Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31results about How to "Calibration will degrade" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
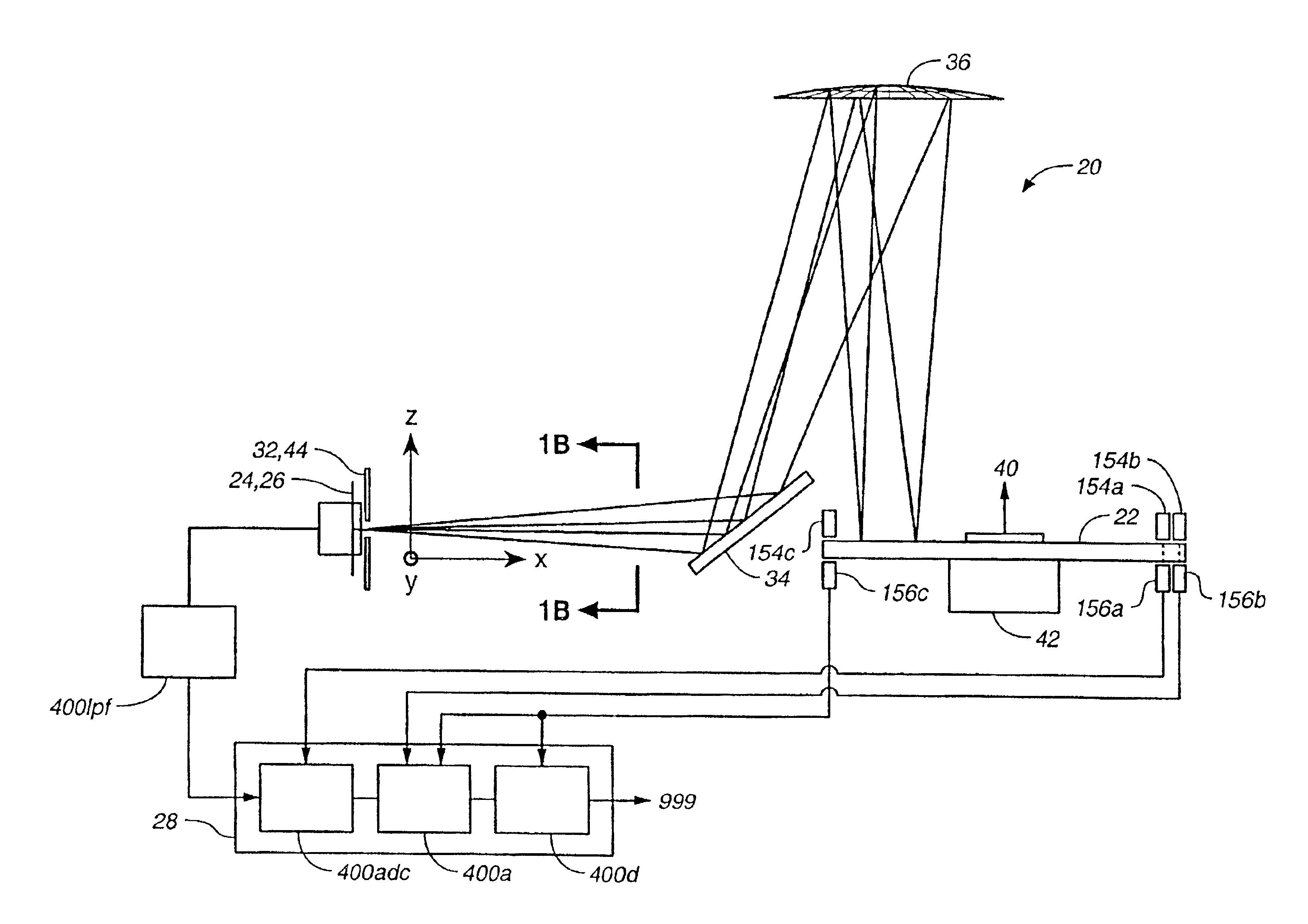
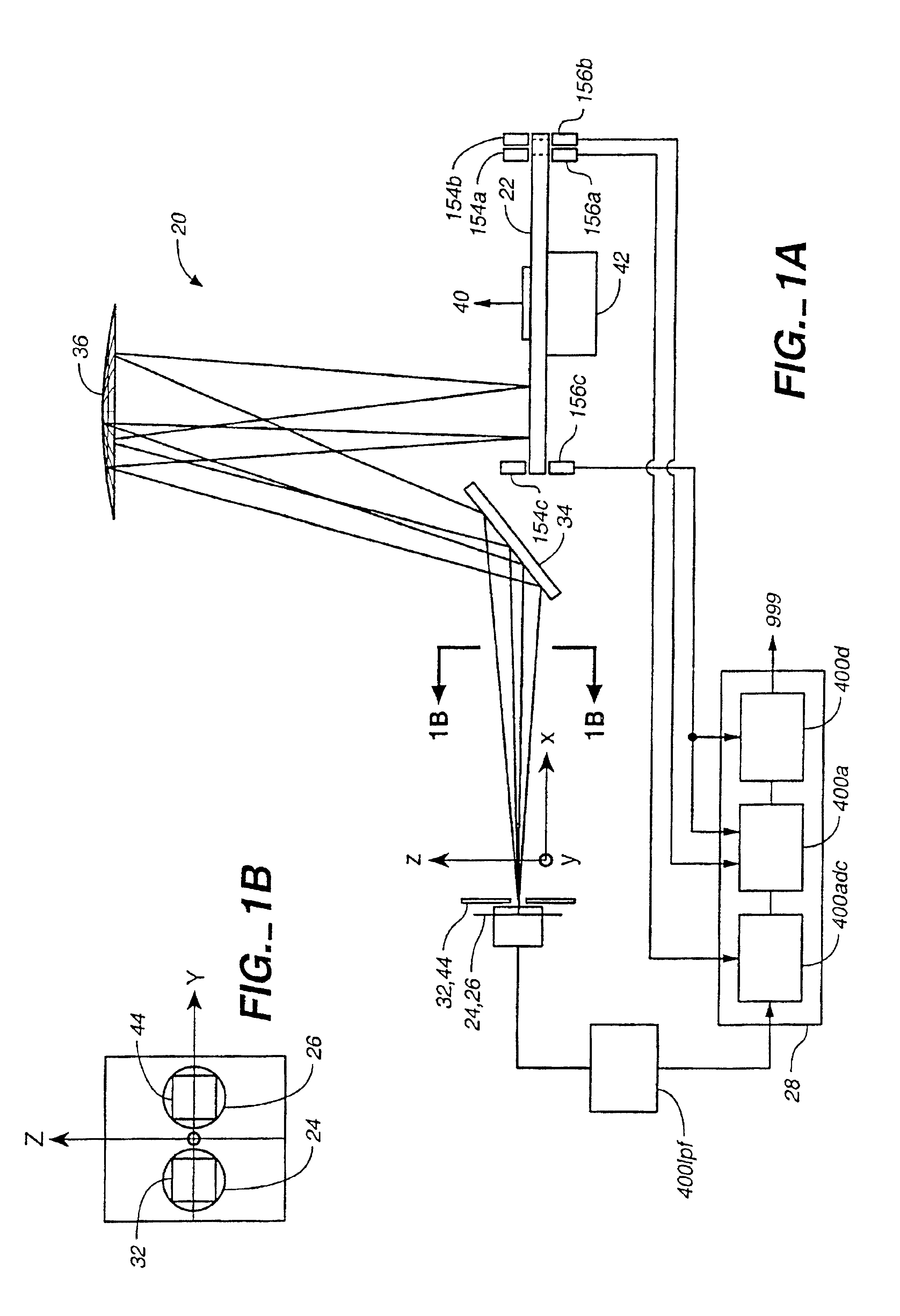
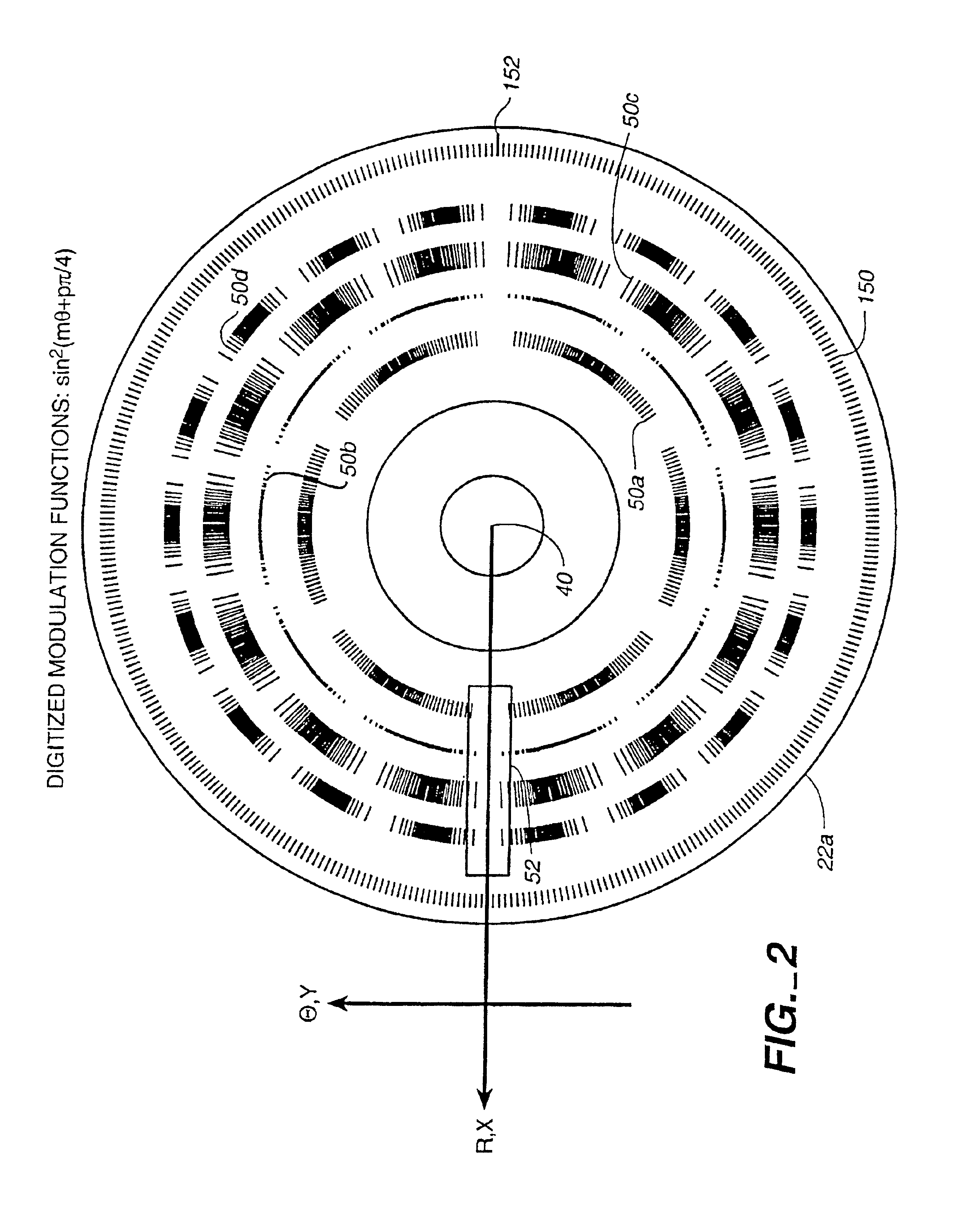
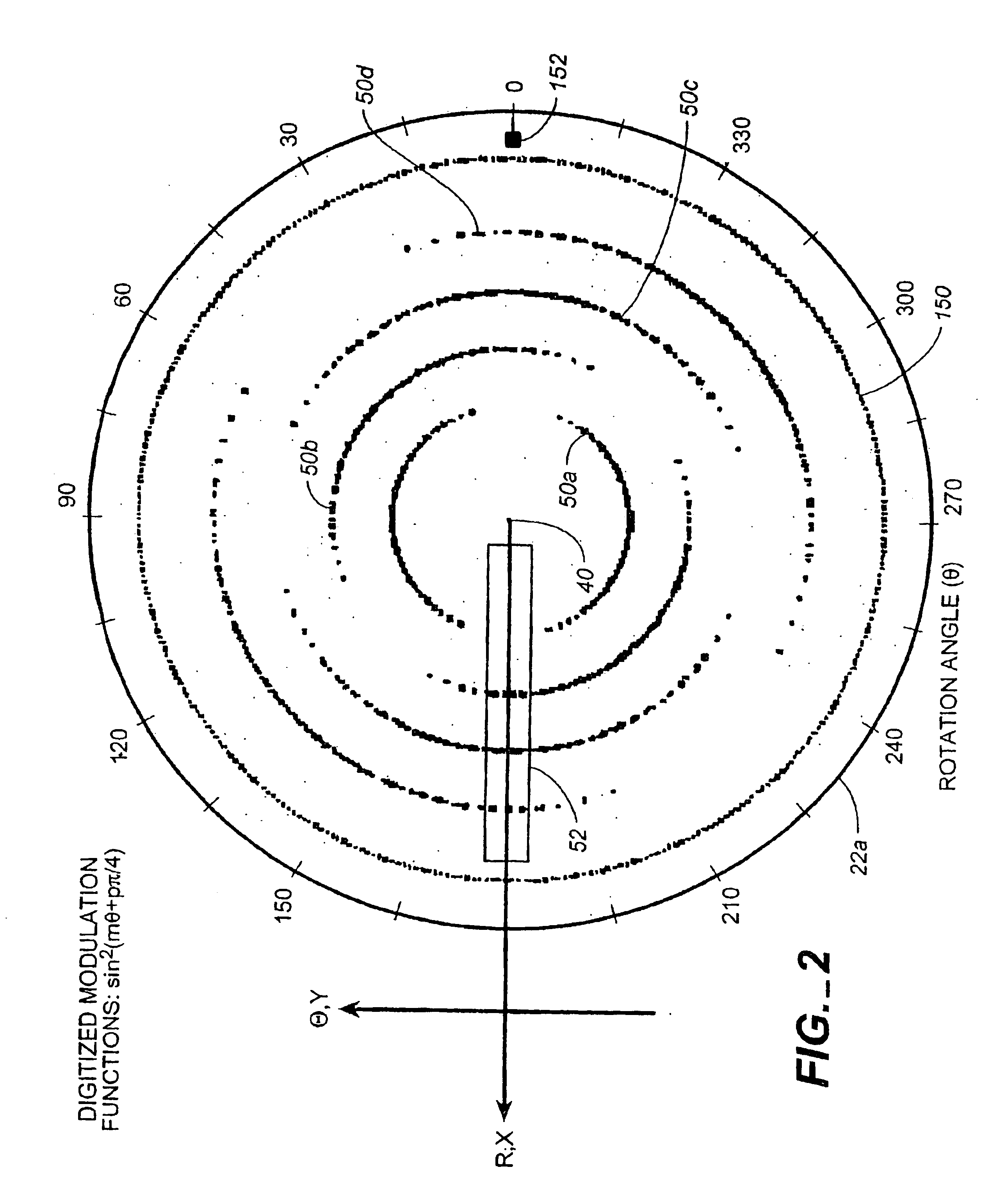
Method and apparatus for spectrum analysis and encoder
InactiveUS6897952B1Increase motor speedReduce motor speedRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsModulation functionFrequency spectrum
A disc serving as a spatial radiation modulator has dispersed radiation filters thereon. Each filter has a transmittance or reflectance modulation function of the form sin2(mθ+pπ / 4), where m is a positive integer and p has one of the four values 0, 1, 2, 3. A radiation beam including selected wavelength components is diffracted into an elongated image dispersed according to wavelength. Different wavelength components are focused onto different filters on the modulator and are encoded by corresponding filters. Since the modulation functions of the filters are orthogonal to one another, it is possible to extract the amplitude of each wavelength component after it has been encoded or modulated by corresponding filter from the total detected signal during one measurement.
