Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
443results about "Computing operations for multiplication/division" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
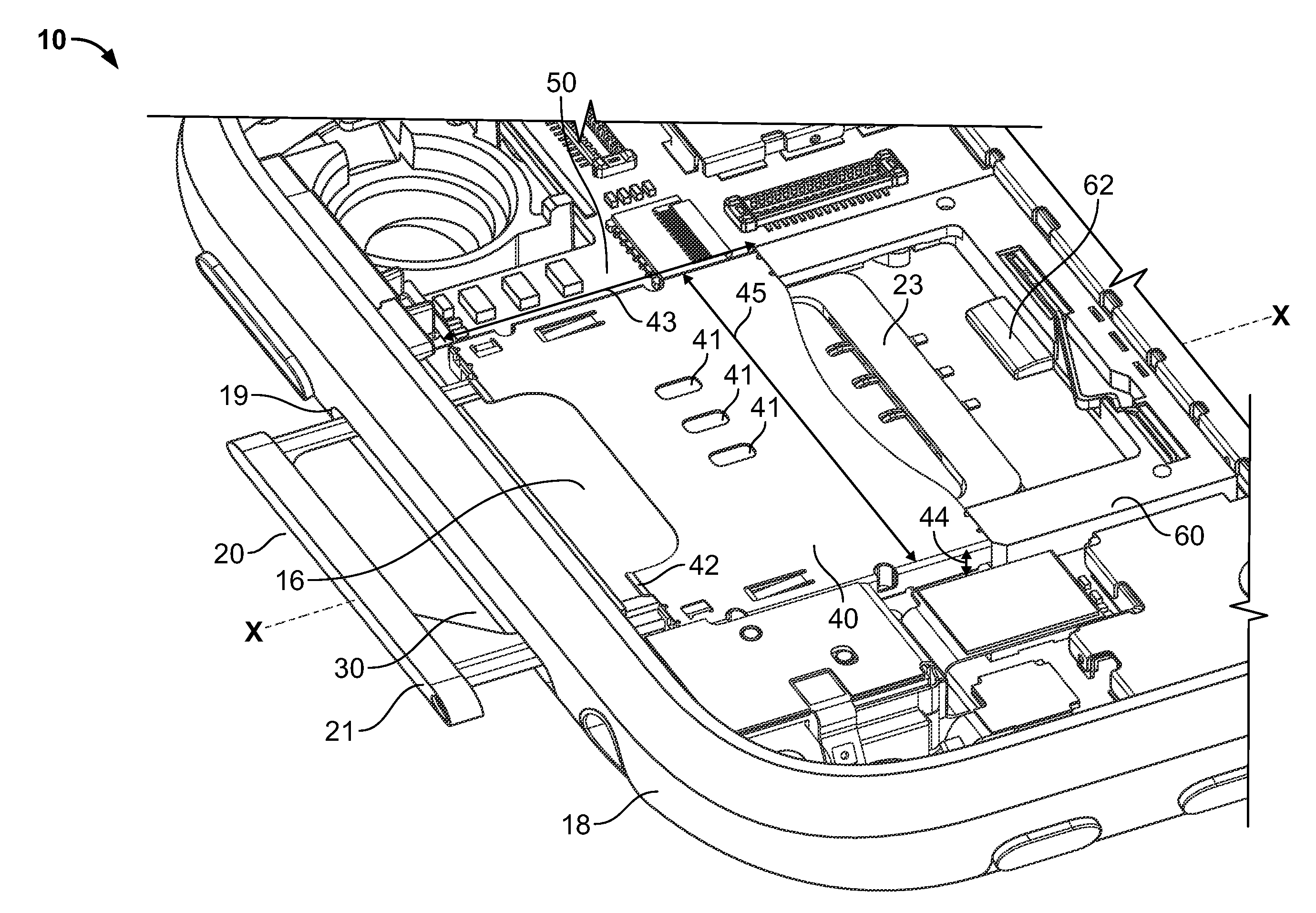
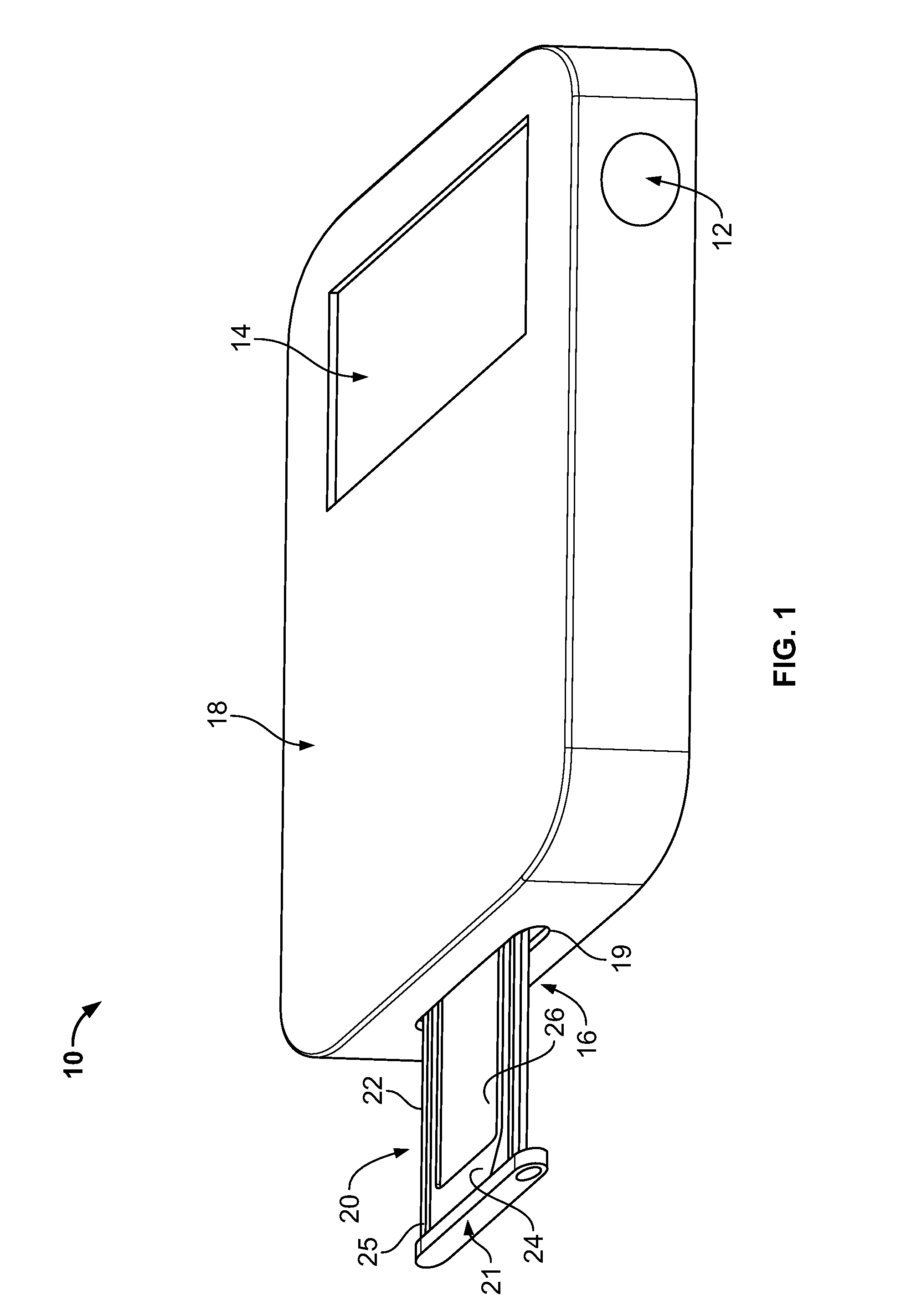
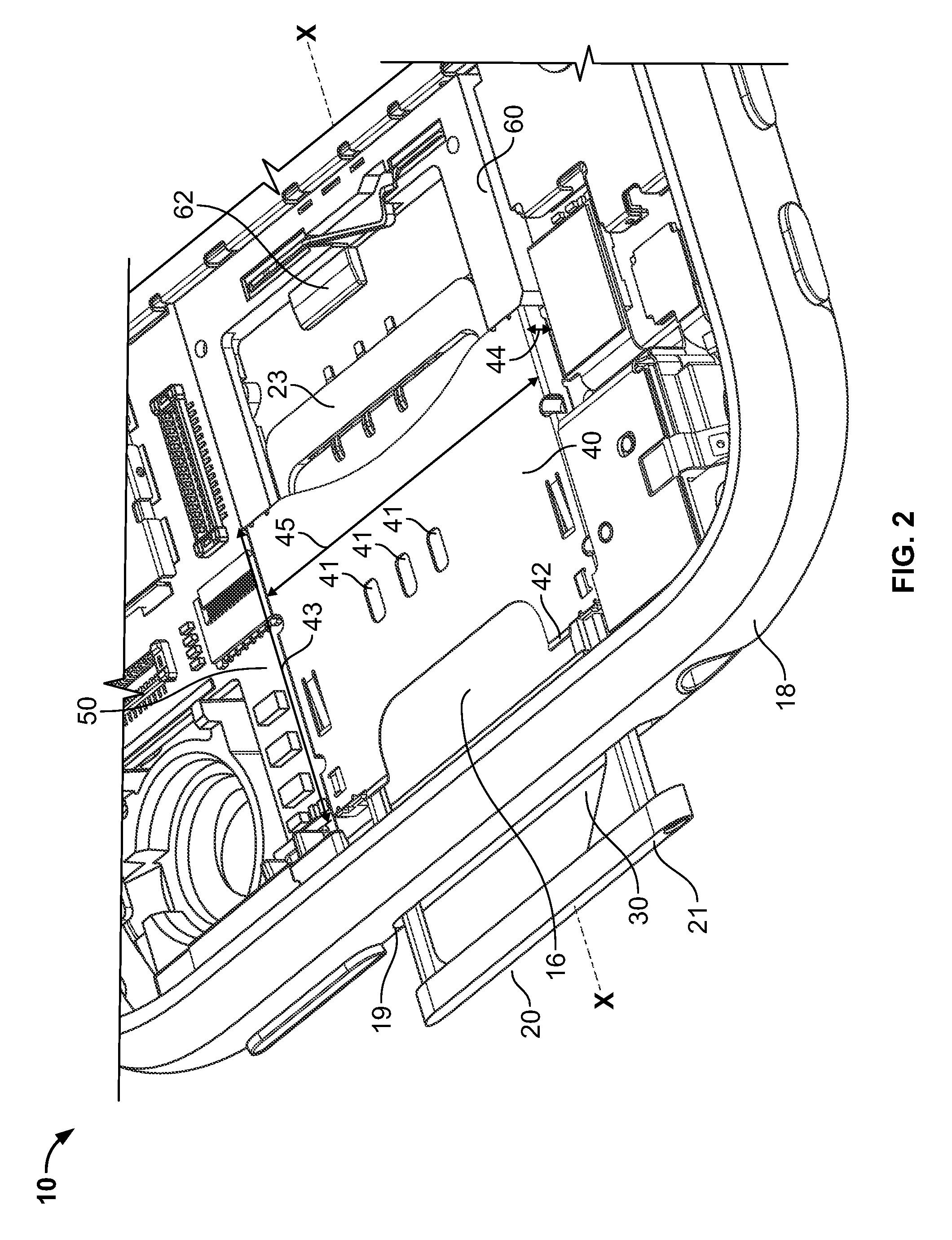
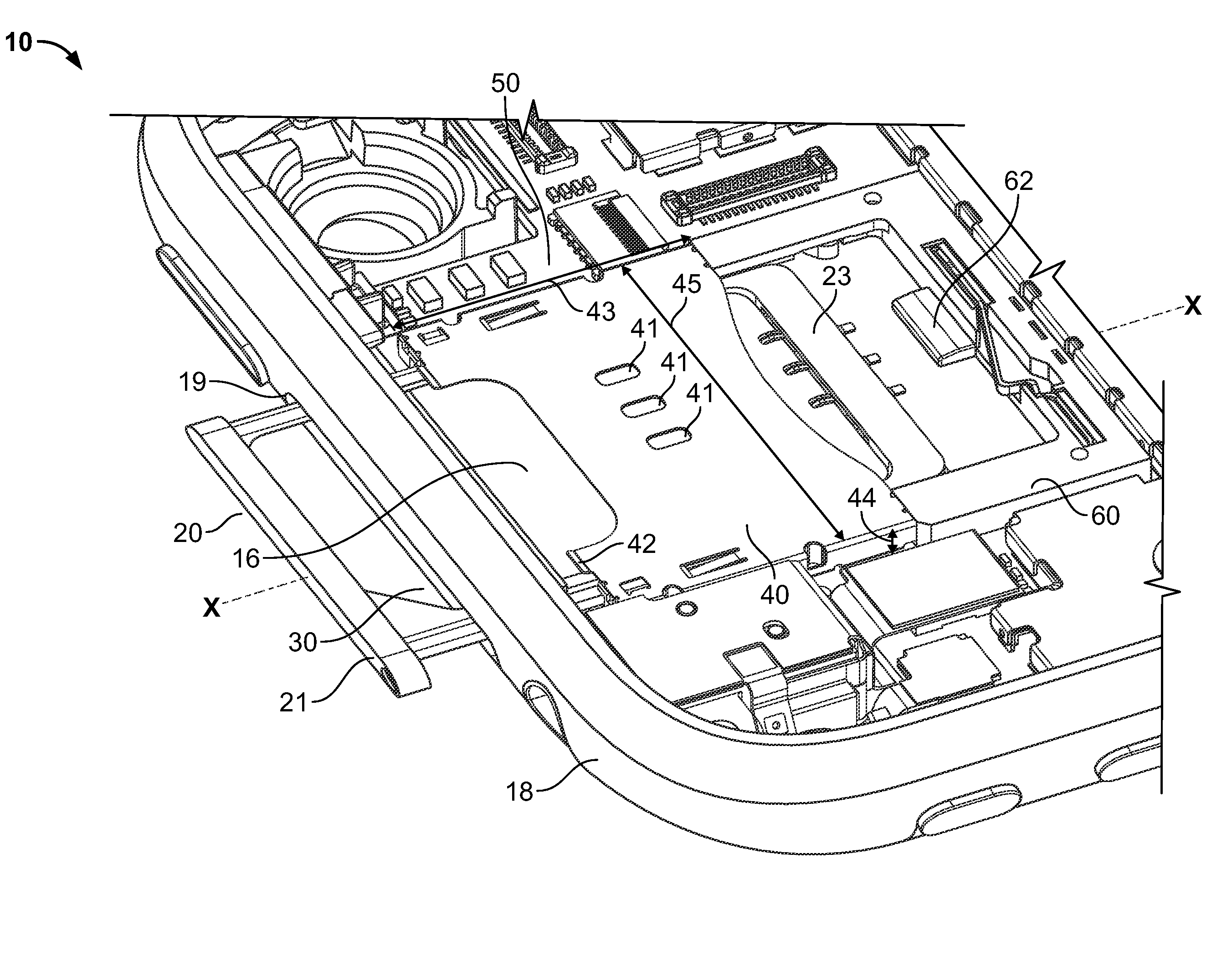
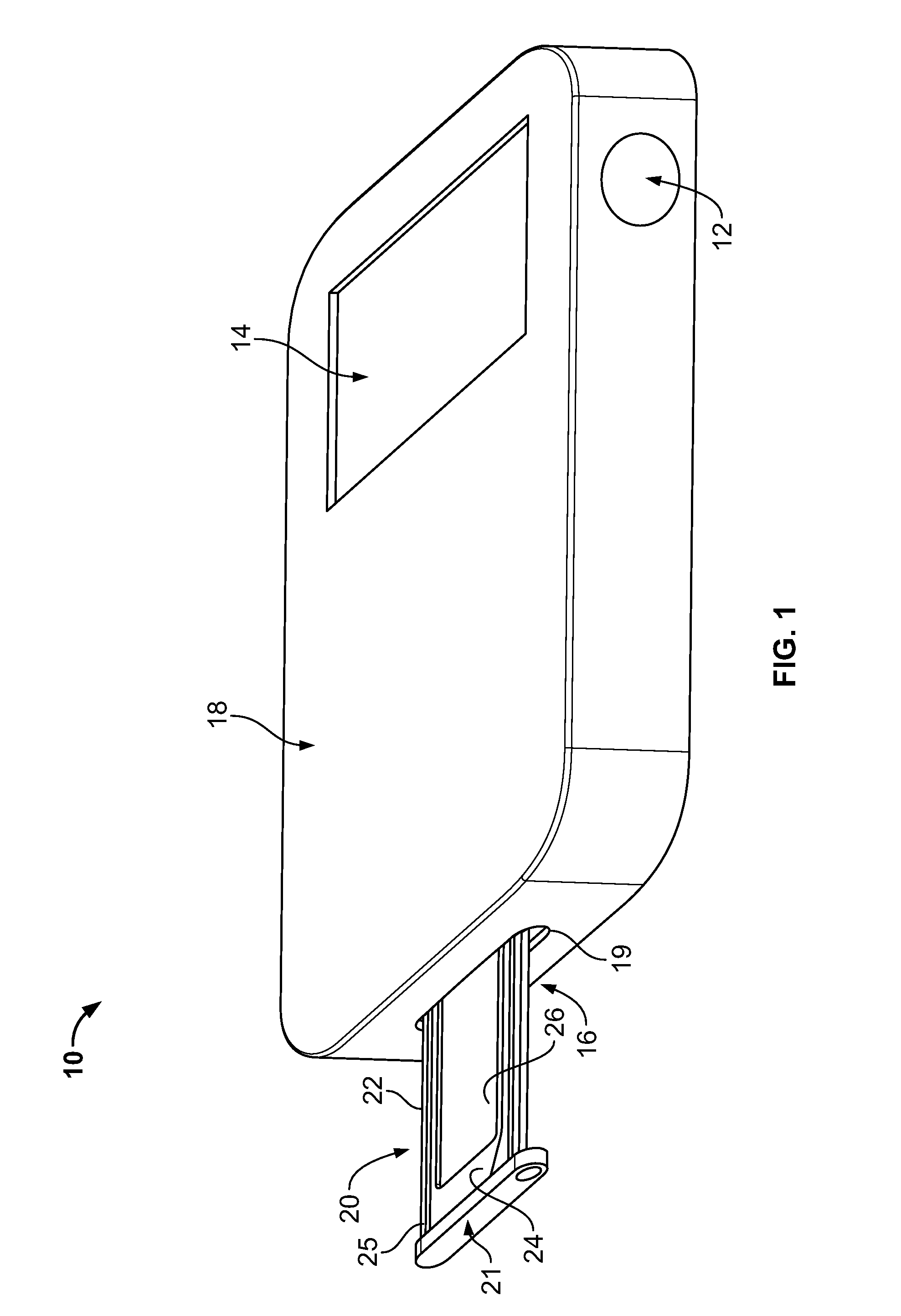
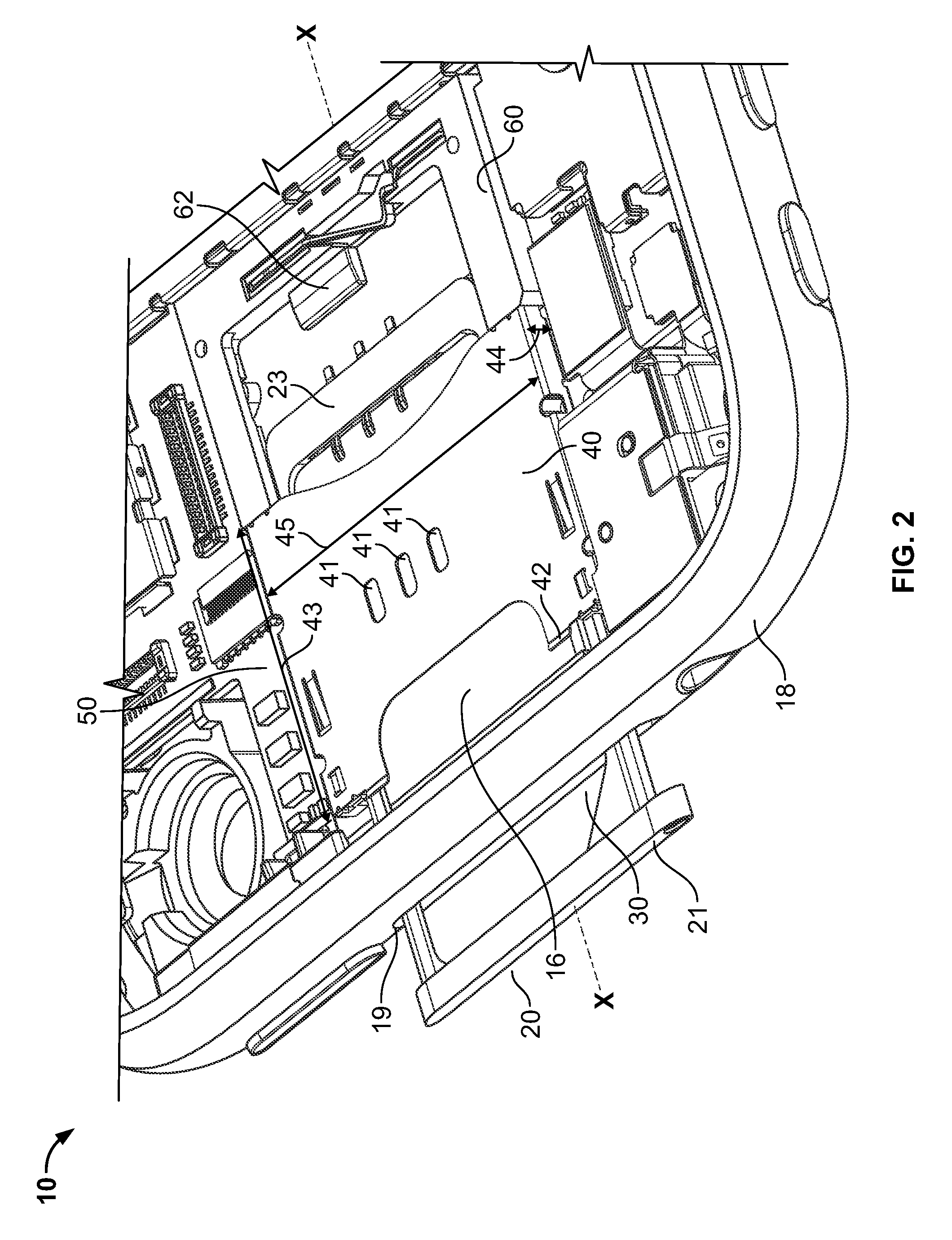
Compact ejectable component assemblies in electronic devices
ActiveUS20090267677A1Computations using contact-making devicesDevices with card reading facilityDetentBiomedical engineering
Electronic devices are provided with ejectable component assemblies. The ejectable component assembly may include a tray that can be loaded with one or more removable modules, wafers coupled to circuit boards, cages and retaining plates to assist in retaining the tray within the assembly. The ejectable component assembly may include springs operative to engage detents in the tray to retain the tray in the assembly. The ejectable component assembly may include a tray ejector mechanism for ejecting the tray from the assembly.
