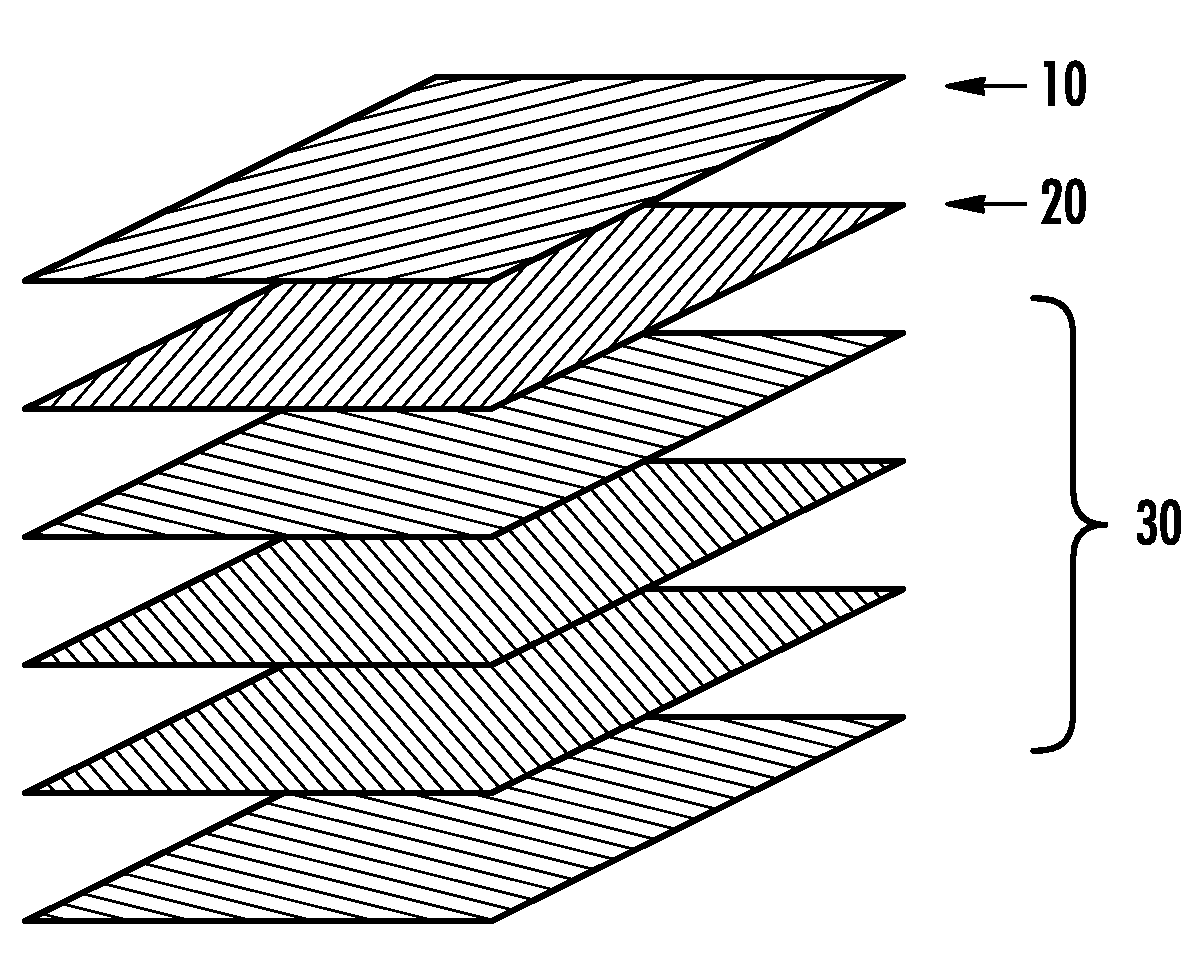
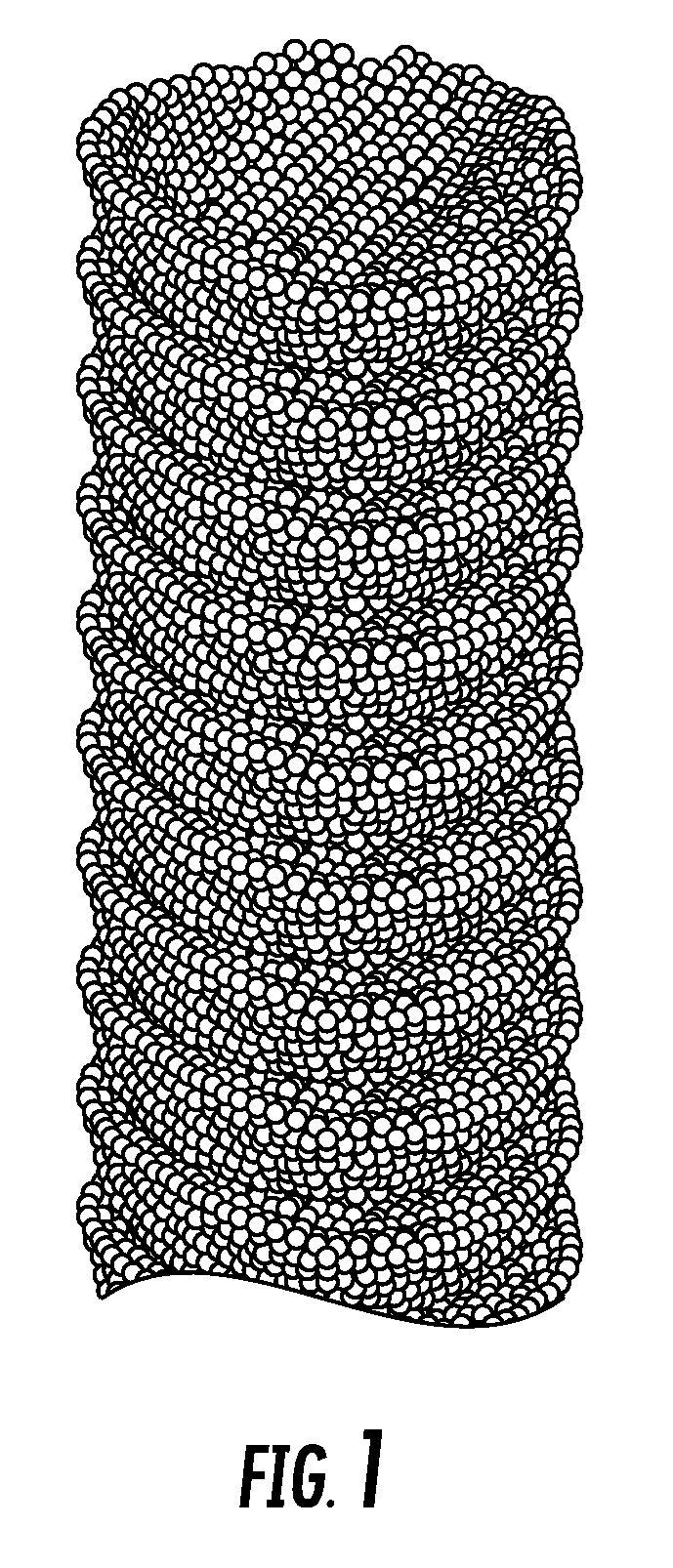
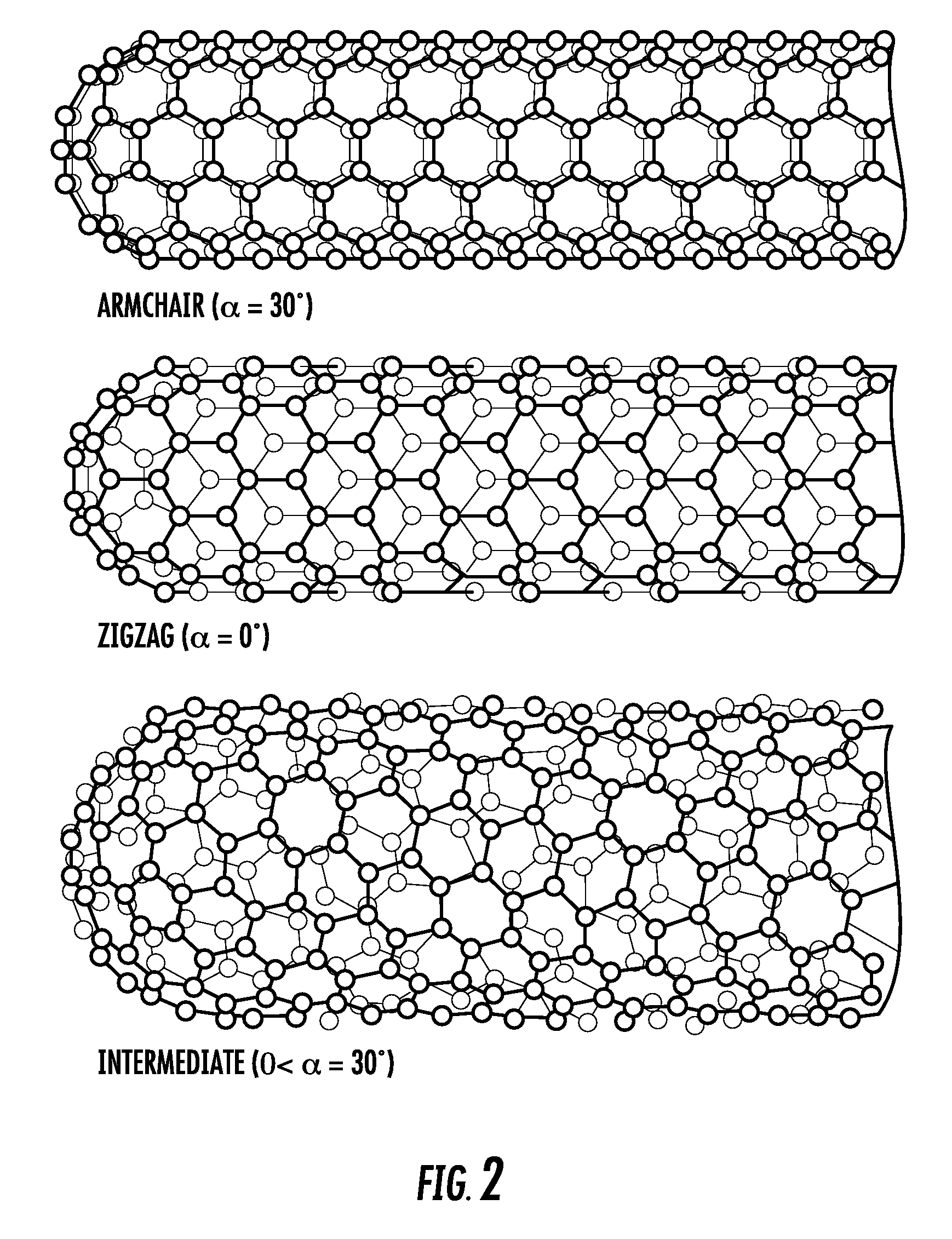
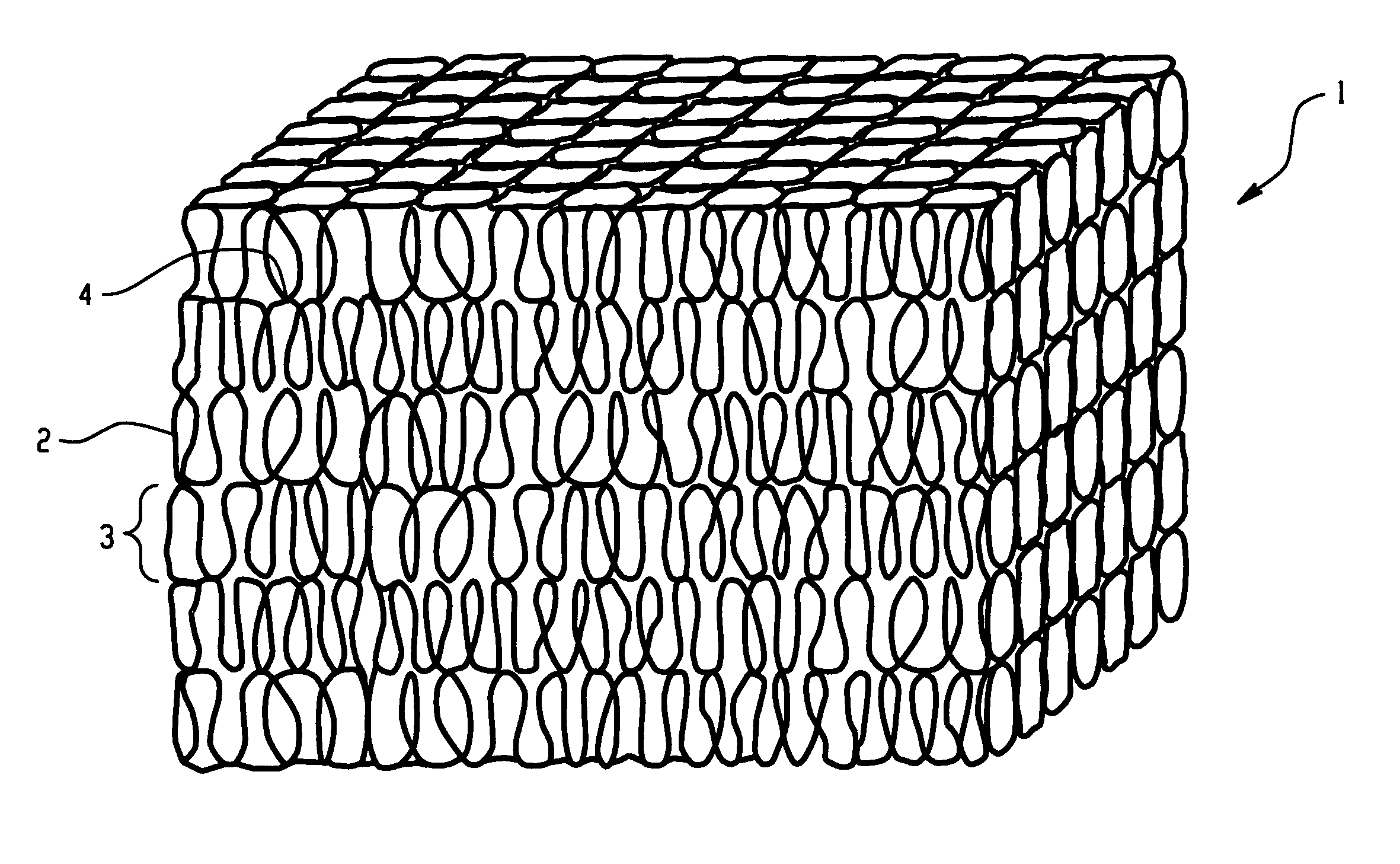
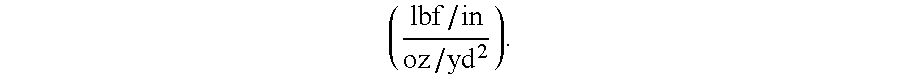Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
976results about "Open work fabrics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nonwoven fabric liner and diaper including a nonwoven laminate liner
The present invention provides a bodyside liner for a disposable absorbent article that is a nonwoven fabric laminate that includes a thin layer of fine fibers that has a basis weight of less than 2.5 grams per square meter. The present invention also provides disposable absorbent garments, such as diapers, that in such a nonwoven fabric laminate to reduce the migration of particles in absorbent garments.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
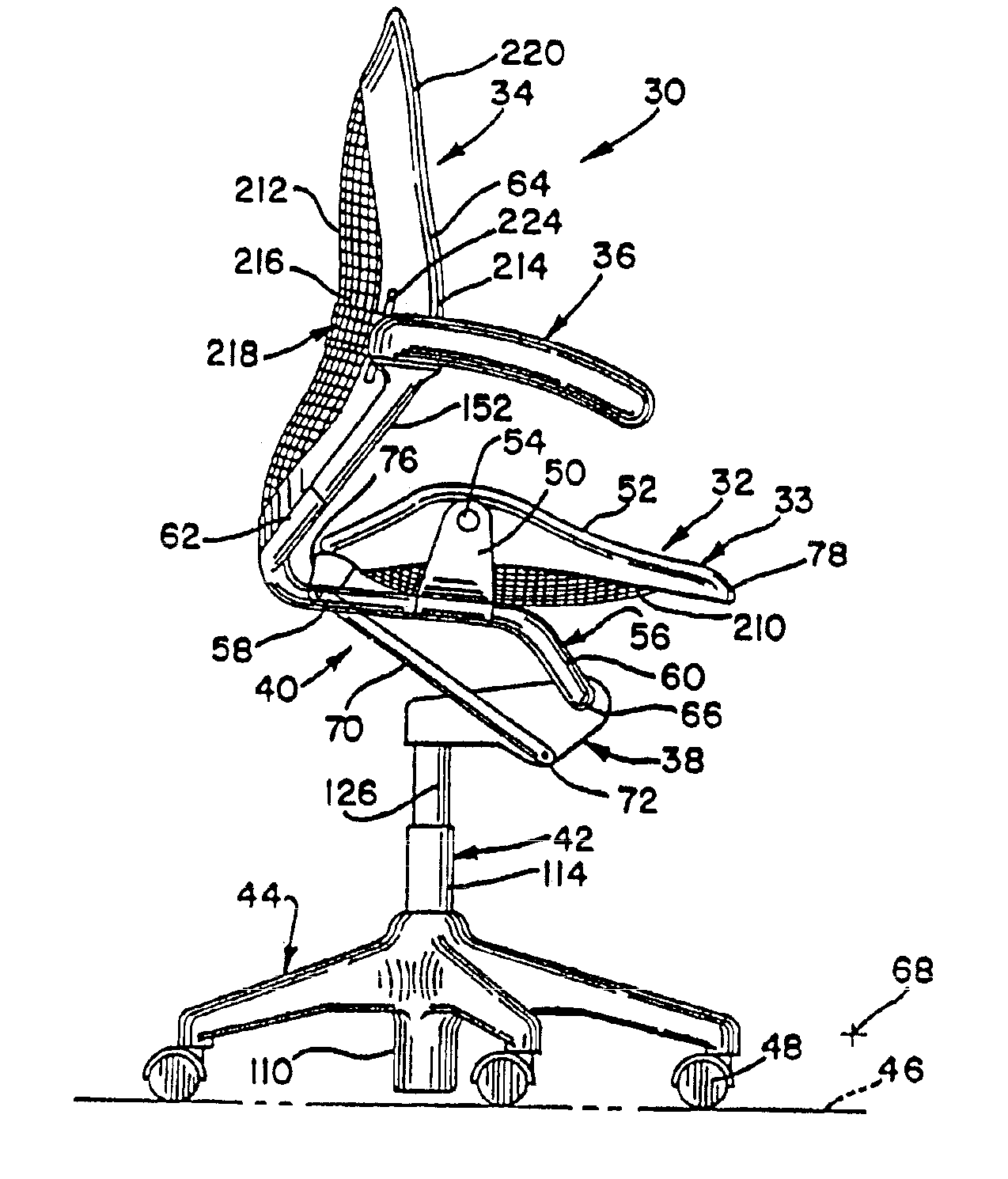
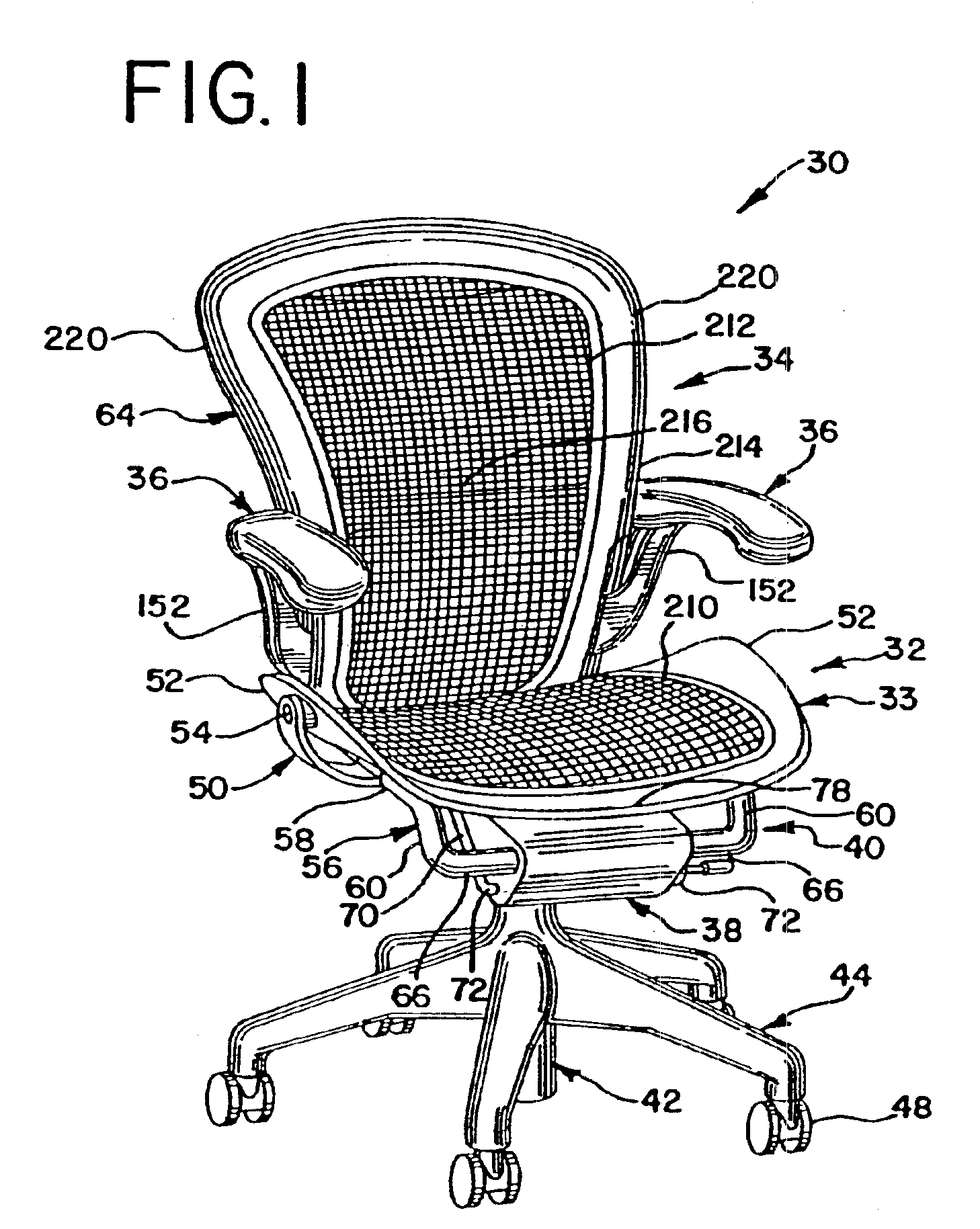
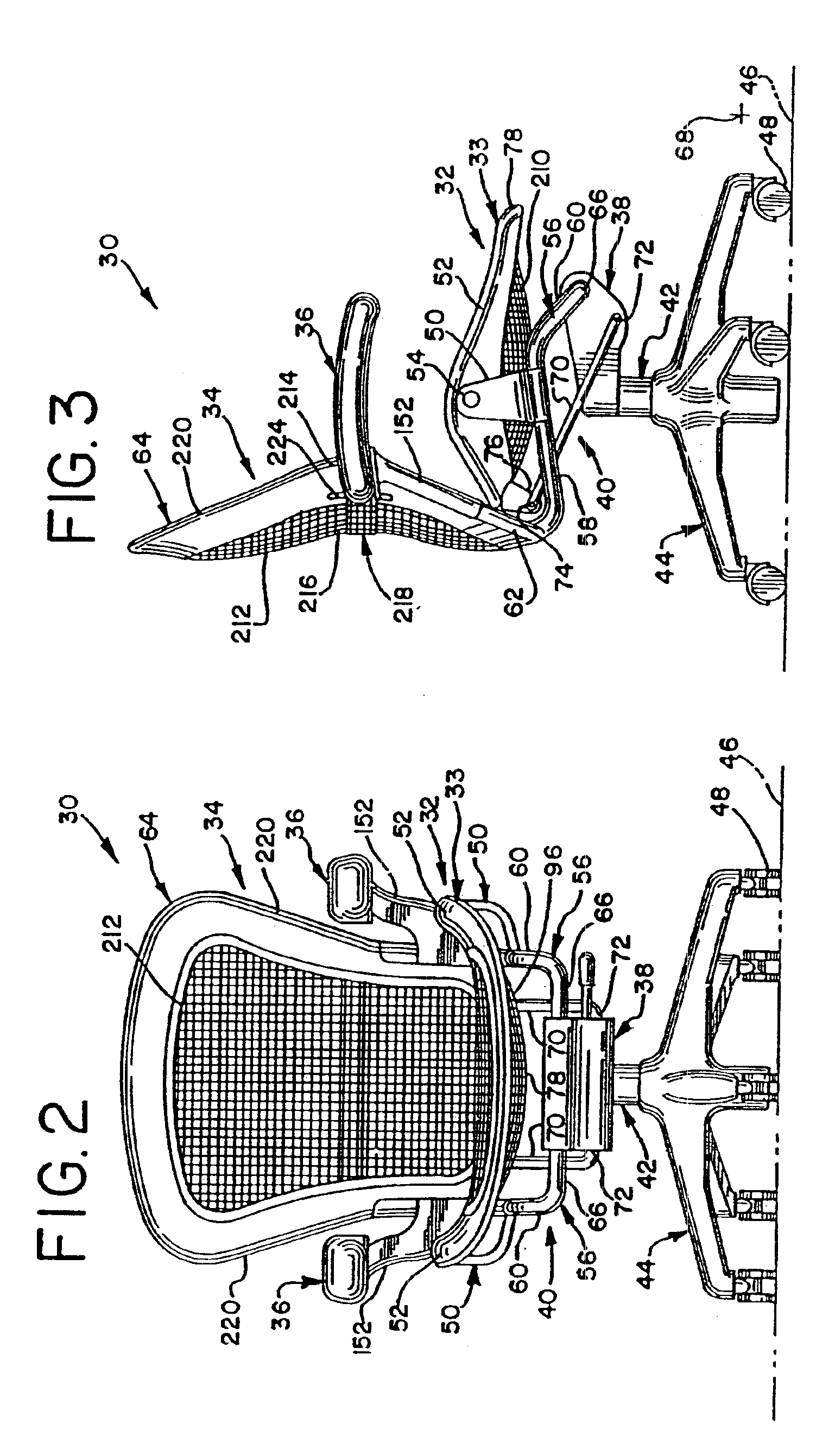
Chair with a linkage assembly
InactiveUS6966604B2Tilt is limitedEffective pointingStuffed mattressesSpring mattressesEngineeringBack support
A chair includes a control housing, a seat and a back support including an upwardly extending upright portion and a link portion extending forwardly from a lower portion of the upright portion. The link portion is pivotally connected to the control housing about a first pivot axis. The seat is connected to the link portion and is pivotable relative thereto. A linkage is coupled to the seat and is pivotally connected to the control housing at a second pivot axis positioned rearwardly and downwardly from the first pivot axis.
