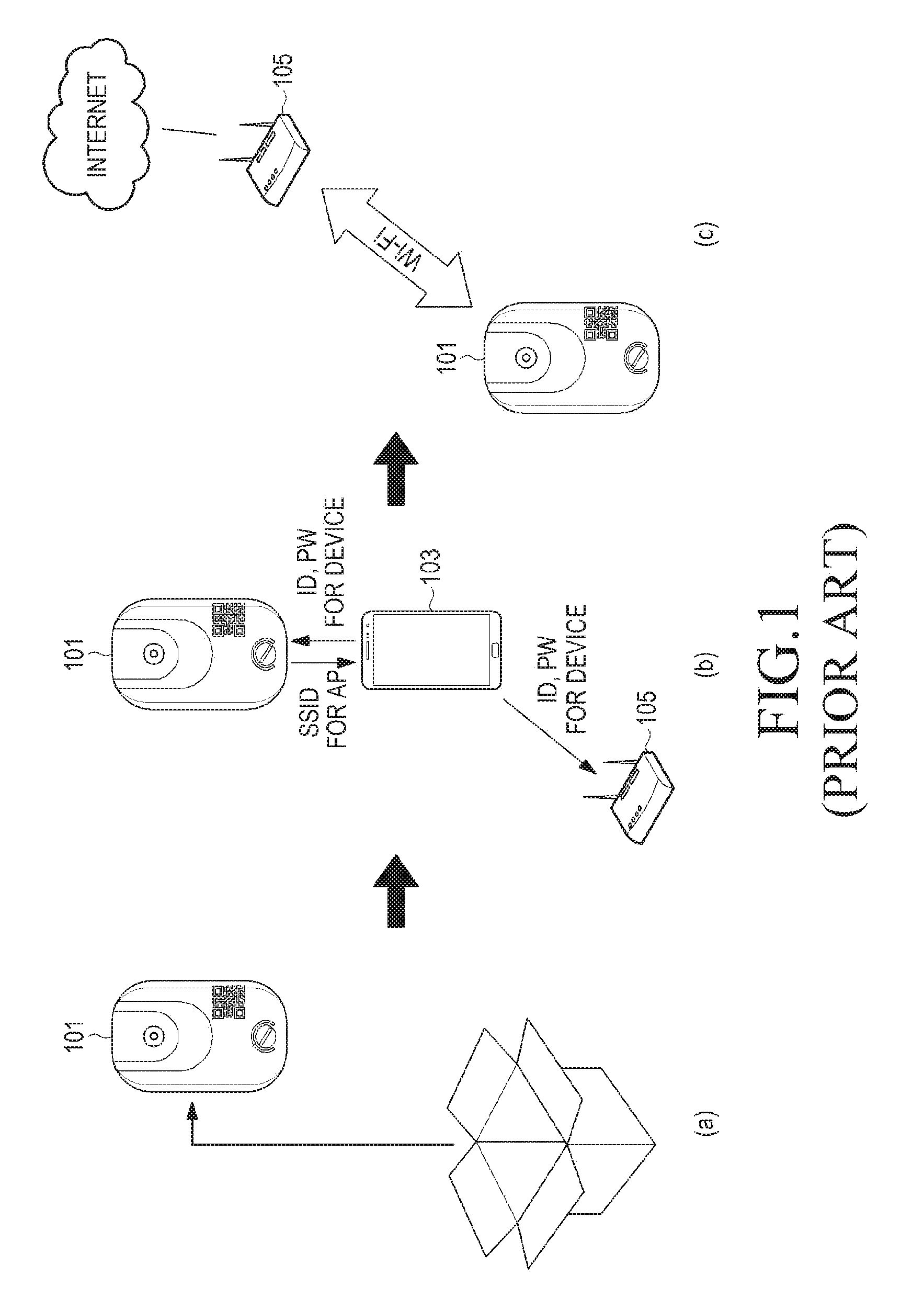
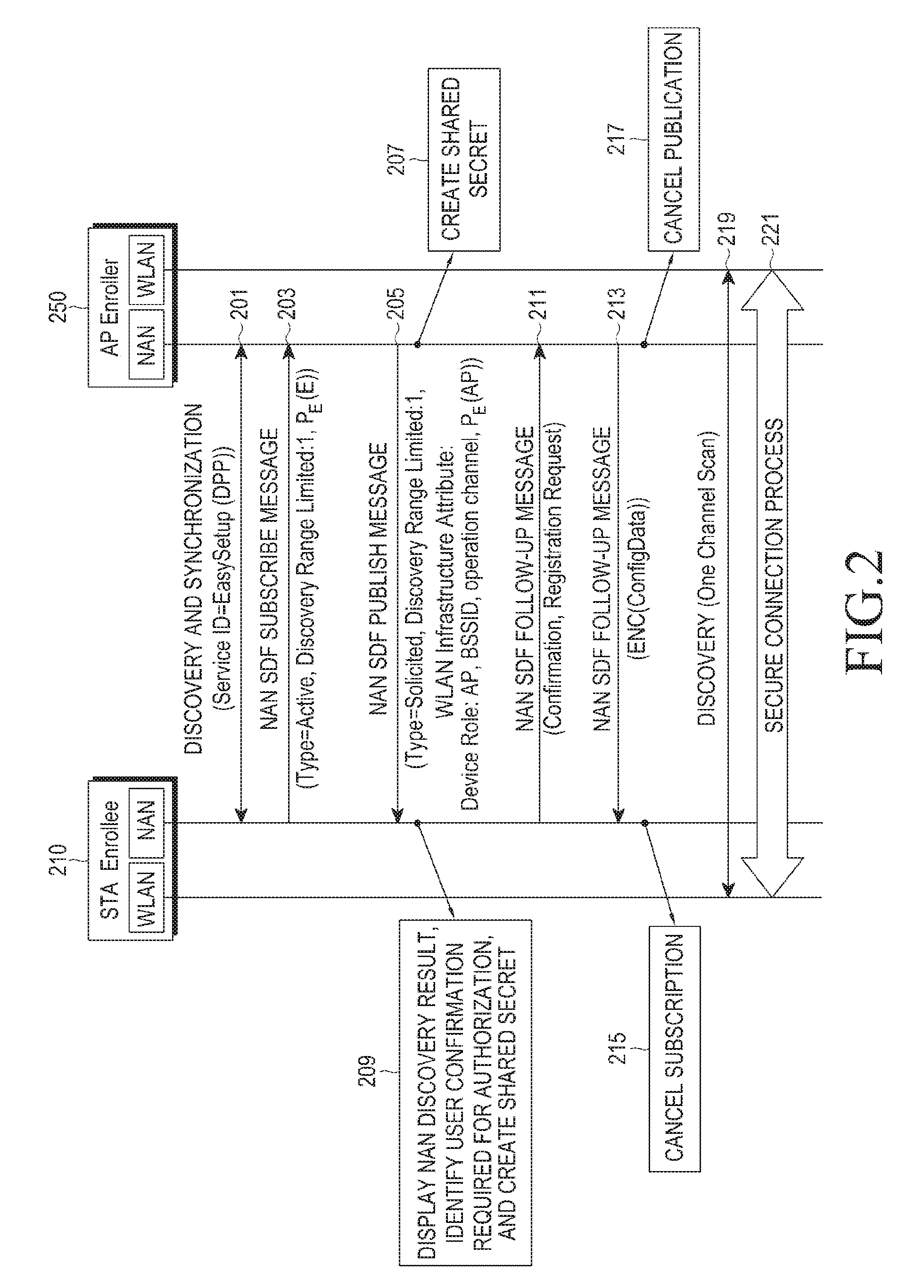
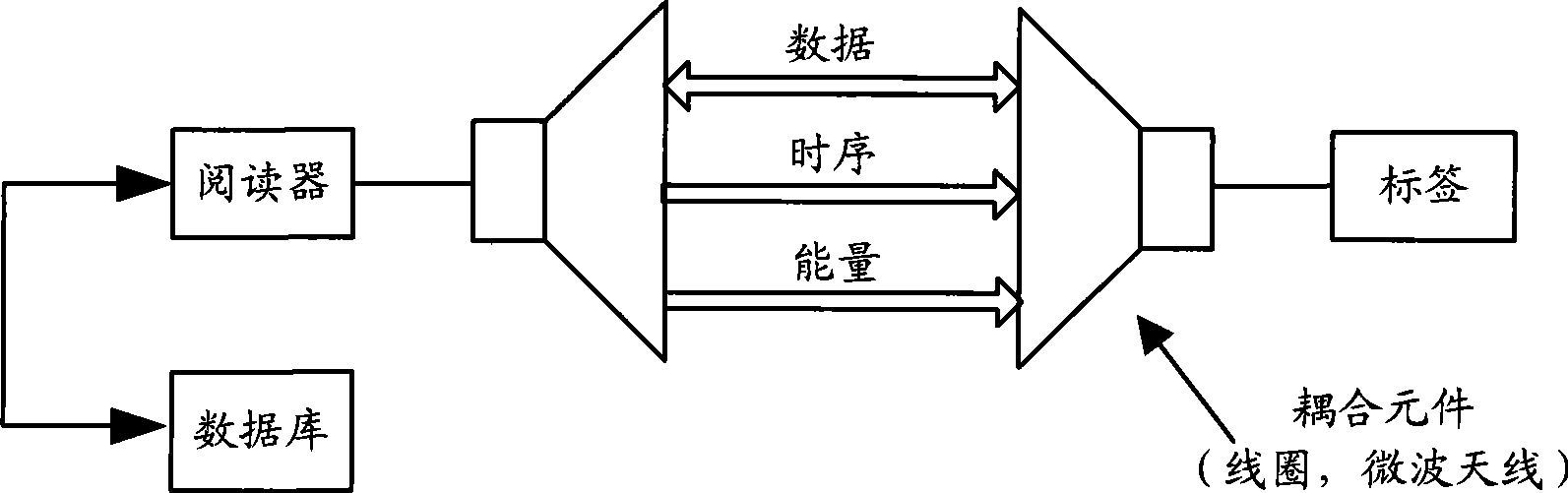
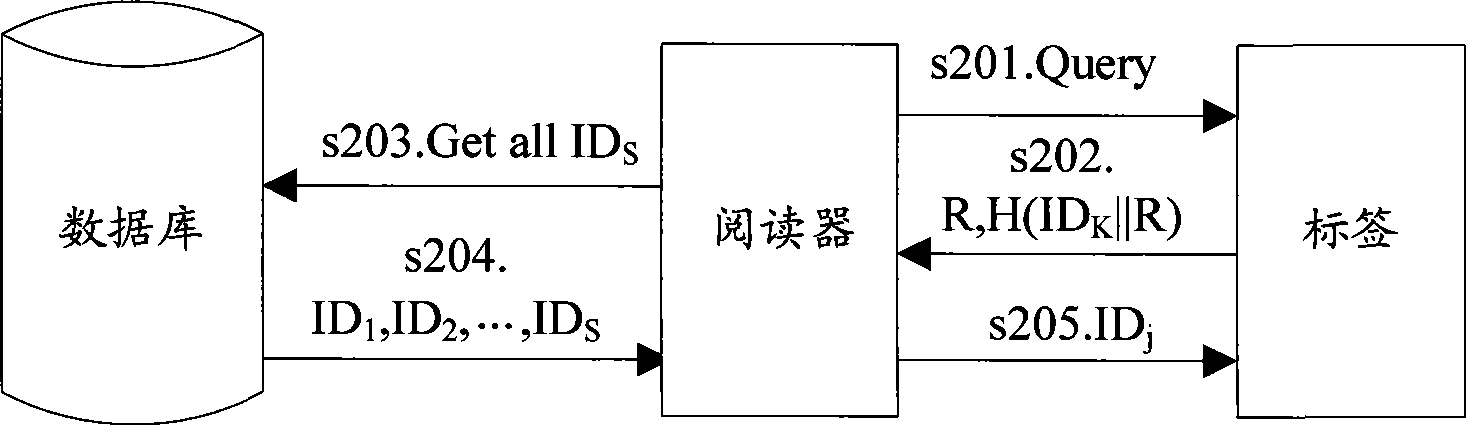
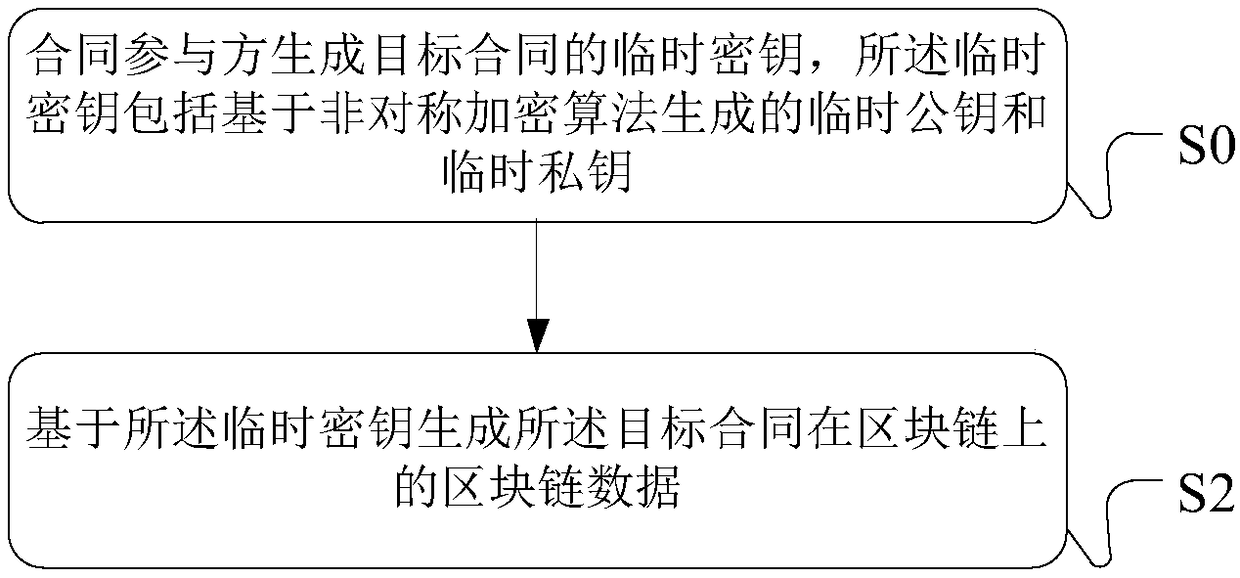
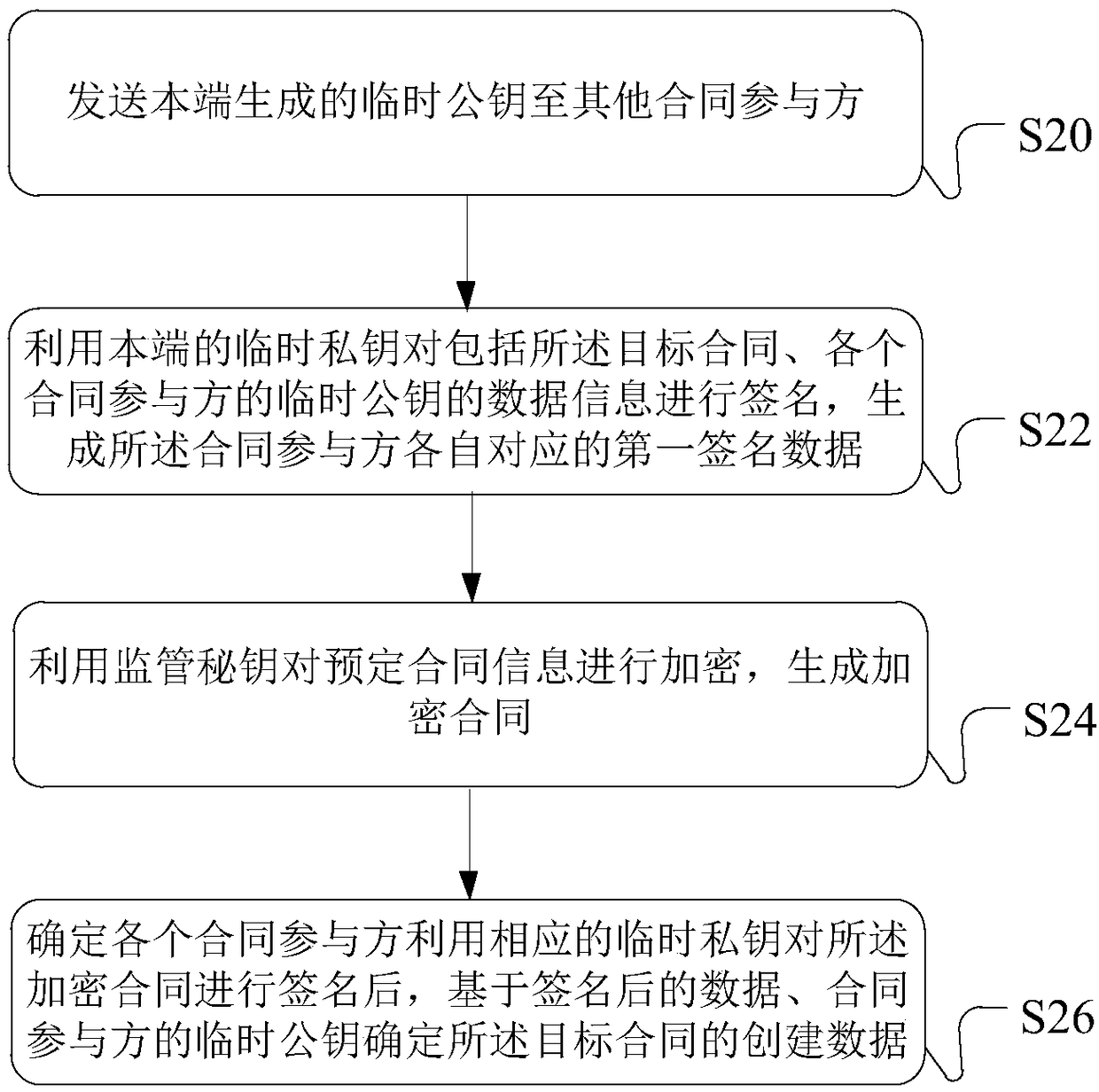
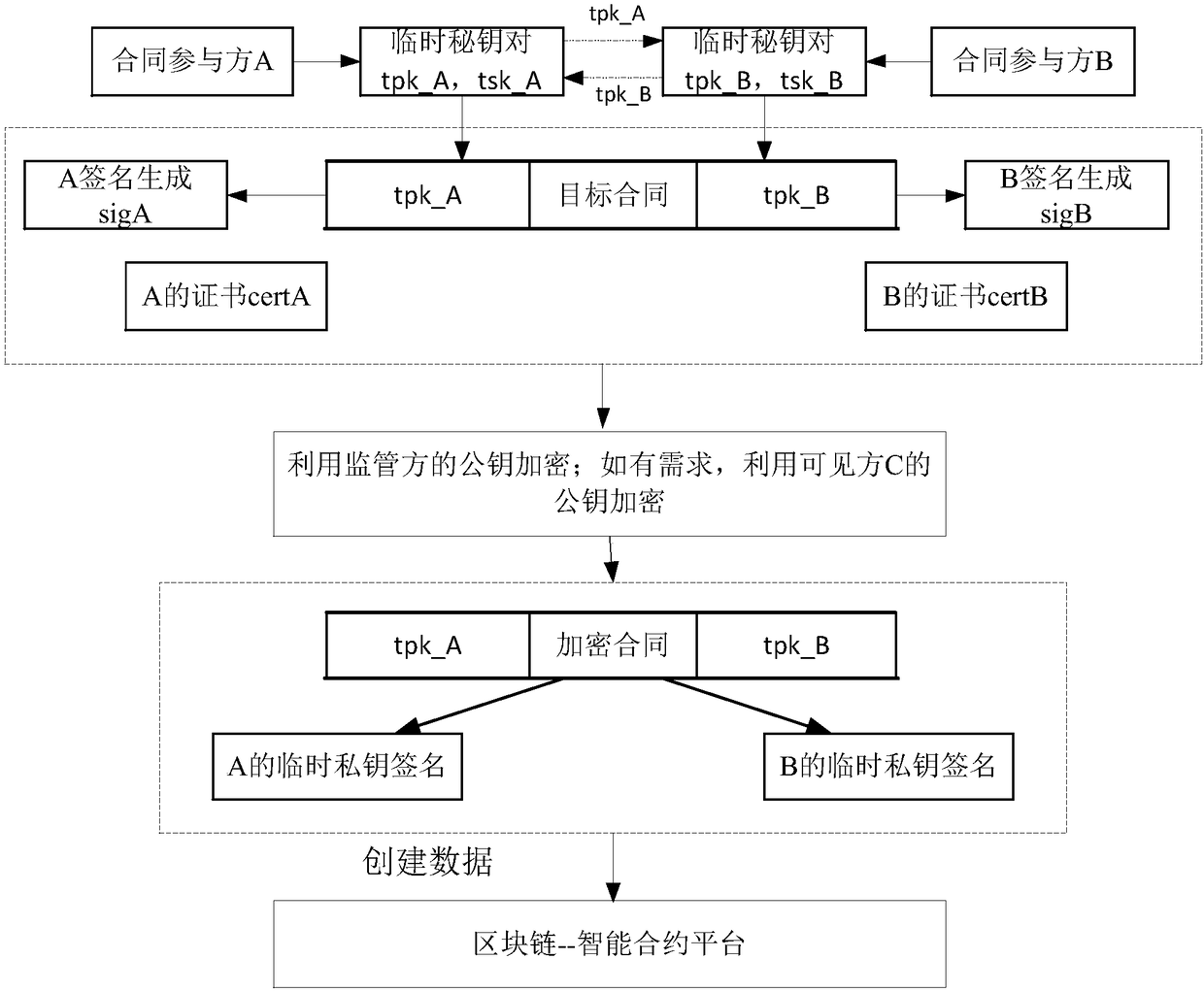
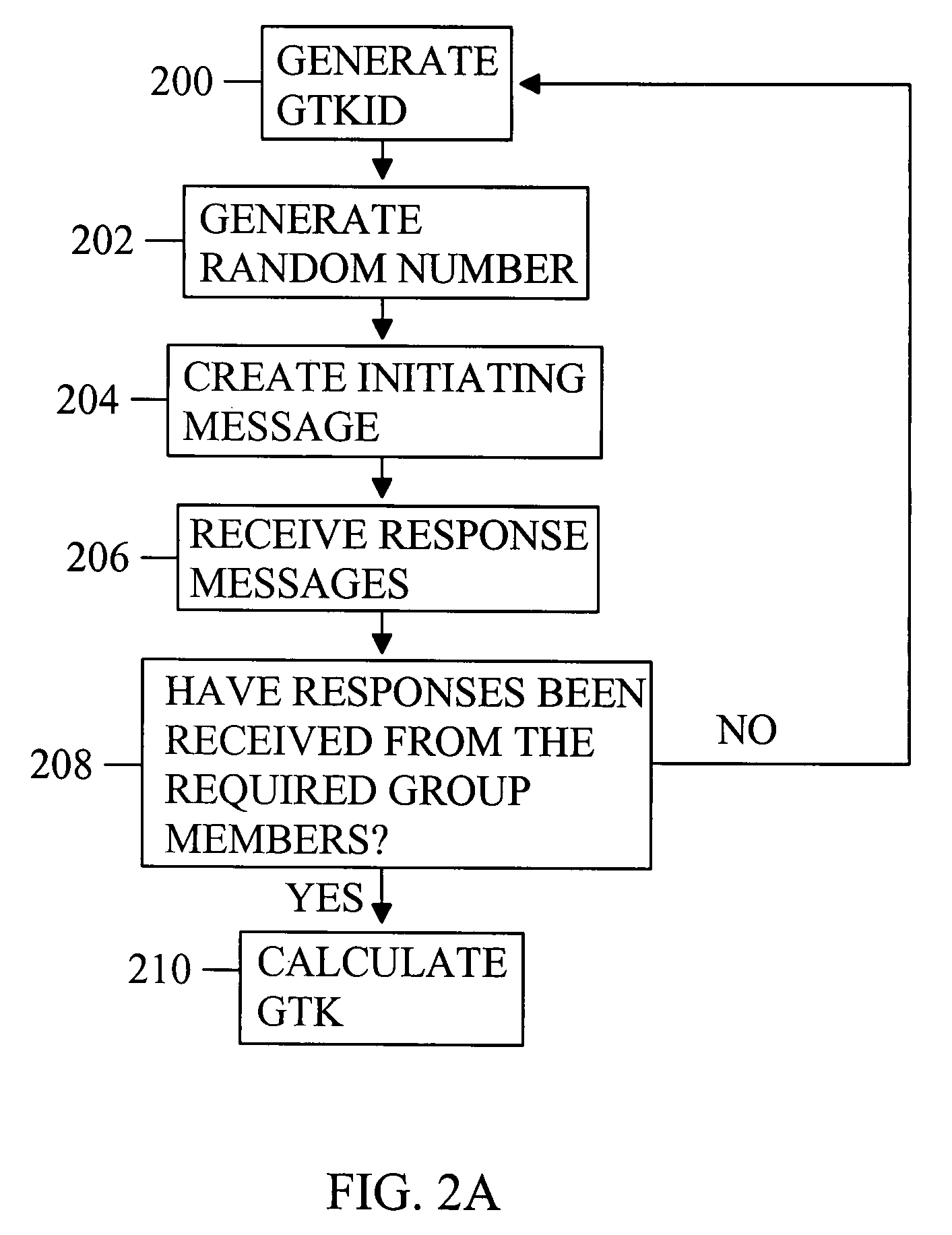
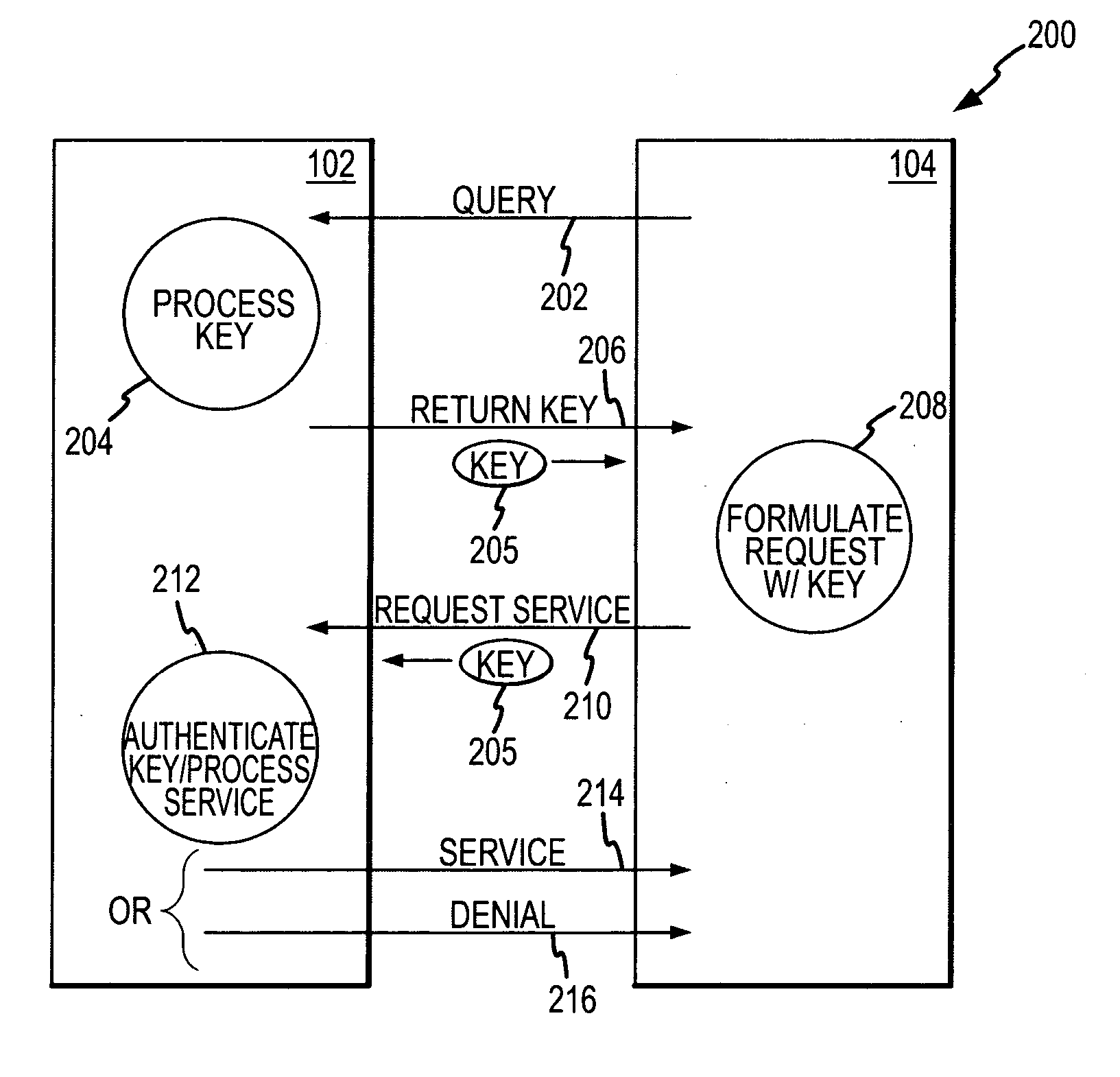
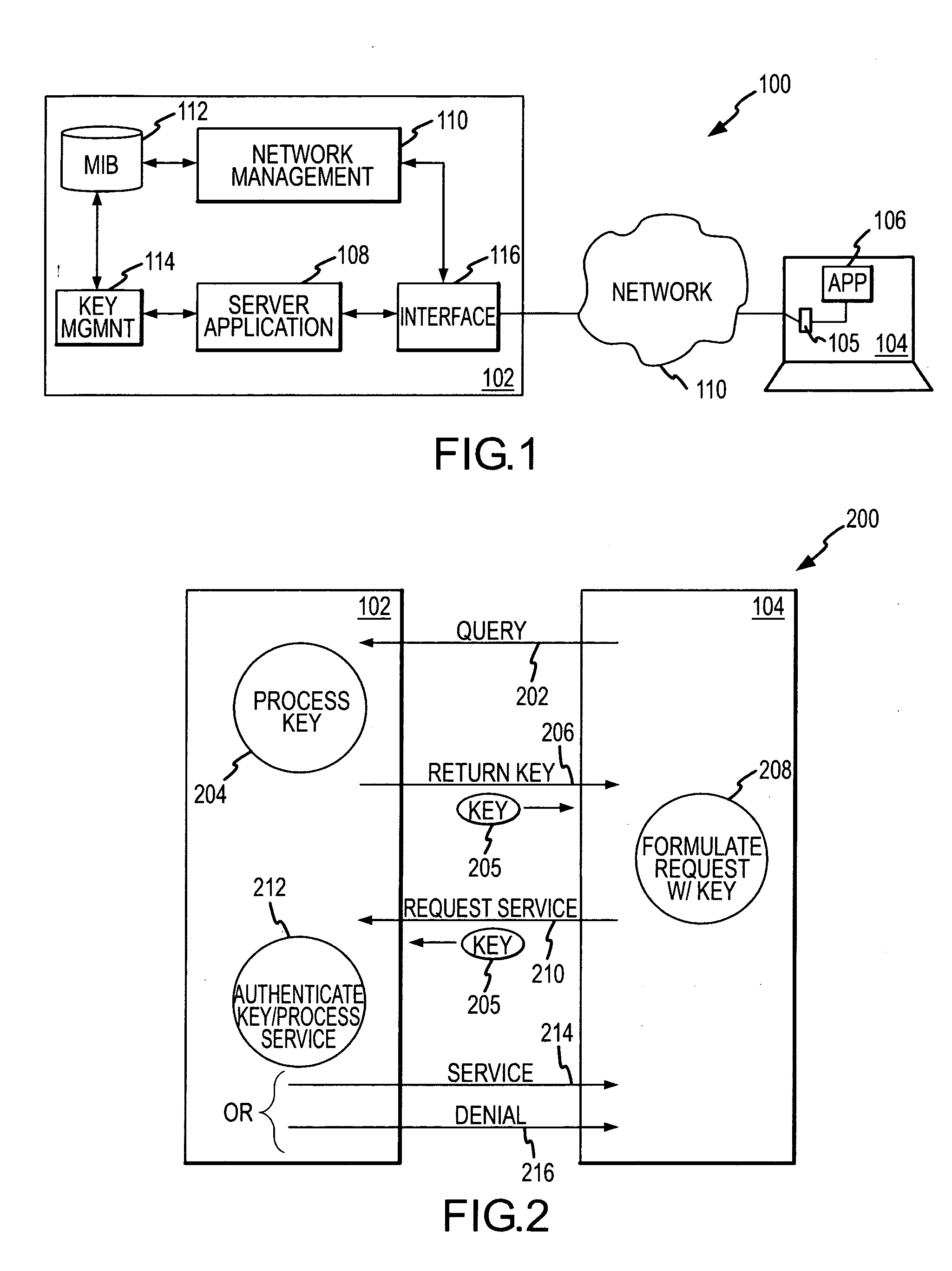
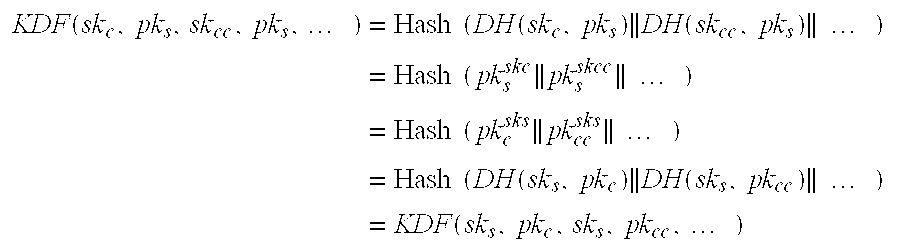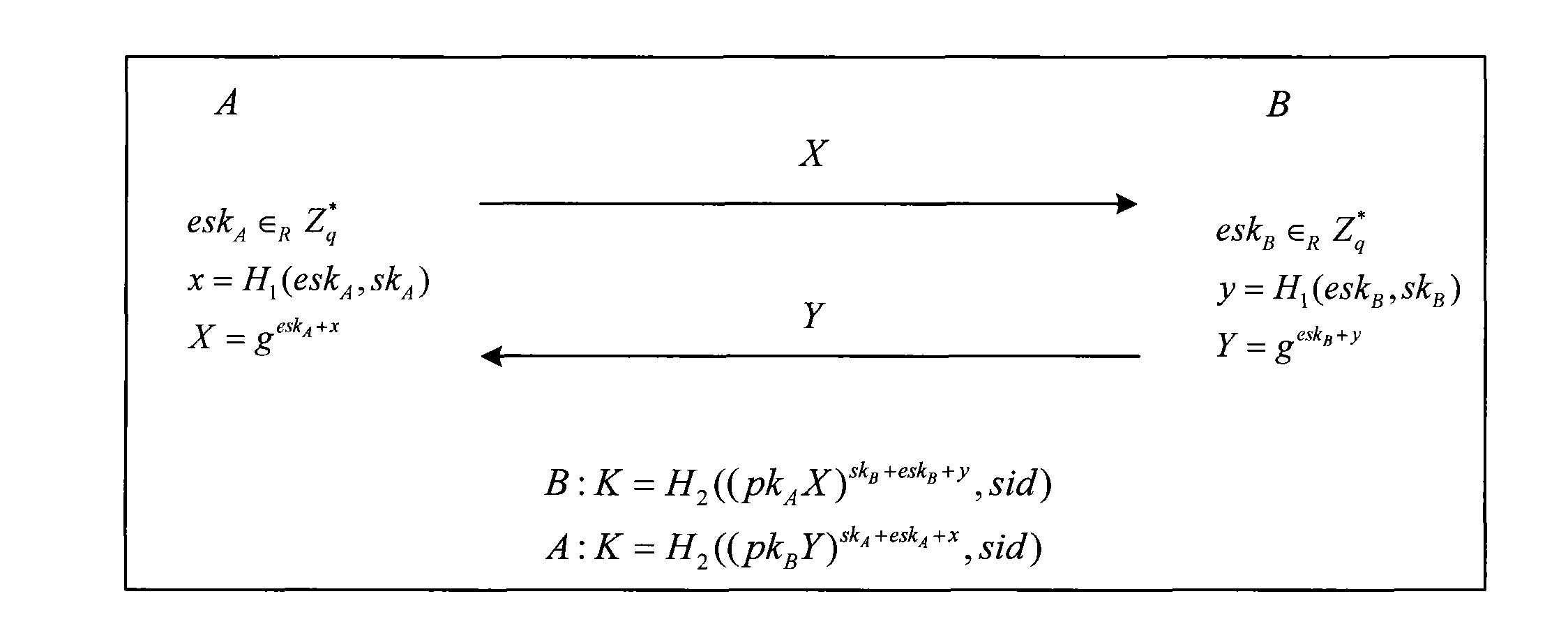Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
284 results about "Ephemeral key" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A cryptographic key is called ephemeral if it is generated for each execution of a key establishment process. In some cases ephemeral keys are used more than once, within a single session (e.g., in broadcast applications) where the sender generates only one ephemeral key pair per message and the private key is combined separately with each recipient's public key. Contrast with a static key.
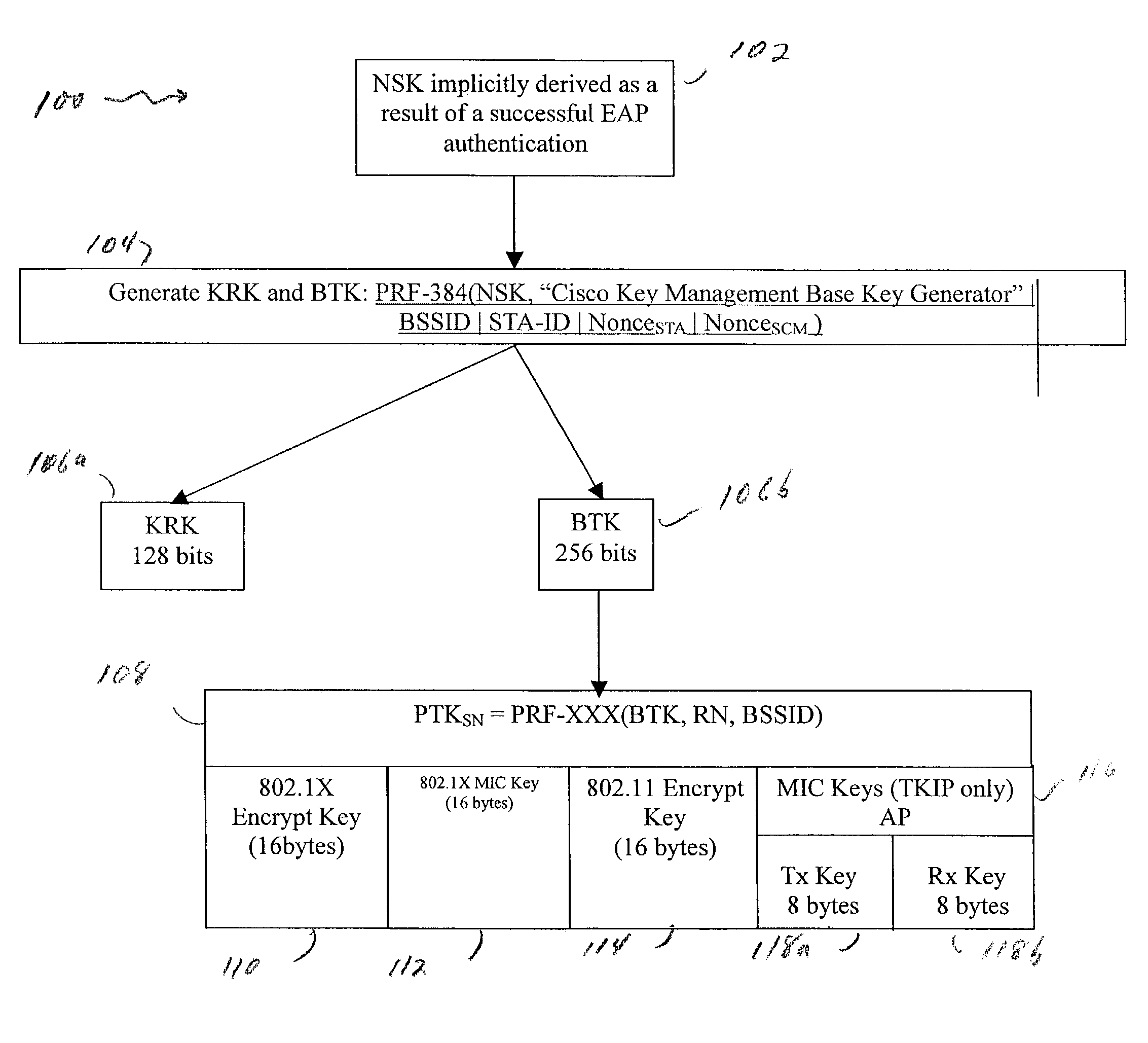
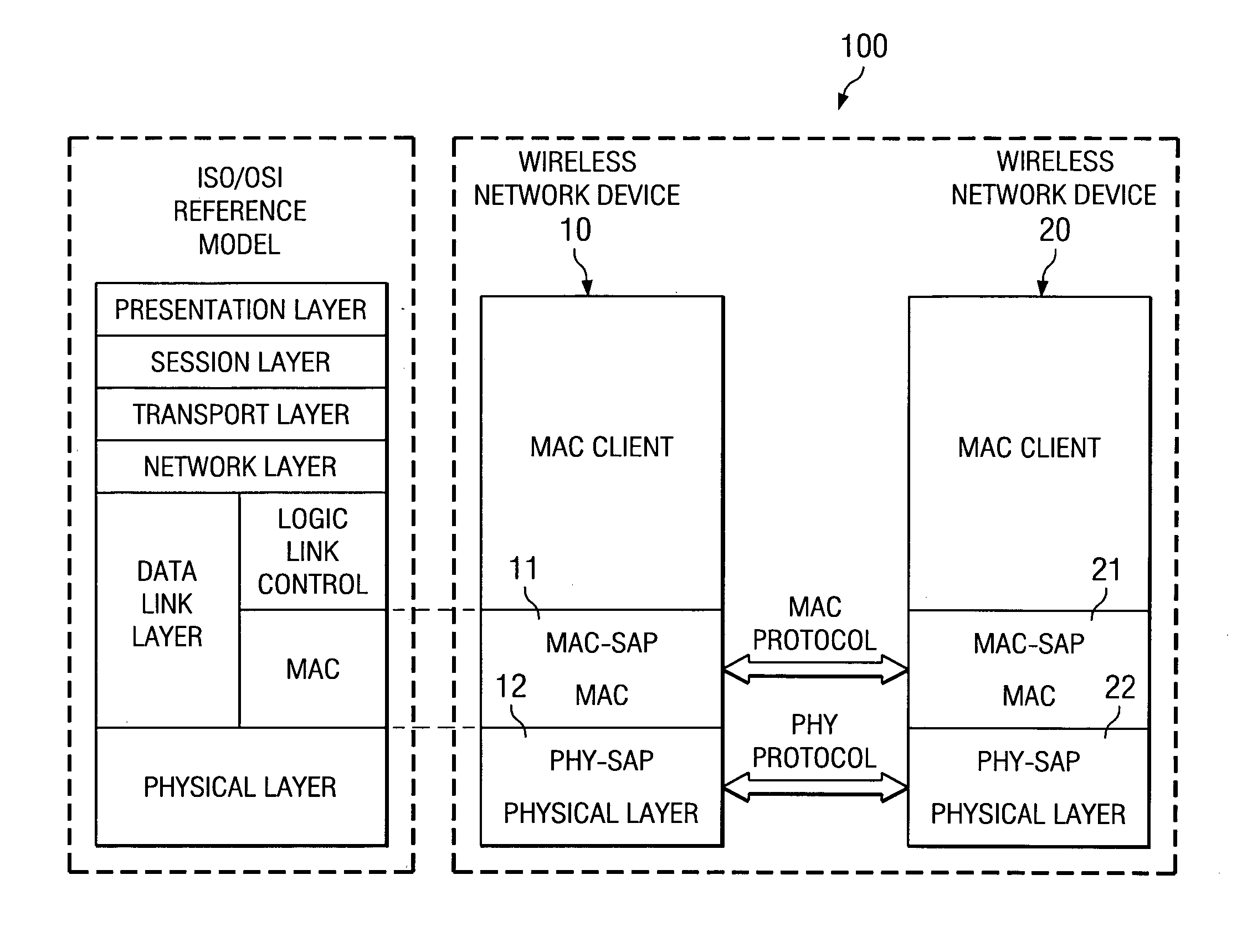
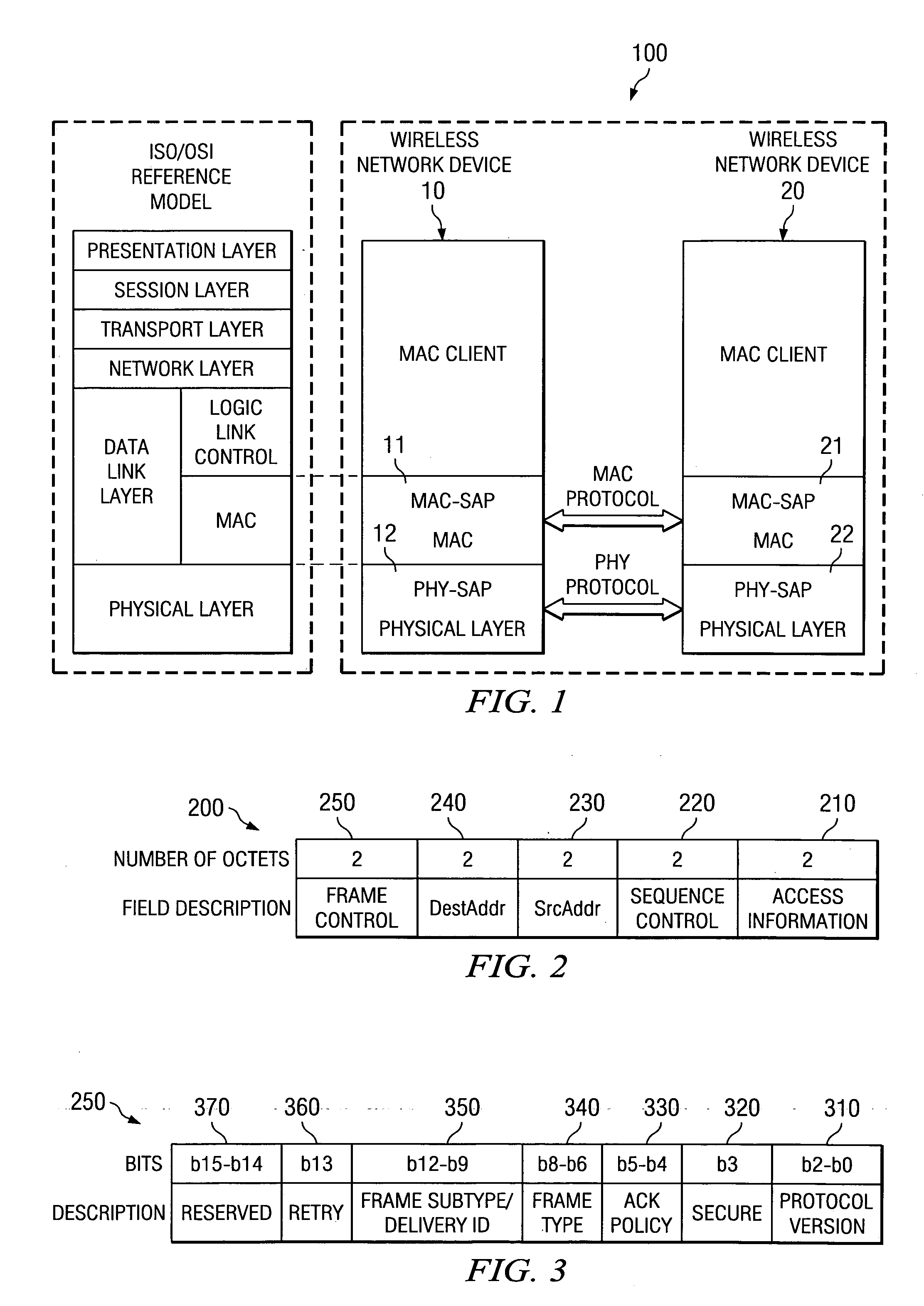
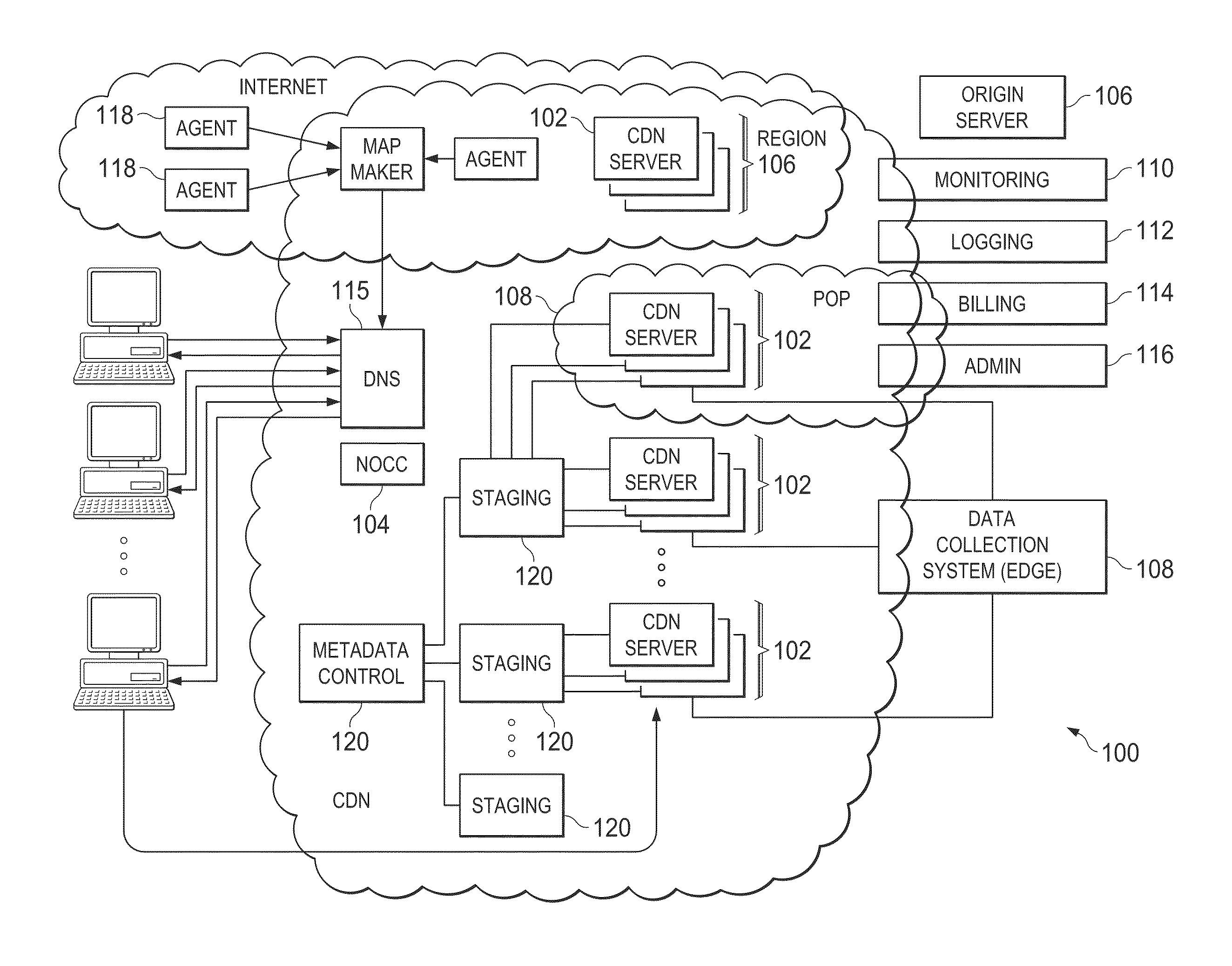
802.11 using a compressed reassociation exchange to facilitate fast handoff
ActiveUS7350077B2Reduce the burden onUser identity/authority verificationNetwork topologiesComputer networkRogue access point
A method and system for handling roaming mobile nodes in a wireless network. The system uses a Subnet Context Manager to store current Network session keys, security policy and duration of the session (e.g. session timeout) for mobile nodes, which is established when the mobile node is initially authenticated. Pairwise transit keys are derived from the network session key. The Subnet Context Manager handles subsequent reassociation requests. When a mobile node roams to a new access point, the access point obtains the network session key from the Subnet Context Manager and validates the mobile node by computing a new pairwise transient key from the network session key.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
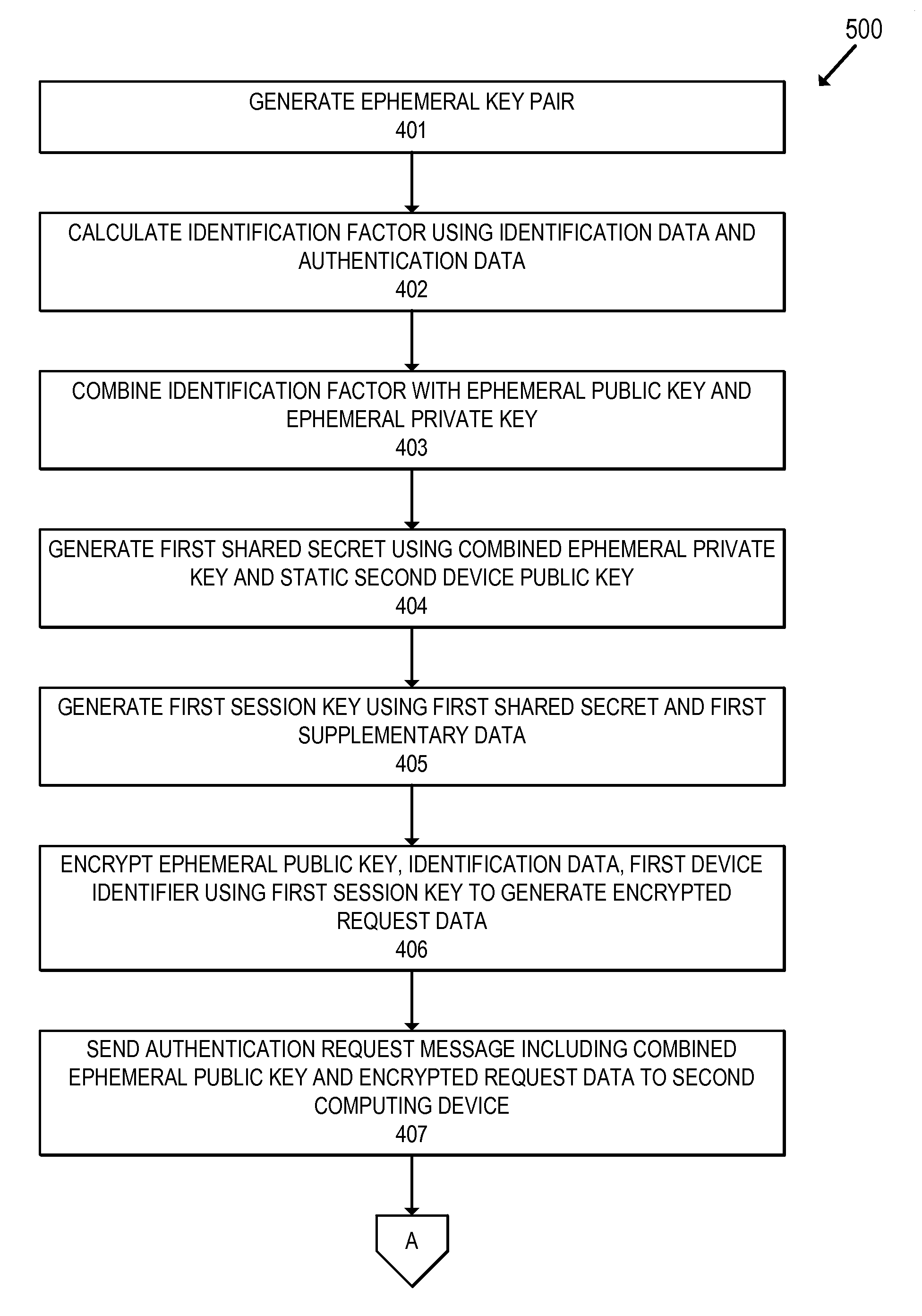
Efficient methods for authenticated communication
ActiveUS20150372811A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationEphemeral keyServer
Embodiments of the invention relate to efficient methods for authenticated communication. In one embodiment, a first computing device can generate an ephemeral key pair comprising an ephemeral public key and an ephemeral private key. The first computing device can generate a first shared secret using the ephemeral private key and a static second device public key. The first computing device can encrypt request data using the first shared secret to obtain encrypted request data. The first computing device can send a request message including the encrypted request data and the ephemeral public key to a server computer. Upon receiving a response message from the server computer, the first computing device can determine a second shared secret using the ephemeral private key and the blinded static second device public key. The first computing device can then decrypt the encrypted response data from the response message to obtain response data.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
