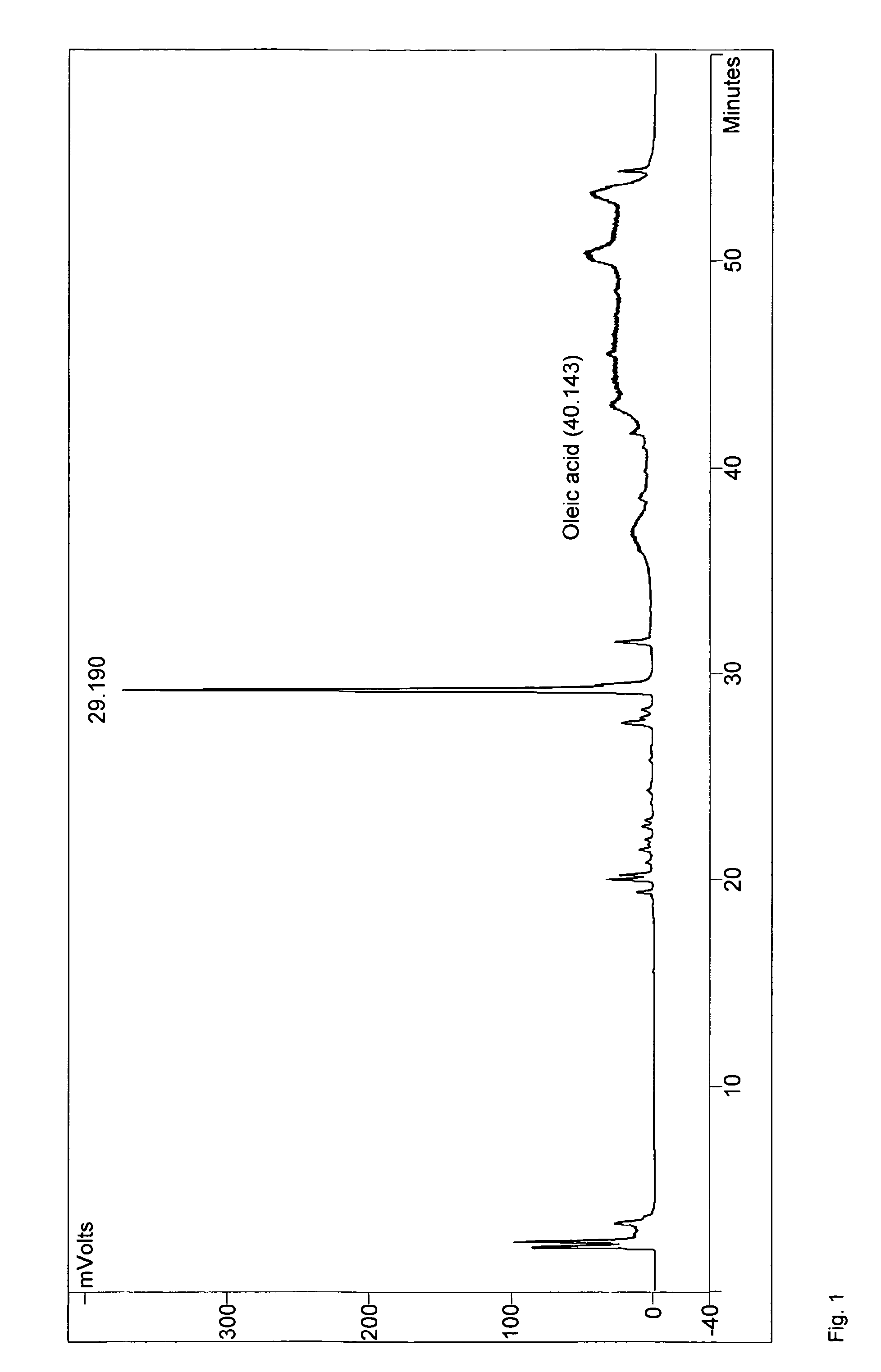
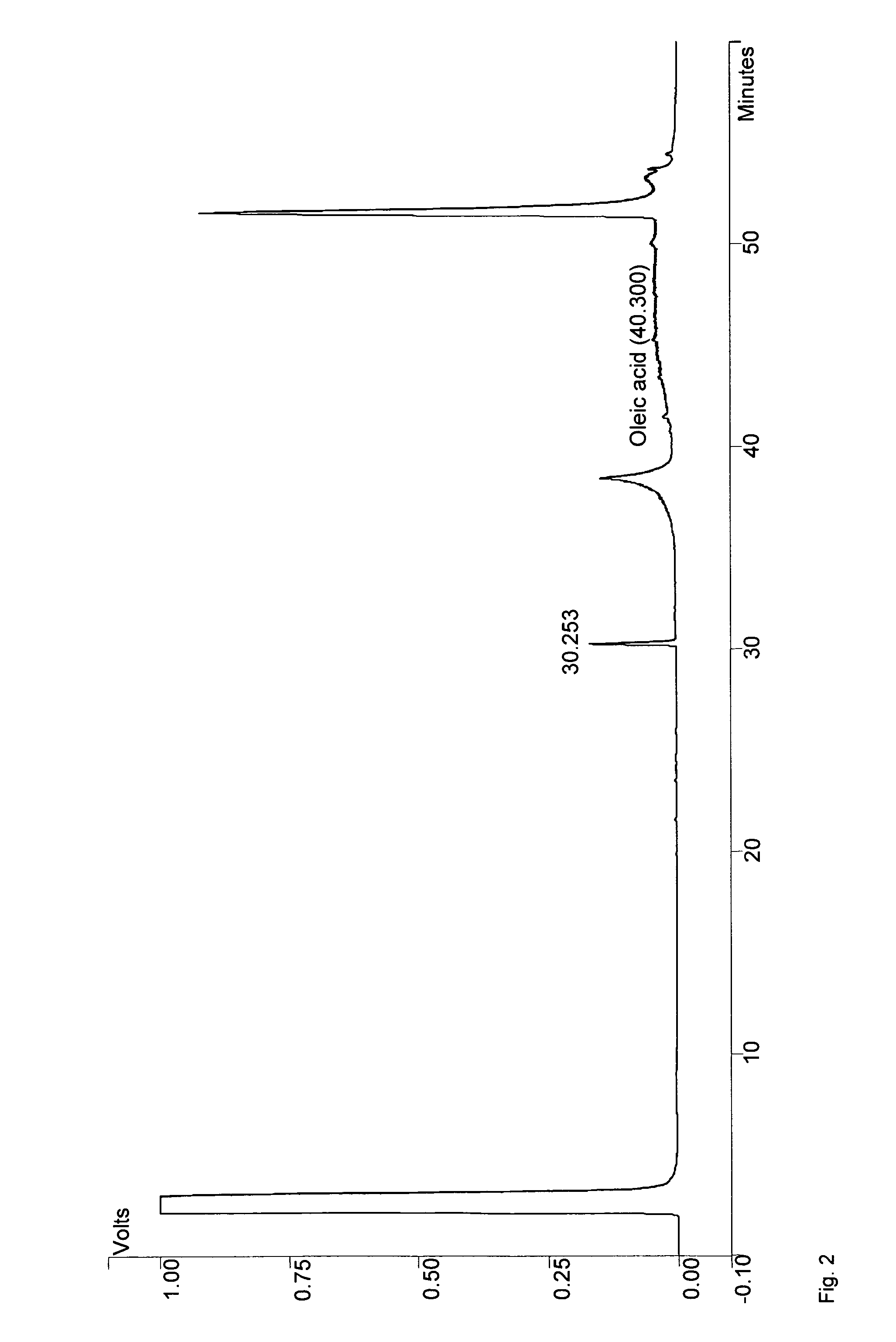
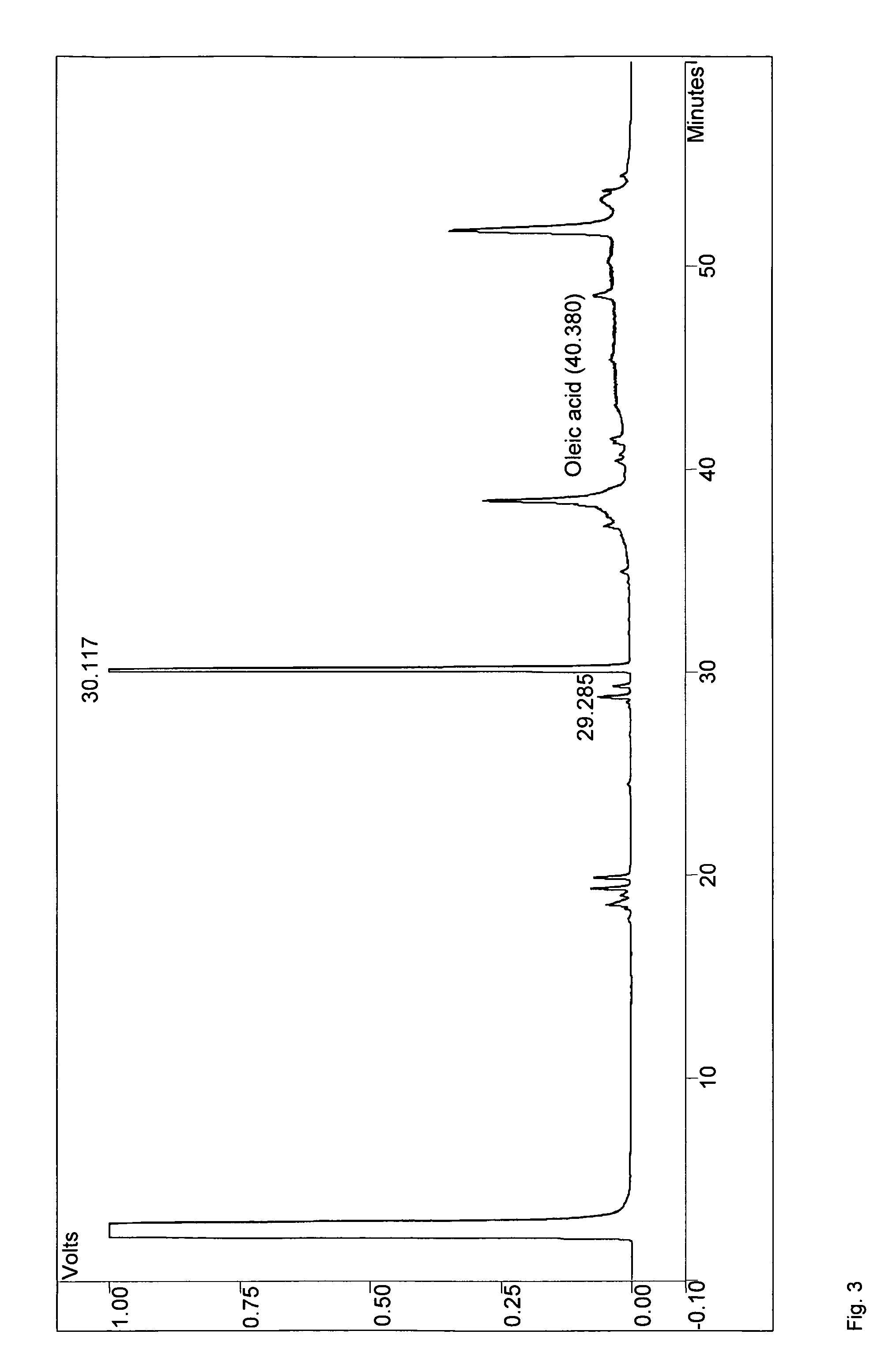
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
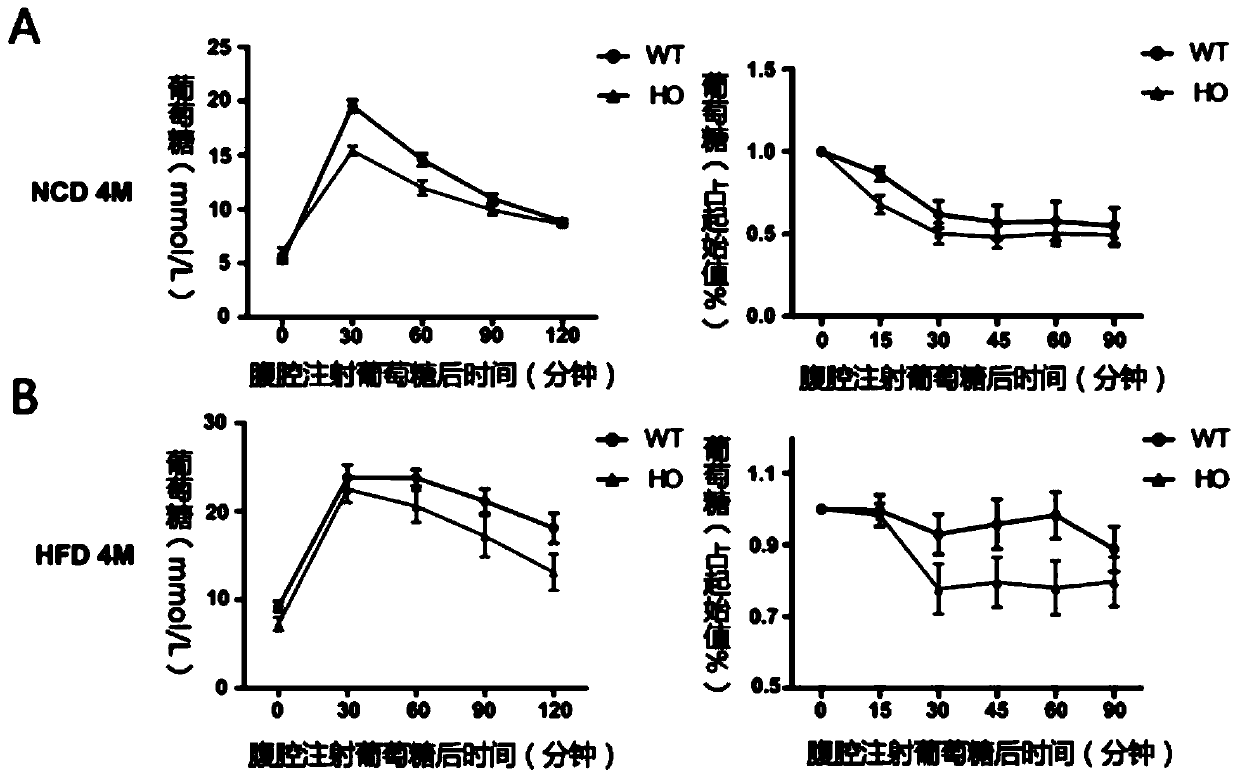
42 results about "Beta oxidation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
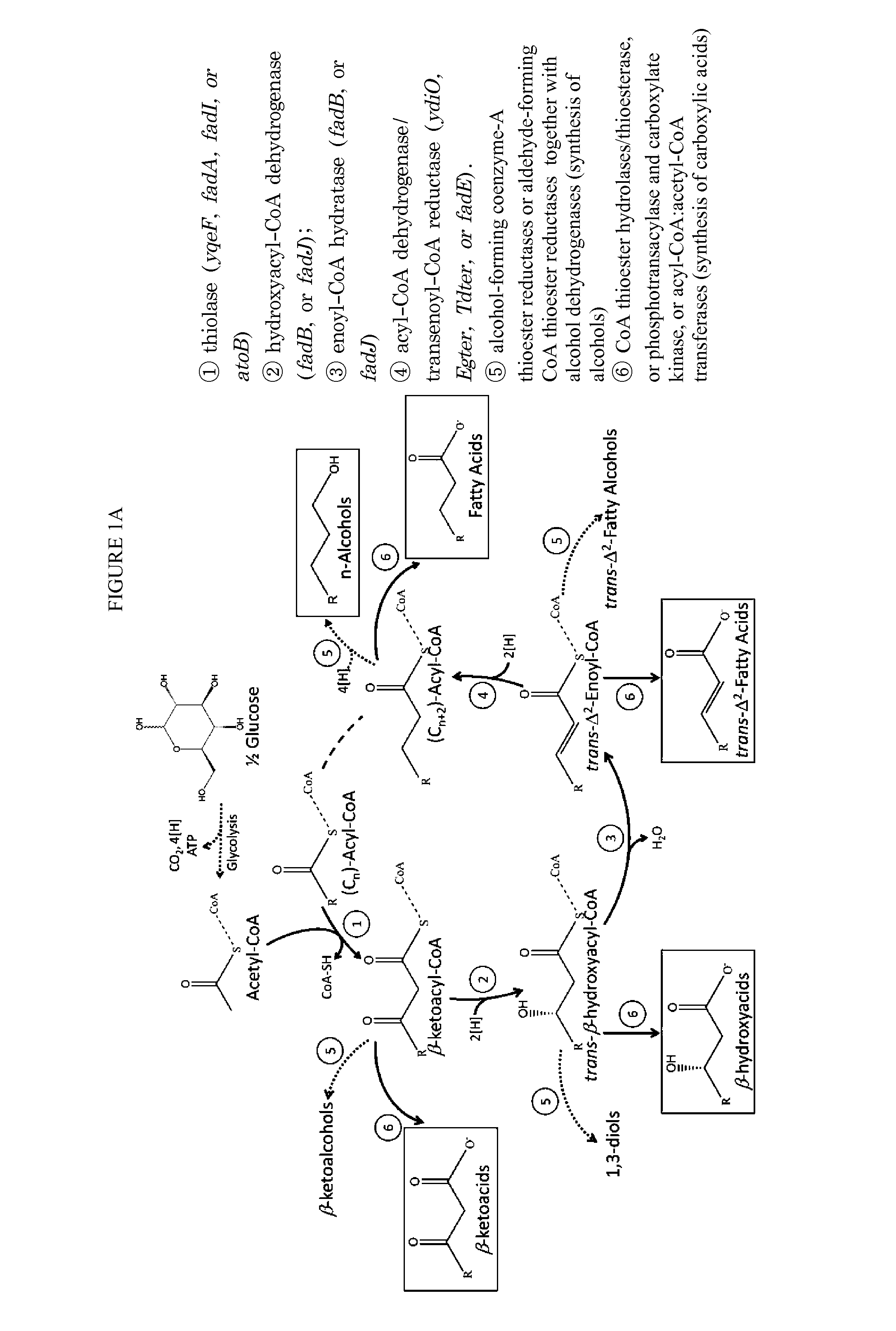
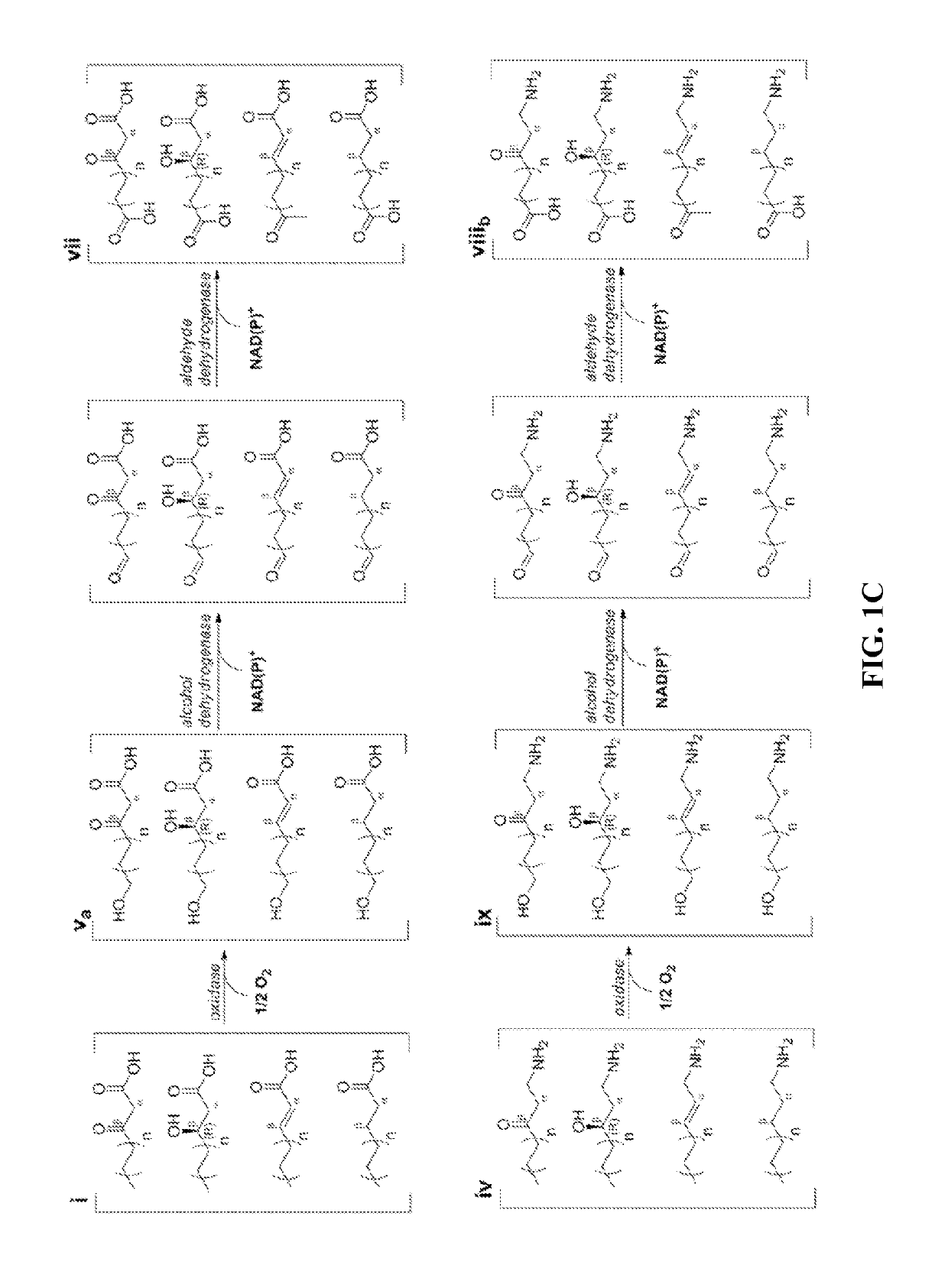
In biochemistry and metabolism, beta-oxidation is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle, and NADH and FADH₂, which are co-enzymes used in the electron transport chain. It is named as such because the beta carbon of the fatty acid undergoes oxidation to a carbonyl group. Beta-oxidation is primarily facilitated by the mitochondrial trifunctional protein, an enzyme complex associated with the inner mitochondrial membrane, although very long chain fatty acids are oxidized in peroxisomes.
