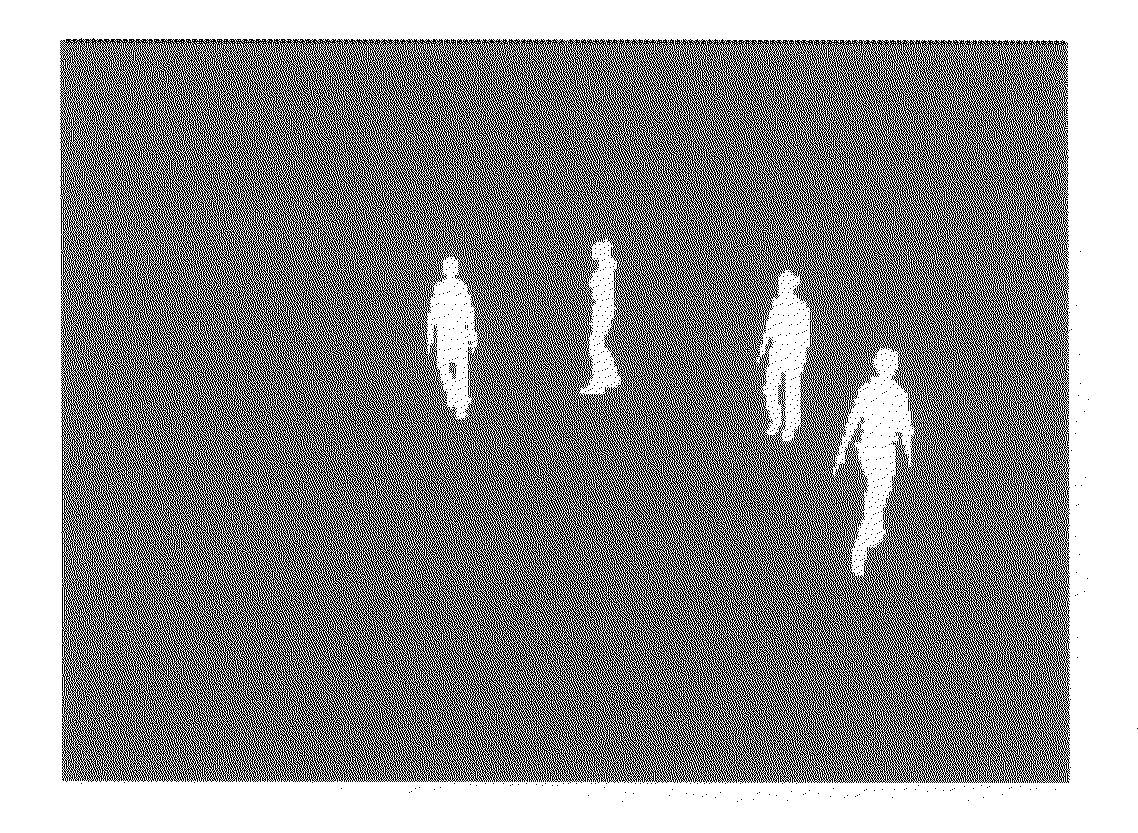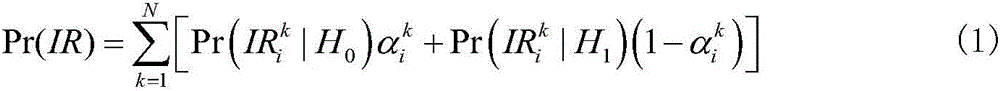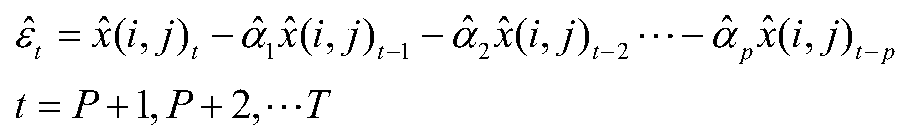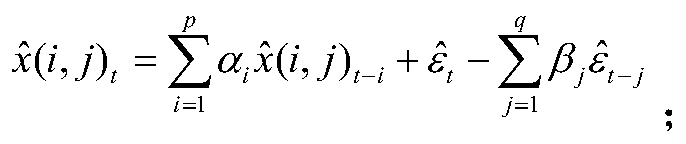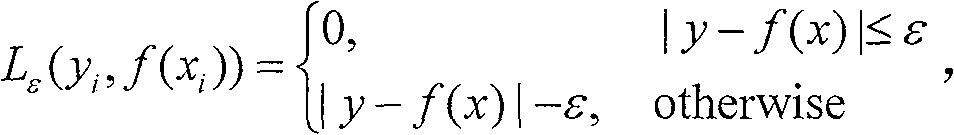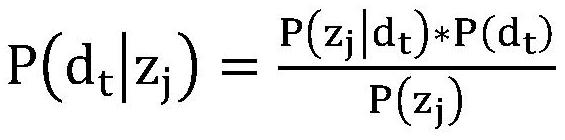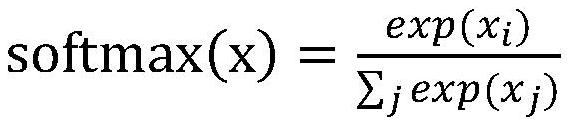Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Bayes' rule" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In probability theory and applications, Bayes' rule relates the odds of event to the odds of event, before and after conditioning on another event . The odds on to event is simply the ratio of the probabilities of the two events. The prior odds is the ratio of the unconditional or prior probabilities, the posterior odds is the ratio of conditional or posterior probabilities given the event . The relationship is expressed in terms of the likelihood ratio or Bayes factor, . By definition, this is the ratio of the conditional probabilities of the event given that is the case or that is the case, respectively. The rule simply states: posterior odds equals prior odds times Bayes factor. When arbitrarily many events are of interest, not just two, the rule can be rephrased as posterior is proportional to prior times likelihood, where the proportionality symbol means that the left hand side is proportional to the right hand side as varies, for fixed or given . In this form it goes back to Laplace and to Cournot; see Fienberg. Bayes' rule is an equivalent way to formulate Bayes' theorem. If we know the odds for and against we also know the probabilities of .
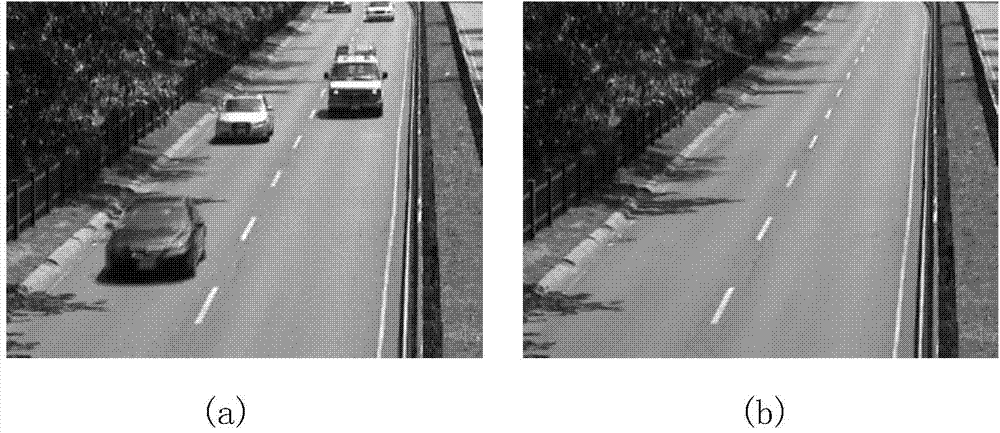
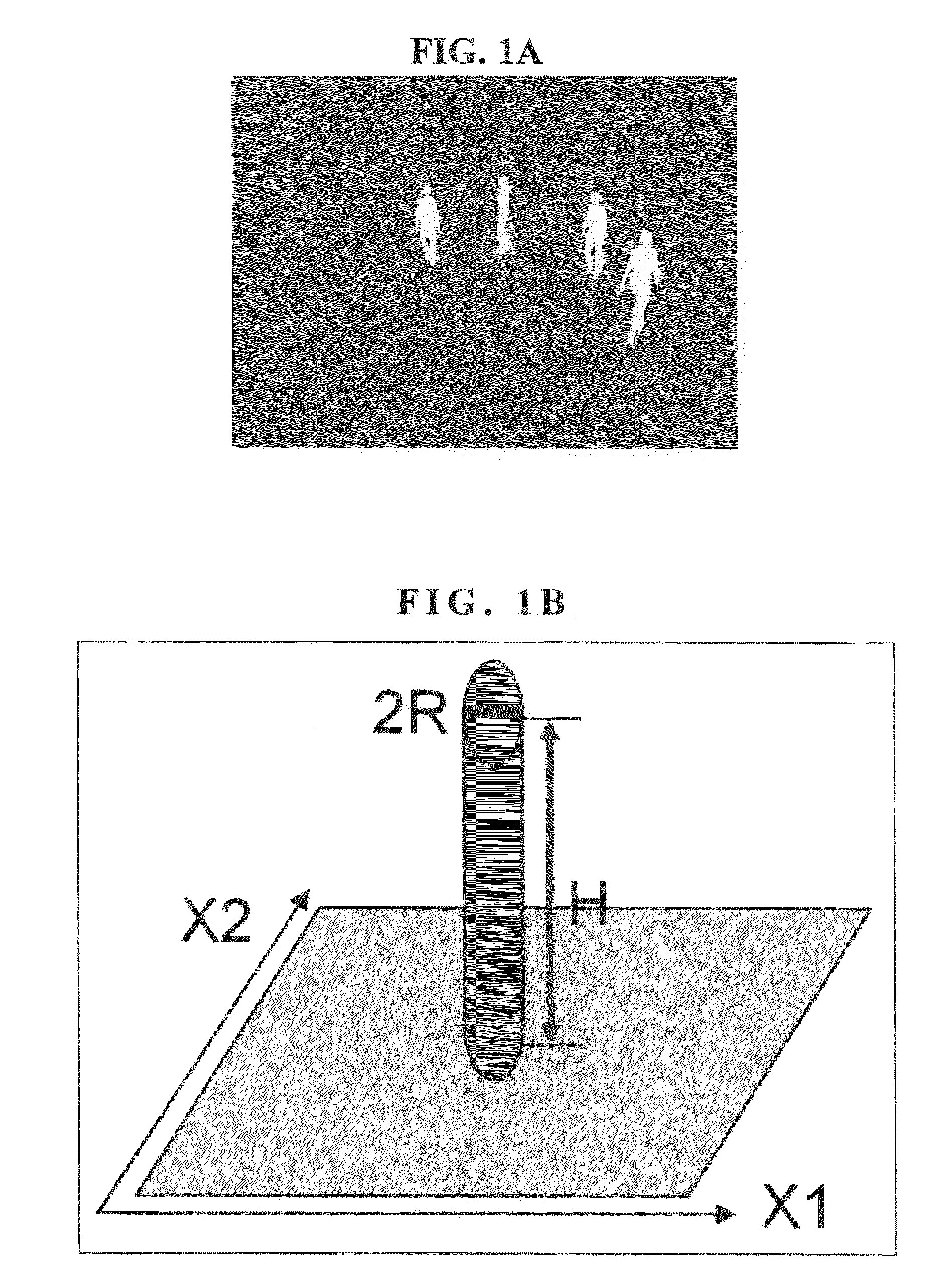
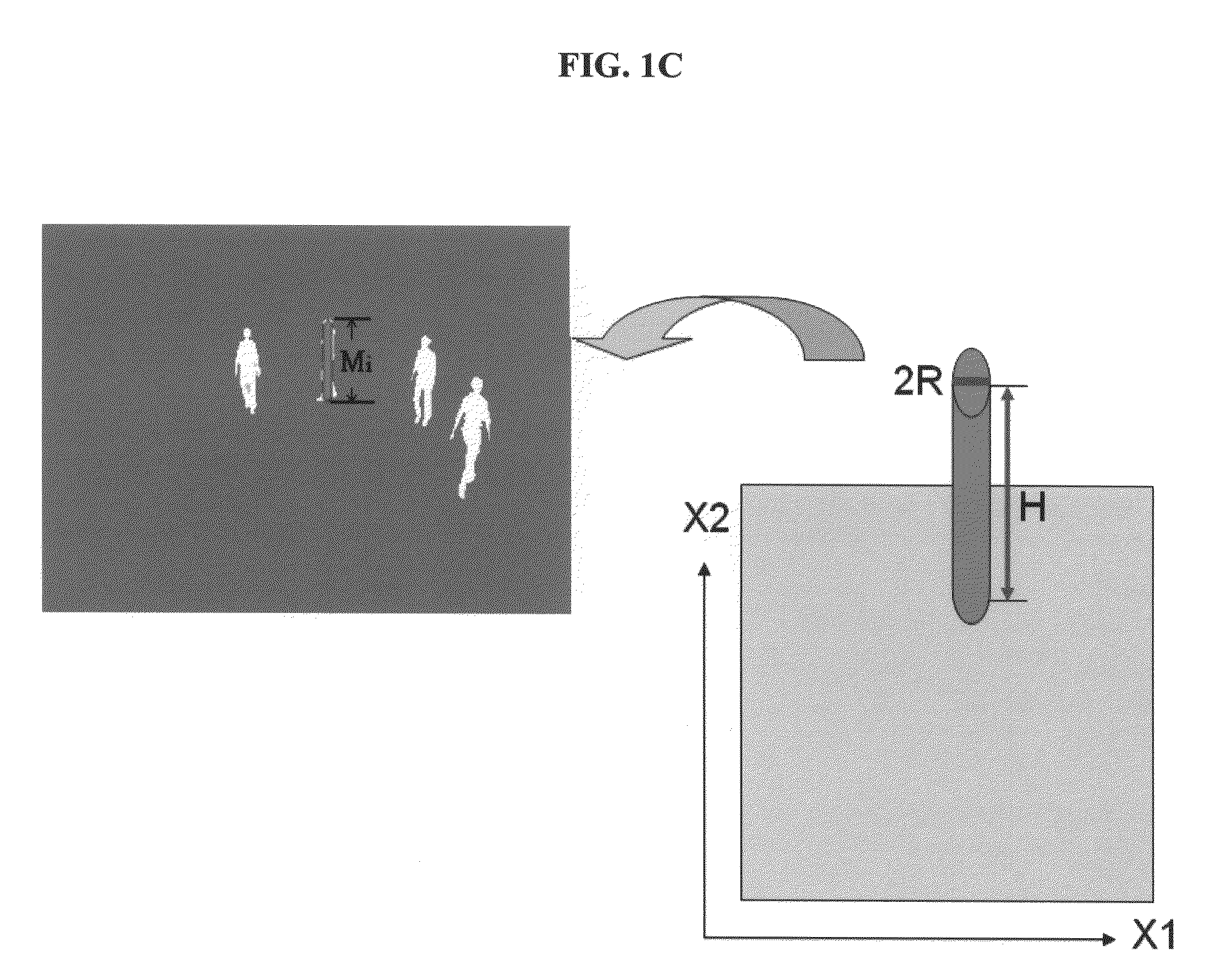
Method for automatic detection and tracking of multiple targets with multiple cameras and system therefor
ActiveUS20100166260A1The result is stable and accurateEfficient integrationCharacter and pattern recognitionClosed circuit television systemsMarkov chainMulti camera
A method for automatically detecting and tracking multiple targets in a multi-camera surveillance zone and system thereof. In each camera view of the system only a simple object detection algorithm is needed. The detection results from multiple cameras are fused into a posterior distribution, named TDP, based on the Bayesian rule. This TDP distribution represents a likelihood of presence of some moving targets on the ground plane. To properly handle the tracking of multiple moving targets with time, a sample-based framework which combines Markov Chain Monte carlo (MCMC), Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC), and Mean-Shift Clustering, is provided. The detection and tracking accuracy is evaluated by both synthesized videos and real videos. The experimental results show that this method and system can accurately track a varying number of targets.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
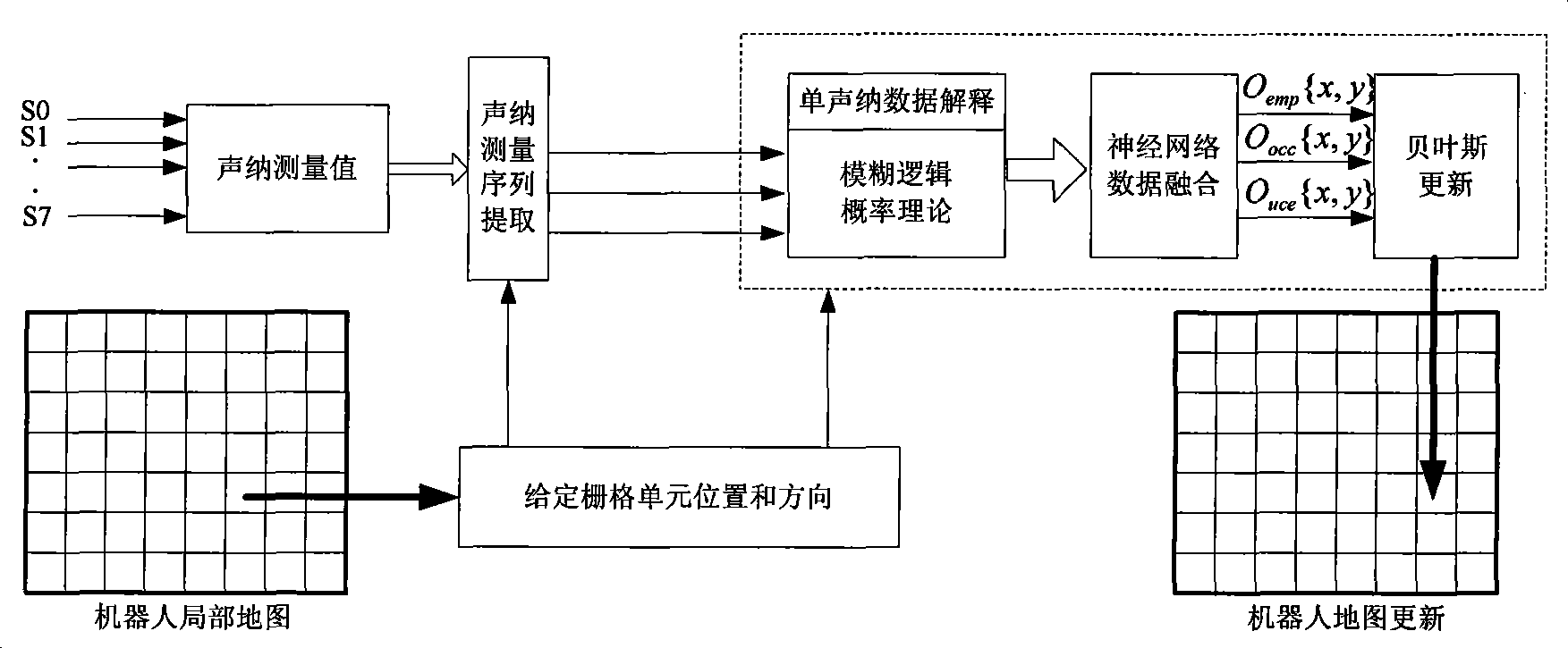
Mobile robot grating map creating method of real-time data fusion
InactiveCN101413806AFast adaptabilityImprove robustnessInstruments for road network navigationPhysical realisationFeature vectorSonar
The invention provides a building method of a grid map by a mobile robot based on real-time data fusion. The method comprises the following steps: artificially dividing an environment into a plurality of grids with the same size, and obtaining the distance information by sonar sensors arranged on the front end of the mobile robot; extracting measured values of three sonar sensors which are closest to a currently computed grid unit at the same time, respectively explaining a single sonar data by a fuzzy logic and a probability theory so as to obtain a group of characteristic vectors which are subject to the data fusion as input vectors of a neural network, wherein, output values of the neural network comprises idle state, busy state and undefined state of the grid; finally updating the state of the grid by the Bayes rule. The mobile robot of the invention obtains the environmental information by sonar ranging finders and completes the environmental modeling, thus providing reliable basis for the subsequent autonomous navigation of the mobile robot.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for automatic detection and tracking of multiple targets with multiple cameras and system therefor
ActiveUS8995712B2The result is stable and accurateEfficient integrationTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionMarkov chainMulti camera
