Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
175 results about "Biogenic substance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A biogenic substance is a product made by or of life forms. The term encompasses constituents, secretions, and metabolites of plants or animals. In context of molecular biology, biogenic substances are referred to as biomolecules.
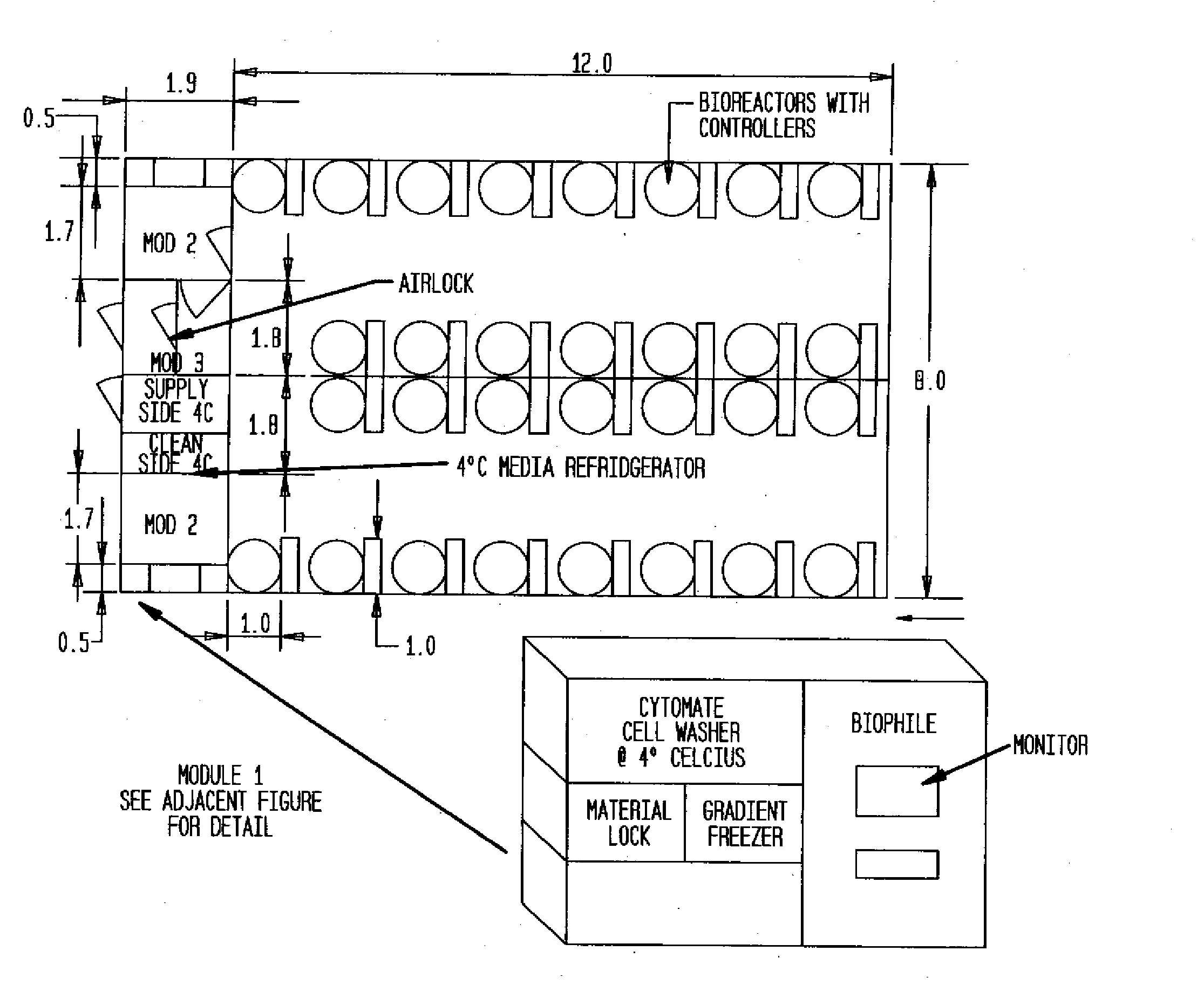
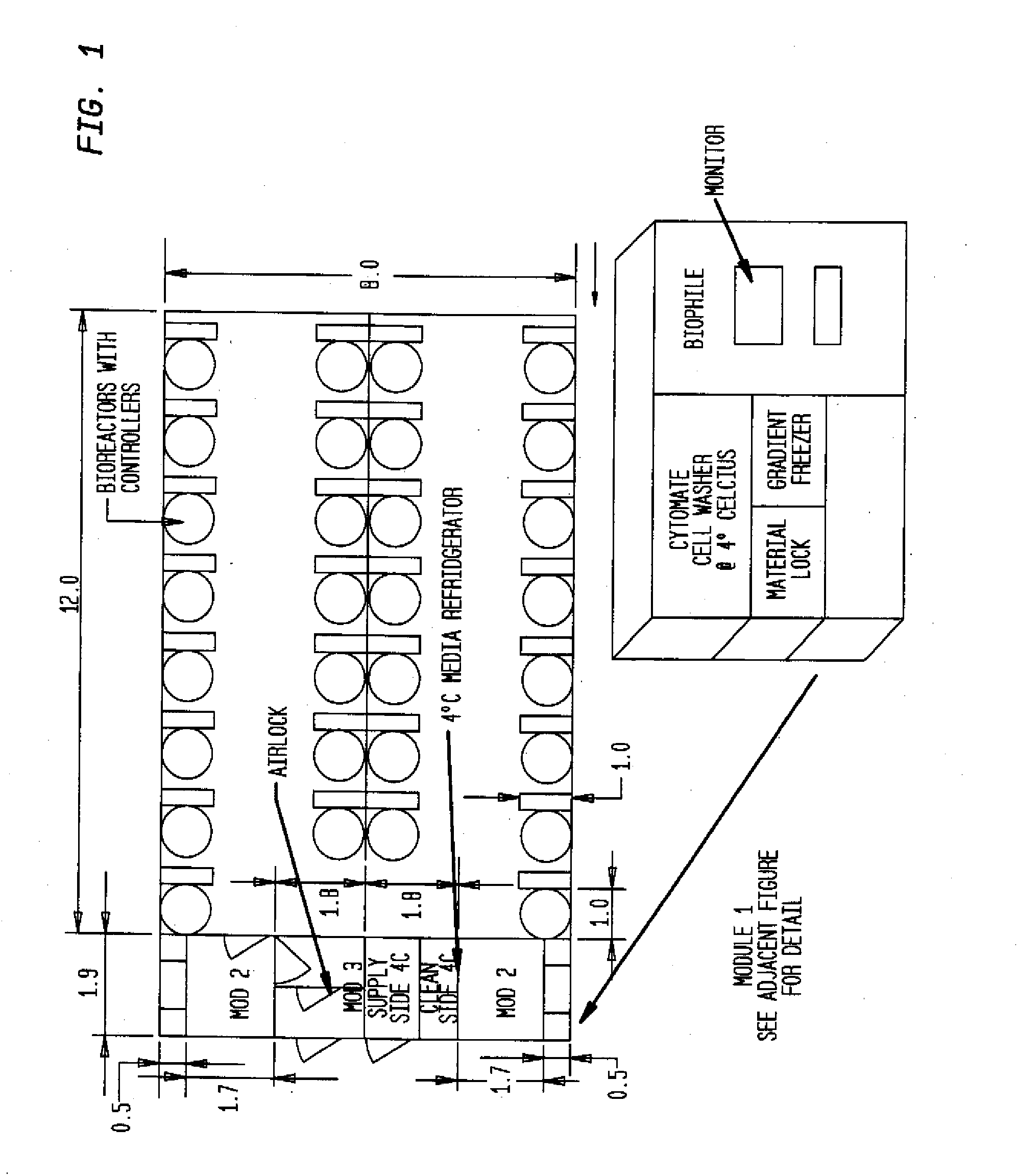
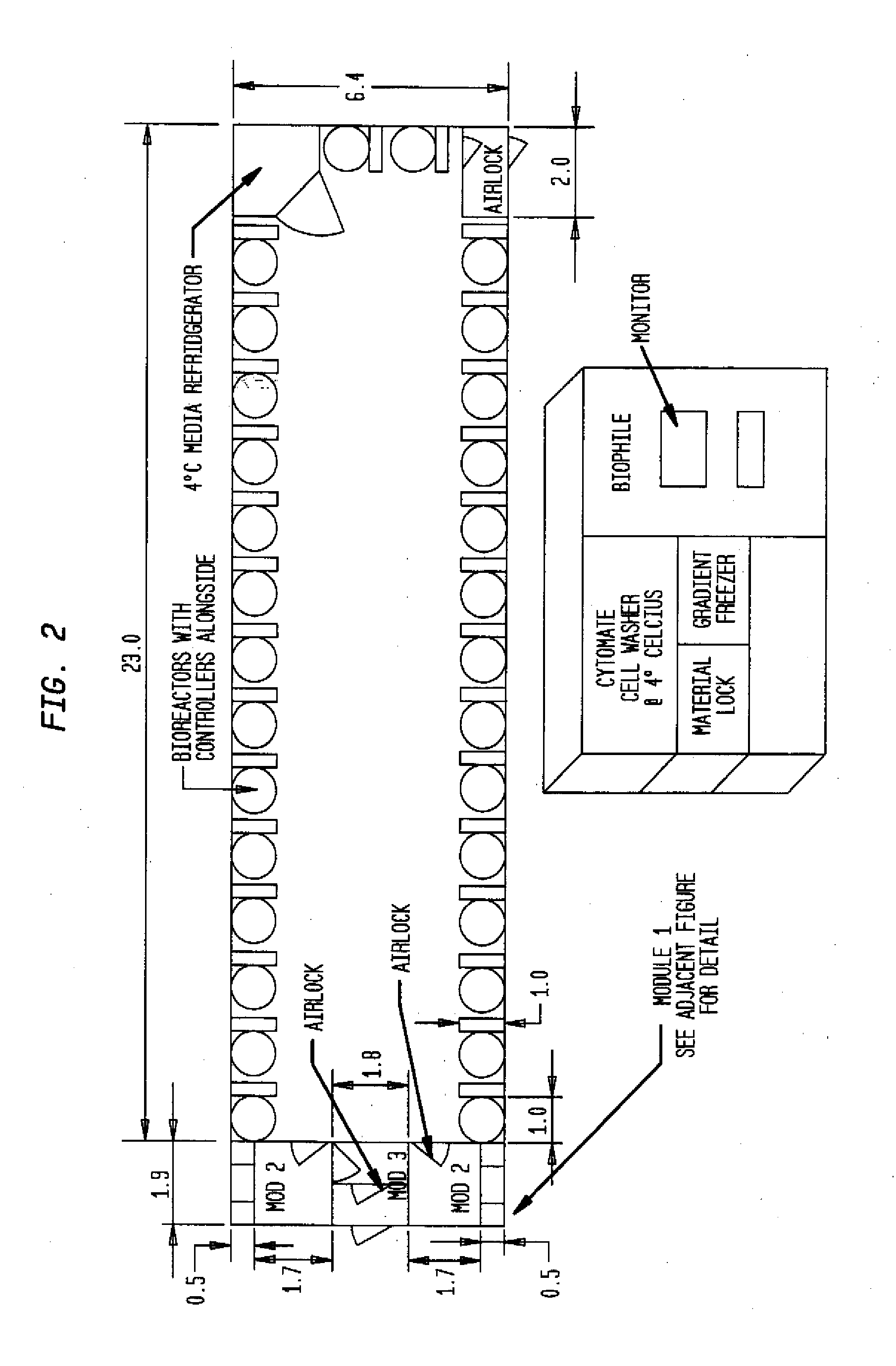
Prevalidated, modular good manufacturing practice-compliant facility
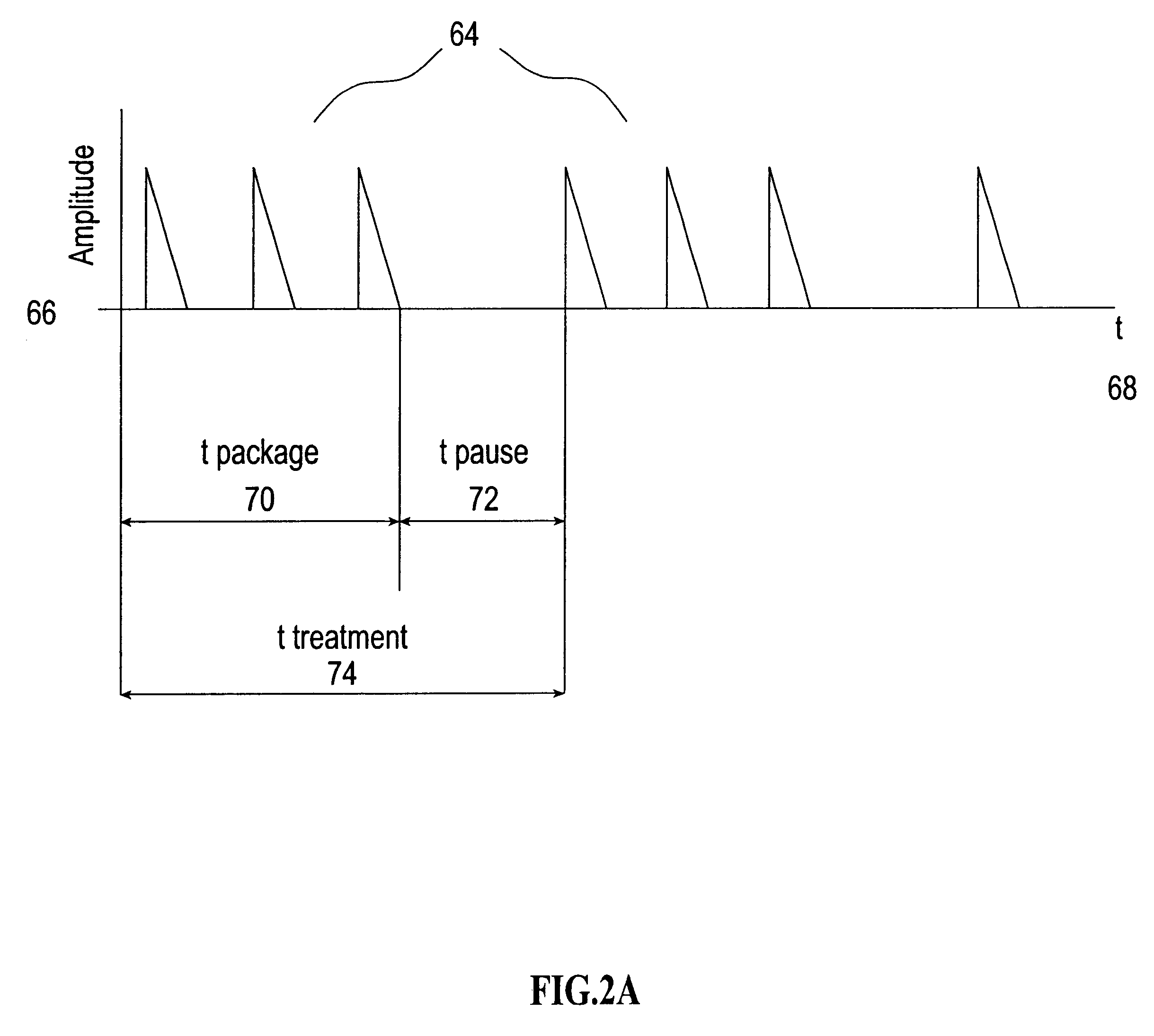
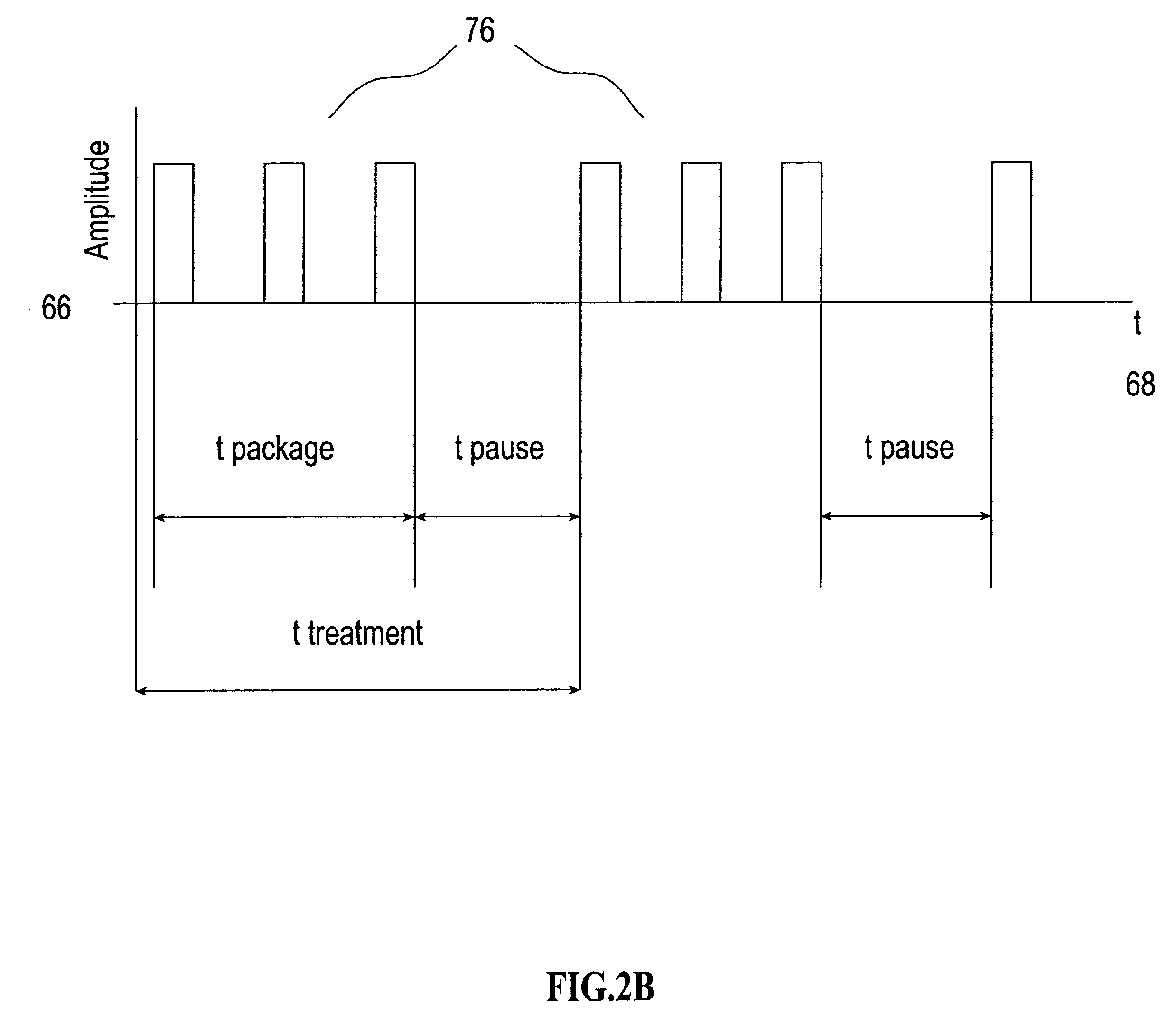
InactiveUS20090305626A1Precious timeShorten the timeApparatus sterilizationDust-free enclosuresInterior spaceGood laboratory practice
