Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38results about How to "Reduce current load" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
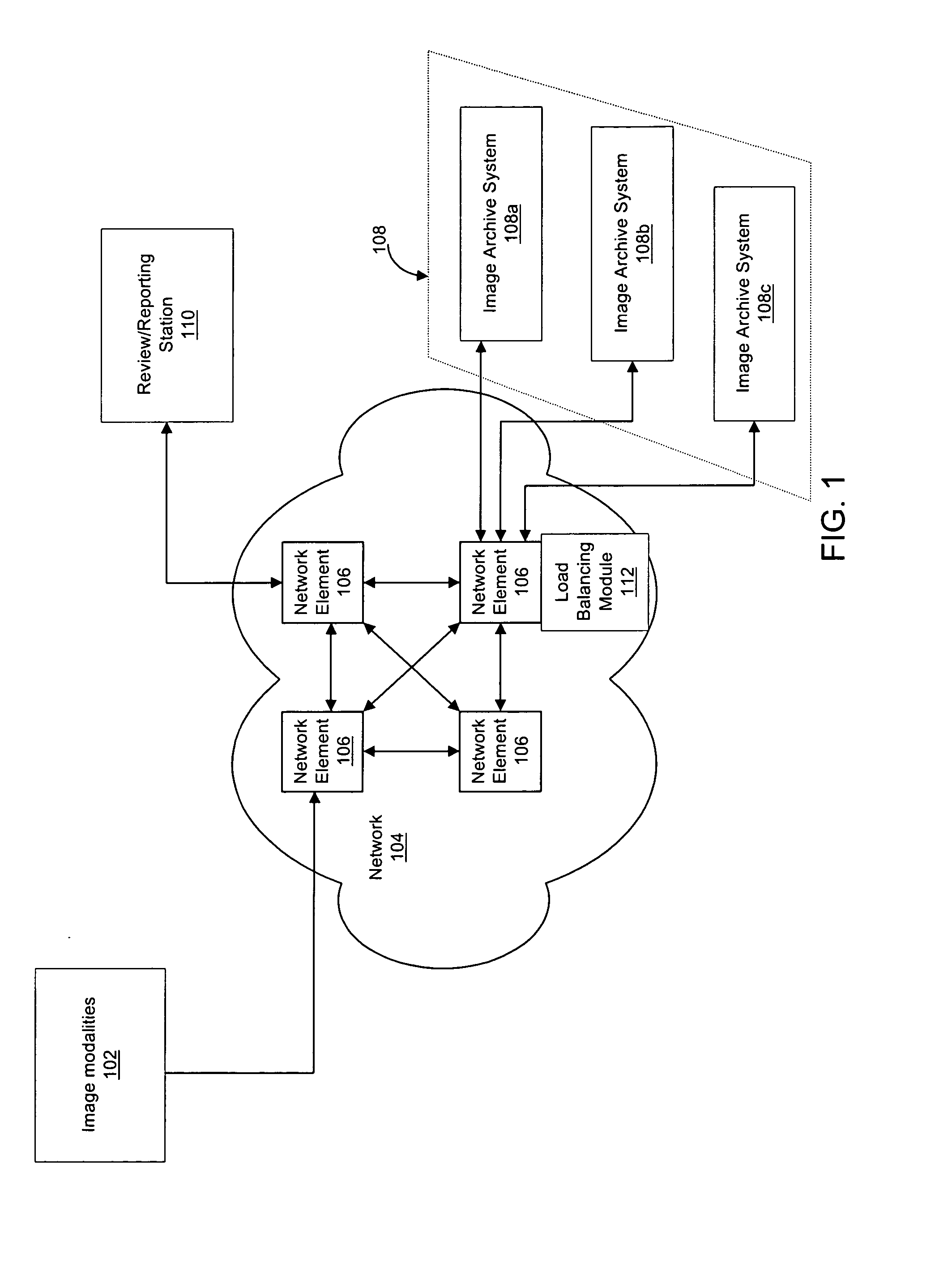
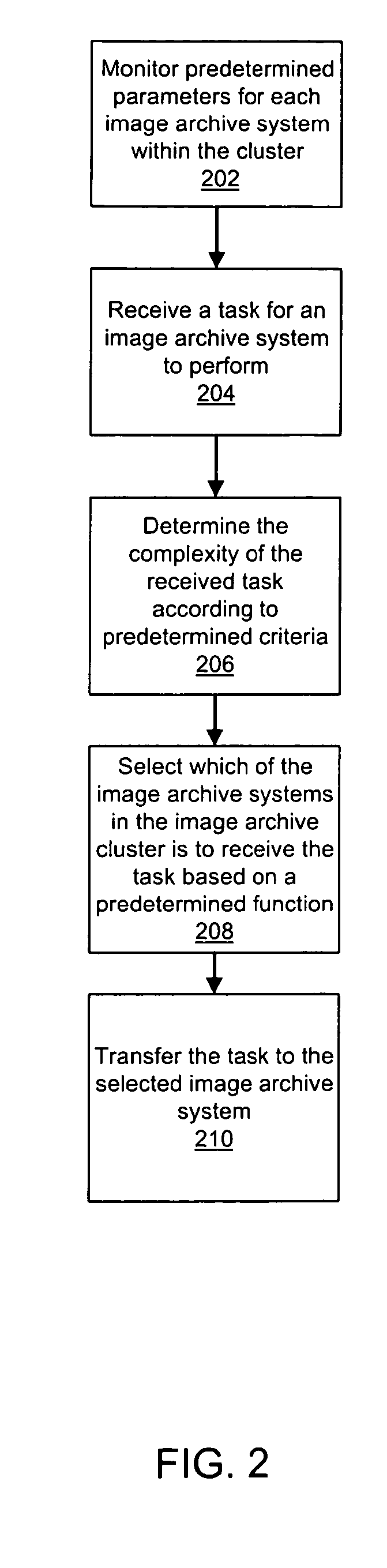
Method and apparatus for providing network based load balancing of medical image data
ActiveUS20050213832A1Reduce current loadIncrease usable capacityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsData processing applicationsLoad SheddingCurrent load
A method and apparatus for providing network based load balancing of medical image data among two or more image archive systems is disclosed. A network element is employed to interface to a network carrying medical image data that may include tasks to be performed on the data. A network service associated with the network element monitors the current load or the available capacity of each of the image archive systems. When a task is received the network service determines the level of complexity of the task and compares the level of complexity to the current load or available capacity of each of the image archive systems. The network service selects the one of the image archive systems to perform the task that has the lowest current load or highest available capacity relative to the level of complexity of the received task.
Owner:AVAYA INC
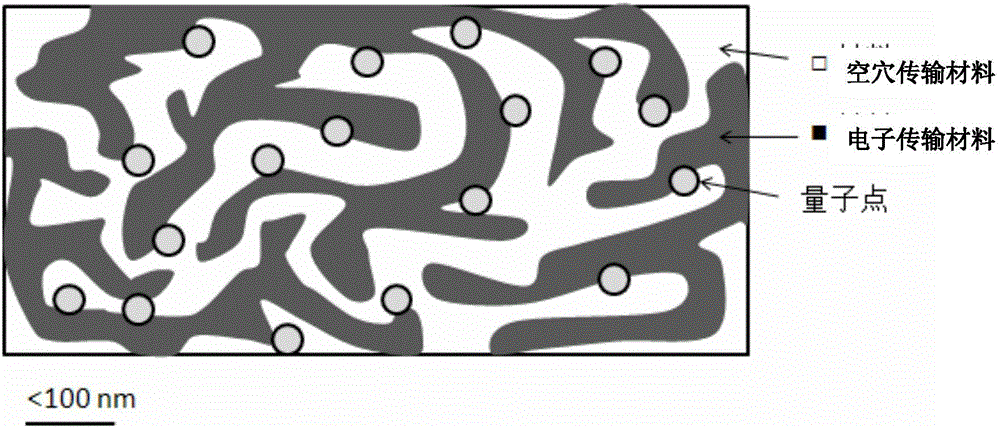
QLED and fabrication method thereof
ActiveCN106328822AImprove luminous efficiencyExtend your lifeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHole injection layerNetwork structure
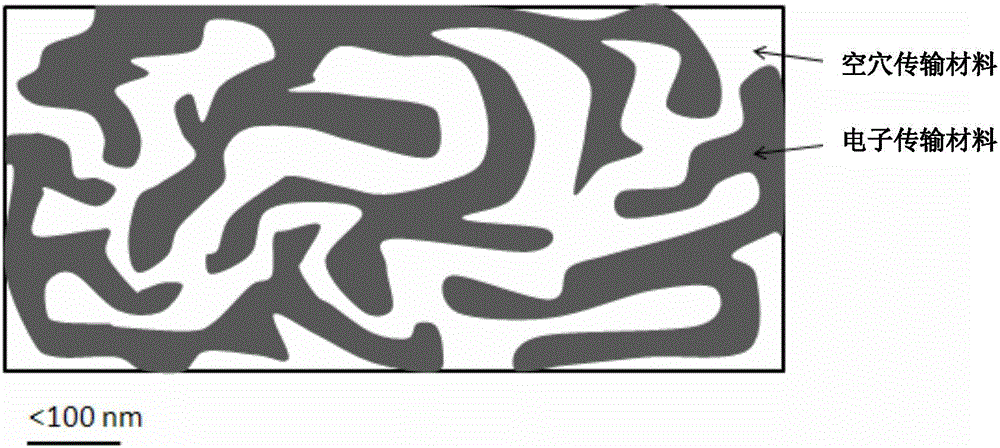
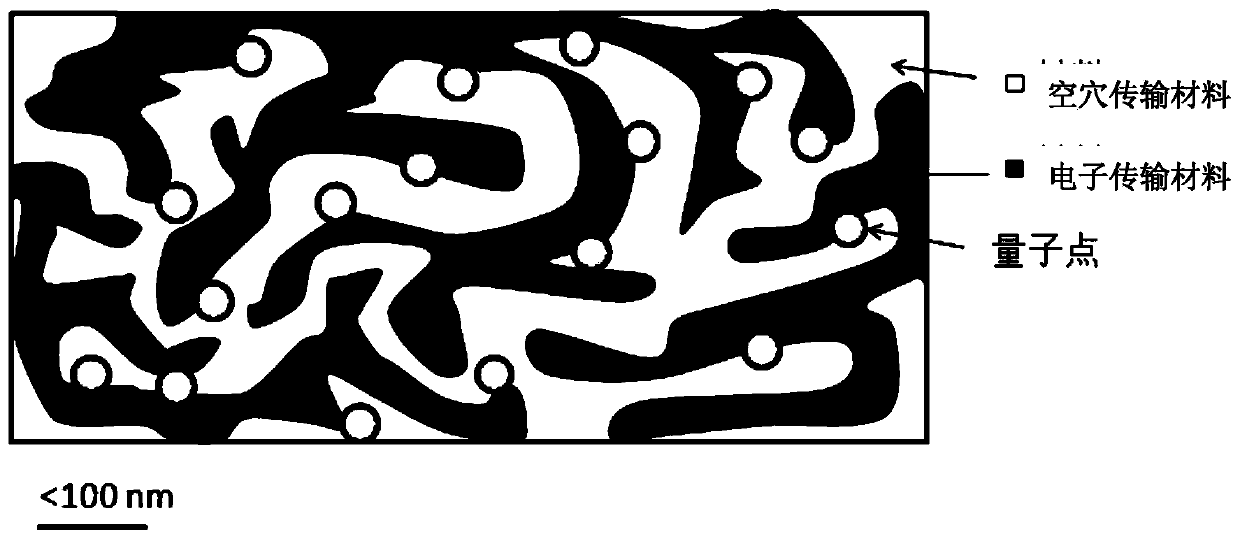
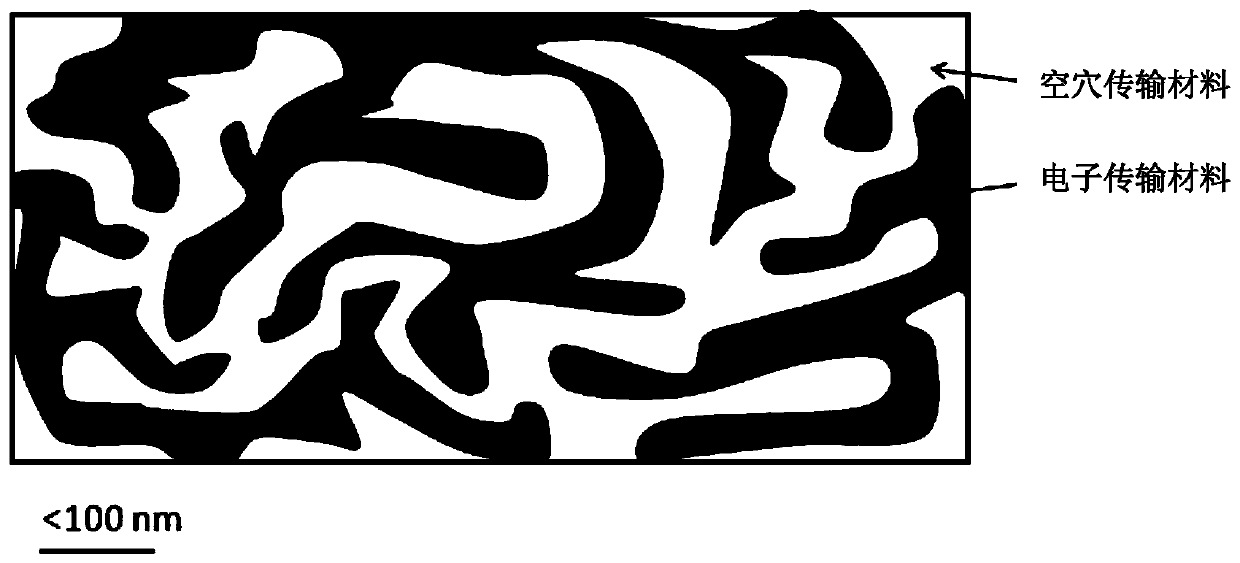
The invention provides a QLED, which comprises, in sequence, the first electrode, hole injection layer, hole transport layer, emitting layer, electron transport layer and the second electrode. The emitting layer comprises quantum dots luminescent materials and mixed transport materials. The mixed transport materials comprise hole transport material and electron transport material. The hole transport material and electron transport material form double continuous network structure in the emitting layer, with the quantum dots luminescent materials scattered in the double continuous network structure.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
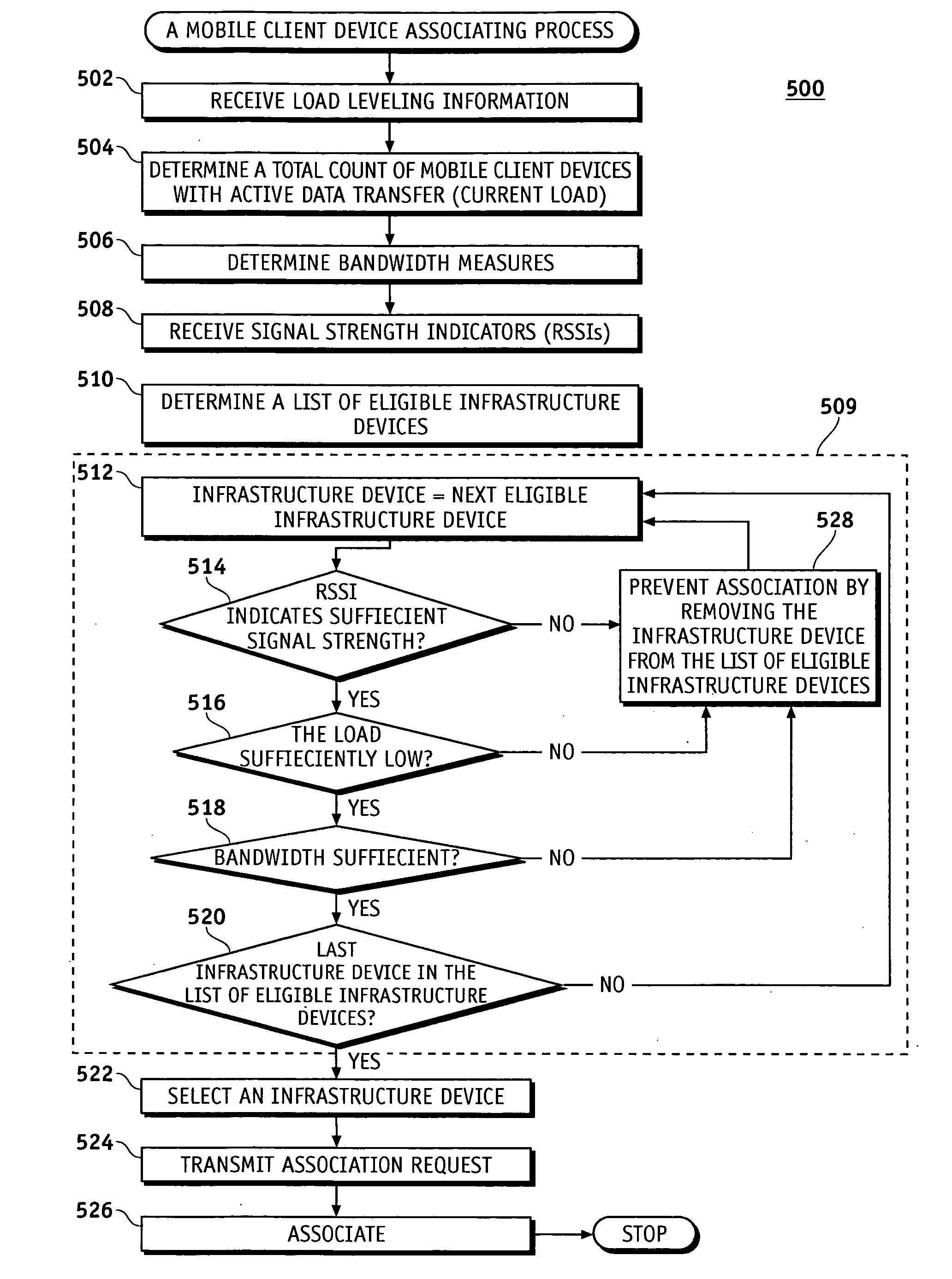
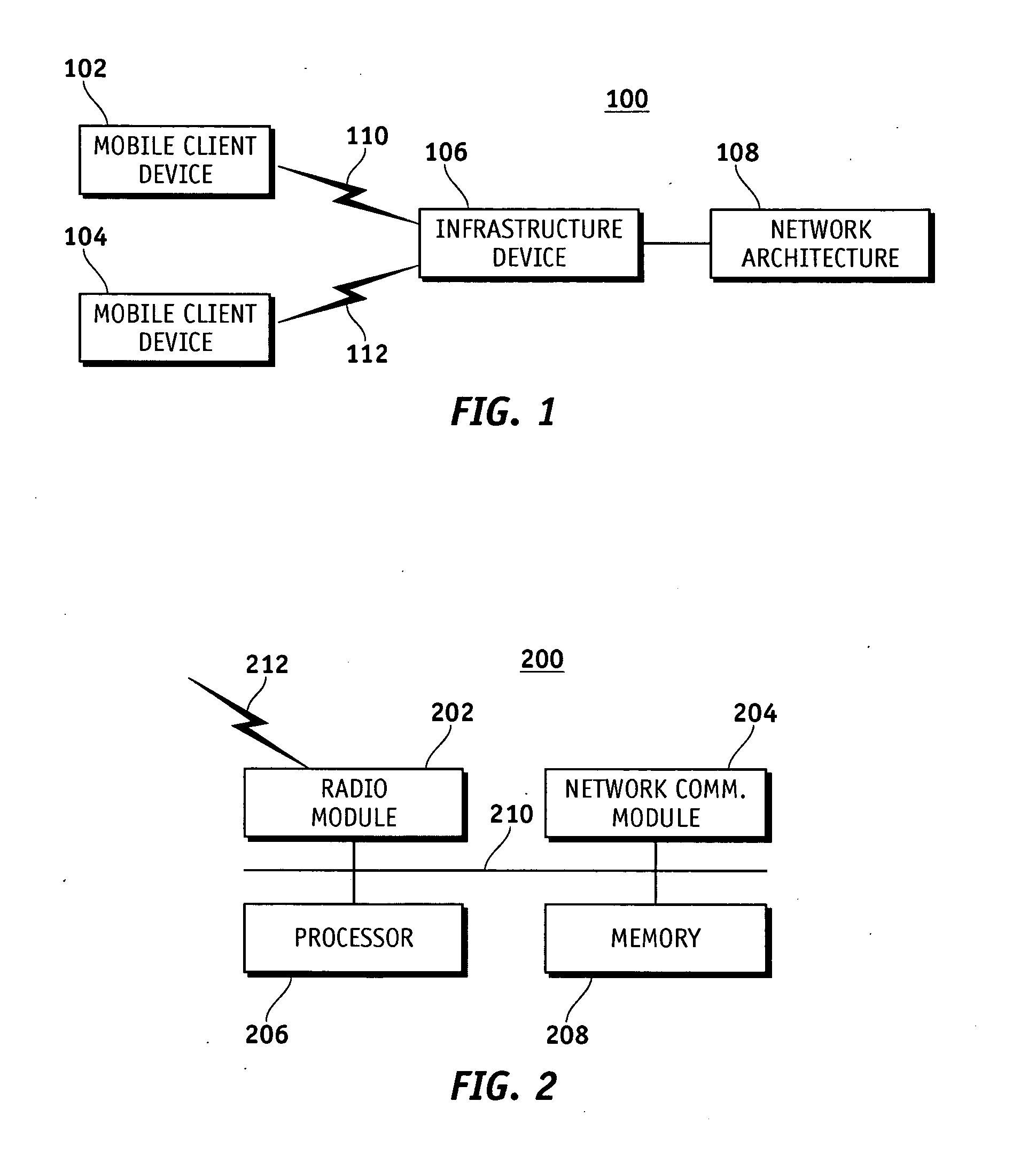
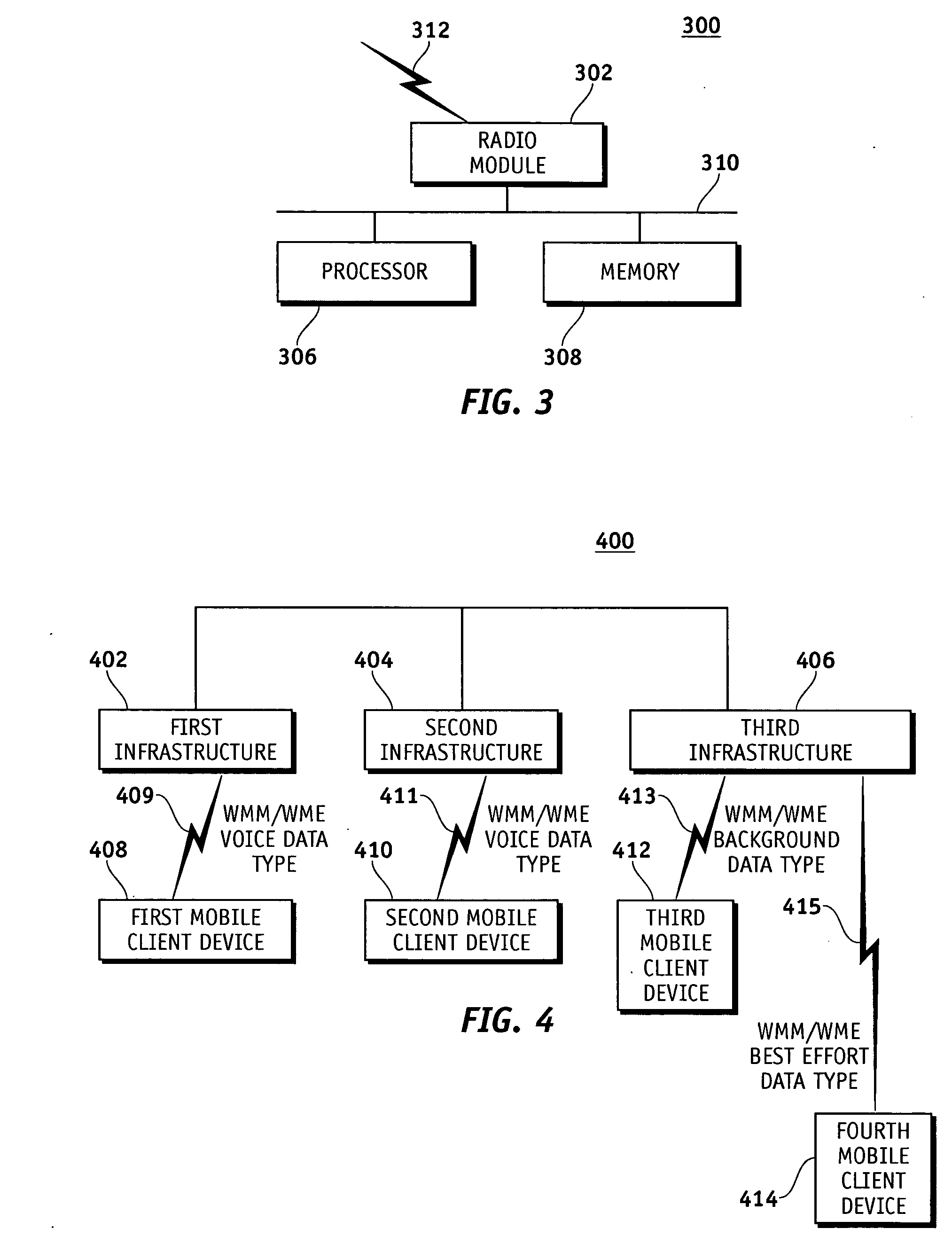
Media type access category based load leveling for a wireless network
InactiveUS20080002641A1Sufficient unutilized bandwidthSolve insufficient bandwidthNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionMedia typeClient-side
A method for automatically determining the amount of currently utilized bandwidth on infrastructure devices such as wireless access points in a wireless network is disclosed. The method begins by a mobile client device receiving load leveling information from infrastructure devices corresponding to media type access categories. Based upon the load leveling information, the amount of currently utilized bandwidth by media type access categories on the infrastructure devices is determined and an infrastructure device with bandwidth sufficient to support at least one of the media type access categories intended for use by the mobile client device is selected.