A method for automatically detecting and tracking multiple targets in a multi-camera surveillance zone and system thereof. In each camera view of the system only a simple object detection algorithm is needed. The detection results from multiple cameras are fused into a posterior distribution, named TDP, based on the Bayesian rule. This TDP distribution represents a likelihood of presence of some moving targets on the ground plane. To properly handle the tracking of multiple moving targets with time, a sample-based framework which combines Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC), Sequential Monte Carlo (SMC), and Mean-Shift Clustering, is provided. The detection and tracking accuracy is evaluated by both synthesized videos and real videos. The experimental results show that this method and system can accurately track a varying number of targets.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
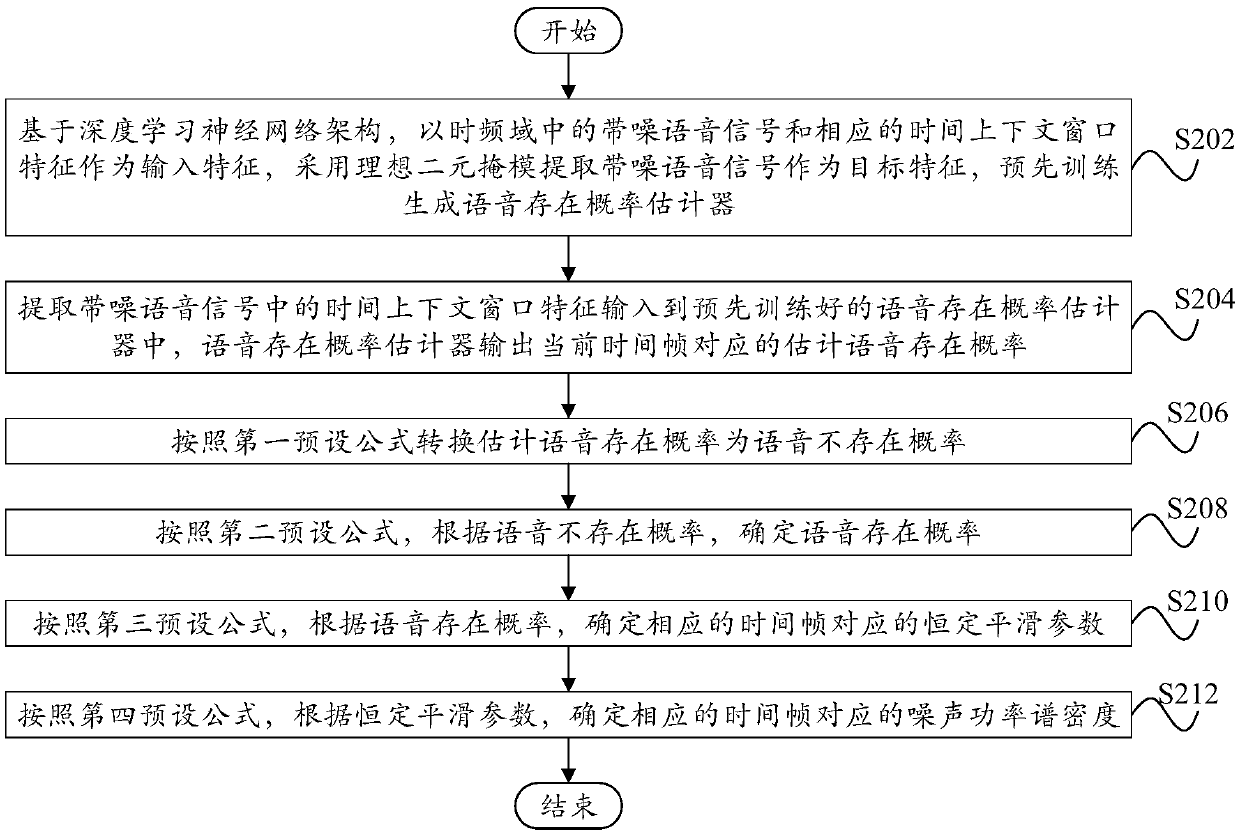
Method and device for estimating noise power spectral density of speech signal
PendingCN109616139AImprove estimation accuracyImprove speech enhancement performanceSpeech analysisBayes' ruleNoise power spectrum
The invention relates to the technical field of speech processing and specifically provides a method and a device for estimating a noise power spectral density of a speech signal. The method comprisesthe following steps: extracting a time context window feature from a noise speech signal, inputting the time context window feature to a pre-trained speech existence probability estimator which outputs an estimated speech existence probability corresponding to a current time frame; correcting the estimated speech existence probability according to a Bayes rule to determine a speech existence probability; determining the noise power spectral density corresponding to the corresponding time frame based on the speech existence probability according to a recursive smoothing formula. Through the technical scheme of the invention, the estimation accuracy of the noise power spectral density is improved in the case of small computing resources, thereby being beneficial to effectively eliminating noise signals, minimizing distortion in the speech processing process and improving speech enhancement performance.
Owner:PING AN TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Robustness prospect detection method based on multi-view learning
InactiveCN104766065AAchieve segmentationCharacter and pattern recognitionBayes' ruleEnergy functional
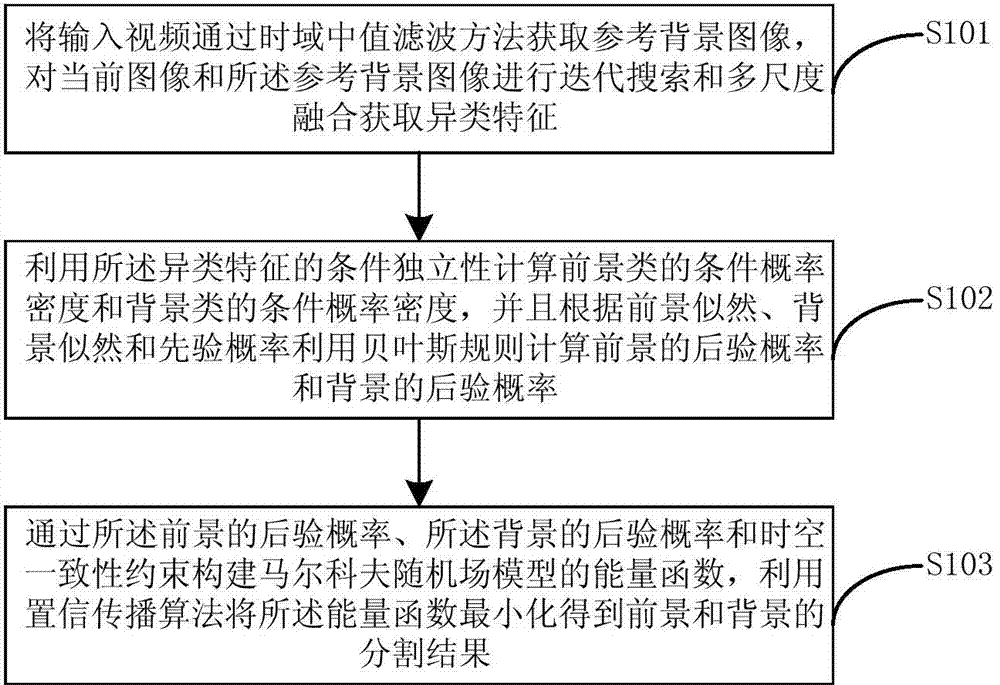
The invention provides a robustness prospect detection method based on multi-view learning. The method includes the steps that a reference background image is acquired by an input video through time domain median filtering method, and iterative search and multi-scale fusion are conducted on a current image and the reference background image to acquire heterogeneous characteristics; conditional probability density of prospects and conditional probability density of backgrounds are calculated by using condition independence of the heterogeneous characteristics, and a prospect posteriori probability and a background posteriori probability are calculated by using Bayes rules according to prospect likelihood, background likelihood and a prior probability; an energy function of a Markov random field model is established by means of the prospect posteriori probability, the background posteriori probability and space-time consistency constraint, the energy function is minimized by using a belief propagation algorithm, and segmented results of the prospect and the background are obtained. By means of the method, in a complex challenging environment, robustness prospect detection is achieved.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
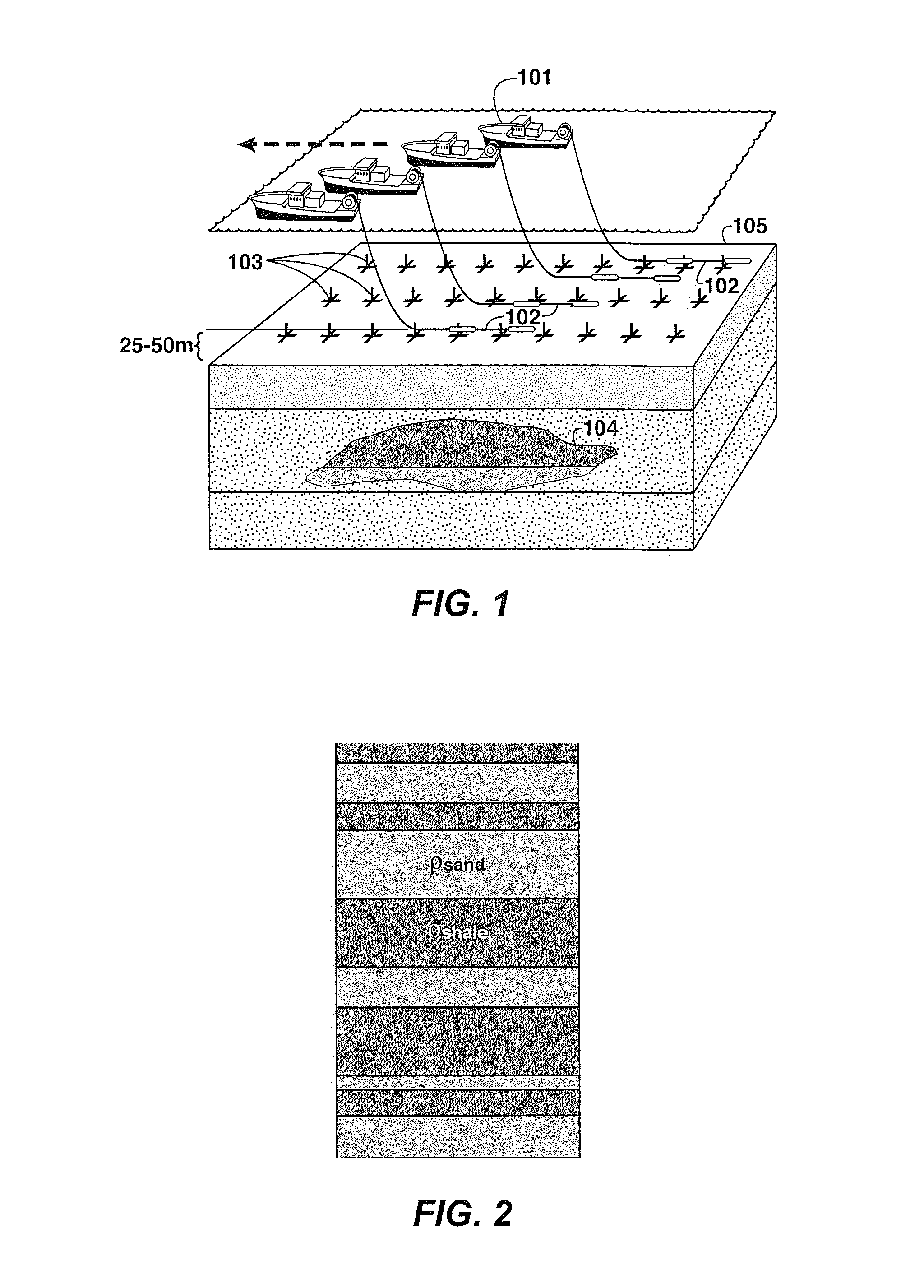
Classifying potential hydrocarbon reservoirs using electromagnetic survey information
ActiveUS8185313B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingProbabilistic methodBayes' rule
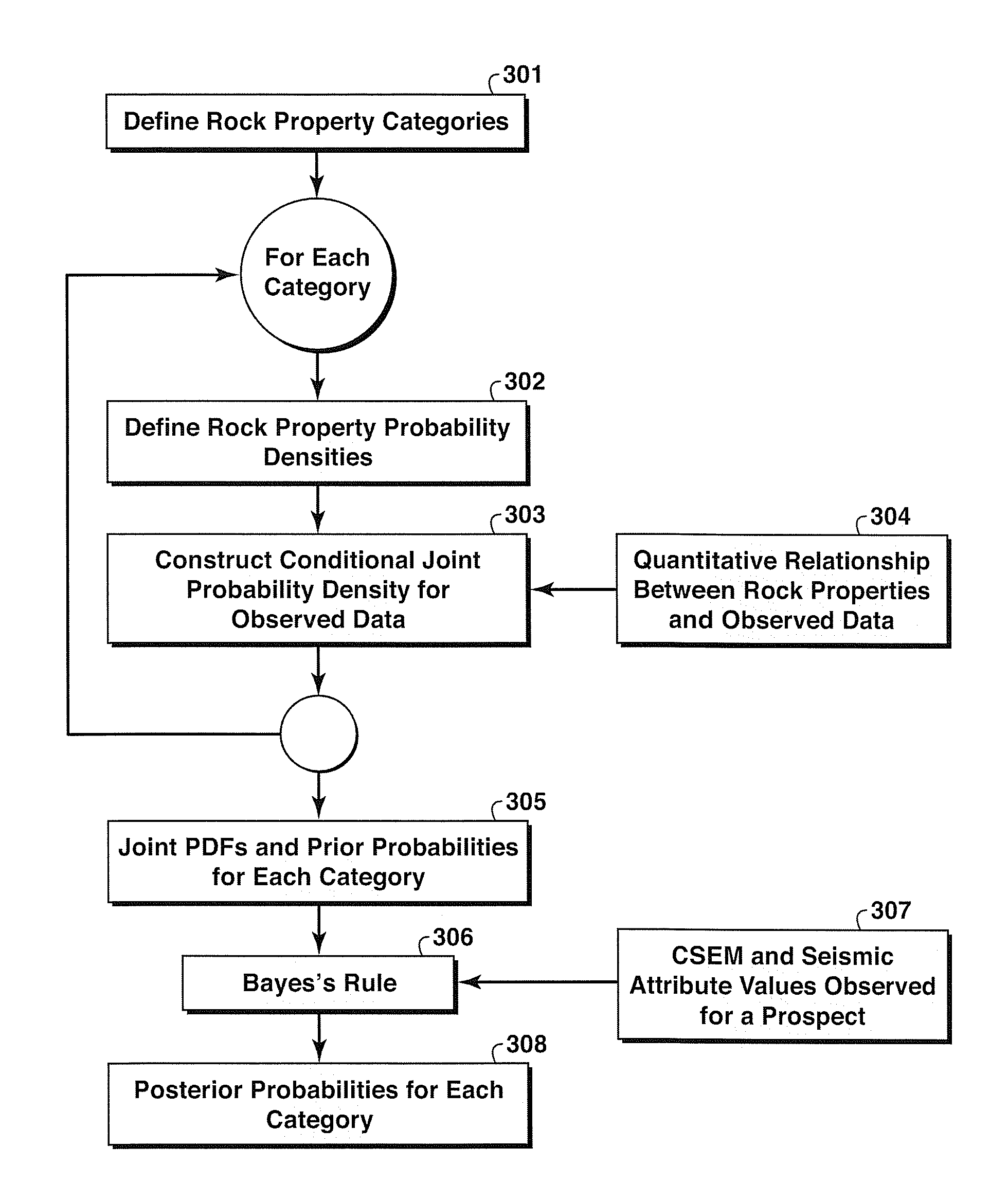
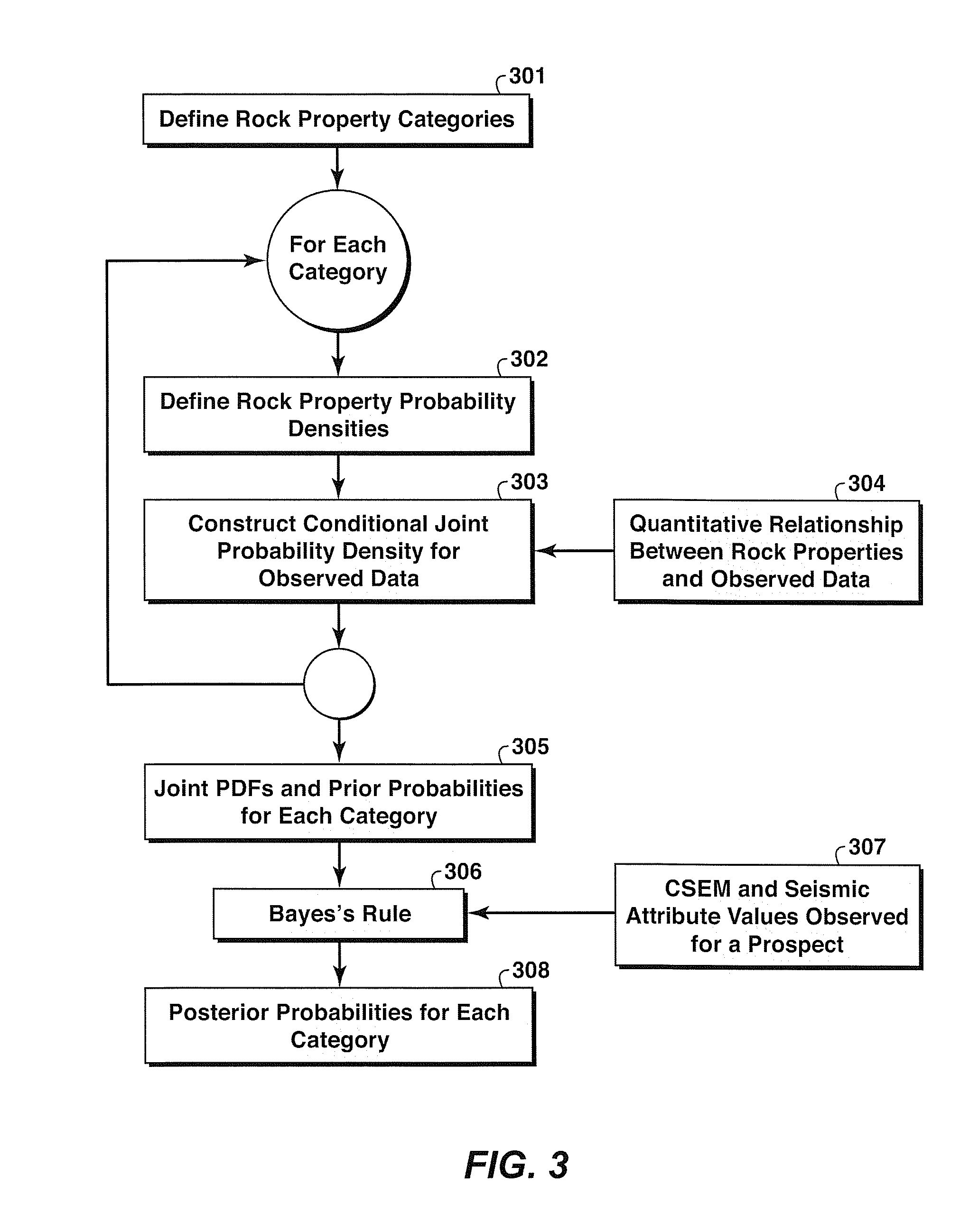
A probabilistic method for classifying observed CSEM response for a resistive anomaly to classify the response into multiple geologic categories indicative of hydrocarbon production potential. Each category is assigned a prior probability (301). For each category, conditional joint probability distributions for observed CSEM data in the anomaly region are constructed (303) from rock property probability distributions (302) and a quantitative relationship between rock / fluid properties and the CSEM data (304). Then, the joint probability distributions and prior probabilities for each category (305) are combined with observed data (307) and used in Bayes' Rule (306) to update the prior category probabilities (308). Seismic data may be used to supplement CSEM data in the method.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Integrity risk probability distribution method supporting satellite navigation positioning reliability requirement
InactiveCN106779082AHigh reliability requirementsSatisfy Integrity Risk RequirementsMathematical modelsBayes' ruleRequired navigation performance
