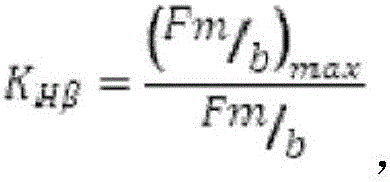Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39results about How to "Compensate for inhomogeneity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
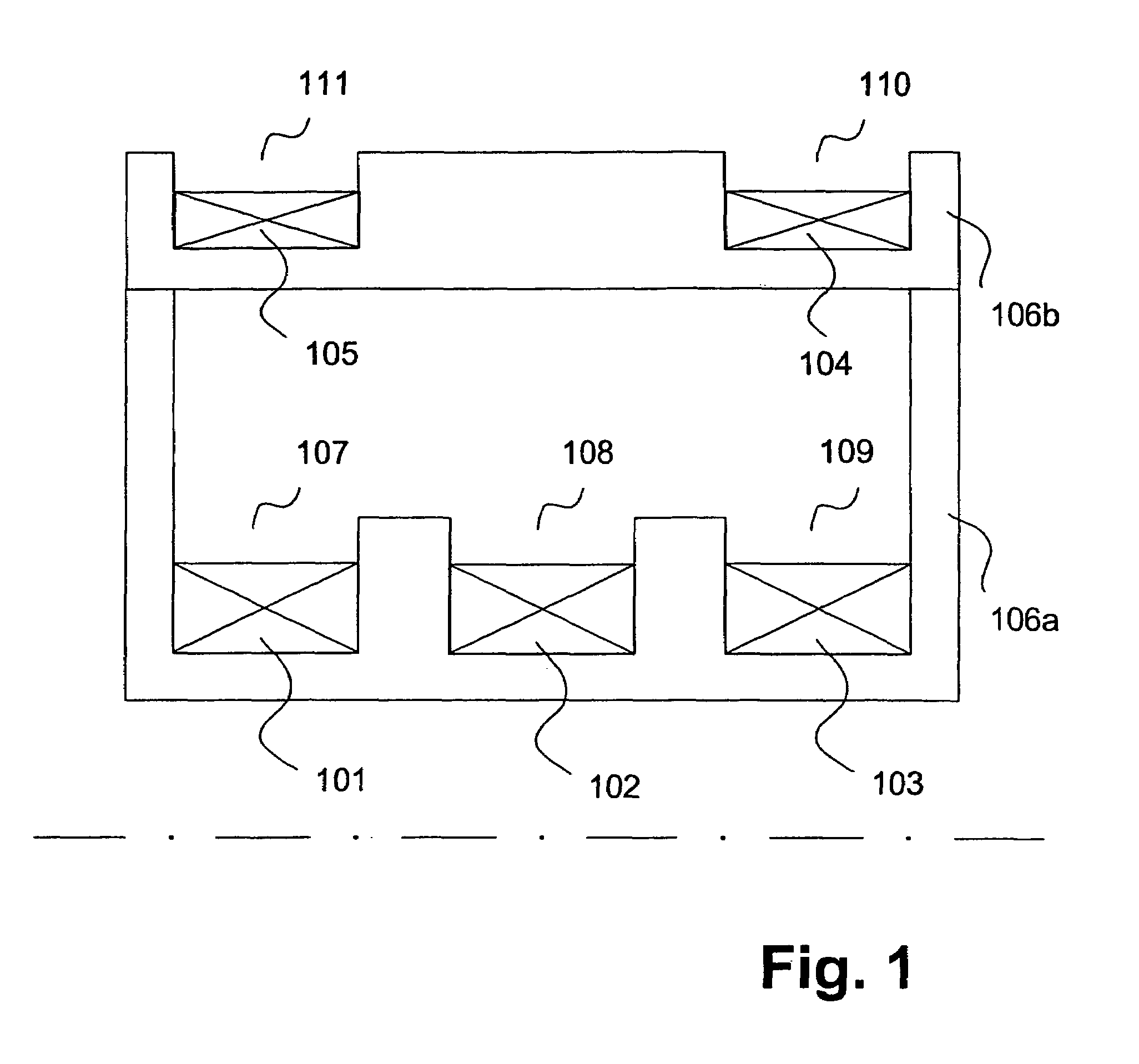
Heating system comprising semiconductor light sources
ActiveUS20160381732A1Improve homogeneityHeating system be improvedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor structureEngineering
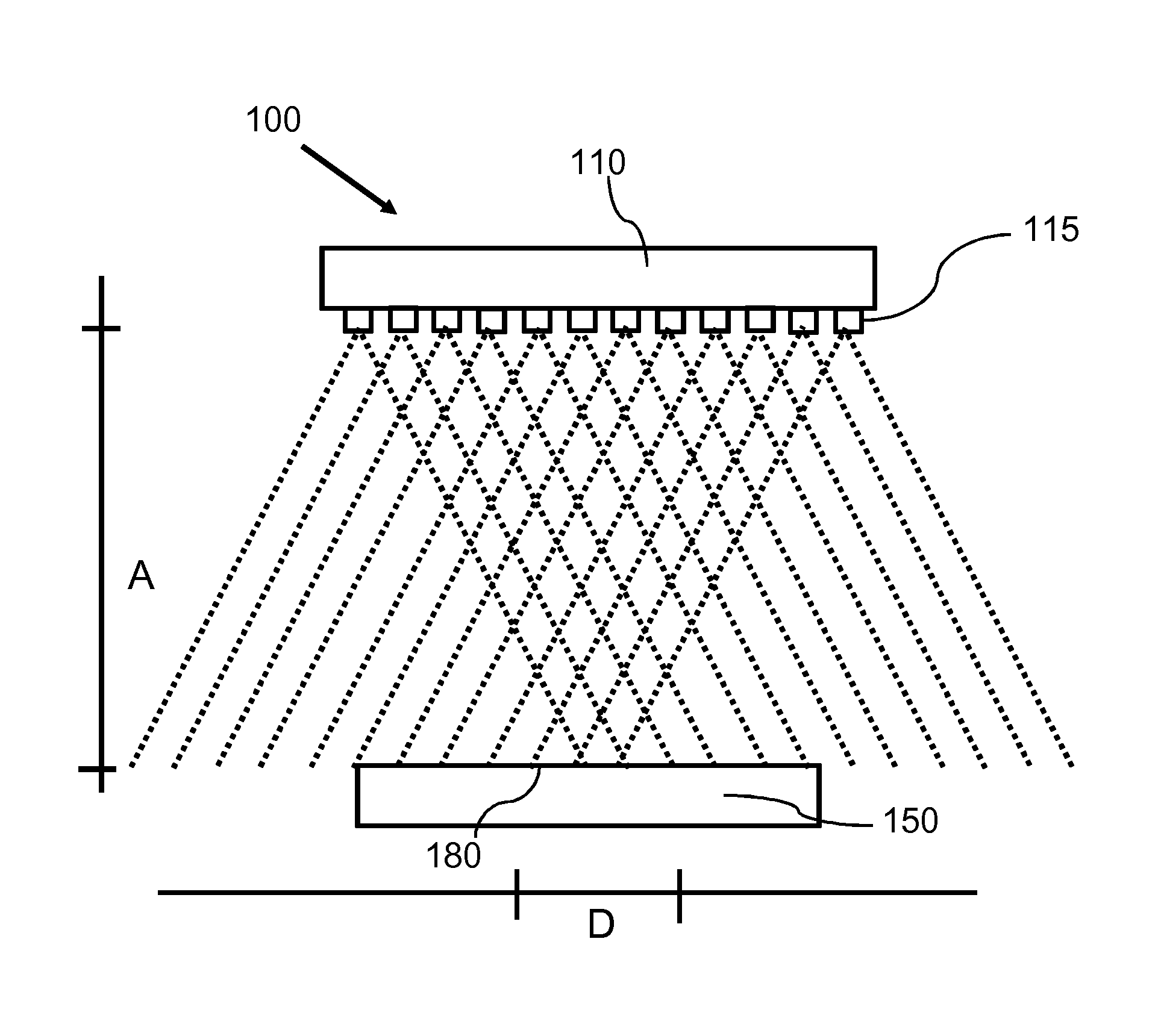
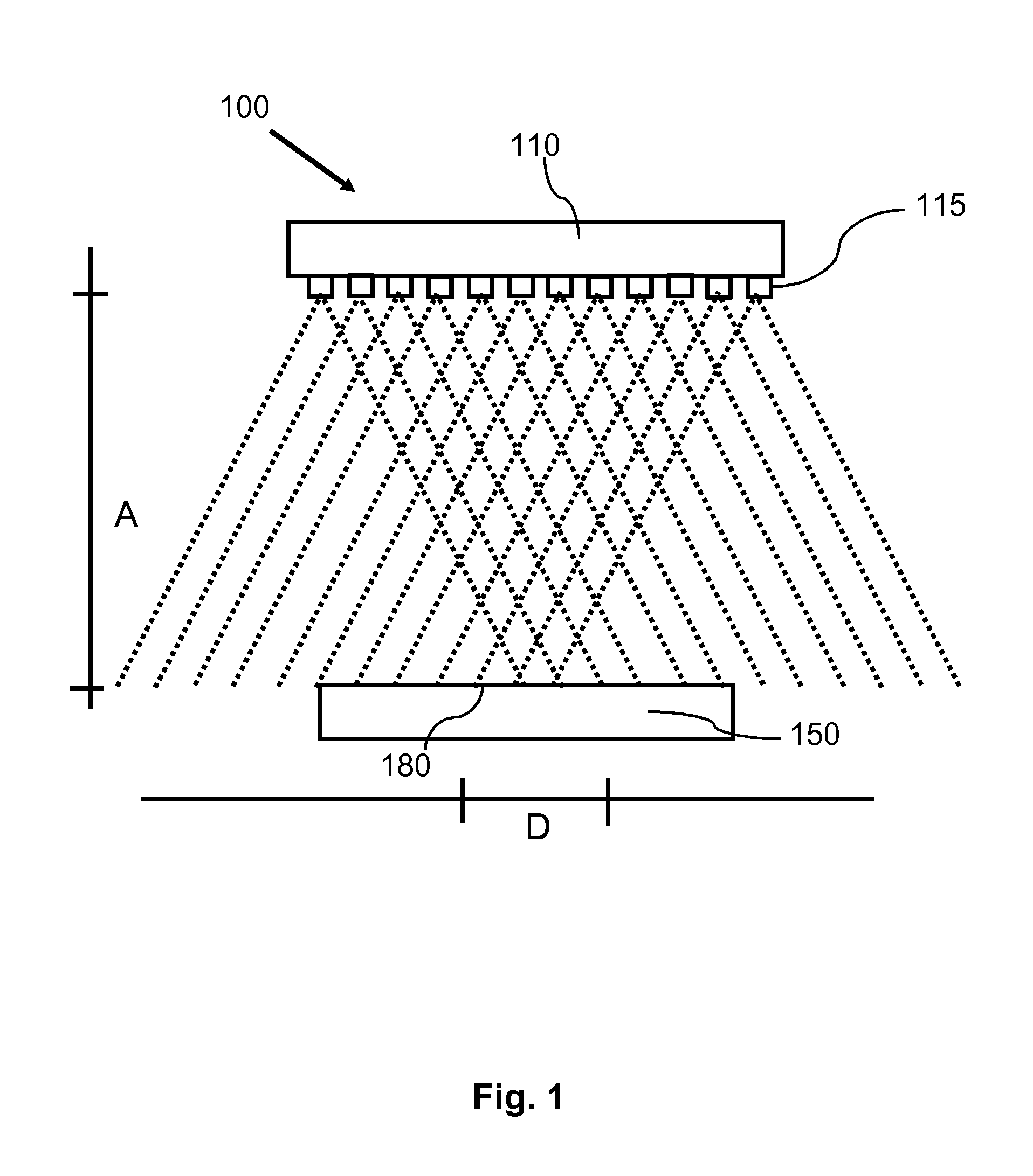
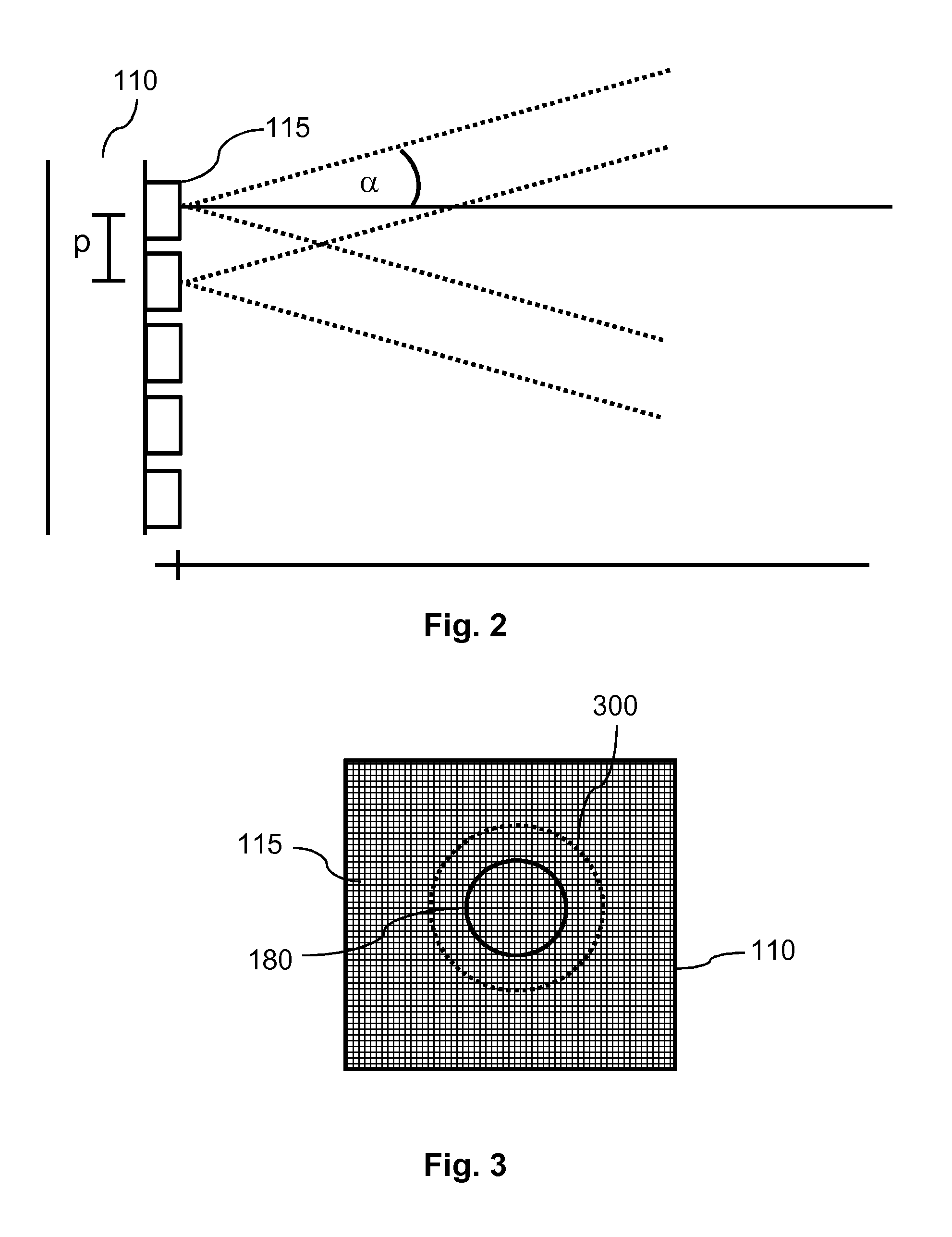
The invention describes a heating system (100) and a corresponding method of heating a heating surface (180) of an object (150, 950) to a processing temperature of at least 100° C., wherein the heating system (100) comprises semiconductor light sources (115), and wherein the heating system (100) is adapted to heat an area element of the heating surface (180) with at least 50 semiconductor light sources (115) at the same time. The heating system (100) may be part of a reactor for processing semiconductor structures. The light emitted by means of the semiconductor light sources (115) overlaps at the heating surface (180). Differences of the characteristic of one single semiconductor light source (115) may be blurred at the heating surface (180) such that a homogeneous temperature distribution across a processing surface of a, for example, wafer may be enabled.
Owner:TRUMPF PHOTONIC COMPONENTS GMBH
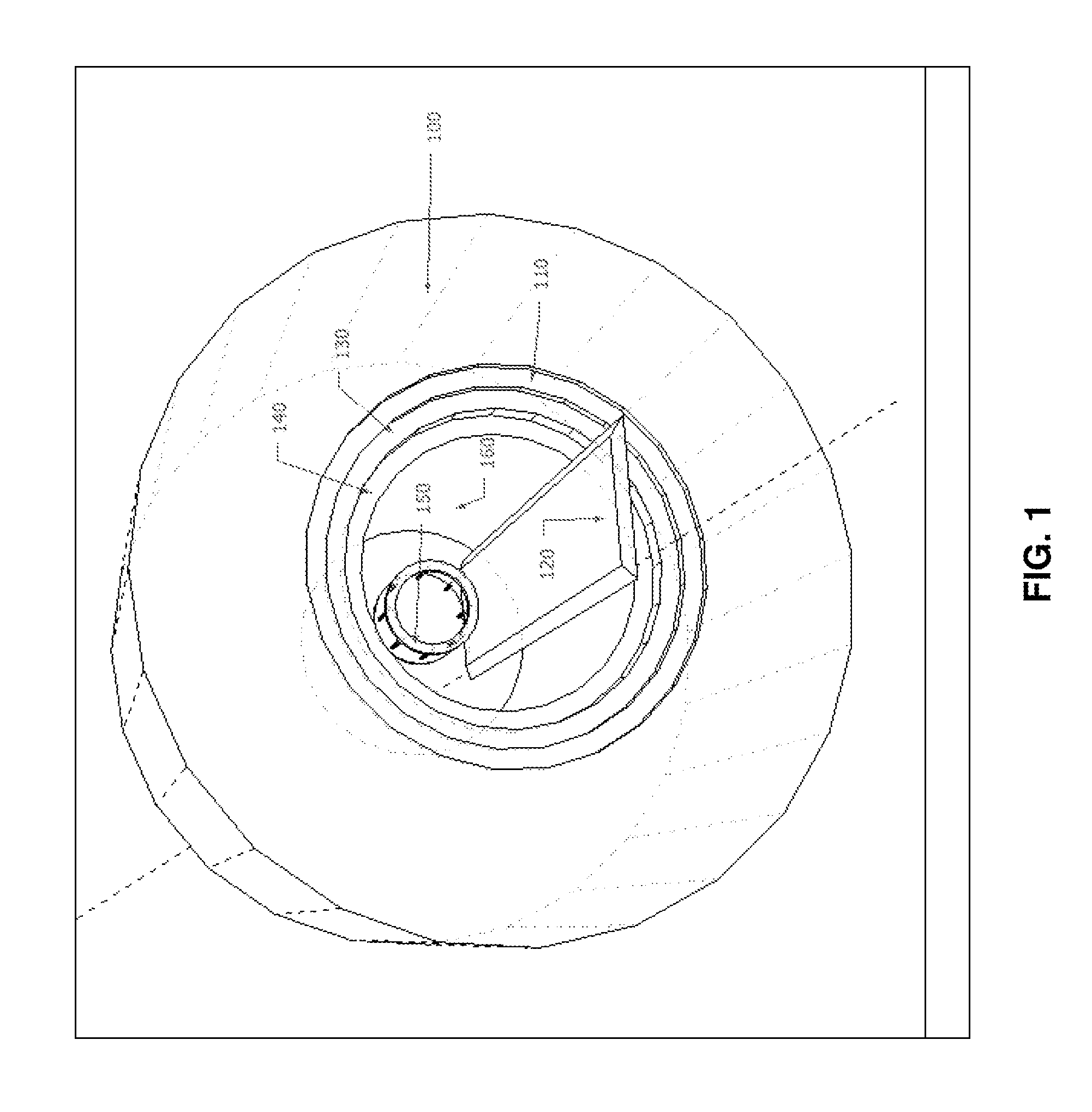
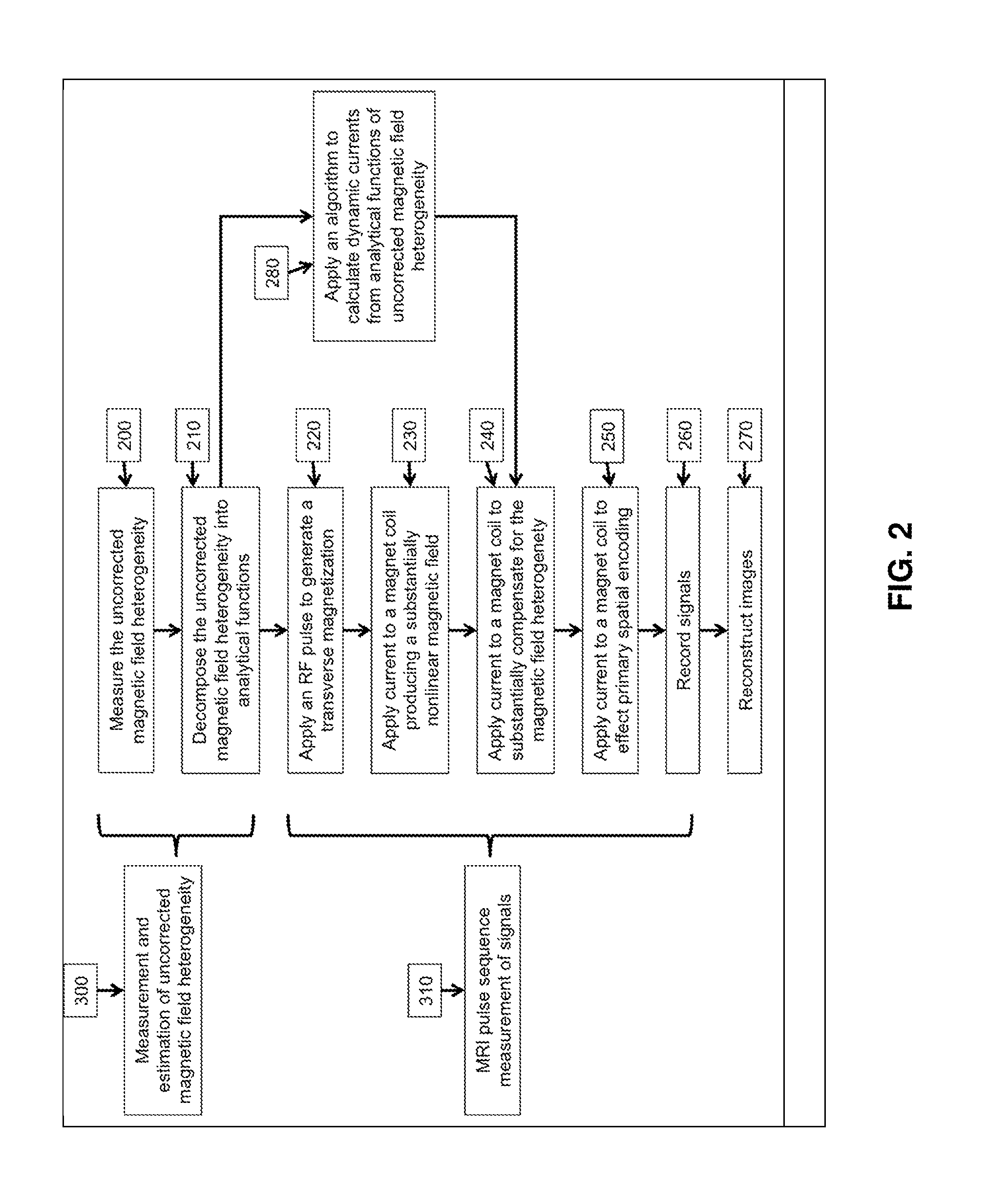
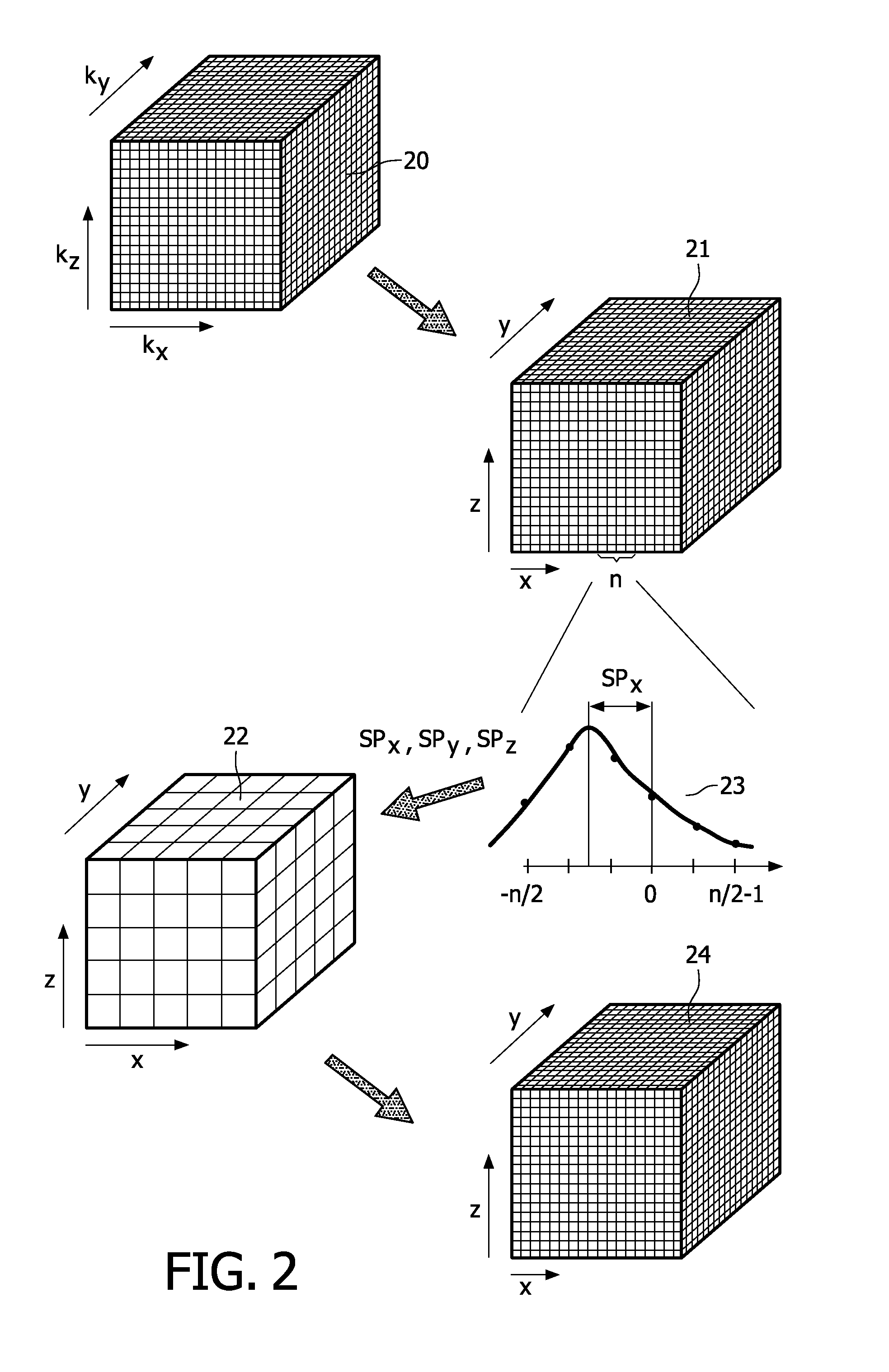
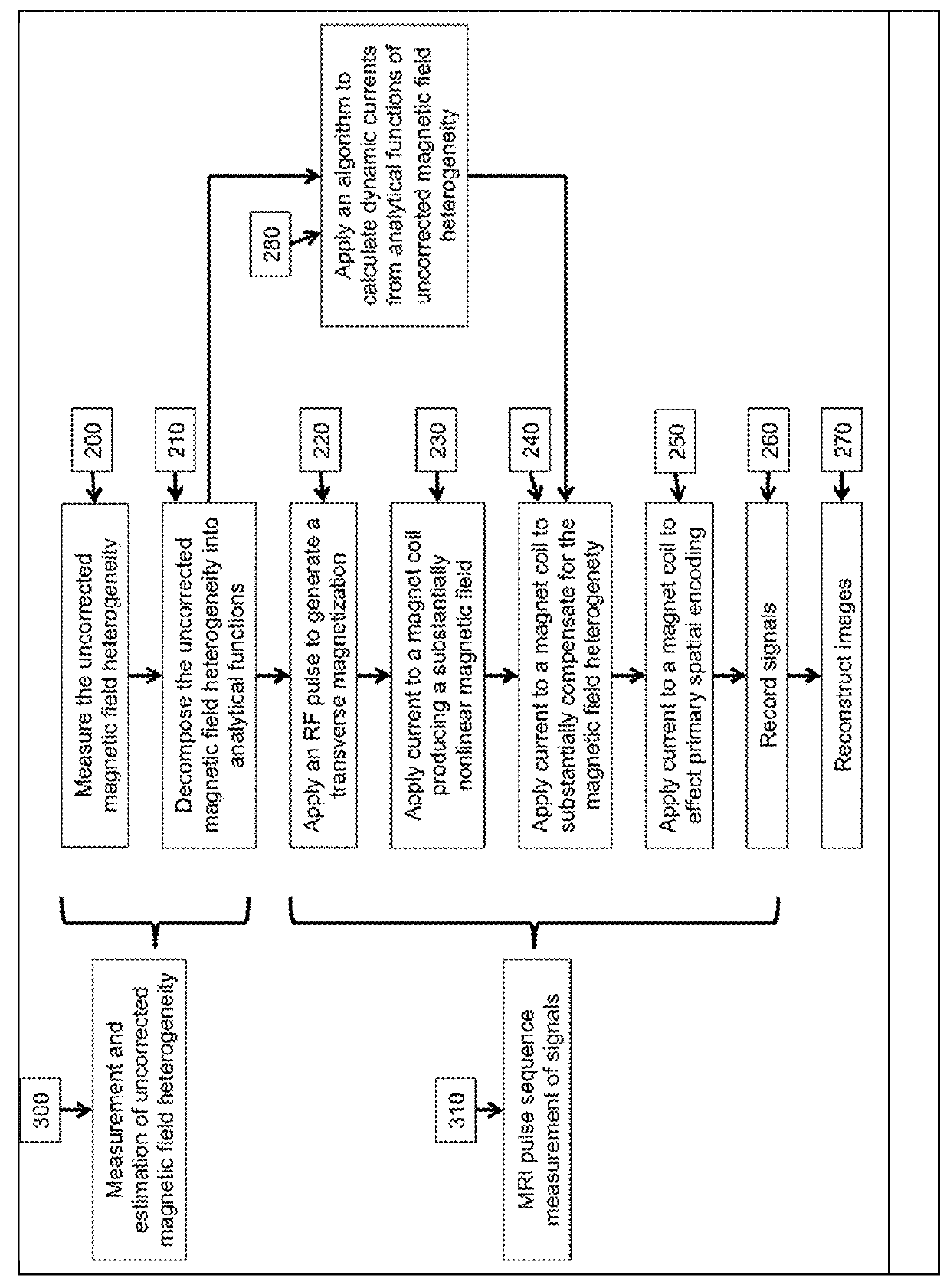
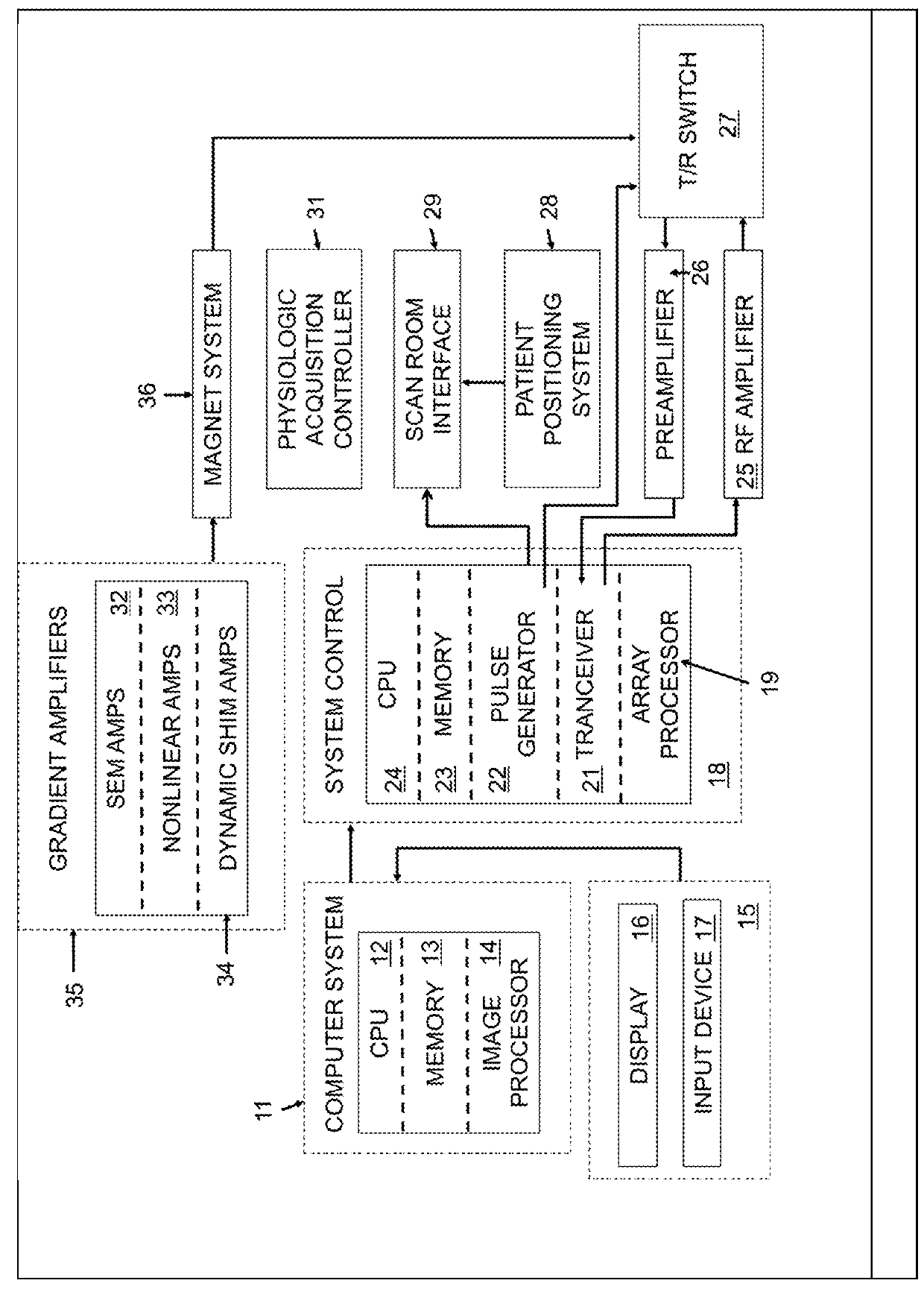
Method of dynamically compensating for magnetic field heterogeneity in magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20120249137A1Lower requirementMinimize homogeneityMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse magnetizationMR - Magnetic resonance
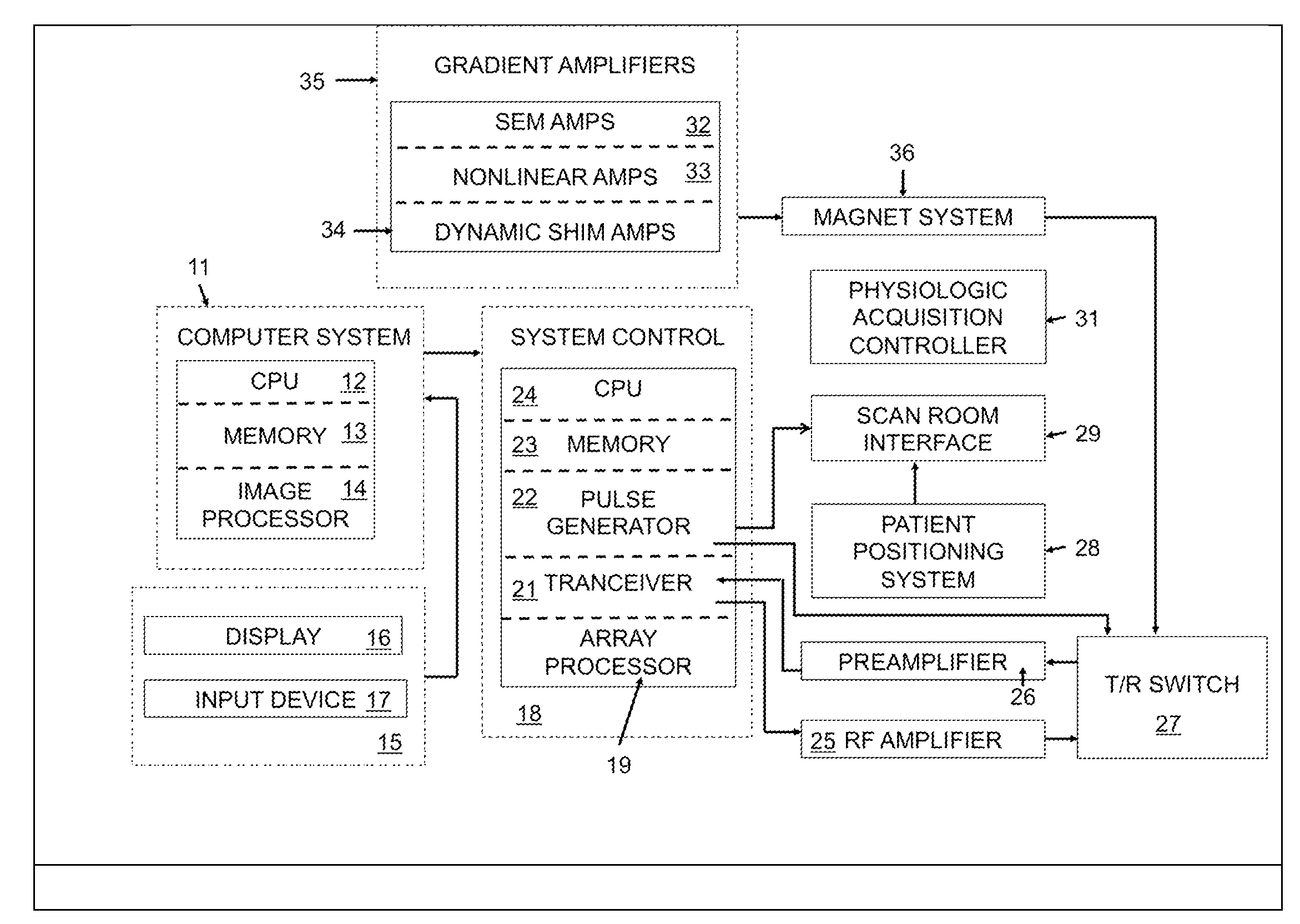
A method to compensate for the magnetic field heterogeneity inside an object of investigation in a MR device obtains an uncorrected magnetic field distribution of the object and executes an MR sequence with a desired k-space coverage by applying RF pulses to generate a transverse magnetization within the object. MR signal data is recorded, magnetic field shimming parameters are dynamically updated and MR signal data are reconstructed to produce images or localized spectroscopic data. Artifacts in a reconstructed image resulting from an uncorrected magnetic field distribution are suppressed by temporally separating MR signals originating from at least two different sub-volumes within a volume of transverse magnetization by generating a nonlinear phase distribution within the object and by dynamically updating shimming parameters to compensate for the field inhomogeneity distributions within the different sub-volumes in the volume of transverse magnetization.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