Owner:APPLE INC
Compact ejectable component assemblies in electronic devices
ActiveUS8462514B2Devices with card reading facilityComputations using contact-making devicesBiomedical engineering
Electronic devices are provided with ejectable component assemblies. The ejectable component assembly may include a tray that can be loaded with one or more removable modules, wafers coupled to circuit boards, cages and retaining plates to assist in retaining the tray within the assembly. The ejectable component assembly may include springs operative to engage detents in the tray to retain the tray in the assembly. The ejectable component assembly may include a tray ejector mechanism for ejecting the tray from the assembly.
Owner:APPLE INC
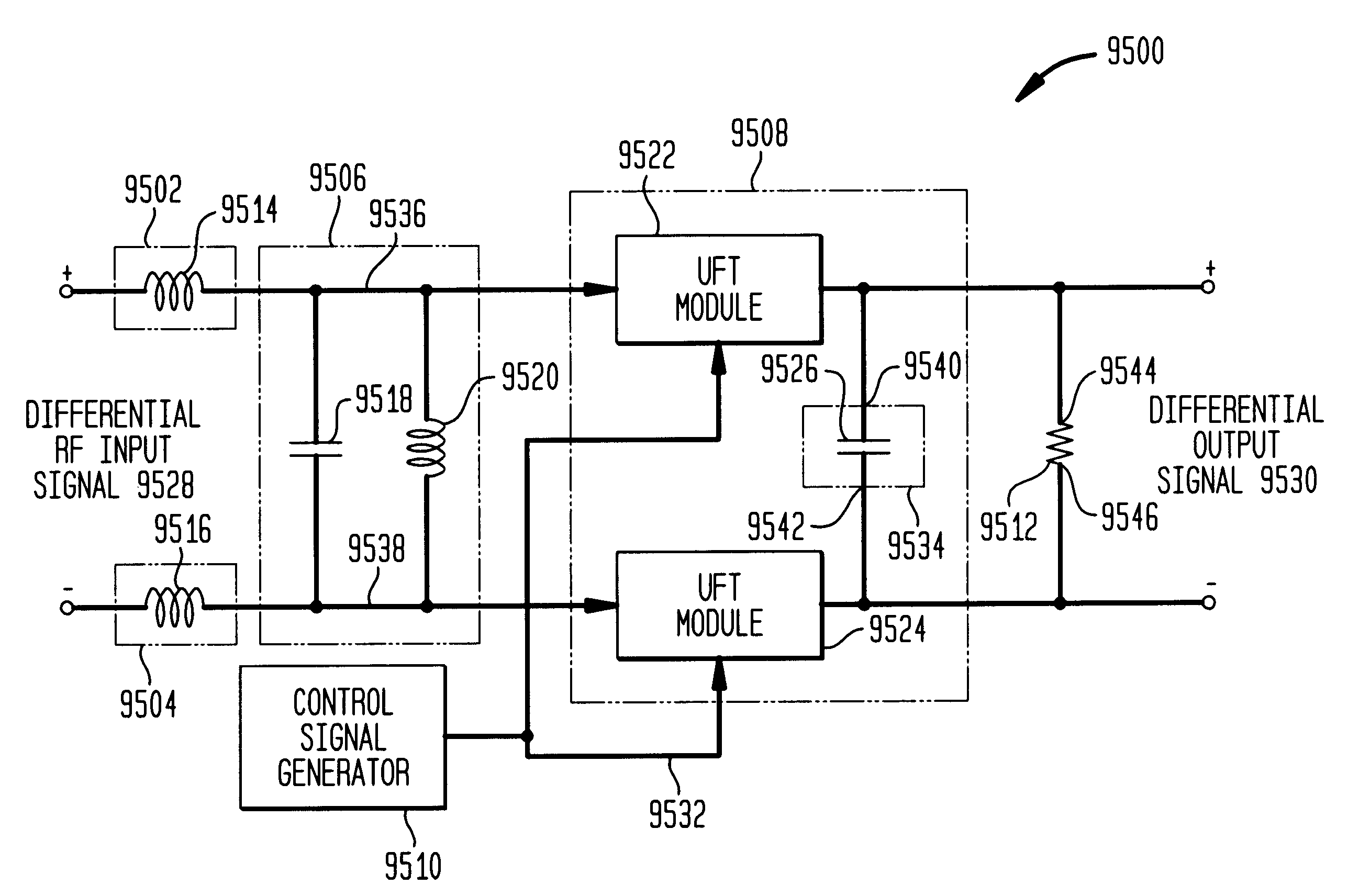
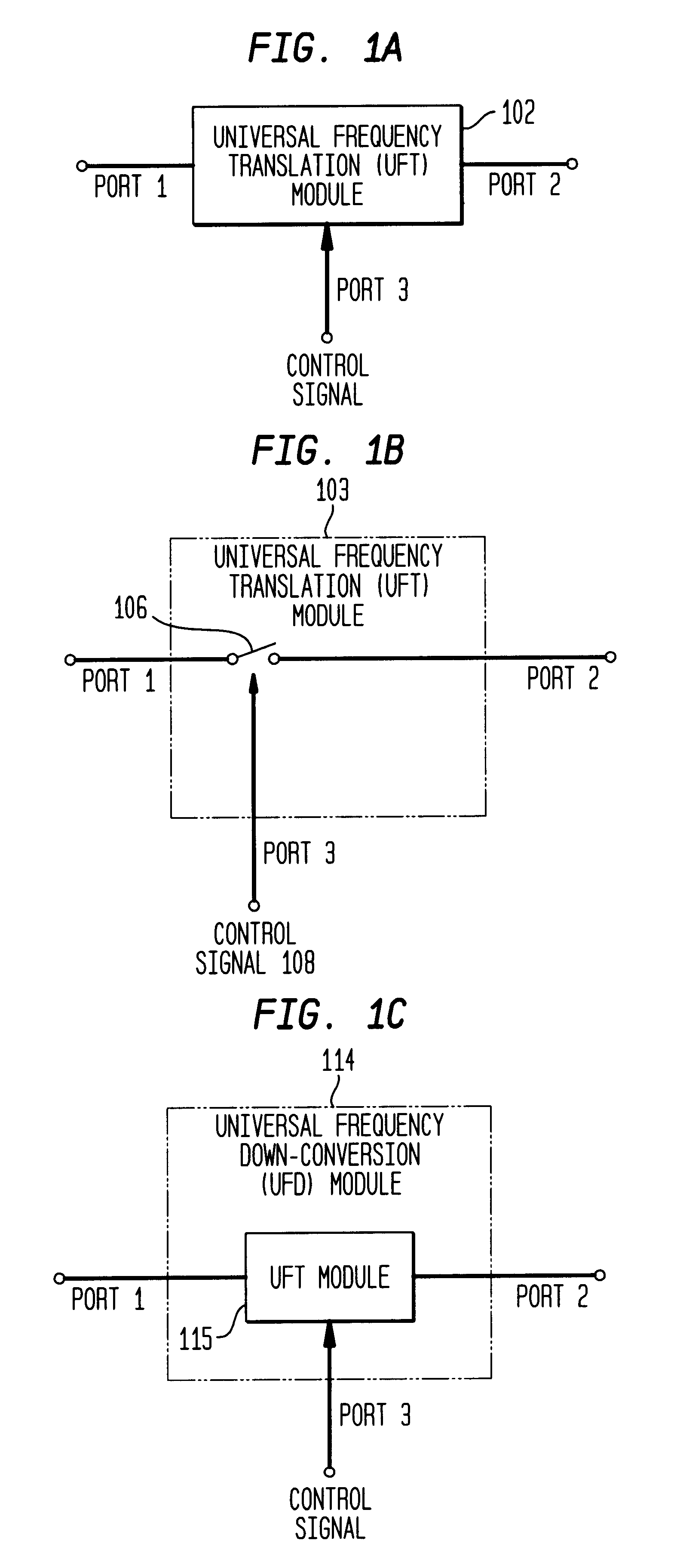
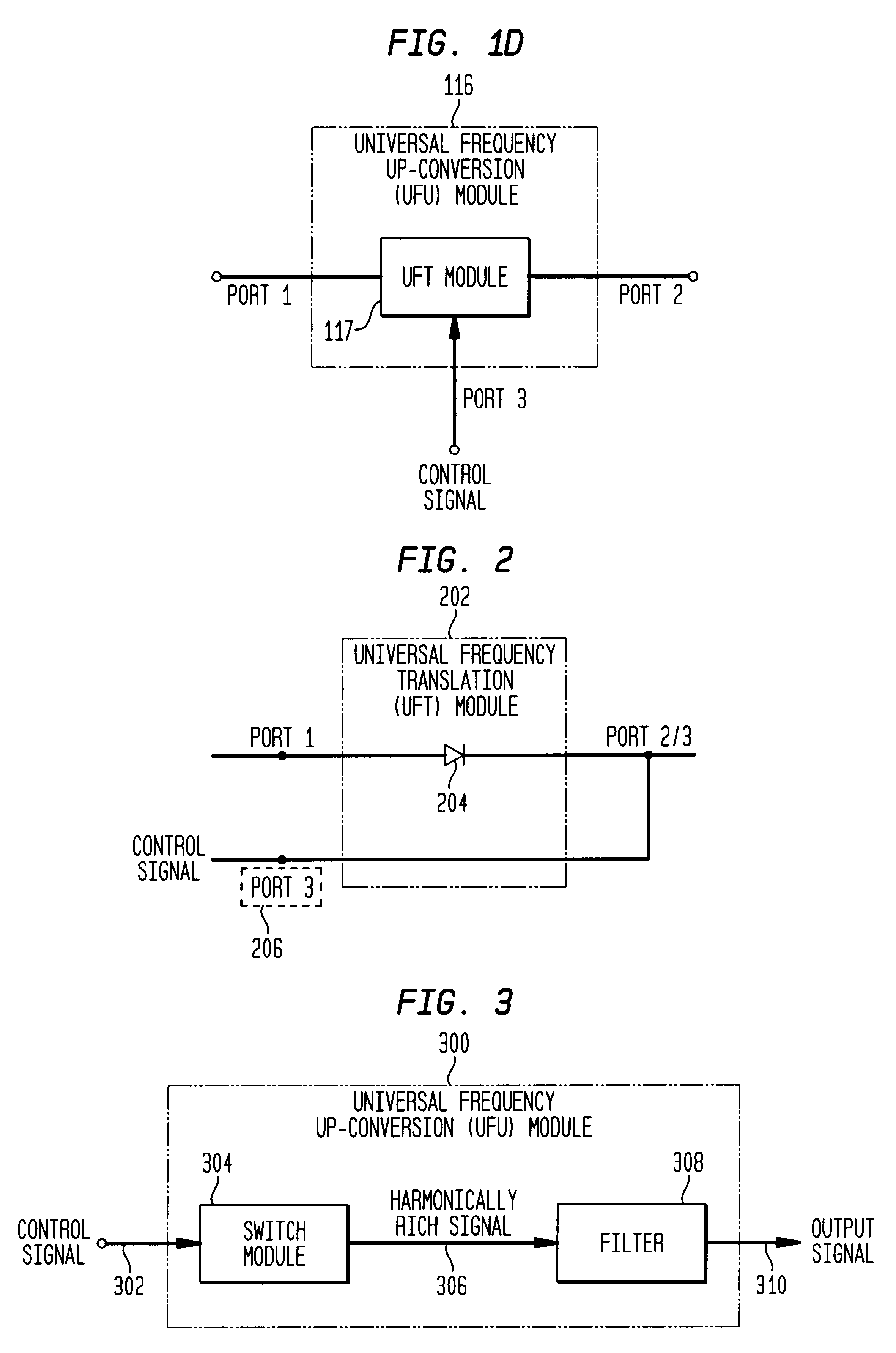
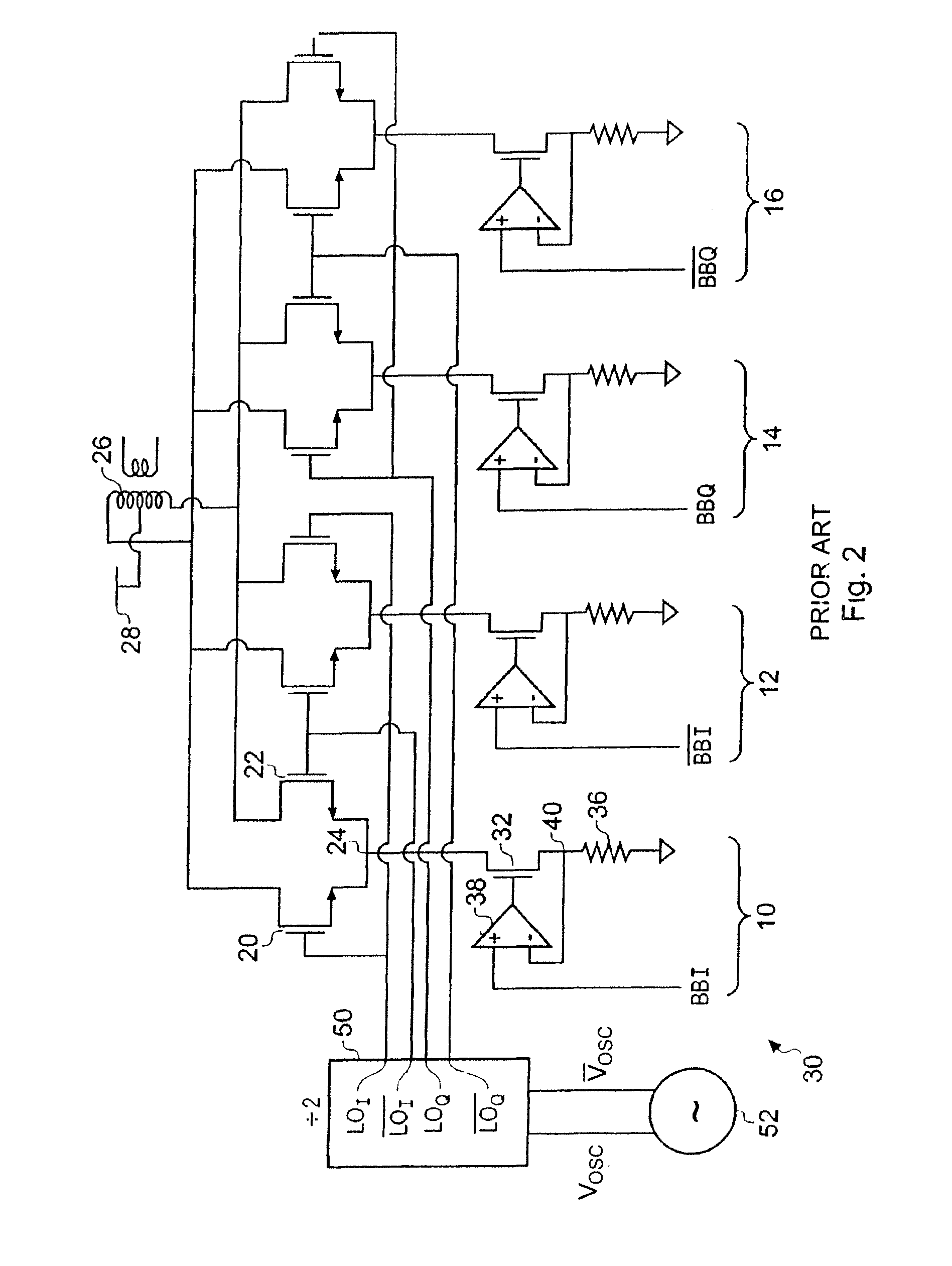
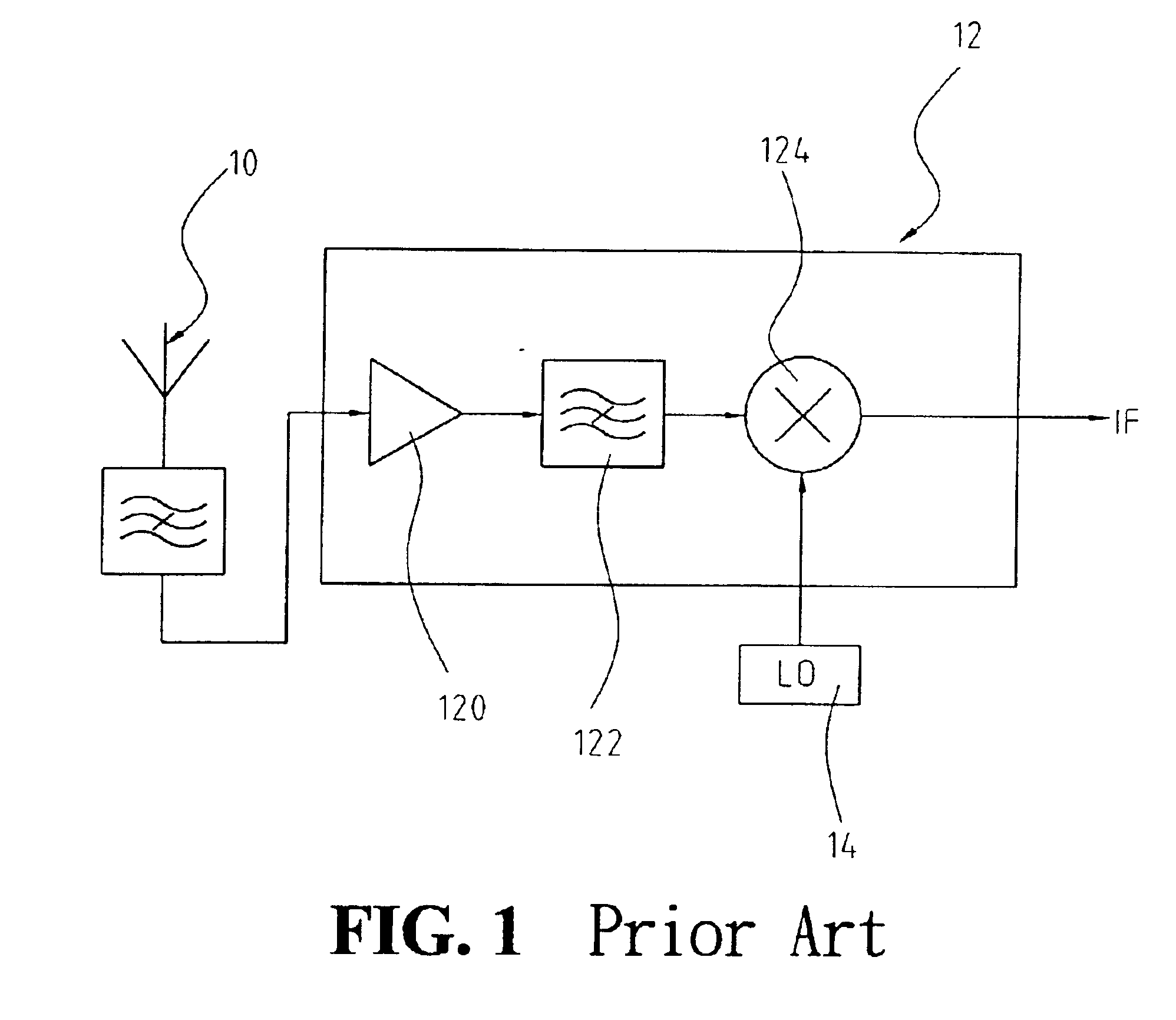
Differential frequency down-conversion using techniques of universal frequency translation technology
