Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
100results about "Reliability increase by circuit redundancy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
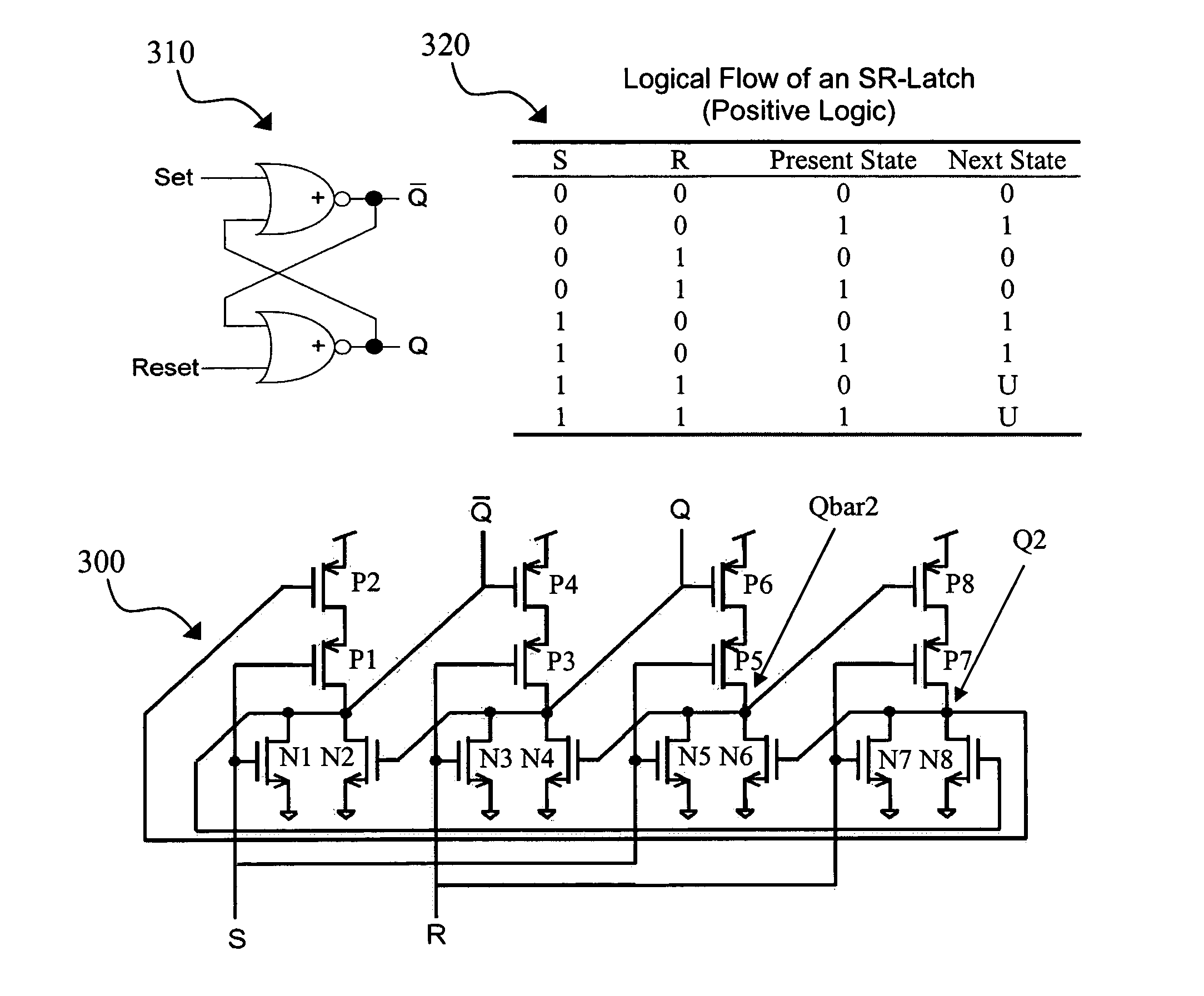
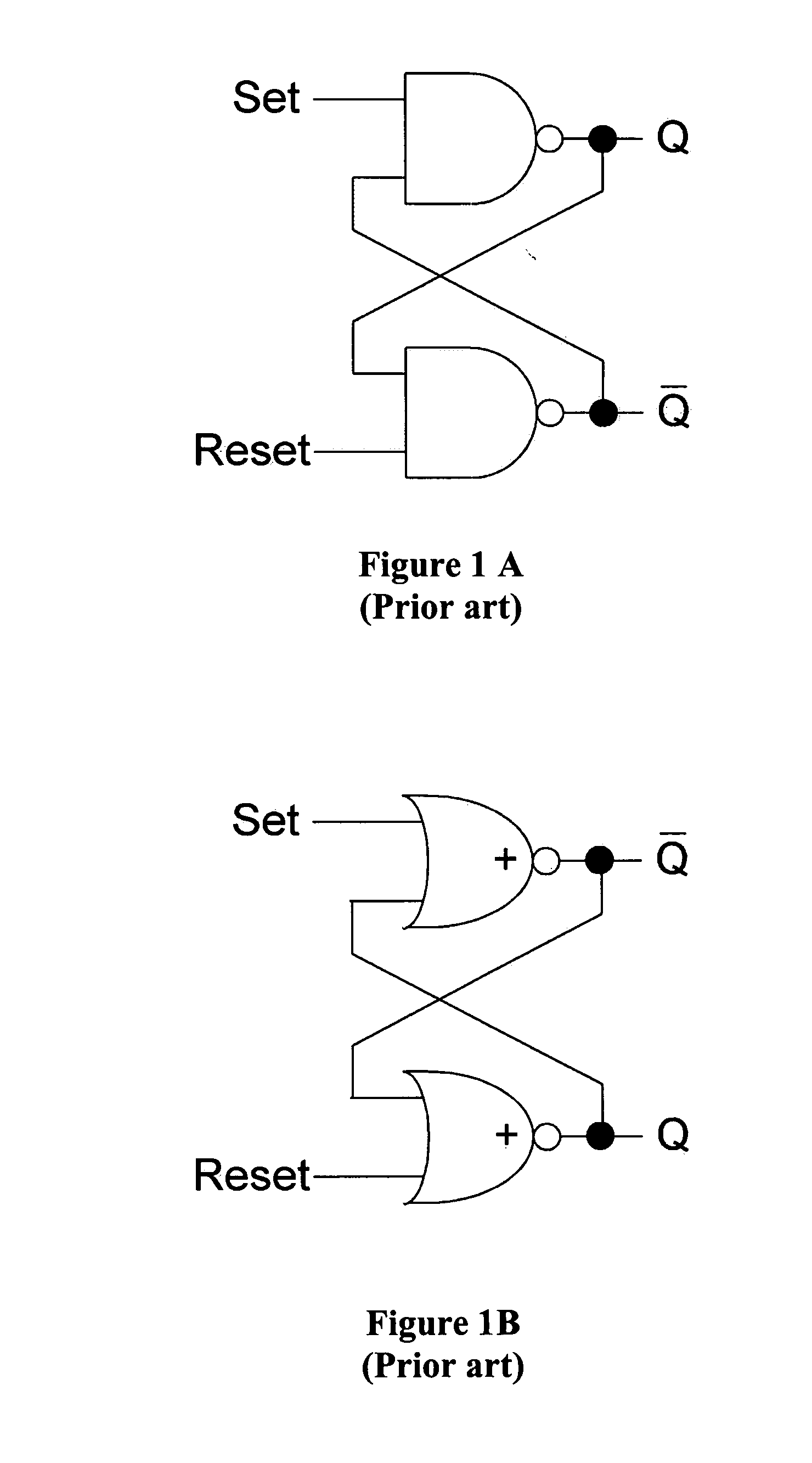
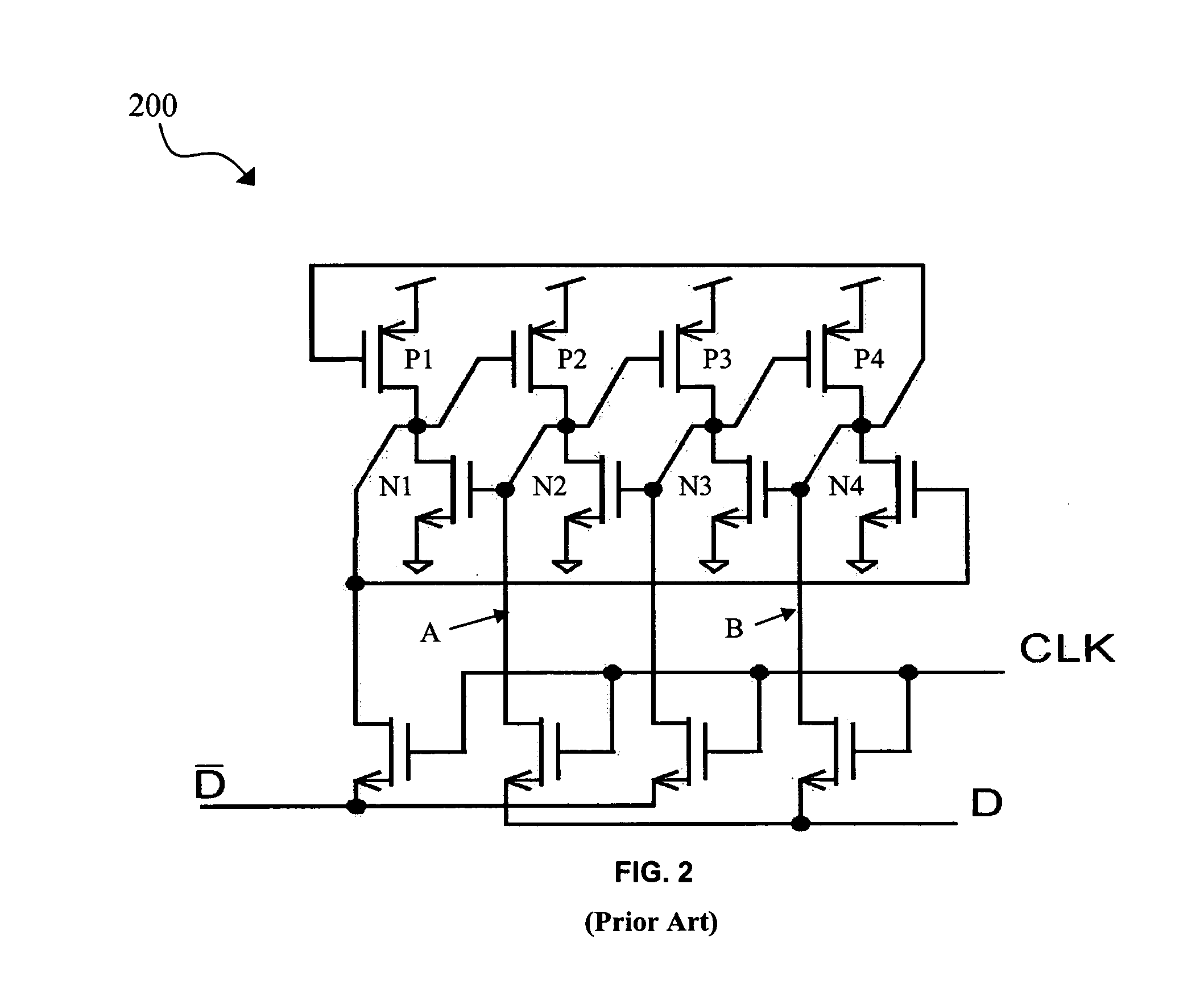
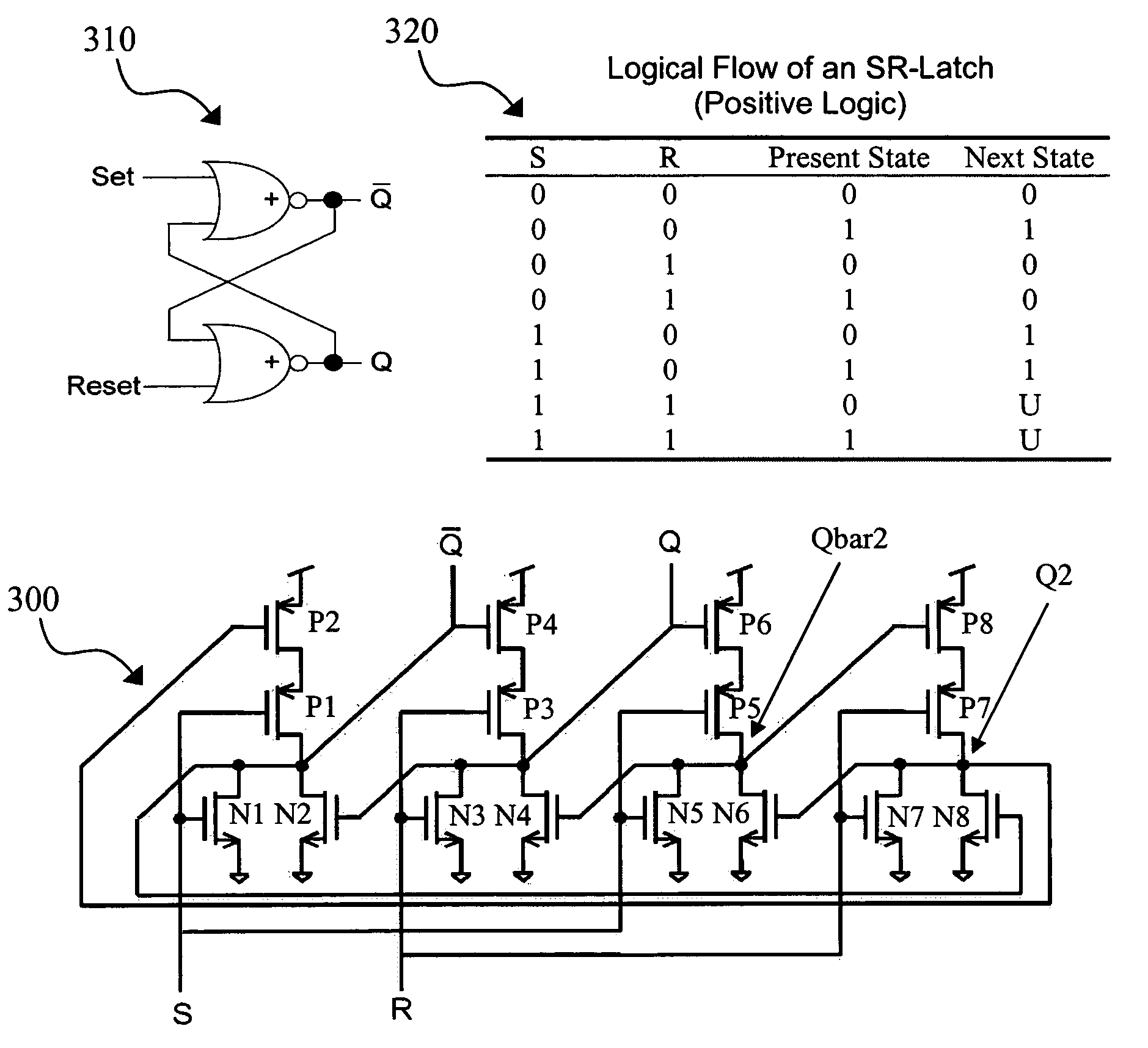
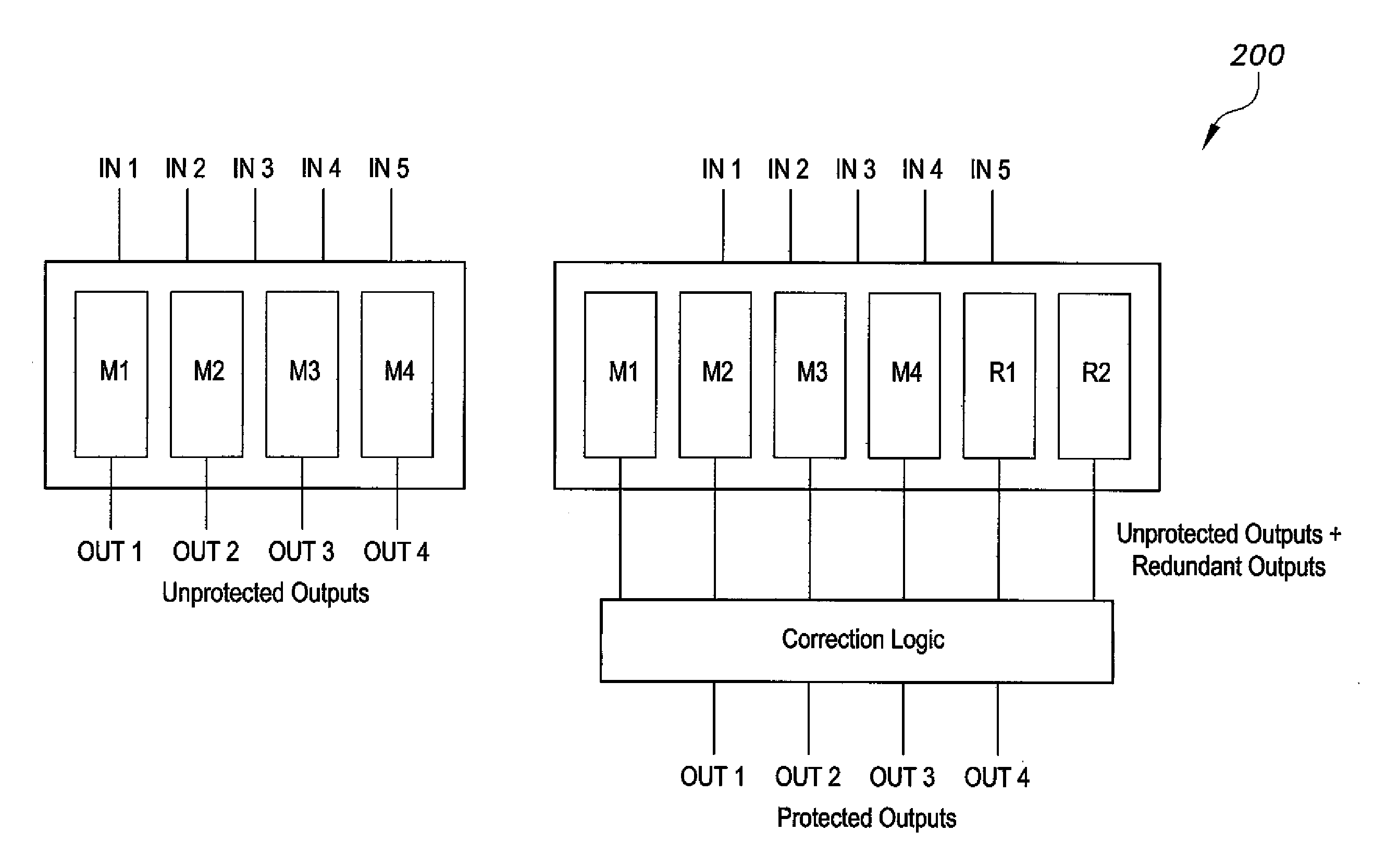
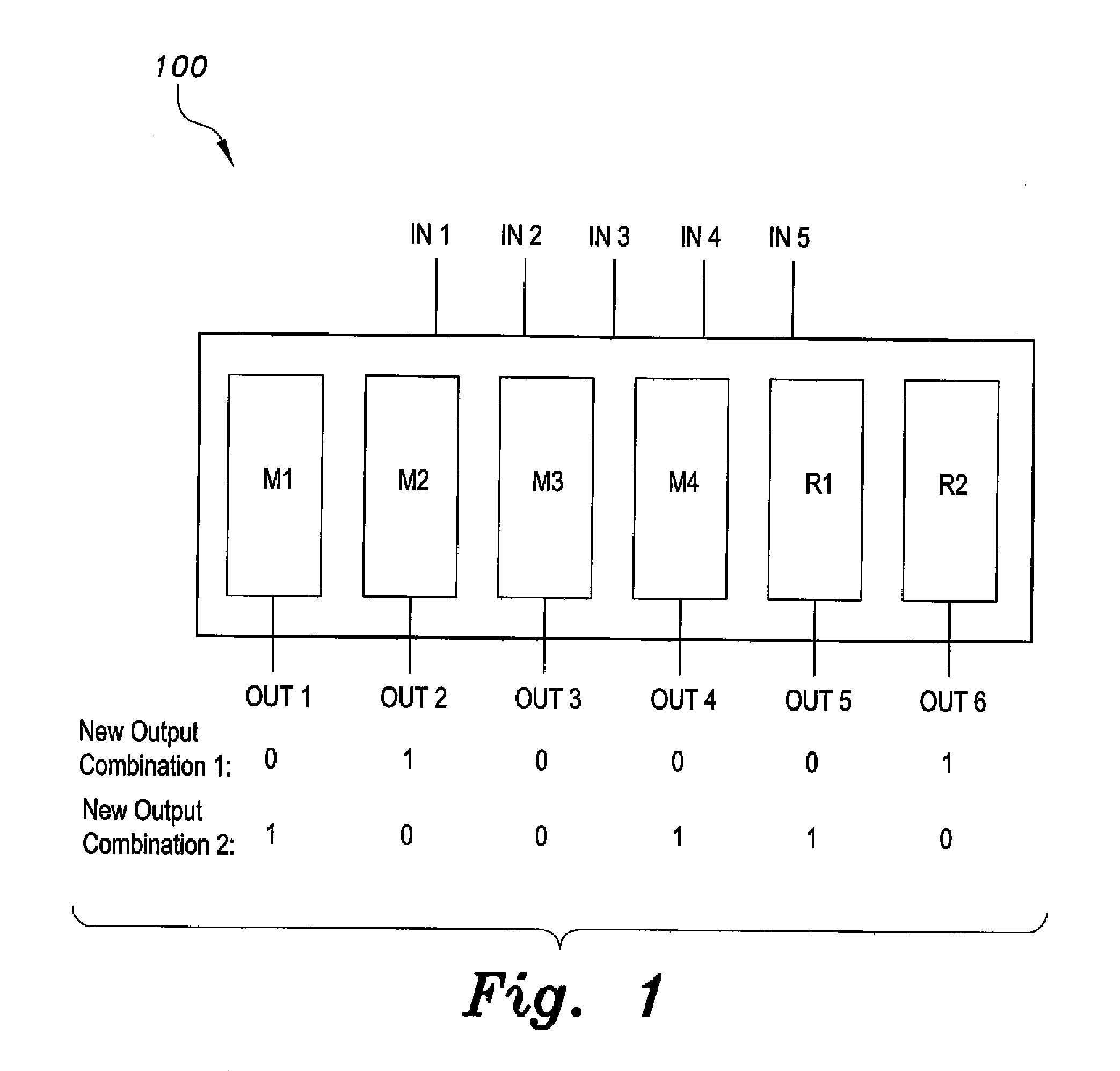
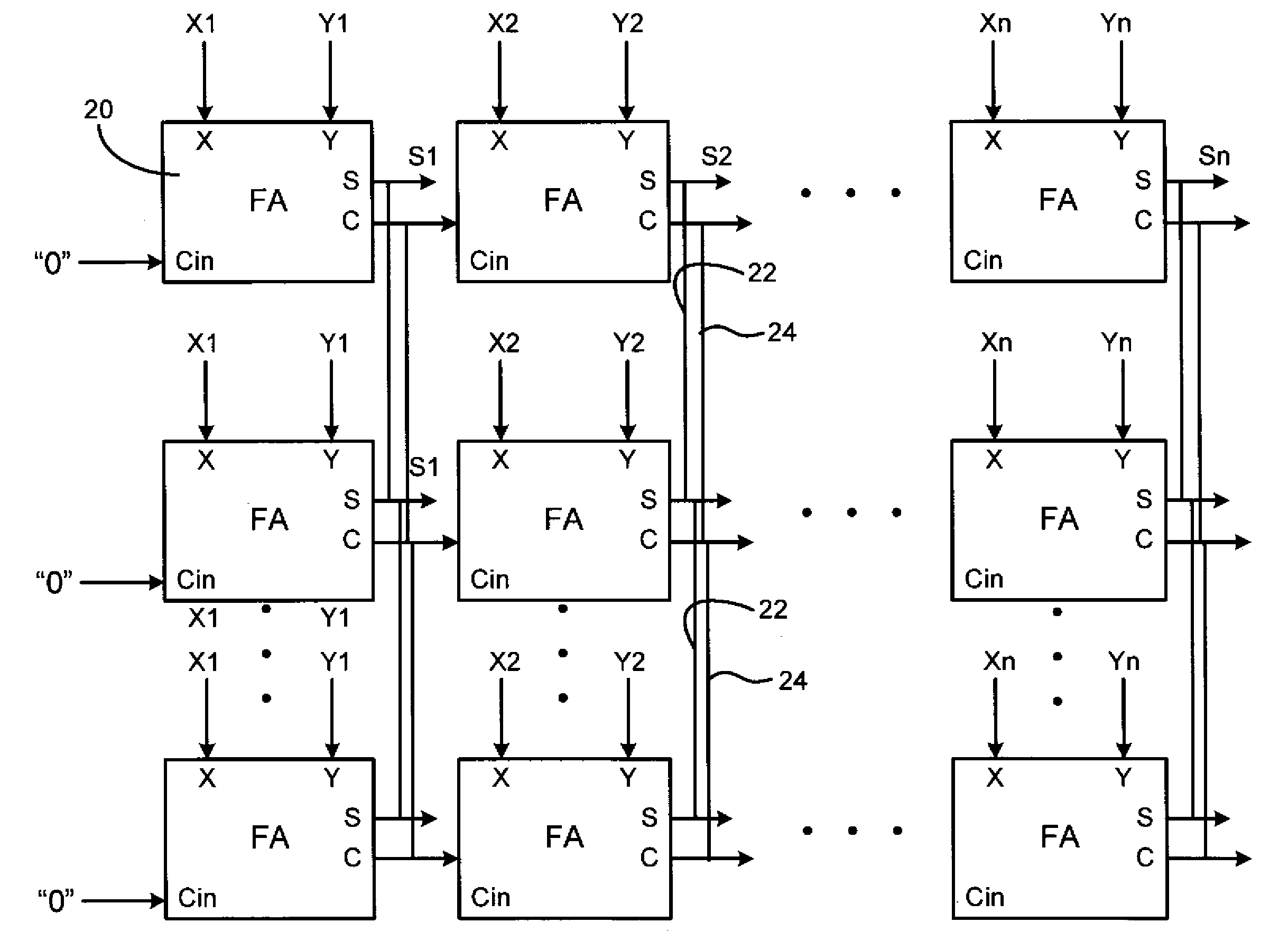
Redundant single event upset supression system
CMOS transistors are configured to operate as either a redundant, SEU-tolerant, positive-logic, cross-coupled Nor Gate SR-flip flop or a redundant, SEU-tolerant, negative-logic, cross-coupled Nand Gate SR-flip flop. The register can operate as a memory, and further as a memory that can overcome the effects of radiation. As an SR-flip flop, the invention can be altered into any known type of latch or flip-flop by the application of external logic, thereby extending radiation tolerance to devices previously incapable of radiation tolerance. Numerous registers can be logically connected and replicated thereby being electronically configured to operate as a redundant circuit.