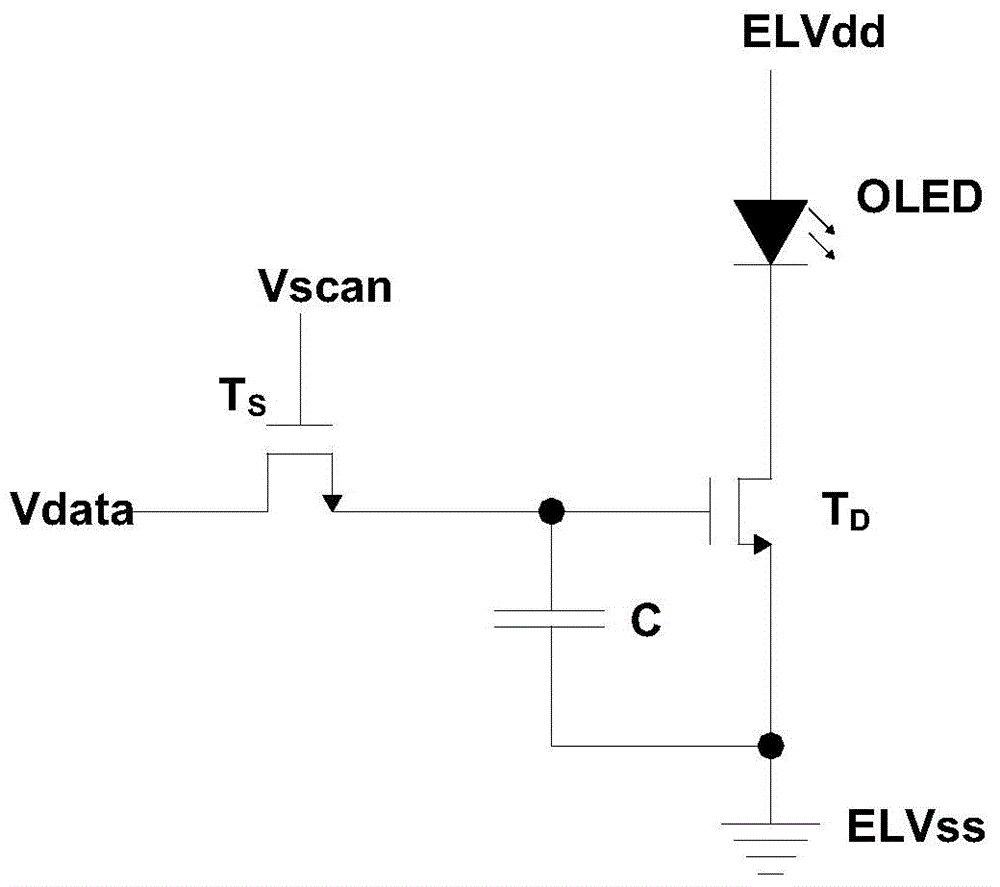
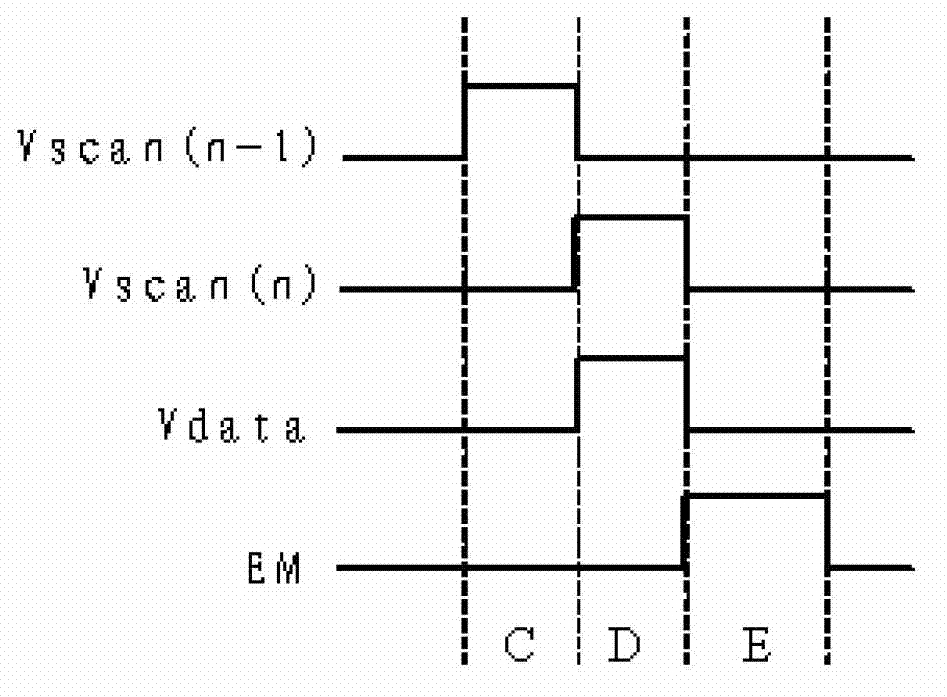
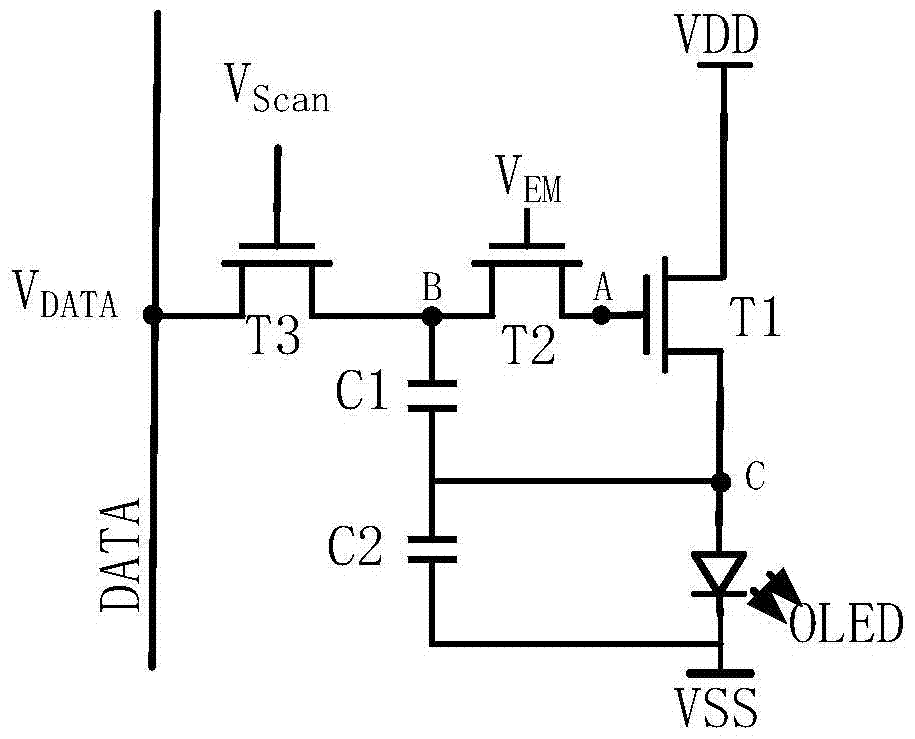
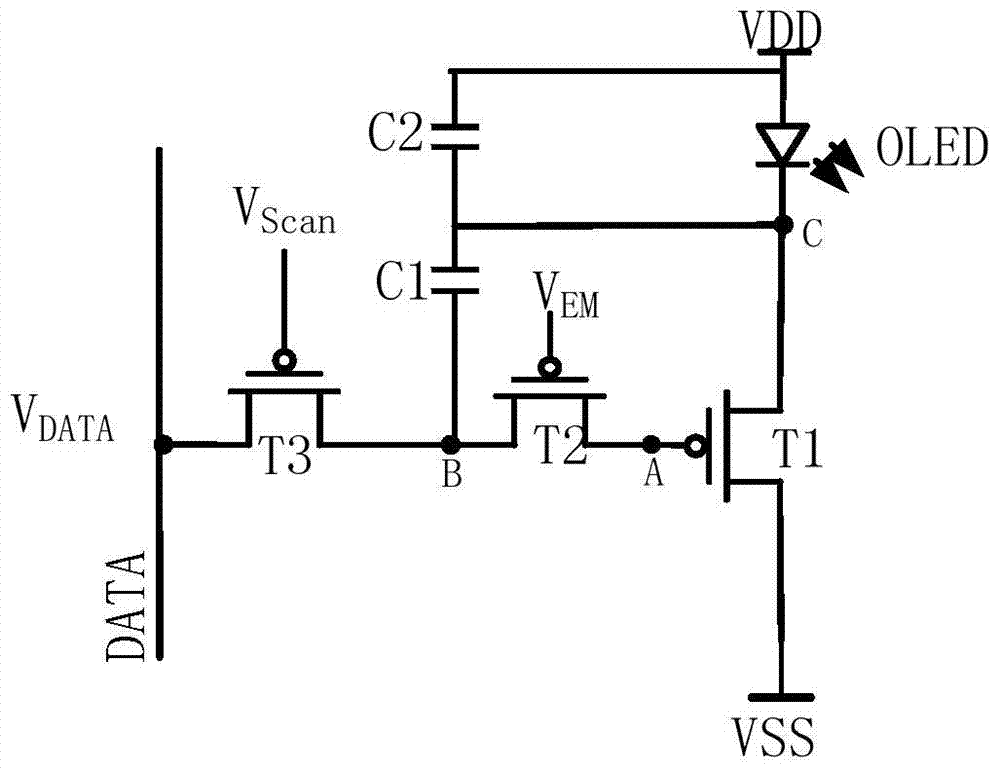
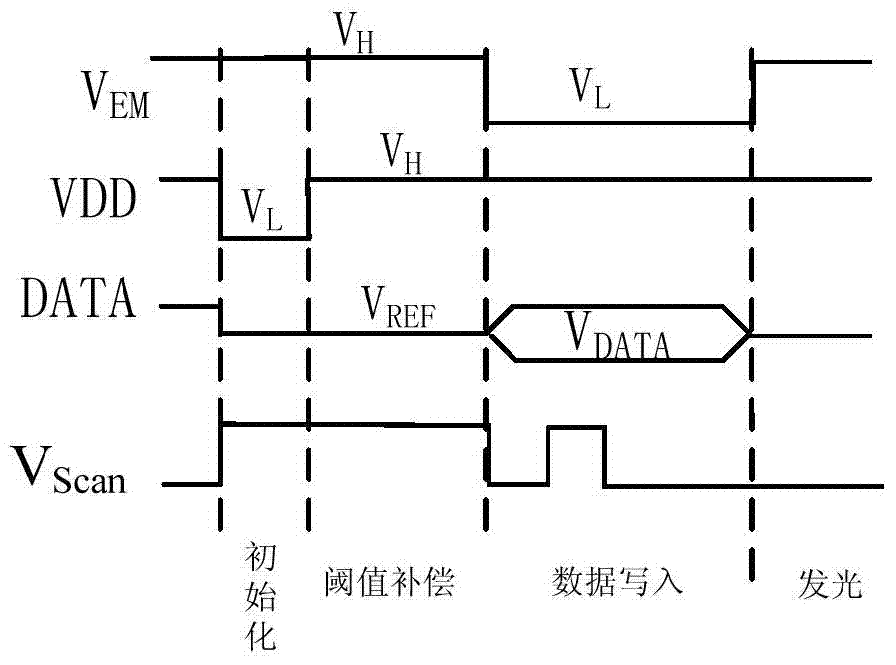
Pixel circuit, driving method thereof and display device
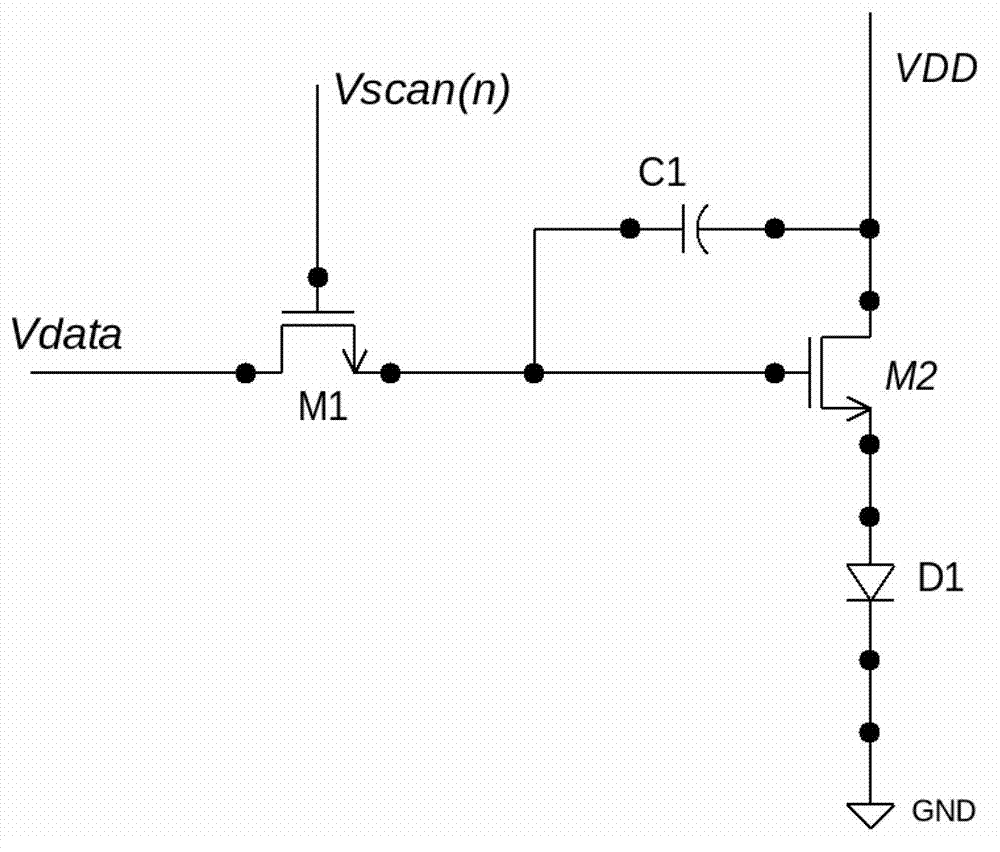
ActiveCN104821150ACompensate for inhomogeneitySimple structureStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesCapacitanceDisplay device
The invention provides a pixel circuit. The pixel circuit includes a driving transistor and a light-emitting element which are connected in series between a first electric level end and a second electric level end, and as well a second transistor, a third transistor, a fourth transistor, a first capacitor and a second capacitor, wherein the second capacitor is connected between the control pole of the driving transistor and the second end of the light-emitting element. Threshold voltage is stored through the first capacitor, so that threshold voltage compensation of the driving transistor and the light-emitting element can be realized, and therefore, the nonuniformity of the display of the pixel circuit can be compensated. According to the above pixel circuit, the invention also provides a display device. According to the display device, a first control line and a light-emitting control line are both global lines. The invention further discloses a pixel circuit driving method.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Compact superconducting magnet configuration with active shielding having a shielding coil contributing to field formation
ActiveUS7898258B2Sizable impactImprove field uniformityMagnetic measurementsMagnetsSuperconducting CoilsHomogeneous magnetic field
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
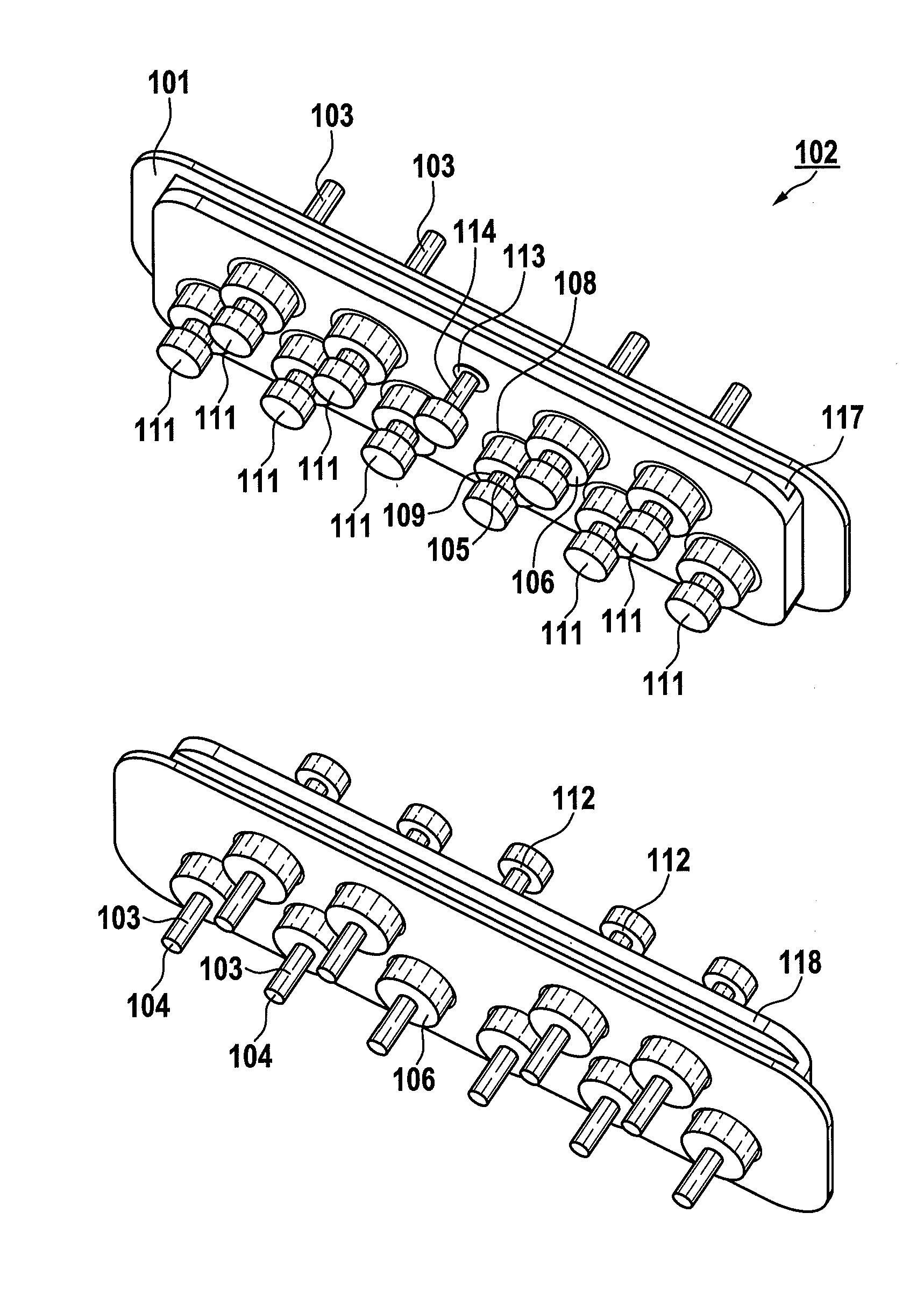
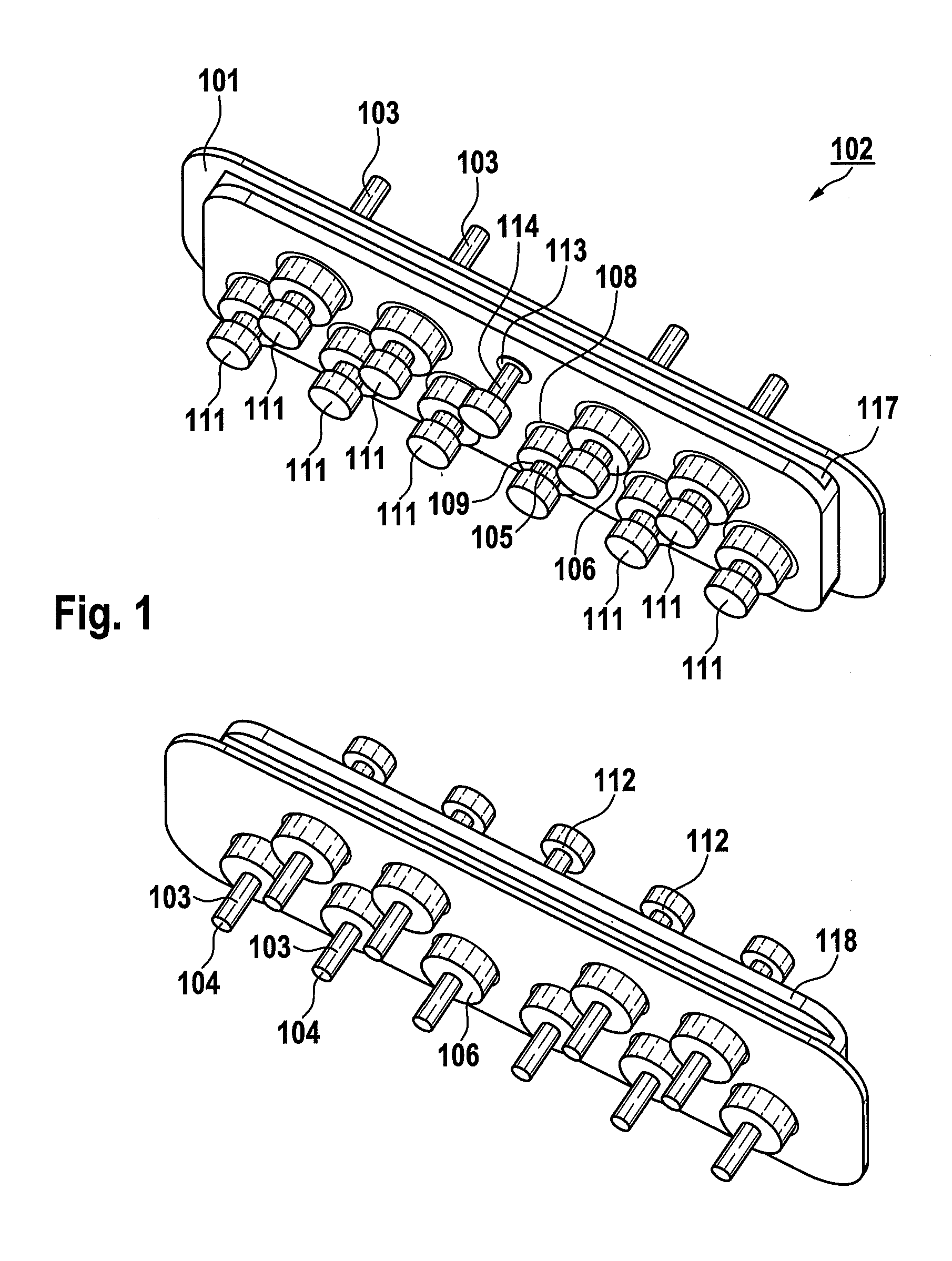
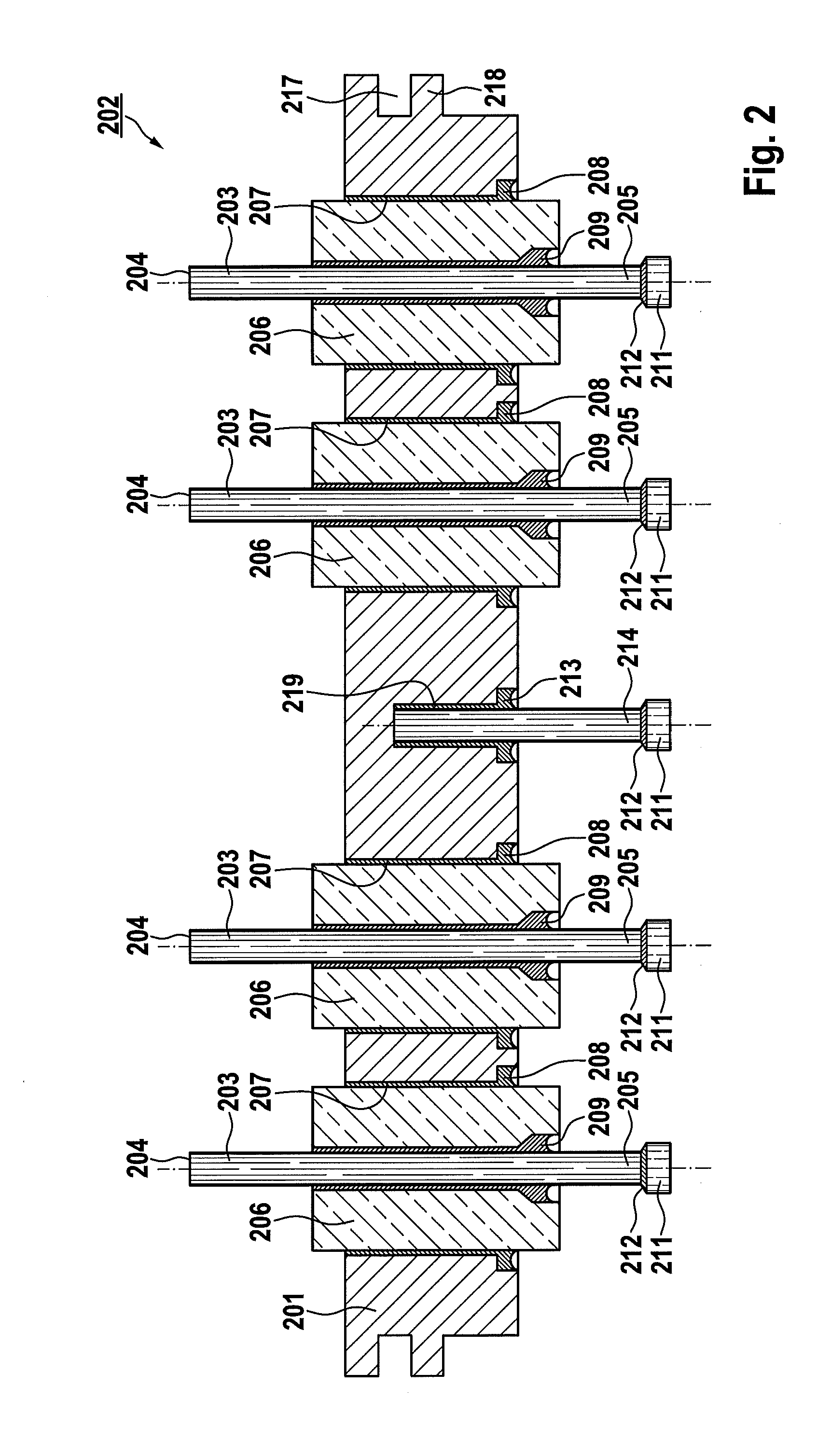
Electrical Feedthrough, in Particular for Medical Implants
ActiveUS20110232961A1Improve carrying capacityFirmly connectedAnti-noise capacitorsElectrotherapyBiomedical engineeringMedical treatment
An electrical feedthrough, in particular for use in an electro-medical implant, having a flange enclosing at least one feedthrough bushing and at least one terminal pin enclosed by the at least one feedthrough bushing, the terminal pin having at least one section which can be joined at a lower energy in the interior of the implant.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Pixel circuit and driving method thereof, array substrate and display device