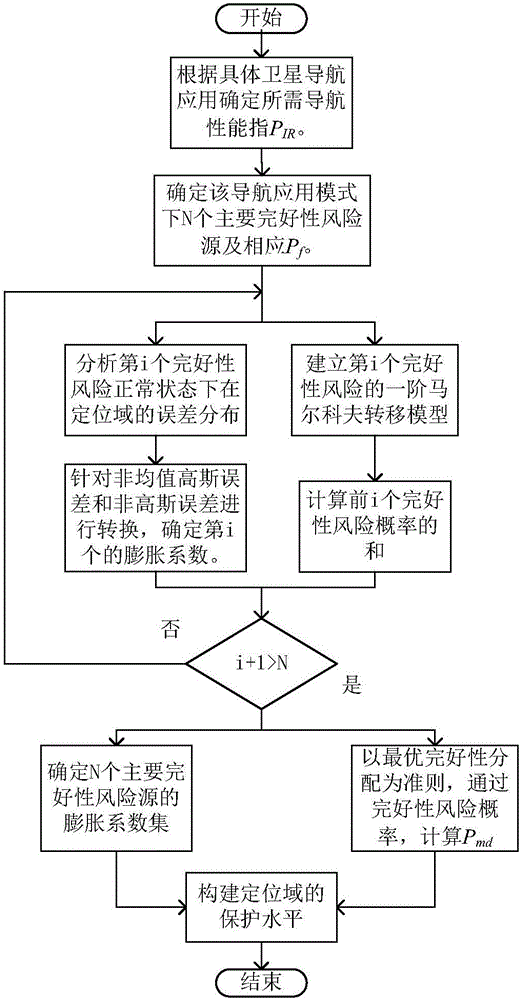
The invention belongs to the technical field of satellite navigation positioning, and particularly relates to an integrity risk probability distribution method supporting a satellite navigation positioning reliability requirement. The method comprises steps of according to navigation performance required in different navigation applications, establishing fault tree modules for integrity risk sources in different applications; according to the Bayes rule, finishing an optimal distribution scheme of the integrity risk probability; establishing an one order Markov switching module for each main integrity risk source, according to a specific integrity risk source, setting an initial condition and prior information of the module, and finally determining the P<md>; and determining a sigma expansion coefficient subset according to counting features on positioning errors imposed by specific integrity risk sources in different applications. According to the invention, an improved sigma expansion algorithm based on the expansion coefficient set is provided and expansion coefficients are determined, so theoretical basis is provided for ideal error hypothesis required by integrity monitoring; and a minimal protection level is finally designed, so the requirement of high reliability of satellite navigation positioning is met.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
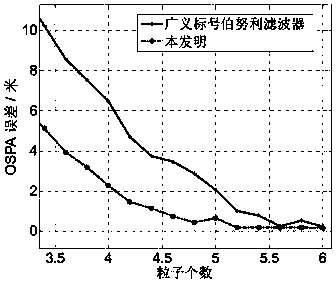
Multi-target tracking method based on theory of random sets
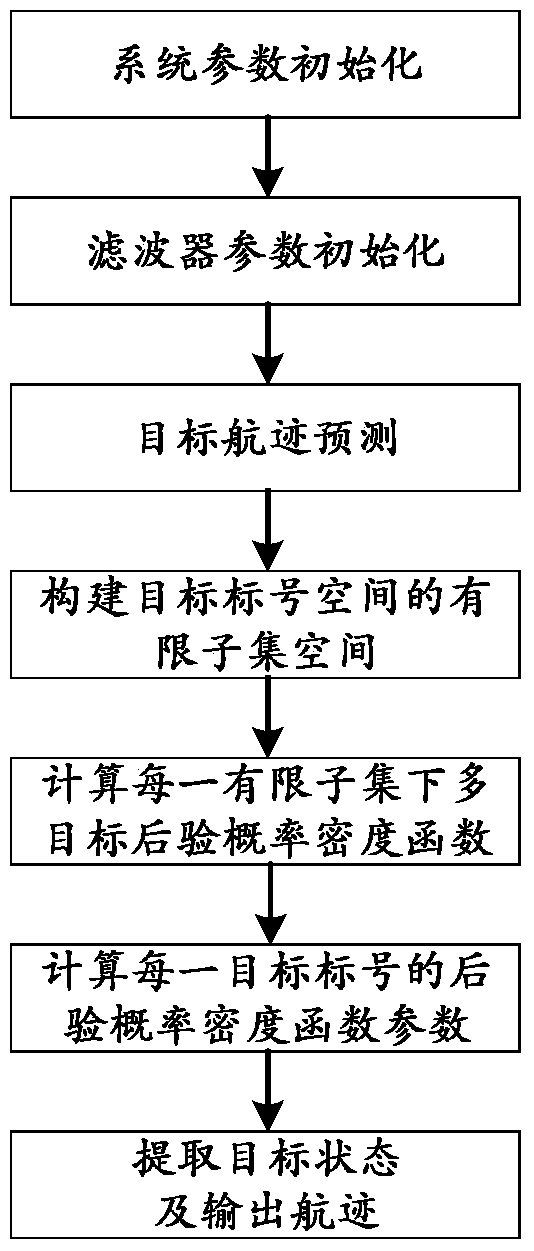
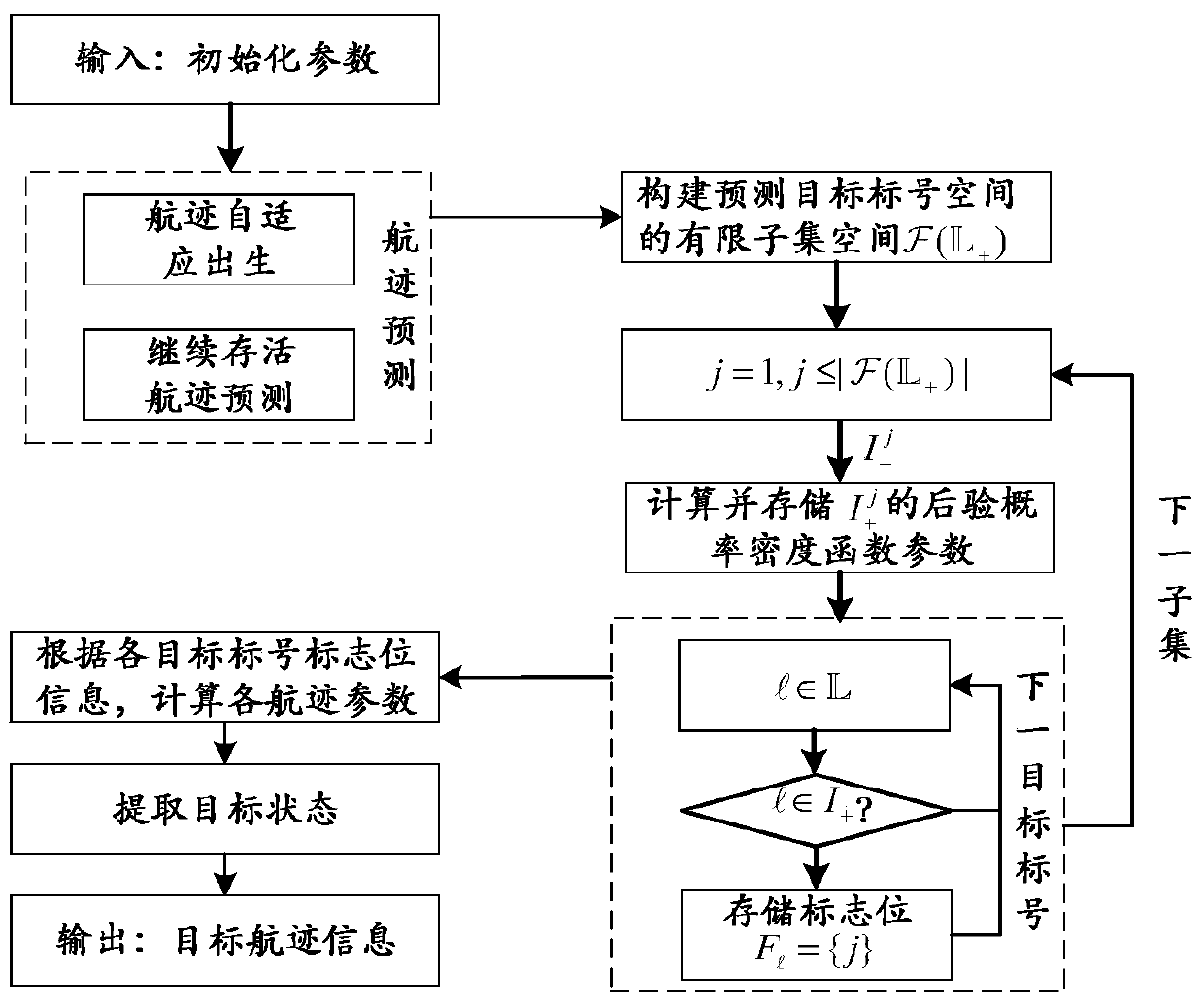
ActiveCN106707272ASave computing resourcesOccupies less computing resourcesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLimited resourcesBayes' rule
The invention provides a multi-target tracking method based on the theory of random sets, and aims at realizing multi-target state effective tracking in a complex scene under the restricted condition of limited resources. According to the method, firstly each continue live track is further predicted according to the Bayes rule in the track prediction stage, and then a target track is self-adaptively generated according to target prior information; and in the track updating stage, firstly the corresponding existence weight probability and a combined multi-target probability density function are computed under each assumption, and then the posterior probability parameter of each target mark number is computed, including the existence probability and the corresponding probability density function. The method has the advantages of being low in approximation cost and excellent in performance under the limited resources and has the robustness suitable for any measurement models. Besides, the algorithm occupies less system computing resources so as to have great engineering application prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
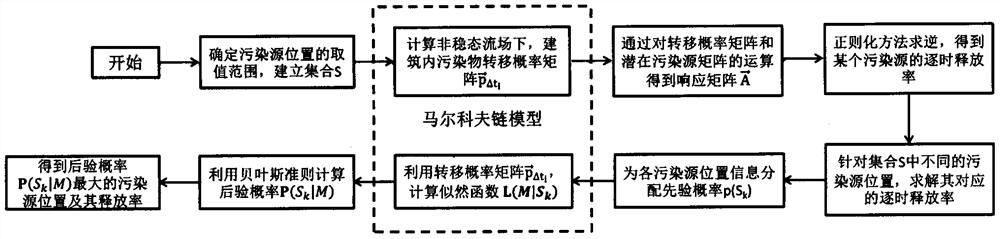
Reverse recognition algorithm of pollution source in unsteady state flow field based on Markov chain
ActiveCN107145737AIdentify locationRecognition release rateInformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsTransfer probabilityBayes' rule
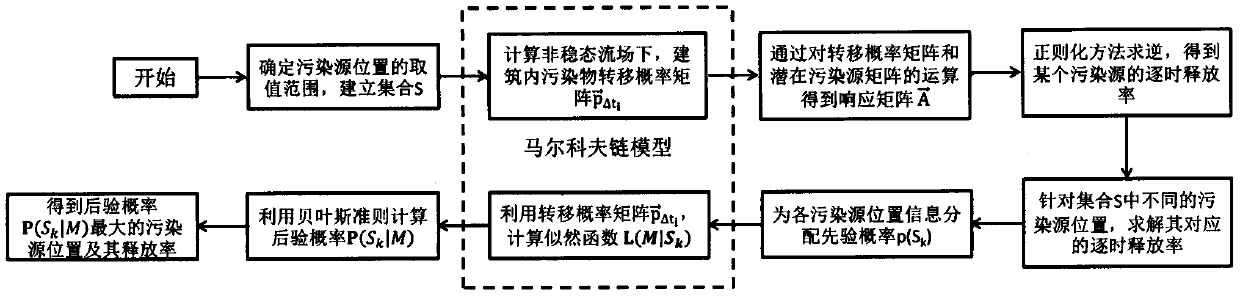
The invention discloses a reverse recognition algorithm of a pollution source in an unsteady state flow field based on a Markov chain, which belongs to the technical field of indoor pollutant control, and aims to solve the problem of pollution source recognition in multiregion buildings in an unsteady state flow field. The reverse recognition algorithm comprises the following steps: determining a position value range of a pollution source; calculating a pollutant transfer probability matrix in a building in an unsteady state flow field; operating the transfer probability matrix and a potential pollution source matrix to obtain a responsive matrix; performing inversion by a regularization method to obtain a hourly release rate of a certain pollution source; solving hourly release rates corresponding to different positions of pollution sources in a set; distributing prior probability to pollution source position information; calculating a likelihood function by means of the transfer probability matrix; calculating posterior probability by means of Bayes rule, thereby obtaining the pollution source position and the release rate thereof with the maximum posterior probability. Compared with numerical value calculation, the reverse recognition algorithm has the advantages that the calculating speed is increased, and reversal calculation of the positions and release rates of pollution sources in multiregion buildings in a unsteady state flow field can be realized.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
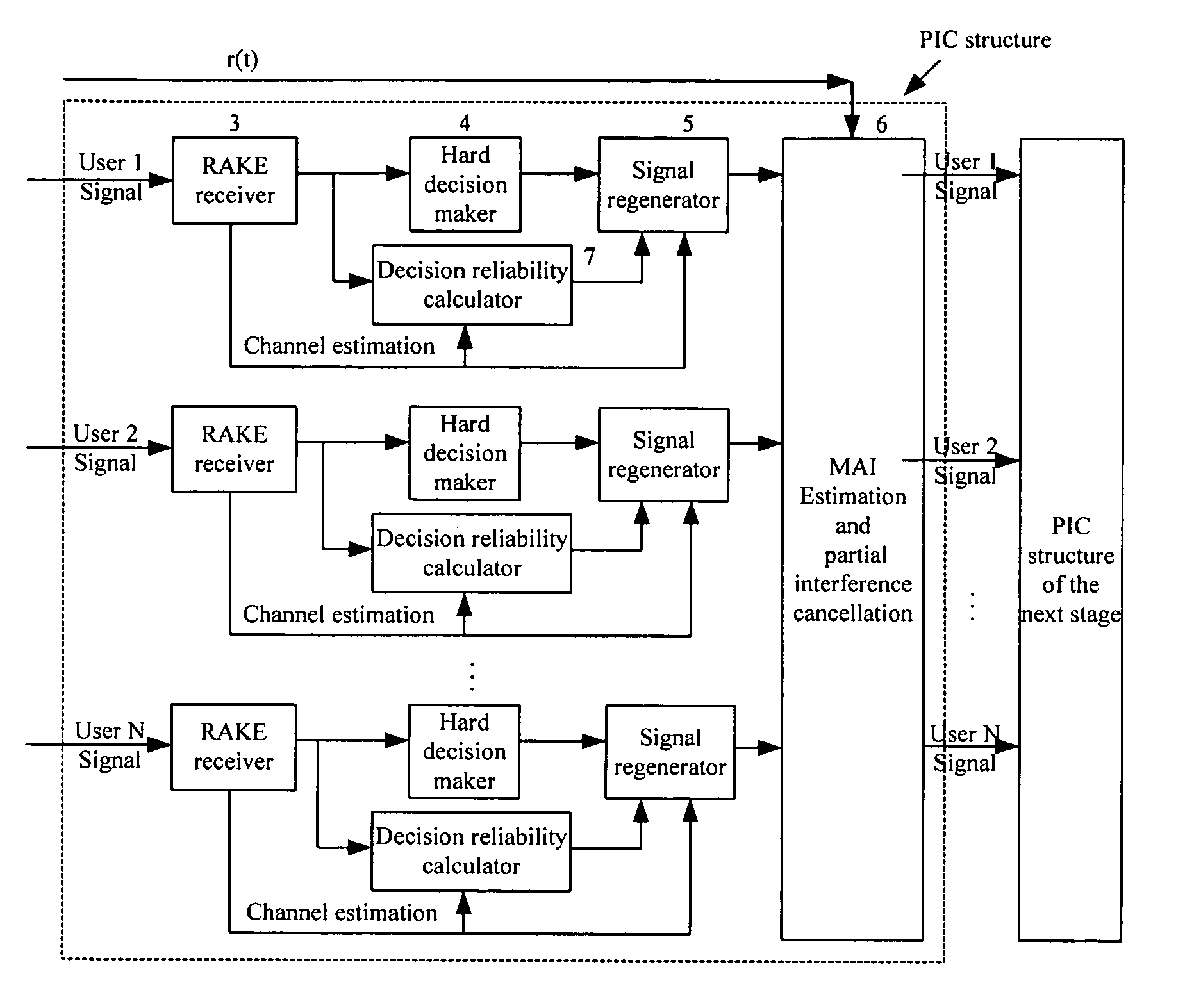