Owner:HERMAN MILLER INC
Fluoropolymer fine fiber
ActiveUS20090032475A1Advantageously employedHeat stableDispersed particle filtrationLiquid suspension thickening by filtrationPolymer scienceFiltration
A layer of fluoropolymer fine fiber can be made. The fine fiber can be made by electrospinning from a solvent or a solvent blend. The layers of the invention are useful in general filtration of fluid streams including gaseous and liquid streams. The fine fiber layers are also useful as hydrophobic filtration layers that can be used to separate water from a hydrocarbon stream.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Conductive pressure sensitive textile
InactiveUS7365031B2Low production costReduce edge effectsForce measurementInsulated cablesElectrical conductorEngineering
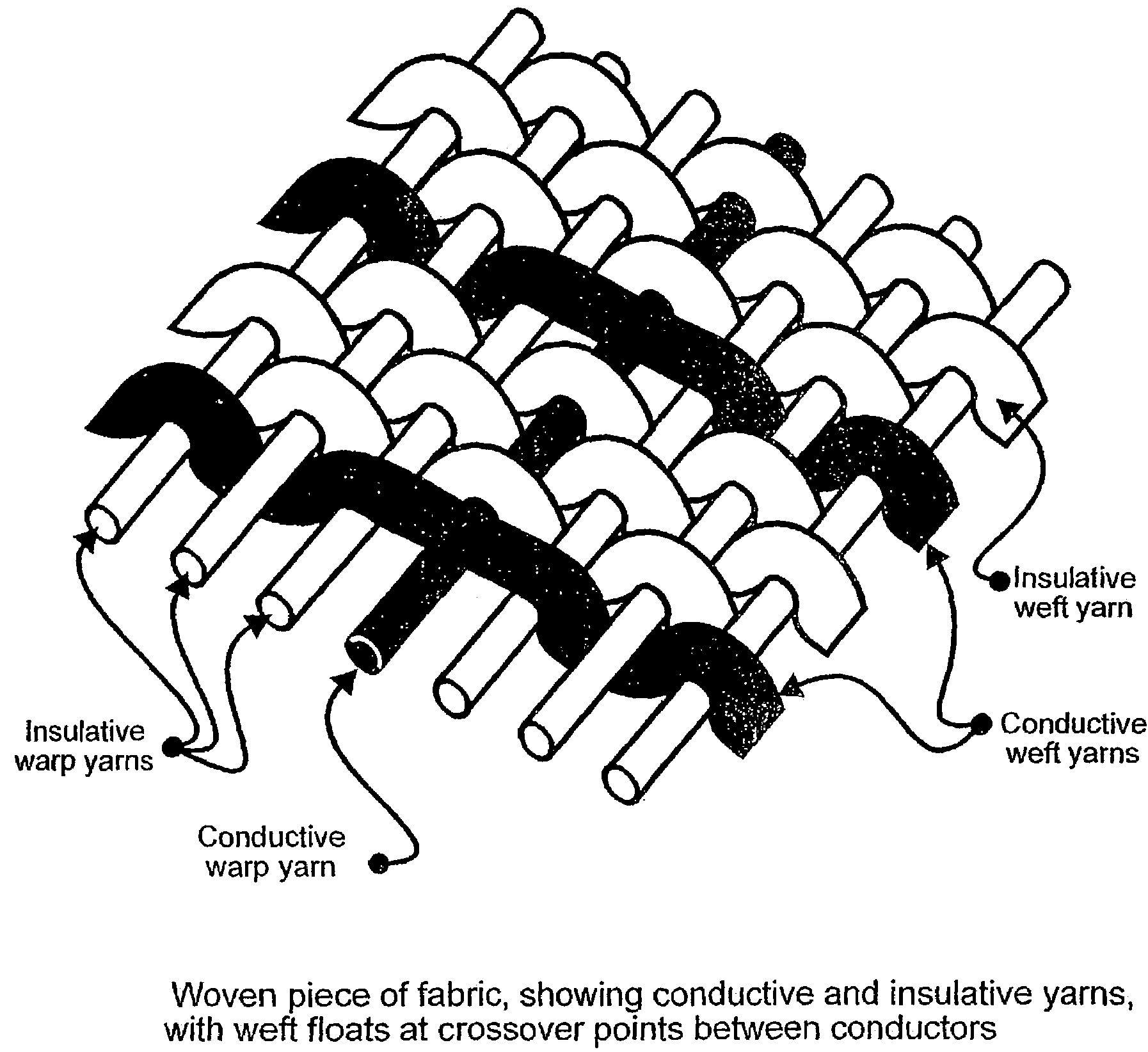
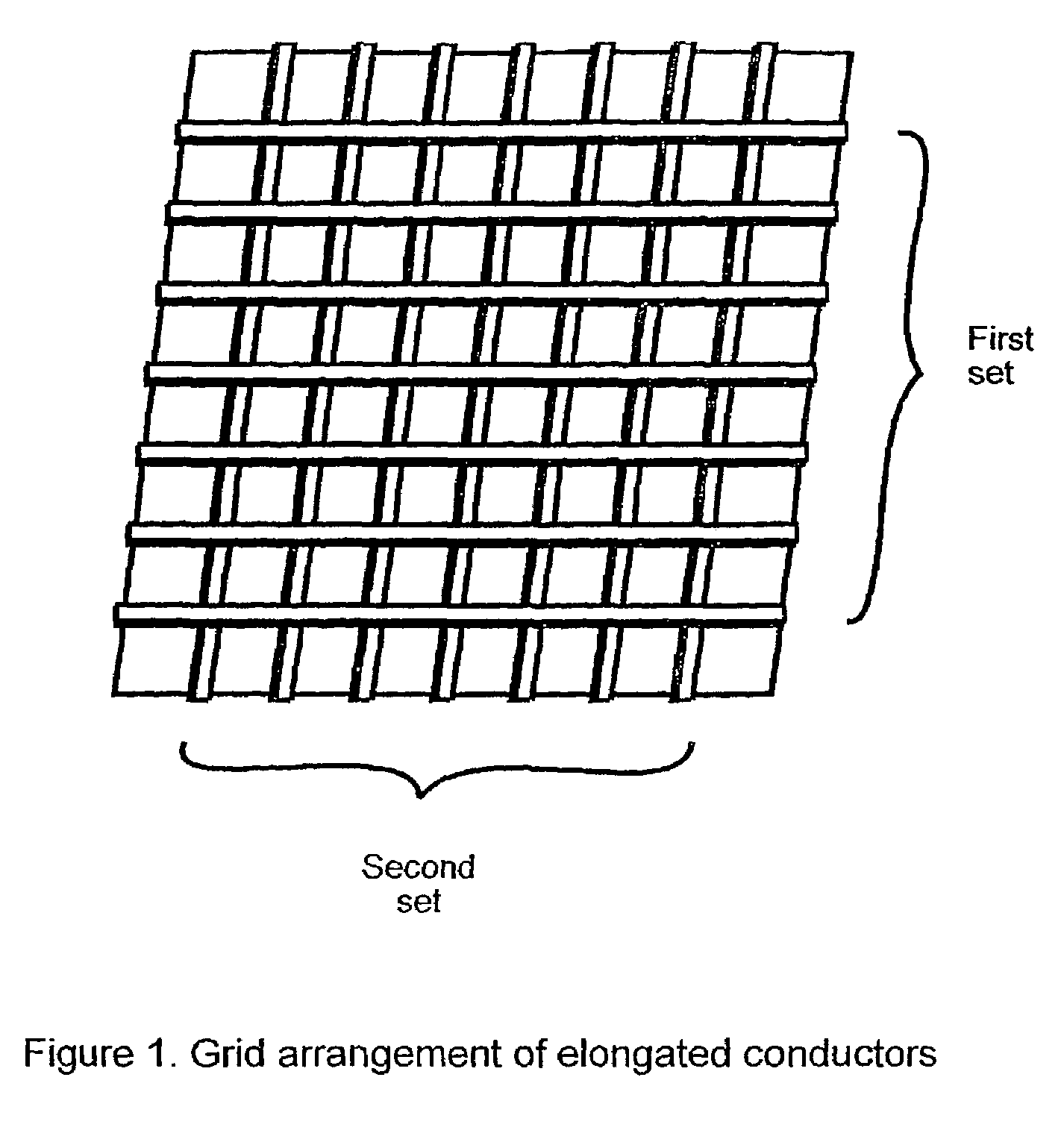
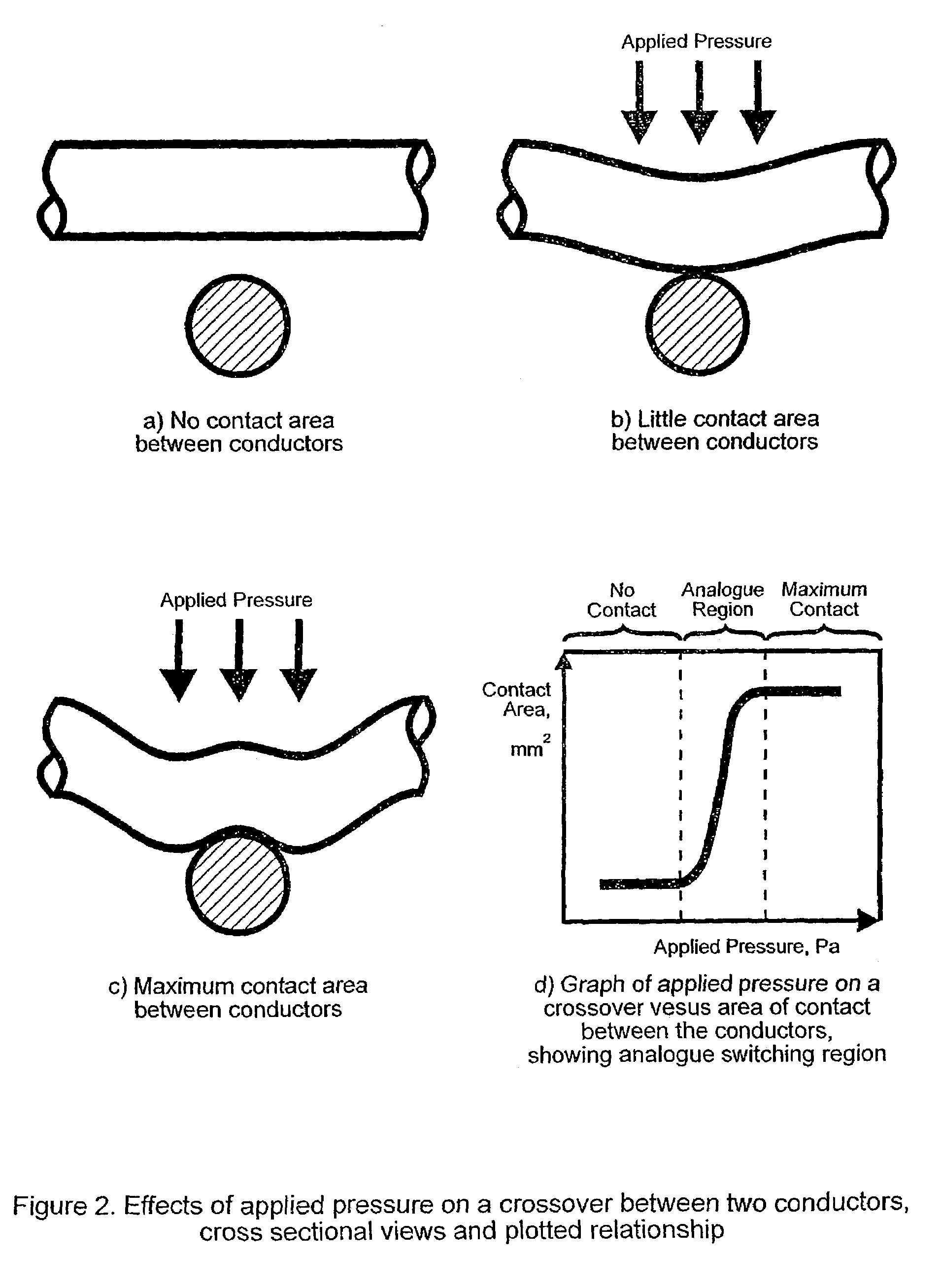
A fabric including within its construction a first elongated electrical conductor crossed by a second elongated electrical conductor, the conductors being normally biased apart at a crossover point of said fibres with an air gap between them, whereby application of pressure in a direction substantially normal to a plane of the fabric causes the conductors to make contact. The fabric may be woven, knitted, non-woven or plaited. The fabric can be used as a pressure sensor, switch or other sensor.
