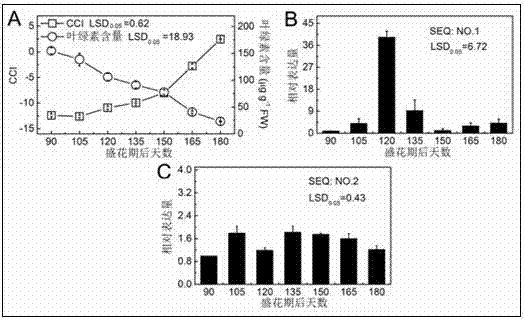
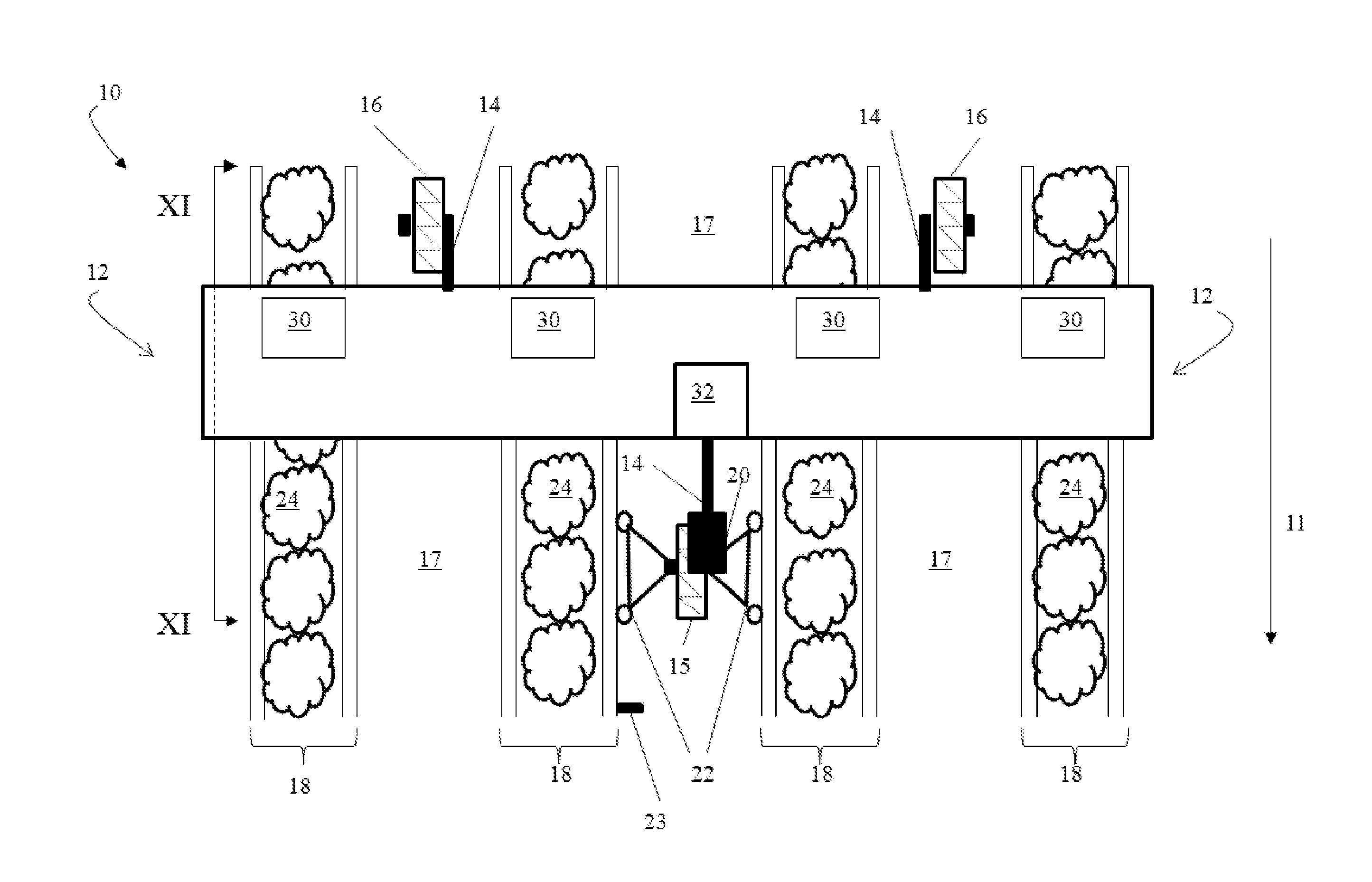
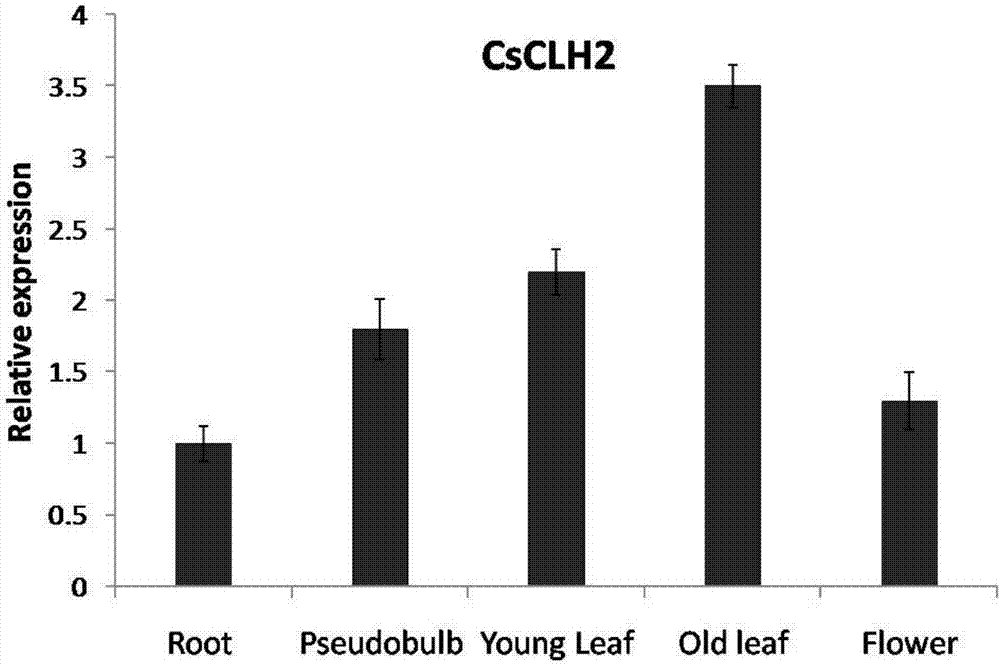
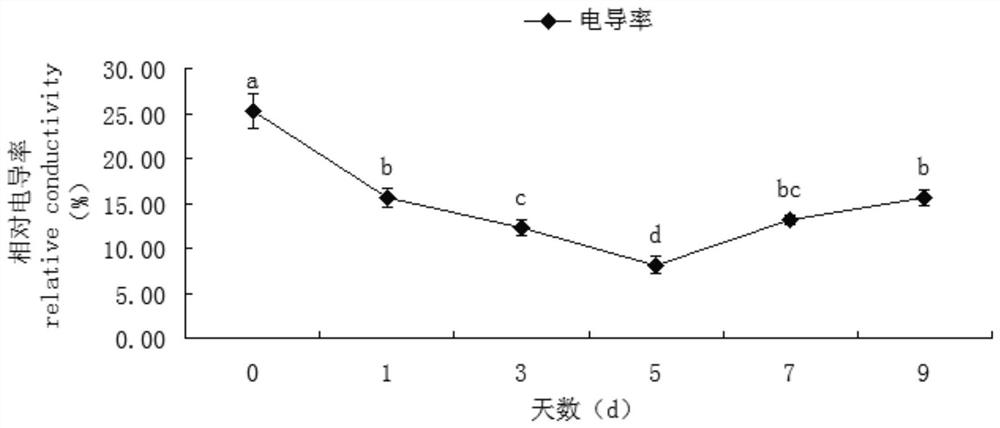
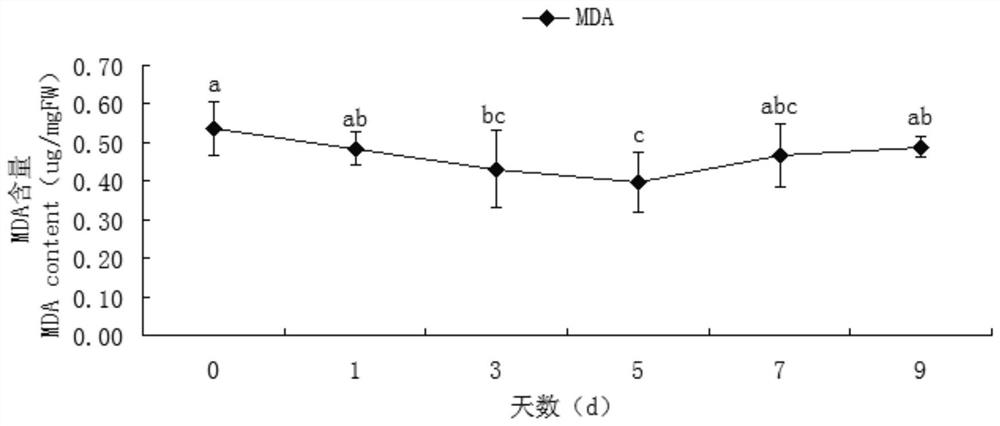
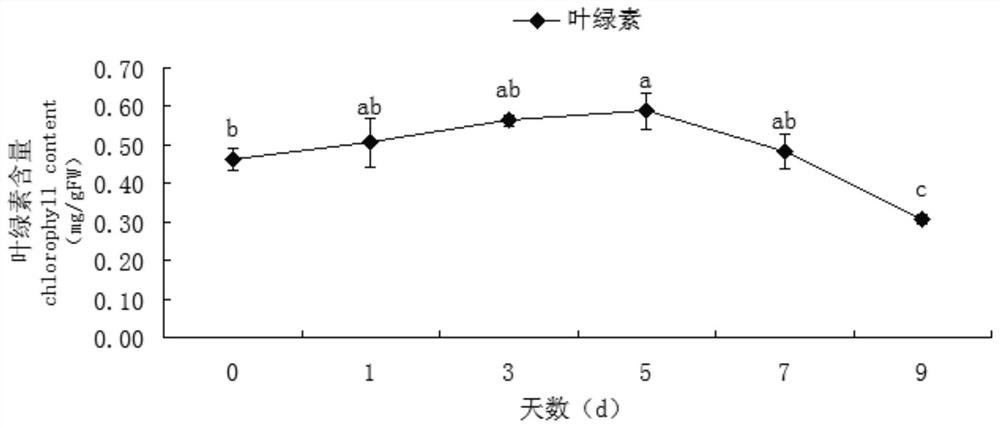
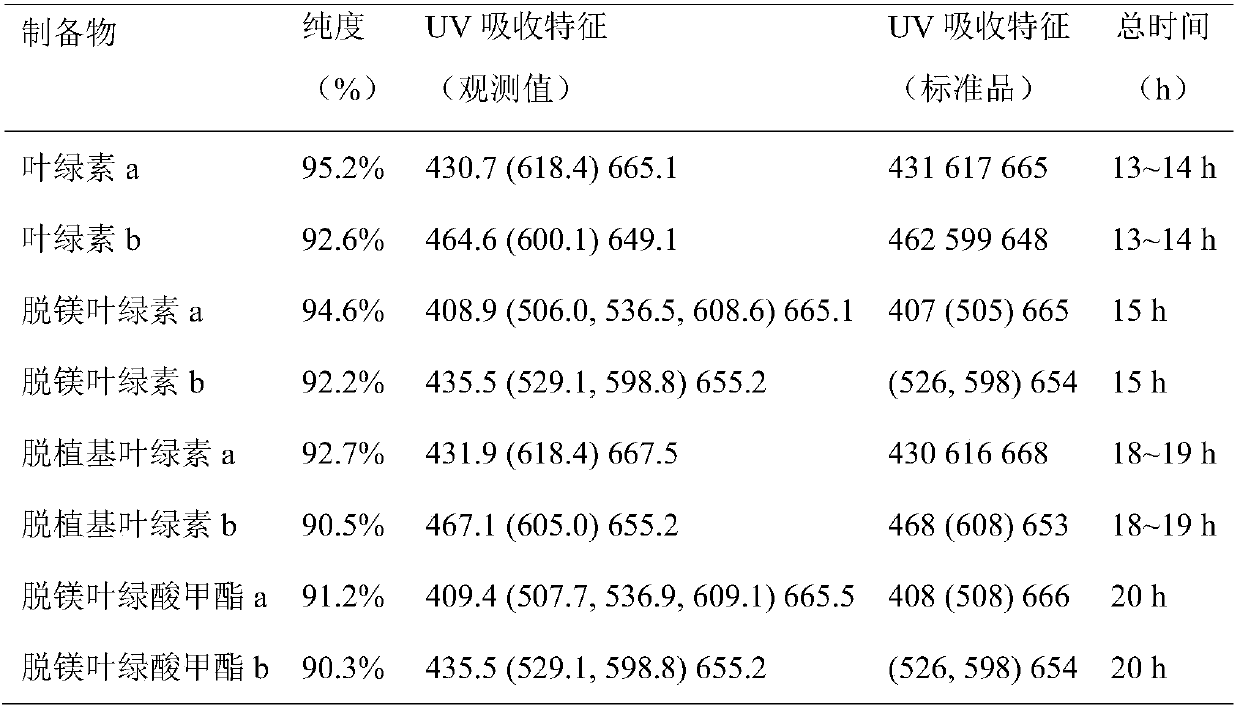
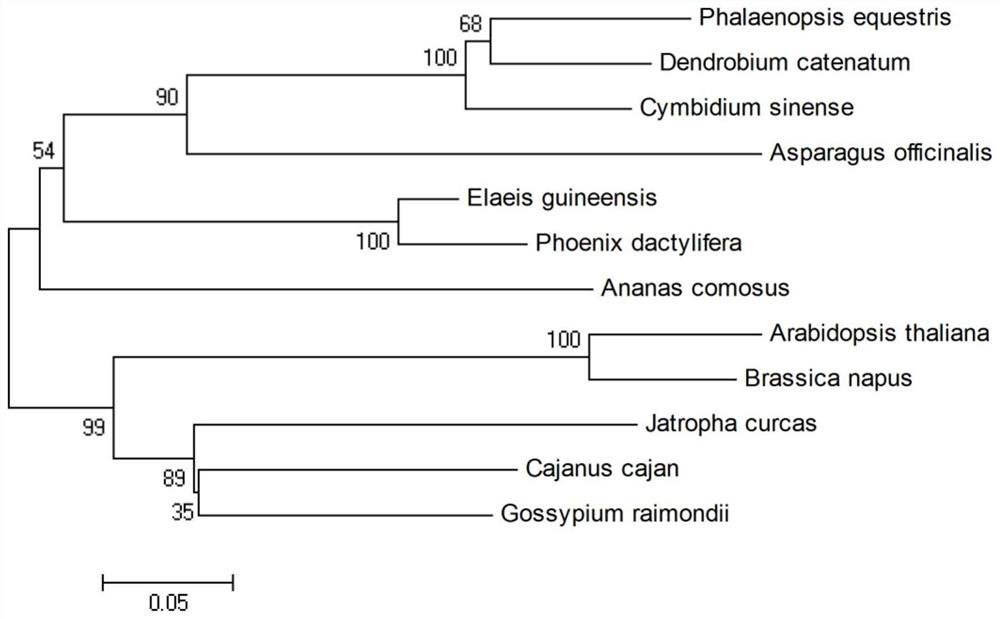
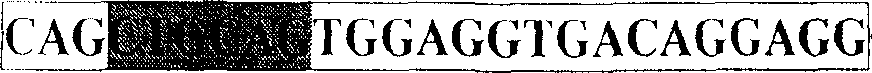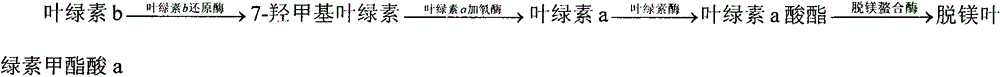Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38 results about "Chlorophyll degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
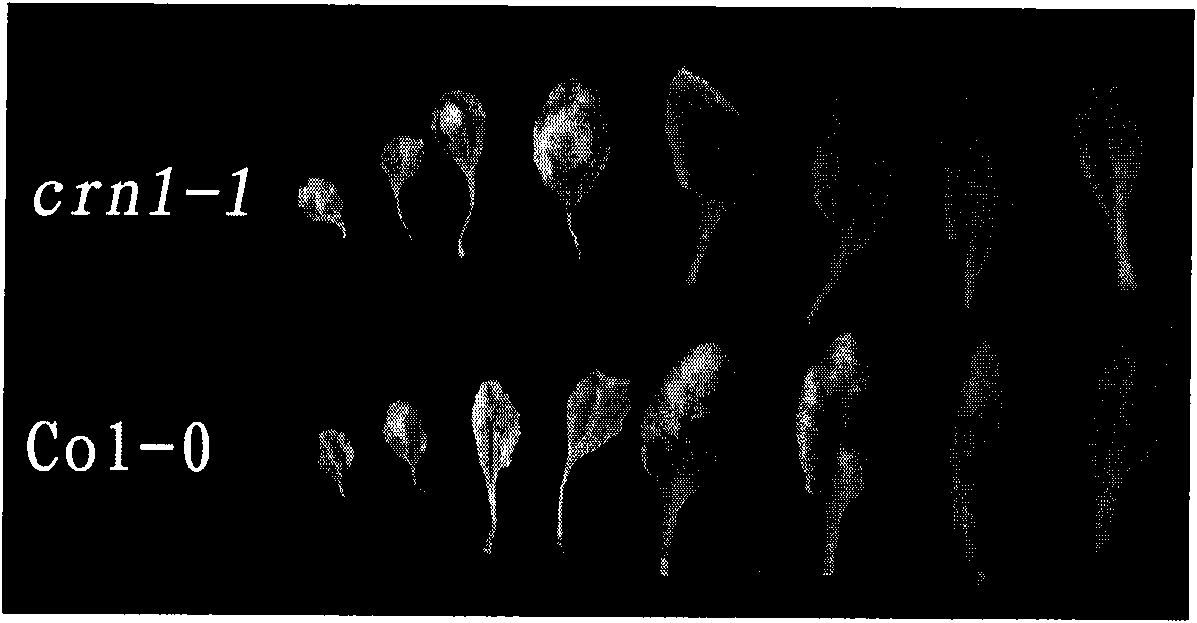
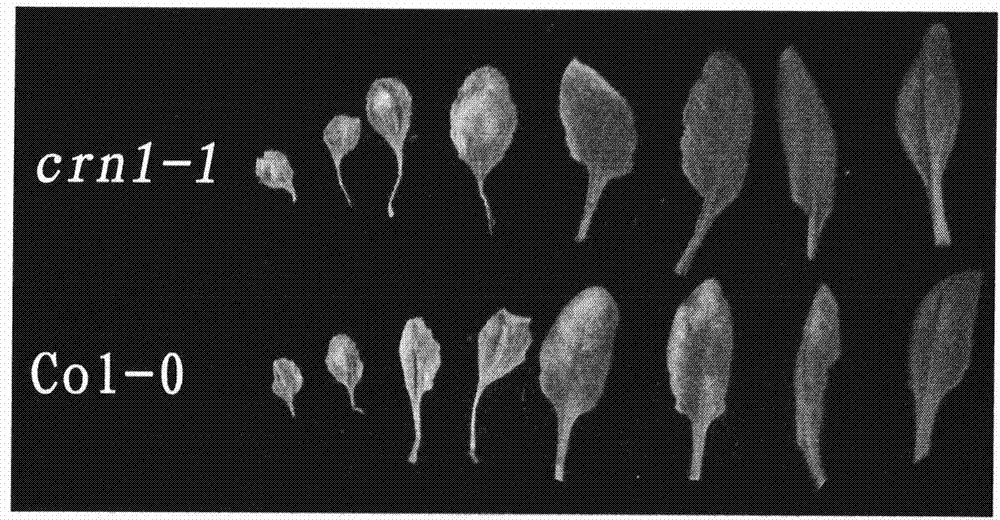
Key gene for regulating and controlling chlorophyll degradation in the senescence process of plant and application thereof
InactiveCN101831450AExtend the life of the priceExtended postharvest green periodFermentationPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyNutrition
The invention relates to a new key gene participating in the regulation and the control of chlorophyll degradation and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of plant gene engineering. Stay-green traits can prolong the commodity price service life of green leafy vegetables and the postharvest green period of fodder crops so as to increase the content of main nutrition constituents, i.e. chlorophylls and proteins; and the stay-green traits can also outstandingly improve the green period and the landscape effect of lawn plants. The invention provides the key gene AtCRN1 for regulating and controlling the chlorophyll degradation and metabolism of plants. An amino acid coding sequence of the key gene AtCRN1 is characterized by being SEQ ID No: 2. The invention also provides a method for establishing a stay-green plant strain, comprising the following steps of: inducing the gene AtCRN1 of a target plant to generate mutation through chemical or physical factors; and destroying or reducing the expression of the gene AtCRN1. Besides, detecting whether the gene AtCRN1 with overall length is contained in a plant genome or not can also be used as a molecular auxiliary breeding method for screening / identifying the stay-green plant strain.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Key ethylene response factor for regulating chlorophyll degradation of citrus peels
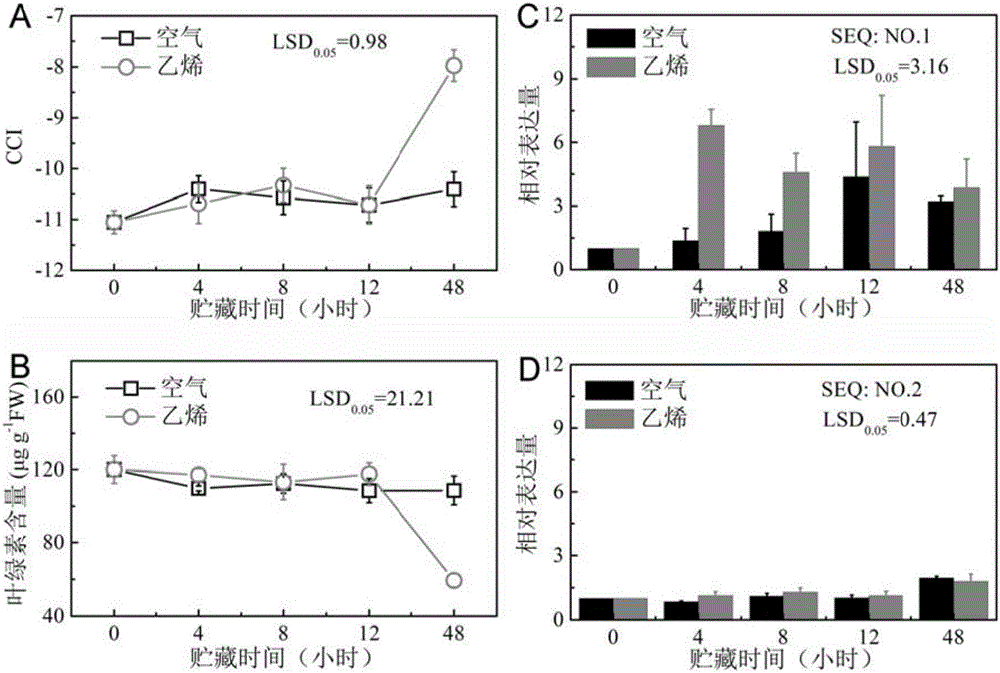
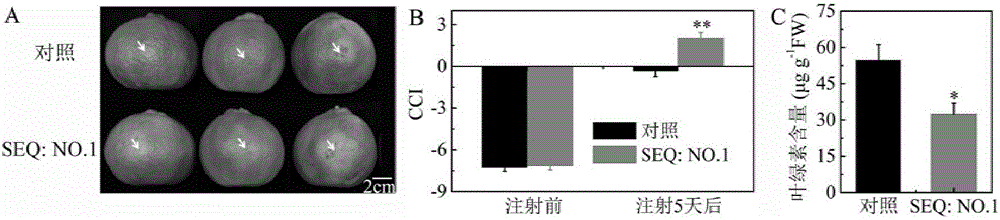
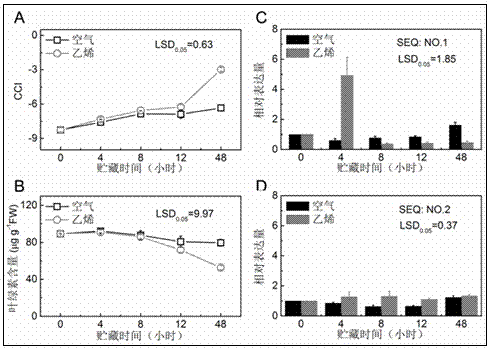
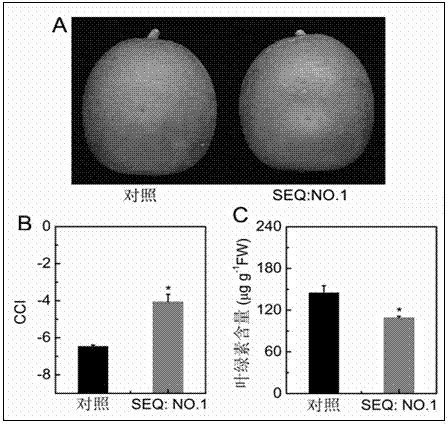
The invention provides a key ethylene response factor CitERF6 (SEQ: NO. 1) for regulating the chlorophyll degradation of citrus peels. The key ethylene response factor comprises a conservative AP2 / ERF structural domain and a Pat4(RKRK) nuclear localization signal. During the ethylene treatment of harvested citrus fruits, the expression of CitERF6 is enhanced under external ethylene induction. When the CitERF6 instantly overexpresses in the citrus peels, the chlorophyll degradation of the citrus peels can be promoted and accelerated. The key ethylene response factor has the