Owner:MUDLOGGING SYST
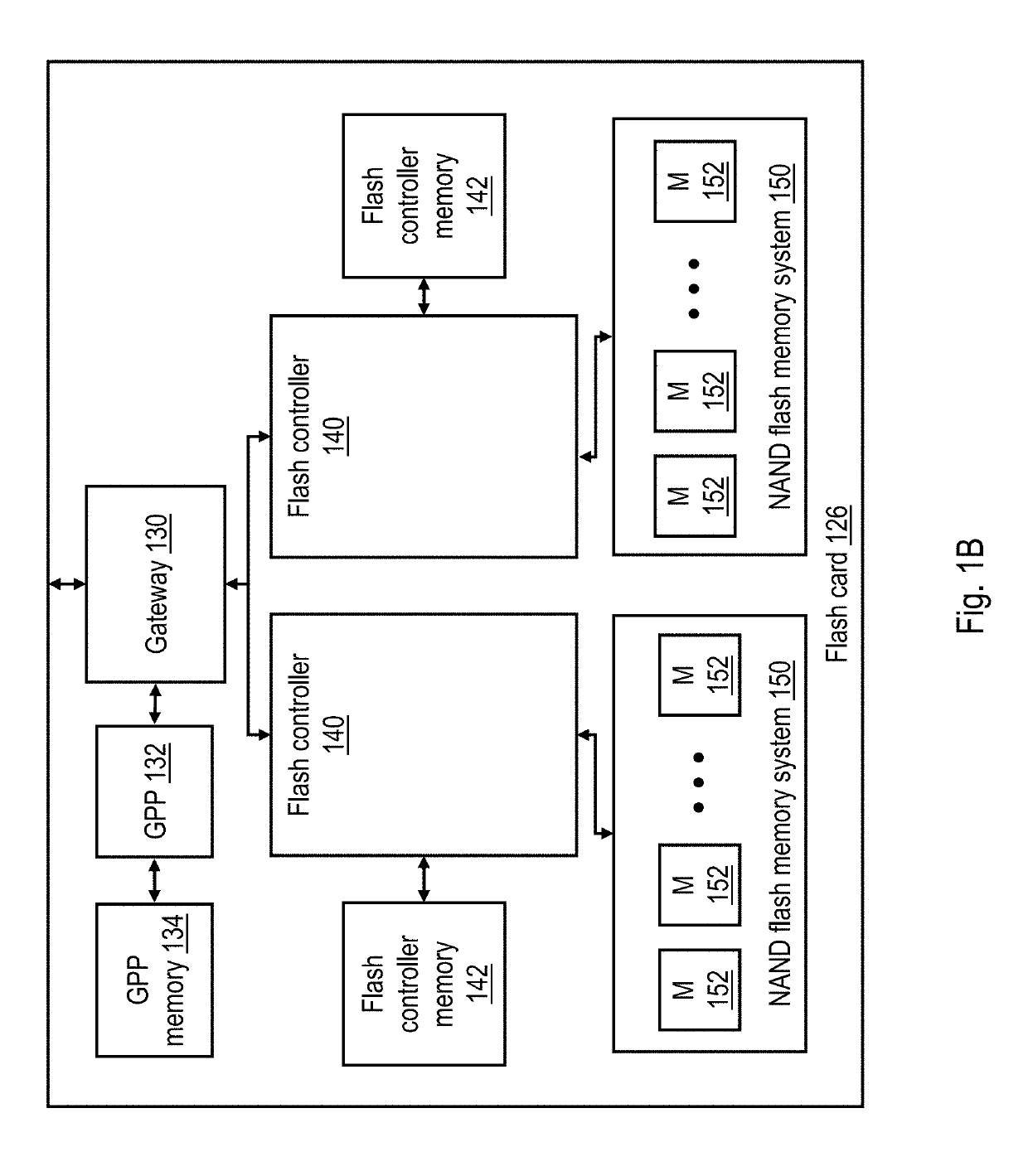
Reducing unnecessary calibration of a memory unit for which the error count margin has been exceeded
ActiveUS20190171381A1Error rateIncreased longevityInput/output to record carriersNon-redundant fault processingNon-volatile memoryBit error rate
A controller sets an error count margin for each of multiple units of a non-volatile memory and detects whether the error count margin of any of the multiple units has been exceeded. In response to detecting that the error count margin of a memory unit is exceeded, the controller determines whether calibration of the memory unit would improve a bit error rate of the memory unit sufficiently to warrant calibration. If so, the controller performs calibration of the memory unit. In some implementations, the controller refrains from performing the calibration in response to determining that calibration of the memory unit would not improve the bit error rate of the memory unit sufficiently to warrant calibration, but instead relocates a desired part or all valid data within the memory unit and, if all valid data has been relocated from it, erases the memory unit.
Owner:IBM CORP
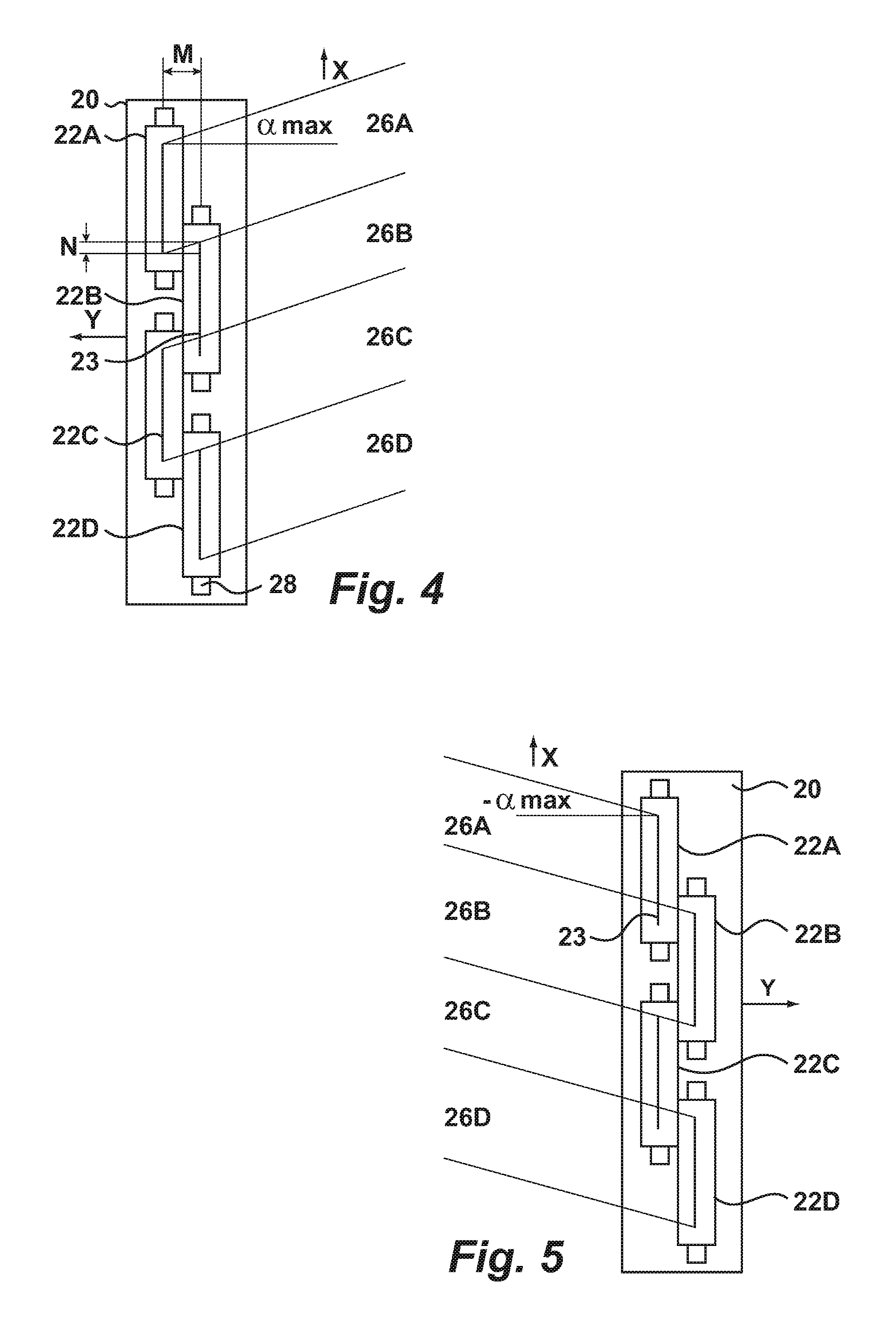
Print head module
ActiveUS20140028748A1Calibration will degradeEliminate possible variationInking apparatusSpacing mechanismsSpray nozzleEngineering
A print head module (20) for depositing a substance has an axis and a plurality of print heads (22) provided with nozzles (23). The heads are distributed along the axis to form an elongate compound head having nozzle redundancy by arranging the heads in partially overlapping relation to one another. This allows deposition of the substance from the nozzles in uniform swathes having different angles transverse to the axis.
