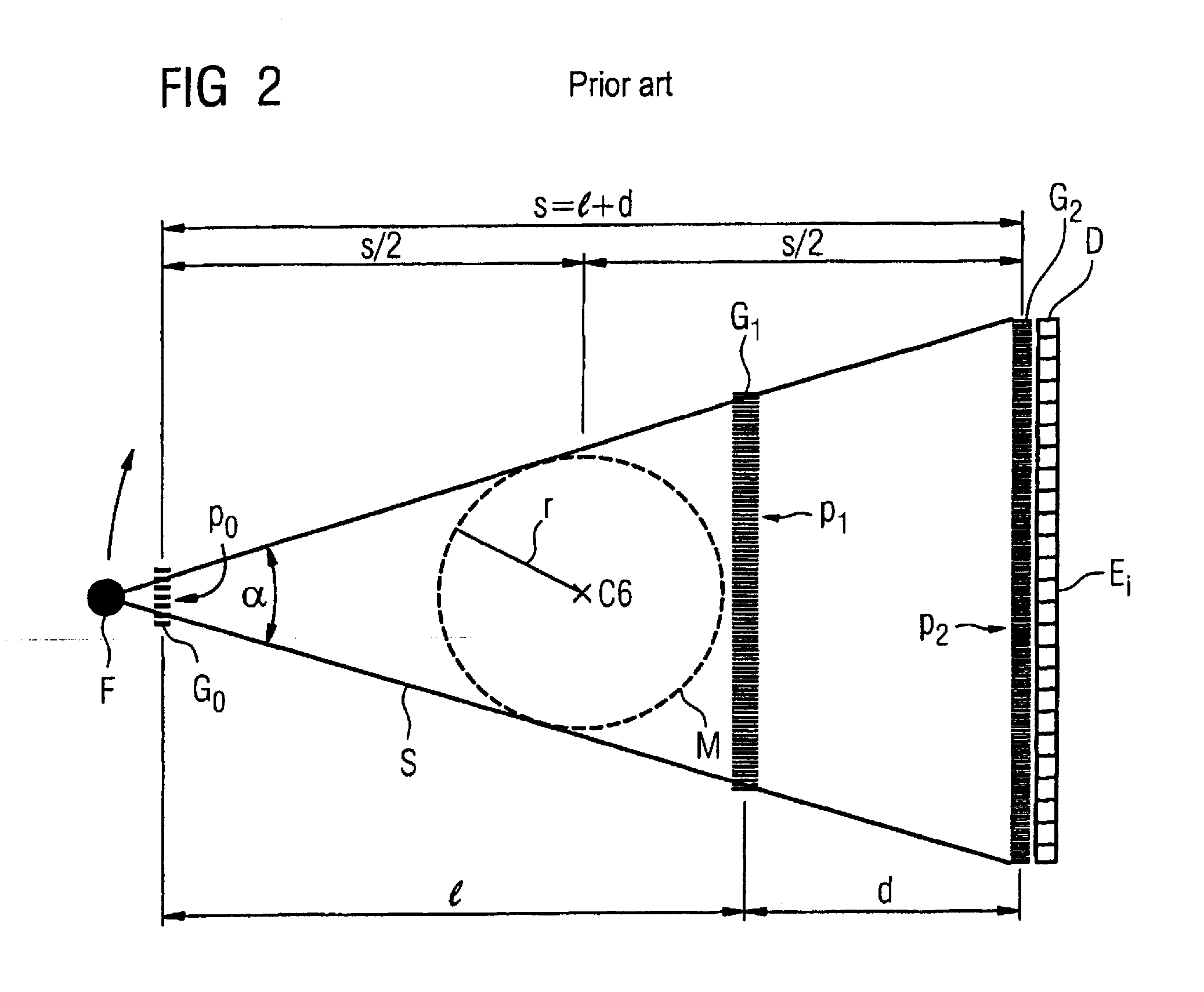
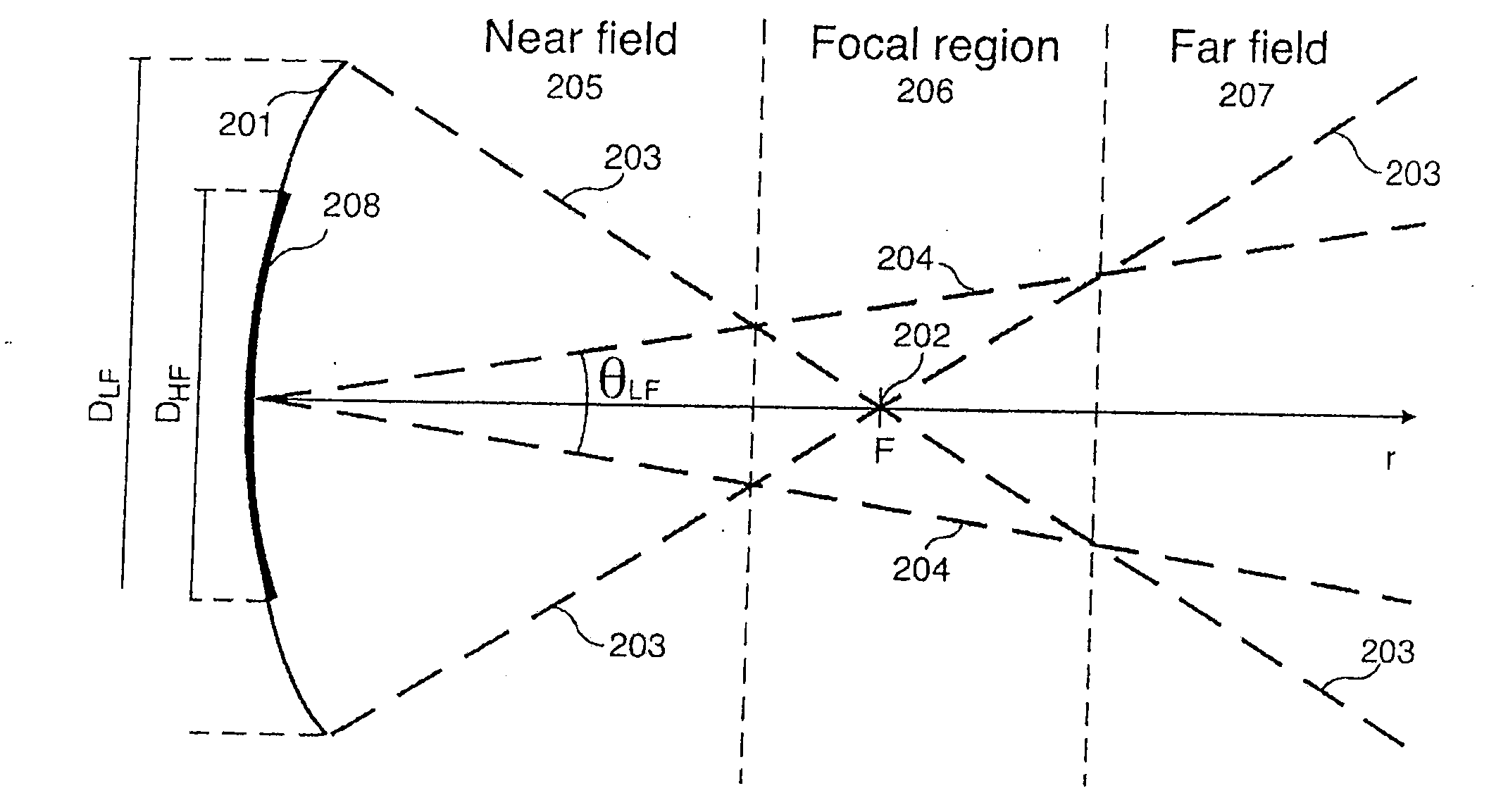
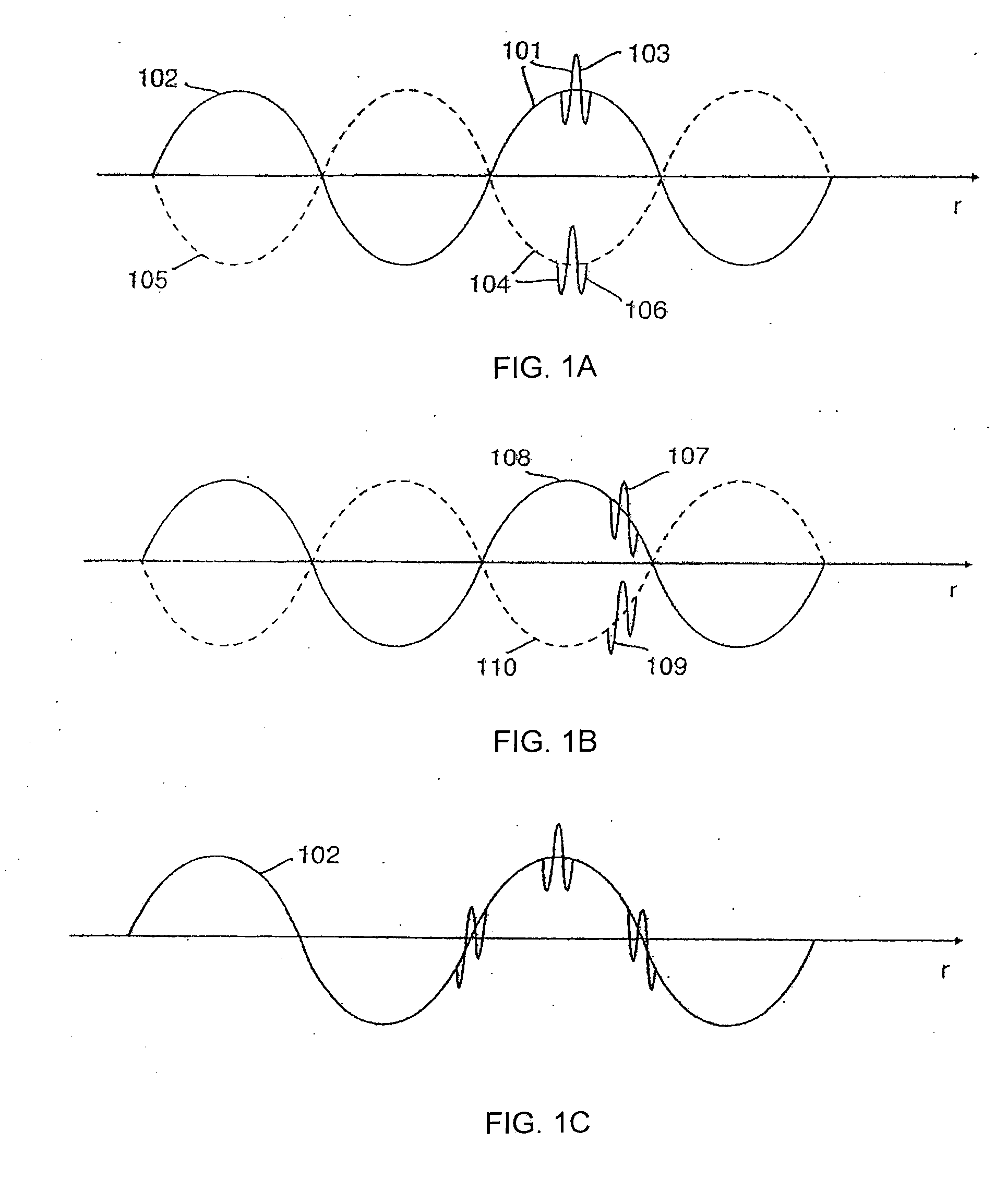
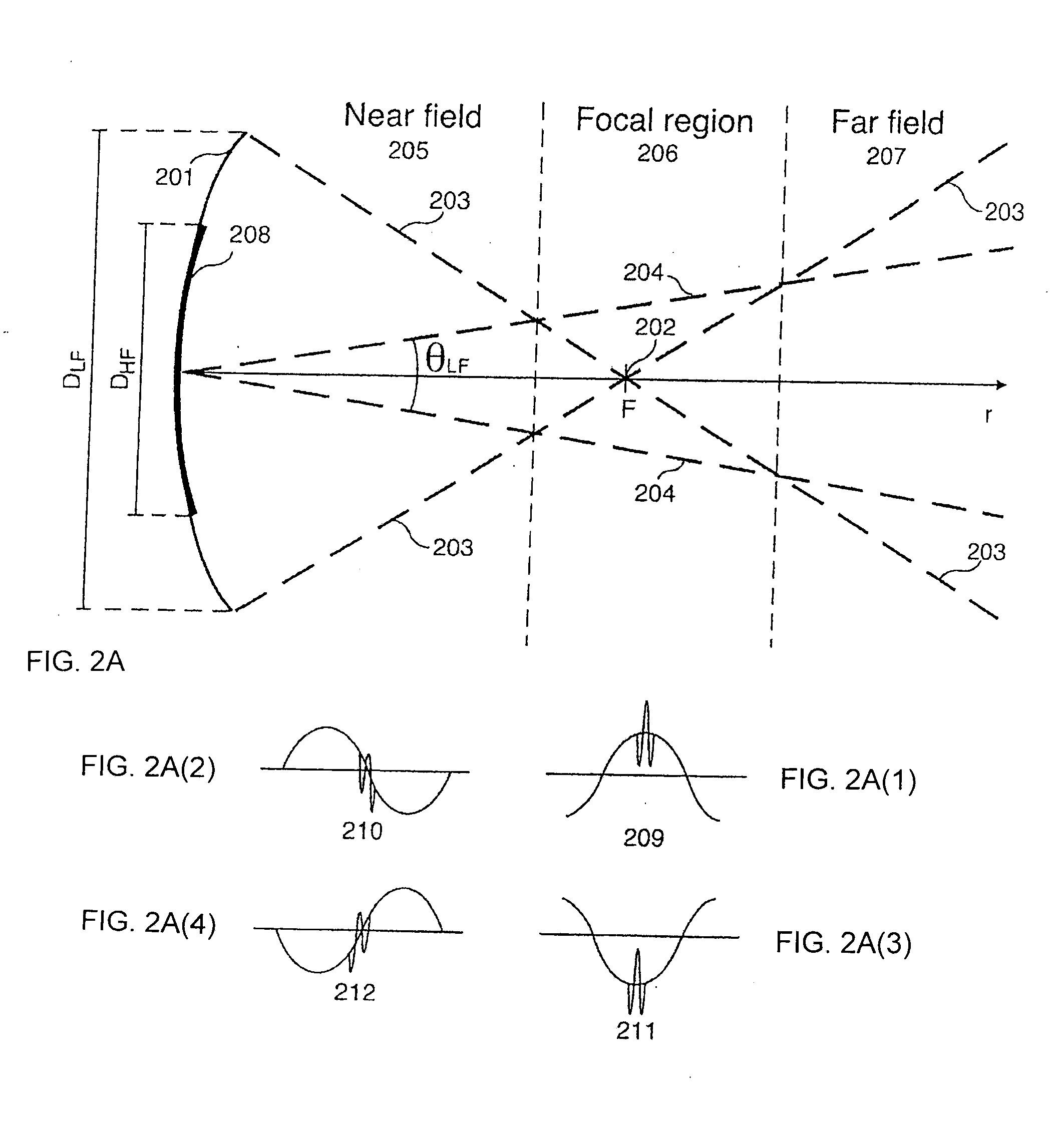
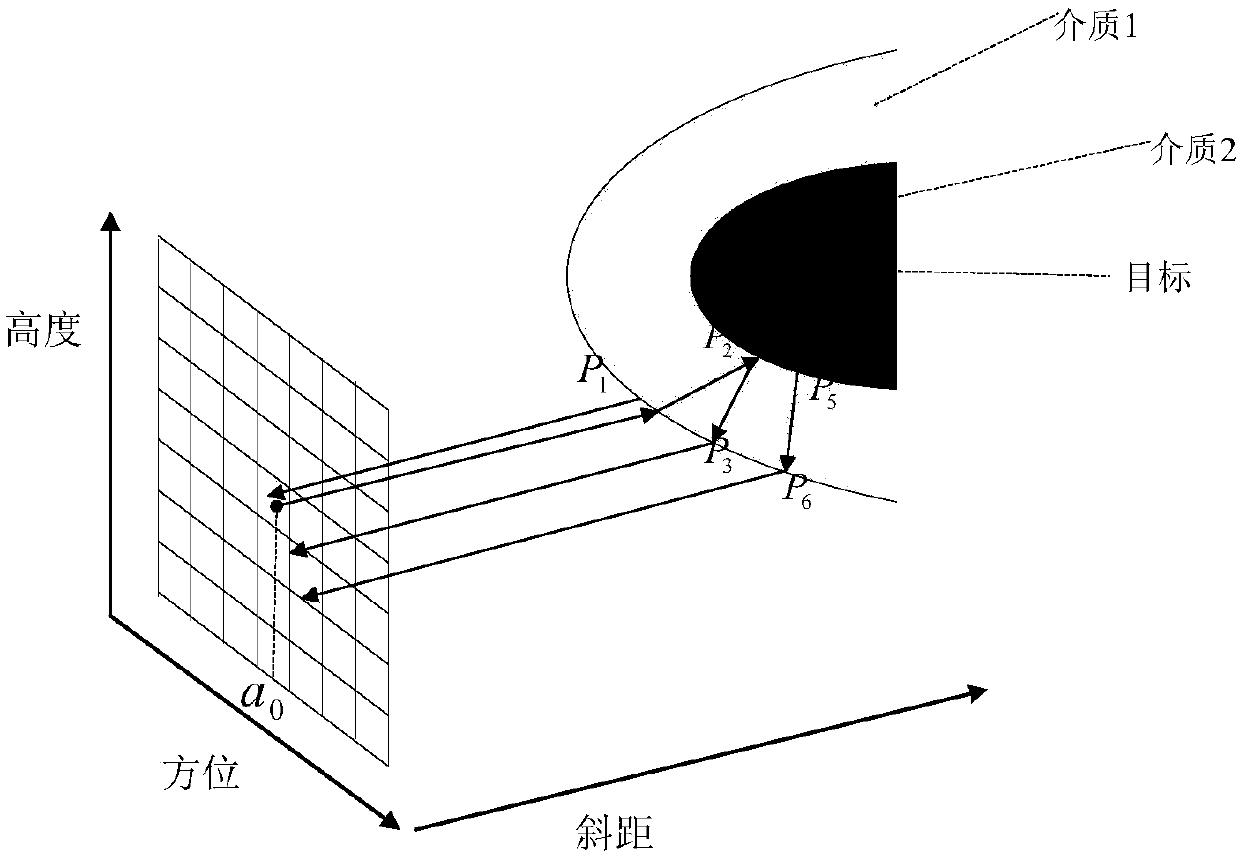
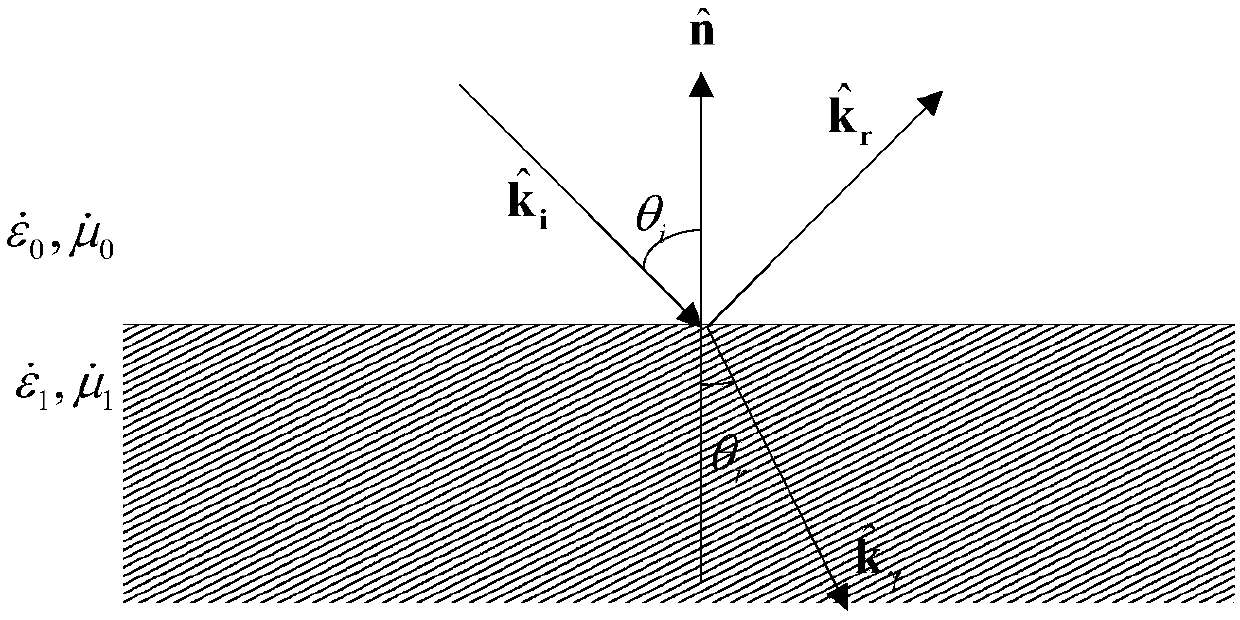
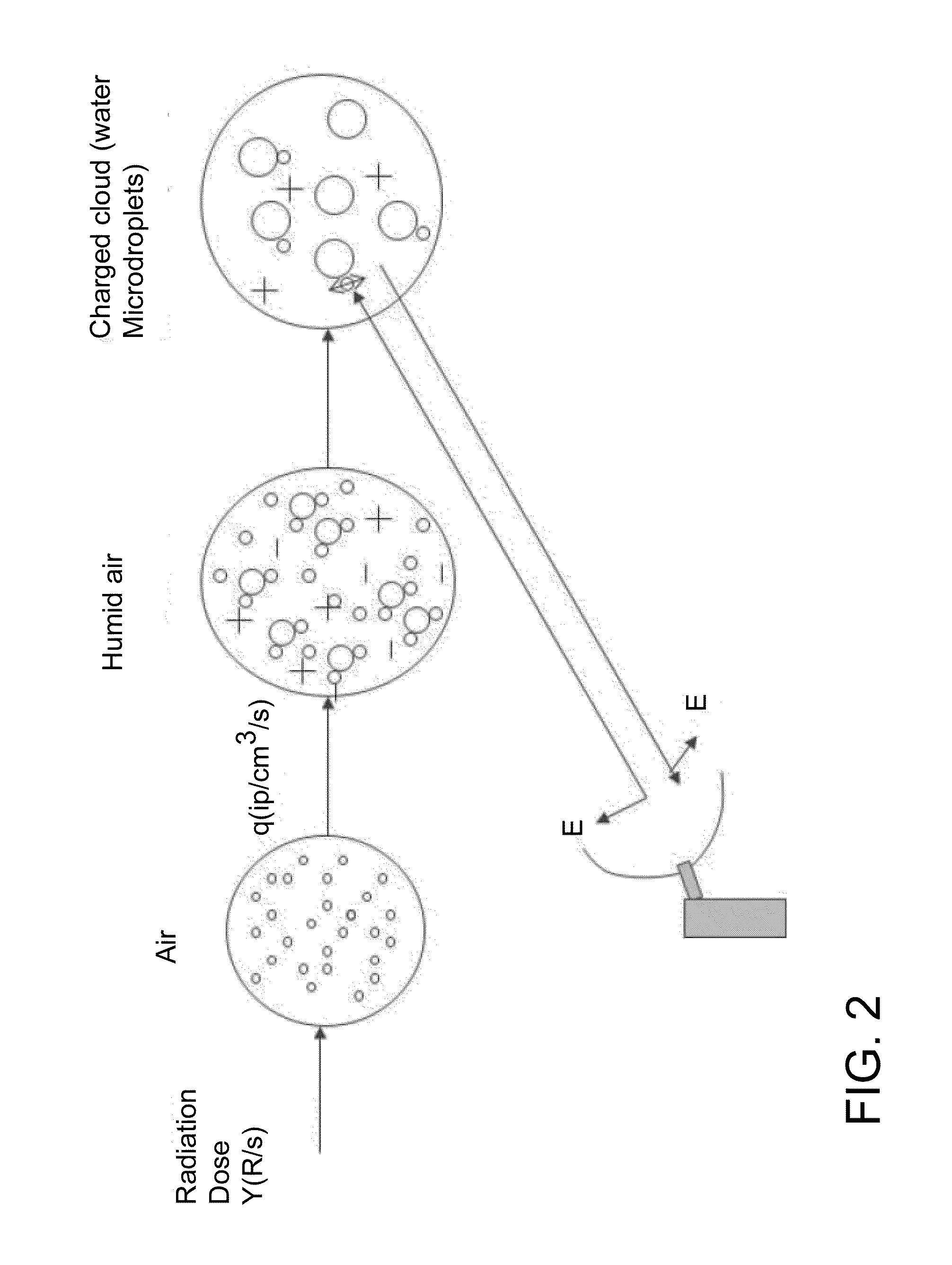
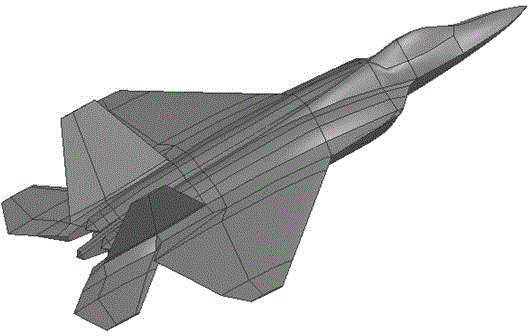
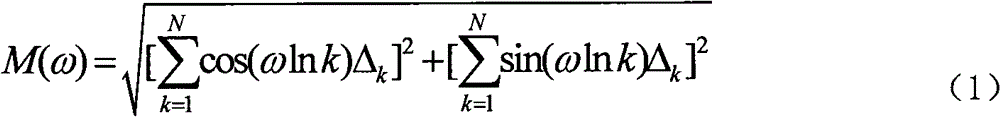Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
194 results about "Em scattering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Elliptical diffusers used in displays
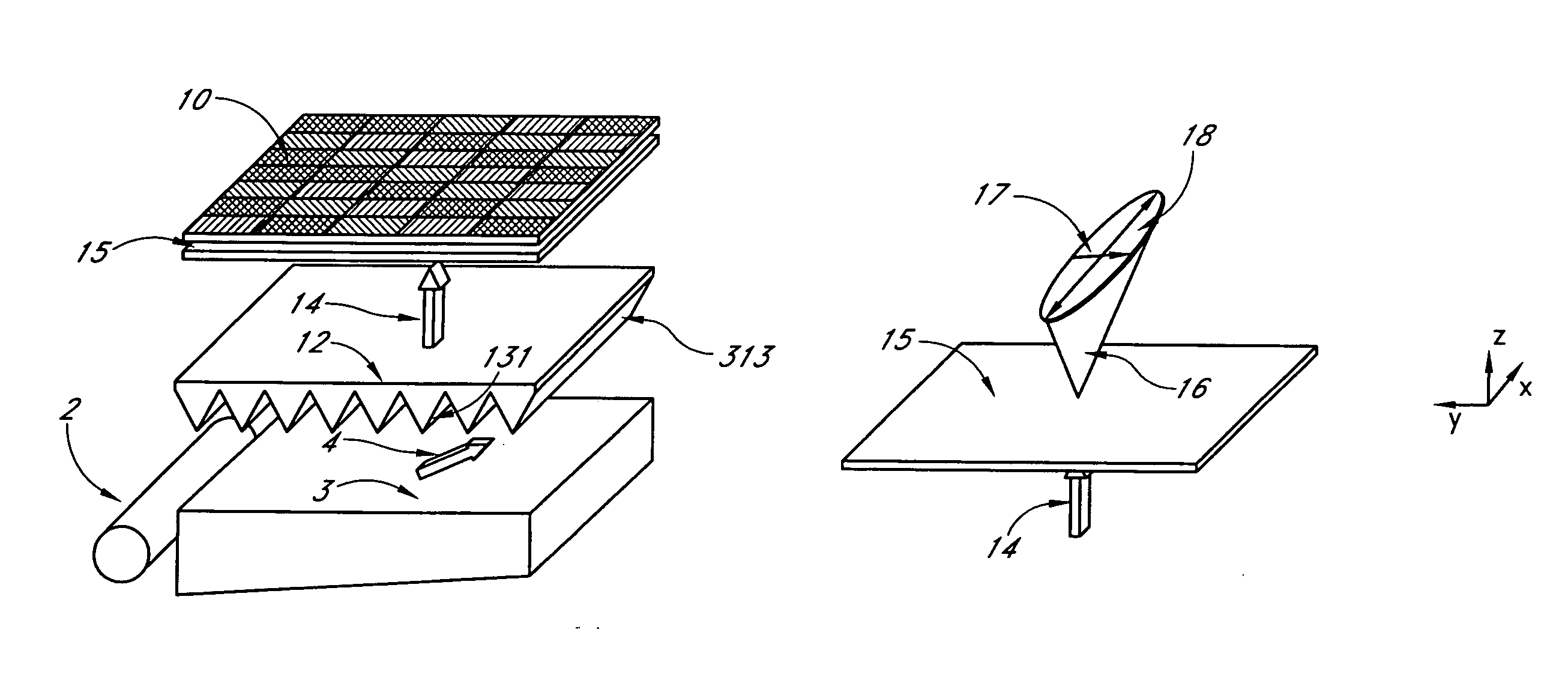
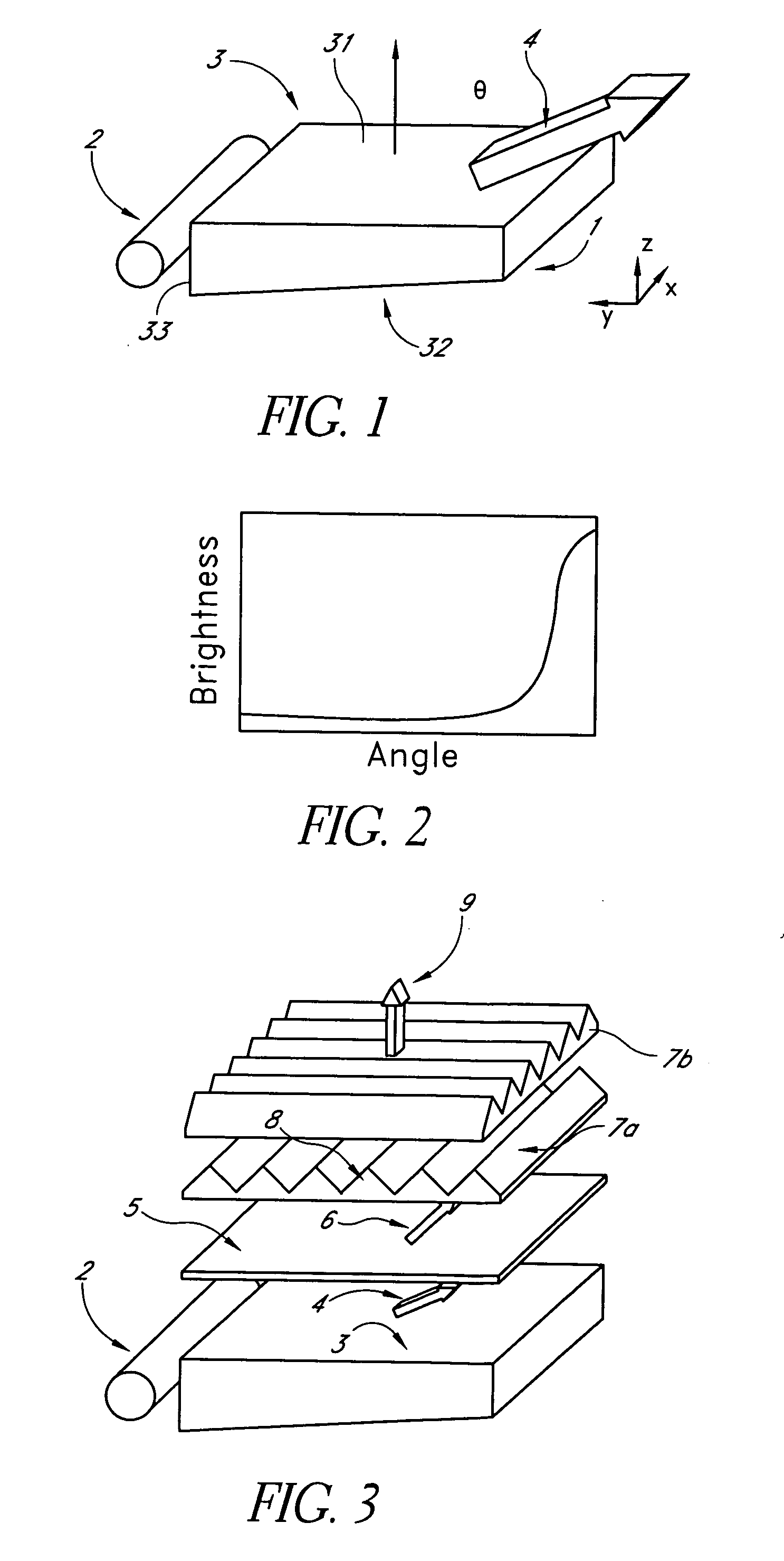
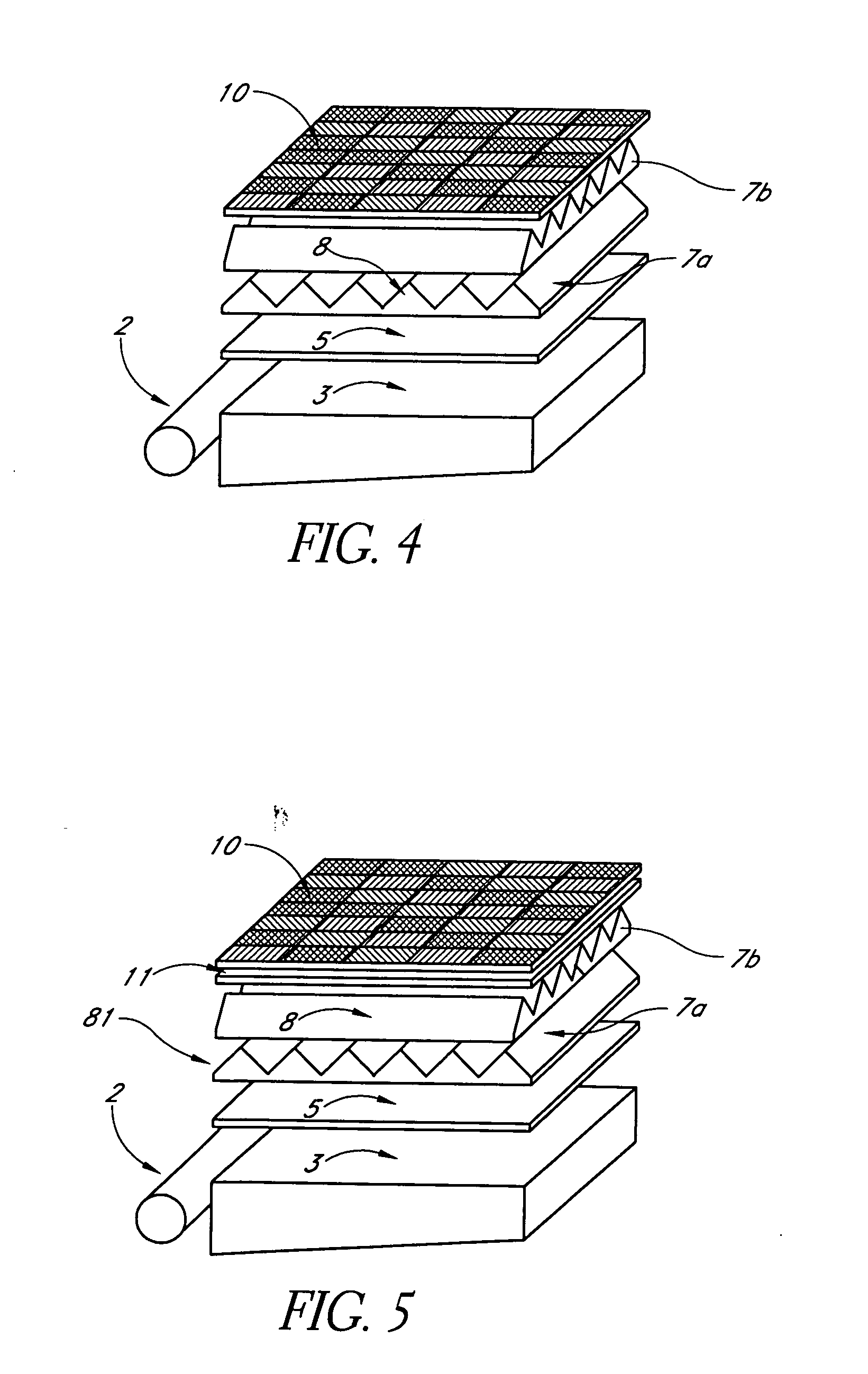
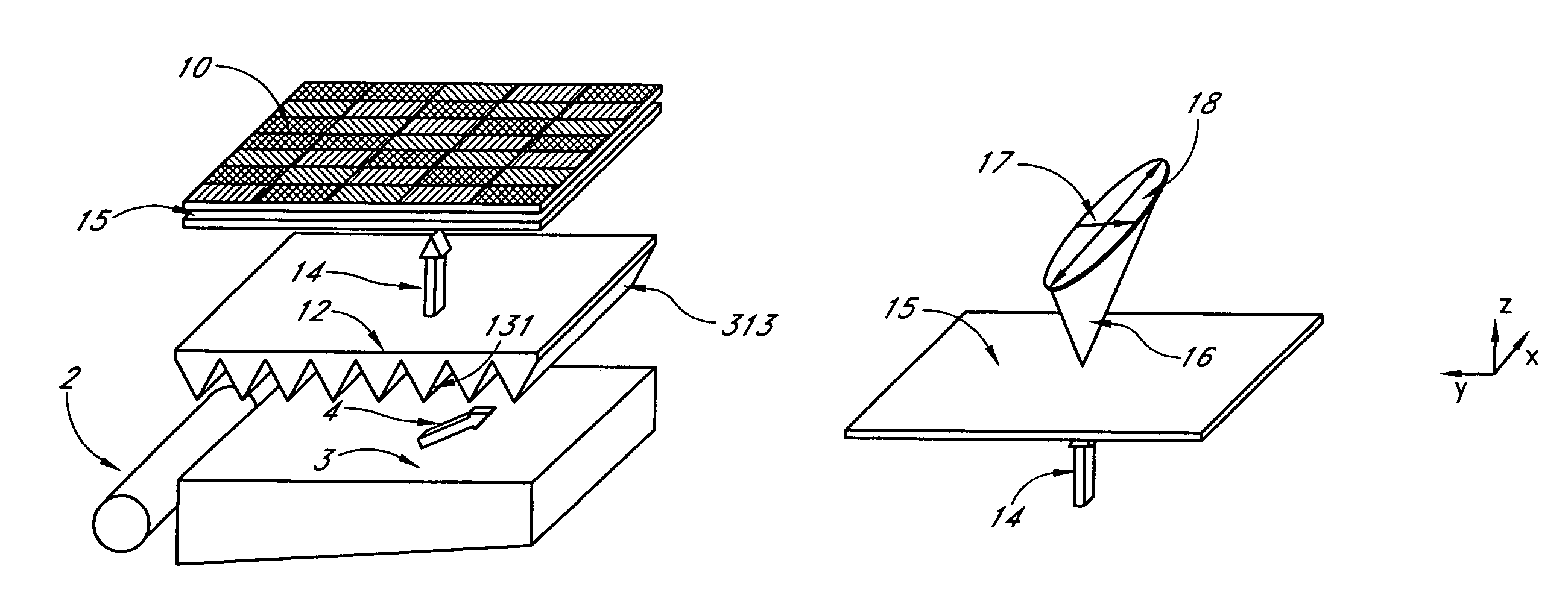
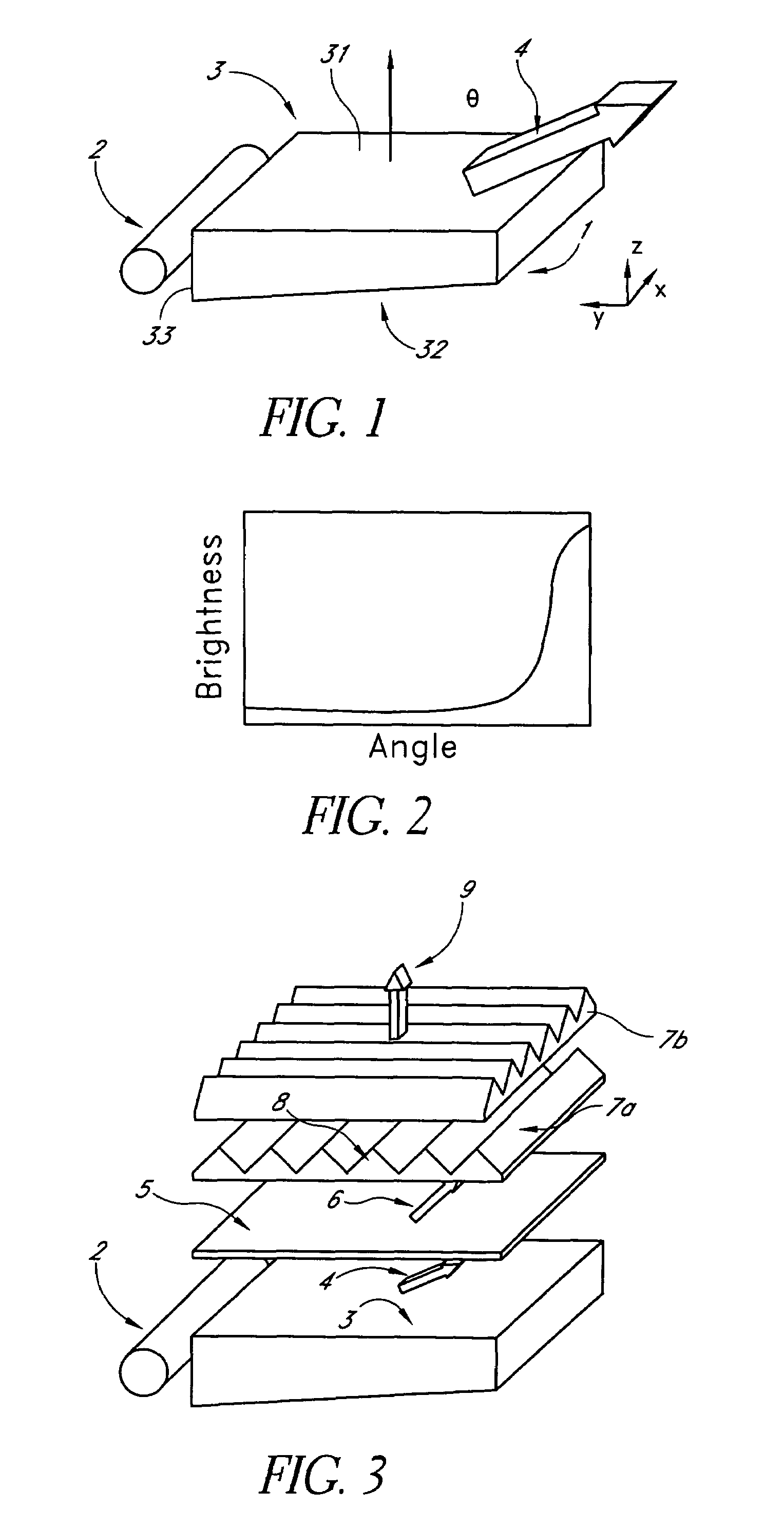
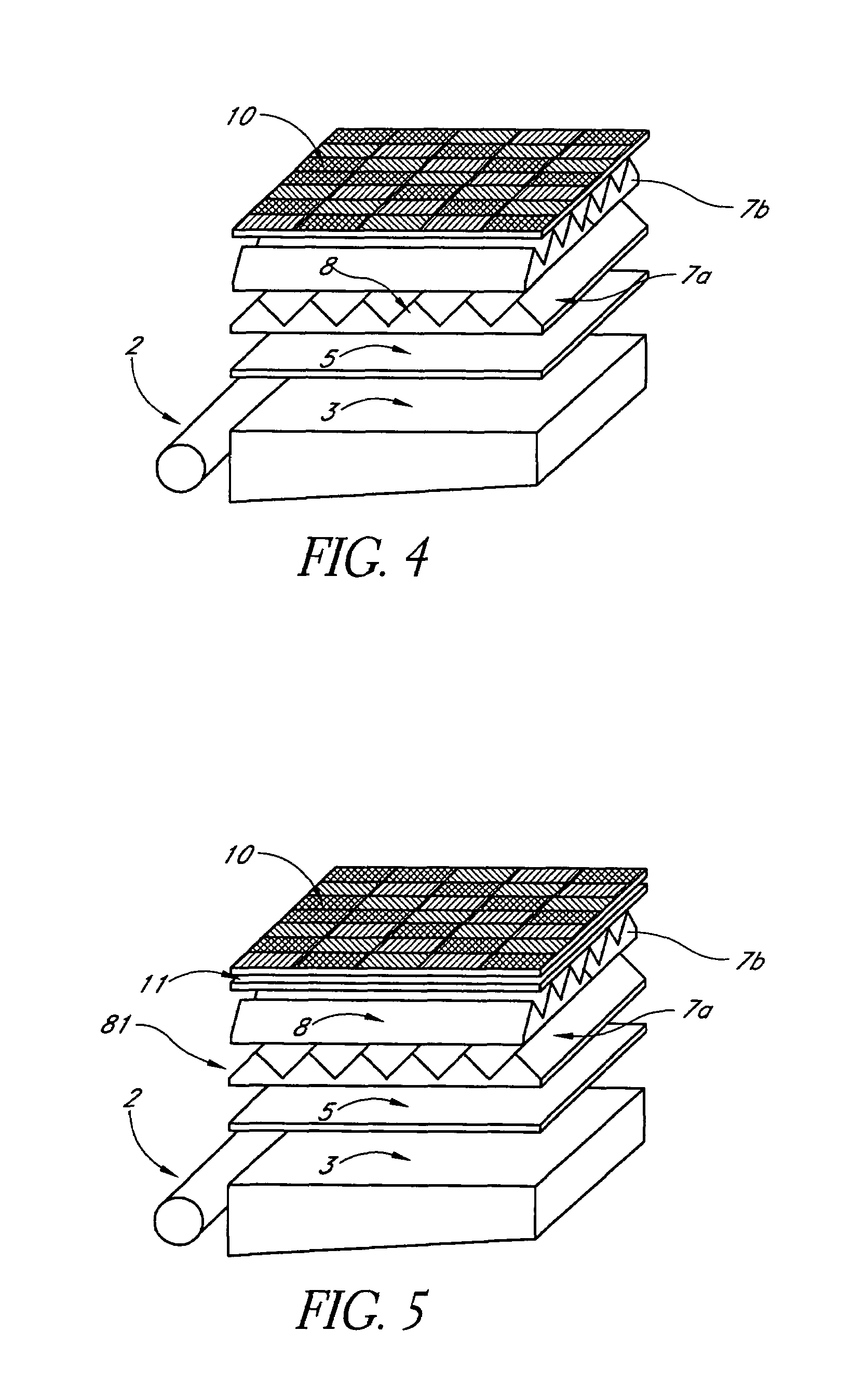
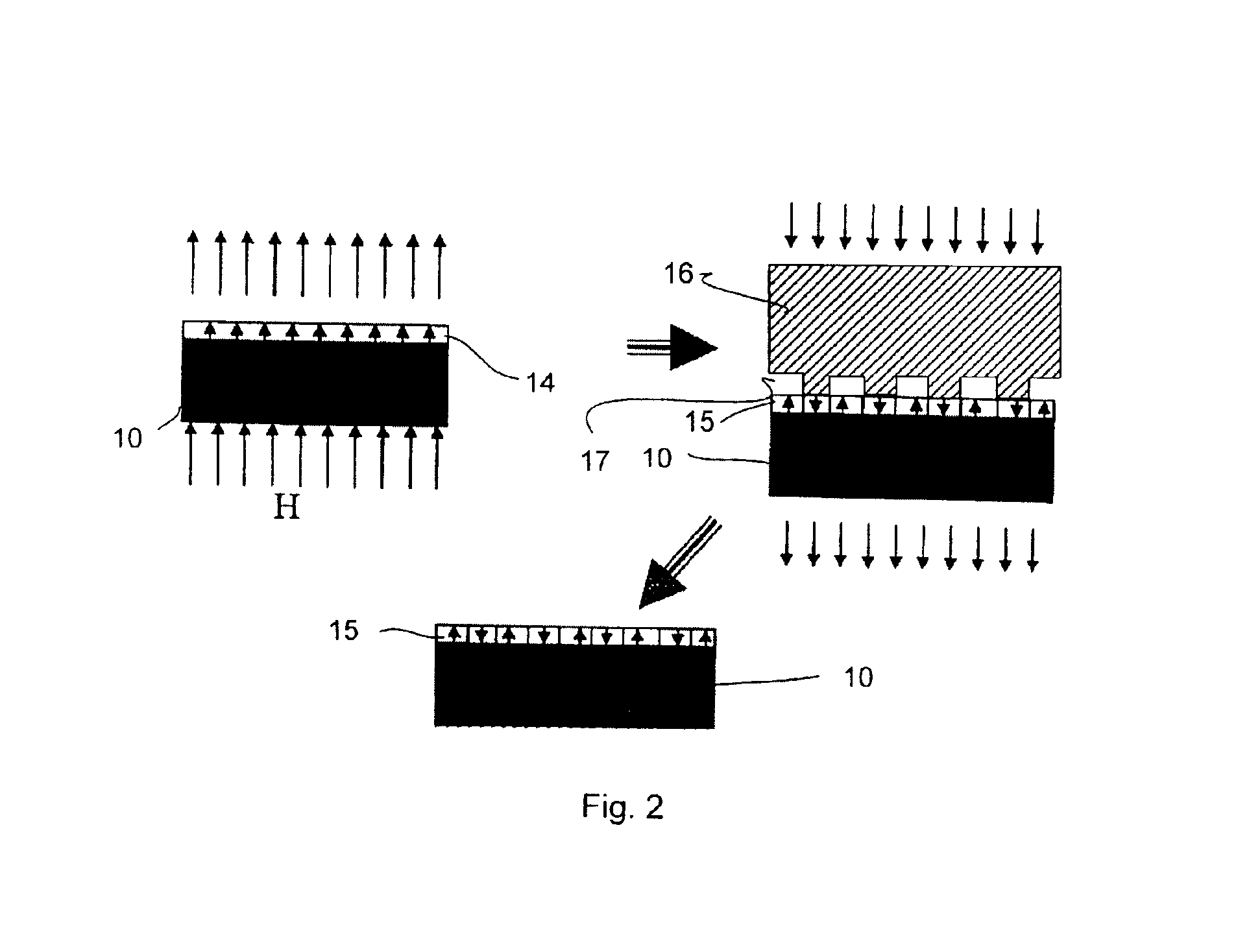
A backlit light display comprises a light guide panel, a prismatic film, an asymmetric top diffuser and an LCD. A linear light source is disposed along a side face of the light guide panel. Light from the linear light source is transmitted though the light guide panel where it is spread and uniformly output through a front face to the prismatic film. Light incident on the prismatic film is redirected more along a first direction than along a second direction. This light is directed more normal to the LCD. An asymmetric diffuser is applied