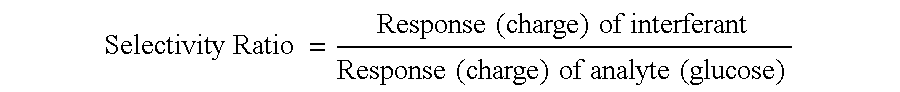Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
673results about "Refining by electric/magnetic means" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
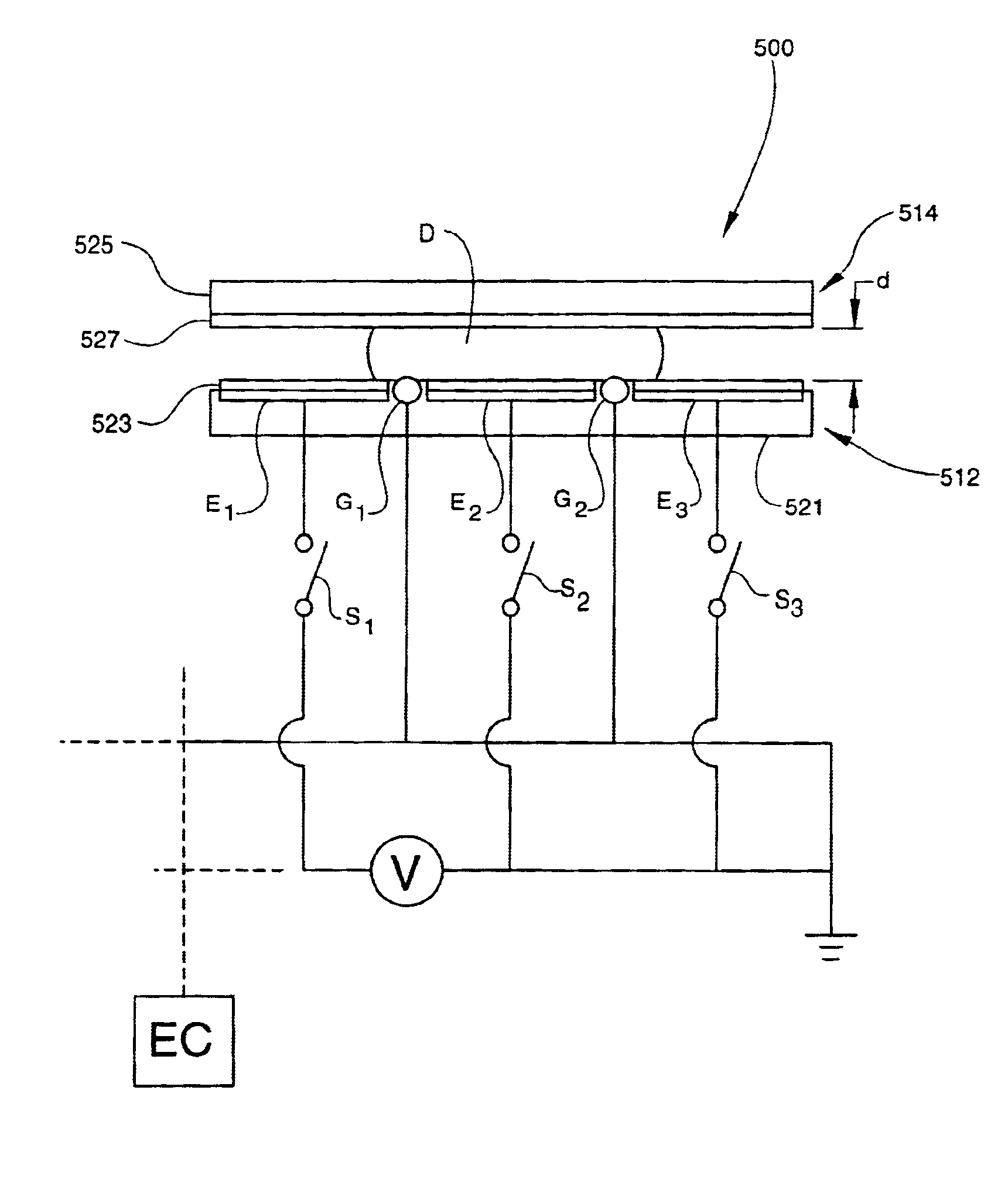
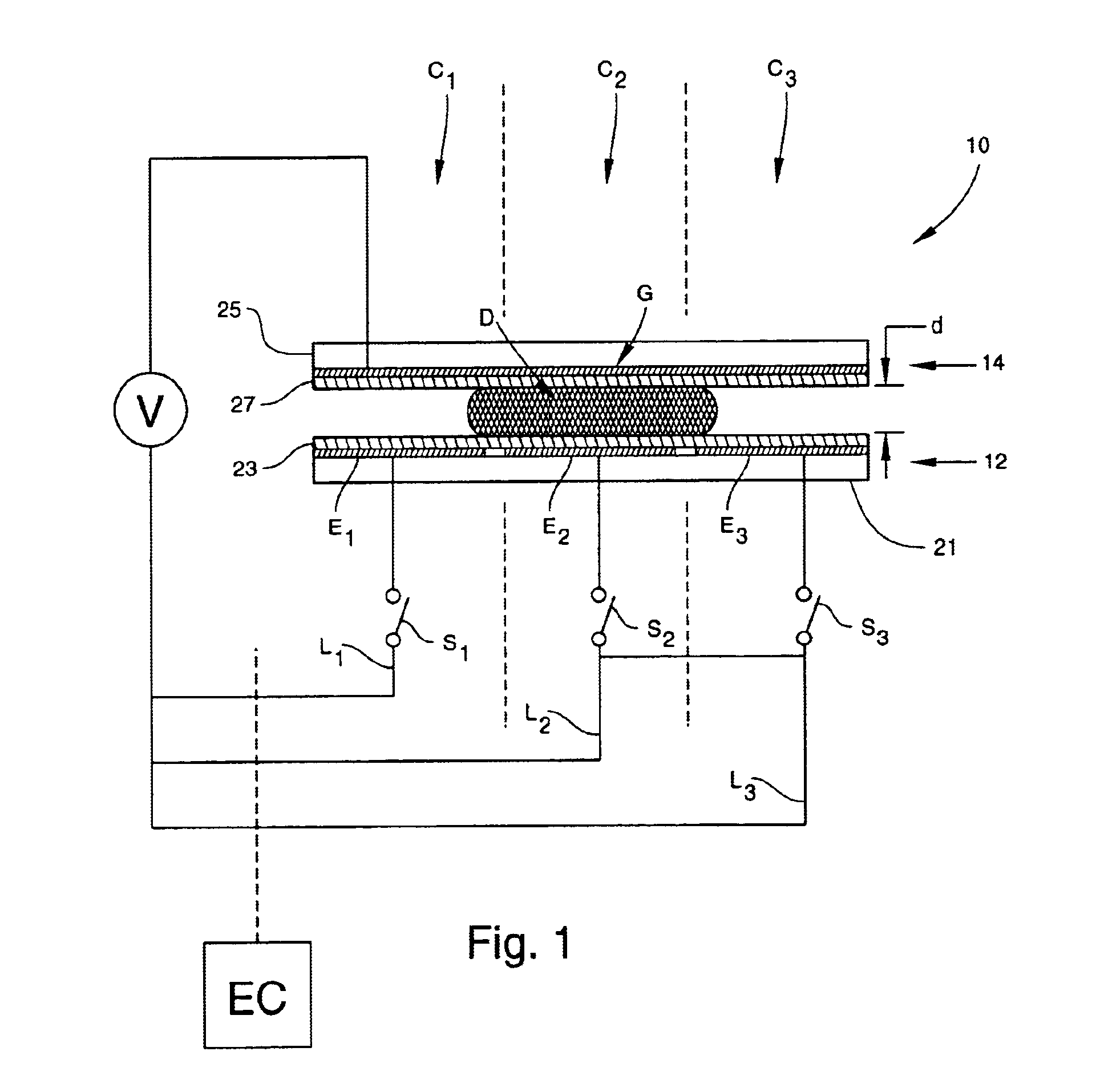
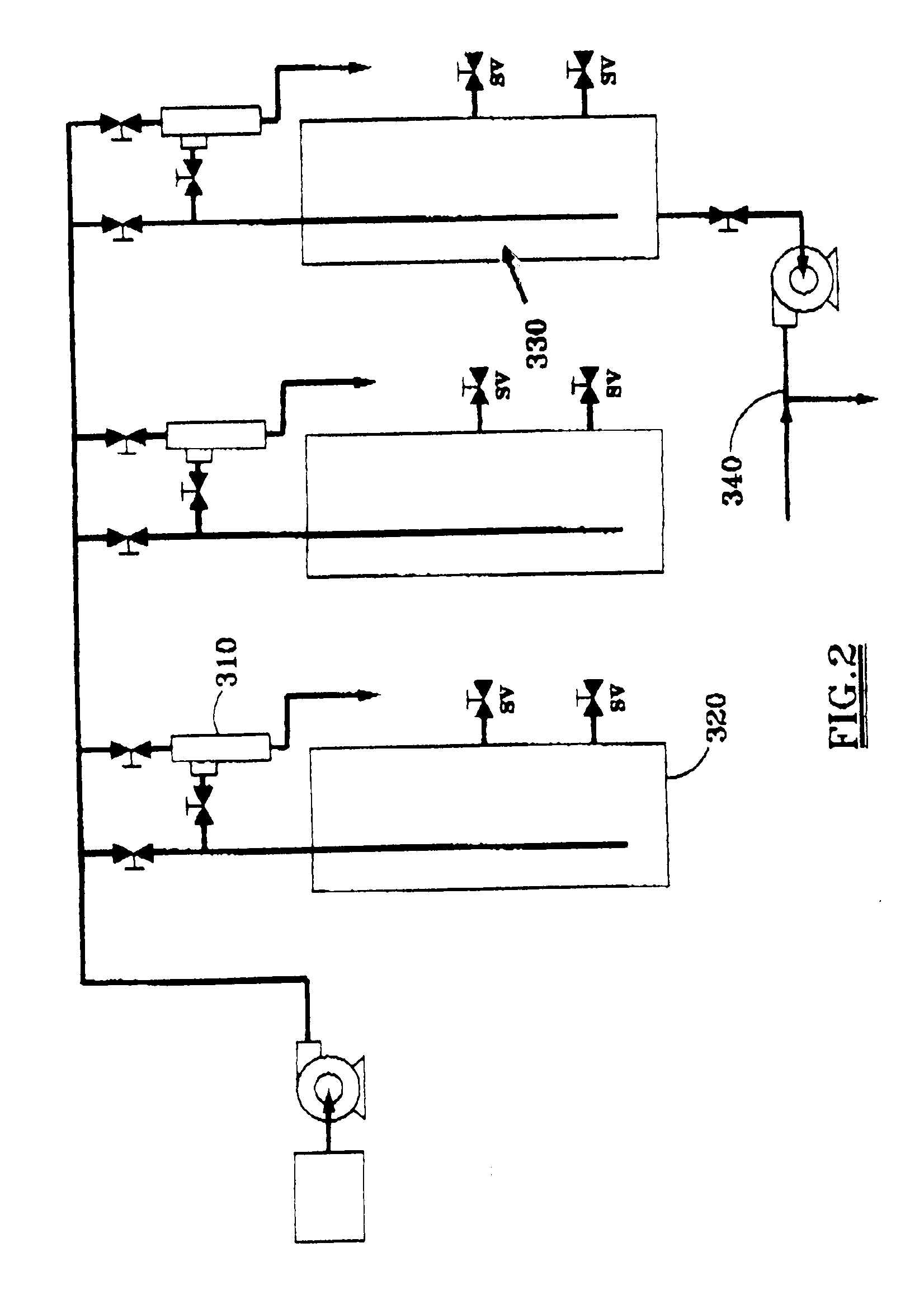
Apparatus for manipulating droplets by electrowetting-based techniques
InactiveUS6911132B2Improve controllabilityImprove accuracyBurnersElectrostatic separatorsElectricityControl manner
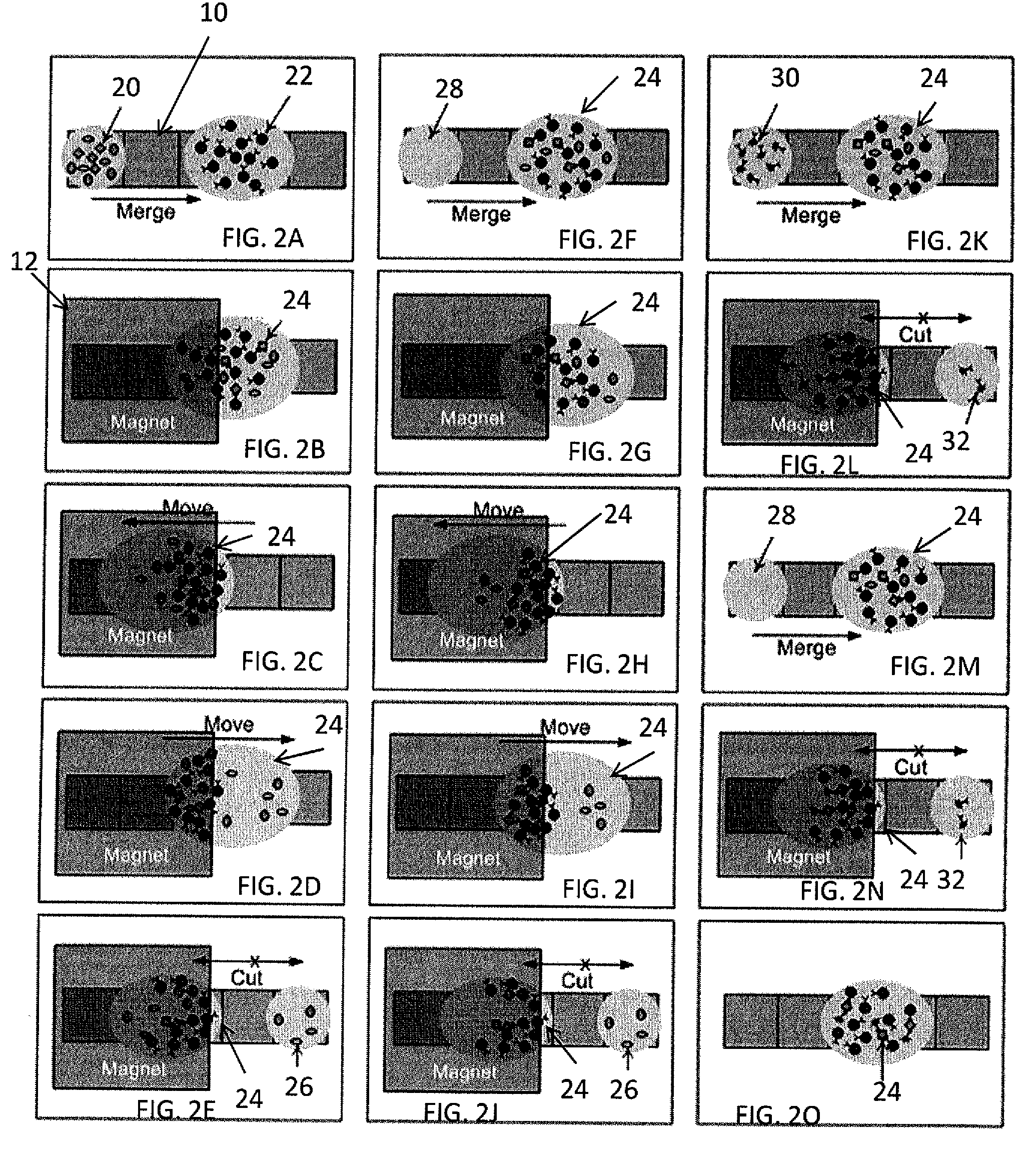
An apparatus is provided for manipulating droplets. The apparatus is a single-sided electrode design in which all conductive elements are contained on one surface on which droplets are manipulated. An additional surface can be provided parallel with the first surface for the purpose of containing the droplets to be manipulated. Droplets are manipulated by performing electrowetting-based techniques in which electrodes contained on or embedded in the first surface are sequentially energized and de-energized in a controlled manner. The apparatus enables a number of droplet manipulation processes, including merging and mixing two droplets together, splitting a droplet into two or more droplets, sampling a continuous liquid flow by forming from the flow individually controllable droplets, and iterative binary or digital mixing of droplets to obtain a desired mixing ratio.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
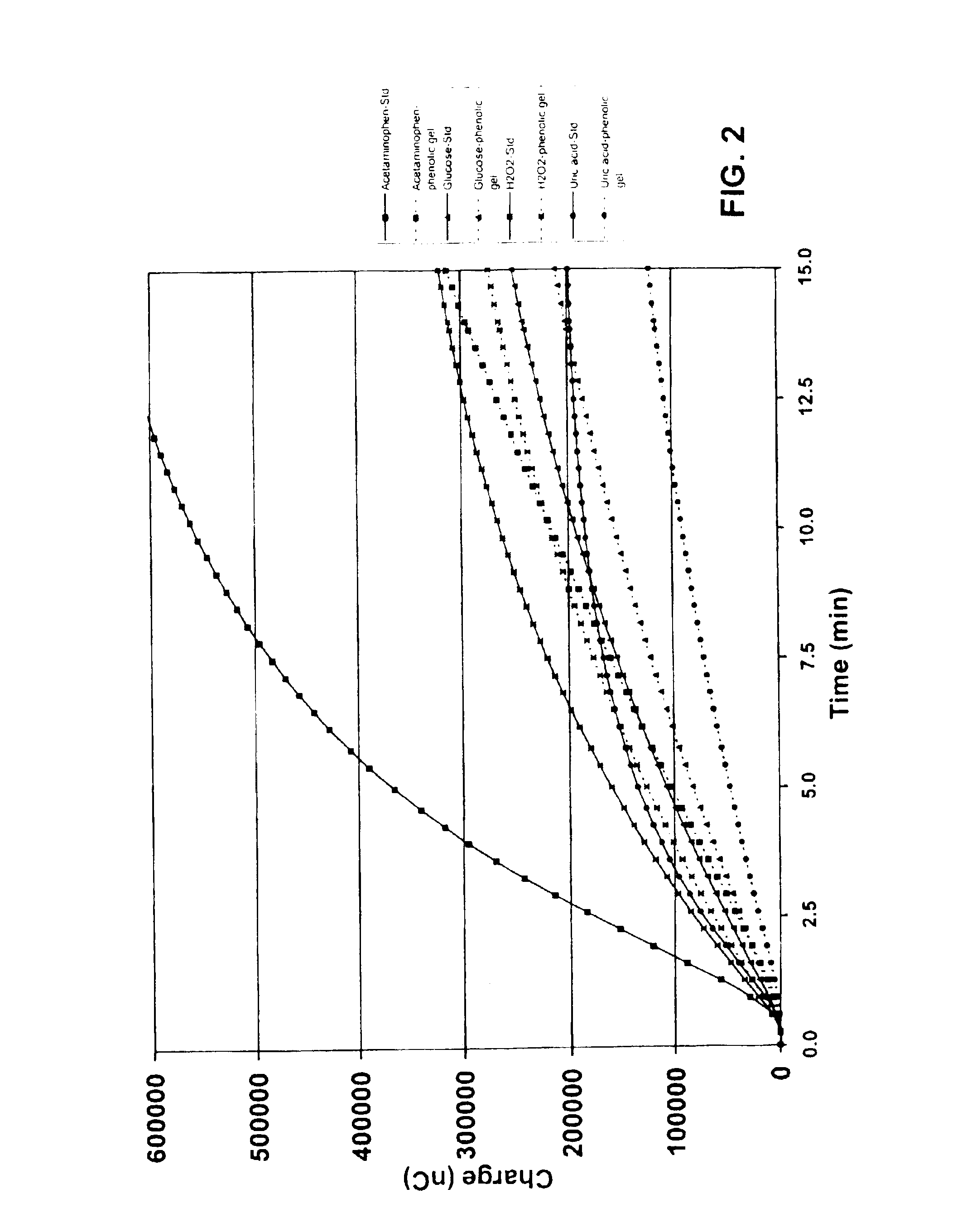
Glucose measuring assembly with a hydrogel
InactiveUS6902905B2Reduce presenceIncrease percentagePowder deliveryElectrotherapyIontophoresis therapyAnalyte
This invention relates to methods for reducing the presence of a compound in an ionically conductive material, e.g., for use in iontophoretic devices, wherein the presence of the compound interferes with detecting a selected analyte. Removal of the compound can typically take place either during or after the manufacture of the ionically conductive material or an assembly comprising this material. Also disclosed are methods for generating selectively permeable barriers on the reactive faces of electrodes. Further, this invention relates to hydrogels comprising one or more biocides, as well as assemblies containing such hydrogels.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC +1
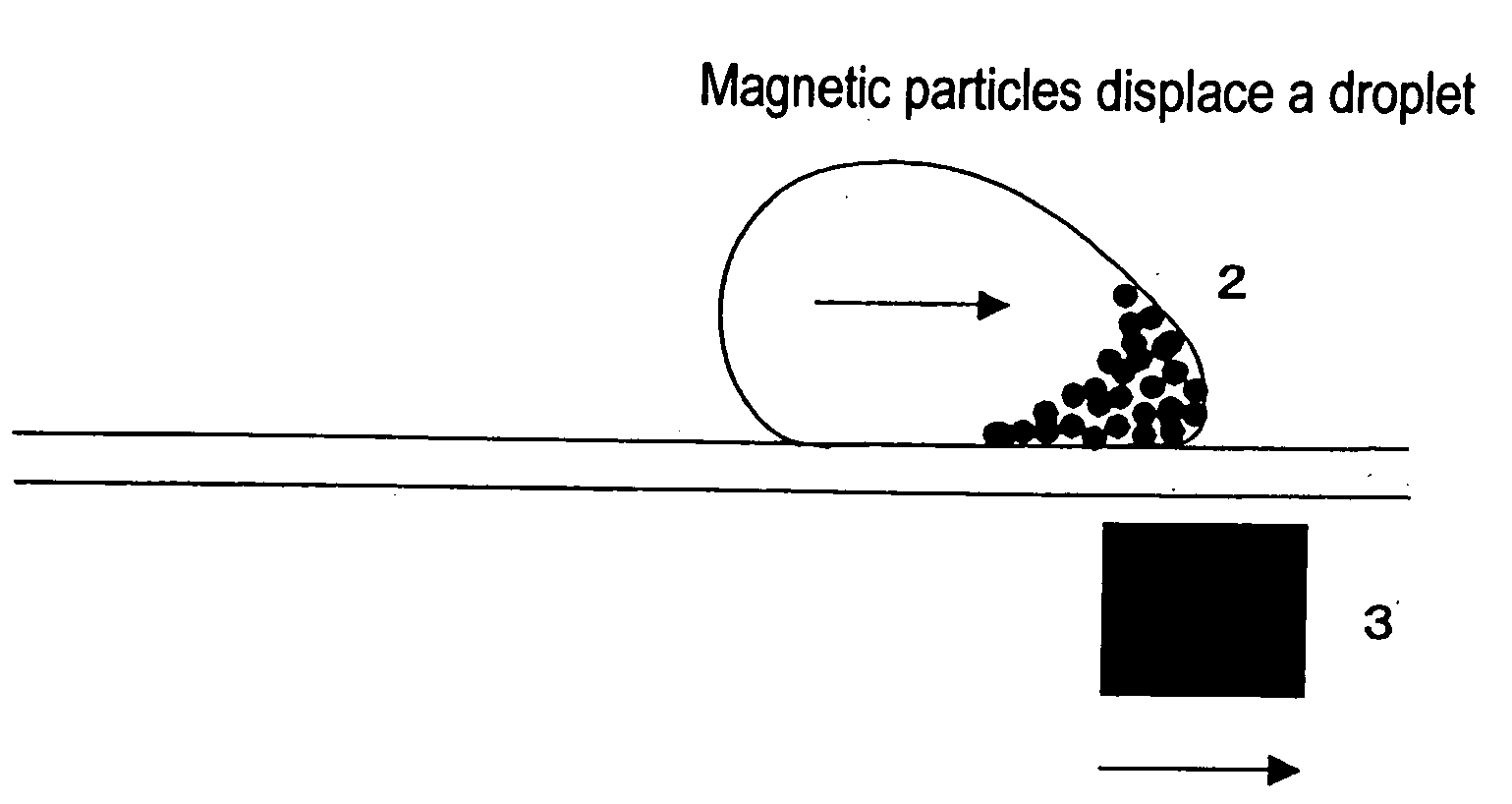
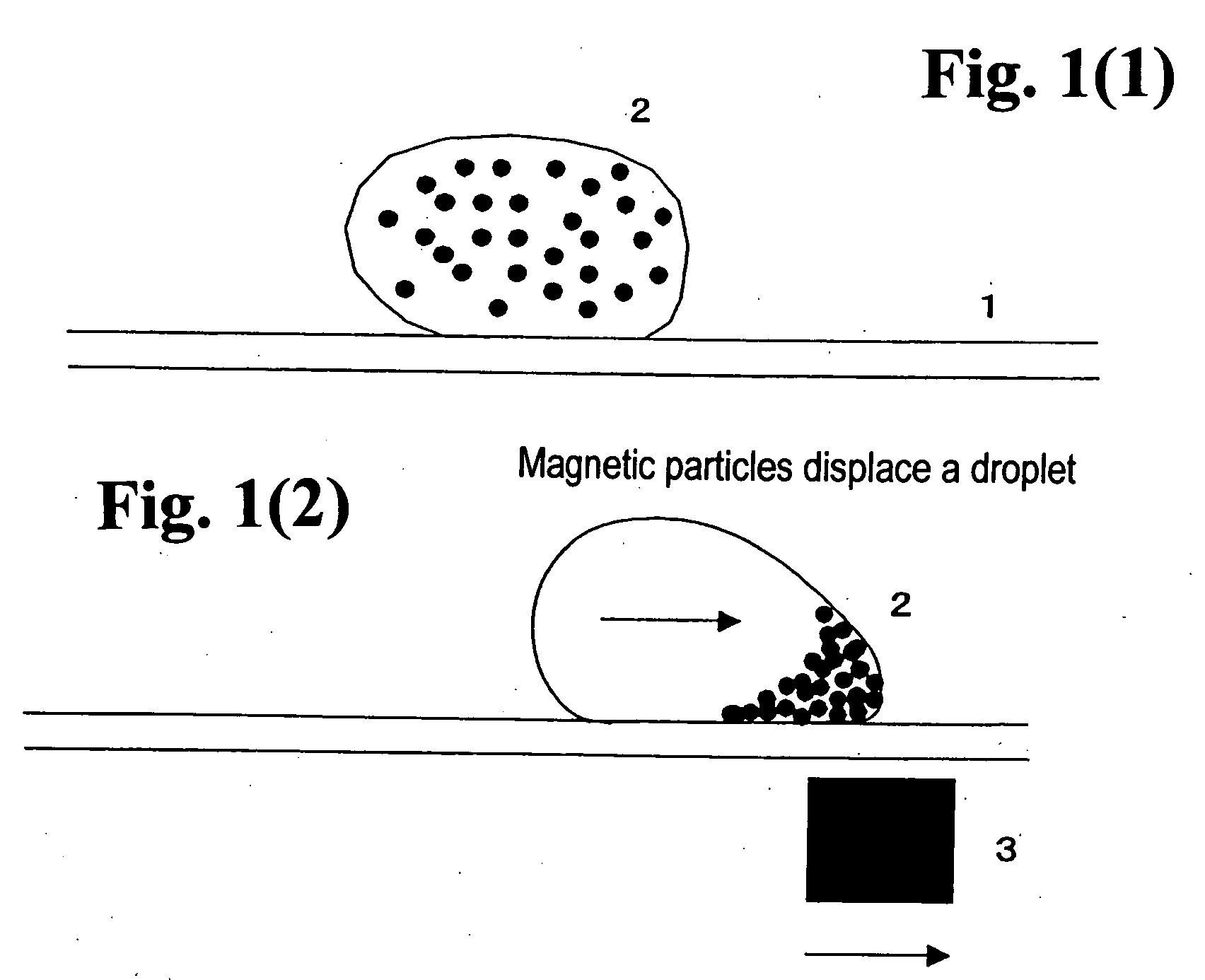
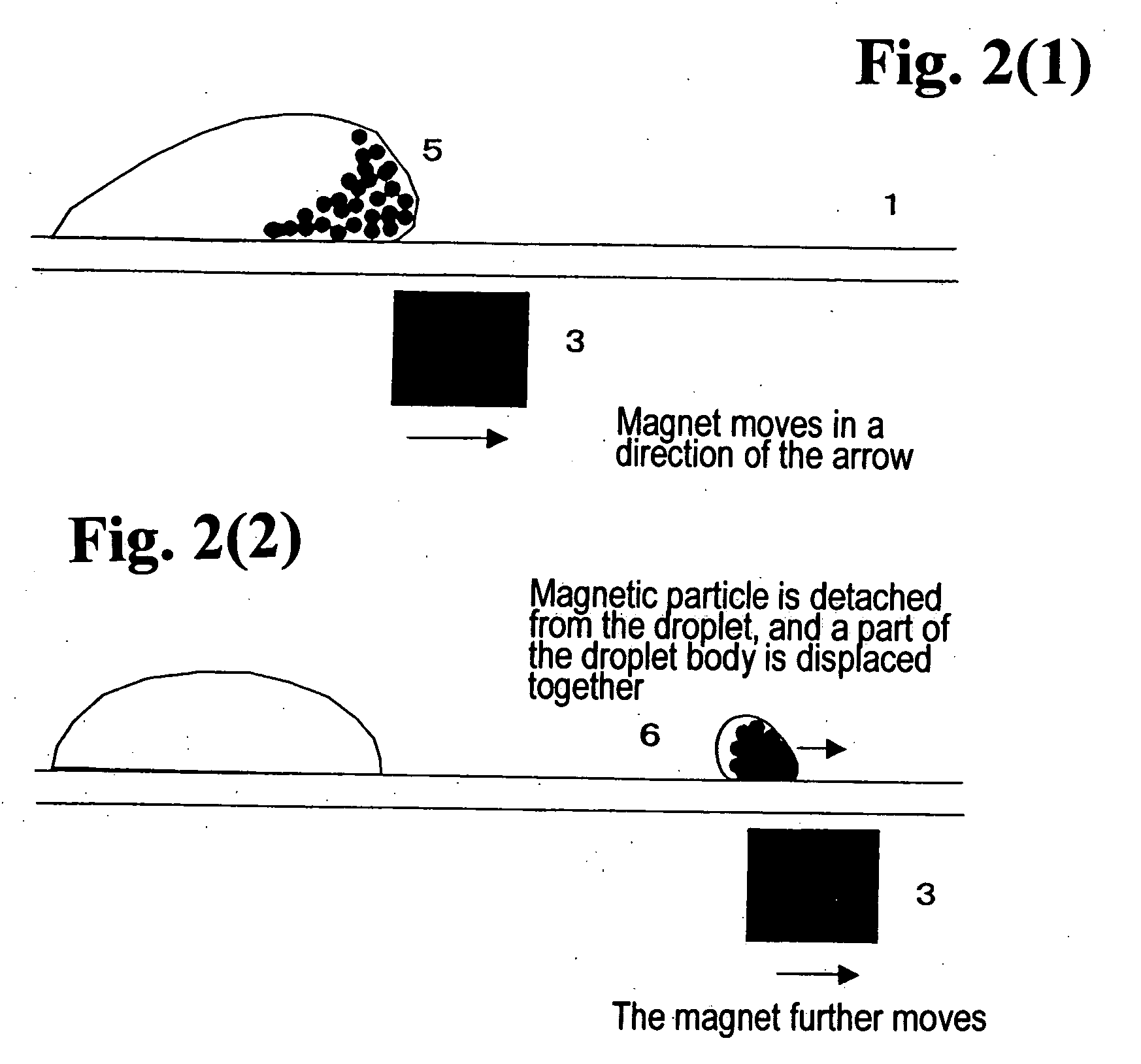
Method for using magnetic particles in droplet microfluidics
ActiveUS20090283407A1Increasing concentration of targetReduce concentrationElectrostatic separatorsLiquid separation by electricityEngineeringDroplet microfluidics