Owner:INTELLIGENT TEXTILES
Article of apparel incorporating a zoned modifiable textile structure
ActiveUS20050204449A1Improve understandingGarment special featuresWeft knittingEngineeringE-textiles
An article of apparel is disclosed that includes zones with a textile having a structure that changes or is otherwise modified by a physical stimulus, such as the presence of water or a temperature change, to modify a property of the textile. The zones may be along a center back area and side areas of the apparel, and the textile may increase in air permeability when exposed to water. The zones may also be in an upper area of the torso and in a lower back area, and the textile may increase in texture when exposed to water. In some embodiments, slits are formed in the textile.
Owner:NIKE INC
Nonwoven material for acoustic insulation, and process for manufacture
An improved acoustically and thermally insulating composite material suitable for use in structures such as buildings, appliances, and the interior passenger compartments and exterior components of automotive vehicles, comprising at least one airlaid fibrous layer of controlled density and composition and incorporating suitable binding agents and additives as needed to meet expectations for noise abatement, fire, and mildew resistance. Separately, an airlaid structure which provides a reduced, controlled airflow therethrough useful for acoustic insulation is provided, and which includes a woven or nonwoven scrim.
Owner:GLATFELTER CORP
Nonwoven containing acoustical insulation laminate
The present invention relates to an acoustical insulation material containing a first layer formed from a nonwoven web having a density of at least 50 kg / m3 wherein the nonwoven web is formed from thermoplastic [meltblown] fibers having an average fiber diameter of less than about 7 microns; and a second layer of a high loft material. The high loft material of the present invention provides bulk to the first layer and may or may not have sound attenuating properties. Examples of the high loft material include, for example, fiberglass and high loft nonwoven webs. Also disclosed in a method of attenuating sound waves passing from a sound source area to a second area. The method includes positioning an acoustical insulation material containing a first layer formed from a nonwoven web having a density of at least 50 kg / m3 wherein the nonwoven web is formed from thermoplastic [meltblown] fibers having an average fiber diameter of less than about 7 microns; and a second layer of a high loft material, between the sound source area and the second area.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Low density lightning strike protection for use in airplanes
ActiveUS20090227162A1Minimize micro-crackingWeight optimizationConductive materialWarp knittingFiberEpoxy
Surface films, paints, or primers can be used in preparing aircraft structural composites that may be exposed to lightning strikes. Methods for making and using these films, paints or primers are also disclosed. The surface film can include a thermoset resin or polymer, e.g., an epoxy resin and / or a thermoplastic polymer, which can be cured, bonded, or painted on the composite structure. Low-density electrically conductive materials are disclosed, such as carbon nanofiber, copper powder, metal coated microspheres, metal-coated carbon nanotubes, single wall carbon nanotubes, graphite nanoplatelets and the like, that can be uniformly dispersed throughout or on the film. Low density conductive materials can include metal screens, optionally in combination with carbon nanofibers.
Owner:ROHR INC +1
Three dimensional random looped structures made from interpolymers of ethylene/alpha-olefins and uses thereof
Cushioning net structures comprise random loops, such as three-dimensional random loops, bonded with one another, wherein the loops are formed by allowing continuous fibers, made of ethylene / α-olefin interpolymers, to bend to come in contact with one another in a molten state and to be heat-bonded at most contact points. The structures provided herein have desirable heat resistance, durability and cushioning property. The cushioning structures are used in furniture, vehicle seats etc.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Flame resistant fabrics and garments made from same
InactiveUS20080057807A1Inexpensive and comfortable to wearerCotton-low durability-isWarp knittingAnimal housingPolymer scienceNatural fiber
Unique blends of fibers that incorporate synthetic cellulosic fibers to render fabrics made with such blends more durable than fabrics made with natural cellulosic fibers such as cotton. While more durable than cotton, the synthetic cellulosic fibers used in the blends are still inexpensive and comfortable to the wearer. Thus, the benefits of cotton (affordability and comfort) are still attained while a drawback of cotton—low durability—is avoided. In one embodiment, the fiber blend includes FR modacrylic fibers and synthetic cellulosic fibers, preferably, but not necessarily non-FR lyocell fibers such as TENCEL™ and TENCEL A100™. Other fibers may be added to the blend, including, but not limited to, additional types of inherently FR fibers, anti-static fibers, anti-microbial fibers, stretch fibers, and / or high tenacity fibers. The fiber blends disclosed herein may be used to form various types of FR fabrics. Desired colors may be imparted in a variety of ways and with a variety of dyes to the fabrics disclosed herein. Fabrics having the fibers blends disclosed herein can be used to construct the entirety of, or various portions of, a variety of protective garments for protecting the wearer against electrical arc flash and flames, including, but not limited to, coveralls, jumpsuits, shirts, jackets, vests, and trousers.
Owner:SOUTHERN MILLS
Adhesive-containing wound closure device and method
InactiveUS20060009099A1Enlarging woundShorten operation timeWeft knittingWarp knittingPolymerizationChemistry
An article, such as a tissue bonding article, includes a flexible material, a polymerization initiator or rate modifier disposed in or on the flexible material, and a polymerizable adhesive composition permeated throughout at least a portion of the flexible material, where the polymerization initiator or rate modifier is a polymerization initiator or rate modifier for the polymerizable adhesive composition.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Structurally reinforced panels
InactiveUS6855652B2Satisfies needSynthetic resin layered productsBuilding componentsFiberEngineering
Owner:ZEPHYROS INC
Composite mesh devices and methods for soft tissue repair
InactiveUS20100318108A1Reduce adhesionDifferent and simple configurationCovering/liningsWarp knittingComposite meshSoft tissue repair
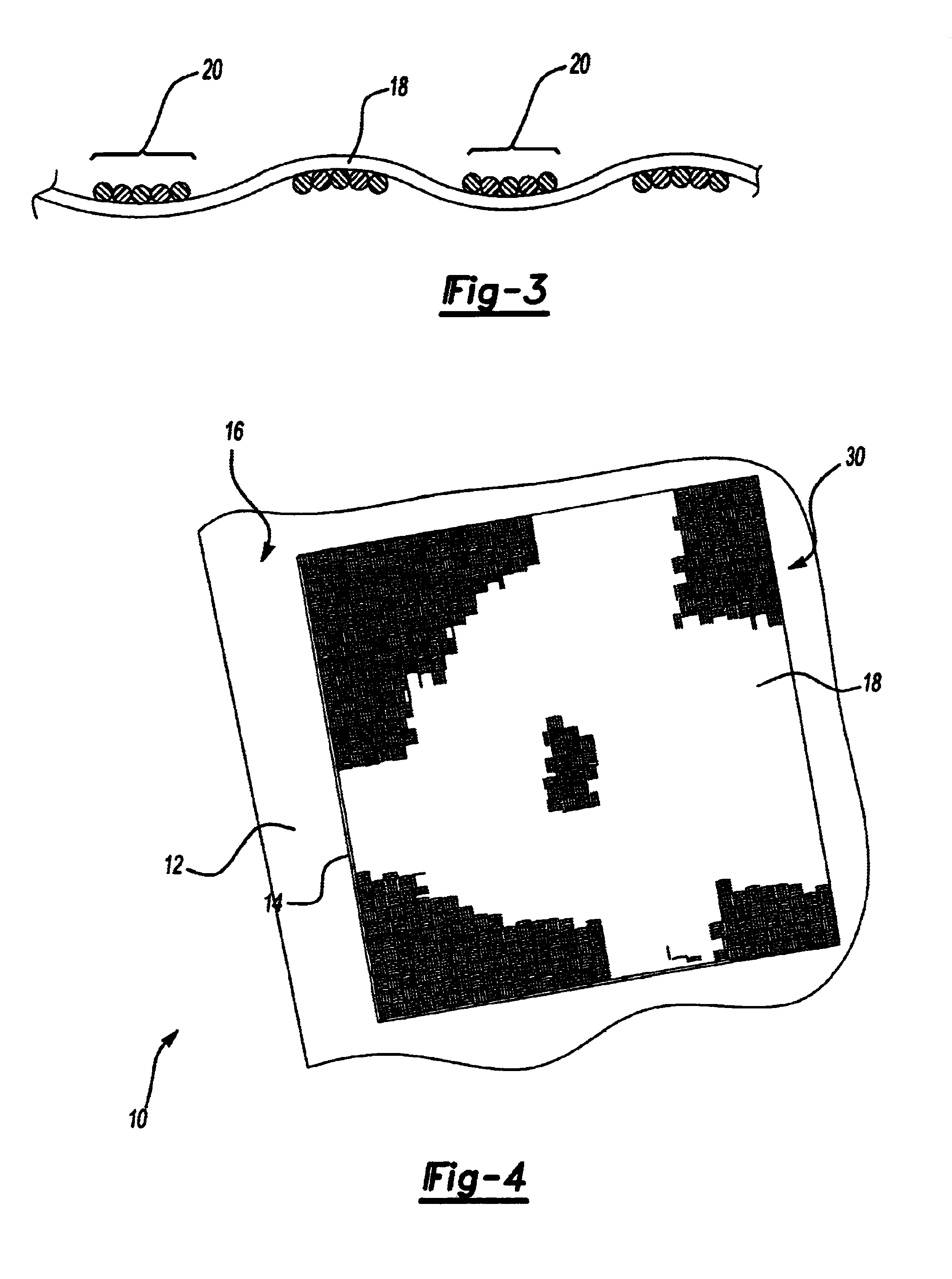
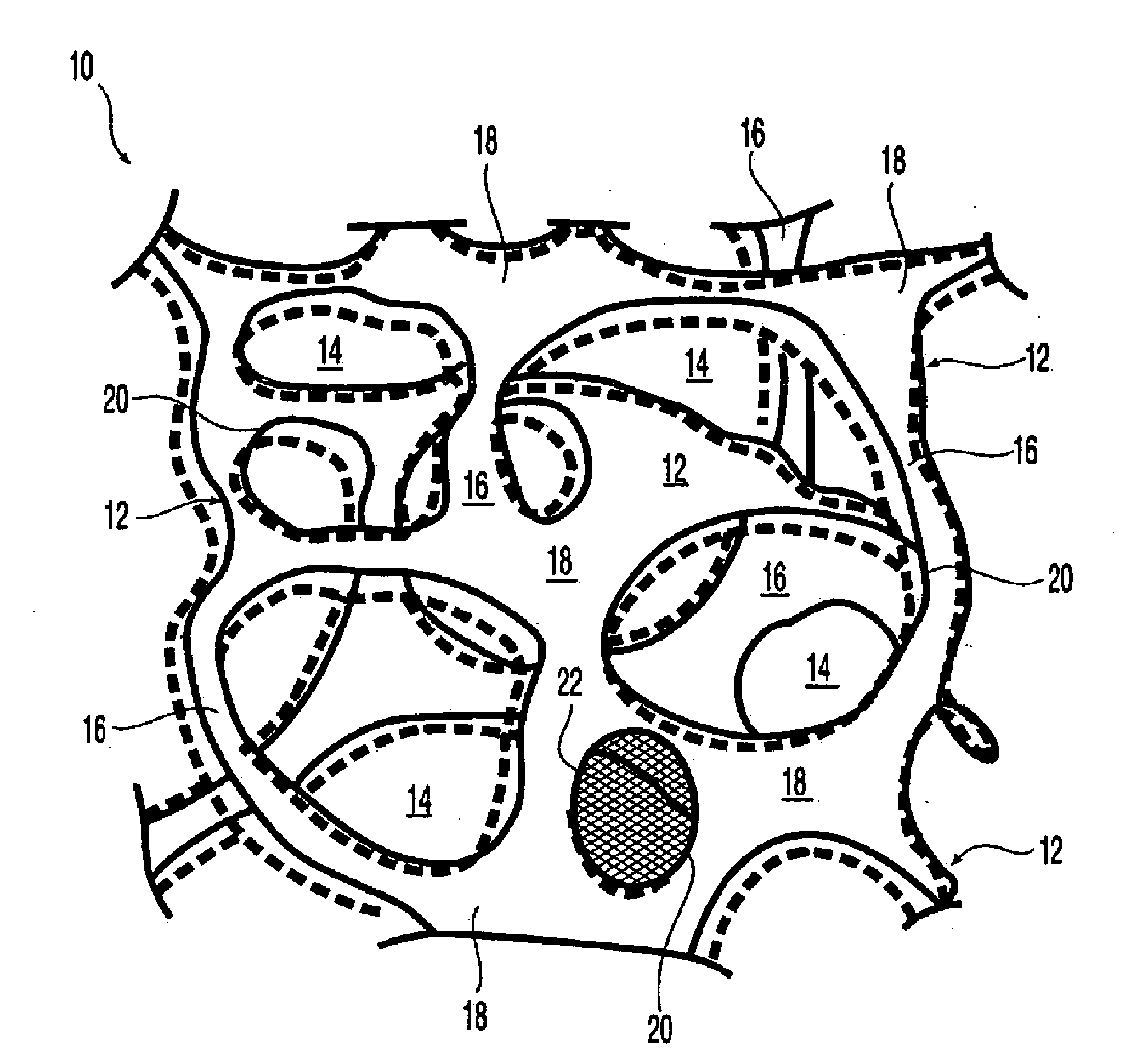
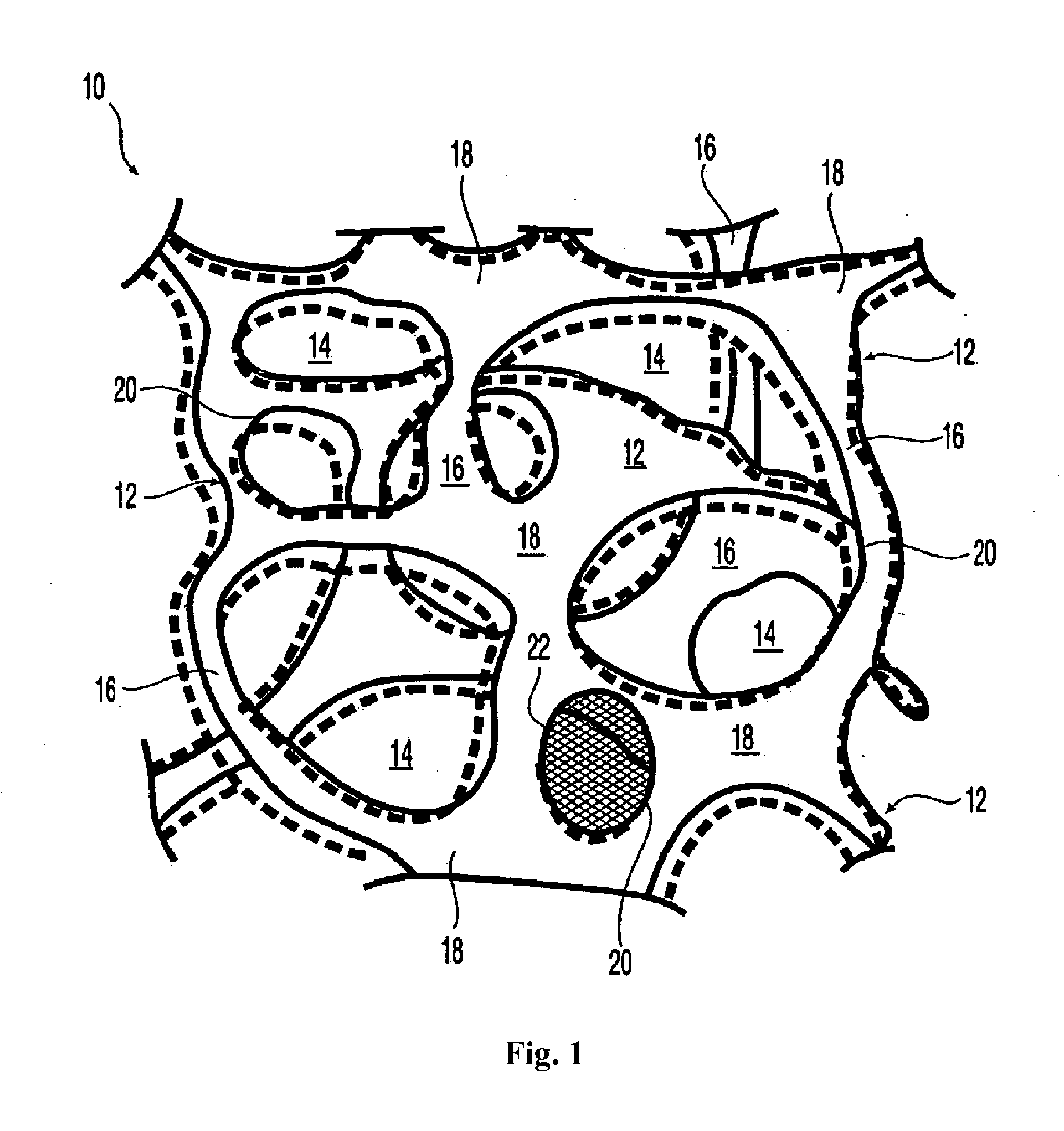
A composite implantable device for promoting tissue ingrowth therein comprising a biodurable reticulated elastomeric matrix having a three-dimensional porous structure having a continueous network of interconnected and intercommunicating open pores and a support structure is disclosed. The support structure may be a polymeric surgical mesh comprising a plurality of intersecting one-dimensional reinforcement elements, wherein said mesh is affixed to a face of said first matrix. Methods of making and using the implantable device are also provided.