Owner:SYMBOL TECH INC
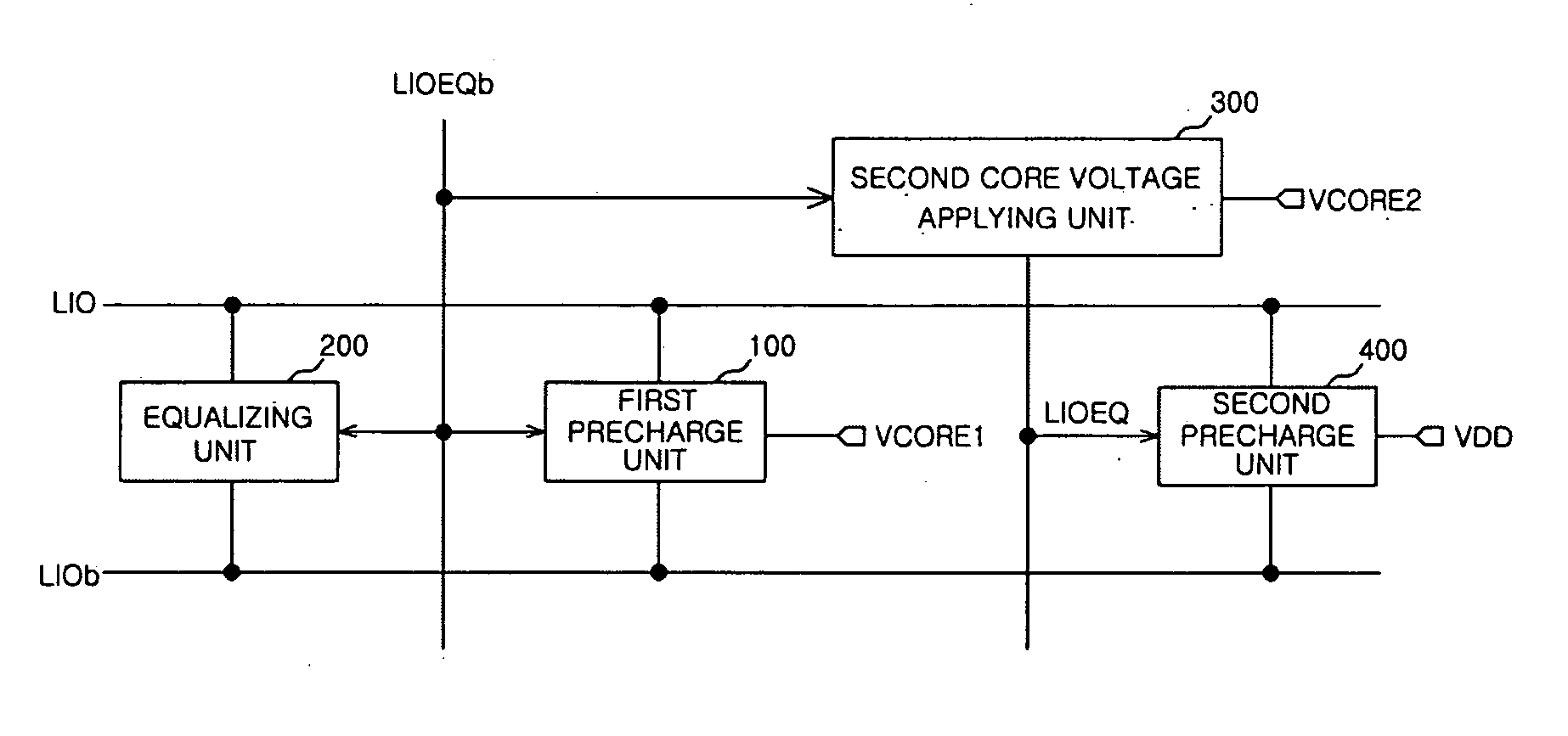
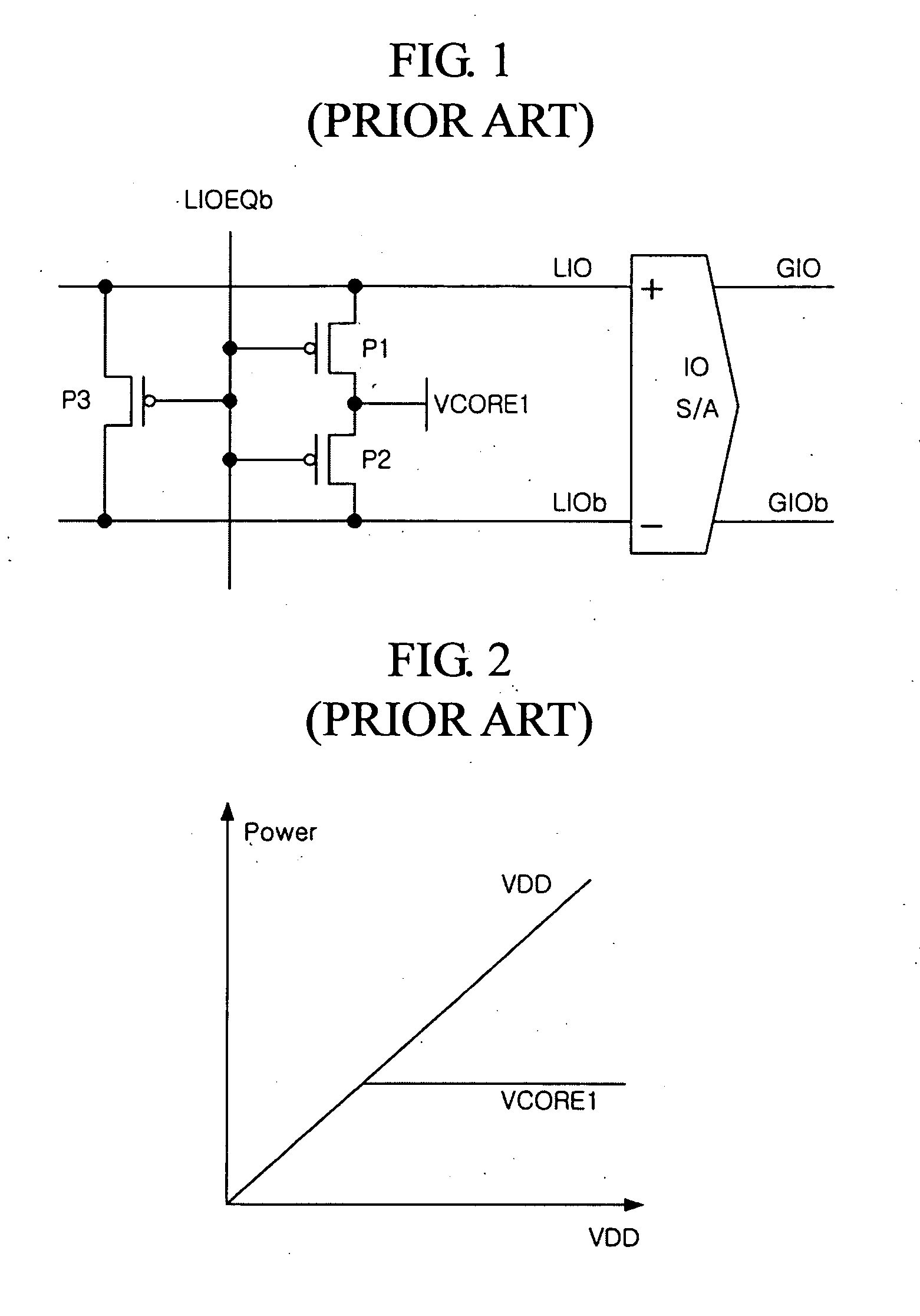
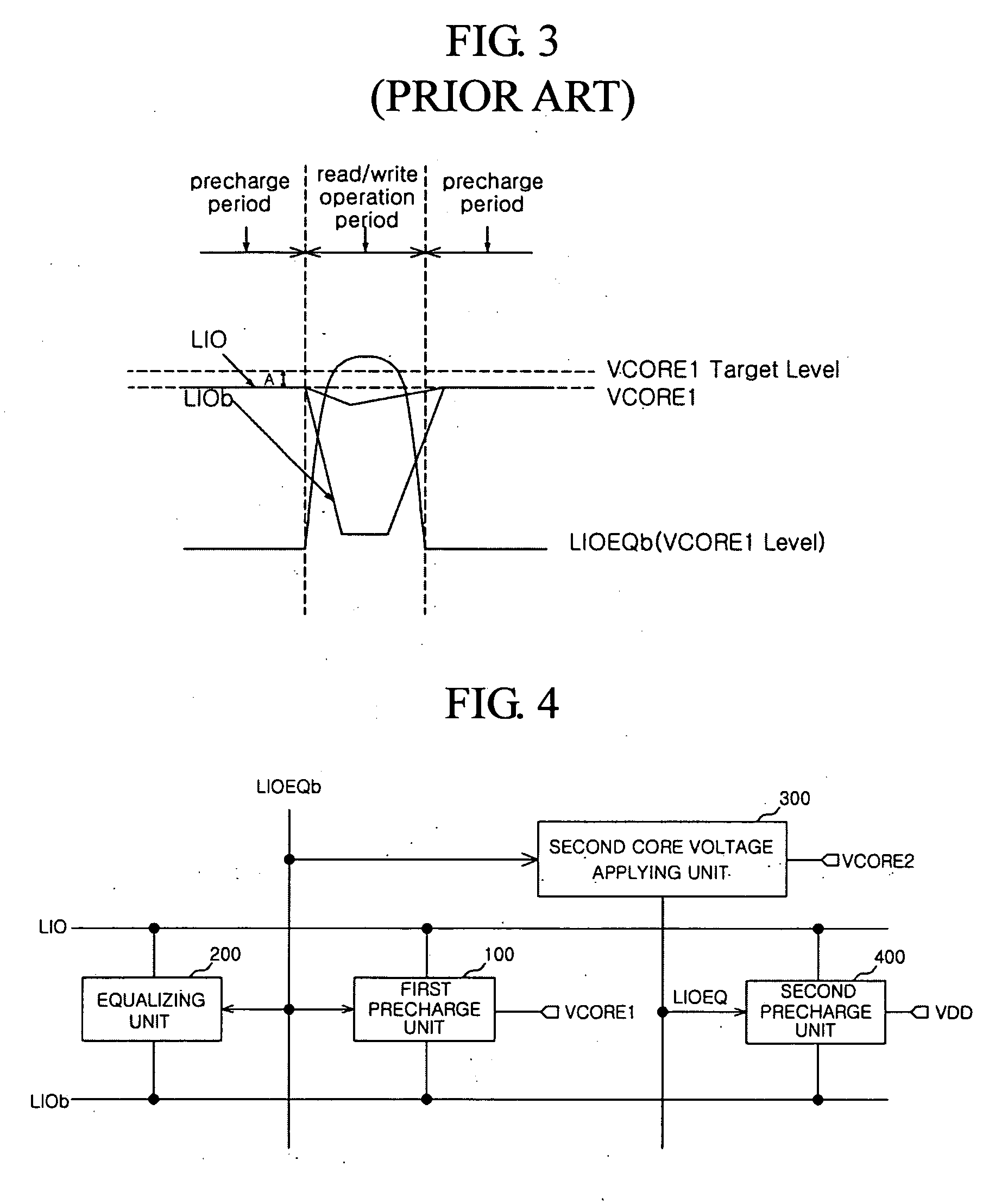
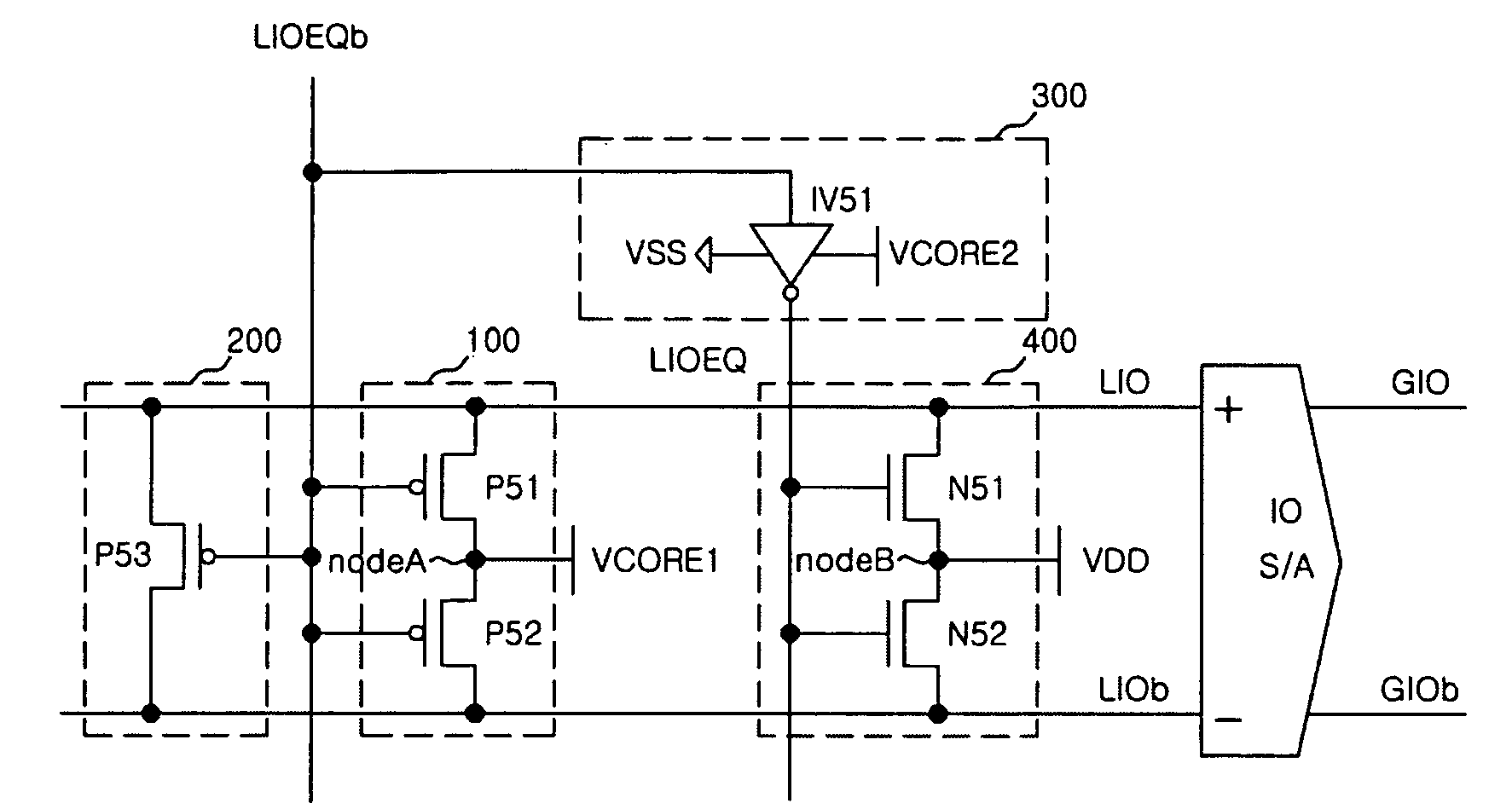
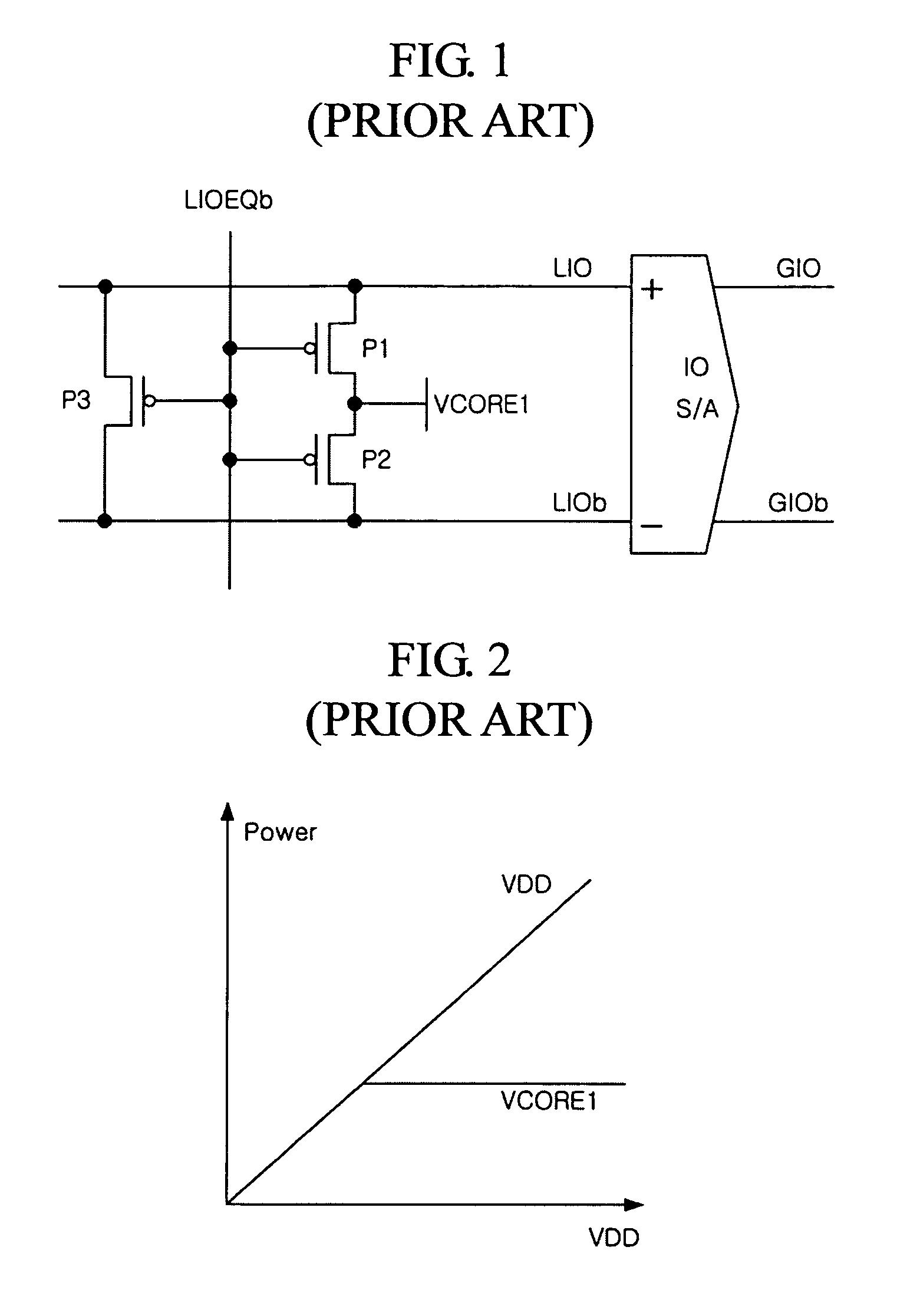
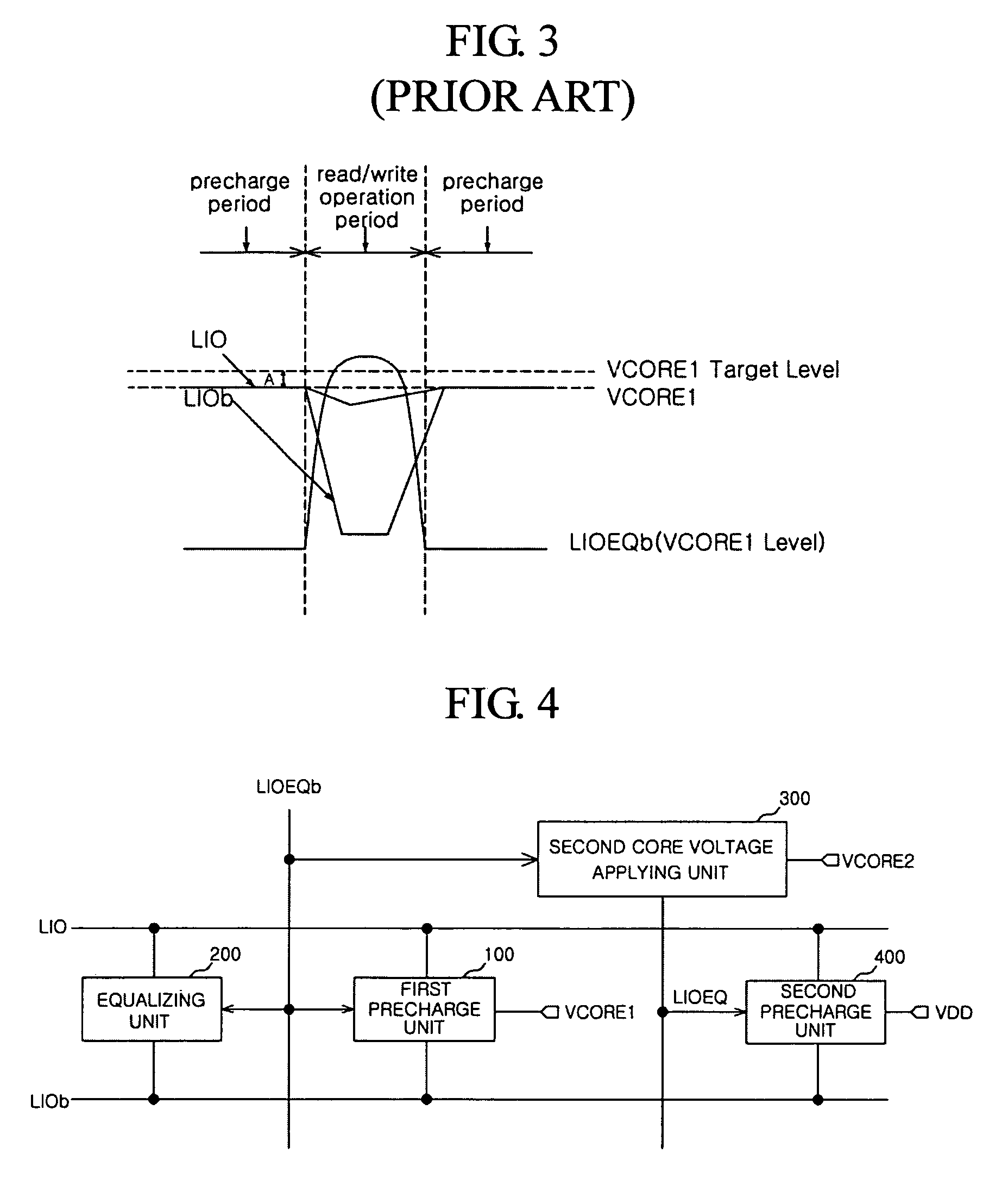
Precharge circuit of semiconductor memory apparatus
Disclosed is a precharge circuit of a semiconductor apparatus. The precharge circuit of a semiconductor memory apparatus includes a first precharge unit and a second precharge unit. The first precharge unit applies a first core voltage to a pair of local input / output lines, in response to a first precharge signal, to precharge the pair of local input / output lines. The second precharge unit applies a clamp voltage, which is generated using a first supply voltage, to the pair of local input / output lines, in response to the first precharge signal, to precharge the pair of local input / output lines.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Floating type wind power generation platform
InactiveCN111891308AIncrease heightRealize positive floating stateWaterborne vesselsWind energy generationMarine engineeringBallast tank
The invention provides a floating type wind power generation platform. The floating type wind power generation platform comprises a floating type foundation and a fan unit. The floating foundation comprises three buoyancy units, three truss units and a fan base arranged on one or two of the buoyancy units. Each buoyancy unit comprises a stand column and a swash deep cabin fixed to the bottom of the stand column. Ballast tanks are arranged in the stand column and the swash deep tank; the section size of the top of the stand column is larger than that of the bottom of the stand column, and any first position and any second position located above the first position in the height direction of the stand column meet the conditions that the section size of the stand column at the second positionis larger than or equal to that of the first position; the swash deep cabin is used as a vertical damping structure; the section size of the swash deep cabin is larger than that of the stand column. The draught fan unit is installed on the draught fan base, and the height of the swash deep cabin of the buoyancy unit where the draught fan unit is located is larger than that of the swash deep cabinof the buoyancy unit where the draught fan unit is not arranged. The wind power generation device has good movement performance, and the power generation efficiency is improved.
Owner:YANTAI RAFFLES SHIPYARD +3
Precharge circuit of semiconductor memory apparatus
InactiveUS7539064B2Reduce current loadRead-only memoriesDigital storageSemiconductorElectrical and Electronics engineering