Owner:FERMI RESEARCH ALLIANCE LLC
Redundant single event upset supression system
CMOS transistors are configured to operate as either a redundant, SEU-tolerant, positive-logic, cross-coupled Nor Gate SR-flip flop or a redundant, SEU-tolerant, negative-logic, cross-coupled Nand Gate SR-flip flop. The register can operate as a memory, and further as a memory that can overcome the effects of radiation. As an SR-flip flop, the invention can be altered into any known type of latch or flip-flop by the application of external logic, thereby extending radiation tolerance to devices previously incapable of radiation tolerance. Numerous registers can be logically connected and replicated thereby being electronically configured to operate as a redundant circuit.
Owner:FERMI RESEARCH ALLIANCE LLC
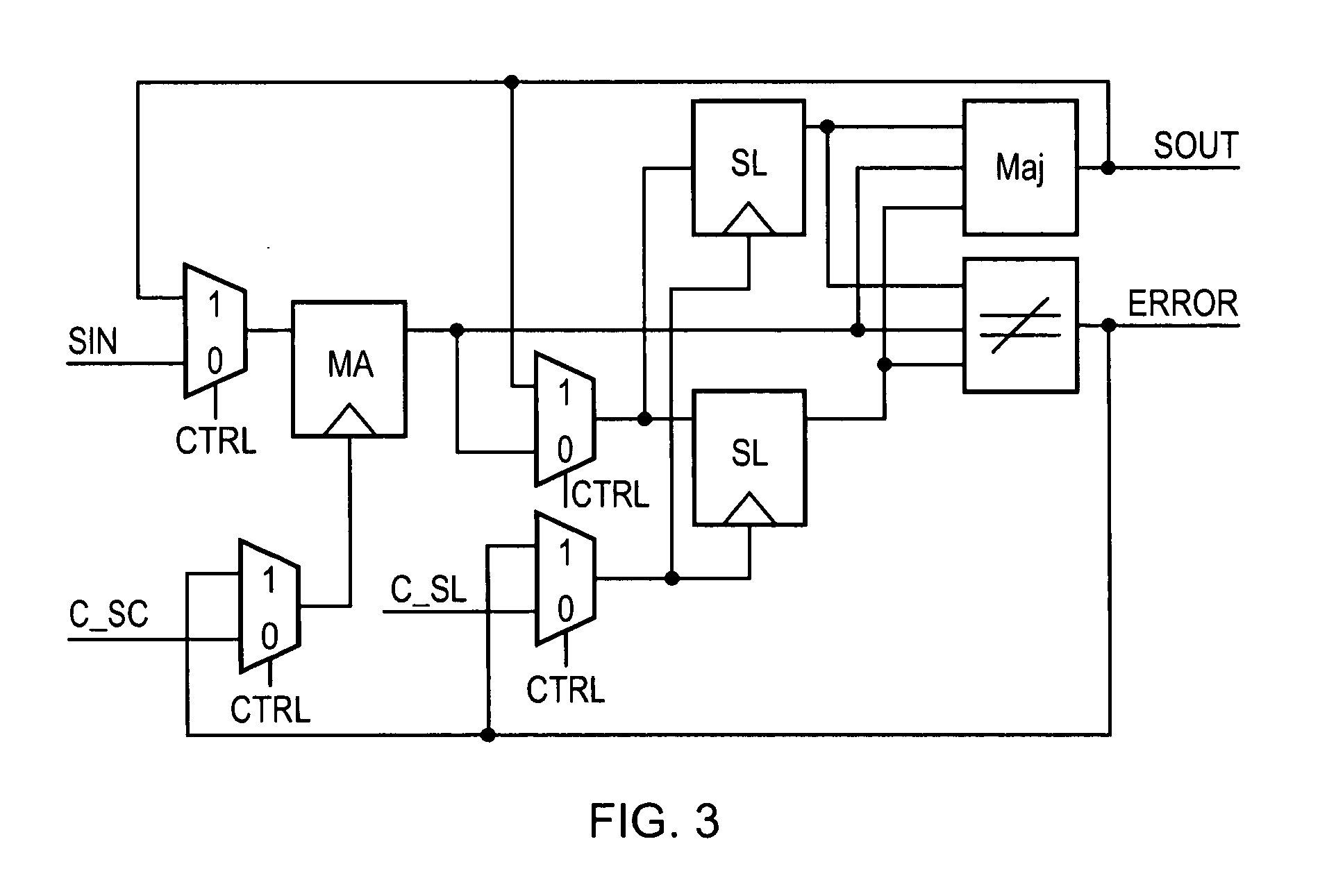
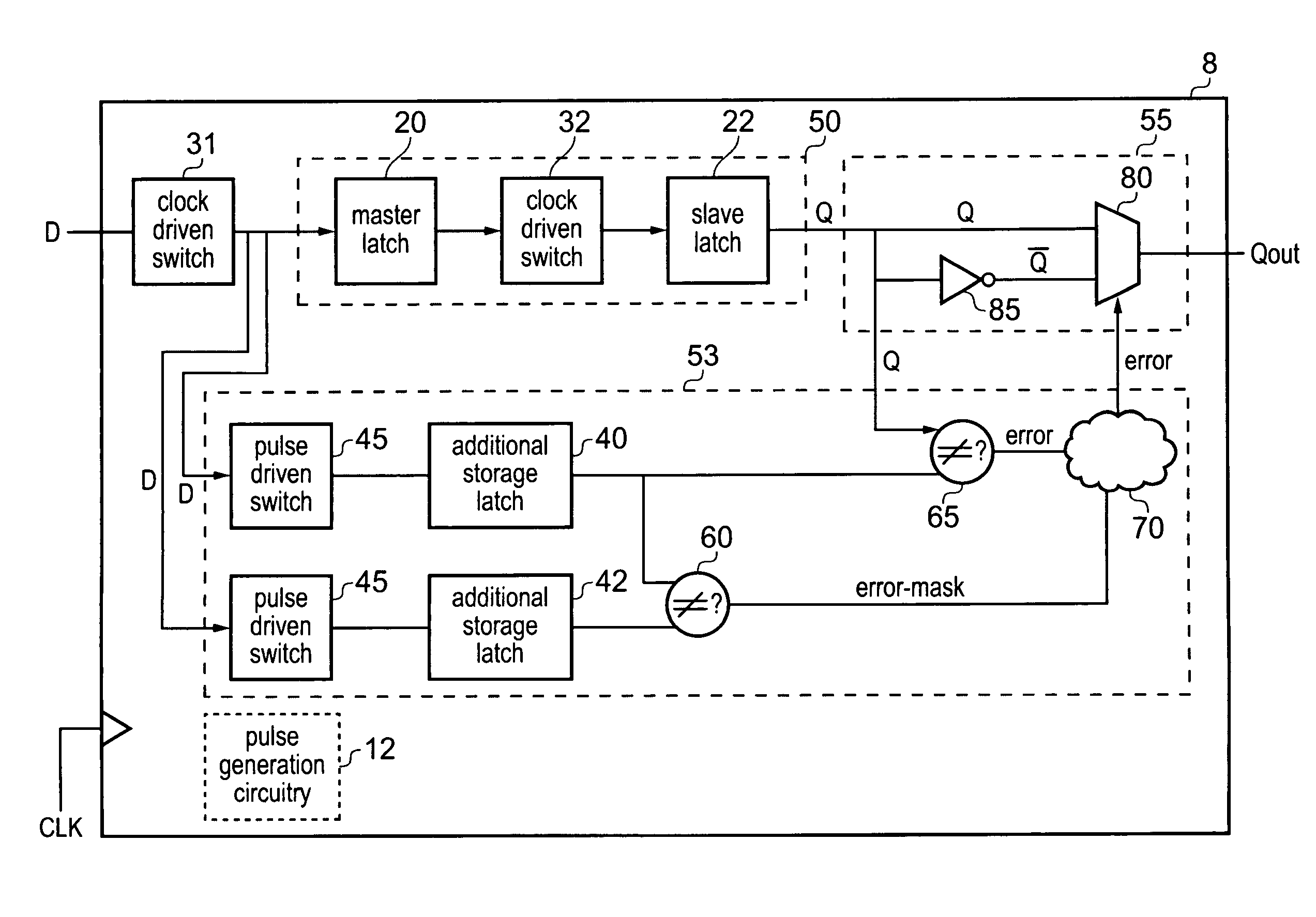
Correction of single event upset error within sequential storage circuitry of an integrated circuit
ActiveUS20100088565A1False errorRapid responseError preventionTransmission systemsSingle event upsetData value
Sequential storage circuitry for an integrated circuit is disclosed that comprises storage circuitry comprising: a first storage element for storing, during a first phase of a clock signal, a first indication of an input data value received by said sequential storage circuitry; a second storage element coupled to an output of said first storage element, for storing a second indication of said input data value during a second phase of said clock signal; and error detection circuitry for detecting a single event upset error in any of said first and second storage elements comprising: two additional storage elements for storing third and fourth indications of said input data value respectively in response to a pulse signal derived from said clock signal; comparison circuitry for comparing said third and fourth indications of said input data value; and further comparison circuitry for comparing during a first phase of said clock signal said first indication and at least one of said third and fourth indications, and for comparing during a second phase of said clock signal said second indication and at least one of said third and fourth indications; and output circuitry for correcting any detected errors in said storage circuitry and for outputting an output value; said output circuitry being responsive to no match by said comparison circuitry to output said first indication during a first phase of said clock signal and said second indication during said second phase of said clock signal, and said output circuitry being responsive to a match by said comparison circuitry to output a value in dependence upon comparisons performed by said further comparison circuitry; said output circuitry being responsive to a match by said further comparison circuitry during a first phase of said clock signal to output said first indication during said first clock cycle and to a no match to output an inverted value of said first indication; and said output circuitry being responsive to a match by said further comparison circuitry during a second phase of said clock signal to output said second indication during said second phase of said clock signal and to a no match to output an inverted value of said second indication.
