Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56results about How to "Suppresses light absorption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
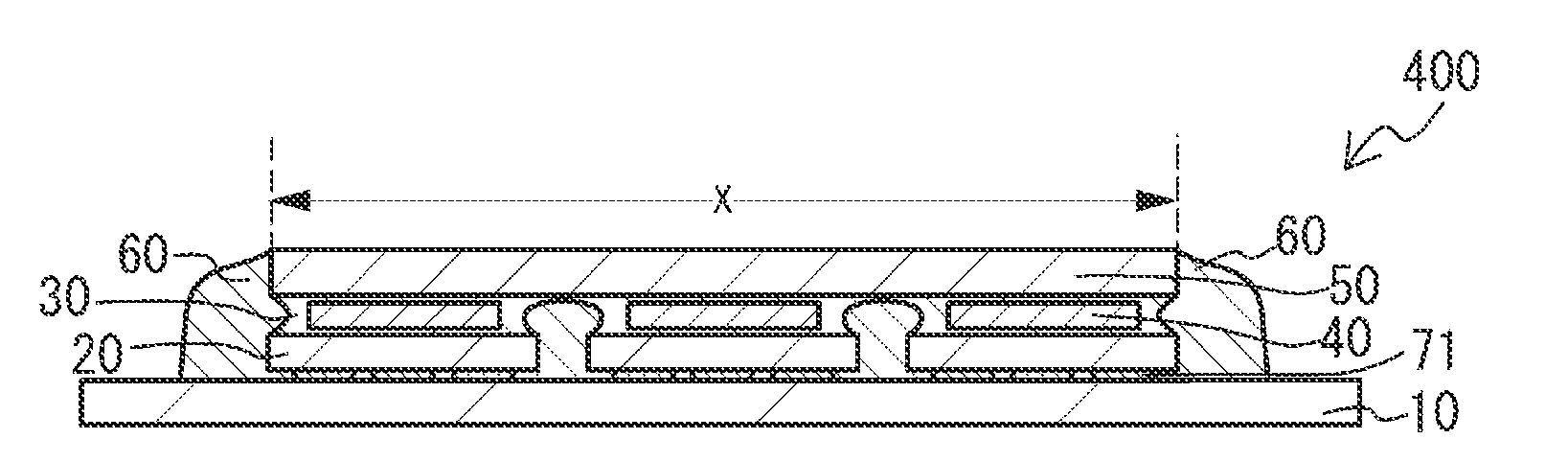
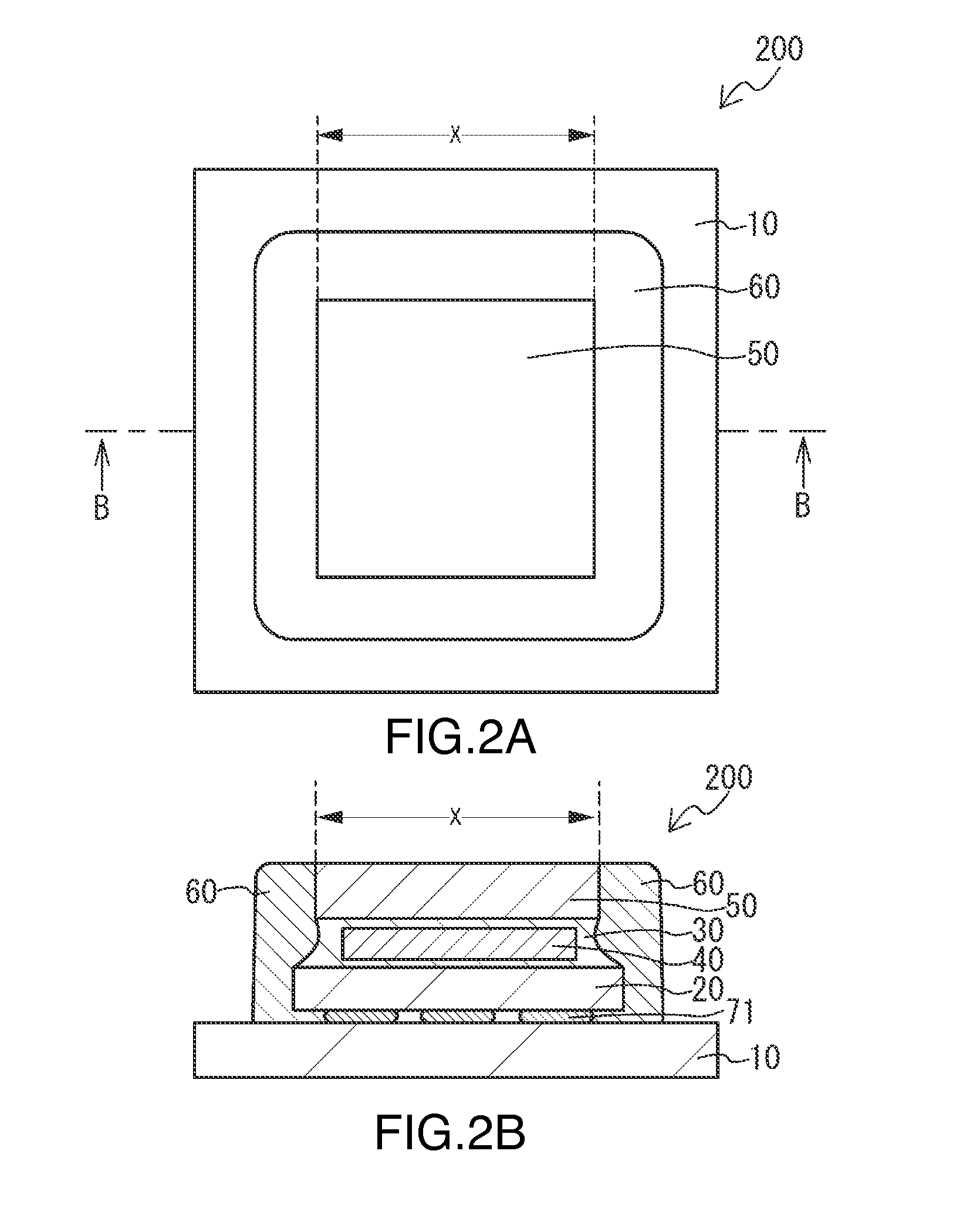
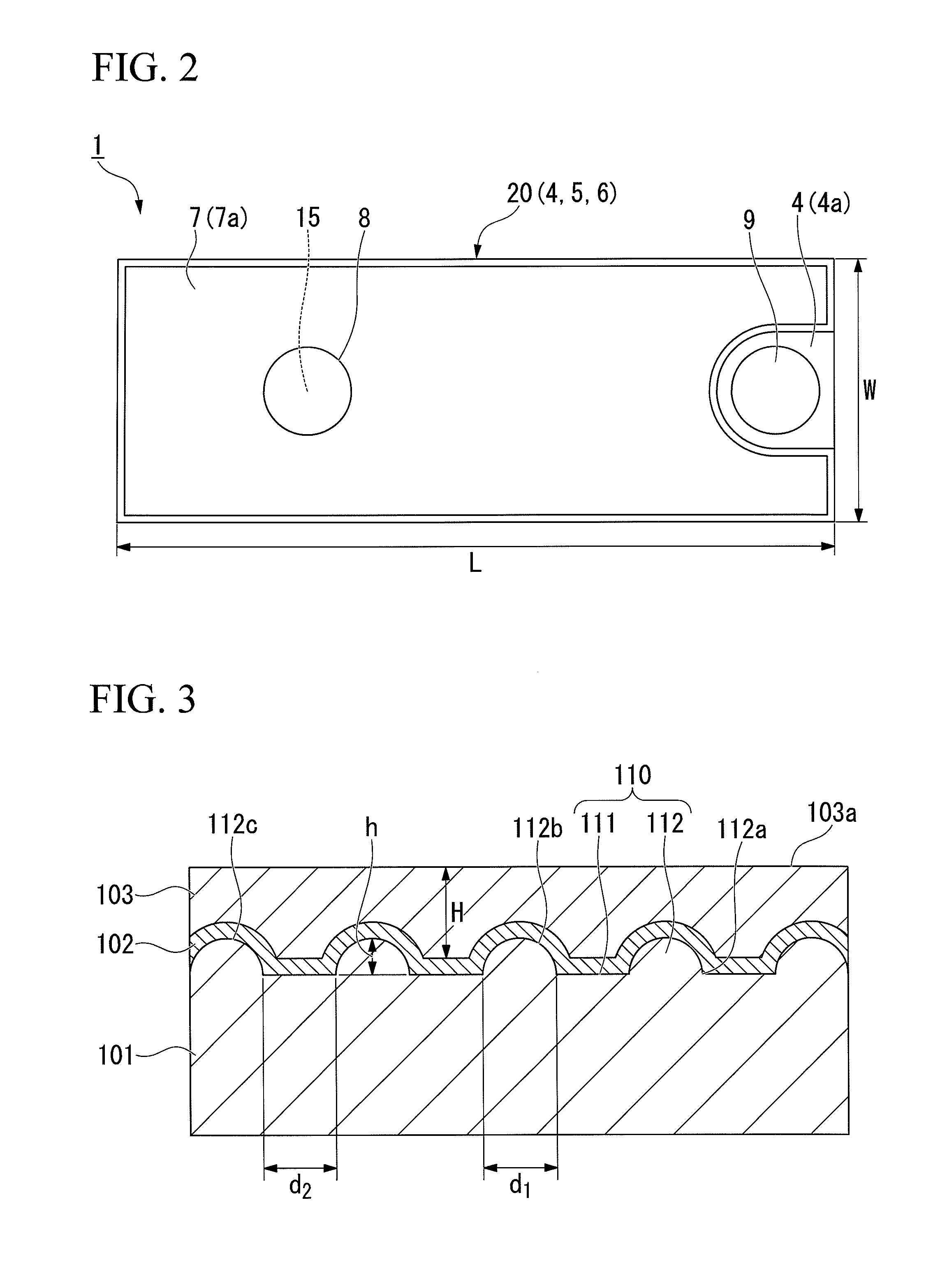
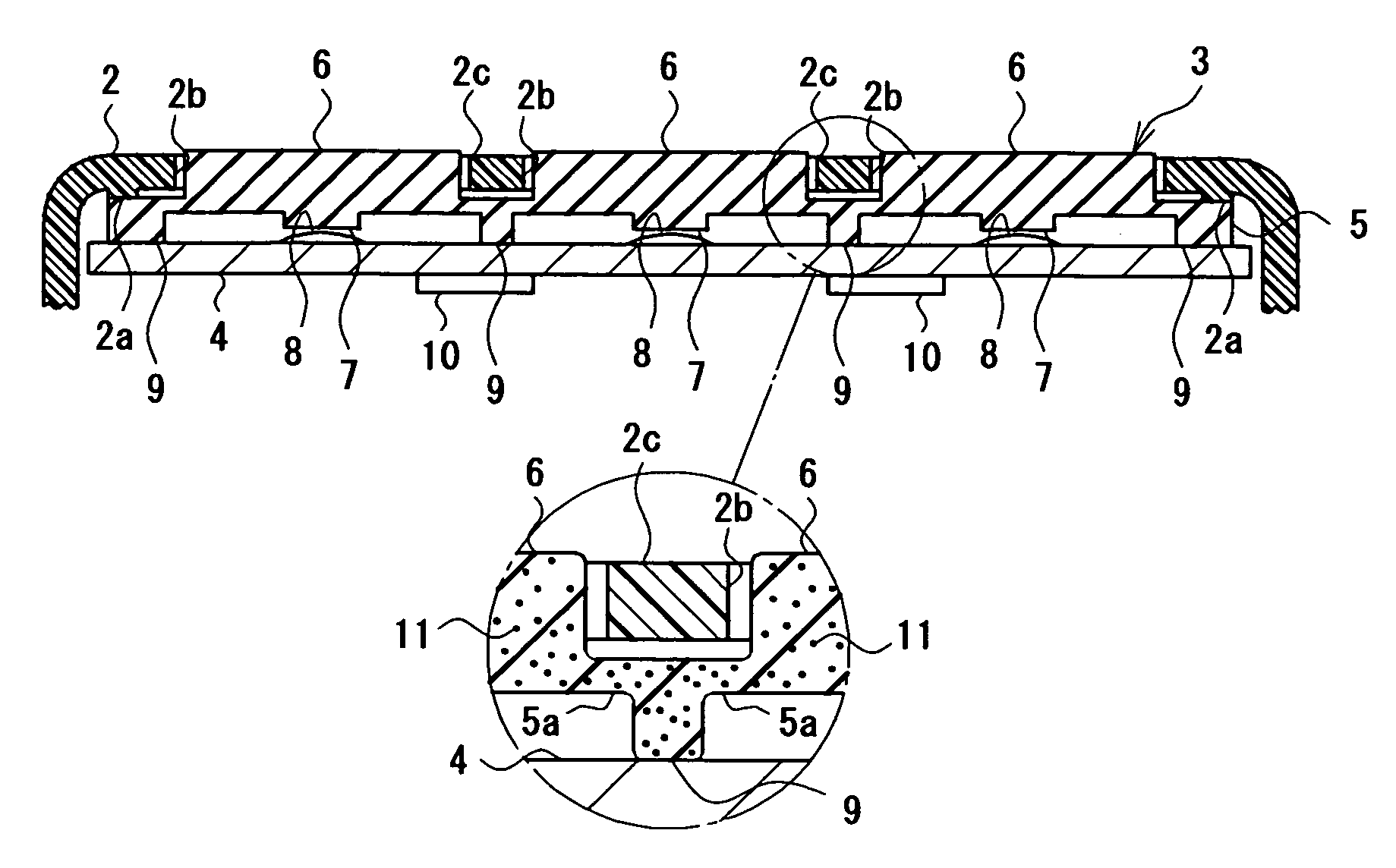
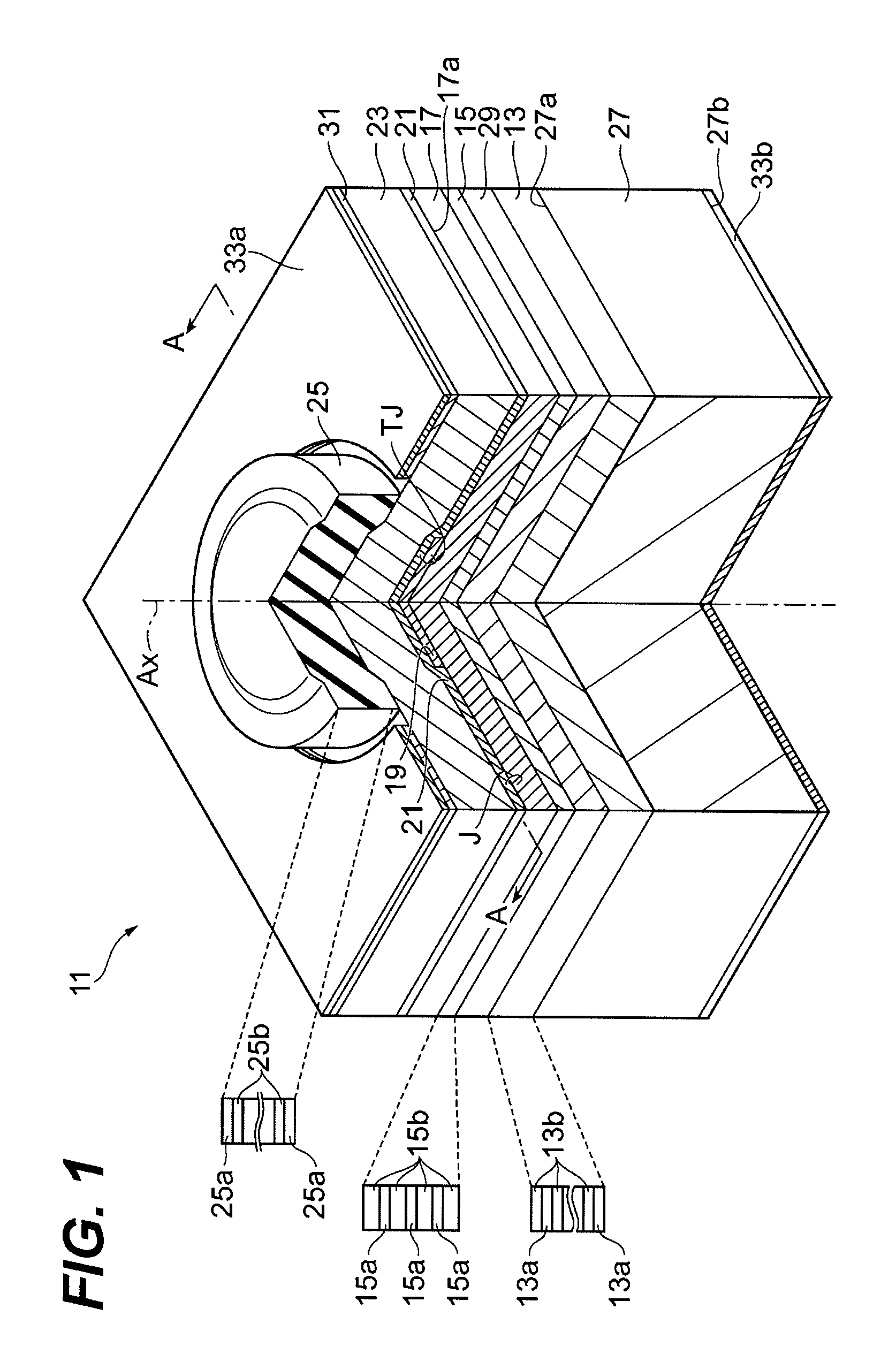
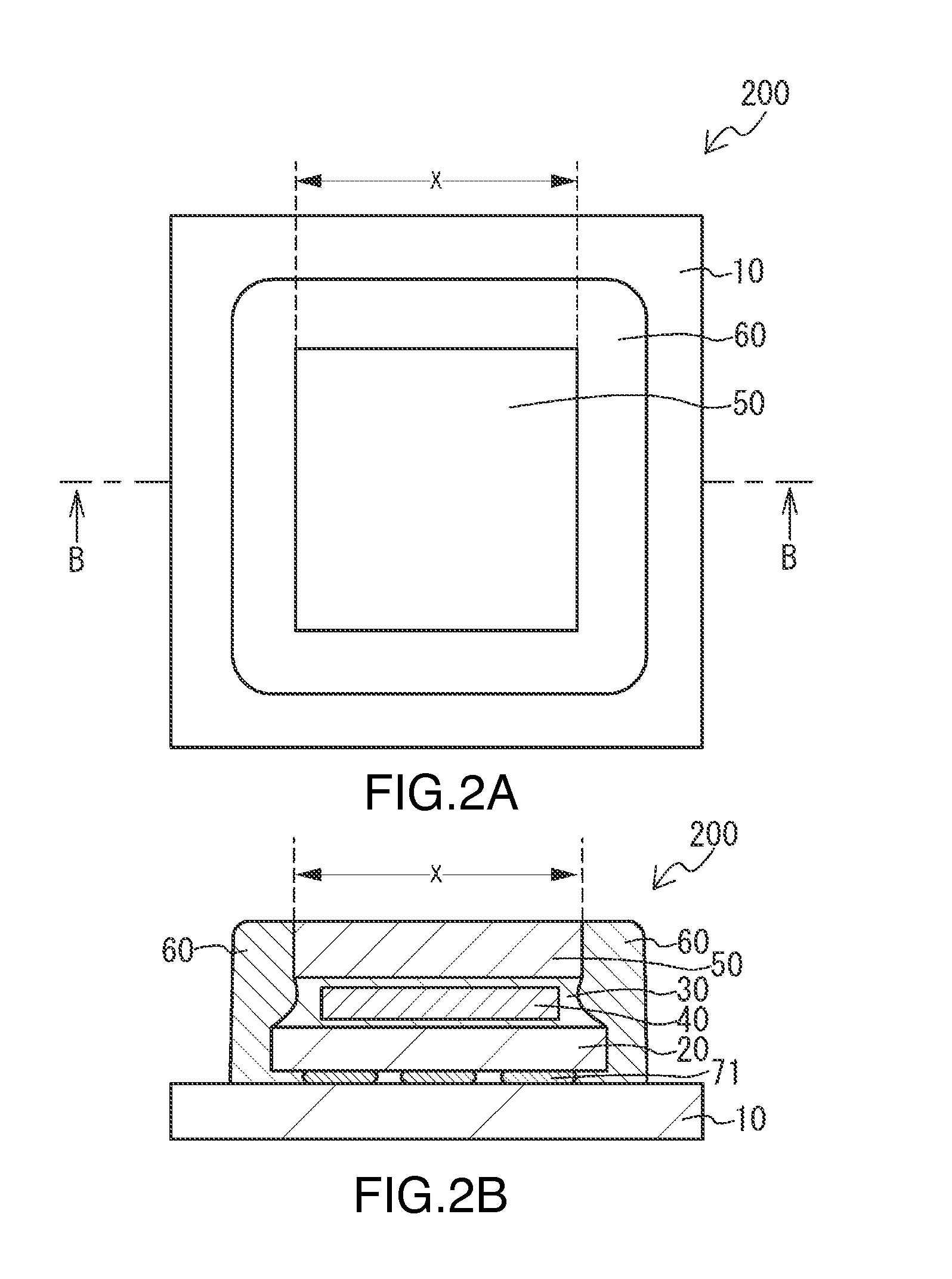
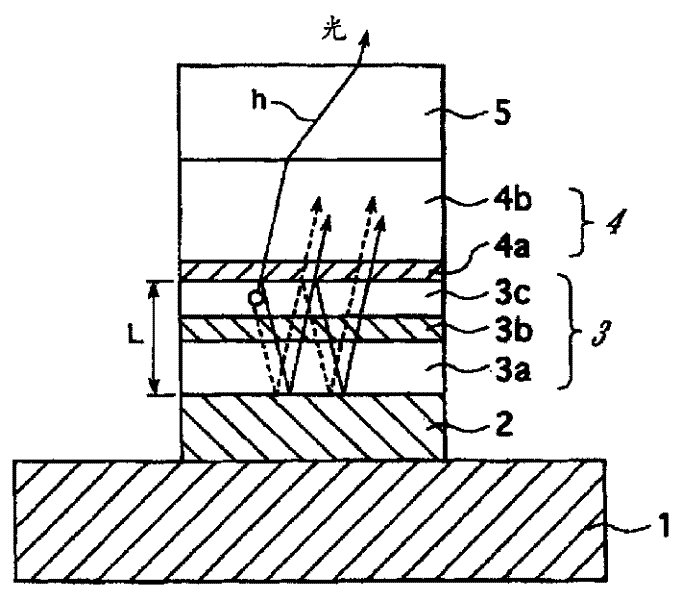
Light emitting device and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20150263254A1Suppresses light absorptionImprove light outputSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringLight emitting device
A light-emitting device includes a substrate; a light-emitting element mounted on the substrate; a first light-transmissive member bonded to an upper surface of the light-emitting element via an adhesive; and a second light-transmissive member placed on an upper surface of the first light-transmissive member. In a plan view of the light-emitting device, a peripheral edge of a lower surface of the first light-transmissive member is positioned more inward than a peripheral edge of the upper surface of the light-emitting element. The adhesive extends from the upper surface of the light-emitting element to a lower surface of the second light-transmissive member, the adhesive covers a side surface of the first light-transmissive member, and the adhesive is separated from the substrate.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Optical element, electro-optical device, and mounted display apparatus
ActiveUS20160124229A1Improve display qualityImprove usabilityDiffraction gratingsPlanar/plate-like light guidesGratingLight guide
An optical element includes a light guide is provided with a incidence section and a emission section, a semitransmissive reflective film is provided in the inside of the light guide, a first diffraction element is provided in the incidence section, and is provided with a plurality of gratings, a second diffraction element is provided in the emission section, and is provided with a plurality of gratings, and a reflective film is provided in the incidence section in a periphery of the first diffraction element, in which the pitch of the plurality of gratings of the first diffraction element is equivalent to the pitch of the plurality of gratings of the second diffraction element, and each extension direction of the plurality of gratings of the first diffraction element is the same direction as each extension direction of the plurality of gratings of the second diffraction element.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Semiconductor device and its manufacturing method, and display device and electronic appliance