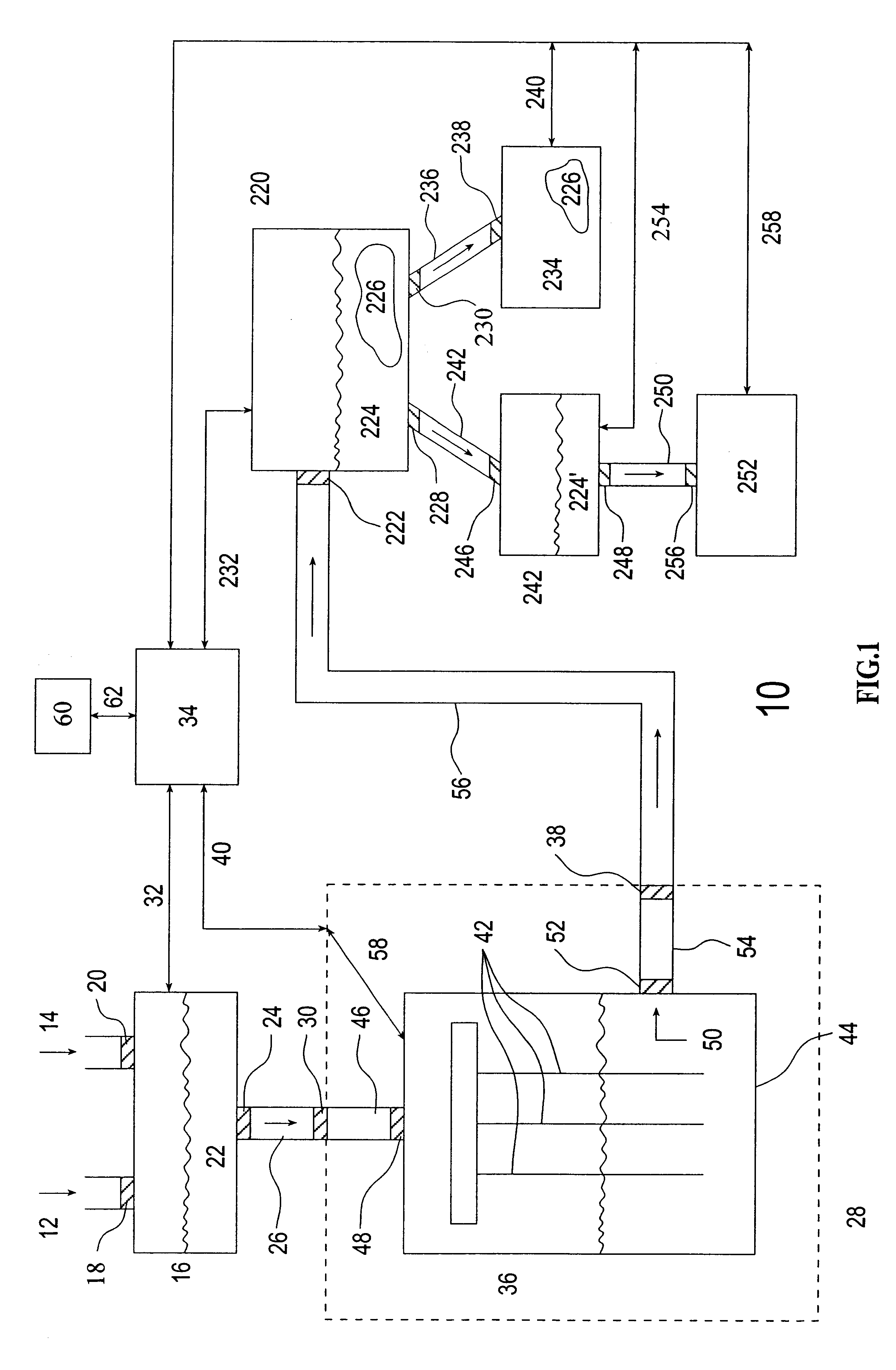
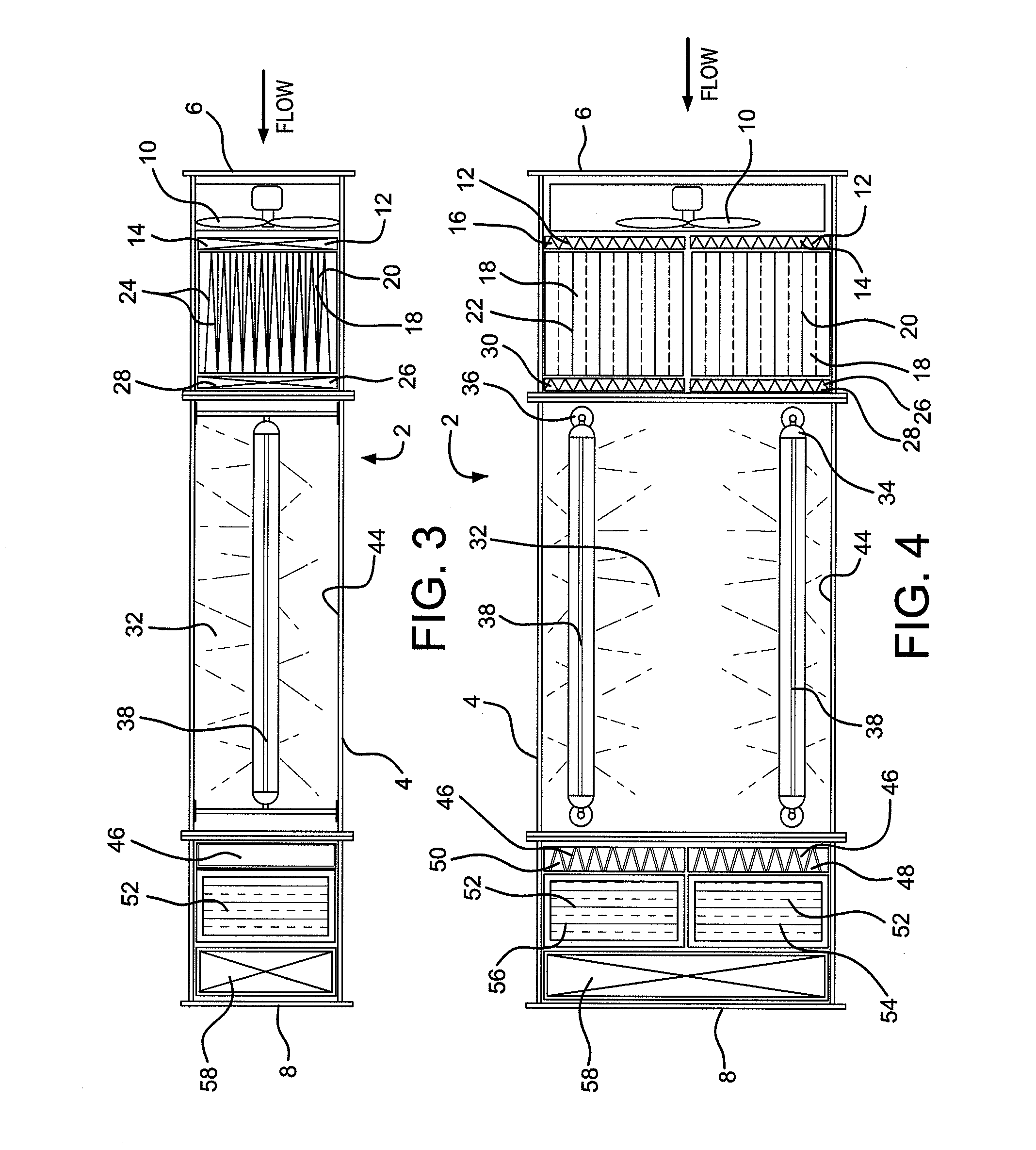
The invention is directed to a ready-to-use modular cleanroom and facility, in particular for the production of drugs and biological substances, which is equipped with pre-approved manufacturing equipment cores. The modular cleanroom is implemented in the interior space of a container, such as a standard shipping container, and includes at least one bioreactor station. The modular facility can be installed on-site from pre-approved cleanroom modules without further regulatory approval. The cleanroom and facility comply with FDA-approved good manufacturing practices (GMP) and good laboratory practices (GLP).