Methods of utilizing magnetic particles or beads (MBs) in droplet-based (or digital) microfluidics are disclosed. The methods may be used in enrichment or separation processes. A first method employs the droplet meniscus to assist in the magnetic collection and positioning of MBs during droplet microfluidic operations. The sweeping movement of the meniscus lifts the MBs off the solid surface and frees them from various surface forces acting on the MBs. A second method uses chemical additives to reduce the adhesion of MBs to surfaces. Both methods allow the MBs on a solid surface to be effectively moved by magnetic force. Droplets may be driven by various methods or techniques including, for example, electrowetting, electrostatic, electromechanical, electrophoretic, dielectrophoretic, electroosmotic, thermocapillary, surface acoustic, and pressure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Alignment of carbon nanotubes using magnetic particles
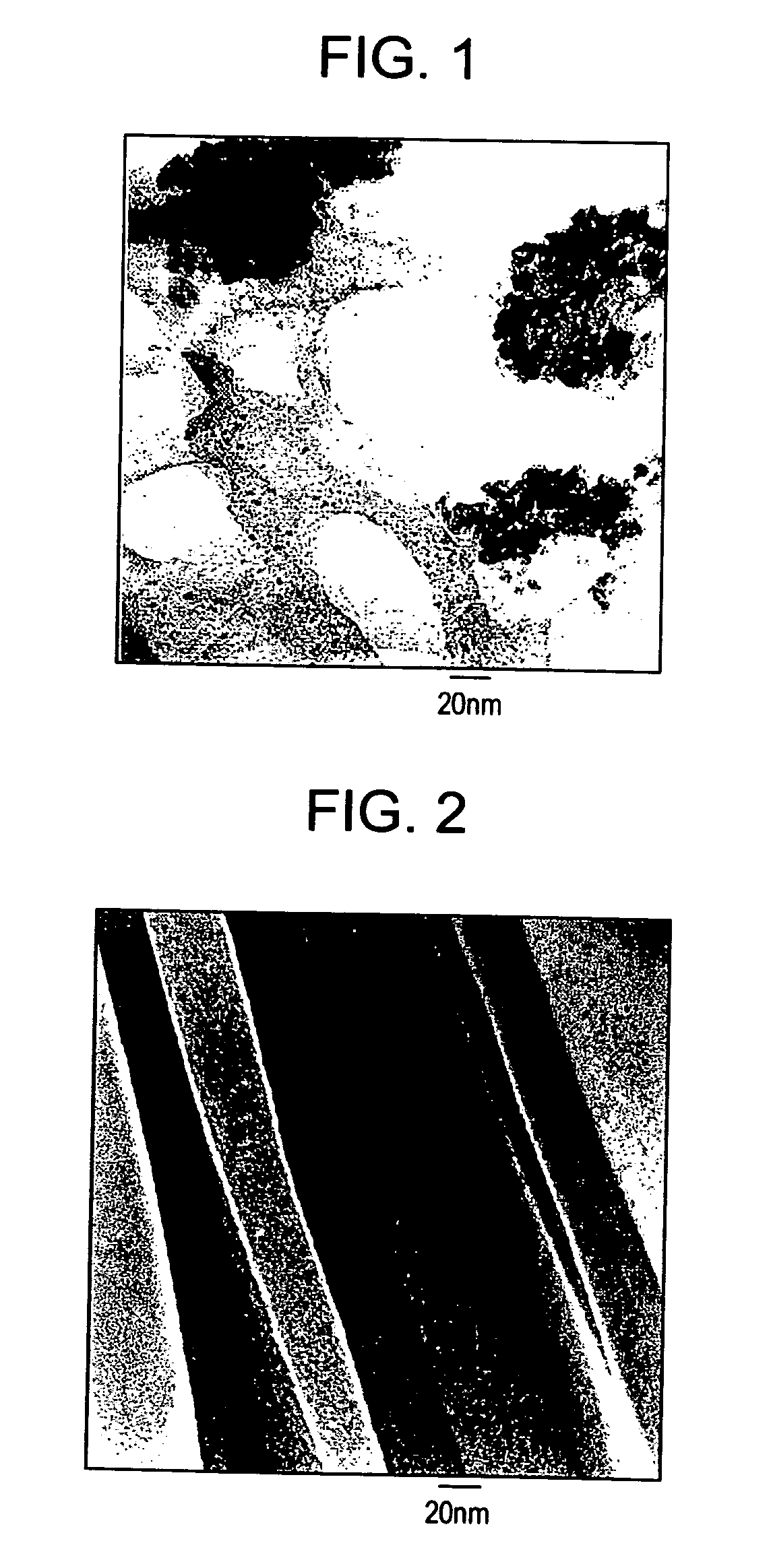
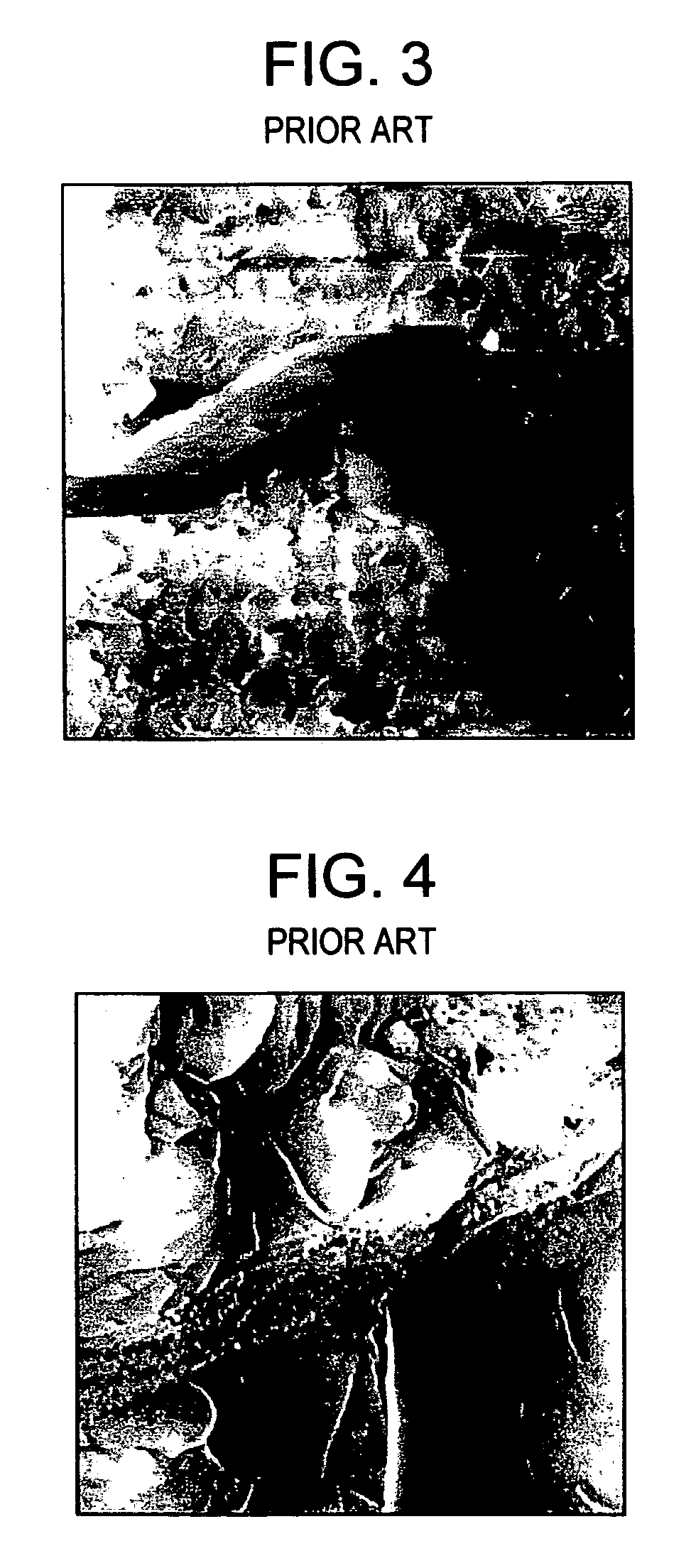
InactiveUS20050239948A1Material nanotechnologyLiquid separation by electricityMagnetite NanoparticlesNanometre
Methods are provided for aligning carbon nanotubes and for making a composite material comprising aligned carbon nanotubes. The method for aligning carbon nanotubes comprises adsorbing magnetic nanoparticles to carbon nanotubes dispersed in a fluid medium to form a magnetic particle-carbon nanotube composite in the fluid medium; and exposing the composite to a magnetic field effective to align the nanotubes in the fluid medium. The method for making a composite material comprising aligned carbon nanotubes comprises (1) adsorbing magnetic nanoparticles to carbon nanotubes to form a magnetic particle-carbon nanotube composite; (2) dispersing the magnetic particle-carbon nanotube composite in a fluid matrix material to form a mixture; (3) exposing the mixture to a magnetic field effective to align the nanotubes in the mixture; and (4) solidifying the fluid matrix material to form a nanotube / matrix material composite comprising the aligned nanotubes which remain aligned in the absence of said magnetic field.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE RES FOUND +1
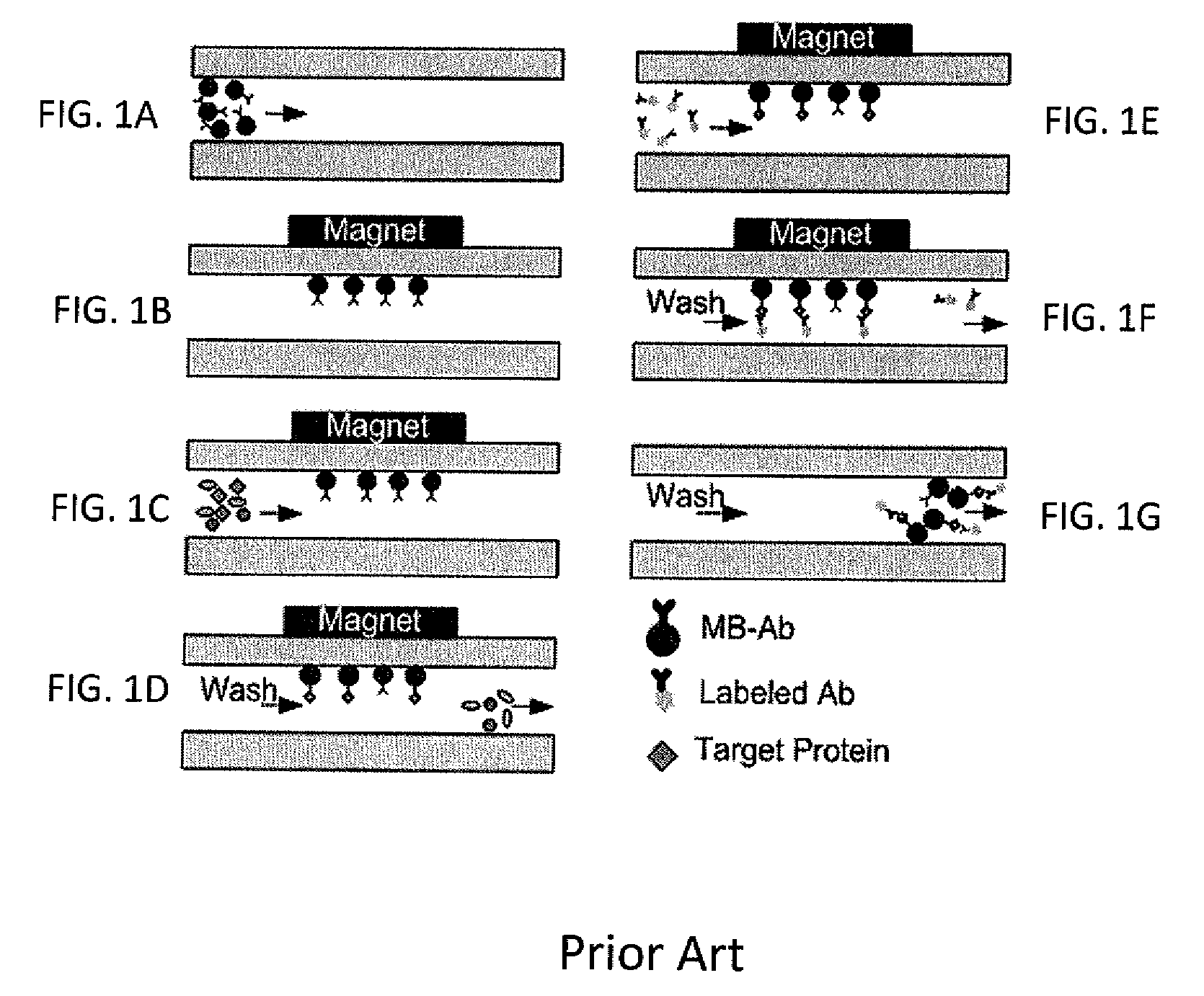
Bead Incubation and Washing on a Droplet Actuator
The present invention relates to bead incubating and washing on a droplet actuator. Methods for incubating magnetically responsive beads that are labeled with primary antibody, a sample (i.e., analyte), and secondary reporter antibodies on a magnet, on and off a magnet, and completely off a magnet are provided. Also provided are methods for washing magnetically responsive beads using shape-assisted merging of droplets. Also provided are methods for shape-mediated splitting, transporting, and dispensing of a sample droplet that contains magnetically responsive beads. The apparatuses and methods of the invention provide for rapid time to result and optimum detection of an analyte in an immunoassay.
Owner:ADVANCED LIQUID LOGIC
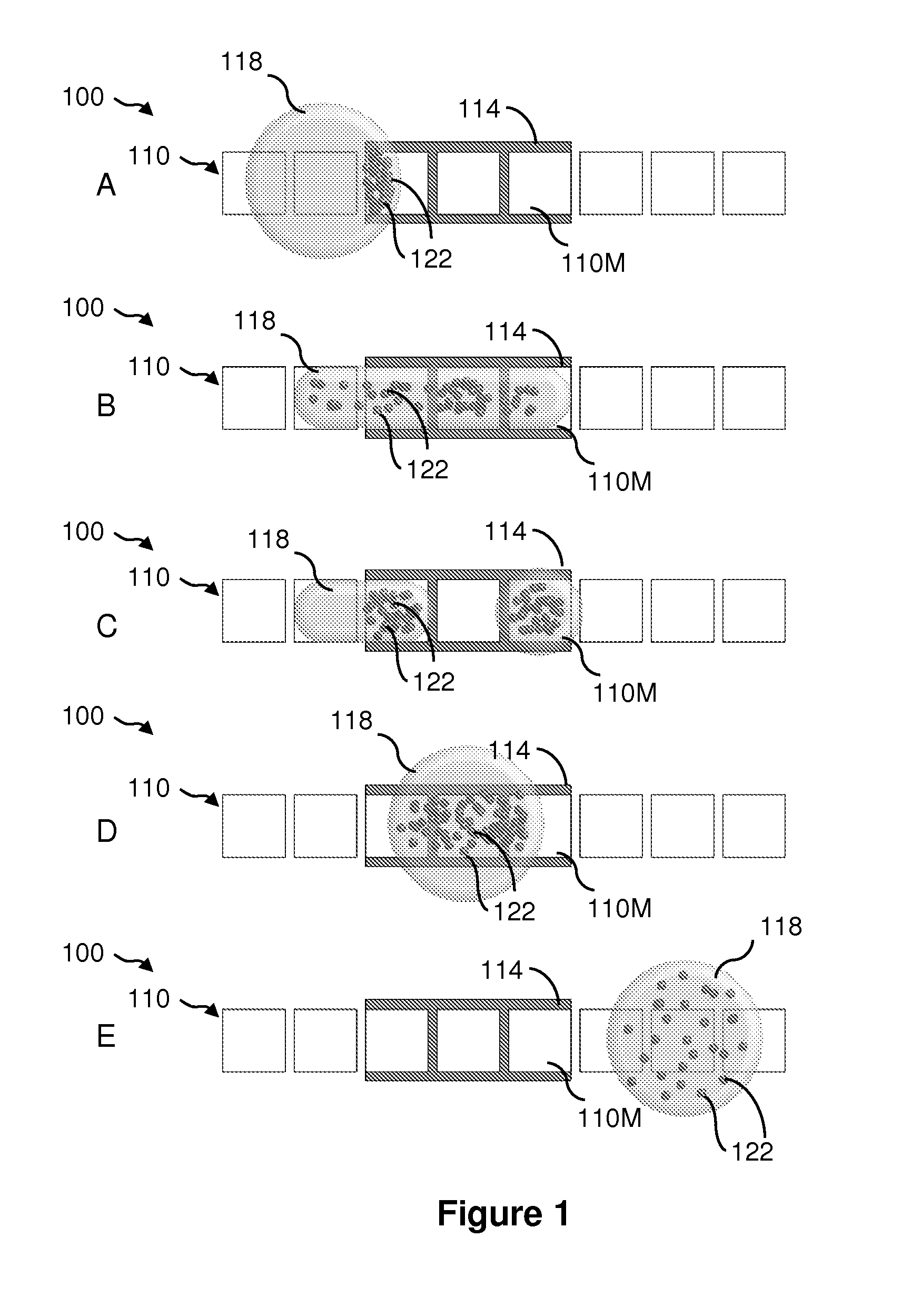
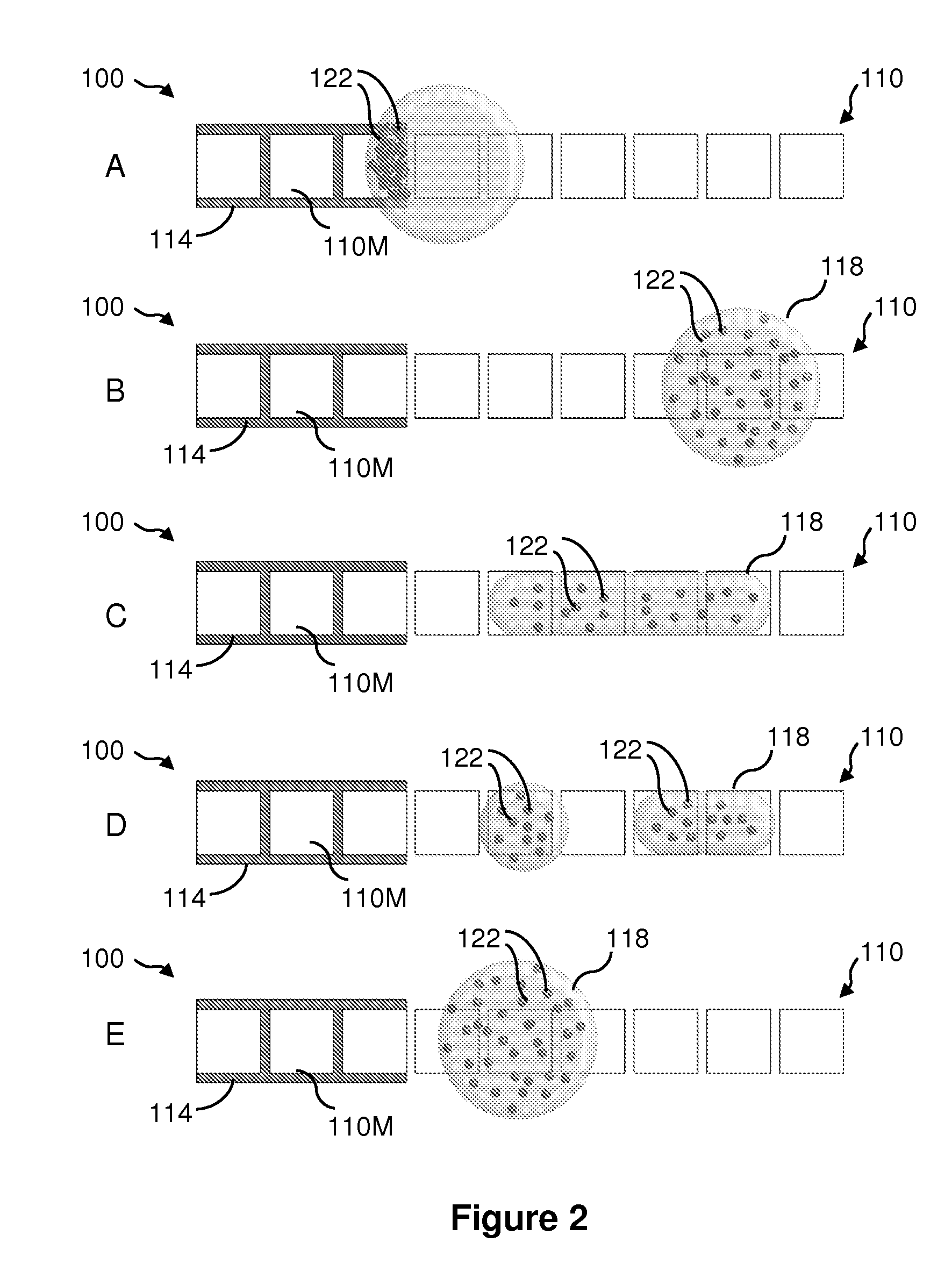
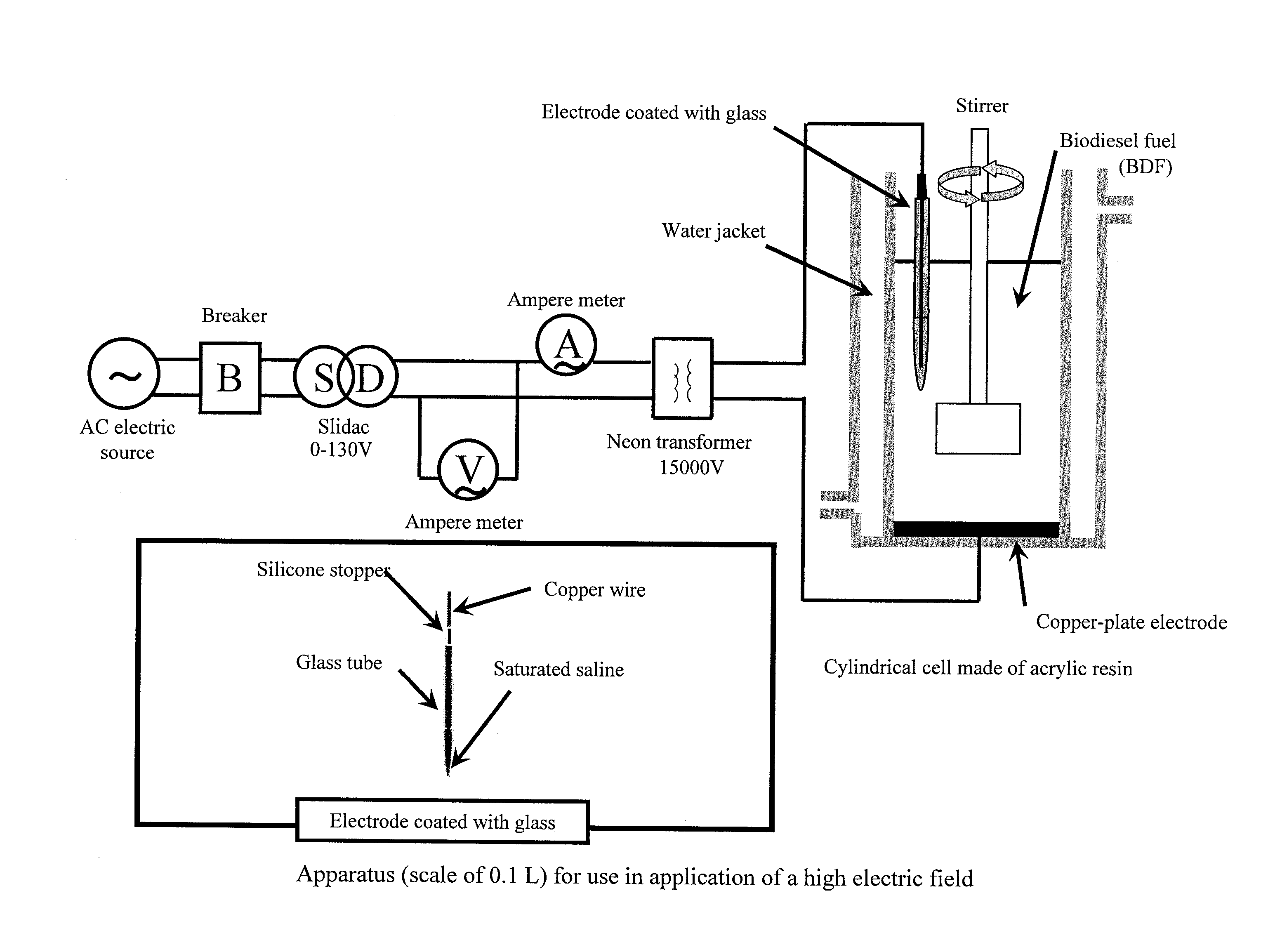
