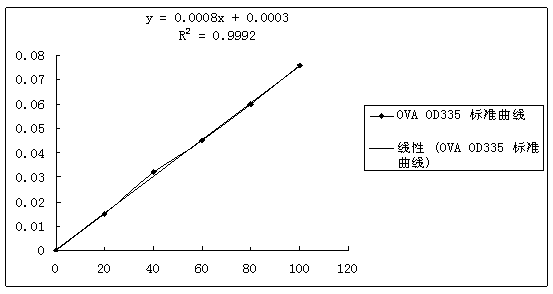
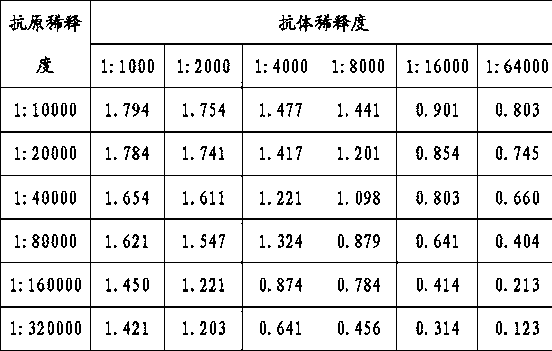
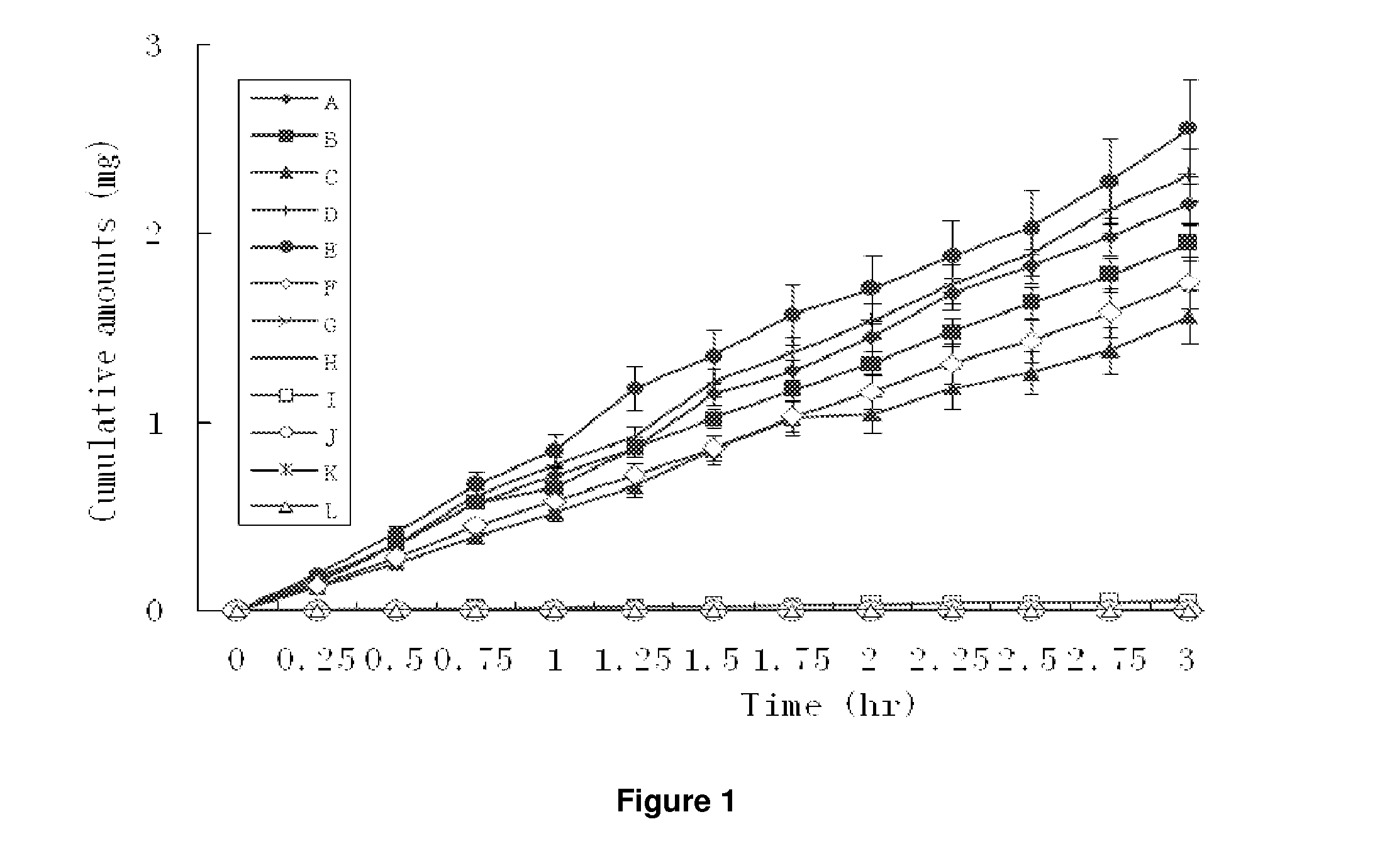
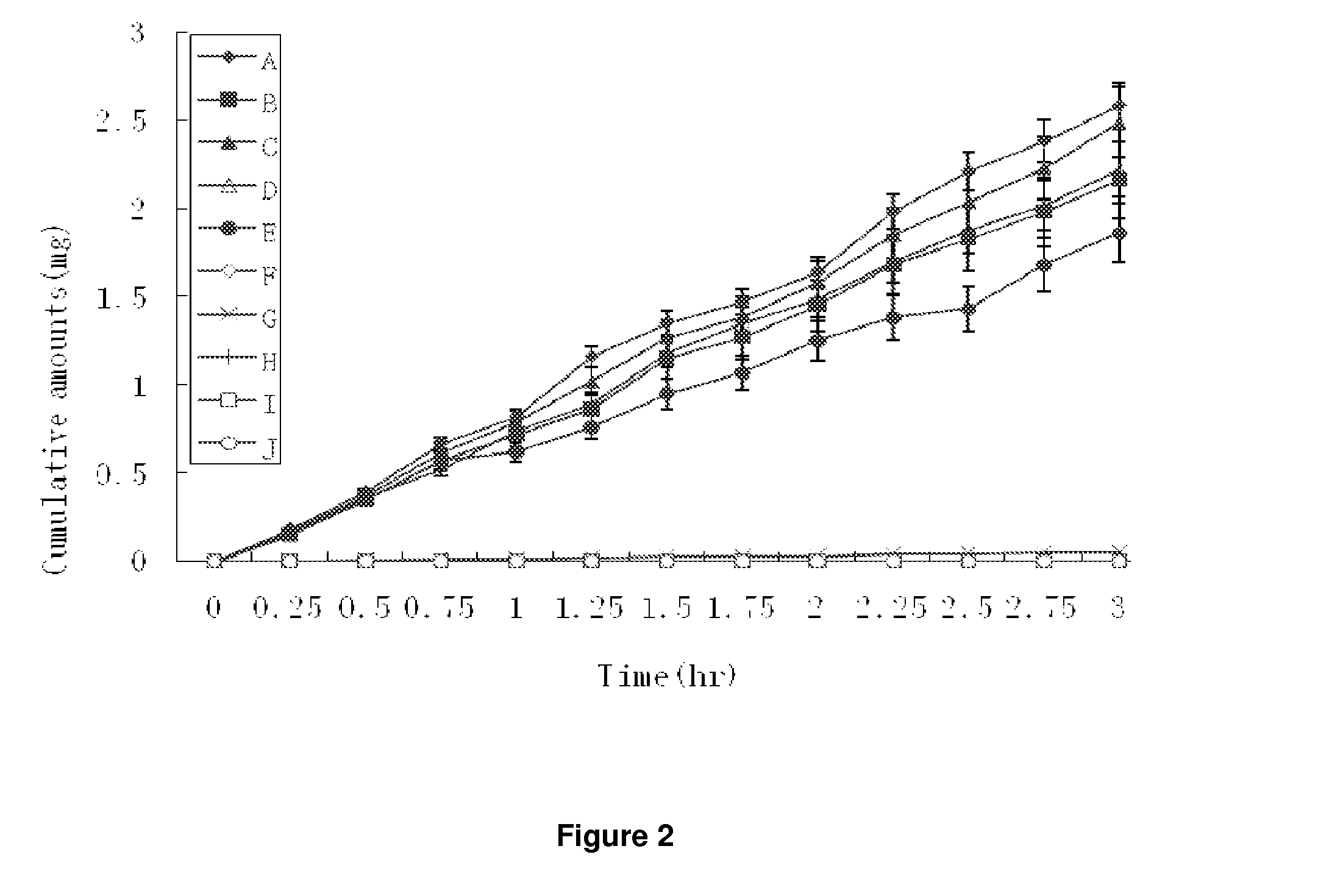
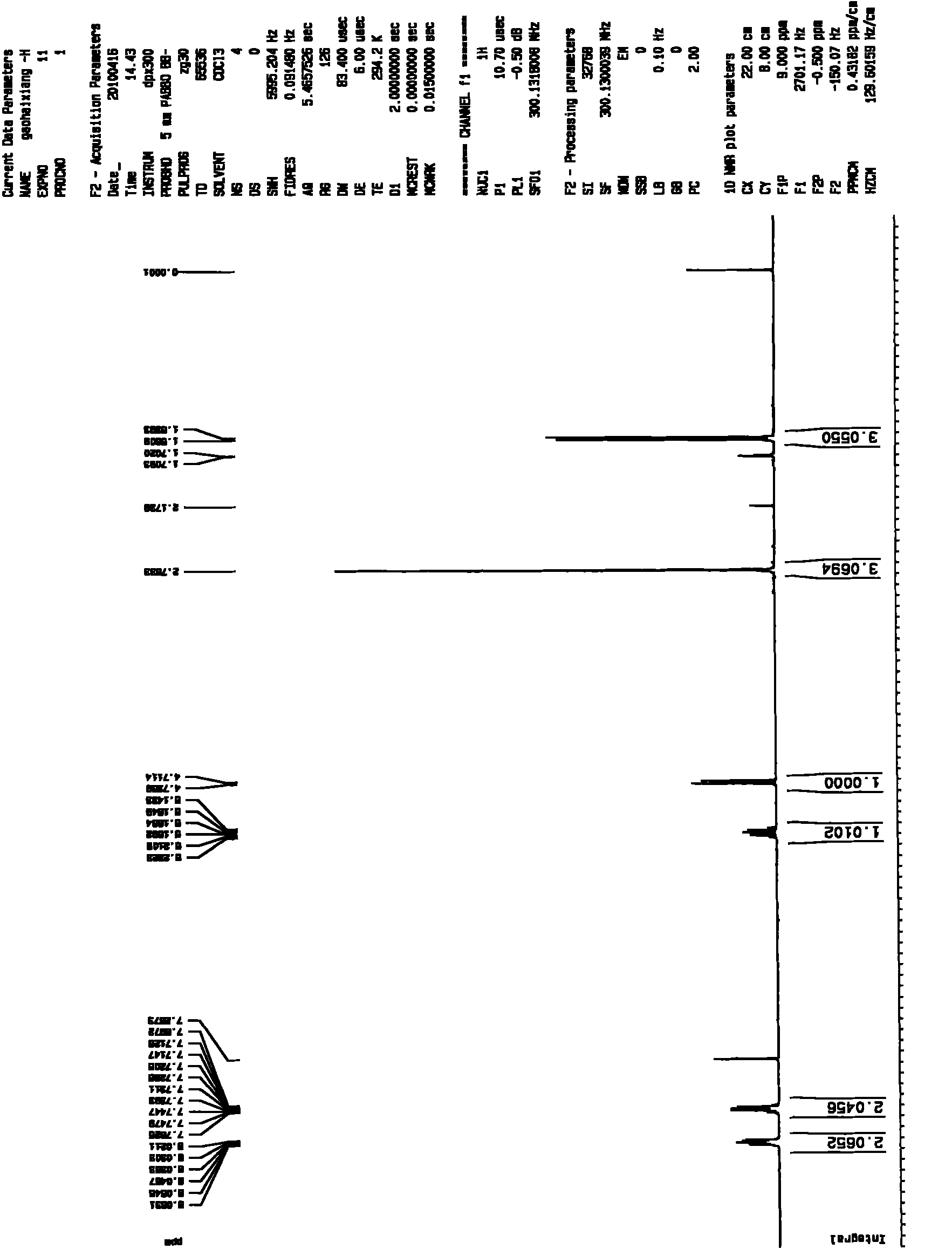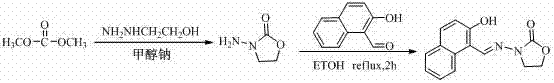Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
79 results about "Drug metabolite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A drug metabolite is a byproduct of the body breaking down, or “metabolizing,” a drug into a different substance. The process of metabolizing a drug is predictable and certain; everyone metabolizes drugs the same way. Some metabolites stay in the body much longer than the parent drug.
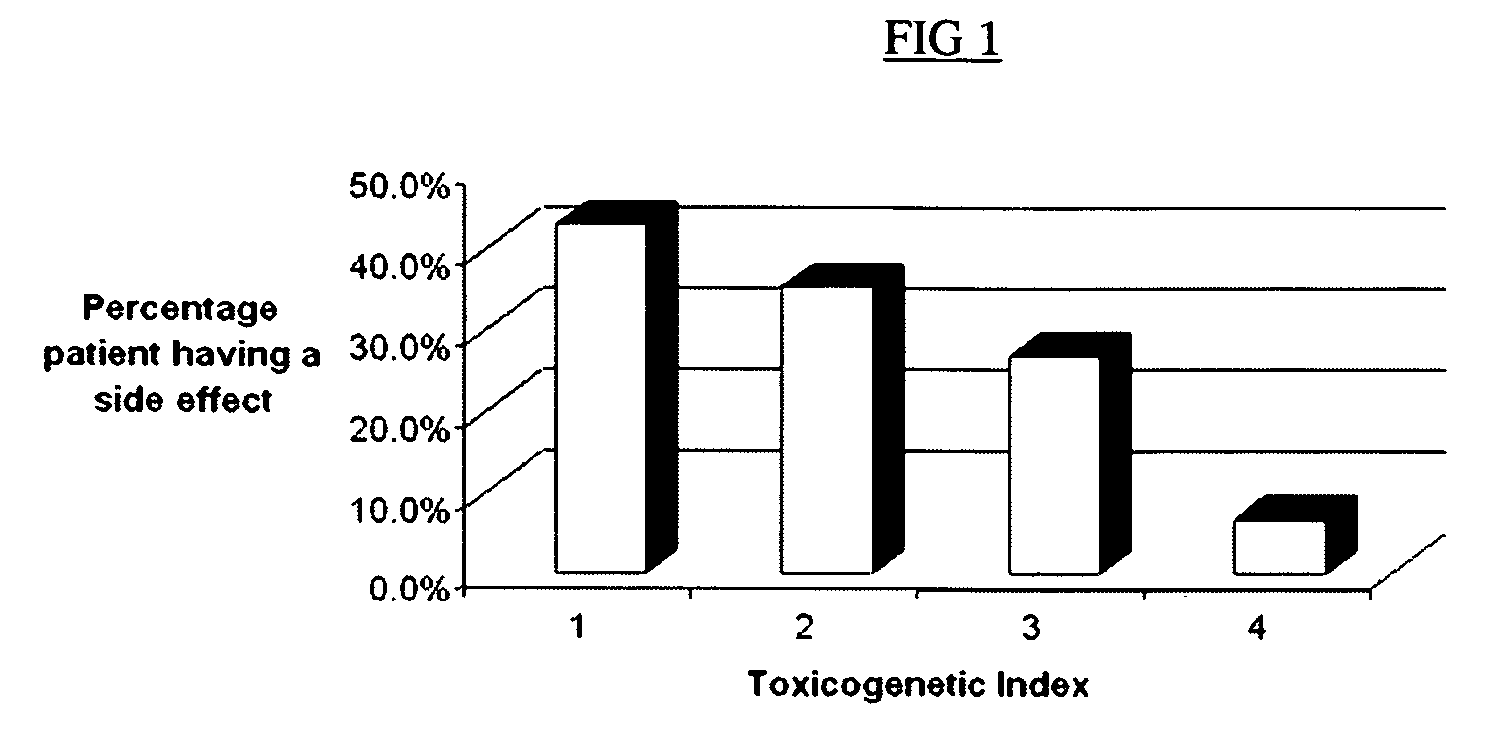
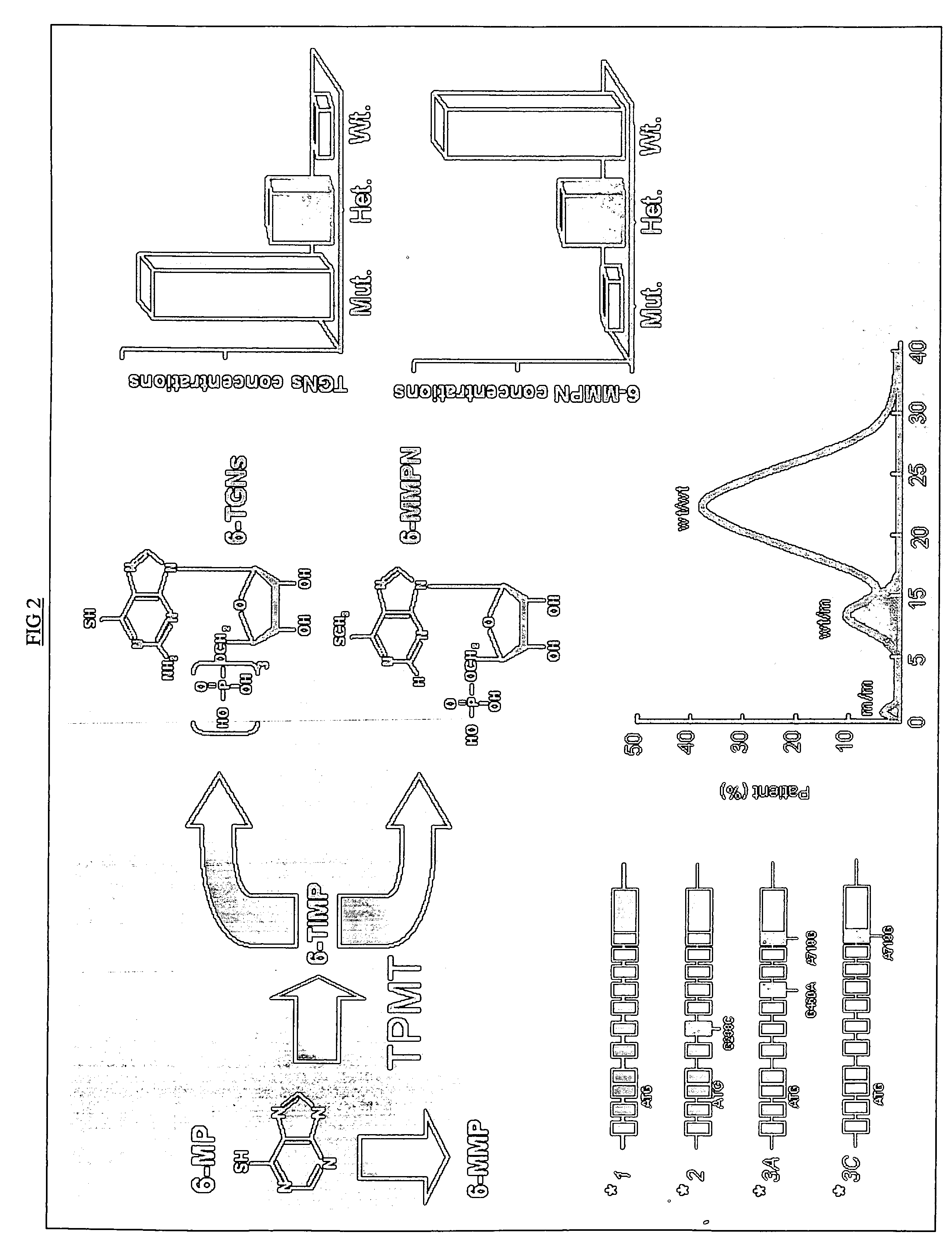
Method of treating IBD/Crohn's disease and related conditions wherein drug metabolite levels in host blood cells determine subsequent dosage
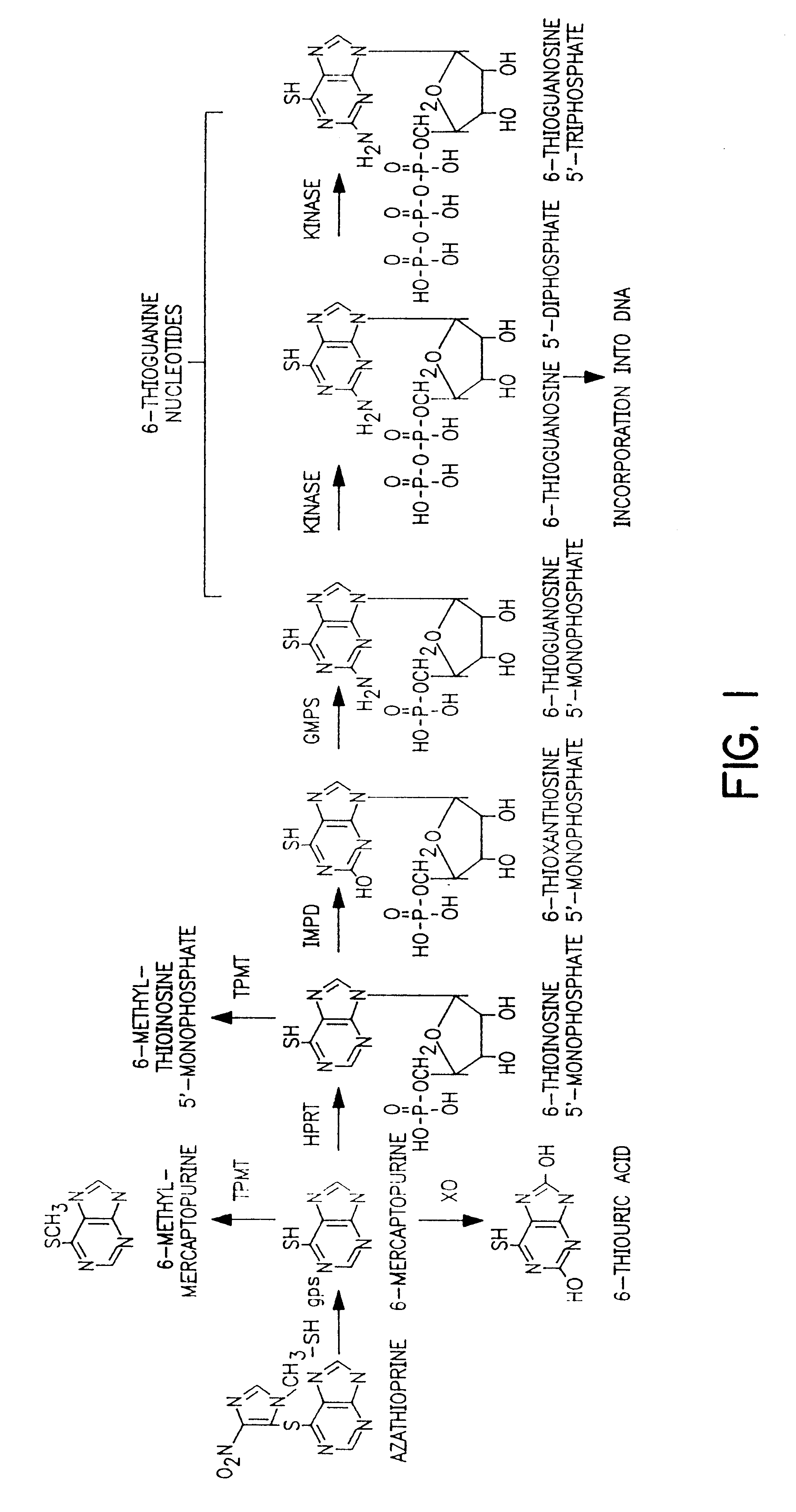
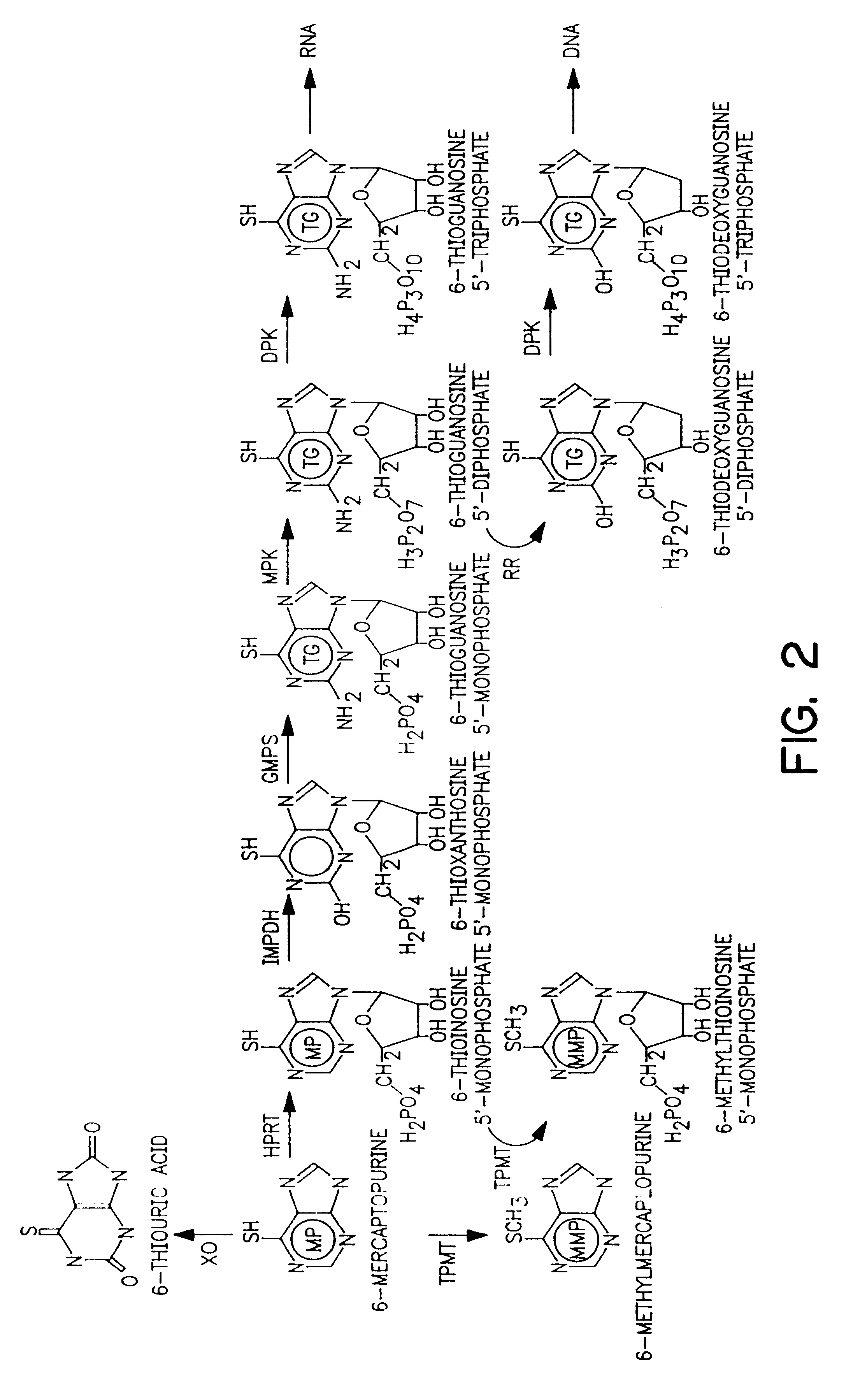
The present invention provides a method of optimizing therapeutic efficacy and reducing toxicity associated with 6-mercaptopurine drug treatment of an immune-mediated gastrointestinal disorder such as inflammatory bowel disease. The method of the invention includes the step of determining the level of one or more 6-mercaptopurine metabolites in the patient having an immune-mediated gastrointestinal disorder.