Owner:HOPE ERNEST G
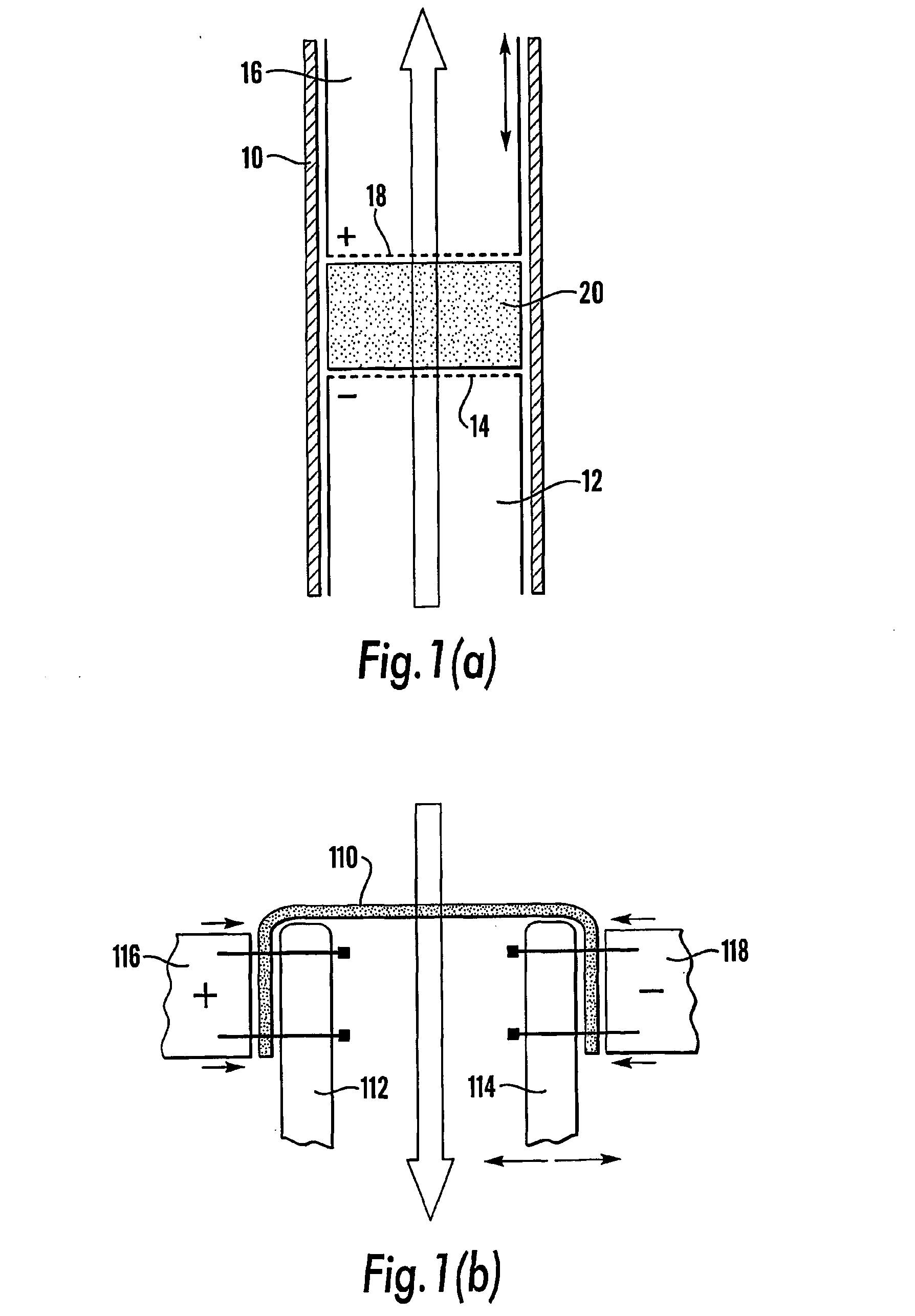
Process and system for electrical extraction of intracellular matter from biological matter
InactiveUS6344349B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectrolysisCell membrane
A process and system for electrical extraction of intracellular matter from biological matter, and intracellular matter products formed thereby, based on preparing a mixture of biological matter featuring cells, and an electro-conductive liquid, and electrifying the mixture by transmitting controlled cycles of pulses and pauses of electrical current into the mixture by using electrodes, whereby the pulses of electrical current pierce holes into or perforate the cell membranes of the cells, enabling the release of intracellular matter for collecting and separating into target intracellular matter extract and solid waste. Pauses included in each cycle of transmitting pulses of electrical current enable firm control of electrical extraction processing conditions, including extent of extraction, temperature effects, and pressure effects, during the electrical extraction process. Electrical extraction of the present invention is applicable to a wide variety of biological matter originating from human, animal, and plant entities. Intracellular matter extracts so obtained include highly concentrated liquid fertilizer, valuable elements, nutrients, oils, and fats, which are used for manufacturing a diversity of end products of the agricultural, pharmaceutical, cosmetic, and food industries.
Owner:DECANT TECH
Analytical method, kit, and apparatus
Owner:NISSUI PHARMA CO LTD
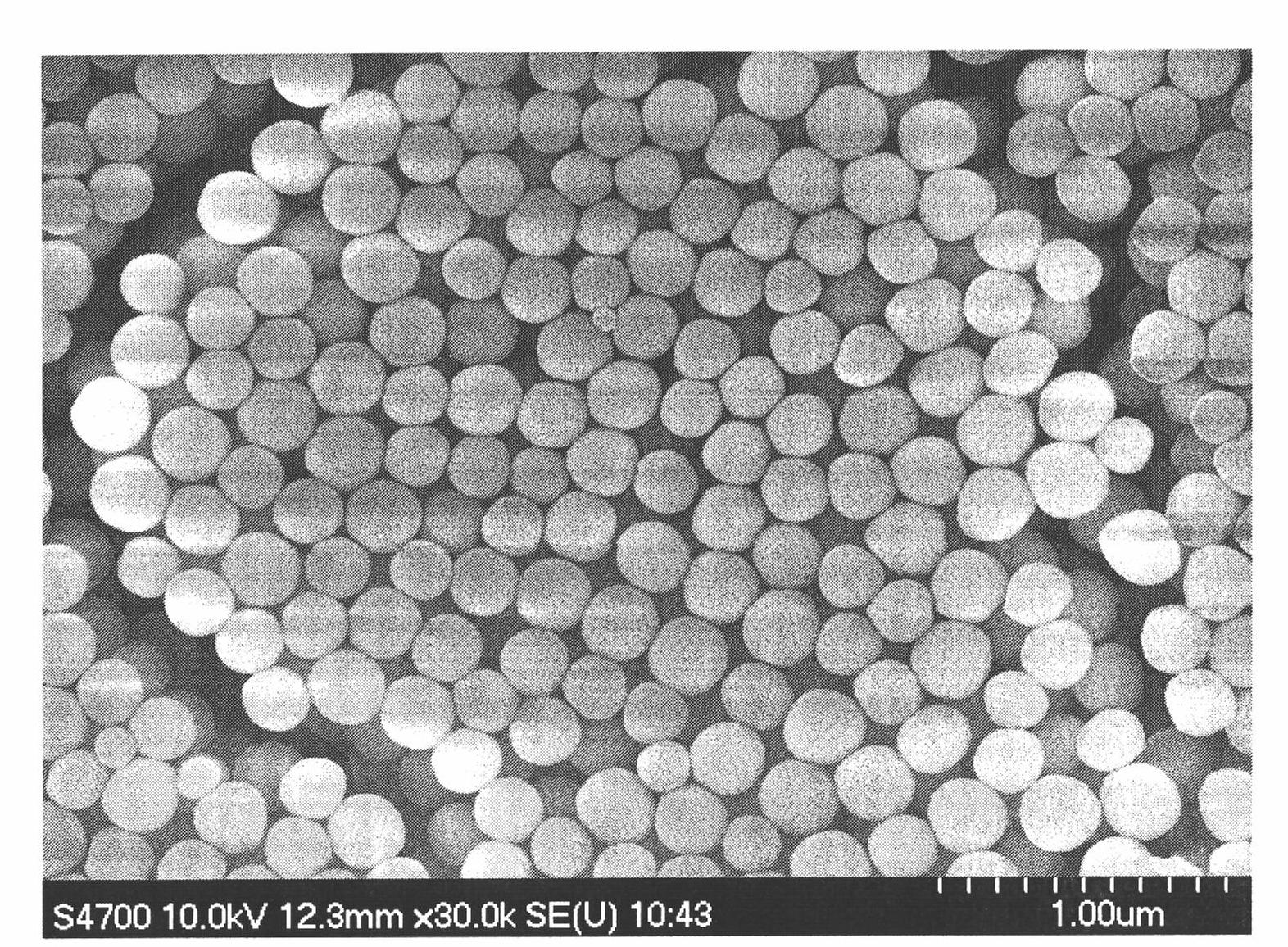
Mono-dispersed nano/micron polymer hollow microsphere resin and method for synthesizing the same
The invention relates to a preparation method of isodisperse nano / micron polymer hollow microsphere. The hollow microsphere with 10 nano-10 micron inner diameter and 10 nano-200 nano wall thickness is polyene type monomer homopolymer or copolymer (20-100 percent crosslinking) of polyene type monomer and other functional monoene type monomer. The polyene type monomer or the polyene type monomer and other functional monoene type monomer are distilled with the existence of a template to prepare a series of sodisperse sodisperse hollow microsphere with different inner diameters and wall thicknesses after precipitation polymerization. The invention has the advantages of simple conditions, easy operation, pure products and being easy to get raw materials and environment protective and so on. The nano / micron polymer hollow microsphere of the invention can be applied to systems with controllable transportation and release such as dyes, cosmetics, medicine, enzymes, proteins, etc. as well as light fillings, nano micro vessels, low dielectric constant materials, catalyst carrier and has very important application value in aspects such as artificial cell, disease diagnosis, biological material separation, etc.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Carriers having biological substance
InactiveUS7122378B1Improve alignment-defining powerEase difficulty in alignmentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAmount of substanceBiological substances
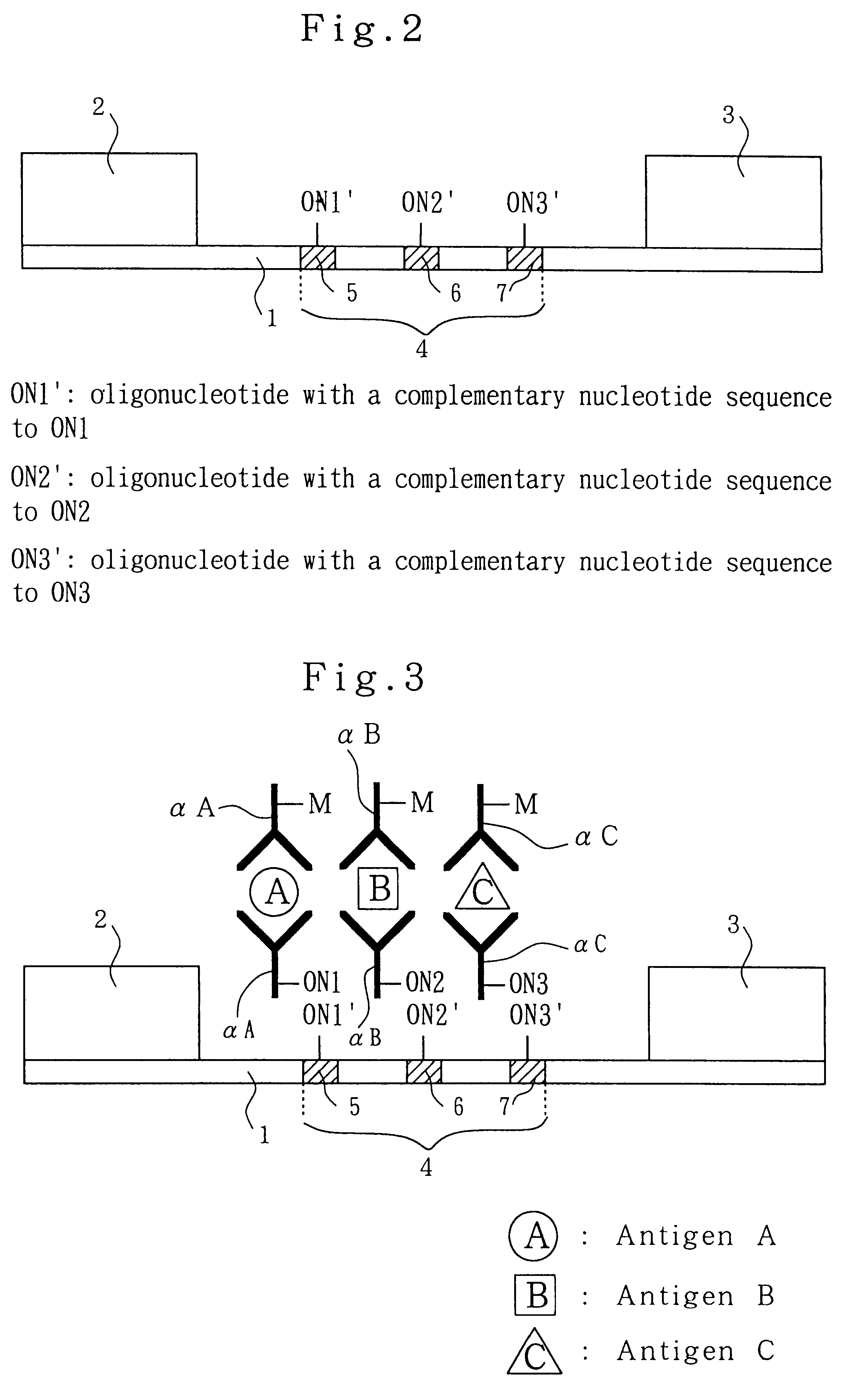
By the present invention, there is provided a fiber having nucleic acid immobilized thereon, an alignment of fibers having nucleic acid immobilized thereon, and a slice thereof.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Apparatus and method for identification of biomolecules, in particular nucleic acid sequences, proteins, and antigens and antibodies
InactiveUS20050079598A1Improve chip resistanceThe result is accurateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntigenNucleic acid sequencing
An electrical detection system and method using an array of conductive sense sites within a sensing substrate for electrically detecting the successful hybridization or binding reaction between two chemical substances, particularly between biogenic substances such as nucleotides, proteins and ligands, and antigens and antibodies. The method and apparatus provide a an inexpensive, robust, small, repeatable, and intuitively easy to use apparatus for detection of low levels of hybridization with large numbers of closely spaced conductive sense sites within a single substrate.
Owner:DAVIS RANDALL W
Kit for Immobilizing Organic Substance, Organic Substance-Immobilized Structure, and Manufacturing Methods Therefor
InactiveUS20080108132A1Good reproducibilityImprove stabilitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidePhysiological function
To provide an organic substance-immobilized structure employing a novel immobilizing technique and a manufacturing method thereof using the novel immobilizing technique, where, when an organic substance, particularly a biological substance is immobilized on the surface of a substrate, the organic substance, particularly the biological substance can be stably immobilized on the surface of the substrate through orientation of the organic substance, particularly the biological substance suitable for exerting physiological functions thereof. At least part of the substrate's surface is constructed of one or more substrates containing aluminum oxide. The immobilization of the organic substance to the surface of the substrate is carried out by binding at least part of the binding domain to the surface of the substrate through a binding domain containing a peptide having an affinity to aluminum oxide and composed of at least one or more amino acids, which is coupled with the organic substance.