advantages that by the PCR, real-time and quantitative PCR and citrus fruit instant expression technologies, the citrus ethylene response factor CitERF6 is cloned, and identification of the CitERF6 shows that the CitERF6 can participate in the chlorophyll degradation; the CitERF6 is applicable to genetic engineering breeding of plant color modification and especially to the regulation of the chlorophyll degradation of the citrus peels, and a theoretical basis is provided for the further researches of the peel coloring technology and the acting mechanism of the CitERF6.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Critical ethylene response factor (ERF) for regulating and controlling orange peel chlorophyll removal and application of critical ERF
InactiveCN104774849AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyChlorophyll degradation
The invention provides a critical ethylene response factor (ERF) CitERF13 for regulating and controlling orange peel chlorophyll removal. The gene contains a conservative AP2 / ERF structural domain and a Pat4 (RKRK) core positioning signal. During the development of orange fruits, the expression peak of the CitERF13 is degraded in advance of peel chlorophyll, and is enhanced by exogenous ethylene. When the CitERF13 is excessively expressed instantaneously in orange peels, the degradation of chlorophyll can be promoted, and the peel chlorophyll removal is accelerated. A technology of PCR (polymerase chain reaction), real-time quantitative PCR and orange fruit instantaneous expression is utilized to clone and identify the critical ERF CitERF13 which can be used for regulating and controlling the chlorophyll degradation, and can be applied to plant color modified genetic engineering breeding especially to regulation and control of orange peel chlorophyll removal.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Key gene for controlling chlorophyll metabolism and method for establishing plant green residence character therewith
InactiveCN1831127ADoes not cause adverse morphological changesPlant peptidesFermentationResidenceMethod of images
The invention uses fast neutron mutagenesis mode plant south-leaf mustard to filter to gain stay-green mutant. Separating crucial adjusting gene AtNYE1 would be gained by the method of image-location clone. And the stay-green feature would be created by RNA interrupt or other technology, and through NYE1 gene or the expression to restrain the gene, and lower the albumen activity of NYE1.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
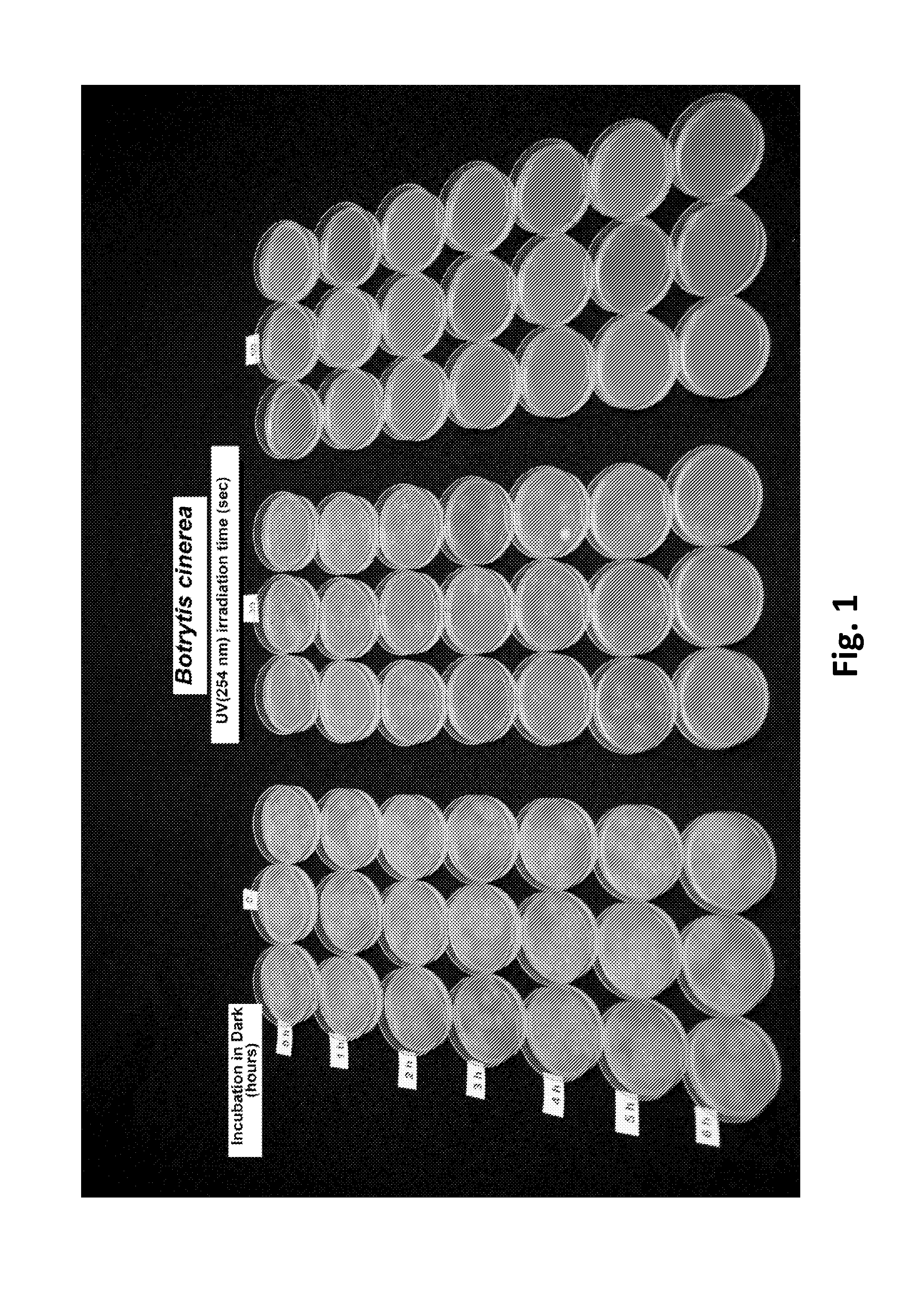
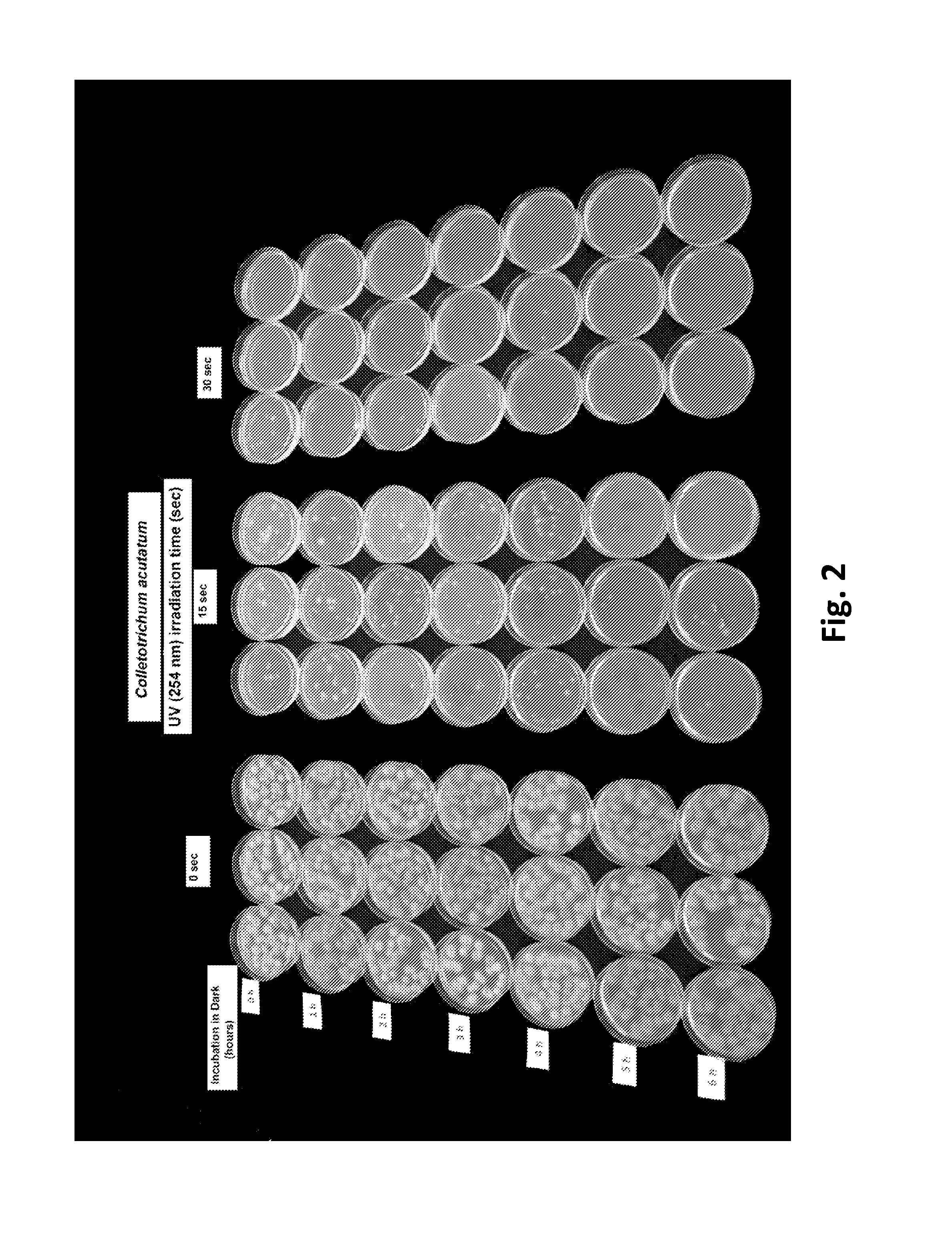
Method for Controlling Fungal Plant Pathogens Using a Combination of UV Radiation Followed by Antagonist Application and Dark Period
InactiveUS20150283276A1Reduced survivalReduce infectionBiocideMaterial analysis by optical meansDiseasePollen