Owner:BIOMERIX CORP
Designed composite degradation for spinal implants
InactiveUS20050136764A1Avoid problemsRelieve pressureInternal osteosythesisSynthetic resin layered productsSpinal columnIn vivo
The invention includes a composite material for use in the construction of orthopedic devices and methods for using these composites. The composite material is comprised of at least one filament or cord that can be non-biodegradable and a biodegradable matrix. In other forms the composite material contains at least two components formed of a biodegradable material, which components can be a matrix or a filament or a combination of matrices and filaments. The degradation rate of the two components need not be the same. The composite material is used in the construction of orthopedic devices such as bone plates, bone rods, spinal rods, and laminate sheets that change physical properties in vivo.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
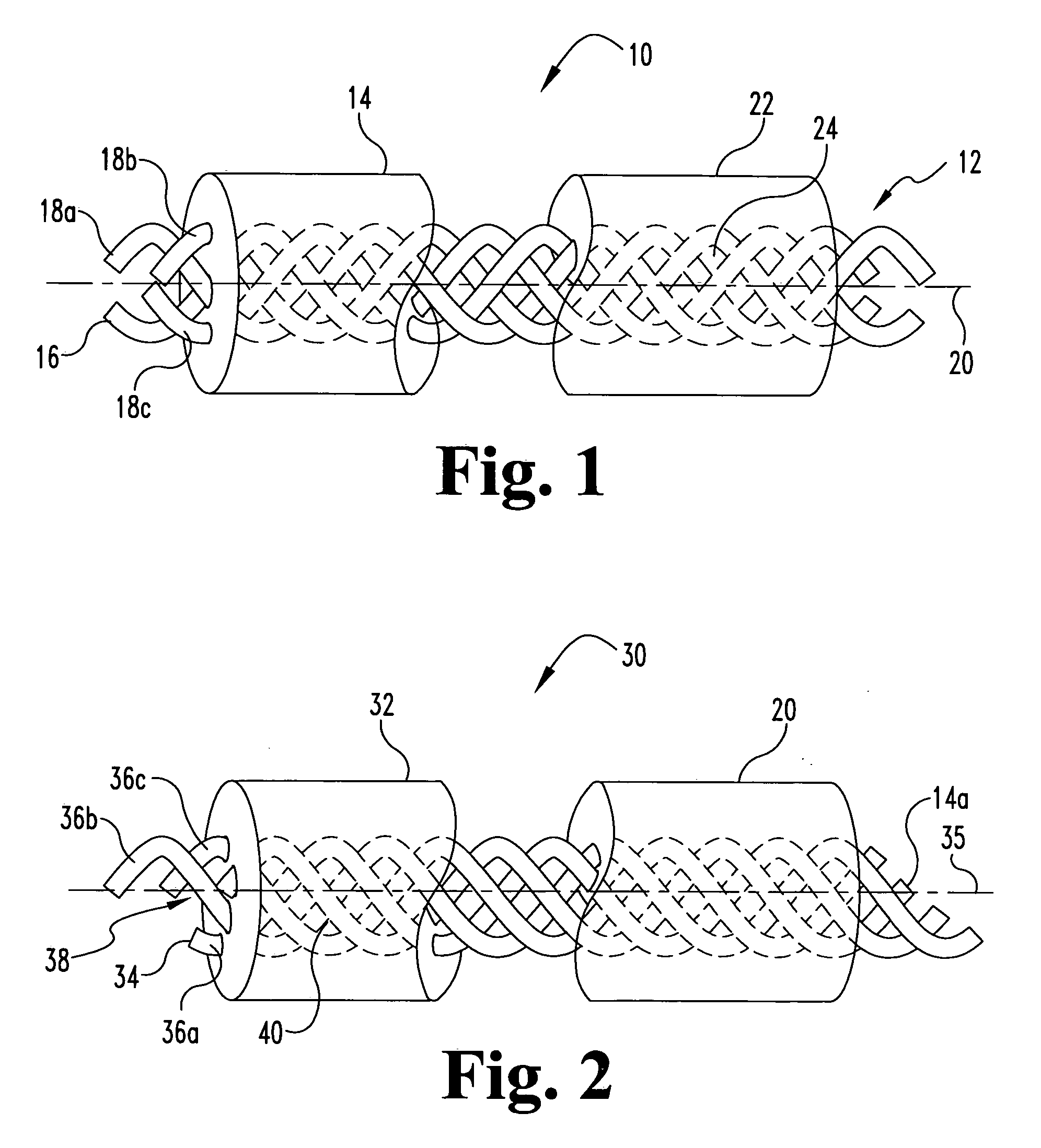
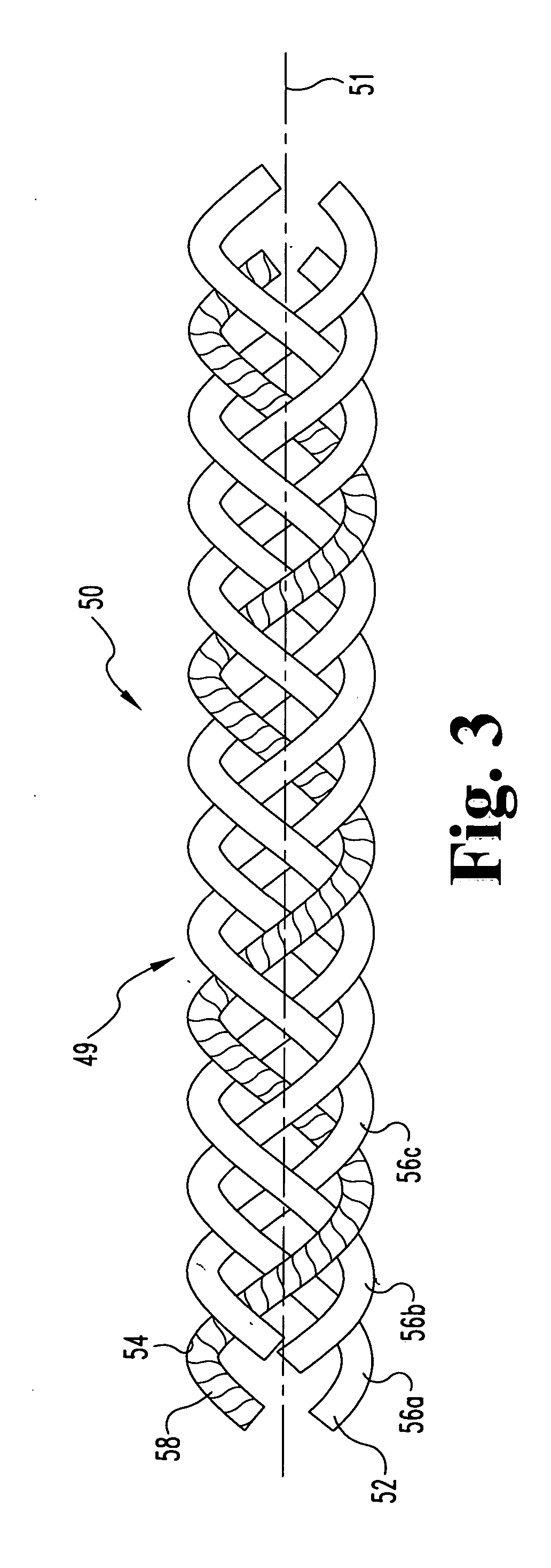
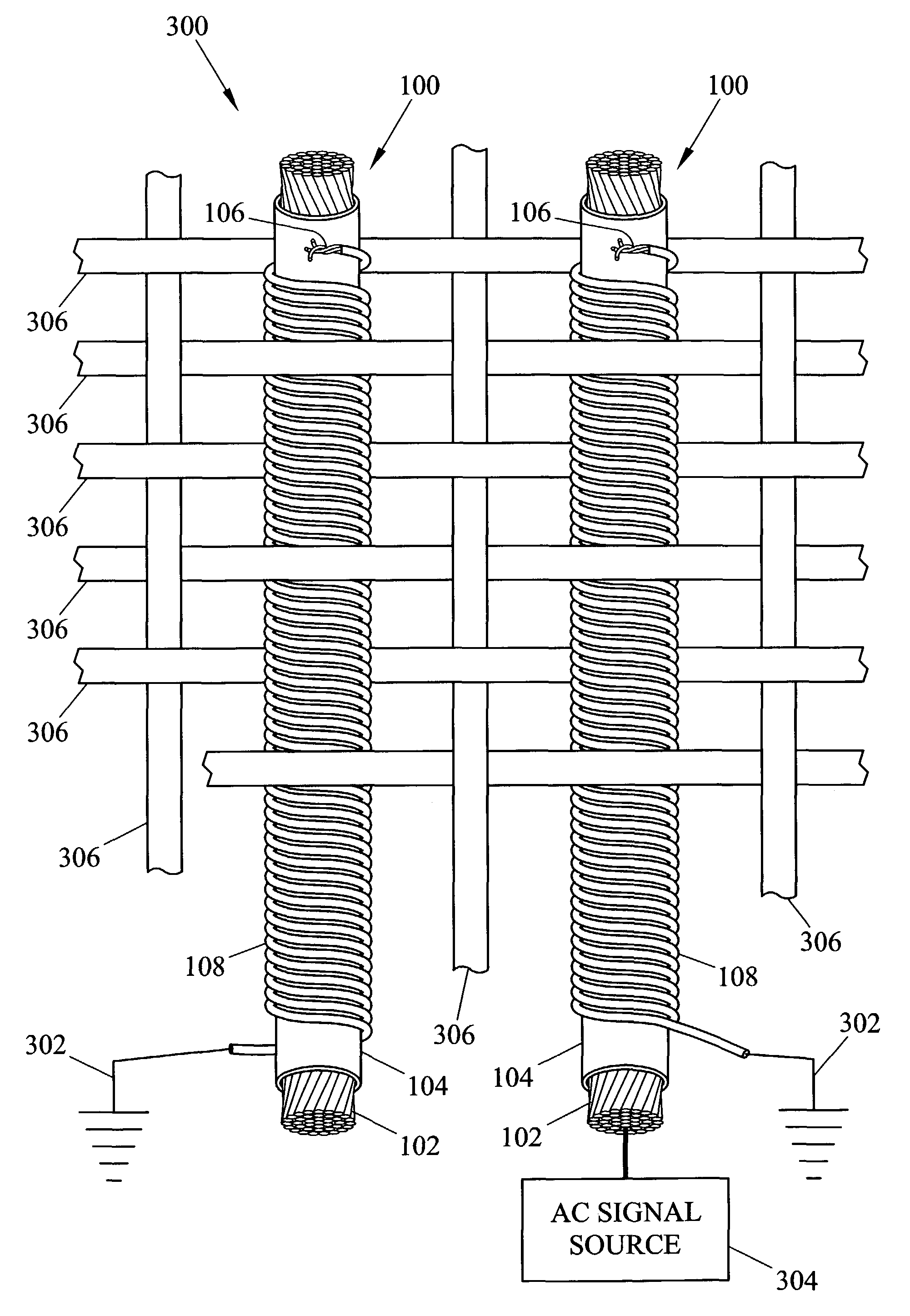
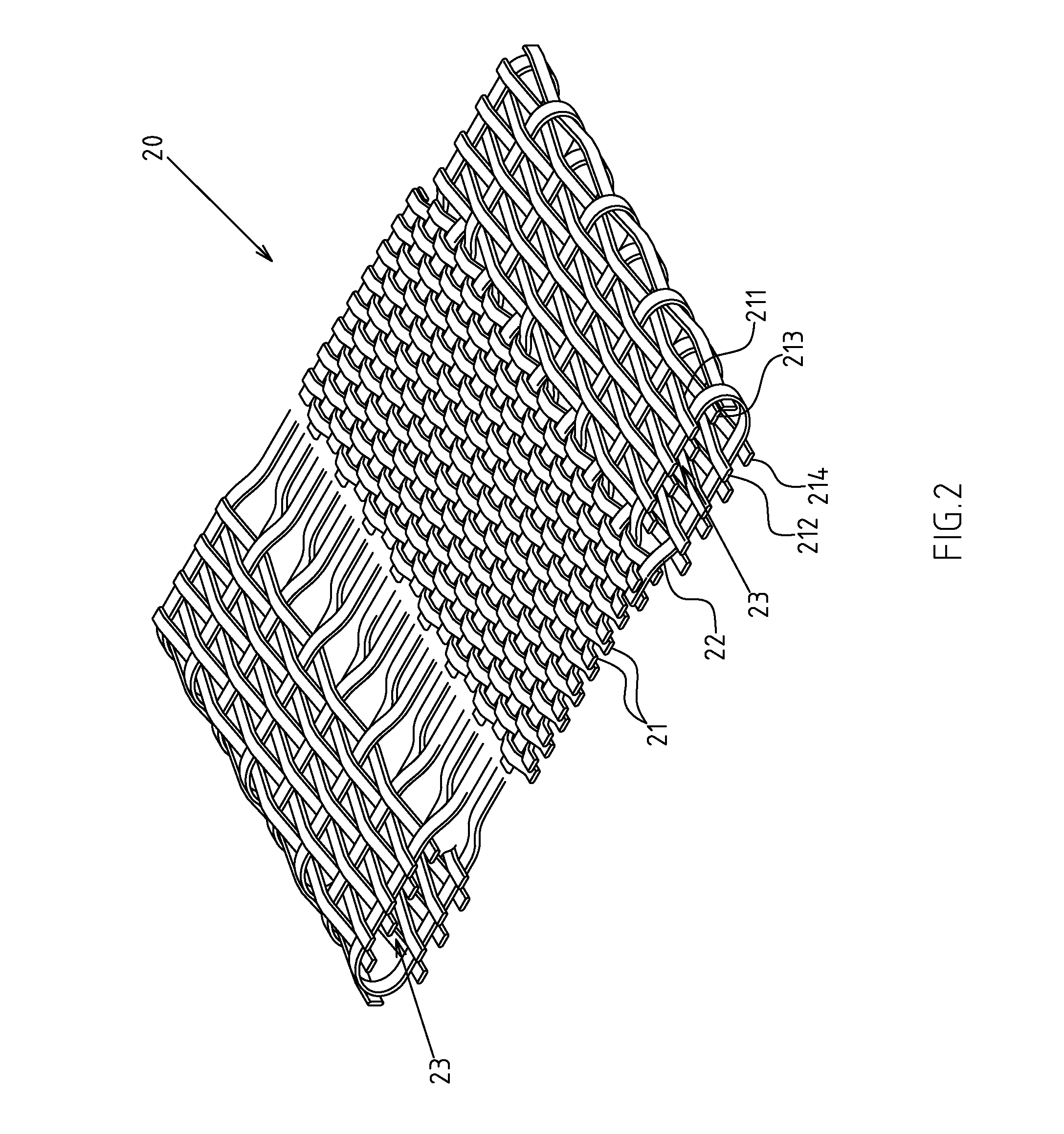
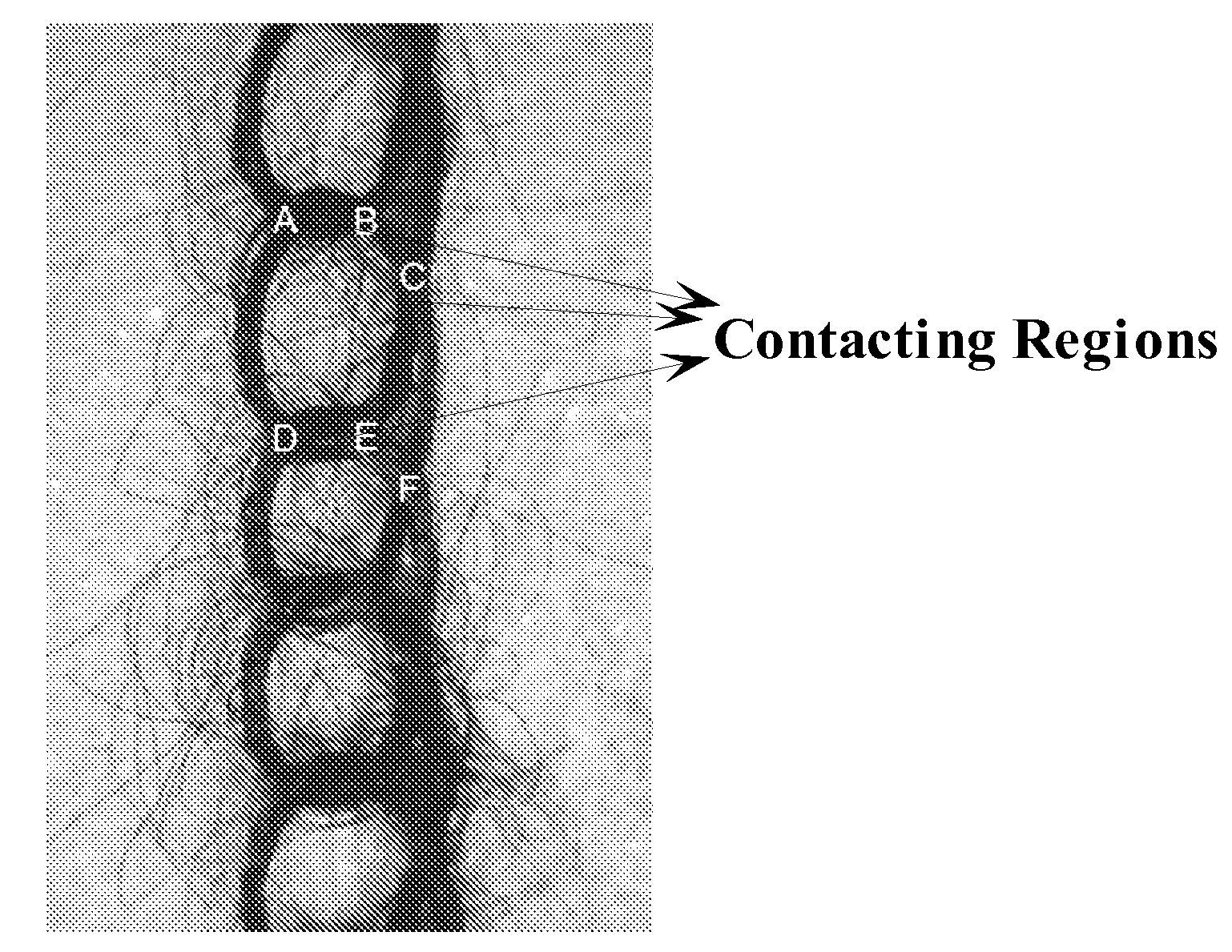
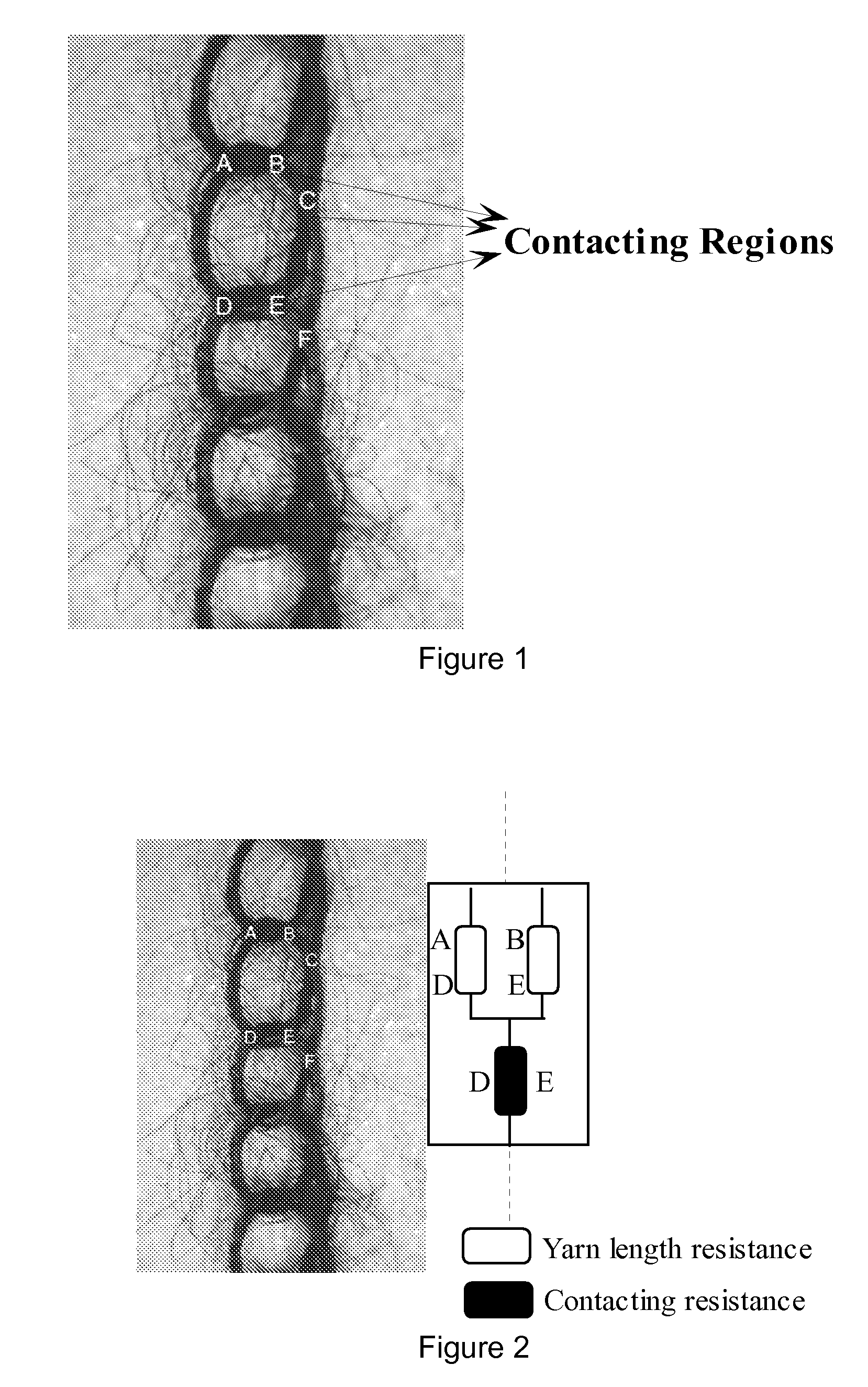
Fabric and yarn structures for improving signal integrity in fabric-based electrical circuits