InactiveCN105096826ACompensate for inhomogeneityImprove uniformityStatic indicating devicesElectricityActive matrix
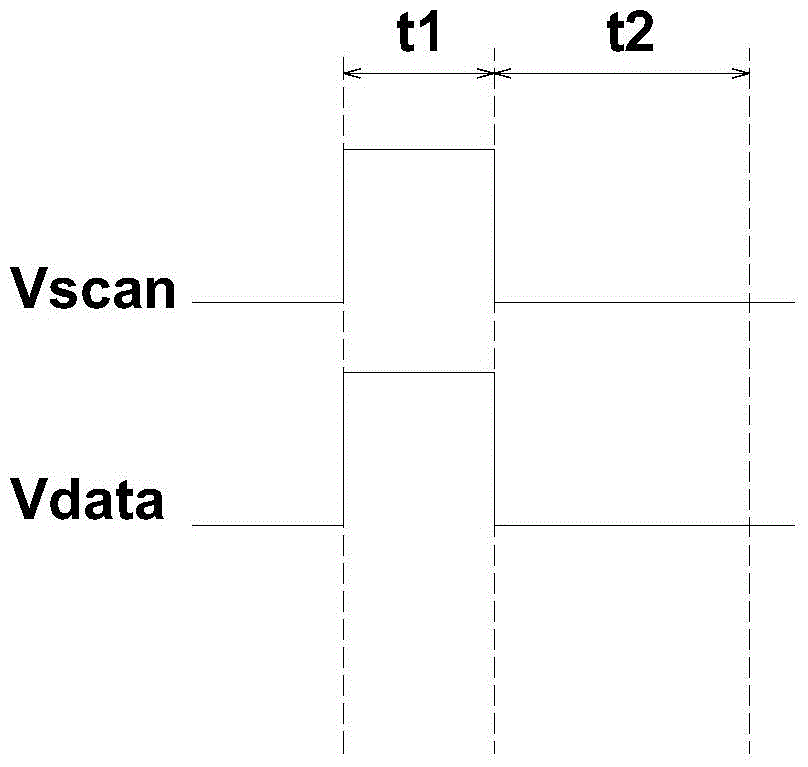
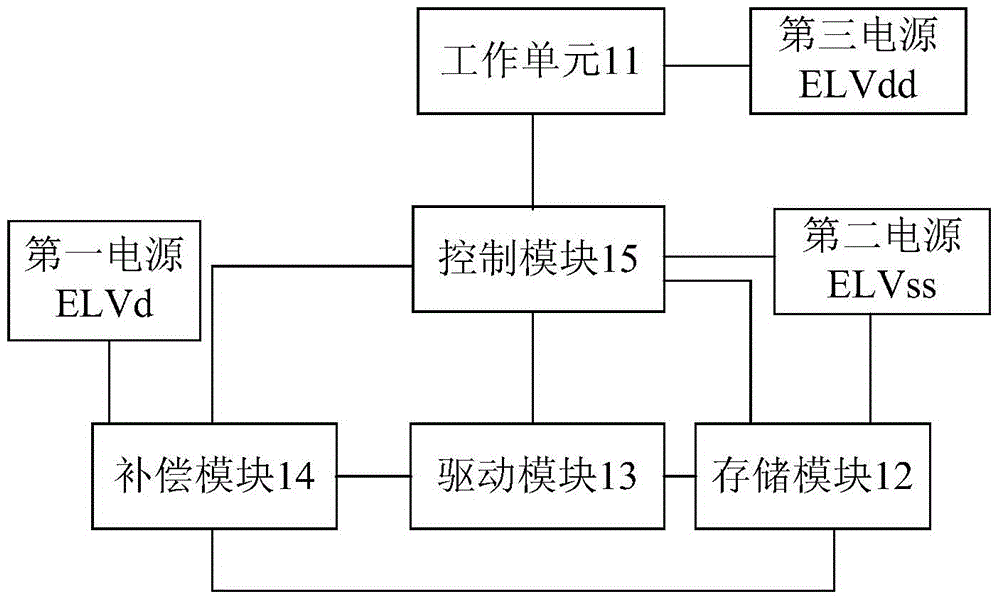
The invention provides a pixel circuit and a driving method thereof, an array substrate and a display device, belongs to the technical field of display, and can solve the problems that the threshold voltage change of an existing driving transistor influences the brightness uniformity of an OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) and an AMOLED (Active Matrix / Organic Light Emitting Diode) does not emit light uniformly due to the driving voltage change of the gate of the driving transistor caused by electric leakage of a switching transistor. The pixel circuit comprises a working unit, a storage module, a driving module, a compensation module and a control module; at the initialization phase, the compensation module and the driving module are initialized under the control of a first power supply; at the data write-in and compensation phase, a data signal input end charges the storage module through the compensation module; and at the display phase, the control module is enabled, and the storage module discharges electricity to the working unit through the driving module, so that the working unit emits light, and the influence of the threshold voltage drift of the driving module on the performance of the working unit is reduced.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Pixel circuit and driving method thereof, array substrate and display device
InactiveCN103208254AImprove picture uniformityCompensate for inhomogeneityStatic indicating devicesIdentification meansCapacitanceEngineering
The invention provides a pixel circuit and a driving method thereof, an array substrate and a display device and belongs to the technical field of organic light-emitting display. The pixel circuit comprises a driving transistor, a first switch transistor, a storage capacitor and a light-emitting device and further comprises a threshold compensating circuit. The threshold compensating circuit is formed by a second switch transistor, a third switch transistor, a fourth switch transistor and a coupling capacitor. The threshold compensating circuit can effectively compensate for non-uniformity of threshold voltage of the driving transistor. The driving method comprises a precharge stage, a compensation stage and a light-emitting stage. The array substrate comprises a pixel unit circuit and is stable in performance. The display device comprises the array substrate, and picture uniformity is greatly improved.