InactiveUS7439545B2Effectively exitSuppresses light absorptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDisplay deviceEngineering
A semiconductor device having a light-emitting element with excellent light-emitting characteristics is provided. The semiconductor device is provided with a first depressed portion or opening portion formed in an insulating film; a first electrode which is formed over the insulating film around the first depressed portion or opening portion, which is positioned in the first depressed portion or opening portion, and which forms a second depressed portion together with the first depressed portion or opening portion; a semiconductor layer of a first conductivity type which is formed over the first electrode and which forms a third depressed portion together with the second depressed portion; a light-emitting layer which is formed over the semiconductor layer of the first conductivity type and which forms a fourth depressed portion together with the third depressed portion; a semiconductor layer of a second conductivity type which is formed over the light-emitting layer and which forms a fifth depressed portion together with the fourth depressed portion; and a second electrode formed over the semiconductor layer of the second conductivity type that forms a bottom surface and a side surface of the fifth depressed portion.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
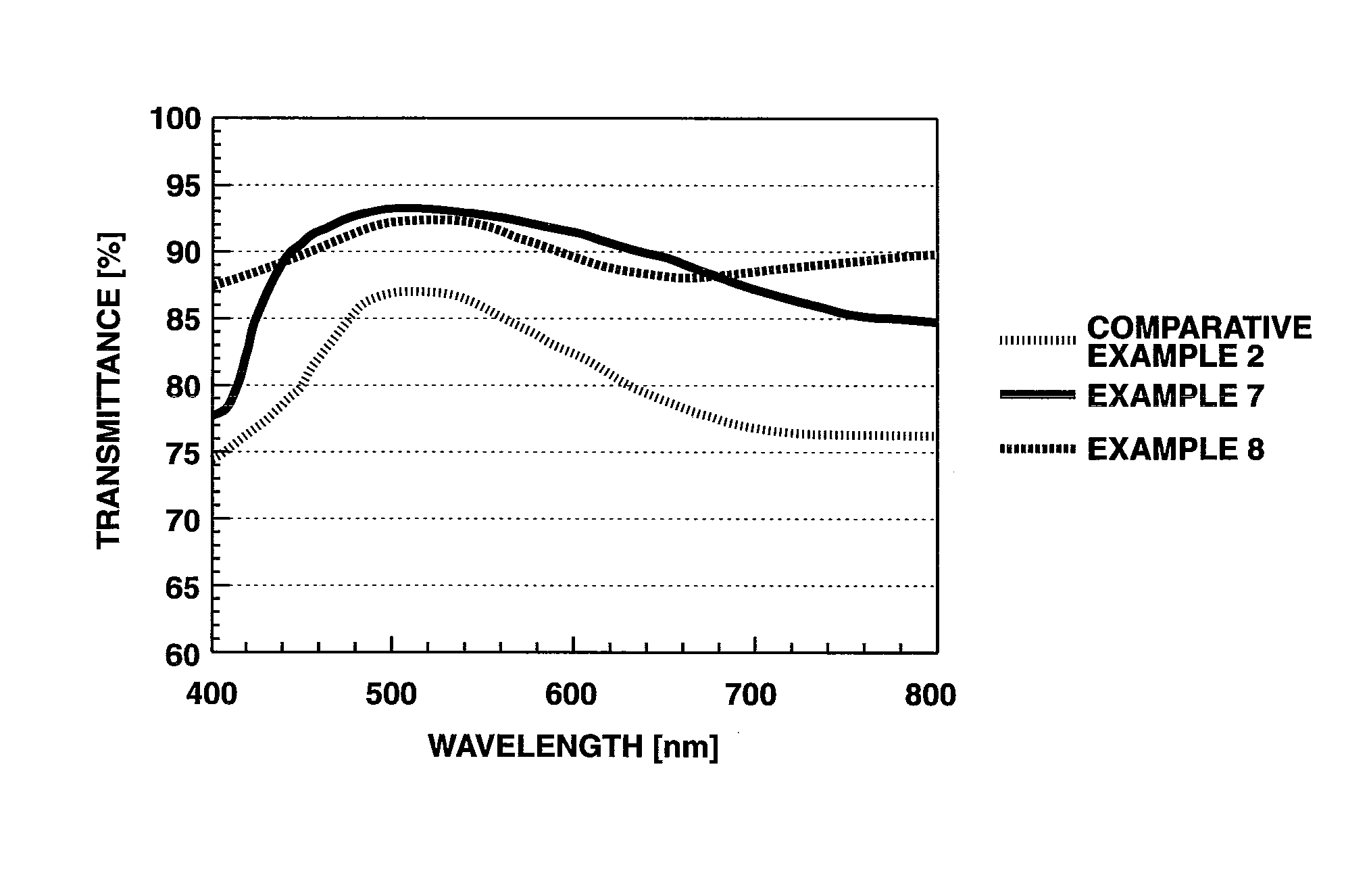
Charge-Preventing Optical Film, Charge-Preventing Adhesive Optical film, Manufacturing Method Thereof, and Image Display Device
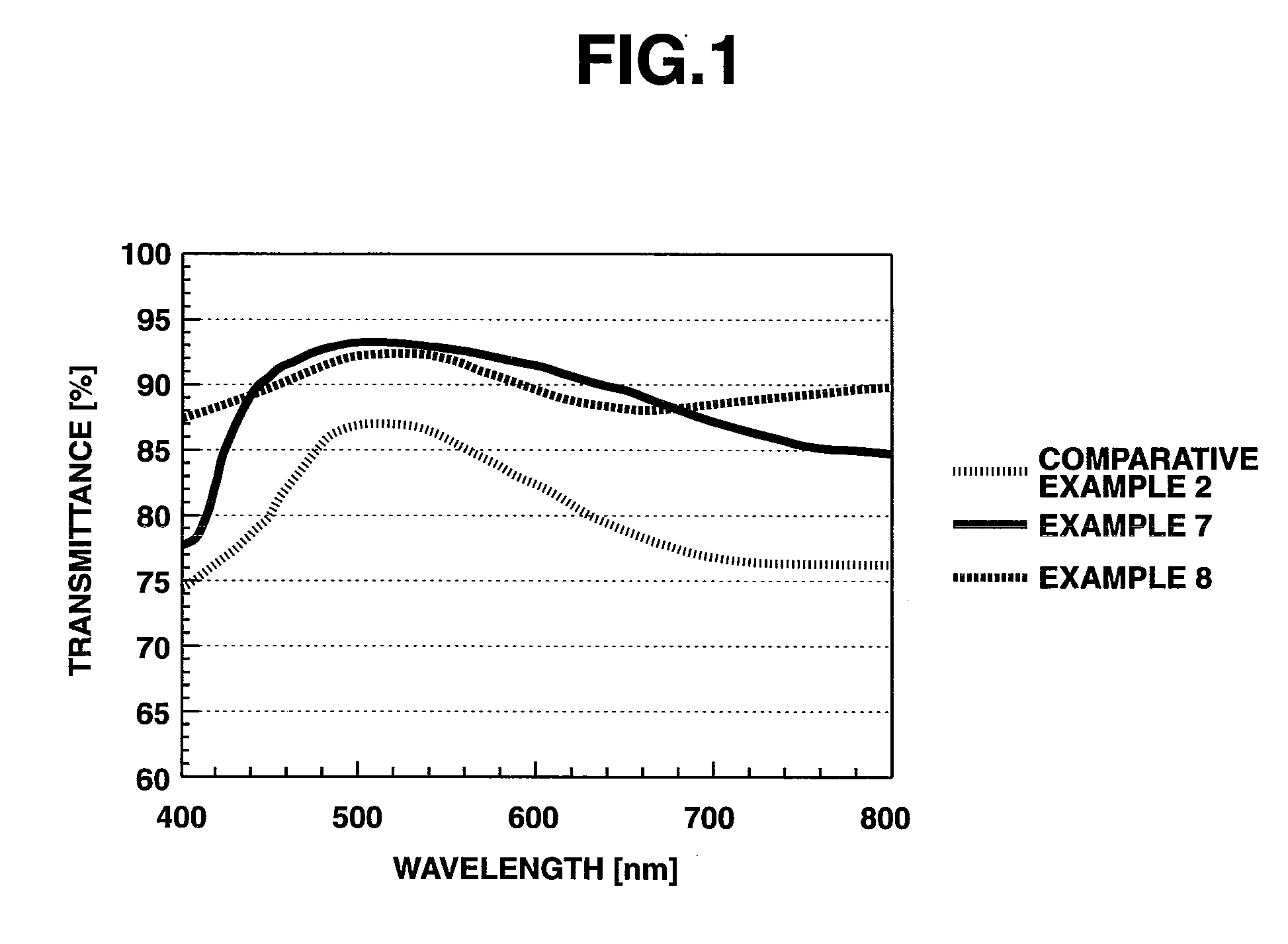
InactiveUS20080044674A1Good effectImprove transmittanceElectroluminescent light sourcesSynthetic resin layered productsConductive polymerTransmittance
The present invention aims at providing an antistatic optical film having excellent antistatic effect and high light transmittance, wherein an antistatic layer laminated on at least one side of the optical film. An antistatic optical film having an antistatic layer laminated on at least one side of the optical film, wherein rubbing treatment is performed on a surface of the optical film on which the antistatic layer is laminated, and a conductive polymer in the antistatic layer is aligned.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
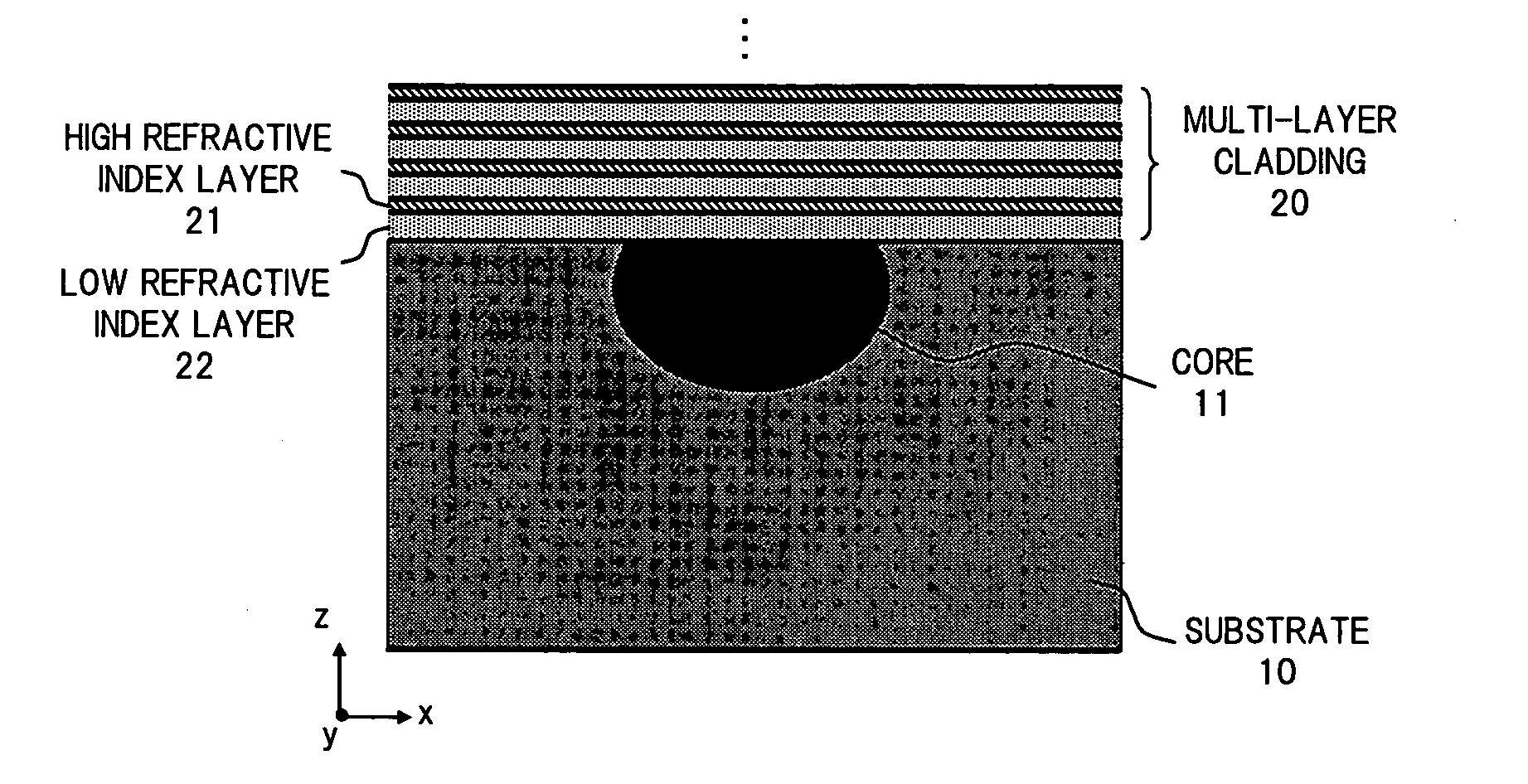
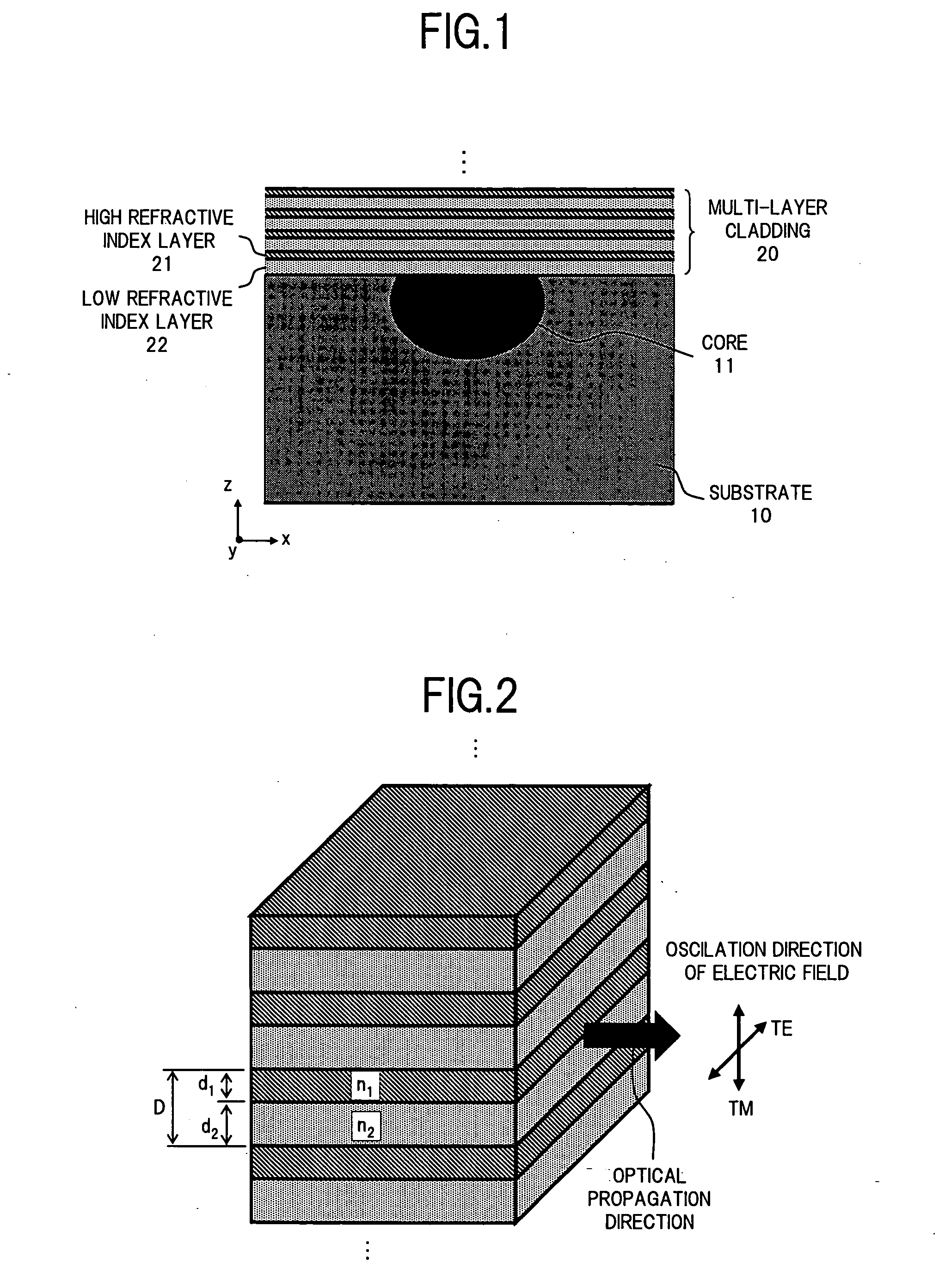