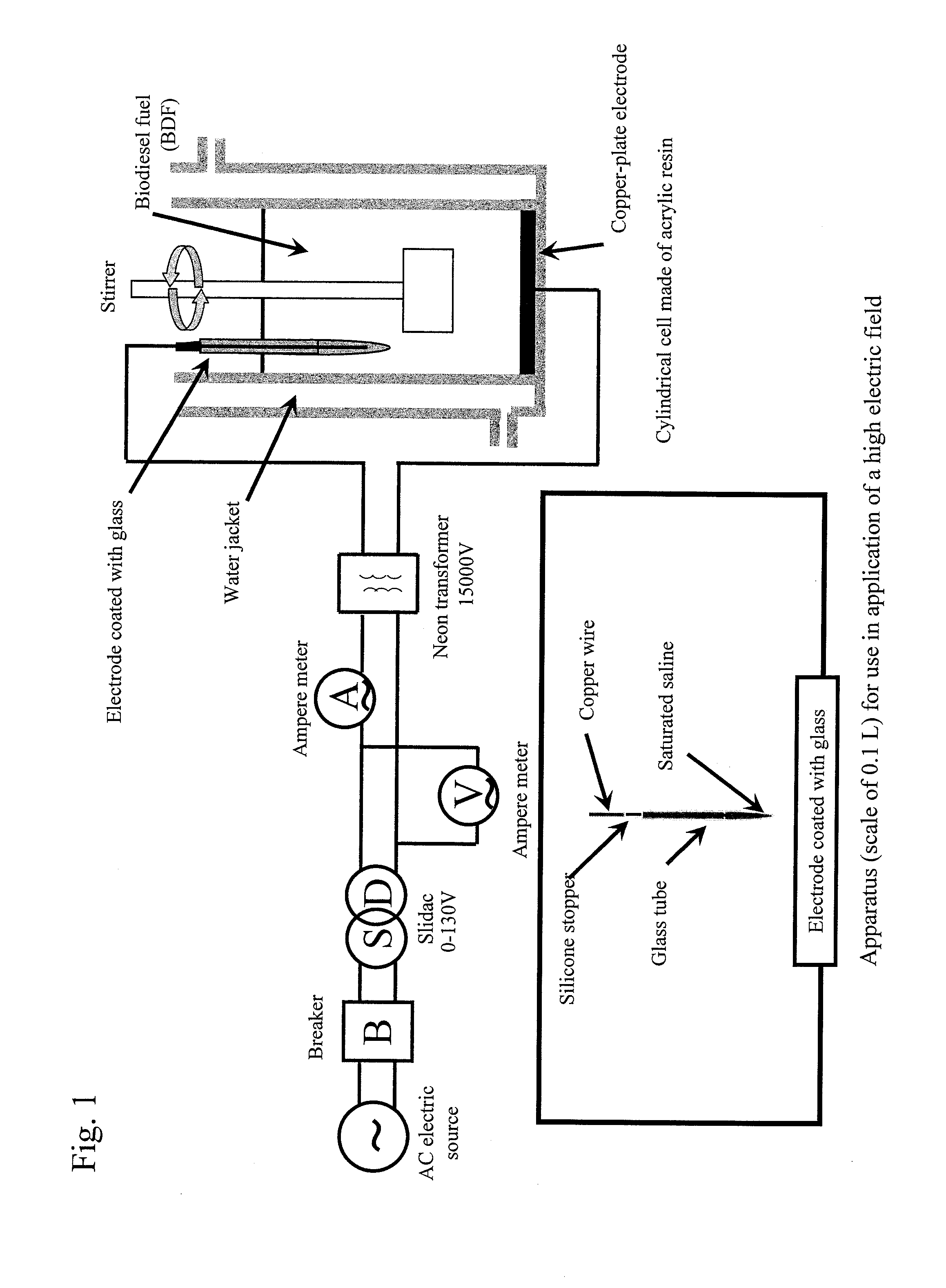
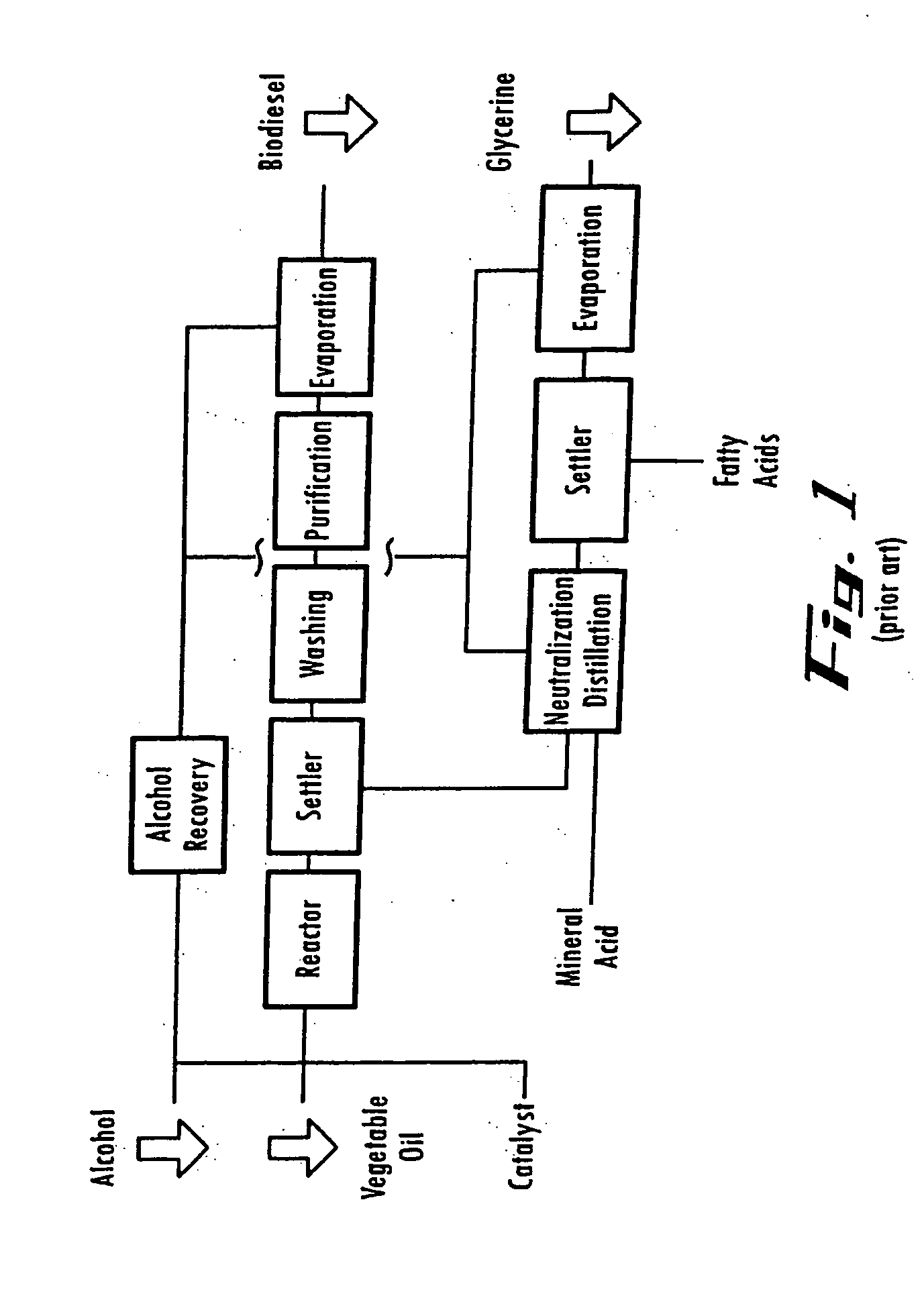
Method for purifying biodiesel fuel
InactiveUS20090025277A1Preventing and greatly reducing generationWater/sewage treatment by irradiationLiquid separation by electricityDemulsifierBiodiesel
Provided is a method for purifying a biodiesel fuel while completely preventing or greatly reducing generation of waste water. The present invention relates to a method for purifying a biodiesel fuel characterized by applying an electric field to or heating a crude biodiesel fuel and a method for purifying a biodiesel fuel characterized by adding water (preferably containing a demulsifier such as an inorganic calcium salt or a magnesium salt) to a crude biodiesel fuel to form W / O emulsion, and breaking the emulsion by application of an electric field or heating, etc.
Owner:KAGOSHIMA UNIV
Component separation device
ActiveUS8273302B2High collecting percentageEfficient separationElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentInlet channelSolid particle
A component separating device includes a flow channel, an acoustic wave generator for generating an acoustic wave in the flow channel, a first inlet channel for introducing a fist solution containing solid particles into the flow channel, a second inlet channel for introducing a second solution, and outlet channels for discharging a solution from the flow channel. A density grade generator is provided at the first inlet channel for forming a density grade of the solid particles. This component separating device extracts the solid particles into a high-purity solution at a high collecting rate.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Bilge water reclamation system and process
InactiveUS6902678B2Reduce pollutantsEasy to processLiquid separation by electricityAuxillariesOil retentionBilge
A system and method for treating and removing hydrocarbon and other contaminants in bilge and ballast water, utilizing a multiple progressive process that chemically and electrically treats-and removes contaminants. Wastewater, received by a sump, is transmitted to a holding tank and treated, over a period of time while-influent wastewater continues off loading. The wastewater is pumped to an oil / water separator tank that decants free-floating oil from the wastewater to an oil retention tank. The wastewater then undergoes an electrocoagulation process where emulsions are broken and compounds that further aid treatment are created. The treated water flows to a retention / separation tank where contaminant particles coalesce and separate. Water is decanted and transferred to a clean water holding tank through an ozone injection system and an activated carbon filter. Treated water is recirculated until it exits the system meeting discharge limits for organics and metals allowing release into the environment.
Owner:TIPTON GARY A
System and Process for Treatment and De-halogenation of Ballast Water