Method of double weighting parallel interference cancellation
ActiveUS7321581B2Reduce Algorithmic ComplexityPerformance unchangedRadio transmissionCommunications systemInterference cancelation
A method for double weighting parallel interference cancellation in CDMA mobile communication system, integrates ideas of both partial weighting method and weighting method based on Bayes rule. When making a decision on each symbol of the user, calculating reliability coefficient of a decision result on the symbol of the user according to the weighting algorithm based on Bayes rule; weighting regenerated signal of the symbol of the user with the reliability coefficient. During process of MAI estimating and removing, obtaining the MAI on the expected user from weighted regenerated signal of other users in chip level; and then setting a weight value, weighting the MAI with the weight value. Finally, removing weighted MAI from received signal, which means partially removing MAI produced by other users on the expected user. At the same time, the present invention also discloses a double weighting PIC method with simplified algorithm, which transfers weighting in chip level to weighting in symbol level, replacing a Hyperbolic tangent decision with a piecewise linear decision method or a look-up table method.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
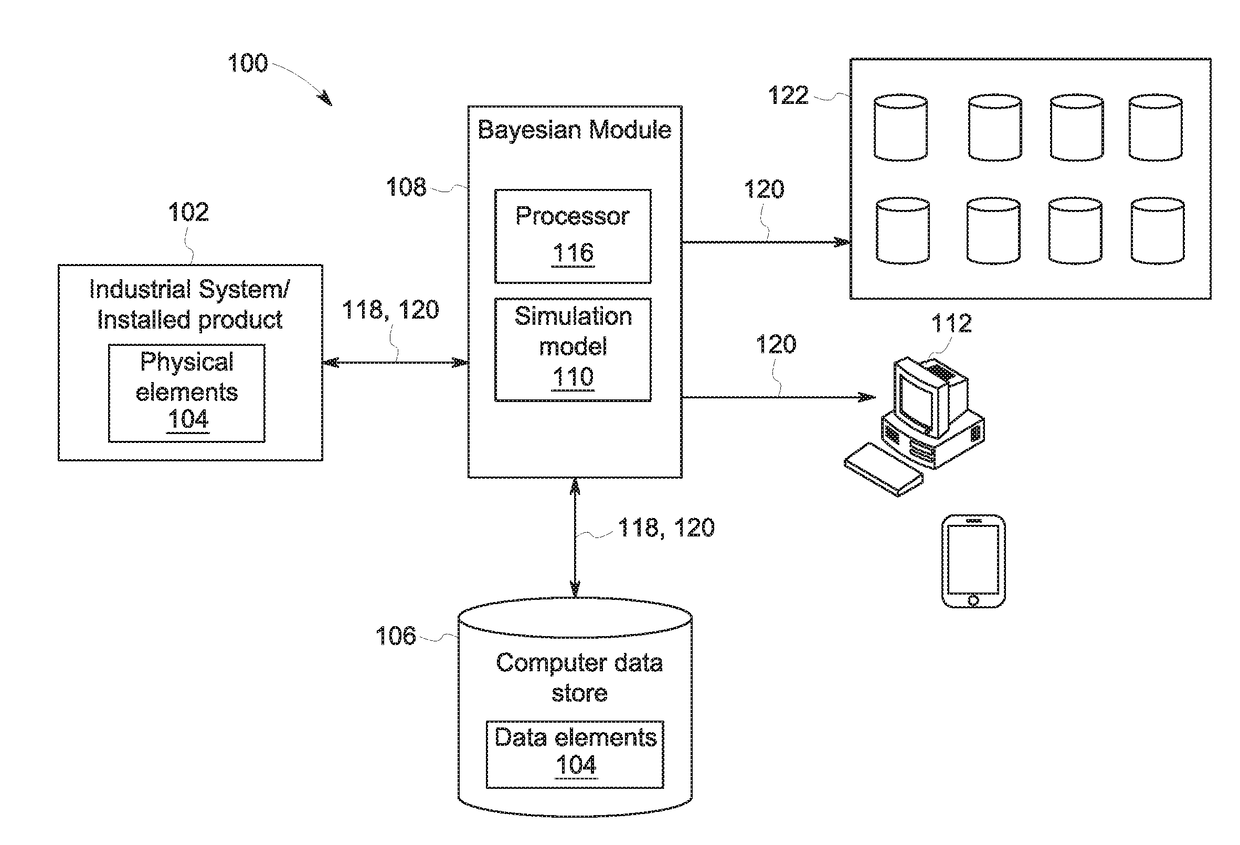
Massively accelerated bayesian machine
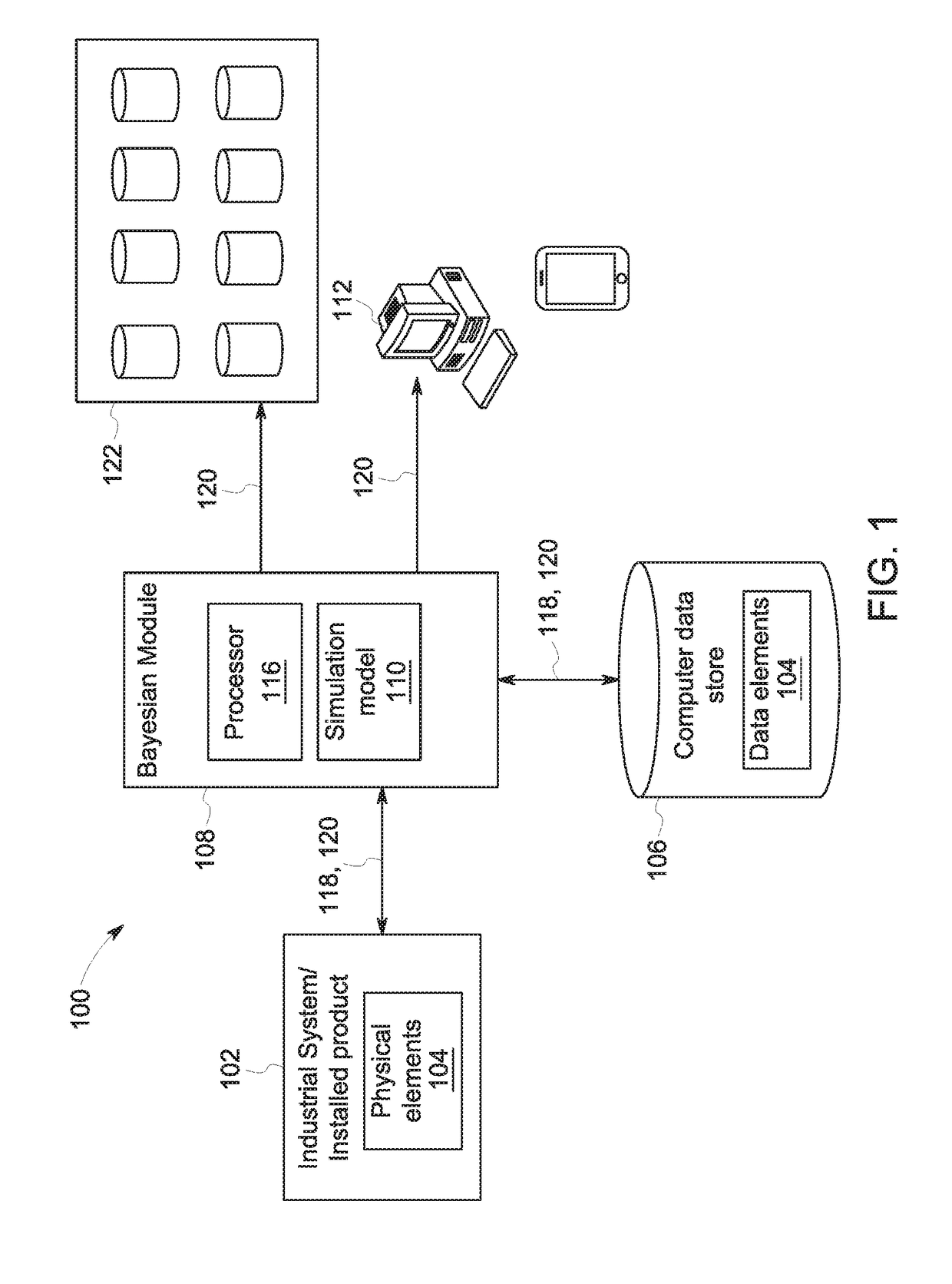
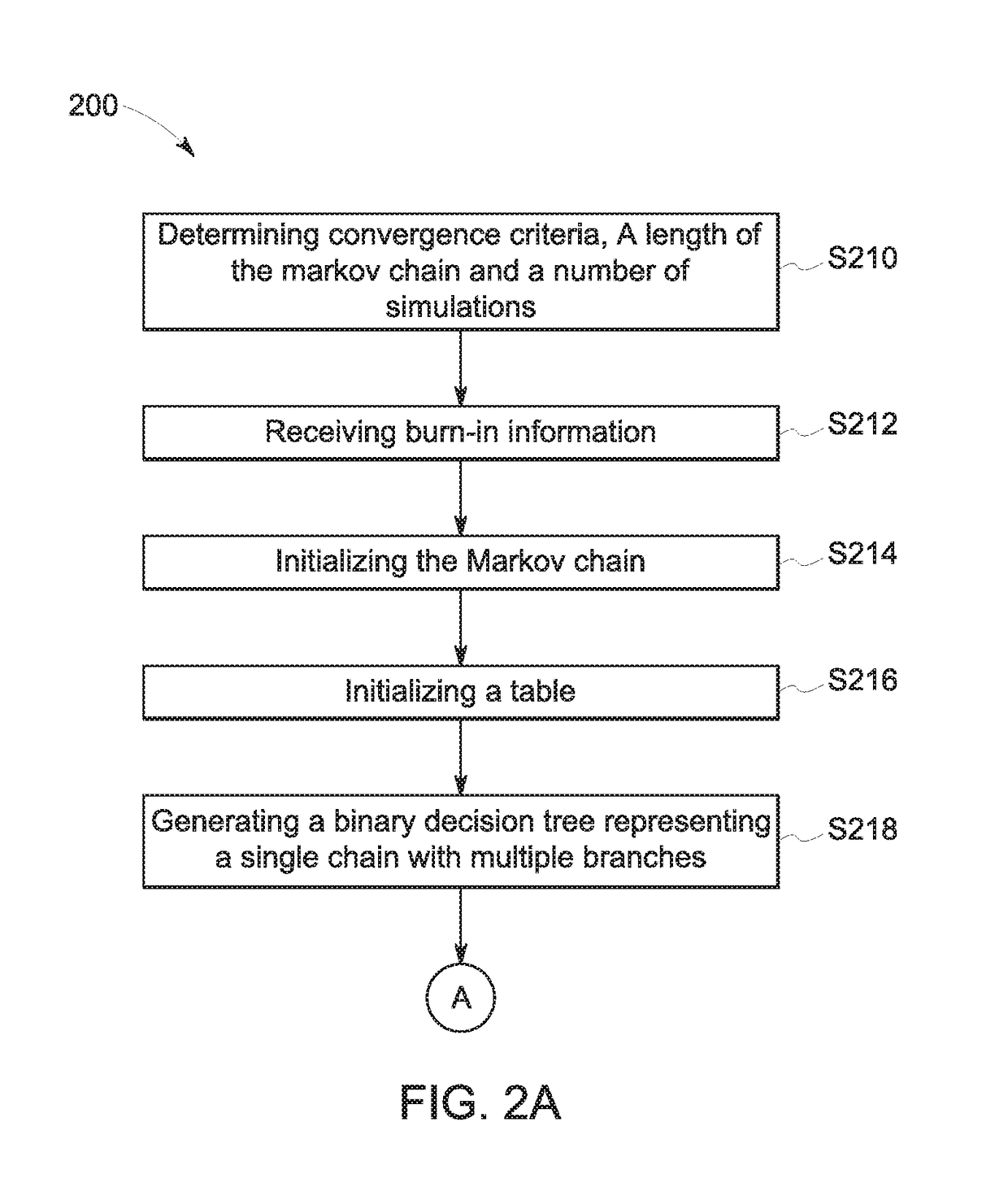
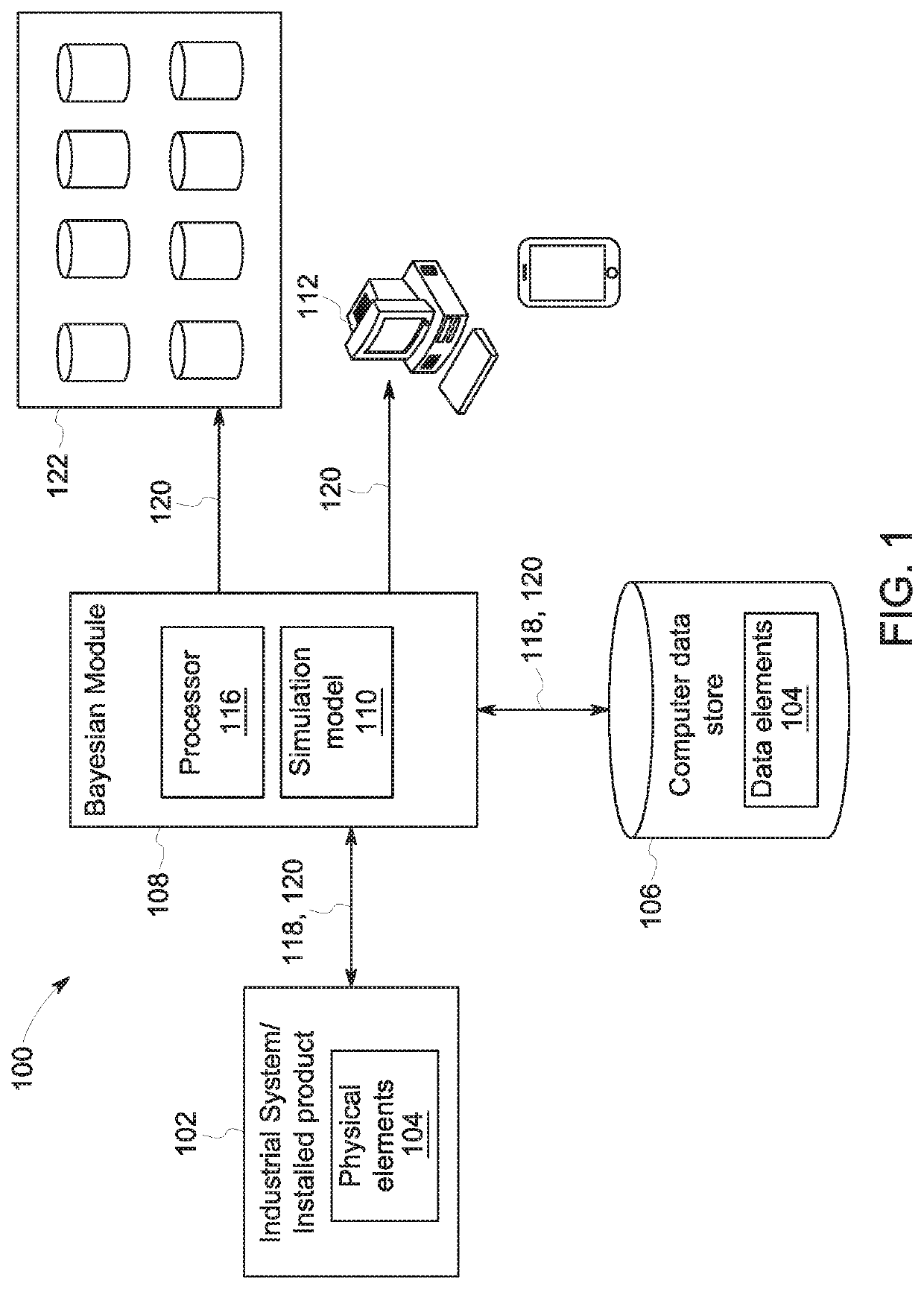
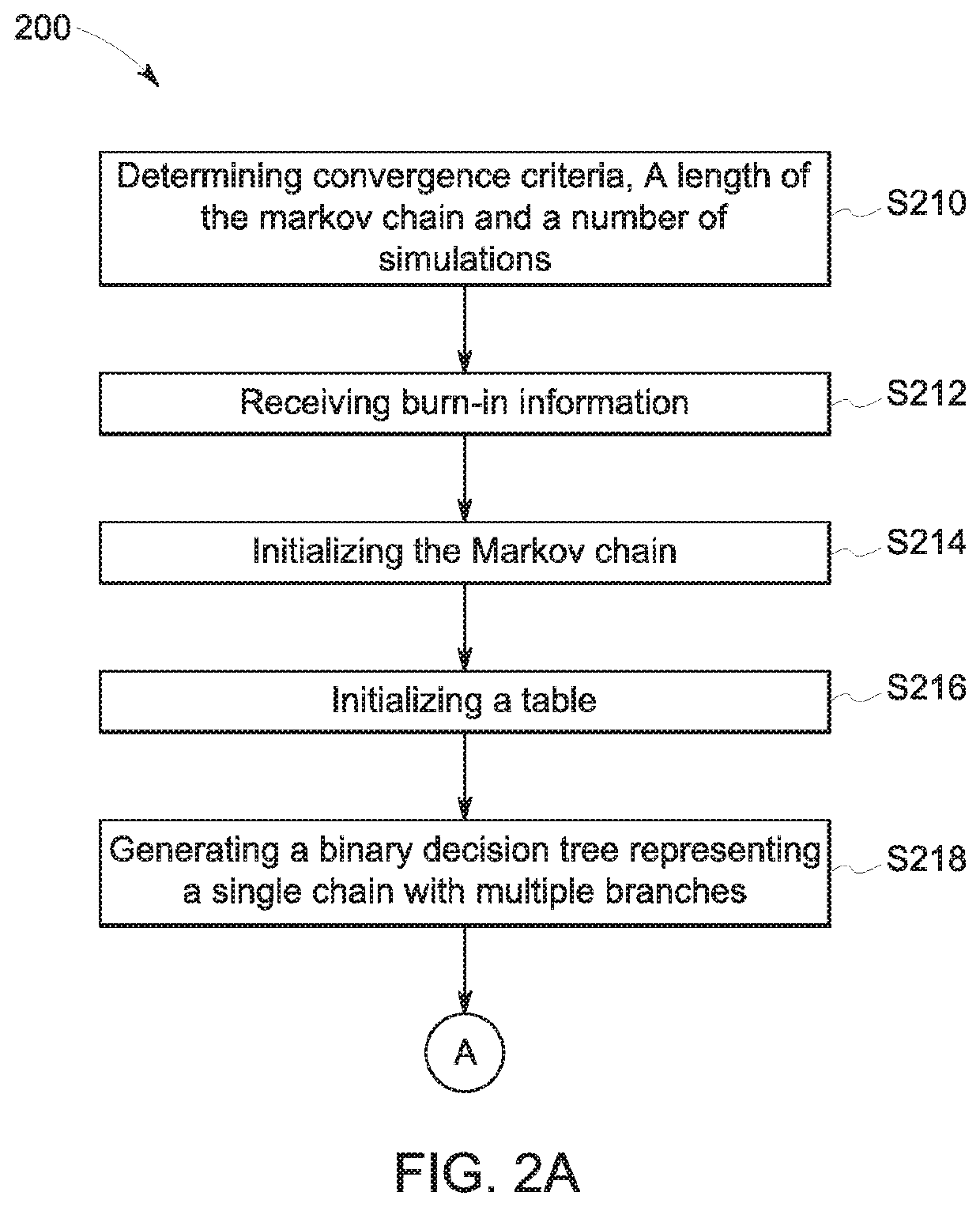
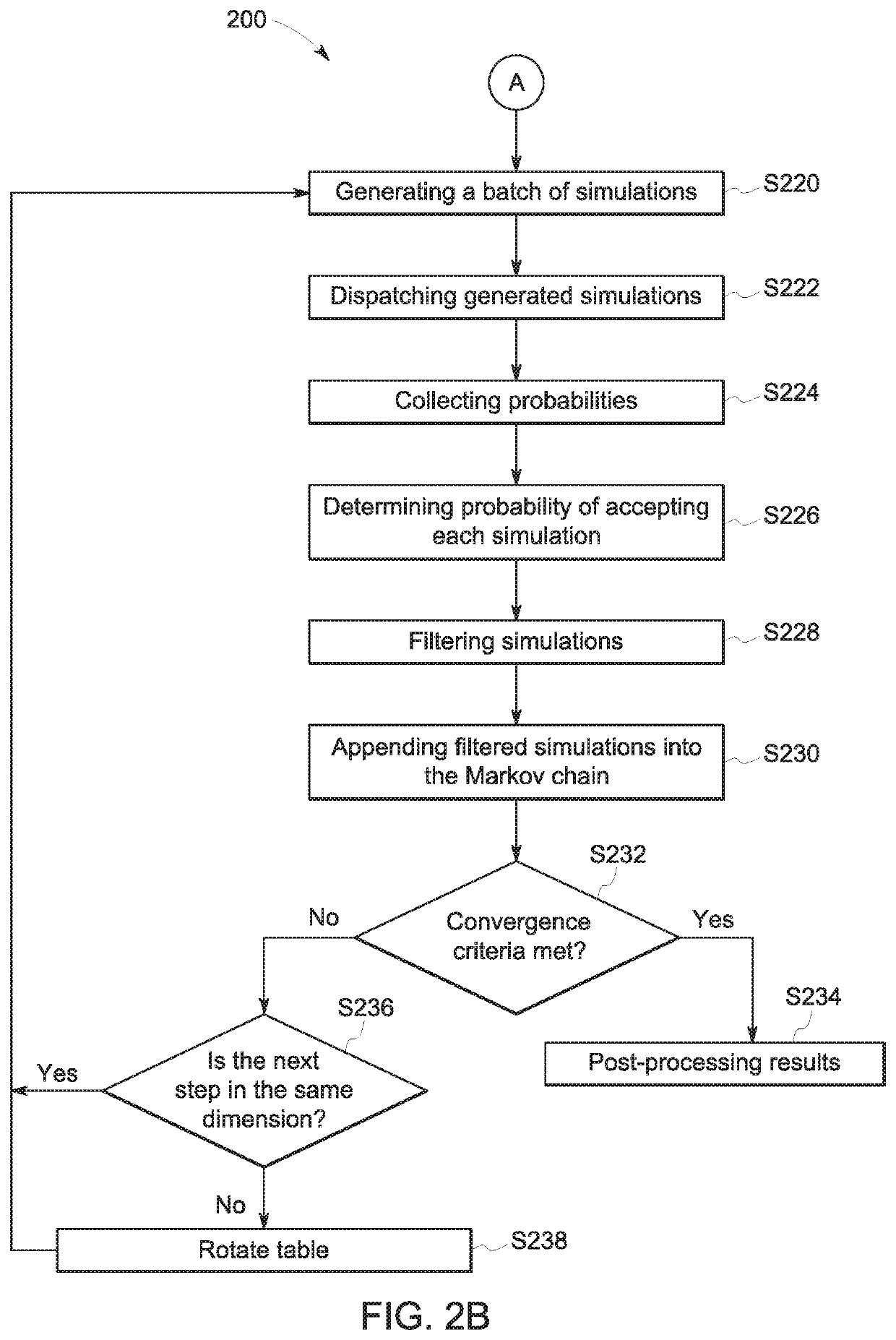
ActiveUS20180196892A1Increase speedSacrificing convergenceMathematical modelsDesign optimisation/simulationBayes' ruleSimulation based
According to some embodiments, system and methods are provided comprising: receiving data; providing a simulation model for the data; generating one or more simulations via a Bayesian module based on the data, wherein the simulation includes one or more nodes in a chain; executing the Bayesian module to determine the acceptability of the nodes in the simulation based on a Bayesian rule, wherein execution of the Bayesian module further comprises: generating a binary decision tree representing the chain in the simulation, wherein the chain includes one or more nodes; prioritizing which nodes in the tree to simulate; generating one or more simulations; executing the simulation model with data associated with the prioritized nodes in the tree in parallel to determine a posterior probability for each prioritized node; and determining whether each prioritized node is accepted or rejected based on the posterior probabilities. Numerous other aspects are provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Autonomous positioning method used for robot and implemented on basis of ARMA model
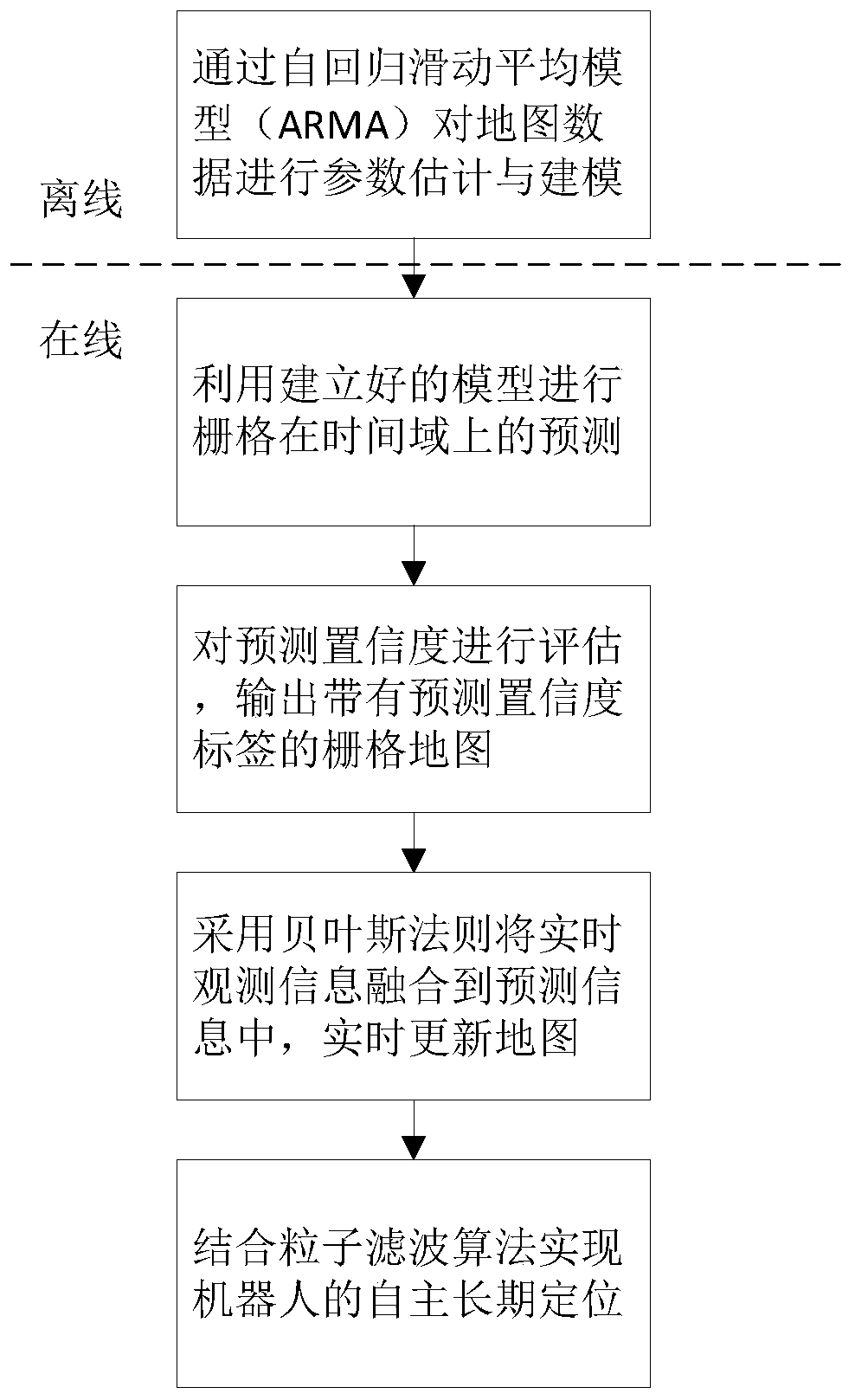
ActiveCN110068330AHigh positioning accuracyPrecise positioningNavigational calculation instrumentsTime domainBayes' rule
The invention provides an autonomous positioning method used for a robot and implemented on the basis of an ARMA model. The autonomous positioning method comprises the following steps: performing parameter estimation on data and state of a map in a long-term changing environment by virtue of an autoregressive moving average model (ARMA), and ultimately building a changing map model of the environment and in a probability grid form; performing follow-up prediction on a grid time domain of the built map model, and evaluating prediction confidence, so that a predicted grid map provided with a prediction confidence label is obtained; and finally fusing real-time observation information into the predicted grid map by adopting Bayes rules, so that an updated environment map available for the robot is obtained, and realizing autonomous long-term positioning in the changing environment by the robot by combining a particle filter algorithm under the map. Therefore, the effect that the robot hasrelatively high positioning accuracy and positioning robustness in the long-term changing environment is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
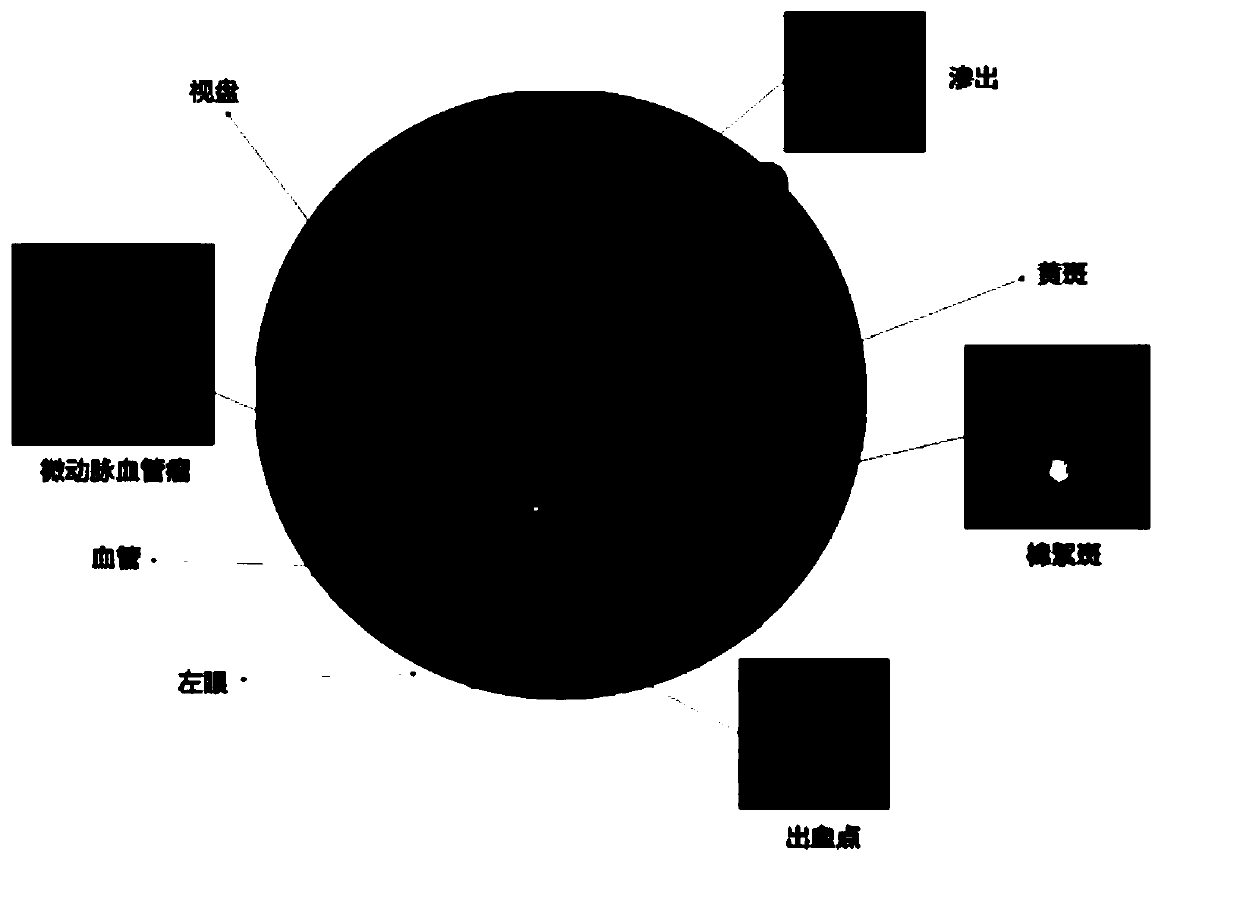
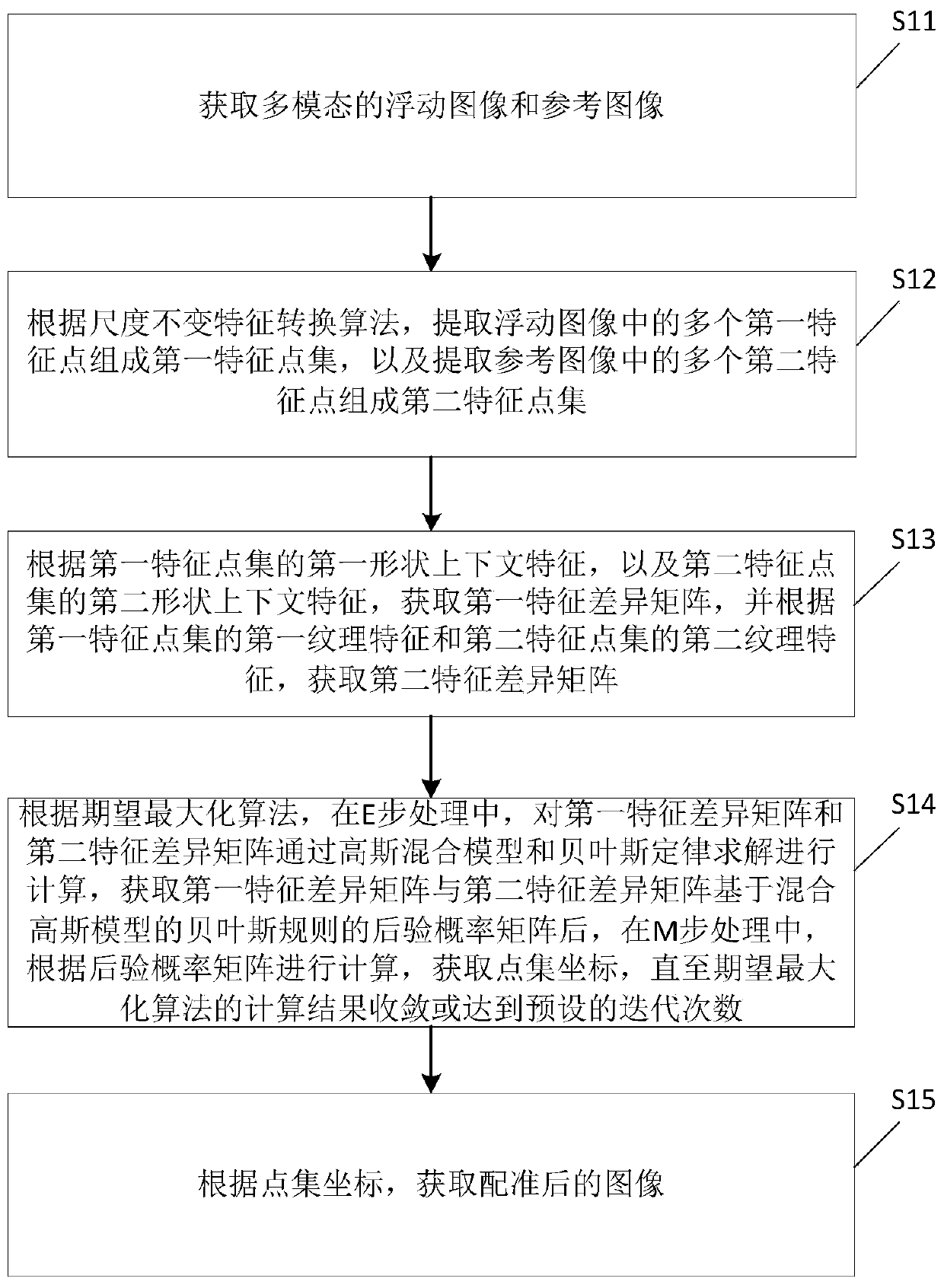
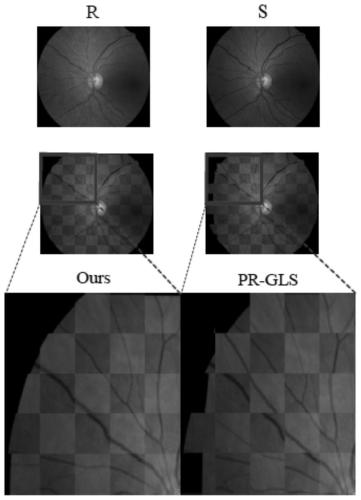
Multi-mode retinal fundus image registration method and device
PendingCN111260701AHigh precisionAvoid misjudgmentImage enhancementImage analysisExpectation–maximization algorithmBayes' rule
