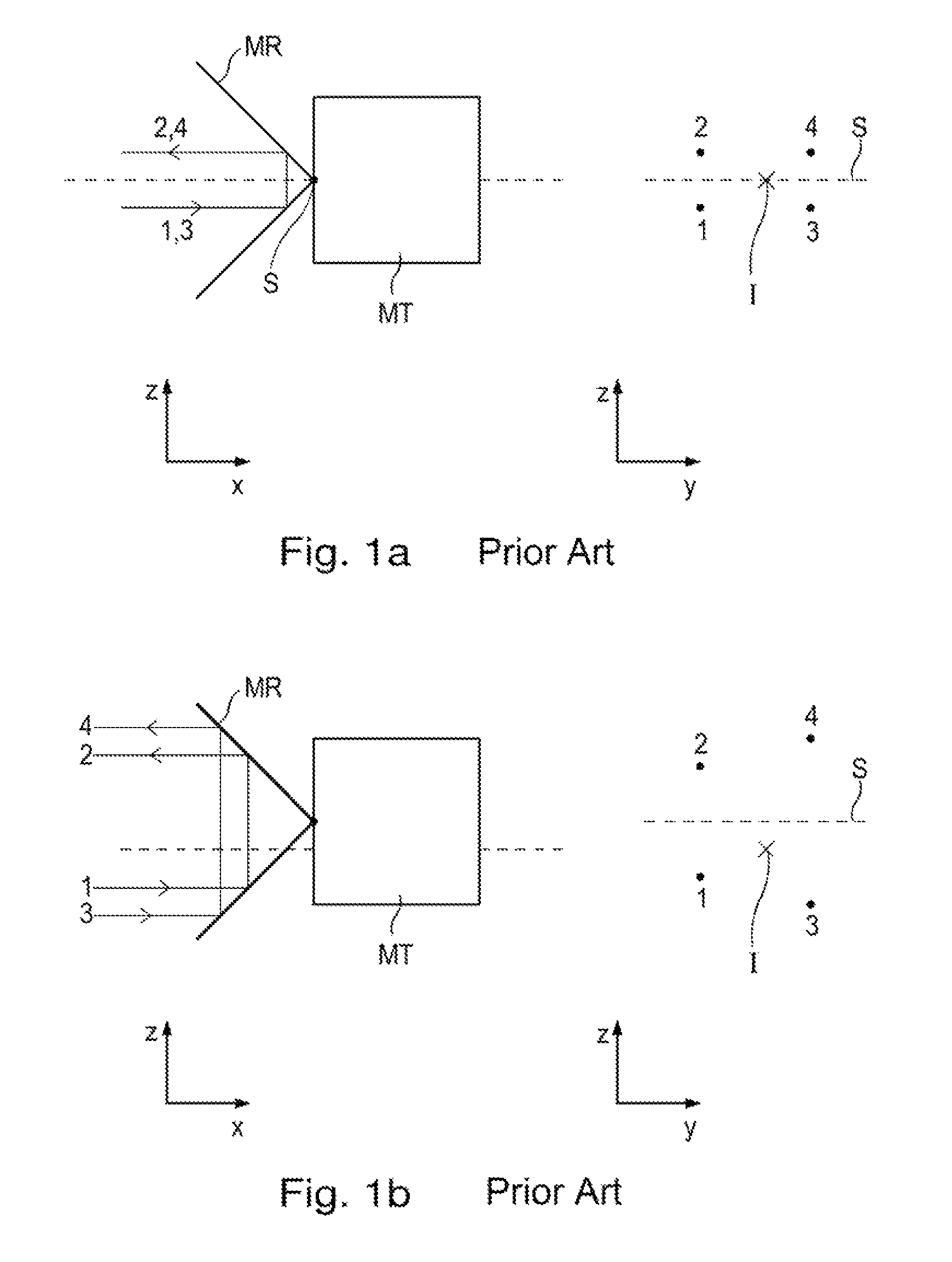Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42results about How to "High expenditure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
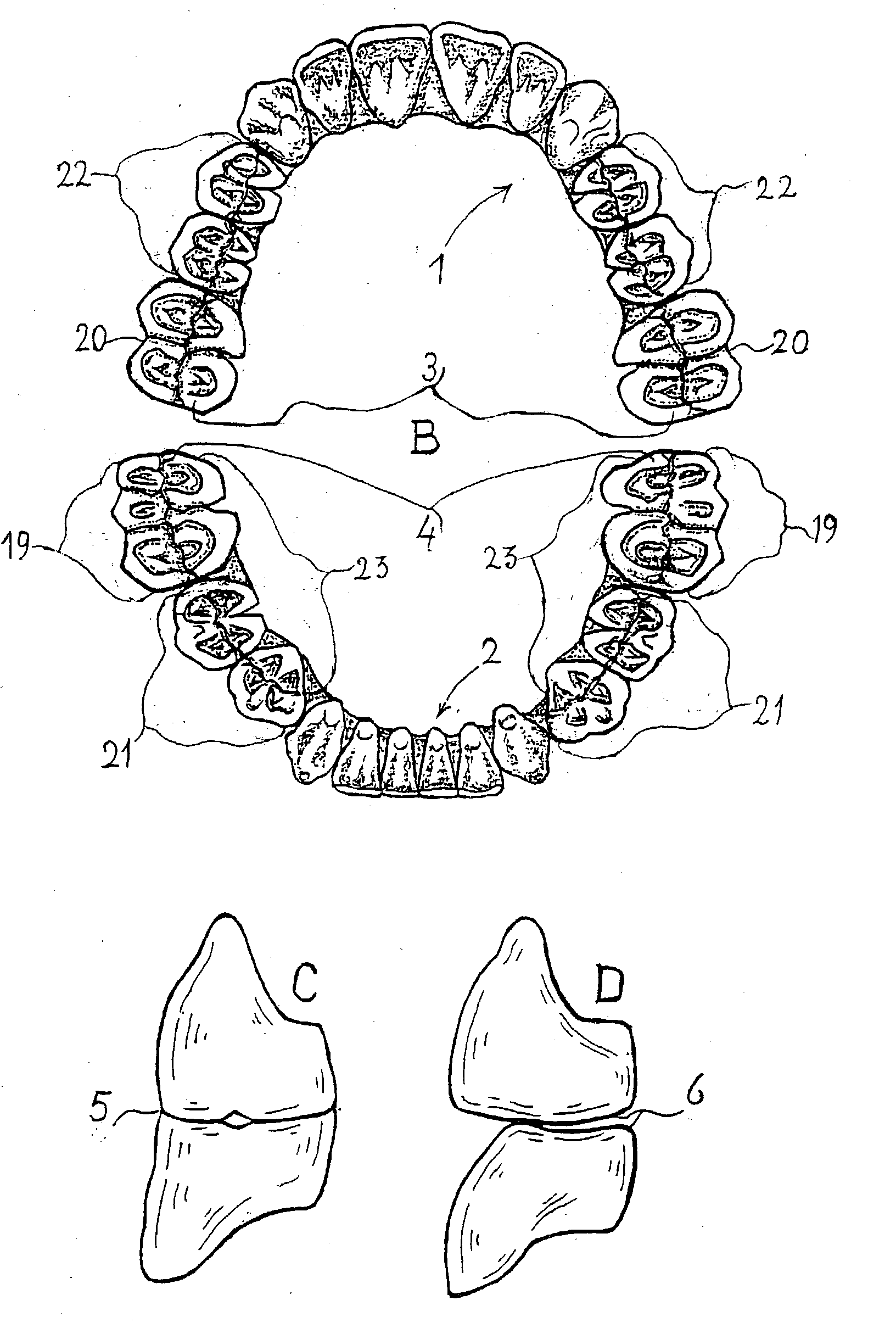
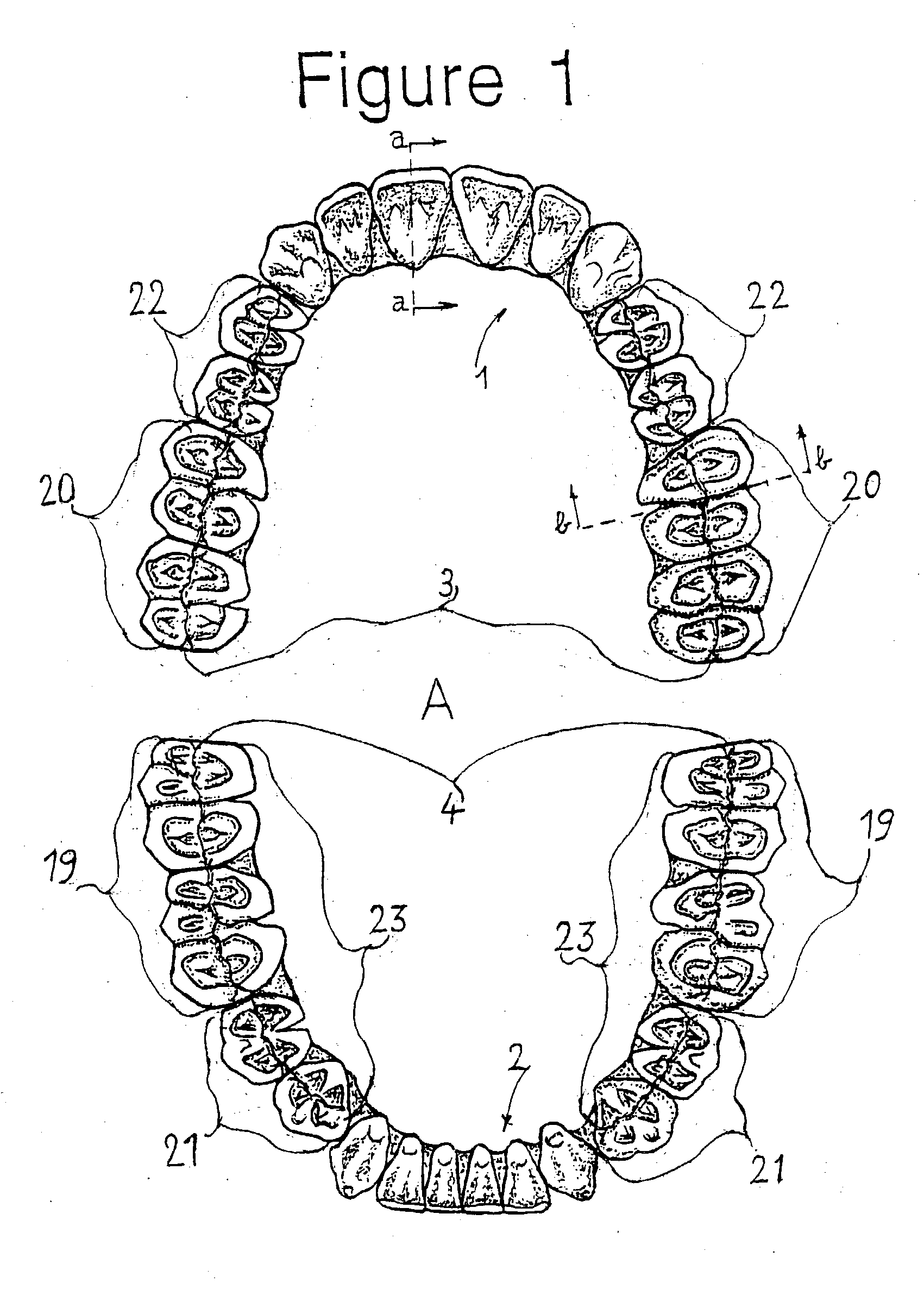
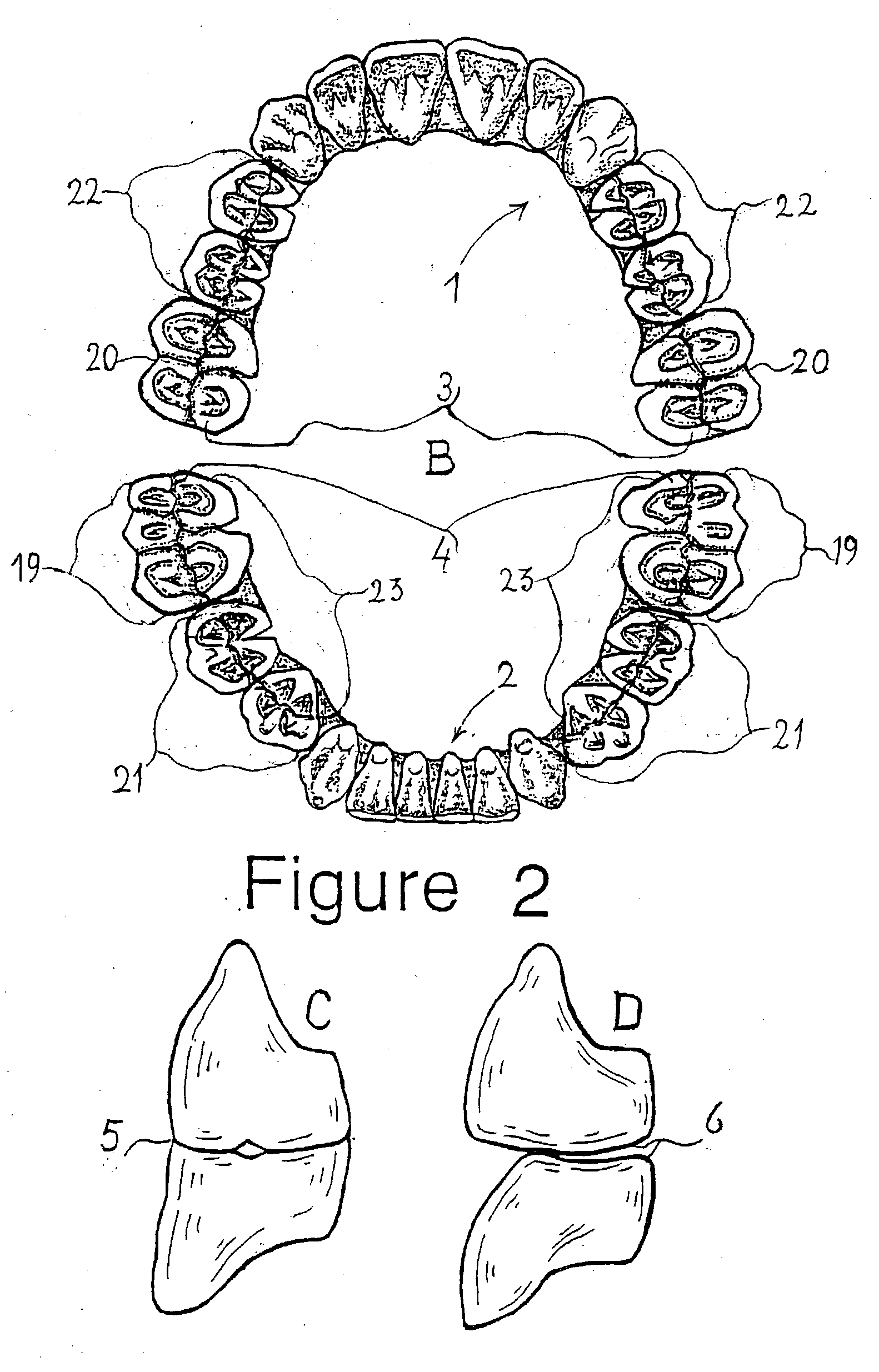
Combination set of denture teeth units for setting-up dentures in balanced articulation
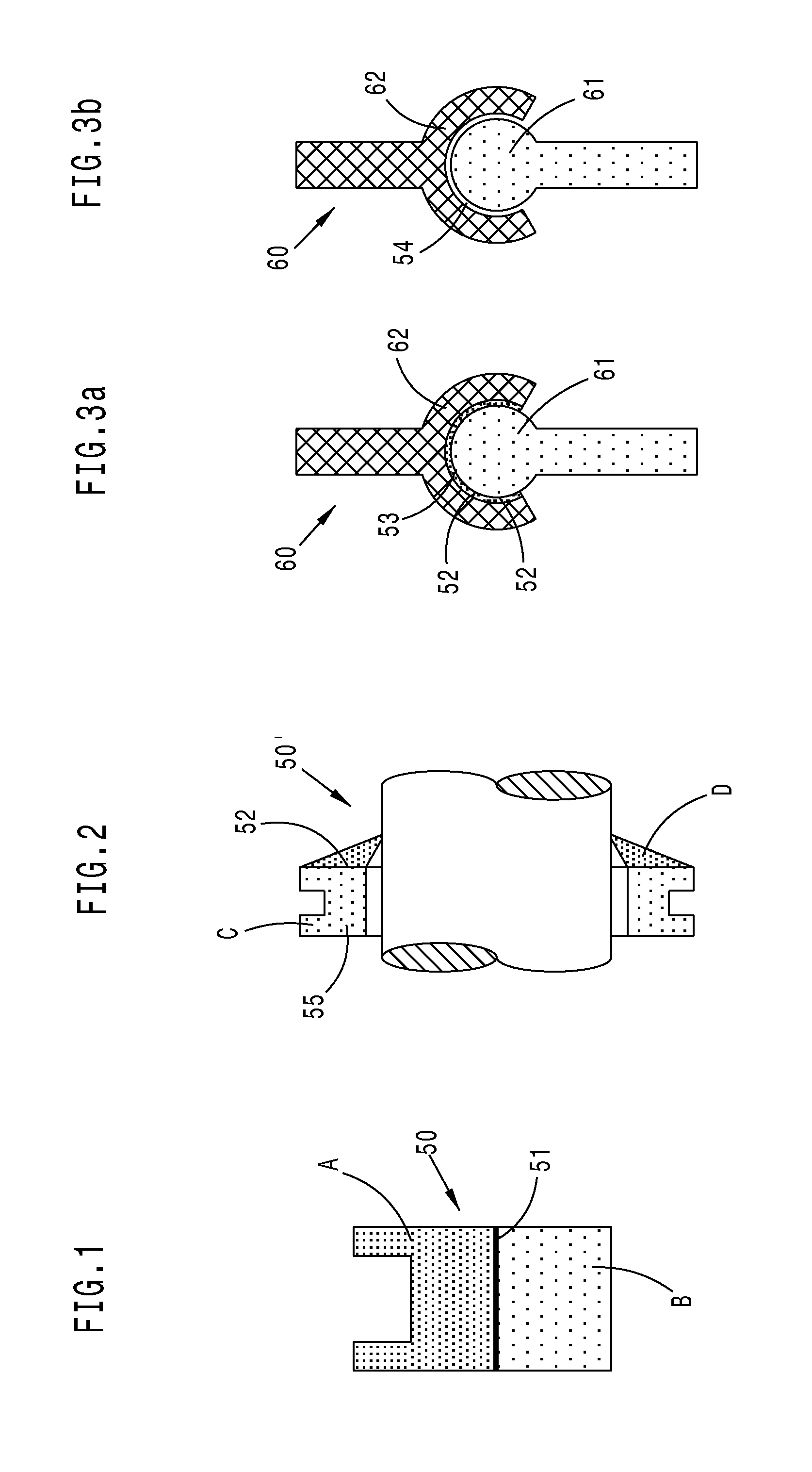
A combination set (FIG. 1, A,B), at least in a medium size or different sizes, includes complete arched denture teeth units (1), (2) preformed without denture base, for setting up denture teeth instantly and adjustable in a full balanced articulation during custom denture work. The set(s) is composed of a complete upper (1) and separate complementary complete lower (2) arched denture teeth unit, each including anterior and posterior denture teeth inter-connected either in a complete (A) or under-extended complete (B) tooth arch at least in an oval form. Each of the units includes a total unitary inter-occlusal bite plane preformed in a corresponding centric occlusion and full balanced articulation. In order to prevent to setting-up denture teeth, one by one in the centric and full balanced articulation, as regularly, hereto the unitary inter-occlusal bite plane is pre-set according to interconnected anterior and posterior denture teeth. While the posterior denture teeth are formed cuspless spheroellipsoidal, conforming a 4 inch (11 cm.) radius, thereby pre-set either in a planar or anterio-posterior or curved sphero-ellipsoidal arrangement including a free centric inter-occlusal contact (FIG. 2) either full (C, 5) or partly (D,6) and a free eccentric bi-lateral balanced articular contact. Having the last molar posterior denture teeth either broader or not than regularly and pre-set without tongue interference to ascertain individually the balanced articular contact. Having the set(s) non-bendable from a durable tooth aesthetic material. The invention includes further a method A for preforming the set(s) from the material by providing a durable economised mould structure and yet a method B for setting up the set(s) in an instant and adjustable full balanced articulation with the provision of an auxiliary set of tools.
Owner:DEQUEKER FRANS A B
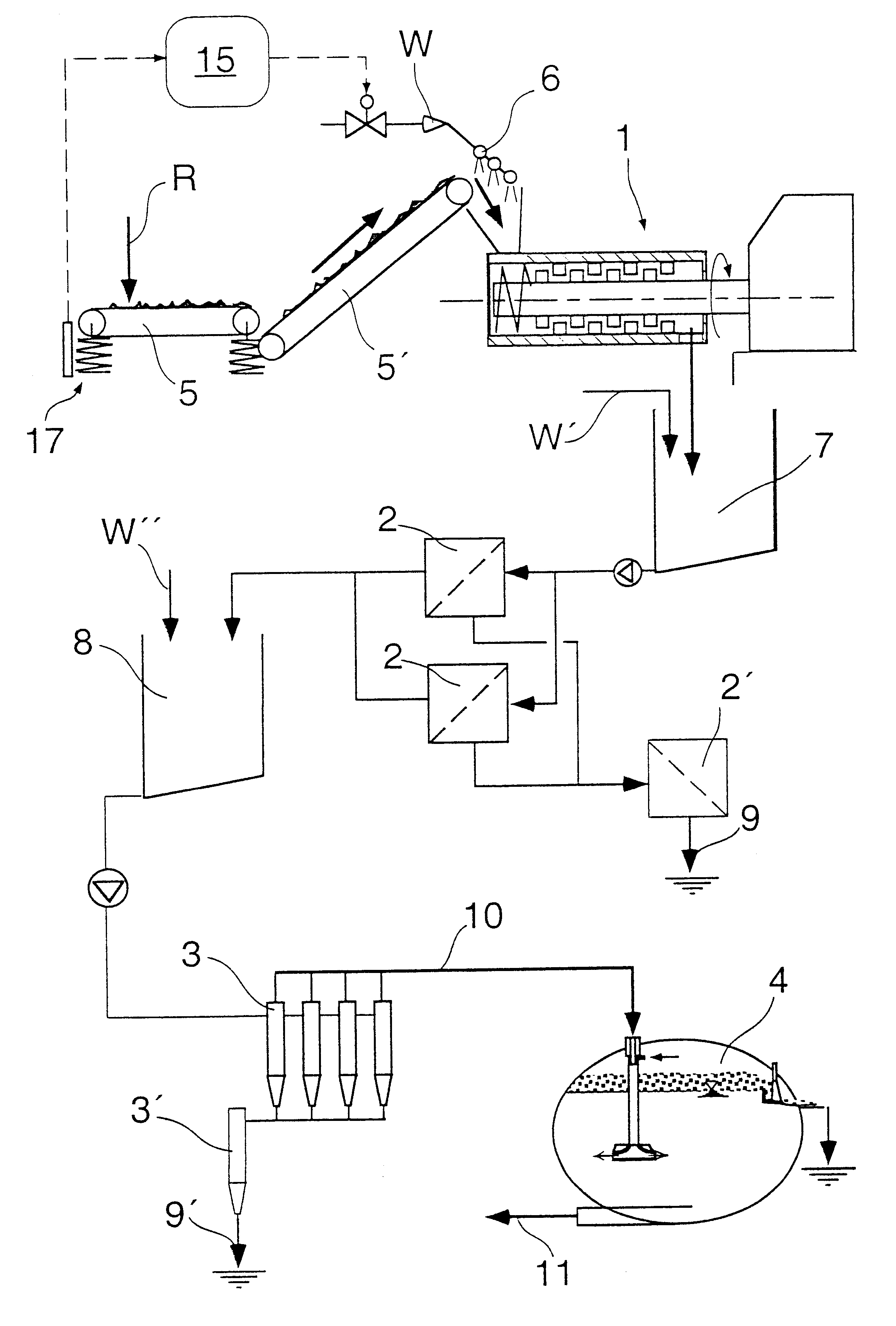
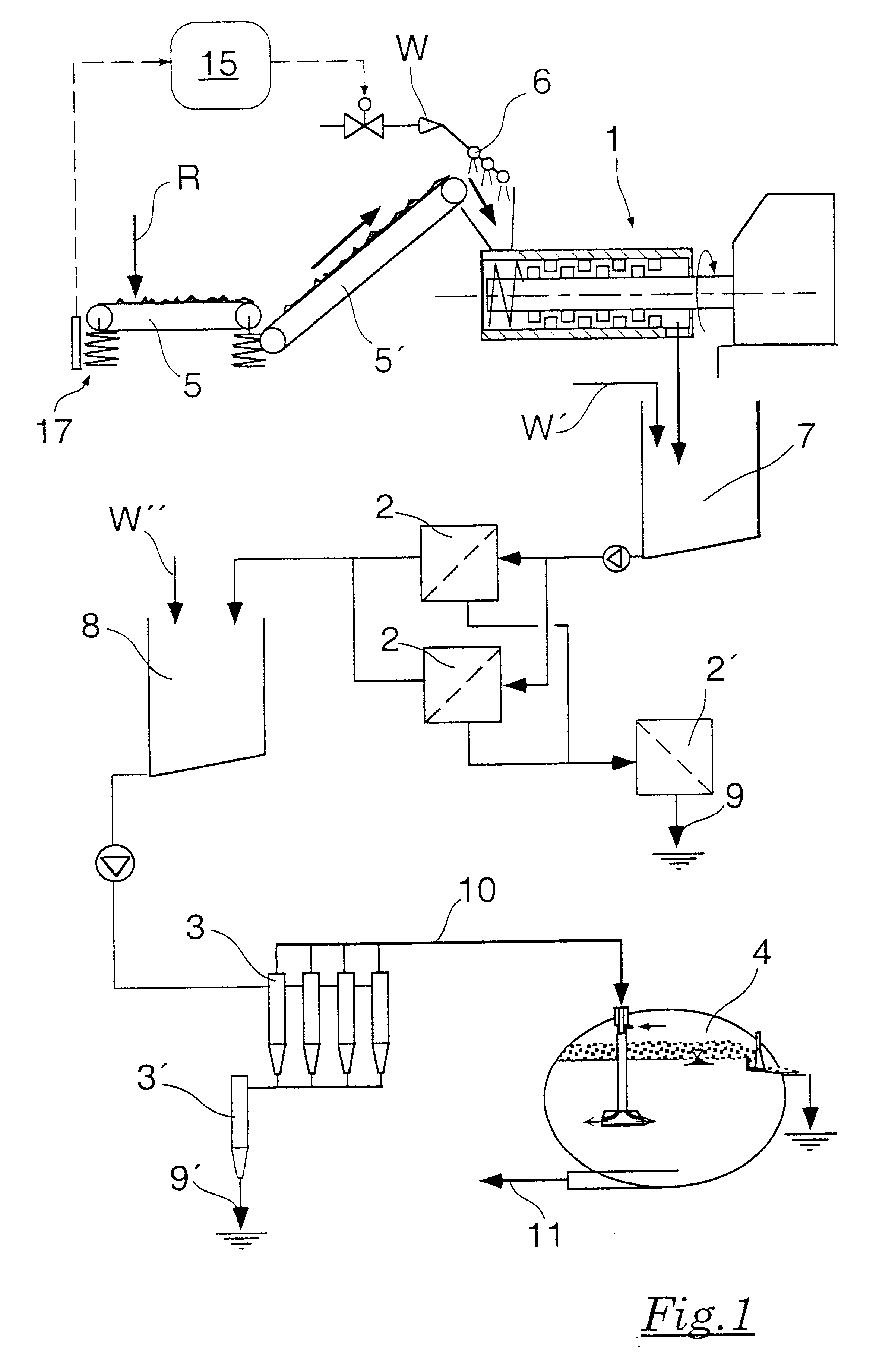
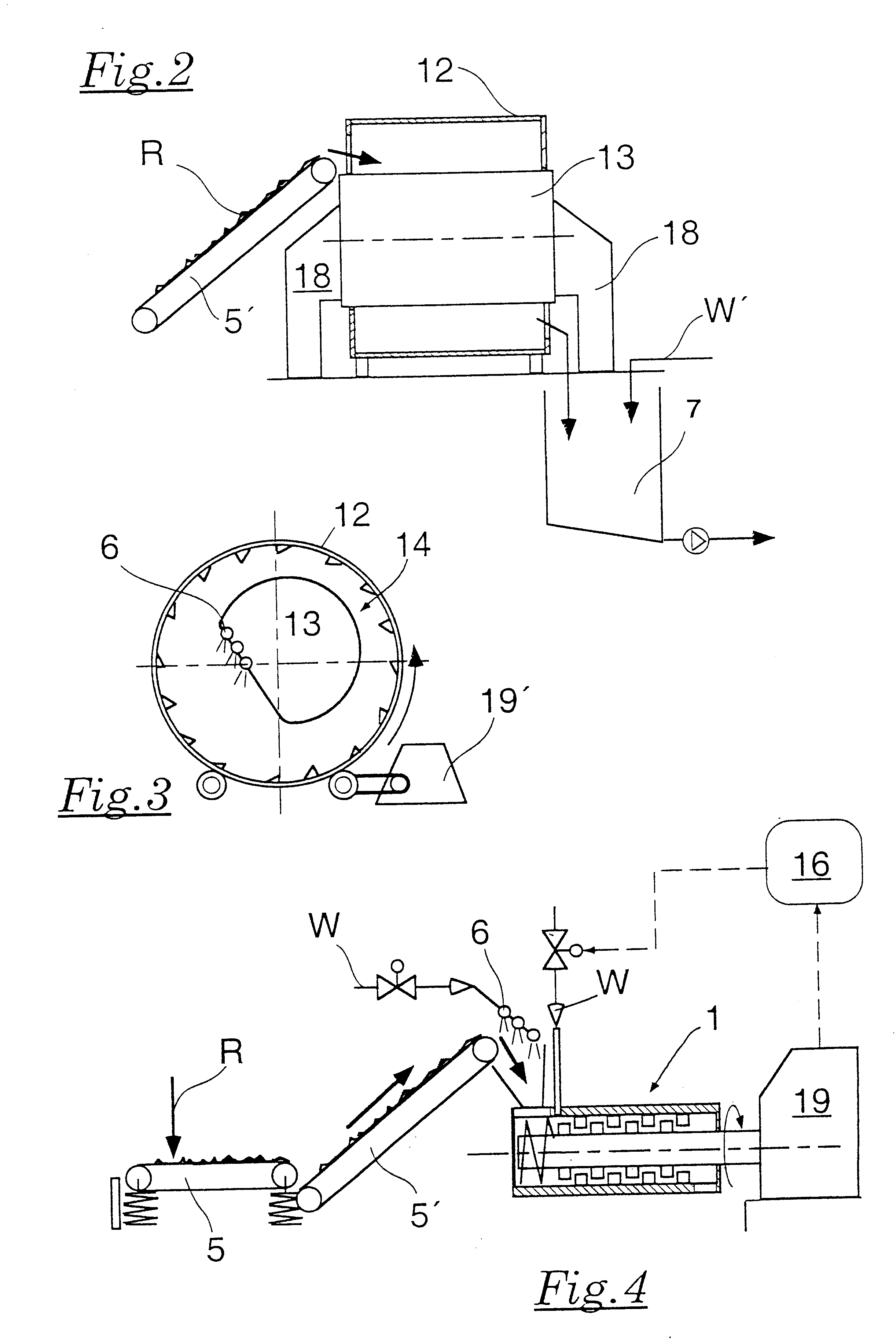
Method for gasifying organic materials and mixtures of materials
InactiveUS7077878B1High expenditureGreat amountThermal non-catalytic crackingGasifier feeding meansProcess engineeringProduct gas
The aim of the invention is to provide a method for gasifying organic materials which is simple to carry out and requires minimal equipment and which produced an undiluted gas of high calorific value. The inventive method should eliminate the need to use fluid beds and heat exchangers with high temperatures on both sides, with the heat being transferred from the furnace to a heat-carrying medium in a particularly defined way. To this end, the feed material is divided into a volatile phase and a solid carbon-containing residue in the pyrolysis reactor by circulating a hot heat-carrying medium. After the reaction agent has been added, said volatile phase is converted into the product gas by further heating in the reaction area, also using the heat-carrying medium. The solid, carbon-containing residue is separated from the heat-carrying medium in the separating stage and burnt in the furnace. The heat-carrying medium is heated by the waste gases of the furnace in the heating area and then returned to the reformer and then the pyrolysis reactor.