InactiveUS6963734B2Reduce voltageImprove dynamic rangeModulation transferenceComputations using contact-making devicesEngineeringDynamic range
Methods, systems, and apparatuses for down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal by aliasing the EM signal, and applications thereof are described herein. Reducing or eliminating DC offset voltages and re-radiation generated when down-converting an electromagnetic (EM) signal is also described herein. Down-converting a signal and improving receiver dynamic range is also described herein.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
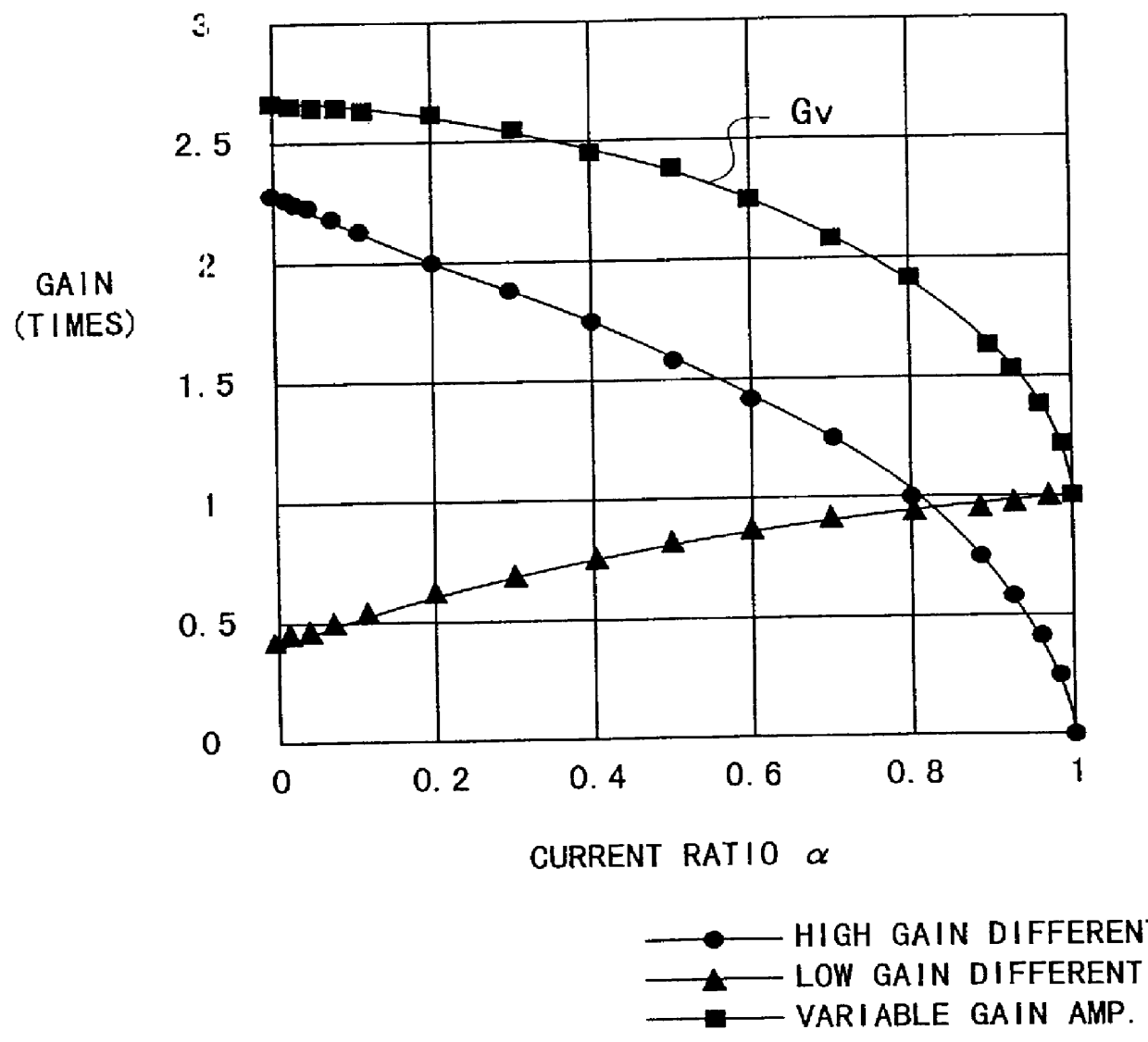
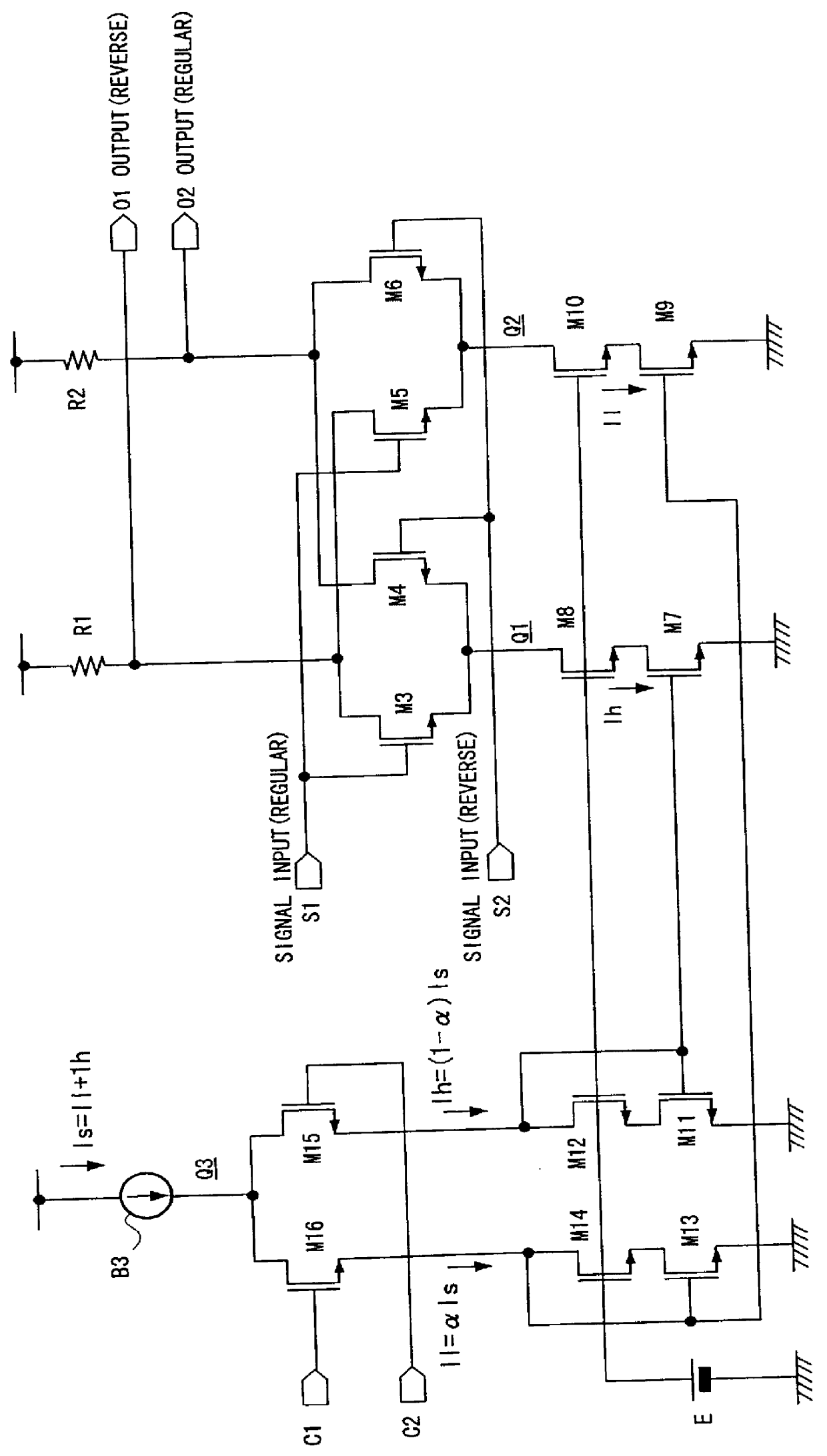
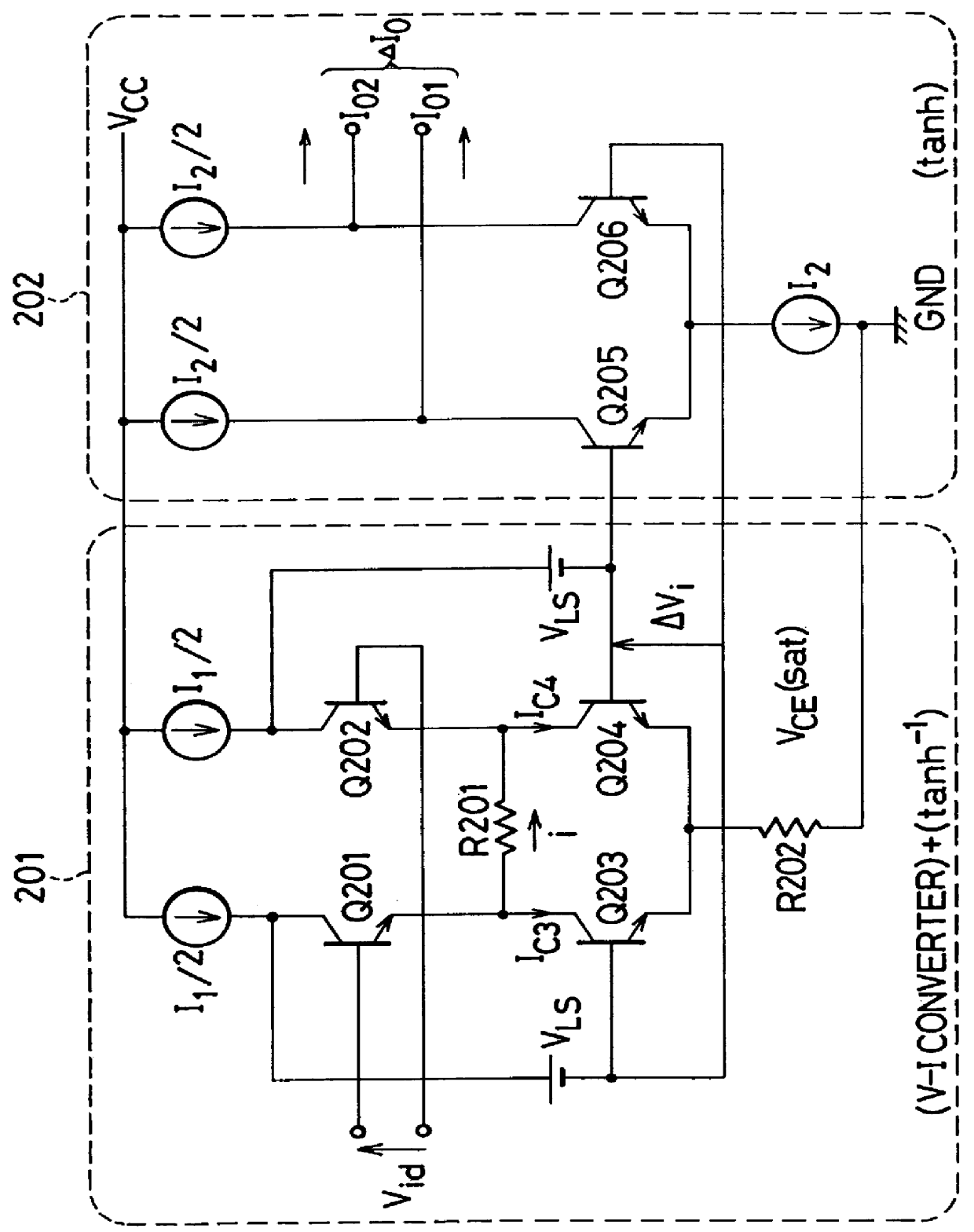
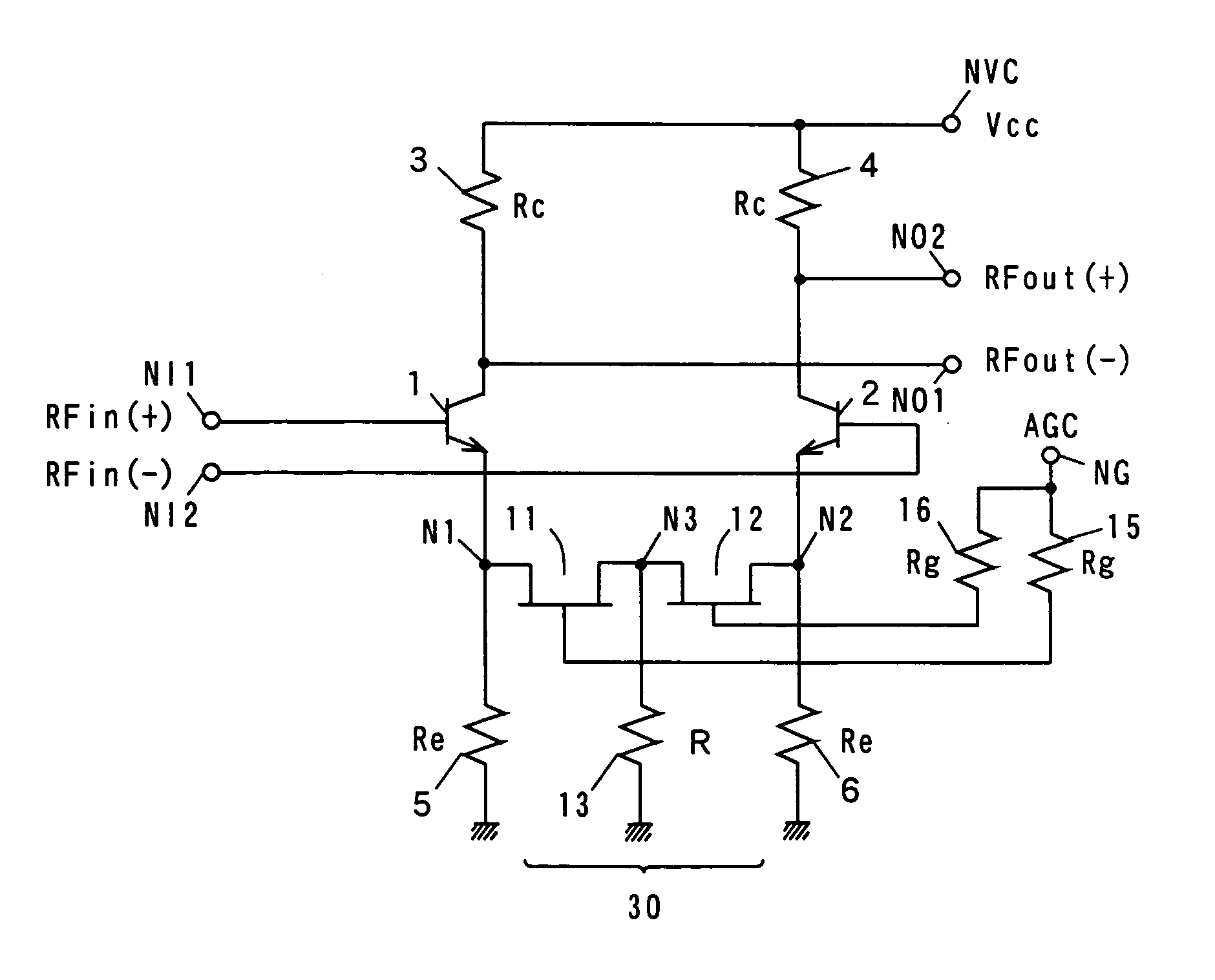
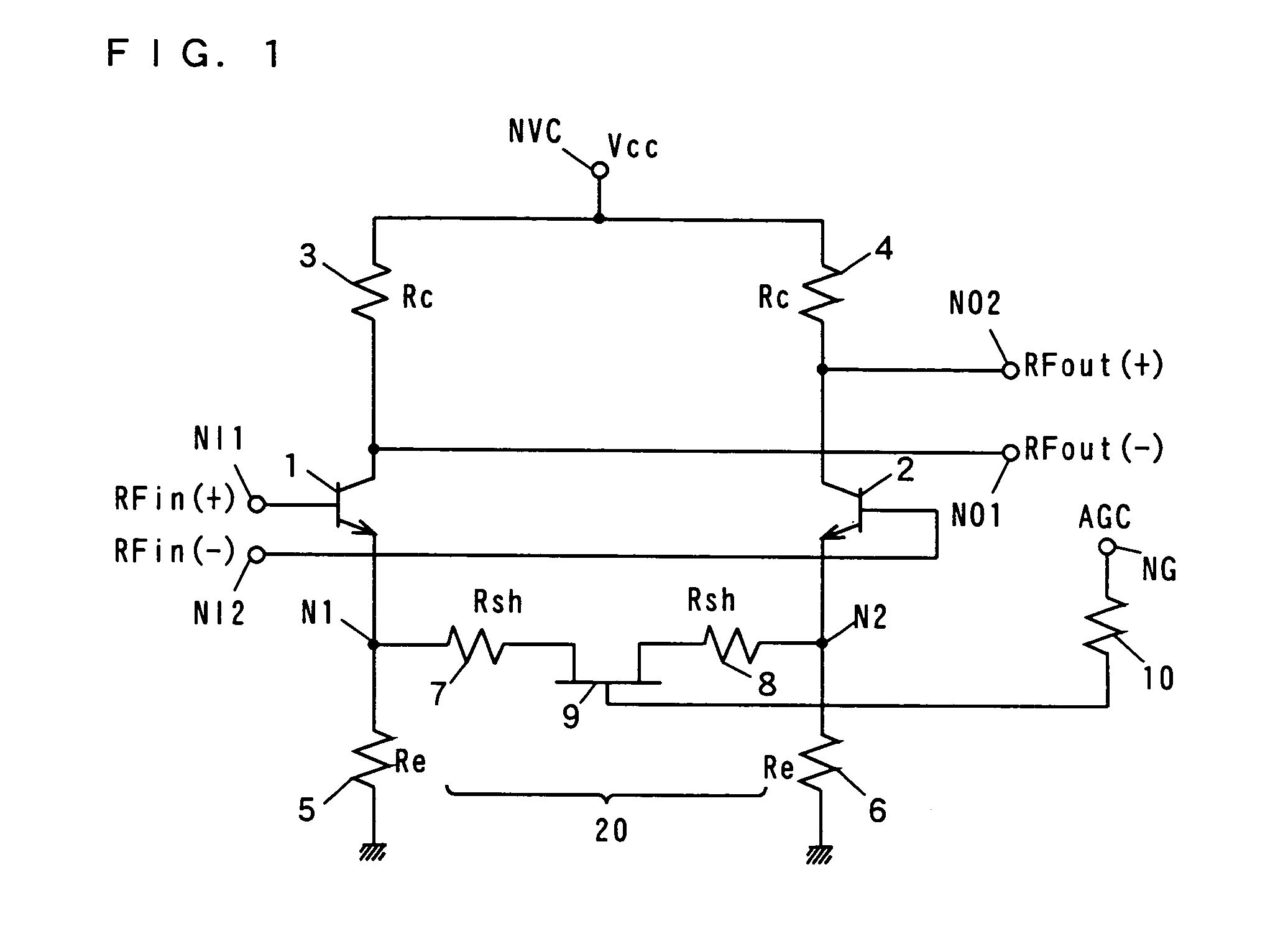
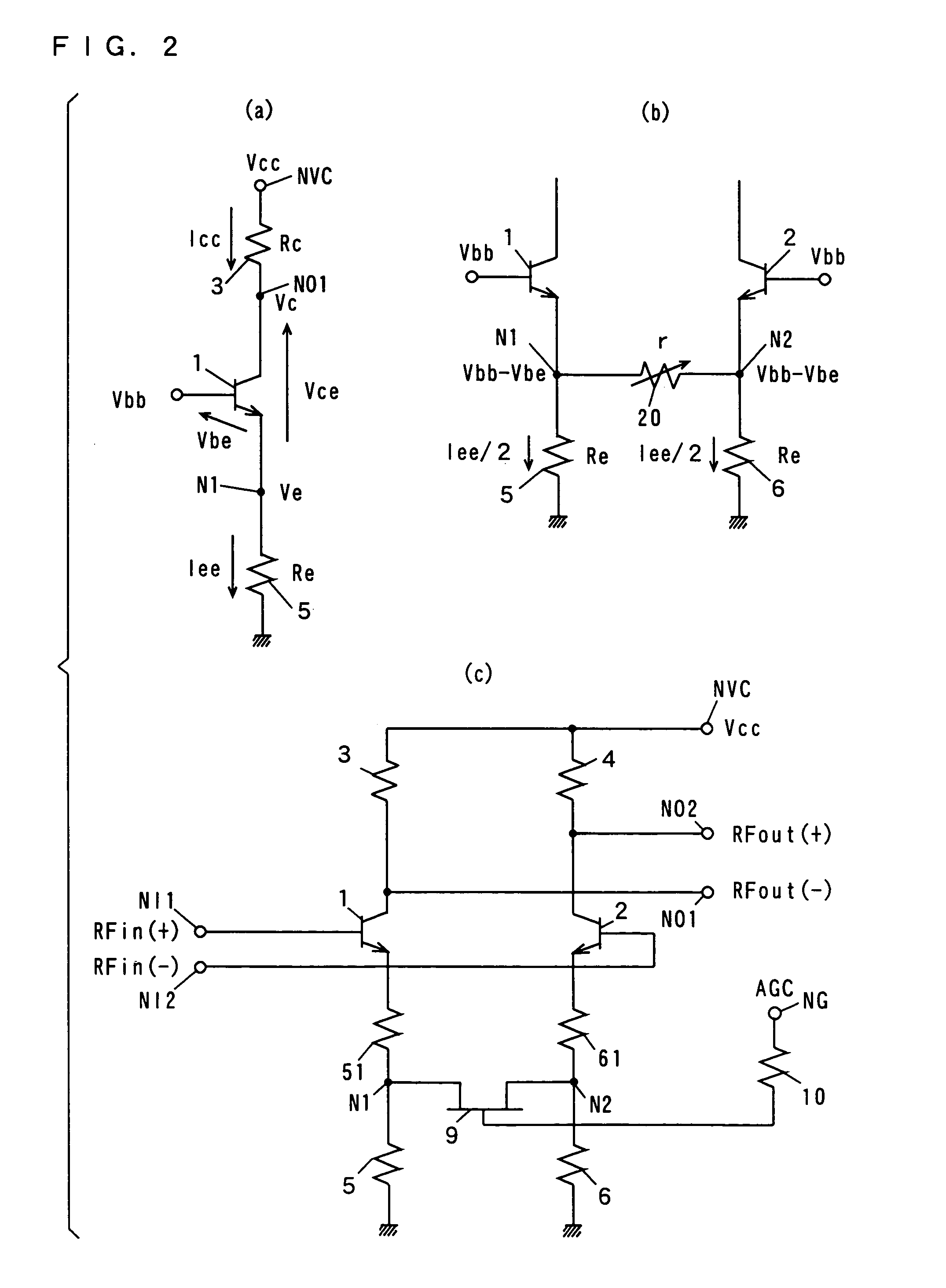
Variable gain amplifier
InactiveUS6163215AComputations using contact-making devicesGain controlAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
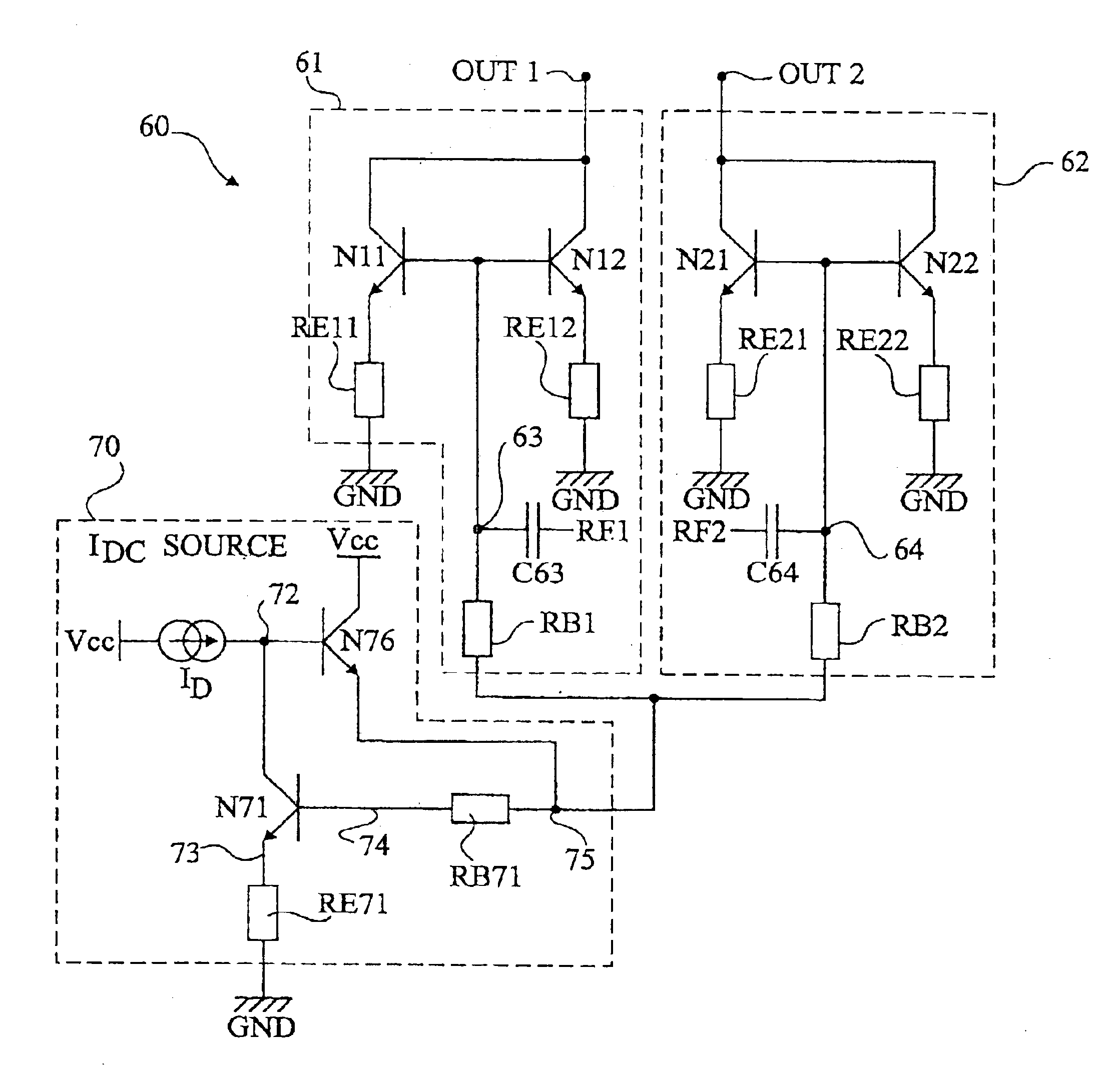
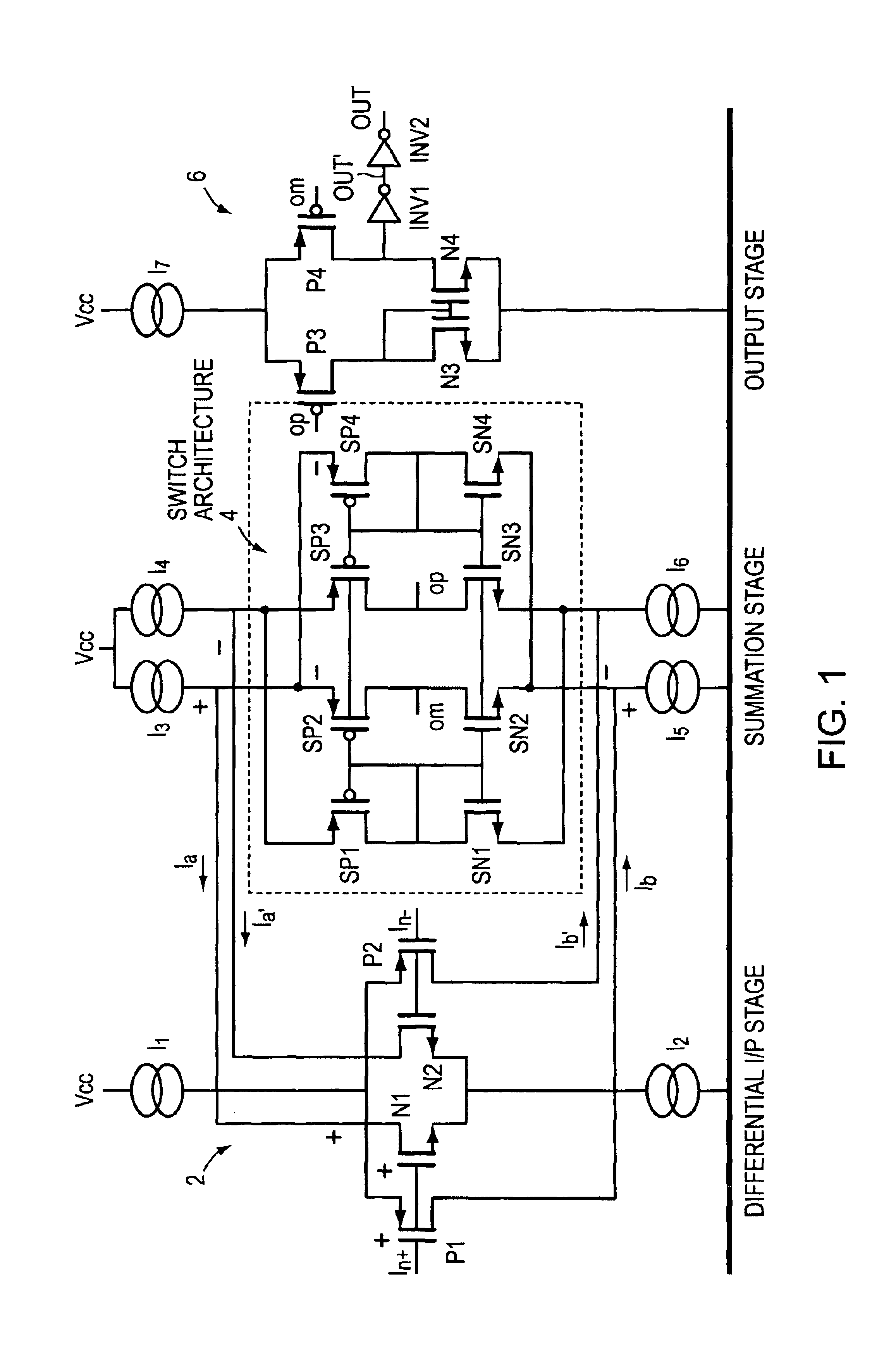
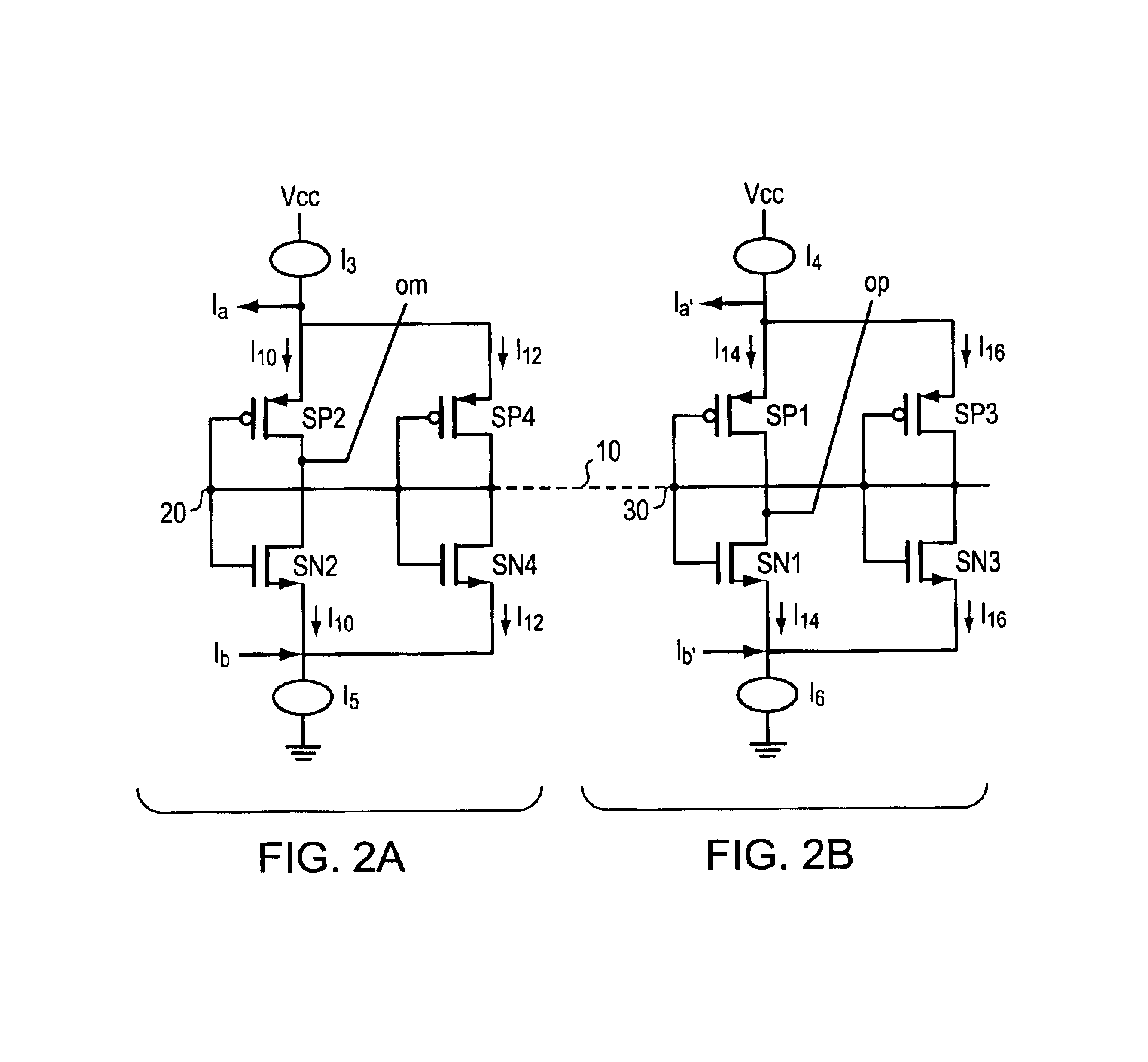
In a variable gain amplifier controlling a gain by using differential amplifiers with a gain control signal, a gain switchover differential amplifier or a bias circuit which composes a current mirror with the gain switchover differential amplifier is connected between a high and a low gain differential amplifier for the same bias current which are mutually connected to share load resistances for the same output polarity and a bias current source common to both of the differential amplifiers, to perform switchover operations of the high and the low differential amplifier by a gain control signal, and a current source which flows a fixed offset current through at least the low one of the high and the low differential amplifier is provided.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Apparatus, methods and articles of manufacture for electromagnetic processing
Apparatus, methods and articles of manufacture are shown for modifying electromagnetic waves. Through using various wave characteristics such as amplitude to regulate a current source, a current is output that may be used in any number of ways, such as driving an antenna or other load.
