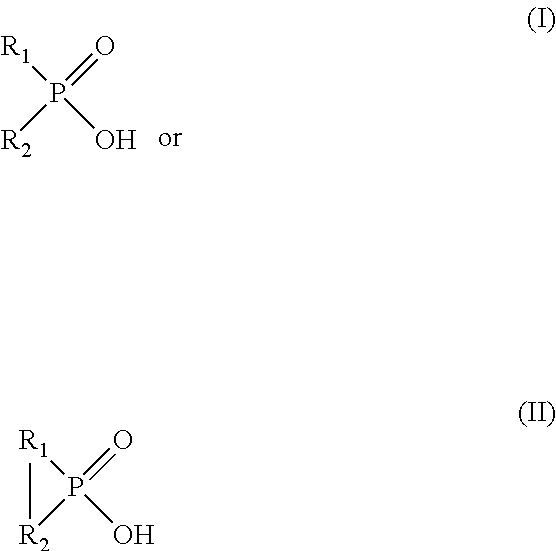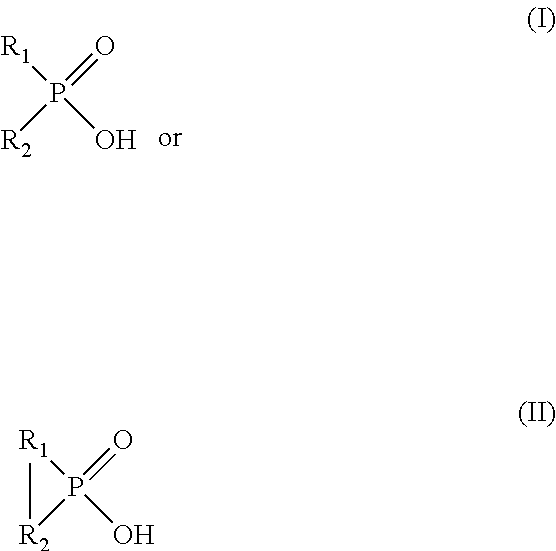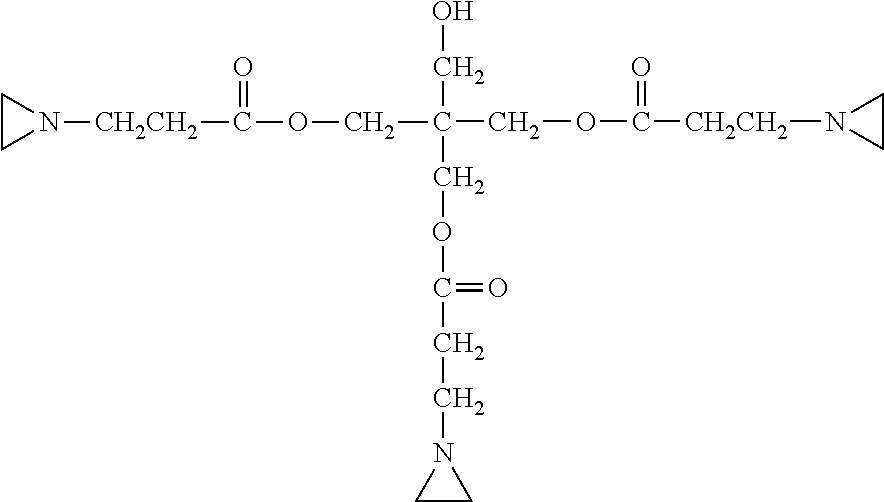Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34results about How to "Efficient and economical manner" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
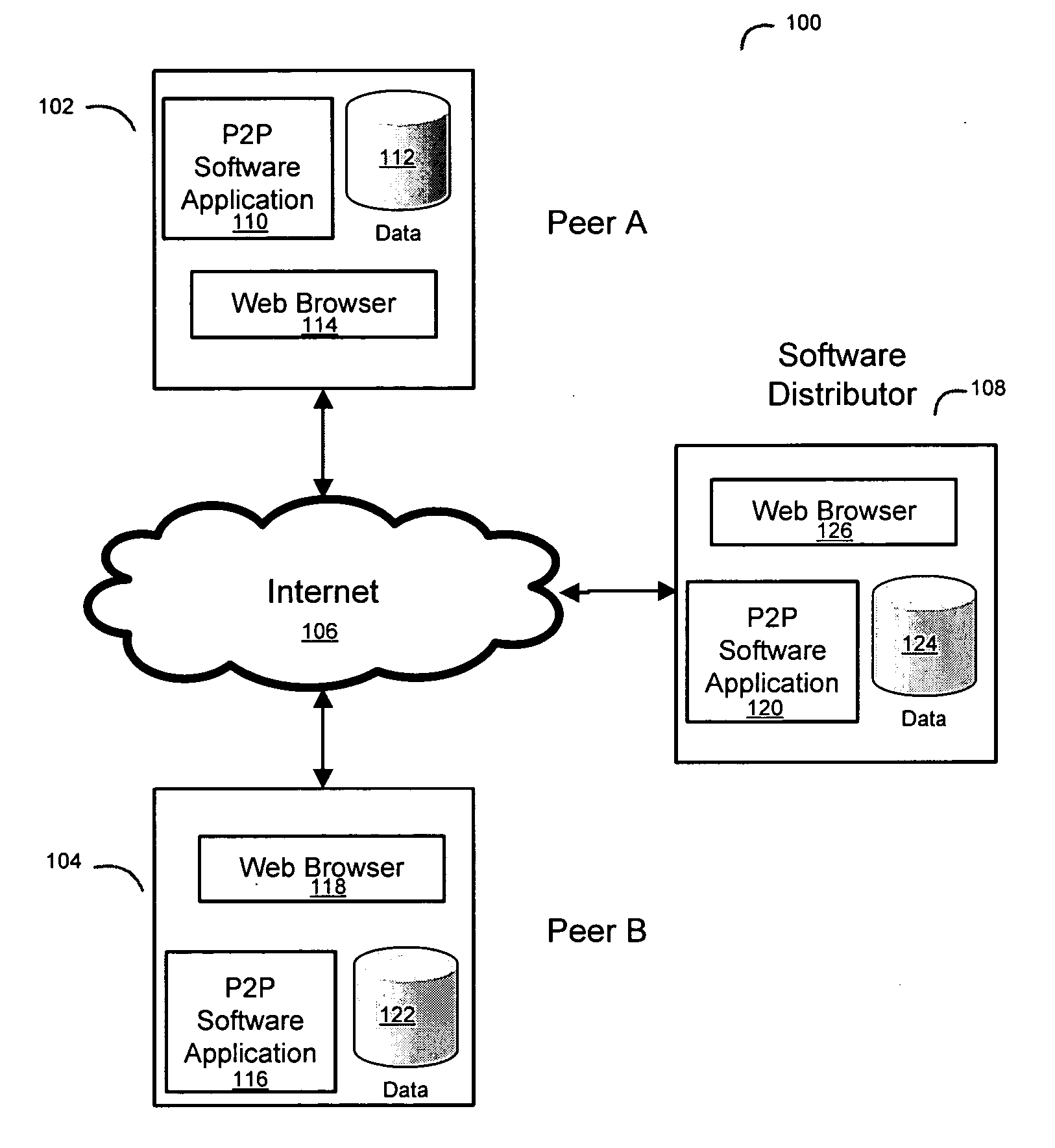
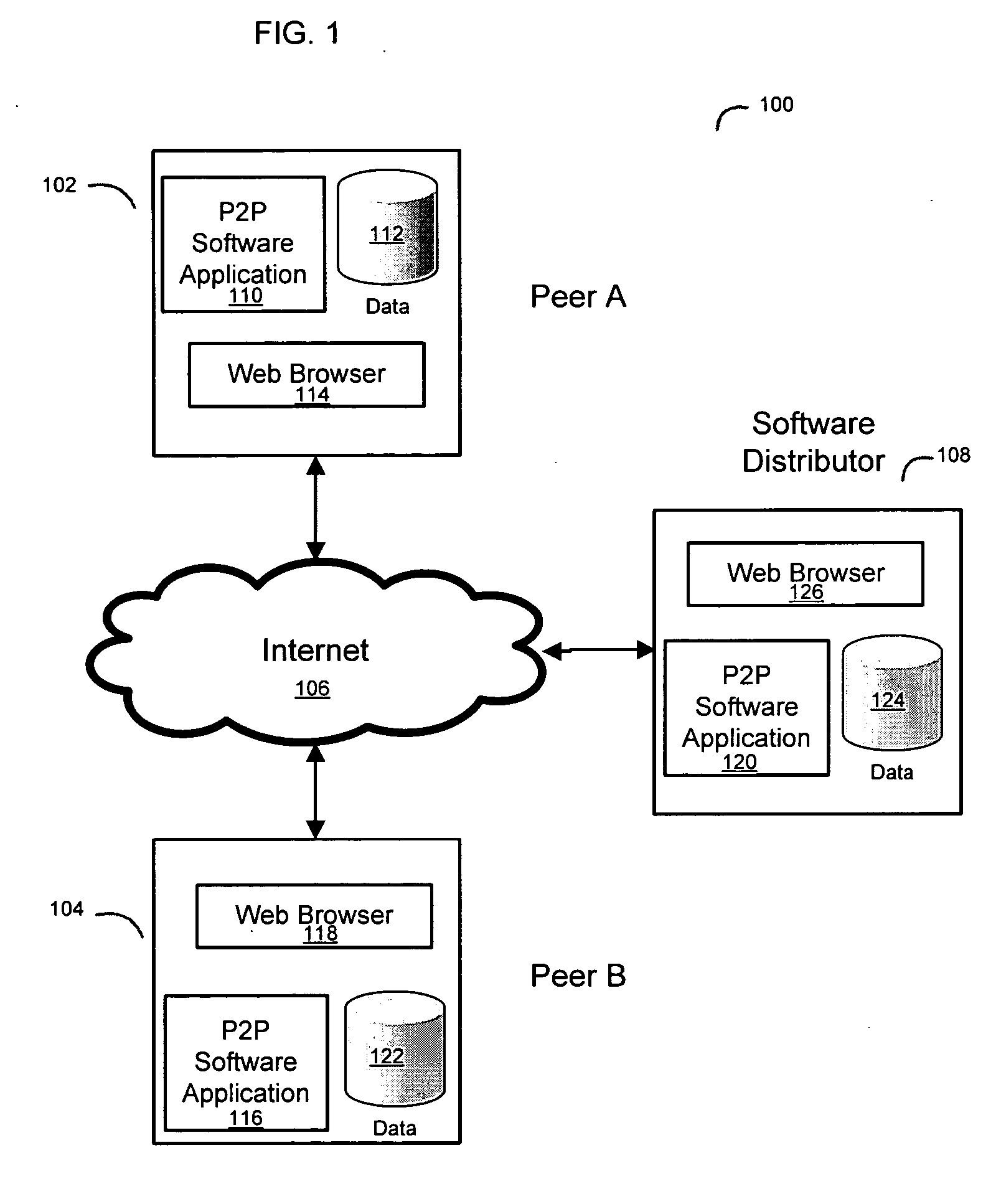
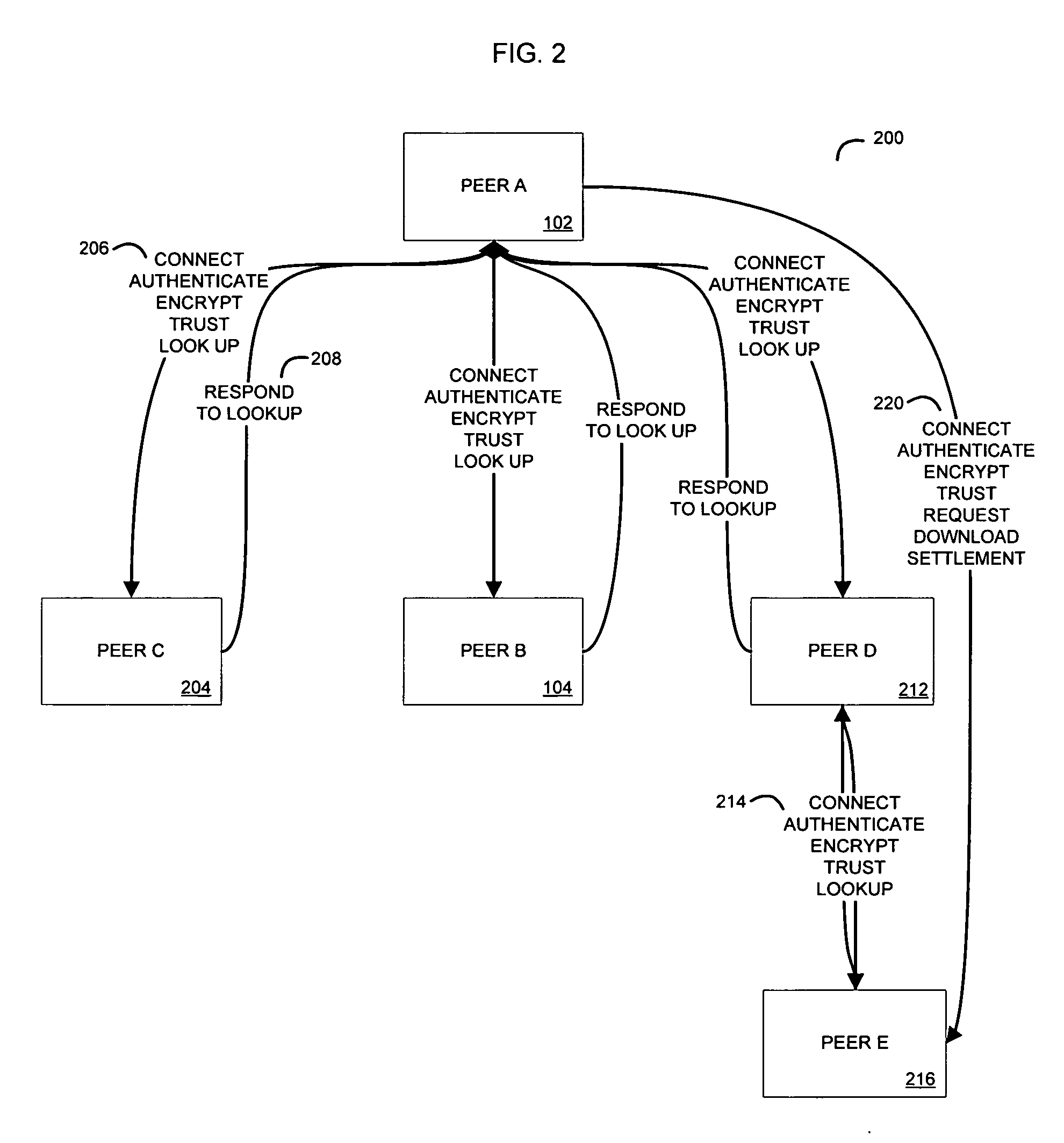
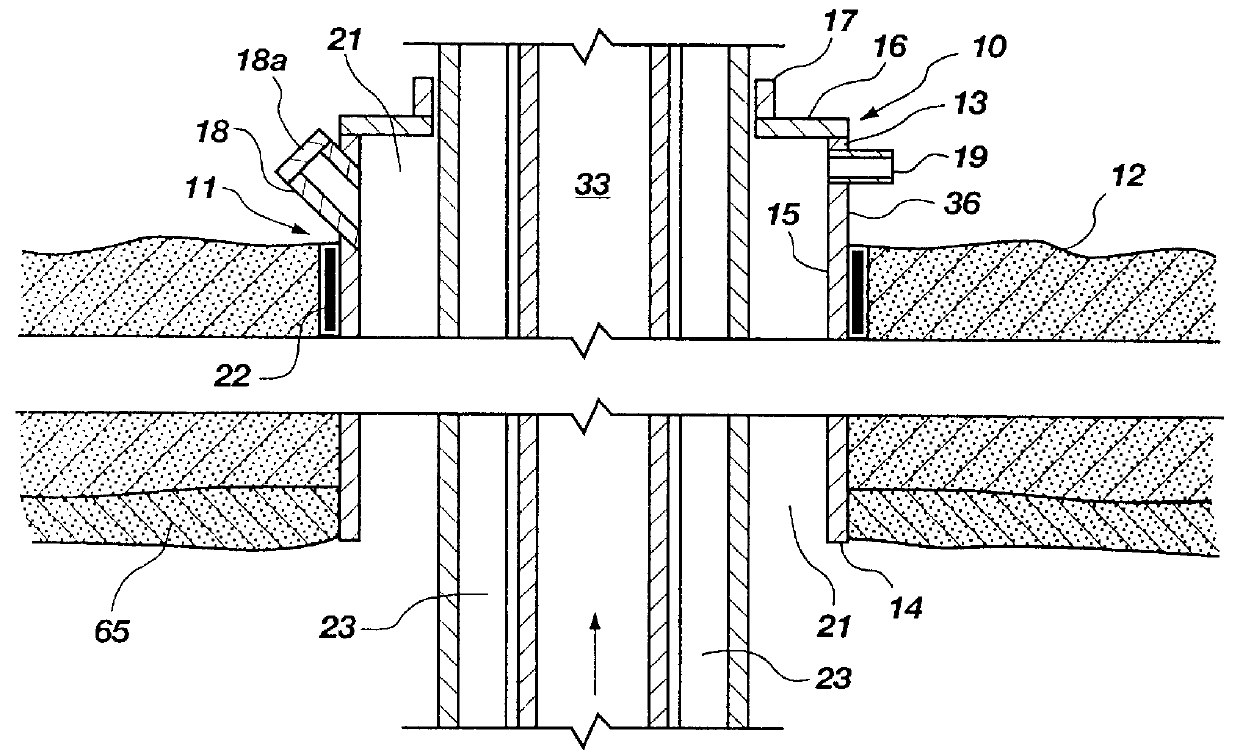
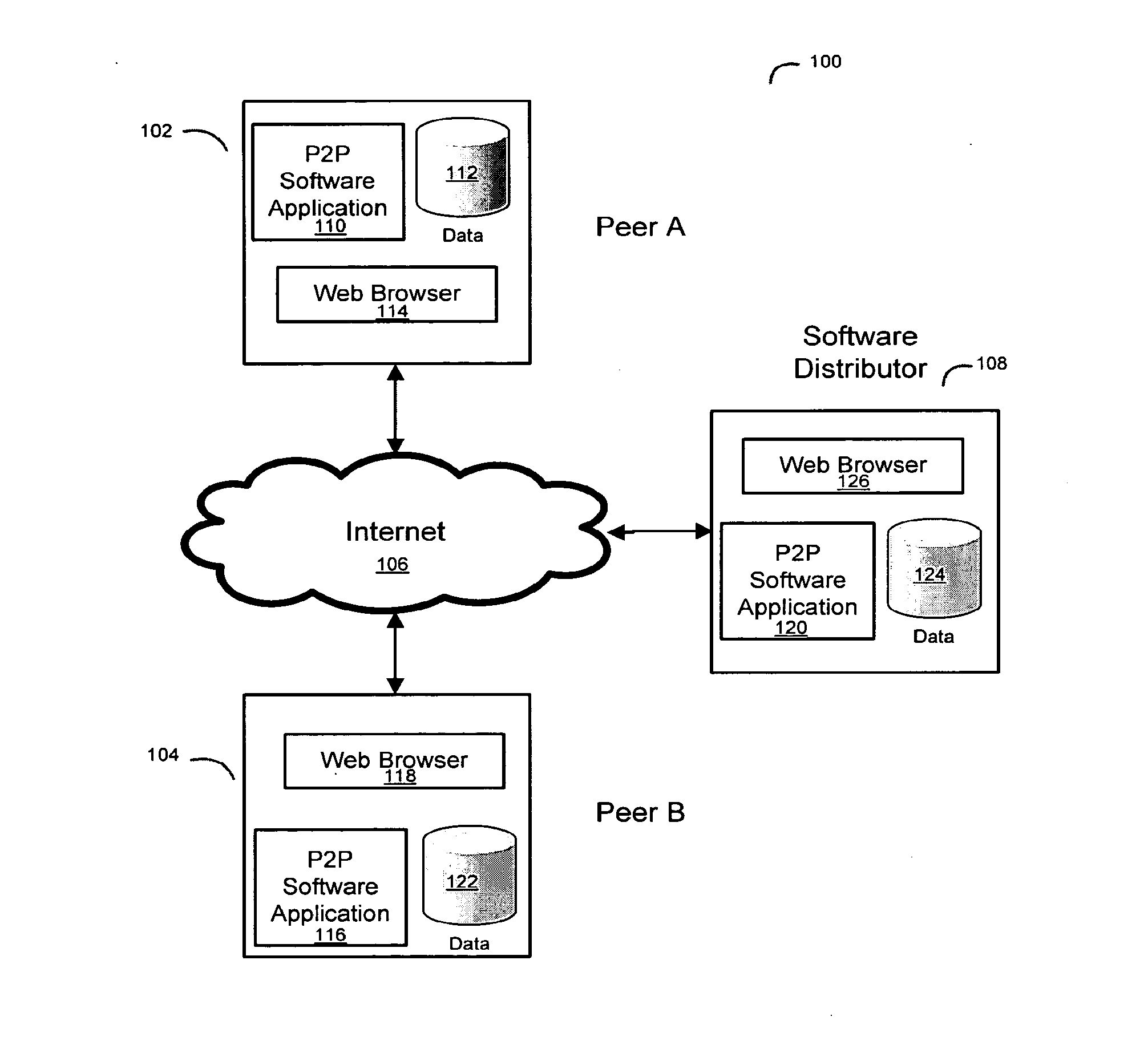
System and method for a peer to peer exchange of consumer information
InactiveUS20060277092A1Facilitate communicationEfficient and economical mannerDigital data information retrievalFinancePaymentInvoice
Using peer-to-peer networking to exchange consumer information in a secure environment. The seeker of consumer information transmits an encrypted query to authenticated and trusted peers which includes legal representations stating the legally permissible purpose for seeking the information. A peer, acting as a maintainer of consumer information, determines if the query matches any consumer information held by the maintainer. The maintainer then informs the seeker of the results of the match, the type of information available, the data format, and the price for such consumer information. A payment invoice can be generated and electronically presented by maintainer. The payment may be electronically debited from the designated account of seeker and remitted to maintainer. In addition, a portion of such funds may be delivered to an entity which maintains the peer-to-peer software.