Owner:ELFGEN HERTA MRS +3
Device for two-dimensional imaging of scenes by microwave scanning
InactiveUS20090224993A1Acceptable image qualityHigh expenditureAntennasRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMoving speedMicrowave
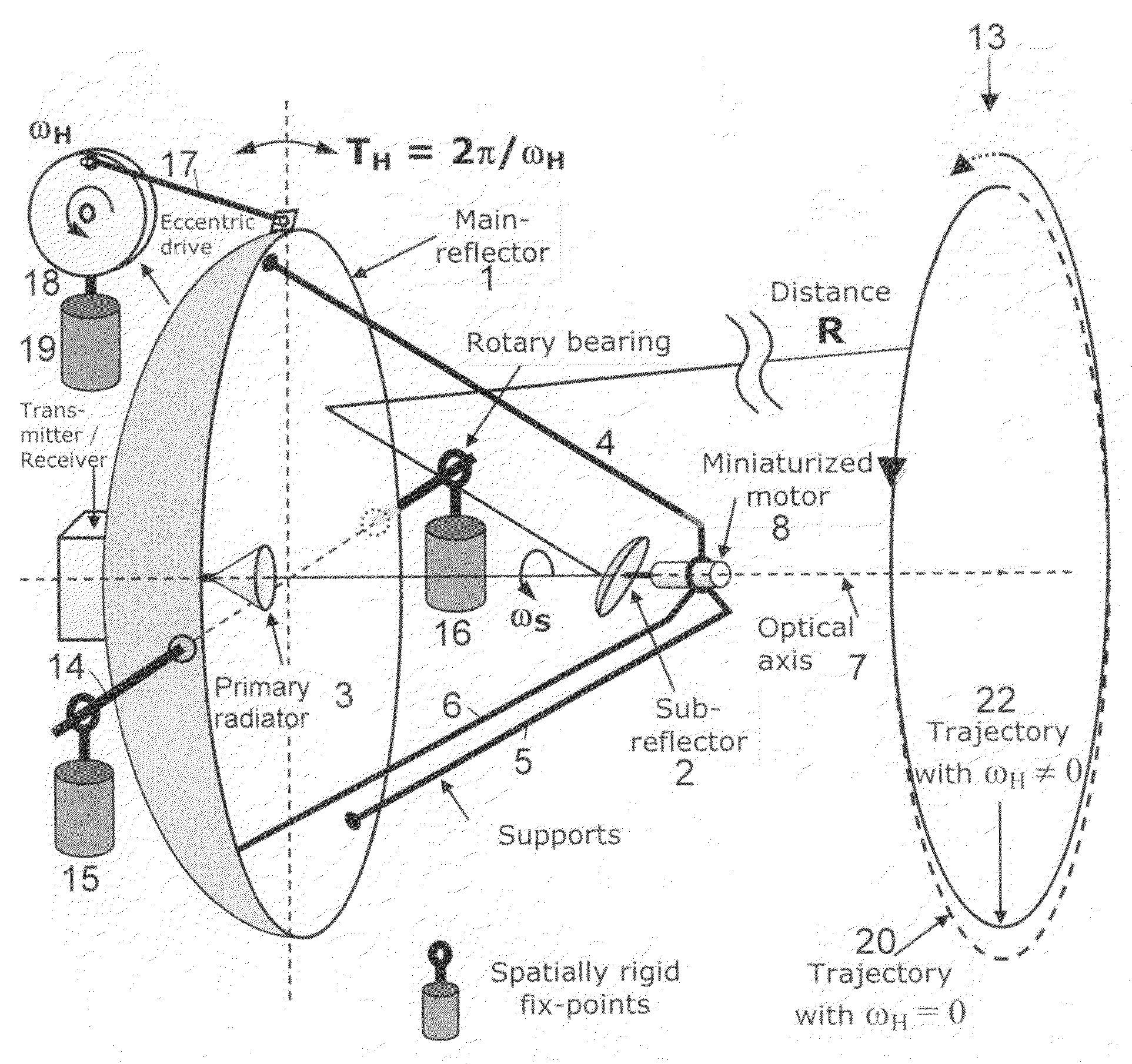
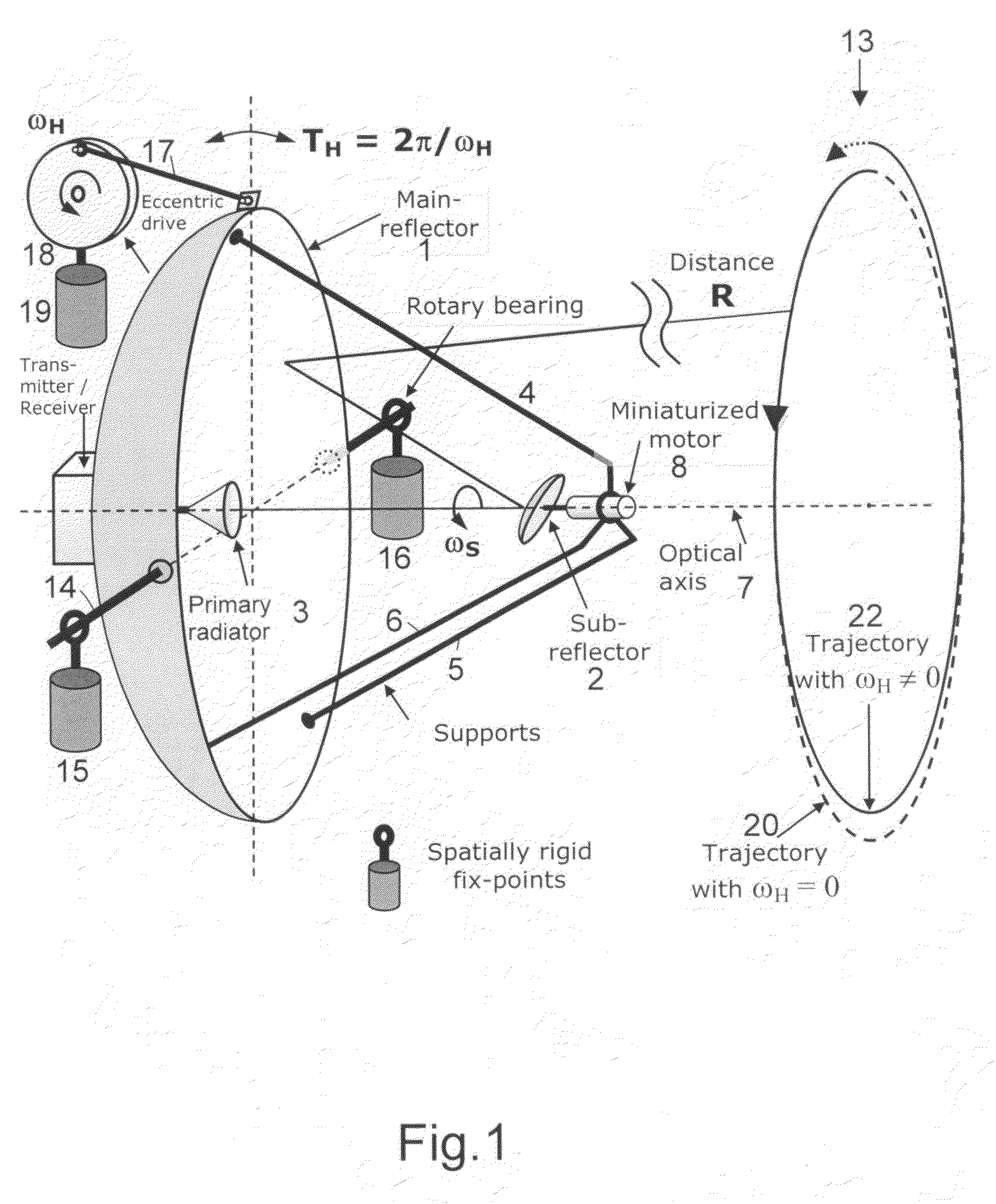
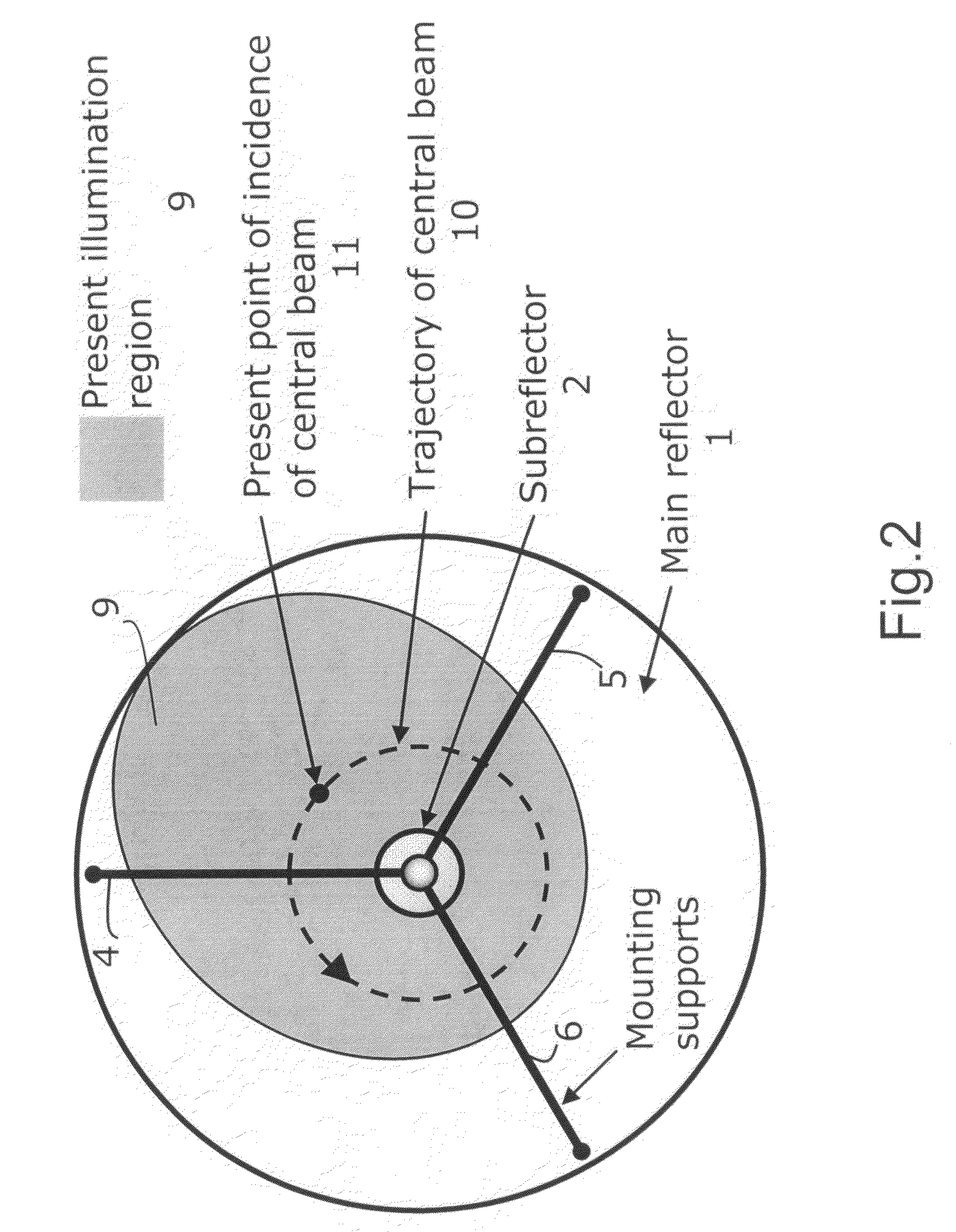
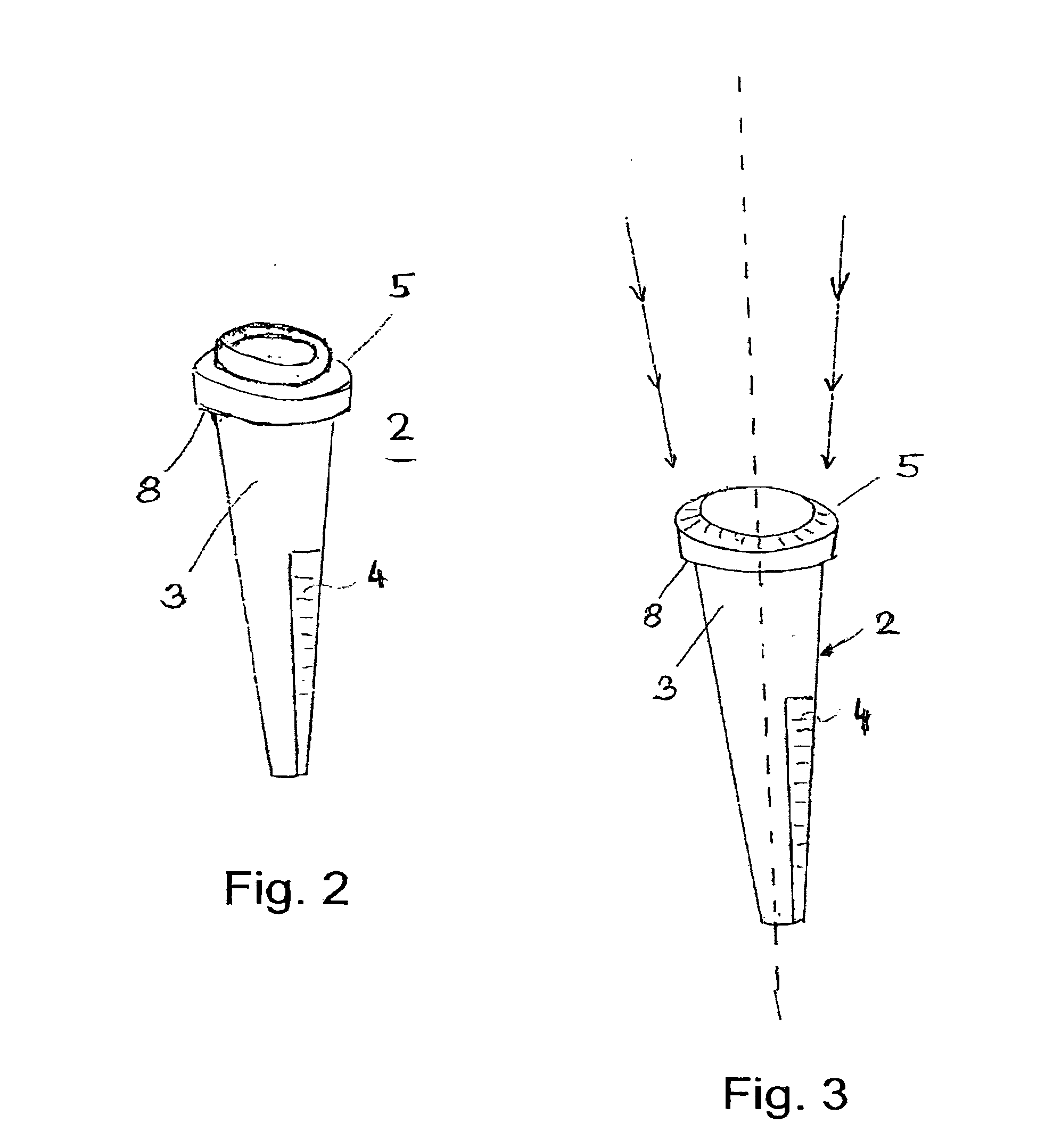
For two-dimensional imaging of scenes through continuous passive or active microwave scanning, use is made of a fully mechanized directional antenna array comprising a main reflector (1), a primary radiator array (3) and a subreflector (2) having a small size in comparison to the main reflector and being tilted relative to the optical axis (7) of the directional antenna array. First drive means (8) are operative to rotate the subreflector (2) about the optical axis (7), and second drive means (17,18) are operative to move the total directional antenna array in a direction approximately vertical to the optical axis (7). The moving speed of the subreflector (2) is very high in comparison to that of the total directional antenna array. The shape of the main reflector (1), the shape of the subreflector (2), the primary radiator (3), the distance between primary radiator and subreflector and the distance between subreflector and main reflector as focusing parameters are attuned to each other in such a manner that, for a given scene distance, an optimum focusing and an optimum size of the field of view are achieved. The focusing parameters and the moving speeds of the two drive means are set in a manner allowing for a gapless, continuous scanning of the scene with the aid of the focusing spot (12) moving at the scene distance.Applicability in remote investigation, particularly in earth observation and in safety technology.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
Clock pulse control device of a microwave pulse radar
InactiveUS20060274871A1High frequencySave powerLevel indicatorsPulse manipulationPulse controlMicrowave
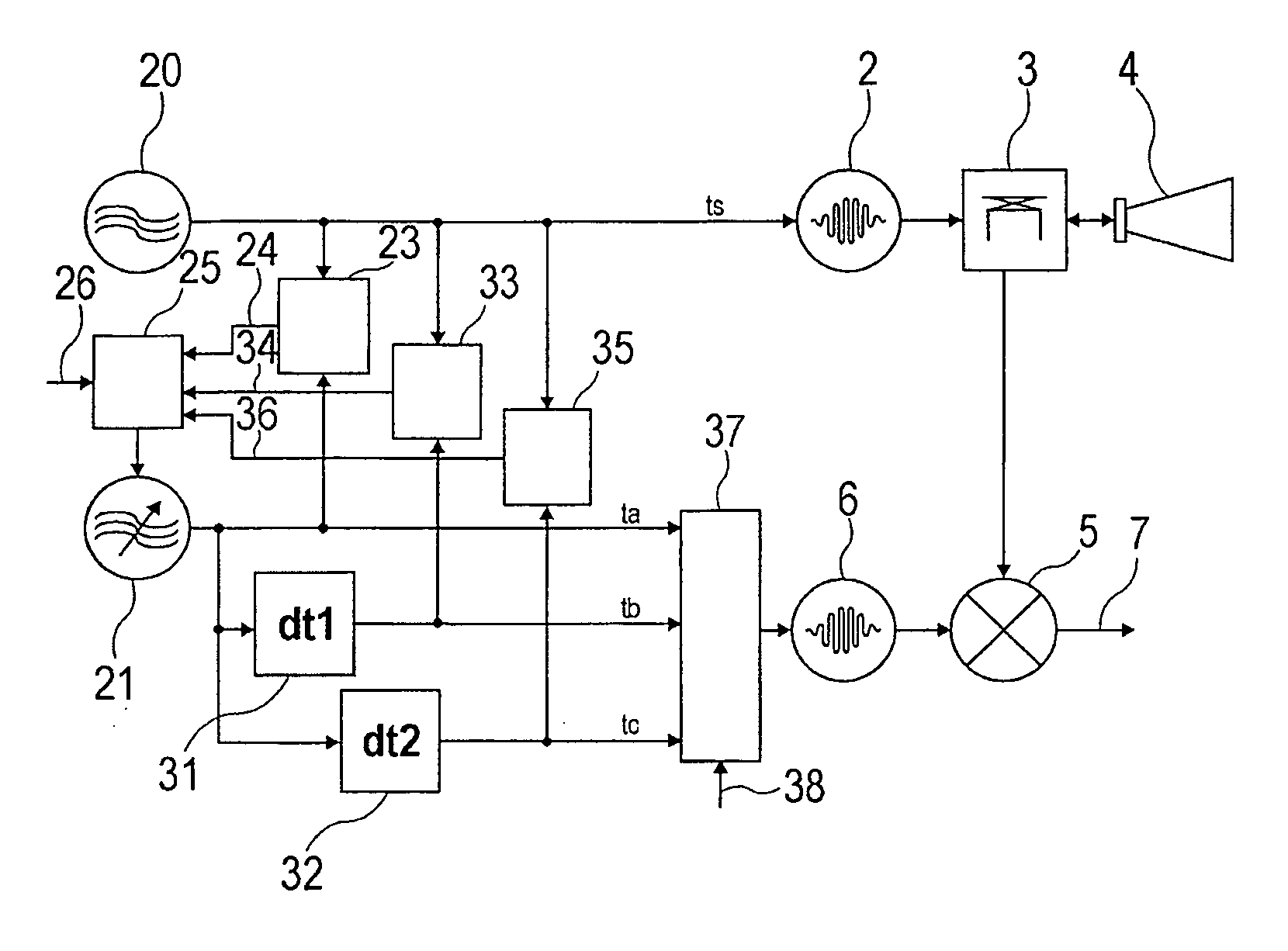
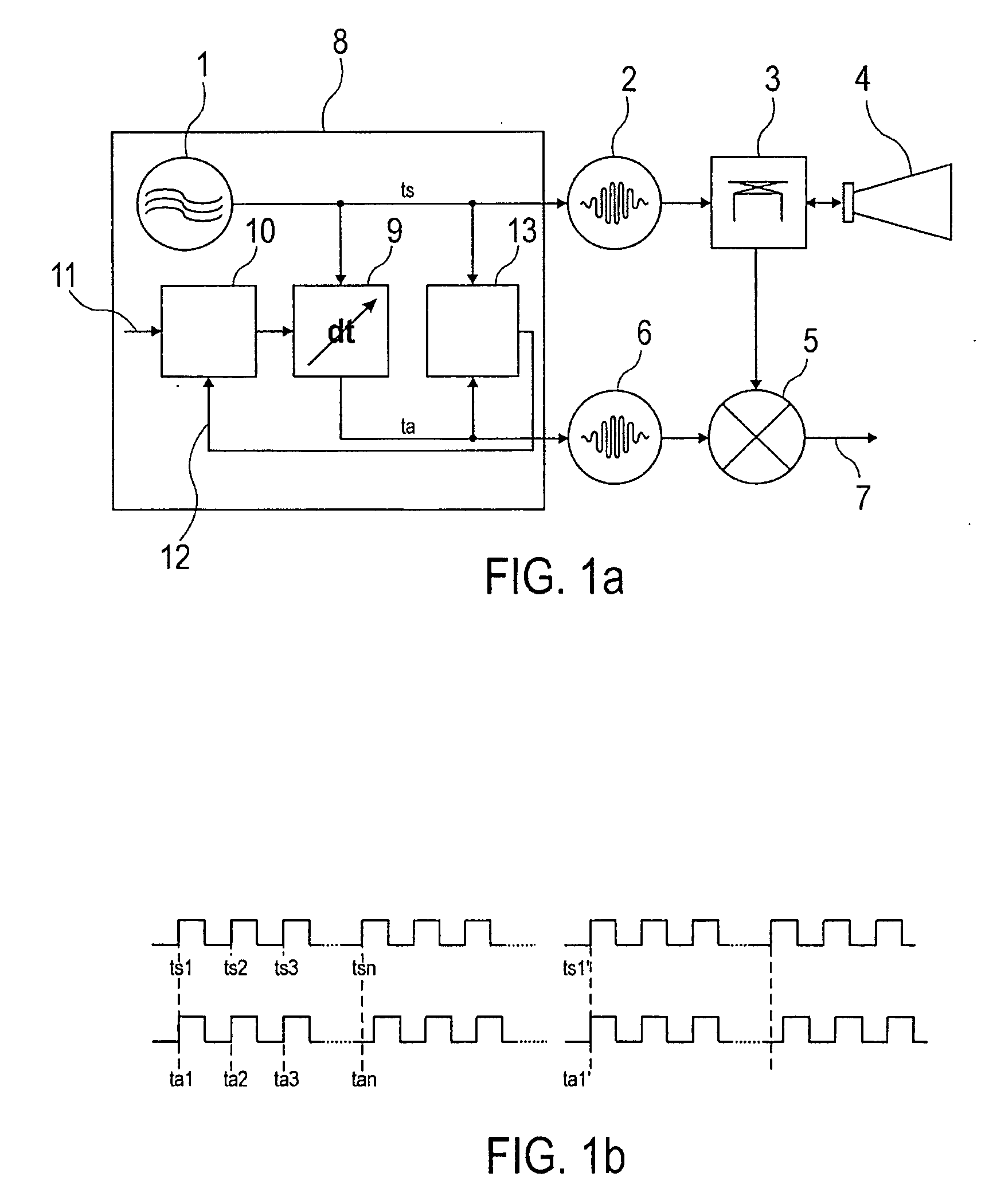
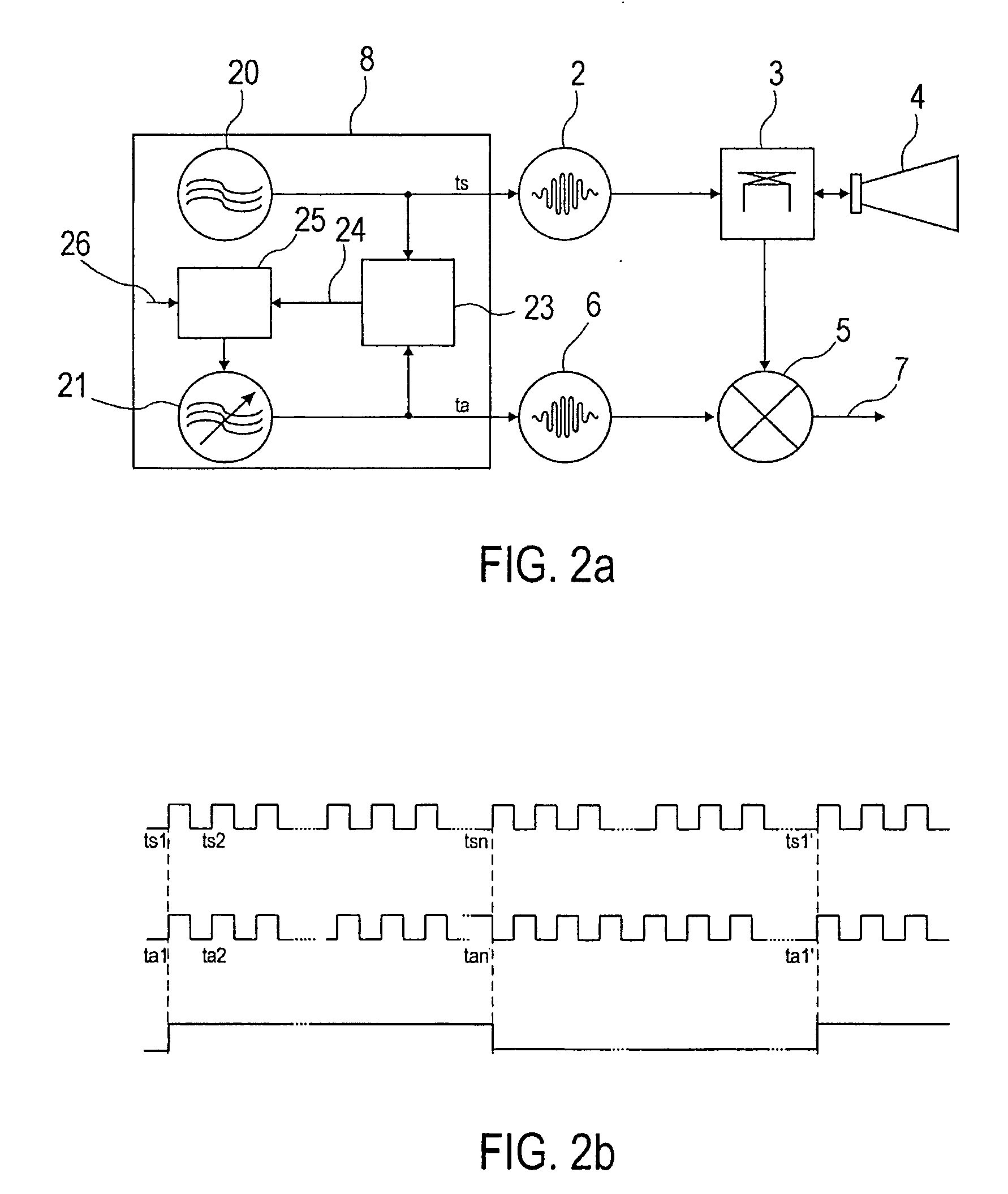
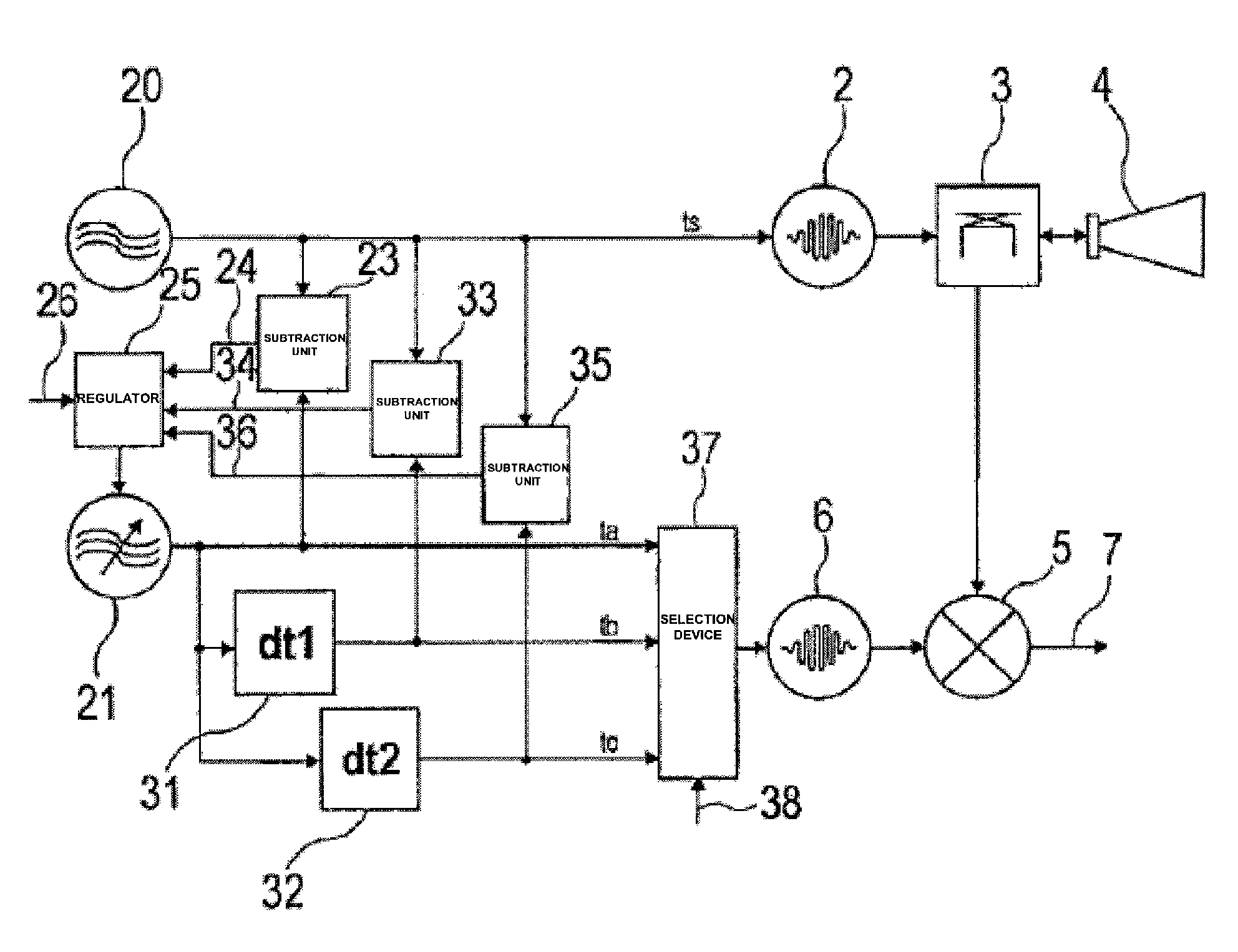
The invention relates to a clock pulse control circuit for generating a transmit clock pulse (ts) and a sampling clock pulse (ta; tb; tc), wherein the clock pulse control circuit comprises a first oscillator (20) for generating a first clock pulse (ts) of a first frequency, and a second oscillator (21) for generating a plurality of second clock pulses (ta; tb; tc), that are shifted in time in relation to each other, of a second frequency. The clock pulse control circuit is designed such that based on the first clock pulse (ts) and the plurality of second clock pulses (ta; tb; tc) the transmit clock pulse (ts) is providable to a transmit pulse generator (2), and the sampling clock pulse (ta; tb; tc) is providable to a sampling pulse generator (6).