between the prismatic film and the LCD panel to smear the periodic information from the prismatic film and eliminate the Moiré fringe pattern resulting from interference between the periodic structure of the prismatic film and the periodic arrangement of pixels in the LCD. The asymmetric diffuser is aligned with respect to the prismatic film such that it scatters and spreads light more in a second direction than the first direction.
Owner:WAVEFRONT TECH INC
Elliptical diffusers used in displays
A backlit light display comprises a light guide panel, a prismatic film, an asymmetric top diffuser and an LCD. A linear light source is disposed along a side face of the light guide panel. Light from the linear light source is transmitted though the light guide panel where it is spread and uniformly output through a front face to the prismatic film. Light incident on the prismatic film is redirected more along a first direction than along a second direction. This light is directed more normal to the LCD. An asymmetric diffuser is applied between the prismatic film and the LCD panel to smear the periodic information from the prismatic film and eliminate the Moiré fringe pattern resulting from interference between the periodic structure of the prismatic film and the periodic arrangement of pixels in the LCD. The asymmetric diffuser is aligned with respect to the prismatic film such that it scatters and spreads light more in a second direction than the first direction.
Owner:WAVEFRONT TECH INC
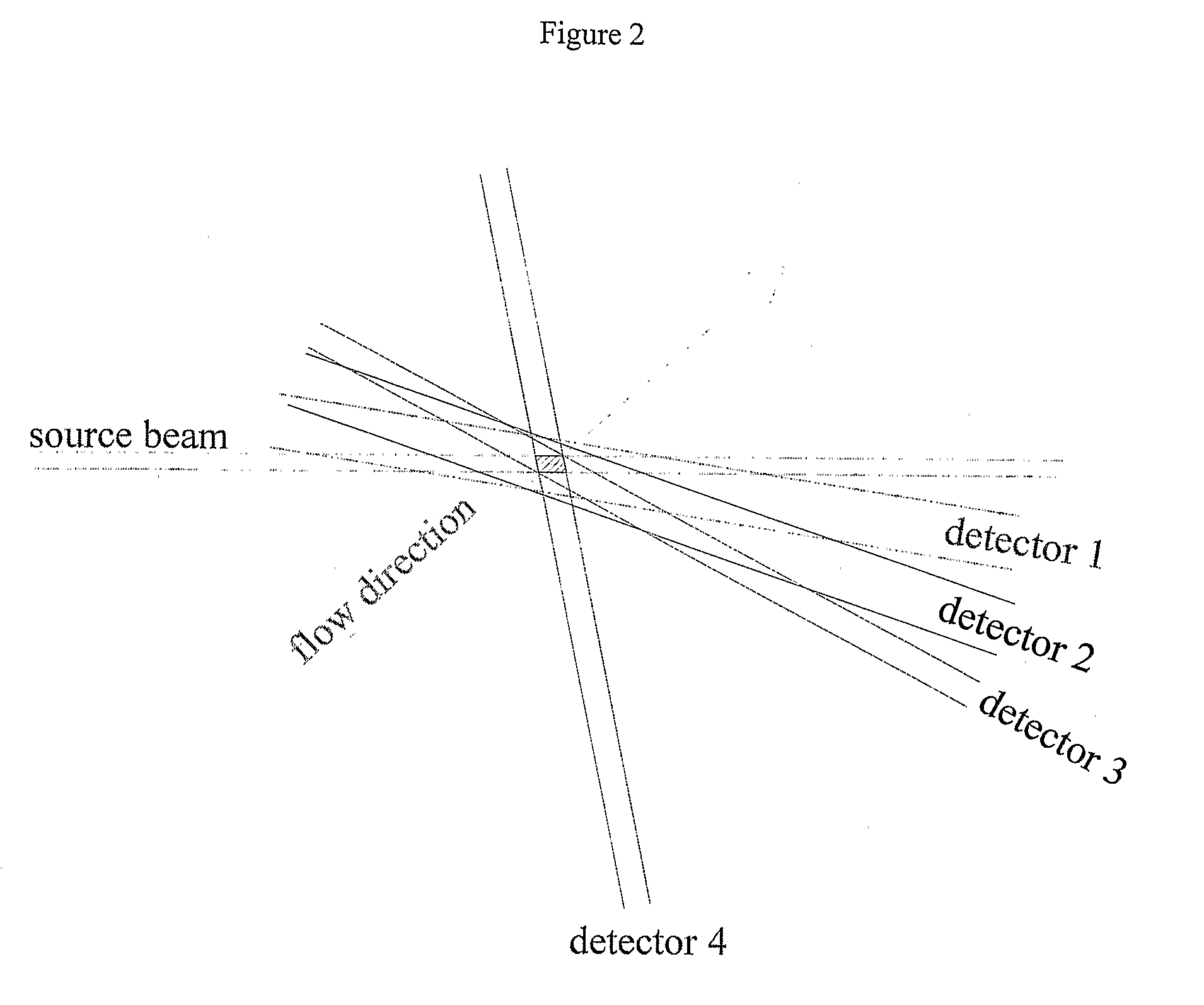
Methods and apparatus for determining the size and shape of particles
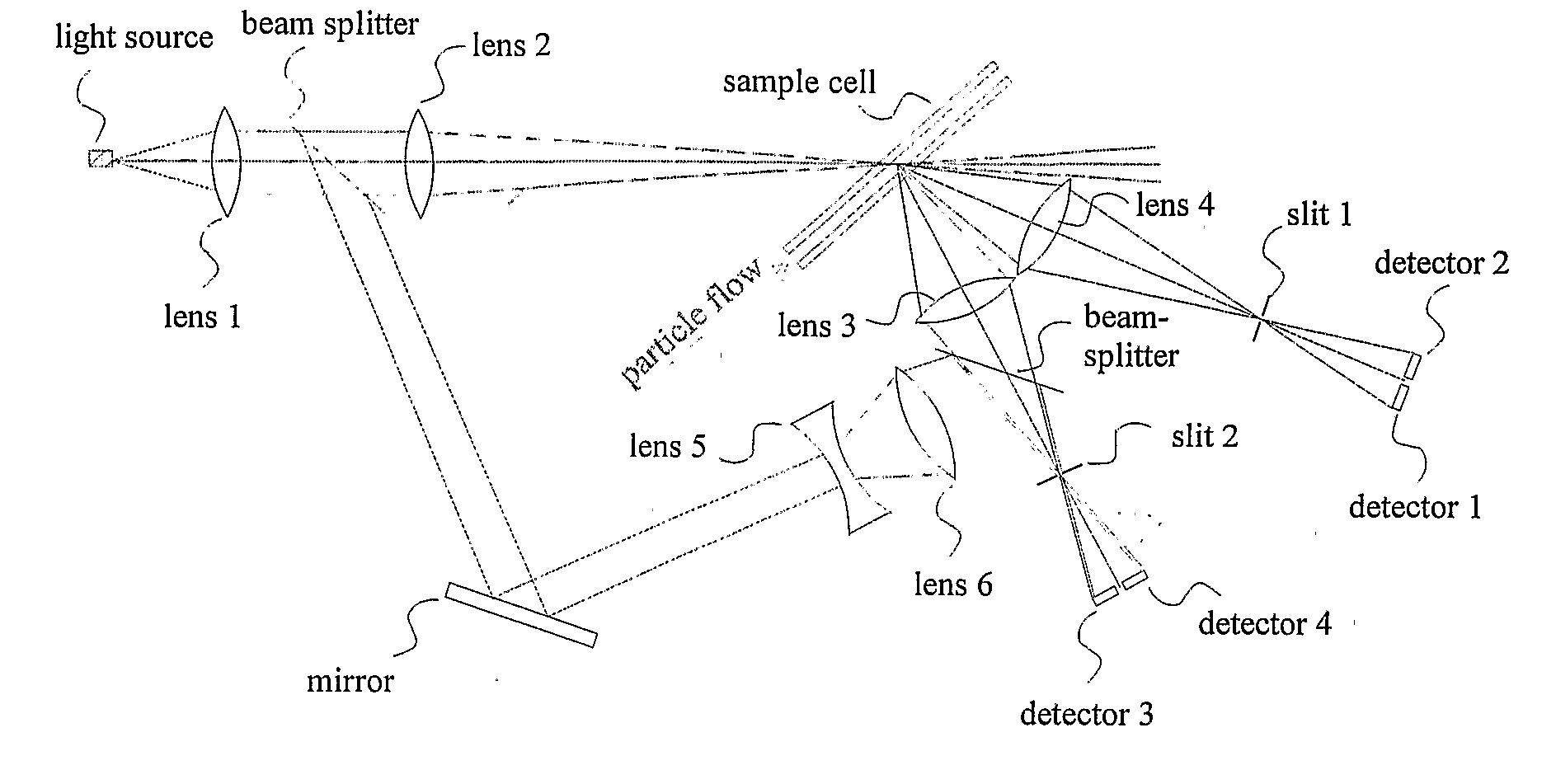
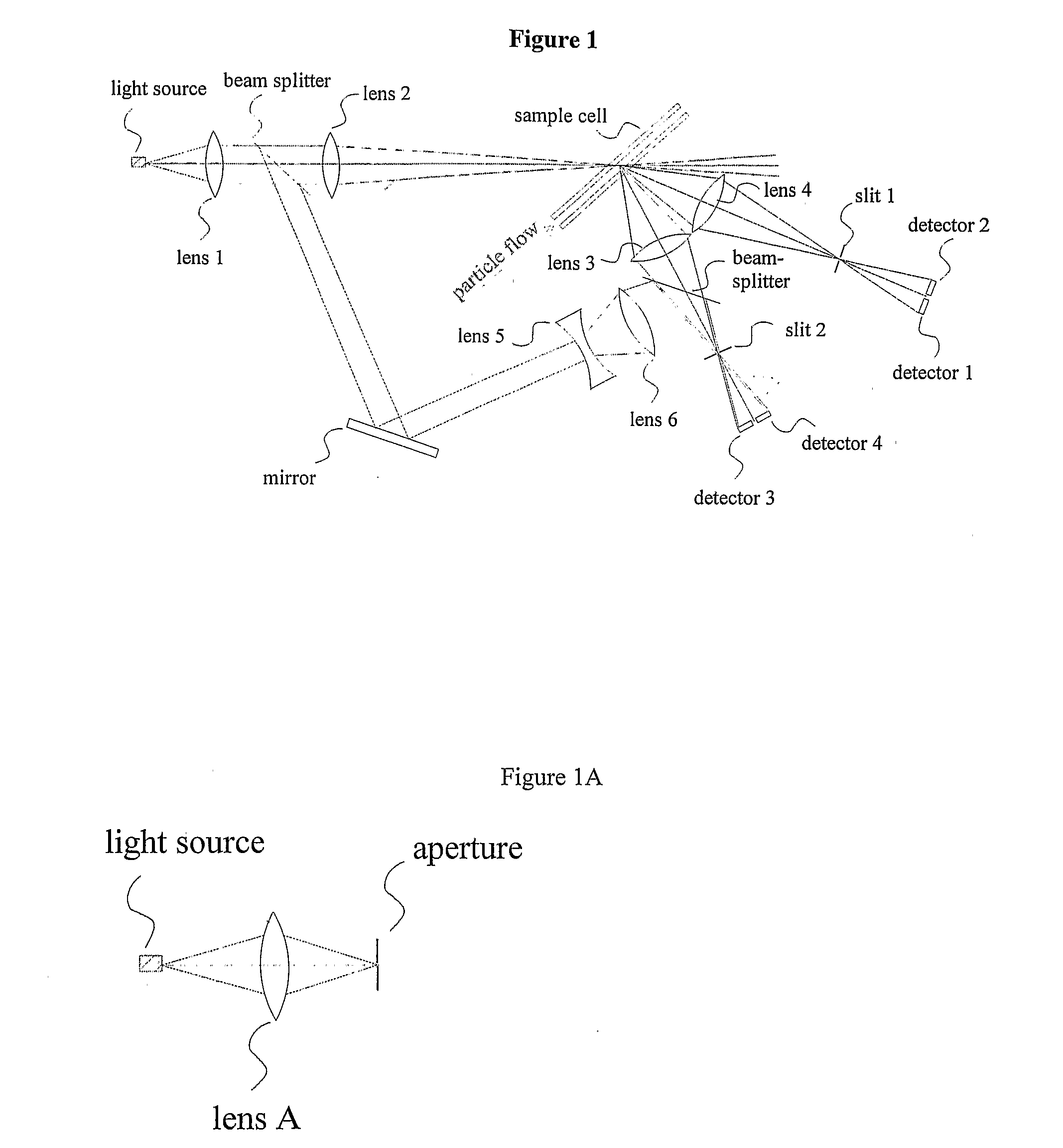
An instrument for measuring the size distribution of a particle sample by counting and classifying particles into selected size ranges. The particle concentration is reduced to the level where the probability of measuring scattering from multiple particles at one time is reduced to an acceptable level. A light beam is focused or collimated through a sample cell, through which the particles flow. As each particle passes through the beam, it scatters, absorbs, and transmits different amounts of the light, depending upon the particle size. So both the decrease in the beam intensity, due to light removal by the particle, and increase of light, scattered by the particle, may be used to determine the particle size, to classify the particle and count it in a certain size range. If all of the particles pass through a single beam, then many small particles must be counted for each large one because typical distributions are uniform on a particle volume basis, and the number distribution is related to the volume distribution by the particle diameter cubed.
