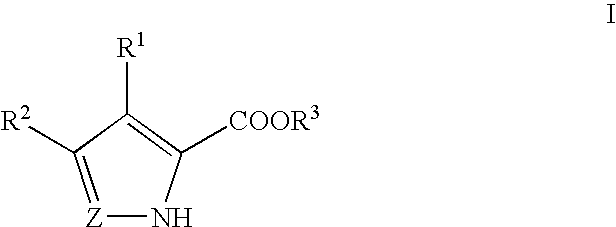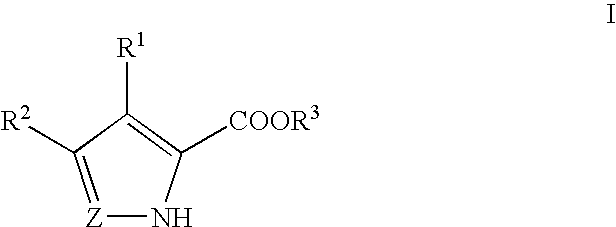Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
105results about How to "Potent inhibition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
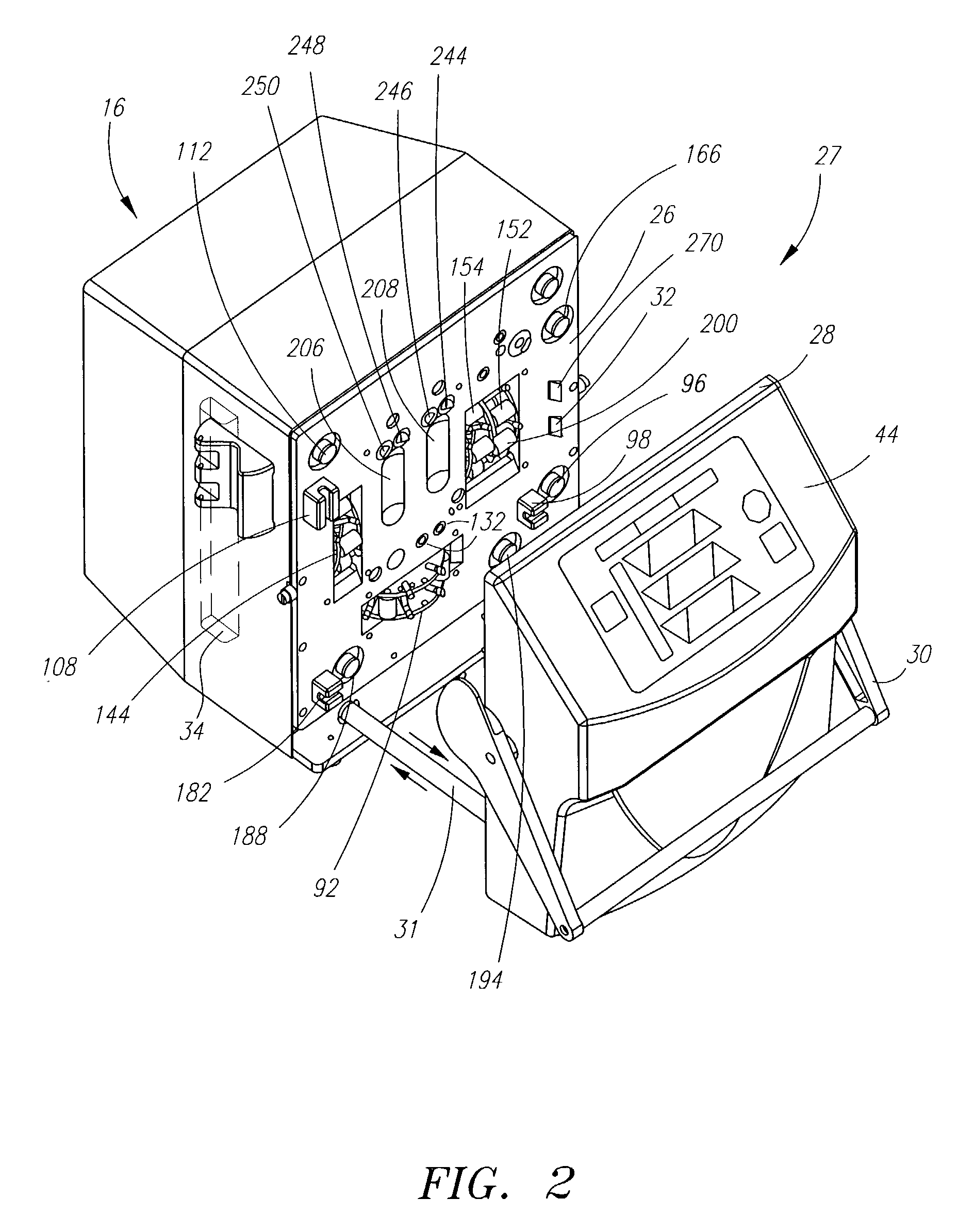
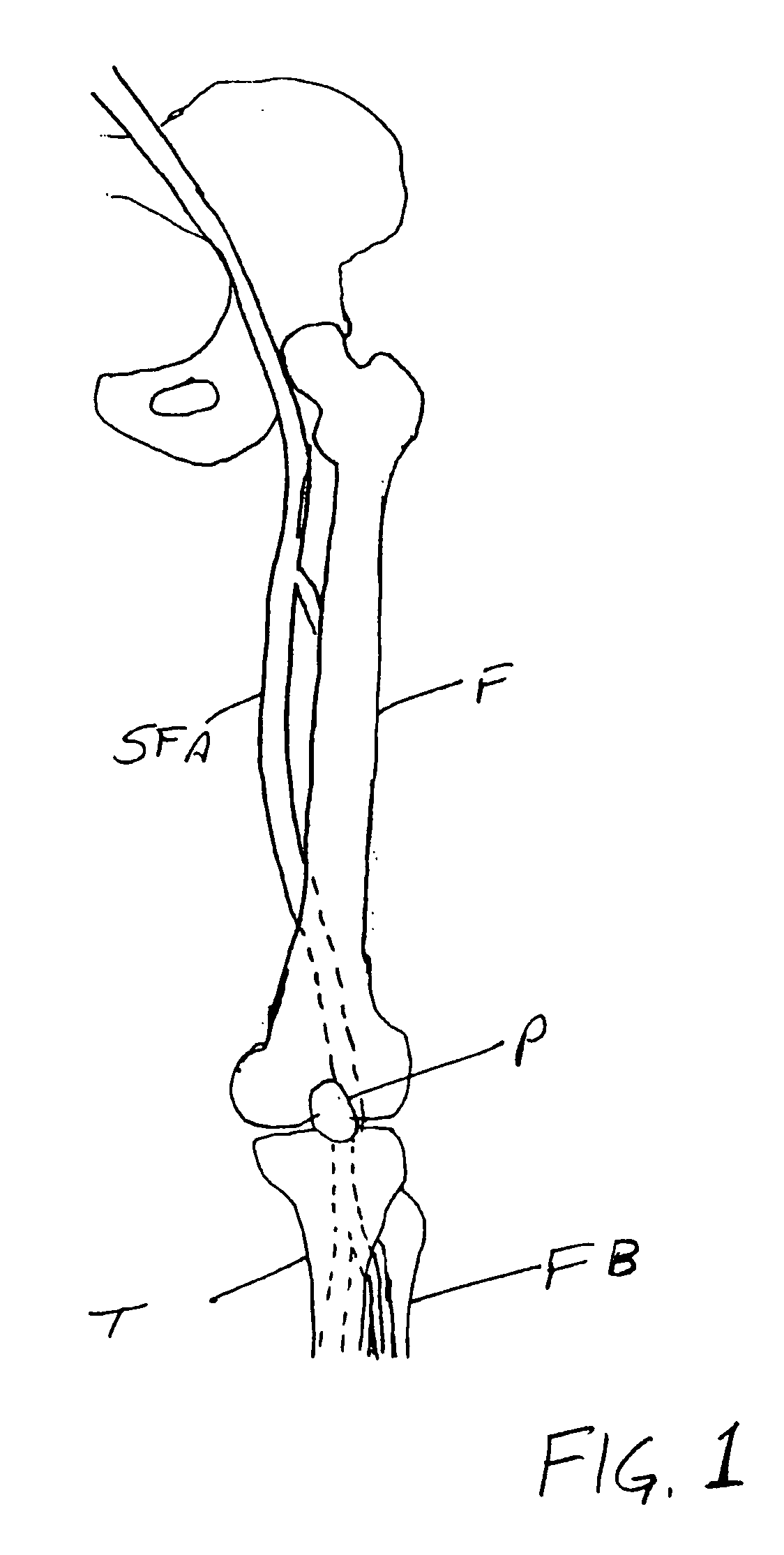
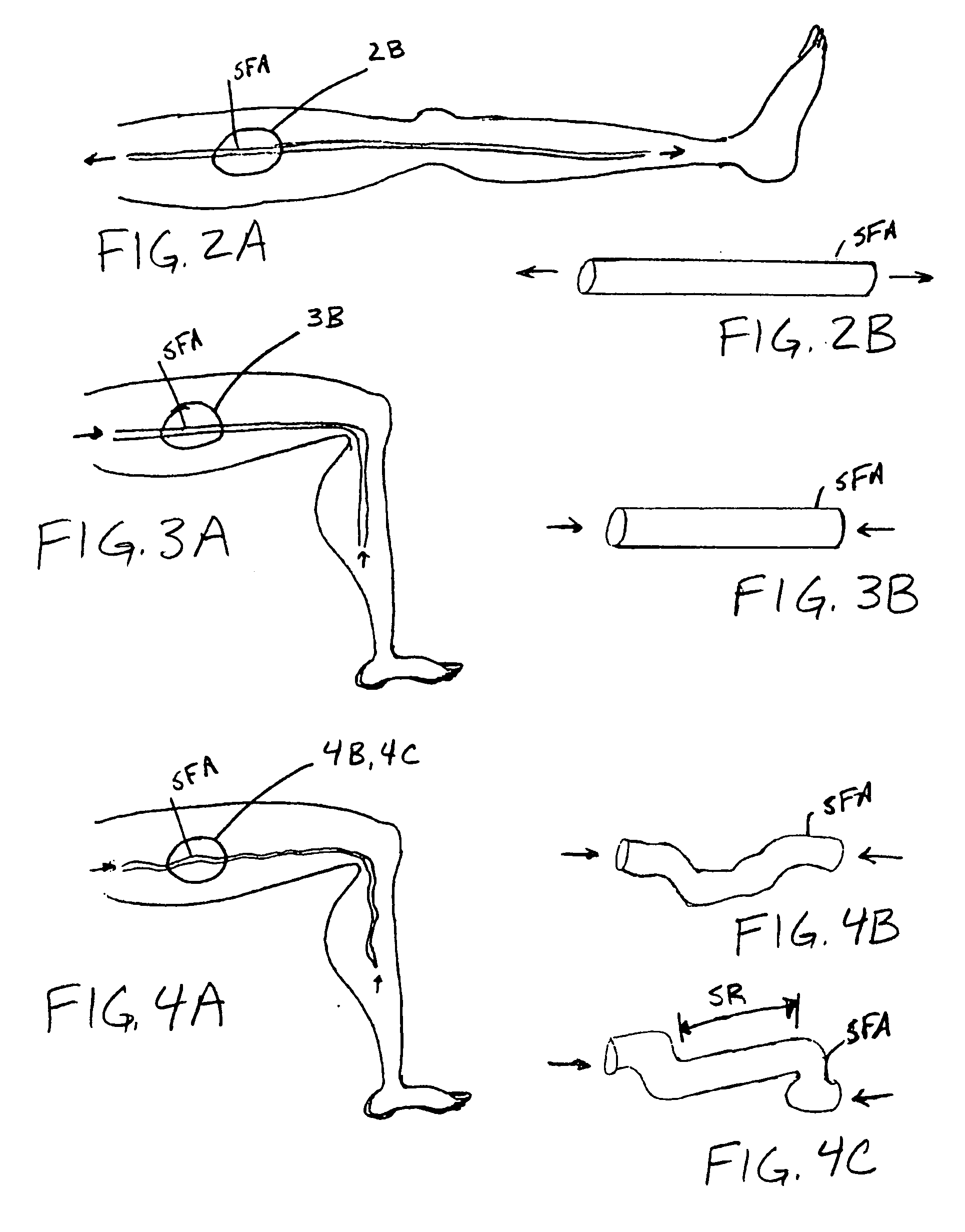
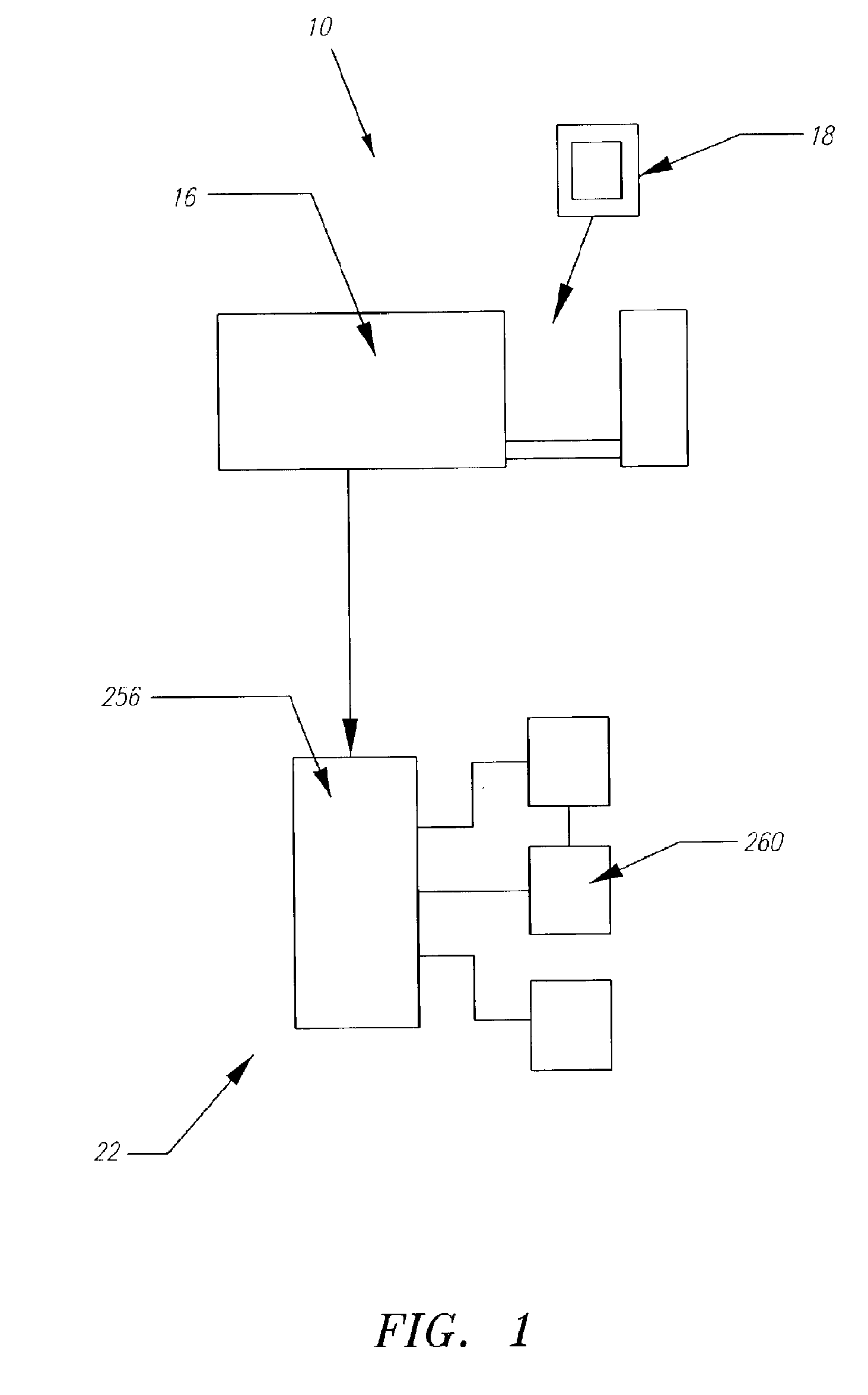
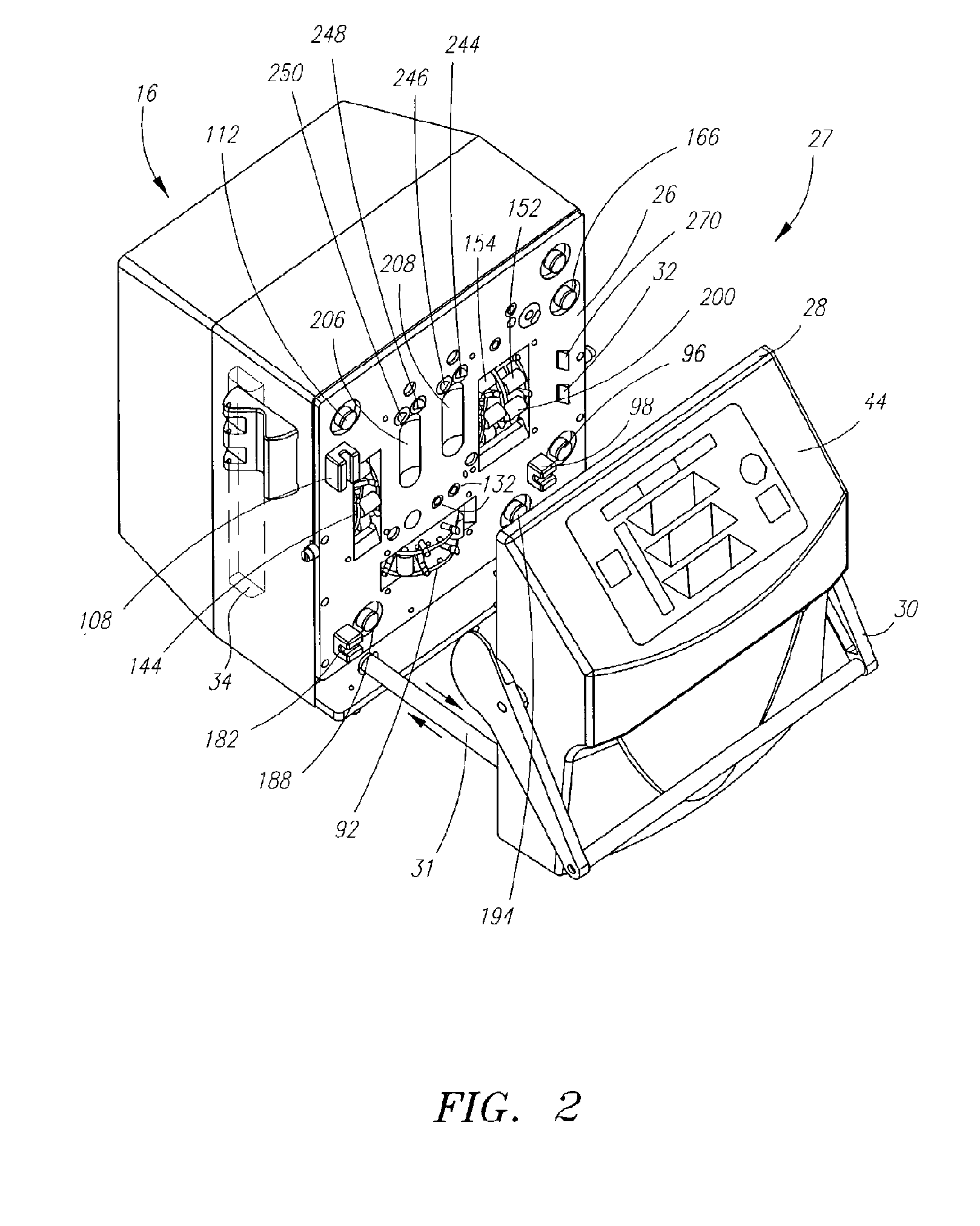
Systems and methods for performing blood processing and/or fluid exchange procedures
InactiveUS6979309B2Fast and convenient and one step process for loading processingPotent inhibitionSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionBlood treatmentsEngineering
A flow management system for extracorporeal blood treatment application helps to ensure proper balance of incoming and outgoing fluids by precise balancing of relatively small balance chambers. The invention employs combinations of features that help to ensure accuracy including underfilling of the waste flow side of a fixed volume chamber and mechanical connections to synchronize valves and pumps.