Owner:VEGA GRIESHABER GMBH & CO
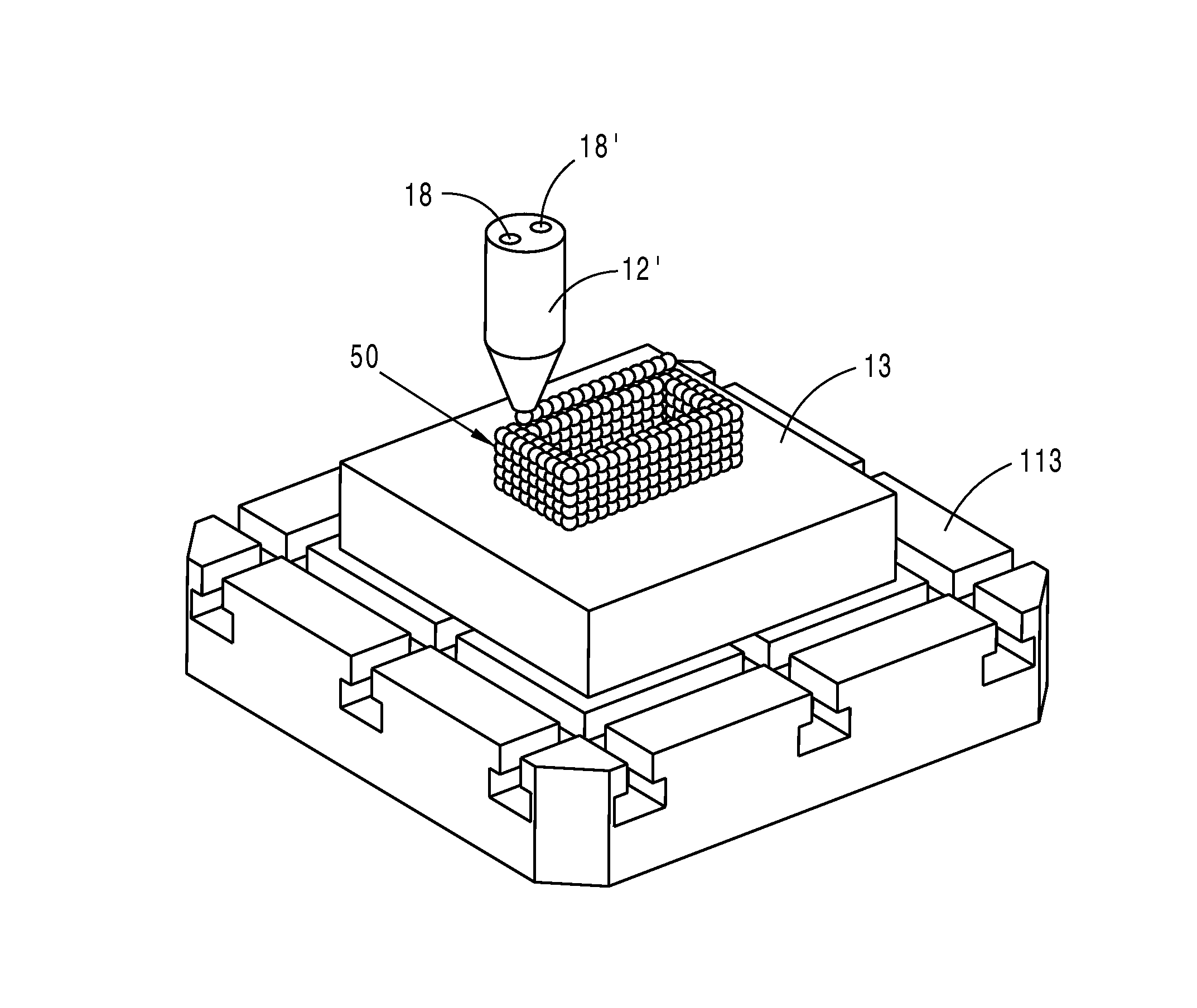
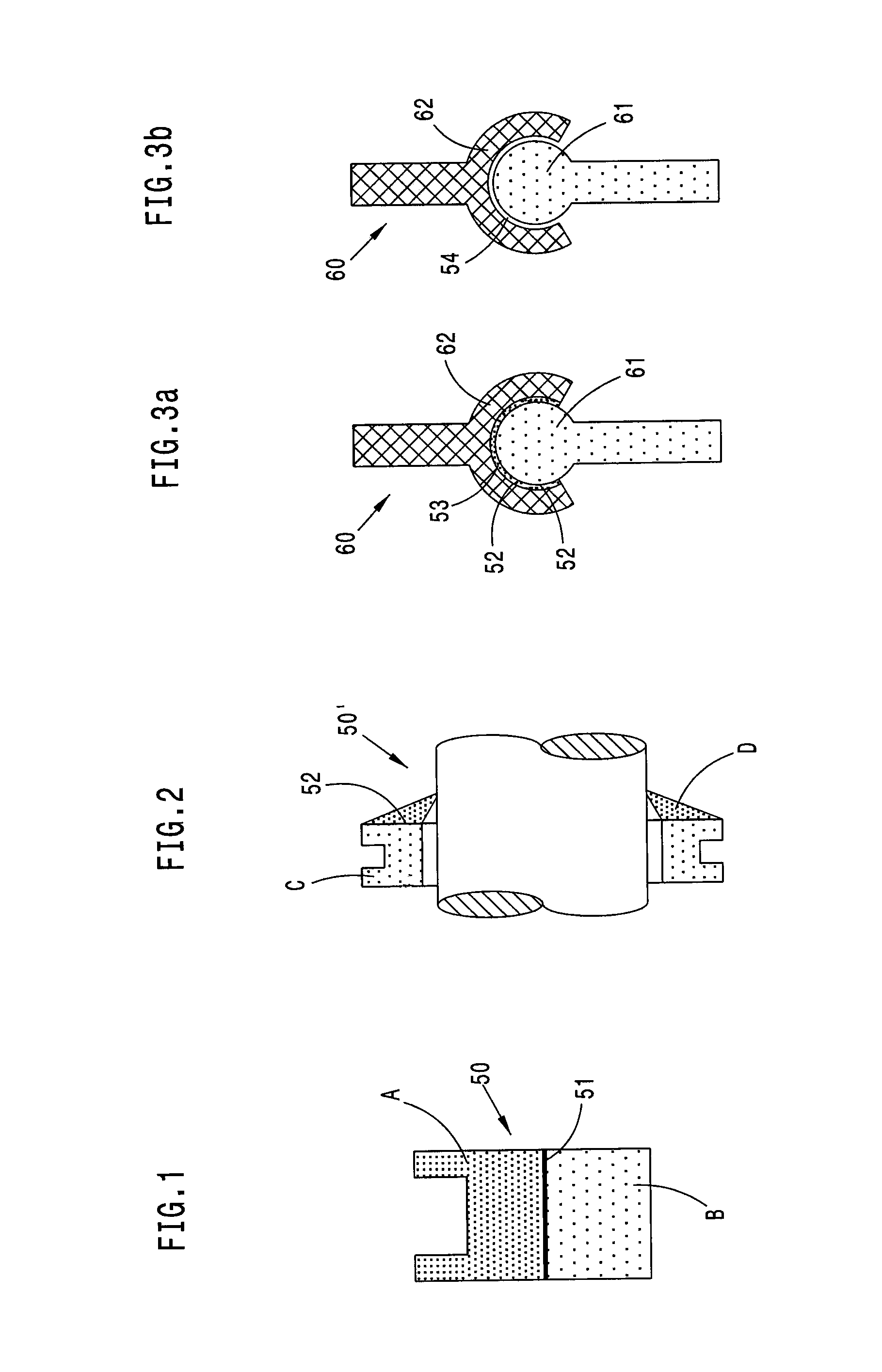
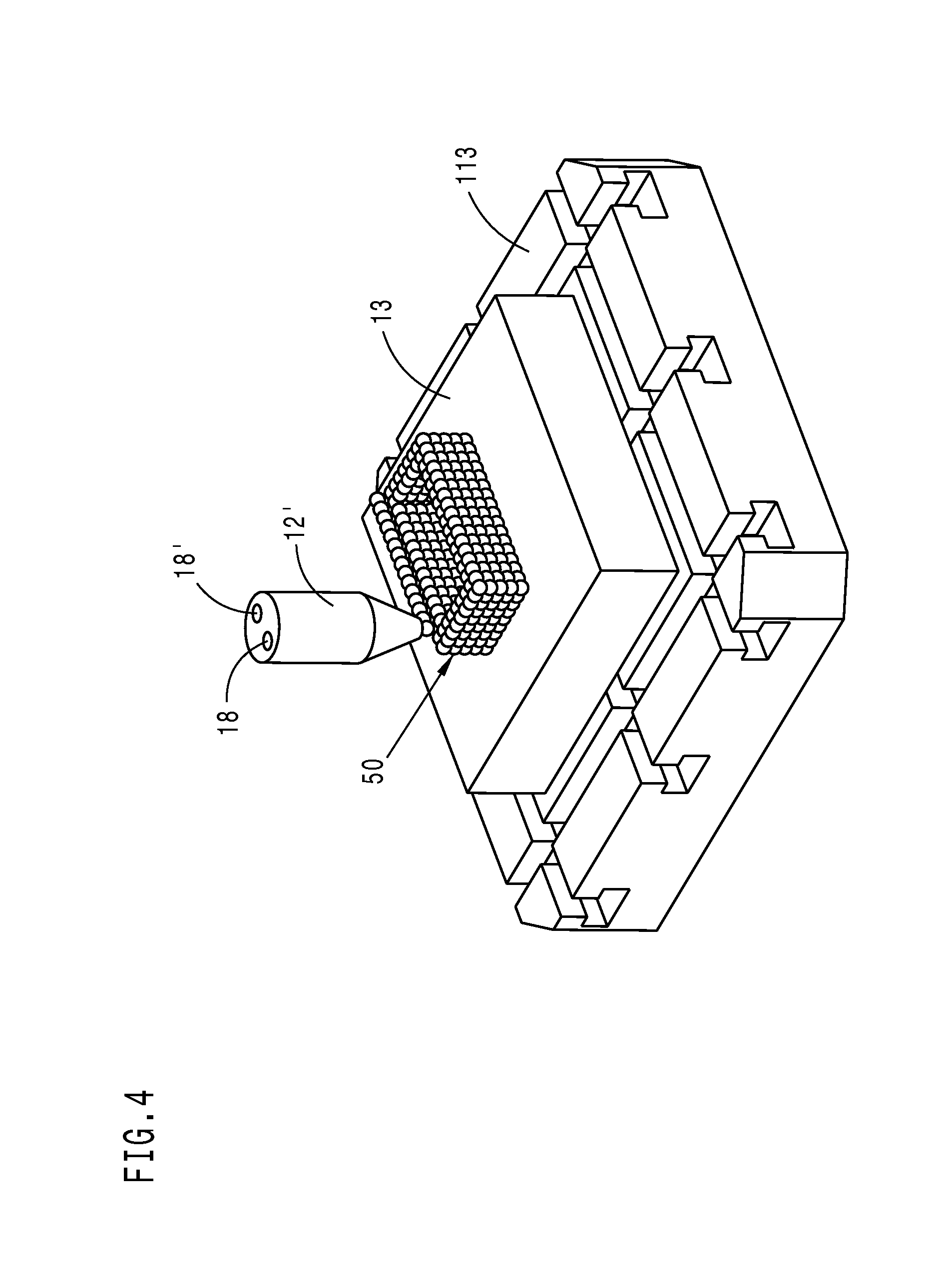
Method for producing a three-dimensional object from solidifiable material as well as an object produced therewith
ActiveUS20130071599A1High expenditureAdditive manufacturing apparatusLayered productsMulti materialFluid phase
A method serves to produce a three-dimensional object by additive construction in direct construction sequence from solidifiable material, which is either present in the starting state in a fluid phase or can be liquefied, where multiple material components are discharged alternately in a programmable manner by means of multiple discharge units and configure different parts of the object joined to one another as a result of the discharge, where the geometric proportions obtained during discharge already correspond to the object, and because the material components form between them either edge regions merging into one another without boundaries or boundary regions of the different material components abutting one another without joining, a method and an object produced therewith can be provided, in which boundary and edge regions are formed “as if from one piece” between different material components even in the case of complex geometries.
Owner:ARBURG GMBH & CO KG
Implant analog
Implant analog for custom production of prosthetic superstructures for inserted dental implants, inserted into a master cast directly or indirectly via a model sleeve comprising an implant head equipped with elements to hold and fasten an implant system; a base of said implant analog having a cross section that tapers over at least part of its length; an implant head having a working surface and a connecting piece; a tenon-like projection on a bottom end surface of said implant head; and an external thread dimensioned to connect with a screw element. The analog may be removable through the bottom of the base.
Owner:BIOMED EST
Solid Bowl Screw Centrifuge Comprising a Centripetal Pump
InactiveUS20080153687A1Optimizes of regulatingHigh expenditureRotary centrifugesMechanical engineeringConoid
A solid bowl screw centrifuge including: a drum having a solids discharge at a conical end and at least one discharge opening at an end opposite the conical end, the at least one discharge opening arranged with an axial drum lid; a screw rotatable at a different speed relative to the drum; a centripetal chamber section connected behind the drum lid with the at least one discharge opening; a centripetal pump arranged to discharge a liquid phase from the solid bowl screw centrifuge; and an adjustable throttling device connected in front of the centripetal pump in the centripetal chamber section, the adjustable throttling device being assigned to the at least one discharge opening.
Owner:WESTFALIA SEPARATOR AG
Clock pulse control device of a microwave pulse radar
Owner:VEGA GRIESHABER GMBH & CO
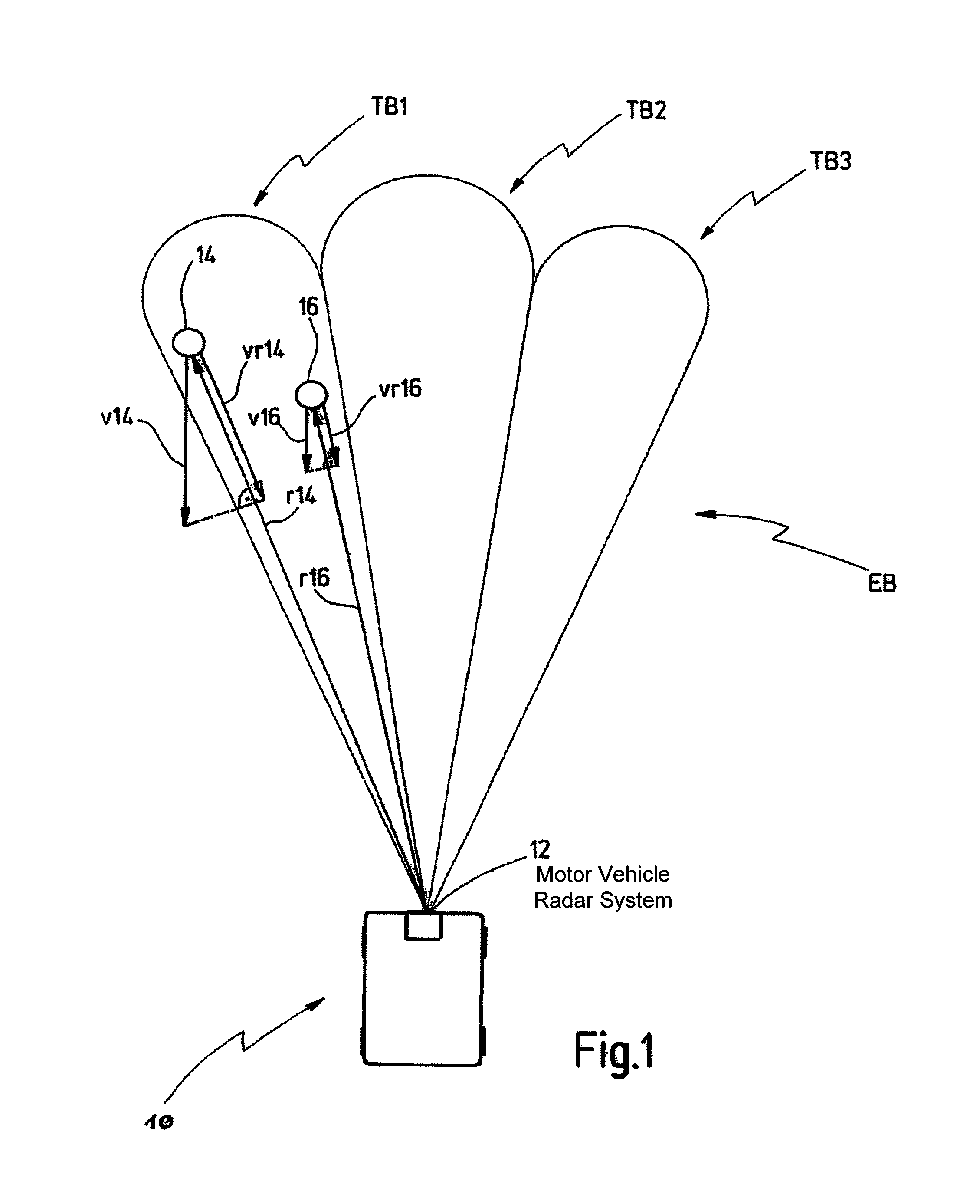
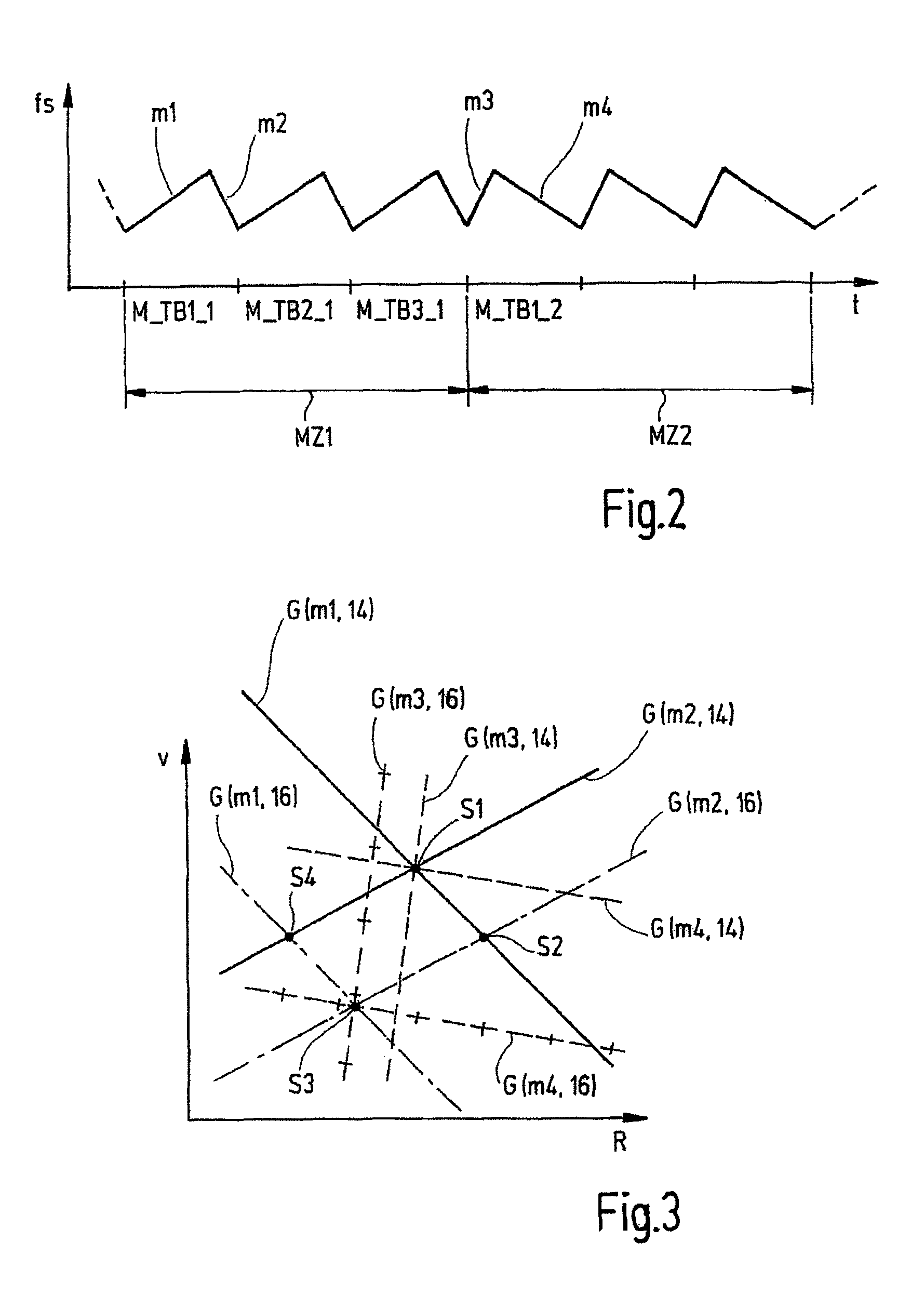
Motor vehicle radar system, and method for determining speeds and distances of objects
ActiveUS8704704B2Little required measuring timeImprove update rateRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsHypothesis
Presented is a method for determining speeds (vr14, vr16) and distances (r14, r16) of objects (14, 16) relative to a radar system (12) of a motor vehicle (10), wherein a coverage area (EB) of the radar system (12) is divided into at least two part-areas (TB1, TB2, TB3), the coverage area (EB) is examined for reflecting objects (14, 16) in successive measuring cycles (MZ1, MZ2; MZi, MZi+1), wherein radar signals received in a measuring cycle (MZ1, MZ2; MZi, MZi+1) are processed separated in accordance with part-areas (TB1, TB2, TB3) and processed signals are assembled to form a total result differentiated in accordance with spatial directions. The method is characterized in that from signals received in a first measuring cycle (MZ1; MZi), hypotheses for the distance (r14, r16) and speed (vr14, vr16) of reflecting objects (14, 16) are formed and the hypotheses are validated in dependence on signals received in at least one further measuring cycle (MZ2; MZi+2). Furthermore, a radar system (12) is presented which carries out such a method.