Owner:HOPITAL SAINTE JUSTINE
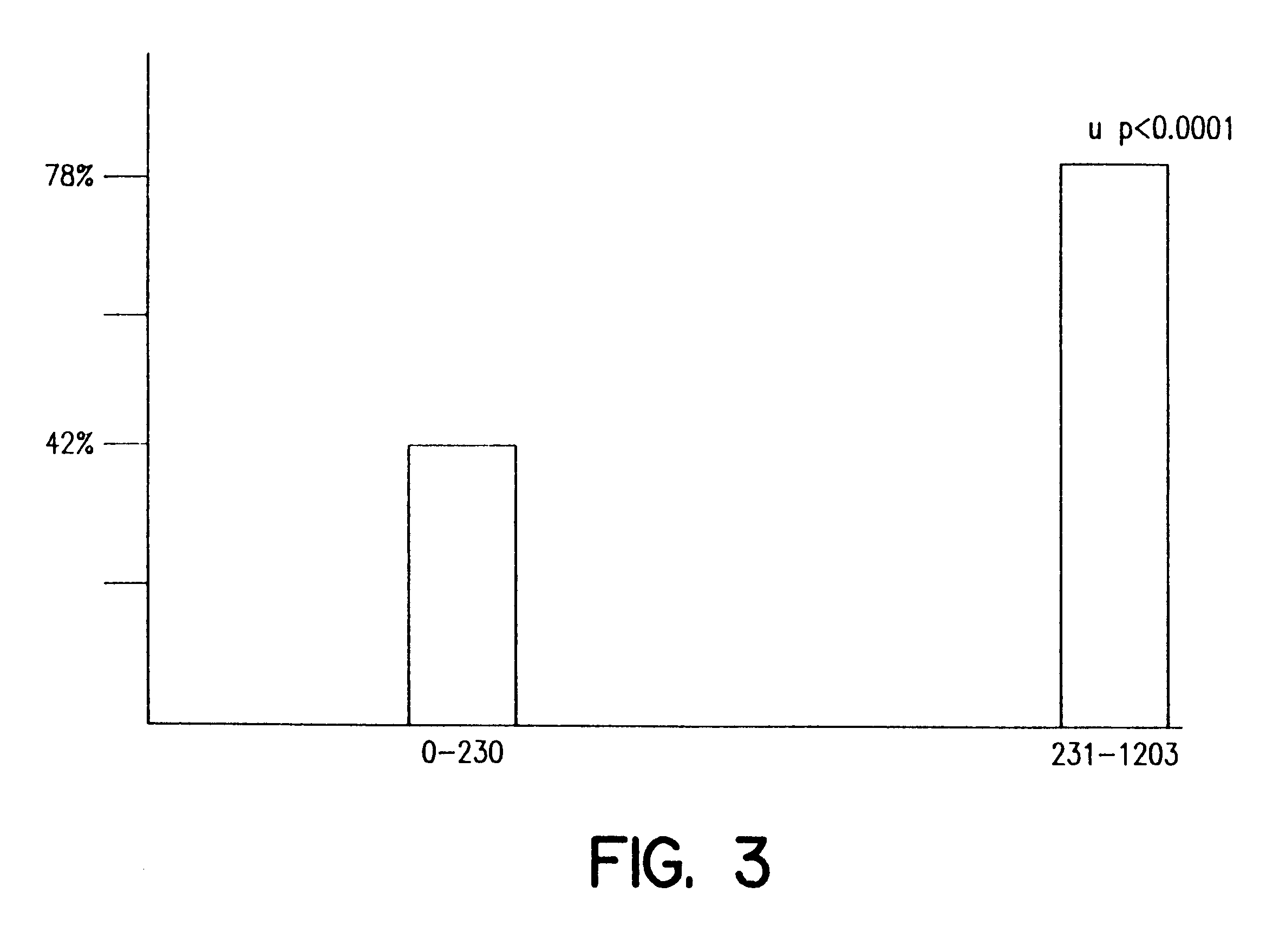
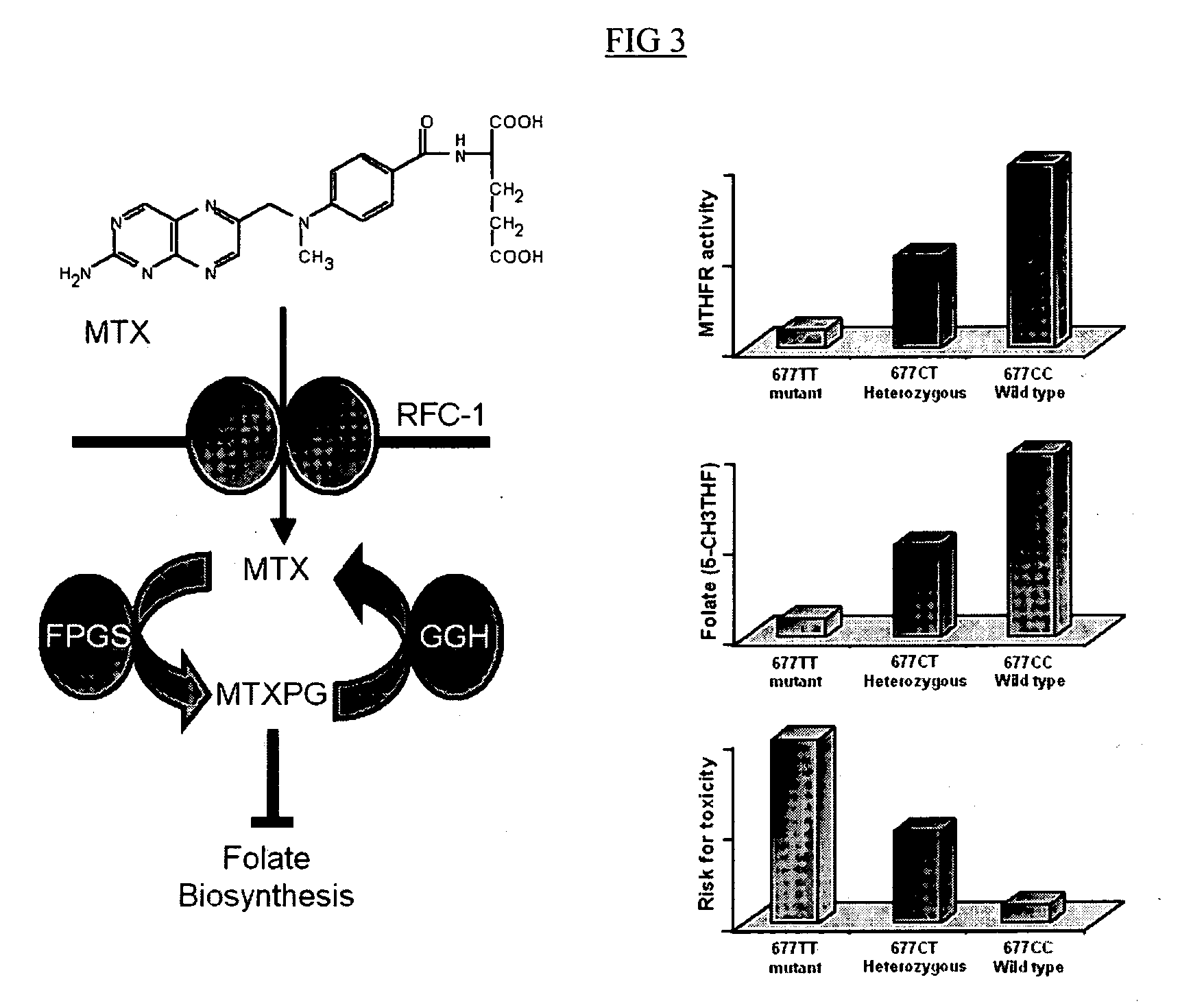
Method to optimize drug selection, dosing and evaluation and to help predict therapeutic response and toxicity from immunosuppressant therapy
InactiveUS20060253263A1Good curative effectMinimizing toxic side effectMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsMaintenance therapyAutoimmune condition
The present invention provides a method of effectively measuring risk for therapeutic toxicity of a subject having an autoimmune disorder or cancer and predicting and evaluating therapeutic efficacy of immunosuppressive therapies for autoimmune diseases and cancers before or after starting therapy. The present invention also provides for determining a drug metabolite level of a subject during therapy and measuring periodically the drug metabolite level of a subject on maintenance therapy to ensure treatment compliance and continued therapeutic response by measuring minimal clinical important differences (MCID) in the drug metabolite levels. The present invention also provides for a method to effectively optimize the selection and dose of immunosuppressive therapies of a subject having an autoimmune disease or cancer to improve therapeutic efficacy and reduce therapeutic toxicity prior to starting concomitant biologic therapy and before or after the subject has failed to respond to the at least one immunosuppressive agent.
Owner:MESHKIN BRIAN JAVAADE
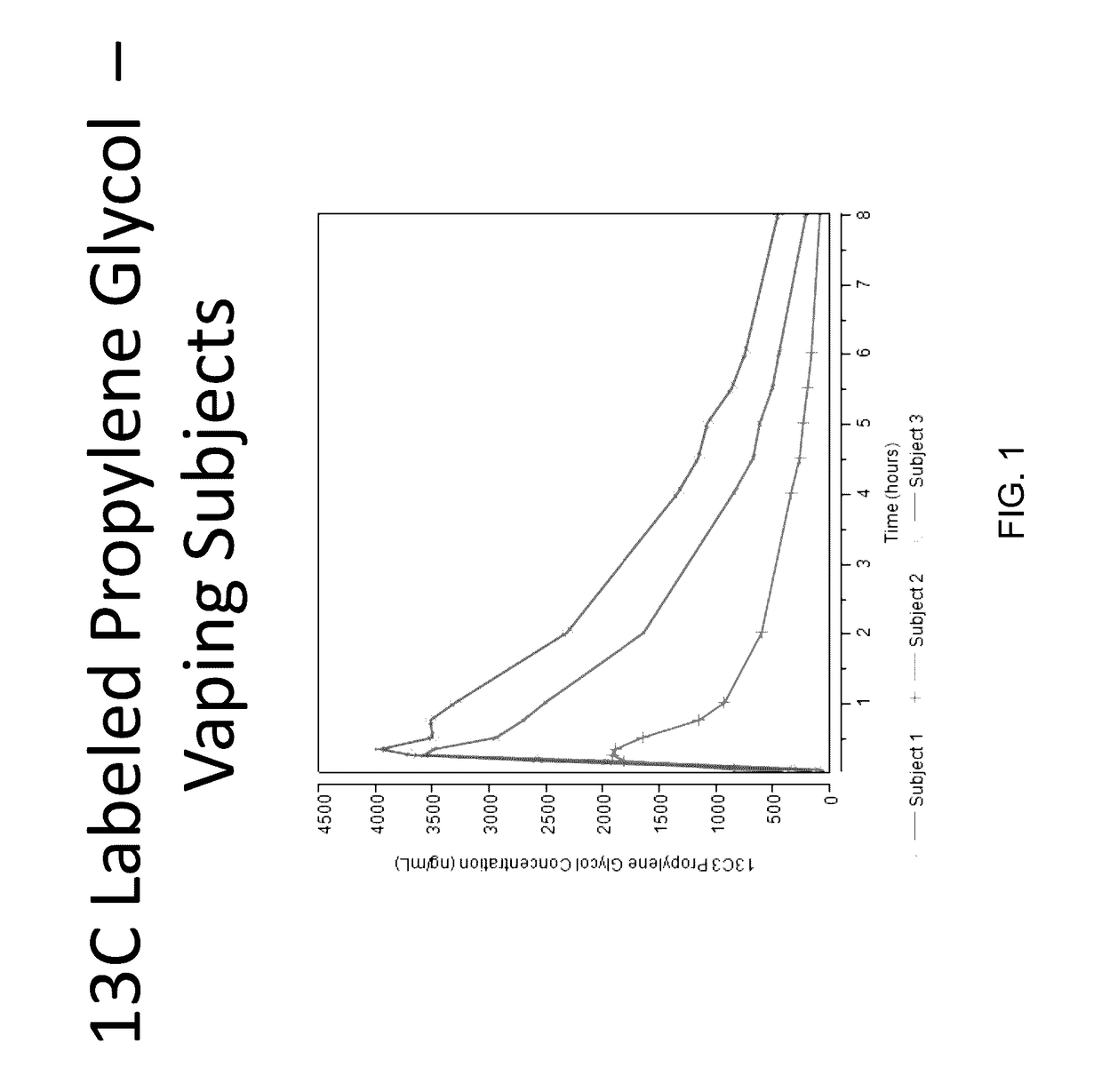
Isotopically-labeled solvents and the use of same in testing e-cigarettes
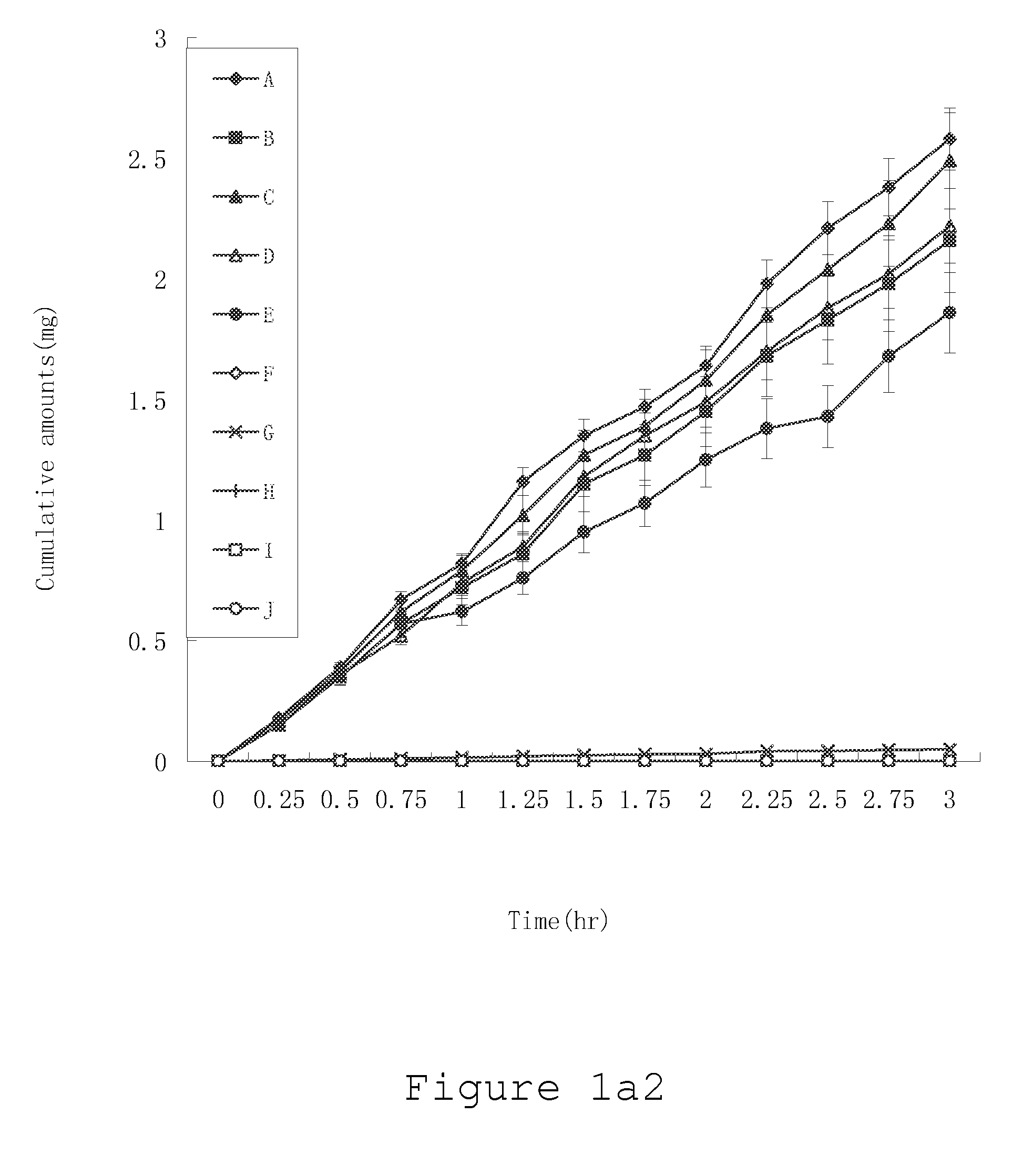
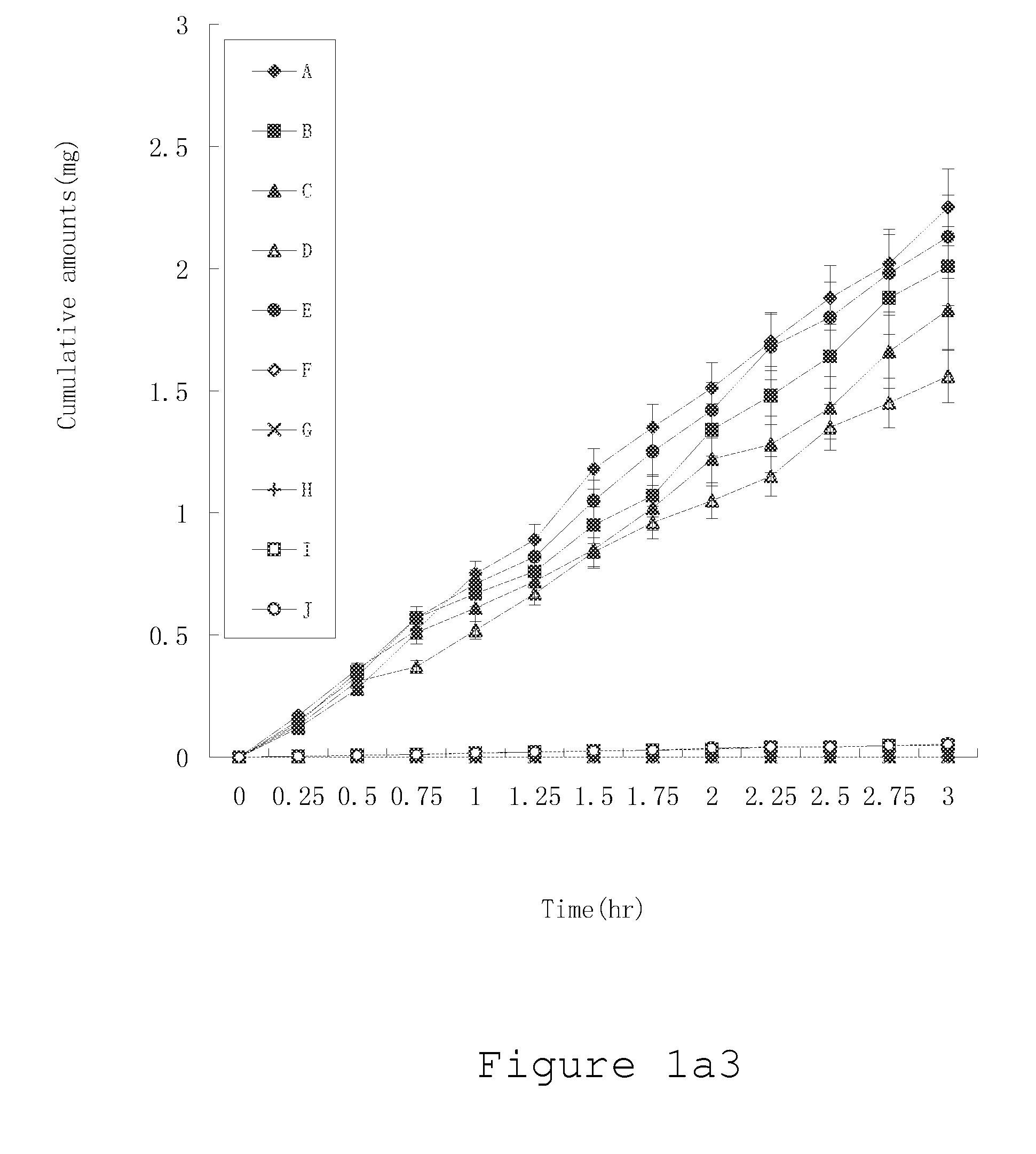
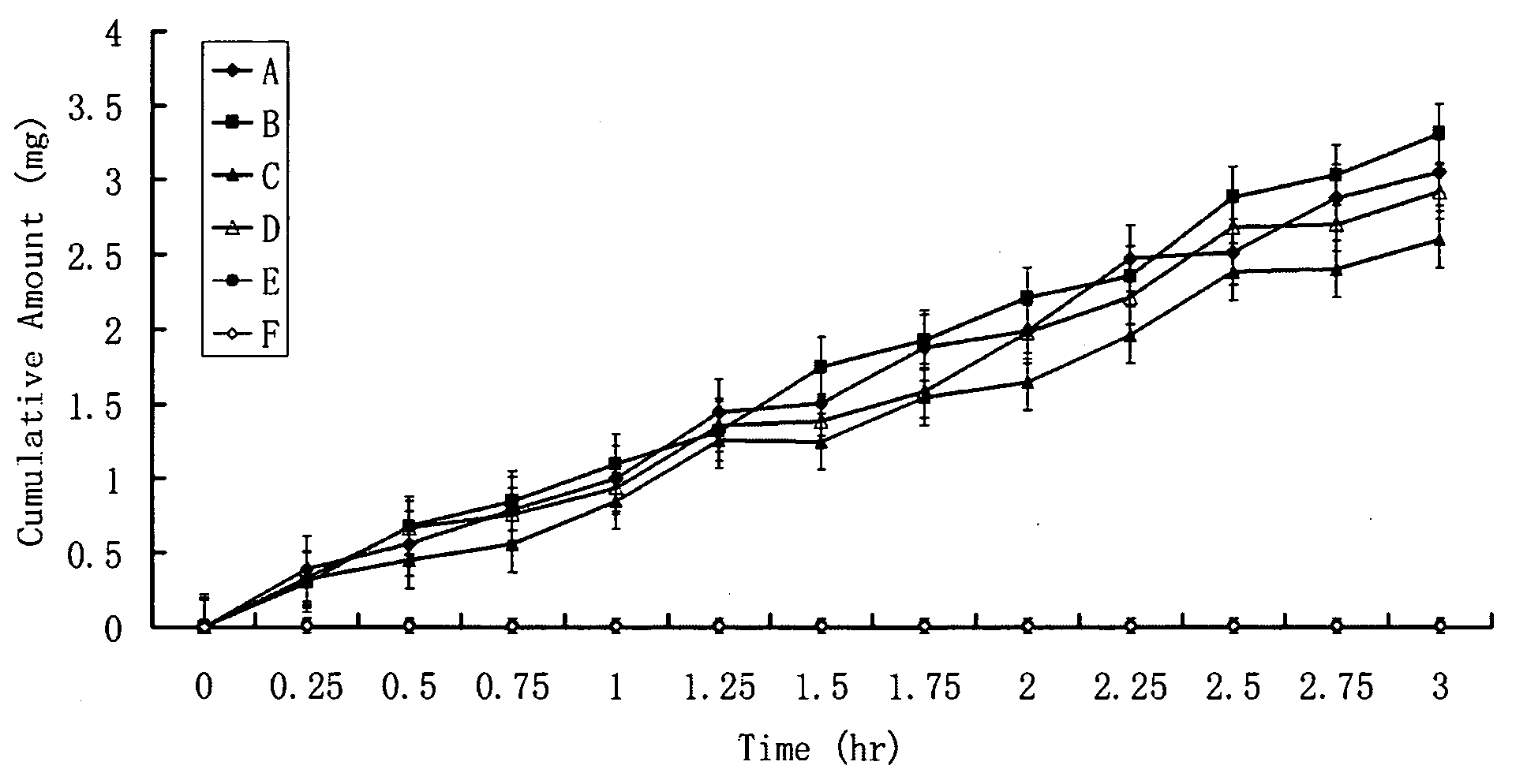
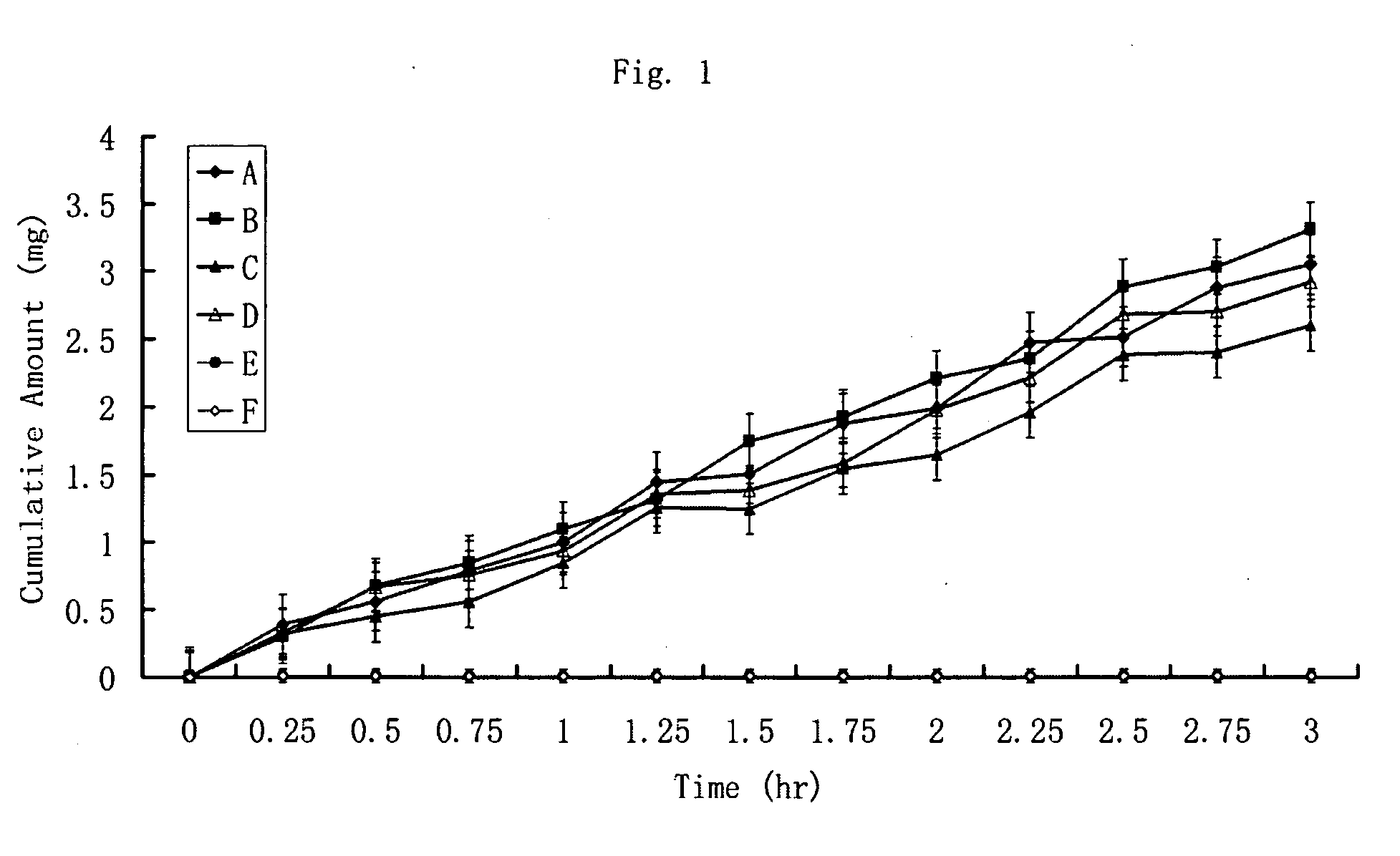
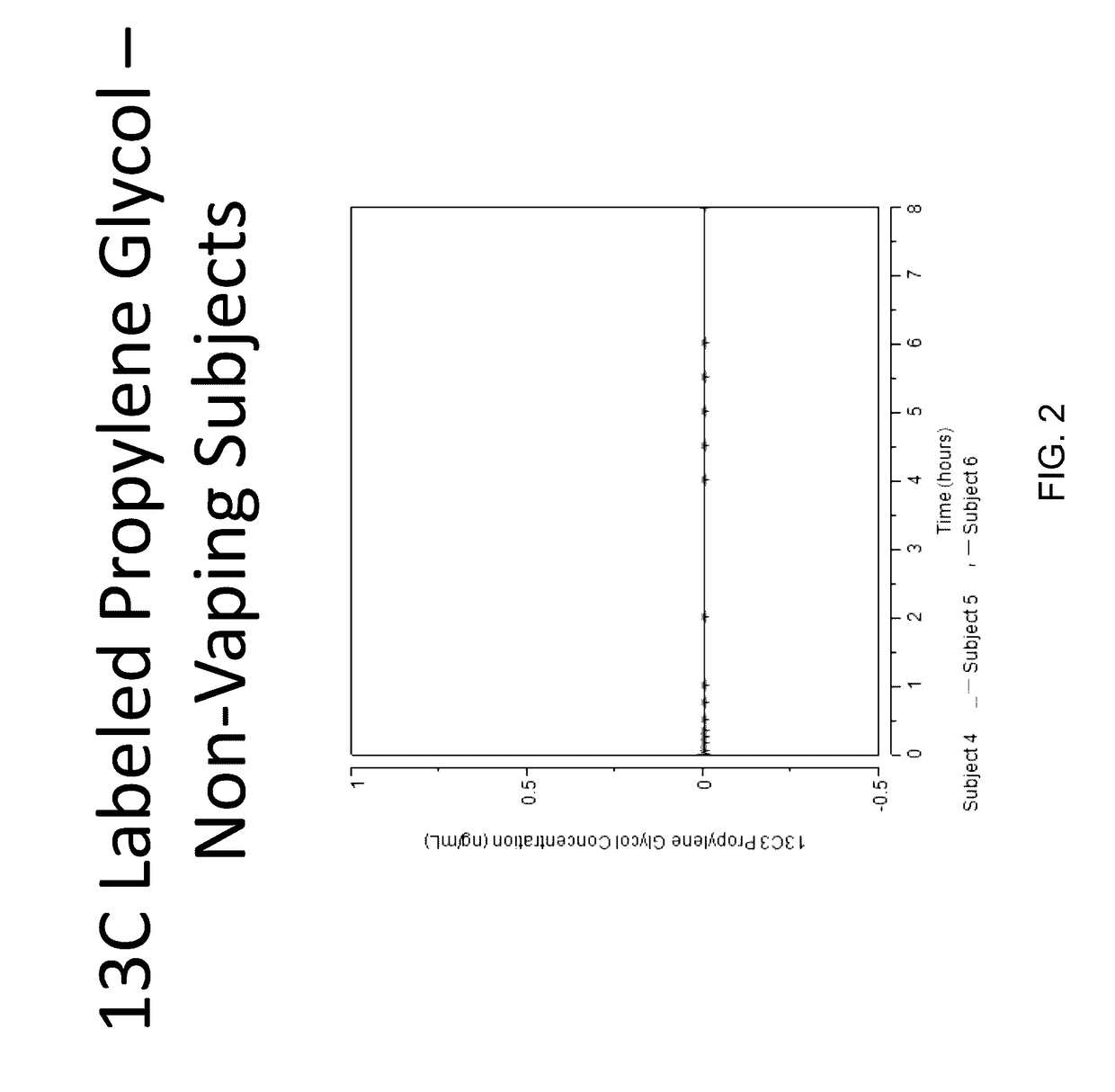
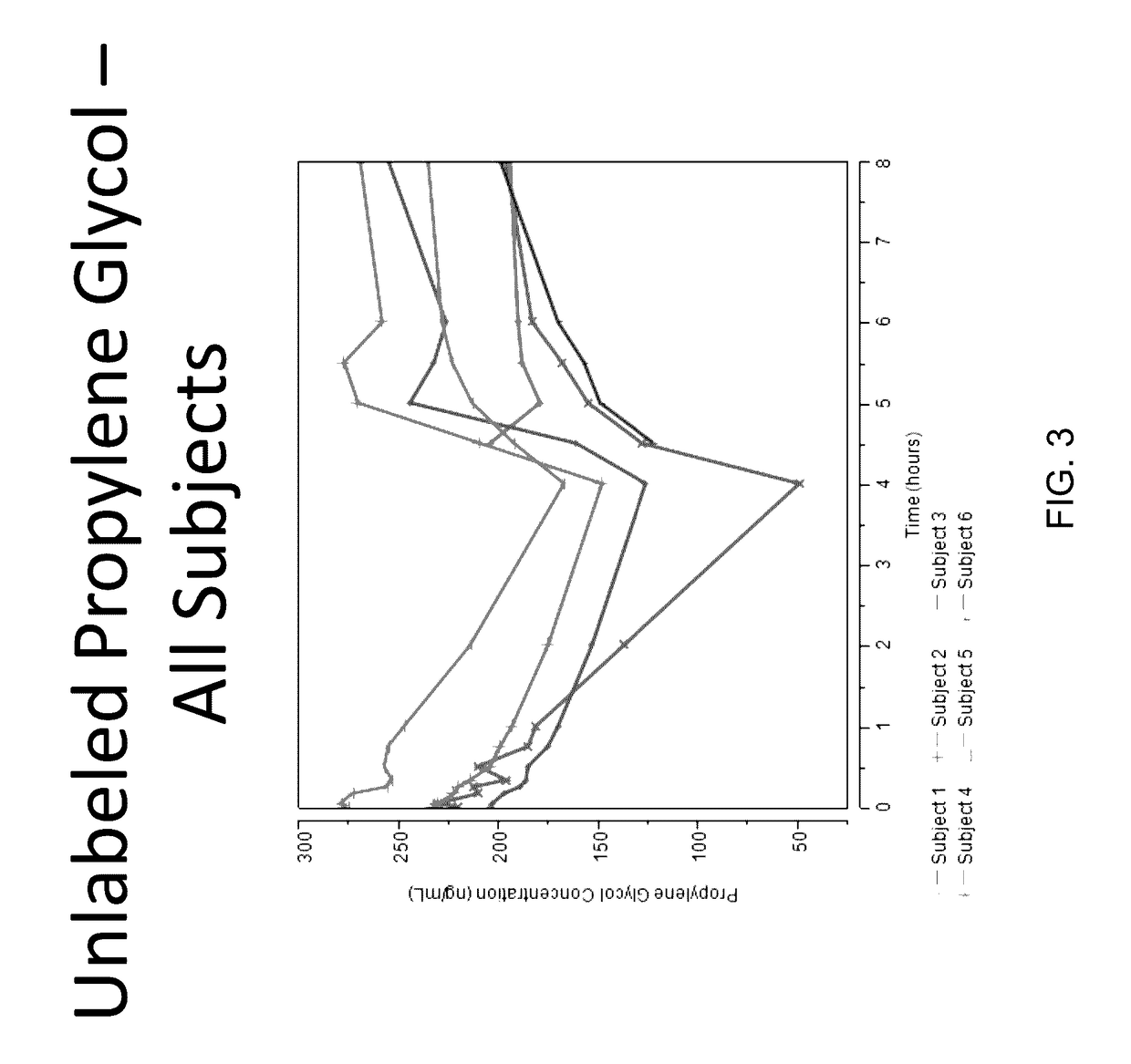
Isotopically-labeled species of propylene glycol and glycerol are provided as solvents for use in electronic nicotine delivery systems (e.g., as disposed in a cartridge in an e-cigarette). The isotopically-labeled species are distinguishable from the non-isotopically-labeled species (e.g., by mass spectrometry). Thus, methods are provided for the measurement of the quantity of solvent or of a solvent heating by-product (e.g., formaldehyde, acetaldehyde), or of a metabolite of the drug, delivered to a user by analysis of blood samples taken subsequent to dosing by use of the electronic nicotine delivery system. An example of an isotopically-labeled species of propylene glycol for use in such measurement methods is [13C]3H8O2. A clinical study of e-cigarettes loaded with this isotopically-labeled species resulted in the following blood plasma concentration profiles in “vaping” subjects.