Owner:CREDIGY TECH
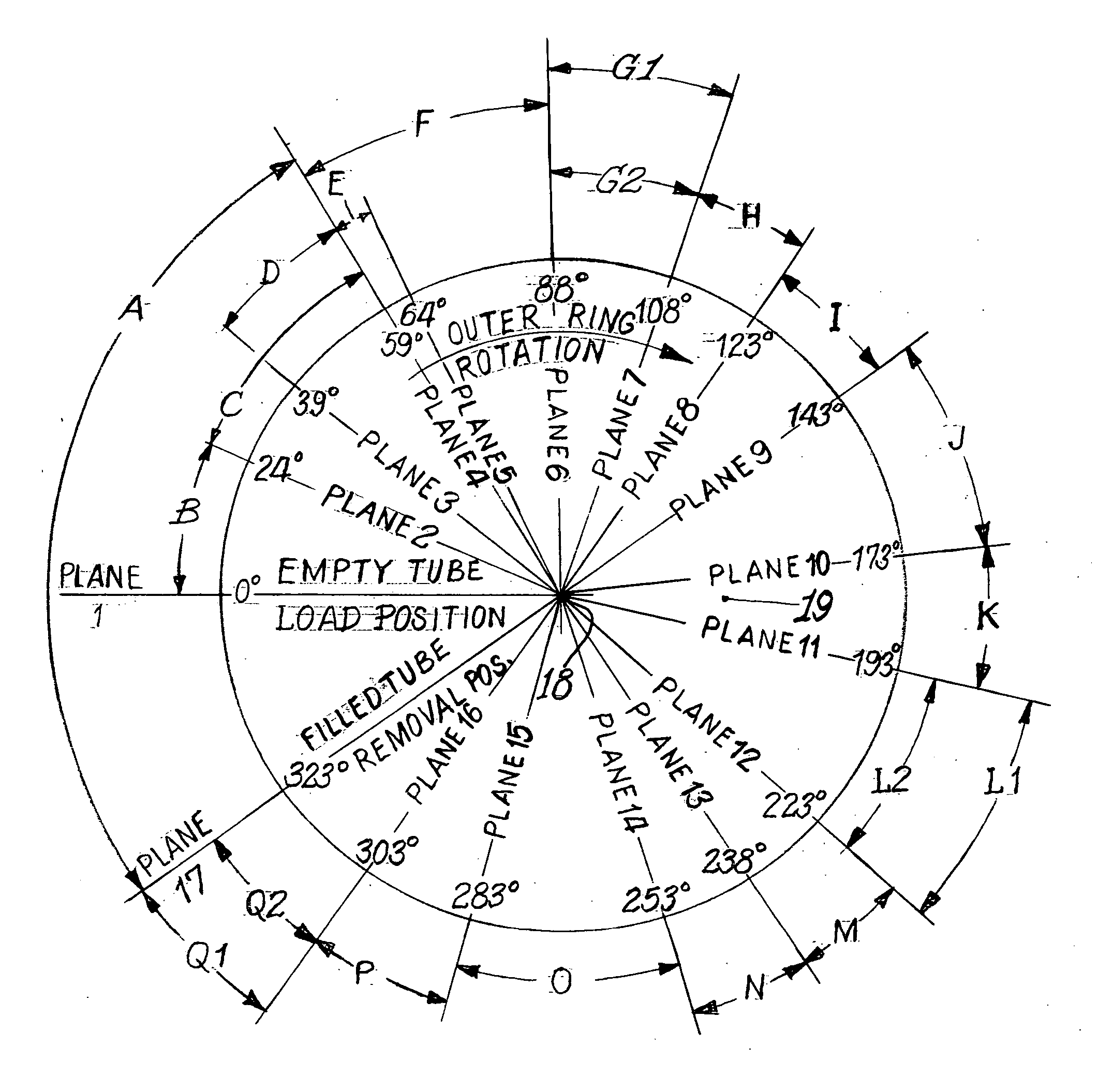
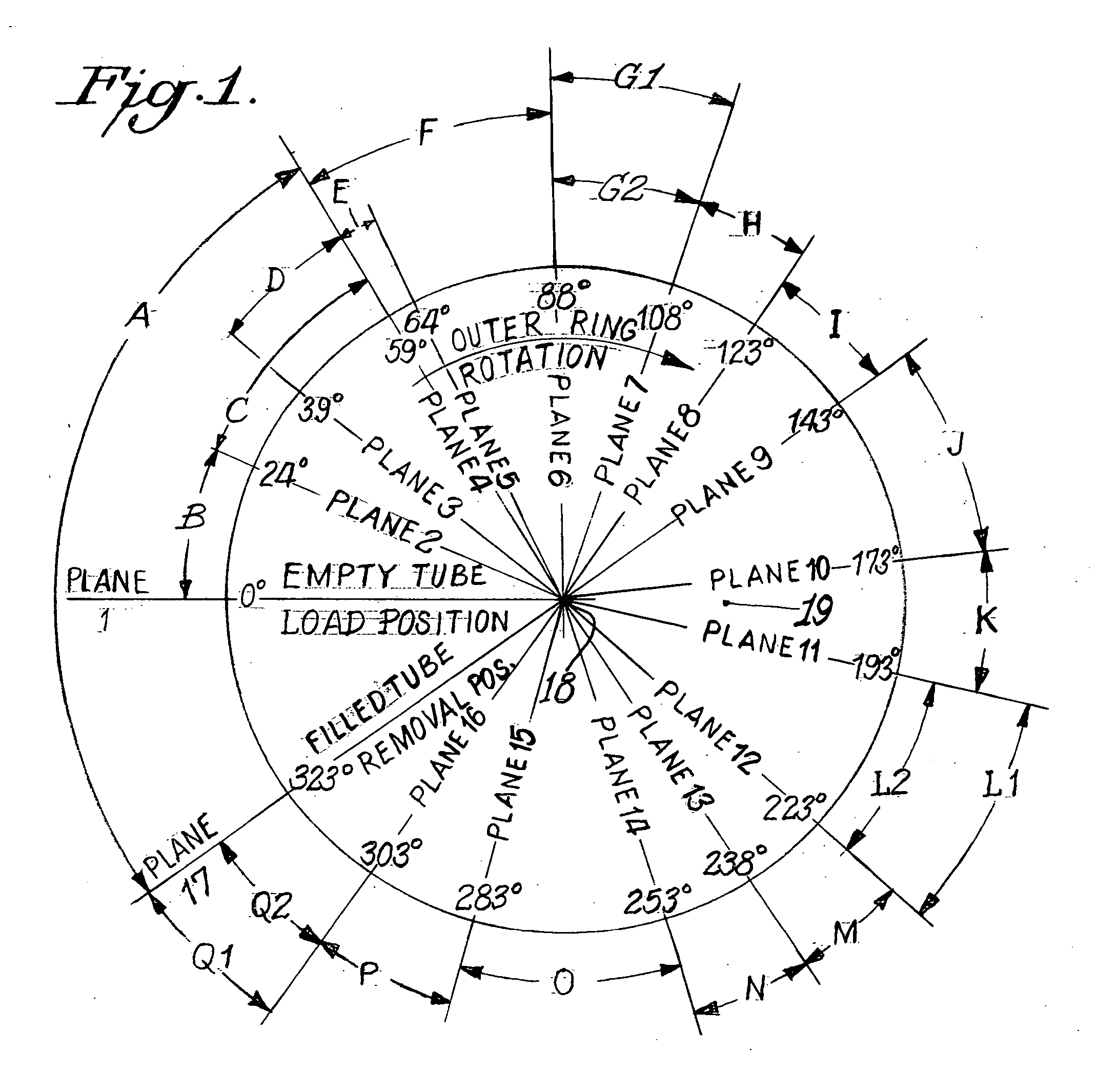
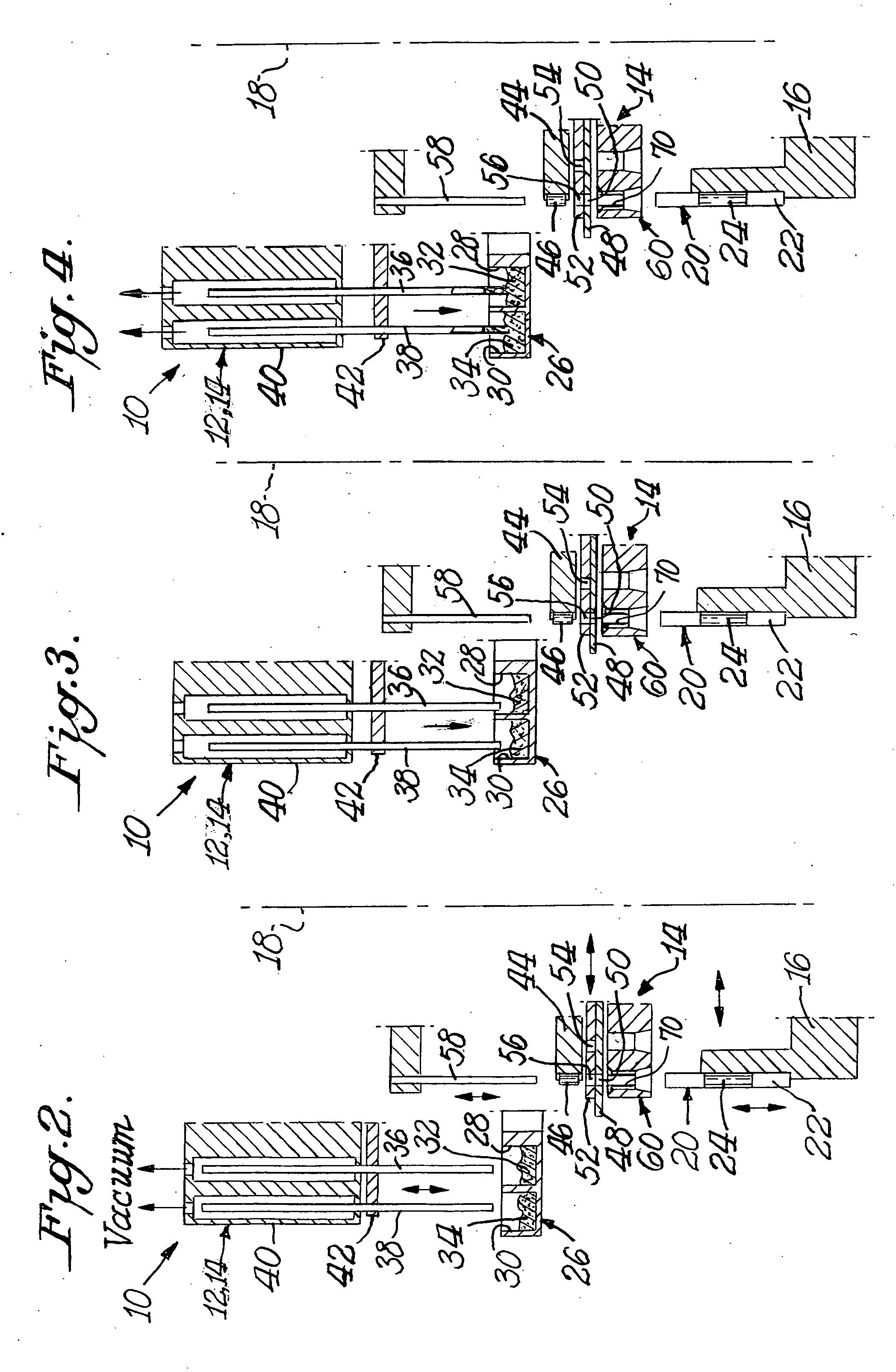
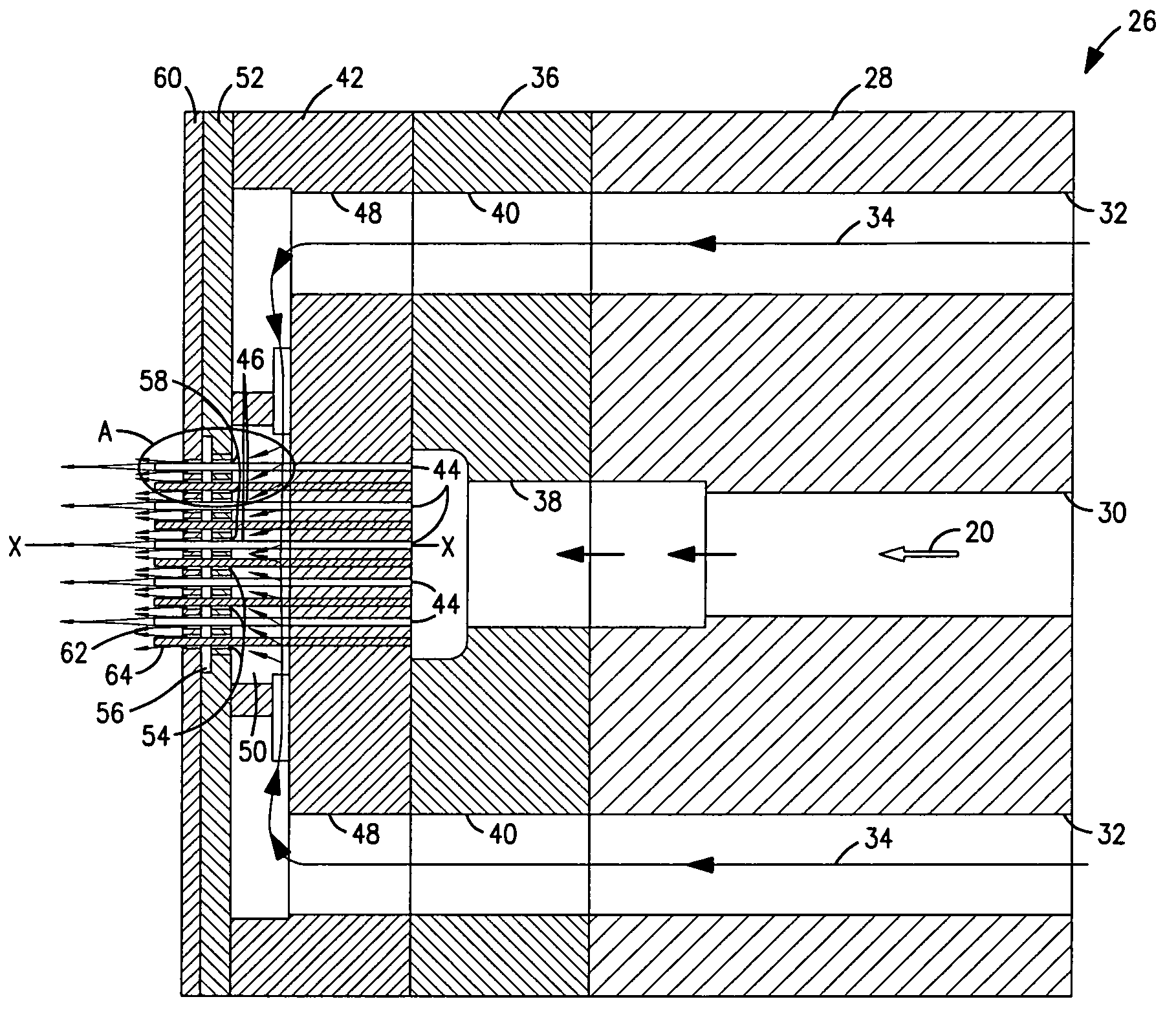
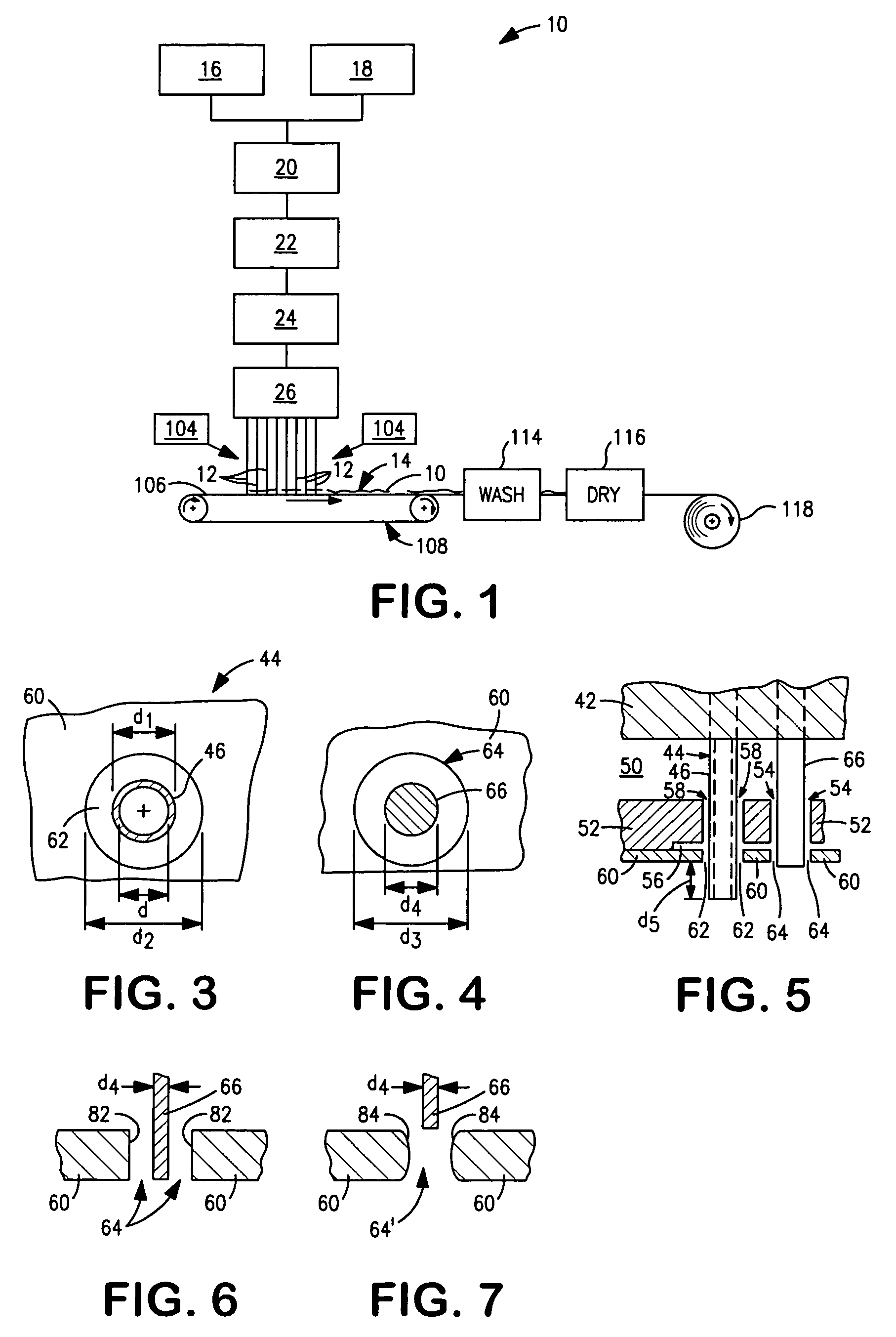
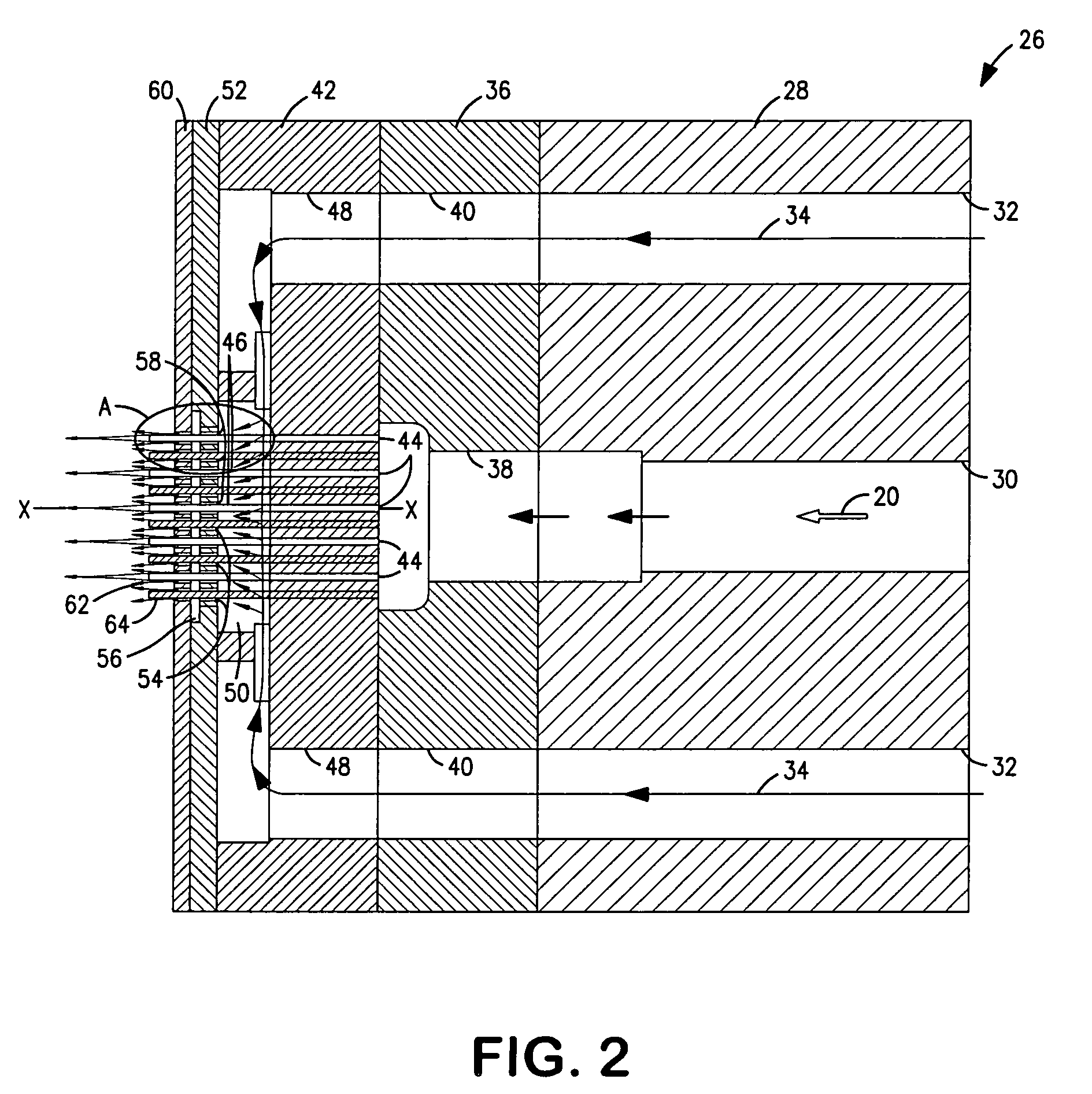
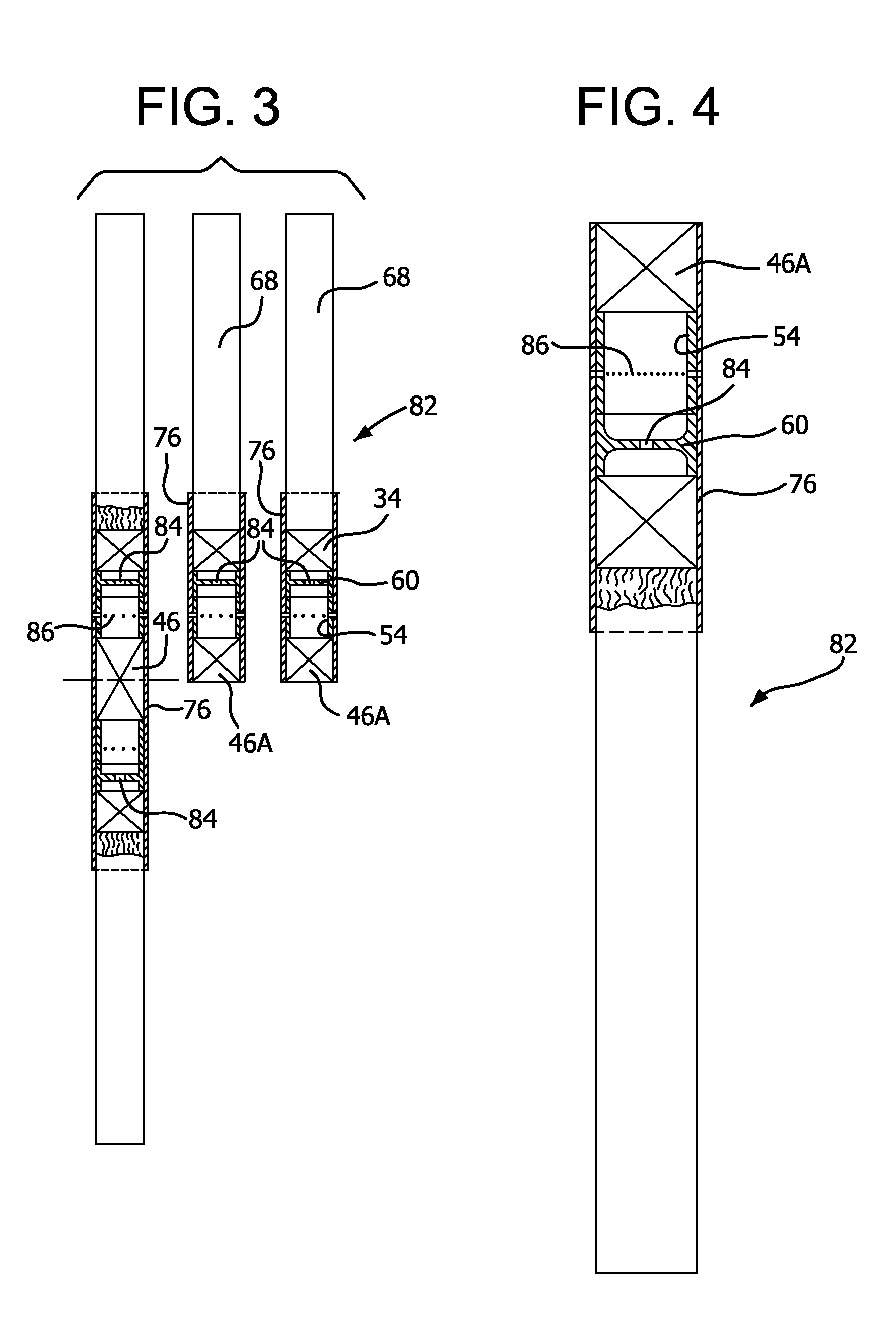
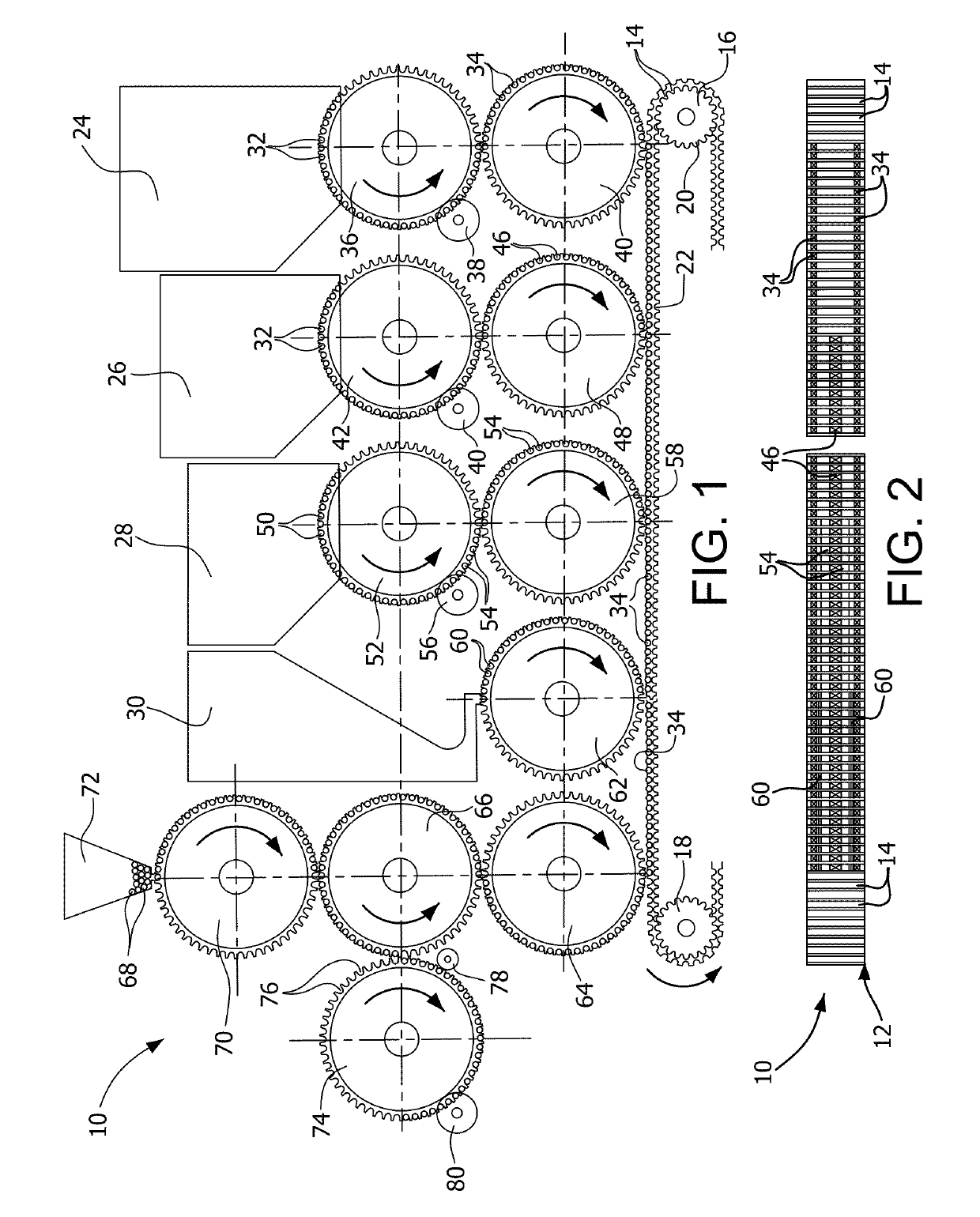
Vertical filter filling machine and process
ActiveUS20060112963A1Efficient and economical mannerIncrease chanceTobacco treatmentPaper/cardboard wound articlesVertical filterFilter material
Process and apparatus for the mass production of compound cigarette filters function to deposit granular filter material into the open ends of vertically oriented filter tubes. Predetermined amounts of diverse granular material are withdrawn by suction from sources of such material, and these amounts are deposited into the tubes. Solid filter segments seal the granular material within the tube. After one half of each filter tube is filled with granular material and sealed, the tube is inverted and the opposite end is filled in substantially the same manner. When cut in half each filter tube produces two cigarette filters.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS USA INC
Apparatus for extruding cellulose fibers
ActiveUS20090256277A1Efficient and economical mannerEconomical and efficientFrozen sweetsConfectioneryAqueous solutionAirflow
An apparatus is disclosed for extruding cellulose fibers. The apparatus includes a first member, a second member and a third member all secured together. Multiple nozzles extend outward from the first member and each is designed to direct an aqueous cellulose solution therethrough. As the aqueous solution is extruded, it is accentuated and accelerated by pressurized gas flowing through the first member and the second member and out through first openings formed in the third member. The pressurized gas at least partially surrounds each nozzle and shelters the molten filaments extruded therefrom. The third member also has multiple second openings formed therethrough which are also connected to a source of pressurized gas. The pressurized gas streams exiting each of the second openings function to keep each of the molten filaments from contacting an adjacent molten filament.