A system and process for de-halogenating ballast water before releasing the ballast water from the vessel. In one embodiment, the system comprises a means for measuring the halogen content of the ballast water, a reducing agent source in fluid communication with the ballast water, and a means for controlling the amount of reducing agent supplied to the ballast water. In one aspect, the means for measuring the halogen content comprises one or more oxidation / reduction potential analyzers. In another embodiment, the system comprises one or more hypochlorite electrolytic cells for generating hypochlorite to treat the ballast water.One embodiment of the process for de-halogenating ballast water comprises measuring the oxidation / reduction potential of the ballast water and adding one or more reducing agents to the ballast water to de-halogenate the ballast water in response to the measured oxidation / reduction potential. In one aspect, the oxidation / reduction potential is modulated so that excess reducing agent is present in the ballast water.
Owner:DE NORA WATER TECH
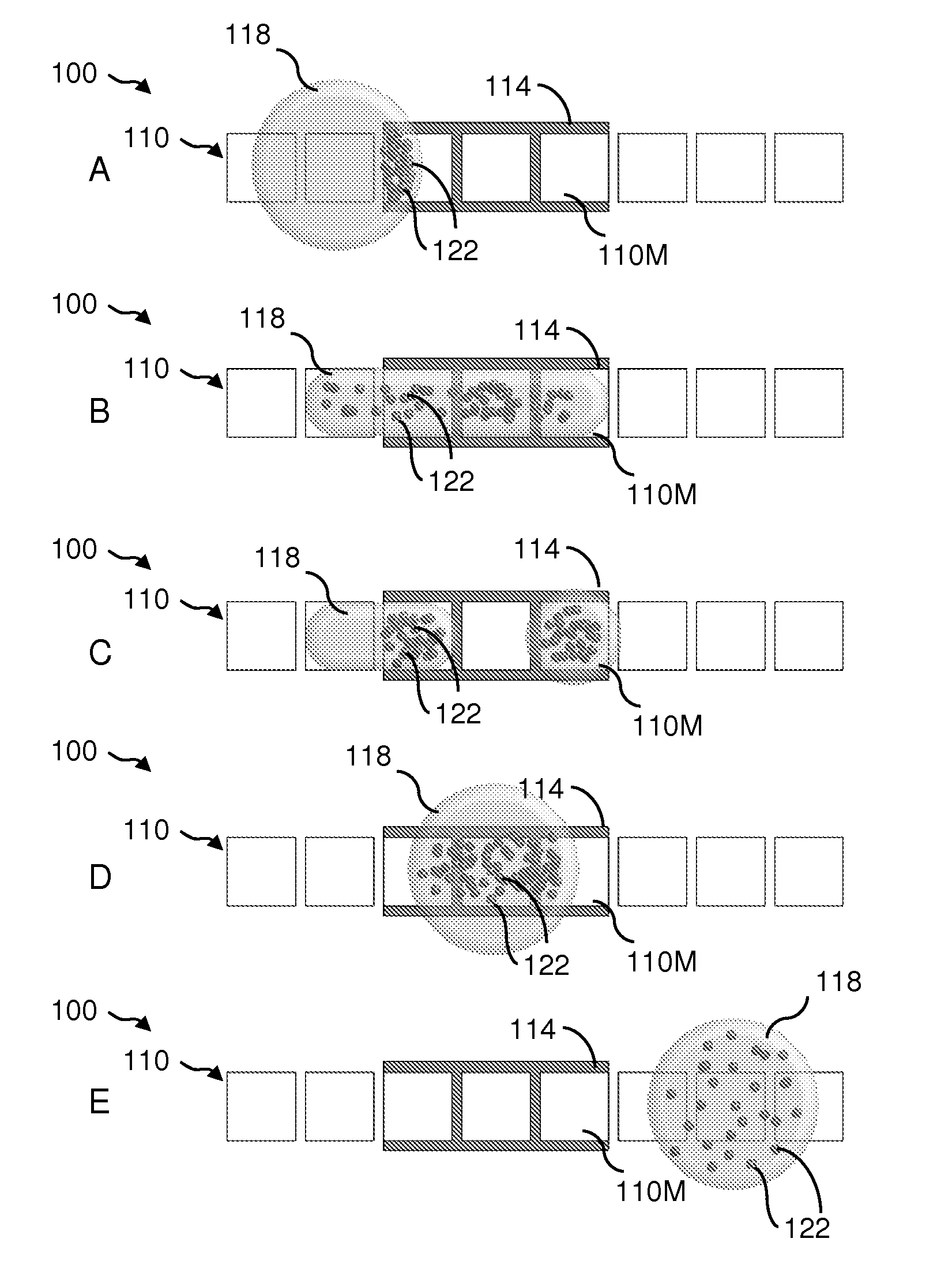
Microchemistry reaction method and device
A chemical reaction is conducted in a fluid of a droplet inside a reaction receptacle or on a surface of a reaction substrate. Fluctuations of a magnetic field are applied to the droplet including an aqueous solution having magnetic body particles with a hydrophilic surface, and a physical force is transmitted to the surrounding aqueous solution through the magnetic body particles. The droplet is thus moved by the physical force to conduct an operation necessary for a chemical reaction.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
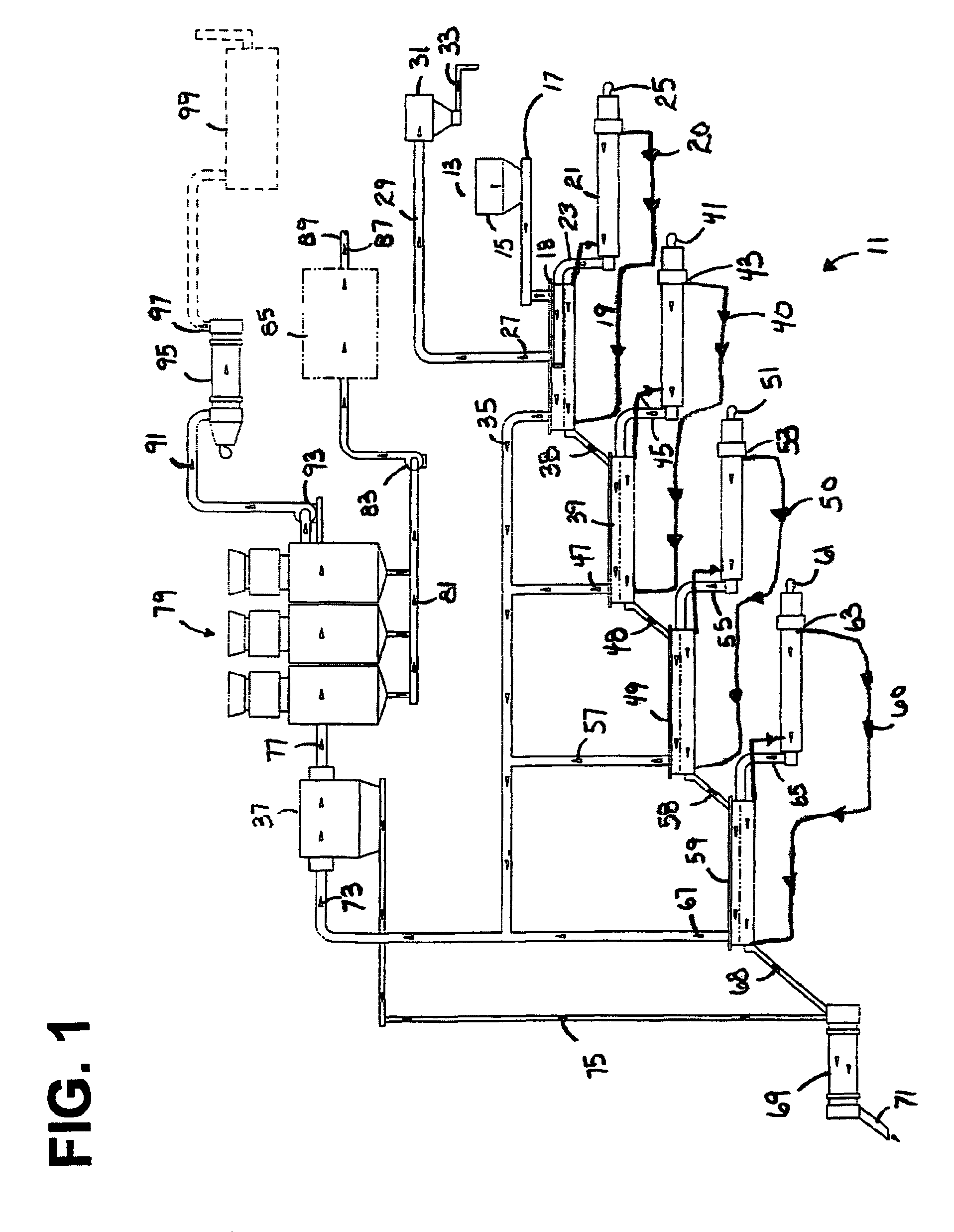
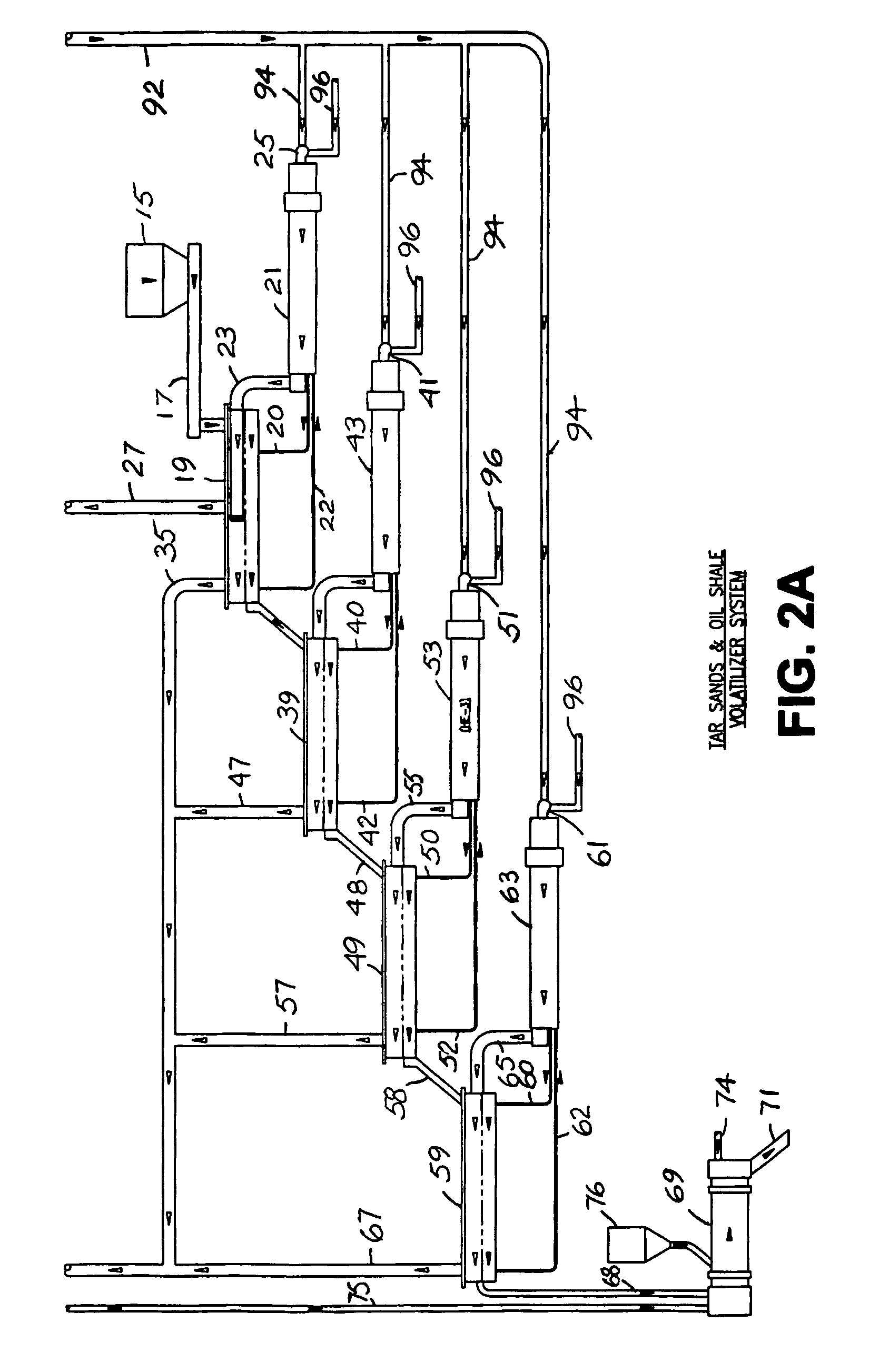
Thermal recovery of petroleum crude oil from tar sands and oil shale deposits
InactiveUS7807048B2Rule out the possibilityEliminate needHydrocarbon oil cracking processIndirect heating destructive distillationParticulatesFuel oil
A tar sand volatilizer system thermally removes petroleum crude oil from tar sands or shale oil. A series of heated augers or thermal screws are used to elevate material temperature gradually using conductive heat transfer. The thermal screws blades and auger case receive a heated fluid. The screws are driven by variable speed drive systems. The unit is sized for any throughput rate desired. Hot clean material discharges into a rotary cooler and re-hydrator unit. The exhaust gases are pulled through a high temperature filter collector for particulate removal. The particulate free petroleum vapor laden hot gas exits the filter house into a multi stage condenser system with water chillers where the vapor temperature is gradually cooled. A microwave upgrader system processes crude oil using catalyst injected microwave technology to produce a diesel like fuel oil in a continuous process stream.