The invention discloses a multi-modal retinal fundus image registration method and device. The method comprises the steps: extracting a second feature point set in a first feature point set referenceimage in a floating image according to a scale invariant feature conversion algorithm; obtaining a first feature difference matrix according to the second shape context features of the first feature point set and the second feature point set, and obtaining a second feature difference matrix according to the second texture features of the first feature point set and the second feature point set; algorithm according to expectation maximization, solving and calculating the first characteristic difference matrix and the second characteristic difference matrix through a Gaussian mixture model and aBayesian law; after a posterior probability matrix of Bayesian rules of the first feature difference matrix and the second feature difference matrix based on a Gaussian mixture model is obtained, calculation is conducted according to the posterior probability matrix, and point set coordinates are obtained until the calculation result of the expectation maximization algorithm converges or reachesthe preset number of iterations; and obtaining a registered image according to the point set coordinates.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Moving target tracking method based on progressive unscented Kalman
ActiveCN107966697AImprove tracking accuracyImprove robustnessRadio wave reradiation/reflectionBayes' ruleCalculation error
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
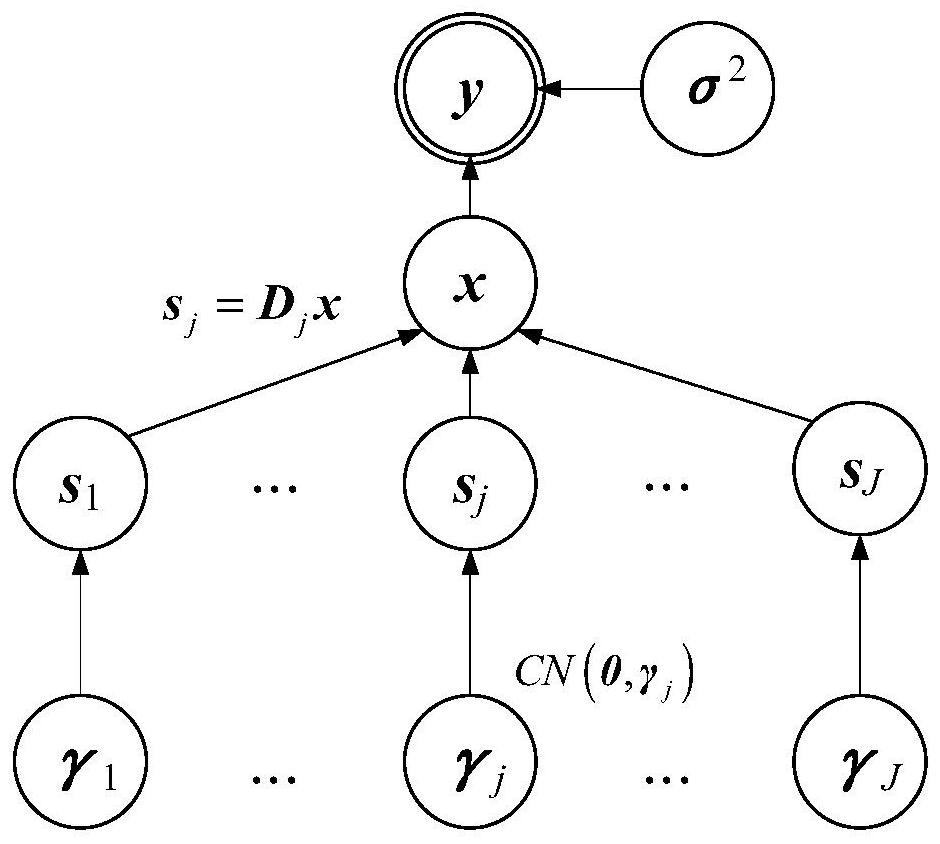
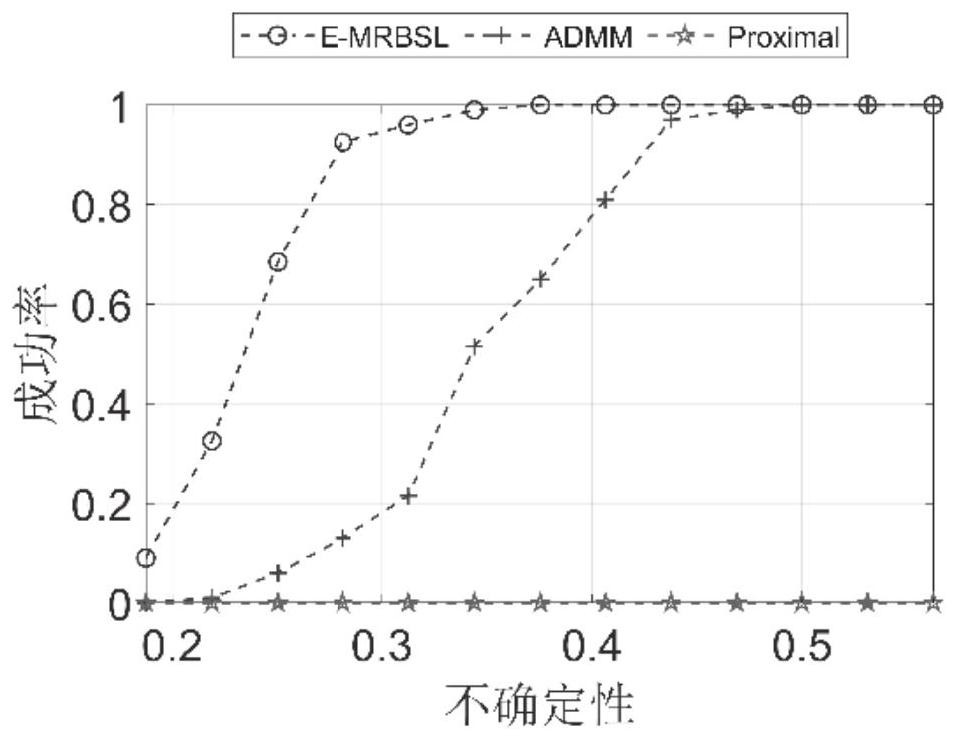
Underdetermined broadband signal DOA estimation method based on sparse Bayesian in unknown noise field
PendingCN112487703ASolving non-convex optimization problemsEasy to handleDesign optimisation/simulationDirection/deviation determination systemsBayes' ruleTarget signal
The invention discloses an underdetermined broadband signal DOA estimation method based on sparse Bayesian in an unknown noise field, and the method comprises the following steps: firstly introducinga co-prime array which employs a minimum sparse scale to reconstruct a space covariance matrix, and employing a non-uniform sampling method; vectorizing the covariance matrix, and obtaining a virtualmanifold matrix from the co-prime array by utilizing a Kronecker product; secondly, preprocessing the vectorized covariance matrix, preliminarily inhibiting unknown noise signals in the acquired signals, and weakening the interference of noise on target signal positioning; and finally, introducing a sparse Bayesian algorithm, applying the sparse Bayesian algorithm to a sparse signal recovery model, obtaining a posterior probability through a Bayesian rule, estimating all hyper-parameters, and updating the real DOA estimation of the target signal. According to the invention, the problem of non-convex optimization can be solved, the sparsity is automatically determined by utilizing fixed-point updating, and a better processing effect is achieved under the condition that a small number of samples are collected, especially under the condition of a low signal-to-noise ratio.
Owner:南京信息工程大学滨江学院
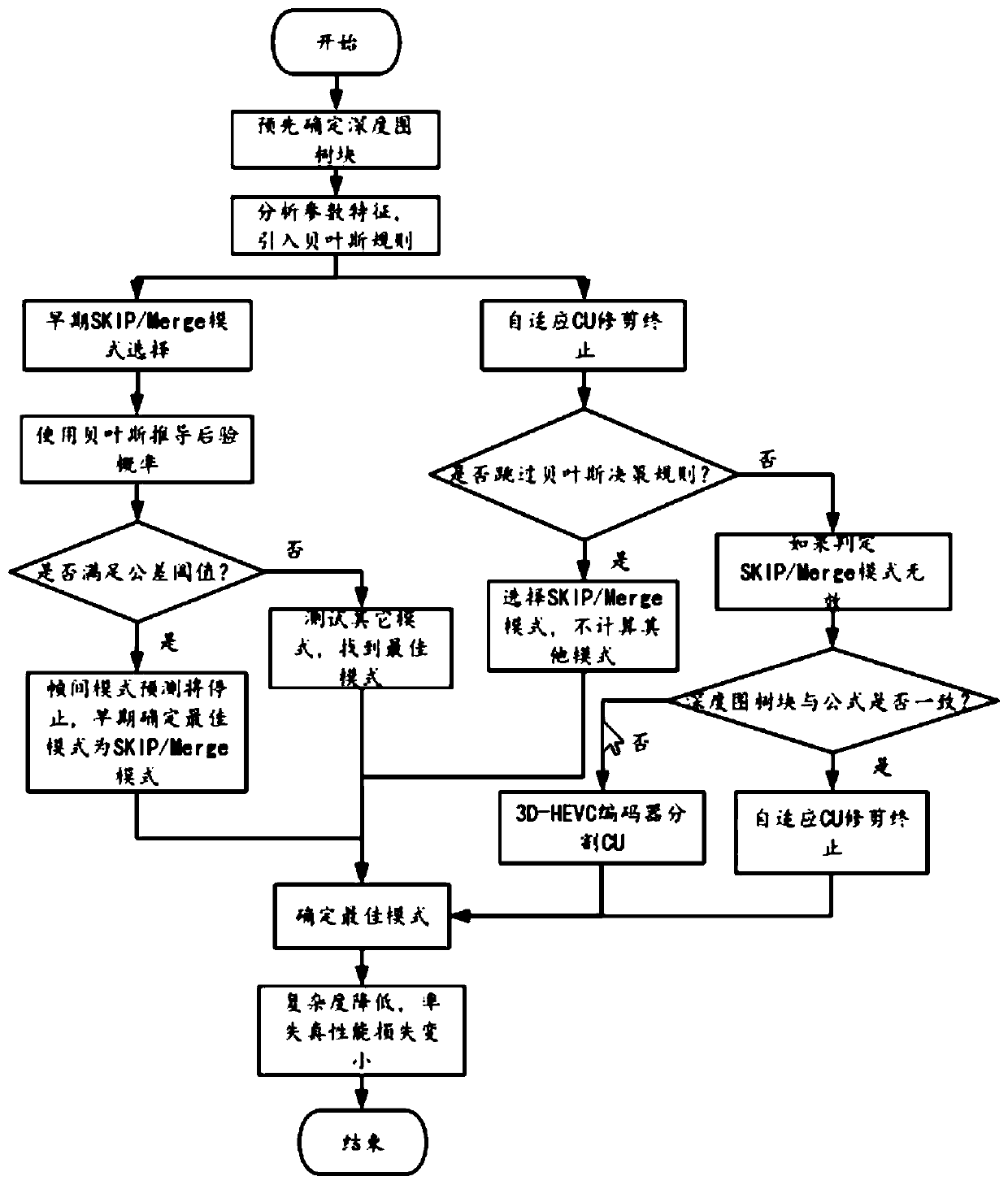
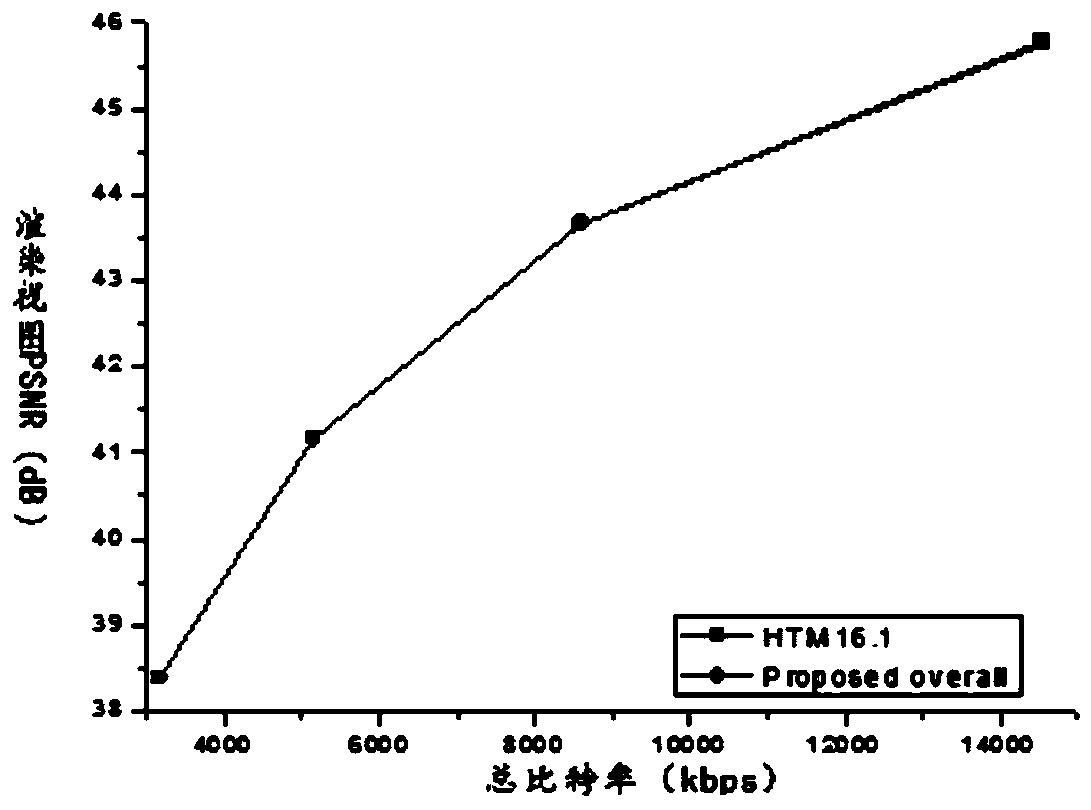
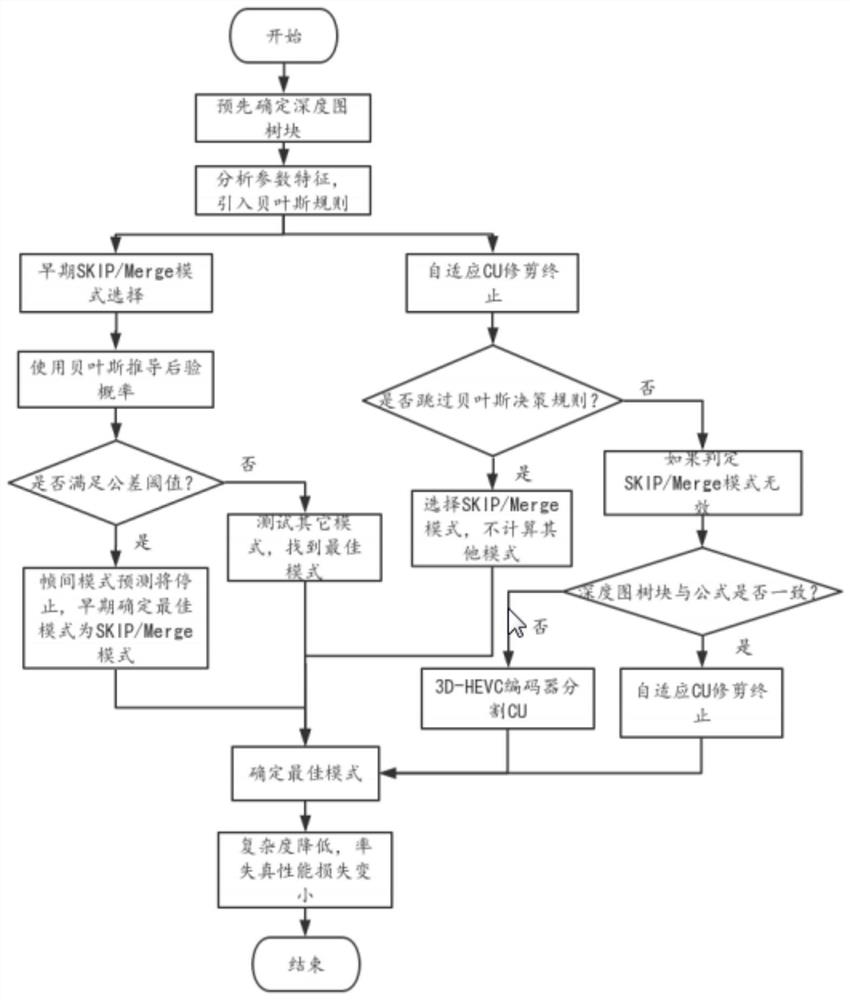
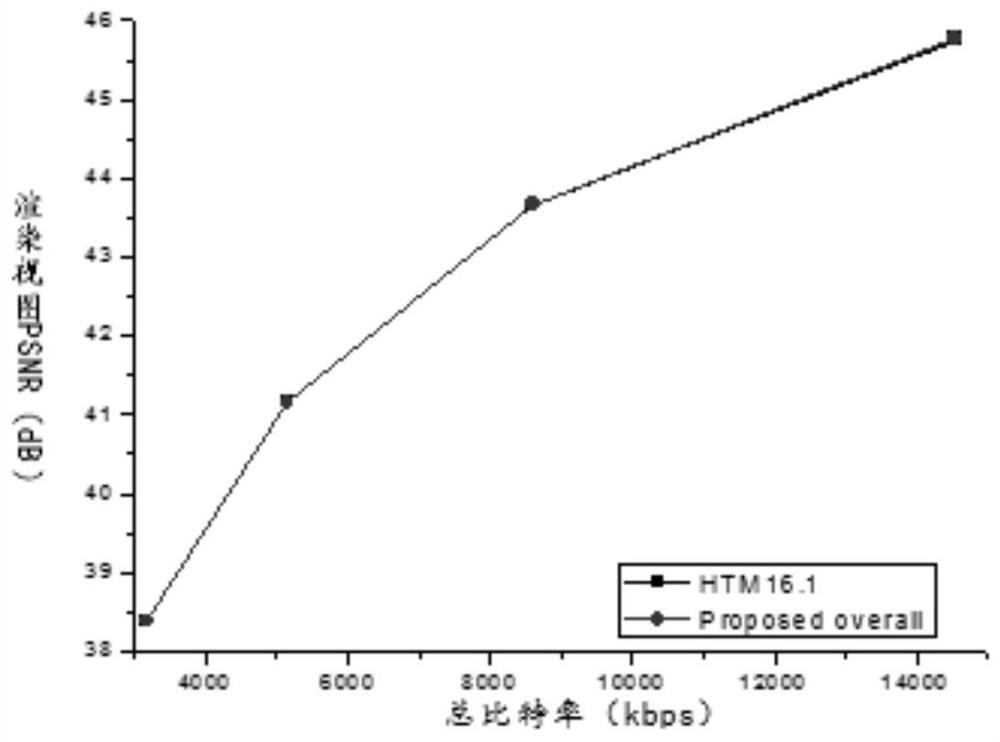
3D-HEVC fast depth coding method based on Bayesian decision theorem
ActiveCN111031303AReduce complexityReduce performance lossDigital video signal modificationSteroscopic systemsBayes' ruleDepth map coding
The invention provides a 3D-HEVC fast depth coding method based on the Bayesian decision theorem. The method comprises the steps of firstly determining a depth map tree block, and analyzing the inter-frame mode distribution among different quantification parameters; on one hand, adopting a Bayesian rule to calculate the posterior probability of a depth map tree block, and judging whether the interaction mode of the depth map tree block is optimal to determine that the optimal coding mode of the depth map tree block is an SKIP / Merge mode; on the other hand, calculating the Bayesian cost of thedepth map tree block according to a Bayesian rule; and according to whether the Bayesian cost is less than the tolerance parameter, early determining to terminate CU trimming of the depth map tree block and determining an optimal coding mode, or segmenting the CU of the depth map tree block by using a 3D-HEVC encoder, testing other coding modes of the depth map tree block, and finding the optimalcoding mode. According to the invention, by introducing the Bayesian rule, other inter-frame modes of test depth map coding are avoided; the quality of similar virtual viewpoints is ensured; and the 3D-HEVC depth coding complexity is obviously reduced.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Massively accelerated Bayesian machine
ActiveUS10719639B2Increase speedSacrificing convergenceDesign optimisation/simulationProbabilistic networksBayes' ruleTheoretical computer science
Owner:GE DIGITAL HLDG LLC
3d-hevc fast depth coding method based on Bayesian decision theorem
