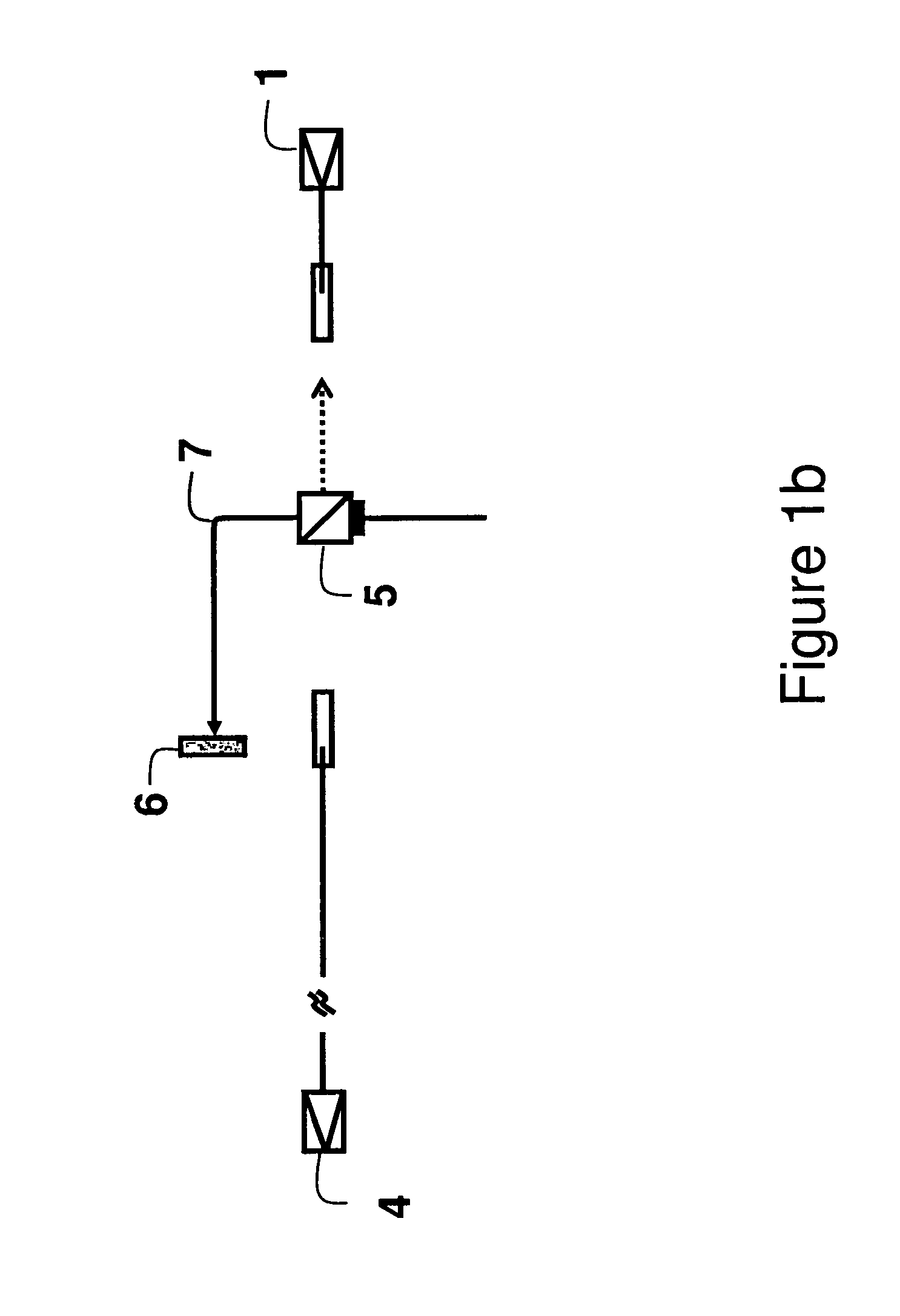
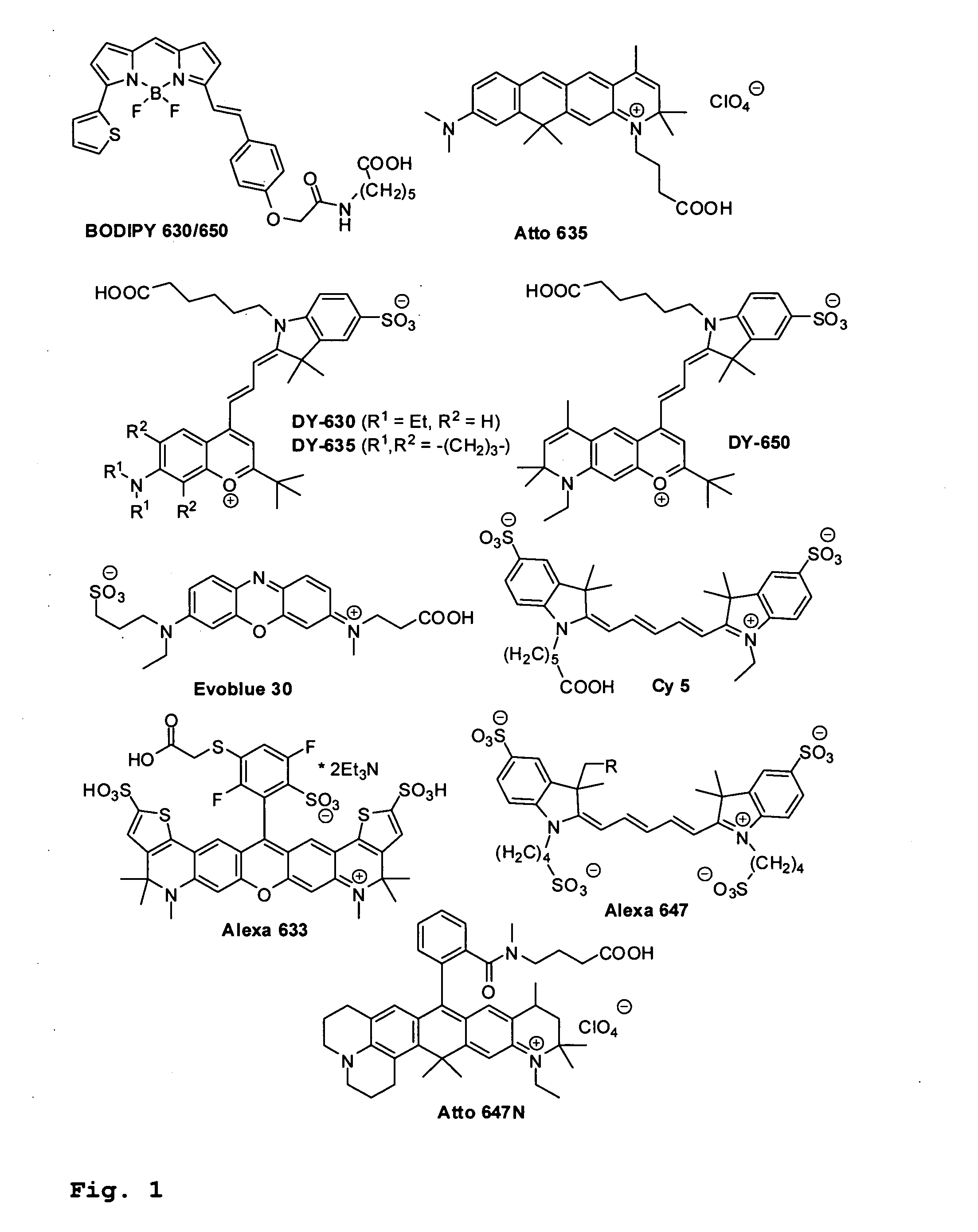
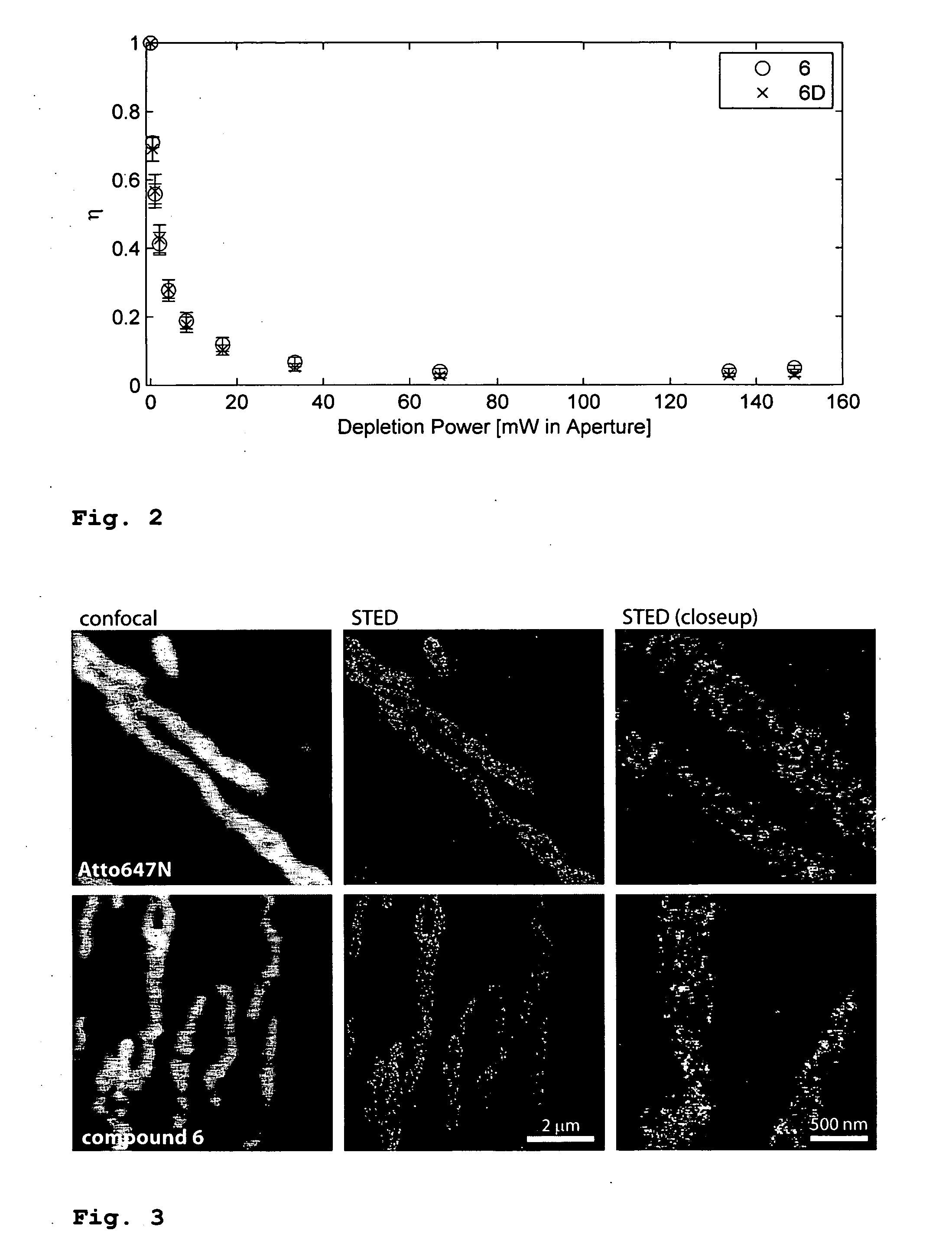
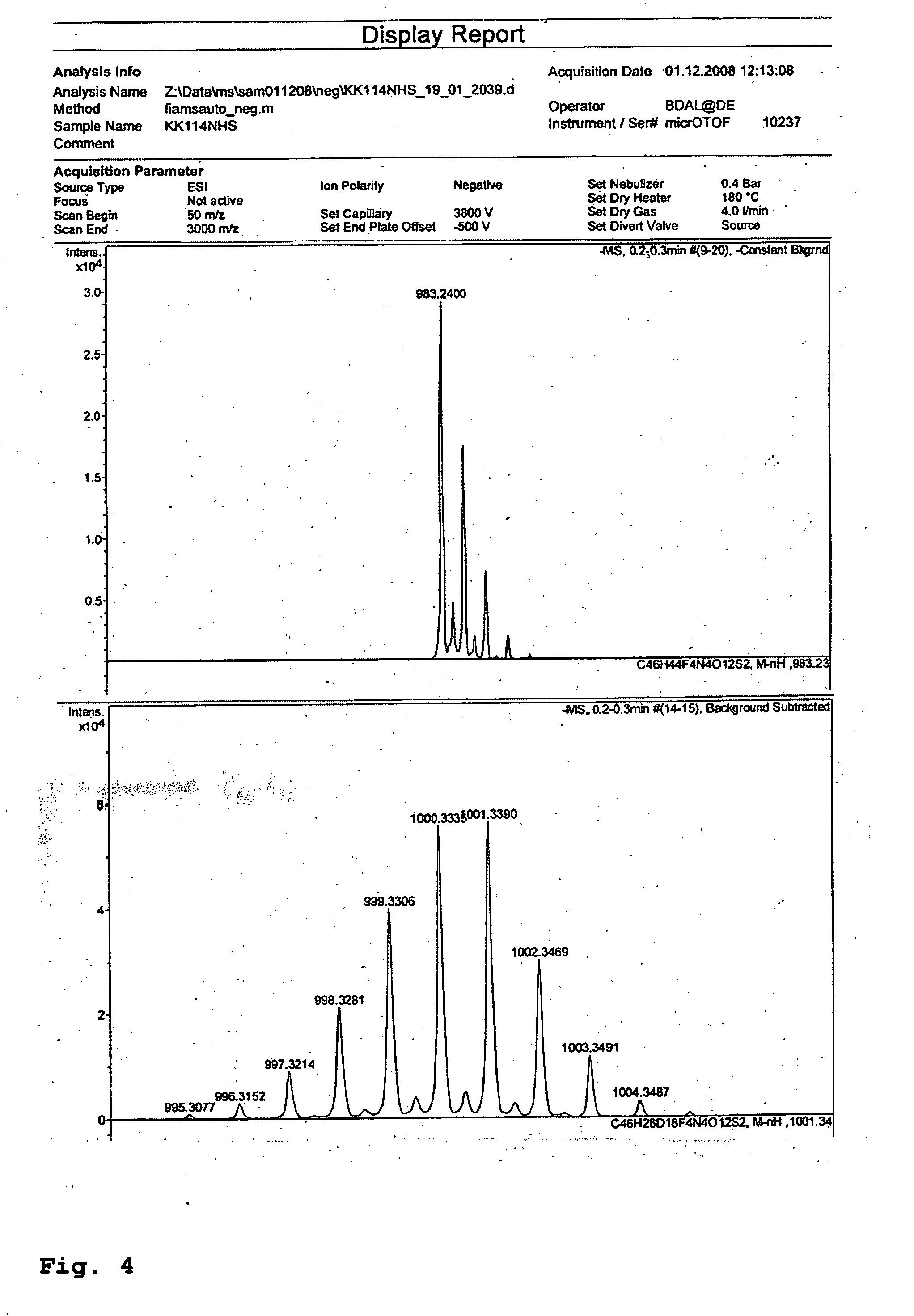
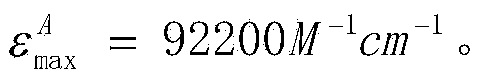Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
48 results about "Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
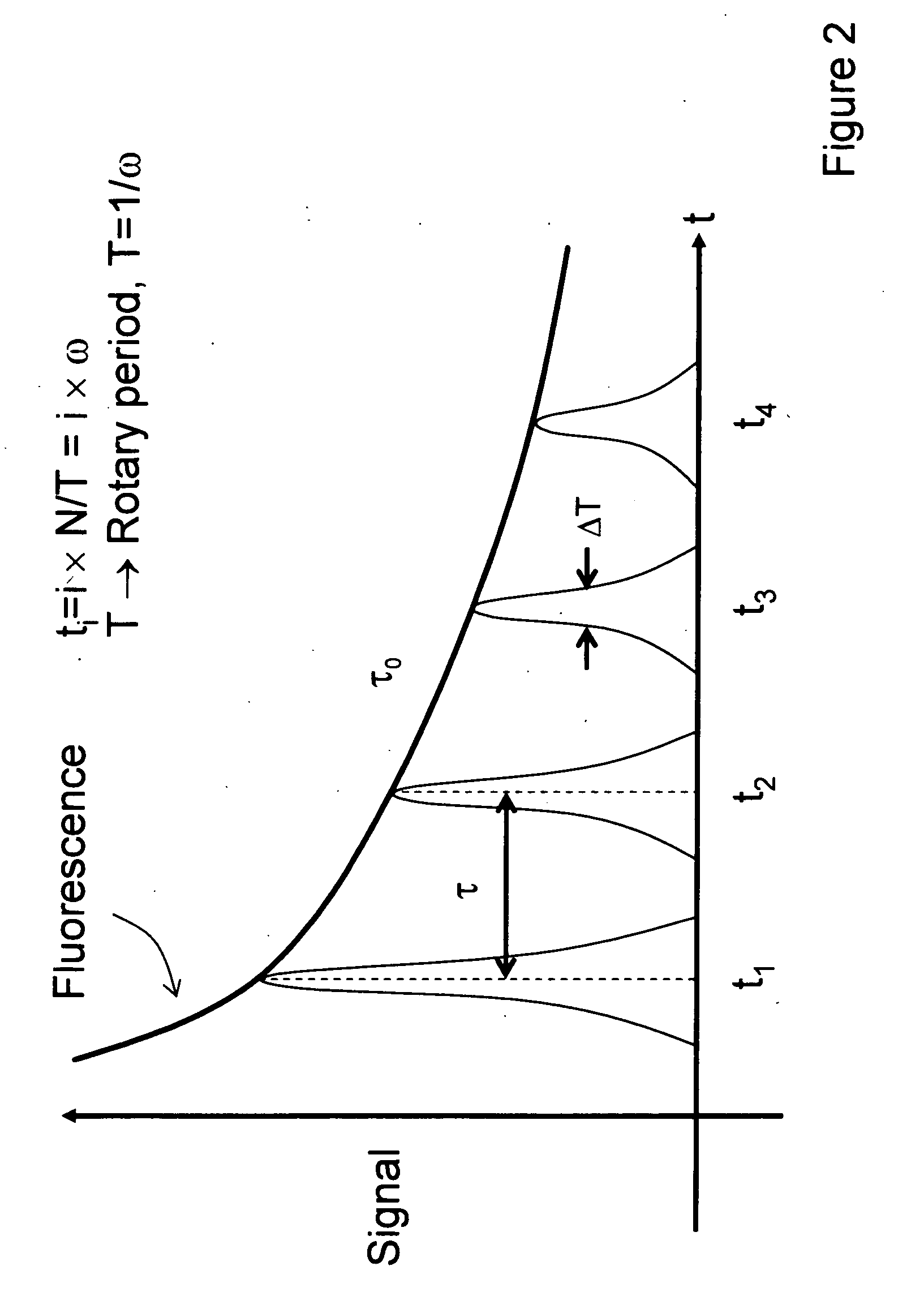
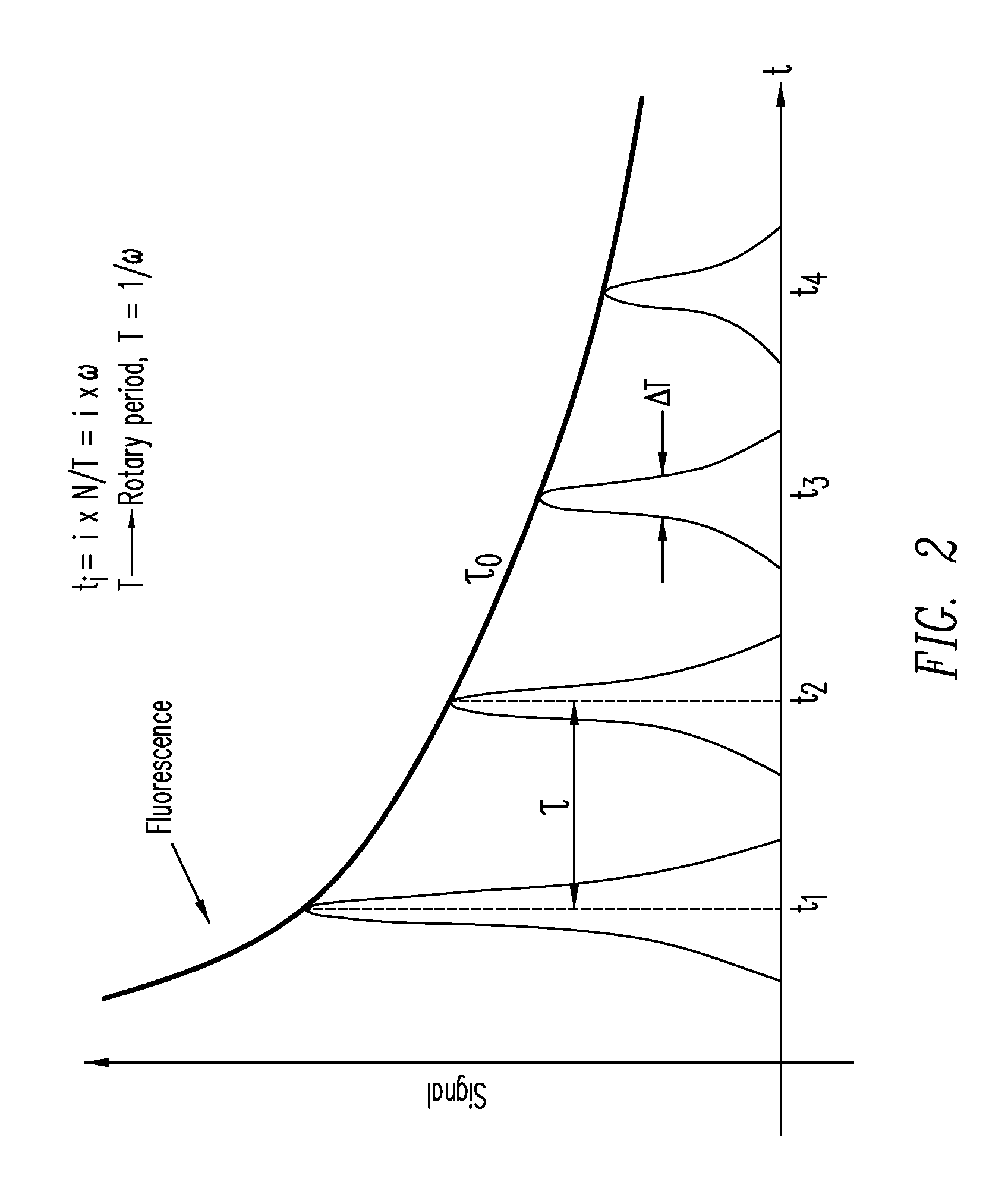
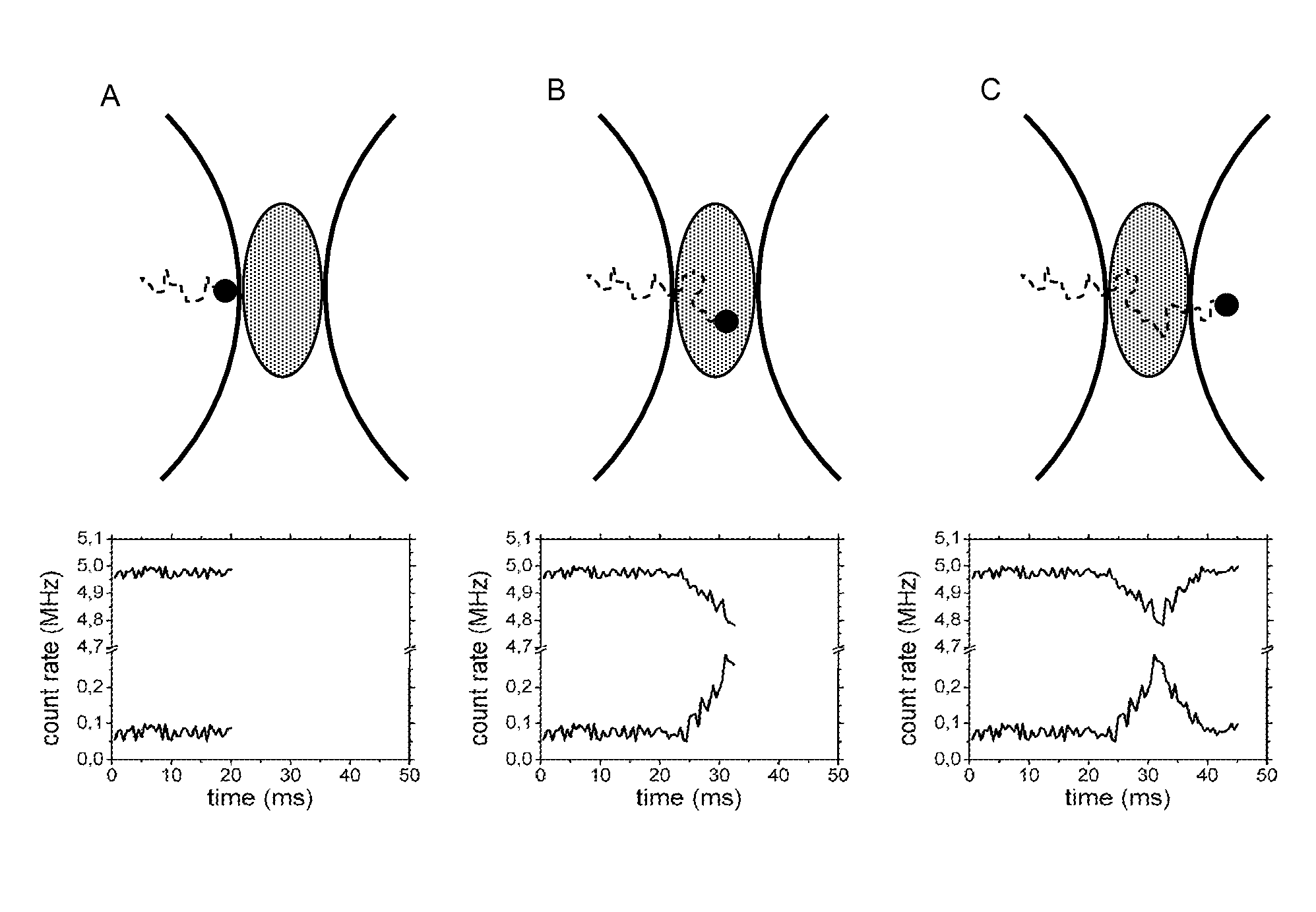
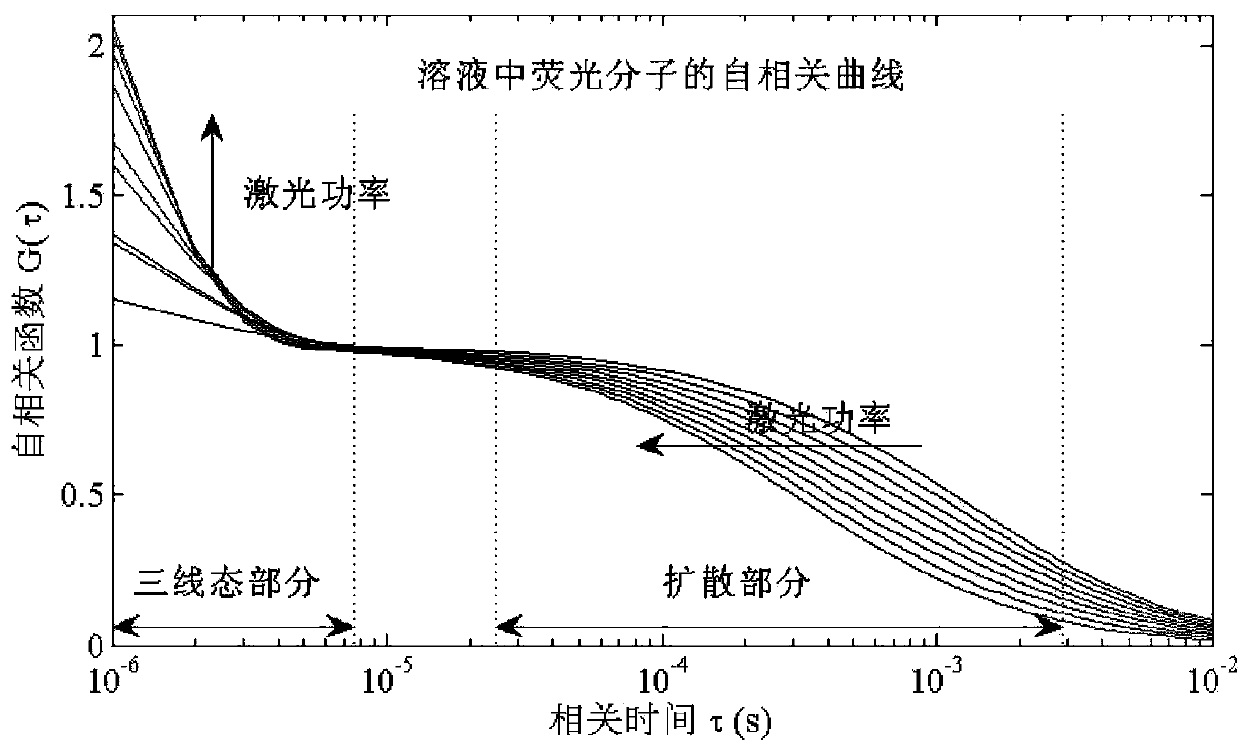
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS) is a correlation analysis of fluctuation of the fluorescence intensity. The analysis provides parameters of the physics under the fluctuations. One of the interesting applications of this is an analysis of the concentration fluctuations of fluorescent particles (molecules) in solution. In this application, the fluorescence emitted from a very tiny space in solution containing a small number of fluorescent particles (molecules) is observed. The fluorescence intensity is fluctuating due to Brownian motion of the particles. In other words, the number of the particles in the sub-space defined by the optical system is randomly changing around the average number. The analysis gives the average number of fluorescent particles and average diffusion time, when the particle is passing through the space. Eventually, both the concentration and size of the particle (molecule) are determined. Both parameters are important in biochemical research, biophysics, and chemistry.