A precharge circuit of a semiconductor memory apparatus includes a first precharge unit and a second precharge unit. The first precharge unit applies a first core voltage to a pair of local input / output lines, in response to a first precharge signal, to precharge the pair of local input / output lines. The second precharge unit applies a clamp voltage, which is generated using a first supply voltage, to the pair of local input / output lines, in response to the first precharge signal, to precharge the pair of local input / output lines.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
System for and method of edge welding using projections
InactiveCN101396761AReduce current loadReduce energy consumptionResistance welding apparatusElectrical resistance and conductanceCurrent load
A method of edge welding a plurality of workpieces particularly useful for minimizing edge deformation and reducing the electrode size, flange size, welding force and current load necessary to produce a given weld, including the steps of forming at least one distending projection along the edge of a first workpiece, securing the projection against a second workpiece and applying a force and current load to the projection so as to fuse a portion of the projection, and a system for performing the method, including a dedicated projection forming fixture, a resistance welding apparatus preferablyhaving specialized electrodes and a controller communicatively coupled to the fixture and apparatus.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
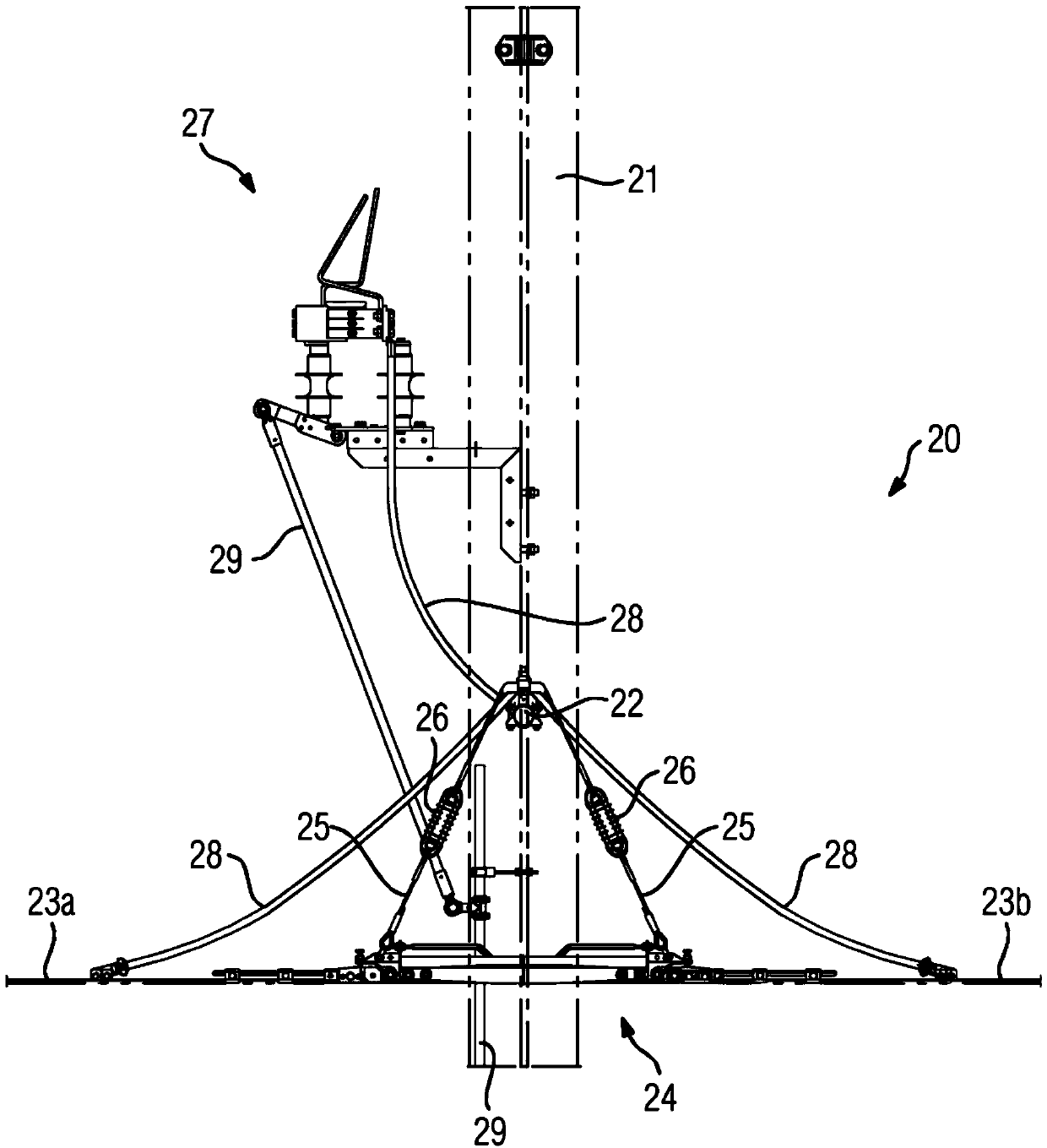
System for operating an electric tractive unit
InactiveCN103857556AReliable transmissionSmall structure sizeElectric devicesPropulsion using ac induction motorsElectricityUnit system
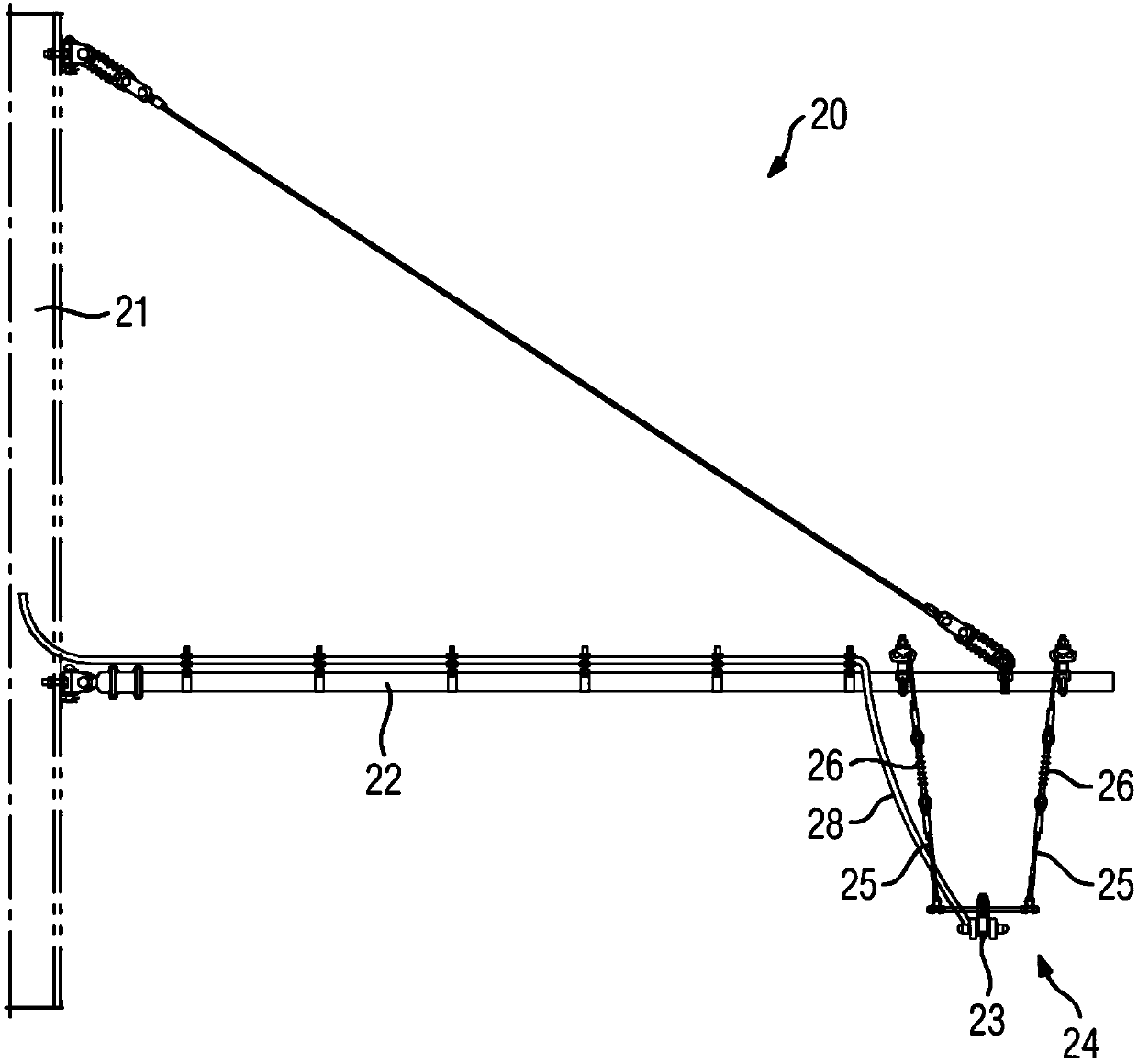
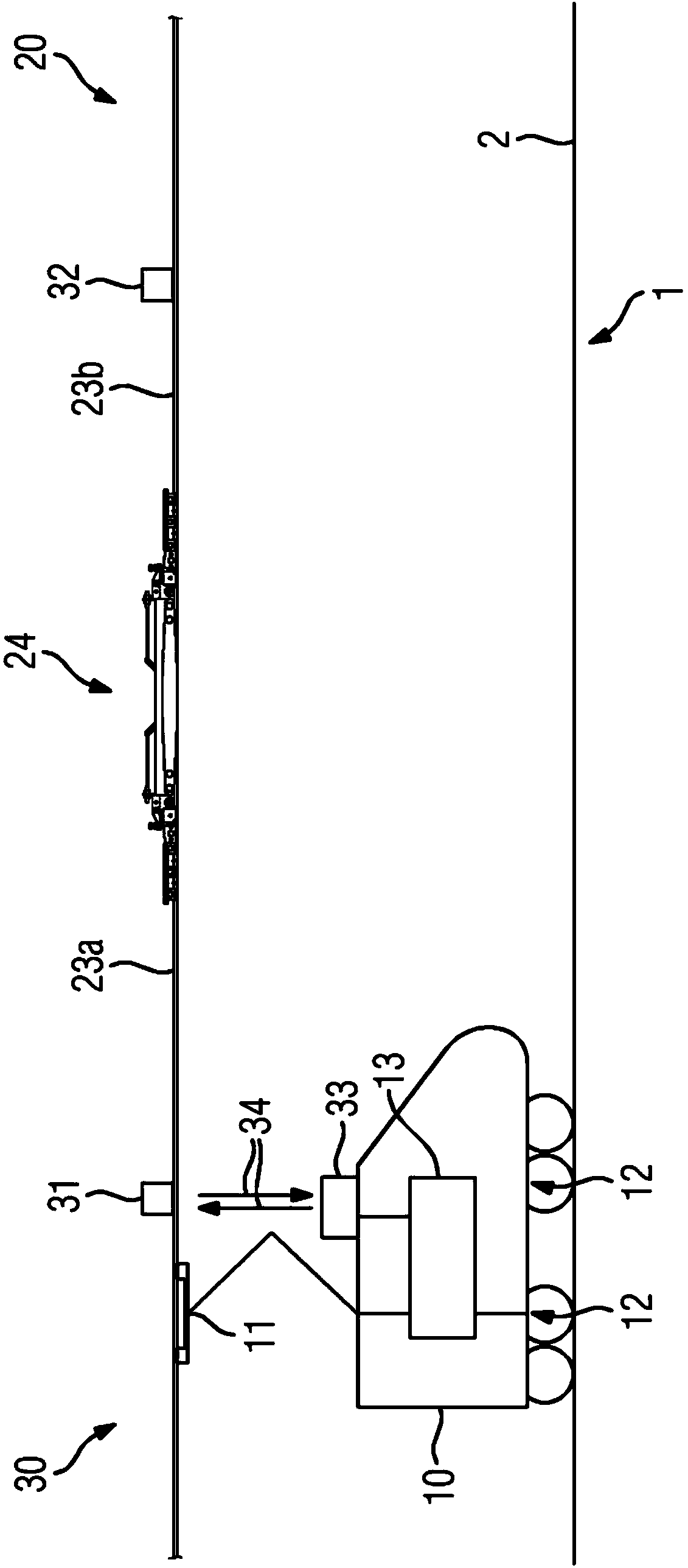
System for operating an electric tractive unit. The invention relates to a system (1) for operating an electric tractive unit (10), having a contact line system (20) which is arranged along a route (2) of the tractive unit (10). In this context, a current collector (11) of the tractive unit (10) for transmitting energy can be placed in sliding contact with a contact line (23) of the contact line system (20). In addition, the contact line (23) is divided by a section insulator (24), along which the current collector (11) can travel with sliding contact, into contact line sections (23a, 23b) which are supplied with electricity separately from one another. According to the invention, a detection device (30) is designed to detect when travel over the section insulator (24) by tractive unit (10) is imminent. Said detection device (30) interacts with a drive controller (13) for an electric drive (12) of the tractive unit (10) in such a way that transmission of energy via the current collector (11) while the section insulator (24) is being travelled over is automatically reduced or switched off. As a result, the wear on section insulators (24) can be reduced.