Owner:NORTH SOUTH HLDG
Class AB differential mixer
InactiveUS6882194B2Reduce power consumptionModulation transference by semiconductor devices with minimum 2 electrodesModulation transference balanced arrangementsLow voltageReference line
A differential mixer including at least two input / output stages, each stage including two identical branches, each branch of one of the two stages including at least two bipolar transistors the bases of which define a first pair of input / output terminals of the stage and are connected to a same D.C. current source individually by a respective isolating resistor; the collectors of which define a second pair of input / output terminals of the stage which forms a pair of input / output terminals of another stage of the mixer; and the emitters of which are individually connected to a low voltage reference line by a respective degenerative impedance.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
High linearity circuits and methods regarding same
InactiveUS20020126767A1Improve linearitySufficient gainAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionComputations using contact-making devicesHarmonicLinearity
Circuits and methods that improve linearity with use of cancellation of at least a portion, and preferably, substantially all of, at least one significant harmonic from the output of a primary circuit, e.g., the 3.sup.rd harmonic, using the output of a substantially functionally identical auxiliary circuit.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
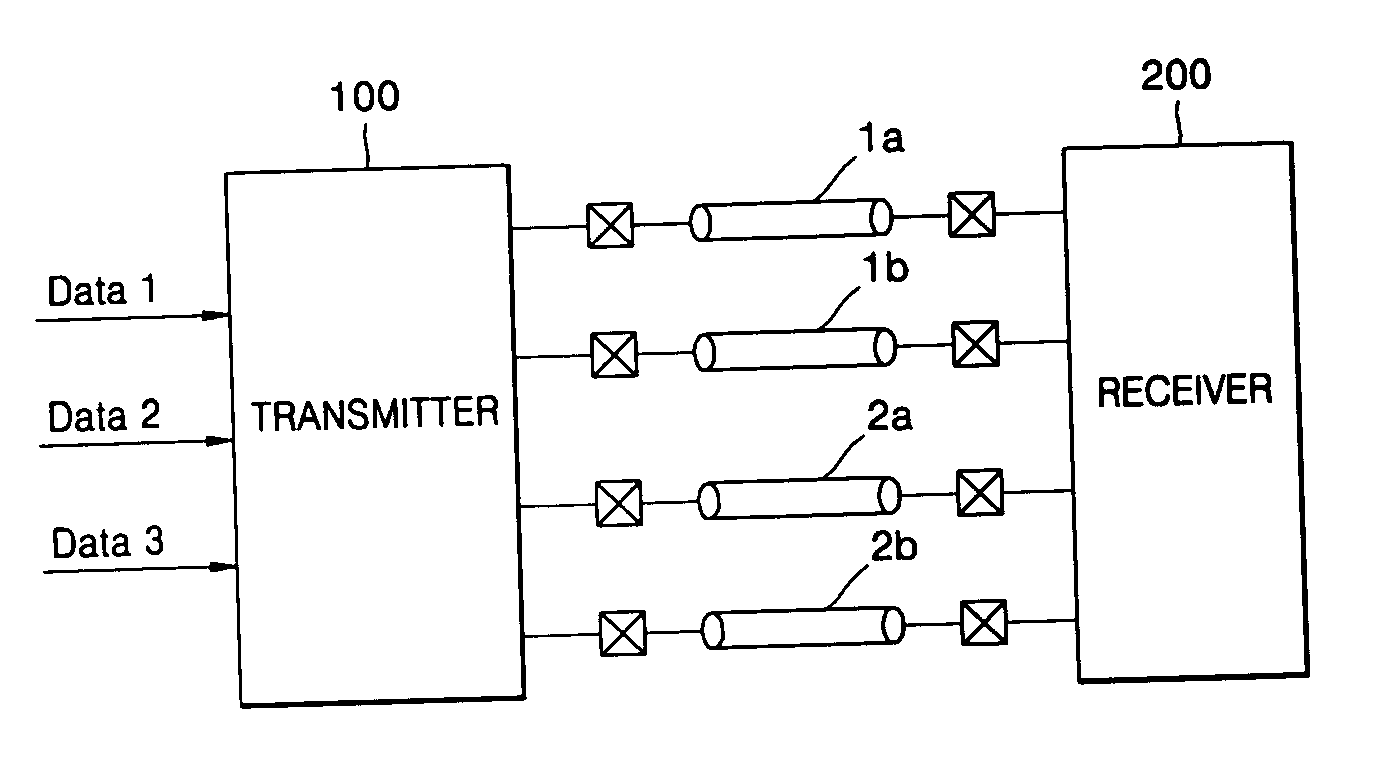
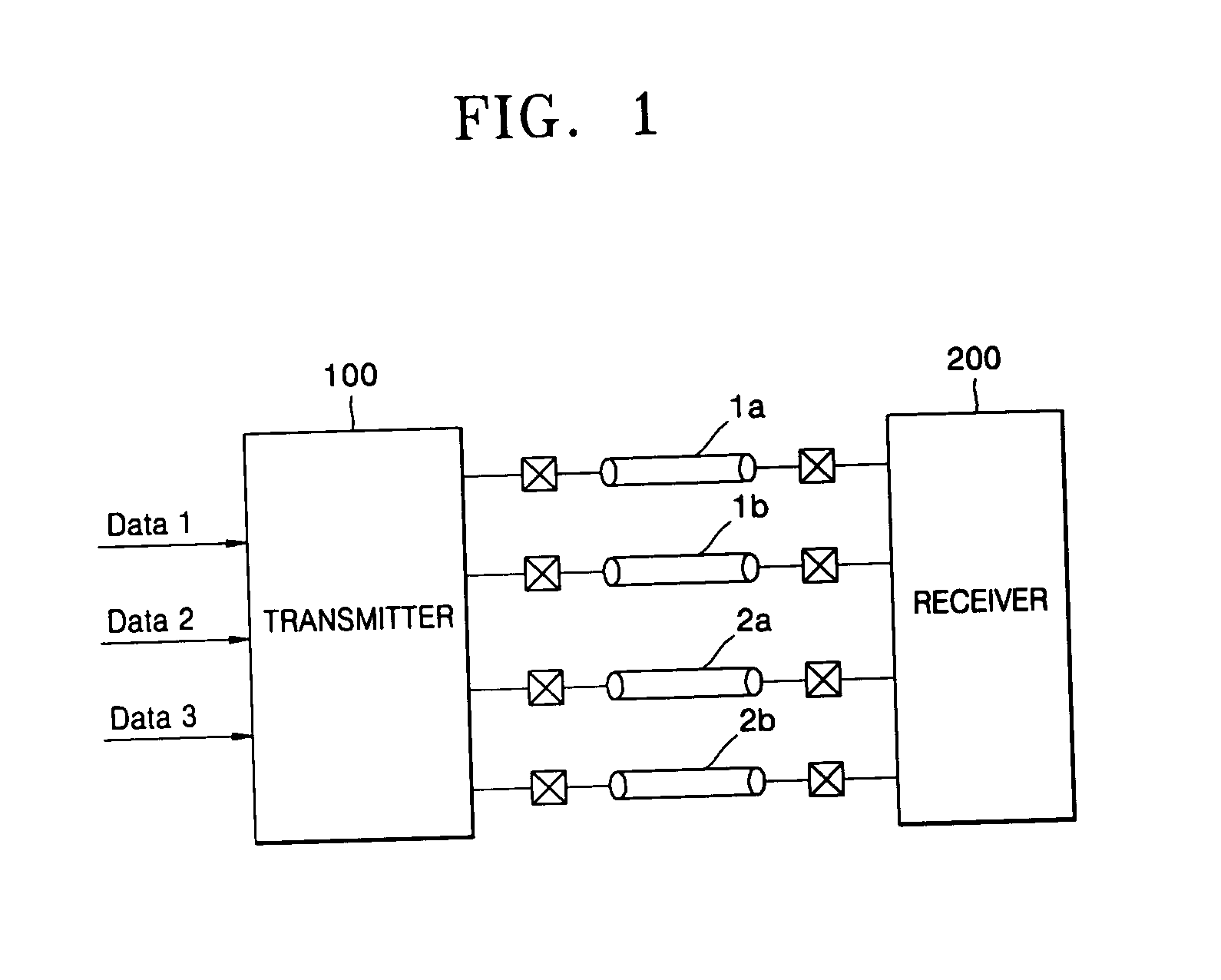
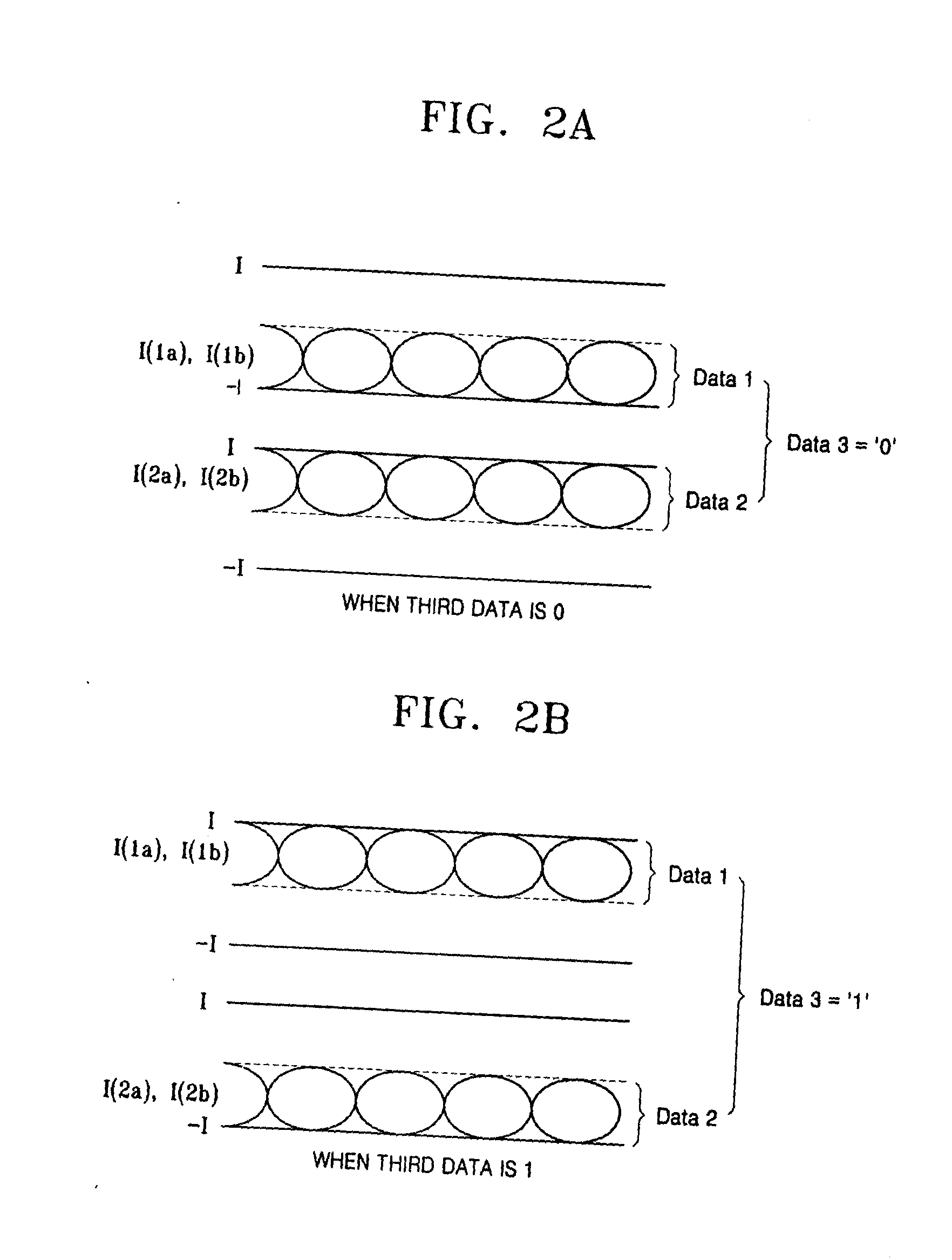
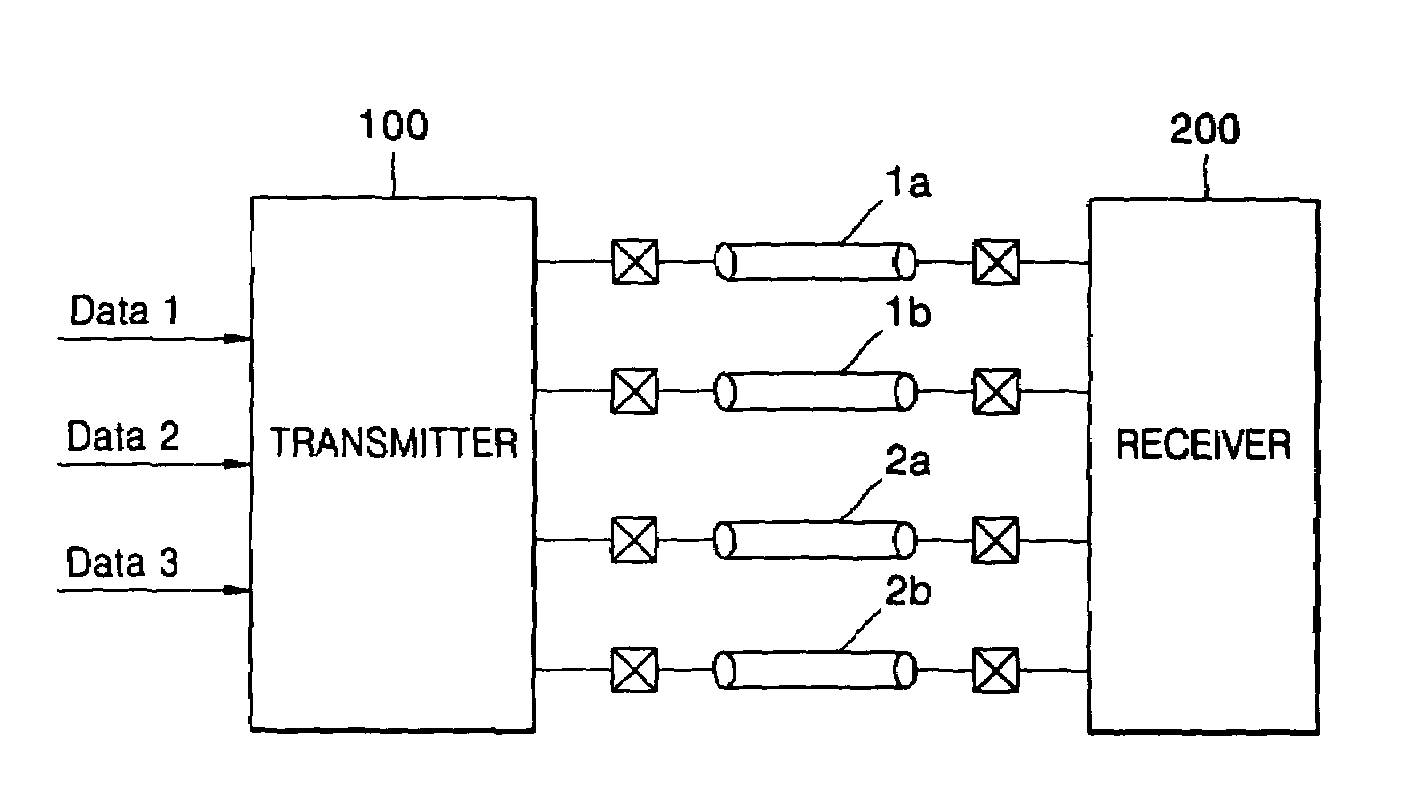
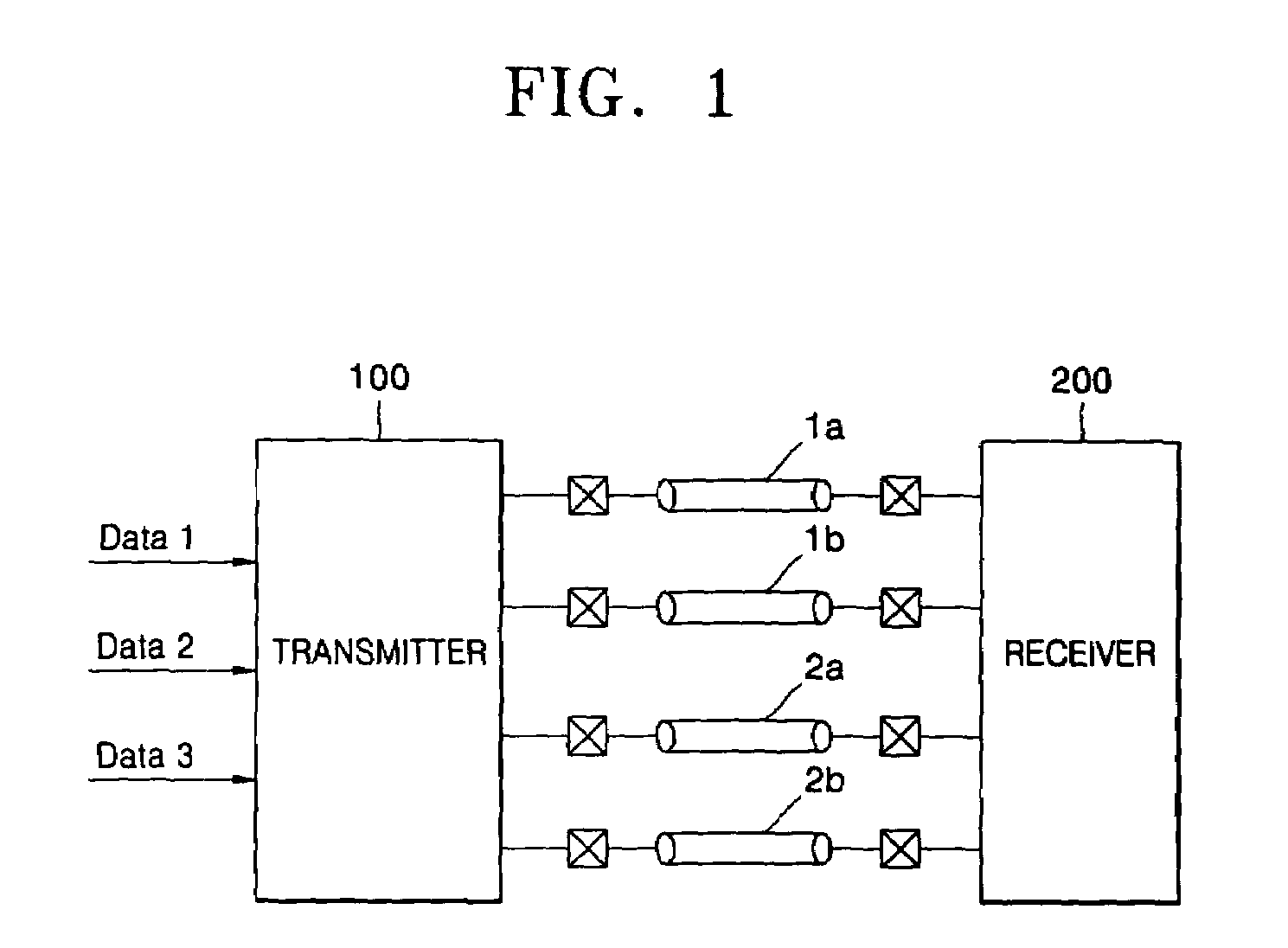
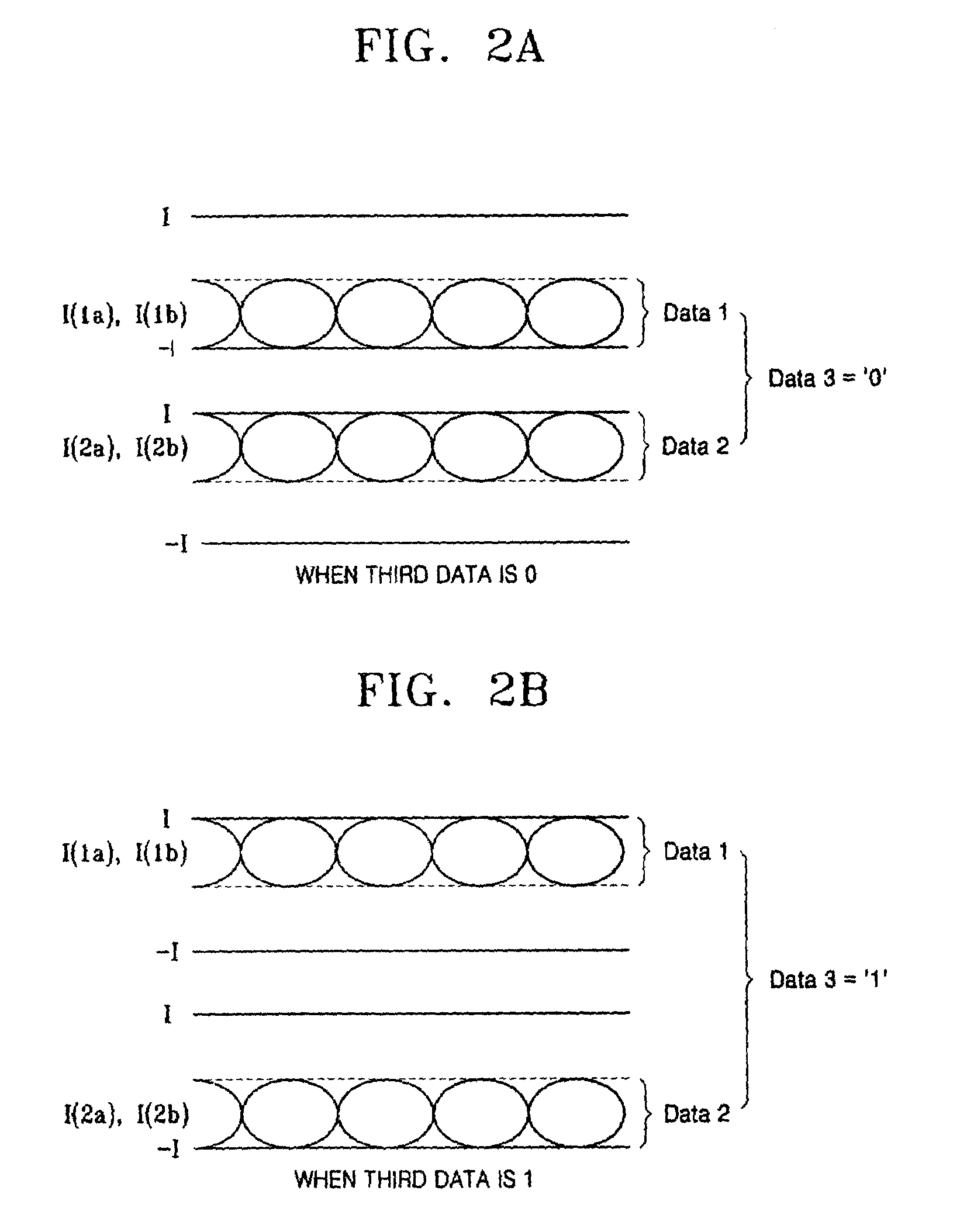
Current mode differential transmission method and system for transmitting three units of data using four signal lines
InactiveUS20060013331A1Reduce in quantityChannel dividing arrangementsComputations using contact-making devicesDifferential transmissionEngineering
Provided are a current mode differential transmission method and system for differentially transmitting three units of data using four signal lines. The method includes: dividing the four signal lines 1a, 1b, 2a and 2b into two pairs of signal lines 1a / 1b and 2a / 2b, and differentially transmitting respective data (first data and second data) via the two pairs of signal lines 1a / 1b and 2a / 2b; and transmitting the other data (third data) by differentially changing common mode currents of the two pairs of signal lines 1a / 1b and 2a / 2b.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