Owner:ARM LTD
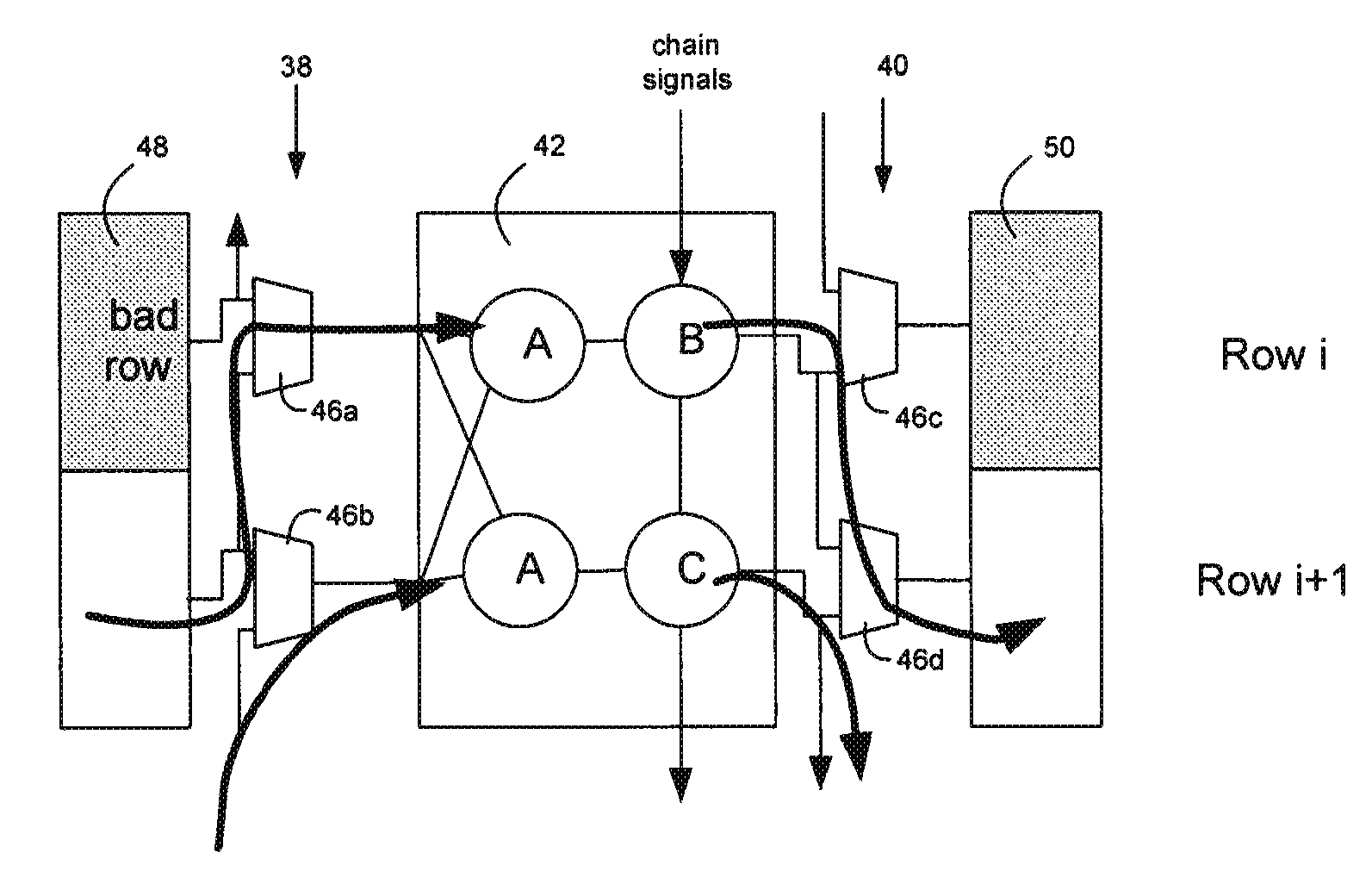
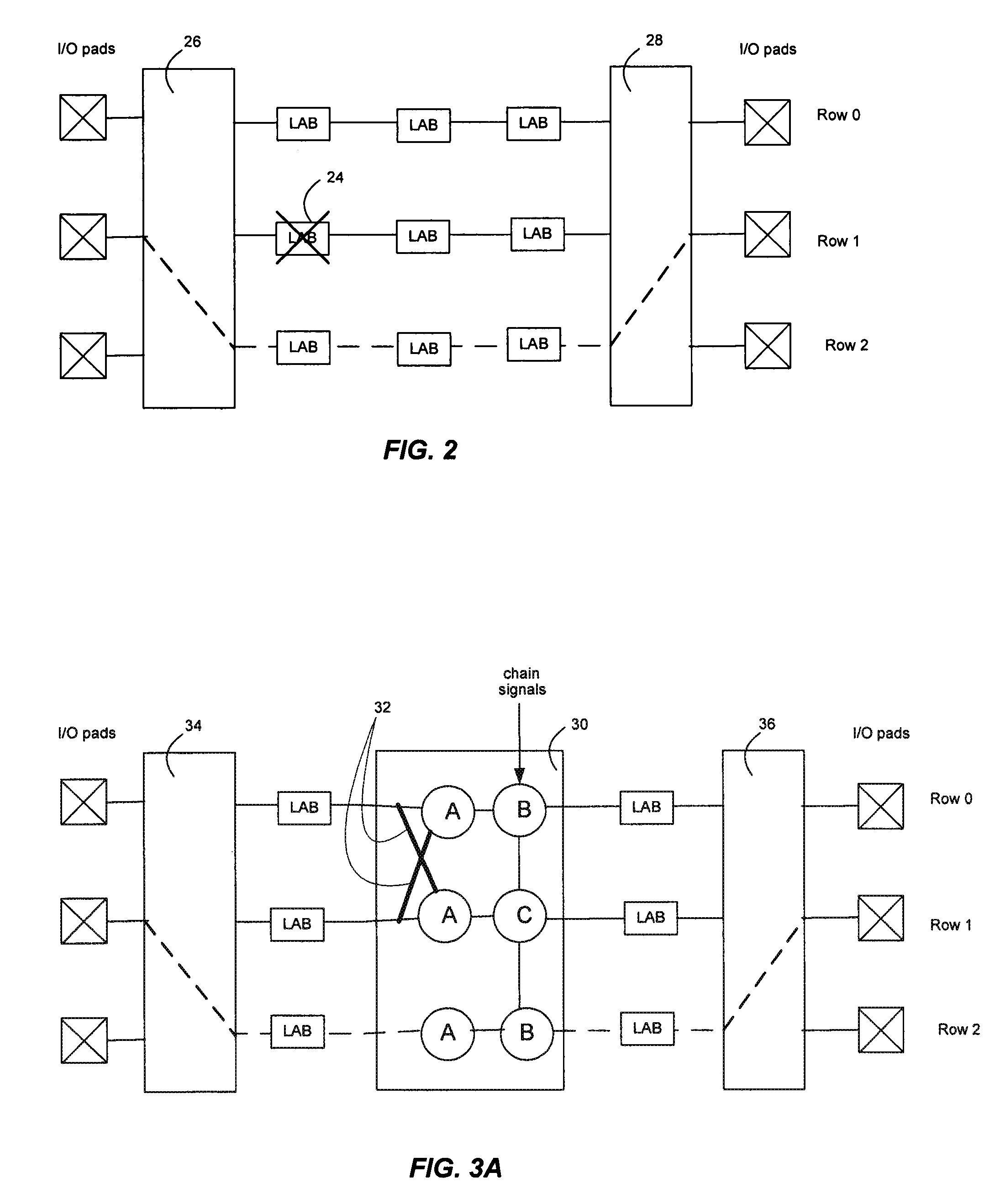
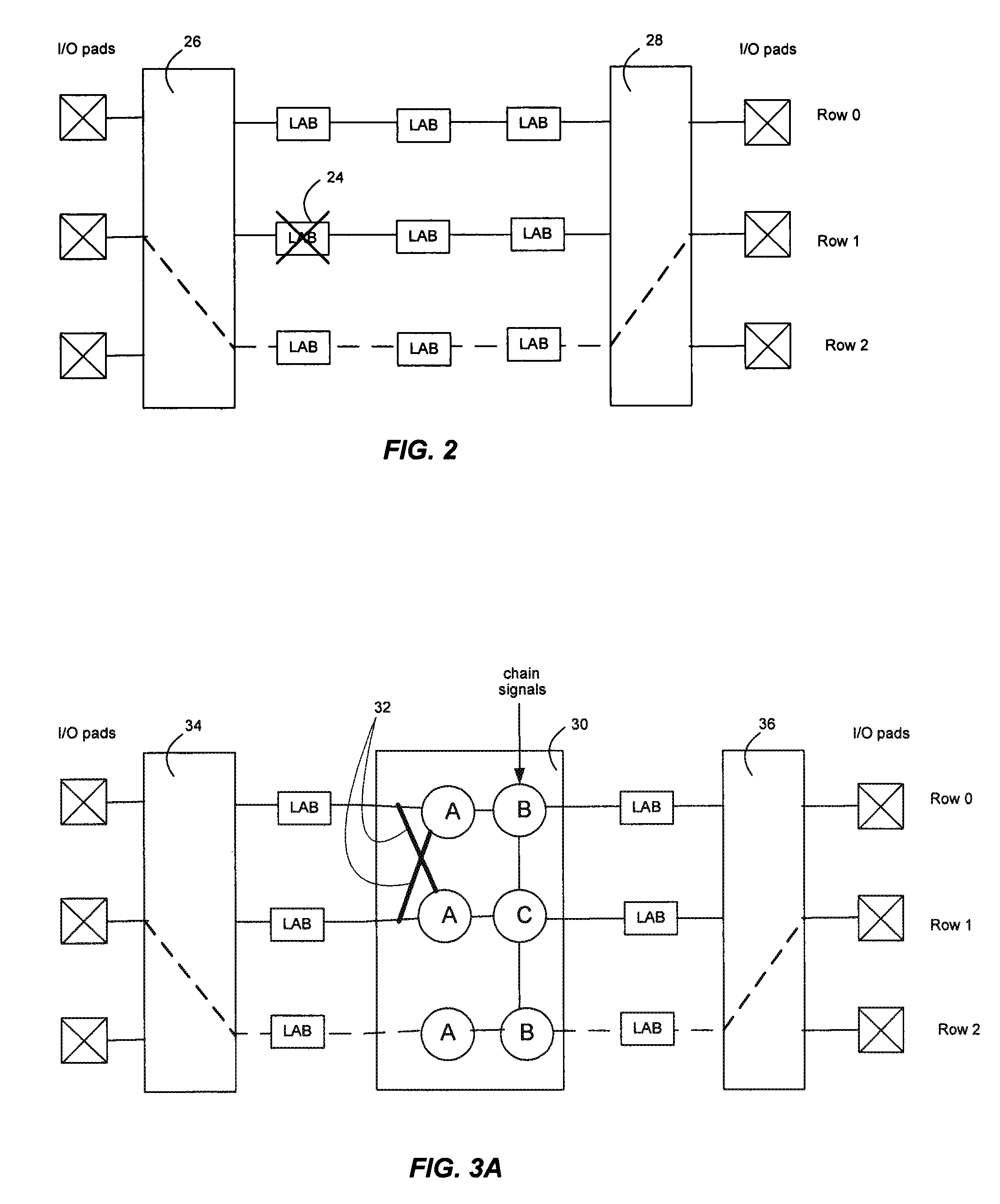
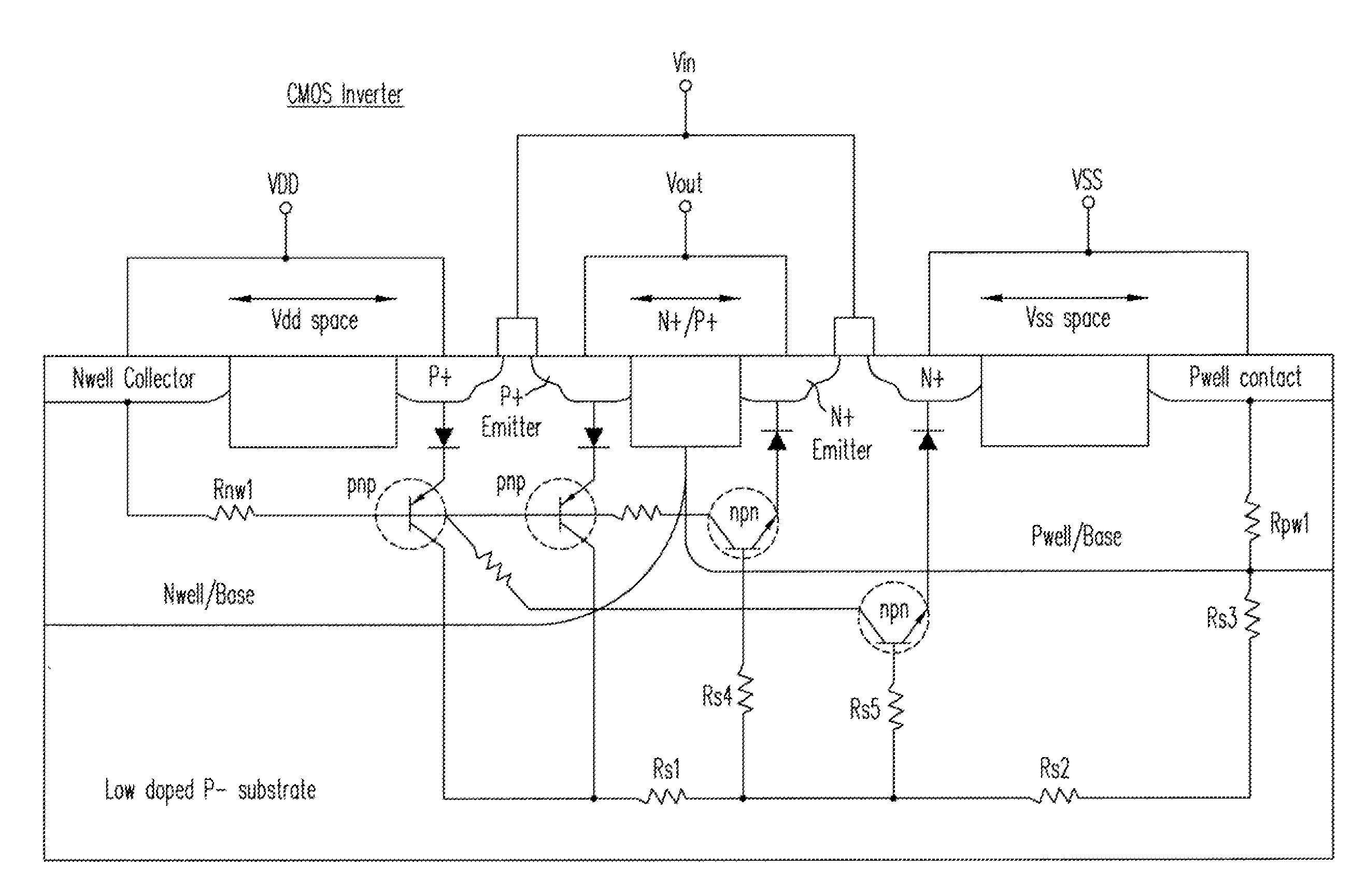
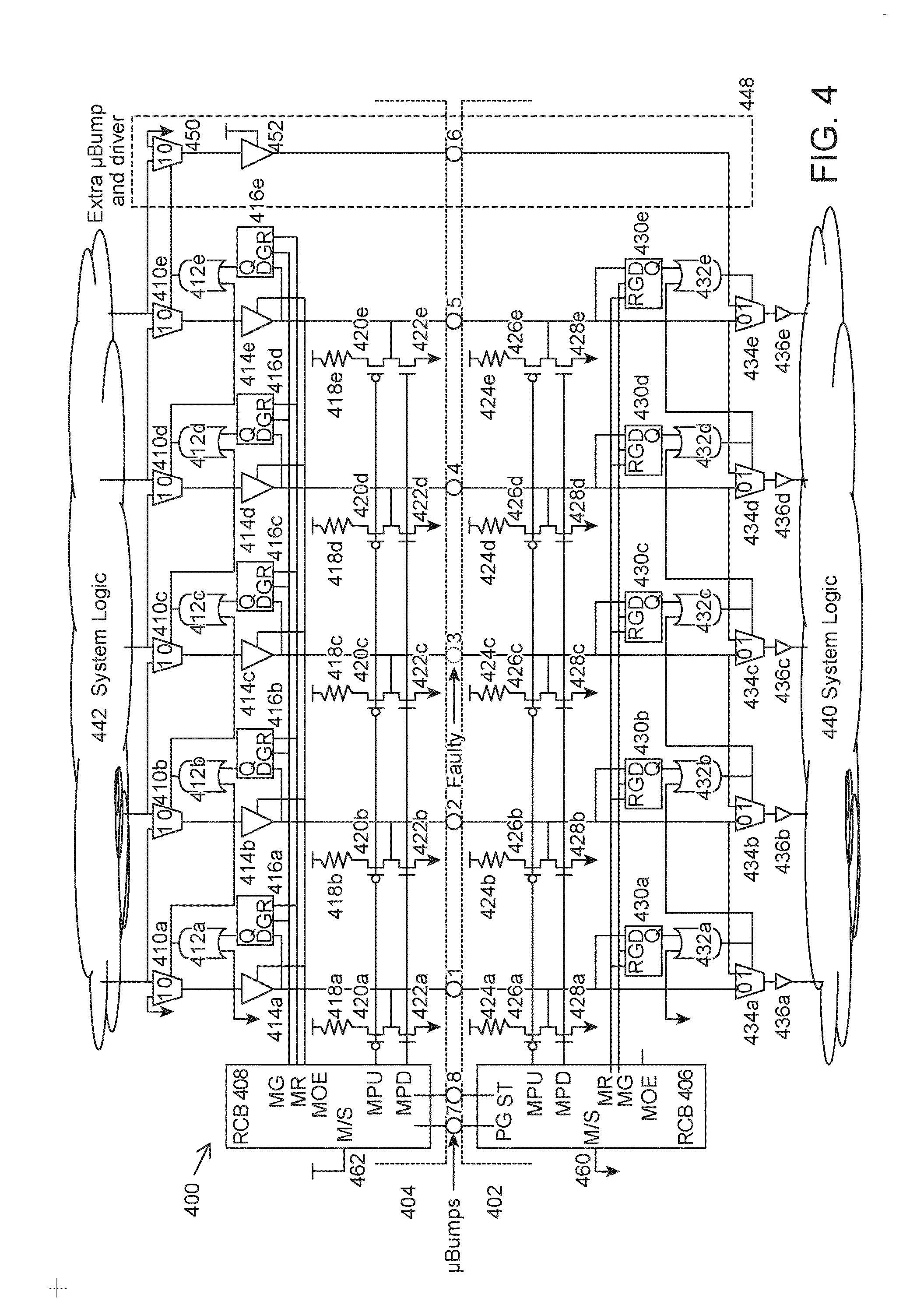
Multi-row block supporting row level redundancy in a pld
InactiveUS20100060309A1Solid-state devicesReliability increase by circuit redundancyComputer architectureProgrammable logic device
In a Programmable Logic Device (PLD), a multi-row block that has internal logic connections between rows has redundant internal connections between rows to replace the internal logic connections when a fault occurs. The redundant internal logic connections extend through a row, linking the row above a defective row with a row below the defective row. Elements in a multi-row block are configurable to perform a default function and a function of an element in a neighboring row, if the functions are different.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
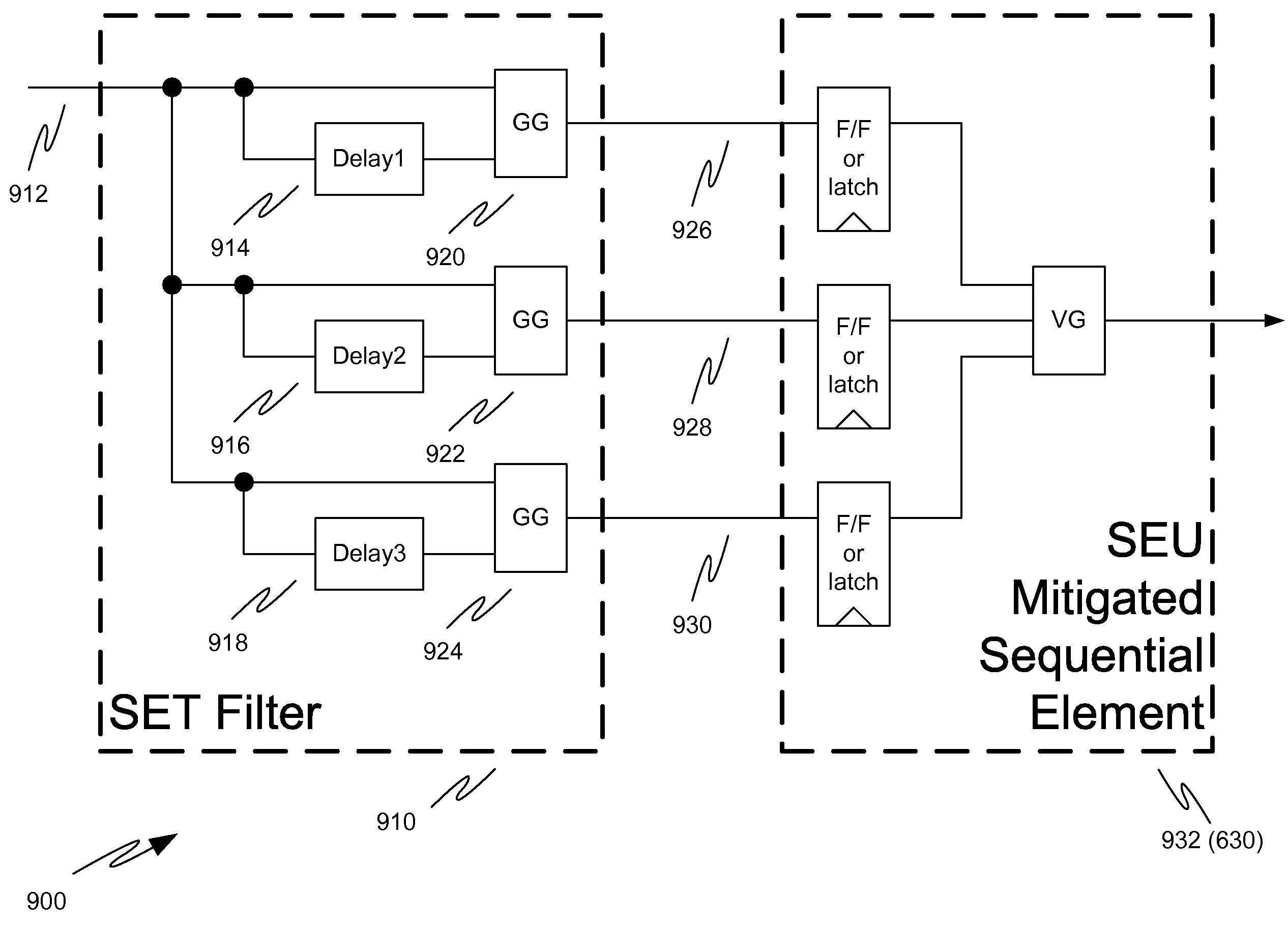
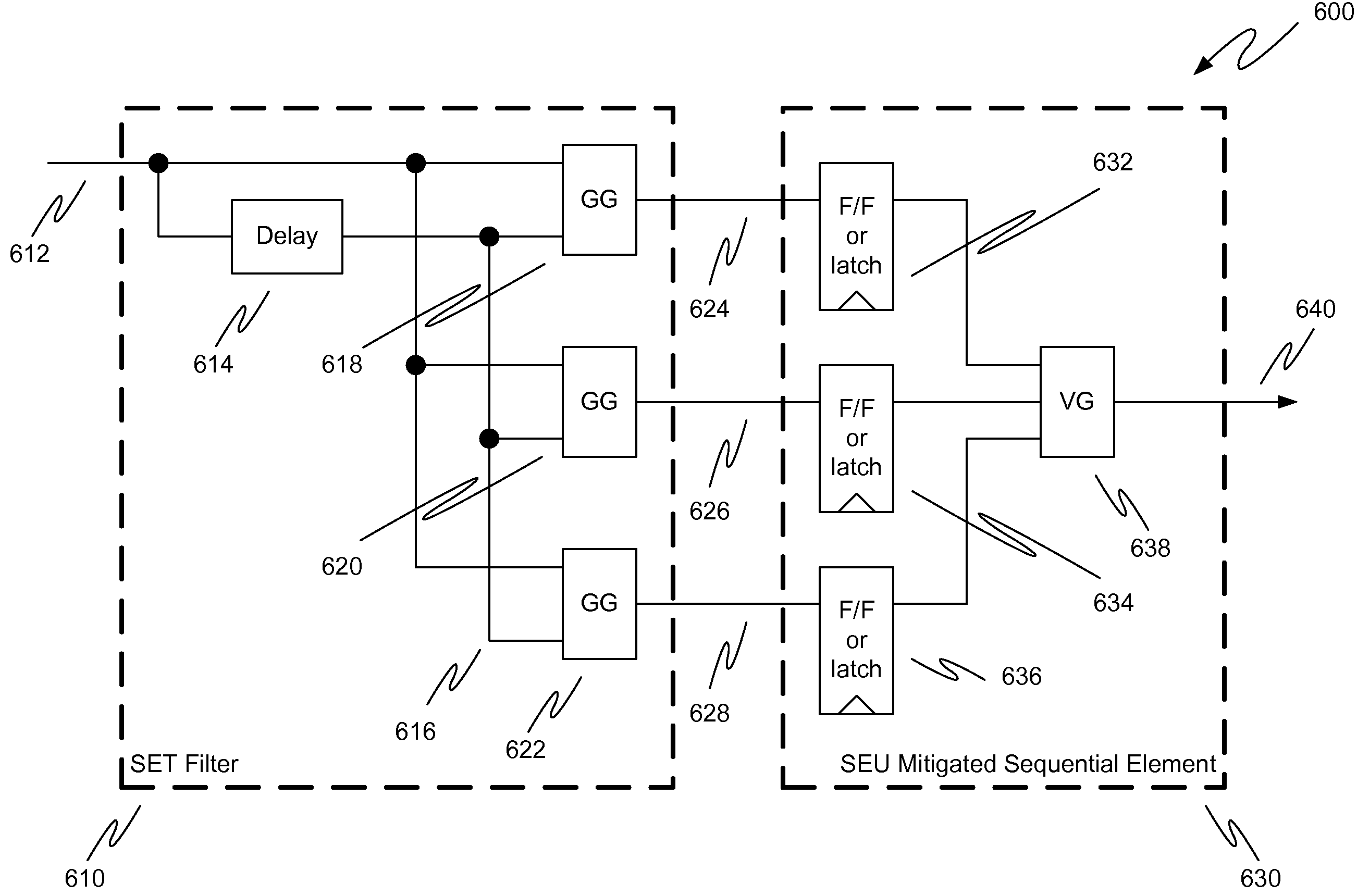
Single event transient mitigation and measurement in integrated circuits
ActiveUS20090189634A1Electronic switchingReliability increase by circuit redundancyComputer scienceSET domain
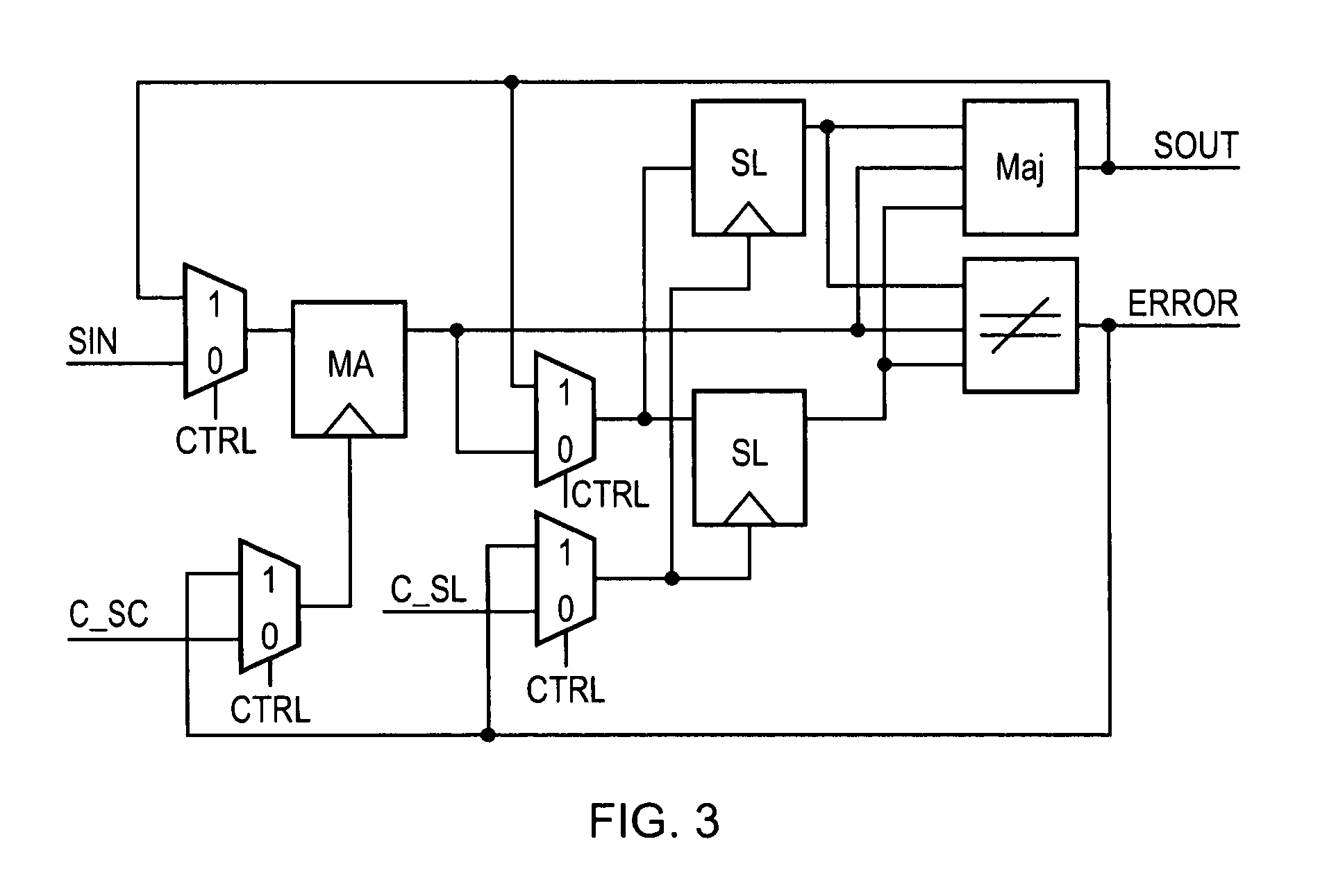
A method for single event transient filtering in an integrated circuit device is described. The device comprises three sequential elements, each having a data input and a data output with each of the three data outputs coupled to one of three inputs of a voting gate. The method comprises generating first and second nominally equivalent logic signals in first and second SET domains, converting the first and second nominally equivalent logic signals into first, second and third nominally equivalent data channels, and transmitting the first, second and third nominally equivalent data channels to the data inputs of the first, second and third sequential elements.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
Interleaved memory cell with single-event-upset tolerance
ActiveUS7515452B1Digital storageReliability increase by circuit redundancyComputer architectureInterleaved memory
A memory array has a first memory cell with a plurality of transistors connected so as to restore a data value to a node of the memory cell to an initial value following an event upsetting the initial value. A first portion of the plurality of transistors is in a first cell portion and a second portion of the plurality of transistors is in a second cell portion. A second memory cell has a third cell portion and a fourth cell portion. The third cell portion is between the first cell portion and the second cell portion and adjacent to each of the first cell portion and the second cell portion. In a particular embodiment, the memory cell is a single-event-upset (“SEU”) tolerant memory cell and the first and second cell portions are each a half cell of a sixteen transistor memory cell.