Owner:REIFENHAUSER GMBH & CO
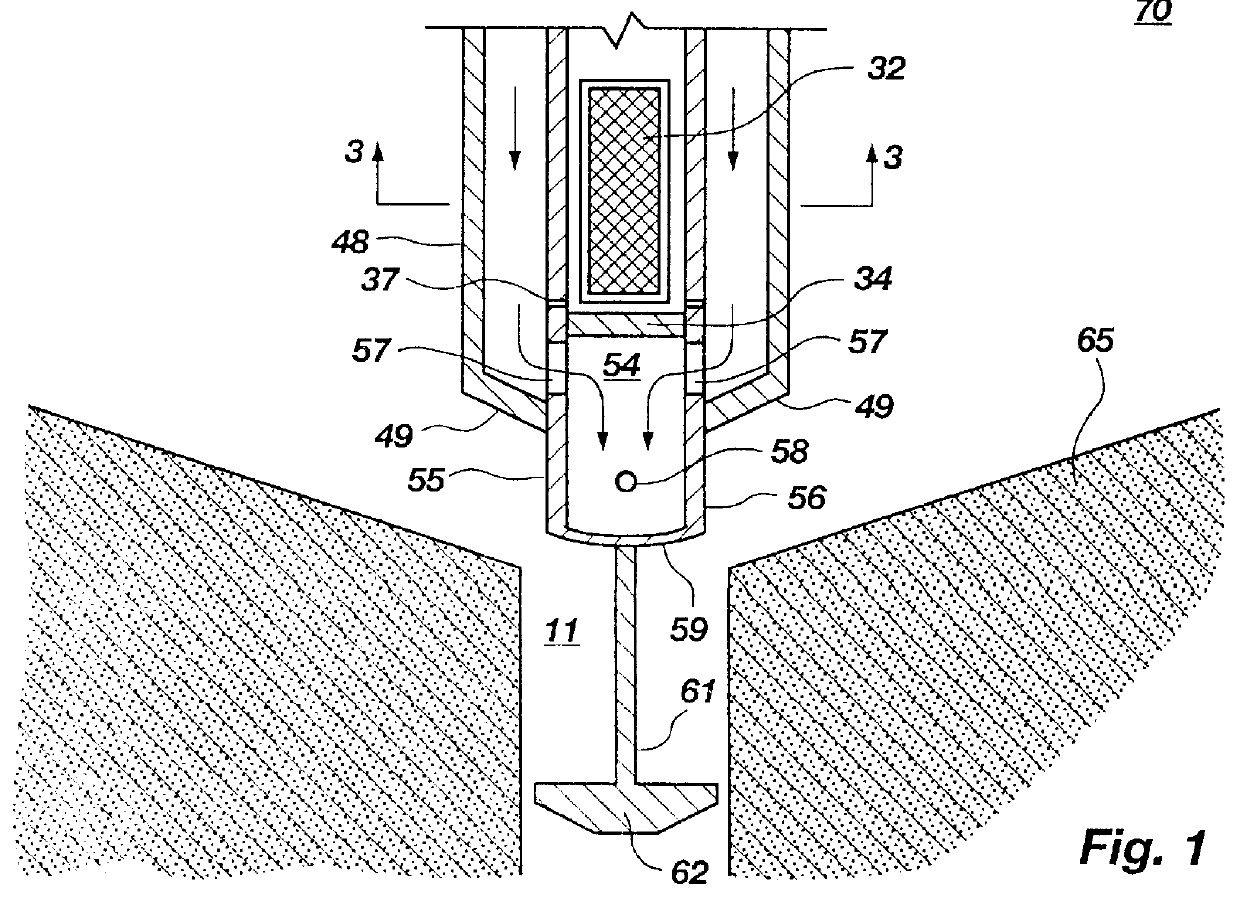
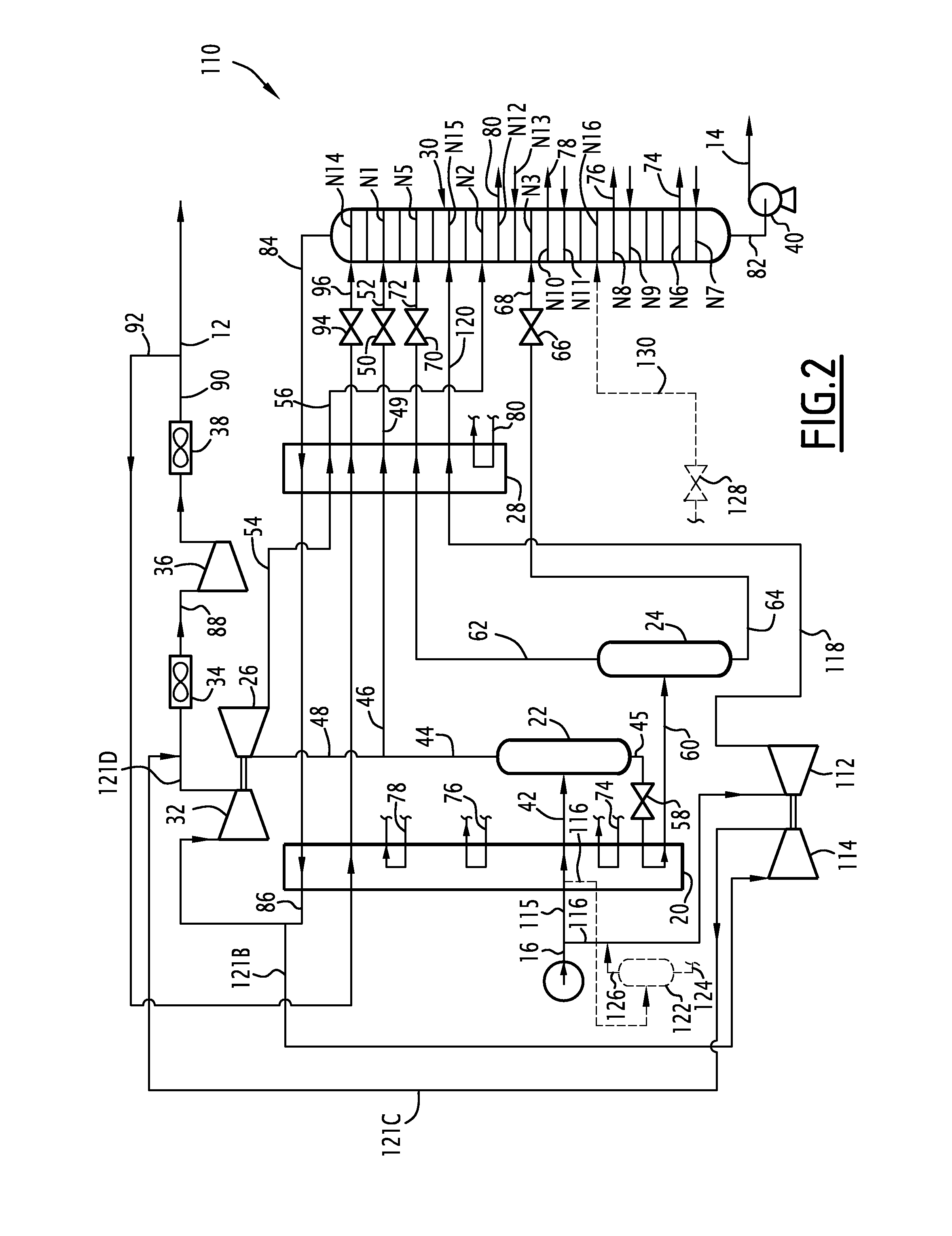
Hydraulic mining of tar sand bitumen with aggregate material
A method and apparatus for the hydraulic removal of bitumen from a tar sand deposit comprises forming a borehole into the tar sand deposit and securing a casing into the borehole. Into the casing is inserted a mining tool having a water / diluent channel and a slurry exit channel. Through the casing the borehole is charged with crushed aggregate. At the lower end of the tool are nozzles through which high pressure hot water / diluent is injected as a jet from the water / diluent channel into the tar sand deposit causing a cavity to form in the tar sand deposit. The heat of the water / diluent jets and dissolving action of the diluent softens the tar sand contacted and the impact of the jets and the scouring action of the aggregate, as impinged upon by the jets, removes the tar sand from the surface of the developing cavity into a water phase. A bitumen / diluent phase rises to the surface of the water phase and is removed from the cavity through the casing. A water sand slurry at the bottom of the developing cavity is removed from the slurry exit channel where sand is subsequently removed and the water is recovered and reintroduced back into the process along with makeup water and diluent. Water temperature and pressures are controlled to optimize the hydraulic mining process.
Owner:RAAM
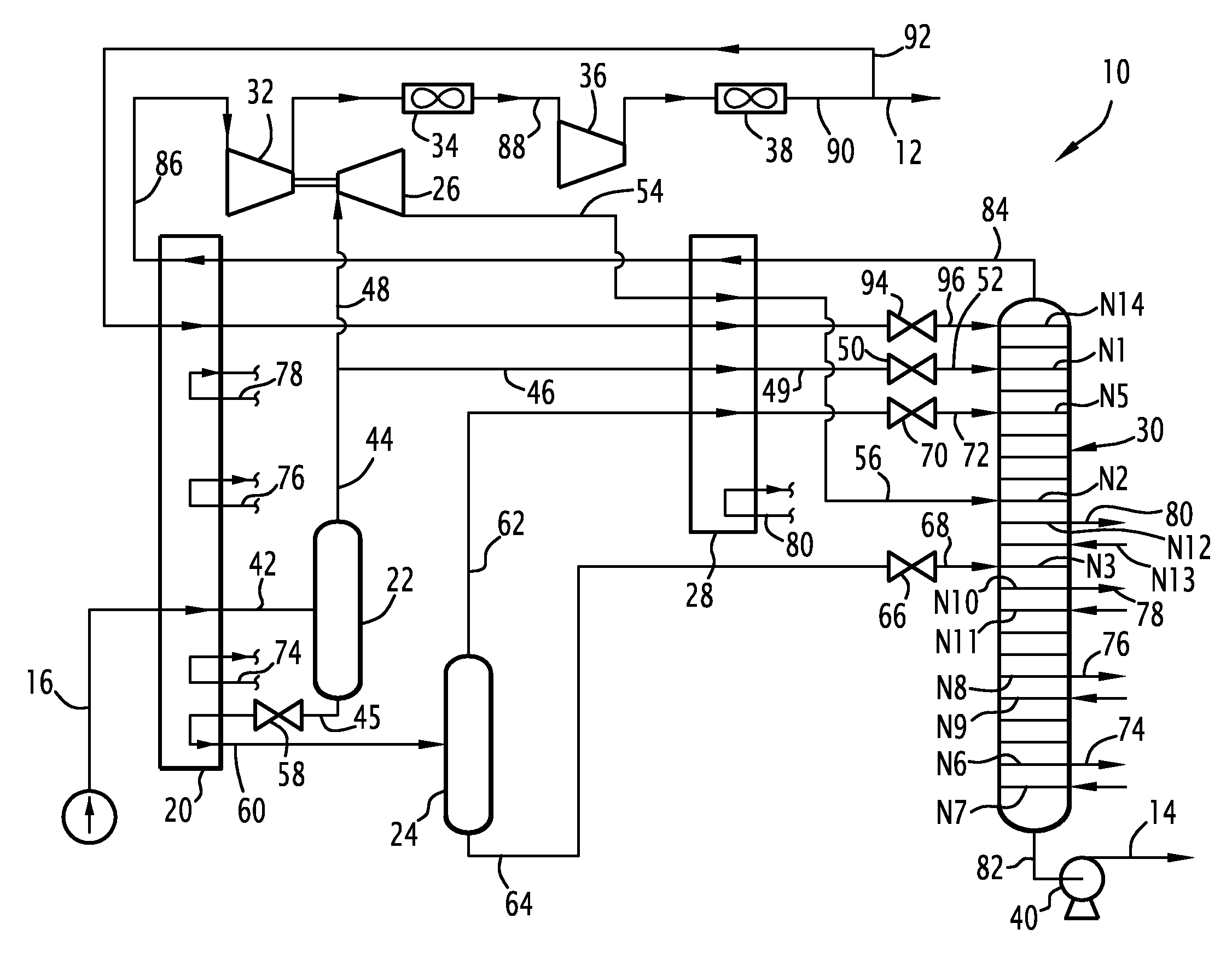
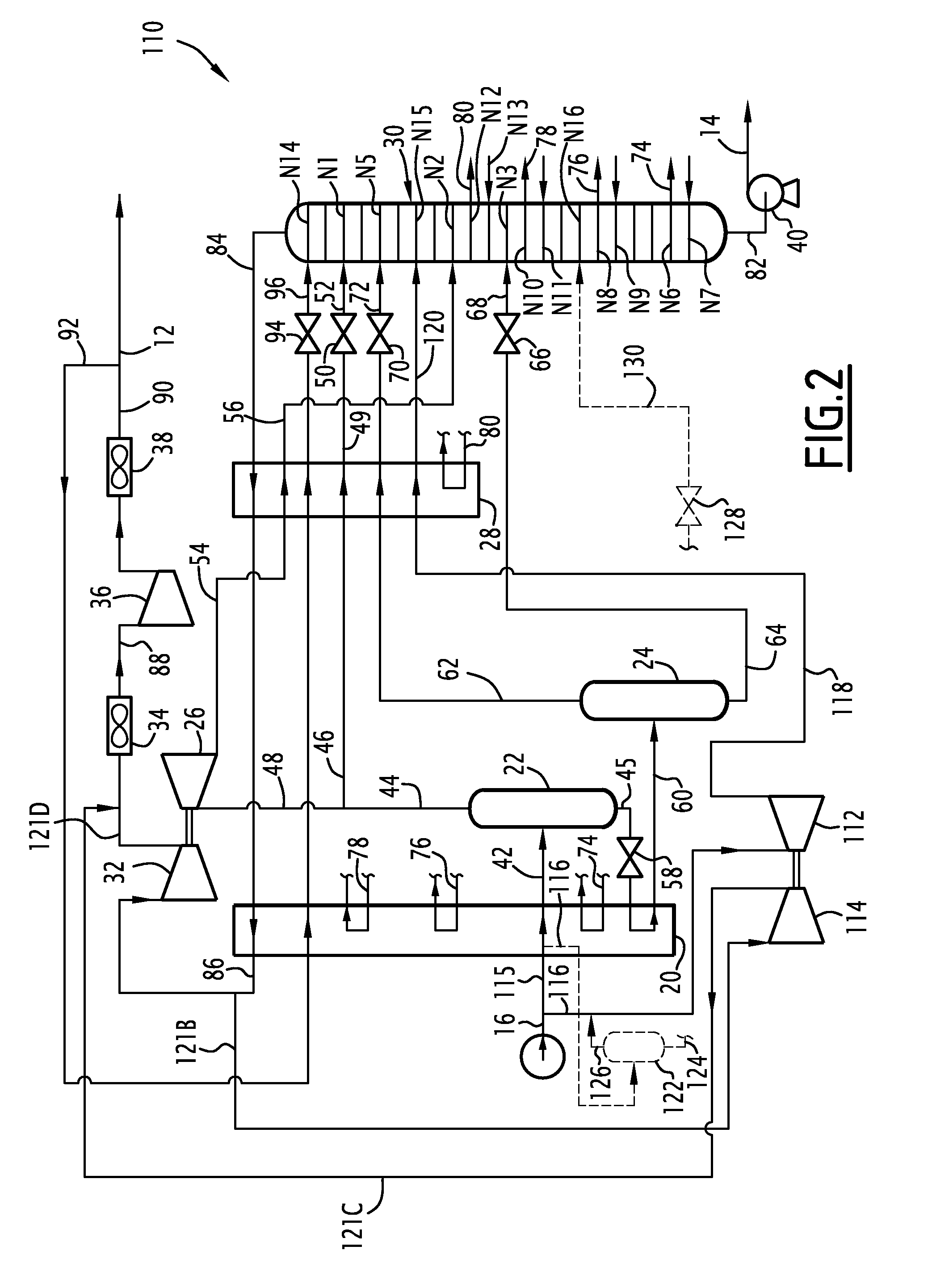
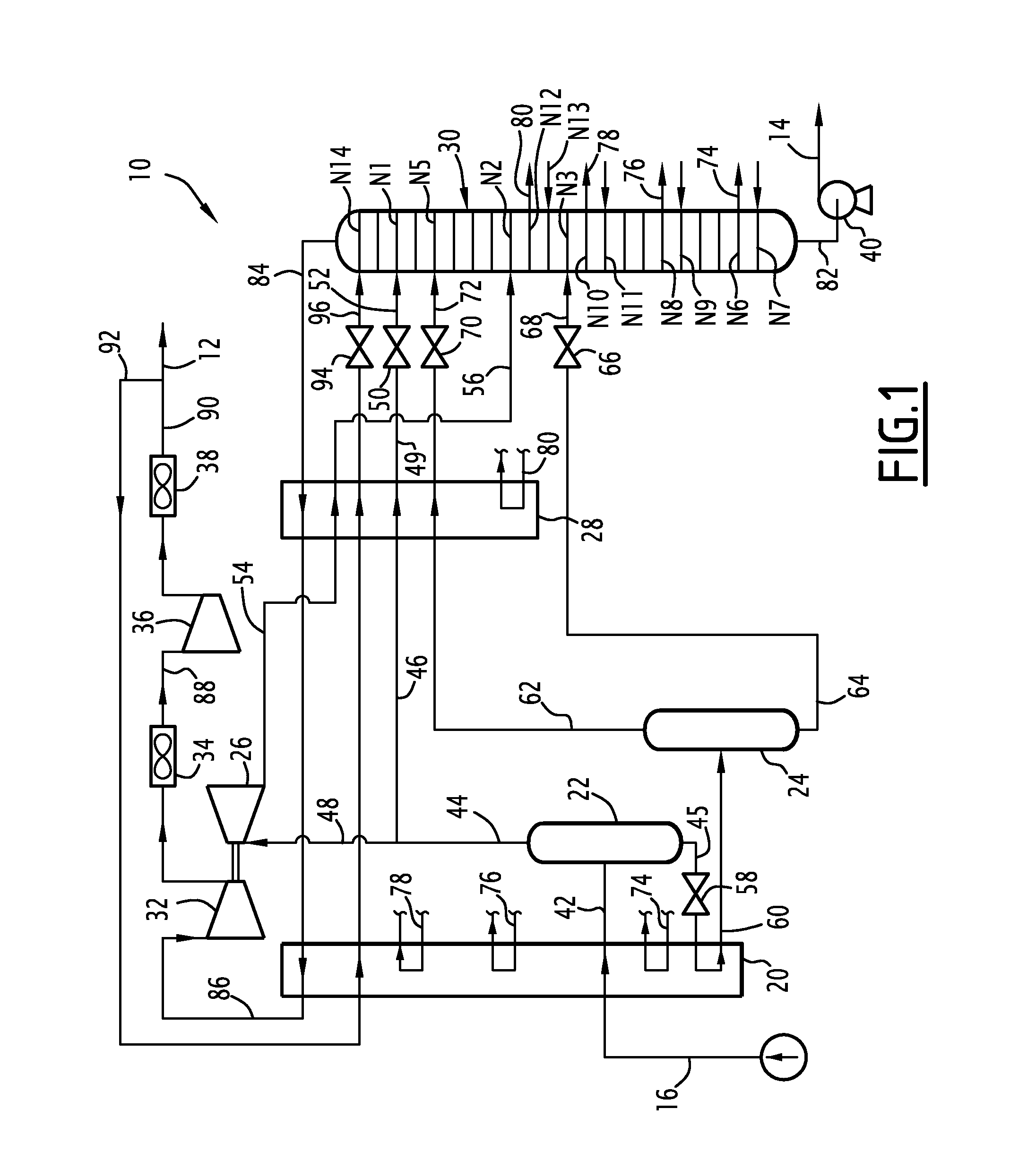
Method for producing a flow rich in methane and a flow rich in c2+ hydrocarbons, and associated installation
ActiveUS20110005273A1Economical and very efficient mannerSpace minimizationSolidificationLiquefactionFractionating columnProcess engineering
This method comprises cooling the supply flow in a first heat exchanger, separation in a first separation flask in order to produce a light upper flow and a heavy lower flow and dividing the light upper flow into a supply fraction of a dynamic pressure reduction turbine and a supply fraction of a first distillation column.The method comprises forming a cooled reflux flow from an effluent from a dynamic pressure reduction turbine, the portion of the effluent being cooled and at least partially liquefied in a heat exchanger.It comprises introducing the cooled reflux flow from the heat exchanger into the first distillation column.