Owner:CELERION INC
Dynamic Lab on a Chip Based Point-Of-Care Device For Analysis of Pluripotent Stem Cells, Tumor Cells, Drug Metabolites, Immunological Response, Glucose Monitoring, Hospital Based Infectious Diseases, and Drone Delivery Point-of-Care Systems
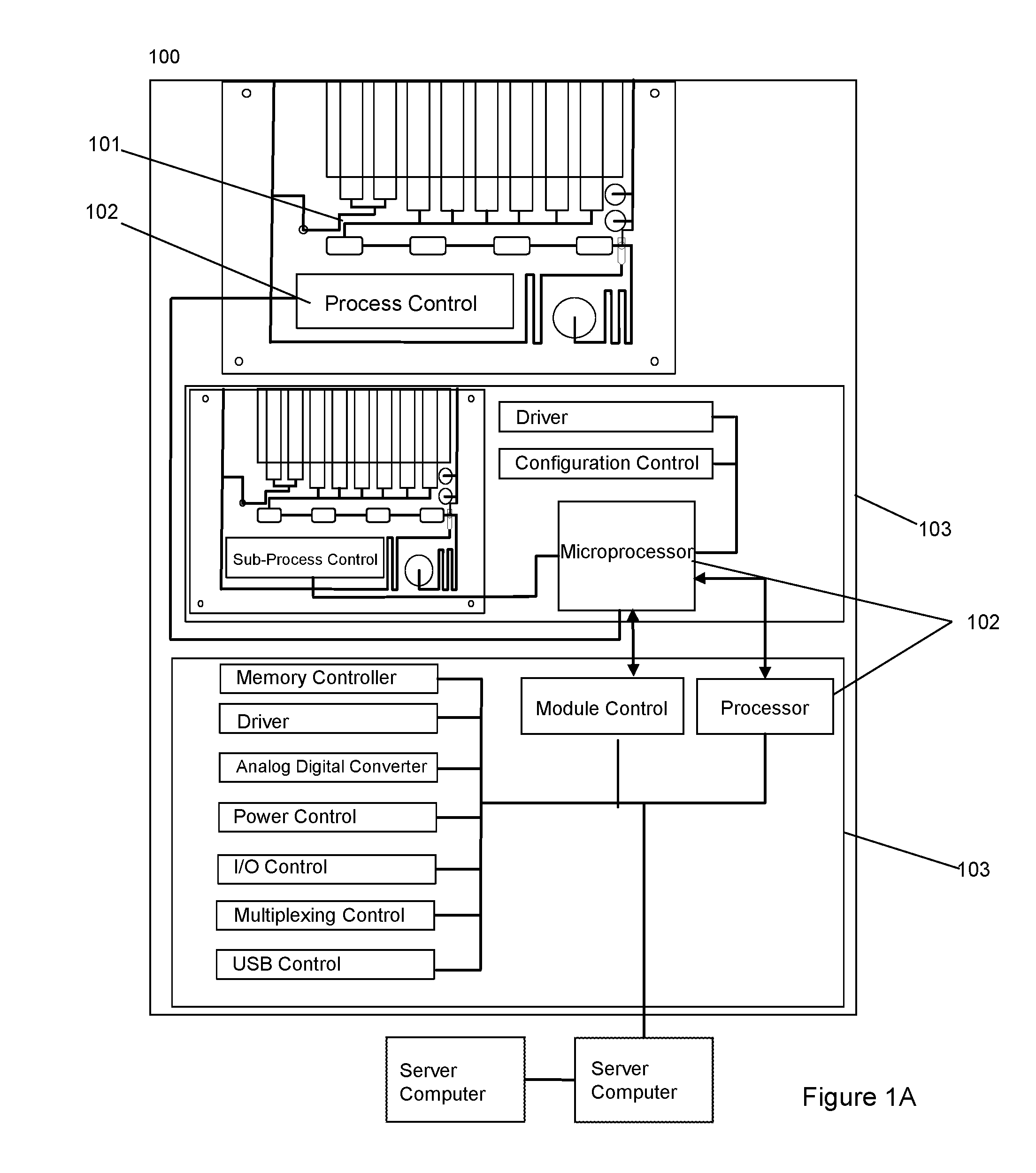
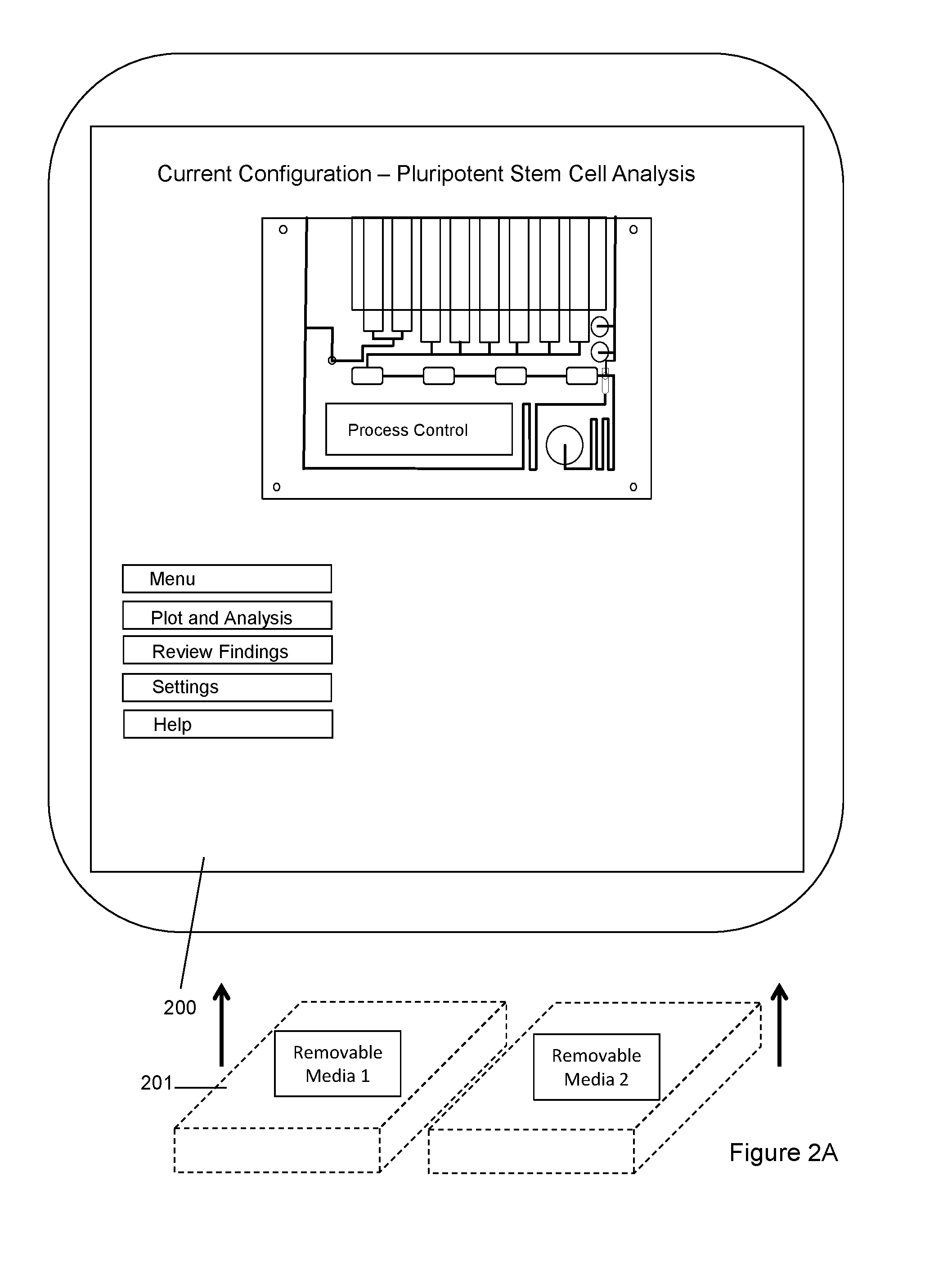
The invention provides for a novel dynamically configurable point-of-care device for clinical diagnostics and research for analysis of activity associated with pluripotent stem cells, tumor cells, drug metabolites, immunological response, glucose monitoring, cardiovascular diseases, liver cell therapy, cell-cell signaling, epidemic outbreaks, hospital based infectious diseases, pathogens, germ cells, pharmacological compounds, oxidation reduction, microscopy, tomography, flow cytometry, clinical lab testing, and for providing immunoassays, ELISA, electrophoresis, PCR, chromatography, and other laboratory functions. The device comprises a biochemical processing module further comprising a processor and at least one controller, receiving microfluidic elements, sensors, software scripts, an electrically operated interface, flow ports, a user interface, memory, and a communications link, configurable based on analysis of patient data. The invention further provides for multiple-criteria decision analysis for hospital administrators, a wearable device, mobile medical device, molecular electronics configuration, touchscreen recognition, data analytics application, and a drone delivery based point-of-care system.
Owner:PATEL NILESH
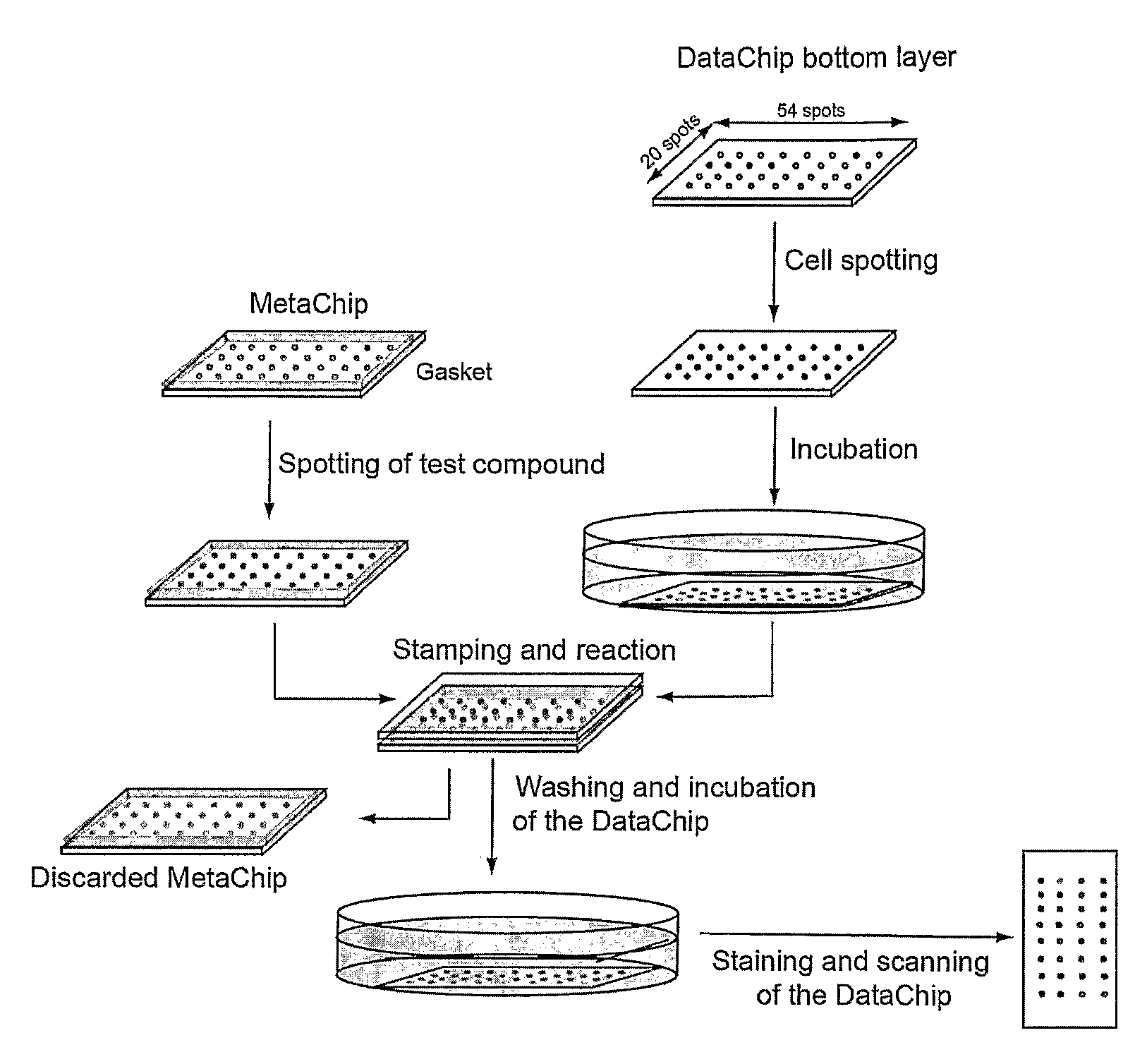
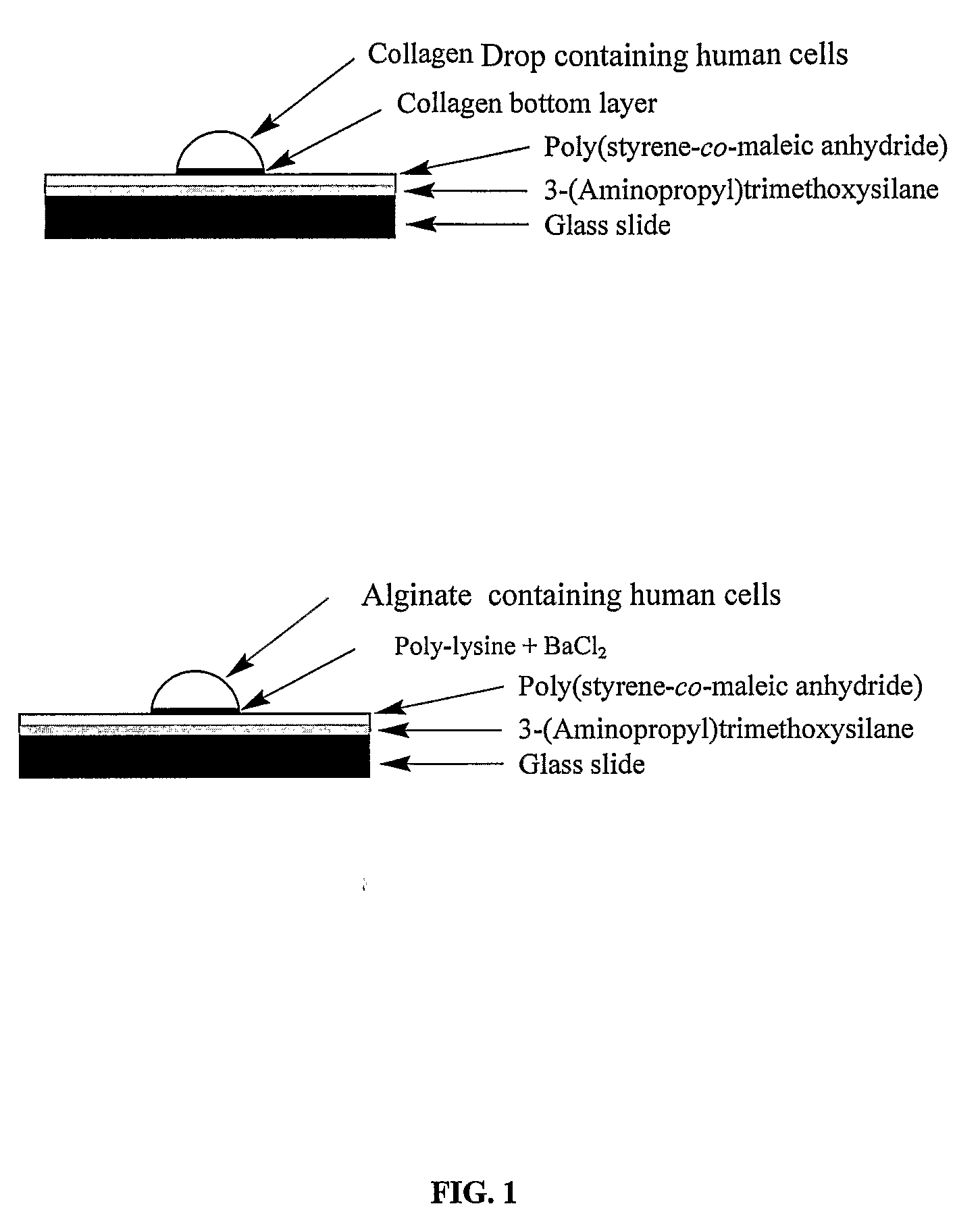
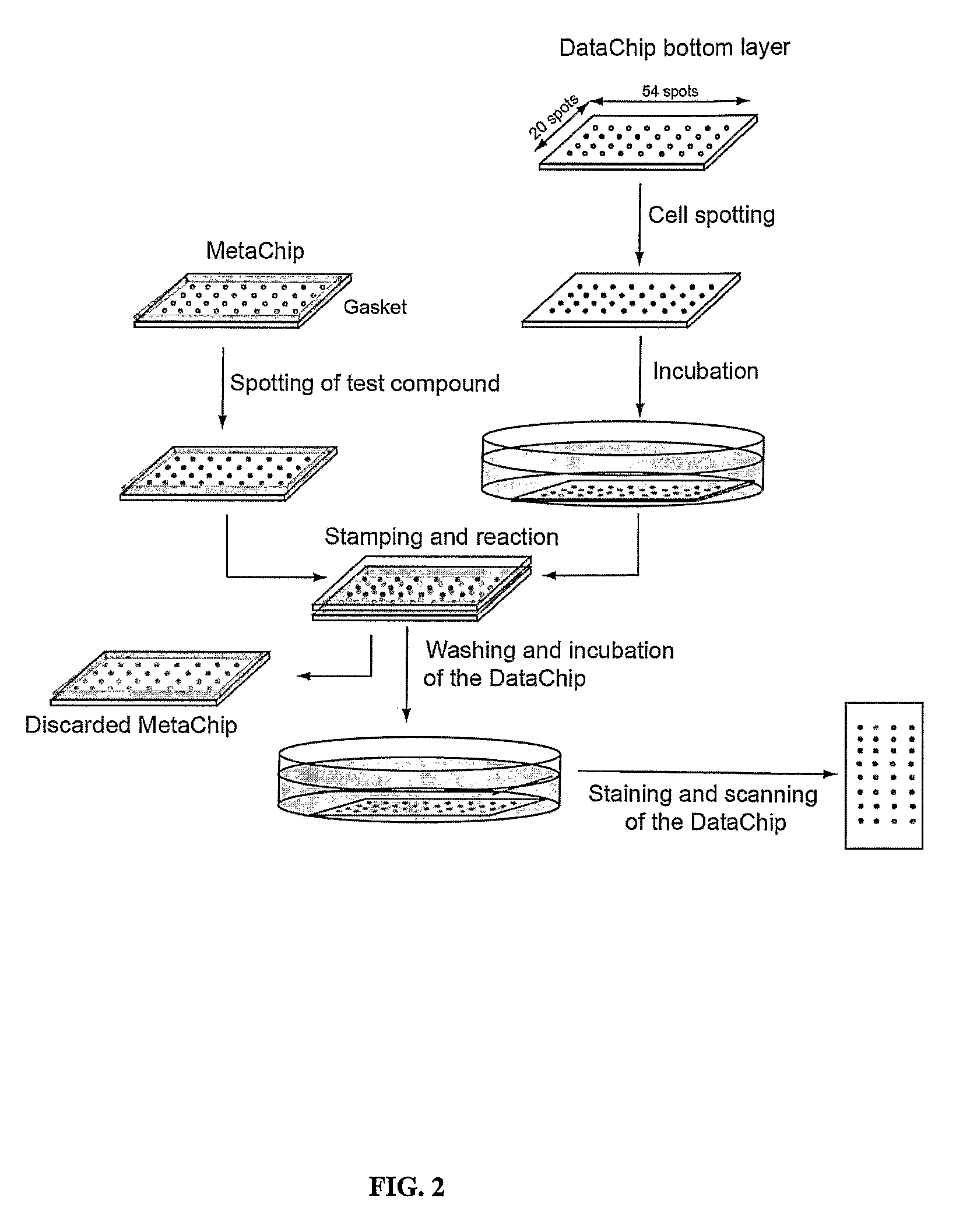
Three-dimensional cellular array chip and platform for toxicology assays
The present invention is directed to a screening platform employing a miniaturized three-dimensional cell chip for high-throughput toxicology screening of test and lead compounds, prodrugs, drugs and P-450 generated drug metabolites. To this end, the three-dimensional cell chip, employs human cells encapsulated in a matrix (e.g., collagen or alginate gels) in volumes as small as 10 nL arrayed on a functionalized substrates (e.g., glass microscope slides) for spatially addressable screening against multiple test compounds. With the present platform, over 3,000 cell-matrix islands may be spotted providing for simultaneous screening against multiple compounds at multiple doses and in high replicate.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
