Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
640results about How to "Accurate distance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
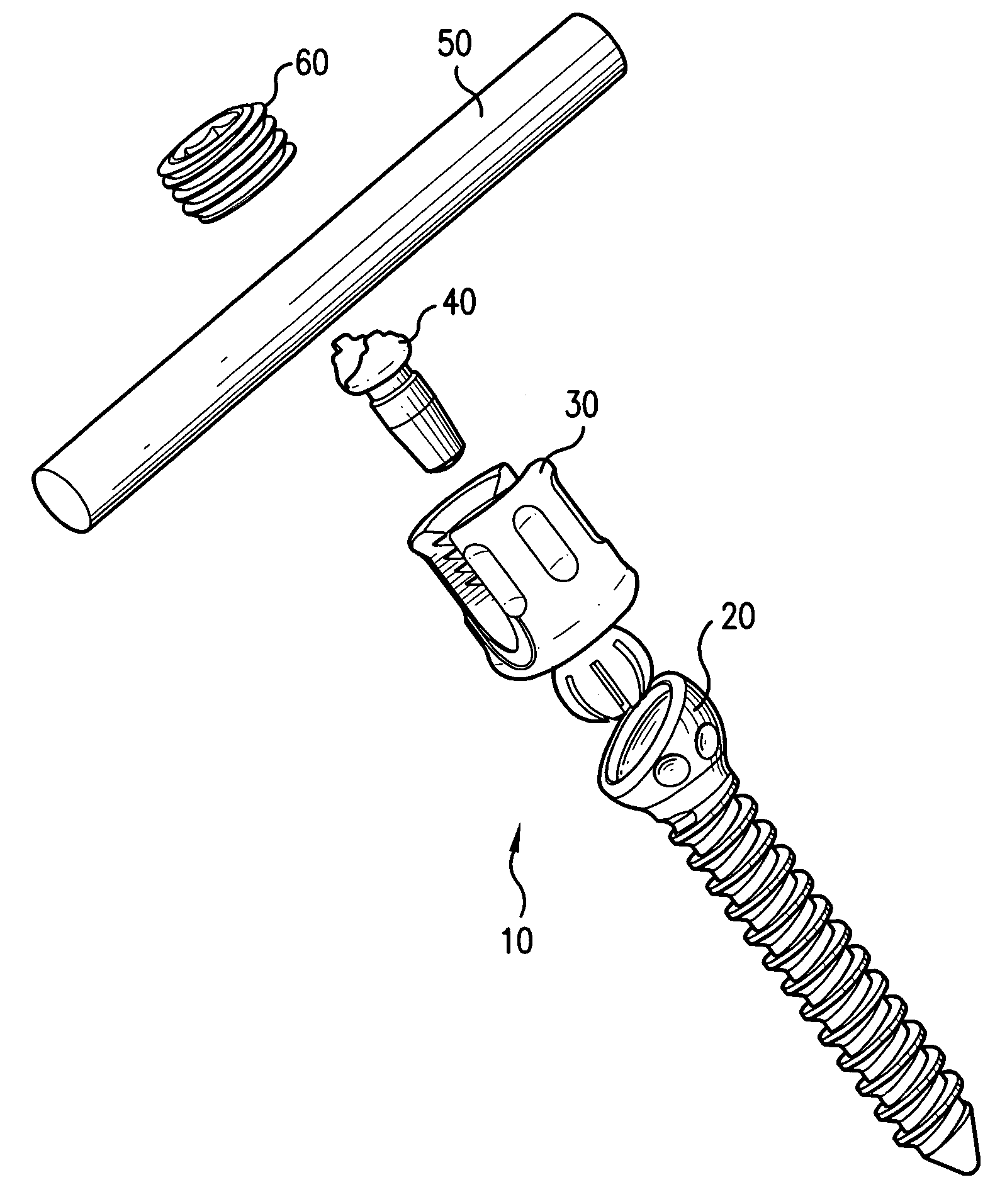
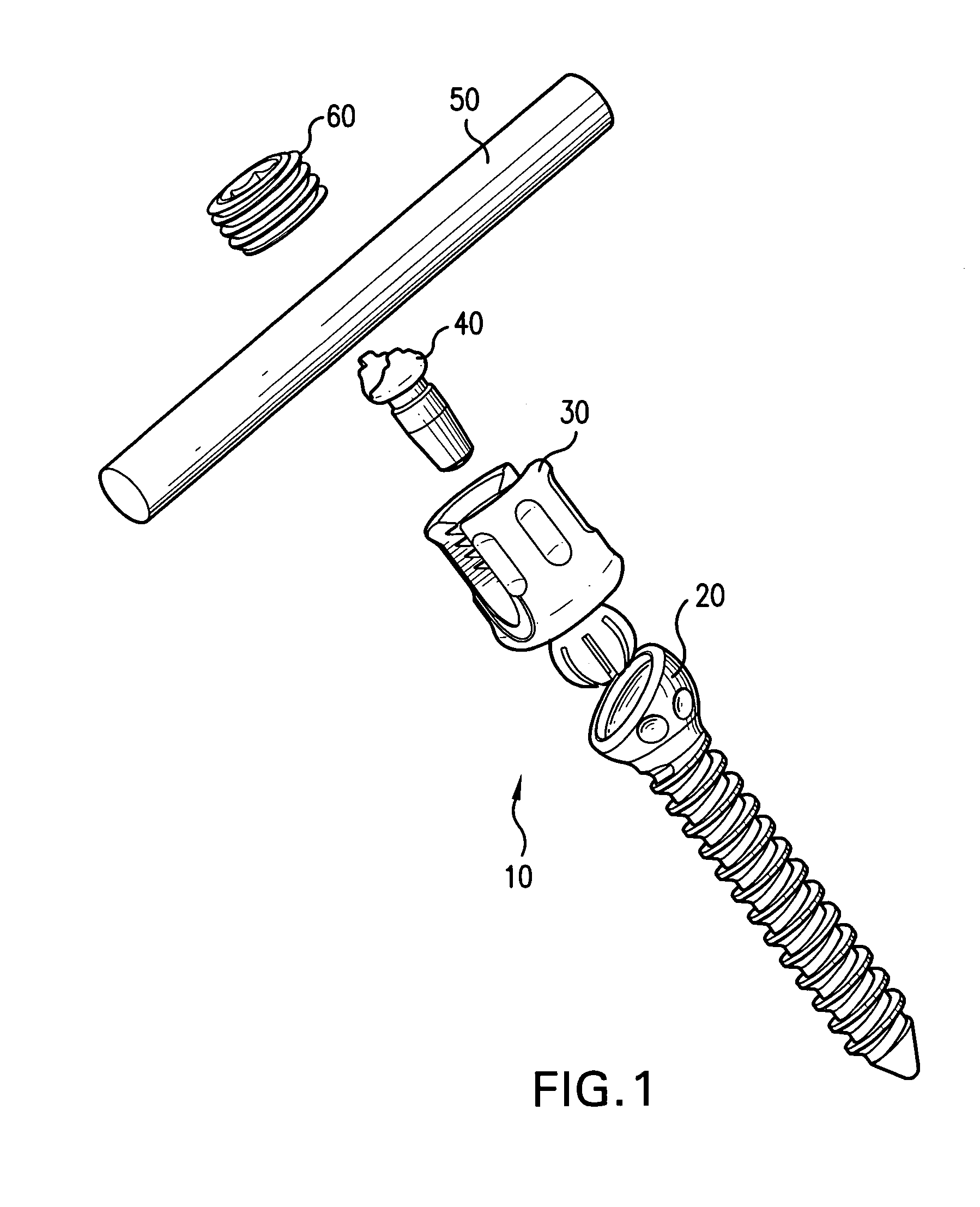
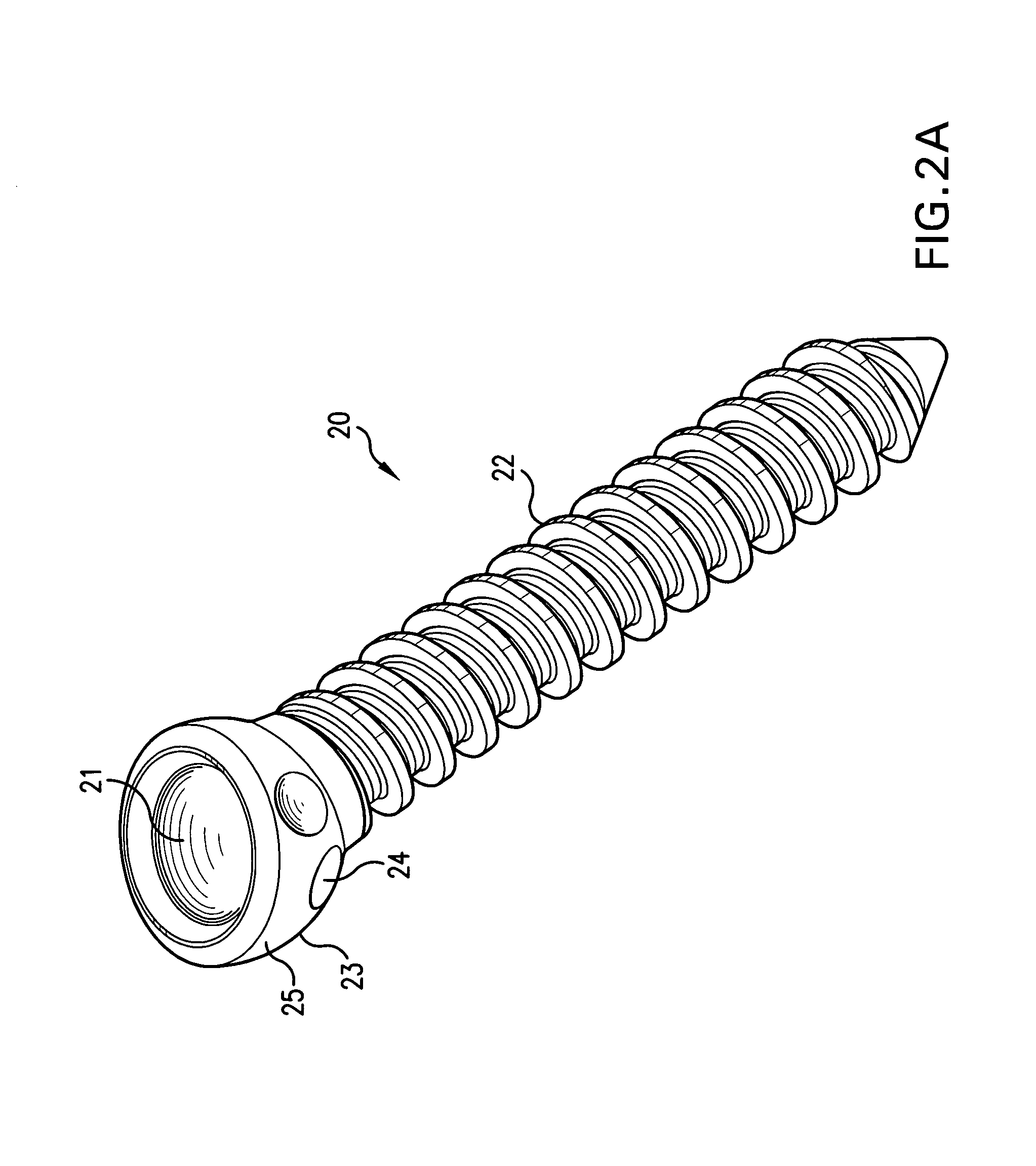
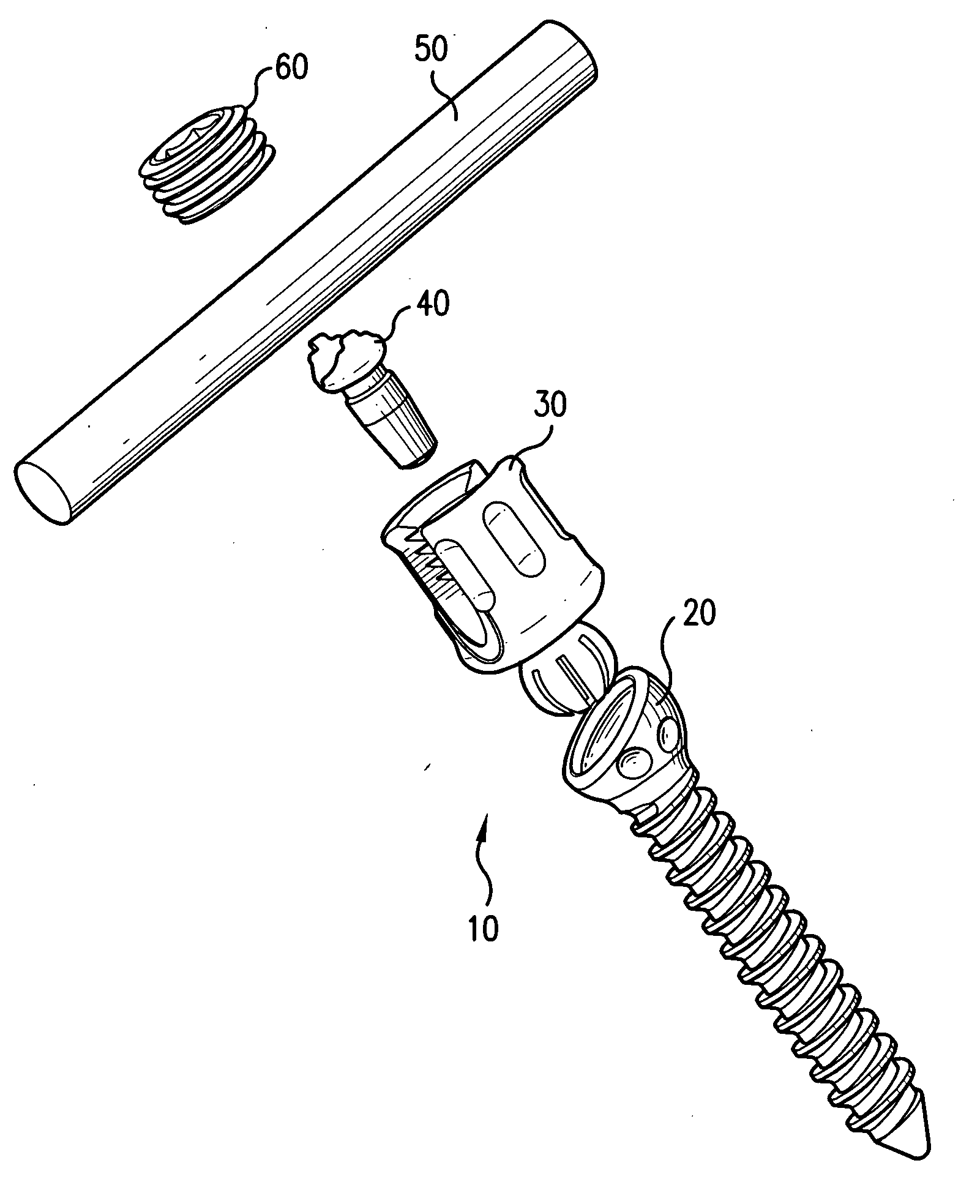
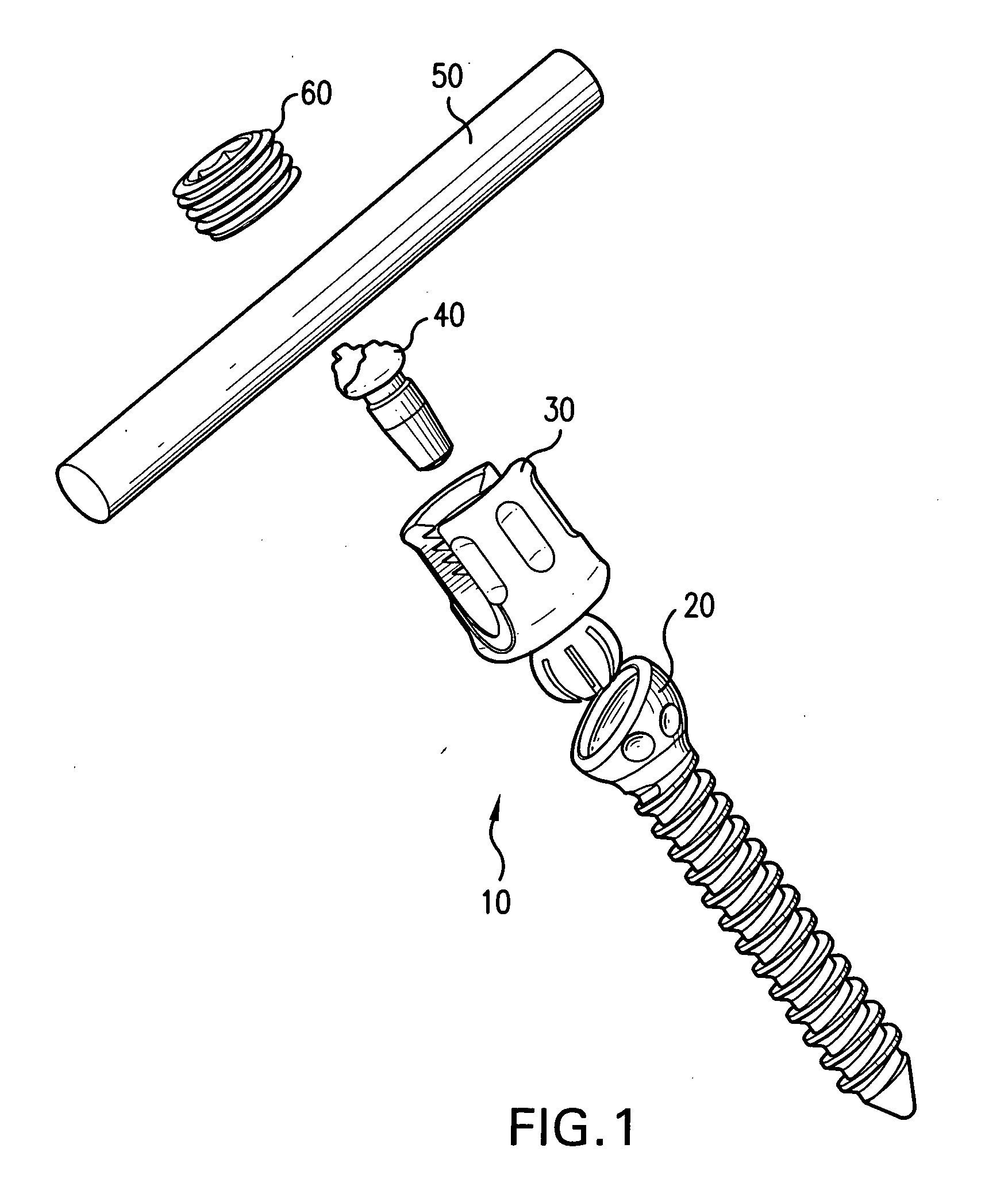
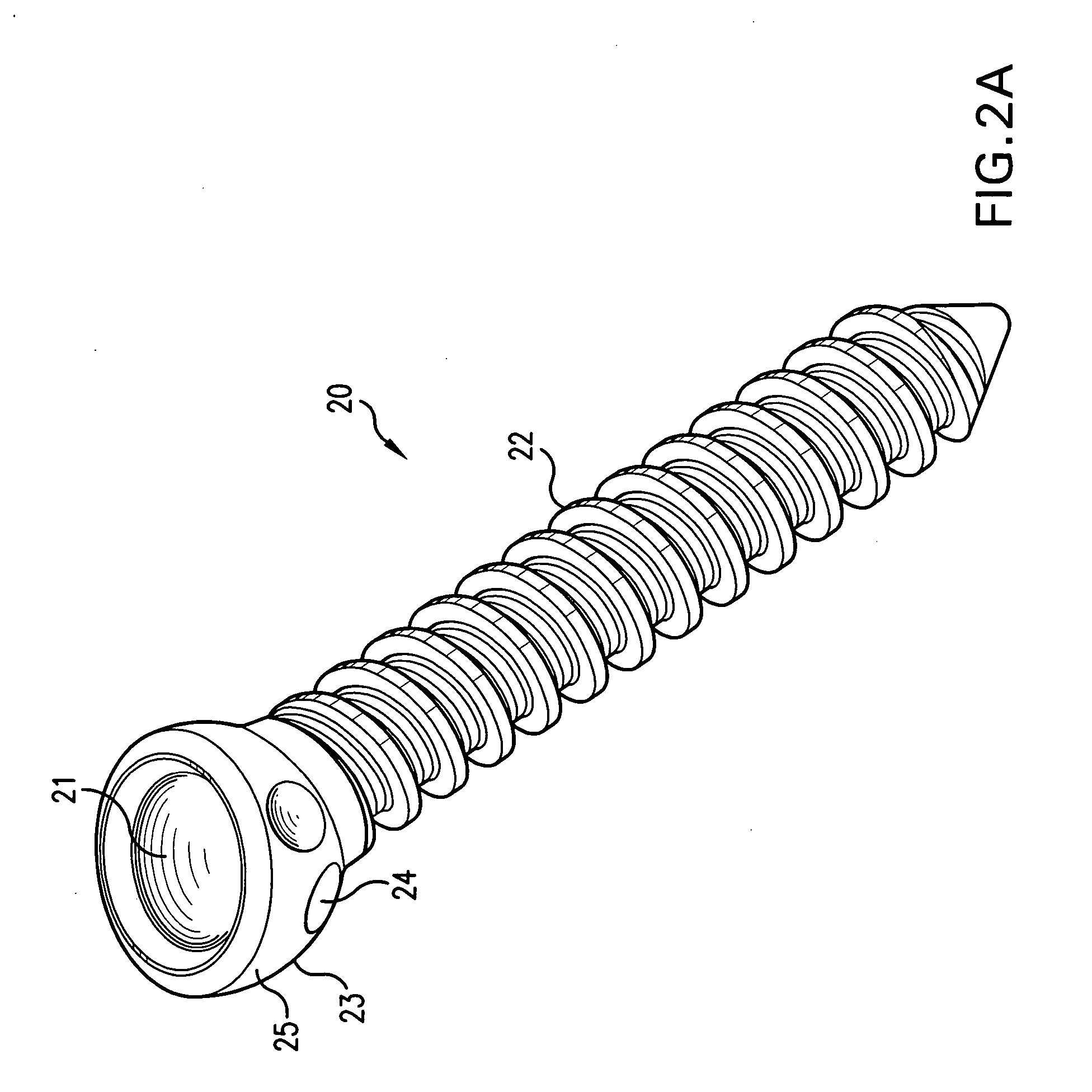
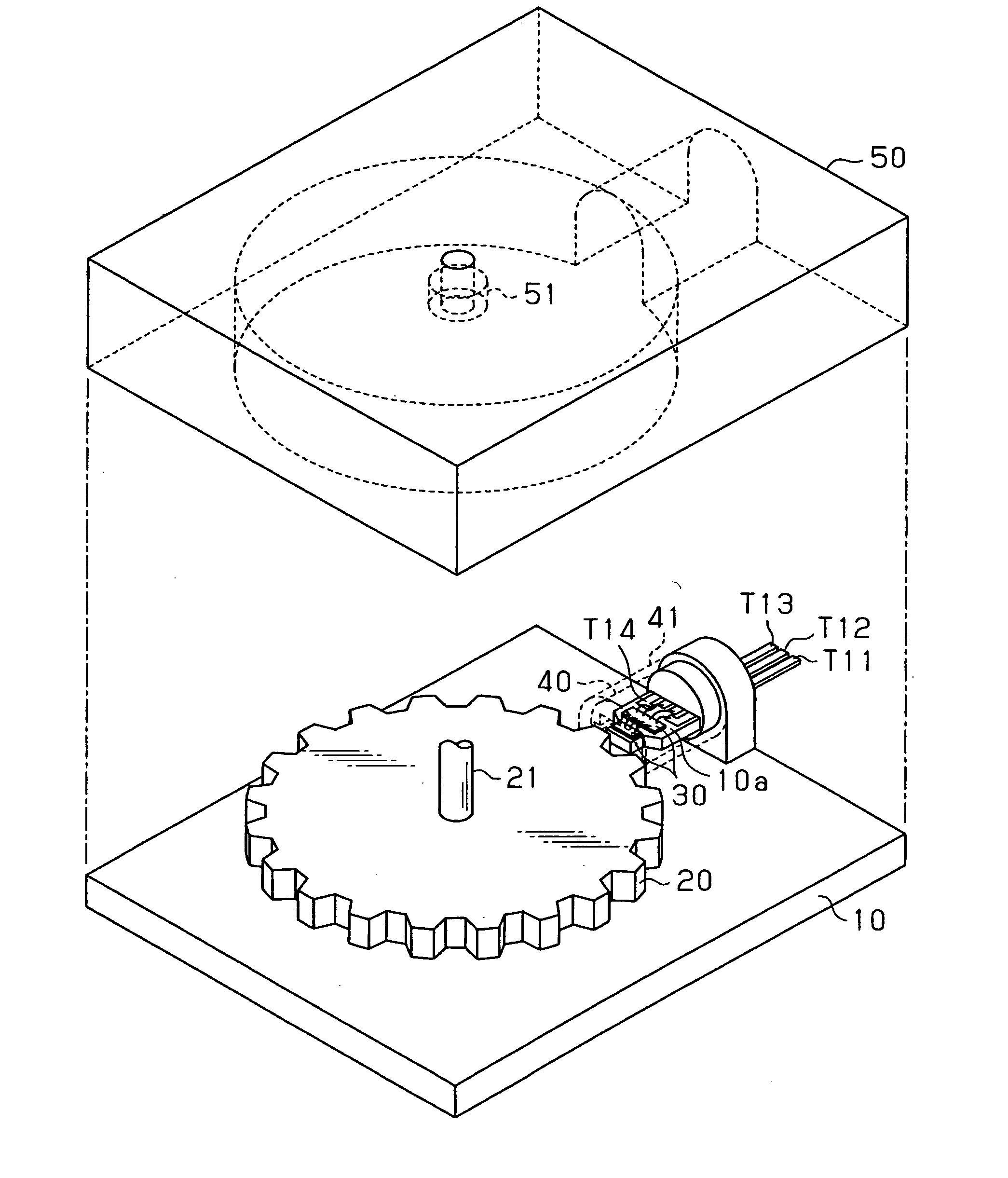
Biased angle polyaxial pedicle screw assembly
A pedicle screw assembly and method of assembly comprises a longitudinal member; a screw head comprising a bulbous end, wherein the screw head has a slot adapted to receive the longitudinal member; a bone fixator component comprising a concave socket having a biased angled top and a rounded bottom adapted to receive the screw head; a locking pin adapted to engage the screw head, the bone fixator component, and the longitudinal member; and a blocker adapted to engage the screw head and to secure the longitudinal member. Additionally, the bone fixator component may be configured as any of a bone screw and a hook.