InactiveUS7348285B2Reduce crosstalkImprove signal integrityAlcoholic beverage preparationPower cables with screens/conductive layersPower gridTwisted pair
Coaxial and twisted pair conductive yarn structures reduce signal crosstalk between adjacent lines in woven electrical networks. A coaxial conductive yarn structure includes an inner conductive yarn having a plurality of conductive strands twisted together. An outer conductive yarn is wrapped around the inner conductive yarn. An insulating layer separates the inner and outer yarns. A twisted pair conductive yarn structure includes first and second conductive yarns, each including a plurality of conductive strands being twisted together. The first and second conductive yarns are twisted together to form a helical structure. In a woven electrical network, at least one conductor of adjacent conductive yarn structures is connected to ground to reduce signal crosstalk. Coaxial and twisted pair yarn structures may also be formed simultaneously with weaving or knitting the threads that make up the structures into a fabric.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
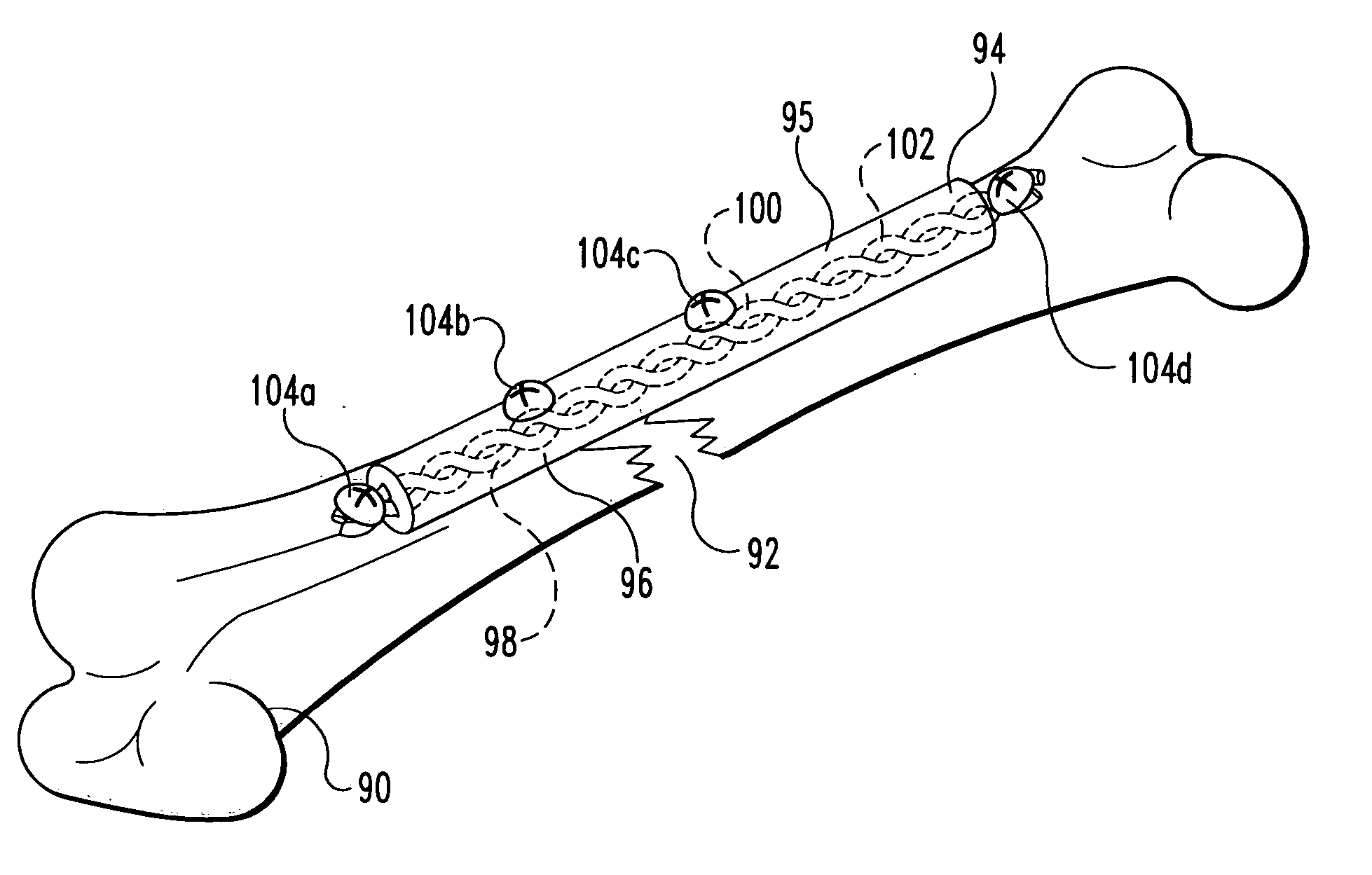
Rope for a hoisting device, elevator and use
ActiveUS20110000746A1Increase ROPDrawback can be obviatedWarp knittingCeramic layered productsGlass fiberFiber