Optical waveguide device and optical modulator
InactiveUS7450811B2Simple structureRaise the ratioOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsRefractive indexWaveguide
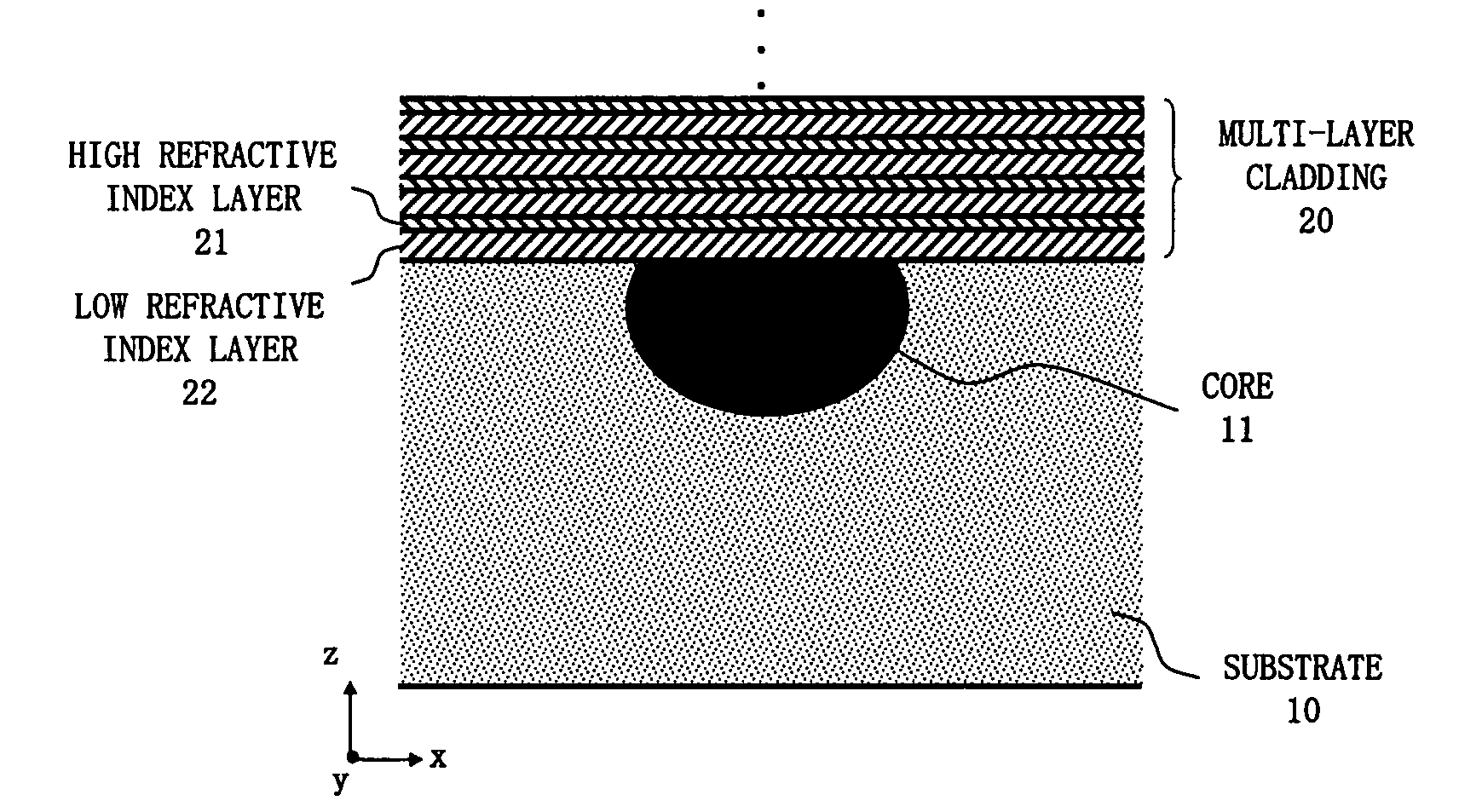
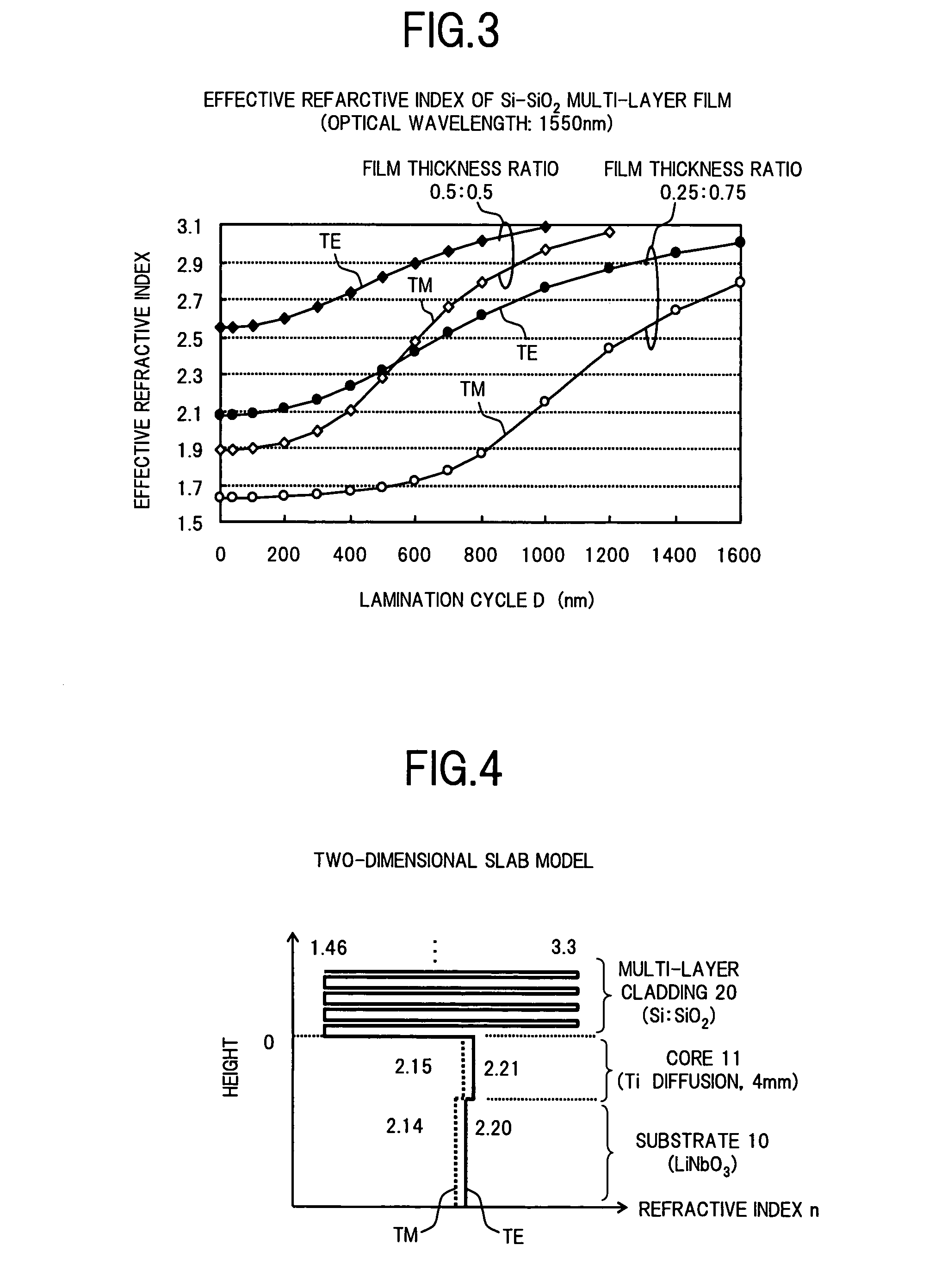
In an optical waveguide device according to the present invention, a multi-layer cladding which is formed by laminating one or more high refractive index layers having the refractive index higher than that of a core and one or more low refractive index layers having the refractive index lower than that of the core, is disposed on a substrate on which an optical waveguide is formed, and utilizing the structural birefringence of this multi-layer cladding, the polarization-dependence of the optical waveguide is increased. As a result, it becomes possible to provide the optical waveguide device having a simple optical waveguide structure for selectively attenuating one of polarization modes of a propagated light.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
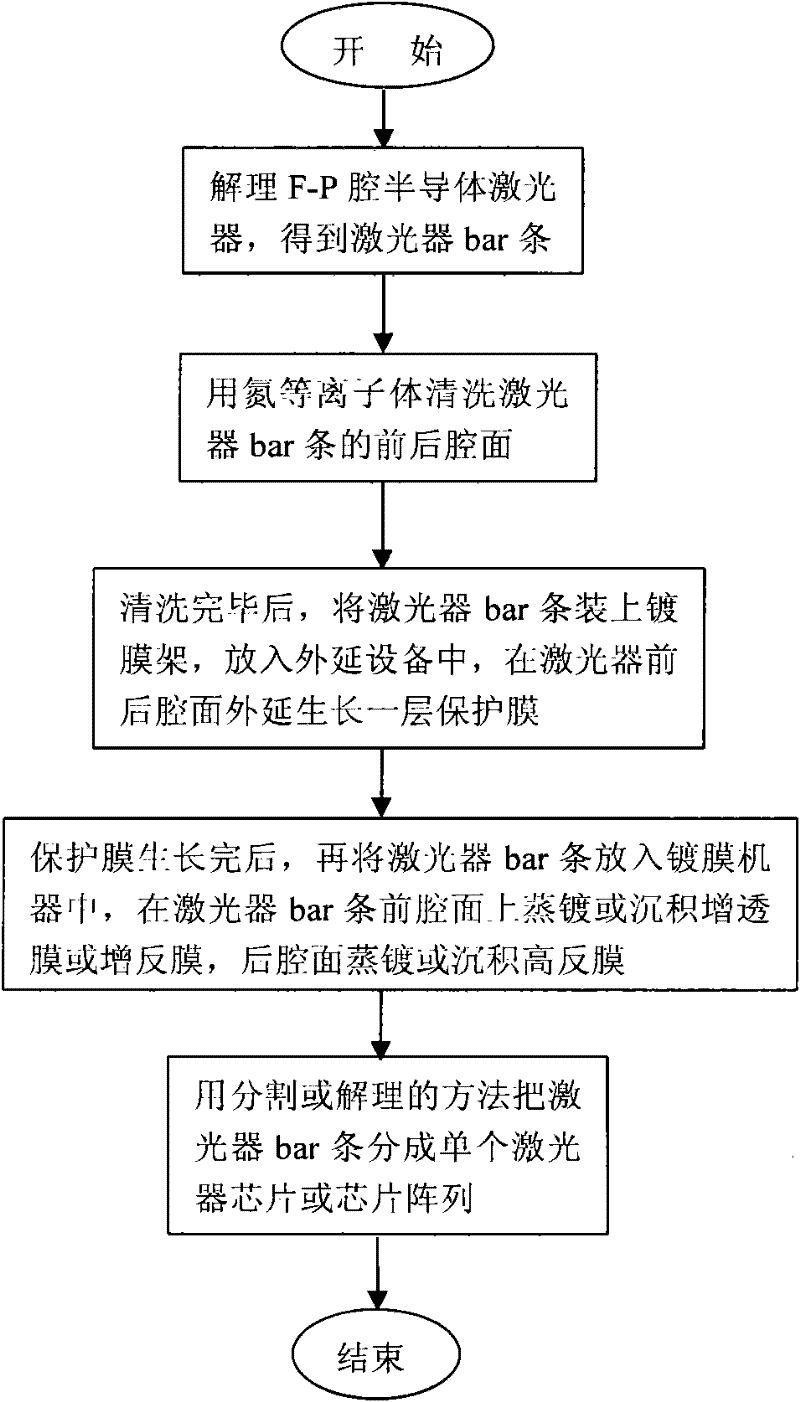
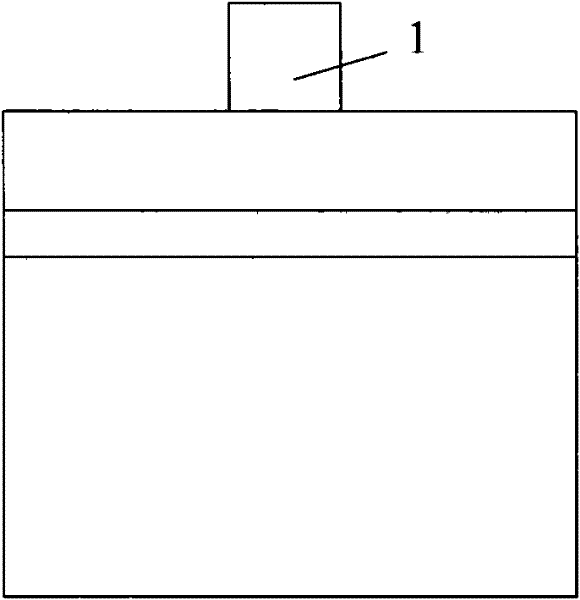
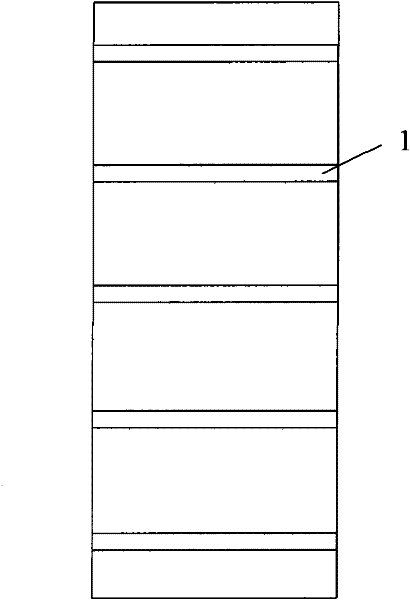
Passivation Method of Cavity Surface of f-p Cavity Semiconductor Laser
InactiveCN102299479ASuppressed Lasing Threshold Current DensityImproving the Optical Catastrophe Damage Threshold of the Cavity SurfaceLaser optical resonator constructionVacuum evaporation coatingTectorial membraneNitrogen plasma
A method for passivating the cavity surface of an F-P cavity semiconductor laser, comprising the following steps: 1, cleaving the F-P cavity semiconductor laser to obtain a laser bar; 2, cleaning the front and rear cavity surfaces of the laser bar with nitrogen plasma; 3, applying epitaxy Growth technology epitaxially grows a layer of protective film on the front and rear cavity surfaces of the laser; 4. Evaporate or deposit an anti-reflection film on the front cavity surface of the laser bar, and evaporate or deposit a high-reflection film on the rear cavity surface; 5. Use segmentation or solution A reasonable approach divides the laser bar into individual laser chips or chip arrays. The invention can effectively reduce the dangling bonds and surface states at the laser cavity surface, and suppress the light absorption of the laser cavity surface; at the same time, the epitaxially grown thin film is a wide bandgap material, which absorbs very little outgoing light, and can greatly suppress the laser cavity The light absorption at the surface and the resulting temperature rise improve the stability and reliability of the laser.