Owner:COLLETTE JERRY R
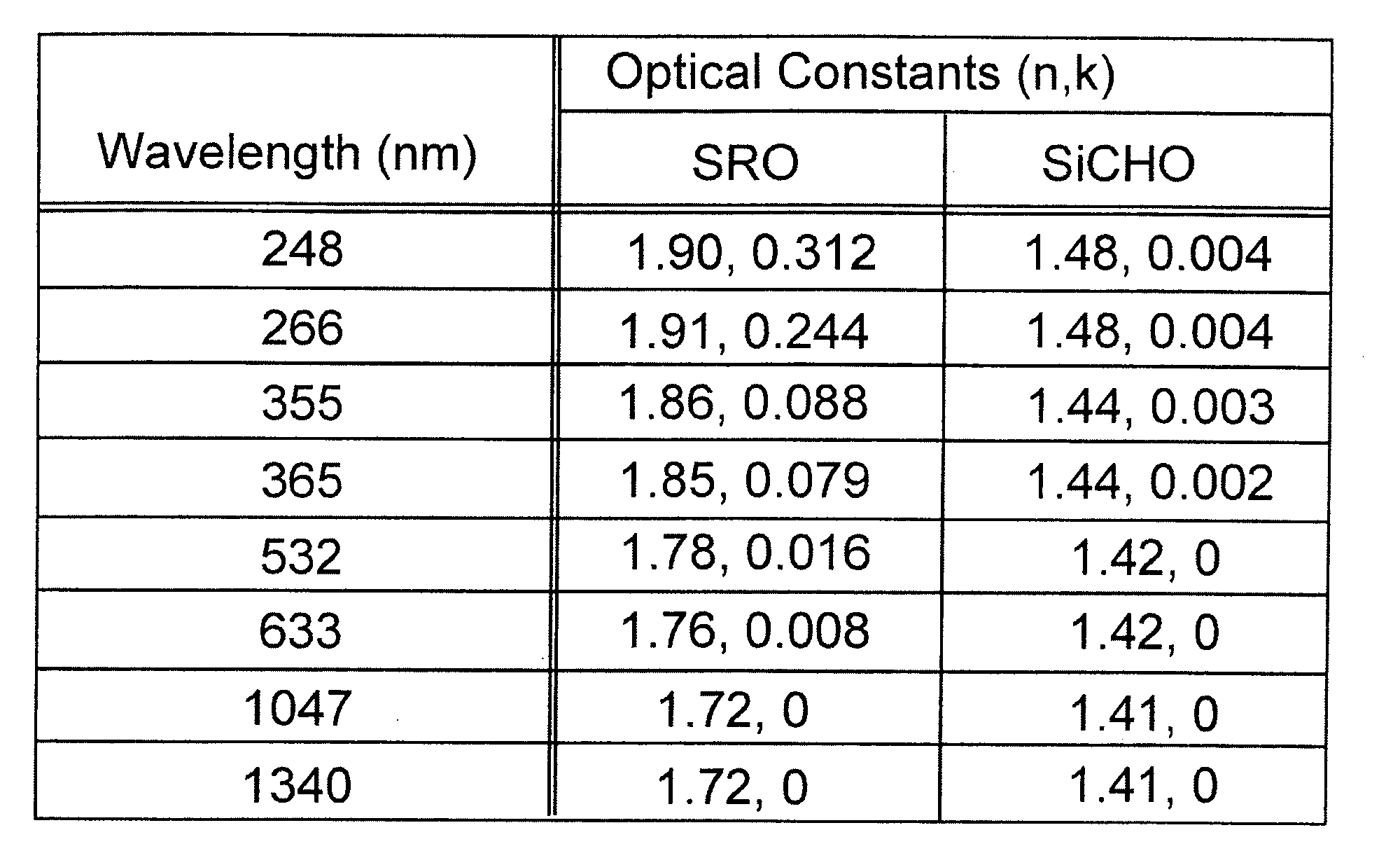
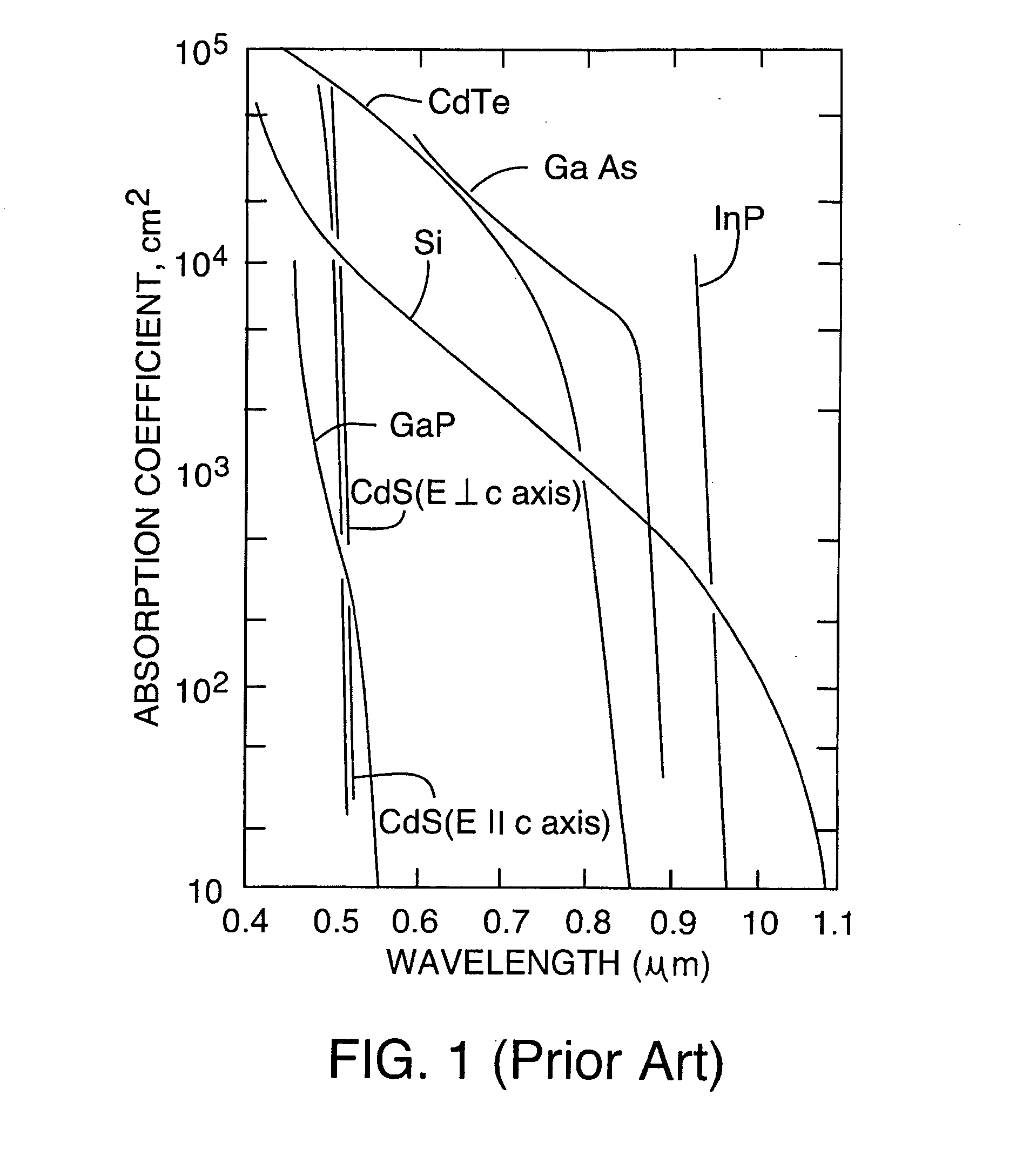
Laser processing of workpieces containing low-k dielectric material
InactiveUS20070272555A1Liquid separation by electricityElectrostatic separationLaser processingLength wave
Laser output including at least one laser pulse having a wavelength greater than 1.1 μm and shorter than 5 μm (preferably at about 1.1 μm) and having a pulsewidth shorter than 100 ps (preferably shorter than 10 ps) permits low-k dielectric material, such as SRO or SiCOH, to be removed without damaging the substrate. An oscillator module in cooperation with an amplification module are used to generate the laser output.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Alignment of carbon nanotubes using magnetic particles
InactiveUS7803262B2Material nanotechnologyLiquid separation by electricityMagnetite NanoparticlesNanometre
Methods are provided for aligning carbon nanotubes and for making a composite material comprising aligned carbon nanotubes. The method for aligning carbon nanotubes comprises adsorbing magnetic nanoparticles to carbon nanotubes dispersed in a fluid medium to form a magnetic particle-carbon nanotube composite in the fluid medium; and exposing the composite to a magnetic field effective to align the nanotubes in the fluid medium. The method for making a composite material comprising aligned carbon nanotubes comprises (1) adsorbing magnetic nanoparticles to carbon nanotubes to form a magnetic particle-carbon nanotube composite; (2) dispersing the magnetic particle-carbon nanotube composite in a fluid matrix material to form a mixture; (3) exposing the mixture to a magnetic field effective to align the nanotubes in the mixture; and (4) solidifying the fluid matrix material to form a nanotube / matrix material composite comprising the aligned nanotubes which remain aligned in the absence of said magnetic field.
Owner:FLORIDA STATE RES FOUND +1
Chemical synthesis methods using electro-catalysis
Synthesis methods are provided using electro-chemical catalysis. In one method, diesel fuel is made by (1) flowing a mixture of a triglyceride source and an alcohol through a high voltage electrical field, effective to convert the triglyceride into saturated mono alkyl esters; and (2) adding the saturated mono alkyl esters to a petroleum-derived diesel fuel to form a diesel fuel blend. In another method, a high temperature, oxidatively stable lubricant is made by (1) flowing a renewable oil including unsaturated fatty acids through a high voltage electrical field effective to convert the unsaturated fatty acids into saturated fatty acids; and (2) adding one or more functional additives to the saturated fatty acid-containing renewable oil to form a synthetic lubricant. In another method, ethanol is made by flowing a liquid which comprises a simple sugar through a high voltage electrical field effective to convert the sugar into ethanol without fermentation.
Owner:ECR TECH
Desalting adjunct chemistry
InactiveUS6120678AImproves separation of waterReduce decreaseDewatering/demulsification with chemical meansLiquid separation by electricityChemical treatmentMeth-
Improved performance in the phase separation of aqueous brines from hydrocarbons within an electrostatic desalter operation is obtained by the addition to the crude oil emulsions entering the desalter of an effective asphaltene dispersing amount of an alkyl phenol-formaldehyde liquid resin polymer, optionally in the presence of a lipophilic / hydrophilic vinylic polymer. The preferred resin is a nonyl phenol-formaldehyde resin having a molecular weight of from 1,000-20,000, and the preferred vinylic polymer is a copolymer of lauryl (meth)acrylate and hydroxyethyl (meth)acrylate. Best results from the electrostatic desalter are obtained when also using a demulsifier chemical treatment along with the asphaltene dispersing treatments. Desalter efficiency is increased and desalter brine effluent quality is greatly increased.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC +1
Bilge water reclamation system and process
A system and method for treating and removing hydrocarbon and other contaminants in bilge and ballast water, utilizing a multiple progressive process that chemically and electrically treats-and removes contaminants. Wastewater, received by a sump, is transmitted to a holding tank and treated, over a period of time while-influent wastewater continues off loading. The wastewater is pumped to an oil / water separator tank that decants free-floating oil from the wastewater to an oil retention tank. The wastewater then undergoes an electrocoagulation process where emulsions are broken and compounds that further aid treatment are created. The treated water flows to a retention / separation tank where contaminant particles coalesce and separate. Water is decanted and transferred to a clean water holding tank through an ozone injection system and an activated carbon filter. Treated water is recirculated until it exits the system meeting discharge limits for organics and metals allowing release into the environment.
Owner:TIPTON GARY A
Hydrocarbon oil demetalizing agent, and preparing method and use method thereof
InactiveCN1454967AEasy to separateReduce oil contentRefining with non-metalsRefining with acid-containing liquidsPetroleumChemistry
The present invention relates to a hydrocarbon oil demetallization agent, its preparation method and application method. Said hydrocarbon oil demetallization agent comprises demetallization agent, demulsifier and demetallization adjuvant. Its application method includes the following steps: fully mixing hydrocarbon oil demetallization agent or its aqueous solution and hydrocarbon oil according to a certain ratio and adopting conventional electric desalting process to make treatment so as to obtain demetallized hydrocarbon oil. At the same time of desalting it can remove other metal ions of calcium, magnesium, iron, vanadium and nickel, etc. from hydrocarbon oil, so that its oil and water separation effect is good.
Owner:PETROCHINA KARAMAY PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
Method of using triaxial magnetic fields for making particle structures
A method of producing three-dimensional particle structures with enhanced magnetic susceptibility in three dimensions by applying a triaxial energetic field to a magnetic particle suspension and subsequently stabilizing said particle structure. Combinations of direct current and alternating current fields in three dimensions produce particle gel structures, honeycomb structures, and foam-like structures.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Treatment of crude oils
InactiveUS6955753B1Quality improvementImprove efficiencyWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by selective extractionSolvent extractionHydrogenPetroleum
A process and apparatus to extract and recover heavy metals and sulfur from crude oil or petroleum fuel products including the steps of emulsifying the crude oil with an emulsifying agent, adding a leach solution to the emulsified crude oil and leaching the emulsified crude oil at elevated temperature and pressure to give a leached emulsified crude oil. The leach solution may be acid or alkali. A proportion of the leach solution is extracted for recovering heavy metals. There can also be a microwave hydro-treating step using hydrogen gas at a temperature below 220° C. to ensure there is no quality degradation in the crude feed to produce a desulfurized crude oil and a hydrogen sulphide by-product and recovering sulfur from the hydrogen sulphide by-product.
Owner:RODOLFO ANTONIO M GOMEZ
Method and apparatus for preventing scale deposits and removing contaminants from fluid columns
ActiveUS20050161405A1Improve efficiencyProcess environmental protectionElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentCouplingEngineering
A method and apparatus provide fluid treatment at a plurality of distinct points using a length of energized magnetically conductive conduit in fluid communication with non-magnetic coupling devices. The instant invention prevents the formation and accumulation of contaminants within conduits and on equipment utilized in the transportation, delivery and processing of fluid columns. It may also be utilized to accelerate the separation of oil and water and increase the efficiency of oil / water separation equipment.