Treatment of fatty liver
InactiveUS20070265340A1Shorten the progressIncreased riskBiocideDigestive systemFatty liverBeta oxidation
Methods and compositions comprising peroxisomal and / or mitochondrial beta oxidation stimulating agents to reverse or resolve, slow the progression of, treat or prevent the development of fatty liver and conditions stemming from fatty liver, such as NASH, liver inflammation, cirrhosis and liver failure. An active agent that by itself is associated with an increased risk of fatty liver development and conditions stemming from fatty liver, such as NASH, liver inflammation, cirrhosis and liver failure, may be administered in combination with peroxisomal and / or mitochondrial beta oxidation stimulating agents. A combination regimen involving such agents, as simultaneous or concomitant therapy, or as a fixed dosage form, is also provided.
Owner:RELIANT PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Treatment of Fatty Liver
InactiveUS20090182022A1Shorten the progressAvoid developmentBiocideDigestive systemBeta oxidationActive agent
Methods and compositions comprising peroxisomal and / or mitochondrial beta oxidation stimulating agents to reverse or resolve, slow the progression of, treat or prevent the development of fatty liver and conditions stemming from fatty liver, such as NASH, liver inflammation, cirrhosis and liver failure. An active agent that by itself is associated with an increased risk of fatty liver development and conditions stemming from fatty liver, such as NASH, liver inflammation, cirrhosis and liver failure, may be administered in combination with peroxisomal and / or mitochondrial beta oxidation stimulating agents. A combination regimen involving such agents, as simultaneous or concomitant therapy, or as a fixed dosage form, is also provided.
Owner:RELIANT PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Method for the production of medium-chain sophorolipids
The MFE2 gene of a microorganism capable of producing glycolipids, such as, but not limited to C. bombicola is disrupted with the purpose of blocking the beta-oxidation pathway in the strain. Fermentation of a such strain having such disrupted genes on primary or secondary alcohols or diols, preferably on primary alcohols produces short chained glycolipids in high yield and purity.
Owner:ECOVER CO ORDINATION CENT
Method for increasing long-chain biatomic acid fermentation production rate
This invention relates to one method of improving fermentation efficiency of long chain diacid. In this method, normal alkane is the material, and animalcule fermentation method is adopted to produce correspondent diacid. Its major character is to add catastaltica, which includes halogeno-aliphatic acid, methyl fat acid and one or two kinds of its salt or ester, to reduce beta oxidation ability of bacterial strain. The concentration of the catastaltica is 0.01-5mmol / L. the added catastaltica can efficiently reduce beta oxidation ability of bacterial strain, lowers the alkane consumption, and improves greatly the fermentation efficiency, the acid-producing rapidity and is particularly suitable for long chain diacid.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Reverse beta oxidation pathway
ActiveUS20130316413A1Prevents/minimizes the metabolism of acetyl-CoABacteriaBiofuelsMicroorganismBeta oxidation
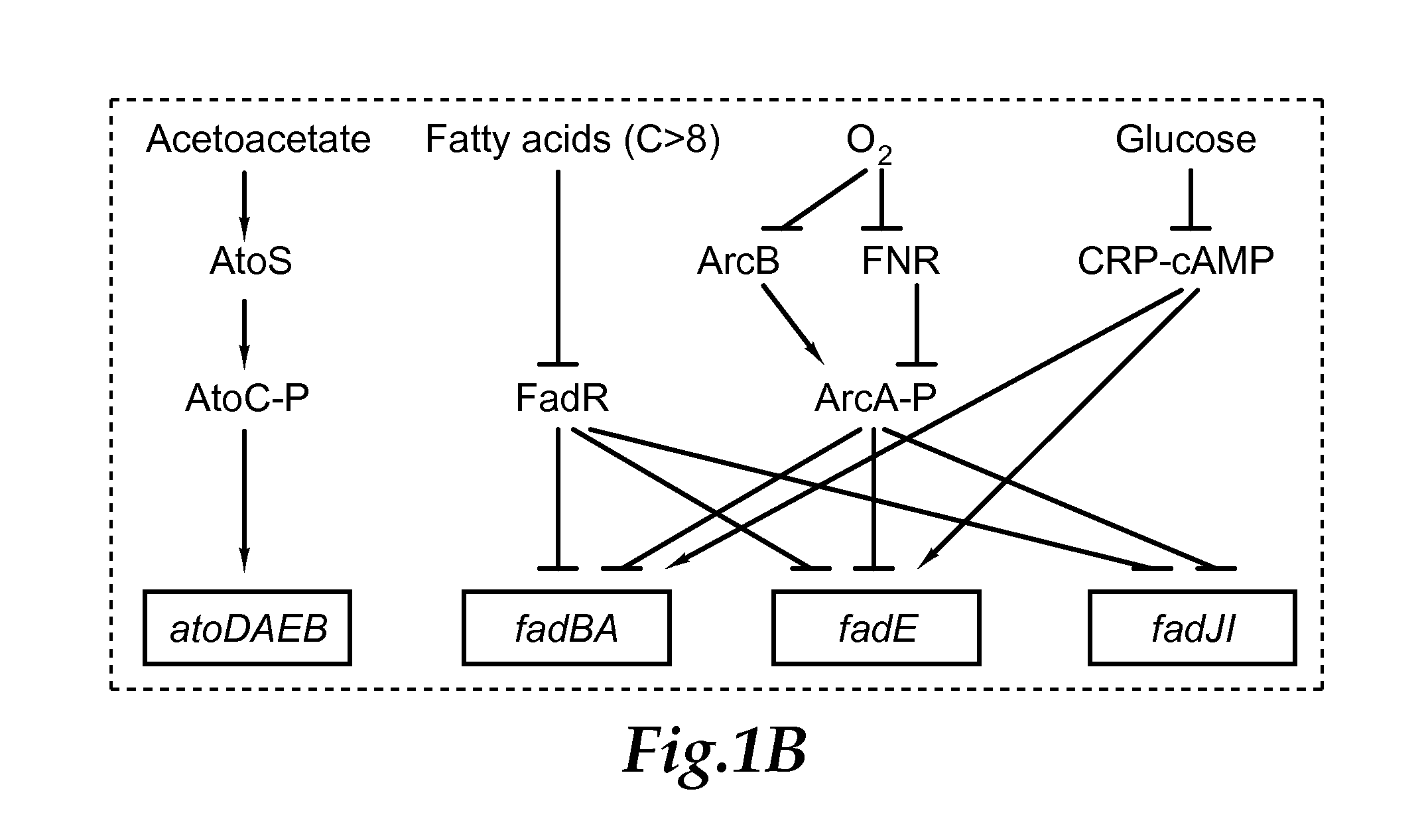
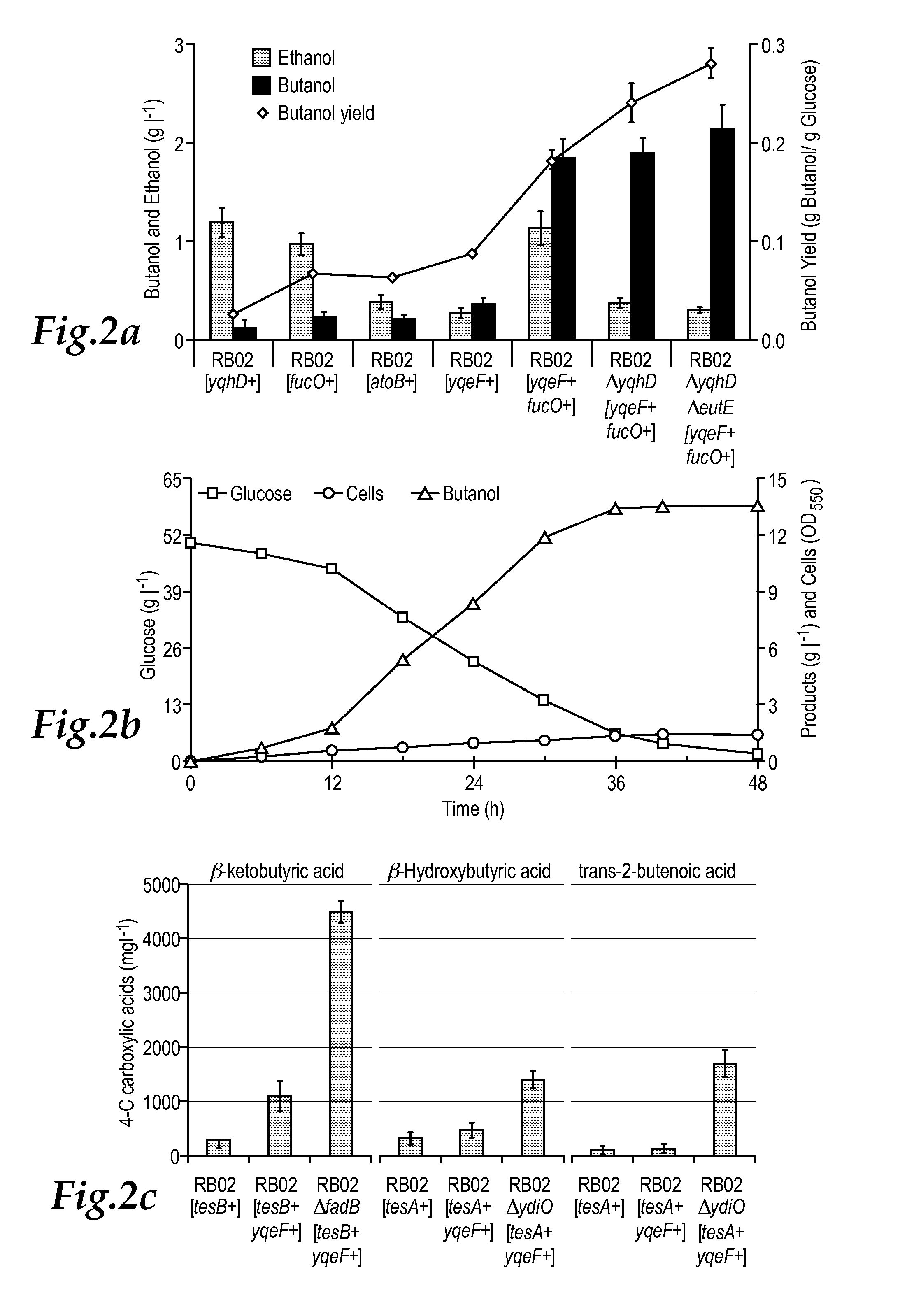
The invention relates to recombinant microorganisms that have been engineered to produce various chemicals using genes that have been repurposed to create a reverse beta oxidation pathway. Generally speaking, the beta oxidation cycle is expressed and driven in reverse by modifying various regulation points for as many cycles as needed, and then the CoA thioester intermediates are converted to useful products by the action of termination enzymes.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Functionalized carboxylic acids and alcohols by reverse fatty acid oxidation
ActiveUS20140273110A1Reduce expressionReducing lactate productionBacteriaHydrolasesAlcoholBeta oxidation
Bacteria that run the beta oxidation cycle in reverse anabolic direction are provided, along with many novel primers to start the reverse cycle, pathways to make such primers, and a large variety of products produced thereby. Methods for making desired product by using such primers in the reverse pathway are also disclosed.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Method for activating the lipid catabolic metabolism in enteric epithelium and improving the lipid metabolism in enteric epithelium
InactiveUS20030158257A1Easy to burnImprove energy consumptionBiocideMetabolism disorderIntestinal structureLipid formation
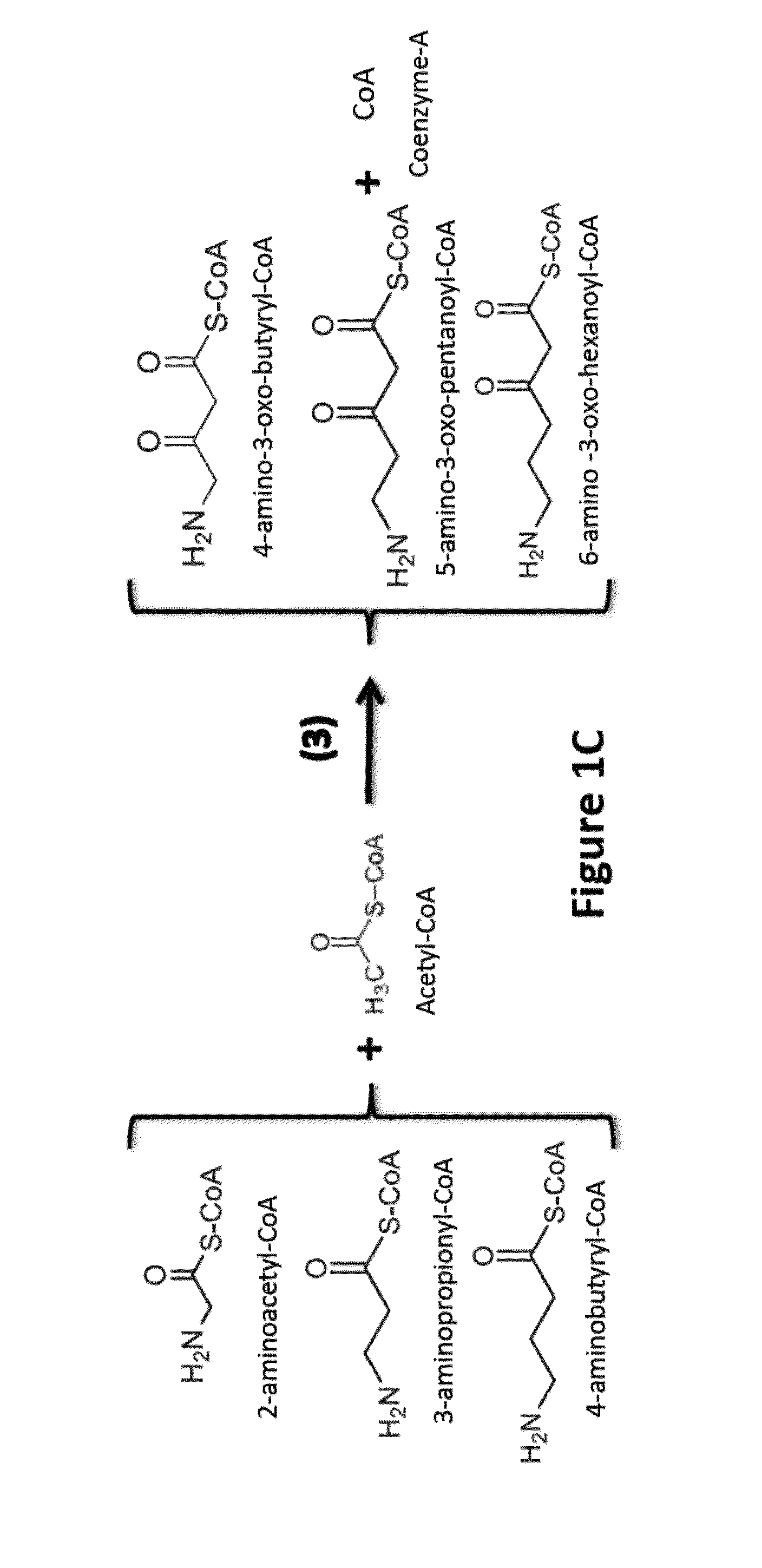
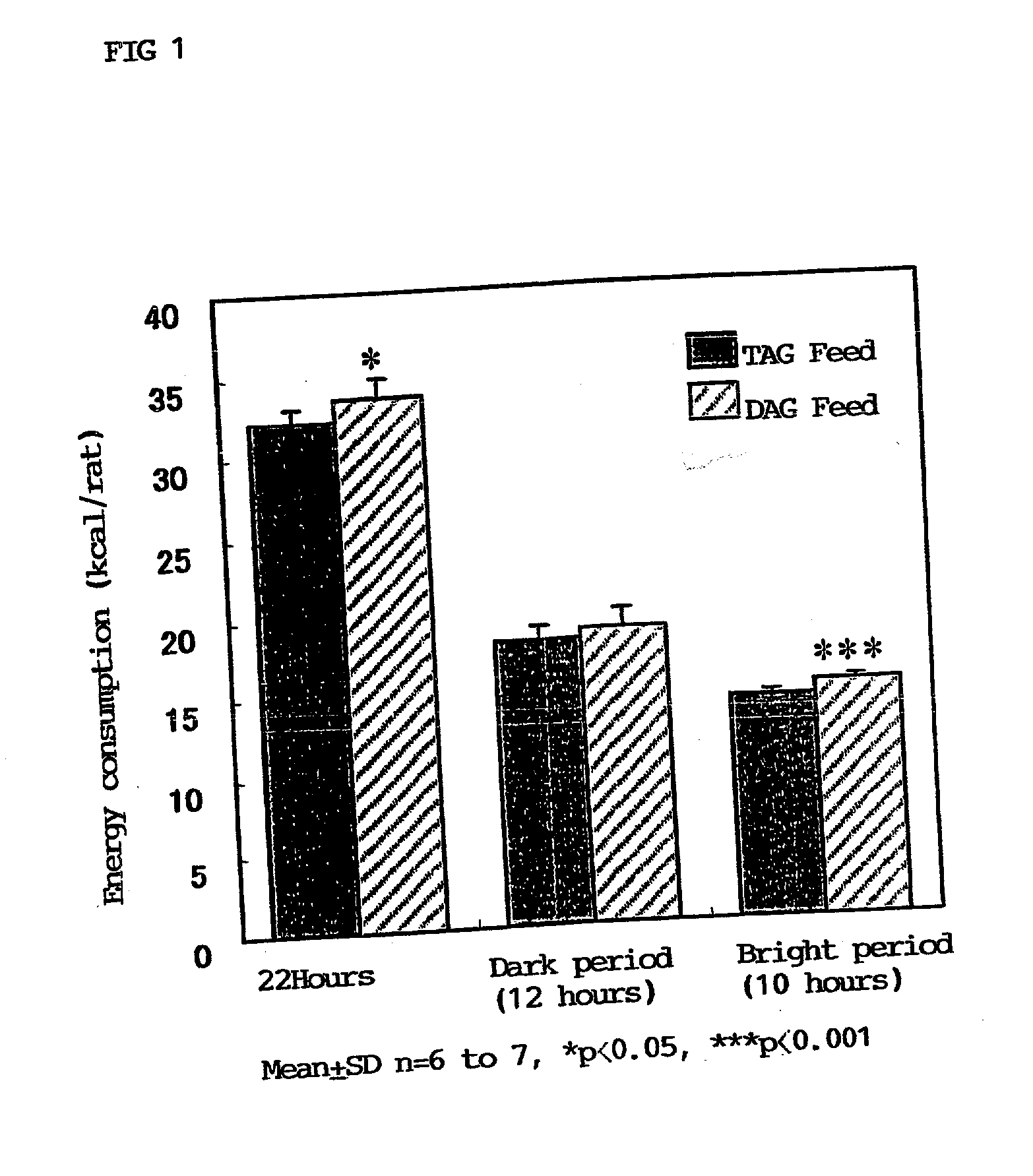
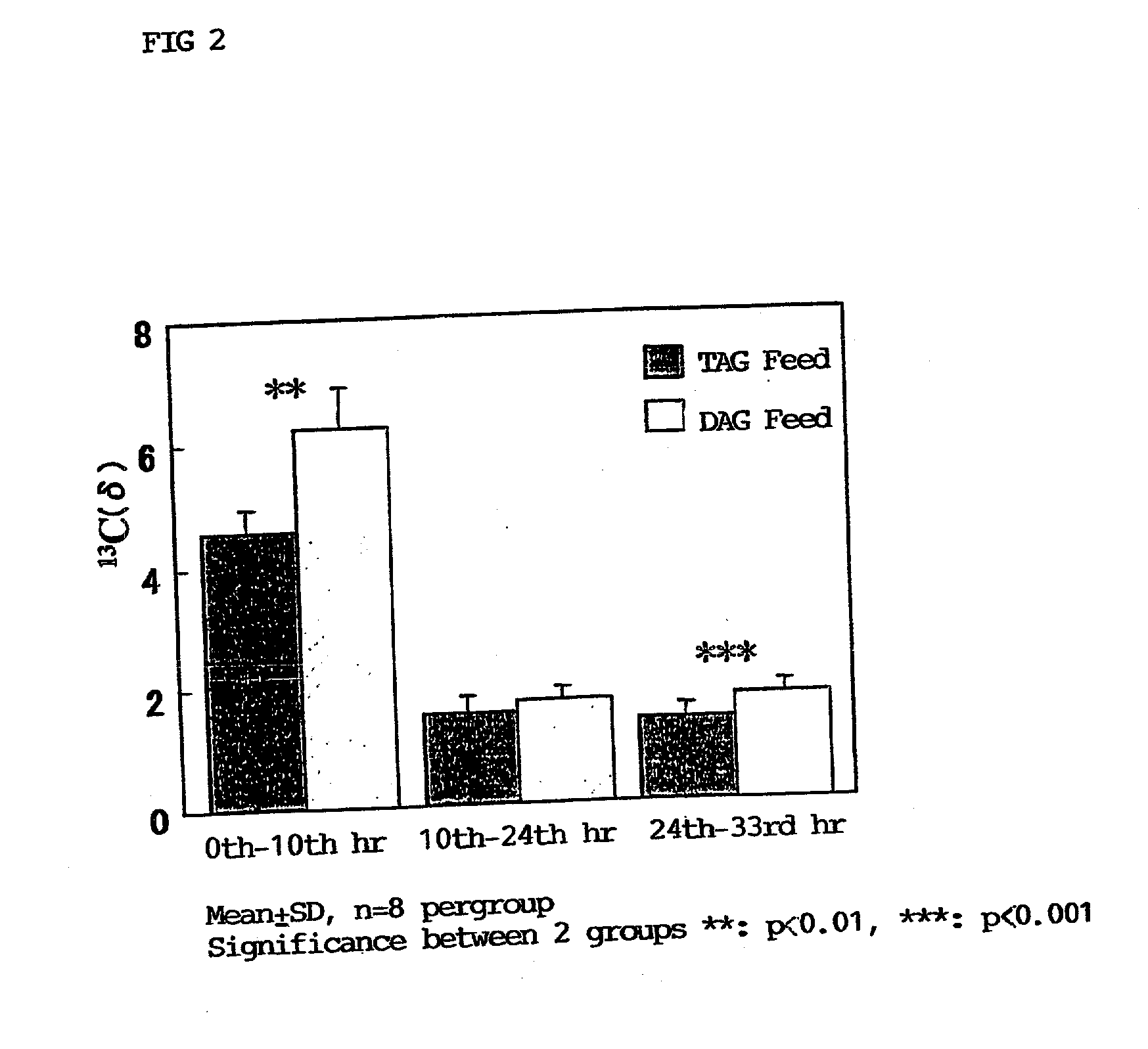
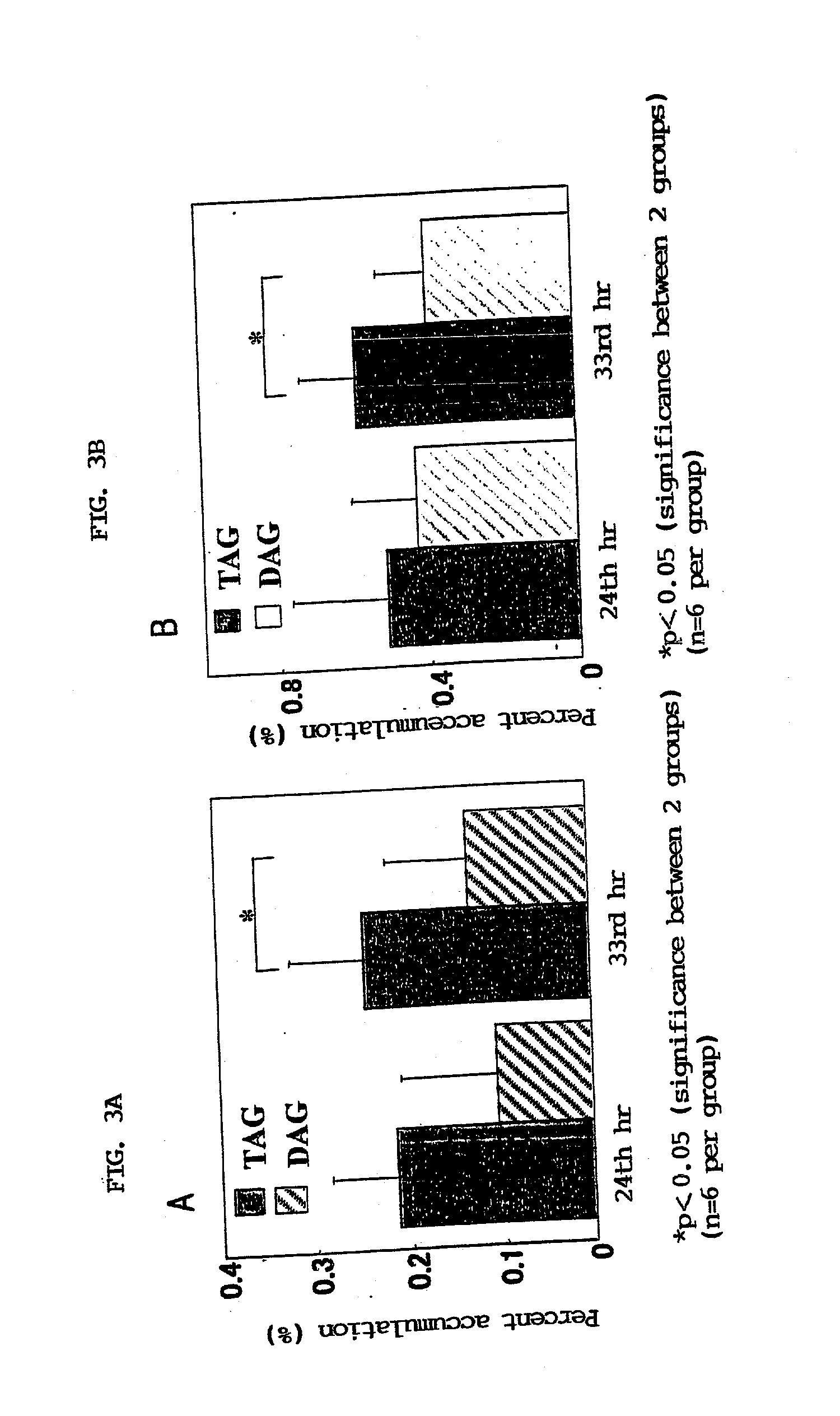