Time-resolved fluorescence spectrometer for multiple-species analysis
InactiveUS20080117418A1Accurate profileLong excited state lifetimesRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyGratingOpto electronic
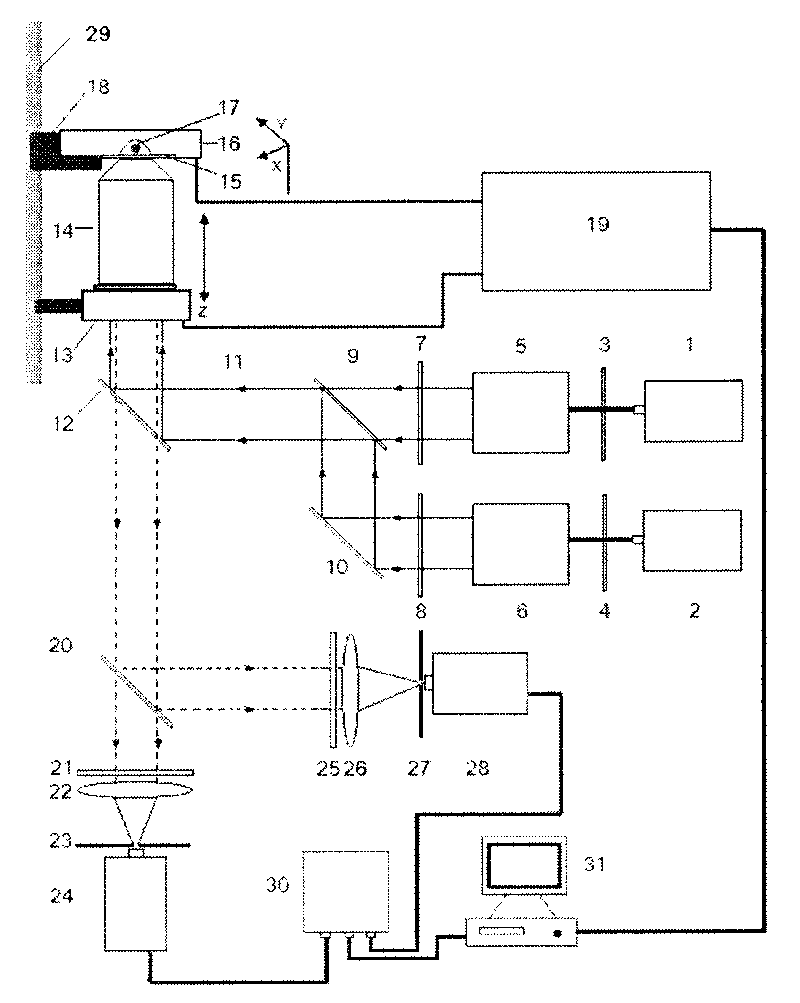
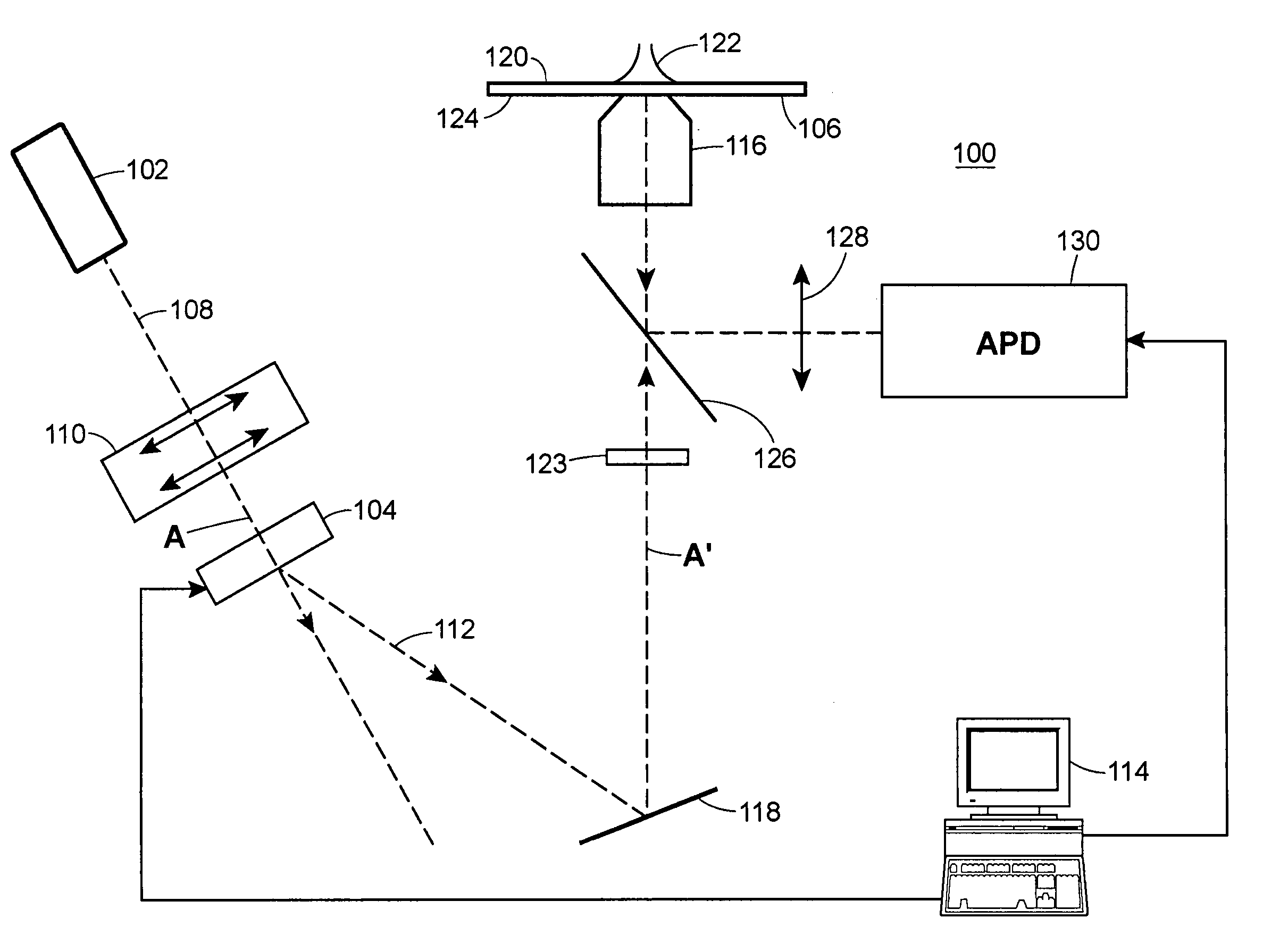
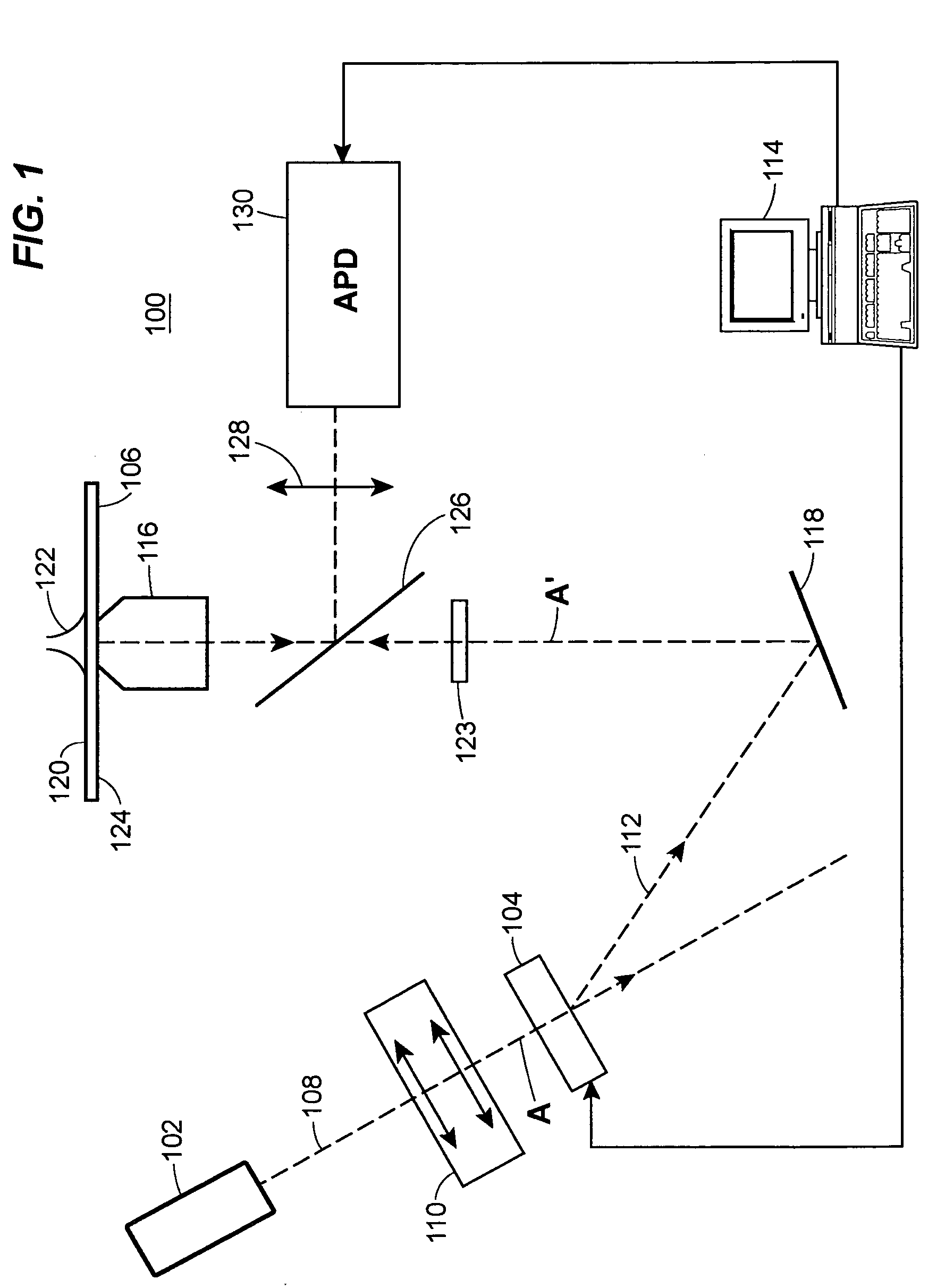
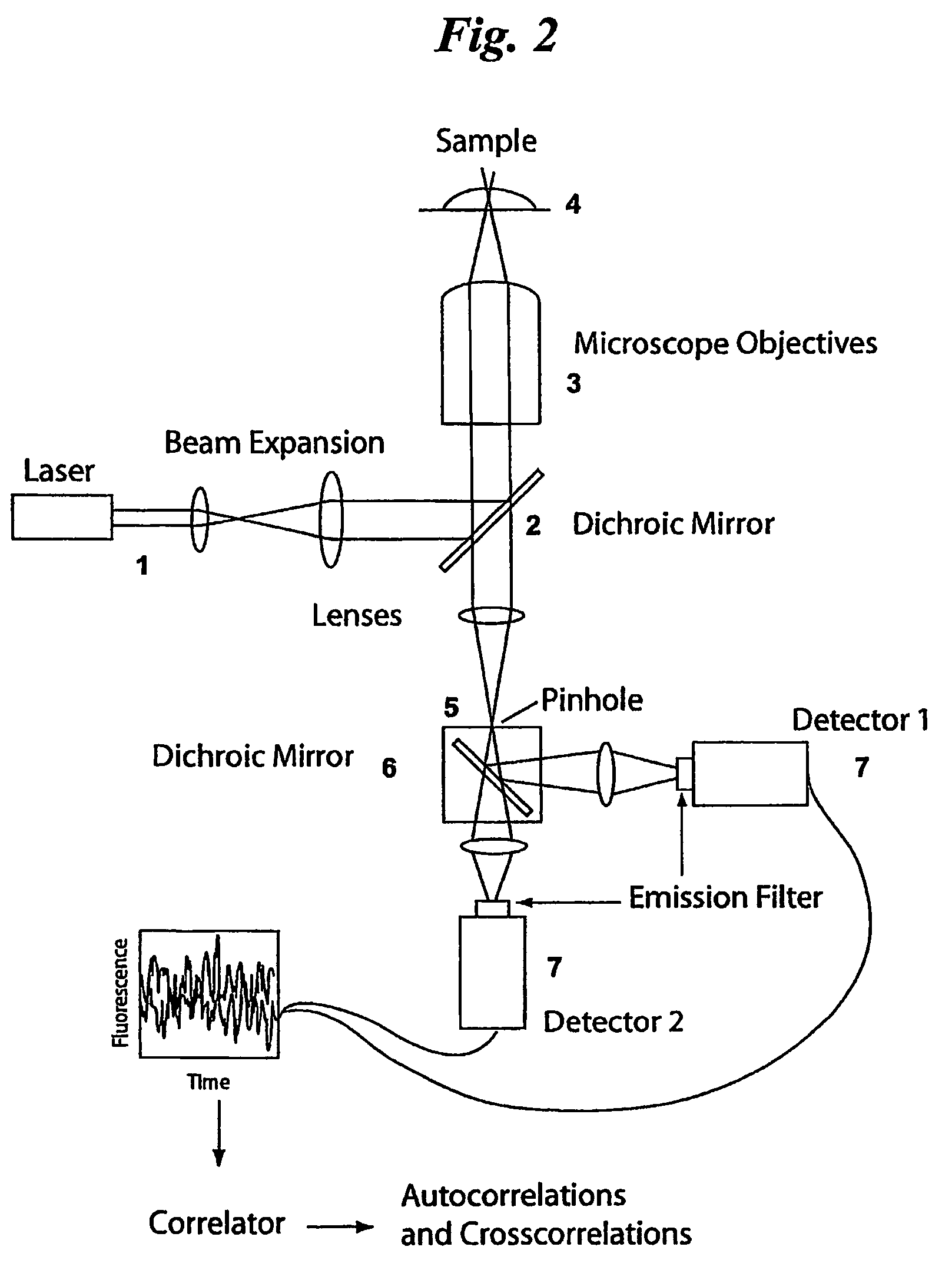
A time-resolved, fluorescence spectrometer makes use of a RadiaLight® optical switch and no dispersive optical elements (DOE) like gratings. The structure is unique in its compactness and simplicity of operation. In one embodiment, the spectrometer makes use of only one photo-detector and an efficient linear regression algorithm. The structure offers a time resolution, for multiple species measurements, of less than 1 s. The structure can also be used to perform fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy.
Owner:OPTICAL ONCOLOGY
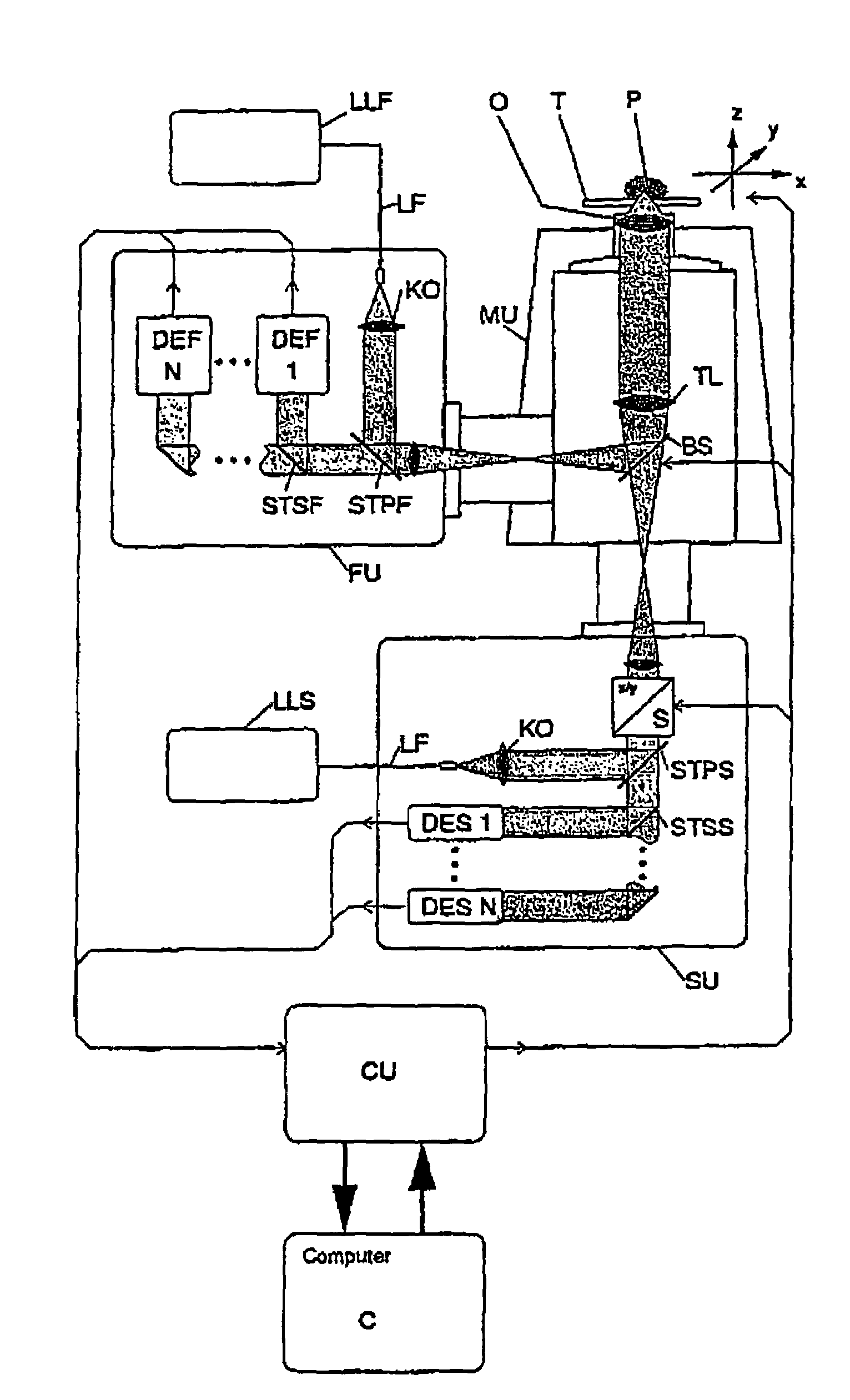
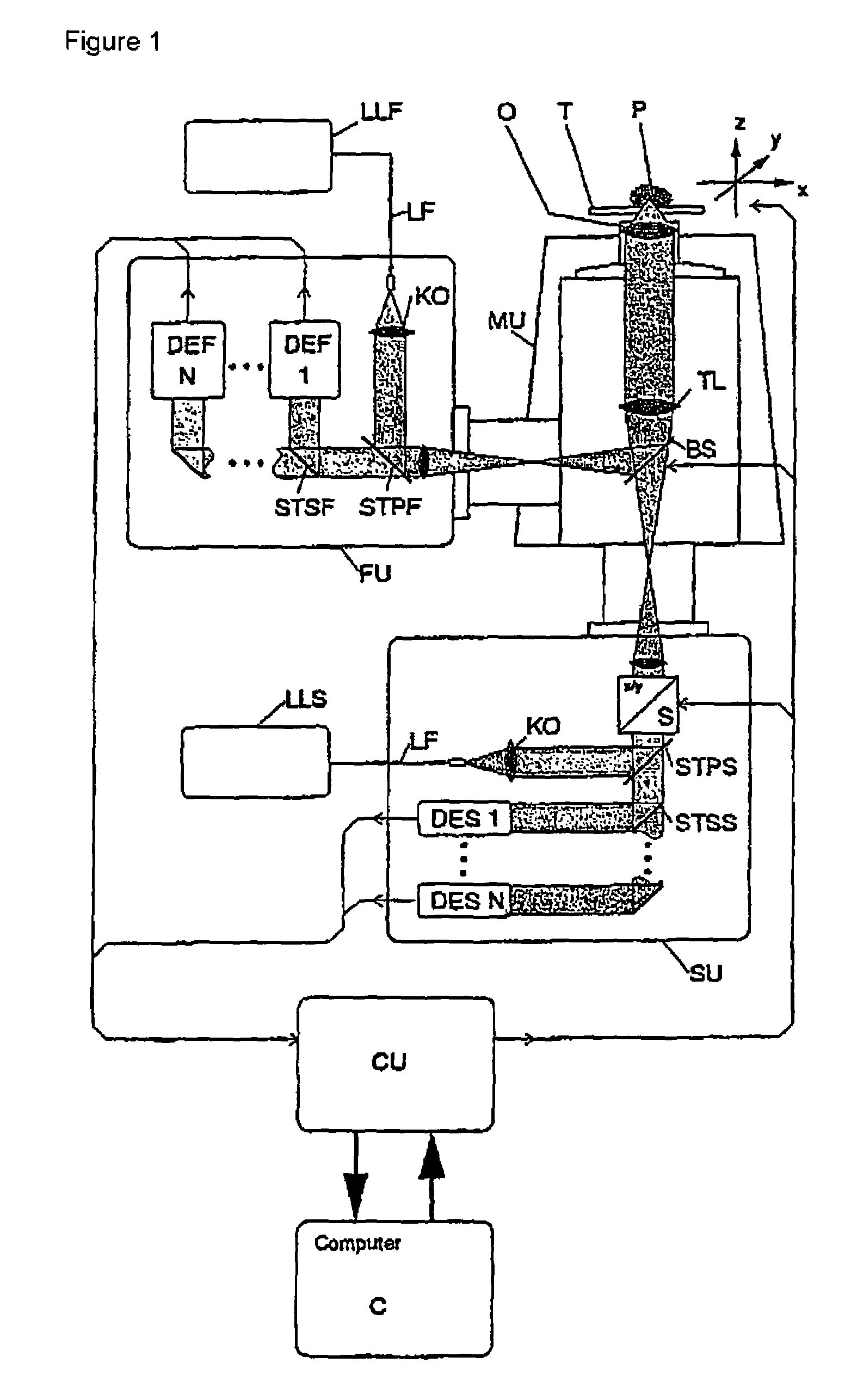
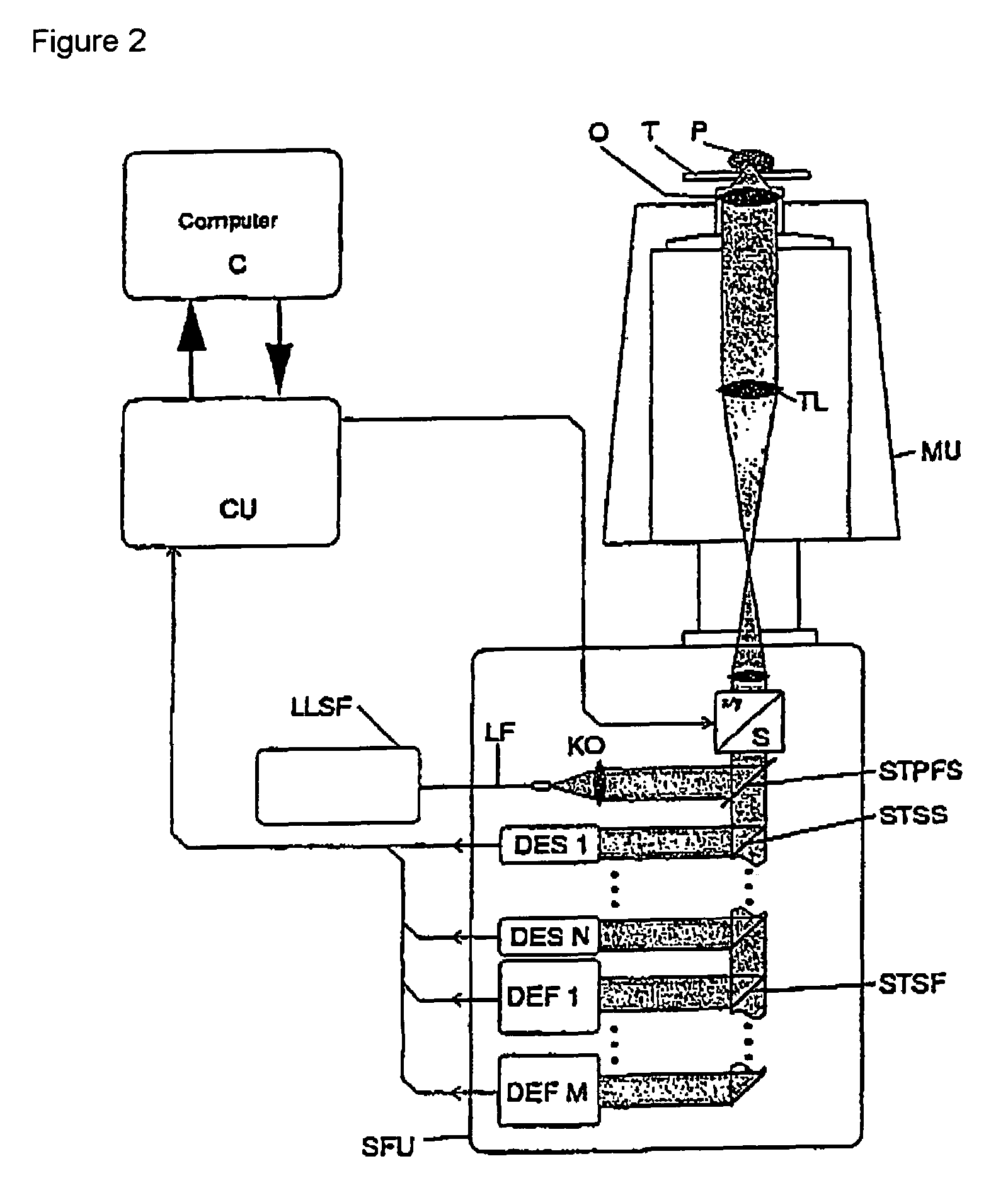
Lasing fluorescence scanning imaging-fluorescence correlation spectrum unimolecule detecting instrument
InactiveCN101718696AEasy to replaceEasy to operateFluorescence/phosphorescencePhoton detectionData acquisition
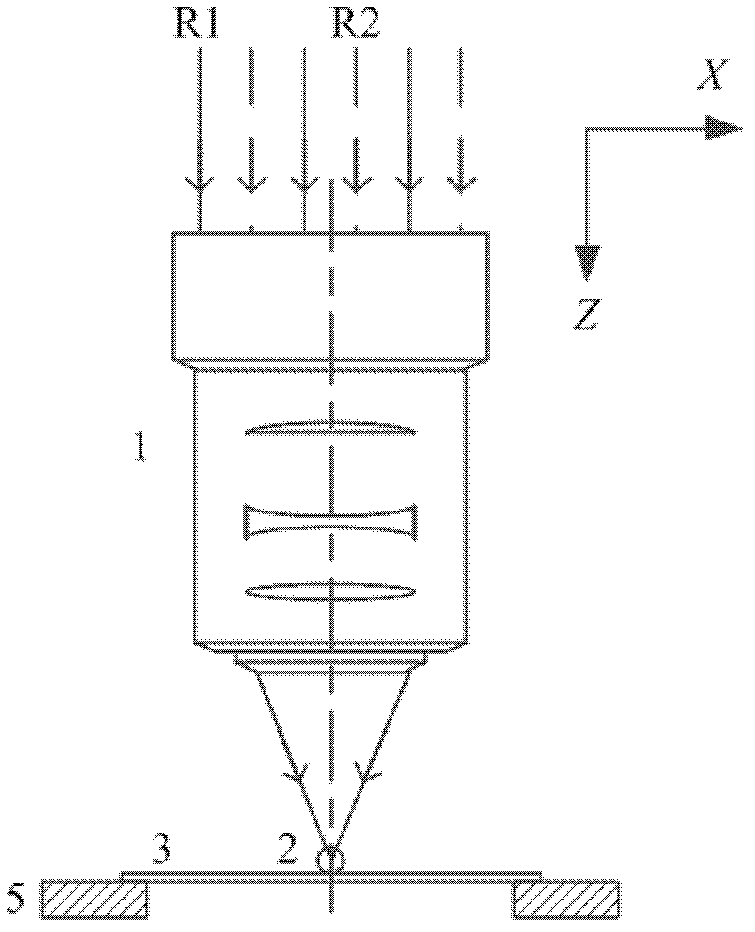
The invention relates to a lasing fluorescence scanning imaging-fluorescence correlation spectrum unimolecule detecting instrument. Cover glass or a sample cell is arranged on an X-Y scanning platform; a microscope objective is installed on a Z-direction locator. Expended laser is filtered by an excitation filter, and then reflected into the objective by a dichroic mirror, and finally radiated in a sample above the cover glass after being focused by the objective; the sample generates fluorescence; and the generated fluorescence is collected by the same objective, passes through the dichroic mirror, and stray light is filtered off by an emission filter, and finally the filtered fluorescence is focused by a focusing lens on a small hole which is coupled with a single photon detector; and a signal generated by the single photon detector enters a computer through a data acquisition card. In the computer, three-dimension displacement and positioning system control software control the X-Y scanning platform to do X-Y two-dimension movement, and the Z-direction locator controls the focus of the objective to do Z-direction movement, thereby forming the three-dimension scanning to the sample; and three-dimension space position information and the signal generated by the single photon detector construct three-dimension scanning images and fluorescence correlation spectrum curves in the computer.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
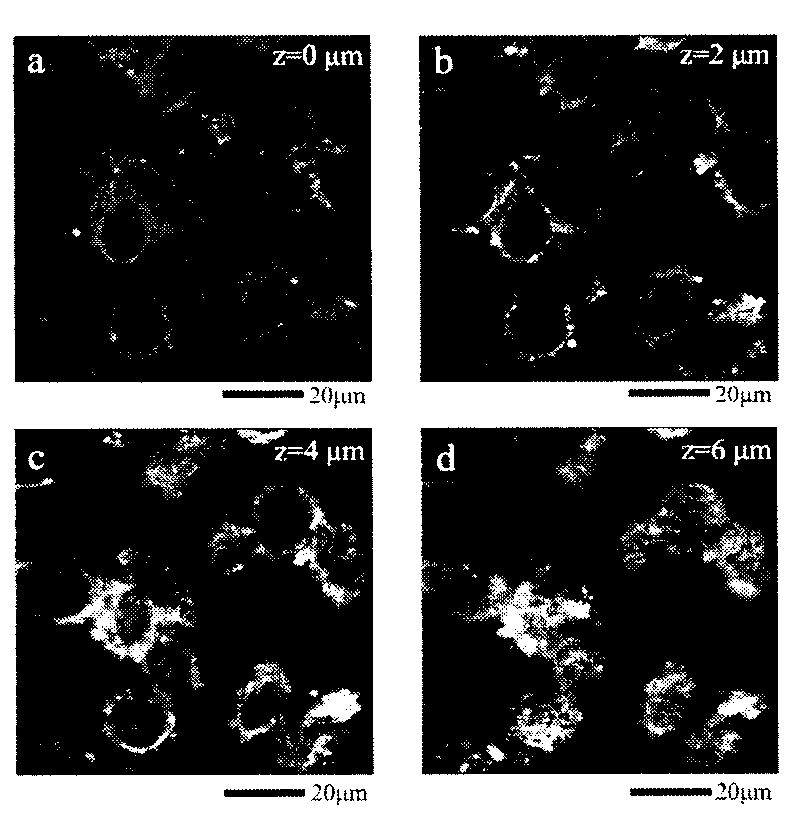
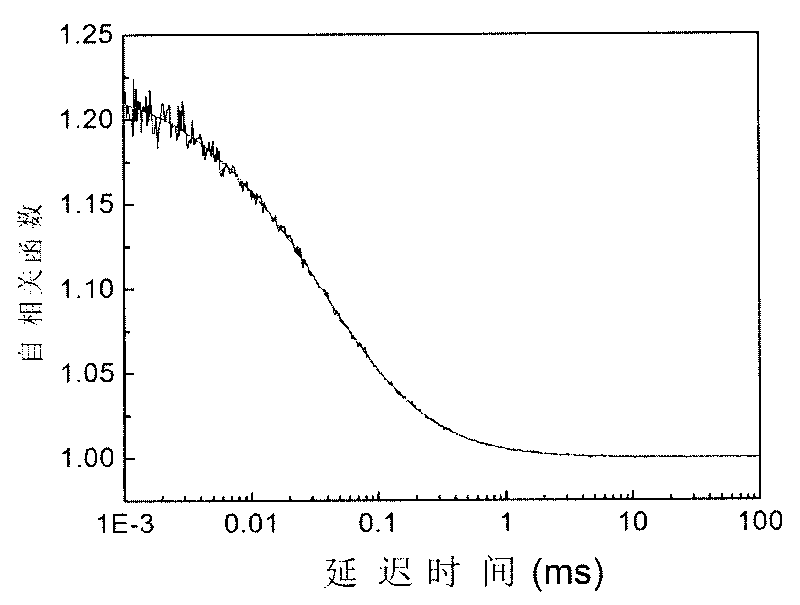
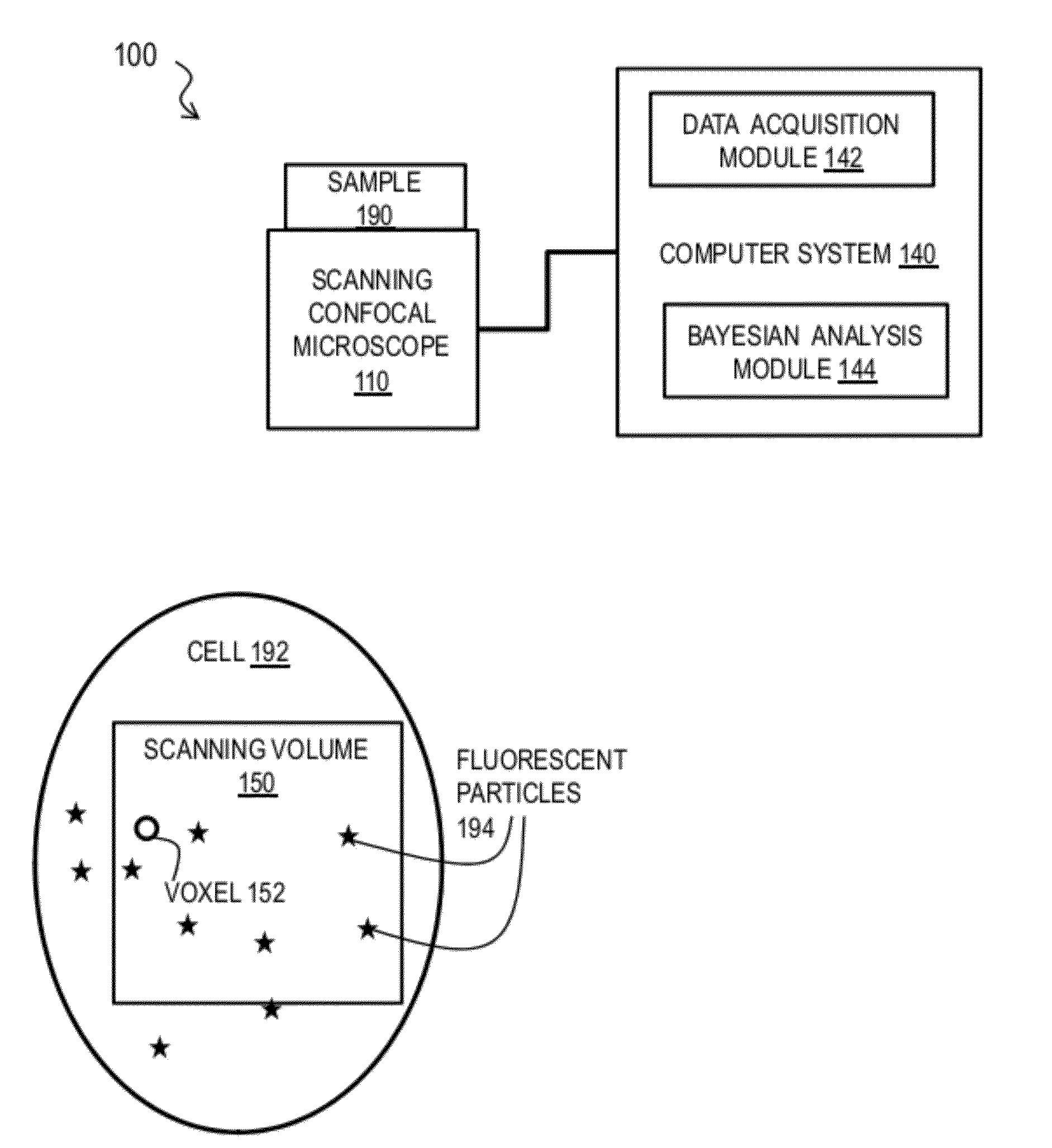
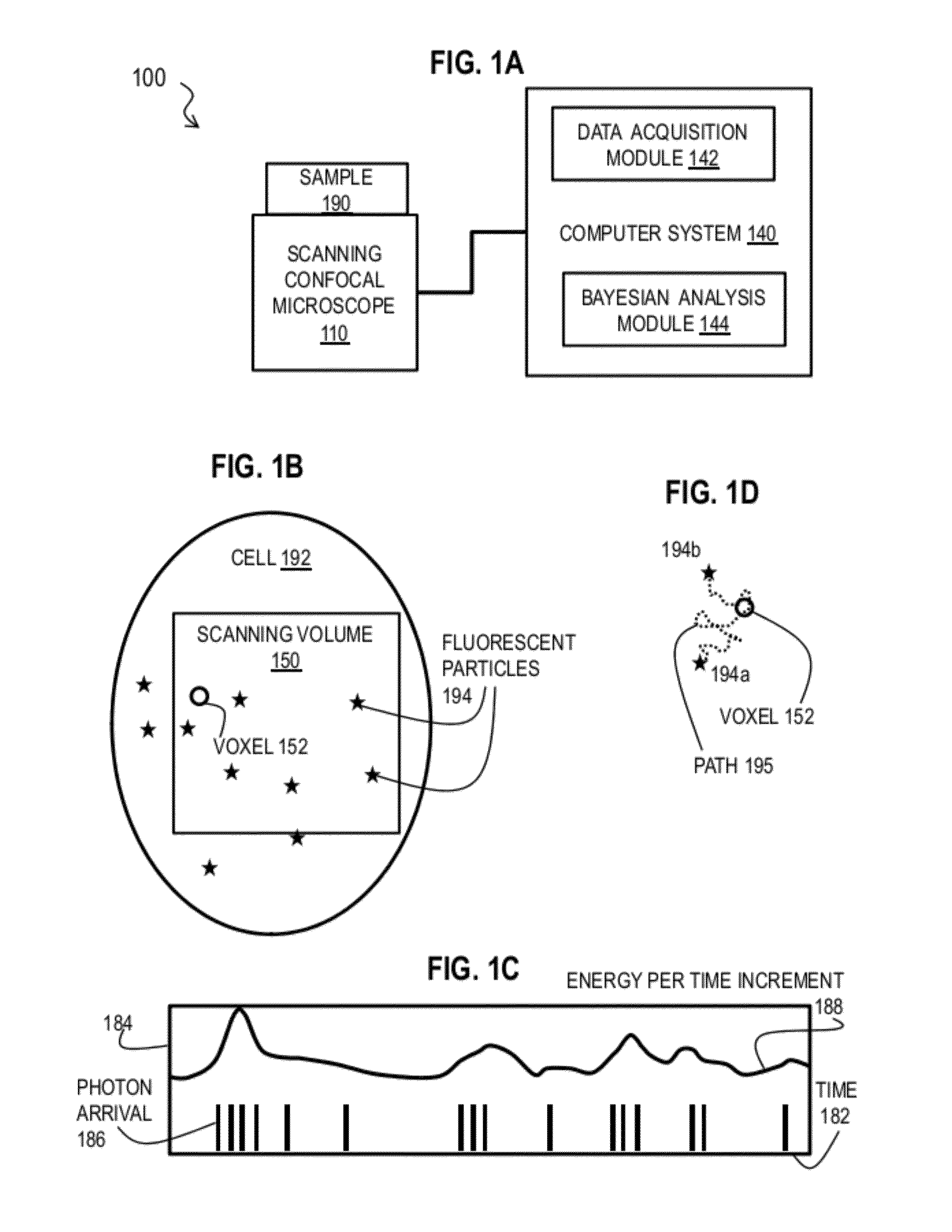
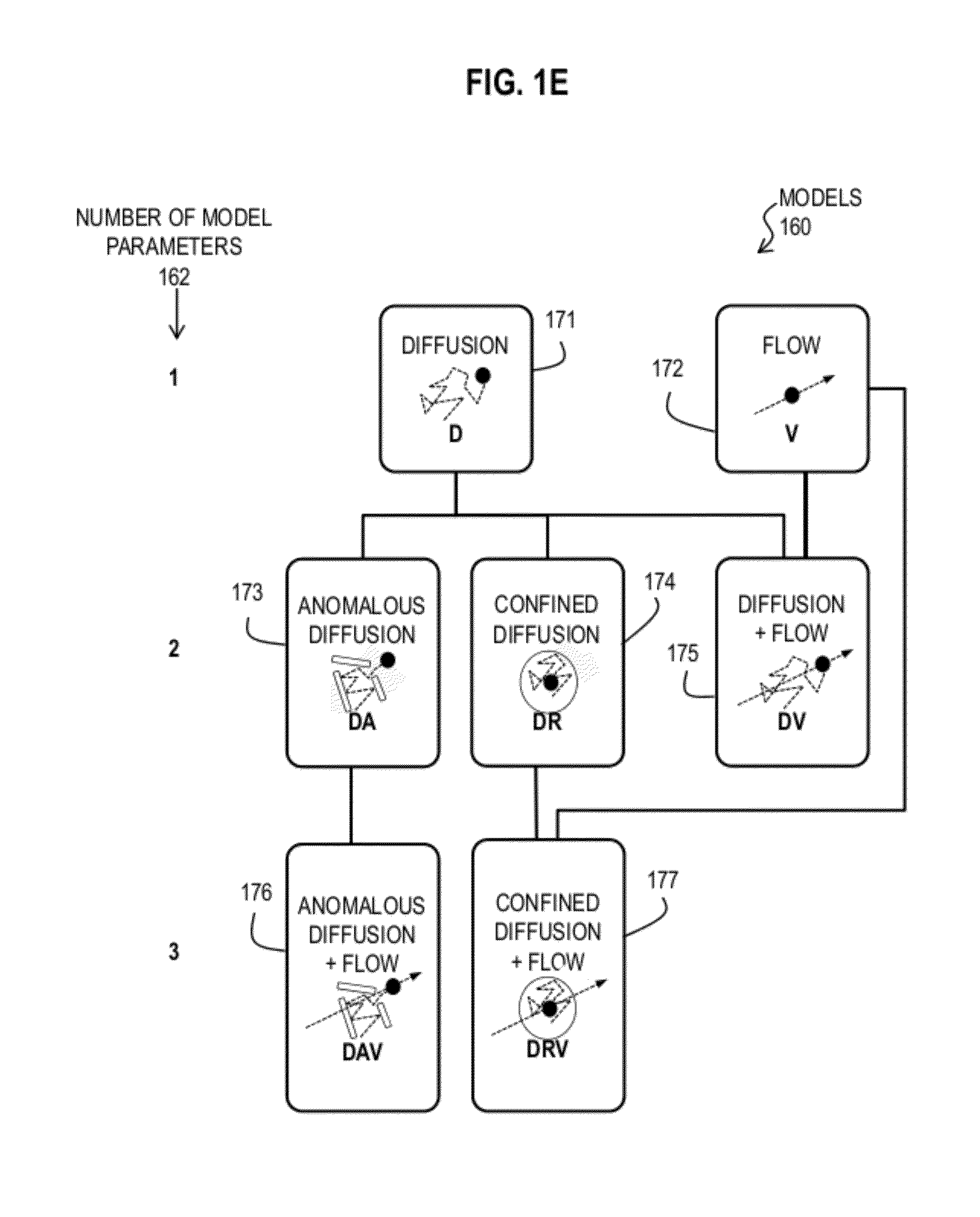
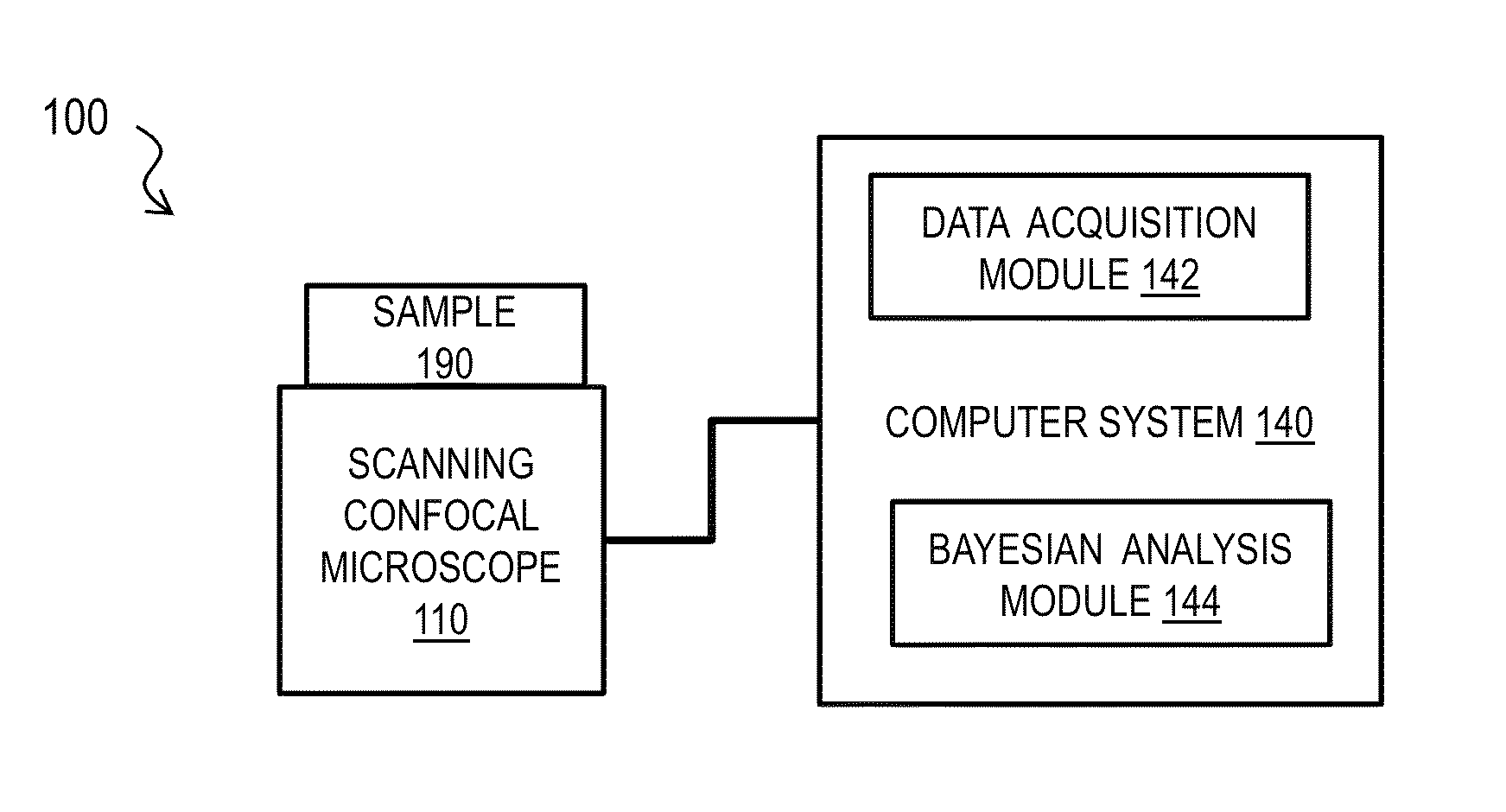
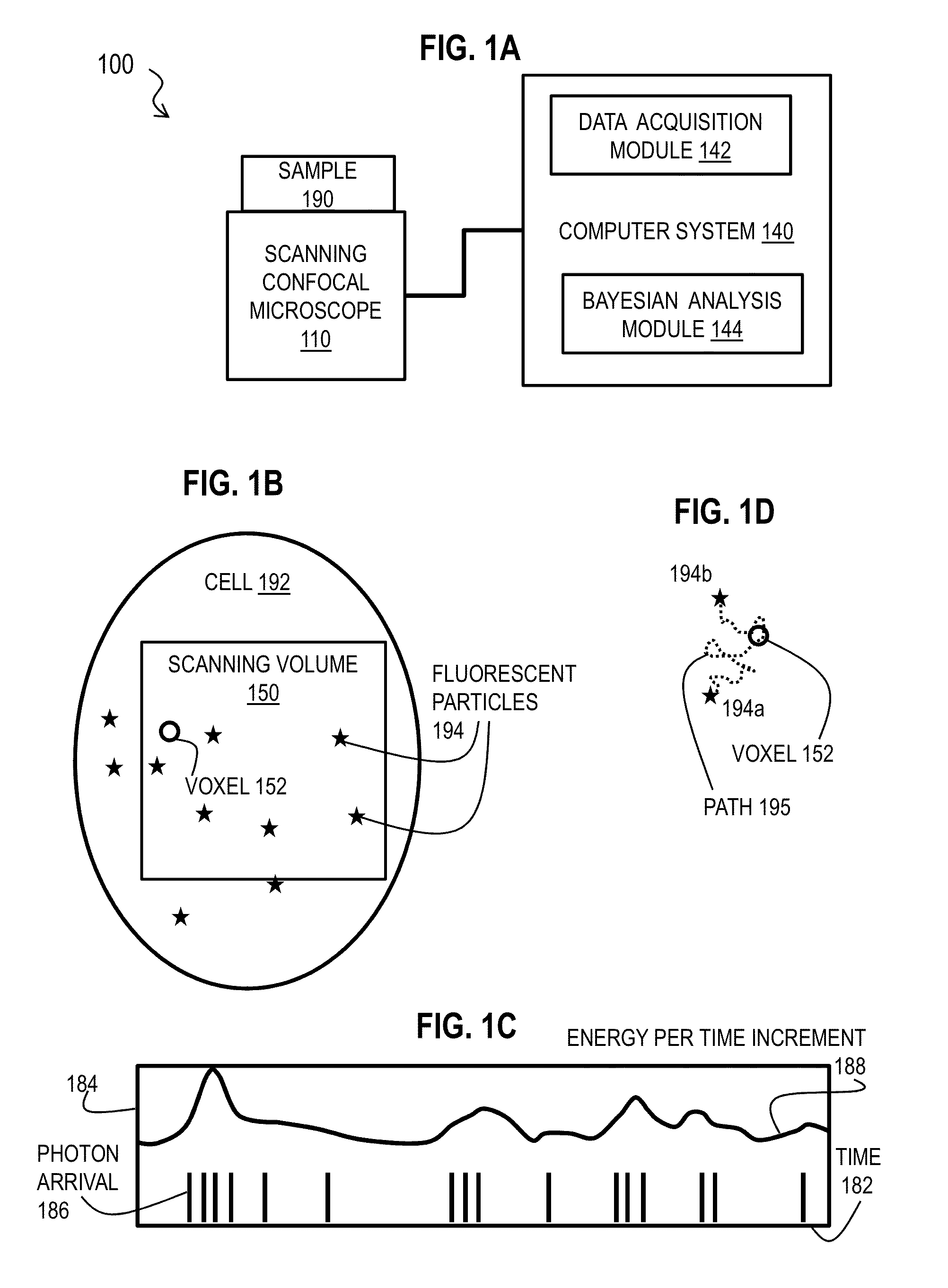
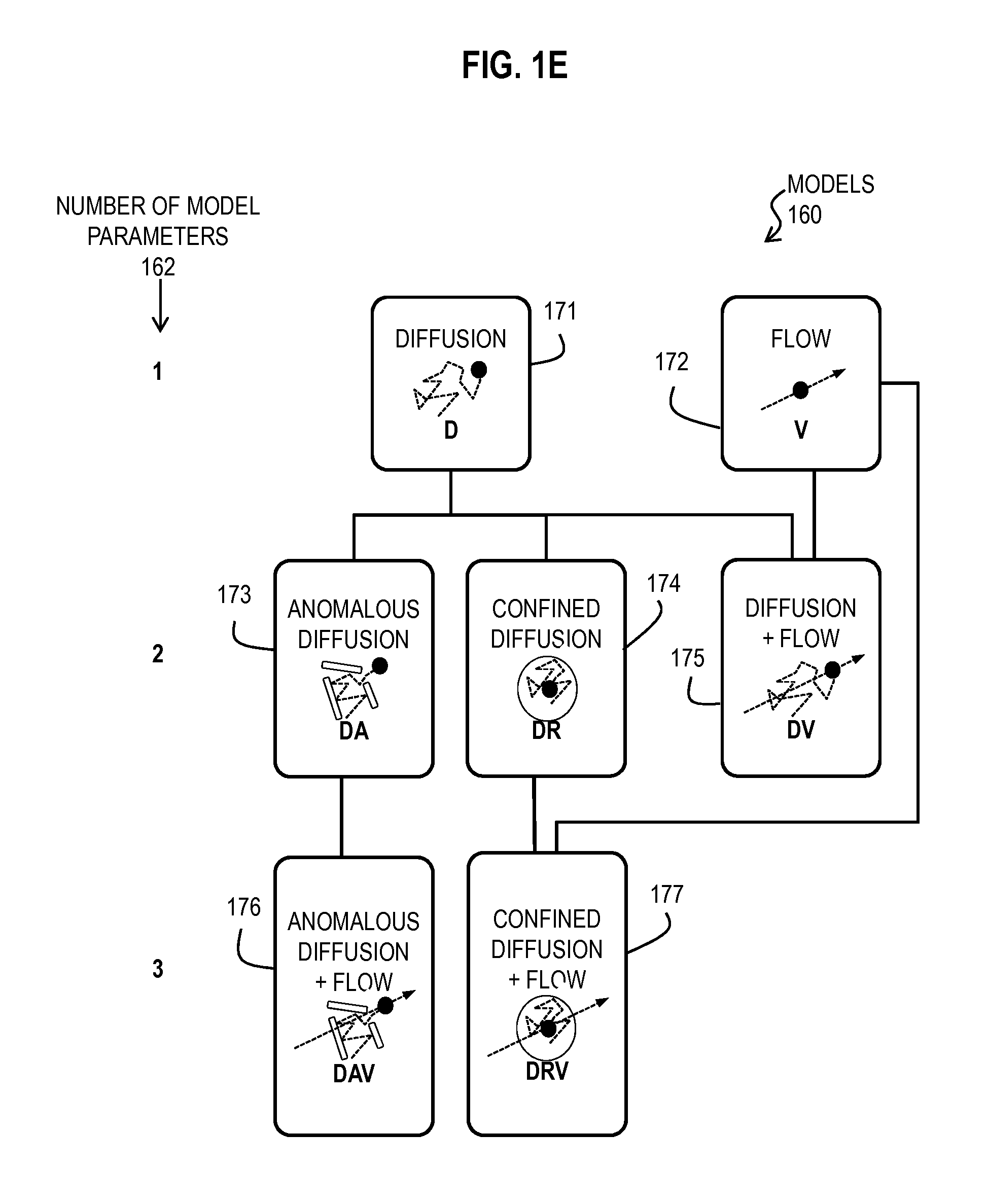
Bayesian Inference of Particle Motion and Dynamics from Single Particle Tracking and Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy
Techniques for inferring particle dynamics from certain data include determining multiple models for motion of particles in a biological sample. Each model includes a corresponding set of one or more parameters. Measured data is obtained based on measurements at one or more voxels of an imaging system sensitive to motion of particles in the biological sample; and, determining noise correlation of the measured data. Based at least in part on the noise correlation, a marginal likelihood is determined of the measured data given each model of the multiple models. A relative probability for each model is determined based on the marginal likelihood. Based at least in part on the relative probability for each model, a value is determined for at least one parameter of the set of one or more parameters corresponding to a selected model of the multiple models.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Novel fluorinated rhodamines as photostable fluorescent dyes for labelling and imaging techniques
ActiveUS20120135459A1High fluorescence quantum yieldLow rateSugar derivativesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceStimulated emissionCombinatorial chemistry
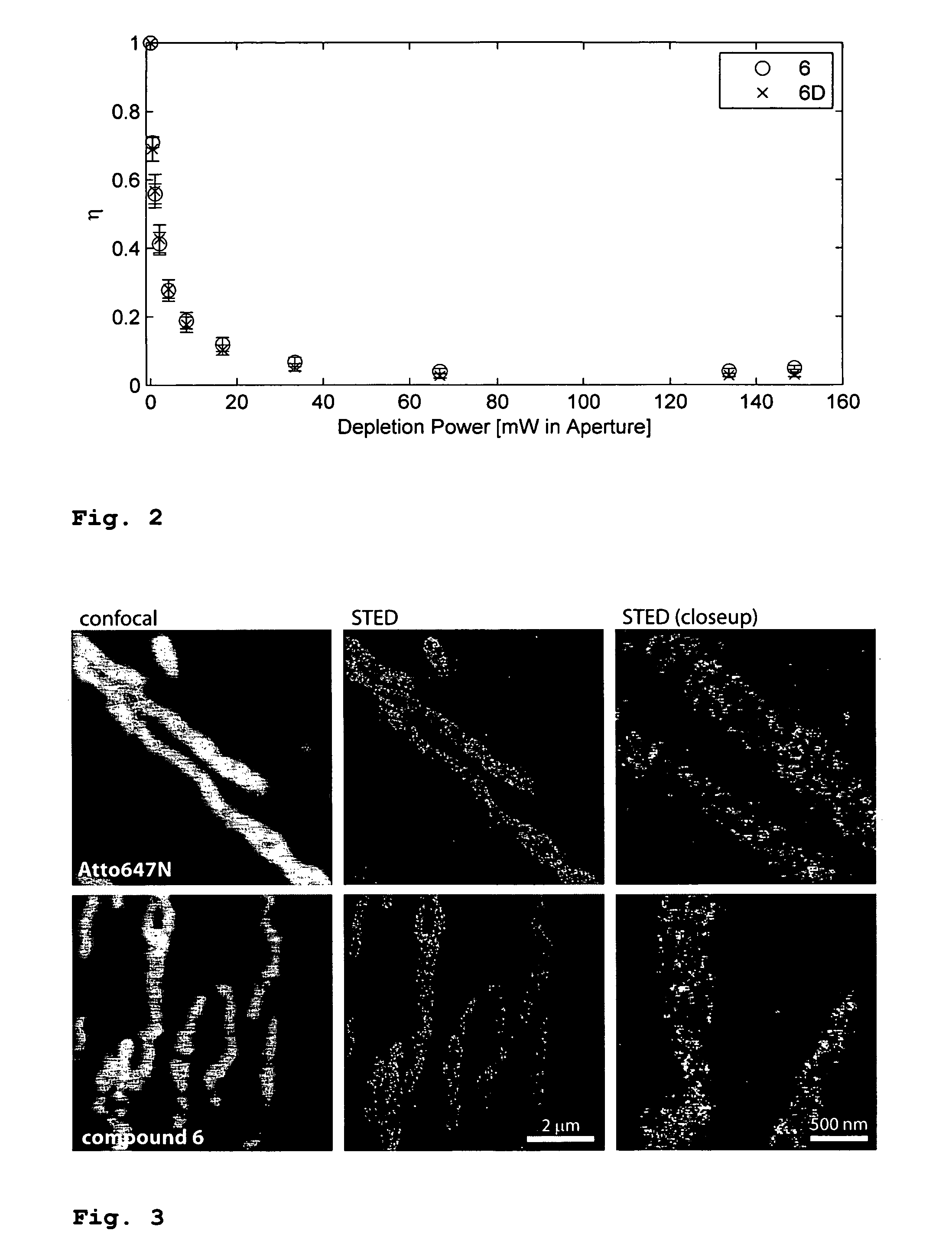
The present invention relates to novel fluorinated 3,6-diaminoxanthene compounds derived from the basic structural formula (I) and to their uses as photostable fluorescent dyes, e.g. for immunostainings and spectroscopic and microscopic applications, in particular in conventional microscopy, stimulated emission depletion (STED) reversible saturable optically linear fluorescent transitions (RESOLFT) microscopy, and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. The claimed compounds are also useful as molecular probes in various spectroscopic applications.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Time-resolved fluorescence spectrometer for multiple-species analysis
InactiveUS7679745B2Accurate profileLong excited state lifetimesRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyGratingPhotovoltaic detectors
A time-resolved, fluorescence spectrometer makes use of a RadiaLight® optical switch and no dispersive optical elements (DOE) like gratings. The structure is unique in its compactness and simplicity of operation. In one embodiment, the spectrometer makes use of only one photo-detector and an efficient linear regression algorithm. The structure offers a time resolution, for multiple species measurements, of less than 1 s. The structure can also be used to perform fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy.
Owner:OPTICAL ONCOLOGY INC
Time-Resolved Spectroscopy System and Methods for Multiple-Species Analysis in Fluorescence and Cavity-Ringdown Applications
InactiveUS20100165338A1Raman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryLinear regressionTime-division multiplexing
A time-resolved spectroscopy system employing a time-division multiplexing optical device with no dispersive optical elements to perform lifetime and concentration measurements in multi-species samples, is disclosed. Some examples include fluorescence and cavity ring-down spectroscopy. The system is unique in its compactness and simplicity of operation. In one embodiment, the system makes use of only one photo-detector and an efficient linear regression algorithm. The system offers a measurement time for multiple species measurements of less than 1 s. The system can also be used to perform fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy. Four methods to de-convolve a multi-component, exponentially decaying optical signal such as obtained with the system disclosed here, are presented. These methods may be applied to the measurement of fluorescence decay lifetimes and cavity ring-down times, the latter used extensively for the measurement of gas and trace-gas concentrations in complex mixtures, via absorption spectroscopy.