Owner:TRAINER MICHAEL
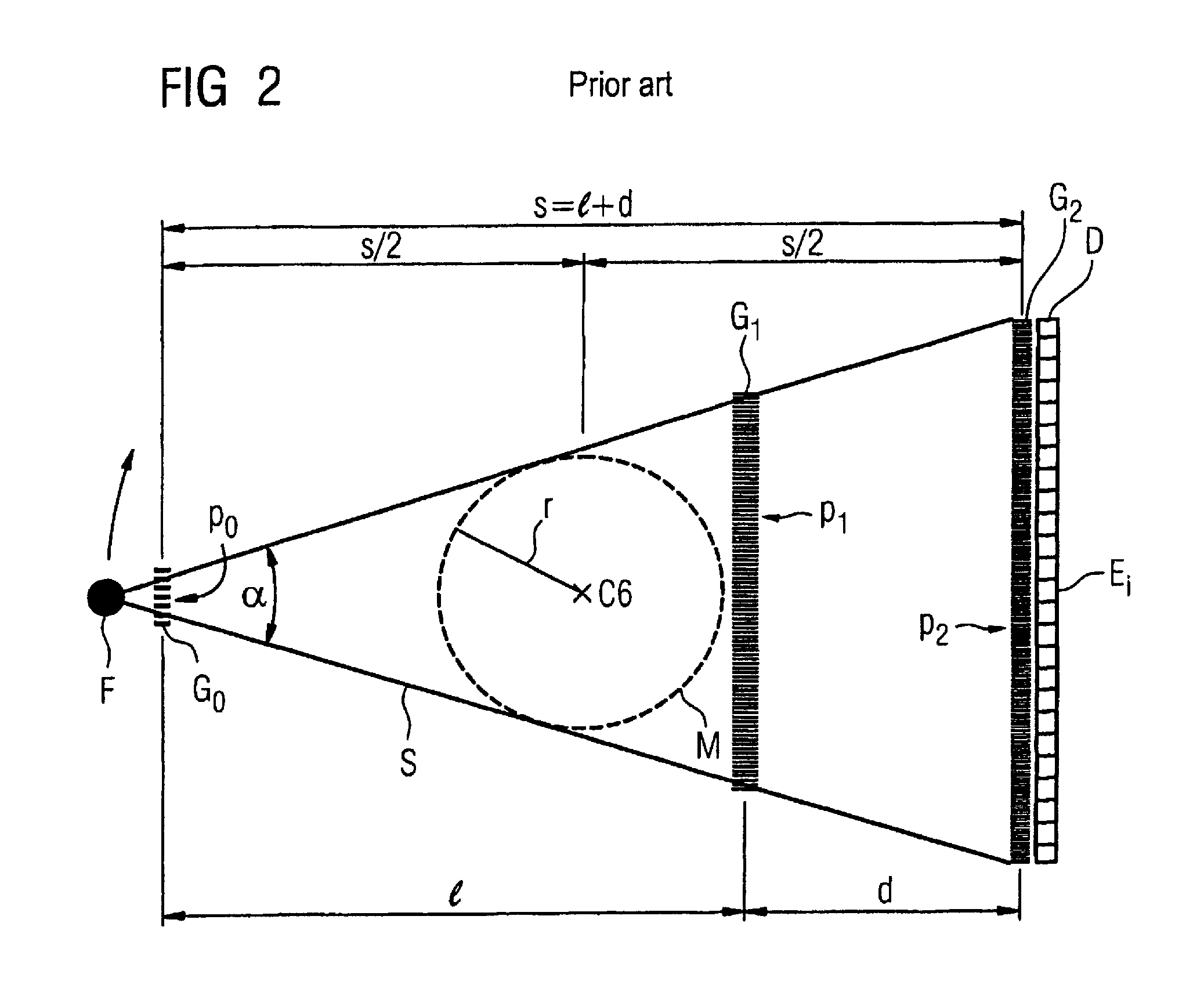
X-ray CT system for x-ray phase contrast and/or x-ray dark field imaging
ActiveUS7983381B2Technical requirementPractical operationImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayGrating interferometer
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
Compound electromagnetic scattering value simulation method of electrically large complex object and rough surface background
InactiveCN102176017AReduce complexityIncrease the number of raysRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRough surfaceRadar imaging
The invention belongs to the technical field of radar target imaging and monitoring, in particular relates to a compound electromagnetic scattering value simulation method of electrically large complex object and rough surface background. The method comprises the following steps of: synthesizing a two-dimensional arc aperture by using a frequency stepping radar in a down spotlight mode, simulating (observing) a electromagnetic scattered radar echo value of a electrically large complex three-dimensional target through the frequency stepping radar to obtain a three-dimensional back scattering matrix containing amplitude and phase; obtaining a uniform re-sampling data in an X-Y-Z coordinate system through a three-dimensional interpolation in a wave number domain; performing the three-dimensional rapid Fourier conversion on the re-sampling data to obtain a three-dimensional focus image to further reconstruct a geometric feature of the three-dimensional complex target. A numerical value execution result proves that the compound electromagnetic scattering value simulation method has feasible, accurate and high-efficient performance in the simulation of the three-dimensional complex target scattering monitoring, radar imaging and geometric feature reconstructing on a rough surface background.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Ultra-High Temperature Distributed Wireless Sensors
InactiveUS20100290503A1Thermometers using electric/magnetic elementsForce measurementLine sensorResonance
A passive wireless sensor is disclosed. The sensor has at least a measurand sensitive member and an electromagnetically resonant member positioned proximate to each other. The resonant member comprises a preselected resonance frequency, such that it scatters at least a portion of an interrogating signal as a scattered signal proximate to its resonance frequency, and the measurand sensitive member alters the scattered signal as a function of the measurand to change the shape of the scattered signal. The reactive field of the sensor is kept within the sensor to minimize environment interference and to maximize its signal strength. Almost bond-free packaging mitigates problems with delamination or internal stresses due to differing coefficients of thermal expansion.
Owner:PRIME PHOTONICS LC
Multi-resolution precondition method for analyzing aerial radiation and electromagnetic scattering
ActiveCN102156764AGood mannersIterative convergence is fastSpecial data processing applicationsLow demandElectromagnetic shielding
The invention discloses a multi-resolution precondition method for analyzing aerial radiation and electromagnetic scattering problems in electromagnetic simulation. The method is a method for generating a multi-resolution basis function by using a geometrical mode on a laminar grid constructed in a grid aggregation mode and further generating multi-resolution preconditions, wherein the multi-resolution basis function is formed by linear combination of a classical vector triangle basis function (RWG), and can be conveniently applied to the conventional moment method electromagnetic simulation program to effectively improve the behavior of a matrix formed in the moment method electromagnetic simulation process so as to realize acceleration of the iterative solution process of a matrix equation and fulfill the purpose of accelerating the moment method electromagnetic simulation process. Meanwhile, the multi-resolution pre-processing technology can also be conveniently combined with a quick algorithm such as a quick multi-pole algorithm. The method has the advantages of short calculation time and capability of ensuring high precision of the program and low demand of a computing memory, and can effectively improve the computing efficiency of the conventional electromagnetic simulation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
X-ray ct system for x-ray phase contrast and/or x-ray dark field imaging
ActiveUS20100091936A1Decline in technical requirementsPractical operationImaging devicesRadiation/particle handlingGrating interferometerSoft x ray
An x-ray CT system for x-ray phase contrast and / or x-ray dark field imaging has a grating interferometer that has a first grating structure that has a number of band-shaped x-ray emission maxima and minima arranged in parallel, the maxima and minima exhibiting a first grating period, a second band-shaped grating structure that produces, as a phase grating, a partial phase offset of x-ray radiation passing therethrough and that exhibits a second grating period, a third band-shaped grating structure with a third grating period with which relative phase shifts of adjacent x-rays and / or their scatter components are detected, and a device for value-based determination of the phase between adjacent x-rays and / or for value-based determination of the spatial intensity curve per detector element perpendicular to the bands of the grating structures. The third grating structure has a grating period that is larger by a factor of 2 to 5 than the grating period of the first grating structure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
Model-based measurement of semiconductor device features with feed forward use of data for dimensionality reduction
ActiveUS7716003B1Reduce dimensionalityResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial analysis by optical meansNonlinear dimensionality reductionScattering function
The present application discloses a new technique which reduces the dimensionality of a feature model by re-use of data that has been obtained by a prior measurement. The data re-used from the prior measurement may range from parameters, such as geometrical dimensions, to more complex data that describe the electromagnetic scattering function of an underlying layer (for example, a local solution of the electric field properties).
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Measurement and Imaging of Scatterers with Memory of Scatterer Parameters Using at Least Two-Frequency Elastic Wave Pulse Complexes
ActiveUS20140150556A1Solve insufficient capacityImprove performanceMultiple-port networksAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcousticsLow frequency