Owner:NXSTAGE MEDICAL
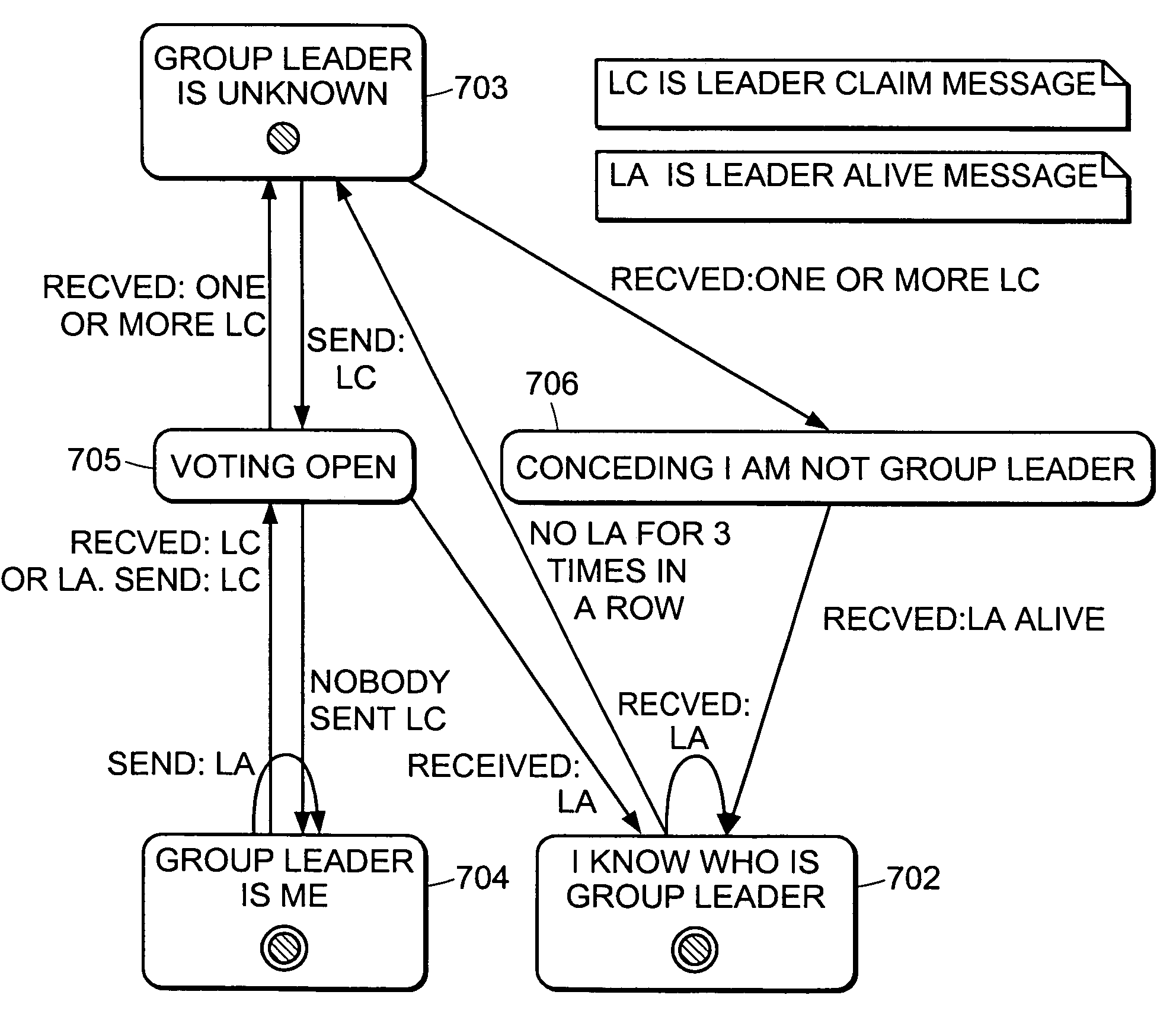
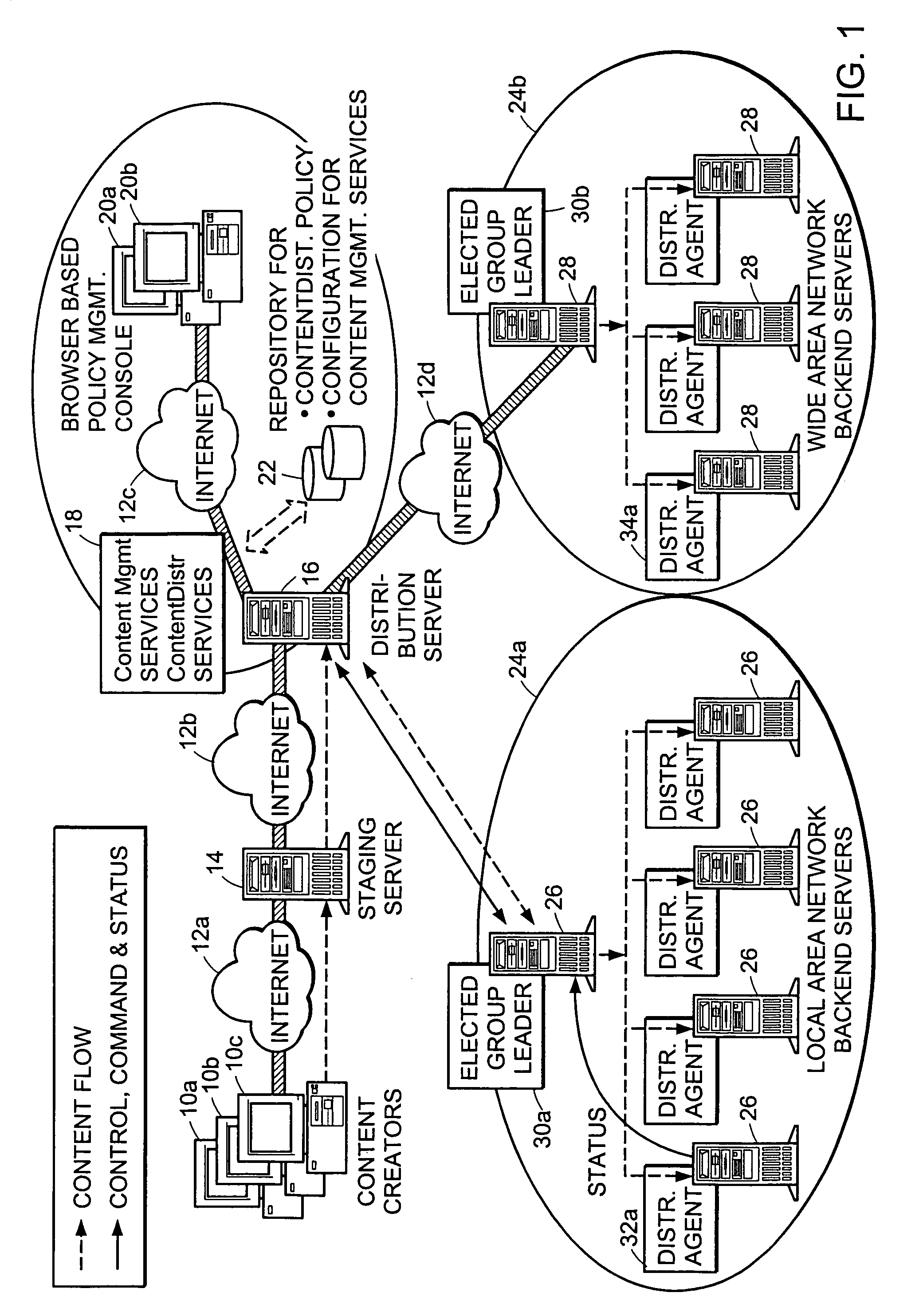
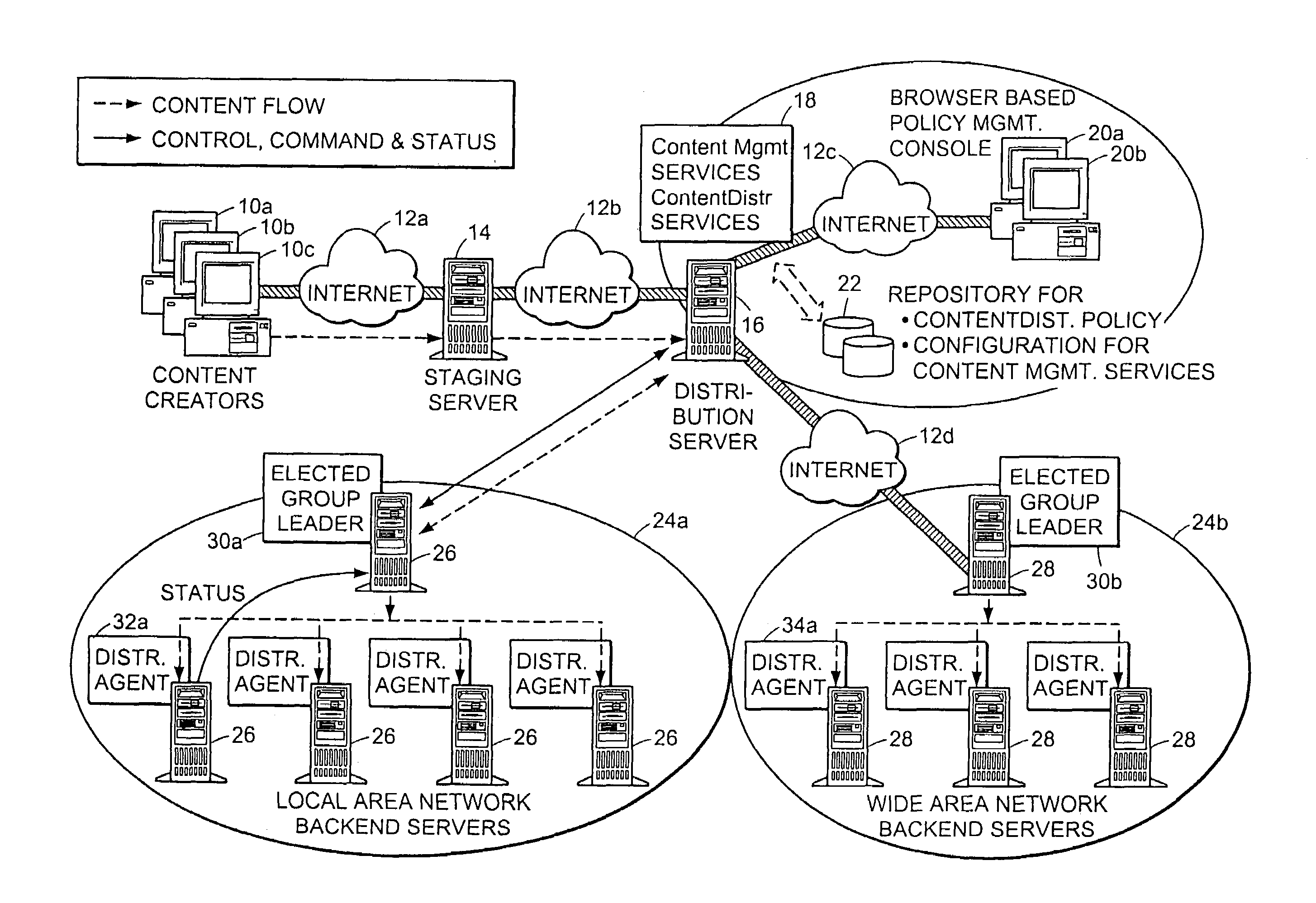
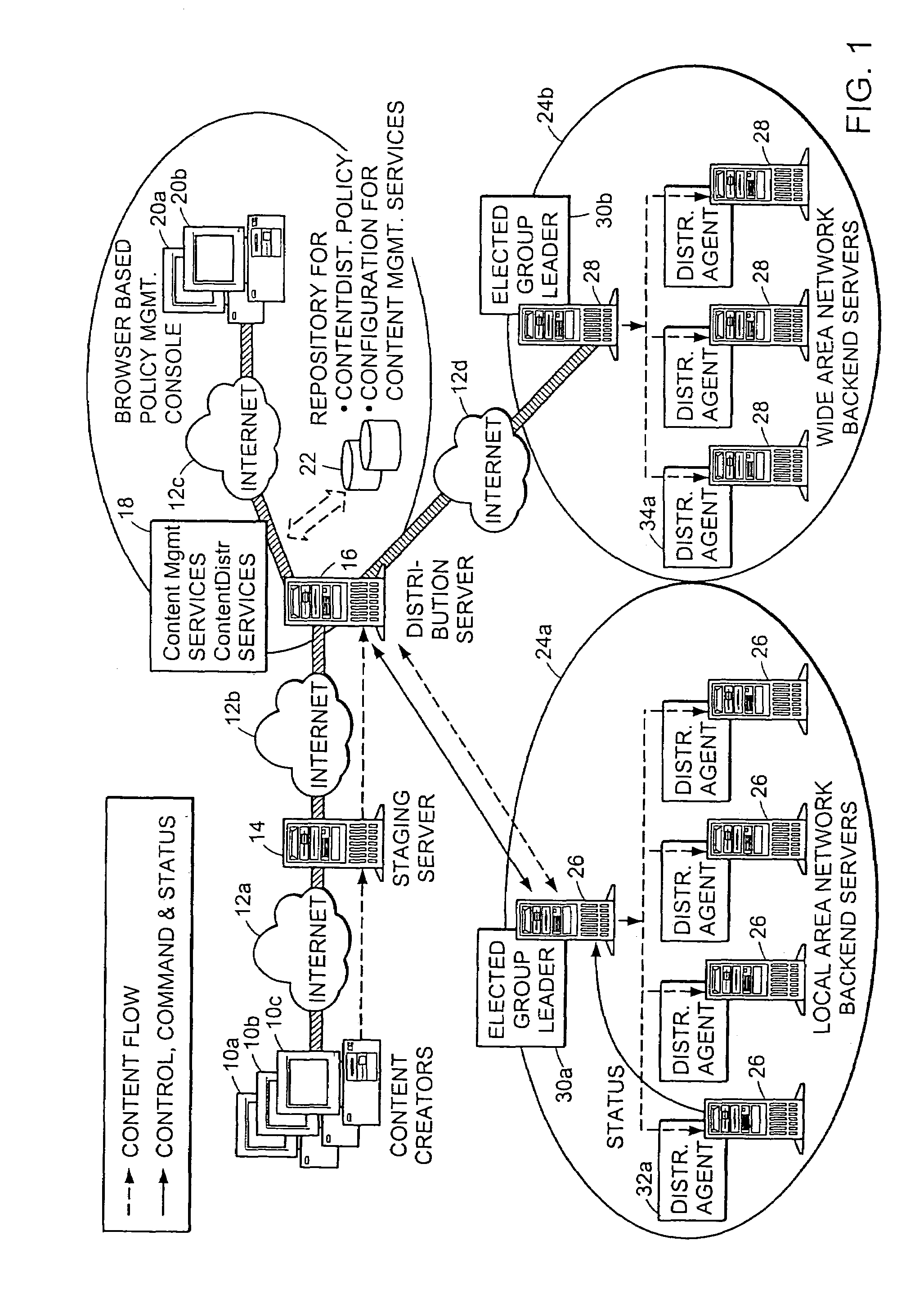
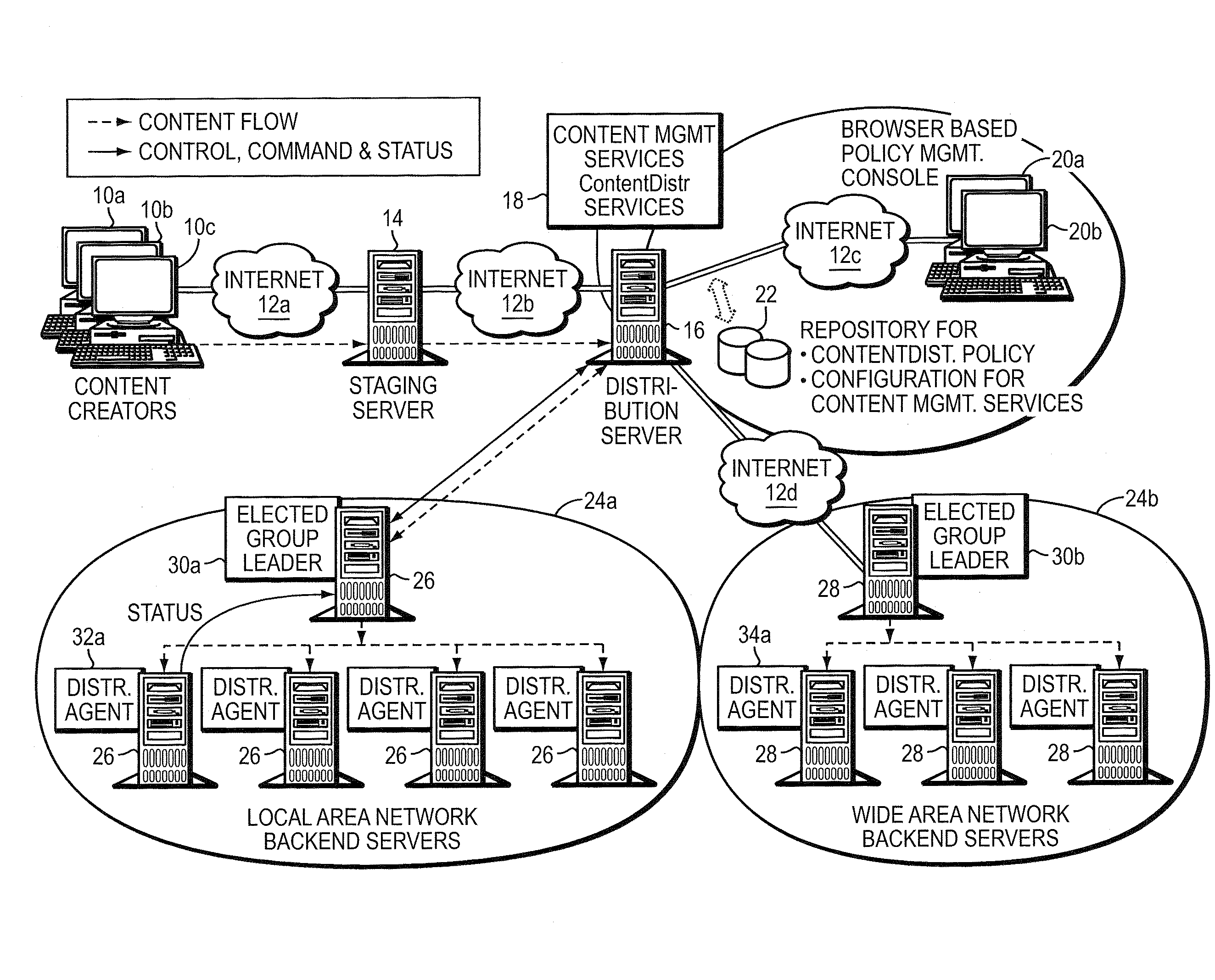
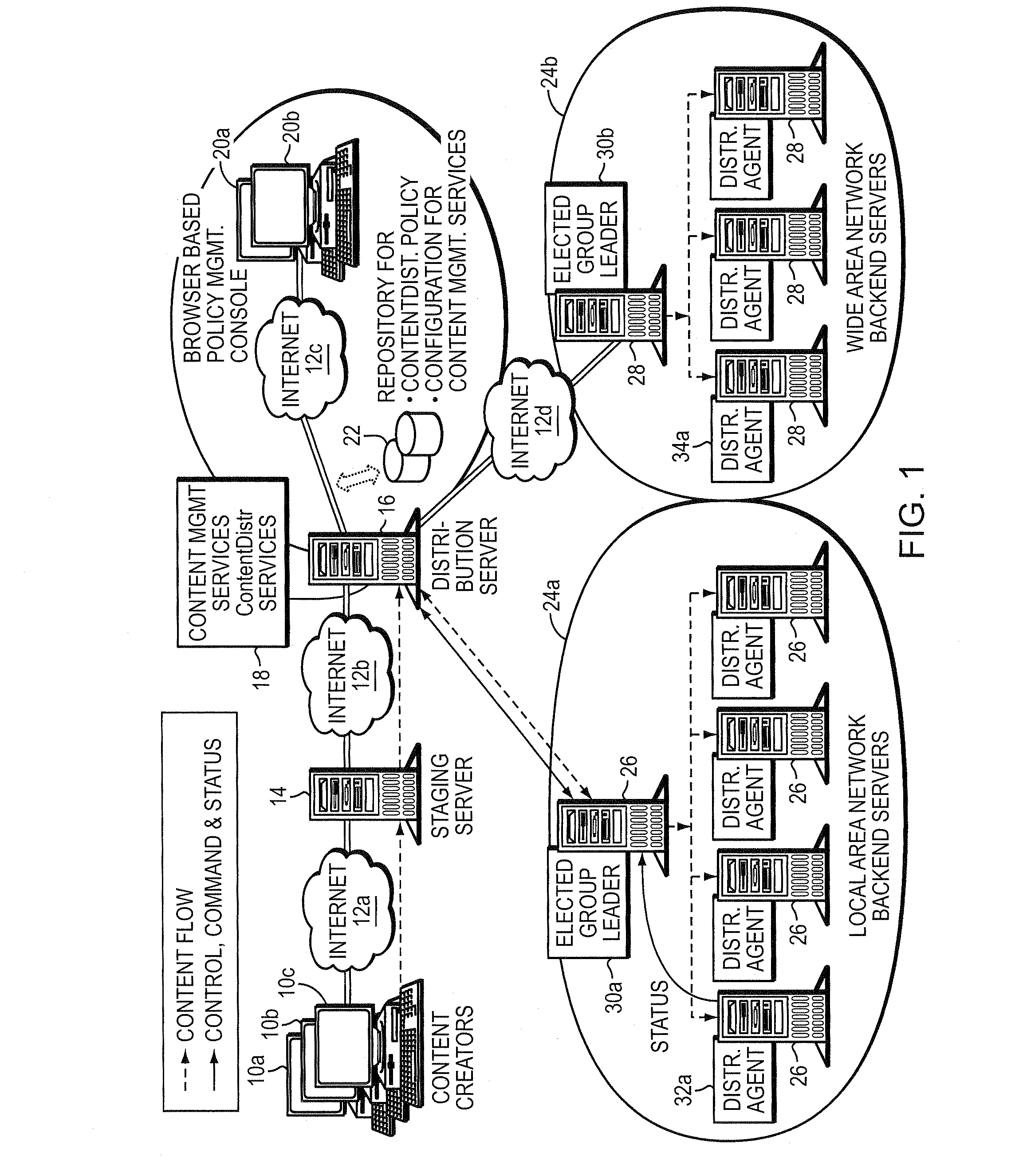
Method and apparatus for election of group leaders in a distributed network
InactiveUS6993587B1Effective controlEffective distributionMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionData fileMulticast network
The present invention provides a system and apparatus for efficient and reliable, control and distribution of data files in large-scale distributed networks. The members of a group of servers in a multicast network elect a group leader whenever a new group leader is required, as when the prior group leader become unavailable, as detected by absence of a periodic heartbeat message published by the leader. The election is carried out by a system of voting by each candidate whereby each candidate has a priority calculated from its configuration, and the server with the highest priority is configured to claim the leadership faster than the other candidates. As part of the claim, each candidate multicasts its priority. Each candidate that receives a multicast claim for leadership from another candidate compares its own priority against the claimant and only votes for itself if its own priority is higher. After a preconfigured period of hearing no other claimants with higher priority, the candidate with the highest priority becomes the new leader.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Method and apparatus for election of group leaders in a distributed network
InactiveUS20050198359A1Effective controlEffective distributionMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionGroup controllerData file
A system and apparatus for control and distribution of data files in large-scale distributed networks. Members of a group of servers in a multicast network elect a group leader whenever a new group leader is required, as detected by absence of a periodic message published by the leader. Election is carried out by a system of voting by each candidate whereby each candidate has a priority calculated from its configuration, and the server with the highest priority is configured to claim the leadership faster than the other candidates. As part of the claim, each