Owner:TECH FRANCE SA
Method for removing contaminating gaseous components from a natural gas stream
InactiveUS20060225386A1Efficient and economical mannerCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationGas compositionGas phase
A method for removing contaminating gaseous components, such as CO2 and / or H2S, from a contaminated natural gas stream. The method includes the steps of expanding the contaminated gas stream in an expander to form an expanded gas stream; allowing at least part of the contaminants in the expanded gas stream to liquify to form a dispersion of a contaminants enriched liquid phase in a contaminants depleted gaseous phase; and separating at least part of the contaminants enriched liquid phase from the contaminants depleted gaseous phase in one or more centrifugal separators.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Method for removing contaminating gaseous components from a natural gas stream
InactiveUS7550032B2Efficient and economical mannerCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationGas phaseLiquid phase
A method for removing contaminating gaseous components, such as CO2 and / or H2S, from a contaminated natural gas stream. The method includes the steps of expanding the contaminated gas stream in an expander to form an expanded gas stream; allowing at least part of the contaminants in the expanded gas stream to liquefy to form a dispersion of a contaminants enriched liquid phase in a contaminants depleted gaseous phase; and separating at least part of the contaminants enriched liquid phase from the contaminants depleted gaseous phase in one or more centrifugal separators.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
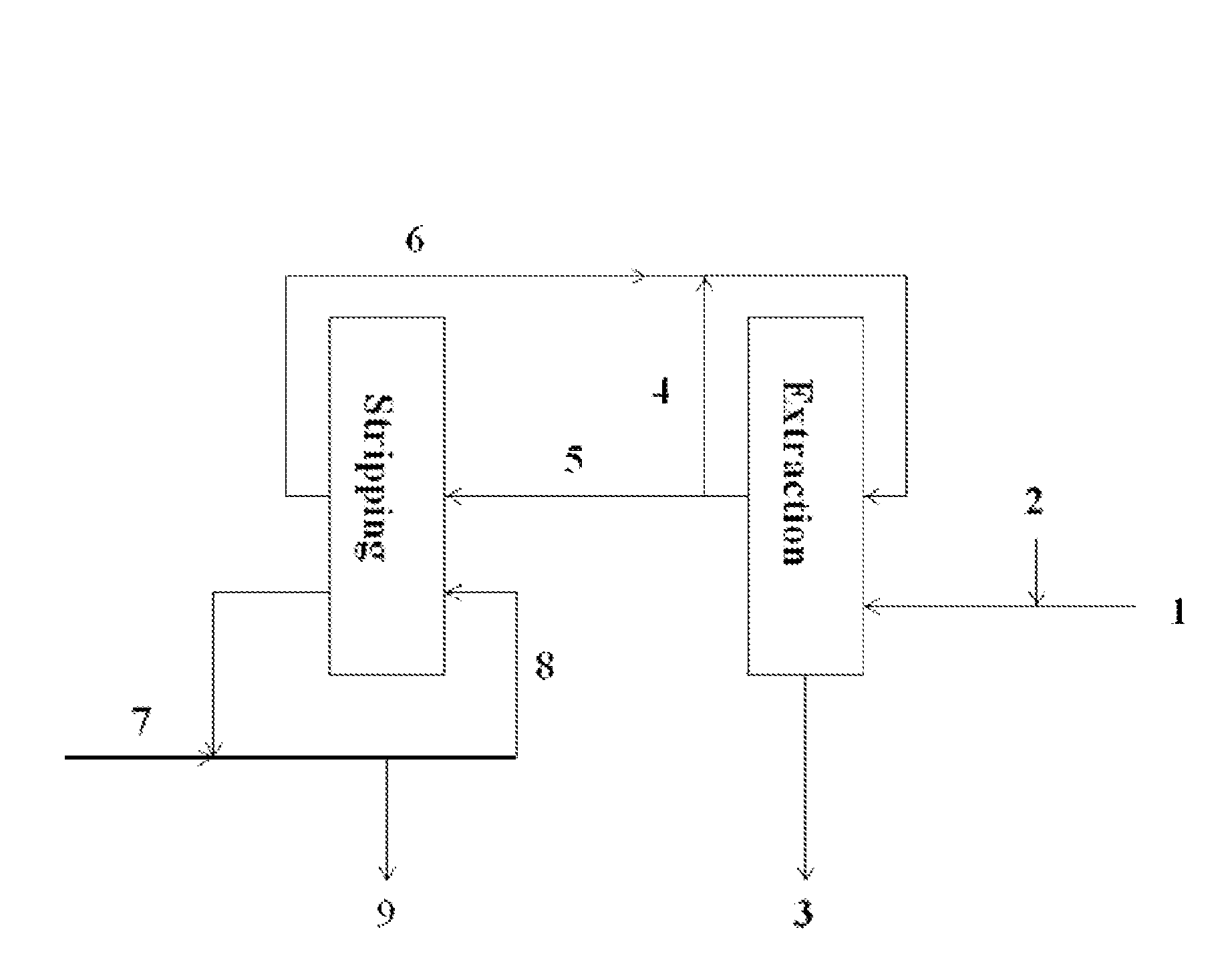
Processes for recovering metals from aqueous solutions
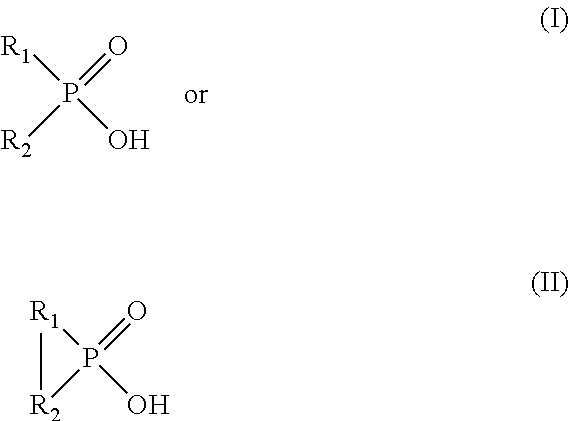
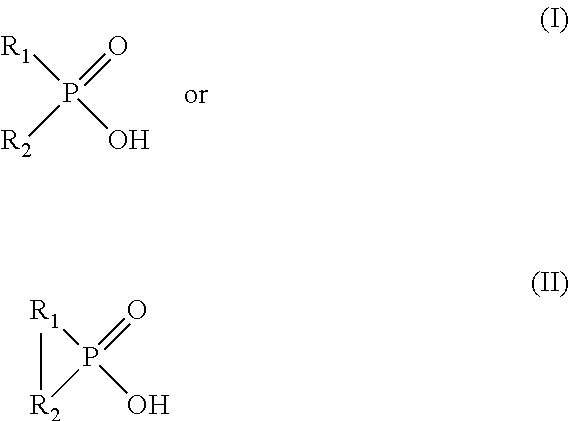
ActiveUS8328900B2Speed up extractionEfficient and economical mannerSolvent extractionMolybdeum compoundsGramInorganic compound
Provided herein are processes for recovering molybdenum and / or other value metals (e.g., uranium) present in aqueous solutions from a large range of concentrations: from ppm to grams per liter via a solvent extraction process by extracting the molybdenum and / or other value metal from the aqueous solution by contacting it with an organic phase solution containing a phosphinic acid, stripping the molybdenum and / or other value metal from the organic phase solution by contacting it with an aqueous phase strip solution containing an inorganic compound and having a ≦1.0 M concentration of free ammonia, and recovering the molybdenum and / or other value metal by separating it from the aqueous phase strip solution. When the molybdenum and / or other value metal are present only in low concentration, the processes can include an organic phase recycle step and / or an aqueous phase strip recycle step in order to concentrate the metal prior to recover.
Owner:CYTEC TECH CORP
Poultry wing deboning apparatus and method
ActiveUS8591298B1Easy quantityEfficient and economical mannerPoultry deboningFish filletingAerospace engineering
An apparatus and method for deboning a poultry wing including multiple stations. The poultry wing is cut and then placed with bones extending through a plate for engagement by a subsequent rotary disboner. The mechanism includes a convey or with the plates secured thereto and motor and controls for moving the conveyor and plates and rotary deboner.
Owner:THREE DICK FARMS
Continuous feed inter-dental brush assembly and device
An inter-dental brush device has a handle with a cartridge removably housed therein. The cartridge has a plurality of chambers each appointed for housing at least one replaceable inter-dental brush. The cartridge is appointed to be rotated to align and select one of the chambers for feed out of the selected inter-dental brush. A base portion is removably attached to the handle, which includes rotation engagement means adapted to interact with the cartridge for rotational engagement, alignment and selection of the chamber and visa vie the inter-dental brush housed therein. An oral portion is removably attached to the other end of the handle, and includes an aperture for feeding out the selected inter-dental brush. A delivery means in association with the handle and the oral portion is provided and is adapted to feed out the selected inter-dental brush. Used, worn out brush is removed or cut off by an optional slidable cutter provided on the brush device.
Owner:WEISS ROGER E
Electron microscope with integrated detector(s)
ActiveUS8334511B2Efficient and economical mannerMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesElectron sourceX-ray
An electron microscope including a vacuum chamber for containing a specimen to be analyzed, an optics column, including an electron source and a final probe forming lens, for focusing electrons emitted from the electron source, a specimen stage positioned in the vacuum chamber under the probe forming lens for holding the specimen, and an x-ray detector positioned within the vacuum chamber. The x-ray detector includes an x-ray sensitive solid-state sensor and a mechanical support system for supporting and positioning the detector, including the sensor, within the vacuum chamber. The entirety of the mechanical support system is contained within the vacuum chamber. Multiple detectors of different types may be supported within the vacuum chamber on the mechanical support system. The mechanical support system may also include at least one thermoelectric cooler element for thermo-electrically cooling the x-ray sensors.
Owner:FEI CO
In-line digital printing system for textile materials
ActiveUS20160023454A1Efficient and economicalEfficient and economical mannerSynthetic resin layered productsPretreated surfacesDigital printingDigital ink
Compositions for and methods of digitally printing an ink image onto a woven textile material are provided. A base application is applied to the surface of a woven textile material, especially one comprising synthetic resin fibers prior to application of an ink image layer. The base application comprises an acrylic latex material that is formulated to imprinted upon with a digital ink while still wet, thereby eliminating the need for an intermediate drying cycle in between base application deposit and printing of the ink image.
Owner:DONALD D SLOAN TRUSTEE OF THE DONALD D SLOAN TRUST ETC +1
Vertical filter filling machine and process
ActiveUS20090036284A1Accurate measurementPacked tightlyPaper/cardboard wound articlesTobacco smoke filtersVertical filterFilter material
A process and apparatus for the mass production of compound cigarette filters function to deposit granular filter material into the open ends of vertically oriented filter tubes. Predetermined amounts of diverse granular material are withdrawn by suction from sources of such material, and these amounts are deposited into the tubes. Solid filter segments seal the granular material within the tube. After one half of each filter tube is filled with granular material and sealed, the tube is inverted and the opposite end is filled in substantially the same manner. When cut in half each filter tube produces two cigarette filters.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS USA INC
Process for resin phase separation by plate decantation
InactiveUS6420517B1Efficient separationEfficient and economical mannerNon-miscible liquid separationInterfacial reactionCentrifugation
This invention relates to an economical and efficient process for purifying a reaction mixture obtained in a two-phase interfacial reaction for the preparation of polycarbonate. More particularly, the method of the invention provides for separating the reaction mixture into an organic phase, which includes the desired polycarbonate and undesirable impurities, and an aqueous phase. The organic phase is further purified by using a plate decanter in combination with coalescence and centrifugation.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Transparent conductive composite films
ActiveUS9199438B2Efficient and economical mannerSimple methodSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationNanowireComposite film
A process for the manufacture of a transparent conductive film comprising: (i) a polymeric substrate comprising a polymeric base layer and a polymeric binding layer, wherein the polymeric material of the base layer has a softening temperature TS-B, and the polymeric material of the binding layer has a softening temperature TS-HS; and (ii) a conductive layer comprising a plurality of nanowires, wherein said nanowires are bound by the polymeric matrix of the binding layer such that the nanowires are dispersed at least partially in the polymeric matrix of the binding layer, said process comprising the steps of providing a polymeric substrate comprising a polymeric base layer and a polymeric binding layer; disposing said nanowires on the exposed surface of the binding layer; and heating the composite film to a temperature T1 wherein T1 is equal to or greater than TS-HS, and T1 is at least about 5° C. below TS-B; and transparent conductive films derived from said process.
Owner:DUPONT TEIJIN FILMS U S LLP
Vertical filter filling machine and process
ActiveUS7479099B2Efficient and economical mannerIncrease chanceTobacco treatmentPaper/cardboard wound articlesVertical filterMechanical engineering
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS USA INC
Processes for recovering metals from aqueous solutions
ActiveUS20110005354A1Efficient and economical mannerImprove the mixing effectPhotography auxillary processesProcess efficiency improvementPhosphinic AcidsAqueous solution
Provided herein are processes for recovering molybdenum and / or other value metals (e.g., uranium) present in aqueous solutions from a large range of concentrations: from ppm to grams per liter via a solvent extraction process by extracting the molybdenum and / or other value metal from the aqueous solution by contacting it with an organic phase solution containing a phosphinic acid, stripping the molybdenum and / or other value metal from the organic phase solution by contacting it with an aqueous phase strip solution containing an inorganic compound and having a ≦1.0 M concentration of free ammonia, and recovering the molybdenum and / or other value metal by separating it from the aqueous phase strip solution. When the molybdenum and / or other value metal are present only in low concentration, the processes can include an organic phase recycle step and / or an aqueous phase strip recycle step in order to concentrate the metal prior to recover.
Owner:CYTEC TECH CORP
Power systems for transportation and residential uses
InactiveUS20070017718A1Efficient and economical mannerDependency on fossil fuels can be greatly diminishedHybrid vehiclesPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingMagnetic layerElectromagnetic radiation
A power wheel system includes a first wheel member that is attachable to a vehicle, an electric motor that selectively rotates the first wheel member and that is mounted at least partially within the first wheel member and a receiver that is attachable to the vehicle that receives wireless power from a power source, preferably electromagnetic radiation energy from the Earth's magnosphere. The power wheel system may also include a first transformer that receives an input voltage from the receiver and supplies a corresponding output voltage to the electric motor. This transformer may be positioned at least partially within the wheel member. The power wheel system may also include a control mechanism that is used to control the power wheel system. In another embodiment some of the same components can be arranged to provide a power residence system.