Strawberries are available year-around from production in the field or from controlled environments (e.g. high and low tunnel culture and greenhouse). Diversity of production conditions results in challenges in controlling diseases before, during, and after harvest. Fungicides, traditionally used to control diseases, have limitations. UV-C irradiation followed by a dark period was used to kill two major pathogens of strawberry, Botrytis cinerea and Colletotrichum acutatum. The UV-C irradiation and dark period was followed by repopulation with beneficial biocontrol microorganisms. The 4 hr dark period prevented activation of a light-dependent UV-C damage repair mechanism in the pathogens. This combination protocol makes it possible to use a lower dose of UV-C for reduction and / or elimination of pathogens. A mobile treatment apparatus was designed to provide the appropriately timed UV-C doses, dark period, and sprayable doses of biocontrol microorganisms. The UV-C dose and repeated exposure did not affect pollen germination or cause chlorophyll degradation in strawberry leaves.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
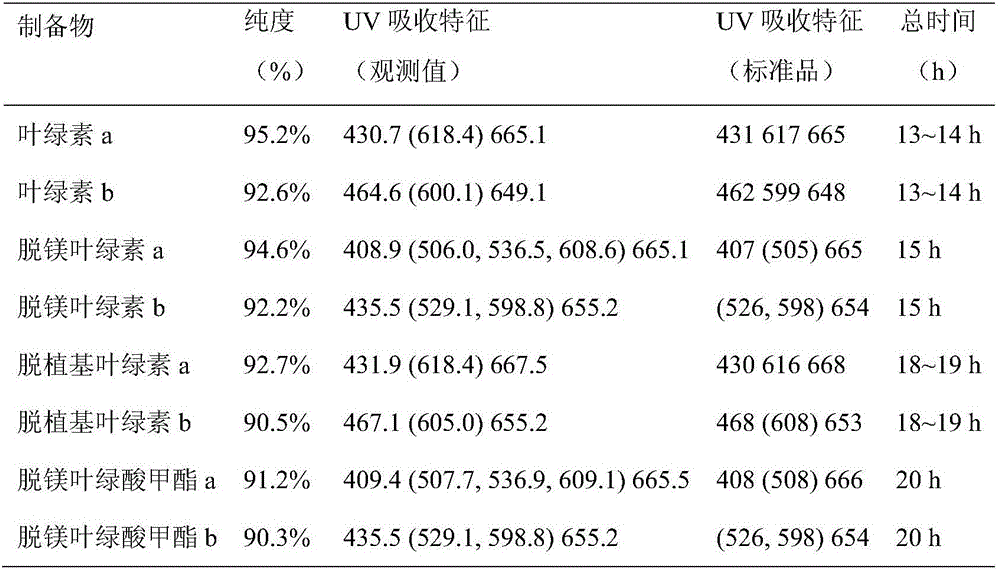
Method for quickly preparing high-purity chlorophyll and chlorophyll degradation products
ActiveCN105906638AGood effectLow costOrganic chemistryFermentationChlorophyll degradationLaboratory facility
The invention discloses a method for quickly preparing high-purity chlorophyll and chlorophyll degradation products. Satsuma mandarin peels and sweet potato leaves are used as raw materials for the first time to prepare the chlorophyll and derivatives thereof. The method disclosed by the invention is convenient and quick for taking materials, low in cost and easy to operate, and can complete the preparation of all the 8 products within three days. The purity of the obtained products can reach 90-95%, and the cost is much lower than the price of the same type of imported standard substance. The method can efficiently and quickly prepare the standard reference substances of the milligram-level chlorophyll and derivatives thereof required by the experiment, is suitable for popularization and application in commercial laboratories and enterprises, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Preservation method of fresh lotus seedpods
ActiveCN105123902AEasy to handleShort timeFruits/vegetable preservation by coatingBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a refrigerating preservation method of fresh lotus seedpods. The method includes the following steps of 1, low-temperature cleaning of fresh-picked lotus seedpods; 2, low-temperature soaking and ozone water sterilization; 3, composite color-protecting preservative film formation treatment; 4, polypropylene preservation bag packaging, and conduction of low-temperature refrigeration at the temperature of 0-2 DEG C to obtain finished products. According to the method, microorganisms on the surfaces of the lotus seedpods can be effectively restrained or killed, photosynthesis, respiration, rising, glycometabolism and other physiological metabolism activities of the fresh lotus seedpods are retarded, and ethylene release and chlorophyll degradation can