A hoisting device rope has a width larger than a thickness thereof in a transverse direction of the rope. The rope includes a load-bearing part made of a composite material, said composite material comprising non-metallic reinforcing fibers, which include carbon fiber or glass fiber, in a polymer matrix. An elevator includes a drive sheave, an elevator car and a rope system for moving the elevator car by means of the drive sheave. The rope system includes at least one rope that has a width that is larger than a thickness thereof in a transverse direction of the rope. The rope includes a load-bearing part made of a composite material. The composite material includes reinforcing fibers in a polymer matrix.
Owner:KONE CORP
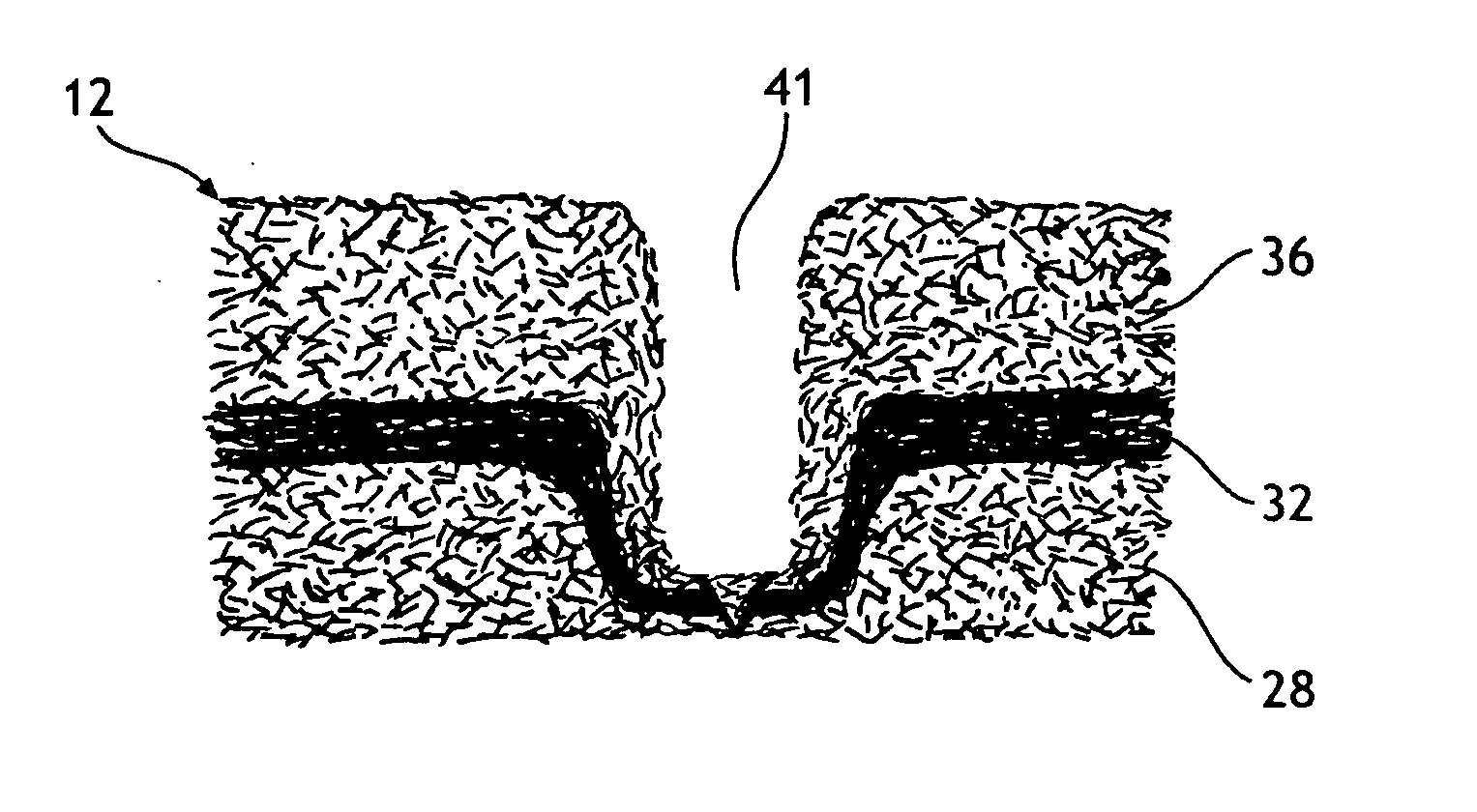
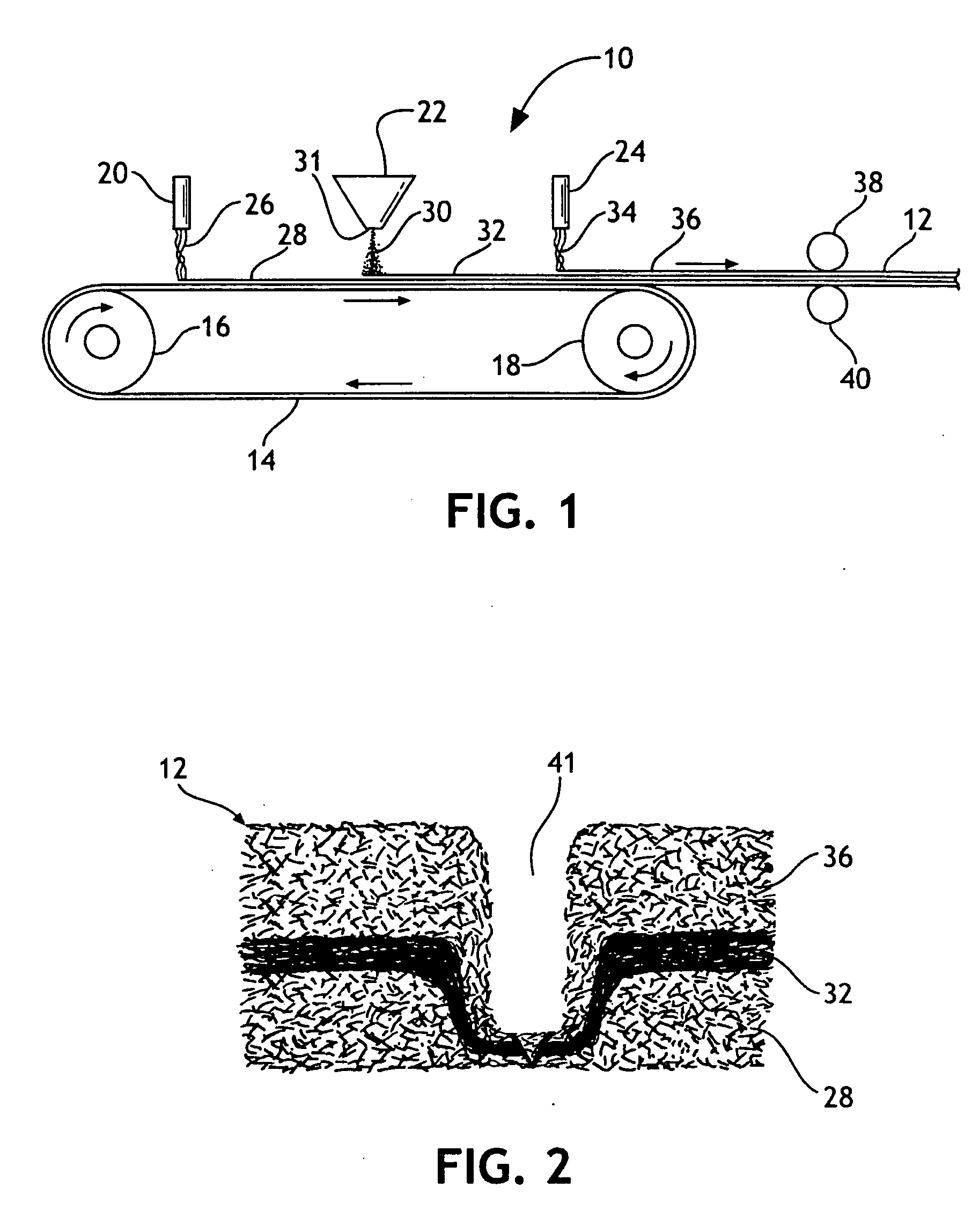
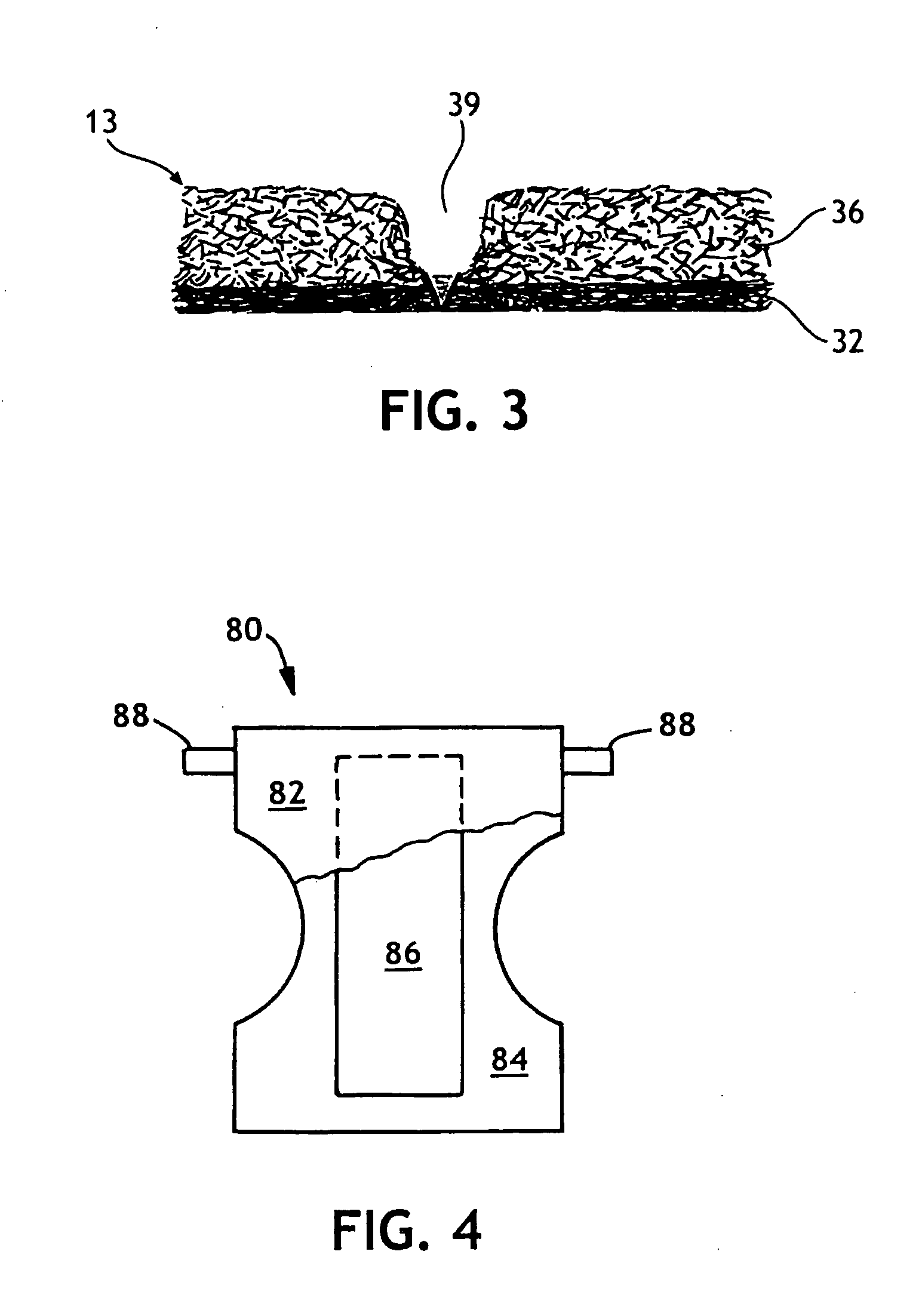
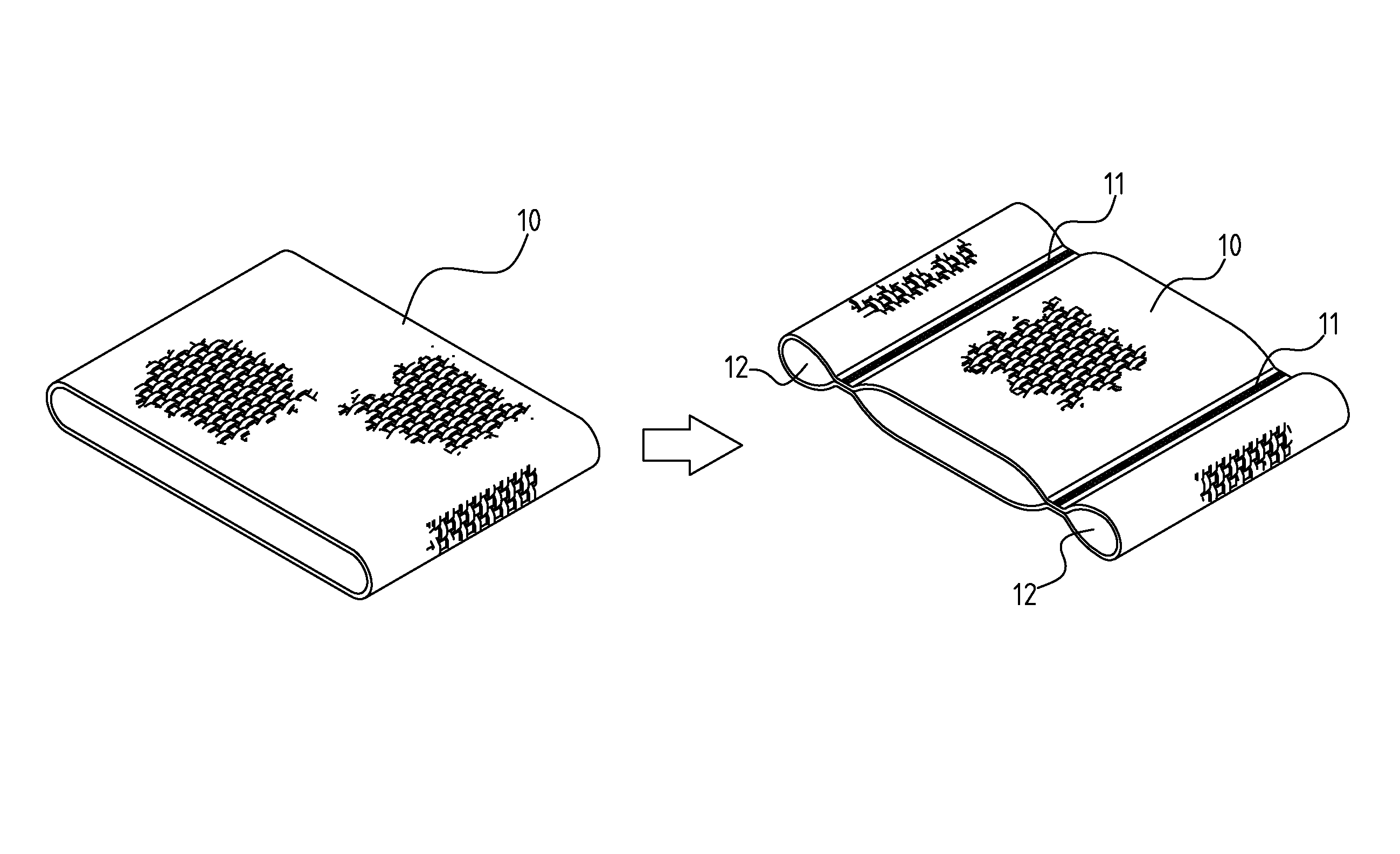
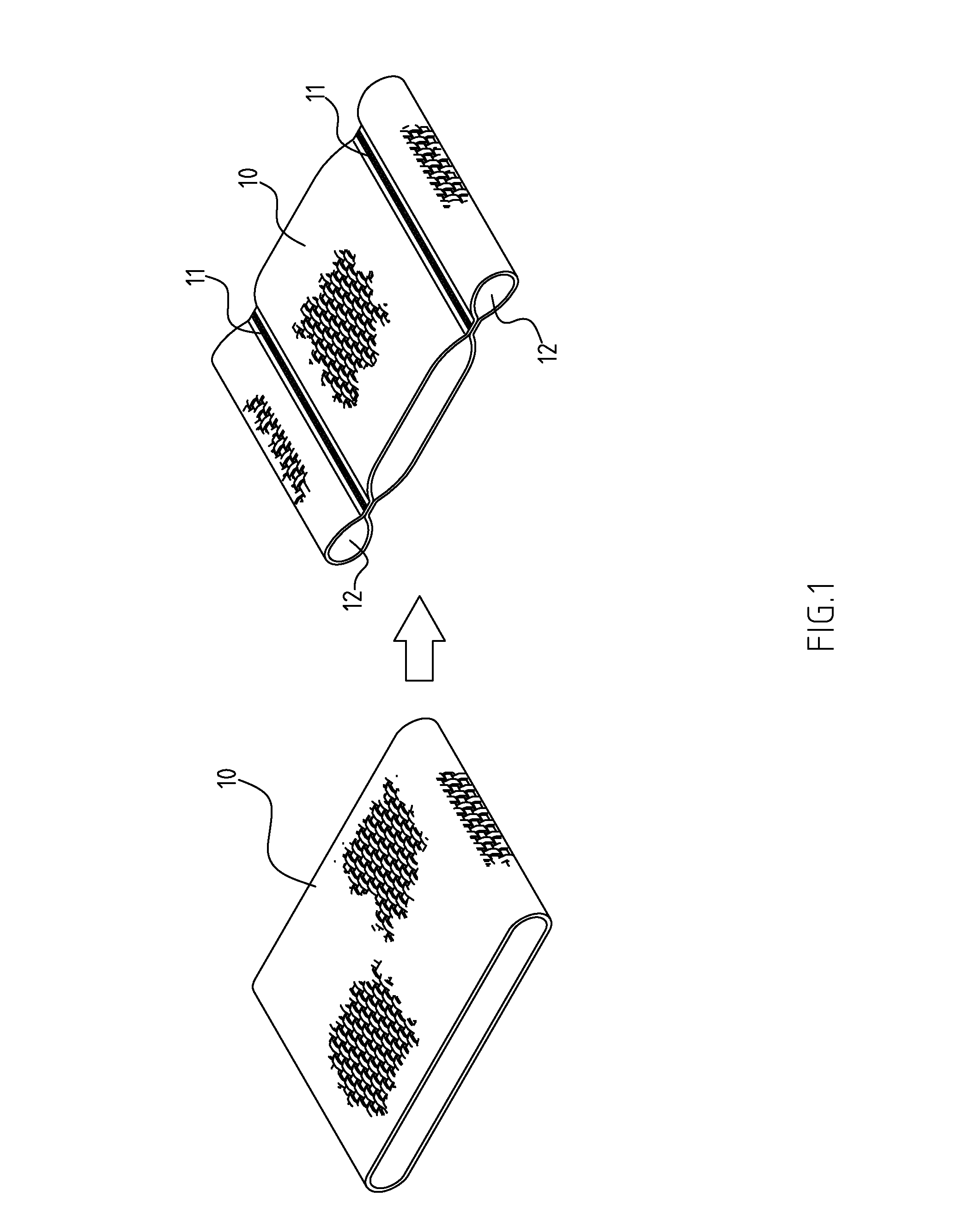
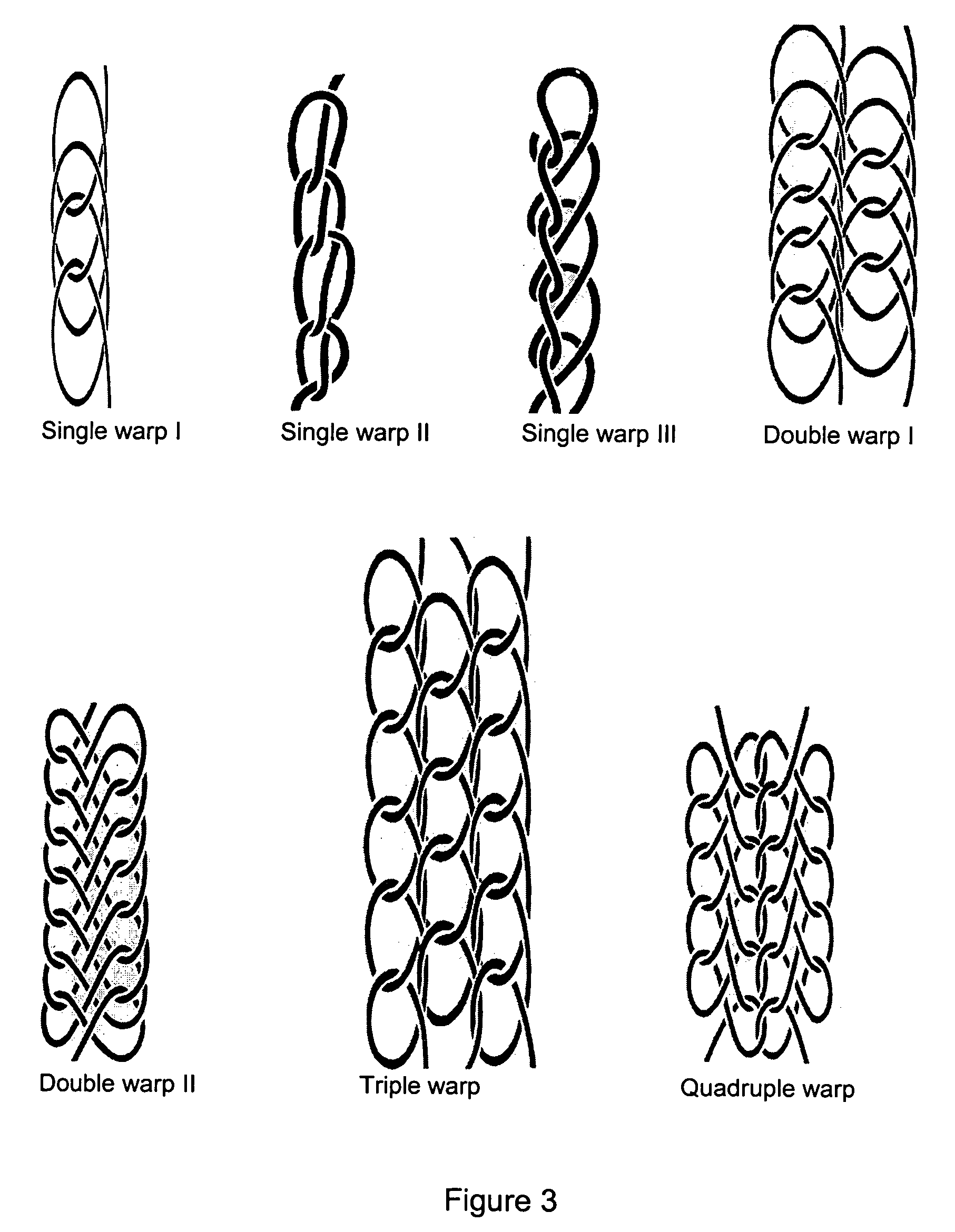
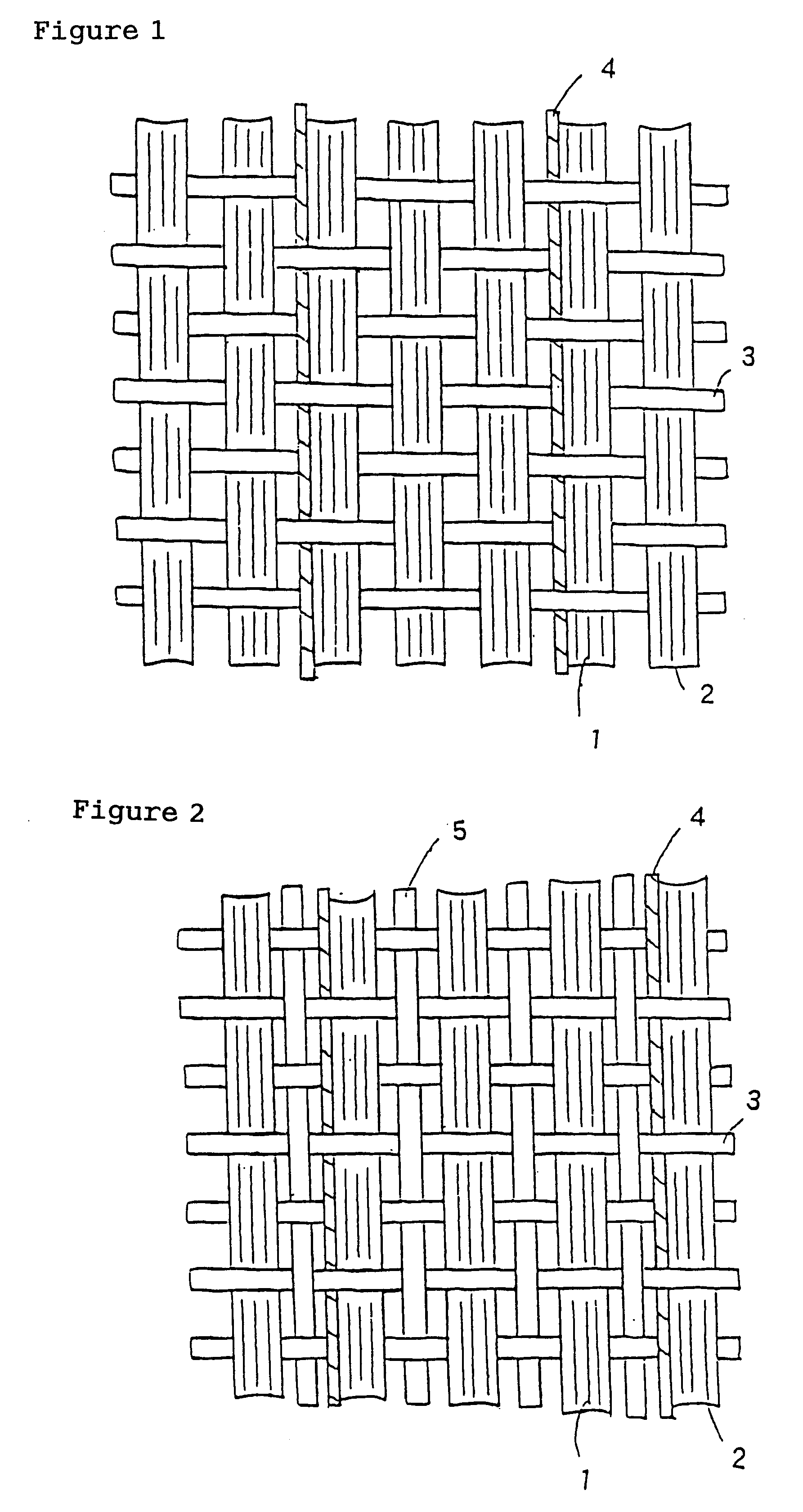
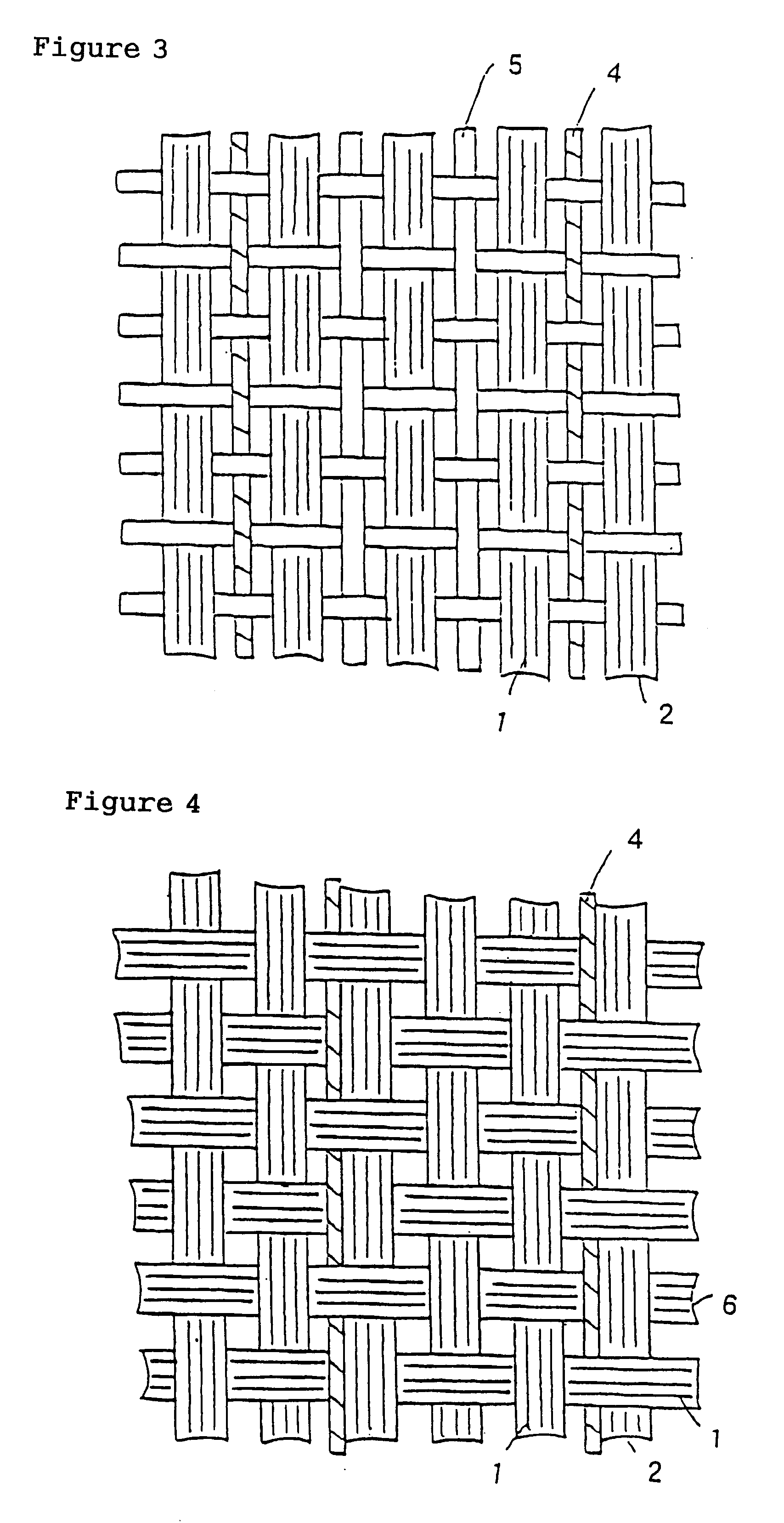
Shaping method and structure of woven fabric with a groove
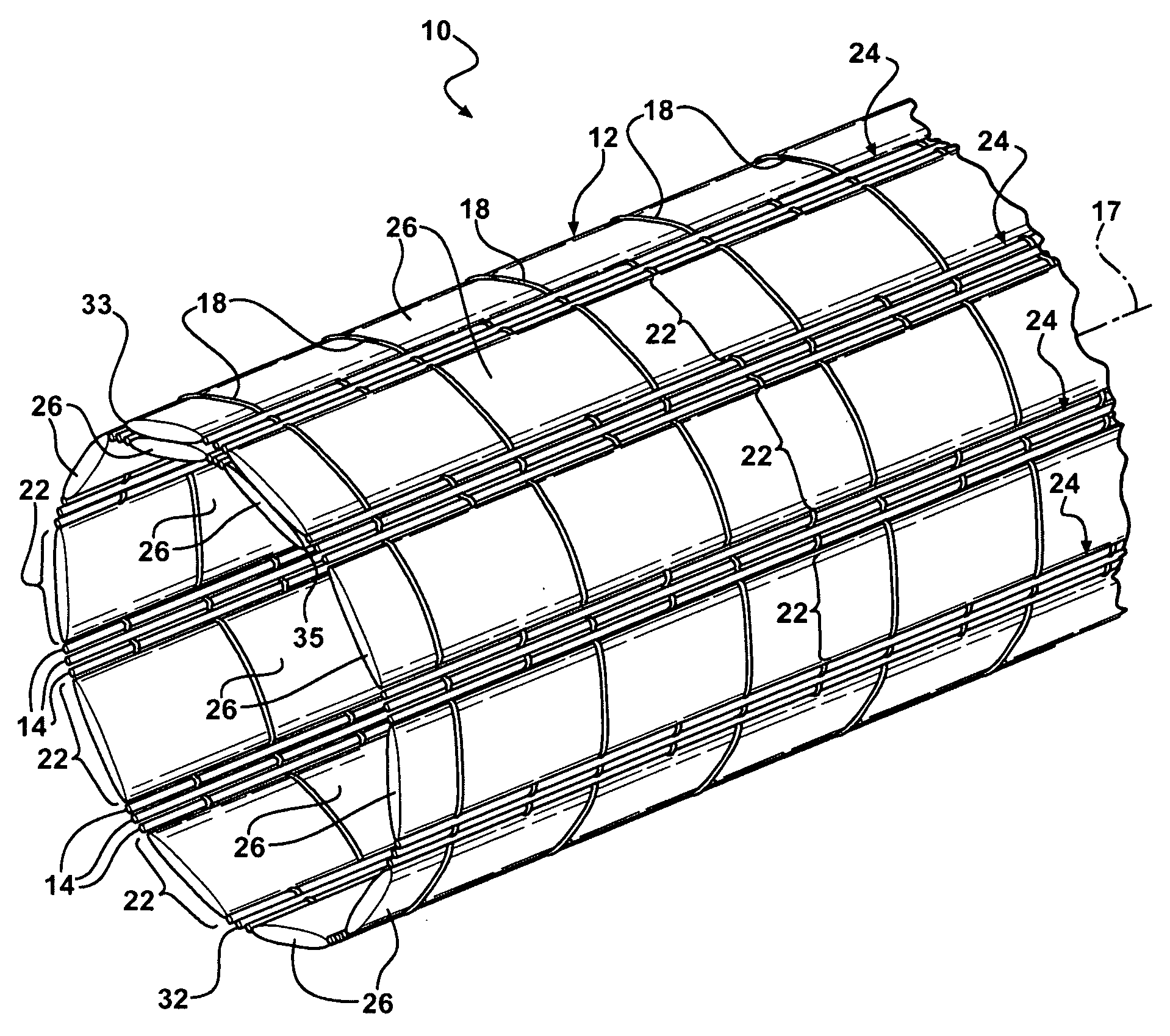
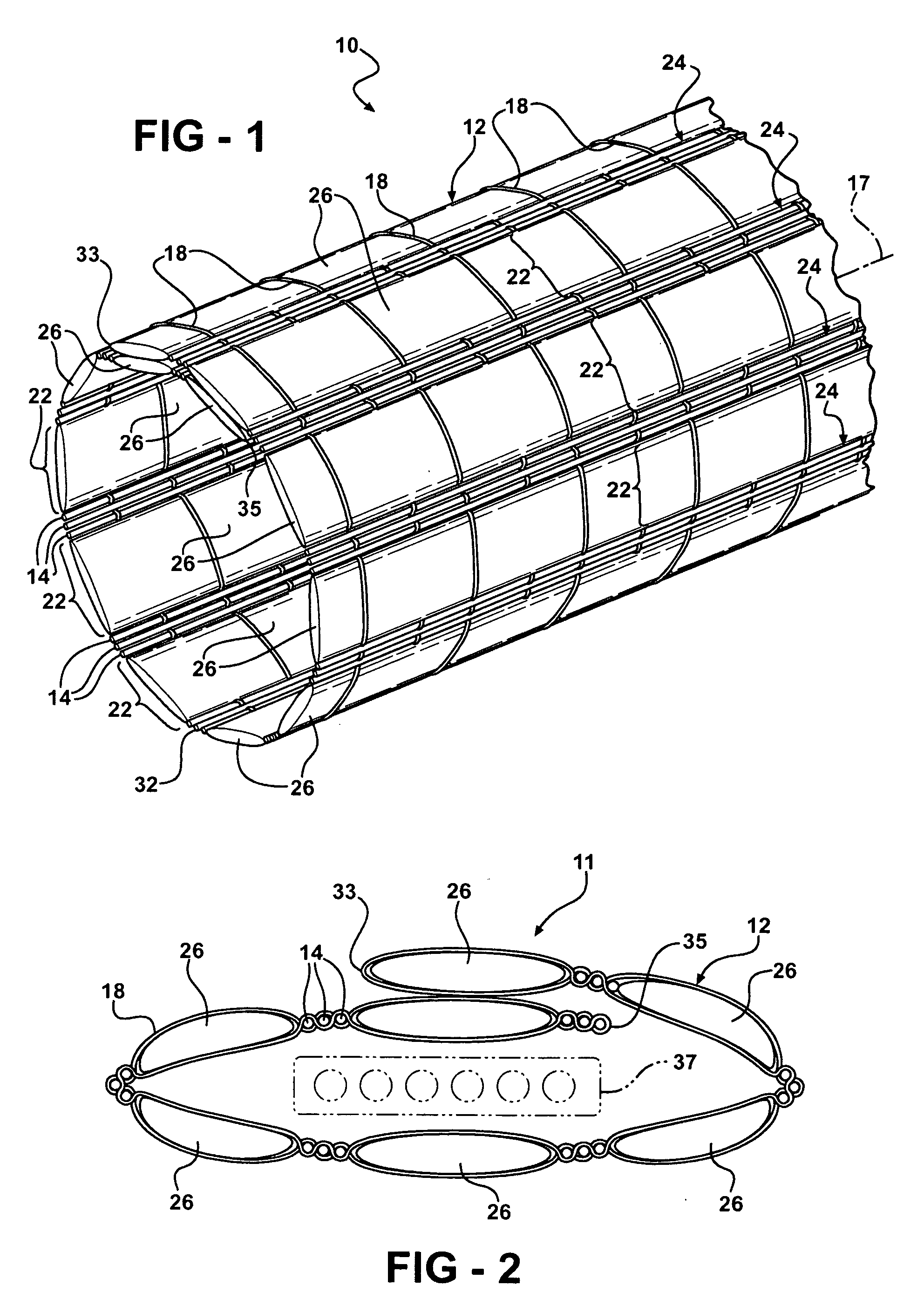
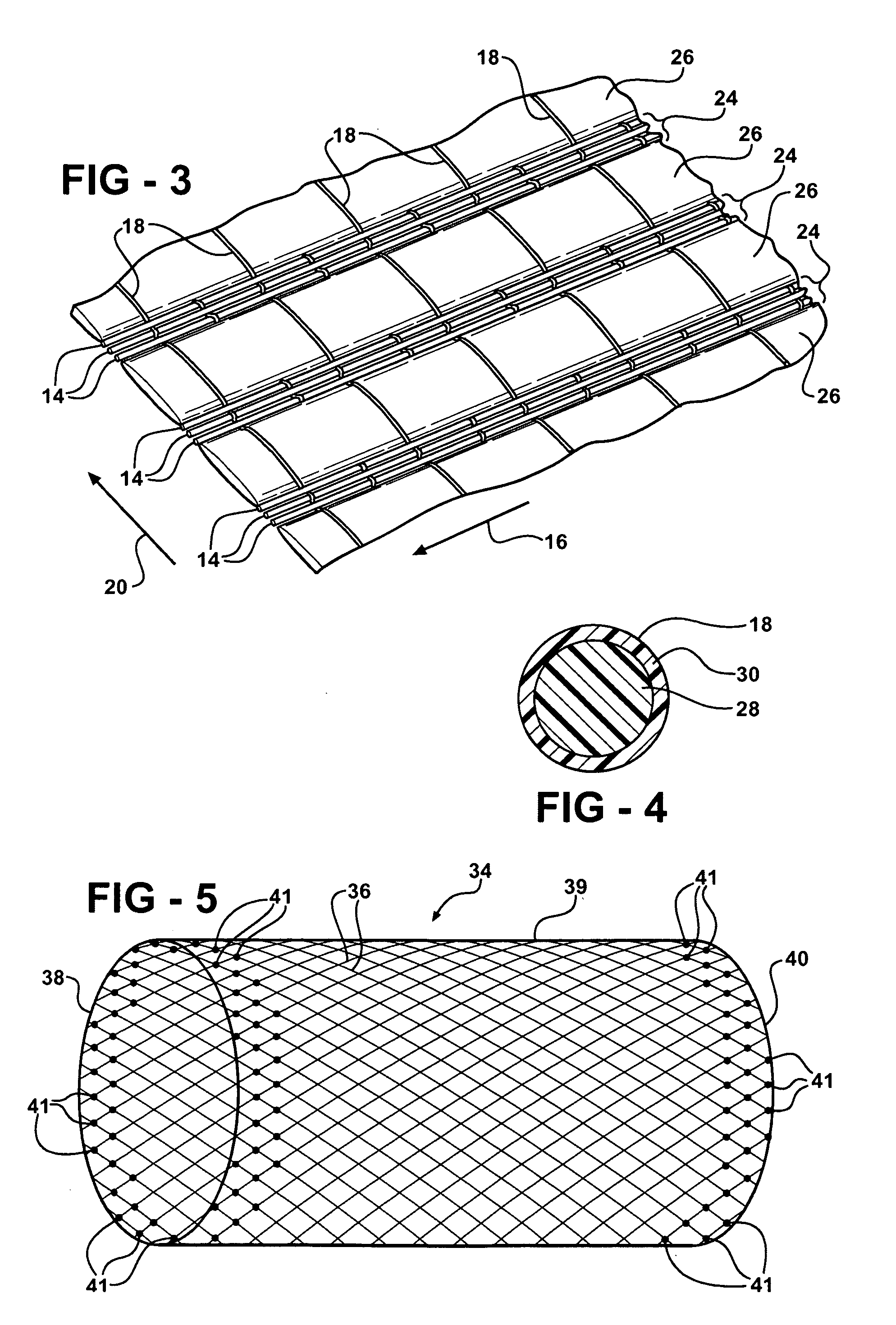
InactiveUS7484539B1Low efficiencyIncrease costMulti-ply fabricsOpen work fabricsMechanical engineeringWoven fabric
A shaping method for a woven fabric having a hollow looped portion includes the steps of laying top longitudinals and bottom longitudinals in a pattern corresponding to a shape and size of the hollow looped portions, forming top warps and bottom warps in a generally planar pattern, flat weaving a weft through and between the top warps and the bottom warps such that the top warps reside above the weft and said bottom warps reside below the weft, passing the weft between the top longitudinals and the bottom longitudinals in the hollow looped portion such that the top longitudinals reside above the weft and the bottom longitudinals reside below the weft.
Owner:CHING SHI IND
Heat weldable roofing membrane
InactiveUS6864195B2Roof covering using flexible materialsSynthetic resin layered productsThermoplasticPolyolefin
A roofing membrane includes a substrate sheet formed of a thermoplastic vulcanizate (TPV) and a film layer of thermoplastic polyolefin (TPO) adhered to at least one surface of the substrate sheet. The TPV preferably includes a copolymer of ethylene and a carbonyl containing monomer dynamically vulcanized in a polyolefin thermoplastic, preferably metallocene-catalyzed polyethylene. A scrim reinforcement layer is optionally embedded in the TPV layer. When installed on a roof substrate, the membrane can be sealed by heat welding the seams of the membrane sheets.