ActiveCN111031303BReduce complexityReduce performance lossDigital video signal modificationSteroscopic systemsBayes' ruleRound complexity
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
A Reverse Identification Algorithm of Pollution Sources in Unsteady Flow Field Based on Markov Chain
ActiveCN107145737BOvercome the defect that the unsteady flow field cannot be calculatedIncrease computing speedInformaticsComplex mathematical operationsBayes' ruleTransition probability matrix
The invention discloses a reverse recognition algorithm of a pollution source in an unsteady state flow field based on a Markov chain, which belongs to the technical field of indoor pollutant control, and aims to solve the problem of pollution source recognition in multiregion buildings in an unsteady state flow field. The reverse recognition algorithm comprises the following steps: determining a position value range of a pollution source; calculating a pollutant transfer probability matrix in a building in an unsteady state flow field; operating the transfer probability matrix and a potential pollution source matrix to obtain a responsive matrix; performing inversion by a regularization method to obtain a hourly release rate of a certain pollution source; solving hourly release rates corresponding to different positions of pollution sources in a set; distributing prior probability to pollution source position information; calculating a likelihood function by means of the transfer probability matrix; calculating posterior probability by means of Bayes rule, thereby obtaining the pollution source position and the release rate thereof with the maximum posterior probability. Compared with numerical value calculation, the reverse recognition algorithm has the advantages that the calculating speed is increased, and reversal calculation of the positions and release rates of pollution sources in multiregion buildings in a unsteady state flow field can be realized.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
A Multi-target Tracking Method Based on Random Set Theory
ActiveCN106707272BSave computing resourcesOccupies less computing resourcesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLimited resourcesPrior information
In order to realize effective tracking of multi-target states in complex scenes under the condition of limited resources, the present invention provides a multi-target tracking method based on random set theory. In the track prediction stage, the method first predicts each surviving track in one step according to the Bayesian criterion, and then adapts the birth target track according to the target prior information; in the track update stage, first calculates Corresponding existence weight probability and joint multi-target probability density function, and then calculate the posterior probability parameters of each target label, including existence probability and corresponding probability density function. This method has the advantages of low approximation cost, excellent performance under limited resources, and robustness applicable to any measurement model. In addition, since the algorithm of the invention occupies less system computing resources, it has good engineering application prospects.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Soft measuring method of industrial process under condition of small sample
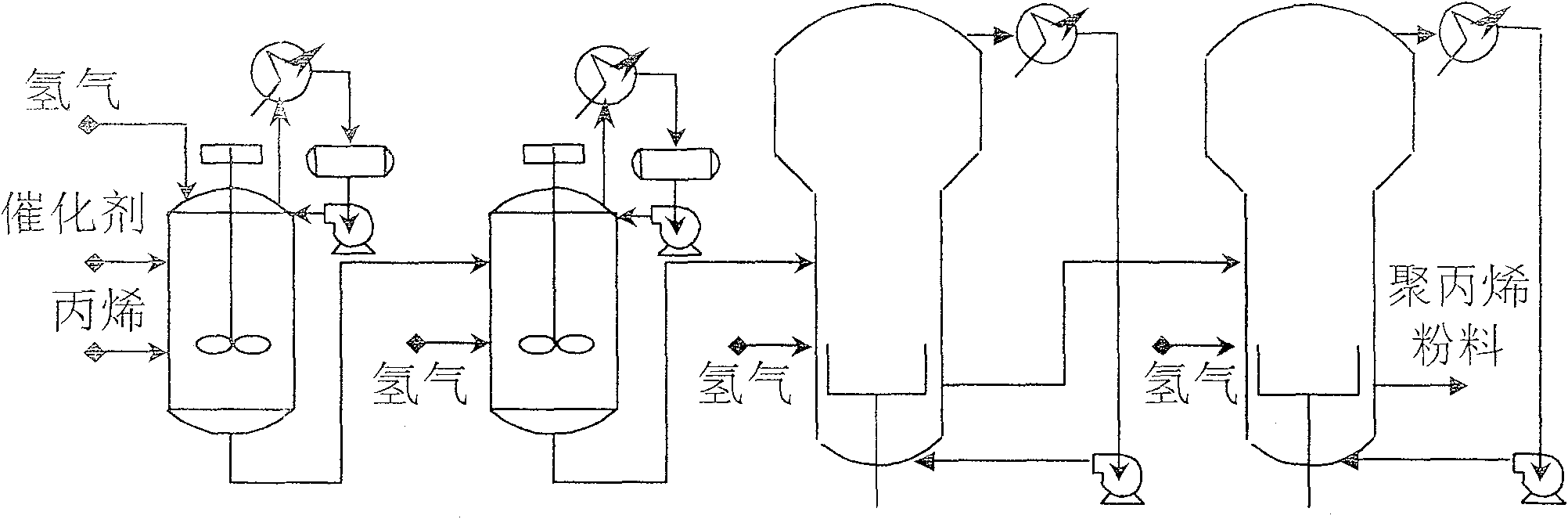
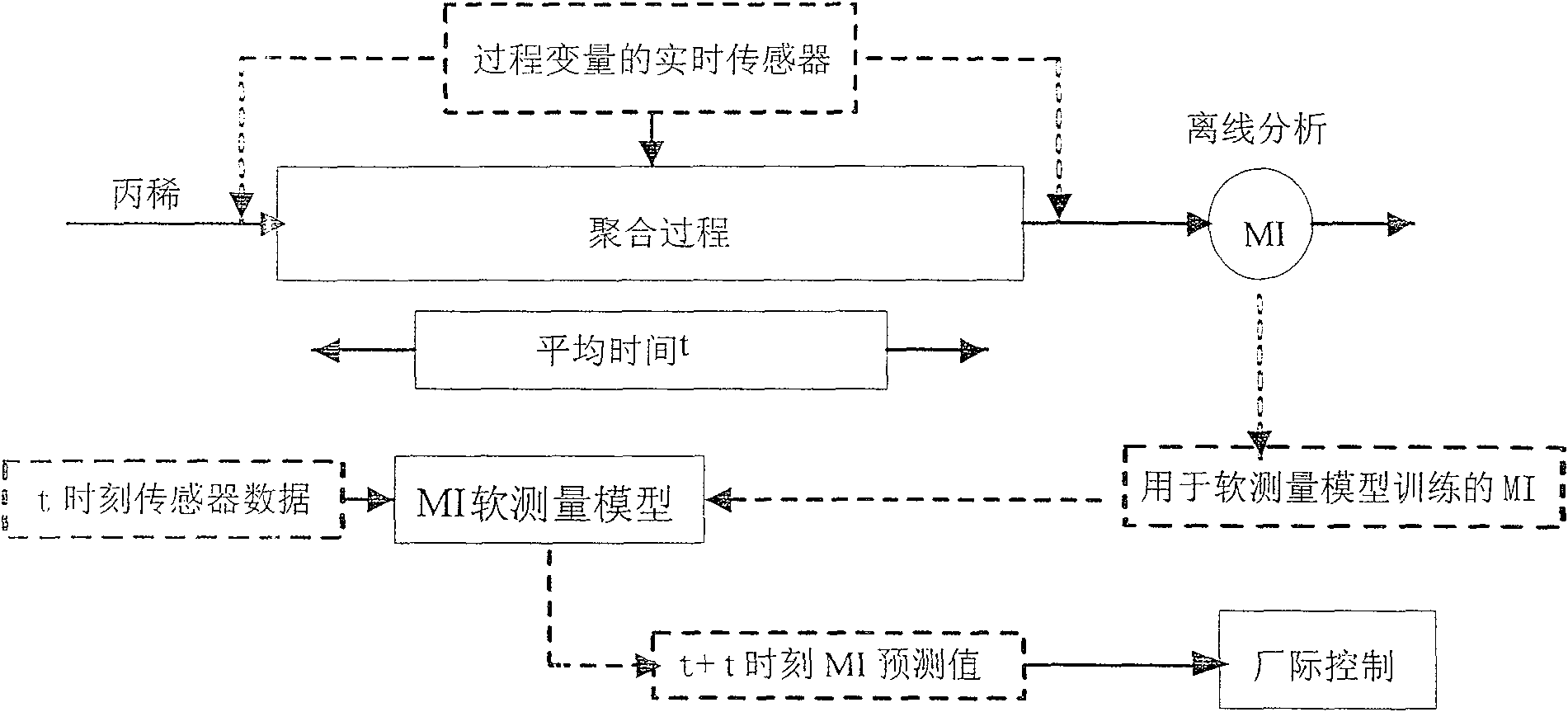
InactiveCN100580585CAvoid the disadvantage of too much calculationSimulator controlAdaptive controlSupport vector machineSmall sample
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A Multi-UAV Cooperative Search Method Based on Gaussian Distribution Prediction
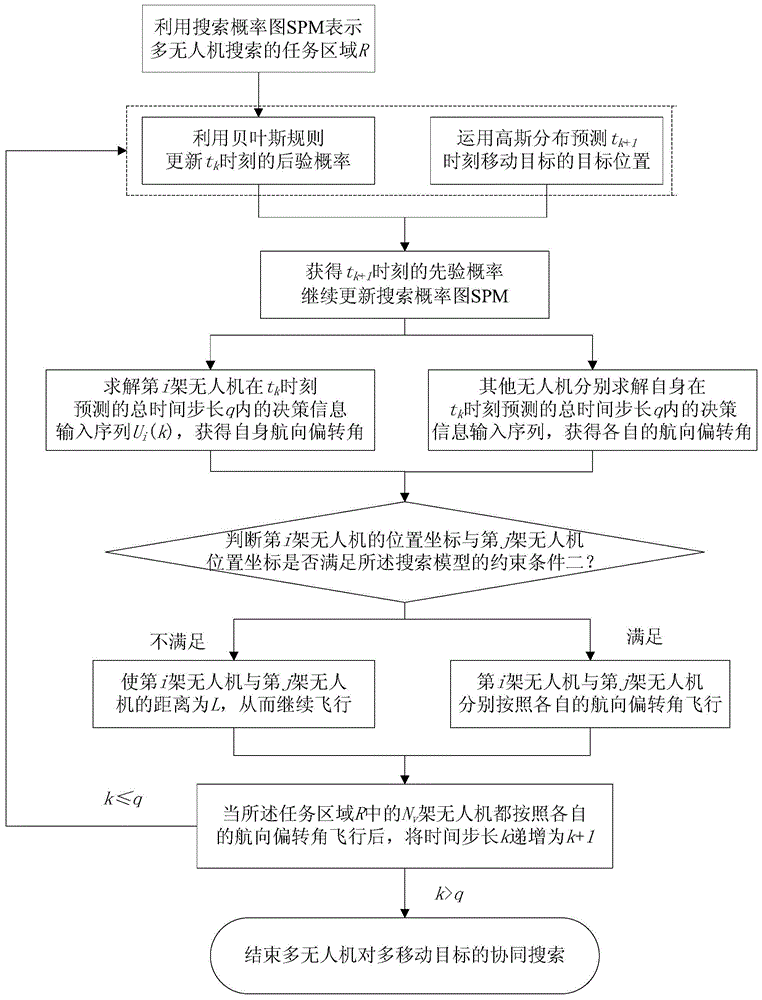
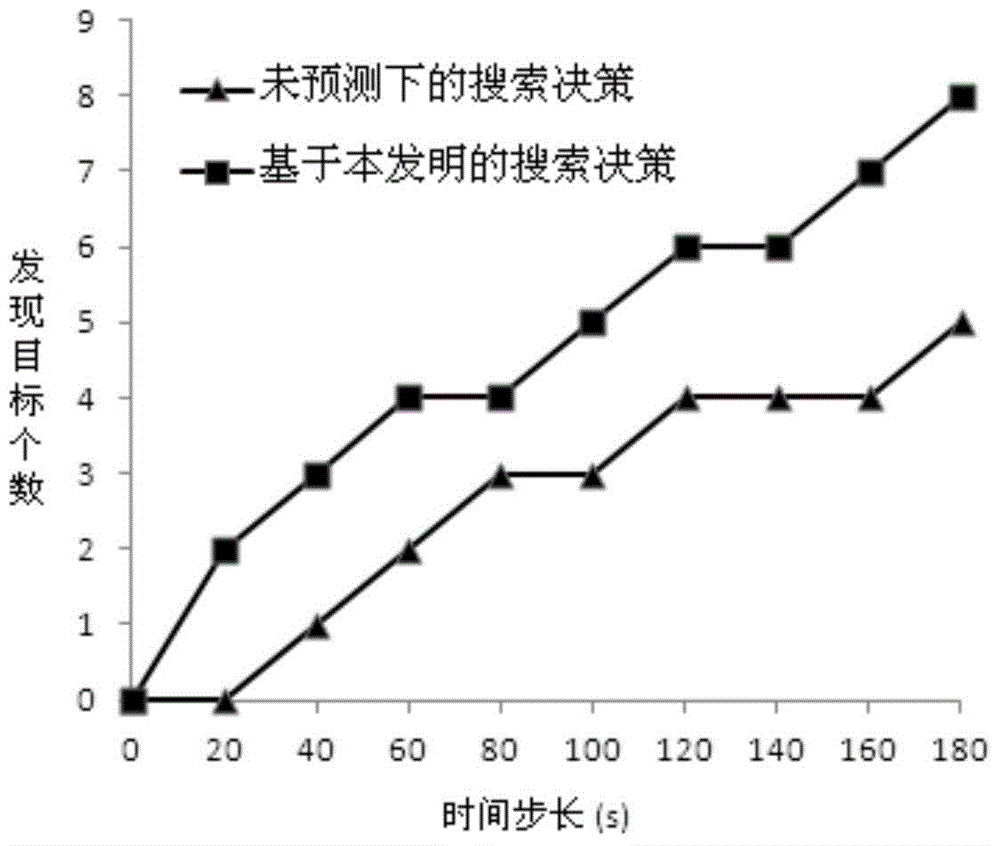
ActiveCN103472850BImplement searchOvercome blindnessTarget-seeking controlAdaptive controlTask completionBayes' rule
The invention discloses a multi-unmanned aerial vehicle collaborative multi-moving object search search method based on Gaussian distribution prediction. The multi-unmanned aerial vehicle collaborative multi-moving object search method based on Gaussian distribution prediction is characterized by comprising the steps that 1, a task area R is represented by a search probability graph; 2, the Bayes rule is used to update the posterior probability; 3, the objective positions of moving objects are predicted through the application of the Gaussian distribution, and the search probability graph is updated; 4, a distribution model prediction control method is used for constructing the search model of the multi-unmanned vehicle collaborative multi-moving objects search; 5, unmanned aerial vehicles solve a decision information input sequence and obtain heading deflection angles and fly according to the heading deflection angle when the constraint condition is met; 6, a time step is progressively increased, the step 2, the step 3, the step 5 and the step 6 are executed repetitively until the time step exceeds the total time step of search of the unmanned aerial vehicles, and then searching is over. The multi-unmanned aerial vehicle collaborative search method based on the Gaussian distribution prediction can achieve the task of searching multiple moving objects by multiple unmanned aerial vehicles in a collaborative mode, improve the accuracy of searching of the unmanned aerial vehicles, and ensure the accomplished accuracy of the searching task.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