Owner:HEFEI BOE OPTOELECTRONICS TECH +1
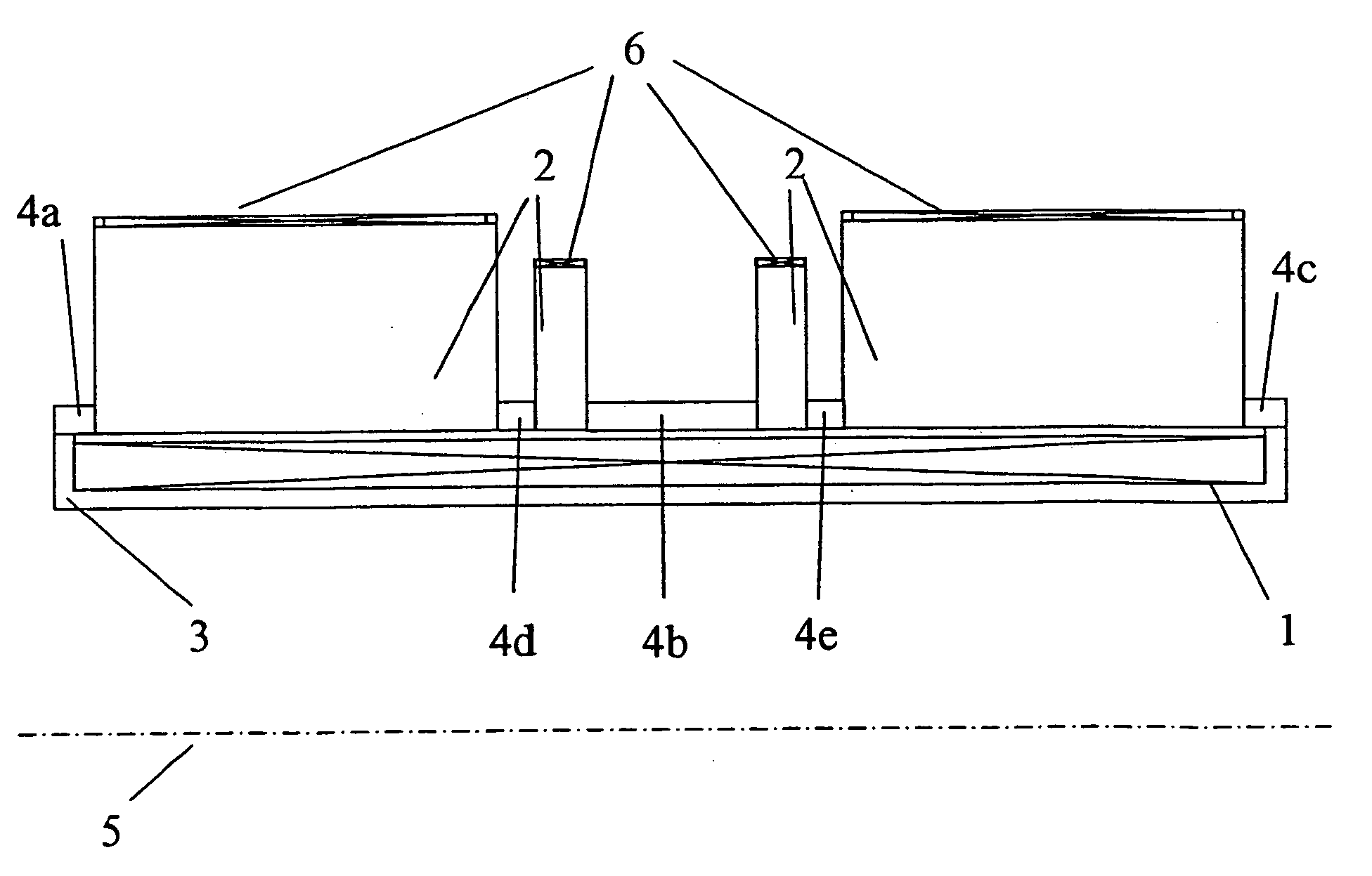
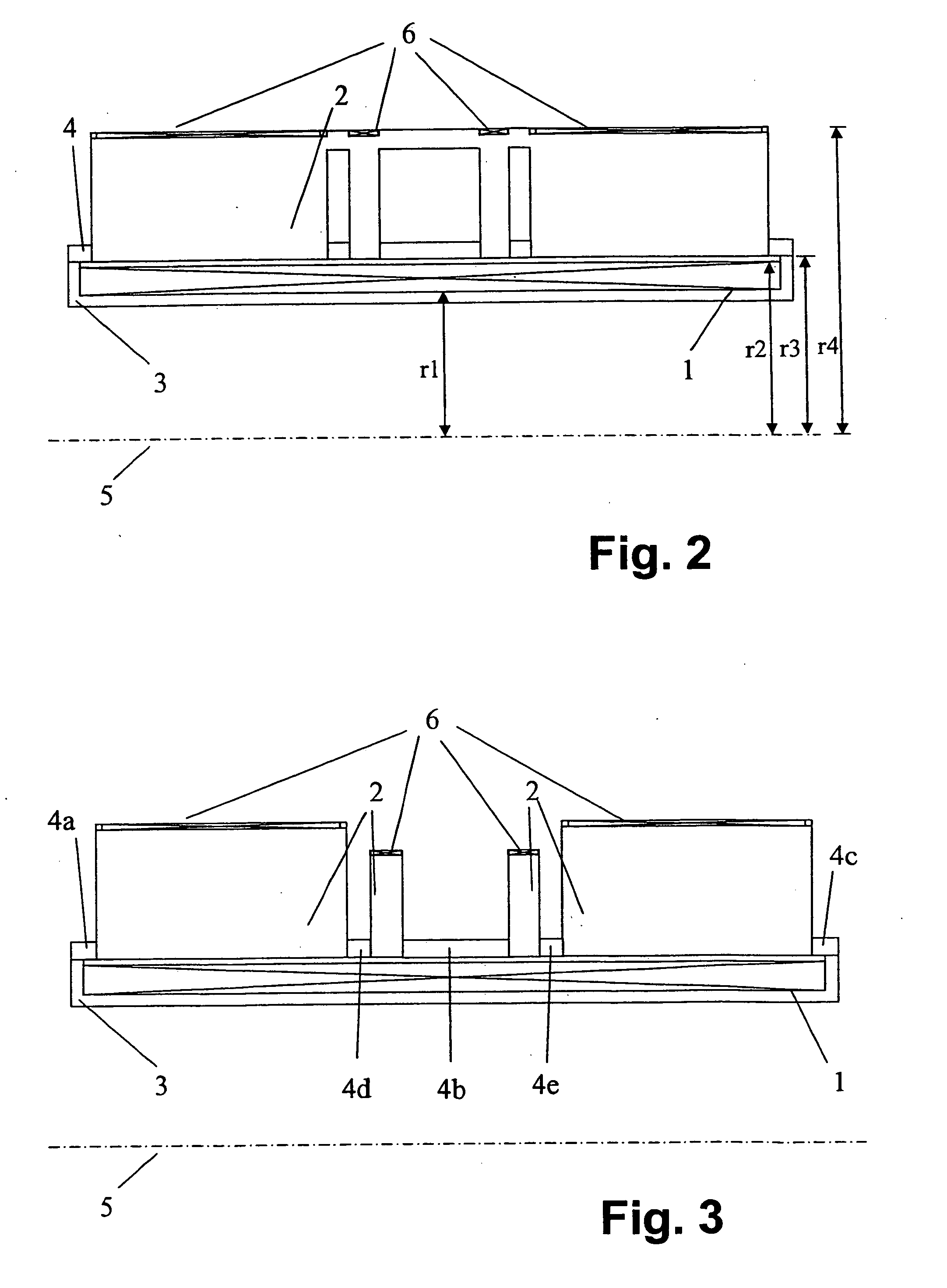
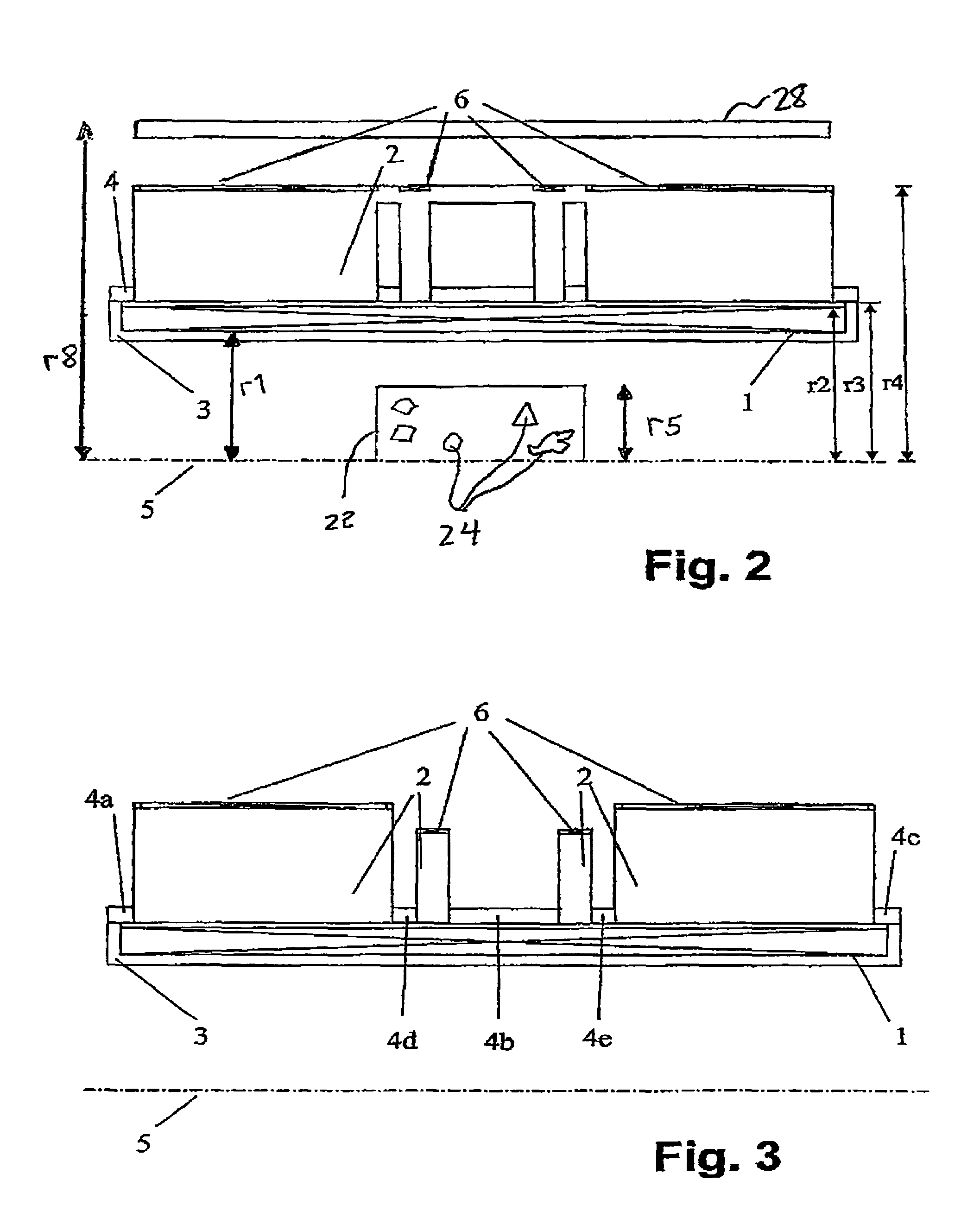
Hybrid magnet configuration
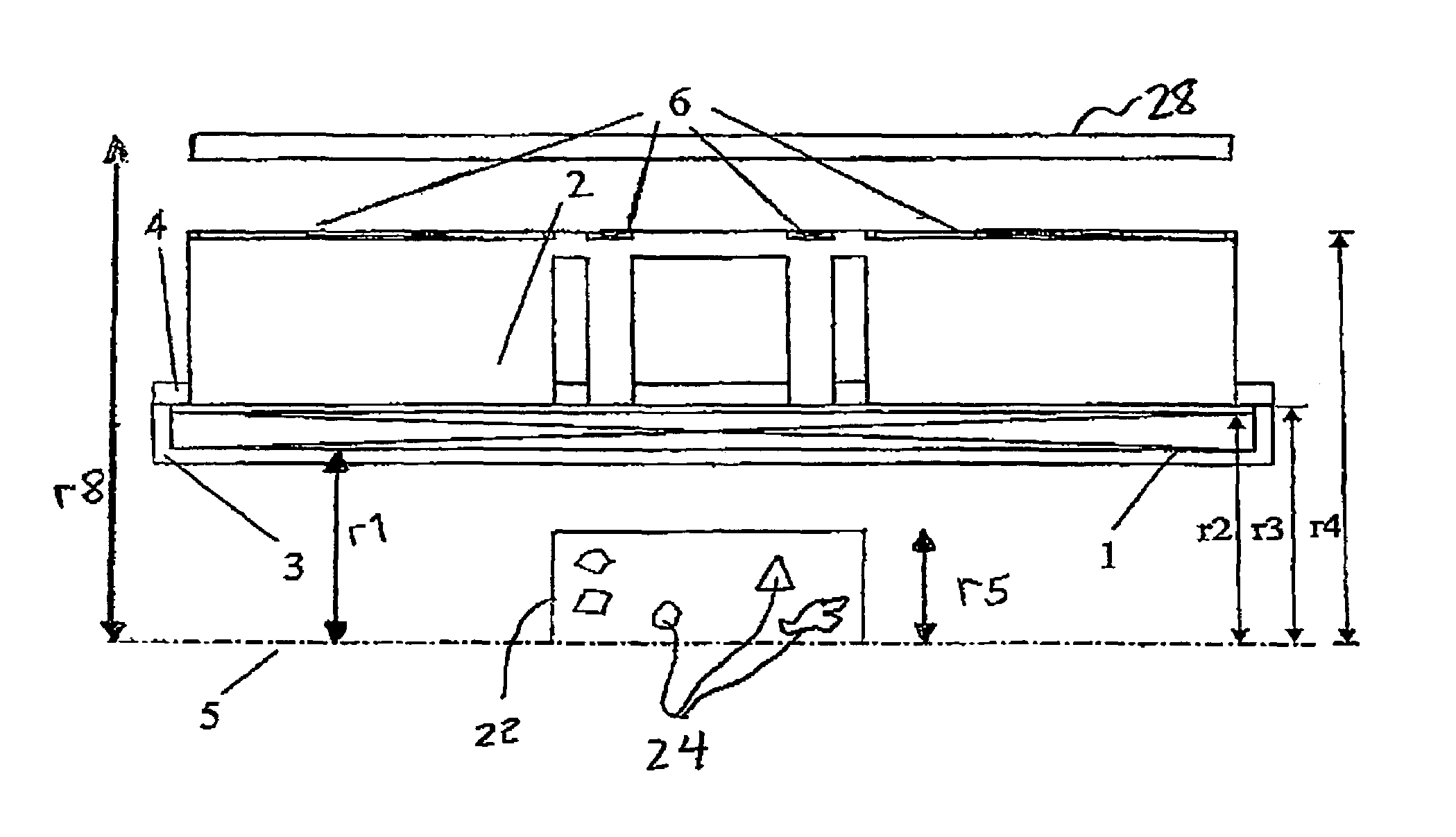
ActiveUS20060061361A1Facilitates individual adjustmentMinimize magnetic fringe fieldMagnetic measurementsMagnetsNuclear magnetic resonanceMagnet
A co-axial magnet configuration for the production of a magnetic field and investigational volume which is suitable for measurement of magnetic resonance has at least one superconducting solenoid coil or solenoid coils which are radially nested within each other, wherein the windings of the solenoid coil(s) in a radial region about the axis of the magnetic configuration are disposed between r1 and r2, wherein r1<r2 is characterized in that the windings are surrounded by at least one rotationally symmetric magnet body made from ferromagnetic material which extends over a radial region between r3 and r4 wherein r3<r4 wherein r2<r3<1.3 r2 and r4>1.3 r3, wherein the rotationally symmetric magnet body or bodies are structured, dimensioned and positioned in such a fashion that the magnetic field is homogenized in the investigational volume and the magnetic fringe field outside the magnet configuration is essentially suppressed to permit the production of strong magnetic fields of high homogeneity without requiring notches in the coil configuration.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Compact superconducting magnet configuration with active shielding having a shielding coil contributing to field formation
ActiveUS20090261246A1Good effectEasy alignmentElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMagnetic measurementsSuperconducting CoilsHomogeneous magnetic field
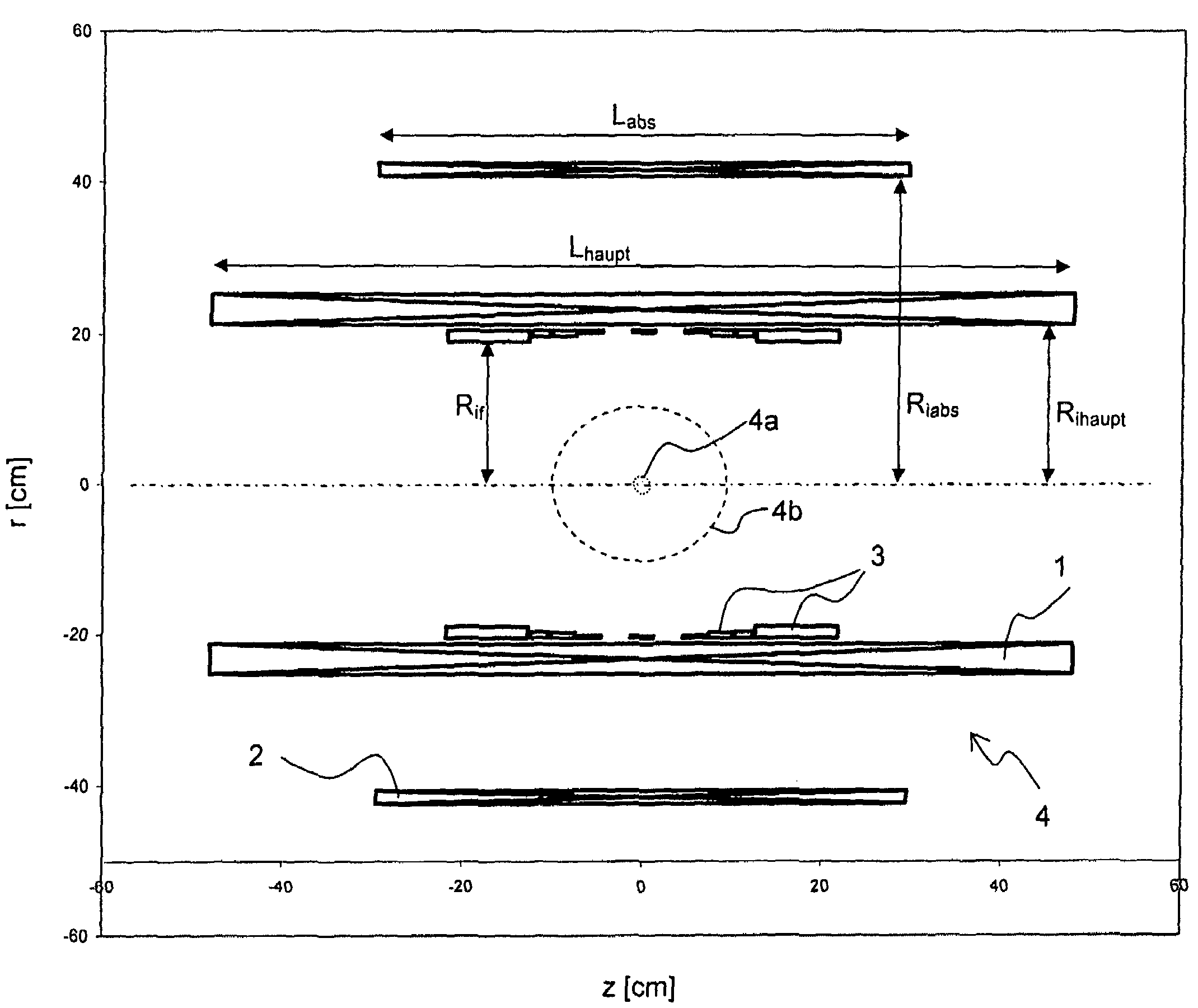
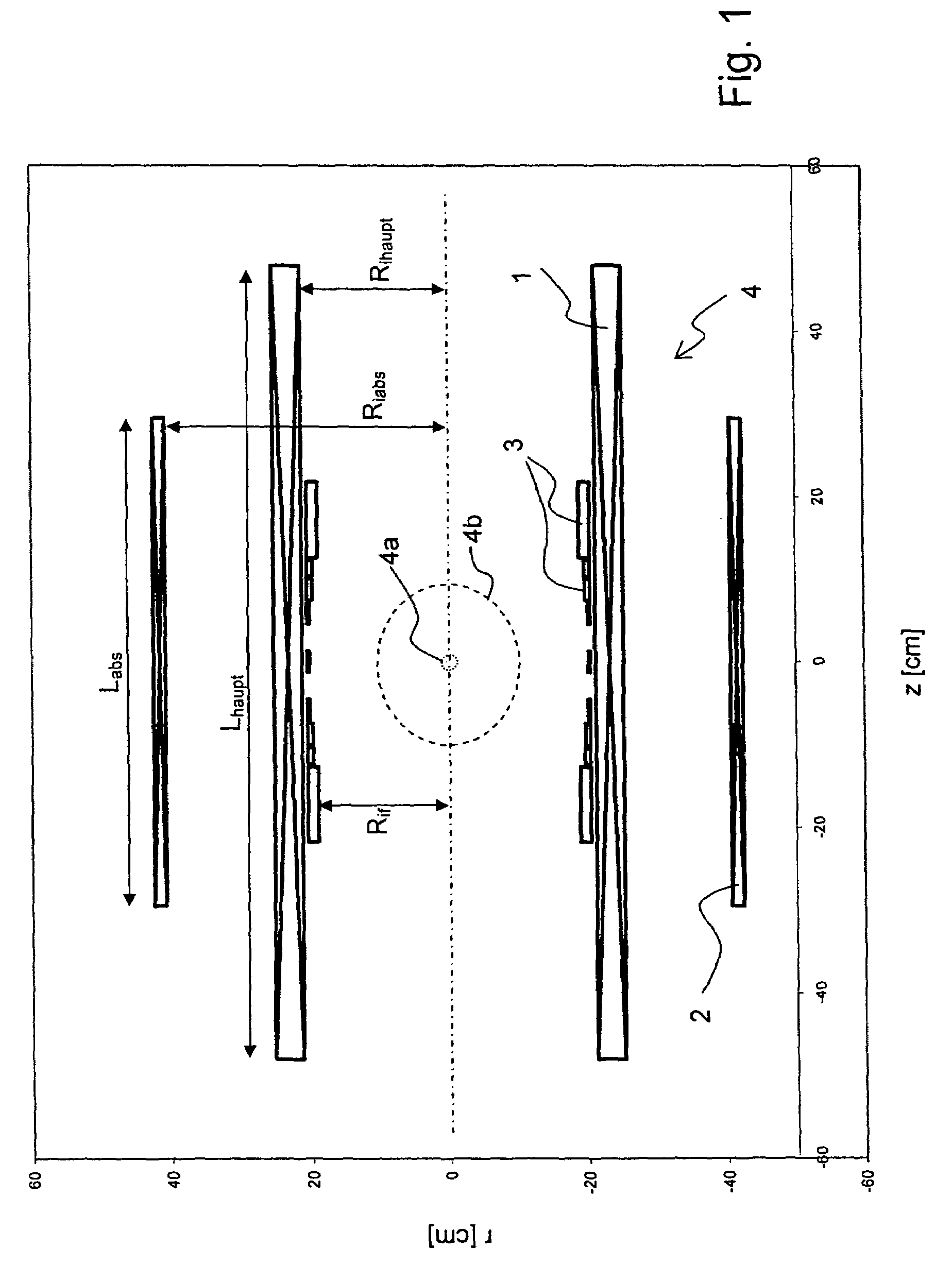
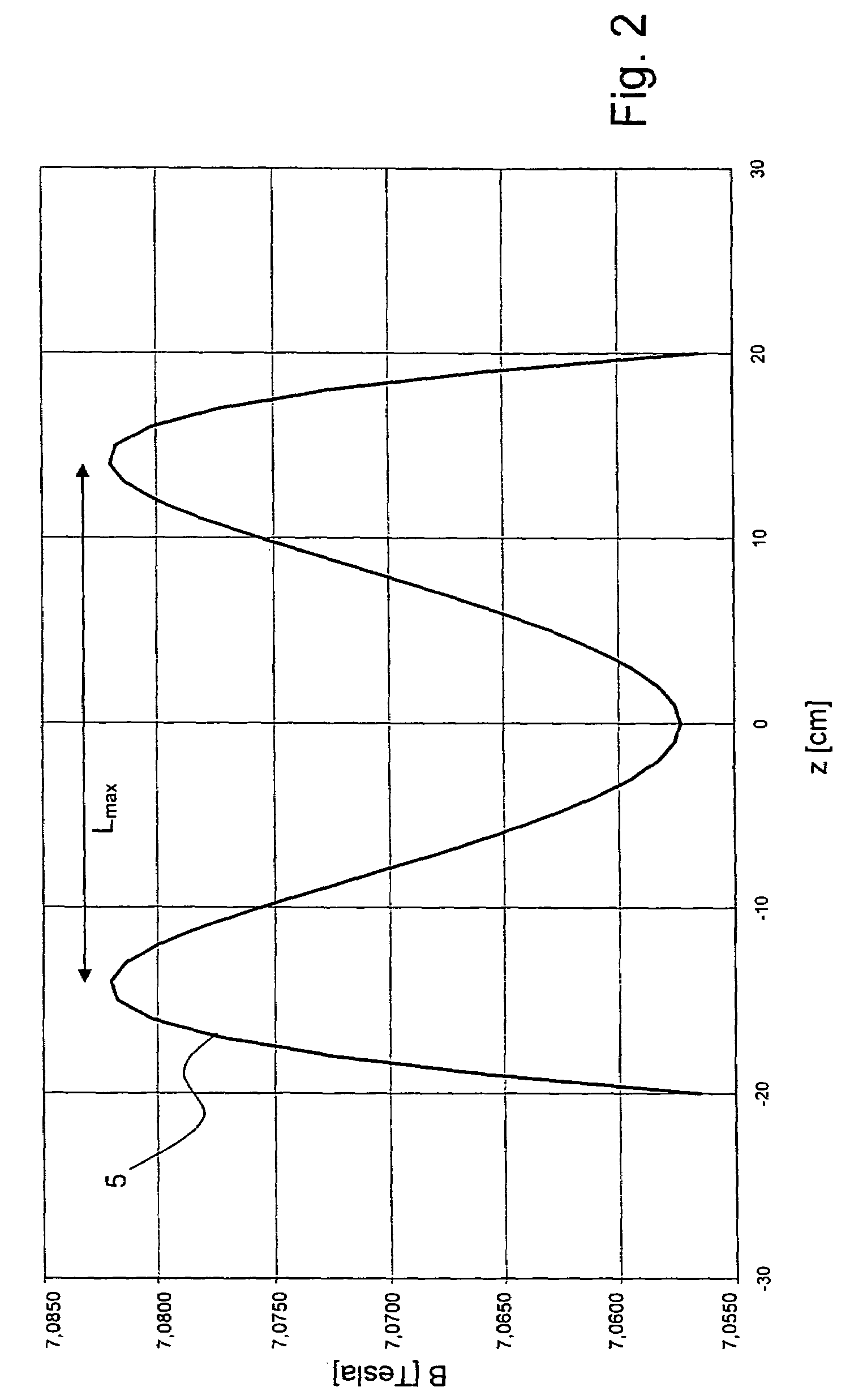
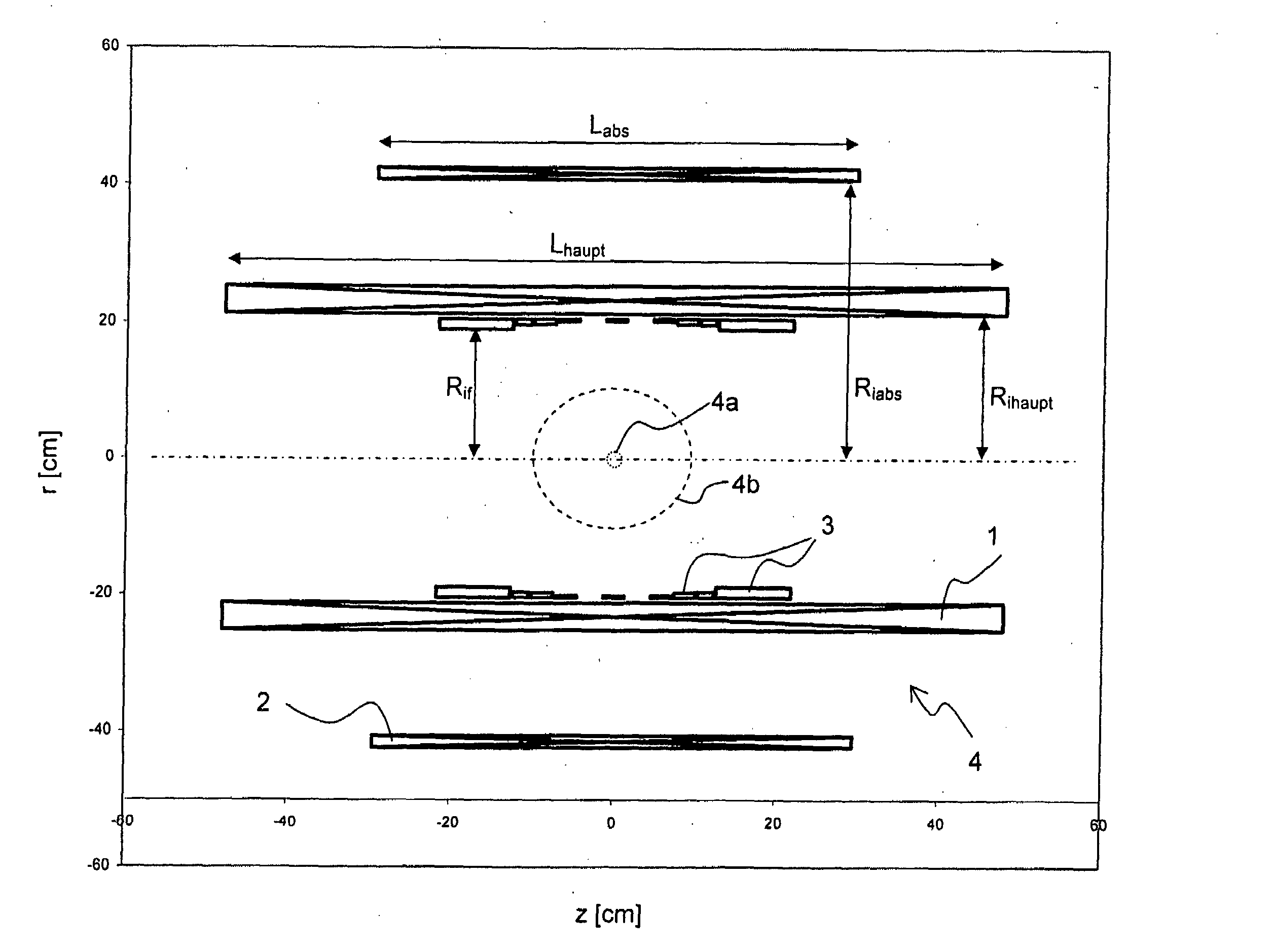
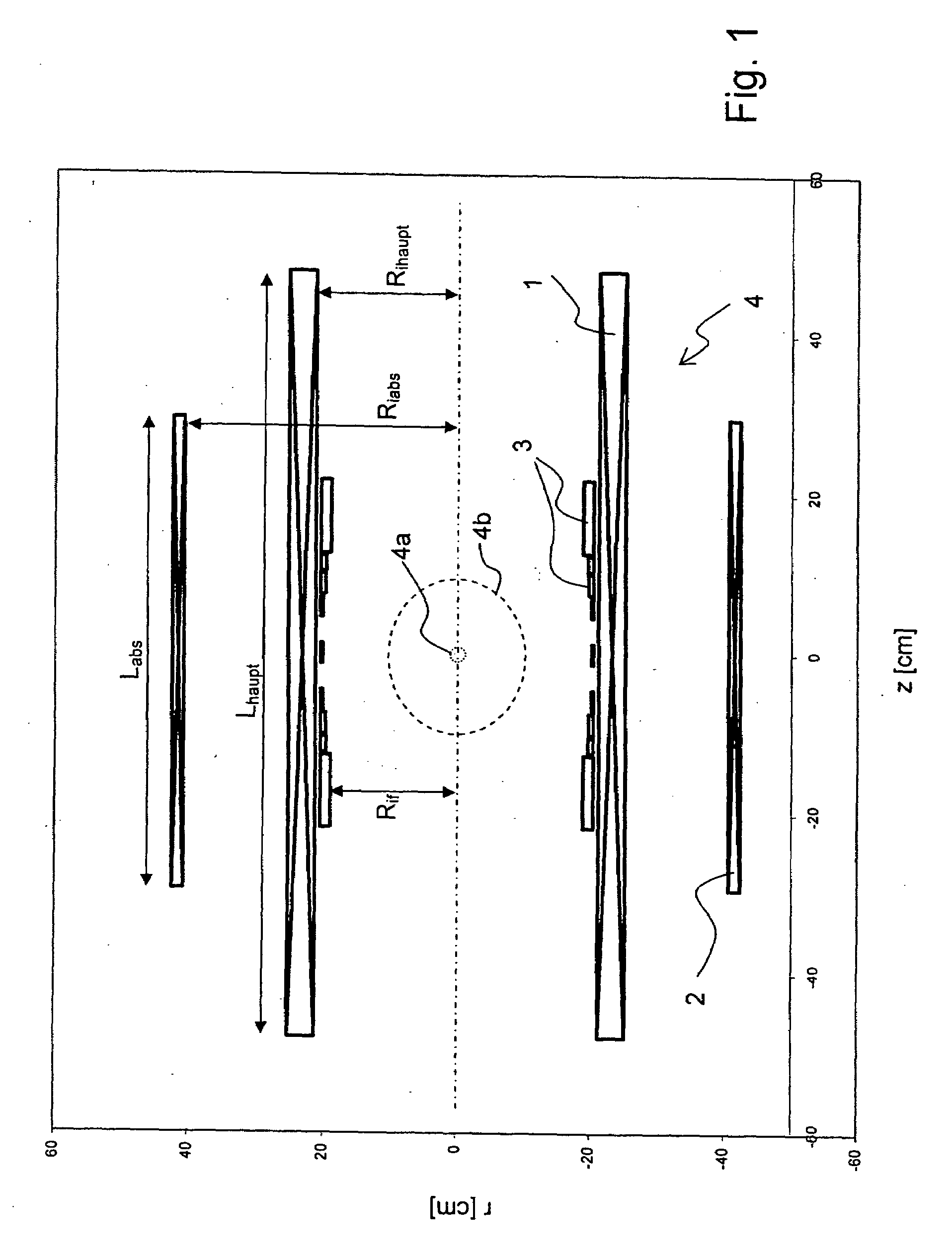
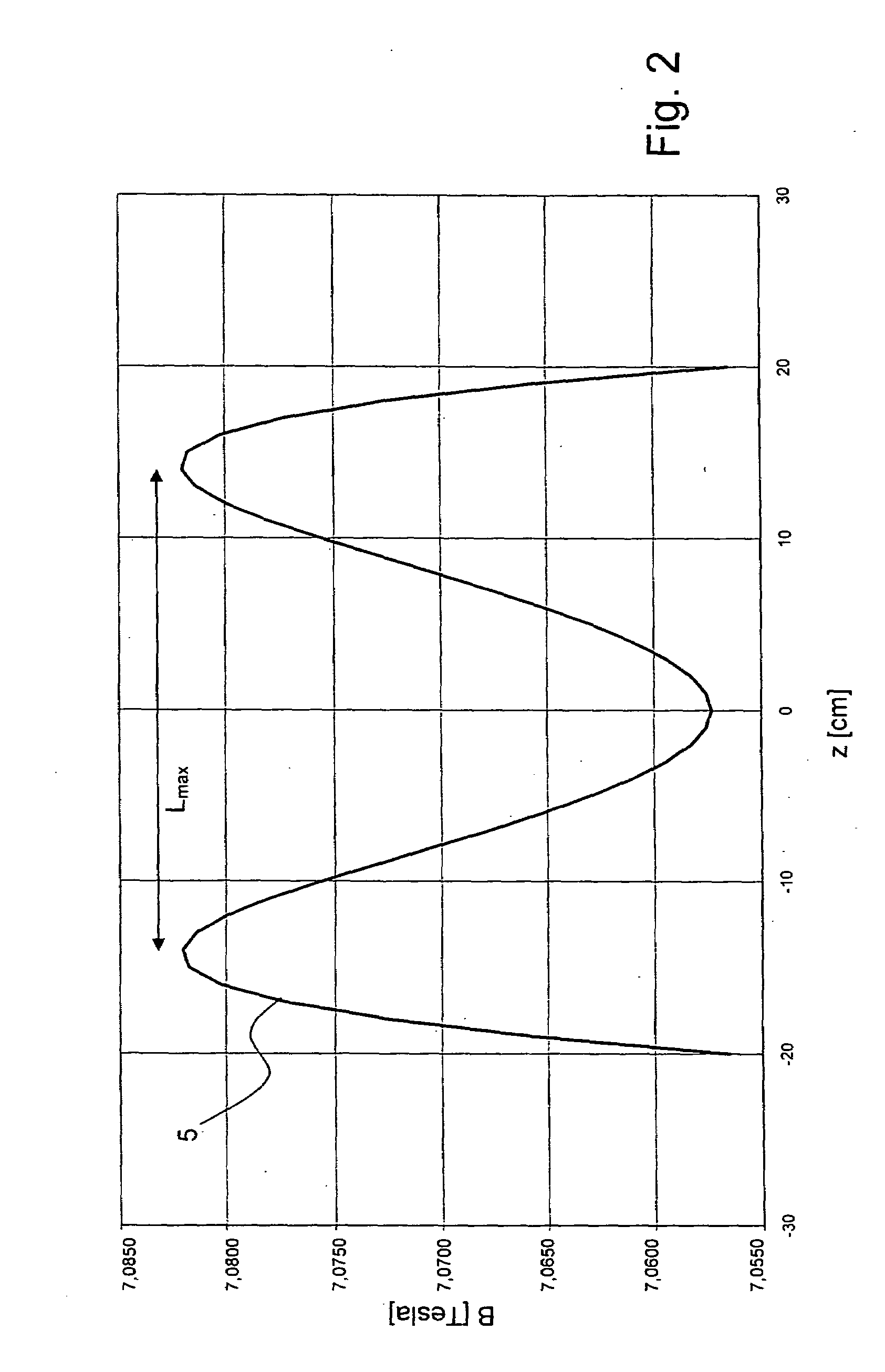
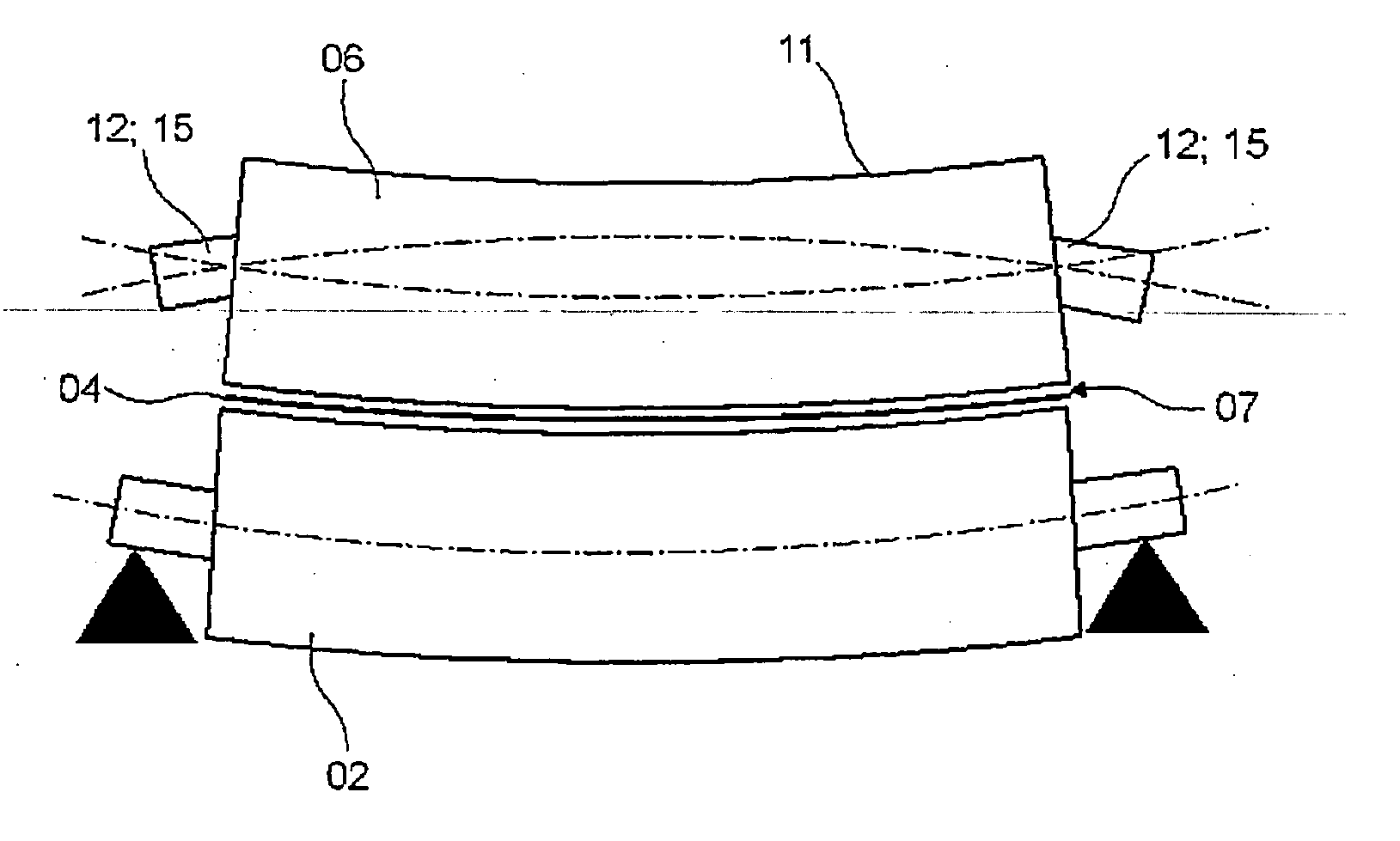
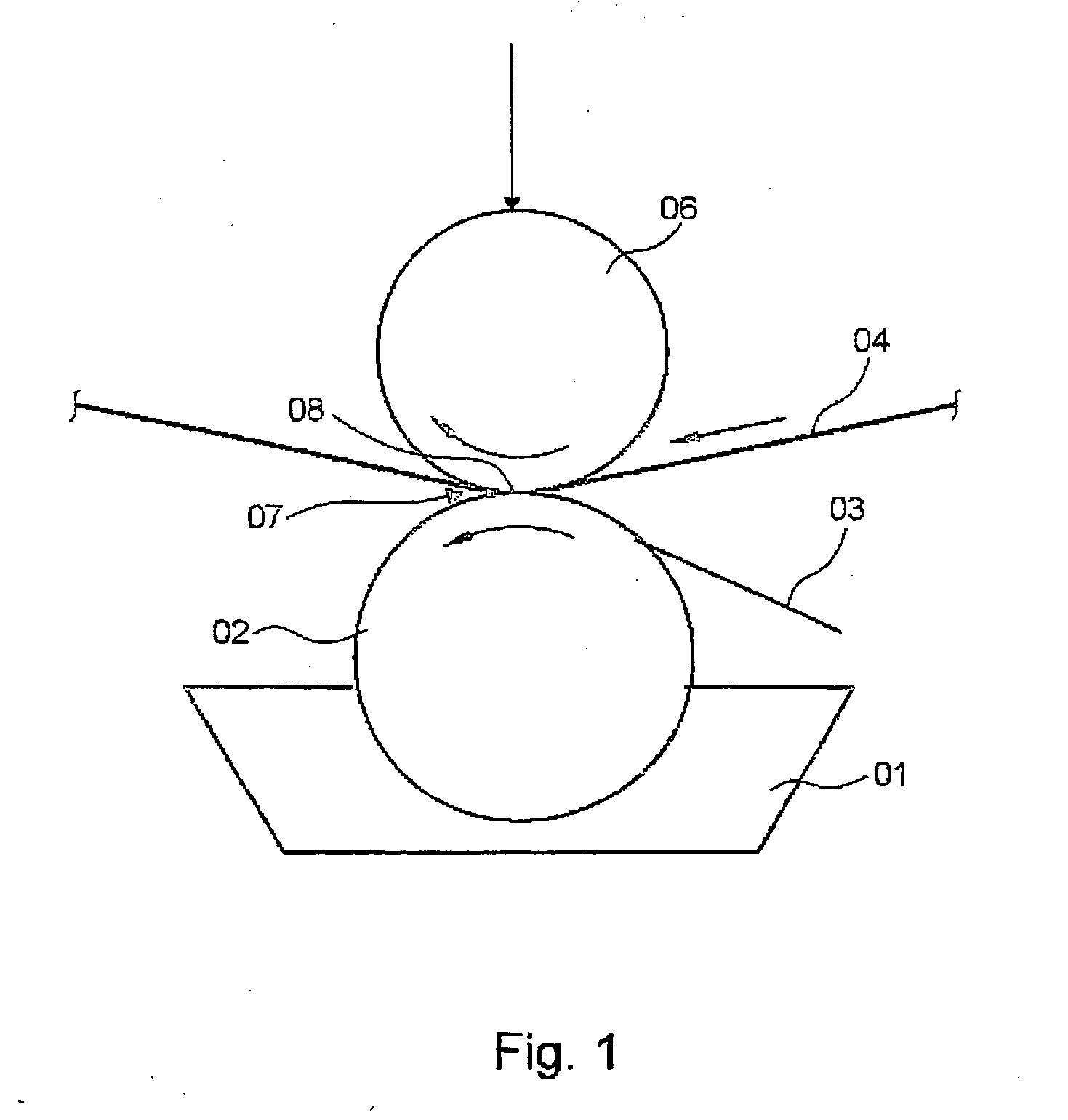
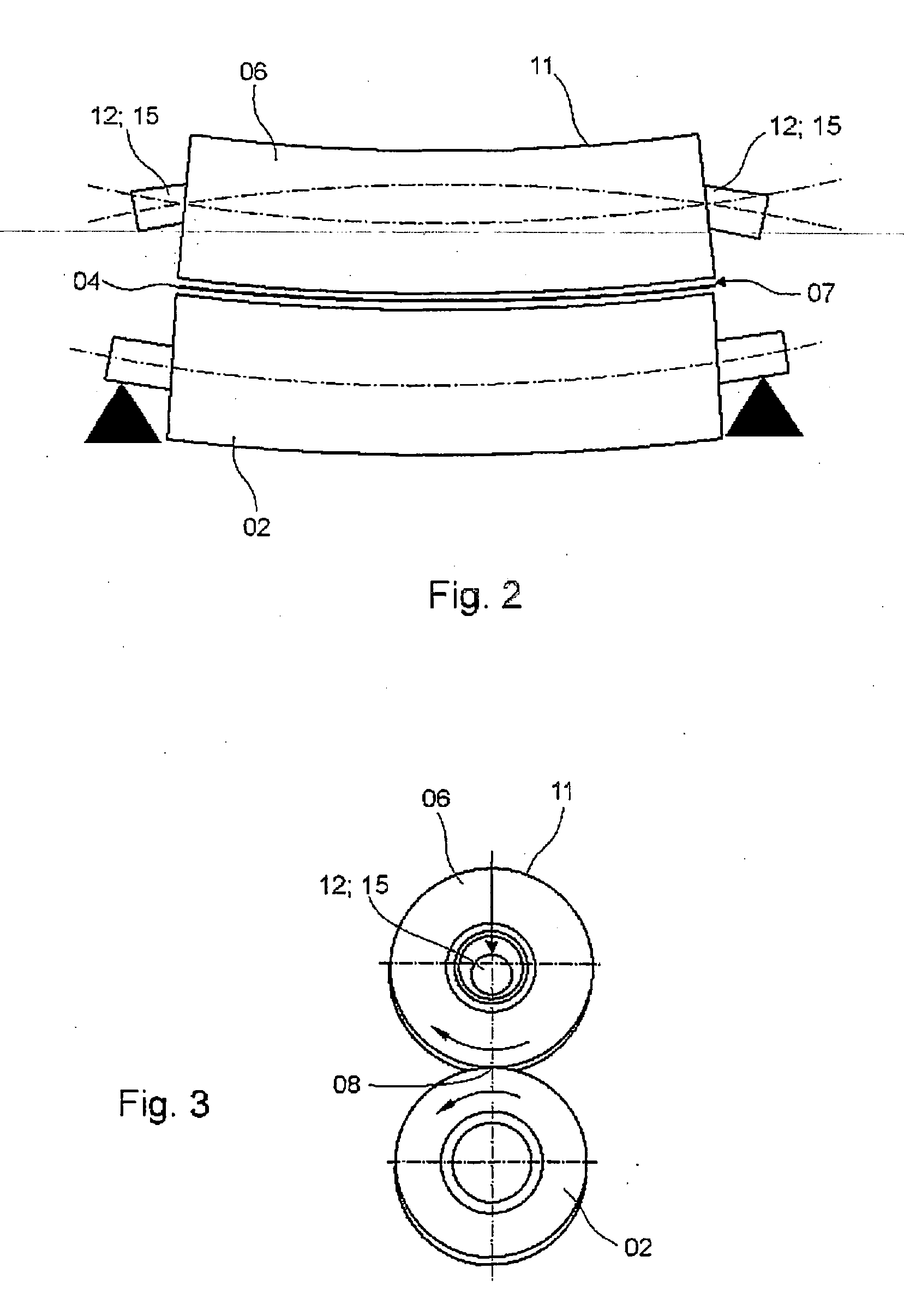
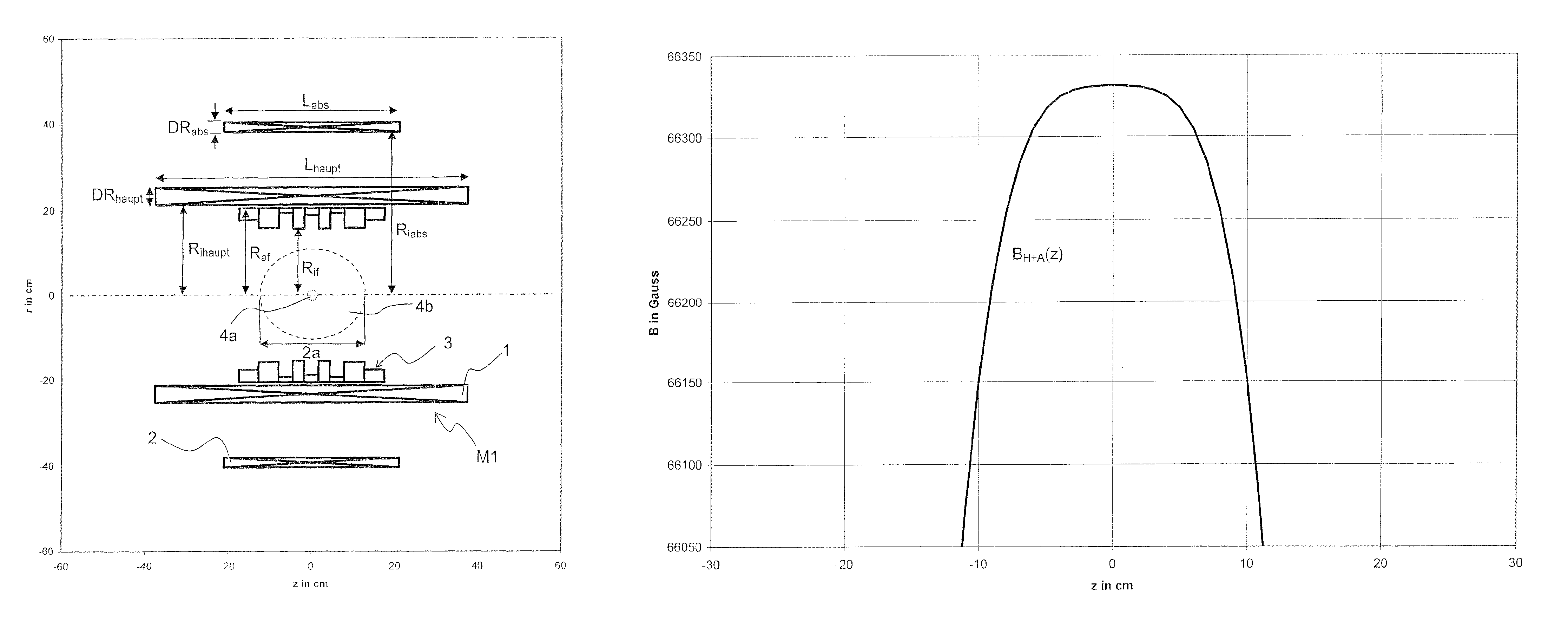
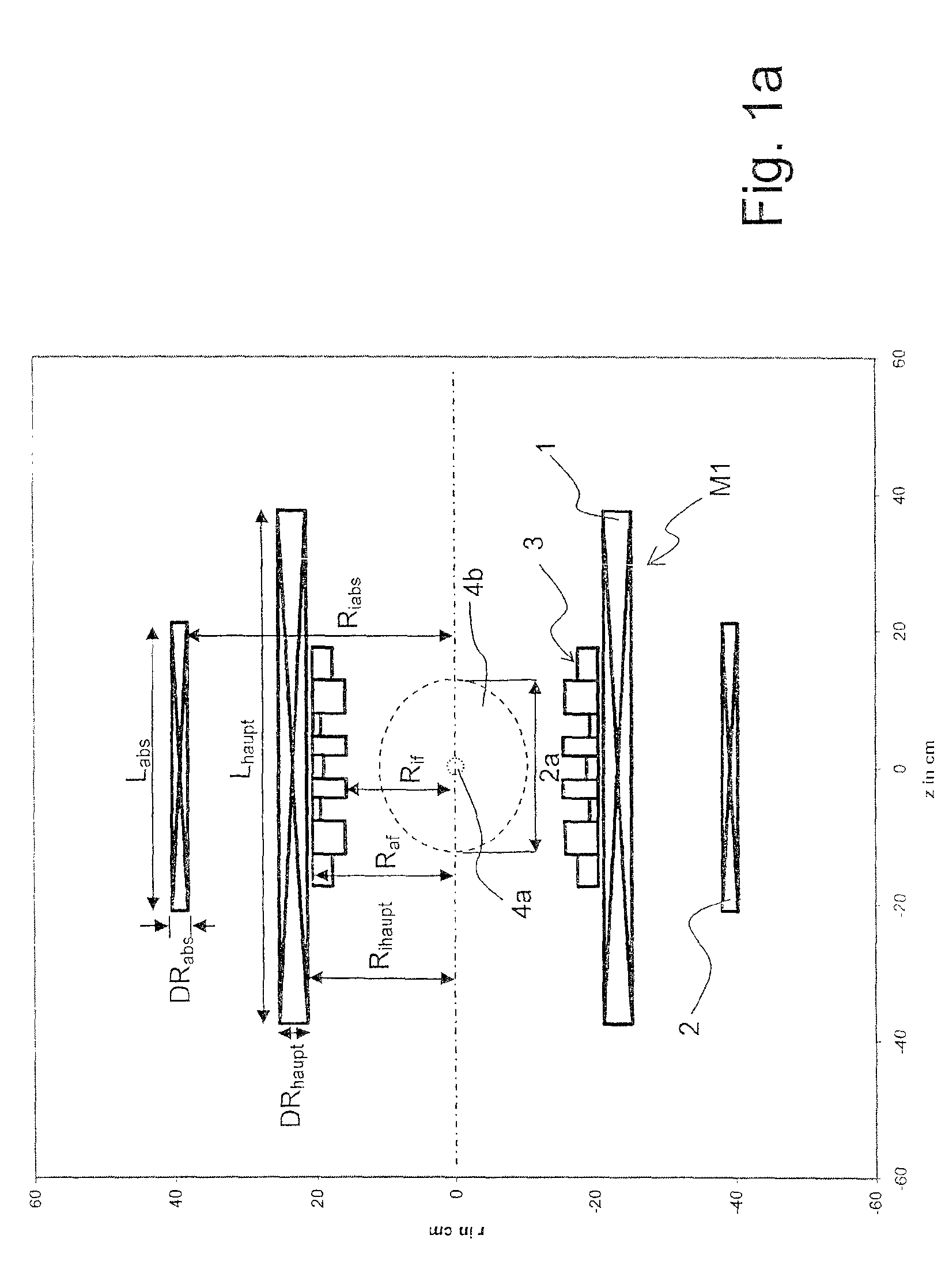
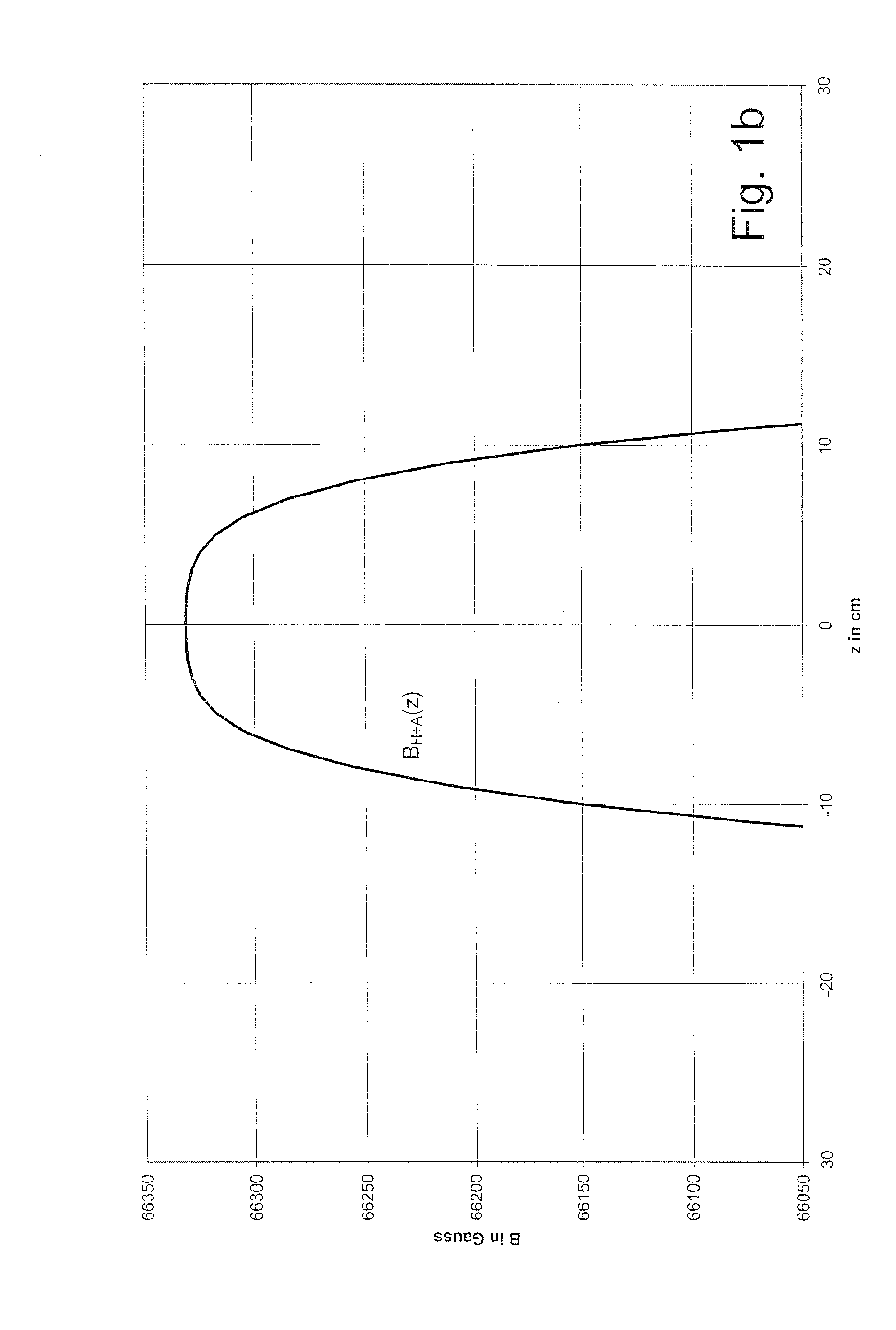
A superconducting magnet configuration (4; 14) for generating a homogeneous magnetic field B0 in an examination volume (4b), has an interior radial superconducting main field coil (1) which is disposed rotationally symmetrically about an axis (z-axis) and an oppositely driven coaxial radially exterior superconducting shielding coil (2) is characterized in that the magnet configuration (4; 14) consists of the main field coil (1), the shielding coil (2), and a ferromagnetic field formation device (3; 18), wherein the ferromagnetic field formation device (3; 18) is located at the radially inside of the main field coil (1), the main field coil (1) consisting of an unstructured solenoid coil or of several radially nested unstructured solenoid coils (15, 16) which are driven in the same direction, the axial extent Labs of the shielding coil (2) being smaller than the axial extent Lhaupt of the main field coil (1), wherein the axial magnetic field profile (5) generated by the main field coil (1) and the shielding coil (2) during operation has a minimum of the field strength along the axis (z-axis) in the center (4a) and a maximum of the field strength on each side of the center (4a), and wherein the axial magnetic field profile (6) generated by the ferromagnetic field formation device (3; 18) during operation has a maximum of the field strength along the axis (z-axis) in the center (4a) and a minimum of the field strength on each side of the center (4a). The magnet configuration in accordance with the invention has a very simple structure.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