Owner:WILSA HLDG
Multiple frequency electrostatic coalescence
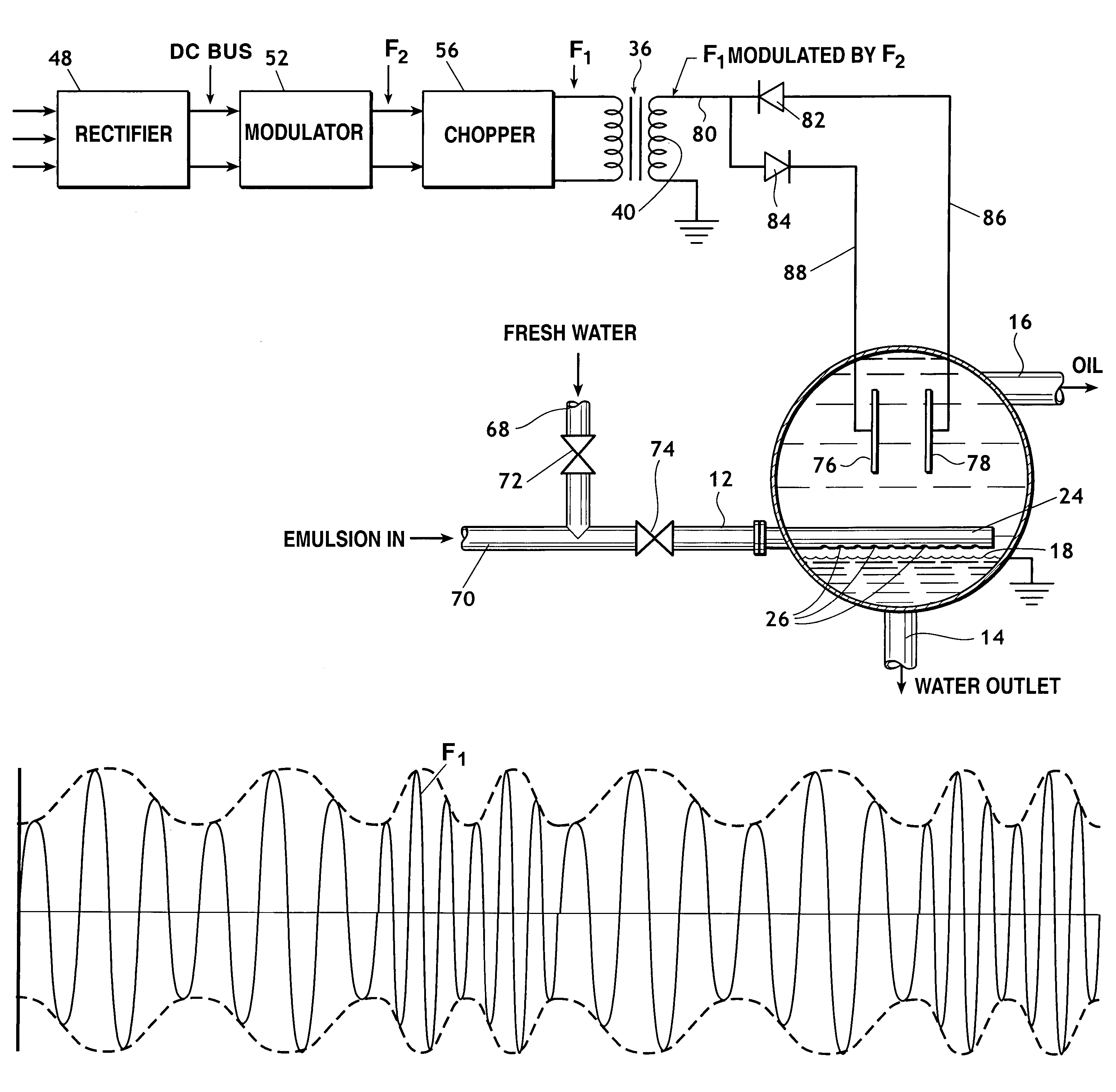
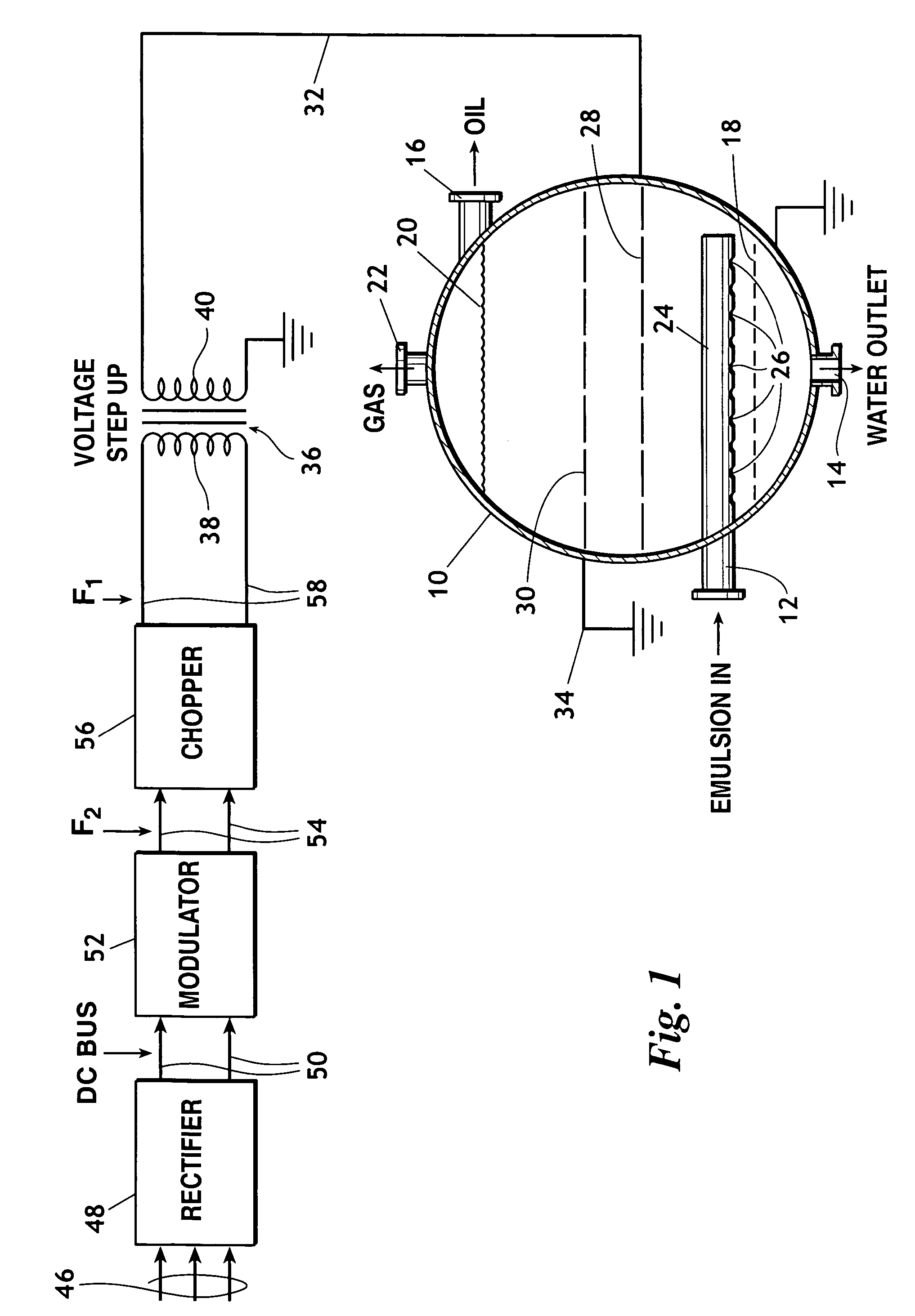
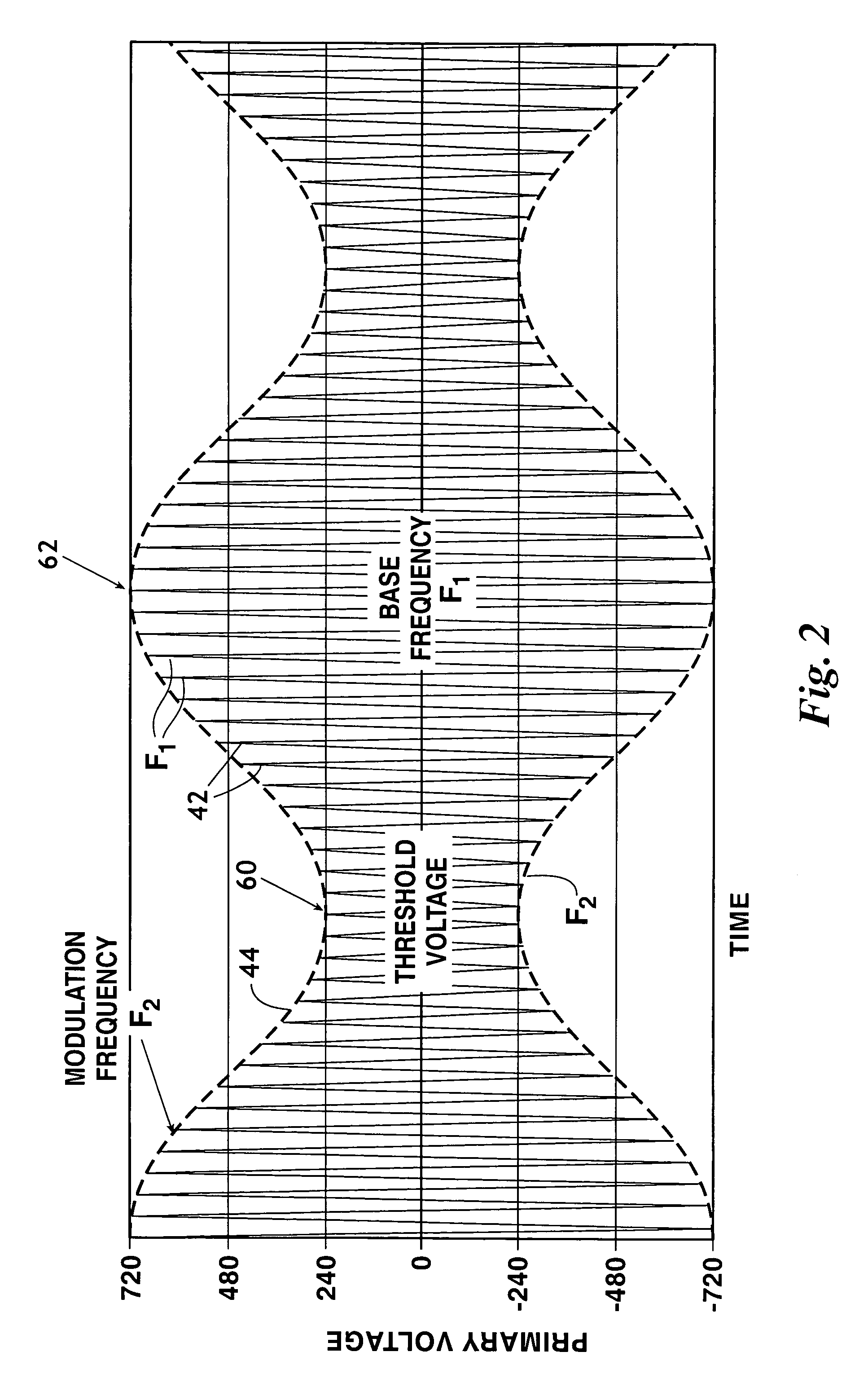
A method of augmenting the separation of immiscible heavier and lighter components of an emulsion including the steps of conducting the emulsion into a treatment vessel, providing an AC voltage source, employing from the source an AC voltage of at least one selected frequency F1 to establish at least one electric filed within the vessel through which the emulsion passes, and cyclically modulating the AC voltage with a method of modulation selected from: (a) amplitude modulation; (b) frequency modulation; and (c) combined amplitude and frequency modulation.
Owner:NAT TANK
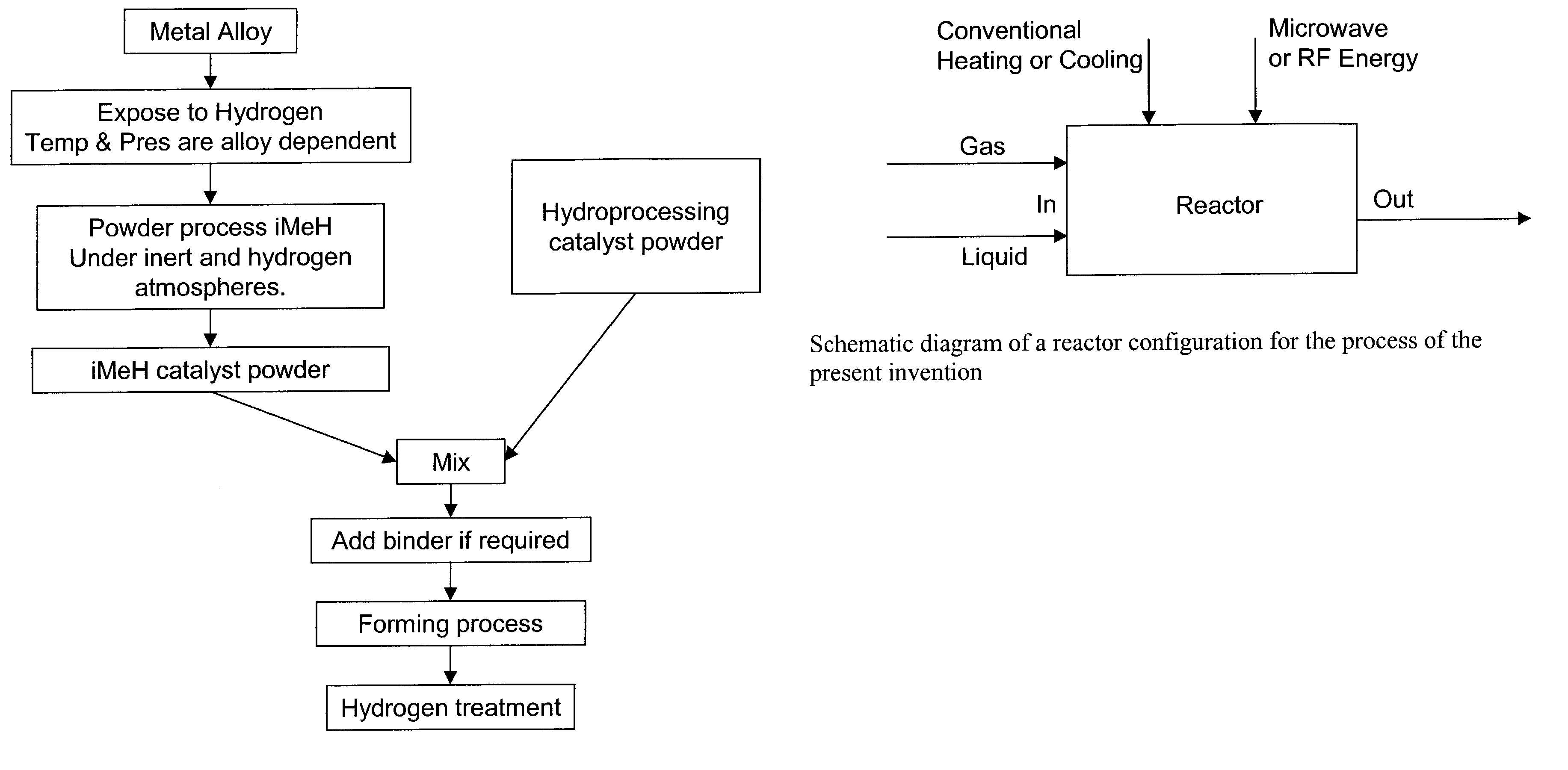
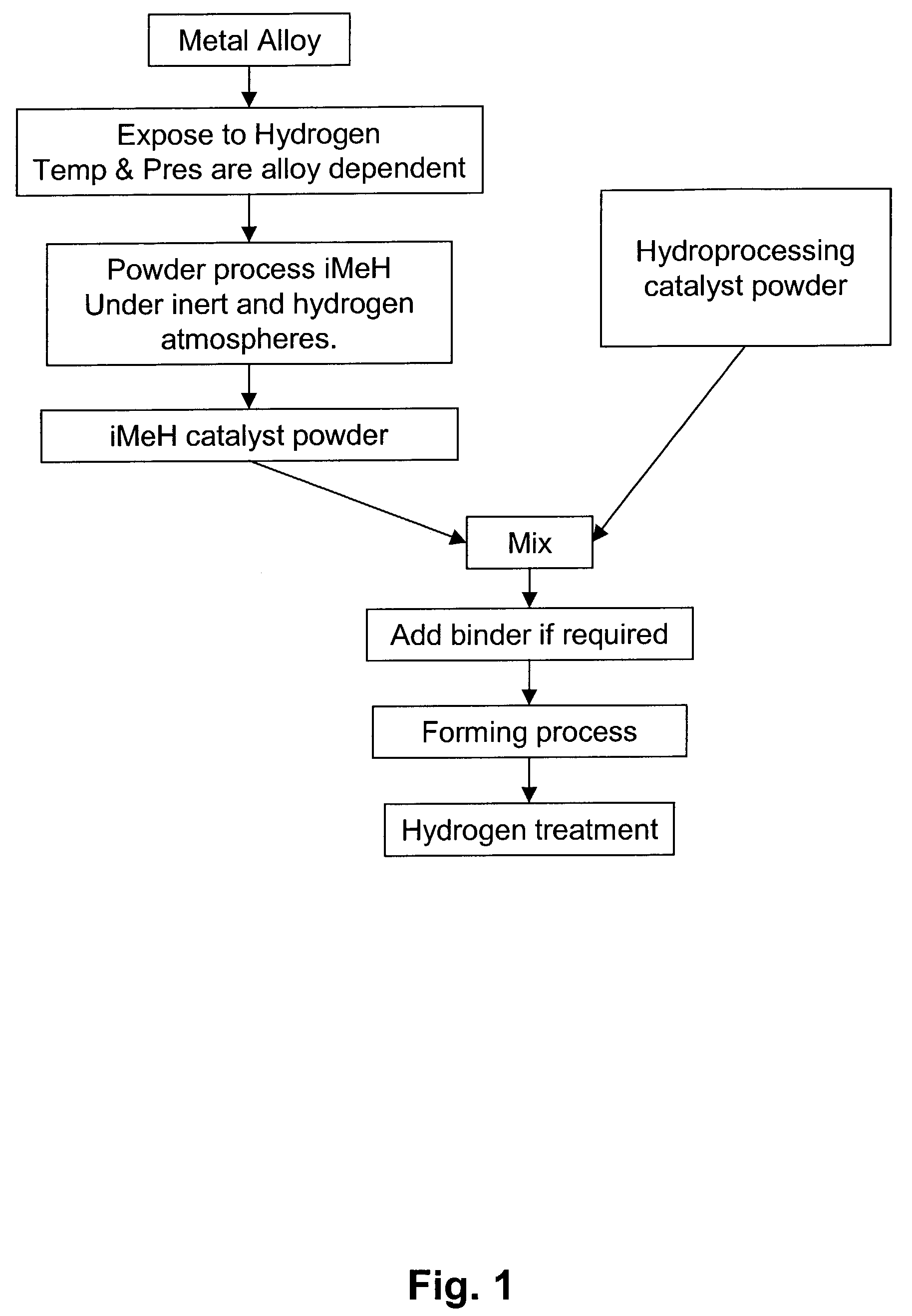
Catalytic process for the treatment of organic compounds
InactiveUS7387712B2Group 1/11 element organic compoundsCatalytic crackingSimple Organic CompoundsPtru catalyst
A process for the catalytic reaction of organic compounds, in which the organic compounds are contacted with a catalyst comprising an interstitial metal hydride, having a reaction surface, to produce a catalyst-organic compound mixture, energy is applied, monatomic hydrogen is produced at the reaction surface of the interstitial metal hydride, and the organic compounds are reacted with the monatomic hydrogen. Reactions accomplished by this process include petroleum hydrocracking and hydrotreating processes. The method's performance can be further enhanced using radio frequency (RF) or microwave energy.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
System and Process for Treating Ballast Water
ActiveUS20080000775A1Prevent outbreakLiquid separation by electricityElectrostatic separationHypochloriteWater treatment system
A system and process for treating ballast water within an ocean going vessel by generating hypochlorite for treating the ballast water. The system comprises one or more hypochlorite electrolytic cells in fluid communication with ballast water. The total organic carbon content of the ballast water is ascertained and the amount of hypochlorite generated is modulated in response to the total organic carbon content of the ballast water. In one embodiment the system comprises a total organic carbon analyzer for measuring total organic carbon content. In one embodiment of the process of the invention, hypochlorite production is modulated so that the residual halogen-containing oxidizing agent is maintained in the ballast water. In another embodiment of the process, hypochlorite production is modulated to maintain a weight ratio of hypochlorite to total organic carbon in the ballast water ranging from about 1.0 to about 3.0.
