Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
249results about How to "Reduce alignment errors" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
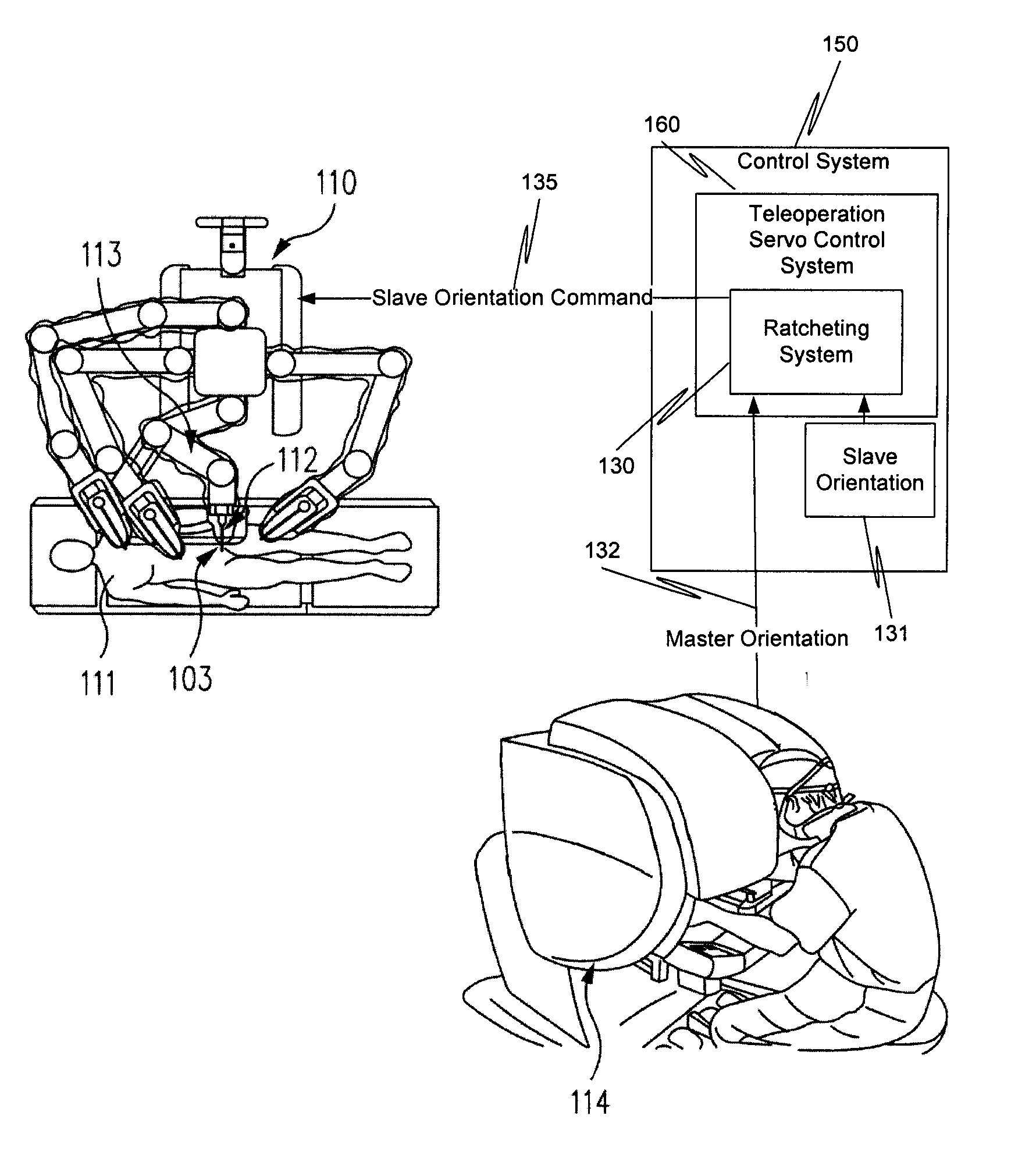
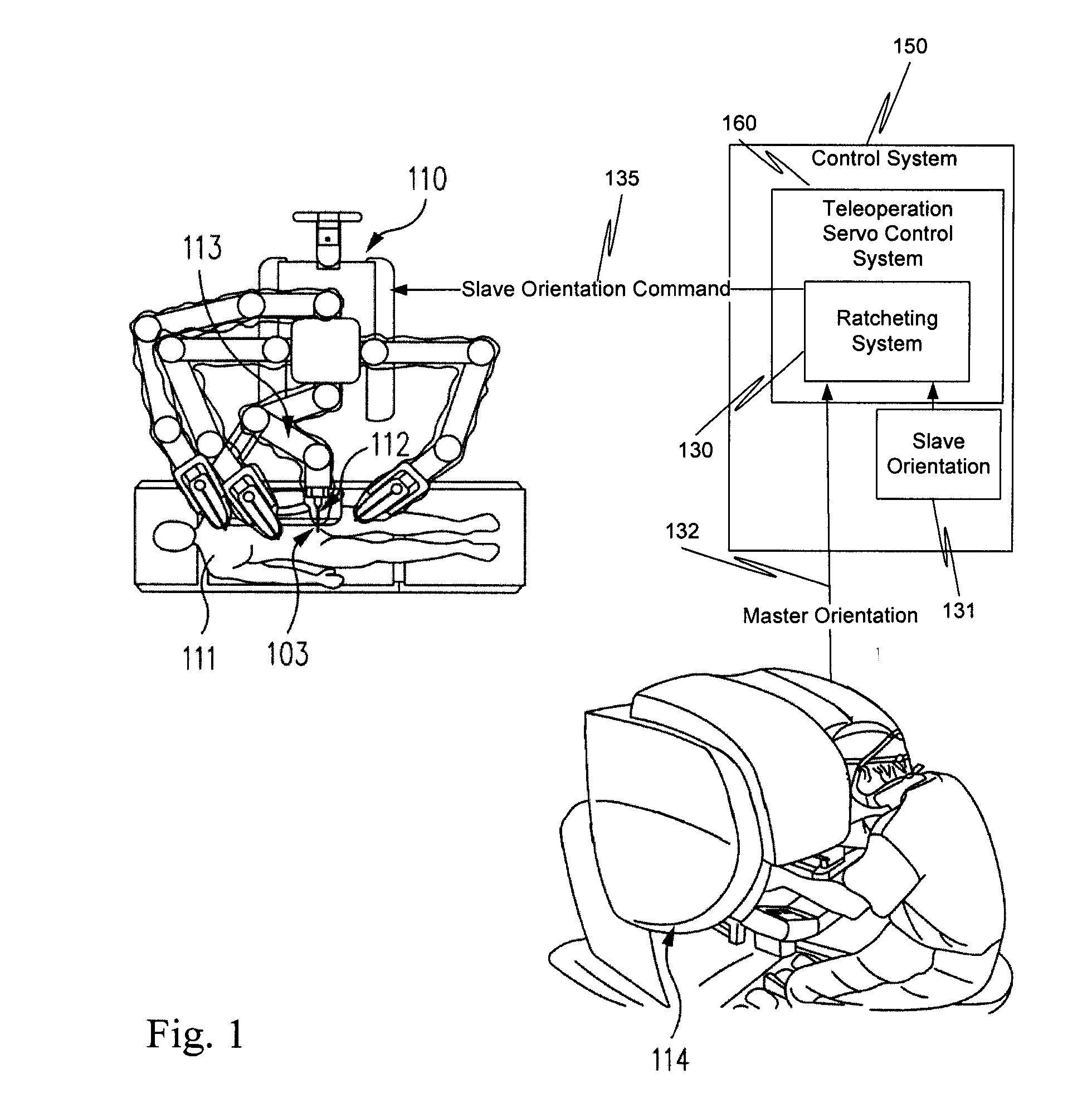
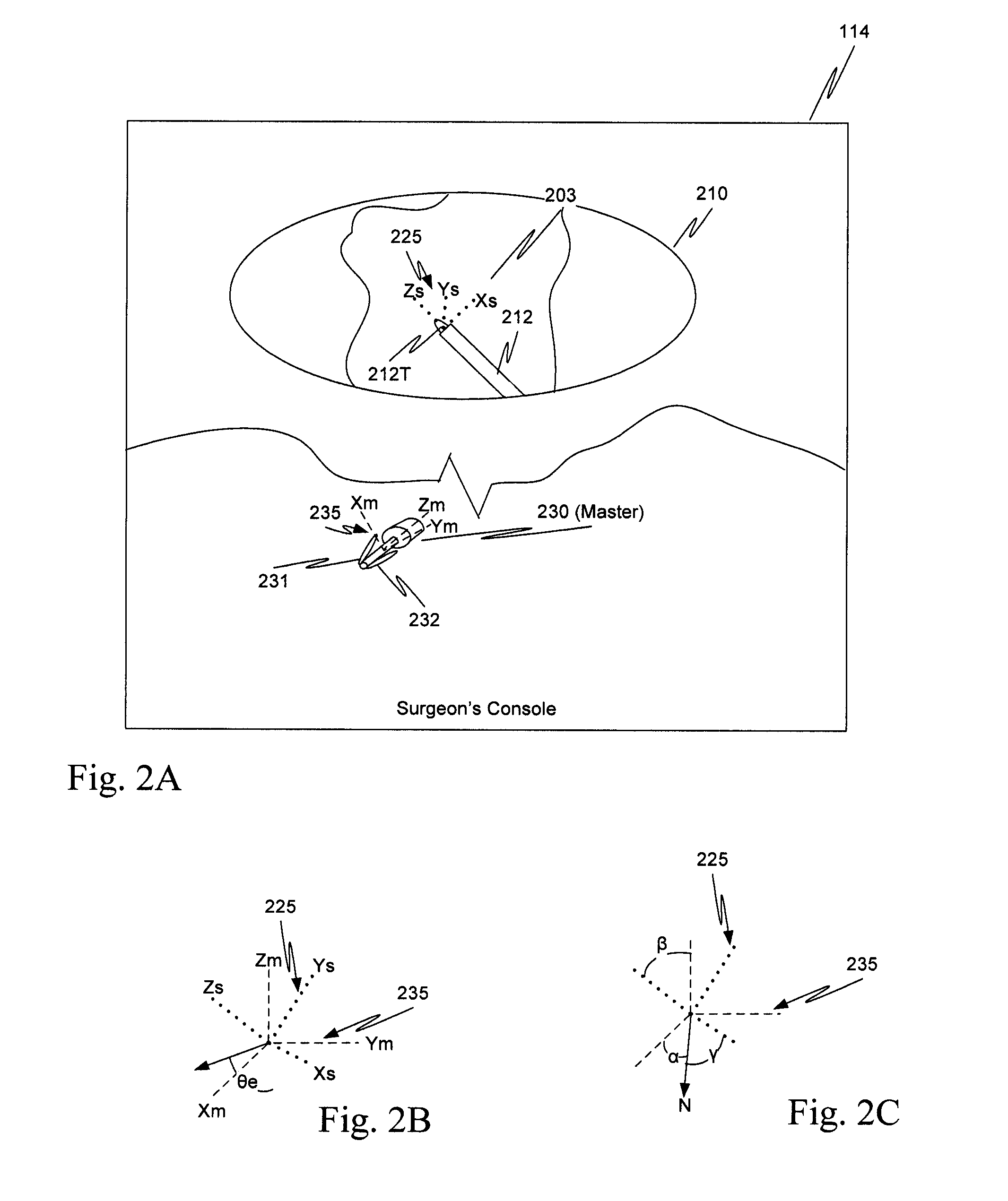
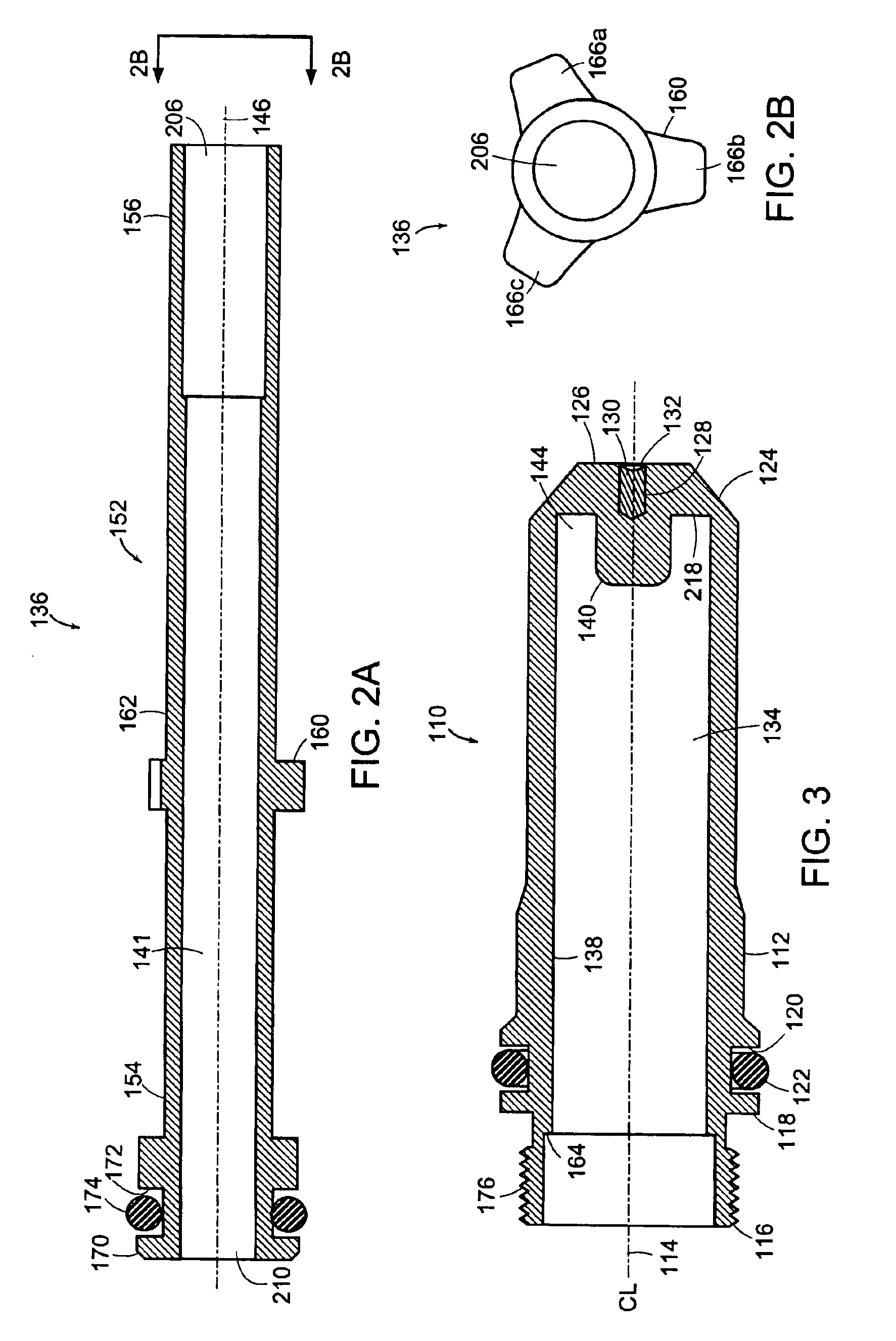
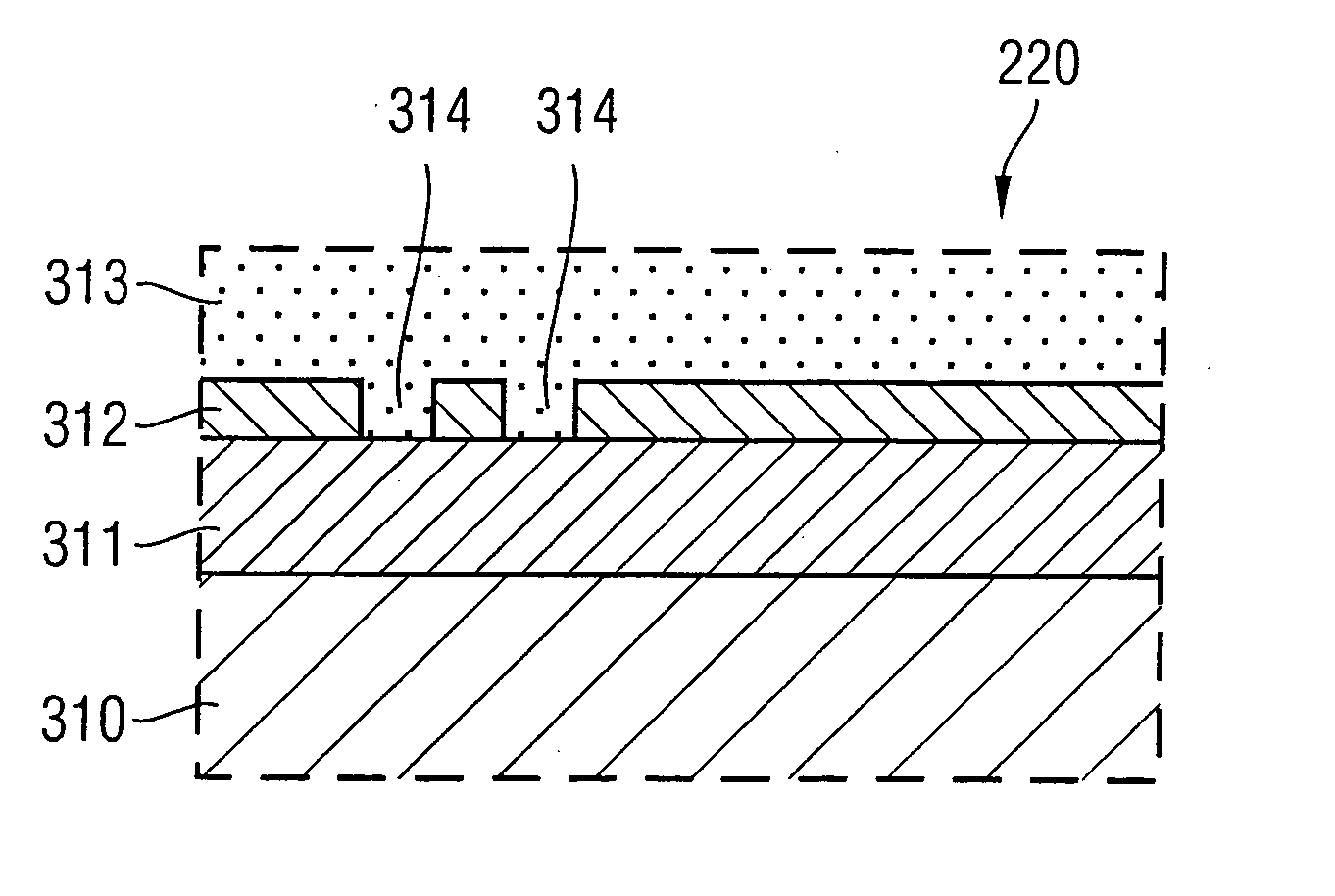
Ratcheting for master alignment of a teleoperated minimally-invasive surgical instrument
ActiveUS20100332031A1Easy alignmentLow costProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorLess invasive surgeryEngineering
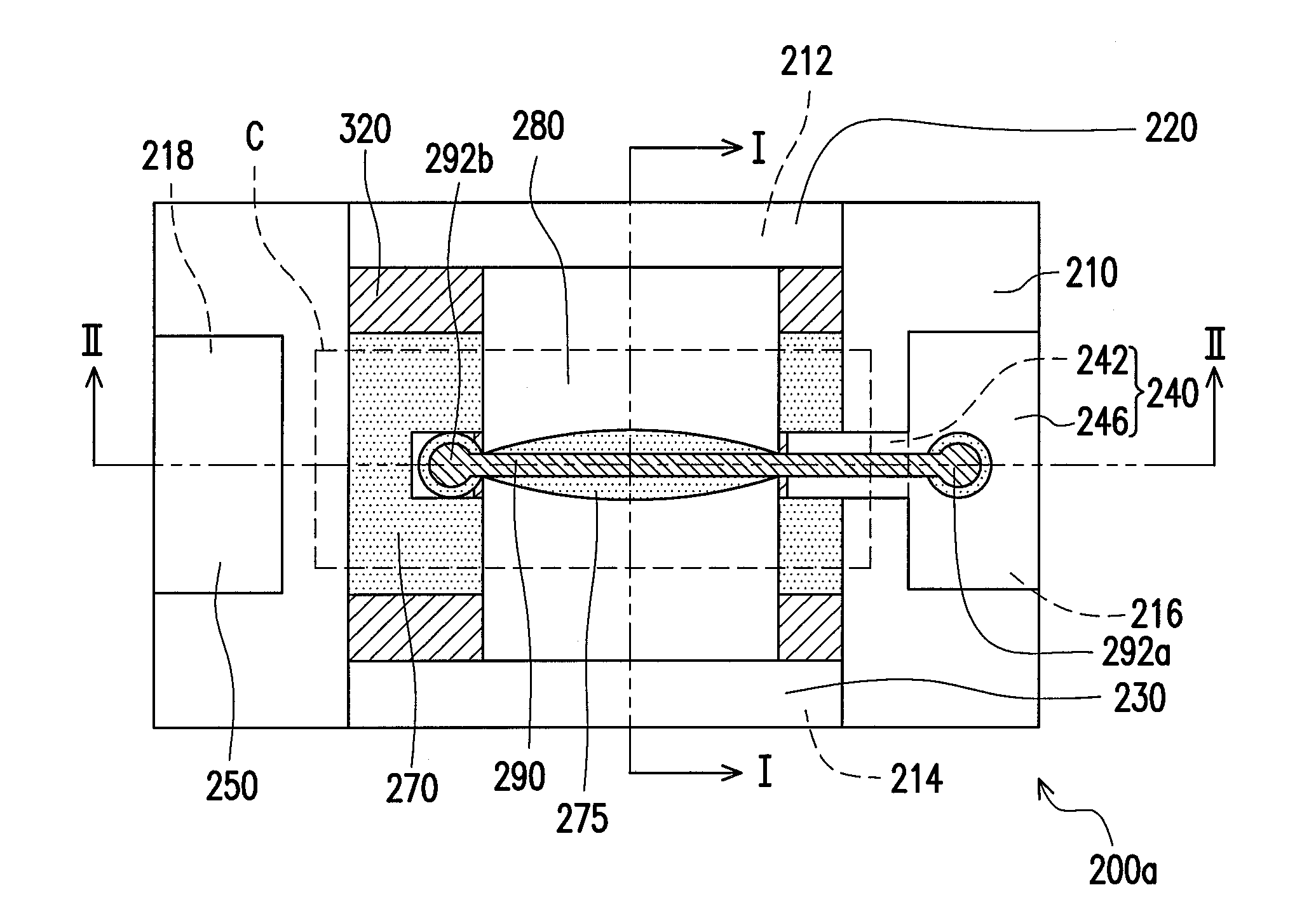
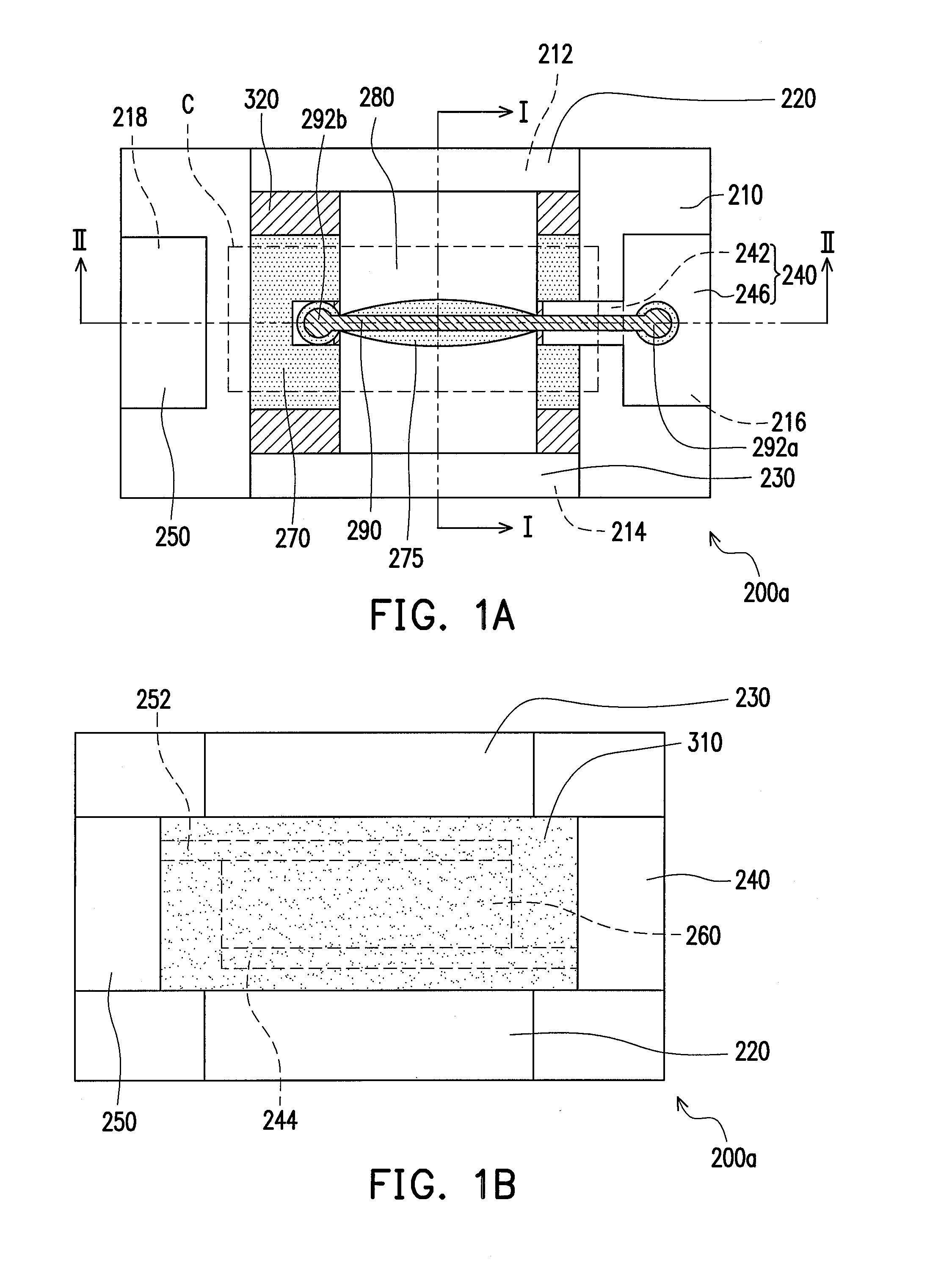
A minimally-invasive surgical system includes a slave surgical instrument having a slave surgical instrument tip and a master grip. The slave surgical instrument tip has an alignment in a common frame of reference and the master grip, which is coupled to the slave surgical instrument, has an alignment in the common frame of reference. An alignment error, in the common frame of reference, is a difference in alignment between the alignment of the slave surgical instrument tip and the alignment of the master grip. A ratcheting system (i) coupled to the master grip to receive the alignment of the master grip and (ii) coupled to the slave surgical instrument, to control motion of the slave by continuously reducing the alignment error, as the master grip moves, without autonomous motion of the slave surgical instrument tip and without autonomous motion of the master grip.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Ratcheting for master alignment of a teleoperated minimally-invasive surgical instrument
ActiveUS8423186B2Easy alignmentLow costProgramme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlLess invasive surgeryEngineering