Owner:苏州纳睿光电有限公司
Oligoaniline compounds
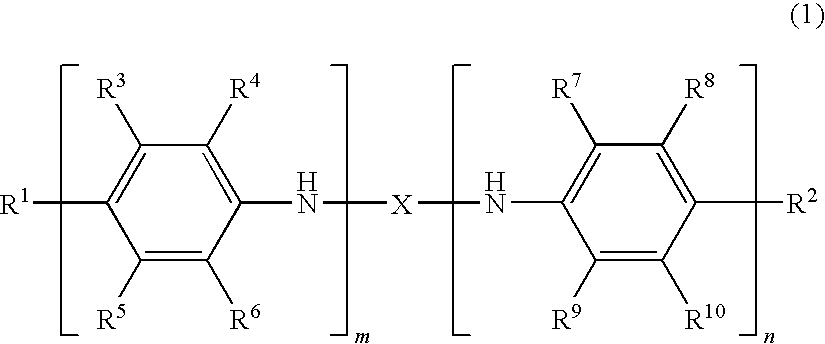
InactiveUS20100159279A1Suppresses light absorptionLight absorptionOrganic compound preparationLayered productsHalogenHydrogen atom
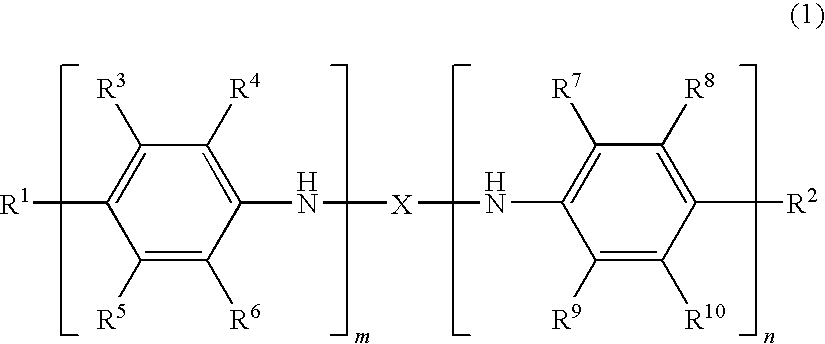
An oligoaniline compound represented by the formula (1) can provide a charge transporting thin film which shows a suppressed coloration in the visible range. Use of this thin film makes it possible to ensure a color reproducibility of a device without lowering the color purity of an electroluminescent light or a light having passed through a color filter.wherein R1 to R10 independently represent each a hydrogen atom, a halogen, etc.; m and n independently represent each an integer of 1 or more while satisfying the condition m+n≦20; and X is a structure represented by any of the following formulae (4) to (10), etc.;wherein R21 to R36 independently represent each a hydrogen atom, a hydroxyl group, etc.; p and q represent each an integer of 1 or more while satisfying the conditions p≦20 and q≦20; and W1s independently represent each —(CR1R2)p-, —O—, —S—, etc.
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
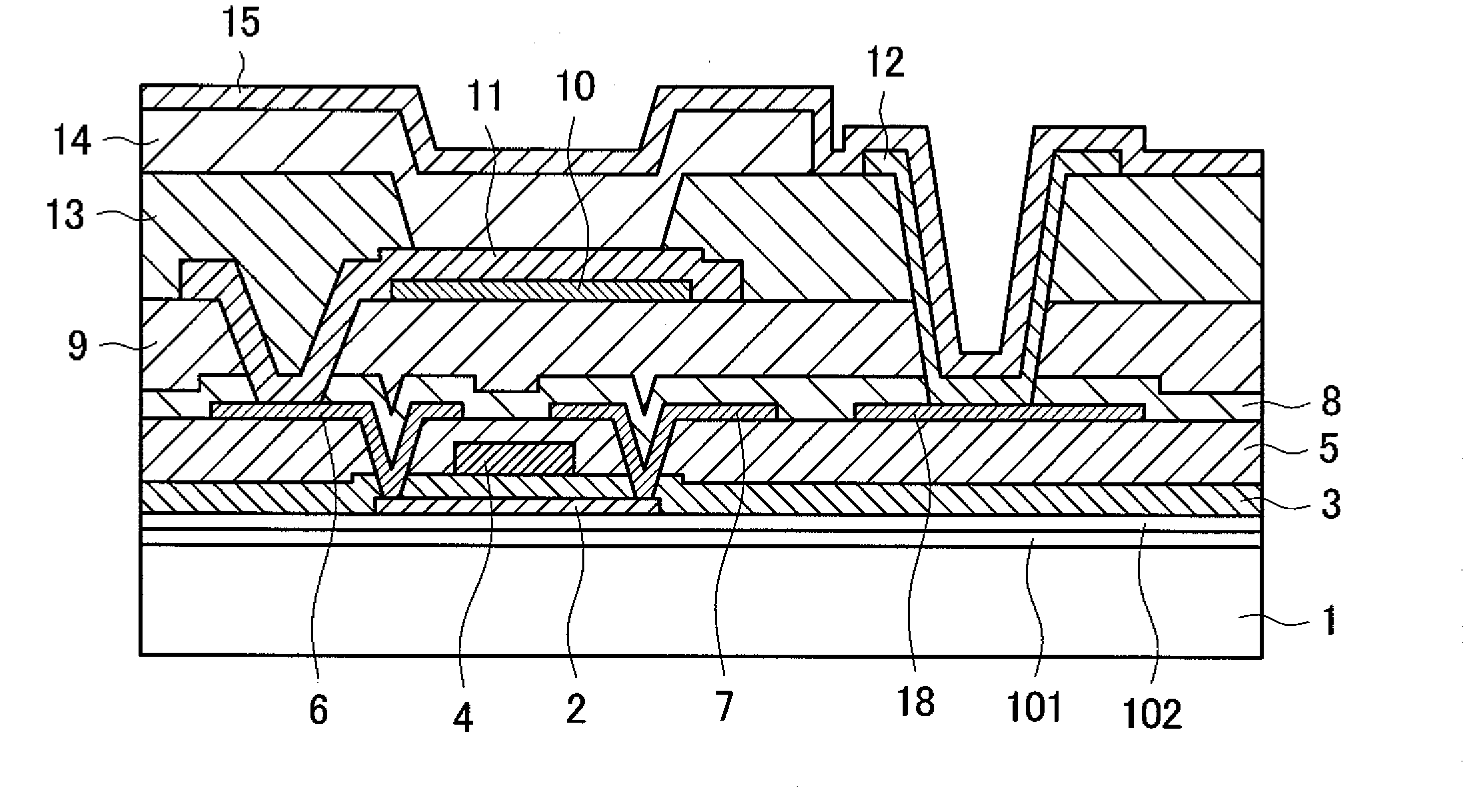
Group iii nitride semiconductor light-emitting device and method of manufacturing the same, and lamp
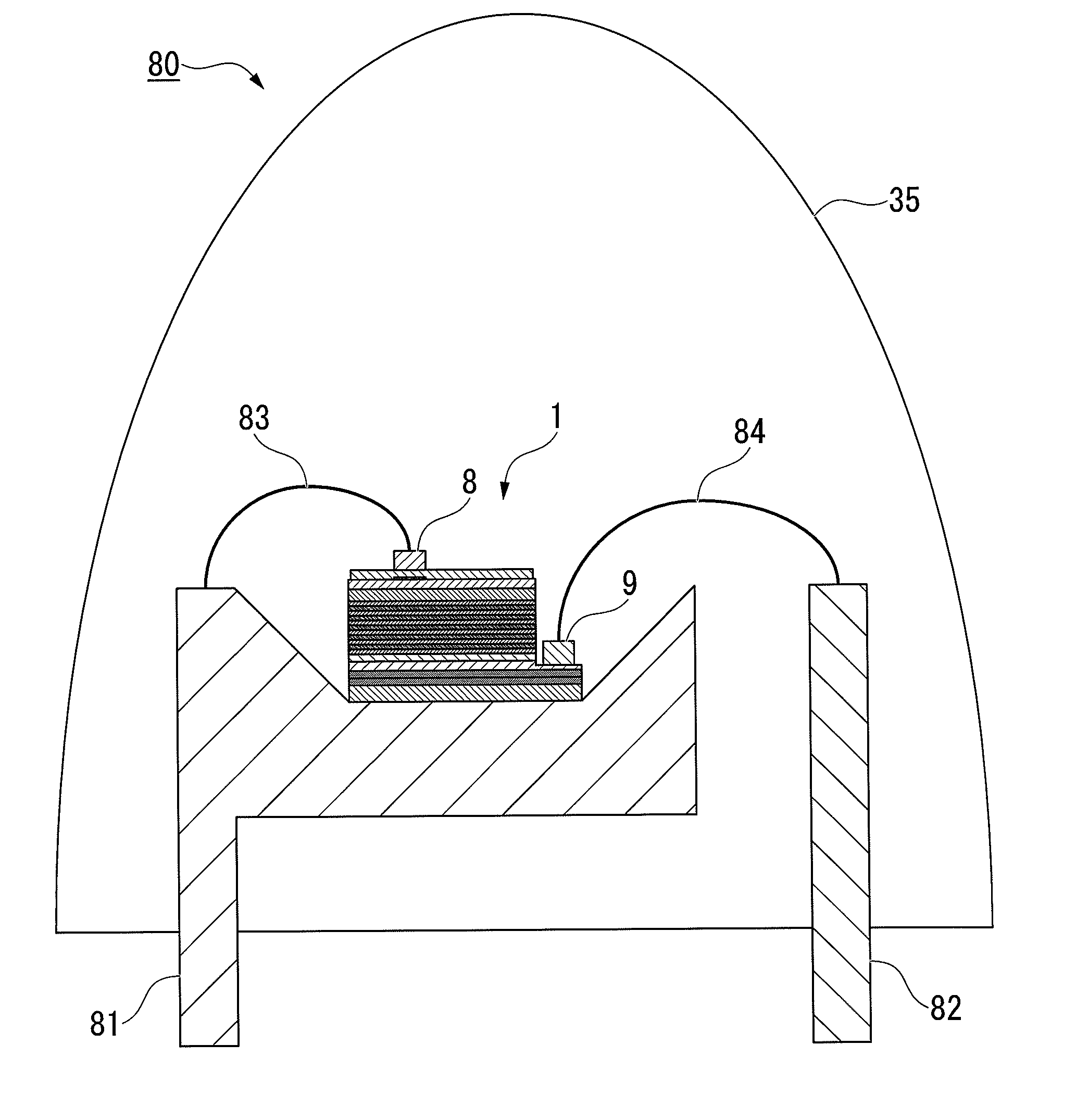
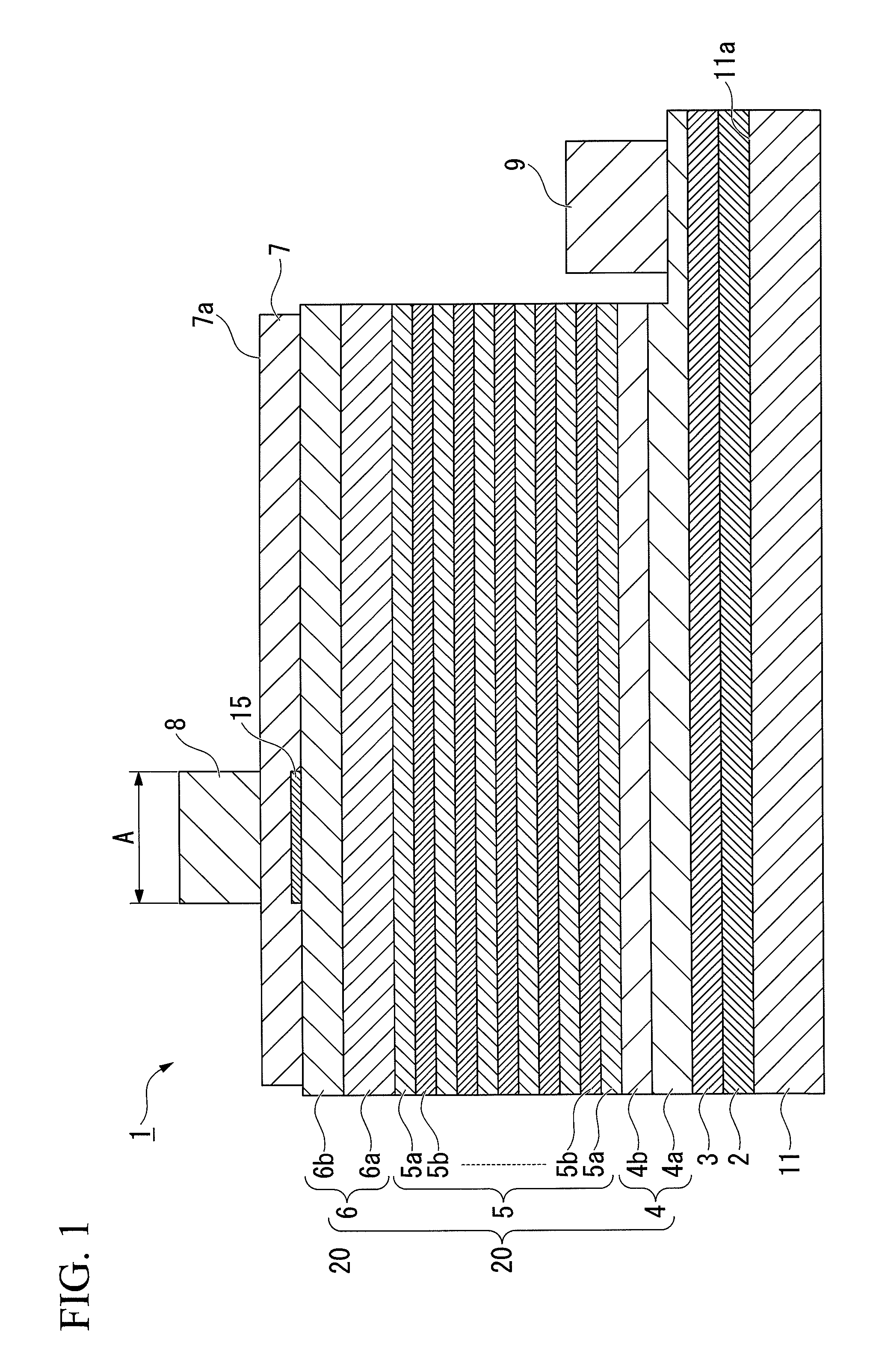
ActiveUS20120001220A1Improve emission efficiencySuppresses light absorptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingQuantum efficiencyInsulation layer
Disclosed is a group III nitride semiconductor light-emitting device which suppresses electric current concentration in a light-transmitting electrode and a semiconductor layer directly below an electrode to enhance light emission efficiency, suppresses light absorption in the electrode or light loss due to multiple reflection therein to enhance light extraction efficiency, and has superior external quantum efficiency and electric characteristics. A semiconductor layer (20), in which an n-type semiconductor layer (4), a light-emitting layer (5) and a p-type semiconductor layer (6) are sequentially layered, is formed on a single-crystal underlayer (3) which is formed on a substrate (11). A light-transmitting electrode (7) is formed on the p-type semiconductor layer (6). An insulation layer (15) is formed on at least a part of the p-type semiconductor layer (6), and the light-transmitting electrode (7) is formed to cover the insulation layer (15). A positive electrode bonding pad (8) is provided in a position A corresponding to the insulation layer (15) provided on the p-type semiconductor layer (6), on a surface (7a) of the light-transmitting electrode (7). A sheet resistance of the n-type semiconductor layer (4) is lower than a sheet resistance of the light-transmitting electrode (7).
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Organic EL Display Device
ActiveUS20100007272A1Suppress shadowsKeeping screen brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDisplay deviceLength wave
In a top emission type organic EL display device, brightness gradient in a screen is reduced while keeping a screen brightness. A reflection film is formed under a lower electrode and the light from an organic EL layer is emitted through an upper electrode. Light absorption of the upper electrode is larger on the side of a shorter wavelength. When a film thickness of the upper electrode is enlarged in order to reduce the brightness gradient in a screen, the film thicknesses of the upper electrodes for a red pixel and a green pixel are enlarged without enlarging the film thickness of the upper electrode for a blue pixel. This makes it possible to reduce the brightness gradient as well as to suppress the light absorption of the upper electrode.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Group-III nitride semiconductor device
ActiveUS20070126009A1Reduce dislocation densitySuppresses light absorptionLaser detailsSemiconductor laser structural detailsUltravioletEngineering
An object of the present invention is to provide a Group III nitride semiconductor element which comprises a thick AlGaN layer exhibiting high crystallinity and containing no cracks, and which does not include a thick GaN layer (which generally serves as a light-absorbing layer in an ultraviolet LED). The inventive Group III nitride semiconductor element comprises a substrate; a first nitride semiconductor layer composed of AlN which is provided on the substrate; a second nitride semiconductor layer composed of Alx1Ga1-x1N (0≦x1≦0.1) which is provided on the first nitride semiconductor layer; and a third nitride semiconductor layer composed of Alx2Ga1-x2N (0<x2<1 and x1+0.02≦x2) which is provided on the second nitride semiconductor layer.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Group-III nitride semiconductor device
ActiveUS8134168B2Reduce dislocation densitySuppresses light absorptionLaser detailsSemiconductor laser structural detailsUltravioletCrystallinity
An object of the present invention is to provide a Group III nitride semiconductor element which comprises a thick AlGaN layer exhibiting high crystallinity and containing no cracks, and which does not include a thick GaN layer (which generally serves as a light-absorbing layer in an ultraviolet LED).The inventive Group III nitride semiconductor element comprises a substrate; a first nitride semiconductor layer composed of AlN which is provided on the substrate; a second nitride semiconductor layer composed of Alx1Ga1-x1N (0≦x1≦0.1) which is provided on the first nitride semiconductor layer; and a third nitride semiconductor layer composed of Alx2Ga1-x2N (0<x2<1 and x1+0.02≦x2) which is provided on the second nitride semiconductor layer.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
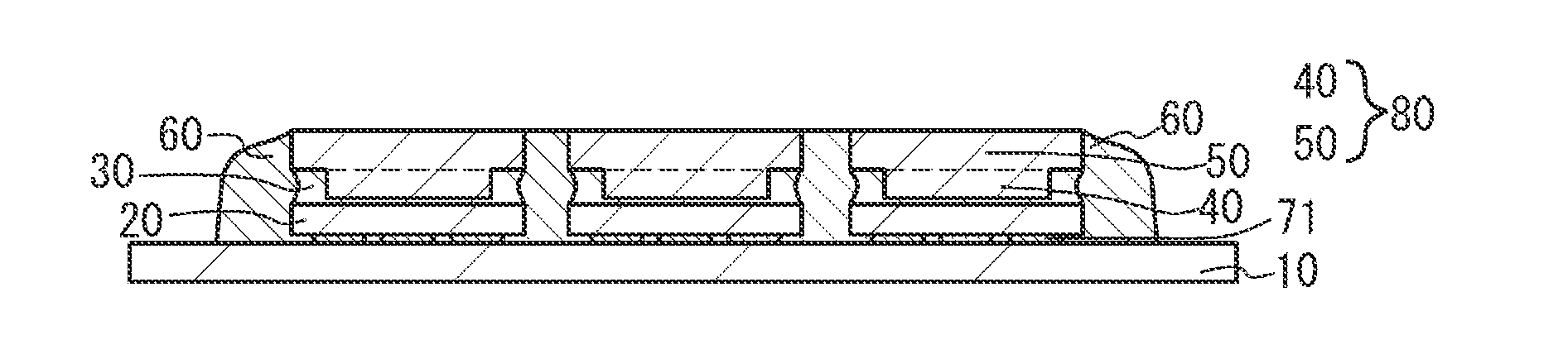
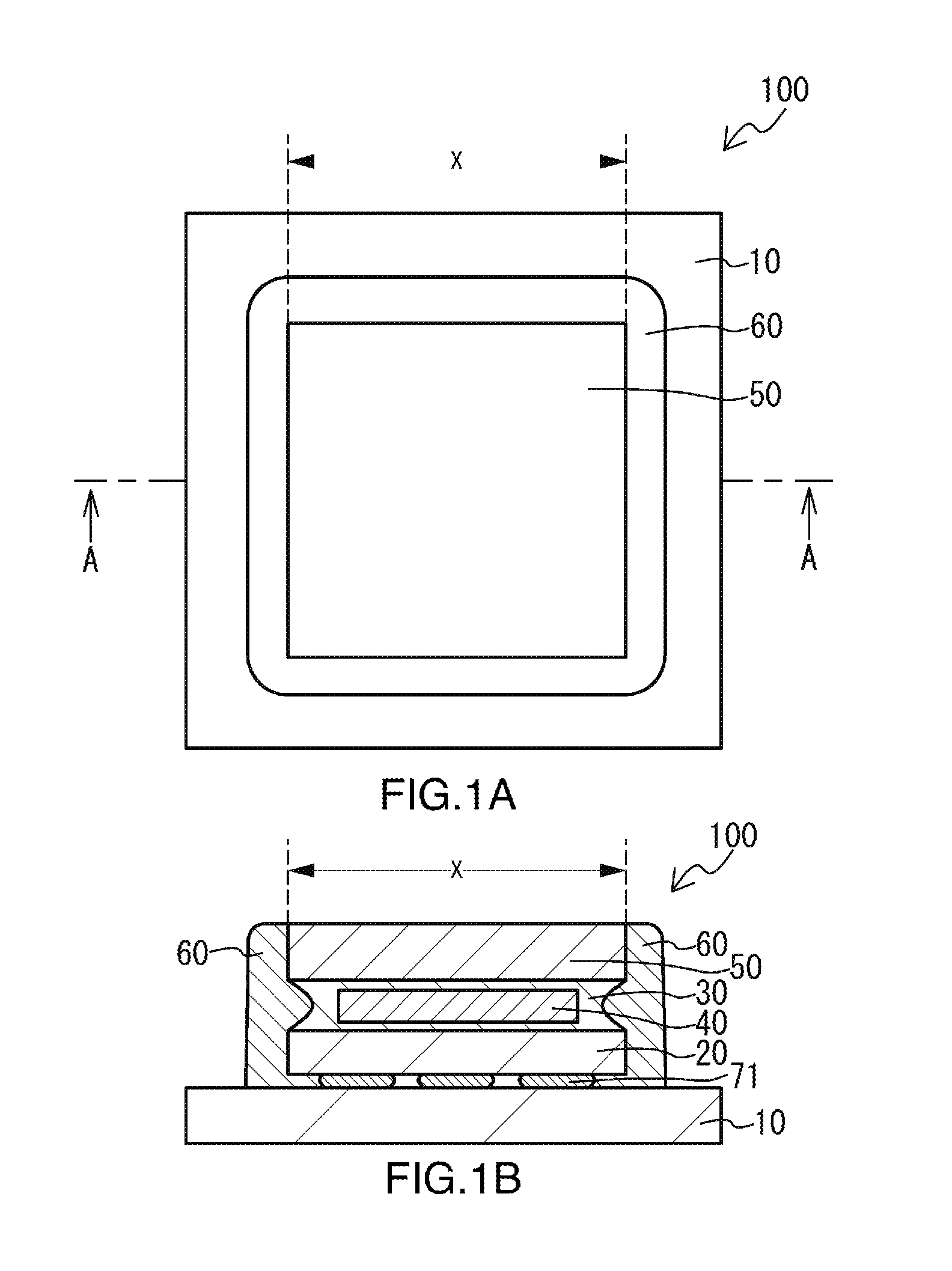
Key sheet
InactiveUS20070084709A1Suppresses light absorptionBrighter illuminationContact operating partsEmergency protective devicesDevice materialEngineering
Disclosed is a key sheet efficiently diffusing local heat generated by a device mounted on a board. A key sheet has a base sheet formed of a rubber-like elastic material in which a heat conductive filler is mixed. Thus, if a semiconductor device on a board generates heat, it is possible to suppress local heat storage by the heat conductive filler of the base sheet. Further, there is no need to provide a separate member for heat diffusion between the board and the key sheet, making it possible to realize a reduction in thickness. Thus, with the key sheet, it is possible to meet the requirement for heat diffusion to eliminate local heat storage in electronic apparatuses, and the requirement for a reduction in the thickness and weight of electronic apparatuses.