candidate multicasts its priority. Each candidate that receives a multicast claim for leadership from another candidate compares its own priority against the claimant and only votes for itself if its own priority is higher. After a preconfigured period of hearing no other claimants with higher priority, the candidate with the highest priority becomes the new leader.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
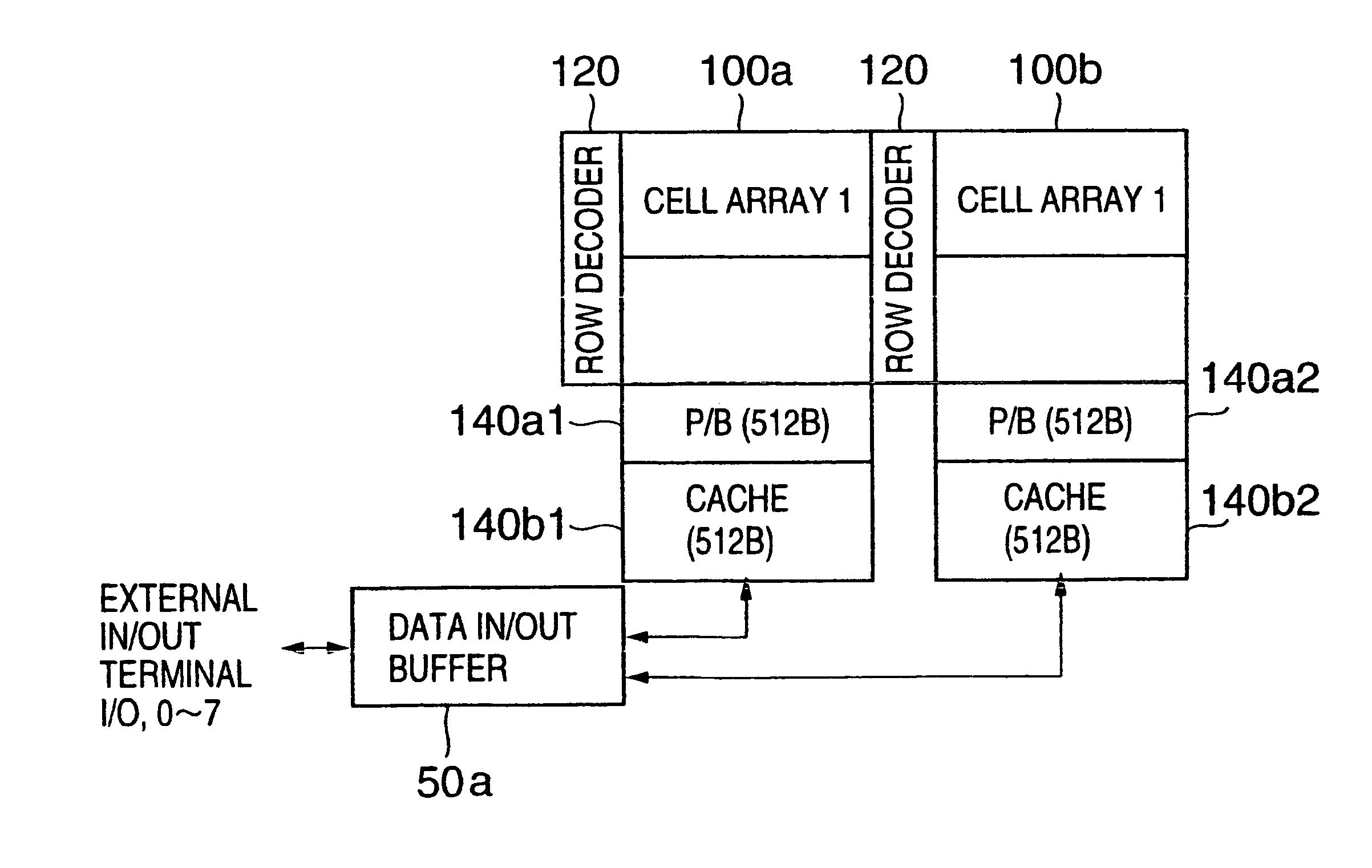
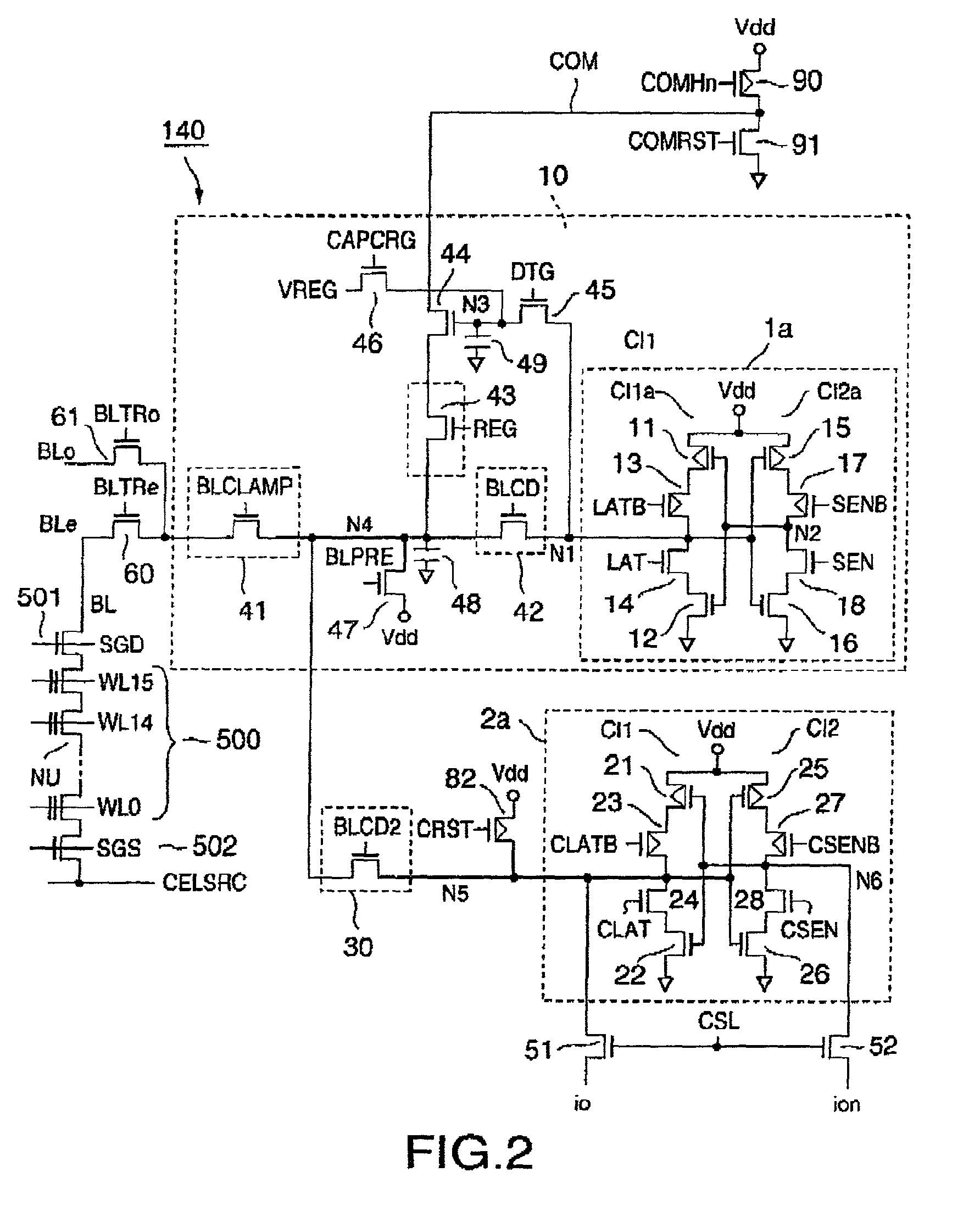
Non-volatile semiconductor memory
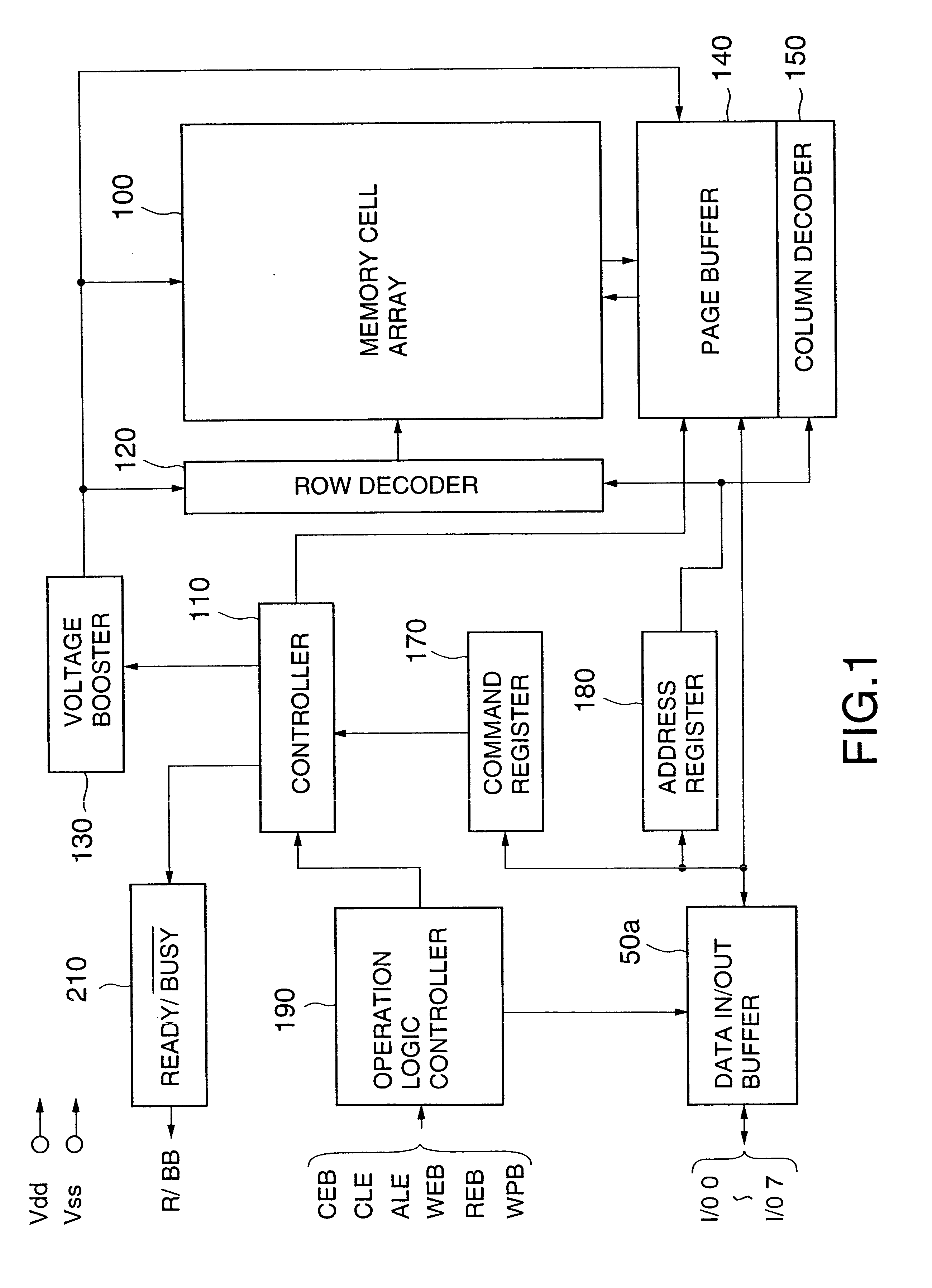
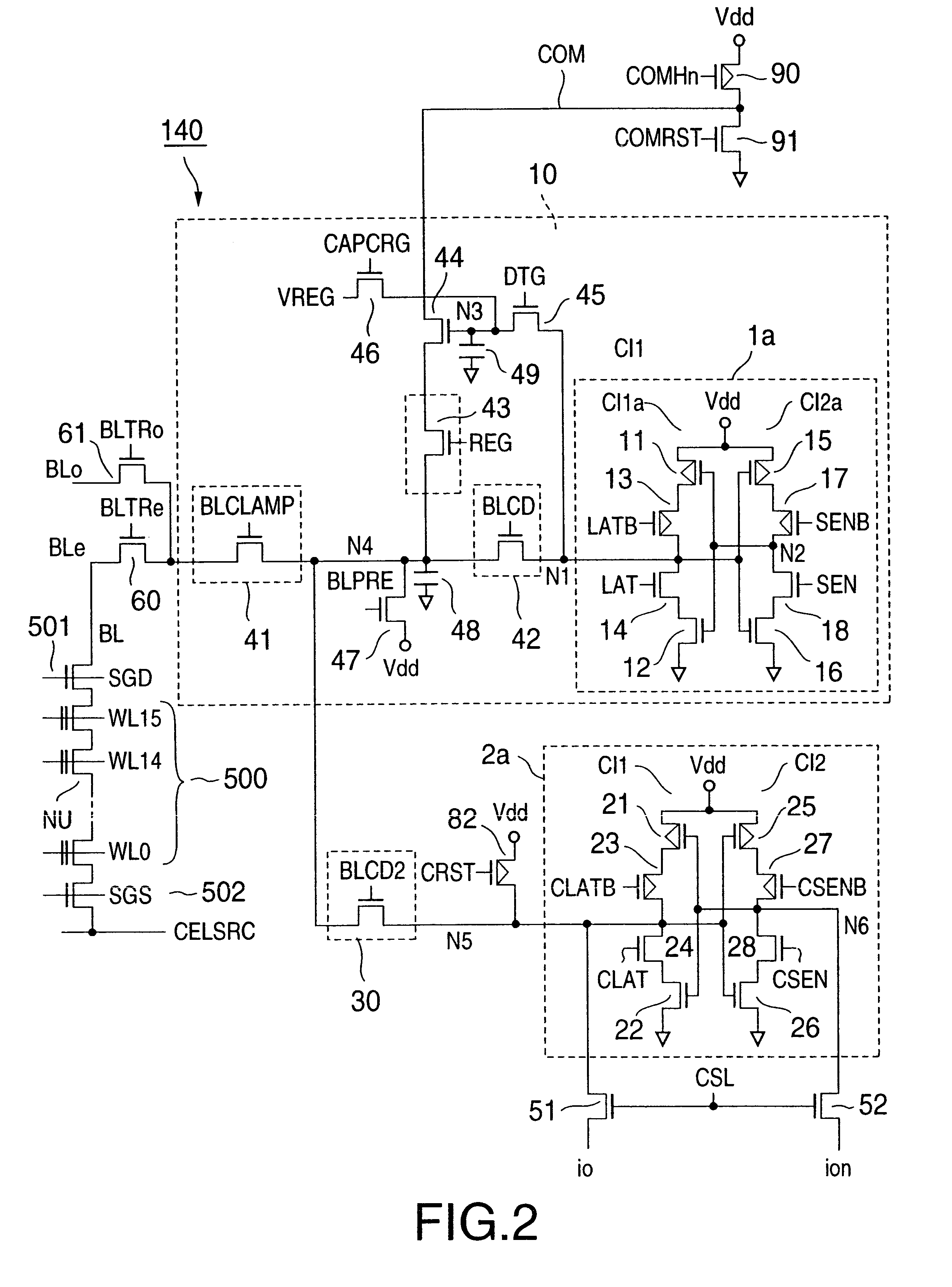
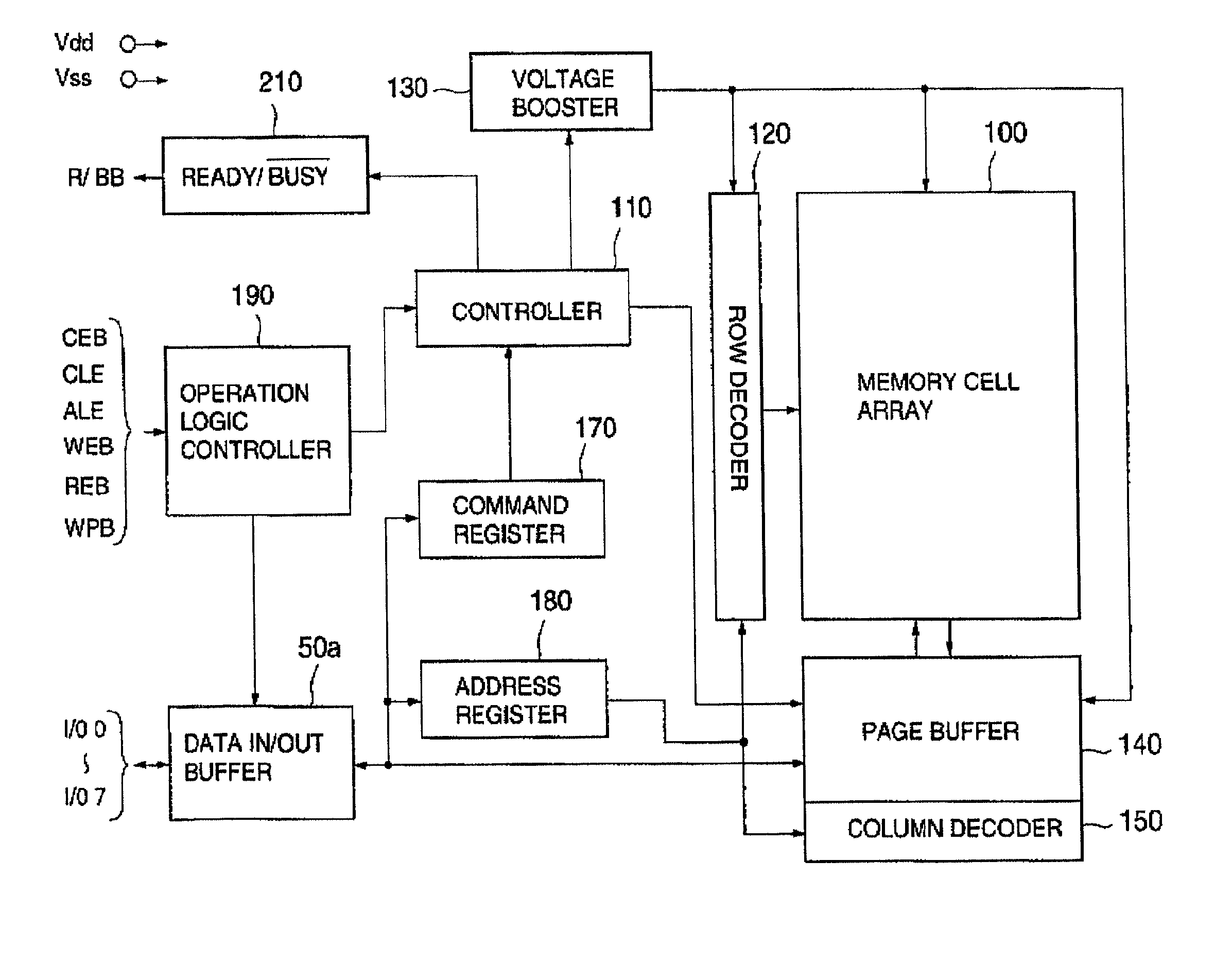
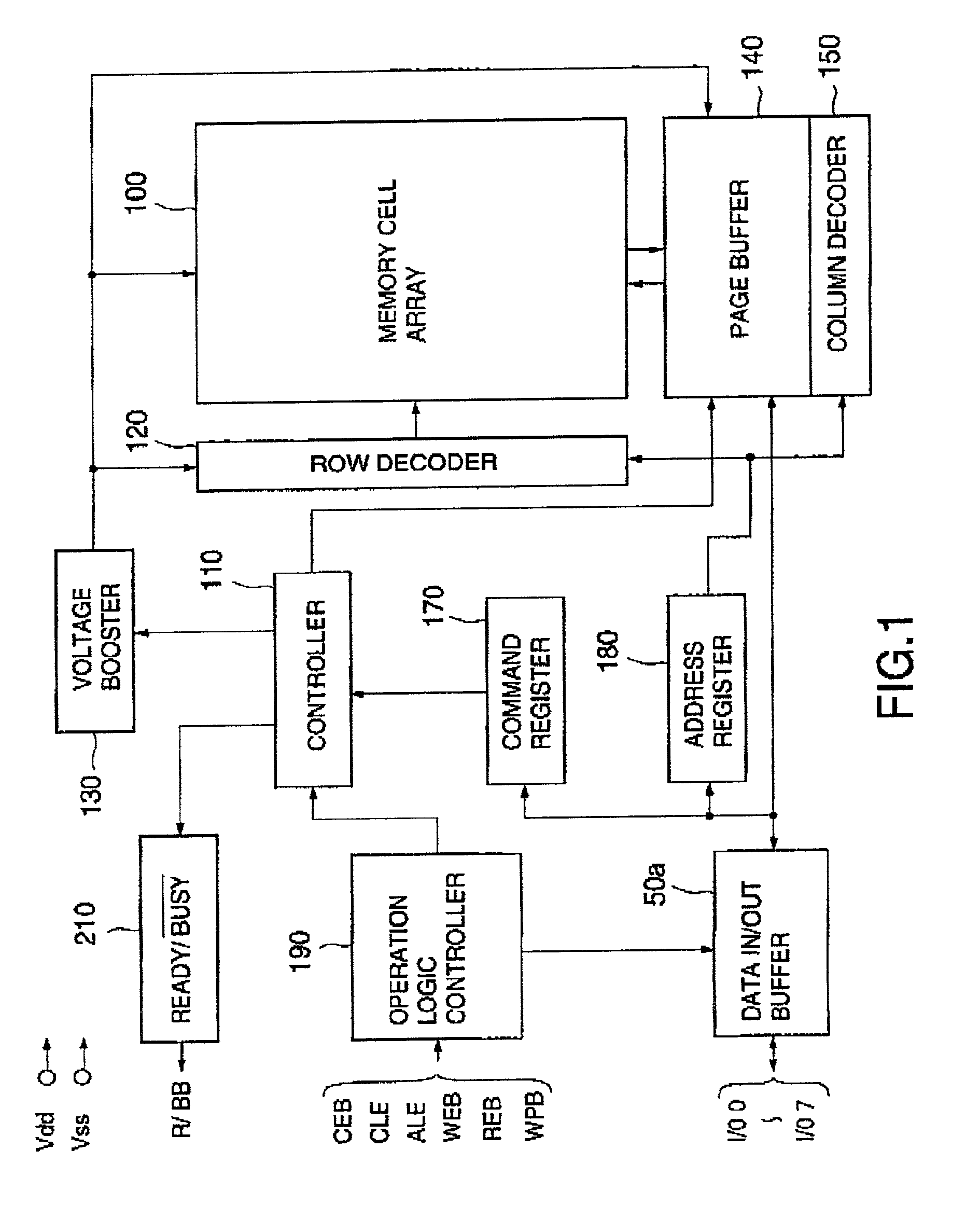
InactiveUS6937510B2Large storage capacityWider marginRead-only memoriesDigital storageSensing dataData retrieval
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Non-volatile semiconductor memory
ActiveUS20020126531A1Large storage capacityWider marginRead-only memoriesDigital storageData transmissionLevel data
A non-volatile semiconductor device has a memory cell array having electrically erasable programmable non-volatile memory cells, reprogramming an retrieval circuits that temporarily store data to be programmed in the memory cell array and sense data retrieved from the memory cell array, each reprogramming and retrieval circuit having a first latch and a second latch that are selectively connected to the memory cell array and transfer data each other, and a controller that controls the reprogramming and retrieval circuits on data-reprogramming operation to and data-retrieval operation from the memory cell array. Each reprogramming and retrieval circuit has a multilevel logical operation mode and a caching operation mode, in the multilevel logical operation mode, re-programming and retrieval of upper and lower bits of two-bit four-level data being performed using the first and the second lathes in storing the two-bit four-level data in one of the memory cells in a predetermined threshold level range, in the caching operation mode, data transfer between one of the memory cells selected in accordance with a first address and the first latch being performed while data transfer is being performed between the second latch and input output terminals in accordance with a second address with respect to one-bit two-level data to be stored in one of the memory cells.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