A minimally-invasive surgical system includes a slave surgical instrument having a slave surgical instrument tip and a master grip. The slave surgical instrument tip has an alignment in a common frame of reference and the master grip, which is coupled to the slave surgical instrument, has an alignment in the common frame of reference. An alignment error, in the common frame of reference, is a difference in alignment between the alignment of the slave surgical instrument tip and the alignment of the master grip. A ratcheting system (i) coupled to the master grip to receive the alignment of the master grip and (ii) coupled to the slave surgical instrument, to control motion of the slave by continuously reducing the alignment error, as the master grip moves, without autonomous motion of the slave surgical instrument tip and without autonomous motion of the master grip.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
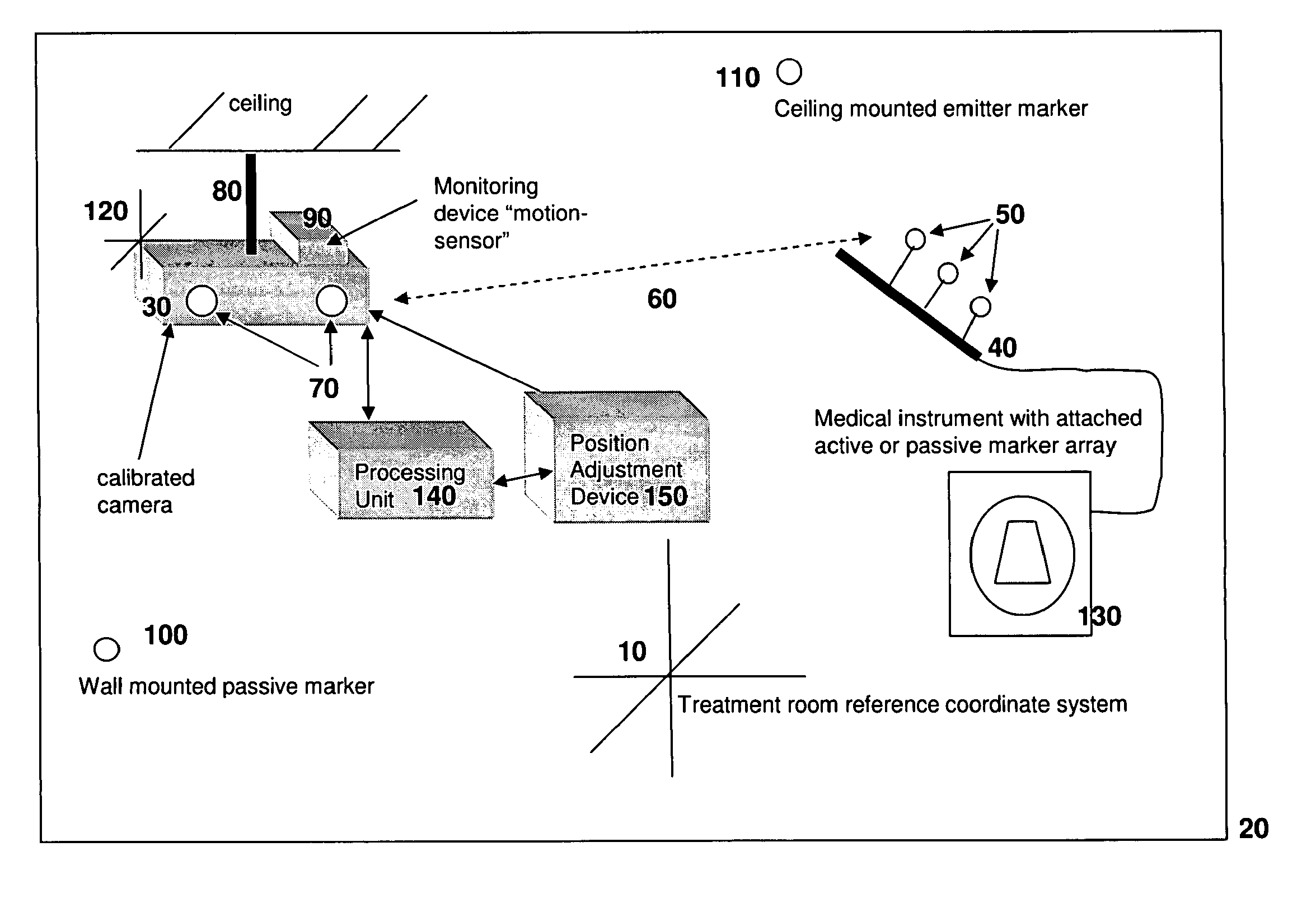
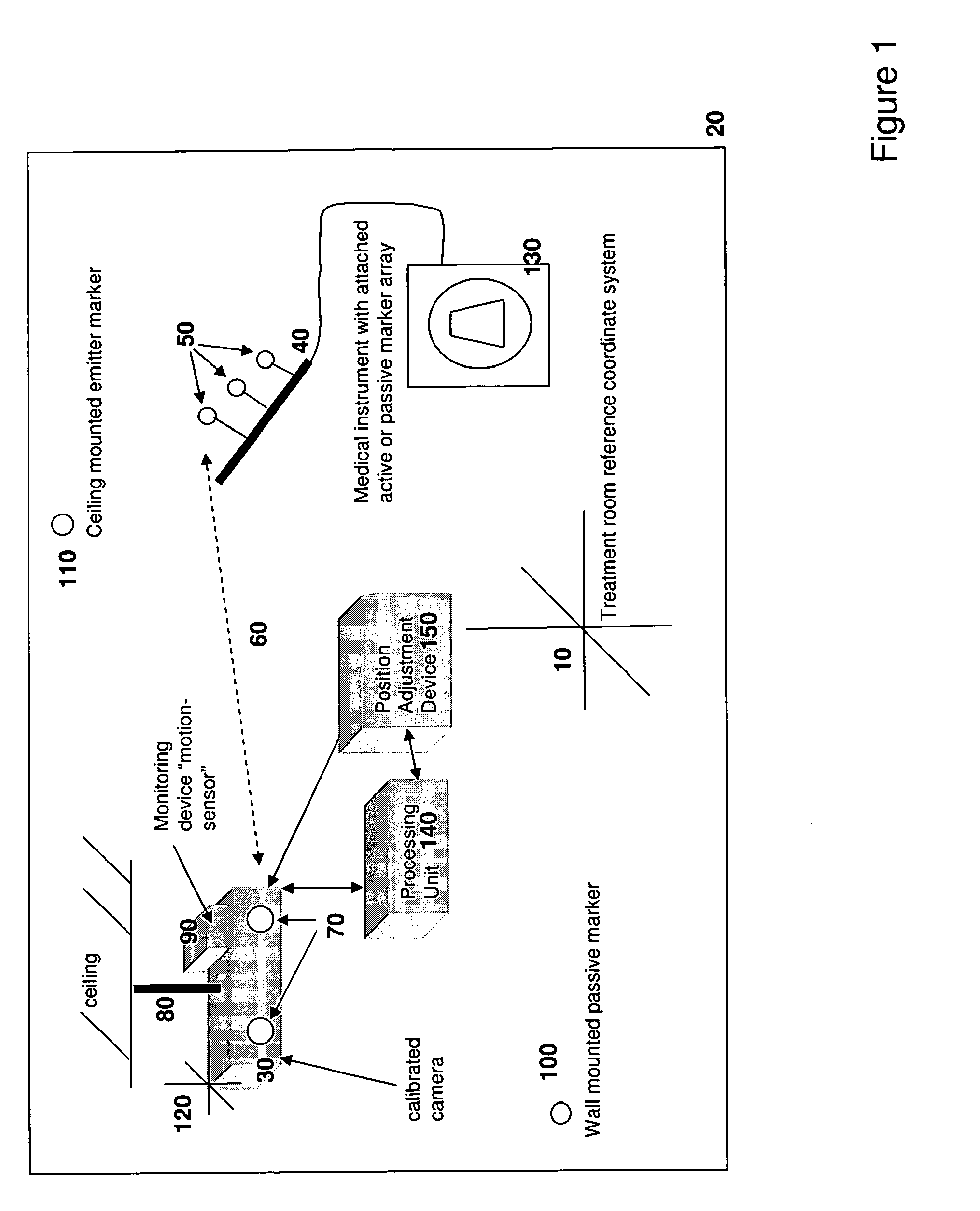
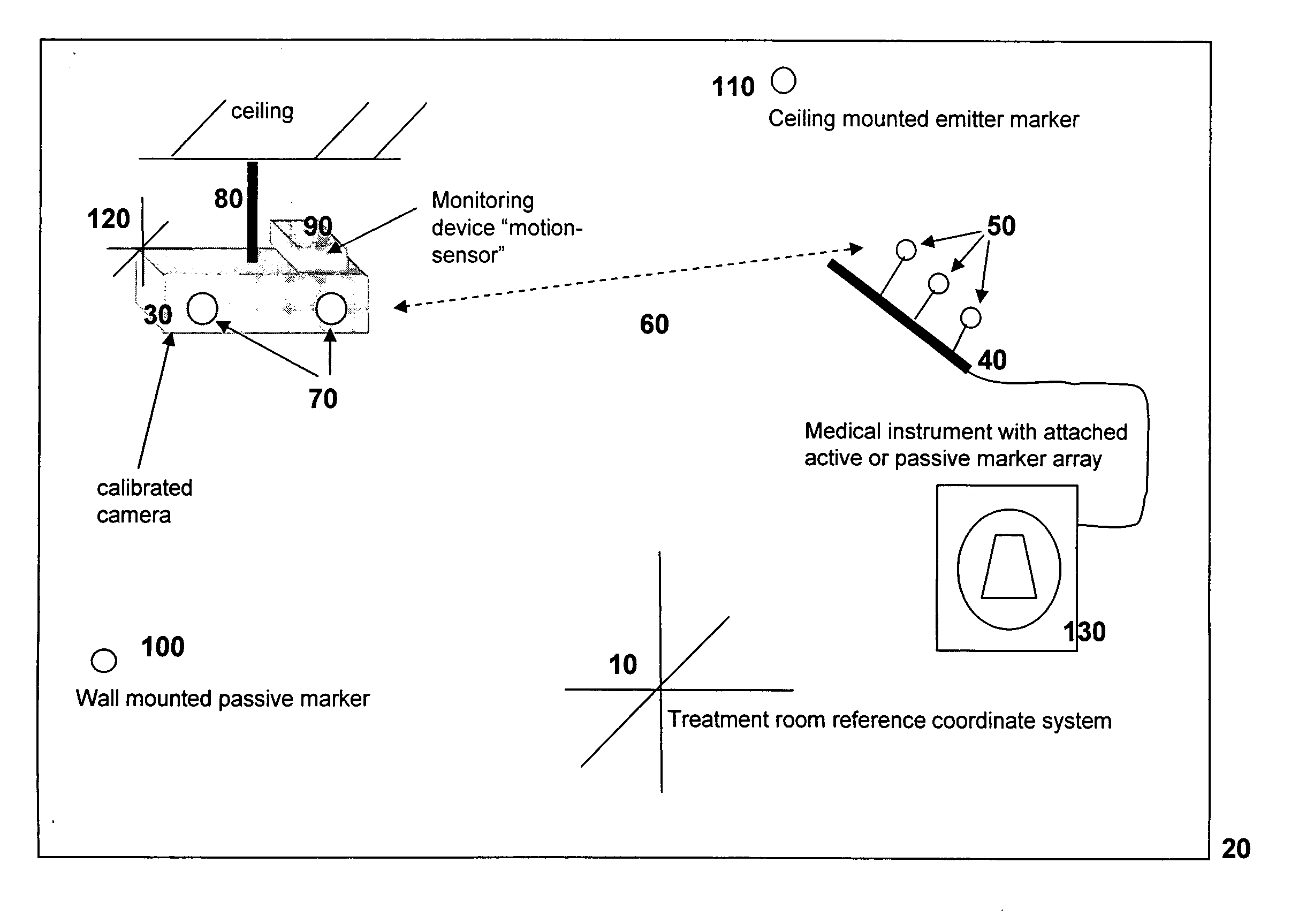
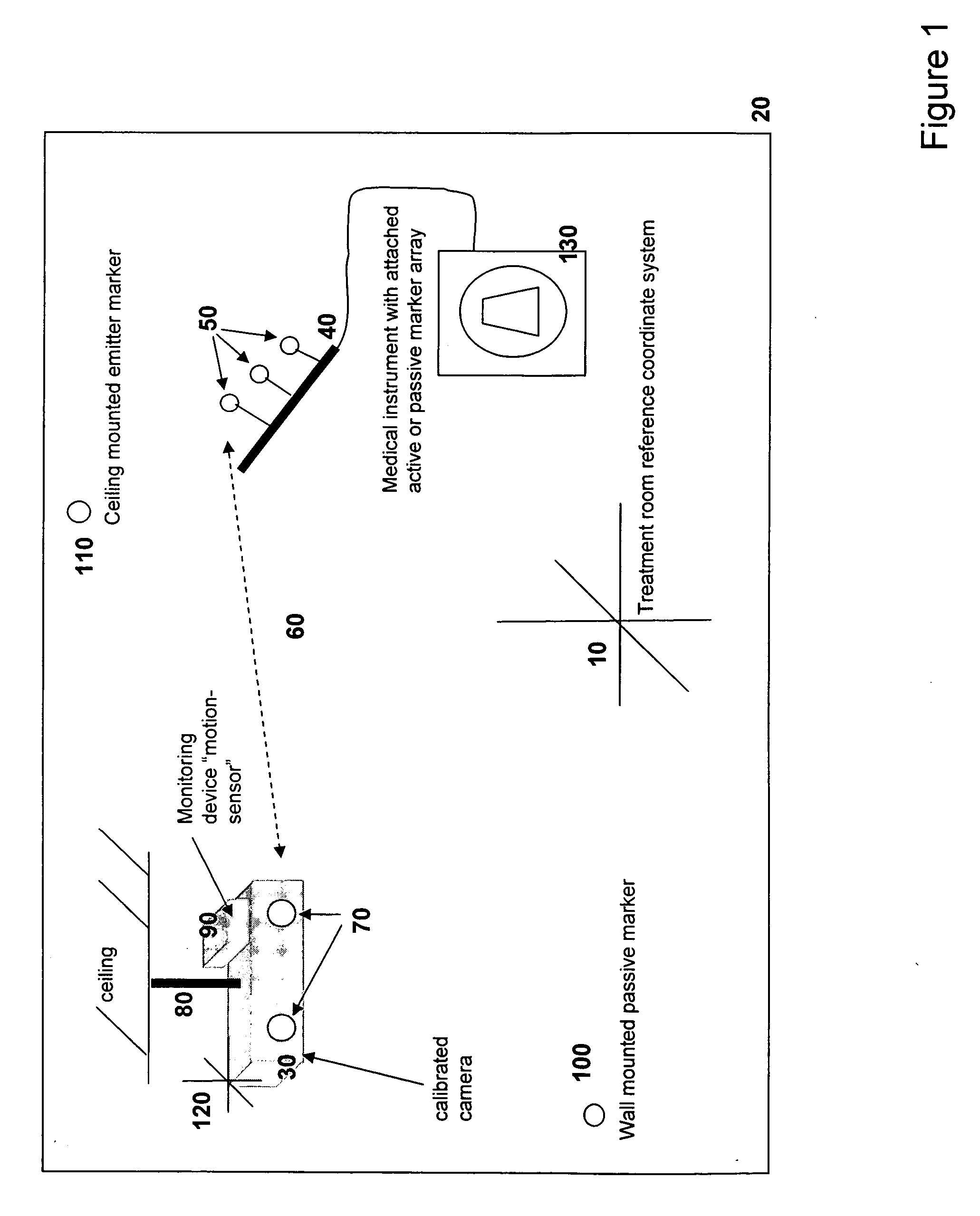
System and method for detecting drifts in calibrated tracking systems
ActiveUS7535411B2Reduce and eliminate errorReduce alignment errorsMeasurement arrangements for variableDiagnostic recording/measuringMedical deviceMedical treatment
A method and system for detecting drift in calibrated tracking systems used to locate features with respect to one or more coordinate systems allows medical devices to be accurately tracked within a reference coordinate system, and facilitates detection and compensation for changes in the orientation of the tracking system with respect to the coordinate system over time.