Owner:TEN CATE ADVANCED TEXTILES BV
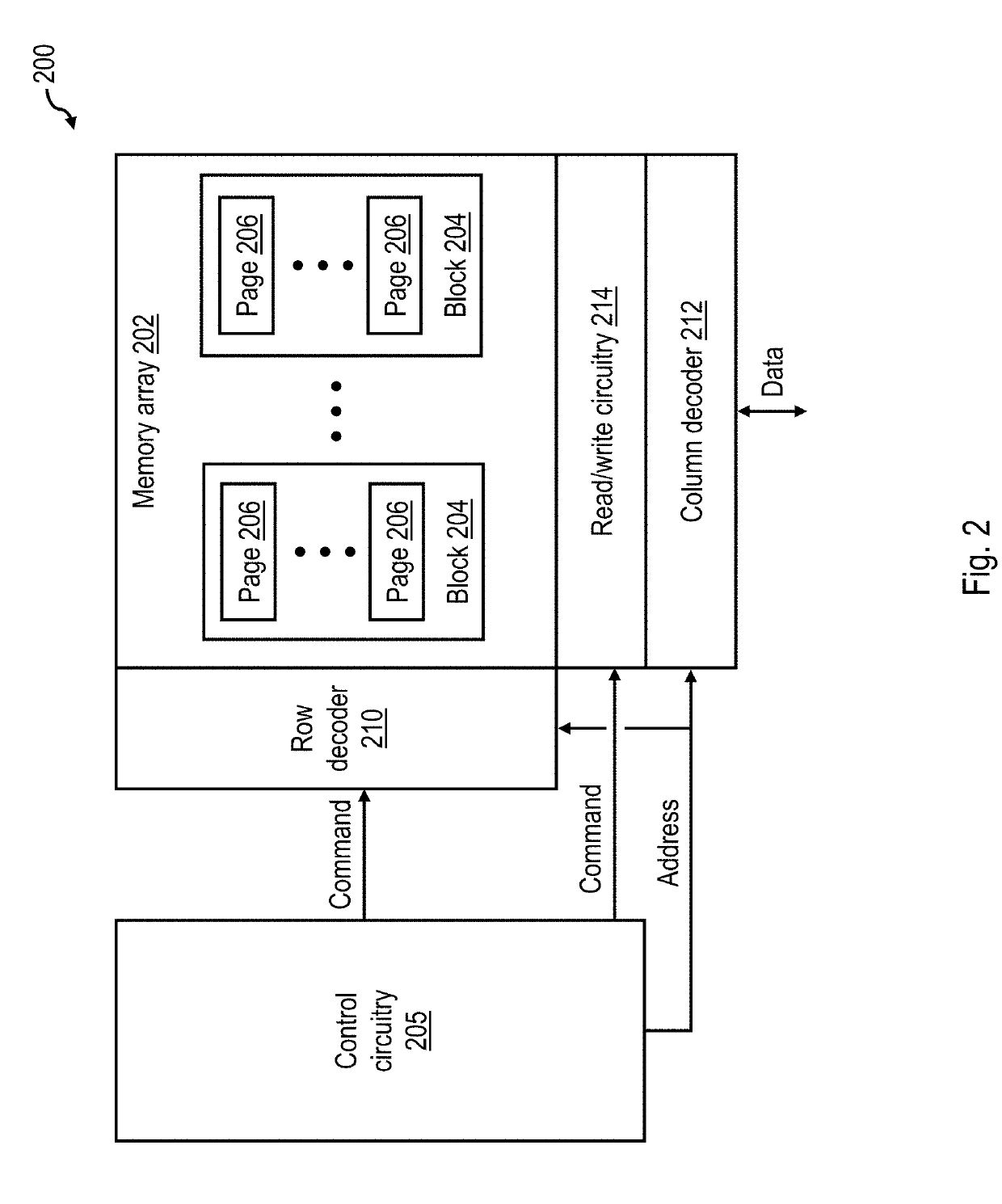
Computer readable medium recording a calibration program, calibration method, and calibration system
InactiveUS20070024928A1Accurate detectionImprove accuracyColour-separation/tonal-correctionPictoral communicationPattern recognitionImage formation
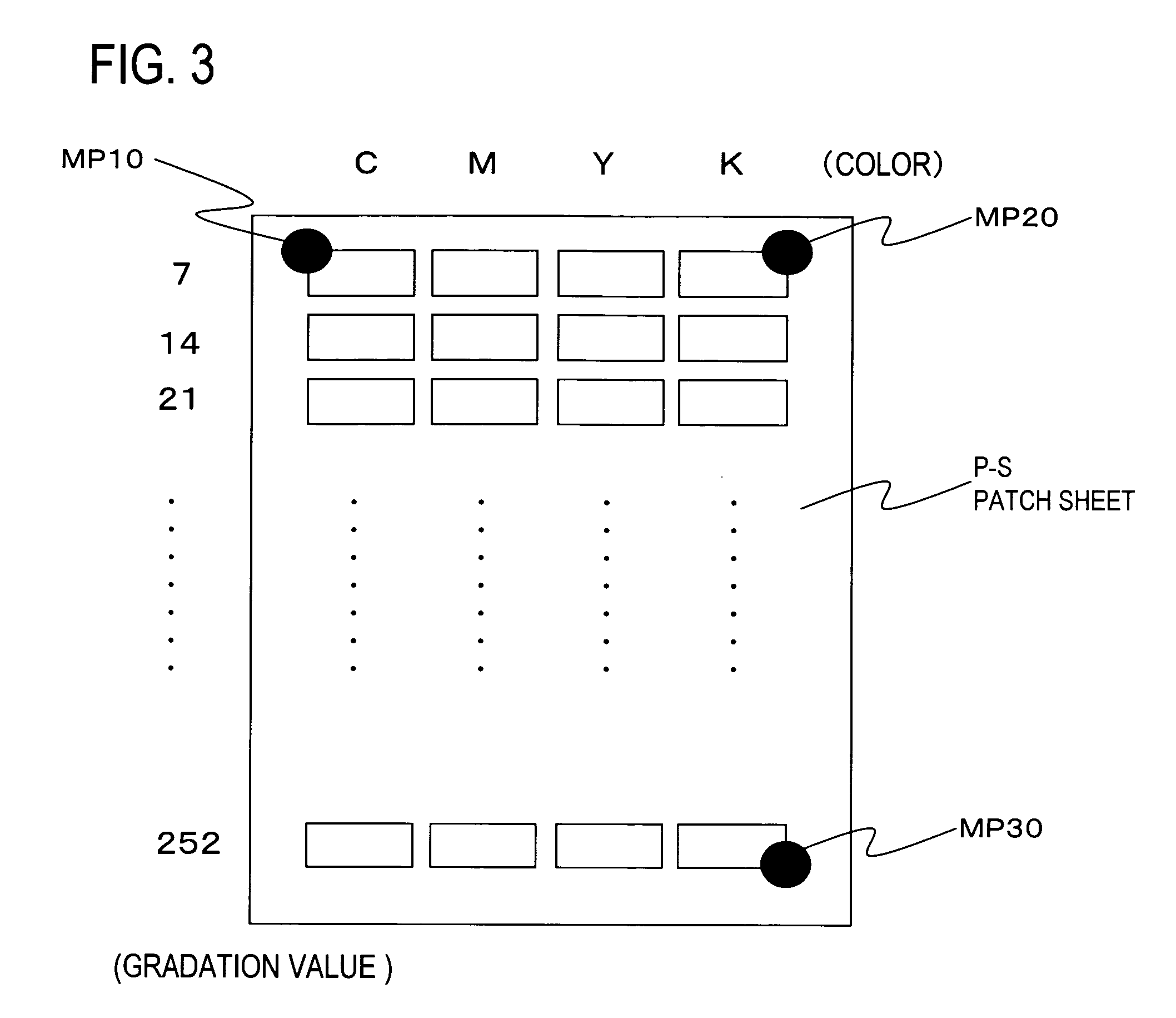
A computer readable medium records a calibration program, which causes a control device to execute calibration processing of reading as image data a patch sheet output from an image formation device, having a plurality of patch patterns formed as images based on different density-gradation value data for each color, acquiring calorimetric values for each of the patch patterns from the read-out image data, and adjusting the density of the image formation device based on the density-gradation values and the acquired calorimetric values for each of the patch patterns. The program causes the control device to execute displaying the read-out image data of the patch sheet, detecting and displaying the position of each of the patch patterns in the image data of the patch sheet, and acquiring the calorimetric values for each the patch pattern based on the displayed patch pattern positions, in response to confirmation input by a user of the displayed patch pattern position.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
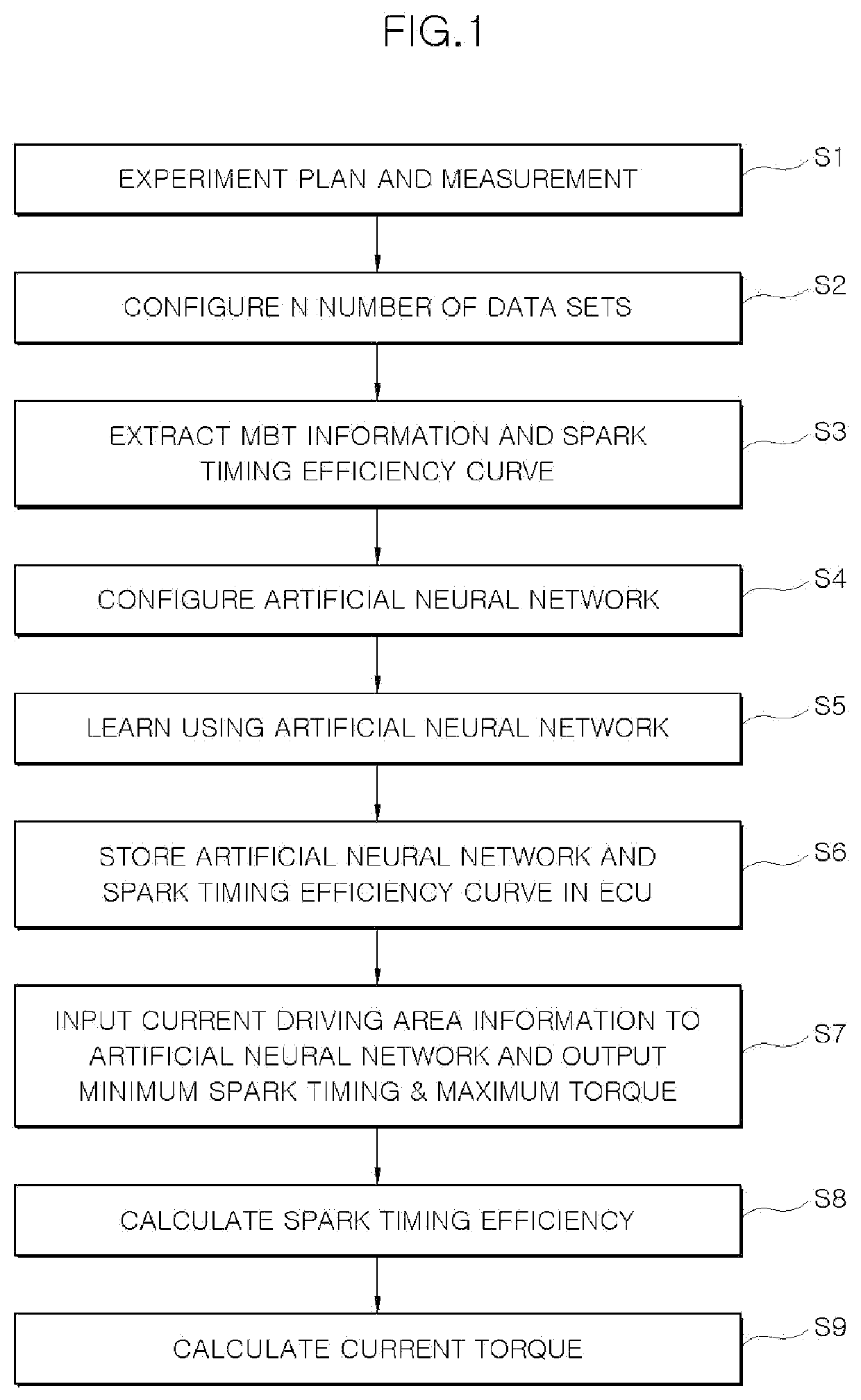
System and method of predicting vehicle engine torque using artificial neural network
ActiveUS20210222662A1Improve accuracyReduce development costsValve arrangementsAutonomous decision making processComputed torqueEngineering
A method of predicting vehicle engine torque using an artificial neural network is provided. A data-based artificial neural network model is applied to more accurately calculate. torque and reduce development costs for calibration and logics.