Owner:CUSTOM SPINE INC
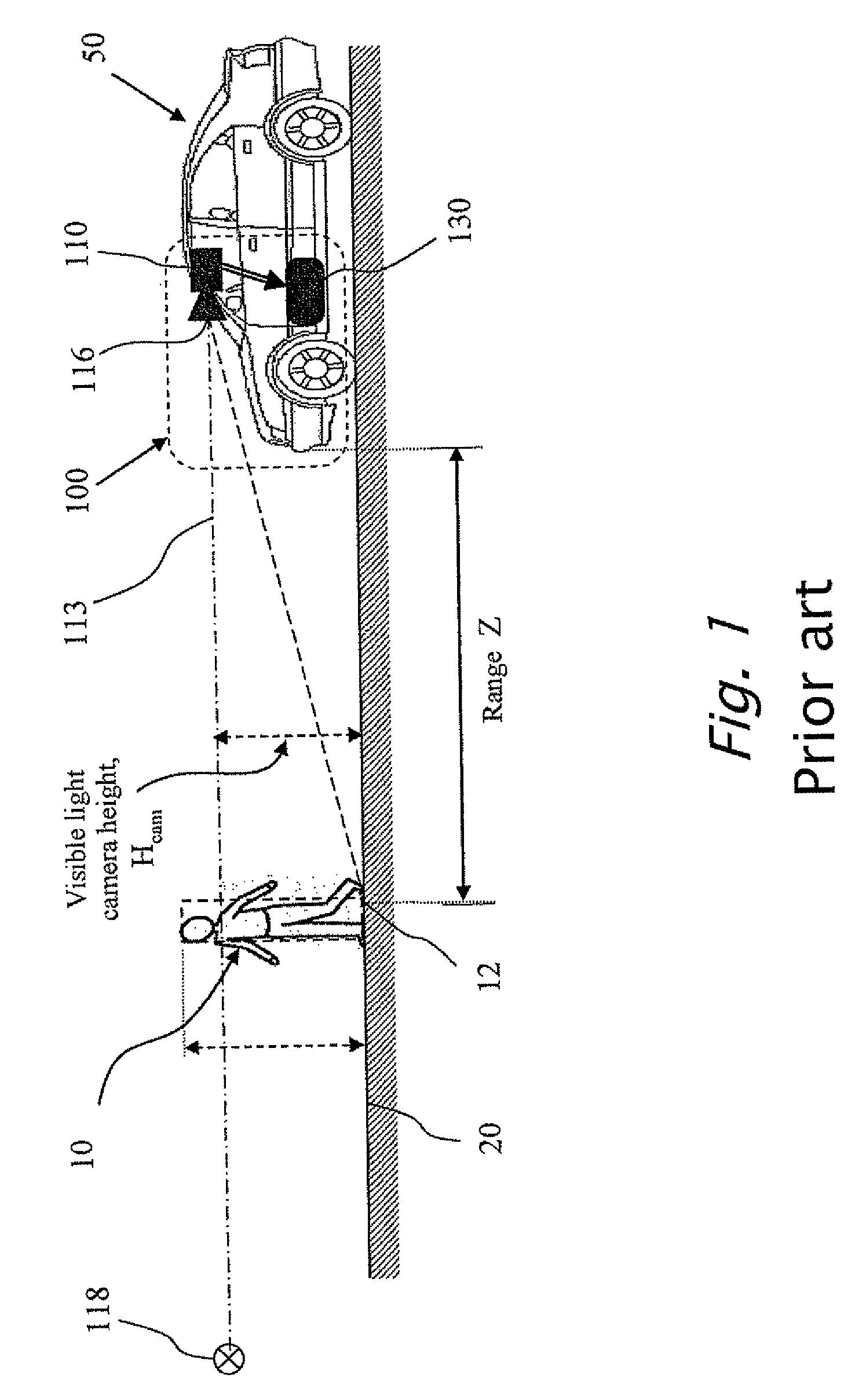
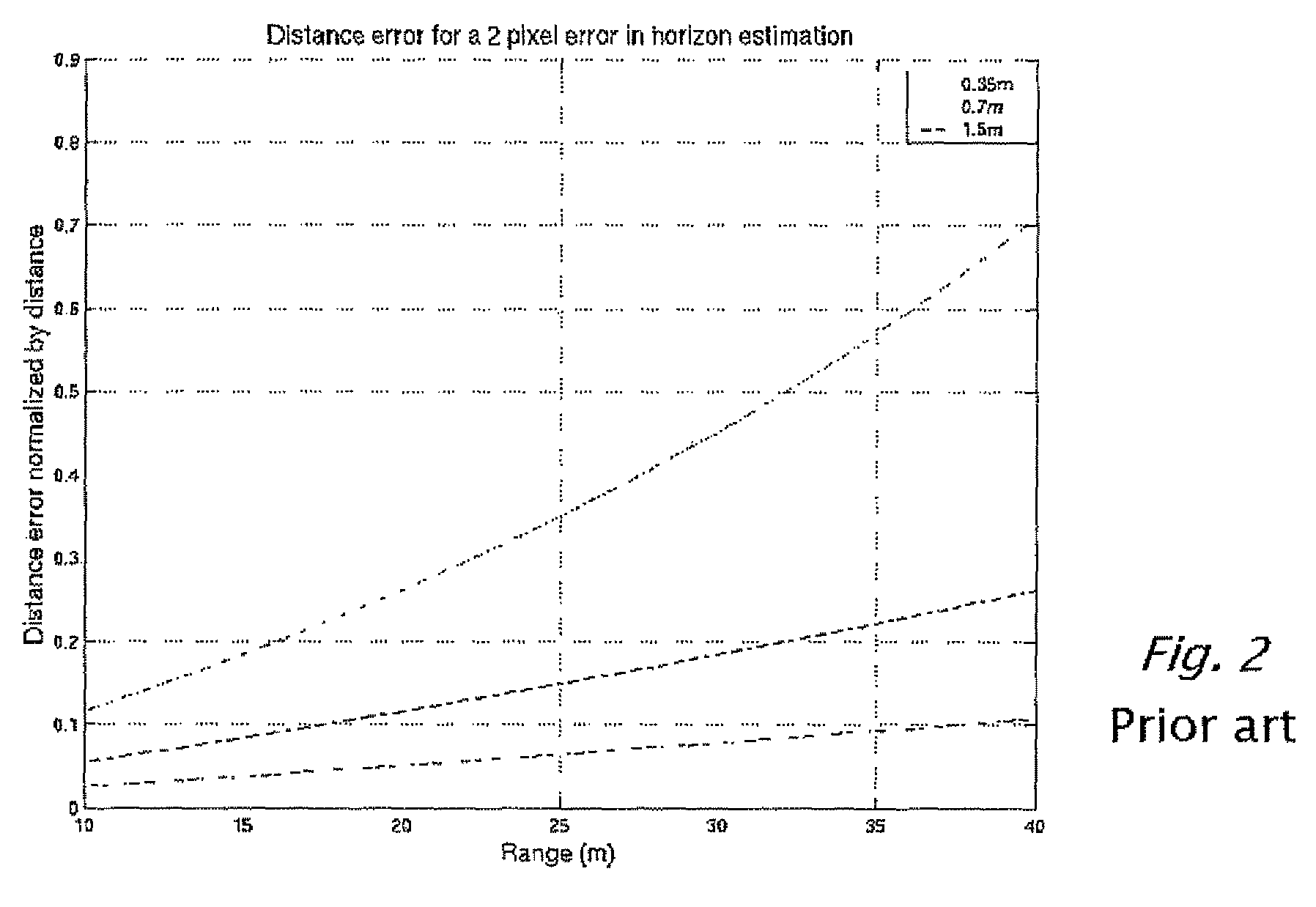
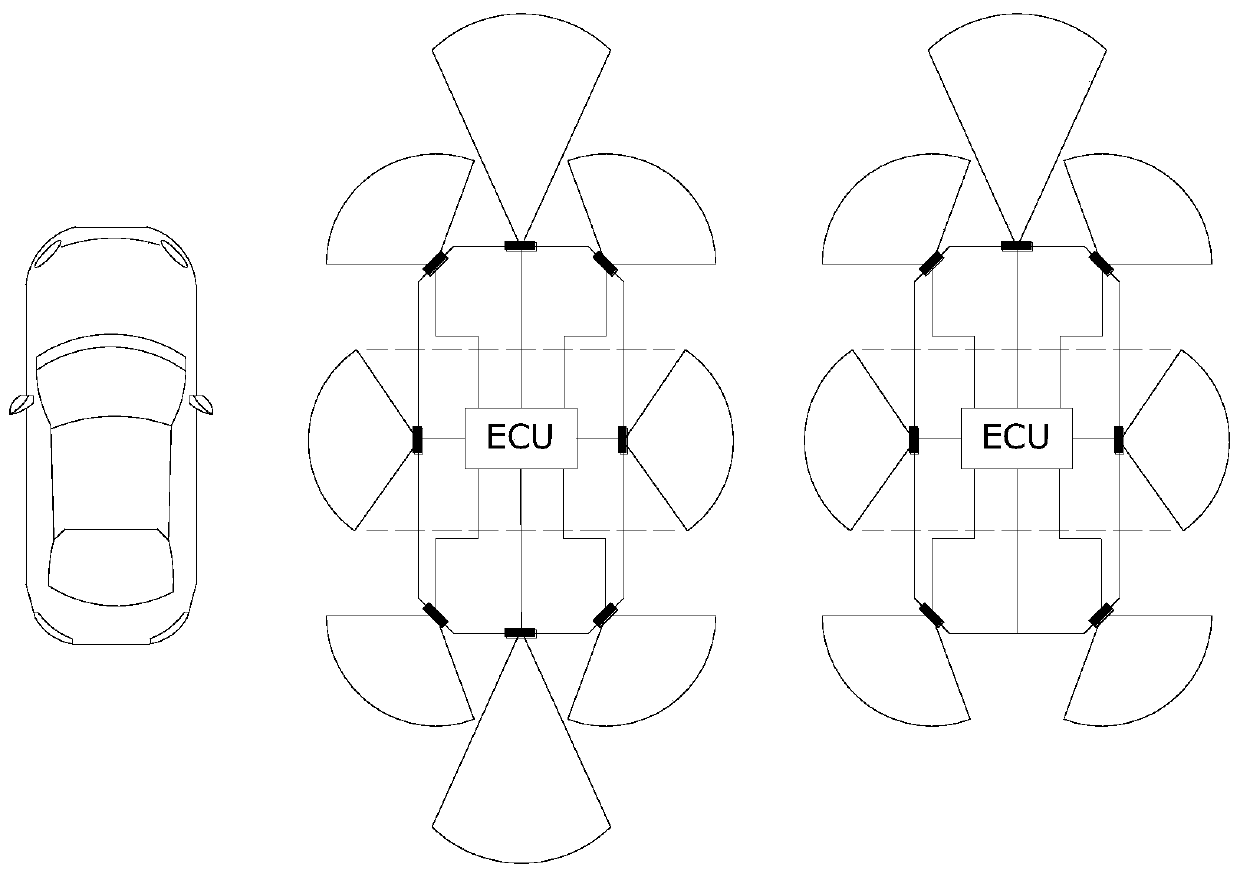
Fusion of far infrared and visible images in enhanced obstacle detection in automotive applications
InactiveUS7786898B2Improve visibilityBetter triangulationImage enhancementImage analysisComputerized systemFar infrared
A method in computerized system mounted on a vehicle including a cabin and an engine. The system including a visible (VIS) camera sensitive to visible light, the VIS camera mounted inside the cabin, wherein the VIS camera acquires consecutively in real time multiple image frames including VIS images of an object within a field of view of the VIS camera and in the environment of the vehicle. The system also including a FIR camera mounted on the vehicle in front of the engine, wherein the FIR camera acquires consecutively in real time multiple FIR image frames including FIR images of the object within a field of view of the FIR camera and in the environment of the vehicle. The FIR images and VIS images are processed simultaneously, thereby producing a detected object when the object is present in the environment.
Owner:MOBILEYE VISION TECH LTD
Biased angle polyaxial pedicle screw assembly
ActiveUS20050192573A1Accurate distanceSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisEngineeringPedicle screw
A pedicle screw assembly and method of assembly comprises a longitudinal member; a screw head comprising a bulbous end, wherein the screw head has a slot adapted to receive the longitudinal member; a bone fixator component comprising a concave socket having a biased angled top and a rounded bottom adapted to receive the screw head; a locking pin adapted to engage the screw head, the bone fixator component, and the longitudinal member; and a blocker adapted to engage the screw head and to secure the longitudinal member. Additionally, the bone fixator component may be configured as any of a bone screw and a hook.
Owner:CUSTOM SPINE INC
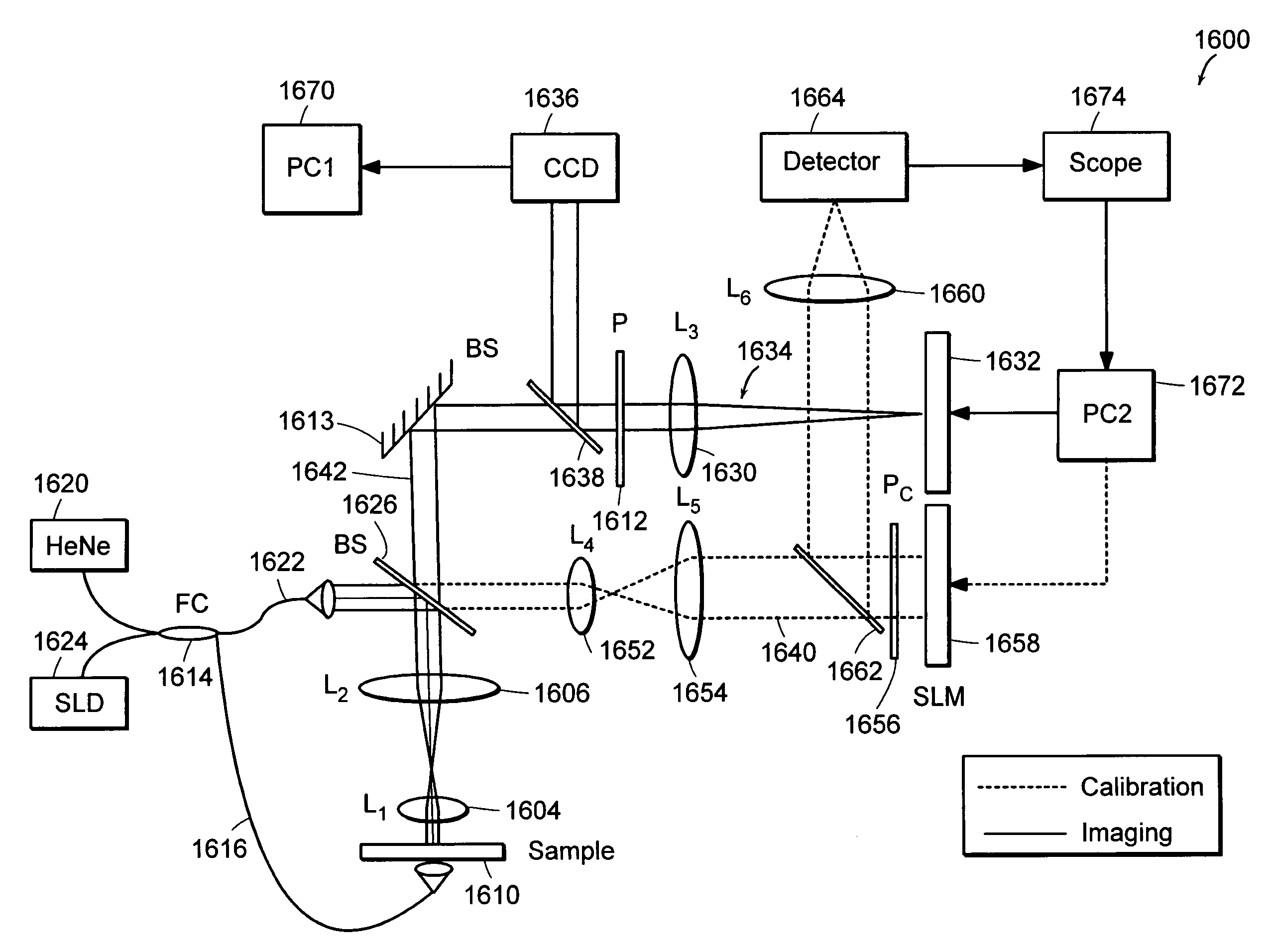
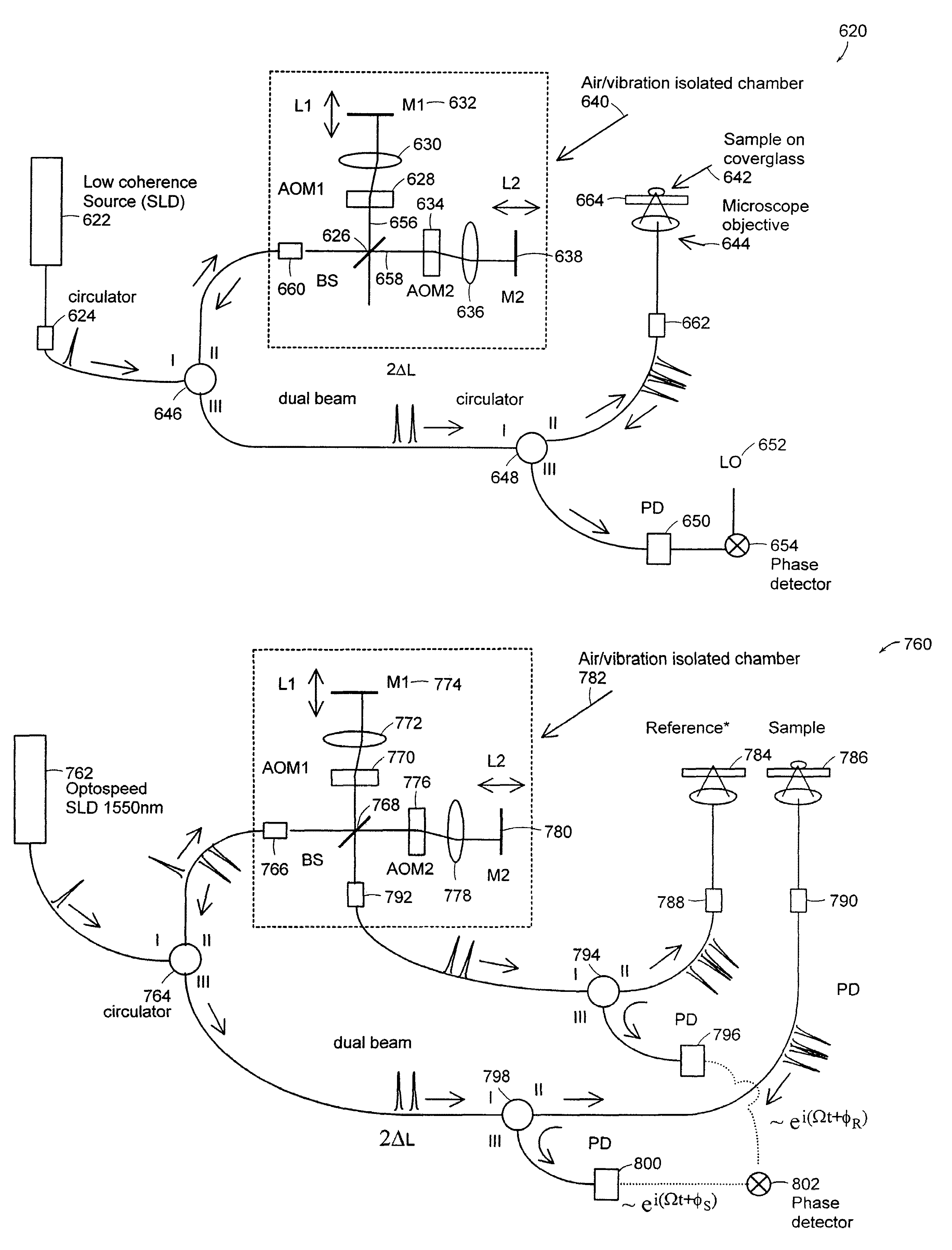
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS20050105097A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
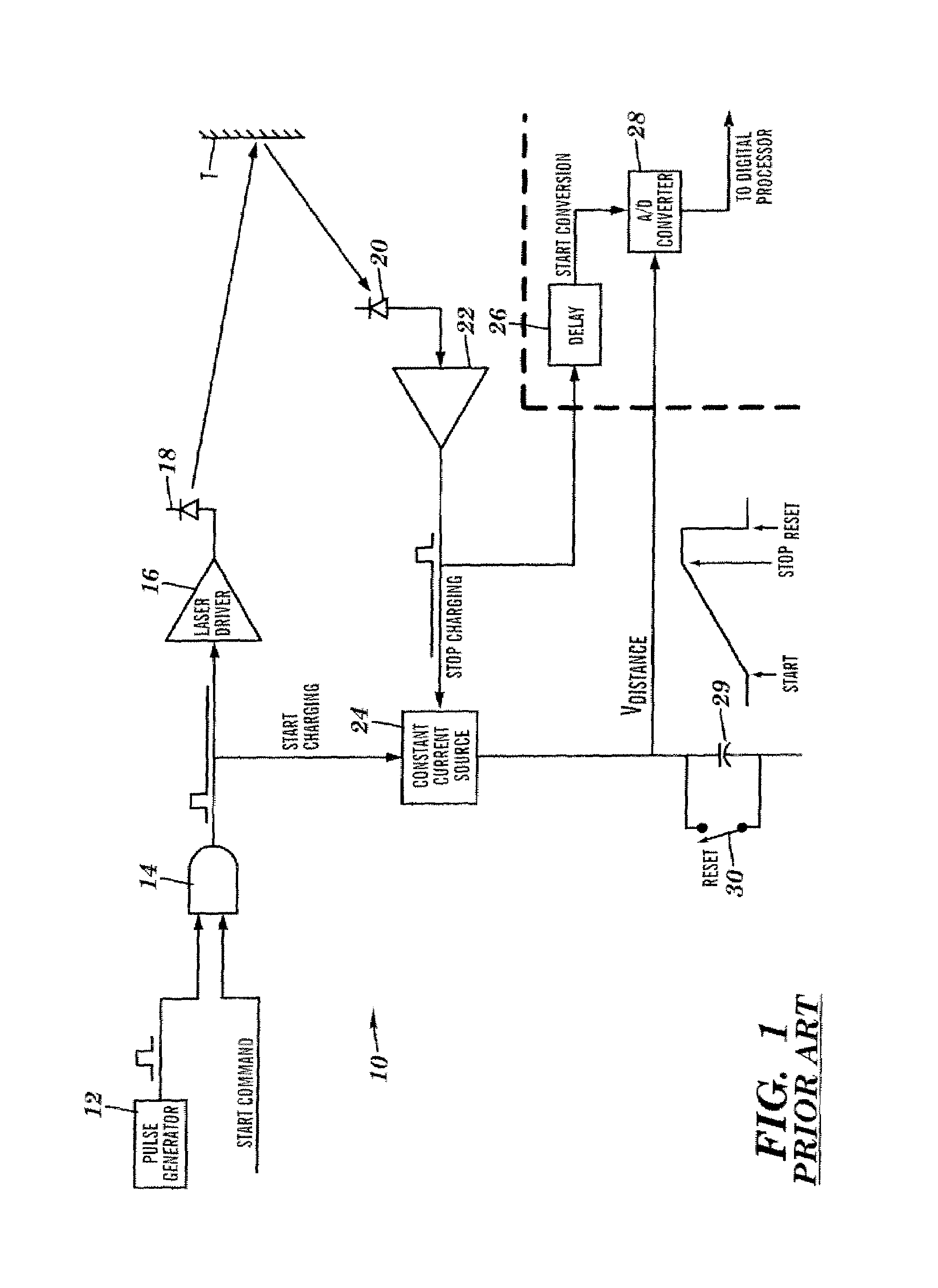
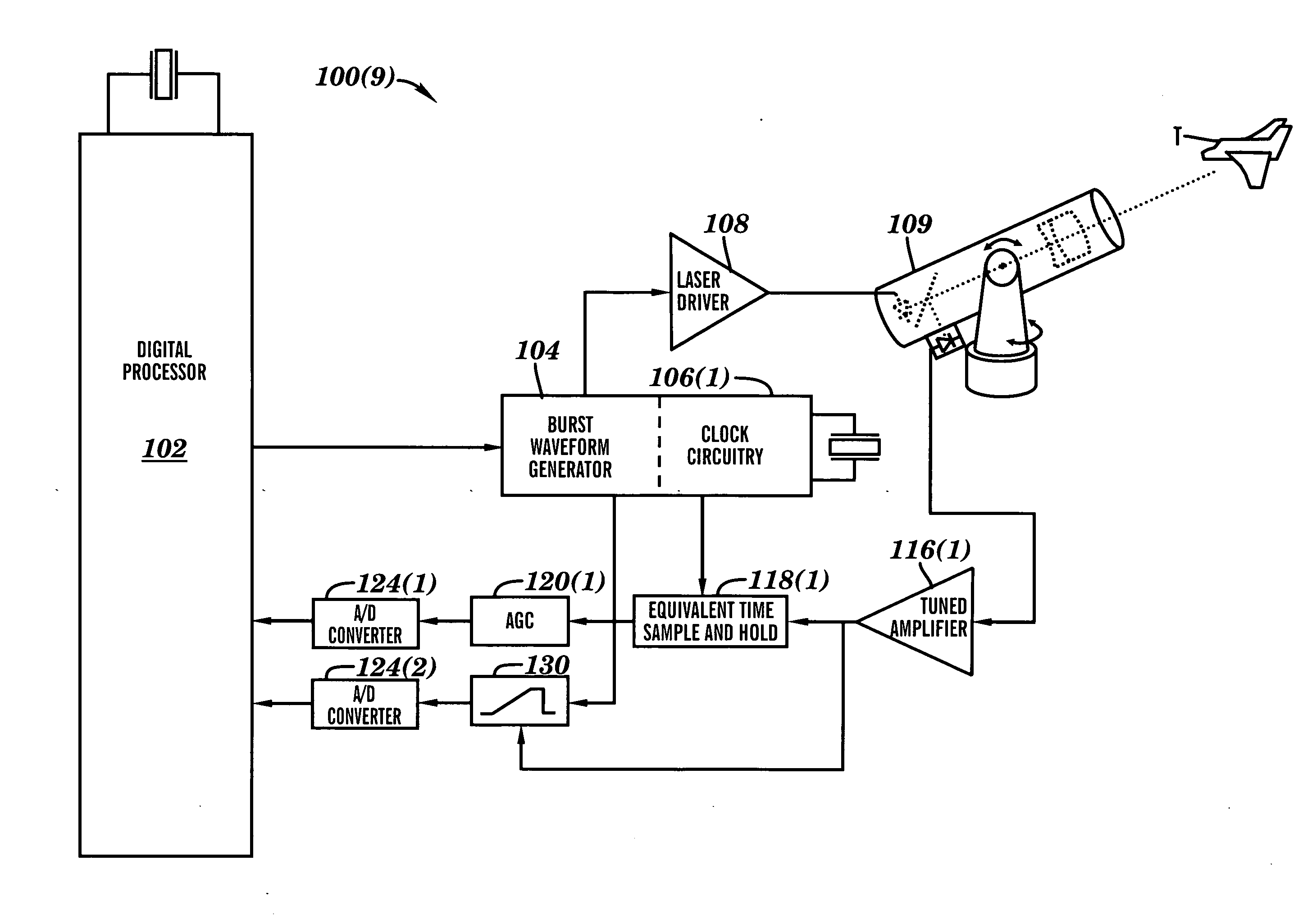
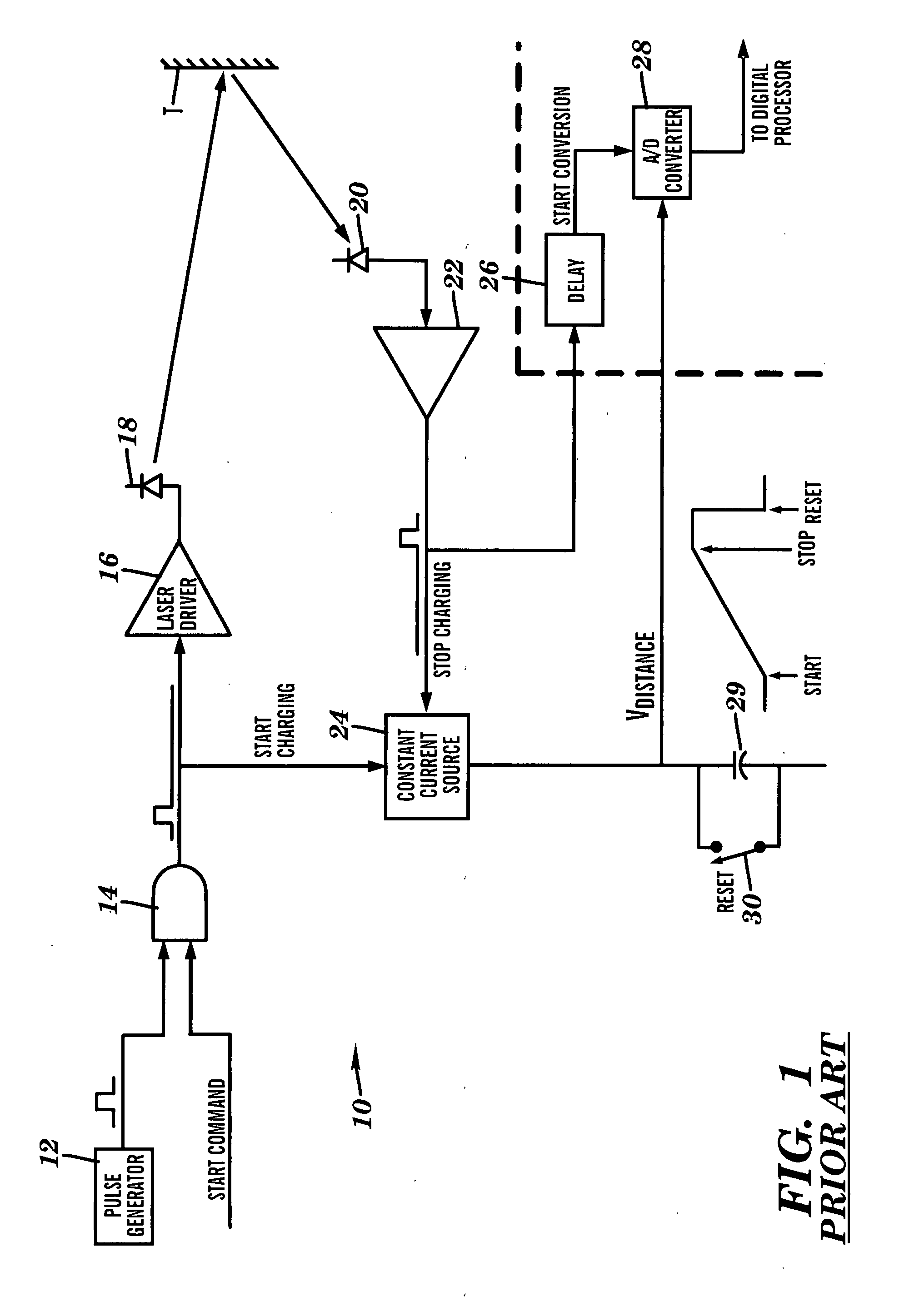
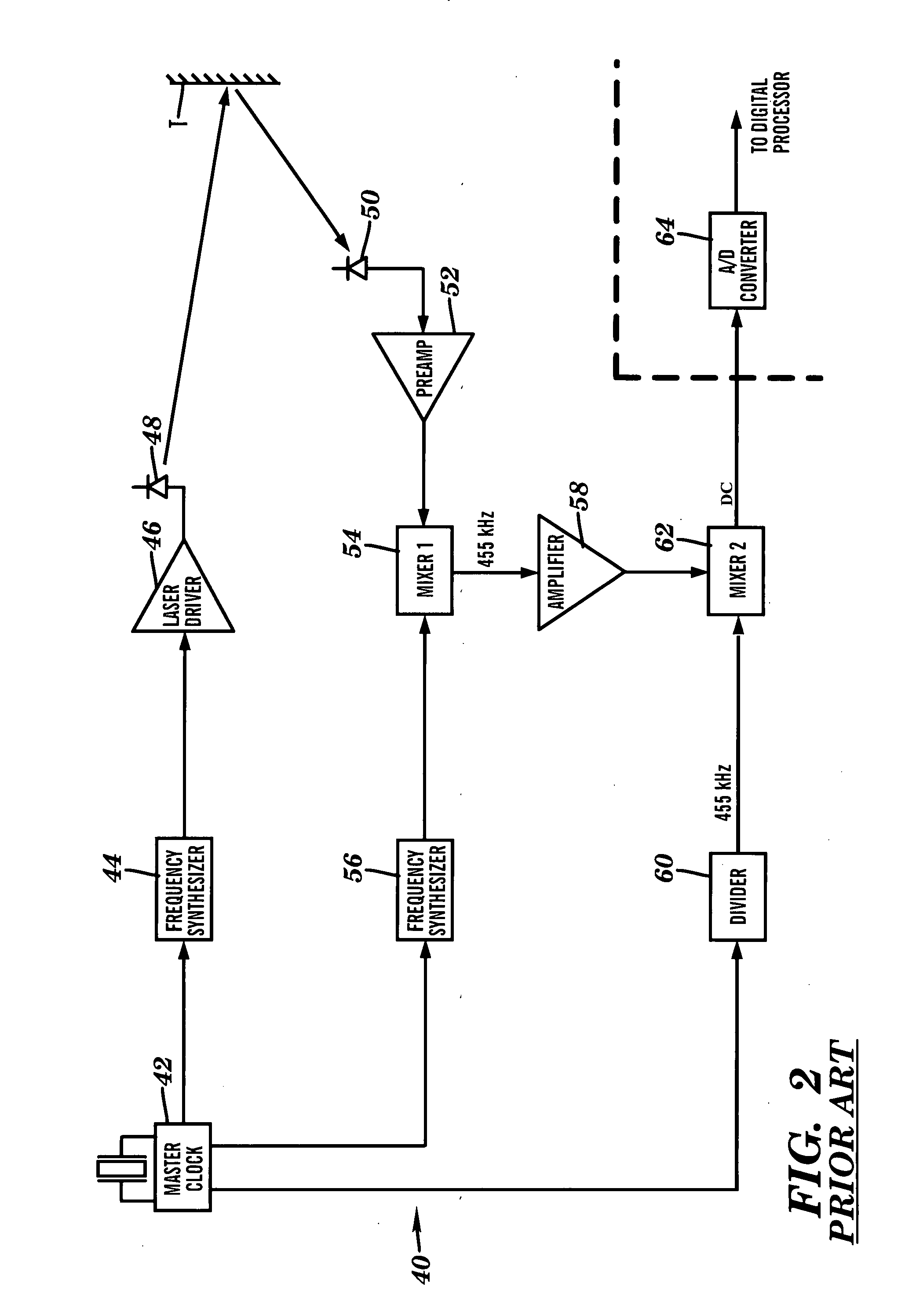
Apparatus for high accuracy distance and velocity measurement and methods thereof
InactiveUS7202941B2Increase costLow costOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationEngineeringDiscrete Fourier transform
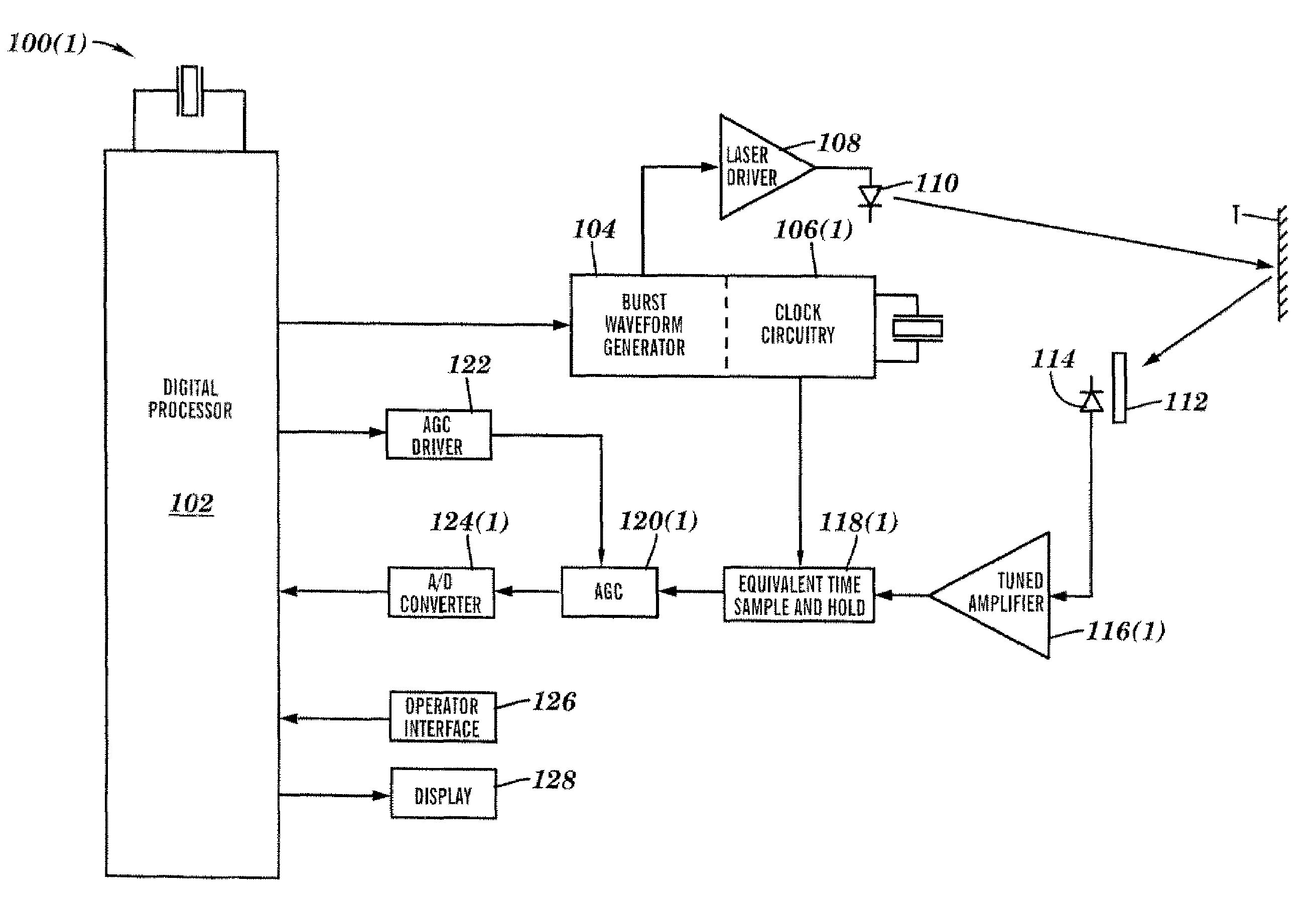
A system and method for measuring a parameter of a target in accordance with embodiments of the present invention includes transmitting at least one signal towards a target and receiving at least a portion of the transmitted signal back from the target. The measured parameter is one of distance velocity, or reflectivity. The transmitted signal is of the coherent burst waveform, and upon reception is processed with equivalent time sampling, AGC with minimal, if any, error, and a discrete Fourier transform.
Owner:MUNRO JAMES F
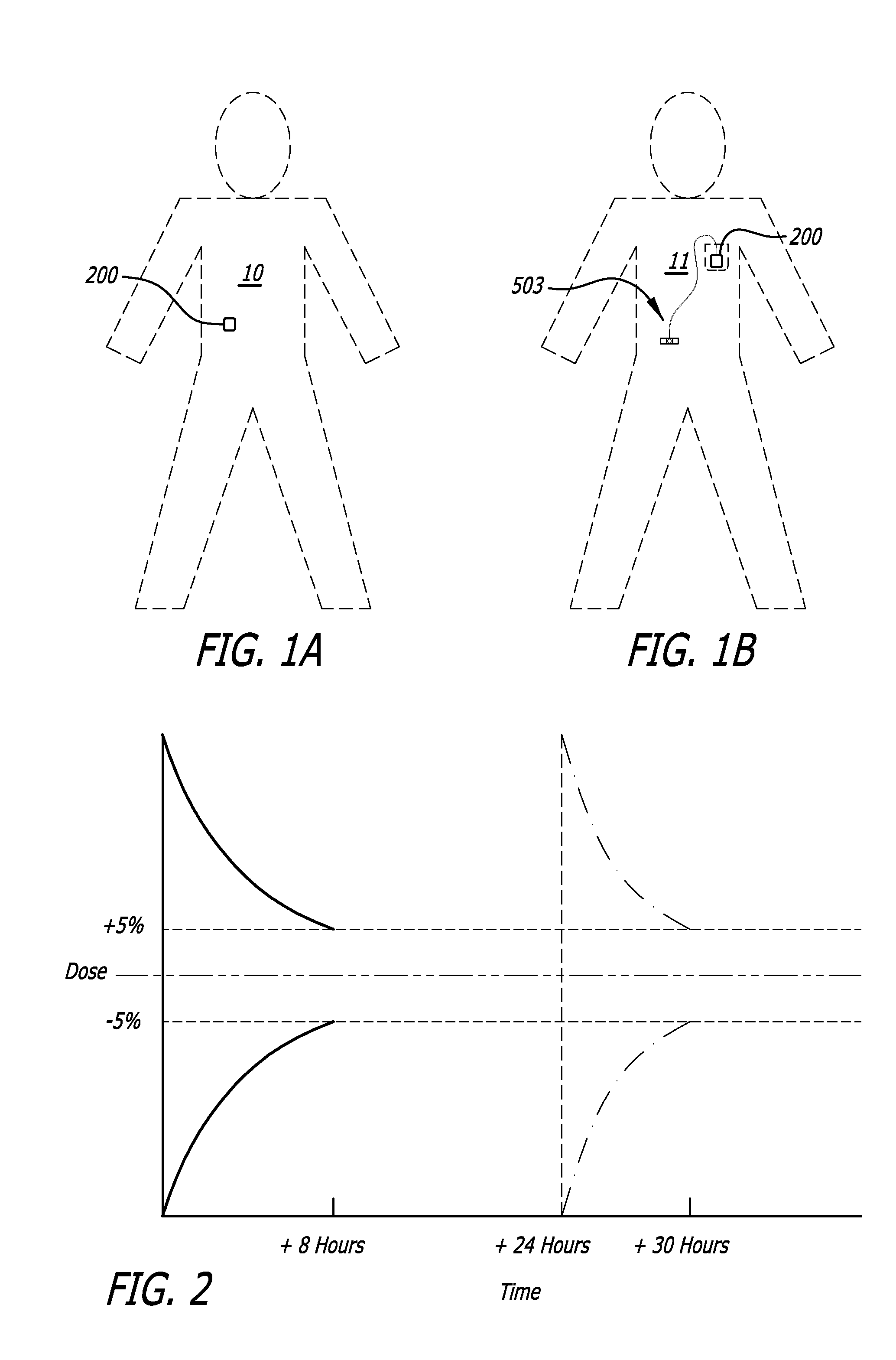
Infusion pumps
ActiveUS20120078181A1Constant controlAccurate distanceDiagnosticsSurgeryBiomedical engineeringAmbulatory infusion pumps
Ambulatory infusion pumps, pump assemblies, cartridges, baseplates, cannulas, insertion tools, and related components as well as combinations thereof and related methods.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS7365858B2No loss of precisionReduce coherenceOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Digital telecommunications call management and monitoring system
ActiveUS20060285650A1Restricting communication optionAccurate distanceSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsSubstation equipmentComputer basedCall management
The present invention discloses a centralized, digital, computer-based telephone call management system for authenticating users of a telephone system in an institutional facility. The system includes the capacity to allow an institution to control, record, monitor, and bill and report usage and access to a telephone network. The telephone call management system further includes both accounting and management software for use in controlling, monitoring, billing, recording, and reporting usage and access. Also, it can operate over both a Public Switch Telephone Network (PSTN) and a Voice over Internet Protocol (VOIP) infrastructure.