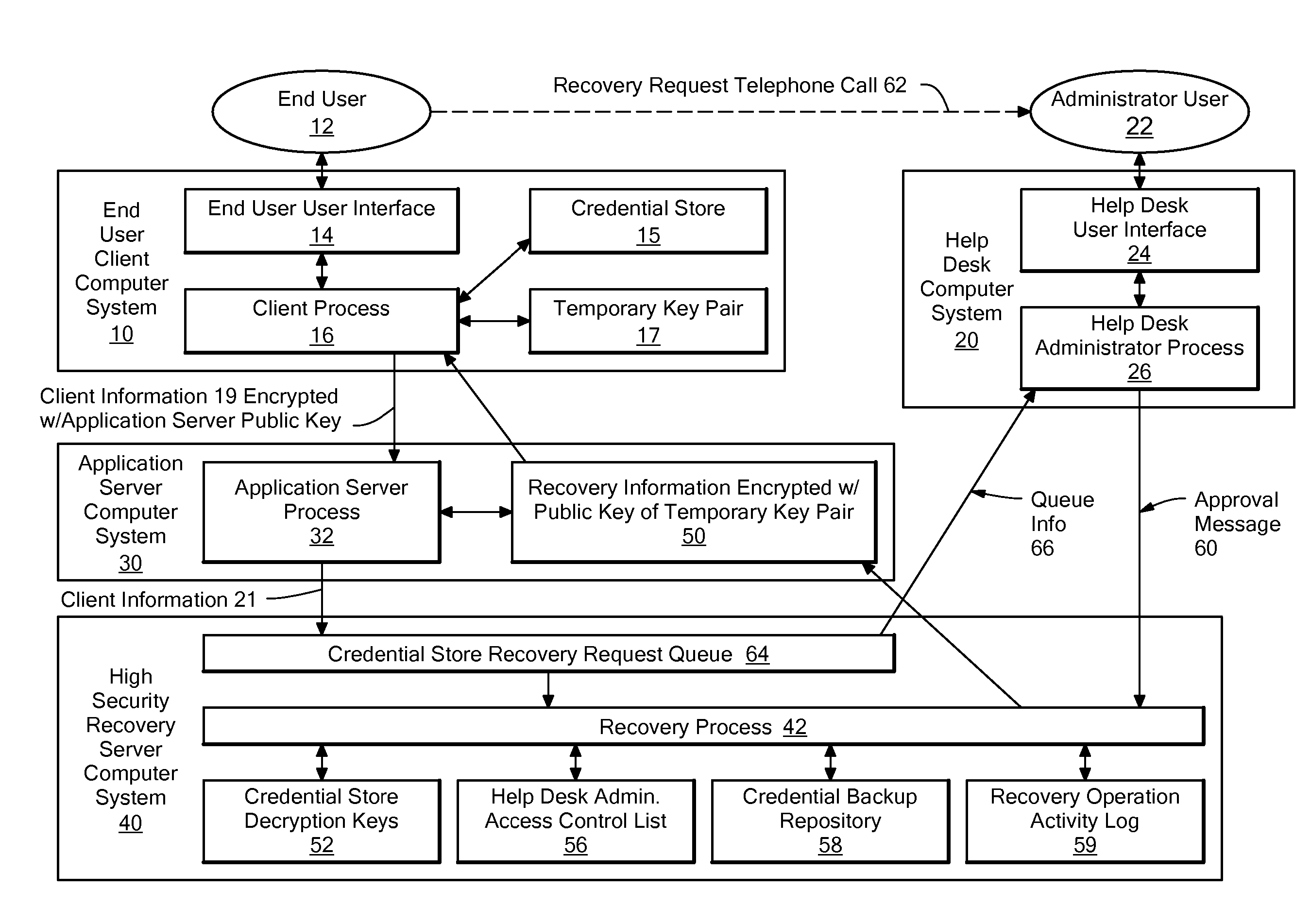
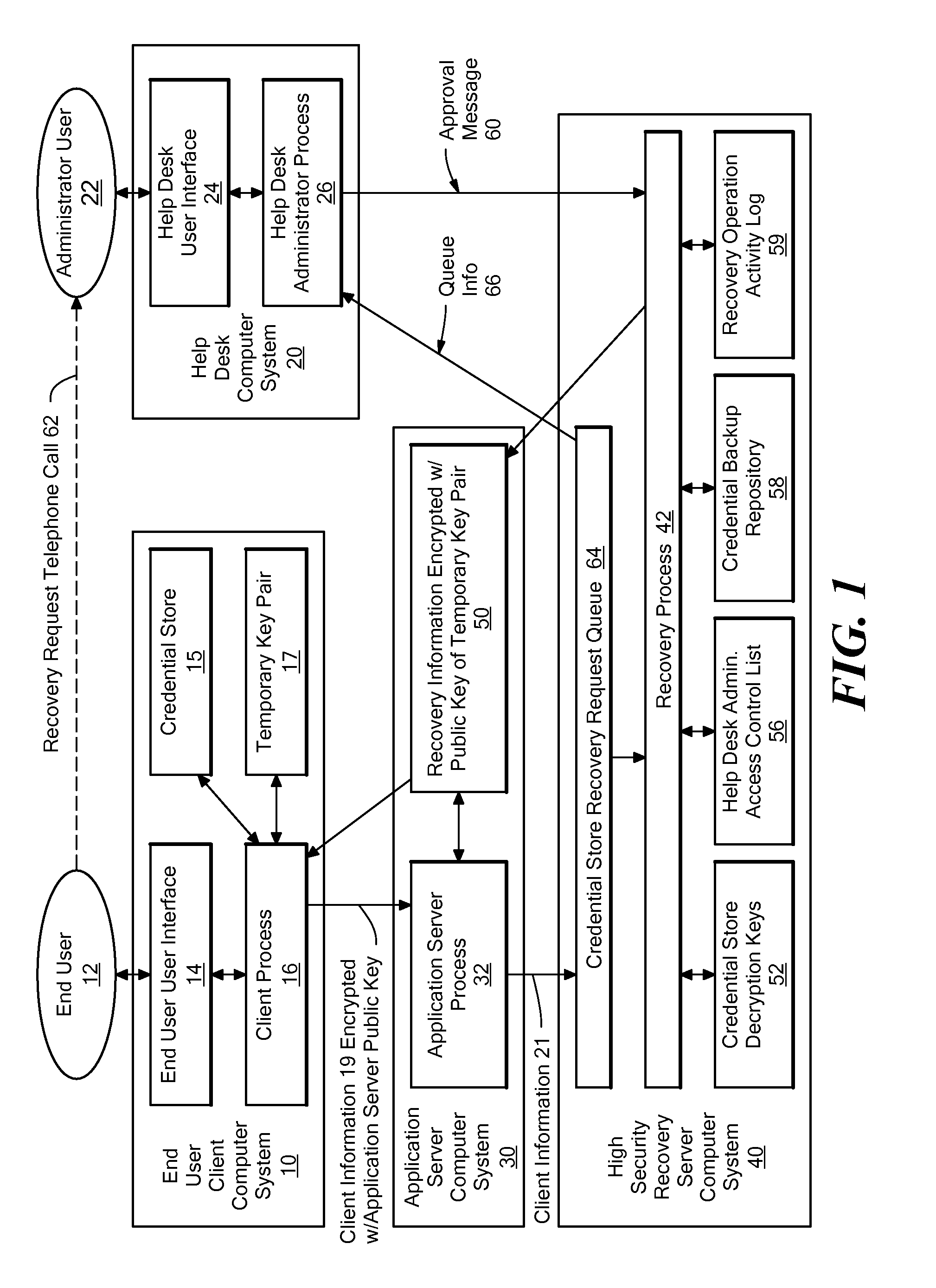
Method and system for automating the recovery of a credential store
A system for automating the recovery of a credential store, in which client software generates a temporary key pair based on a new password, and sends client information including the user's name, the public half of the temporary key pair, and the host name of the client computer system to a server system, from which the client information is passed to a recovery process. The client software process displays a prompt indicating that the user should call a help desk. A help desk administrator verifies the user's identity and approves the user's request by causing an approval message to be sent to the recovery process. The recovery process obtains recovery information consisting of either the decryption key(s) for the credential store, or a decrypted copy of the credential store, and encrypts the recovery information using the temporary public key. The client process downloads the recovery information from the server, and decrypts it using private key of the temporary key pair. The credential store can then be decrypted using the recovery information if necessary, then re-encrypted based on the new password. The encrypted recovery information is stored on the server and re-used for a certain period of time, after which it is deleted, thus allowing multiple copies of the credential store to be conveniently recovered.
Owner:IBM CORP
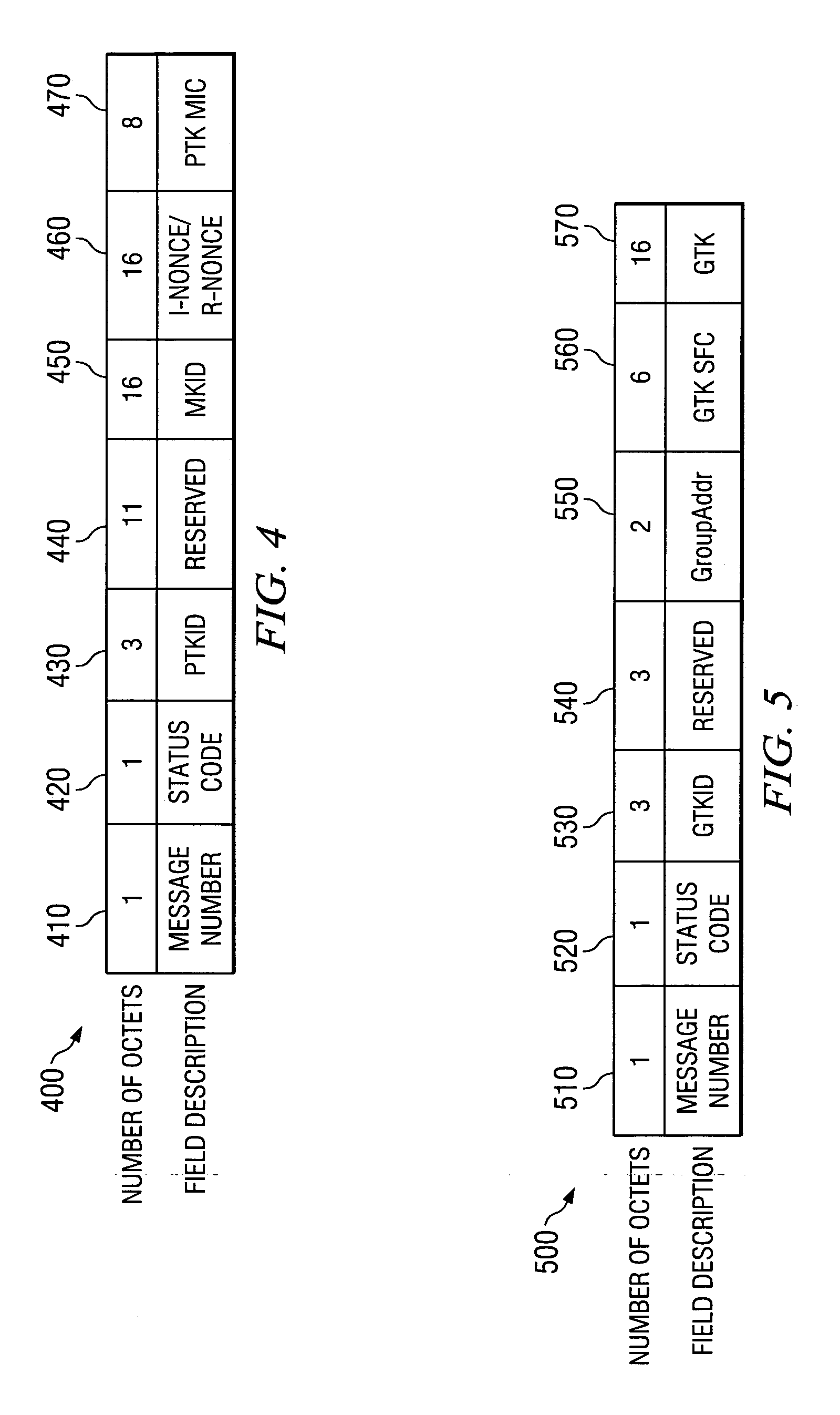
System and method for establishing secure communications between devices in distributed wireless networks
A method of establishing secure communications between devices in a network is described. According to an embodiment, messages included in pairwise temporal key (PTK) command frames and group temporal key (GTK) command frames are defined. According to another embodiment, service primitives representing message exchanges between management entities within a device are defined. According to another embodiment, method for using defined messages and primitives for a 4-way handshake to derive a PTK between two devices are also described.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Remote secure authorization
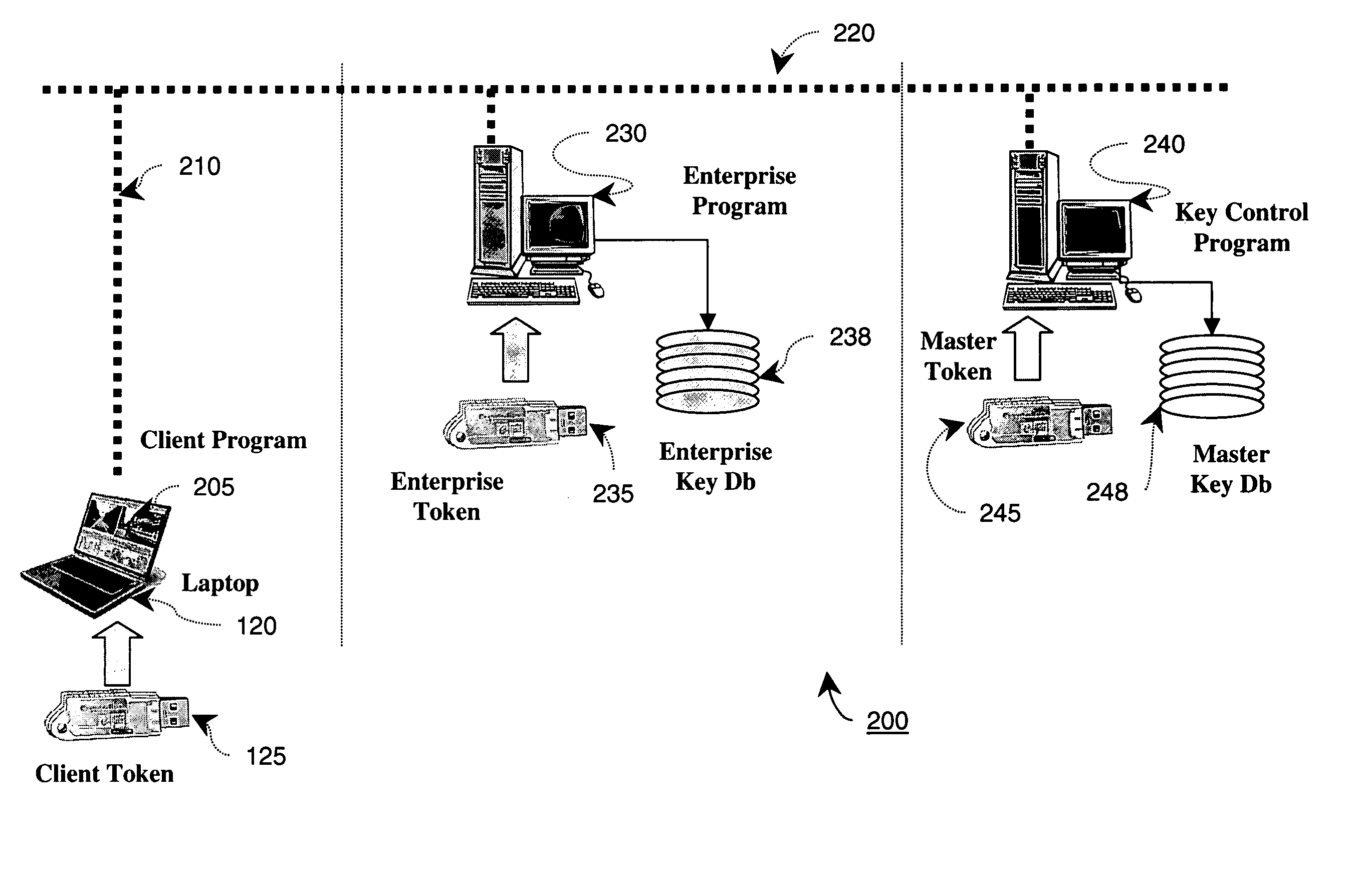
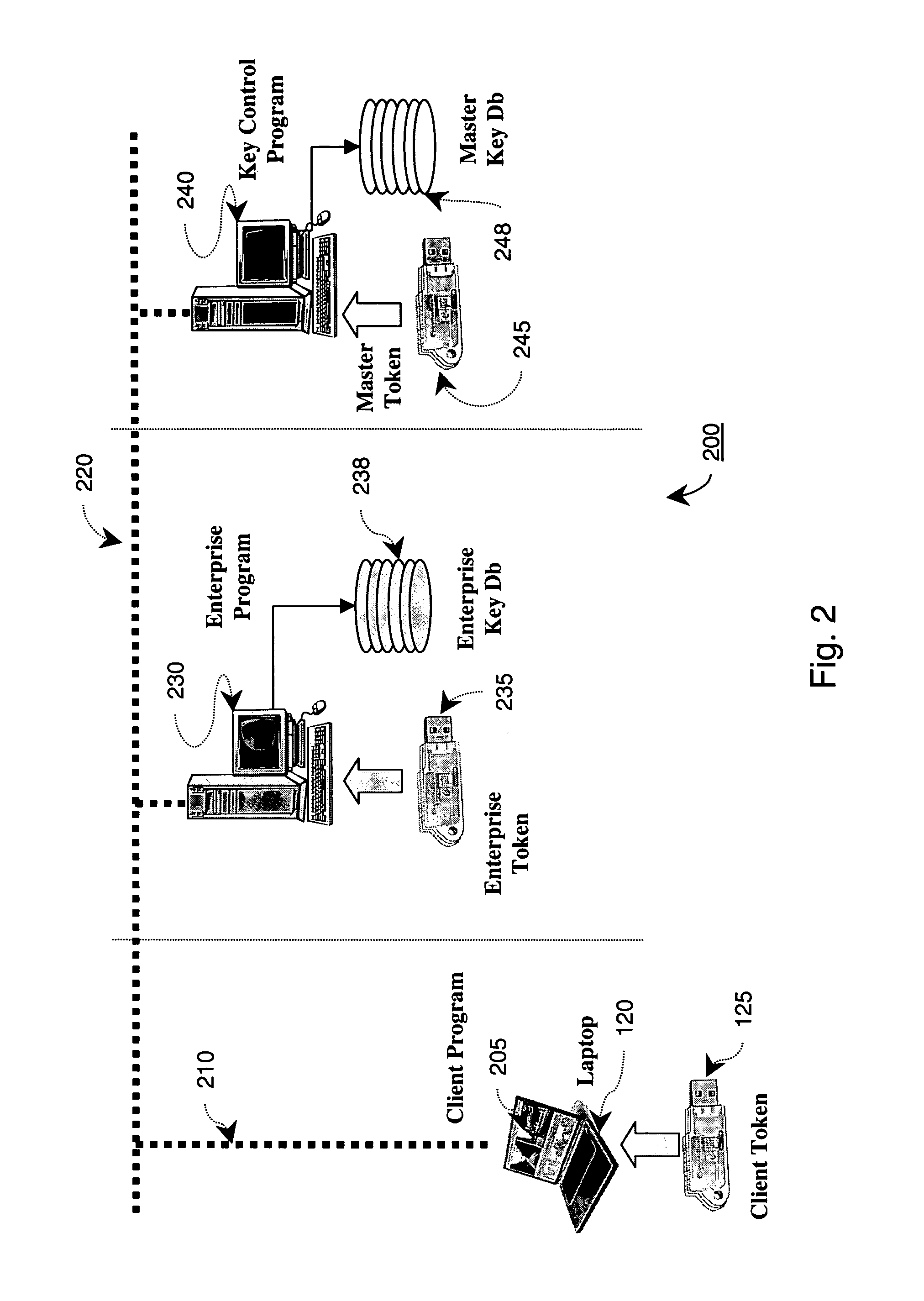
The present invention discloses a technique provisioning network cryptographic keys to a client when direct physical transfer is not feasible. In an embodiment of the invention, a client token generates a temporary key encrypted with a first secret key known only in a master token database and passes this on to an enterprise network token of a network to which service is requested. The enterprise network token then further encrypts the encrypted temporary key with a second secret key and passes that on to the master token database. Since the second secret key is also known by the master token database, the originally encrypted temporary key can be securely decoded only by a master token coupled to the master token database. The decrypted temporary key can then be re-encrypted with a key known only by the enterprise network token and the master token, and returned to the enterprise network token. This allows the enterprise network token to gain secure access to the temporary key of the client token, thereby allowing the enterprise network token to securely provision the remote client token with the appropriate enterprise Network Keys.