Owner:VALEO SCHALTER & SENSOREN
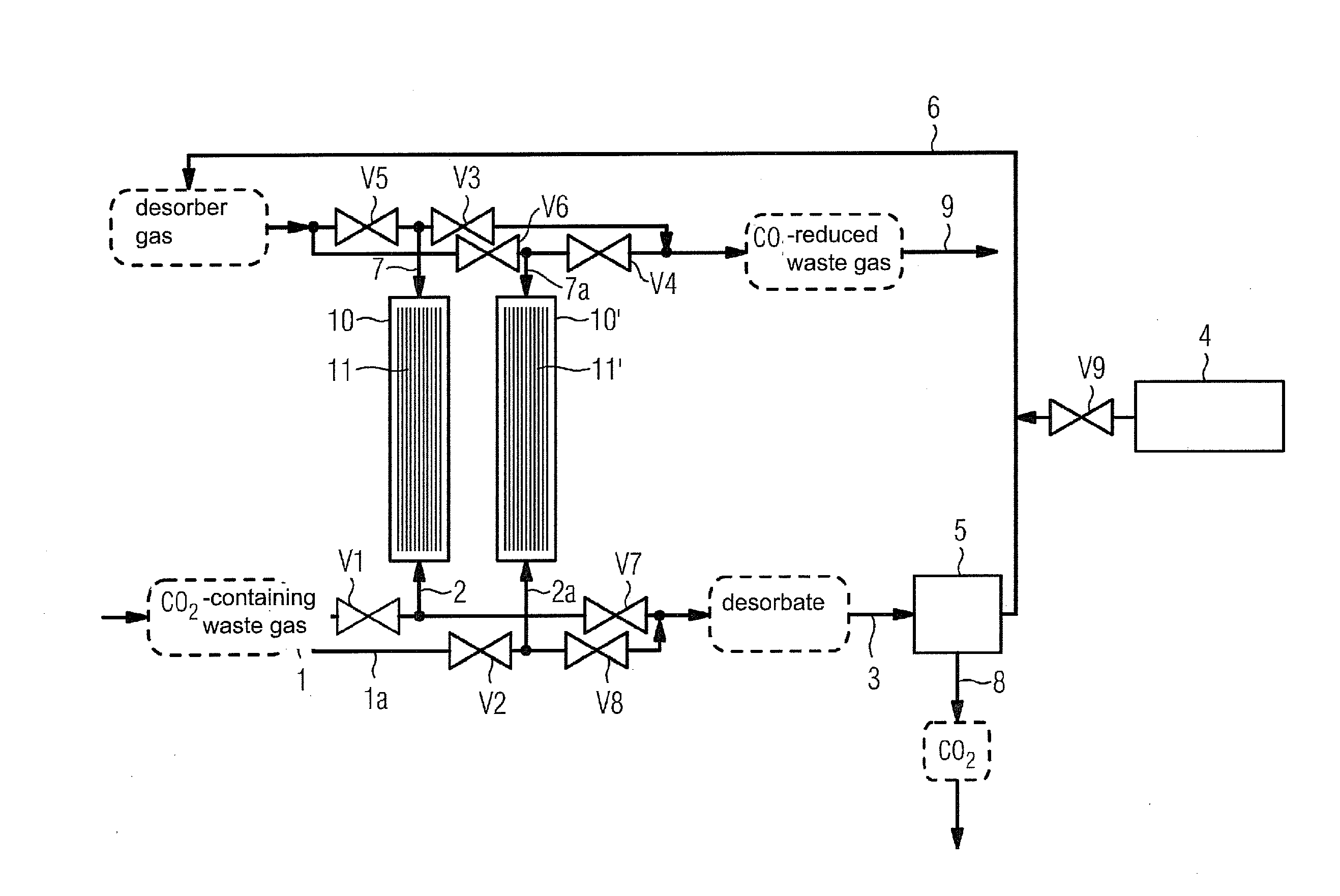
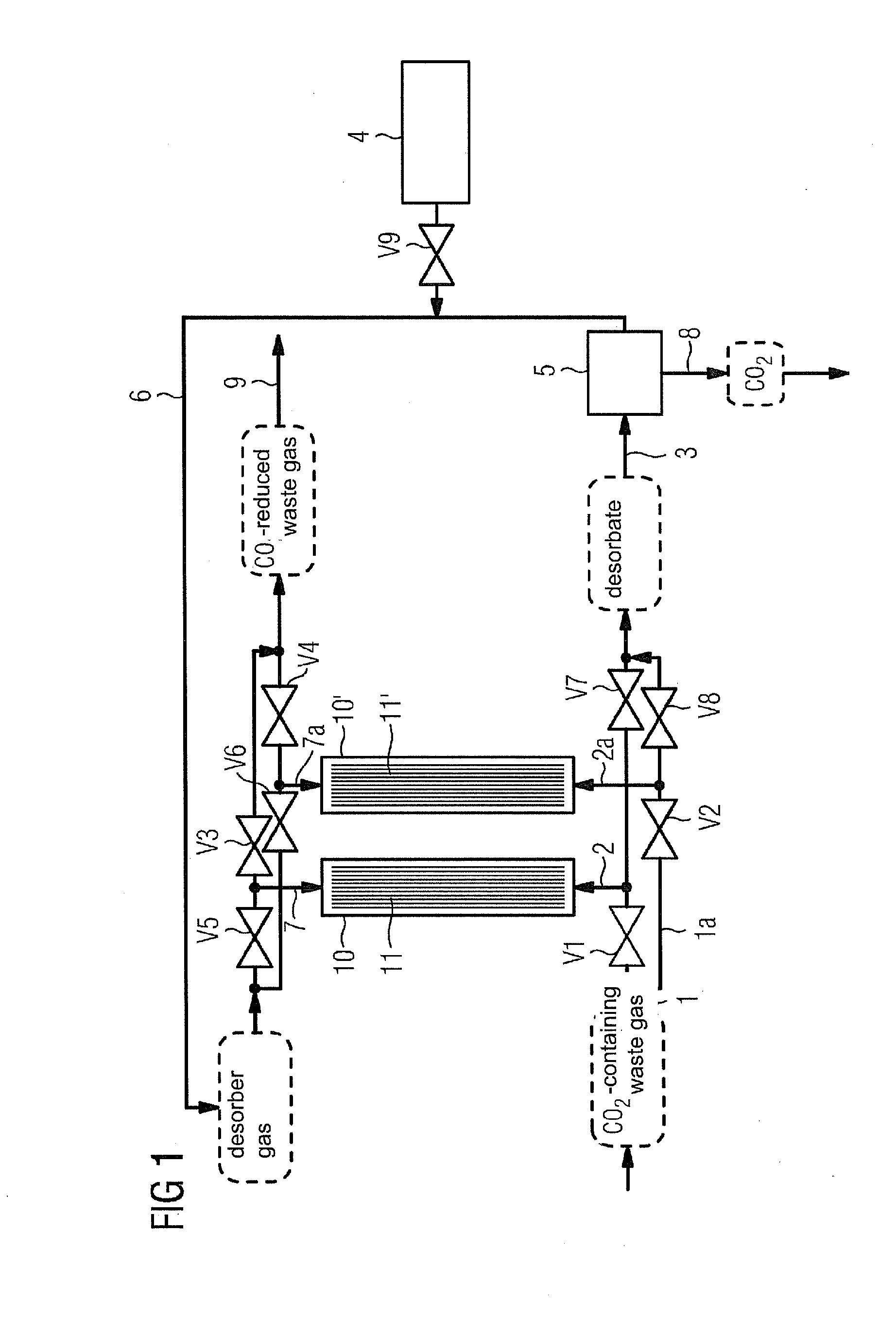
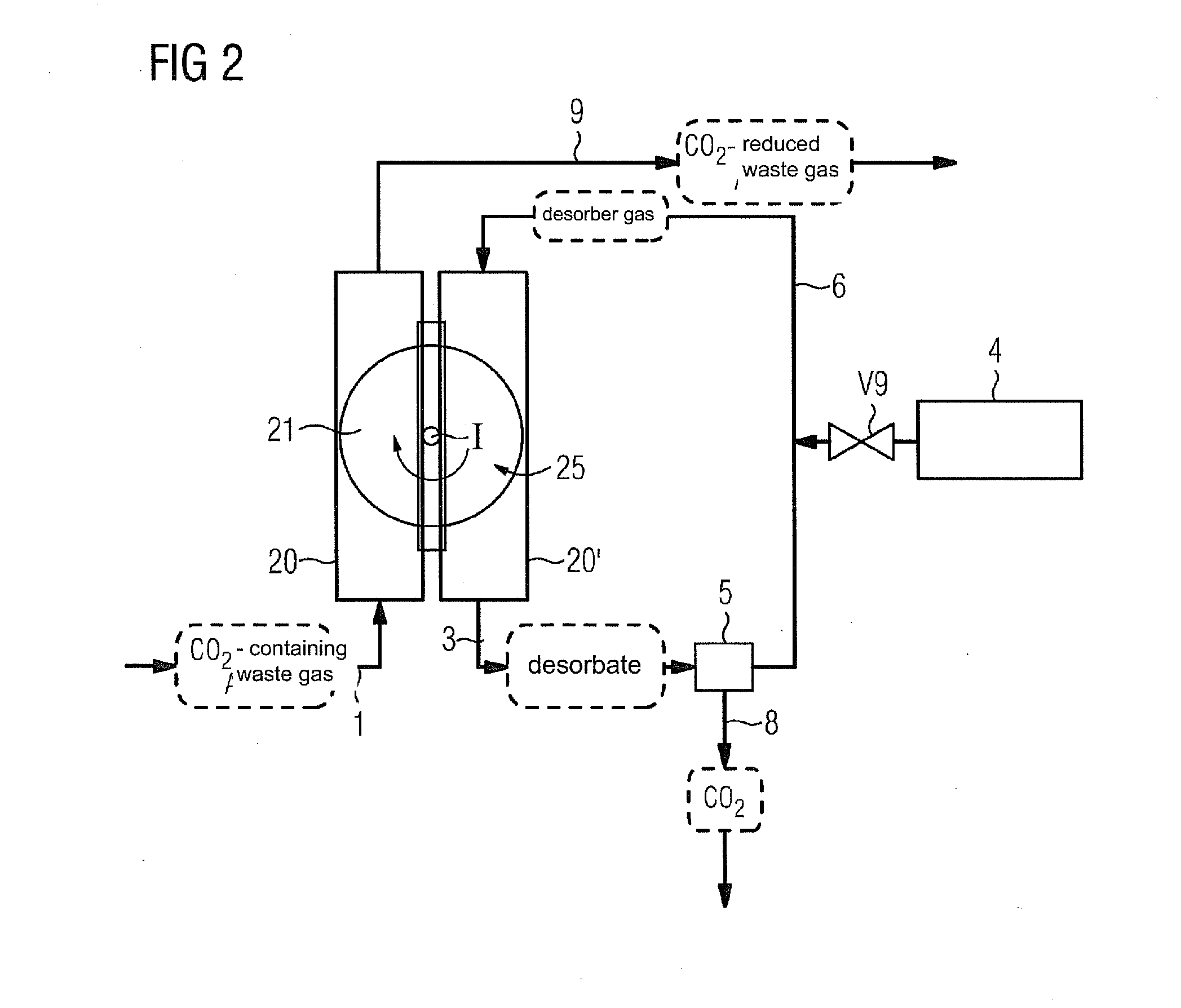
Method for separating carbon dioxide from flue gases and associated device
InactiveUS20100196234A1Simple methodPossible to useCombination devicesGas treatmentFlue gasCompound (substance)
A method in which CO2 is placed on an adsorber and an adsorption reaction with ammonia, that is used as a chemical absorption agent, occurs, is provided. The CO2 extracted from the waste gas is joined to the ammonia on the catalytic surface using a heterogeneous, catalytic reaction. At least two reactors are provided in the associated device. The reactors, which operate alternately, are switched between the adsorption of CO2 and the regeneration of the absorption agent.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Solid bowl screw centrifuge comprising a distributor
InactiveUS7060019B2Shorten speedNo lowering of relative velocityRotary centrifugesDistributorSurface structure
The present invention relates to solid bowl screw centrifuge comprising a centrifuging chamber having a rotatable screw with a center axis and a rotatable drum surrounding the centrifuging chamber. Also included is an axially extending inflow tube for guiding material to be centrifuged into a distributor. The distributor is oriented in a substantially perpendicular manner with respect to the center axis of the screw and configured for introducing the material to be centrifuged into the centrifuging chamber. The distributor further includes at least one wall having a surface structure that includes projections configured such that a substantial portion of the material to be centrifuged flowing through the distributor must flow around at least one of the projections.
Owner:WESTFALIA SEPARATOR AG
Method for producing a three-dimensional object
ActiveUS9039953B2High expenditureAdditive manufacturing apparatusLayered productsMulti materialFluid phase
A method serves to produce a three-dimensional object by additive construction in direct construction sequence from solidifiable material, which is either present in the starting state in a fluid phase or can be liquefied, where multiple material components are discharged alternately in a programmable manner by means of multiple discharge units and configure different parts of the object joined to one another as a result of the discharge, where the geometric proportions obtained during discharge already correspond to the object, and because the material components form between them either edge regions merging into one another without boundaries or boundary regions of the different material components abutting one another without joining, a method and an object produced therewith can be provided, in which boundary and edge regions are formed “as if from one piece” between different material components even in the case of complex geometries.
Owner:ARBURG GMBH & CO KG
Method and Device For Representing the Microstructure of the Lungs
InactiveUS20080208038A1High expenditureSmall shrinkageBiocideMagnetic measurementsFluorinated gasesMedicine
The invention relates to an apparatus and a method for imaging the microstructure of an animal or human lung by way of introducing a fluoric contrast gas into the lung which is to be imaged; definition of the apparent diffusion coefficient of the contrast gas by way of diffusion weighted 19fluorine magnetic resonance tomography and based on the determined apparent diffusion coefficients; and imaging of the lung's microstructure.The current invention also describes a device for the implementation of the inventive method. The science of the current invention allows for the first time the production of a high resolution image of the microstructures of the lung through non-invasive measures, by way of fluorinated gases.
Owner:JOHANNES GUTENBERG UNIV
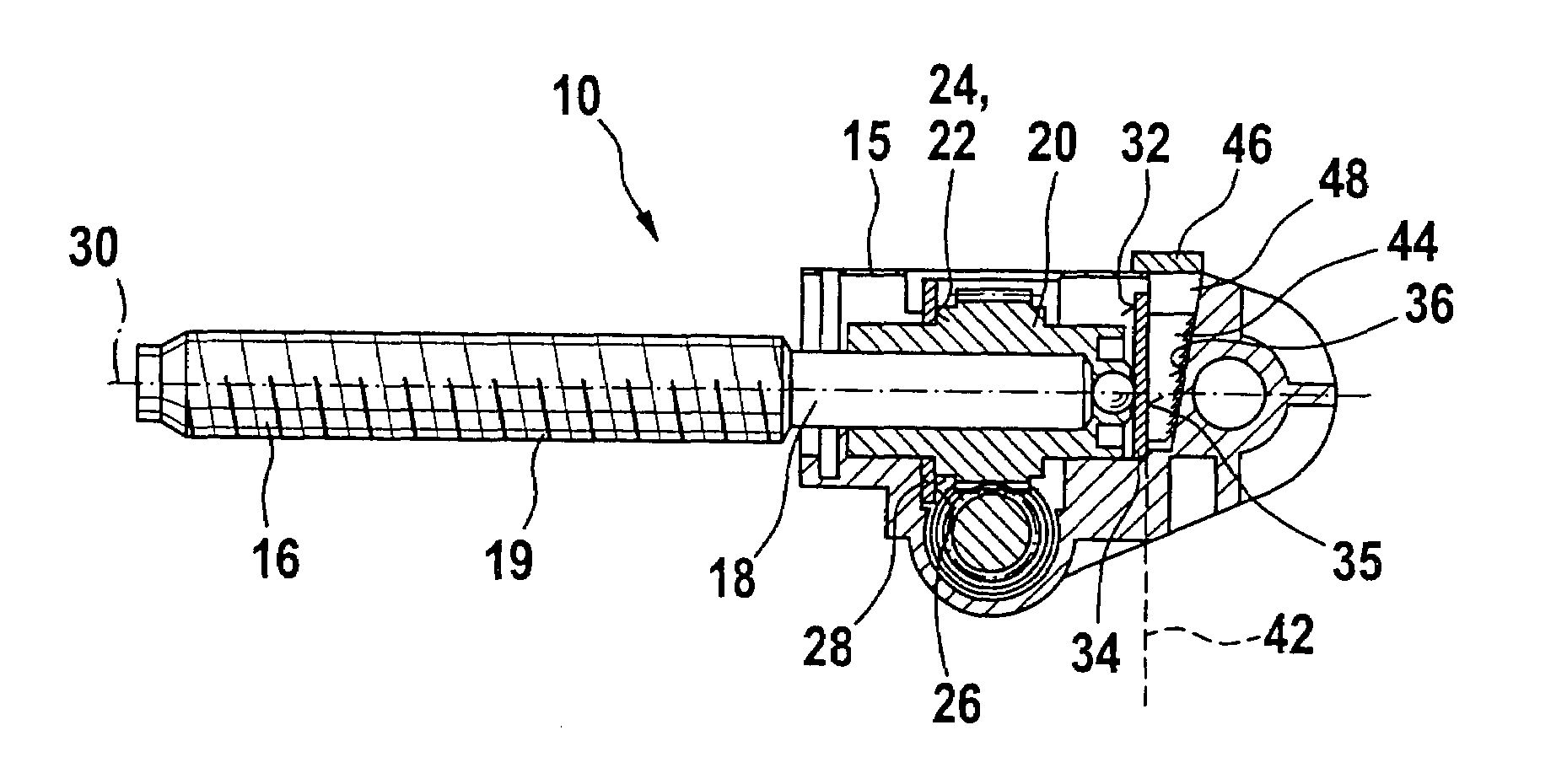
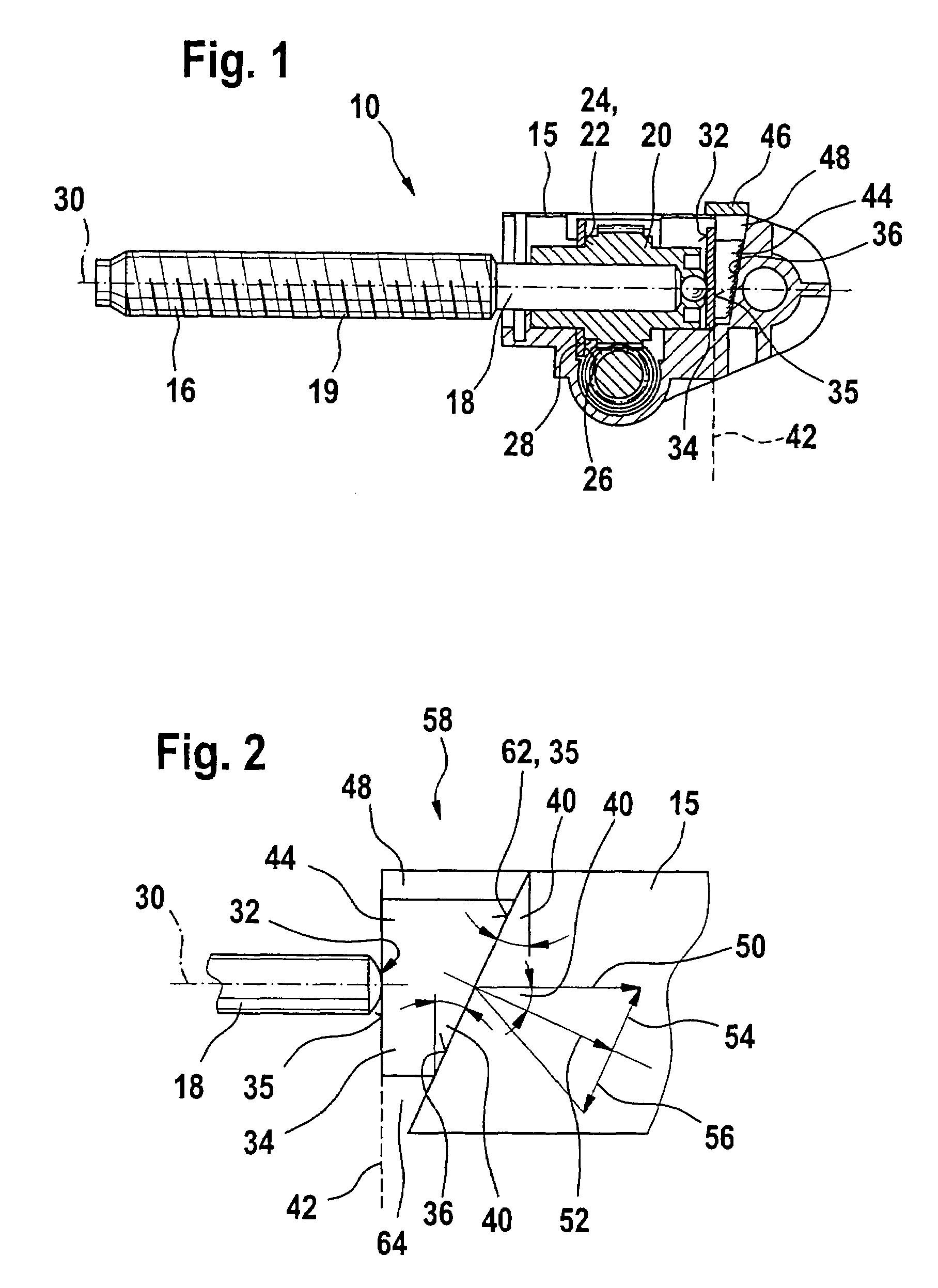
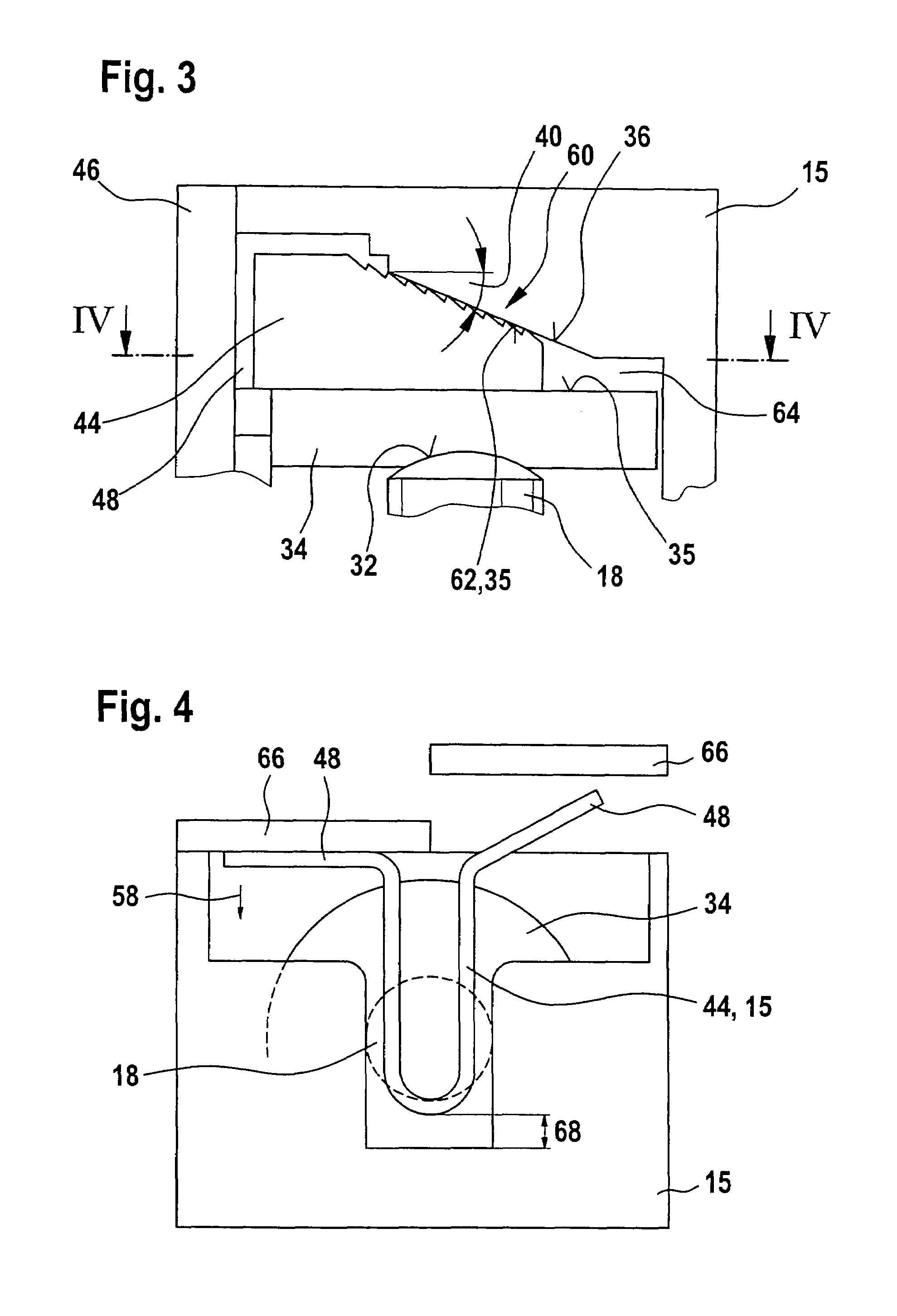
Gearbox drive unit with an inclined stop surface
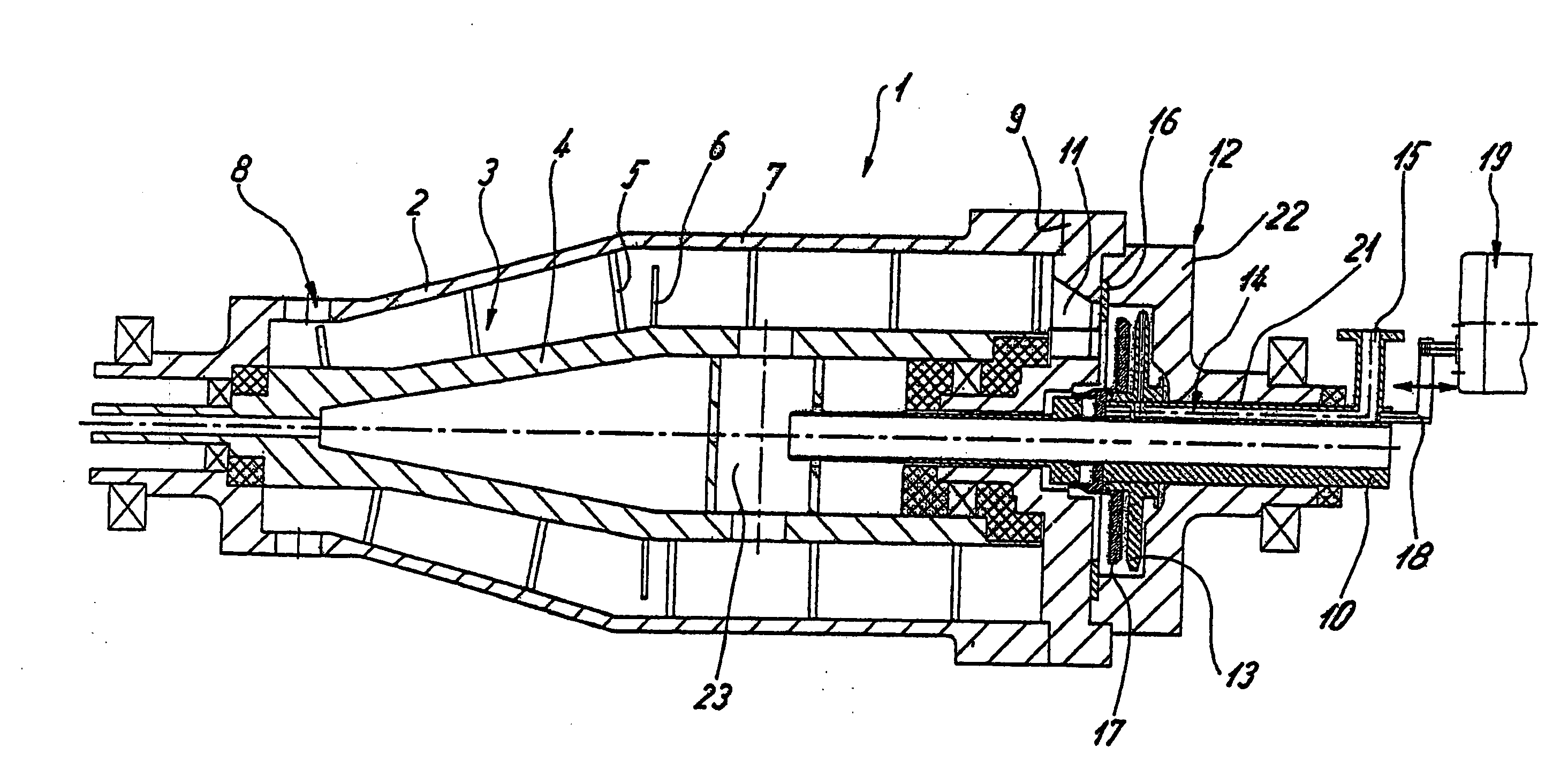
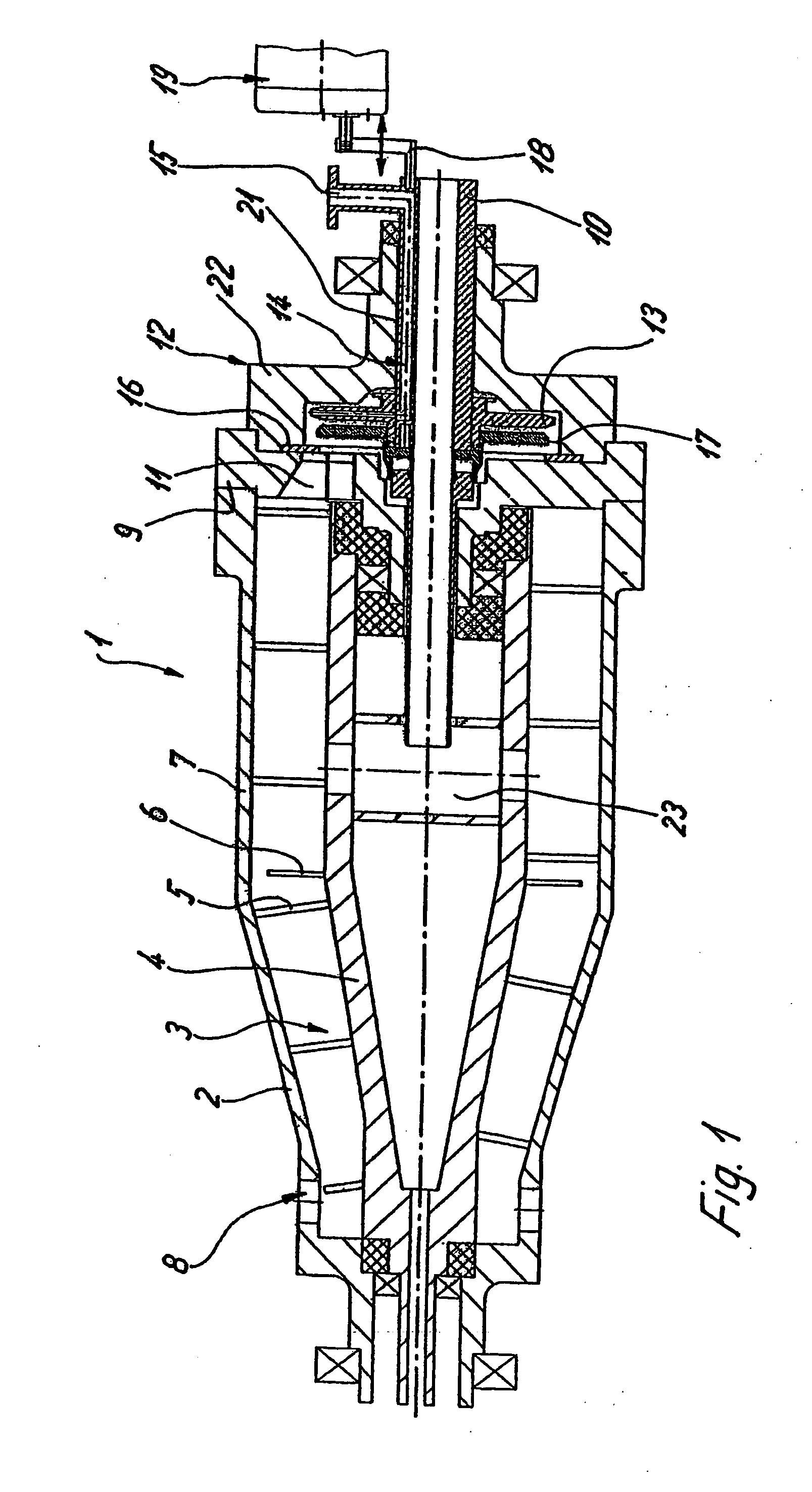
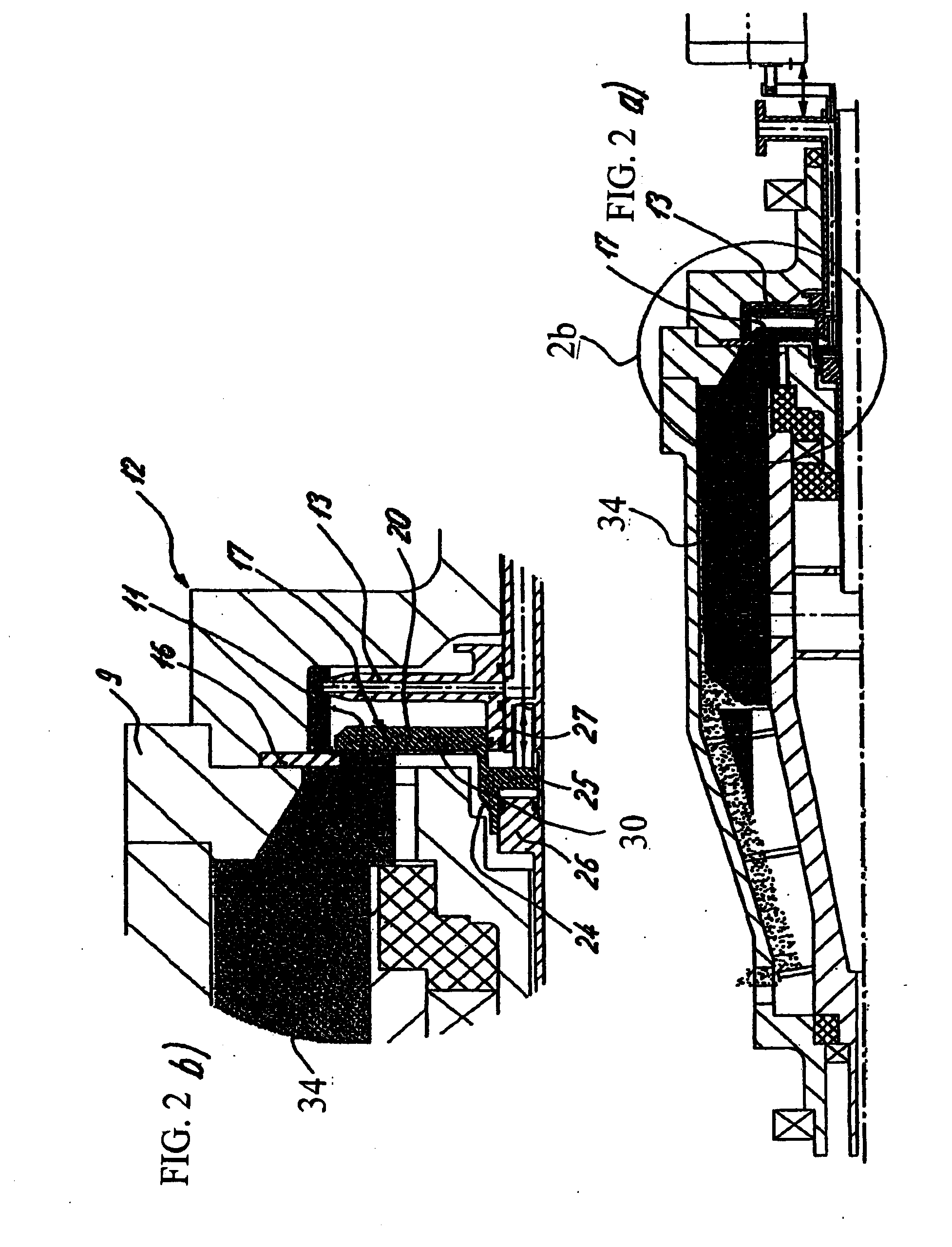
InactiveUS7467565B2Reliably eliminating the longitudinal play of the shaftReduce in quantityToothed gearingsPortable liftingGear driveEngineering