Catheter with catheter hub
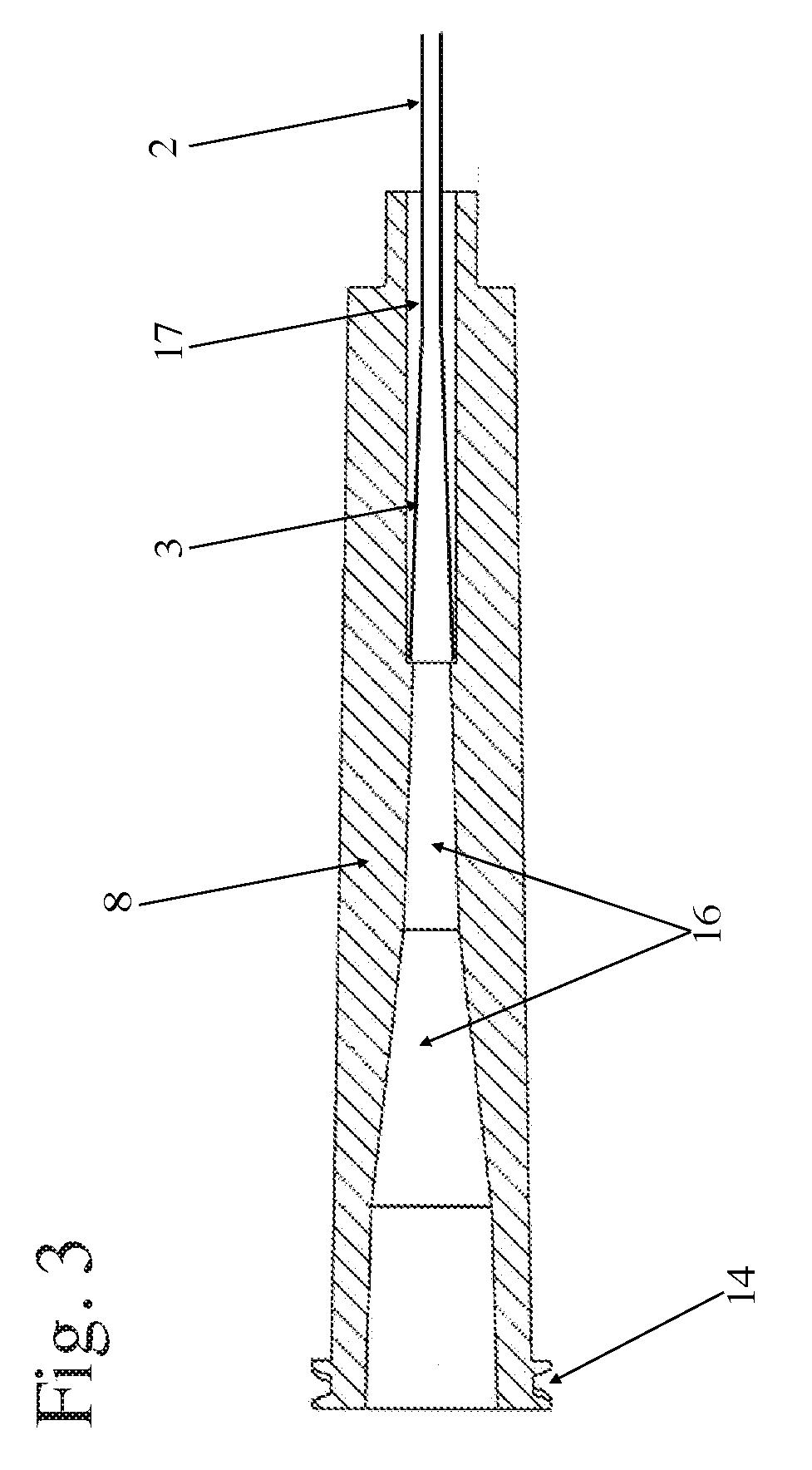
ActiveUS20190275294A1Rigid enoughSmooth transitionBalloon catheterTube connectorsCatheter hubMedical device
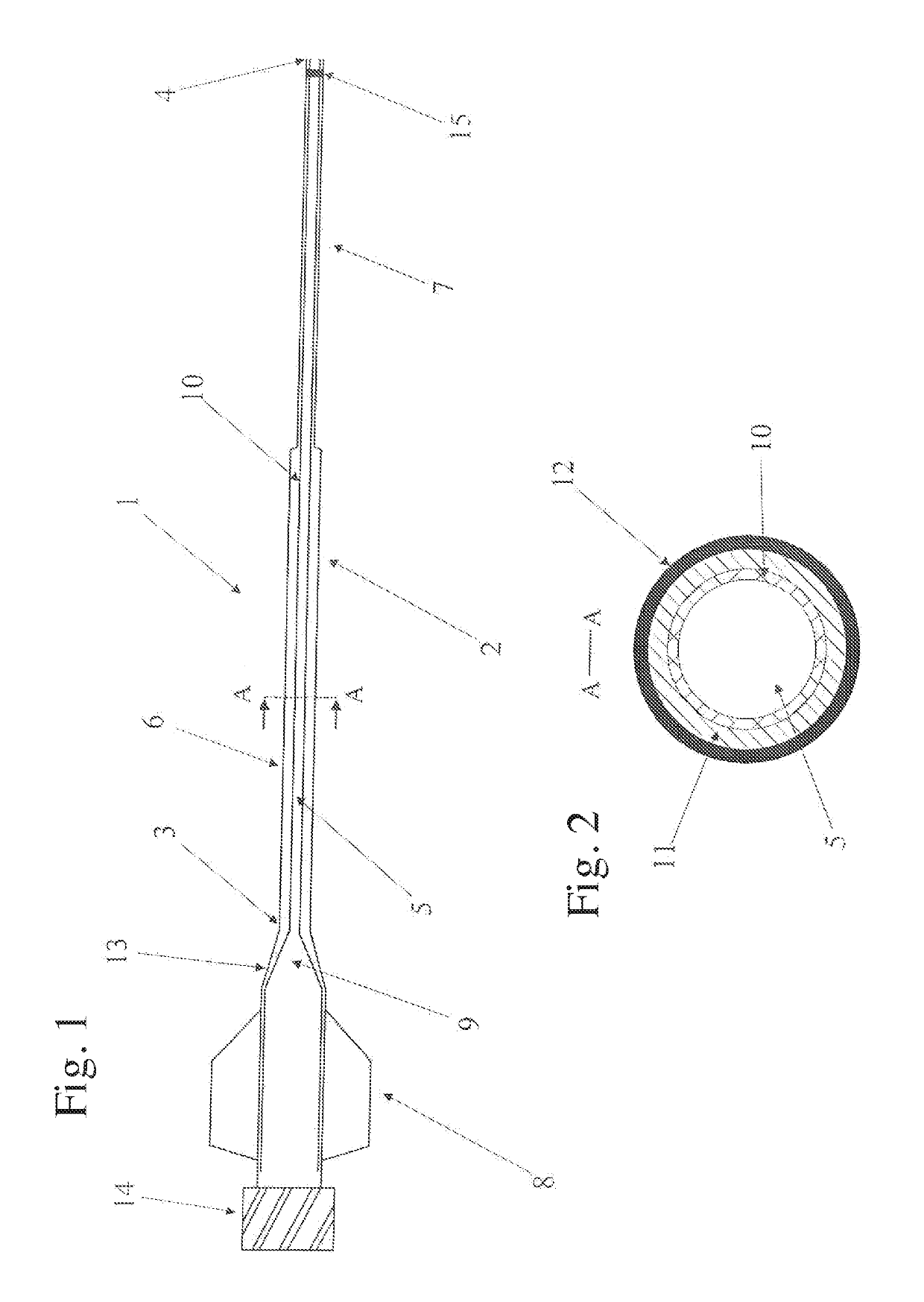
A catheter (1) comprising an elongate tubular body (2) having a proximal end (3), a distal end (4), and an inner lumen (5) extending through the elongate tubular body (2), wherein the elongate tubular body (2) comprises a proximal section (6) and a distal section (7), wherein at least the proximal section (6) comprises at least two layers, wherein the proximal end (3) is connected with a catheter hub (8) being an adapter of greater radial outside dimension than the elongate tubular body (2), wherein the catheter hub (8) has an inner lumen (9) of larger inside diameter than the elongate tubular body (2), and wherein the innermost layer (10) of the proximal section (6) extends into the catheter hub (8) and flares from the proximal section (6) to the catheter hub (8). The catheter ensures a smooth transition of a medical device, e.g. a stent to be transferred from a storage device like a sheath into the tubular body of the catheter.
Owner:PHENOX LTD
System achieving uniform lighting with three-primary-color laser
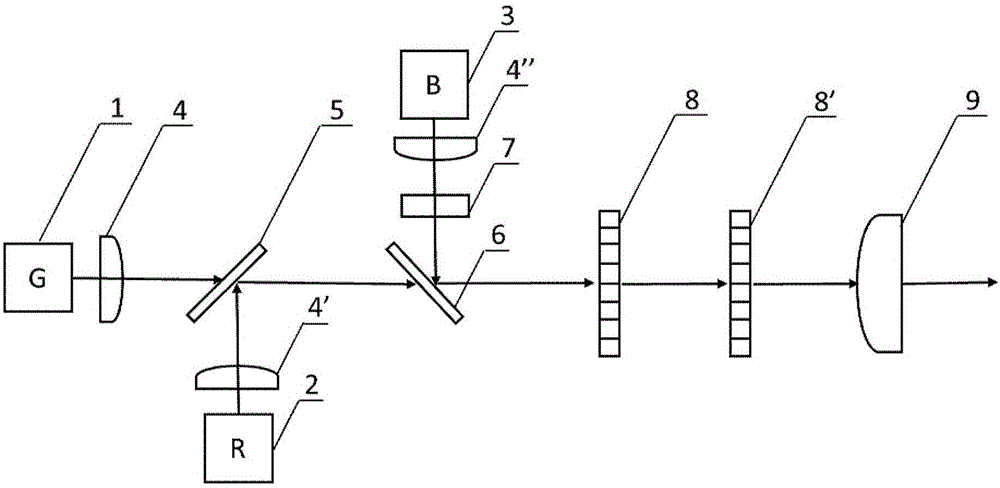
InactiveCN106773073AIncoherent good uniformityCompensate for inhomogeneityOptical elementsMicro lens arraySemiconductor
Provided is a system achieving uniform lighting with a three-primary-color laser. The system comprises a green semiconductor laser, a red semiconductor laser, a blue semiconductor laser, a long wave cut-off filter, a short wave cut-off filter, a neutral density filter, a first microlens array, a second microlens array and a convergent lens, wherein the front ends of the three semiconductor lasers are provided with a first collimating lens, a second collimating lens and a third collimating lens; the long wave cut-off filter is located on an output light path of the green semiconductor laser, and forms an incline angle with the output light path of the green semiconductor laser; the short wave cut-off filter is located on the output light path of the green semiconductor laser, and forms an incline angle with the output light path of the green semiconductor laser; the neutral density filter is located on an output light path of the blue semiconductor laser; the first microlens array and the second microlens array are respectively located on the output light path of the green semiconductor laser in sequence and behind the short wave cut-off filter; the convergent lens is located behind the second microlens array, and on the output light path of the green semiconductor laser.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Filter sealing system
ActiveCN1911487AMutual sealing is effectiveGood compressibilityDispersed particle filtrationMembrane filtersStream flowEngineering
Owner:MANN HUMMEL GMBH
Device for rolling an eccentric rotational component, rolling machine, method, and eccentric rotational component
InactiveUS20120196092A1High pressing forceAdvantageously compensateLayered productsBurnishing machinesRotational componentEngineering