Owner:RESONANT MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for alignment of components of a plasma arc torch
InactiveUS6946617B2Reliable and repeatable positioningReduce alignment errorsArc welding apparatusPlasma welding apparatusEngineeringTorch
A coolant tube and electrode are adapted to mate with each other to align the tube relative to the electrode during operation of the torch. Improved alignment ensures an adequate flow of coolant along an interior surface of the electrode. In one aspect, an elongated body of the coolant tube has a surface adapted to mate with the electrode. In another aspect, an elongated body of the electrode has a surface adapted to mate with the coolant tube. The surfaces of the tube and electrode may, for example, be flanges, tapered surfaces, contours, or steps.
Owner:HYPERTHERM INC
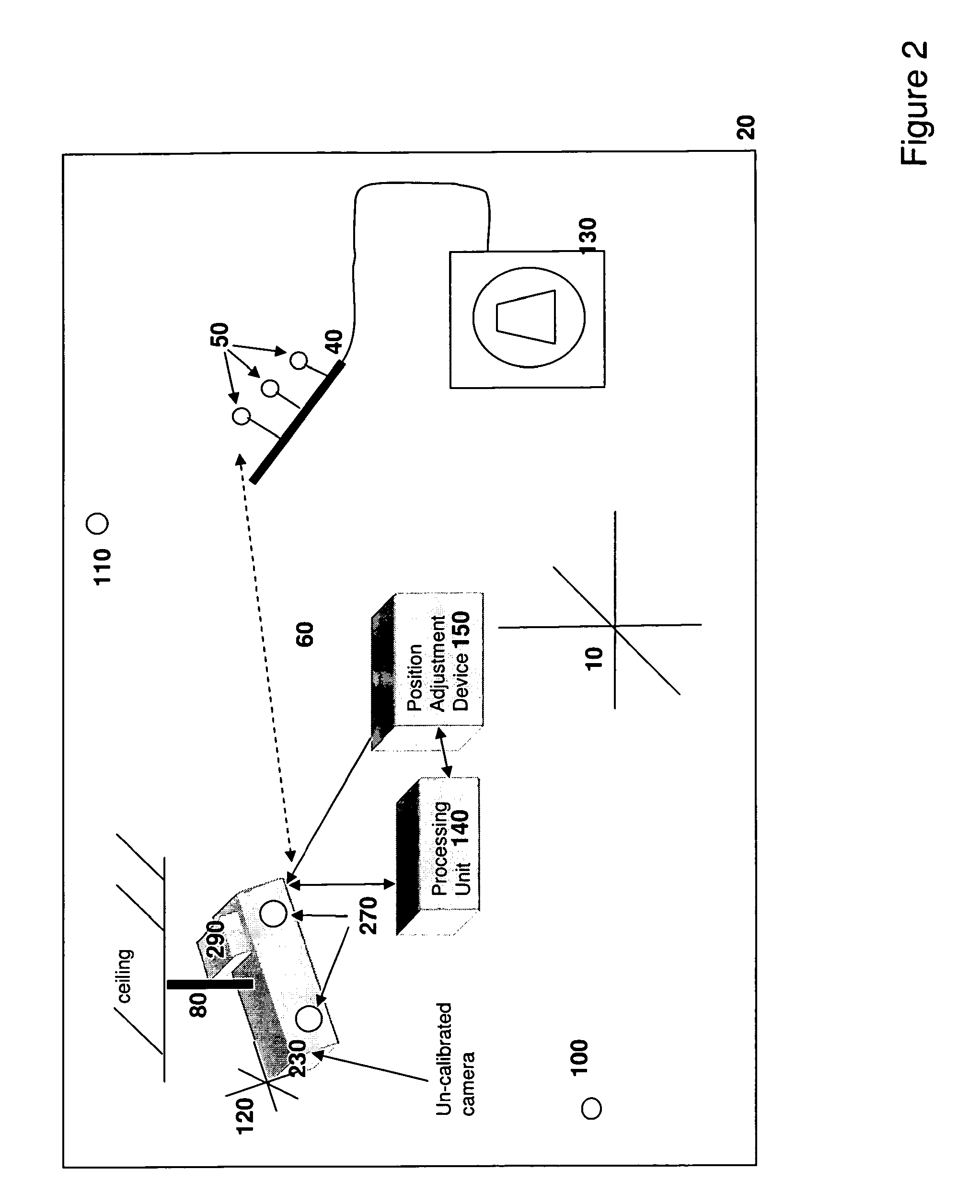
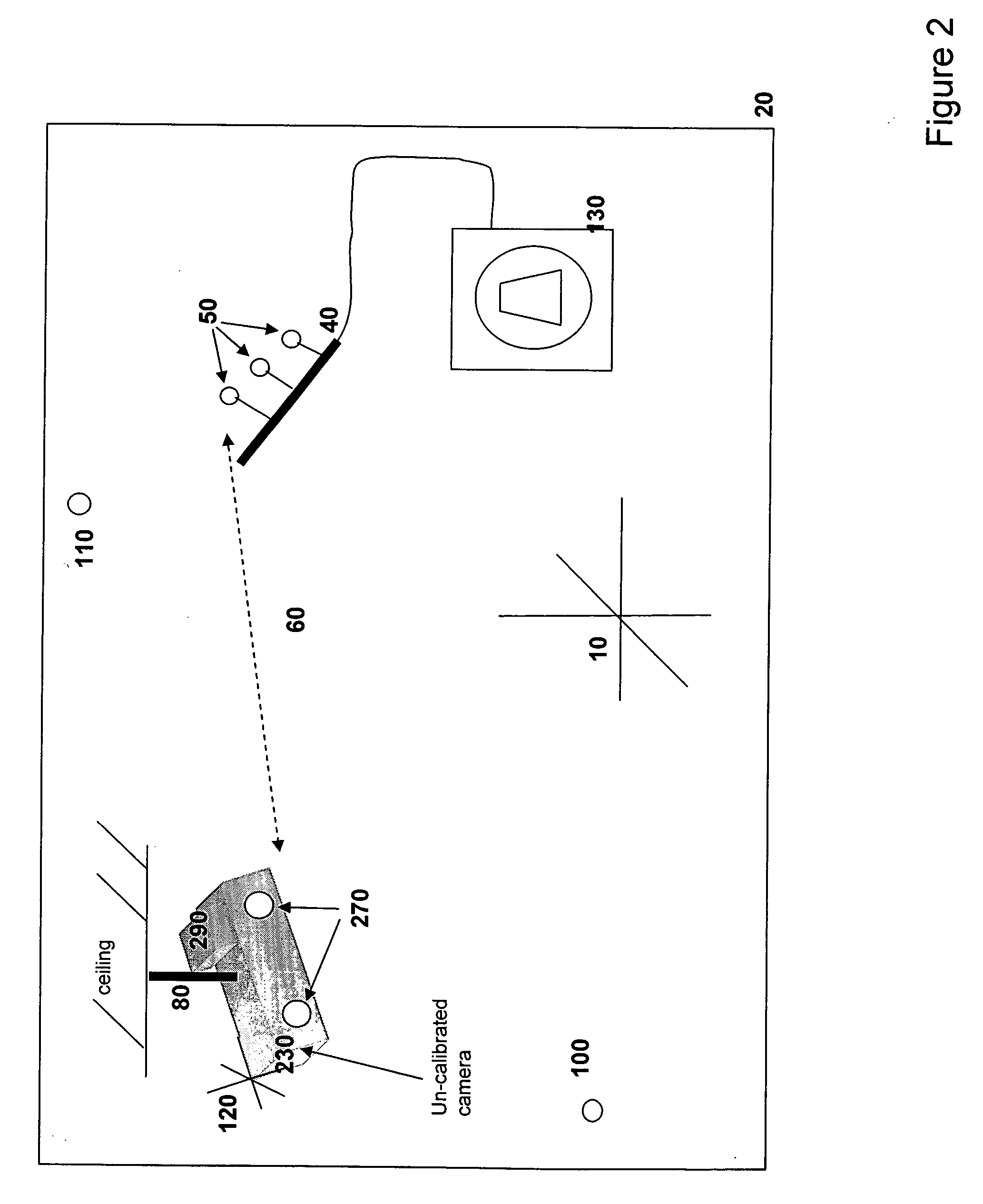
System and method for detecting drifts in calibrated tracking systems
ActiveUS20070034731A1Reduce and eliminate errorReduce alignment errorsMeasurement arrangements for variableDiagnostic recording/measuringCompensatory trackingMedical device
A method and system for detecting drift in calibrated tracking systems used to locate features with respect to one or more coordinate systems allows medical devices to be accurately tracked within a reference coordinate system, and facilitates detection and compensation for changes in the orientation of the tracking system with respect to the coordinate system over time.
Owner:RESONANT MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for alignment of components of a plasma arc torch
InactiveUS20080116179A1Reduce alignment errorReliable and repeatable positioningArc welding apparatusPlasma welding apparatusEngineeringFlange
A coolant tube and electrode are adapted to mate with each other to align the tube relative to the electrode during operation of the torch. Improved alignment ensures an adequate flow of coolant along an interior surface of the electrode. In one aspect, an elongated body of the coolant tube has a surface adapted to mate with the electrode. In another aspect, an elongated body of the electrode has a surface adapted to mate with the coolant tube. The surfaces of the tube and electrode may, for example, be flanges, tapered surfaces, contours, or steps.