Owner:POLYMATECH CO LTD
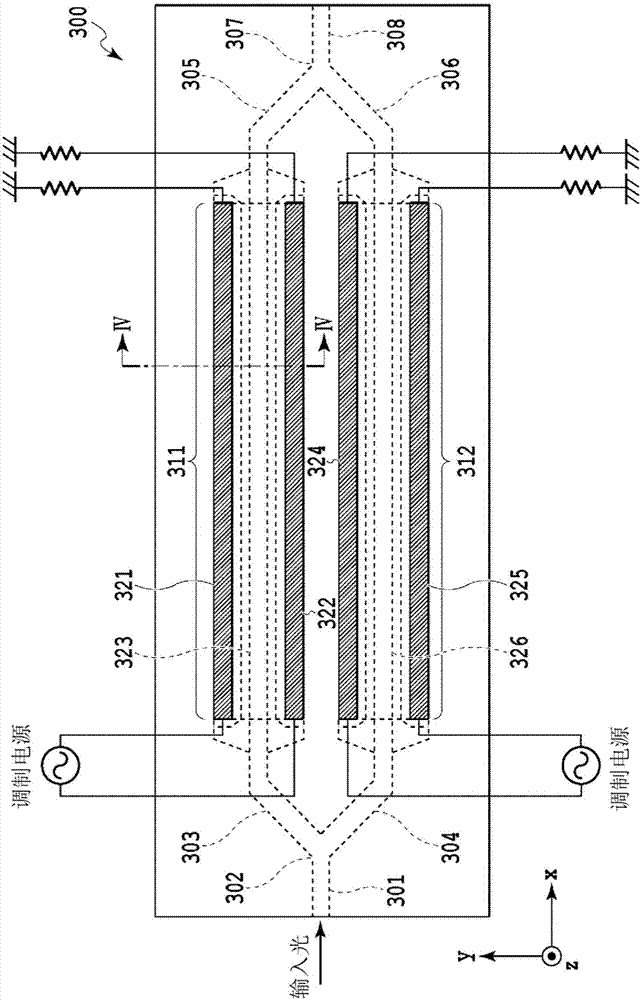
Optical modulator
This optical modulator includes a substrate and a phase modulation unit on the substrate, said phase modulation unit including: a first traveling-wave electrode, a second traveling-wave electrode, and an optical waveguide configured from a first cladding layer, a semiconductor layer, which is laminated on the first cladding layer, and has a refractive index that is higher than that of the first cladding layer, and a second cladding layer, which is laminated on the semiconductor layer, and has a refractive index that is lower than that of the semiconductor layer. The semiconductor layer is provided with: a rib section, which is formed in the optical axis direction of the optical waveguide, and is to be the core of the optical waveguide; a first slab section formed in the optical axis direction on one side of the rib section; a second slab section formed in the optical axis direction on the other side of the rib section; a third slab section formed in the optical axis direction on the first slab section side opposite to the rib section; and a fourth slab section formed in the optical axis direction on the second slab section side opposite to the rib section. The first slab section is formed thinner than the rib section and the third slab section, and the second slab section is formed thinner than the rib section and the fourth slab section.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Method for forming electrode for Group-III nitride compound semiconductor light-emitting devices
ActiveUS20080293231A1Improve reflectivityIncrease contact areaSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor lasersLight emitting deviceNitride
A method for forming an electrode for Group-III nitride compound semiconductor light-emitting devices includes a step of forming a first electrode layer having an average thickness of less than 1 nm on a Group-III nitride compound semiconductor layer, the first electrode layer being made of a material having high adhesion to the Group-III nitride compound semiconductor layer or low contact resistance with the Group-III nitride compound semiconductor layer and also includes a step of forming a second electrode layer made of a highly reflective metal material on the first electrode layer.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Vcsel with reduced light scattering within optical cavity
InactiveUS20090213892A1Avoid problemsImprove activation efficiencyLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAtomic physicsLight scattering
A VCSEL with a structure able to reduce the scattering within the optical cavity and its manufacturing method are disclosed. The VCSEL of the present invention provides, on the semiconductor substrate, the first DBR, the active layer, the p-type spacer layer, the heavily doped p-type mesa, the heavily doped n-type layer, the first n-type spacer and the second DBR in this order. The heavily doped n-type layer, which is formed so as to cover the p-type spacer layer and the heavily doped p-type mesa, forms the tunnel junction with respect to the heavily doped p-type mesa. Because the height, which is appeared in the surface of the n-type spacer layer, reflects the height of the heavily doped p-type mesa and is comparatively small, the light scattering between the second DBR and the n-type spacer layer is suppressed.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Semiconductor laser device and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20050279993A1High crystallinityImprove surface morphologyOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsElectrical conductorGallium nitride