Owner:SIEMENS MOBILITY GMBH
Circuit arrangement for operating a low-pressure gas discharge lamp and corresponding method
InactiveCN101888735ALow costReduce voltageElectrical apparatusElectric lighting sourcesPower inverterGas-discharge lamp
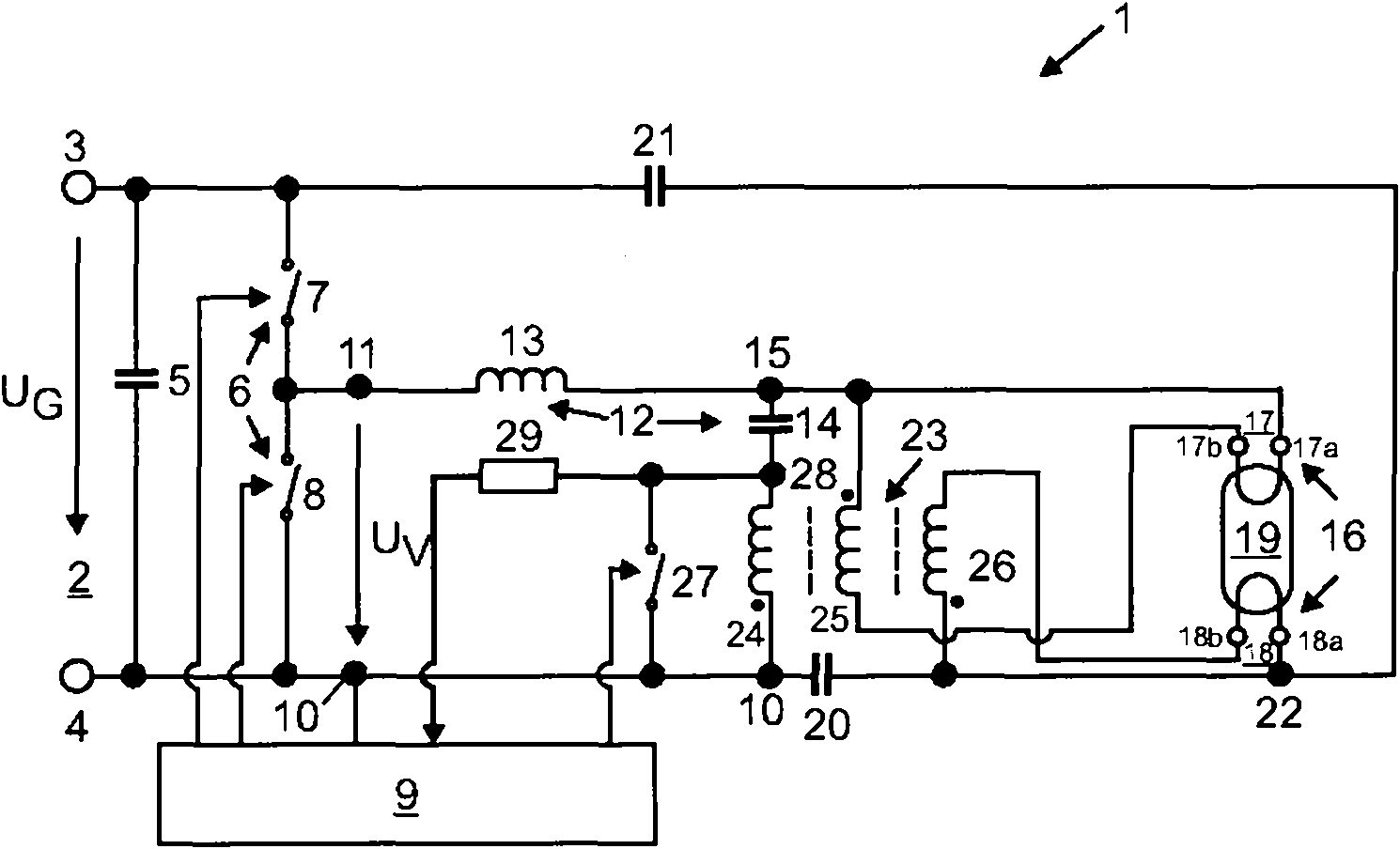
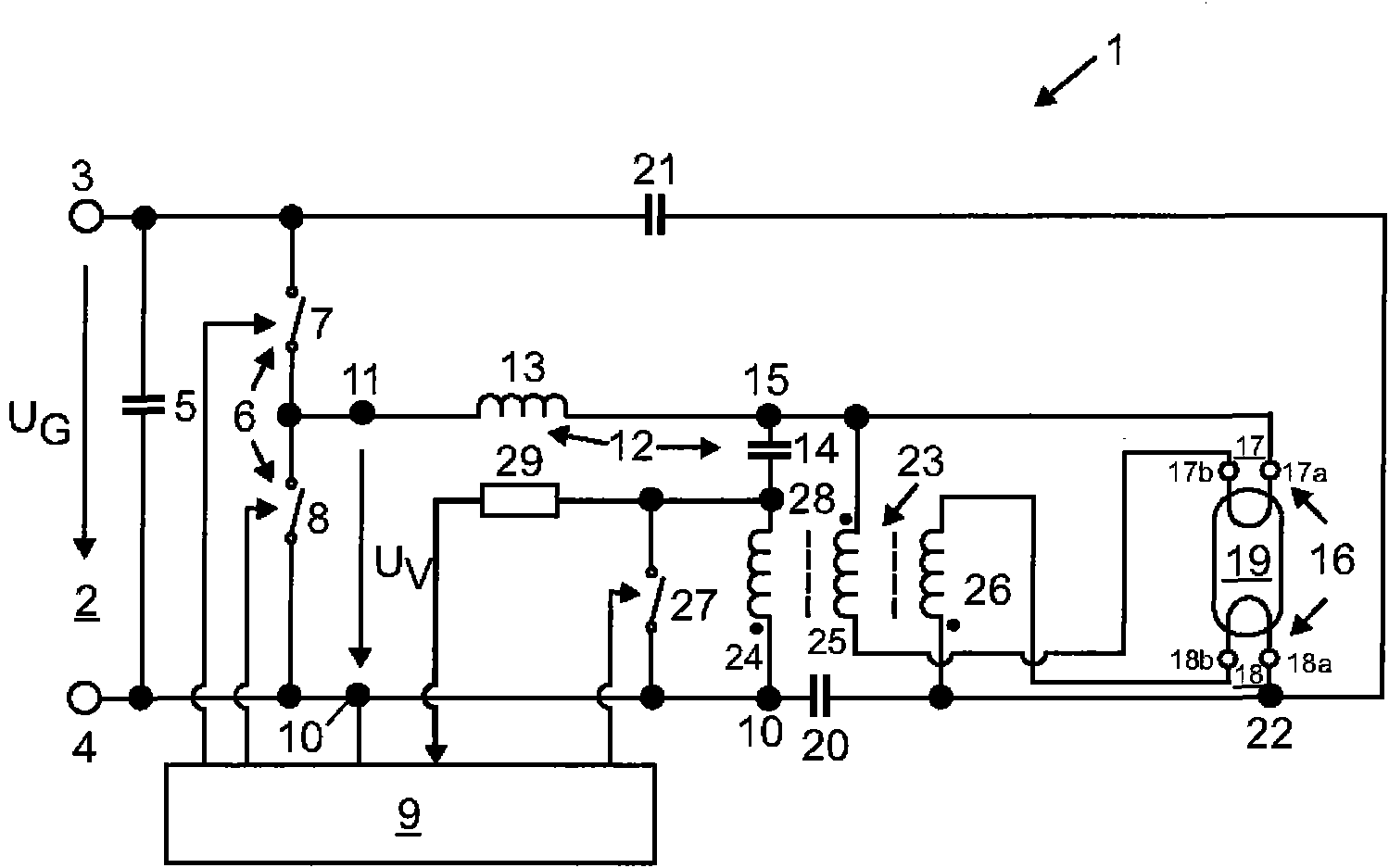
A circuit arrangement is provided, which may include an inverter, configured to provide an AC supply voltage from a DC supply voltage; a control device configured to drive the inverter, the control device being configured to initiate a preheating phase once a preheating criterion has been met; a resonant circuit having a resonant inductor and having a resonant capacitor; and a transformer configured to preheat electrodes of a gas discharge lamp; wherein the primary winding of the transformer is connected in series with the resonant capacitor and is connected directly to the reference potential of the control device, and an electrical switch is coupled in parallel with the primary winding of the transformer, which switch has a control connection, which is coupled to the control device being configured to transfer the electrical switch into its electrically conducting switching state once the starting criterion has been met.
Owner:OSRAM GMBH
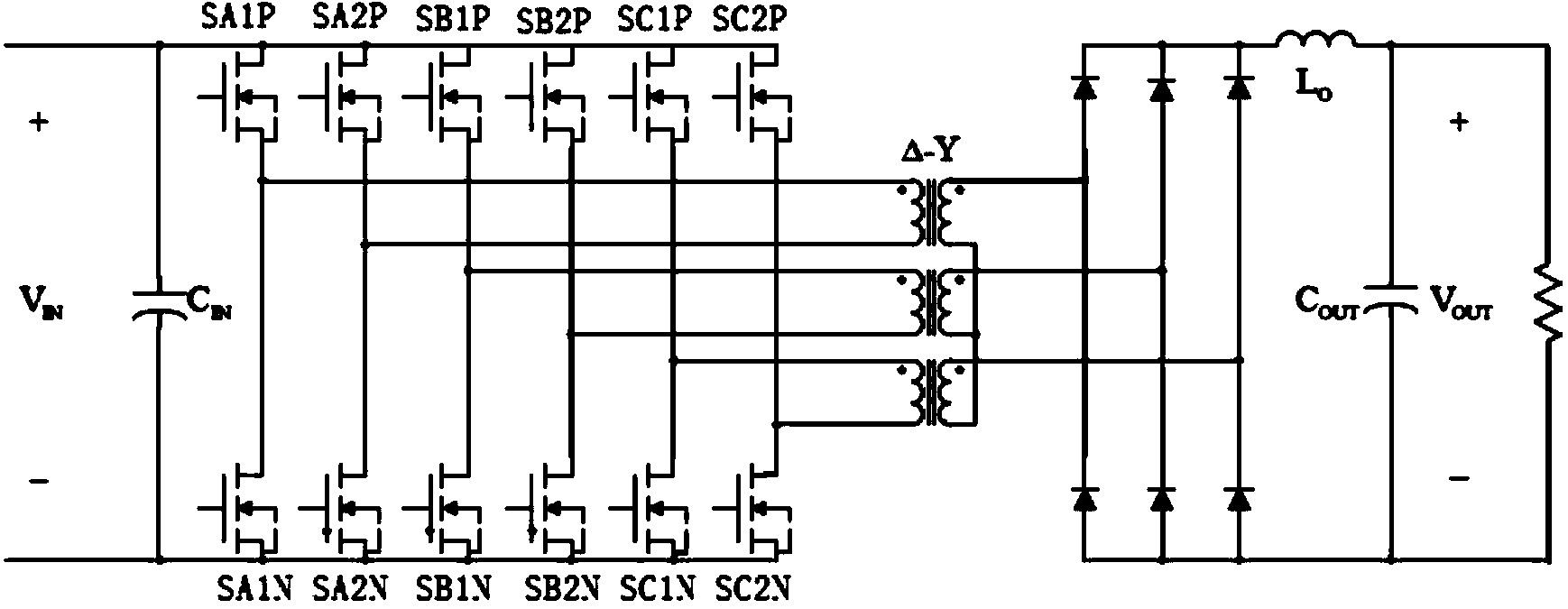
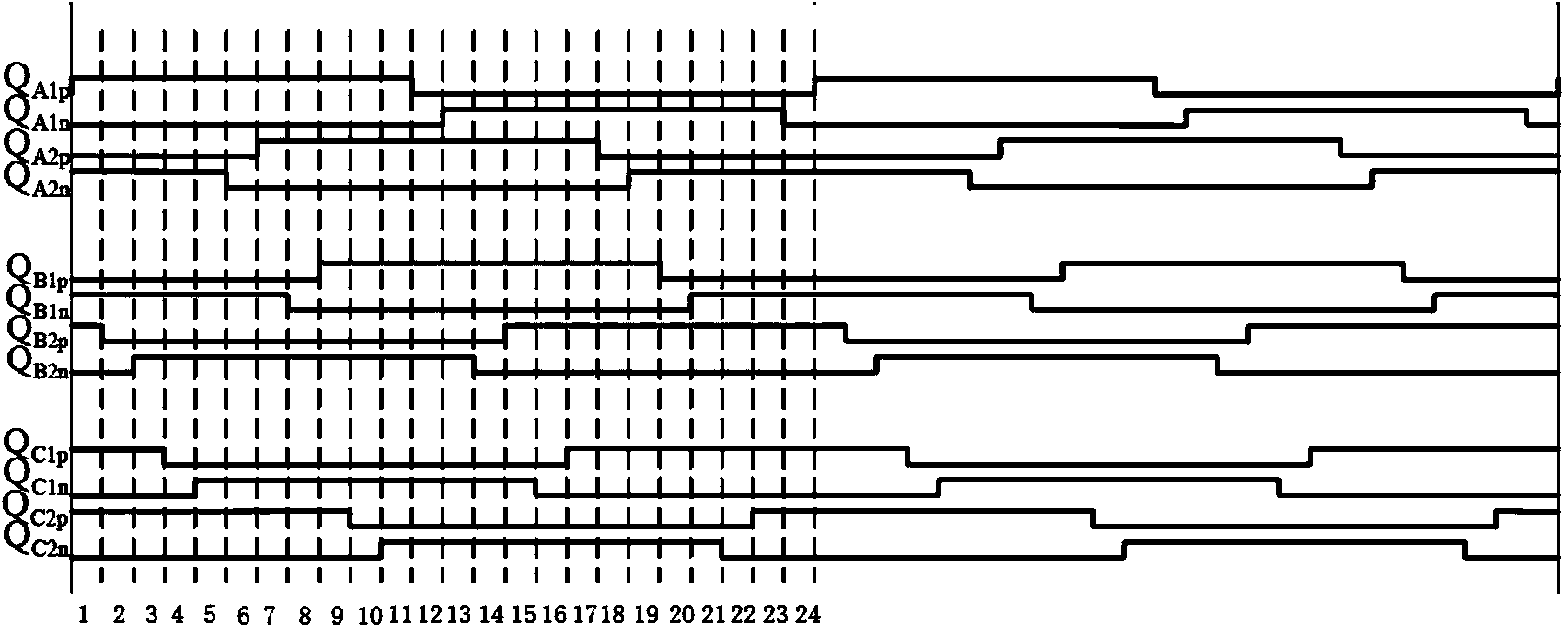
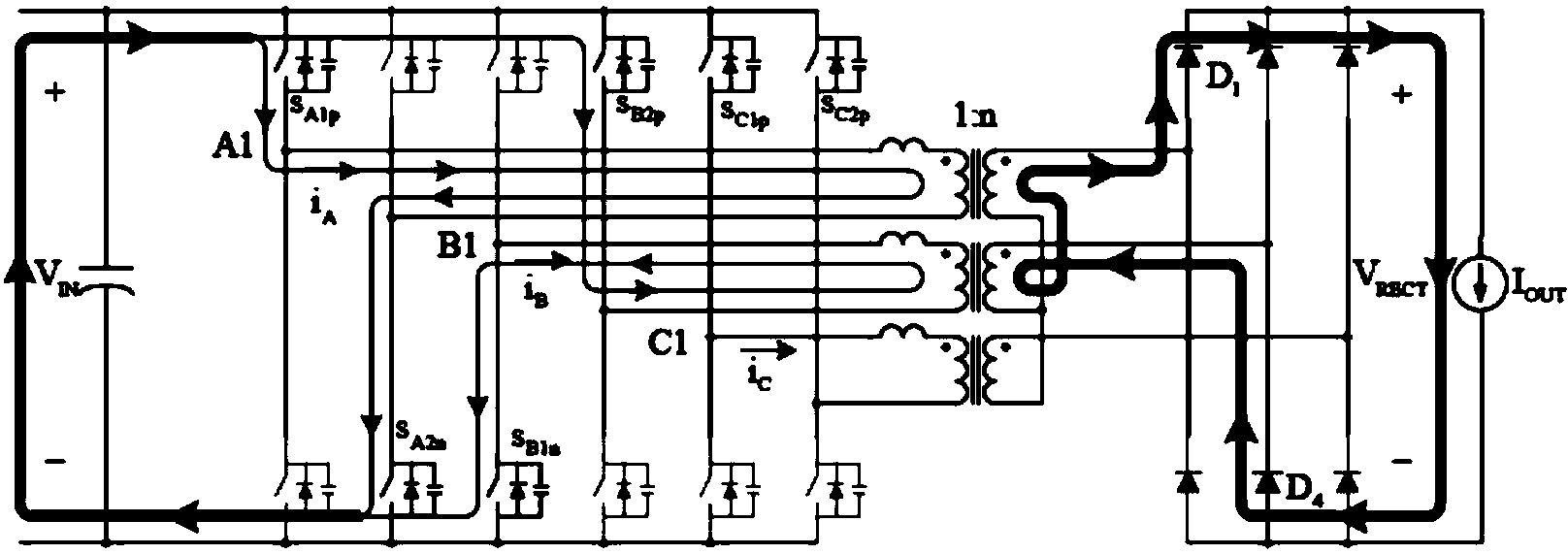
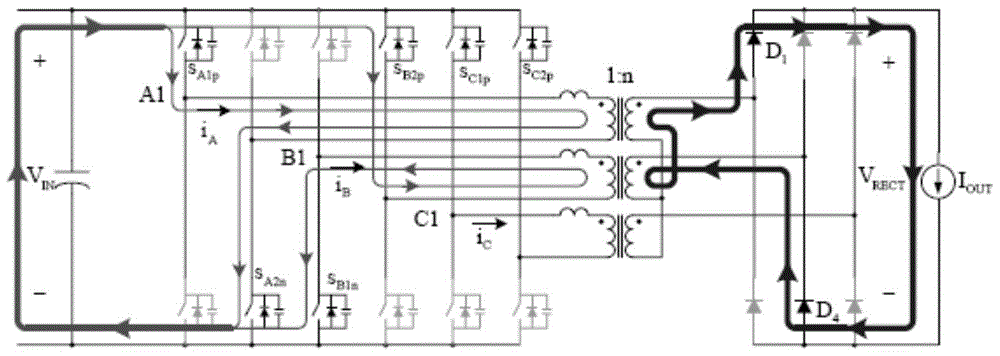
High-efficiency DC-DC converter
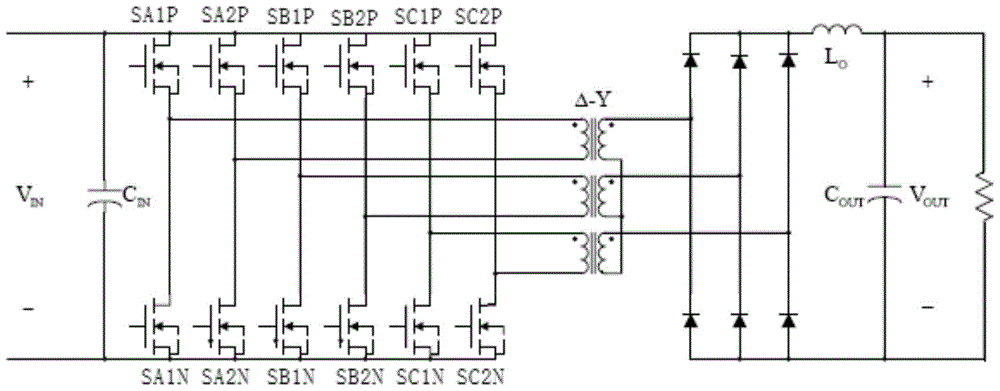
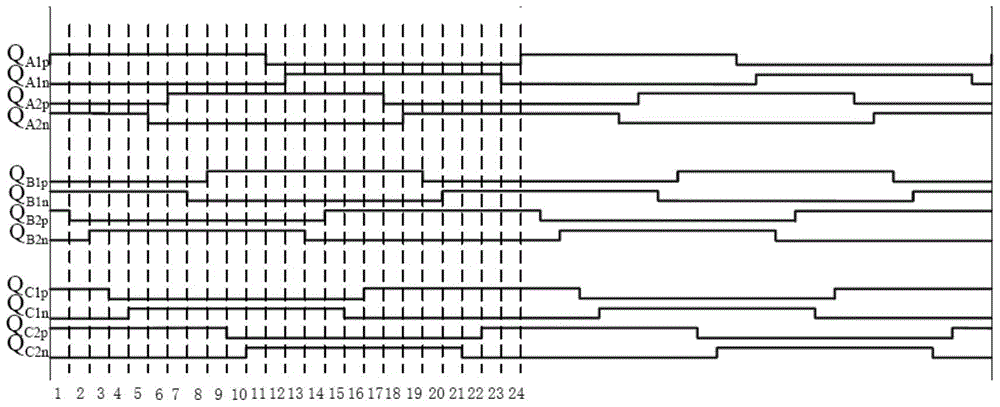
ActiveCN103731040AReduce current loadReduce lossDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCurrent loadCurrent limiting
The invention relates to a high-efficiency DC-DC converter which comprises a first full bridge, a second full bridge and a third full bridge, wherein the first full bridge, the second full bridge and the third full bridge are identical in structure. Bridge arms of the full bridges are all connected with an input power supply in parallel, and the difference between the phase position of the first full bridge, the phase position of the second full bridge and the phase position of the third full bridge is 120 degrees. An on-bridge tube of the advancing bridge arm is driven first, and an under-bridge tube of the advancing bridge arm is driven half a period later than the on-bridge tube. An on-bridge tube of the lagging bridge arm is driven X periods of time later than the on-bridge tube of the advancing bridge arm. Due to the fact that in the five states for energy transmission at each order, at least one phase and at most two phases of the first full bridge, the second full bridge and the third full bridge work, in the whole process, currents are shared by the full bridges which work simultaneously, the current load of each full bridge is reduced, as a result, circuit loss is lowered effectively, the current limiting problem generated during power amplification through a traditional full bridge is solved, and the current resisting requirement of a device is also lowered. Due to the fact that the soft switching state is realized in a part of period, switching tube loss caused by the hard switching state of a switching tube is lowered, and the conversion efficiency of the DC-DC converter is improved.