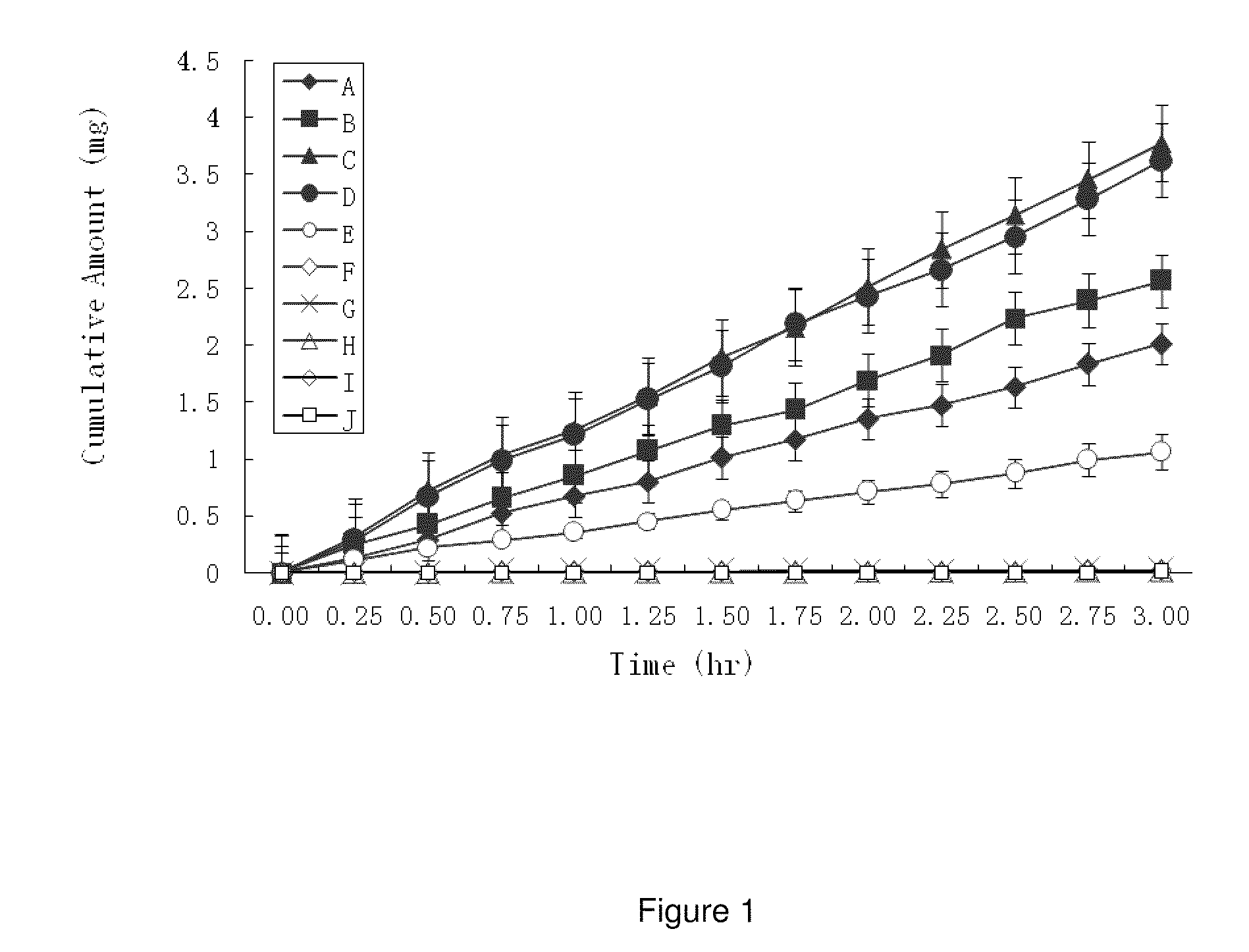
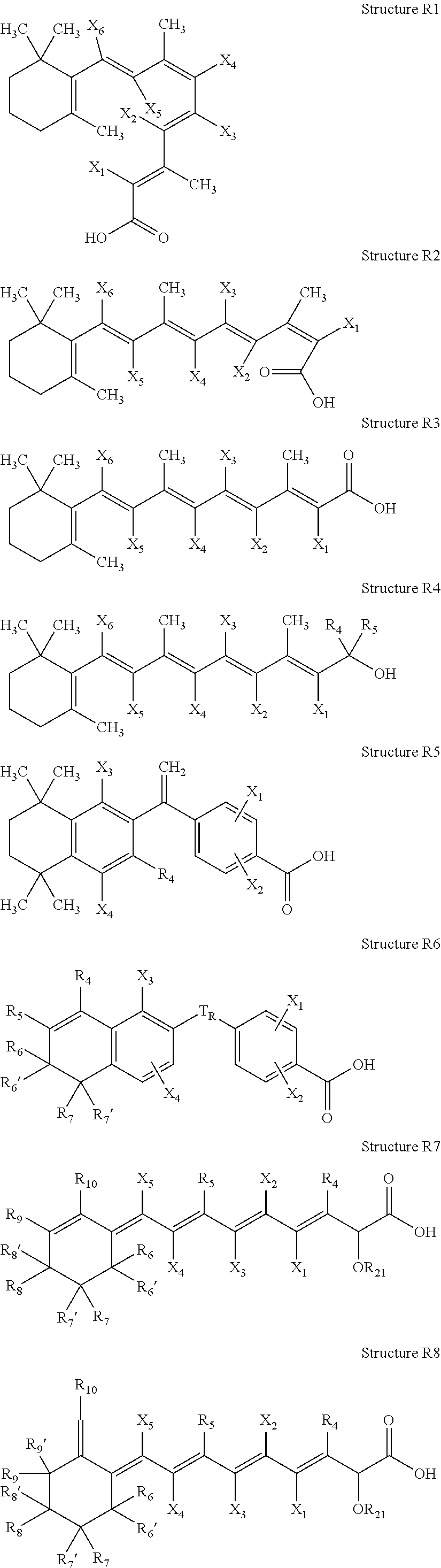
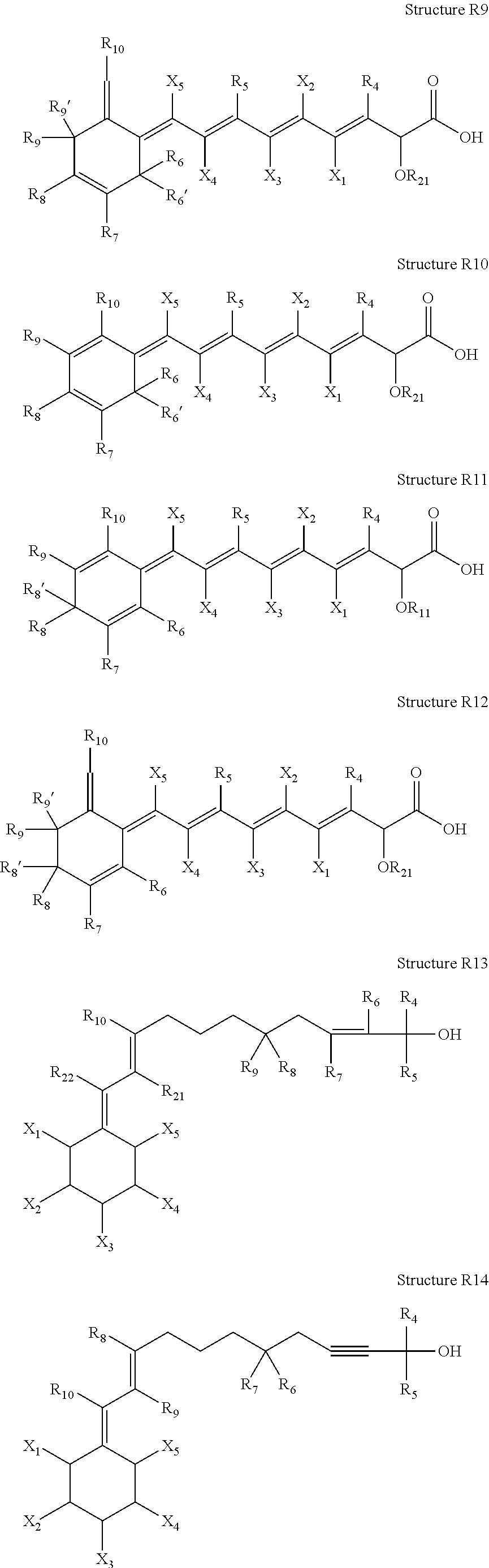
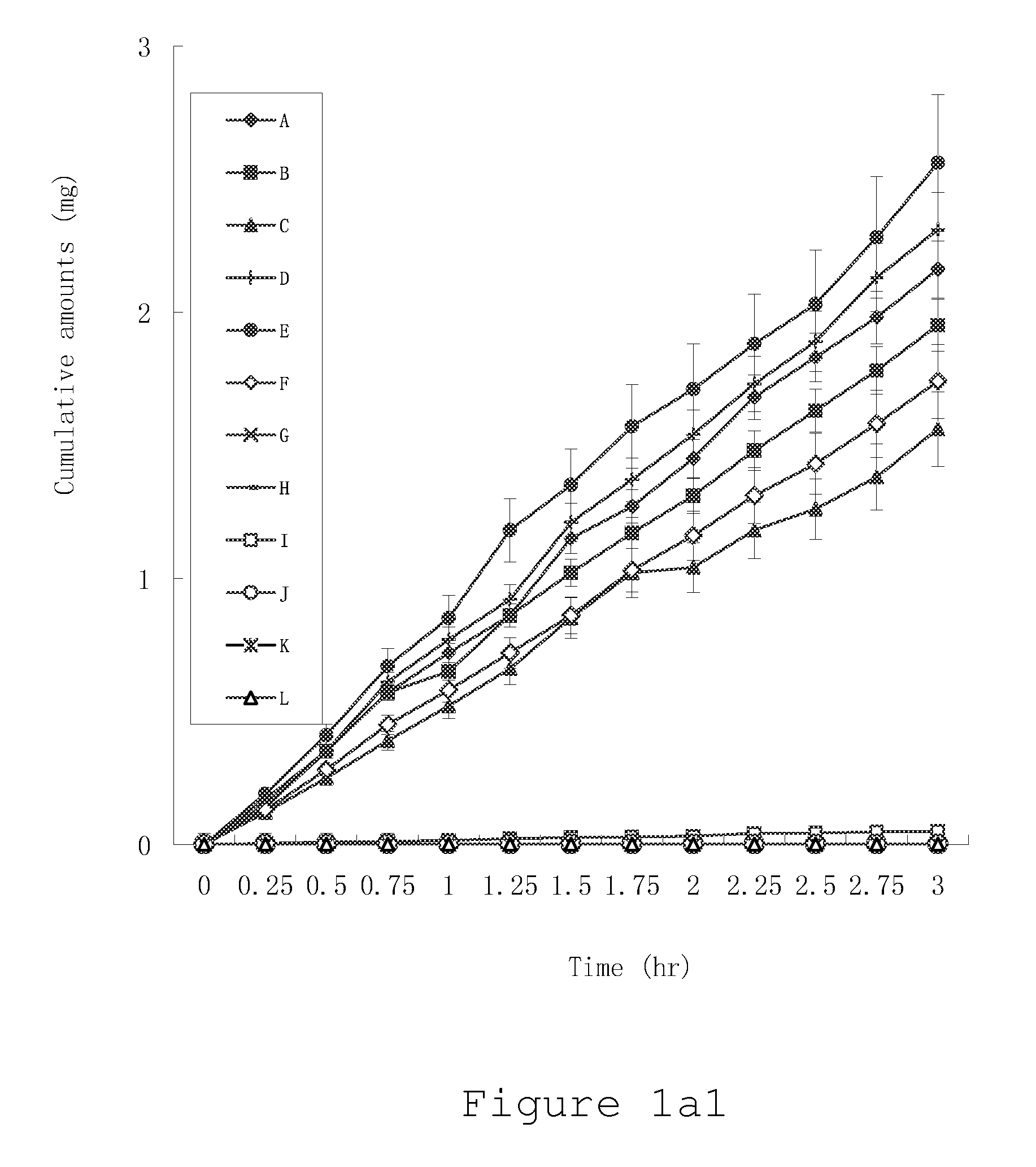
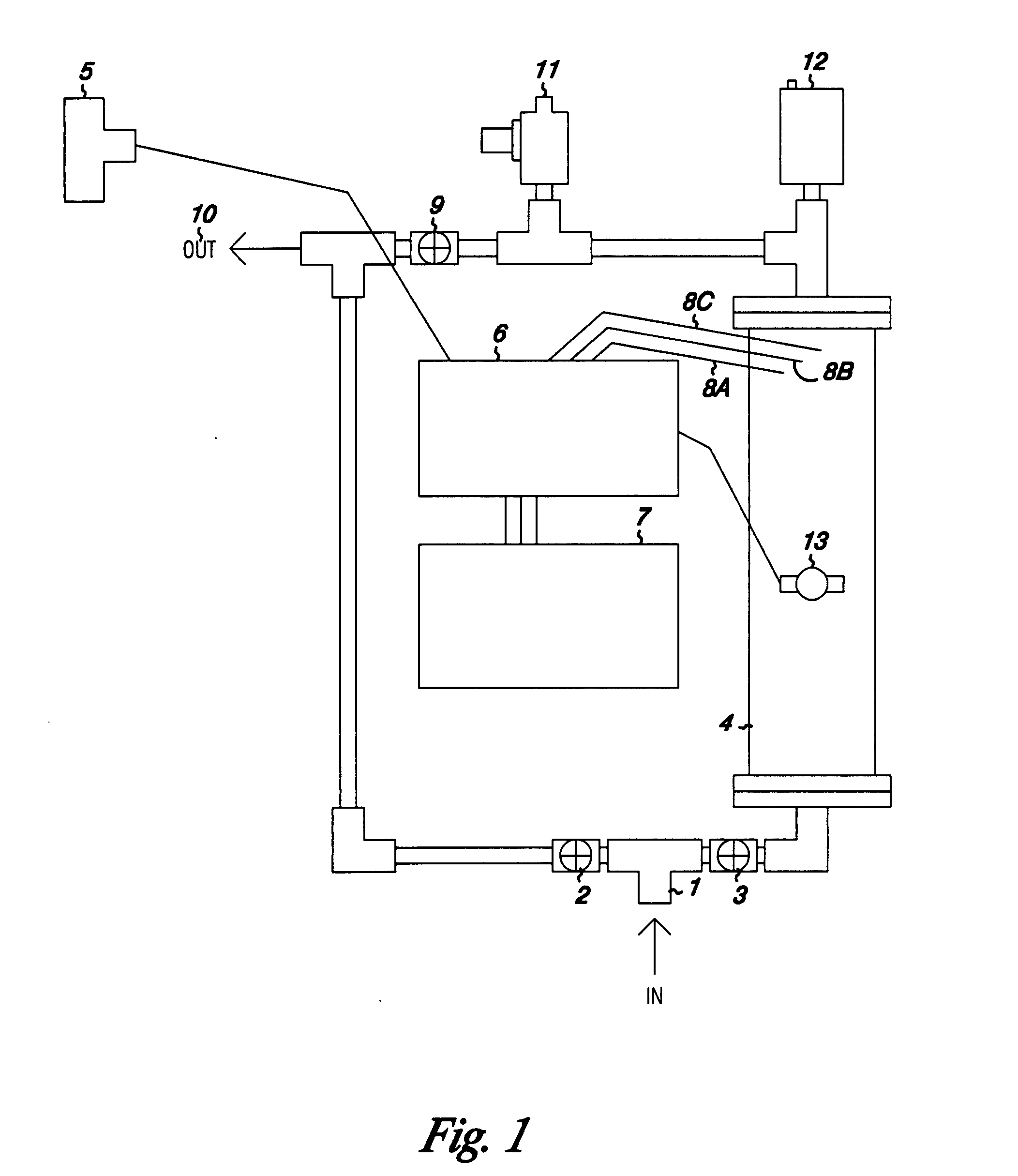
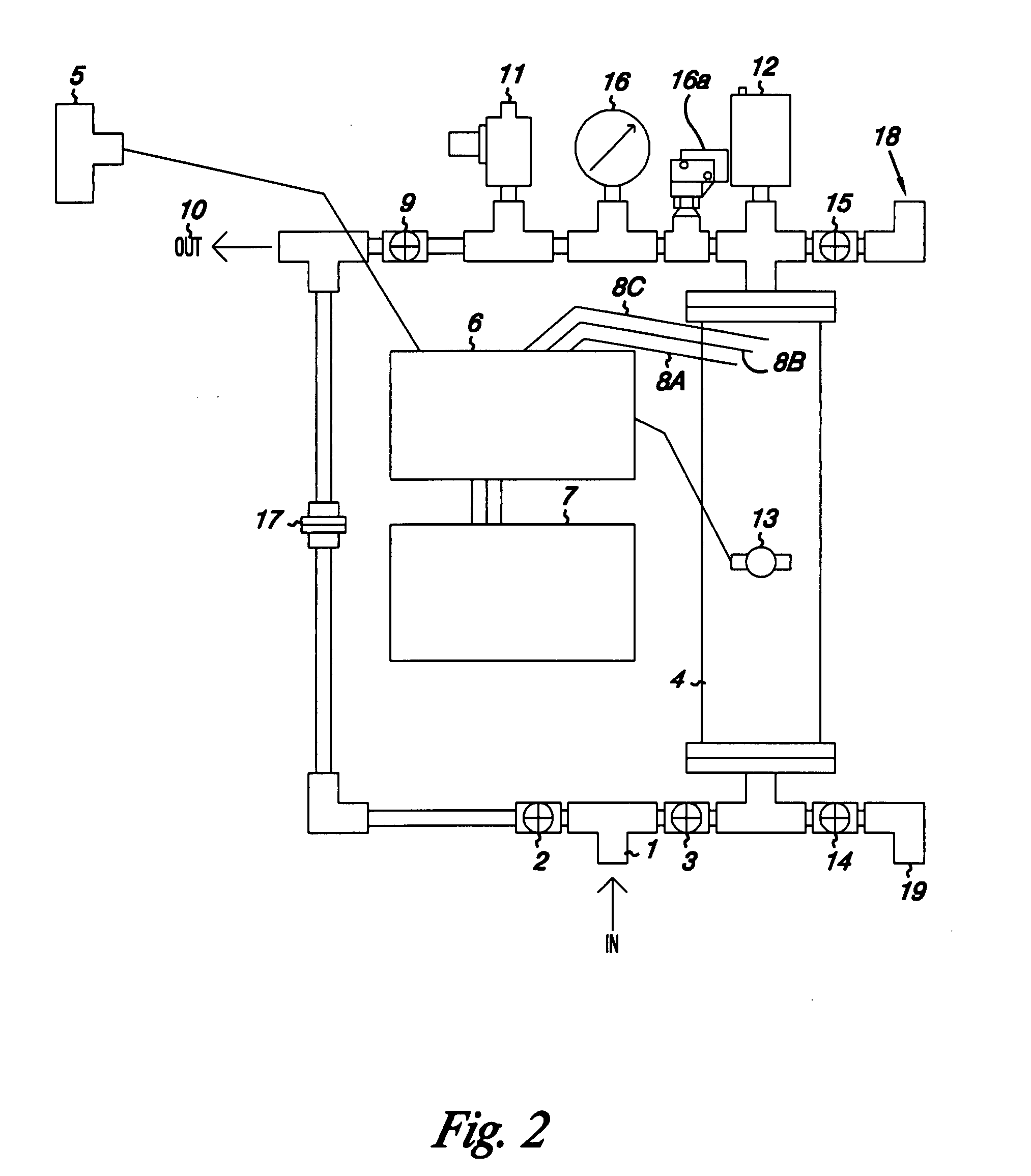
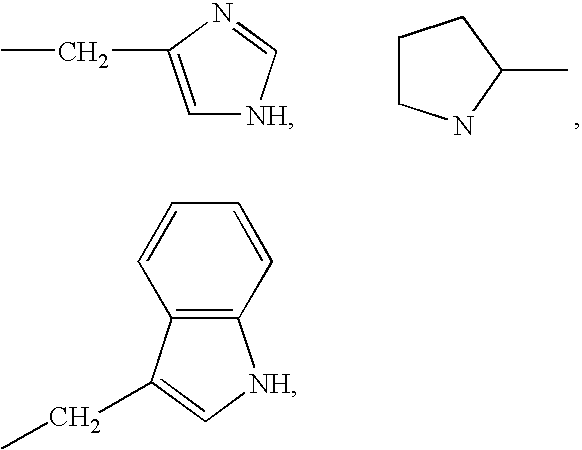
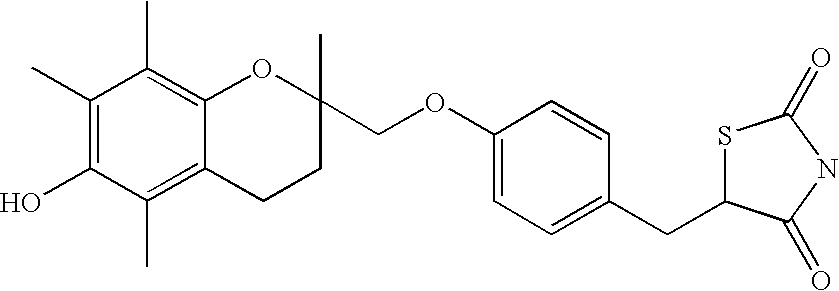
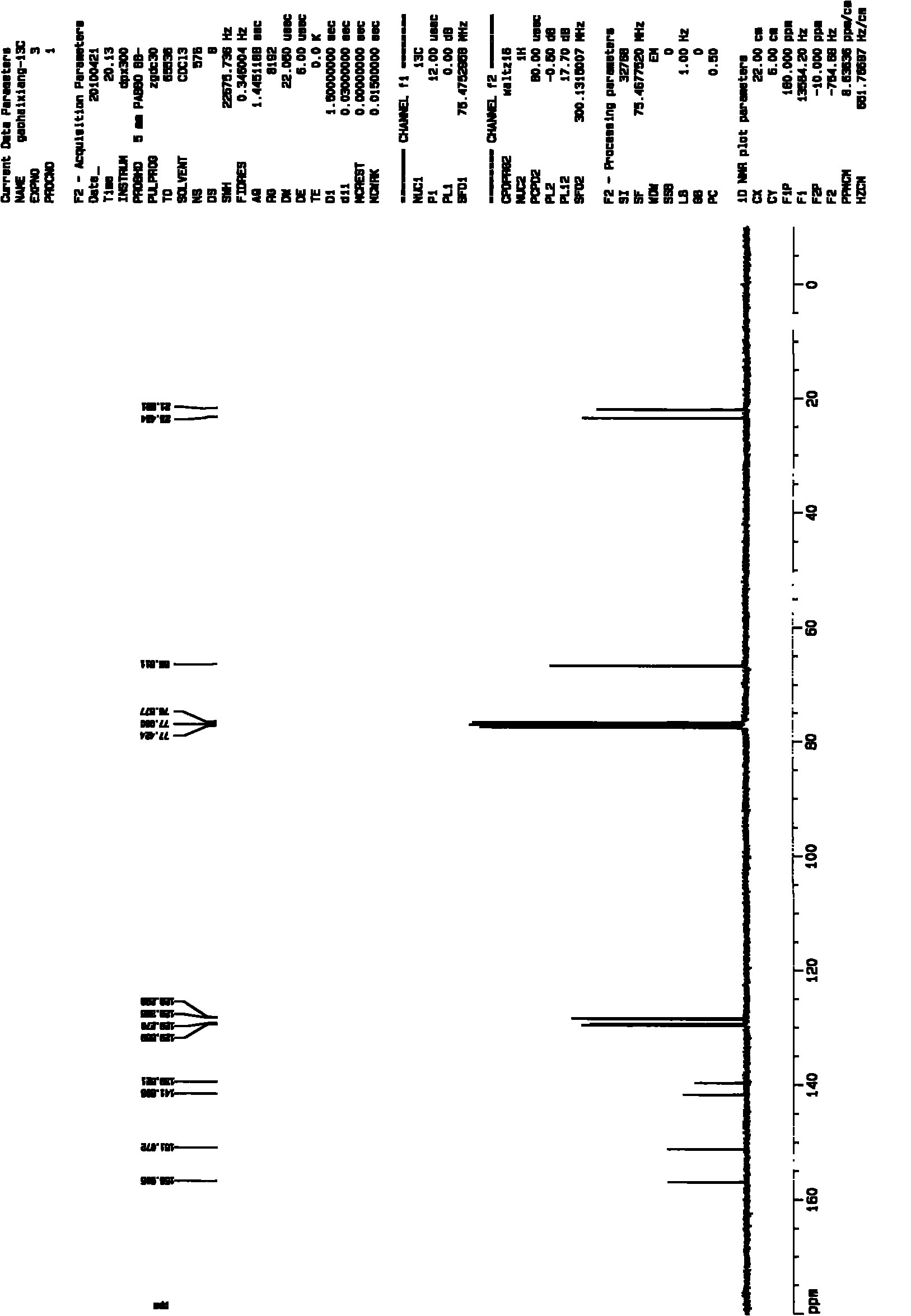
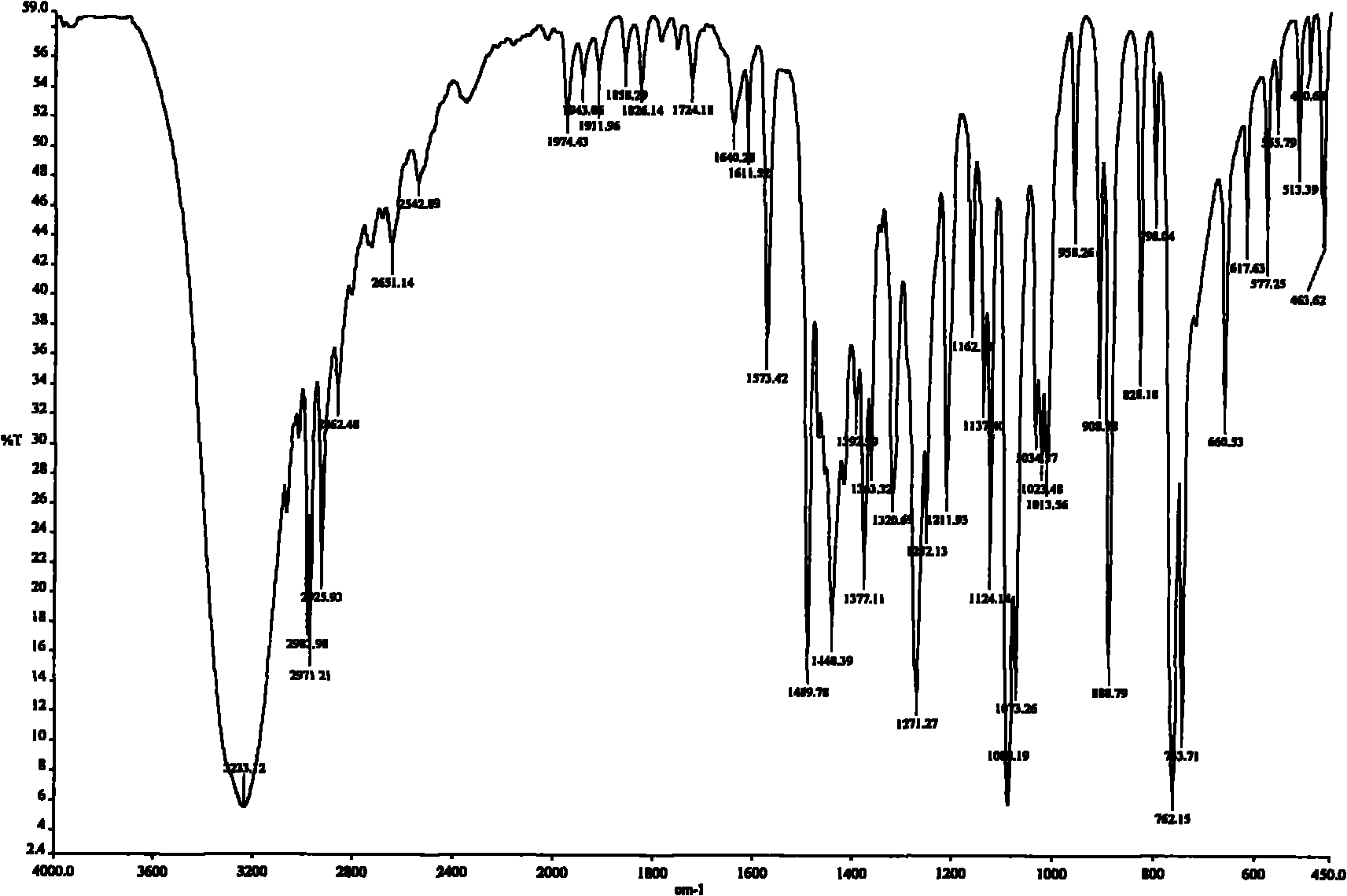
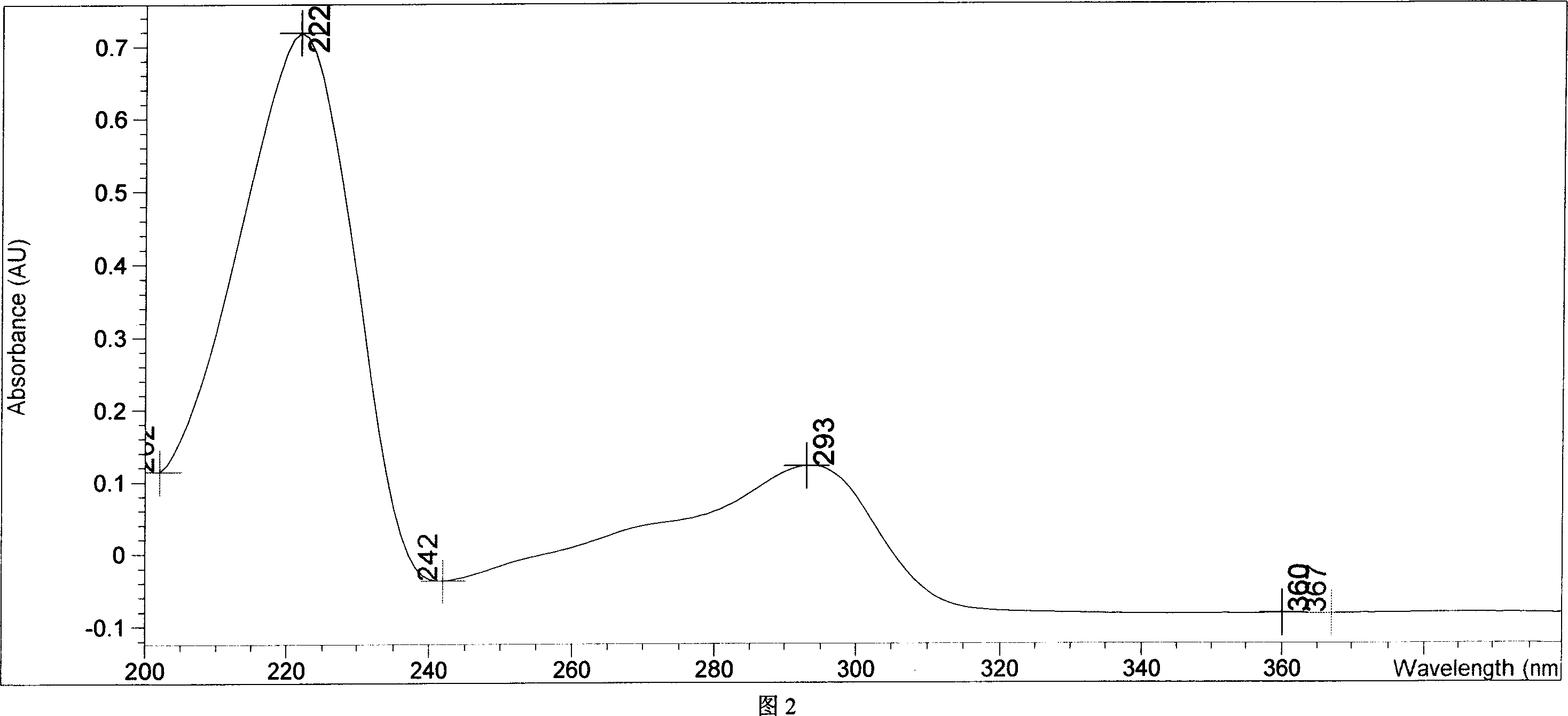
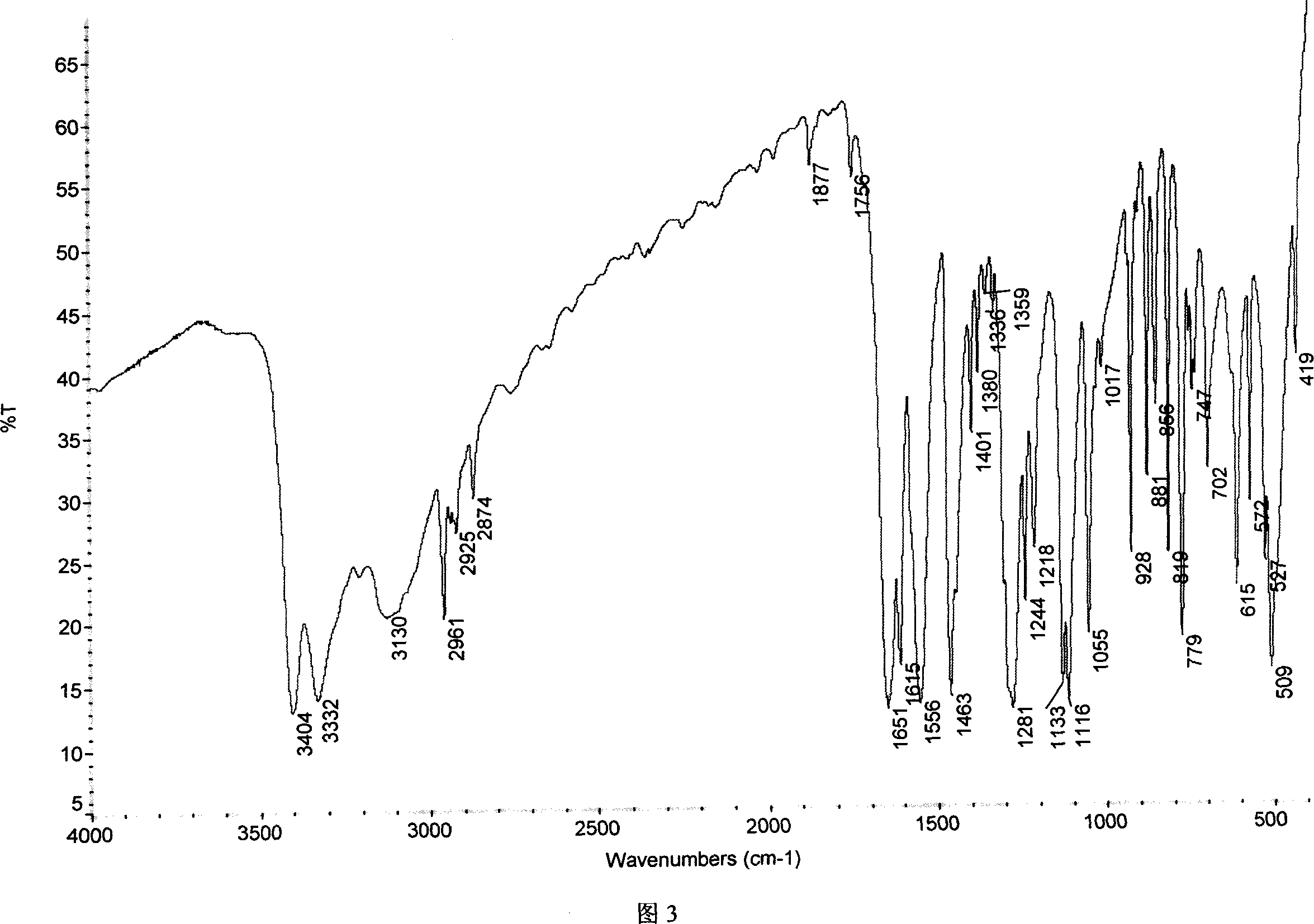
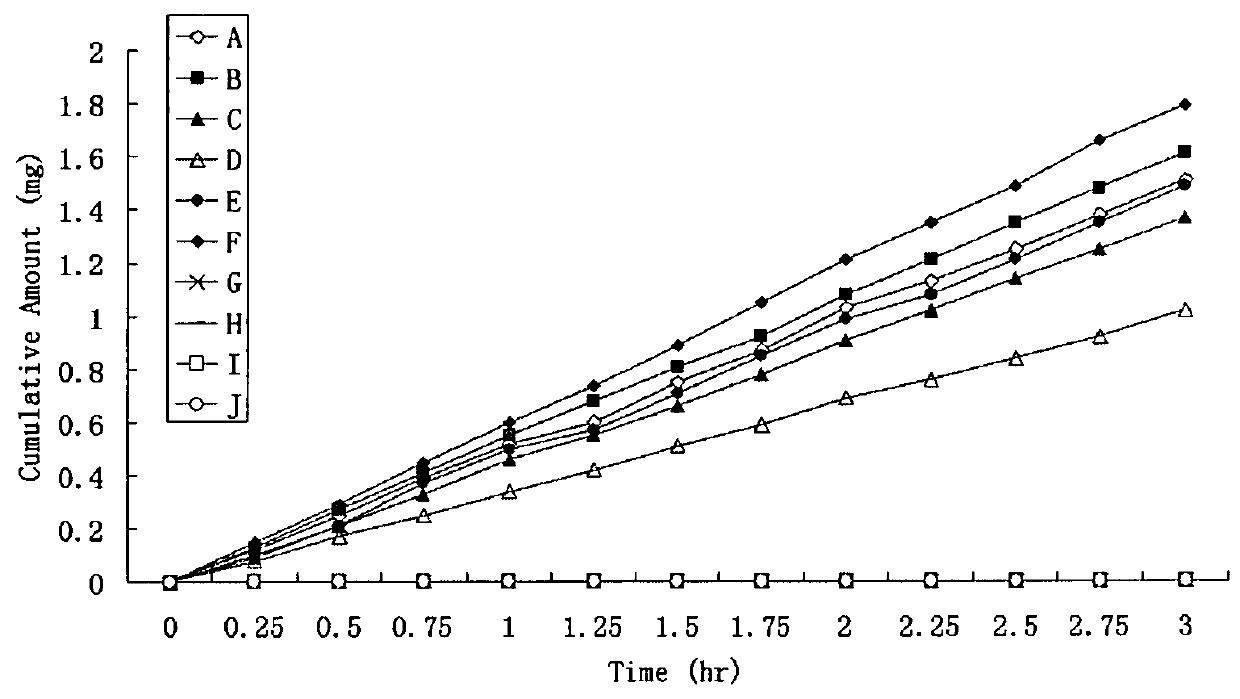
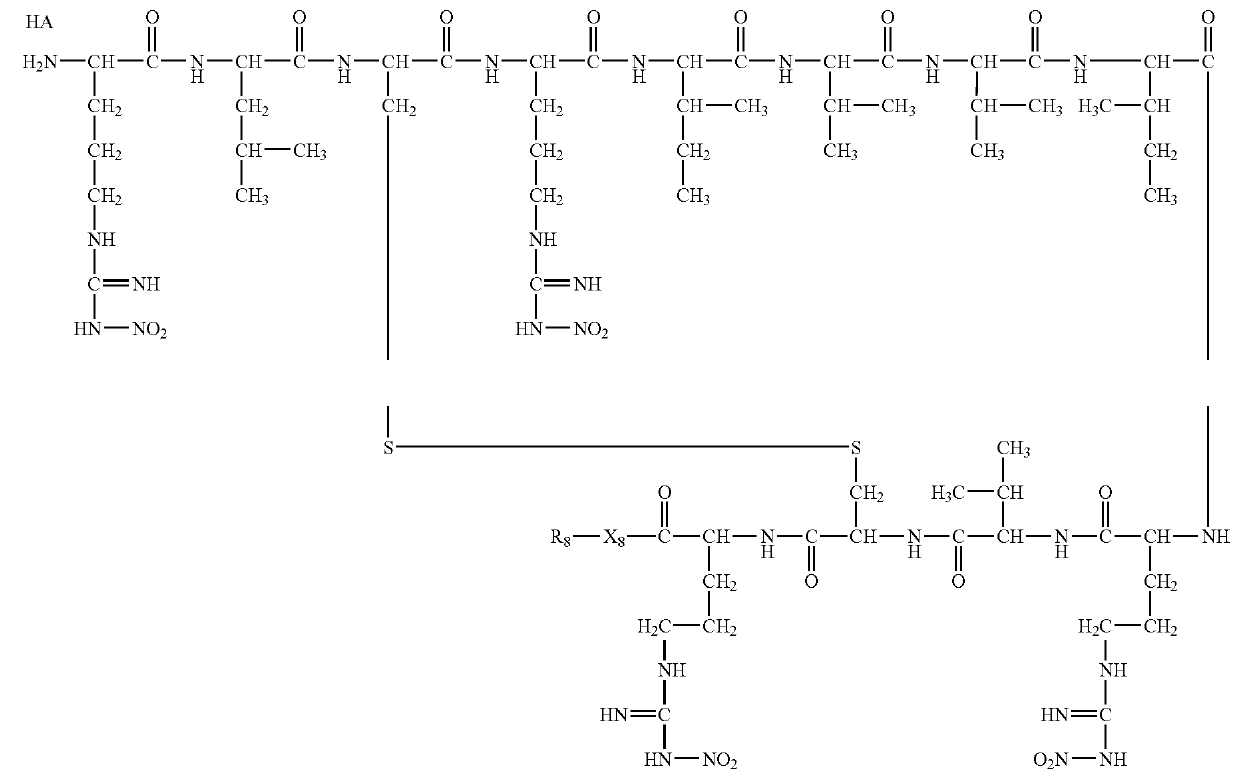
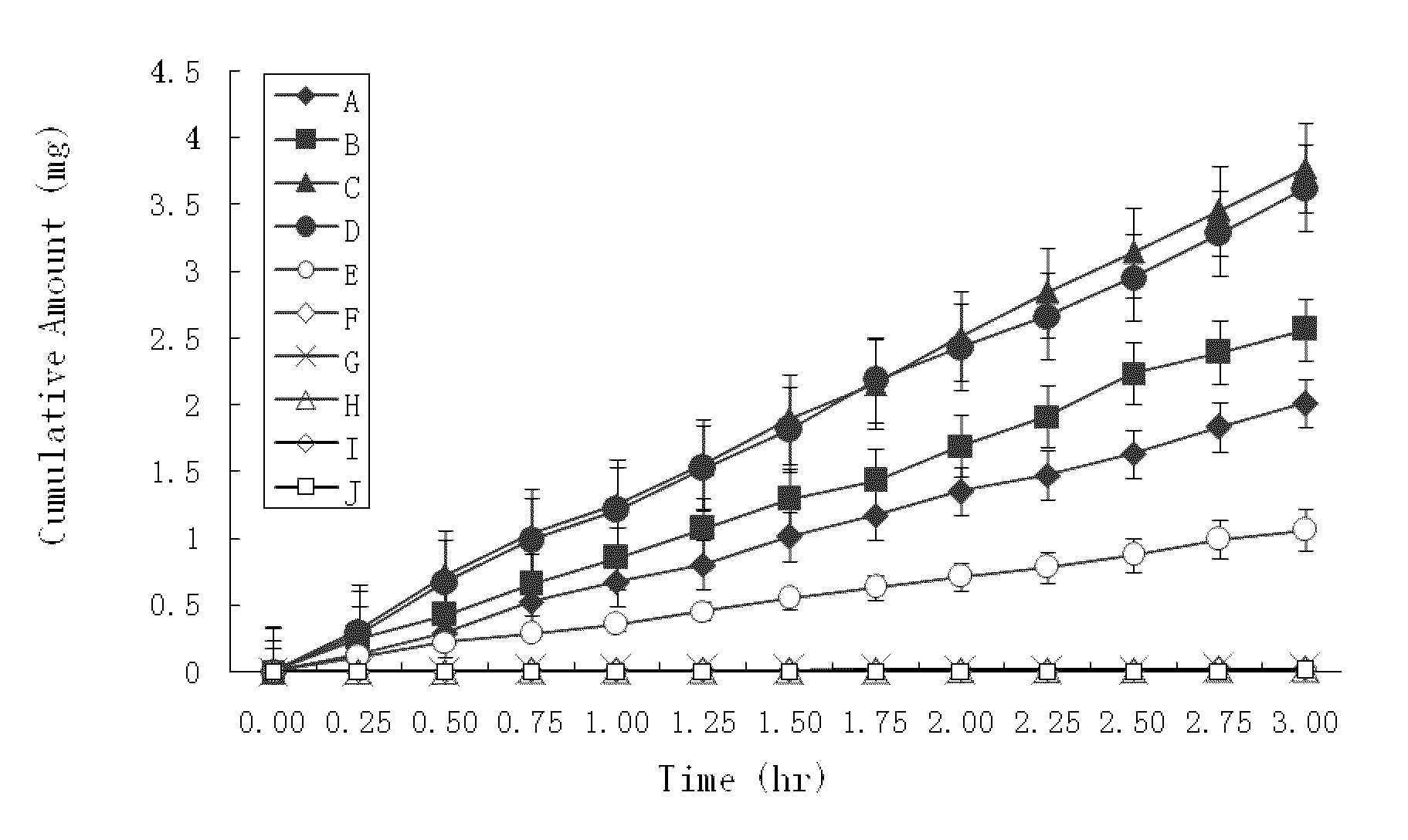
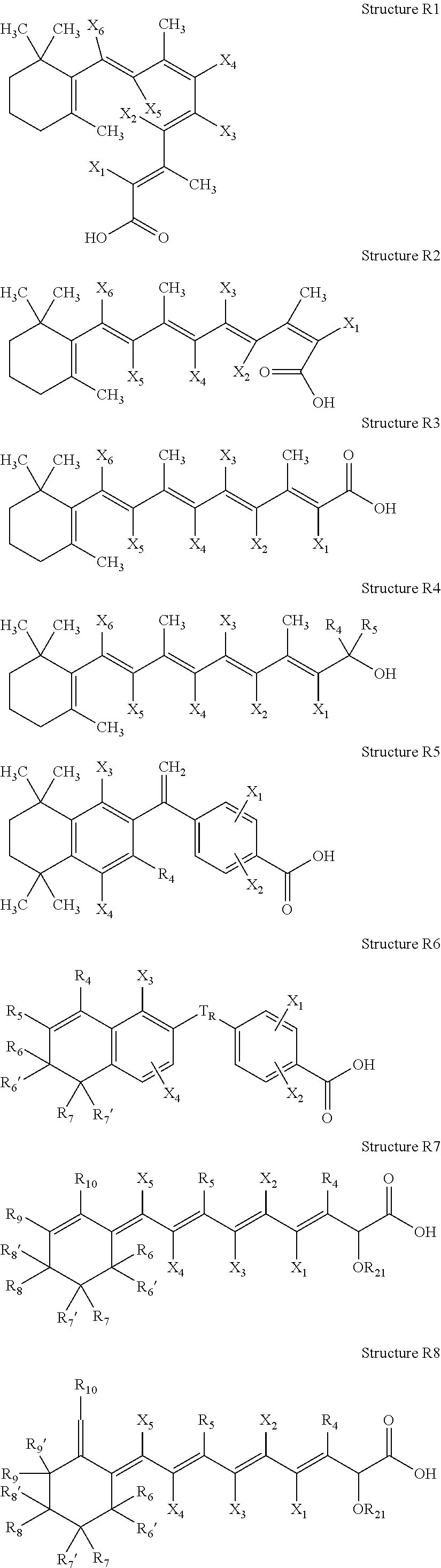
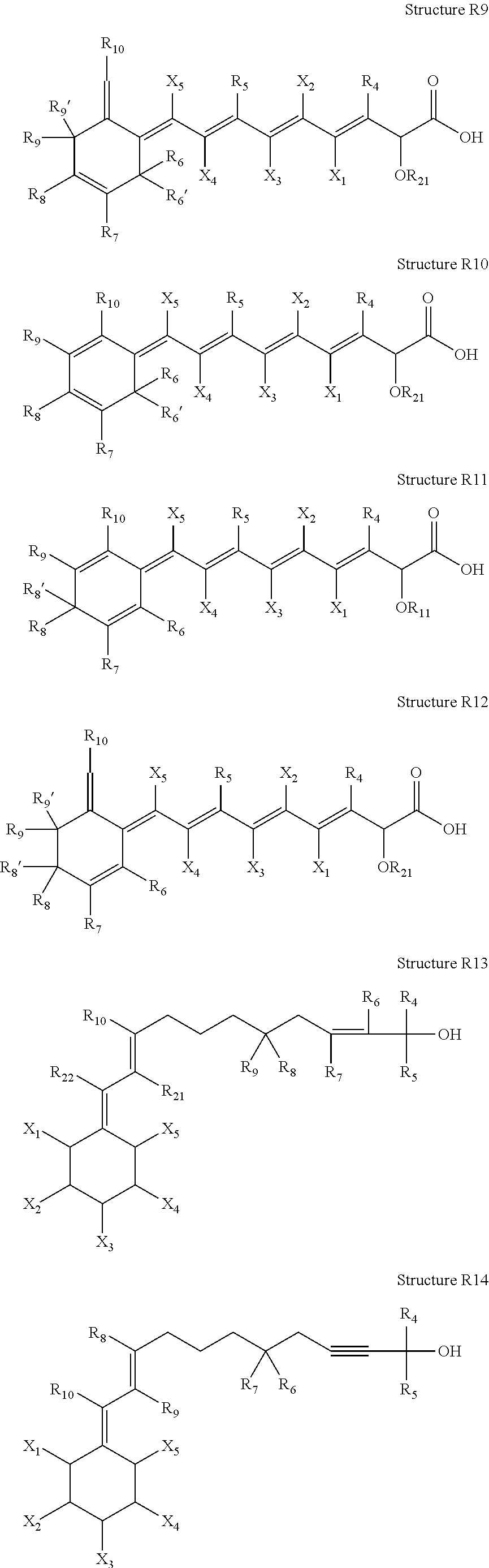
High penetration prodrug compositions of 1h-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amines and 1h-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine-related compounds
ActiveUS20100021394A1Reduce solubilitySkin to slackenBiocideNervous disorderHigh concentrationMetabolite
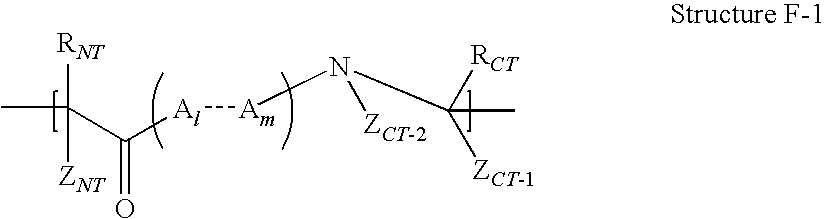
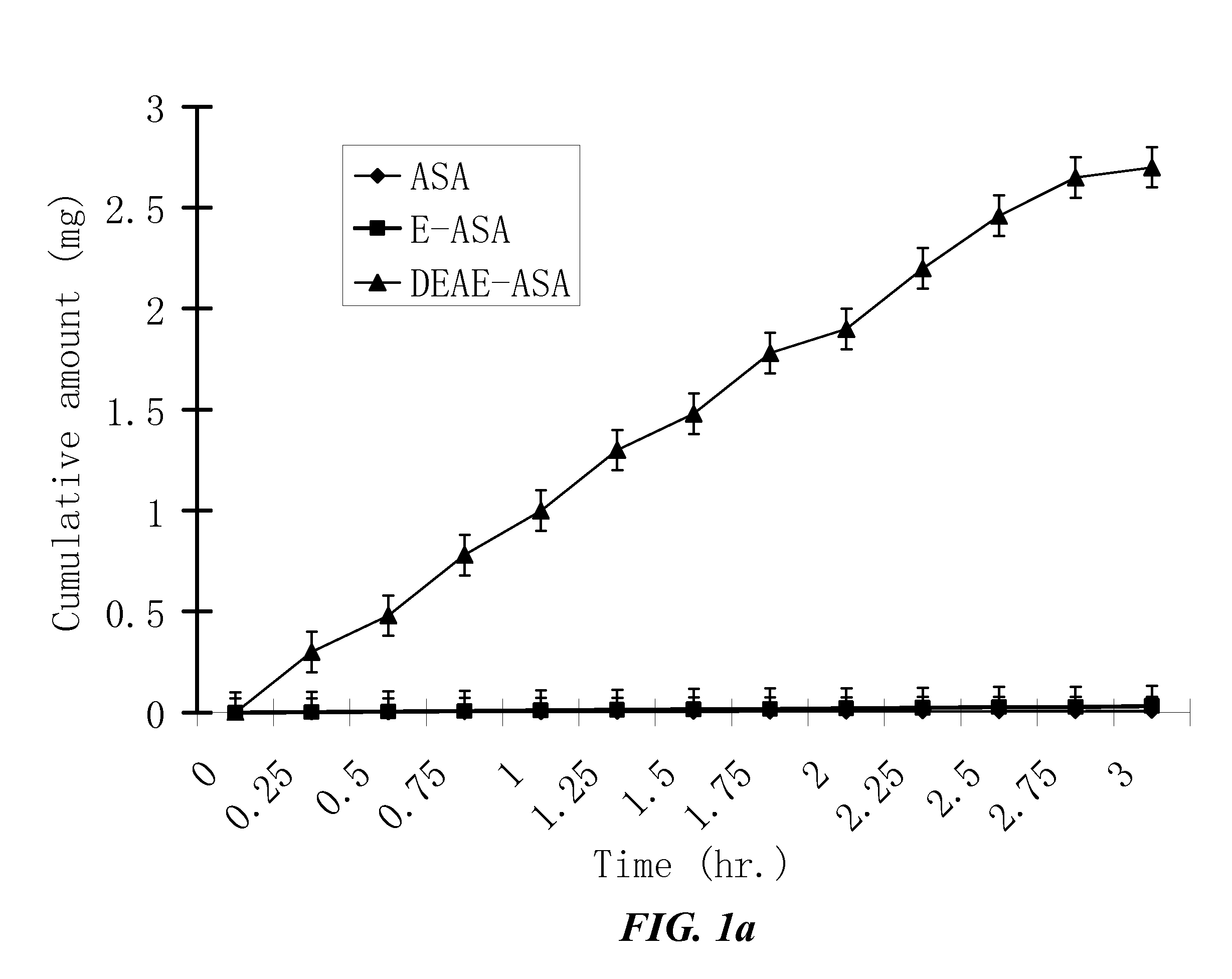
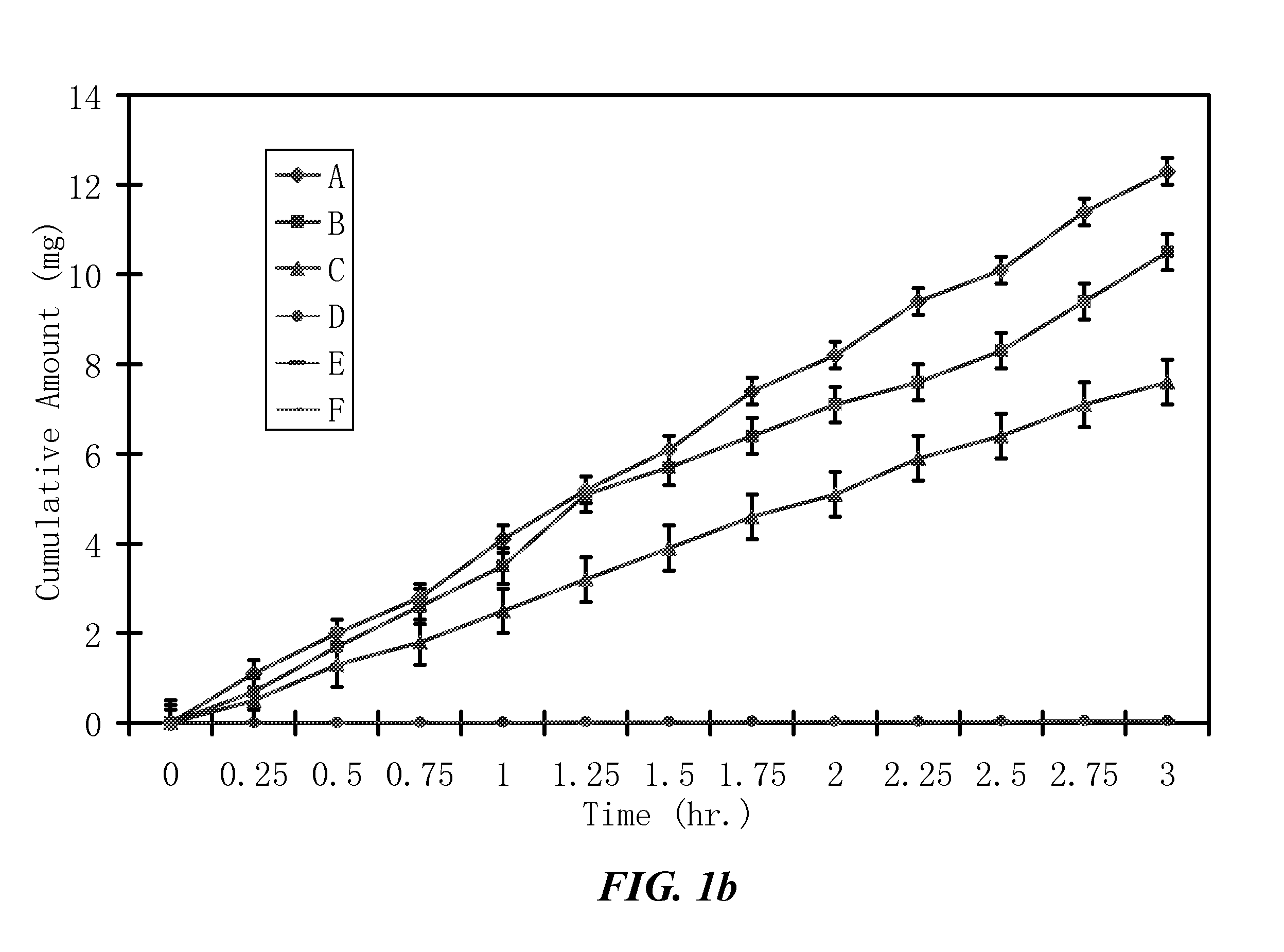
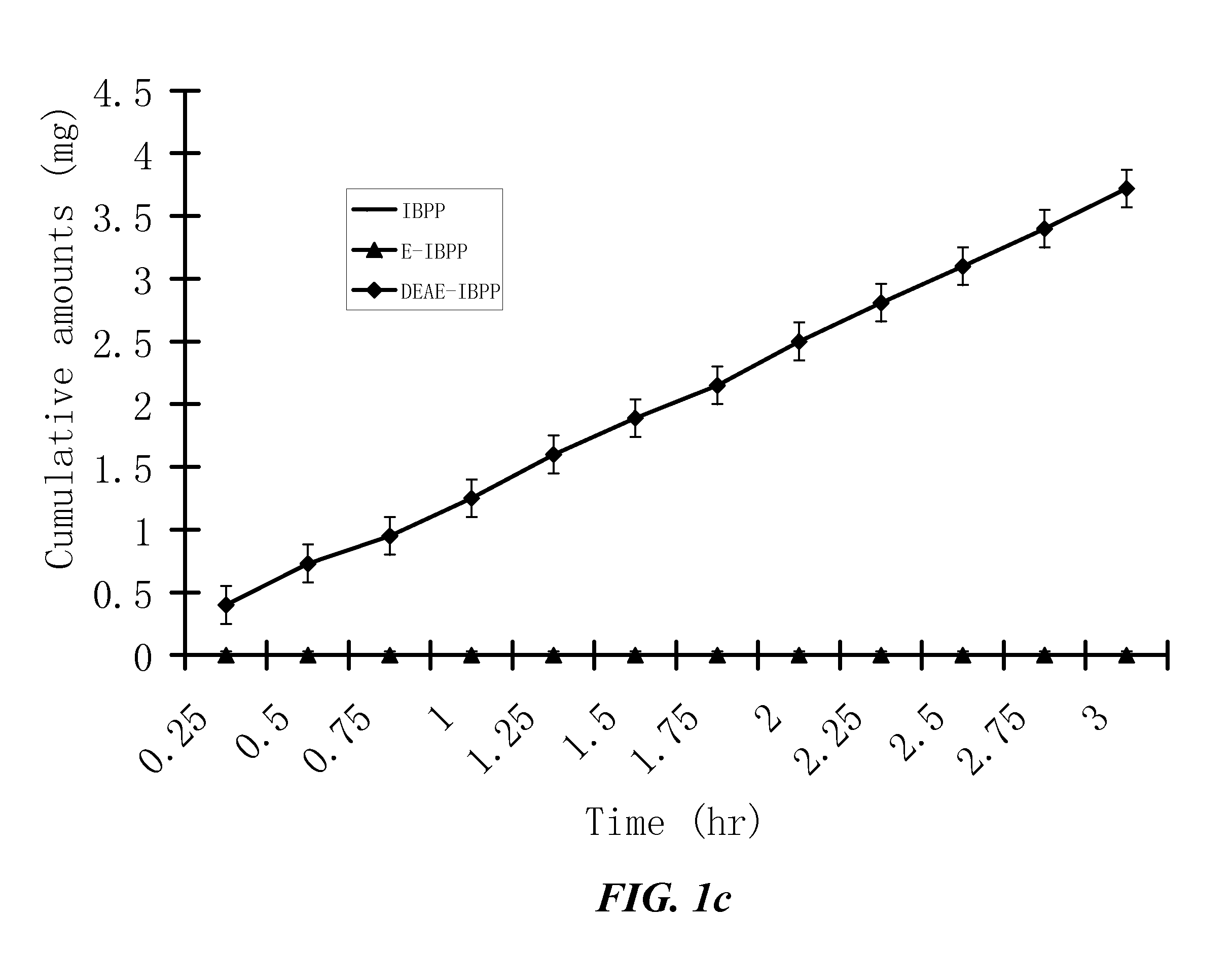
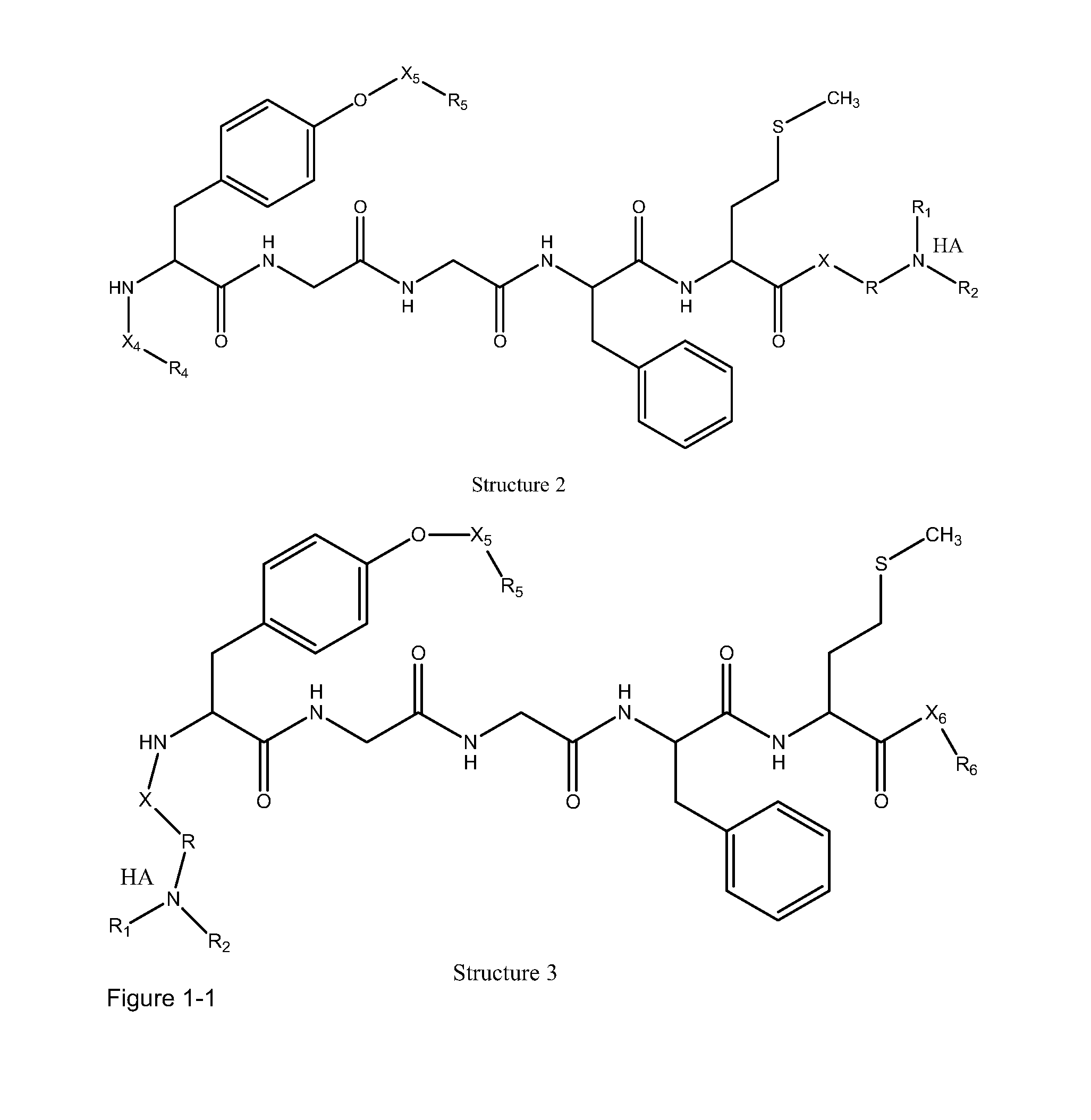
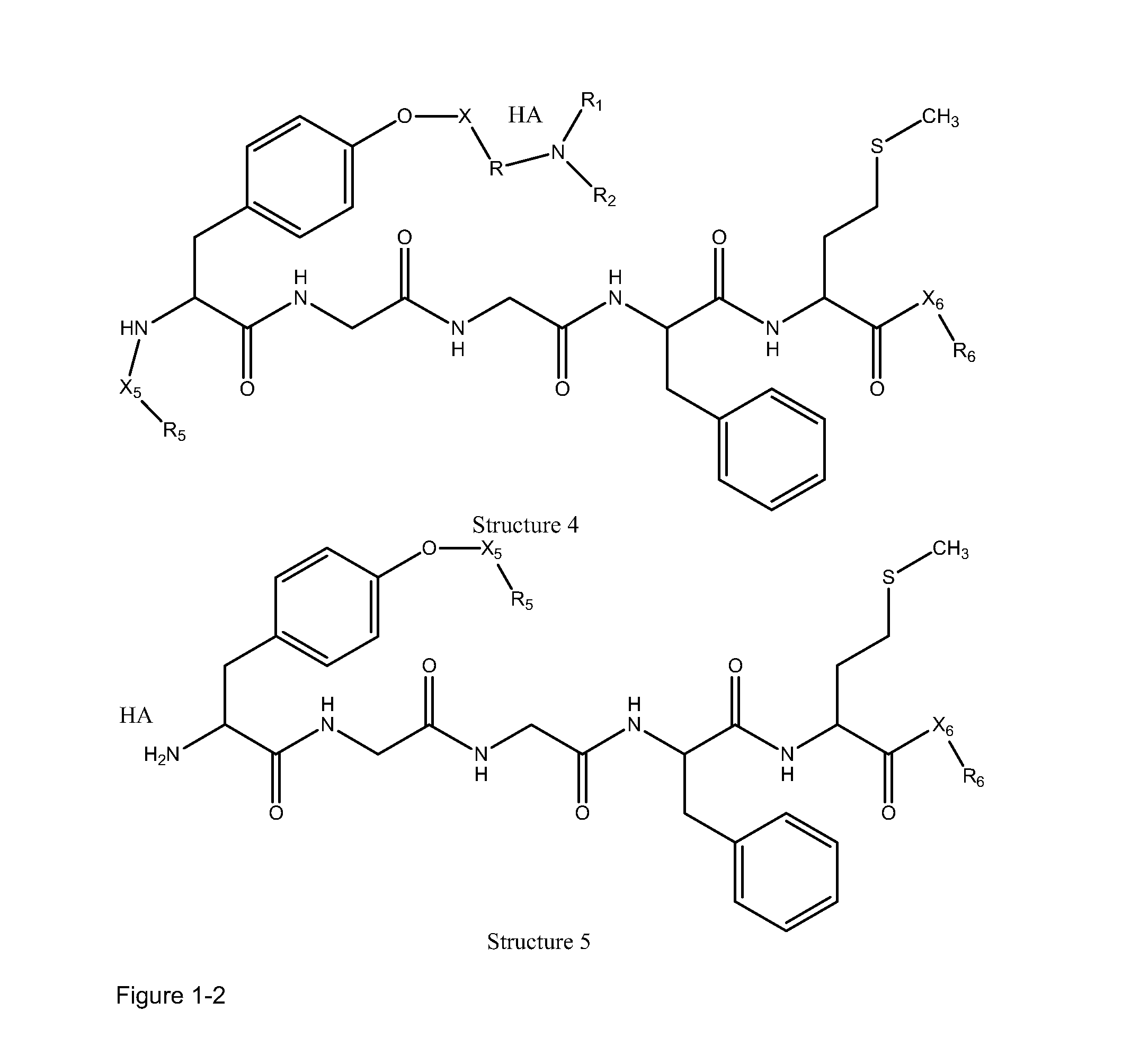
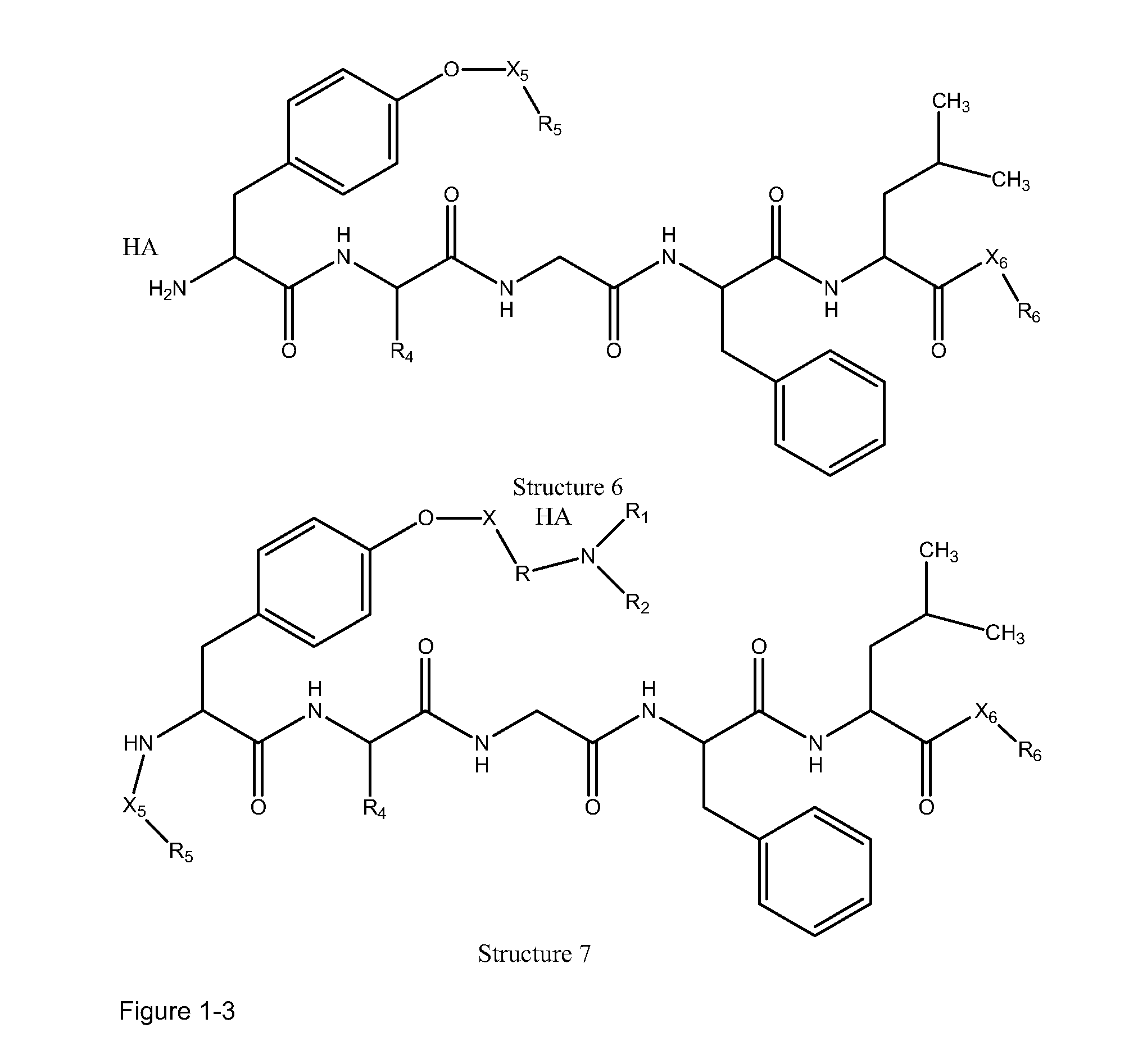
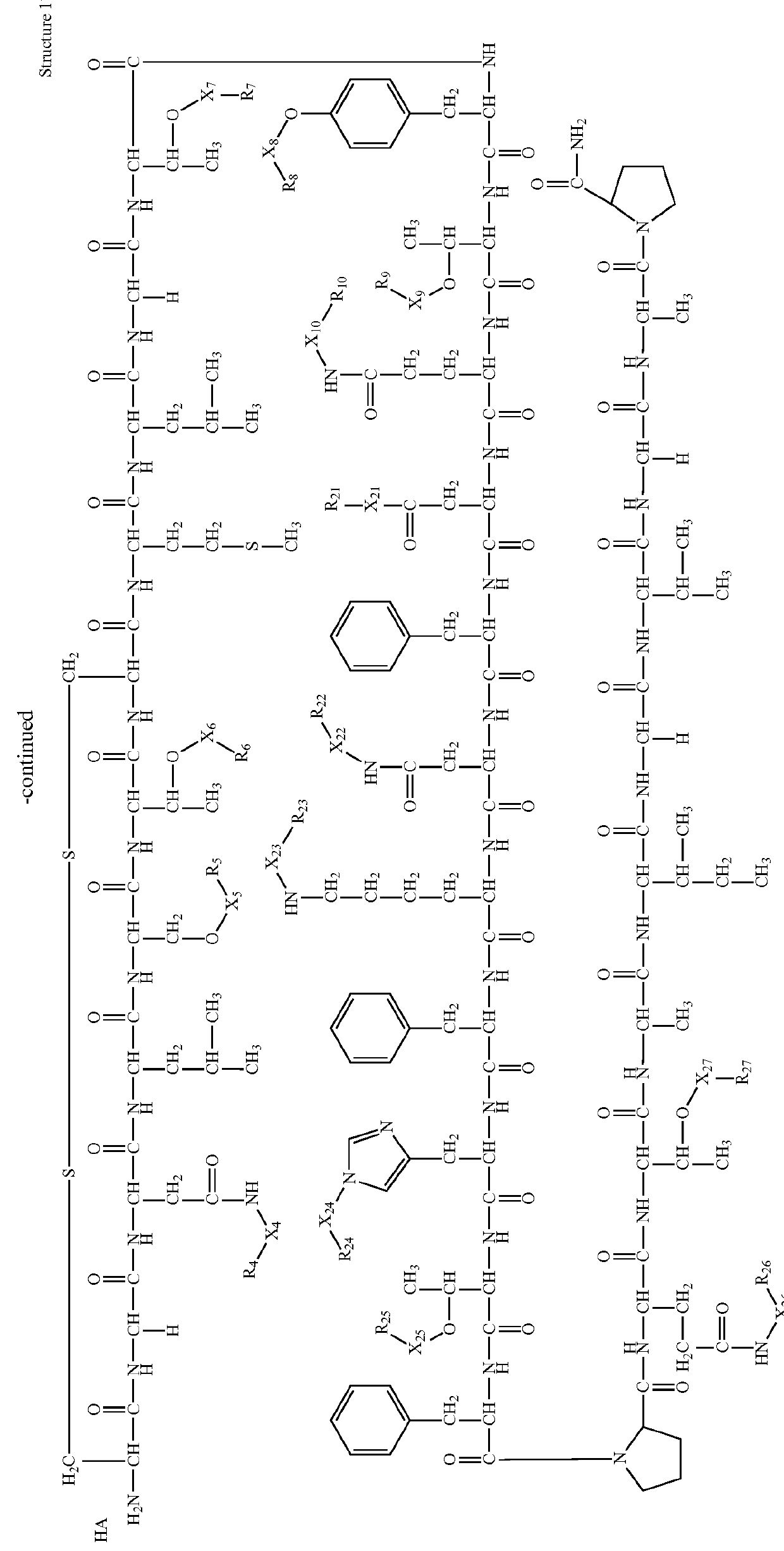
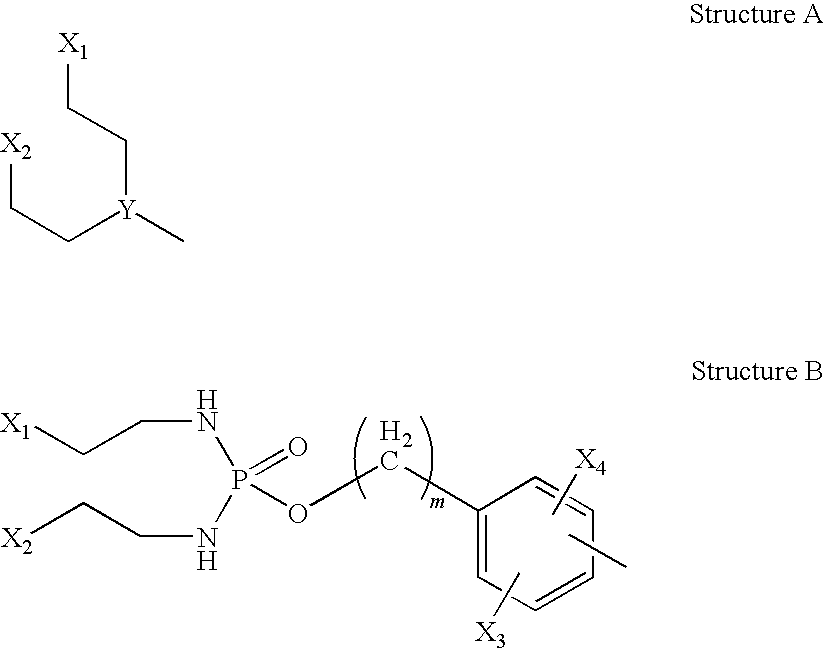
The invention provides compositions of novel high penetration compositions (HPC) or high penetration prodrugs (HPP) of 1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amines and 1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine-related compounds, which are capable of crossing biological barriers with high penetration efficiency. The HPPs are capable of being converted to parent active drugs or drug metabolites after crossing the biological barrier and thus can render treatments for the conditions that the parent drugs or metabolites can. Additionally, the HPPs are capable of reaching areas that parent drugs may not be able to access or to render a sufficient concentration at the target areas and therefore render novel treatments. The HPPs can be administered to a subject through various administration routes, e.g., locally delivered to an action site of a condition with a high concentration or systematically administered to a biological subject and enter the general circulation with a faster rate.
Owner:TECHFIELDS BIOCHEM CO LTD