be restrained; color browning of the fresh lotus seedpods in the storage period is retarded, the appearance quality of the fresh lotus seedpods is fully reserved, and the nutritional quality and flavor of lotus seeds are well kept; the effective length for preservation of the fresh lotus seedpods can be kept for as long as 50 days through the preservation method. The method is simple and easy to carry out, high in operability, low in energy consumption cost and free of excessive investment, the process is environment-friendly, safe and free of pollution, the obtained products are practical and convenient to eat, the shelf life of the fresh lotus seedpods is greatly prolonged, and a new way is developed for high-value utilization of the lotus seed products.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
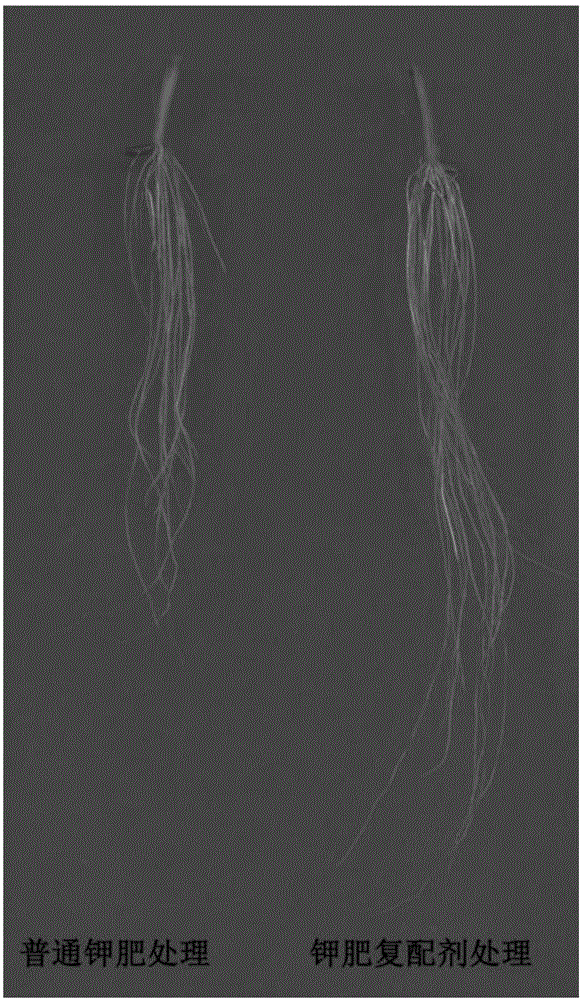
Compounded agent of potassium fertilizer for rice as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105967857APromote absorptionReduce dosagePotassium fertilisersFertilizer mixturesWarm waterPotassium
The invention discloses a compounded agent of a potassium fertilizer for rice as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The compounded agent comprises the following components according to a certain ratio: potassium chloride, ibuprofen, Tween-20, and laurocapram. The method comprises the following steps: (1) potassium chloride is weighed, water is added for dissolving, and a solution A is obtained; (2) ibuprofen and laurocapram weighed and mixed uniformly, ethyl alcohol is added for dissolving, dissolving liquid is dropped into warm water with continuously stirring, and a mixed solution B is obtained; (3) at a normal temperature, the mixed solution B obtained in the step (2) is dropped into the solution A, uniform mixing is carried out, and a mixed solution C is obtained; (4) the Tween-20 is weighed and dropped into the mixed solution C, a mixed solution D is obtained, uniform mixing is carried out, volumetric flask preparation is carried out, and the compounded agent of the potassium fertilizer for rice is obtained. The method has the advantages of low cost, easy and simple operation; the compounded agent can substantially promote growth of rice root, inhibit chlorophyll degradation, and delay leaf aging; with the same application amount of the potassium fertilizer, compared with the common potassium fertilizer, the compounded agent of the potassium fertilizer has obvious yield increasing effects, and yield of rice is increased by 9.1-15.9%.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Chlorophyll degradation metabolism regulation related proteins of non-heading Chinese cabbage and their coding genes and application