Owner:XILINX INC
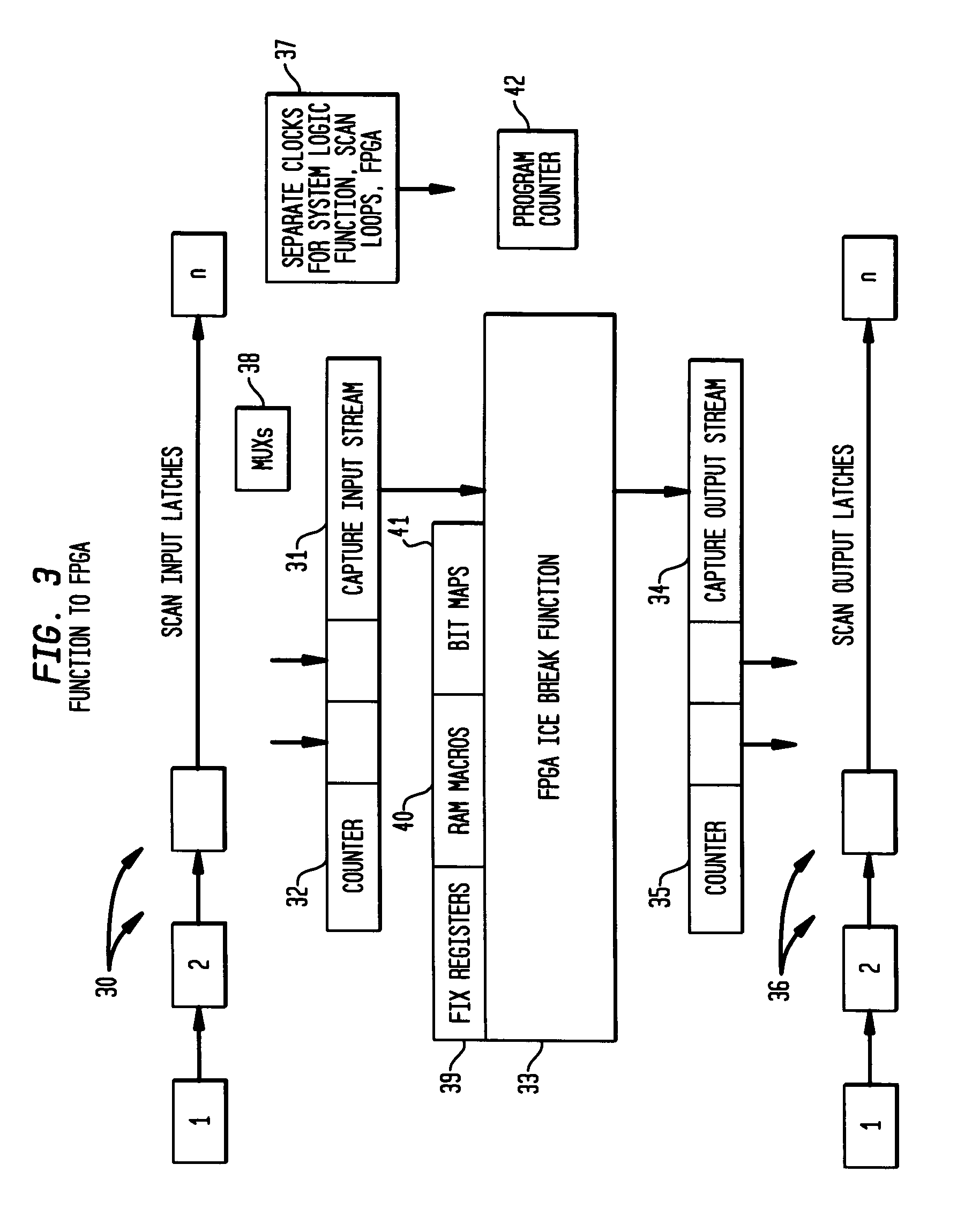
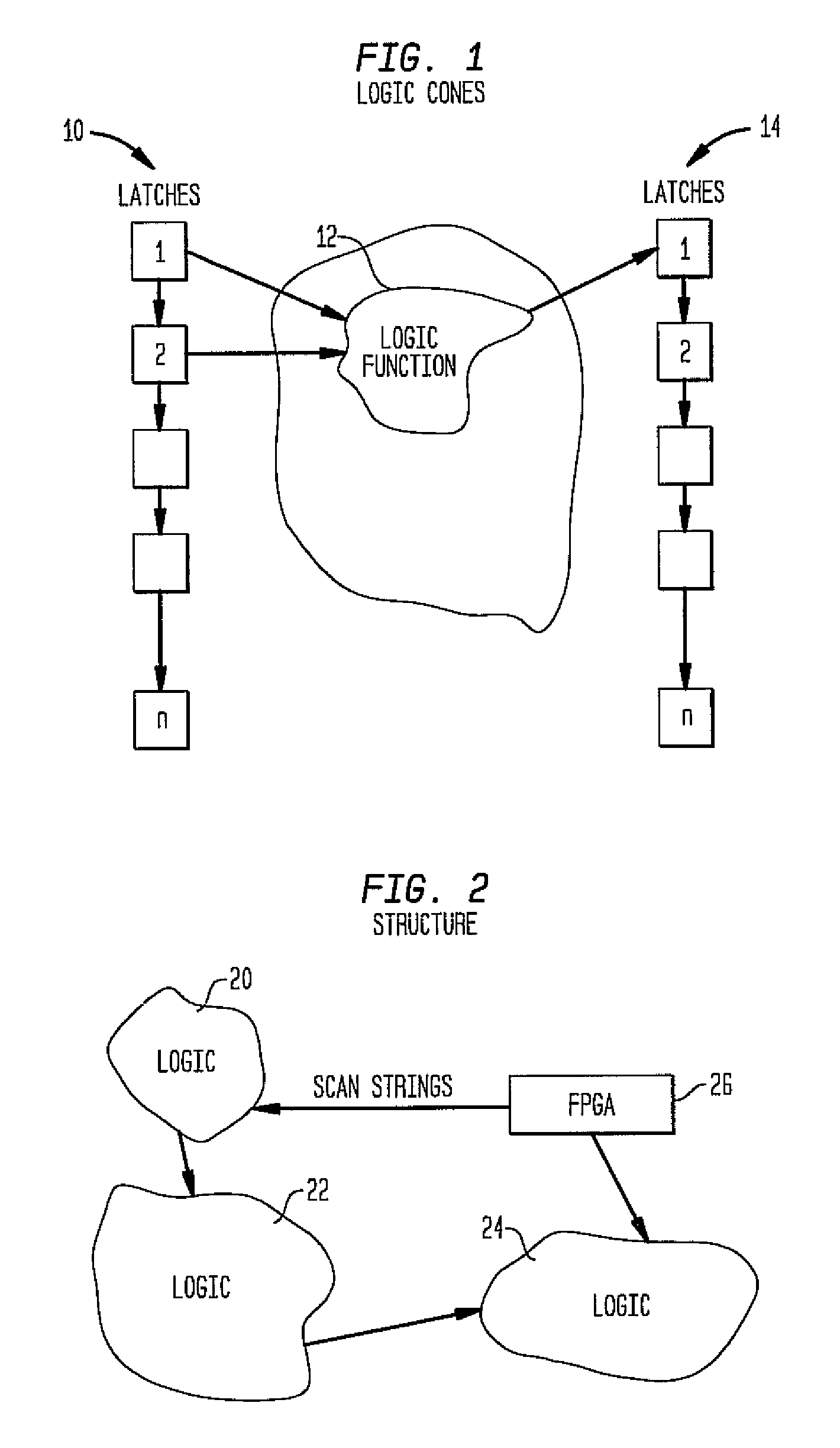
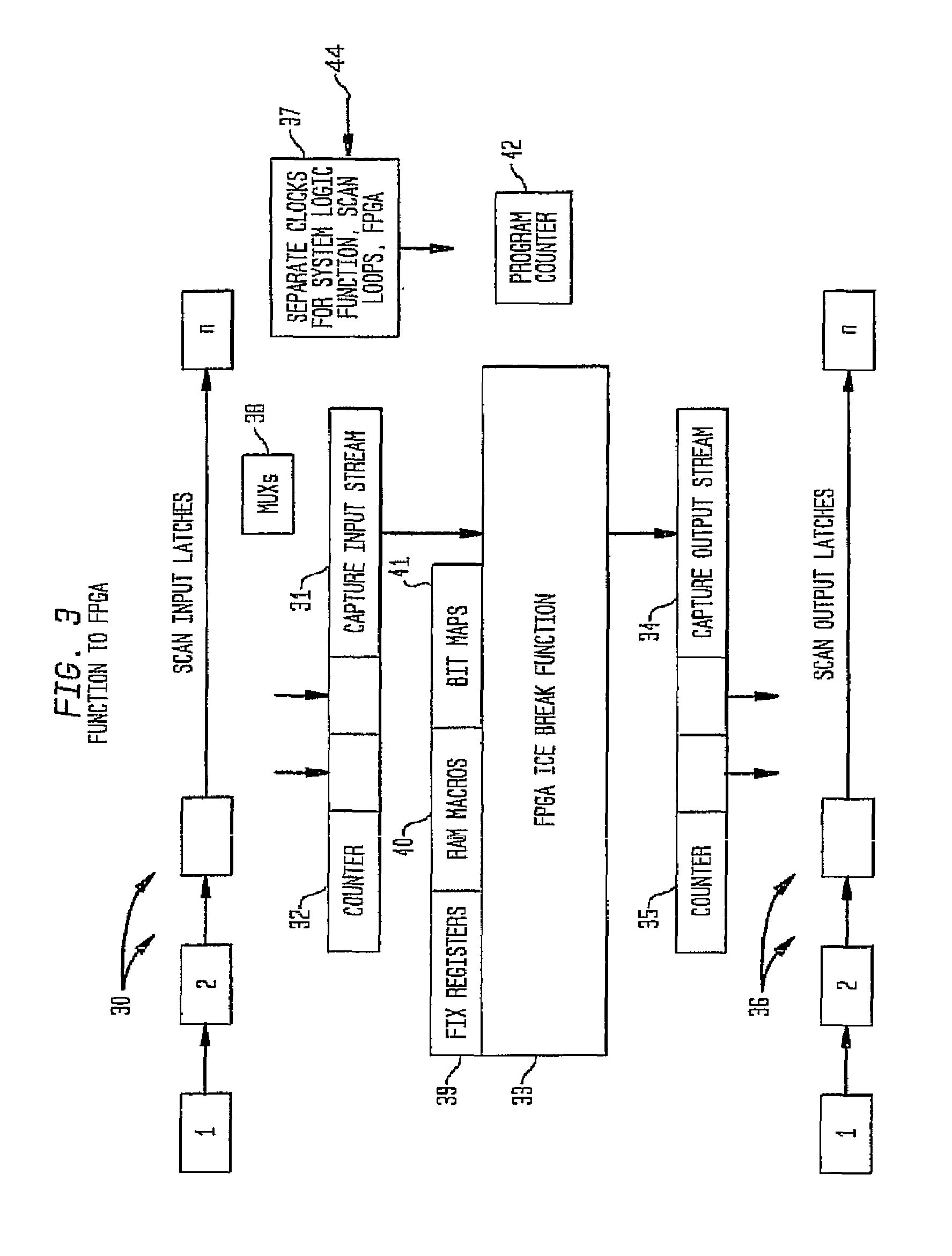
A system and method of providing error detection and correction capability in an integrated circuit using redundant logic cells of an embedded FPGA
A system and method of providing error detection and correction capability in an IC using redundant logic cells and an embedded field programmable gate array (FPGA). The system and method provide error correction (EC) to enable a defective logic function implemented within an IC chip design to be replaced, wherein at least one embedded FPGA is provided in the IC chip to perform a logic function. If a defective logic function is identified in the IC design, the embedded FPGA is programmed to correctly perform the defective logic function. All inputs in an input cone of logic of the defective logic function are identified and are directed into the embedded FPGA, such that the embedded FPGA performs the logic function of the defective logic function. All outputs in an output cone of logic of the defective logic function are identified, and the output of the FPGA is directed to the output cone of logic of the defective logic function, such that logic EC is provided within the embedded FPGA structure of the IC chip.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Correction of single event upset error within sequential storage circuitry of an integrated circuit
ActiveUS8161367B2Rapid responseLess powerError preventionTransmission systemsSingle event upsetComputer science
Sequential storage circuitry includes first and second storage elements storing first and second indications of input data values received by the circuitry during first and second phases of a clock signal. Error detection circuitry detects a single event upset error in any of the first and second storage elements. Two additional storage elements are provided for storing third and fourth indications of the input data value respectively in response to a pulse signal derived from the clock signal. Included is comparison circuitry for comparing the third and fourth indications of the input data value and further comparison circuitry for comparing, during a first phase of the clock signal, the first indication and at least one of the third and fourth indications, and for comparing, during a second phase of the clock signal, the second indication and at least one of the third and fourth indications.