Owner:CANON KK
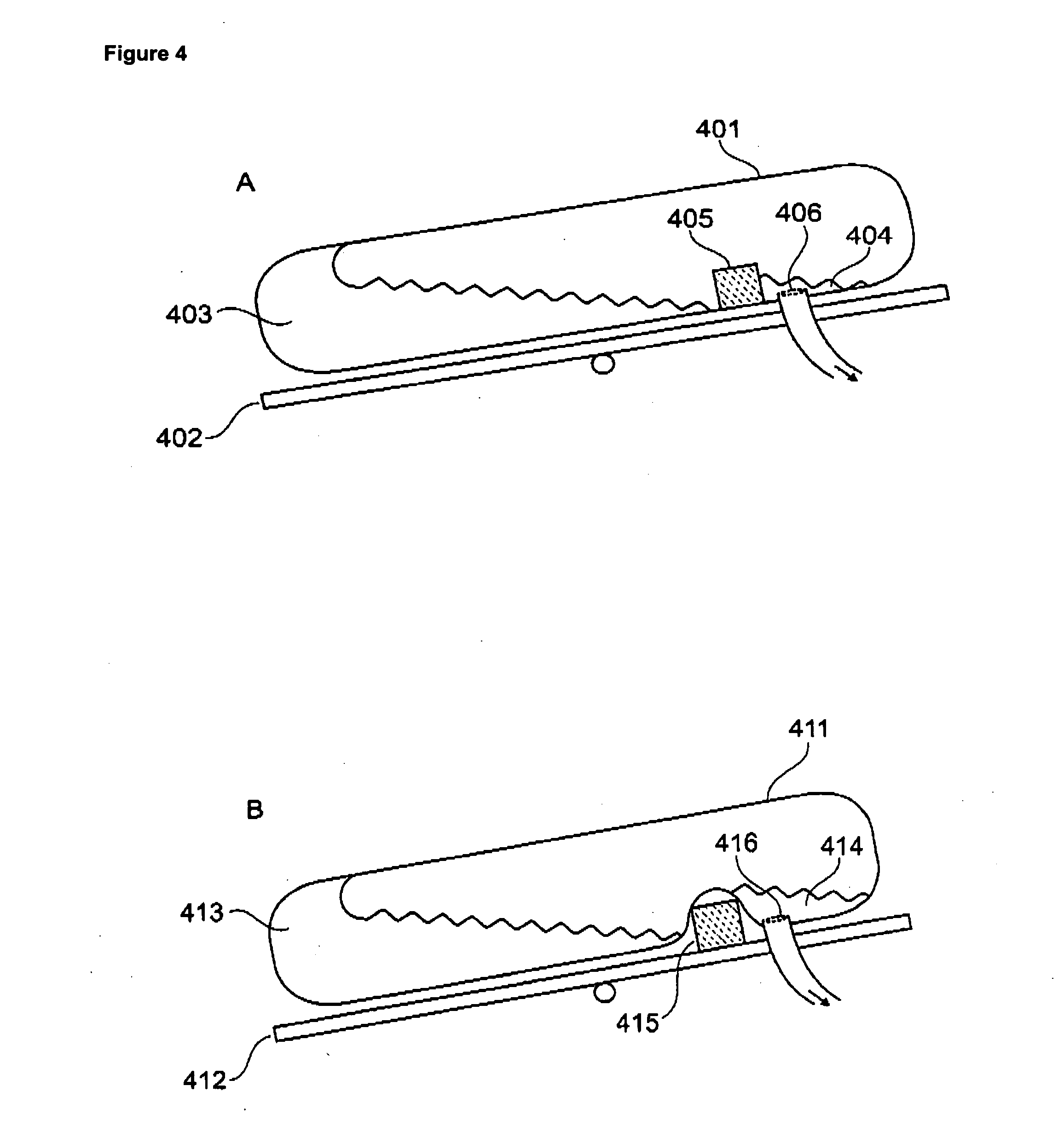
Method for separating biological substances by using photoresist
InactiveUS6194157B1Easy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsBiopolymerLength wave
After a photoresist (2) is used to fix a biological sample, in order to obtain a particular biological substance, for example, a certain cell or biopolymer, from the biological sample embedded in the photoresist (2), properties of the photoresist are changed by exposing the portion of the photoresist (2) that covers the biological substance to light L which has an appropriate wavelength. The biological substance embedded in the changed photoresist is collected.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Analytical device
InactiveUS7186356B2Decrease in electrical conductanceDecrease quantum tunnelling conductanceConductive materialResistors adjusted by auxillary driving meansBiological speciesFiller metal
A sensor for chemical species or biological species or radiation presenting to test fluid a polymer composition comprises polymer and conductive filler metal, alloy or reduced metal oxide and having a first level of electrical conductance when quiescent and being convertible to a second level of conductance by change of stress applied by stretching or compression or electric field, in which the polymer composition is characterized by at least one of the features in the form of particles at least 90% w / w held on a 100 mesh sieve; and / or comprising a permeable body extending across a channel of fluid flow; and / or affording in-and-out diffusion of test fluid and / or mechanically coupled to a workpiece of polymer swellable by a constituent of test fluid.
Owner:PERATECH HOLDCO
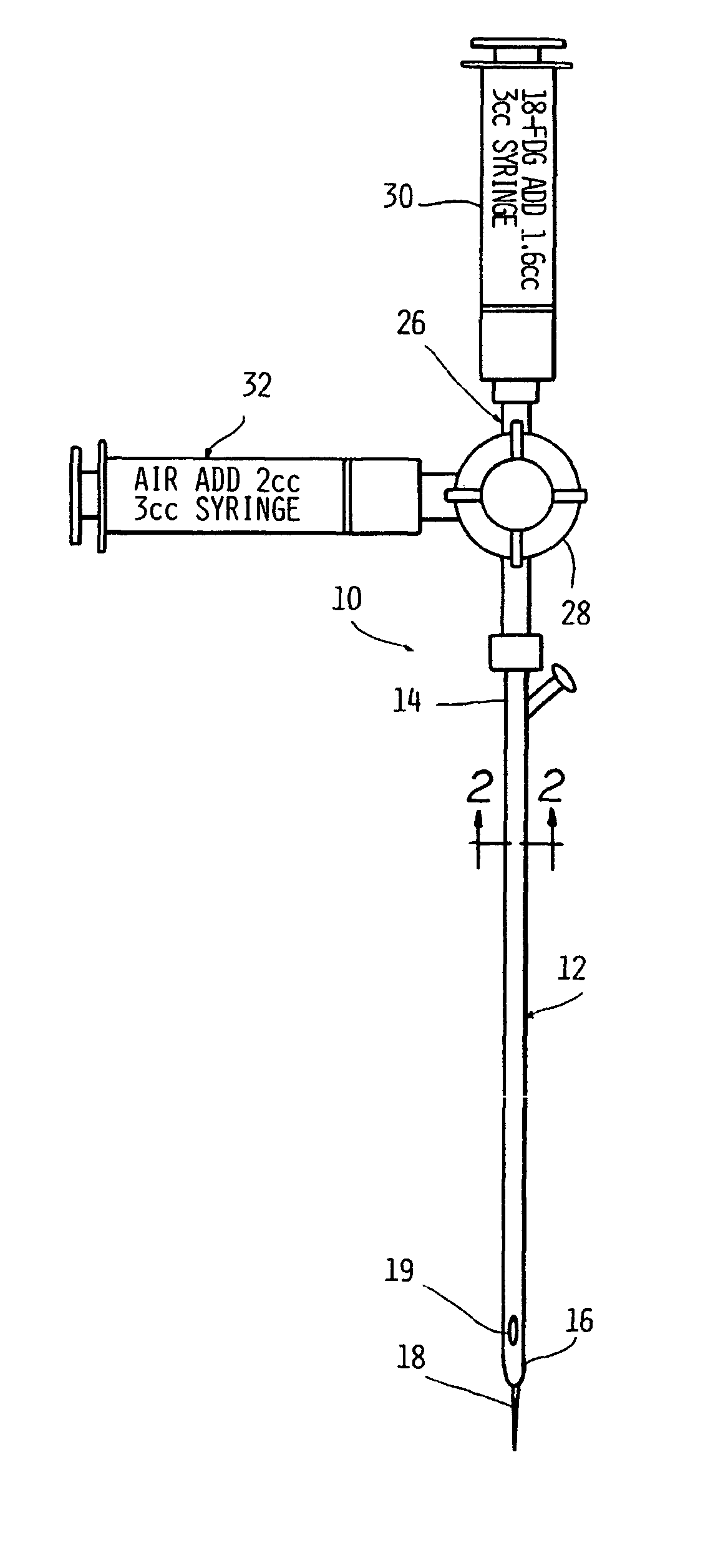
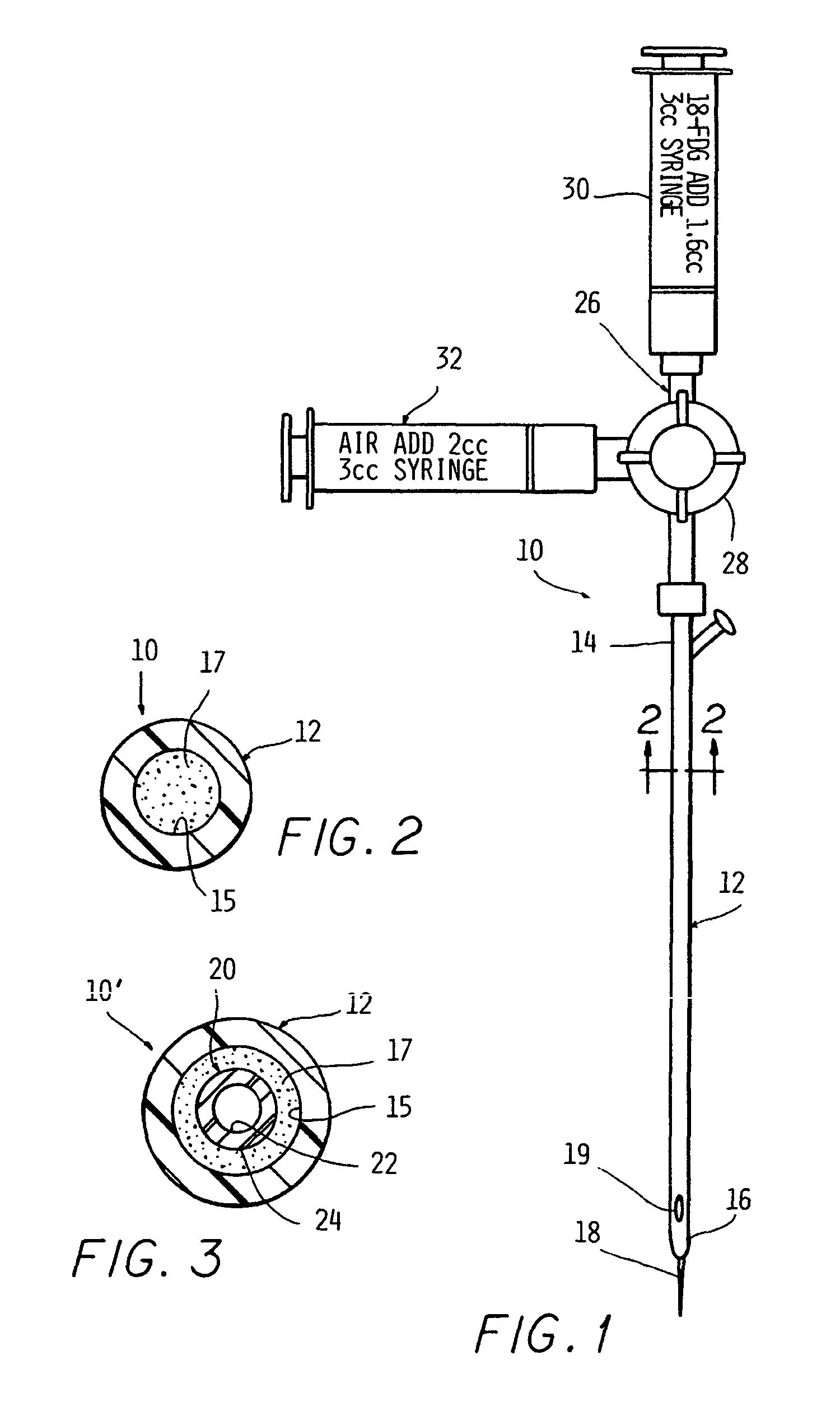
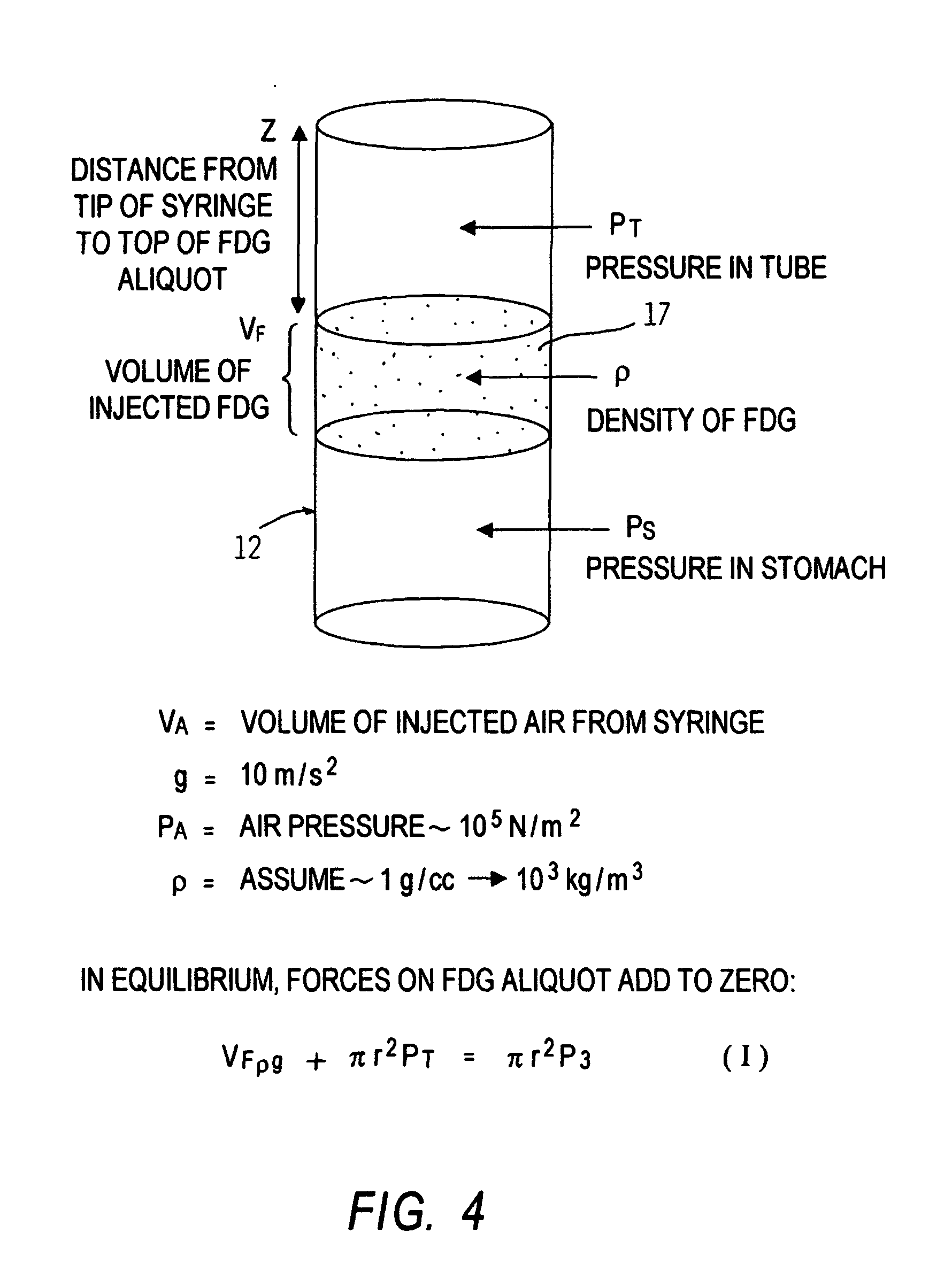
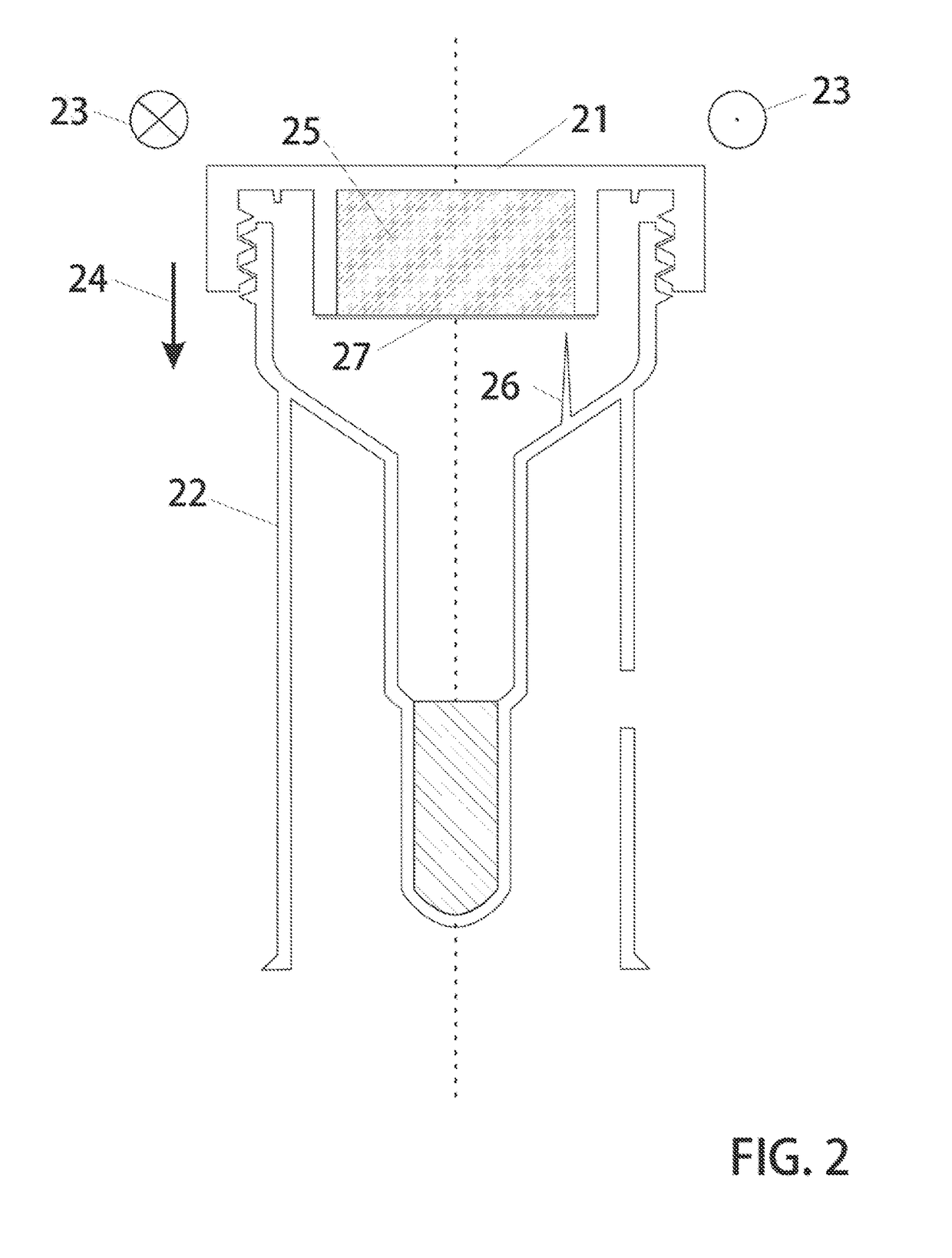
Internal marker device for identification of biological substances
InactiveUS20050004456A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationSurgeryCritical structureComputing tomography
A device for visualizing structure located on the interior of a biological substance. The device includes a marker member that may be a solid cylinder or lumen having an interior volume having a distal end removably insertable in the biological substance relative to the interior structure to be visualized. An image-enhancing material is contained relative to the marker member in a manner such that the imaging material does not directly contact the biological substance. The imaging material of choice is one capable of producing an emission or