Owner:GLOBAL TELLINK
Video endoscope with a rotatable video camera
A video endoscope includes a tube fitted at its distal end with an affixed objective lens, a video camera mounted behind the objective lens in the tube, the camera together with an elongated rotation element constituting a swivel unit that is supported both at the distal and proximal end zones in each case by swivel bearing at the tube. The swivel element being rotationally adjustable relative the tube by a swivel drive system. The distal swivel bearing is axially and radially bearing and the proximal swivel bearing is only radially bearing.
Owner:OLYMPUS WINTER & IBE
Imaging device, semiconductor integrated circuit and imaging method
ActiveUS20140184883A1Accurately estimateAccurate distanceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensIntegrated circuit
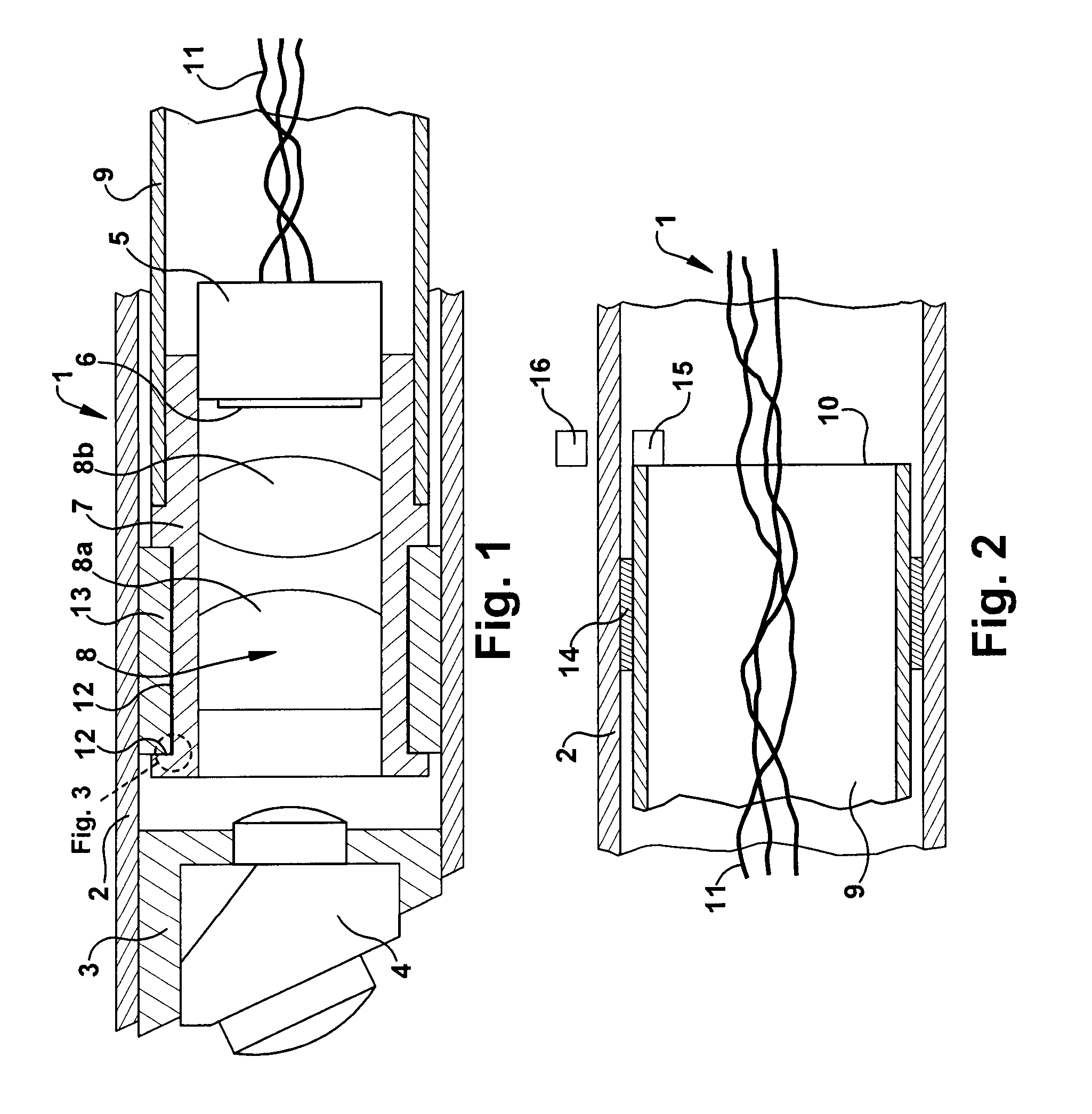
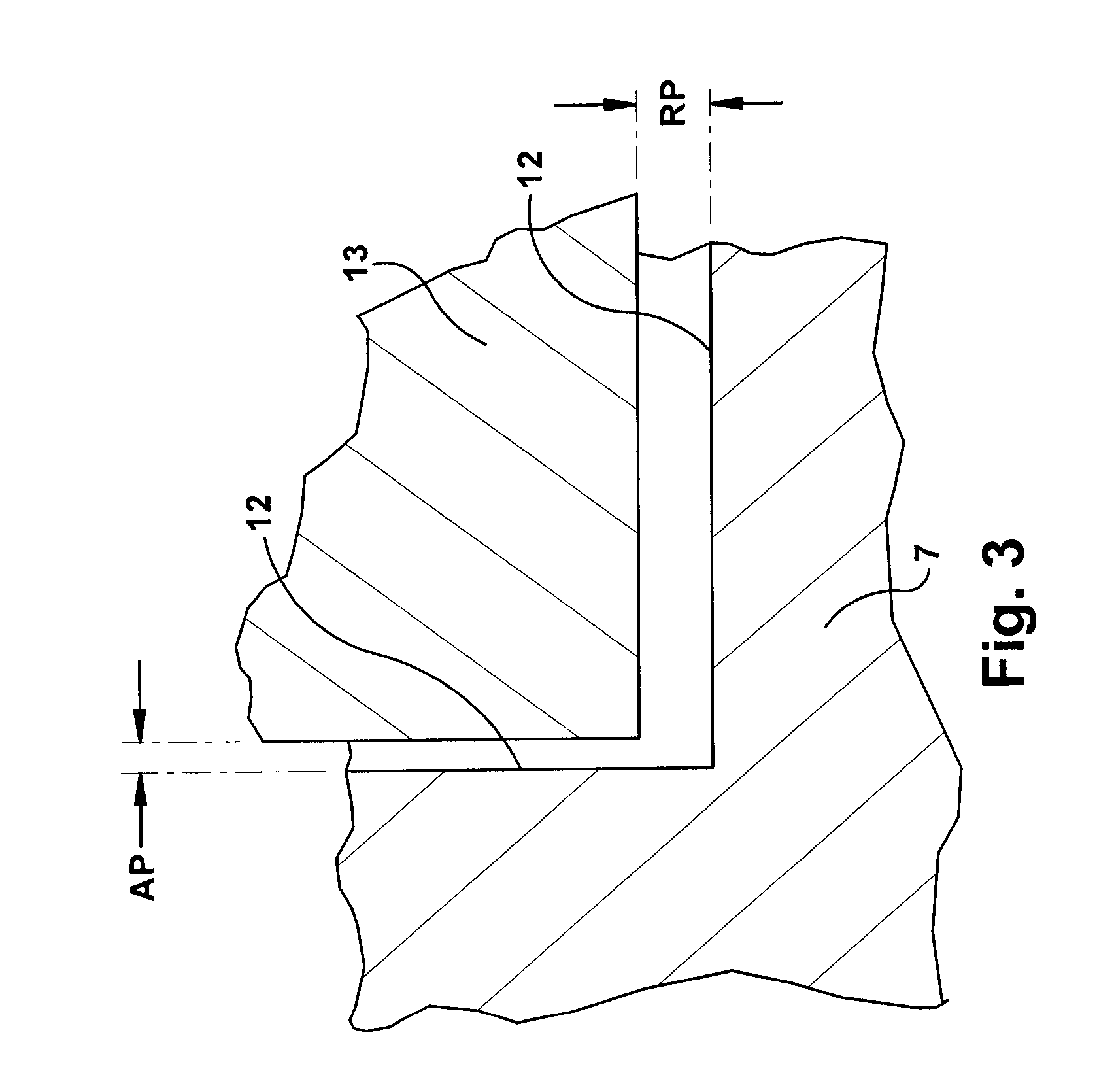
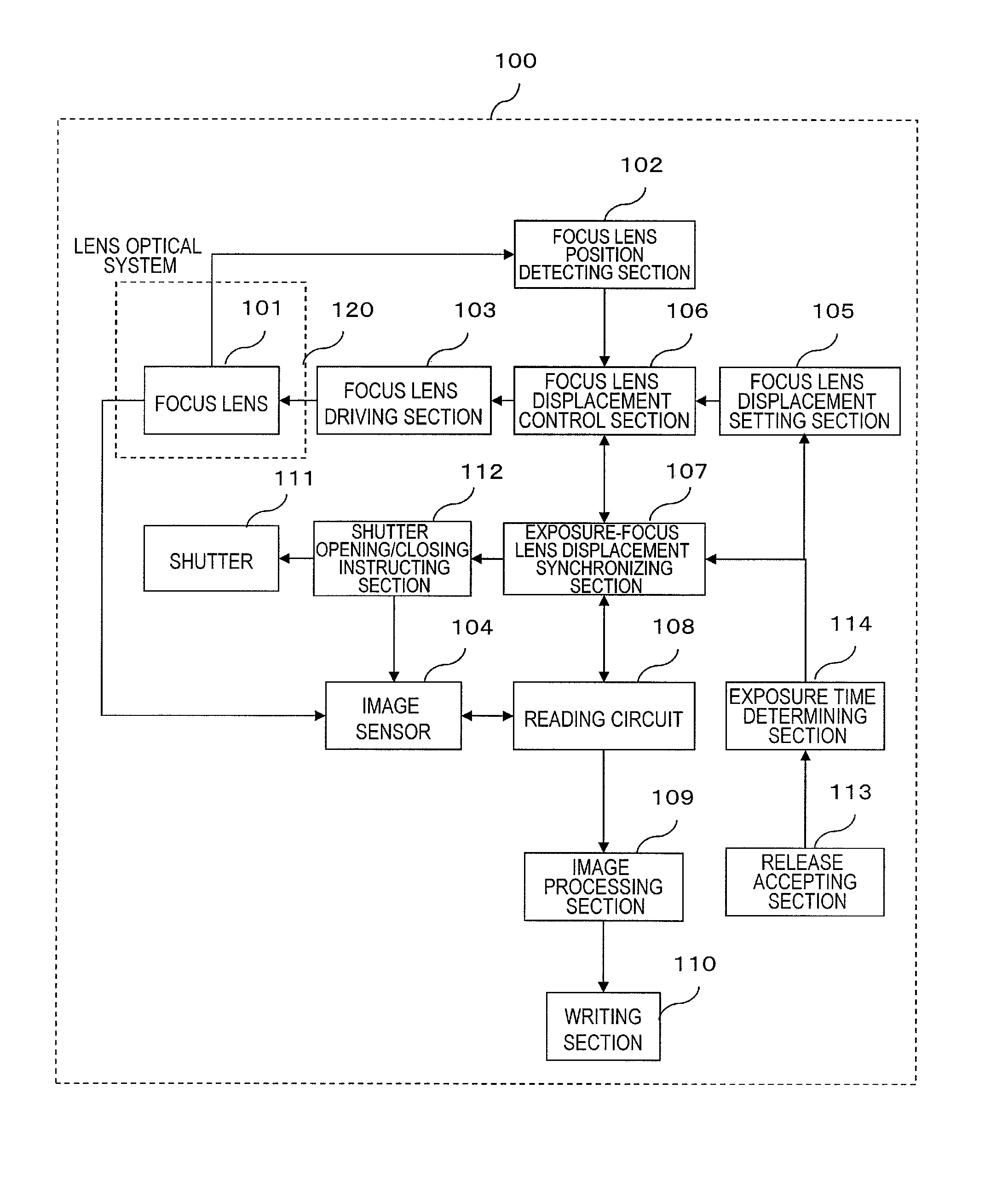
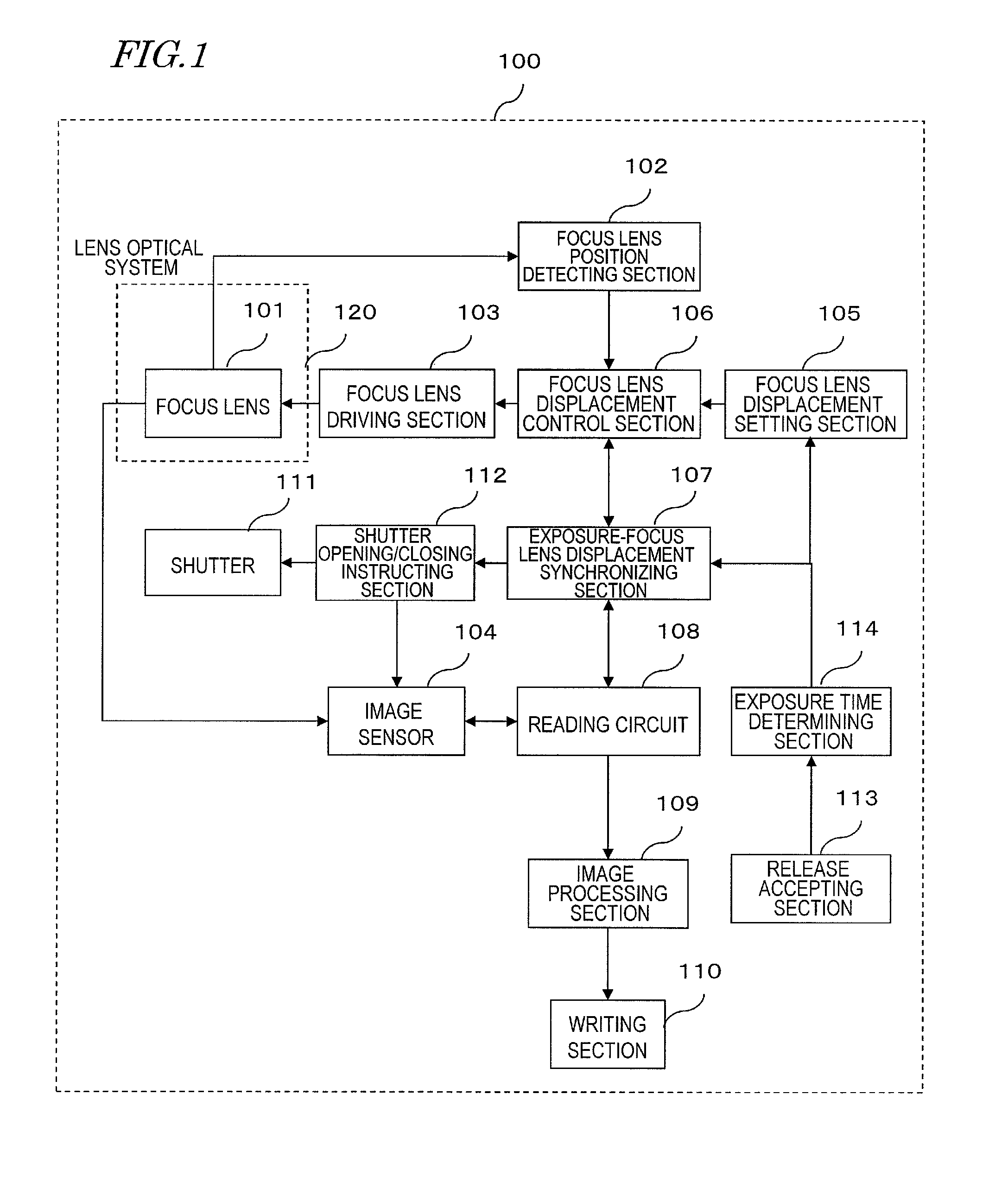
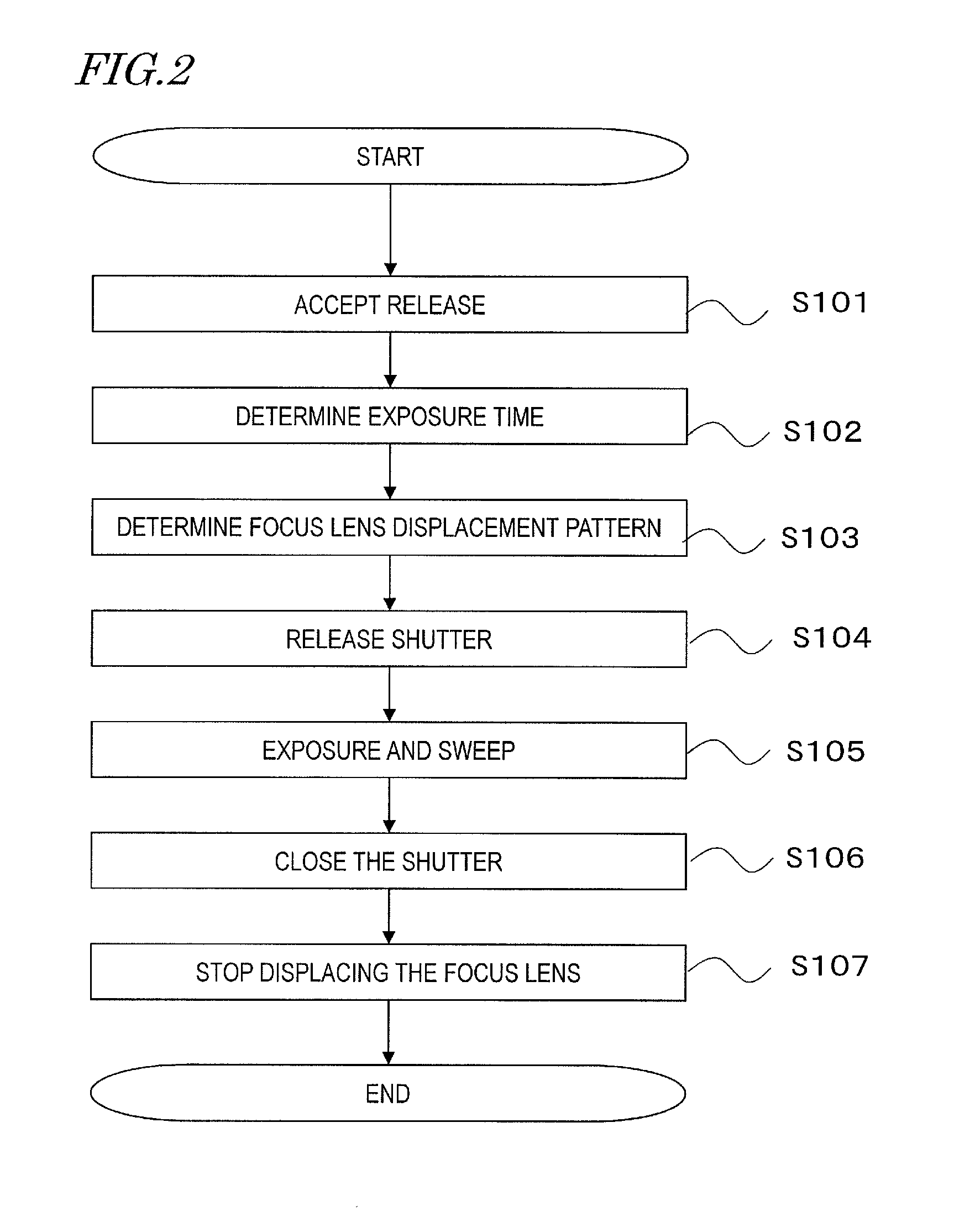
An image capture device according to the present disclosure includes: an image sensor; a lens optical system condensing light onto the image sensor and including a focus lens; a driving section driving one of the image sensor and the focus lens to change a distance between the image sensor and the focus lens; a displacement control section configured to control the displacement of the one being driven according to a predetermined displacement pattern by outputting an instruction to the driving section; and a synchronizing section configured to control the displacement control section by reference to timing of exposure of the image sensor. The displacement range of the image sensor or focus lens includes a first range, a second range separated from the first range, and a third range interposed between the first and second ranges. The predetermined displacement pattern includes first, second and third types of displacement patterns according to which one of the image sensor and the focus lens is displaced at least once in each of the entire first, second and third ranges. And one of the first and second types of displacement patterns and the third type of displacement pattern are repeated alternately.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Method and system of aligning x-ray detector for data acquisition
ActiveUS20060109958A1Precise alignmentPrecise positioningRadiation beam directing meansX-ray apparatusData acquisitionTransmitter
A method and system of aligning an x-ray detector and x-ray tube for data acquisition are presented. The x-ray detector and x-ray tube are equipped with transmitters and receivers designed to provide feedback relating to the orientation, spacing, and general position thereof. In this regard, a user can effectively and efficiently position the x-ray tube and x-ray detector relative to one another for data acquisition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
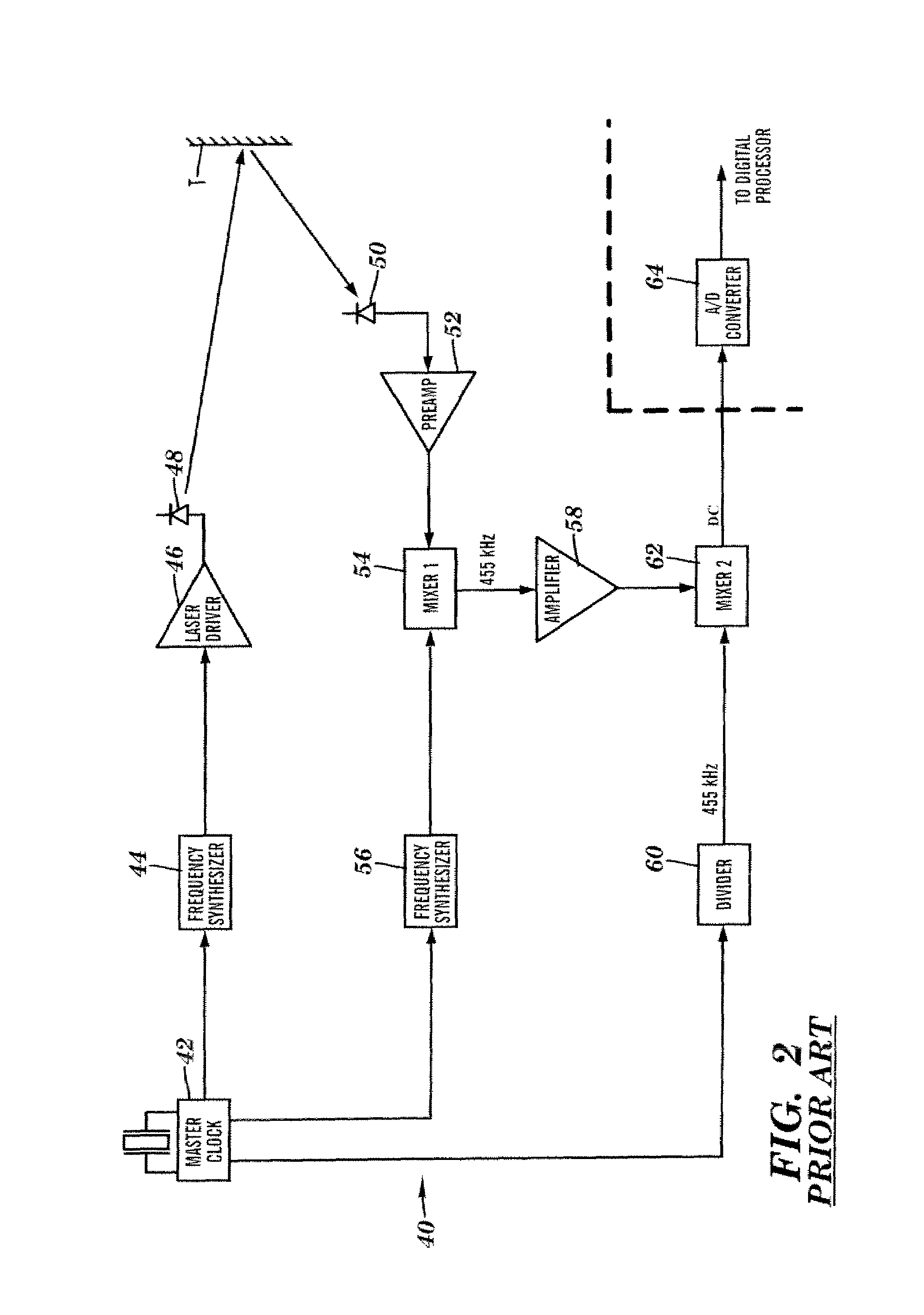
Apparatus for high accuracy distance and velocity measurement and methods thereof
InactiveUS20080100822A1Accurate distanceVelocity accuratelyOptical rangefindersScattering properties measurementsEngineeringDiscrete Fourier transform
Owner:MUNRO JAMES F
Digital telecommunications call management and monitoring system
ActiveUS7783021B2Accurate distanceAccurate for determining location of individualSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsSubstation equipmentMonitoring systemTelephone network
The present invention discloses a centralized, digital, computer-based telephone call management system for authenticating users of a telephone system in an institutional facility. The system includes the capacity to allow an institution to control, record, monitor, and bill and report usage and access to a telephone network. The telephone call management system further includes both accounting and management software for use in controlling, monitoring, billing, recording, and reporting usage and access. Also, it can operate over both a Public Switch Telephone Network (PSTN) and a Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) infrastructure.
Owner:GLOBAL TELLINK