Owner:ARM LTD
Multi-row block supporting row level redundancy in a PLD
InactiveUS7772872B2Solid-state devicesReliability increase by circuit redundancyComputer architectureProgrammable logic device
In a Programmable Logic Device (PLD), a multi-row block that has internal logic connections between rows has redundant internal connections between rows to replace the internal logic connections when a fault occurs. The redundant internal logic connections extend through a row, linking the row above a defective row with a row below the defective row. Elements in a multi-row block are configurable to perform a default function and a function of an element in a neighboring row, if the functions are different.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
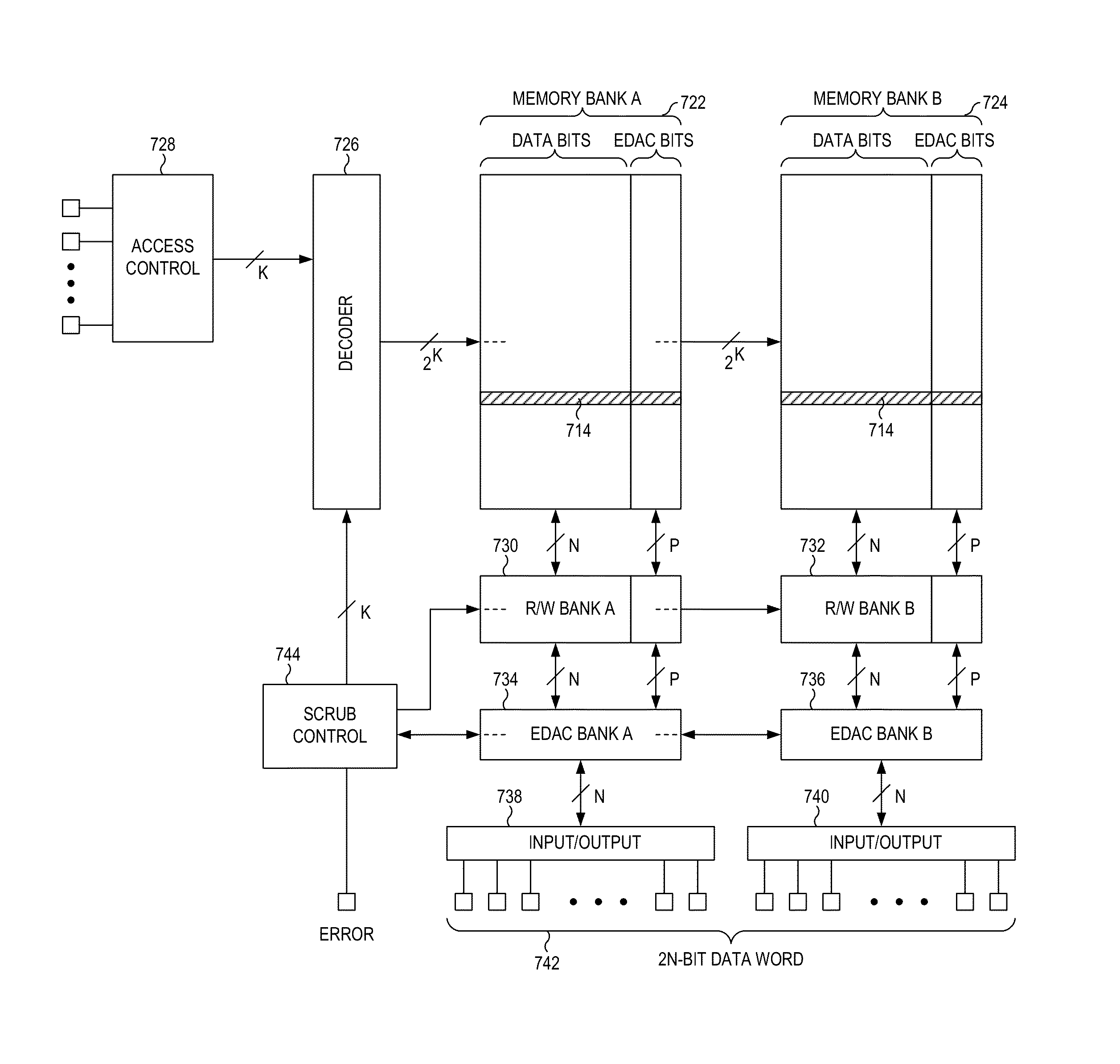
Memory circuit incorporating radiation-hardened memory scrub engine
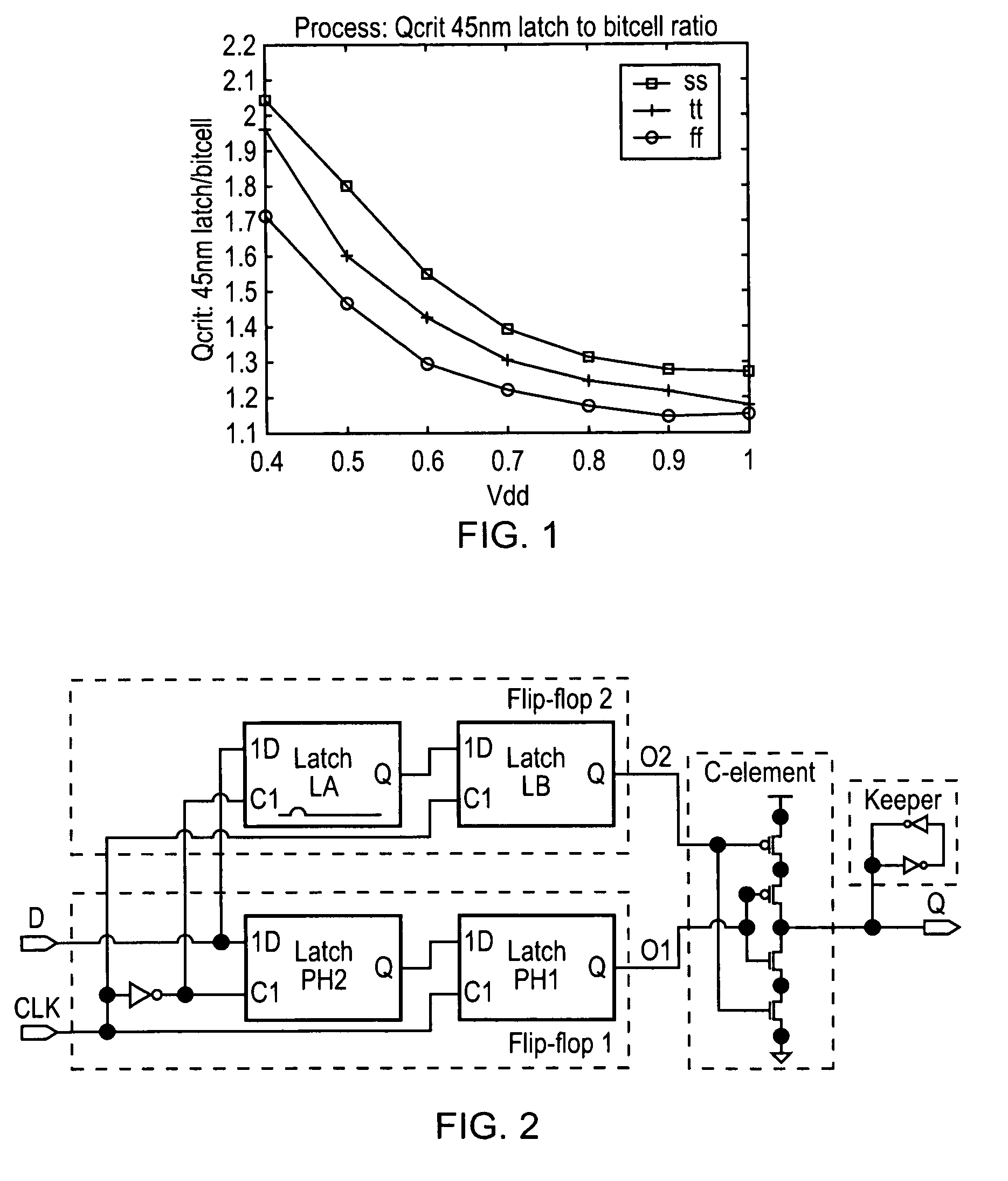
An example integrated circuit includes a first memory array including a first plurality of data groups, each such data group including a respective plurality of data bits. The integrated circuit also includes a first error detection and correction (EDAC) circuit configured to detect and correct an error in a data group read from the first memory array. The integrated circuit also includes a first scrub circuit configured to access in a sequence each of the first plurality of data groups to correct any detected errors therein. Both the first EDAC circuit and the first scrub circuit include spatially redundant circuitry. The first EDAC circuit and the first scrub circuit may include buried guard ring (BGR) structures, and may include parasitic isolation device (PID) structures. The spatially redundant circuitry may include dual interlocked storage cell (DICE) circuits, and may include temporal filtering circuitry.
Owner:SILICON SPACE TECH
Single event transient mitigation and measurement in integrated circuits
ActiveUS7772874B2Electronic switchingReliability increase by circuit redundancyComputer scienceSignal transition
A method for single event transient filtering in an integrated circuit device is described. The device comprises three sequential elements, each having a data input and a data output with each of the three data outputs coupled to one of three inputs of a voting gate. The method comprises generating first and second nominally equivalent logic signals in first and second SET domains, converting the first and second nominally equivalent logic signals into first, second and third nominally equivalent data channels, and transmitting the first, second and third nominally equivalent data channels to the data inputs of the first, second and third sequential elements.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
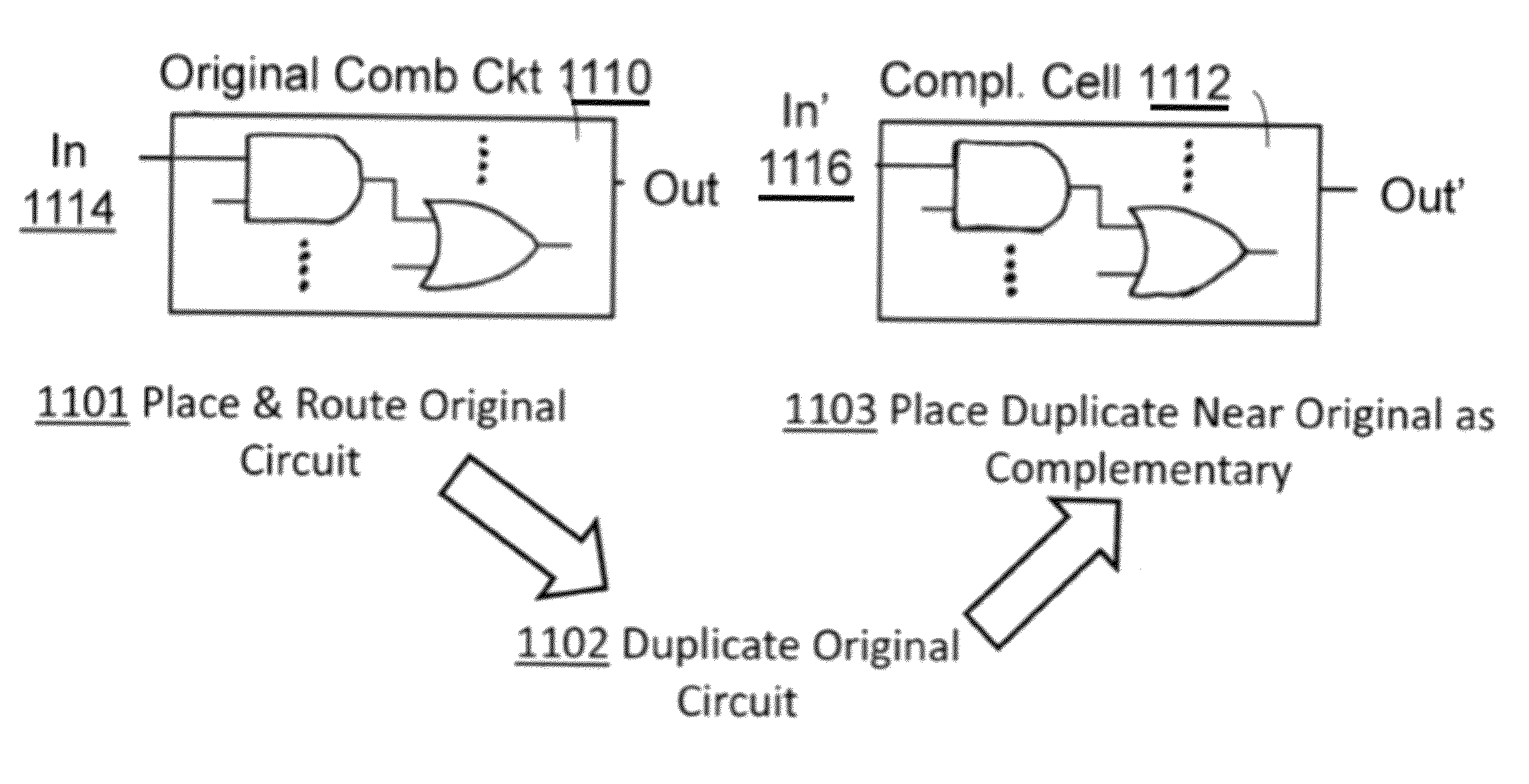
Homogeneous dual-rail logic for DPA attack resistive secure circuit design
ActiveUS8395408B2Reliability increase by circuit redundancySpecial data processing applicationsNegationPrimary cell
Homogenous dual-rail logic for DPA attack resistive secure circuit design is disclosed. According to one embodiment, an HDRL circuit comprises a primary cell and a complementary cell, wherein the complementary cell is an identical duplicate of the primary cell. The HDRL circuit comprises a first set of inputs and a second set of inputs, wherein the second set of inputs are a negation of the first set of inputs. The HDRL circuit has a differential power at a level that is resistive to DPA attacks.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Radiation-tolerant flash-based FPGA memory cells
ActiveUS7768317B1Logic circuits characterised by logic functionRead-only memoriesTransistorElectrical and Electronics engineering
A radiation-tolerant flash-based FPGA switching element includes a plurality of memory cells each having a memory transistor and a switch transistor sharing a floating gate. Four such memory cells are combined such that two sets of two switch transistors are wired in series and the two sets of series-wired switch transistors are also wired in parallel. The four memory transistors associated with the series-parallel combination of switch transistors are all programmed to the same on or off state. The series combination prevents an “on” radiation-hit fault to one of the floating gates from creating a false connection and the parallel combination prevents an “off” radiation-hit fault to one of the floating gates from creating a false open circuit.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
Techniques for bypassing defects in rows of circuits
An integrated circuit includes rows of circuits. A first region of the integrated circuit includes a first portion of each of the rows of circuits, and a second region of the integrated circuit includes a second portion of each of the rows of circuits. The integrated circuit shifts functions for a first subset of the rows of circuits to a second subset of the rows of circuits in the first region based on a first defect in a first one of the rows of circuits in the first region. The integrated circuit shifts functions for a third subset of the rows of circuits to a fourth subset of the rows of circuits in the second region based on a second defect in a second one of the rows of circuits in the second region.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Three-dimensional integrated circuit having redundant relief structure for chip bonding section