Owner:KOOLSPAN
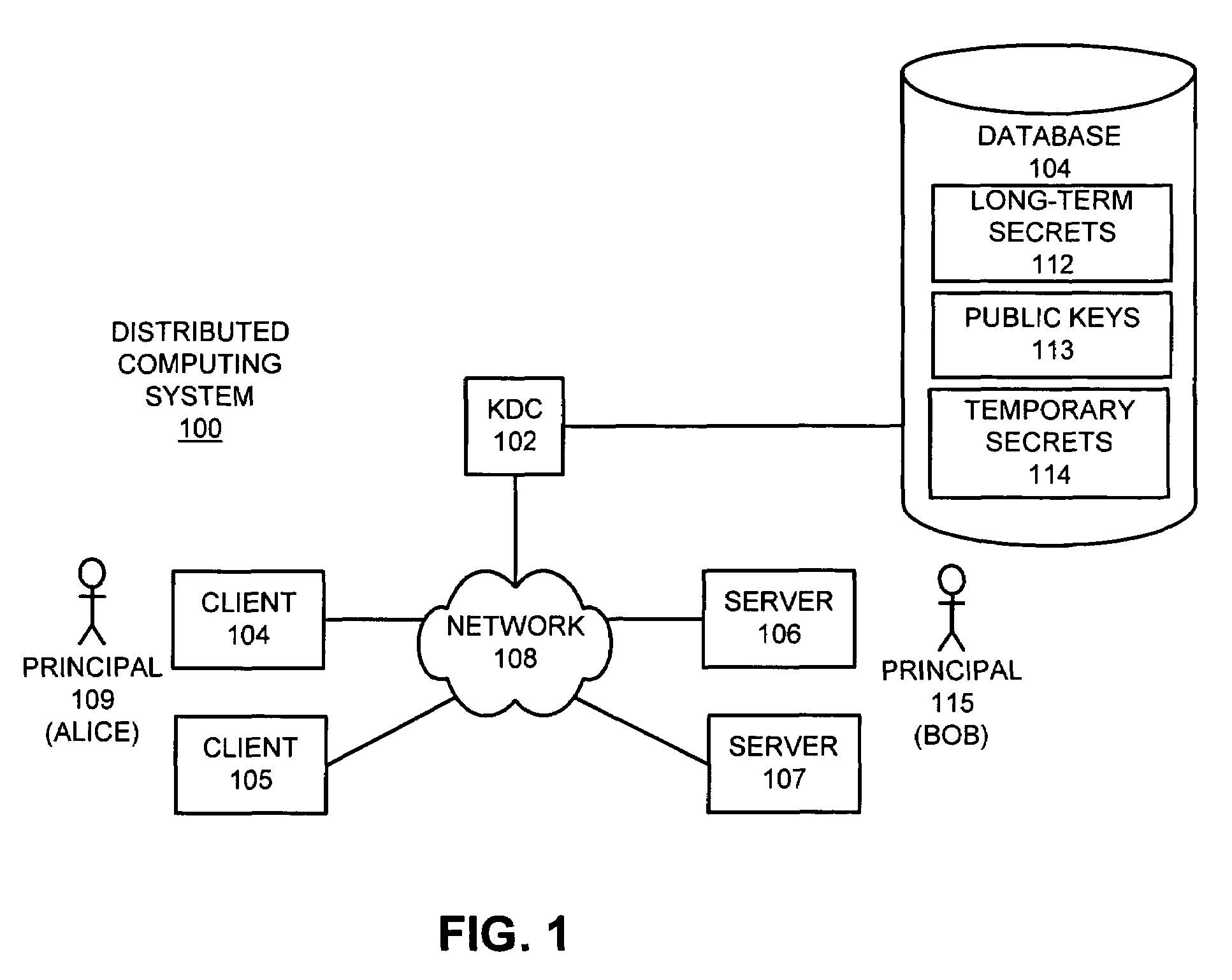
Method and apparatus for providing a key distribution center without storing long-term server secrets
InactiveUS7395549B1Facilitates secure communicationFacilitate communicationKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsSecure communicationClient-side
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system for operating a key distribution center (KDC) that provides keys to facilitate secure communications between clients and servers across a computer network, wherein the system operates without having to store long-term server secrets. The system operates by receiving a communication from a server at the KDC. This communication includes an identifier for the server, as well as a temporary secret key to be used in communications between a client and the server for a limited time period. In response the communication, the system attempts to authenticate the server. If the server is successfully authenticated, the system stores the temporary secret key at the KDC, so that the temporary secret key can be subsequently used to facilitate communications with the server. Upon subsequently receiving a request at the KDC from a client that desires to communicate with the server, the system produces a session key to be used in communications between the client and server, and then creates a ticket to the server by encrypting an identifier for the client and the session key with the temporary secret key for the server. Next, the system assembles a message that includes the identifier for the server, the session key and the ticket to the server, and sends the message to the client in a secure manner. The system subsequently allows the client to forward the ticket to the server in order to initiate communications between the client and the server.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Providing forward secrecy in a terminating SSL/TLS connection proxy using ephemeral Diffie-Hellman key exchange
ActiveUS20150067338A1Promote exchangeKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageTerminal serverDigital signature
An infrastructure delivery platform provides a proxy service as an enhancement to the TLS / SSL protocol to off-load to an external server the generation of a digital signature, the digital signature being generated using a private key that would otherwise have to be maintained on a terminating server. Using this service, instead of digitally signing (using the private key) “locally,” the terminating server proxies given public portions of ephemeral key exchange material to the external server and receives, in response, a signature validating the terminating server is authorized to continue with the key exchange. In this manner, a private key used to generate the digital signature (or, more generally, to facilitate the key exchange) does not need to be stored in association with the terminating server. Rather, that private key is stored only at the external server, and there is no requirement for the pre-master secret to travel (on the wire).