Disclosed are a method for activating lipid metabolism in the small intestine epithelium and also a method for promoting accumulation of fatty acids into the small intestine epithelium, each of which features administering an effective amount of a diacylglycerol. Also disclosed are methods for improving various symptoms in diabetes, which have ingesting a diacylglycerol. Ingestion of the diacylglycerol leads to accumulation of the fatty acids in the small intestine. The fatty acids so accumulated promote induction of beta-oxidation, thereby not only activating lipid catabolism but also making it difficult to allow lipids to accumulate as triacylglycerols. This series of actions eventually results in development of lowering action for blood remnant-like lipoprotein level and also lowering action for blood leptin level, and hence, lipid metabolism is improved. Further, energy consumption is enhanced by promoting the induction of beta-oxidation and activating lipid catabolism.
Owner:KAO CORP
Non-revertible beta-oxidation blocked candida tropicalis
ActiveUS20100167361A1Improve productivityIncreased quantitative yieldFungiFungi based processesBeta oxidationCandida famata
Owner:COGNIS IP MANAGEMENT GMBH
Oil or fat composition
InactiveCN1675344AInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsEdible oils/fats ingredientsDocosahexaenoic acidOil and grease
The present invention relates to an oil or fat composition containing the following components (A) and (B): (A) from 80 to 99.9 wt.% of a monoglyceride comprising 20 to 75 wt.% of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and 0.1 to 25 wt.% of icosapentaenoic acid (IPA), as the constituent fatty acids thereof, wherein the weight ratio of DHA / IPA being 2 or more; and (B) from 0.1 to 20 wt.% of a diglyceride. The oil or fat compositions according to the present invention are excellent in processability, have a good flavor, and are excellent in PPAR activating effects and beta oxidation activating effects so that they are beneficial as foods and animal feeds as well as pharmaceuticals for diabetes, hyperlipidemia and obesity.
Owner:KAO CORP
Methods for regulating beta-oxidation in plants
InactiveUS6914170B2Decreasing β-oxidationEnhanced oil levelHydrolasesFermentationPlant tissueBeta oxidation
The invention relates to the genetic manipulation of plants to increase oil accumulation in plant tissues, particularly seeds. Methods for decreasing β-oxidation in plants and optimizing oil accumulation in a seeds are provided. The methods find use in increasing the accumulation of oil or particular oil constituents in plant seeds. Isolated nucleotide molecules, isolated proteins, expression cassettes and transformed plants, plant tissues and plant cells are additionally provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Method for improving fermentation yield of long-chain dicarboxylic acid
InactiveCN102808004AReduce unit consumptionImprove conversion rateMicroorganism based processesFermentationAlkaneBeta oxidation
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical products, and relates to a method for improving the fermentation yield of long-chain dicarboxylic acid. According to the method, the long-chain dicarboxylic acid is produced by a microbiological fermentation method by taking C10 to C18 n-alkanes as raw materials; the method is characterized in that alpha oxidative decarboxylation inhibitor and beta-oxidation inhibitor are added in a fermentation production process to reduce the alpha-oxidative decarboxylation and beta-oxidation capacities of strains, wherein the alpha oxidative decarboxylation inhibitor is one or mixture of more of chlorpromazine hydrochloride, phenobarbital sodium, crylic acid and polyacrylic acid, and the concentration is 0.01 to 1mmol / L; and the beta-oxidation inhibitor is one or mixture of more of mercaptoacetic acid, sodium thioglycollate, ranolazine, ranolazine dihydrochloride and mildronate, and the concentration is 0.01 to 1 mmol / L. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of high acid producing speed, weak alpha oxidative decarboxylation and beta-oxidation capacity, low unit consumption of alkane, and high fermentation alkane conversion rate, and is particularly suitable for preparing the long-chain dicarboxylic acid.
Owner:ZIBO GUANGTONG CHEM
Method for the production of medium-chain sophorolipids
The MFE2 gene of a microorganism capable of producing glycolipids, such as, but not limited to C. bombicola is disrupted with the purpose of blocking the beta-oxidation pathway in the strain. Fermentation of a such strain having such disrupted genes on primary or secondary alcohols or diols, preferably on primary alcohols produces short chained glycolipids in high yield and purity.
Owner:ECOVER CO ORDINATION CENT
Fat beta-oxidation enhancing and carbohydrate absorption inhibition supplement
InactiveUS20080102144A1Promote oxidationMaintain blood sugar levelsOrganic active ingredientsBiocideBeta oxidationCarbohydrate absorption
The present invention relates to a method for increasing the β-oxidation of fatty acids while substantially simultaneously maintaining blood glucose concentration through the inhibition of carbohydrate absorption. Furthermore, the present invention additionally provides a composition for increasing the β-oxidation of fatty acids while substantially simultaneously maintaining blood glucose concentration through the inhibition of carbohydrate absorption comprising an Extract of Green Coffee Bean, and an Extract of Salacia oblonga. The composition may further comprise diacylglycerol.