The invention relates to a gear drive unit (10), in particular to adjust moveable parts in a motor vehicle, with a gear housing (15) and a shaft (18) positioned therein along a longitudinal axis (30), which shaft is supported on the housing (15) via an axial stopping face (35) on a counter stopping face (36), wherein at least one of the stopping faces (35, 36) is inclined perpendicular to the longitudinal axis (30) against a plane (42) by an angle of inclination (40) in order to generate an axial force, and a component (44), which cooperates with at least one of the stopping faces (35, 36), is arranged in a displaceable manner perpendicular to the longitudinal axis (30). In doing so, the coefficient of friction between the at least one stopping face (35, 36) and the component (44) is greater than the tangent of the angle of inclination (40).
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Solid bowl screw centrifuge comprising a centripetal pump with a throtting device
InactiveUS7510519B2High expenditureImproving operation and adjustabilityRotary centrifugesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A solid bowl screw centrifuge including: a drum having a solids discharge at a conical end and at least one discharge opening at an end opposite the conical end, the at least one discharge opening arranged with an axial drum lid; a screw rotatable at a different speed relative to the drum; a centripetal chamber section connected behind the drum lid with the at least one discharge opening; a centripetal pump arranged to discharge a liquid phase from the solid bowl screw centrifuge; and an adjustable throttling device connected in front of the centripetal pump in the centripetal chamber section, the adjustable throttling device being assigned to the at least one discharge opening.
Owner:WESTFALIA SEPARATOR AG
Preparation comprising thiol-group-containing proteins
InactiveUS6358918B1High nitrosation level of proteinWithout adversely nativityBiocideNervous disorderCombinatorial chemistryVirus
There is disclosed a stable, virus-safe, pharmaceutical preparation comprising thiol-group-containing proteins which are heat-treated and processed such that at least 40% of the thiol groups are capable of being nitrosated, a method of preparing such preparations as well as the use of these preparations.
Owner:HALLSTROM SETH +1
Process for dissolving used paper
InactiveUS20010006098A1Easy to tearImprove solubilityFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpPaper recyclingHeavy particleSolid particle
Process for dissolving used paper including adjusting a content of solid particles of used paper to a range between about 15 and 35%, kneading the used paper with a specific work of at least about 10 kWh / t, diluting the kneaded used paper to a content of solid particles below about 6%, separating non-fibrous contaminants with wet screening, adjusting a solid material content to less than about 3%, and separating heavy particles with at least one hydrocyclone.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
System and method for removing foreign particles from an aqueous fibrous suspension
A method and system is used for removing foreign particles, e.g., printing ink particles, from an aqueous fibrous suspension, in particular recovered paper suspension. The method includes dividing the suspension in a fractionation into a fine fraction, in particular short-fiber fraction, and a coarse fraction, in particular long-fiber fraction. Both of the fractions thus formed are then treated in respectively differently operated flotations in order to carry away the foreign particles in the flotation foam. The parameters and apparatuses used of the two flotations can be optimally adjusted thereby to the conditions present in the individual fractions.
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
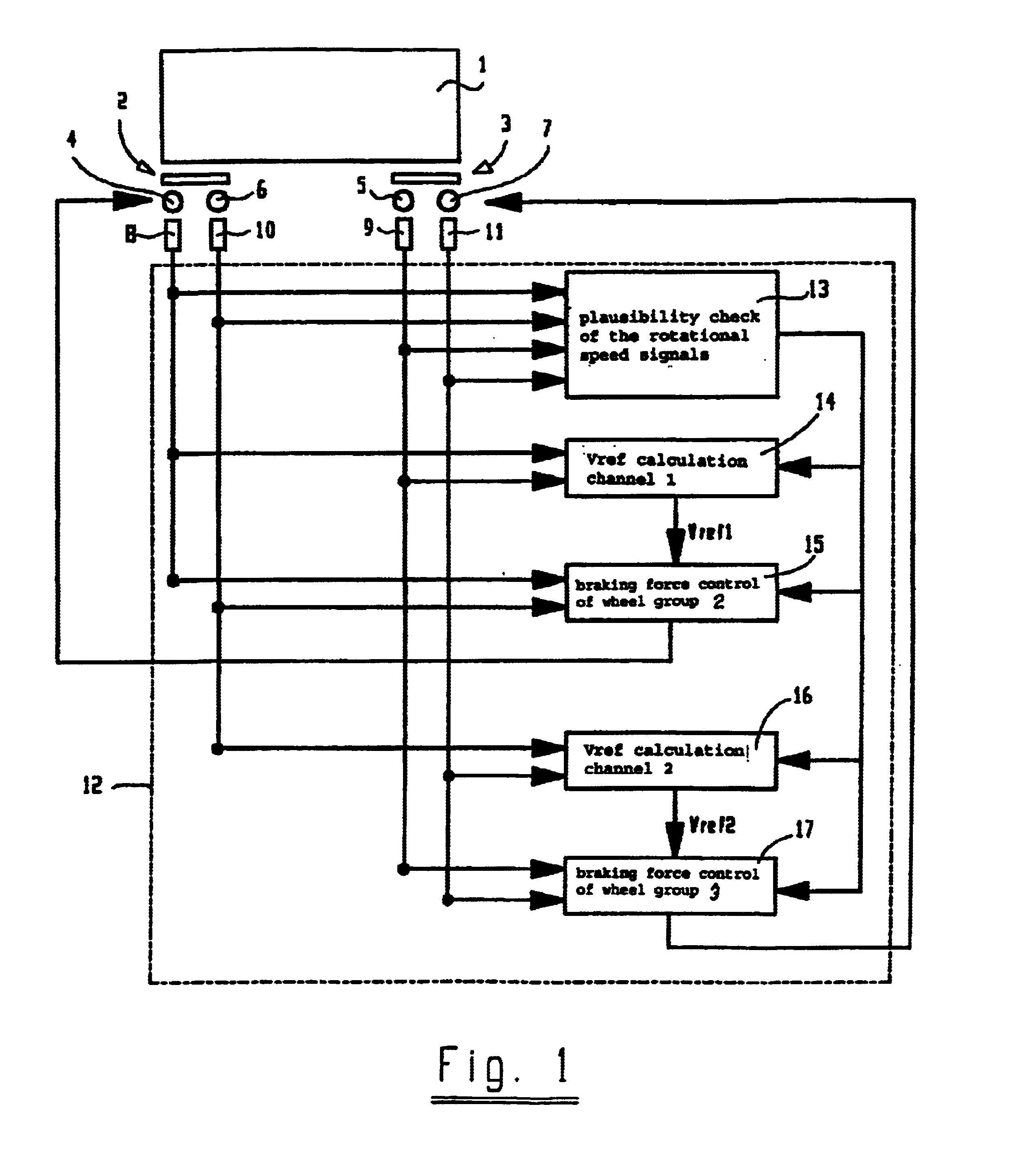
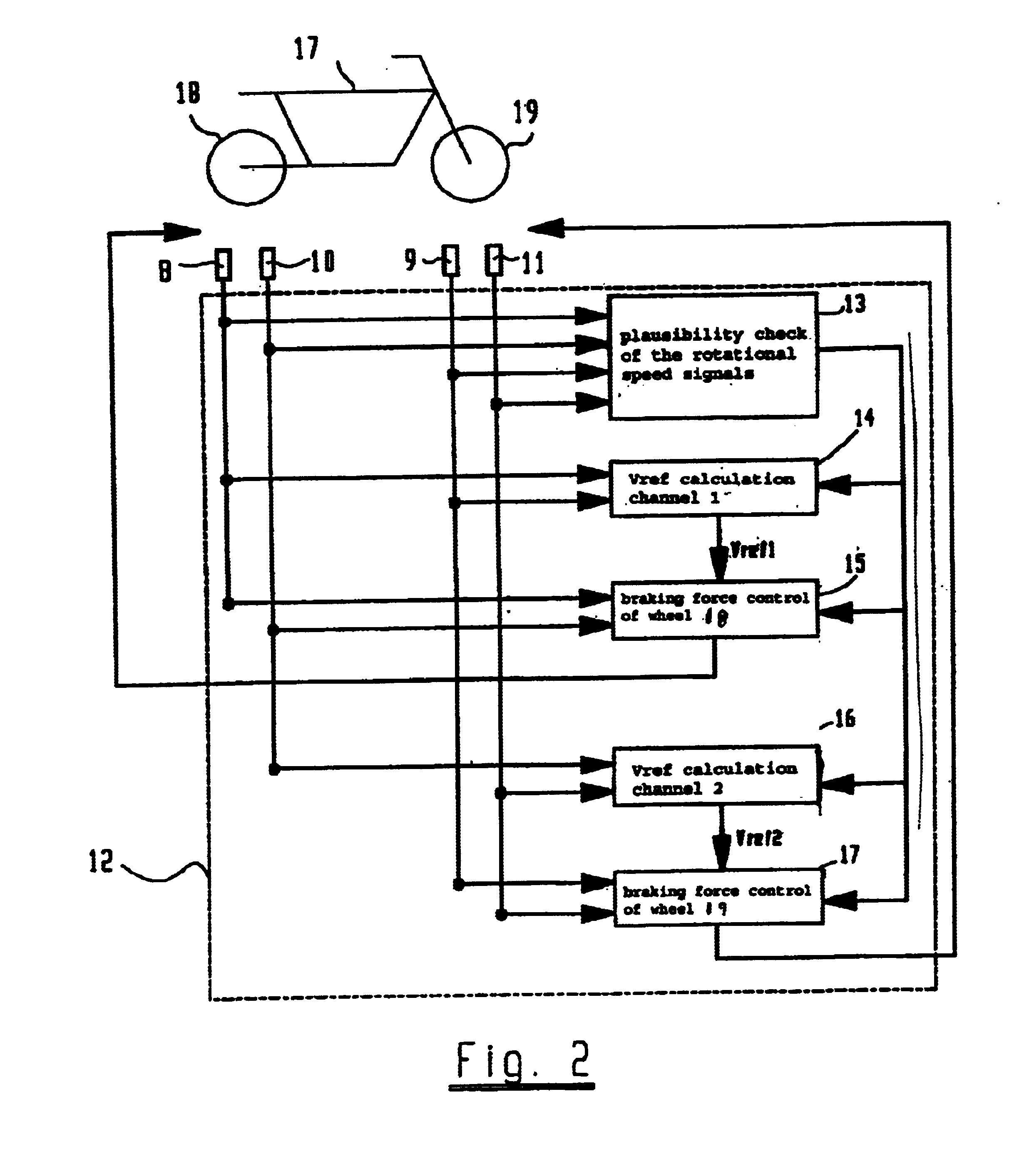
Braking system for vehicle provided with ABS or an anti-skid protection system
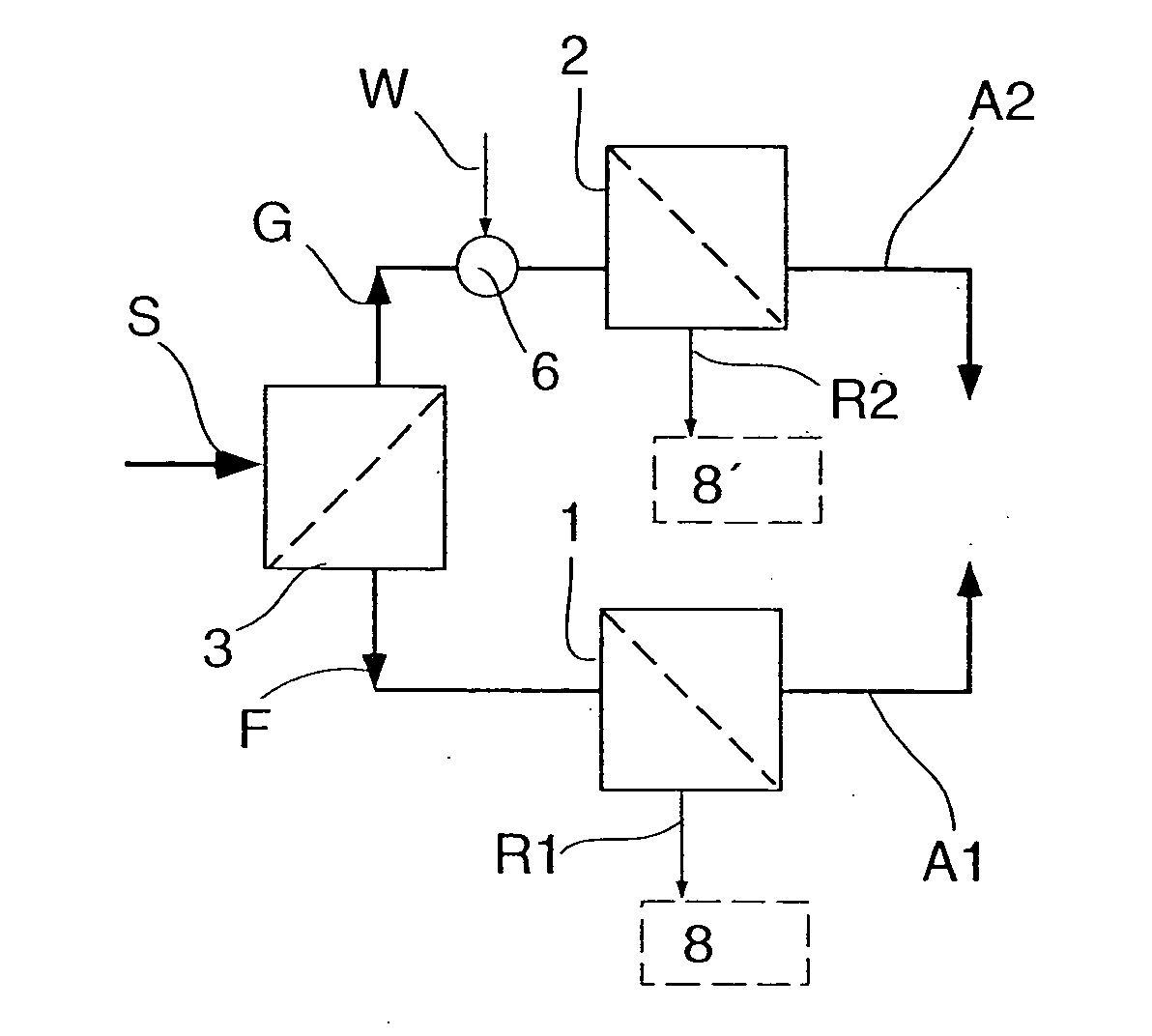
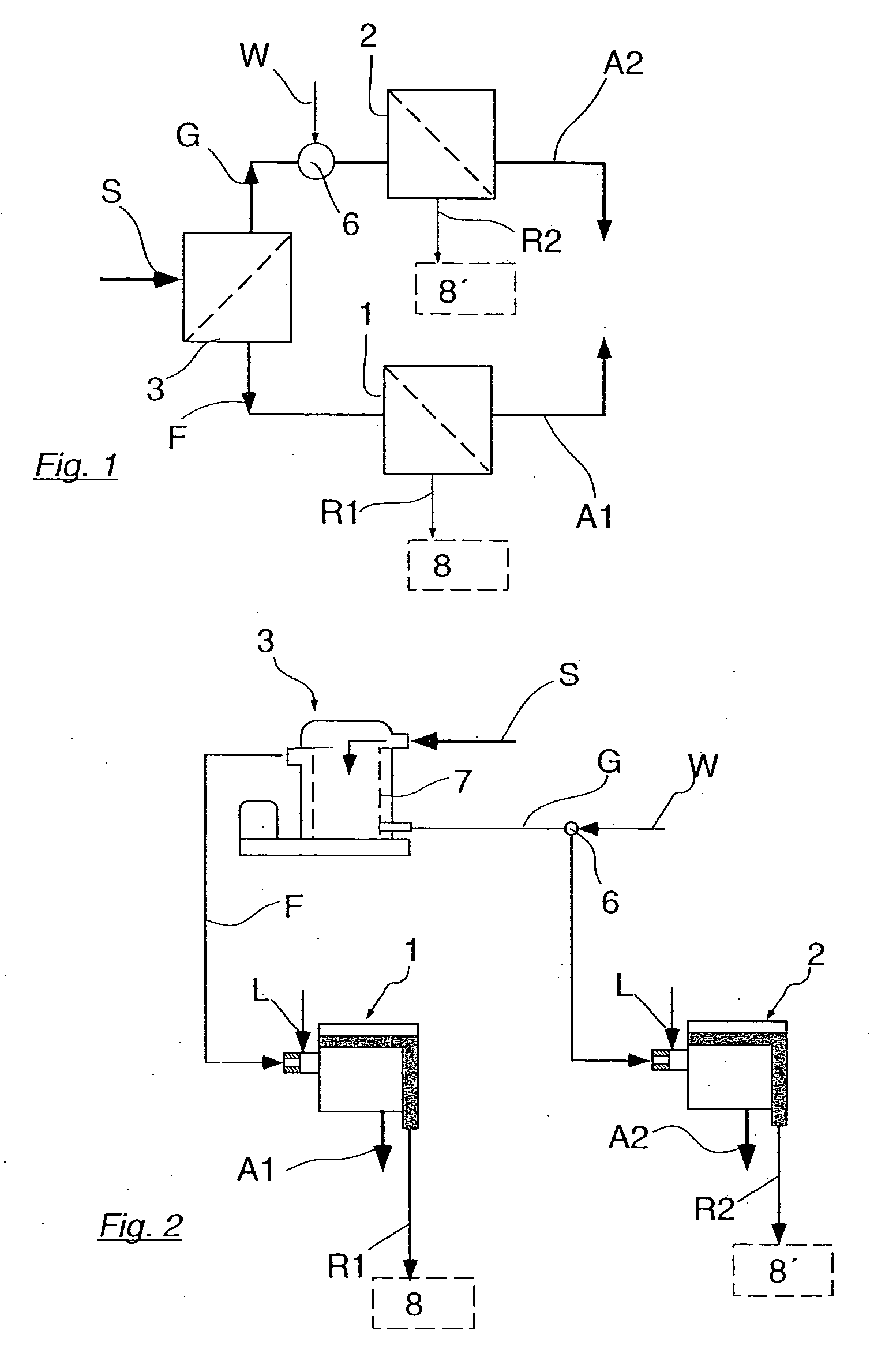
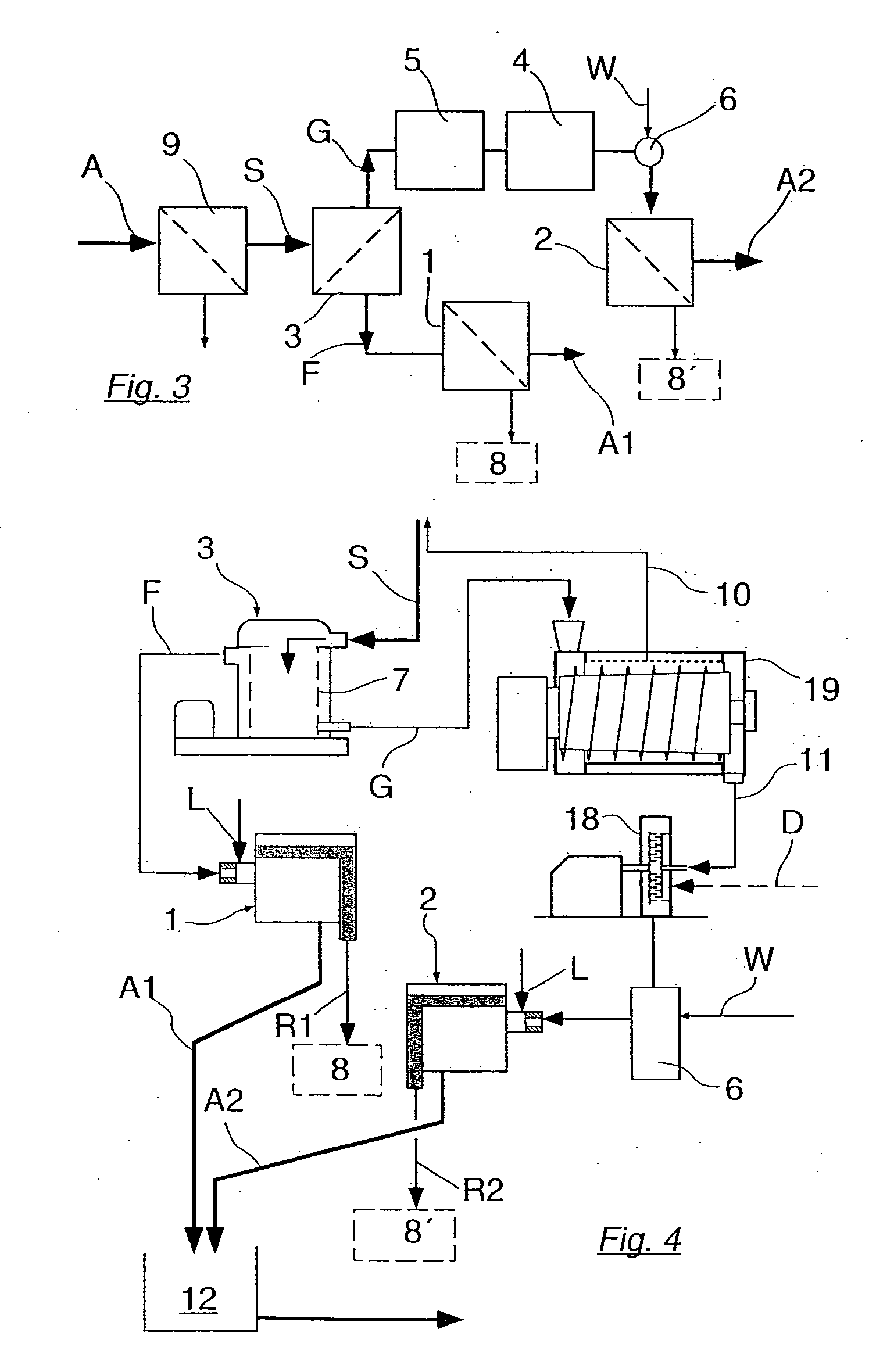
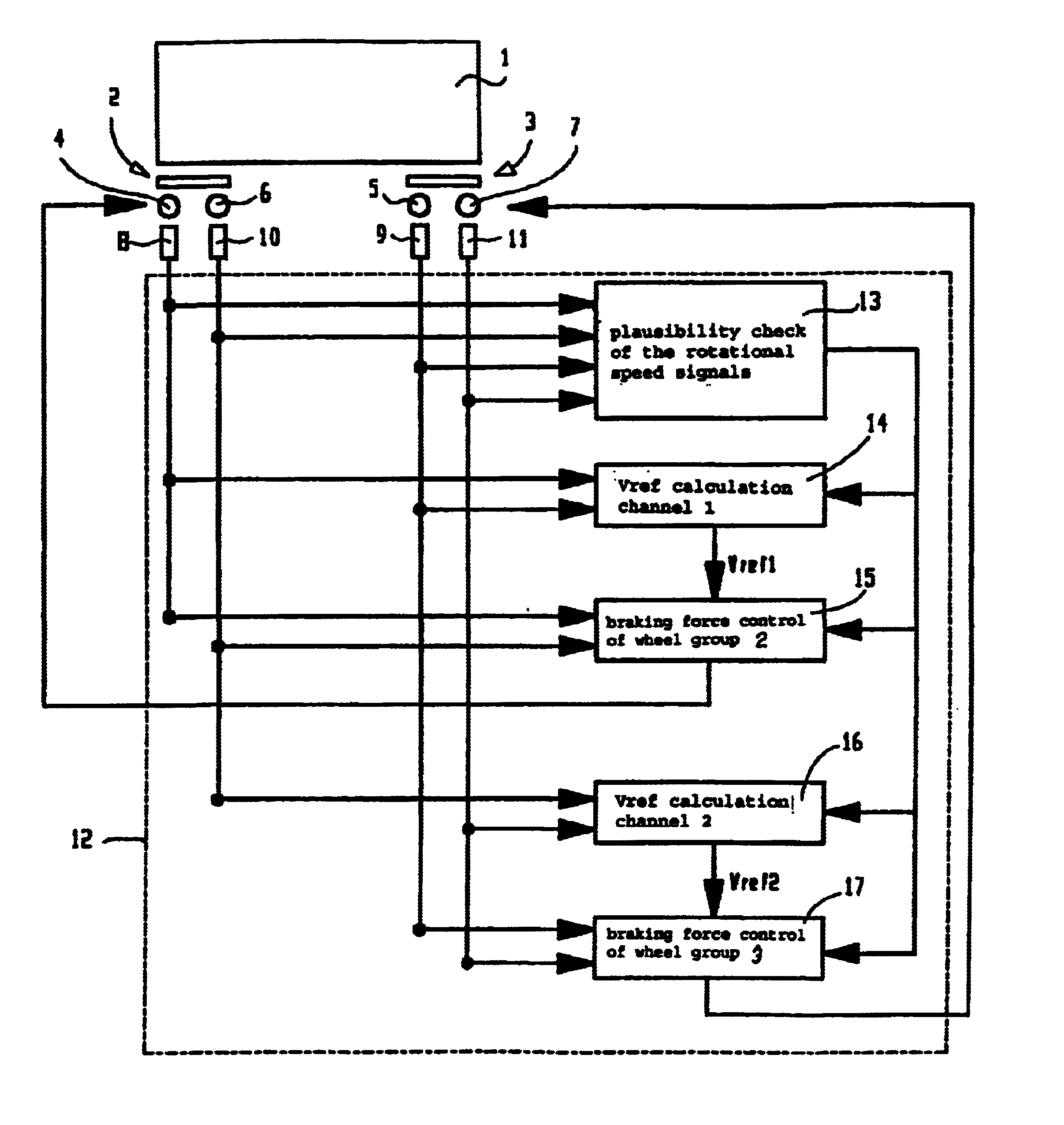
InactiveUS6945611B2Improve driving safetyHigh expenditureBraking action transmissionApplication and release valvesProtection systemBraking system
The general principle underlying the invention is a braking system that is provided with an arithmetic unit with at least two independent channels for determining the reference speeds approximated to the actual vehicle speed. The at least two determined reference speeds are used only for regulating a part of the brakes installed in the vehicle.