Owner:DE NORA WATER TECH
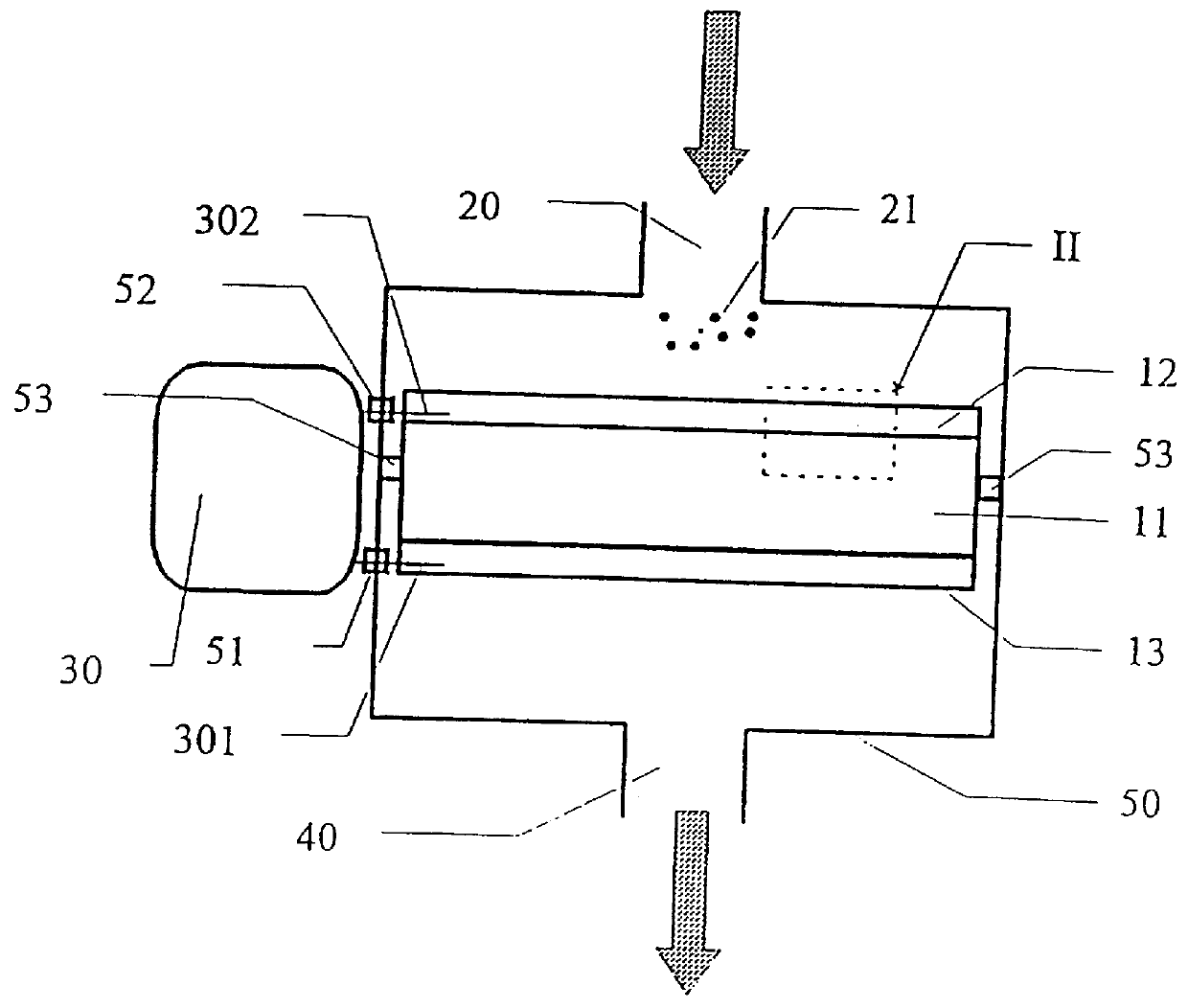
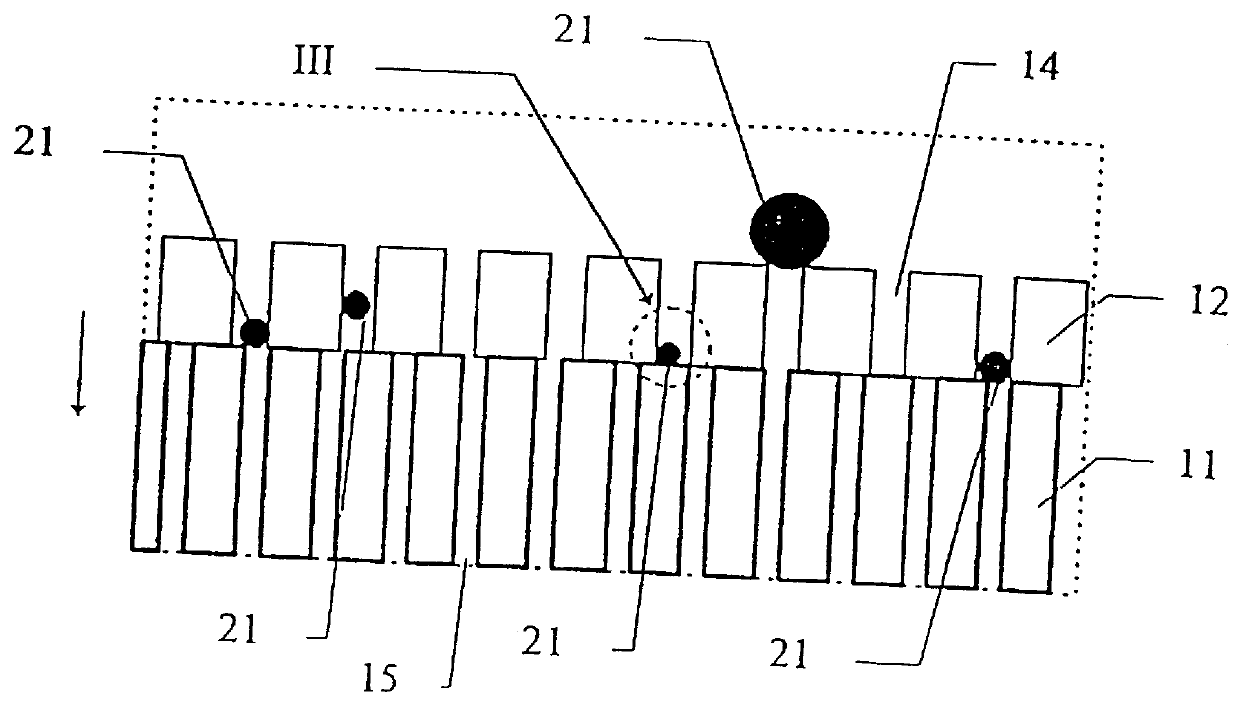
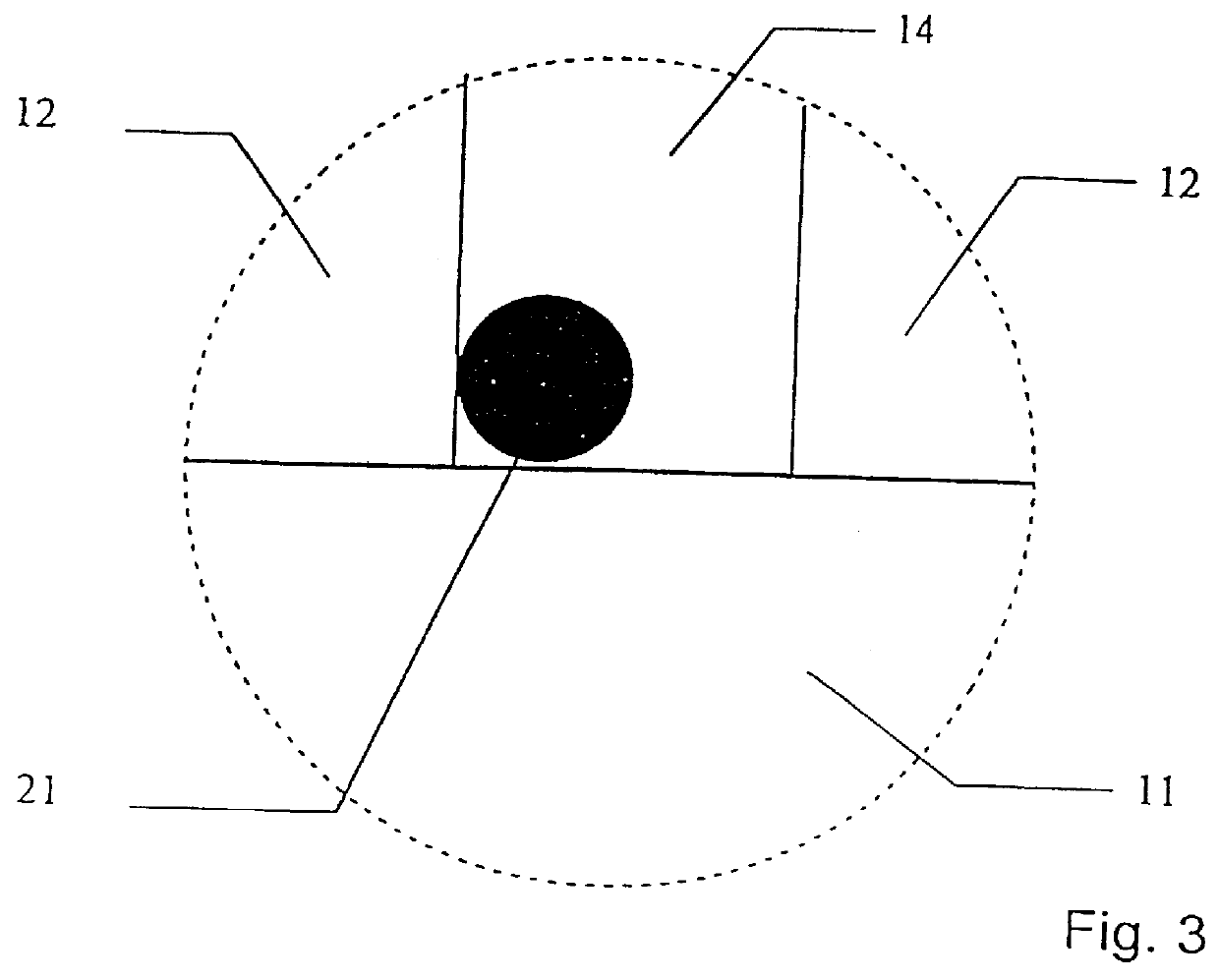
Method and a reactor for electrochemical conversion of a material e.g. soot particles being insoluble in a fluid
InactiveUS6036840AInternal combustion piston enginesLiquid separation by electricityElectricityFlue gas
A method and a reactor for electrochemical conversion of a material (21) being insoluble in a fluid into a material being soluble in the fluid, which method comprises that a flow of the fluid is passed to a reaction zone which comprises an internal circuit consisting of: one or more working electrodes (12), one or more counter-electrodes (13), and one or more ion-selective electrolytes (11), and which internal circuit is applied with an electrical voltage difference sufficient for the electrochemical processes; and use thereof for removal of soot particles from flue gasses and removal of oil in waste water.
Owner:DINEX AS
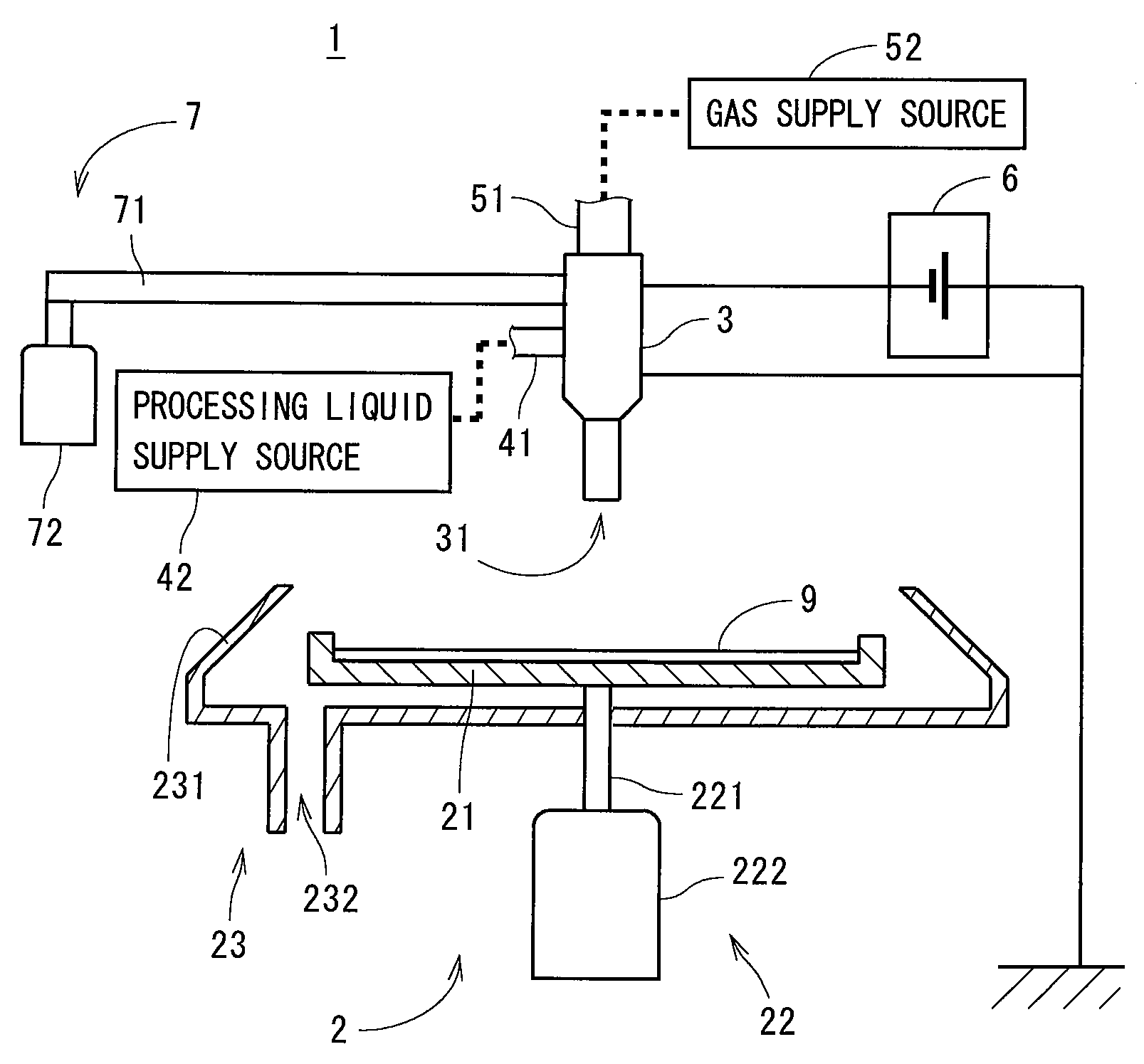
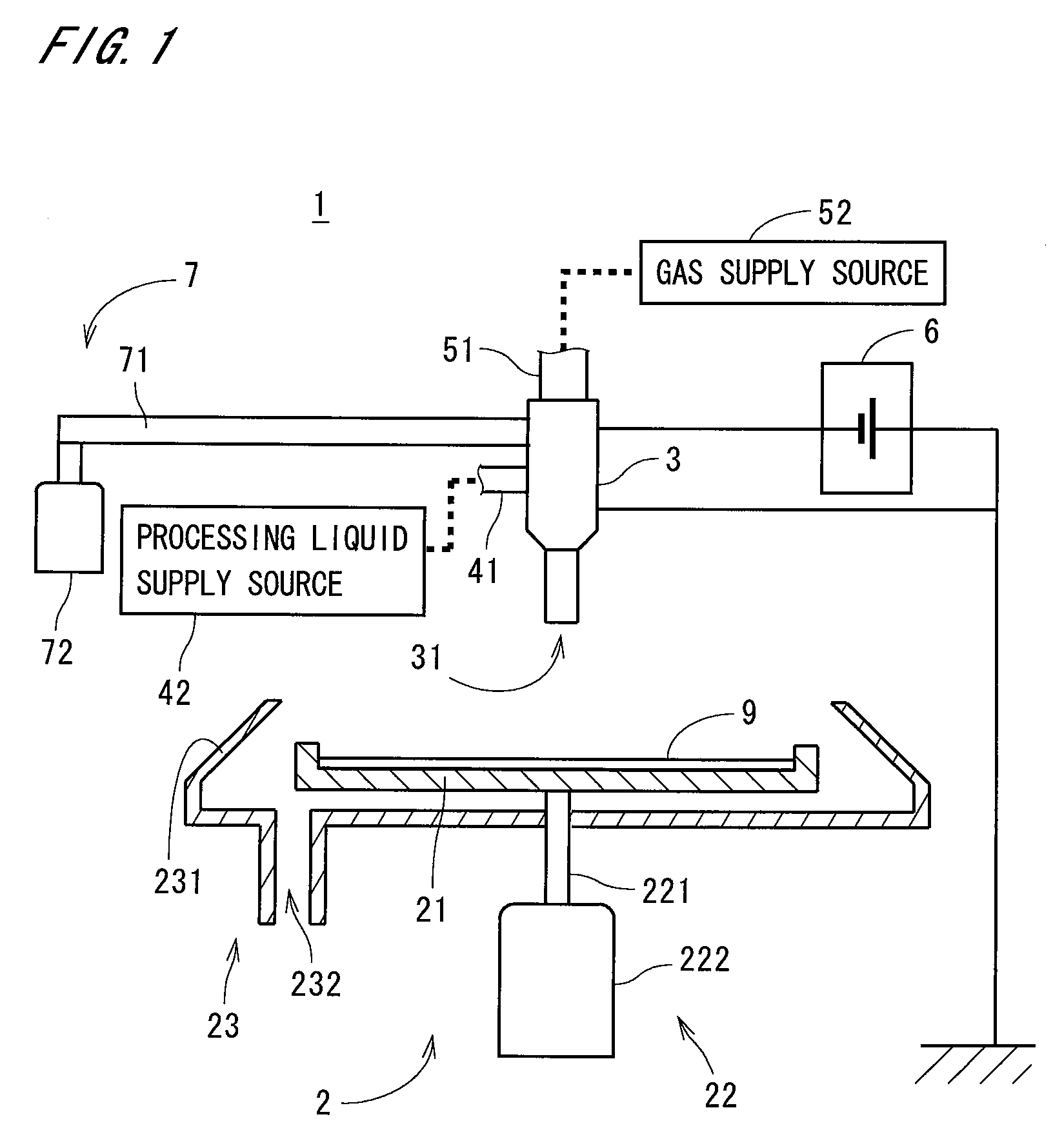
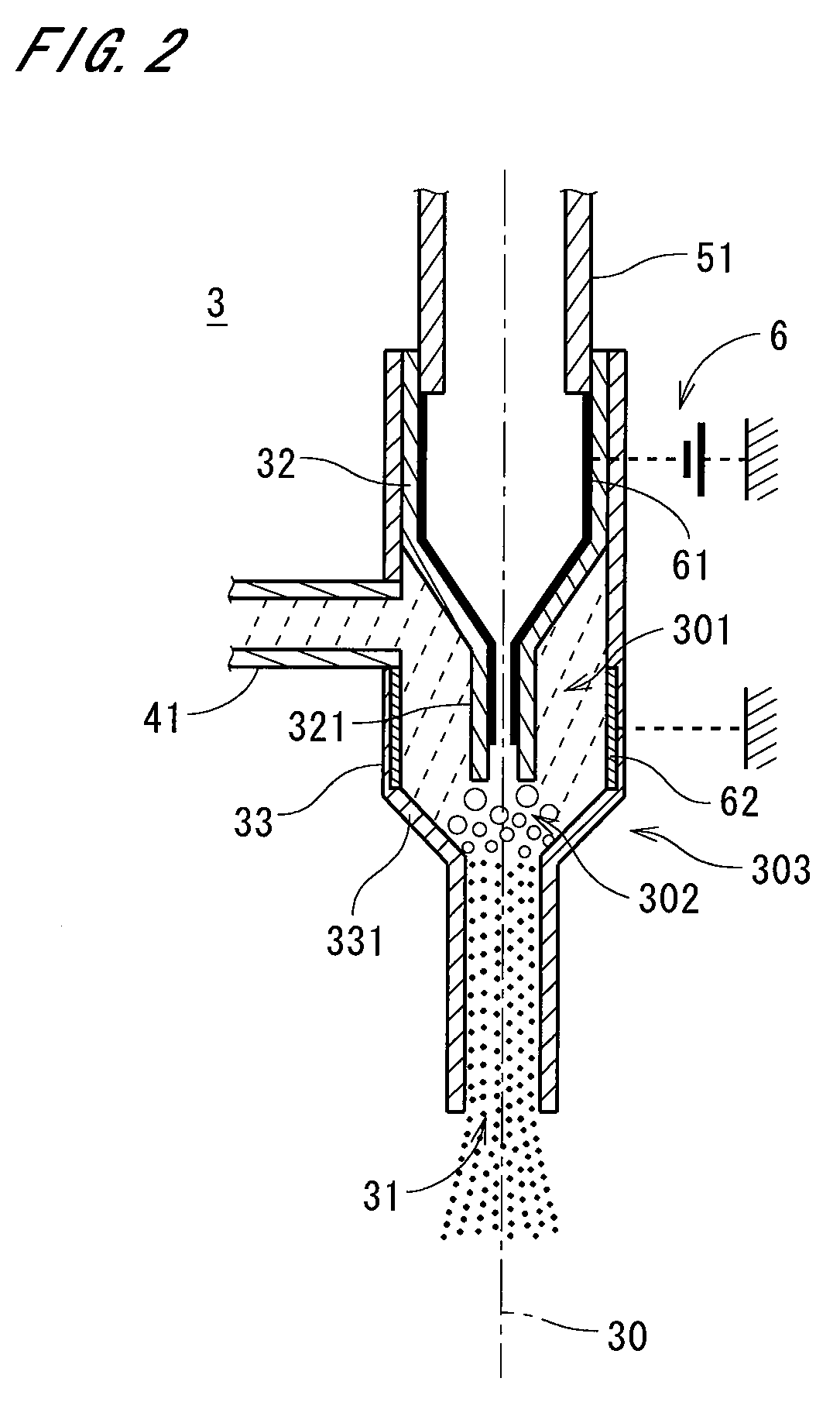
Two-fluid nozzle, substrate processing apparatus, and substrate processing method
InactiveUS20080173327A1Efficiently charge dropletEasy constructionBurnersSludge treatmentEngineeringMechanical engineering
A substrate processing apparatus has a two-fluid nozzle having an inner cylindrical member and an outer cylindrical member. Gas flows in the inner cylindrical member which is a gas passage and the processing liquid downwardly flows in a processing liquid passage constituted of the inner and outer cylindrical members. The gas and the processing liquid are mixed in a mixing area below the inner cylindrical member to generate fine droplets, and the droplets are ejected from an outlet of a lower end of the outer cylindrical member onto a substrate. Charge is induced on the processing liquid by generating an electric potential difference between a first electrode provided in the gas passage and a second electrode provided in the processing liquid passage, to generate charged droplets. In the nozzle, the first electrode is isolated from the processing liquid with a simple construction, and the droplets can be charged efficiently.