Owner:IOMEDIX DEV INT
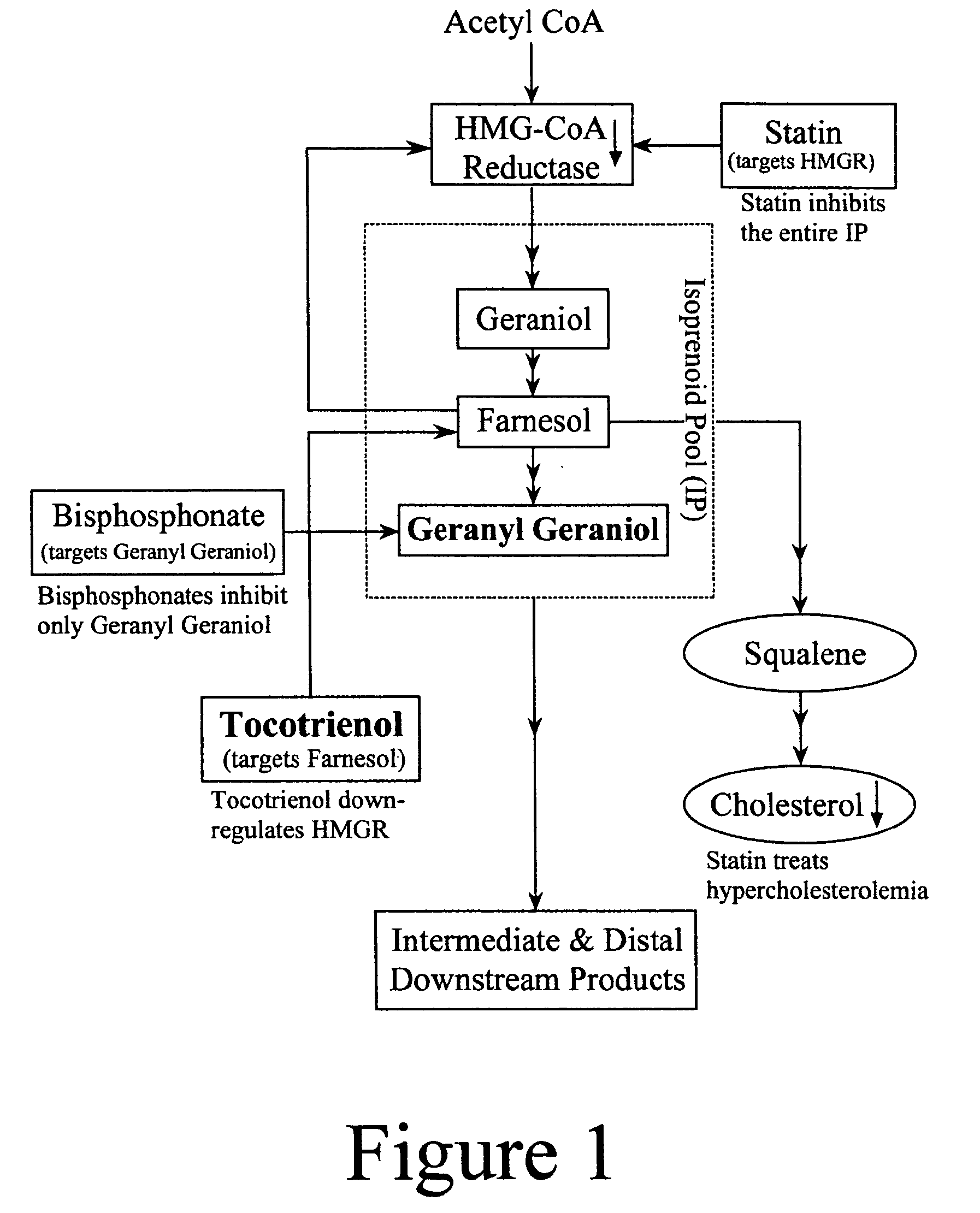
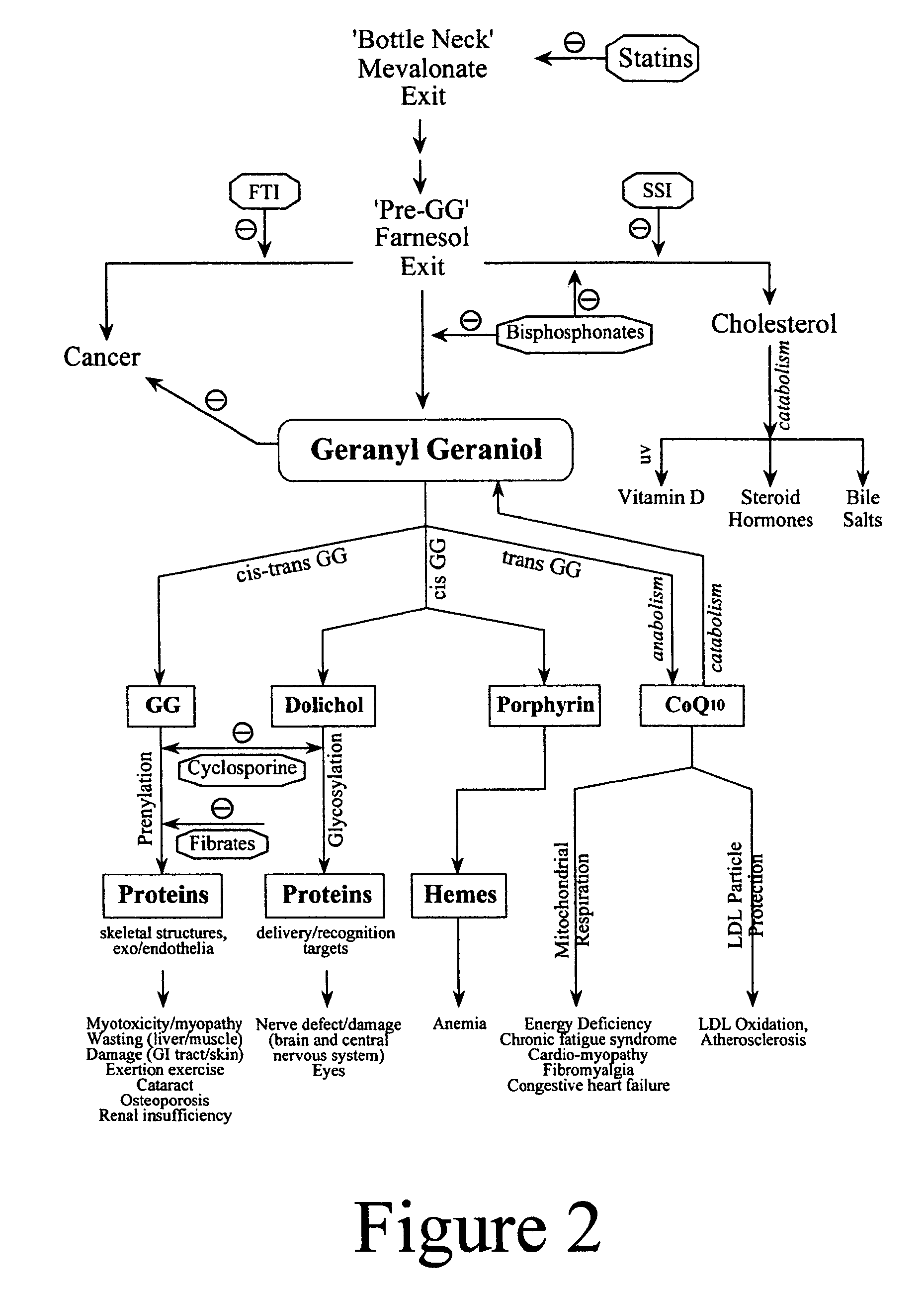
Annatto extract compositions, including geranyl geraniols and methods of use
ActiveUS7989006B2Reduce disease riskIncreasing cellular uptakeBiocideSenses disorderEnergeticsPhysiology
Owner:AMERICAN RIVER NUTRITION LLC
Annatto Extract Compositions, Including Geranyl Geraniols And Methods Of Use
ActiveUS20080031985A1Preventing statin toxicityIncreasing CoQBiocideSenses disorderEnergeticsSide chain
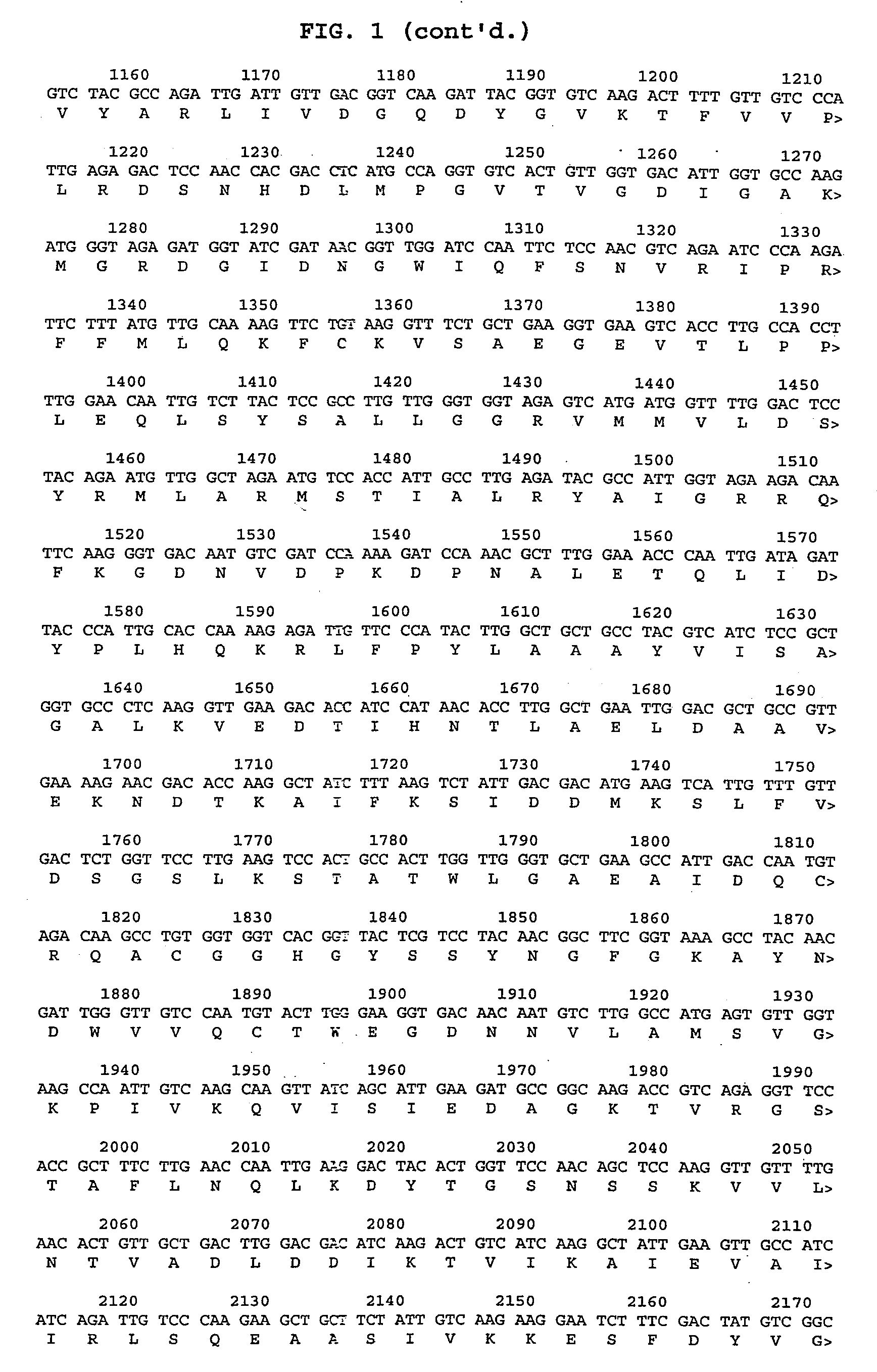
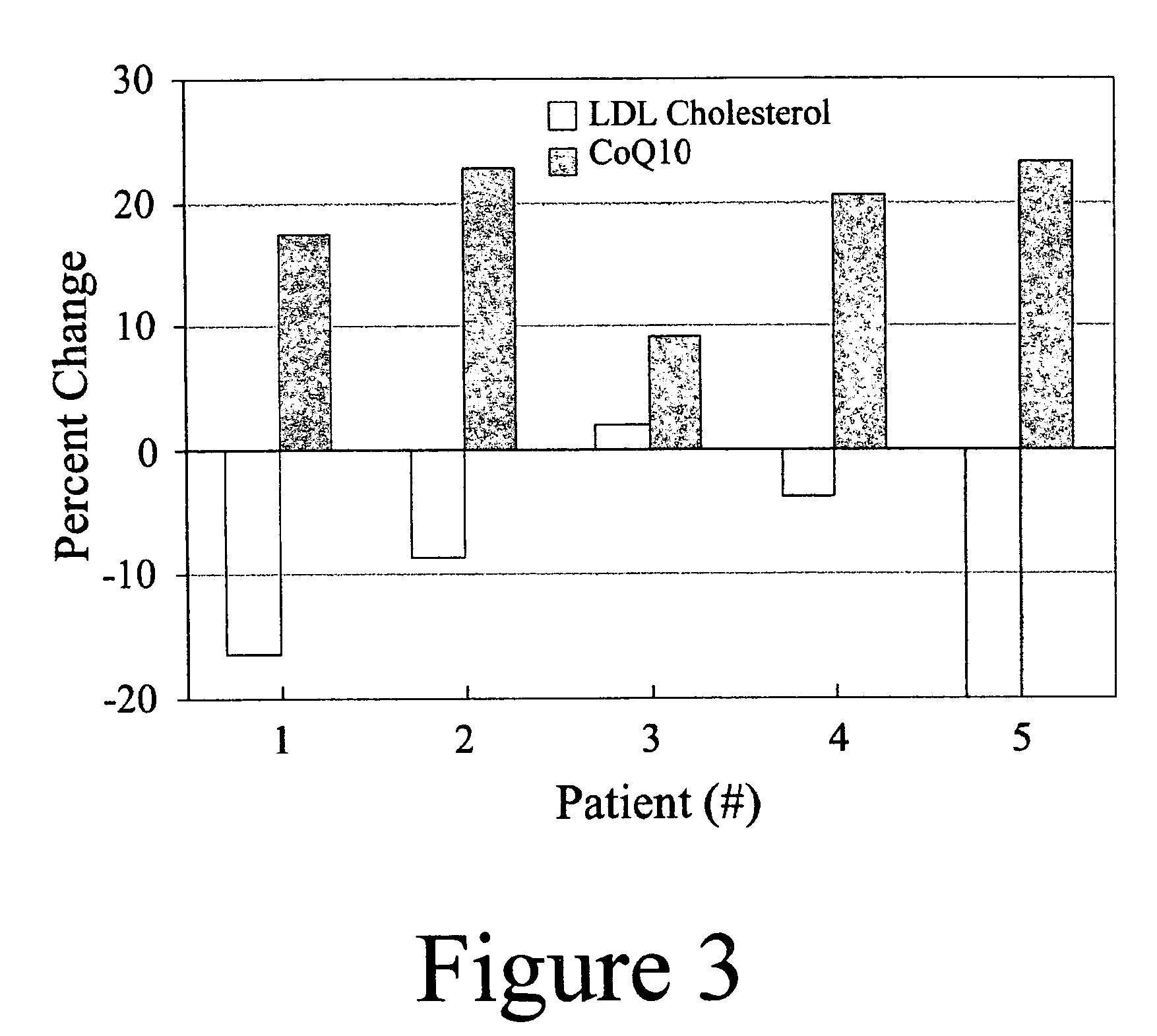
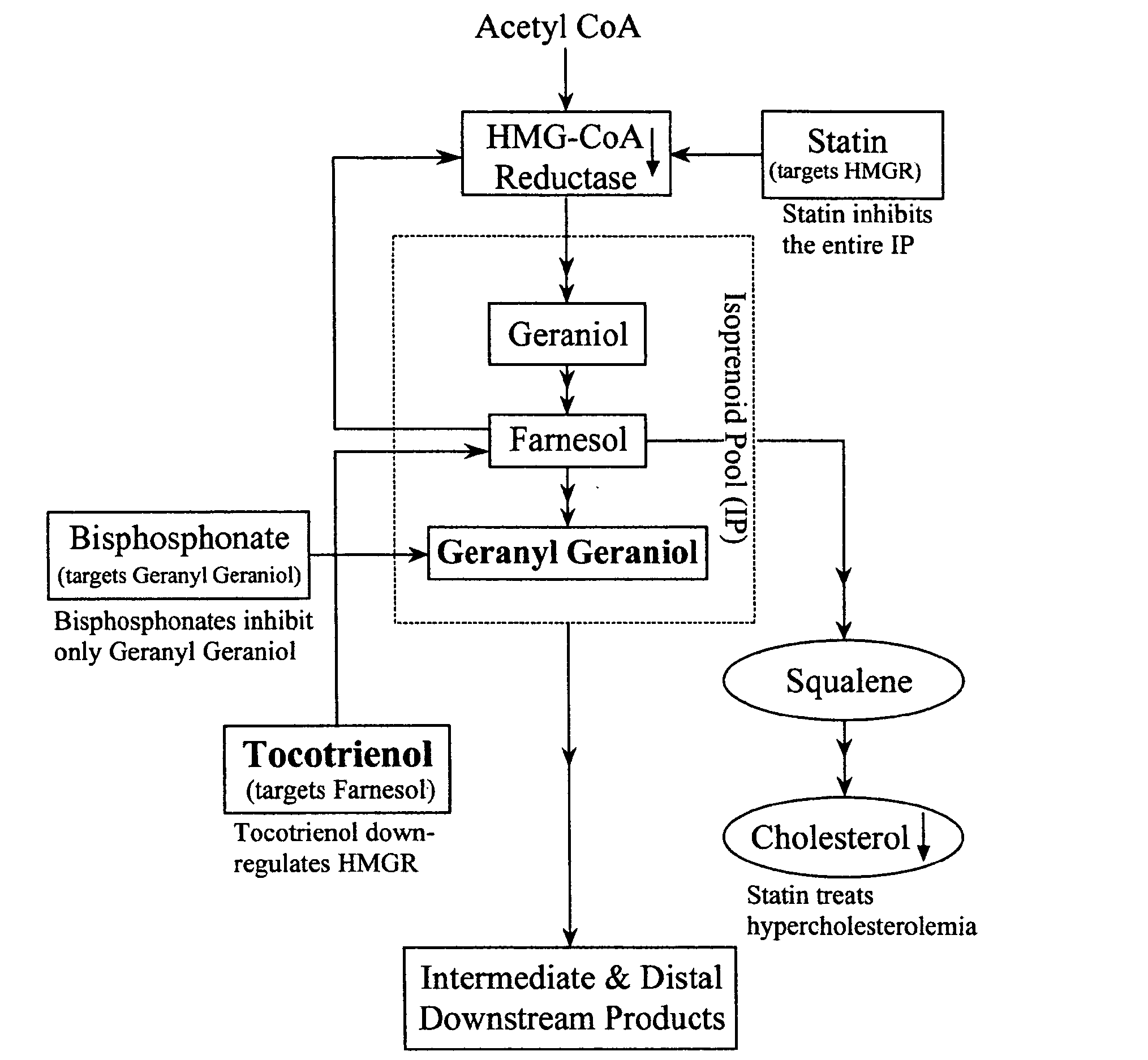
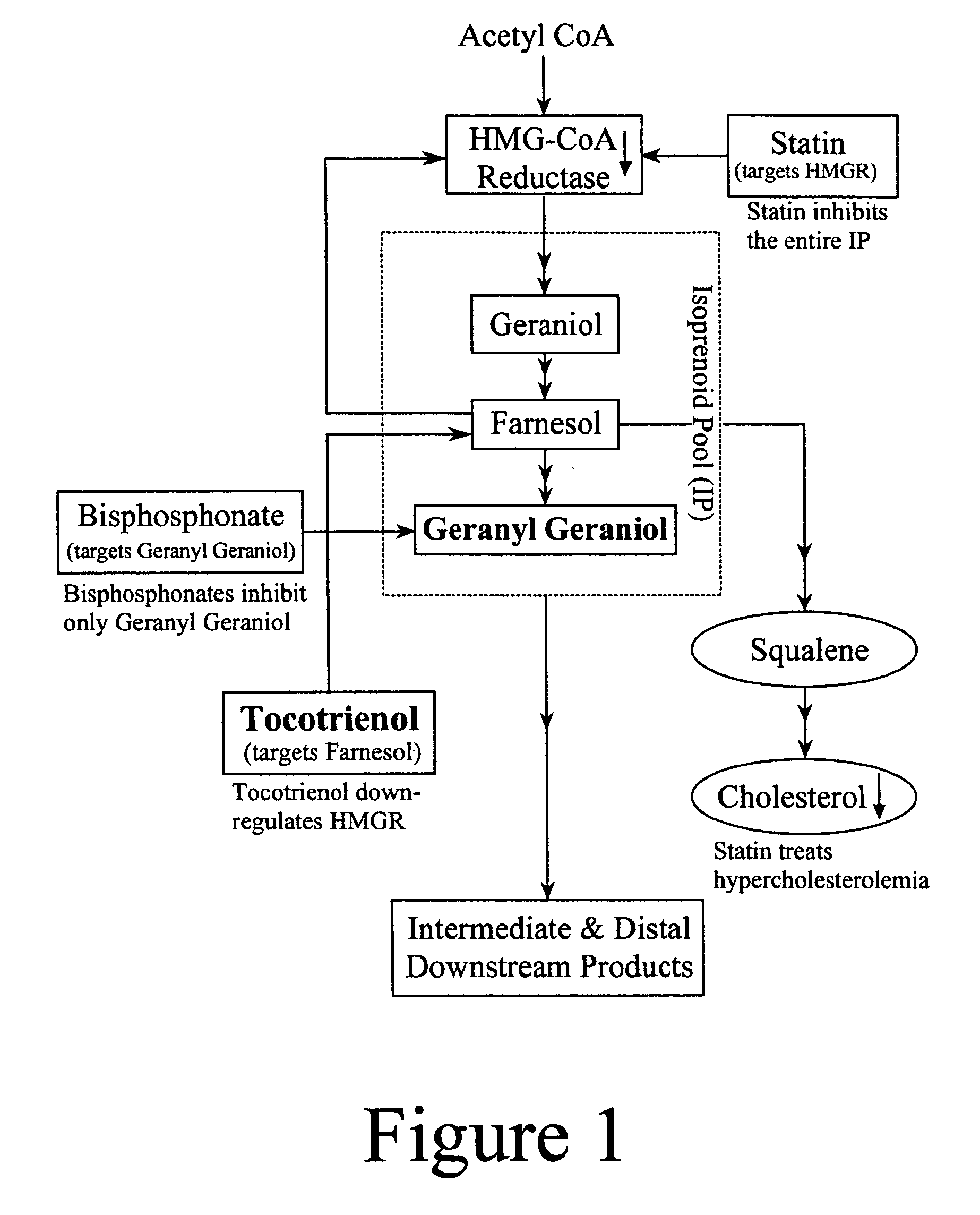
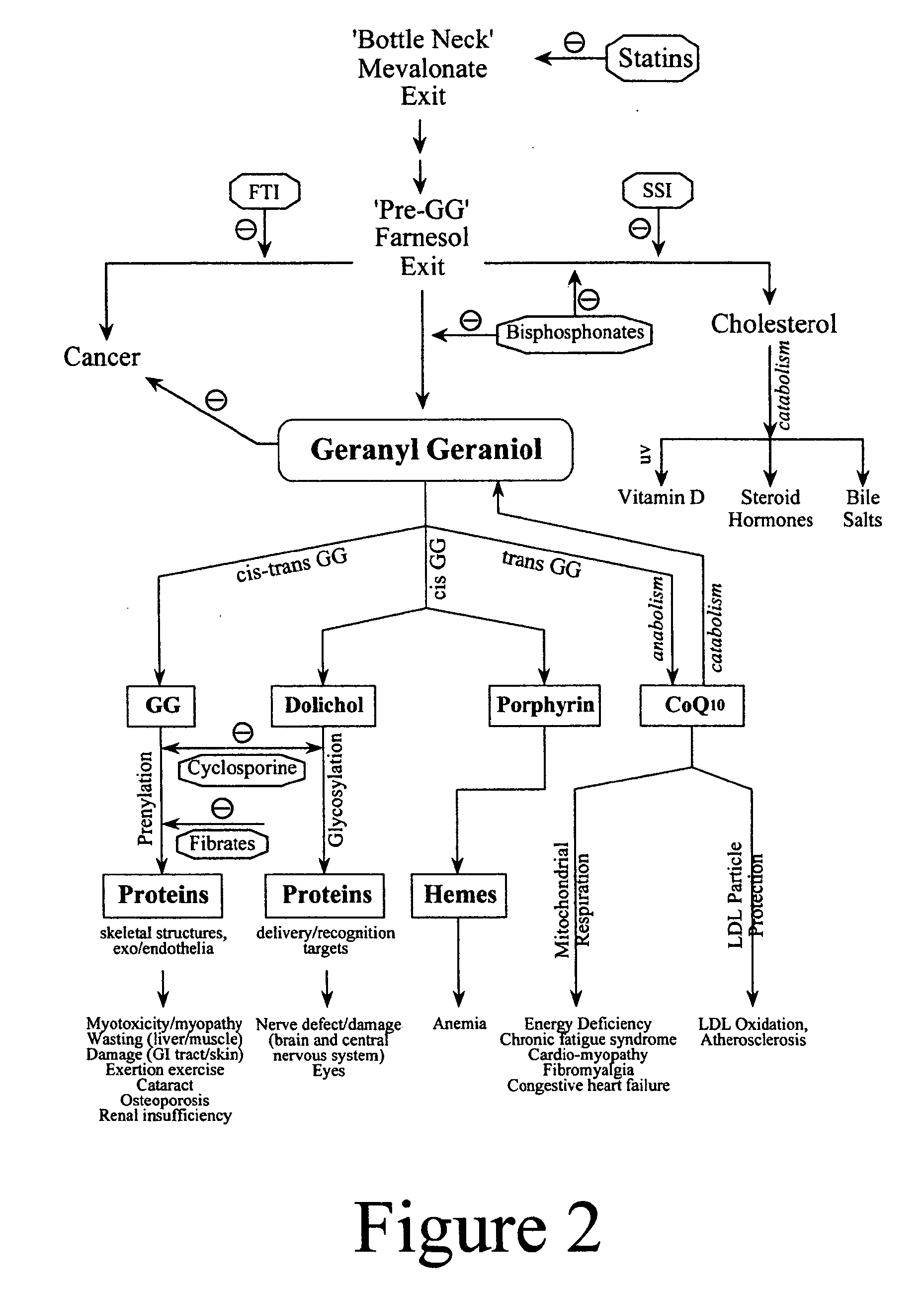
Annatto extract composition (AEC), including cis and trans geranyl geraniols (GG) and tocopherol-free C-5 unsubstituted tocotrienols (T3), increases the de novo synthesis of intermediate isoprenoid and distal protein products, including endogenous coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), dolichols (DL) and all subsequent GG-prenylated and DL-glycosylated proteins, including GG-porphyrinated hemes. This intermediate and distal product replenishment by AEC reverses maladies of myotoxicity (of both drug and non-drug origins), including maladies that affect the muscle, kidney, eye, GI tract and skin, nerve, blood, and CoQ10-related syndromes of energetics and LDL protection. AEC anabolically increases the endogenous de novo CoQ10 synthesis via GG elongation / prenylation of side-chain and conversely CoQ10 catabolically increases the endogenous de novo GG synthesis via beta-oxidation of CoQ10. Also, such AEC decreases de novo synthesis and increases disposal of triglycerides (TG) in humans via PPAR activation and SREBP deactivation. Such drop in TG by AEC reverses maladies of insulin resistance (IR) and metabolic syndrome (MS), prediabetes, diabetes and diabetes-related cardiovascular diseases (CVD). GG activates PPAR and down regulates SREBP transcription factors. This AEC, containing GG, inhibits cancer growth whether or not GG involvement in protein prenylation is required.