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and particularly discloses a chlorophyll katabolism control associated protein of non-heading Chinese cabbage as well as an encoding gene and application thereof. The chlorophyll katabolism control associated protein provided by the invention is sourced from the non-heading Chinese cabbage with the variety of 'Xiadongqing',and has the name of BcNYE1 and the amino acid sequence shown as SEQIDNO:2. The encoding gene of the chlorophyll katabolism control associated protein of the non-heading Chinese cabbage has the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQIDNO:1 or the polynucleotide sequence of the amino acid sequence with the code of SEQIDNO:2. The gene disclosed by the invention can be applied to chlorophyll katabolism molecular mechanism research of the non-heading Chinese cabbage and improvement of plant stay-green property on the aspects of delaying blade chlorophyll degradation and blade senescence of plants.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Bambusa emeiensis 'viridiflavus' chlorophyll degradation pathway related protein and encoding gene thereof as well as application of encoding gene
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering, and in particular relates to a Bambusa emeiensis 'viridiflavus' chlorophyll degradation pathway related protein and an encoding gene thereof as well as an application of the encoding gene. The chlorophyll degradation related protein provided by the invention is derived from Bambusa emeiensis 'viridiflavus'; and the name of the protein is BeCRN1, and the amino acid sequence of the protein is as shown in SEQIDNO: 2. The nucleotide sequence of the encoding gene of the Bambusa emeiensis 'viridiflavus' chlorophyll degradation pathway related protein BeCRN1 is as shown in SEQIDNO: 1, or a polynucleotide sequence for encoding the SEQIDNO: 2 amino acid sequence. The gene disclosed by the invention can be used for research on a Bambusa emeiensis 'viridiflavus' chlorophyll degradation mechanism and is used for color character improvement of ornamental bamboo plants, including improvement of green characters of ornamental bamboo plants and the like.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Chlorophyll katabolism control associated protein of non-heading Chinese cabbage as well as encoding gene and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and particularly discloses a chlorophyll katabolism control associated protein of non-heading Chinese cabbage as well as an encoding gene and application thereof. The chlorophyll katabolism control associated protein provided by the invention is sourced from the non-heading Chinese cabbage with the variety of 'Xiadongqing',and has the name of BcNYE1 and the amino acid sequence shown as SEQIDNO:2. The encoding gene of the chlorophyll katabolism control associated protein of the non-heading Chinese cabbage has the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQIDNO:1 or the polynucleotide sequence of the amino acid sequence with the code of SEQIDNO:2. The gene disclosed by the invention can be applied to chlorophyll katabolism molecular mechanism research of the non-heading Chinese cabbage and improvement of plant stay-green property on the aspects of delaying blade chlorophyll degradation and blade senescence of plants.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Yellow tea of new technology, and production method thereof