signal detectable external to the biological substance by suitable imaging instrumentation. Also disclosed is a method for visualizing critical structures or radiation therapy targets in imaging processes such as positron emission tomography and / or single photon emission computerized tomography, MRI, or ultrasound either used alone or in combination or in registration with anatomical imaging processes such as computed tomography or mammography.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN +1
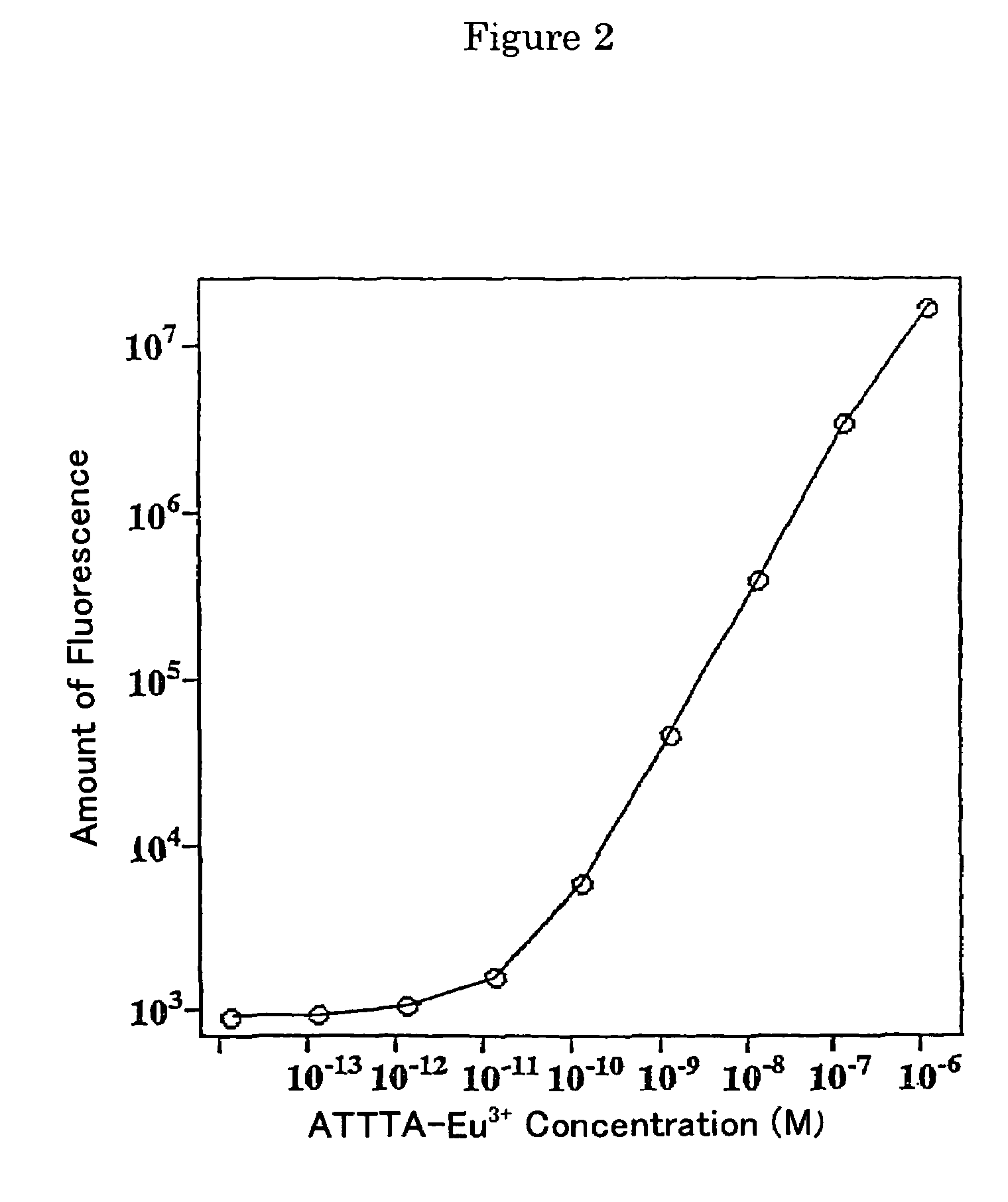
Fluorescent label compounds
InactiveUS7465747B2Long fluorescence lifetimeSufficiently stableBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementCoordination complexFluorescence assay
It is intended to provide novel labeling reagents characterized by having a group capable of binding to a substance to be labeled (for example, a biological substance, a physiologically active substance, etc.), easily forming a complex together with a rare earth ion, the complex being stable in an aqueous solution, and having a sufficient fluorescence intensity and a long fluorescence life time regardless of buffer types; complexes composed of the above labeling reagent with a rare earth ion; fluorescence labels containing the above complex; a fluorescence assay method using the above fluorescent label; etc. Namely, labeling reagents comprising a compound having a 2,2′:6′,2″-tripyridine skeleton or a 2,6-dipyrazolopyridine skeleton and having a group capable of binding to a substance to be labeled (for example, a biological substance, a physiologically active substance, etc.) and a group capable of forming a complex together with a rare earth ion; complexes composed of the above labeling reagent with a rare earth ion; fluorescence labels containing the above complex; a fluorescence labeling method using the above complex as a label; and a fluorescence assay method using the above fluorescent label.
Owner:TOKYO CHEM IND +1
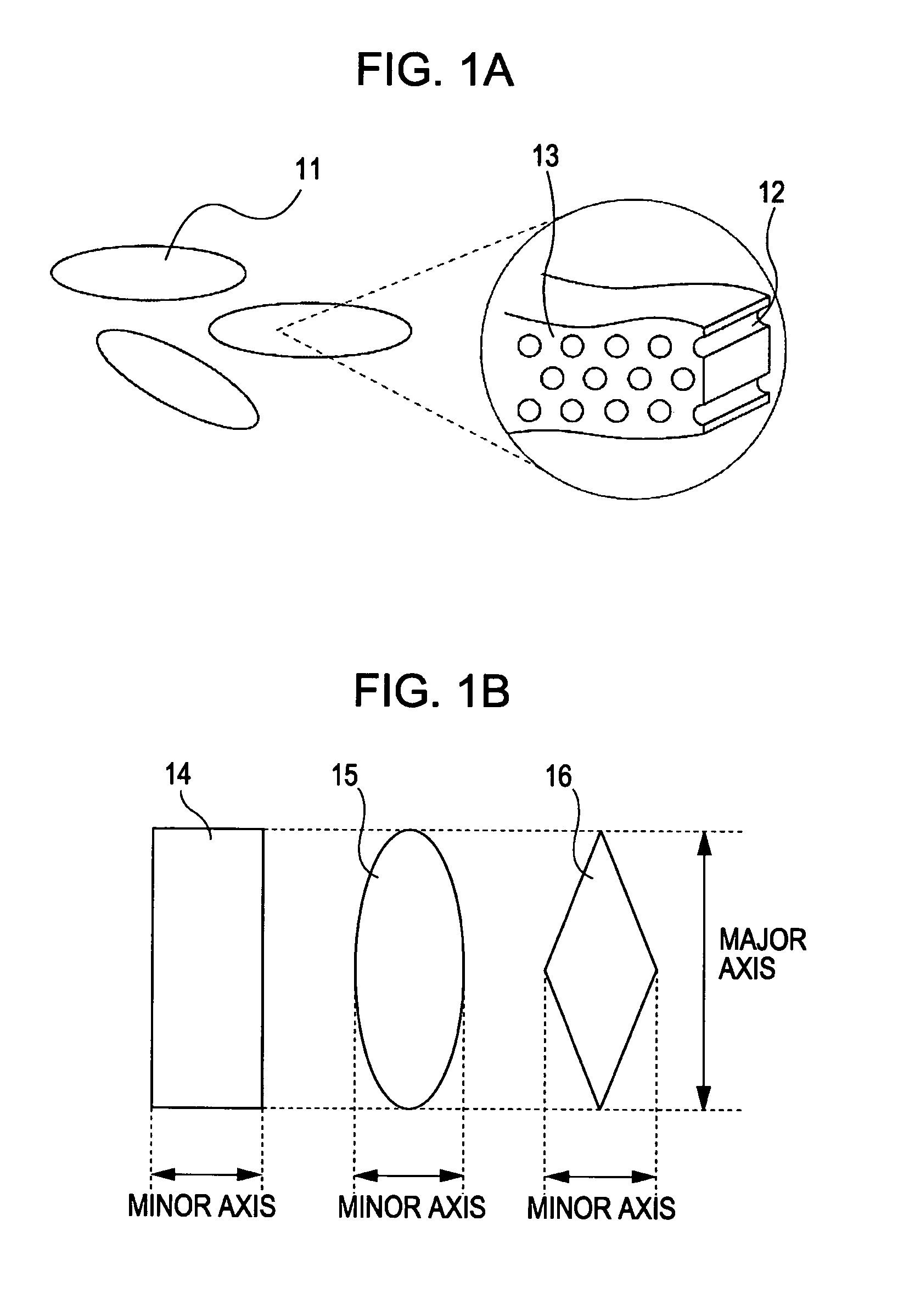
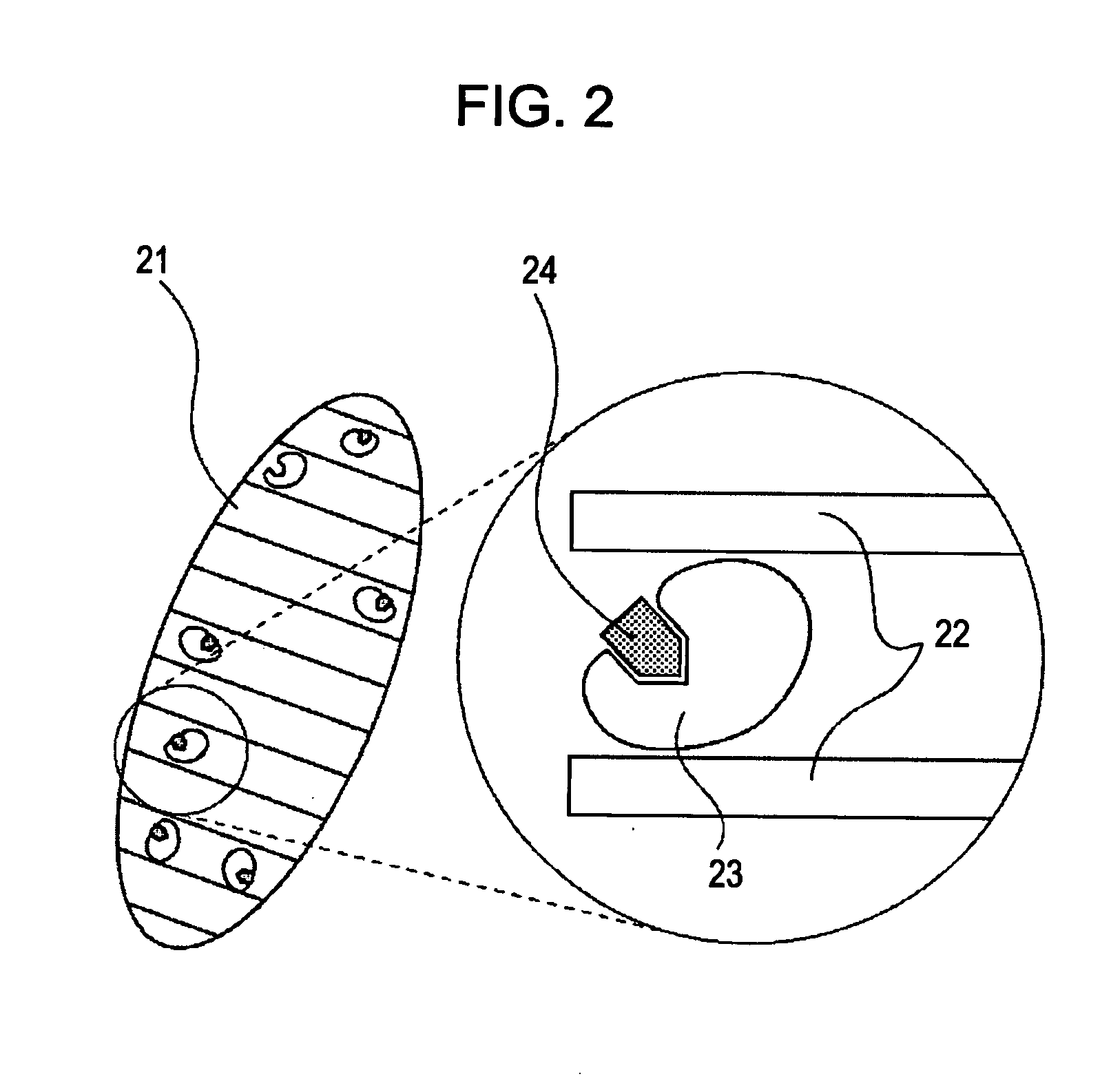
Particle having mesopore loaded with biological substance, sensor including the same, and method for detecting specimen
InactiveUS20070148044A1Small aspect ratioHigh sensitivityCurrent/voltage measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLong axisPorous particle
The present invention provides a porous particle loaded with a larger amount of biological substance. A rod-shaped particle according to the present invention includes a plurality of mesopores that crosses the major axis of the rod-shaped particle and that is loaded with the biological substance.