A semiconductor laser device of the present invention includes: an active layer formed on a substrate; a first semiconductor layer formed on the active layer and made of a nitride semiconductor of a first conductivity type; a multilayer film formed on the first semiconductor layer and having a groove; and a second semiconductor layer formed on the multilayer film to fill the groove and made of a nitride semiconductor of the first conductivity type. The multilayer film is composed of a plurality of thin films containing a nitride semiconductor of a second conductivity type, and one of the thin films formed as the uppermost film is made of gallium nitride.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
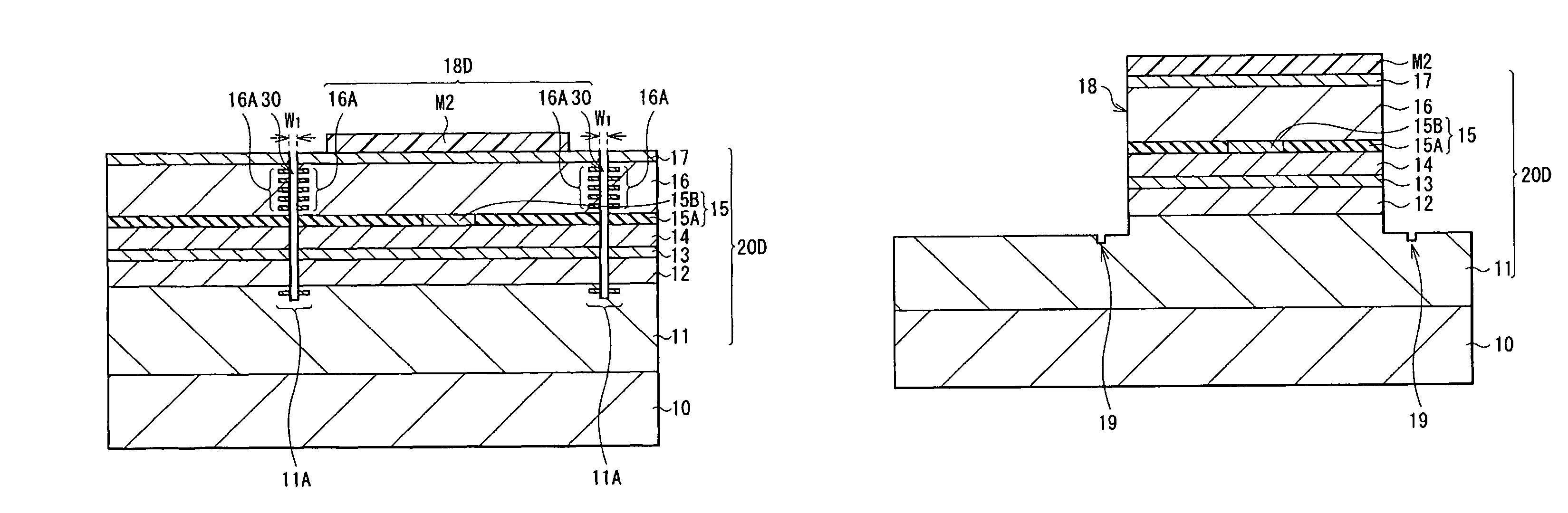
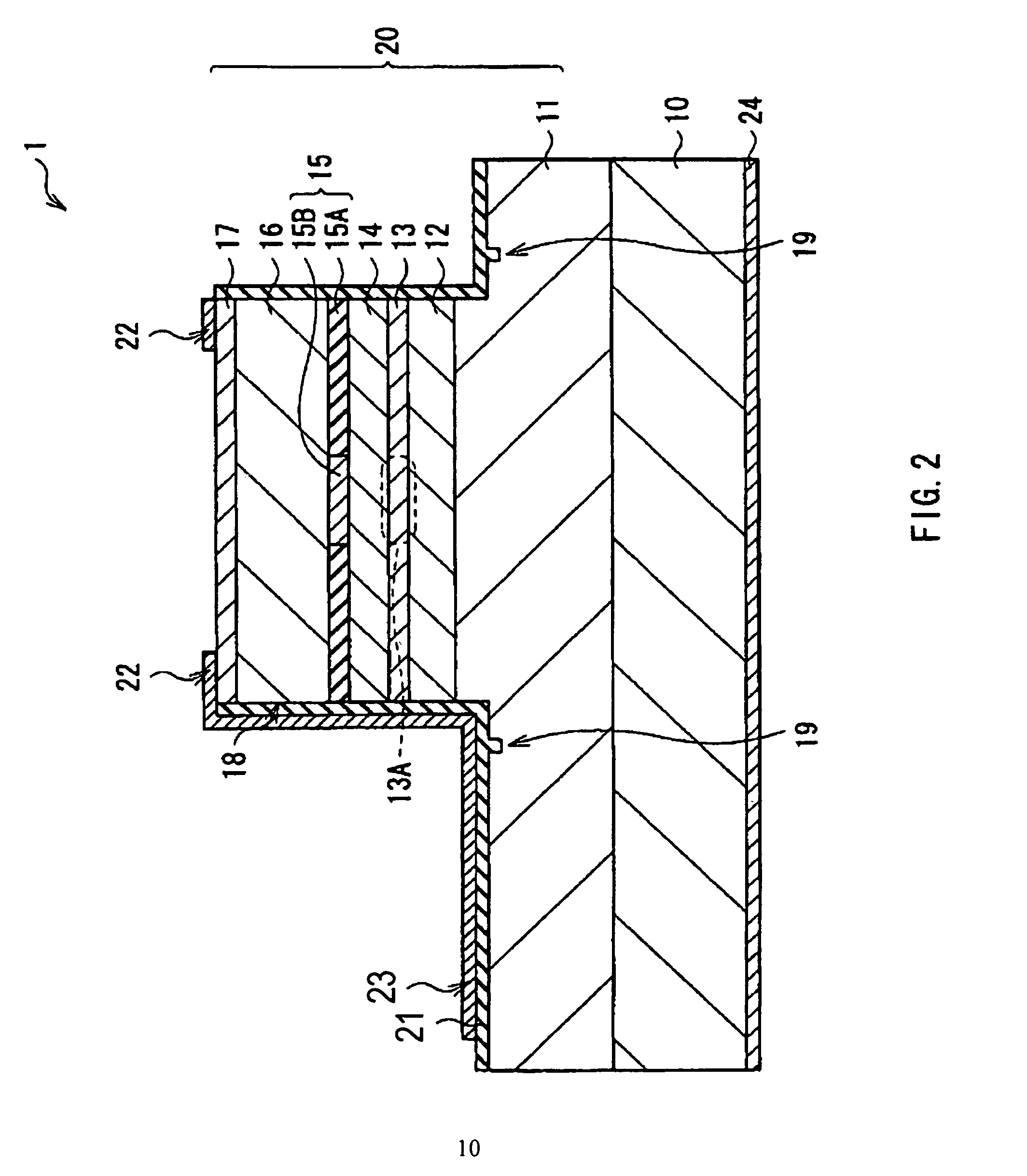
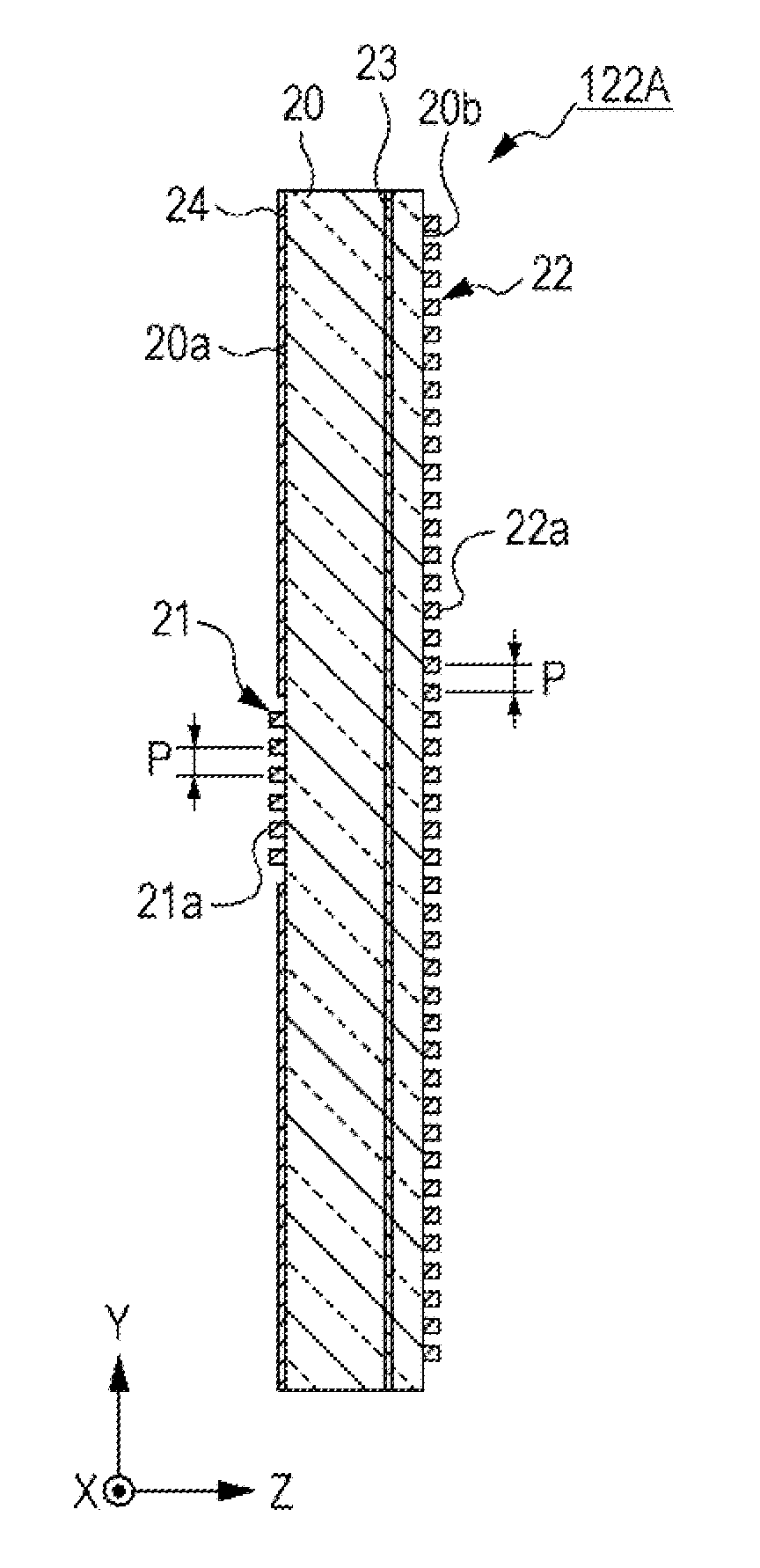
Light-emitting device and method of manufacturing same
ActiveUS20160380165A1Suppresses light absorptionImprove light outputSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLight emitting deviceMechanical engineering
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Optical waveguide device and optical modulator
InactiveUS20070297737A1Simple structureRaise the ratioOptical waveguide light guideNon-linear opticsRefractive indexWaveguide
In an optical waveguide device according to the present invention, a multi-layer cladding which is formed by laminating one or more high refractive index layers having the refractive index higher than that of a core and one or more low refractive index layers having the refractive index lower than that of the core, is disposed on a substrate on which an optical waveguide is formed, and utilizing the structural birefringence of this multi-layer cladding, the polarization-dependence of the optical waveguide is increased. As a result, it becomes possible to provide the optical waveguide device having a simple optical waveguide structure for selectively attenuating one of polarization modes of a propagated light.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Organic electroluminescence element
InactiveCN101989647ASuppresses light absorptionImprove patienceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSimple Organic CompoundsCharge-transfer complex
Owner:YAMAGATA PROMOTIONAL ORG FOR INDAL TECH
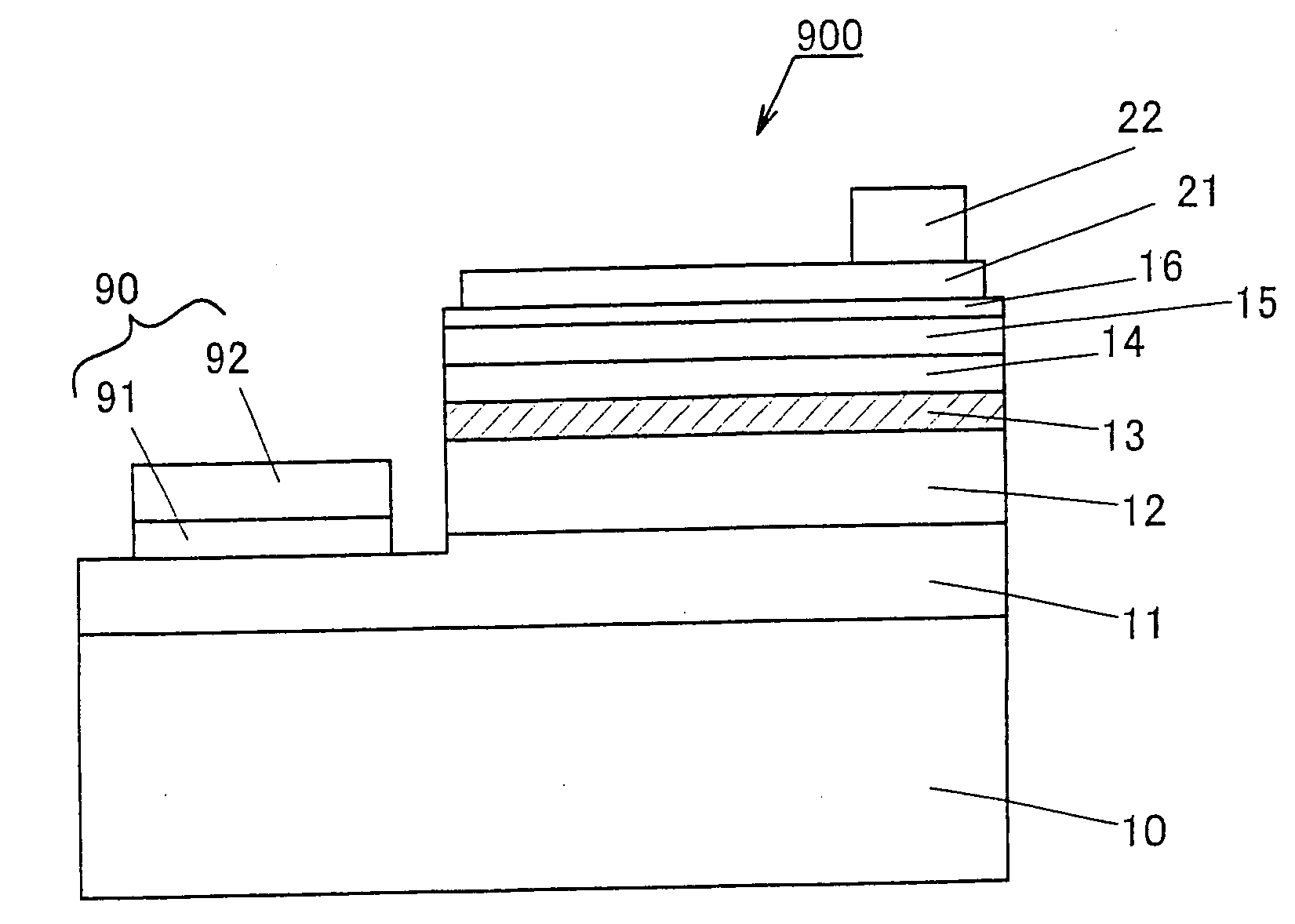
Light emitting device and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS7511314B2Increase brightnessSuppresses light absorptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPeak valueLength wave
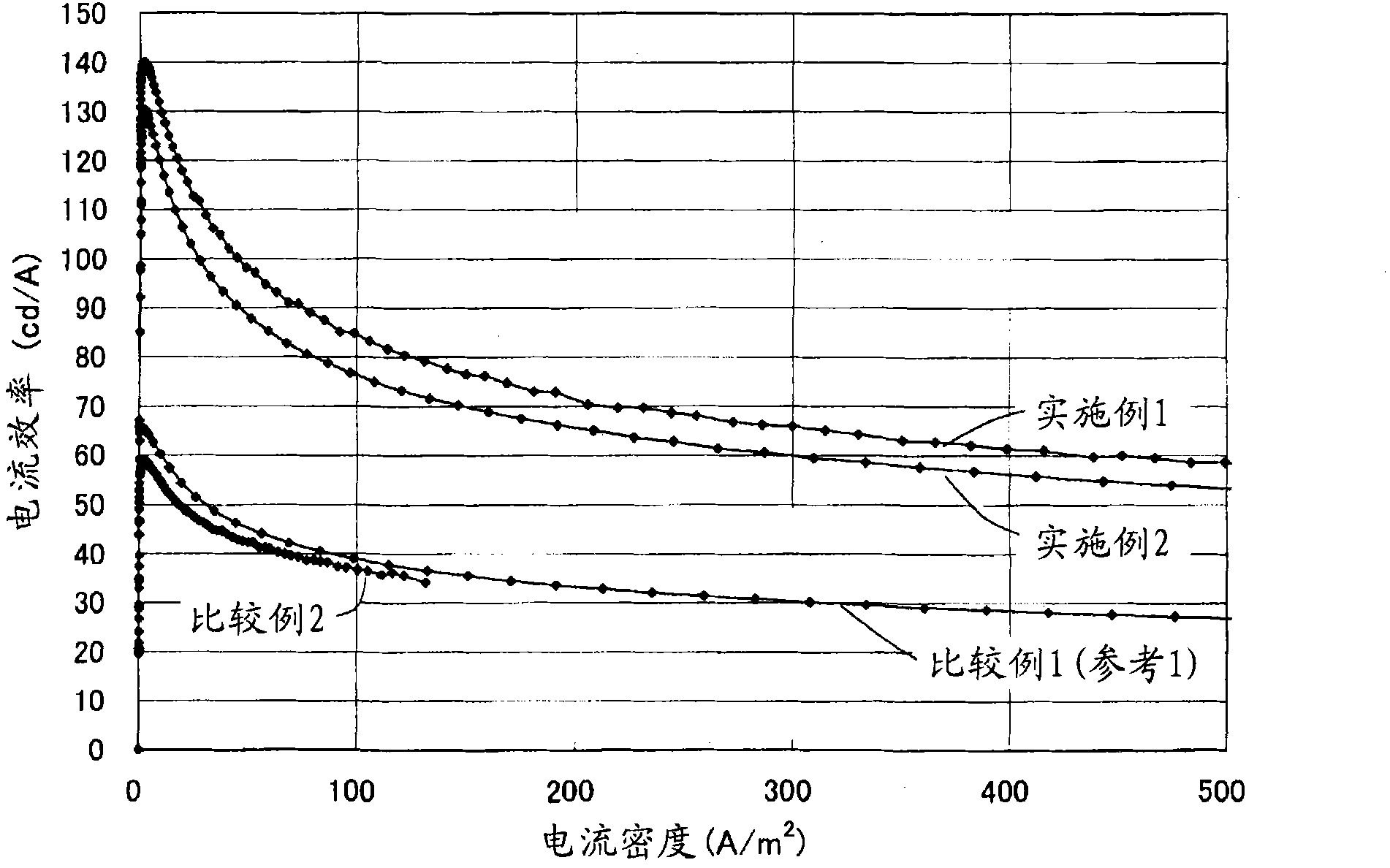
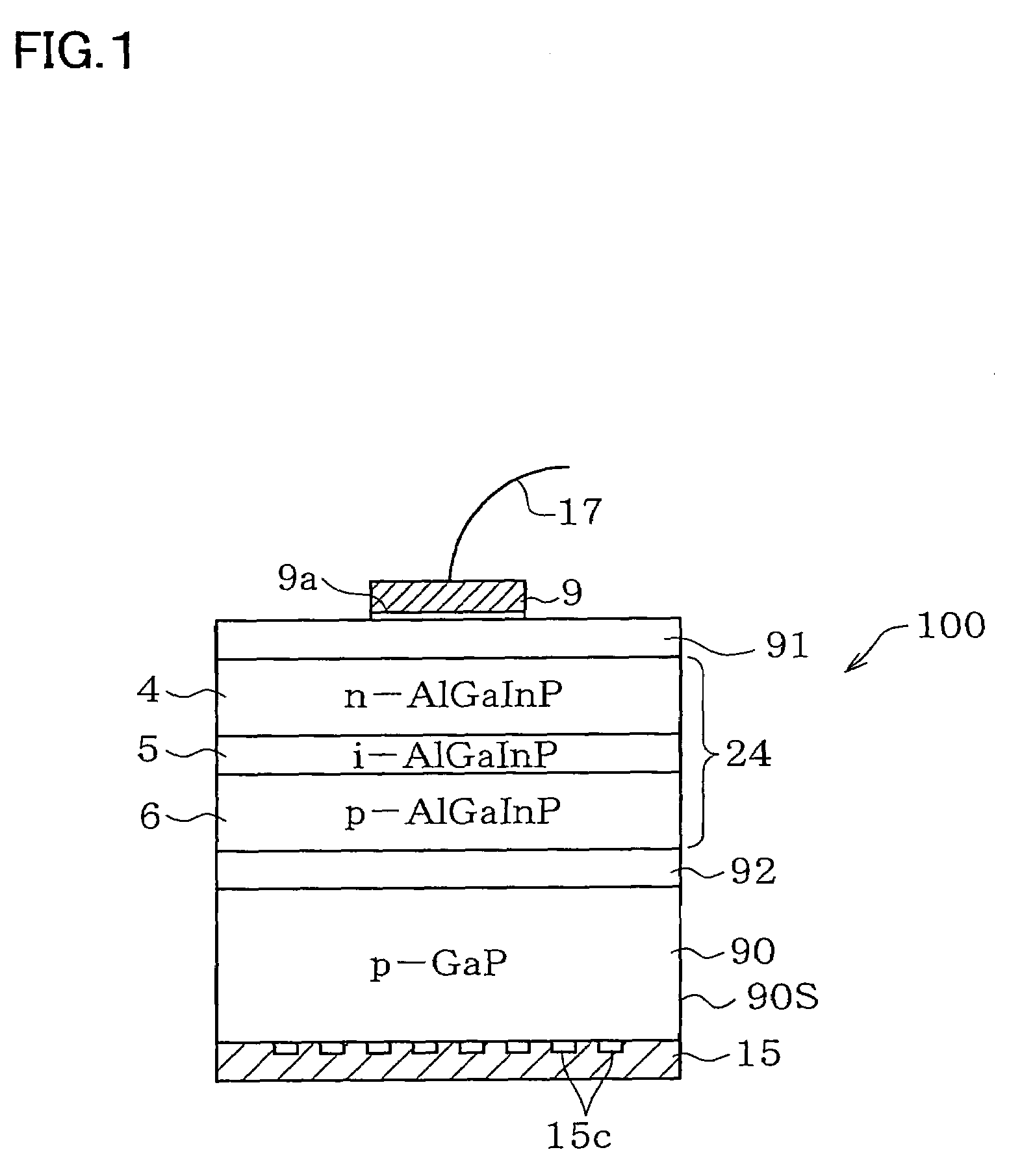
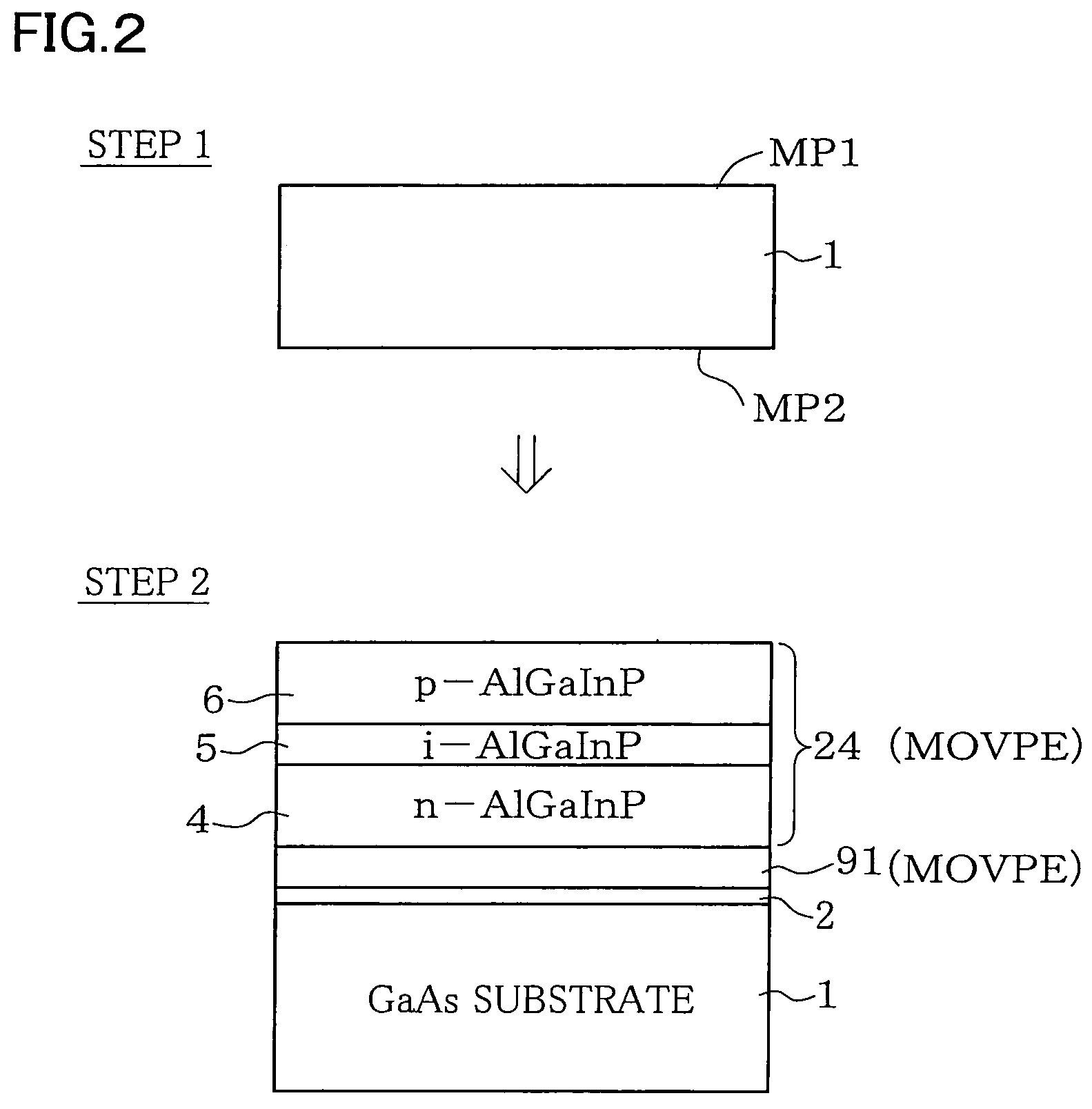
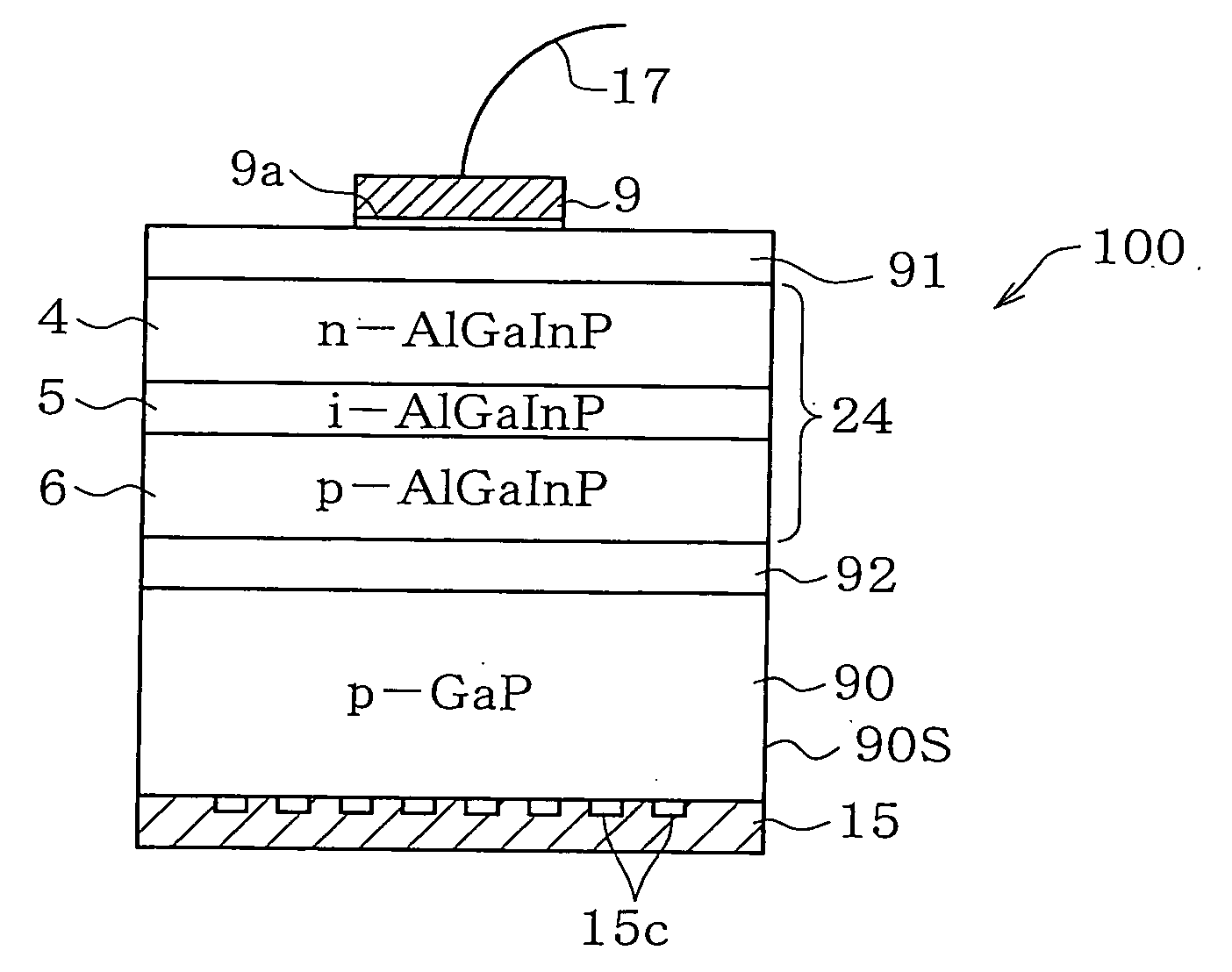
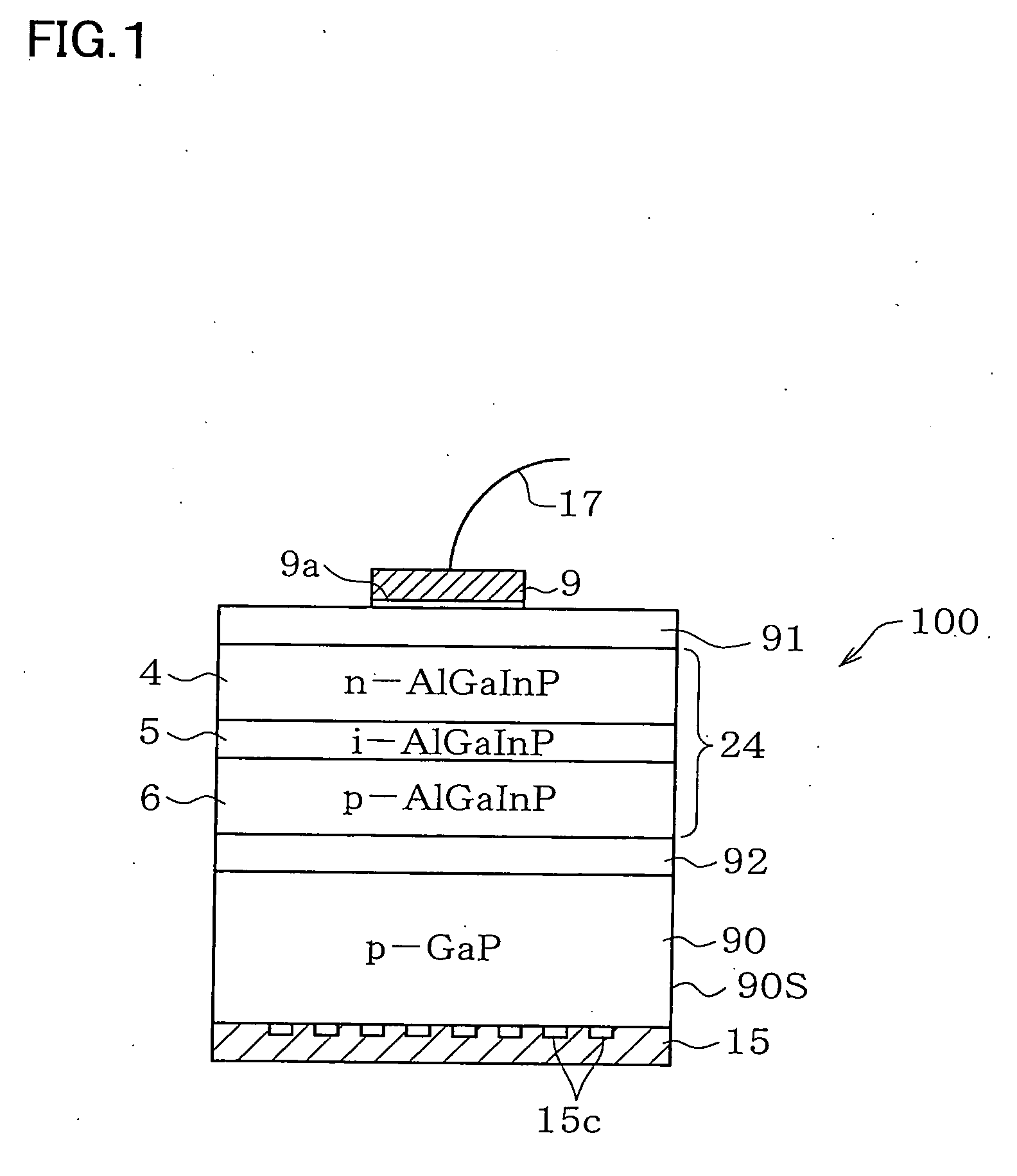
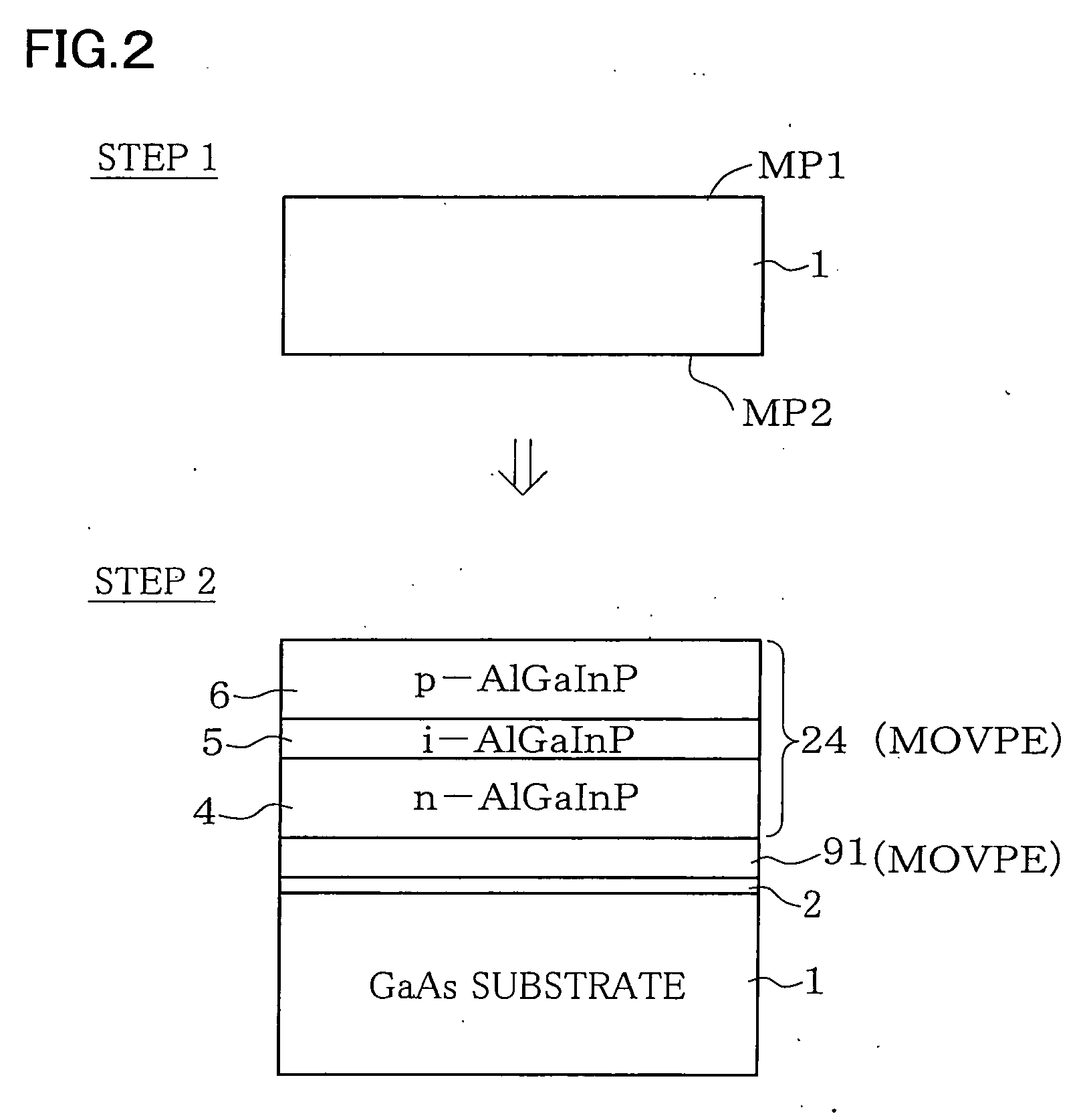
Disclosed is a light-emitting device (100) has a light-emitting layer portion (24) which is composed of a group III-V compound semiconductor and a transparent thick-film semiconductor layer (90) with a thickness of not less than 40 μm which is formed on at least one major surface side of the light-emitting layer portion (24) and composed of a group III-V compound semiconductor having a band gap energy larger than the photon energy equivalent of the peak wavelength of emission flux from the light-emitting layer portion (24). The transparent thick-film semiconductor layer (90) has a lateral surface portion (90S) which is a chemically etched surface. The dopant concentration of the transparent thick-film semiconductor layer (90) is not less than 5×1016 / cm3 and not more than 2×1018 / cm3. The light-emitting device can have a transparent thick-film semiconductor layer while being significantly improved in light taking-out efficiency from the lateral surface portion.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Surface emitting laser