ActiveCN108812984AReduce moisture contentPromote degradationPre-extraction tea treatmentUltravioletBud
The invention relates to yellow tea of new technology, and a production method thereof. The method particularly includes: with fresh tea tree leaves, with one bud and one leaf or one bud and two leaves, being a raw material, carrying out the steps of withering, deactivation of enzymes, rolling, heaping for yellowing, drying, and fragrance enhancing. The production method is used for producing high-quality yellow tea, which has the characters of sweet (fresh) corn-like fragrance or rice crust-like fragrance. In the method, withering time is prolonged, so that water content of the fresh leaves is reduced; the step of heaping for yellowing is carried out under sun to form a high-temperature and -humidity environmental conditions, thereby largely damaging chlorophyll; and yellow substances, such as theaflavin which is generated through non-enzymic auto-oxidization of polyphenols under the high-temperature and -humidity condition, are exposed, thereby improving the color quality of the yellow tea; the polyphenols are oxidized and the chlorophyll is degraded, and by means of ultraviolet ray in sunshine, generation of mildews and other adverse microorganisms in a tea base can be inhibited, so that the produced yellow tea have excellent quality and safety.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for improving drought resistance of apples
ActiveCN110024687AIncrease net photosynthetic rateIncrease water contentGraftingCultivating equipmentsInduced mutationCarbon ion irradiation
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Cultivation method for making ginkgo leaf color change in advance
InactiveCN106857143AGuaranteed healthy growthGive full play to the ornamental valueClimate change adaptationGrowth substratesDiameter at breast heightChlorophyll degradation
The invention relates to a cultivation method for making a ginkgo leaf color change in advance. The cultivation method comprises the specific steps that a matrix prepared by 25-30% of yellow sand, 20-30% of animal manure, 20-30% topsoil, 20-30% of composted straw and 0.03-0.05% of crosslinked polyacrylamide is used on the ground without planting hole digging, field planting is conducted on ginkgoes having the diameter at breast height of 8-15 cm by using tapered piled soil after even mixing, wherein the line spacings of plants are 3.5-4.5 m * 3.5-5.5 m; at the beginning of March in each year, 150-300g of urea is additionally applied to culture healthy leaves. The ginkgoes have poor resistance, if it rains in the middle ten days of September, protection is provided by using plastic cloth and other facilities sheltering from the rain, the moisture content of the matrix is reduced to 18-26%, drought stress is performed for 15 days, chlorophyll degradation can be accelerated, and a yellow leaf enjoying period of the ginkgoes can be advanced to the early of October.