Owner:CANON KK
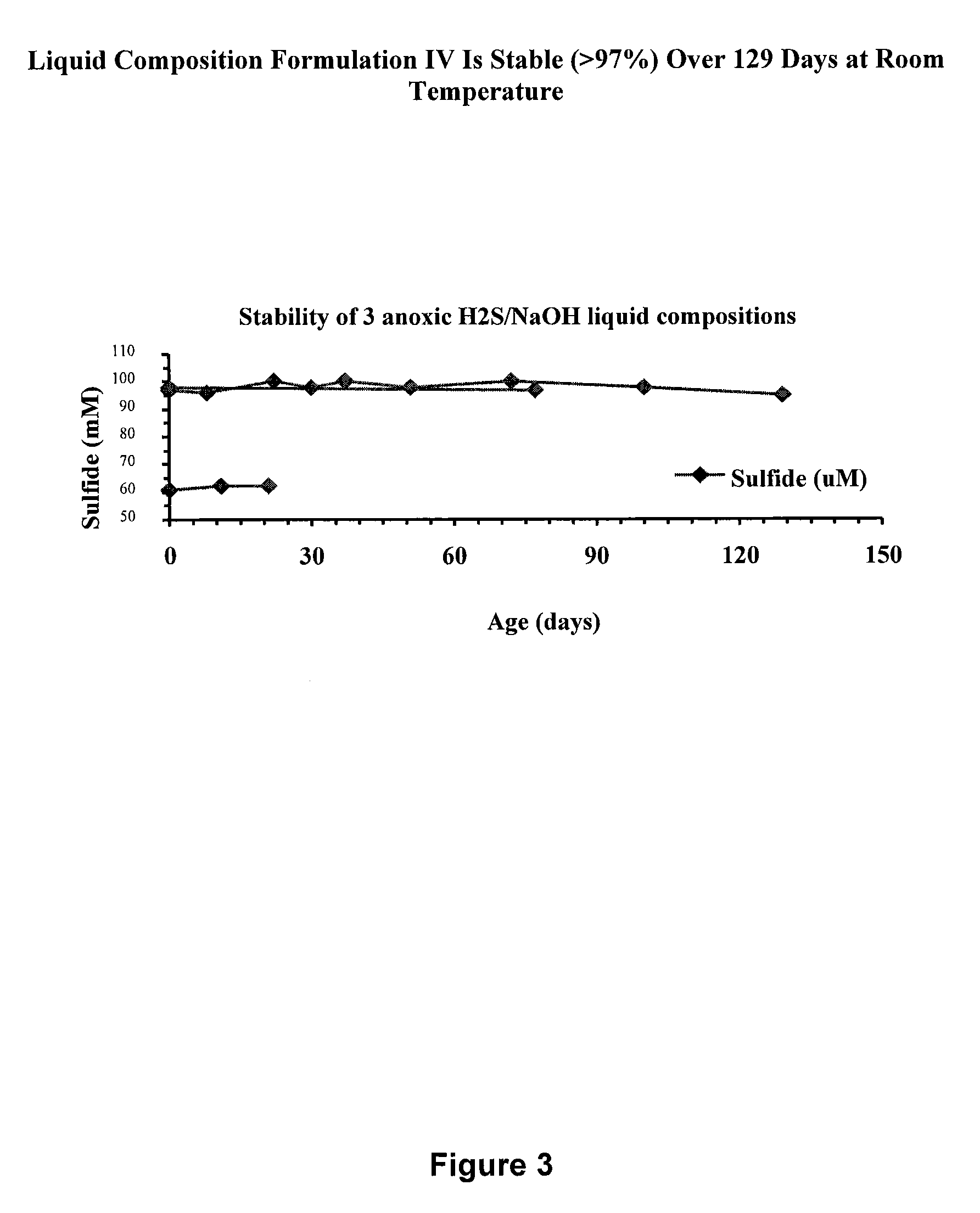
Liquid chalcogenide compositions and methods of manufacturing and using the same
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
Detection Device Based on Surface Plasmon Resonance Effect
InactiveUS20100021347A1Properly detectRapidly understandMaterial analysis by optical meansLaboratory glasswaresAmount of substanceElectrically conductive
The present invention describes a detection device based on the surface plasmon resonance effect, comprising: (1) a rotational microfluidic substrate (40) with channels (45), valves (50) and reservoirs (41,44) and at least one Detection Zone (42) wherein said Detection Zone comprises a Detection Surface (DS) built on top of a dif tractive thin electrically conductive layer, —(2) a system comprising a light emitter (20) and a light detector (30) capable of transducing the occurrence of events near the DS by exploiting the surface plasmon resonance effect in the diffractive conductive layer, —(3) a mechanism for controlling the rotation speed, duration and positioning of the rotational microfluidic substrate, in order to move a predefined liquid volume from an initial reservoir into a Detection Zone and finally into a final reservoir. The sensor described in the present invention enables the determination of the concentration of specific chemical and / or biological substances present at the DS or present in the fluid near the DS.
Owner:BIOSURFIT
Solids discharge centrifugal separator with disposable contact elements
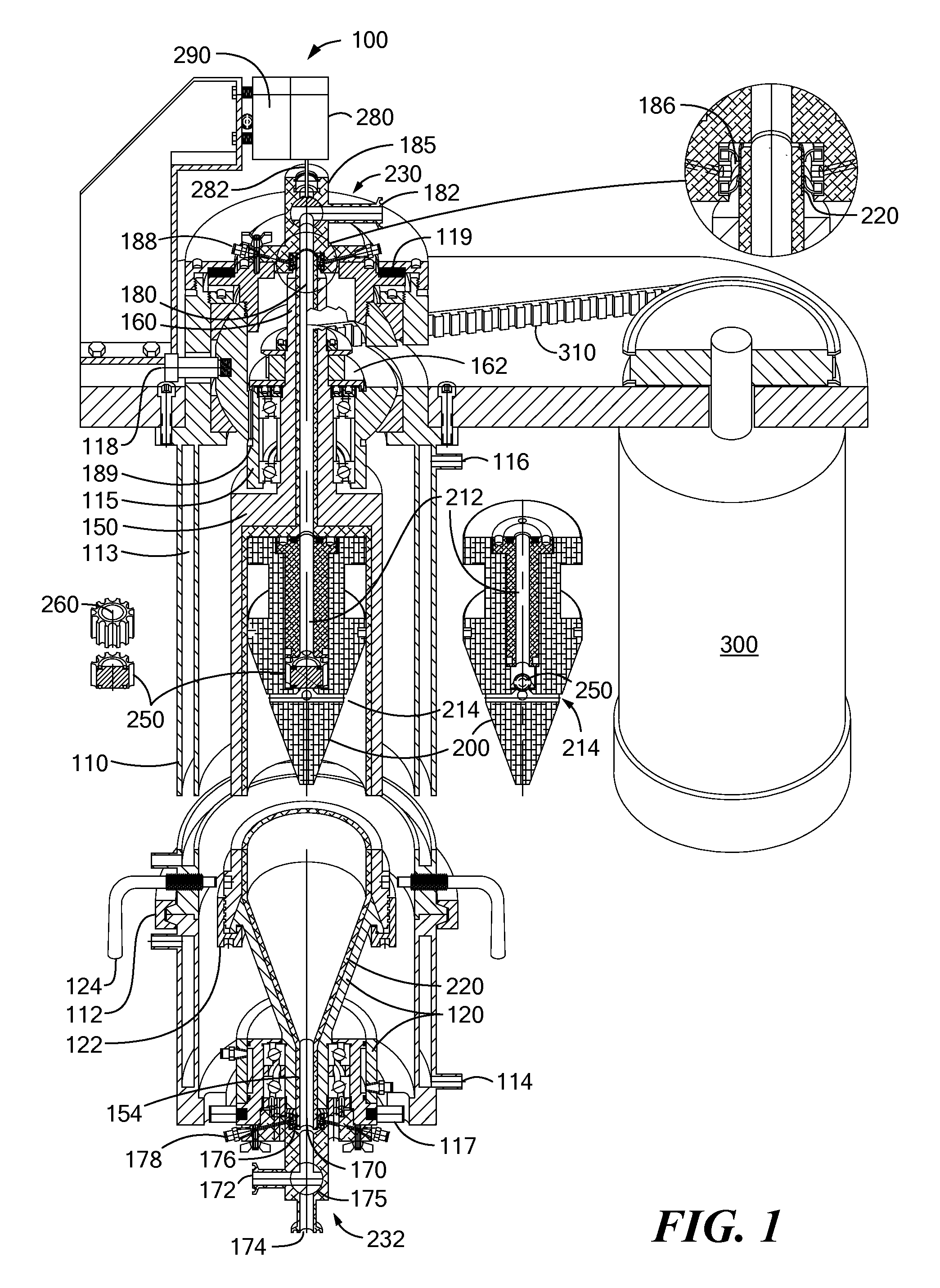
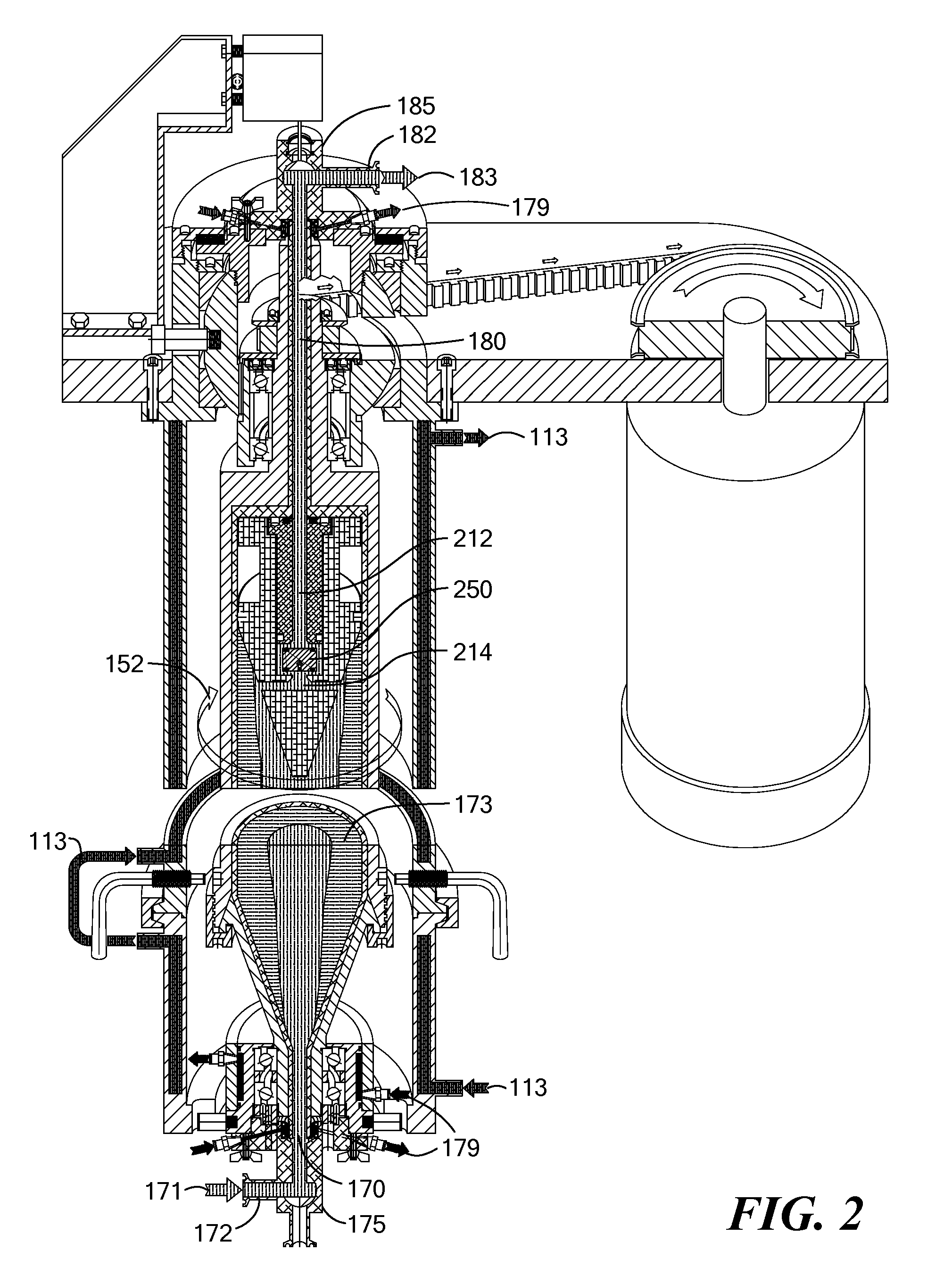
ActiveUS20100167899A1Effective recoveryLow-shear fillingDispersed particle separationRotary centrifugesEngineeringContact element
A hermetically sealed solids discharge centrifugal separator exhibits low-shear filling, acceleration, and separation of feed material. The separator can be particularly useful for separation and recovery of sensitive solids such as chemical or biological substances. The separator accommodates disposable sample contacting elements to eliminate the need for clean-in-place and sterilize-in-place operations. Some embodiments of the separator feature dual solids discharge pistons, which fully optimize recovery of valuable solids.