Owner:HYUNDAI KEFICO CORP
Method and apparatus for spectrum analysis and encoder
InactiveUS6982788B2Little effectOptimize timingRadiation pyrometrySpectrum generation using diffraction elementsModulation functionFrequency spectrum
Owner:MUDLOGGING SYST
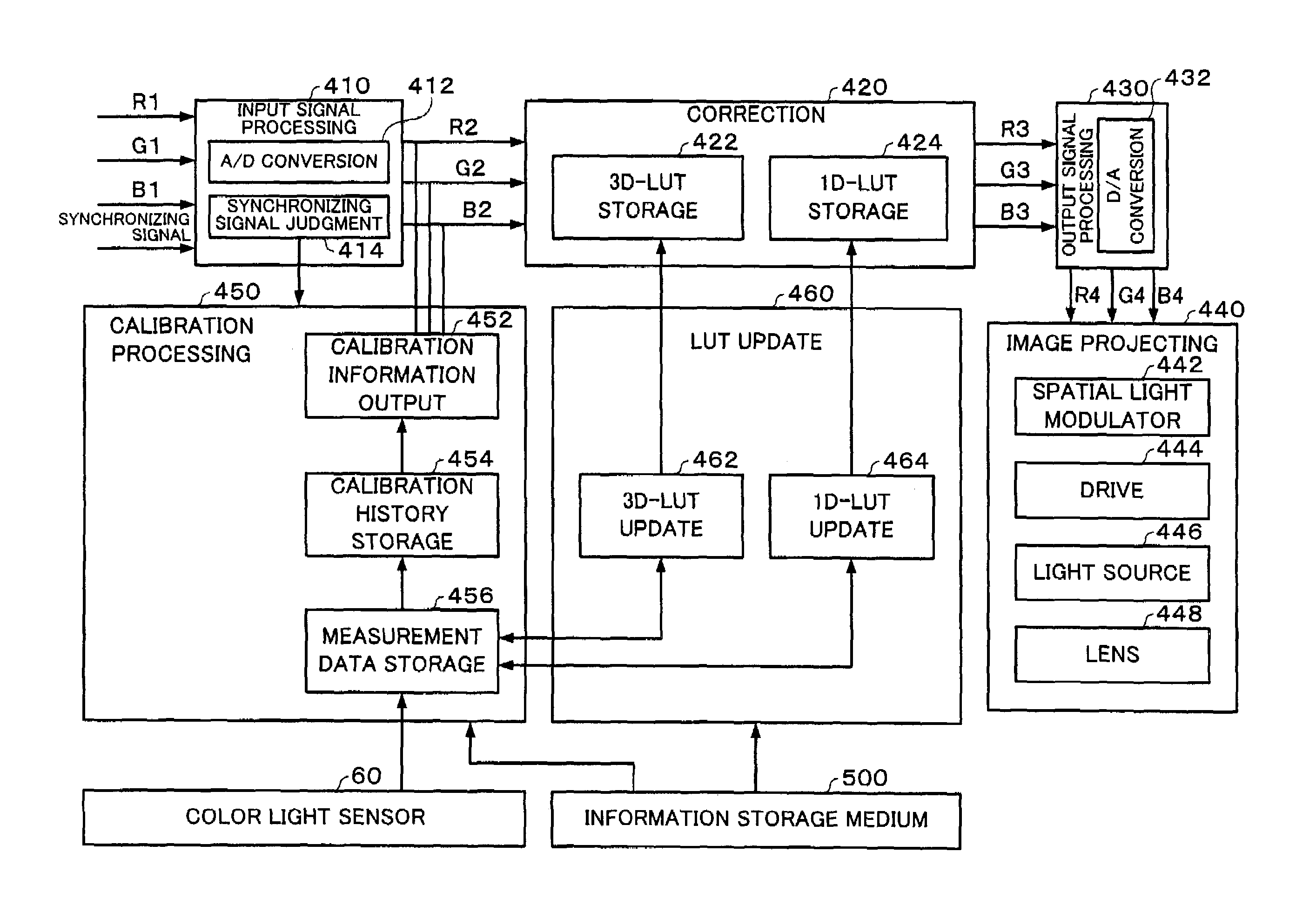
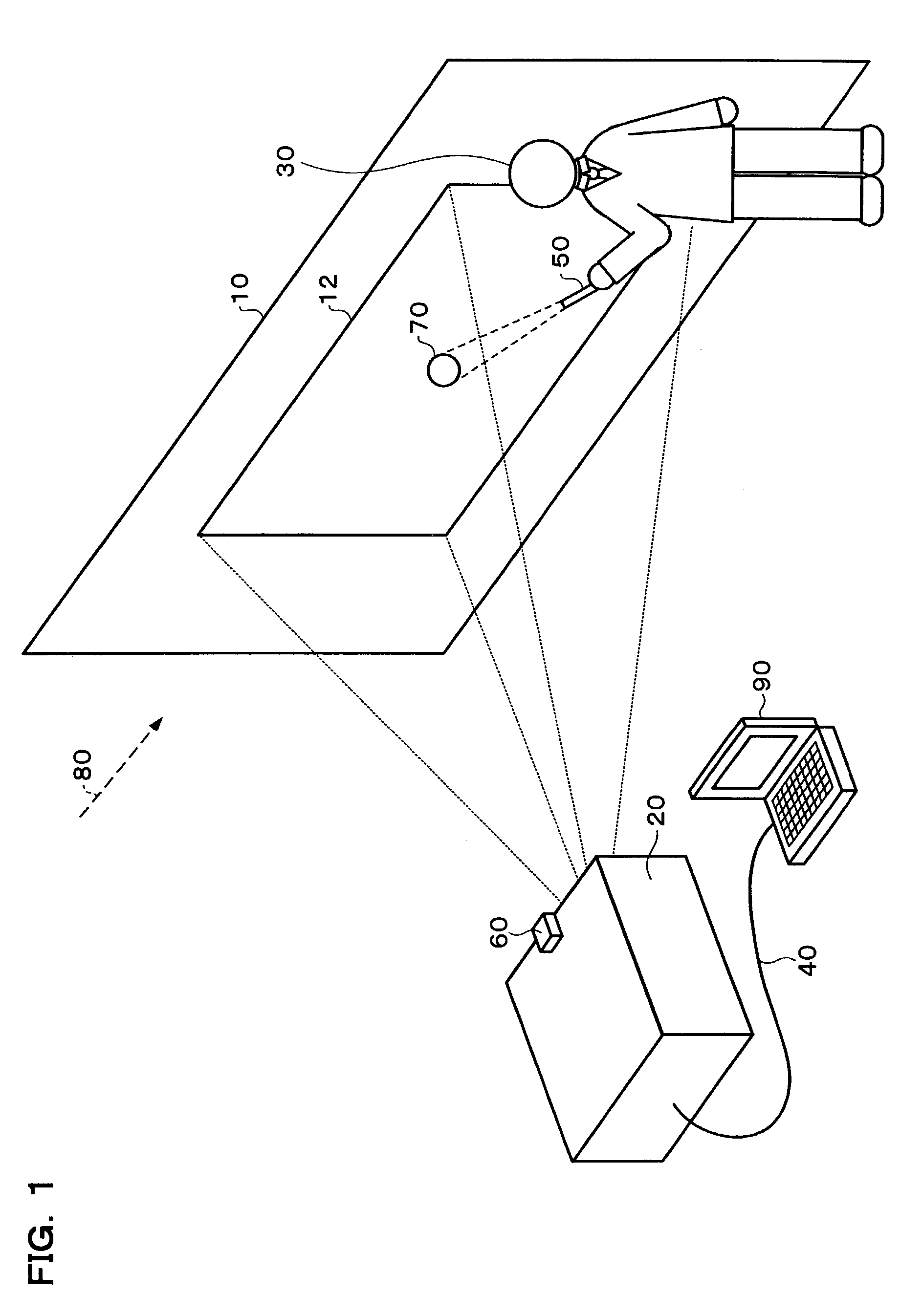
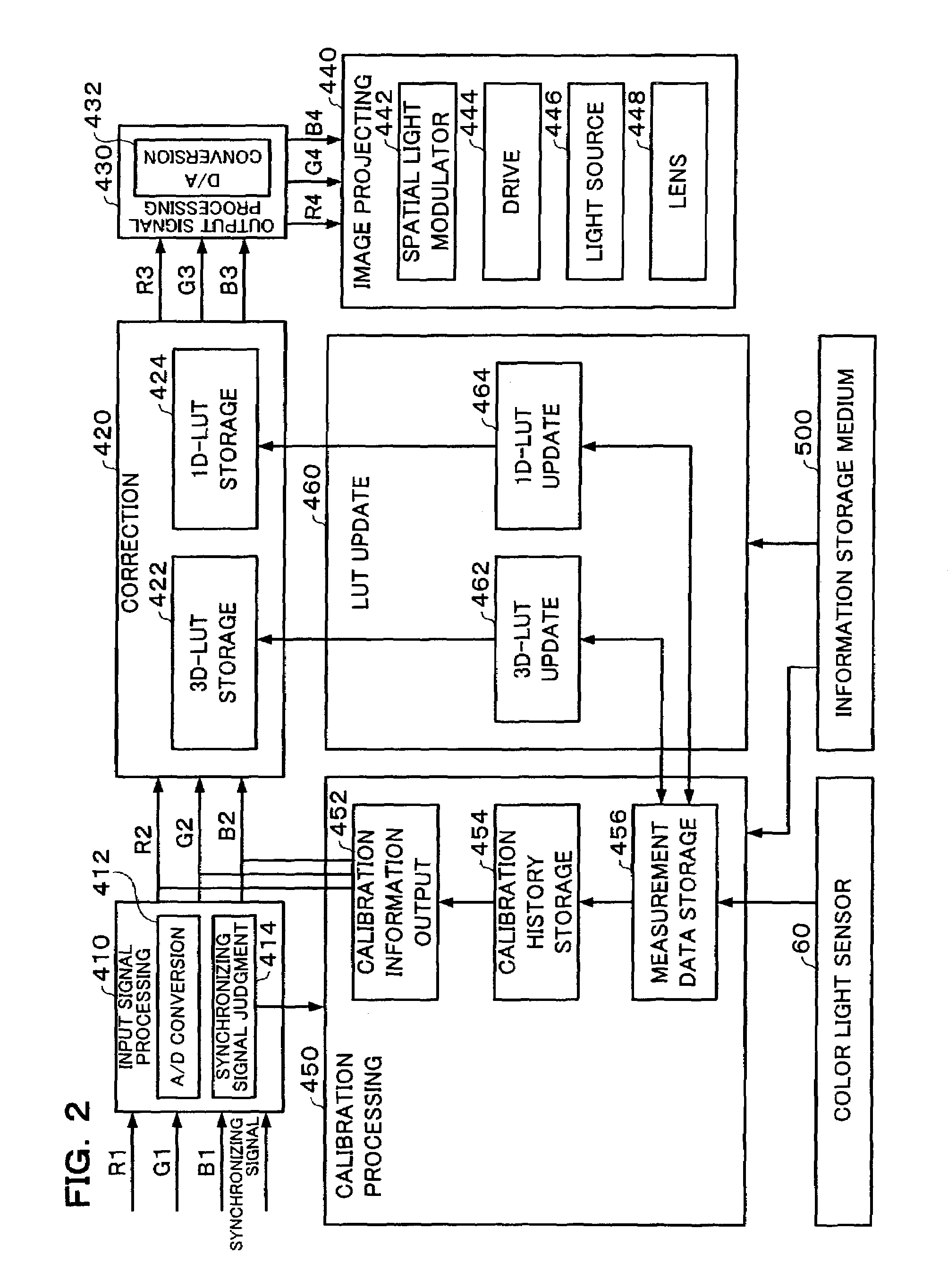
Projection system, projector, program, information storage medium and image processing method
ActiveUS7034852B2Reduce unpleasantnessCalibration will degradeTelevision system detailsImage enhancementComputer hardwareImaging processing
In order to provide a projection system, projector, program, information storage medium and image processing method which can reduce an unpleasantness to an observer in an image calibration when it is executed in consideration of the ambient light, a calibration information output section selects and outputs calibration information, a color light sensor then measures XYZ values in the respective projected calibration images, and a measurement data is then stored in a sensing value holding section, when a synchronizing signal judgment section judges that no synchronizing signal has been inputted. When all the color correcting measurement data have been provided, a 3D-LUT update section updates a 3D-LUT stored in the 3D-LUT storage section, based on the measurement data. When all the brightness correction measurement data have been provided, a 1D-LUT update section updates a 1D-LUT stored in a 1D-LUT storage section to execute the calibration, based on the measurement data.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
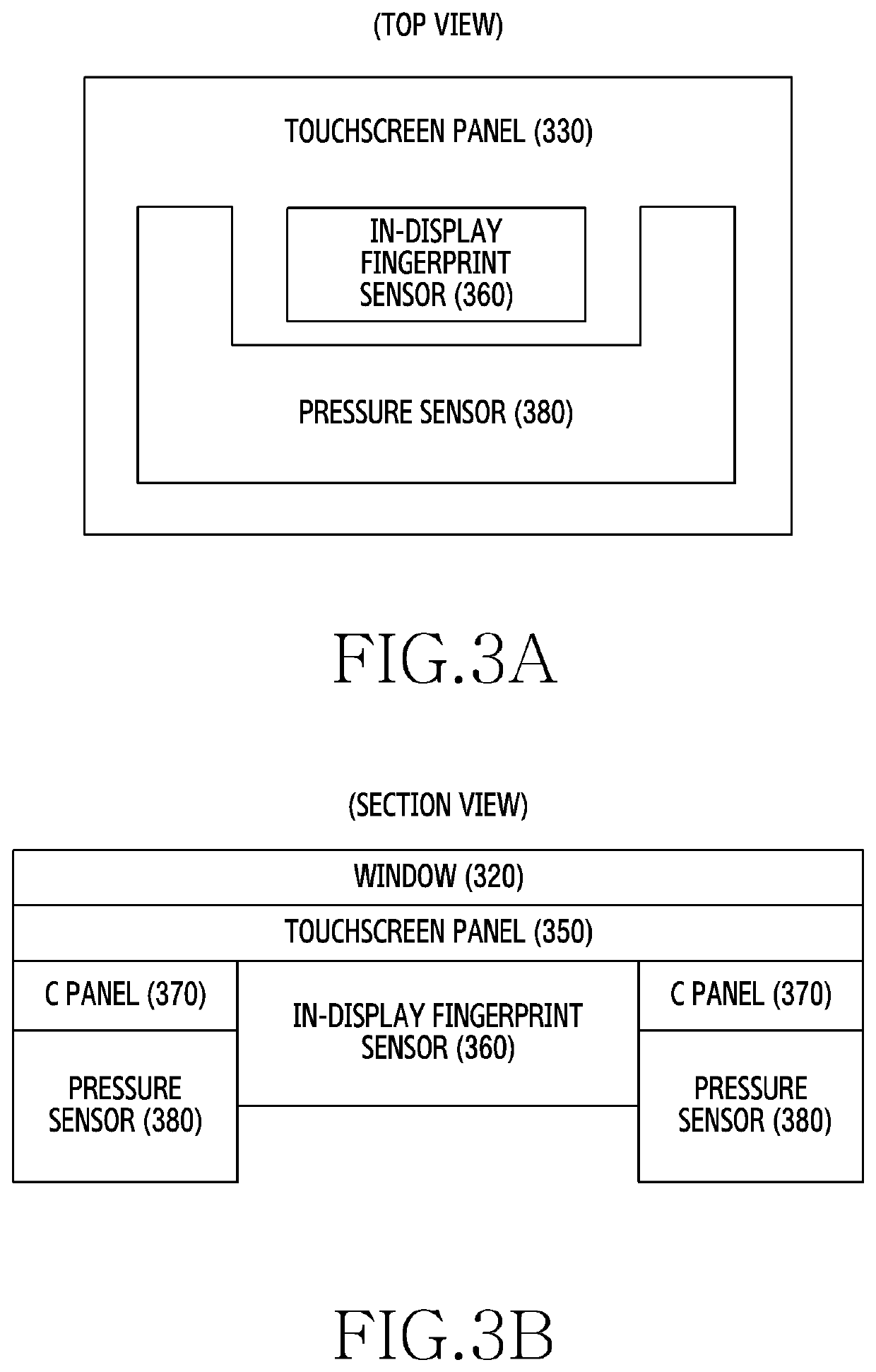
Electronic device including ultrasonic in-display fingerprint sensor and operating method thereof
ActiveUS20200074134A1Reduce abnormal calibrationEasy to identifyThermometer detailsInternal/peripheral component protectionMedicineDisplay device
Various embodiments of the disclosure relate generally to an electronic device and its operating method for creating a calibration condition of an in-display fingerprint sensor and calibrating the fingerprint sensor according to the created condition, using a touchscreen display. The electronic device may according to various embodiments of the disclosure include a housing, a touchscreen display disposed inside the housing and viewable through one surface of the housing, an ultrasonic fingerprint sensor disposed inside the housing an overlapping one area of the touchscreen display when viewed from above the one surface of the housing, the ultrasonic fingerprint sensor further comprising a temperature measuring sensor, at least one processor operatively coupled with the touchscreen display and the ultrasonic fingerprint sensor, and at least one memory operatively coupled with the at least one processor, and configured to store a first reference fingerprint image relating to authentication using the ultrasonic fingerprint sensor, wherein the at least one memory may be configured to store instructions that, when executed, cause the at least one processor to control the electronic device to: measure a temperature change using the temperature measuring sensor, determine a presence of a foreign substance on the one area using the touchscreen display, and determine whether to calibrate the ultrasonic fingerprint sensor according to the temperature change, based at least in part on determining the presence of a foreign substance.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Calibration measurements for network analyzers
ActiveUS20130134990A1Reduce numberReduced calibration standardResistance/reactance/impedencePhysicsTest fixture