Measurement or imaging of elastic wave nonlinear scatterers with a memory of scattering parameters comprises selecting LF pulses having characteristics to change the scattering parameters of nonlinear scatterers. A transmit time relation is selected so that the incident HF pulse propagates sufficiently close to the LF pulse that the effect of the incident LF pulse on its scatterer parameters is observed by the HF pulse. At least two elastic wave pulse complexes comprising a high frequency (HF) pulse and a selected low frequency (LF) pulse are transmitted towards the region. Received HF signals are combined to form nonlinear HF signals representing the scatterers with memory, with suppression of received HF signals from other scatterers. At least one of the received HF signals may be corrected by time delay correction and / or speckle correction with a speckle correction filter, determined by movement of the scattering object. Systems are also disclosed.
Owner:SURF TECH AS
Single-layer earth surface dielectric parameter and roughness parameter fast inversion combined optimization algorithm based on measured radar back scattering data
ActiveCN103617344AEnables real-time forecastingOvercome timeSpecial data processing applicationsSupport vector machineRadar
The invention discloses a combined optimization algorithm of an inheritance multi-output support vector machine. The combined optimization algorithm combines with measured radar back scattering data for fast inversion of single-layer earth surface (root-mean-square height ksigma<1.5, and root-mean-square slope s<0.3) dielectric parameters and roughness parameters. The algorithm includes: using single-layer earth surface HH and VV measured polarizing radar back scattering coefficient data to obtain homo-polarization ratio; using a rough earth surface electromagnetic scattering small slope approximation method to calculate back homo-polarization ratio; combining a genetic algorithm with the small slope approximation homo-polarization ratio and the measured data to invert the earth surface dielectric constant; substituting the inversion result into an electromagnetic scattering integral equation model to generate a data file of back scattering coefficient changing with roughness; combining two kinds of measured polarized radar back scattering data to form a target function, using M-SVR optimization algorithm to invert the earth surface roughness parameters, and evaluating inversion errors and efficiency. By the combined optimization algorithm, real-time prediction of earth surface parameters can be achieved while inversion precision is guaranteed.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Volcanic ash detection by optical backscatter using standard aircraft lights
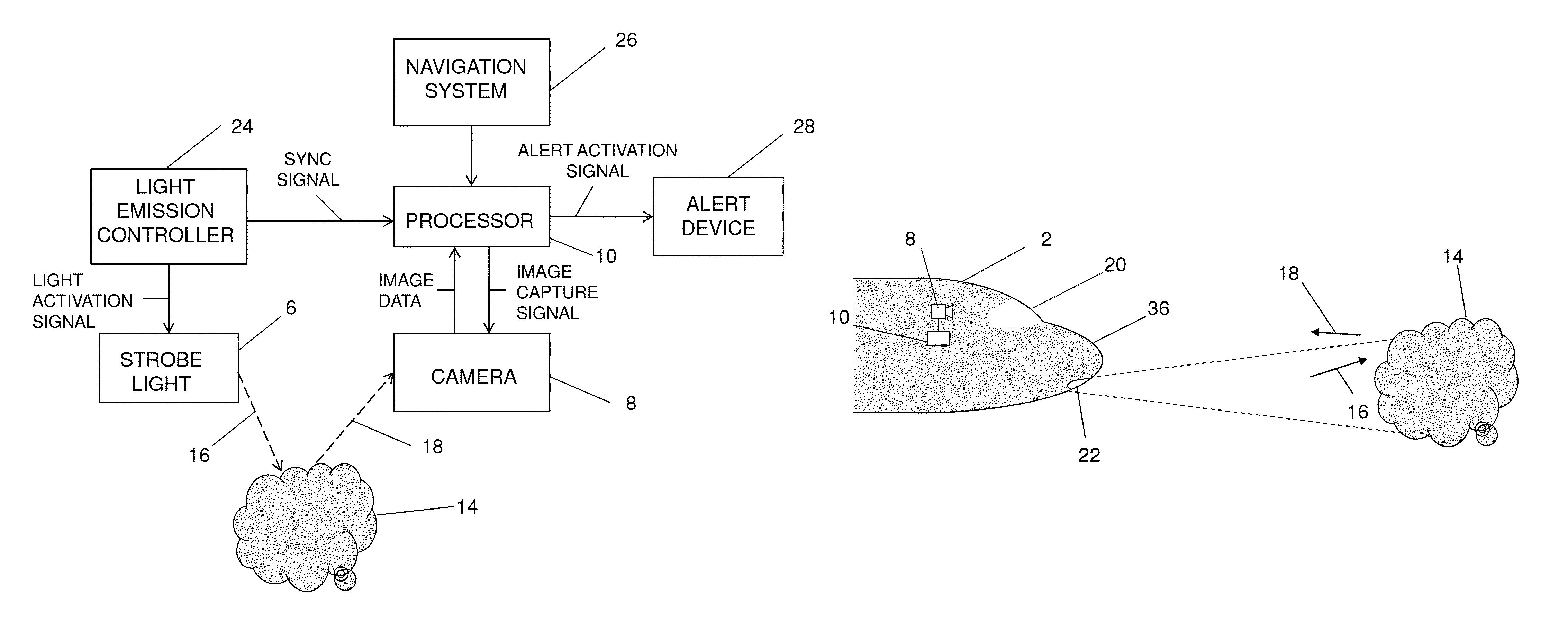
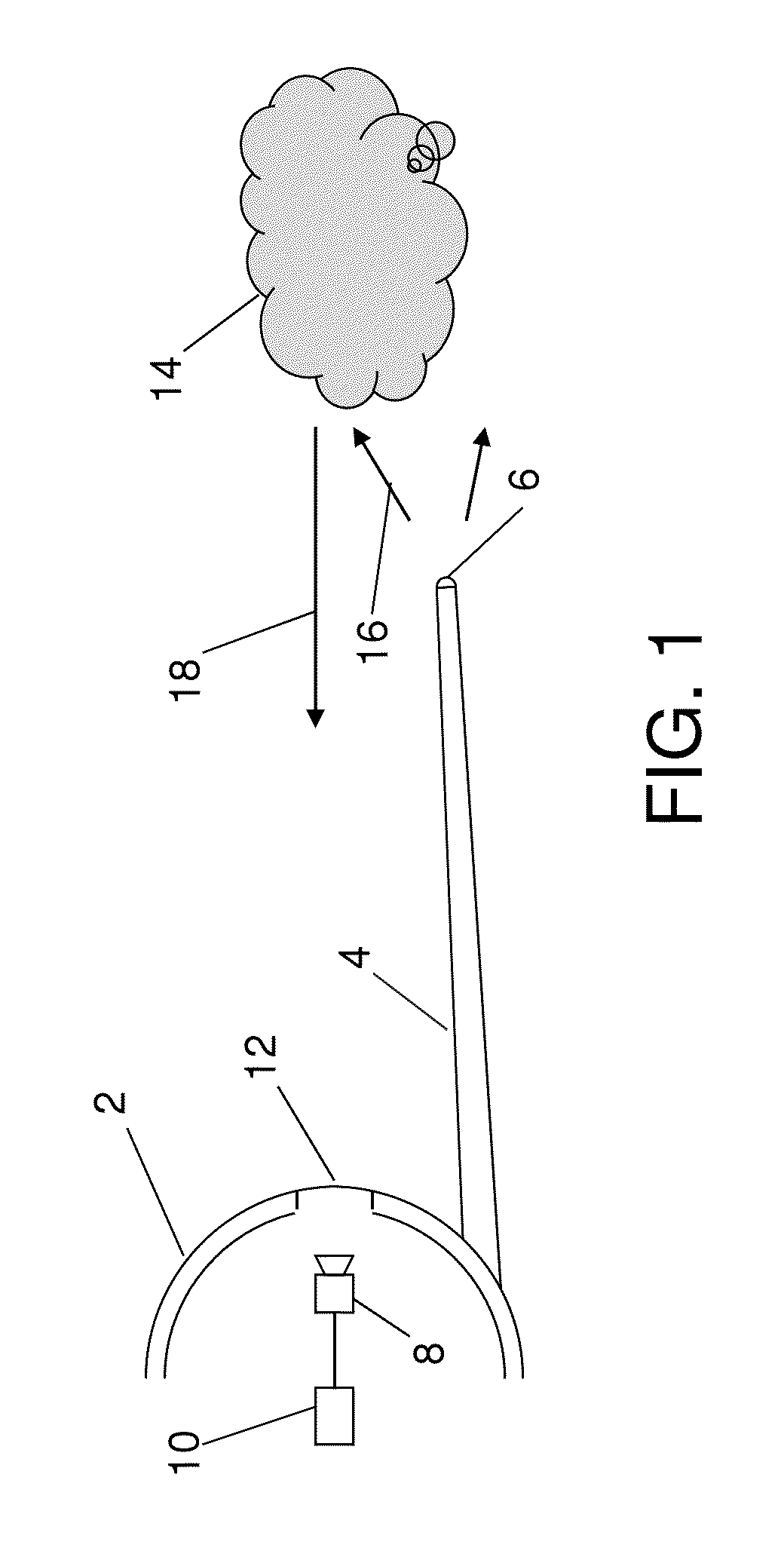
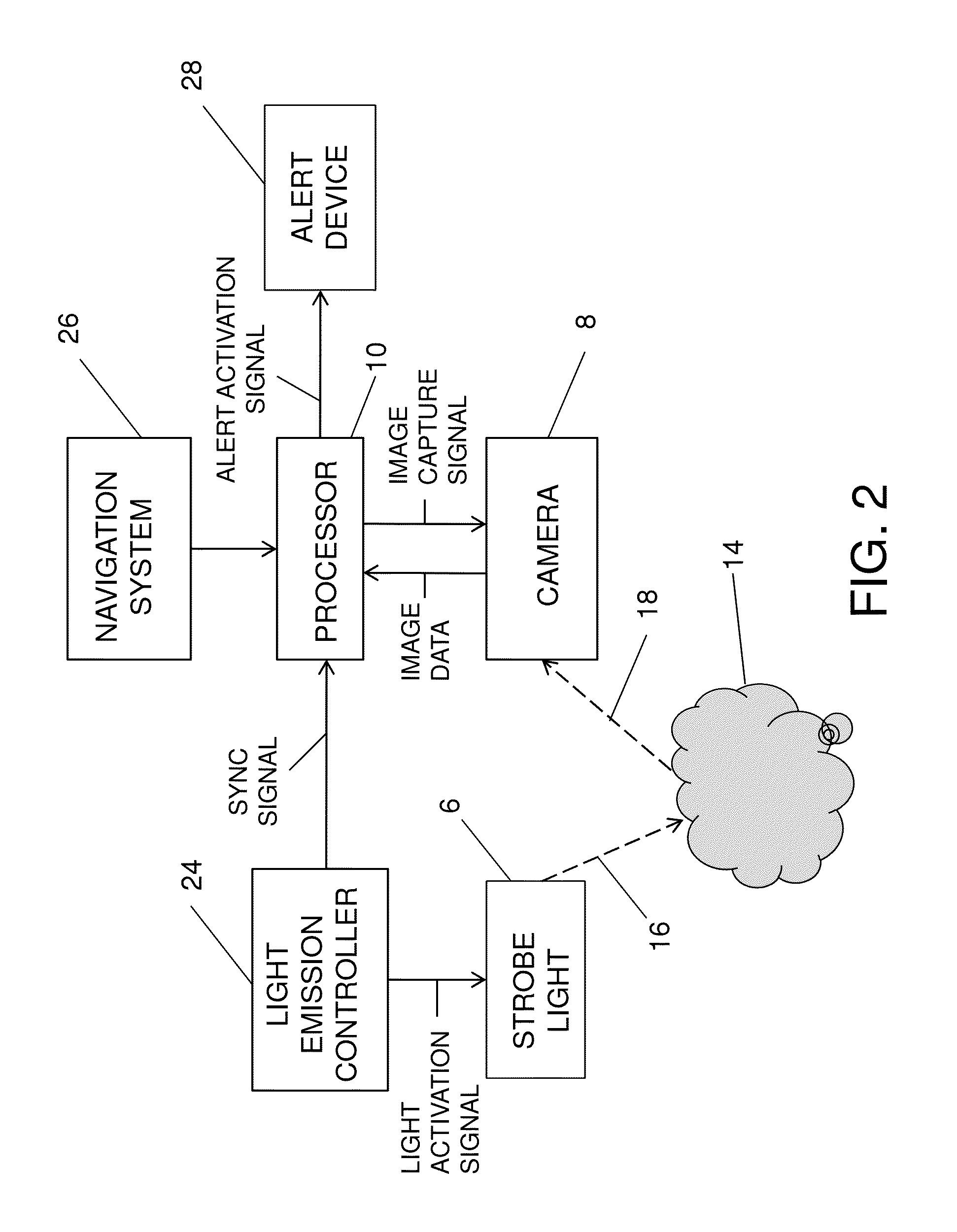
ActiveUS8666570B1Avoids and minimizes costAvoids and minimizes and delayImage enhancementImage analysisDigital dataNose
Onboard systems and methods for detection of airborne volcanic ash. One or more cameras are added to an aircraft. Each camera is configured to view a volume of air illuminated by a standard aircraft light, such as a strobe warning light (e.g., located on a wing tip) or a forward-facing landing light (e.g., located in the nose). Each camera is connected to a data processor. When diffuse volcanic ash is present, it scatters light transmitted from the standard aircraft light. Each camera converts impinging backscattered light into digital data which is sent to the processor. The processor processes the data from the camera or cameras to derive a measurement of the backscattered light and issues an alert when the amount and type of backscatter are compatible with the presence of volcanic ash.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
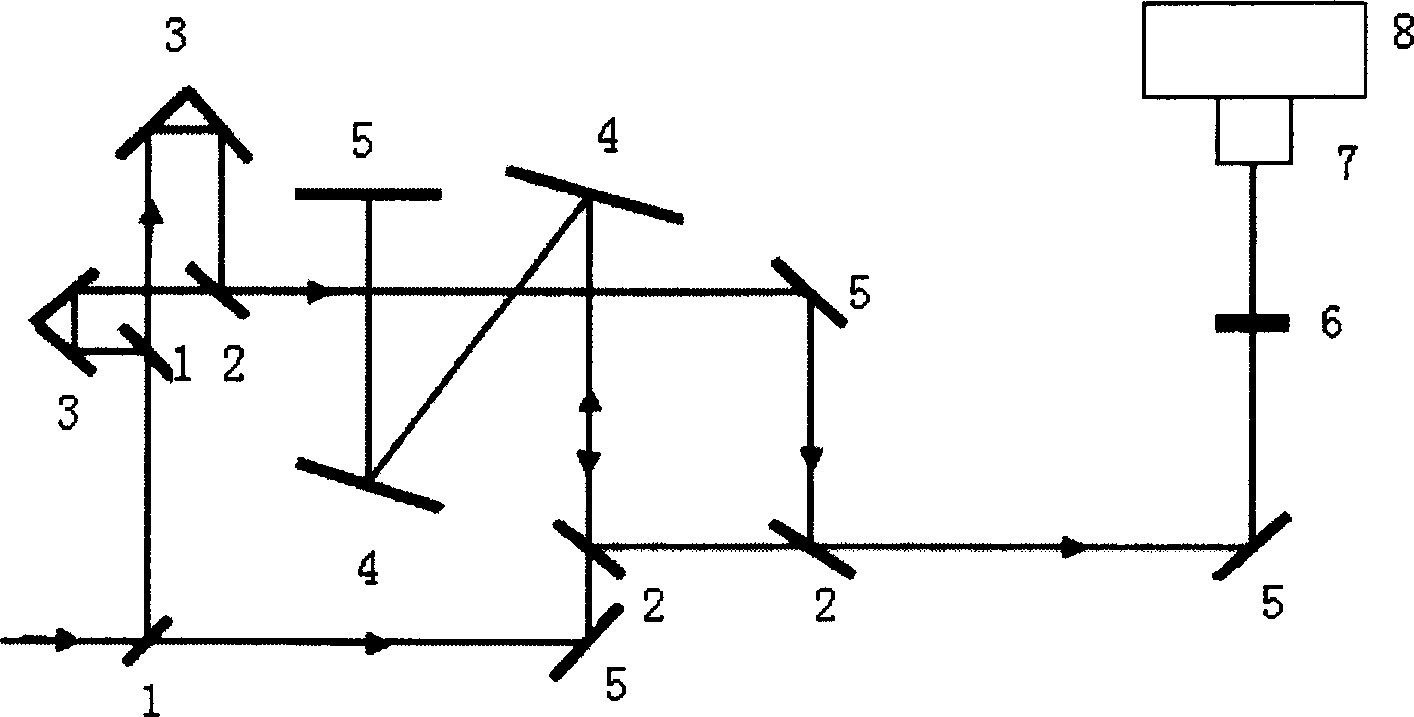
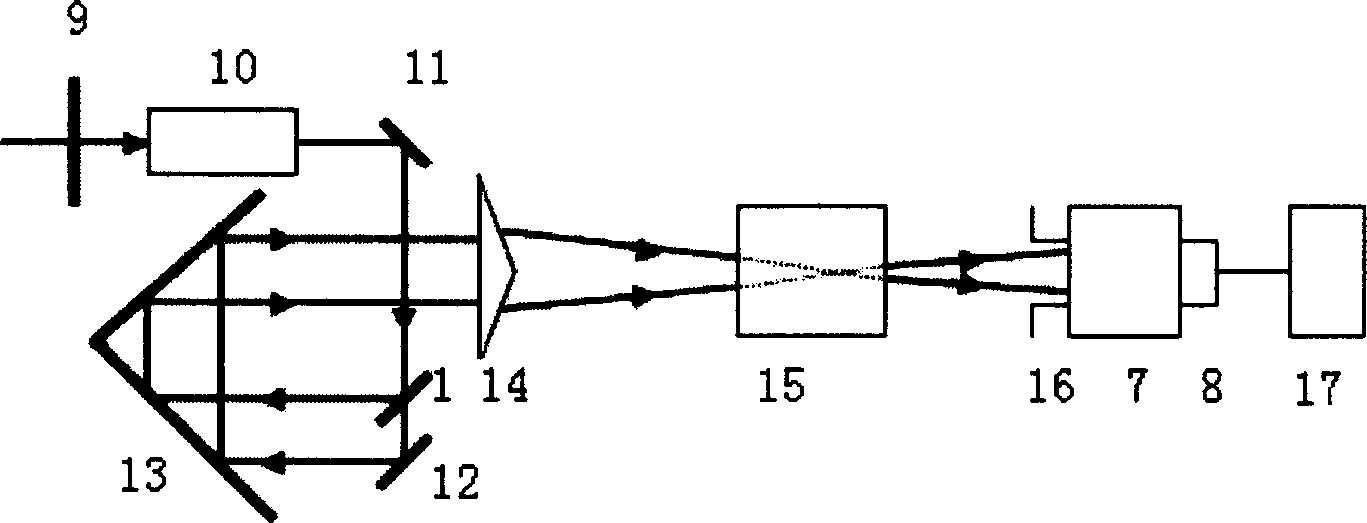
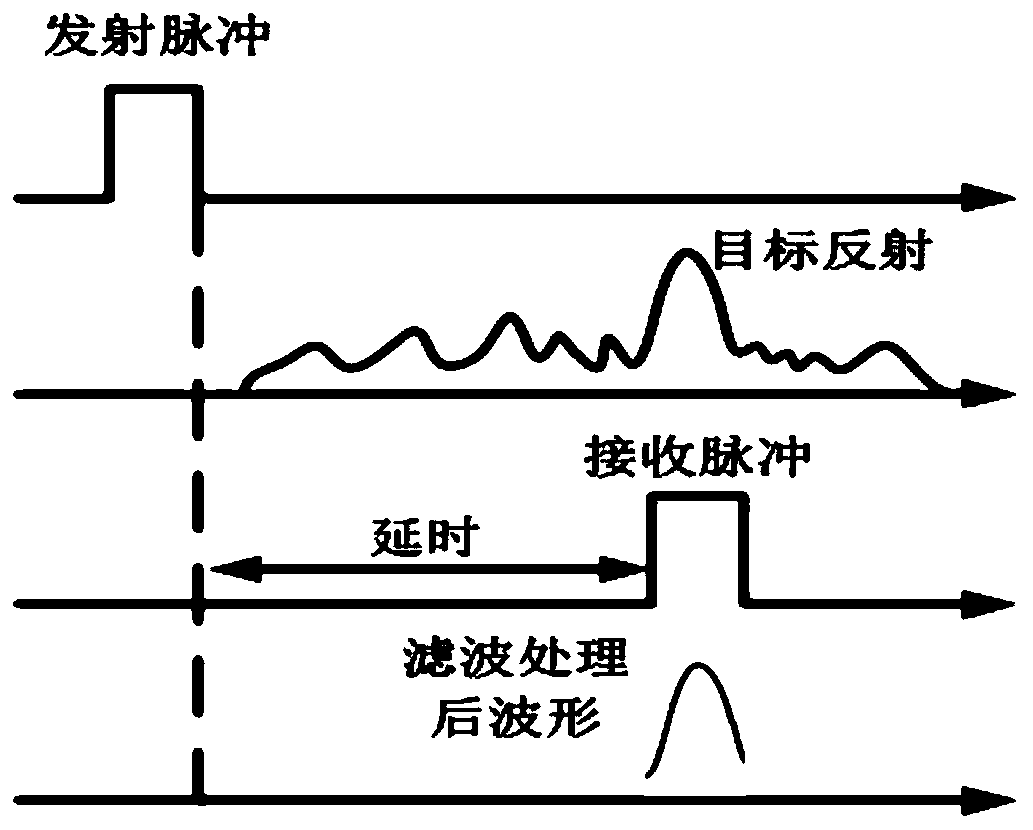
Flying second pulse simple real-time measuring instrument
InactiveCN1888836AOptimizing light pathLess componentsInstrumentsMeasuring instrumentReconstruction method
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
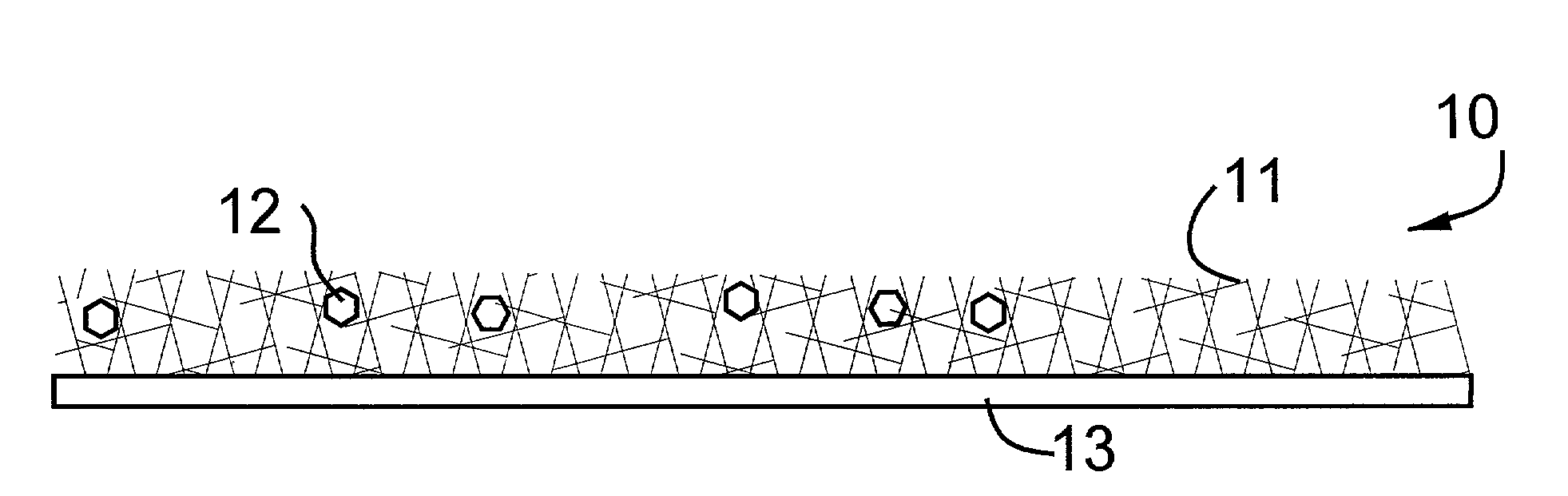
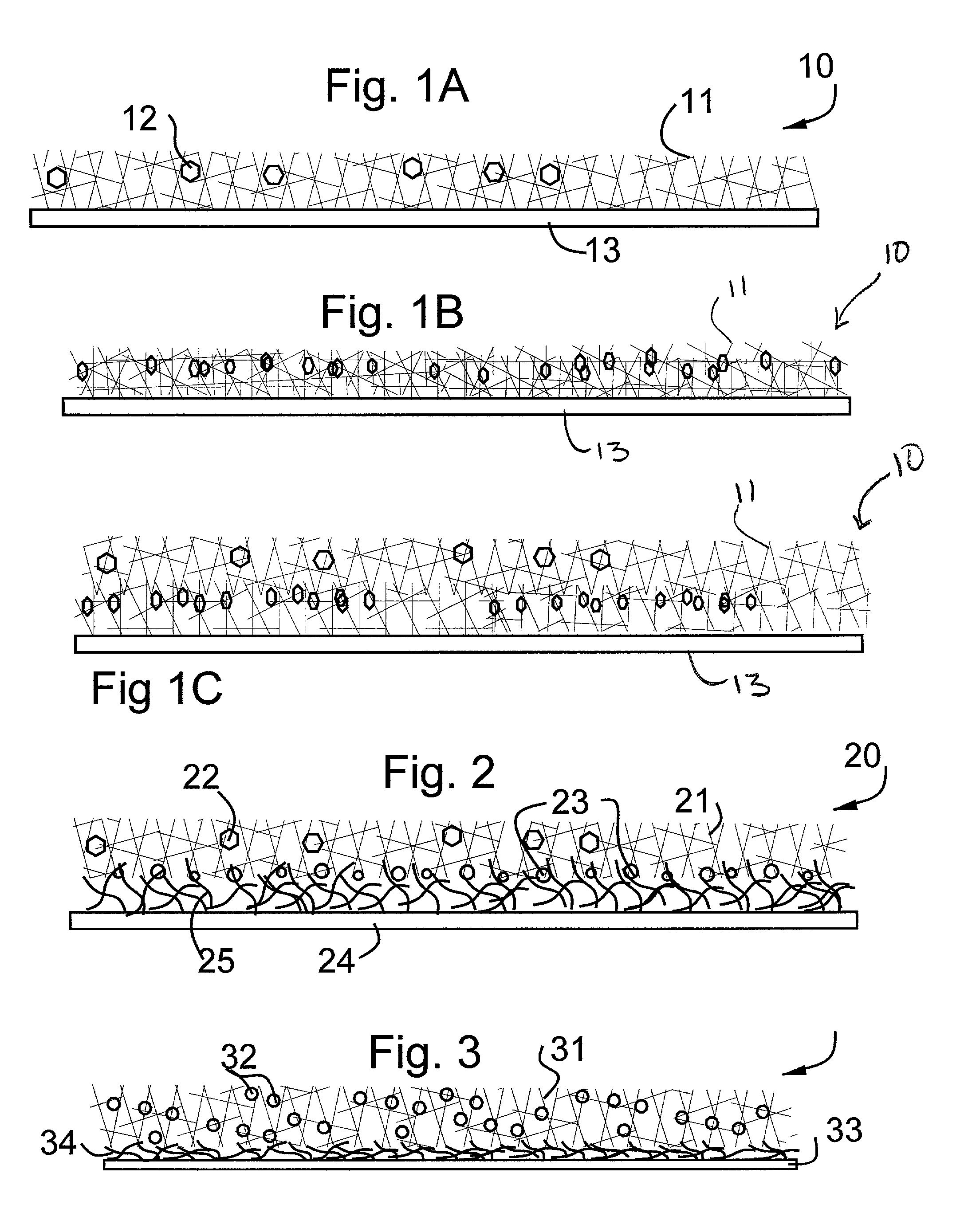
Absorbent pad for entrapping small and coarse particles, retaining liquids and eliminating odors
InactiveUS7726260B1Excellent liquid absorption rateExcellent planar diffusionKitchenware cleanersPaper/cardboard layered productsEngineeringAbsorbent material
A layered pad comprising a bottom impervious layer, a top layer of a fibrous high loft non woven capable of entrapping fine or coarse particles and preventing their scatter, optionally combined with a middle layer of fibers and super absorbent agent, wherein liquids pass through the top layer, become absorbed by the middle layer, and evaporate. As particles from an animal litter box or cage, shoes, metal cutting, wood shavings, and copy machines are generated, they immediately encounter the high loft non-woven top layer, which immediately immobilizes and then entraps them, preventing them from scattering. The filament count of the non-woven can be varied to design the pads to be more effective in trapping smaller or larger particles. In addition, a film of oily substance can be applied to the fibers to make them more sensitive to absorbing and entrapping extremely small particles. If absorbency is required under the high loft fibrous non-woven, a layer of absorbent material is added between the two layers. The layered pad is optionally treated with super absorbent polymer, deodorants, antibacterial agents, anti-fungal agents, and other substances depending on the use of pad.
Owner:YANANTON PAT
Absorbent pad for entrapping small and large particles, retaining liquids and eliminating odors
InactiveUS7654227B1Eliminate odorEnhance particle entrapmentAnimal housingOther apparatusFiberInter layer
A layered pad comprising a bottom impervious layer, a top layer of a fibrous high loft non woven capable of entrapping small or large particles and preventing their scatter, optionally combined with a middle layer of fibers and super absorbent agent, wherein liquids pass through the top layer, become absorbed by the middle layer, and evaporate; and a method for manufacturing a non-woven pad layer having an at least partially open-ended configuration. The method of manufacturing the open-ended non-woven layer includes cutting at least one surface of the non-woven layer and then abrading the cut surface with an abrading tool.
Owner:YANANTON PAT
Reduction in scattering from a turbid medium by photo-bleaching
ActiveUS7536213B2Reduce absorptionReduce dispersionRadiation pyrometryDiagnostics using lightAnalyteFluorescence
A method is proposed whereby photo-bleaching is used not only to change the absorption and fluorescence of a sample but is also employed to change its scattering characteristics. When the compounds which are bleached are contained in regions wherein the real part of the index of refraction is greater than or equal to the average index of the medium, the bleaching will result in reduction in the scattering at wavelengths longer than the wavelength of the bleaching source. This reduction can be useful in measuring the concentration of analytes located at significant depths within turbid media.