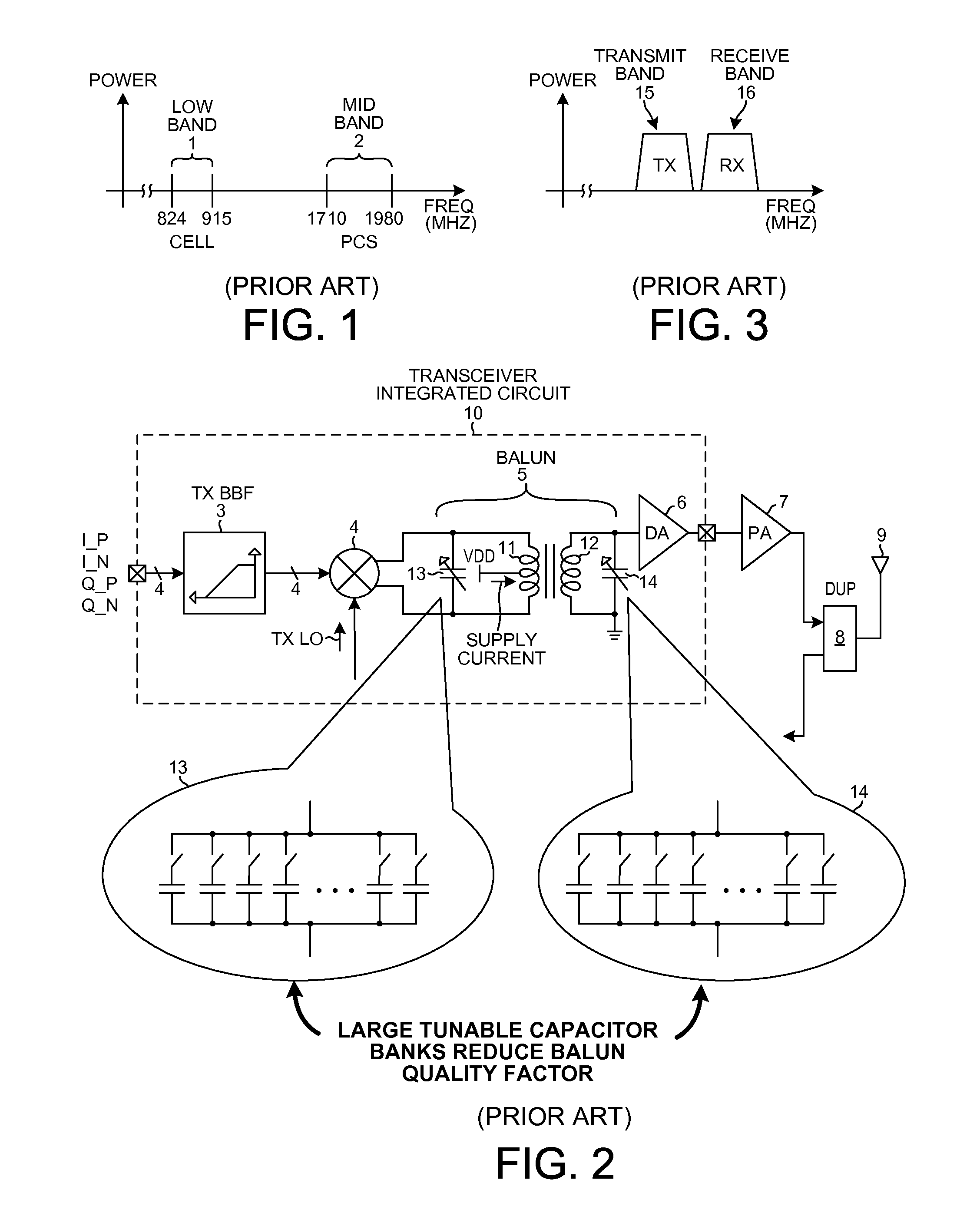
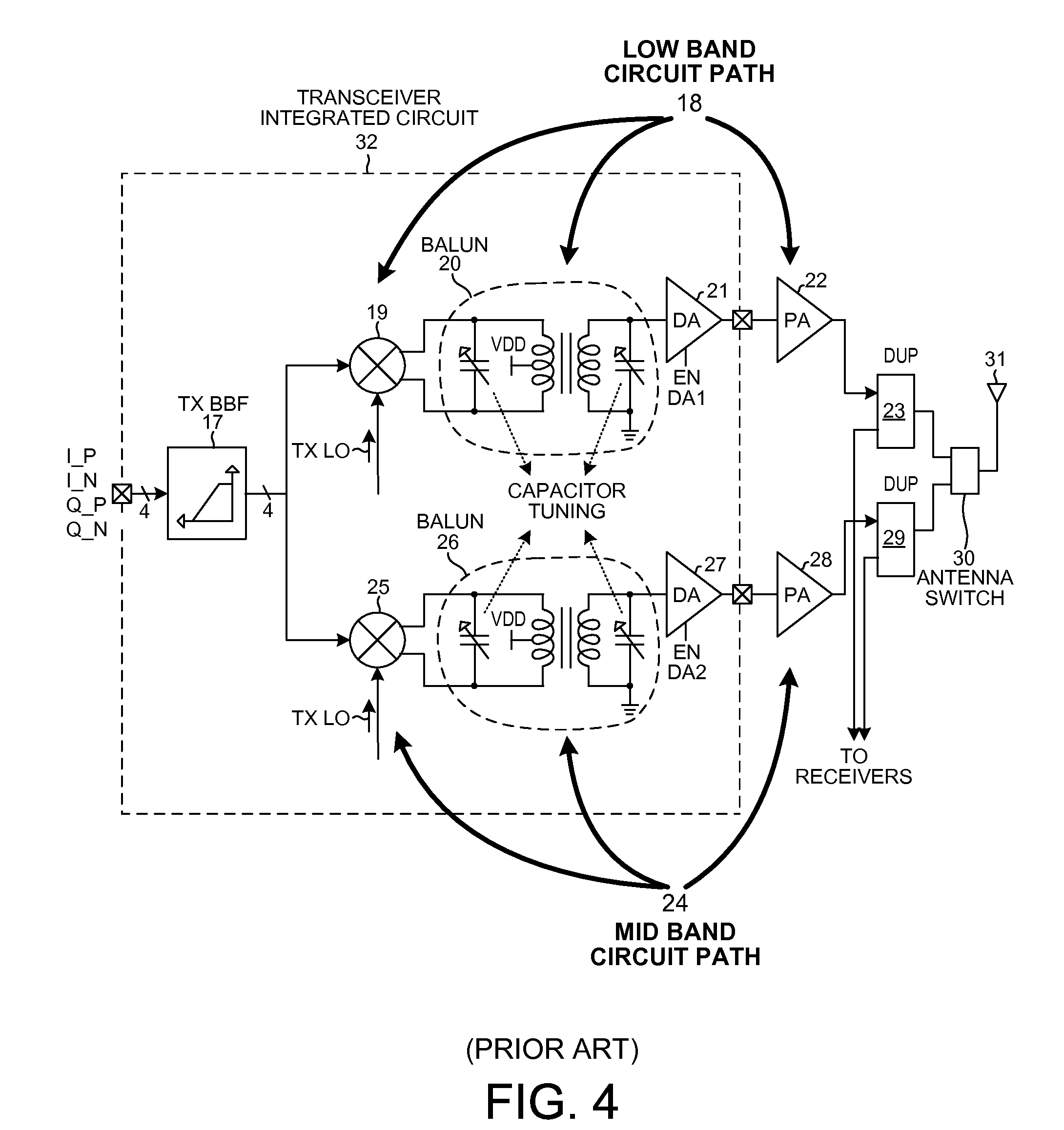
Wideband balun having a single primary and multiple secondaries
ActiveUS20120013387A1Reduce power consumptionPerformance requirementMultiple-port networksModulation transferenceWideband balunAudio power amplifier
An RF transmitter capable of transmitting over a wide range of frequencies includes a mixer, a wideband high-Q balun, a first driver amplifier and a second driver amplifier. The balun has a single primary winding and two secondary windings. A differential output of the mixer is coupled to the primary winding. A first of the two secondary windings is coupled to drive the first driver amplifier. A second of the two secondary windings is coupled to drive the second driver amplifier. One driver amplifier is used when transmitting at lower frequencies whereas the other driver amplifier is used when transmitting at higher frequencies. By appropriate sizing of the inductances of the secondary windings and by switching out one of the secondary windings at certain times, the balun is tunable to operate over the wide frequency range while having a high quality factor Q, thereby facilitating reduced power consumption while simultaneously meeting performance requirements.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
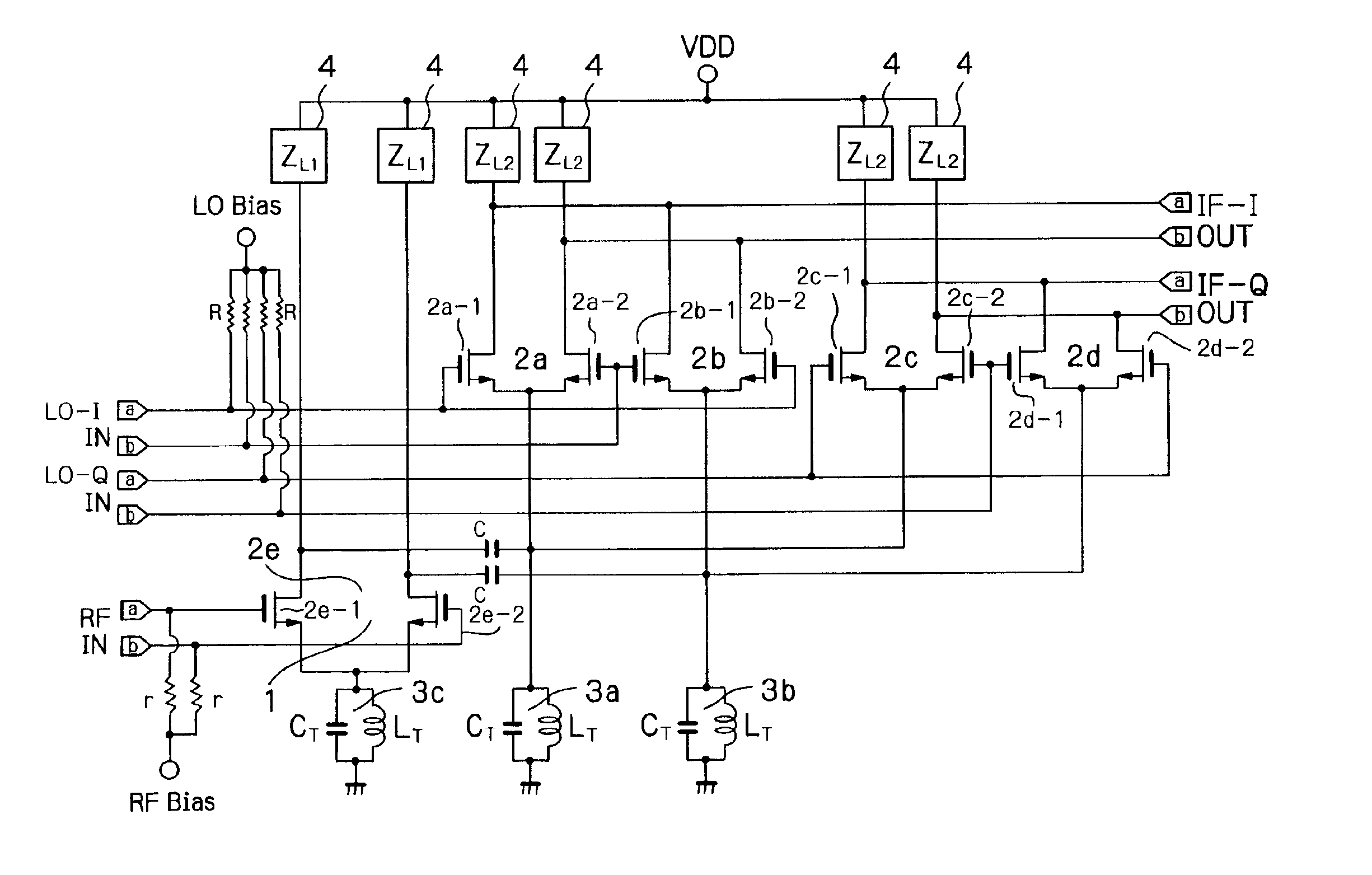
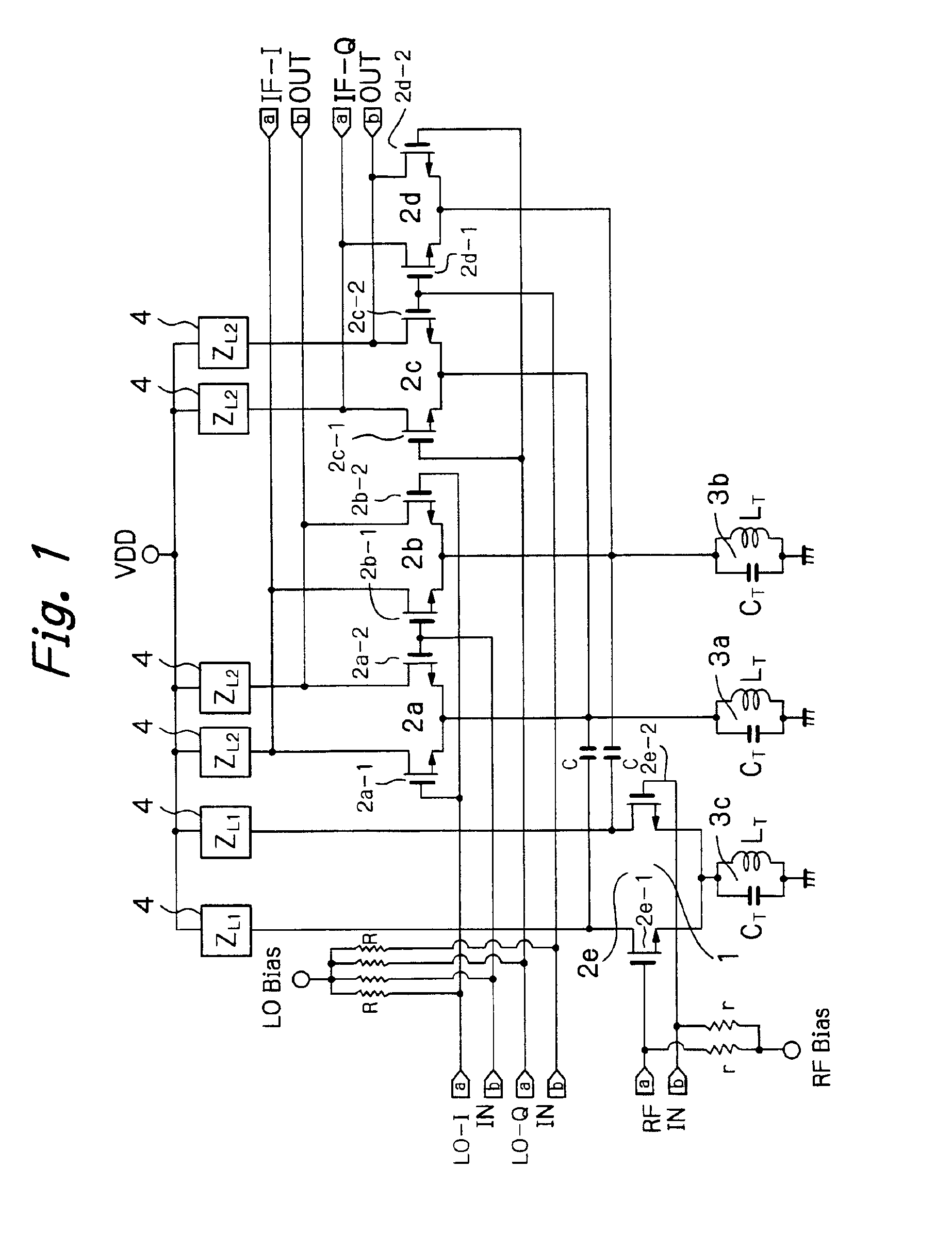
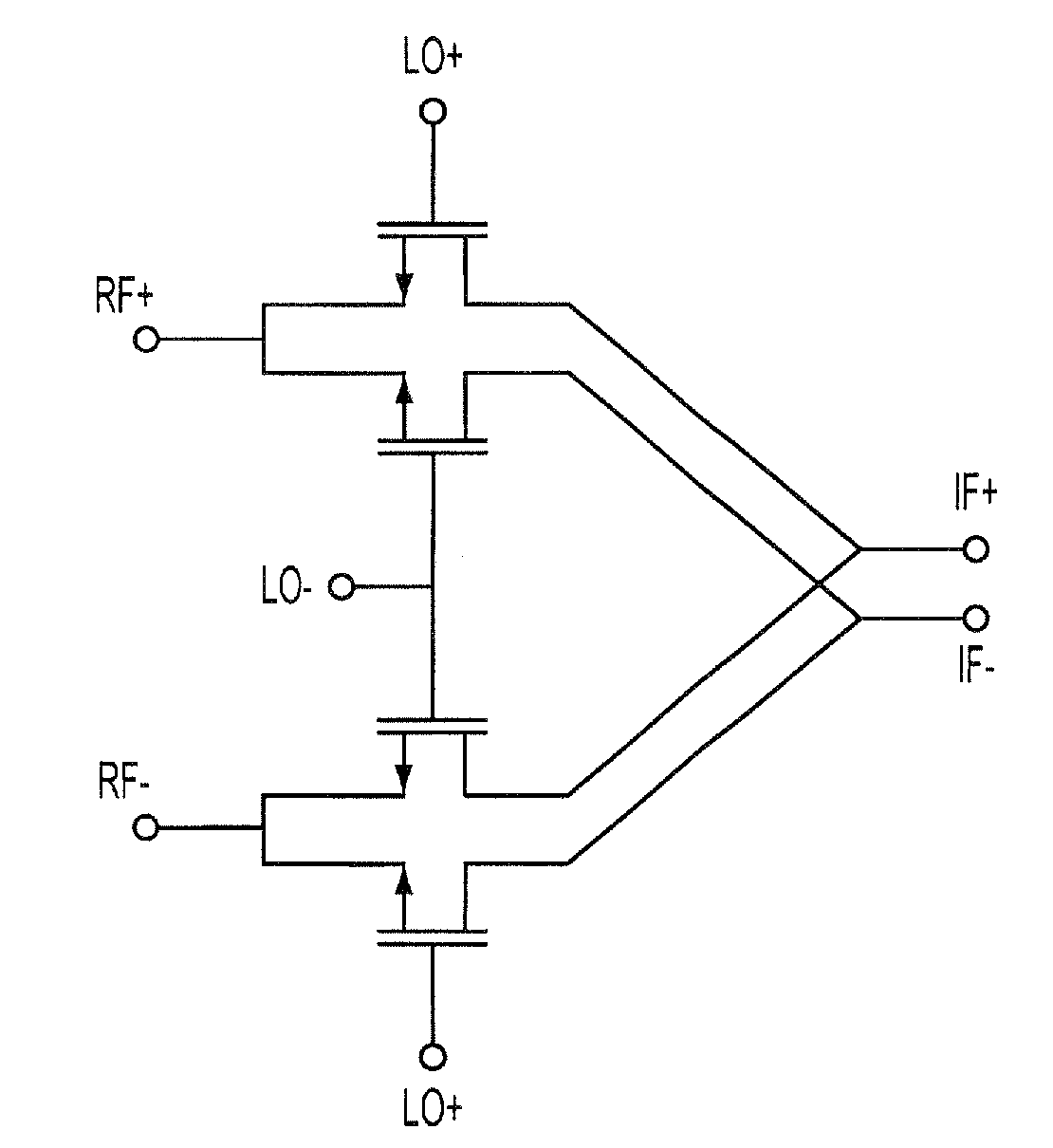
Mixer circuit
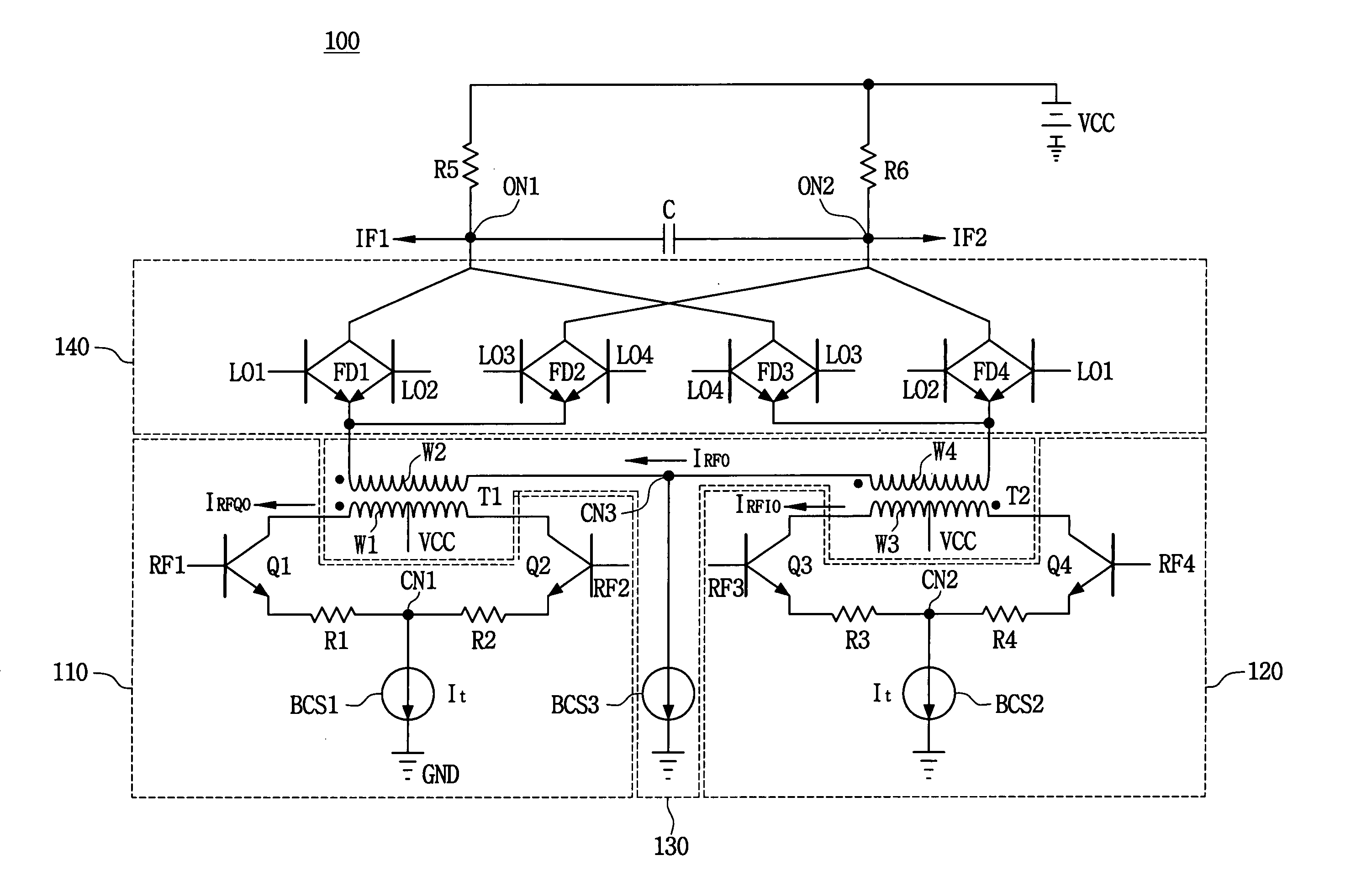
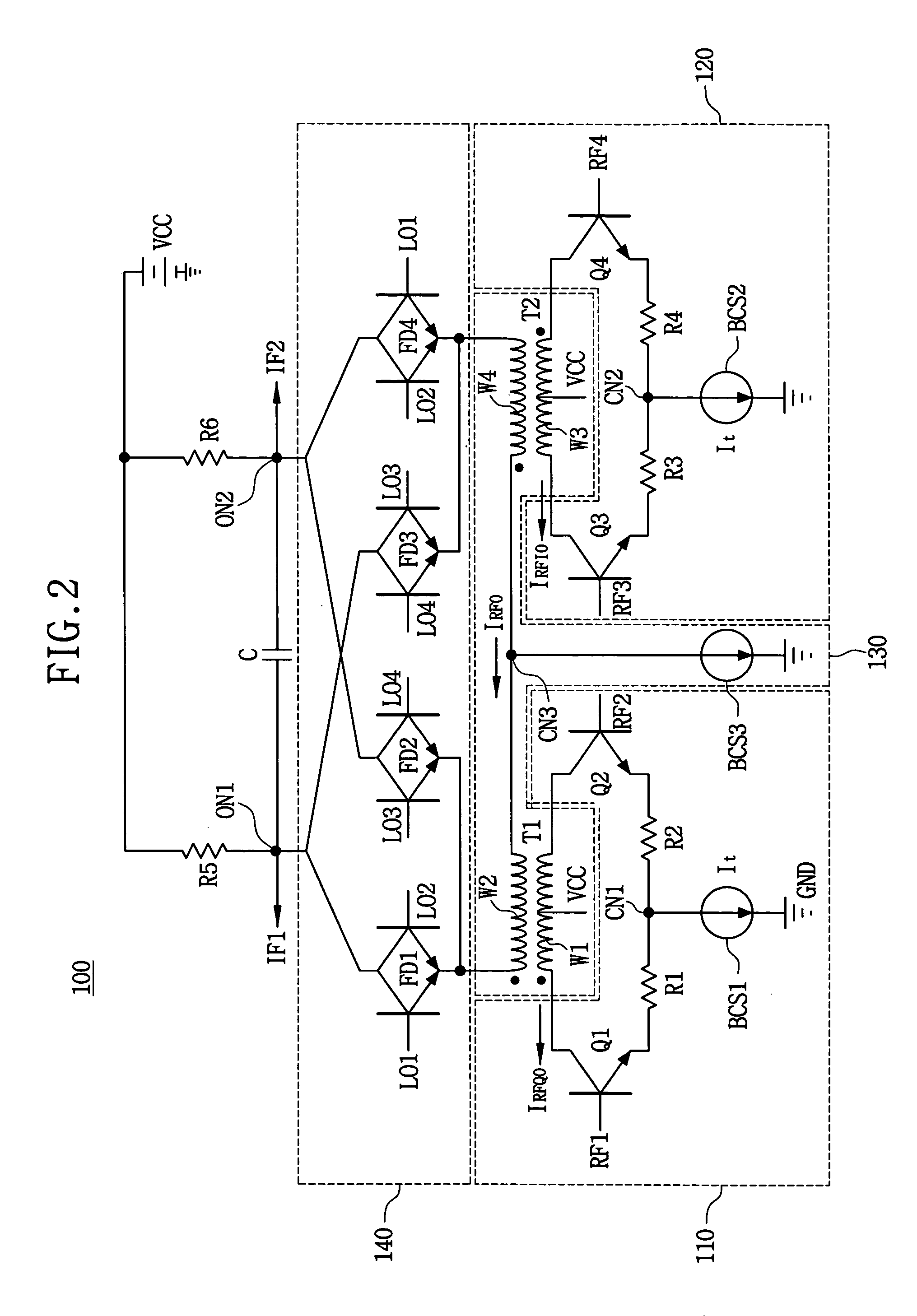
InactiveUS6871057B2Increase working frequencyMinimum errorModulation transference balanced arrangementsComputations using contact-making devicesFrequency mixerIntermediate frequency
A mixer circuit used in a radio receiver for mixing two frequencies and providing an intermediate frequency which is the difference of the two frequencies. Excellent image rejection is provided by decreasing an amplitude error and a phase error of an output IF signal in differential form.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Embedded phase noise measurement system