Owner:AKAMAI TECH INC
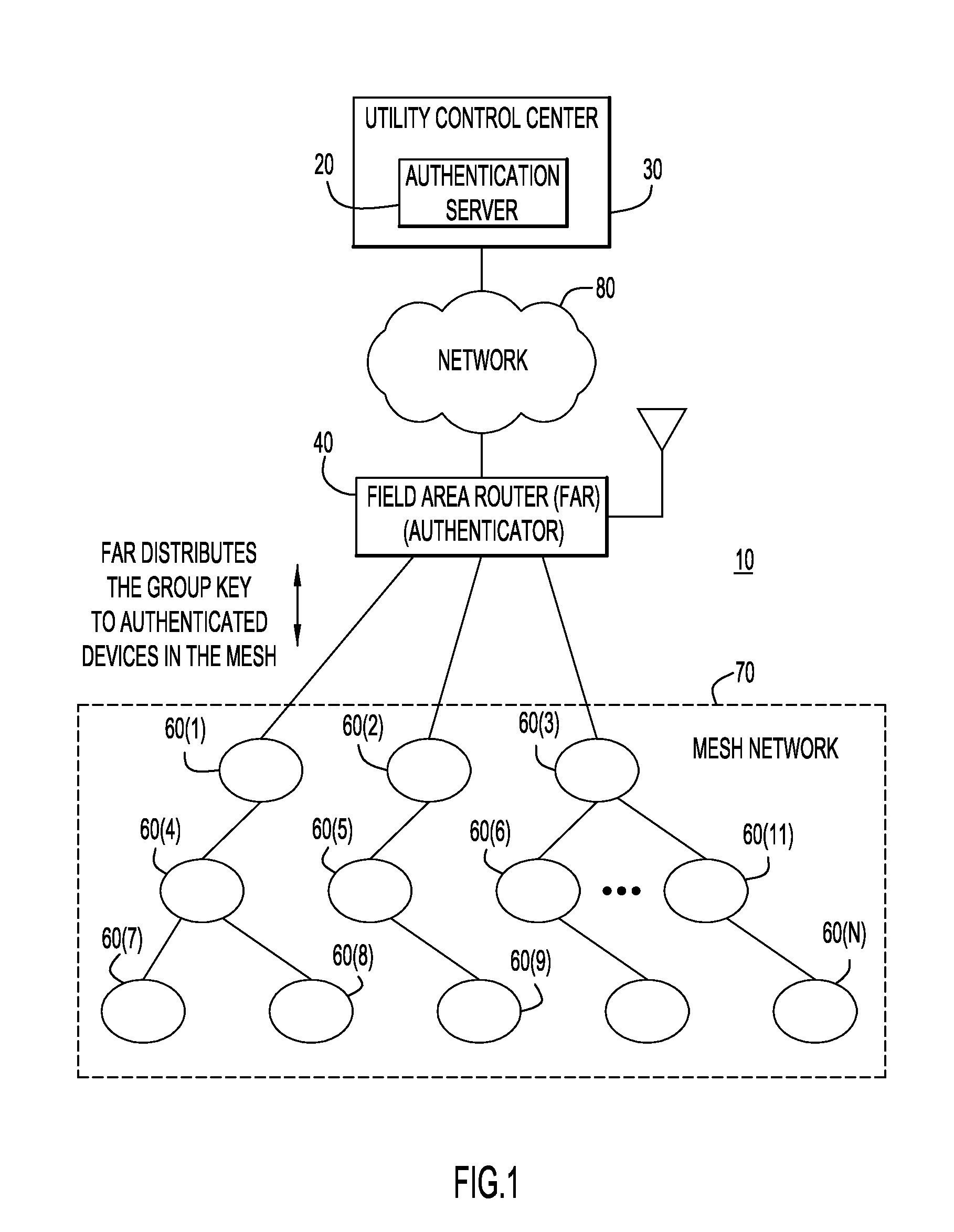
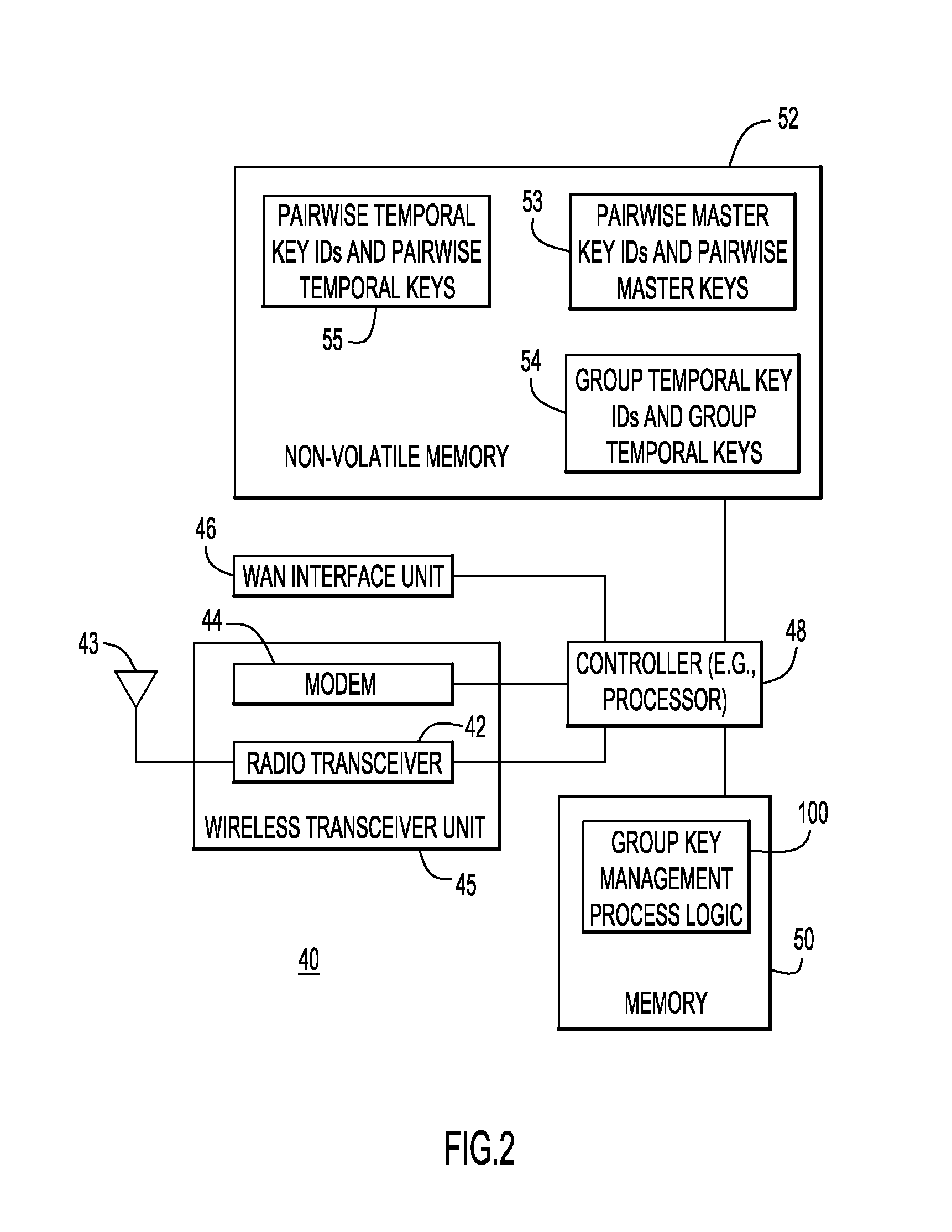
Group Key Management and Authentication Schemes for Mesh Networks
ActiveUS20130036305A1Multiple keys/algorithms usageUser identity/authority verificationSecure communicationMaster key
According to one embodiment, techniques are provided to enable secure communication among devices in a mesh network using a group temporal key. An authenticator device associated with a mesh network stores a pairwise master key for each of a plurality of devices in a mesh network upon authentication of the respective devices. Using the pairwise master key, the authenticator device initiates a handshake procedure with a particular device in the mesh network to mutually derive a pairwise temporal key from the pairwise master key. The authenticator device encrypts and signs a group temporal key using the pairwise temporal key for the particular device and sends the group temporal key encrypted and signed with the pairwise temporal key to the particular device.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
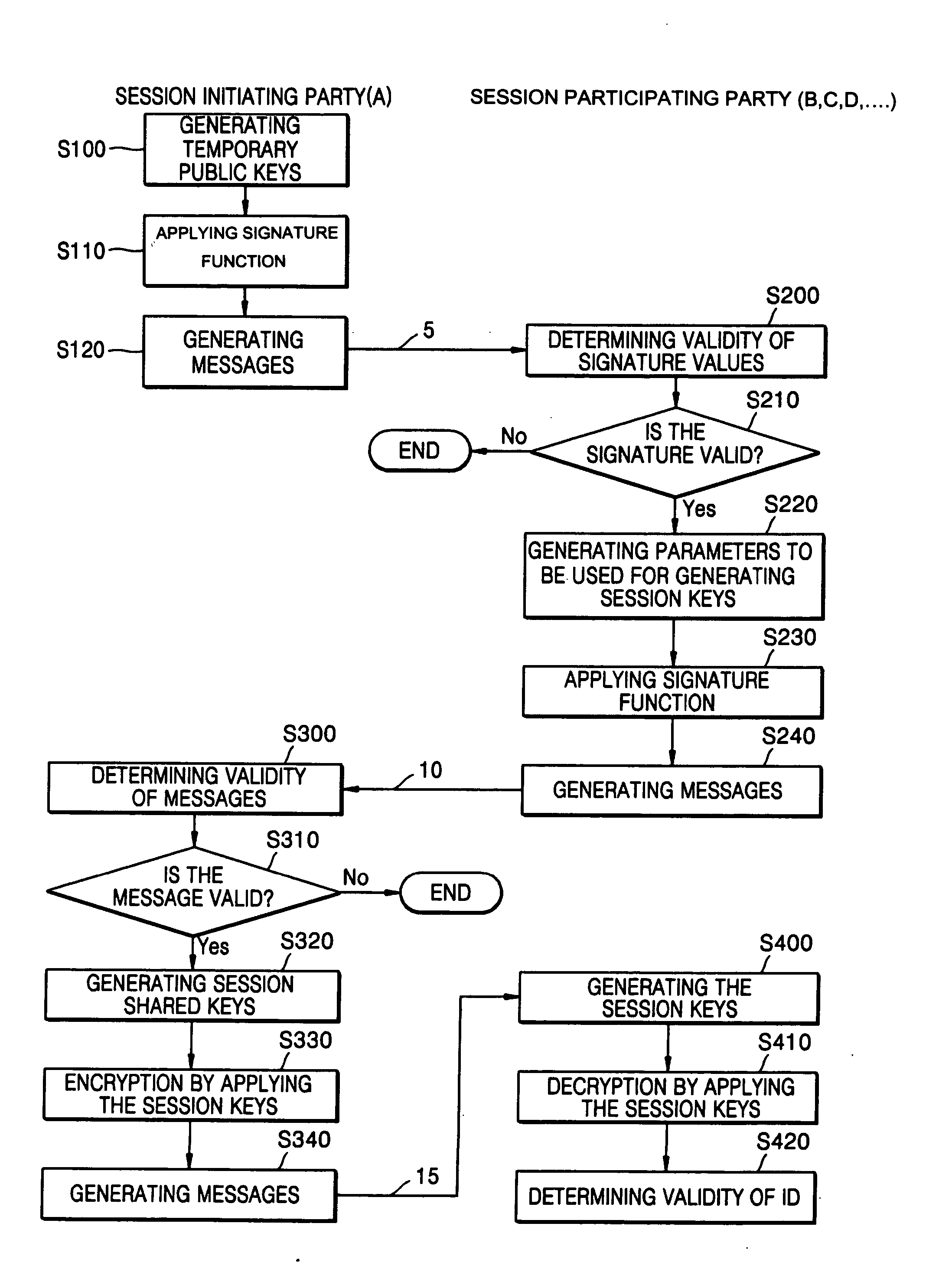
Conference session key distribution method in an ID-based cryptographic system
InactiveUS20050084114A1Avoid attackKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDistribution methodEphemeral key
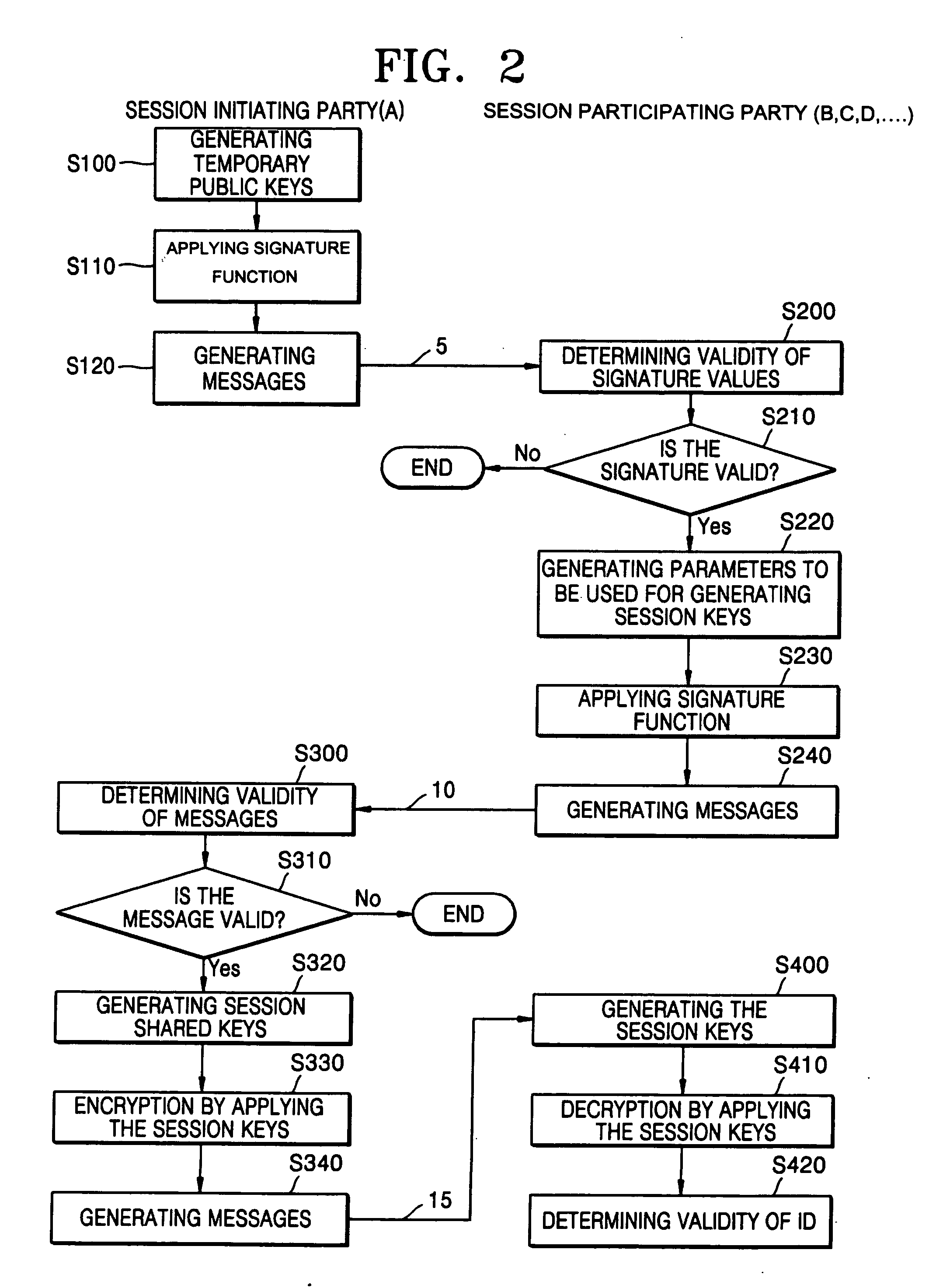
A conference session key distribution method used in an ID-based cryptographic system includes selecting two different temporary secret keys, generating a message and generating session key generation variables using the temporary secret keys of a session initiating party. Only valid participating parties receive the session key generation variables. Each party determines the session shared key from the session key generation variables.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Public key encryption with digital signature scheme
InactiveUS7707420B1Mitigate such drawbackReduce computational processingPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDigital signatureDigital signature forgery
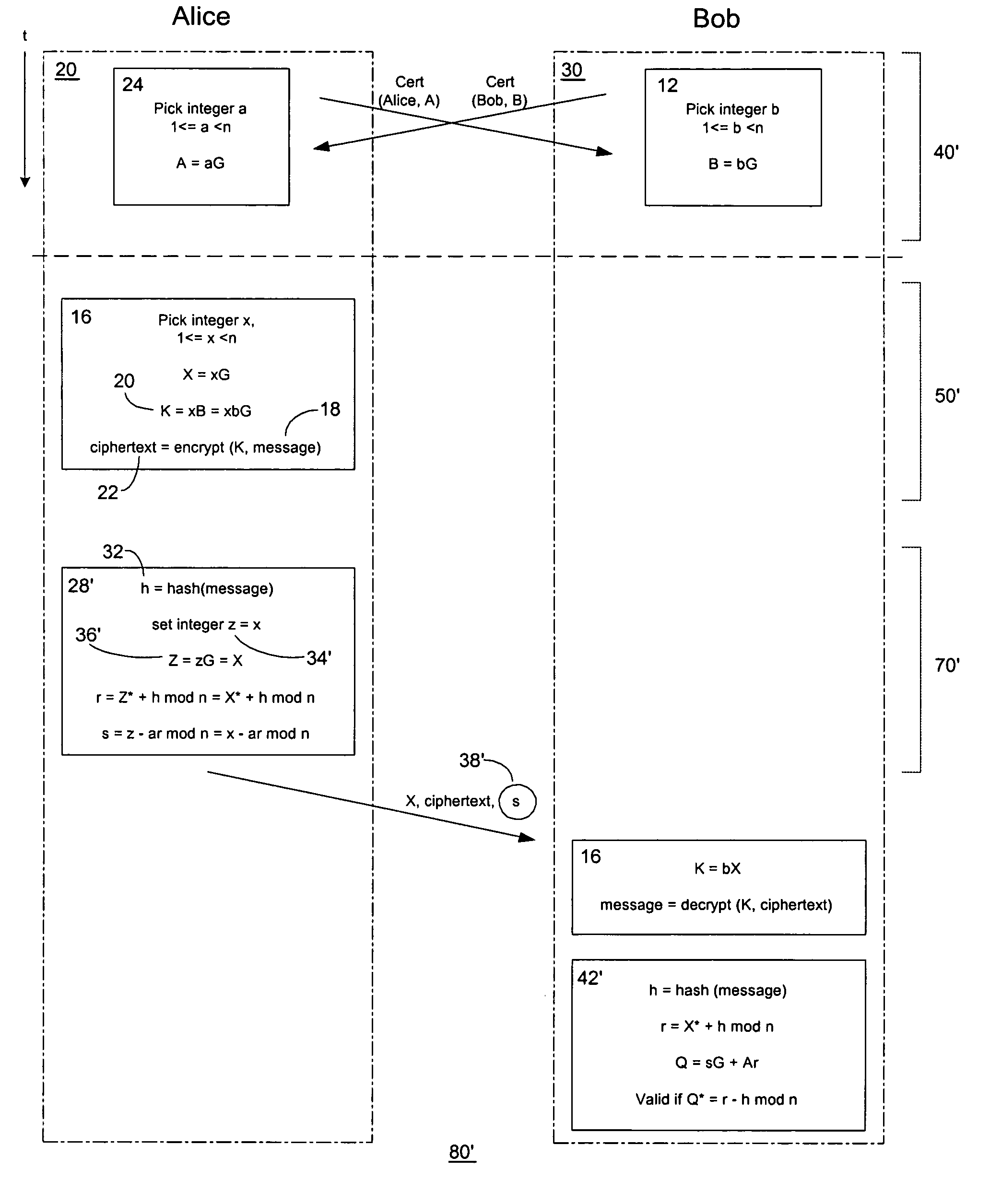
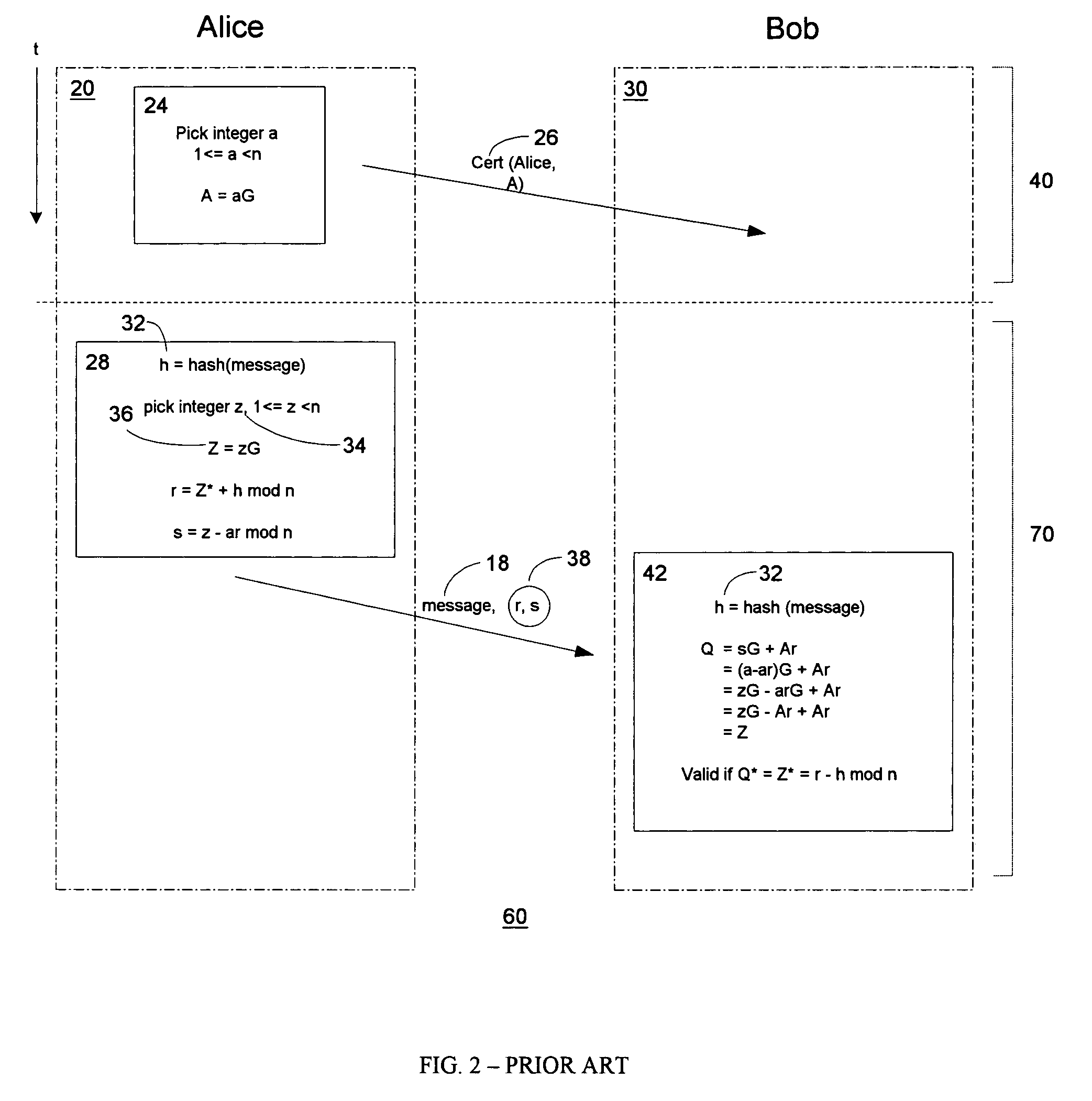
An improved encryption and digital signature system and method in accordance with the invention reuses an encryption ephemeral key pair from an encryption process in a digital signature process. The reuse of the encryption ephemeral key pair in the digital signature process advantageously results in reduced byte size of the digital signature and reduction of costly computation overhead. In a preferred embodiment, the invention is based on the El Gamal encryption scheme and the Nyberg-Rueppel signature scheme. The present invention is particularly useful for operation in conjunction with small communication devices having limited processing and storage, wherein such devices may communicate via bandwidth sensitive RF links.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
System and method for point of sale payment data credentials management using out-of-band authentication
ActiveUS20160307194A1Easy to usePromote disseminationMultiple keys/algorithms usagePublic key for secure communicationMalwareHardware authentication
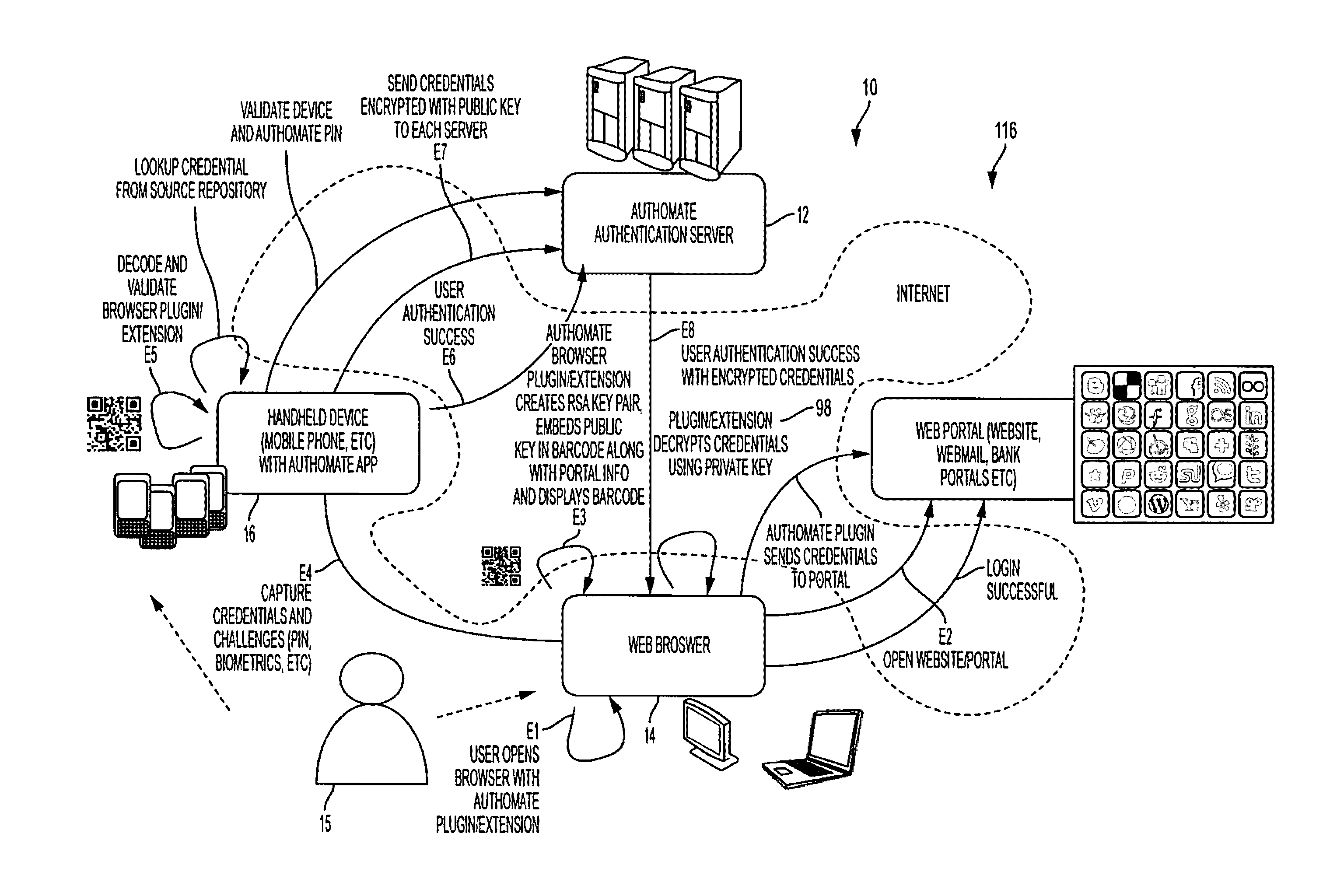
The invention provides an easy to use credential management mechanism for multi-factor out-of-band multi-channel authentication process to protect payment credentials without the risk of malware and skimming attacks.When opened, the secure payment application generates a multi-dimensional transitory key. The user authenticates the multi-dimensional transitory key and validates the secure payment application, triggering an out-of-band outbound mechanism. The portable mobile device invokes the authentication server and the authentication server authenticates the user based on the authenticated transitory key. After authentication, the merchant is allowed access to the payment credentials to complete the transaction.The process of the invention includes an authentication server, a secure payment application to generate an authentication vehicle or an embodiment (i.e. multi-dimensional transitory key) and handle incoming requests, and a portable communication device with a smartphone application.