InactiveUS20130127028A1High yieldReduce areaSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringThree-dimensional integrated circuit
A chip is layered on a rewiring member. A plurality of connecting members and a plurality of redundant connecting members are arranged in the chip, and electrically connect the chip to the rewiring member. Redundant circuits are embedded in each of the rewiring member and the chip. When one of the connecting members is faulty, the redundant circuits cause one of the redundant connecting members to transmit a signal between the rewiring member and the chip, instead of the faulty connecting member. The connecting members have first and second subsets arranged in first and second regions, respectively. A distance between the rewiring member and the chip exceeds a predetermined threshold value in the first region in contrast to the second region. The first subset has a higher proportion of connecting members that the redundant circuits can replace with a subset of the redundant connecting members than the second subset.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and apparatus for self-annealing multi-die interconnect redundancy control
ActiveUS20130009694A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:XILINX INC
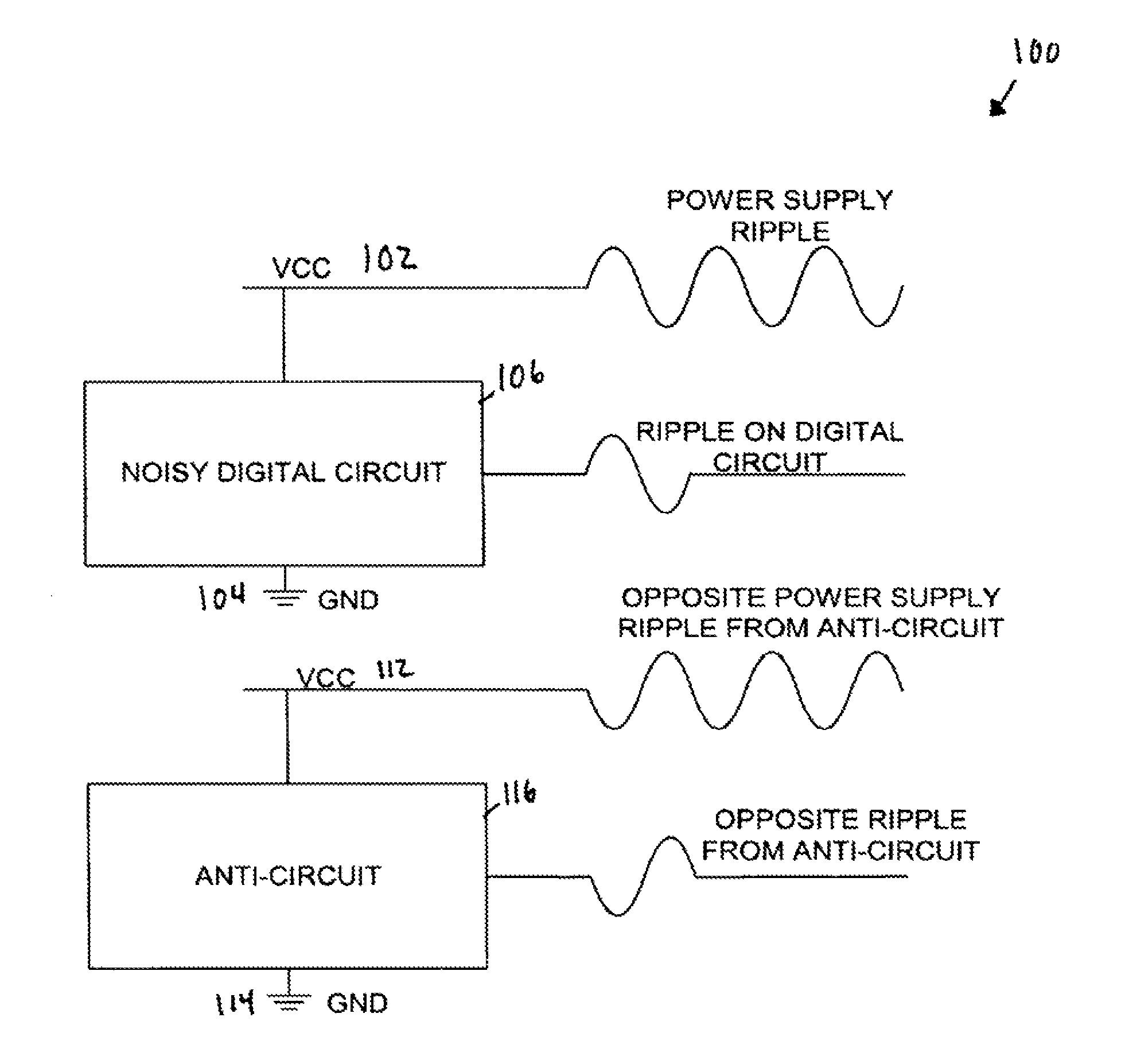
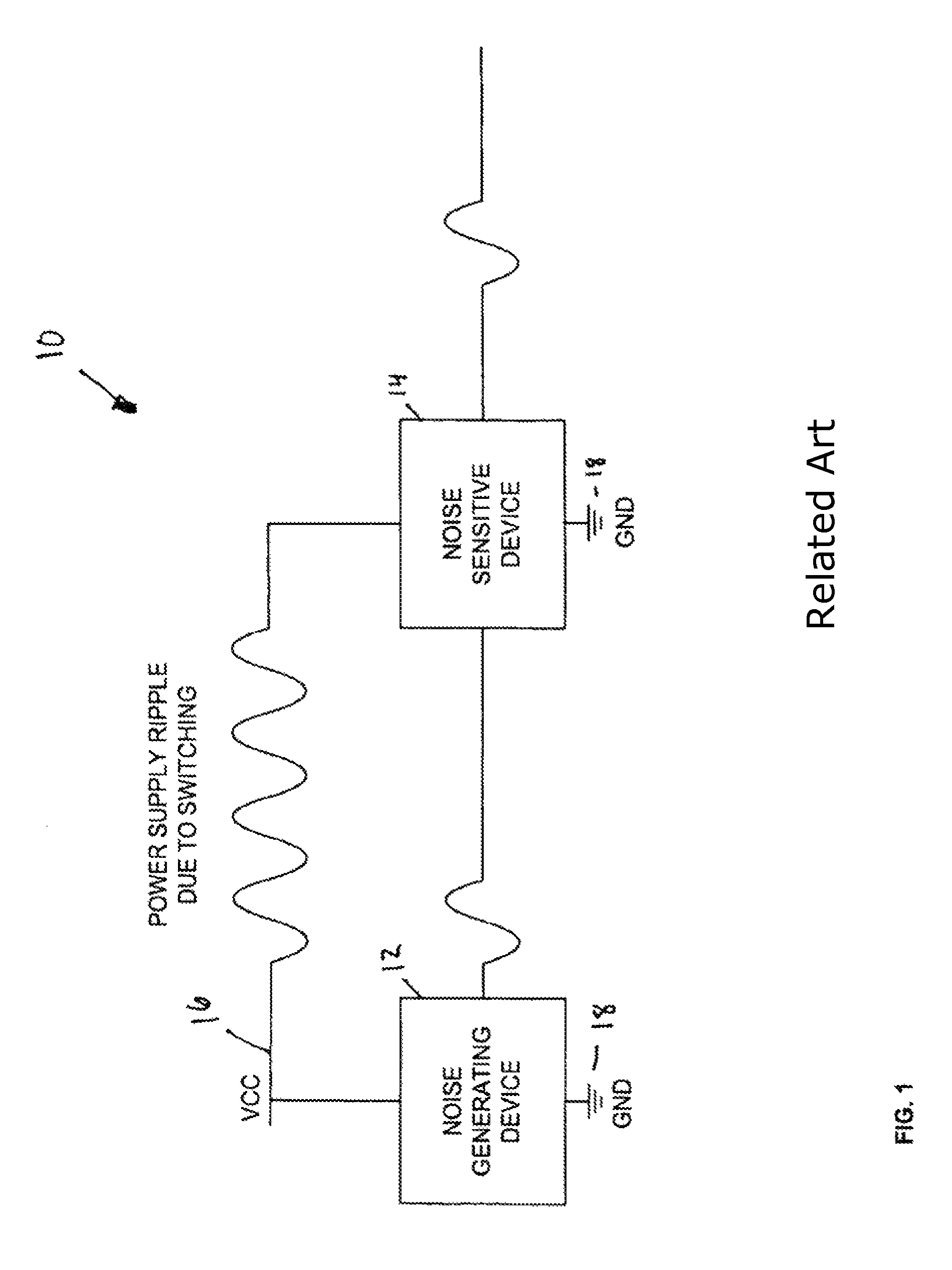
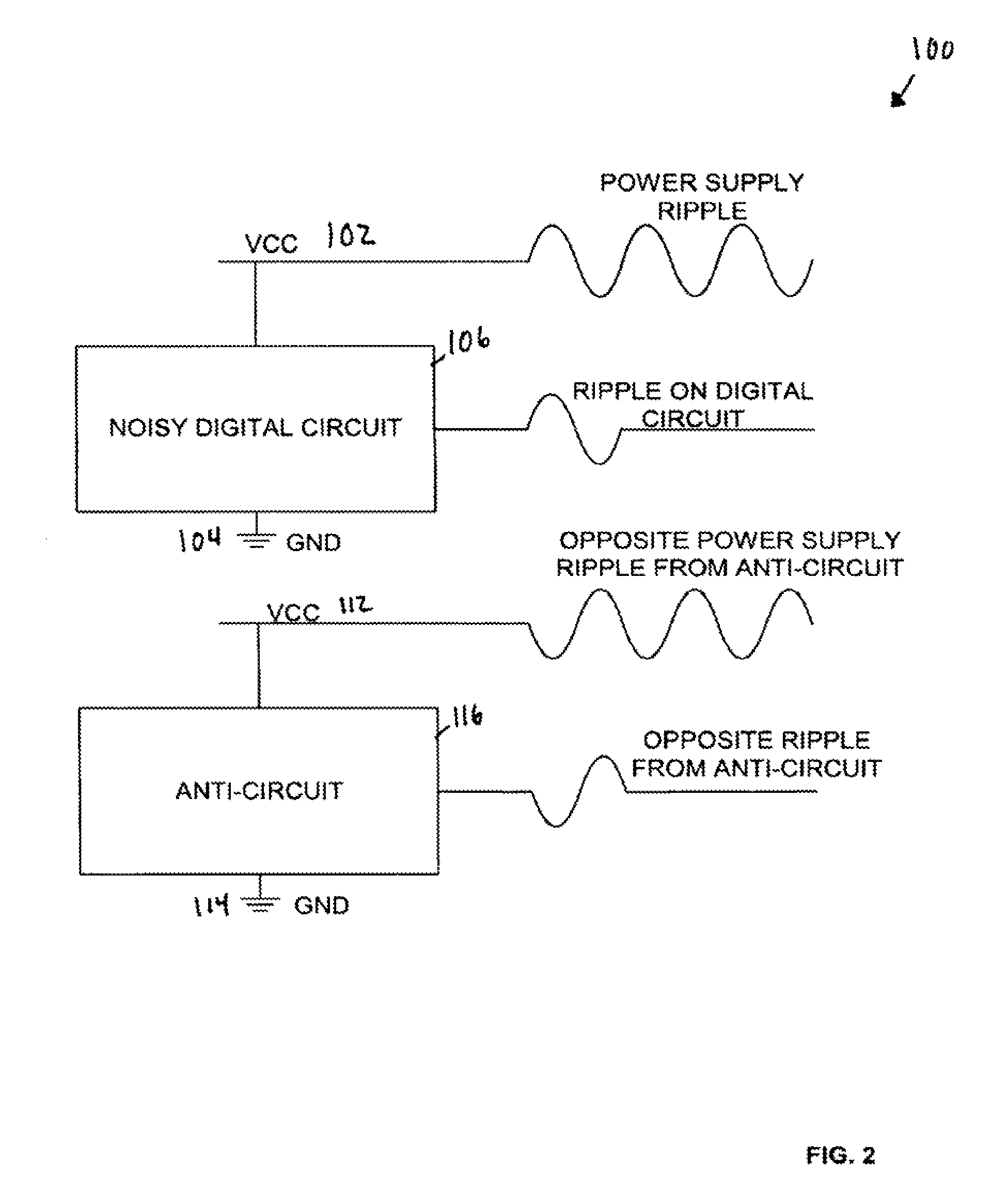
System for noise reduction in circuits
InactiveUS8093765B1Reduce noiseDc network circuit arrangementsPower distribution line transmissionEngineeringNoise reduction
Disclosed is an improved noise reducing apparatus using an anti-circuit, including a digital logic circuit and a digital anti-circuit corresponding to the digital logic circuit. The digital anti-circuit functions to cancel noise generated by the digital logic circuit. The anti-circuit includes logic to generate a similar number of switching edges as the logic circuit, where the anti-circuit edges are in the opposite direction as the logic circuit. The anti-circuit may have a circuit structure close to that of the noisy circuit, or can be formed of components different in structure but generating an output pattern similar to (and opposite from) the noisy circuit. In some embodiments, the differently structured components can include a state machine coupled to a memory or look-up-table.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
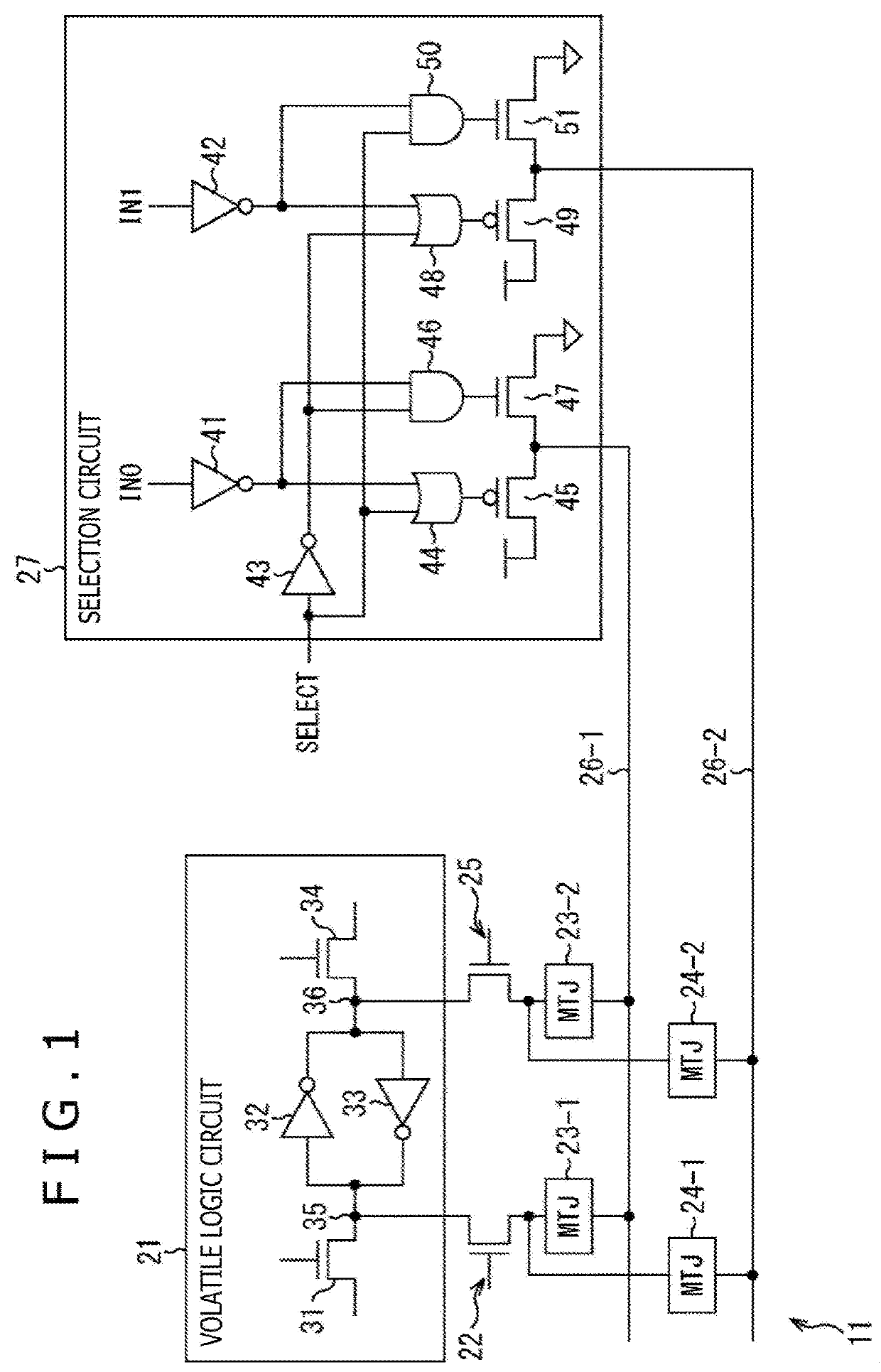
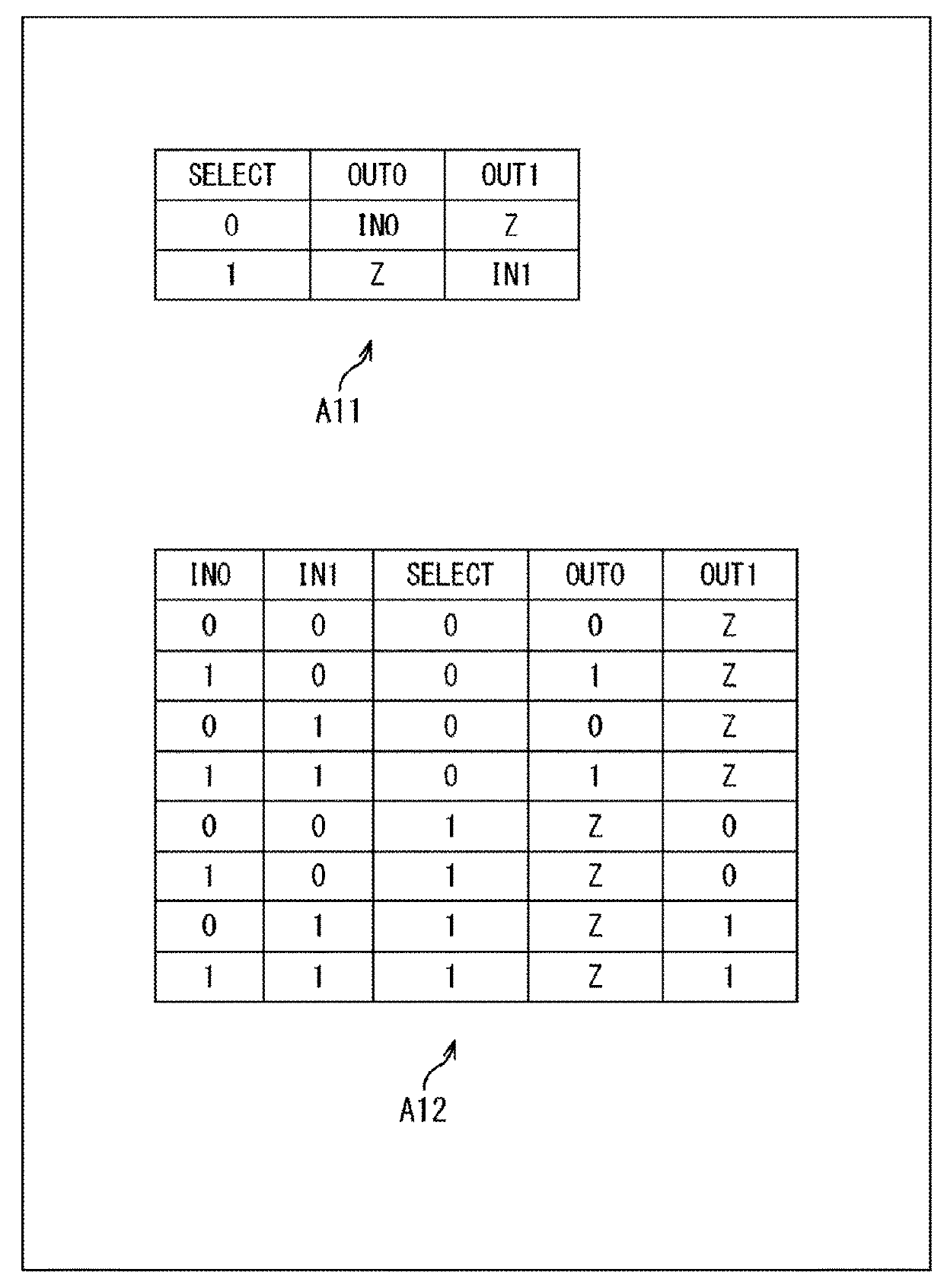
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20180277594A1Increase productionTransistorMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsDevice materialControl line
The present technology relates to a semiconductor device which enables yield to be enhanced. A volatile logic circuit has a storage node, and stores inputted information. A plurality of non-volatile elements are connected to the storage node of the volatile logic circuit through the same connection gate, and control lines for control for these non-volatile elements are connected to the respective non-volatile elements, every non-volatile element. A plurality of non-volatile elements are connected to the volatile logic circuit through the same connection gate in such a way, thereby enabling the yield to be enhanced. The present technology can be applied to a semiconductor device.
Owner:SONY CORP
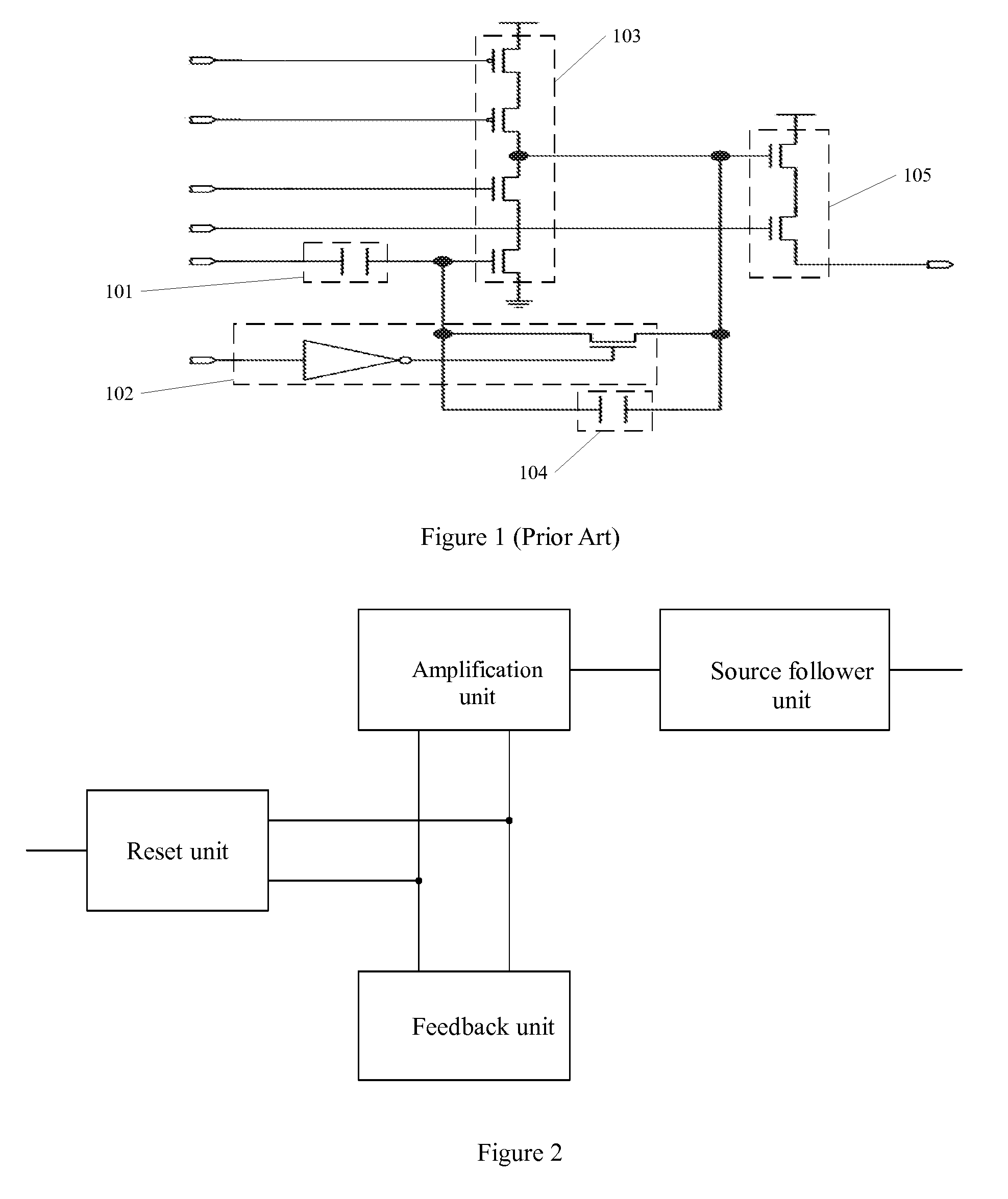
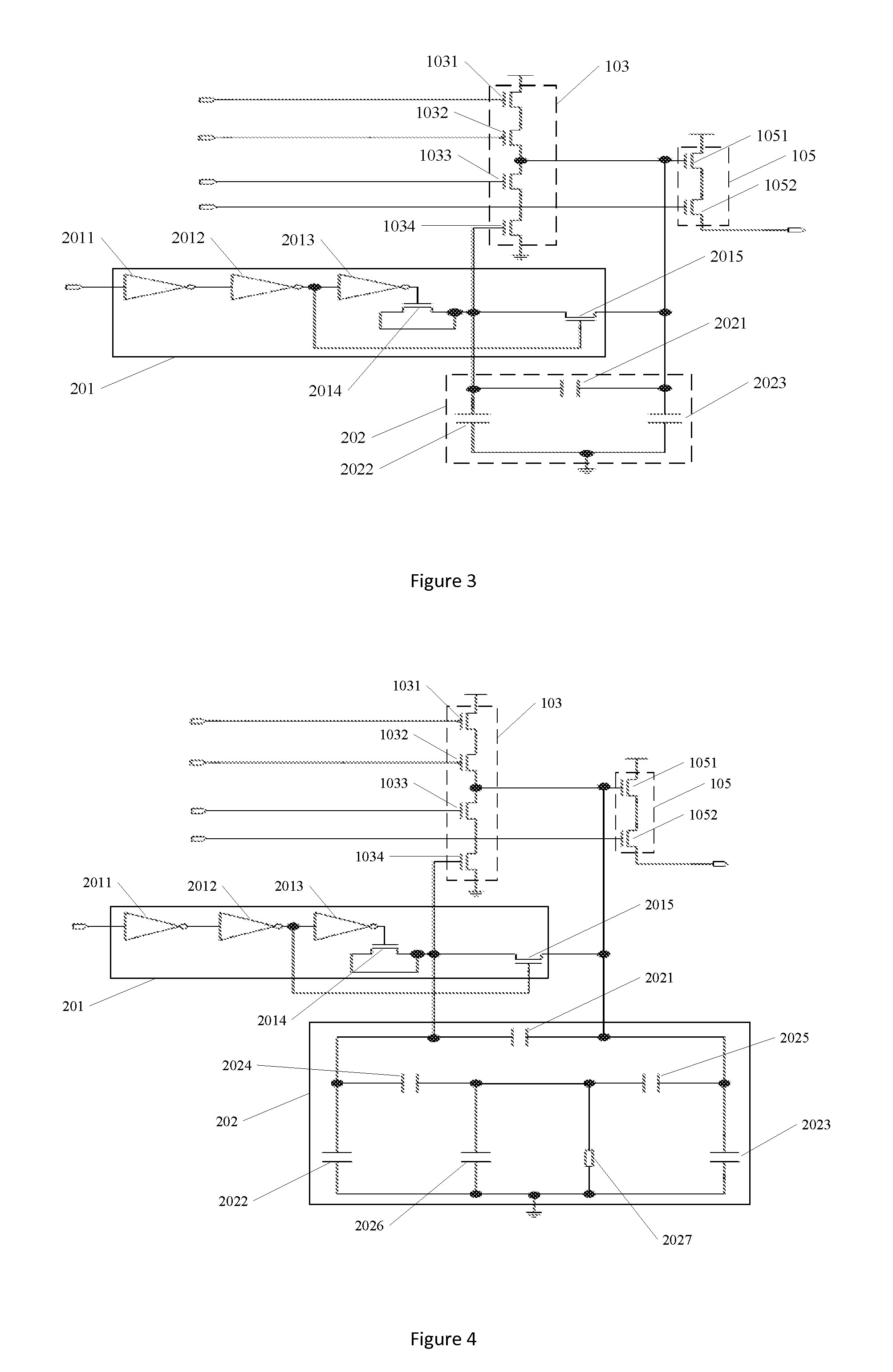
Fingerprint information detection circuit
ActiveUS20160275331A1Accurate representationAccurate distanceTransistorSolid-state devicesLevel shiftingCharge injection
The present invention relates to a chip design and discloses a fingerprint information detection circuit. The invention includes a reset unit, a feedback unit, an amplification unit and a source follower unit; the reset unit is connected to the feedback unit and amplification unit, while the feedback unit is connected to the amplification unit, and the amplification unit is connected to the source follower unit; when the reset transistor built-into the reset unit is on, it stores an electric charge, and resets the feedback unit; when the reset transistor is off, the stored electric charge is injected into the feedback unit and amplification unit; the feedback unit receives the electric charge, and outputs the second voltage signal generated when it detects fingerprints to the source follower unit; the amplification unit amplifies the received signal and outputs it to the source follower unit; the source follower unit receives the signal, performs voltage level shifting before outputting the first voltage signal that carries the detected fingerprint information. The present invention enables the circuit to use a reduced chip area, hence, saving the cost of the chip.