Owner:HYPERTHERM INC
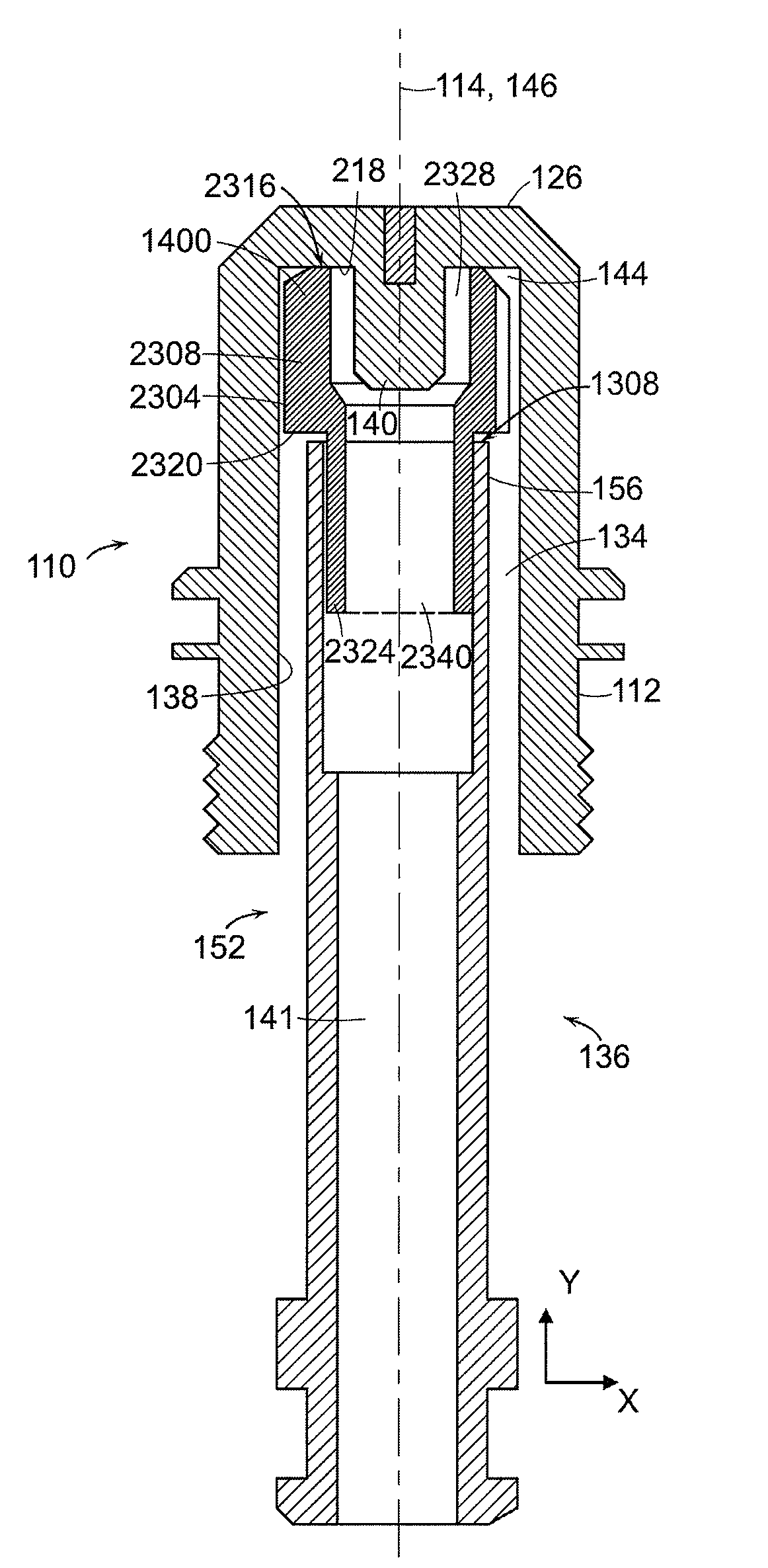
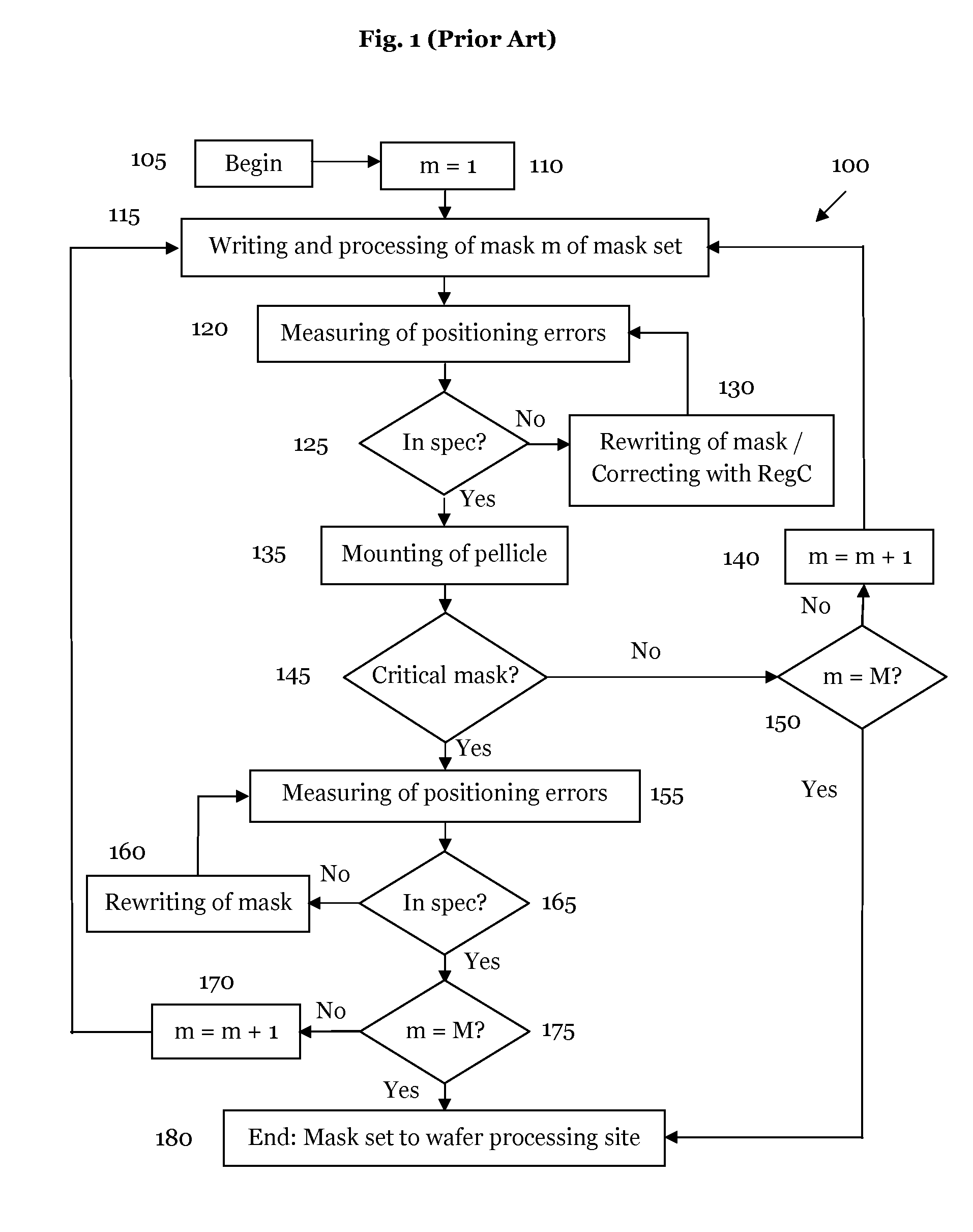
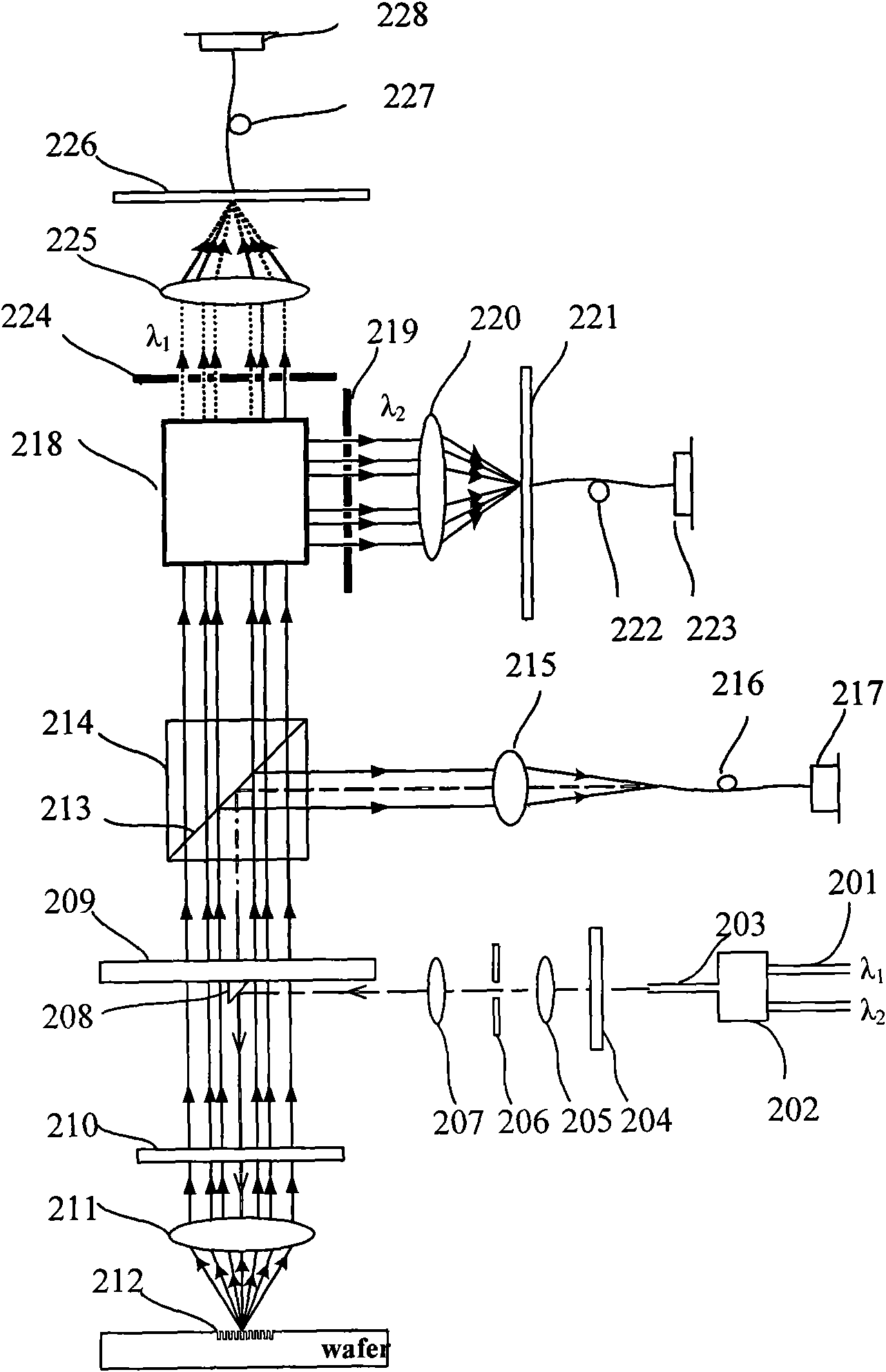
Method and apparatus for correcting errors on a wafer processed by a photolithographic mask
ActiveUS20140036243A1Reduce alignment errorsPhotomechanical apparatusOriginals for photomechanical treatmentComputer scienceProcessing Site
The invention relates to a method for correcting at least one error on wafers processed by at least one photolithographic mask, the method comprises: (a) measuring the at least one error on a wafer at a wafer processing site, and (b) modifying the at least one photolithographic mask by introducing at least one arrangement of local persistent modifications in the at least one photolithographic mask.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMS GMBH +1
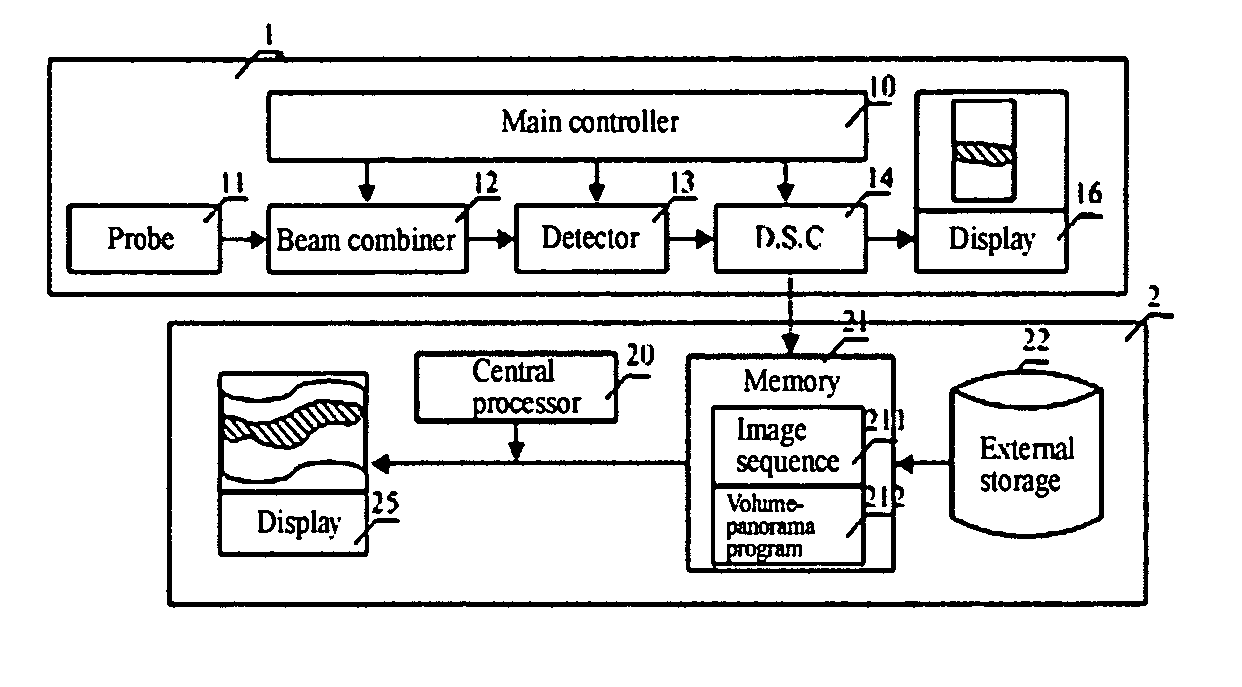
Method of volume-panorama imaging processing
ActiveUS20060239571A1Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingSonification
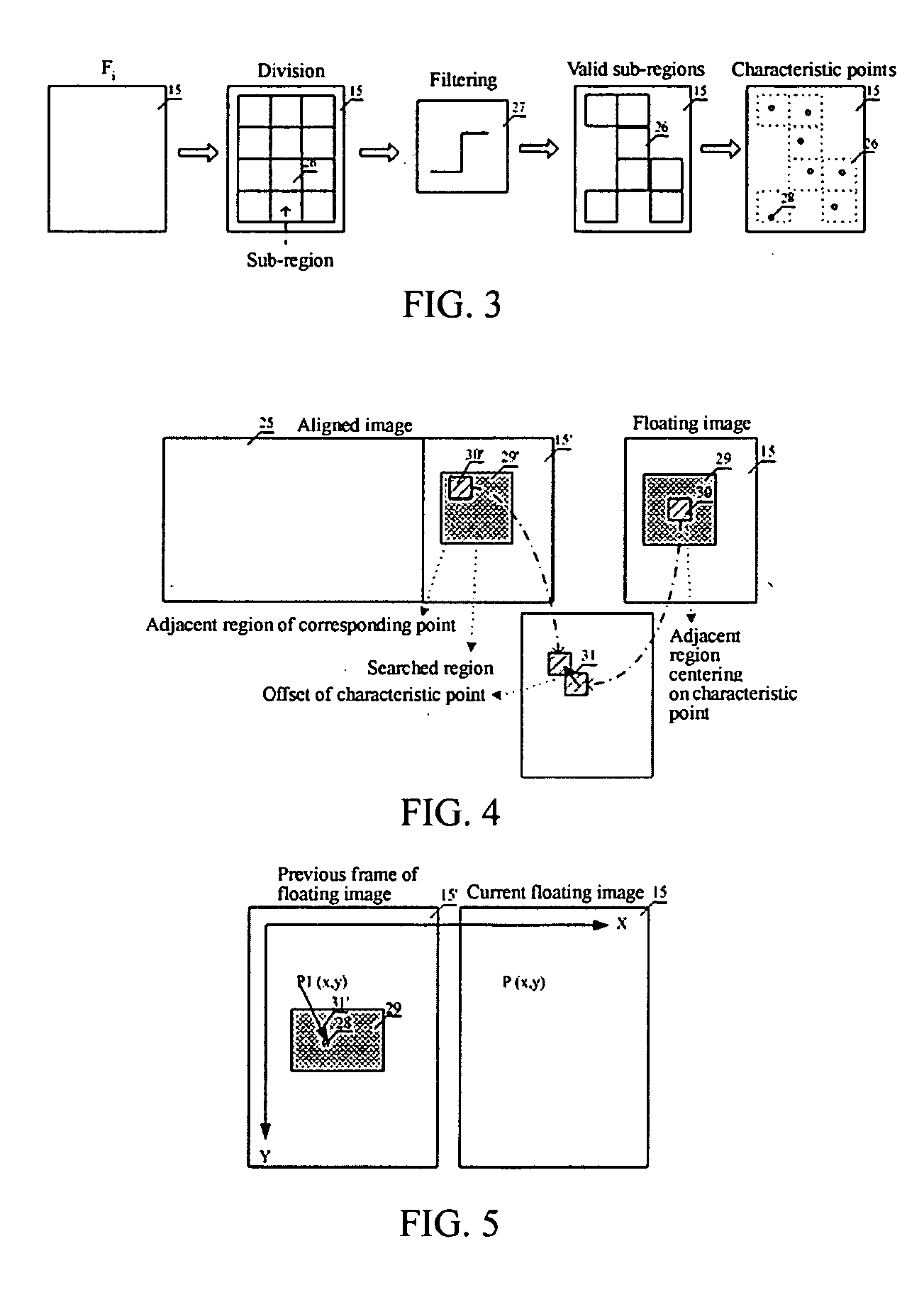
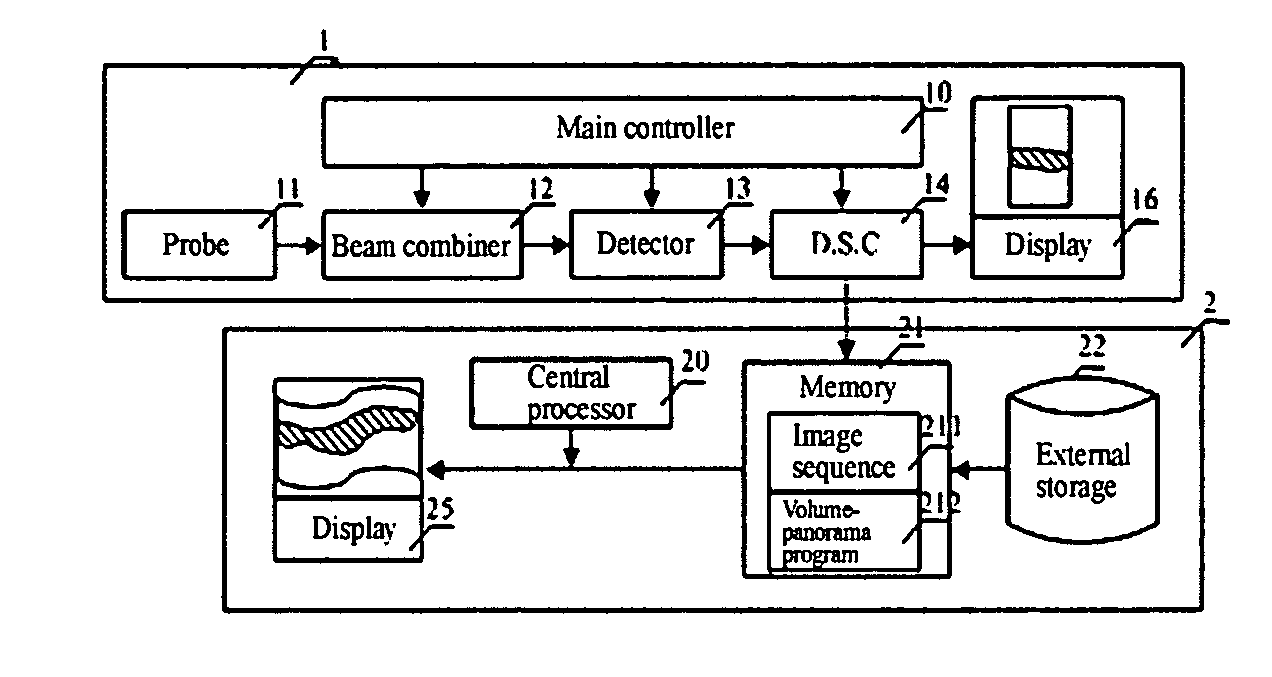
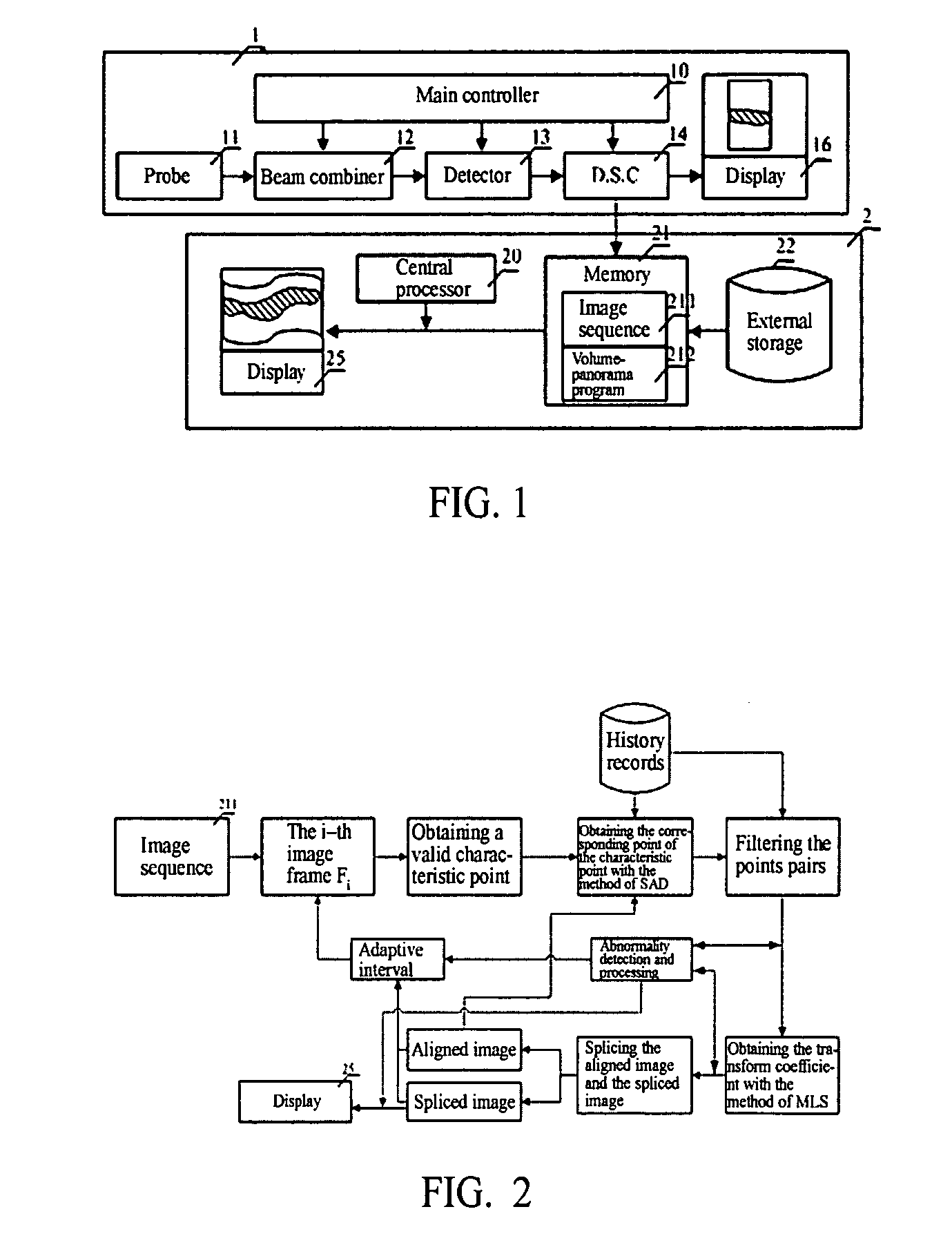
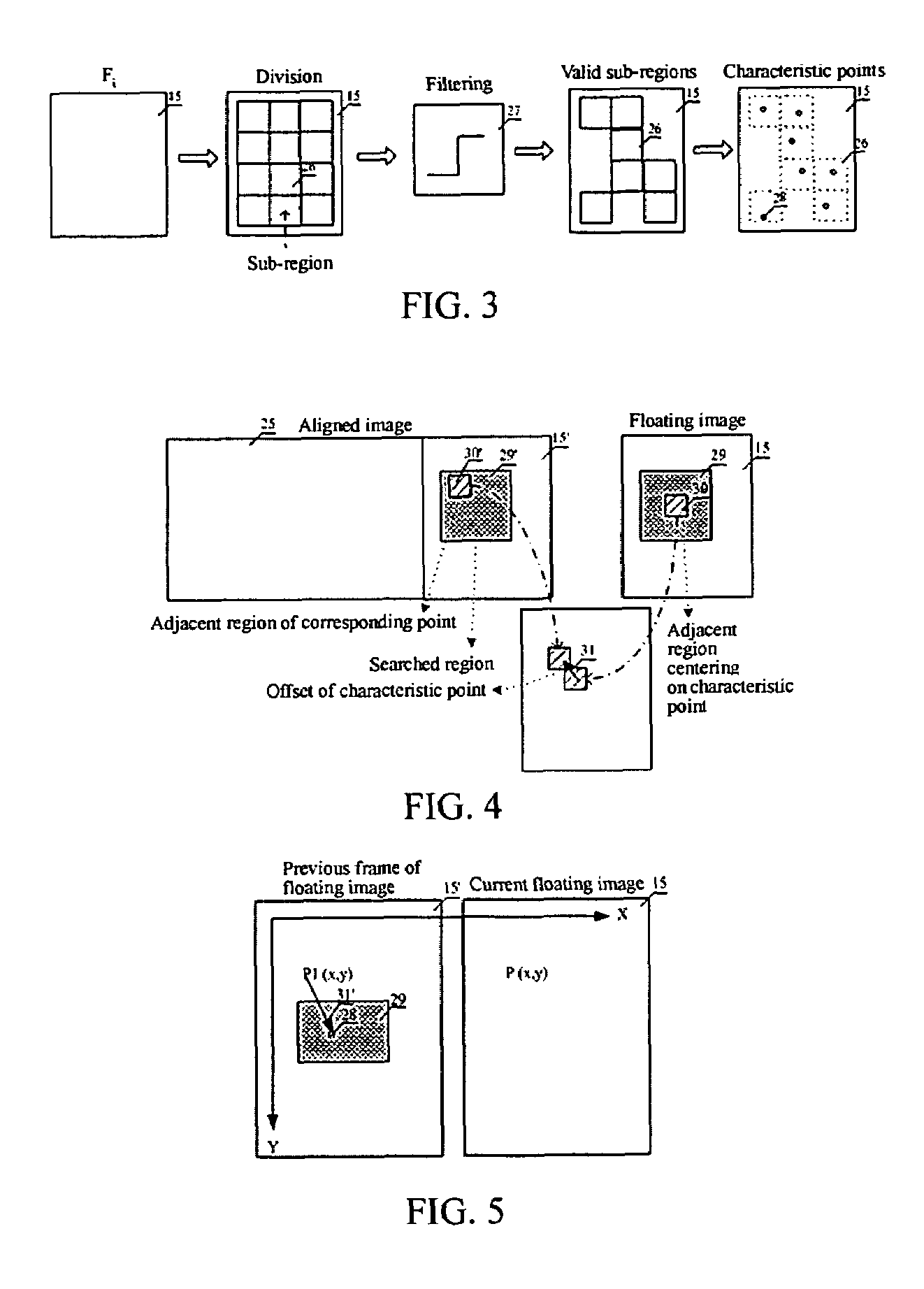
The present invention discloses a method of volume-panorama imaging processing, which generates a volume-panorama image by subsequently splicing respective image frames from an image sequence obtained in a real-time way or stored in a medium based upon the fact that the immediately adjacent image frames have the largest correlation. The method comprises the steps of: reading the image sequence, and firstly initializing an aligned image and a spliced image; dividing the i-th image frame Fi into a plurality of sub-regions; calculating a motion vector of the i-t image frame with respect to the aligned image; fitting the motion vector to calculate a transform coefficient; splicing the Fi to the current spliced image based upon the transform coefficient, and updating the aligned image; entering into a self-adaptive selection of a next image frame until the end of the splicing; and outputting the current spliced image as a resultant image. Additionally, when the image Fi is spliced, double-filtering architecture of selecting characteristic points through a filtering and selecting the valid motion vector of the selected characteristic points through the other filtering to reduce an alignment error may be adopted. According to the present invention, the volume-panorama imaging can be done quickly and accurately so that the reliability of images particularly meets a very high requirement of the ultrasonic iatric diagnose.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method To Control Semiconductor Device Overlay Using Post Etch Image Metrology
InactiveUS20090186286A1Reduce alignment errorsIntroducing additional costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesIntegrated circuitPhotolithography
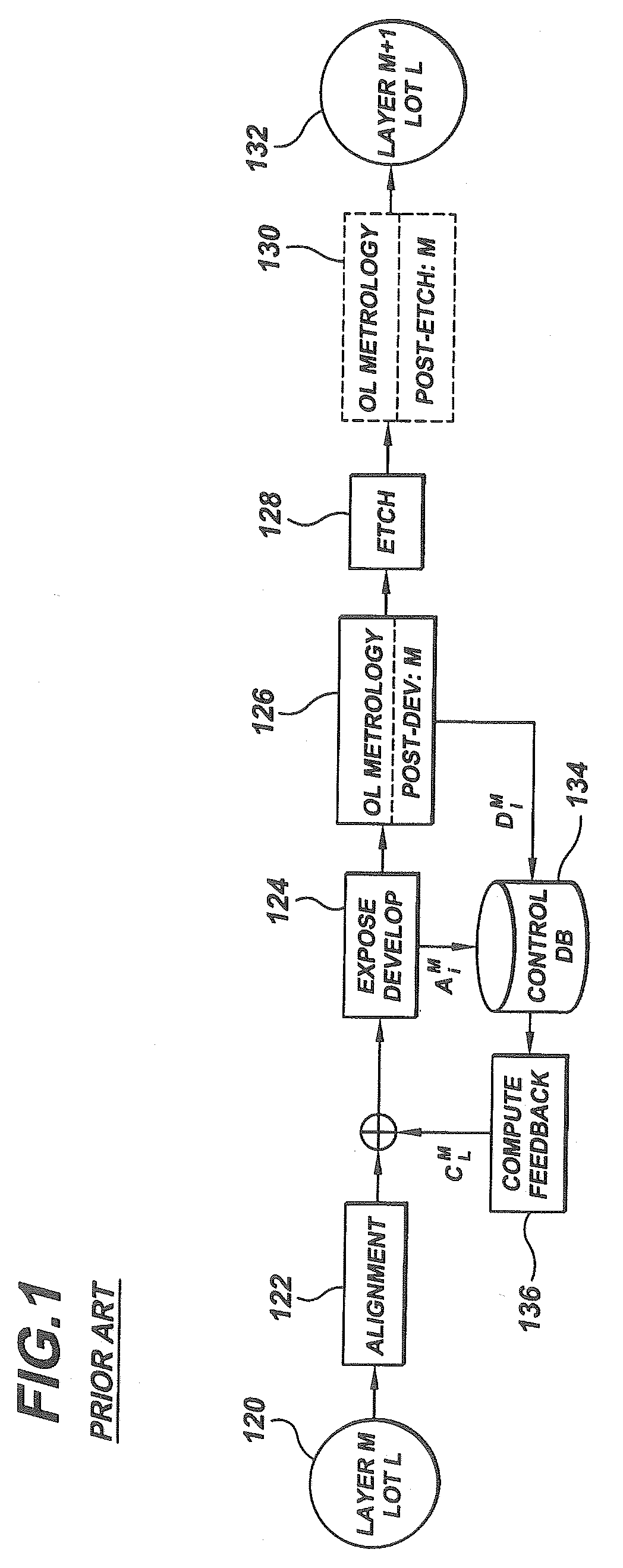
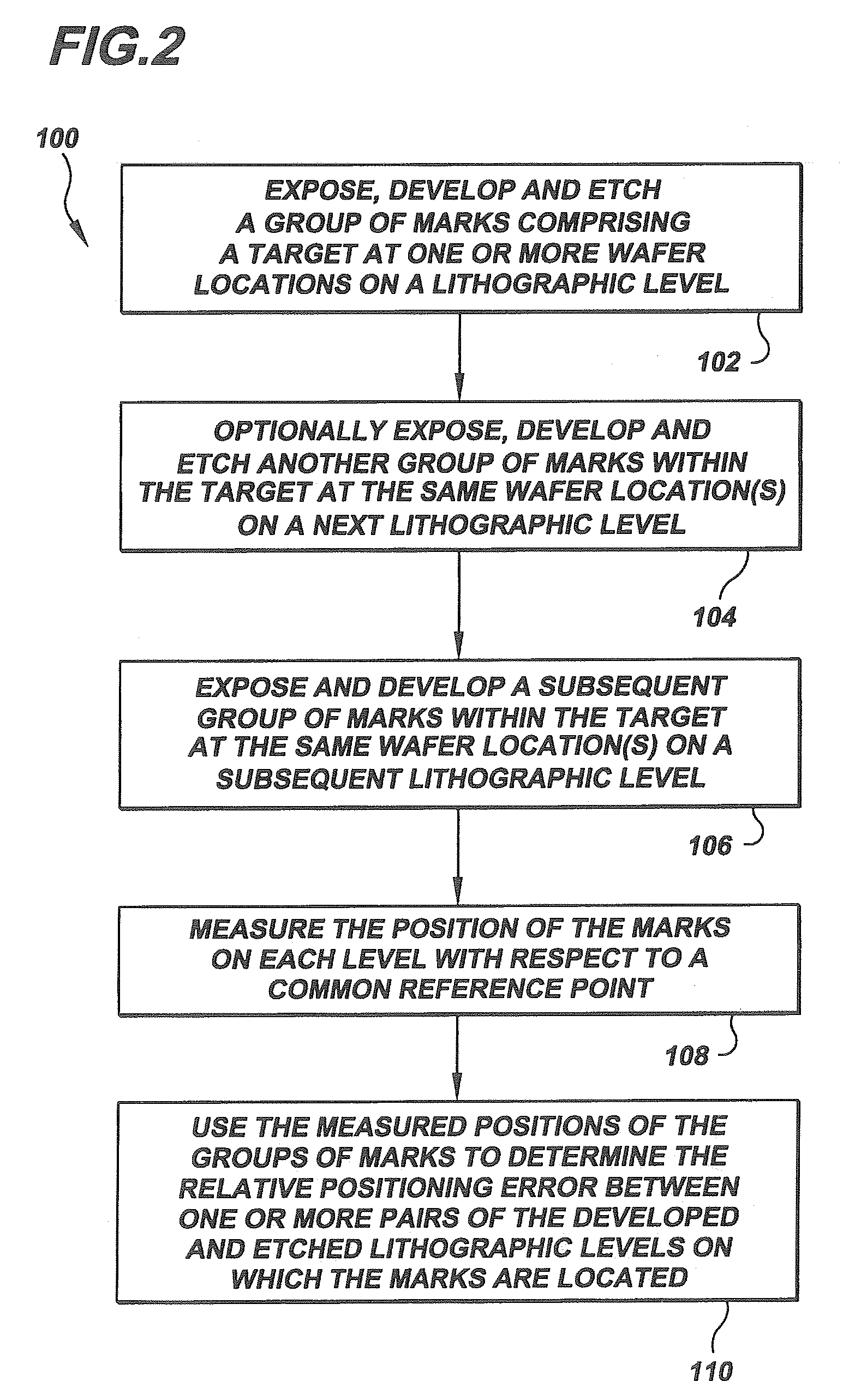
A method of determining positioning error between lithographically produced integrated circuit patterns on at least two different lithographic levels of a semiconductor wafer comprising. The method includes exposing, developing and etching one or more lithographic levels to create one or more groups of marks comprising a target at one or more wafer locations. The method then includes exposing and developing a subsequent group of marks within the target on a subsequent lithographic level. The method then comprises measuring the position of the marks on each level with respect to a common reference point, and using the measured positions of the groups of marks to determine the relative positioning error between one or more pairs of the developed and etched lithographic levels on which the marks are located.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Thin film transistor array substrate as well as application and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101740581AReduce alignment errorsReduce color castSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid-crystal displayTransistor