Owner:GCOM IP LLC
Identity authentication system and method based on electronic identification card
ActiveCN104994114AProtect identity privacyImprove reliabilityUser identity/authority verificationElectronic identificationOnline identity
The invention provides an identity authentication system and method based on an electronic identification card. The identity authentication system comprises an intelligent terminal, an operator server, a network identity authentication center and an application platform. The intelligent terminal is used for storing a first temporary secret key only associated with the electronic identification card of a user, and generating to-be-authenticated encryption information and first encryption information. The operator server is used for acquiring the first encryption information, authenticating the first encryption information preliminarily, and then generating second encryption information. The network identity authentication center is used for acquiring the second encryption information, generating a second temporary secret key and authenticated encryption information, and comparing the to-be-authenticated encryption information with the authenticated encryption information so as to realize authentication of the user identity. The application platform is connected with a secret key server. The application platform sends an authentication request and is used for acquiring a result of user identity authentication from the operator server. The first temporary secret key is stored in a safe area of the intelligent terminal, so that the user does not need to carry a hardware carrier and are not worry about risks, such as information leakage and so on when in online payment or online identity authentication.
Owner:尤磊
Systems and methods of performing link setup and authentication
ActiveUS20130263223A1Digital data processing detailsNetwork topologiesAuthentication systemMobile device
Systems and methods of performing link setup and authentication are disclosed. A first method utilizes an unprotected association request and an association response that includes an access point nonce (ANonce). A second method includes receiving, during a first link setup using a first ANonce, a second ANonce for use in a second link setup. A third method utilizes a temporary key to protect an association request. A fourth method includes generating an ANonce at a mobile device based on an ANonce-seed received from an access point.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method for establishing a secure communication channel
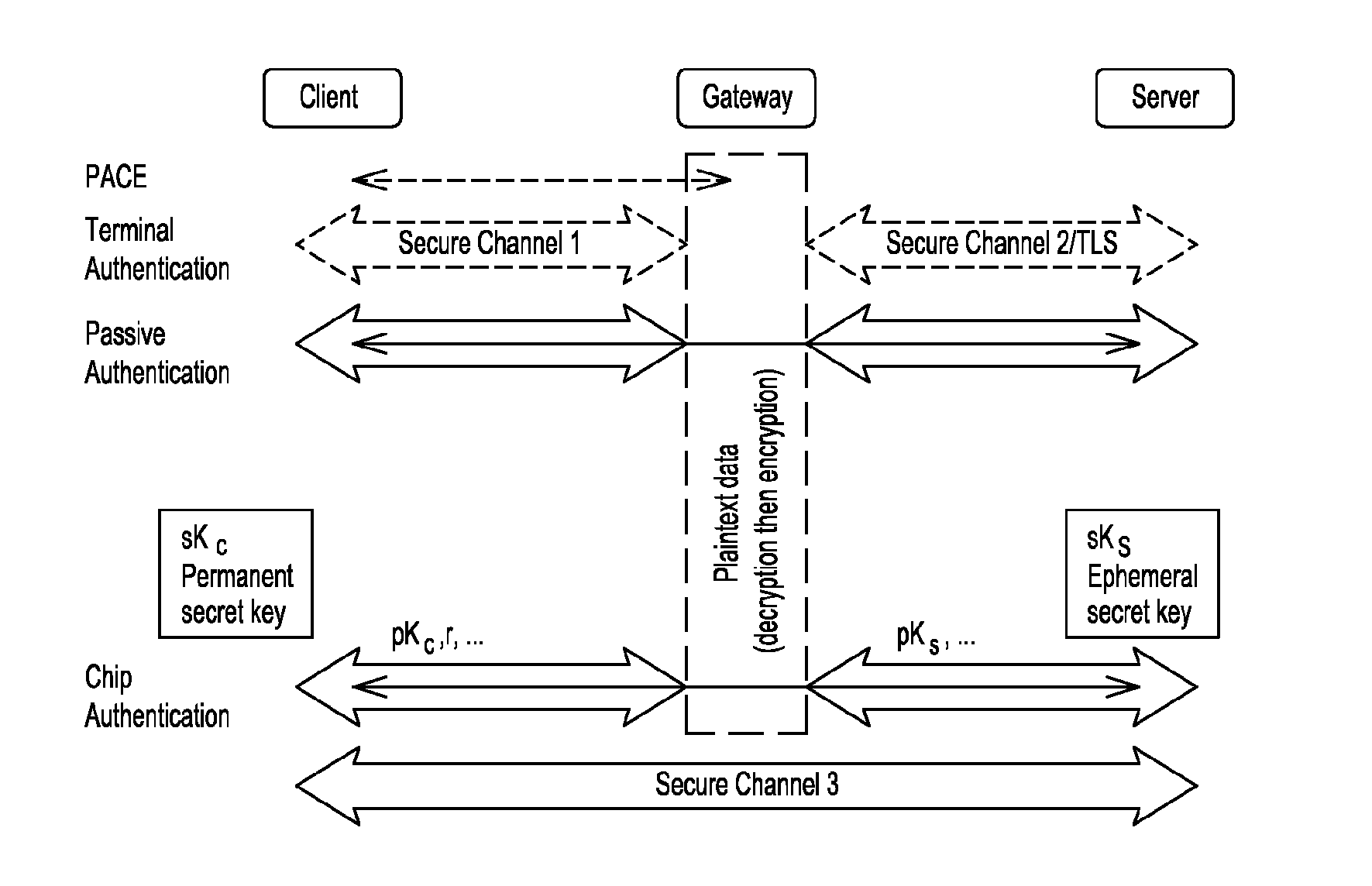
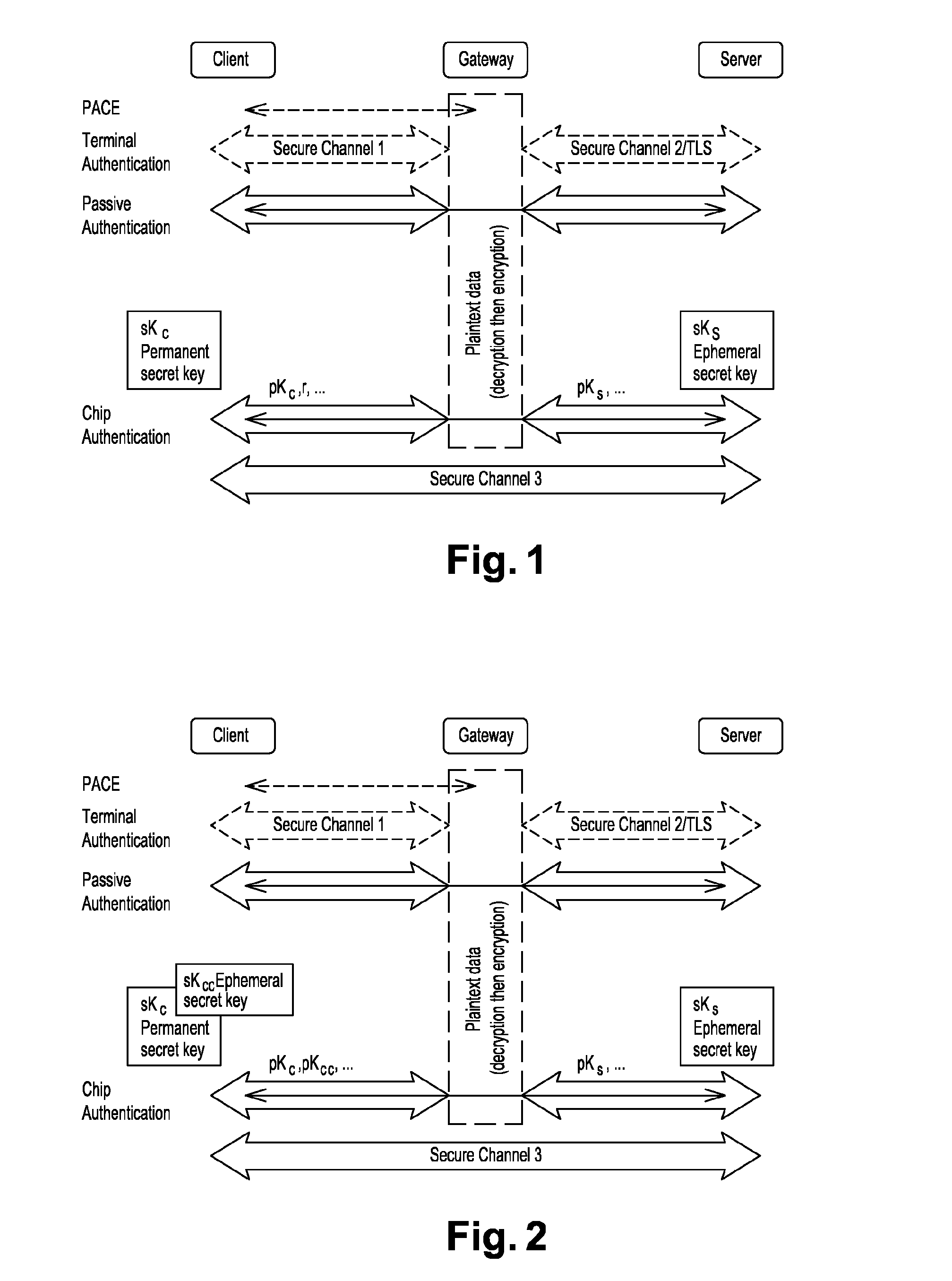
ActiveUS20130301828A1Key distribution for secure communicationSecure communicationSecure communication channel
The present invention provides a method for establishing a secure communication channel between a client (C) and a remote server (S), said client (C) and remote server (S) exchanging data through an intermediate entity (G), said client (C) having a long-term key pair (skc,pkc), said remote server generating an ephemeral key (sks,pks), the method comprising a mutual authentication step wherein the client (C) sends a public key (pkc) of said long-term key pair (skc, pkc) and the proof that said public key (pkc) is valid to the server (S), and wherein the remote server (S) sends the public key (pks) of said ephemeral key pair (sks,pks) to the client (C). The client (C) generates an ephemeral key pair (skCc,pkCc) and sends the public key (pKcc) of said ephemeral key pair (skcc,pkcc) to the server (S) so as to generate a secret common to the client (C) and to the remote server (S) for opening the secure communication channel.
Owner:THALES DIS FRANCE SA
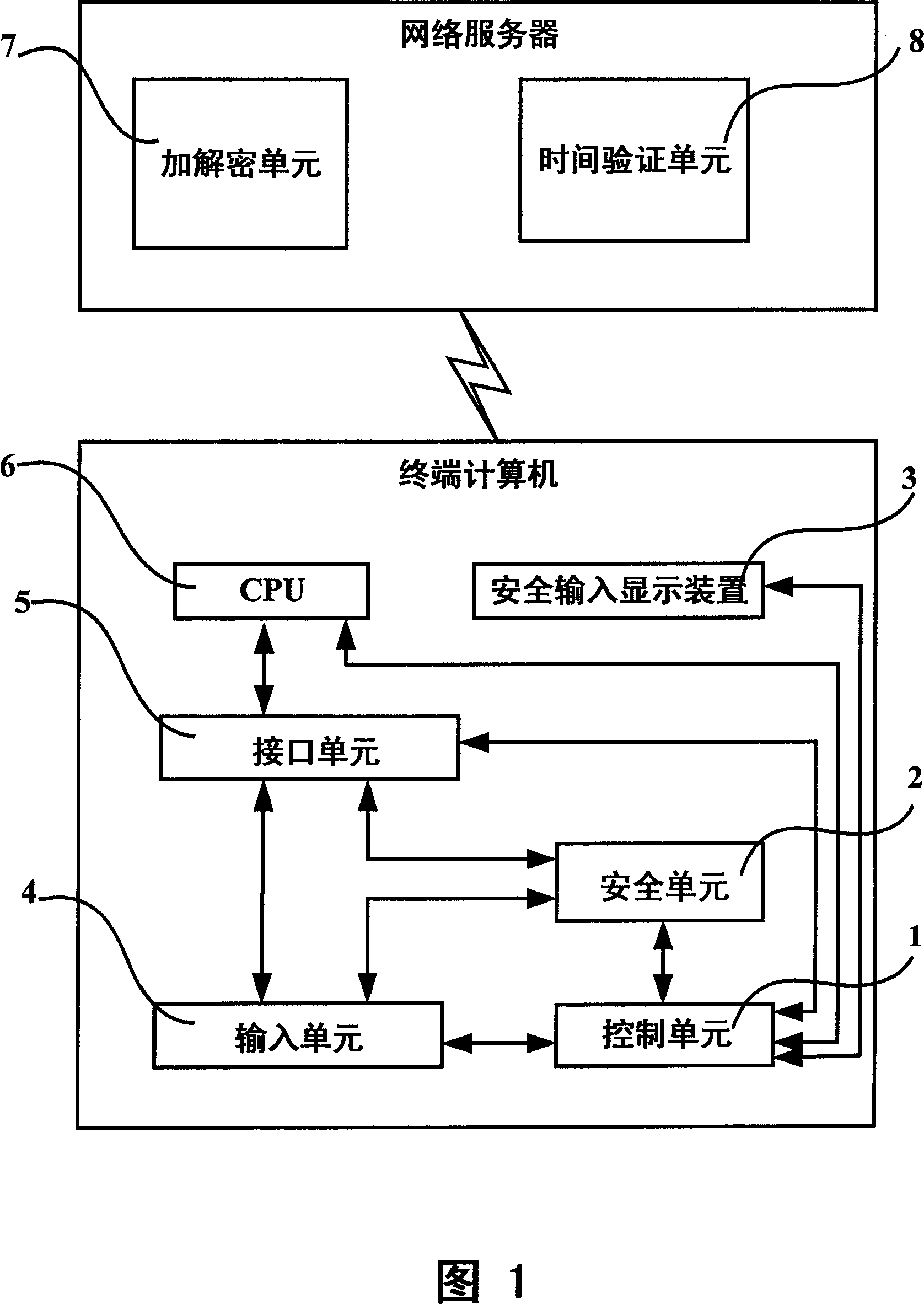
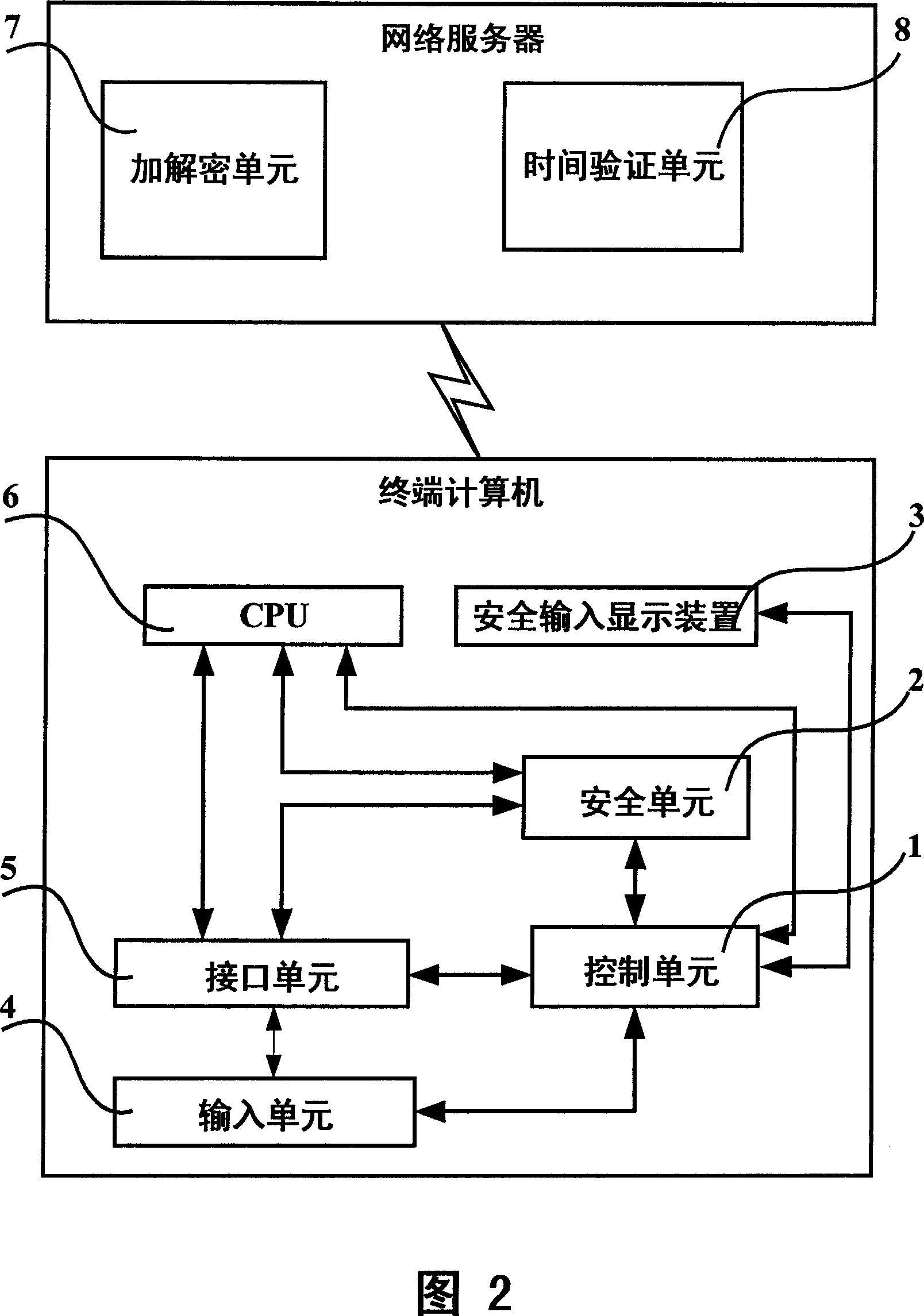
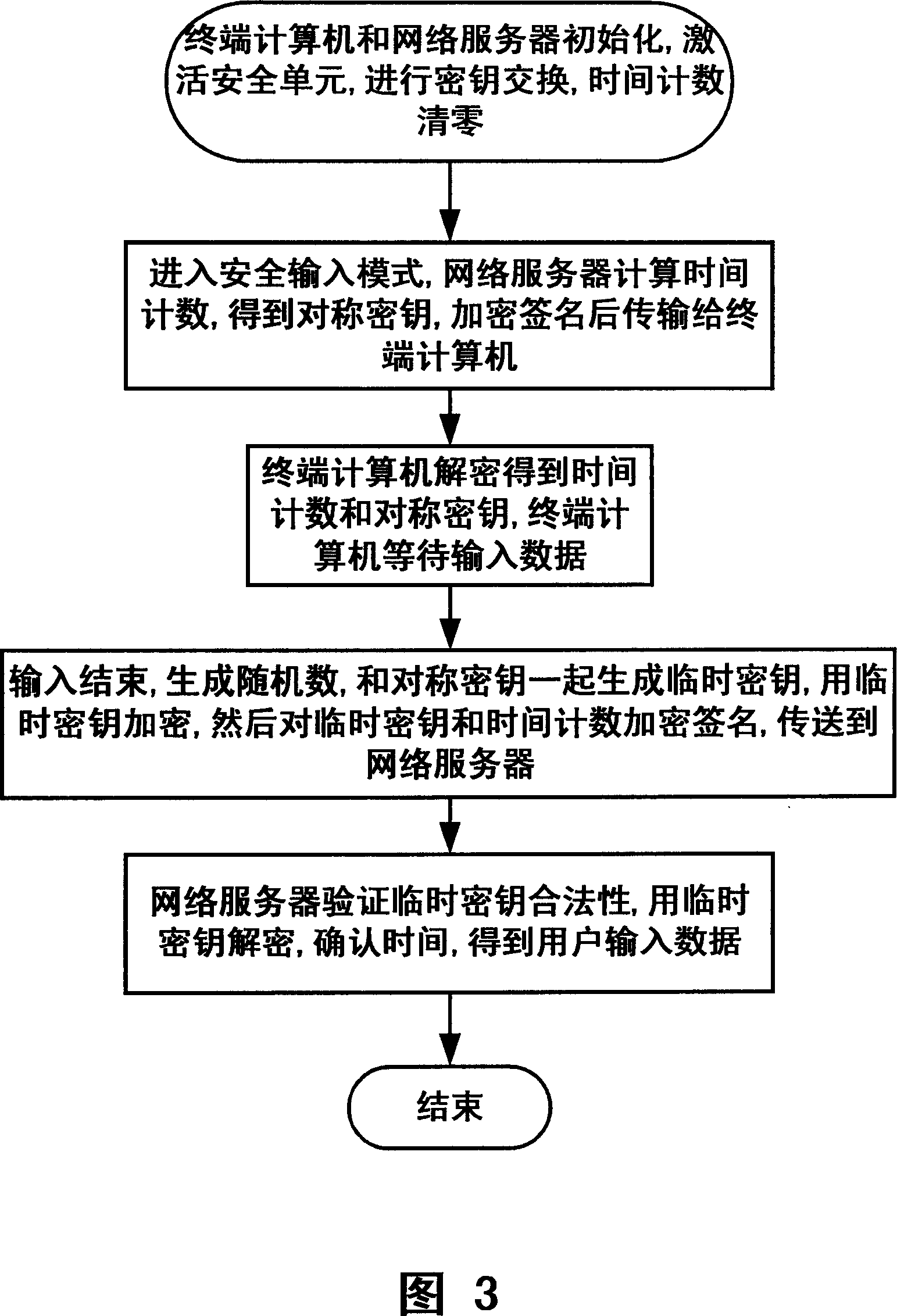
Computer network safe input authentication system and method
ActiveCN101064595ASafe loginSolving Security Authentication IssuesSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSecuring communicationUser inputNetwork packet
The invention discloses a computer network safety attestation system and method that comprises terminal computer and network server, the input equipment of the terminal computer includes input unit (4) and interface unit (5), said terminal computer also includes control unit (1) and safe unit (2); the safe unit (2) receives the data input from the input unit (4) in safe inputting mode, encrypting data input with symmetry arithmetic by key, temporary key is encrypted and underwritten by the server general key transmitted by the network server with asymmetric arithmetic; said network server includes encrypting and deciphering unit(7); the encrypting and deciphering unit(7) deciphers the data package transmitted from the terminal computer with corresponding asymmetric arithmetic using server private key to obtain the key, validating the validity of temporary key, then the encrypted character string is deciphered with corresponding symmetry arithmetic using the temporary key to obtain data input by user. The inventions can guarantees the input data of computer not be filched, decrypted or forged.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) CO LTD
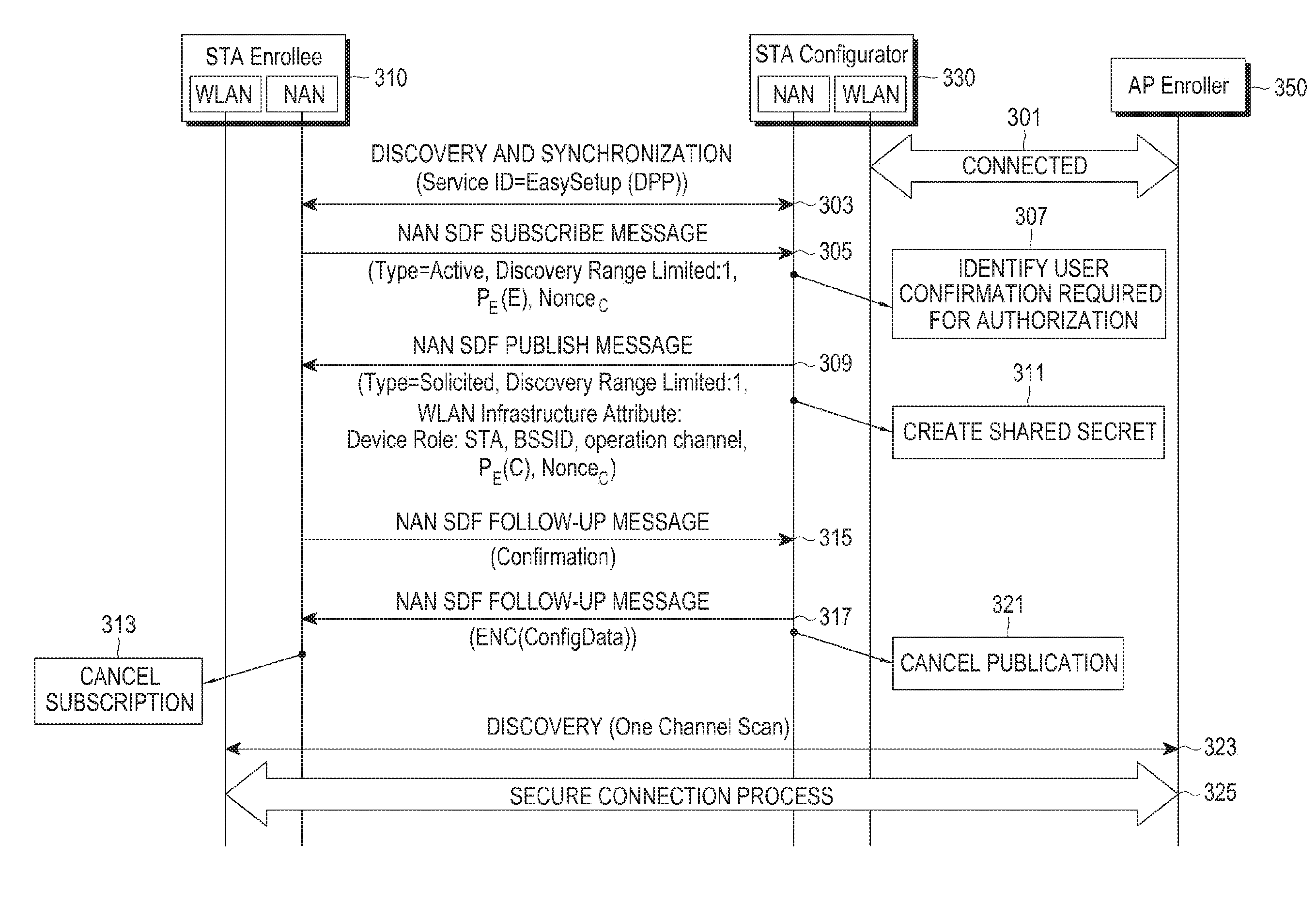
Method and apparatus for configuring connection between devices in communication system
Disclosed are a communication scheme and a system thereof for converging an IoT technology and a 5G communication system for supporting a high data transmission rate beyond that of a 4G system. A method and an apparatus for configuring a connection with a second device, which provides access to a network, by a first device in a communication system, is provided. The method includes discovering the second device supporting a neighbor awareness network (NAN) and located within a predetermined range from the first device, exchanging an ephemeral key of the first device for identifying the first device and an ephemeral key of the second device for identifying the second device, and performing a secure connection between the first device and the second device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Wireless RFID system authentication method and apparatus
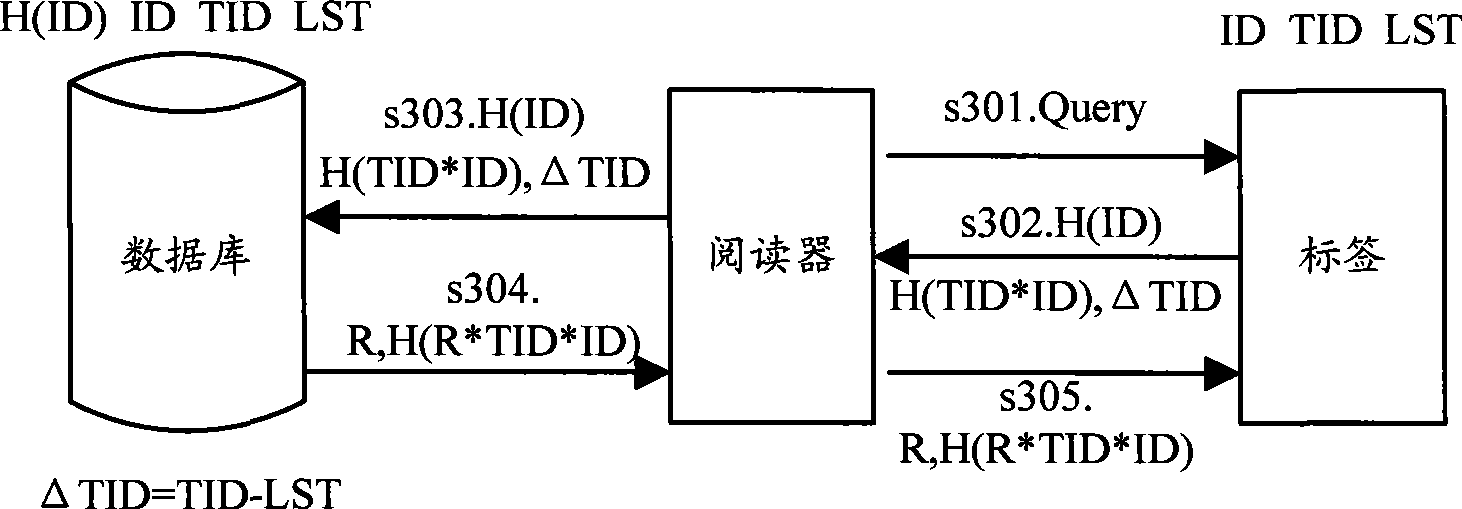
InactiveCN101488854AKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationPlaintextTransfer mode
The embodiment of the invention discloses an authentication method in wireless radio frequency recognition RFID for bidirectional authentication between a label, a reader and a database. The embodiment of the invention also discloses a system and apparatus for authentication in RFID, according to the method and apparatus provided by the invention embodiment, the ID can be divided on the transferring mode of the label ID, and the ciphering and the transmitting can be performed respectively, the mode enables the ID information not to be transmitted by the clear text form, the information can be transmitted to the reader by the label at the anonymous mode, so that the information of the label ID can be protected. In addition, the embodiment of the invention also provides a label enquiring type communication mode, according to the method for increasing and storing temporary cipher key on the network side and transmitting the request for updating the cipher key before the database updates the cipher key forward label to affirm whether the cipher key is updated or not, the reliability for updating the cipher key between the label and the network side synchronously can be improved.