Owner:SILEAD
Power switch device
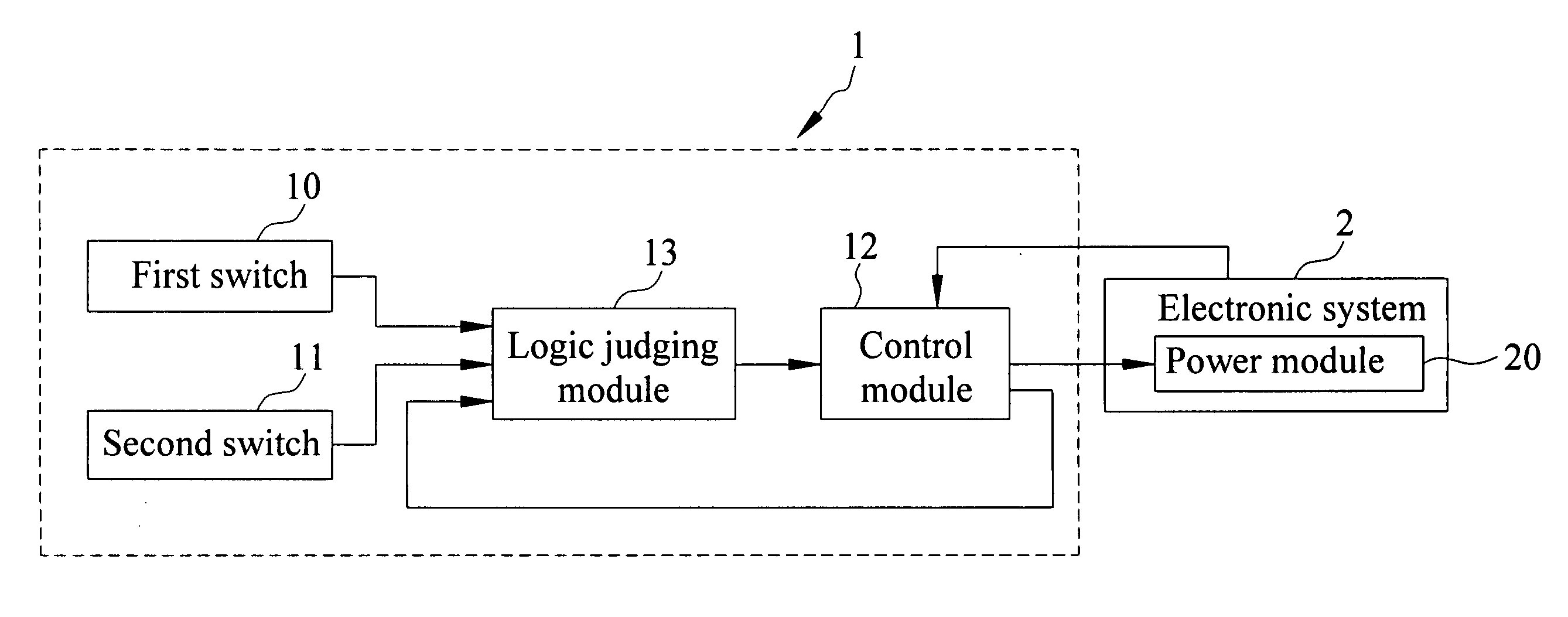
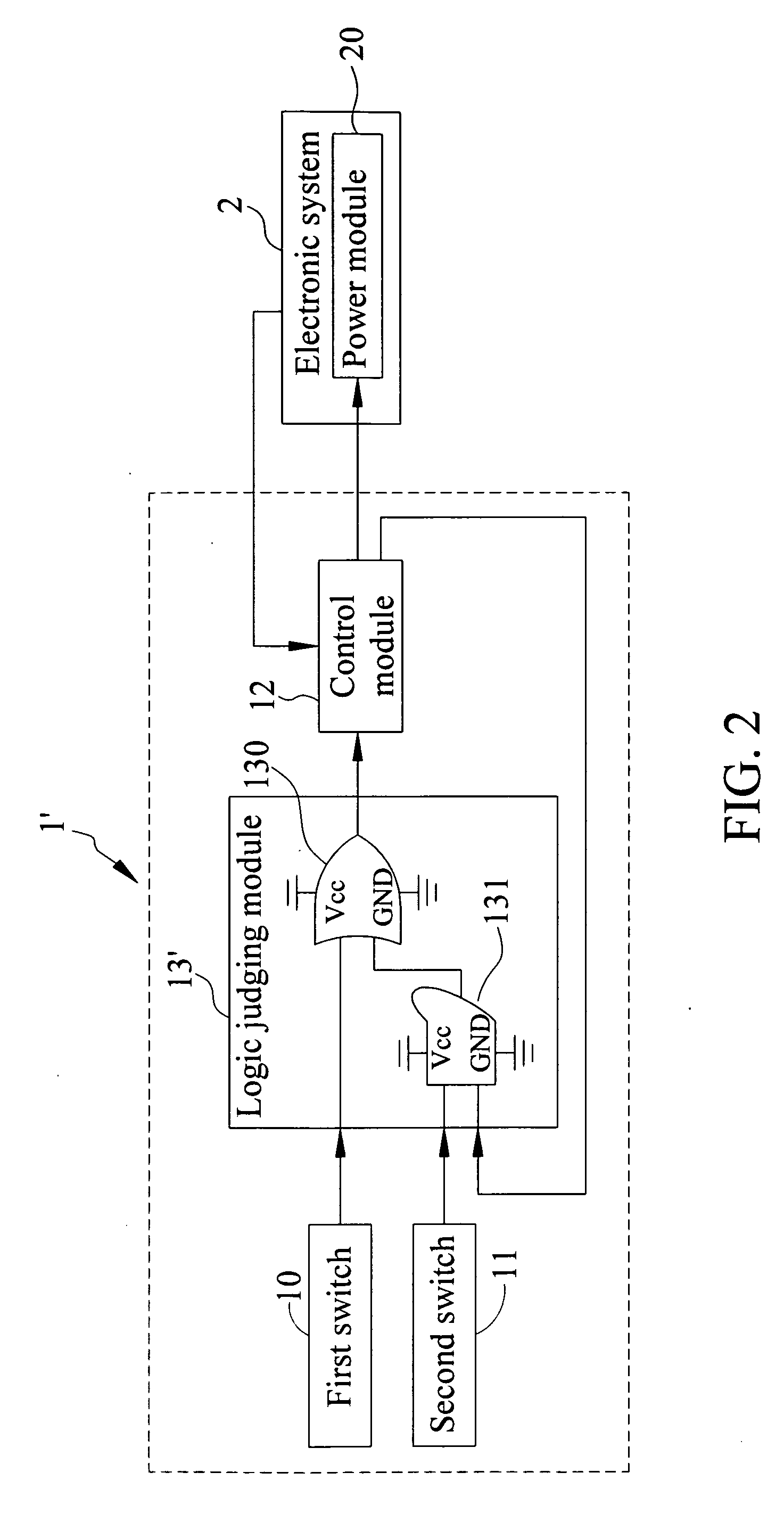
InactiveUS20090066165A1Avoid powerEasy to operateBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsComputer controlElectricityElectronic systems
The invention provides a power switch device for electronic systems equipped having a power module. The power switch device includes a first switch for activating a first signal, a second switch for activating a second signal, a logic judging module for receiving the first and second signals for logic algorithm processing, and a control module electrically connected to the electronic system and the logic judging module. The control module is adapted to generate and transmit on and off signals of the electronic system to the logic judging module. Further, the control module controls switching on the power module according to the off signal and the logic algorithm processing based on the first signal, and also controls switching off the power module according to the on signal and the logic algorithm processing based on the first and second signals.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
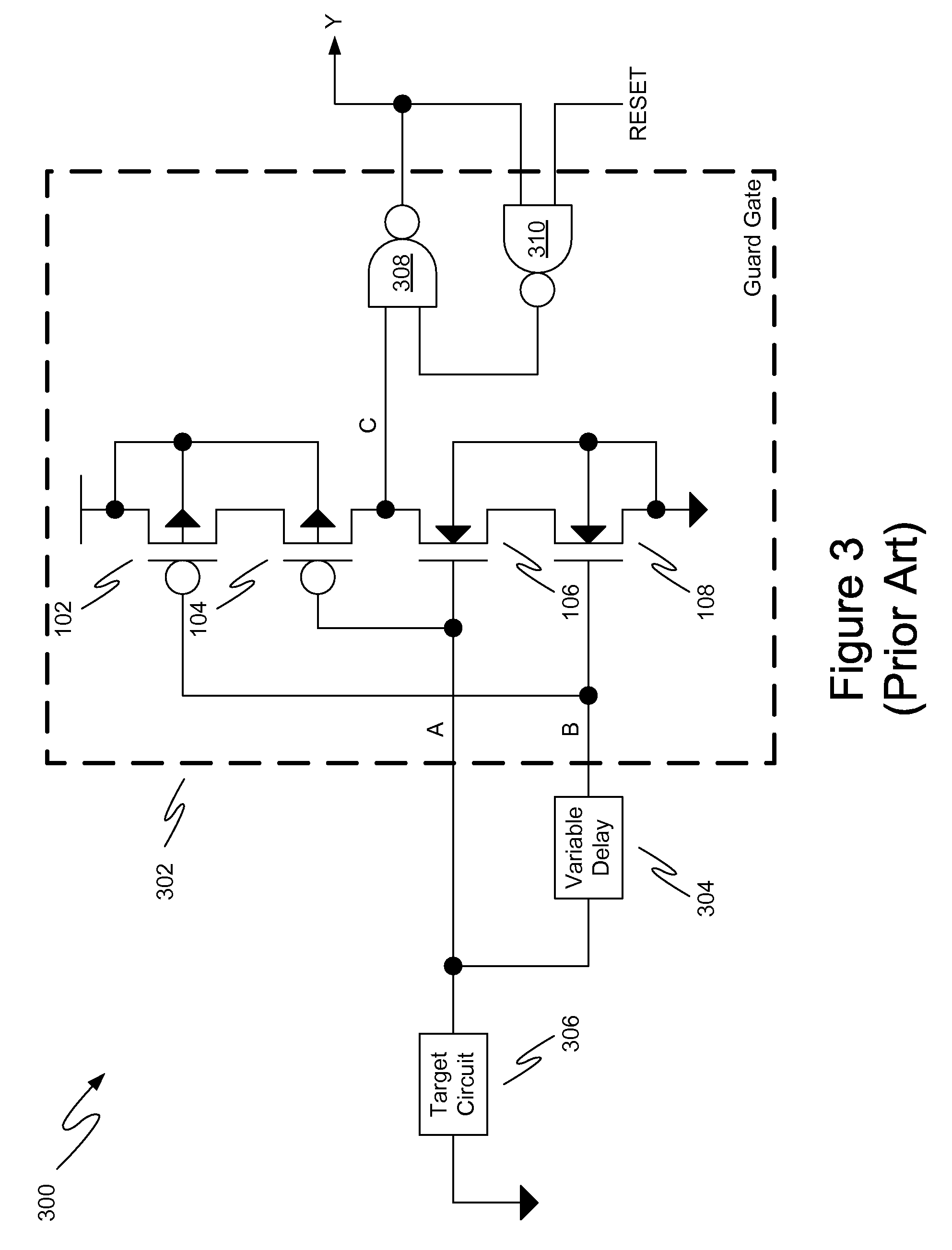
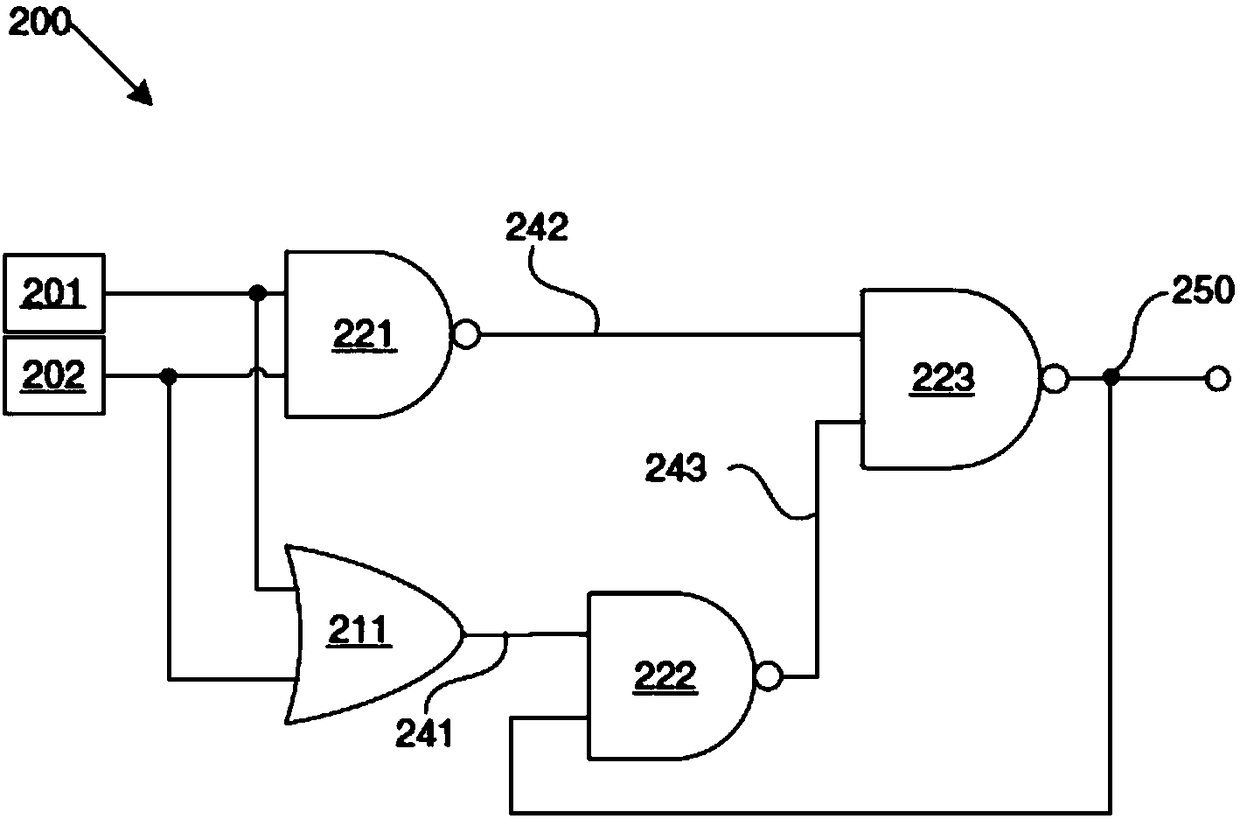
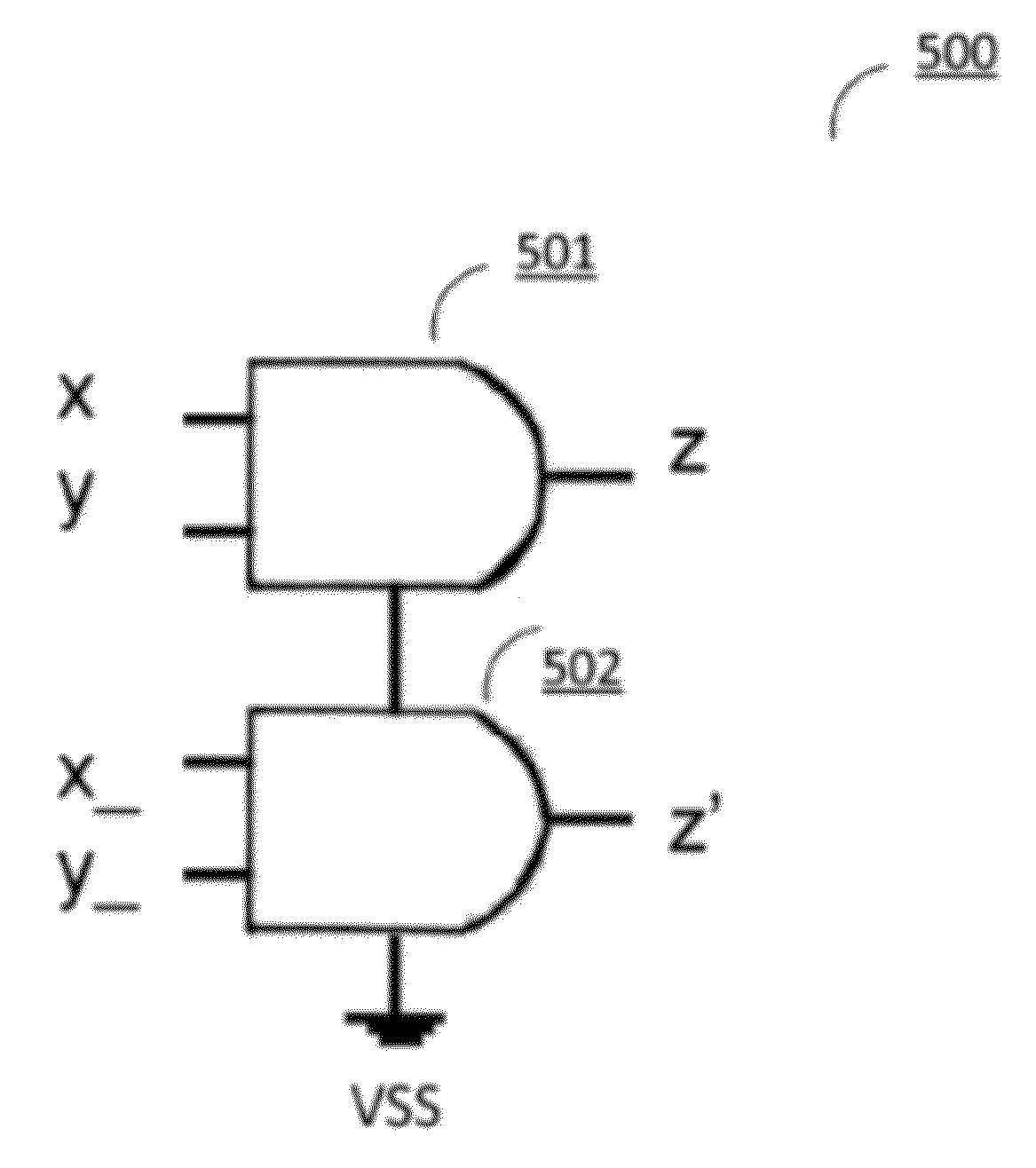
Method and circuit structure for suppressing single event transients or glitches in digital electronic circuits
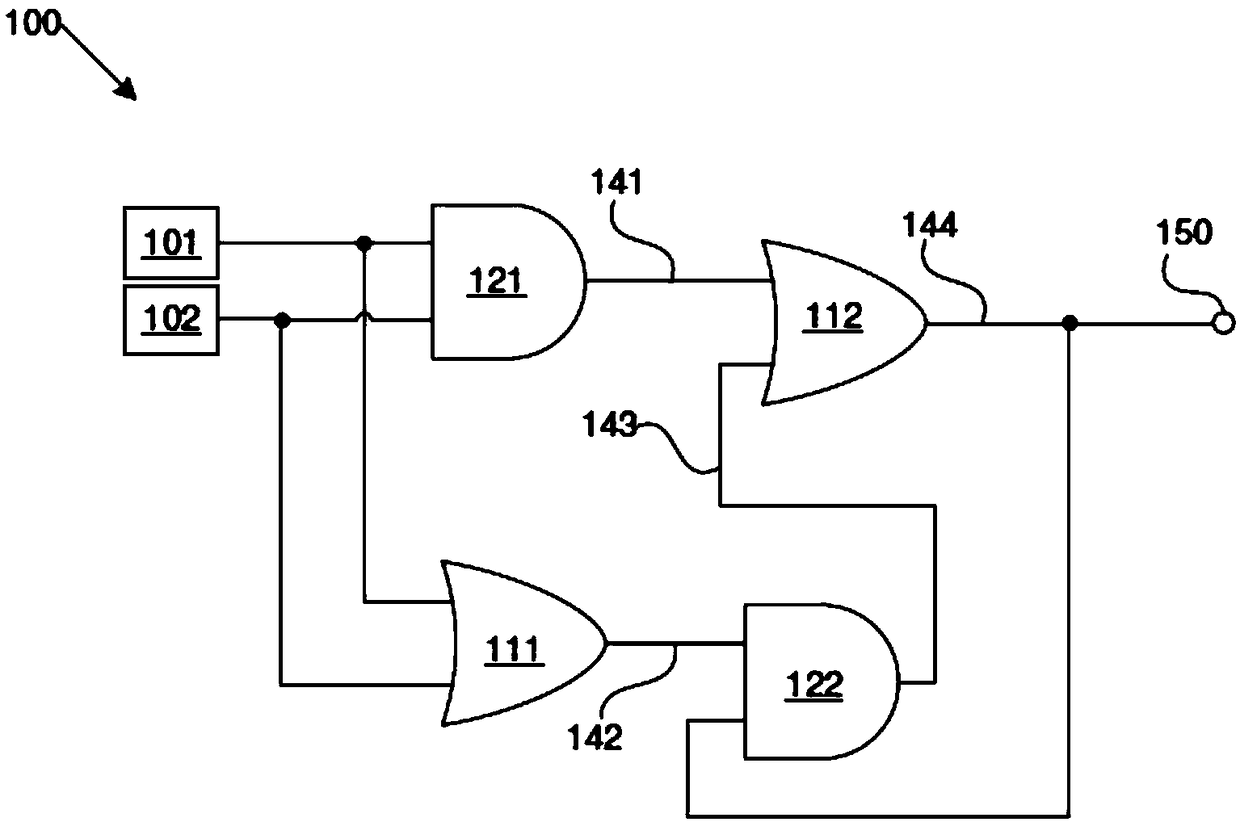
A circuit structure and a method for supressing single event transients (SETs) or single event upset (SEU) in digital electronic circuits are provided. The circuit includes a first input which receives an output of a digital electronic circuit and a second input which receives a redundant or duplicated output of the digital electronic circuit. The circuit includes only four two-input gates of twodifferent kinds selected from AND, OR, NAND and NOR gates. The four two-input gates being arranged so that a final circuit output is impervious to a change in a logic level of only the first input oronly the second input, and the final circuit output is equivalent to the logic level of the first and second inputs when the logic level of the first and second inputs match.