A method for measuring s-parameters of an N-port device under test (DUT), using an N-port test fixture and a network analyzer. The method includes: measuring calibration errors of the N-port test fixture using a reduced set of N / 2 calibration standards; measuring calibration errors due to the network analyzer by calibrating only the network analyzer using analyzer-only calibration standards; isolating test fixture s-parameters errors using results of the analyzer-only calibration standards measurement and the N-port test fixture calibration standard measurement; measuring the s-parameters errors of the DUT; and correcting the s-parameters errors of the DUT corresponding to the isolated test fixture s-parameters errors and the calibration errors of the network analyzer.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Method for operating a metering unit of a catalytic converter
InactiveUS7452724B2Simple processSimple methodSamplingInternal combustion piston enginesCombustion systemNitrogen oxides
In order to ensure optimum metering of a reagent to be metered into an exhaust gas during operation of a metering unit of a catalytic converter of a combustion system, in particular an internal combustion engine of a motor vehicle, in any operating state of the catalytic converter and / or in any operating state of the combustion system, a method and a device for operating a metering unit of a catalytic converter of a combustion system provide that, based on a steady-state value of the reagent quantity to be metered during a steady-state operating state of the catalytic converter and / or the combustion system, the quantity of the at least one reagent is determined and adjusted using at least one dynamic correction factor which is dependent on at least one of the performance characteristics of the catalytic converter and on at least one of the performance characteristics of the combustion system. The dynamic correction factor and / or a nitrogen oxide correction factor are obtained from a dynamic correction characteristics map or a nitrogen oxide correction characteristics map only as a function of performance characteristics of the internal combustion engine, in particular the engine speed and the injected fuel quantity, and of performance characteristics of the catalytic converter, preferably the nitrogen oxide emission and the temperature of the exhaust gas downstream from the catalytic converter.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Luminance-chrominance calibration production line of LED display module
ActiveUS20150371405A1Data errorReduce calibration manpowerImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageData acquisition
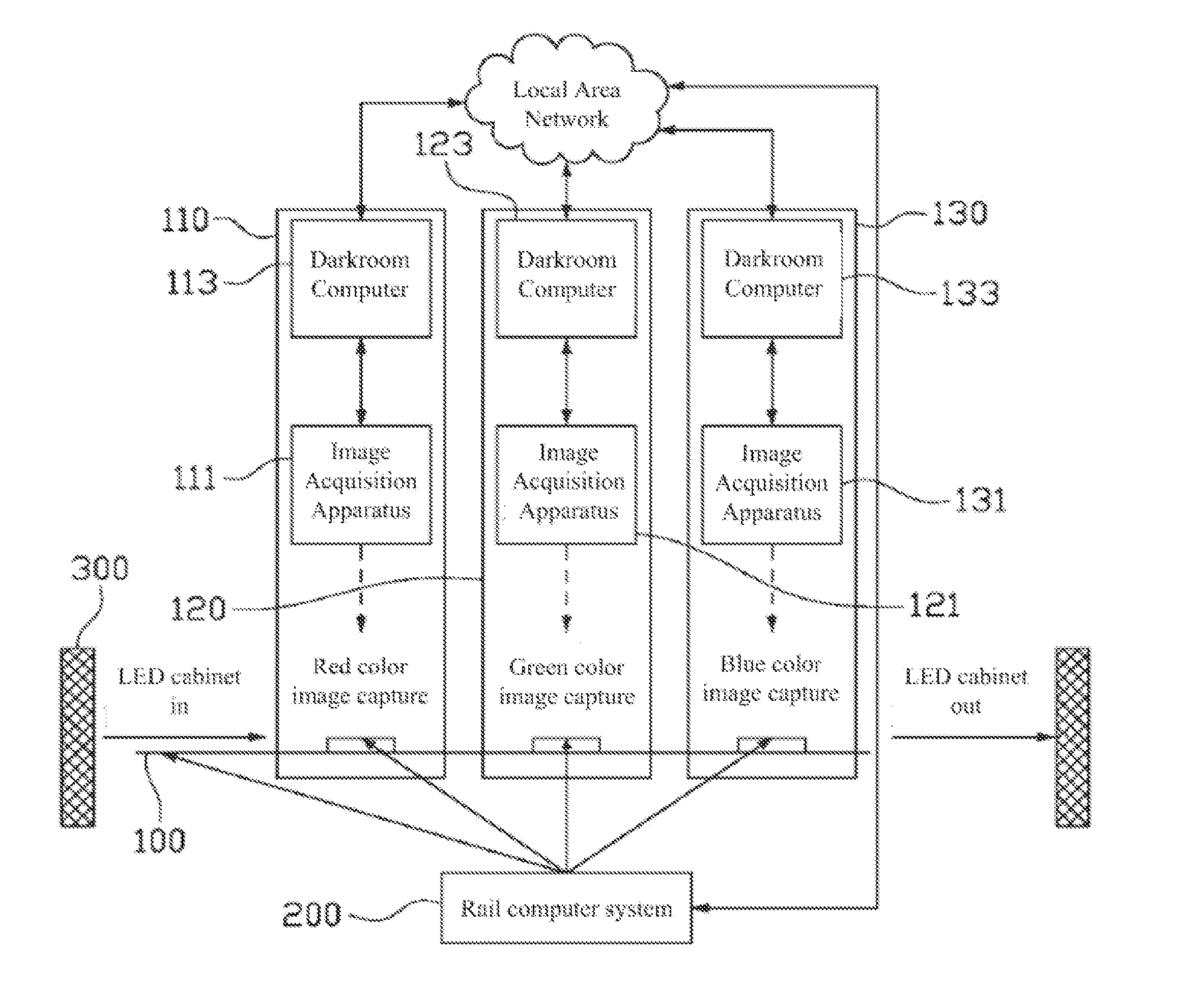
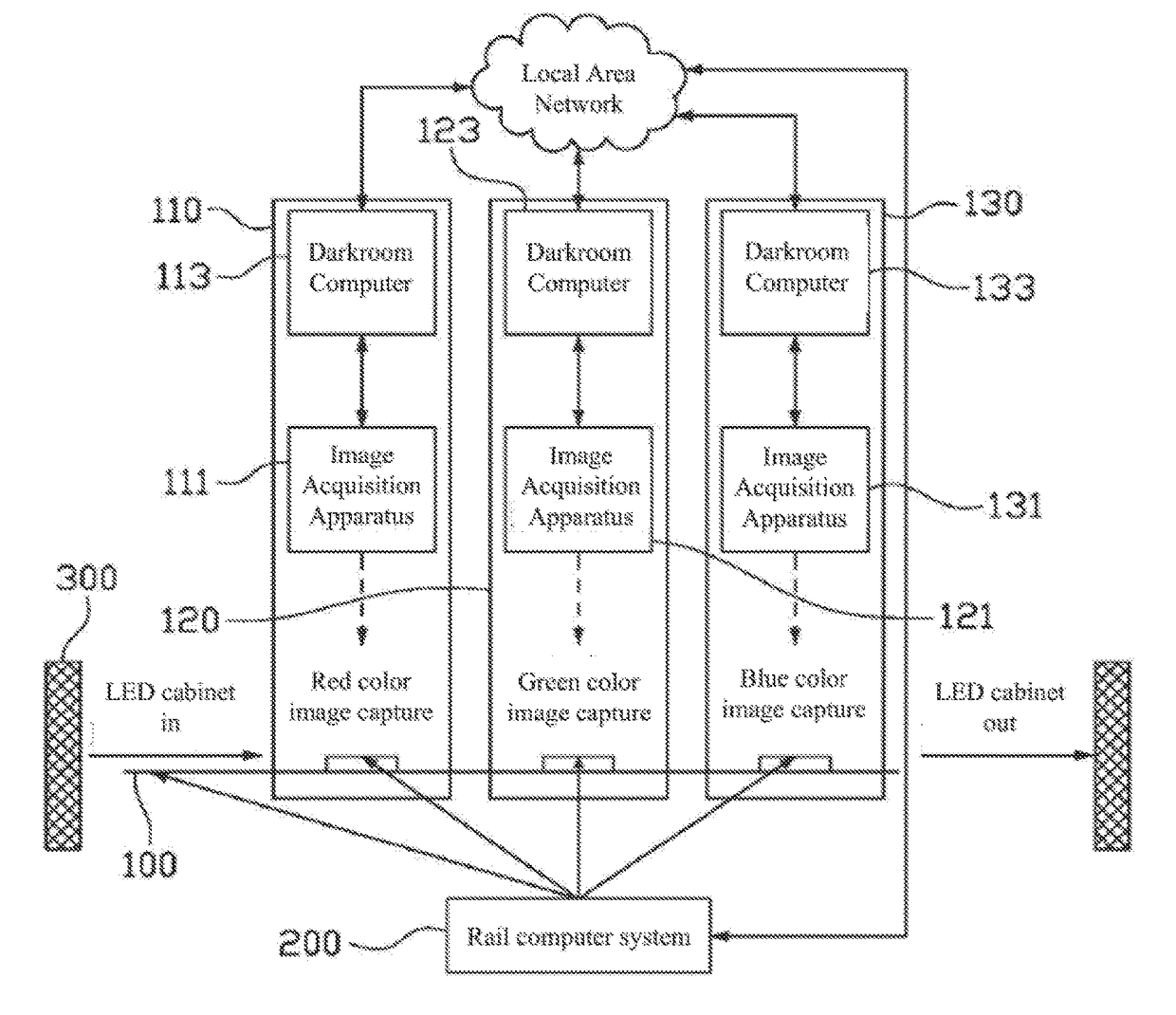
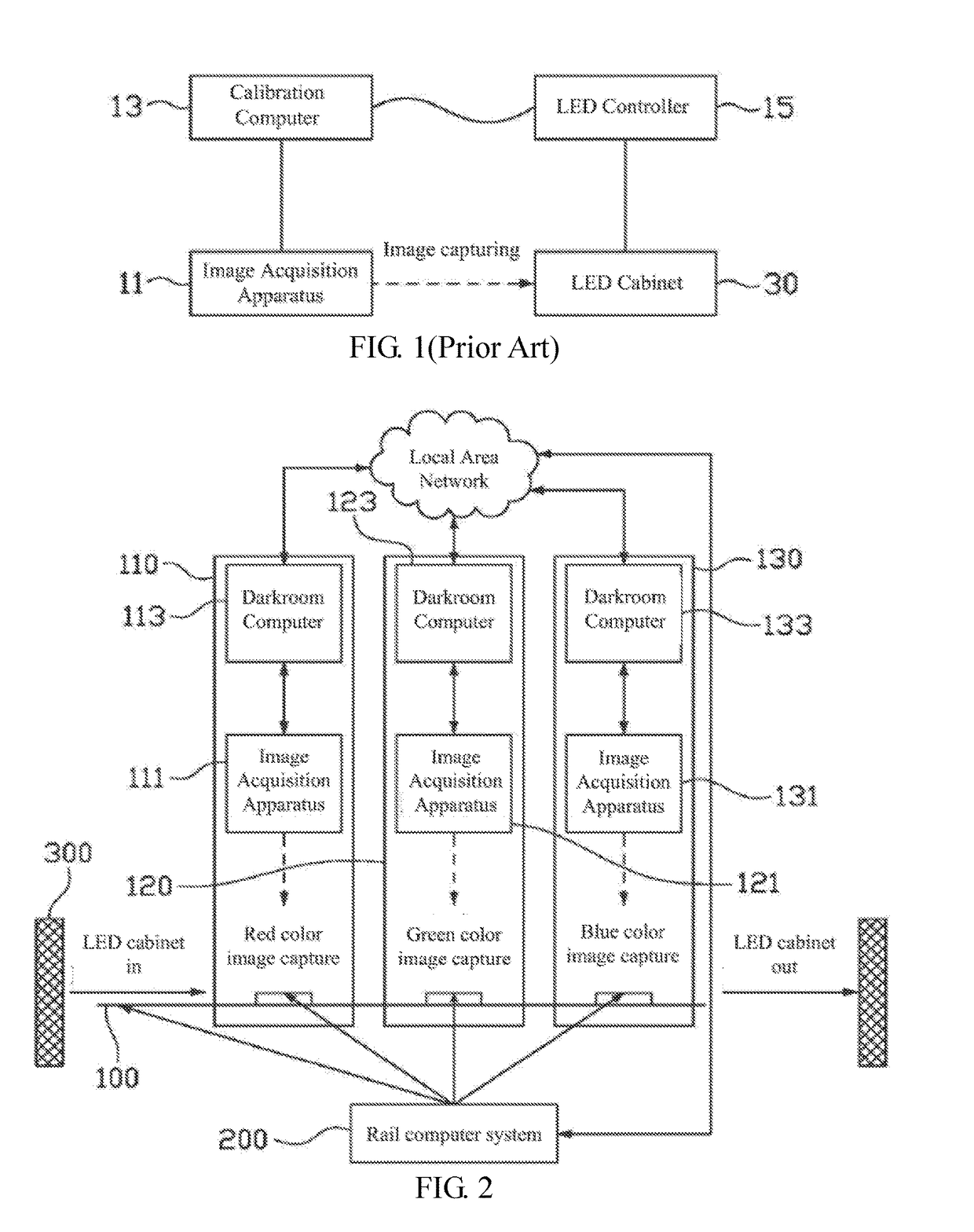
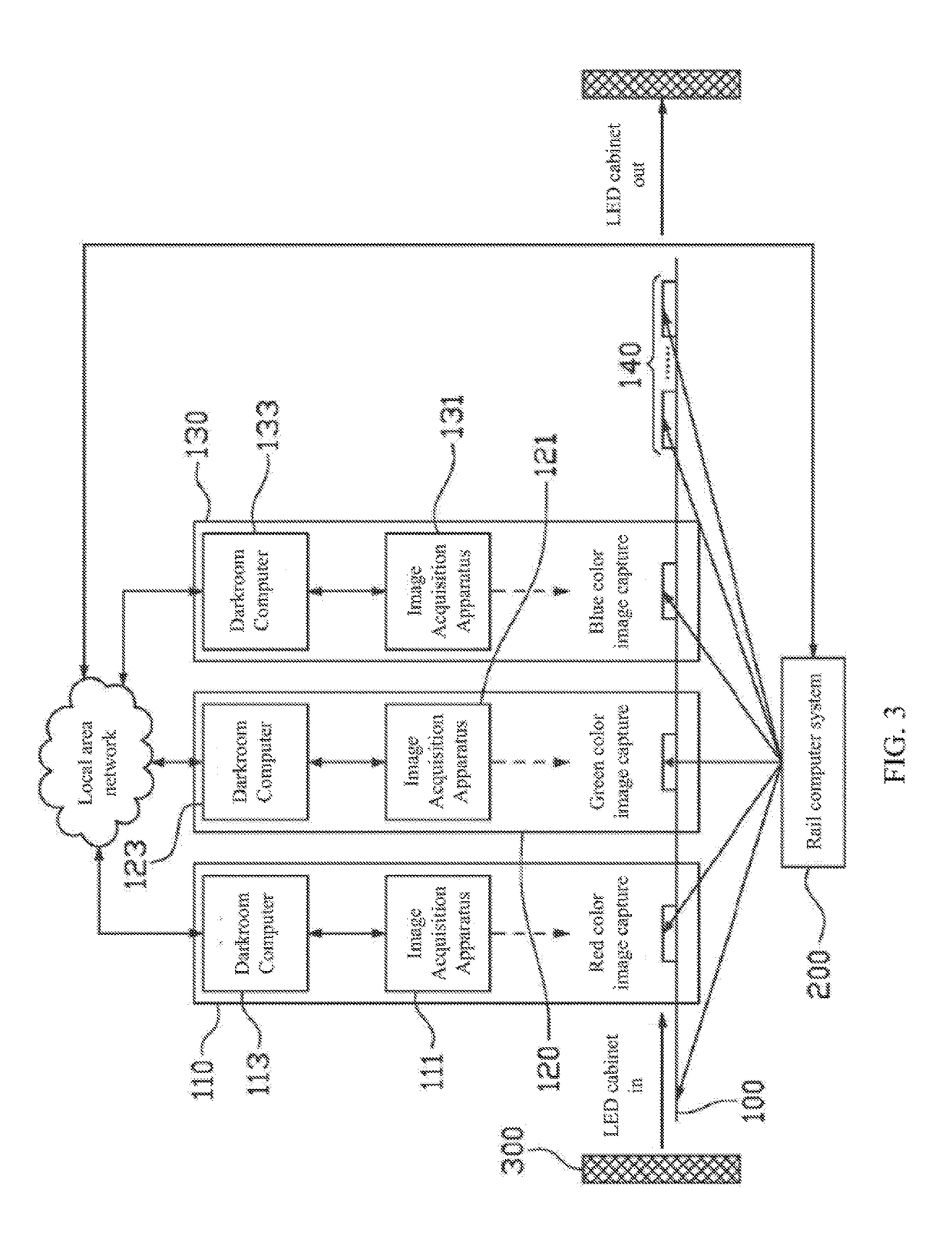
A luminance-chrominance calibration production line includes: a rail; multiple stations disposed along the rail and including multiple first darkroom stations; multiple image acquisition apparatuses respectively disposed in the first darkroom stations and for capturing different color images sequentially displayed by a to-be-calibrated LED display module loaded on the rail to acquire color image data; and a rail computer system for controlling a transport movement on the rail and controlling the to-be-calibrated LED display module to display the different color images, and being signally connected to the image acquisition apparatuses to obtain the color image data. By using multiple image acquisition apparatuses to collect various color image information of LED display module in pipelined manner, calibration efficiency is improved, data collection is accurate, data collection error caused by using different image acquisition apparatuses to calibrate different LED display modules is avoided and calibration manpower is reduced.