Owner:DIABESEN TECH BEIJING CO LTD
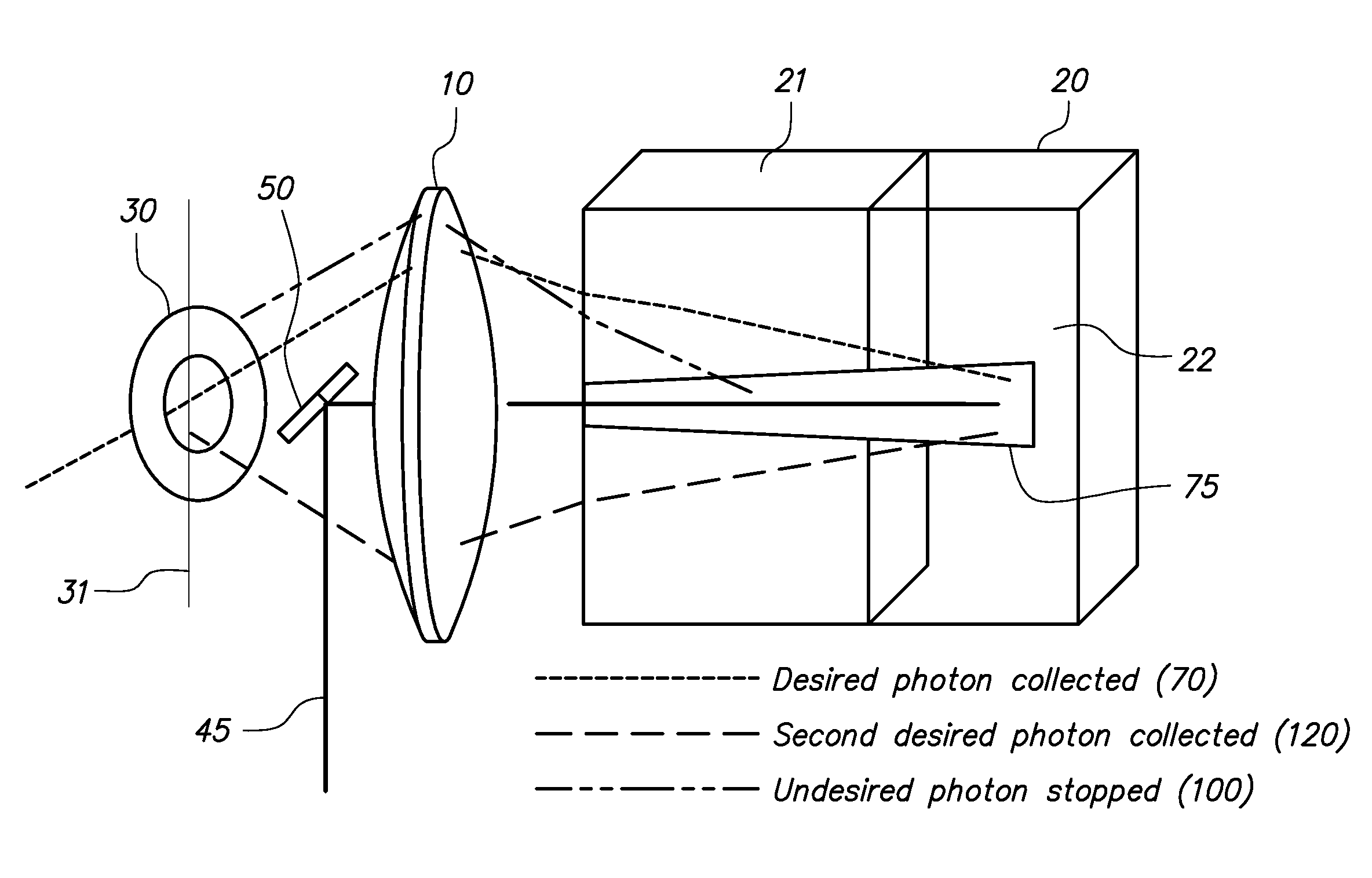
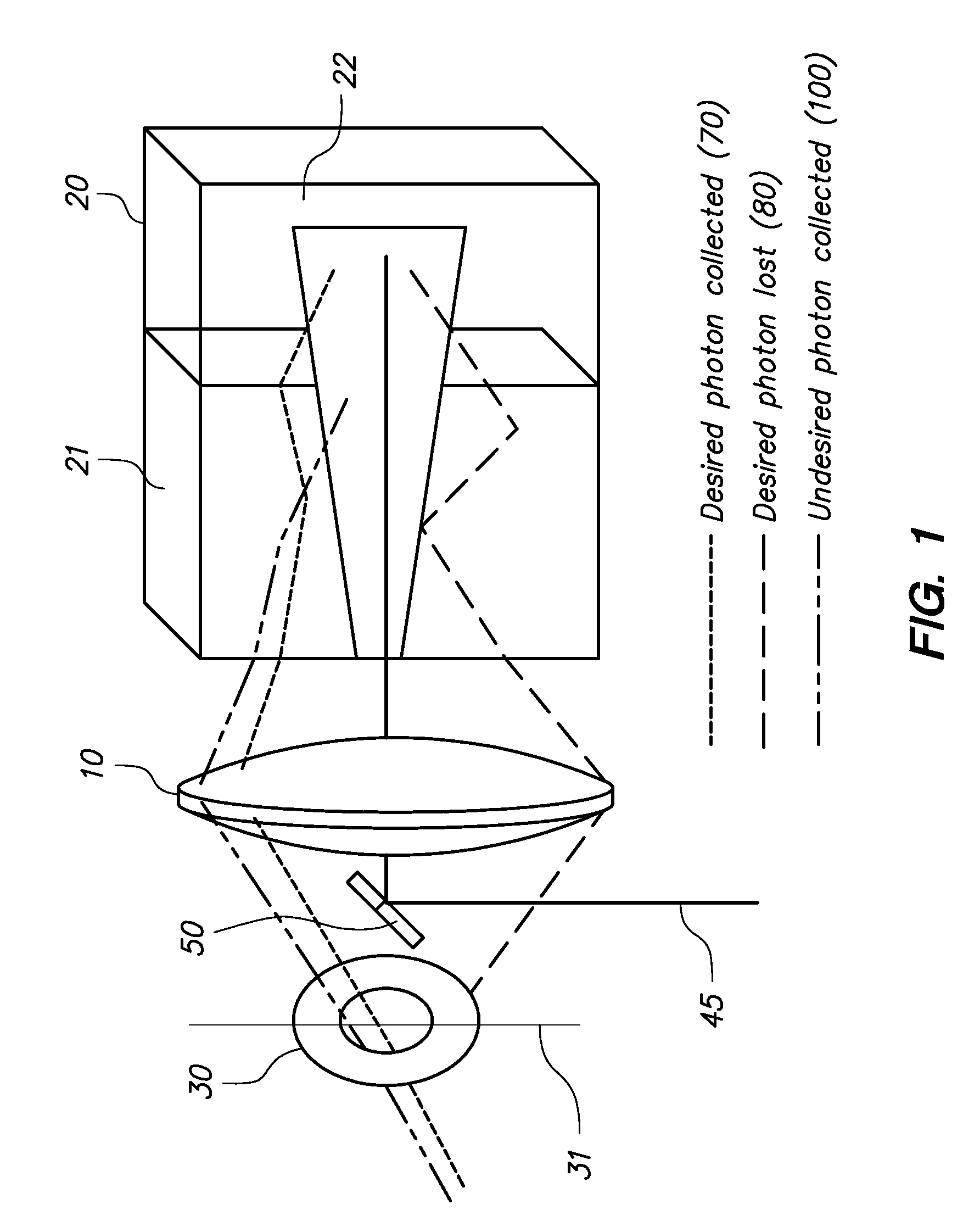
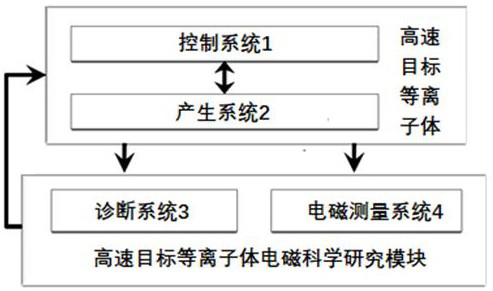
Near space high-speed target plasma electromagnetic measurement system
ActiveCN112816795ADetermine the lengthAccurately calculate the radiusElectromagentic field characteristicsMagnetic measurementsEngineering
The invention discloses a near space high-speed target plasma electromagnetic measurement system which comprises a cylindrical horizontal vacuum cavity, wherein a nozzle plane of plasma entering the vacuum cavity cannot be coplanar with the end face of the vacuum cavity; transmitting and receiving antennas of a transmission measurement system are respectively erected on the lower guide rails on the two sides, the transmitting and receiving antennas of the transmission measurement system are symmetrically erected and can perform two-dimensional movement along the axis direction and the radial direction of the plasma, a to-be-measured target of a scattering measurement system is erected on the lower guide rail in the middle, and transmitting and receiving antennas of the scattering measurement system are all erected on the upper guide rail; and a transmitting antenna of an internal electromagnetic field measurement system is erected on any group of lower guide rails on the two side edges, and an electric field / magnetic field probe for receiving an electromagnetic field is erected on the lower guide rail in the middle. According to the invention, three measurement systems, namely, the transmission measurement system, the scattering measurement system and the internal electromagnetic field measurement system, in plasma electromagnetic measurement are considered at the same time, so that an electromagnetic scattering experiment and a transmission experiment can be configured at the same time and do not influence each other.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Electromagnetic scattering analysis method of target with cavity on the basis of moment method and parabolic equation
ActiveCN104778151AWell formedQuick and easy to formComplex mathematical operationsAnalysis methodRadar cross-section
The invention discloses an electromagnetic scattering analysis method of a target with a cavity on the basis of a moment method and a parabolic equation. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, filling the cavity body of the target with the cavity with solid metal, establishing a discrete model, determining the axial direction of a parabola as an x axis, and dispersing a target along the axial direction of the parabola by a mesh; in an x-axis direction, utilizing a CN (Crank-Nicolson) difference scheme to obtain a relationship between two adjacent tangent planes; in y-axis and z-axis directions, independently adopting an RPIM (Radial Point Interpolation Method) constructing fractal function and a spatial derivative to construct a matrix equation; successively carrying out recursive solving on a node electric field value on each tangent plane; carrying out solving on a cavity body part in the target separately by a fast multipole algorithm, applying an electric field integral equation to obtain current on the surface of the cavity body, and obtaining the electric field value of each discrete point required by the parabolic equation on an opening surface of the cavity body; and finally, carrying out postprocessing on the electric field on a last tangent plane to obtain a radar scattering sectional area. A meshless parabola and a fast multipole acceleration moment method are combined, and the electromagnetic scattering analysis method has the advantages of being efficient and reliable.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
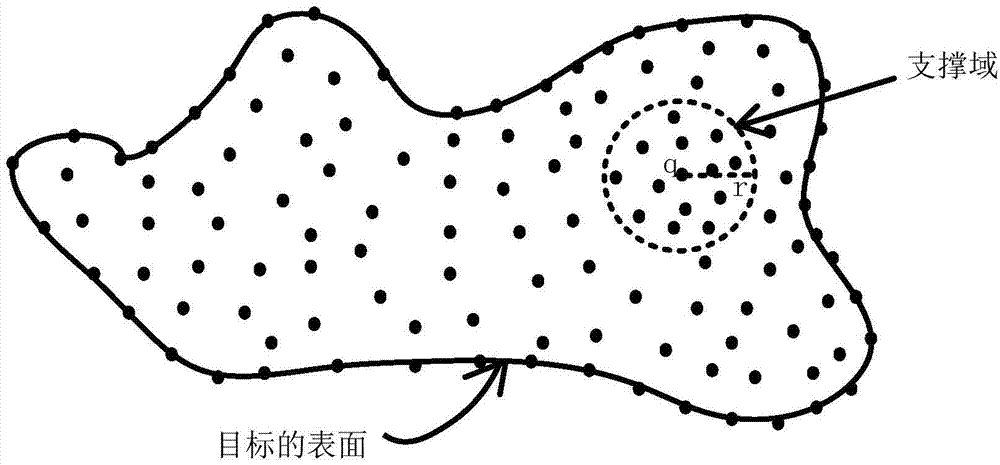
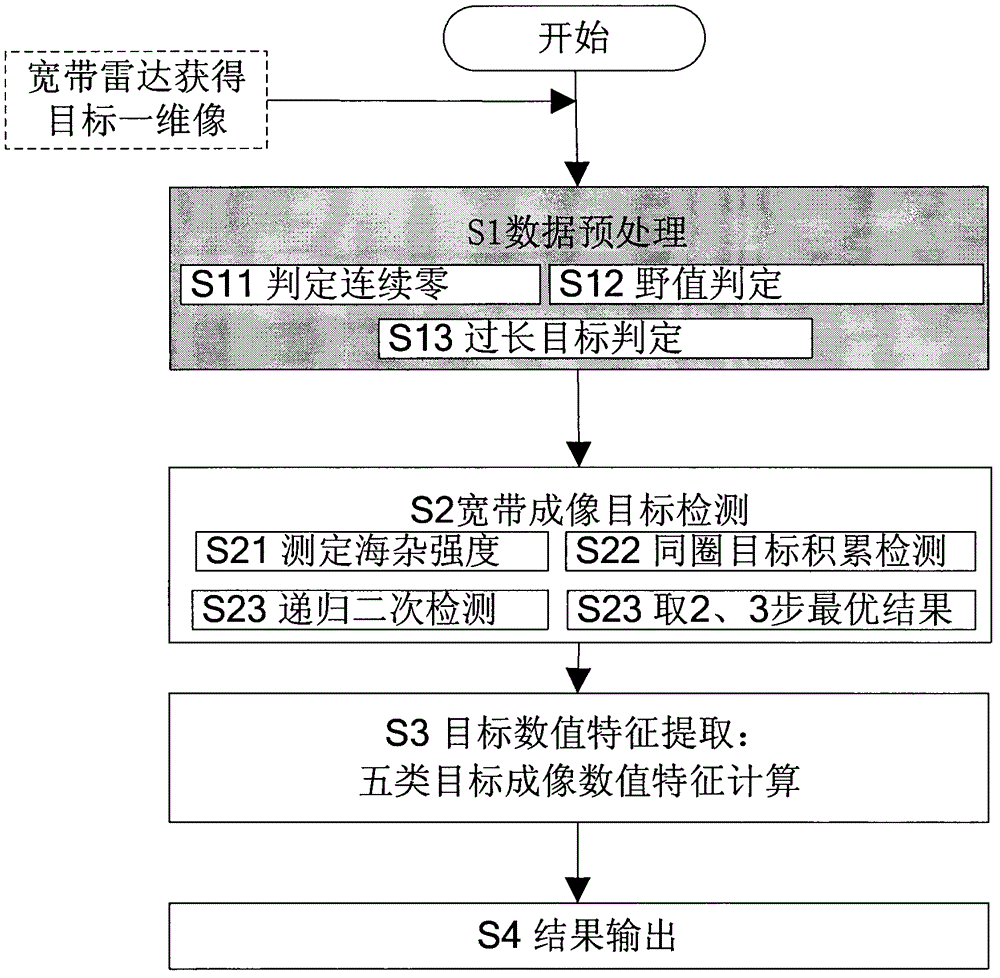
Target feature extraction method for one-dimensional imaging of target by using broadband radar
InactiveCN102721963ASolve the problem of object recognition feature extractionImprove adaptabilityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarImaging Feature
The invention relates to a target feature extraction method for one-dimensional imaging of a target by using a broadband radar. The target feature extraction method is used for solving the problems that the target features of a sea target are easily unstable under the influence of sea clutters when the sea target is subjected to broadband imaging, and the like, caused by the fact that the current broadband radar one-dimensional imaging method for the target mainly acquires the electromagnetic scattering characteristics of the external shape of the target. In order to obtain more stable identification results, a one-dimensional high-resolution distance feature extraction algorithm is provided by the technical scheme adopted by the invention, so that the accurate extraction of one-dimensional image features is realized, the discrimination and identification of one-dimensional broadband images of the sea target are realized. The target feature extraction method comprises the following specific steps of: judging the correctness of one-dimensional imaging data of the target so as to eliminate singular values which affect data computed results; accurately judging imaging starting and ending positions of the target so as to provide a basis for the judgment of target size and a support for back-end processing; and carrying out extraction and computation on numerical features of the target. The target feature extraction method provided by the invention has the advantages that the difficult problem in extraction of identification features of the target is solved, and a technical support for identification of broadband images of the target is provided.
Owner:THE 724TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND
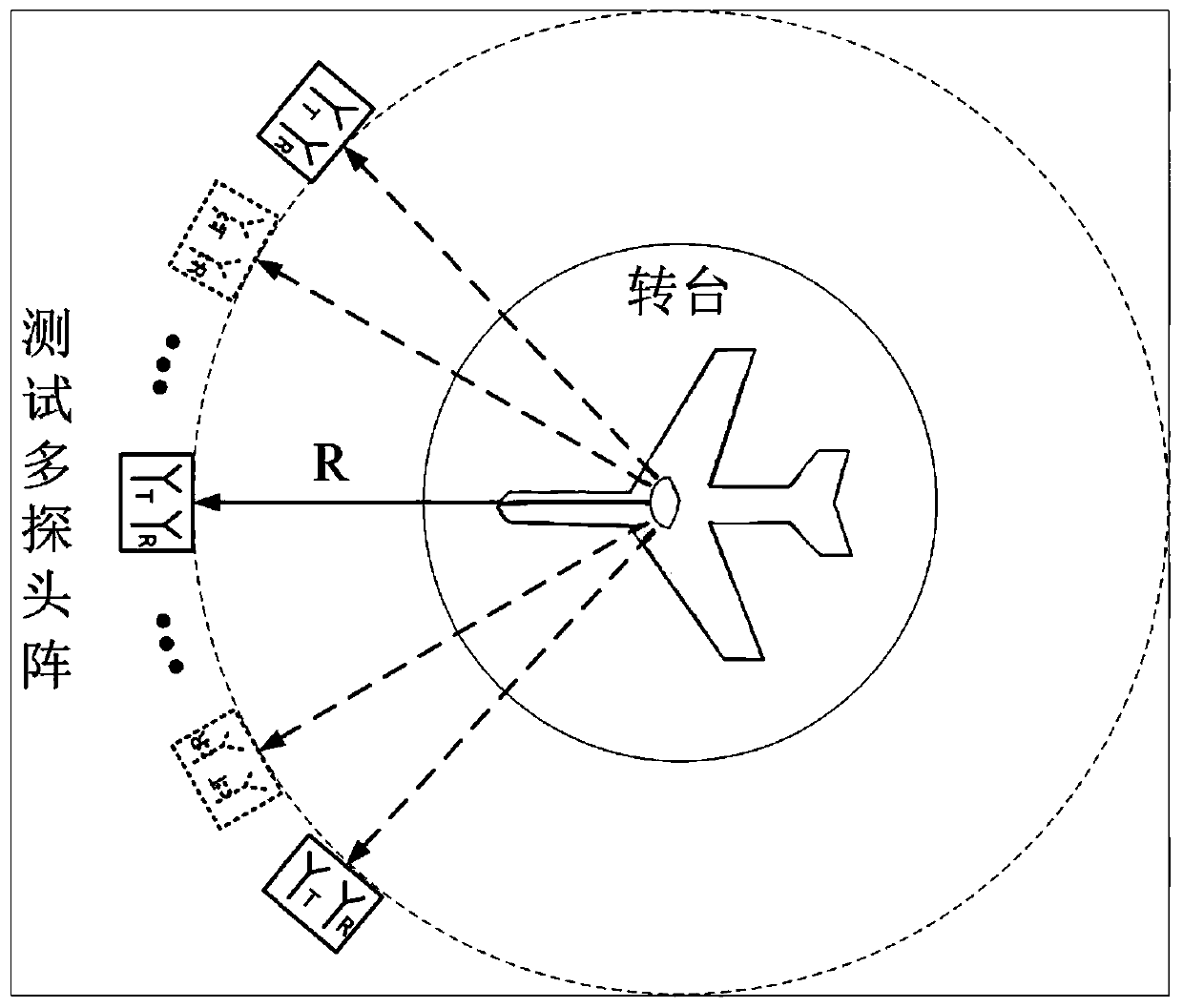
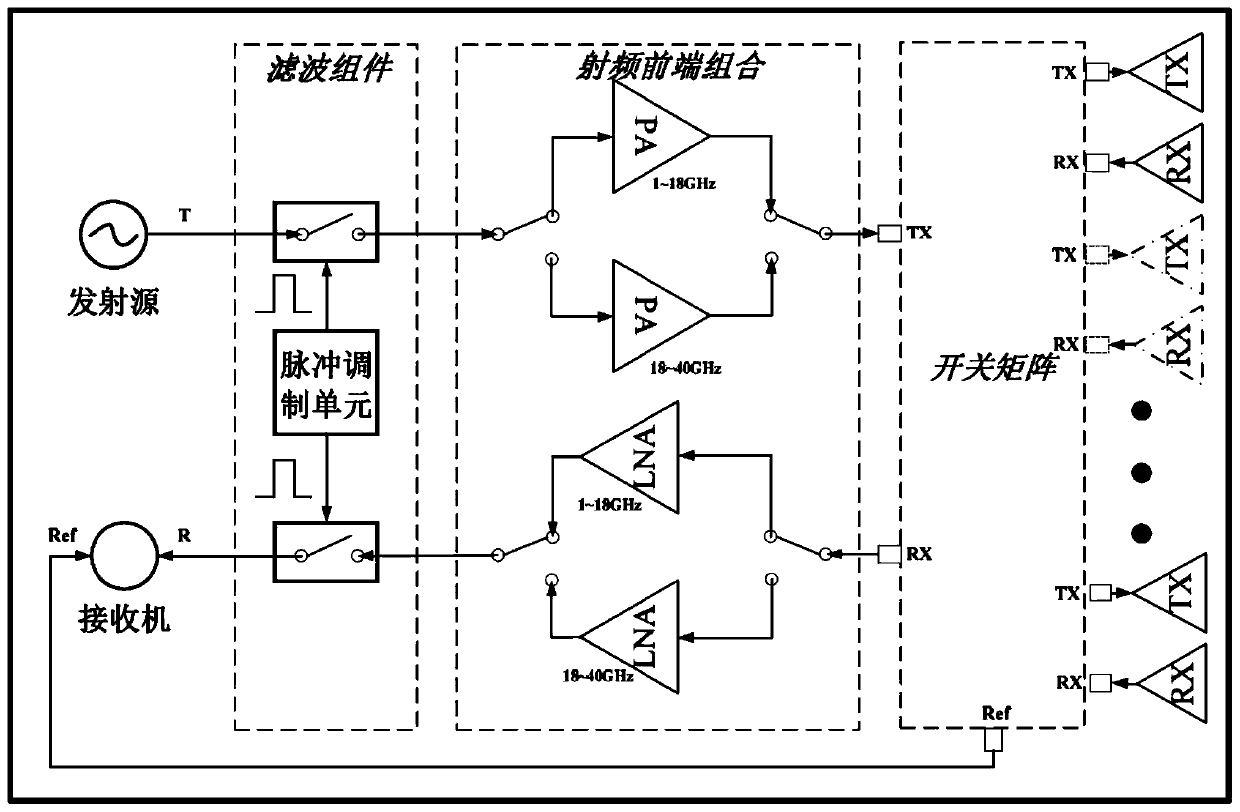
Ultra-wideband target electromagnetic scattering characteristic test system and method
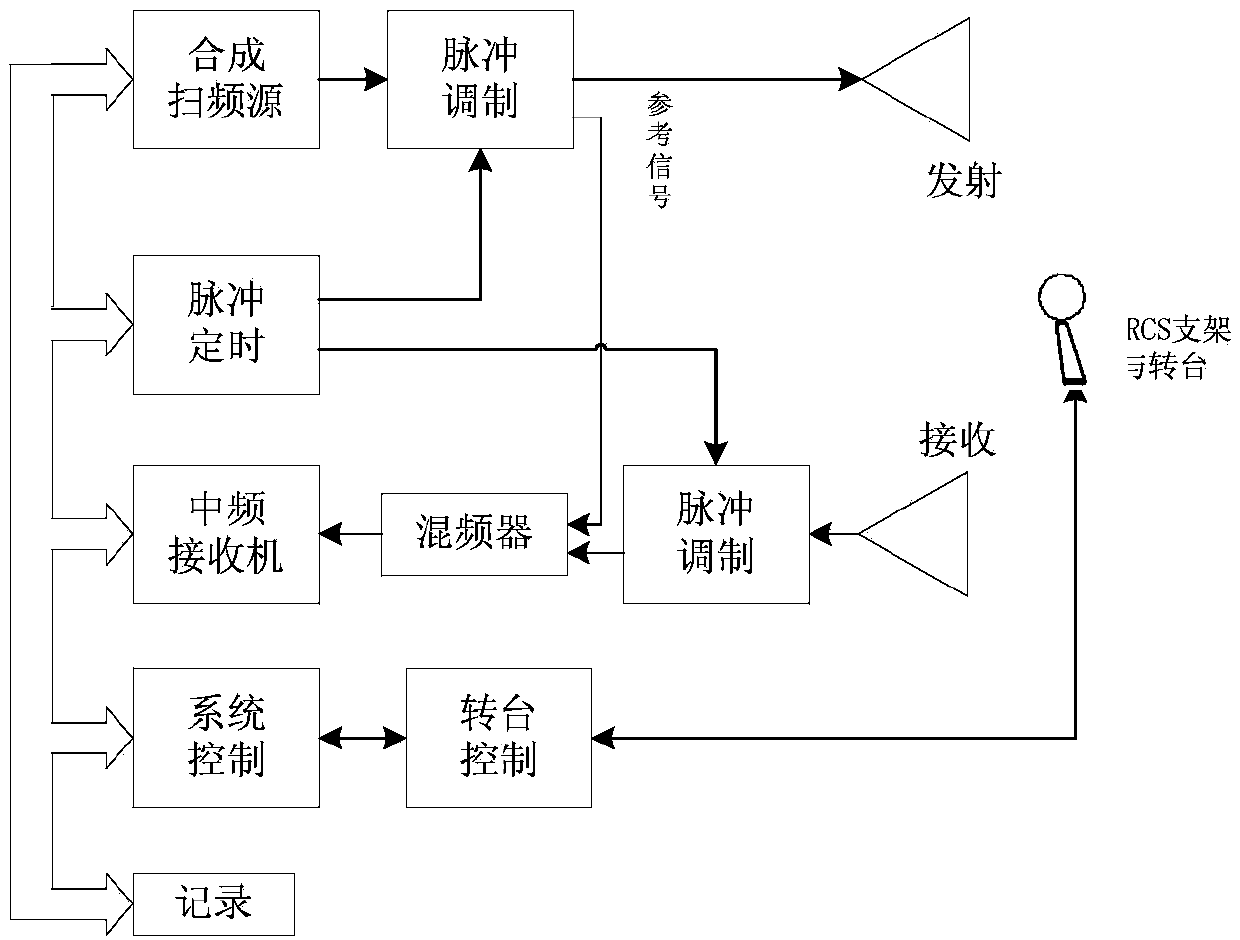
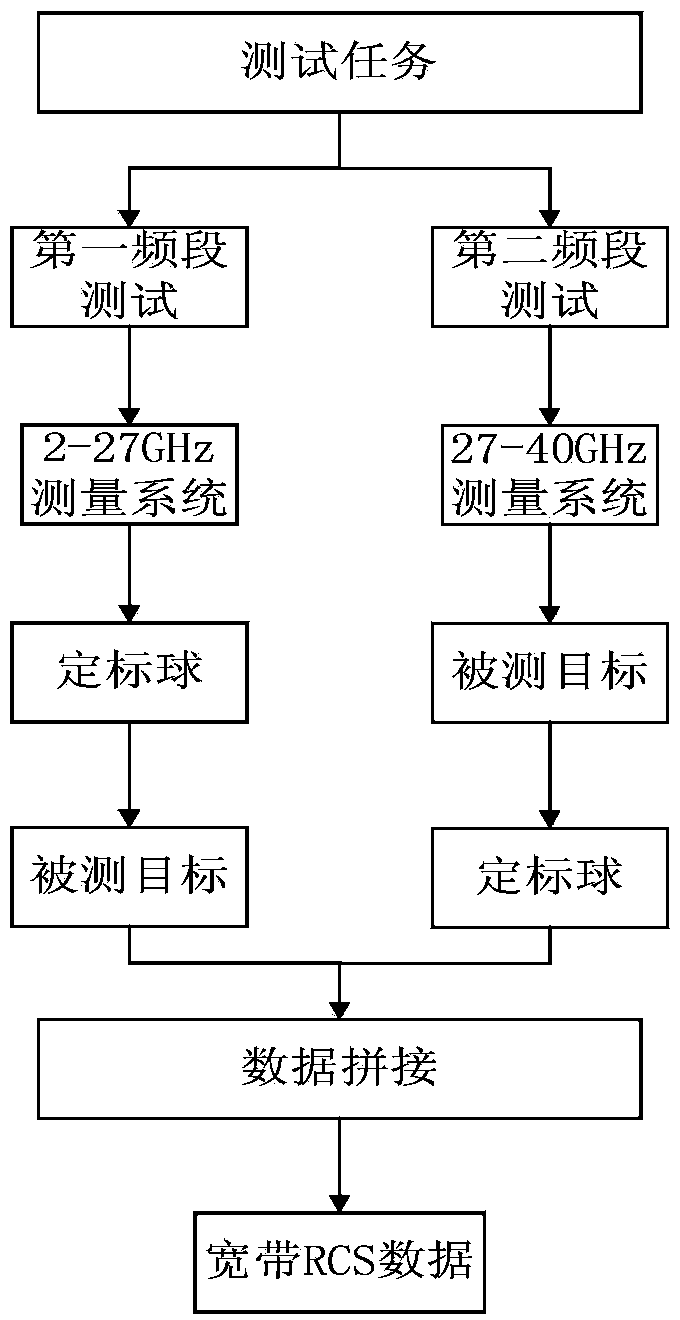
ActiveCN104515908AAvoid disadvantagesGet quickly and efficientlyWave based measurement systemsElectromagentic field characteristicsUltra-widebandMechanical engineering
The invention provides an ultra-wideband target electromagnetic scattering characteristic test system and method. The method includes: firstly, measuring a calibration object on a rotary table by fixing a first group of feed sources working on a first frequency band on a support capable of automatically switching the feed sources so as to continuously switch 2-27GHz plane waves emitted by the feed sources, and receiving reflected echo data; secondly, still performing 2-27GHz measurement by replacing a target object at the position of the calibration object; thirdly, after test ends, keeping the target object stationary, measuring the target object on the rotary table by 27-40GHz plane waves emitted by a second group of feed sources working on a second frequency band and receiving reflected echo data; fourthly, placing the previous calibration object at the position of the target object, performing calibration testing through the second frequency band, and receiving calibrated reflected echo data. Through the test data and by combining the data integrating technology, ultra-wideband target electromagnetic scattering characteristics of the target object can be acquired.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL FEATURES
Flexible electromagnetic scattering regulation and control structure and manufacturing method thereof
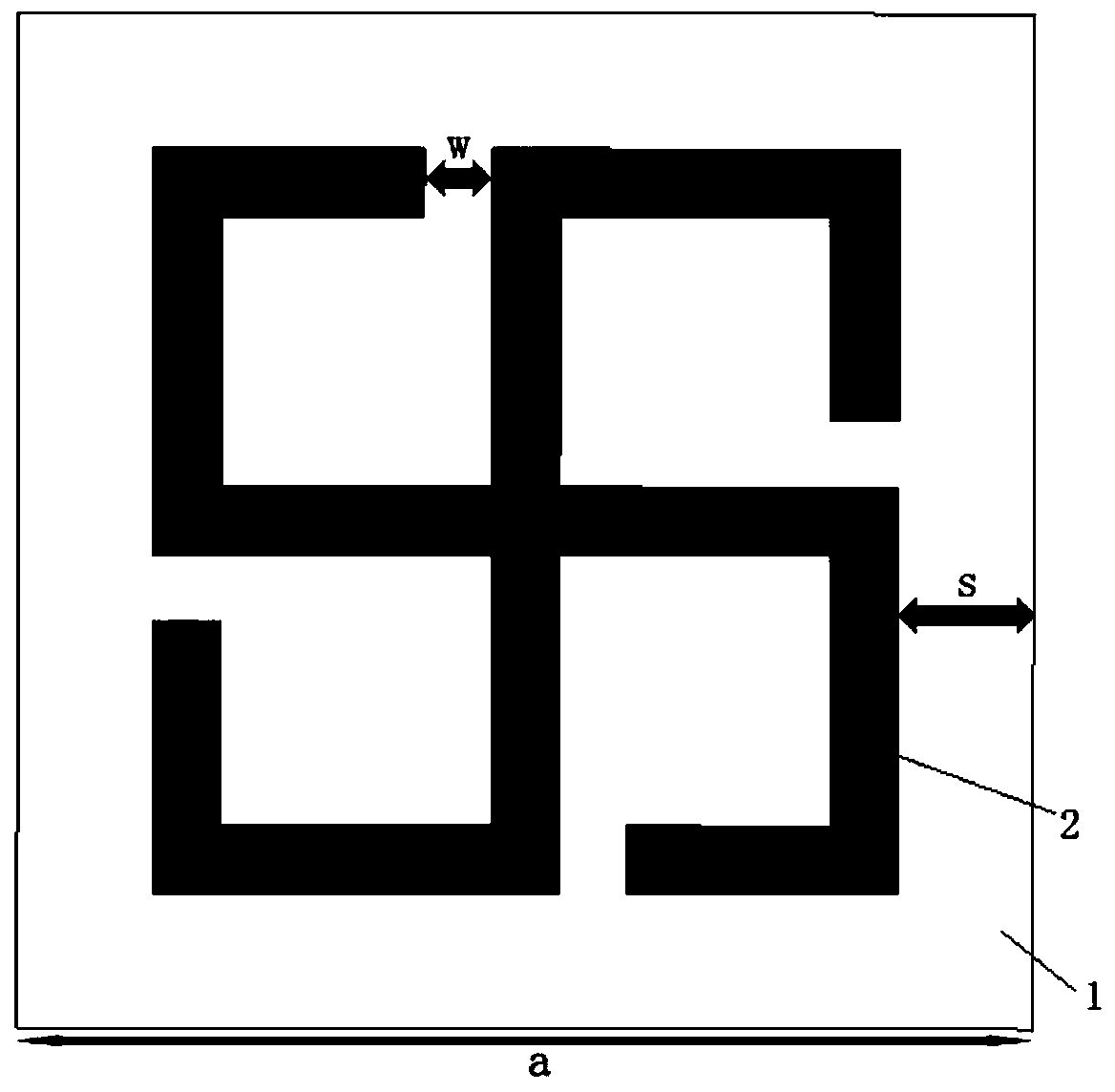
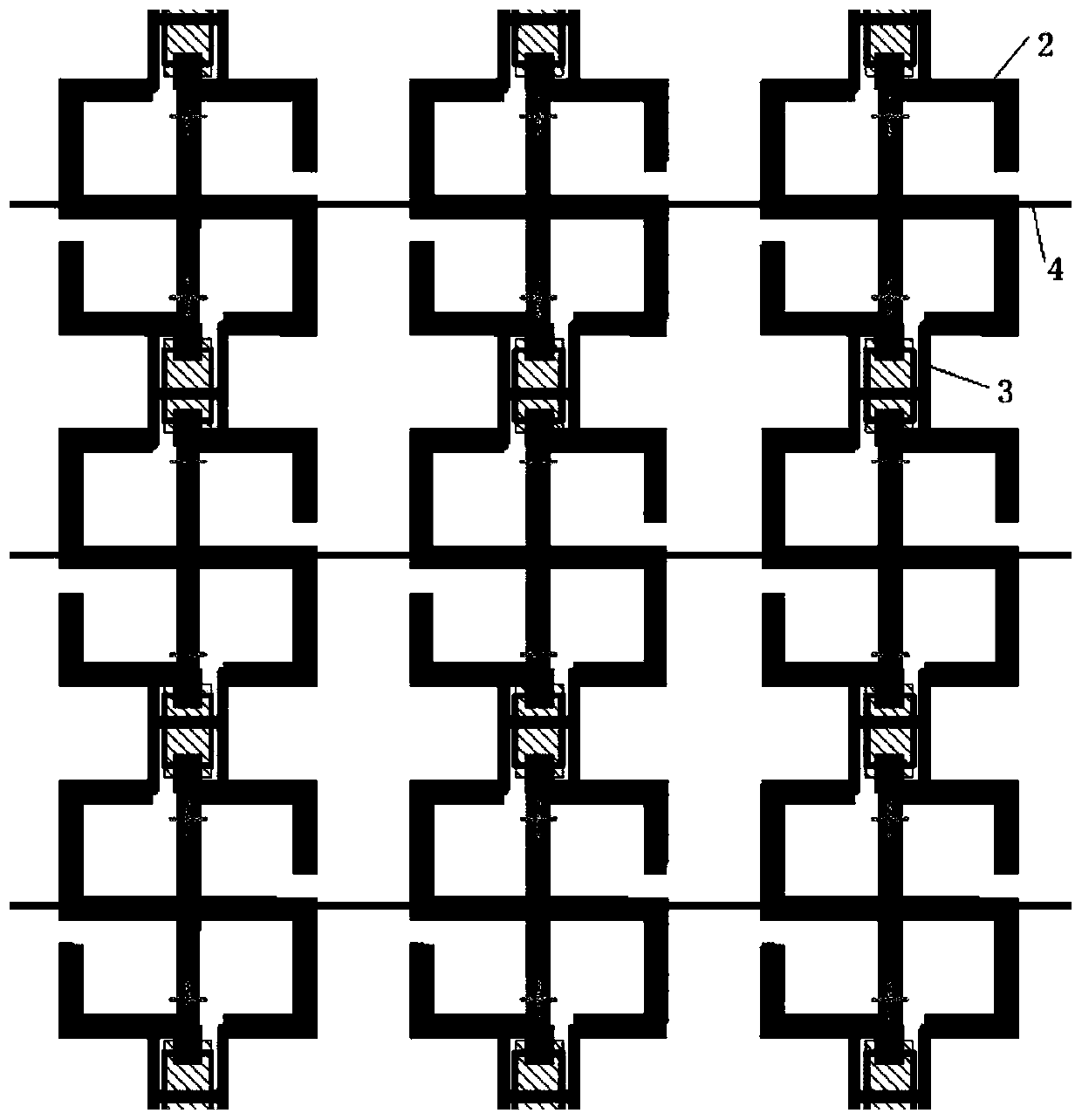
ActiveCN111478050AReduce the probability of detectionIncrease the areaAntennasElectrical polarityMechanical engineering
The invention provides a flexible electromagnetic scattering regulation and control structure. The structure comprises a flexible dielectric layer and a conductive pattern arranged on the flexible dielectric layer; the conductive pattern comprises conductive units arranged in an array; every two longitudinally adjacent conductive units are connected through a varactor; every two transversely adjacent conductive units are connected through a transverse direct-current bias line, and positive and negative voltage power supply buses are arranged on the two sides of each transverse column to form apower supply network; the varactors arranged in the same transverse row are the same in polarity; the varactors arranged longitudinally and adjacently are opposite in polarity; and all the varactorsare arranged in parallel. The invention further provides a manufacturing method of the electromagnetic scattering regulation and control structure. Flexible conformal coverage can be realized by utilizing the flexible electromagnetic scattering regulation and control structure, a greater role is played in electronic countermeasure, the probability that weaponry is detected is greatly reduced, andthe survivability of the weaponry is improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Method for accurately calculating electromagnetic scattering of bianisotropic medium ball
InactiveCN103235888AElectromagnetic scattering appliesSpecial data processing applicationsMaxwell's equationsCondensed matter physics
The invention provides a method for accurately calculating electromagnetic scattering of a bianisotropic medium ball. The method comprises the steps of 1, using passive maxwell's equations and an intrinsic equation of a bianisotropic medium to deduce a differential equation of the magnetic induction intensity B; 2, expressing factors related to the B in the differential equation in the form of spherical vector wave functions, then using orthogonality properties of spherical vector wave functions M and N to obtain a parameter-contained matrix equation, firstly, calculating parameters of the matrix equation under the condition that the matrix equation meets a non-zero solution, and then substituting parameters into the parameter-contained matrix equation to obtain the non-zero solution of the matrix equation; and 3, constructing a new function, expressing the magnetic induction intensity B again through the new function, then an electromagnetic field inside the medium ball is calculated, and substituting the electromagnetic field inside the medium ball and an incident electromagnetic field and a scattering electromagnetic field outside the ball into boundary conditions to obtain a scattering matrix. The method is applicable to solving of the electromagnetic scattering of the bianisotropic medium ball of the small electrical size.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
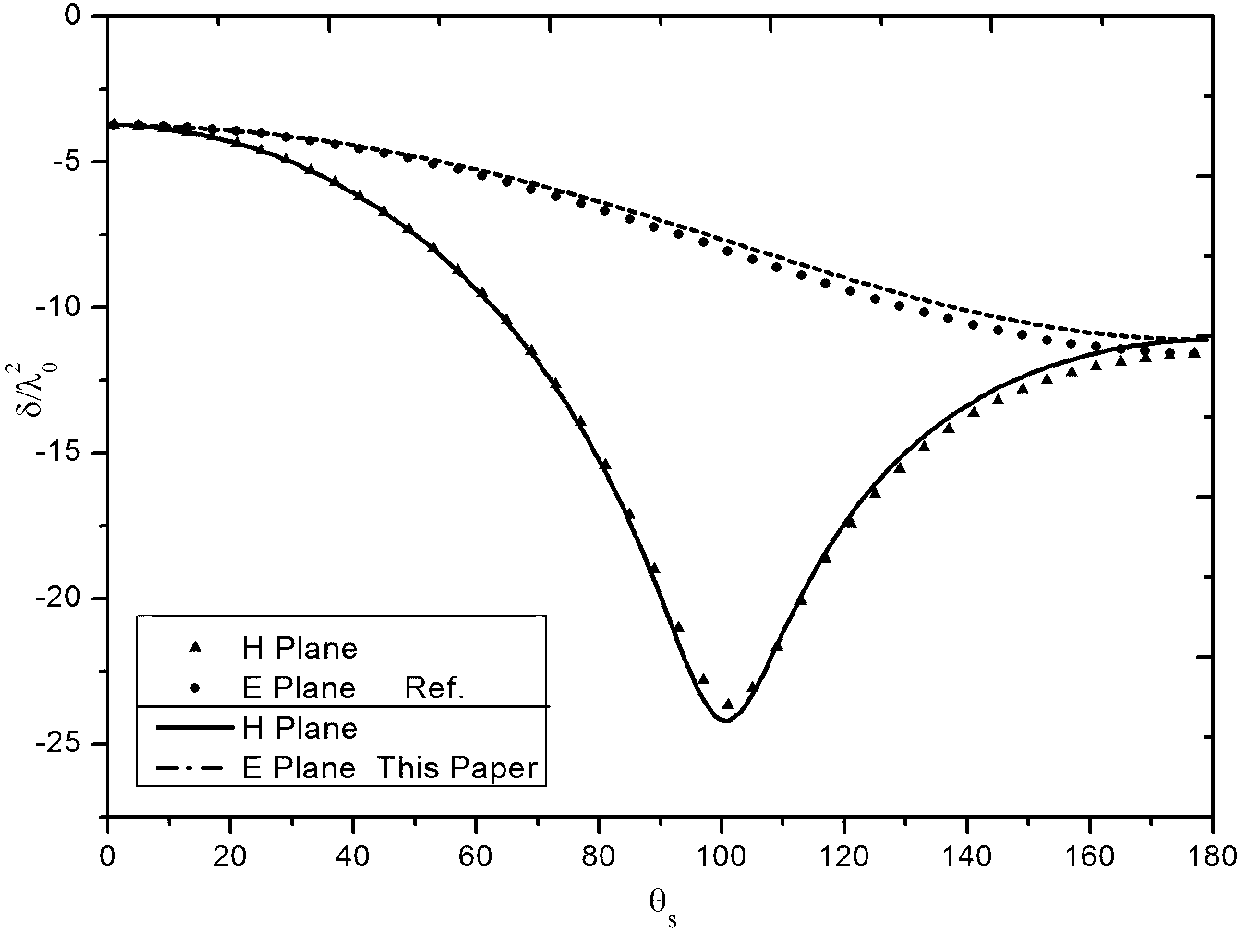
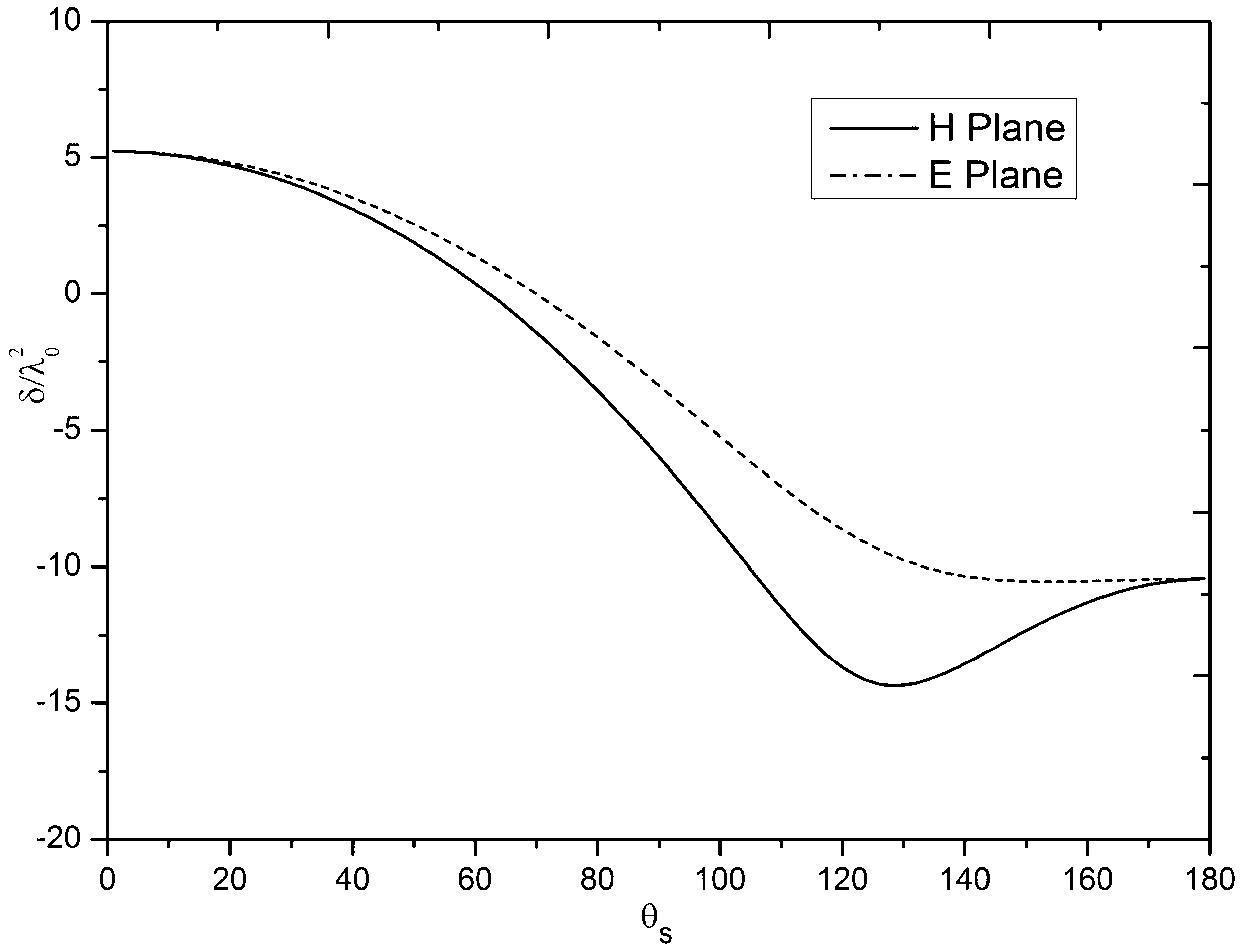
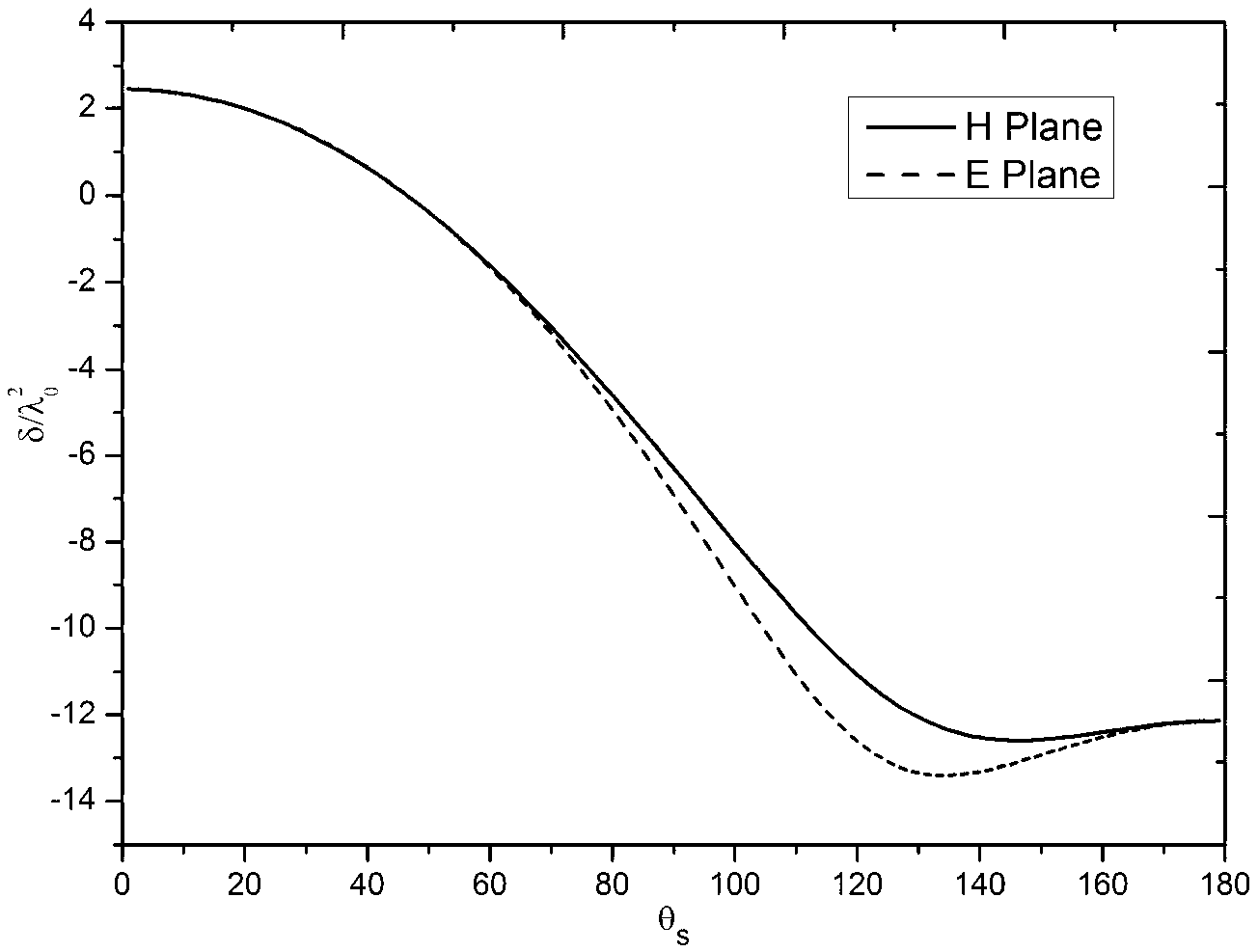
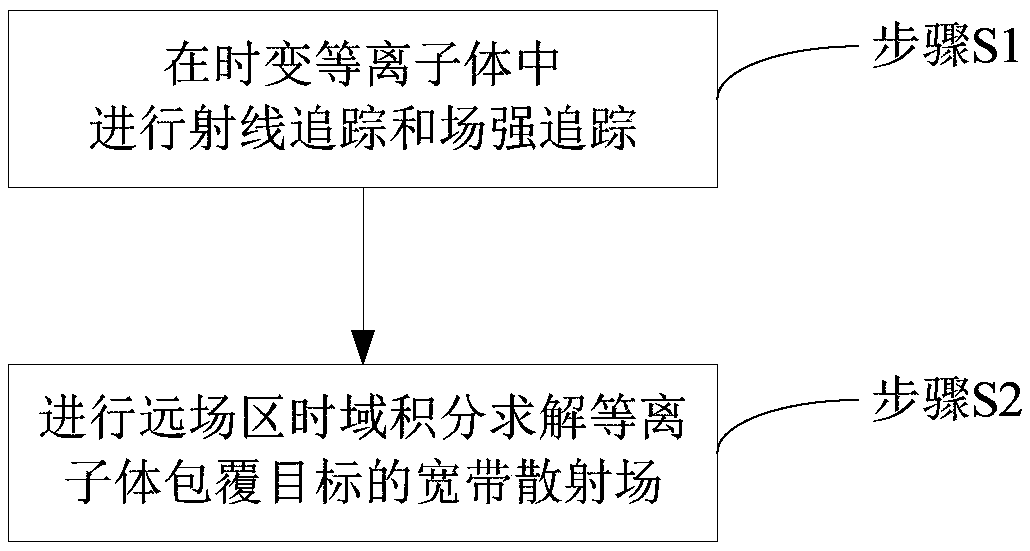
Plasma electromagnetic scattering modeling method based on time domain shooting and bouncing rays method
The invention discloses a plasma electromagnetic scattering modeling method based on the time domain shooting and bouncing rays method. The method utilizes rays to simulate the reflection and the refraction of electromagnetic waves in a multilayer plasma, and realizes electromagnetic scattering modeling of a plasma coated target by field strength tracking and far field solution of the rays. The method is an effective electromagnetic scattering modeling scheme for superhigh speed target in lean atmosphere, which enables the rapid modeling of the broadband scattering characteristics of the plasma coated target and greatly expands the scope of application.