Owner:CLAPS RICARDO
Total internal reflection fluorescence apparatus
InactiveUS20060126063A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationTotal internal reflectionHigh numerical aperture
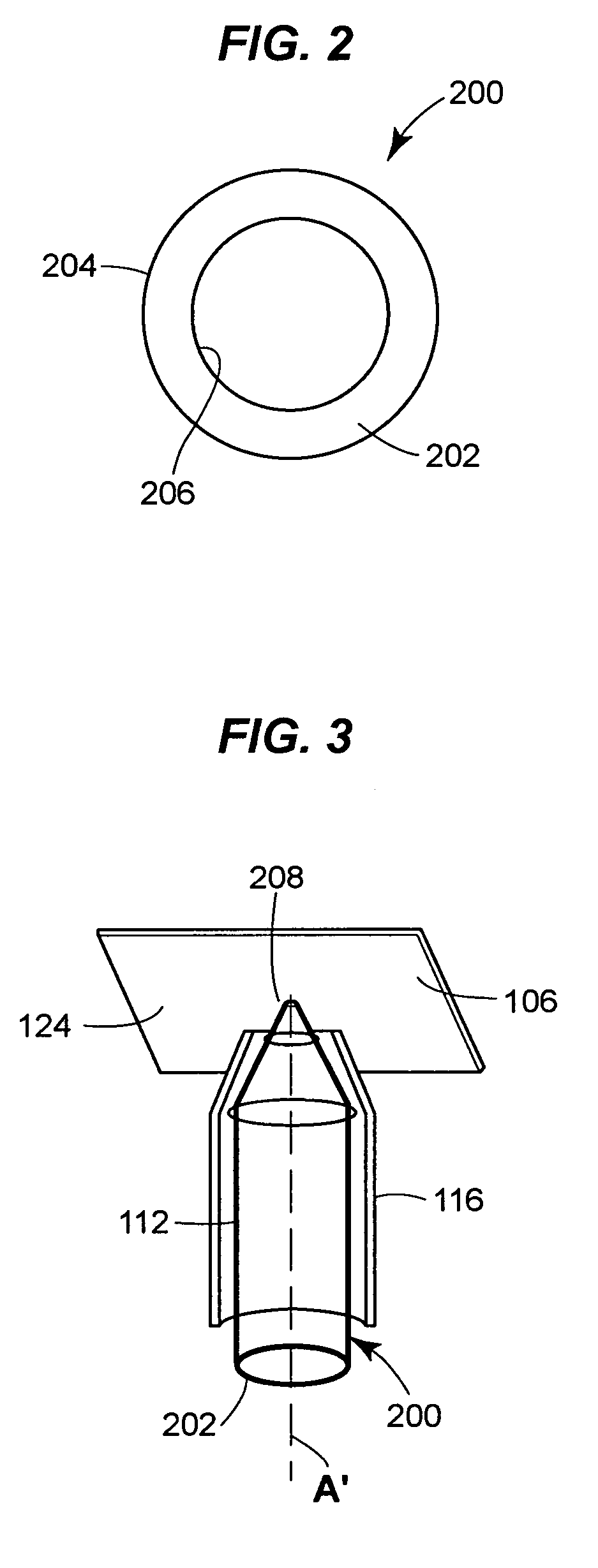
Techniques are provided for illuminating a sample by using total internal reflection (TIR) from a diffraction limited focused annular illumination beam. The illumination forms an affected region and an overlapping confocal region that may have dimensions the below 1 μm. An adjustable diffractive optical element, for example, may create a second order Bessel profile laser beam that is focused on a sample using a high-numerical aperture objective under TIR. An evanescent field excites fluorescent biological material in the confocal region, and fluorescence from the material is analyzed in fluorescence correlation spectroscopy system.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF
Hydrophilic and lipophilic rhodamines for labelling and imaging
ActiveUS8580579B2High fluorescence quantum yieldLow rateSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPhoto stabilityMass spectrometry
The invention relates to novel and improved photostable rhodamine dyes of the general structural formulae I or II and their uses as fluorescent markers, e.g. for immunostainings and spectroscopic and microscopic applications, in particular in conventional and stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. The partially deuterated analogues are useful as molecular mass distribution tags in mass spectroscopic applications, wherein R1=an unsubstituted or substituted alkyl group, including a cycloalkyl group, or heterocycloalkyl group; R2=H, an unsubstituted or substituted alkyl group, including a cycloalkyl group, or heterocycloalkyl group, or an unsubstituted or substituted aryl group or heteroaryl group, or any combination of such groups; X=CH2, C═O, C═NORa, C═NNRaNRb, CH(ORa), O, S, SO, SO2, or any other derivatives of these groups, with Ra and Rb independently being H or an organic residue, in particular an unsubstituted or substituted (cyclo)alkyl group or heterocycloalkyl group, an unsubstituted or substituted aryl group or heteroaryl group; Z=a negatively charged group with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 charges per anion.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Apparatus, method and computer program for fluorescence correlation spectroscopy
InactiveUS20100301231A1Reduce computationReduce the number of timesRaman/scattering spectroscopyPhotometryDiffusionComputer science
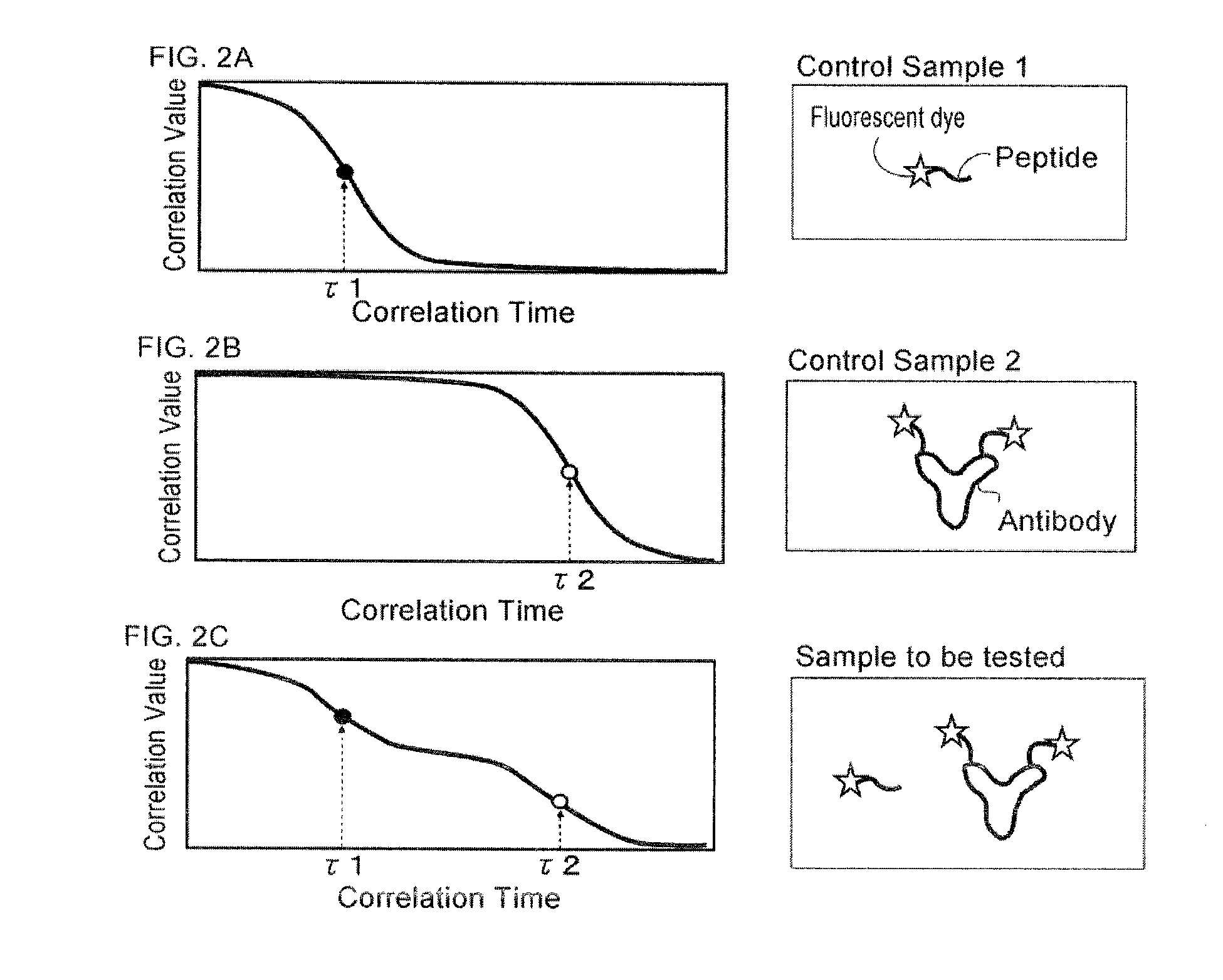
There are provided an apparatus, a method and a computer program for fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS), which can reduce the number of times of fluorescence measurements of control samples as few as possible for a measurement by FCS in detecting existence ratios of the respective components contained in a sample. In the inventive apparatus, method and computer program for detecting an existence ratio of each of components with a fluorescent label contained in a solution sample by FCS, using a value of a ratio of a translational diffusion time of each of the components based upon the knowledge that a ratio of a translational diffusion time of each of the components is conservative under different measurement conditions etc.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Fluorinated rhodamines as photostable fluorescent dyes for labelling and imaging techniques
ActiveUS8735444B2High fluorescence quantum yieldLow rateBiocideChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceStimulated emissionCombinatorial chemistry
The present invention relates to novel fluorinated 3,6-diaminoxanthene compounds derived from the basic structural formula (I) and to their uses as photostable fluorescent dyes, e.g. for immunostainings and spectroscopic and microscopic applications, in particular in conventional microscopy, stimulated emission depletion (STED) reversible saturable optically linear fluorescent transitions (RESOLFT) microscopy, and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. The claimed compounds are also useful as molecular probes in various spectroscopic applications.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Bayesian inference of particle motion and dynamics from single particle tracking and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy
Techniques for inferring particle dynamics from certain data include determining multiple models for motion of particles in a biological sample. Each model includes a corresponding set of one or more parameters. Measured data is obtained based on measurements at one or more voxels of an imaging system sensitive to motion of particles in the biological sample; and, determining noise correlation of the measured data. Based at least in part on the noise correlation, a marginal likelihood is determined of the measured data given each model of the multiple models. A relative probability for each model is determined based on the marginal likelihood. Based at least in part on the relative probability for each model, a value is determined for at least one parameter of the set of one or more parameters corresponding to a selected model of the multiple models.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and device for analyzing fluorescent correlation spectroscopy based on medium microsphere
InactiveCN102305782ASimple structureHigh-resolutionRaman/scattering spectroscopyMicroscopesHigh concentrationMicrosphere
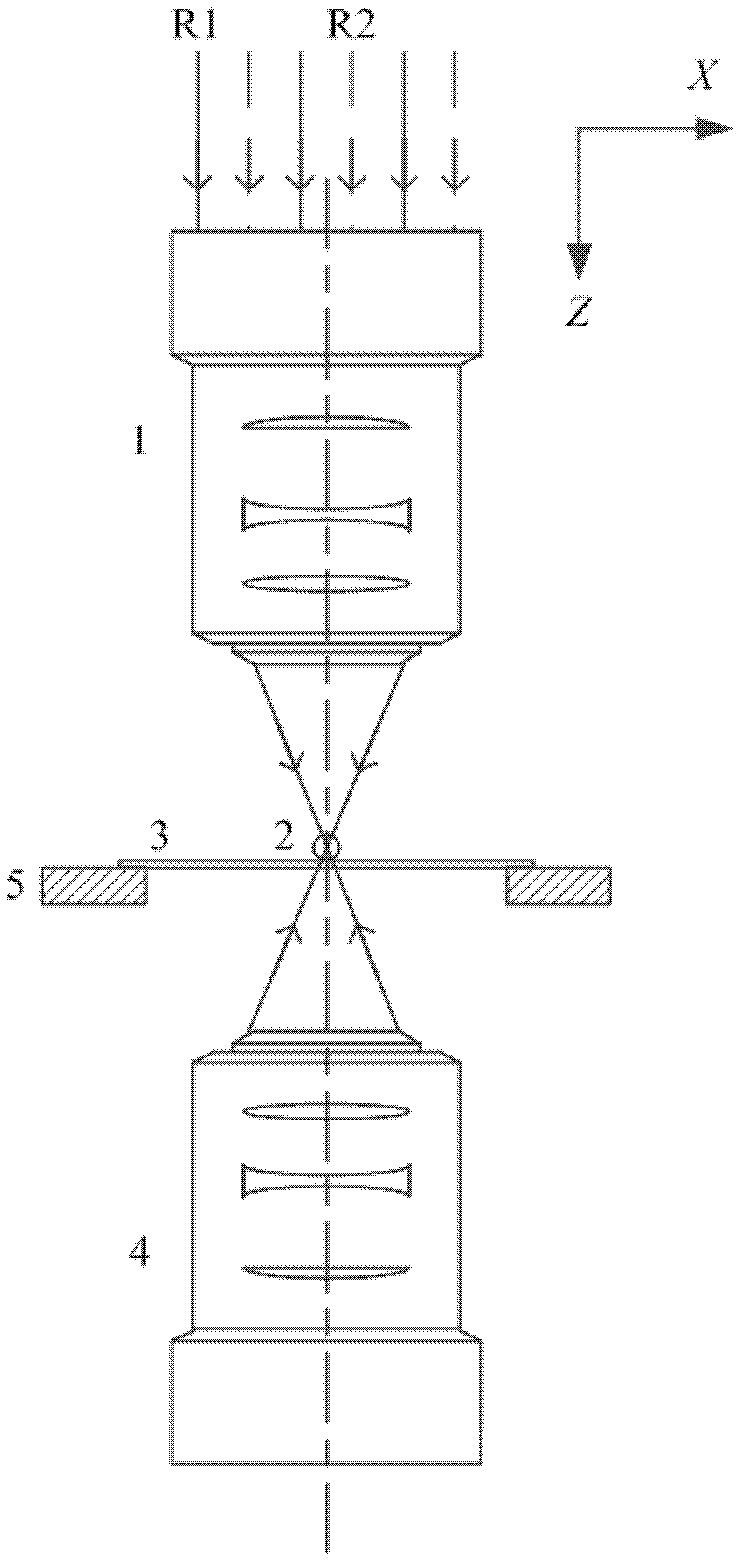
The invention discloses a method and device for analyzing the fluorescent correlation spectroscopy based on a medium microsphere. In the method, radial polarized light and tangential polarized light are respectively used as a fluorescent excitation beam and a fluorescent inhibition beam which are sequentially focused by a microobjective, then are subjected to nanometer spraying by virtue of the medium microsphere and then act on a fluorescent sample and excite a fluorescent signal; and fluorescent correlation spectroscopy analysis is completed by collecting and analyzing the fluorescent signal. The device sequentially comprises a light source generating the radial polarized light and the tangential polarized light, a first microobjective, the medium microsphere, a sample frame provided with the fluorescent sample and a second microobjective in sequence as well as a fluorescent signal analysis processing device connected with the second microobjective; the first microobjective, the medium microsphere, the fluorescent sample and the second microobjective are located on a coaxial optical path of the radial polarized light and the tangential polarized light; and the medium microsphere is arranged on the object focal plane of the first microobjective. The method and device provided by the invention can be effectively applied to a high-concentration fluorescent molecule sample.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
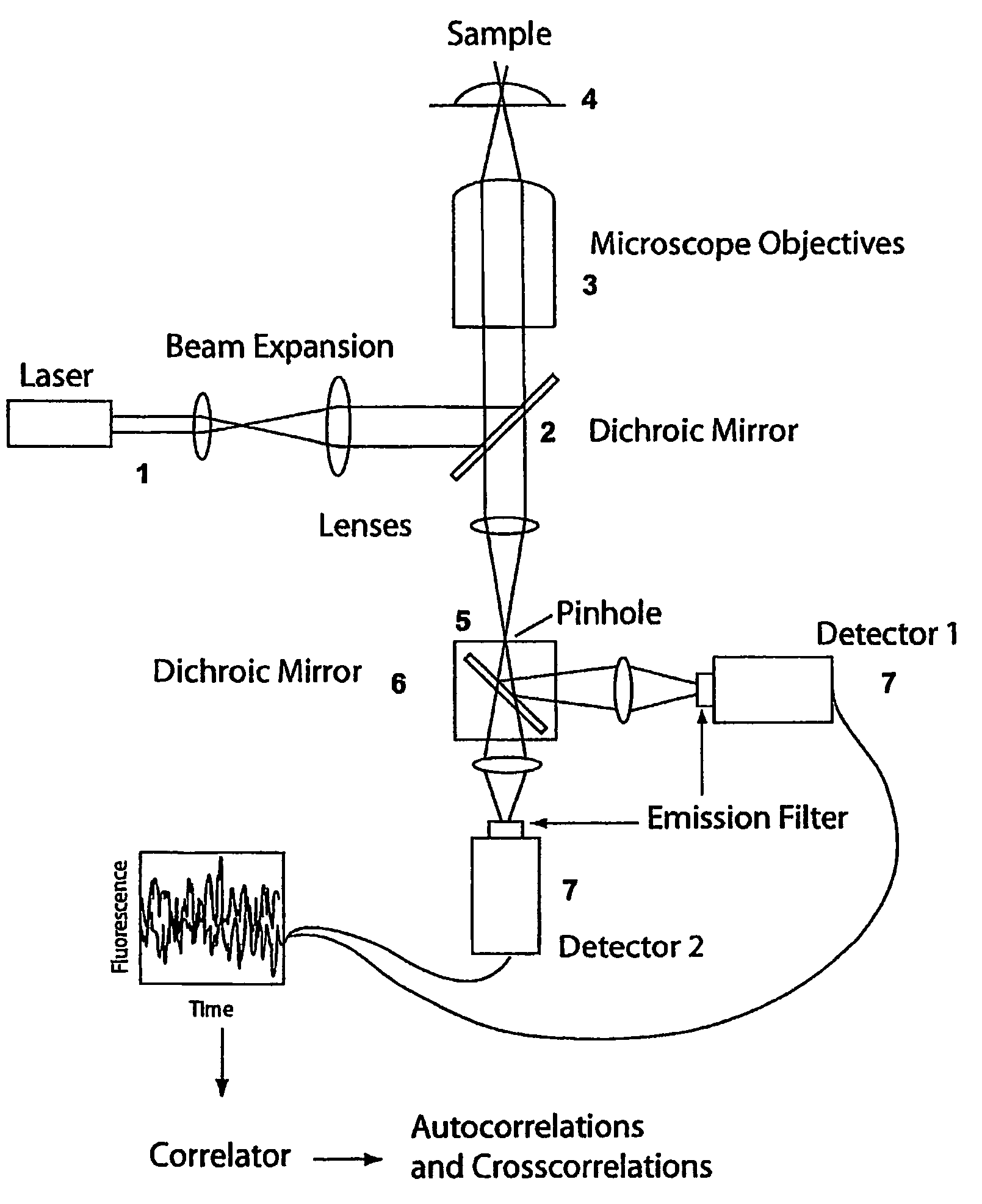
Fluorescent correalated spectrometric analysis device
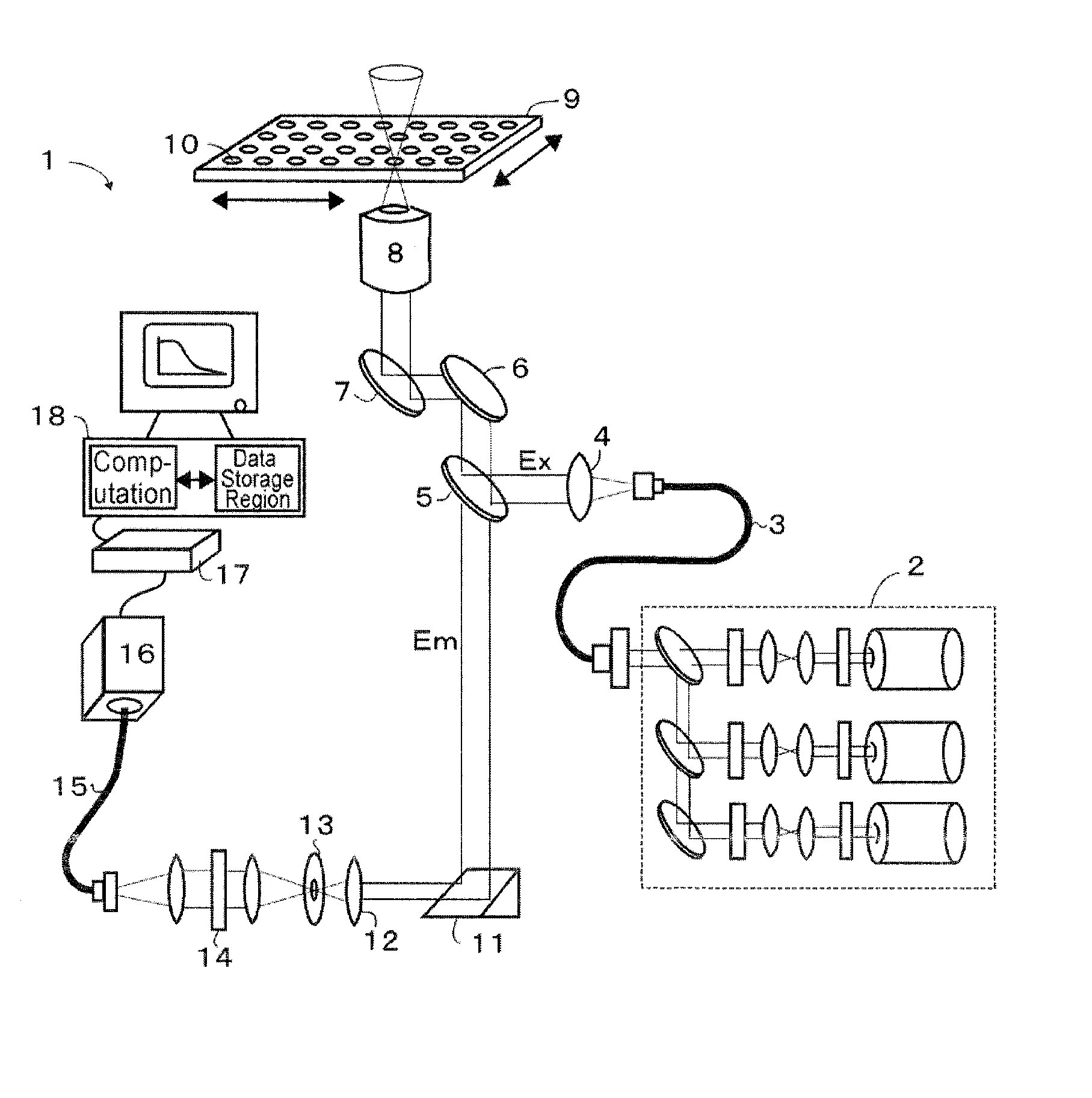
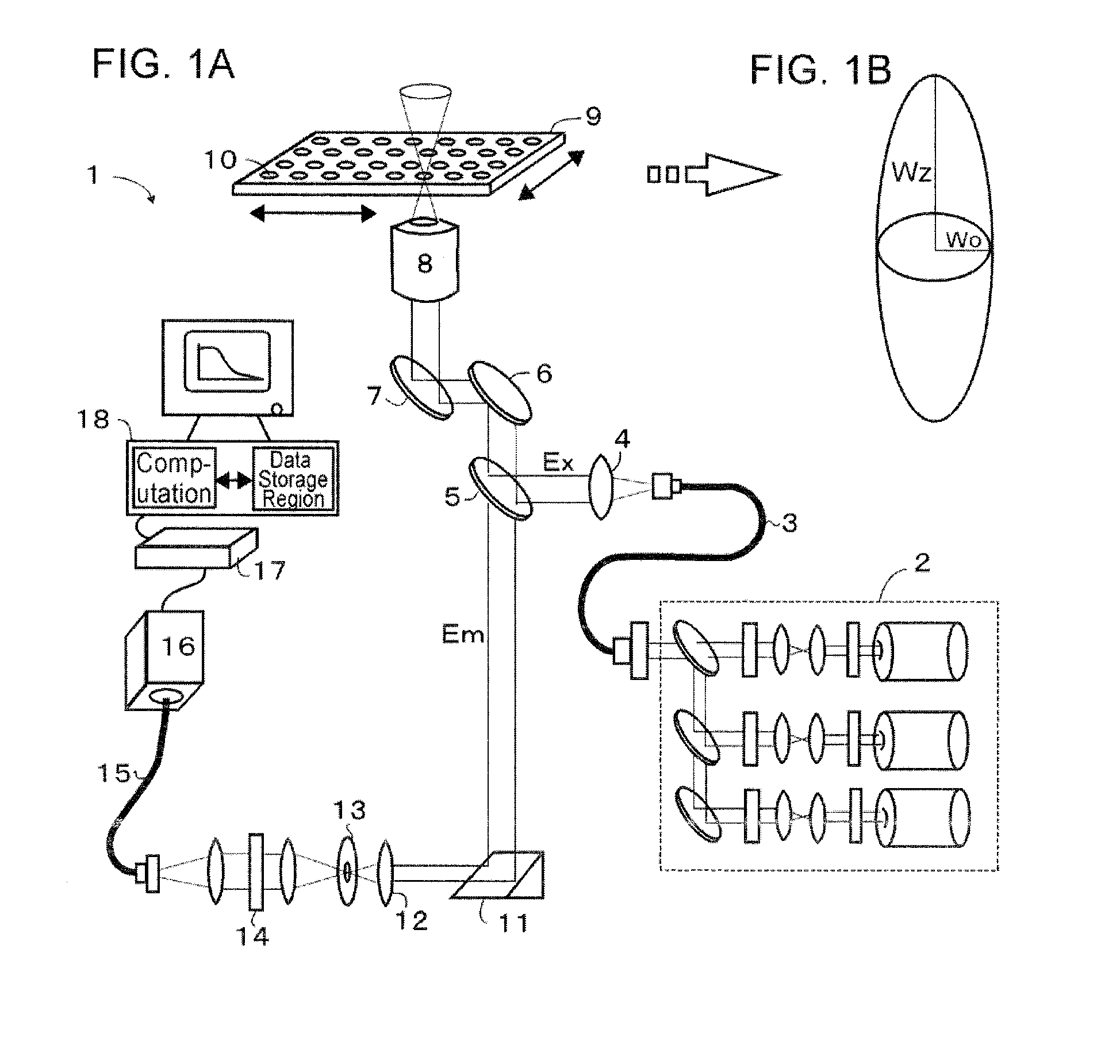
ActiveUS20060262301A1High-speed performanceIncrease speedTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryPhotoelectric conversionMultiple point
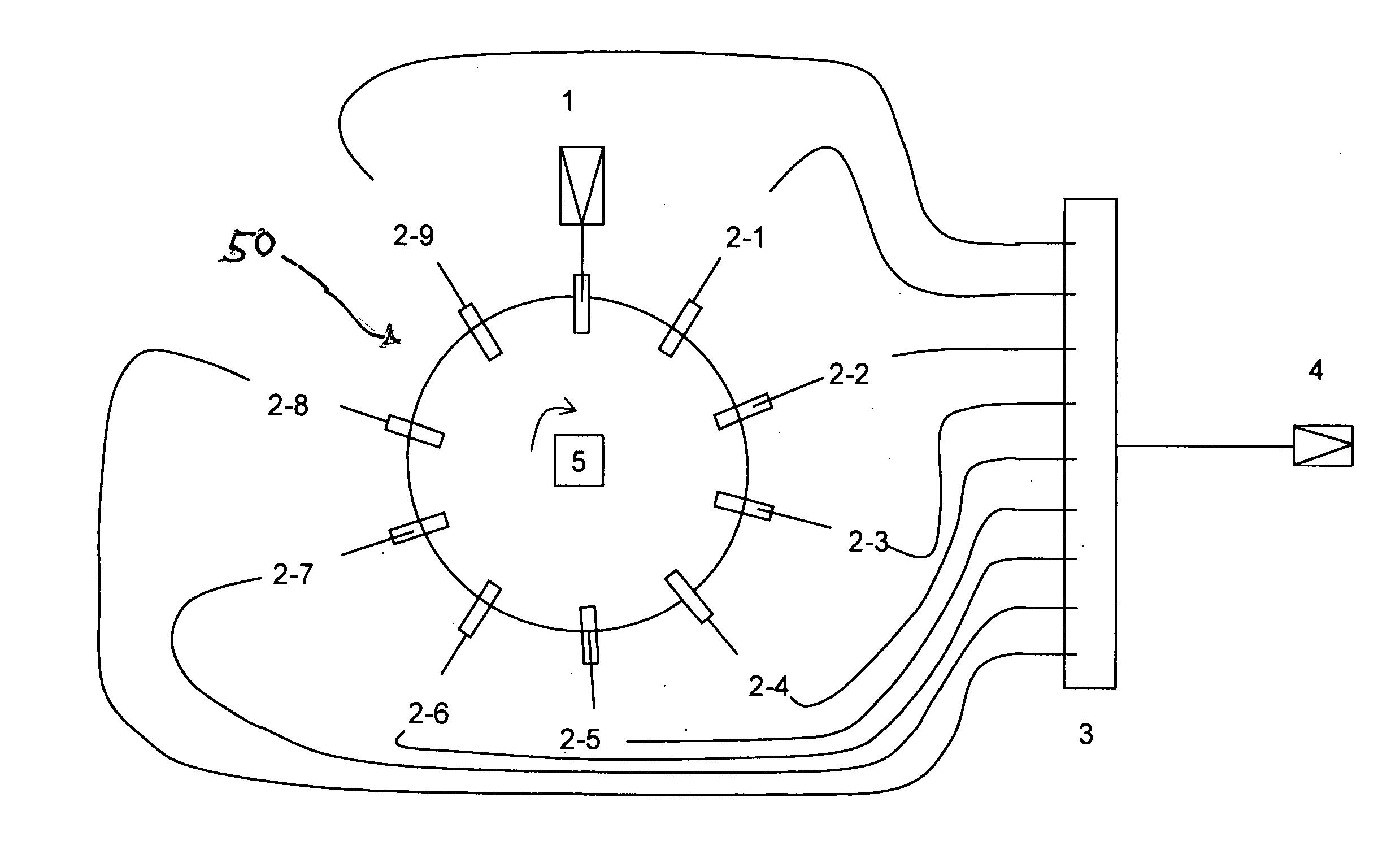
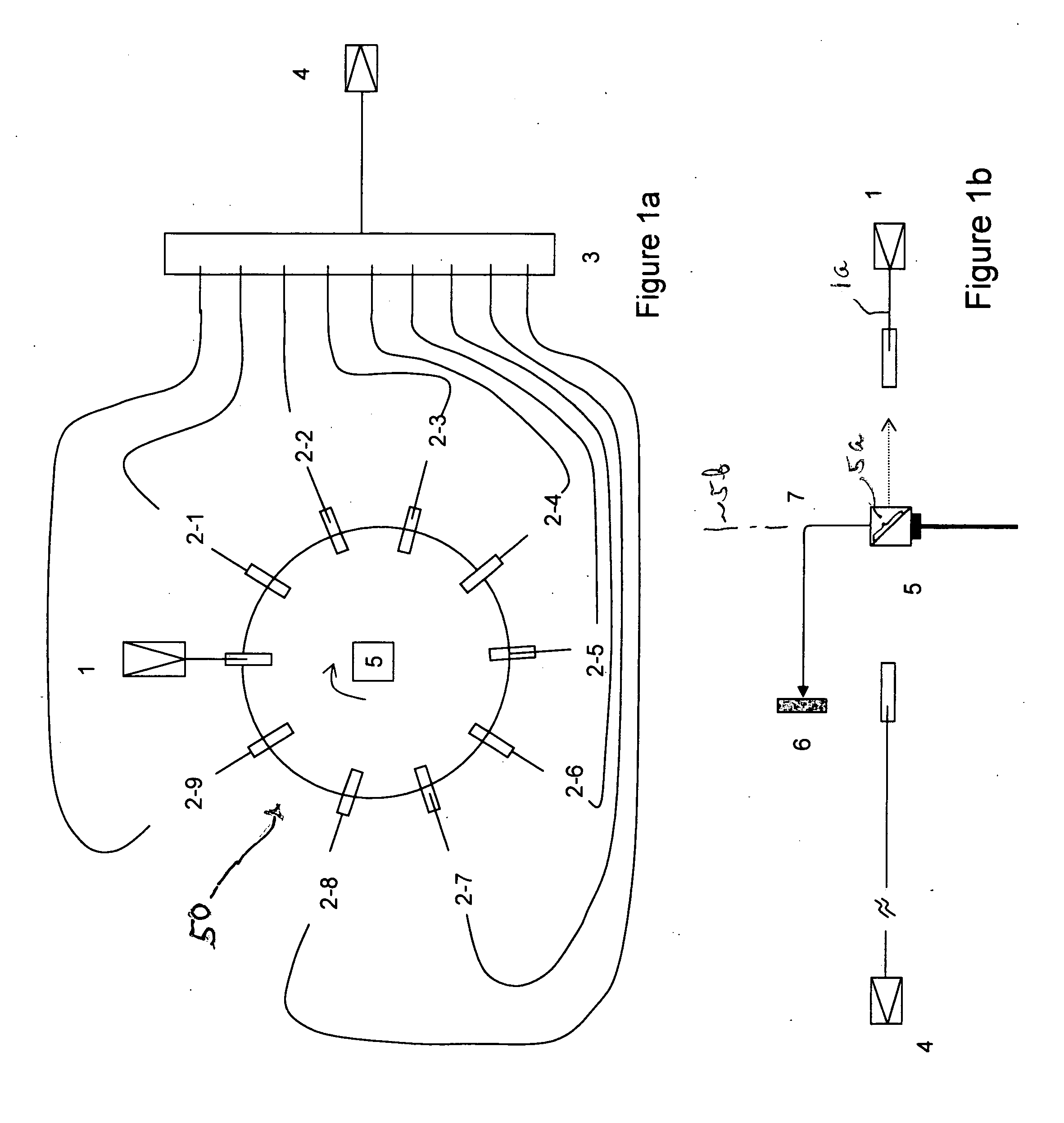
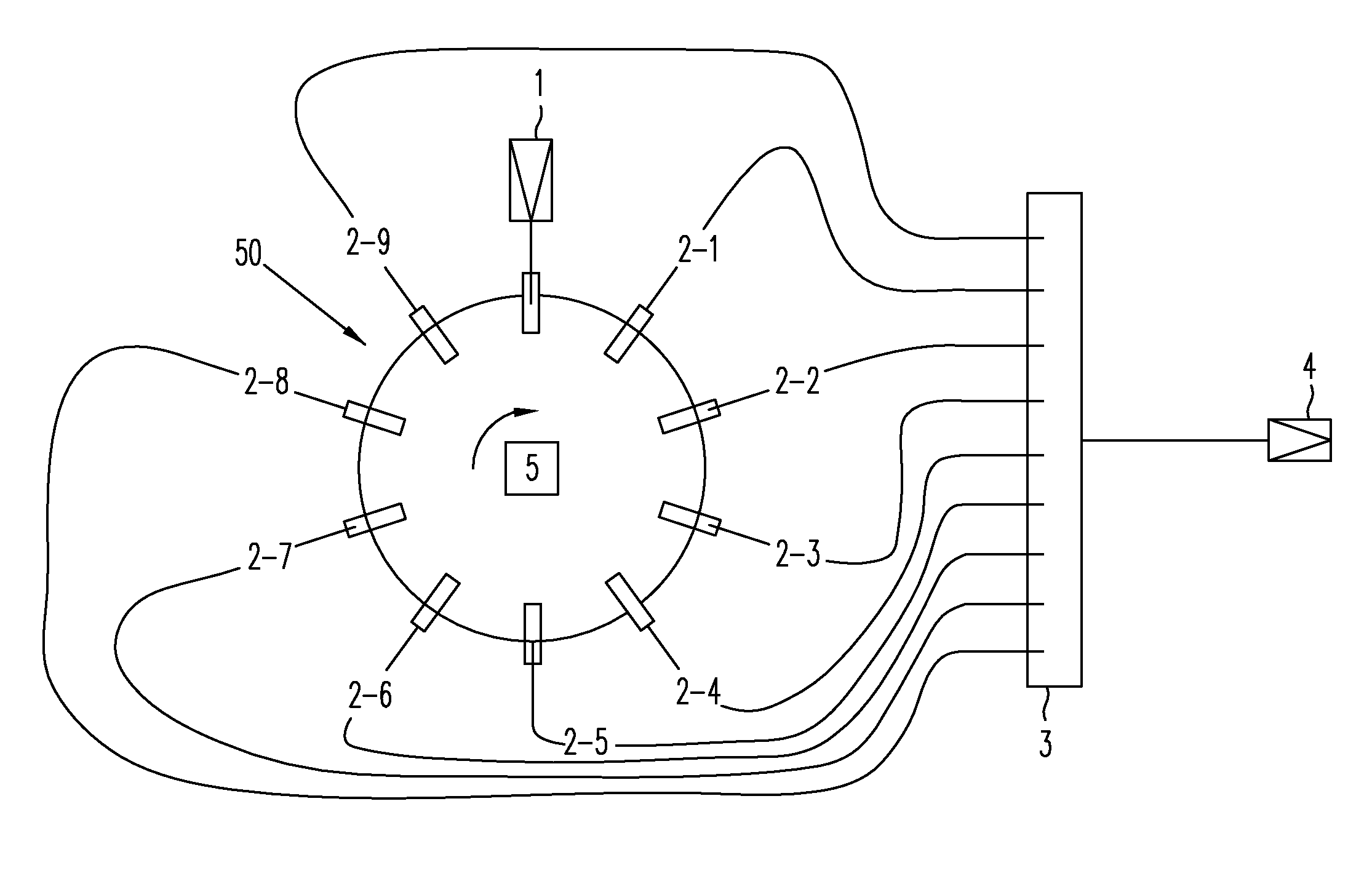
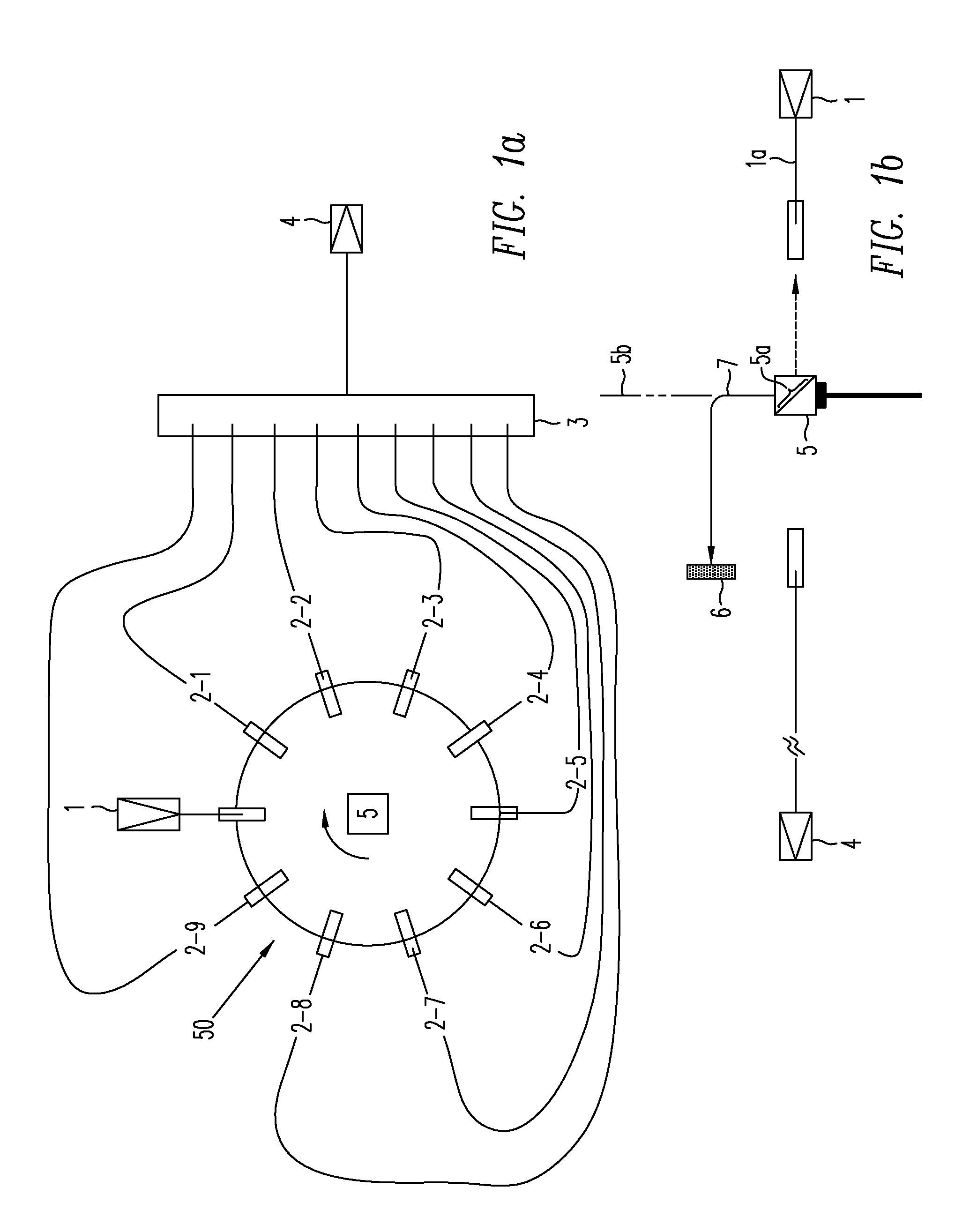
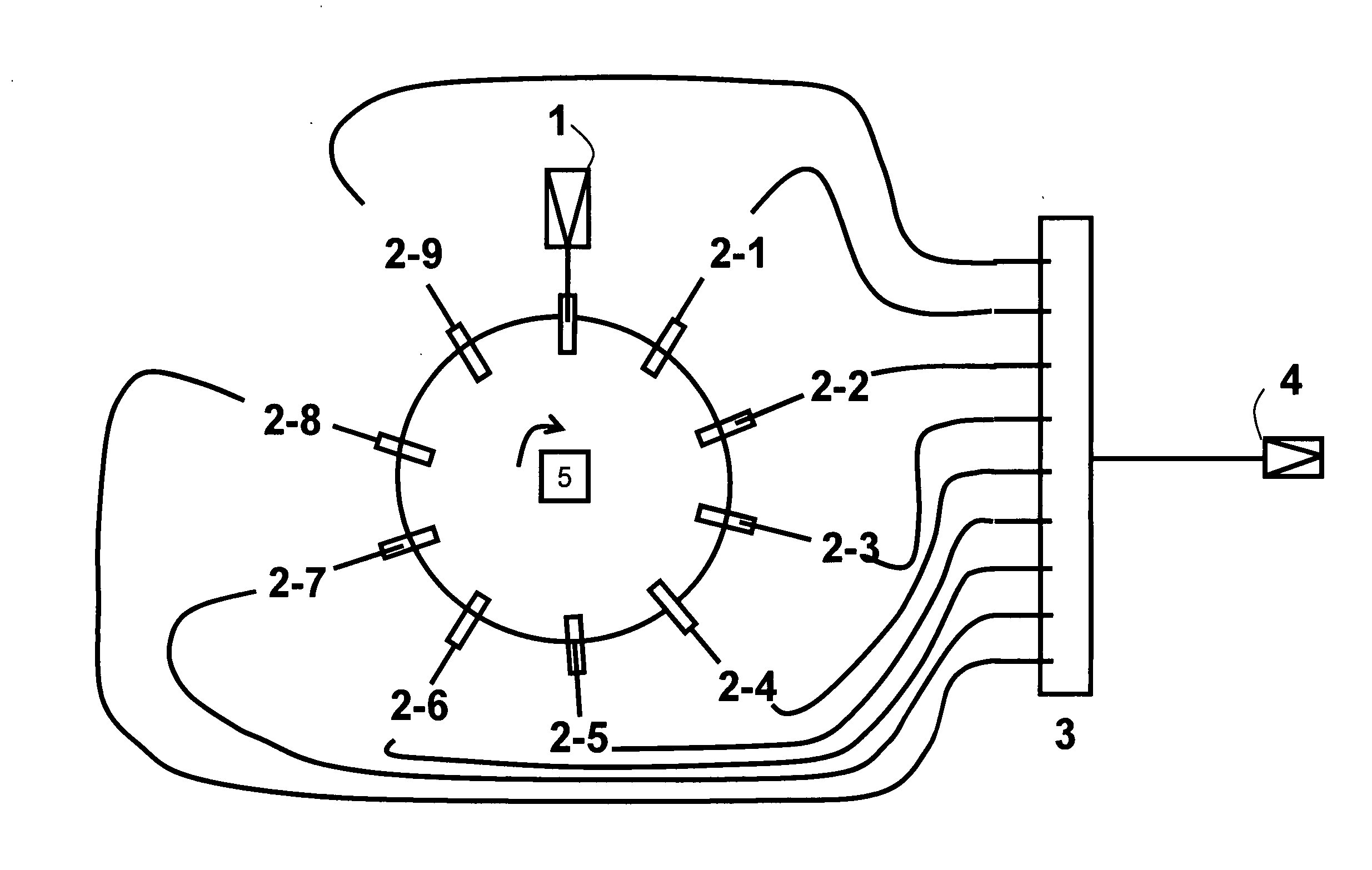
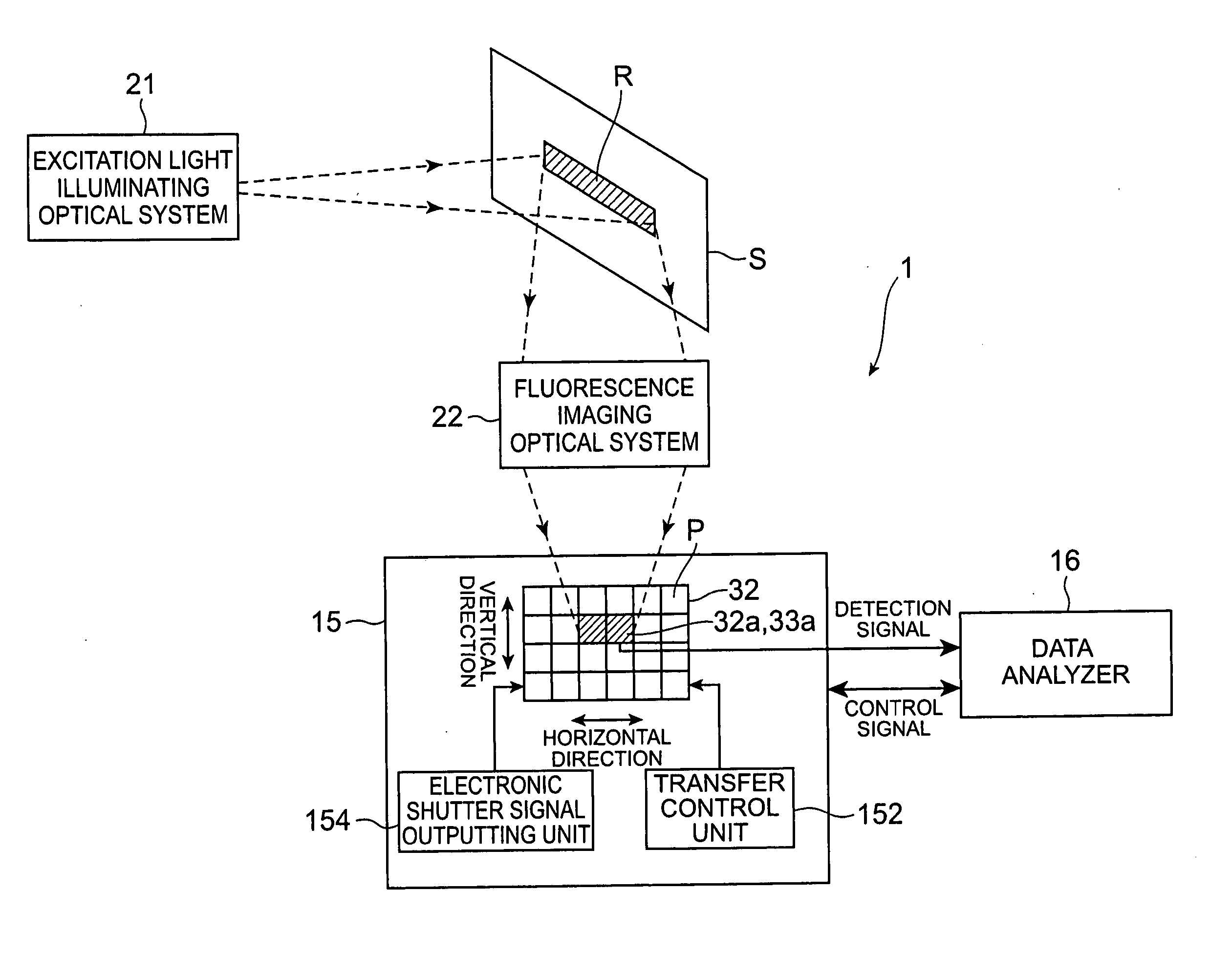
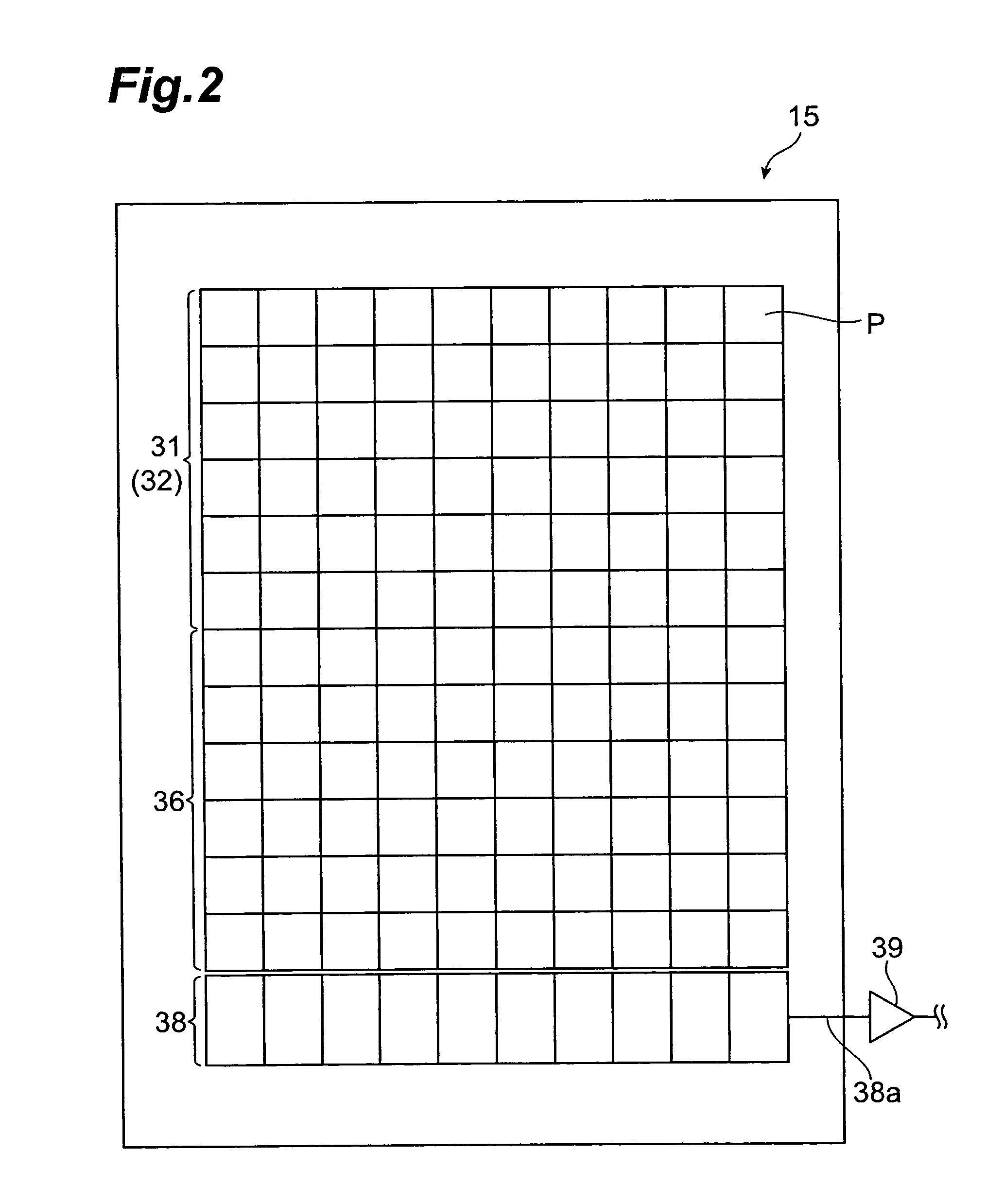
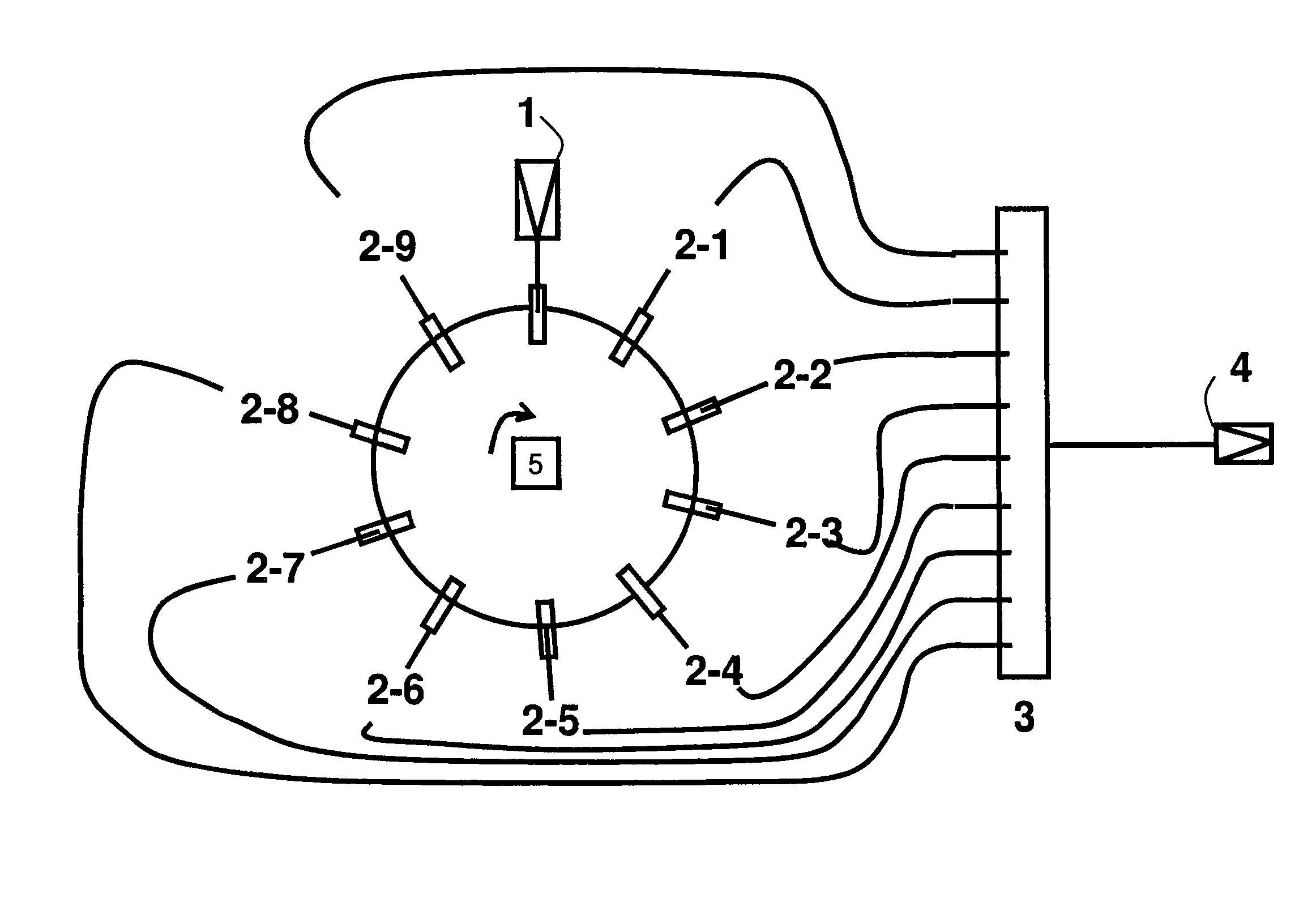
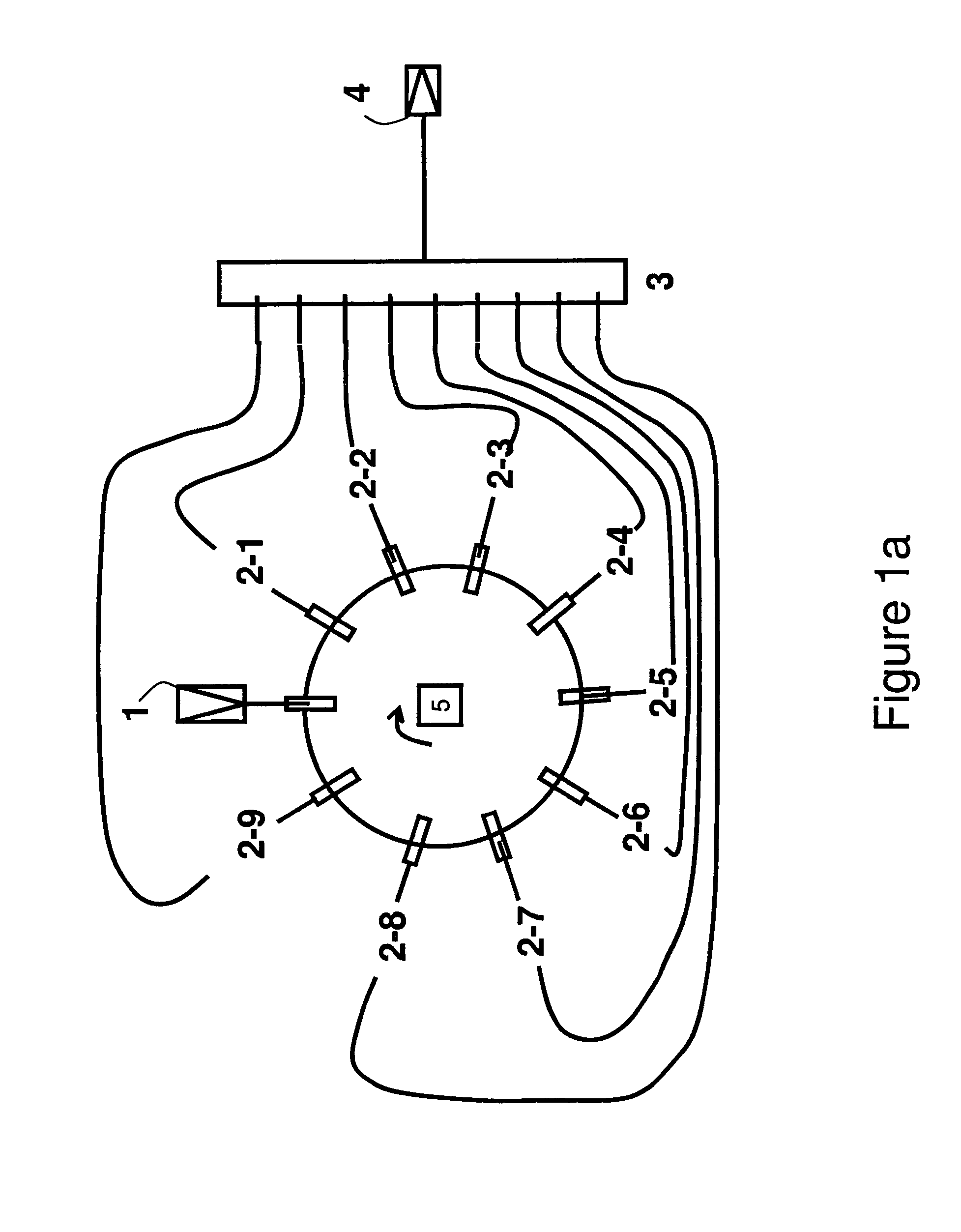
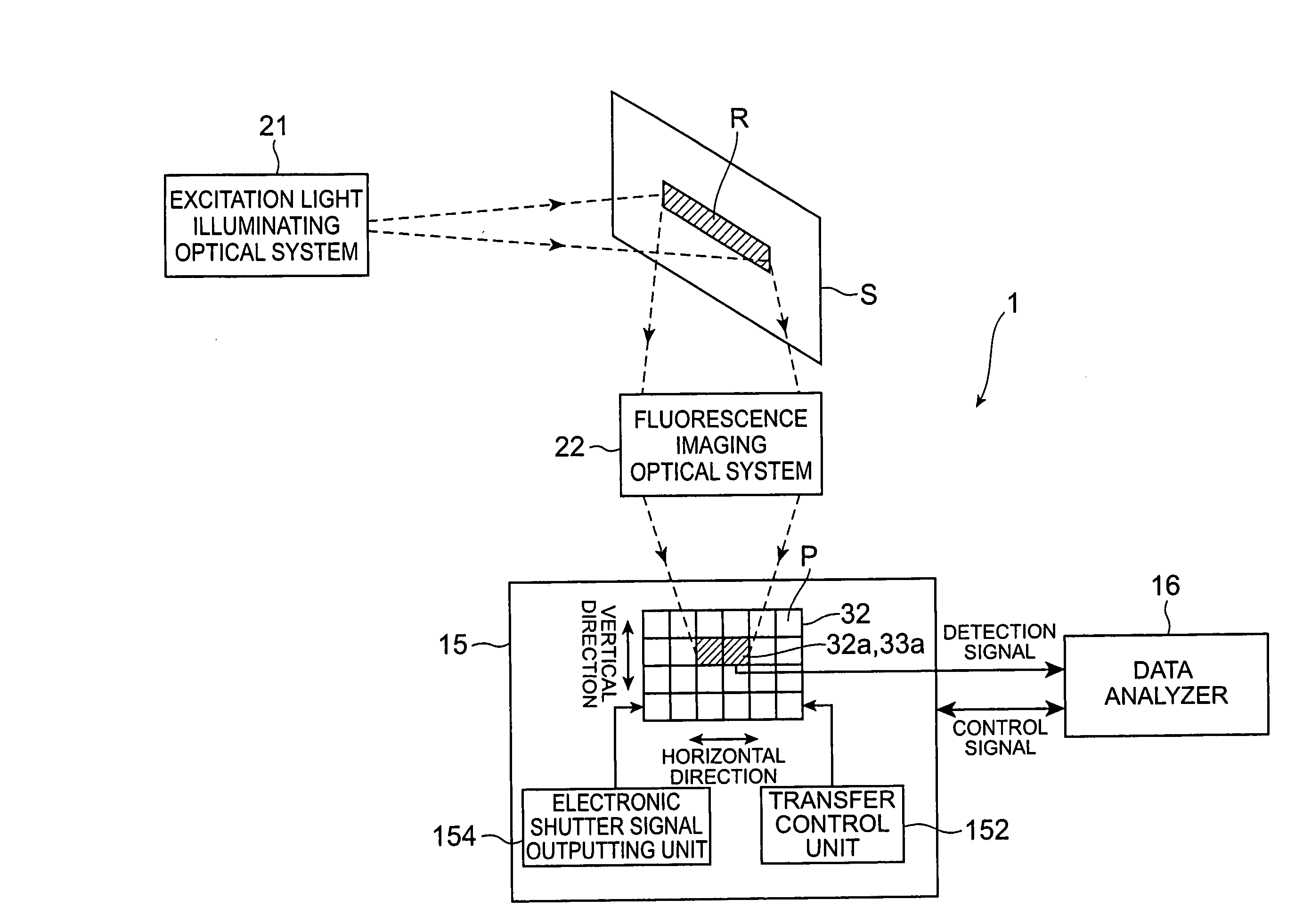
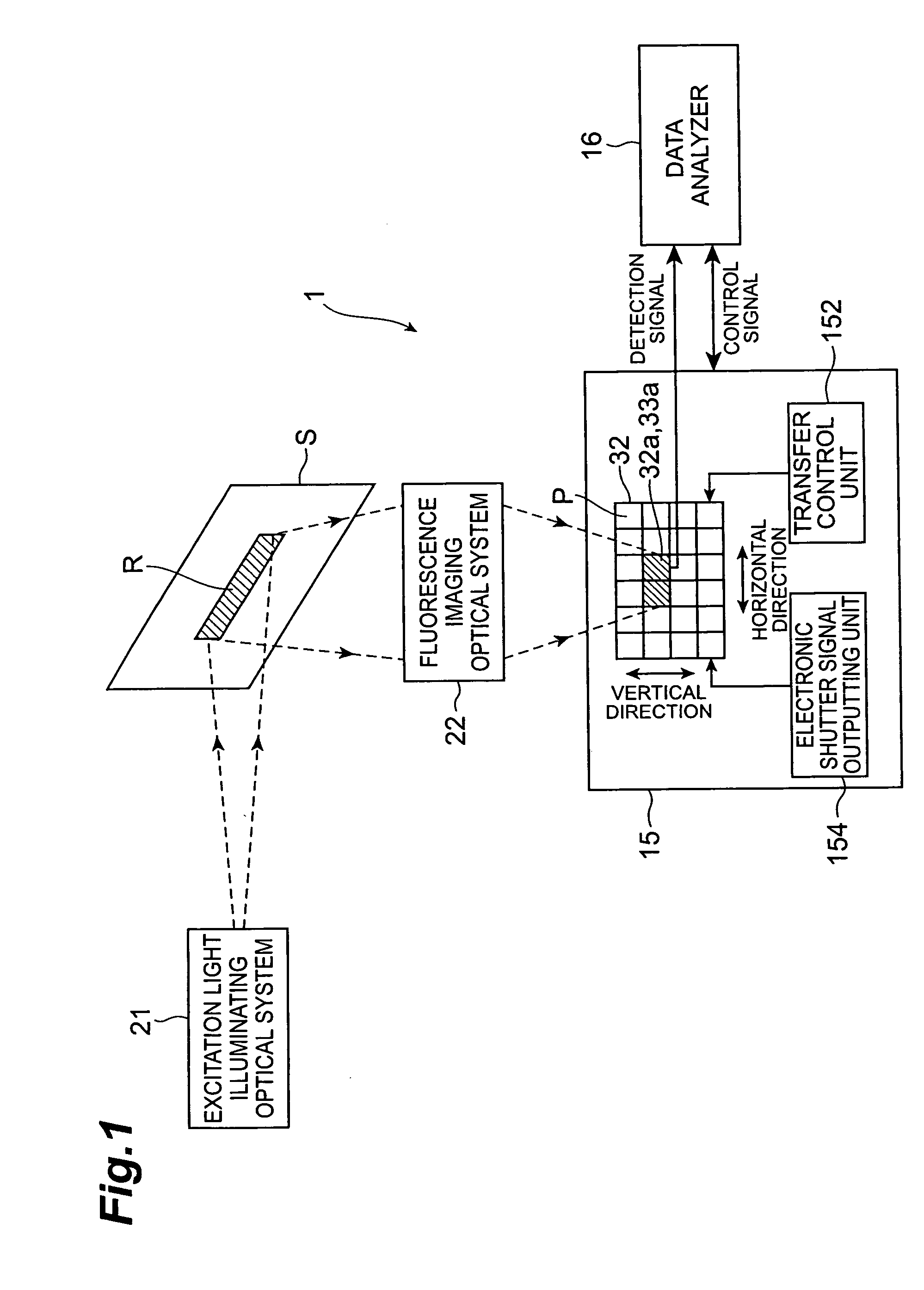
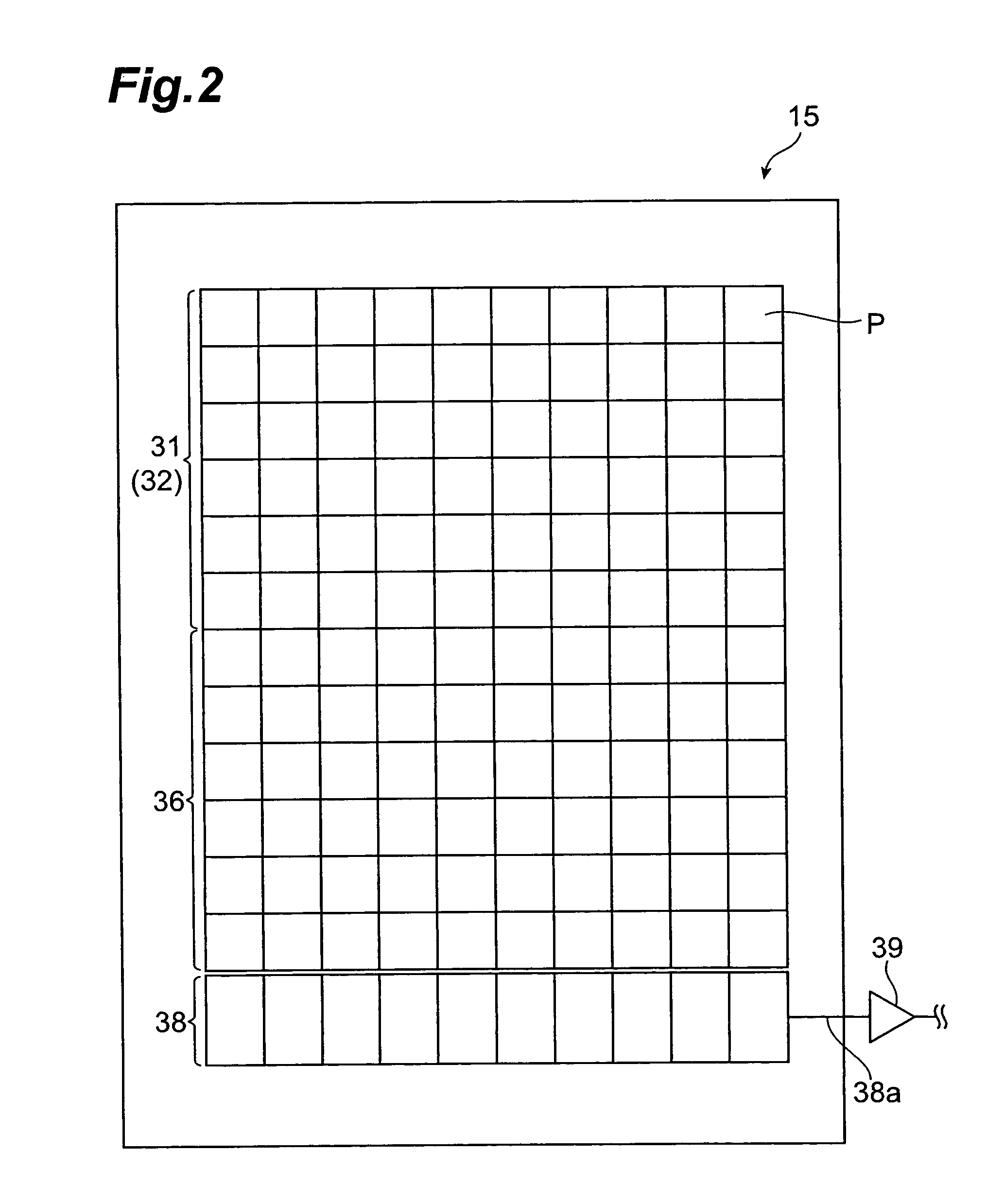
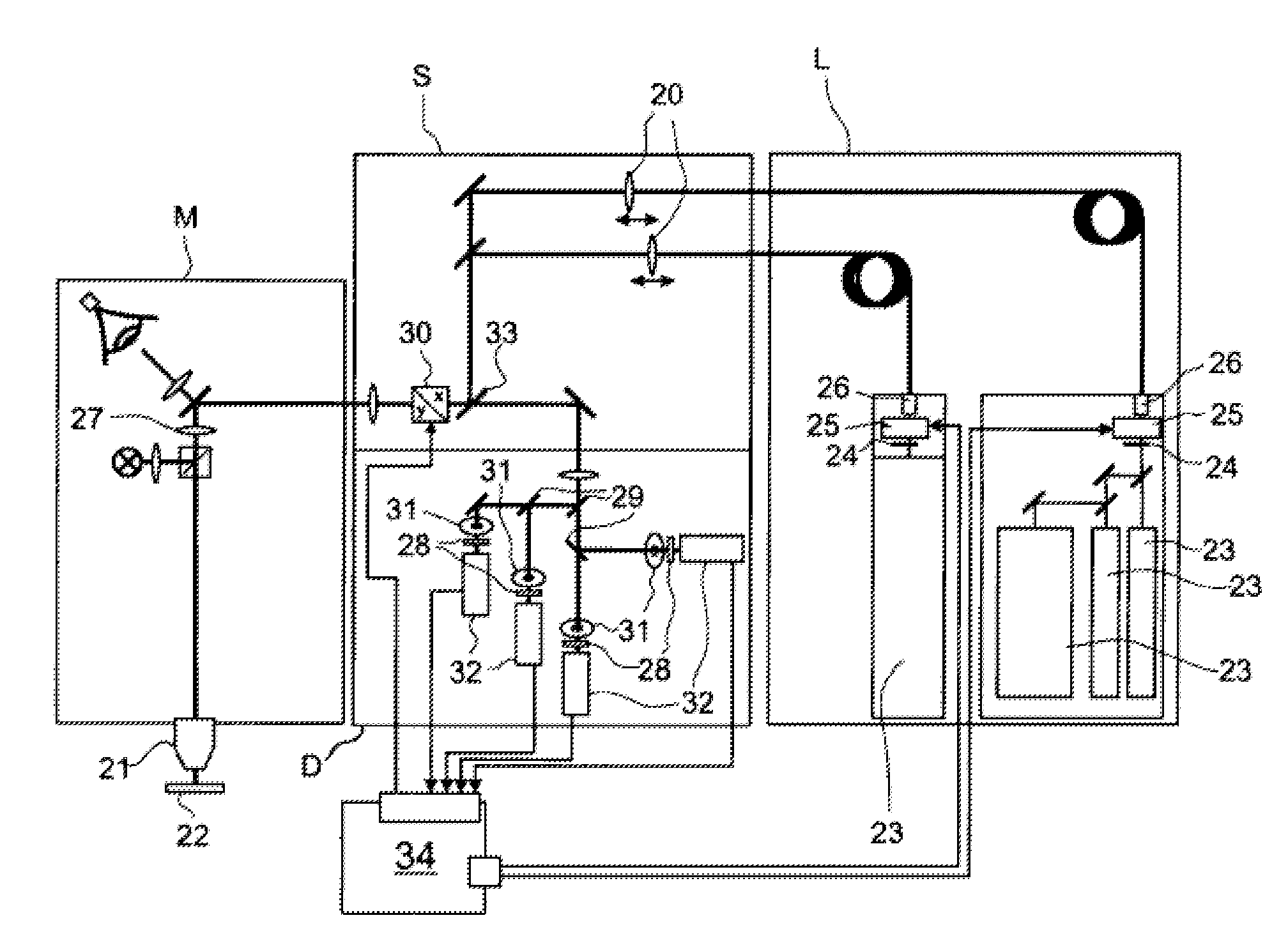
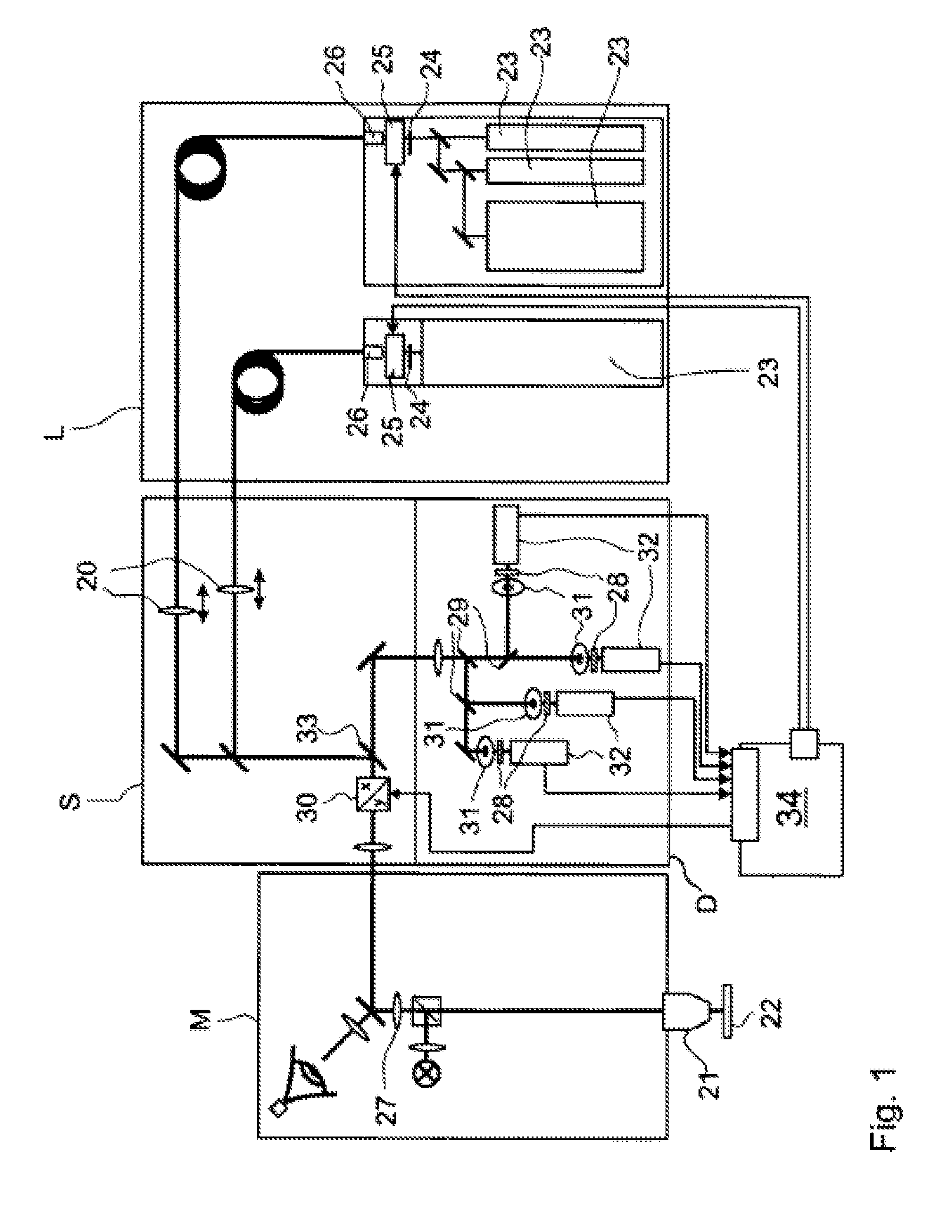
A fluorescence correlation spectroscopy analyzer 1 is equipped with an excitation light illuminating optical system 21, a fluorescence imaging optical system 22, a CCD camera 15, and a data analyzer 16. The excitation light illuminating optical system 21 illuminates excitation light onto a predetermined region of a measured sample S. The fluorescence imaging optical system 22 images the fluorescence generated at the measured sample S onto the photodetection surface of the CCD camera 15. The CCD camera 15 performs photoelectric conversion of the fluorescence made incident onto the photodetection surface in accordance with the respective pixels and outputs the charges generated by the photoelectric conversion as detection signals from an output terminal. The data analyzer 16 inputs the detection signals based on the charges generated at the pixels, among the pixels of the CCD camera 15, that belong to an analyzed pixel set and computes autocorrelation functions of the input detection signals according to each pixel. A fluorescence correlation spectroscopy analyzer, which is enabled to perform fluorescence correlation spectroscopy analysis on multiple points of a measured sample simultaneously and at high speed, is thus provided.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Inverse-fluorescence correlation spectroscopy
InactiveUS20120050734A1Increase brightnessRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationPhotomultiplierExcited molecule