Owner:北京智讯伙伴科技有限公司
Secret key management method, device and system
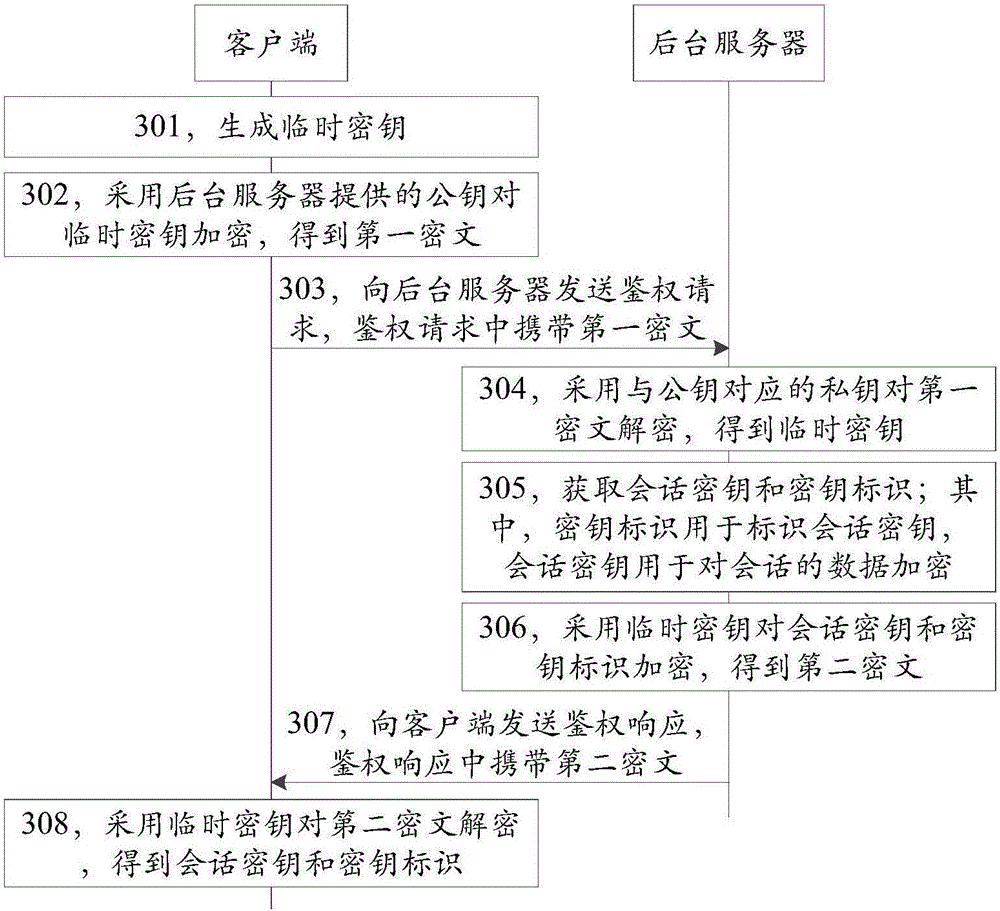
ActiveCN106712932ASolve the problem of requiring a lot of resources to manage symmetric keysSimplify complexityKey distribution for secure communicationCiphertextClient-side
The invention discloses a secret key management method, device and system, and belongs to the technical field of information security. The method comprises the steps that a client side generates a temporary secret key, and the temporary secret key is encrypted by using a public key provided by a background server so that a first cryptograph is obtained and transmitted to the background server; the background server applies a private key corresponding to the public key to decrypt the first cryptograph so as to obtain the temporary secret key, a session key and a key identifier are acquired, and the session key and the key identifier are encrypted by using the temporary secret key so that a second cryptograph is obtained and transmitted to the client side; and the client side applies the temporary secret key to decrypt the second cryptograph so as to obtain the session key and the key identifier, wherein the key identifier is used for identifying the session key, and the session key is used for encrypting the session data. The management complexity of the background server for the secret key can be simplified under the premise of considering the security of the secret key and the efficiency of encryption and decryption so that the processing and storage resources of the background server can be saved.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
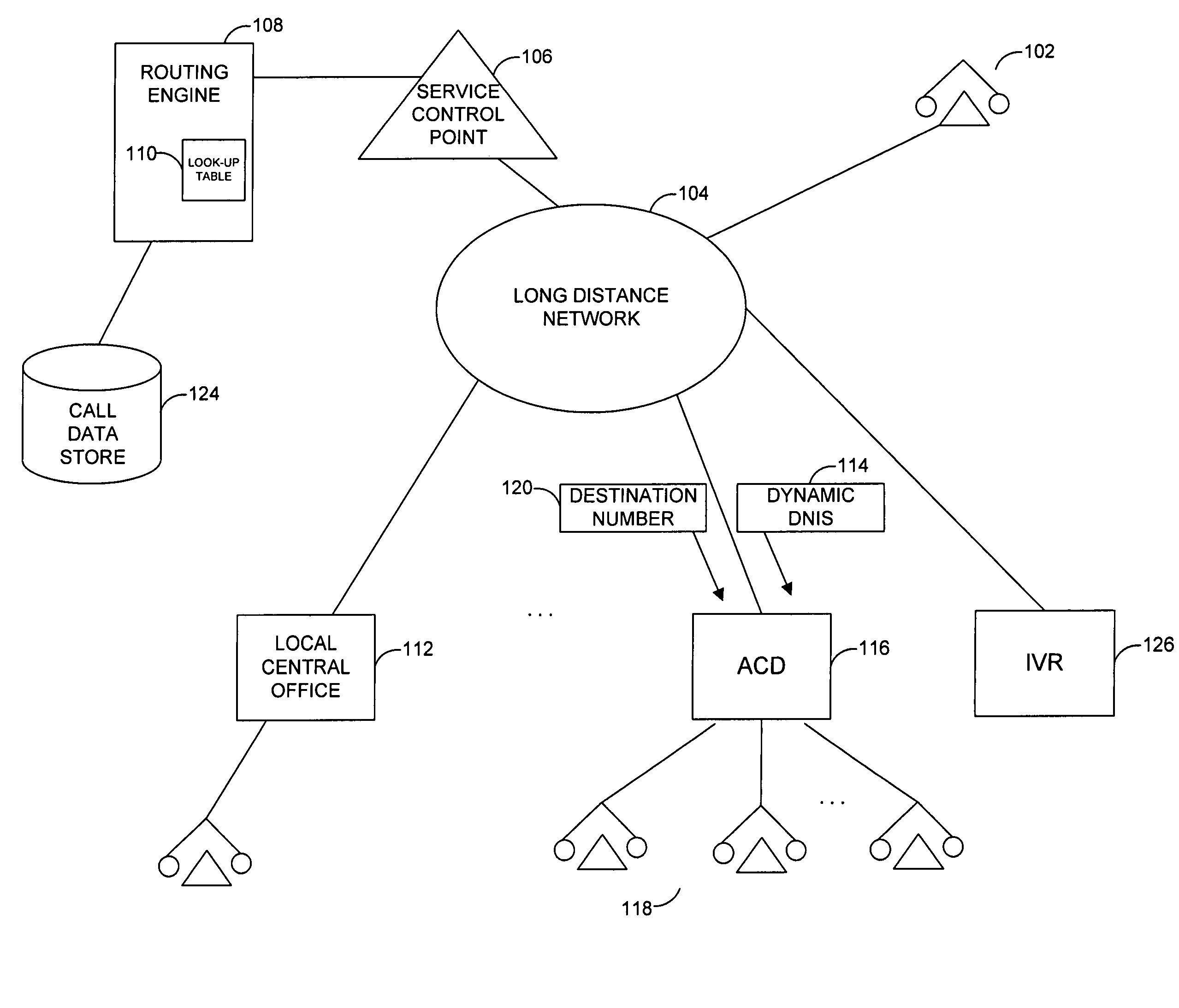
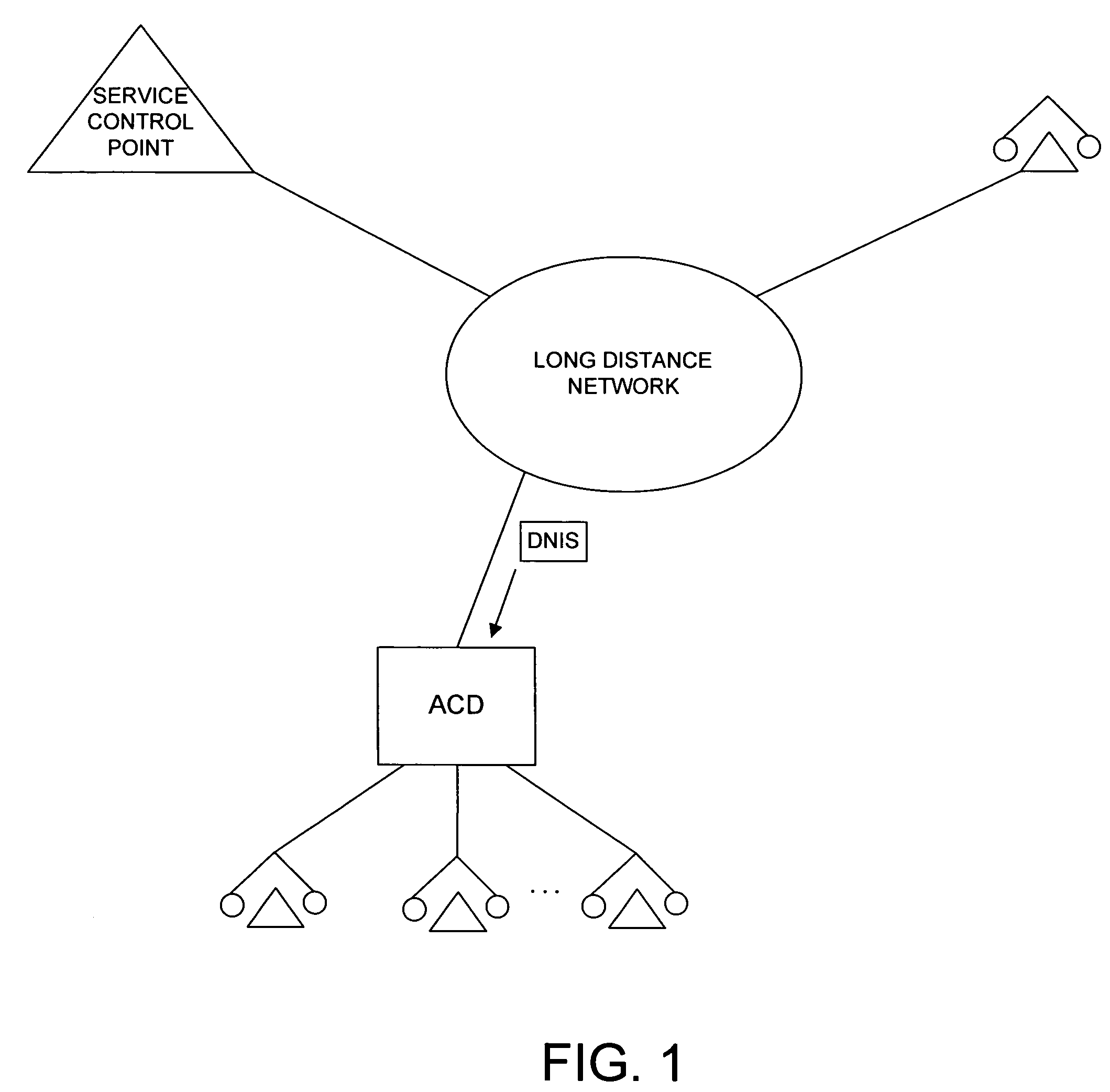
System and method for dynamic assignment of dialed number identification services in call distribution system
ActiveUS7894587B1Capacity of systemIncrease capacityInterconnection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersDistribution systemData memory
A system and related techniques enhance the generation and delivery of dialed number identification service (DNIS) data to automatic call distributors and other destinations. Unlike conventional DNIS-based (800) or other call centers or other resources whose available DNIS-based identifications can become overtaxed during comparatively high call volumes, according to embodiments of the invention DNIS numbers are dynamically generated from an available pool on a per-call basis under call router supervision. According to embodiments of the invention in one regard, the dynamic DNIS may be associated with that call to the call's particular destination, such as an automatic call distributor, interactive voice response unit or other resource, during the duration of the call for the operative destination, with other calls being locked out from using that DNIS assignment while the call is in progress. The DNIS digits along with other tag or label information may likewise be used as a temporary key to access associated call data, such as dialed number, caller entered or other data or information, which may be stored in a data store for access by customer service representatives (CSRs) or others. After the call is completed, the temporarily assigned DNIS number may be released back to the pool for use by other calls to that destination.
Owner:T MOBILE INNOVATIONS LLC
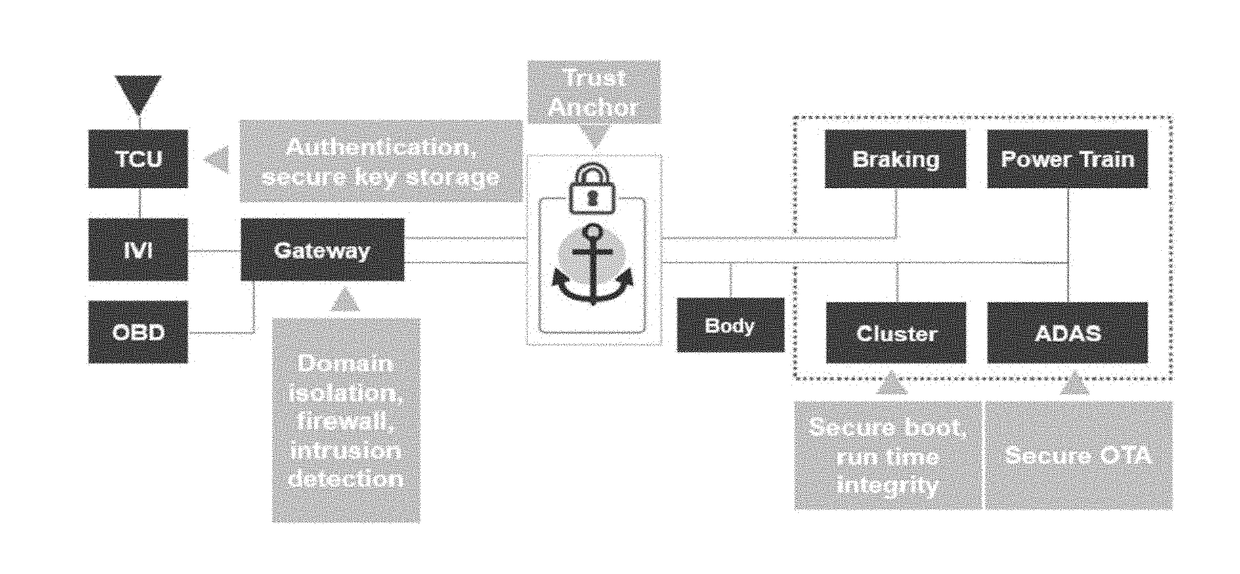
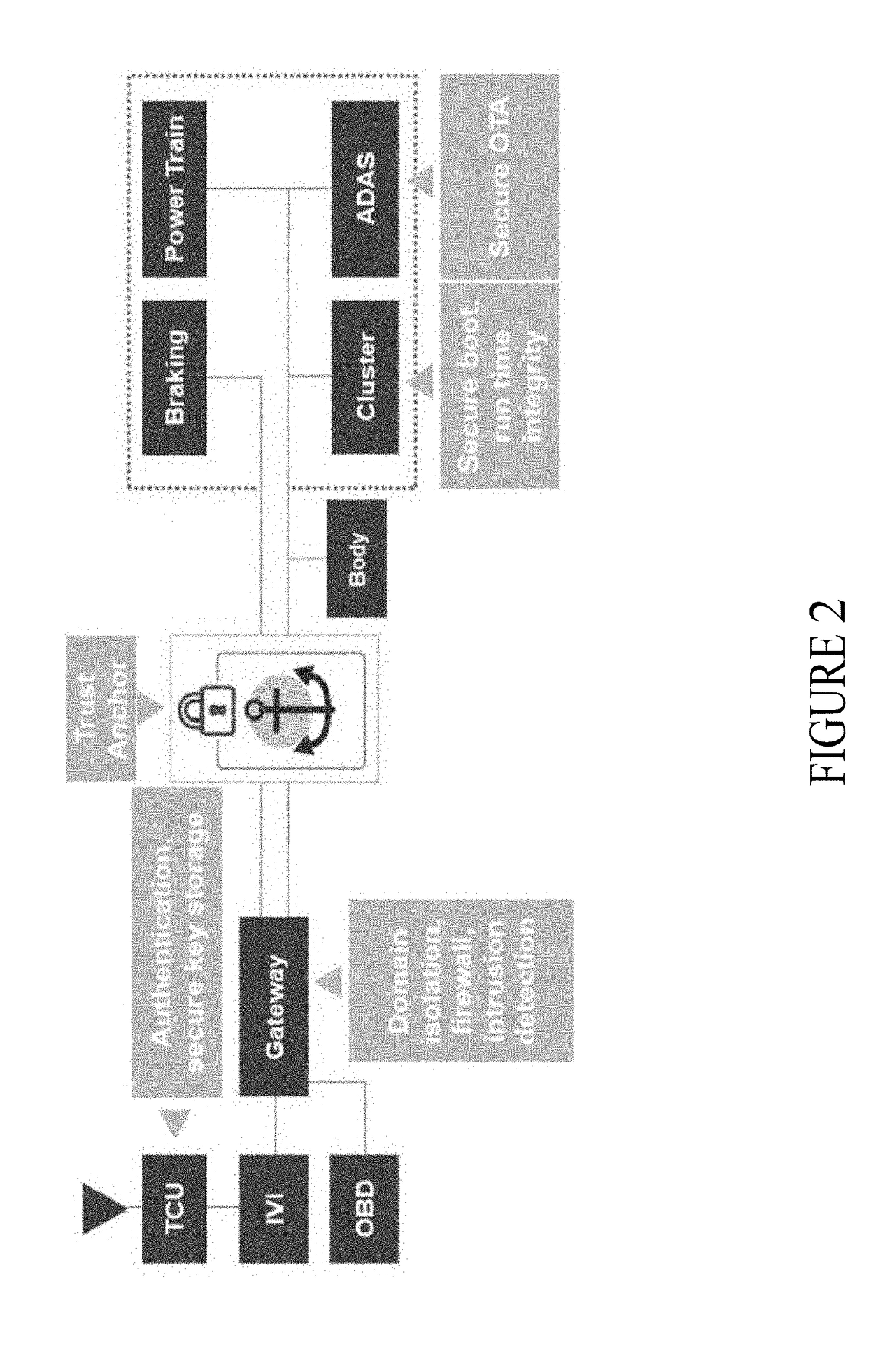
In-vehicle networking
A system and method for securing communication across an in-vehicle bus, includes establishing a connection between a gateway in a vehicle and the in-vehicle bus; generating a session key at the gateway within the vehicle; transmitting a public key certificate and ephemeral key to the gateway and an electronic control unit of the vehicle; generating a shared secret at the gateway and the electronic control unit, respectively; encrypting the session key with the shared secret at the gateway; receiving the encrypted session key through the in-vehicle bus at the electronic control unit; and decrypting the encrypted session key based on the shared secret generated at the electronic control unit.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
Blockchain data processing method, device, processing equipment and system
ActiveCN108600272AGuaranteed safe handlingImprove securityUser identity/authority verificationData informationData store
The embodiment of the specification discloses a blockchain data processing method, device, processing equipment and system. For encryption processing in related operations related to a target contract, such as signature, encryption, verification and the like of the contract, contract participants can use a temporarily generated key to carry out processing. Data information after the temporary keyprocesses is uploaded into a blockchain to carry out storage, safety processing of each contract participant on the contract data under the chain can be effectively guaranteed, and meanwhile, safety of data storage in the blockchain is improved.