Owner:ネルソンマンデラユニバーシティ
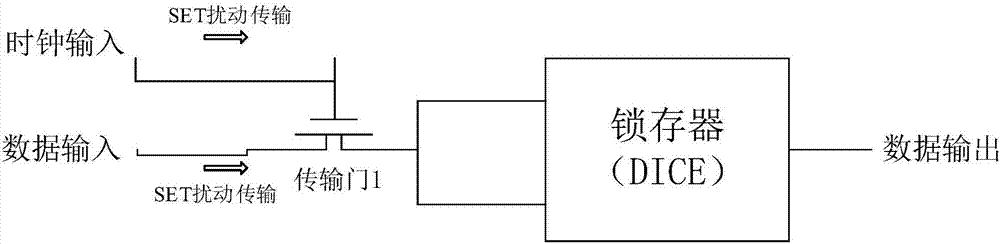
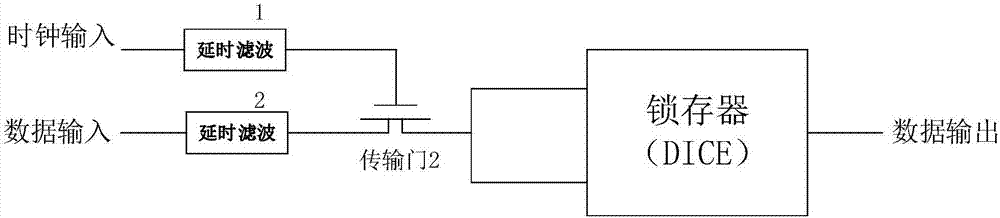
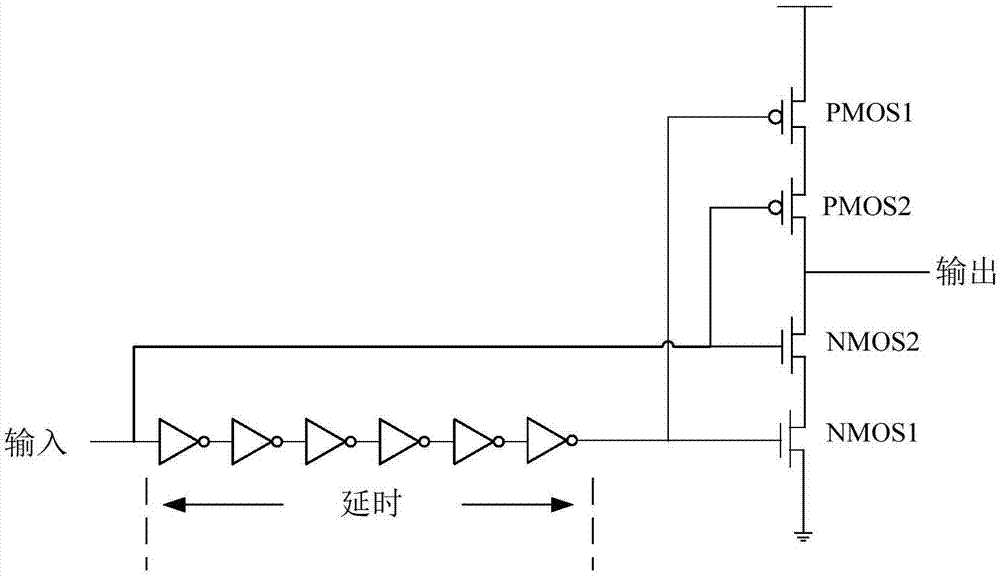
Single event transient disturbance reinforced latch circuit
InactiveCN107124176ADoes not affect the working frequencySimple structureReliability increase by circuit redundancyEngineeringOperating frequency
The invention relates to a single event transient disturbance reinforced latch circuit and belongs to the field of circuit design. The single event transient disturbance reinforced latch circuit comprises a first lowpass filter unit and a latch. First way data input of a data input end is connected with a first input end of the latch. Second data input of the data input end is connected with a second input end of the latch through the first lowpass filter unit. The first lowpass filter unit is a circuit unit which is composed of a passive device and is used for removing a high-frequency signal. The first lowpass filter unit for removing the high-frequency signal is composed of the passive device, the filter capacity only needs to be greater than the maximum pulse width produced by single event transient disturbance, the working frequency of the latch circuit is not influenced, and a circuit structure is simple. The passive device itself does not produce the single event transient disturbance and an area and the power consumption of a storage unit are not increased, so the single event effect resistance of logic circuits such as the latch and a trigger can be effectively improved.
Owner:58TH RES INST OF CETC
Homogeneous Dual-Rail Logic for DPA Attack Resistive Secure Circuit Design
ActiveUS20120105099A1Reliability increase by circuit redundancySpecial data processing applicationsNegationPrimary cell
Homogenous dual-rail logic for DPA attack resistive secure circuit design is disclosed. According to one embodiment, an HDRL circuit comprises a primary cell and a complementary cell, wherein the complementary cell is an identical duplicate of the primary cell. The HDRL circuit comprises a first set of inputs and a second set of inputs, wherein the second set of inputs are a negation of the first set of inputs. The HDRL circuit has a differential power at a level that is resistive to DPA attacks.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System and method of providing error detection and correction capability in an integrated circuit using redundant logic cells of an embedded FPGA
A system and method of providing error detection and correction capability in an IC using redundant logic cells and an embedded field programmable gate array (FPGA). The system and method provide error correction (EC) to enable a defective logic function implemented within an IC chip design to be replaced, wherein at least one embedded FPGA is provided in the IC chip to perform a logic function. If a defective logic function is identified in the IC design, the embedded FPGA is programmed to correctly perform the defective logic function. All inputs in an input cone of logic of the defective logic function are identified and are directed into the embedded FPGA, such that the embedded FPGA performs the logic function of the defective logic function. All outputs in an output cone of logic of the defective logic function are identified, and the output of the FPGA is directed to the output cone of logic of the defective logic function, such that logic EC is provided within the embedded FPGA structure of the IC chip.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Three-dimensional integrated circuit having redundant relief structure for chip bonding section
InactiveUS8704226B2Reduce yieldReduce areaSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringThree-dimensional integrated circuit
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
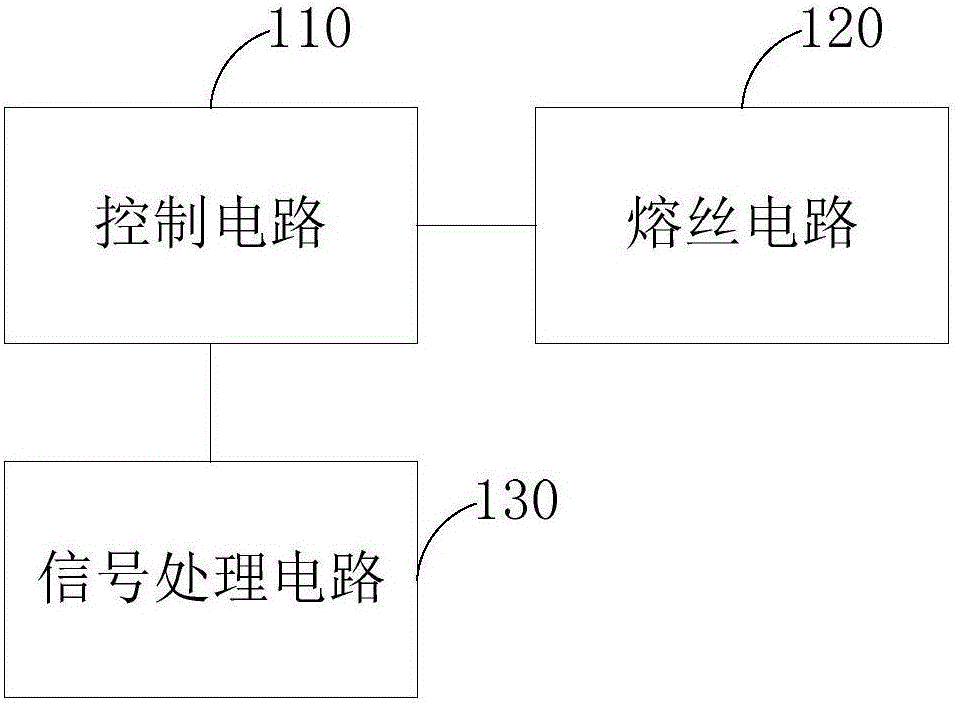
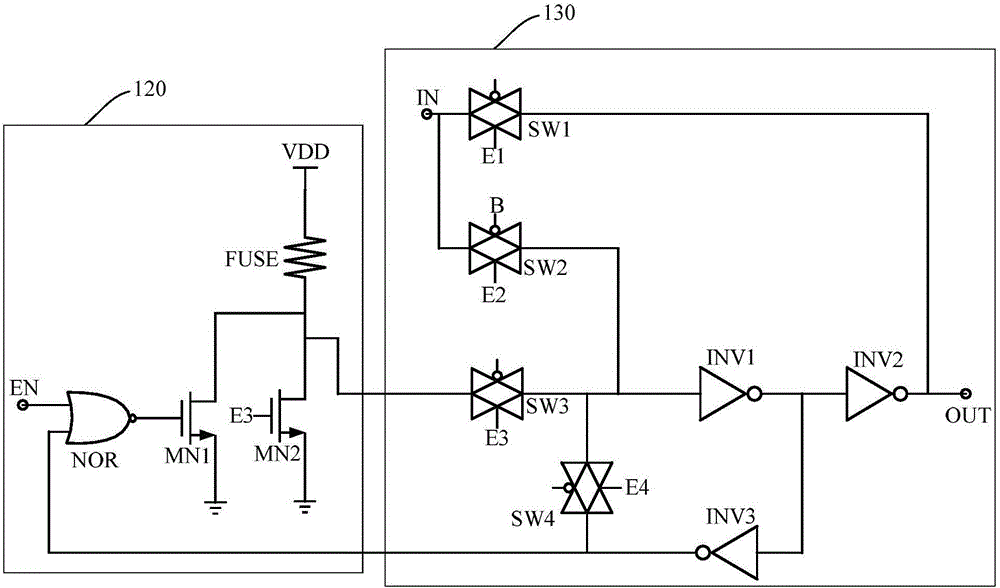
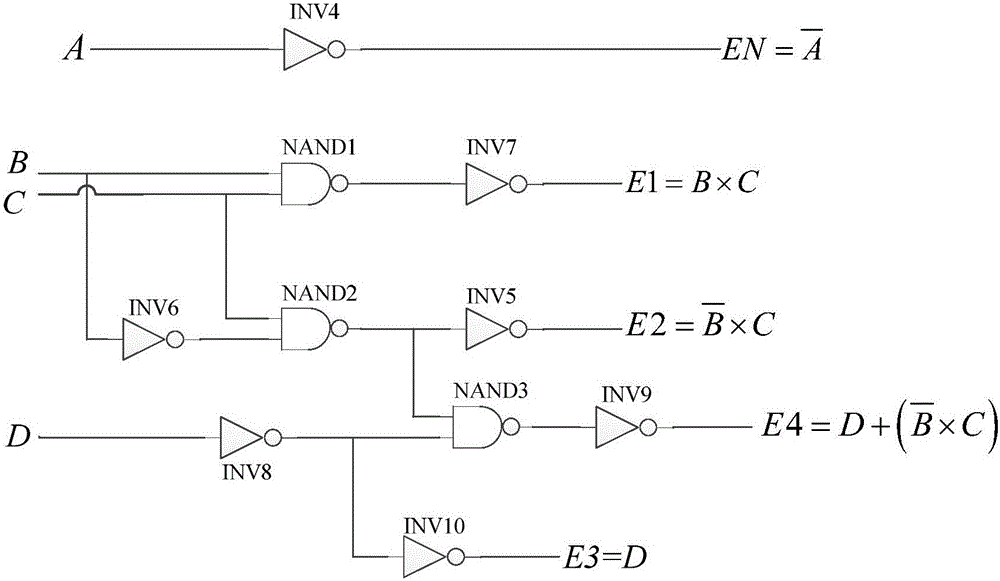
Fuse trimming device
ActiveCN106209061AIncrease diversityReduced adjustment costsReliability increase by circuit redundancySignal processing circuitsControl signal
The invention provides a fuse trimming device, comprising a control circuit, a fuse circuit and a signal processing circuit, wherein the control circuit is used for controlling the signal processing circuit to output a virtual fusing signal input by the control circuit to the fuse circuit during virtual fusing; the control circuit is used for controlling the signal processing circuit to output a real fusing signal input by the control circuit to the fuse circuit during real fusing, and sending a signal indicating whether a fuse in the fuse circuit determined according to the performance of a corresponding circuit should be fused in the corresponding circuit after the real fusing signal is output to the corresponding circuit as the virtual fusing signal; and the fuse circuit is used for executing a fusing operation or a non-fusing operation on the fuse according to the received real fusing signal, generating a trimming signal the same as the real fusing signal after the operation is terminated, and outputting the trimming signal to the corresponding circuit. Since the fuse trimming device provided by the invention can carry out virtual fusing and real fusing, the variety of structures and functions of the fuse trimming device can be realized, and the trimming cost is reduced.
Owner:NO 24 RES INST OF CETC
Generalized modular redundancy fault tolerance method for combinational circuits
ActiveUS20150100839A1Improve soft error reliabilityImprove reliabilityMajority/minority circuitsElectronic circuit testingModularityComputer science
The generalized modular redundancy fault tolerance method for combinational circuits utilizes redundancy techniques to improve soft error reliability and is based on probability of occurrence for combinations at the outputs of circuits. The generalized modular redundancy method enhances the reliability of combinational circuits. Types of redundant modules, complexity of voters and single versus multiple outputs protection are explored.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Memory circuit incorporating radiation-hardened memory scrub engine
Owner:SILICON SPACE TECH
Programmable logic device having redundancy with logic element granularity
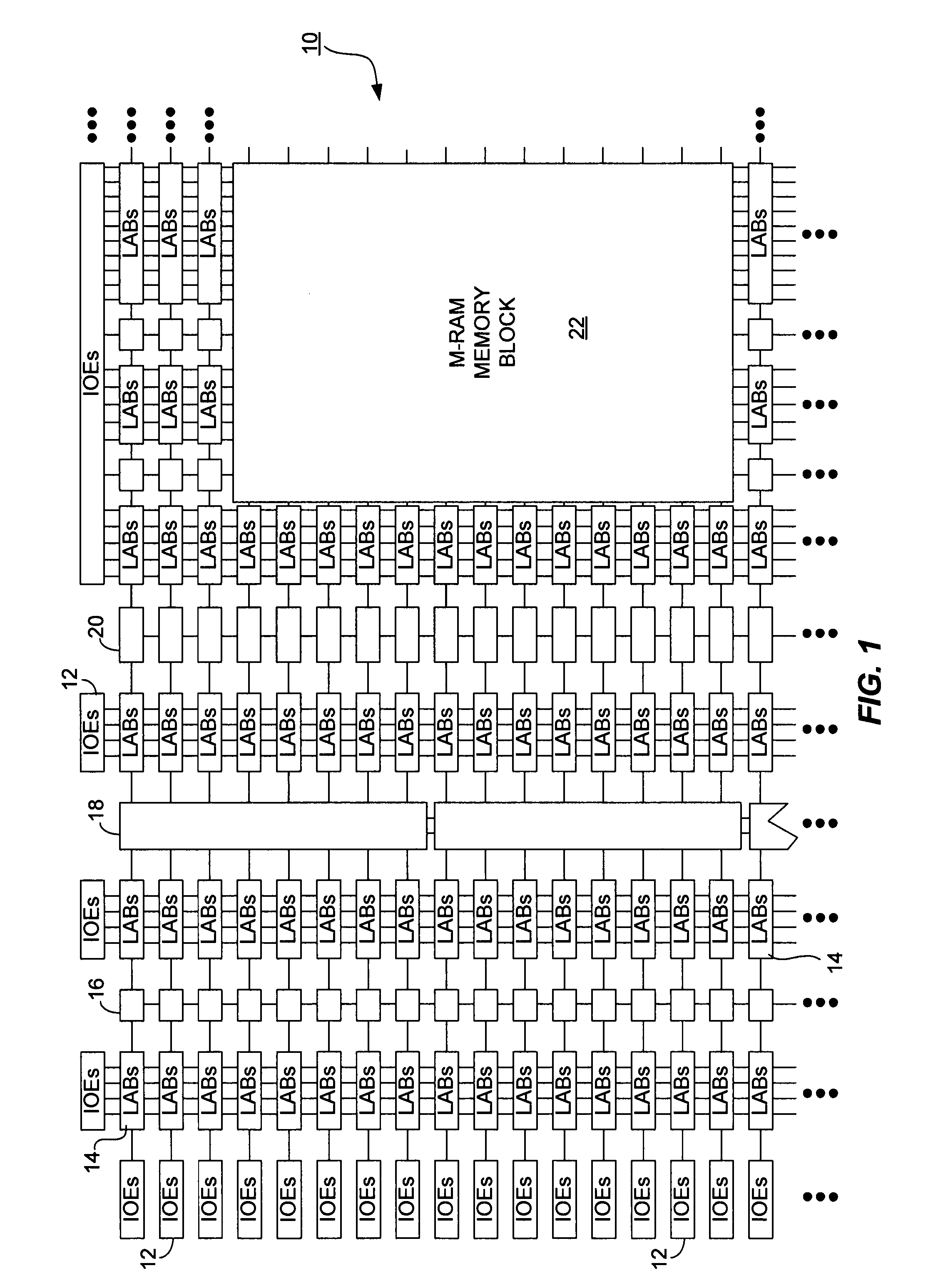
ActiveUS20080218197A1Switching accelaration modificationsSolid-state devicesGranularityProgrammable logic device
A PLD having logic element row granularity redundancy is disclosed. The PLD includes a plurality of LABs arranged in an array and a plurality of horizontal and vertical inter-LAB lines interconnecting the LABs of the array. Each of the LABs further includes a predetermined number of logic elements and redundancy circuitry to replace a defective logic element with a non-defective logic element among the predetermined logic elements by shifting programming data intended to for the defective logic element to the non-defective logic element.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Nanoelectronics
InactiveUS20080133635A1Simple and robust solutionTransistorComputation using non-contact making devicesElectricityEngineering
A circuit element includes a plurality of computation blocks connected at least partially in series for processing multi-bit numbers. Each of the computation blocks includes a plurality of transistors having characteristic threshold voltages. The circuit element is configured so that the transistors will each operate at a voltage below its threshold voltage. The circuit element includes a plurality of circuit sub-elements each having an output. The circuit sub-element outputs are connected together.
Owner:AUNET SNORRE
Popular searches
Hardware monitoring Coding details Logic circuits using elementary logic circuit components Semiconductor devices Computation using denominational number representation Static storage Logic circuit coupling/interface arrangements Redundant hardware error correction Electric power transfer ac network Noise generation
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com