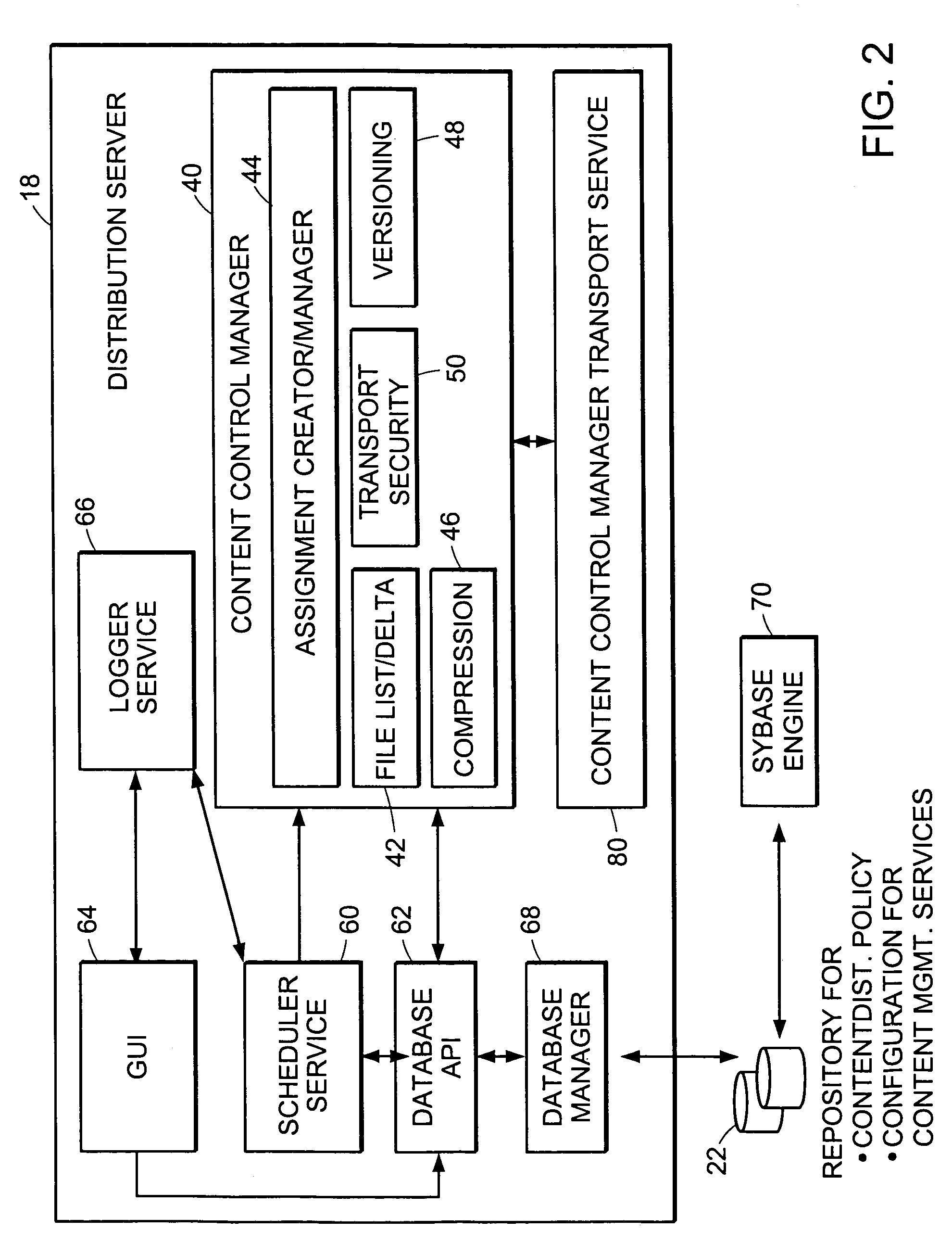
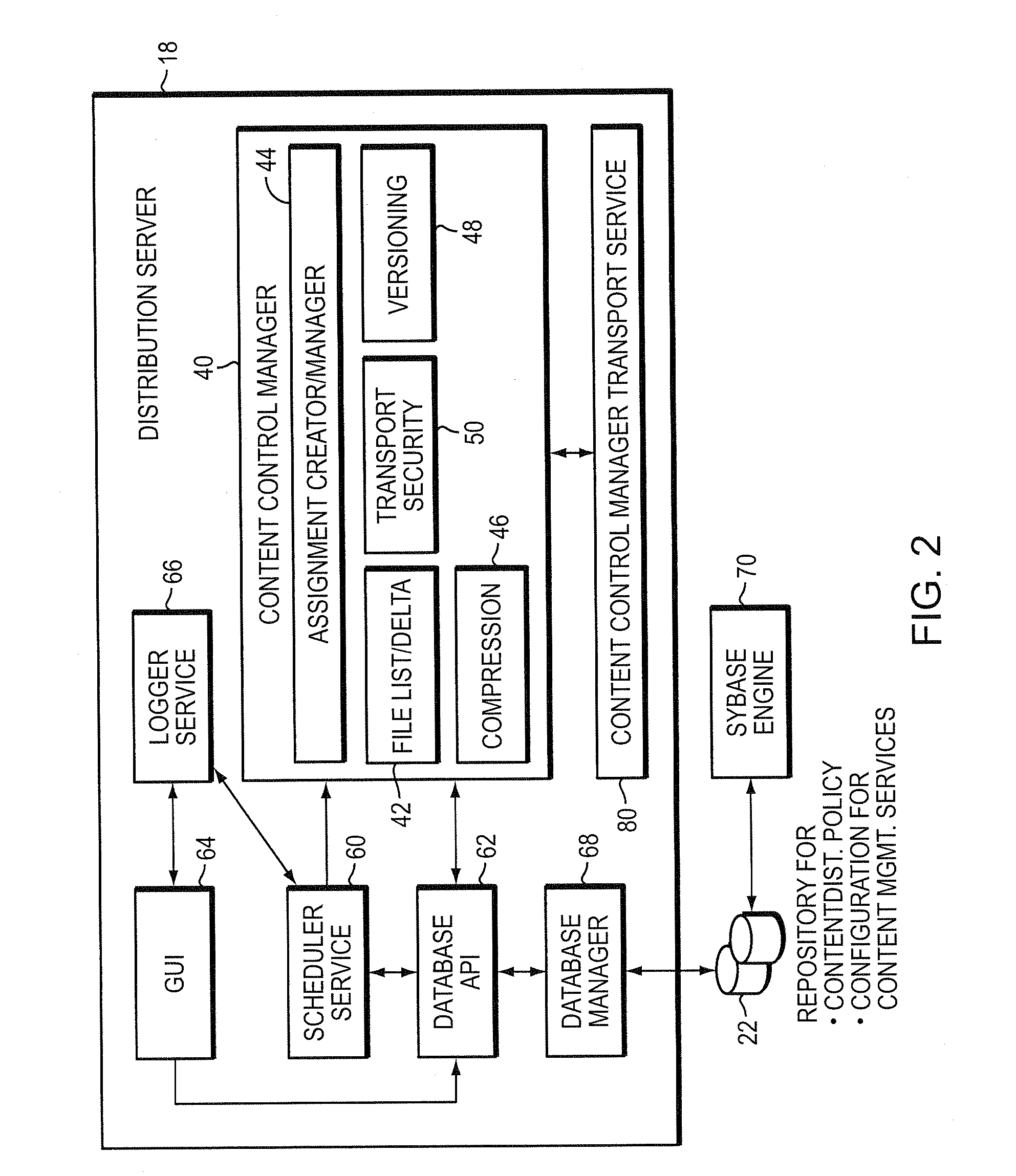
System for creating and distributing prioritized list of computer nodes selected as participants in a distribution job
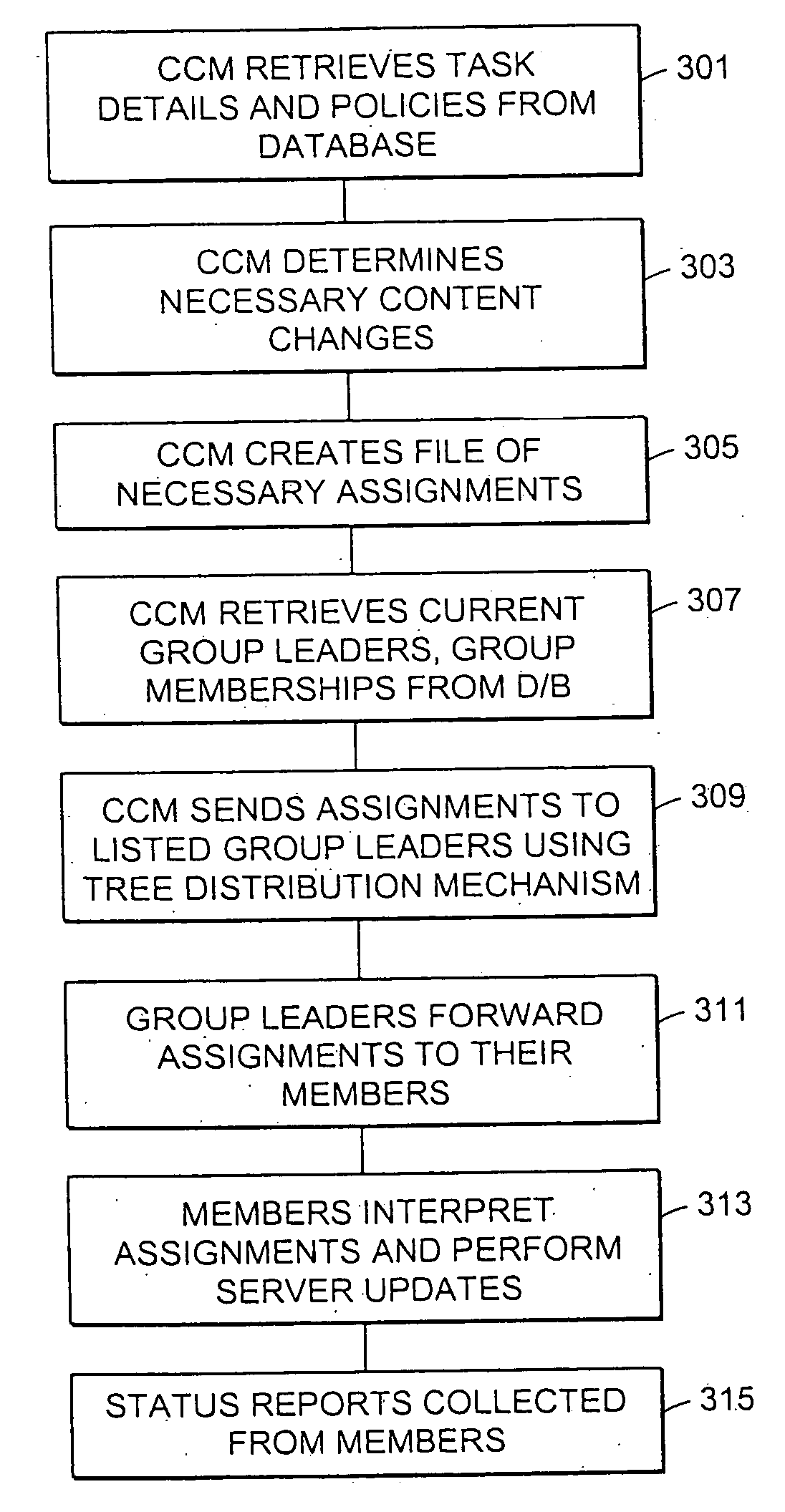
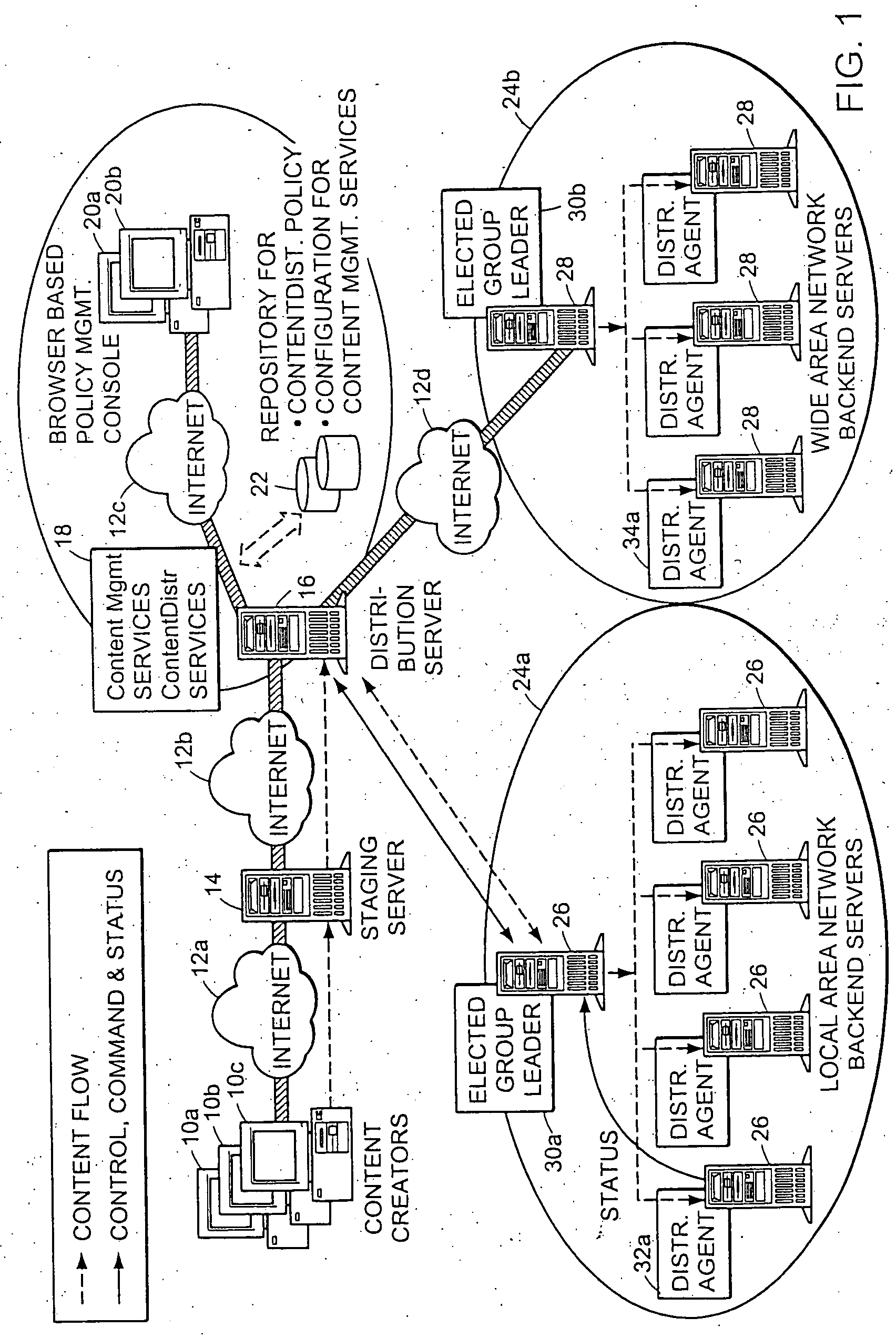
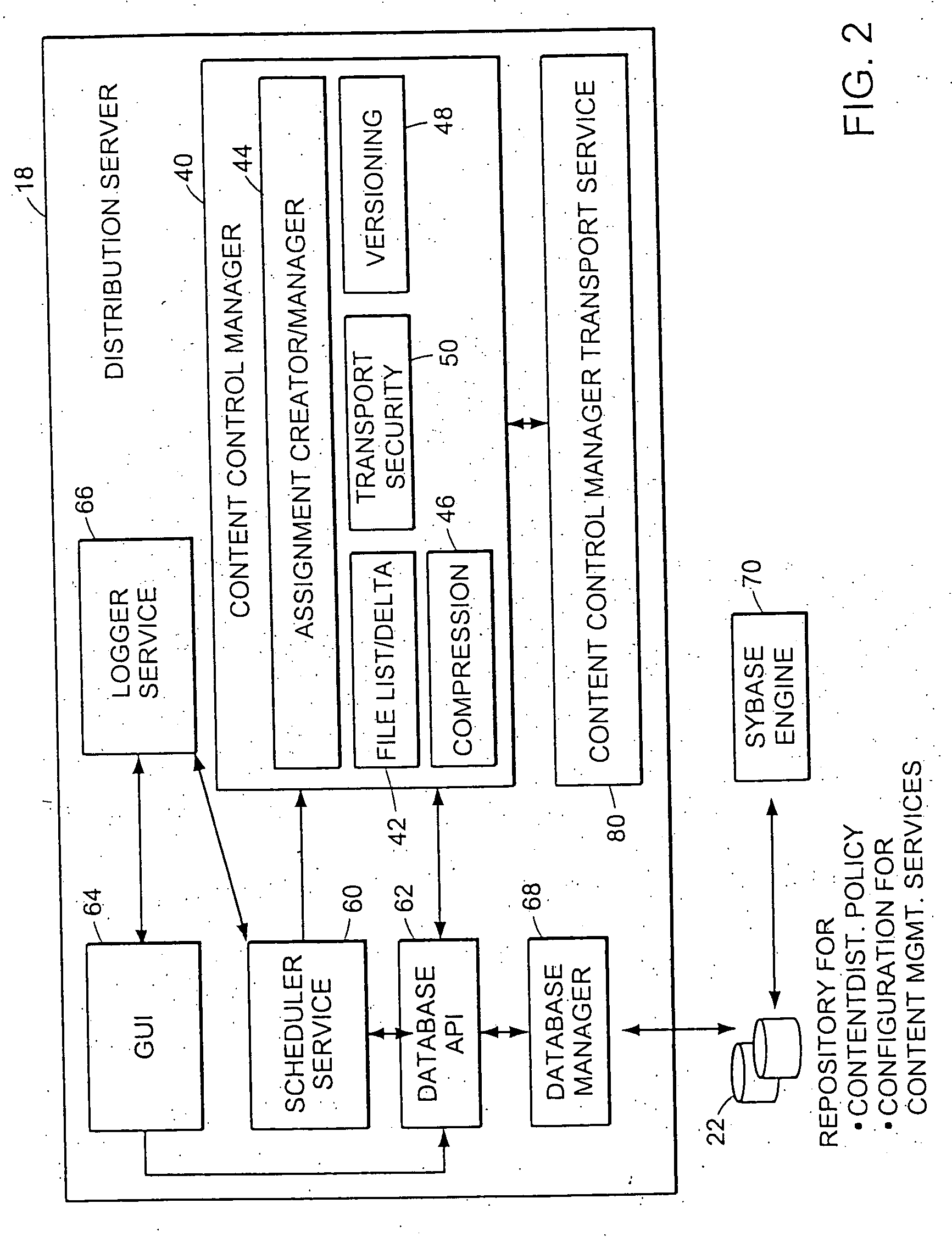
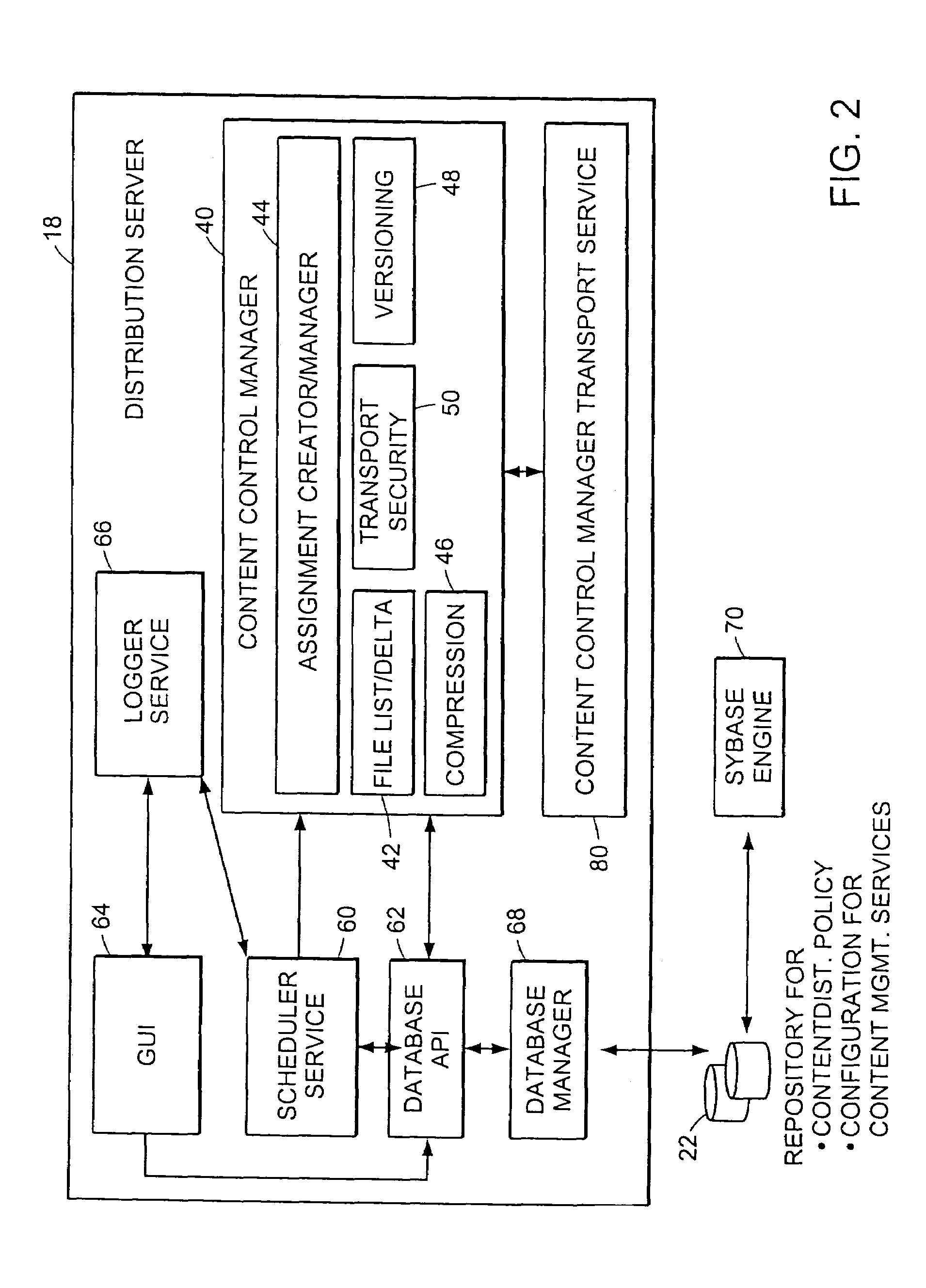
InactiveUS7346682B2Improve scalabilityEfficient data transferMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionContent distributionStore and forward
The present invention provides a system and apparatus for efficient and reliable, control and distribution of data files or portions of files, applications, or other data objects in large-scale distributed networks. A unique content-management front-end provides efficient controls for triggering distribution of digitized data content to selected groups of a large number of remote computer servers. Network distribution messages are dispatched according to a sorted list of servers, based on factors such as nearness, server processor speed, reliability, and CPU Usage. For large numbers of servers, a store-and-forward approach becomes much more efficient. A first selected server receives the message from a content control manager (CCM). The first server requests instructions for the next server listed on an ordered list in the CCM and forwards a copy of that message to the next identified server. Each server reports its completion and requests further instructions from the CCM. This mechanism permits highly efficient and robust distribution of assignments and data content from the CCM to each required GL using a store-and-forward tree structure.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
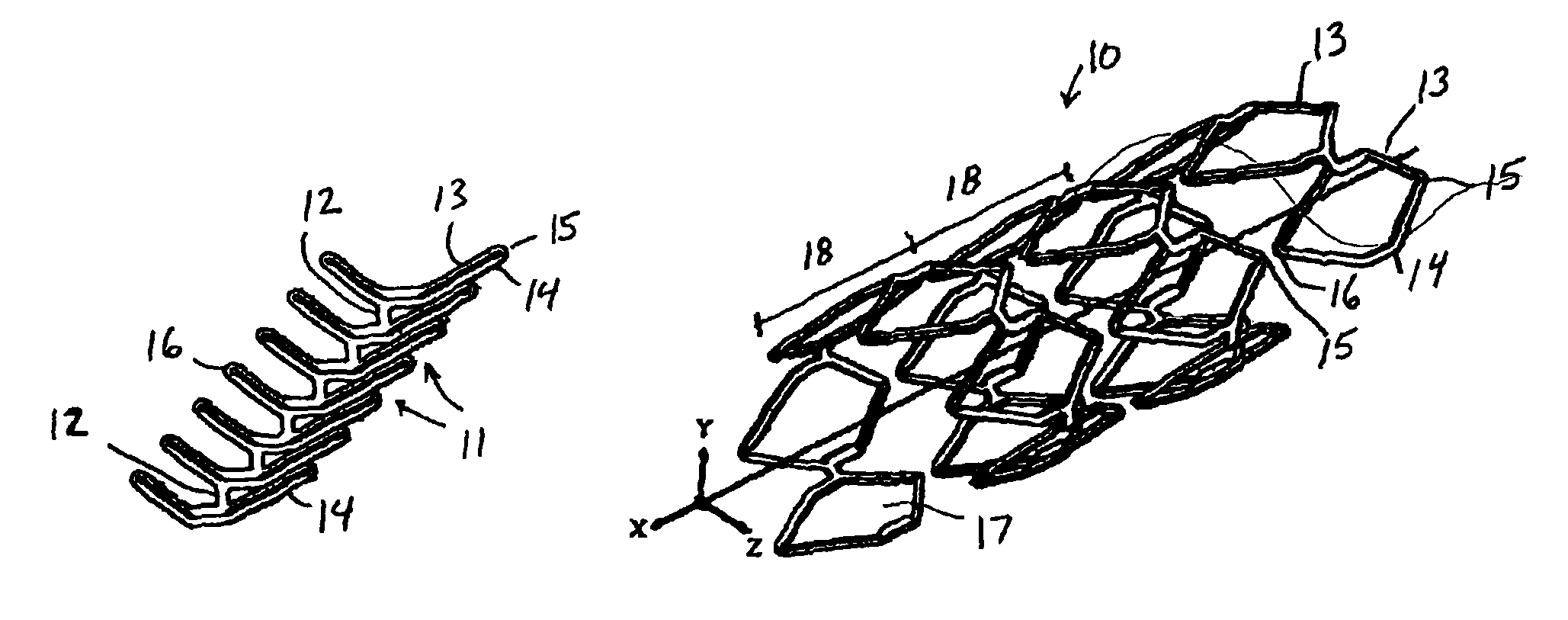
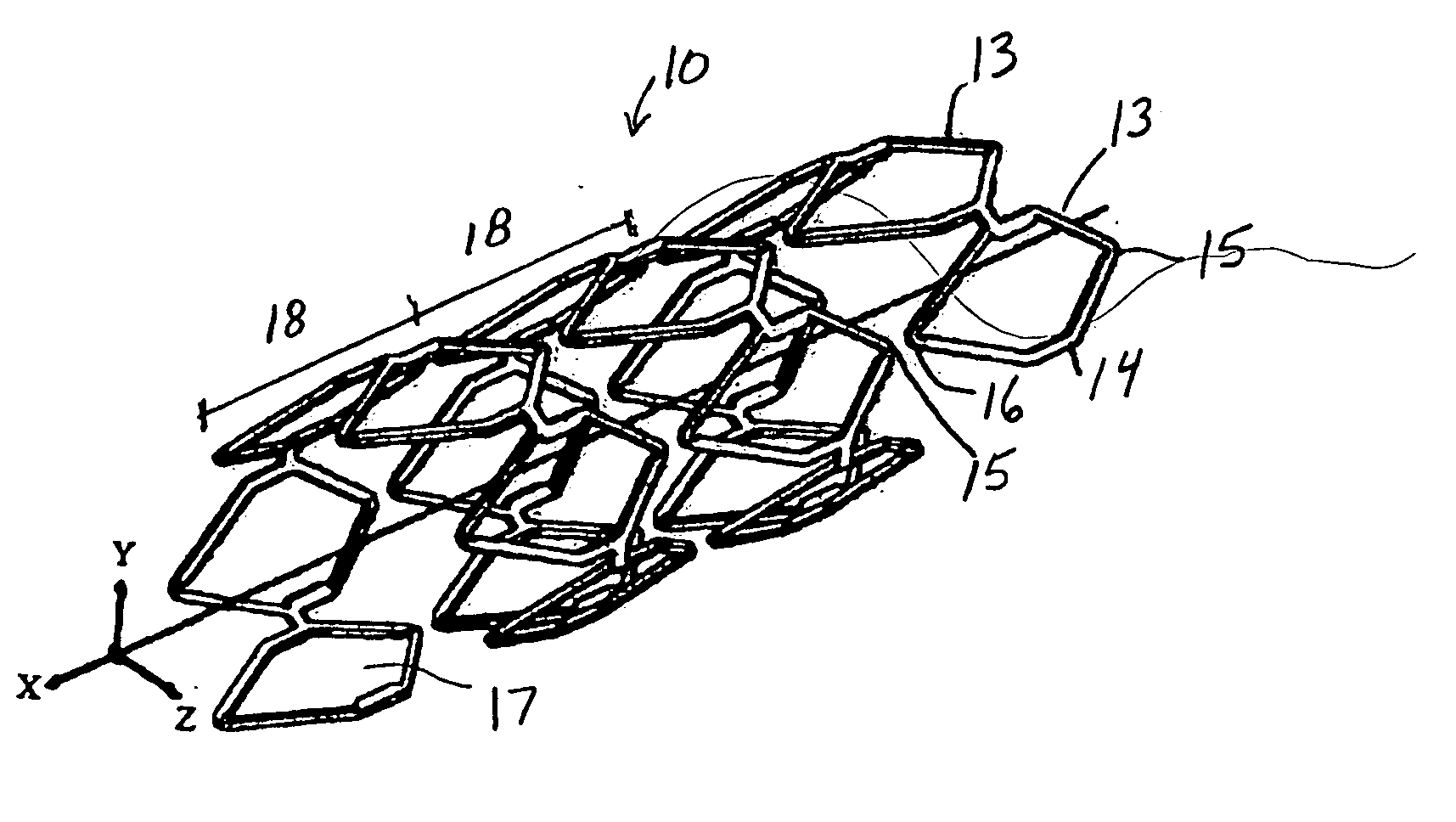
Fracture-resistant helical stent incorporating bistable cells and methods of use
InactiveUS20060217795A1Increased compressive loadPotent inhibitionStentsSurgeryVascular prosthesisLesion
Vascular prostheses and methods of use are provided, wherein the vascular prosthesis includes a plurality of bistable unit cells configured to form a helical structure. A visualization catheter also is provided for use ensuring accurate measurement of a lesion and ensuring delivery and placement of the vascular prosthesis.