A tool for rolling an eccentric rotational component having an eccentric portion, in particular an eccentric worm shaft, wherein the tool has a rotational device having rolling device, by means of which the surface edge zone of the eccentric rotational component is strengthened in order to increase the service life thereof. In an embodiment example, a cutting process is performed before the rolling process.
Owner:ECOROLL WERKZEUGTECHN
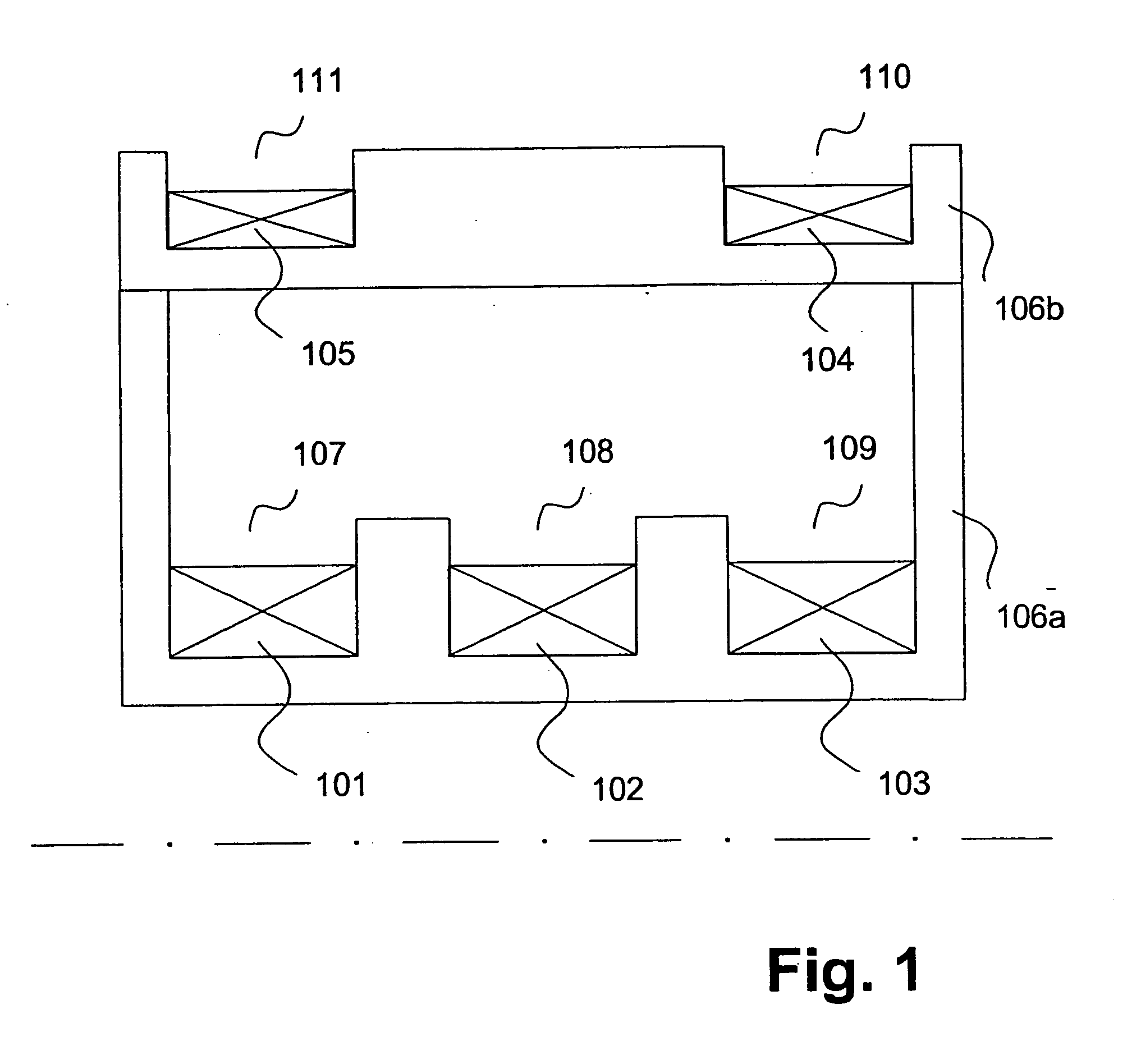
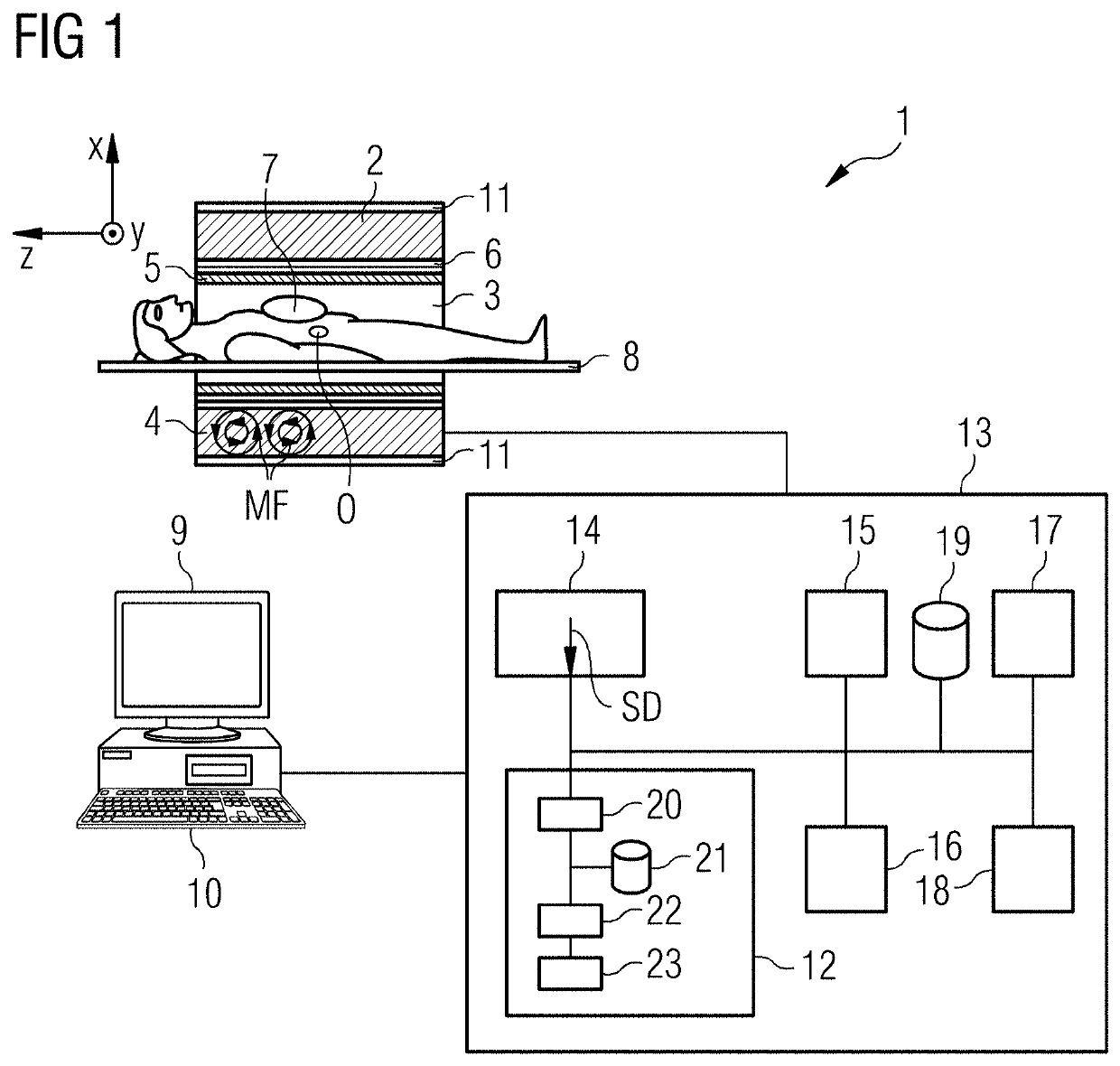
Determination of susceptibility-induced magnetic field gradients by magnetic resonance
InactiveUS20100002926A1Enables imagingSharp contrastCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientMagnetic susceptibility
The invention relates to a device for magnetic resonance imaging of a body (7). The device (1) comprises means (2) for establishing a substantially homogeneous main magnetic field in the examination volume, means (3, 4, 5) for generating switched magnetic field gradients superimposed upon the main magnetic field, means (6) for radiating RF pulses towards the body (7), control means (12) for controlling the generation of the magnetic field gradients and the RF pulses, means (10) for receiving and sampling magnetic resonance signals, and reconstruction means (14) for forming MR images from the signal samples. In accordance with the invention, the device is arranged to a) generate a series of MR echo signals (20) by subjecting at least a portion of the body (7) to an MR imaging sequence of RF pulses and switched magnetic field gradients, b) acquire the MR echo signals for reconstructing an MR image data set (21) therefrom, c) calculate a gradient map (22) by computing echo shift parameters (SPx, SPy, SPz) from subsets of the MR image data set, the echo shift parameters (SPx, SPy, SPz) indicating magnetic field gradient induced shifts of the echo positions in k-space, wherein each subset comprises a number (n) of spatially adjacent pixel or voxel values of the MR image data set (21).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method of dynamically compensating for magnetic field heterogeneity in magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS9377517B2Improve image qualitySolve the real problemMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse magnetizationMR - Magnetic resonance
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
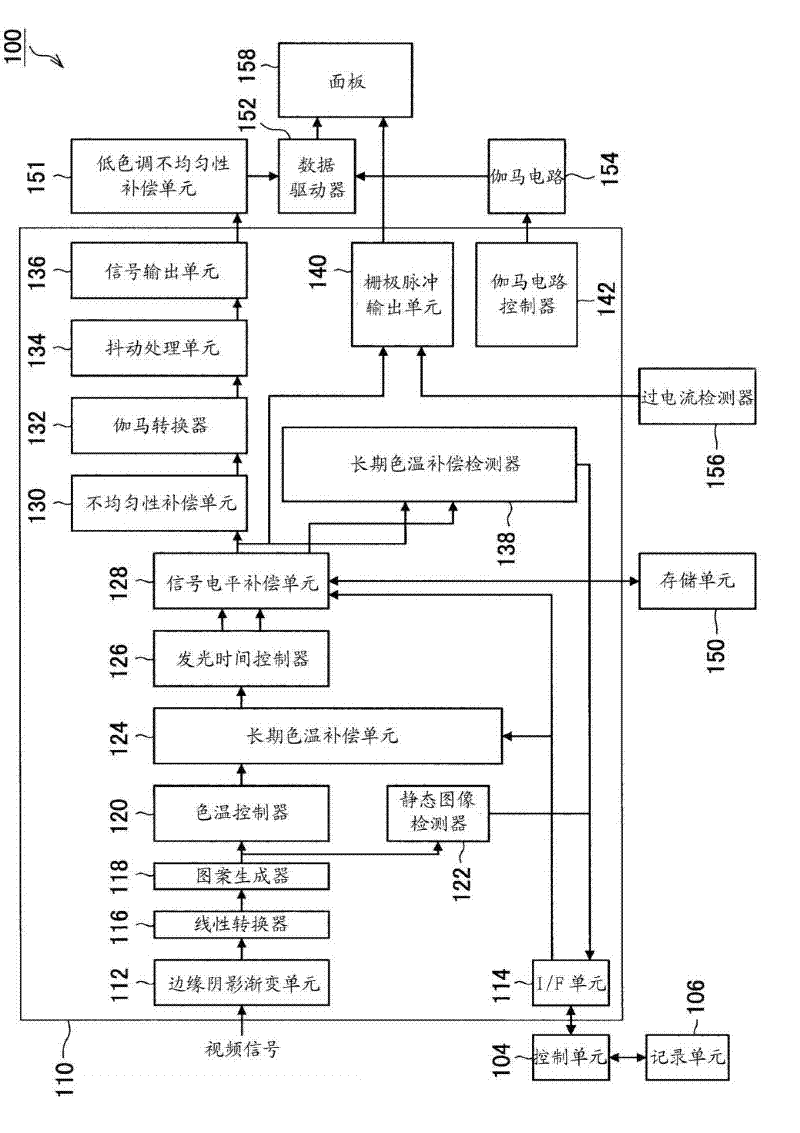
Display device, unevenness correction method, and computer program
InactiveCN102598101ACompensate for inhomogeneityReduce areaStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesScan lineDisplay device
Disclosed is a display device that can both correct unevenness in a linear space and set one unevenness-correction plane outside the linear space, correcting unevenness in ultra-low-brightness regions, thereby effectively correcting unevenness in ultra-low-brightness regions while minimizing increases in power consumption and circuit size. The disclosed display device is provided with: pixels provided with light-emitting elements, which emit light according to levels of current, and pixel circuits that control currents applied to said light-emitting elements in accordance with a video signal; a display unit in which scan lines, which with a prescribed scan period supply the pixels with a selection signal that selects the pixels to be turned on, and data lines, which supply the aforementioned video signal to the pixels, are arranged in a matrix; a first unevenness-correction unit which corrects brightness unevenness in video signals with linear characteristics; and a second unevenness-correction unit which corrects brightness unevenness in video signals with gamma characteristics, in prescribed regions and those below.