Owner:ADVANCED NEW TECH CO LTD
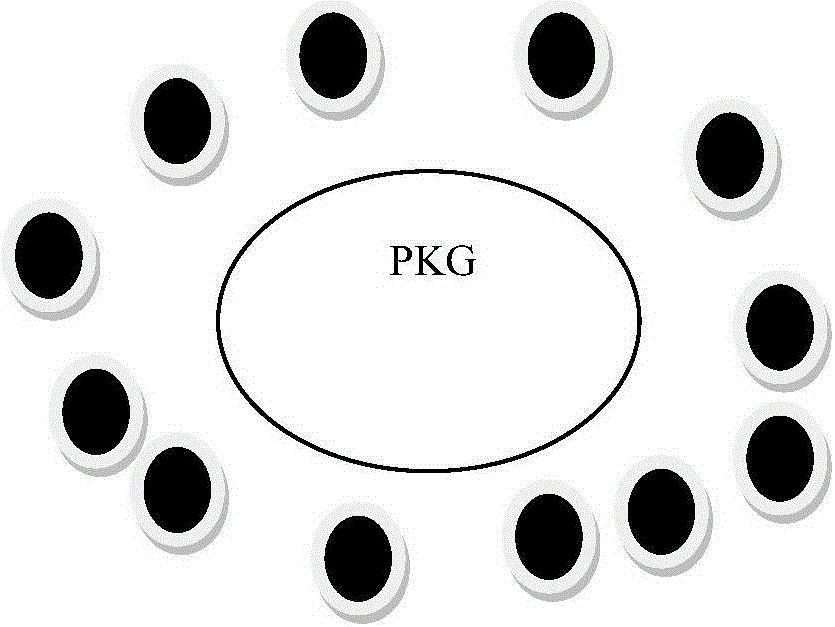
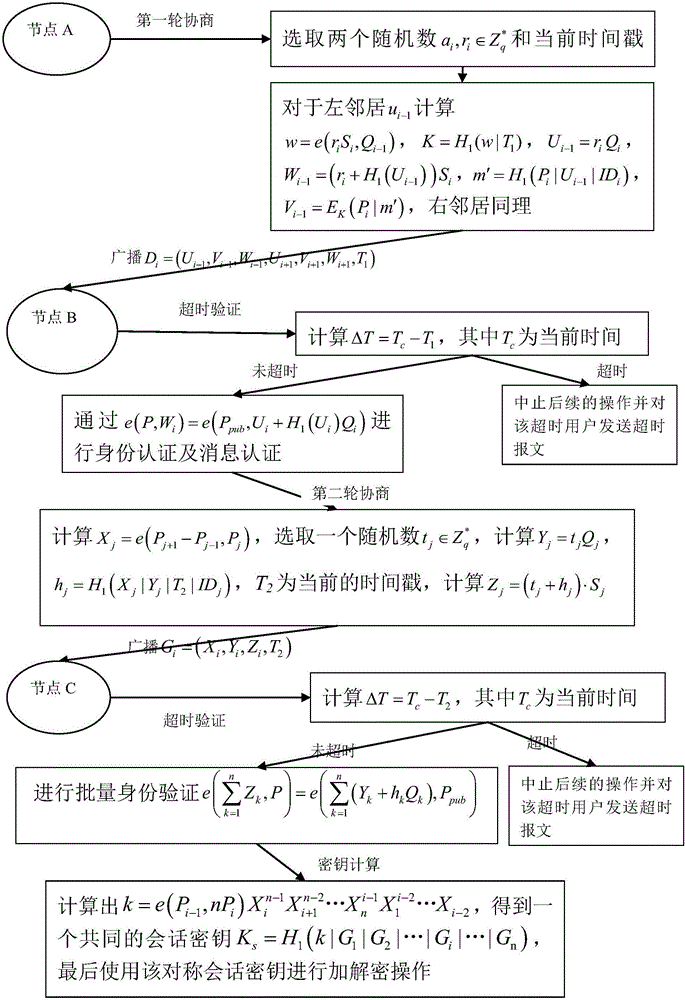
ID-based authenticated dynamic group key agreement method
ActiveCN105959269ATroubleshoot certificate issuesAvoid complex calculationsKey distribution for secure communicationRelevant informationNetwork communication
The invention relates to an ID-based authenticated dynamic group key agreement method, and belongs to the network communication safety technology field. The method is characterized in that 1, system initialization: a PKG is generated, and system parameters are disclosed; 2, private key extraction generation: every user sends a public key to the PKG, which is used to return a private key to the corresponding user; 3, two rounds of key agreement: a first round of key agreement is carried out in order to authenticate validity of neighbors of a group users and transmit an own temporary key, and a second round of key agreement is carried out after the successful authentication of the neighbors in order to disclose the related information used for generating the group conversation key; 4, the conversation key is calculated by using the information of the last step, and is used for the encryption and the decryption of the inter-group communication. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention is advantageous in that the user dynamic event is supported at the same time of realizing the key agreements, and then the network is provided with the good dynamic performance and the expansibility, and at the same time, the internal attacker can be detected, and under the precondition of guaranteeing the safety performance, the encrypted items are less, and then the calculation quantity and the communication traffic are reduced.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
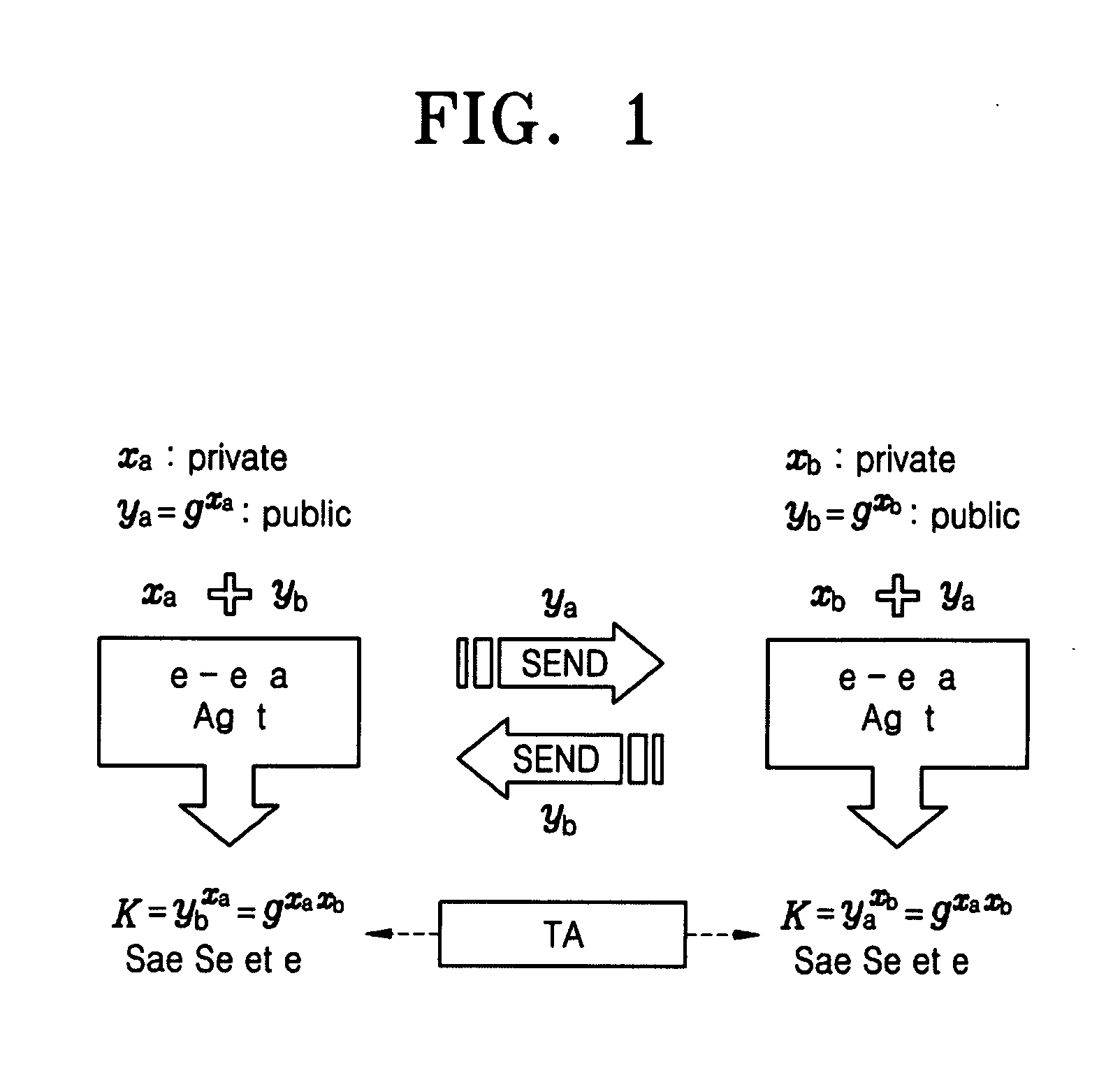
Key agreement method and device
InactiveCN101582906AImprove efficiencyEnsure safetyPublic key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCertificate authorityEphemeral key
The invention discloses a key agreement method and a device. The method comprises the steps: a first user end obtains a long-term public key of a second user end conducting key agreement session with the first user end from a certificate authority; an ephemeral key of the first user end is selected randomly and the first hash calculation is conducted on the ephemeral key of the first user end and a long-term private key of the first user end to obtain a first intermediate value; according to the first intermediate value and the ephemeral key, first key agreement information is generated; after the first key agreement information is sent to the second user end, second key agreement information returned back from the second user end is received; and according to the second key agreement information, the long-term public key of the second user end, the ephemeral key of the first user end, the long-term private key of the first user end and the session identification of the key agreement session, the first user end conducts the second hash calculation to obtain a shared key. The method and the device improve the efficiency of the key agreement, and the long-term key and the ephemeral key of any party can not be simultaneously divulged, thus being capable of guaranteeing the security of agreement.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
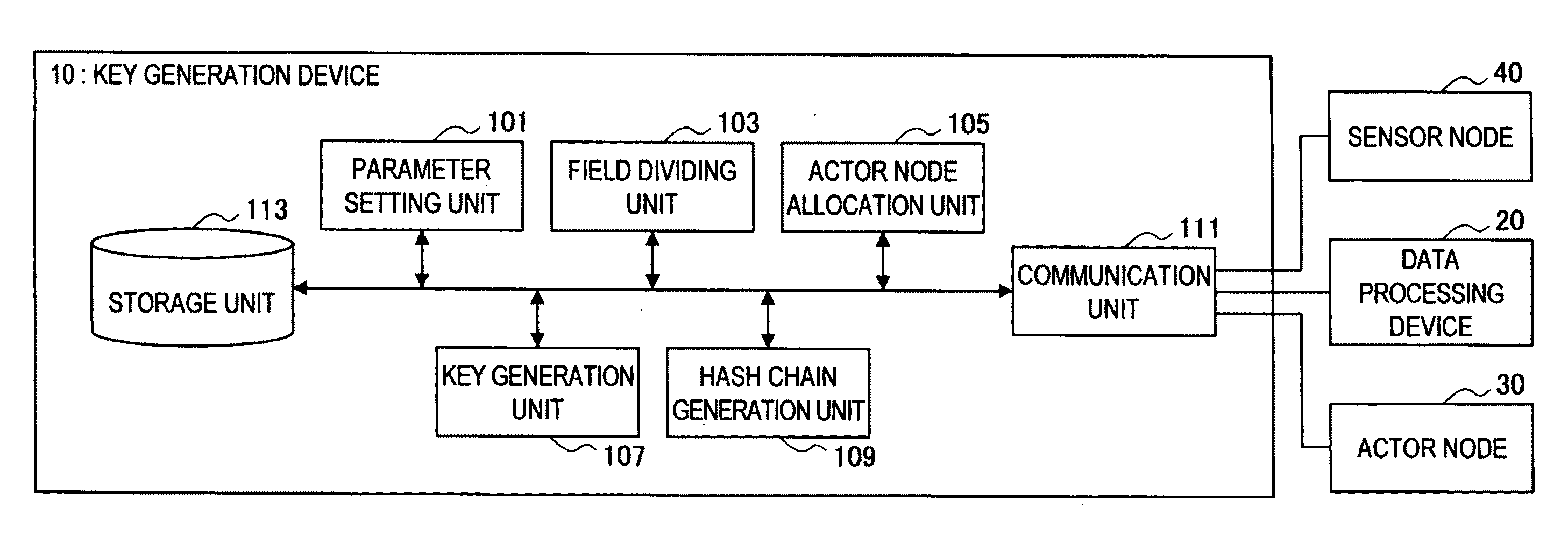
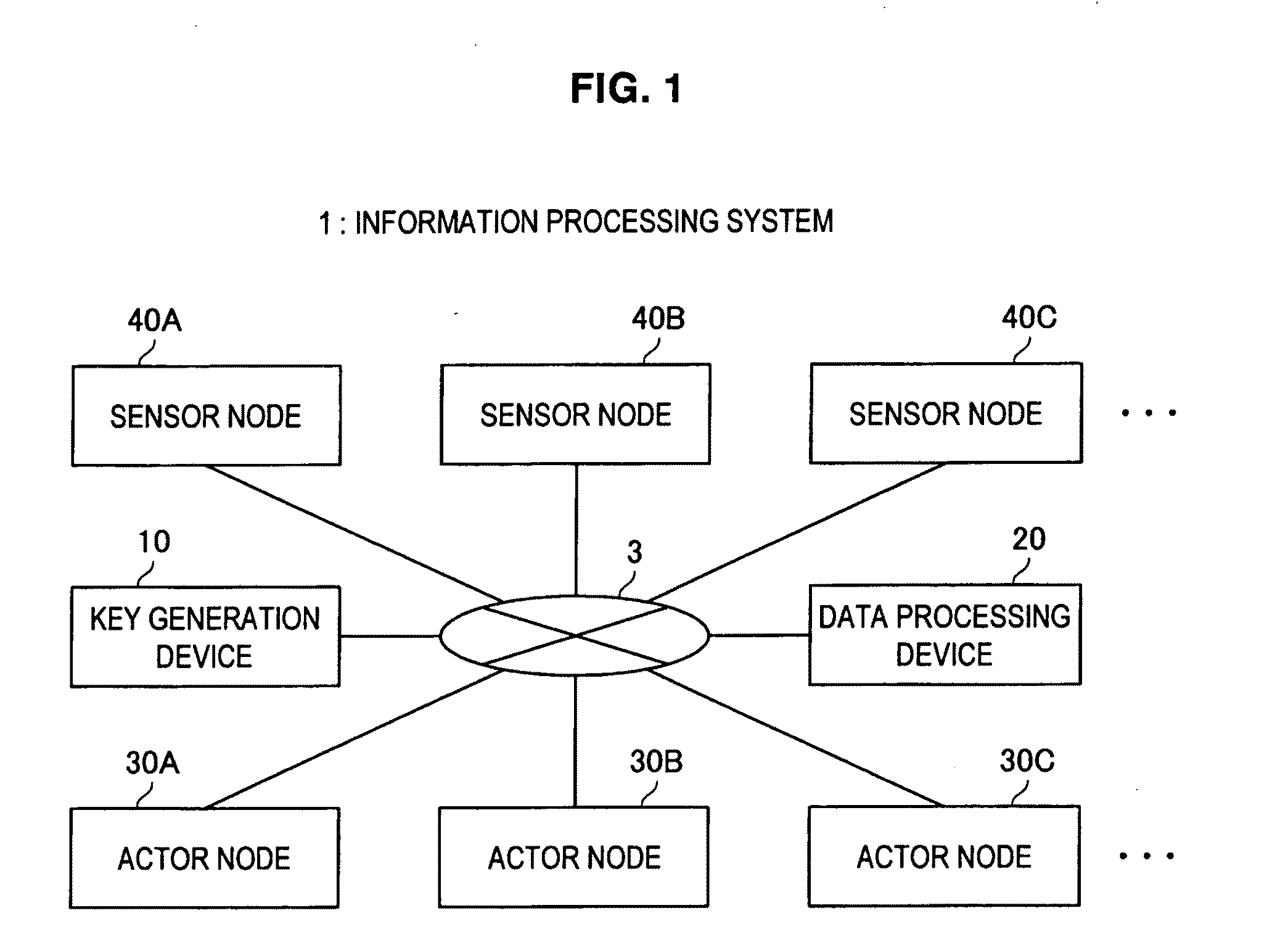
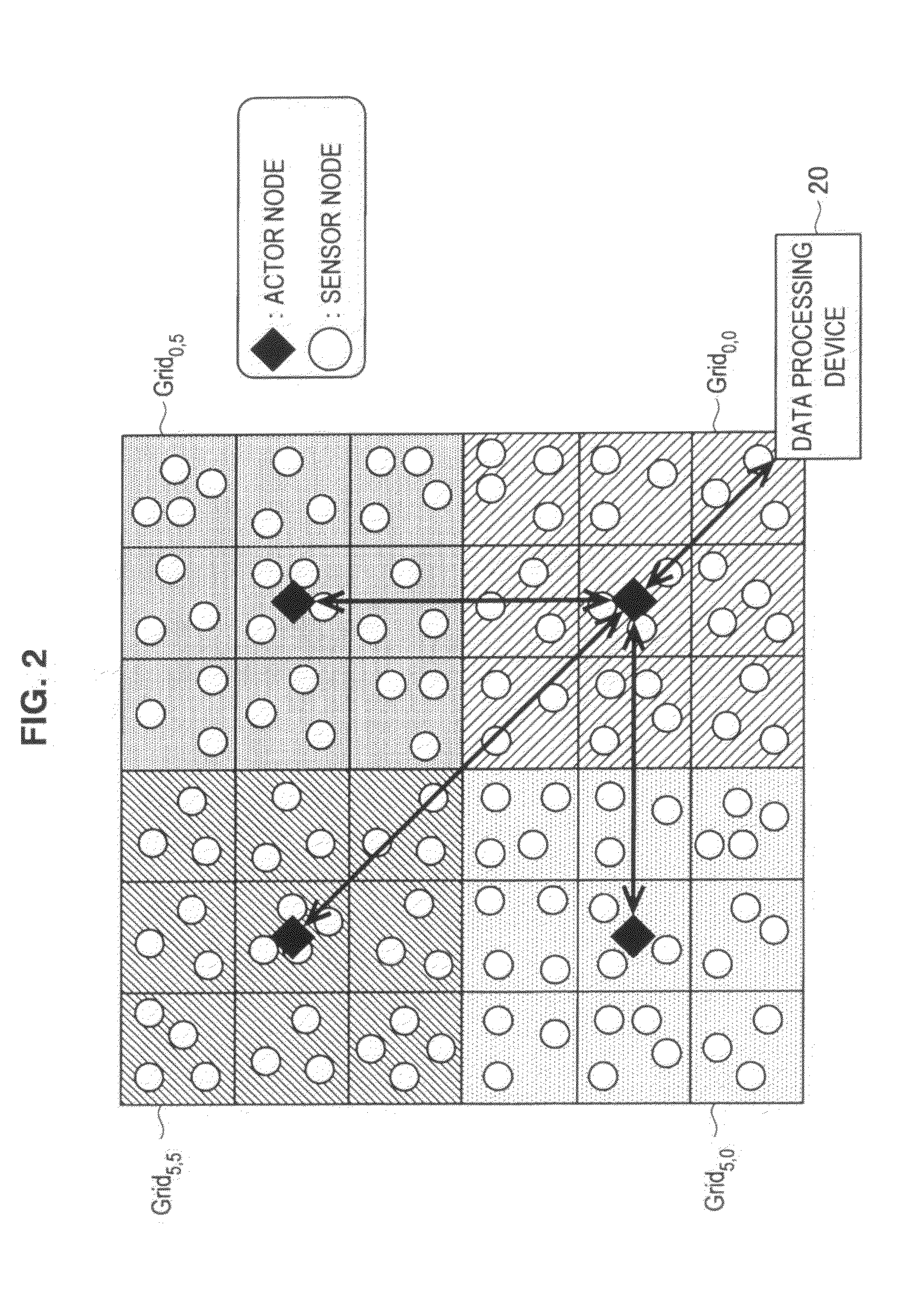
Actor node, sensor node, coverage block change method, parameter change method, program, and information processing system
InactiveUS20110145578A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationInformation processingSensor node
An actor node according to the present invention includes a dynamic change unit for temporarily changing a coverage block in which data are obtained from a sensor node and temporarily causing another actor node to obtain, on behalf of the actor node, data from the sensor node arranged in a partial region of at least a portion of the coverage blocks. The dynamic change unit obtains identification information unique to the another actor node from the another actor node. The dynamic change unit notifies, to the sensor node arranged in the partial region, the obtained identification information. The dynamic change unit notifies, to the another actor node, a portion of the hash chain and a temporary key generated using the obtained identification information and the key used for communication with the sensor node arranged in the partial region.
Owner:SONY CORP
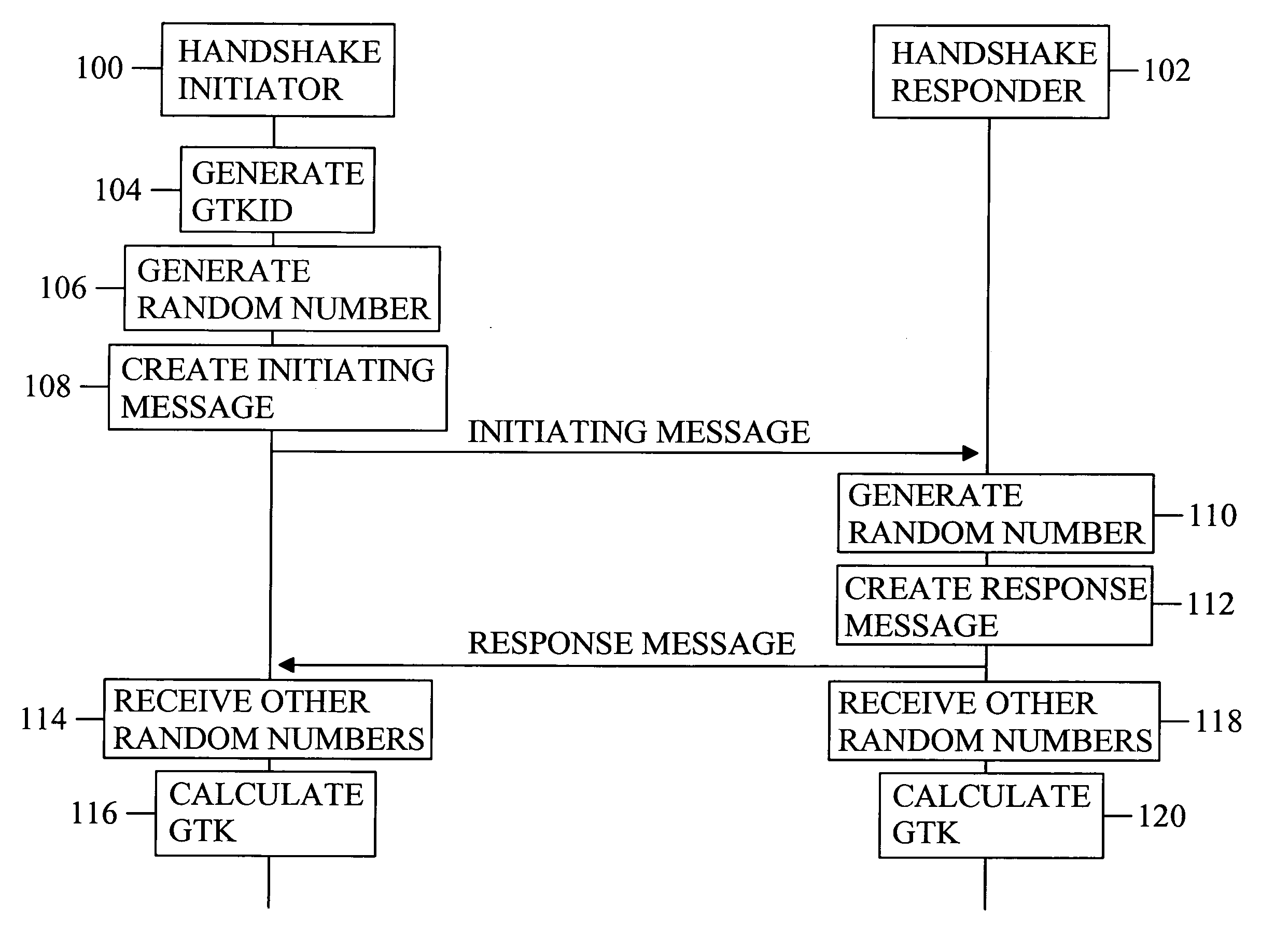
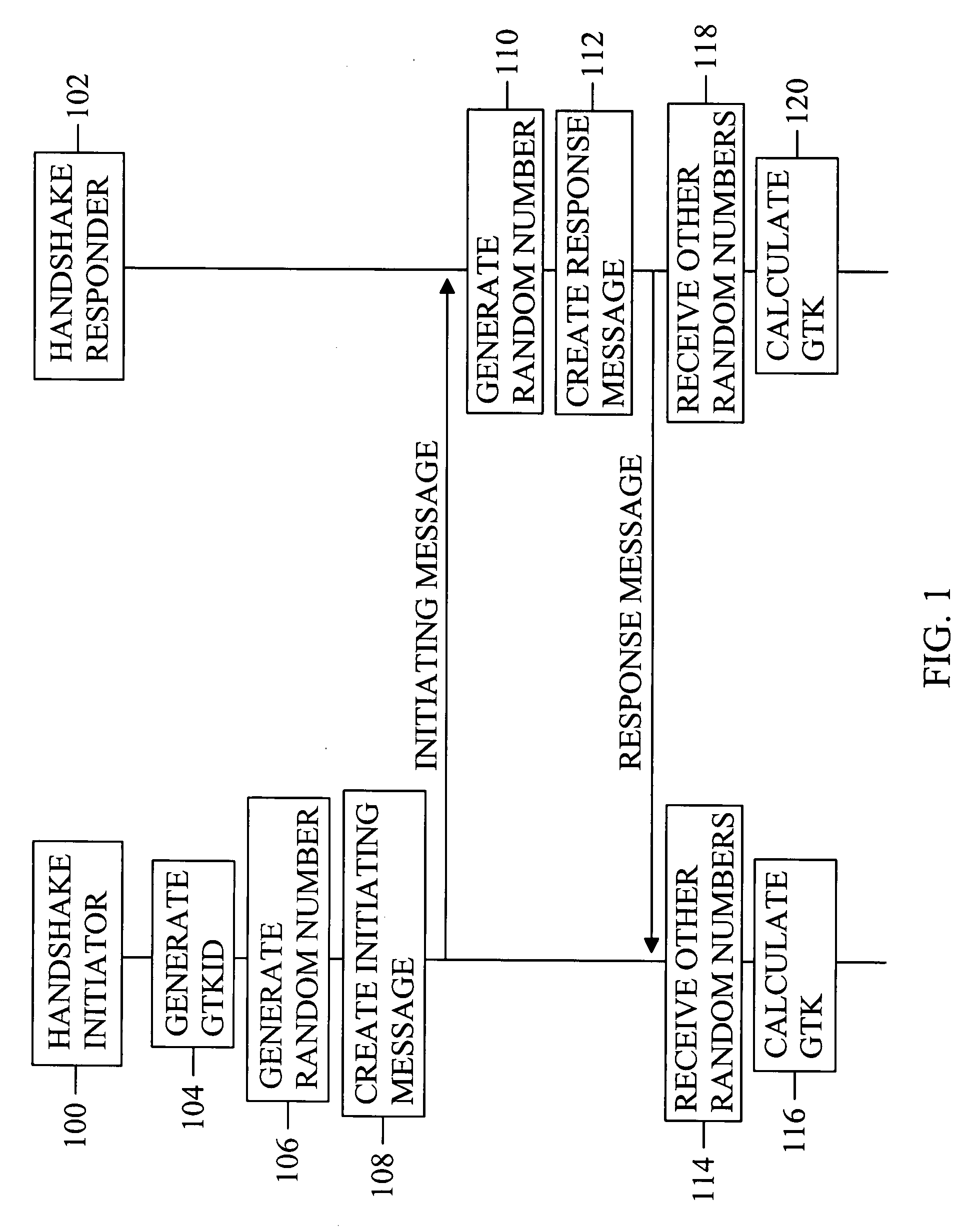
Handshake procedure
InactiveUS20080253562A1Improve efficiencyPublic key for secure communicationSecret communicationComputer scienceEphemeral key
The invention discloses a solution for establishing by a handshake procedure a group temporal key for group communication. The group temporal key is established by a group procedure and is a group-specific temporal key.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Systems and methods for providing access to network resources based upon temporary keys
InactiveUS20070204156A1User identity/authority verificationSecurity arrangementResource basedClient-side
Secure access to a wireless switch or other server node is provided through the use of a temporary key. The server initially receives a key request from a remotely-located client application that is formatted according to a first protocol such as the simple network management protocol (SNMP). In response to the key request, the server generates a temporary key that is provided to the client application and also stored at the server. After receiving the temporary key, the client application creates a service request that includes the temporary key. Examples of suitable protocols for the server request include the common gateway interface (CGI) and active server pages (ASP) formats. After receiving the service request, the server provides access to the network service if the temporary key in the service request matches the temporary key stored in the database, and otherwise does not provide access to the network service
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