System and method for determining position and distance of objects using road fiducials
ActiveUS8880273B1Accurately determineAccurate distanceRoad vehicles traffic controlCharacter and pattern recognitionDriver/operatorObject based
Owner:WAYMO LLC
Base, payload and connecting structure and methods of making the same
InactiveUS6850675B1Relieve stiffnessHigh intrinsic precisionCoupling light guidesMountingsKinematicsMachining
Micromachined passive alignment assemblies and methods of using and making the same are provided. The alignment assemblies are used to align at least one optical element. The alignment assemblies may be configured with kinematic, pseudo-kinematic, redundant or degenerate support structures. One alignment assembly comprises a base and a payload, which supports at least one optical element. The payload may be coupled to the base via connecting structures. The base, the payload and / or the connecting structures may have internal flexure assemblies for preloading a connection, thermal compensation and / or strain isolation.
Owner:DIGITALPTICS MEMS
Image capturing module, method for manufacturing the image capturing module, and electronic information device
InactiveUS20090160998A1Improve accuracyFixed and accurateTelevision system detailsLaminationComputer moduleElectronic information
An image capturing module according to the present invention includes a holder member, which accommodates therein a focusing lens for forming an image of a subject light on an image capturing chip attached on a substrate and is attached to the substrate to cover the image capturing chip, where the holder member is directly supported on a surface of the image capturing chip.
Owner:SHARP KK
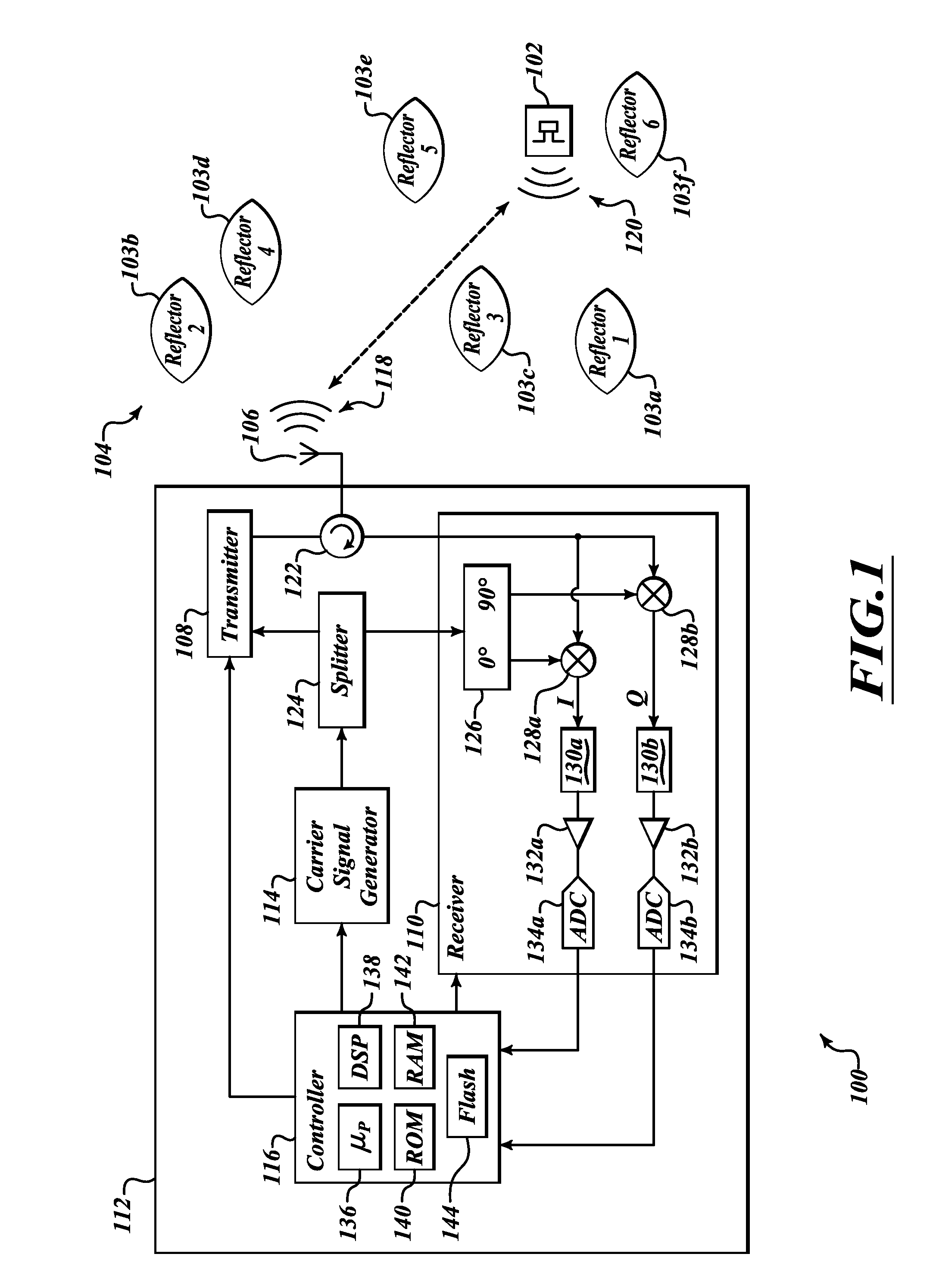
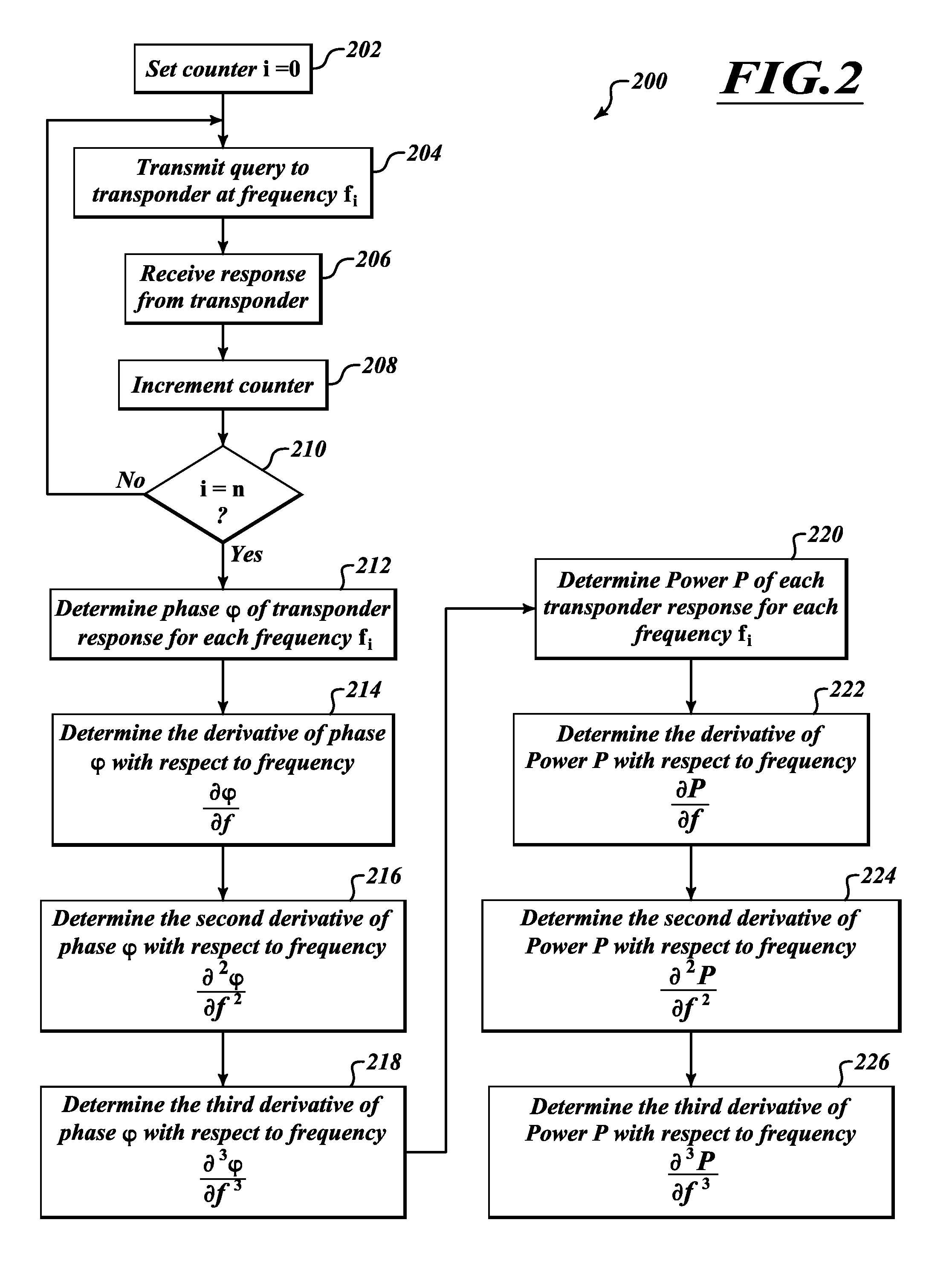
Method and apparatus to mitigate multipath in RFID
InactiveUS20120176227A1Accurately determineRange errorTicket-issuing apparatusSensing detailsTelecommunicationsMultipath interference
A distance between at least one antenna of an interrogation system and a transponder, such as an RFID tag, is determined based on derivatives with respect to frequency of the phase and the signal strength of responses transmitted by the transponder and received at the at least one antenna. The derivatives of the phase and the signal strength facilitate compensating for sources of multipath interference. Determining changes in distance may further facilitate determining location, speed, or bearing of the transponder by the interrogation system.
Owner:INTERMEC IP
Lens Mount
ActiveUS20140002676A1Accurate distancePlace safeTelevision system detailsProjector film strip handlingElectrical connectionEngineering
A lens mount design is presented. The mount can be used on a variety of imaging systems but is targeted at small camera systems such as might be used on mobile phones, cameras, sports cameras, computers and computer peripherals where interchangeable lenses are currently not common place. Embodiments include different attachment mechanisms, environmental barriers, electrical connections, a serial number marking system on the replaceable lens body and methods for using the lens mount and system.
Owner:NING ALEX
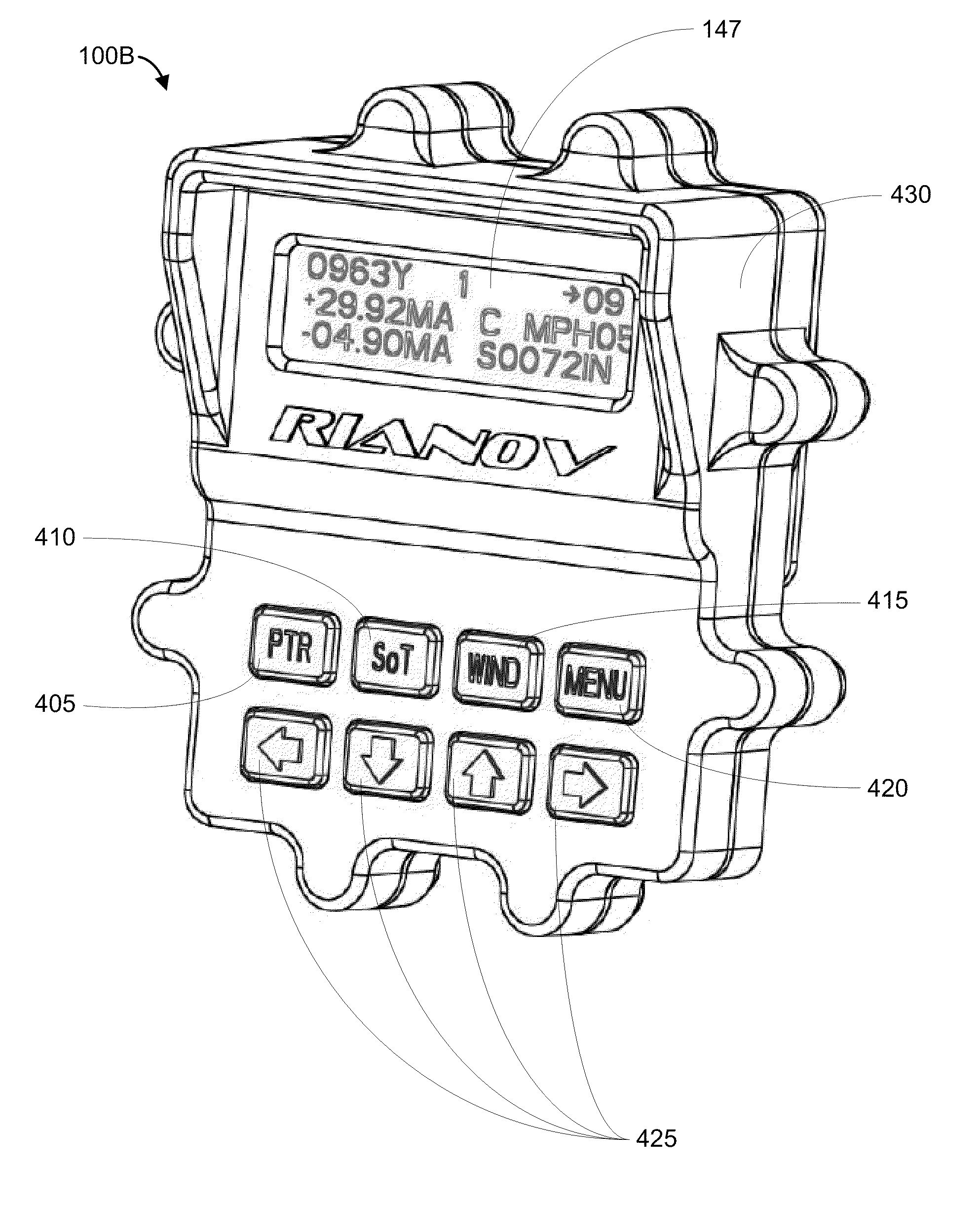
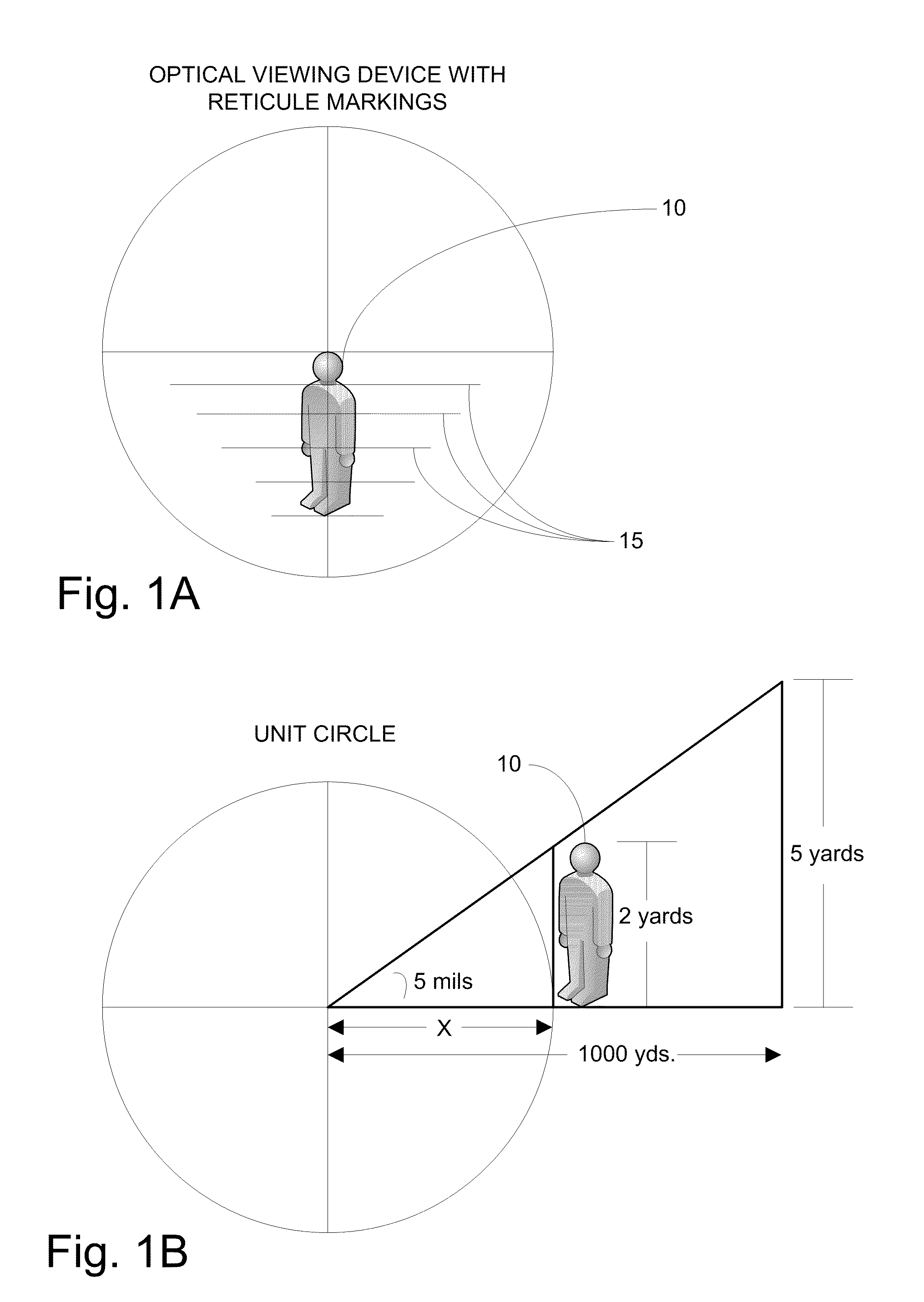
System and Method for Ballistic Solutions
ActiveUS20110168777A1Good estimateIncrease investmentAngle measurementWeapon control systemsDistance to targetMagnification
Disclosed embodiments, as well as features and aspects thereof, are directed towards providing a system, device and method for calculating comprehensive ballistic solutions, or portions thereof, via a varying magnification optical range determining and ballistic trajectory calculating apparatus referred to as a ballistic solutions device. Advantageously, embodiments of a ballistic solutions device may drastically reduce marksman error in milling targets by employing a measurement component configured to measure angular movement of a projectile launching device, such as a rifle, thus delivering consistently accurate distance to target estimations. Additionally, embodiments of a ballistic solutions device may also comprise features and aspects that enable a user to leverage available real-time field data such that error associated with the measurement of those variables is minimized prior to calculating and rendering a comprehensive ballistic solution derived from stored DOPE.