Owner:AMERICAN RIVER NUTRITION LLC
Complex microbial inoculant rich in grease raw material for medium-temperature biogas fermentation system and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104498415APromote degradationImprove gas production efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLong chain fatty acidProduction rate
The invention provides a complex microbial inoculant for a grease-rich raw material medium-temperature biogas fermentation system and a preparation method and application thereof. The complex microbial inoculant is mainly used for strengthening degradation (beta-oxidation) of long-chain fatty acid and methane production of a degradation product (acetic acid+CO2+H2) of the long-chain fatty acid, improving gas production rate of a grease-rich raw material, shortening fermentation dwell time and meanwhile avoiding severed accumulation of fermentation liquid upper-layer grease.
Owner:CHENGDU ZHONGKE ENERGY & ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION CO LTD
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for synthesizing squalene and application thereof
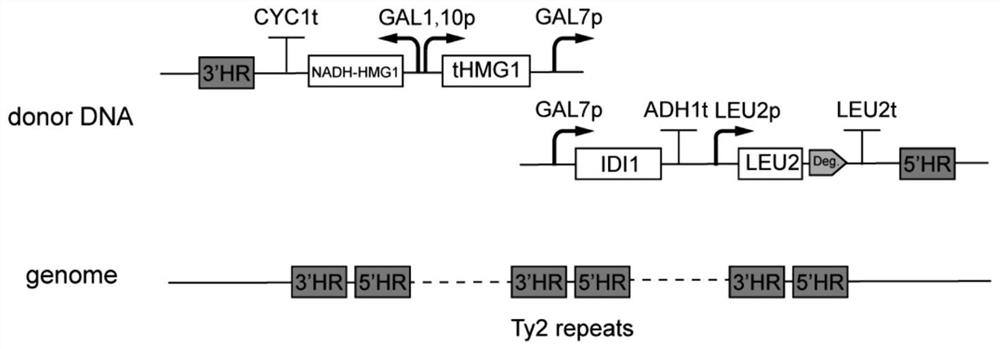
ActiveCN113234610AEnhancing Pathway Metabolic FluxIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesHeterologousBeta oxidation
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for synthesizing squalene and an application of the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the invention, tHMG1 and IDI1 are integrated at a multi-copy site Ty2 of saccharomyces cerevisiae, so that synthesis and accumulation of squalene are remarkably promoted, NADH-dependent HMG1 is heterologously expressed, the redox level in yeast cells is balanced, a promoter HXT1 with a remarkable inhibition effect on ERG1 transcription is further replaced, conversion of squalene to the downstream is hindered, ACL1 and ACL2 are heterologously expressed, PEX11 and FOX3 are over-expressed, accumulation of a squalene synthesis precursor acetyl coenzyme A in cytoplasm is enhanced through beta oxidation, accumulation of squalene is further promoted, and the squalene yield can reach 1253.4 mg / L after saccharomyces cerevisiae is fermented for 96 h.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Reverse beta oxidation pathway
ActiveUS9416364B2Prevents/minimizes the metabolism of acetyl-CoABacteriaBiofuelsThioester synthesisMicroorganism
Owner:RICE UNIV
Natamycin fermentation technology based on addition of exogenous saturated fatty acid