The invention discloses thin film transistor array substrate as well as application and manufacturing method thereof. The manufacturing method comprises at least the following steps of: providing a substrate; forming a plurality of thin film transistors on the substrate; forming a plurality of first pixel electrodes on the substrate; forming an electrode insulating layer on the first pixel electrodes; and forming a plurality of second pixel electrodes on the electrode insulating layer. The thin film transistor array substrate can be used in a liquid crystal display panel or a liquid crystal display device.
Owner:INNOLUX CORP
Highly aligned thin film tape head
InactiveUS6496329B2Improved tape head element alignmentEasy alignmentManufacturing heads with multiple gapsManufacture unitary devices of plural headsComputer hardwareData density
Reducing alignment errors between a read element and corresponding write elements permits narrower data tracks and, hence, greater data density on magnetic tape. A method for manufacturing a thin film tape head having multiple write elements and at least one read element corresponding to each write element is provided. Excess material is trimmed from each write element to align the write element with corresponding read elements. The excess material may be track trimmed using a focused ion beam.
Owner:STORAGE TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
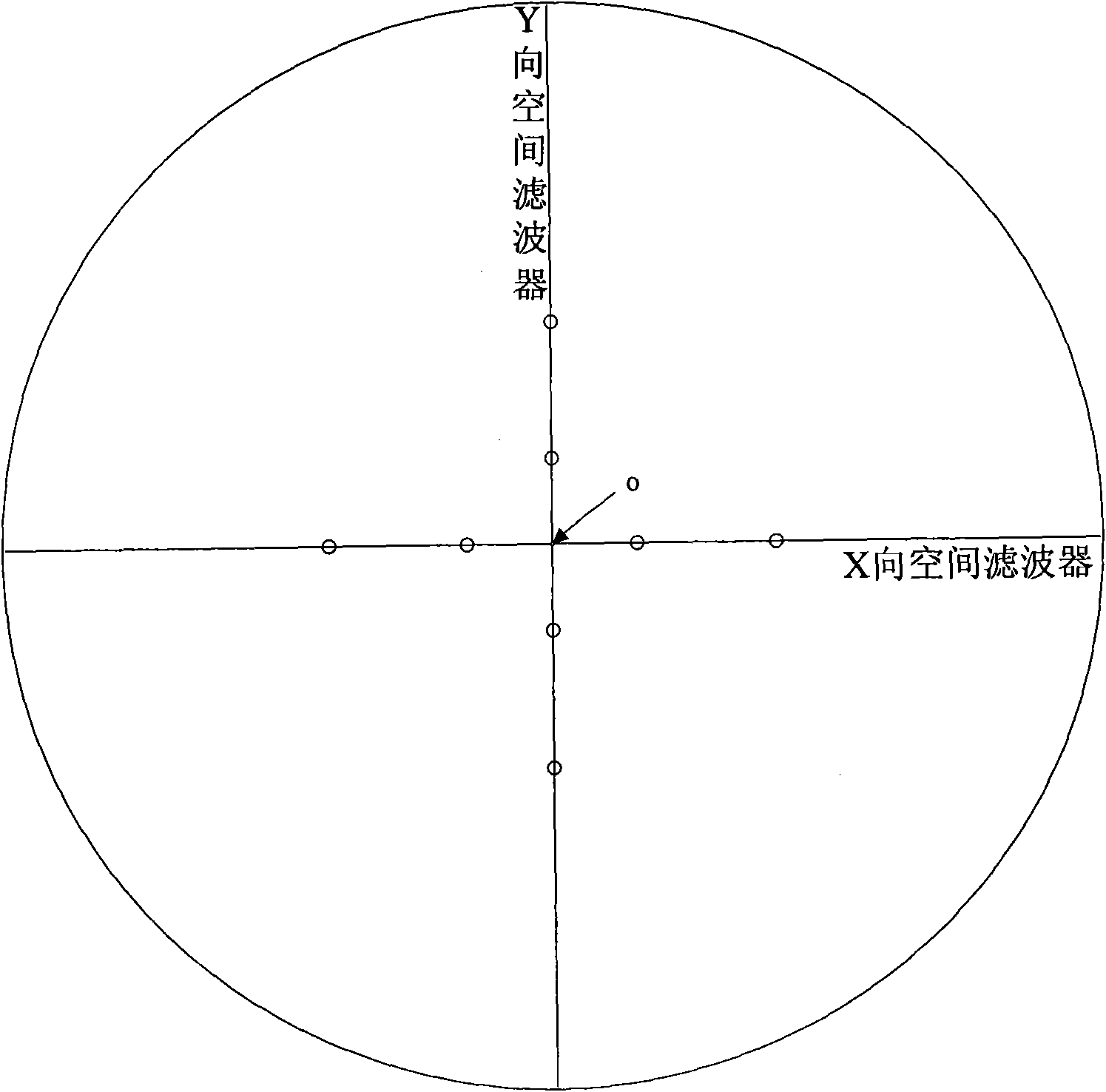
Aligning mark used for photolithography equipment aligning system and its use method
ActiveCN101299132AAvoid crosstalkImprove energy utilizationPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusGratingPosition error
The present invention provides an aligning mark which is used for the aligning system of the photo-etching device and a using method thereof. The aligning mark comprising at least three groups of raster with different periods is used. The + / -1 grade diffraction lights of three groups of raster are used in the aligning process. Two large-period raster in three groups of raster are used for coarse alignment. A small-period raster is used for refined alignment. The alignment position error caused by the asymmetrical deformation of the aligning mark is reduced. The small period raster and the large period raster are spatially staggered. The corresponding interface images are spatially divided in the image surface. The crosstalk problem of signal is effectively settled. The energy usage of light source is increased. The intensity of aligning signal and the dynamic range of detection are facilitated to increase.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD +1
Reflection-type TFT LCD and making method thereof
The invention relates to a reflection-type TFT (Thin Film Transistor) LCD (liquid crystal display) and a making method thereof. A light absorption layer is arranged below a reflection surface, rays can enter the light absorption layer below the reflection surface through a light absorption gap and can be absorbed by the light absorption layer without irradiating the upper surface of a driving part to cause the failure of the driving part. Accordingly, the light absorption layer can substitute a black light-shielding layer in the prior art, and a black border region is formed between two adjacent pixels. The pixel electrodes or the reflection layer is extremely thin, and the pattern making thereof has extremely high accuracy so that the pattern of the black border region also has extremely high accuracy. Moreover, the black border region and the pixel electrodes are formed on the same substrate, the problem of pattern pasting contraposition errors among different substrates is inessential, and contraposition errors of different film layers of the same substrate are generally very small so that the black border region can be designed very narrow to acquire a larger pixel reflection display area and an effective reflection area ratio.