Owner:CHROBAK DENNIS S
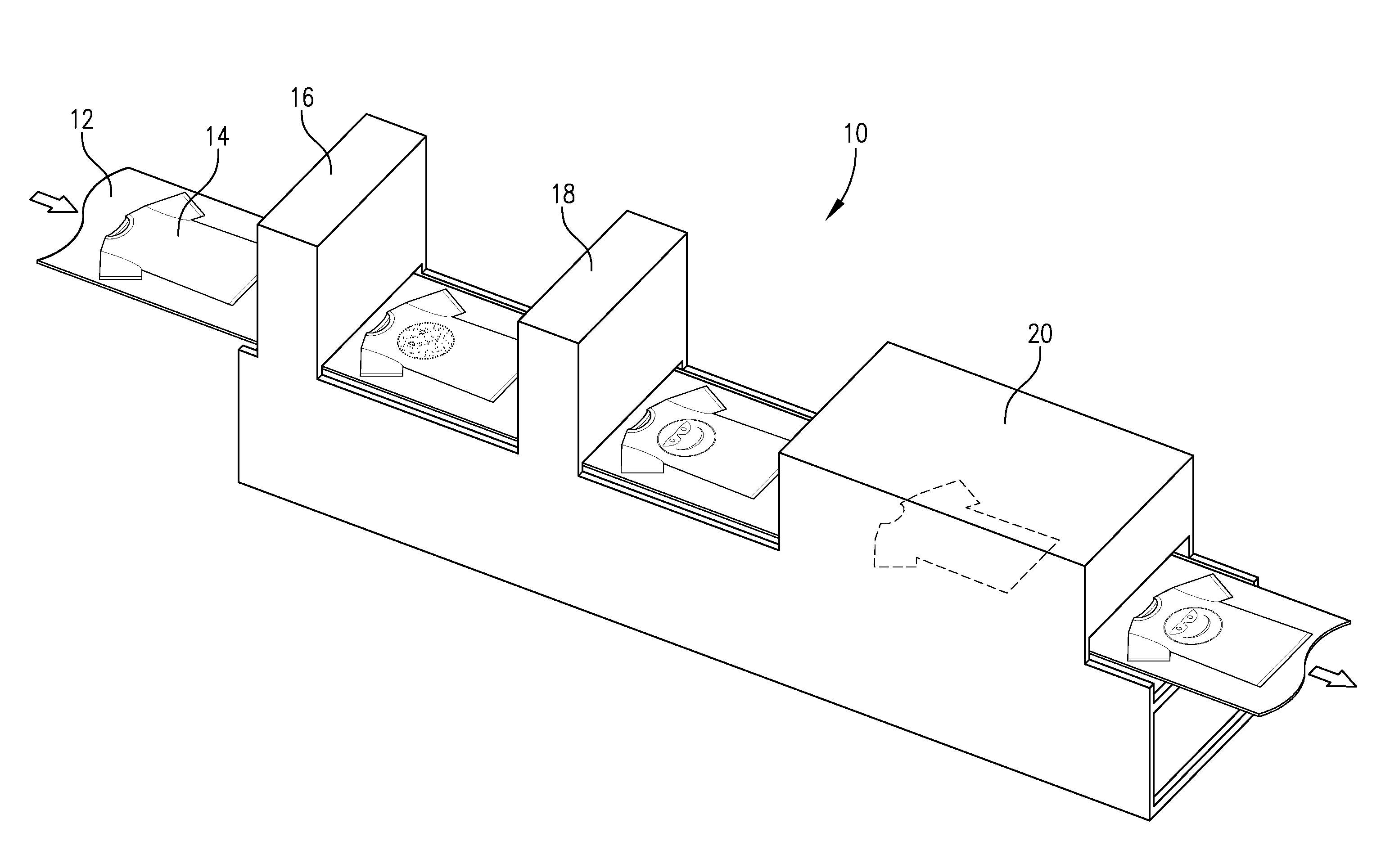
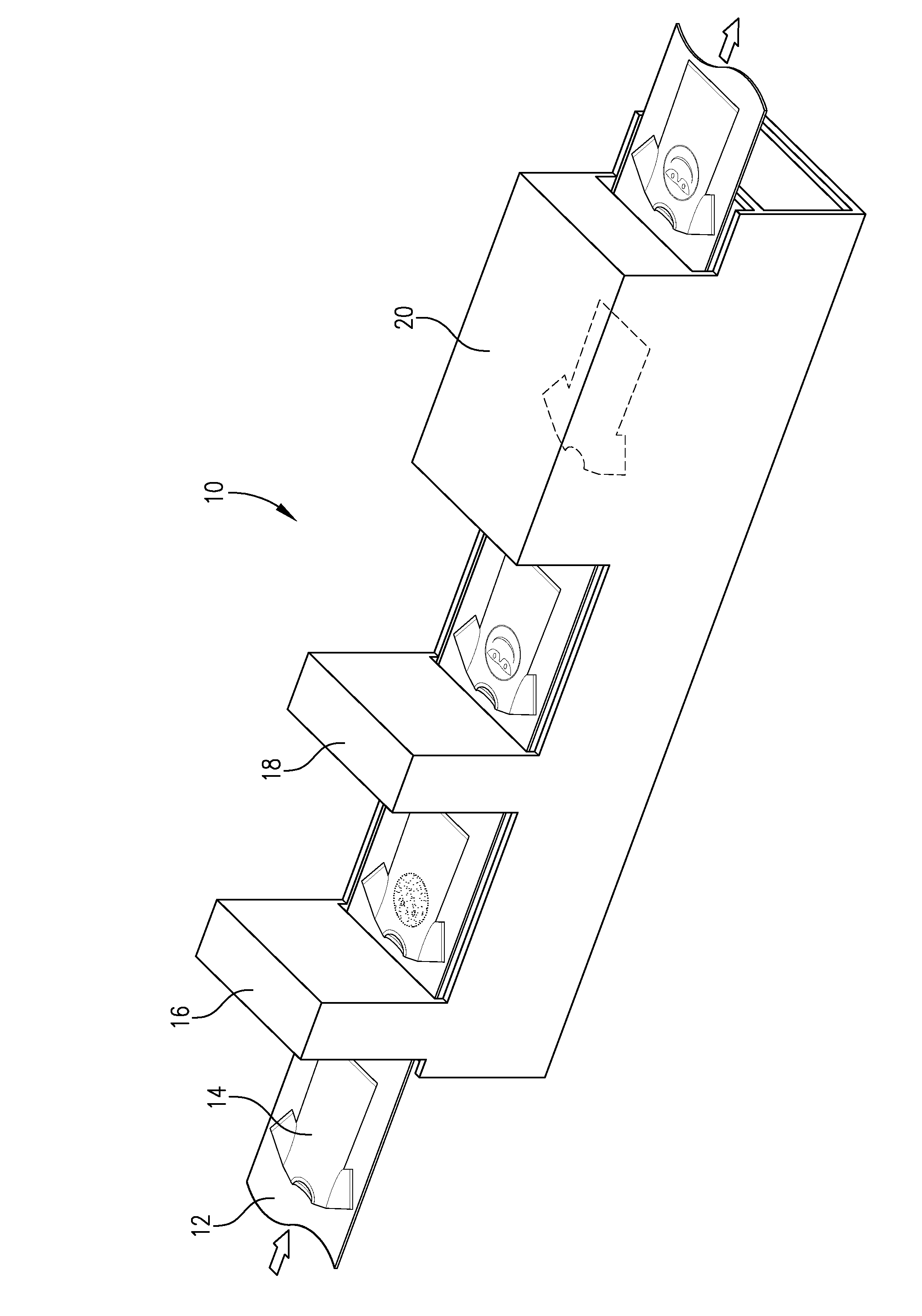
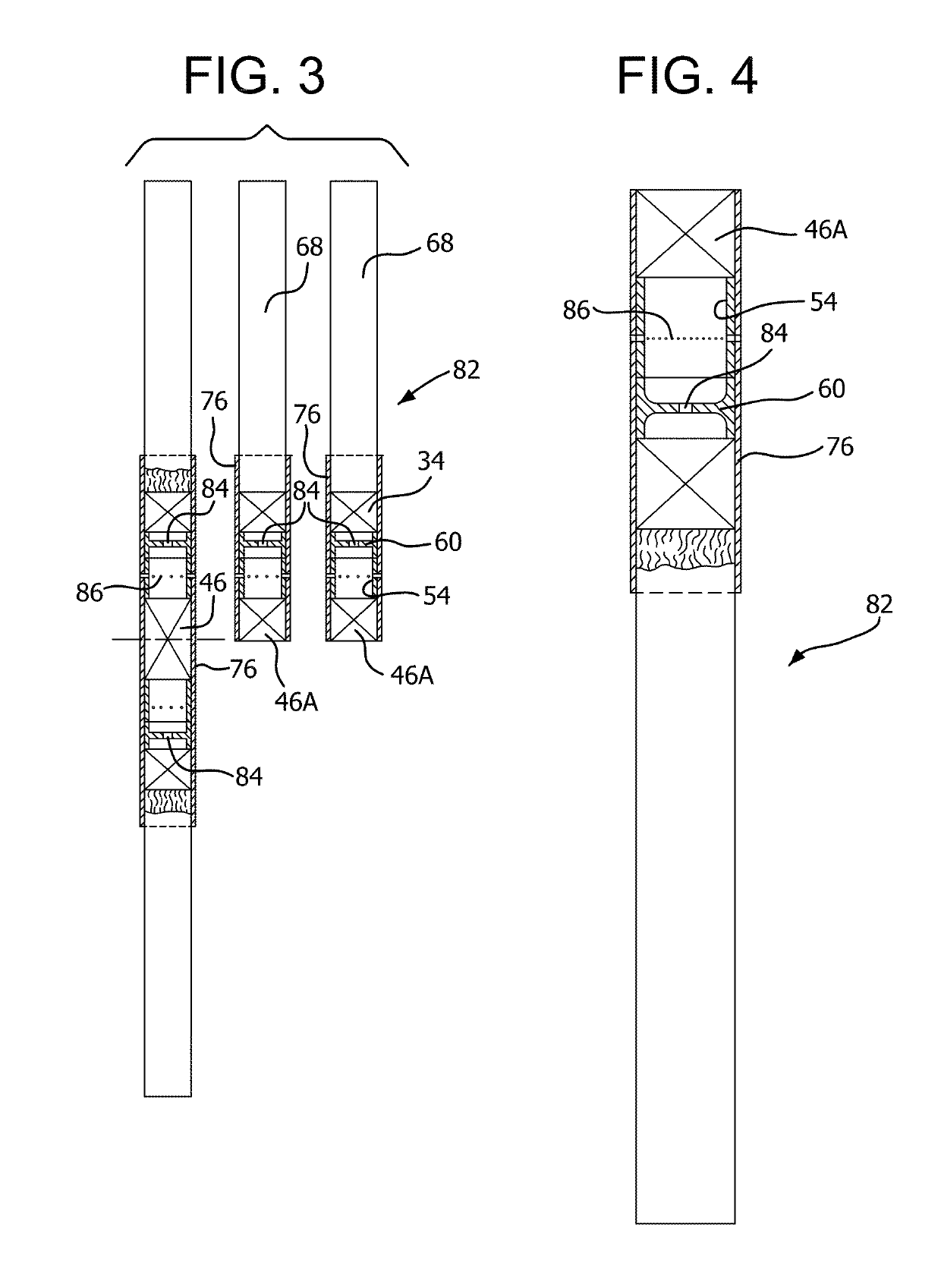
Compound horizontal filter assembly machine and process
ActiveUS20110290263A1Efficient and economical mannerIncrease chancePaper/cardboard wound articlesCigarette manufactureEngineeringComposite filter
An apparatus and processes for producing compound cigarette filters by horizontally assembling multiple filter segments onto the horizontally oriented transverse flutes of a continuous belt. Spaced apart hoppers are serially arranged above the belt, and each hopper contains at least one of the multiple segments of the compound filter being assembled. A transfer structure between each hopper and the belt serially delivers the filter segments to the flutes on the belt, and after such assembly the various filter segments are removed as a group from each flute of the continuous belt. The filter segments are then combined as a group with wrapped tobacco rods to thereby produce filtered cigarettes.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS USA INC
System And Method for a Peer to Peer Exchange of Consumer Information
InactiveUS20160284020A1Facilitate communicationEfficient and economical mannerFinanceApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingPaymentInvoice
Using peer-to-peer networking to exchange consumer information in a secure environment. The seeker of consumer information transmits an encrypted query to authenticated and trusted peers which includes legal representations stating the legally permissible purpose for seeking the information. A peer, acting as a maintainer of consumer information, determines if the query matches any consumer information held by the maintainer. The maintainer then informs the seeker of the results of the match, the type of information available, the data format, and the price for such consumer information. A payment invoice can be generated and electronically presented by maintainer. The payment may be electronically debited from the designated account of seeker and remitted to maintainer. In addition, a portion of such funds may be delivered to an entity which maintains the peer-to-peer software.
Owner:CREDIGY TECH
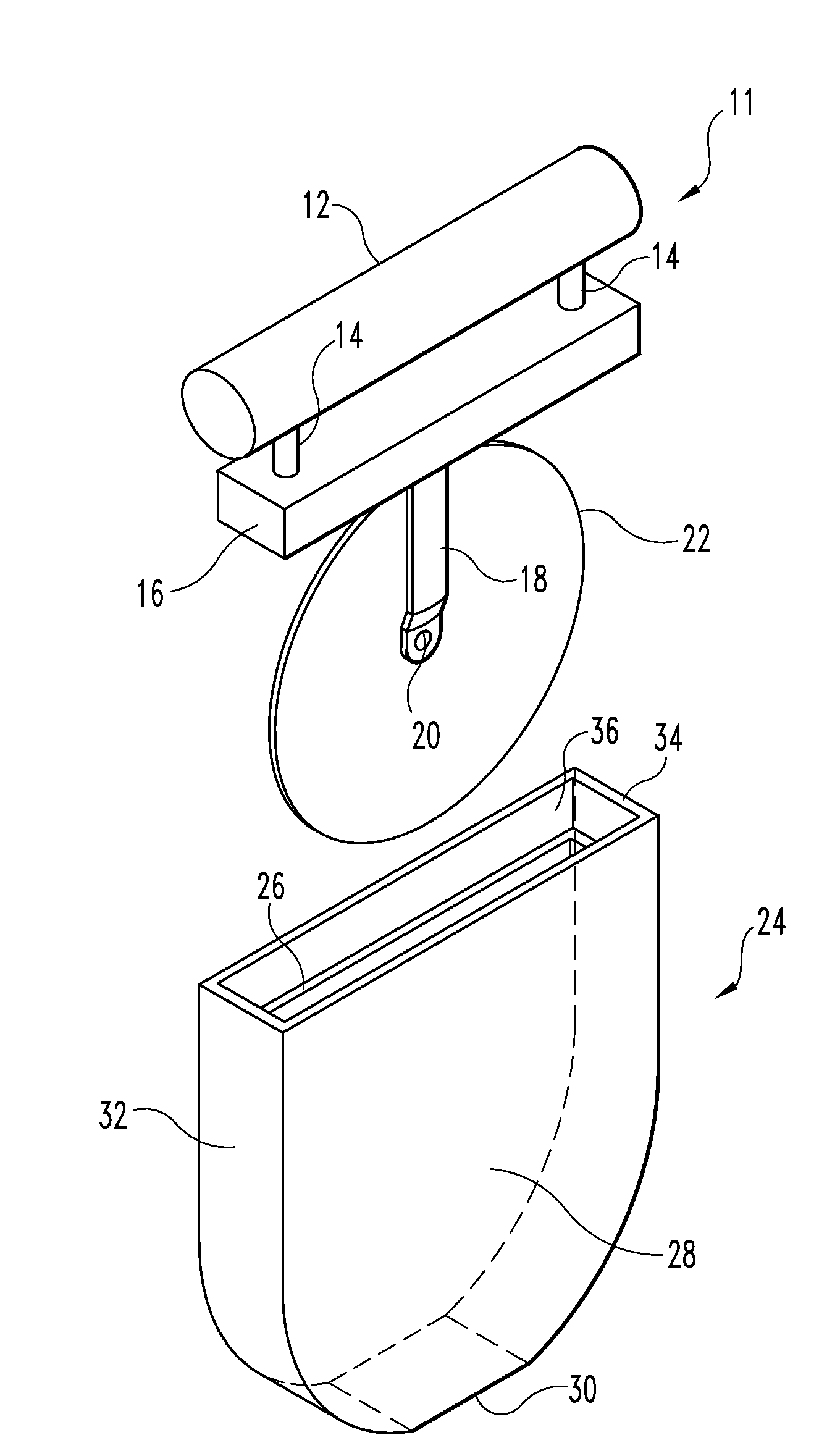
Cutting wheel assembly
InactiveUS7681319B2Easy to useEfficient and economical mannerThrusting weaponsWeapon componentsEngineeringKnife blades
Owner:GEHLHAUSEN TINA M
Continuous feed inter-dental brush and device
An inter-dental brush is provided with a handle that accepts a cartridge housing continuous inter-dental brush feedstock. Used, worn out brush is cut off by a slidable cutter provided on an angled portion of the handle. Fresh inter-dental brush is fed out from the continuous inter-dental feedstock by turning a knob on the handle. The protrusion length of the inter-dental brush is controlled by the number of turns. The knob is connected to a gear that pushes against the feedstock, driving the brush through an aperture in the angled portion of the handle. Within the cartridge, the feedstock is removably attached to one swivel and is wrapped around a second swivel. The swivels have a brake that produces a taut feedstock as the brush is fed out. The cartridge may contain a single roll with a brake instead of a pair of swivels.
Owner:WEISS ROGER E
Method and Apparatus for Coating a Substrate and Printed Matter
InactiveUS20080044618A1Efficient and economical mannerImprove material efficiencySpecial visual effect coatingsLayered productsEngineeringSolid content
A method and an apparatus for coating a substrate (7), in which a coating agent (9) is applied onto the substrate (7) in order to form a printing surface, and in which the coating agent (9) is brought into contact with the substrate (7) with a solids content above 80%, and the coating agent (9) is fixed to the substrate (7), the coating being performed during a printing process in a printing machine (10), between the input of the substrate (10) and the output of the printed matter (1), before the actual information (2, 3, 4) is printed.
Owner:VALMET TECH INC
Method for producing a flow rich in methane and a flow rich in c2+ hydrocarbons, and associated installation
ActiveUS20150292798A1Efficient and economical mannerSpace minimizationSolidificationLiquefactionFractionating columnEngineering
This method envisions cooling the supply flow in a first heat exchanger, separation in a first separation flask in order to produce a light upper flow and a heavy lower flow and dividing the light upper flow into a supply fraction of a dynamic pressure reduction turbine and a supply fraction of a first distillation column. A cooled reflux flow is formed from an effluent from a dynamic pressure reduction turbine, the portion of the effluent being cooled and at least partially liquefied in a heat exchanger. The cooled reflux flow is introduced from the heat exchanger into the first distillation column.
Owner:TECH FRANCE SA
In-line digital printing system for textile materials
Compositions for and methods of digitally printing an ink image onto a woven textile material are provided. A base application is applied to the surface of a woven textile material, especially one comprising synthetic resin fibers prior to application of an ink image layer. The base application comprises an acrylic latex material that is formulated to imprinted upon with a digital ink while still wet, thereby eliminating the need for an intermediate drying cycle in between base application deposit and printing of the ink image.
Owner:DONALD D SLOAN TRUSTEE OF THE DONALD D SLOAN TRUST ETC +1
Processes for recovering metals from aqueous solutions
ActiveUS8968698B2Speed up extractionEfficient and economical mannerSolvent extractionTantalum compoundsPhosphinic AcidsInorganic compound
Provided herein are processes for recovering molybdenum and / or other value metals (e.g., uranium) present in aqueous solutions from a large range of concentrations: from ppm to grams per liter via a solvent extraction process by extracting the molybdenum and / or other value metal from the aqueous solution by contacting it with an organic phase solution containing a phosphinic acid, stripping the molybdenum and / or other value metal from the organic phase solution by contacting it with an aqueous phase strip solution containing an inorganic compound and having a ≦1.0 M concentration of free ammonia, and recovering the molybdenum and / or other value metal by separating it from the aqueous phase strip solution. When the molybdenum and / or other value metal are present only in low concentration, the processes can include an organic phase recycle step and / or an aqueous phase strip recycle step in order to concentrate the metal prior to recover.