Owner:AGRI ENG INST ANHUI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Key gene for regulating and controlling chlorophyll degradation in the senescence process of plant and application thereof
InactiveCN101831450BExtend the life of the priceExtended postharvest green periodFermentationPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyNutrition
The invention relates to a new key gene participating in the regulation and the control of chlorophyll degradation and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of plant gene engineering. Stay-green traits can prolong the commodity price service life of green leafy vegetables and the postharvest green period of fodder crops so as to increase the content of main nutrition constituents, i.e. chlorophylls and proteins; and the stay-green traits can also outstandingly improve the green period and the landscape effect of lawn plants. The invention provides the key gene AtCRN1 for regulating and controlling the chlorophyll degradation and metabolism of plants. An amino acid coding sequence of the key gene AtCRN1 is characterized by being SEQ ID No: 2. The invention also provides a method for establishing a stay-green plant strain, comprising the following steps of: inducing the gene AtCRN1 of a target plant to generate mutation through chemical or physical factors; and destroying or reducing the expression of the gene AtCRN1. Besides, detecting whether the gene AtCRN1 with overall length is contained in a plant genome or not can also be used as a molecular auxiliary breeding method for screening / identifying the stay-green plant strain.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Metal complex of chlorophyll degradation product chlorin e6 derivatives as well as preparation method and applications of metal complex
ActiveCN104277046AClear structureHigh activityOrganic chemistryDigestive systemAlkaneDivalent metal ions
The invention discloses a metal complex of chlorophyll degradation product chlorin e6 derivatives as well as a preparation method and applications of the metal complex. The metal complex of the chlorin e6 derivatives is shown in the formula I (shown in the specification), wherein R1 and R2 are H or CH3, CH2CH3, CH2CH2CH3, n-C4H9 and other common alkane groups, M is common divalent metal ions such as Cu<2+>, Zn<2+>, Fe<2+>, Mn<2+>, Ni<2+>, Co<2+> and Pd<2+>. The compound is clear in structure and excellent in activity, and has potential for developing anti-gastric ulcer and liver protection drugs. The metal complex is low in sources of raw materials, the preparation method is simple and fast to react, and suitable for large-scale industrial production. The formula is shown in the specification.
Owner:海宁凤鸣叶绿素有限公司
Cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory protein as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN107488643AReduce chlorophyll contentGood characterHydrolasesFermentationNucleotideChlorophyll degradation
The invention discloses cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory protein as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory protein disclosed by the invention comprises 307 amino acid residues and is shown in SEQ ID NO:2; the nucleotide sequence of a cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory gene for coding the cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory protein comprises 924 basic groups and is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory protein disclosed by the invention has the activity of chlorophyll degrading enzyme; after the expression quantity of the cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory protein is increased, the content of chlorophyll in arabidopsis thaliana leaf blades can be decreased; after the cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory protein is highly expressed in cymbidium sinense, the contents of chlorophyll in leaf blades and flowering branches of cymbidium sinense are obviously decreased. The cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory gene and the cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory protein coded by the same can be used for research on a chlorophyll degradation molecular mechanism and character improvement of leaf color or flower color of plants.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL HORTICULTURE RES INST OF GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Cut flower preservative and application thereof in lily cut flower preservation
InactiveCN112120015AImprove liquidityNo change in preservation propertiesDead plant preservationChlorophyll degradationChlorophyllin
The invention discloses a cut flower preservative. The preservative comprises the following components in parts by weight: 100-400 parts of inorganic salt, 10-20 parts of a bacteriostatic agent, 10-20parts of isoniazid, 500-1000 parts of sulfamic acid, 100-200 parts of a nutritional supplement, 0-200 parts of anhydrous magnesium sulfate and 10000 parts of a nutritional substrate. The preservativecan effectively delay the occurrence time of the maximum flower diameter of cut flowers through mutual cooperation of the components, prolong the ornamental time of the cut flowers, relieve chlorophyll degradation of the leaves of thecut flowers and prolong the vase life of the cut flowers. On the other hand, the invention discloses a cut flower preservative bottling liquid which is obtained by mixing and dissolving the cut flower preservative and water according to the mass-volume ratio of 1: 50-200kg / L.
Owner:四川润尔科技有限公司
Method for quickly preparing water-soluble pigment by using enteromorpha
ActiveCN104725892AImprove adsorption capacityEasy accessOrganic chemistryNatural dyesDistillationInstability
The invention relates to a method for quickly preparing a water-soluble pigment by using enteromorpha. The method mainly comprises the following steps: performing pretreatment on raw material enteromorpha in a water phase; cleaning and performing filter pressing to obtain pretreated enteromorpha powder; performing acetone extraction and alkaline reaction to obtain an enteromorpha chlorophyll water-soluble pigment precipitant; removing impurities out of reaction supernatant by petroleum ether and performing reduced-pressure distillation to obtain an enteromorpha chlorophyll degradable product water-soluble pigment; mixing the pigment precipitants which are obtained in the two steps to obtain an enteromorpha water-soluble pigment finished product. Compared with the traditional chlorophyll water-soluble pigment preparation process, the method provided by the invention aims at instability and high degradation rate of enteromorpha chlorophyll, has the characteristics of easiness for operation, good economical performance, environment friendliness, high efficiency and quickness.
Owner:青岛海济润生生物科技有限公司
A kind of new process yellow tea and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108812984BReduce moisture contentPromote degradationPre-extraction tea treatmentMicroorganismTheaflavin
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for improving cold resistance of red bract pineapples
The invention provides a method for improving cold resistance of red bract pineapples, and belongs to the field of plant cultivation. The method for improving cold resistance of the red bract pineapples comprises the following steps that S1, tissue culture seedlings of the red bract pineapples are inoculated into an MS culture medium containing a low-temperature treating agent for culture; and S2, low-temperature exercise treatment is conducted after culture is completed. According to the method for improving cold resistance of the red bract pineapples, the activity of protective enzyme systems (SOD, POD and CAT in bodies of the red bract pineapples can be improved, so that the damage of low-temperature stress to the red bract pineapples is reduced, the integrity of leaf structures is kept, chlorophyll degradation is relieved, photosynthesis is promoted, and the overall cold resistance of the red bract pineapples is improved.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
A kind of method for rapidly preparing water-soluble pigment by utilizing Protissae
ActiveCN104725892BImprove adsorption capacityEasy accessOrganic chemistryNatural dyesEnvironmental resistanceDistillation
Owner:青岛海济润生生物科技有限公司
Greenness-protecting and brittleness-keeping compound agent for heracleum moellendorffii hance
InactiveCN107801769ASpeed up entryReduce loss rateFruit and vegetables preservationDecompositionPeroxidase
The invention relates to a greenness-protecting and brittleness-keeping compound agent for heracleum moellendorffii hance and belongs to the technical field of processing of agricultural products. A method comprises the concrete steps: after grading and cleaning fresh heracleum moellendorffii hance, soaking the heracleum moellendorffii hance into a greenness-protecting and brittleness-keeping water solution composed of 0.03%-0.30%(w / v) of tea polyphenol, 0.02%-0.25%(w / v) of ascorbic acid, 0.06%-0.50%(w / v) of nobiletin, 0.01%-0.30%(w / v) of calcium lactate and 0.01%-0.30%(w / v) of zinc chloride;and performing treatment with an ultrasonic wave device for 10-15min, rinsing, dewatering, cooling, vacuum packaging and low-temperature storage. After the heracleum moellendorffii hance is treated bythe above steps, degradation of chlorophyll and decomposition and browning of pectin can be obviously postponed and the respiratory intensity and peroxidase activity of the heracleum moellendorffii hance can be obviously reduced. The method is a green, environment-friendly, safe, economic and high-efficiency greenness-protecting and brittleness-keeping method and provides a research basis for theresearch and development of the related products of the heracleum moellendorffii hance in the future.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A kind of bacterial strain and degradation method for degrading chlorophyll
ActiveCN102286382AFast degradationImprove degradation rateFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismNatural product
The invention discloses a strain and method for degrading chlorophyll. The name of the strain determined by China Center for Type Culture Collection is Aspergillus GLHZB319, and the collection number is CCTCC NO:M2011101. The residual chlorophyll on the plant is degraded by a microbial fermentation method. When the strain ferments and degrades chlorophyll, no additional carbon source, nitrogen source or inorganic sodium salt is needed; and in the strain growth and development process, the chlorophyll can be used as a substrate for degrading chlorophyll. The strain has the characteristics of high degradation speed, high degradation rate, low cost, no residue, no pollution, high safety and environmental protection for chlorophyll, and can partially substitute decolorizing resin in the existing natural product extraction process.