Owner:湖南终南山科技发展有限公司
Electroosmosis sludge modifying and drying device
ActiveCN103613266ASolve the phenomenon of sparks caused by poor contactIncrease wrap angleSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningElectricitySludge
The invention relates to a drying device, and in particular relates to an electroosmosis sludge modifying and drying device, aiming at solving the problems of an existing electroosmosis sludge modifying and drying device that anode loss is serious, an anode roller leaks after being electrolyzed so as not to be capable of working normally, a conveying chain easily looses, and a power distribution device is arranged in a stand in nude. A driving shaft of the electroosmosis sludge modifying and drying device is arranged on the left side of the middle of the stand; a plurality of driving chain wheels, a plurality of driven chain wheels and a plurality of guide wheels are sheathed in a conveying chain group; an anode roller component is arranged in the middle of the stand; a conductive resistance shaft is arranged at the upper part of the stand; the conductive resistance shaft is sheathed in a conductive resistance roller; the two ends of the anode roller component are respectively provided with an anode power distribution assembly; the two ends of the driving shaft are respectively provided with a cathode power distribution assembly; the two ends of the driven shaft are respectively provided with a cathode power distribution assembly. The electroosmosis sludge modifying and drying device is used for the field of sludge treatment.
Owner:哈尔滨北方环保工程有限公司
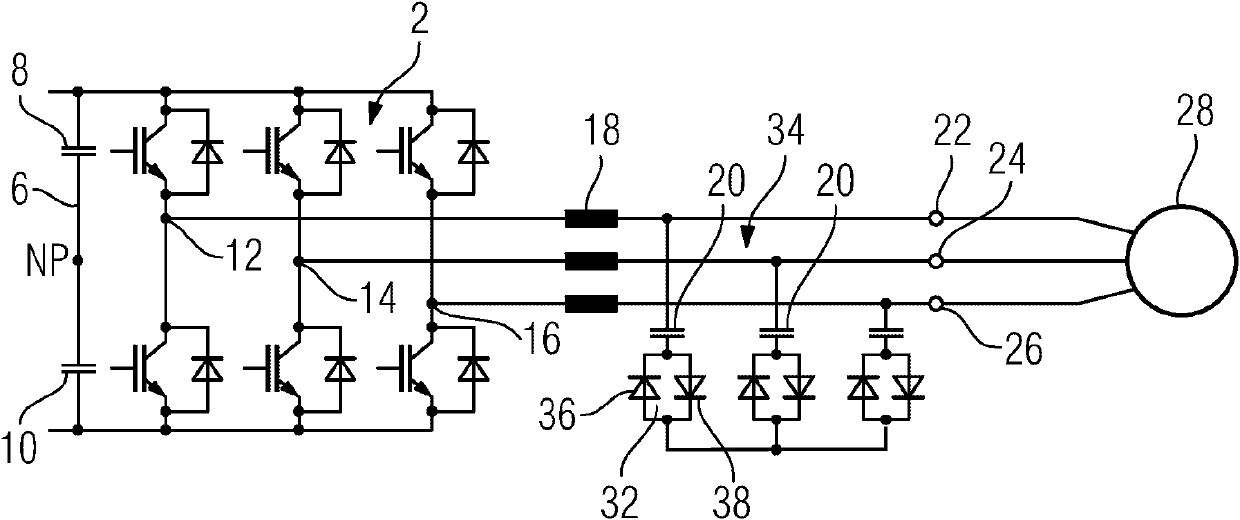
Lossy triphase low-pass filter
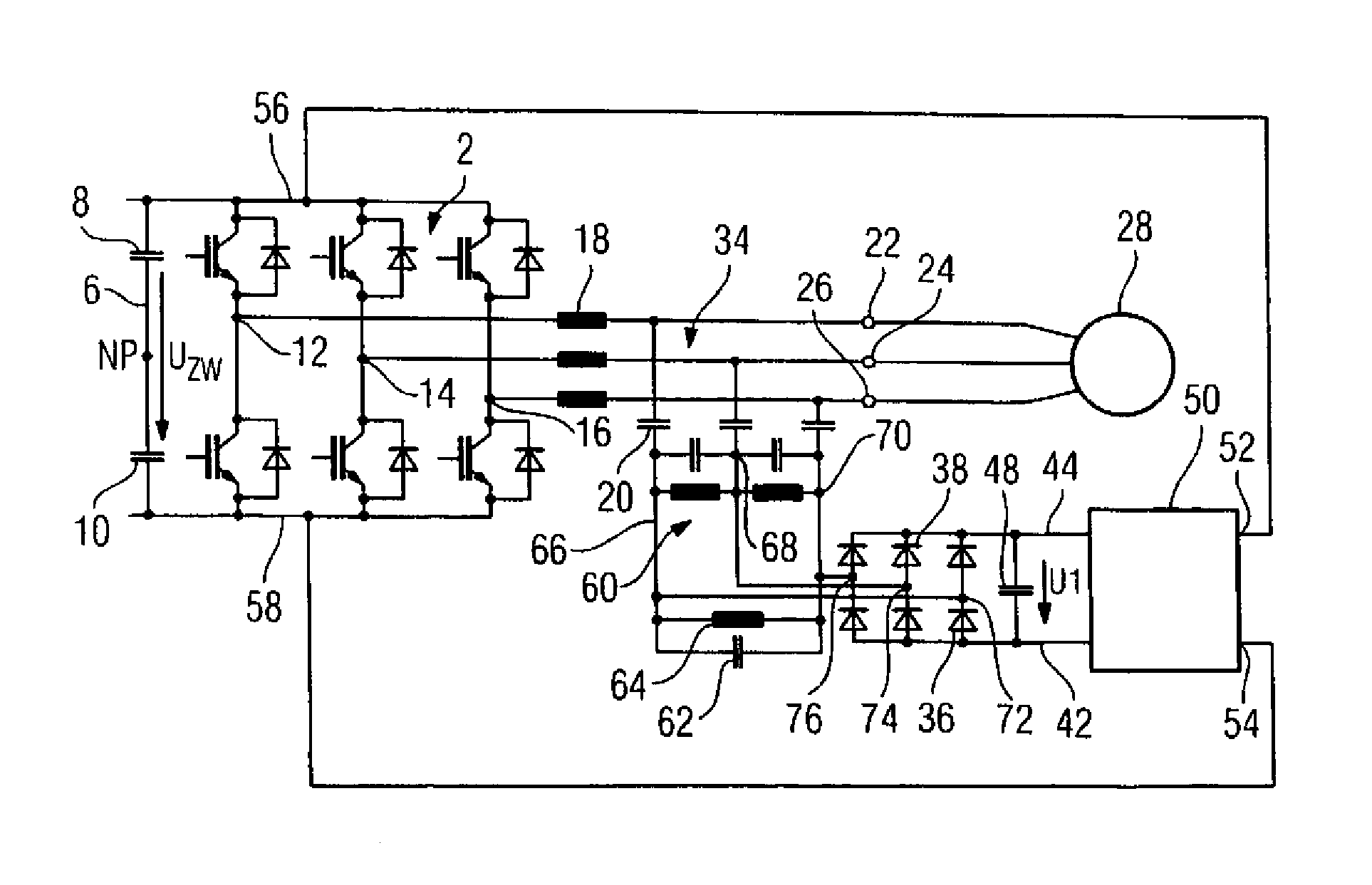
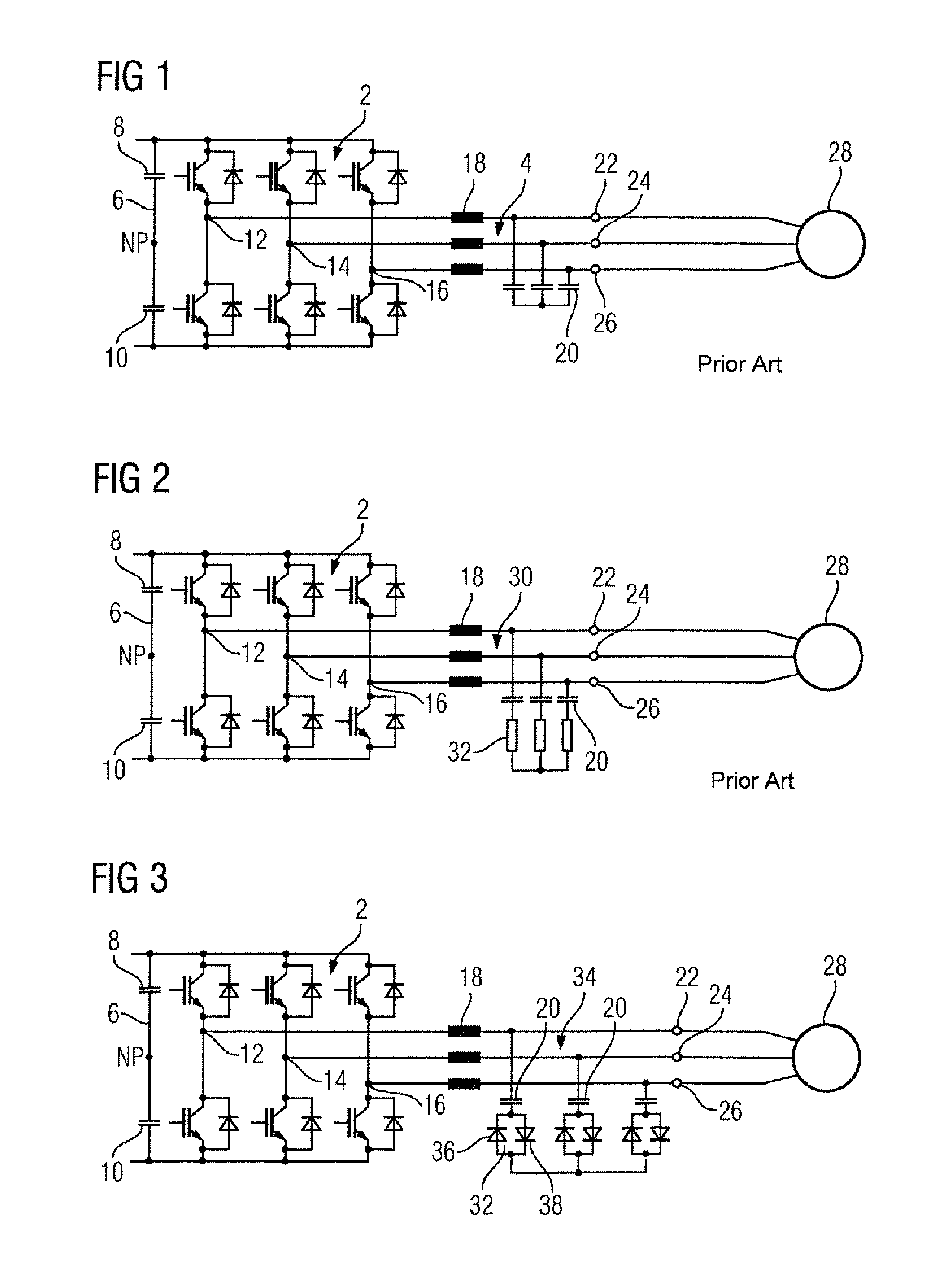
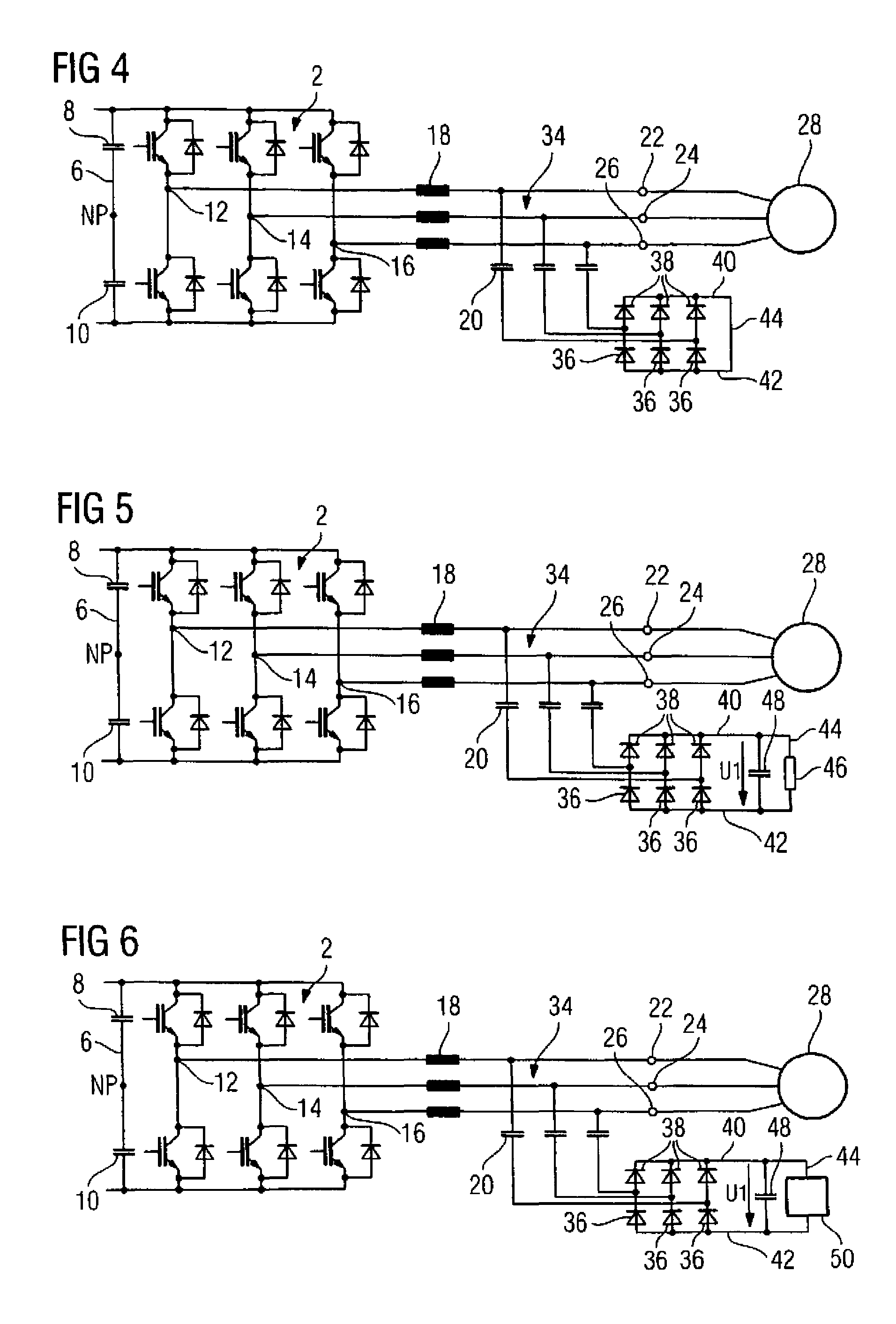
ActiveCN102027677AReduce current loadSave spaceImpedence networksPower conversion systemsAttenuation coefficientUltrasound attenuation
The invention relates to a lossy triphase low-pass filter (34) having a filter choke (18), a filter capacitor (20), and an attenuation element (32) per phase of said low-pass filter (34), wherein one filter capacitor (20) and one attenuation element (32) each are electrically connected in series. According to the invention, two diodes (36, 38) are provided as attenuation elements, which are electrically connected to each other in an anti-parallel manner. In this manner a lossy triphase low-pass filter (34) is obtained, the power loss of which is significantly reduced without any loss of the attenuation effect.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method for producing a part with a coil and electric machine comprising such a part
InactiveCN1585237AReduce voidsGap retentionManufacturing dynamo-electric machinesElectric machineLacquer
The invention relates to a method for producing a part (1) of a motor with a coil (9) comprising following steps: winding one or more wires (10) to a coil (9), whereby the wire is a baked lacquer wire with an electrically conducting core, an insulating coating and an external baked coating; pressing the wound coil with a pressing tool (8) and baking the pressed coil (9) to fix the geometric shape of the coil.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Lossy triphase low-pass filter
ActiveUS8743572B2Reduce loadReduce current loadMultiple-port networksPower conversion systemsUltrasound attenuationBand-pass filter
The invention relates to a lossy triphase low-pass filter having a filter choke, a filter capacitor, and an attenuation element per phase of said the low-pass filter, wherein one filter capacitor and one attenuation element each are electrically connected in series. Two diodes are provided as attenuation elements, which are electrically connected to each other in an anti-parallel manner. In this manner a lossy triphase low-pass filter is obtained, the power loss of which is significantly reduced without any loss of the attenuation effect.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Whole equipment cabinet server and power supply method
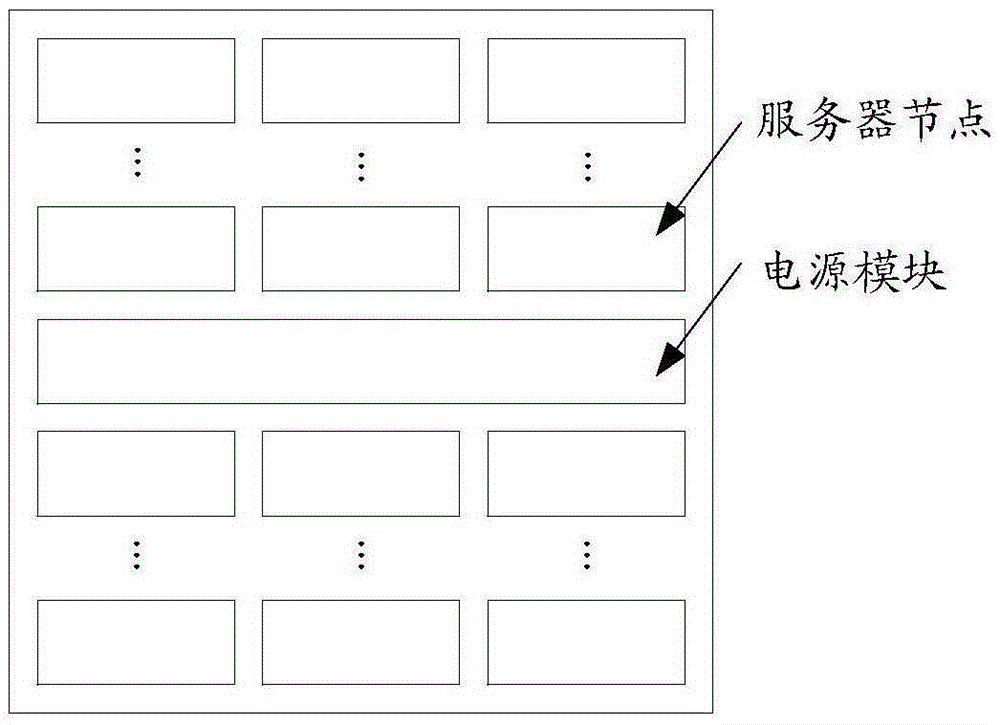
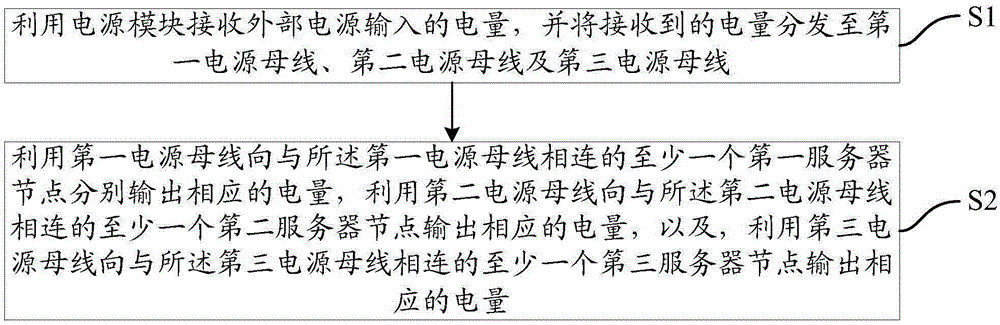
InactiveCN105302258AReduce current loadReduce power consumptionPower supply for data processingDigital processing power distributionComputer moduleElectric power