Owner:CELONOVA STENT
Transverse connector
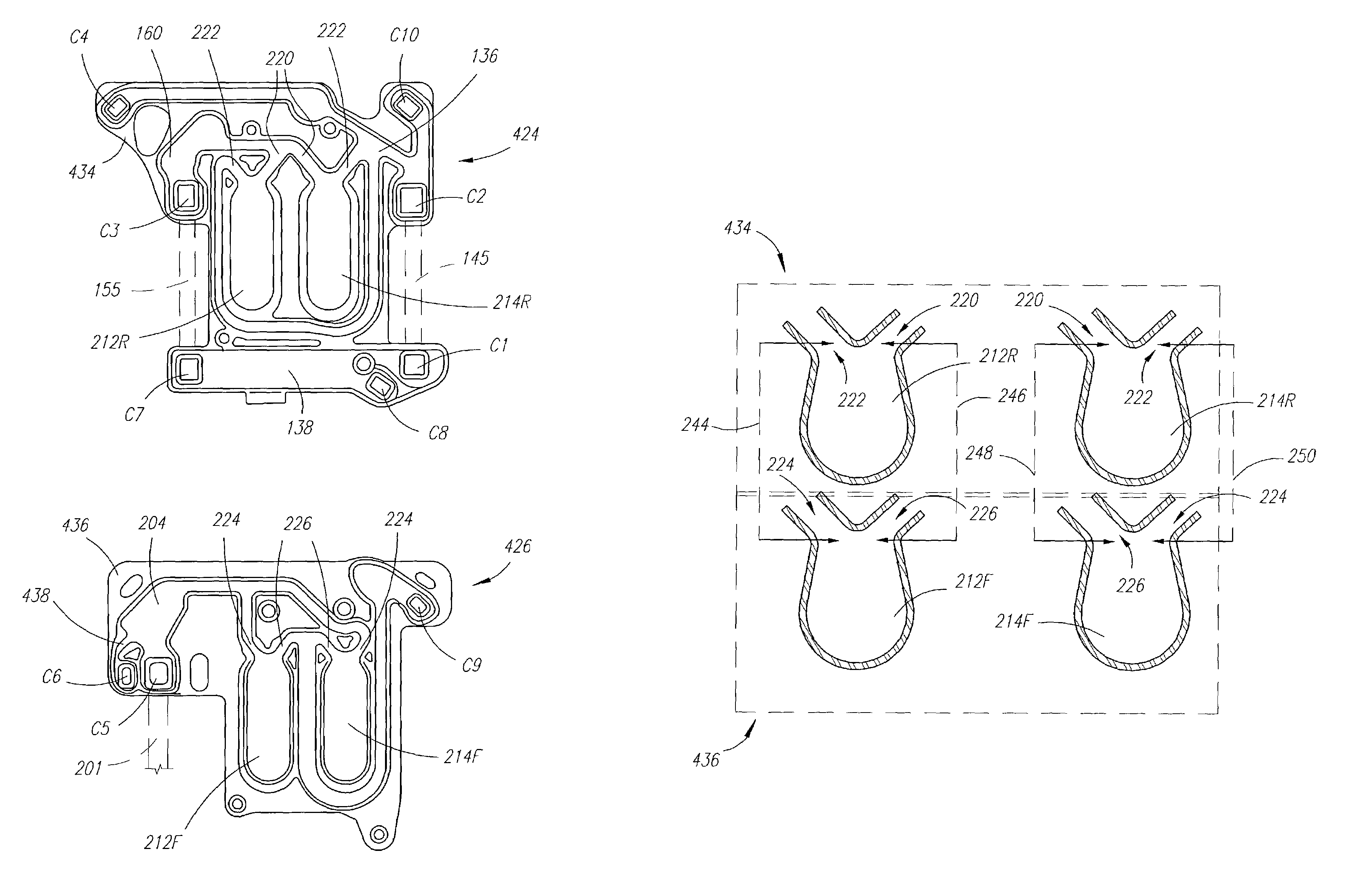
ActiveUS7842071B2Prevent movementPotent inhibitionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A crosslink or connecting assembly is provided to secure multiple spinal rods in relation to each other. The connecting assembly is disposed transversely between two spinal rods and has moveable components for rotating, pivoting, and extending portions of the connecting device in order to accommodate the positioning of the spinal rods.
Owner:XTANT MEDICAL HLDG INC
Optical Device Characterization
ActiveUS20070274626A1Distortion of optical propertyReduce eye damageChecking apparatusOther accessoriesElectricityDevice material
A method and system for determining the orientation of an optical device, the optical device having data carrier means for carrying data related to the optical device, the data carrier having data carrier means operable in at least one of an electrical mode and a magnetic mode; the data carrier means being associated with an optical device by at least at least one of the group of depositing on or printing on a posterior surface or anterior surface of the optical device, including the data carrier with the optical device material, wherein data carrier means emits a data signal periodically or in response to a external signal from an external means.
Owner:SABETA ANTON
Systems and methods for performing blood processing and/or fluid exchange procedures
InactiveUS20060084906A1Fast and convenient and one step process for loading processingPotent inhibitionOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationFlow managementBlood processing
A flow management system comprising a first panel having a fluid pathway and a second panel having a fluid pathway for passing a second fluid. The fluid pathway of the first panel passes a first fluid. The first panel includes a first compartment to receive a volume of the first fluid. The second panel includes a second compartment to receive a volume of the second fluid. The first and second panels are aligned so that the first compartment overlays the second compartment. The flow management system may be placed within a gap defined by a first surface and a second surface. The first and second compartments are disposed within the gap so that the second compartment bears against the second surface as the second fluid fills the second compartment and forces the first fluid out from the first compartment as the first compartment bears against the first surface.
Owner:NXSTAGE MEDICAL INC
Method & system for tracking the wearable life of an ophthalmic product
ActiveUS20060267768A1Potent inhibitionRegistering/indicating time of eventsChecking apparatusLapse timeEngineering
A method for tracking the wearable life of an ophthalmic product, the method comprising the steps of: providing the ophthalmic product with at least one data carrier for carrying data related to the ophthalmic product, the data carrier having a first device operable in a magnetic and / or electrical mode; providing an activation signal from an external means; activating the first device with the activation signal to cause the first device to emit the data in response to the activating signal; recording the time the first device is interrogated, processing the received data to determine the wearable life of the ophthalmic product based on the lapsed time.
Owner:SABETA ANTON
Transverse Connector
ActiveUS20080015588A1Prevent movementPotent inhibitionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A crosslink or connecting assembly is provided to secure multiple spinal rods in relation to each other. The connecting assembly is disposed transversely between two spinal rods and has moveable components for rotating, pivoting, and extending portions of the connecting device in order to accommodate the positioning of the spinal rods.
Owner:XTANT MEDICAL HLDG INC
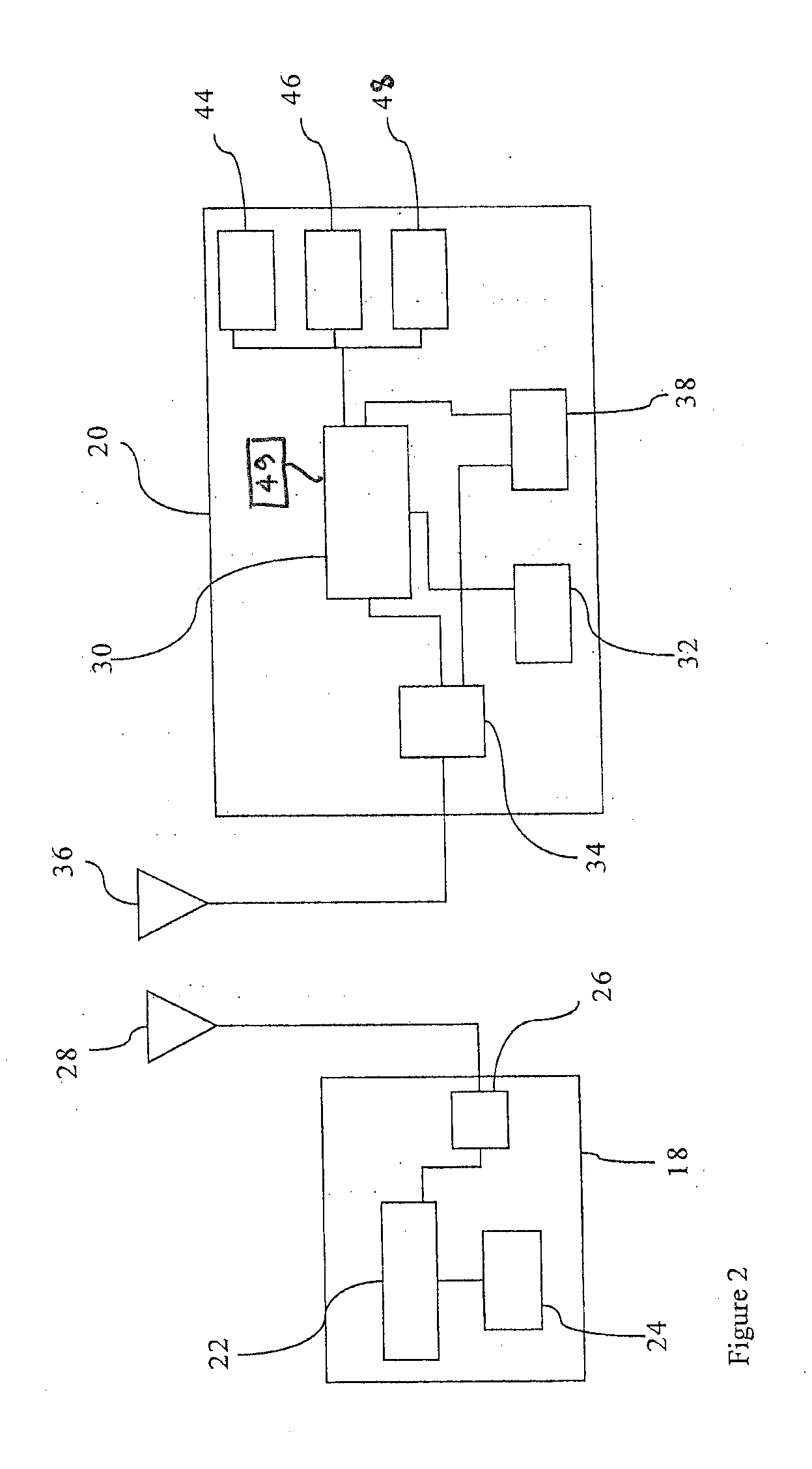
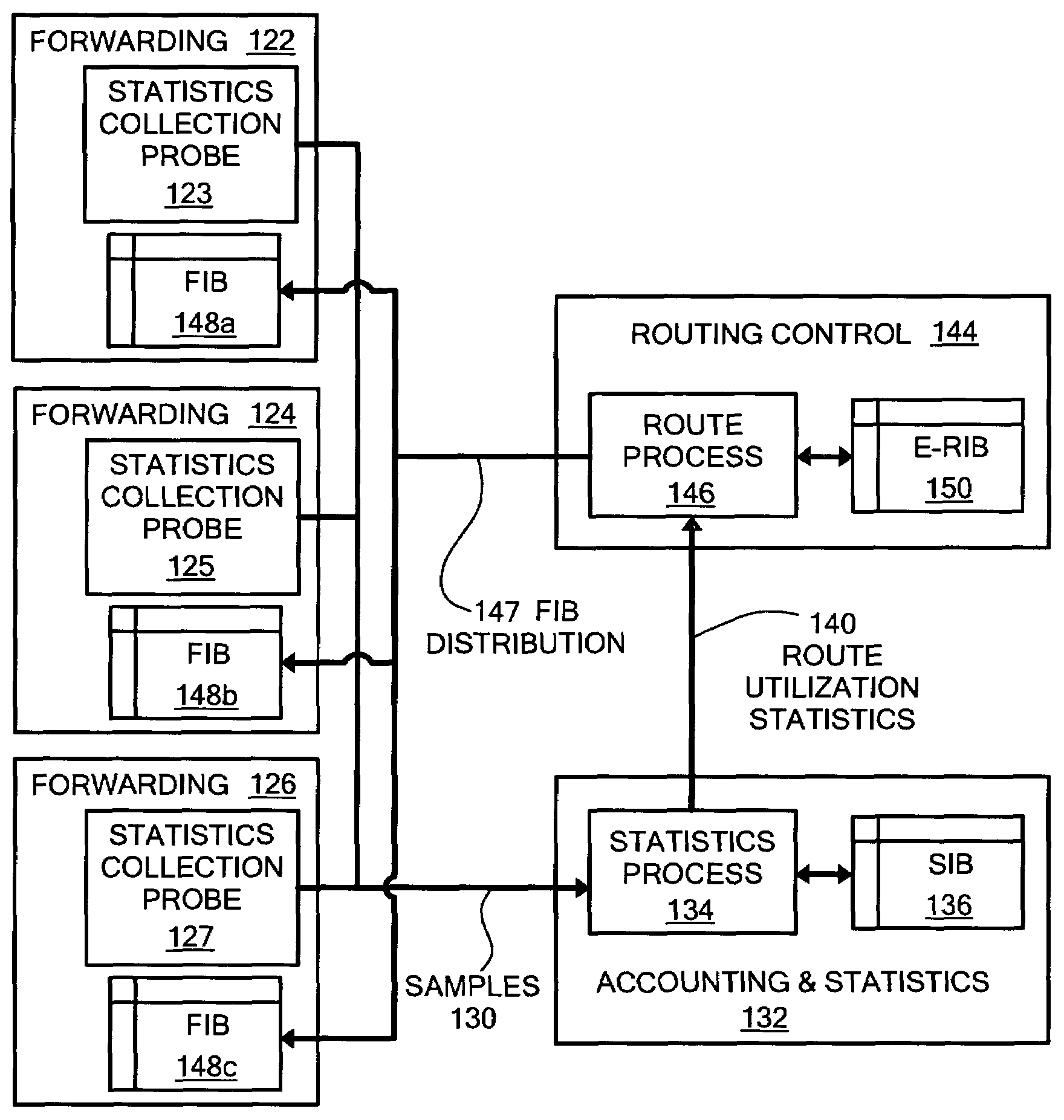
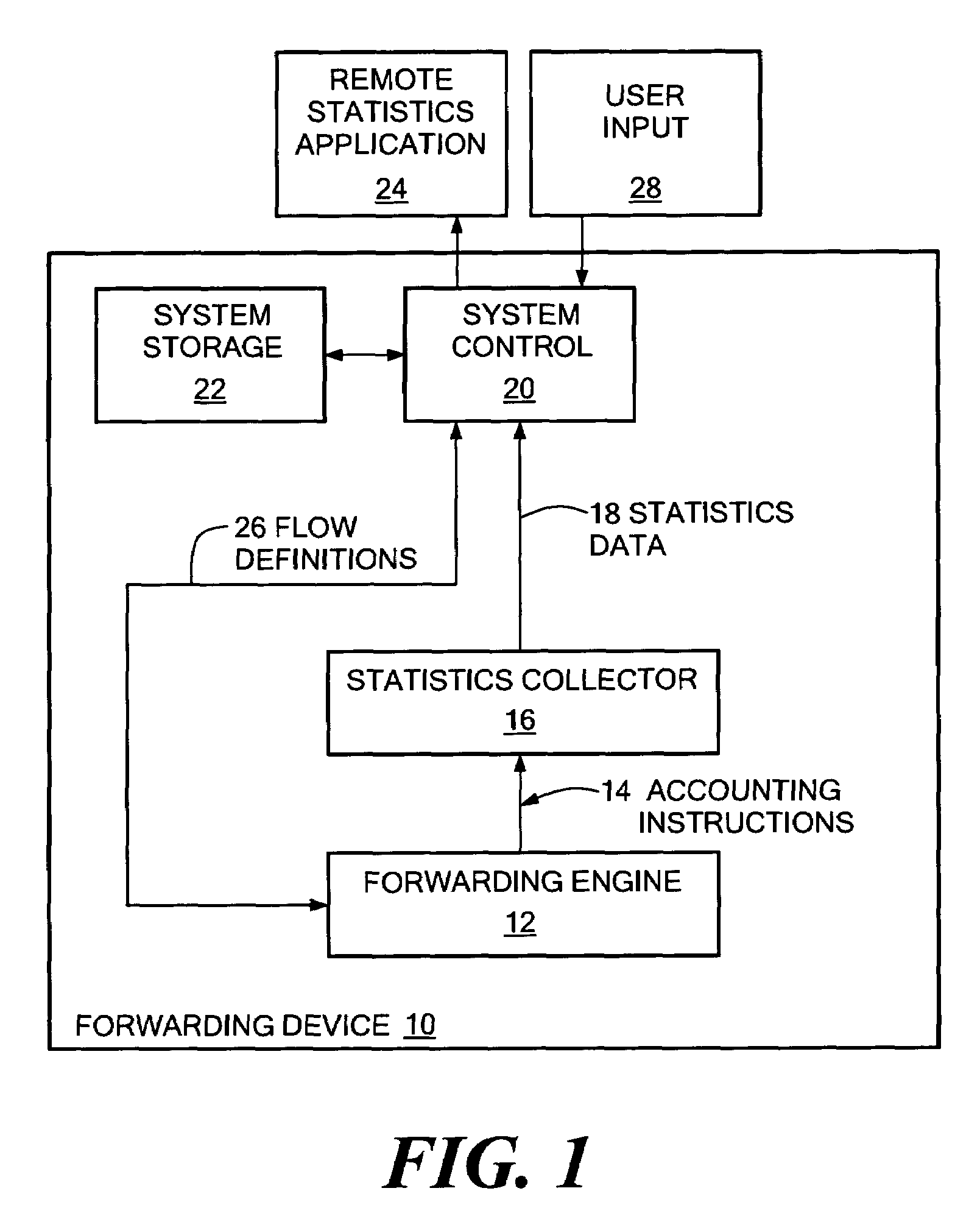
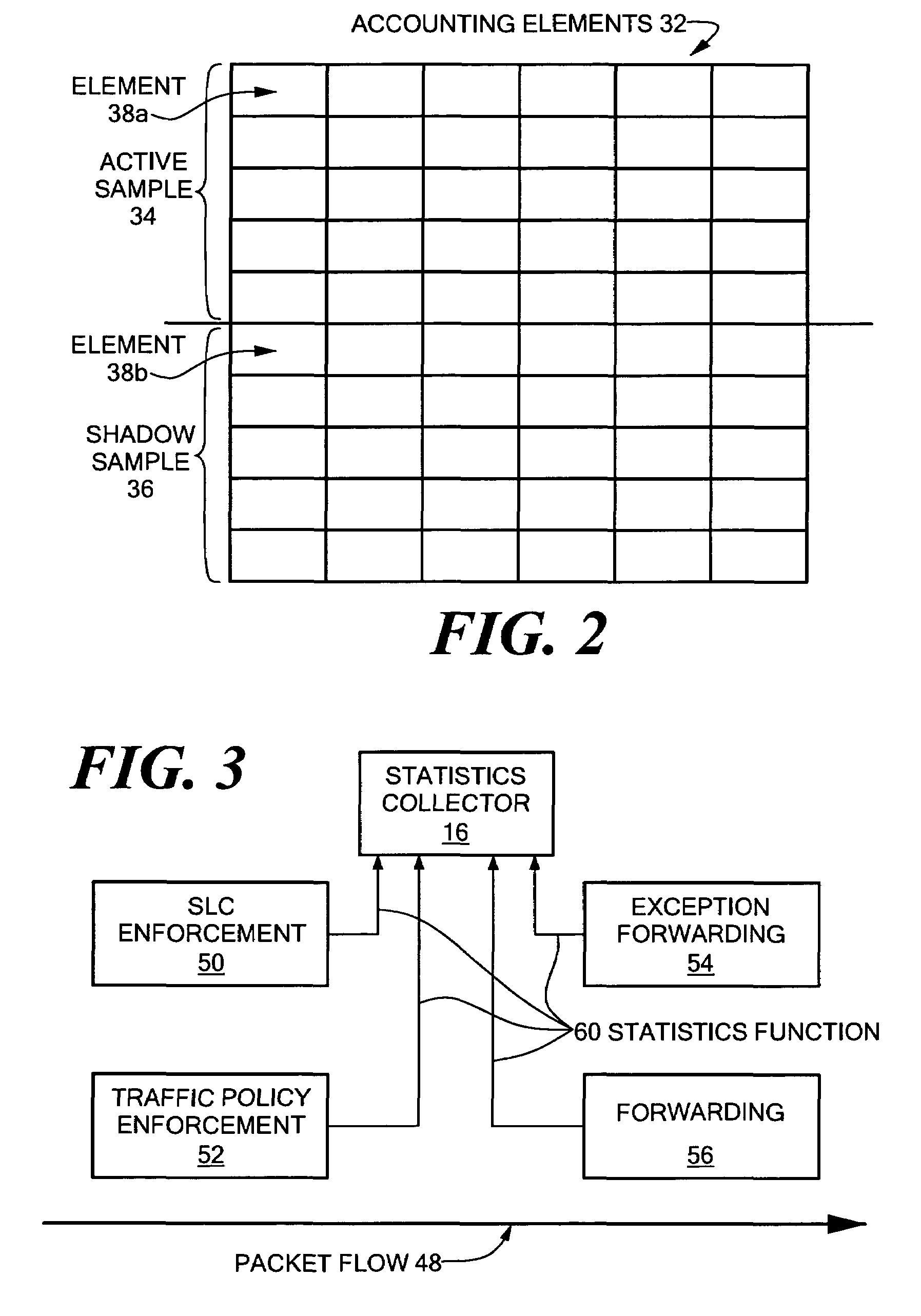
Network accounting statistics collection
InactiveUS7577736B1Improve the level ofReduce transmission bandwidthMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsError preventionPrimitive operationCollection system
A system for network accounting statistics collection including a statistics collector associated with each packet forwarding engine. Each statistics collector has one or more accounting elements, each of which includes some number of counters, such as packet and byte counters. Each statistics collector receives accounting instructions from the associated forwarding engine for packets processed by the forwarding engine, including packets that will be discarded without being forwarded. Each accounting instruction includes an identifier uniquely indicating one of the accounting elements, and information used to increment the counters within the accounting element. Upon receipt of an accounting instruction, the receiving statistics collector increments the counters in the accounting element. The accounting instruction is a relatively simple primitive operation in the disclosed system, enabling high-speed operation. Each statistics collector collects data over a fixed sampling interval that may range from a number of milliseconds to one or more minutes. Each sampling period begins with a reset of an accounting element store, and ends with at least one set of data being flushed to a management system for further processing and / or formatting.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Method and apparatus for dynamic resource discovery and information distribution in a data network
InactiveUS20080177861A1Effective controlEffective distributionMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionDynamic resourceBack end server
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Benzo[d]isoxazol-3-ol DAAO inhibitors
Methods for increasing D-Serine concentration and reducing concentration of the toxic products of D-Serine oxidation, for enhancing learning, memory and / or cognition, or for treating schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease, ataxia, or neuropathic pain, or preventing loss in neuronal function characteristic of neurodegenerative diseases involve administering to a subject in need of treatment a therapeutic amount of a compound of formula I, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof:whereinZ1 is N or CR3;Z2 is N or CR4;Z3is O or S;A is hydrogen, alkyl or M+;M is aluminum, calcium, lithium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, zinc or a mixture thereof;R1, R2, R3 and R4 are independently selected from hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy alkoxy, aryl, acyl, halo, cyano, haloalkyl, NHCOOR5 and SO2NH2;R5 is aryl, arylalkyl, heteroaryl or heteroarylalkyl;at least one of R1, R2, R3 and R4 is other than hydrogen; andat least one of Z1 and Z2 is other than N.