ActiveCN109943610AIncreased biosynthetic levelsDoes not affect growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBeta oxidationSide effect
The invention discloses a natamycin fermentation technology based on addition of exogenous saturated fatty acid. By adding a slow-release precursor source, namely the saturated fatty acid, which has no toxic or side effects on cells, when beta-oxidation utilization is conducted in the cells, the exogenous saturated fatty acid generates a large quantity of acetyl CoA precursors and NADH, thus supply of natamycin macrolide precursors and ATP is guaranteed, and product synthesis is promoted. Since the saturated fatty acid is in a solid state under normal temperature and is not dissolved in water,the concentration of the saturated fatty acid cannot influence cell growth and metabolism in a fermentation liquor, and therefore, in the technology, rigid control over the concentration of the saturated fatty acid is not needed. By means of the technology, the biosynthesis level of the natamycin can be effectively improved, the detection and material supply operation load of precisely regulatingthe precursor concentration in the fermentation liquor is greatly lowered, and the technology has important application value in the industry.
Owner:山东元泰生物工程有限公司
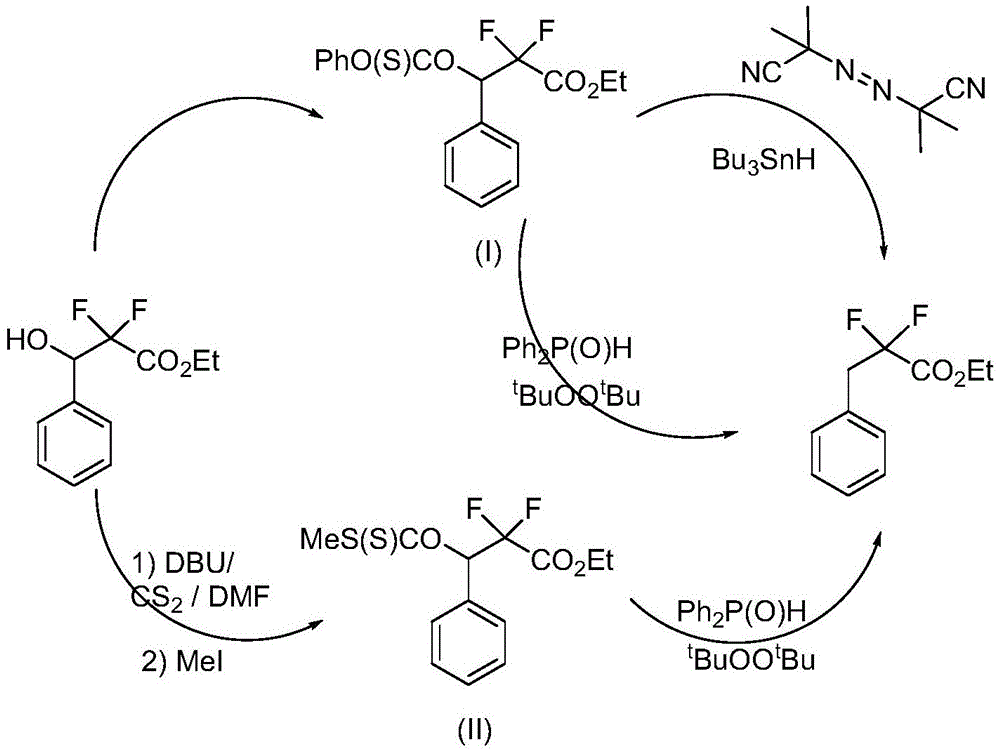
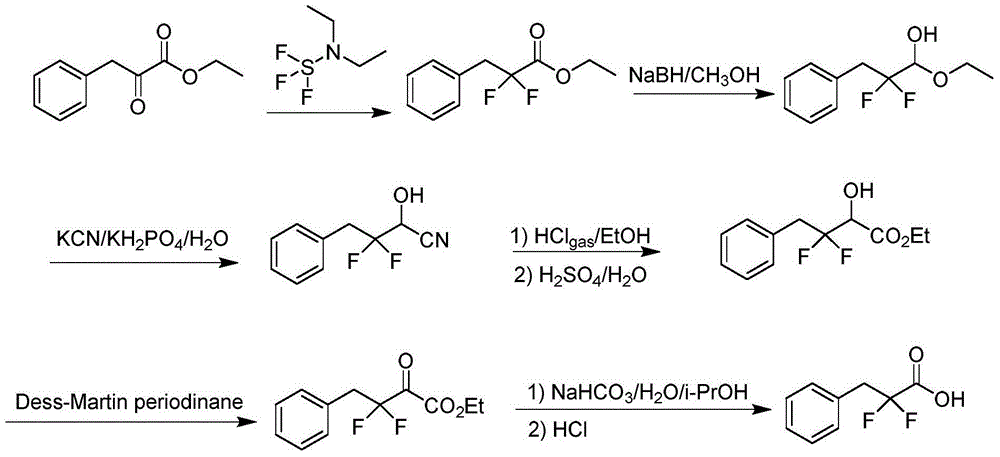
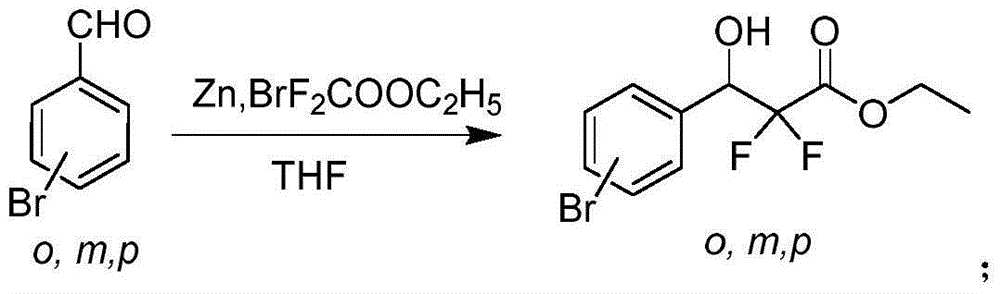
Preparation method of 3-(bromophenyl)-2,2'-difluoropropanoic acid
InactiveCN104557512ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getLow costPreparation from carboxylic acid saltsOrganic compound preparation3-Hydroxypropionic acidBeta oxidation
The invention provides a preparation method of 3-(bromophenyl)-2,2'-difluoropropanoic acid. Specifically, bromobenzaldehyde serving as a raw material and ethyl bromodifluoroacetate undergo addition reaction to obtain 3-(bromophenyl)-2,2'-difluoro-3-ethyl hydroxyropanoate; the 3-(bromophenyl)-2,2'-difluoro-3-ethyl hydroxyropanoate is subjected to bromo-substitution to obtain 3-(bromophenyl)-2,2'-difluoro-3-ethyl bromopropionate; and the 3-(bromophenyl)-2,2'-difluoro-3-ethyl bromopropionate is subjected to hydroxy reduction and hydrolytic degreasing reaction to obtain the 3-(bromophenyl)-2,2'-difluoropropanoic acid. The preparation method is simple in synthetic route, easy to operate, cheap and readily available in raw materials and mild in reaction condition, the intermediate and the product are easy to separate, and the yield is relatively high, so the preparation method is suitable for industrialized production. The prepared 3-(bromophenyl)-2,2'-difluoropropanoic acid has a wide application value in a beta-oxidation process inhibitor in pest control and pheromone bio-synthesis.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