Owner:XIAN NOVASTAR TECH
Control approach for use with dual mode oxygen sensor
InactiveUS7197866B2Accurate locationCalibration will degradeElectrical controlExhaust apparatusDual modeOxygen sensor
Electronic circuitry and control algorithms are described to automatically establish the output voltage of a linear exhaust gas oxygen sensor (e.g., a UEGO sensor) corresponding to an exhaust air-fuel ratio of stoichiometry. The apparatus and control logic herein described may be used to adaptively correct the setpoint of an air-fuel ratio control system in which a UEGO sensor is used in a feedback loop to adjust the fuel injection quantity of an internal combustion engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Print head module
ActiveUS8960855B2Eliminate variationEffective placementInking apparatusSpacing mechanismsEngineeringNozzle
Owner:TEN CATE ADVANCED TEXTILES BV
RF input transconductor stage
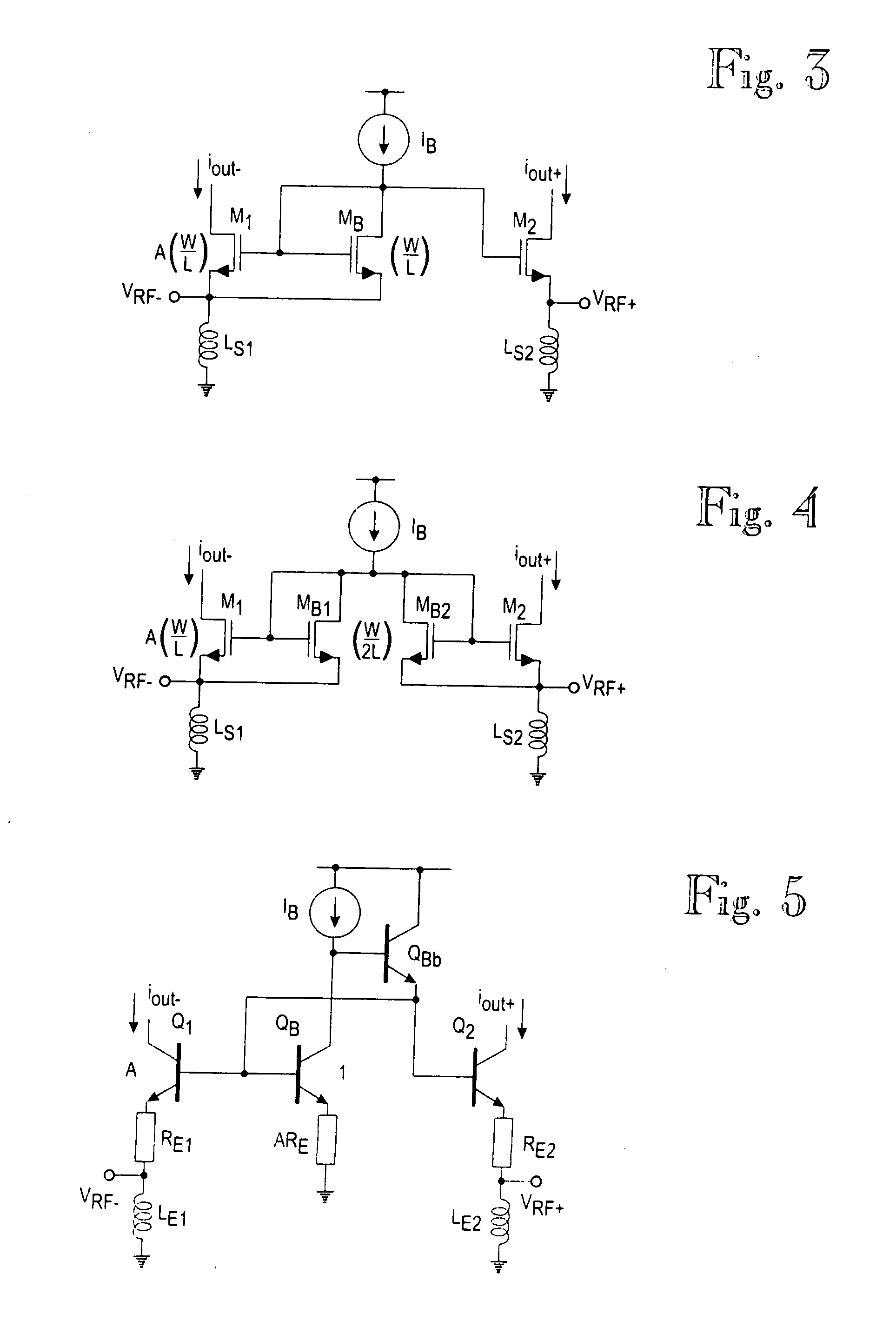
ActiveUS20080261553A1Low costIncrease productionComputations using contact-making devicesGain controlDirect-conversion receiverRf filters
A transconductor input circuit for a down converting quadrature mixer stage of a direct-conversion receiver comprises a pair of common-gate input transistors whose source electrodes are coupled to a differential radio frequency (RF) input signal outputted from an interstage RF filter. The transconductor circuit further comprises a pair of equally-sized biasing transistors for biasing the pair of common-gate input transistors. Source electrodes of the biasing transistors are coupled to the source electrodes of the transistors to sense the differential radio frequency input signal for canceling intermodulation distortion.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Computer readable medium recording a calibration program, calibration method, and calibration system for detecting patch positions during acquisition of calorimetric values from a patch sheet
InactiveUS7978382B2Accurate detectionImprove accuracyColour-separation/tonal-correctionPictoral communicationPattern recognitionComputer graphics (images)
A computer readable medium records a calibration program, which causes a control device to execute calibration processing of reading as image data a patch sheet output from an image formation device, having a plurality of patch patterns formed as images based on different density-gradation value data for each color, acquiring calorimetric values for each of the patch patterns from the read-out image data, and adjusting the density of the image formation device based on the density-gradation values and the acquired calorimetric values for each of the patch patterns. The program causes the control device to execute displaying the read-out image data of the patch sheet, detecting and displaying the position of each of the patch patterns in the image data of the patch sheet, and acquiring the calorimetric values for each the patch pattern based on the displayed patch pattern positions, in response to confirmation input by a user of the displayed patch pattern position.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Hybrid fuel system
InactiveUS20180149096A1Reduce signalingCalibration will degradeElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesExternal combustion engineLiquid fuel
A hybrid fuel supply system for diesel and other fuel injected internal combustion engines; the system including separate liquid fuel and compressed hydrogen gas sources; and wherein a hydrogen gas supply module calculates of “maps” instant liquid fuel requirements based on engine size and capacity and at least one parameter output from the engine's control unit (ECU) to derive an instant volume of hydrogen gas for addition to the engine's fuel injection system.