InactiveUS20100327940A1Improve featuresComputations using contact-making devicesVoltage-current phase anglePhase detectorPhase noise
Phase noise detection systems for a device under test (DUT) are provided that can be embedded within a chip. According to one embodiment, the embedded phase noise detection system can include an active delay line cell, a phase shifter, and a phase detector. The active delay line and phase shifter separately receive the output signal of the DUT. The phase detector can include a double-balanced mixer followed by an active RC filter. The double-balanced mixer receives, as input, the outputs from the active delay line and phase shifter and can produce different dc voltages proportional to the difference from the input phase quadrature. An auto-adjustment circuit can also be included to help the input signal from the phase shifter to the mixer maintain quadrature.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
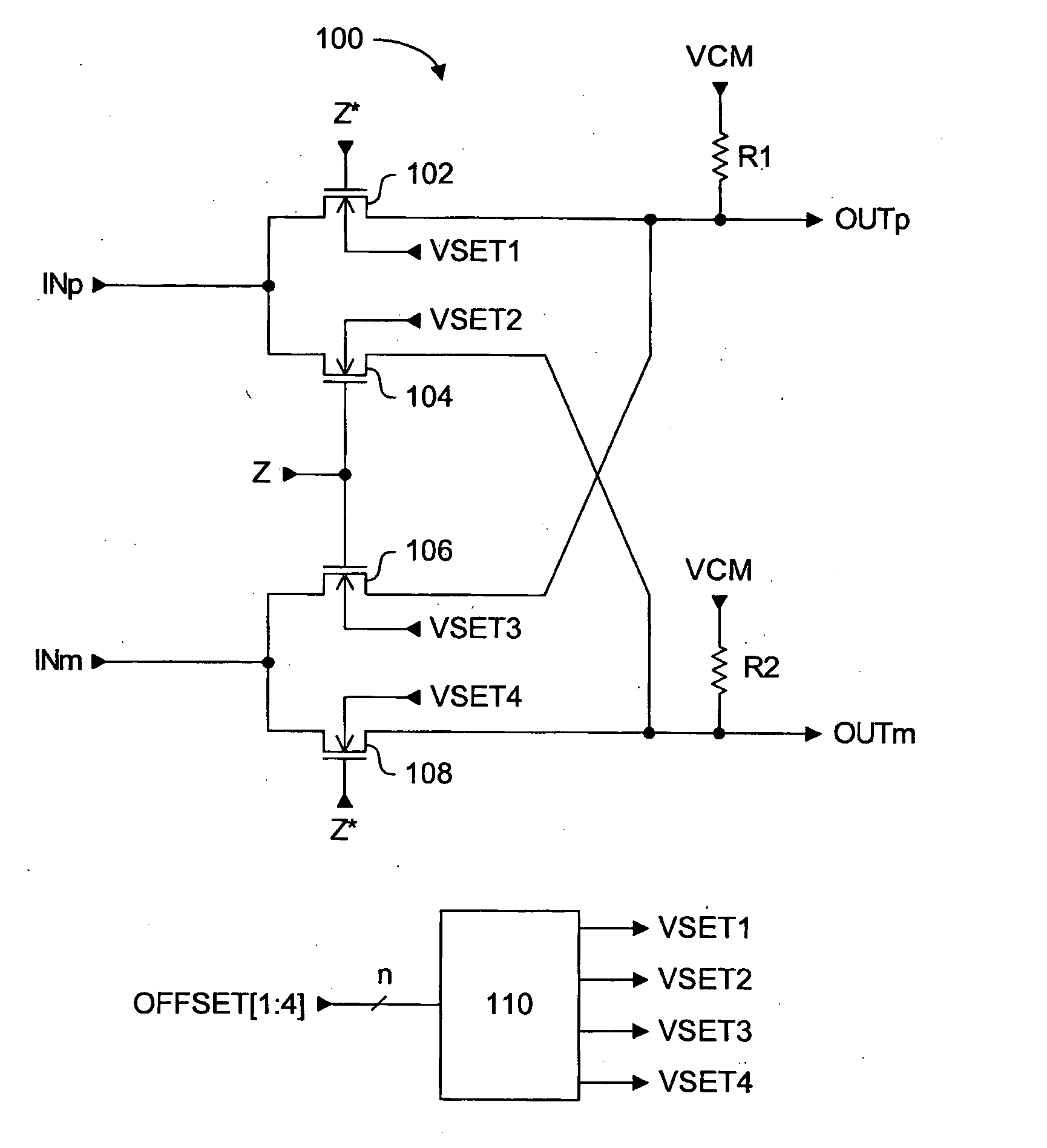
System for reducing second order intermodulation products from differential circuits
ActiveUS20070132500A1Reduce decreaseLow intermodulationModulation transferenceComputations using contact-making devicesCMOSDc current
A passive CMOS differential mixer circuit with a mismatch correction circuit for balancing the electrical characteristics of the two output paths. Once the output paths of the differential circuit are balanced, or matched as closely as possible, second order intermodulation product generation can be inhibited or at least reduced to acceptable levels. The mismatch correction circuit receives a digital offset signal, and generates one or more voltage signals to be selectively applied to the signal paths of the passive differential mixer circuit. The voltage signals can be adjusted back gate bias voltages applied to the bulk terminals of selected transistors to adjust their threshold voltages, or the voltage signals can be adjusted common mode voltages applied directly to a selected signal path. Since the differential mixer circuit is passive, no DC current contribution to noise is generated. The switching transistors of the mixer circuit can be maintained at minimal dimensions to reduce switching signal drive loading, resulting in lower power consumption and higher operating frequencies than if larger switching transistors were used.