Owner:BAY LAURENCE ANDREW
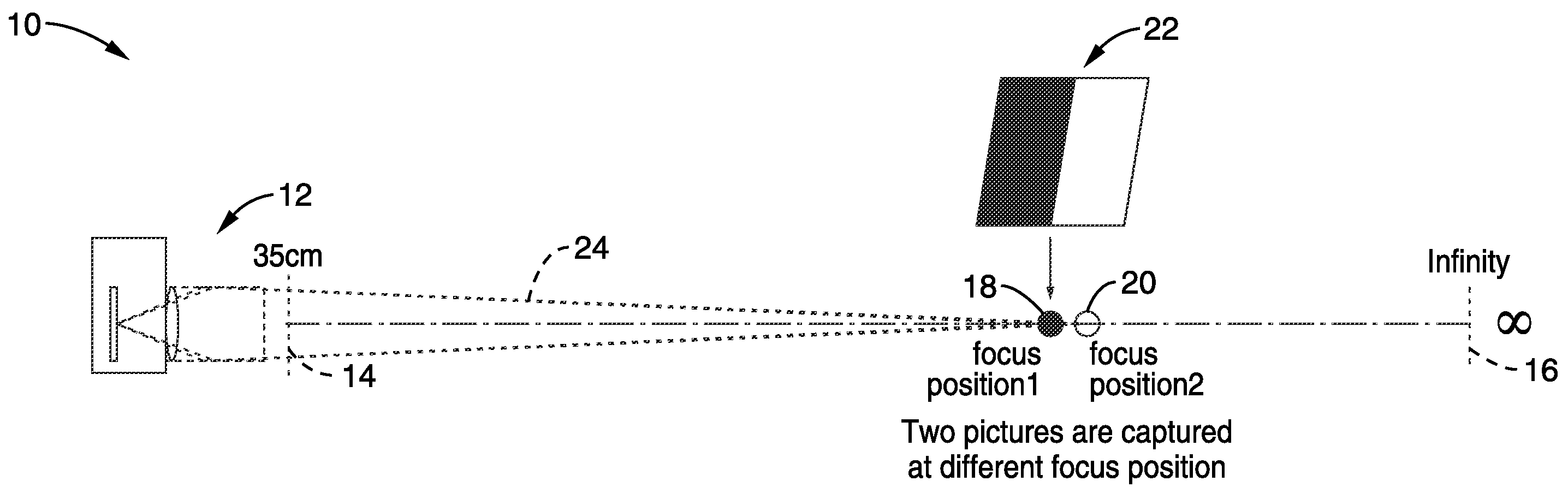
Two-dimensional polynomial model for depth estimation based on two-picture matching
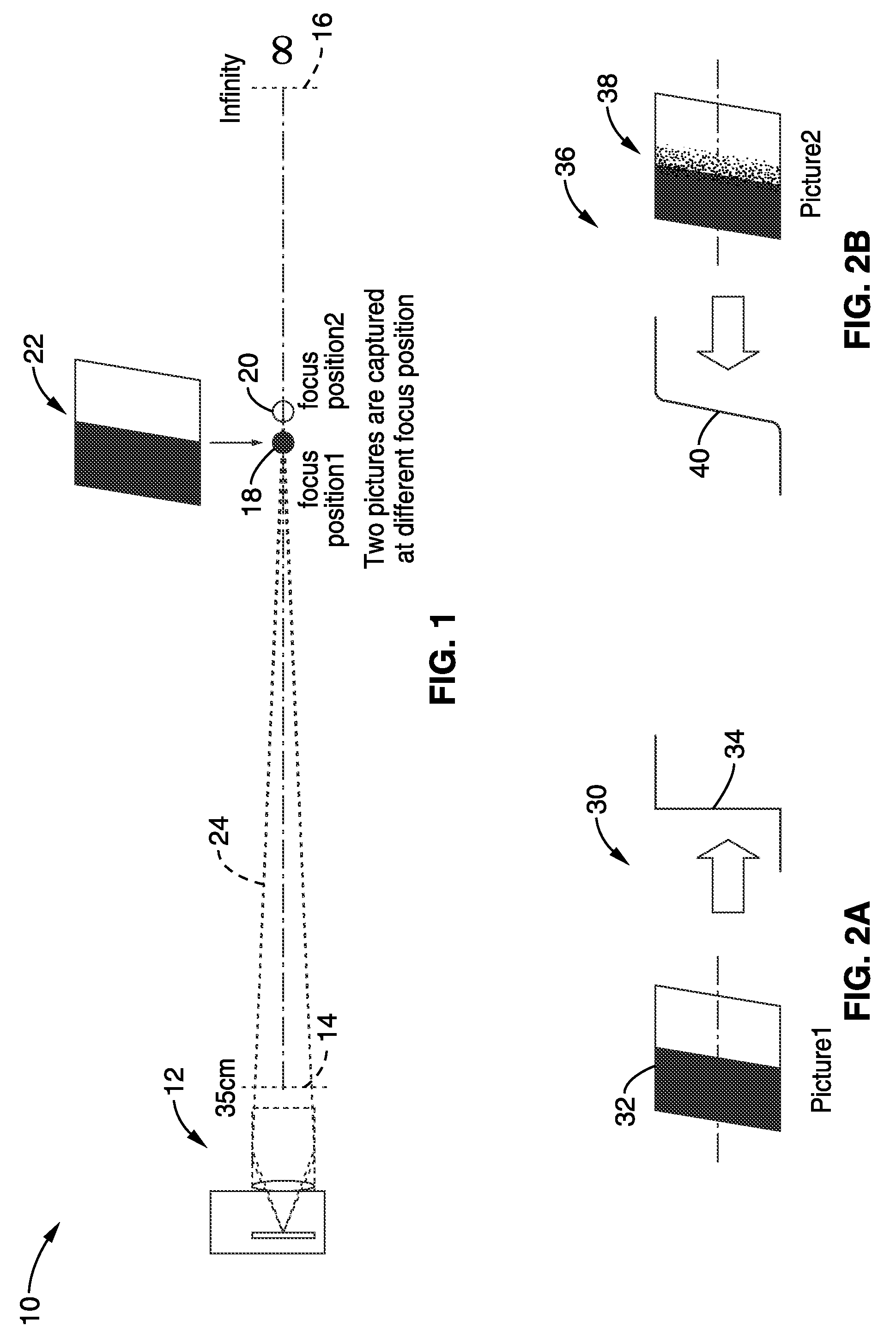
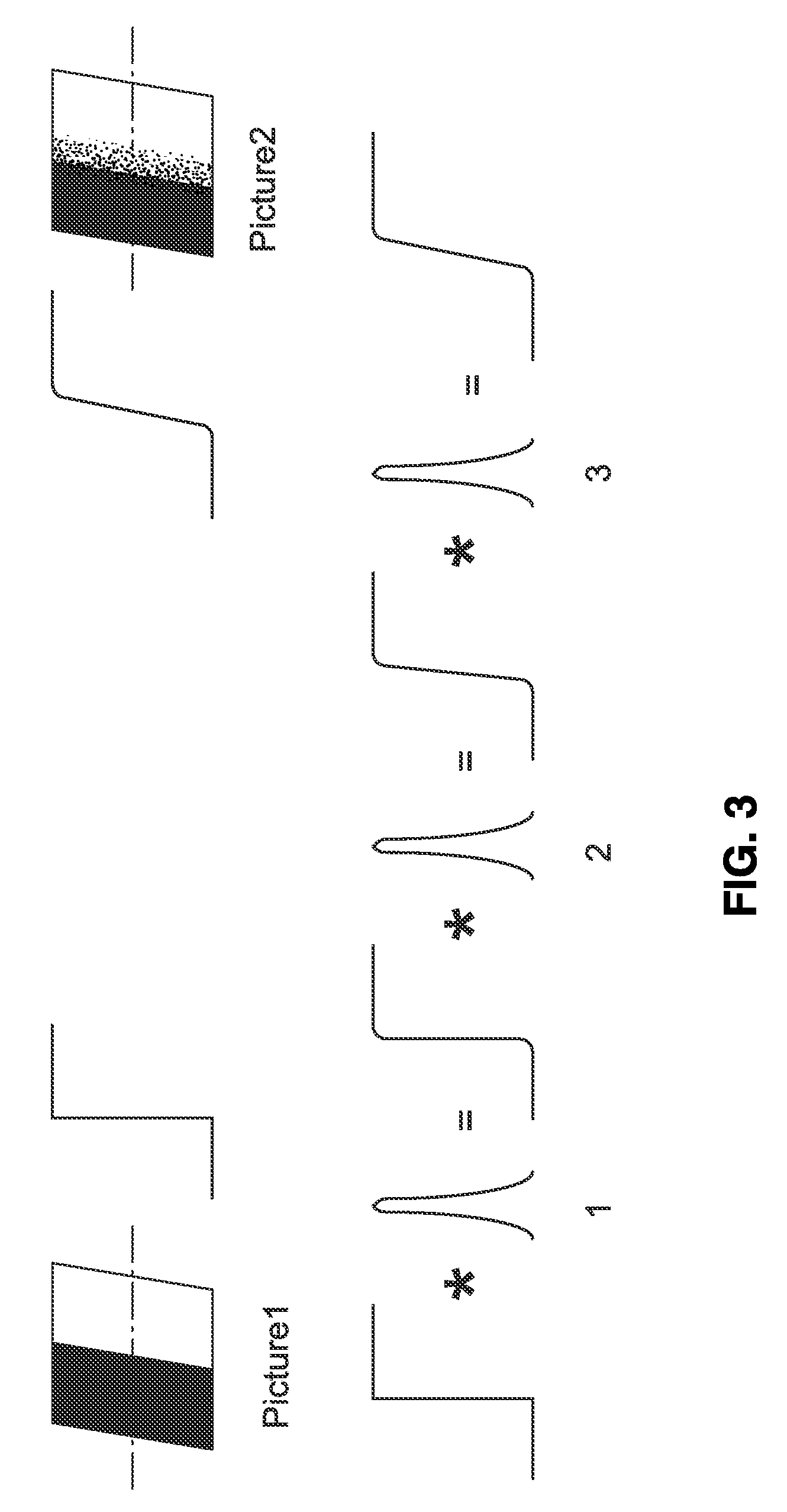
InactiveUS20100194971A1Accurate distanceReducing noiseTelevision system detailsImage analysisImage estimationFocal position
Apparatus and method for electronically estimating focusing distance between a camera (still and / or video camera) and a subject. Images at different focal positions of a calibration target are collected with distances between subject positions. In one aspect, histogram matching is performed to reduce noise error. A focus matching model is then generated in response to detected blur differences between successive images of the calibration target. The focus matching model is preferably converted to a polynomial equation of a desired order to smooth out image collection noise. The focus matching model is stored for access during operation. In use, the distance to subject is estimated in response to capturing images, detecting blur differences between the images and entering the blur difference information into the matching model.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
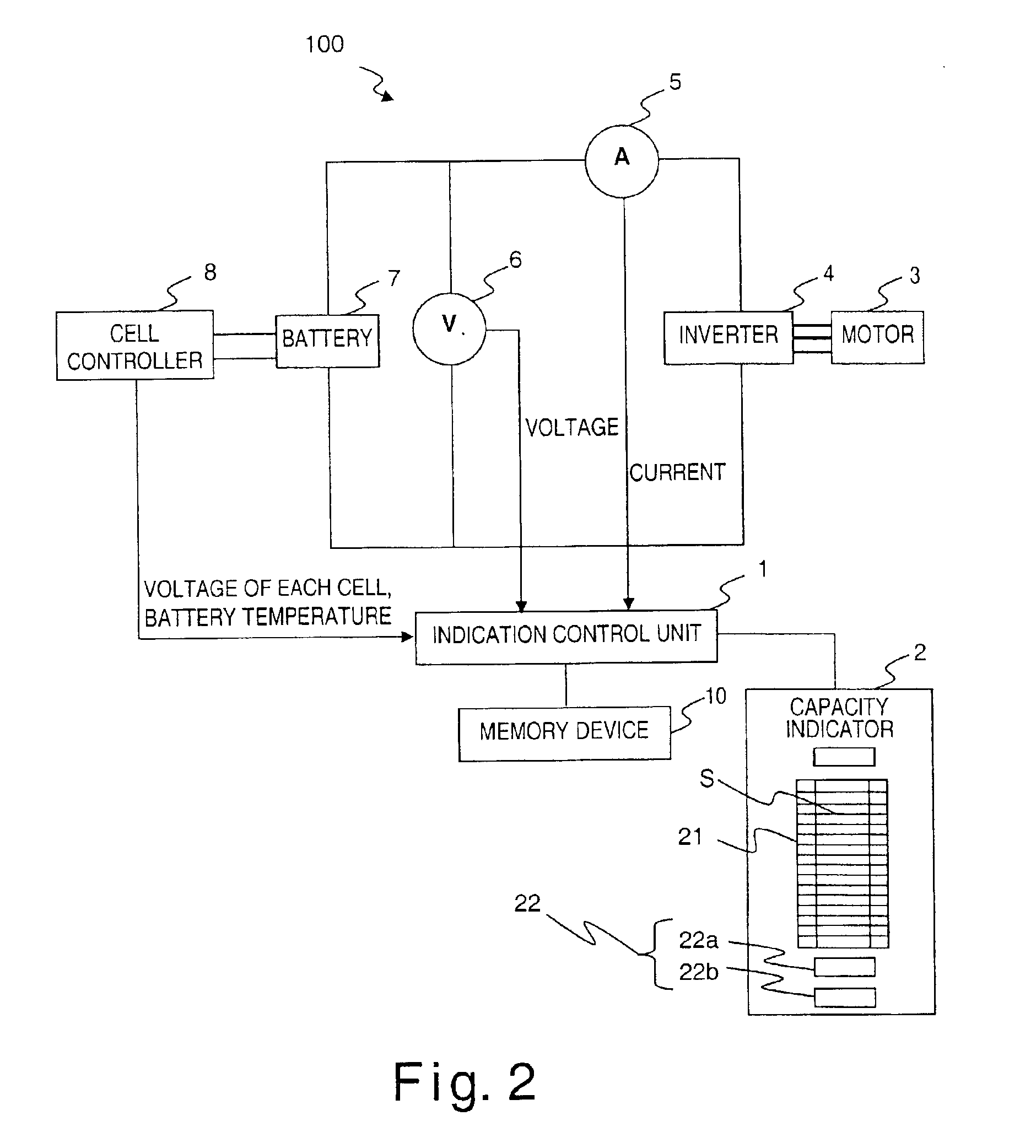
Capacity indicating device and method thereof
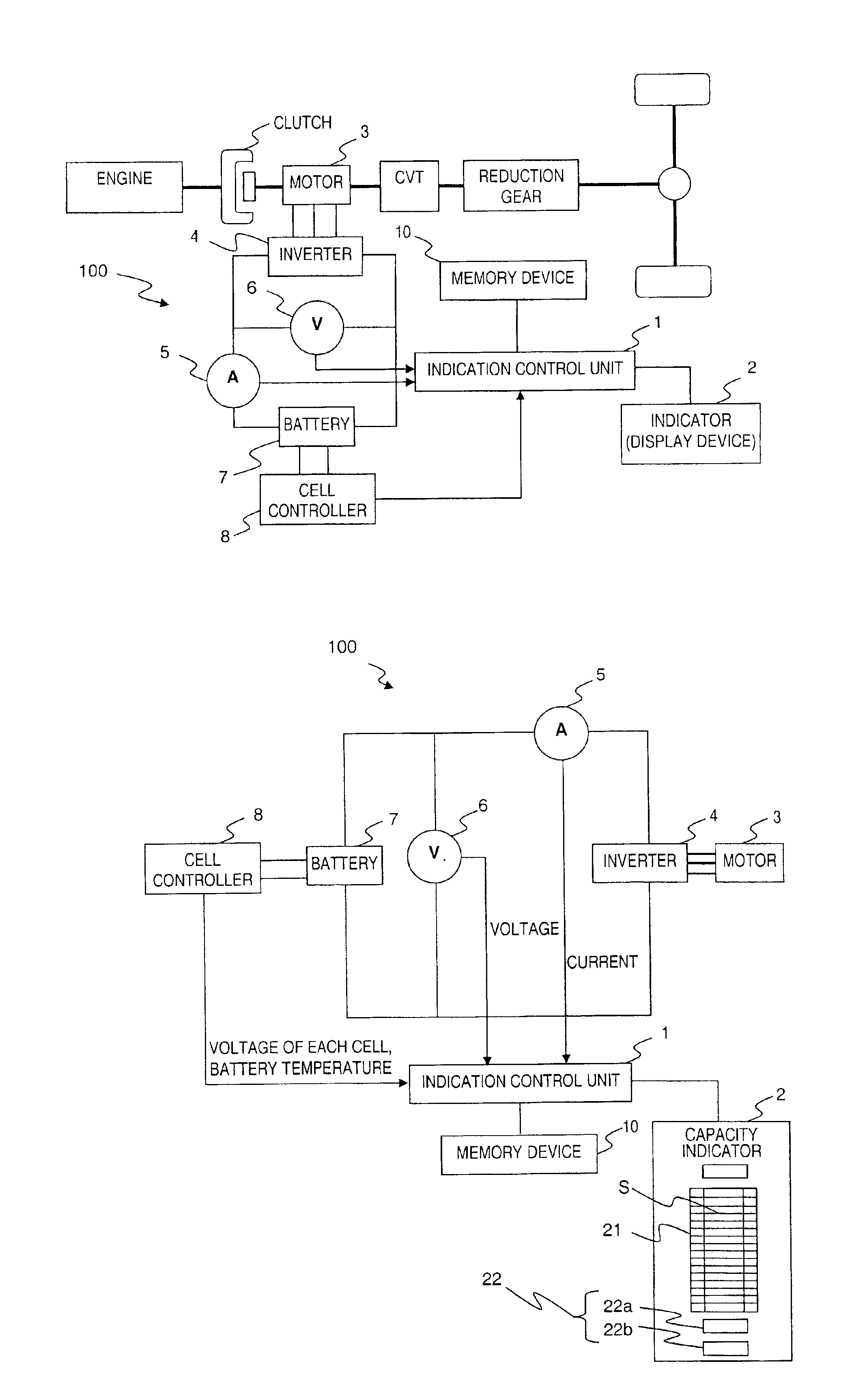
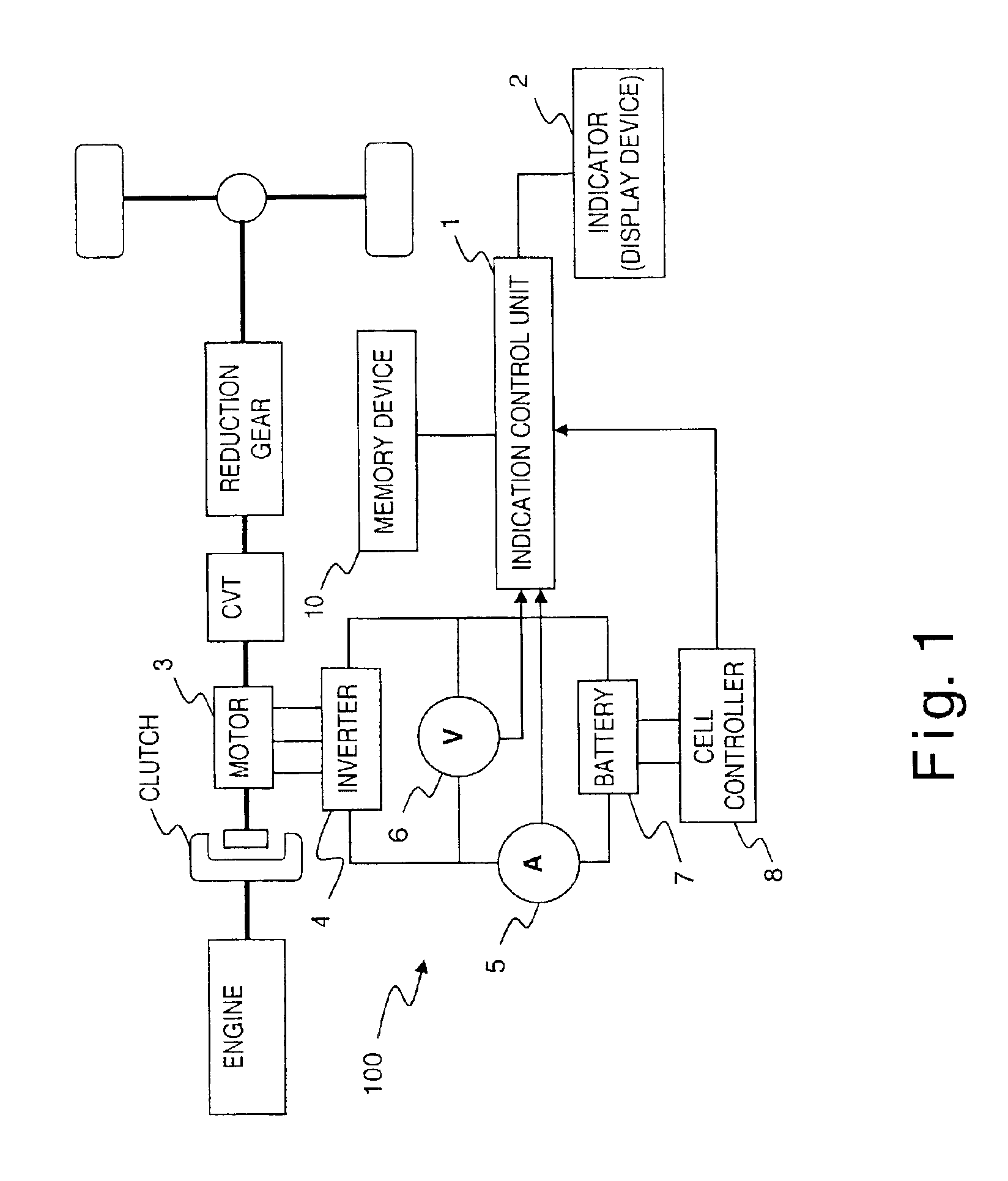
InactiveUS6932174B2Accurate distanceEvenly distributedHybrid vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsBattery capacityEmbedded system
A capacity indicating device is configured to indicate a fully charged state when full recharging has been conducted even if the battery is degraded; hold the possible traveling distance per segment roughly constant; and make it easy to estimate the possible cruising distance. The capacity indicating device has an indication control unit that: (1) allocates a prescribed portion of the battery capacity of a vehicle to a capacity adjustment region that serves to adjust the battery capacity as it decreases due to degradation of the battery; (2) calculates the degradation degree of the battery based on the detected voltage value and current value; (3) corrects the capacity adjustment region a based on the calculated degradation degree; and (4) indicates the present battery capacity using segments that are not affected by the degradation of the battery.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS7557929B2No loss of precisionReduce coherenceOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
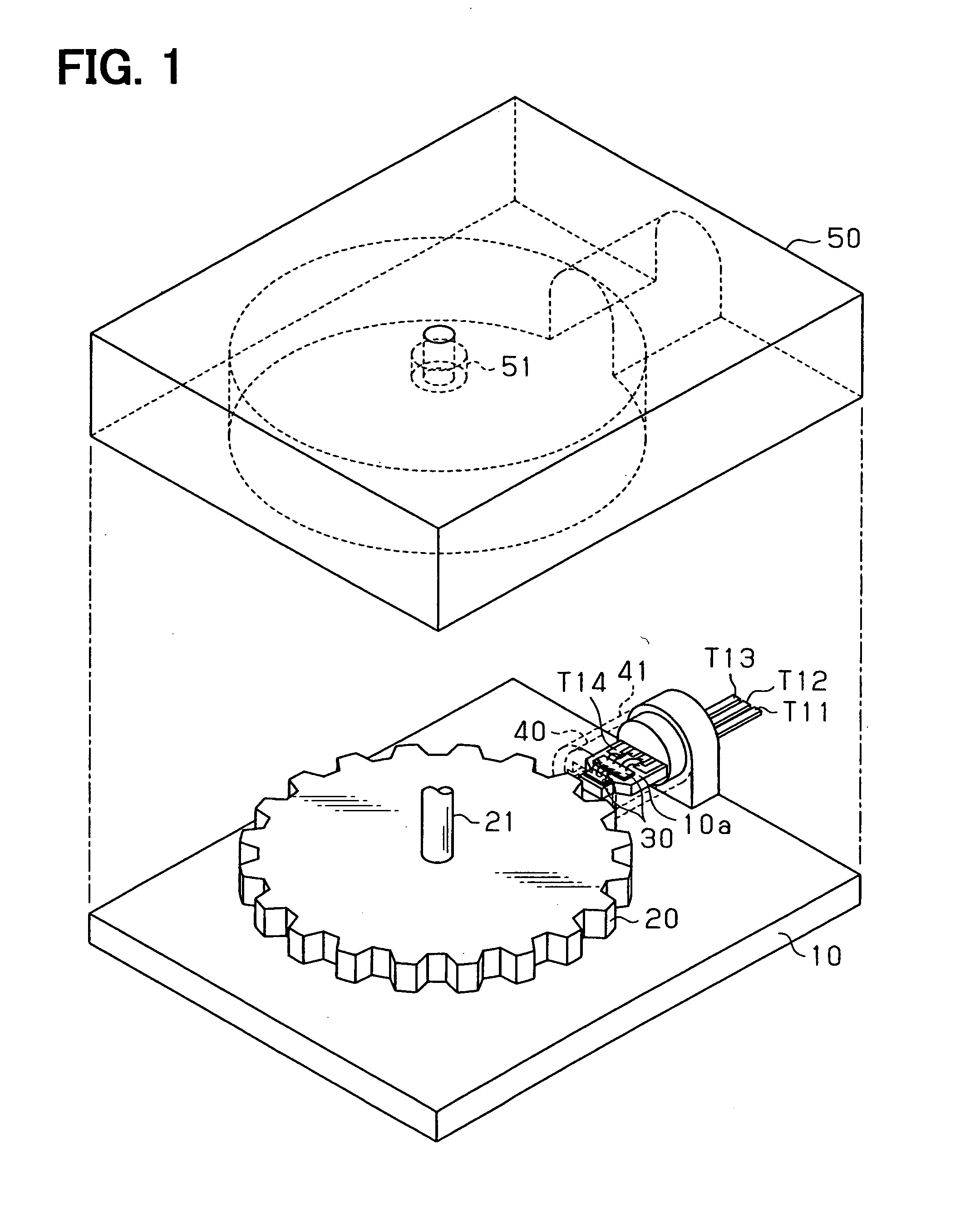
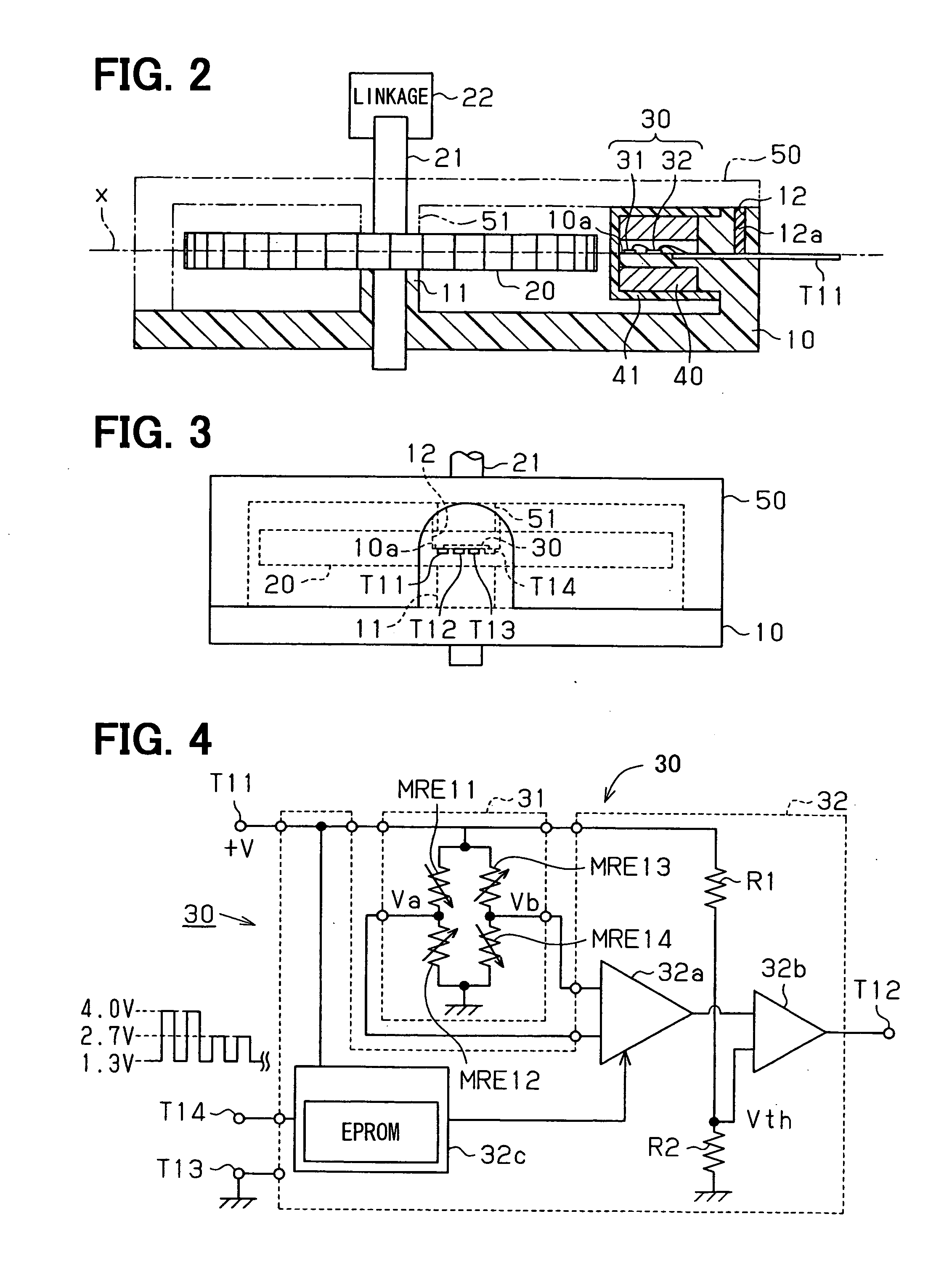
Rotation detecting device
ActiveUS20060097717A1Accurate distanceEasy to correct detection errorUsing electrical meansLinear/angular speed measurementSignal processingMagnet
A rotation detecting device for detecting a rotating object includes a housing having a bearing and an mounting surface, a rotor member having magnetic peripheral portion and a rotary shaft that is supported by the bearing, a biasing permanent magnet for providing magnetic field around the mounting surface and the magnetic peripheral portion, an IC sensor chip including plural magnetic sensor elements disposed on the mounting surface to provide a sensing signal related to change in magnetic field around the sensor elements, and an IC signal processing chip that provides a rotation signal according to the sensing signal. In this device, the bearing and the mounting surface are integrally formed into the housing at a prescribed distance to secure an unchanged air gap distance.