Owner:SHANTOU GOWORLD DISPLAY (PLANT II) CO LTD
Thermally enhanced thin semiconductor package
InactiveUS20090057852A1Accelerated dissipationReduce alignment errorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipSemiconductor package
A semiconductor die package is disclosed. The semiconductor die package includes a semiconductor die comprising an input at a first top semiconductor die surface and an output at a second bottom semiconductor die surface. A leadframe having a first leadframe surface and a second leadframe surface opposite the first leadframe surface is in the semiconductor die package and is coupled to the first top semiconductor die surface. A clip having a first clip surface and a second clip surface is coupled to the second bottom semiconductor die surface. A molding material having exterior molding material surfaces covers at least a portion of the leadframe, the clip, and the semiconductor die. The first leadframe surface and the first clip surface are exposed by the molding material, and the first leadframe surface, the first clip surface, and the exterior molding material surfaces of the molding material form exterior surfaces of the semiconductor die package.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
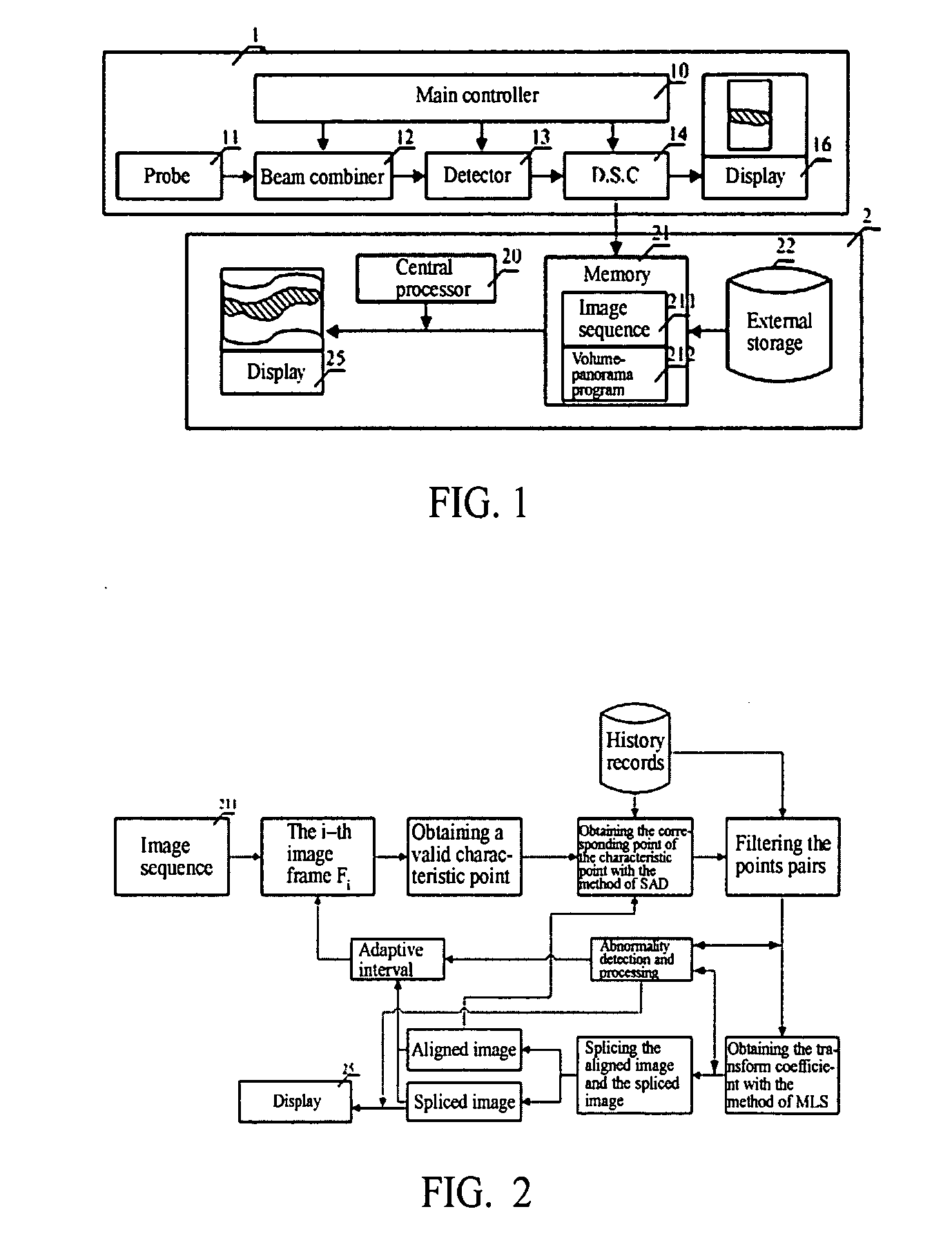
Method of volume-panorama imaging processing
ActiveUS7565019B2Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingPanorama
The present invention discloses a method of volume-panorama imaging processing, which generates a volume-panorama image by subsequently splicing respective image frames from an image sequence obtained in a real-time way or stored in a medium based upon the fact that the immediately adjacent image frames have the largest correlation. The method comprises the steps of: reading the image sequence, and firstly initializing an aligned image and a spliced image; dividing the i-th image frame Fi into a plurality of sub-regions; calculating a motion vector of the i-t image frame with respect to the aligned image; fitting the motion vector to calculate a transform coefficient; splicing the Fi to the current spliced image based upon the transform coefficient, and updating the aligned image; entering into a self-adaptive selection of a next image frame until the end of the splicing; and outputting the current spliced image as a resultant image. Additionally, when the image Fi is spliced, double-filtering architecture of selecting characteristic points through a filtering and selecting the valid motion vector of the selected characteristic points through the other filtering to reduce an alignment error may be adopted. According to the present invention, the volume-panorama imaging can be done quickly and accurately so that the reliability of images particularly meets a very high requirement of the ultrasonic iatric diagnose.
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Aligning system and aligning method for lithography equipment
ActiveCN101566800AImprove reliabilityReduce complexityPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusGratingLithographic artist
The invention provides an aligning system and an aligning method for a lithography equipment, which adopts two or more groups of amplitude-type reference grating and aligning marks of different periods; each branch grating of the reference grating and the aligning marks consist of bar-shaped structures with equidifferent arrangement widths so as to lead the scanning intensity signal peak to be sharper and improve the reliability of the aligning system; during the aligning process, only (plus and minus) 1 stage of diffracted beam with aligned marks is used; after the small period grating coherent image and corresponding reference gratings in the aligned marks are scanned, the obtained scanning signal intensity peak is used as coarse capture; based on coarse capture, the precise capture information is obtained by the phase information of the large period grating coherent images in the aligned marks; furthermore, the phase information obtained by scanning the large period grating coherent image and the corresponding reference grating in the aligned marks is used for precise alignment; and the alignment position error caused by asymmetric deformation of the alignment marks is reduced, the complexity of the optical system is reduced and the utilization ratio of the optical energy is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD +1
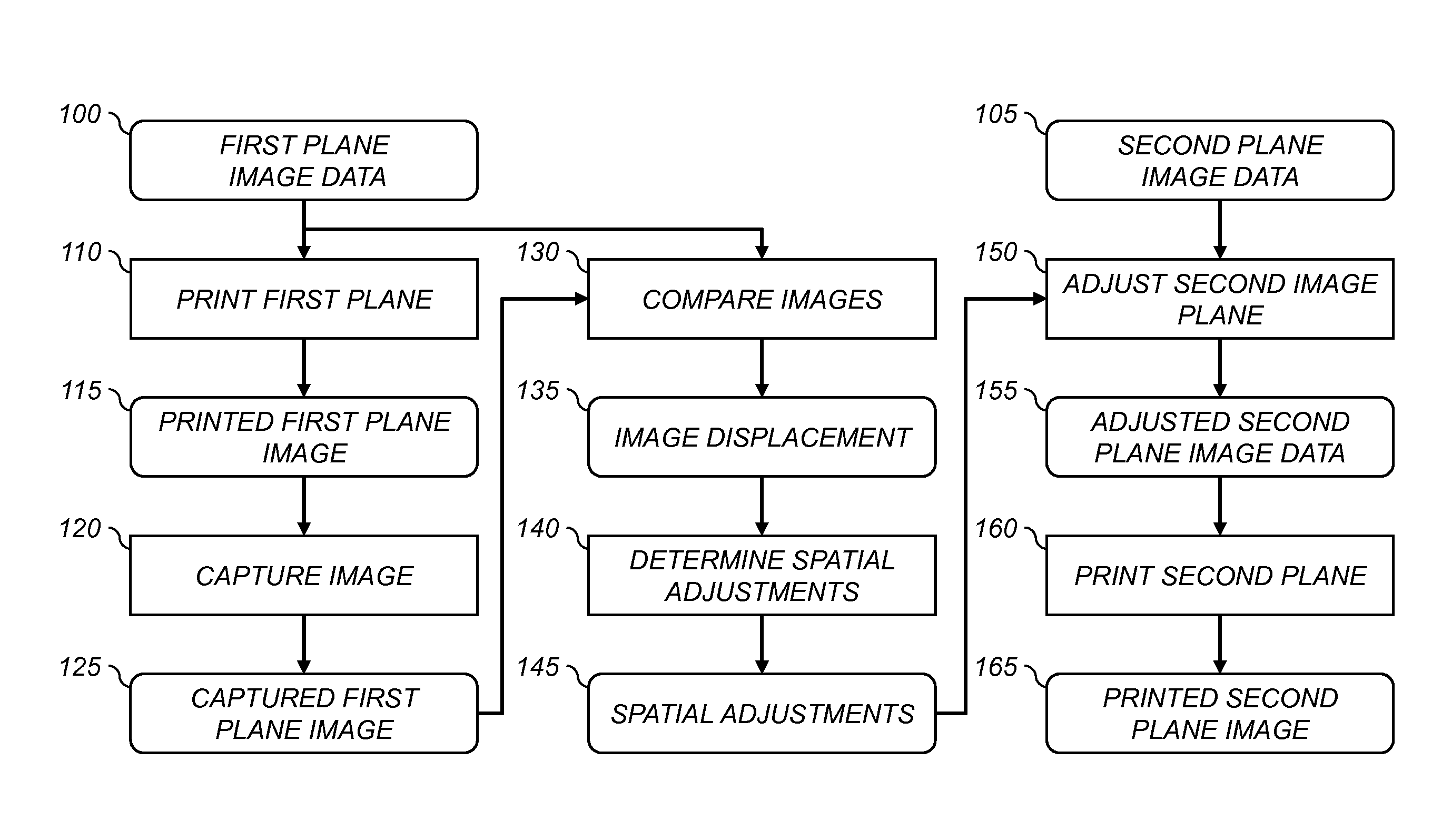
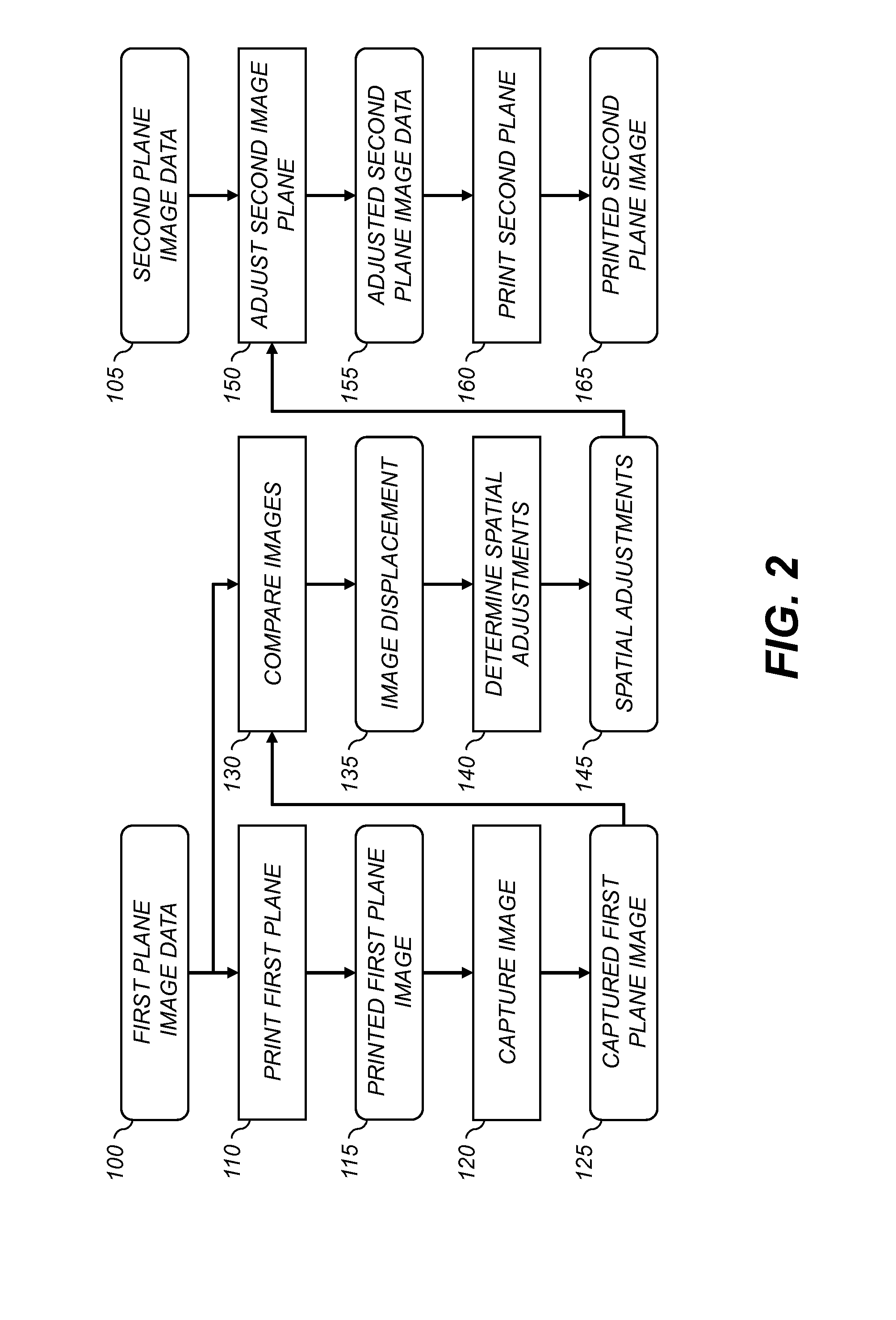
Printer with image plane alignment correction
InactiveUS20150116734A1Reduce alignment errorsCorrect distortionImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersComputer graphics (images)Computer printing
A printer includes first and second marking units for printing respective first and second image planes on a receiver medium. A digital image capture system is positioned between the first and second marking units, and is used to capture an image of a printed first image plane. Image data for the first image plane is compared to the captured image to determine a displacement between a nominal location and an actual location of the printed image data. Corresponding spatial adjustments are applied to image data for the second image plane to reduce alignment errors between the printed image data for the first and second image planes.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Alignment location device
ActiveCN102849444AGuaranteed synchronicityImprove alignment rateConveyor partsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:SHENNAN CIRCUITS
Semiconductor device having align mark layer and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS7482703B2Reduce alignment errorsCost-effectiveSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialSemiconductor
A semiconductor device includes a pad electrode layer and an align mark layer, formed on the semiconductor substrate. A passivation layer is formed on the semiconductor substrate and exposes at least a portion of the top of the pad electrode layer and at least a portion of the top of the align mark layer. A light-transmitting protecting layer covers at least a portion of the passivation layer, exposes the top portion of the pad electrode layer exposed from the passivation layer, and covers the portion of the align mark layer exposed from the passivation layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
A method to determine an alignment errors in image data and performing in-track alignment errors correction using test pattern
ActiveUS20140285828A1Improve visibilityReduce alignment errorsDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsPattern recognitionImaging data
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Aligning system, mark, method for lithographic device and lithographic device thereof
ActiveCN101251725AReduce alignment errorSolve signal crosstalkPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusCoherent imagingLight source
The present invention discloses an alignment system, an alignment mark and an alignment method for photoetching devices, as well as a photoetching device. By detecting light intensity changes of +-1 grade diffraction light of a first grating, a second grating and a third grating of the alignment mark on an image plane, wherein the +-1 grade diffraction light is modulated via a reference grating after coherent imaging, the center position of the alignment mark is acquired through the phase information of transmitted light signals, wherein the rough position information of the alignment mark is acquired through the alignment signals of the first grating and the second grating of the alignment mark; the exact position information of the alignment mark is acquired through the alignment signals of the third grating of the alignment mark. The alignment system reduces alignment position error caused by the asymmetrical deformation of the alignment mark, effectively solves the problems of signal crosstalk, improves the energy utilization ratio of a light source, and is beneficial to improve the intensity of alignment signals and the dynamic range of detection.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Aligning correction device and method for space navigation detector ground calibration
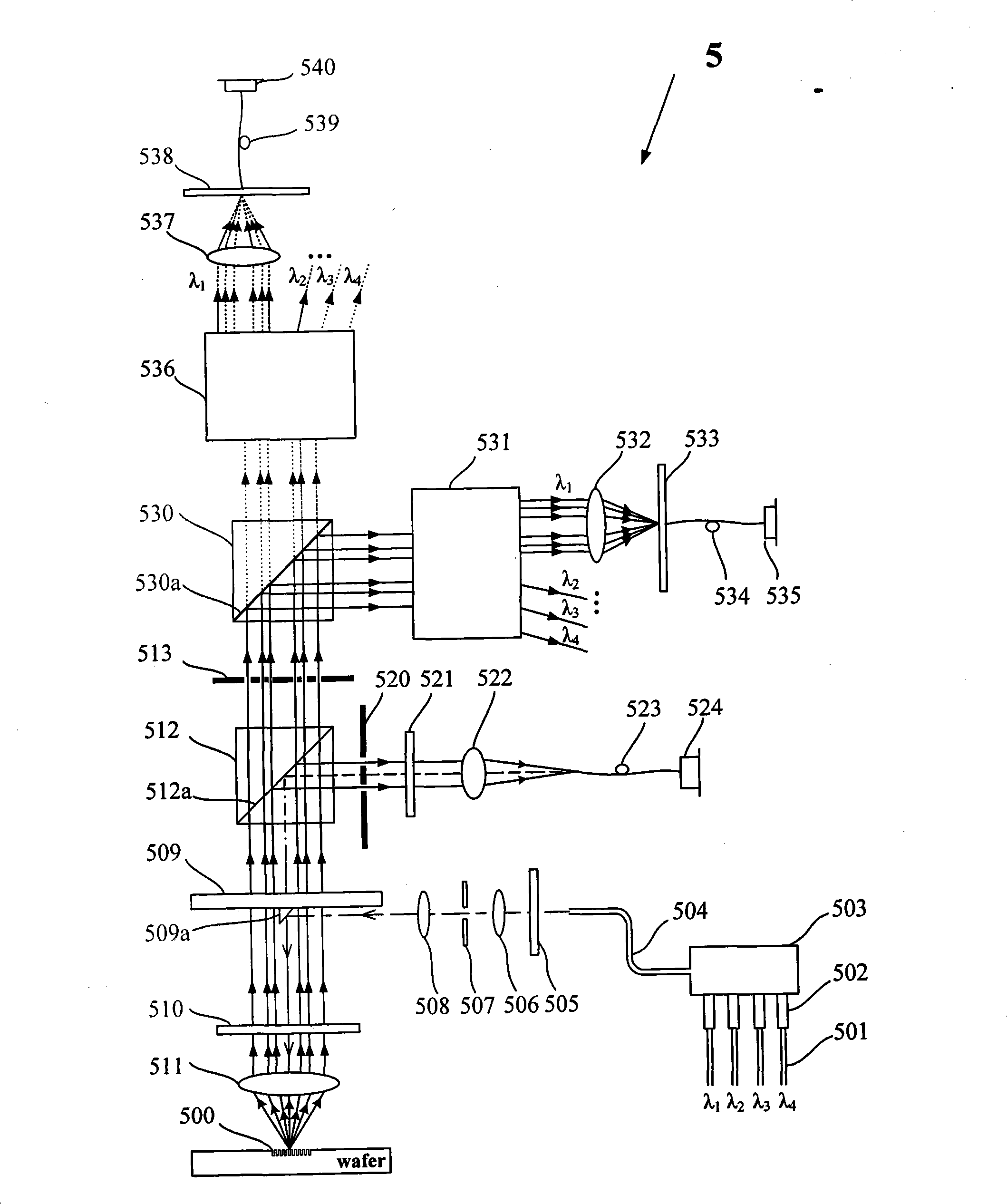
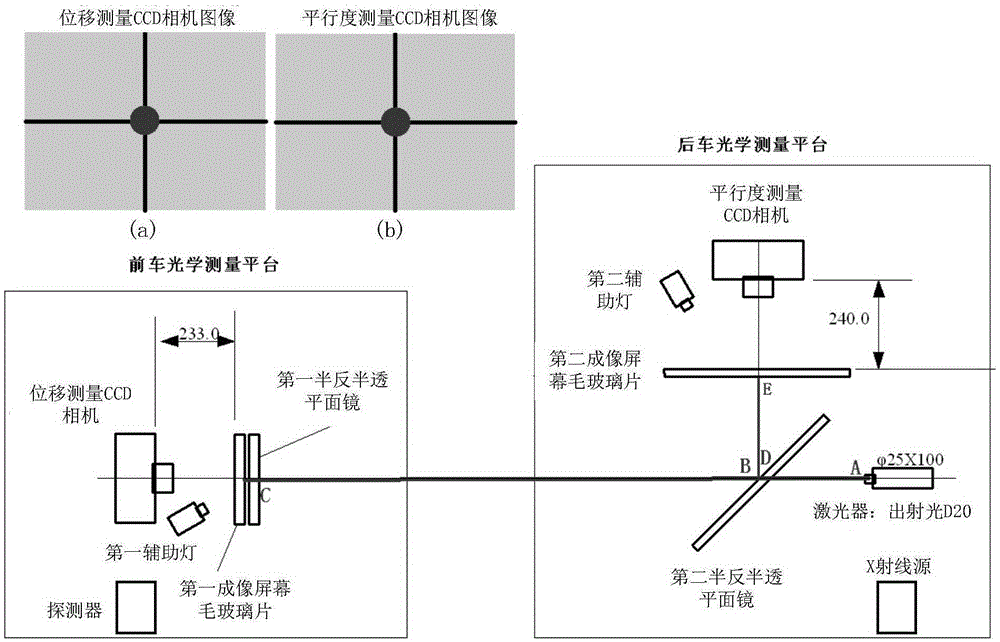
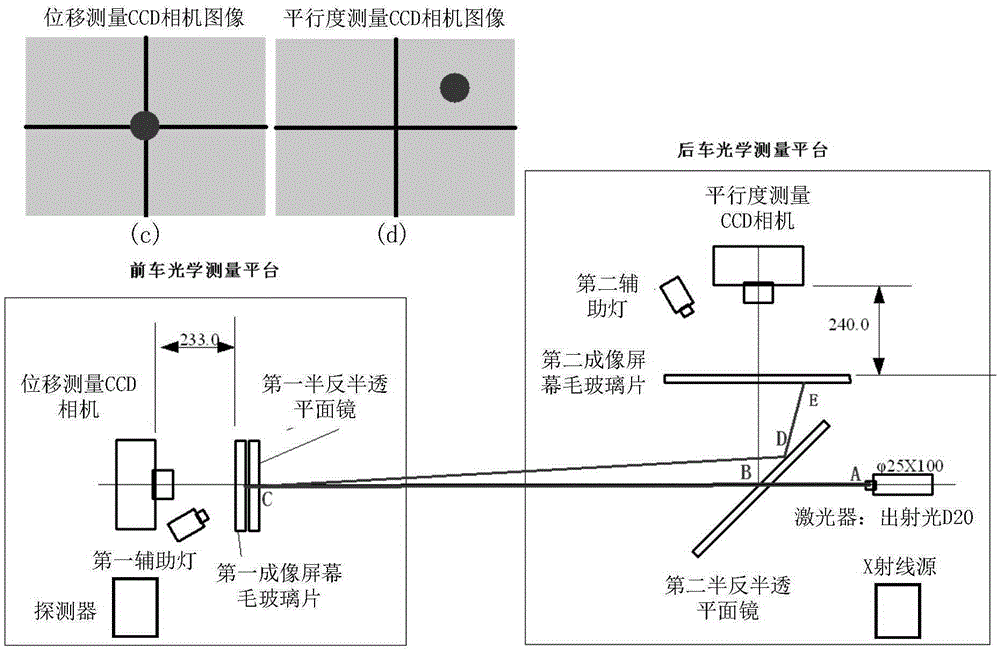
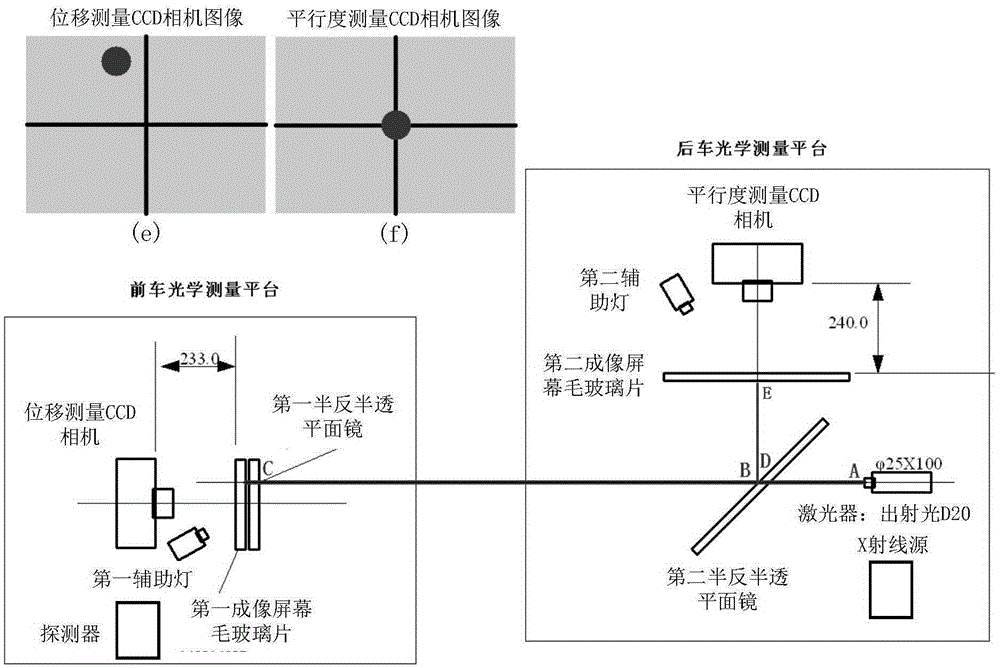
ActiveCN105352514APrecise alignmentMeet the calibration needsInstruments for comonautical navigationX-rayLaser light
The invention discloses an aligning correction device and method for space navigation detector ground calibration. Accuracy aligning of an X radiation source and a detector can be achieved through the device, and the parallel aligning error is less than 0.02 degree and the central aligning error is less than 1mm. The device comprises a front-vehicle optical measuring platform and a rear-vehicle optical measuring platform. A detector is fixedly installed on the front-vehicle optical measuring platform. An X radiation source is fixedly installed on the rear-vehicle optical measuring platform. The front-vehicle and rear-vehicle optical measuring platforms are located at front and rear ends of a vacuum beam line channel respectively. Firstly, parallelism aligning is carried out, the posture of the front-vehicle or rear-vehicle optical measuring platform is adjusted, and thus an image of a laser light spot is located at an imaging center of a parallelism measuring CCD camera; then height and horizontal displacement aligning is carried out, the posture of the front-vehicle or rear-vehicle optical measuring platform is adjusted, thus the image of the laser light spot is located at the imaging center of the displacement measuring CCD camera, and finally aligning of the X radiation source and the detector is achieved.
Owner:CHINA GREAT WALL IND CORP +1
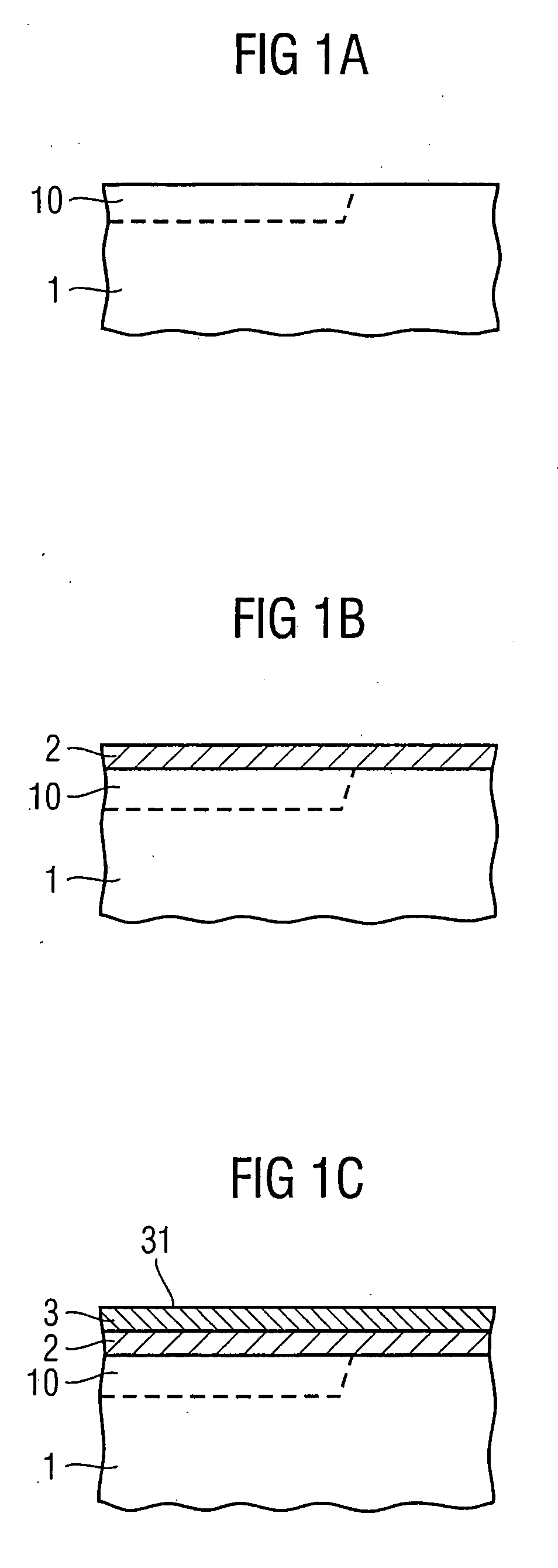
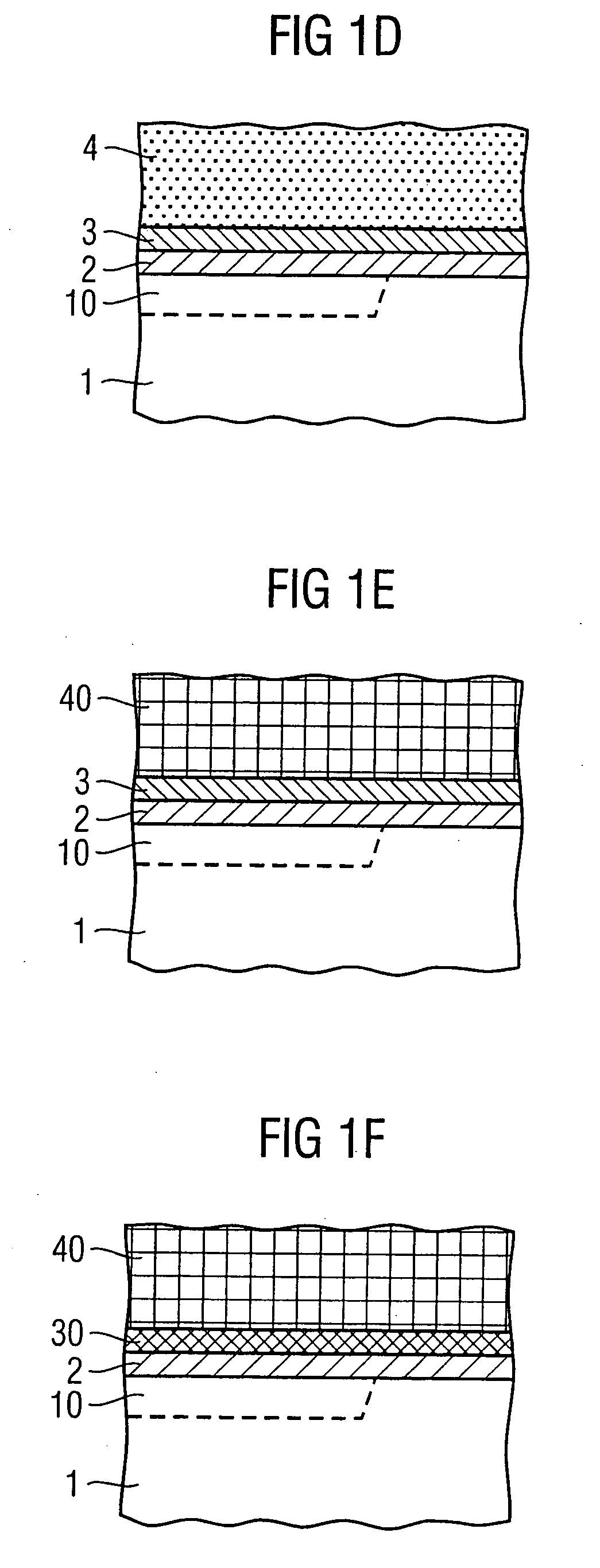
Method for fabricating an integrated circuit on a semiconductor substrate
ActiveUS20070155139A1Reduce numberOptimize efficiencyTransistorSolid-state devicesIntegrated circuitPolycrystalline silicon
Integrated circuit device comprising a conductive layer and a poly-crystalline silicon layer, wherein the integrated circuit device further comprises an intermediate counter-stress layer. This intermediate counter-stress layer is arranged between the poly-crystalline silicon layer and the conductive layer, and enables stress-reduced crystallization of the poly-crystalline silicon layer. Further, the intermediate counter-stress layer is amorphous at and below a poly-silicon crystallization temperature.
Owner:CHANGXIN MEMORY TECH INC
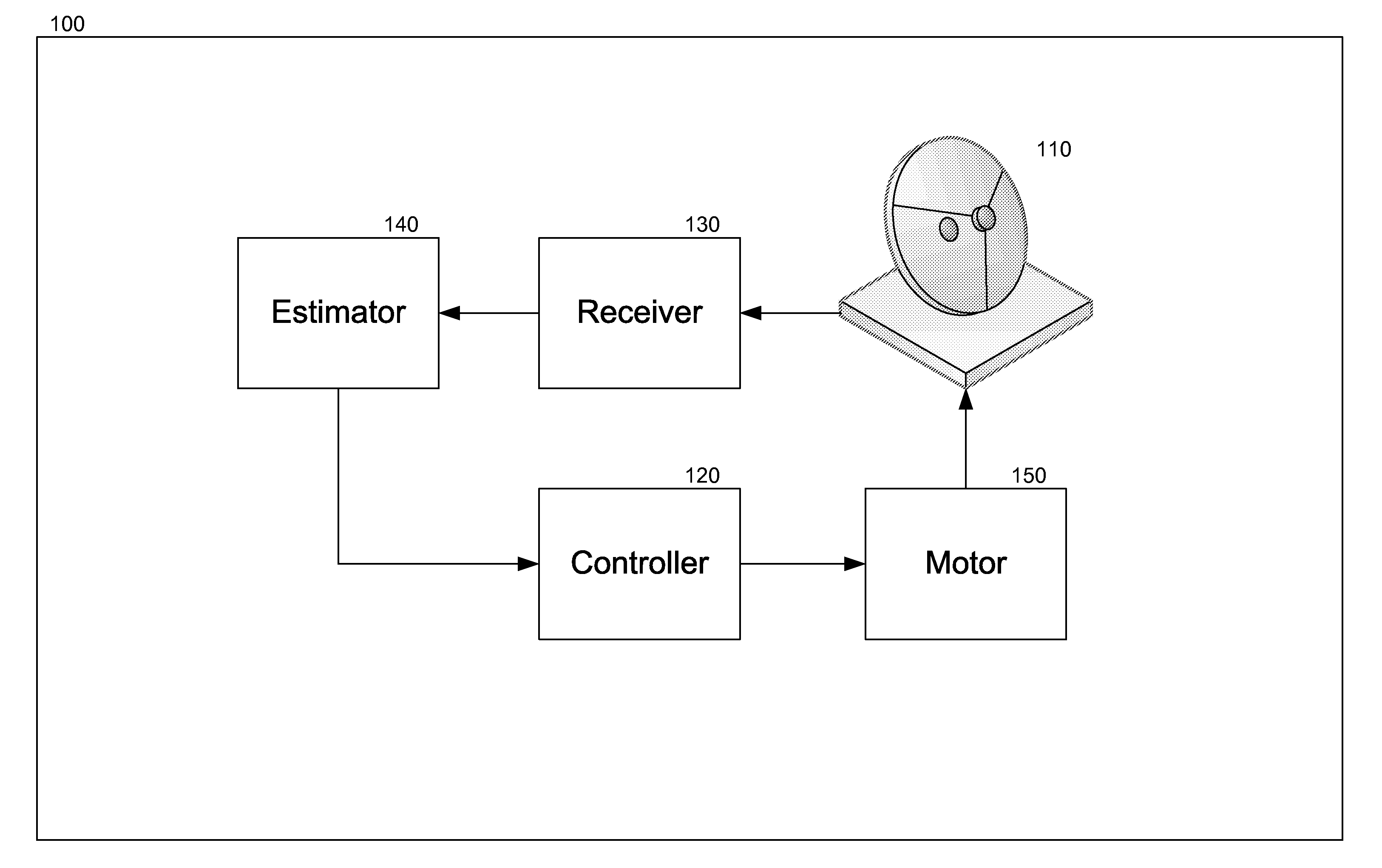
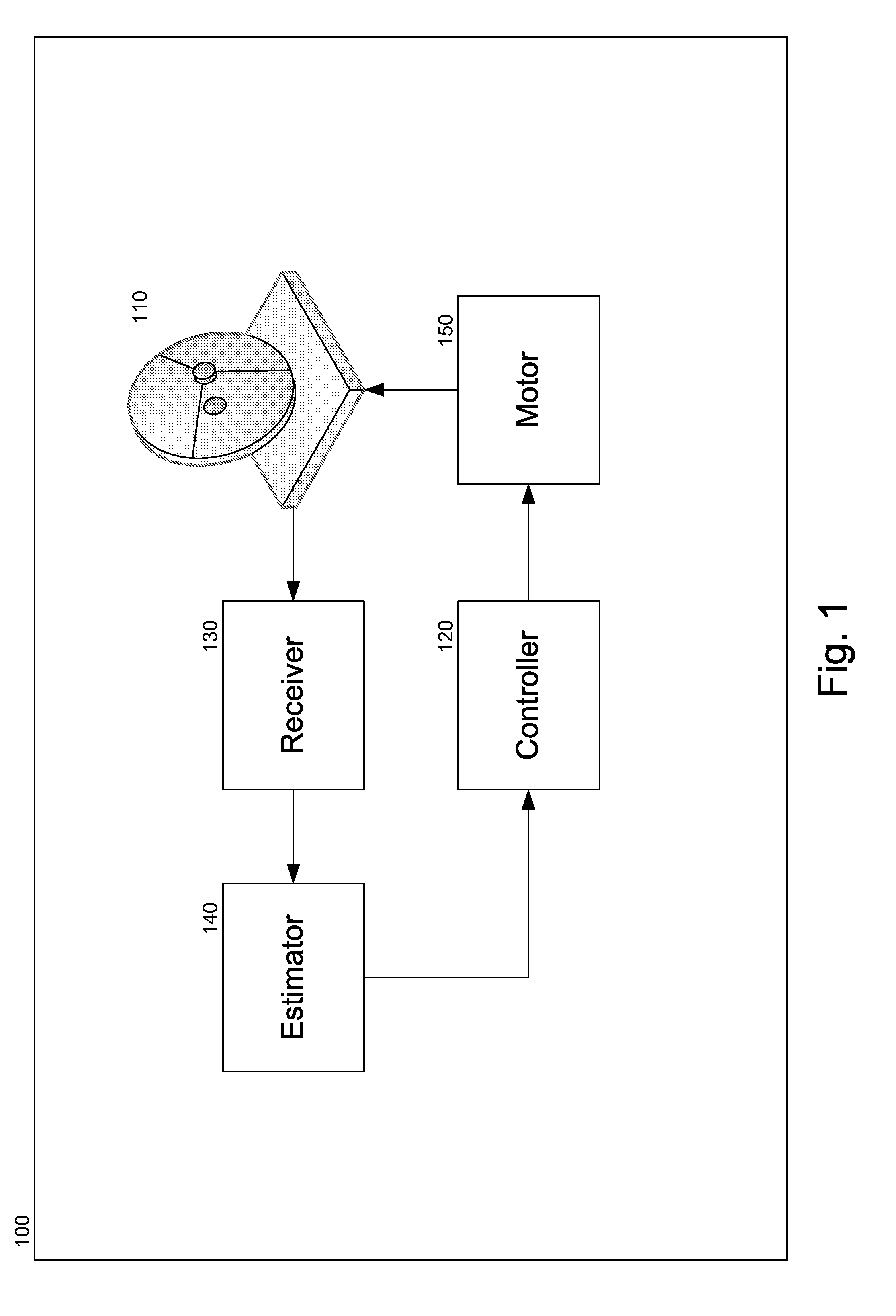
Satellite Tracking Method and Apparatus Thereof
InactiveUS20120013506A1Reduce alignment errorsReduce signalingCosmonautic vehicle trackingAntenna detailsSatellite trackingInclined orbit
A satellite communication ground station configured for communicating over an inclined orbit geostationary satellite may include a tracking antenna having three fixed axis and one moving axis, a motor for swinging the antenna along the moving axis, a controller for controlling the motor, a receiver configured to receive a signal arriving from the satellite via the tracking antenna and an estimator configured to estimate reception quality of a signal received by the receiver. The invention described herein presents a method for tracking an inclined orbit geostationary satellite, the method comprising a learning step and a tracking step, wherein the learning step includes use of a filter for reducing alignment errors and reducing the amount of peaking required for aligning the antenna with the satellite and tracking its movement.