High penetration prodrug compositions of retinoids and retinoid-related compounds
The invention provides compositions of novel high penetration compositions (HPC) or high penetration prodrugs (HPP) of retinoids and retinoid-related compounds, which are capable of crossing biological barriers with high penetration efficiency. The HPPs are capable of being converted to parent active drugs or drug metabolites after crossing the biological barrier and thus can render treatments for the conditions that the parent drugs or metabolites can. Additionally, the HPPs are capable of reaching areas that parent drugs may not be able to access or to render a sufficient concentration at the target areas and therefore render novel treatments. The HPPs can be administered to a subject through various administration routes, e.g., locally delivered to an action site of a condition with a high concentration or systematically administered to a biological subject and enter the general circulation with a faster rate.
Owner:TECHFIELDS BIOCHEM CO LTD
High penetration prodrug compositions of antimicrobials and antimicrobial-related compounds
InactiveUS20100040548A1Not easy to penetrateReduce potential sufferingAntibacterial agentsBiocideHigh concentrationMetabolite
The invention provides compositions of novel high penetration compositions (HPC) or high penetration prodrugs (HPP) of antimicrobials and antimicrobial-related compounds, which are capable of crossing biological barriers with high penetration efficiency. The HPPs are capable of being converted to parent active drugs or drug metabolites after crossing the biological barrier and thus can render treatments for the conditions that the parent drugs or metabolites can. Additionally, the HPPs are capable of reaching areas that parent drugs may not be able to access or to render a sufficient concentration at the target areas and therefore render novel treatments. The HPPs can be administered to a subject through various administration routes, e.g., locally delivered to an action site of a condition with a high concentration or systematically administered to a biological subject and enter the general circulation with a faster rate.
Owner:TECHFIELDS BIOCHEM CO LTD
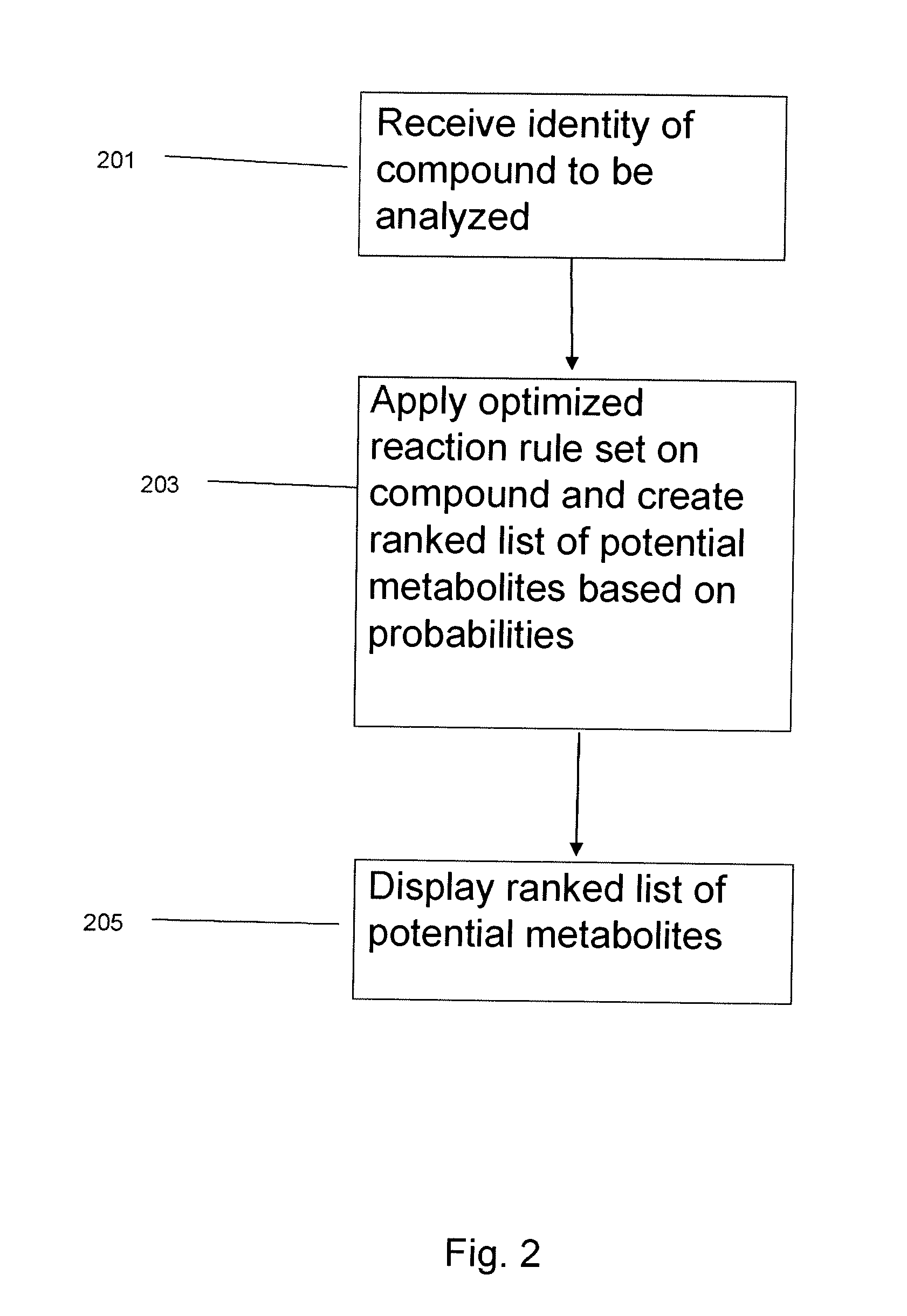
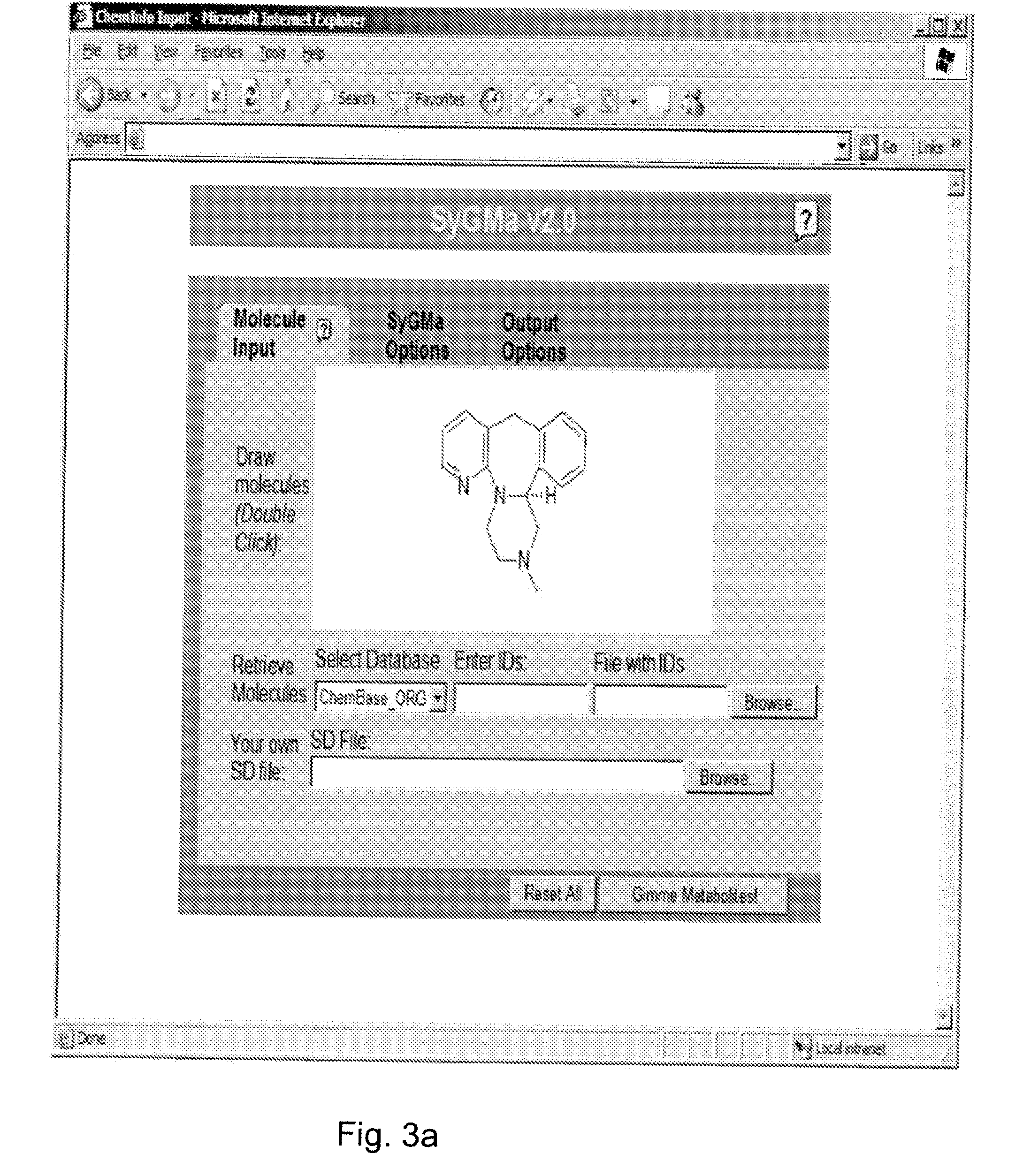
System and method to identify the metabolites of a drug
InactiveUS20080120041A1Improve efficiencyImprove accuracyMolecular entity identificationChemical processes analysis/designReaction ruleMetabolite