Owner:KNORR BREMSE SYST FUR SCHIENENFAHRZEUGE GMBH
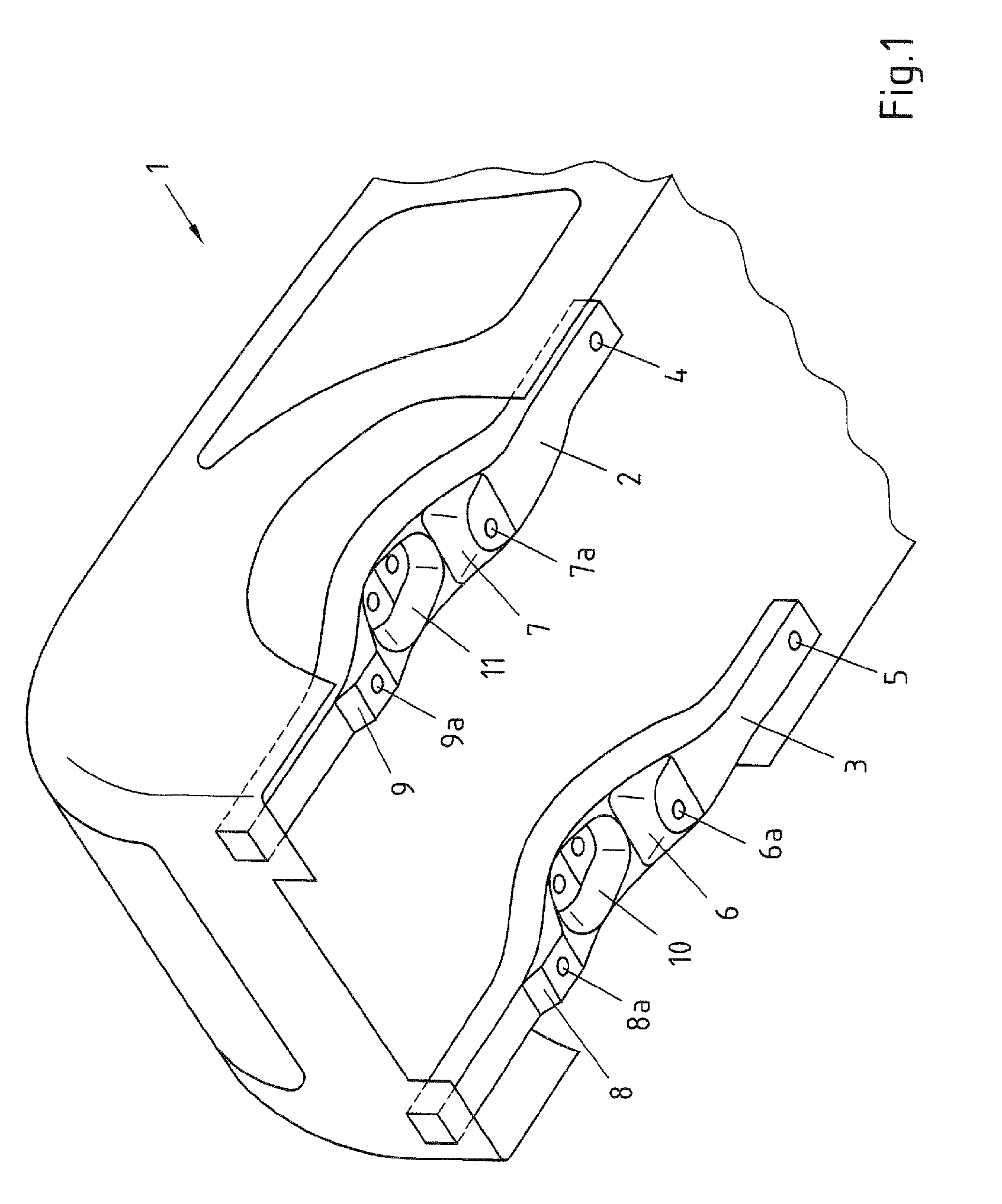
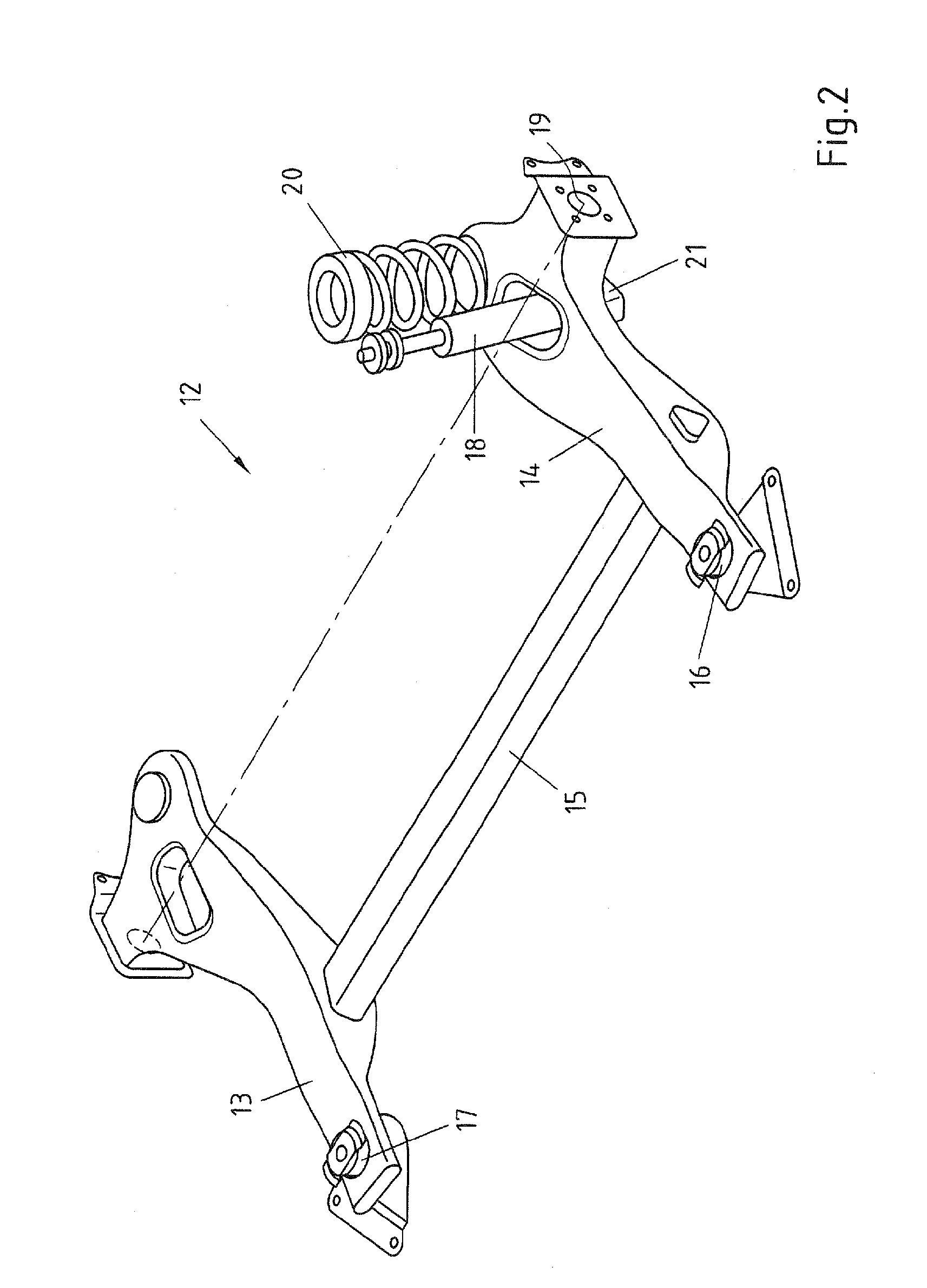
Vehicle chassis having modular rear axle construction
InactiveUS8925947B2Increase in weightHigh expenditure can be avoidedUnderstructuresInterconnection systemsMobile vehicleMulti link
The invention relates to a bodywork of a motor vehicle comprising side members and a rear axle construction which is connected to the bodywork, the rear axle construction having means for attaching the rear axle construction to the bodywork and having a suspension, and the rear axle construction being configured as a torsion-beam axle or as a multi-link axle. The object to provide a generic bodywork of a motor vehicle with a rear axle construction which allows, in a financially favorable manner, a modular rear axle concept, i.e. the selective use of a torsion-beam axle or of a multi-link axle is achieved in that the bodywork has means for receiving the attachment means of a torsion-beam axle and of a multi-link axle and has means for receiving the attachment means and the suspension of a torsion-beam axle and of a multi-link axle.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP AUTOMOTIVE SYST +1
Vehicle Chassis having Modular Rear Axle Construction
InactiveUS20120211962A1Increase in weightHigh expenditure can be avoidedUnderstructuresInterconnection systemsMobile vehicleMulti link
The invention relates to a bodywork of a motor vehicle comprising side members and a rear axle construction which is connected to the bodywork, the rear axle construction having means for attaching the rear axle construction to the bodywork and having a suspension, and the rear axle construction being configured as a torsion-beam axle or as a multi-link axle. The object to provide a generic bodywork of a motor vehicle with a rear axle construction which allows, in a financially favourable manner, a modular rear axle concept, i.e. the selective use of a torsion-beam axle or of a multi-link axle is achieved in that the bodywork has means for receiving the attachment means of a torsion-beam axle and of a multi-link axle and has means for receiving the attachment means and the suspension of a torsion-beam axle and of a multi-link axle.
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP AUTOMOTIVE SYST +1
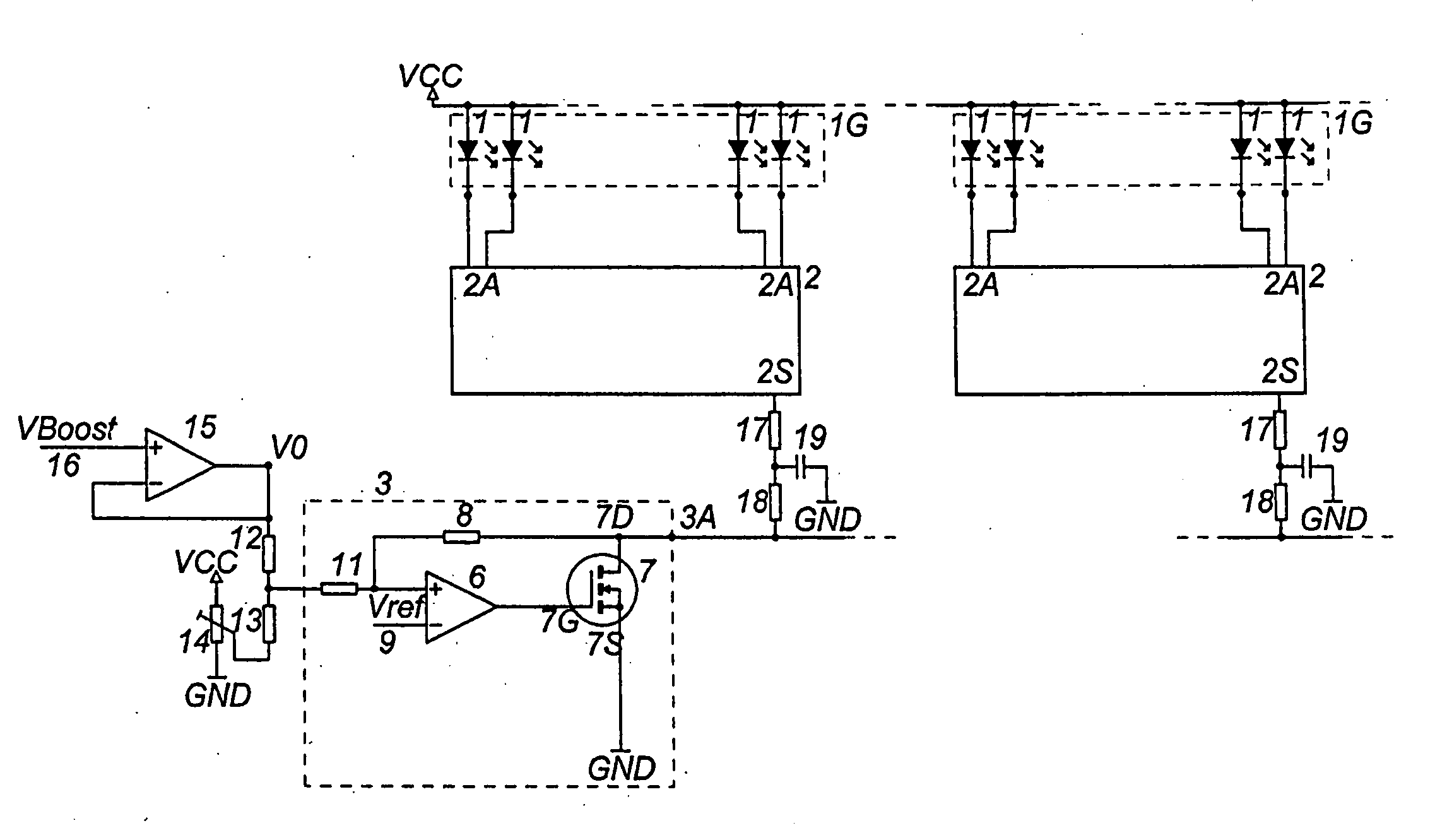
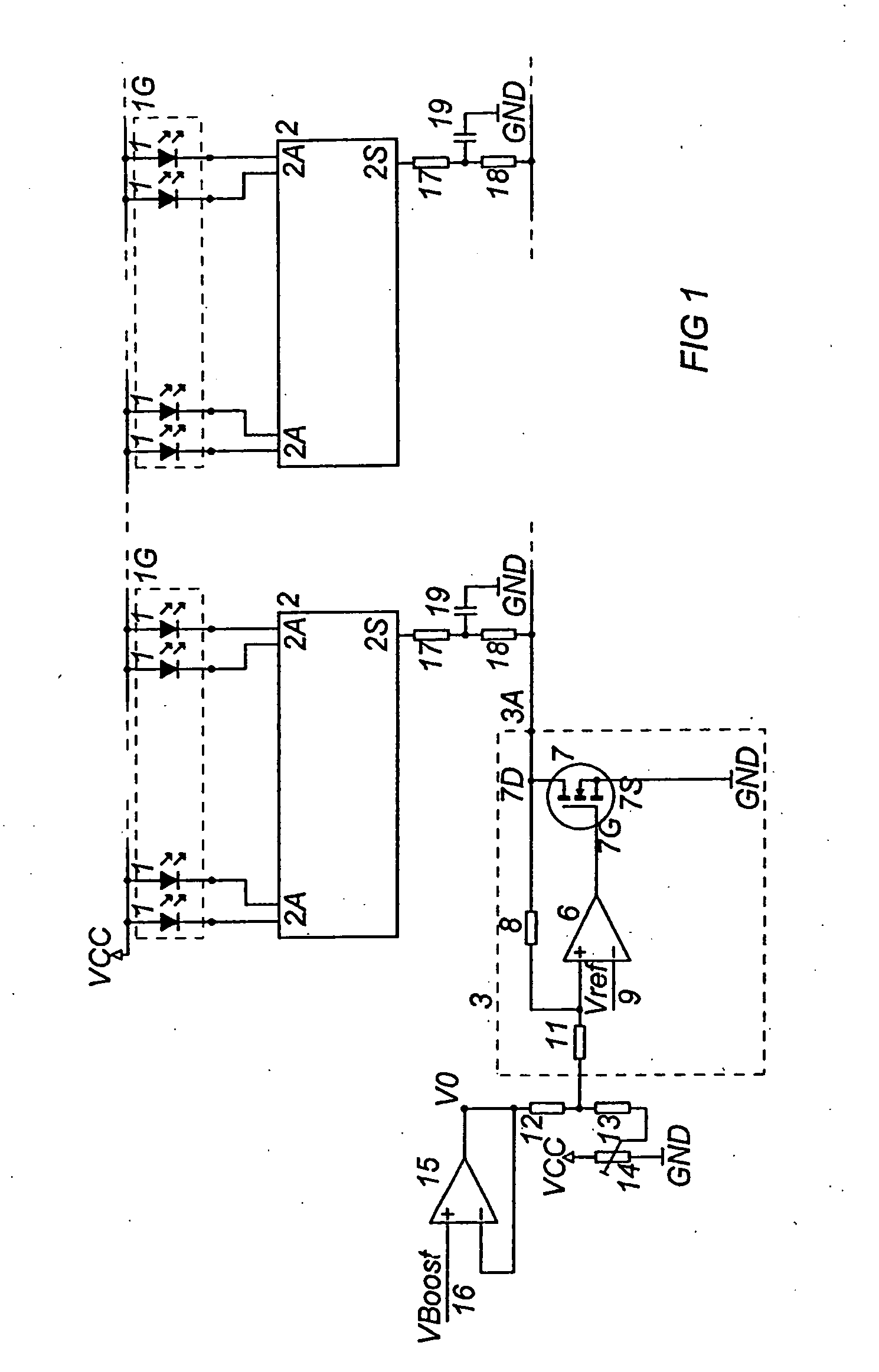
Circuit arrangement for controlling light emitting diodes
InactiveUS20100327770A1Easy to adjustIncreasing applied voltageElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesEngineeringVoltage source
In a circuit arrangement for controlling light emitting diodes (LED's) combined in groups, with at least one driver which has current outputs, via which current can be delivered to the LED's, as well as a control input by which the current supplied to the LED's is adjustable, the current control input is connected to the voltage output of a voltage source.
Owner:INIT INNOVATIVE INFORMATIKANWENDUNGEN & TRANSPORT VERKEHRS UND LEITSYSTN
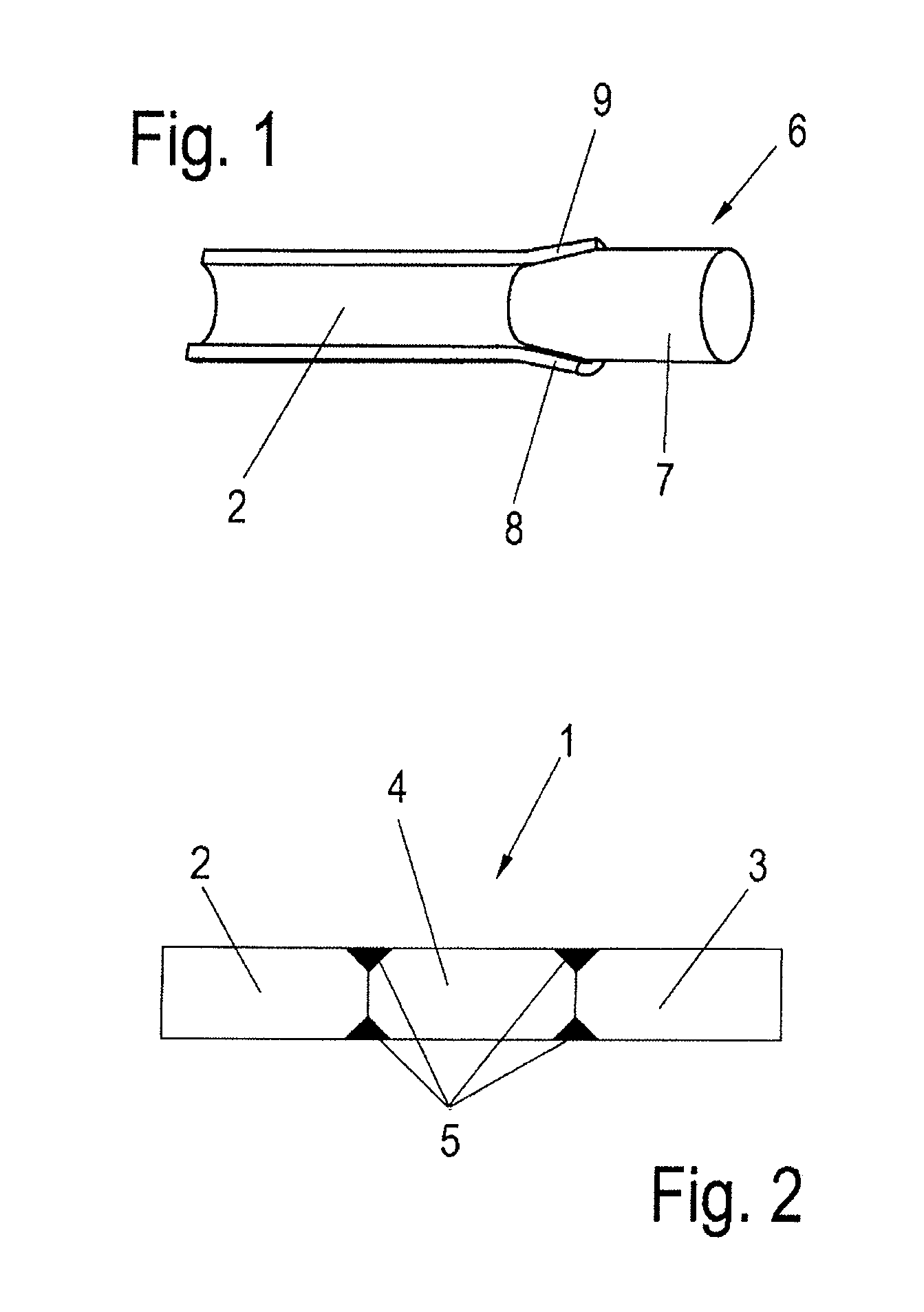
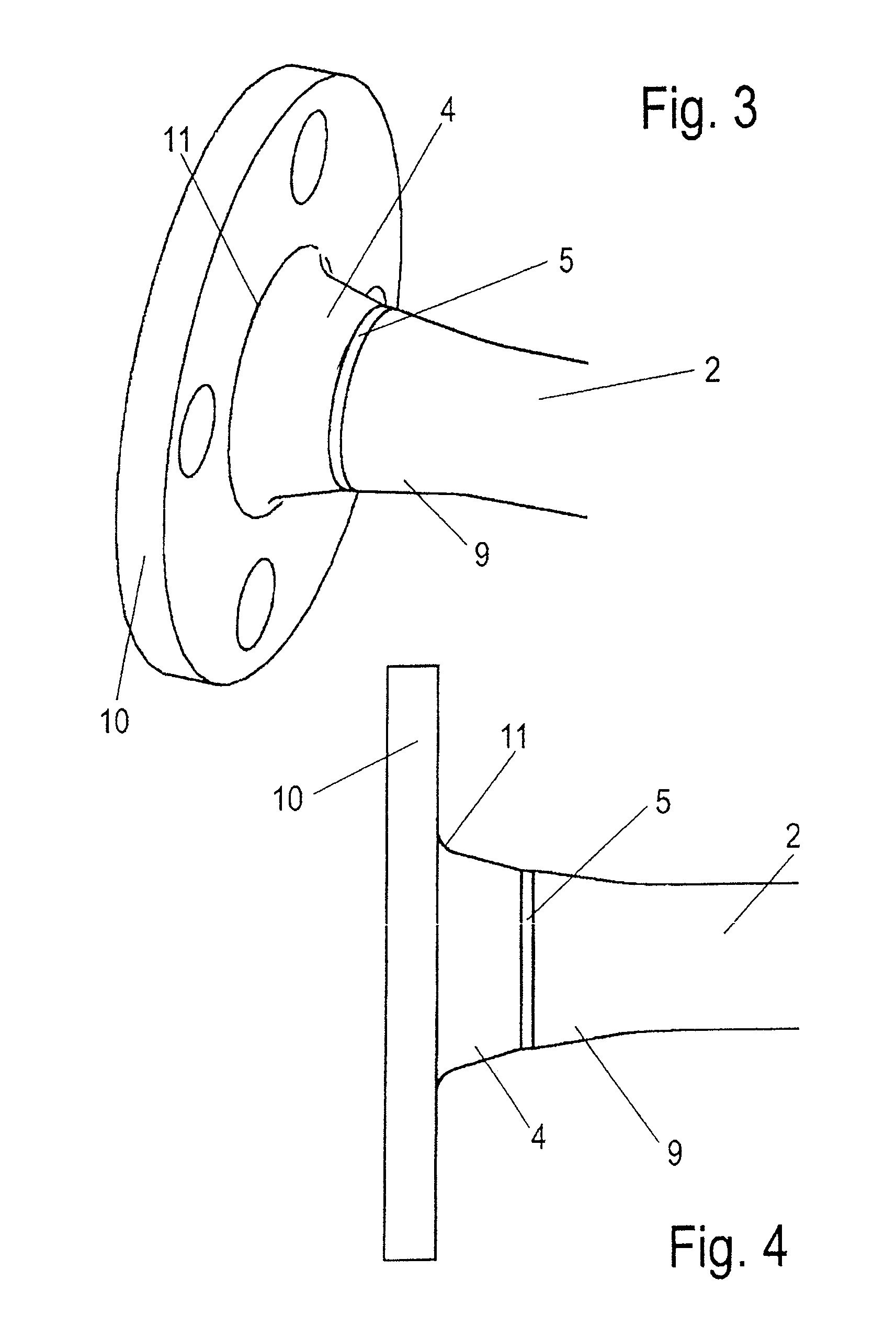
Process for connecting a tube stabilizer part of a divided tube stabilizer having an intermediate element, and a tube stabilizer
InactiveUS20110020569A1High expenditureReliable controlEnvelopes/bags making machineryLayered productsEngineeringActuator
A process for connecting a tube stabilizer part of a divided tube stabilizer with an intermediate element, such as an actuator or shift transmission. The process steps include providing the tube stabilizer part, providing the intermediate element, widening an end-side section of the tube stabilizer part using a conical mandrel, and bending the tube stabilizer part, and connecting the tube stabilizer part with the intermediate element.