Owner:SEPACOR INC
Substituted Isoquinolinones and Quinazolinones
The invention relates to substituted nitrogen containing bicyclic heterocycles of the formula (I)wherein Z is CH2 or N—R4 and X, R1, R2, R4, R6, R7 and n are as defined in the description. Such compounds are suitable for the treatment of a disorder or disease which is mediated by the activity of MDM2 and / or MDM4, or variants thereof.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
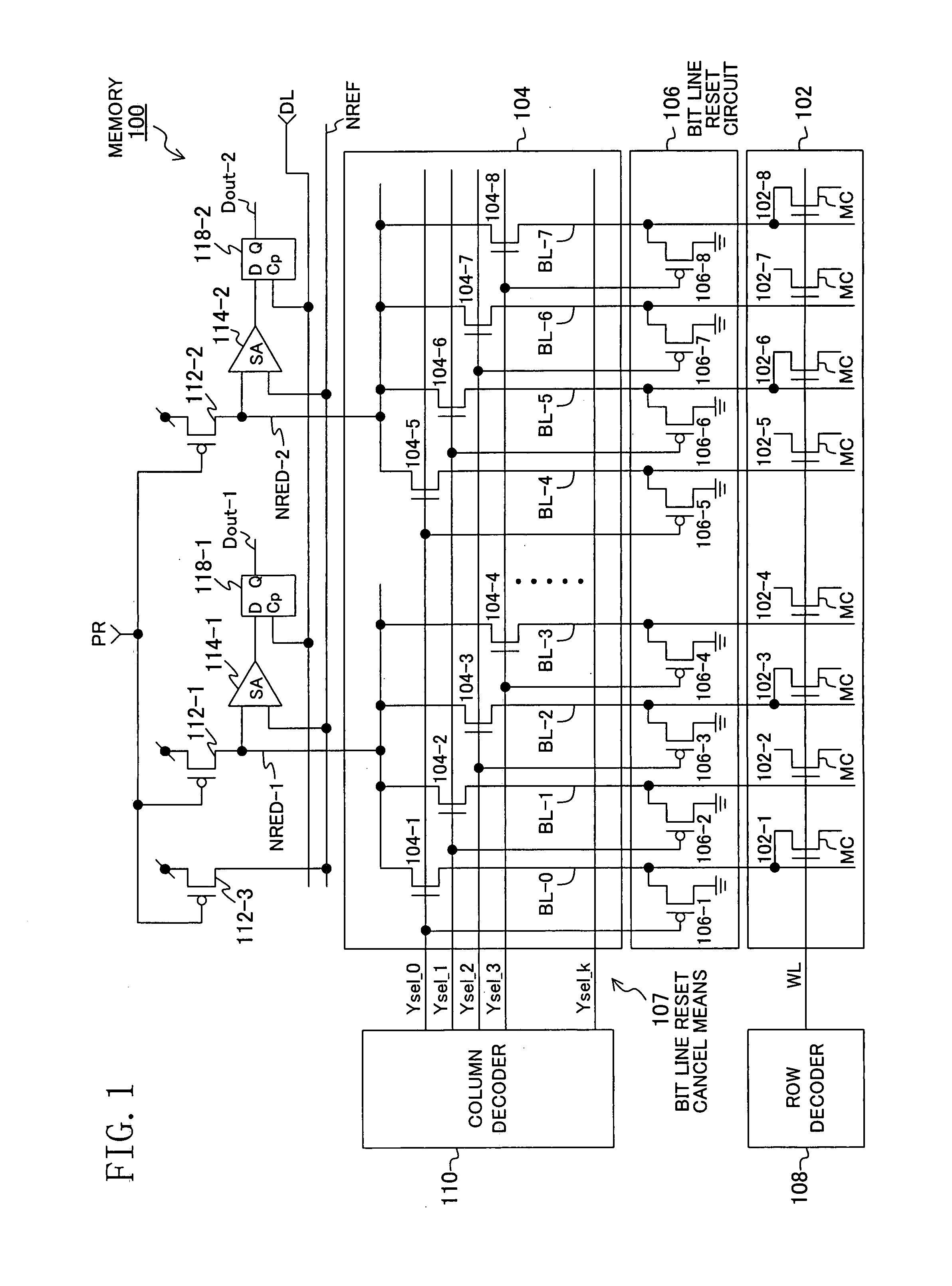
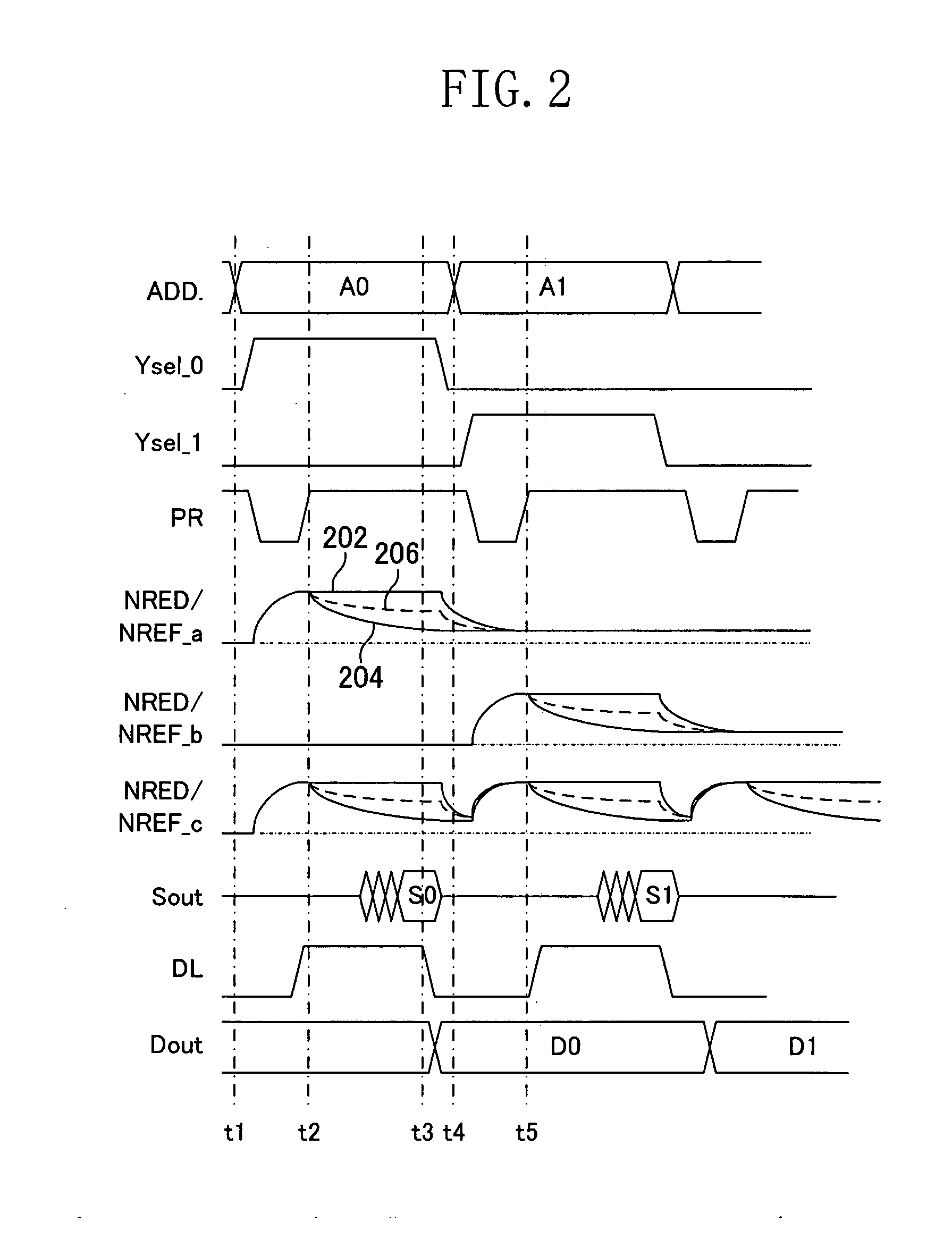
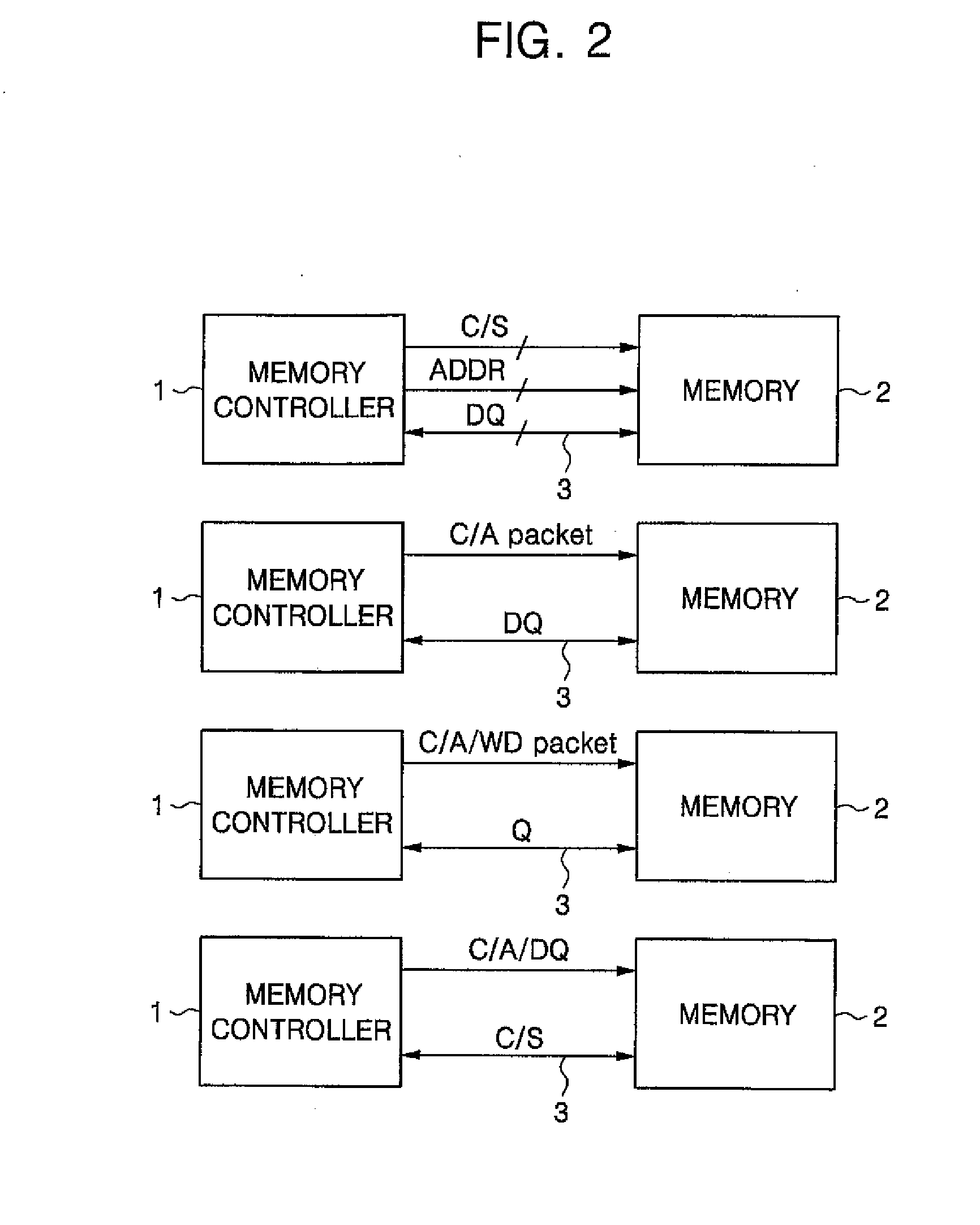
Memory system and command handling method
ActiveUS20080195922A1Potent inhibitionEnsure data integrityCode conversionCoding detailsTerm memoryMemory controller
A memory system including a memory controller and a memory and a related method are disclosed. The method includes communicating a command and error detection / correction (EDC) data associated with the command from the memory controller to the memory, decoding the command and executing an EDC operation related to the EDC data in parallel, and if the command is a write command, delaying execution of a write operation indicated by the write command until completion of the EDC operation, else immediately executing an operation indicated by the command without regard to completion of the EDC operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
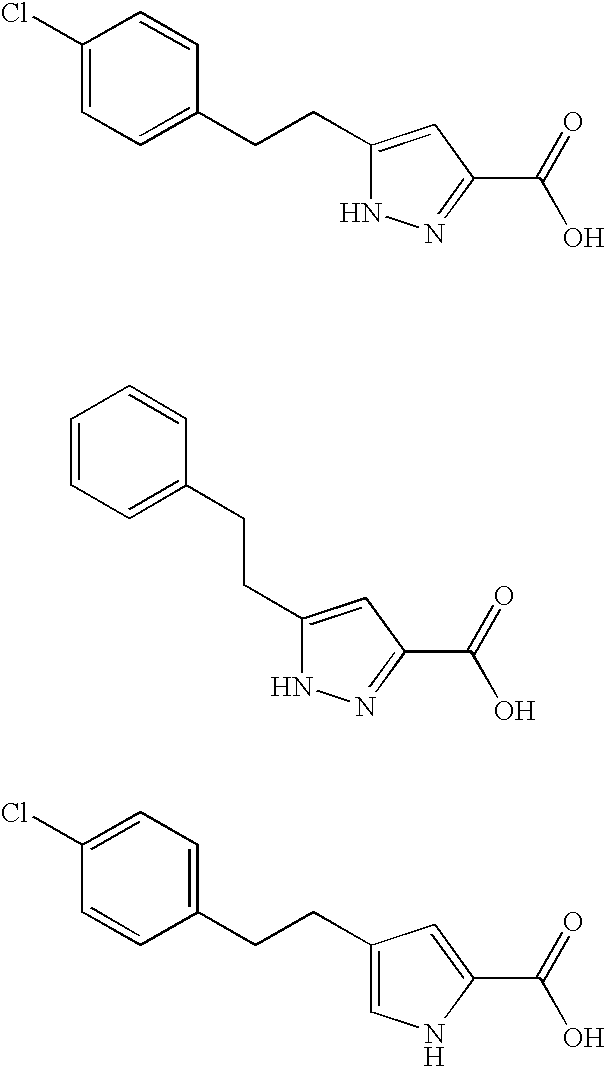
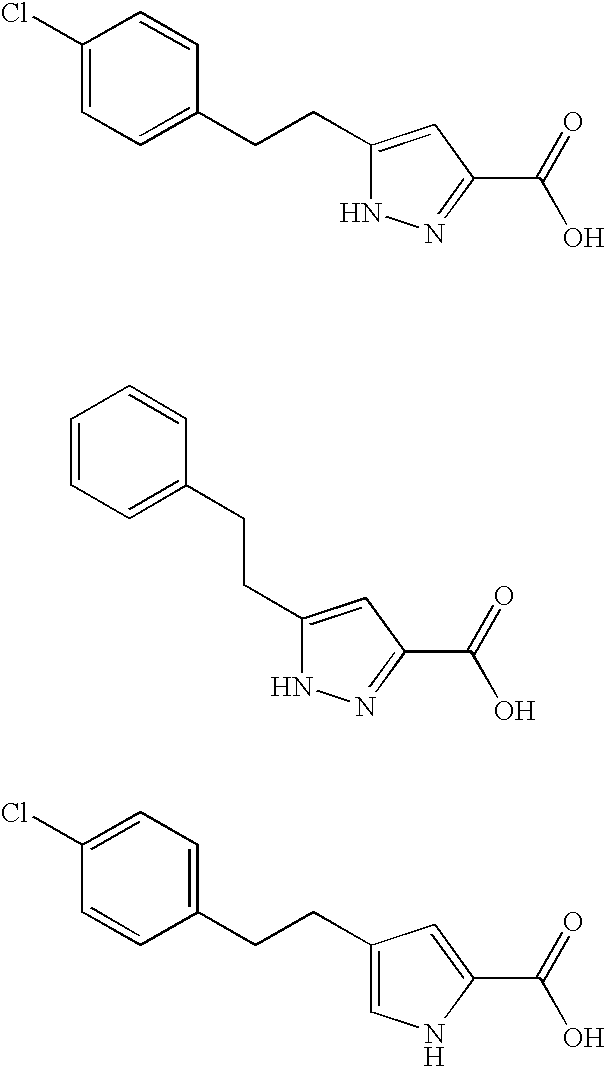
Pyrrole and pyrazole DAAO inhibitors
Methods for increasing D-Serine concentration and reducing concentration of the toxic products of D-Serine oxidation, for enhancing learning, memory and / or cognition, or for treating schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease, ataxia or neuropathic pain, or preventing loss in neuronal function characteristic of neurodegenerative diseases involve administering to a subject in need of treatment a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula I, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof: wherein [0001]R1 and R2 are independently selected from hydrogen, halo, nitro, alkyl, acyl, alkylaryl, and XYR5; [0002]or R1 and R2, taken together, form a 5, 6, 7 or 8-membered substituted or unsubstituted carbocyclic or heterocyclic group; [0003]X and Y are independently selected from O, S, NH, and (CR6R7)n; [0004]R3 is hydrogen, alkyl or M+; M is aluminum, calcium, lithium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, zinc ion or a mixture thereof; [0005]Z is N or CR4; [0006]R4 is from selected from hydrogen, halo, nitro, alkyl, alkylaryl, and XYR5; [0007]R5 is selected from aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl; [0008]R6 and R7 are independently selected from hydrogen and alkyl; n is an integer from 1 to 6; [0009]at least one of R1, R2 and R4 is other than hydrogen; and [0010]at least one of X and Y is (CR6R7)n. D-serine or cycloserine may be coadministered along with the compound of formula I.