Owner:DAINIPPON SCREEN MTG CO LTD
Water treatment turbine apparatus and method
InactiveUS20060226060A1Consume energyConstant energy consumptionLiquid separation by electricityGeneral water supply conservationElectric powerElectric generator
The present invention provides an improved water purifier and method. In one possible embodiment, the present invention provides a turbine mounted in or to piping of a pool or spa filtering system. The turbine comprises one or more rotatable elements such as fins, paddles, blades, propellers, or the like which are responsive to water flow through the piping to produce rotation. The rotatable element may comprise magnets which rotate along with the rotatable element to produce a rotating magnetic field. The rotating magnetic field may be utilized for generating electricity utilizing various types of electric power generators. Electricity so produced may be utilized to power a water purification unit such as a chlorine generator, UV generator, or an ozone generator. In one embodiment, the output of the water purification unit is directed into turbulence, such as turbulence produced by the rotatable element, so that the purification efficiency is enhanced.
Owner:MERCER RICHARD D
Component separation device
ActiveUS20100126922A1High collecting percentageEfficient separationSludge treatmentElectrostatic separatorsInlet channelSolid particle
A component separating device includes a flow channel, an acoustic wave generator for generating an acoustic wave in the flow channel, a first inlet channel for introducing a fist solution containing solid particles into the flow channel, a second inlet channel for introducing a second solution, and outlet channels for discharging a solution from the flow channel. A density grade generator is provided at the first inlet channel for forming a density grade of the solid particles. This component separating device extracts the solid particles into a high-purity solution at a high collecting rate.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
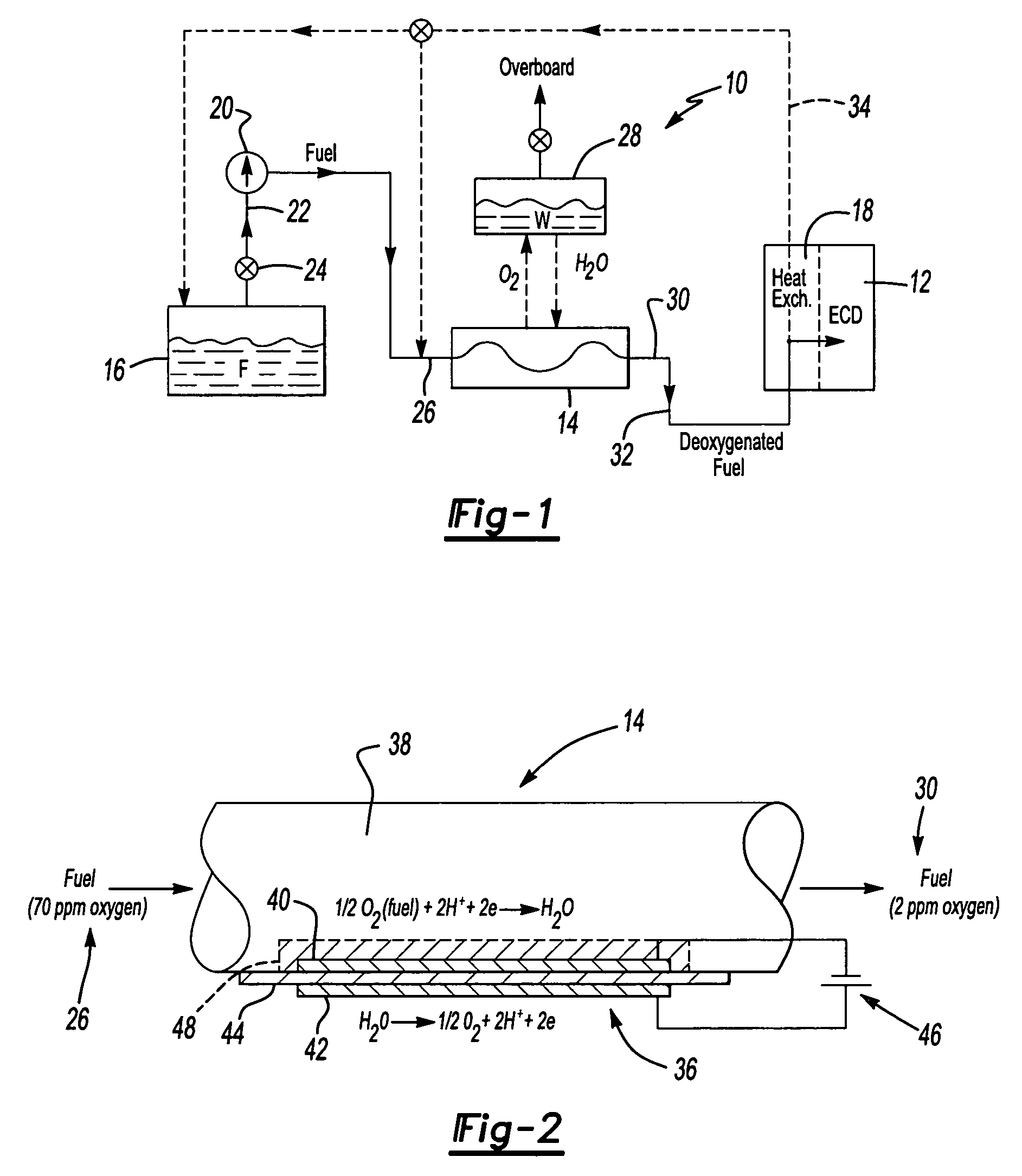
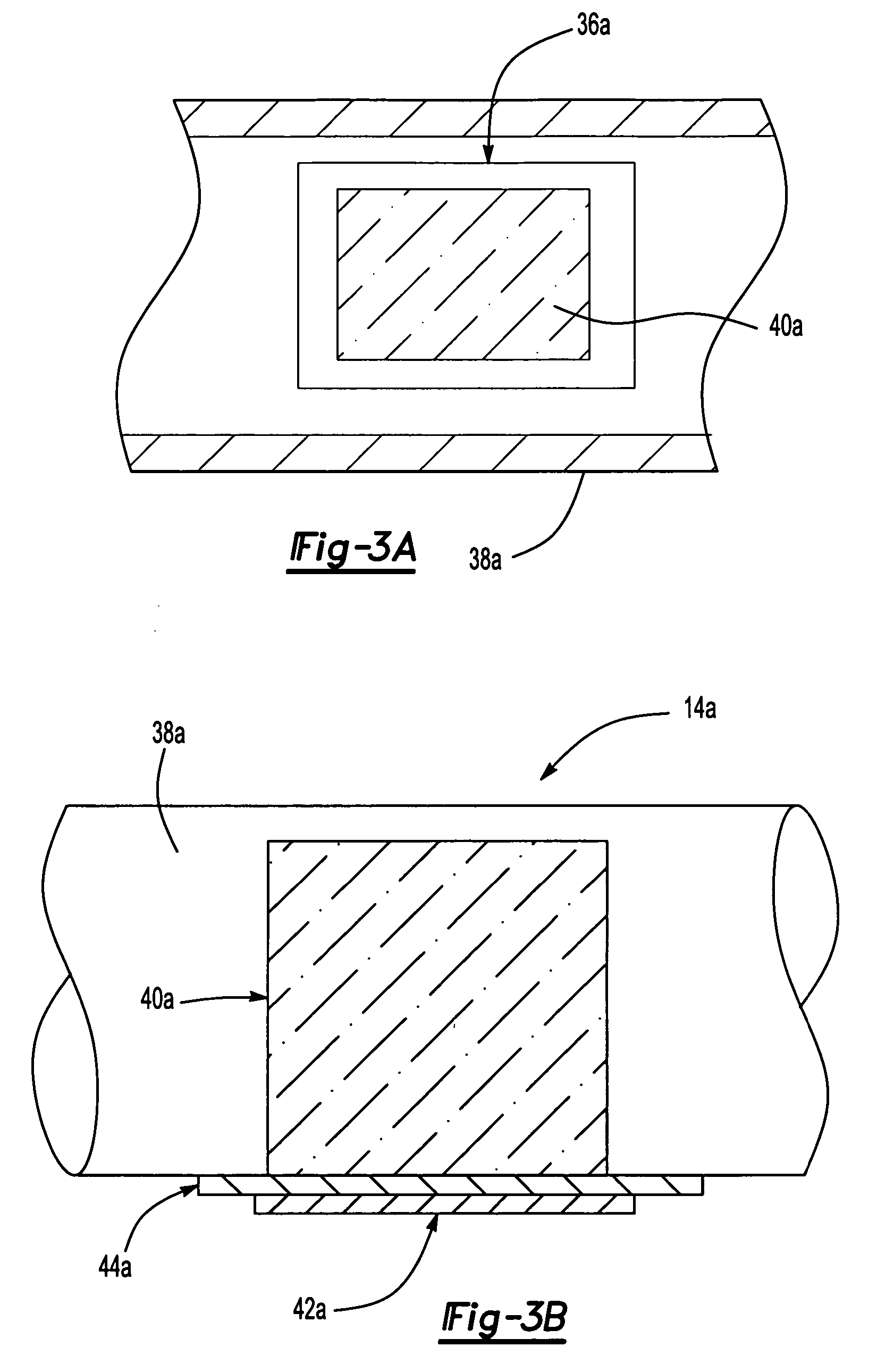
Electrochemical fuel deoxygenation system
ActiveUS7431818B2Minimize cokingInexpensive sizeCellsLiquid fuel feeder/distributionElectricityElectrochemistry
A fuel system for an energy conversion device includes a deoxygenator system with an electrochemical conversion system to remove oxygen from fuel through conversion of the oxygen to water. The electrochemical conversion system is located within a fuel flow. On the fuel side ½O2+2H++2e−=>H2O while on the reverse side the opposite reaction occurs. From the electrochemical conversion system the water is then collected and / or expelled from the system.
Owner:RTX CORP
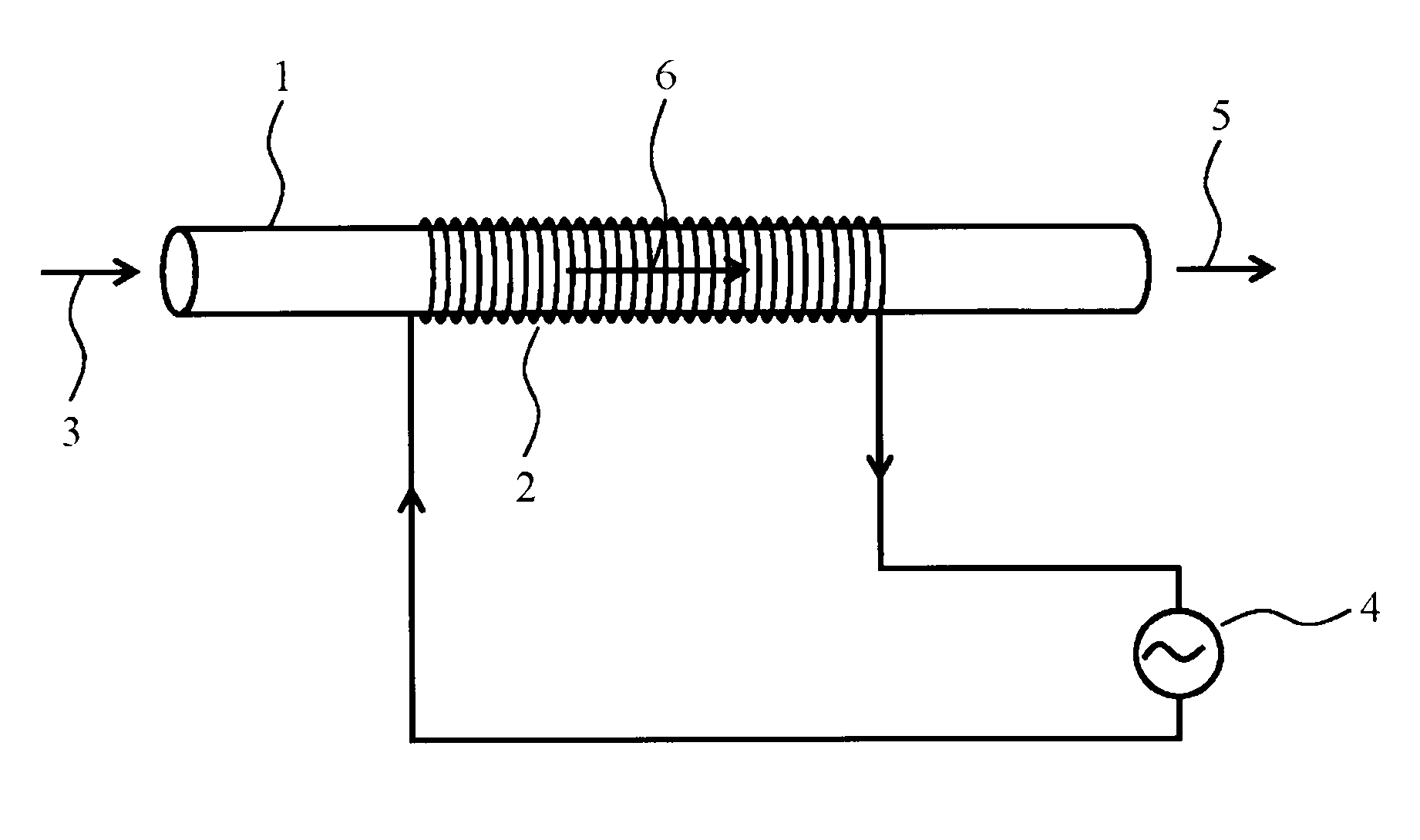
Electromagnetic field treatment method and electromagnetic field treatment equipment of water
InactiveUS20090242407A1Improve universalityImprove stabilityElectrostatic separatorsLiquid degasificationWater channelPeak current
For example, a coil 2 is provide on the outer side of a water pipe 1 of a water channel, water to be treated 3 is fed, and a specific alternating current having a specific frequency or a specific peak current is supplied from an AC power supply 4 to the coil 2. As a frequency of the specific alternating current, one resonant frequency is selected out of a resonant frequency group having plural resonant frequencies. A resonant magnetic field is induced in the channel by the specific peak current. An oscillating electromagnetic field induced by such a specific alternating current is imparted to the water to be treated 3 and subjecting the water to be treated 3 to electromagnetic field treatment, whereby active treated water 5 that is simply and easily and highly efficiently activated can be obtained.
Owner:SHIGA FUNCTIONAL WATER LAB CORP
Useful energy product
InactiveUS7714258B2Enhanced radiationLow efficiencyHydrogenHydrocarbon oil cracking processChemical speciesSusceptor
A useful energy product created by a process where a chemical species flow passes through a macroscopic artificial dielectric structure for a gas-permeable susceptor having (a) first regions in the structure that are primarily transparent to applied electromagnetic energy and (b) second regions in the structure that are not primarily transparent to applied electromagnetic energy.
Owner:DALTON ROBERT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com