A method is disclosed for analyzing particles or biomolecules in a liquid sample, including: detecting a signal and fluctuations in the signal from a detection volume in the sample; wherein the signal is generated from signal-generating molecules in the medium surrounding the particles or biomolecules and the fluctuations are transient reductions in the signal as the particles or biomolecules transit through the detection volume; and analyzing the detected fluctuations to obtain information about the particles or biomolecules in the liquid sample. At least one example embodiment of the present invention relates to a fluorescence correlation spectroscopy system including a laser, a zero-mode waveguide, guiding device for guiding the laser into the zero-mode waveguide, device for collecting fluorescence emission from excited molecules within the waveguide, a detector for detecting the fluorescence emission and means for autocorrelating the detected fluorescence signal, wherein the detector comprises a photomultiplier tube. Moreover, at least one embodiment relates to the use of a fluorescence correlation spectroscopy system for analyzing molecules of interest in a sample by detecting and analyzing fluctuations in a fluorescence signal that is generated from sample molecules surrounding the molecules of interest, wherein the fluctuations are transient reductions in the detected fluorescence signal.
Owner:WENNMALM STEFAN +1
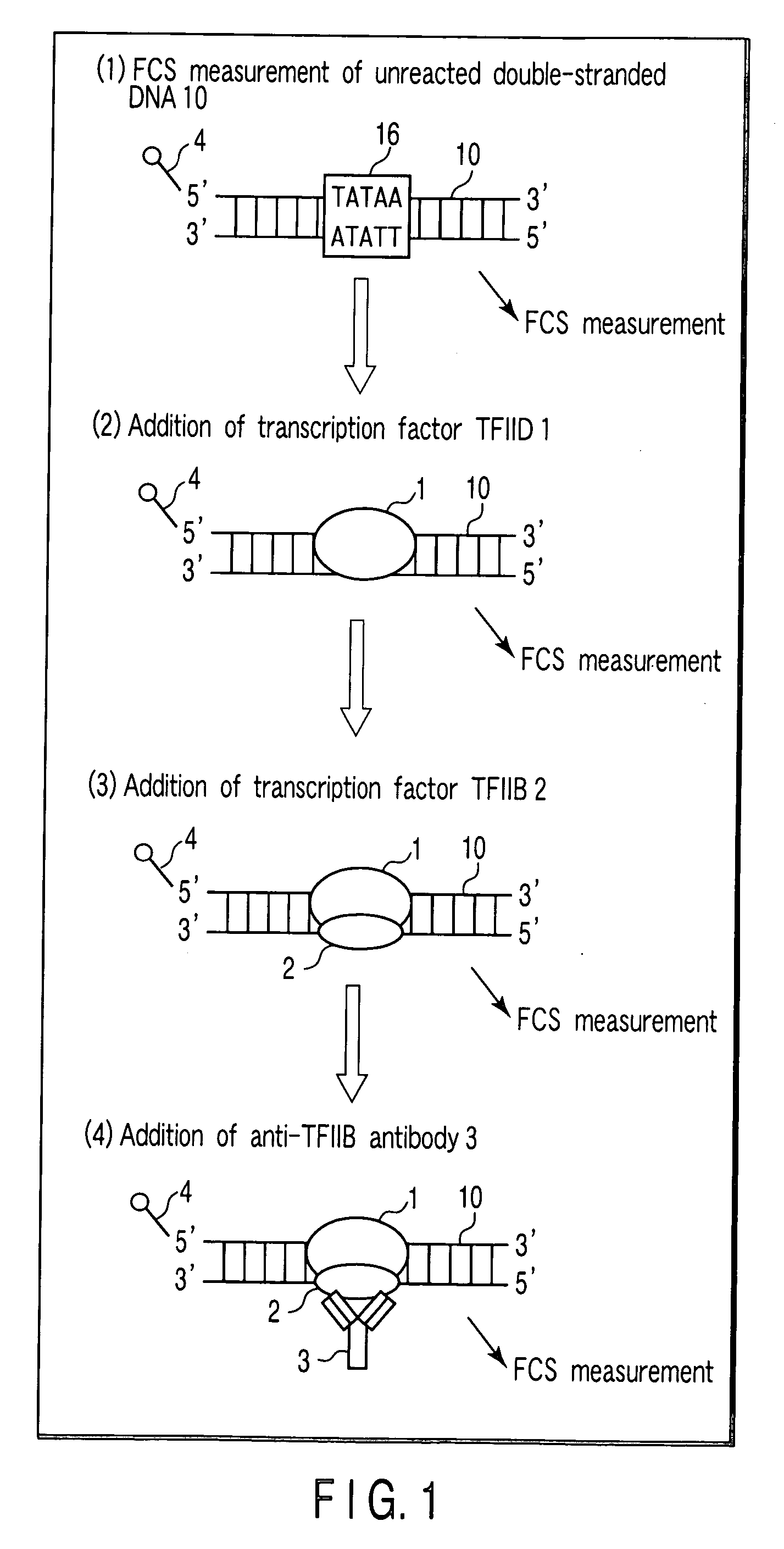
Method of detecting reaction of DNA and DNA-binding protein
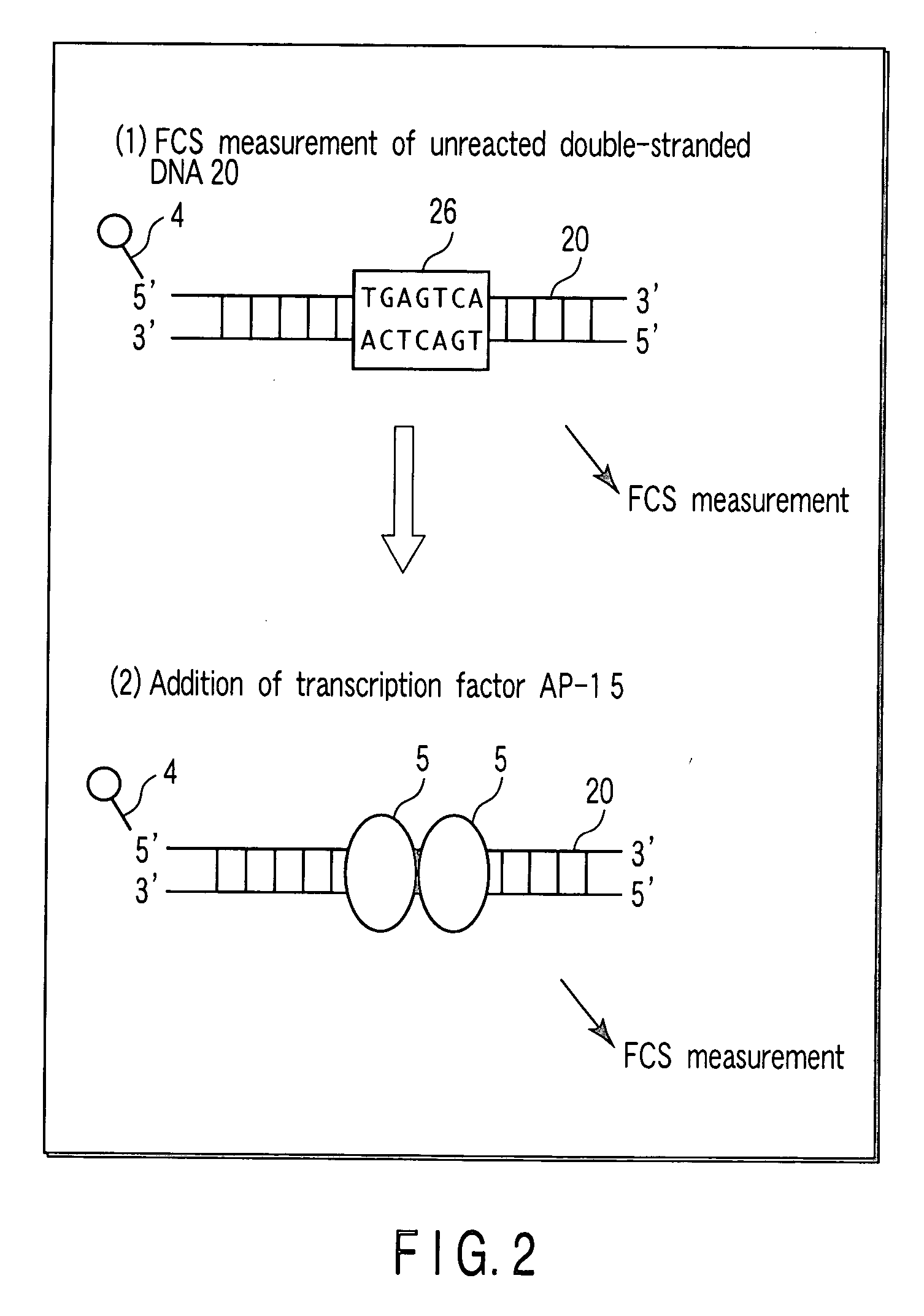
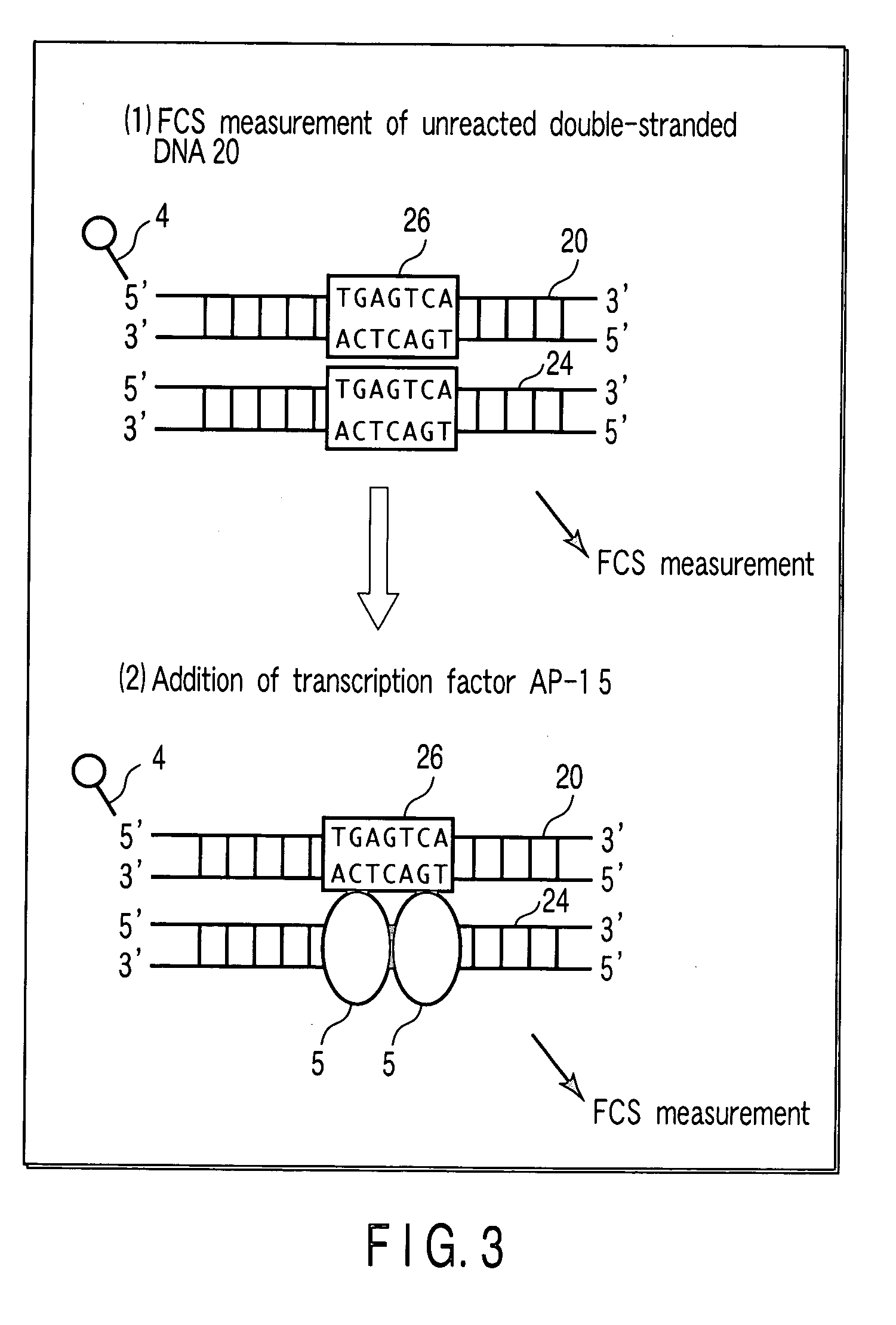
InactiveUS20060166237A1Short timeNo longer be detectedMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementDiffusionBinding site
In the case of detecting whether or not a binding site of a transcription factor TFIID and a transcription factor TFIIB is present in a labeled DNA, the presence of a binding site can be detected precisely by adding all of a transcription factor TFIID, a transcription factor TFIIB and an anti-TFIIB antibody to a DNA-containing solution, and obtaining a translational diffusion time of the binding product by FCS-measurement. Information for obtaining a translational diffusion time is obtained, by mixing the sample and measuring it by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS), and as a result, detection result can be simply obtained in a short time, without performing troublesome operation such as utilization of a radioisotope and selection by an electrophoresis method or immobilization of a molecule on a solid substrate.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Time-resolved spectroscopy system and methods for multiple-species analysis in fluorescence and cavity-ringdown applications
InactiveUS8405827B2Radiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyTime-division multiplexingLinear regression
Owner:CLAPS RICARDO
Novel hydrophilic and lipophilic rhodamines for labelling and imaging
The invention relates to novel and improved photostable rhodamine dyes of the general structural formulae I or II and their uses as fluorescent markers, e.g. for immunostainings and spectroscopic and microscopic applications, in particular in conventional and stimulated emission depletion (STED) microscopy and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. The partially deuterated analogues are useful as molecular mass distribution tags in mass spectroscopic applications. wherein R1=an unsubstituted or substituted alkyl group, including a cycloalkyl group, or heterocycloalkyl group; R2═H, an unsubstituted or substituted alkyl group, including a cycloalkyl group, or heterocycloalkyl group, or an unsubstituted or substituted aryl group or heteroaryl group, or any combination of such groups; X═CH2, C═O, C═NORa, C═NNRaNRb, CH(ORa), O, S, SO, SO2, or any other derivatives of these groups, with Ra and Rb independently being H or an organic residue, in particular an unsubstituted or substituted (cyclo) alkyl group or heterocycloalkyl group, an unsubstituted or substituted aryl group or heteroaryl group; Z=a negatively charged group with 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5 charges per anion.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Total internal reflection fluorescence apparatus
InactiveUS7330255B2Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationTotal internal reflectionHigh numerical aperture
Techniques are provided for illuminating a sample by using total internal reflection (TIR) from a diffraction limited focused annular illumination beam. The illumination forms an affected region and an overlapping confocal region that may have dimensions the below 1 μm. An adjustable diffractive optical element, for example, may create a second order Bessel profile laser beam that is focused on a sample using a high-numerical aperture objective under TIR. An evanescent field excites fluorescent biological material in the confocal region, and fluorescence from the material is analyzed in fluorescence correlation spectroscopy system.