Mutually authenticated ecdhe key exchange for a device and a network using multiple pki key pairs
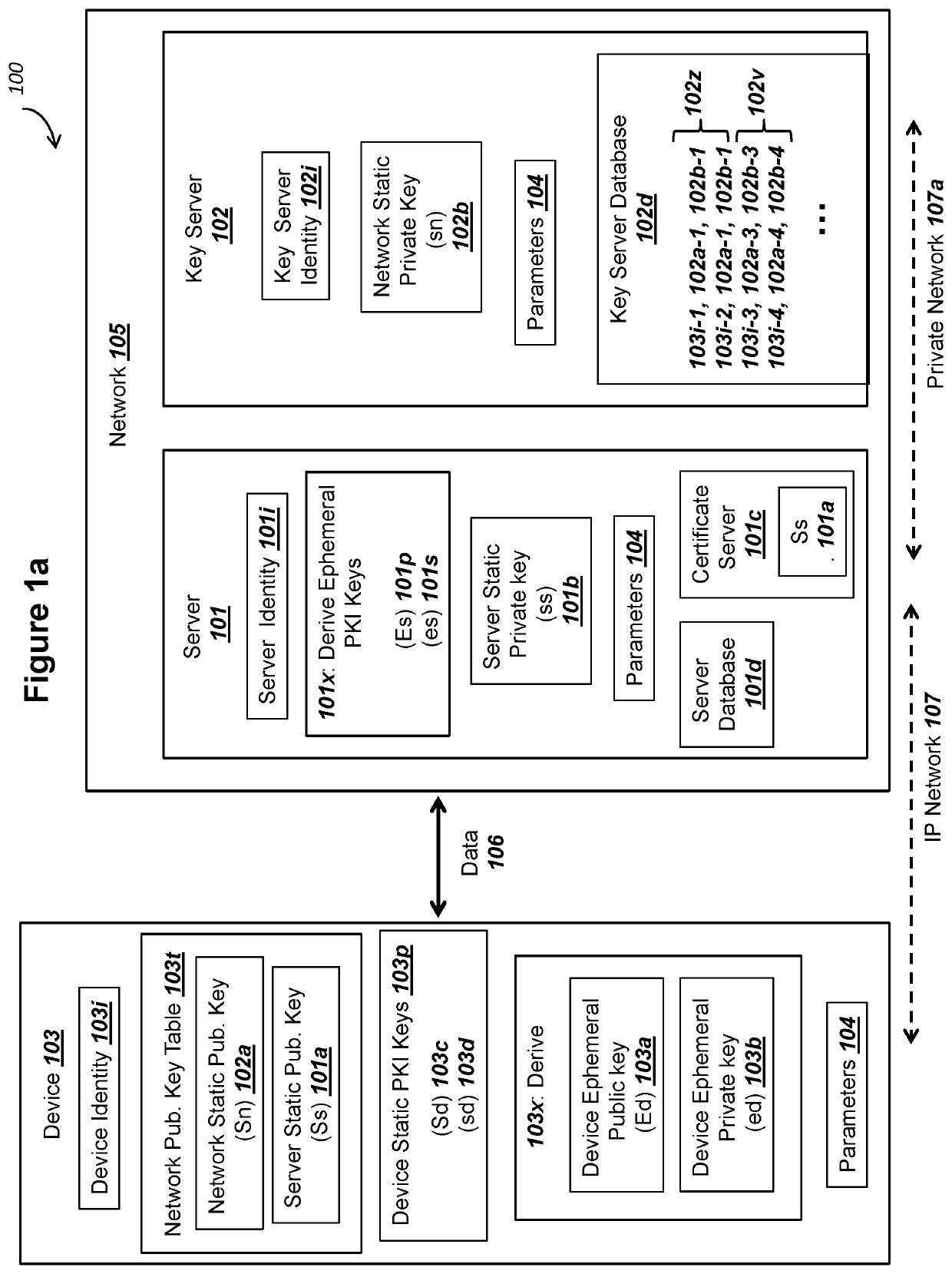
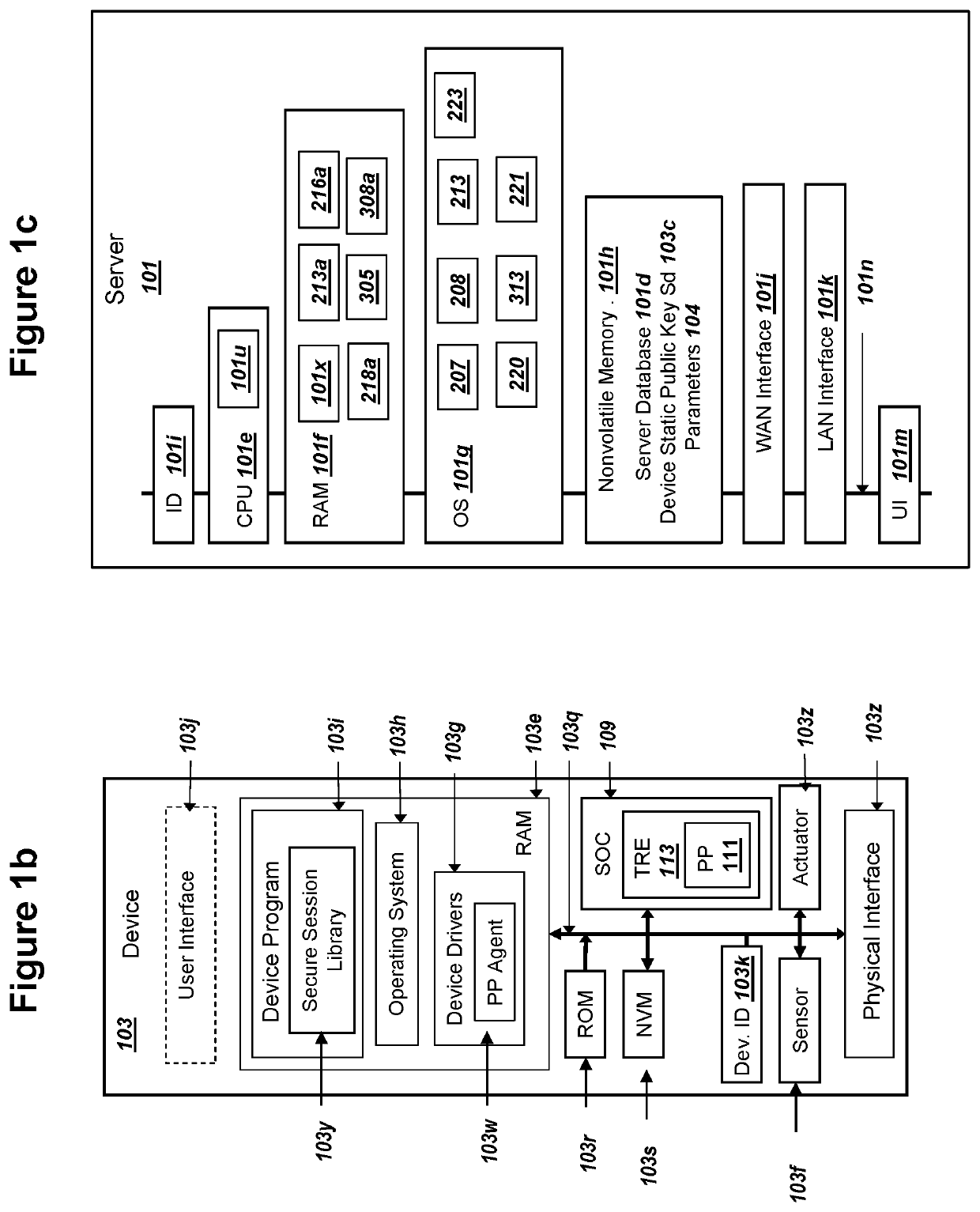
ActiveUS20200162269A1Only successfulMultiple keys/algorithms usagePublic key for secure communicationKey exchangeComputer network
A device can (i) store public keys Ss and Sn for a network and (ii) record private key sd. A network can record a corresponding private keys ss and sn. The device can (i) generate a device ephemeral PKI key pair (Ed, ed) and (ii) send public key Ed to the network. The device can receive an ephemeral public key Es from the network. The device can calculate values for A: an elliptic curve point addition over Ss, Sn, and Es, and B: (sd+ed) mod n. The device can input values for X and Y into an elliptic curve Diffie Hellman key exchange (ECDH) in order to determine a mutually derived shared secret X5, where the network can also derive shared secret X5. The device can (i) use X5 to derive a key K2 and (ii) decrypt a ciphertext from the network using key K2.
Owner:IOT & M2M TECH LLC
Single interaction authenticated key agreement protocol of identity-based cryptosystem
ActiveCN106209369AReduce usageResist attackKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationCryptosystemMaster key
The invention discloses a single interaction authenticated key agreement protocol of an identity-based cryptosystem, and relates to the field of cryptography. The key agreement efficiency can be effectively enhanced and the interaction frequency can be reduced. The solving technical scheme is that a random number is self-selected through combination of an opposite side public key and an own side private key, and a session key of both communication sides is constructed through bilinear operation and Hash operation. The single interaction authenticated key agreement protocol of the identity-based cryptosystem comprises the following steps that 1) a PKG generates system parameters and generates and distributes corresponding private keys to all the hosts in a local domain; and 2) a client side initiates a key agreement request to a server side and transmits key information, and generates the session key according to the algorithm and stores the session key. Natural binding of the identity and the public key is completed based on the identity-based cryptographic technology so that use of a certificate can be avoided; a master key and a temporary key are combined so as to meet the known session key security, partial forward security, partial key resistant disguise leaking, unknown key resistant sharing, message independence and known session temporary secret information security and resist the man-in-the-middle attack; and operation is easy and convenient and the computational complexity is low.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
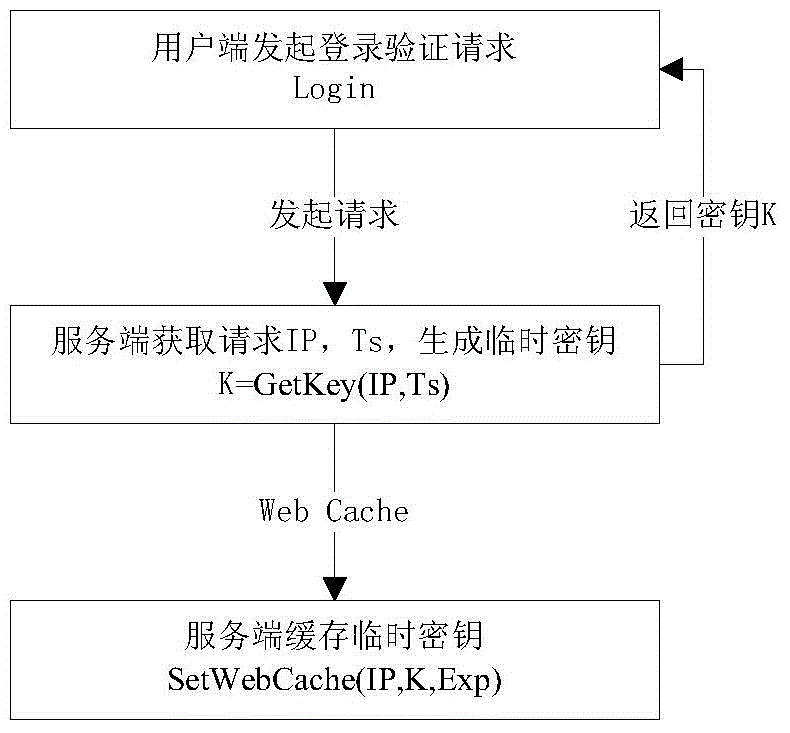
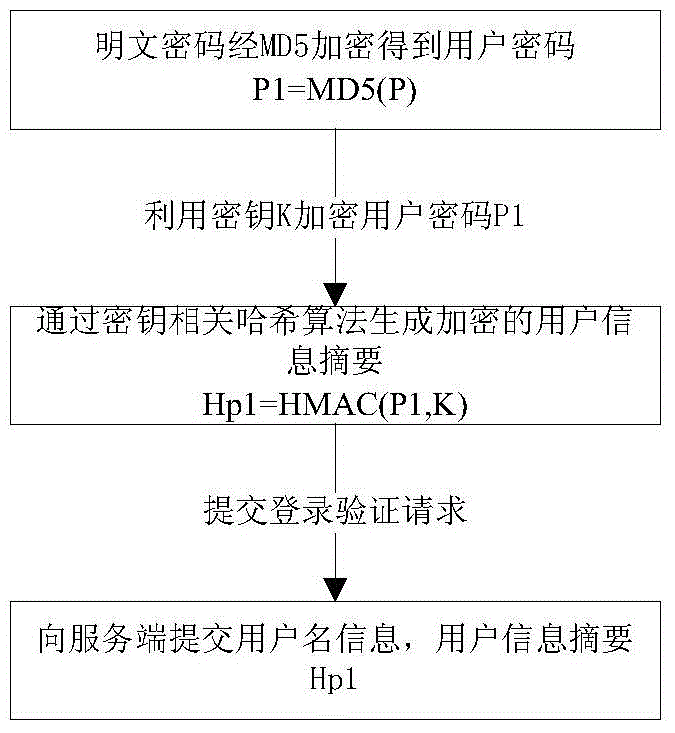
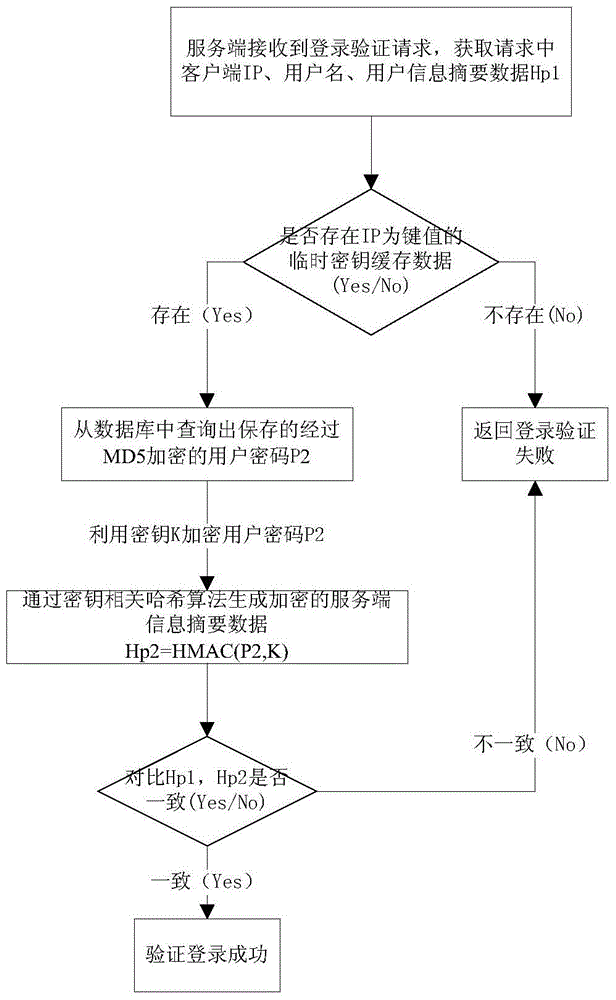
Secured logon method for variable secret key encryption under HTTP
The invention relates to a secured logon method for variable secret key encryption under an HTTP. The method includes the following steps that a server terminal generates a temporary secret key K according to a login authentication request of a client terminal, and the temporary secret key is sent back to the client terminal and cached at the client terminal; the client terminal generates user information abstract data Hp1 according to a clear-text password and the temporary secret key in an encryption mode; whether the temporary secret key K with the IP being a key value exists or not is inquired by the server terminal according to the login authentication request, and if not, it is judged that the login authentication fails; if yes, a user password of the server terminal is inquired, server terminal information abstract data Hp2 are generated according to the user password of the server terminal and the temporary secret key, the Hp2 is compared with the Hp1, and whether the login authentication fails or succeeds is judged. According to the secured logon method, the secret key and the data are both dynamic, an illegal third party cannot calculate the password data used by current login, and therefore the technical problem that the security is low due to the fact that the passwords are likely to be leaked or forged during login authentication in the prior art can be solved.
Owner:中復保有限公司
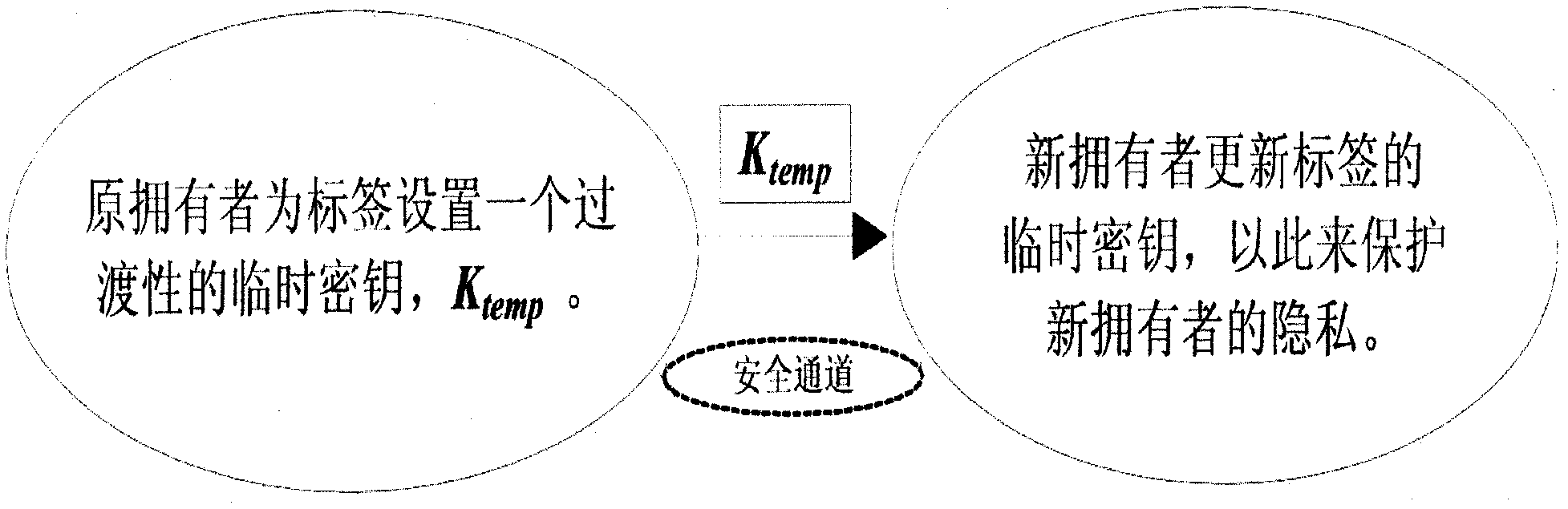
Method and device for ownership transfer of radio frequency identification (RFID) tag
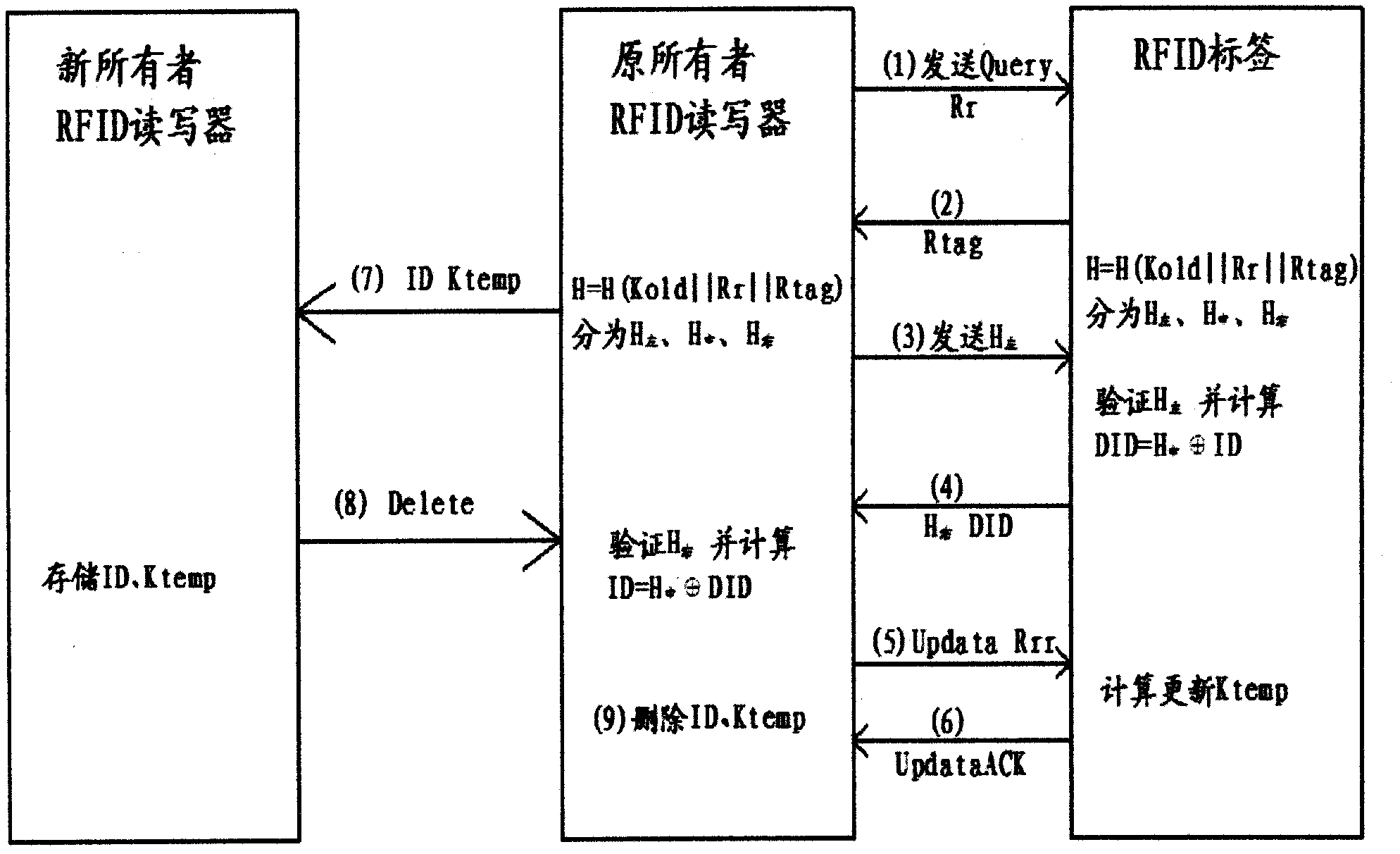
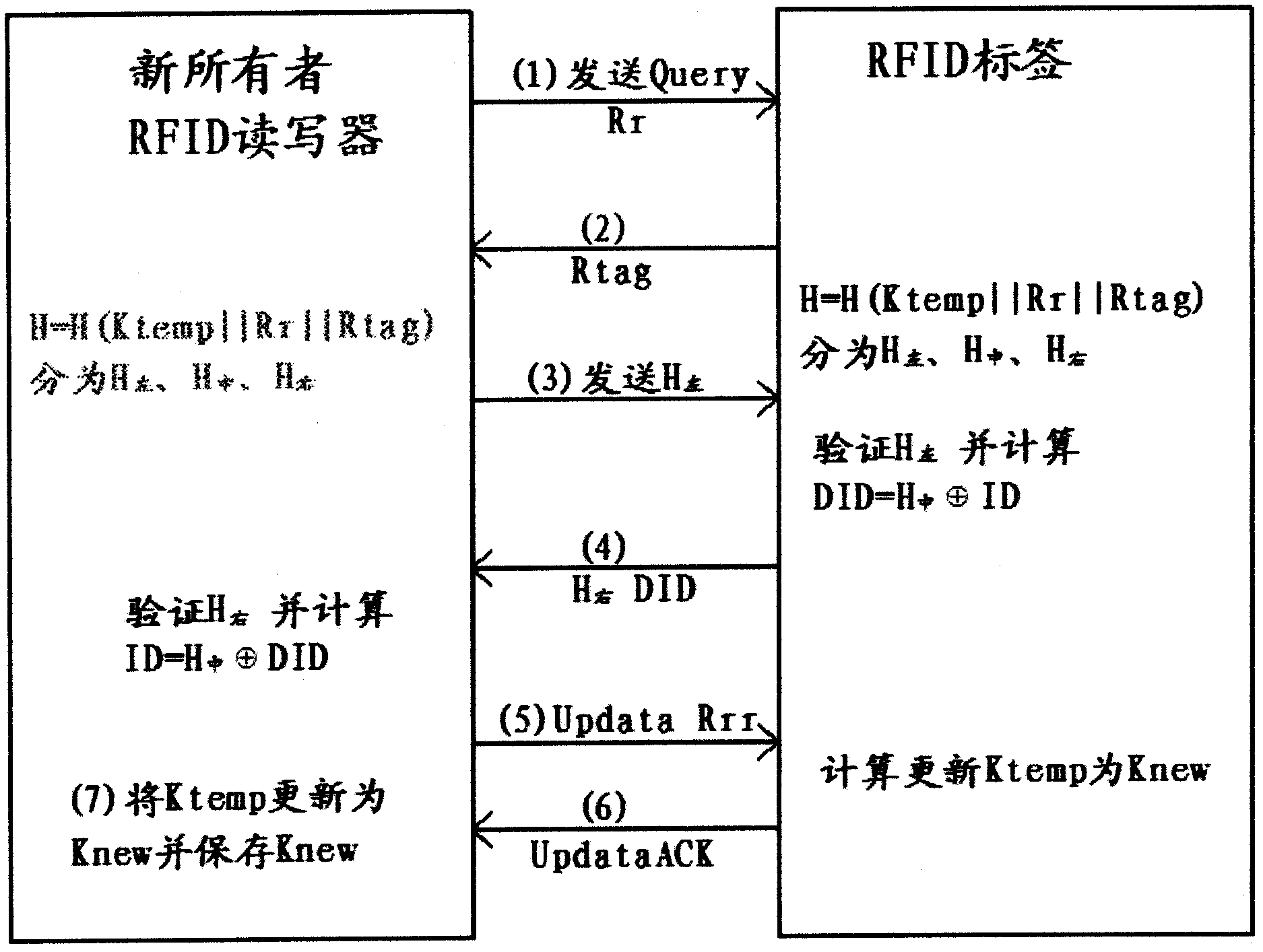
InactiveCN102855504APrivacy protectionPrevent illegal theftCo-operative working arrangementsComputer hardwareHash function
The invention discloses a method and a device for ownership transfer of a radio frequency identification (RFID) tag. Ownership transfer of the RFID tag is achieved through the RFID tag and a RFID reader-writer of an original owner and secret key updating of the RFID tag and a RFID reader-writer of a new owner. A temporary secret key Ktemp for the RFID tag is arranged by the RFID reader-writer of the original owner through shared ciphertext Kold. After the Ktemp is transmitted to the RFID reader-writer of the new owner through a secure channel, a temporary secret key in the RFID reader-writer of the original owner is deleted. After the RFID tag is read and authenticated by the RFID reader-writer of the new owner through tag identification (ID) and the temporary secret key save in a background server, a new secret key Knew is updated and set to replace the temporary secret key Ktemp. A hash function and an exclusive-or operation are led in the transfer of the RFID tag, secret keys of the RFID reader-writer of the original owner and the RFID reader-writer of the new owner are updated successively through the RFID tag so as to achieve that ownership of the RFID tag is transferred from a commercial retail organization to consumers really, the RFID tag on purchased commodities can be controlled by the consumers totally, and tag information illegal stealing of other people can be prevented.
Owner:深联致远(北京)科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com