Owner:GHP IP
Calibration method and calibration tool of camera
ActiveUS20190037204A1Simplify workCalibration will degradeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAngle of viewFocal length
A calibration method for calibrating a first camera and a second camera which are different in at least one of an angle of view and a focal length includes capturing images which include a calibration tool having a first pattern configured with a plurality of first marks and a second pattern configured with a plurality of second marks, different in at least one of a shape between the first mark and the second mark, a size between the first mark and the second mark, and arrangement between the first marks and the second marks, by the first camera and the second camera, and calibrating the first camera and the second camera using patterns corresponding respectively to the first camera and the second camera.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Automatic calibration device for conveyor belt integrating scales
ActiveUS20180195893A1Enhance transportation mechanismReadily availableWeighing apparatus testing/calibrationWeighing apparatus for continuous material flowEngineeringActuator
“AUTOMATIC CALIBRATION DEVICE FOR CONVEYOR BELT INTEGRATING SCALES”, the automatic calibration device for integrating conveyor belt scales (100) is incorporated to a mounted-type integrating conveyor belt scale, mounted to bulk material conveyors, featuring a structure that supports racks with rolled cylinders, which, when assembled, are able to support the conveyor belt; the automatic calibration device (100) with the movement mechanism, comprised in this implementation, by a pair of parallelograms comprised of the beams (1) and (2) connected by rotating joints (7), (8), (9), (10) to the minor arms, (22), (23), (24), (25) which, in turn, are connected to the parallel shafts (3) and (4), with the distances between centers being equal to the distance between rotating joints of the beams; an actuator (14) is used to move standard weights (11) and (12), initially supported onto cavities (16), (17), (18) and (19) provided on the beams (1) and (2) of the parallelograms, until reaching the berths (30), (31), (32) and (33) connected to the weigh bridge (41) of the scale.
Owner:CHVAICER BRENO
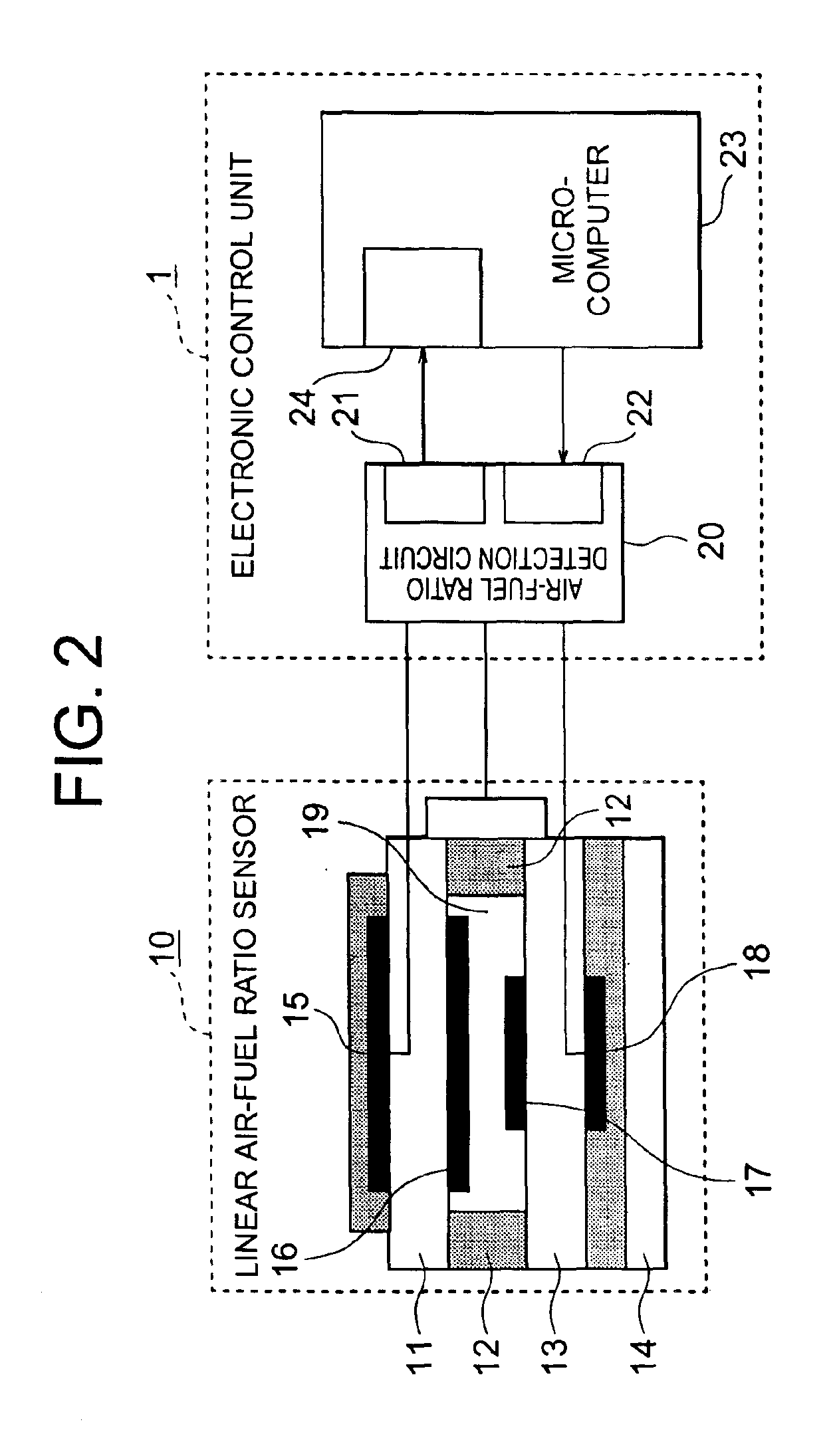
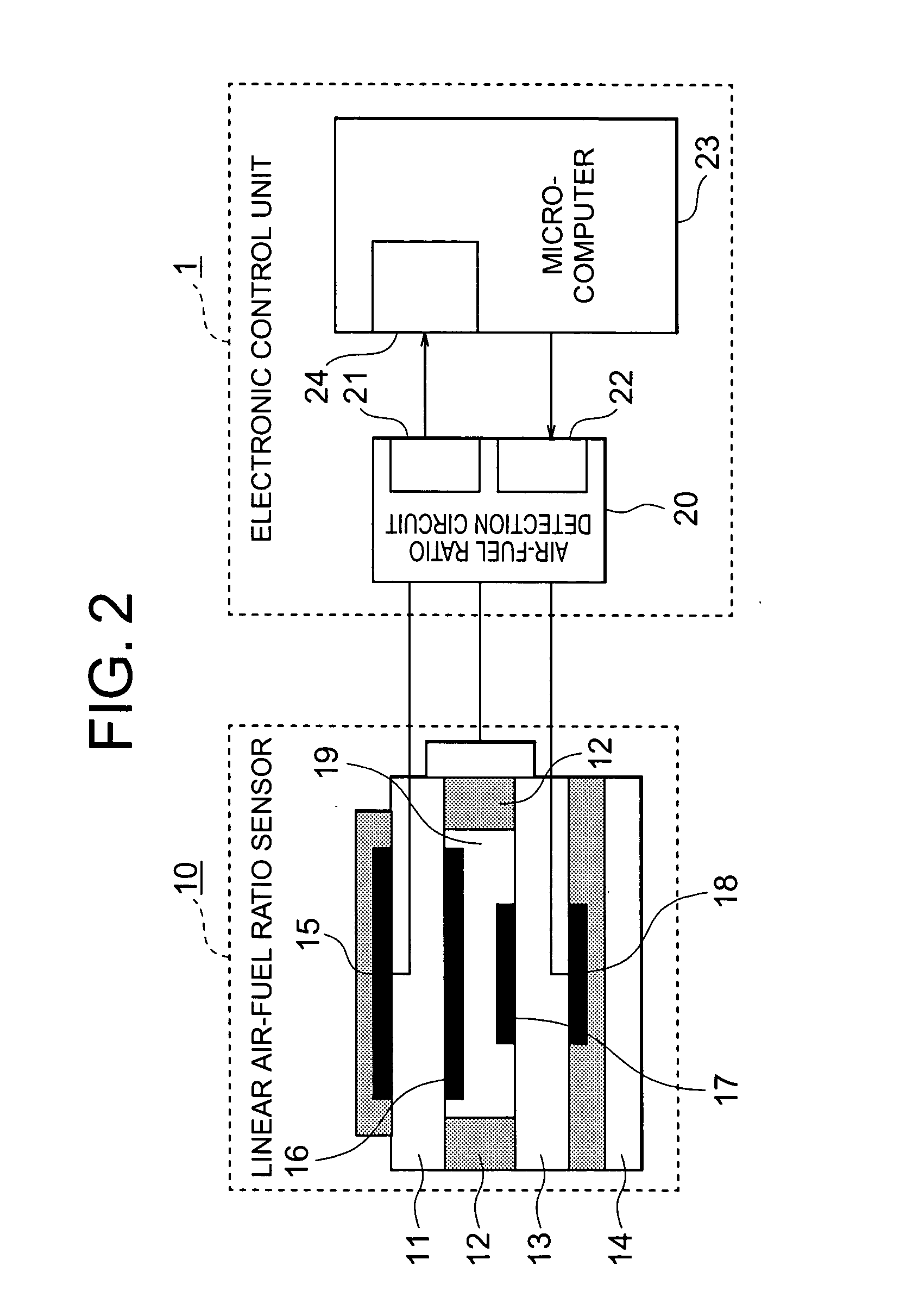
Air-fuel ratio computing apparatus
ActiveUS6915213B2Inhibition effectCalibration will degradeElectrical controlUsing mechanical meansFilter gainControl theory
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Air-fuel ratio computing apparatus
ActiveUS20050049798A1Guaranteed ResponsivenessOscillation suppressionElectrical controlMachines/enginesFilter gainControl theory
The air-fuel ratio computing apparatus includes a linear air-fuel ratio sensor for measuring an air-fuel ratio of exhaust gas and an electronic control unit for repeatedly performing filter processing on the air-fuel ratio, using a formula Vf(n)=(1−G)×Vf(n-1)+G×V(n). In a case where a temperature of the sensor is low, the unit cuts off a pump current to the sensor, performs the filter processing with the filter gain G set to a large value, and transforms a computed value from the filter processing into a theoretical air-fuel ratio voltage and in a case where the temperature of the sensor rises to or above a predetermined temperature, the unit performs the filter processing with a filter gain G set to a small value, and computes an air-fuel ratio from the difference between a computed value from the filter processing and the theoretical air-fuel ratio voltage.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Apparatus and method for reducing rx calibration delay in wireless communication system
InactiveUS20130235961A1Reduce signal distortionReduce delaysTransmissionCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
An apparatus and a method for removing RX DC in a wireless communication system are provided. A receiver apparatus includes a local oscillator, a mixer for converting a received signal to a baseband signal using a frequency provided from the local oscillator, and a DC compensator, comprising an operational amplifier and a low pass filter, for compensating DC in an output signal of a frequency converter by adjusting a pass band size of the low pass filter.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Reducing unnecessary calibration of a memory unit for which the error count margin has been exceeded
ActiveUS10824352B2Error rateBER of the physical page can be improvedInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory cellTerm memory
A controller sets an error count margin for each of multiple units of a non-volatile memory and detects whether the error count margin of any of the multiple units has been exceeded. In response to detecting that the error count margin of a memory unit is exceeded, the controller determines whether calibration of the memory unit would improve a bit error rate of the memory unit sufficiently to warrant calibration. If so, the controller performs calibration of the memory unit. In some implementations, the controller refrains from performing the calibration in response to determining that calibration of the memory unit would not improve the bit error rate of the memory unit sufficiently to warrant calibration, but instead relocates a desired part or all valid data within the memory unit and, if all valid data has been relocated from it, erases the memory unit.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
System and method of predicting vehicle engine torque using artificial neural network
ActiveUS11326572B2Accurate calculationCalibration will degradeValve arrangementsElectrical controlComputed torqueEngineering
Owner:HYUNDAI KEFICO CORP
Print carriage
InactiveUS9004647B2Calibration will degradeEnsure overall alignmentSpacing mechanismsEngineeringForward pass
A system and method for depositing a substance onto a continuously moving substrate in first and second transverse swathes, is achieved by providing a print carriage having a first set of inkjet heads and a second set of inkjet heads. The carriage is traversed across the substrate in a forward pass, while depositing the first and second swathes from the respective first and second plurality of inkjet heads and subsequently traversed across the substrate in a reverse pass. The first and second sets of inkjet heads are arranged such that the first and second swathes complement one another on both forward and reverse passes to provide substantially complete coverage of the substrate. In this manner complementary swathes may be deposited from a single head.