Owner:GILAT SATELLITE NETWORKS
Self-reference interference alignment system for photoetching equipment
ActiveCN103365122AQuality improvementEliminate alignment errorsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptical ModuleLight beam
The invention discloses a self-reference interference alignment system for photoetching equipment. The system comprises a laser light source module, an optical module, a signal acquisition module and a processing module, wherein the laser light source module is used for providing illumination beams; the optical module is used for marking the illumination beams to form a diffraction optical signal; the signal acquisition module is used for processing the optical signal to acquire a light intensity signal; the processing module is used for processing the light intensity signal to acquire an alignment position by combining position data of a workpiece table; the optical module comprises a first optical channel and a second optical channel; an optical signal in the second optical channel is processed to be used for eliminating optical noises in the first optical channel.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Method and apparatus for measuring the draft of a vessel
InactiveUS20050188763A1Accurate measurementCarefully and safely and conveniently determineAuxillariesMachines/enginesMarine engineeringPressure sensor
A device for measuring the draft of a vessel including a tube of a known length having a lower end adapted to be immersed in water a fixed distance from a main deck or other reference point on the vessel, and a pressure sensor directly mounted at the lower end of the tube to measure the pressure head of the water at the lower end of the tube. The pressure at the lower end of the tube is used to determine the distance between a fixed reference point (draft line) on the side of the vessel and the actual surface of the water. This depth is then used to calculate the depth of the hull beneath the surface of the water or the draft of the vessel.
Owner:KREJCI JOHN J
Alignment structure for plasma display panel
InactiveUS20050221713A1Reduce alignment errorsAlternating current plasma display panelsVessels or leading-in conductors manufactureEngineeringPlasma display
A plasma display panel (PDP) with alignment structure. A first alignment pattern is disposed on a rear substrate and formed by a rib structure. A second alignment pattern is disposed on a front substrate disposed opposite, over the rear substrate and corresponds to a space defined by the first alignment pattern. The first and second alignment patterns are disposed outside of the display area of the plasma display panel.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
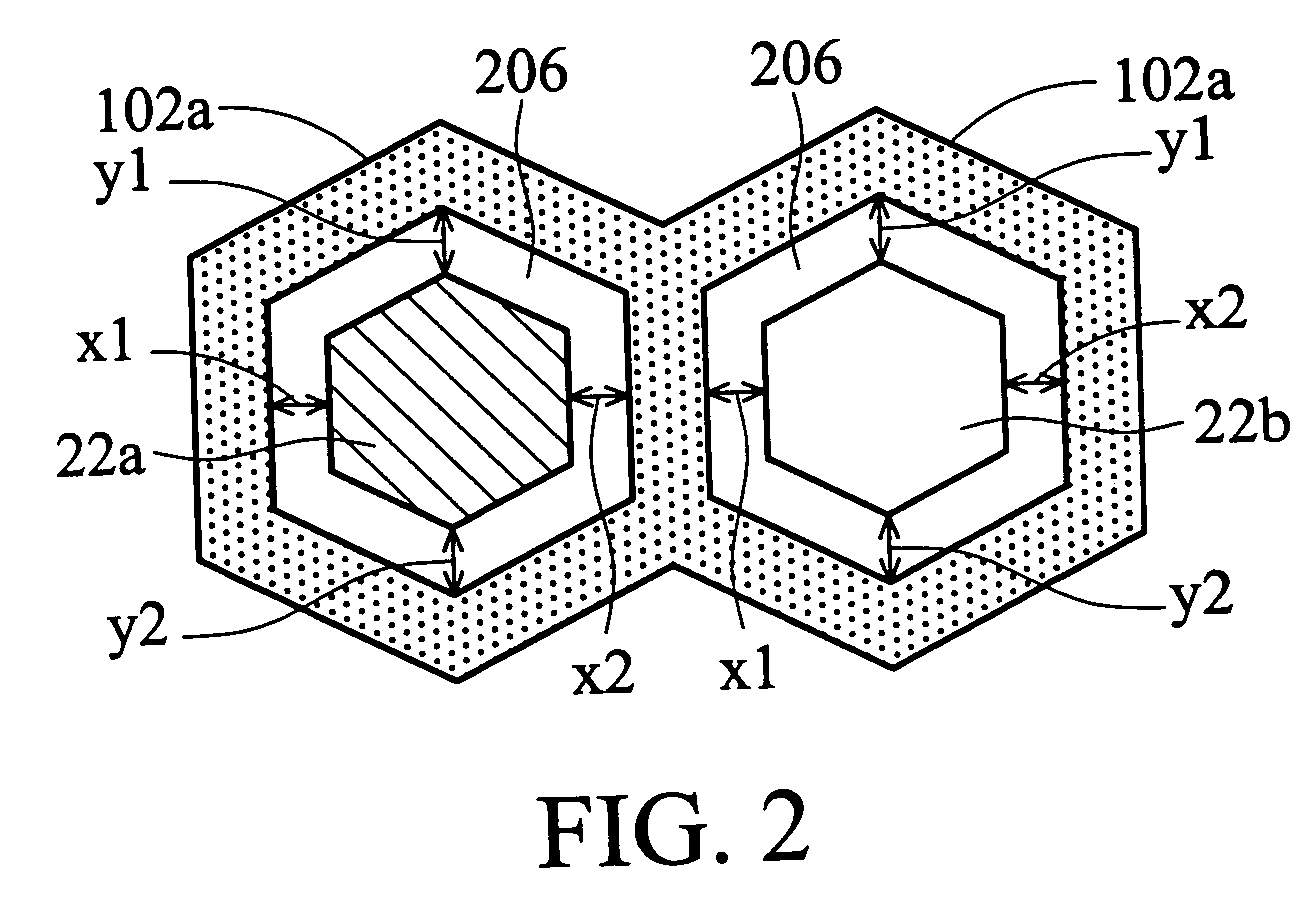
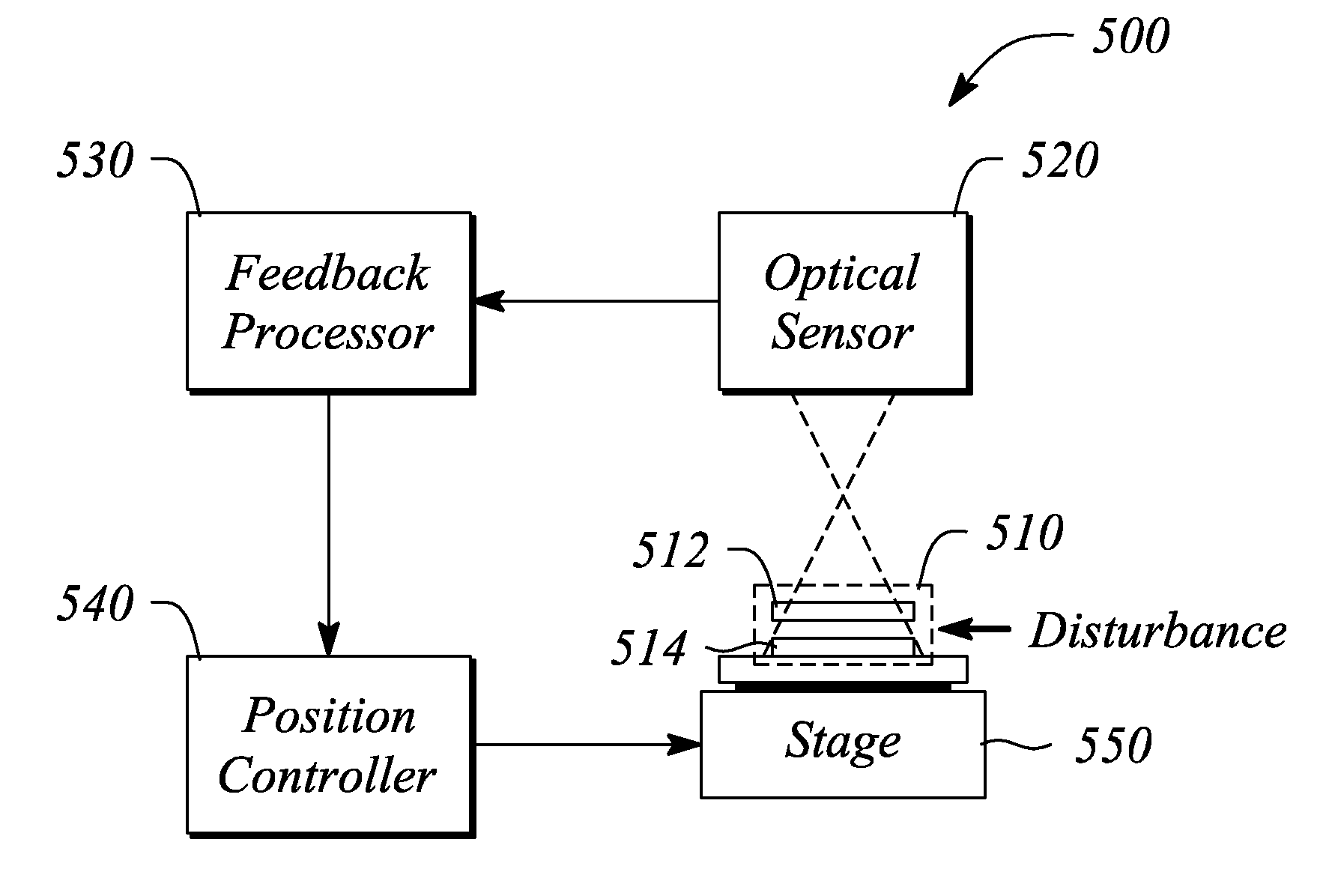
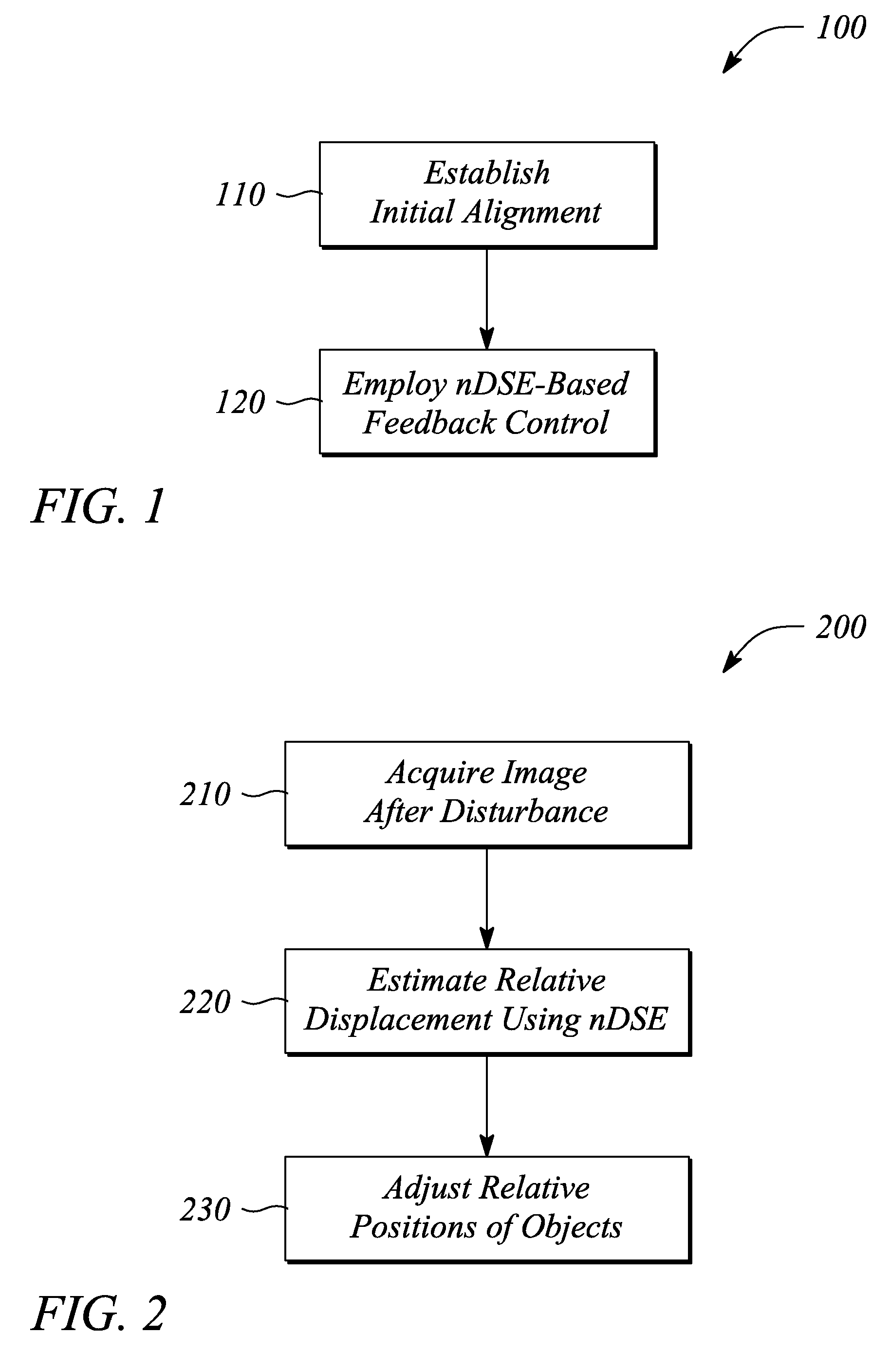
LITHOGRAPHY ALIGNMENT SYSTEM AND METHOD USING nDSE-BASED FEEDBACK CONTROL
InactiveUS20080090312A1Reduce alignment errorsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLithographic artistComputer vision
A contact lithography alignment system and method use nanoscale displacement sensing and estimation (nDSE) to maintain an alignment and compensate for a disturbance of one or more objects during contact lithography. A method of maintaining an alignment includes establishing an initial alignment of one or more objects and employing nDSE-based feedback control of relative positions of more or more of the objects to maintain the alignment during contact lithography. A method of disturbance compensation includes acquiring a first image, acquiring a second image, estimating an alignment error using nDSE applied to the first and second image, and adjusting a relative position to reduce the alignment error. A contact lithography system includes an optical sensor, a feedback processor providing nDSE and a position controller that adjusts relative positions of one or more objects to reduce an alignment error determined using the nDSE.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Quick clamping and alignment method and fixture for milling arc segments of stationary blade grid
ActiveCN104084814AEasy to adjustEasy to operatePositioning apparatusMetal-working holdersModular designMachining process
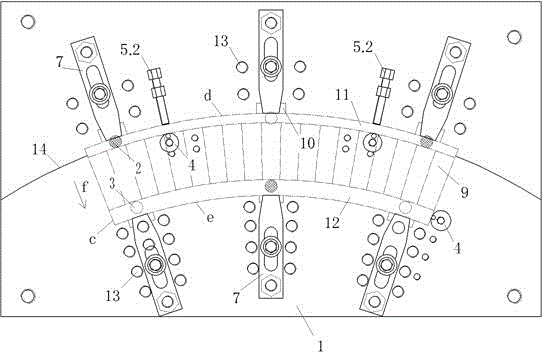
The invention discloses a quick clamping and alignment method and a fixture for milling arc segments of a stationary blade grid and belongs to the technical field of machining of steam turbines. According to the quick clamping and alignment method and the fixture for milling the arc segments of the stationary blade grid, the principle that three points form a plane is utilized, and quick clamping and alignment of the arc segments of the stationary blade grid are achieved through three-point locating and three-point auxiliary supporting; in the application process, adjustment is convenient, operation is easy, the application range is large, the defects that the arc segments of the stationary blade grid have many specifications, the locating accuracy of arc surfaces of the arc segments of the stationary blade grid in the actual machining process is hard to guarantee due to the structure of the arc segments, and a conventional clamping and alignment device is low in universality are overcome, and the alignment efficiency and accuracy are improved; meanwhile, in the method, a modular design thought is adopted for the corresponding clamping and alignment fixture, so that the universality of the device is greatly improved, and operation is convenient, fast and flexible.
Owner:DONGFANG ELECTRIC WUHAN NUCLEAR EQUIP
Protective device
ActiveUS20110057761A1Inhibit currentPrevents voltageEmergency protective device manufacturePower flowOptoelectronics
A protective device including a substrate, a conductive section and a bridge element is provided. The conductive section is supported by the substrate, wherein the conductive section comprises a metal element electrically connected between first and second electrodes. The metal element serves as a sacrificial structure having a melting point lower than that of the first and second electrodes. The bridge element spans across the metal element in a direction across direction of current flow in the metal element, wherein the bridge element facilitates breaking of the metal element upon melting.
Owner:CYNTEC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com