Critical ethylene response factor (ERF) for regulating and controlling orange peel chlorophyll removal and application of critical ERF
A technology of citrus peels and response factors, which can be applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., and can solve problems such as unclear biological mechanisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Example 1 : Gene Cloning
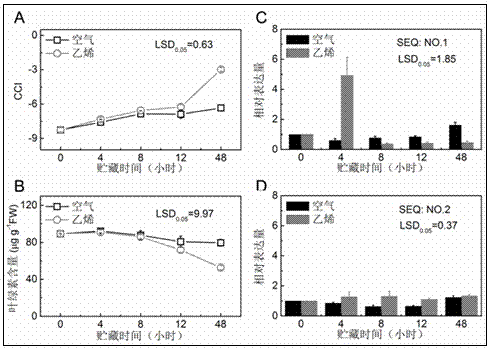
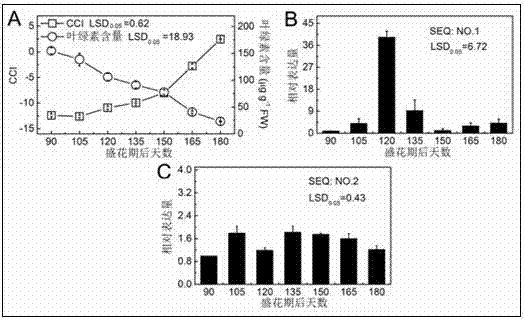
[0022] CitAP2 / ERF gene family members were obtained based on the Citrus Sweet Orange and Clementine Genome Database (http: / / www.citrusgenomedb.org). On the one hand, directly download the genes that may belong to AP2 / ERF according to the annotation, on the other hand, perform BLAST (TBLASTN and BLASTP) analysis on the reported Arabidopsis AP2 / ERF gene, and use the sequences obtained by these two methods to use AP2 / ERF The conserved domains were screened one by one, and then the CAP3 sequence assembly program (http: / / pbil.univ-lyon1.fr / cap3.php) was used to remove repetitive sequences to obtain CitERF13 (SEQ: NO. 1) and CitERF8 (SEQ: NO . 2).
[0023] Combining the primer pair of SEQ: NO. 3 and SEQ: NO. 4, and SEQ: NO. 5 and SEQ: NO. 6, using PCR technology to amplify the two genes obtained respectively, wherein the 30 μl PCR system is: 10×Buffer 3 μl, dNTP 2.4 μl, upstream / downstream primers 0.6 μl each, enzyme 0.15 μl, DEPC-H 2 O 21.3 μl...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Example 2 : Gene expression analysis
[0025] (1) Experimental method
[0026] 1. Fruit material collection
[0027] The fruits of Newhall navel orange in the developing stage were harvested at 90, 105, 120, 135, 150, 165 and 180 days after the full flowering stage. Nine fruits were collected each time and divided into three biological replicates.
[0028] The ponkan fruits 160 days after the full flowering period arrived at the laboratory on the same day after harvest, and the fruits with uniform size and relatively consistent maturity were selected for experiments. The fruits were randomly divided into two groups (100 in each group), and each group was placed in 3 airtight containers on average, and a group of 40 μL·L -1 Ethylene gas was used for 12 h, while the other group was ventilated with air for 12 h, and then placed in a shelf at 20 °C. The two groups of fruits were sampled at 0, 4, 8, 12 and 48 hours of treatment, respectively. Nine fruits were taken ea...
Embodiment 3
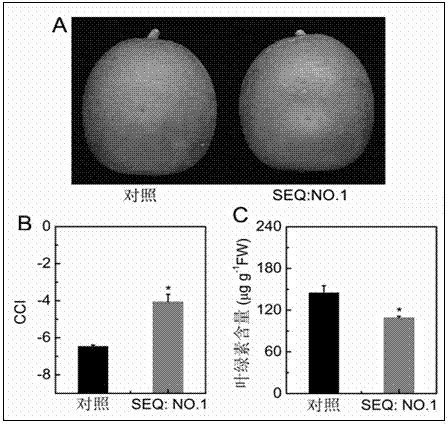
[0038] Example 3 : Gene function verification
[0039] (1) Experimental method
[0040] 1. Recombinant vector construction
[0041] Primers (SEQ: NO. 3 and SEQ: NO. 4) were designed according to the verified full-length sequence of CitERF13 (SEQ: NO. 1) to amplify its open reading frame. Using the cDNA of citrus peel as a template, slightly modify the high-fidelity enzyme system of Invitrogen Company, prepare a PCR system with a final volume of 30 μl: 10×Buffer 3 μl, dNTP 2.4 μl, upstream / downstream primers 0.6 μl, enzyme 0.15 μl, DEPC-H 2 O 21.3 μl, 50 mM MgSO 4 1.2 μl, cDNA 0.75 μl. The reaction conditions were: pre-denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min; denaturation at 95 °C for 10 sec, annealing at 58 °C for 5 sec, extension at 72 °C for 2.5 min, and 35 thermal cycles; extension at 72 °C for 10 min, and storage at 4 °C. After the PCR product was recovered, it was connected to the pGEM-T easy vector, and the recombinant plasmid was introduced into E. coli DH5α competent ce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com