The invention provides for a method for predicting potential metabolites for a compound, comprising the steps of receiving a target compound from a user applying a set of optimized reaction rules to said target compound to generate a list of potential metabolites and calculating a probability score for each product compound on said list of potential metabolites. The reaction set is optimized by starting from a starting set of reaction rules and replacing at least one reaction rule for a reaction center in said starting set of reaction rules by one, or preferably two or more new rules, which are defined to apply to a reaction of said reaction center, but now specifying or differentiating based on the structural environments of said reaction center, if at least one of said new rules has a higher probability score than the replaced reaction rule when the starting set of reaction rules and the optimized set of reaction rules are both tested with a database of known metabolites of compounds.
Owner:NV ORGANON
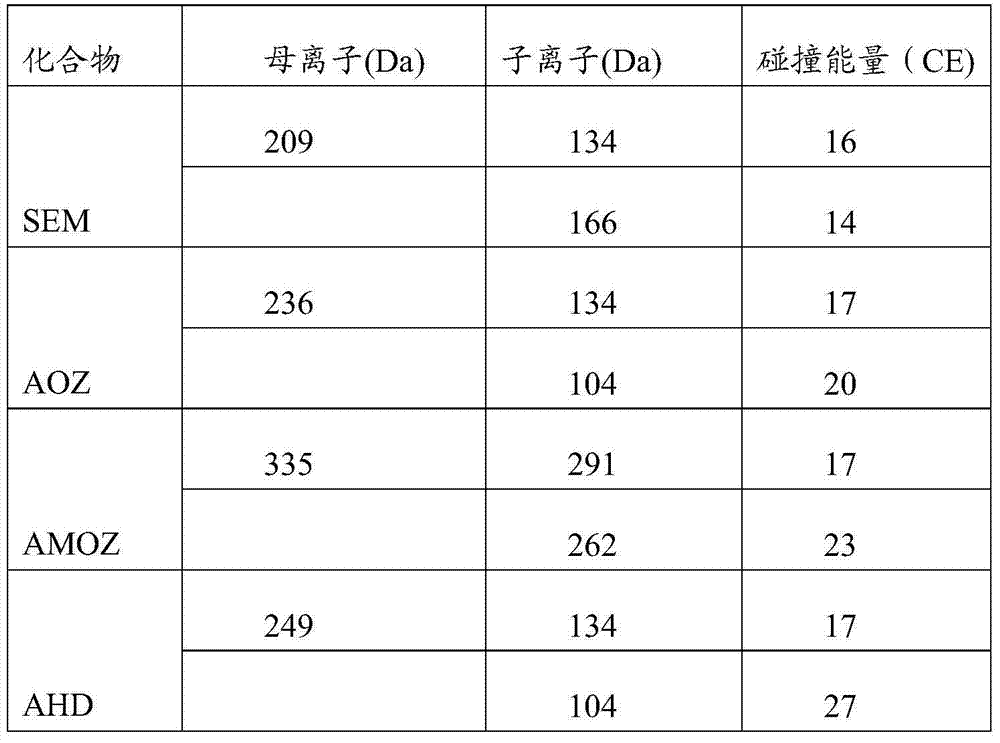
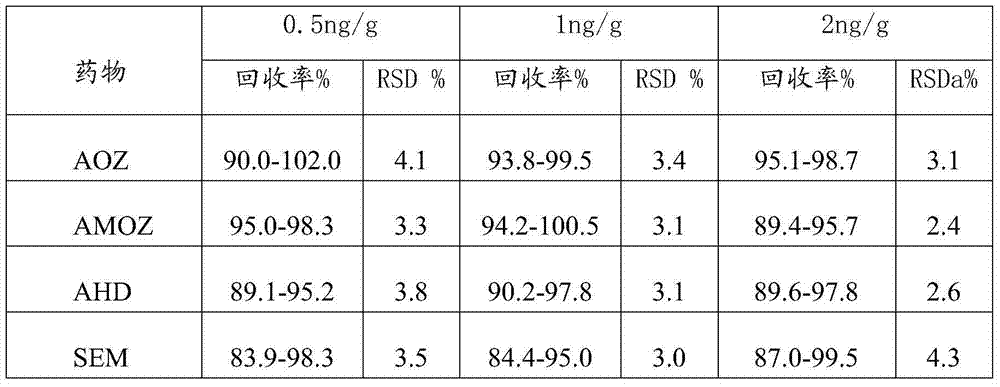
Detection method of nitrofuran drug metabolites in meat product
InactiveCN104297384AShortened hydrolytic derivatization processSimple reagentComponent separationElutionDrug metabolite
The application provides a detection method of nitrofuran drug metabolites in a meat product. The detection method comprises the following steps: (1) pretreatment comprising putting a sample into a pretreatment liquid, oscillating, then carrying out centrifugal separation, removing the clear liquid, and thus obtaining a solid residue; and (2) solid residue treatment comprising adding a derivatization agent into a sample solid residue extract liquid, carrying out derivatization treatment under conditions of heating, acidity and inert gas protection, after the derivatization treatment is completed, cooling, adjusting the pH to neutral, then centrifuging, taking the supernatant, then allowing the supernatant to pass through a solid-phase extraction column, leaching with a leaching liquid, carrying out elution treatment with an eluant to obtain an eluate, concentrating and drying the eluate, re-dissolving with a re-dissolving liquid, and thus obtaining a sample solution. The detection method can be applied to various animal-derived samples, and can shorten the hydrolyzed derivatization process to 30-60 minutes and shorten the whole detection process to 60-120 minutes.