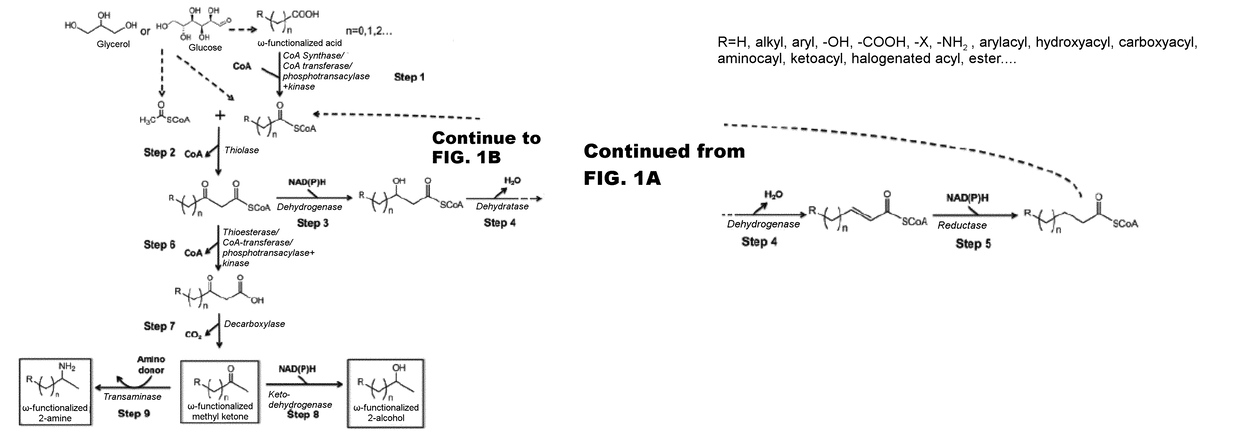
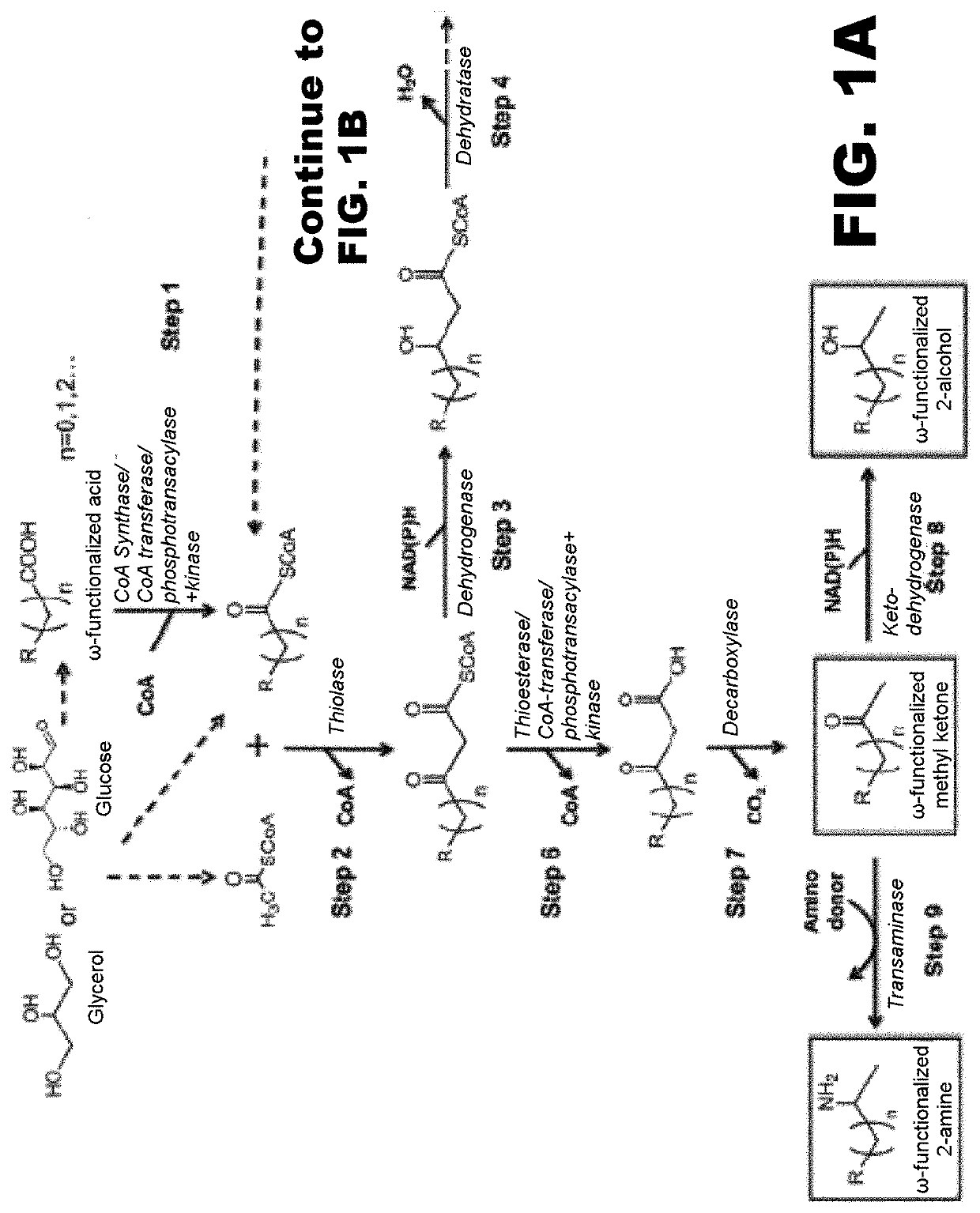
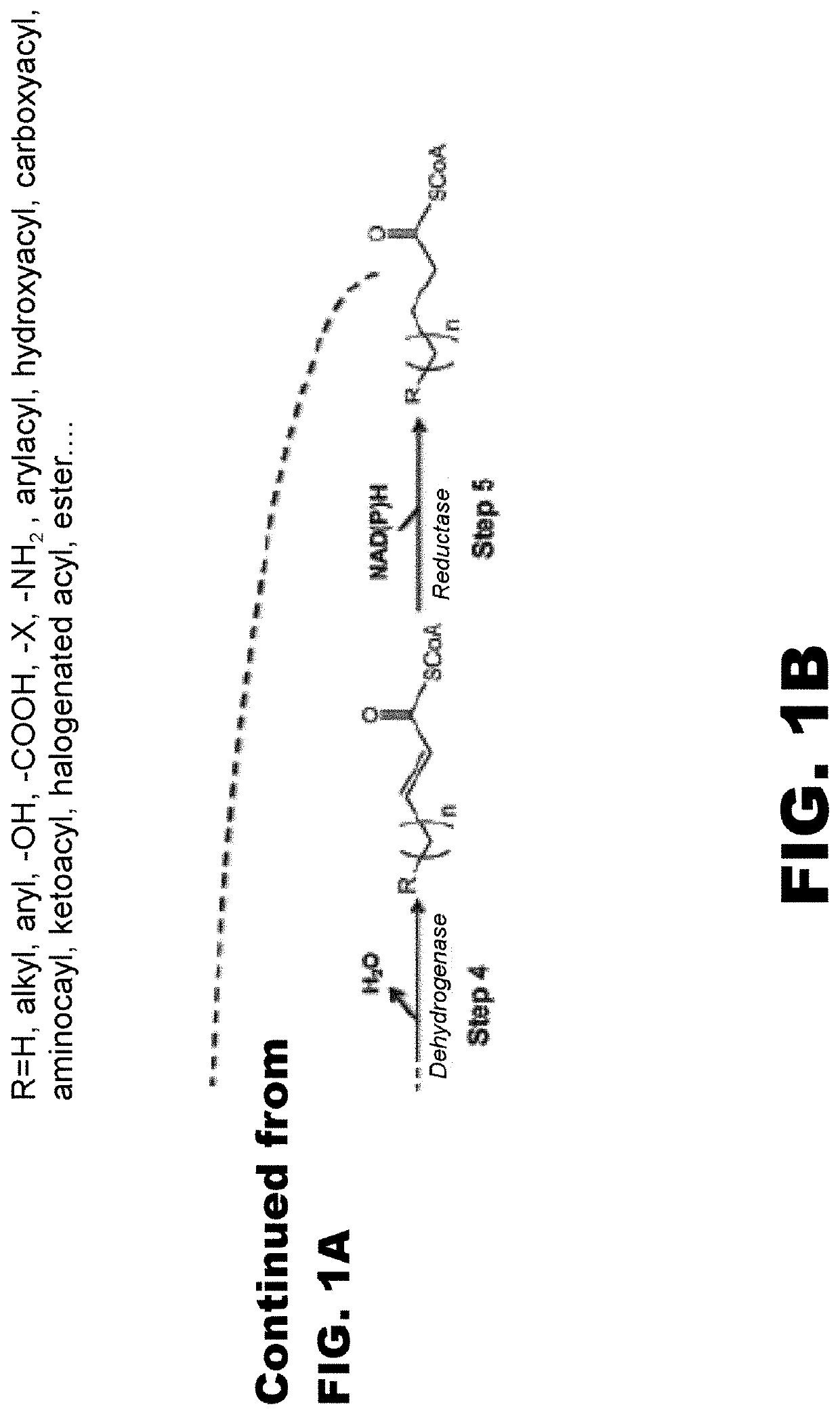
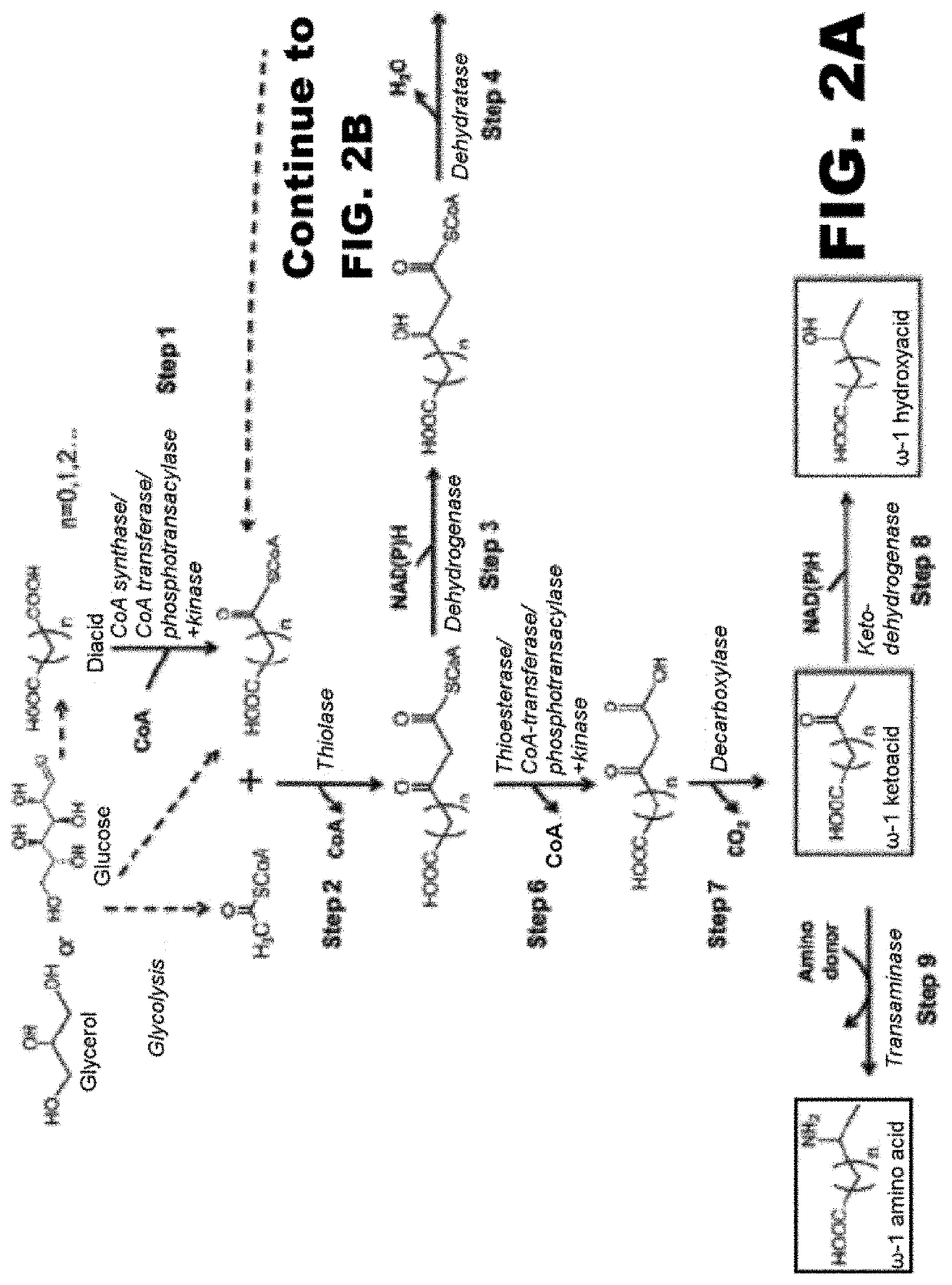
Synthesis of omega functionalized products
InactiveUS20180135059A1Simple designEasy to getPeptide/protein ingredientsUnknown materialsThioester synthesisFatty acid biosynthesis
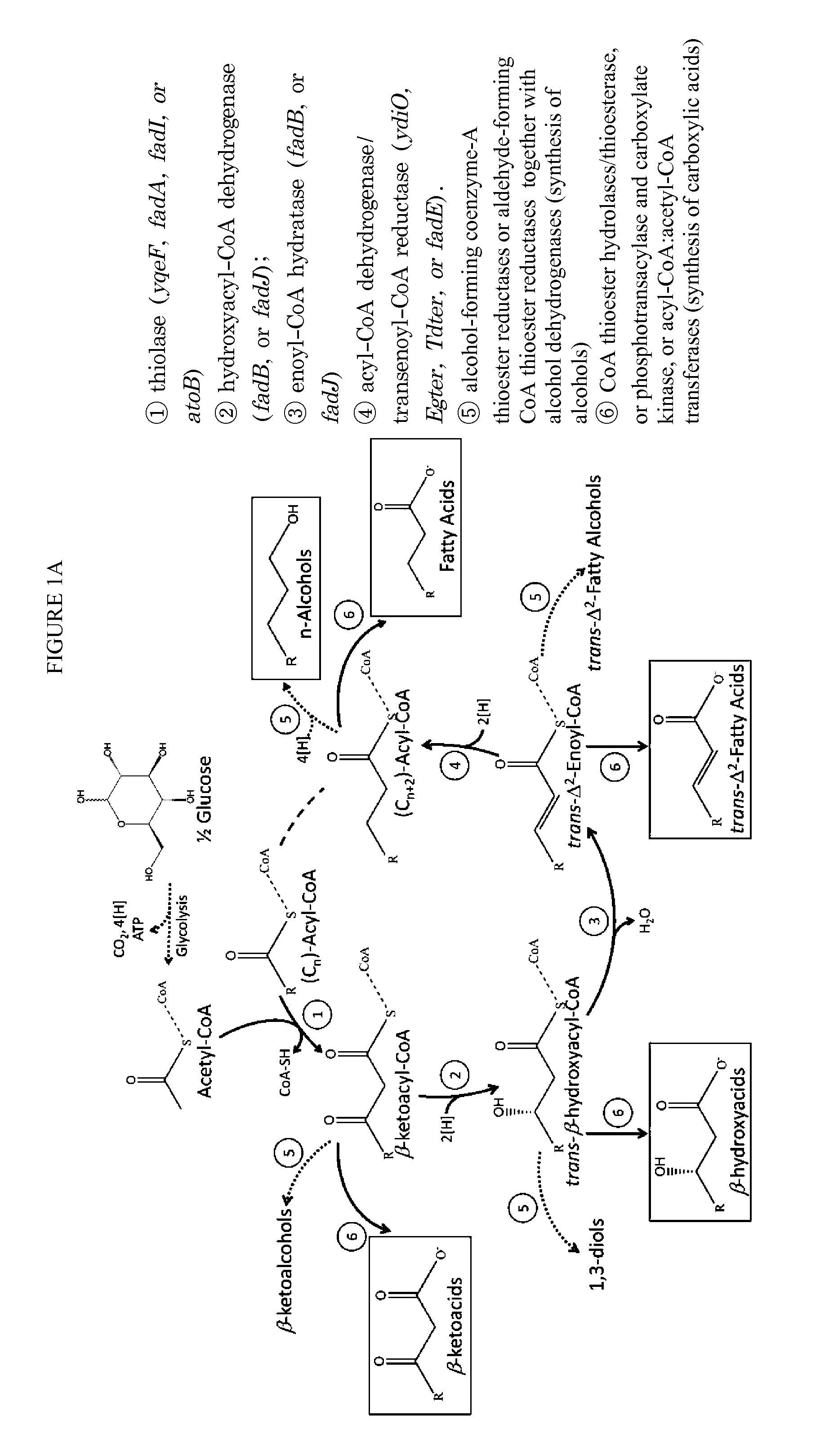
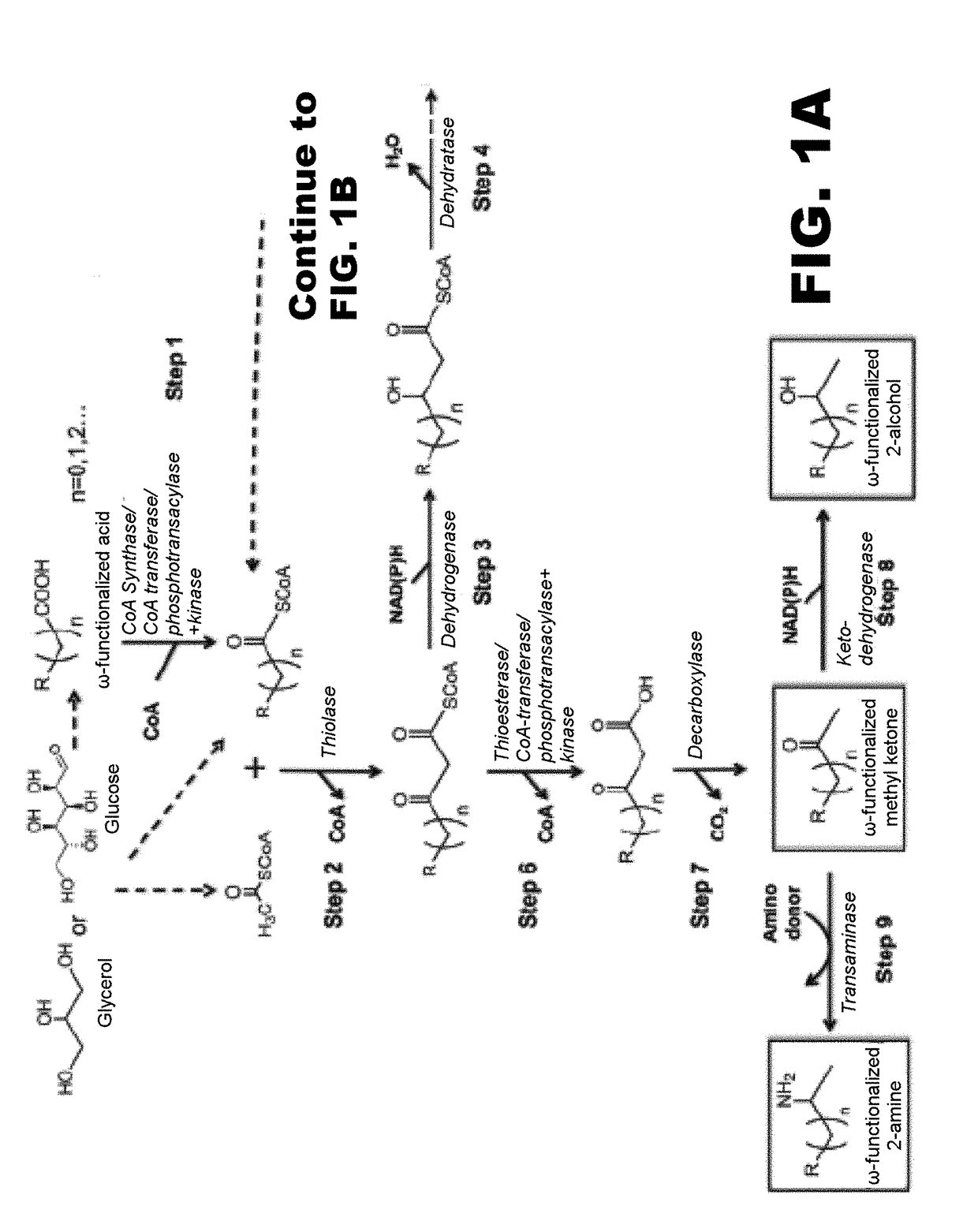
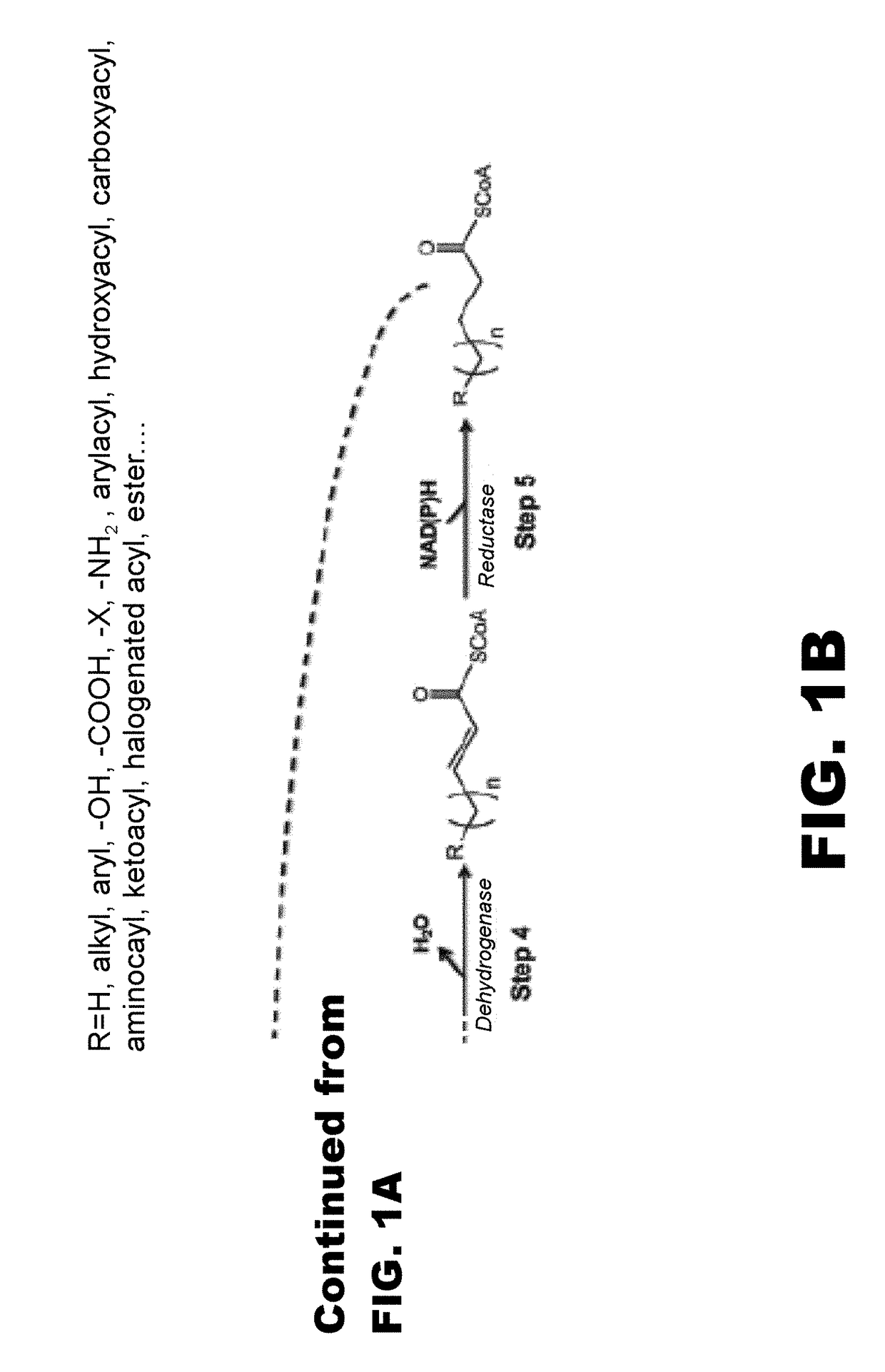
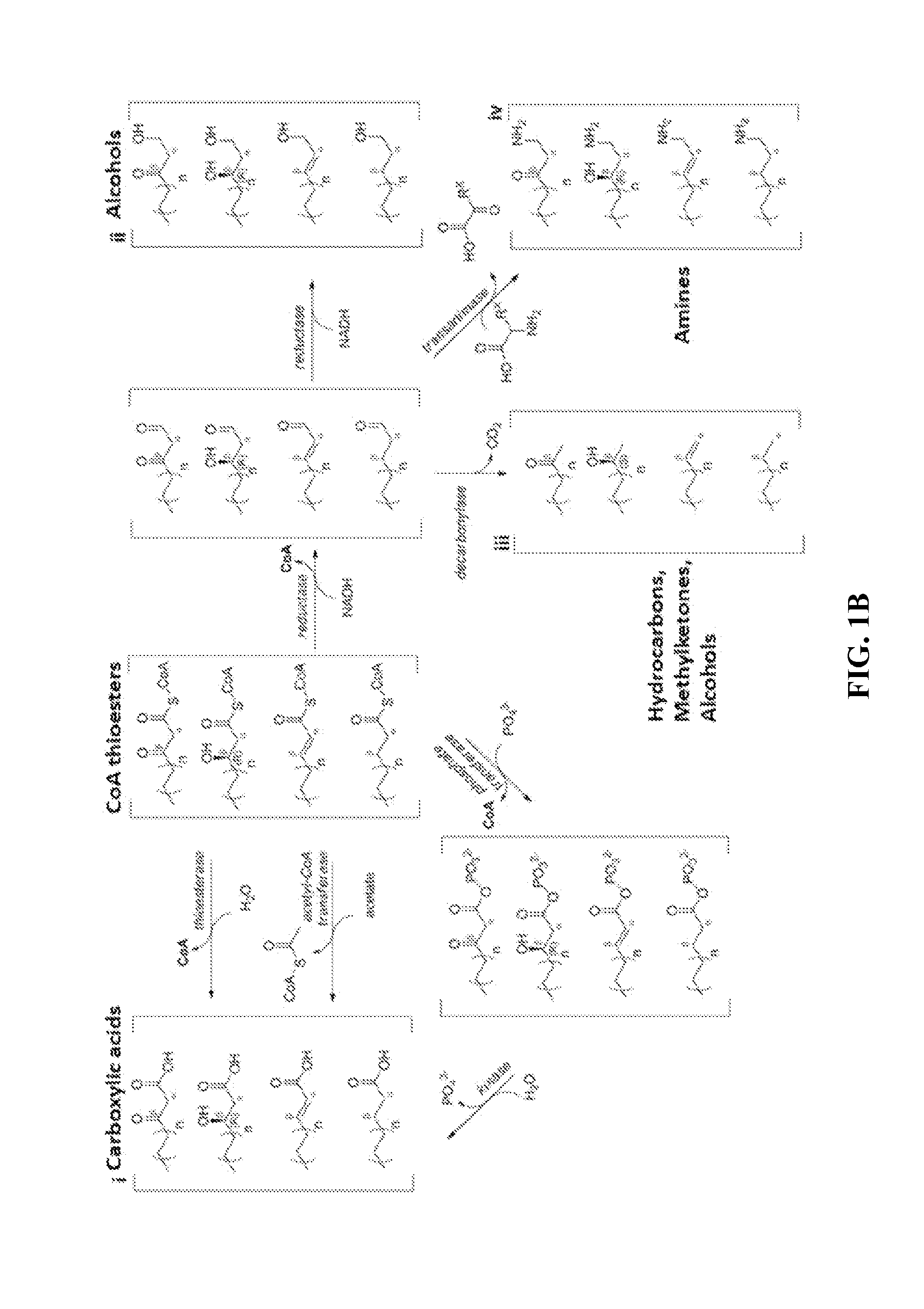
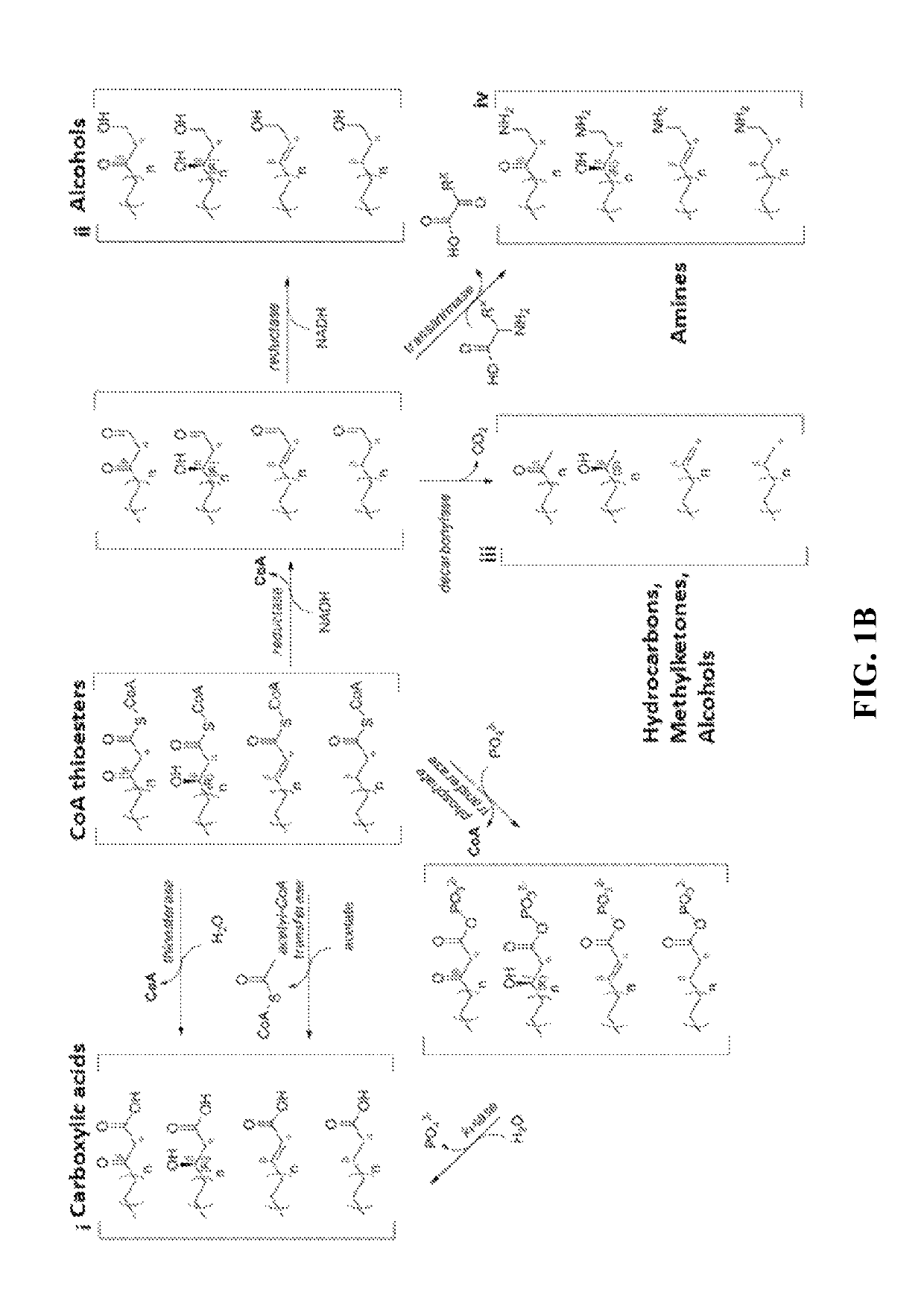
The use of microorganisms to make omega- and / or omega-l-functionalized products through an iterative carbon chain elongation pathway that we call a reverse beta oxidation pathway. The pathway uses omega-functionalized CoA thioesters as primers and acetyl-CoA as the extender unit in a non-decarboxylative Claisen condensation, and then uses beta oxidation or fatty acid synthesis enzymes to complete the cycle, via reductase, dehydratase and reductase reactions. Various termination enzymes that act on the functionalized beta-keto acyl-CoA intermediates of the pathway and produce omega or omega-1 functionalized products. The action of termination enzymes on such intermediates yield a large variety of products.
Owner:GONZALEZ RAMON
Type ii fatty acid synthesis enzymes in reverse ß-oxidation
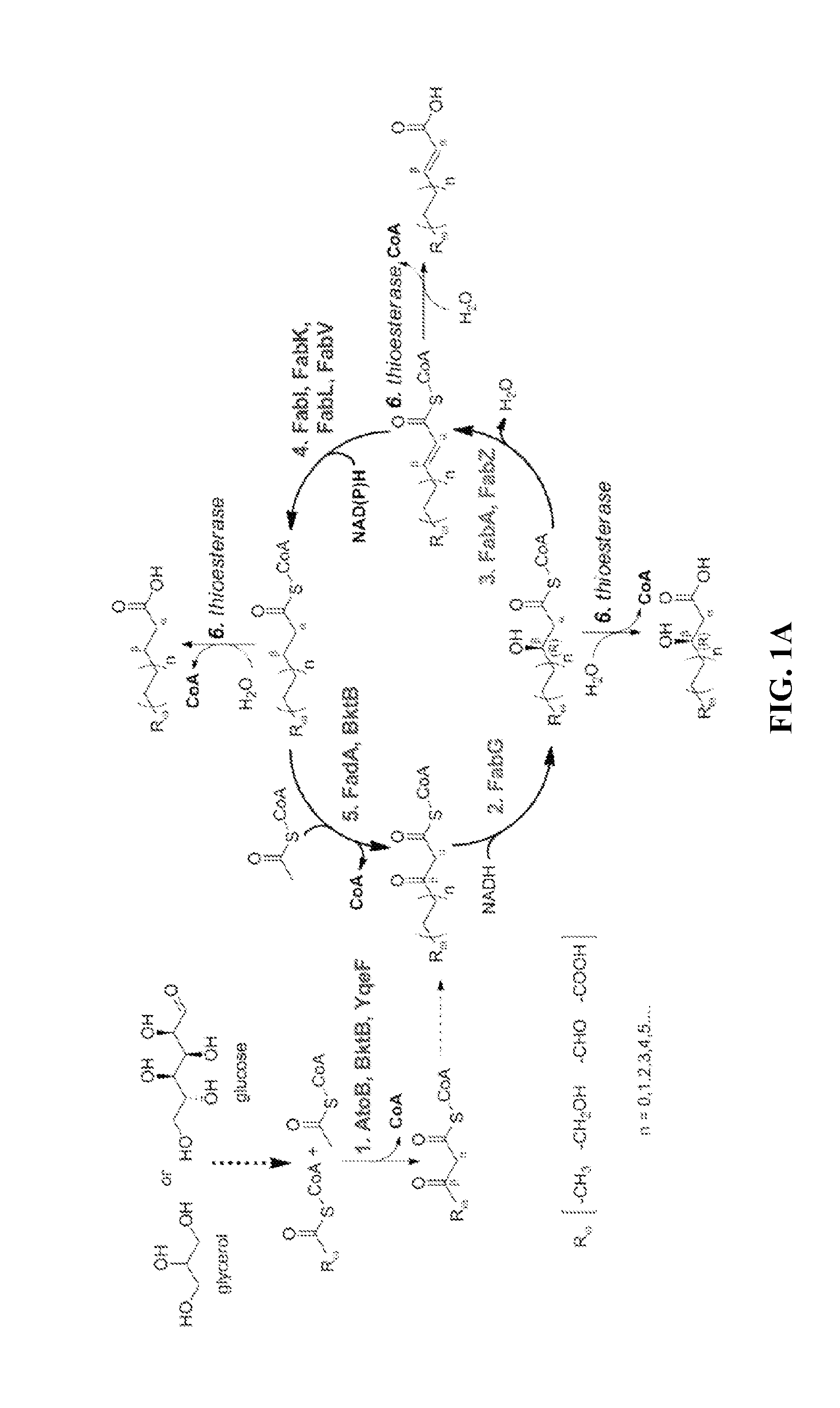
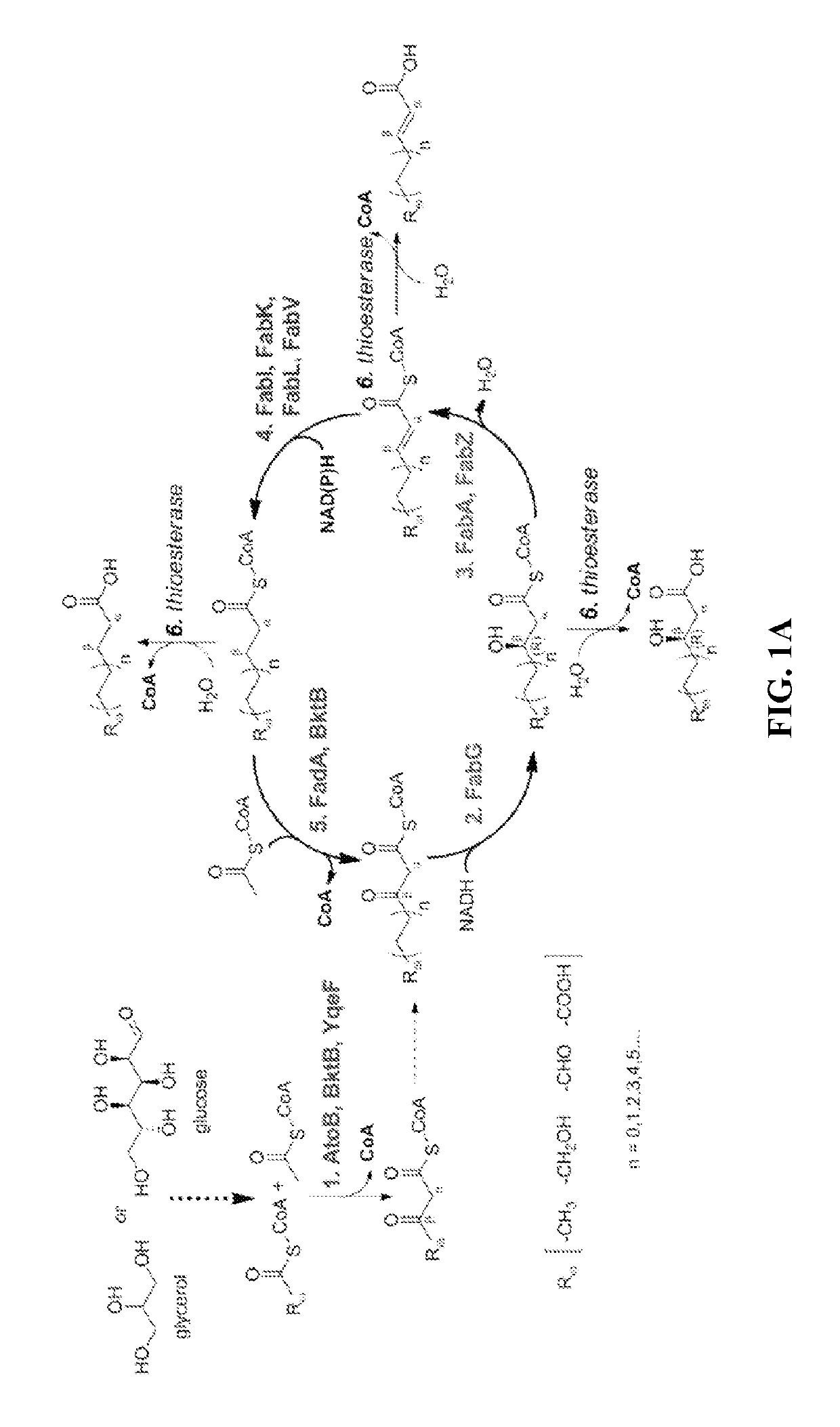
This disclosure describes enzymes from the type II (a discrete set of enzymes) fatty acid synthesis (“FAS”) pathway that can be used in combination with thiolases to operate a functional reversal of the β-oxidation cycle. A combination of thiolases with one or more of 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (FabG, others), 3-hydroxyacyl-[acp] dehydratase (FabA, FabZ, others), and enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (FabI, FabK, FabL, FabV, others) yields a functional reversal of the β-oxidation cycle. If only one or two enzymes are used, the remaining enzymes will be traditional beta oxidation enzymes. Once this cycle is coupled with the appropriate priming and termination pathways, the production of carboxylic acids, alcohols, hydrocarbons, amines and their α-, β-, and ω-functionalized derivatives from renewable carbon sources can be achieved.