Owner:CHICAGO UNIV OF
Donor-acceptor distance distribution measuring method based on fluorescence correlation spectroscopy
ActiveCN103983623AAccurate measurementAvoid measurement failuresFluorescence/phosphorescenceSelf correlationLaser scanning
The invention discloses a donor-acceptor distance distribution measuring method based on fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Fluorescent labeled living cells of donors and acceptors are subjected to a selective donor excitation operation through a fluorescence correlation spectroscopy module of a laser scanning confocal microscope in different laser power. A correlation card acquires photon number fluctuation signals of a donor channel and an acceptor channel to form a self-correlation curve. Energy transfer rate and energy transfer efficiency can be calculated through triplet state analysis of the self-correlation curve of the acceptors. In addition, triplet state distribution of the energy transfer rate and the energy transfer efficiency can be inverted from the self-correlation curve of the triplet state of the acceptors through a maximum entropy algorithm so that donor-to-acceptor distance distribution can be calculated. A fluorescence correlation spectrum analysis method itself is an excellent technology of measuring concentration of a dilute solution, so that the measuring method can be used for measuring donor-acceptor non-paired fluorescence resonance energy transfer efficiency and donor-acceptor non-paired distance distribution after integration items of overlap items of the spectrum being corrected with respect to the donor-acceptor concentration proportion. The measuring method is convenient to use and high in measuring precision.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
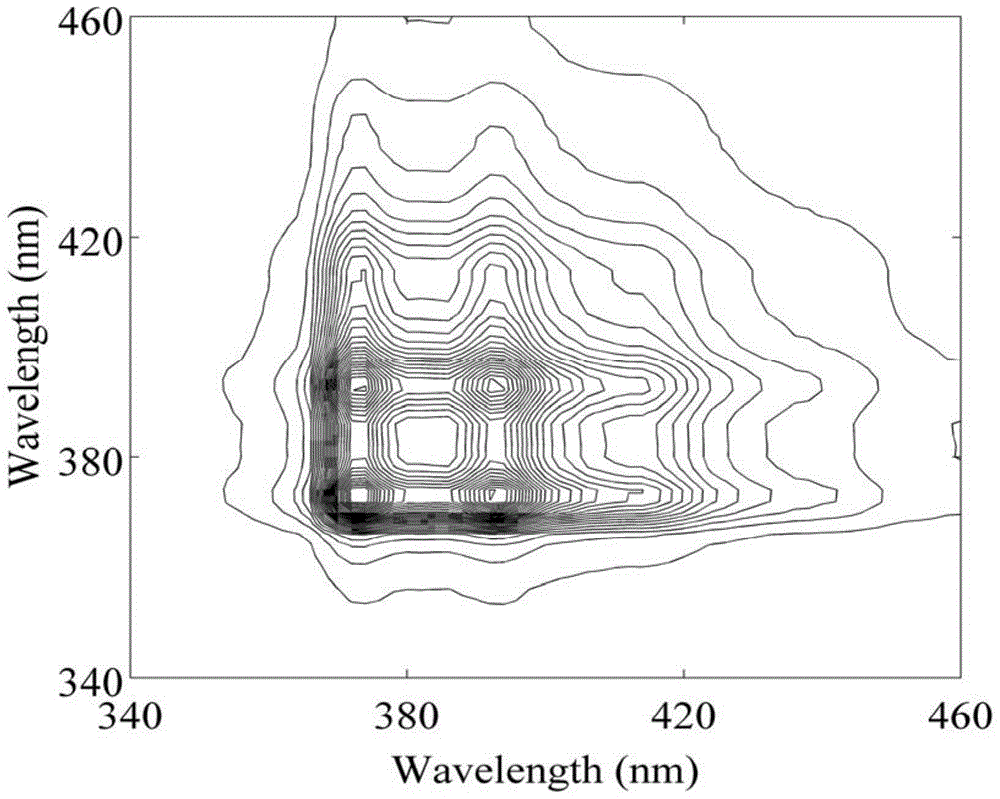
In-water polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon detection method based on two-dimensional fluorescence correlation spectroscopy
ActiveCN105675562AEfficient extractionRealize quantitative analysisFluorescence/phosphorescencePolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonAnthracene
The invention discloses an in-water polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon detection method based on two-dimensional fluorescence correlation spectroscopy.The method includes: (1) preparing mixed experimental polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon aqueous solutions of different concentrations; (2) scanning fluorescence spectrums of each mixed experimental polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon aqueous solution under different excitation wavelengths to obtain one-dimensional dynamic fluorescence spectrums; (3) adopting data of the obtained one-dimensional dynamic fluorescence spectrums to form a spectrum matrix, and carrying out two-dimensional correlation calculation to obtain a synchronous two-dimensional fluorescence correlation spectrum matrix; (4) establishing a quantitative analysis model according to the synchronous two-dimensional fluorescence correlation spectrum matrix and a concentration variable matrix of anthracene, phenanthrene and pyrene in each mixed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon aqueous solution; (5) substituting a synchronous two-dimensional fluorescence correlation spectrum of an unknown sample aqueous solution into the quantitative analysis model established at the step (4) to obtain concentrations of anthracene, phenanthrene and pyrene in the unknown sample aqueous solution.The in-water polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon detection method based on two-dimensional fluorescence correlation spectroscopy has the advantages that feature information of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon pollutants can be extracted more effectively, quantitative analysis of in-water polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is realized, and easiness in operation and high analysis efficiency and analysis precision are achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
Method for acquiring diffusive and directional movement information of single polymer molecules in shear fields
InactiveCN105675561AImprove resolutionHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceLaser lightPolymer solution
The invention discloses a method for obtaining the diffusion and directional motion information of a single polymer molecule under a shear field. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a polymer solution with a concentration below 10nM, and marking the fluorescent molecular probe on the polymer molecule; (2) irradiating the marked polymer solution with laser light while applying a shear field , to collect the emitted fluorescent signal, the diffusion and directional motion information of a single polymer molecule can be obtained; the measurement system used includes an excitation light source unit, a shear application and rheological measurement unit, an optical microscope unit and a fluorescence An associated spectral measurement unit, wherein the shear application and the bottom of the rheological measurement unit are provided with an excitation light optical window. The method of the invention can not only implement precise dynamic shearing to measure the macroscopic rheological properties of the polymer solution, but also can study the microscopic physical image of the polymer solution from the perspective of single molecules.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method of quickly detecting and/or assaying antigen by fluorescence correlation spectrometry
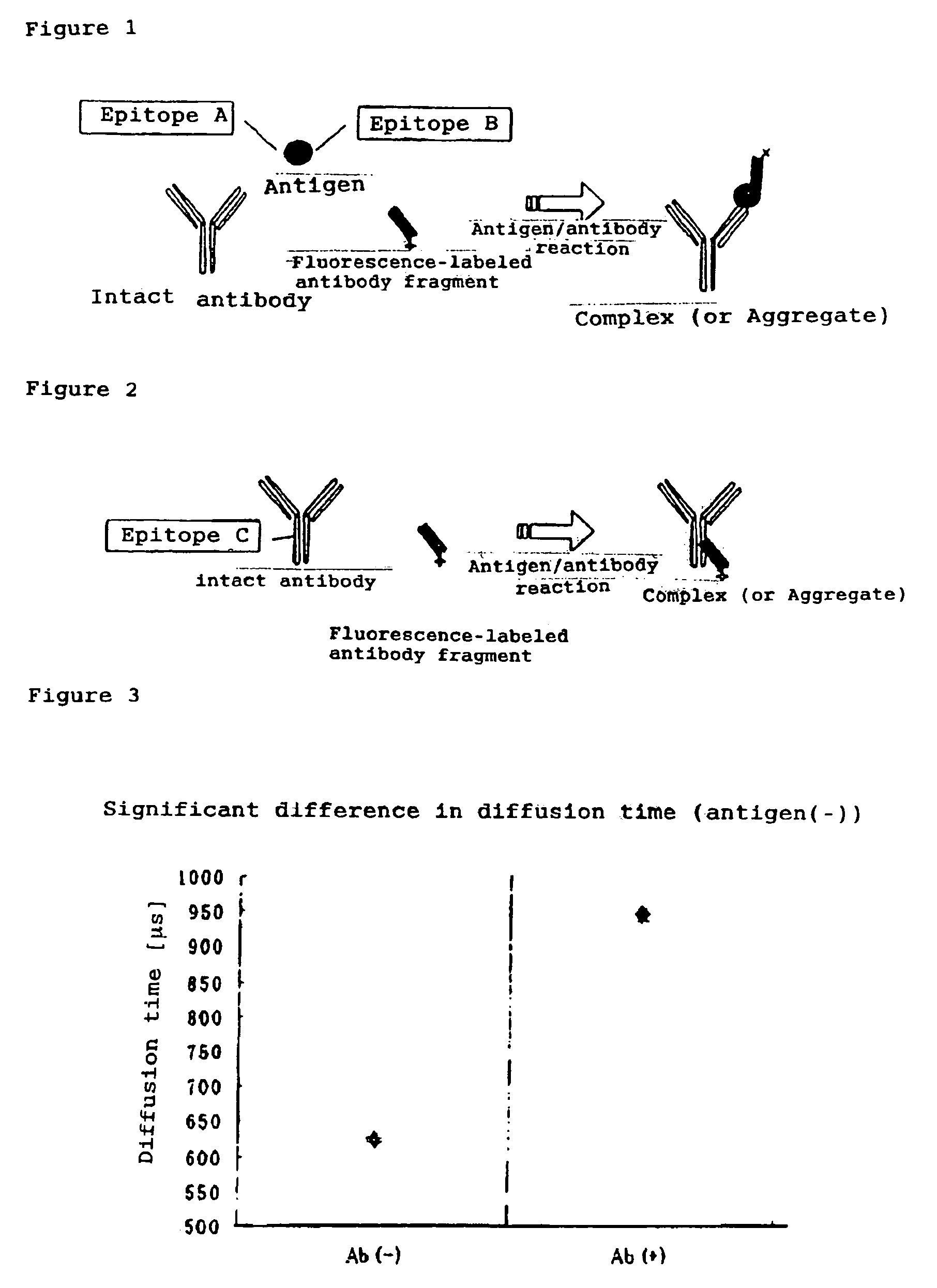
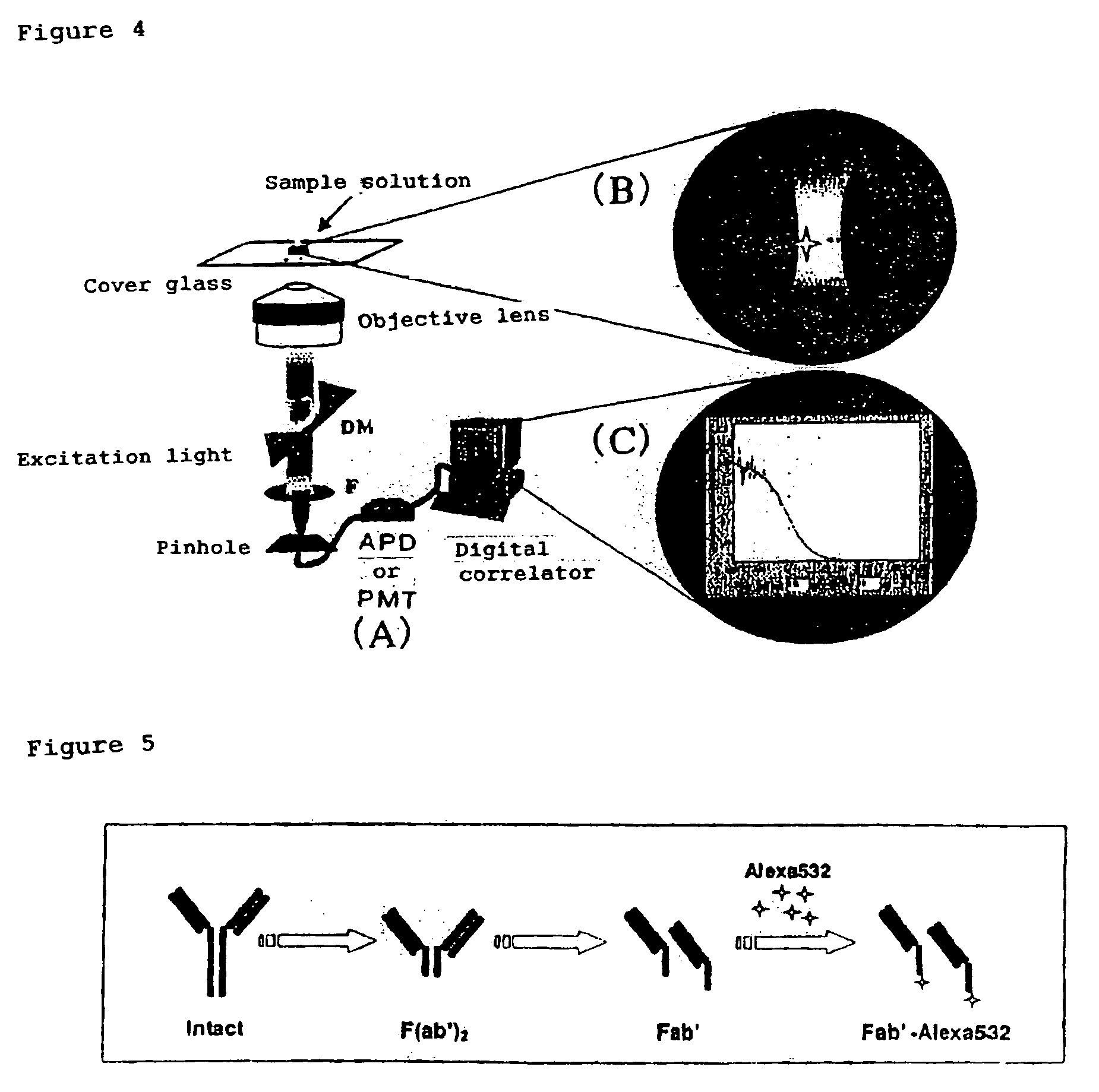
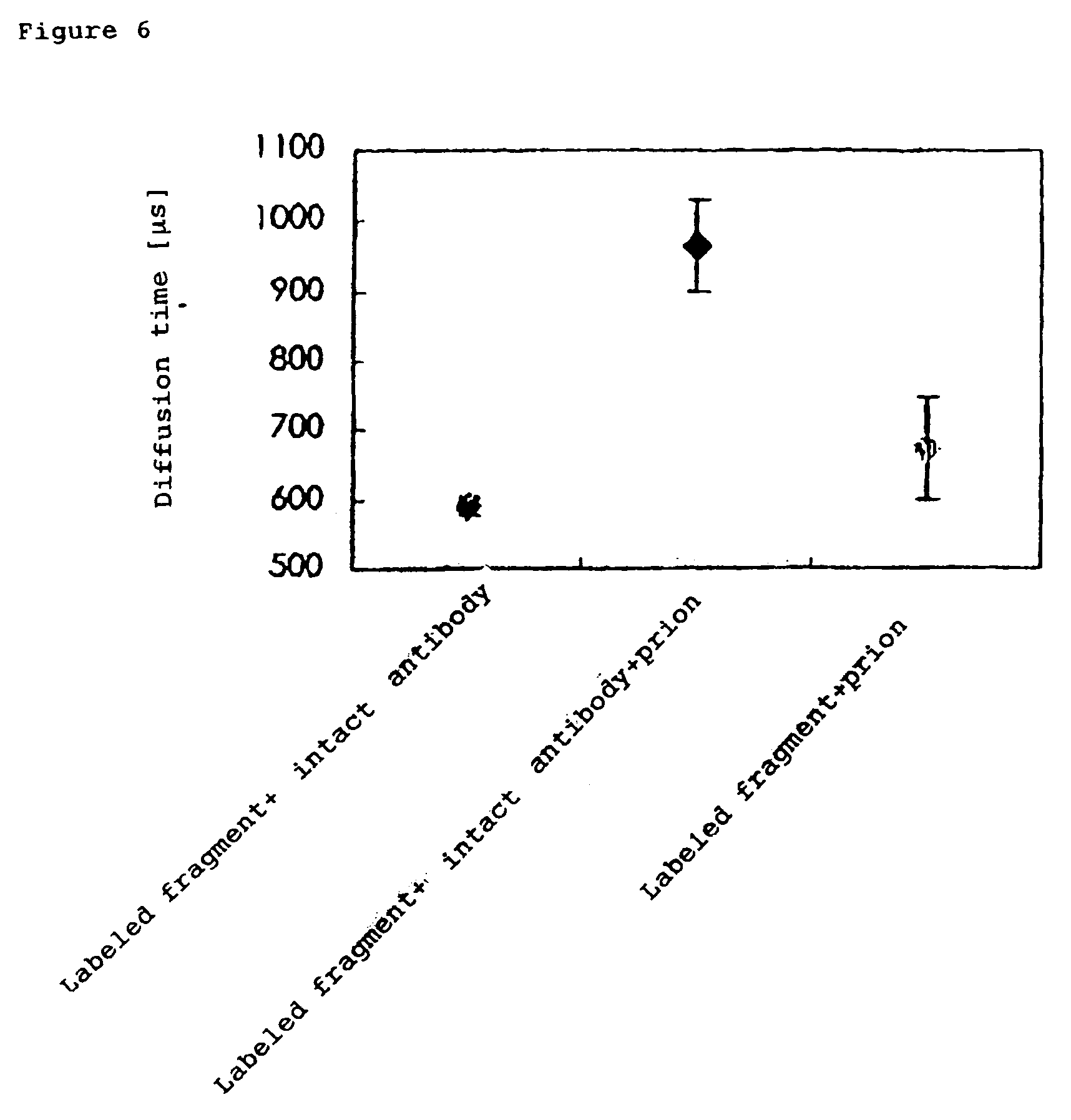
InactiveUS7476545B2Quick and convenient methodAvoid narrow scopeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAntibody fragmentsAntigen binding
The present invention provides a method of quickly and accurately detecting and / or assaying an antigen using fluorescence correlation spectroscopy (FCS), which involves a fluorescence-labeled antibody fragment and a non-fluorescence-labeled intact antibody that form a complex with the antigen. There is a significant difference in diffusion rate between the fluorescence-labeled antibody fragment not bonded to the antigen and the complex formed by the the fluorescence-labeled antibody fragment, the antigen, and the non-fluorescence-labeled intact antibody, and this diffusion rate can be determined using FCS. The antigen can be an antigenic protein, such as an abnormal prion or a harmful protein contained in a food material. According to this method, antigens over a wide scope can be assayed regardless of the shape or molecular weight.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Fluorescent correalated spectrometric analysis device
ActiveUS7400396B2High-speed performanceIncrease speedTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryPhotoelectric conversionFluorescent imaging
A fluorescence correlation spectroscopy analyzer 1 is equipped with an excitation light illuminating optical system 21, a fluorescence imaging optical system 22, a CCD camera 15, and a data analyzer 16. The excitation light illuminating optical system 21 illuminates excitation light onto a predetermined region of a measured sample S. The fluorescence imaging optical system 22 images the fluorescence generated at the measured sample S onto the photodetection surface of the CCD camera 15. The CCD camera 15 performs photoelectric conversion of the fluorescence made incident onto the photodetection surface in accordance with the respective pixels and outputs the charges generated by the photoelectric conversion as detection signals from an output terminal. The data analyzer 16 inputs the detection signals based on the charges generated at the pixels, and computes autocorrelation functions of the input detection signals according to each pixel.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy system for analyzing particles in a medium
InactiveUS20120228518A1Low production costSingle-molecule sensitivityRaman/scattering spectroscopyLuminescent dosimetersParticle physicsWaveguide
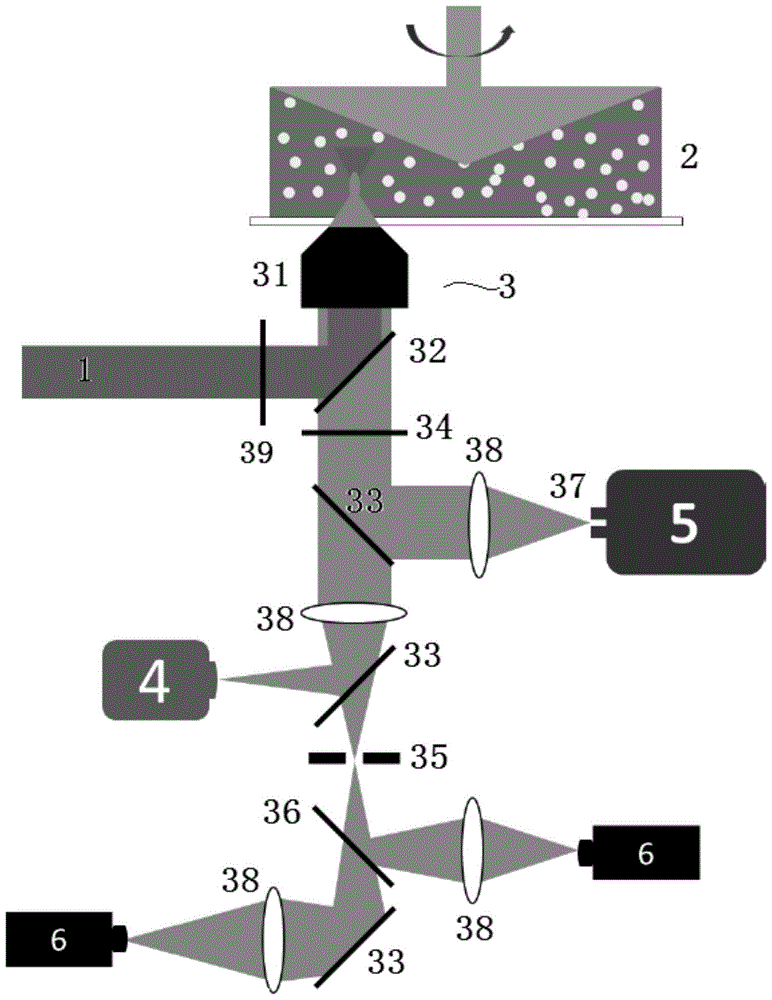
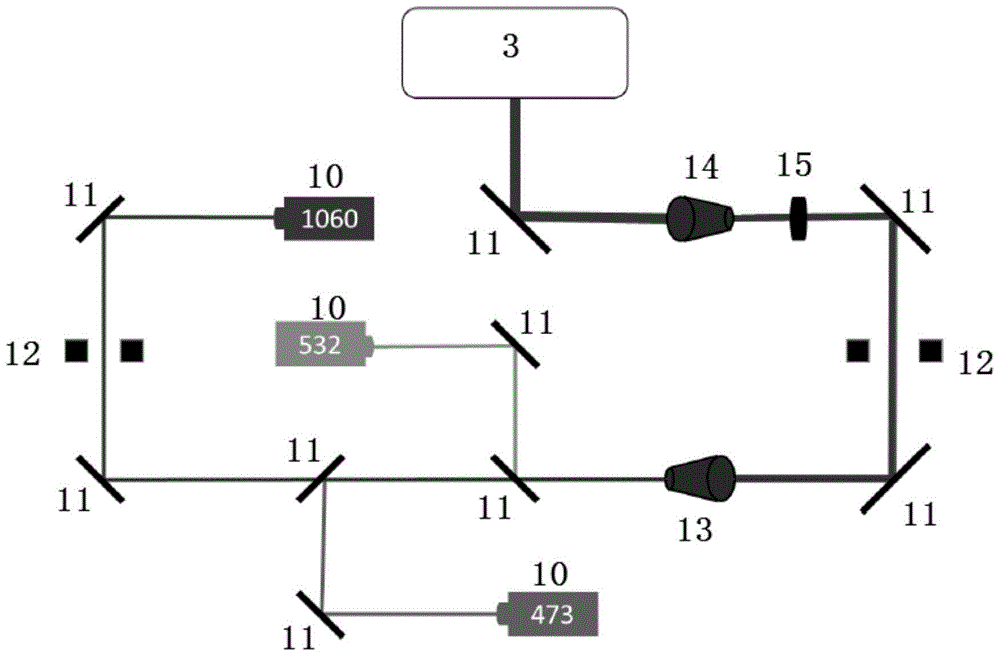
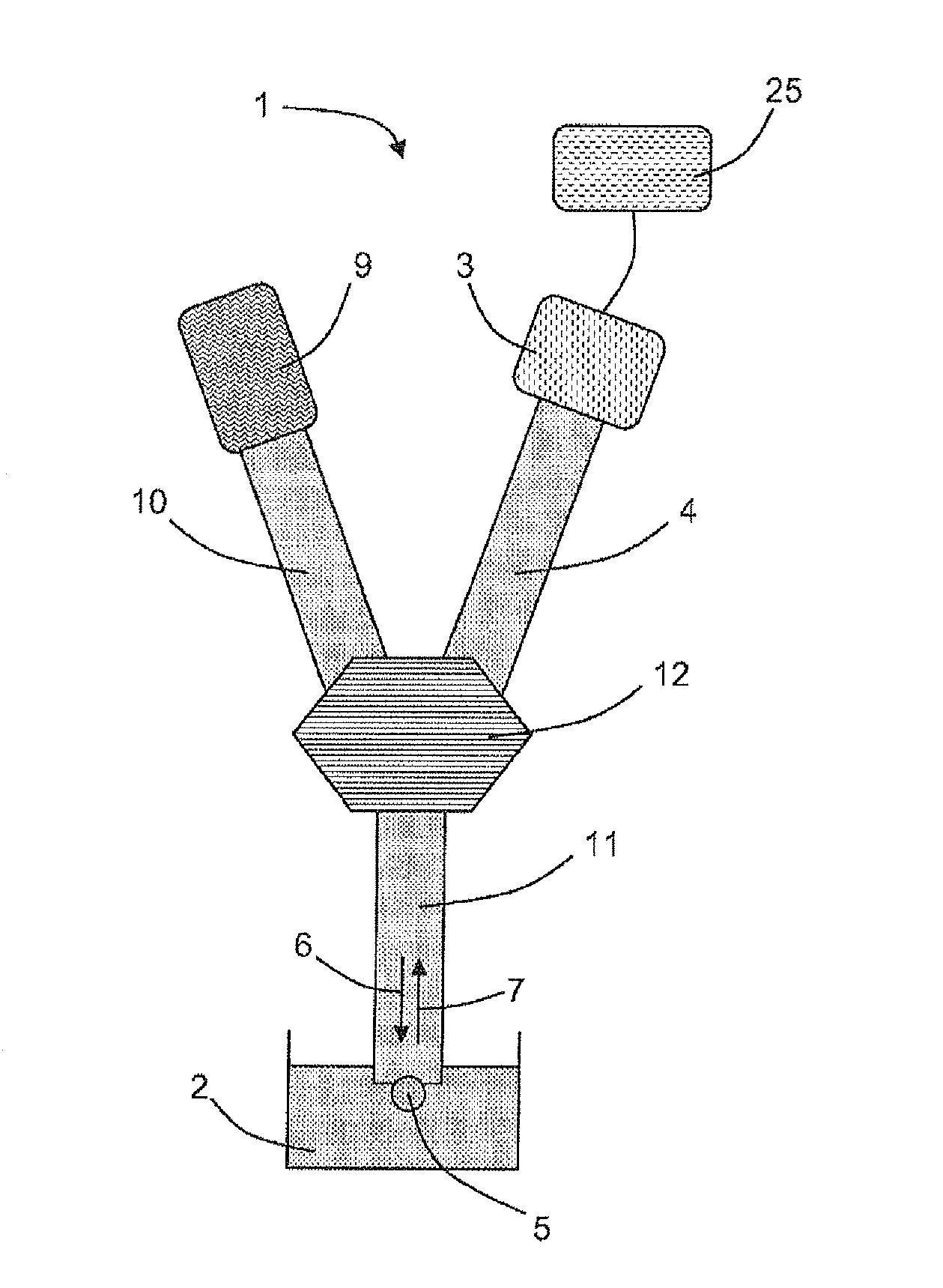
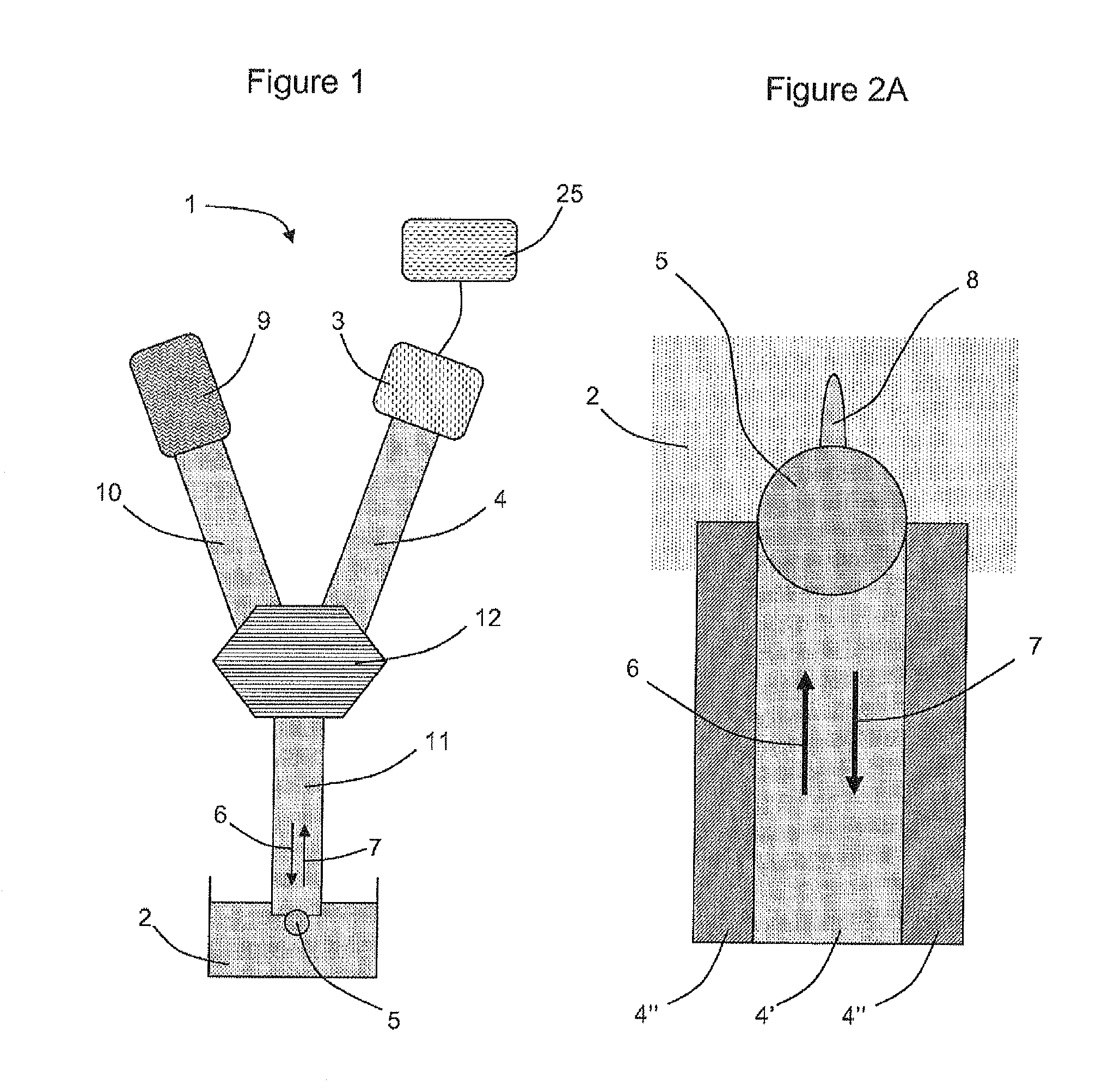
The present invention relates to a fluorescence correlation spectroscopy system (1) for analyzing particles in a medium (2), including a means (3) for detecting the light (7) emitted by the particles in the medium (2), said means (3) being coupled to a waveguide (4), for which purpose the end piece of the guide (4) comprises a means (4b; 5) for confining the light (7) injected into the guide (4).