Owner:SONY CORP
Hybrid magnet configuration
ActiveUS7365540B2High strengthIncrease field strengthMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceSuperconducting solenoid
A co-axial magnet configuration for the production of a magnetic field and investigational volume which is suitable for measurement of magnetic resonance has at least one superconducting solenoid coil or solenoid coils which are radially nested within each other, wherein the windings of the solenoid coil(s) in a radial region about the axis of the magnetic configuration are disposed between r1 and r2, wherein r1<r2 is characterized in that the windings are surrounded by at least one rotationally symmetric magnet body made from ferromagnetic material which extends over a radial region between r3 and r4 wherein r3<r4 wherein r2<r3<1.3 r2 and r4>1.3 r3, wherein the rotationally symmetric magnet body or bodies are structured, dimensioned and positioned in such a fashion that the magnetic field is homogenized in the investigational volume and the magnetic fringe field outside the magnet configuration is essentially suppressed to permit the production of strong magnetic fields of high homogeneity without requiring notches in the coil configuration.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
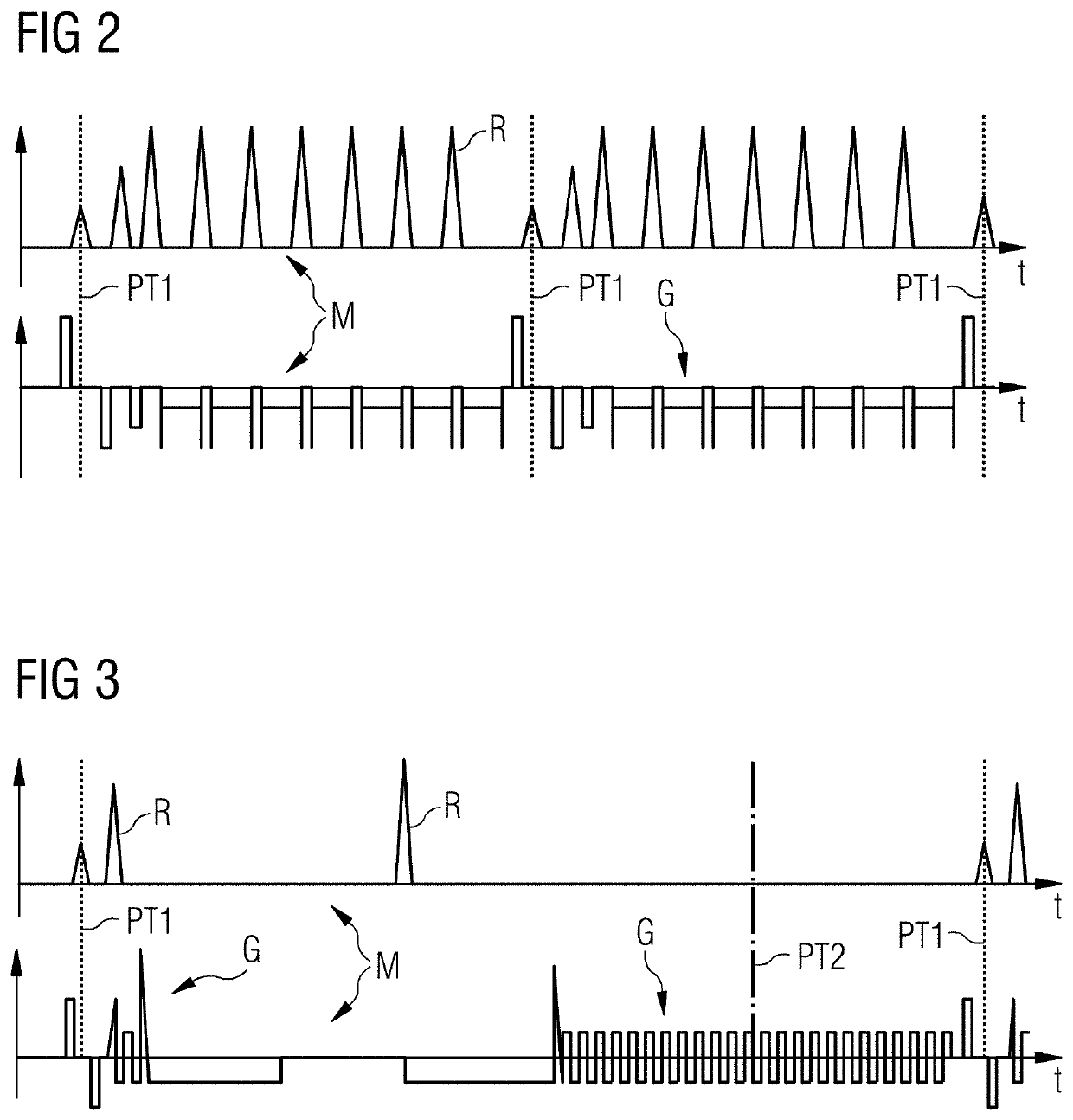
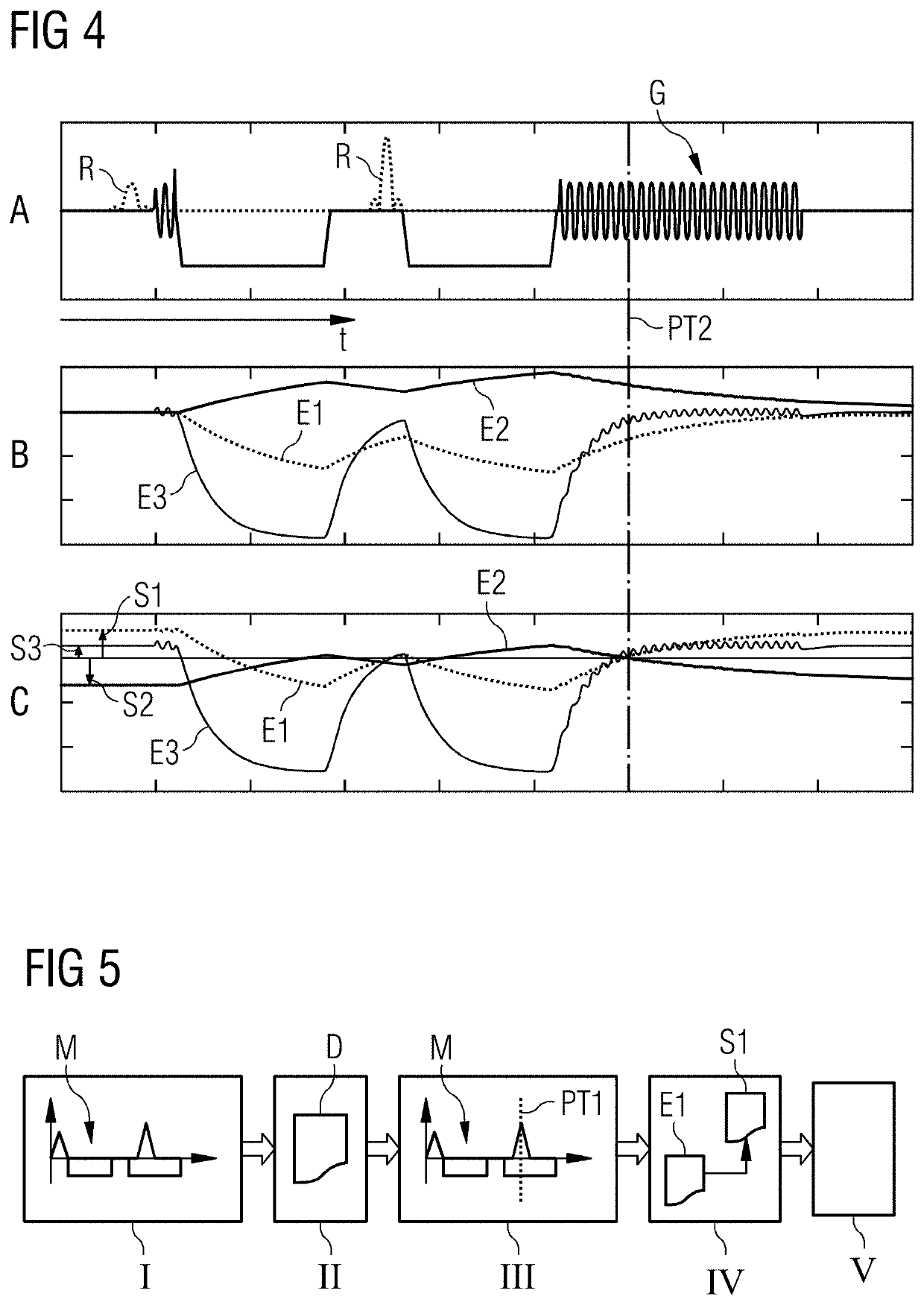
Method And Control Unit For Compensation Of Eddy Current Induced Magnetic Fields In Magnetic Resonance Imaging
PendingUS20200116807A1Good compensationMinimize orDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData setControl cell
Eddy current induced magnetic fields (MF) are compensated in a magnetic resonance imaging system. An MR-sequence (M) includes a number of gradients. A dataset includes values of an amplitude and a time constant of eddy current fields of a number of gradients on at least one gradient axis. A number of points in time within the time period of the MR-sequence are defined. A number of constant currents are calculated for a number of coils of the magnetic resonance imaging system based on the dataset. The number of constant currents is designed to compensate at least at the one defined point in time (PT1, PT2). The calculated number of constant currents are applied on the related coils prior or during the application of the MR-sequence or a section of the MR-sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Reflex multi-time amplification device based on spliced laser crystals
ActiveCN105552707AImprove amplification efficiencyGuaranteed spatiotemporal propertiesActive medium materialOptical elementsOptical pathOptical pathlength
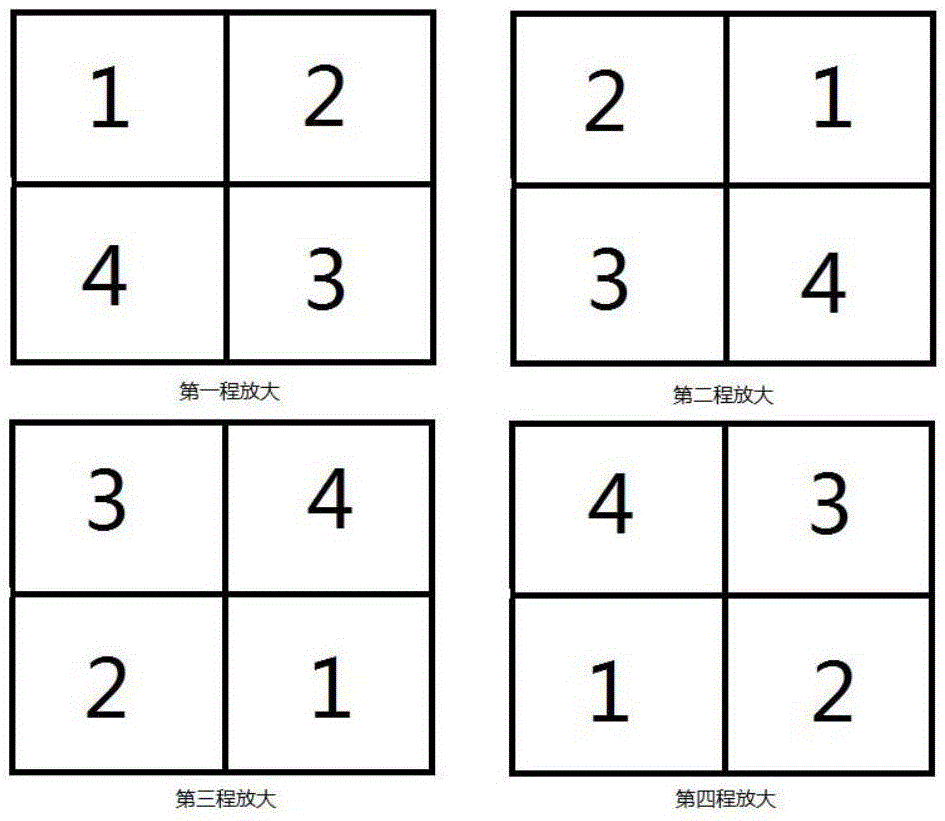
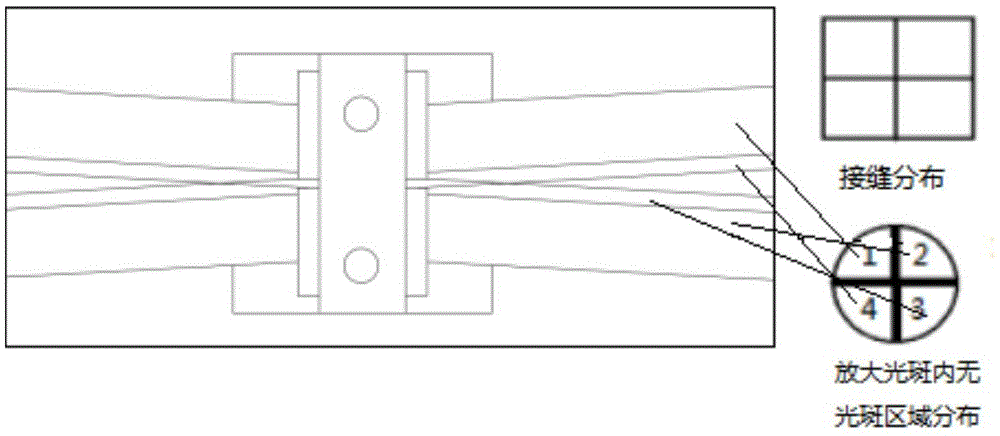
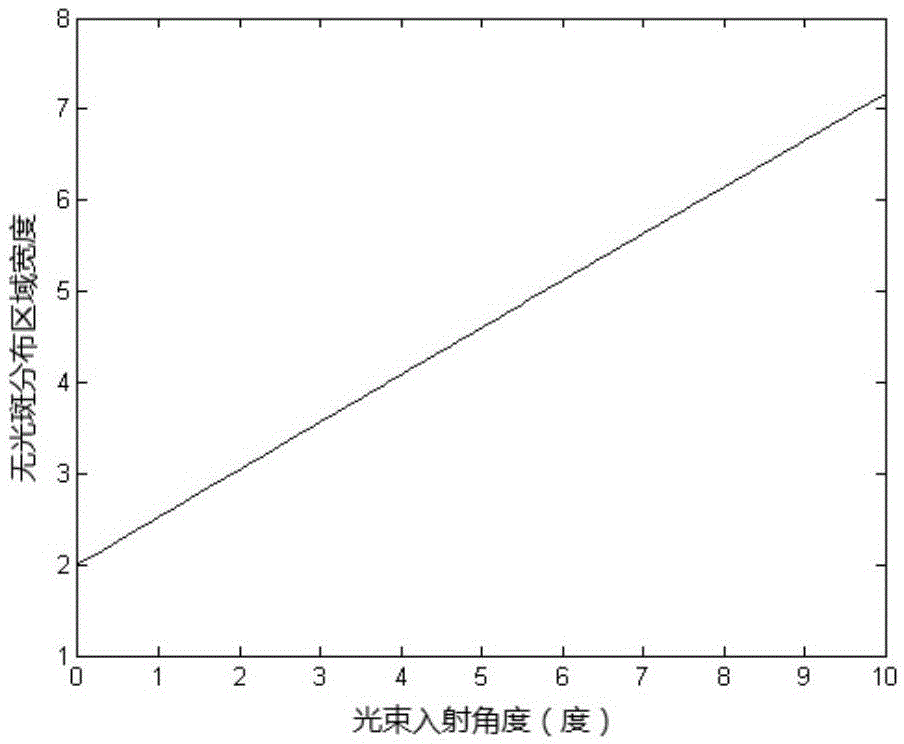
The invention relates to a reflex multi-time amplification device based on spliced laser crystals. The device comprises a spliced laser crystal amplifier, a first reflecting mirror, a second reflecting mirror, a third reflecting mirror, a fourth reflecting mirror, a fifth reflecting mirror, a sixth reflecting mirror, a seventh reflecting mirror and a deformable lens or a splicing reflecting mirror driven by a motor, wherein each of the first reflecting mirror, the second reflecting mirror, the third reflecting mirror, the fourth reflecting mirror, the fifth reflecting mirror, the sixth reflecting mirror and the seventh reflecting mirror is provided with a mirror bracket. The device is characterized in that by the two reflecting mirrors with multiple pairs of normal lines perpendicular to one another, the distribution of an amplified light spot in a space is exchanged in a reflex direction, after reflex amplification for many times, different parts of the light spot sequentially pass through spliced small crystals in each spliced big crystal, the optical path difference caused by different incident angles is compensated by the deformable lens or the spliced reflecting mirror driven by the motor, and thus, the non-uniformity of each small spliced laser crystal of the spliced laser crystal amplifier is compensated. By the device, the optical path difference and a surface-shape error caused by different incident angles due to different times are compensated, and the time-space characteristic of the light spot can be ensured well.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cylinder and device for guiding a material web
InactiveUS20050199144A1Simple wayCompensate for inhomogeneityLiquid surface applicatorsRotary intaglio printing pressEngineeringBiomedical engineering
Owner:OFFICINE MECCANICHE GIOVANNI CERUTTI
Compact superconducting magnet configuration with active shielding, wherein the shielding coil damps the field maximum of the main coil as well as associated magnetic resonance tomograph, NMR spectrometer and ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer
ActiveUS8154368B2Good compensationRelative density is smallMagnetic measurementsMagnetsResonanceSuperconducting Coils
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN
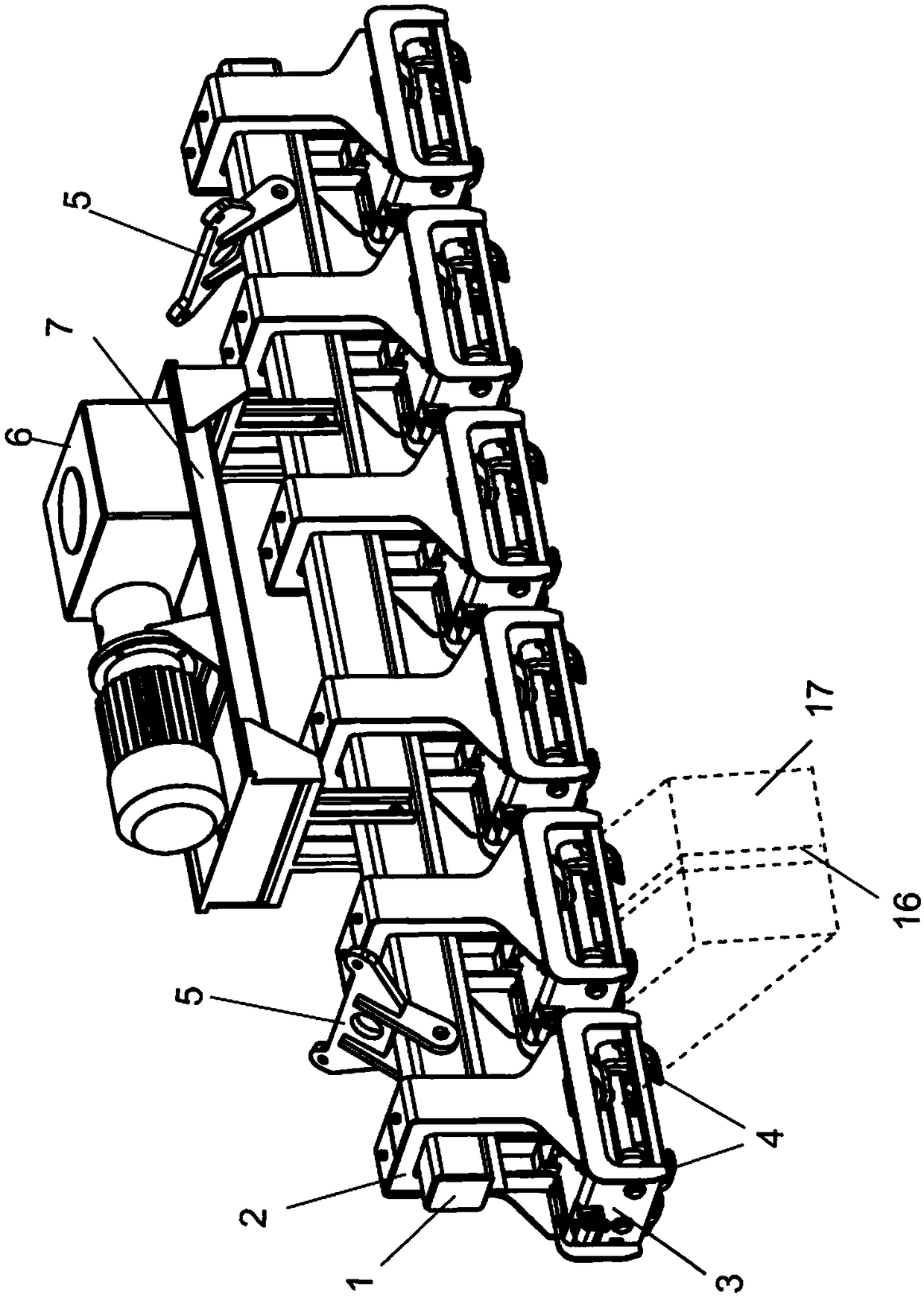
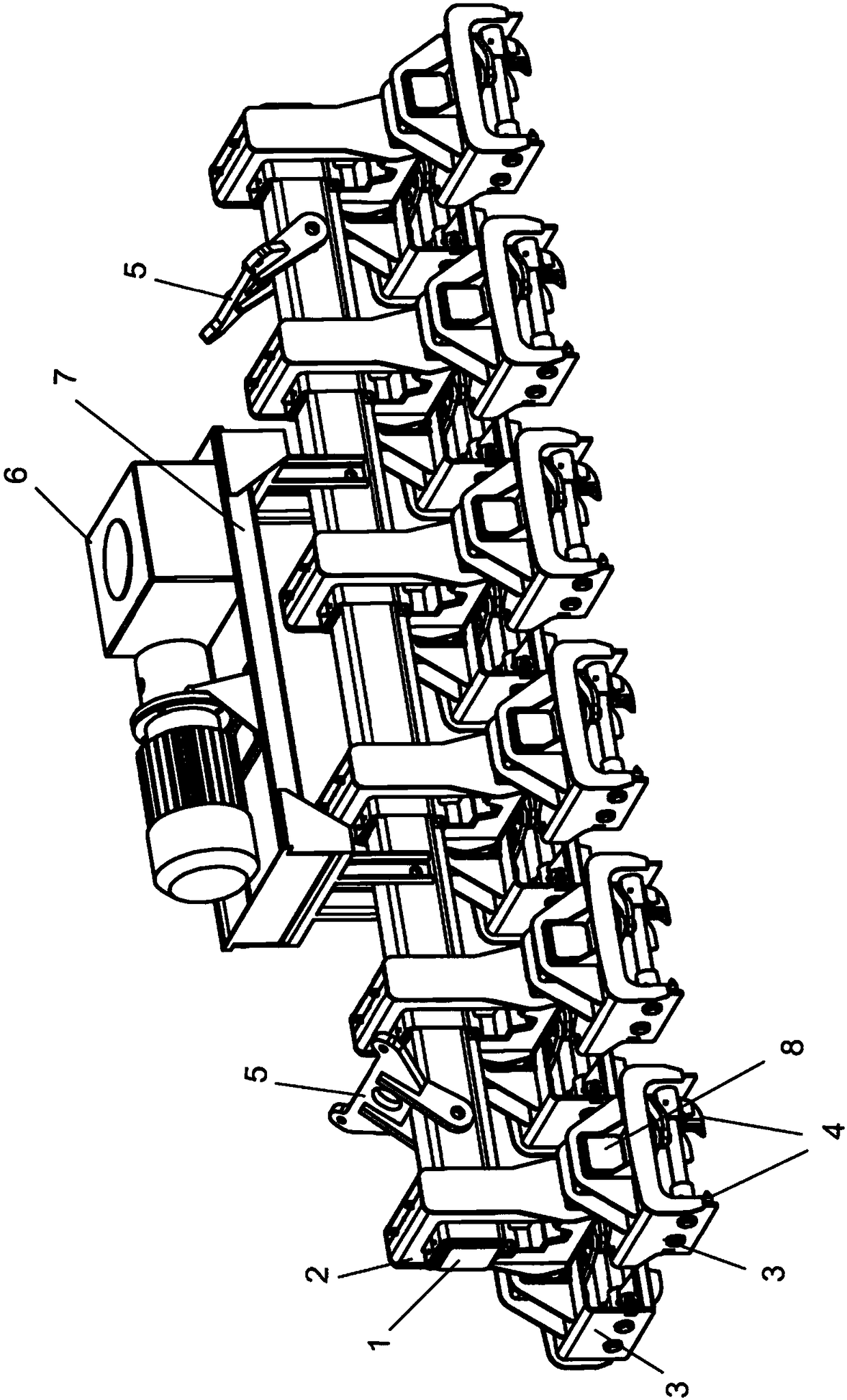
Apparatus for lifting items bound together by strapping means
ActiveCN107148394ACompensate for inhomogeneityCompensation heightLoad-engaging elementsStrappingEngineering
An apparatus for lifting items, such as pulp units, bound together by strapping means, the apparatus including at least one horizontal beam (1) attached to a crane and the beam having a plural number of hook trolleys (3) attached thereto and movable along the beam, each hook trolley (3) located at an item to be lifted being arranged to grab the strapping means of the item when grabbing means (4) belonging to the trolleys are made to approach one another, the strapping means being thus suspended from the grabbing means. The hook trolleys (3) are provided with either one or two grabbing member pairs at a fixed distance from one another, their grabbing movement being a parallel movement and each hook trolley (3) being at an adjustable distance from another one, suspended either by a slot arrangement (2) from said horizontal beam (1), the slot arrangement (2) permitting each hook trolley (3) to move separately in a vertical direction for a predetermined distance and to tilt to a predetermined angle in the slot attachment, or via an intermediate beam (8) from said horizontal beam (1), each intermediate beam (8) being fastened so as to hang from the horizontal beam (1) by the slot arrangement (2), the intermediate beam (8) being transverse to the horizontal beam (1) and the slot arrangement (2) permitting each hook trolley (3) or hook trolley pair to move separately in a vertical direction for a predetermined distance and to tilt to a predetermined angle in the slot attachment.