InactiveUS7876800B2Highly efficient current injectionSuppresses light absorptionLaser optical resonator constructionLaser cooling arrangementsIn planePhotonic crystal
Owner:CANON KK
Photovoltaic device
InactiveUS20100229935A1Increase the amount of lightIncrease currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationLength waveElectric power
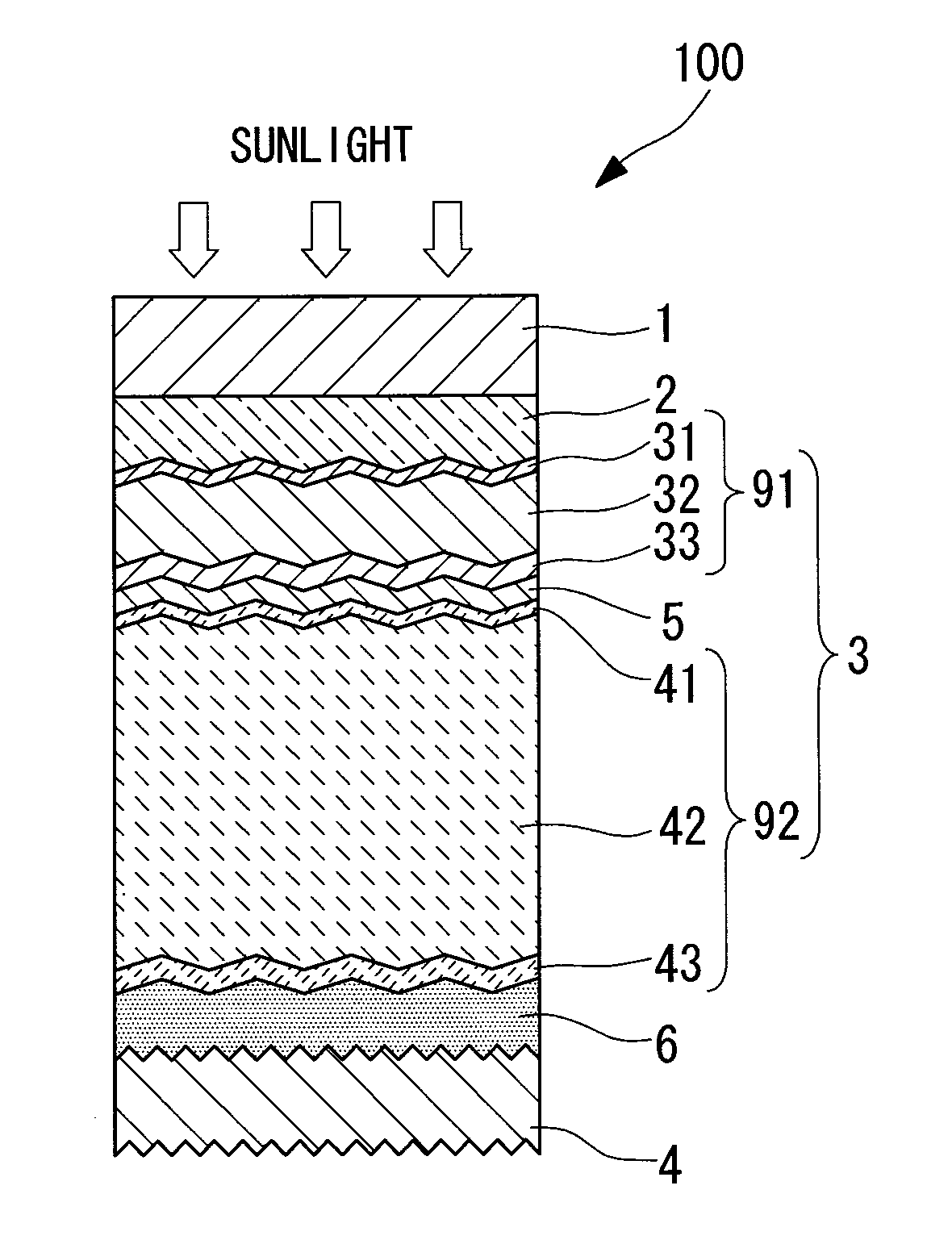
The short-circuit current of a photovoltaic device is improved by optimizing the transparent conductive layer. A photovoltaic device comprising a first transparent electrode layer, an electric power generation layer, a second transparent electrode layer and a back electrode layer on a substrate, wherein the film thickness of the second transparent electrode layer is not less than 80 nm and not more than 100 nm, and the light absorptance for the second transparent electrode layer in a wavelength region from not less than 600 nm to not more than 1,000 nm is not more than 1.5%. Also, a photovoltaic device wherein the film thickness of the second transparent electrode layer is not less than 80 nm and not more than 100 nm, and the reflectance for light reflected at the second transparent electrode layer and the back electrode layer is not less than 91% in the wavelength region from not less than 600 nm to not more than 1,000 nm.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Light emitting device and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20070145405A1Current spreading effect can be made moreImprove current spreading effectSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPeak valueLength wave
Disclosed is a light-emitting device (100) has a light-emitting layer portion (24) which is composed of a group III-V compound semiconductor and a transparent thick-film semiconductor layer (90) with a thickness of not less than 40 μm which is formed on at least one major surface side of the light-emitting layer portion (24) and composed of a group III-V compound semiconductor having a band gap energy larger than the photon energy equivalent of the peak wavelength of emission flux from the light-emitting layer portion (24). The transparent thick-film semiconductor layer (90) has a lateral surface portion (90S) which is a chemically etched surface. The dopant concentration of the transparent thick-film semiconductor layer (90) is not less than 5×1016 / cm3 and not more than 2×1018 / cm3. The light-emitting device can have a transparent thick-film semiconductor layer while being significantly improved in light taking-out efficiency from the lateral surface portion.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Organic electroluminescent element
InactiveCN1481657ASuppresses light absorptionElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesPhysicsOrganic electroluminescence
A self-light-emitting type organic electroluminescence device which makes it possible to restrain to the utmost the absorption of light in an electrode layer, to efficiently take out the light and thereby to obtain sufficient luminance efficiency and the like, in the case of emitting the light through the electrode layer. In an organic electroluminescence device comprising a light-emitting layer ( 3 ) comprised of an organic material based the light-emitting layer ( 3 ) being sandwiched between a first electrode ( 2 ) and a second electrode ( 4 ), and light emitted from the light-emitting layer ( 3 ) being taken out to at least one of the side of the first electrode ( 2 ) and the side of the second electrode ( 4 ), the light absorbance of the electrode or electrodes on the side of taking out the light, of the first electrode ( 2 ) and the second electrode ( 4 ), is not more than 10%.