Owner:DENSO CORP
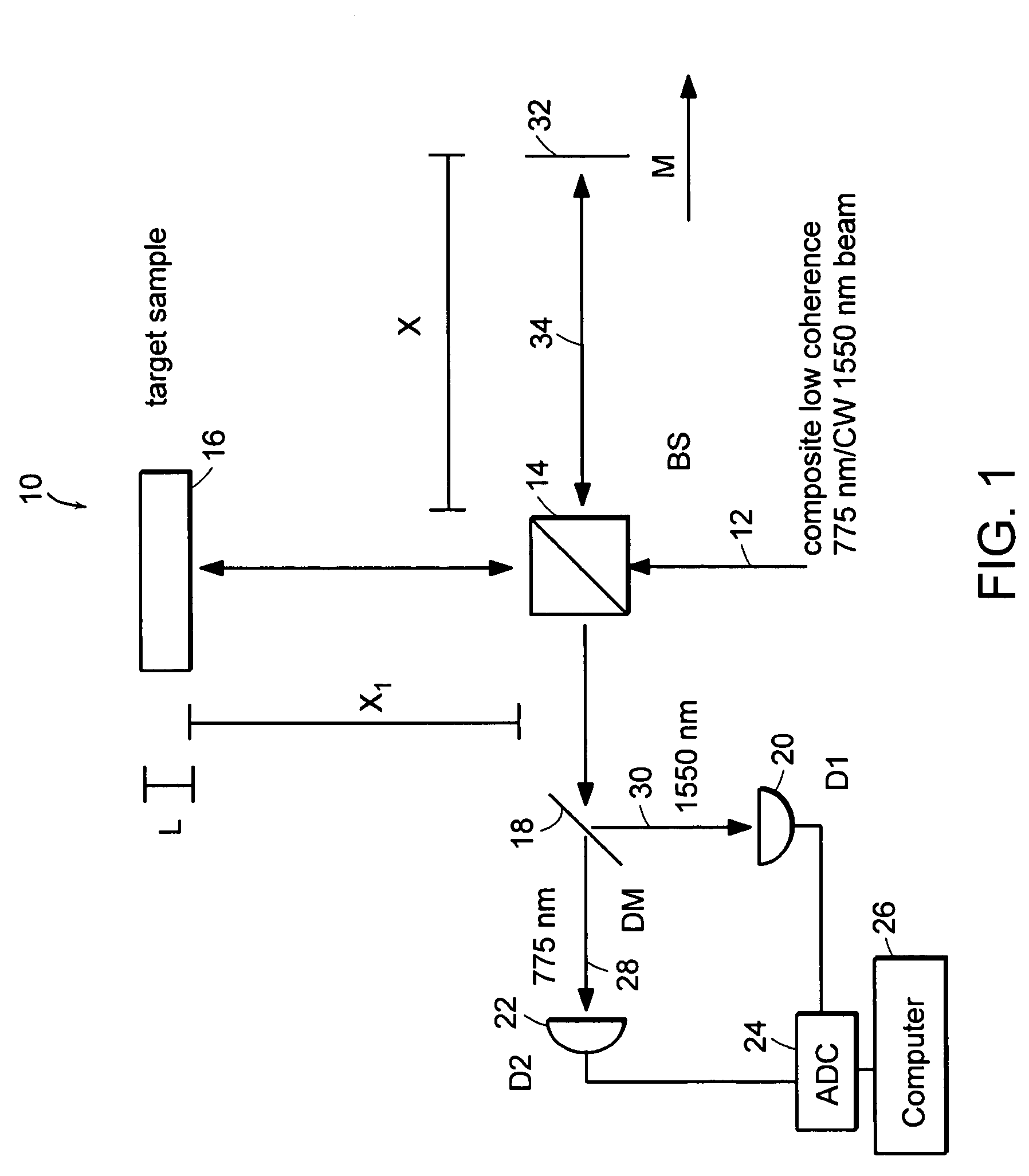
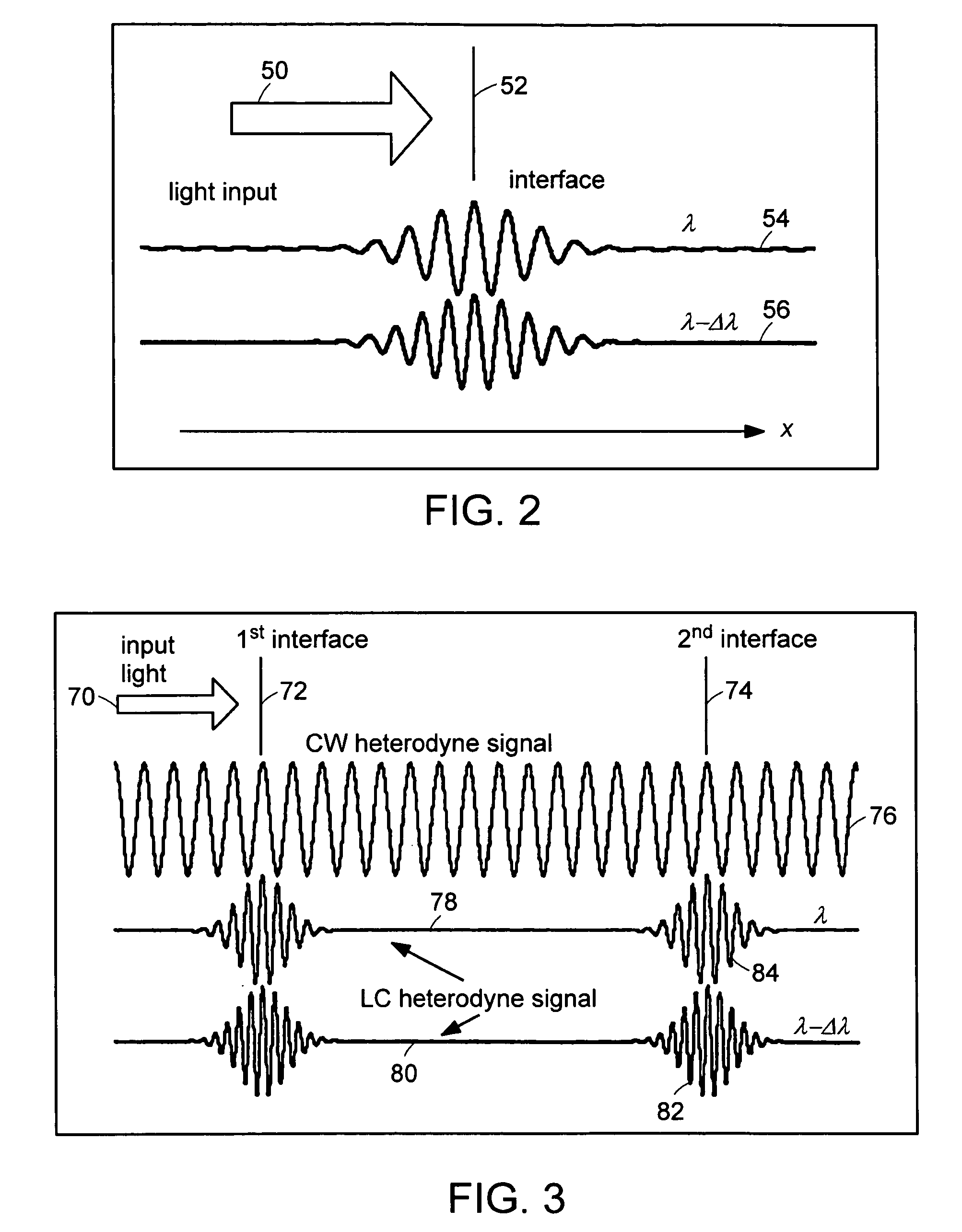
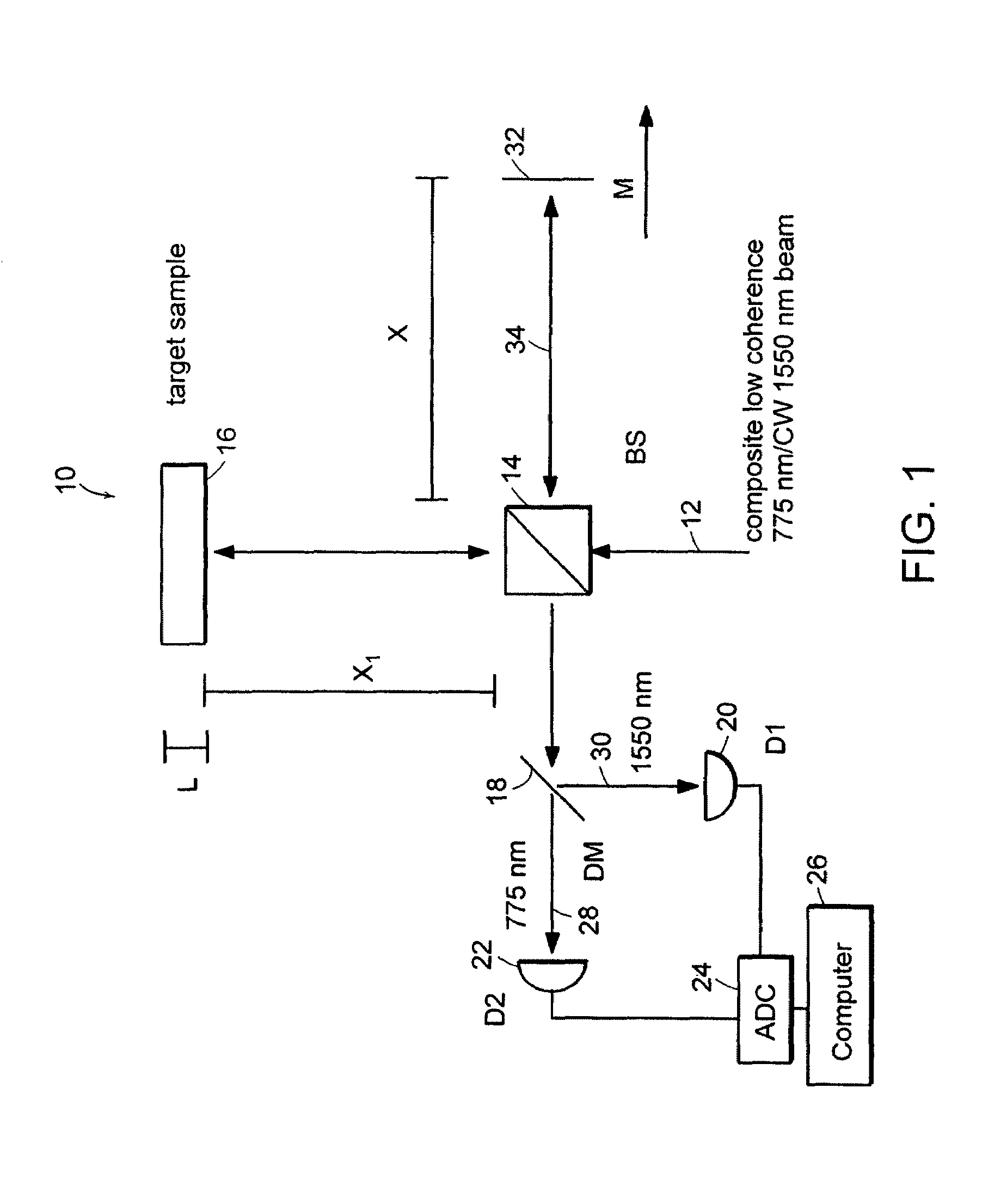
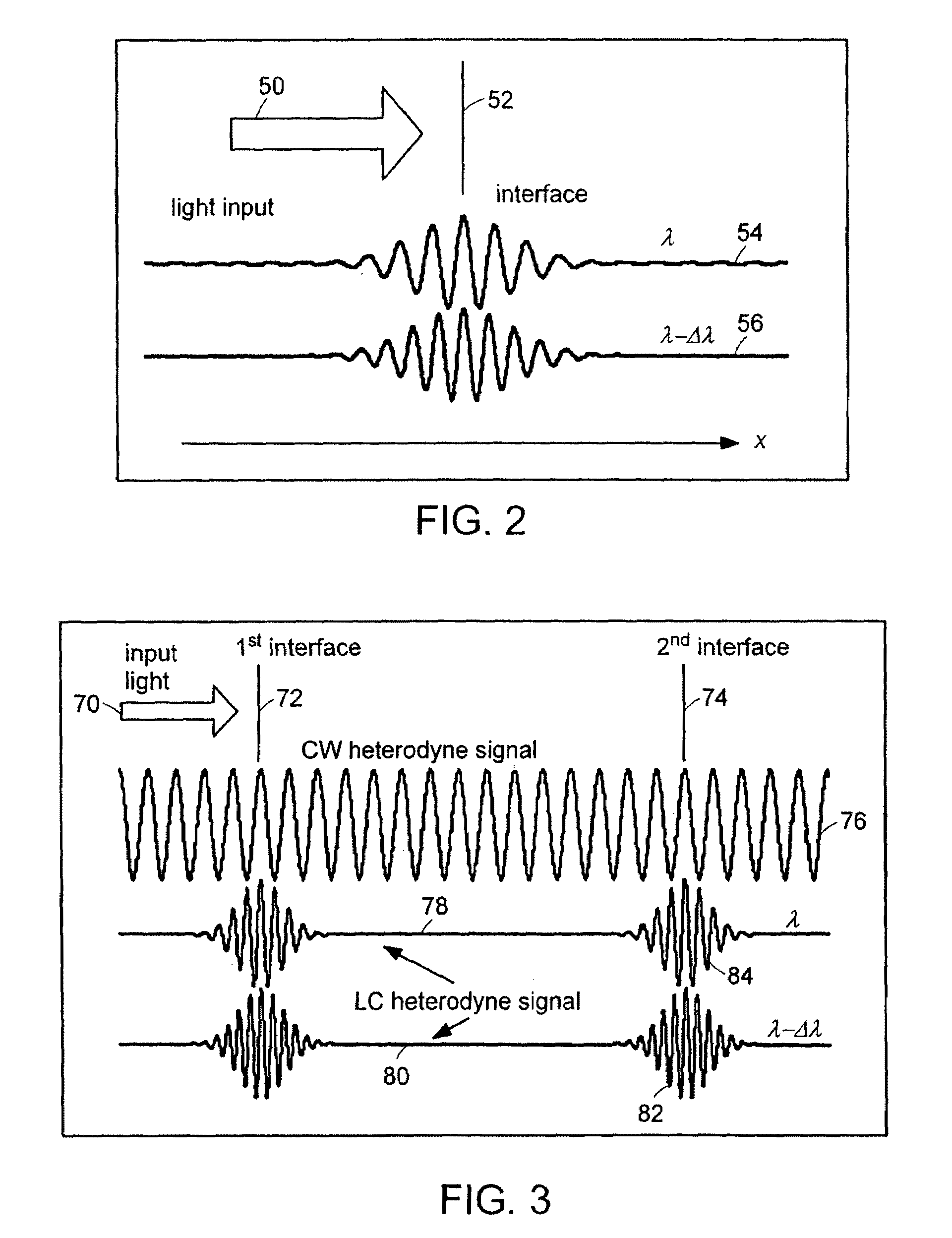
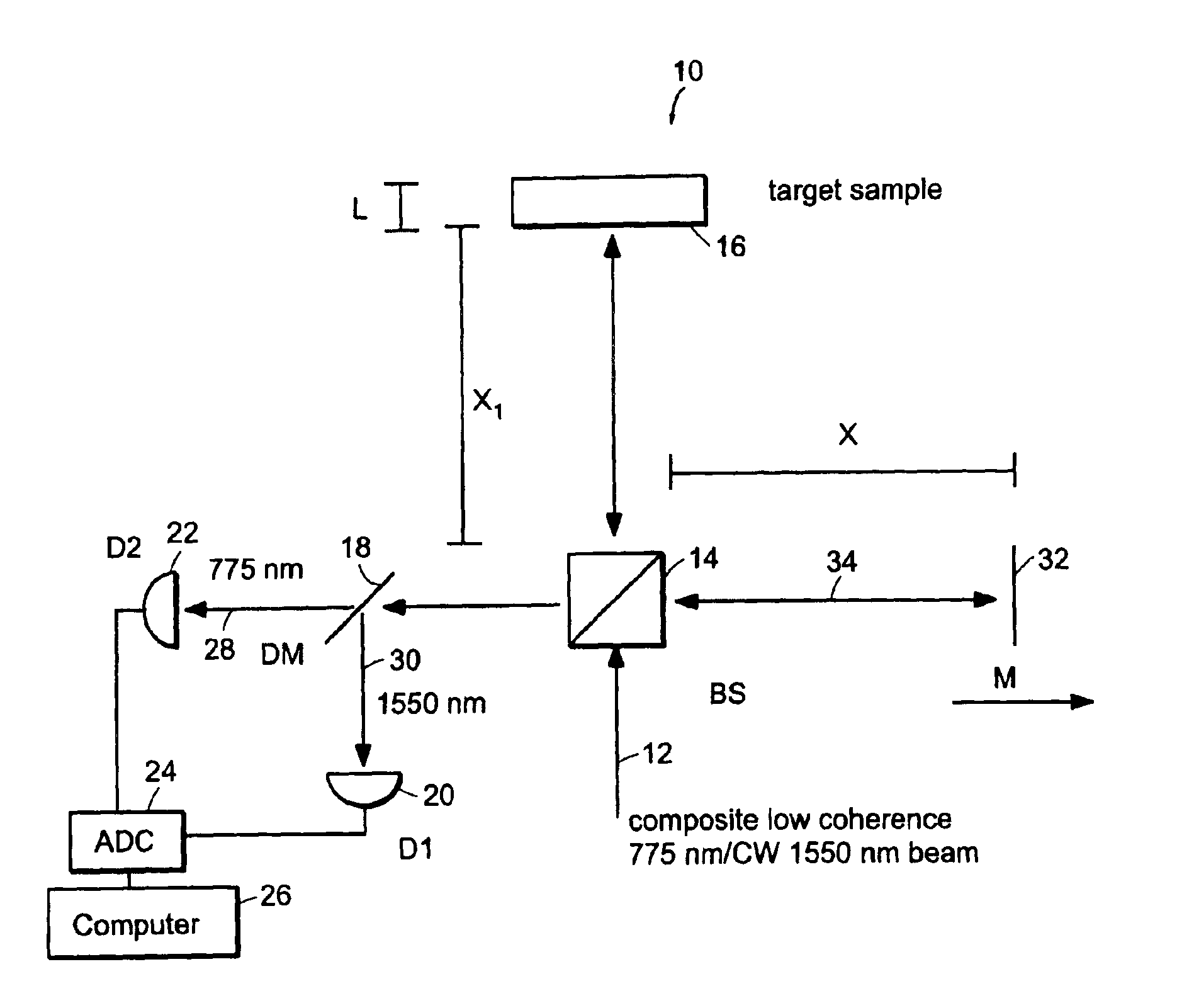
System and method for measuring optical distance
InactiveUS6934035B2Accurately measureAccurately determineOptical measurementsPhase-affecting property measurementsPhysicsMichelson interferometer
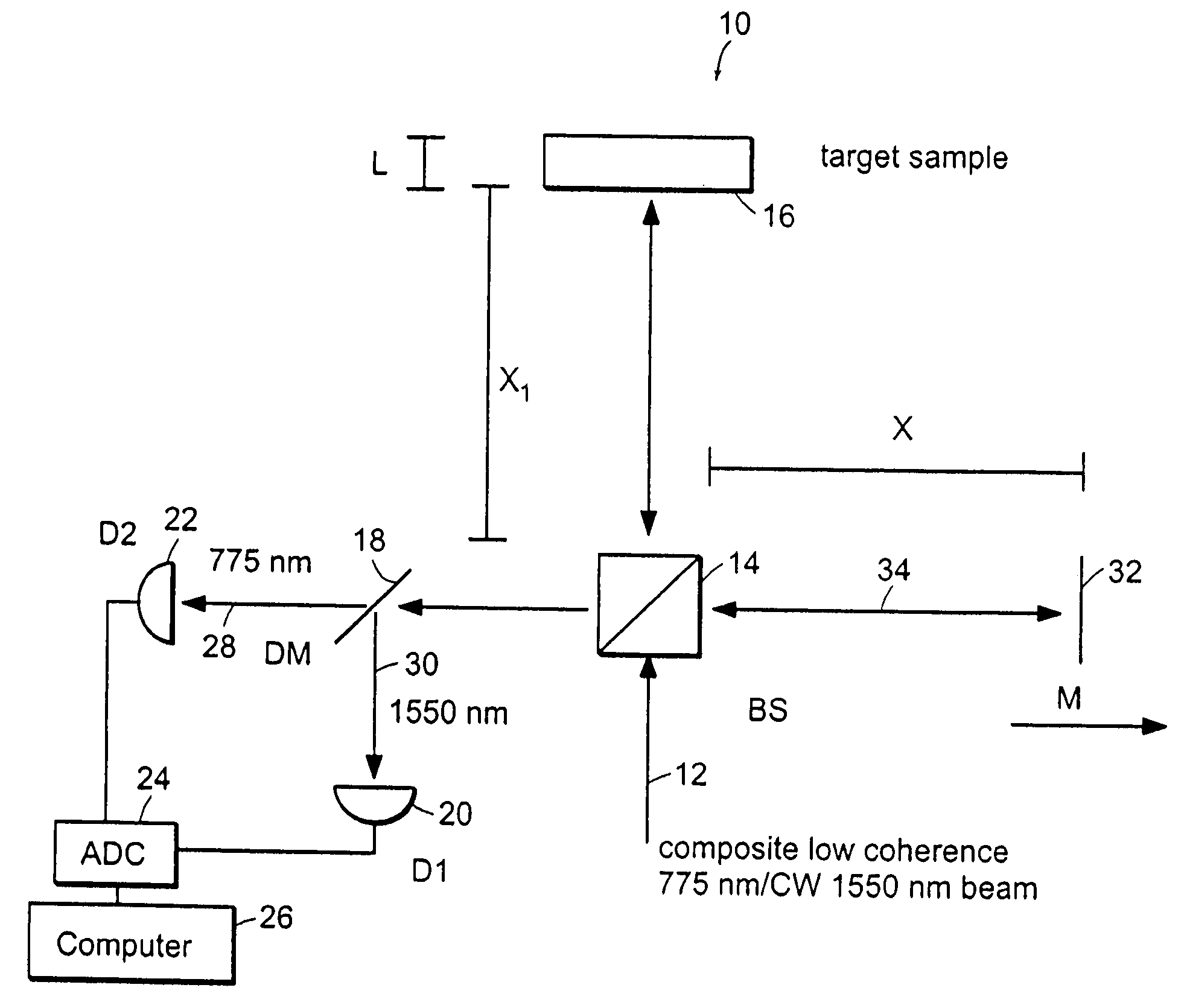
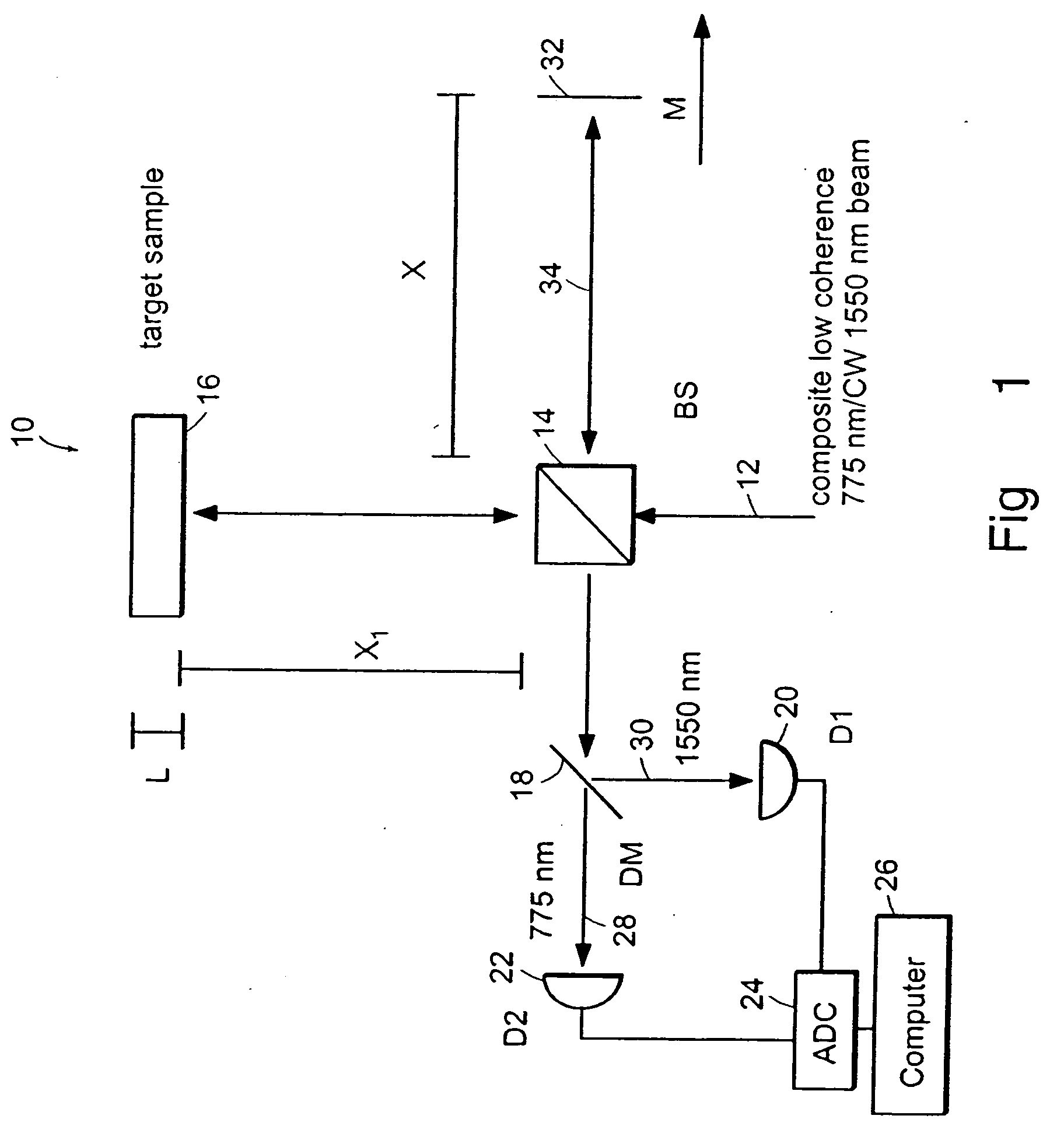
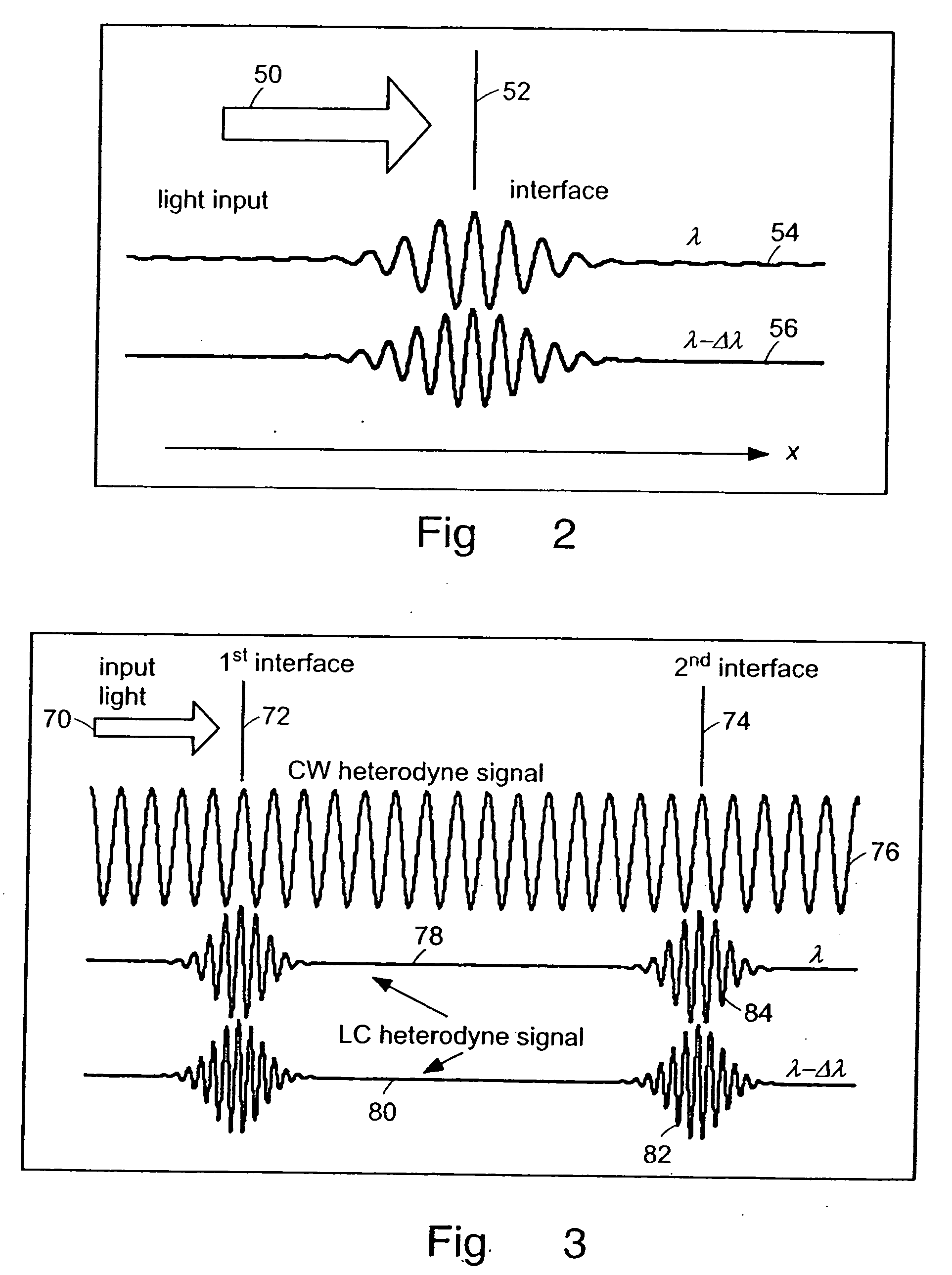
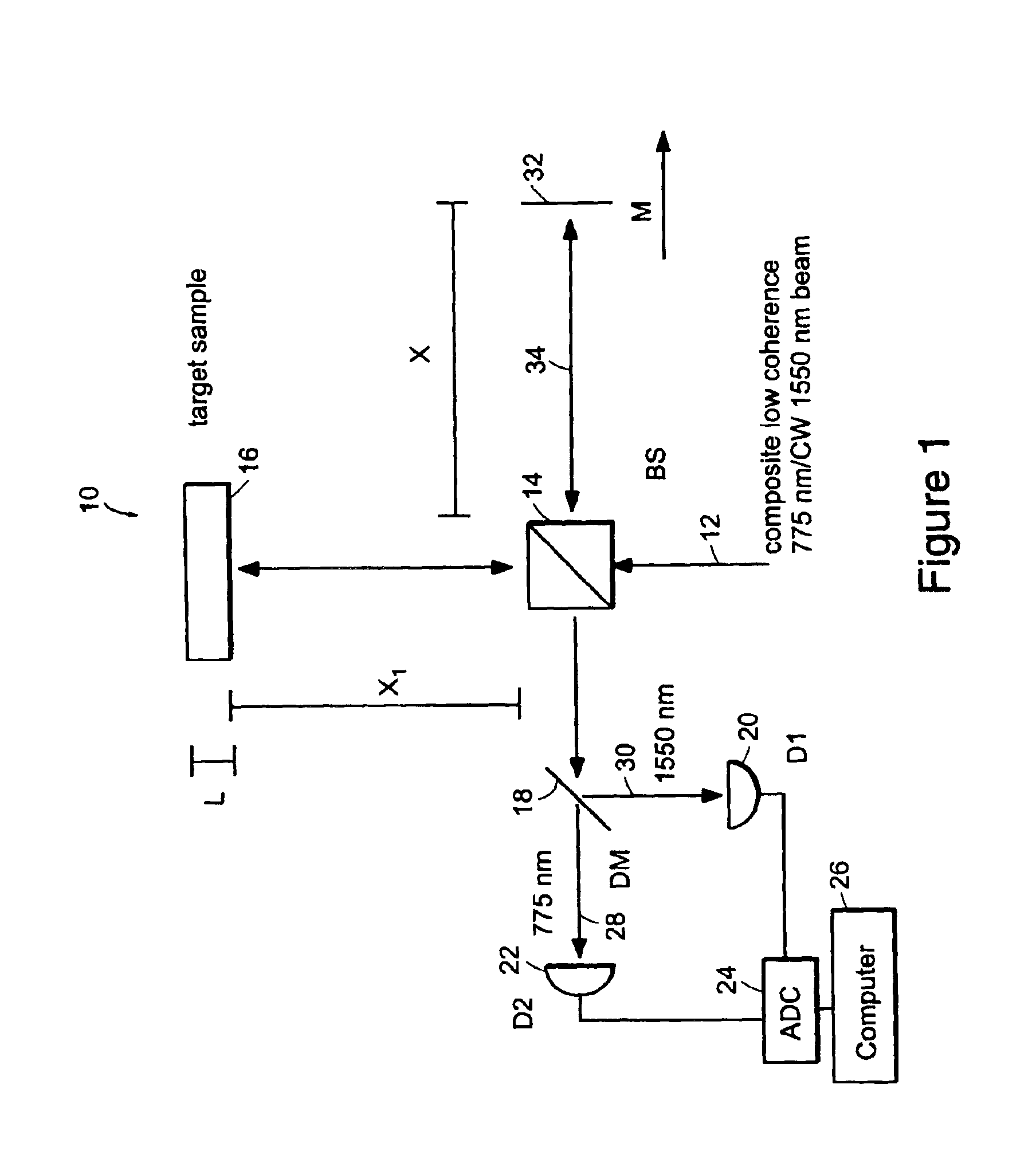
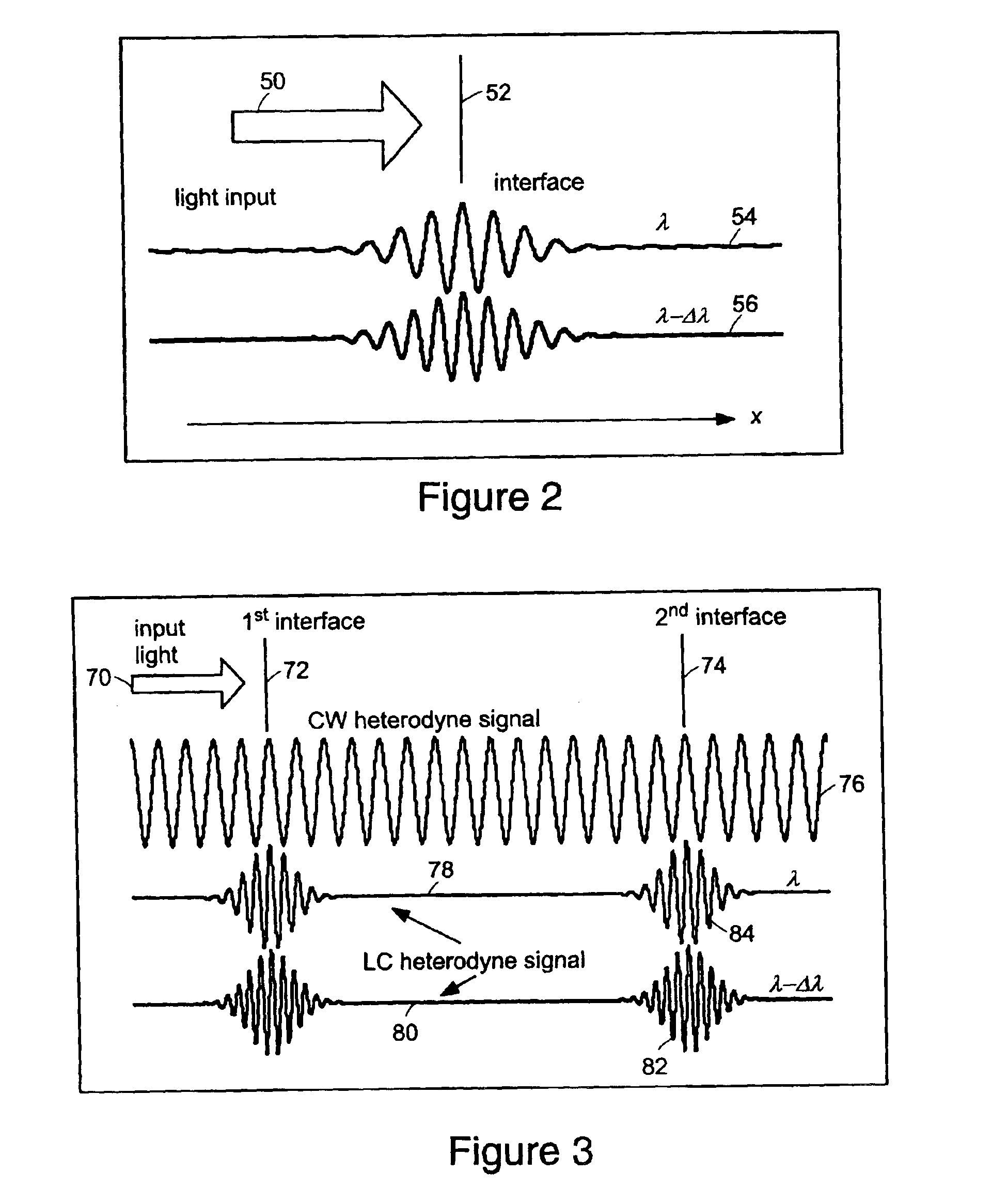
The methods of the present invention are directed at an accurate phase-based technique for measuring arbitrarily long optical distances with sub-nanometer precision. A preferred embodiment of the present invention method employs a interferometer, for example, a Michelson interferometer, with a pair of harmonically related light sources, one continuous wave (CW) and a second source having low coherence. By slightly adjusting the center wavelength of the low coherence source between scans of the target sample, the phase relationship between the heterodyne signals of the CW and low coherence light is used to measure the separation between reflecting interfaces with sub-nanometer precision. As the preferred embodiment of this method is completely free of 2π ambiguity, an issue that plagues most phase-based techniques, it can be used to measure arbitrarily long optical distances without loss of precision.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Driver assistance system and method based on millimetre-wave radar, terminal and medium
ActiveCN110208793AAccurate distanceAccurate speedExternal condition input parametersRadio wave reradiation/reflectionTransceiverOriginal data
The invention provides a driver assistance system and method based on a millimetre-wave radar, a terminal and a storage medium. The driver assistance system based on the millimetre-wave radar comprises at least one millimetre-wave (mmW) transceiver (Tx / Rx), an original data processing unit, a dynamic and static separation unit, a fusion unit, an analysis unit and a decision-making unit. The driverassistance system based on the millimetre-wave radar in the invention does not depend on a visual sensor; point cloud data singly obtained by the millimetre-wave radar is subjected to pre-processing,fusion, dynamic and static separation, individual semantic acquisition, tracking and analysis; therefore, the effect having the same target obtained by image processing through the visual sensor canbe achieved; furthermore, fusion between visual perception data and radar perception data can be utilized in the invention; then, processing or analysis is carried out; for target object tracking, therelative distance, speed and angle data are relatively precise in the invention; and thus, the driver assistance system disclosed by the invention is more suitable for being used in complex scenes having relatively high people flow, such as a parking lot, a garden and a basement.