The invention provides a whole equipment cabinet server and a power supply method. The whole equipment cabinet server comprises a cabinet body, at least one first server node, at least one second server node and at least one third server node, wherein the first server nodes are installed on the left side of a front window region of the cabinet body, the second server nodes are installed in the middle of the front window region of the cabinet body, and the third server nodes are installed on the right side of the front window region of the cabinet body. The whole equipment cabinet server further comprises a first power bus bar, a second power bus bar, a third power bus bar and a power module. The first power bus bar is installed on the left side of a rear window region of the cabinet body, the second power bus bar is installed in the middle of the rear window region of the cabinet body, and the third power bus bar is installed on the right side of the rear window region of the cabinet body. Each first server node is connected with the first power bus bar, each second server node is connected with the second power bus bar, and each third server node is connected with the third power bus bar. The power module is connected with the first power bus bar, the second power bus bar and the third power bus bar. Through the technical scheme, electric resources can be saved.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
Charge pump system and memory
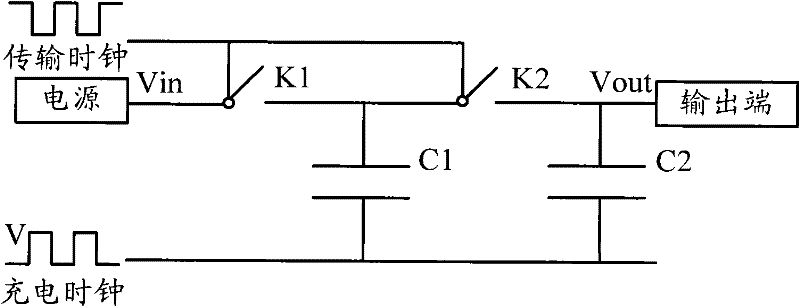
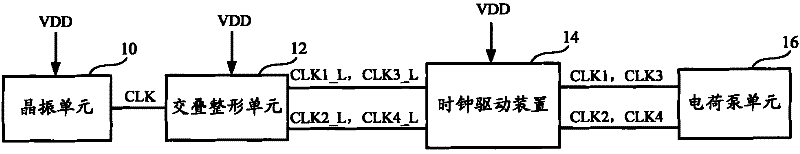
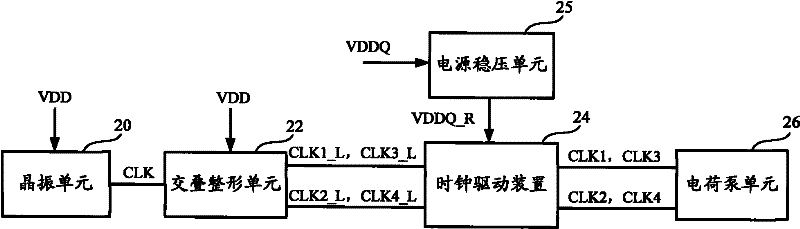
InactiveCN102280997AReduce current loadImprove charging efficiencyApparatus without intermediate ac conversionEngineeringClock signal
A charge pump system and memory, the charge pump system comprising: a charge pump unit; a clock drive device connected to the charge pump unit, the clock drive device has: a first clock drive unit controlled by a first power supply voltage , enhance the obtained current of the first type clock signal and output it to the charge pump unit; the second clock driving unit controlled by the second power supply voltage enhances the obtained current of the second type clock signal and output it to the said charge pump unit A charge pump unit; a power supply voltage stabilizing unit, configured to adjust the second power supply voltage to obtain the first power supply voltage. Compared with the prior art, the present invention improves charging efficiency and transmission efficiency by setting the first clock driving unit and the second clock driving unit separately and providing different power supply voltages respectively.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Test probe suitable for large current
InactiveCN113608102AAvoid the disadvantage of being easy to burn outReduce current loadElectronic circuit testingElectrical measurement instrument detailsMechanical engineeringElectrical current
The invention relates to a test probe suitable for large current. The test probe comprises a probe tube; two ends of the probe tube are provided with probe shafts; at least one of the two probe shafts is arranged in a telescopic manner; one of adjacent ends of the two probe shafts is provided with a plug, the other one is provided with a slot in matched plug connection with the plug; when the plug is inserted into the slot, the parts of the opposite ends of the two probe shafts are located outside the probe tube; and an elastic supporting piece for keeping the plug and the slot in a separated state is arranged between the two probe shafts. The overall structure of the test probe is simple; the defect that a traditional test probe is prone to being burnt out due to the fact that current is too large is overcome; the stability performance effect is excellent in the testing process; and the service life of the test probe is greatly prolonged.
Owner:深圳市美锐精密电子有限公司
Air Conditioner system
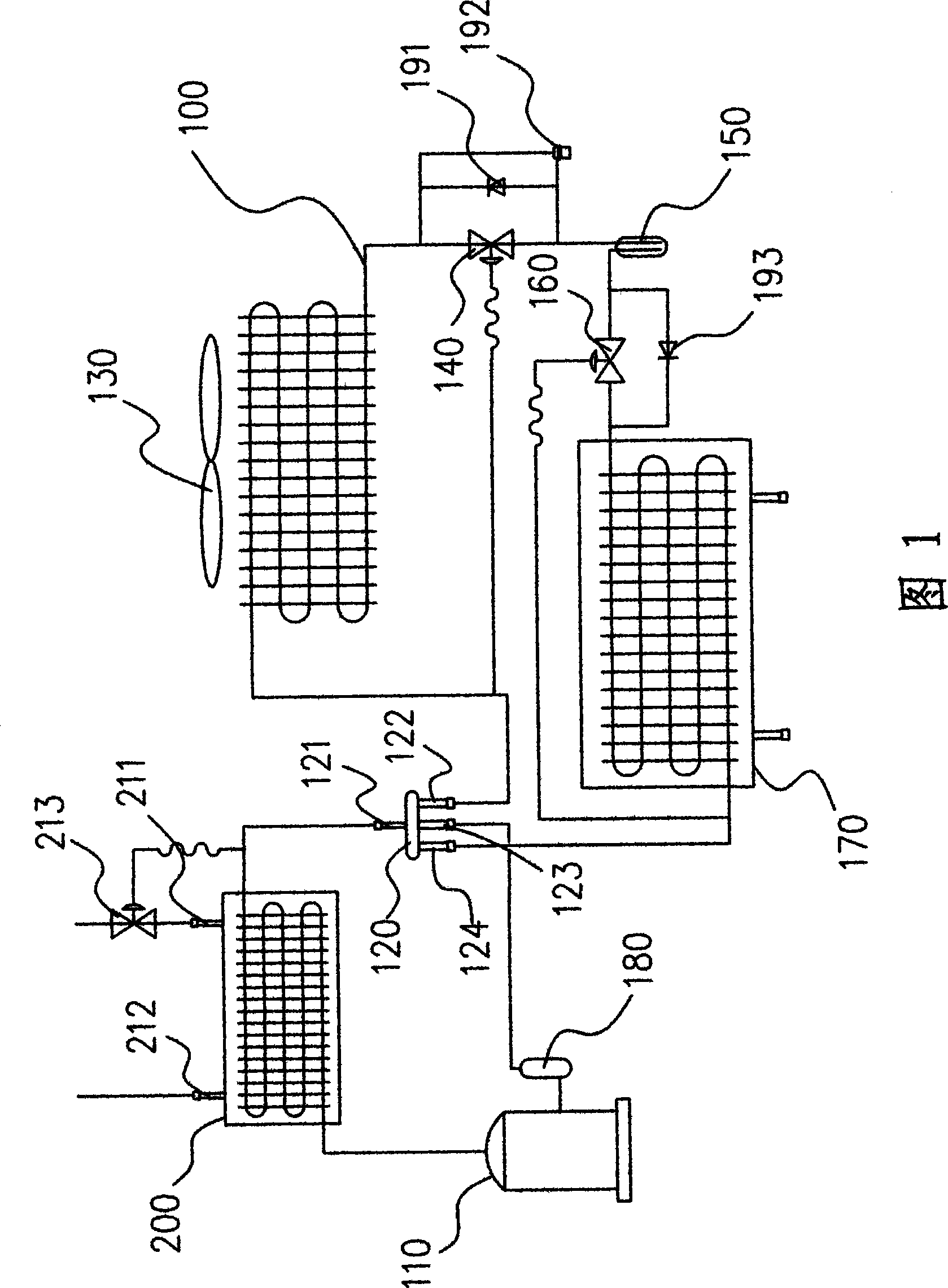
InactiveCN101377341AImprove job stabilityReduce current loadEnergy recovery in ventilation and heatingLighting and heating apparatusCurrent loadPower flow
The invention discloses an air-conditioning system, which comprises a refrigeration device which is provided with a compressor, wherein, a heat recovery heat exchanger used to absorb heat of condensation released from the refrigeration device is arranged at the compressor of the refrigeration device; the heat recovery heat exchanger is provided with a water inlet and a water outlet. Therefore, through supplying tap water to the heat recover heat exchanger to absorb the heat of condensation released by the working medium in the refrigeration device, the heat exchange efficiency is improved, the temperature of the working medium after heat exchange is low, the load of the refrigeration device is too low, thus the working stability of the air-conditioning system is improved, the current load of the air-conditioning system is lowered, and the service life is prolonged.