Owner:SONY CORP
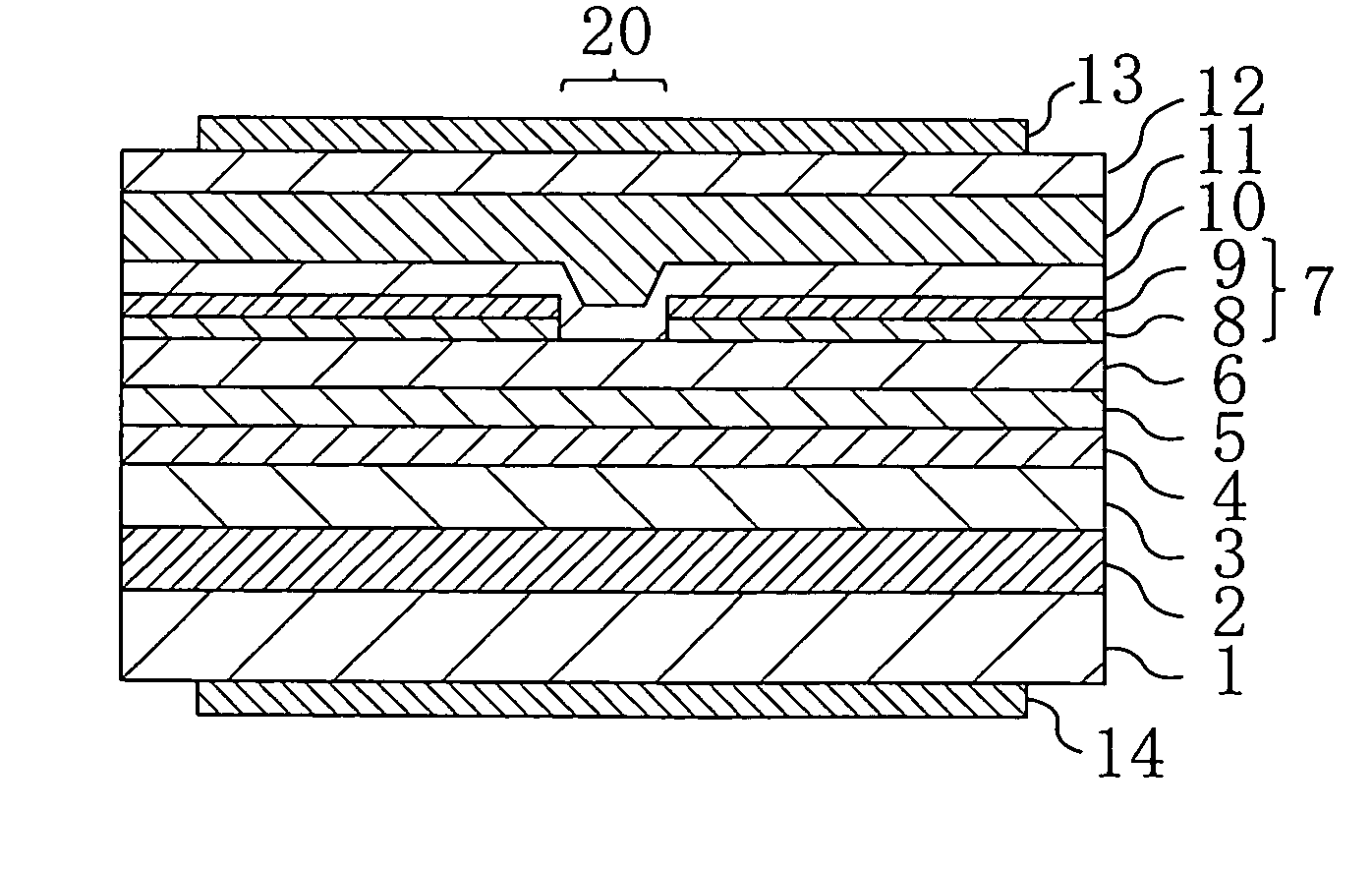
Method for manufacturing semiconductor light-emitting device
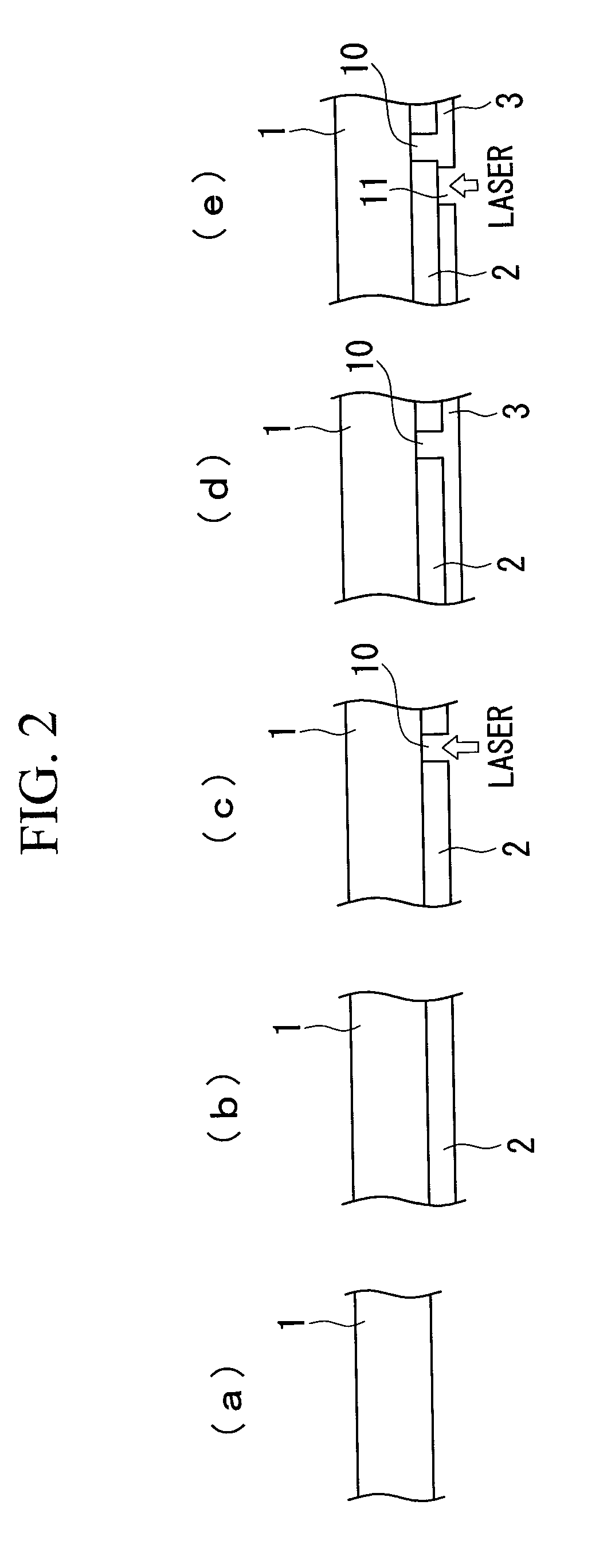
ActiveUS7871841B2Suppresses light absorptionImprove reliabilityOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsEngineeringLight emitting device
Owner:SONY CORP
Optical element, electro-optical device, and mounted display apparatus
ActiveUS9720236B2Suppress deterioration in emitted light intensitySuppresses light absorptionMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesGratingLight guide
An optical element includes a light guide is provided with a incidence section and a emission section, a semitransmissive reflective film is provided in the inside of the light guide, a first diffraction element is provided in the incidence section, and is provided with a plurality of gratings, a second diffraction element is provided in the emission section, and is provided with a plurality of gratings, and a reflective film is provided in the incidence section in a periphery of the first diffraction element, in which the pitch of the plurality of gratings of the first diffraction element is equivalent to the pitch of the plurality of gratings of the second diffraction element, and each extension direction of the plurality of gratings of the first diffraction element is the same direction as each extension direction of the plurality of gratings of the second diffraction element.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Thin film solar cells and preparation methods thereof
ActiveCN109713132AReduce lossesImprove energy conversion efficiencySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHole transport layerMetal electrodes
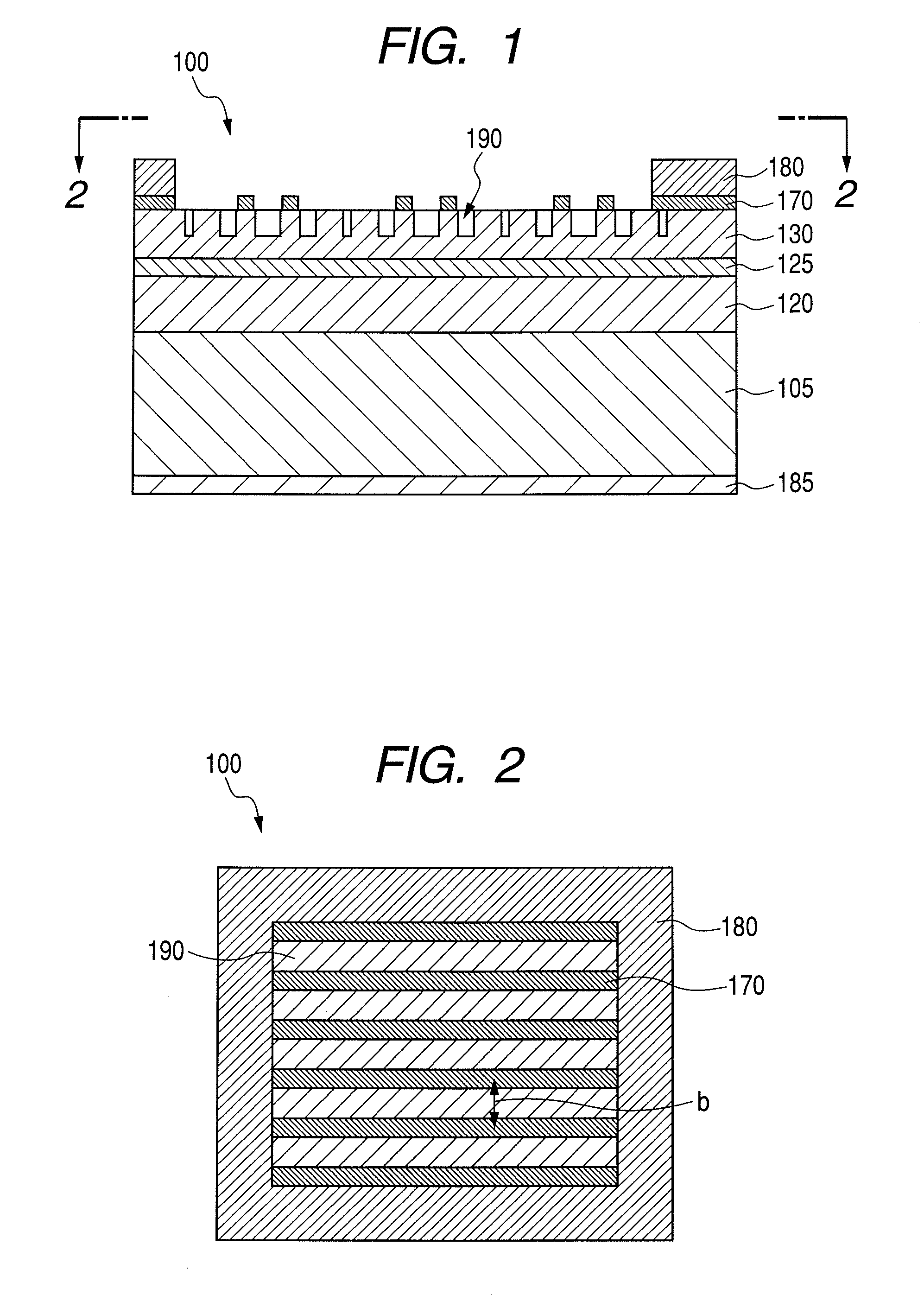
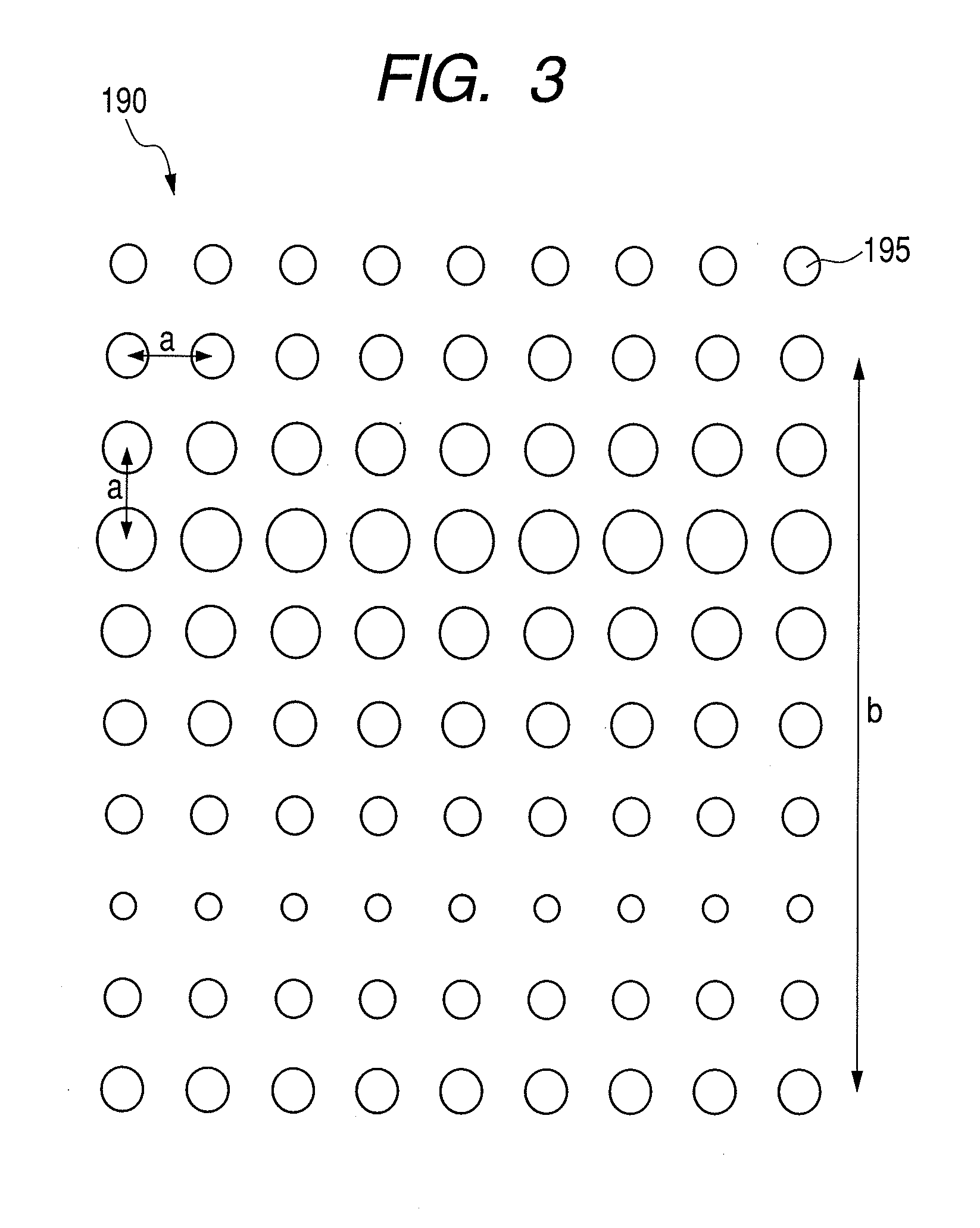
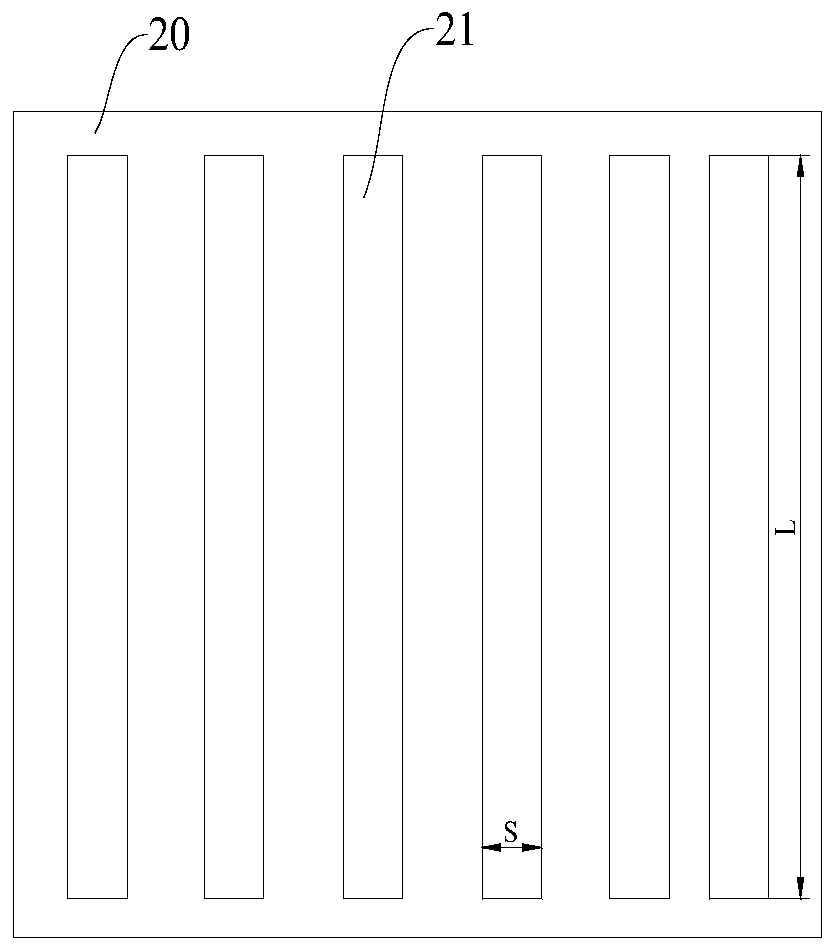
The invention provides thin film solar cells and preparation methods thereof. The thin film solar cell includes a transparent electrode, an electron transfer layer, a perovskite light absorbing layer,a hole transport layer, and a metal electrode which are sequentially are arranged in a laminated manner, wherein the transparent electrode is provided with multiple grooves disposed at intervals. Through arrangement of the grooves in the battery, light absorption of the transparent electrode can be inhibited, and at the same time, obvious resistive loss can not be produced, thereby being capableof improving the utilization rate of sunlight, and the energy conversion efficiency of the battery is improved.
Owner:WUXI UTMOST LIGHT TECH CO LTD
Oligoaniline compounds
InactiveUS8906519B2Suppresses light absorptionLight absorptionOrganic compound preparationElectroluminescent light sourcesHalogenHydrogen atom
Owner:NISSAN CHEM IND LTD
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20200287076A1Improve characteristicOperating voltage decreaseSemiconductor devicesPhysicsElectrically conductive
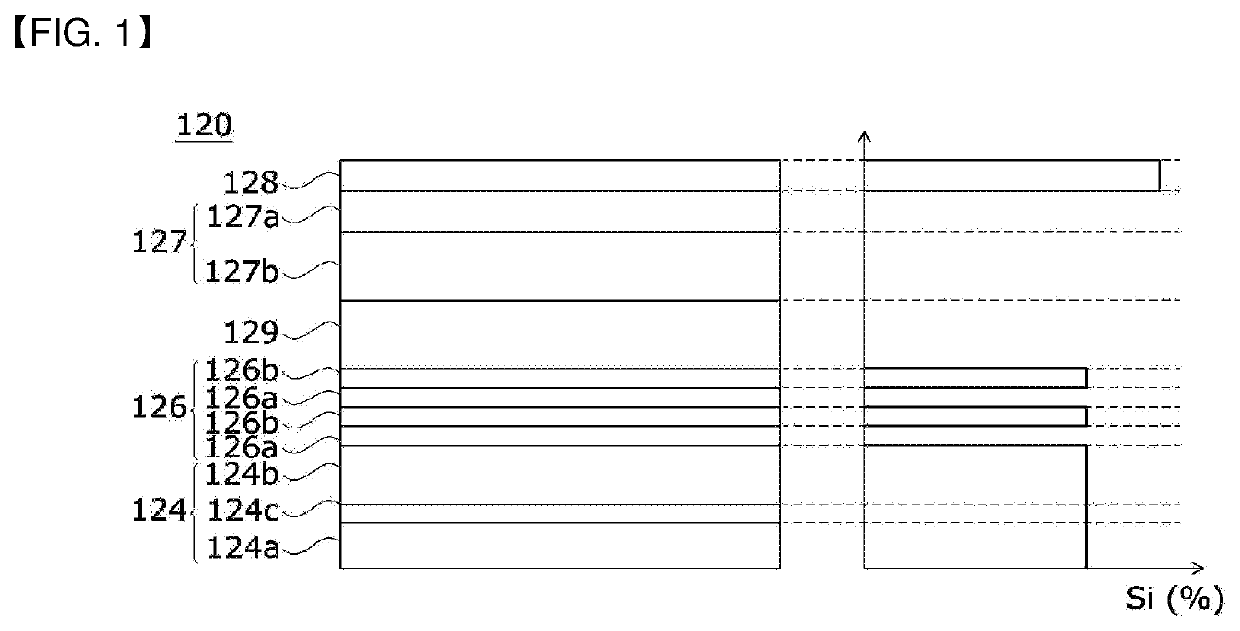
Disclosed according to an embodiment is a semiconductor device comprising: a semiconductor structure including a first conductive semiconductor layer, a second conductive semiconductor layer, and an active layer disposed between the first conductive semiconductor layer and the second conductive semiconductor layer; a first electrode electrically connected to the first conductive semiconductor layer; and a second electrode electrically connected to the second conductive semiconductor layer, wherein the semiconductor structure includes a third conductive semiconductor layer disposed between the second conductive semiconductor layer and the second electrode, the first conductive semiconductor layer includes a first dopant, the second conductive semiconductor layer includes a second dopant, the third conductive semiconductor layer includes the first dopant and the second dopant, and the concentration ratio between the first dopant and the second dopant included in the third conductive semiconductor layer ranges from 0.01:1.0 to 0.8:1.0.
Owner:SUZHOU LEKIN SEMICON CO LTD
Organic EL display device
ActiveUS8237353B2Increase brightnessSuppress shadowsDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com