Owner:XENNIA HOLLAND
Electronic device including ultrasonic in-display fingerprint sensor and operating method thereof
ActiveUS11093727B2Easy to identifyCalibration will degradeThermometer detailsInternal/peripheral component protectionMedicineDisplay device
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Calibration method and calibration tool of camera
ActiveUS10491882B2Simplify workCalibration will degradeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsAngle of viewFocal length
A calibration method for calibrating a first camera and a second camera which are different in at least one of an angle of view and a focal length includes capturing images which include a calibration tool having a first pattern configured with a plurality of first marks and a second pattern configured with a plurality of second marks, different in at least one of a shape between the first mark and the second mark, a size between the first mark and the second mark, and arrangement between the first marks and the second marks, by the first camera and the second camera, and calibrating the first camera and the second camera using patterns corresponding respectively to the first camera and the second camera.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Automatic calibration device for conveyor belt integrating scales
ActiveUS10739185B2Easy CalibrationCalibration will degradeWeighing apparatus testing/calibrationWeighing apparatus for continuous material flowClassical mechanicsActuator
Owner:CHVAICER BRENO
Luminance-chrominance calibration production line of LED display module
ActiveUS20170236264A1Improve calibration efficiencyData errorImage enhancementImage analysisProduction lineColor image
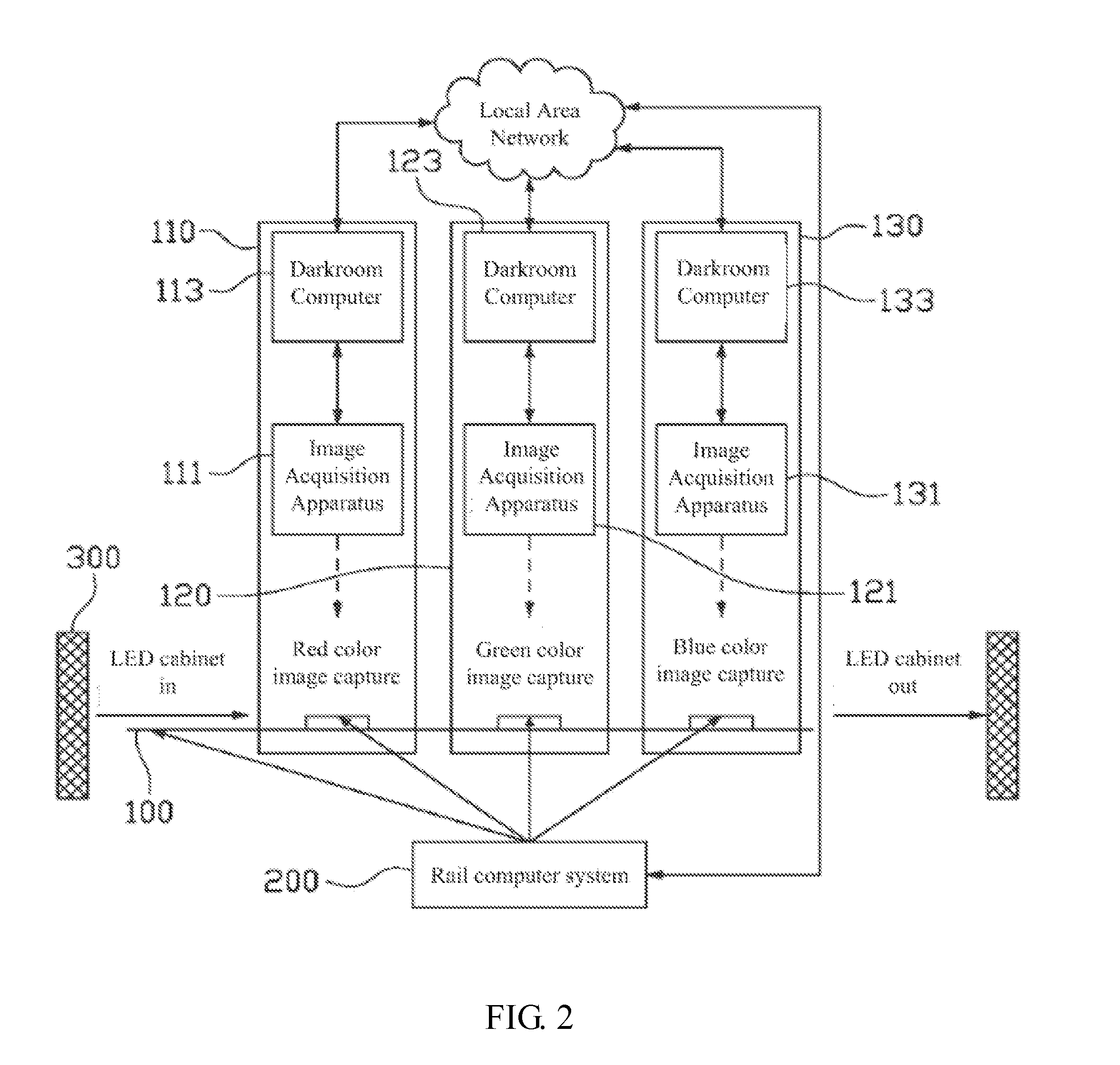
A luminance-chrominance calibration production line system includes: a rail; multiple stations disposed along the rail and including multiple first darkroom stations; multiple image acquisition apparatuses respectively disposed in the first darkroom stations and for capturing different color images sequentially displayed by a to-be-calibrated LED display module loaded on the rail to acquire color image data; and a rail computer system for controlling a transport movement on the rail and controlling the to-be-calibrated LED display module to display the different color images, and being signally connected to the image acquisition apparatuses to obtain the color image data. By using multiple image acquisition apparatuses to collect various color image information of LED display module in pipelined manner, calibration efficiency is improved, data collection is accurate, data collection error caused by using different image acquisition apparatuses to calibrate different LED display modules is avoided and calibration manpower is reduced.
Owner:XIAN NOVASTAR TECH
Method and device for calibrating load sensors
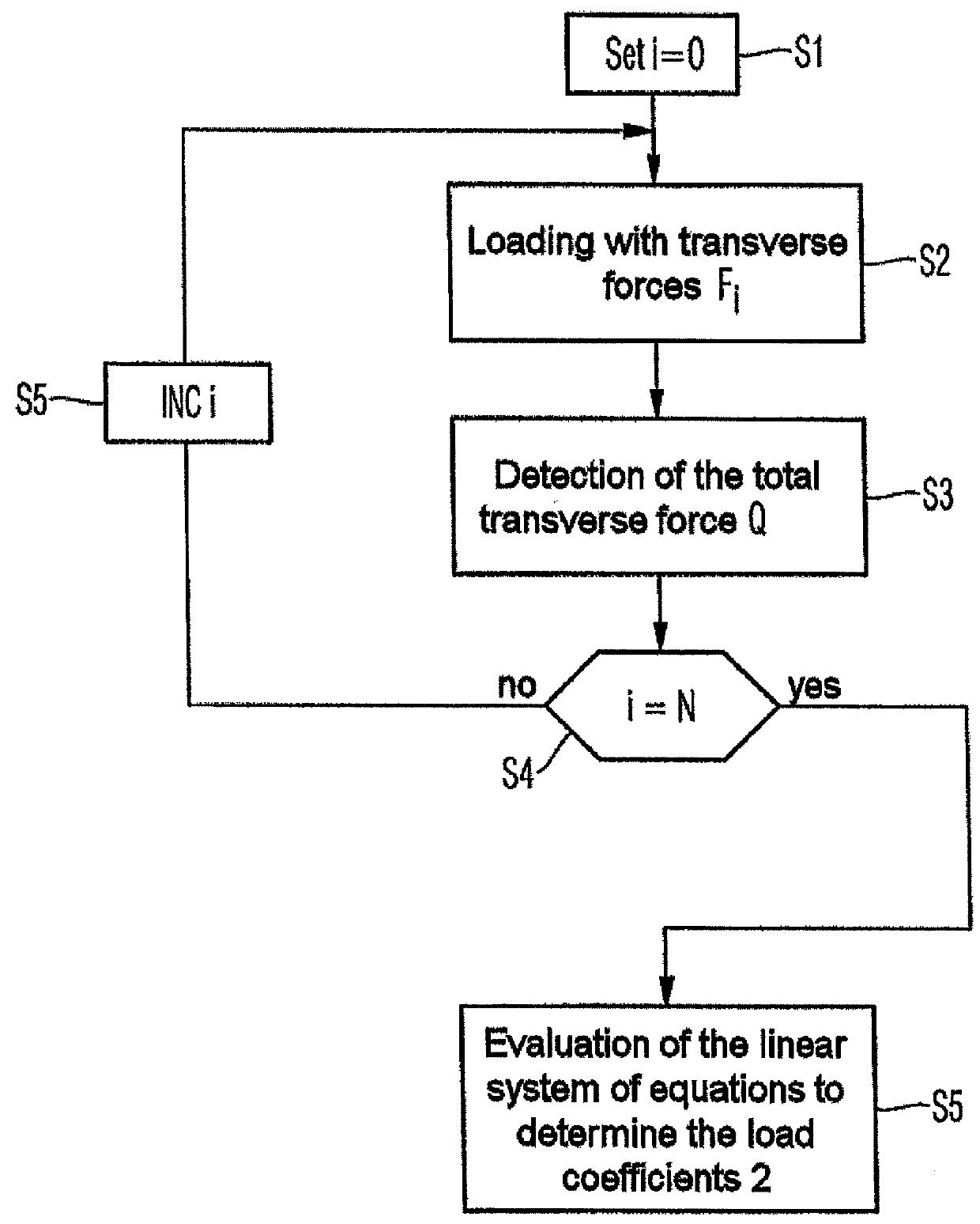
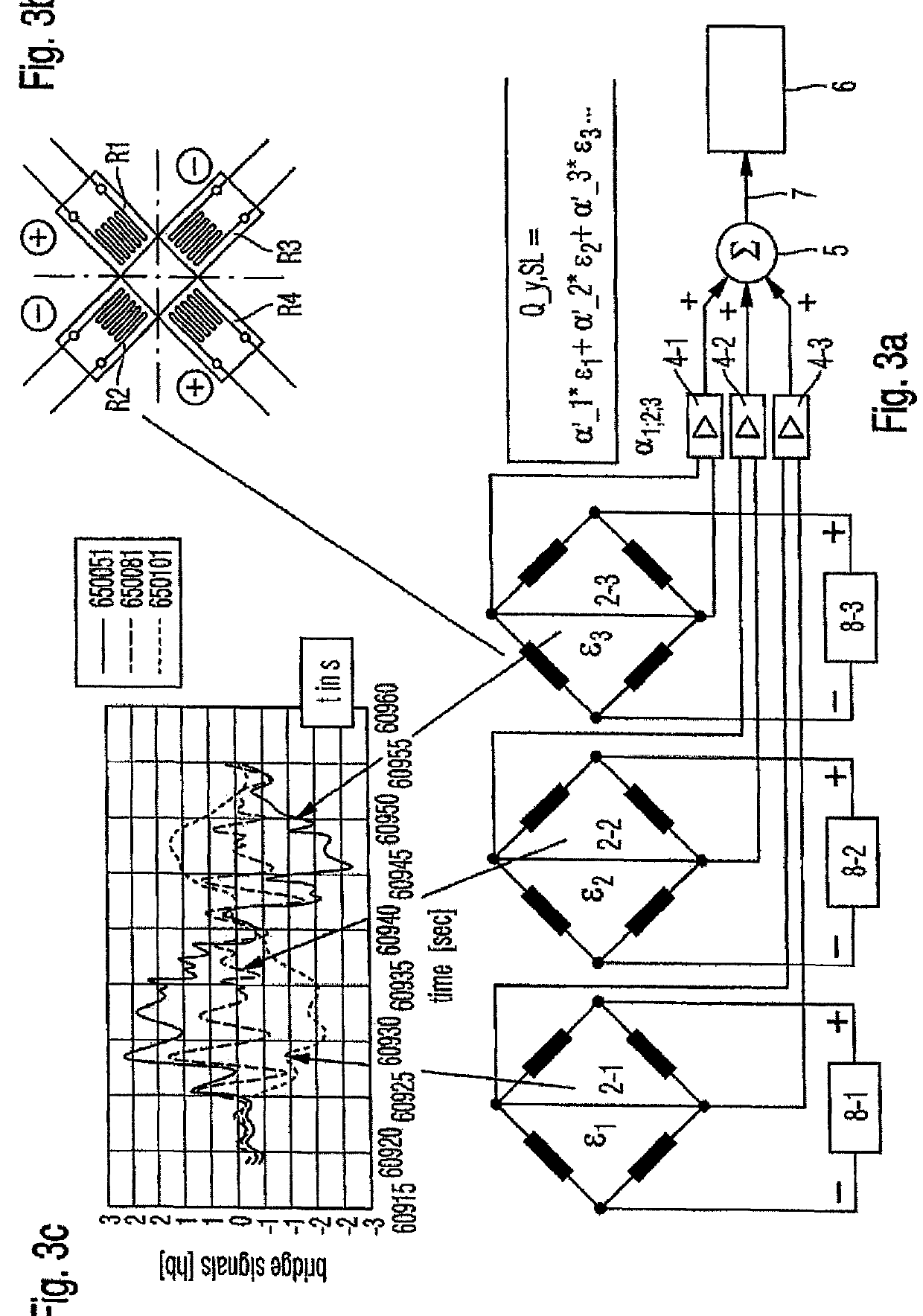
ActiveUS9250152B2Calibration will degradeImprove accuracyForce measurementFluid pressure measurementEngineeringAirplane
A device and a method for calibrating load sensors which are provided at least one load cross-section of an aerofoil or control surface of an aircraft, the load sensors being calibrated on the basis of load coefficients (αi) of the load sensors, which load coefficients a calculation unit calculates by evaluating a linear system of equations formed by means of mechanical loading of the aerofoil or control surface.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Control device, radiography system, control method, and control program
InactiveUS20220265236A1Calibration will degradeImage enhancementImage analysisComputational physicsGate current
Within one imaging period, a processor of a control device supplies a gate voltage, performs control to correct a voltage value of the gate voltage on the basis of a difference between a current value of an estimated anode current, which flows from a power supply voltage generator to an anode unit and is estimated on the basis of a detection value of a cathode current flowing from a cathode unit to a ground and a detection value of a gate current flowing from the power supply voltage generator to a gate electrode, and a target current value of an anode current set for an n-th imaging operation, and performs control to set the voltage value of the gate voltage corresponding to a corrected voltage value of the gate voltage corrected at the end of the n-th imaging operation and a target current value of the anode current set for an (n+1)-th imaging operation as a voltage value of the gate voltage which is supplied to the gate electrode first in the (n+1)-th imaging operation.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com