Owner:CARR ROBERT BRET
Magnetic substance-biosubstance complex structure, peptide fragment capable of linking to magnetic substance and gene therefor, and process for producing the complex structure
InactiveUS20070054315A1Good reproducibilityEfficient executionBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide fragmentAmino acid
A magnetic substance-biosubstance complex structure comprises a magnetic substance-containing carrier and a bio-substance immobilized on the carrier, the biosubstance being immobilized through a spacer comprising an amino acid sequence on a surface of the carrier.
Owner:CANON KK
Computational methods and compositions
The invention in some aspects relates to methods, devices and compositions for evaluating material properties, such as mechanical and rheological properties of substances, particularly biological substances, such as cells, tissues, and biological fluids. In some aspects, the invention relates to methods, devices and compositions for evaluating material properties of deformable objects, such as cells. In further aspects, the invention relates to methods, devices and compositions for diagnosing and / or characterizing disease based on material properties of biological cells.
Owner:BROWN UNIV RES FOUND INC +1
Purification of and air methods of making and using the same
InactiveUS20120283508A1High methodHigh purityMechanical apparatusOrganic chemistryParticulatesPhysical chemistry
Alkaline-tolerant and halophilic aspergillus strain and application thereof in environmental management
InactiveCN103436450AEfficient degradationFungiAgriculture tools and machinesLaboratory cultureEuryhaline
The invention belongs to the field of microbial engineering and technology, and specifically relates to an alkaline-tolerant and halophilic aspergillus strain and an application thereof in environmental management. The strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on April 20th, 2012, with a preservation name of aspergillus JL and a preservation number of CGMCC 6025. The strain has the characteristic of degrading biological substances such as straws in a high salt and alkali environment and can be used for improvement of saline lands and treatment of environmental pollutions.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method of producing membrane vesicles
InactiveCN1426461AEasy to shareIncreased immunogenic potentialAntipyreticSerum albuminCentrifugationBiological materials
The present invention relates to methods of preparing biological material, for use in various experimental, diagnostic or therapeutic uses, including immunotherapy treatment or prophylaxy of tumors. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods of preparing membrane vesicles (in particular exosomes) released by various types of mammalian cells, comprising diafiltration and / or density cushion centrifugation. The invention also provides novel methods for characterizing and analyzing exosome preparations, which can be used in quality control assay for the purpose of pharmaceutical product production. The invention is suitable to produce pharmaceutical grade preparations of such membrane vesicles and to fully characterize said preparations, for use in human beings.
Owner:阿诺塞斯公司
Silica nanoparticle embedding quantum dots, preparation method thereof and biosubstance labeling agent by use thereof
Disclosed is a quantum dot-embedded silica nanoparticle having plural quantum dots embedded within the silica nanoparticle, wherein the number of quantum dots existing in a concentric area within 10% of a radius from a center of the silica nanoparticle accounts for 10 to 70% of the number of total quantum dots embedded in the silica nanoparticle.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA MEDICAL & GRAPHICS INC
Perfusion bioreactor
InactiveUS20120100576A1Improve production yieldMaintaining and even improving quality of productBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFungiPerfusion bioreactorCulture cell
The present invention pertains to a system for culturing cells comprising a culturing bag and a continuous flow centrifuge wherein the cells are continuously separated from the supernatant and are recycled into the culturing bag. Further provided are methods for culturing cells and for producing a biological substance using the device for culturing cells, and the use of a bag for culturing cells in said device or said methods. In particular, a perfusion system for culturing cells is provided wherein the wave technology for culturing cells is combined with continuous flow centrifugation for separating the medium from the cells.
Owner:GLYCOTOPE GMBH
Multiprobe optical fibre evanescent wave biological sensor
InactiveCN1434287AIncrease the angle of incidenceIncrease the number of reflectionsBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceFiberSignal on
The invention is a multiple-probe fibre-optical evanescent-wave biosensor, including the laser exciting light path, the fluoescent receiving light path, the sample flow path and the scan system, respectively used to excite the fluorescence of the measured biological substance on the surface of the fibre-optical core wire, receive the fluorescent signal from the fibre-optical and finish the photoelectric conversion, indraft the sample and make the scanning detection on the fluorescent signal on multiple pieces of fiber-optical.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Nonlinear magnetophoretic separation of biological substances
InactiveUS20100279887A1Highly sensitive separationLibrary screeningMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteBiochemistry
A method of separating a target biological analyte from a mixture of substances in a fluid sample employs nonlinear magnetophoresis. Magnetic particles having the capacity to bind to the target analyte are contacted with the fluid sample so that the analyte is immobilized on the surface of at least some of the particles. The magnetic particles are provided adjacent an array of micromagnets patterned on a substrate so that the particles are attracted the micromagnets. The magnetic particles are then subjected to a traveling magnetic field operating at or above a frequency effective to sweep those particles not bound to analyte to an adjacent micromagnet. Those magnetic particles bound to analyte have a larger size or smaller magnetic moment that prevents them from being moved to adjacent micromagnets, thereby affording separation of the analyte.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
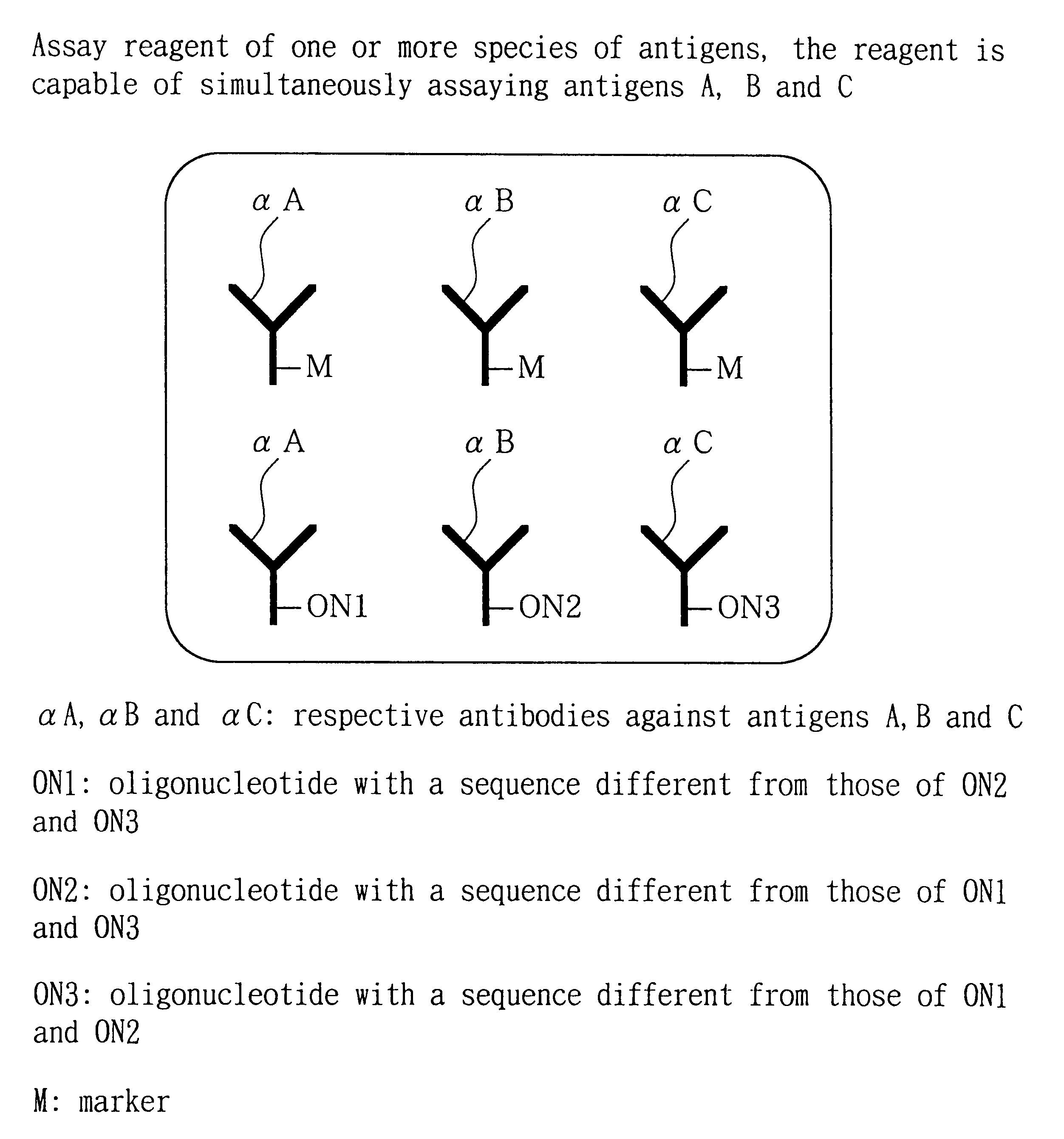
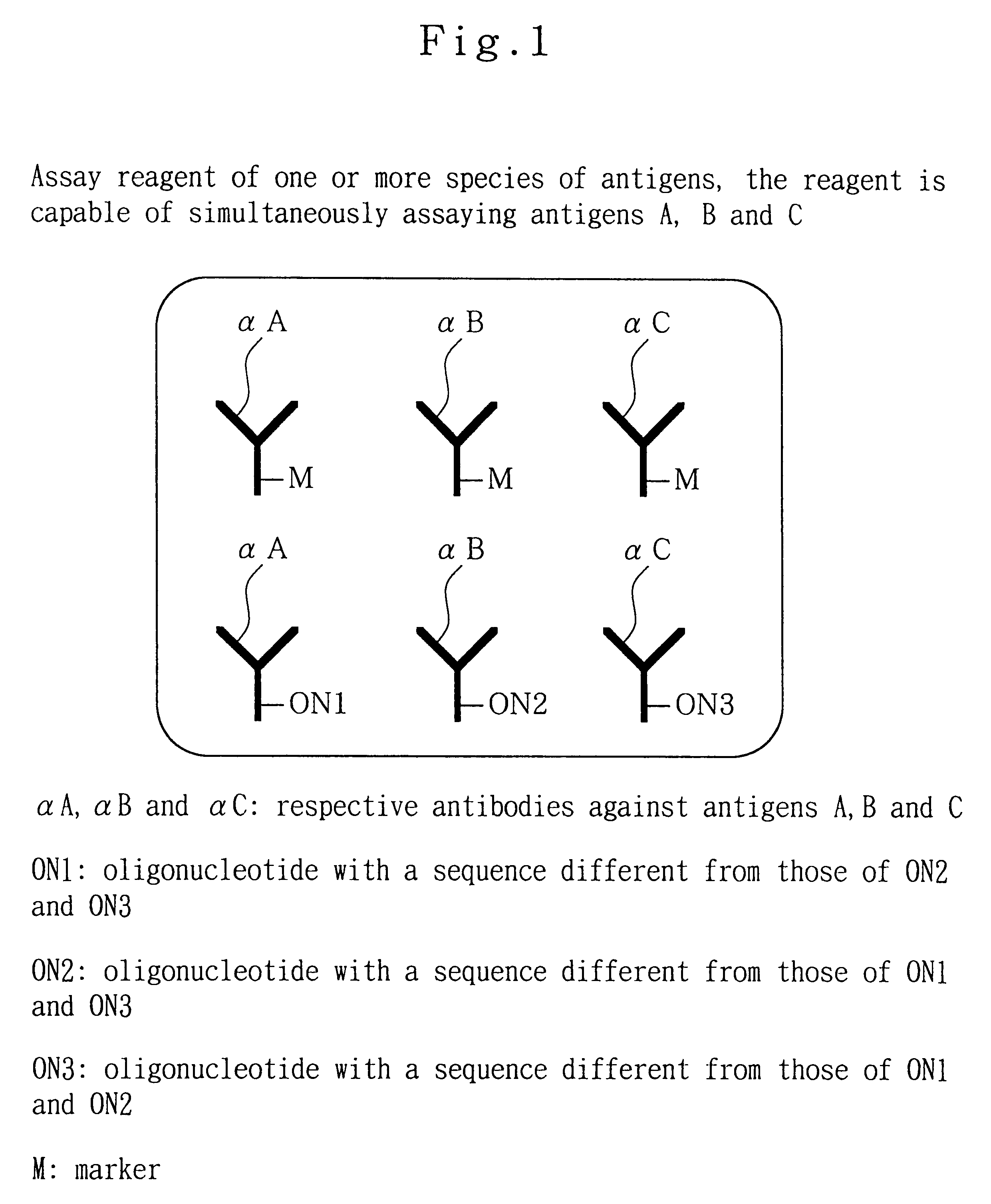
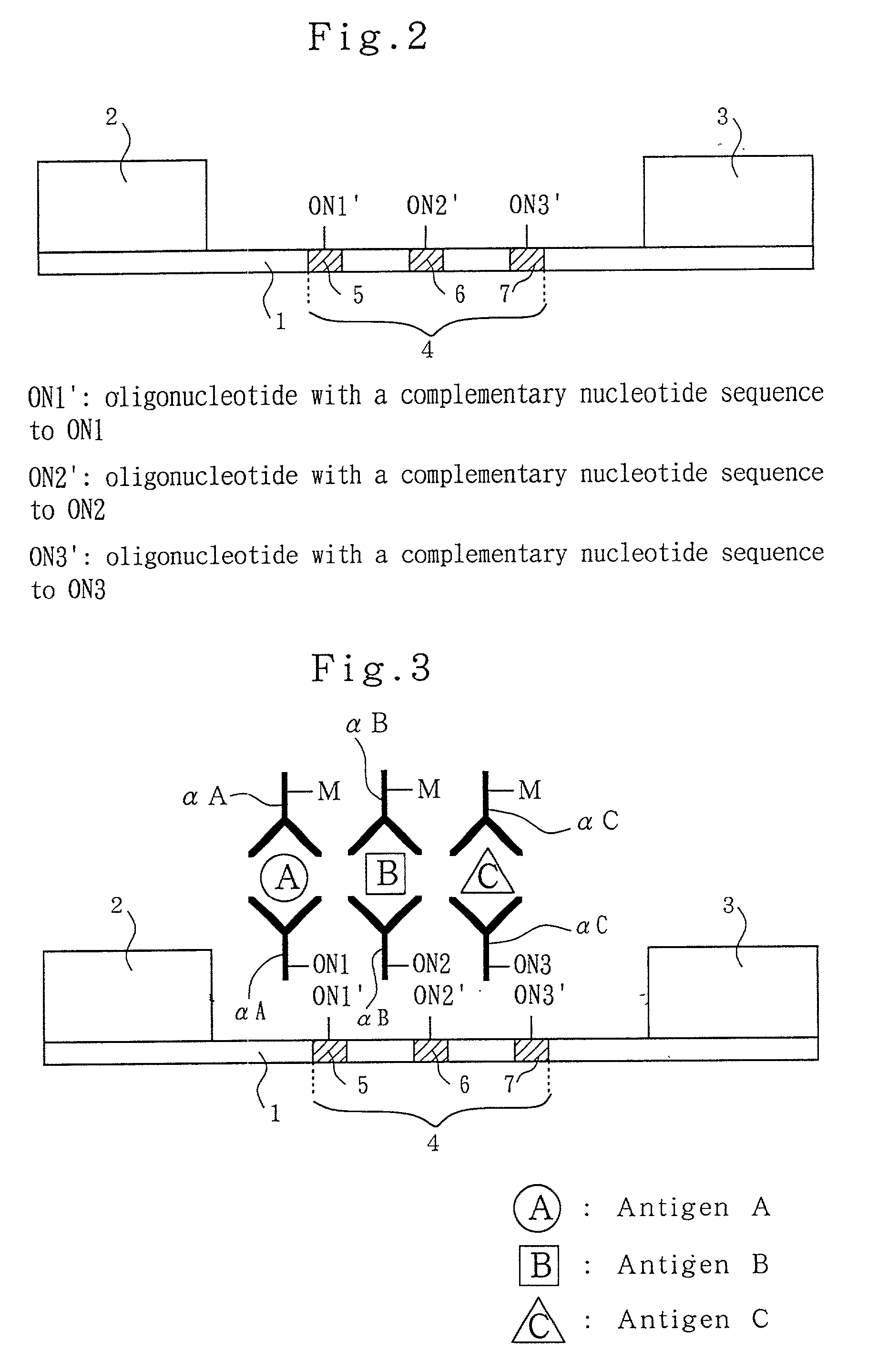
Analytical method, kit, and apparatus
InactiveUS20010006775A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayAnalyte
Providing an assay method capable of simultaneously determining the presence or absence of one or more species of biological substances or assaying the amounts thereof with a single assay device, a kit therefor and an assay device thereof. The amount thereof or the presence thereof is detected, by putting a liquid sample containing one or more species of analytes in contact to a reagent including one or more species of marker-labeled ligands and one or more species of nucleic acid-labeled ligands, to generate one or more species of complexes, developing the generated one or more species of complexes through capillary phenomenon in developing element 11 in a sheet form, capturing the complexes through complementary nucleic acid binding onto anti-bond elements consisting of nucleic acids on detection zones 15, 16 and 17 formed depending on each of one or more species of nucleic acids immobilized on the detection zone 14, thereby capturing a complex depending on the analyte species, through the complementary binding between the anti-bond element and the bond element, to form an independent band and to assay the amount or the presence on the detection part.