Owner:SEPACOR INC
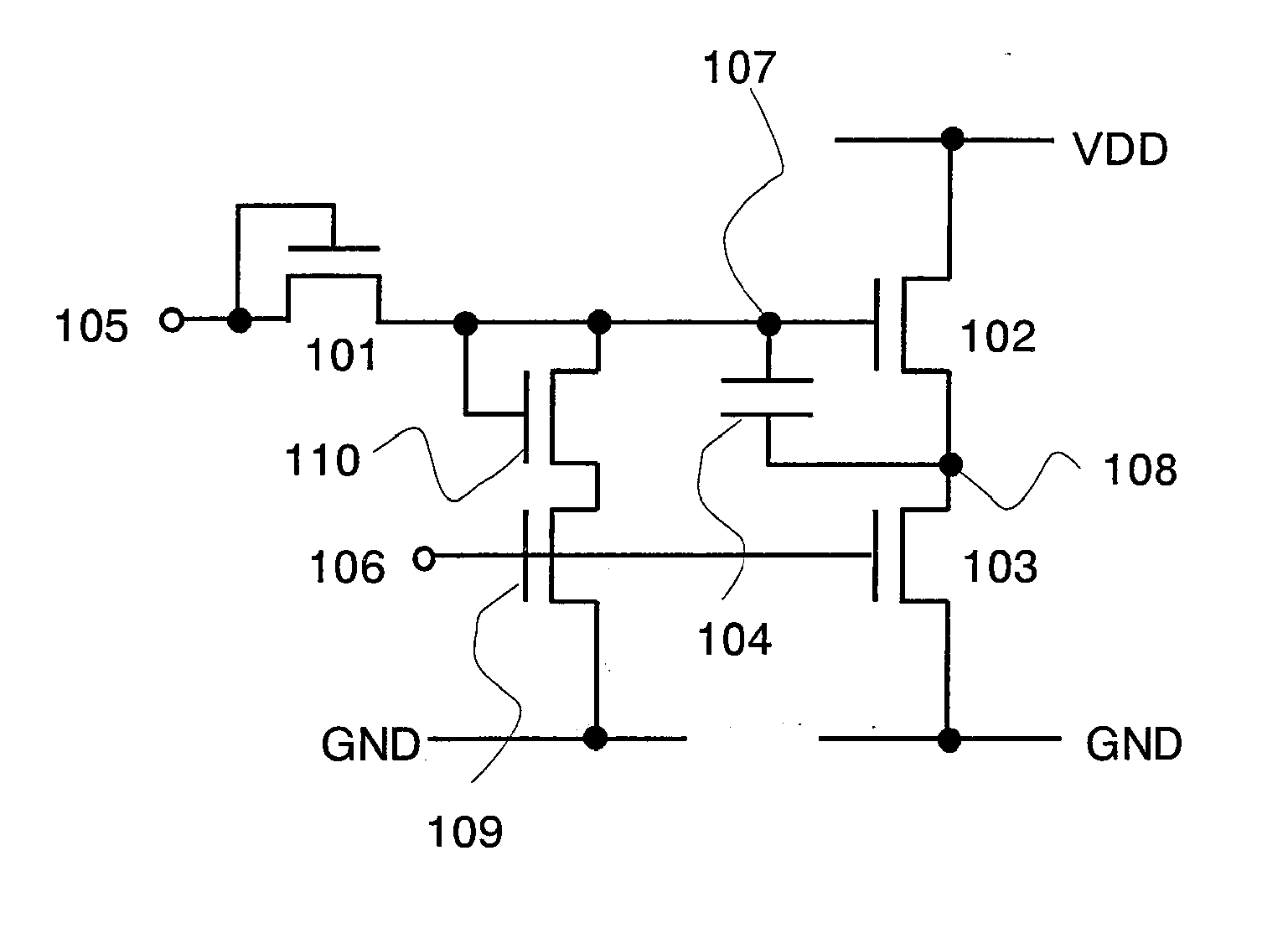
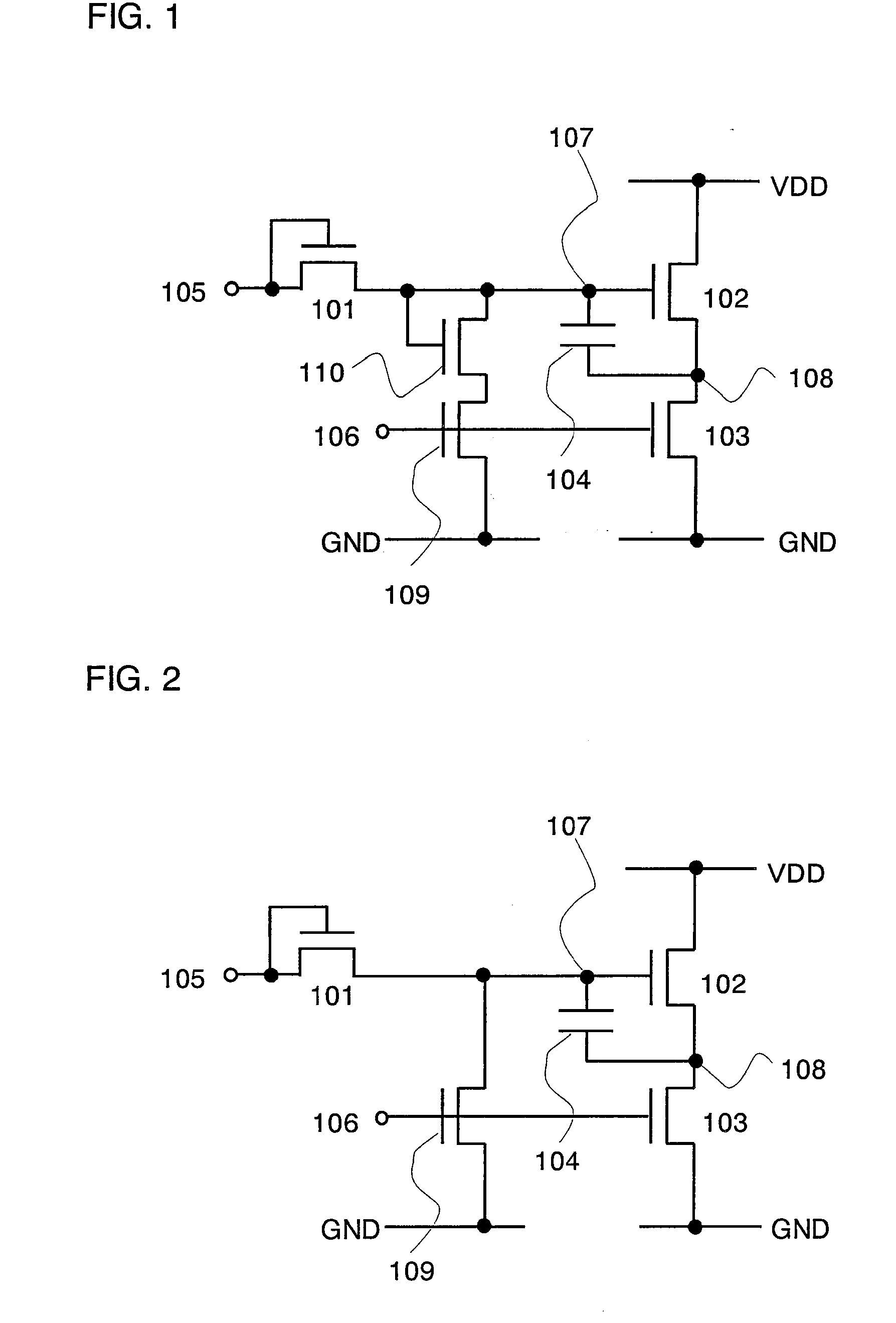
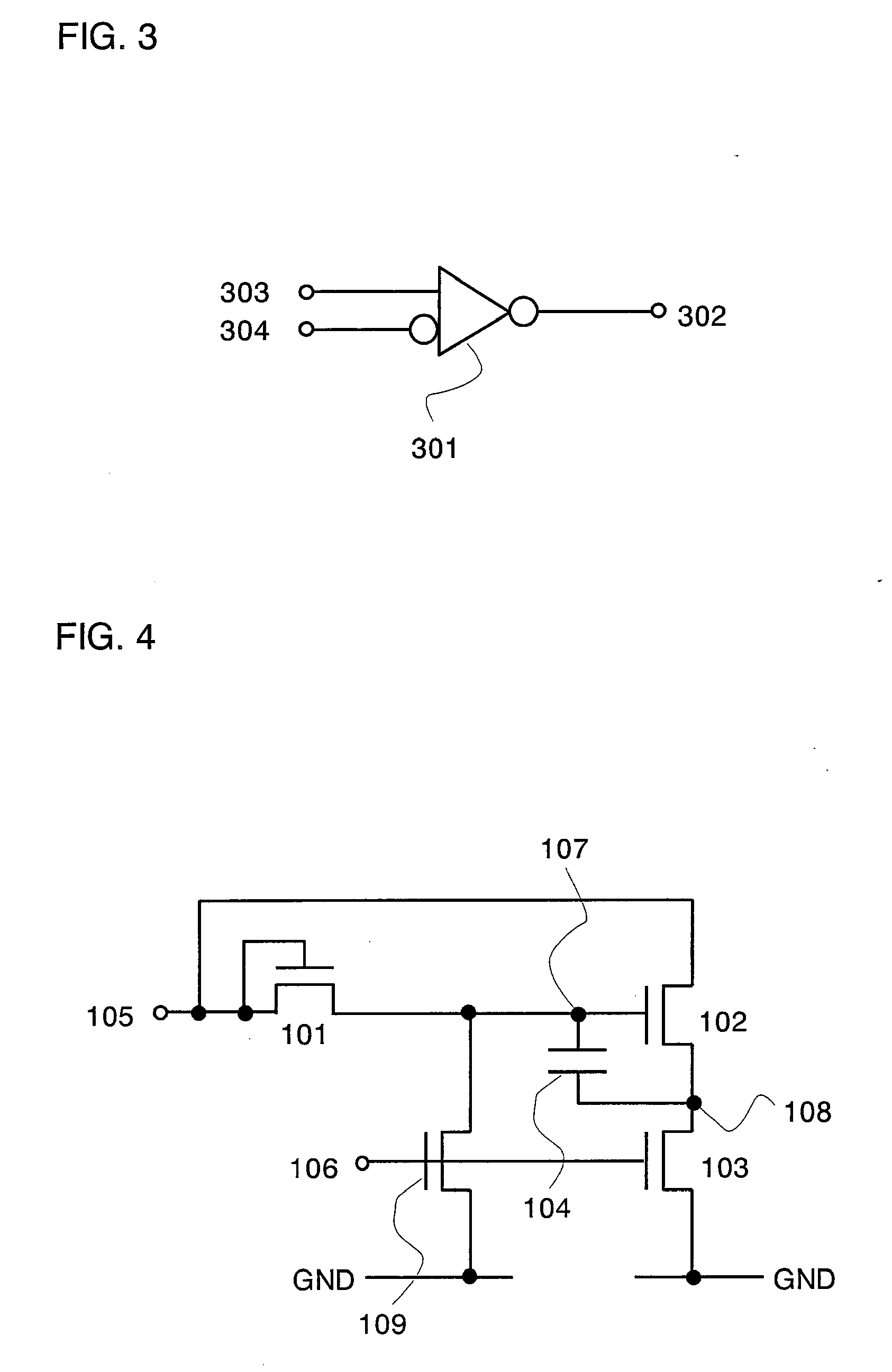
Semiconductor Device, and Display Device and Electronic Device Utilizing the Same
ActiveUS20070132686A1Reduce the amplitudeRaise the potentialSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialDisplay device
A semiconductor device having a normal function means is provided, in which the amplitude of an output signal is prevented from being decreased even when a digital circuit using transistors having one conductivity is employed. By turning OFF a diode-connected transistor 101, the gate terminal of a first transistor 102 is brought into a floating state. At this time, the first transistor 102 is ON and its gate-source voltage is stored in a capacitor. Then, when a potential at the source terminal of the first transistor 102 is increased, a potential at the gate terminal of the first transistor 102 is increased as well by bootstrap effect. As a result, the amplitude of an output signal is prevented from being decreased.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Benzo[d]isoxazol-3-ol DAAO inhibitors
Methods for increasing D-Serine concentration and reducing concentration of the toxic products of D-Serine oxidation, for enhancing learning, memory and / or cognition, or for treating schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease, ataxia, or neuropathic pain, or preventing loss in neuronal function characteristic of neurodegenerative diseases involve administering to a subject in need of treatment a therapeutic amount of a compound of formula I, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof: wherein [0001]Z1 is N or CR3; [0002]Z2 is N or CR4; [0003]Z3is O or S; [0004]A is hydrogen, alkyl or M+; M is aluminum, calcium, lithium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, zinc or a mixture thereof; [0005]R1, R2, R3 and R4 are independently selected from hydrogen, alkyl, hydroxy alkoxy, aryl, acyl, halo, cyano, haloalkyl, NHCOOR5 and SO2NH2; [0006]R5 is aryl, arylalkyl, heteroaryl or heteroarylalkyl; [0007]at least one of R1, R2, R3 and R4 is other than hydrogen; and [0008]at least one of Z1 and Z2 is other than N.
Owner:SEPACOR INC
Fracture-resistant helical stent incorporating bistable cells and methods of use
InactiveUS8353948B2Increased compressive loadPotent inhibitionStentsSurgeryVascular prosthesisLesion
Vascular prostheses and methods of use are provided, wherein the vascular prosthesis includes a plurality of bistable unit cells configured to form a helical structure. A visualization catheter also is provided for use ensuring accurate measurement of a lesion and ensuring delivery and placement of the vascular prosthesis.
Owner:CELONOVA STENT
Hose-end sprayer assembly
A hose-end sprayer has a selectively rotatable rotary valve received within the transverse bore of a housing which includes a carrier liquid inlet passage, a chemical liquid inlet passage and a discharge passage. The valve has a carrier liquid duct and a chemical liquid duct opening into the carrier duct for interconnecting the inlet passage in a first rotative position of the valve, and the valve is capable of closing the inlet passages in a second rotative position of the valve. The rotary valve is selectively rotatable in a third position for interconnecting the liquid passage only with the discharge passage in a rinse position of the valve. Container venting is isolated from a valve chamber in which the rotary valve operates to avoid entry of carrier liquid into the container through the open vent in the ON position of the valve upon its selective rotation.
Owner:SILGAN DISPENSING SYST CORP
Display device and method for driving same
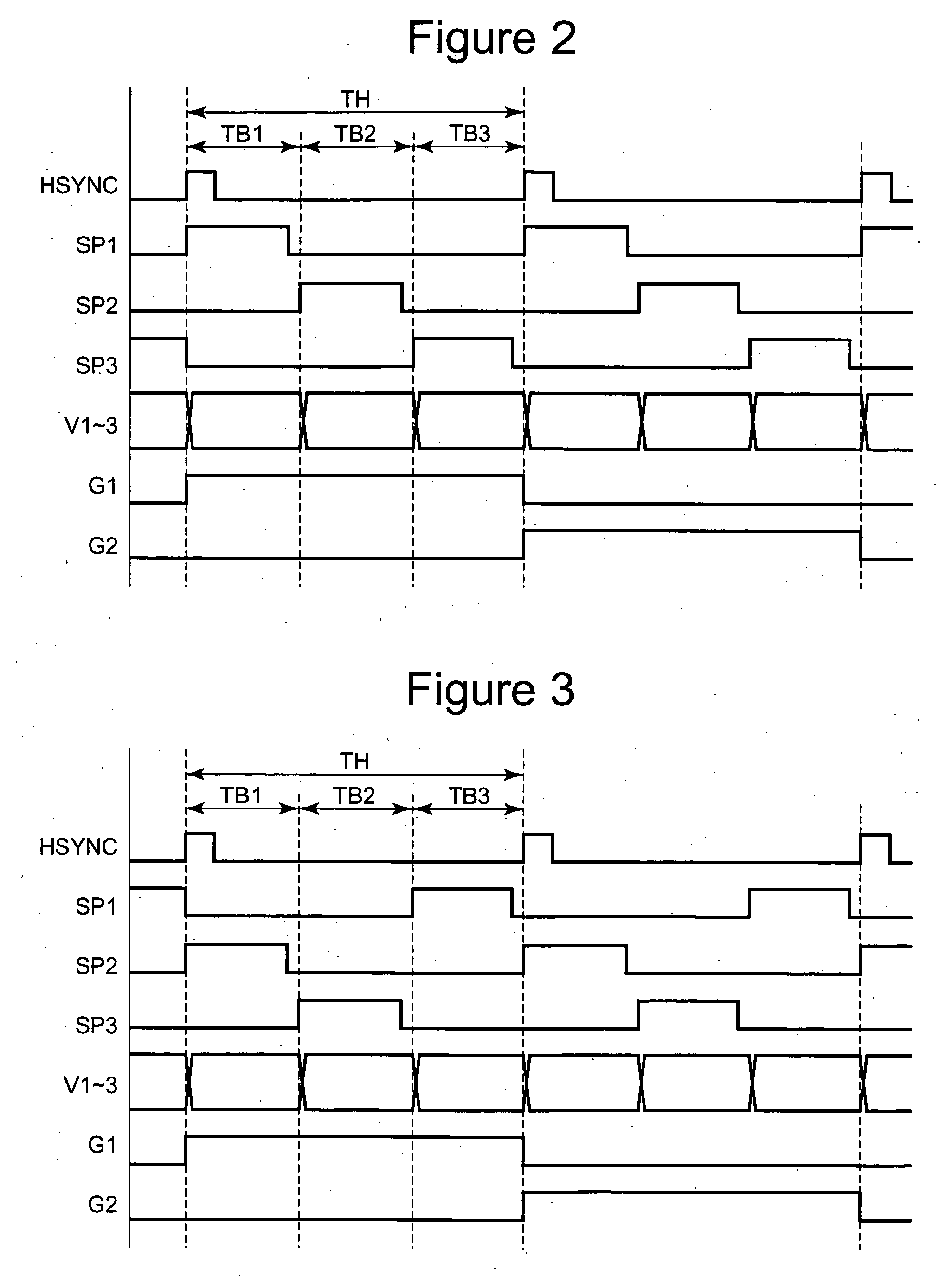
ActiveUS20160300534A1Increase in circuit sizeChange in measurementStatic indicating devicesComputational physicsDigital data
A display device that can compensate for degradation of circuit elements while suppressing an increase in circuit size is implemented.A data signal line (S(j)) is not only used as a signal line that transfers a signal for allowing an organic EL element (OLED) in each pixel circuit (11) to emit light at a desired luminance, but also used as a signal line for characteristic detection. In addition, a switch (334) is provided between the data signal line (S(j)) and an internal data line (Sin(j)). In such a configuration, during an AD conversion period during which analog data obtained for characteristic detection is converted into digital data, the switch (334) is brought into an off state and a potential of the data signal line (S(j)) obtained immediately before the AD conversion period is supplied from through a predetermined control line (CL) to the data signal line (S(j)).
Owner:SHARP KK
Optimizing multi-hit caching for long tail content
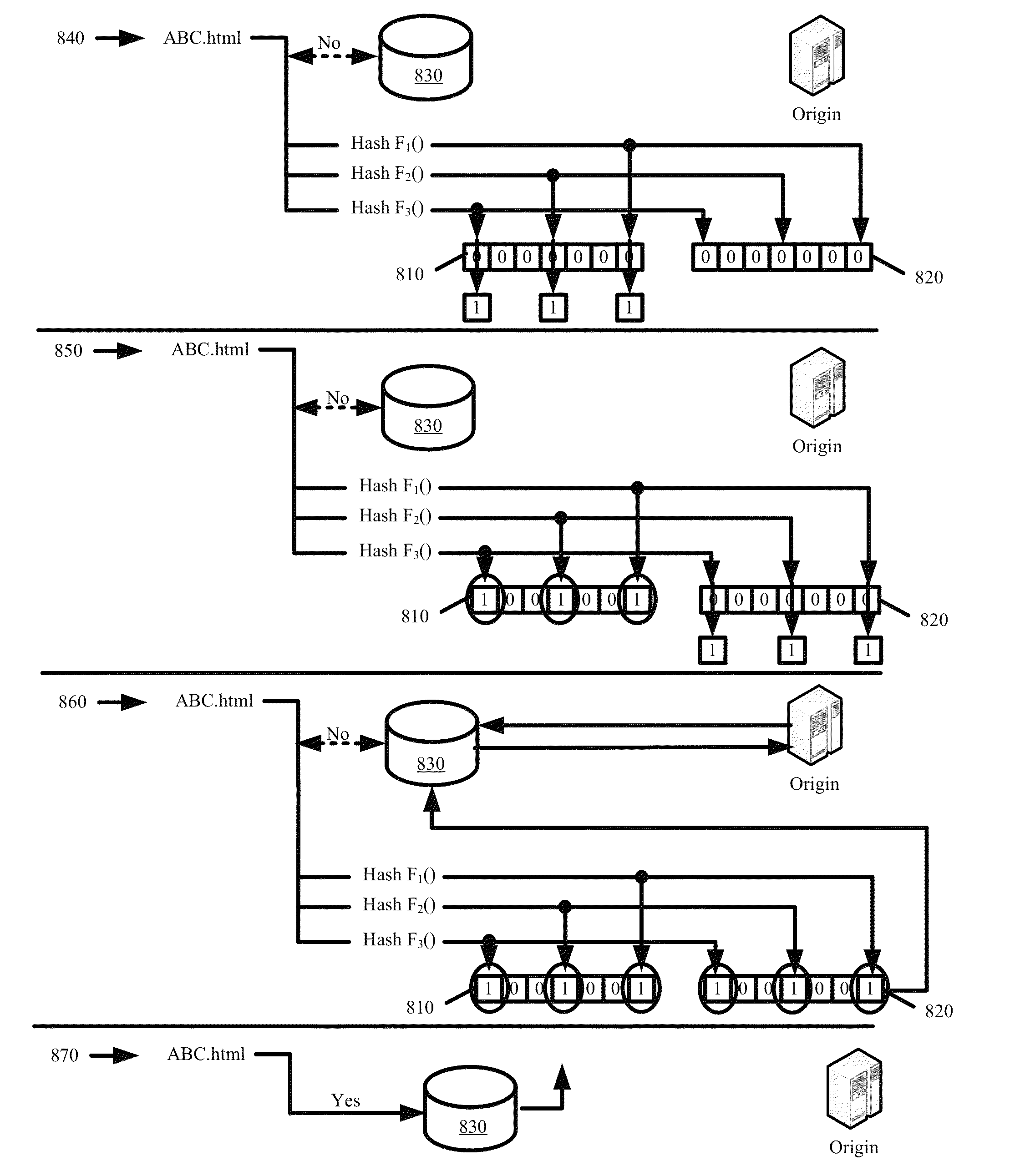
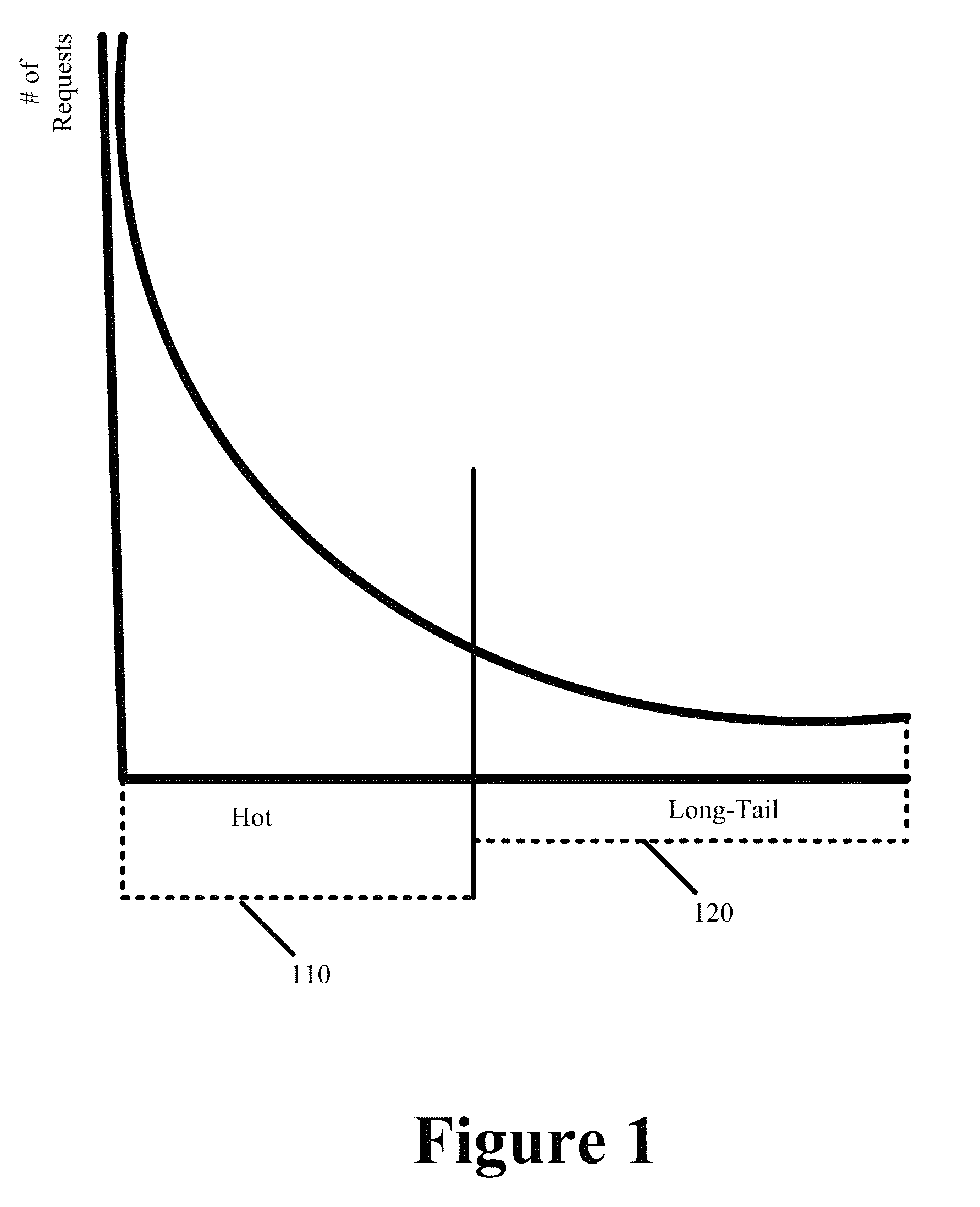
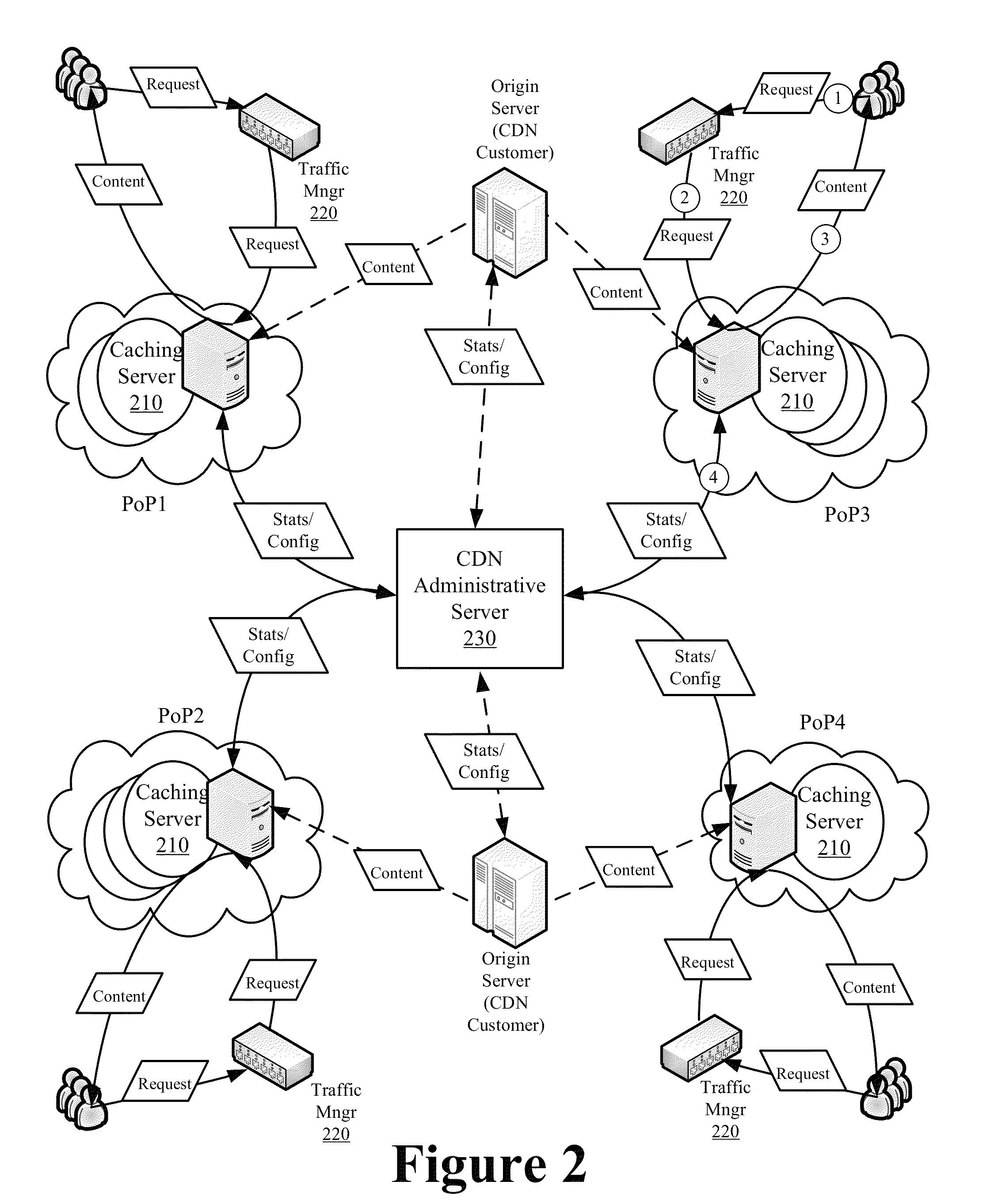
ActiveUS8370460B1Efficient executionAvoid cachingMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionBit arrayParallel computing
Some embodiments provide an optimized multi-hit caching technique that minimizes the performance impact associated with caching of long-tail content while retaining much of the efficiency and minimal overhead associated with first hit caching in determining when to cache content. The optimized multi-hit caching utilizes a modified bloom filter implementation that performs flushing and state rolling to delete indices representing stale content from a bit array used to track hit counts without affecting identification of other content that may be represented with indices overlapping with those representing the stale content. Specifically, a copy of the bit array is stored prior to flushing the bit array so as to avoid losing track of previously requested and cached content when flushing the bit arrays and the flushing is performed to remove the bit indices representing stale content from the bit array and to minimize the possibility of a false positive.