Owner:ZONGMU TECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
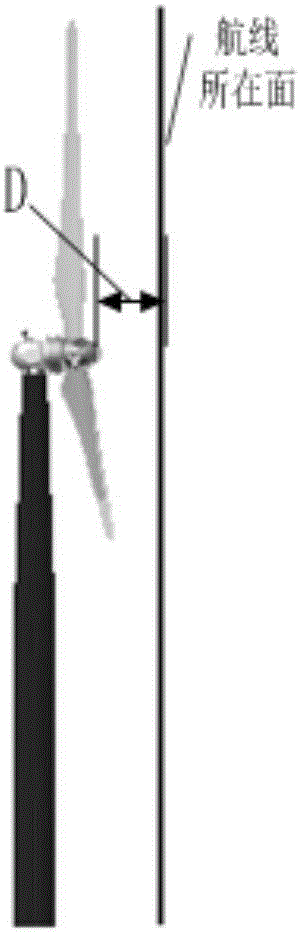
Method, device and system for detecting damage of fan blades based on unmanned aerial vehicle
ActiveCN106762451ADamage detection automaticDamage detection is accurateOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMachines/enginesUncrewed vehicleEngineering
The embodiment of the invention provides a method, device and system for detecting damage of fan blades based on an unmanned aerial vehicle. The method comprises the steps of receiving an image set of the fan blades shot from the unmanned aerial vehicle when the unmanned aerial vehicle flies along a preset airline and information of the located space position when each image in the image set is shot; determining information of the blade region where the unmanned aerial vehicle is located when the unmanned aerial vehicle shoots each image according to the locking state of the draught fan blades and the information of the space position; conducting image recognition on the image set, and obtaining the images of the damaged draught fan blades; conducting damage location on the draught fan blades according to the information of the space position and the information of the blade region which correspond to the images of the damaged draught fan blades, and obtaining damage position information; generating a damage detecting report according to the damage position information. According to the method, device and system for detecting the damage of the fan blades based on the unmanned aerial vehicle, the purpose of utilizing the unmanned aerial vehicle to automatically and accurately detect the damage of the draught fan blades is achieved, the detecting efficiency is improved, technological support is provided for follow-up blade maintenance, and the working hours and cost are saved.
Owner:BEIJING GOLDWIND SCI & CREATION WINDPOWER EQUIP CO LTD
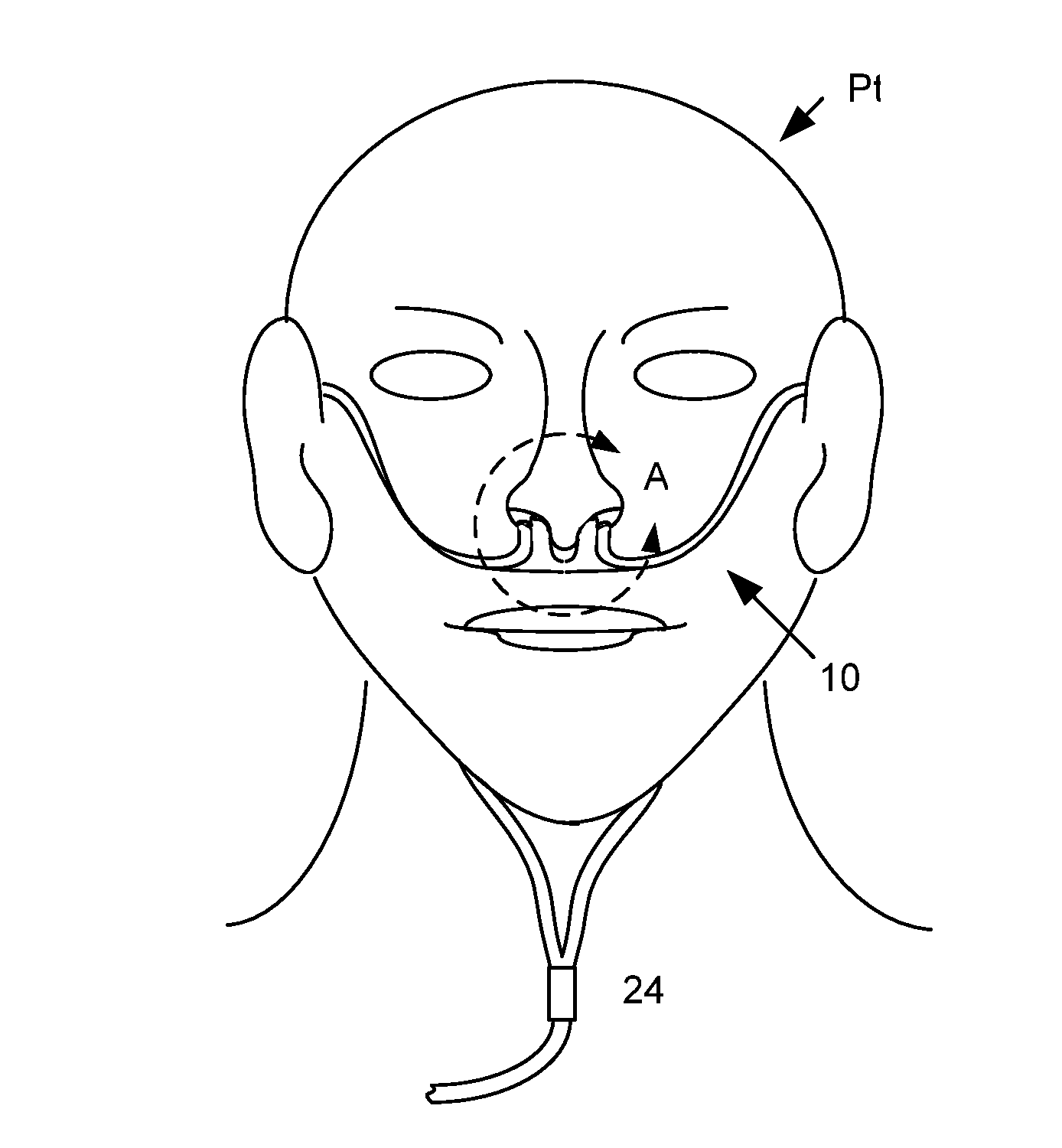
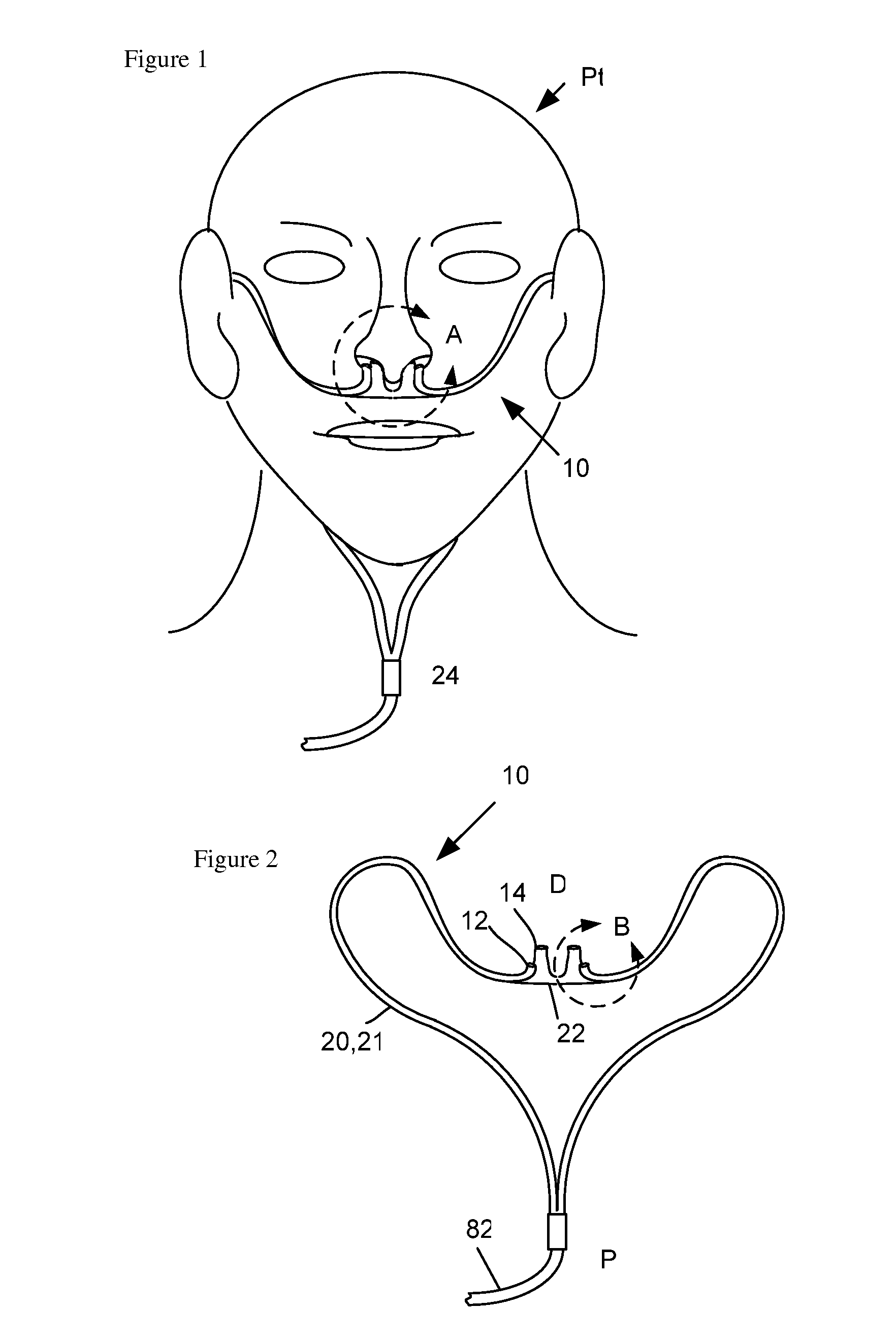
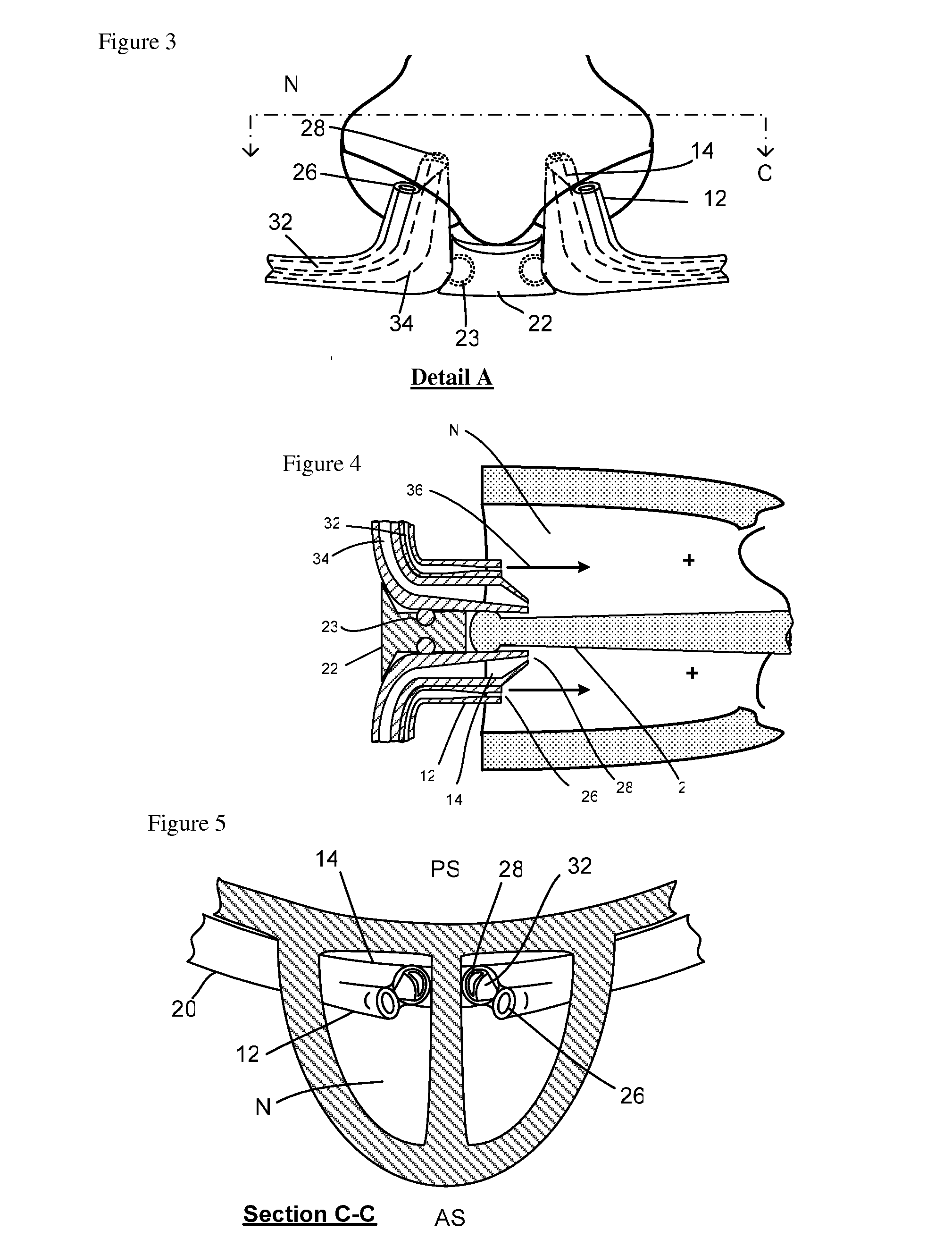
Nasal Ventilation Cannula System and Methods
A nasal cannula ventilation system is described for treating lung disease or for exercise conditioning, incorporating a Venturi system. The ventilation cannula comprises unique positioning features to positively locate a gas delivery nozzle in an optimal location to optimize Venturi performance, patient comfort and fitment to the patient. The cannula is low profile, making it as realistic to wear and use as a standard oxygen cannula, and is simple rending the cost reasonable. The ventilation cannula uses a simple low cost ventilator as a gas delivery control system which is compatible with existing gas sources. The system is used (1) during stationary use to unrest the respiratory muscles to increase tolerance to activity after a treatment session, or (2) to enable activity within a distance from a stationary gas source, (3) during ambulatory use using a portable gas source to enable mobility, and (4) for enhanced fitness conditioning.