Owner:SHANGHAI RADIO EQUIP RES INST
Radar detection of radiation-induced ionization in air
InactiveUS20120242544A1Direction finders using radio wavesRadiation measurementNuclear radiationAir Ionization
A millimeter wave measurement system has been developed for remote detection of airborne nuclear radiation, based on electromagnetic scattering from radiation-induced ionization in air. Specifically, methods of monitoring radiation-induced ionization of air have been investigated, and the ionized air has been identified as a source of millimeter wave radar reflection, which can be utilized to determine the size and strength of a radiation source.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Surface patch normal vector adaptive modification method in electromagnetic scattering simulation modeling
ActiveCN104809258AAdaptableImprove execution efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsModelSimEngineering
The invention discloses a surface patch normal vector adaptive modification method in electromagnetic scattering simulation modeling. A correct outer normal vector of a triangular surface patch can be automatically extracted aiming at the surface subdivision information or face subdivision information of any complex model. Aiming at an electrically large model, millions and even ten millions of grids are formed, and octree subdivision is added in the normal vector modification process to quicken a circulation speed, so the algorithm execution speed is improved by several orders. The conventional complex manual normal vector modification method can be completely substituted, is simple and easy and has a wide application range.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of wheat syrup for beer brewing
The invention discloses a method for preparing for the brewage used wheat syrup which mixes the wheat and the grist and adds them into No 1 pot, then it adds water to adjust the temperature and the glucanase, neuter protease and xylanase, it then adds fire resistant catalyst to boil into wheat liquid after heat preservation high fever. It scatters the grist and adds it into No 2 pot, adds water to adjust the temperature, when the grist into the grist liquid, it puts it into No 1 pot to mix it with the wheat liquid. It puts the maize starch into No 3 pot, adds water to adjust the temperature, adds alpha catalyst, fire resistant catalyst and beta catalyst and at last mixes it with the No 1, 2 pots to adjust the temperature and filter them to obtain the wheat syrup.
Owner:华润雪花啤酒(黑龙江)有限公司
Detection of defects embedded in servo pattern on stamper by using scattered light
Defects of a hard disk drive servo pattern stamper are detected by comparing a scattered light beam pattern against the known servo pattern. A magnetic field is applied to stamper and the beam is linearly polarized. Variations in the physical offset of the beam, its scatter, are indicative of physical defects. Variations in the Kerr rotation of scattered beam are indicative of magnetic defects.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Grain synthesizing method based on multiple master drawings
InactiveCN1570978AStrong random textureStrong randomness3D-image renderingVeinComputer graphics (images)
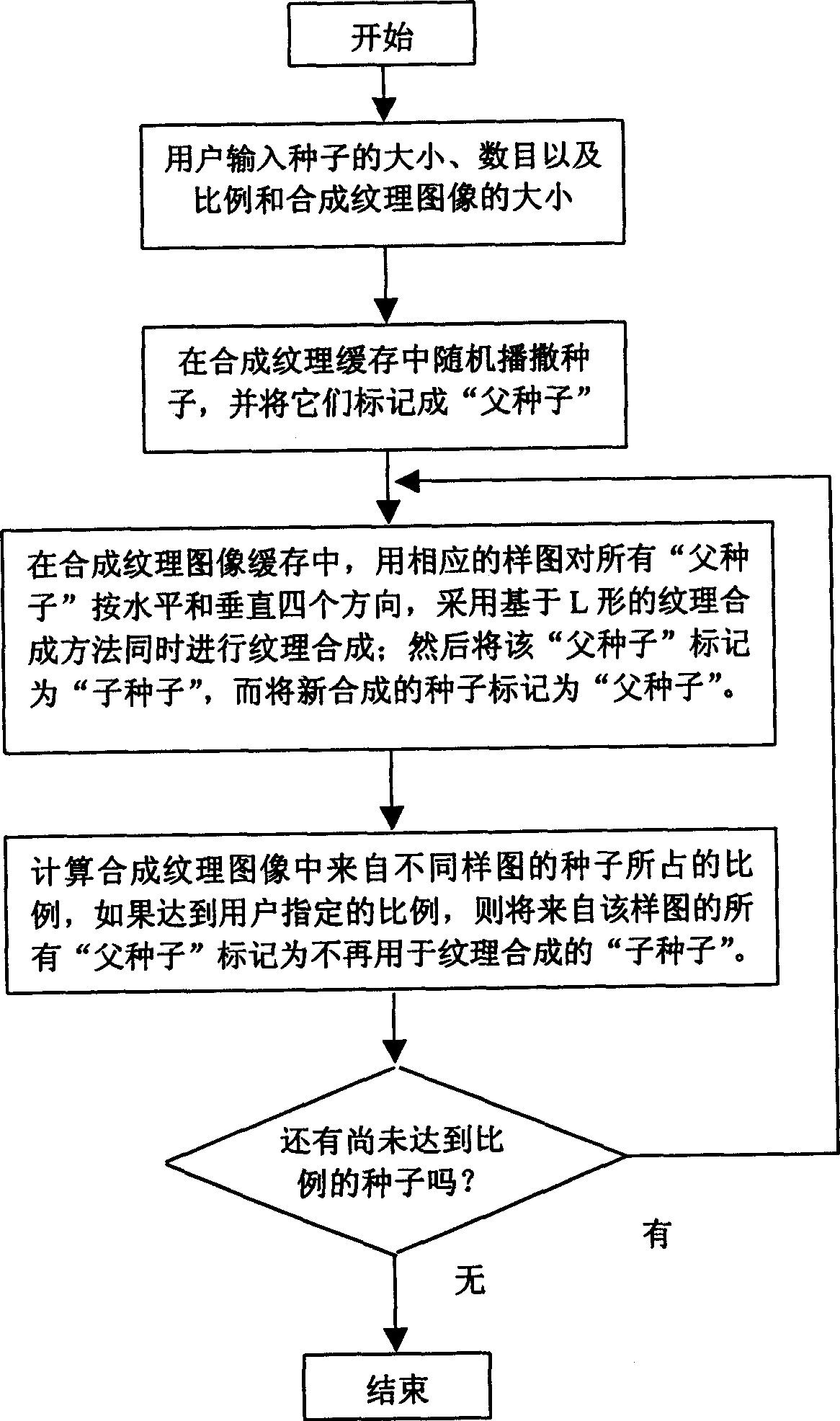
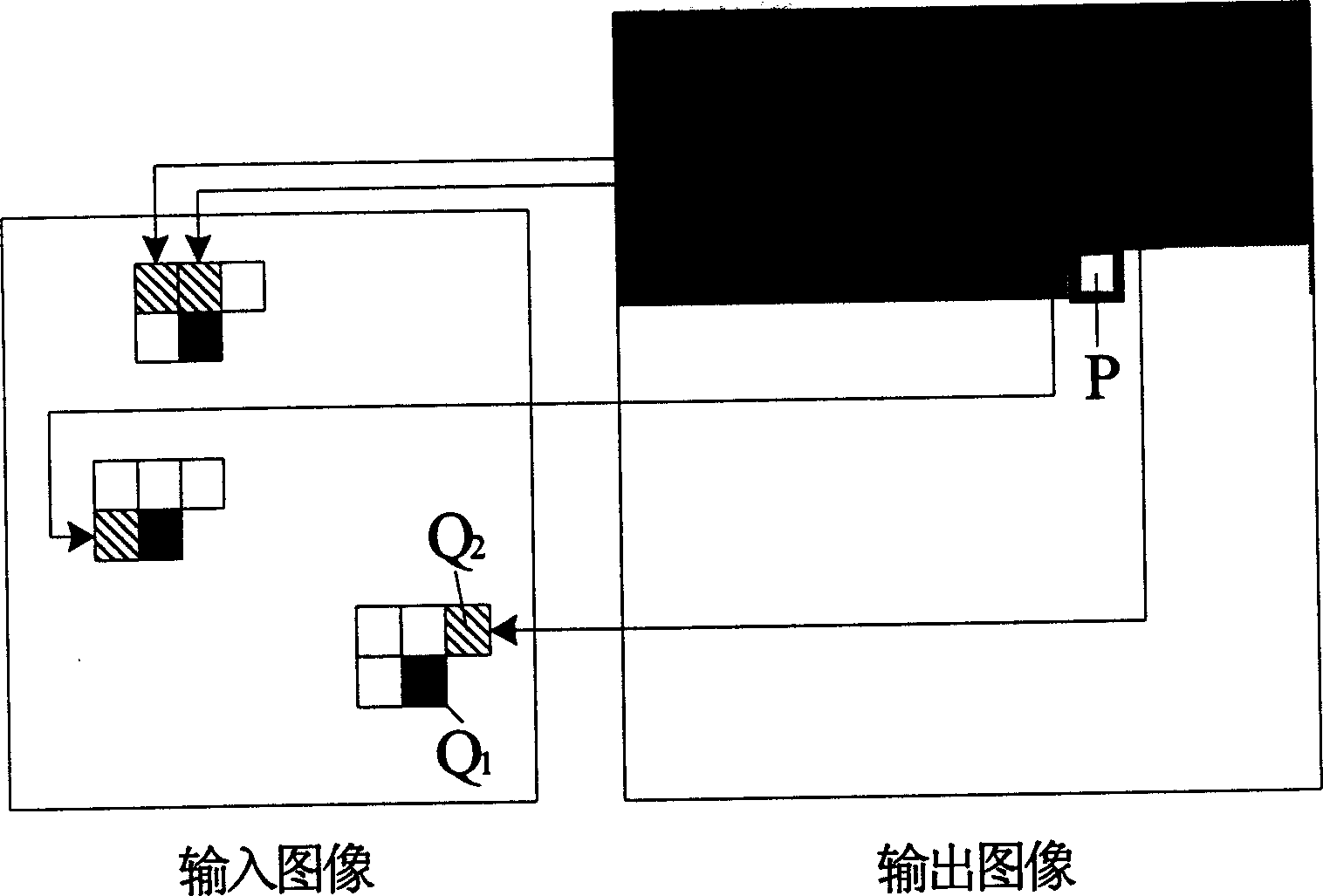
This invention is a vein synthesis method based on multi-pattern. By utilizing existing vein pattern, it scatters the seeds on the synthesized vein image buffer memory random according to the size of synthesized vein, the size and number of seeds that selected by user and different vein's proportion in the new synthesized vein. Then synthesizing vein using the vein synthesis method that L-shape based for all seeds in the four horizontal and vertical direction, until all the pixels in the synthesized vein image buffer memory have been synthesized.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Multi-probe quasi-far-field electromagnetic scattering cross section (RCS) extrapolation test system
PendingCN110764068AWork around limitationsMeet the needs of large-scale testingWave based measurement systemsICT adaptationData processing systemScattering cross-section
The invention discloses a multi-probe quasi-far-field electromagnetic scattering cross section (RCS) extrapolation test system. The system is composed of a quasi-far-field electromagnetic scattering measurement system and a quasi-far-field electromagnetic scattering measurement data processing system. The first part realizes one-dimensional rotation of a target to be tested by controlling a turntable, and acquires an original signal required for quasi-far-field electromagnetic scattering measurement of the target to be tested by using a special test radar multi-probe circuit. The second part realizes acquisition of electromagnetic scattering data, and calculates a far-field horizontal plane RCS of the target to be tested according to a quasi-far-field-far-field transformation extrapolationalgorithm. The test system provided by the invention overcomes the limitation of the traditional electromagnetic scattering test means on the test distance and the size of the measurable target, reduces the influence of physical sizes among multiple probes, and has the advantages of high test efficiency and low cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI HOLLYWELL ELECTRONICS SYST TECH
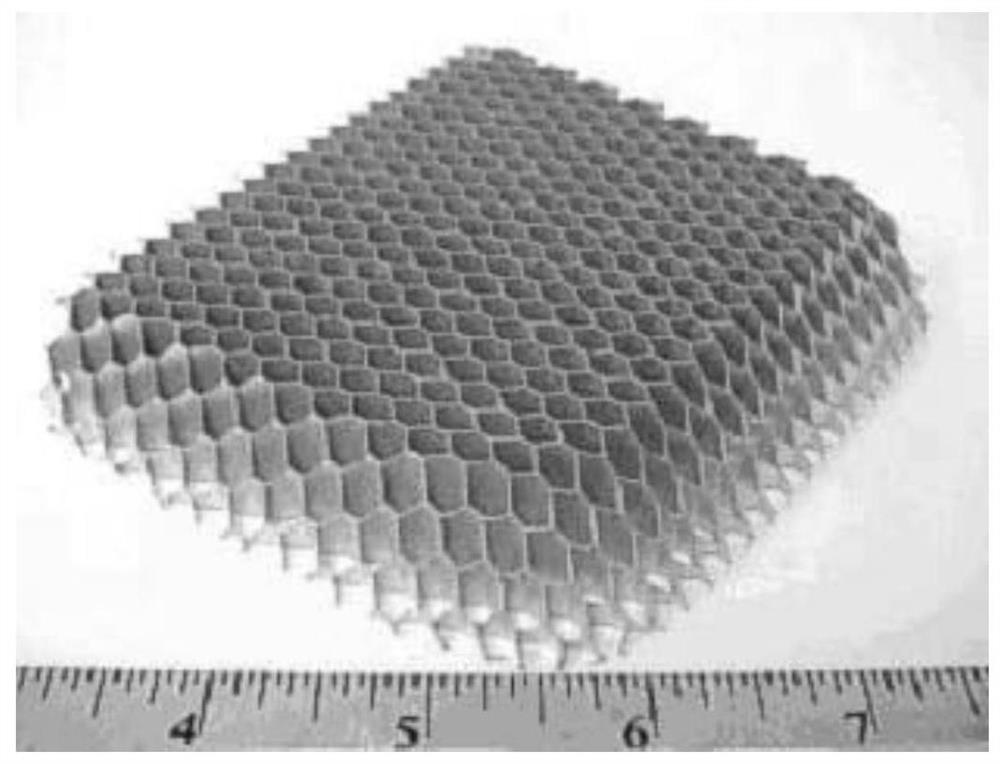
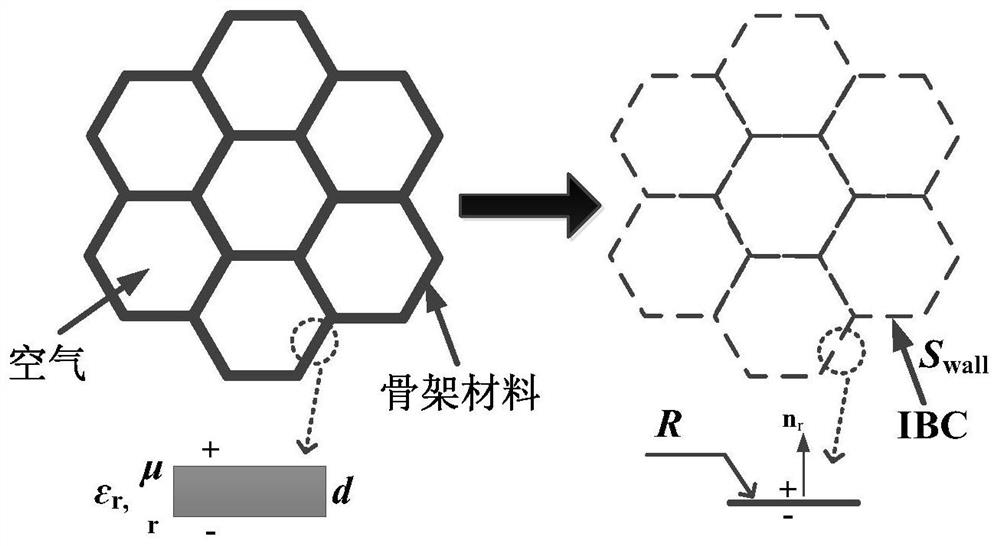
Efficient electromagnetic scattering modeling and calculating method for composite target containing wave-absorbing honeycomb structure
ActiveCN113033053ASimplify the modeling processHigh precisionSustainable transportationDesign optimisation/simulationComputation processEngineering
The invention provides an efficient electromagnetic scattering modeling and calculation method for a composite target containing a wave-absorbing honeycomb structure, and the method comprises the steps: enabling a honeycomb wall to be equivalent to an impedance sheet during modeling of a hexagonal honeycomb structure, only remaining a uniform honeycomb unit as a body, and enabling a whole honeycomb region to become a uniform medium body containing a series of impedance boundary conditions, and simplifying the honeycomb modeling process. A non-conformal region decomposition technology is adopted to independently model a composite target partition containing a wave-absorbing honeycomb structure, so that modeling calculation of honeycomb structures of any shape and size becomes possible, and flexible and free geometric model creation, region division and mesh generation are allowed. After modeling and subdivision, efficient transmission conditions are set for different junctions between the sub-regions to ensure continuity of tangential electromagnetic fields on the surface and normal electromagnetic currents on the line, and the sub-regions are connected together. In the electromagnetic scattering calculation process, a matrix equation is obtained after an equation is dispersed, and the calculation process is simplified by introducing an IBC formula.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com