Owner:EDGIO INC
Pyrrole and pyrazole DAAO inhibitors
Methods for increasing D-Serine concentration and reducing concentration of the toxic products of D-Serine oxidation, for enhancing learning, memory and / or cognition, or for treating schizophrenia, Alzheimer's disease, ataxia or neuropathic pain, or preventing loss in neuronal function characteristic of neurodegenerative diseases involve administering to a subject in need of treatment a therapeutically effective amount of a compound of formula I, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof:whereinR1 and R2 are independently selected from hydrogen, halo, nitro, alkyl, acyl, alkylaryl, and XYR5;or R1 and R2, taken together, form a 5, 6, 7 or 8-membered substituted or unsubstituted carbocyclic or heterocyclic group;X and Y are independently selected from O, S, NH, and (CR6R7)n;R3 is hydrogen, alkyl or M+;M is aluminum, calcium, lithium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, zinc ion or a mixture thereof;Z is N or CR4;R4 is from selected from hydrogen, halo, nitro, alkyl, alkylaryl, and XYR5;R5 is selected from aryl, substituted aryl, heteroaryl and substituted heteroaryl;R6 and R7 are independently selected from hydrogen and alkyl;n is an integer from 1 to 6;at least one of R1, R2 and R4 is other than hydrogen; andat least one of X and Y is (CR6R7)n.D-serine or cycloserine may be coadministered along with the compound of formula I.
Owner:SEPACOR INC
USB upstream device, USB connector, and USB cable
InactiveUS20050228934A1Potent inhibitionAvoid signalingInput/output processes for data processingData transmissionHigh impedance
It is an object to provide a USB upstream device, a USB connector, and a USB cable, capable of operating stably by preventing malfunction due to a signal line defined as a high impedance state depending on a data transmission mode in the USB upstream device, when inserting or removing the USB upstream device into or from the USB. In a USP upstream device 1, a switch circuit 11 is provided between a signal line D− and grounding voltage. When the USB upstream device 1 is connected to the USB, power is supplied through VBUS line in the USB cable and the signal line D− is cut off from the grounding voltage. When cut off from the USB, the power supply through the VBUS line is cut off, and the switch circuit 11 conducts. Then, a discharge route is established. Unnecessary charge such as leak current or the like is discharged to the grounding voltage through the switch circuit 11. As a result, in a state separated from the USB, a voltage level of the signal line D− is maintained at a low voltage level.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
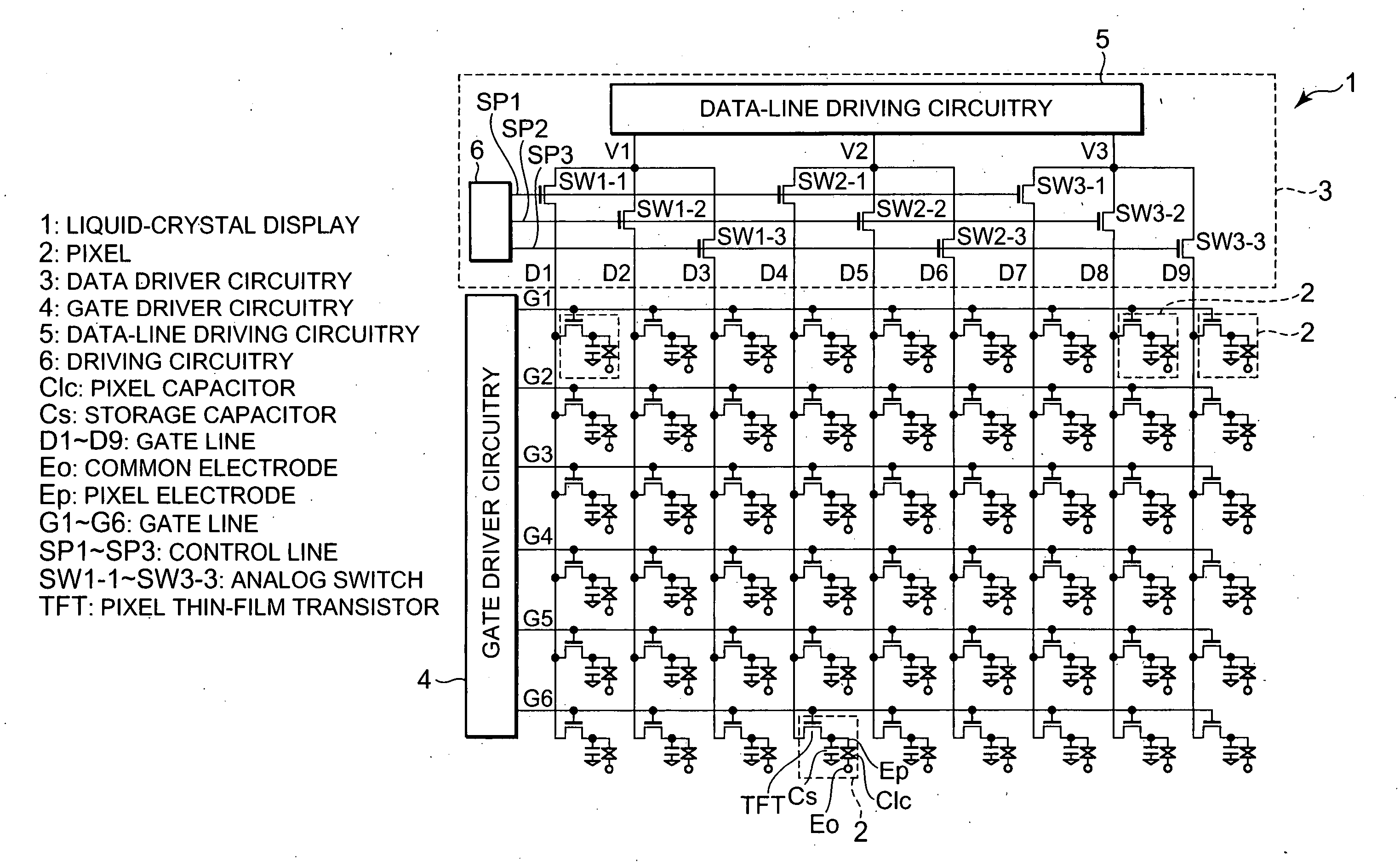
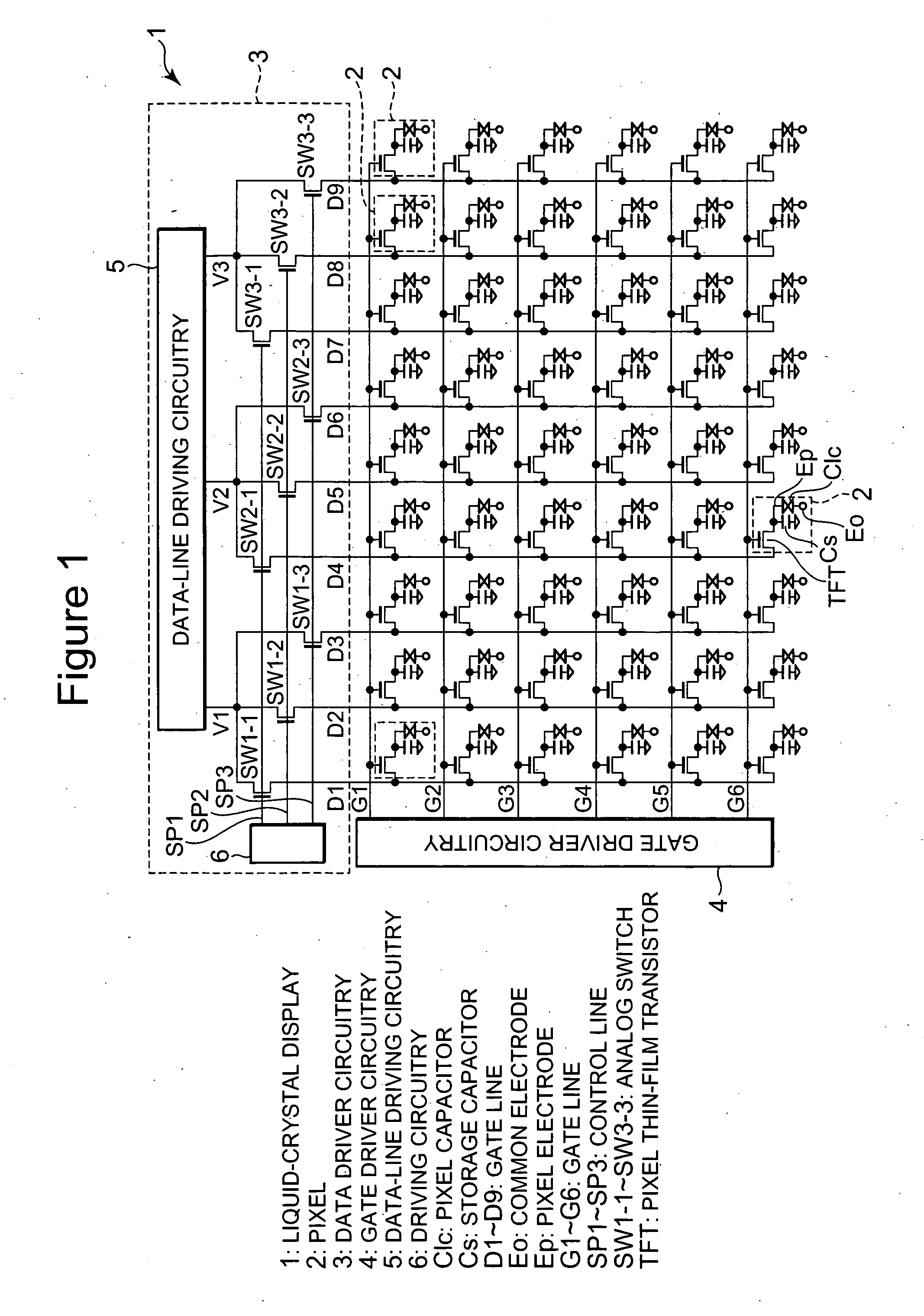
Liquid-crystal display, projector system, portable terminal unit, and method of driving liquid-crystal display
InactiveUS20070103421A1Eliminate streak-like irregularityPotent inhibitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsLiquid-crystal displayControl line
A sequence for applying pulses to control lines in a horizontal period is differentiated for every horizontal period or vertical period and a sequence for data driver circuitry to write signals in data lines in a horizontal period is differentiated for every horizontal period or vertical period so that potential fluctuations of data lines generated at the time of sampling are temporally made uniform so as to make recognition of streak-like irregularity difficult.
Owner:NEC CORP
Implantable cardiac stimulation device having optimized AV/PV delays for improved atrial kick during automatic capture and threshold determinations
An improved device and method for performing automatic capture / threshold determination that is particularly useful in an implantable cardiac stimulation device. While conventional devices use a fixed shortening of the AV / PV delays during automatic capture / threshold determinations, any shortening can unnecessarily cause discomfort to patients with heart blocks and unnecessarily diminish the atrial kick for other patients. Accordingly, embodiments of the present invention periodically measure the AR / PR conduction times and tabulate and / or otherwise process this data. Preferably, these measured conduction times are also correlated with the current heart rate. Finally, when an automatic capture / threshold determination occurs, this measured conduction data, which corresponds to this patient, is used to adjust the AV / PV delays while minimizing patient discomfort and adverse hemodynamic effects. Alternatively, the AV / PV delays may be manually programmable by a medical practitioner.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
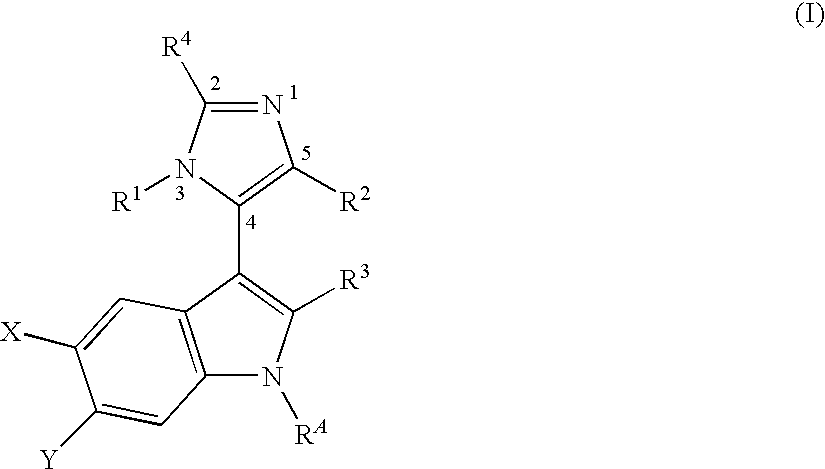
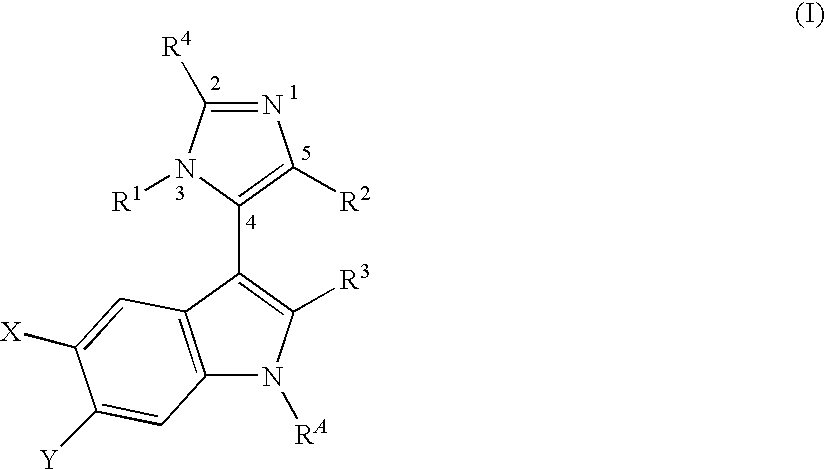
3-Imidazolyl-Indoles for the Treatment of Proliferative Diseases
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Semiconductor memory device, and read method and read circuit for the same
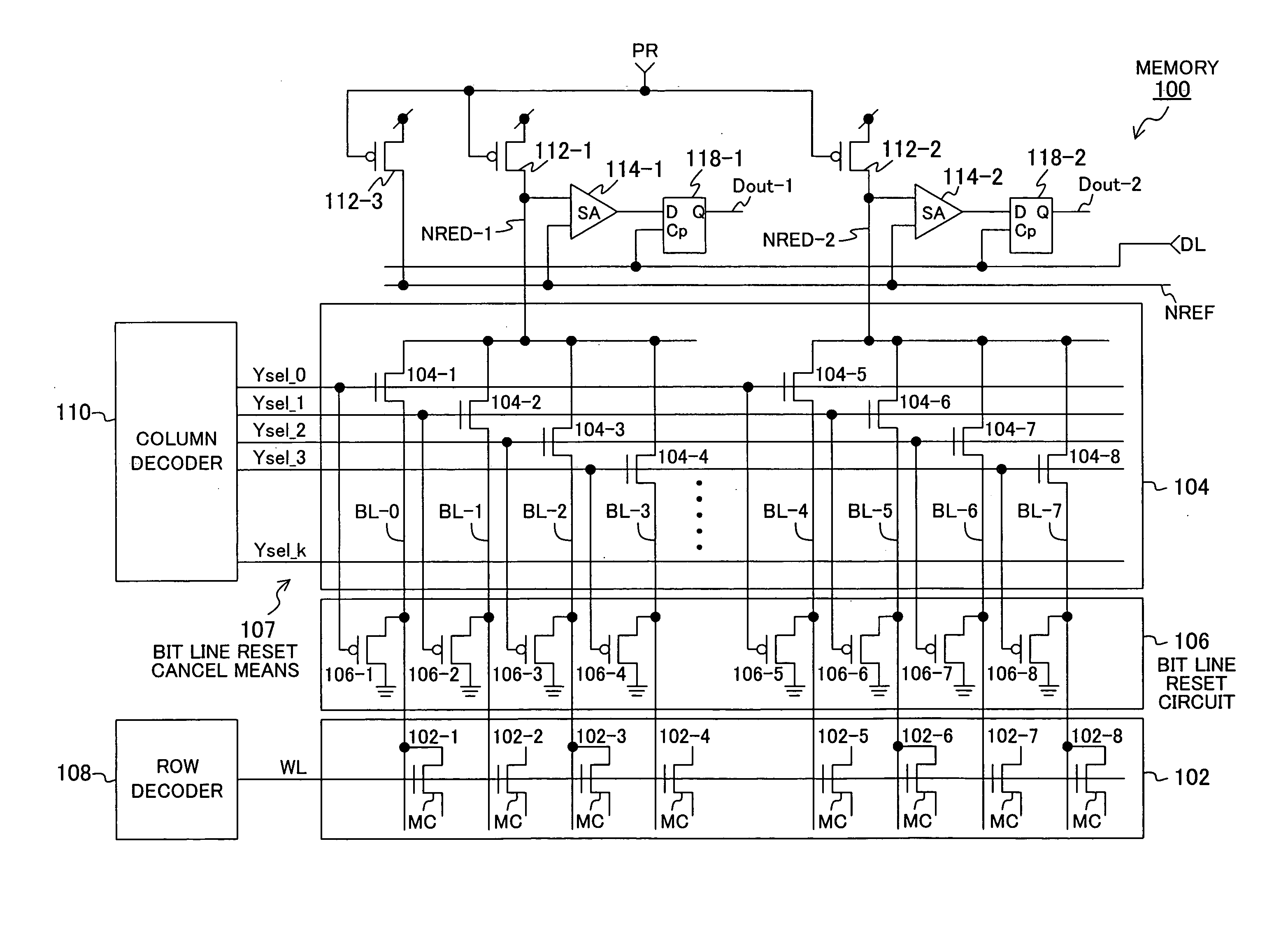
InactiveUS20080008007A1Shortening of read cycleSimple circuit configurationRead-only memoriesDigital storageHemt circuitsResidual charge
In a semiconductor memory device operative to discharge residual charge in a read bit line in a read cycle, the bit line is in the reset state at all times except during read operation. The reset state of a bit line is canceled when selected and connected to a read circuit for read, and information stored in a selected memory cell is read via the selected bit line. Upon completion of the read of the memory cell, the selected bit line is disconnected from the read circuit and reset to thereby complete discharge of residual charge in the read bit line prior to read operation in the next cycle. This ensures that during read determination operation in the next read cycle, the potential of a selected bit line will not vary with the bit line residual discharge in the previous read cycle.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com









![Benzo[d]isoxazol-3-ol DAAO inhibitors Benzo[d]isoxazol-3-ol DAAO inhibitors](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/b133d05f-1952-4ba7-b446-84c7814c238f/US07166725-20070123-C00001.png)
![Benzo[d]isoxazol-3-ol DAAO inhibitors Benzo[d]isoxazol-3-ol DAAO inhibitors](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/b133d05f-1952-4ba7-b446-84c7814c238f/US07166725-20070123-C00002.png)
![Benzo[d]isoxazol-3-ol DAAO inhibitors Benzo[d]isoxazol-3-ol DAAO inhibitors](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/b133d05f-1952-4ba7-b446-84c7814c238f/US07166725-20070123-C00003.png)





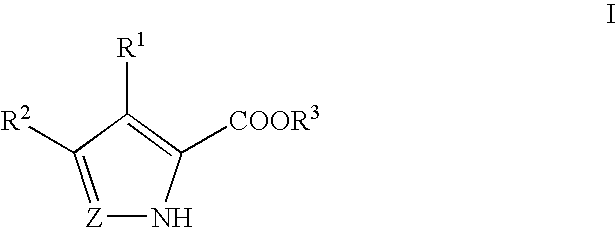
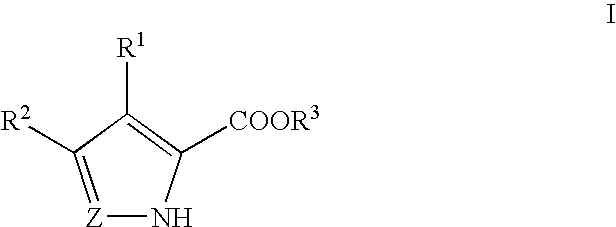
![Benzo[d]isoxazol-3-ol DAAO inhibitors Benzo[d]isoxazol-3-ol DAAO inhibitors](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a77d243c-81f9-48b5-83ca-99e1191687f1/US20050143434A1-20050630-C00001.png)
![Benzo[d]isoxazol-3-ol DAAO inhibitors Benzo[d]isoxazol-3-ol DAAO inhibitors](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a77d243c-81f9-48b5-83ca-99e1191687f1/US20050143434A1-20050630-C00002.png)
![Benzo[d]isoxazol-3-ol DAAO inhibitors Benzo[d]isoxazol-3-ol DAAO inhibitors](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/a77d243c-81f9-48b5-83ca-99e1191687f1/US20050143434A1-20050630-C00003.png)