Owner:CYTEC TECH CORP
Method for separating polishing material and regenerated polishing material
ActiveUS10017675B2Efficient and economical mannerHigh purityOther chemical processesSeparation devicesTemperature controlAlkaline earth metal
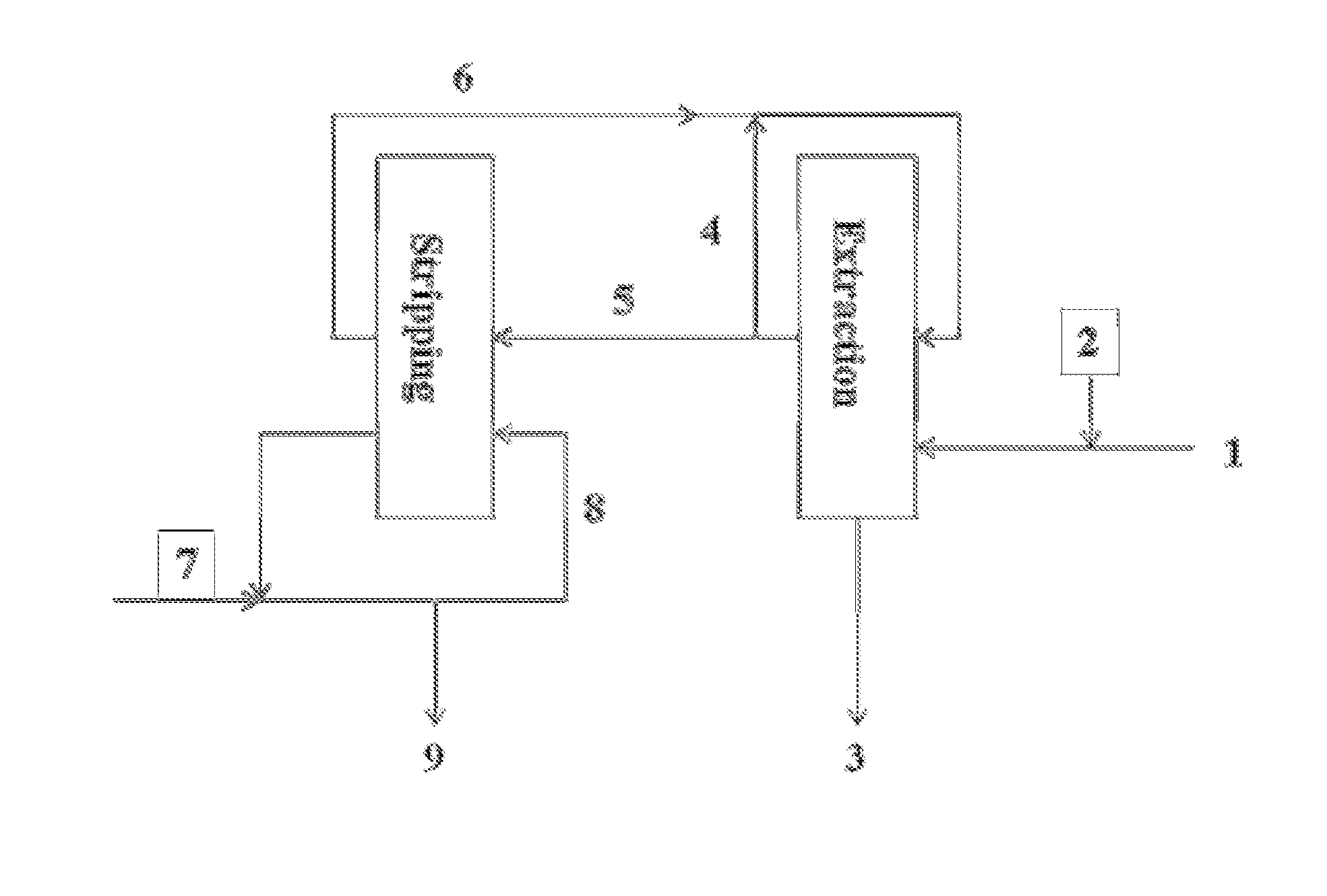
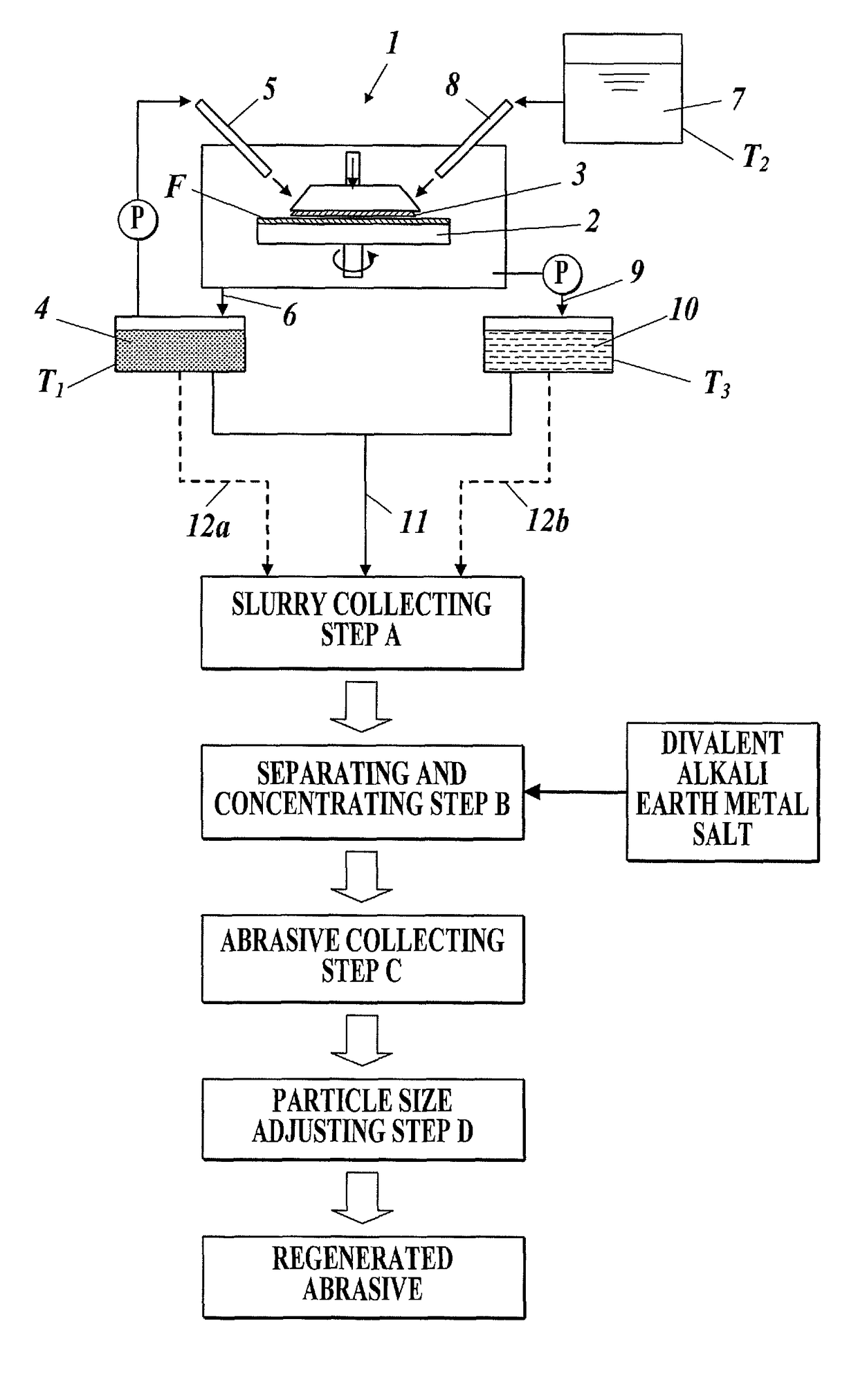
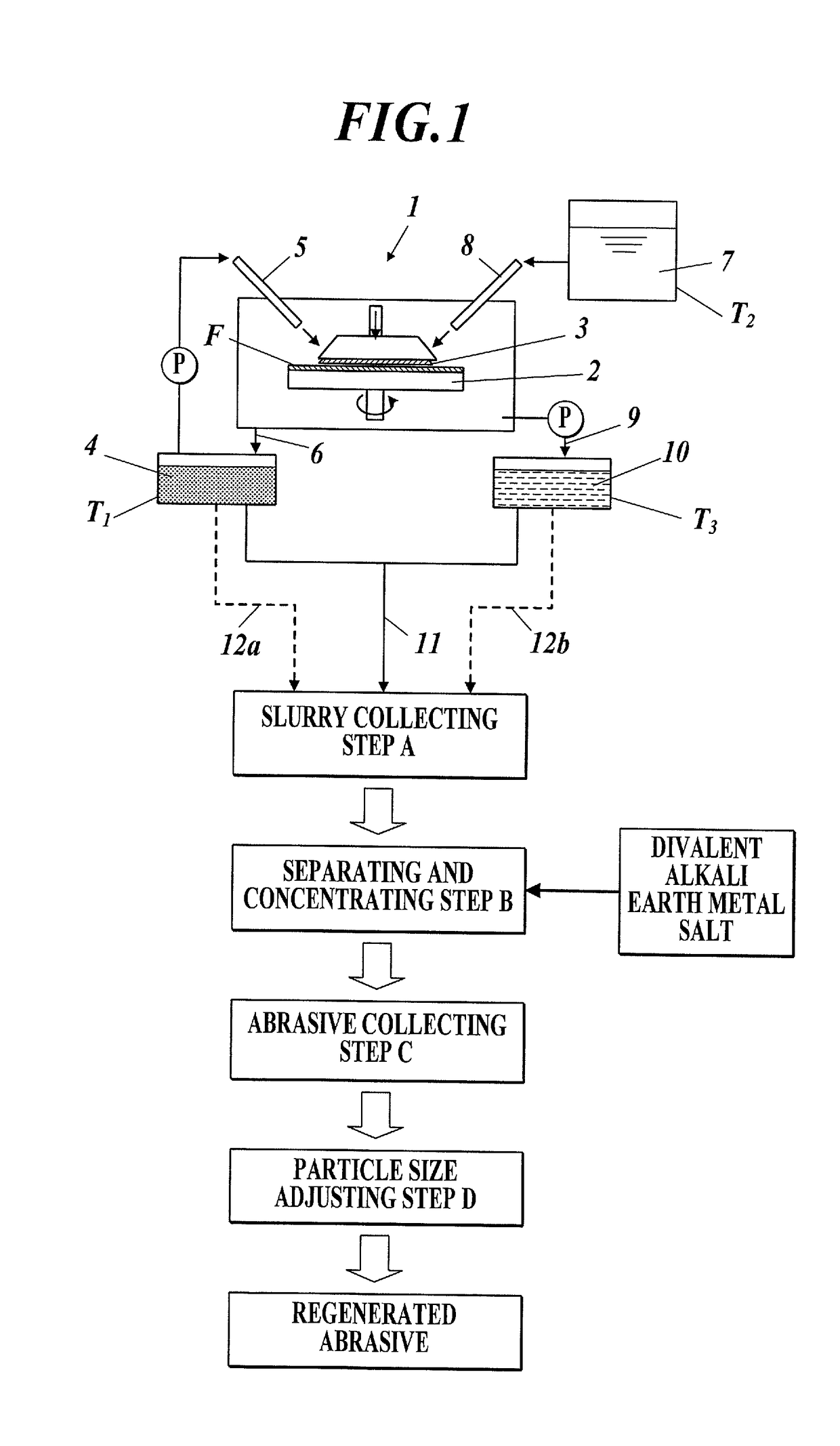
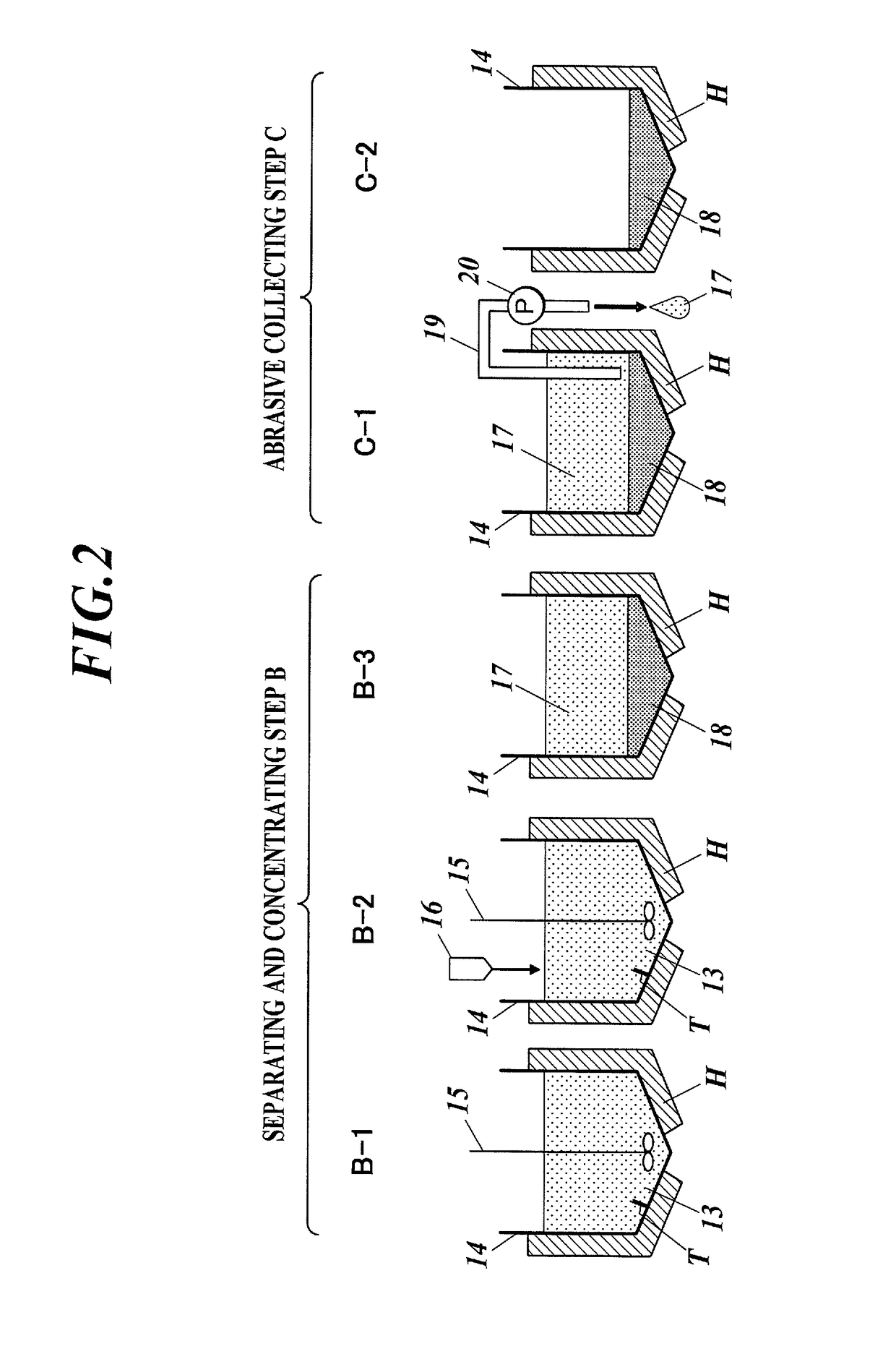
Method for separating a polishing material, which is capable of separating and recovering cerium oxide from a used polishing material that is mainly composed of cerium oxide and a regenerated polishing material which can be obtained by the separation method. This method for separating a polishing material is characterized in that a divalent alkaline earth metal salt is added into the slurry of the used polishing material, while controlling the temperature of the slurry within the range of 10-70 DEG C., thereby causing the polishing material to aggregate under such conditions that the mother liquor has a pH of less than 10.0 as the pH is converted to one at 25 DEG C. so that the polishing material is separated from the mother liquor.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
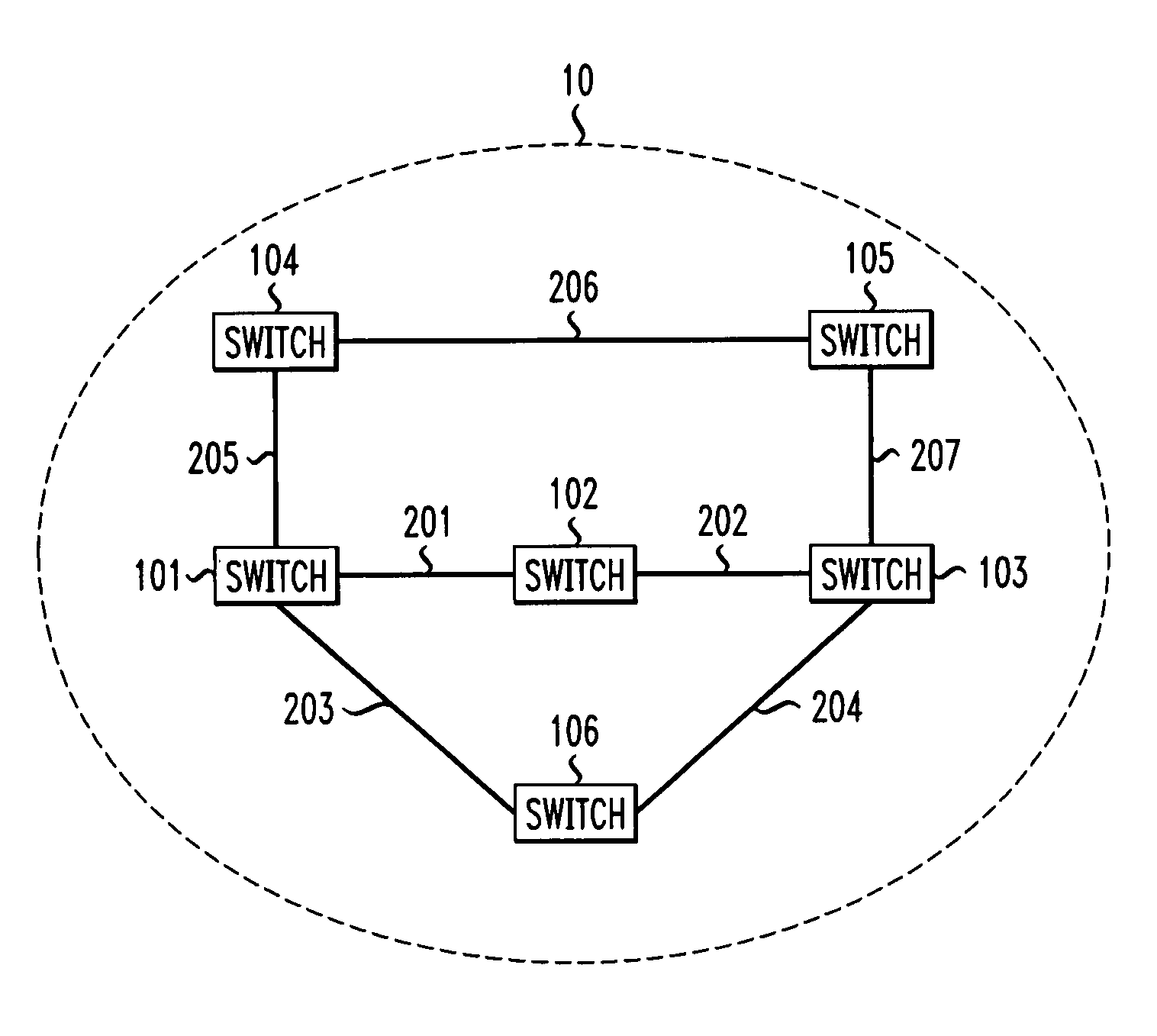
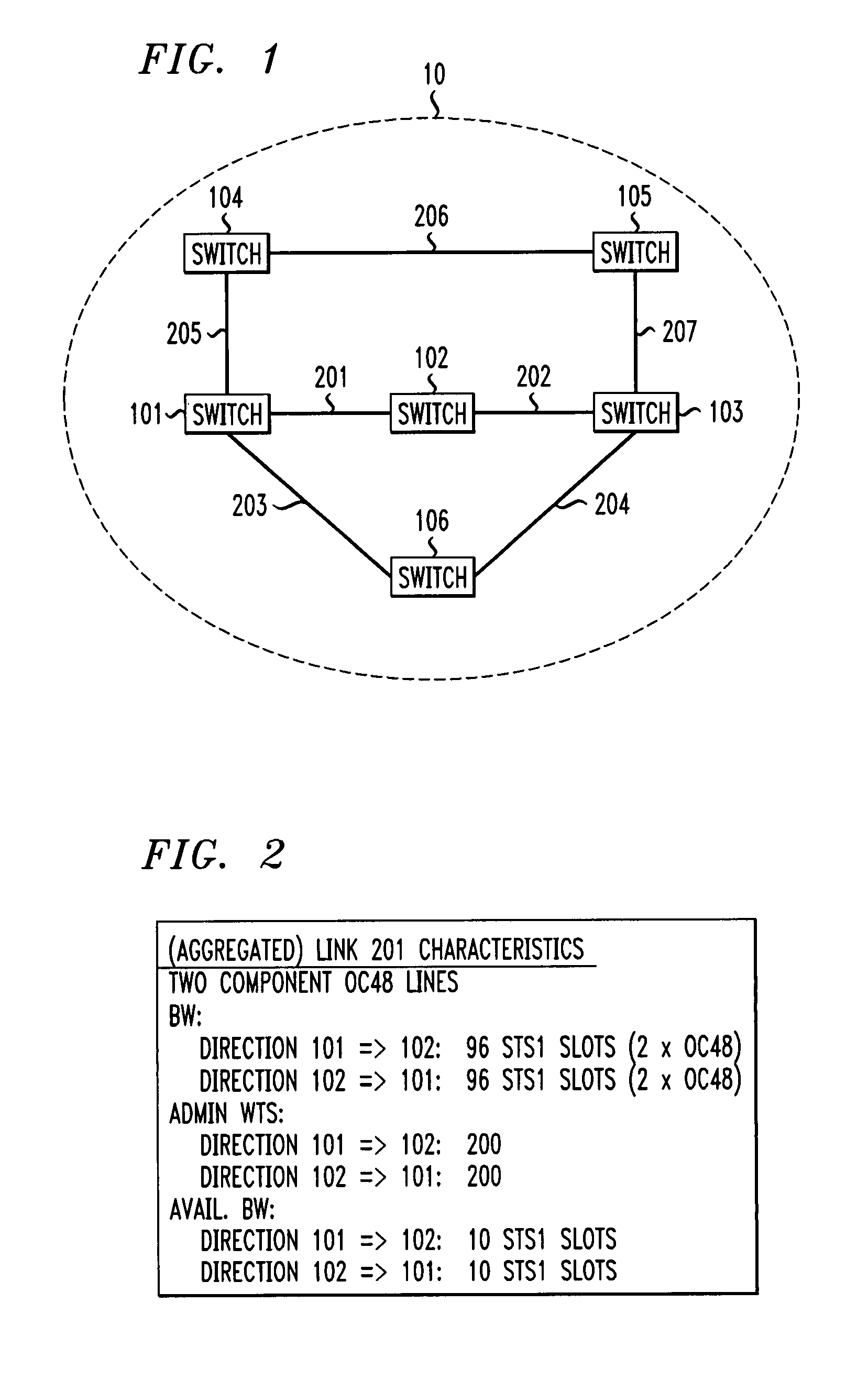
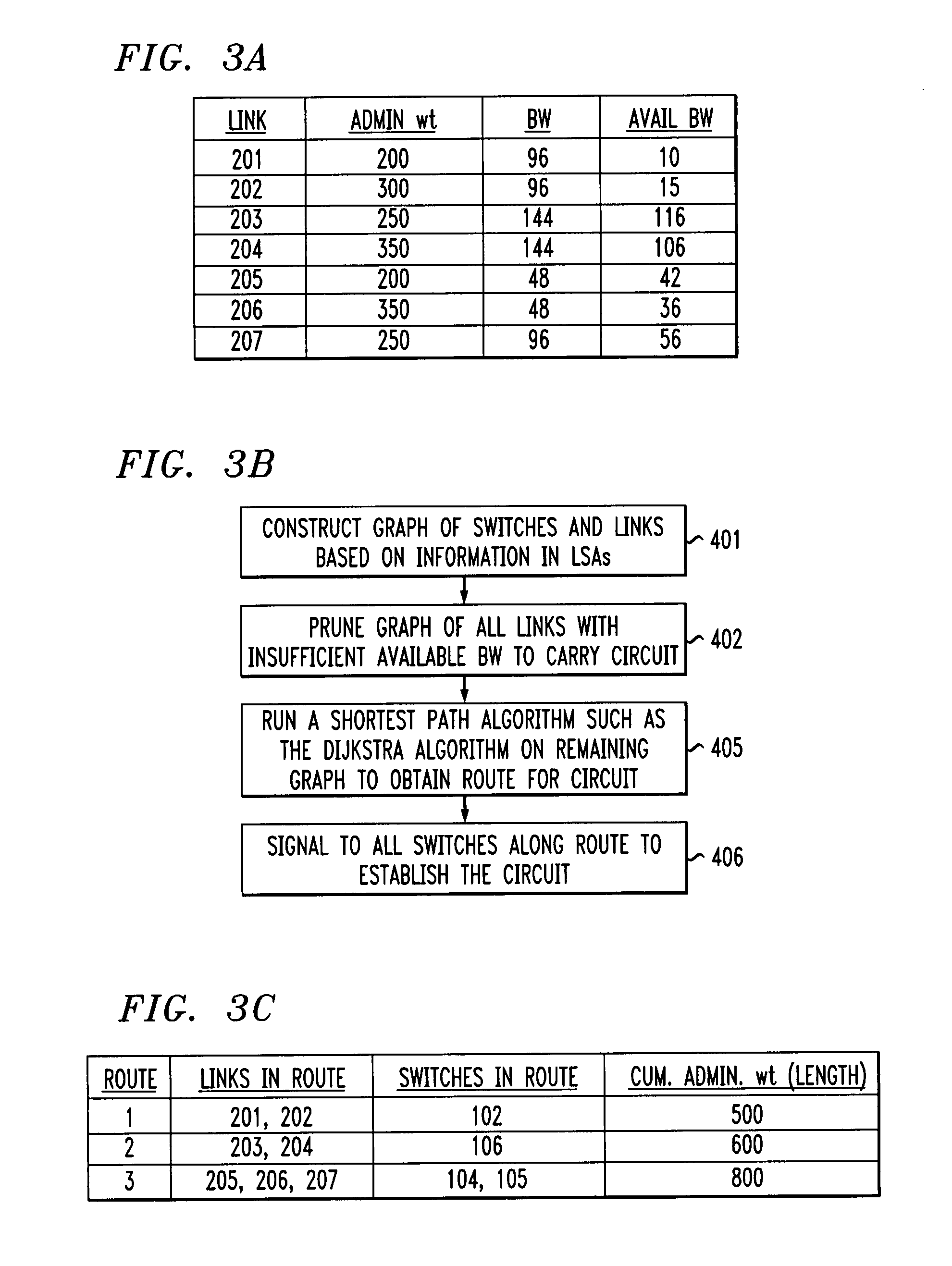
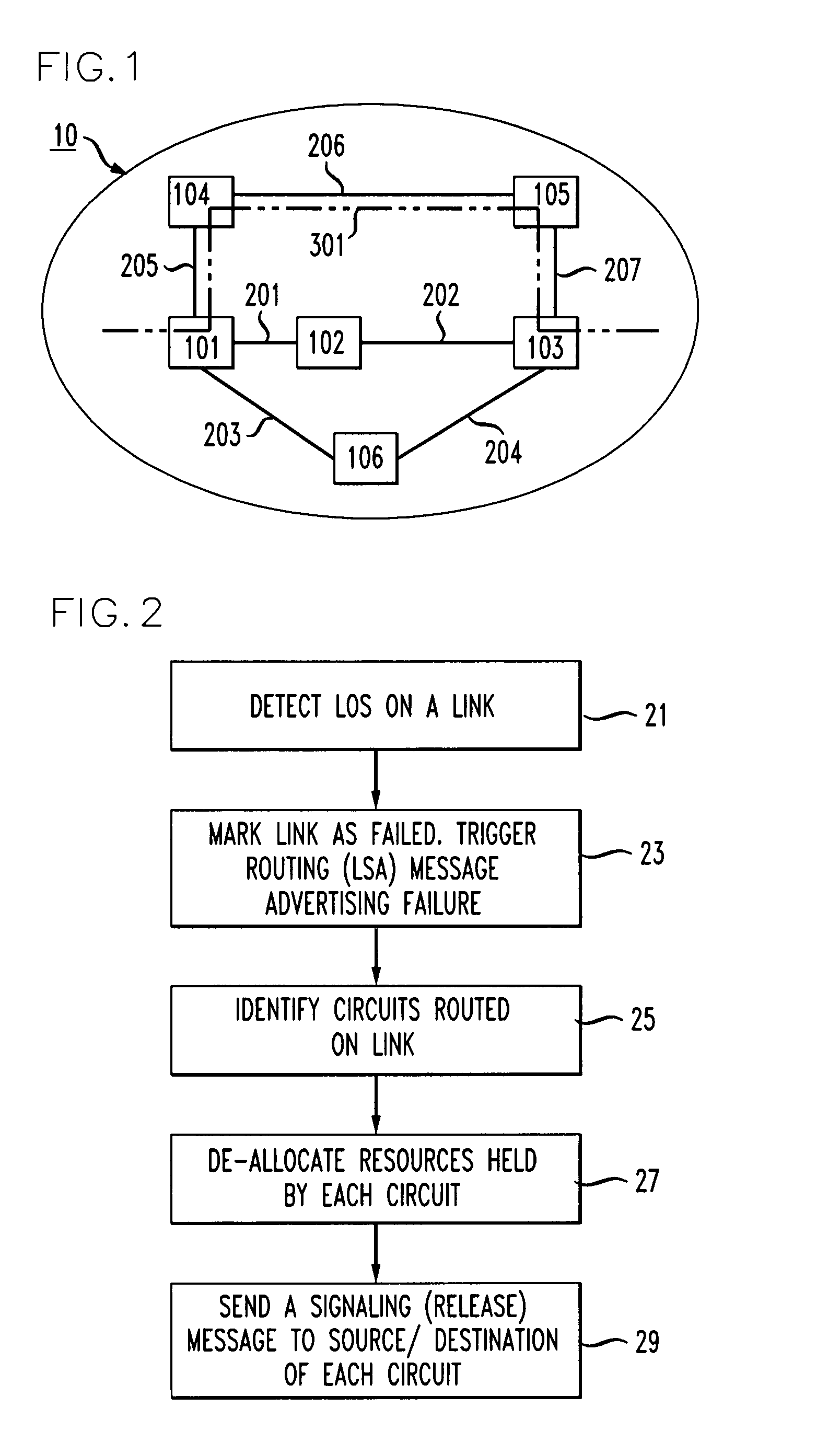
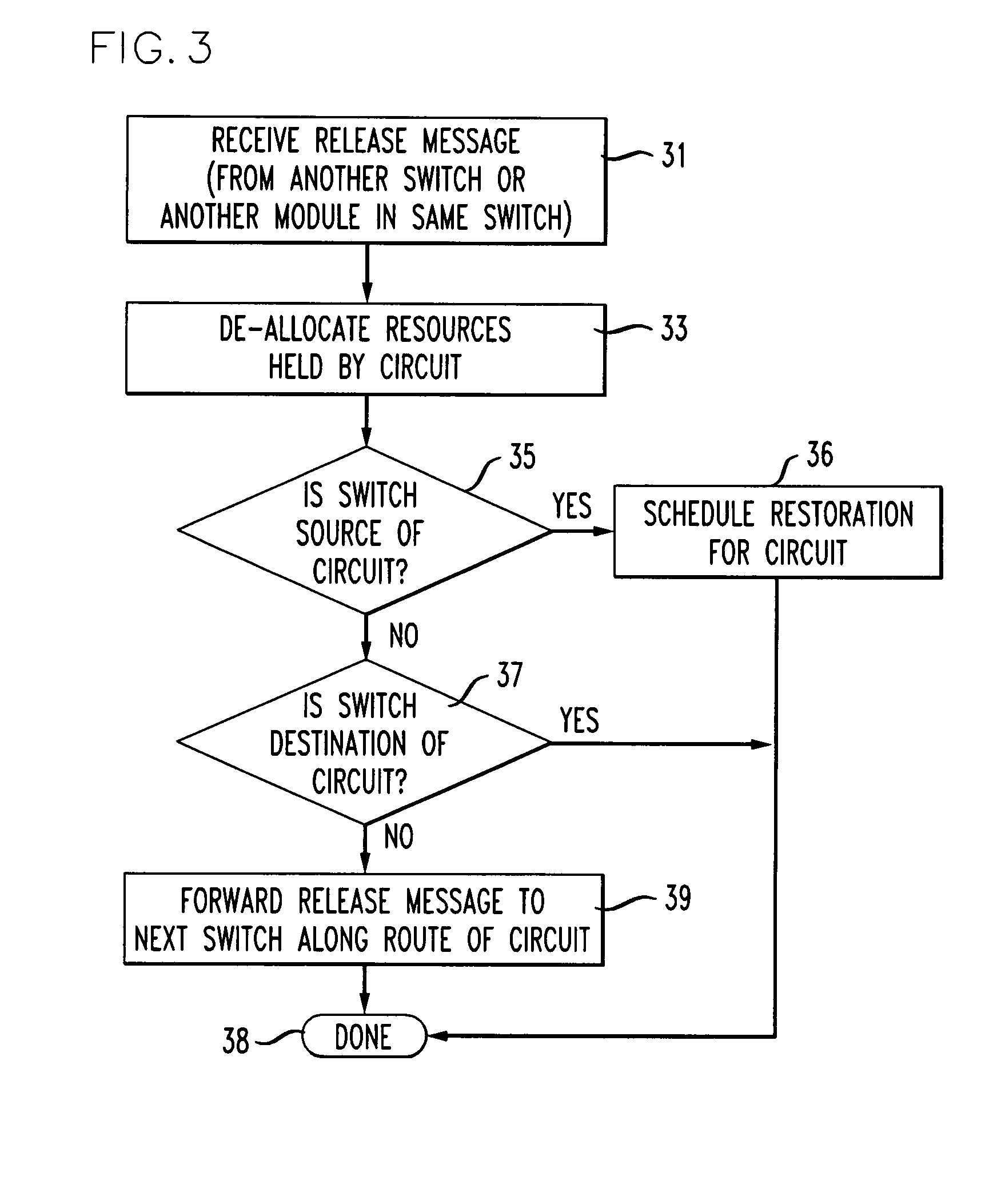
Scheme for routing circuits with dynamic self-adjusting link weights in a network
InactiveUS7613166B1Efficient and economical mannerNetwork can be highData switching by path configurationLink weightCross connection