Owner:赵福龙
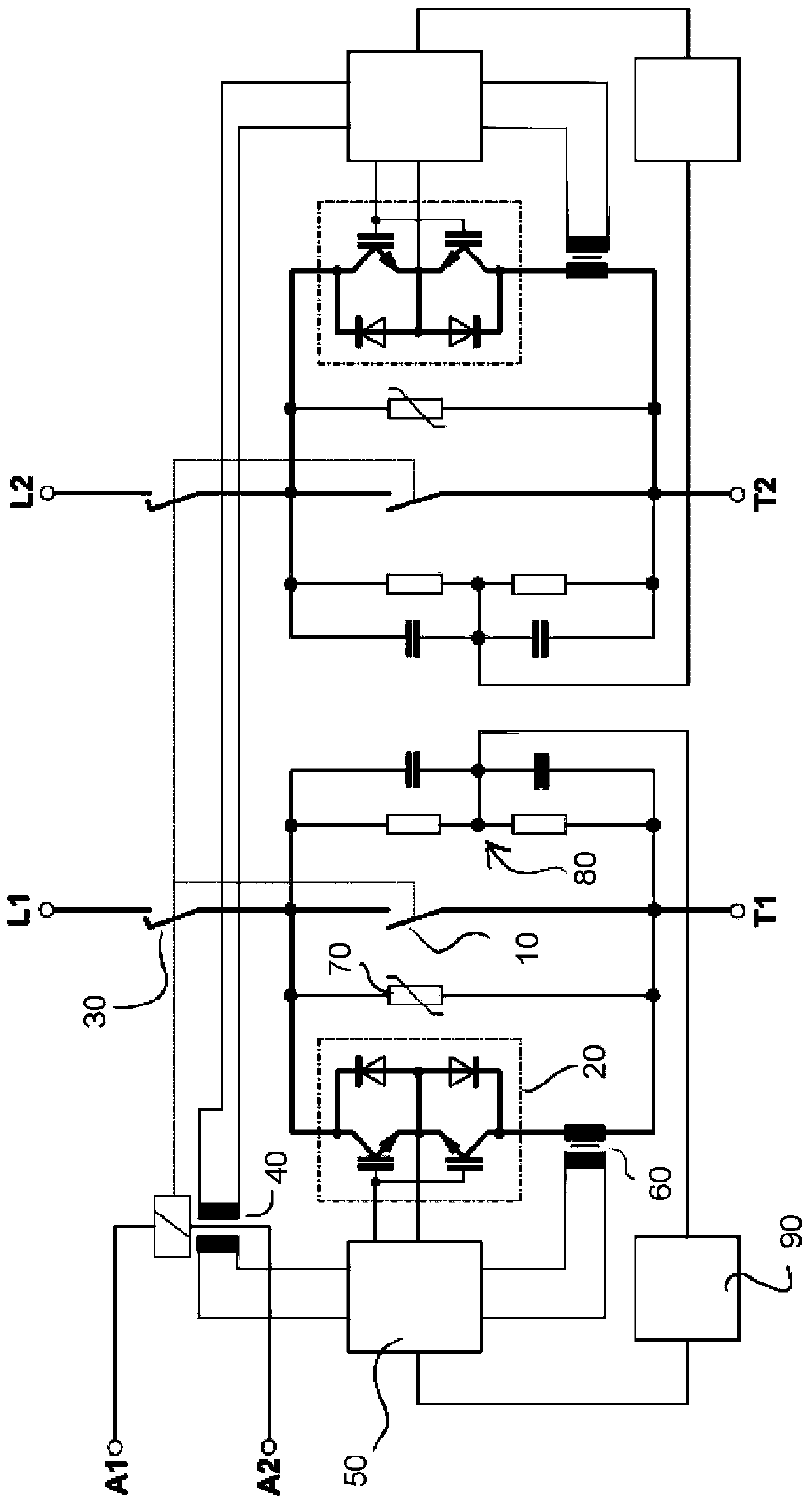
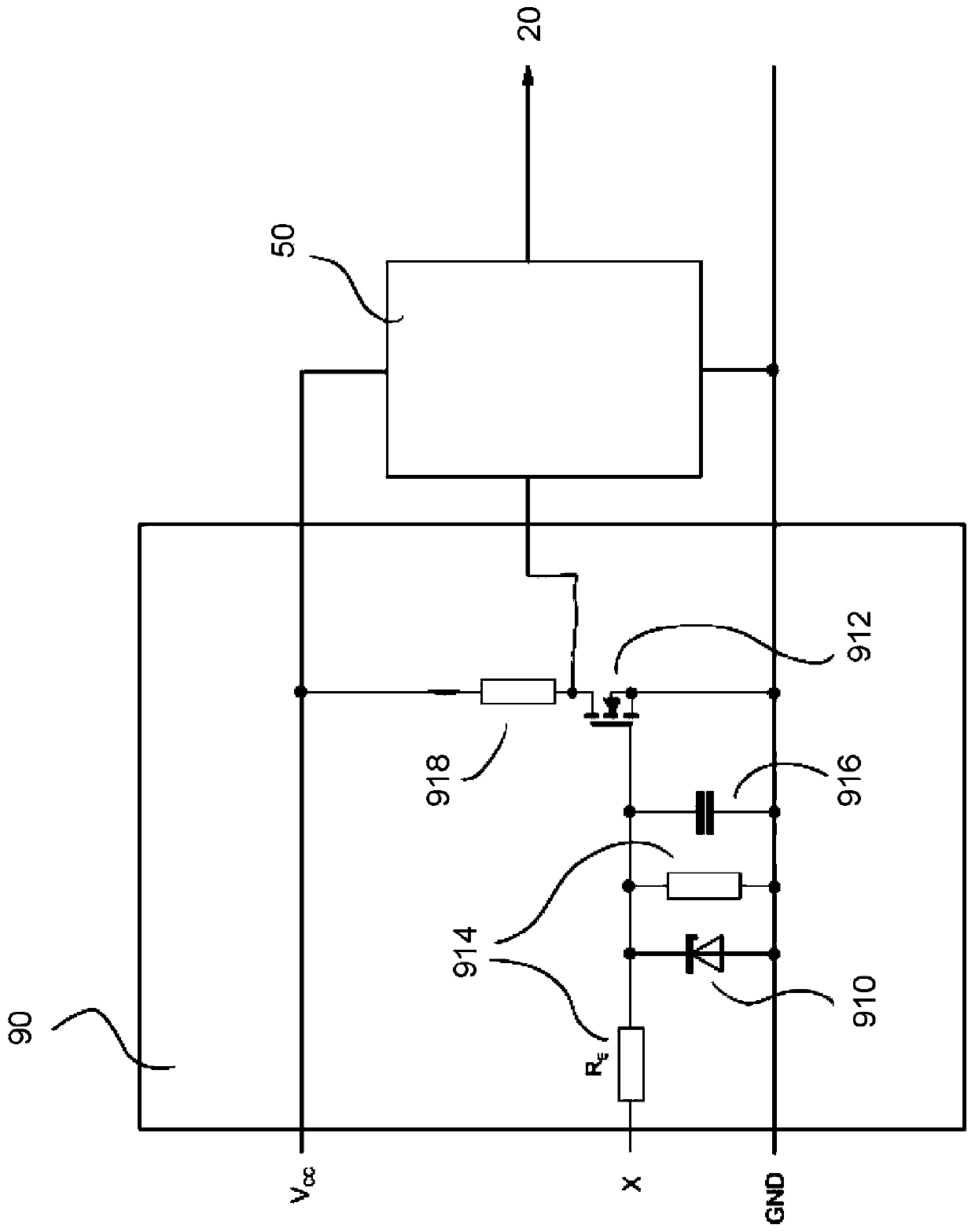
Switching apparatus for carrying and disconnecting electric currents, and switchgear having a switching apparatus of this kind
ActiveCN111492452AReduce current loadElectronic switchingHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesElectronic systemsControl signal
The invention discloses a switching apparatus for carrying and disconnecting electric currents, comprising a first mechanical contact arrangement (10), a second mechanical contact arrangement (30) which is connected in series with the first mechanical contact arrangement, a semiconductor switch (20) which is connected in parallel with the first mechanical contact arrangement, and a switching electronics system (50) which is designed to switch on and switch off the semiconductor switch (20), wherein the switching apparatus is designed in such a way that, during a switching process, the two mechanical contact arrangements (10, 30) are closed with a time delay in relation to one another. The invention further provides a control circuit (90) which is designed to ascertain a voltage across thefirst mechanical contact arrangement (10) and to generate an actuation signal for the switching electronics system (50), which actuation signal switches on the semiconductor switch (20), depending onthe ascertained voltage.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
Electronic gun of single-colour cathode-ray tube with improved structure
InactiveCN1282214CIncrease screen brightnessImprove visual qualityElectrode and associated part arrangementsSingle electronImage resolution
The present invention is an electron gun of a monochromatic cathode ray tube with improved structure at least provided with more than two electron current emitting sources (such as: cathode), so that the electron beams produced by each of the electron current emitting sources have a finer The cross-sectional area of the electron beam (Beam Spot Size), and can be projected to the same focus position on the screen of the monochrome cathode ray tube under the convergence of the focusing lens or the common lens of the electron gun, resulting in better resolution and focusing quality , in this way, it can not only effectively improve the problem that the cross-sectional area of the electron beam caused by the mutual repulsion of the electrons in the electron beam is not easy to shrink when the traditional electron gun applies a large current to the single electron current emission source, but also can greatly improve the monochromatic cathode ray. Tube screen brightness for better visual quality.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
Negative Charge Pump Feedback Circuit
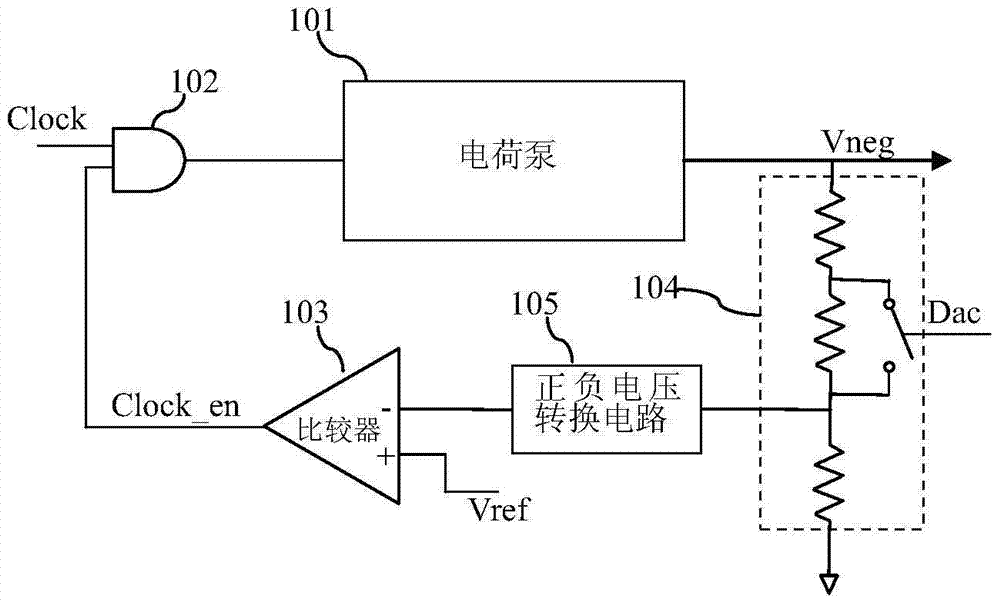
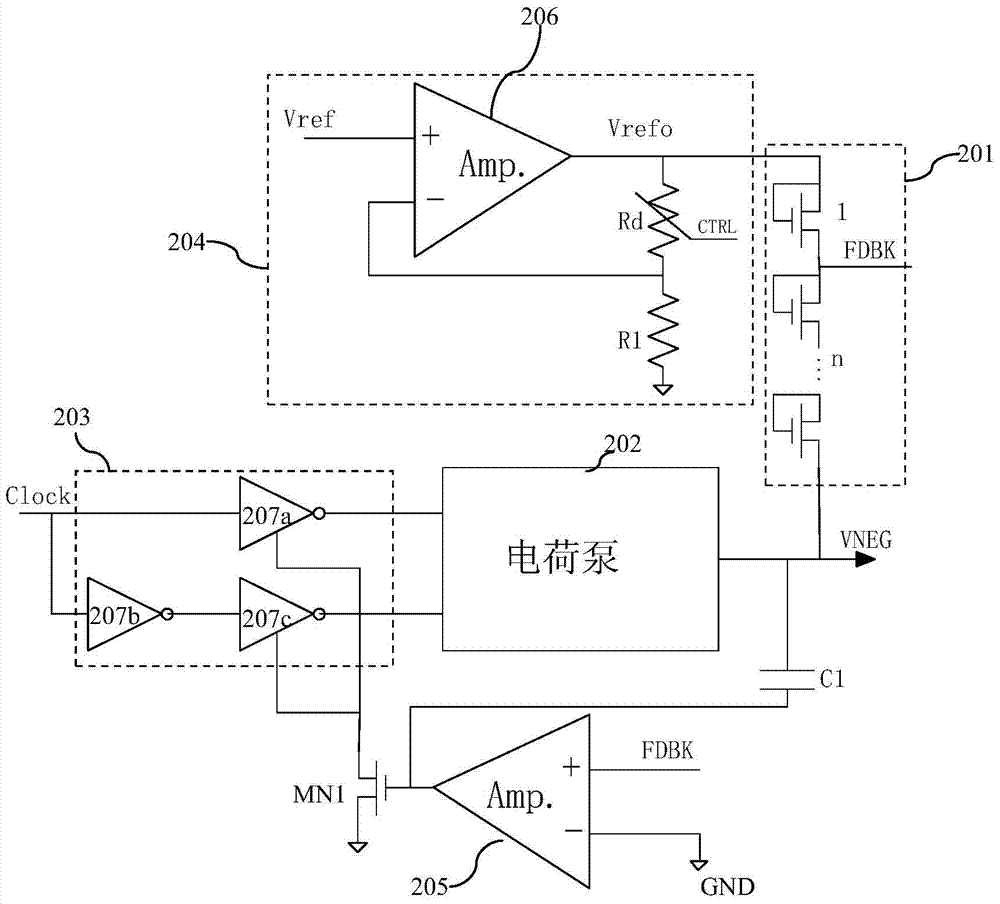
ActiveCN105468075BReduce areaEasy to controlElectric variable regulationAudio power amplifierControl signal
The invention discloses a feedback circuit of a negative voltage charge pump. The circuit comprises a bleeder circuit which is formed by connecting a plurality of MOS transistors in series, the drain electrodes and the grid electrodes of the MOS transistors being in short circuit. The bleeder circuit is connected between the negative voltage output by the charge pump and first reference voltage, and outputs branch voltage as feedback voltage. The feedback voltage is connected with a first input end of a first operational amplifier. The second input end of the first operational amplifier is connected with ground. An amplification signal output by the first operational amplifier is used as a clock control signal. The clock signal inputs to the input end of the charge pump through a clock control circuit. The clock control signal inputs to the clock control circuit to adjust amplitude of the clock signal input to the charge pump, and values of the negative voltage are controlled through adjusting the amplitude of the clock signal. The circuit area is reduced.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Electronic ballast for operating at least two different types of discharge lamps
InactiveCN101861041BAchieve normal operationGuaranteed normal consumptionElectrical apparatusElectric lighting sourcesMicrocontrollerGas-discharge lamp
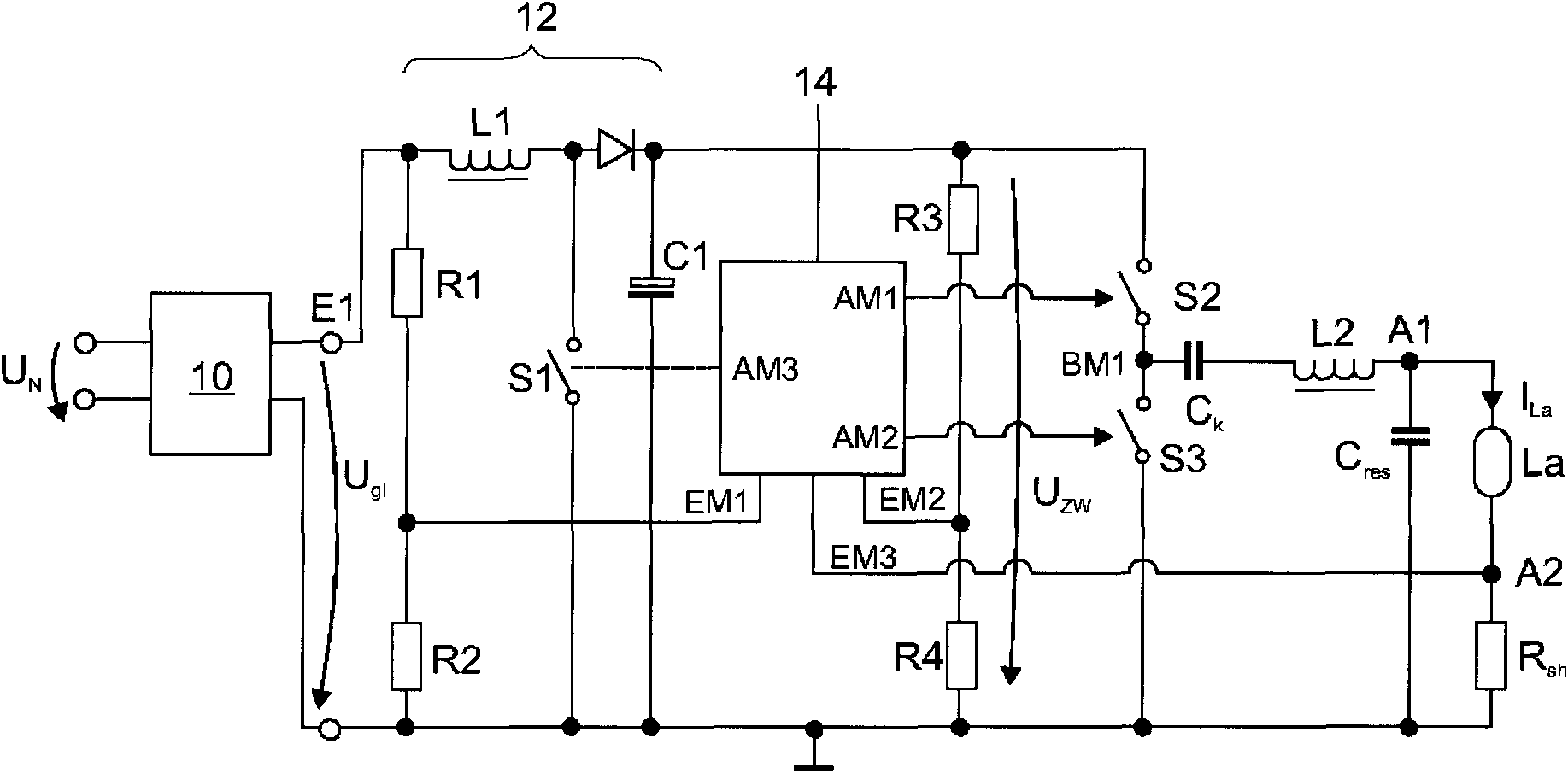
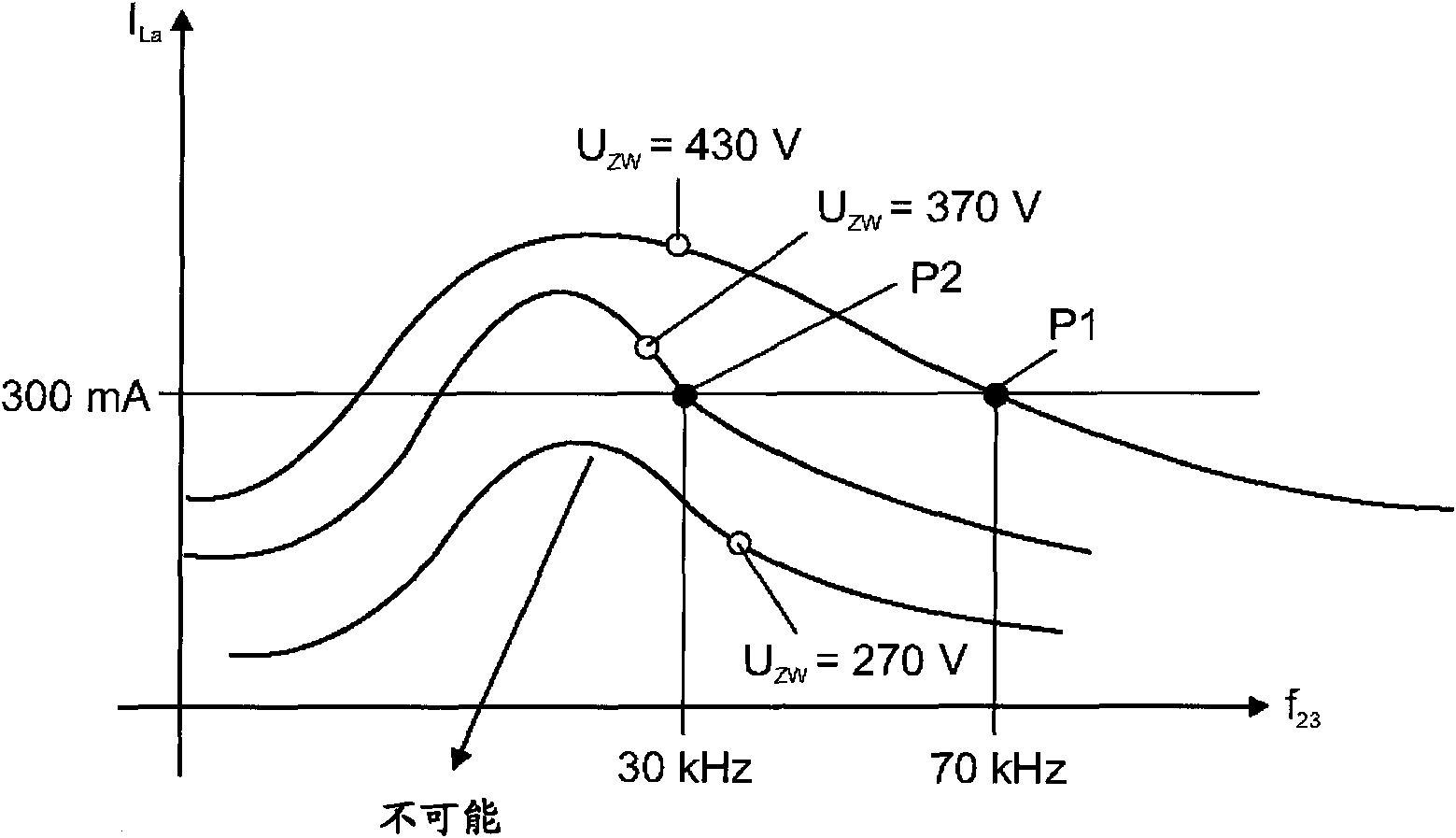
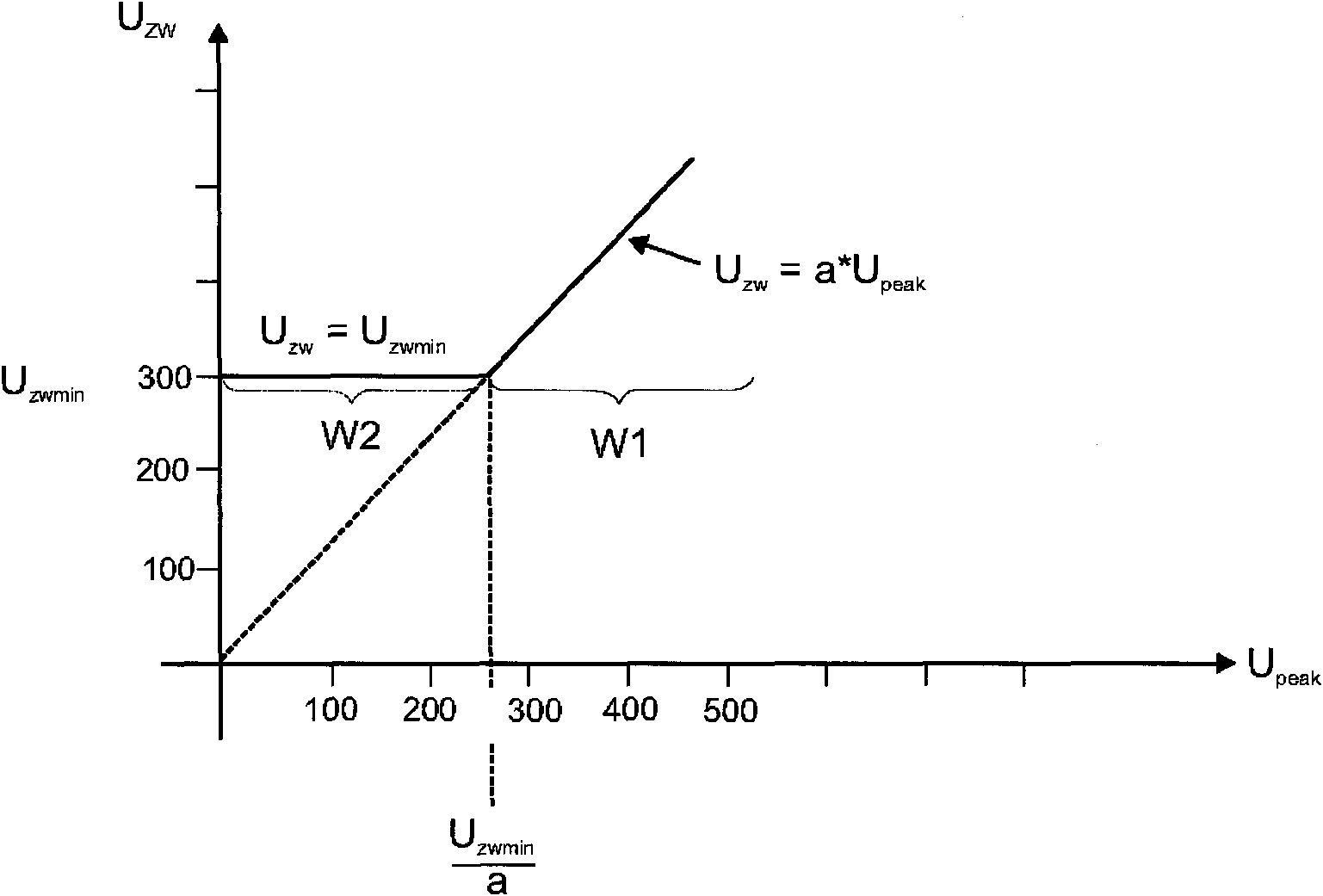
#CMT# # / CMT# The device has an input unit provided with two input connectors (E1) for connection of direct current supply voltage unit (Un). Voltage measuring devices (R1-R4) are provided for measuring voltage between input connectors and output connectors of a boost-converter (12). A microcontroller (14) is provided with two inputs (EM1, EM2), which are coupled with voltage measuring devices. The micro-controller is designed such that voltage (Uzw) between output connectors of the converter is controlled to a value, which depends upon a value of voltage (Ugl) between the input connectors of converter. #CMT#USE : # / CMT# Electronic pre-switching device for operation of two different types of discharge lamps. #CMT#ADVANTAGE : # / CMT# The micro-controller is designed such that voltage between output connectors of the boost converter is controlled to the value, which depends upon the value of voltage between the input connectors, thus operating the pre-switching device at reduced power losses, and reducing electronic interferences, during operation of the discharge lamps. The device is designed such that the voltage stroke between the input and the output of the boost converter is reduced, thus increasing the efficiency of the converter, and reducing power load in all components of the pre-switching device such that compact components are used in the pre-switching device, and hence reducing the cost and space required for the pre-switching device. #CMT#DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS : # / CMT# The drawing shows a schematic circuit diagram of an electronic pre-switching device. E1 : Input connectors EM1, EM2 : Inputs R1-R4 : Voltage measuring devices Ugl, Uzw : Voltage Un : Direct current supply voltage unit 12 : Boost-converter 14 : Microcontroller.