Owner:HOLCIM
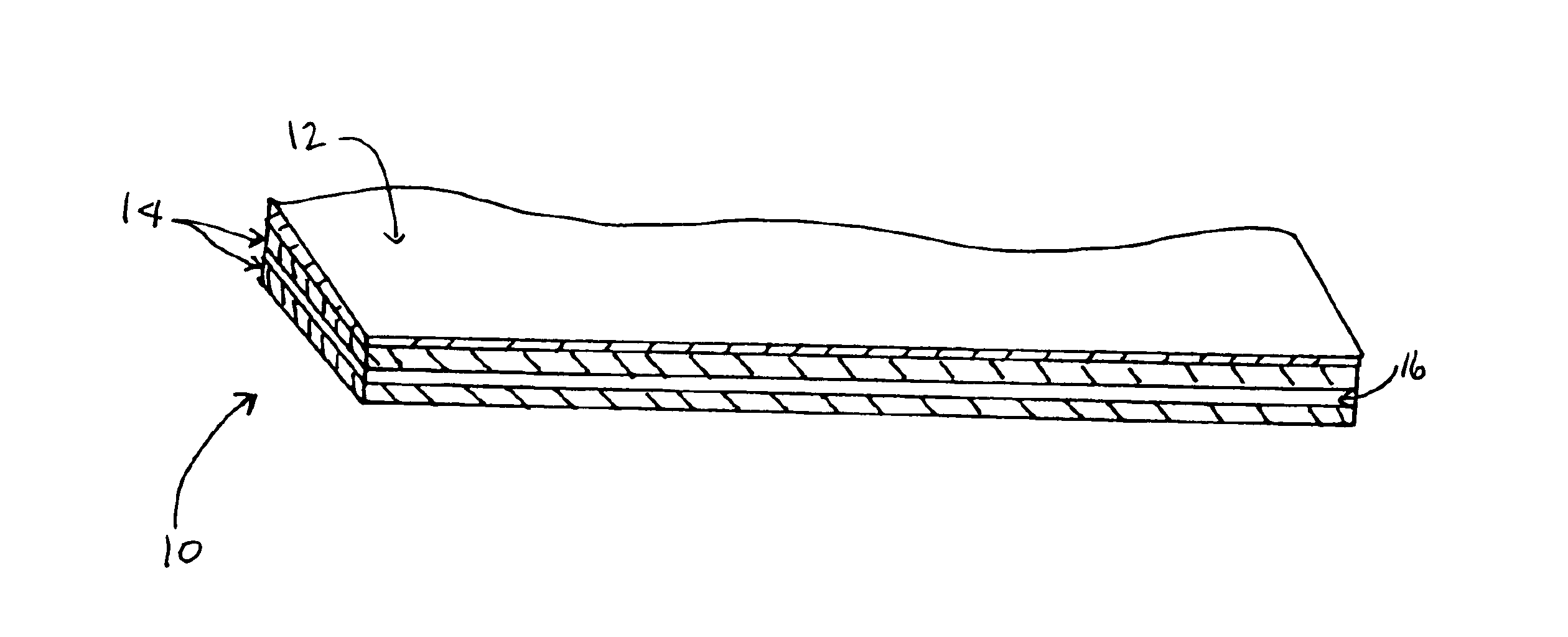
Lightweight ballistic resistant rigid structural panel
InactiveUS6825137B2Without sacrificing ballistic resistanceImprove fatigueFuselage framesFuselage bulkheadsAdhesiveEngineering
A lightweight ballistic resistant rigid structural panel especially for use in aircraft interiors is disclosed. The rigid structural panel is made up of a core layer including a plurality of sheets of flexible, high-tensile strength fabric interleaved with a plurality of sheets of a thermal-fusible film adhesive, and a sheet of cushioning material adhered to the plurality of sheets of flexible, high-tensile strength fabric. Fiber-reinforced face skins are adhered to exterior surfaces of the panel core for structural strength and rigidity. The rigid structural panel is capable of resisting ballistic attack from handguns and like weapons, while maintaining a high degree of strength and rigidity.
Owner:NORDISK AVIATION PRODS A S
Electromagnetic-wave shielding and light transmitting plate
InactiveUS6090473AImprove efficiencySimple processCathode-ray/electron-beam tube vessels/containersMagnetic/electric field screeningEngineering
An electromagnetic-wave shielding and light transmitting plate suitable for an electromagnetic-wave shielding filter for a PDP, which has good electromagnetic-wave shielding efficiency and light transparency, can provide distinct pictures, and can yet be easily made, is provided. The electromagnetic-wave shielding and light transmitting plate is formed of two transparent base plates and an adhesive layer made of EVA in which conductive particles are dispersed and mixed. The base plates are integrally bonded together by the adhesive layer. Adjusting the particle size and the dispersed amount of the conductive particles enables the manufacture of plates having desired electromagnetic-wave shielding efficiency, in addition, good light transparency, without moir+E,acu e+EE phenomenon. Using an adhesive sheet formed by mixing the conductive particles into the EVA facilitates the manufacture of the aforementioned plate.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
High flow, hydrogenated styrene-butadiene-styrene block copolymer and applications
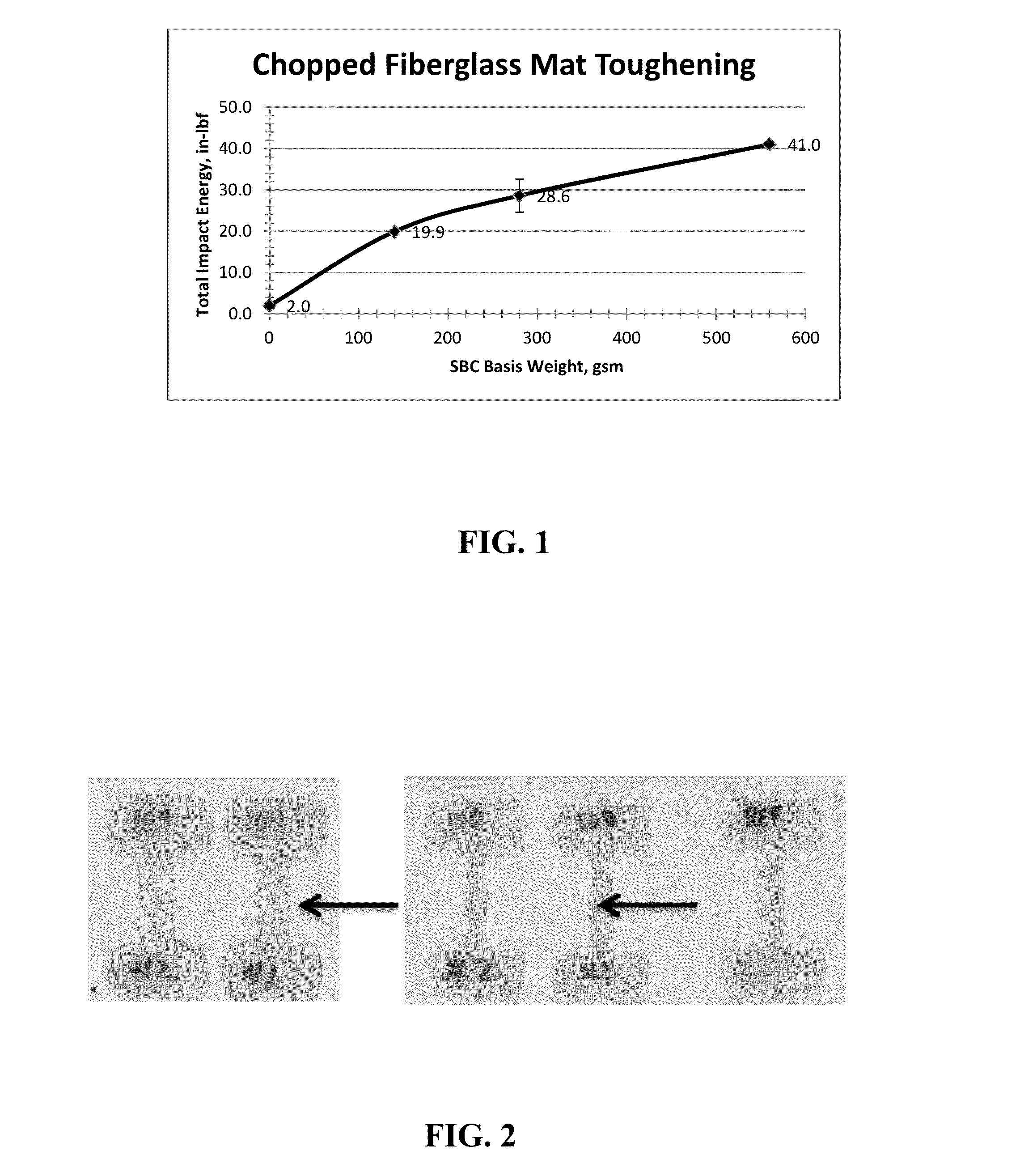
The invention relates to unique applications for the novel high melt flow, low viscosity, selectively hydrogenated styrene-butadiene-styrene (hSBS) or selectively hydrogenated controlled distribution styrene-butadiene / styrene-styrene (hSBSS) block copolymers, wherein the melt flow rate of said block copolymer is at least 100 g / 10 min at 230° C. under 2.16 kg mass according to ASTM D1238. These block copolymers are novel and have the highest melt flow rate of any styrenic block copolymer also possessing high strength and elasticity. It has applications that prior to the present invention were not normally possible due to the normal low melt flow rate of styrenic block copolymers. The present invention also encompasses various fields of use such as a fiberglass hSBS or hSBSS reinforced mat, low viscosity hSBS or hSBSS coatings for industrial uses, hot melt adhesives prepared from hSBS or hSBSS blended with polyalpha-olefins, and elastic film, fiber, and nonwoven constructions using hSBS or hSBSS.
Owner:KRATON POLYMERS US LLC
Conductive films
Conductive films with transparency characteristics are provided. In accordance with various example embodiments, a transparent conductive film includes an inorganic nanowire mesh embedded in an organic substrate layer. The embedding may involve, for example, embedding a majority of, or substantially all of the nanowire mesh in the organic substrate layer to facilitate a resulting surface roughness of the combined nanowire mesh-polymer that is less than a surface roughness of the mesh alone (e.g., or otherwise embedded), and in turn facilitates desirable conductivity characteristics.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Air permeable garment and fabric with integral aerosol filtration
InactiveUS20040116025A1Maintain good propertiesProtect environmentProtective equipmentSynthetic resin layered productsGas phaseFiltration
A multilayer fabric for protection from aerosol and gas phase agents comprising a bilayer structure comprising an unfilled Fine fiber layer substantially free of materials within the pores of the Fine fiber layer secured to an outer shell, the Fine fiber layer acting as an aerosol filter, and an optional interior fabric layer having a reactive layer for the removal of gas phase agents.
Owner:DONALDSON CO INC
Pressure sensing fabric
Existing pressure sensing fabrics may involve two portions, i.e., insulating and conductive portions in the fabric, which increases the complexity of the fabric system and more important, and the instablization of the resistance-strain relationship during dynamic deformation which limits the application fields due to intrinsic properties difference between the two portions. These fabrics commonly employ two or more layers to accomplish the detecting functions. Such arrangements increase the thickness, weight, and cost of the sensors with some other disadvantages such as low accuracy, instability, etc. This invention describes a pressure sensing fabric have a general structure as simple as a plurality of electrically conducting yarns forming interlocking loops of yarns. The pressure sensing fabric is found not only be able to sense pressure but also the magnitude of the pressure.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Three-dimensional net-like structure, and method and device for producing three dimensional net-like structure
ActiveUS7625629B2Efficient use ofIncrease rangeWeft knittingSynthetic resin layered productsVolumetric Mass DensityEngineering
A method of and an apparatus for manufacturing a three-dimensional netted structure which is capable of rendering it unnecessary to carry out a finishing operation in a later stage, improving the degree of straightness of the side surfaces of the netted structure, meeting a demand for finishing the netted structure to modified shapes, and improving the durability of the netted structure. A three-dimensional netted structure (1) using thermoplastic resin as a raw material or a main raw material is characterized by a three-dimensional plate type netted structure, in which a plurality of filaments are helically and randomly entangled and partly and thermally bonded together. The density of any of at least three surfaces or four surfaces on the outer periphery of the three-dimensional netted structure is preferably relatively higher than the density of the other portion excluding these surfaces, and flaked or chipped PET bottles are used as a raw material or a main raw material for thermoplastic resin, such PET bottles being directly crushed and then melted to provide flakes, suiting to recycling promoting age, working well in waste disposal cost reduction, the uses of the three-dimensional netted structure (1) including, chiefly, shock absorbing materials, cushioning materials, and sound-absorbing materials.
Owner:C ENG CO LTD
Fabric for end fray resistance and protective sleeves formed therewith and methods of construction
ActiveUS20070166495A1Prevent the sleeve from frayingElectrical apparatusPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementHot meltEngineering
An elongated protective textile sleeve for protecting elongate members and methods of constructing a fabric substrate therefore. The fabric substrate has a plurality of filamentary members either woven, knitted or braided with one another. At least some of the filamentary members of the substrate extend to cut edges and are fabricated of a multi-component material that includes a core of a first polymeric material and an outer sheath of a second polymeric material. The outer sheath is heat-fusible and the inner core is heat-settable. The outer sheaths of the filamentary members are heat fused at least in the regions near the cut edges to keep the cut edges from fraying or the filamentary members from pulling out of the substrate. The core is heat set to form the desired shape of the protective sleeve.
Owner:FEDERAL MOGUL WORLD WIDE LLC
Water vapor breathable, liquid water resistant material
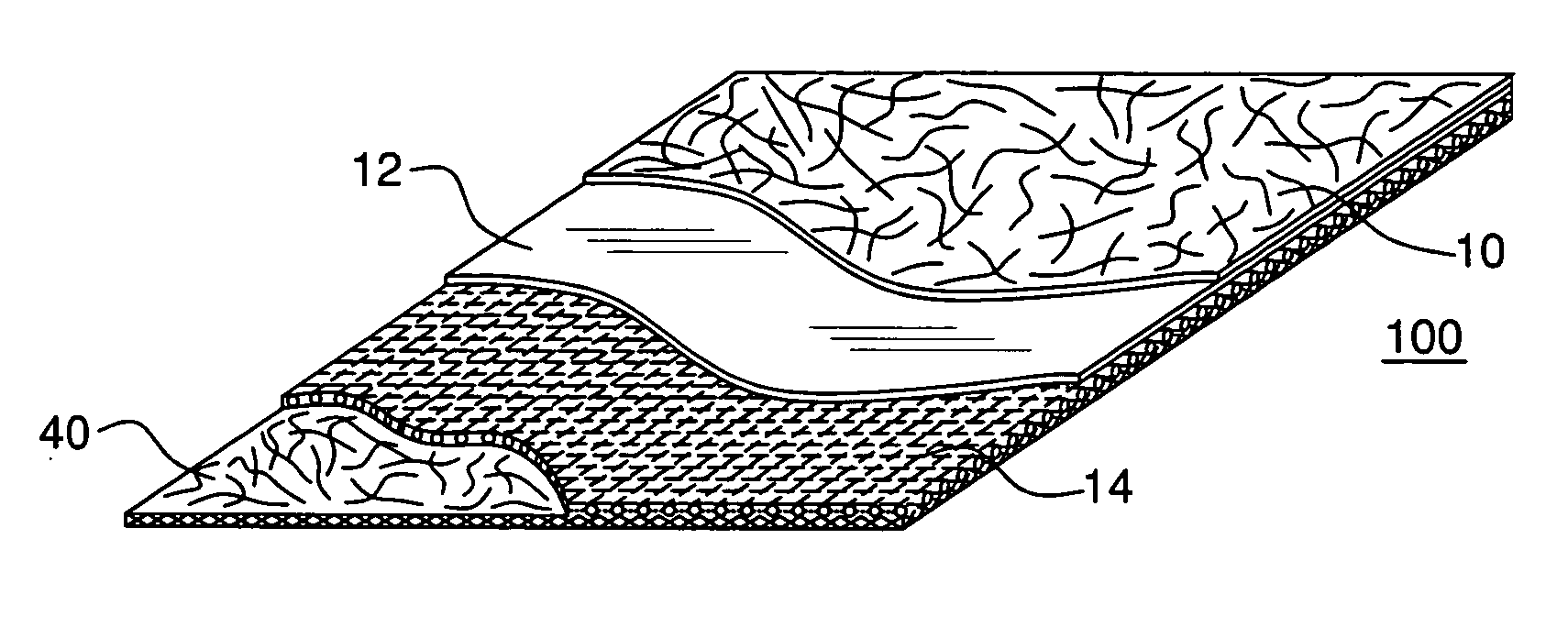
InactiveUS7148160B2Breathability to water retardance ratioMore cost-effectiveSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationLiquid waterHousewrap
The present invention relates to a composite sheet material that is water vapor permeable and substantially liquid water impermeable. The composite sheet material includes an outer layer, a film, and a reinforcing layer and, preferably, has an ASTM D3833 water vapor transmission rate of greater than 250 g / m2 / day, and a tensile strength of at least about 100 N / 5 cm when tested in accordance with ASTM D5035. The sheet material is useful as a membrane for roofing, housewrap, insulation facing and in the fabrication of protective apparel.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN ADFORS CANADA LTD
Auxetic Fabric Structures and Related Fabrication Methods
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Reinforcing carbon fiber material, laminate and detecting method
A sheet-shaped carbon fiber base material is made up from reinforcing carbon fiber and metal wire integrally formed into a carbon fiber base material which may be a a woven fabric, a tow sheet and a prepreg. The volume fraction of metal in the sheet-shaped reinforcing carbon fiber base material is no more than 4% of the carbon fiber. A laminate may also be formed from the sheet-shaped carbon fiber material, where the reinforcing carbon fiber and the metal wire are laid-up in such a way that the metal wire insertion positions are mutually different. Also disclosed is a method of detecting the number of plies in a laminate that includes non-destructively sensing with a detector the presence of metal wire in a laminate of plies of a sheet-shaped carbon fiber base material made up of reinforcing carbon fiber and metal wire integrally formed to make the sheet-shaped carbon fiber laminate material and determining the number of the plies in the laminate based on the metal wires detected.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com