Owner:BENTELER AUTOMOBILTECHNIK GMBH
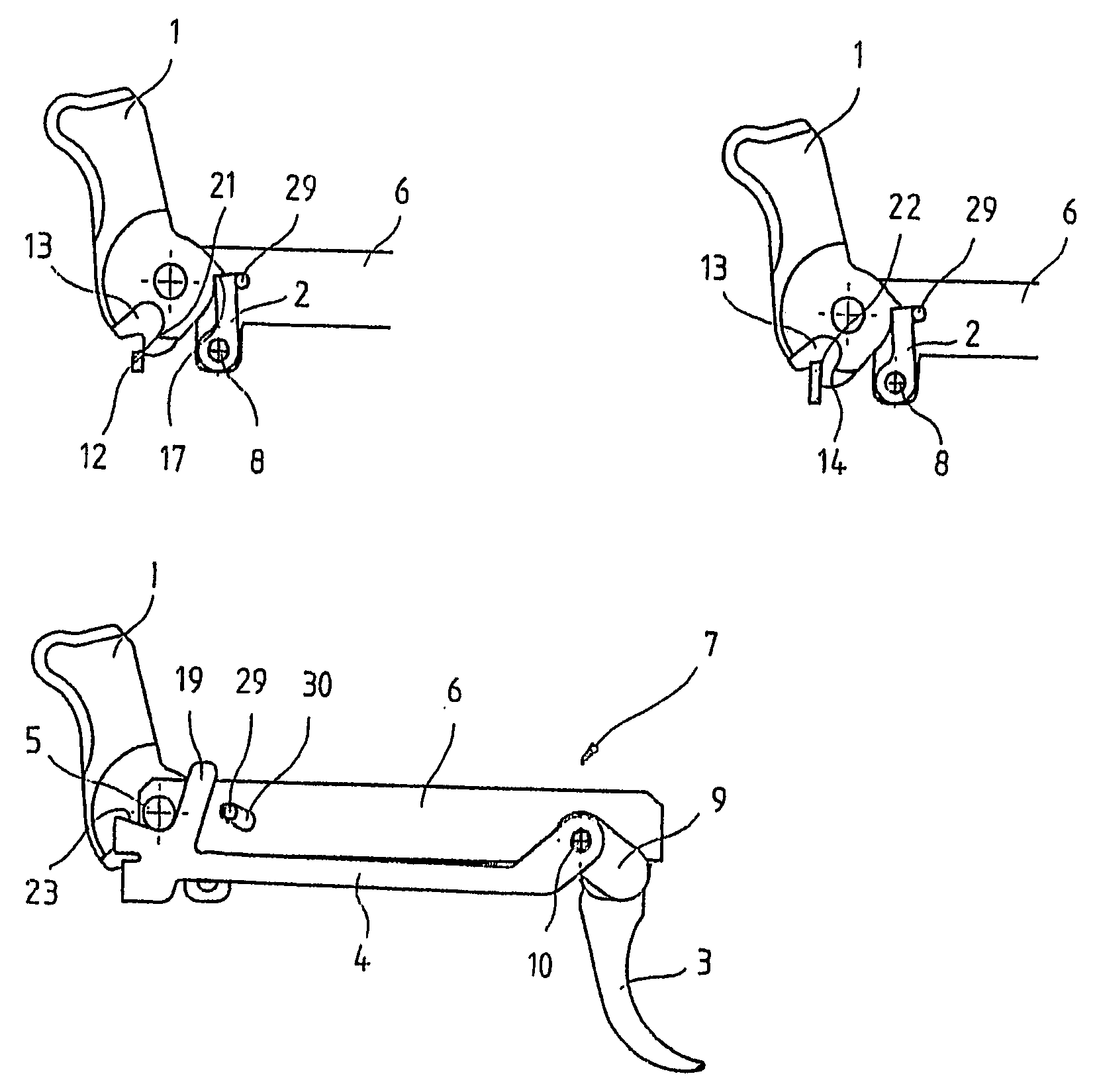
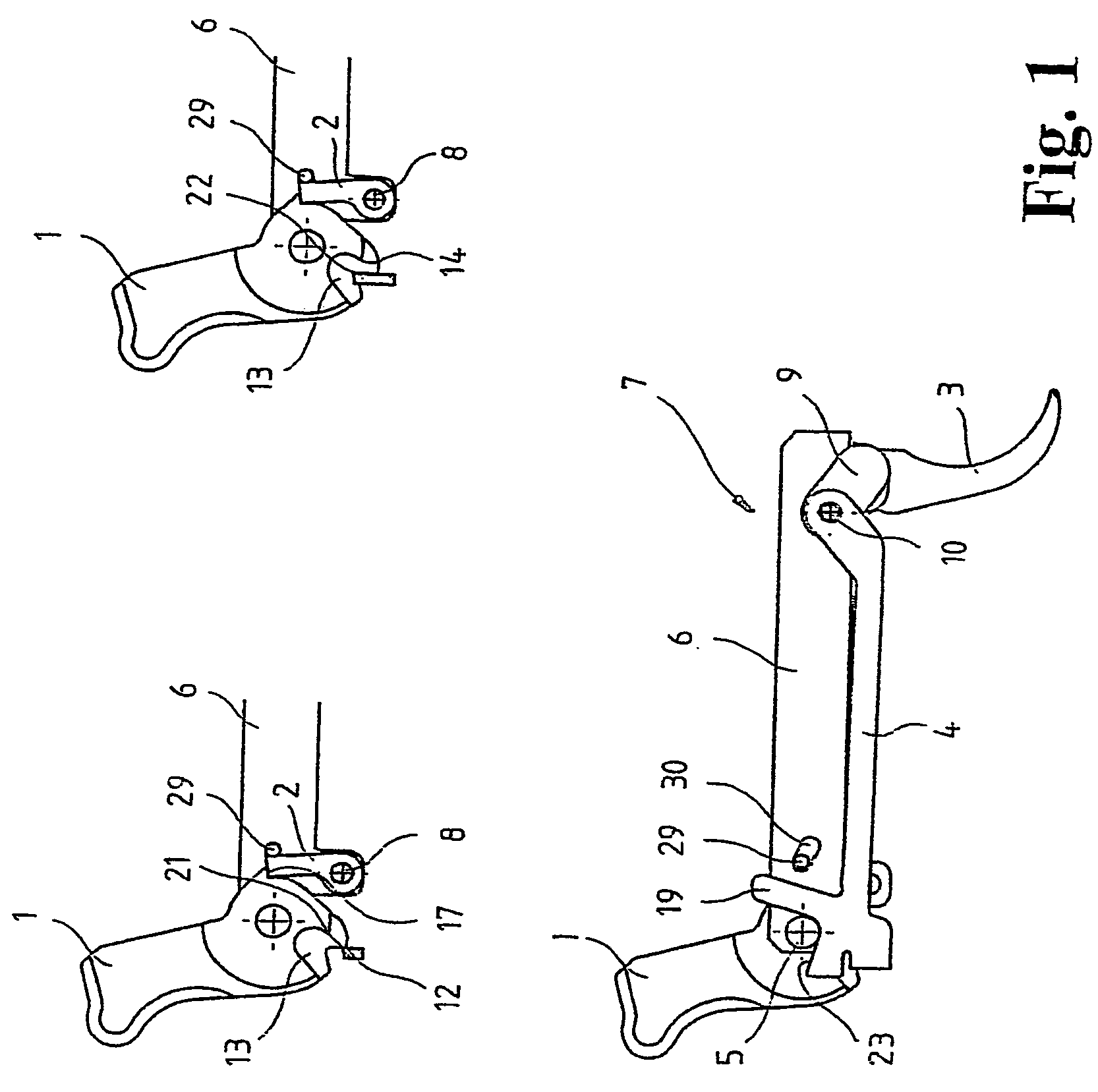
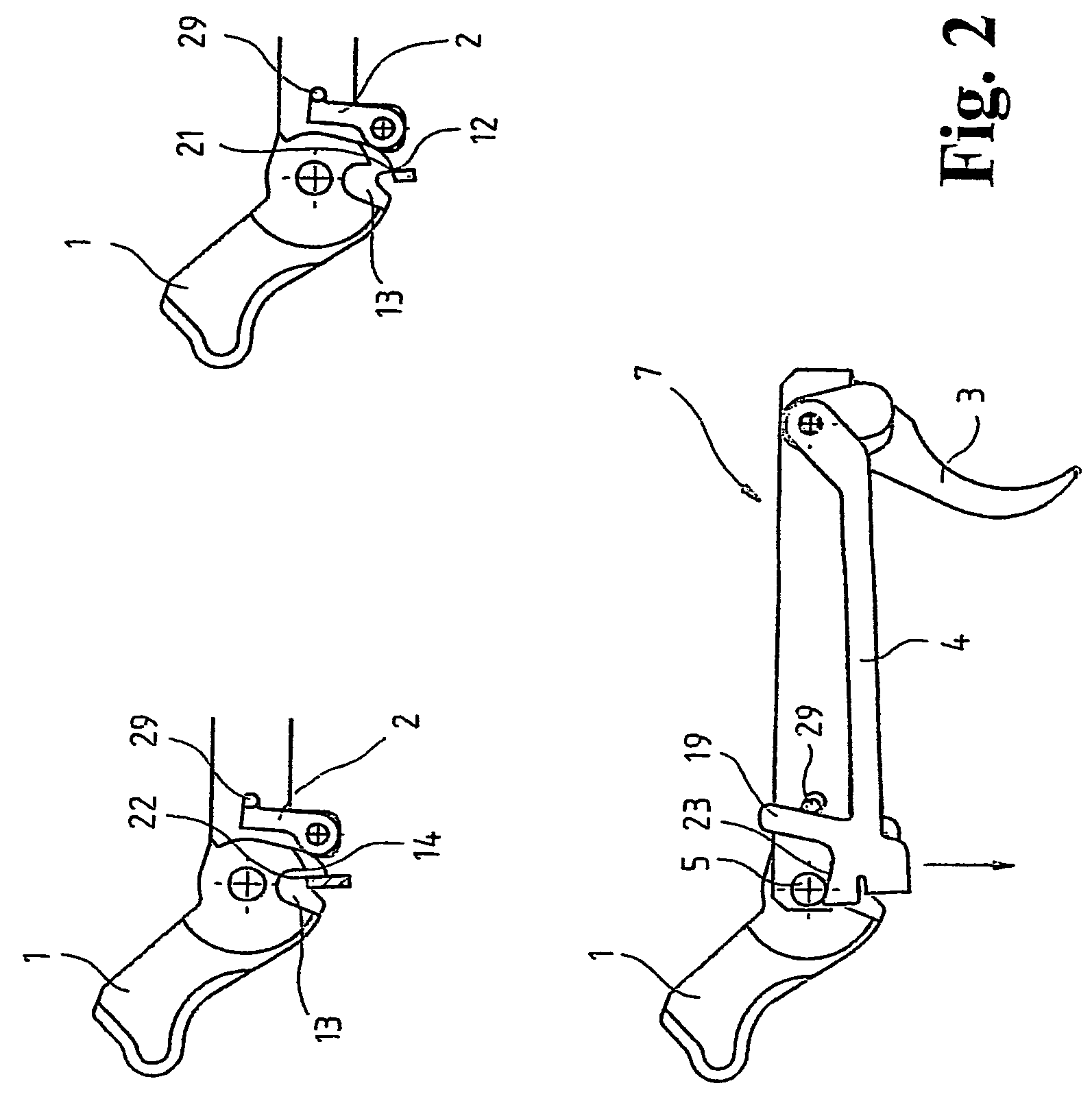
Trigger system for small arms
InactiveUS7213358B2High expenditure of forceHigh expenditureFiring/trigger mechanismsBreech mechanismsMechanical engineeringSmall arms
The invention relates to a trigger system for small arms, said system including a hammer, a catch associated with the hammer, a trigger, and a trigger bar which cooperates with the trigger and has a first locking edge for engaging with a first fire locking element of the hammer. The aim of the invention is to create a trigger system which has a low trigger resistance and remains operable even in the event of firing failure. To this end, the trigger bar has a second locking edge for engaging with a second fire locking element of the hammer.
Owner:T SWISS ARMS TECH
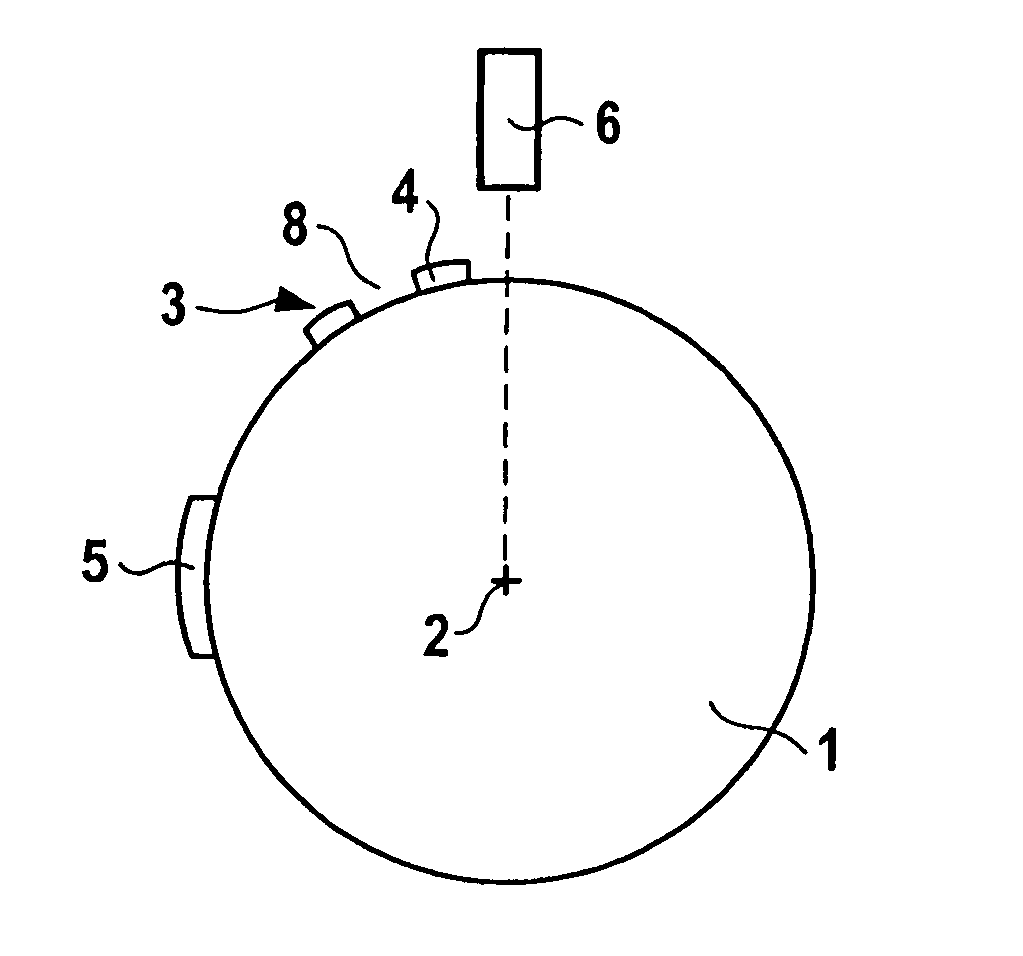
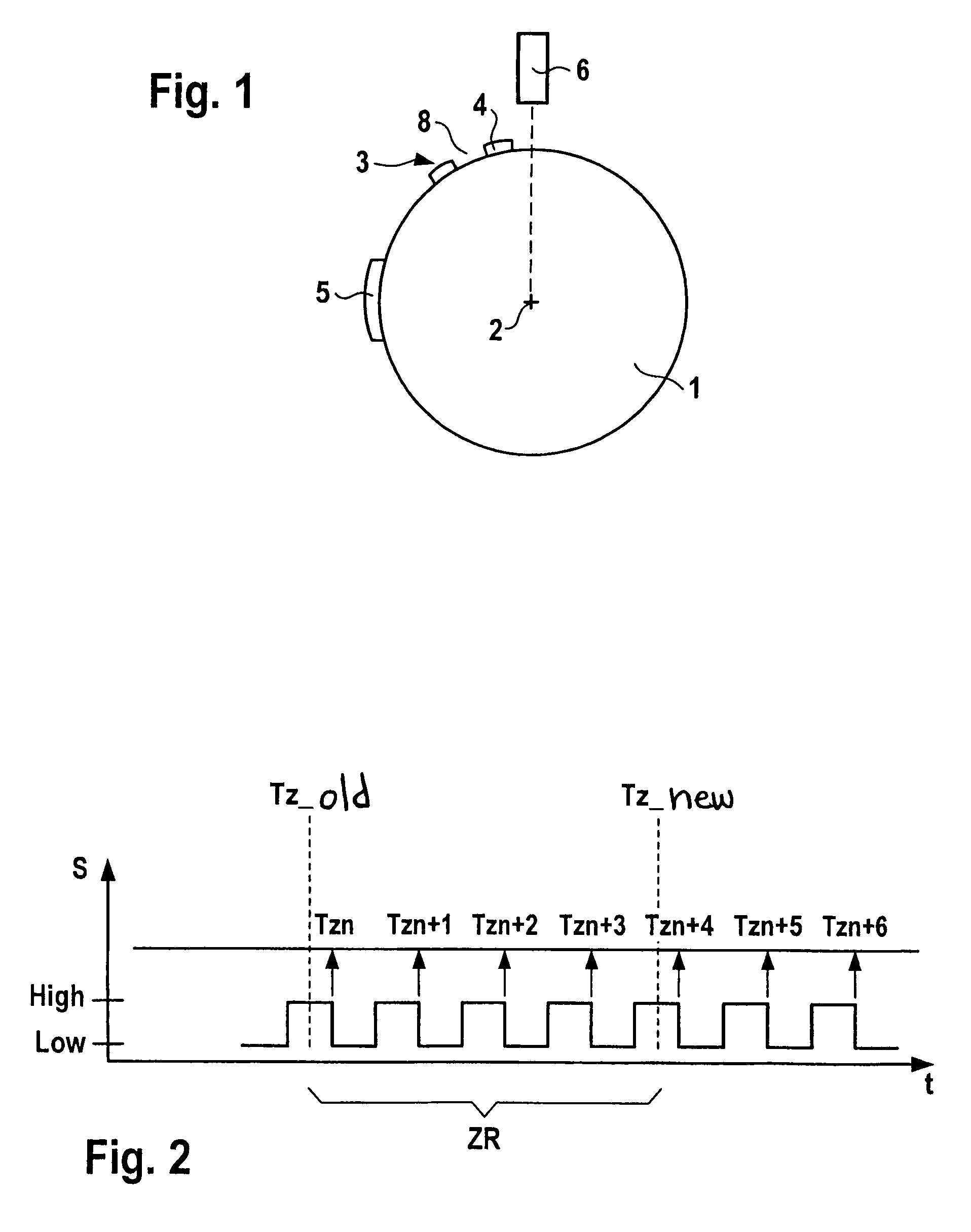
Method for measuring the rotational speed of a crankshaft
InactiveUS7082363B2Low implementation costHigh expenditureAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlControl cellInternal combustion engine
In a method for determining the rotational speed of the crankshaft of an internal combustion engine having a sensor disk which is connected to a crankshaft of the internal combustion engine, the sensor disk having a marking via a system of alternating teeth and tooth spaces, and a first sensor assigned to the sensor disk generating an electrical signal which is able to assume at least two signal levels, one of the signal levels being assigned to a tooth and the other being assigned to a tooth space, the accuracy of the rotational speed determination is increased in that the rotational speed of the crankshaft is determined by the control unit from the angle between two markings divided by the time elapsed between the two markings; additional markings may be situated between the two markings and the number of markings which are situated between the two markings is a function of the rotational speed.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
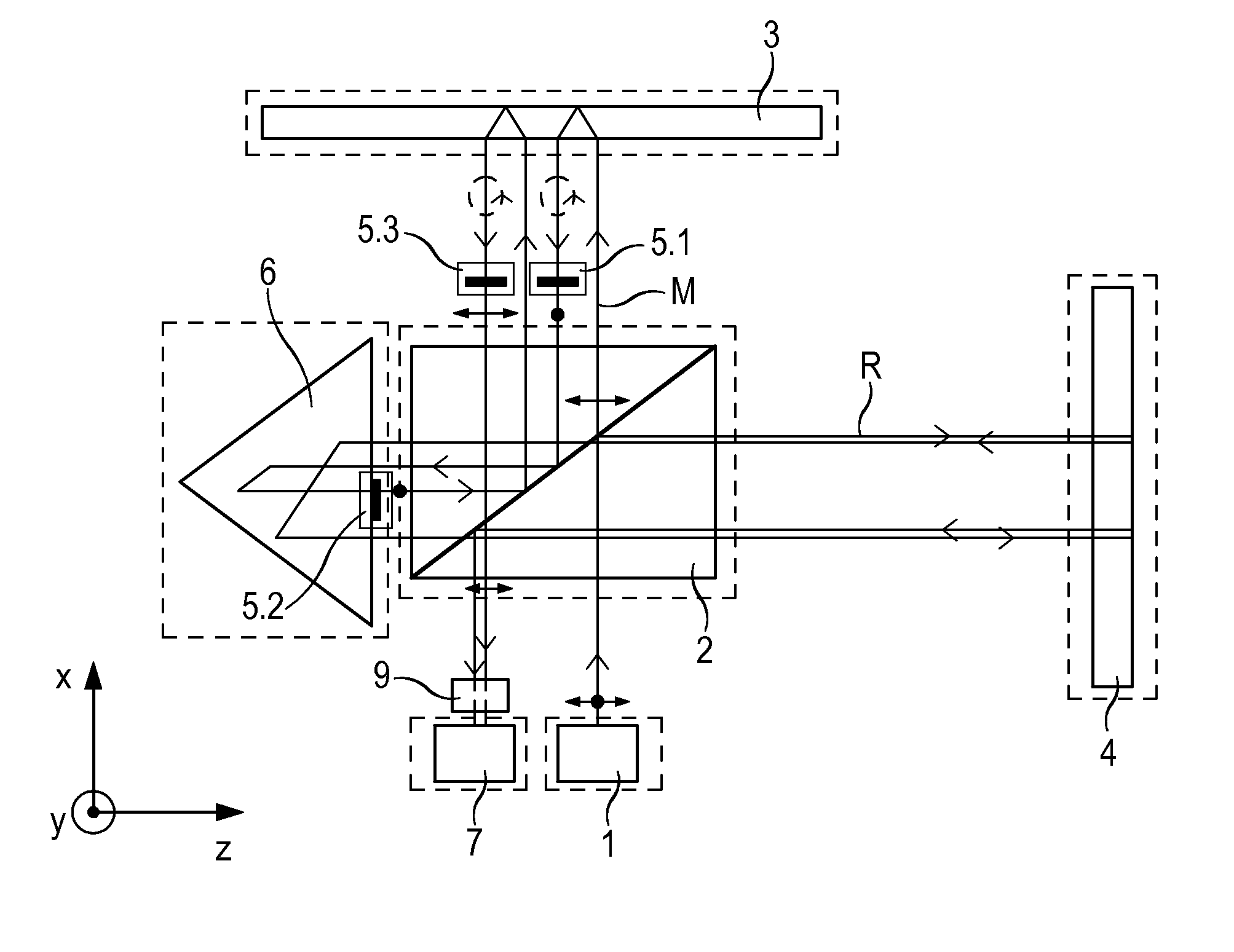
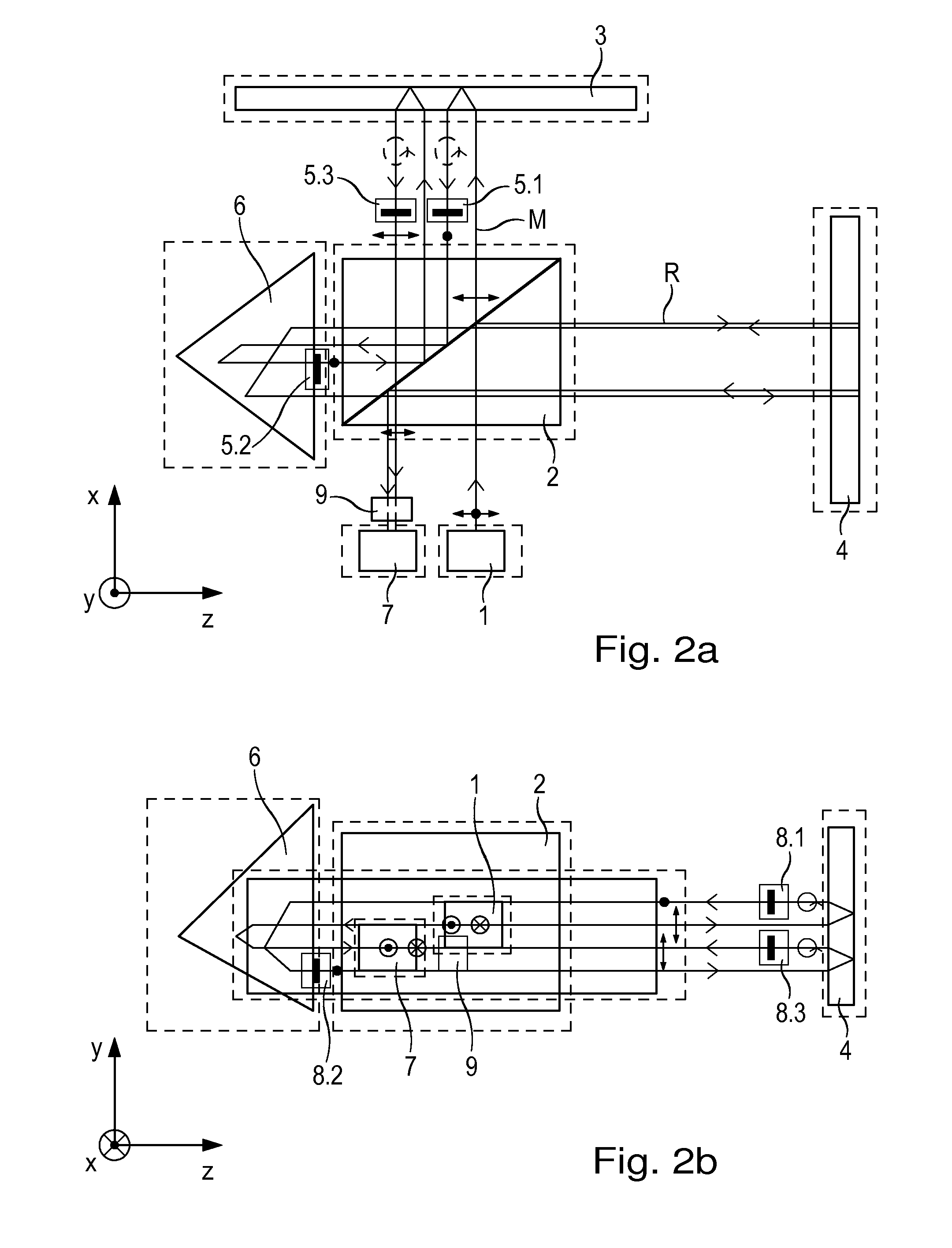
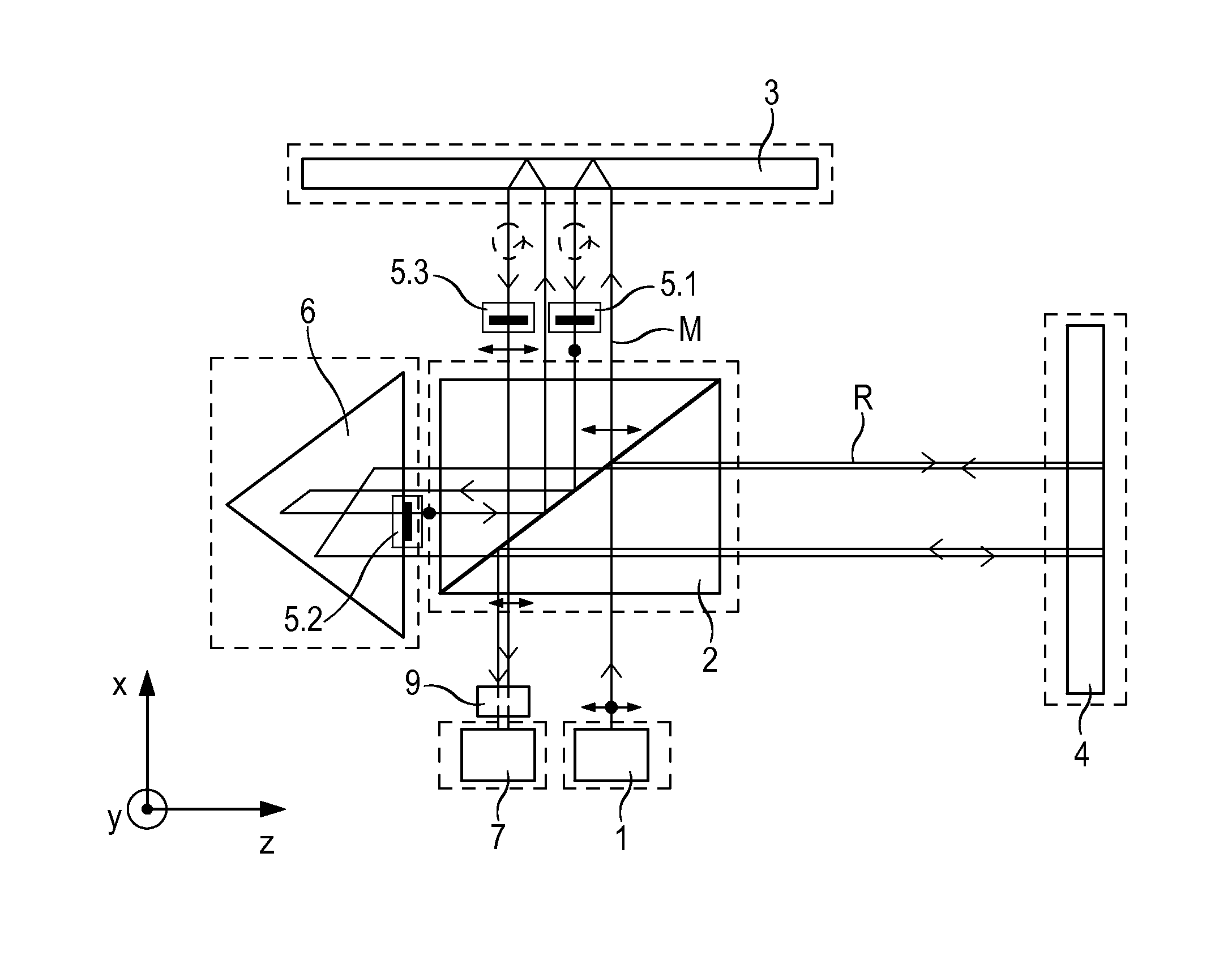
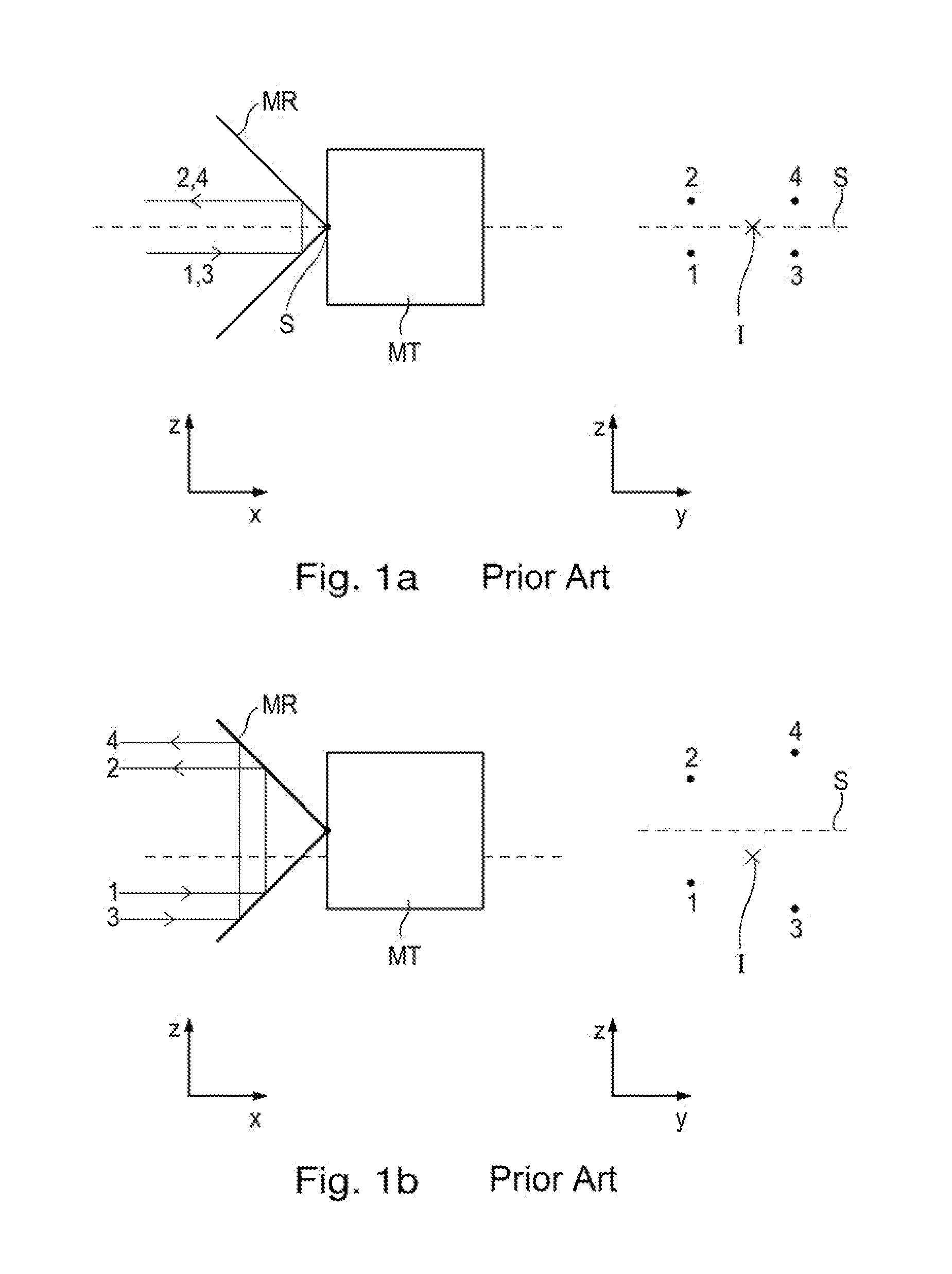
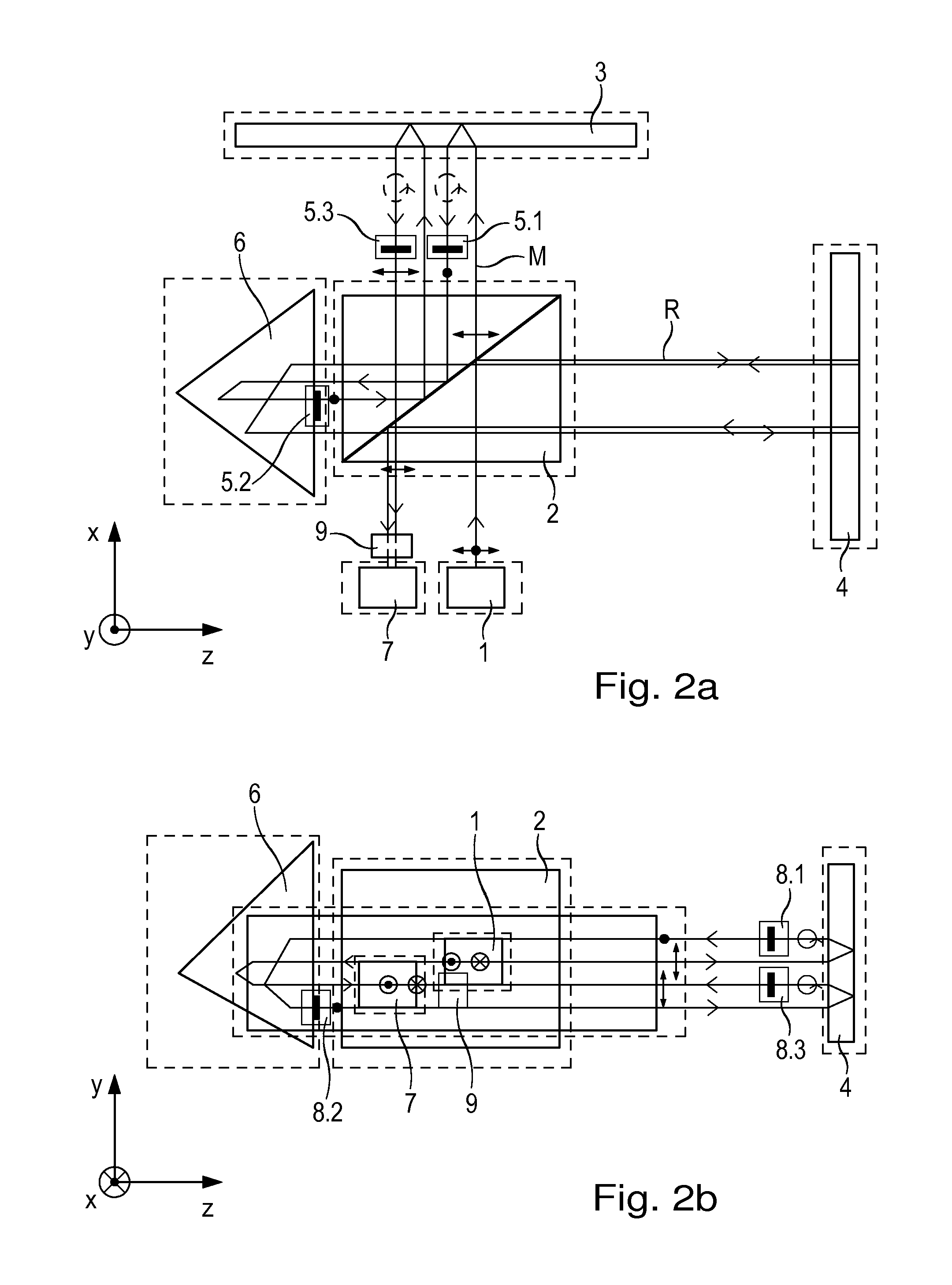
Interferometer
ActiveUS9188424B2Periodic signal errors are sufficiently minimizedThe solution result is accurateUsing optical meansGratingBeam splitter
An interferometer includes a light source and a beam splitter, via which the beam of rays emitted by the light source is split into a measurement beam and a reference beam. The measurement beam propagates in a measuring arm extending in a first direction between the beam splitter and a measuring reflector. The measuring reflector brings about an offset perpendicular to the direction of incidence between the measurement beam falling on it and the measurement beam reflected back by it. In a reference arm extending in a second direction, the reference beam propagates between the beam splitter and a reference reflector. In addition, the interferometer has a detector system, to which the superposed and recombined measurement beam and reference beam are able to be supplied, and via which a distance-dependent interference signal with respect to the position of the measuring reflector is able to be generated. The measuring reflector in each case includes at least one transmission grating as well as a reflector element.
Owner:DR JOHANNES HEIDENHAIN GMBH
Interferometer
ActiveUS20140176962A1Periodic signal errors are sufficiently minimizedThe solution result is accurateUsing optical meansBeam splitterGrating