Owner:WONDKA ANTHONY DAVID
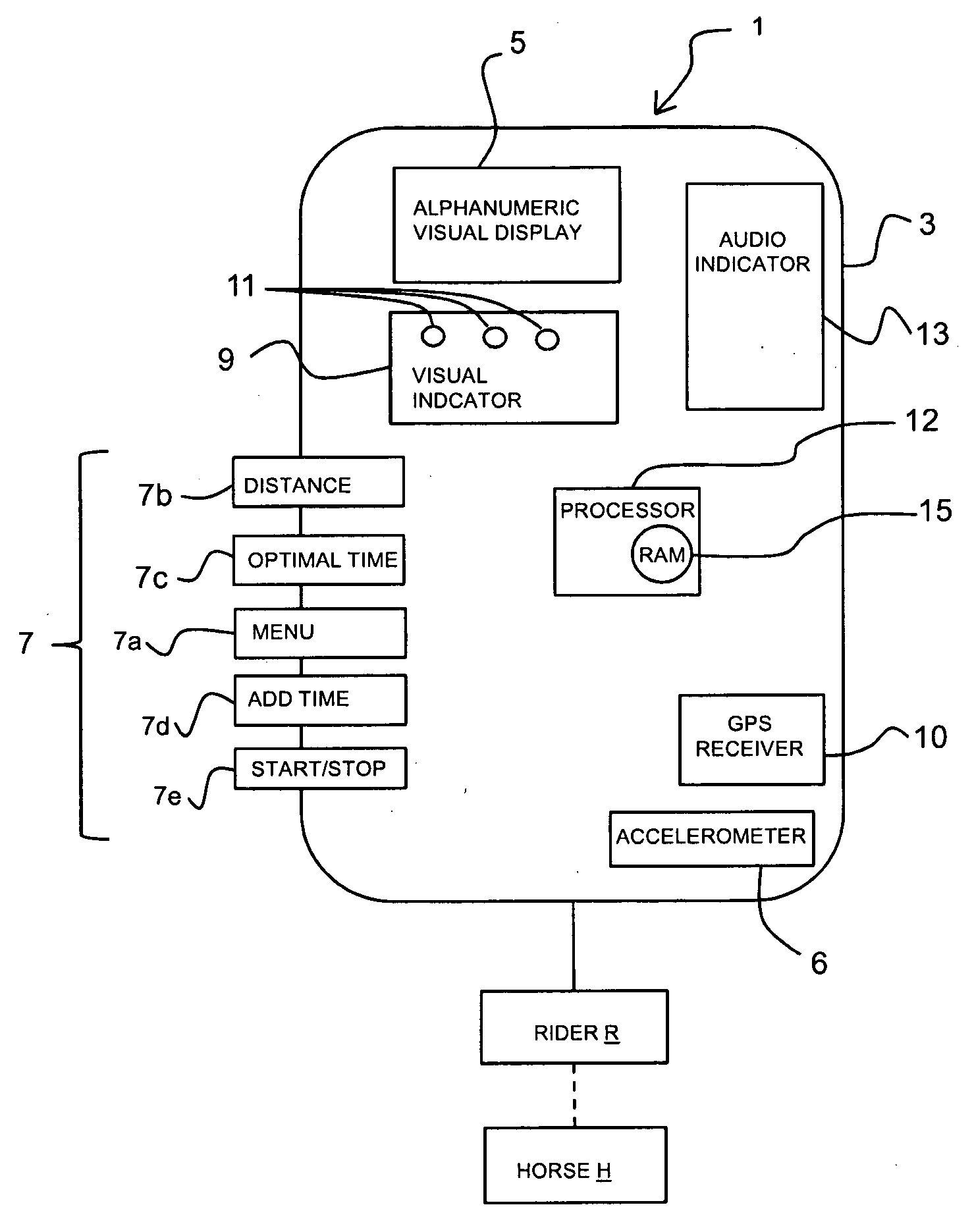
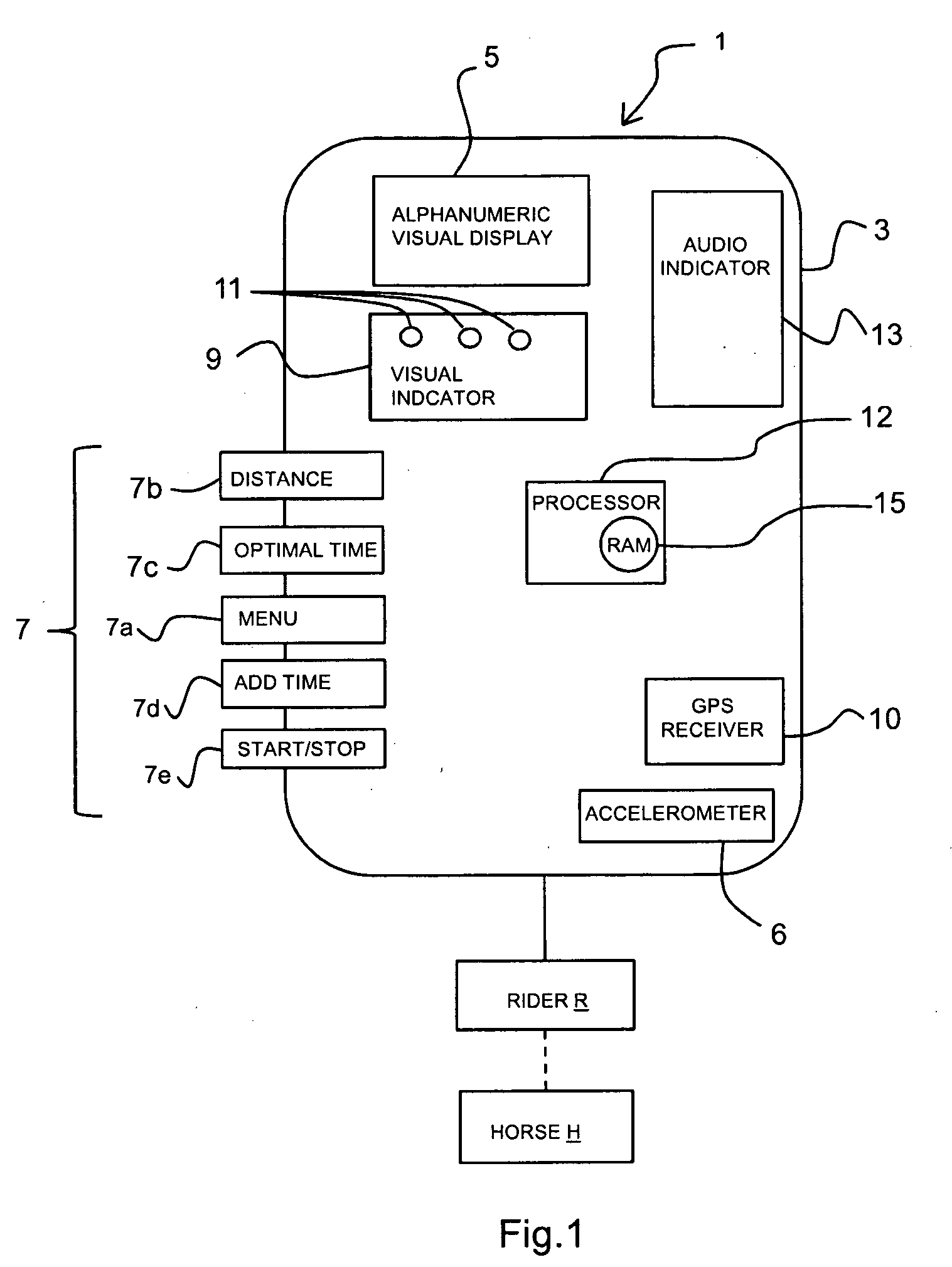
Method and apparatus for measuring and estimating subject motion in variable signal reception environments
InactiveUS20100250179A1Easy to viewLight weightRace-coursesAcceleration measurementTerrainDynamic motion
A dynamic motion and distance measuring device for estimating and measuring speed and distance covered by a subject engaged in an athletic endeavor and more particularly to measuring and estimating the speed and distance and providing a relative indication of a measured speed and distance to an optimal speed and distance and / or time including finish time of the subject engaged in an athletic event, even where the event is occurring in changing environment or terrain conditions where remote data collection and signal reception is inconsistent and variable.
Owner:MARIANO THOMAS +1
Method and system of aligning x-ray detector for data acquisition
ActiveUS7581885B2Precise alignmentPrecise positioningRadiation beam directing meansX-ray apparatusData acquisitionTransmitter
A method and system of aligning an x-ray detector and x-ray tube for data acquisition are presented. The x-ray detector and x-ray tube are equipped with transmitters and receivers designed to provide feedback relating to the orientation, spacing, and general position thereof. In this regard, a user can effectively and efficiently position the x-ray tube and x-ray detector relative to one another for data acquisition.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
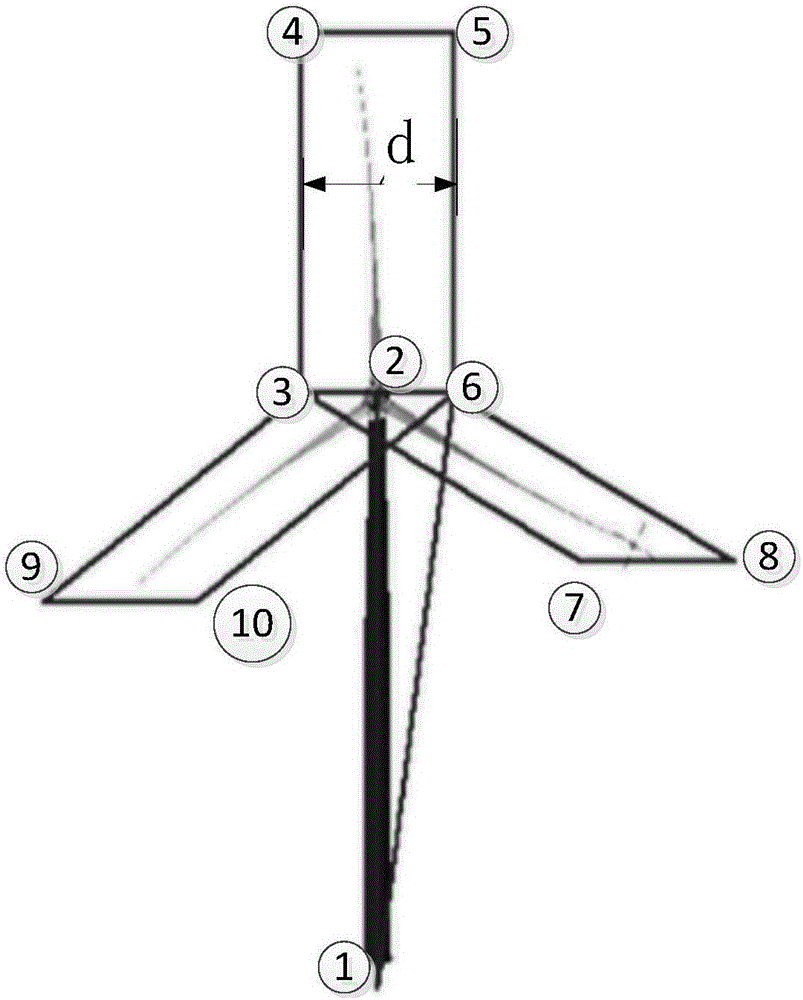
Method for Estimating the Distance of a Receiver from a Radio Transmitter, Relative Methods for Calculating the Position of a Mobile Terminal, Mobile Terminal and Localization Device
ActiveUS20130310074A1Improve phase differenceImprove distance estimatePosition fixationUsing reradiationPhase differenceRadiotransmitter
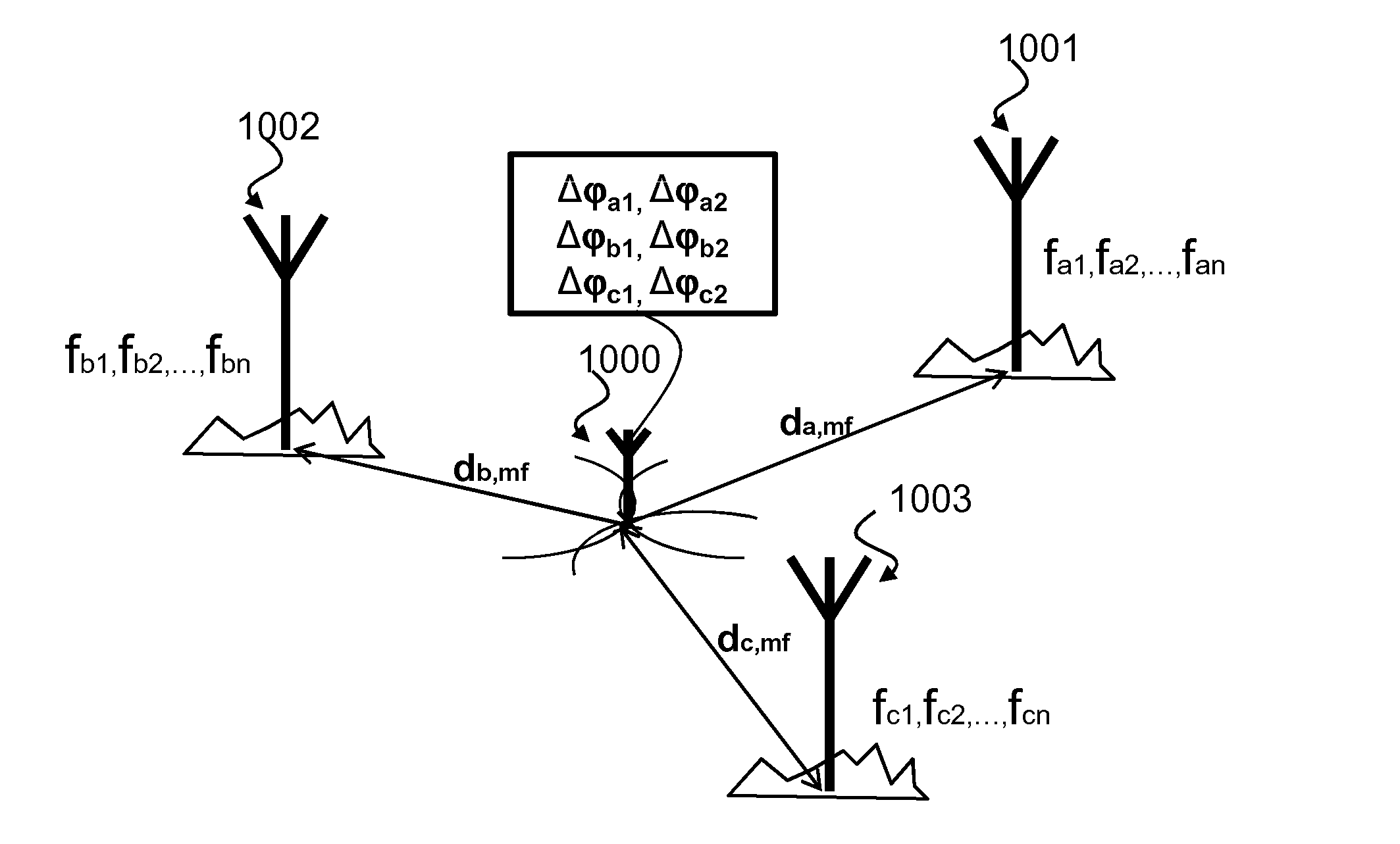
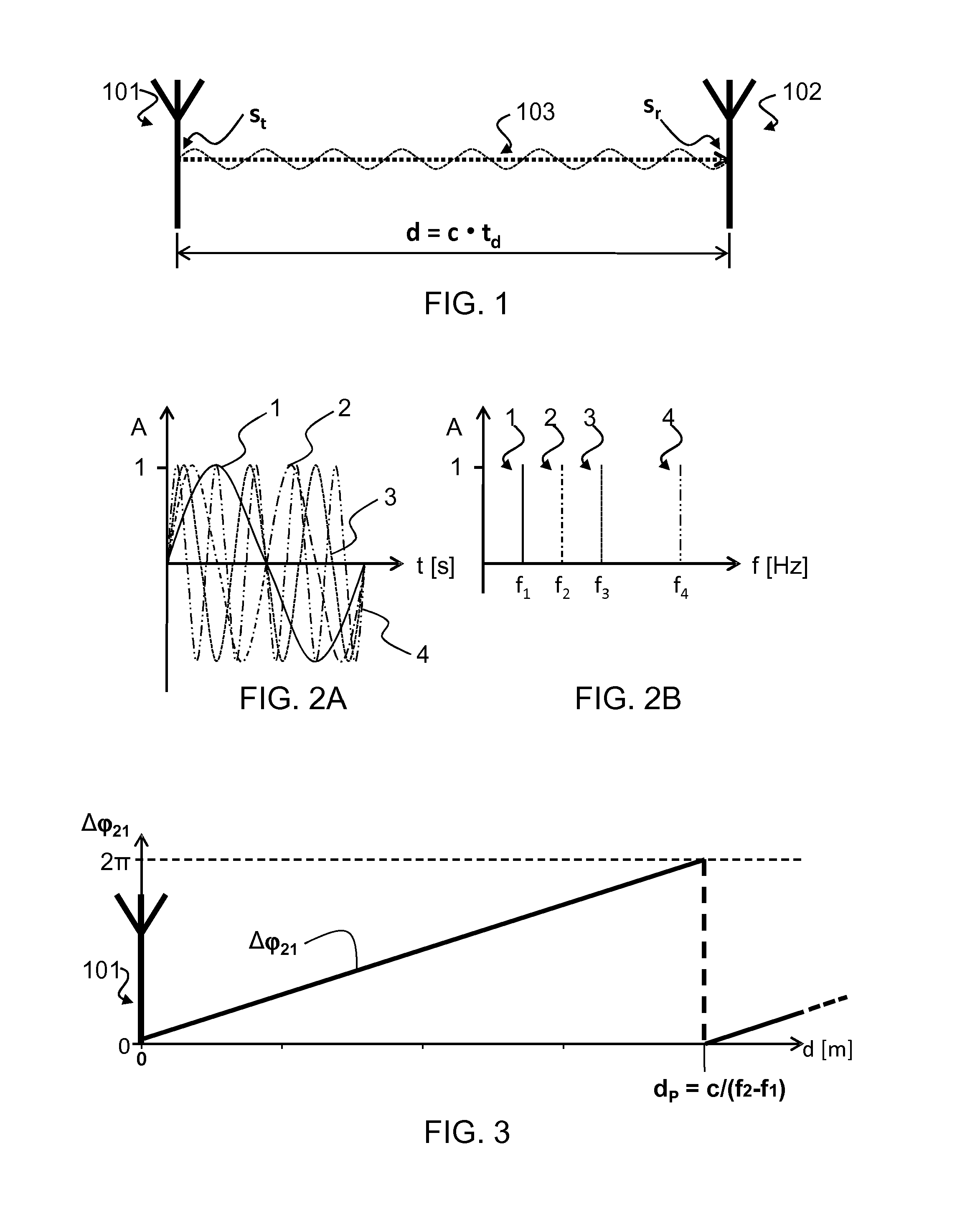
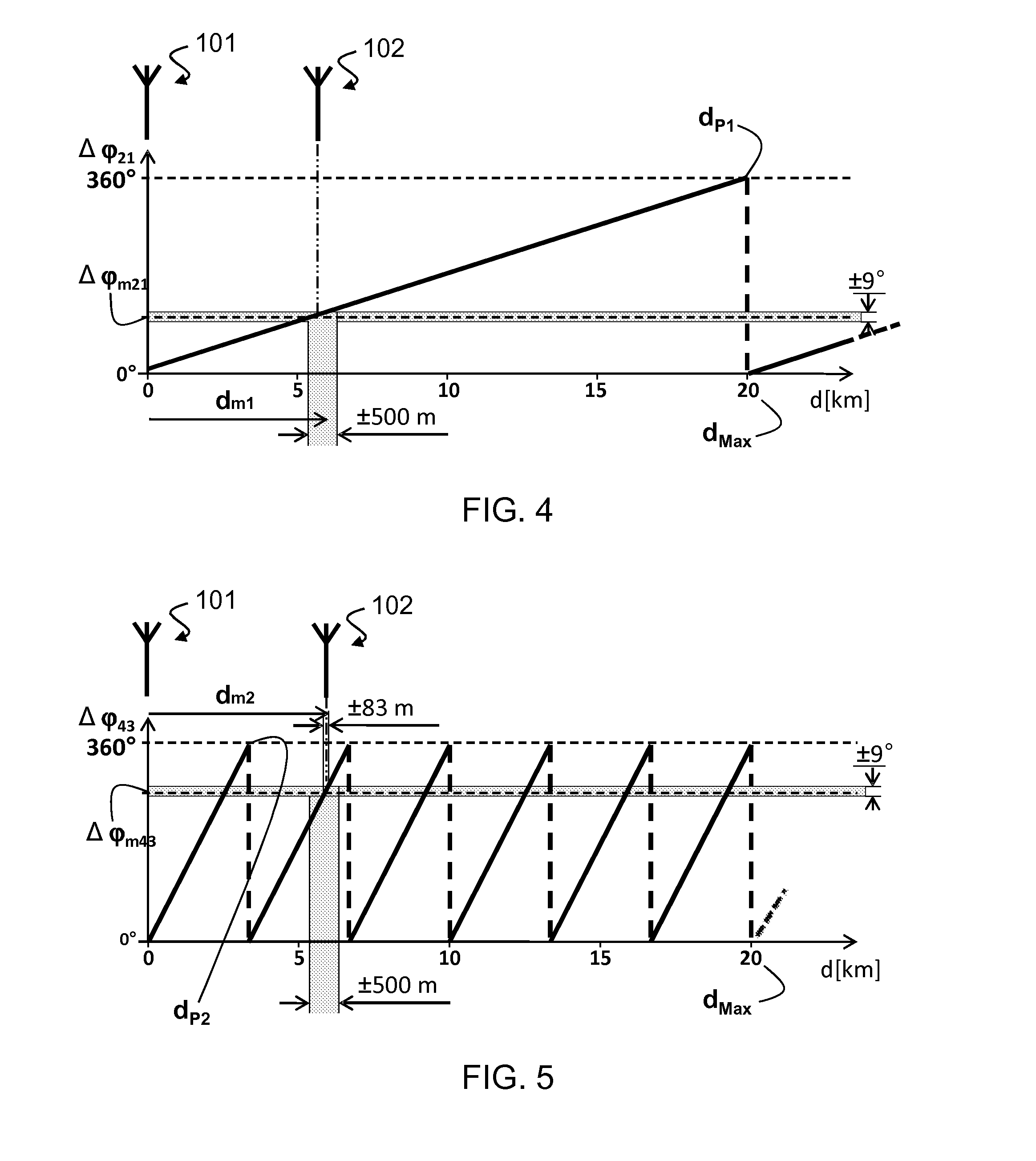
A method for estimating the distance (d) of a receiver (102) from a radio transmitter (101) includes the steps of: receiving (602) radio signals (103, 701) irradiated by the transmitter (101), which include components from which at least three tones (1,2,3,4) are extracted, each having a different frequency; measuring (606) a first phase difference (Δφ21) between first two tones (1, 2) of the at least three tones, whose frequencies (f1, f2) have a first spacing, and measuring a second phase difference (Δφ43) between second two tones (3, 4) of the at least three tones, whose frequencies (f3, f4) have a second spacing, wherein one of the first spacing or second spacing is greater than the other; estimating (607, 611, 613) the distance (d) on the basis of the first phase difference (Δφ21) and the second phase difference (Δφ43).
Owner:EMERGENT MOBILE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com