Owner:RICE UNIV
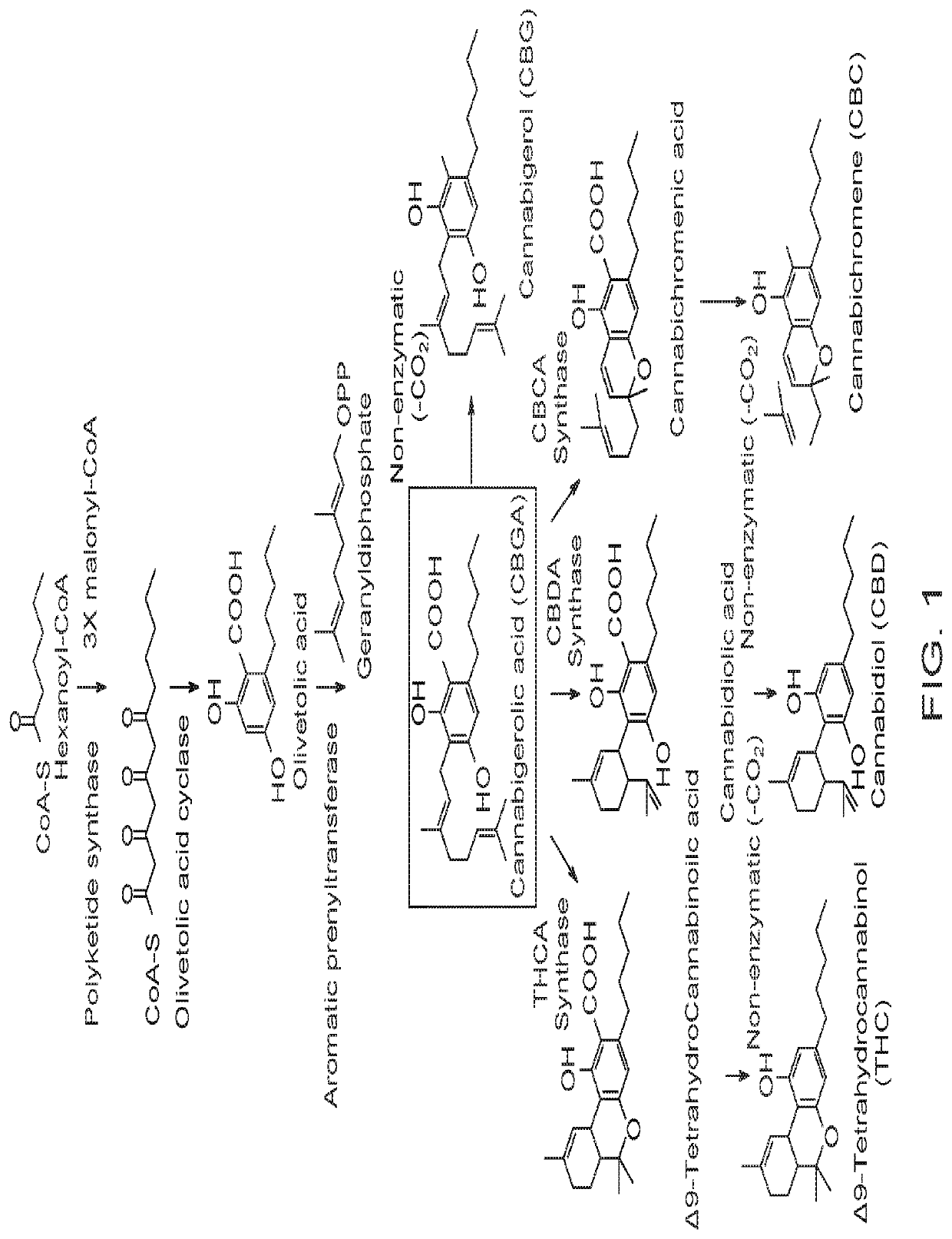
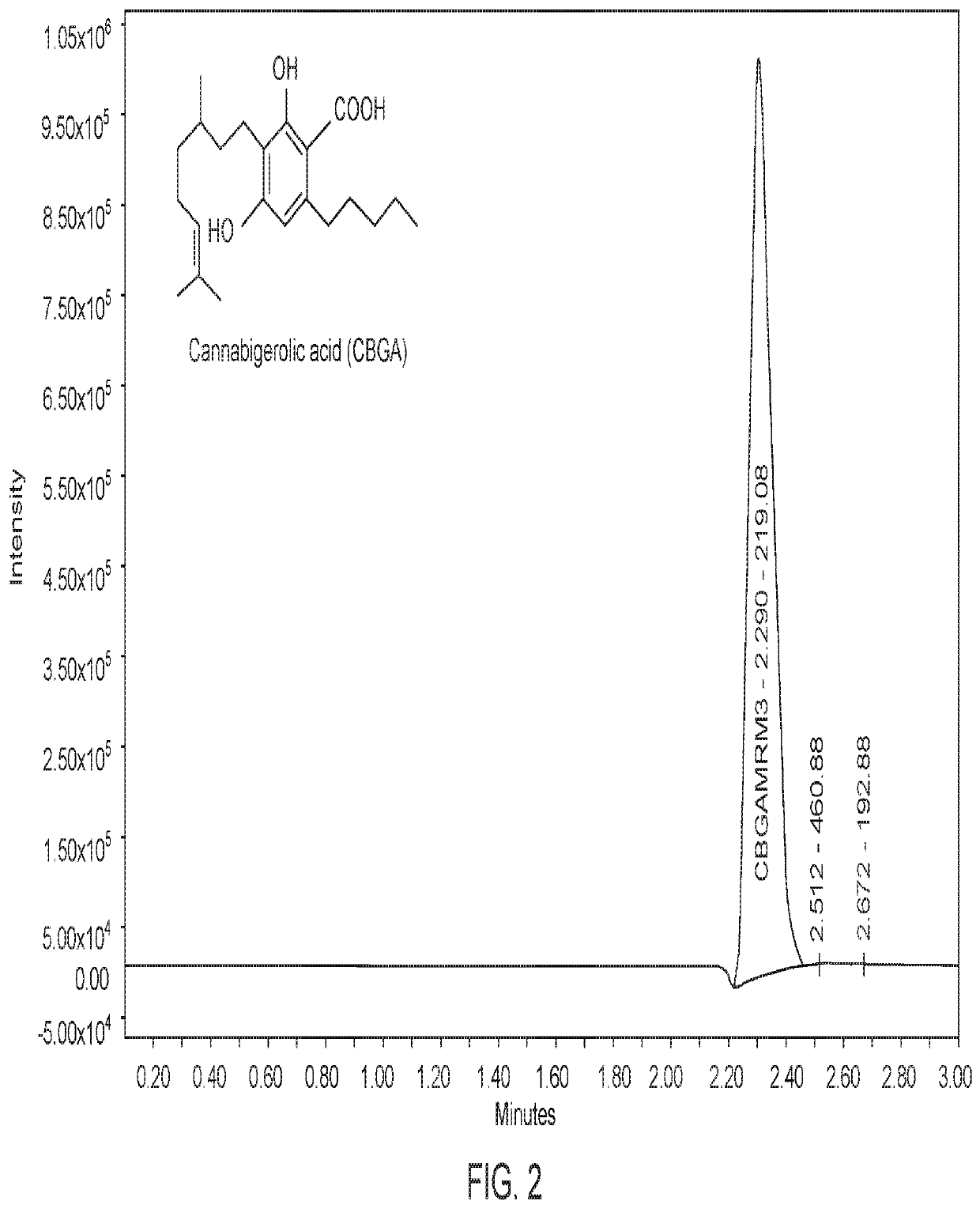
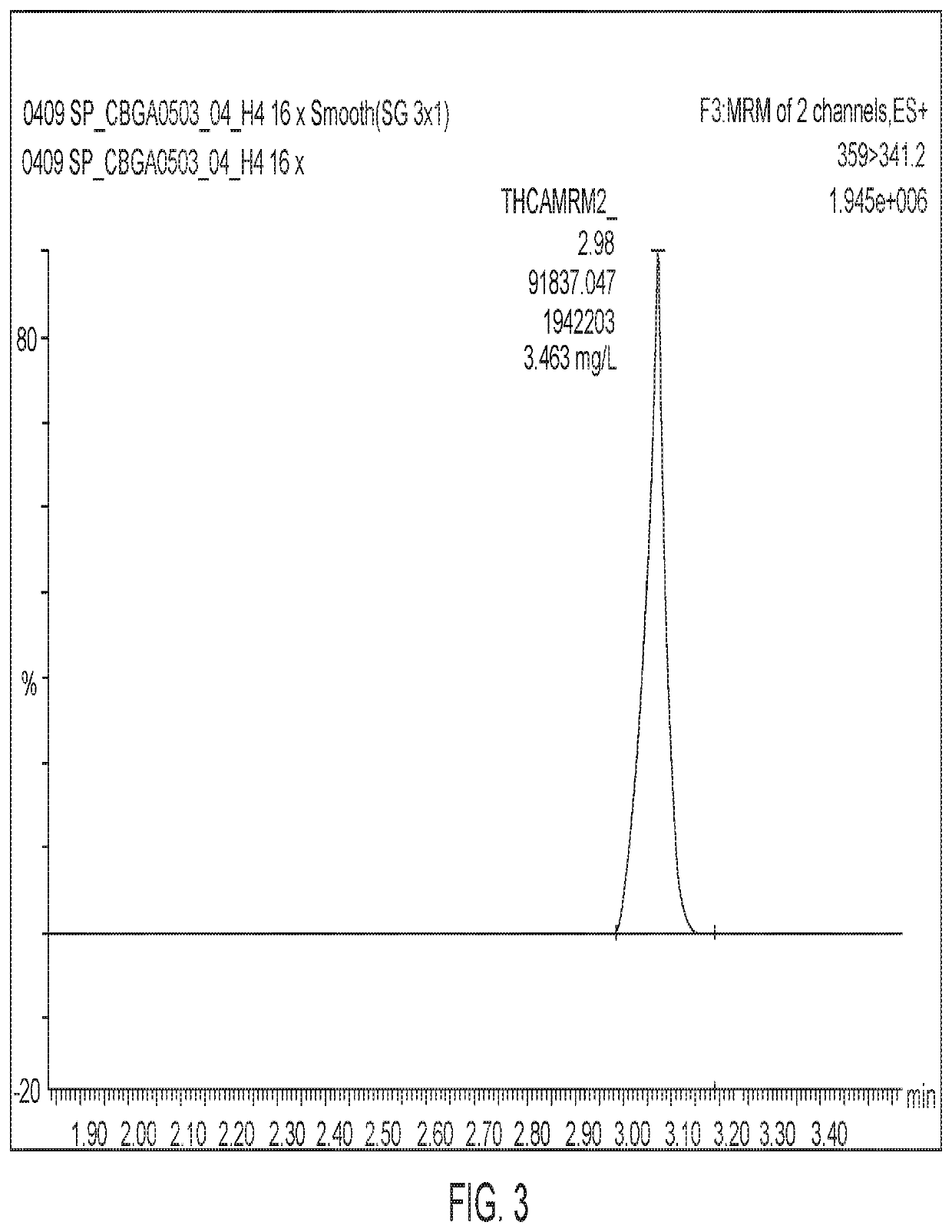
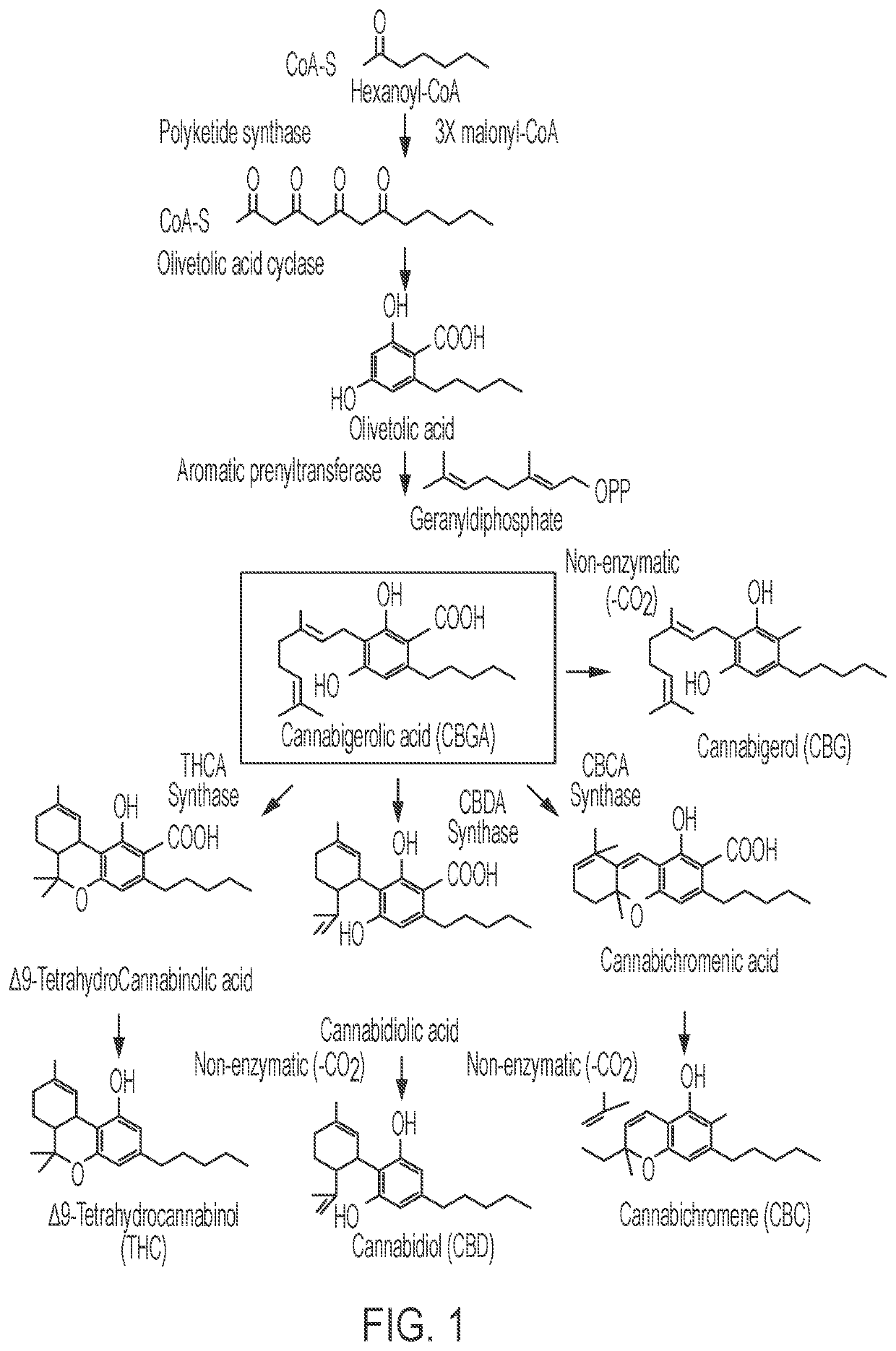
Microorganisms and Methods for the Fermentation of Cannabinoids
PendingUS20210348137A1Improve efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsCarbon-sulfur lyasesCyclaseBeta oxidation
Disclosed herein are microorganism and methods that can be used for the synthesis of cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) and cannabinoids. The methods disclosed can be used to produce CBGA, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), cannabichromenic acid (CBCA), Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD), cannabichromene (CBC). Enzymes useful for the synthesis of CBGA and cannabinoids, include but are not limited to acyl activating enzyme (AAE1), polyketide synthase (PKS), olivetolic acid cyclase (OAC), prenyltransferase (PT), THCA synthase (THCAS), CBDA synthase (CBDAS), CBCA synthase (CBCAS), HMG-Co reductase (HMG1), and / or farnesyl pyrophosphate synthetase (ERG20). The microorganisms can also have one or more genes disrupted, such as gene that that controls beta oxidation of long chain fatty acids.
Owner:ELESZTO GENETIKA INC
Application of ASB3 in preparation of drugs for treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
ActiveCN110478485AReduce fat accumulationReduce contentDigestive systemPharmaceutical active ingredientsBeta oxidationKnockout animal
The invention relates to the field of gene function, and in particular, relates to an application of an ASB3 gene in preparation of drugs for treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The advantages comprise that by constructing an ASB3 gene fully knockout mouse model, the content of E3 ubiquitin ligase ASB3 in vivo can be inhibited, and the beta-oxidation and oxygen consumption of long-chain fatty acids can be enhanced, so as to reduce lipid accumulation in hepatocytes. The invention discloses new functions of the ASB3 gene and provides new targets and ideas for treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
Type II fatty acid synthesis enzymes in reverse β-oxidation
This disclosure describes enzymes from the type II (a discrete set of enzymes) fatty acid synthesis (“FAS”) pathway that can be used in combination with thiolases to operate a functional reversal of the β-oxidation cycle. A combination of thiolases with one or more of 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (FabG, others), 3-hydroxyacyl-[acp] dehydratase (FabA, FabZ, others), and enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (FabI, FabK, FabL, FabV, others) yields a functional reversal of the β-oxidation cycle. If only one or two enzymes are used, the remaining enzymes will be traditional beta oxidation enzymes. Once this cycle is coupled with the appropriate priming and termination pathways, the production of carboxylic acids, alcohols, hydrocarbons, amines and their α-, β-, and ω-functionalized derivatives from renewable carbon sources can be achieved.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Application of P110 alpha in preparation of reagent for regulating and controlling animal energy metabolism
PendingCN113577286AAchieve the effect of treating obesityAvoid side effectsMetabolism disorderPharmaceutical active ingredientsBiotechnologyBeta oxidation
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to application of P110 alpha in preparation of a reagent for regulating and controlling animal energy metabolism. The research finds that the weight of a P110 alpha CKO mouse is reduced. The mouse P110 alpha gene is massively knocked out in the liver and is mainly knocked out in liver sinus endothelial cells (LSECs), and meanwhile, CNP is prompted to be massively expressed in the liver and is mainly expressed in the LSECs. The up-regulation of FGF21 in LSECs of the P110 alpha CKO mouse causes the increase of the FGF21 protein expression of the liver and the FGF21 level of serum, which is possibly caused by the weakening of the synthesis of the liver and white fat (WAT), the enhancement of fatty acid-beta oxidation, the increase of the energy consumption of the body and the weight loss.
Synthesis of omega functionalized products
The use of microorganisms to make omega- and / or omega-1-functionalized products through an iterative carbon chain elongation pathway that we call a reverse beta oxidation pathway. The pathway uses omega-functionalized CoA thioesters as primers and acetyl-CoA as the extender unit in a non-decarboxylative Claisen condensation, and then uses beta oxidation or fatty acid synthesis enzymes to complete the cycle, via reductase, dehydratase and reductase reactions. Various termination enzymes that act on the functionalized beta-keto acyl-CoA intermediates of the pathway and produce omega or omega-1 functionalized products. The action of termination enzymes on such intermediates yield a large variety of products.
Owner:GONZALEZ RAMON
Method of treating diabetic peripheral neuropathy through amendment of pre-neuronal diabetic coagulative micro-angiopathy and neuronal deficiency of mitochondrial ATP production, and through induction of neuronal regeneration
DPN is an intractable and tormenting neurovascular and dermal disorder.Two patients of DPN of stocking-glove pattern were treated with SAG for treatment of microvascuar coagulopathy, induction of vasodilation and possible induction of angioneogenesis; with ALC for ATP generation through mitochondrial beta-oxidation of fats; and with ALA for antioxidative stress to prevent precipitation of vascular damage and to prevent DPN recurrence. SAG+ALC was to cure maceration.Thus, SAG+ALC+ALA was effective in mitigating and curing their distresses. It shall be one of the logical and practical means of prompt DPN therapy not only to alleviate DPN but also to lead to “cure.”
Owner:OKUYAMA SHINICHI +1
Microorganisms and methods for the fermentation of cannabinoids
Disclosed herein are microorganism and methods that can be used for the synthesis of cannabigerolic acid (CBGA) and cannabinoids. The methods disclosed can be used to produce CBGA, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), cannabidiolic acid (CBDA), cannabichromenic acid (CBGA), Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarinic acid (THCVA), cannabidivarinic acid (CBDVA), cannabichromevarinic acid (CBCVA), Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD), cannabichromene (CBC). Enzymes useful for the synthesis of CBGA and cannabinoids, include but are not limited to acyl activating enzyme (AAE1), polyketide synthase (PKS), olivetolic acid cyclase (OAC), prenyltransferase (PT), THCA synthase (THCAS), CBDA synthase (CBDAS), CBC A synthase (CBCAS), HMG-Co reductase (HMG1), and / or famesyl pyrophosphate synthetase (ERG20). The microorganisms can also have one or more genes disrupted, such as gene that that controls beta oxidation of long chain fatty acids.
Owner:ELESZTO GENETIKA INC
Compound formula for preventing and treating obesity by comprehensively correcting metabolic disorders based on gamma-aminobutyric acid
InactiveCN111544425AImprove thermal stabilityGuaranteed stabilityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderFormularyBeta oxidation
The invention discloses a compound formula for preventing and treating obesity by comprehensively correcting metabolic disorders based on gamma-aminobutyric acid. The compound formula comprises the components: gamma-aminobutyric acid (50-500 mg / d), nicotinic acid (20-200 mg / d), riboflavin (3-20 mg / d), pantothenic acid (5-30 mg / d), carnitine (300-2000 mg / d) and magnesium aspartate (30-500 mg / d). The gamma-aminobutyric acid in the formula inhibits nutrient absorption, protects mitochondria from being less continuously damaged by metabolic reactive oxygen species, and plays a role in less absorption and more consumption; the rest components are added to form the compound formula, beta oxidation of a fat-splitting core path is nutritionally supported, metabolism is adjusted in a mild mode, anda safe and healthy weight losing effect is achieved. In formula development, a high-throughput cell experiment and a random double-blind control multi-center volunteer experiment are comprehensivelyutilized; the action range and the toxicity threshold value of each component are accurately detected, so that the use dosage of each component has extremely high tolerance and safety, and the compound formula is suitable for being used as a core formula of a health care product or a nutritional supplement, and is beneficial to development and marketing of subsequent related products.
Owner:陕西哲联生物科技有限公司
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com