Owner:北京华都肉鸡公司
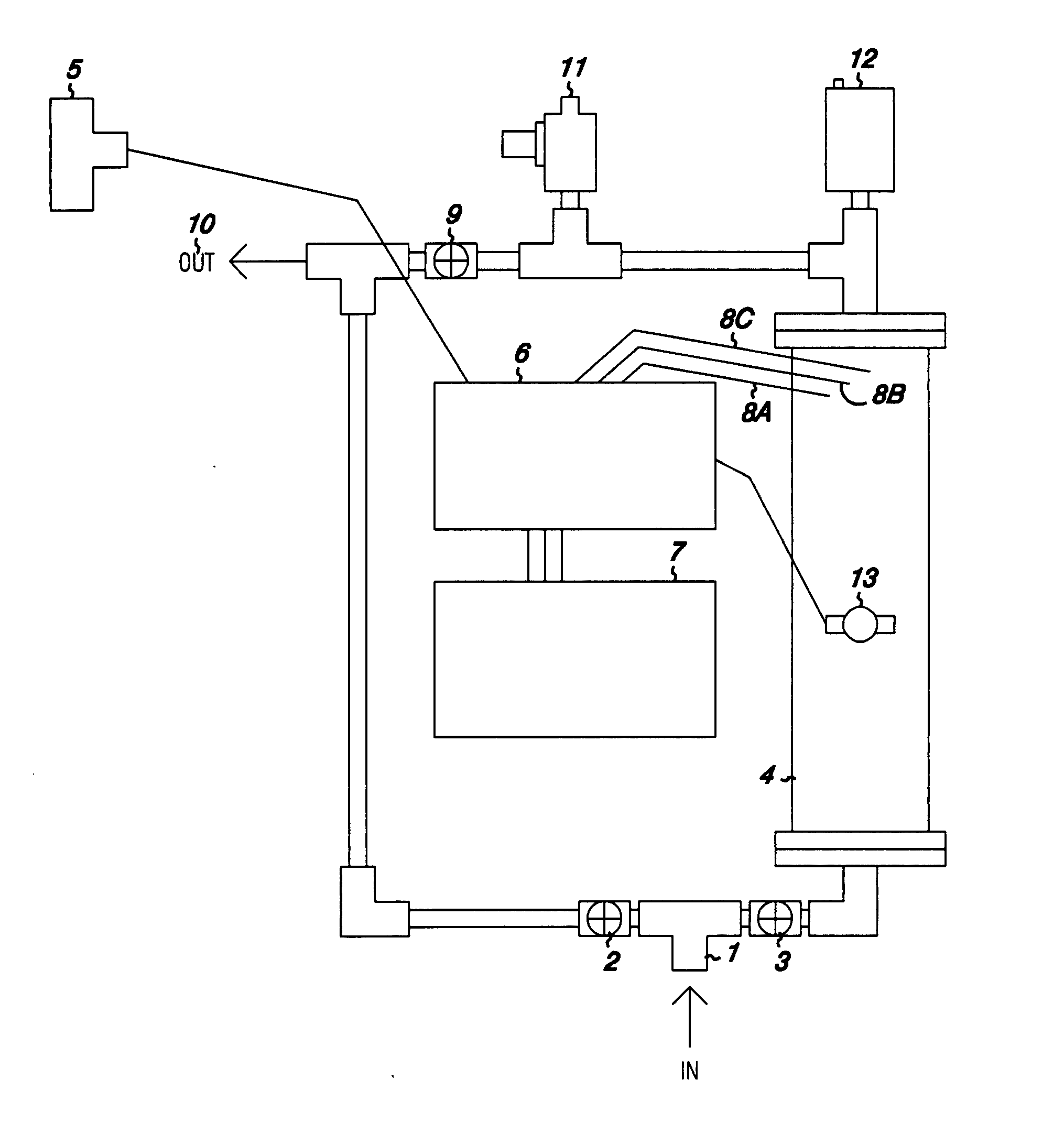
Water treatment system
InactiveUS20070284245A1Water contaminantsTreatment involving filtrationElectrolysisPesticide residue
A system for the treatment of water to remove metals and undesirable substances from well and groundwater so as to render the water potable is disclosed. The system employs microbubbles of oxygen, which remain suspended in water at a concentration above 100% of the calculated saturated concentration at a particular temperature and pressure. These microbubbles oxidize undesirable substances in the water, which substances include iron manganese, arsenic, antimony, chrome, aluminum, reduced sulfur compounds, pesticide residues, drug metabolites and / or bacteria. Microbubbles are produced by electrolysis or by sparging through a microorifice. A control system for the electrolytic system is disclosed.
Owner:OXYGENATOR WATER TECH
High penetration prodrug compositions of peptides and peptide-related compounds
ActiveUS20090311184A1Reduce potential sufferingAvoid the needSenses disorderNervous disorderMetaboliteChemical compound
The invention provides compositions of novel high penetration compositions (HPC) or high penetration prodrugs (HPP) of peptides and peptide-related compounds, which are capable of crossing biological barriers with high penetration efficiency. The HPPs are capable of being converted to parent active drugs or drug metabolites after crossing the biological barrier and thus can render treatments for the conditions that the parent drugs or metabolites can. Additionally, the HPPs are capable of reaching areas that parent drugs may not be able to access or to render a sufficient concentration at the target areas and therefore render novel treatments. The HPPs can be administered to a subject through various administration routes, e.g., locally delivered to an action site of a condition with a high concentration or systematically administered to a biological subject and enter the general circulation with a faster rate.
Owner:TECHFIELDS BIOCHEM CO LTD
Nitrofurans medicament metabolite residue ELISA kit and use method
ActiveCN101241132AAvoid problems requiring detection multiple timesReduce the chance of missed detectionMaterial analysisAntigenWorking fluid
The present invention discloses enzyme-linked immune kits for detecting nitrofurans metabolite residue including antigenic enzyme label plate coated with nitrofuran meatbolites, enzyme labeled antibody working fluid, standard solution, substrate solution, substrate buffer solution, reaction termination liquid, condense washing liquid and sample diluted concentrated liquid. The present invention also discloses using method for detecting by said kits including steps of pretreatment of sample, detecting with kits, result process and analysis and so on. The kits provided by present invention employ directly competing enzyme-linked immunoadsorption analysis to detect not only multiple nitrofurans metabolite residues at the same time, but also singleness nitrofurans metabolite residue, avoid many times detection of the same sample and reduce miss ratio, has merits of high sensitivity, good stability, less steps and low cost, and suit for screening of a large mount of samples, and has importance practical significance.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for identifying drug metabolites with dansylated glutathione
ActiveUS7169576B2Microbiological testing/measurementTripeptide ingredientsDrug metaboliteReactive metabolite
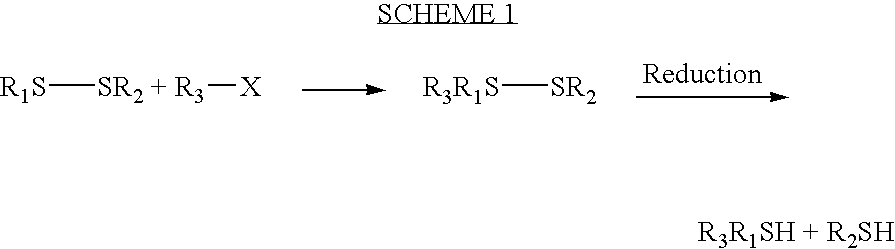
The present application relates to a sensitive and quantitative method using dansylated glutathione as a trapping agent for the detection of reactive metabolites in the field of drug discovery. The fluorescent tag attached to the dansylated glutathione does not impede the ability of glutathione to react with reactive metabolites.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Preparation method of 3-methyl-2-ethanol based quinoxaline
InactiveCN101928252AMeeting the Needs of Metabolism ResearchThe synthesis steps are simpleOrganic chemistryQuinoxalineSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method of 3-methyl-2-ethanol based quinoxaline, comprising the following steps of: (1) in a solvent, carrying out reduction reaction on maquindox in the presence of a reducing agent to obtain 3-methyl-2-acetylquinoline; and (2) in the solvent, carrying out the reduction reaction on the 3-methyl-2-acetylquinoline in the presence of the reducing agent to obtain the 3-methyl-2-ethanol based quinoxaline. The 3-methyl-2-ethanol based quinoxaline of the invention is quinoxaline drug metabolites and can be used as a standard product for the residual and metabolism researches on quinoxaline drugs.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
High penetration compositions and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090238763A1Good curative effectEliminate side effectsPowder deliveryBiocideDrug metaboliteHigh concentration
The present invention relates to compositions and uses of novel high penetration compositions or high penetration prodrugs (HPP), in particular HPPs for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIAs), which are capable of crossing biological barriers with high penetration efficiency. The HPPs herein are capable of being converted to parent active drugs or drug metabolites after crossing the biological barrier and thus can render treatments for the conditions that the parent drugs or metabolites can. Additionally, due to the ability of penetrating biological barriers, the HPPs herein are capable of reaching areas that parent drugs may not be able to access or to render a sufficient concentration at the target areas and therefore render novel treatments. The HPPs herein can be administered to a subject through various administration routes. For example, the HPPs can be locally delivered to an action site of a condition with a high concentration due to their ability of penetrating biological barriers and thus obviate the need for a systematic administration. For another example, the HPPs herein can be systematically administer to a biological subject and enter the general circulation with a faster rate.
Owner:TECHFIELDS BIOCHEM CO LTD
High penetration prodrug compositions of peptides and peptide-related compounds
ActiveUS20120156279A1Administration of has been hamperedReduce adverse effectsSenses disorderNervous disorderHigh concentrationMetabolite
The invention provides compositions of novel high penetration compositions (HPC) or high penetration prodrugs (HPP) of peptides and peptide-related compounds, which are capable of crossing biological barriers with higher penetration efficiency comparing to their parent drugs. The HPPs are capable of being converted to parent drugs or drug metabolites after crossing the biological barrier and thus can render treatments for the conditions that the parent drugs or metabolites can. Additionally, the HPPs / HPCs are capable of reaching areas that parent drugs may not be able to access or to render a sufficient concentration at the target areas and therefore render novel treatments. The HPPs / HPCs can be administered to a subject through various administration routes, e.g., locally delivered to an action site of a condition with a high concentration or systematically administered to a biological subject and enter the general circulation with a faster rate.
Owner:TECHFIELDS BIOCHEM CO LTD
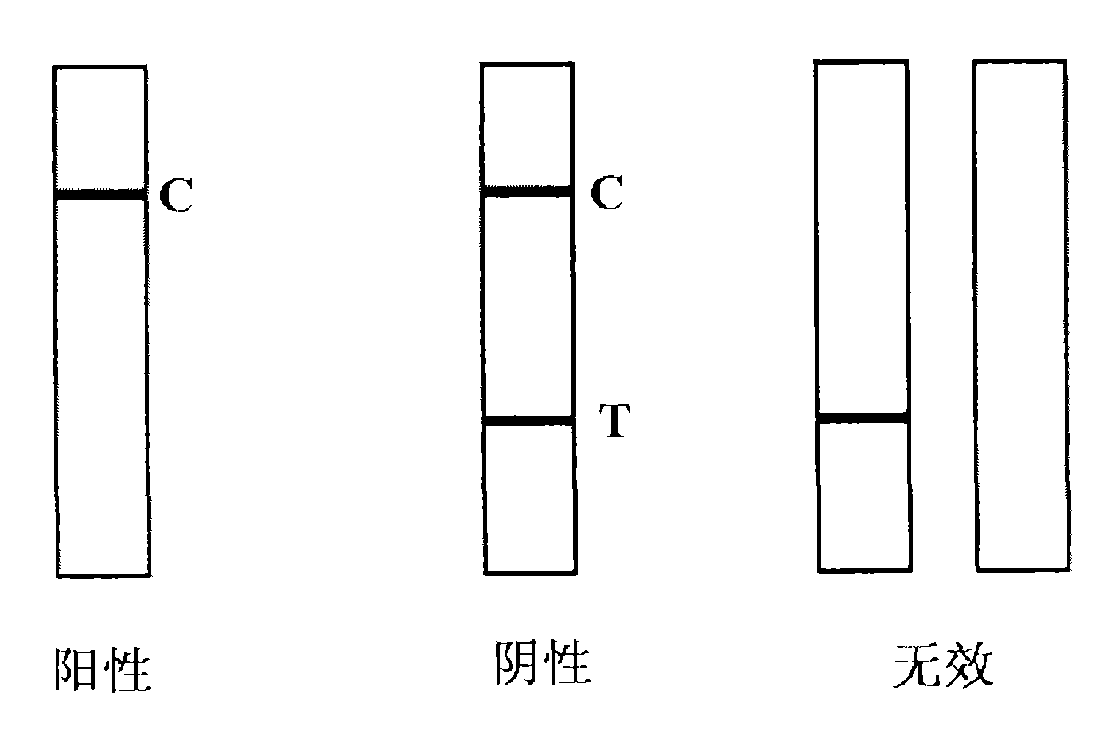
Nitrofurans drug metabolite assay kit and production method thereof
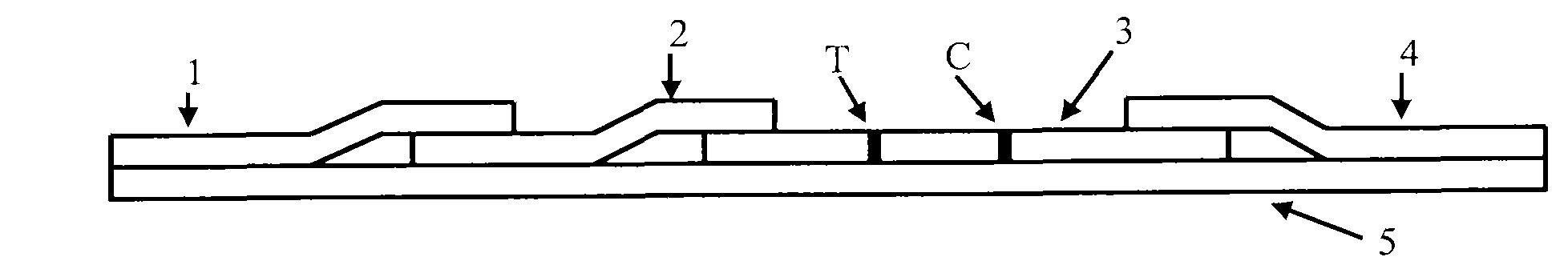
The invention provides a nitrofurans drug metabolite assay kit, which consists of a furazolidone metabolite test paper strip, a furaltadone metabolite test paper strip, a nitrofurazone metabolite test paper strip and a furantoin metabolite test paper strip. Each test paper strip consists of a sample pad, a colloidal gold pad, a nitrocellulose membrane, a sample adsorbing pad and a PVC (polyvinyl chloride) supporting plate, wherein the colloidal gold layer is a nitrofurans drug metabolite monoclonal antibody polyester film marked with colloidal gold, the nitrocellulose membrane is sequentially coated with nitrofurans drug metabolite coupled carrier protein as a test line (a T-line) and goat anti-mouse IgG antibody as a quality control line (a C-line). The nitrofurans drug metabolite assay kit is produced according to the nano colloidal gold technology, antigen-antibody specificity reactions and principles of immunity competitive inhibition reaction, and is used for testing whether samples contain nitrofurans drug metabolites or not.
Owner:宝瑞源生物技术(北京)有限公司
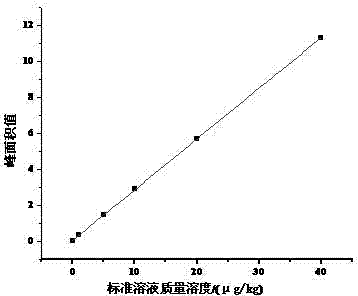
Derivative of nitrofuran medicament metabolites as well as high performance liquid chromatography fluorescence detection
InactiveCN103808821ARealize quantitative analysisQuantitative analysis meetsComponent separationLiquid Chromatography-FluorescenceMetabolite
The invention discloses a derivative of nitrofuran medicament metabolites as well as high performance liquid chromatography fluorescence detection. The method mainly comprises the following step that the derivative of the nitrofuran medicament metabolites is synthesized by matching sodium methylate, methyl alcohol and ethanol hydrazine according to certain dosage, and thus the liquid chromatography fluorescence detection is realized.
Owner:FUYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
High penetration prodrug compositions of peptides and peptide-related compounds
ActiveUS9248109B2Administration of has been hamperedReduce adverse effectsSenses disorderNervous disorderMetaboliteChemical compound
The invention provides compositions of novel high penetration compositions (HPC) or high penetration prodrugs (HPP) of peptides and peptide-related compounds, which are capable of crossing biological barriers with higher penetration efficiency comparing to their parent drugs. The HPPs are capable of being converted to parent drugs or drug metabolites after crossing the biological barrier and thus can render treatments for the conditions that the parent drugs or metabolites can. Additionally, the HPPs / HPCs are capable of reaching areas that parent drugs may not be able to access or to render a sufficient concentration at the target areas and therefore render novel treatments. The HPPs / HPCs can be administered to a subject through various administration routes, e.g., locally delivered to an action site of a condition with a high concentration or systematically administered to a biological subject and enter the general circulation with a faster rate.
Owner:TECHFIELDS BIOCHEM CO LTD
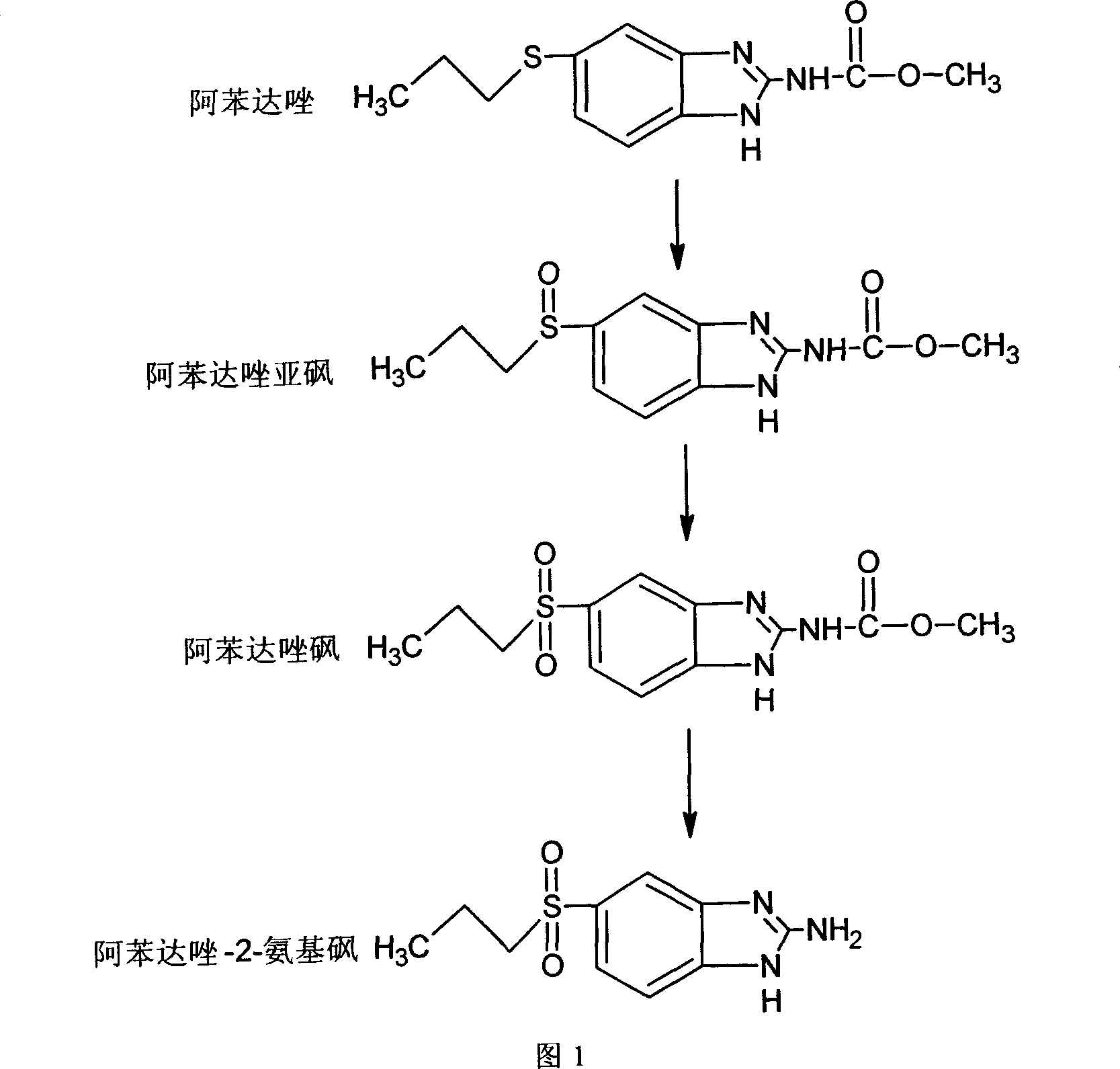
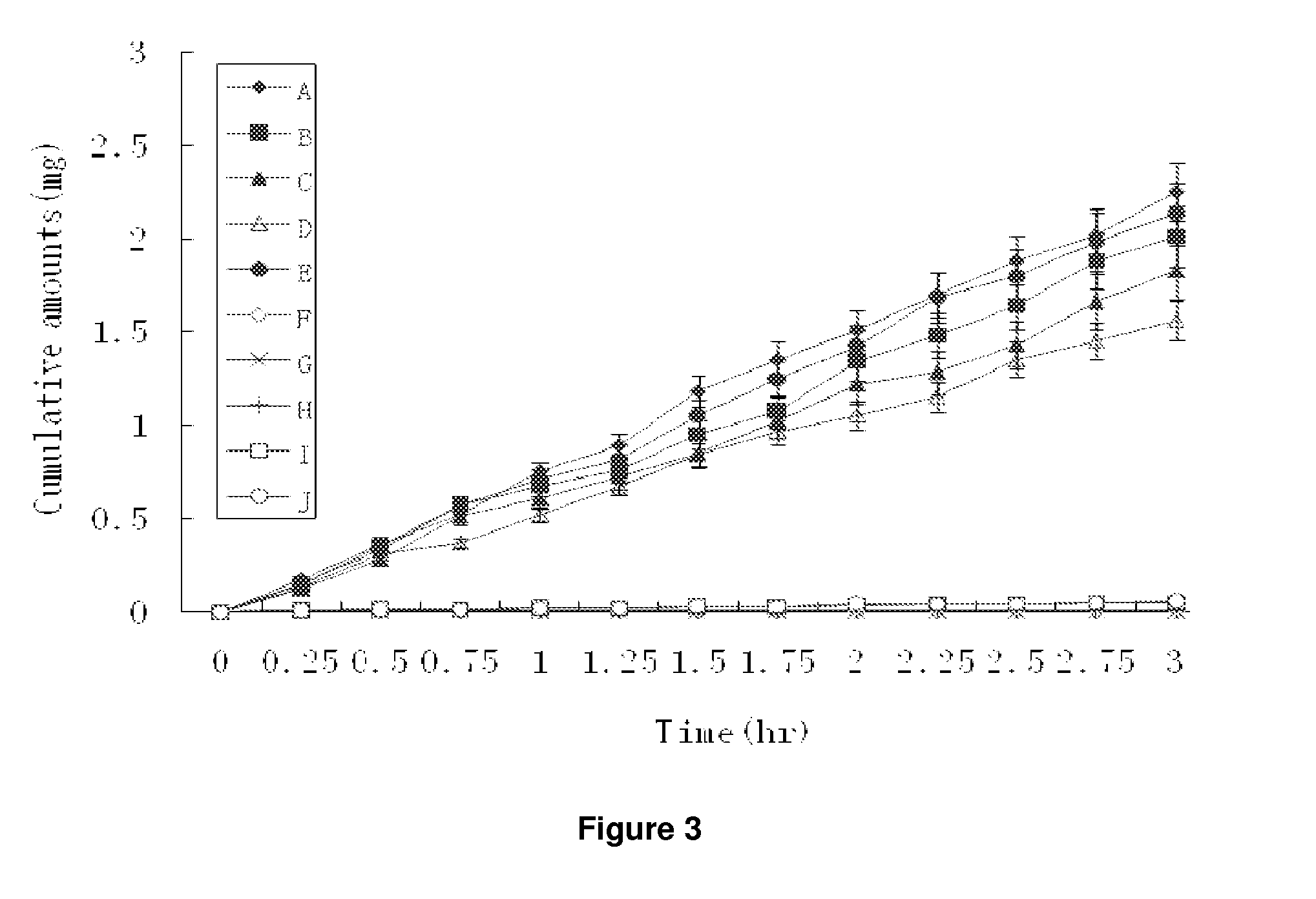
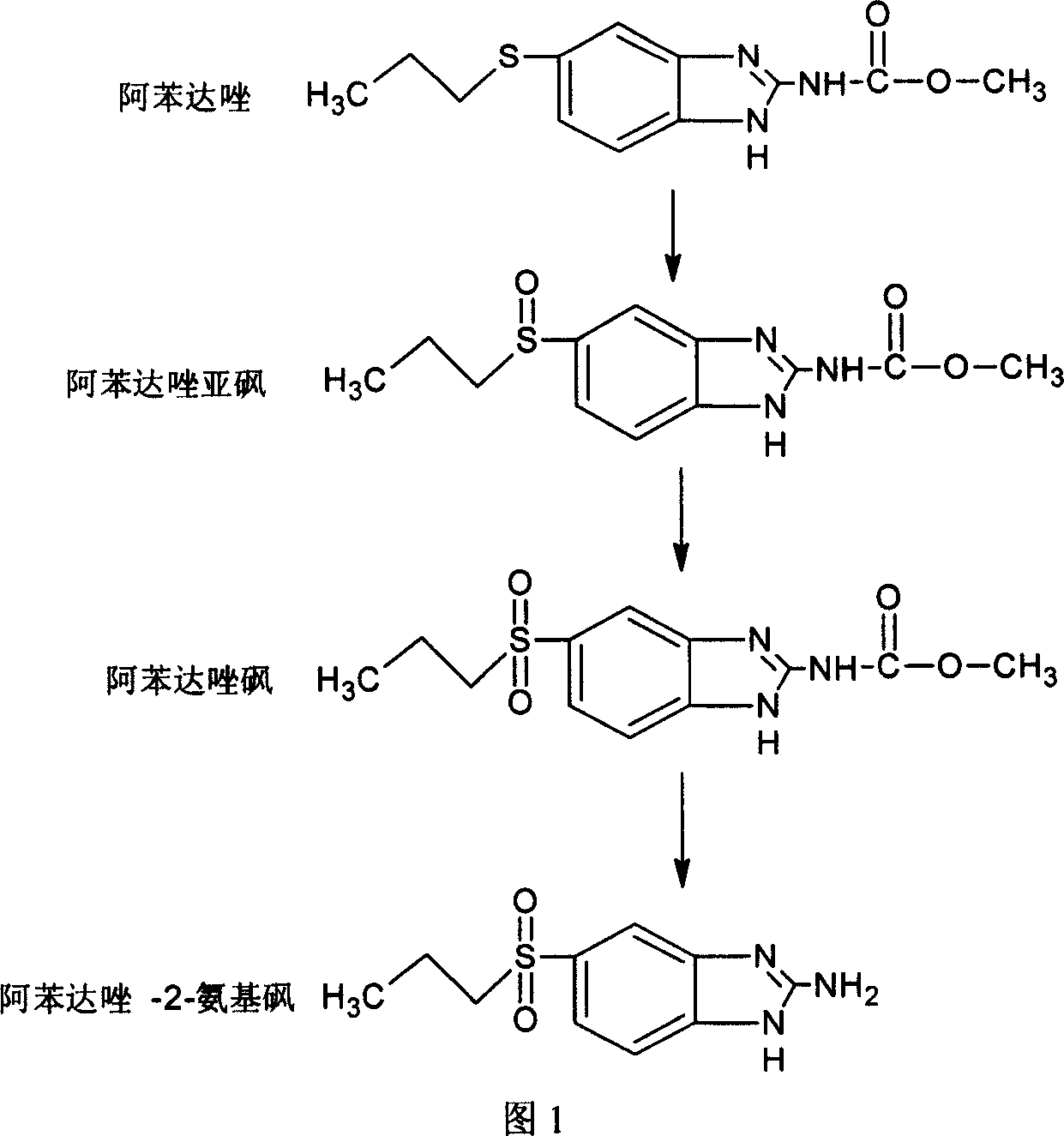
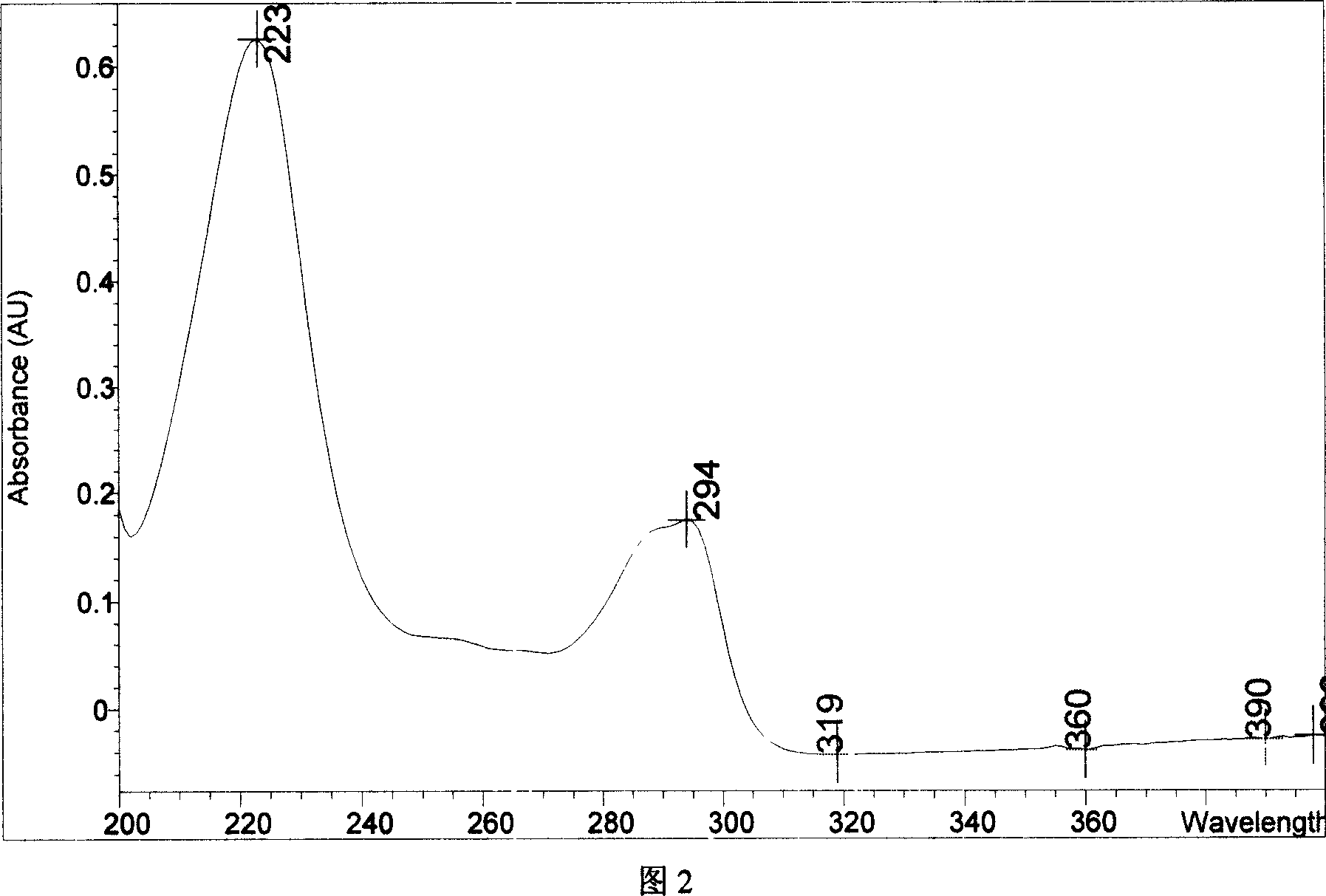
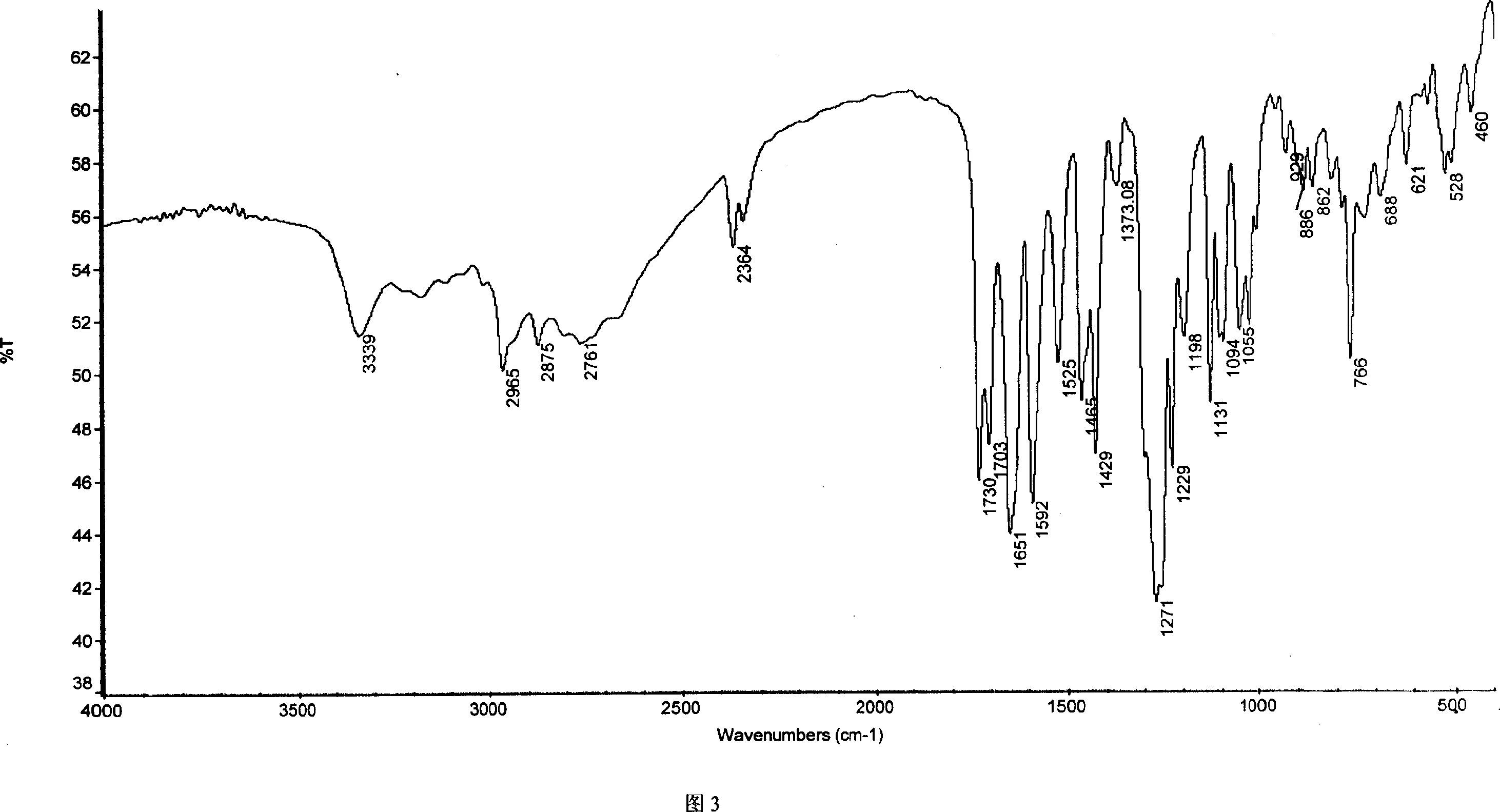
Chemical synthesis of albendazole-2-amino-sulphone
A process for chemically synthesizing albendazole-2-aminosulfone includes such steps as oxidizing reaction between albendazole, glacial acetic acid and H2O2 to obtain albendazole sulfone, reflux reaction in acid solution, regulating pH value to obtain coarse albendazole-2-aminosulfone, and recrystallizing.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
High penetration prodrug compositions of peptides and peptide-related compounds
The invention provides compositions of novel high penetration compositions (HPC) or high penetration prodrugs (HPP) of peptides and peptide-related compounds, which are capable of crossing biological barriers with high penetration efficiency. The HPPs are capable of being converted to parent active drugs or drug metabolites after crossing the biological barrier and thus can render treatments for the conditions that the parent drugs or metabolites can. Additionally, the HPPs are capable of reaching areas that parent drugs may not be able to access or to render a sufficient concentration at the target areas and therefore render novel treatments. The HPPs can be administered to a subject through various administration routes, e.g., locally delivered to an action site of a condition with a high concentration or systematically administered to a biological subject and enter the general circulation with a faster rate.