Owner:STEVENEL
Pixel circuit, driving method thereof, and display device
ActiveCN104821150BCompensate for inhomogeneitySimple structureStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesCapacitanceDisplay device
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
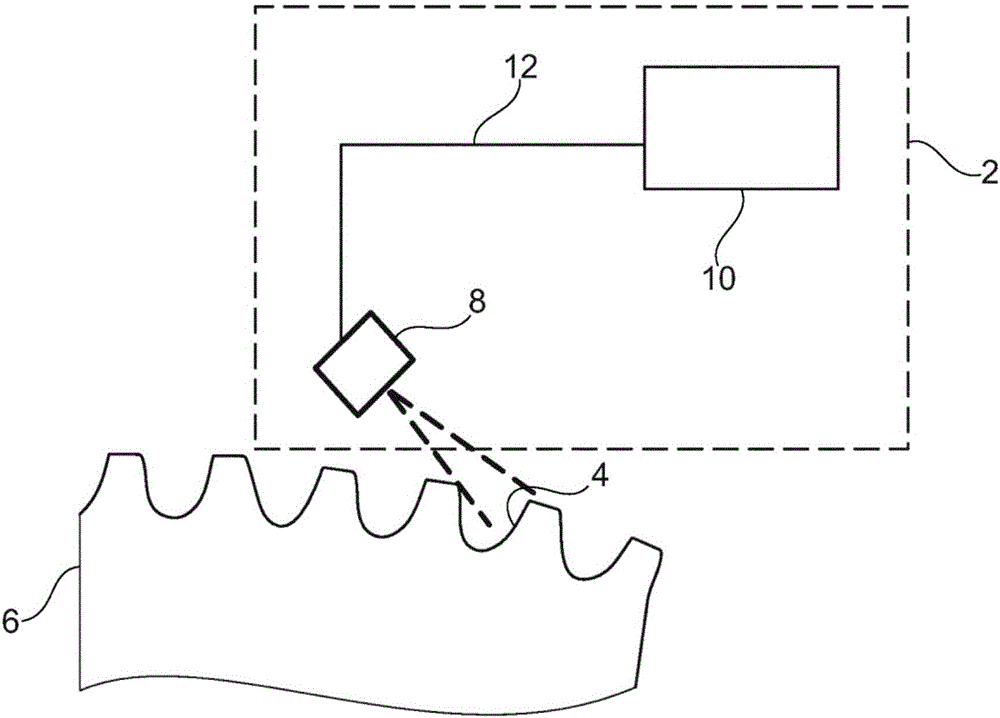
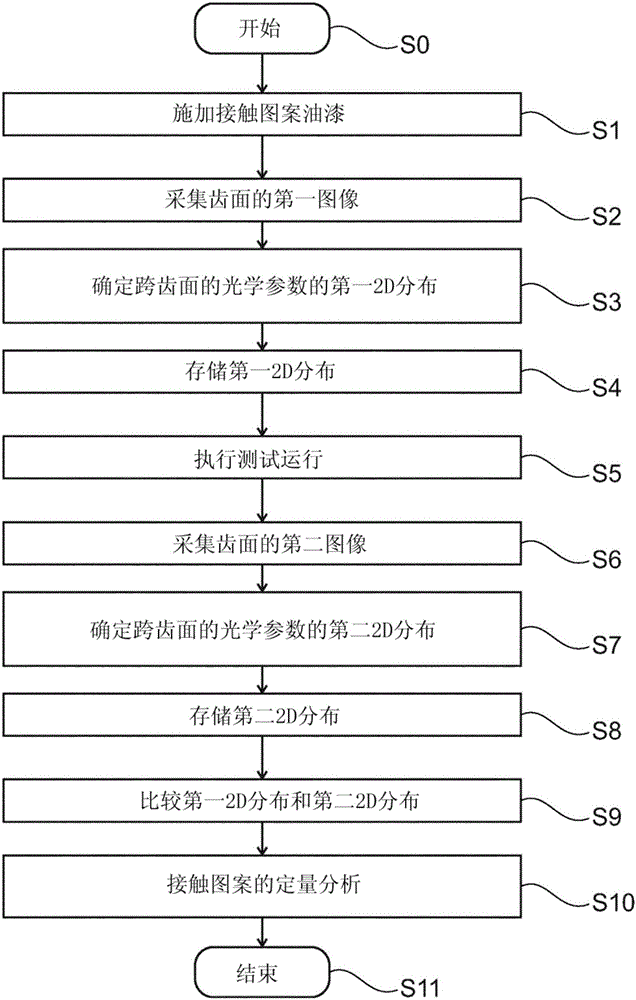
Test unit for quantitative analysis of a contact pattern on a tooth surface of a gear, method for quantitative analysis and use of the test unit
InactiveCN106662500AQuantify or at least estimateDetermine load distributionImage analysisMachine gearing/transmission testingEngineeringControl unit
A test unit for quantitative analysis of a contact pattern and a method for quantitative analysis are provided. The test unit comprises an optoelectronic sensor for capturing images of contact pattern paint on a tooth surface of a gear. Furthermore, the test unit comprises a control unit, which is configured for determining and storing a first distribution of an optical parameter of the contact pattern paint across the tooth surface, from the first image. This is captured prior to testing of the gear. After the tooth surface was exposed to a test load, a second image is captured and a second distribution of the optical parameter is determined. The control unit is configured to perform a quantitative analysis of a contact pattern on the tooth surface by determining a deviation between the first and the second distribution of the optical parameter.
Owner:AREVA WIND
Overlay error measuring device and method
PendingCN113325666AEasy to detectCompensate for inhomogeneityPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusComputer hardwareEngineering
The invention provides an overlay error measuring device and method. The overlay error measuring device comprises an illumination unit, a light splitting device, an objective lens, a first detection unit and a data processor. The first detection unit comprises a first aperture diaphragm, and the first aperture diaphragm comprises at least one adjustable through hole. The through hole is adjusted, when the first aperture diaphragm is in a first state, the first detector obtains a first signal and transmits the first signal to the data processor, and when the first aperture diaphragm is in a second state, the first detector obtains a second signal and transmits the second signal to the data processor. The first signal is a calibration signal, the second signal is calibrated through the first signal, and the overlay error is calculated by using the calibrated second signal. Therefore, more accurate overlay errors can be obtained by using the overlay error measuring device and method, so that the detection performance of the overlay error measuring device is improved, and the working efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Solid-state detector and method for resetting residue charges by illumination in the case of a solid-state detector
ActiveUS7767973B2Uniform Image QualityEasily and effectively matchedTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesSolid state detectorImaging quality
For a uniform image quality of digital X-ray records, a solid-state detector is provided. The detector includes light-sensitive pixel elements arranged in an active matrix, and a reset light source arranged behind them in the radiation direction of X-ray radiation, with the reset light source being in the form of an arrangement with light-emitting diodes and with the light-emitting diodes being designed such that can be driven individually and their intensity can be controlled individually. At least one of a failed and malfunctioning light-emitting diode is detectable. The intensities of the serviceable light-emitting diodes are driven and controlled in the event of a failure or a malfunction of at least one light-emitting diode in such a manner that the intensity and / or the homogeneity of the reset light source remains the same.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Filter
InactiveCN1258387CImprove stabilityAdjust intervalSemi-permeable membranesTransducer circuitsElastomerFilter media
The invention relates to a filter (1) comprising a plurality of rotating filter discs (3) arranged on a shaft (2) and provided with a porous filter medium. The invention is characterized in that elastomer elements (8, 8') are used as separators and are arranged between each individual filter disc (3) on the shaft (2). The invention also relates to a filter disc (3) for such a filter (1).
Owner:ANDRITZ AG
Arrangement for radiation of a radio-frequency field
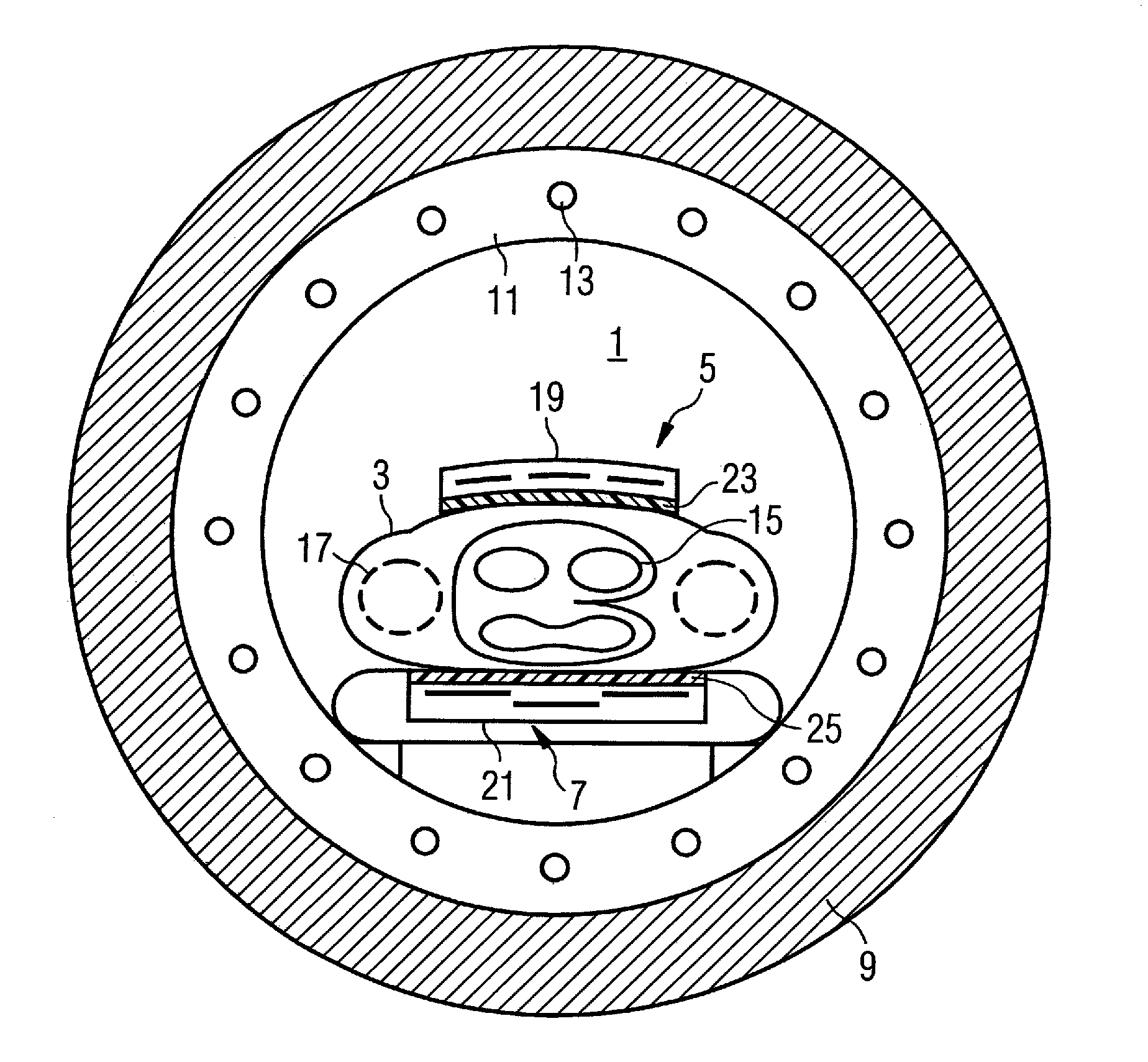
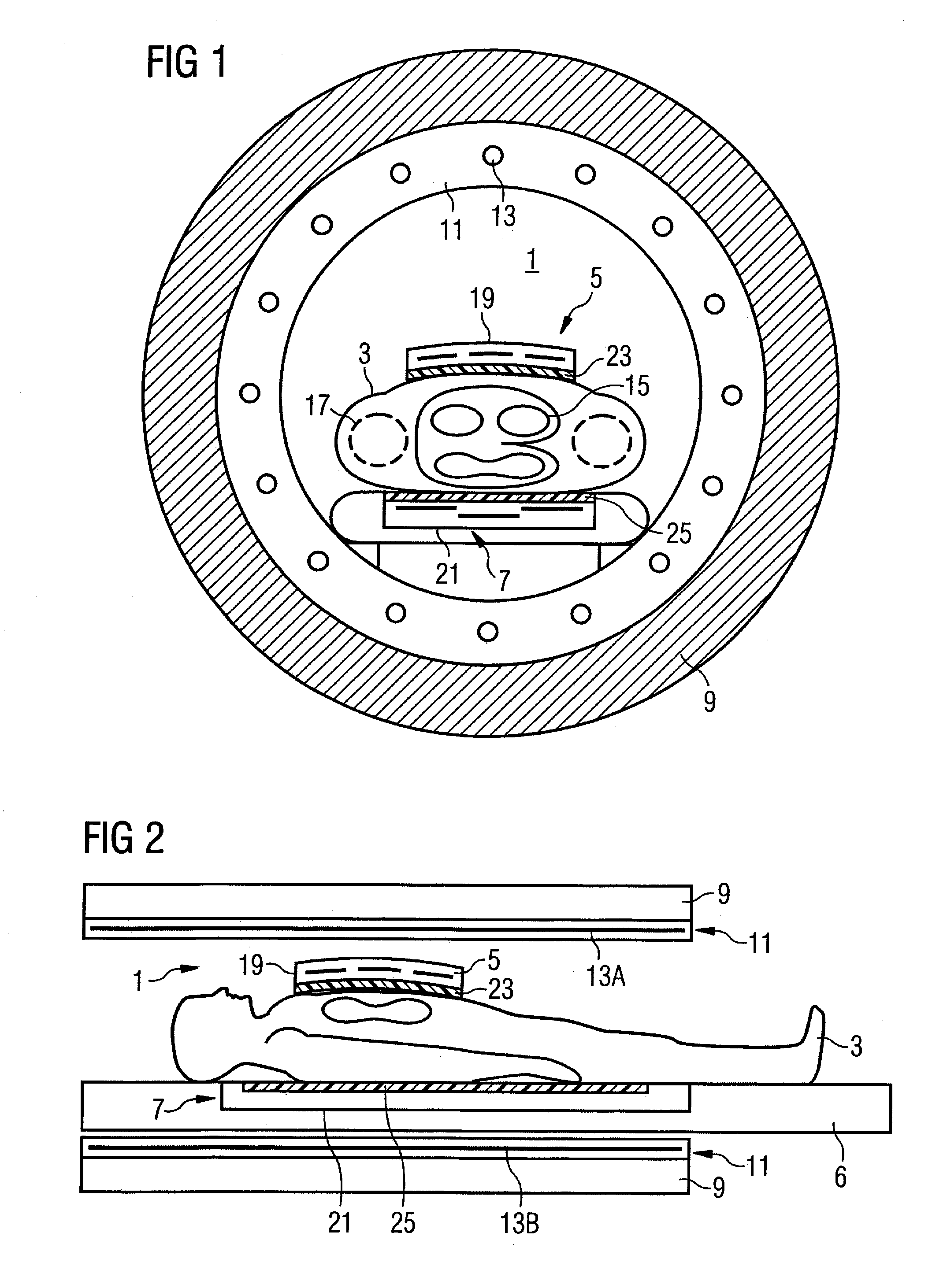
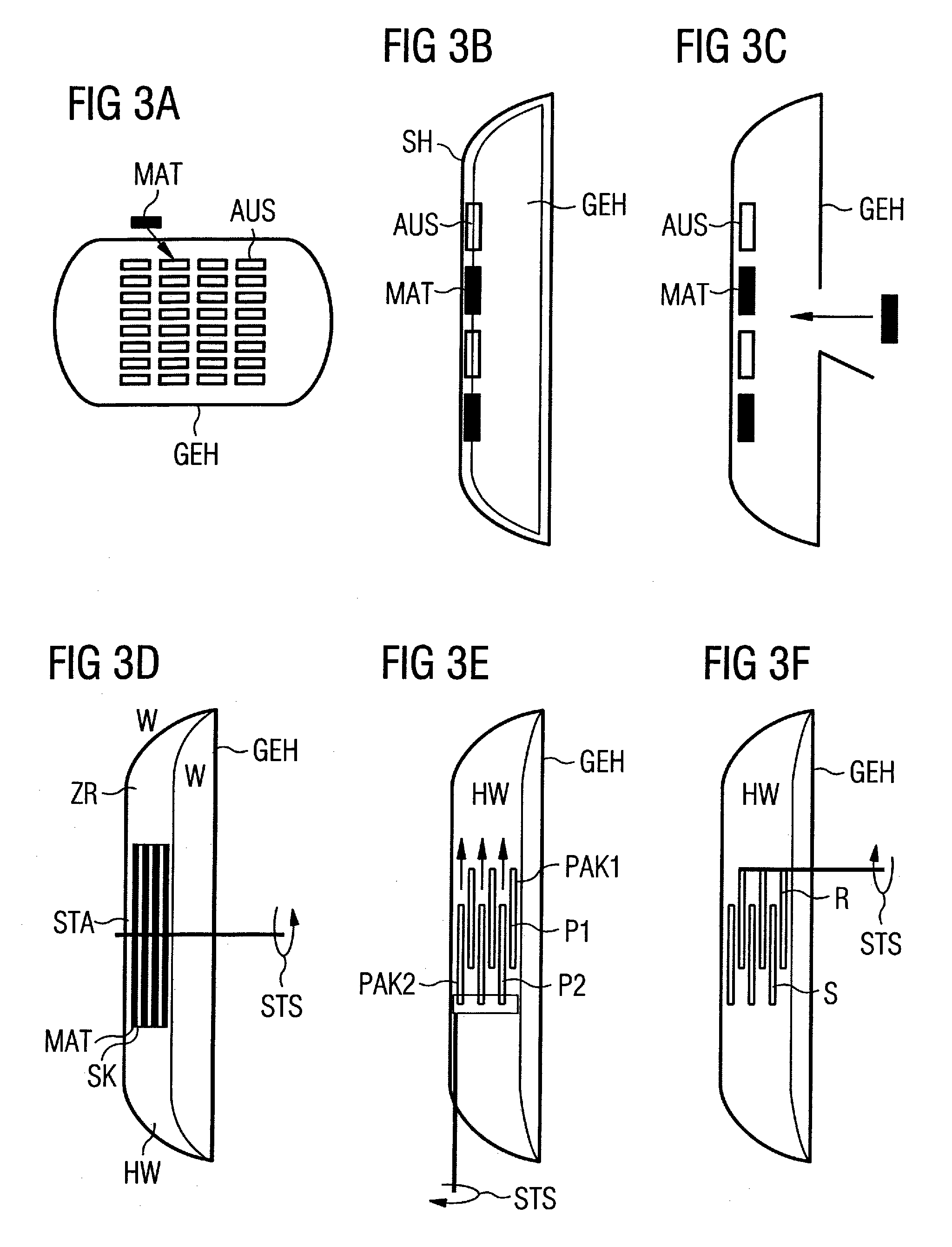
InactiveUS7663368B2Increase inhomogeneityCompensate for inhomogeneityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityB1 field
An arrangement for radiation of a radio-frequency field into an examination subject has a local coil unit with a housing. An insulating dielectric material is embodied at least at one part of the housing in order to passively compensate an inhomogeneity of the B1 field that occurs in the examination subject. An adjustment arrangement allows for fixed but detachable provision of the insulating dielectric material at the housing part.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Display device, pixel circuit and driving method thereof
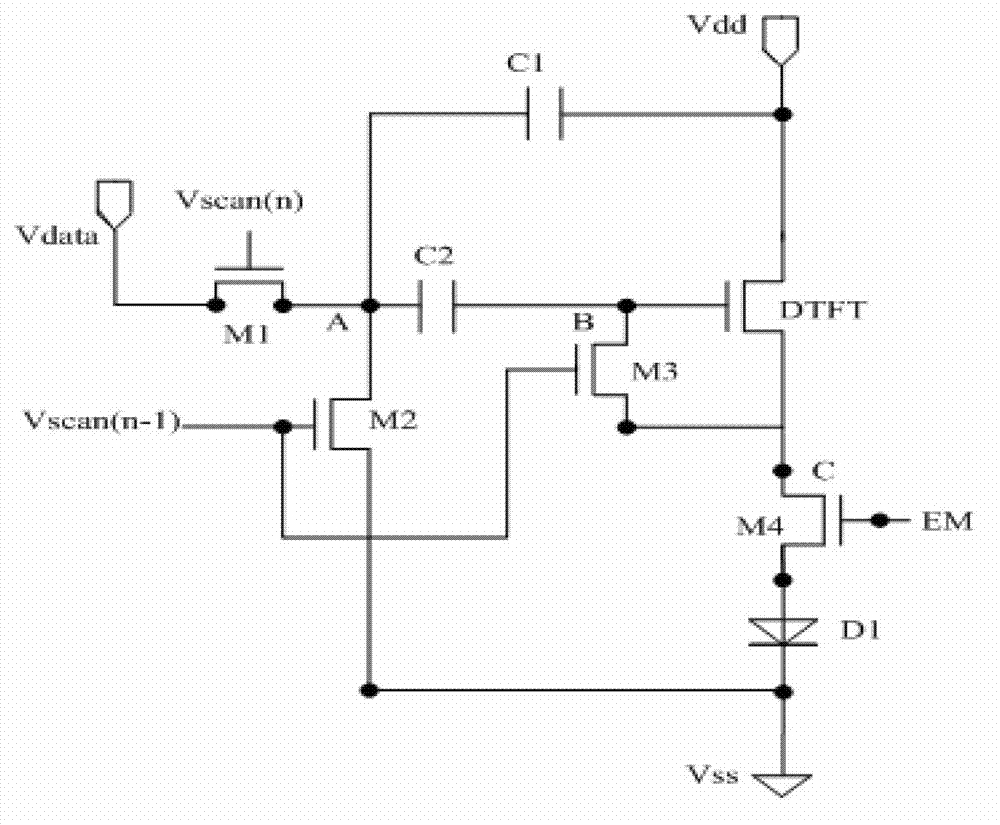
ActiveCN104715723BCompensate for inhomogeneityCompensation Threshold VoltageStatic indicating devicesElectricityCapacitance
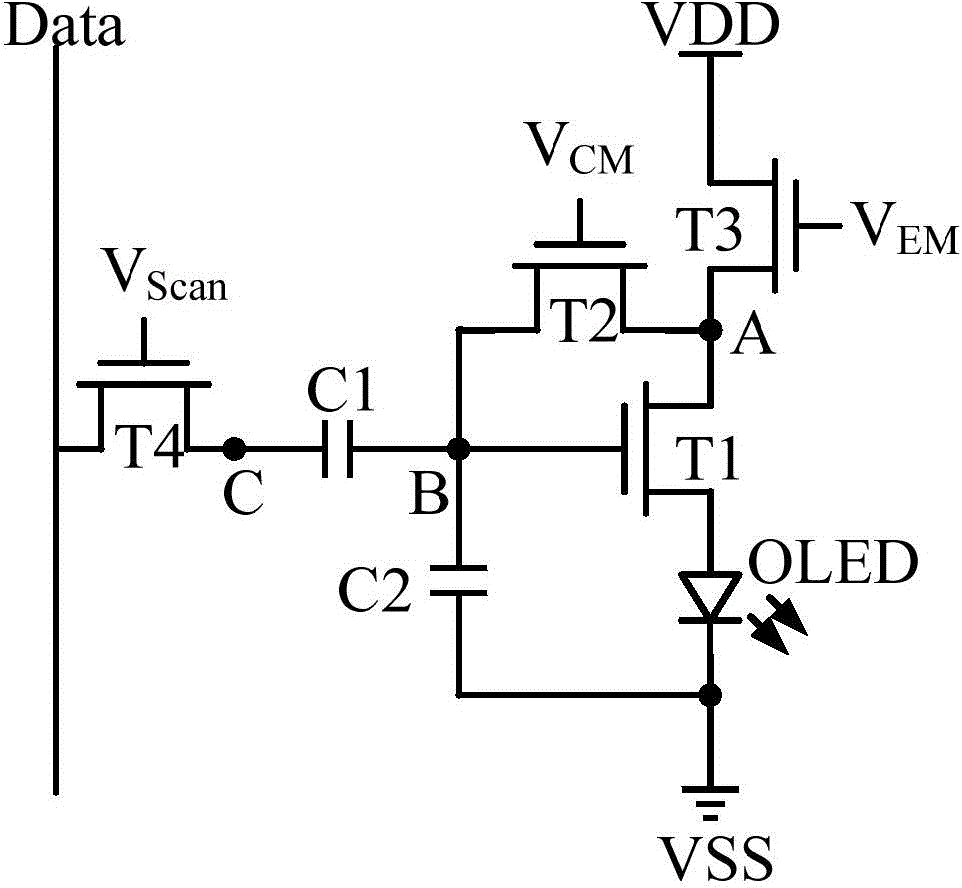
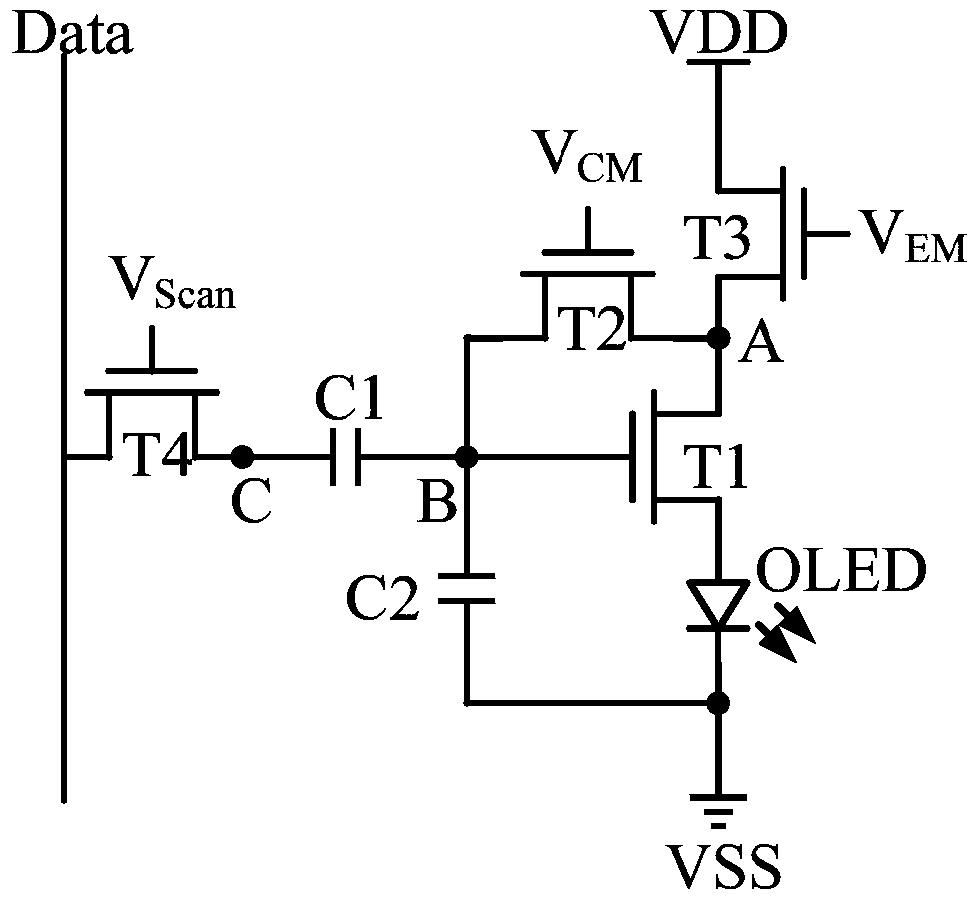
A pixel circuit comprises: a driving transistor (T1) and a light emitting element serially-connected between a first power level end (VDD) and a second power level end (VSS), wherein a first gate of the driving transistor (T1) is connected to a first end of the light emitting element, a second transistor (T2) and a storage capacitor (C1) are connected between a control gate of the driving transistor (T1) and a conduction electrode. At an initialization stage, the second transistor (T2) conducts to separately initialize voltage levels of two ends of the storage capacitor (C1) and a voltage level of the control gate of the driving transistor (T1). At a threshold compensation stage, a reference voltage level (V REF) is provided to the control gate of the driving transistor (T1), so as to read a threshold voltage (V TH) of the driving transistor (T1) and store the same in the storage capacitor (C1), thereby compensating for the threshold voltage (V TH) of the driving transistor (T1) and inhomogeneity shown in the pixel circuit.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com