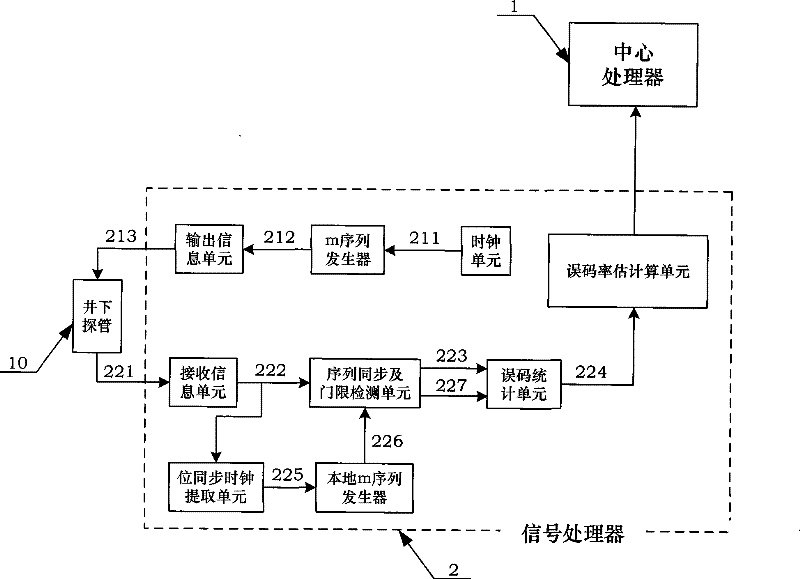
Error rate test system based on Bayes theorem
The invention disclose a bit error rate (BER) testing system based on the Bayes rule, which consists of a clock unit, an m sequencer, an information output unit, an information receiving unit, a sequence synchronizing and threshold detecting unit, a bit error statistical unit, a BER estimating unit, a bit synchronous clock extracting unit and a local m sequencer. A BER estimating method based on the Bayes rule estimates the range of the BER by utilizing the statistical confidence level principle, simultaneously, posterior probability distribution is adopted to substitute normal distribution so as to be similar to a statistical model of a true BER, the posterior probability distribution of the bit error rate is calculated in real time so as to estimate the BER effectively and accurately according to the actually tested bit error points, and the optimal testing time is selected. The system meets the requirement that the BER of a communication system is estimated by the estimated confidence level in a possibly short time in the practical engineering application of a full optical fiber digital clinometer.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
A Moving Target Tracking Method Based on Progressive Unscented Kalman
ActiveCN107966697BImprove tracking accuracyImprove robustnessRadio wave reradiation/reflectionComputation complexityBayes' rule
The invention discloses a target tracking method based on progressive unscented Kalman. The method considers the truncation error problem in a measurement linearization process and puts forwards a progressive unscented Kalman filter algorithm to better handle linearization error and numerical calculation error increasing problems existing in the measurement linearization process. Firstly, a homotopy function for a system state is constructed according to a Bayes rule; through carrying out iteration on a measurement updating process, the current observation information is introduced progressively, and further, the posterior state of the system is obtained; and besides, an innovation judgment condition is introduced during the progressive process, the estimated errors of the system during the progressive process are ensured to be bounded, and the stability of the filter is ensured. Compared with the existing target tracking method, the method thoroughly considers linearization error influences, and on the premise of ensuring the calculation complexity, the target tracking precision and the robustness are improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Distributed signal detection realization method based on mutual correlation suitable for wireless sensing network
InactiveCN102404061BImprove distributed detection performanceNetwork topologiesTransmission monitoringNODALWireless mesh network
The invention relates to a distributed signal detection realization method based on mutual correlation suitable for a wireless sensing network, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, selecting a convergence node which forms a group with each general node respectively; next, broadcasting a signal received by the convergence node, and carrying out mutual correlation treatment on the received signals of the convergence node and the general node by the general node to find out the peak value of a mutual correlation module value or the peak value of a mutual correlation real part; then, selecting the type of a detection value, and estimating first-order or second-order statistical characteristics of the mutual correlation detection value according to the received data; and then, iteratively searching the optimal local detection rule in the Bayes rules by a thought of equal probability division; finally, detecting and judging if unknown transmitter works by each group of nodes according to the optimal local detection rule. When the signal detection values are correlated, an easily realized method for working out the local optimal judgment rule is provided, so that the distributed detection performance of the wireless sensing network in low signal-to-noise ratio situation is improved.