The present invention relates generally to routing of circuits in a network. More particularly, the invention encompasses a method and an apparatus for routing circuits using dynamic self-adjusting link weights within a network. The invention further includes multiple schemes for routing circuits with dynamic self-adjusting link weights in a SCN (Switched Communication Network). The network could consist of optical, ATM, FR, or IP / MPLS switches and cross-connects.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
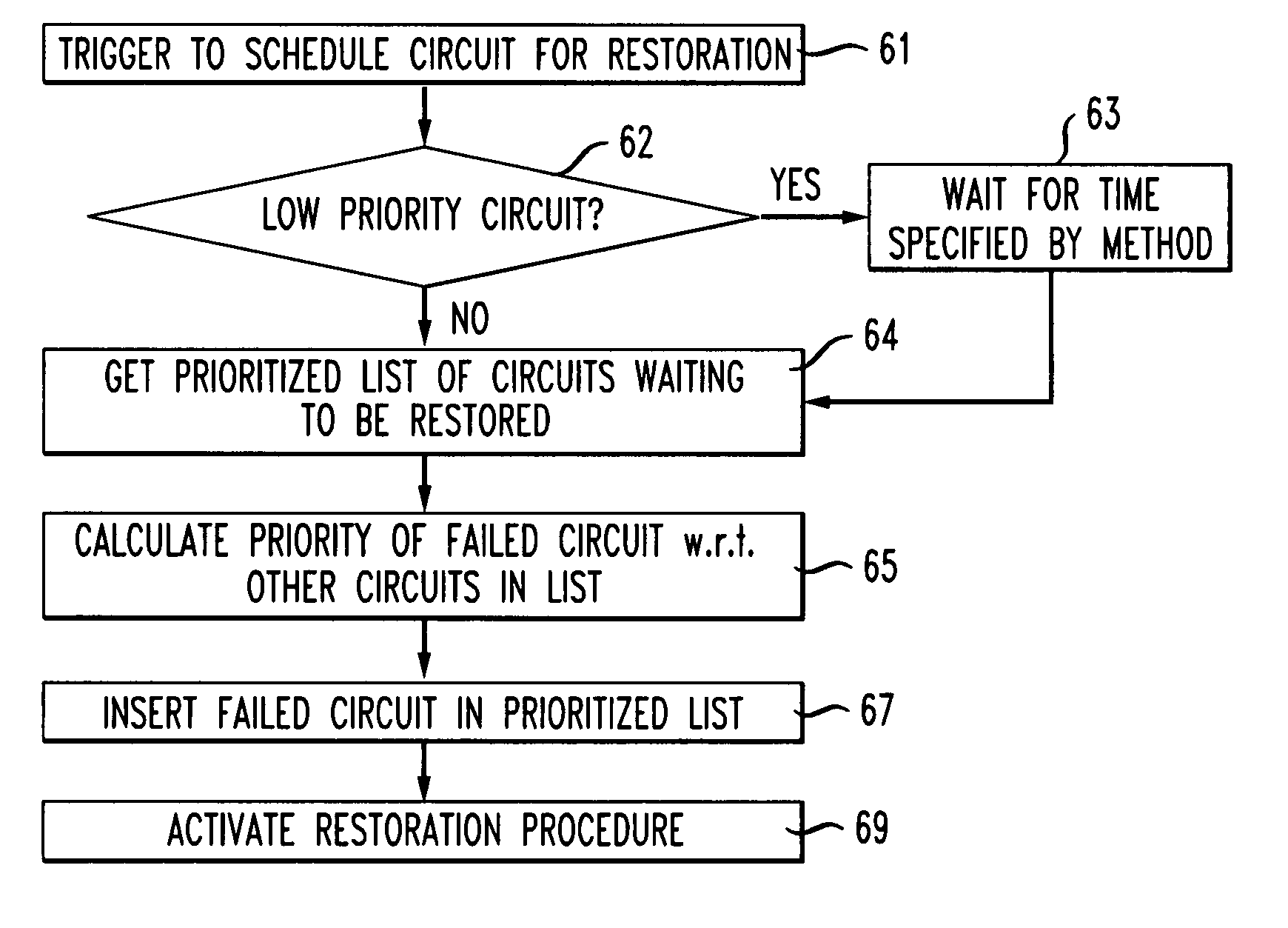
Method and apparatus for delaying start of restoration of low priority services
InactiveUS7542413B1Efficient and economical mannerError preventionTransmission systemsCross connectionDistributed computing
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
Compound horizontal filter assembly machine and process
ActiveUS10299507B2Efficient and economical mannerIncrease chanceCigarette manufactureTobacco smoke filtersComposite filterCigarette filter
An apparatus and processes for producing compound cigarette filters by horizontally assembling multiple filter segments onto the horizontally oriented transverse flutes of a continuous belt. Spaced apart hoppers are serially arranged above the belt, and each hopper contains at least one of the multiple segments of the compound filter being assembled. A transfer structure between each hopper and the belt serially delivers the filter segments to the flutes on the belt, and after such assembly the various filter segments are removed as a group from each flute of the continuous belt. The filter segments are then combined as a group with wrapped tobacco rods to thereby produce filtered cigarettes.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS USA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com