Owner:NISSUI PHARMA
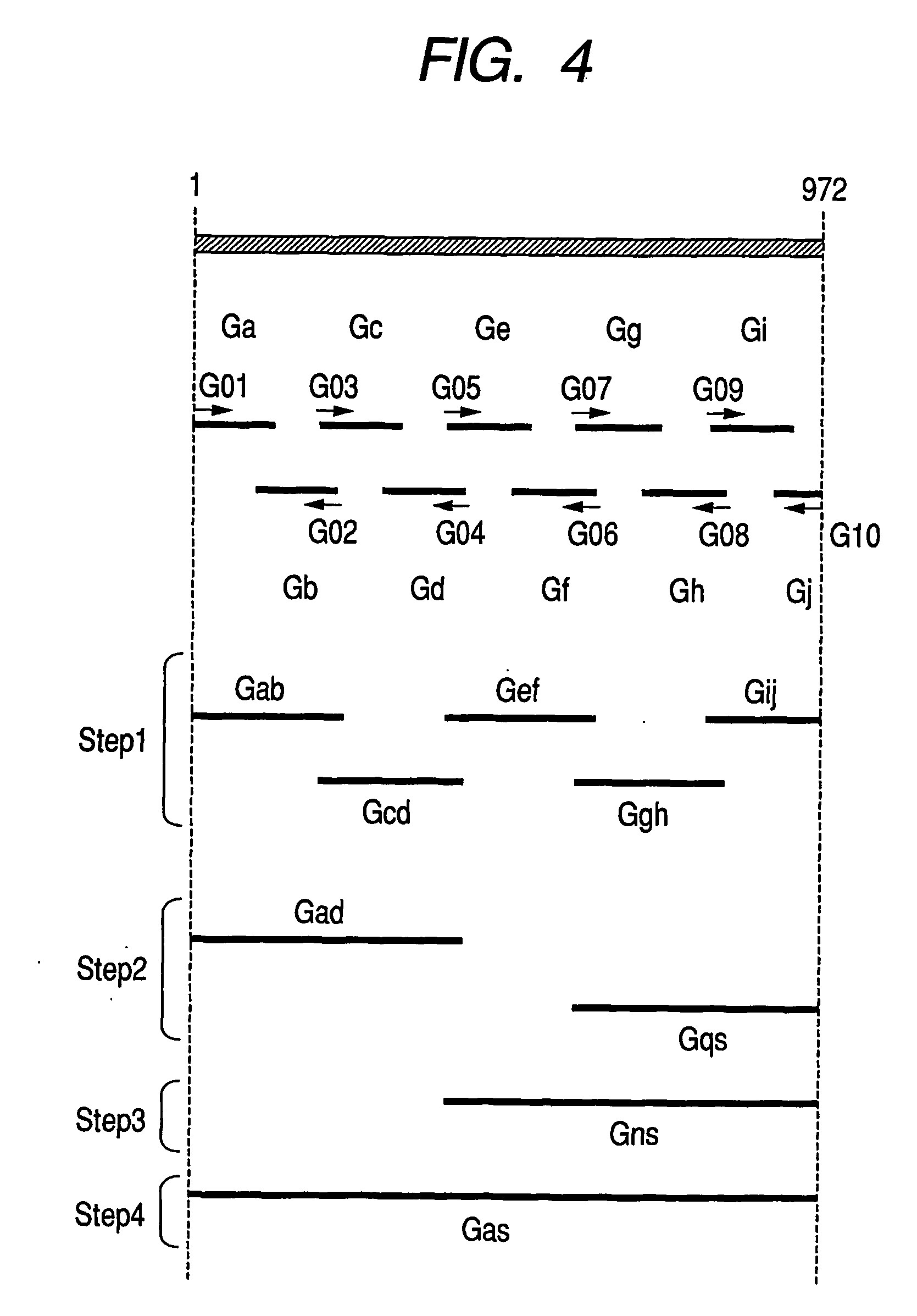
Array having substances fixed on support arranged with chromosomal order or sequence position information added thereto, process for producing the same, analytical system using the array and use of these
InactiveUS20070105103A1Efficient analysisEasy to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnimal reproductionBiological bodySynthetic substance
In fabricating various types of arrays such as a micro array, different kinds of biosubstances, or synthetic substances interacting with the biosubstances, are arranged and immobilized on a support such that the chromosomal order of base sequence blocks, corresponding to the biosubstances, is ascertainable. The biosubstances may be nucleic acids such as DNA, or polypeptides such as protein. The synthetic substances may be compounds that react with the biosubstances. By thus specifying the order of the biosubstances or synthetic substances immobilized on the support, the array can be used, for example, for screening in variety improvement of living organisms.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Genetic sample collection systems
InactiveUS20170246625A1Easy to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSample collectionCollection system
Biological sample collection kits are devised with physical features to enable a high performance collection system which delivers preprocessed biological matter via conventional shipping means to a testing laboratories. In particular, untrained and unskilled users deposit biological matter such as saliva or blood into a receiving vessel. By sealing the container, the user causes release of a premixed solution containing preservatives and optionally lysis reagents. In addition, a purification agent is arranged to bind to target molecules and facilitate their removal from solution. These time consuming processes occur while the sample is in transit to the testing facility such that when it arrives, it is in a preconditioned state immediately ready for execution of washing steps. Thus, the high performance containers taught herein are useful for collection biological samples and performing initial process steps on received matter—steps which are largely effected during the shipping stage of the transfer process.
Owner:PATHYWAY GENOMICS CORP
Near-infrared light-emitting phosphor nanoparticles, method for manufacturing the same, and biological substance labeling agent employing the same
InactiveUS20100171076A1Small particle sizeHigh emission intensitySynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsHigh intensityNanoparti cles
Disclosed are near-infrared light-emitting phosphor nanoparticles with an extremely small particle size, which emit light with a high intensity of emission and which are suitable for a biological substance labeling agent, a method for manufacturing the same, and a biological substance labeling agent employing the same. The near-infrared light-emitting phosphor nanoparticles of the invention are near-infrared light-emitting phosphor nanoparticles with an average particle size of from 2 to 50 nm, which when excited by a near-infrared light with a wavelength in the range of from 700 to 900 nm, emit a near-infrared light with a wavelength in the range of from 700 to 2000 nm, the nanoparticles being characterized in that at least a part of the composition is represented by a specific formula.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA MEDICAL & GRAPHICS INC
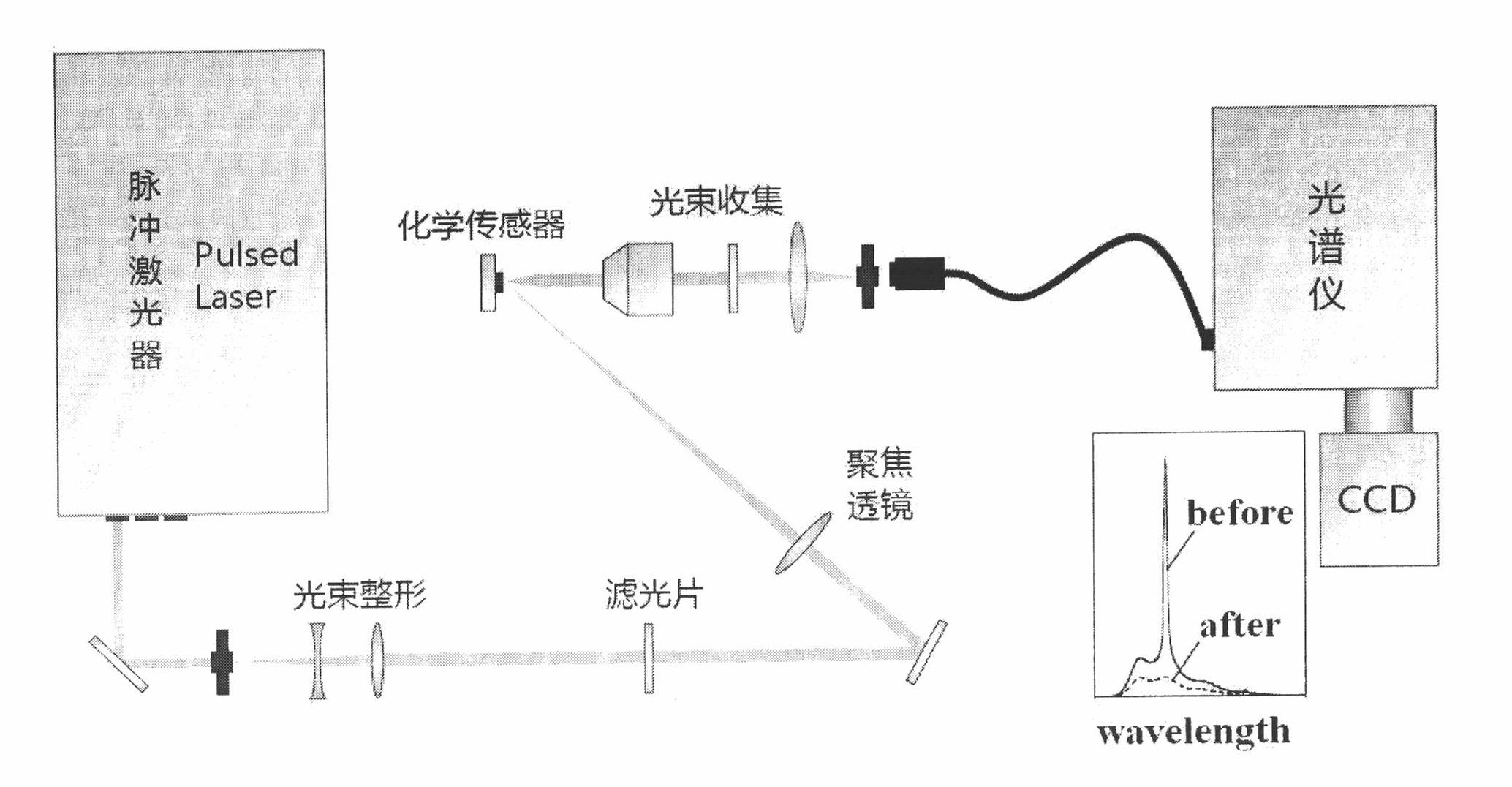
Chemical senor, method and application on basis of laser effects in fluorescence conjugated polymer
InactiveCN102095709AHigh sensitivityStrong anti-interference abilityActive medium materialFluorescence/phosphorescenceLower intensityHigh intensity
The invention relates to a chemical sensor, a method and application on the basis of laser effects in a fluorescence conjugated polymer. The sensor comprises micro resonant cavities and the fluorescence conjugated polymer combined with the micro resonant cavities. The fluorescence conjugated polymer is not only used as a sensing material, but also used as a laser gain medium. The fluorescence conjugated polymer is pumped by pulse laser and is modulated by various micro resonant cavities to generate and output excited and irradiated laser. After the fluorescence conjugated polymer reacts with an analyte, the fluorescence intensity and the gain coefficient of the polymer are changed so as to influence the laser propagation characteristic in the micro resonant cavities and change the output intensity of the laser, namely a sensing function can be realized. In the inention, the high intensity, the monochromaticity and the threshold value characteristic of the laser are utilized, the defects of low intensity, wide spectrum and low anti-interference capacity of fluorescence in the conventional fluorescence chemical sensor are overcome, and the chemical sensor has high sensitivity, high response speed and strong anti-interference capacity. Short-distance and remote detection of chemicals such as environmental pollutants, poison, chemical substances, biological material and the like can be realized simultaneously.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods of using polymers
Provided herein are materials and methods of reducing contamination in a biological substance or treating contamination in a subject by one or more toxins comprising contacting the biological substance with an effective amount of a sorbent capable of sorbing the toxin, wherein the sorbent comprises a plurality of pores ranging from 50Å to 40,000Å with a pore volume of 0.5 cc / g to 5.0 cc / g and a size of 0.05 mm to 2 cm and sorbing the toxin. Also provided are kits to reduce contamination by one or more toxins in a biological substance comprising a sorbent capable of sorbing a toxin, wherein the sorbent comprises a plurality of pores ranging from 50Å to 40,000Å with a pore volume of 0.5 cc / g to 5.0 cc / g and a size of 0.05 mm to 2 cm and a vessel to store said sorbent when not in use together with packaging for same.
Owner:CYTOSORBENTS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com