Owner:NO 63 RES INST HEADQUARTERS OF THE GENERAL STAFF PLA
A Novel Quantum State Transfer Method Based on Hamiltonian Learning
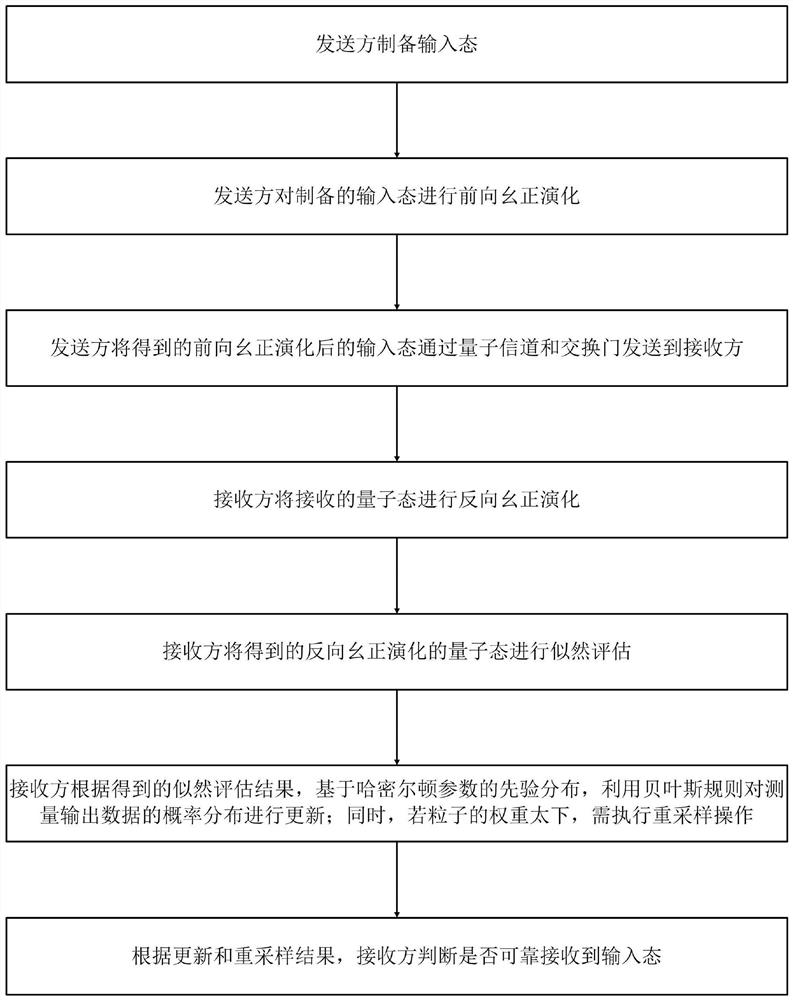
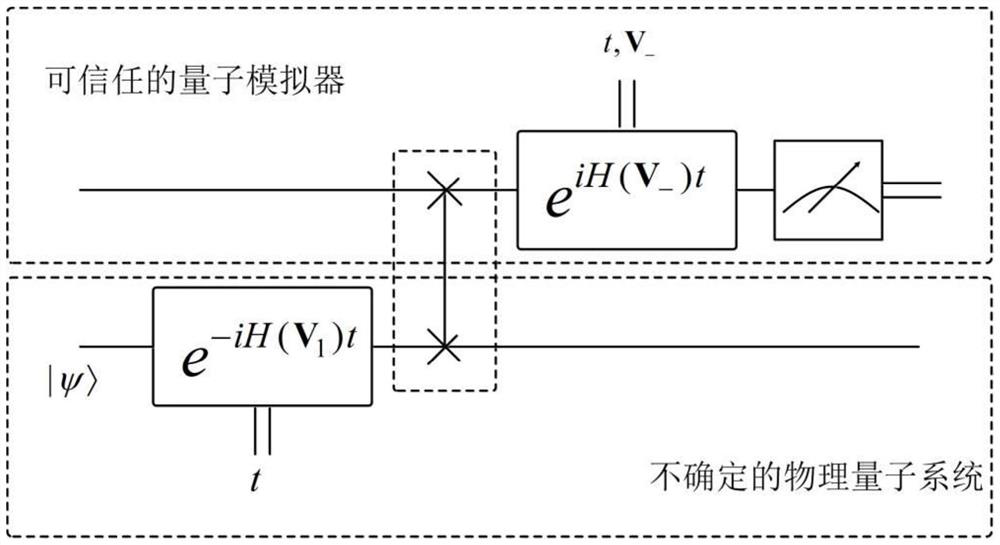
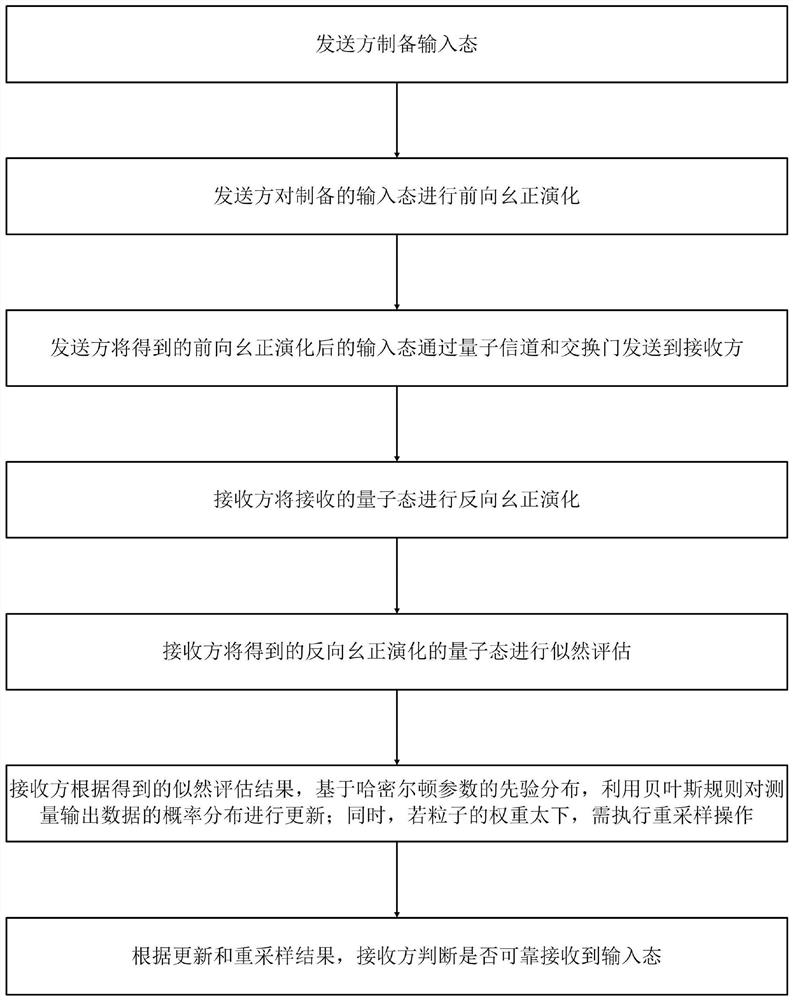
ActiveCN110224763BImprove confidentialityImprove fidelityPhotonic quantum communicationQuantum state transferBayes' rule
The invention discloses a new quantum state transfer method based on Hamiltonian learning, which comprises the steps of preparing the input state by the sender and performing forward unitary evolution on it; the sender sends the input state after forward evolution to the Receiver; the receiver performs reverse unitary evolution of the received evolution quantum state and performs likelihood evaluation; the receiver uses Bayesian rule to update and resample the probability distribution of the measurement output data; the receiver updates and resamples according to As a result, it is judged whether the input state exists and is perfectly transferred to the receiver with probability 1 at a certain moment. The method of the present invention can be evaluated by the likelihood function and the mean square error, the likelihood function is the fidelity of the quantum state transfer, and the mean square error is the Bayesian loss, which is exponential with the measurement times of the interactive quantum likelihood evaluation experiment decline. Therefore, the method of the invention has the characteristics of strong confidentiality, high fidelity and small loss.
Owner:国科蓝盾(北京)科技有限公司
A Chinese question mapping method based on lda
ActiveCN107423439BImprove accuracyReasonable designSpecial data processing applicationsText database clustering/classificationFunction wordPart of speech
The invention discloses an LDA-based Chinese question mapping method, which includes using the LDA topic model to classify the document base, and then using the Softmax regression model to classify the part-of-speech of the question, and according to the difference of the part-of-speech classification, the weight of the content word is higher than that of the function word High, but the weights of different parts of speech in content words are not the same, and then use the syntactic analysis based on dependency grammar to find out the dependency relationship of words in the sentence, and give different weights according to the different components of words in the sentence, so the problem The weight of each word in is obtained by the product of two parts, and finally, according to Bayesian rules, the connection is established through the weighted distribution of words in the question and the distribution of topics and terms in the document. The topic model based on LDA classifies the documents, and at the same time, assigns different weights by referring to the part of speech of the terms in the question sentence and the components in the sentence, so as to improve the role of important terms in classification and improve the mapping of Chinese questions. accuracy.
Owner:识因智能科技(北京)有限公司
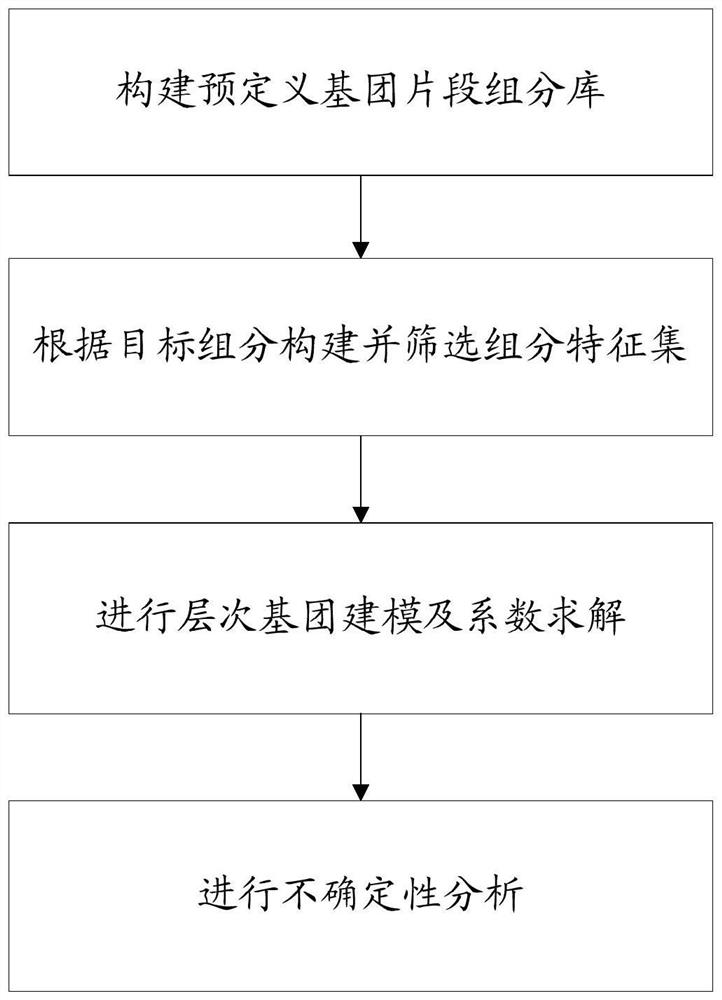
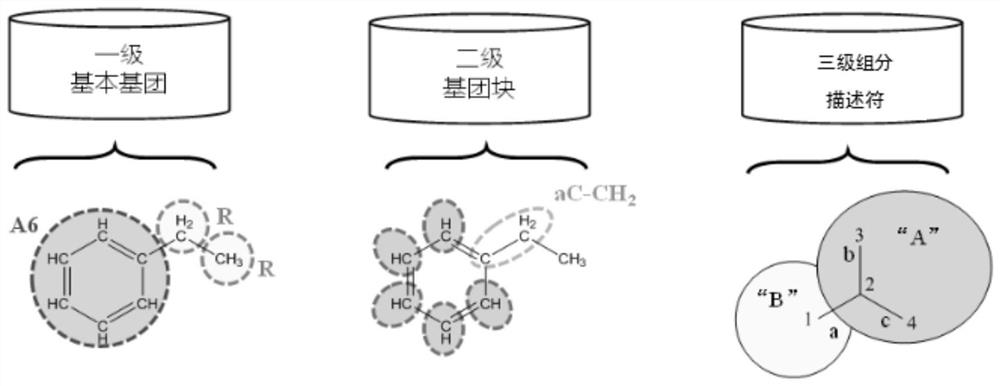
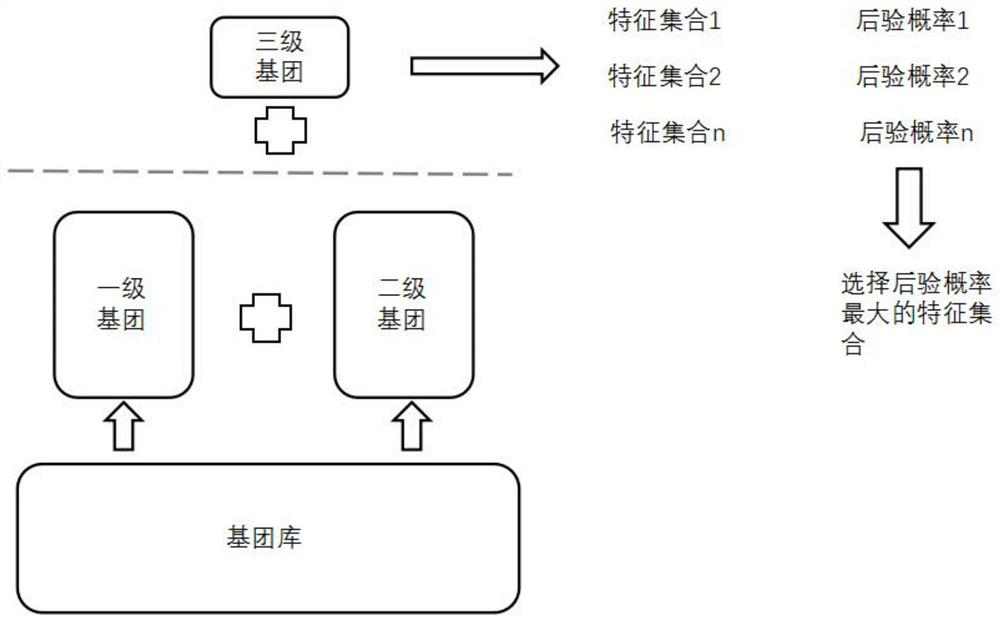
Prediction method for refining property of pure component based on hierarchical group construction
PendingCN114708930AReduce in quantityReduce dependenceChemical property predictionChemical machine learningBayes' rulePetroleum product
The invention discloses a method for predicting refining properties of pure components based on hierarchical group construction, which is used for predicting octane number and cetane number of pure component compounds in petroleum products, and avoids redundancy of feature sets through hierarchical construction of component feature sets and introduction of hierarchical group construction. When a third-level component descriptor is added into a feature set, a Bayesian rule is introduced, so that posterior probability distribution estimation can be carried out on the feature set, and a feature set with a higher posterior probability is selected without only paying attention to prediction precision. On the basis, the Bayesian rule is introduced again, so that posterior probability distribution estimation can be carried out on the final model, and the over-fitting risk of the final prediction model is avoided. The method can be applied to a crude oil and product blending unit in the petrochemical industry, and the petroleum refining precision is effectively improved.
Owner:QUANZHOU INST OF EQUIP MFG
Image Restoration Method and System Based on Multiple Regularization of Equation Structure
ActiveCN113222861BAchieve high-precision reconstructionImprove reconstruction success rateImage enhancementMathematical modelsBayes' ruleNormal density
The invention discloses an image restoration method and system based on multiple regularization of an equation structure. The equation structure is introduced to construct a measured Gaussian likelihood function; based on the constructed measured Gaussian likelihood function, a plurality of sparse transformations are selected, and the sparse transformation coefficient is On the basis, multiple independent probability density functions are given to calculate the conditional prior probability density of the target image; based on the conditional prior probability density of the target image, the mean estimation model of the target image is calculated according to the Bayes rule; Combined with conjugate gradient method, iteratively realizes fast reconstruction of target image, overcomes the invertibility limitation of sparse representation introduced by synthesis method, and allows the use of any number of sparse transformations, and the joint sparse domain can effectively improve the convergence speed of the algorithm.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Target tracking method and tracking system for nonlinear Gaussian system
InactiveCN104318059BReduce mutual interferenceImprove multi-object tracking performanceSpecial data processing applicationsCurrent meterBayes' rule
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com