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
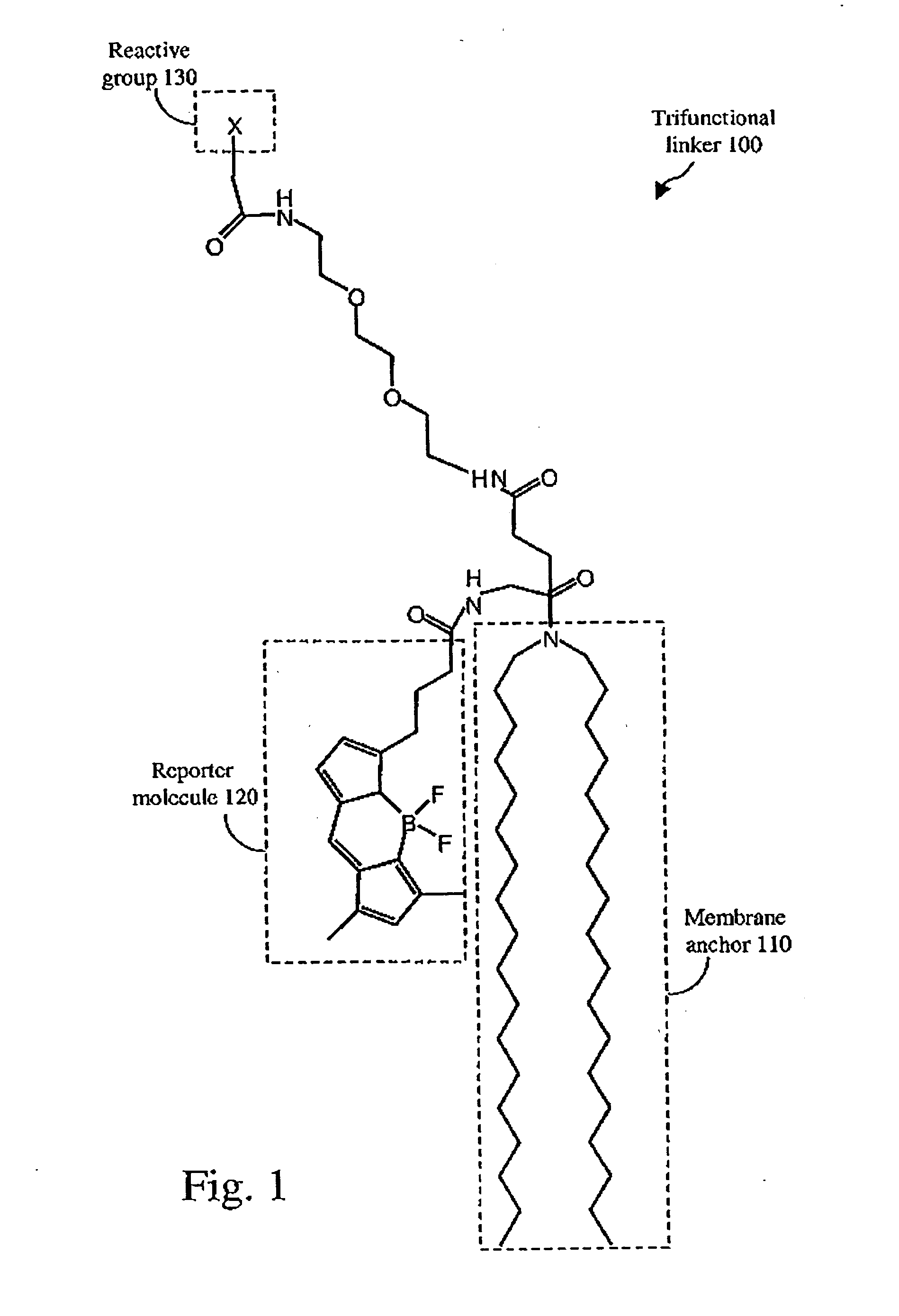
High throughput screening using fluorophore labeled lipid membranes and fluorescence correlation spectroscopy
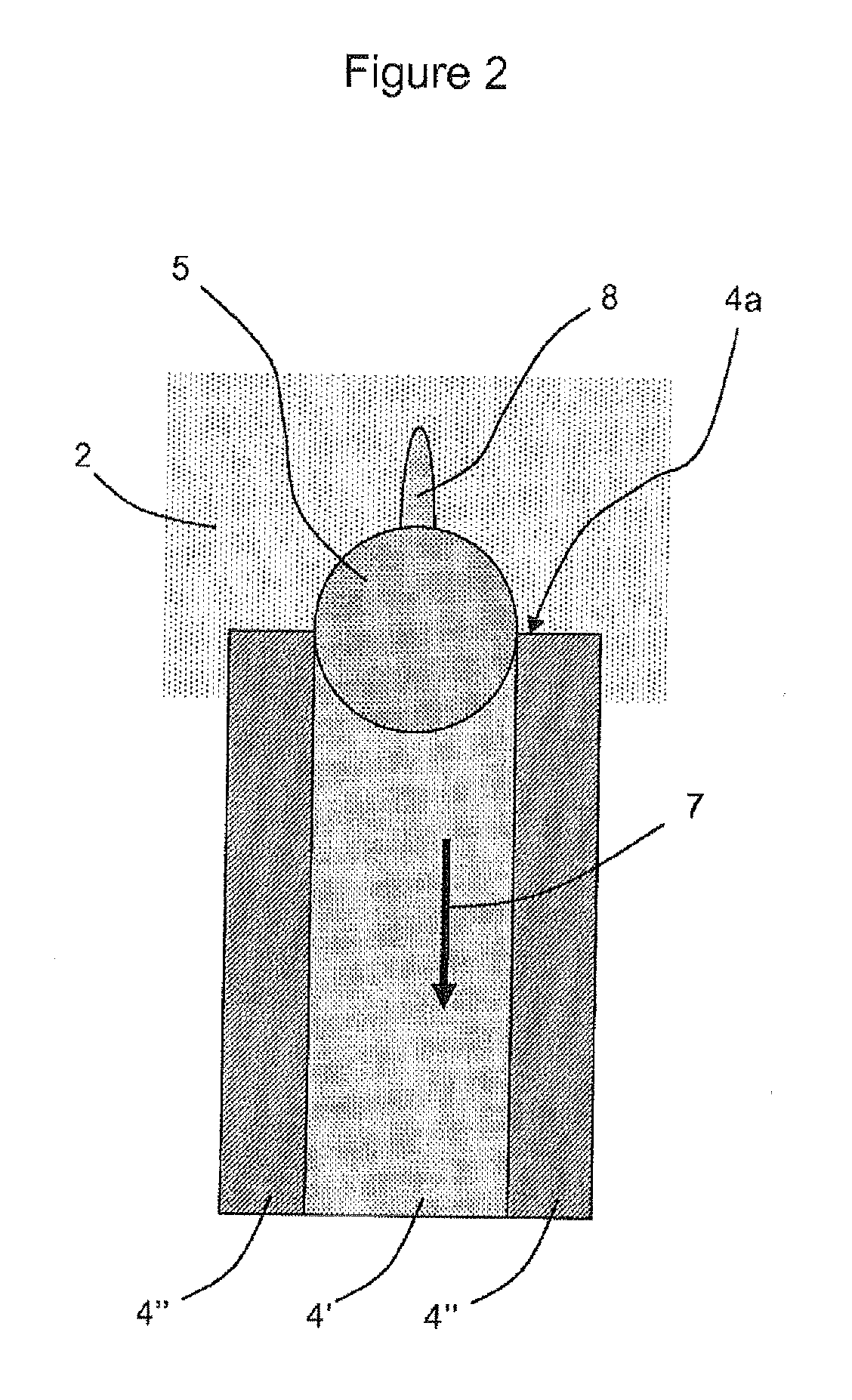
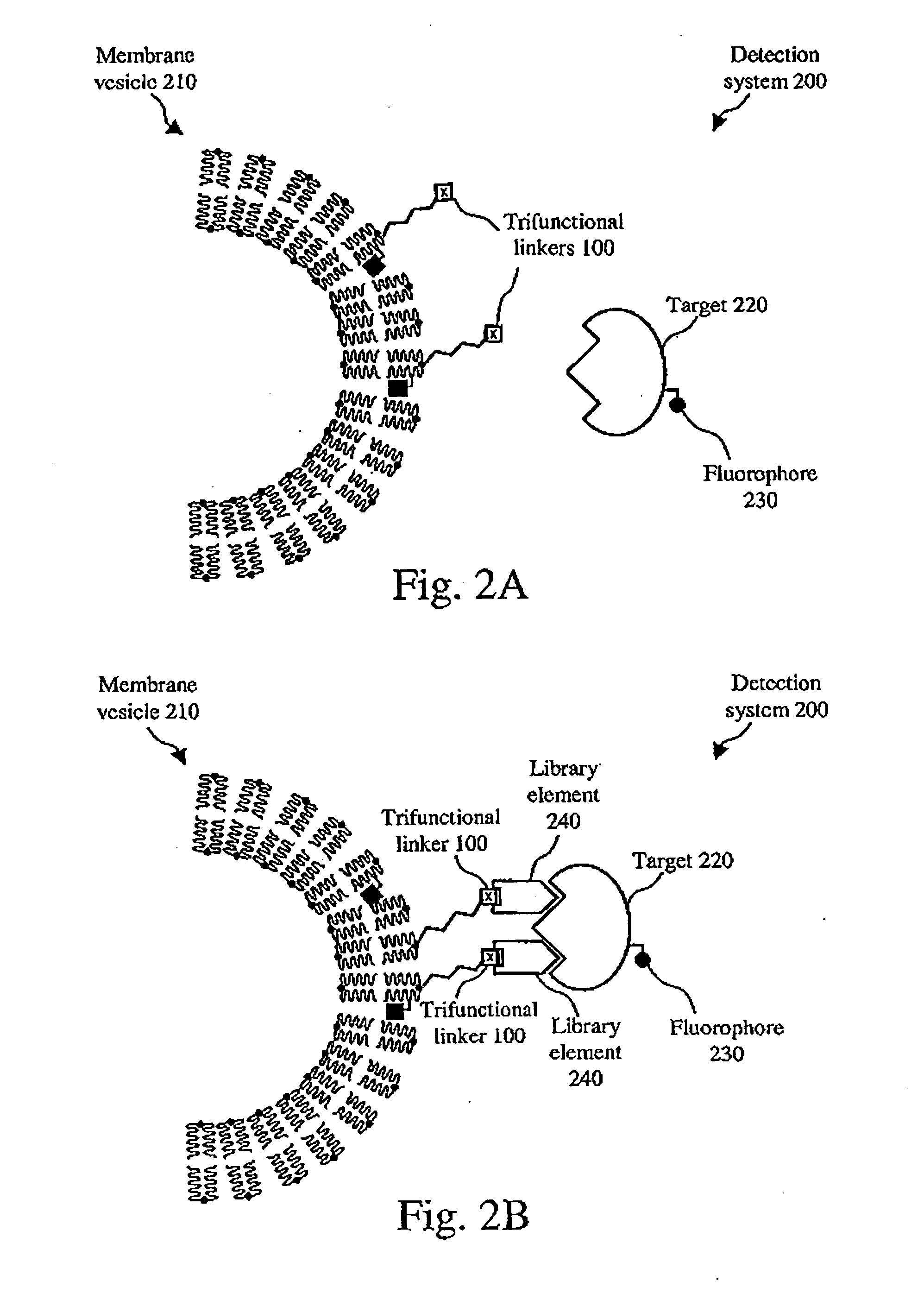
InactiveUS20050191705A1Library screeningBiological testingLipid formationHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
An apparatus for and method of detecting a binding event between biomolecules is disclosed and includes admixing a target molecule including a first fluorophore and membrane vesicles including a trifunctional linker molecule, said trifunctional linker molecule including a second fluorophore, to form a sample, introducing a library of elements into said sample, each of said library elements having a binding affinity for said trifunctional linker molecule, and, screening said sample for fluorescence from said first fluorophore and said second fluorophore, such fluorescence indicative of a binding event between an element from said library of elements and said target molecule.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
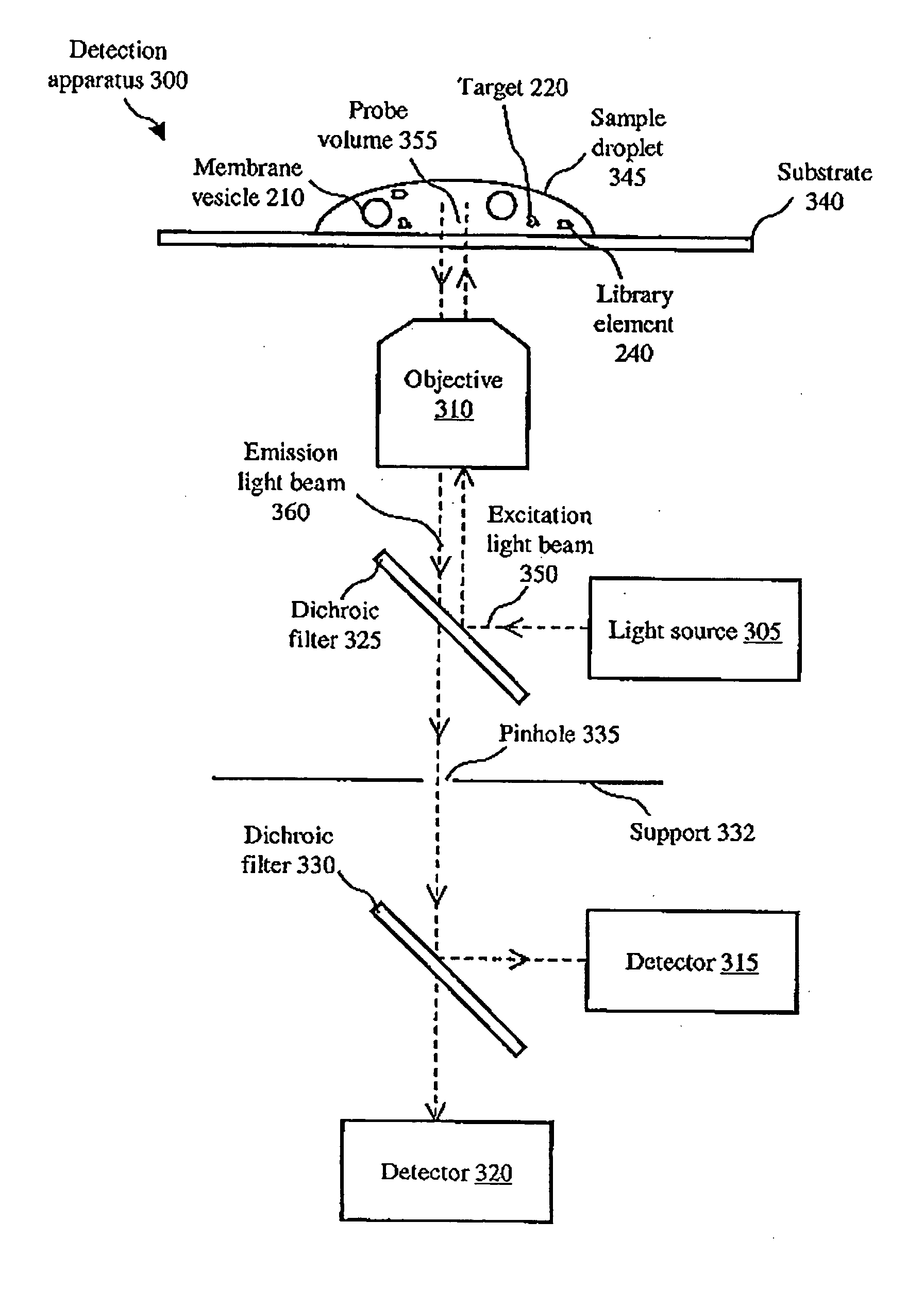
Imaging fluorescence correlation spectroscopy for analysis of molecular interactions in low volumes
InactiveUS7456026B2Chemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAnalysis by electrical excitationFluorescent lightDevice Subassembly
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy with single excitation wavelength
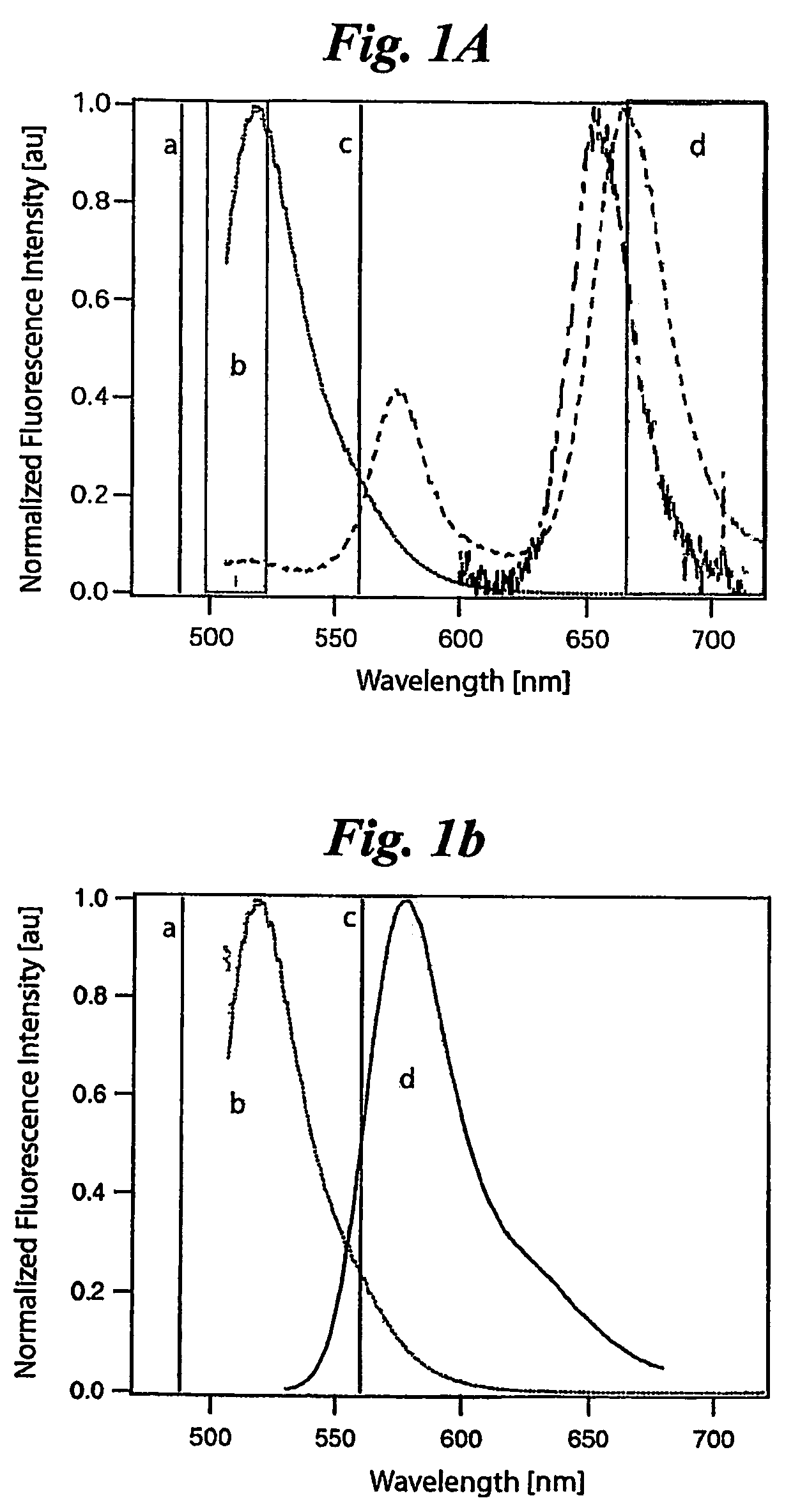
At least two fluorophores (e.g. fluorescein-biotin and tetramethylrhodamine-streptavidin conjugate) for use in fluorescence correlation spectroscopy, characterized in that the fluorophores have substantially the same excitation wavelength (a) and different emission wavelengths (b and d). The fluorophores are used for simultaneous excitation with a single laser wavelength in fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy (FCCS). The central wavelength (c) of the dichroic mirror used for the separation of the emission signal lies between the emission wavelengths of the fluorophores.
Owner:SINGAPORE NAT UNIV OF
Method for evaluating fluorescence correlation spectroscopy measurement data
ActiveUS20110208478A1Prevents unnecessary adjustment computationAffect resultAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsCorrelation analysisComputer science
With the different methods of fluorescence correlation spectroscopy, physical and biological transport processes in or between cells in the microscopic range, for example diffusion processes, can be analyzed. For this purpose, correlations of the fluorescence measurement data are determined for different sample regions and mathematical transport models are adapted thereto. Erroneous fluorescence correlation analyses were previously identified on the basis of the properties of the adapted model function parameters and were discarded. The a-priori knowledge necessary for the identification had to be obtained in time-consuming series of tests. With the invention, sample properties can be determined in a simpler, quicker and more exact way from fluorescence correlations. A suitability degree for one or more regions of the sample is determined for a correlation evaluation, describing quantitatively the information content of the respective region, or the error to be expected from a correlation evaluation, and can thus already be used before a correlation evaluation as a criterion for filtering / selecting the respective region. In this way, elaborate correlation calculations can be dispensed with in non-informative sample regions.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
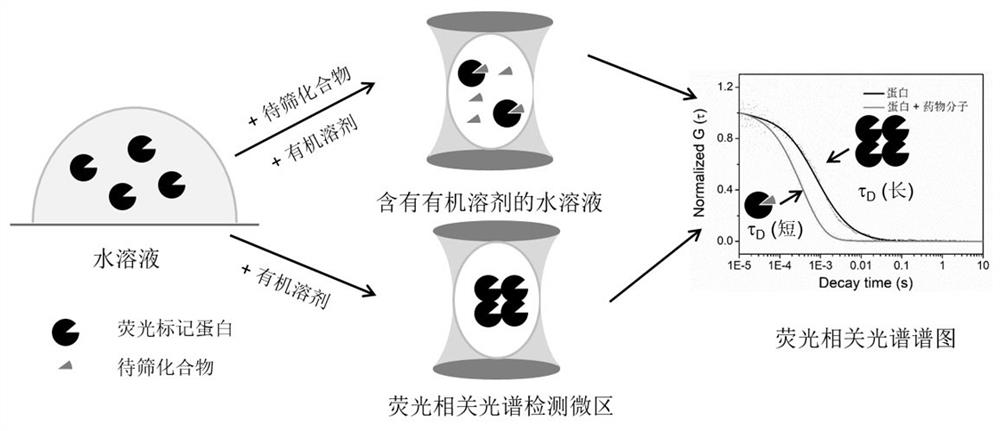
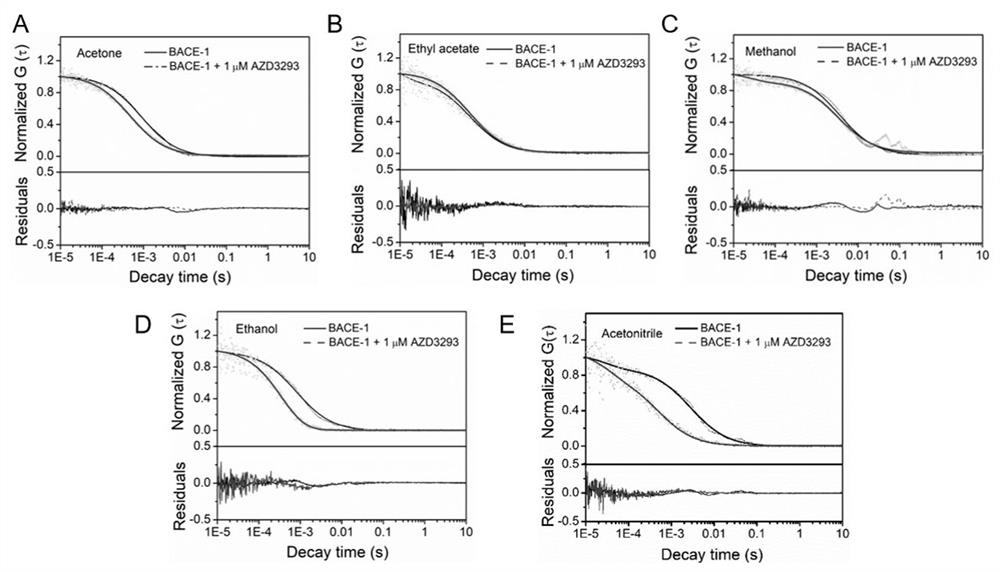
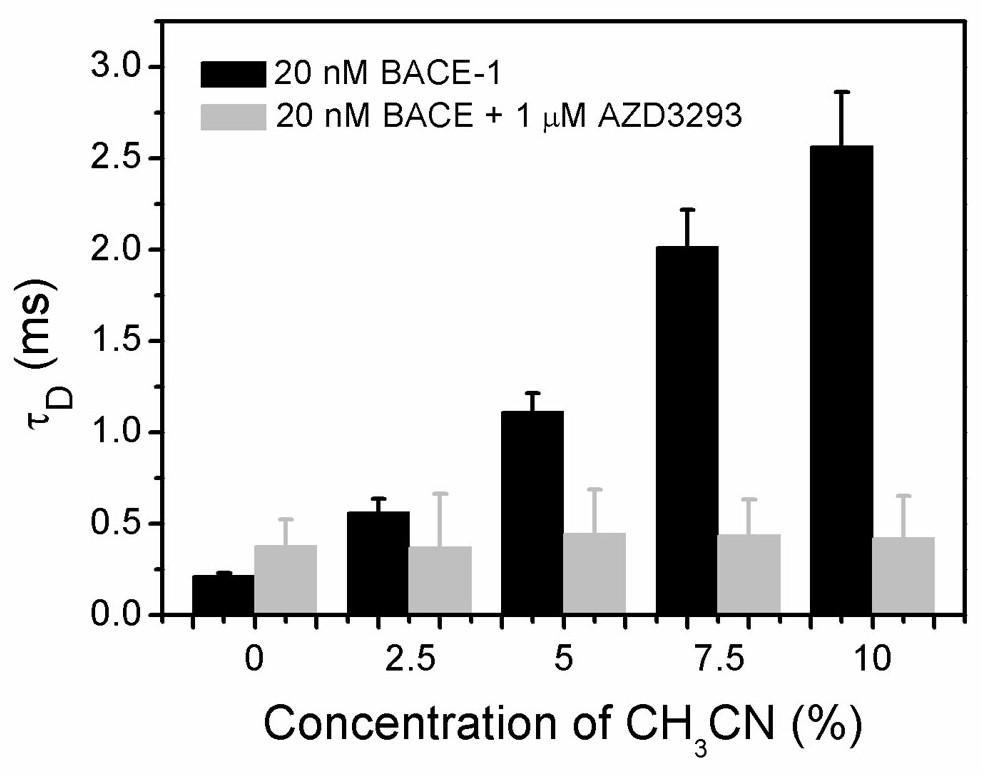
A Drug Screening Method Based on Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy to Detect Protein Aggregation Induced by Organic Solvents
ActiveCN113552102BInhibit aggregationReduce dosageFluorescence/phosphorescenceDiseaseCell Aggregations
The invention relates to a drug screening method based on fluorescence correlation spectrum detection of protein aggregation induced by organic solvents. Fluorescence-labeled proteins produce aggregation in aqueous solutions containing organic solvents. When the compound to be screened interacts with the protein, it will inhibit the protein from Aggregation occurs in aqueous solutions containing organic solvents, and the characteristic diffusion time (diffusion coefficient) of fluorescently labeled protein aggregates is detected by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy to obtain information on the strength of the interaction between the protein and the compound to be screened, thereby realizing the induction of protein aggregation based on organic solvents Drug screening, the method has a small detection volume and high sensitivity. The invention can screen clinical drugs for common diseases and sudden diseases, greatly reduce the time and cost of drug screening, and provide a simpler, faster and more universal method for drug research and development.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for detecting polyelectrolyte conformation transformation in flow field
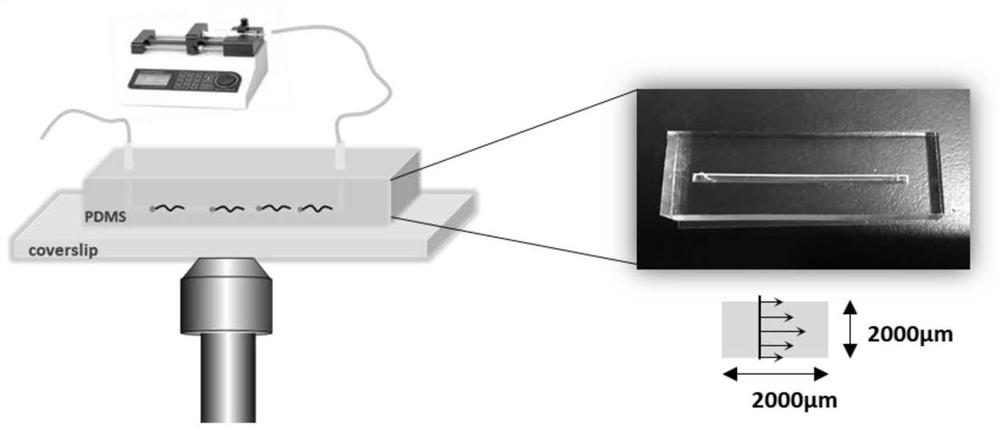
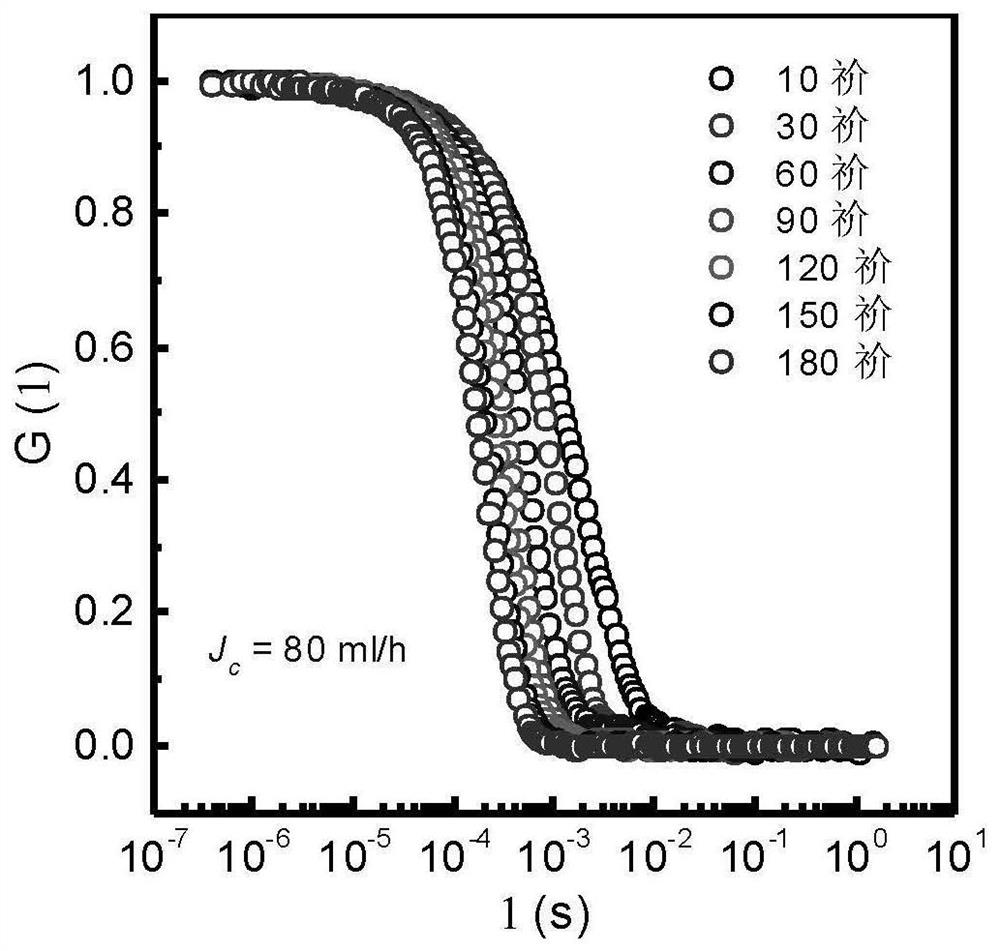
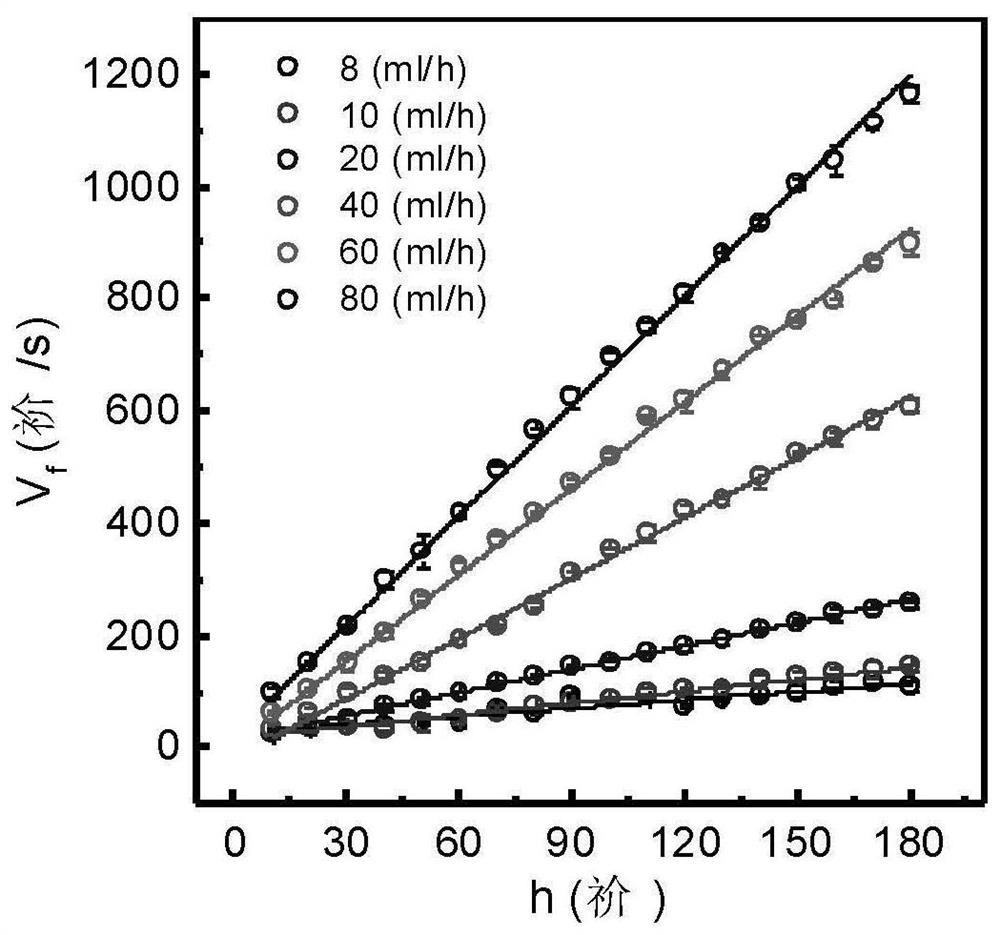
InactiveCN111829994AHigh orienteering speedImprove universalityLaboratory glasswaresFluorescence/phosphorescencePolyelectrolyteChemical physics
The invention discloses a method for detecting polyelectrolyte conformation transformation in a flow field. The method comprises the following steps of: marking a to-be-detected polyelectrolyte by adopting a fluorescent dye capable of reflecting local environmental change; constructing a micro-fluidic channel; measuring the sizes of excitation spaces of the fluorescent dye with the known diffusioncoefficient at different positions in the micro-fluidic channel in the longitudinal height direction by adopting a fluorescence correlation spectrum; determining flow field flow velocities at different positions of the micro-fluidic channel when an external injection pump provides different apparent flows by adopting fluorescence correlation spectroscopy; taking a dilute solution of polyelectrolyte as a flowing medium, and determining spectra of the dilute solution at different positions in the micro-fluidic channel by adopting a single-molecule fluorescence spectrum; obtaining the local environment change of the polyelectrolyte according to the fluorescence intensity of the fluorescent dye marked on the polyelectrolyte, reflecting the concentration change of the counter ions according tothe local environment change, and obtaining the polyelectrolyte conformation transformation information according to the concentration change of the counter ions. The method is suitable for researching the influence on the polyelectrolyte conformation when a flow field and other factors coexist.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com