Owner:广西桂林鹏宇兄弟柑桔产业开发有限责任公司
A method for rapidly preparing chlorophyll and chlorophyll degradation products
ActiveCN105906638BLow costEasy to operateOrganic chemistryFermentationChlorophyll degradationLaboratory facility
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Apple fertilizer nutrient synergist
The invention discloses an apple fertilizer nutrient synergist. The synergist is composed of the following raw materials by weight: 13-30 parts of effective active ingredient, 12-18 parts of traditional Chinese medicine preparation, 25-40 parts of super absorbent resin, 4-7 parts of alkanol milk powder, 8-20 parts of diphenhydramine, 4-10 parts of humic acid chelated magnesium, 6-12 parts of seaweed fermentation residue, 2-4 parts of synergist, 0.5-1. 3 parts of nitrogen-fixing bacteria, 3-8 parts of phosphorylated chitosan, 5-10 parts of camellia seed meal, 13-20 parts of polyacrylamide and 2-6 parts of surfactant. Compared with the prior art, the synergist has the advantages of affecting the development of plant buds, accelerating cell mitosis, promoting cell enlargement and differentiation and preventing fruit and flower dropping, thereby promoting plant growth, premature ripening, delaying aging of crop leaves in the later period and increasing yield. Further, the synergist can promote the growth of apple trees, improve the disease resistance, achieve an insect repellent effect, reduce disease and insect pests, promote plant cell growth, and inhibit plant chlorophyll degradation.
Owner:徐州农丰生物化工有限公司
A kind of regulation protein of orchid chlorophyll degradation metabolism and its coding gene and application
ActiveCN107488643BReduce chlorophyll contentGood characterHydrolasesFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory protein as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory protein disclosed by the invention comprises 307 amino acid residues and is shown in SEQ ID NO:2; the nucleotide sequence of a cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory gene for coding the cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory protein comprises 924 basic groups and is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory protein disclosed by the invention has the activity of chlorophyll degrading enzyme; after the expression quantity of the cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory protein is increased, the content of chlorophyll in arabidopsis thaliana leaf blades can be decreased; after the cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory protein is highly expressed in cymbidium sinense, the contents of chlorophyll in leaf blades and flowering branches of cymbidium sinense are obviously decreased. The cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory gene and the cymbidium sinense chlorophyll catabolism regulatory protein coded by the same can be used for research on a chlorophyll degradation molecular mechanism and character improvement of leaf color or flower color of plants.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL HORTICULTURE RES INST OF GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
A fresh-keeping method for fresh lotus pods
ActiveCN105123902BEasy to handleShort timeFruits/vegetable preservation by coatingOperabilityChlorophyll degradation
The invention discloses a refrigerating preservation method of fresh lotus seedpods. The method includes the following steps of 1, low-temperature cleaning of fresh-picked lotus seedpods; 2, low-temperature soaking and ozone water sterilization; 3, composite color-protecting preservative film formation treatment; 4, polypropylene preservation bag packaging, and conduction of low-temperature refrigeration at the temperature of 0-2 DEG C to obtain finished products. According to the method, microorganisms on the surfaces of the lotus seedpods can be effectively restrained or killed, photosynthesis, respiration, rising, glycometabolism and other physiological metabolism activities of the fresh lotus seedpods are retarded, and ethylene release and chlorophyll degradation can be restrained; color browning of the fresh lotus seedpods in the storage period is retarded, the appearance quality of the fresh lotus seedpods is fully reserved, and the nutritional quality and flavor of lotus seeds are well kept; the effective length for preservation of the fresh lotus seedpods can be kept for as long as 50 days through the preservation method. The method is simple and easy to carry out, high in operability, low in energy consumption cost and free of excessive investment, the process is environment-friendly, safe and free of pollution, the obtained products are practical and convenient to eat, the shelf life of the fresh lotus seedpods is greatly prolonged, and a new way is developed for high-value utilization of the lotus seed products.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
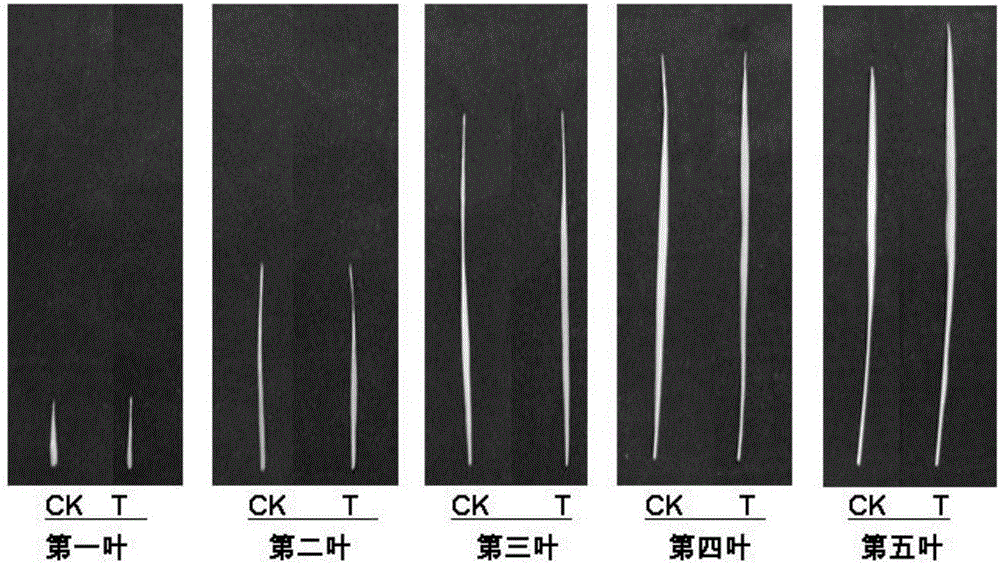
Method for culturing root-growth-enhanced leaf-ageing-delayed transgenic plant
ActiveCN105296503AIncrease productionPromote growthFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyPlant roots
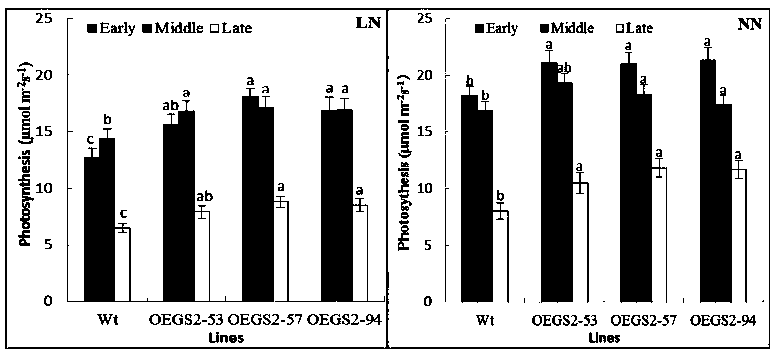
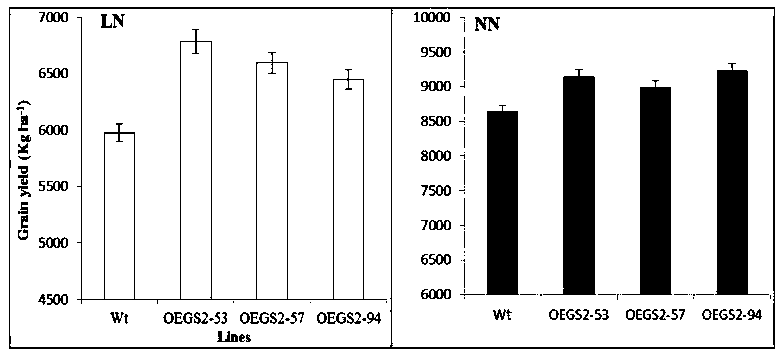
The invention discloses a method for culturing a root-growth-enhanced leaf-ageing-delayed transgenic plant. The gene shown as SEQ ID NO:1 is introduced into a target plant and is stably expressed and inherited, so that the anti-ageing transgenic plant with growth-enhanced root is obtained compared with a non-transgenic contrast plant. Growth of root of the transgenic plant is obviously promoted, also the functional leaf photosynthesis is obviously enhanced at the late growth stage, leaf chlorophyll degradation is delayed, ageing of the transgenic plant is delayed, and therefore crop output is improved.
Owner:河北省农林科学院粮油作物研究所 +1
A method of cultivating transgenic plants with enhanced plant root development and delayed leaf senescence
ActiveCN105296503BIncrease productionPromote growthFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPlant rootsRoot growth
Owner:INST OF CEREAL & OIL CROPS HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com