Owner:TECHFIELDS BIOCHEM CO LTD
High penetration prodrug compositions of mustards and mustard-related compounds
InactiveUS20100069336A1Reduce potential sufferingAvoid the needBiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsHigh concentrationMetabolite
The invention provides compositions of novel high penetration compositions (HPC) or high penetration prodrugs (HPP) of mustards and mustard-related compounds, which are capable of crossing biological barriers with high penetration efficiency. The HPPs are capable of being converted to parent active drugs or drug metabolites after crossing the biological barrier and thus can render treatments for the conditions that the parent drugs or metabolites can. Additionally, the HPPs are capable of reaching areas that parent drugs may not be able to access or to render a sufficient concentration at the target areas and therefore render novel treatments. The HPPs can be administered to a subject through various administration routes, e.g., locally delivered to an action site of a condition with a high concentration or systematically administered to a biological subject and enter the general circulation with a faster rate.
Owner:TECHFIELDS BIOCHEM CO LTD
High penetration prodrug compositions of retinoids and retinoid-related compounds
The invention provides compositions of novel high penetration compositions (HPC) or high penetration prodrugs (HPP) of retinoids and retinoid-related compounds, which are capable of crossing biological barriers with high penetration efficiency. The HPPs are capable of being converted to parent active drugs or drug metabolites after crossing the biological barrier and thus can render treatments for the conditions that the parent drugs or metabolites can. Additionally, the HPPs are capable of reaching areas that parent drugs may not be able to access or to render a sufficient concentration at the target areas and therefore render novel treatments. The HPPs can be administered to a subject through various administration routes, e.g., locally delivered to an action site of a condition with a high concentration or systematically administered to a biological subject and enter the general circulation with a faster rate.
Owner:TECHFIELDS BIOCHEM CO LTD
Furazolidone metabolite derivative monoclonal antibody and applications thereof
ActiveCN102936582ALow cross-reactivityQuick checkMicroorganism based processesTissue cultureMetaboliteAquatic product
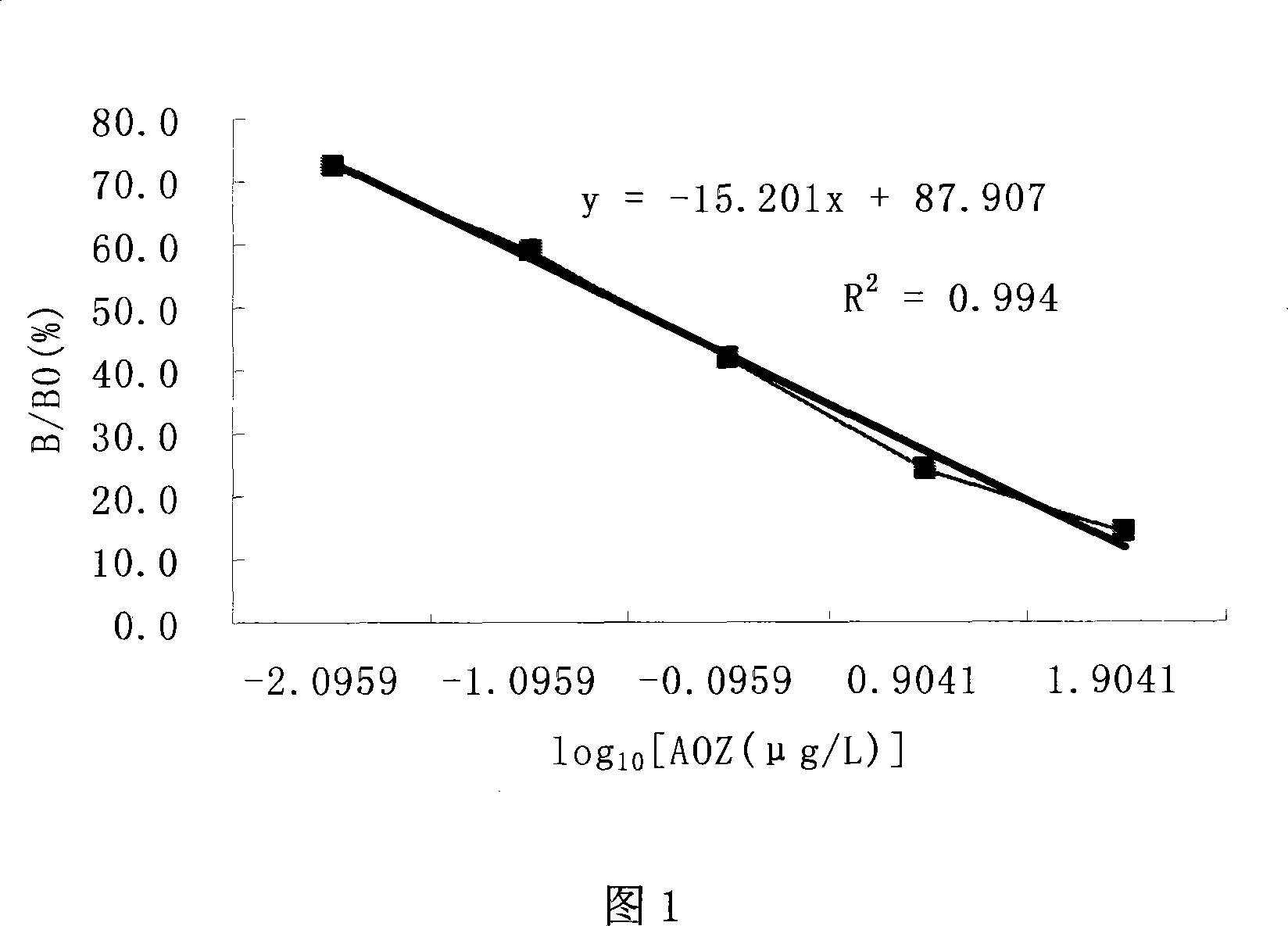
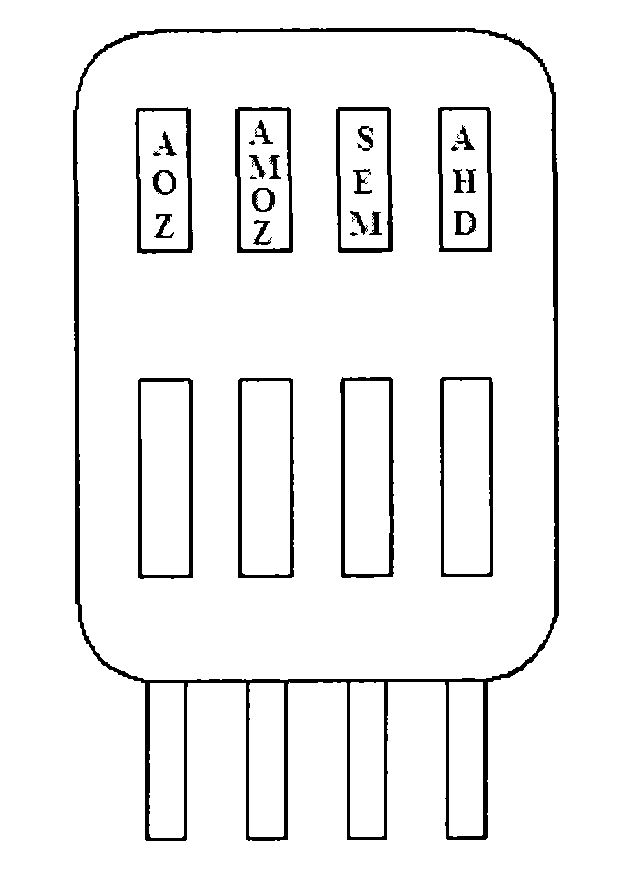
The present invention relates to a monoclonal antibody and applications thereof, especially to a furazolidone metabolite derivative monoclonal antibody and applications thereof, and belongs to the technical field of immunochemistry. The furazolidone metabolite derivative monoclonal antibody 1C3' is produced by mouse hybridoma cell line 1C3, wherein a subtype is IgG1 type. According to the present invention, the monoclonal antibody 1C3' produced by the mouse hybridoma cell line 1C3 can be abundantly produced, and can be used to prepare an enzyme linked immunoassay kit and colloidal gold test paper strips for furazolidone metabolite (AOZ) detection so as to achieve a purpose of rapid and sensitive detection of furazolidone drug metabolites in muscle, liver and aquatic products and establish a foundation for furazolidone metabolite residue detection kit and colloidal gold product development.
Owner:深圳华利达植绒材料有限公司
High penetration prodrug compositions of antimicrobials and antimicrobial-related compounds
ActiveUS20120157371A1Reduce dosageAvoidance of systematic administrationAntibacterial agentsBiocideHigh concentrationMetabolite
The invention provides compositions of novel high penetration compositions (HPC) or high penetration prodrugs (HPP) of antimicrobials and antimicrobial-related compounds, which are capable of crossing biological barriers with high penetration efficiency. The HPCs / HPPs are capable of being converted to parent active drugs or drug metabolites after crossing the biological barrier and thus can render treatments for the conditions that the parent drugs or metabolites can. Additionally, the HPPs are capable of reaching areas that parent drugs may not be able to access or to render a sufficient concentration at the target areas and therefore render novel treatments. The HPCs / HPPs can be administered to a subject through various administration routes, e.g., locally delivered to an action site of a condition with a high concentration or systematically administered to a biological subject and enter the general circulation with a faster rate.
Owner:TECHFIELDS BIOCHEM CO LTD
Chemical synthesis of albendazole-sulfoxide
InactiveCN101029030AAccurately control the dosageReduce generationOrganic chemistryAcetic acidChemical synthesis
A process for chemically synthesizing albendazole sulfoxide includes such steps as oxidizing reaction between albendazole, glacial acetic acid and H2O2 to obtain coarse albendazole sulfoxide, and recrystallizing.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
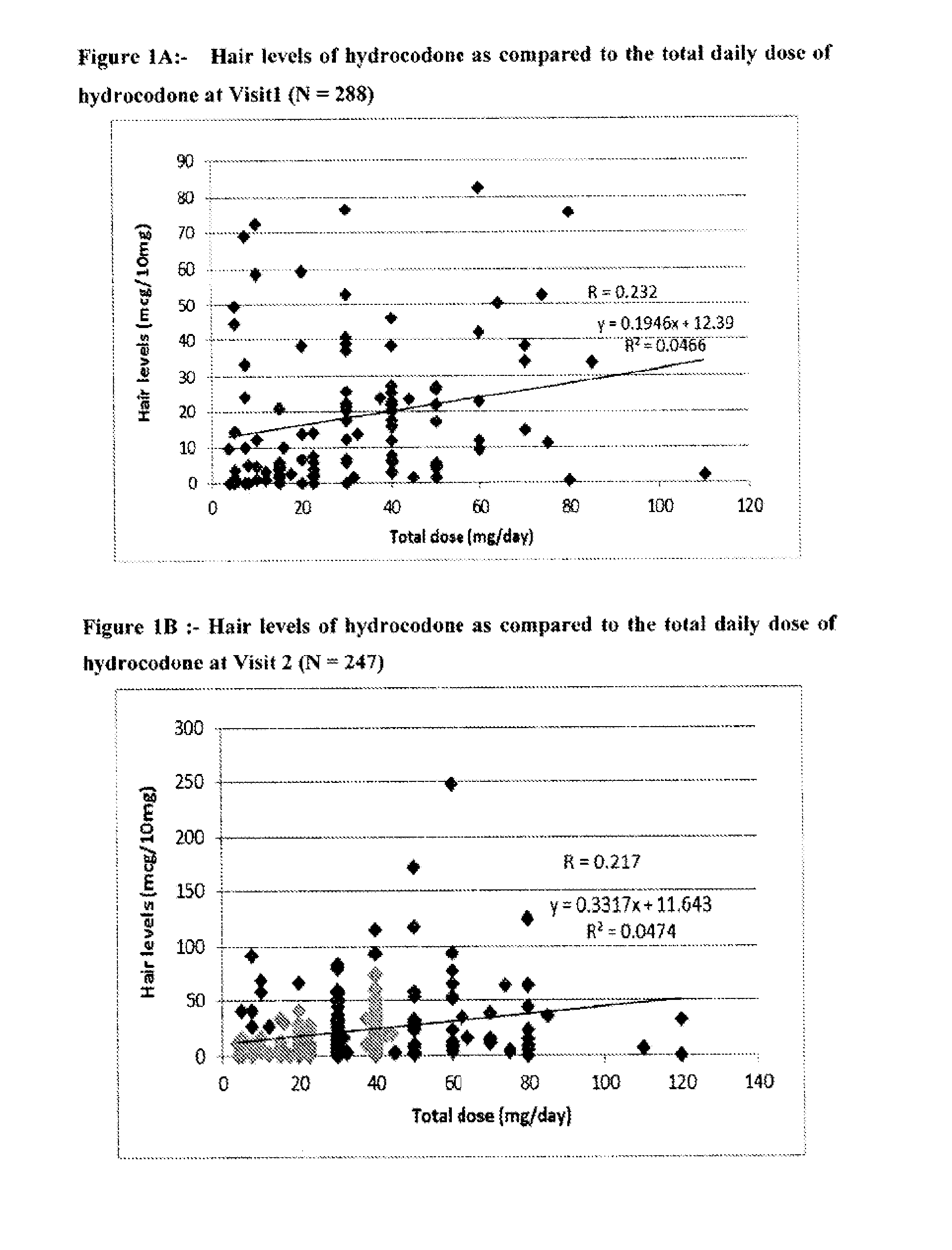
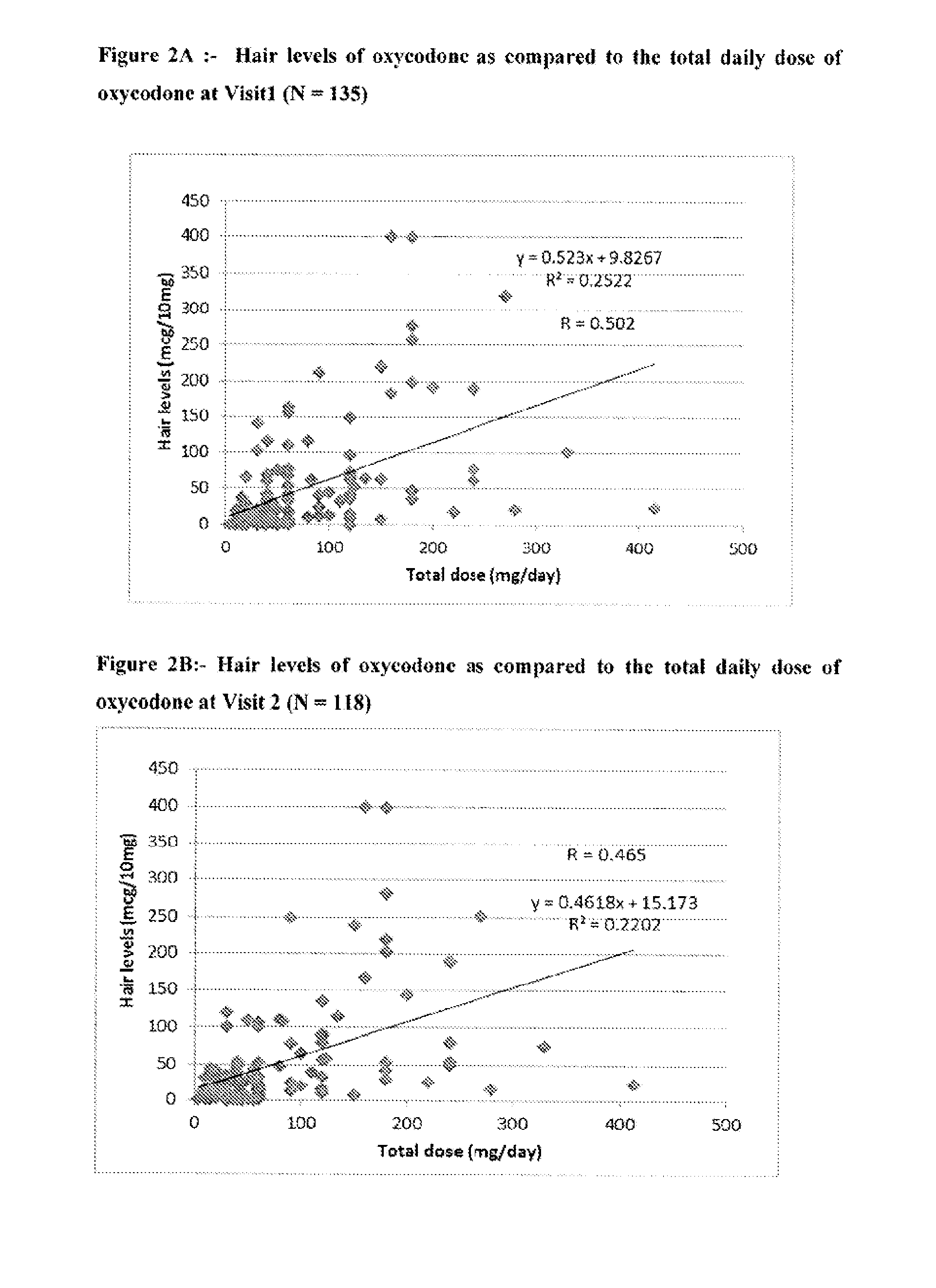
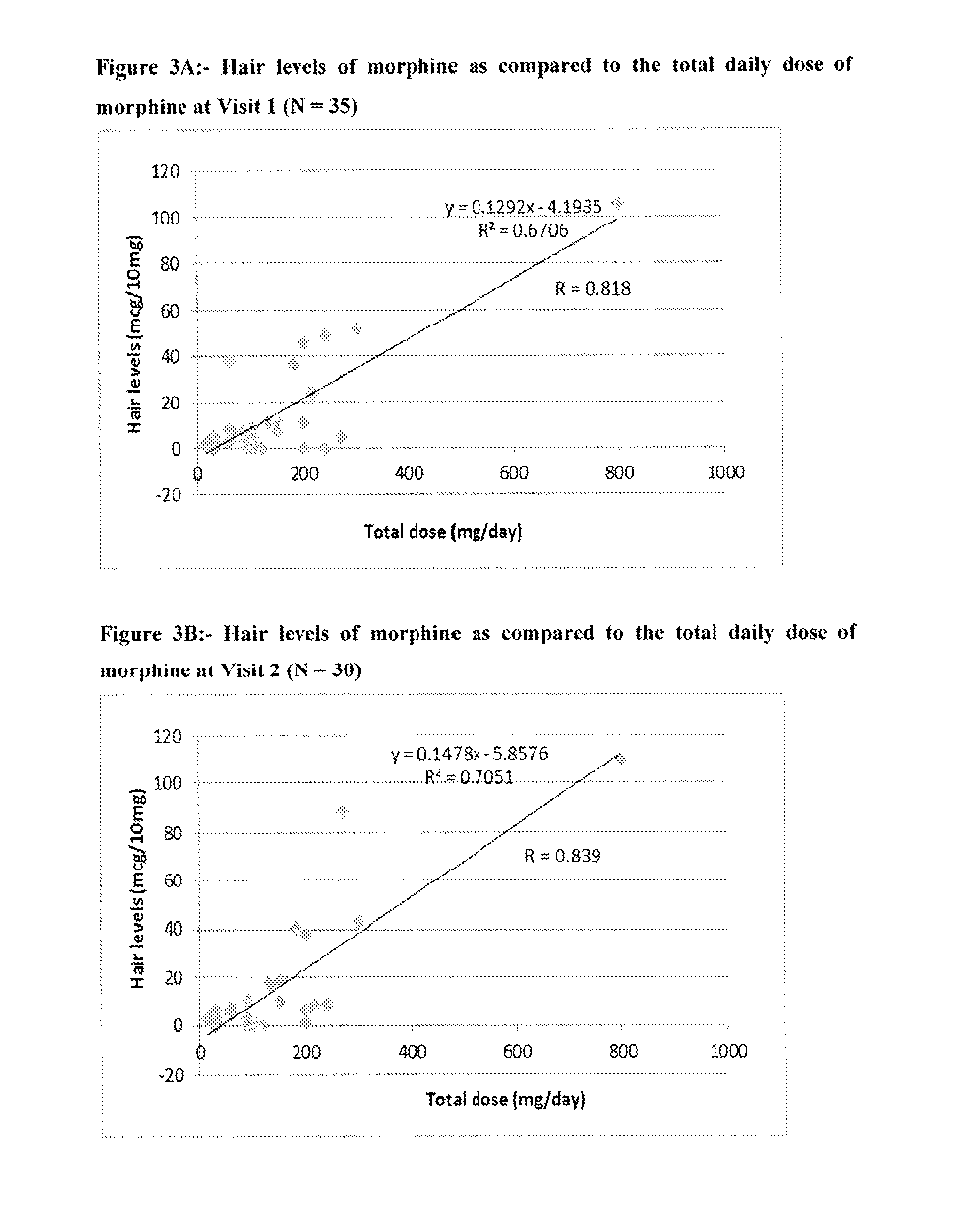
Systems and Methods to Quantify Analytes in Keratinized Samples
InactiveUS20160011220A1Less activeLess effectMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDosing regimenMetabolite
Disclosed in certain embodiments is a method of analysis comprising quantifying the amount of a drug and / or drug metabolite in a keratinized sample of a subject that has been prescribed a dosing regimen of the drug to obtain a result; and comparing the result to a known standard value for the dosing regimen.
Owner:PURDUE PHARMA LP
Water treatment system
InactiveCN101466874AWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsElectrolysisHazardous substance
A system for the treatment of water to remove metals and noxious gases from well and groundwater so as to render the water potable is disclosed. The system employs microbubbles of oxygen, which remain suspended in water at a concentration above 100% of the calculated saturated concentration at a particular temperature and pressure. These microbubbles oxidize undesirable substances in the water, which substances include iron manganese, arsenic, antimony, chrome, aluminum, reduced sulfur compounds, pesticide residues, drug metabolites and / or bacteria. Microbubbles are produced by electrolysis or be sparging through a microorifice. A control system for the electrolytic system is disclosed.
Owner:OXYGENATOR WATER TECH
Construction method of liver unit stent, liver unit stent and application of liver unit stent in field of drug testing
InactiveCN110511905ASuitable for proliferationSuitable for migrationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCross-linkInsertion stent
The invention relates to the field of biomedicine, in particular to a construction method of a liver unit stent, a liver unit stent and application of the liver unit stent in the field of drug testing. The invention aims to provide a construction method of a liver unit stent, a liver unit stent and application of the liver unit stent in the field of drug testing. The construction method of the liver unit stent comprises the following steps: a gelled first composition, which includes hepatic parenchymatous cells and a biodegradable material, is loaded into a biological 3D printer, and an intermediate is printed according to a preset path; a cross-linking agent is dropwise added to the intermediate such that the biodegradable material in the intermediate is cross-linked to form a liver unitstent, wherein a channel is formed in the liver unit stent. In the liver unit stent, cell variety, quantity and position are controllable and the channel is controllable, thus providing a microenvironment for different cells. In addition, the liver unit stent can be used for researching the drug hepatotoxicity of new drugs and is used for detecting drug metabolites, gene expression, protein expression, cell apoptosis and cell proliferation.
Owner:REGENOVO BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

![High penetration prodrug compositions of 1h-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amines and 1h-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine-related compounds High penetration prodrug compositions of 1h-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amines and 1h-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine-related compounds](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/566946cf-52a4-44ad-afcc-6c92fcbdf4a7/US20100021394A1-20100128-D00001.png)
![High penetration prodrug compositions of 1h-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amines and 1h-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine-related compounds High penetration prodrug compositions of 1h-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amines and 1h-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine-related compounds](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/566946cf-52a4-44ad-afcc-6c92fcbdf4a7/US20100021394A1-20100128-C00001.png)
![High penetration prodrug compositions of 1h-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amines and 1h-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine-related compounds High penetration prodrug compositions of 1h-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amines and 1h-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine-related compounds](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/566946cf-52a4-44ad-afcc-6c92fcbdf4a7/US20100021394A1-20100128-C00002.png)