An interferometer includes a light source and a beam splitter, via which the beam of rays emitted by the light source is split into a measurement beam and a reference beam. The measurement beam propagates in a measuring arm extending in a first direction between the beam splitter and a measuring reflector. The measuring reflector brings about an offset perpendicular to the direction of incidence between the measurement beam falling on it and the measurement beam reflected back by it. In a reference arm extending in a second direction, the reference beam propagates between the beam splitter and a reference reflector. In addition, the interferometer has a detector system, to which the superposed and recombined measurement beam and reference beam are able to be supplied, and via which a distance-dependent interference signal with respect to the position of the measuring reflector is able to be generated. The measuring reflector in each case includes at least one transmission grating as well as a reflector element.
Owner:DR JOHANNES HEIDENHAIN GMBH
Method and apparatus for grinding a continuously casting product
InactiveUS8708775B2Reduce cakingQuality improvementEdge grinding machinesWork treatment devicesMetallurgyTreatment use
The invention relates to a method for grinding a continuous casting product (1), in particular a slab, wherein the continuous casting product (1) in the cross-section has a rectangular contour comprising two long sides (2, 3) disposed opposite of each other and two short sides (4, 5) disposed opposite of each other, wherein in a working position (A), in which the continuous casting product (1) rests on a grinding table (6) with one of the long sides (2) thereof, one of the long sides (2) of the continuous casting product (1) is subjected to a surface treatment by means of at least one grinding tool (7). In order to achieve a higher quality in a simple and fast manner when working the continuous casting product and to be able to collect the grinding chips in a simple manner in the process, after or before grinding the long side (2) of the continuous casting product (1) in the working position (A), according to the invention at least one of the short sides (4, 5) is subjected to a surface treatment using the at least one grinding tool (7). The invention further relates to a device for grinding a continuous casting product (1).
Owner:SMS LOGISTIKSYST
Process for dissolving used paper
InactiveUS6391151B2Easy to tearImprove solubilityFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpPaper recyclingHeavy particlePulp and paper industry
Owner:VOITH PATENT GMBH
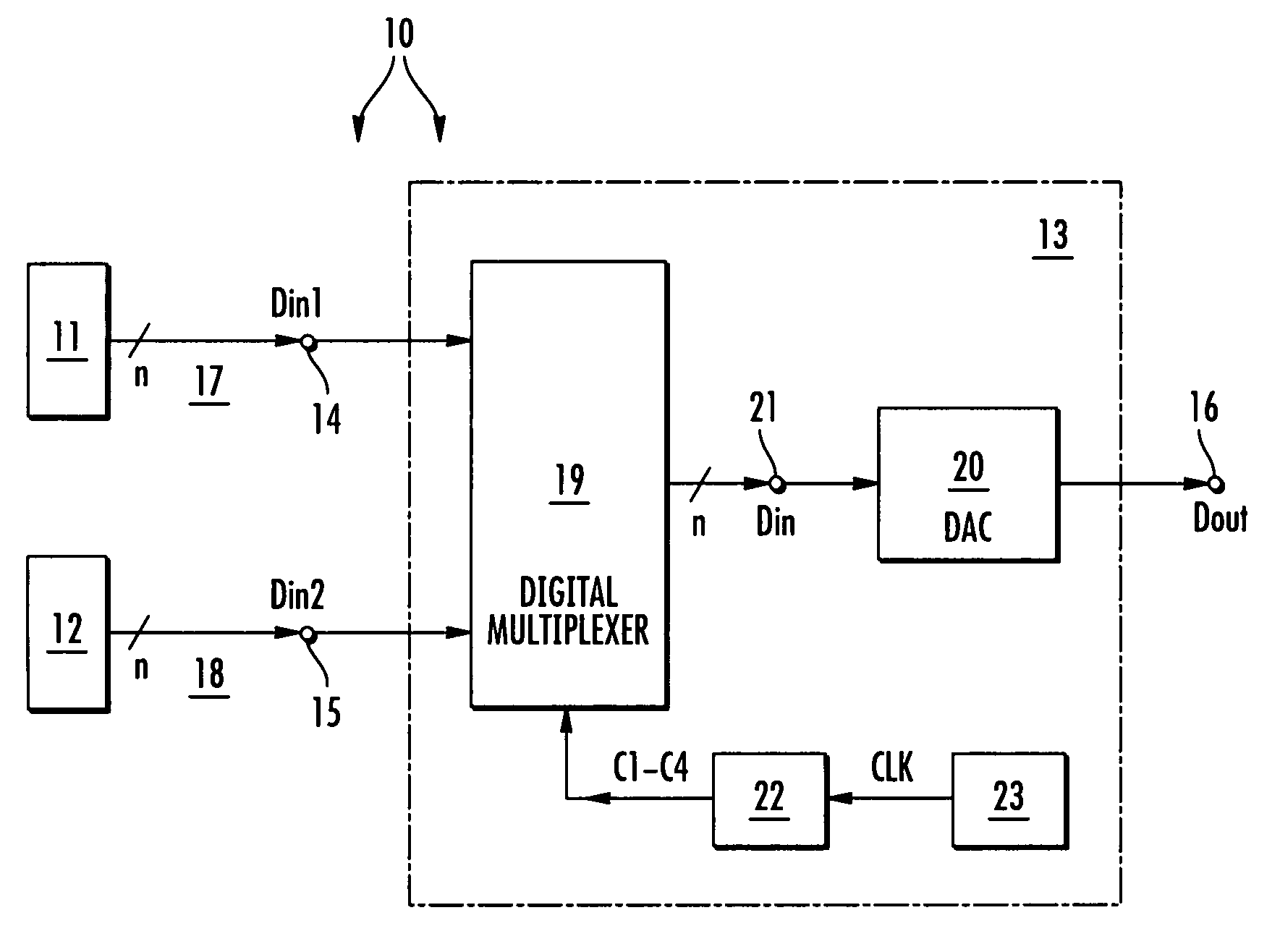
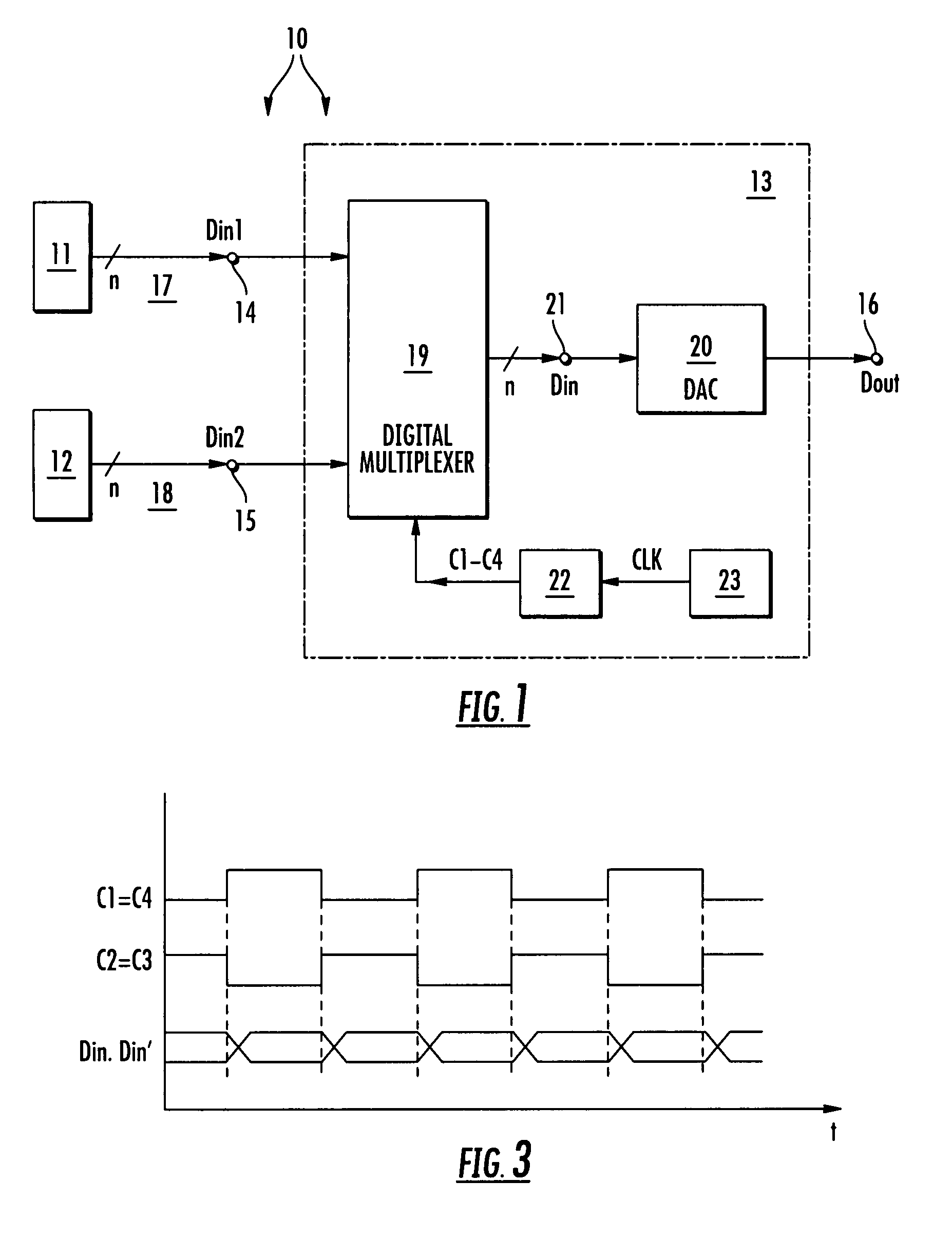
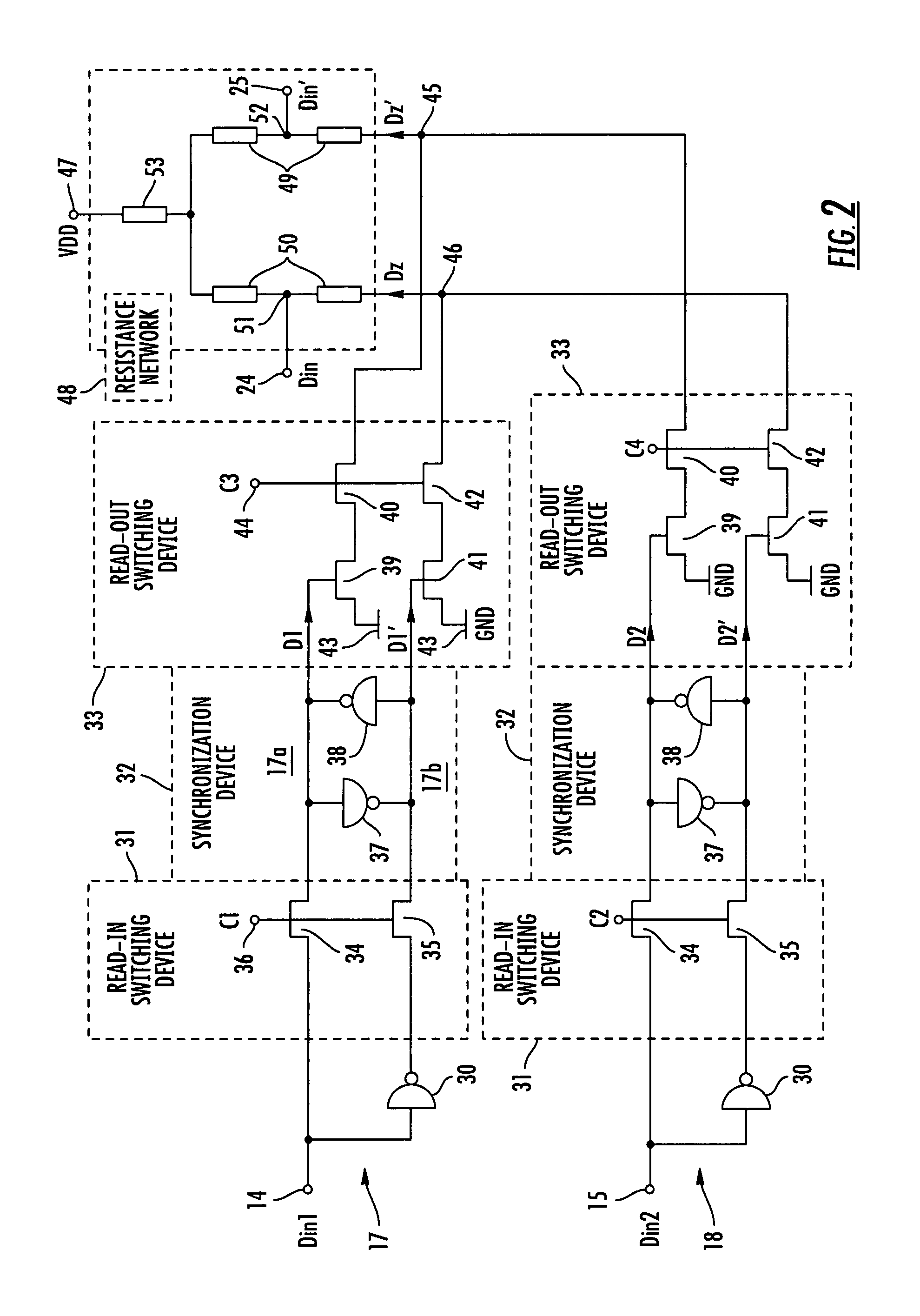
Multi-channel digital/analog converter arrangement
ActiveUS7427937B2Increase data rateHigh expenditureElectric signal transmission systemsElectronic switchingDigital dataMultiplexer
A multi-channel digital / analog converter arrangement comprises at least two data channels for receiving and forwarding a corresponding number of digital data input signals comprising respective time characteristics, a digital multiplexer generating a digital intermediate signal present at a common node by combining the at least two digital data input signals, and a digital / analog converter connected downstream of the multiplexer for converting the digital intermediate signal into an analog output signal. The multiplexer comprises a tuning device for tuning the time characteristics of the at least two digital data input signals in respect to each other.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com