Owner:OSRAM GMBH
Hydraulic fluid pump for a motor vehicle brake system, comprising an eccentric drive
InactiveCN101903225BAnti-lock functionReduce electric powerPump controlPositive-displacement liquid enginesElastomerCounter pressure
Disclosed is a hydraulic fluid pump (80) for a motor vehicle brake system, comprising delivery means (110, 120) for delivering hydraulic fluid against a hydraulic counter-pressure prevailing in one part of the vehicle brake system (140, 150). Said hydraulic fluid pump (80) further comprises means (270), preferably an elastomer component in the motor shaft bearing (200, 220), for modifying the volume delivered by the delivery means (110, 120) in accordance with the level of the hydraulic counter-pressure.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
A High Efficiency DC-DC Converter
ActiveCN103731040BReduce current loadReduce lossDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCurrent loadDc dc converter
The invention relates to a high-efficiency DC-DC converter which comprises a first full bridge, a second full bridge and a third full bridge, wherein the first full bridge, the second full bridge and the third full bridge are identical in structure. Bridge arms of the full bridges are all connected with an input power supply in parallel, and the difference between the phase position of the first full bridge, the phase position of the second full bridge and the phase position of the third full bridge is 120 degrees. An on-bridge tube of the advancing bridge arm is driven first, and an under-bridge tube of the advancing bridge arm is driven half a period later than the on-bridge tube. An on-bridge tube of the lagging bridge arm is driven X periods of time later than the on-bridge tube of the advancing bridge arm. Due to the fact that in the five states for energy transmission at each order, at least one phase and at most two phases of the first full bridge, the second full bridge and the third full bridge work, in the whole process, currents are shared by the full bridges which work simultaneously, the current load of each full bridge is reduced, as a result, circuit loss is lowered effectively, the current limiting problem generated during power amplification through a traditional full bridge is solved, and the current resisting requirement of a device is also lowered. Due to the fact that the soft switching state is realized in a part of period, switching tube loss caused by the hard switching state of a switching tube is lowered, and the conversion efficiency of the DC-DC converter is improved.
Owner:湖南终南山科技发展有限公司
Load Optimization Method for Ion Membrane Electrolyzer
ActiveCN106319560BIncreased operating lifeReduced DC power consumptionElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisPower flow
The invention relates to a load optimization method of an ion membrane electrolyzer, and belongs to the technical field of electrolyzers. The load optimization method is characterized in that the adjusting step is as follows: according to the average load operation situation of each electrolyzer, electrolyzers are divided into high, middle-high, middle, middle-low and low fives grade, under the premise of ensuring the same total current, according to the divided fives grade of the electrolyzers in step 2), partial current of each electrolyzer is adjusted, the partial current of a high grade electrolyzer is reduced to 10% to 30%, the partial current of a middle-high electrolyzer is reduced to 5% to 10%, the partial current of a middle electrolyzer is not changed, the partial current of a middle-low electrolyzer is increased by 5%-10%, and the partial current of a low electrolyzer is increased by 10% to 20%. Through the load optimization method for load optimization of the electrolyzers, low DC power consumption and low acid consumption of the electrolytic device can be achieved, and the operating life of an ionic membrane can be prolonged.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Internally-eccentric ultra-high speed needle machine
PendingCN108914394AReduce centrifugal forceImprove stabilityNeedling machinesCurrent loadUltra high speed
The invention belongs to a needle machine in the technical field of non-woven fabric production machines. In order to resolve technical problems such as great centrifugal force, noise and current loads, the invention provides an internally-eccentric ultra-high speed needle machine. The needle machine comprises a needle beam, a counterweight beam and a crankshaft. The body of the crankshaft is equipped with two first internally-eccentric eccentric parts. The body of the crankshaft is equipped with two second eccentric parts located between the two eccentric parts. The eccentric directions of the first eccentric parts are opposite to those of the second eccentric parts. The top of the needle beam is connected with the first eccentric parts through first opening and closing connecting rods. The top of the counterweight beam is connected with the second eccentric parts through second opening and closing connecting rods. The eccentric parts in two opposite directions on the crankshaft can balance rotary centrifugal force and moment of the crankshaft and can balance reciprocating inertia force and moment of the needle beam and the counterweight beam. When such force and moment reach selfbalance, load of the crankshaft is reduced. When centrifugal force of the crankshaft is on the decrease, the machine operates more stably.
Owner:王永祥
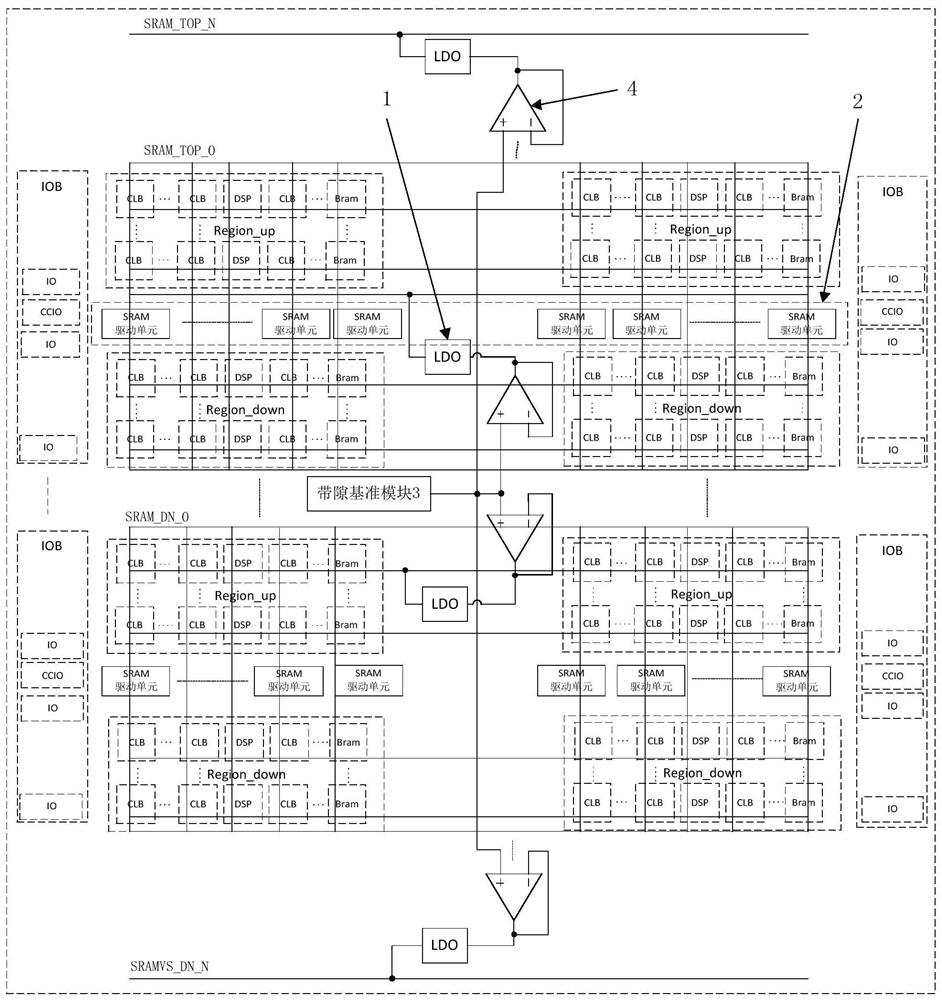
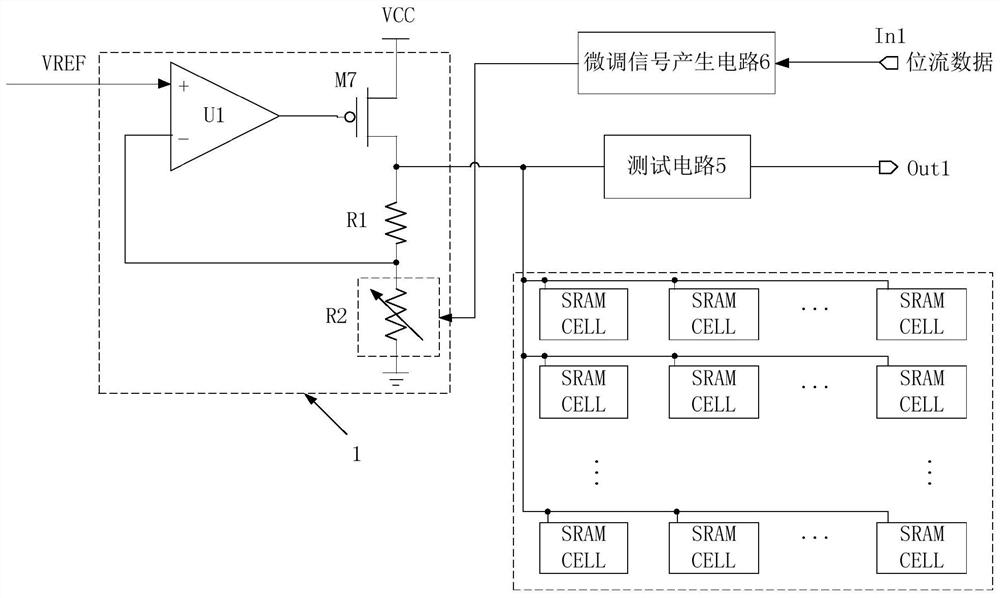
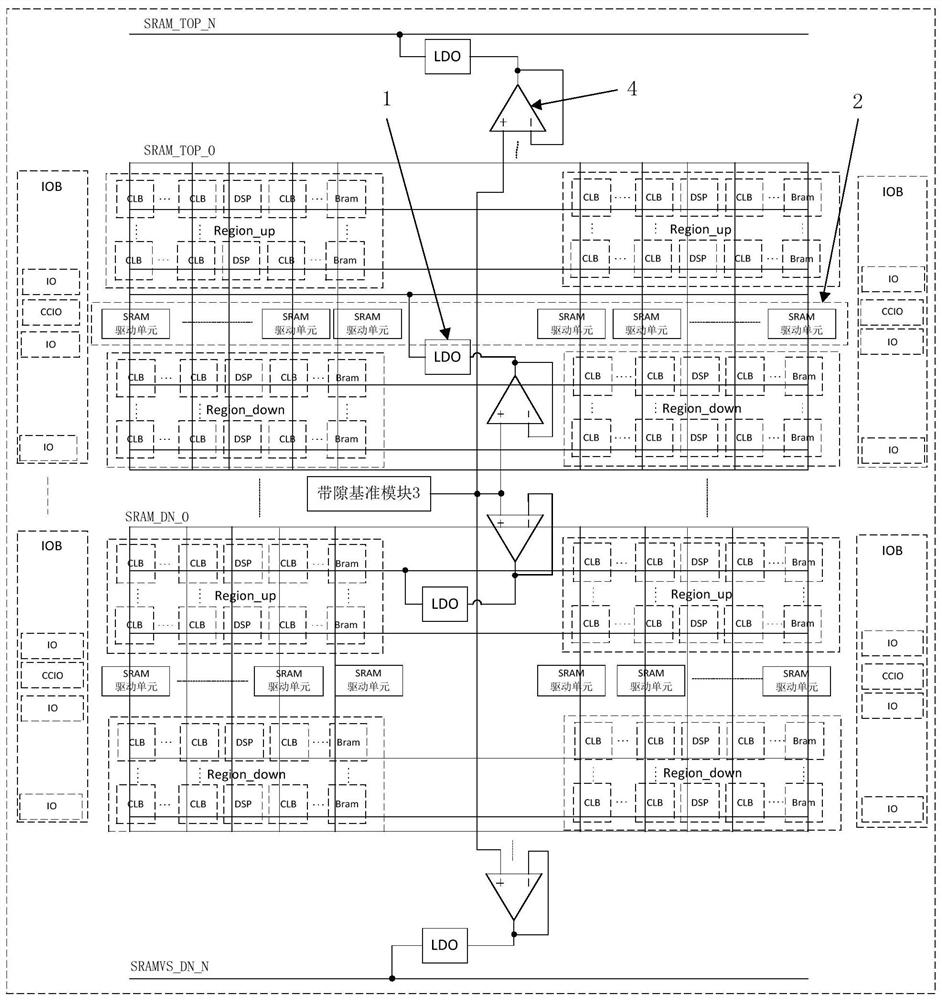
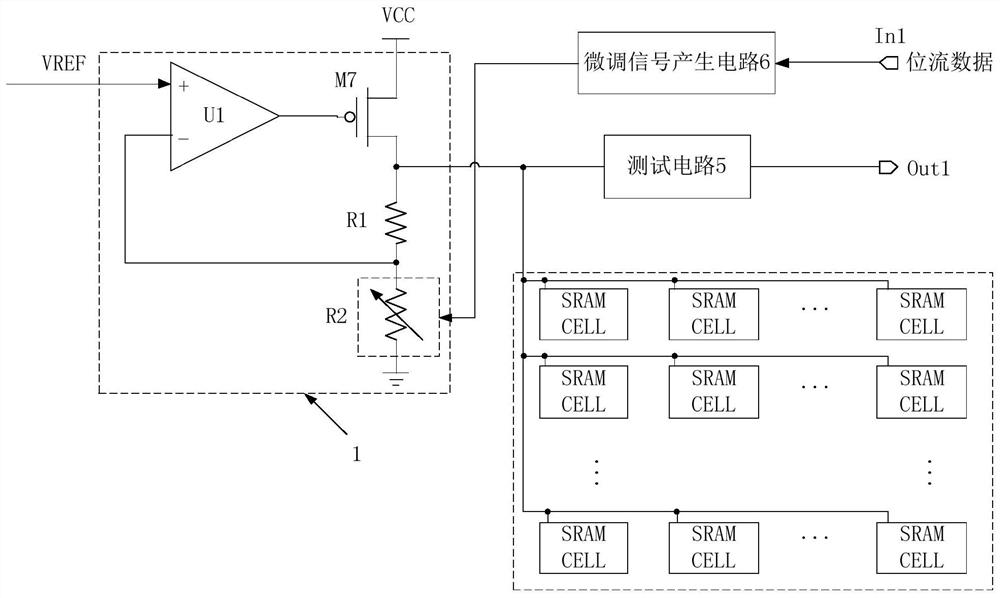
FPGA distributed power supply network with self-test adjustable function
ActiveCN112558669AReduce current loadGuaranteed stabilityElectric variable regulationLinear regulatorCurrent load
The invention discloses an FPGA distributed power supply network with a self-test adjustable function, and relates to the technical field of FPGAs, the distributed power supply network comprises a plurality of independent power supply area blocks, a band-gap reference module is connected with a low dropout regulator in each power supply area block to provide reference voltage, The low-dropout linear voltage regulator in each power supply area block outputs power supply through the driving array, and the voltage of each low-dropout linear voltage regulator is led to the outside through the testcircuit to be tested and is correspondingly adjusted through the fine adjustment signal generation circuit. The distributed power supply design effectively reduces the current load of a single low-dropout linear regulator, the stability of a power supply network is ensured, and the built-in test circuit and the built-in fine tuning signal generation circuit can reduce the voltage error caused bythe process and load between different power supply area blocks. The design bottleneck caused by continuous reduction of the chip manufacturing process and continuous increase of the chip scale is solved, and the reliability and expandability of the chip are improved.
Owner:WUXI ESIONTECH CO LTD +1
Motor FOR HOUSEHOLD APPLIANCE, PUMP, HOUSEHOLD APPLIANCE AND METHOD FOR MANUFACTURING MOTOR
InactiveCN107528440AEasy dischargeReduce current loadWindings insulation shape/form/constructionMagnetic circuit characterised by insulating materialsSynchronous motorElectric machine
The invention relates to a motor (8) for a household appliance (1), wherein the motor (8) is designed as a synchronous motor, with a stator (9) having a stator body (11) and a winding (14), and a rotor (10). The stator (9) is encapsulated at least in regions with protective material (17); the rotor is rotatable relative to the stator (9) and has at least one permanent magnet; and the winding (14) of the stator (9) is formed multi-phase.
Owner:BSH BOSCH & SIEMENS HAUSGERAETE GMBH
qled and its preparation method
ActiveCN106328822BImprove luminous efficiencyExtend your lifeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectron holeHole injection layer
The invention provides a QLED, comprising a first electrode, a hole injection layer, a hole transport layer, a light-emitting layer, an electron transport layer and a second electrode arranged in sequence, and the light-emitting layer is composed of a quantum dot light-emitting material and a mixed transport material The mixed transport material is a hole transport material and an electron transport material, and the hole transport material and the electron transport material form a double continuous network structure in the light-emitting layer, and the quantum dot light-emitting material is dispersed in the In the bicontinuous network structure described above.
Owner:TCL CORPORATION
An fpga distributed power supply network with self-test and adjustable function
ActiveCN112558669BReduce current loadGuaranteed stabilityElectric variable regulationLinear regulatorCurrent load
The invention discloses an FPGA distributed power supply network with a self-test and adjustable function, and relates to the field of FPGA technology. The distributed power supply network includes several independent power supply area blocks, and a bandgap reference module is connected to each power supply area block. The low-dropout linear regulators provide reference voltages. The low-dropout linear regulators in each power supply area block are respectively powered by the drive array output. At the same time, the voltage of each low-dropout linear regulator is drawn to the outside through the test circuit for testing and passed The fine-tuning signal generation circuit is adjusted accordingly. The distributed power supply design effectively reduces the current load of a single low-dropout linear regulator and ensures the stability of the power network. The built-in test circuit and fine-tuning signal generation circuit can reduce the block size of different power supply areas The voltage error caused by the process and load between the chips solves the design bottleneck caused by the continuous shrinking of the chip manufacturing process and the continuous increase of the chip scale, and improves the reliability and scalability of the chip.
Owner:WUXI ESIONTECH CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com