Owner:ICERA CANADA ULC
Switching circuit, and a modulator, demodulator or mixer including such a circuit
ActiveUS7750749B2Improve Noise PerformanceReduce the effect of jitterModulation transferenceComputations using contact-making devicesFrequency mixerControl signal
A switching circuit comprising: first and second steering switches operable to make or break a path between first and second terminals thereof, and each steering switch further having a control terminal for controlling the switch, the first and second steering switches having their control terminals driven by first and second switching signals, the first and second switching signals having a first frequency and the second switching signal being in anti-phase with the first switching signal and a first chopping switch operable to make or break a path between first and second terminals thereof and being connected in series with at least one of the first and second steering switches and receiving at its first terminal an input to be modulated, wherein the control terminal of the chopping switch is driven by a first switching control signal such that the chopping switch is non-conducting while the first and second steering switches are changing between being conducting and being non-conducting.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
System for reducing second order intermodulation products from differential circuits
ActiveUS7554380B2Low intermodulationModulation transferenceComputations using contact-making devicesCMOSElectricity
A passive CMOS differential mixer circuit with a mismatch correction circuit for balancing the electrical characteristics of the two output paths. Once the output paths of the differential circuit are balanced, or matched as closely as possible, second order intermodulation product generation can be inhibited or at least reduced to acceptable levels. The mismatch correction circuit receives a digital offset signal, and generates one or more voltage signals to be selectively applied to the signal paths of the passive differential mixer circuit. The voltage signals can be adjusted back gate bias voltages applied to the bulk terminals of selected transistors to adjust their threshold voltages, or the voltage signals can be adjusted common mode voltages applied directly to a selected signal path. Since the differential mixer circuit is passive, no DC current contribution to noise is generated. The switching transistors of the mixer circuit can be maintained at minimal dimensions to reduce switching signal drive loading, resulting in lower power consumption and higher operating frequencies than if larger switching transistors were used.
Owner:ICERA CANADA ULC
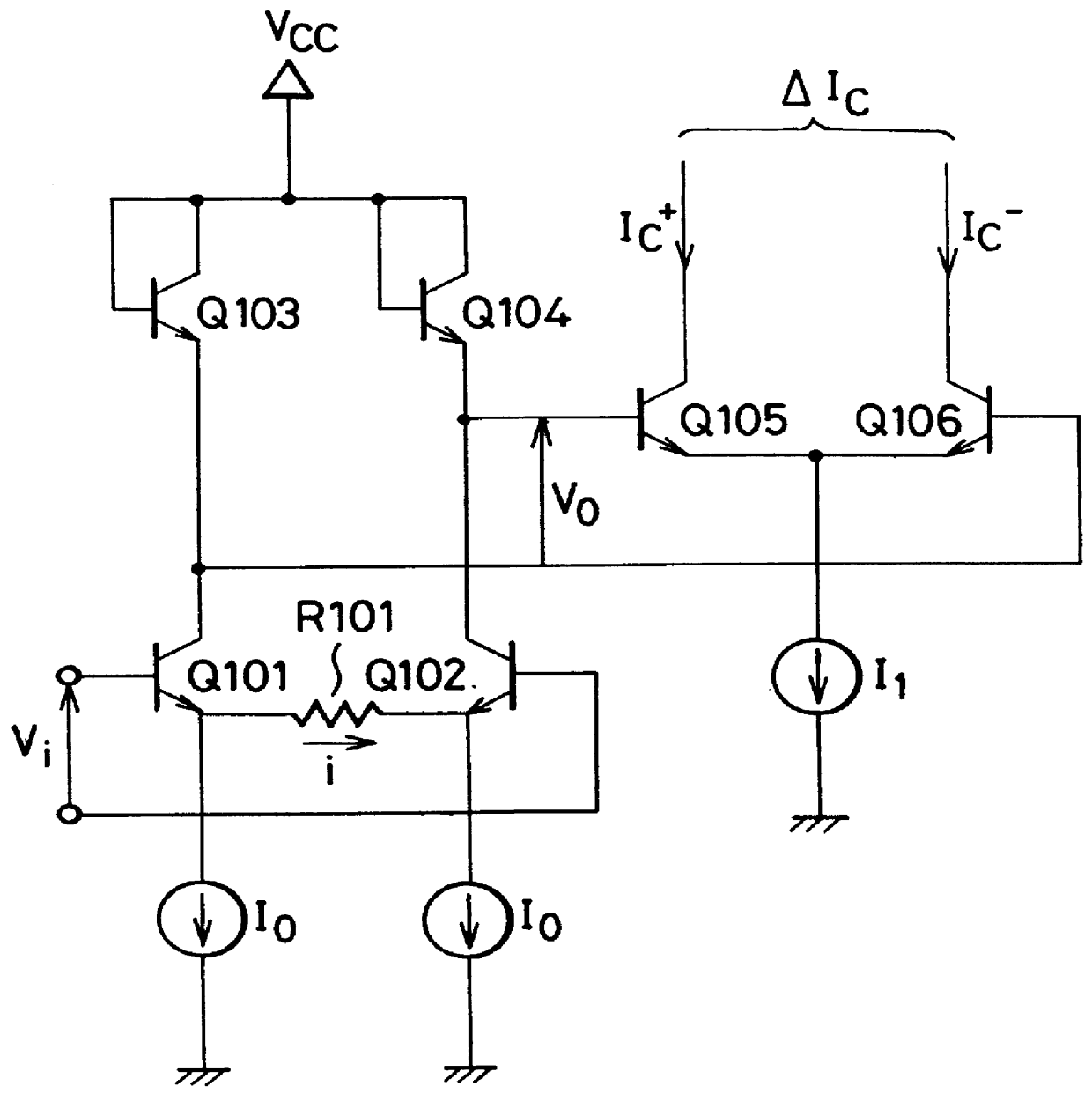
Operational transconductance amplifier and multiplier
InactiveUS6111463AAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionComputations using contact-making devicesAudio power amplifierEngineering
An OTA capable of completely linear operation within the entire operable input range is provided. This OTA includes a differential pair of first and second bipolar transistors, a first current source / sink for driving the first transistor, a second current source / sink for driving the second transistor, and a resistor connected to an emitter of the first transistor and an emitter of the second transistor. The emitters of the first and second transistors are coupled together through the resistor. The differential pair has a pair of input terminals of the OTA. A first current mirror having an input terminal and an output terminal and a second current mirror having an input terminal and an output terminal are provided. The input terminal of the first current mirror is connected to the first transistor. The input terminal of the second current mirror is connected to the second transistor. The output terminal of the first current mirror and the output terminal of the second current mirror form a pair of output terminals of the OTA. An input signal to be amplified is differentially applied across the pair of input terminals of the OTA. An amplified output signal is differentially derived from the pair of output terminals of the OTA.
Owner:NEC CORP
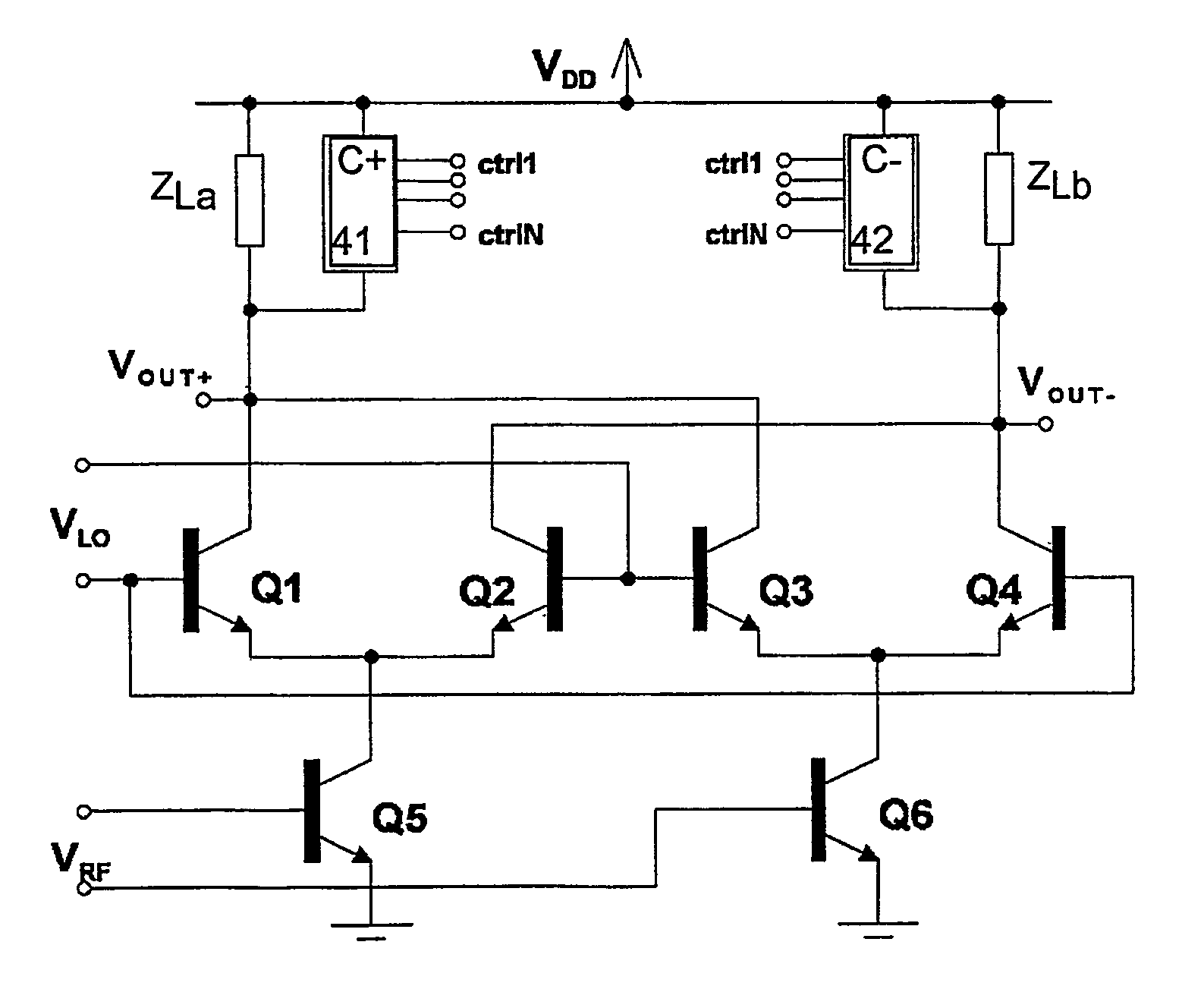
Variable impedance circuit, variable gain differential amplifier, multiplier, high-frequency circuit and differential distributed amplifier
InactiveUS7215196B2Reduce distortion problemsSuppress saturationComputations using contact-making devicesGain controlElectrical resistance and conductanceDistributed amplifier
The collectors of transistors are connected via respective resistances to a power supply terminal receiving a power supply voltage. The emitters of the transistors are connected to a ground terminal via respective resistances. A shunt resistance, a FET, and a shunt resistance are connected in series between nodes connected to the respective emitters of the transistors. The gate of the FET is connected via a resistance to a control terminal receiving a control voltage. The shunt resistances and FET form a variable resistance circuit.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
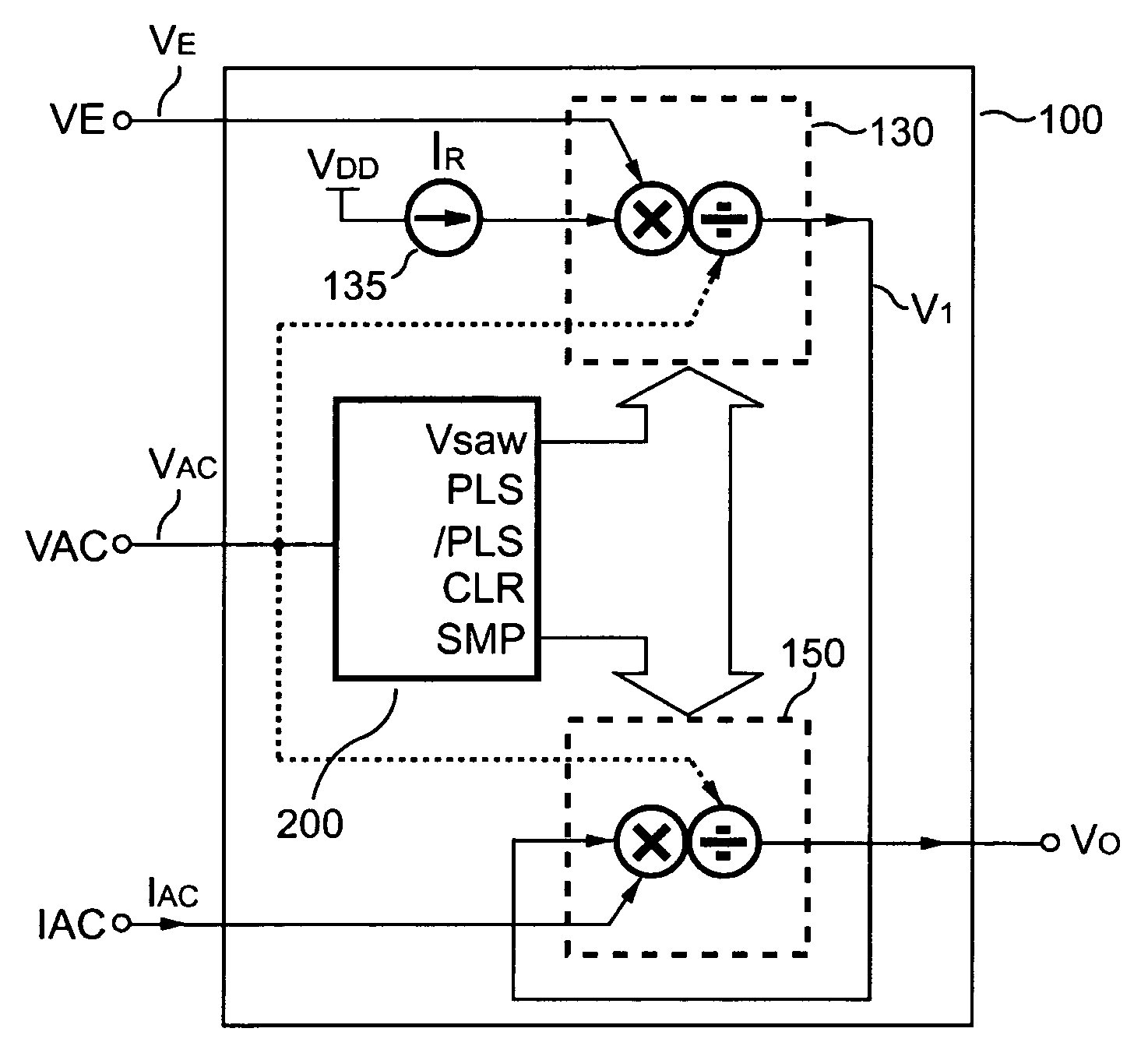
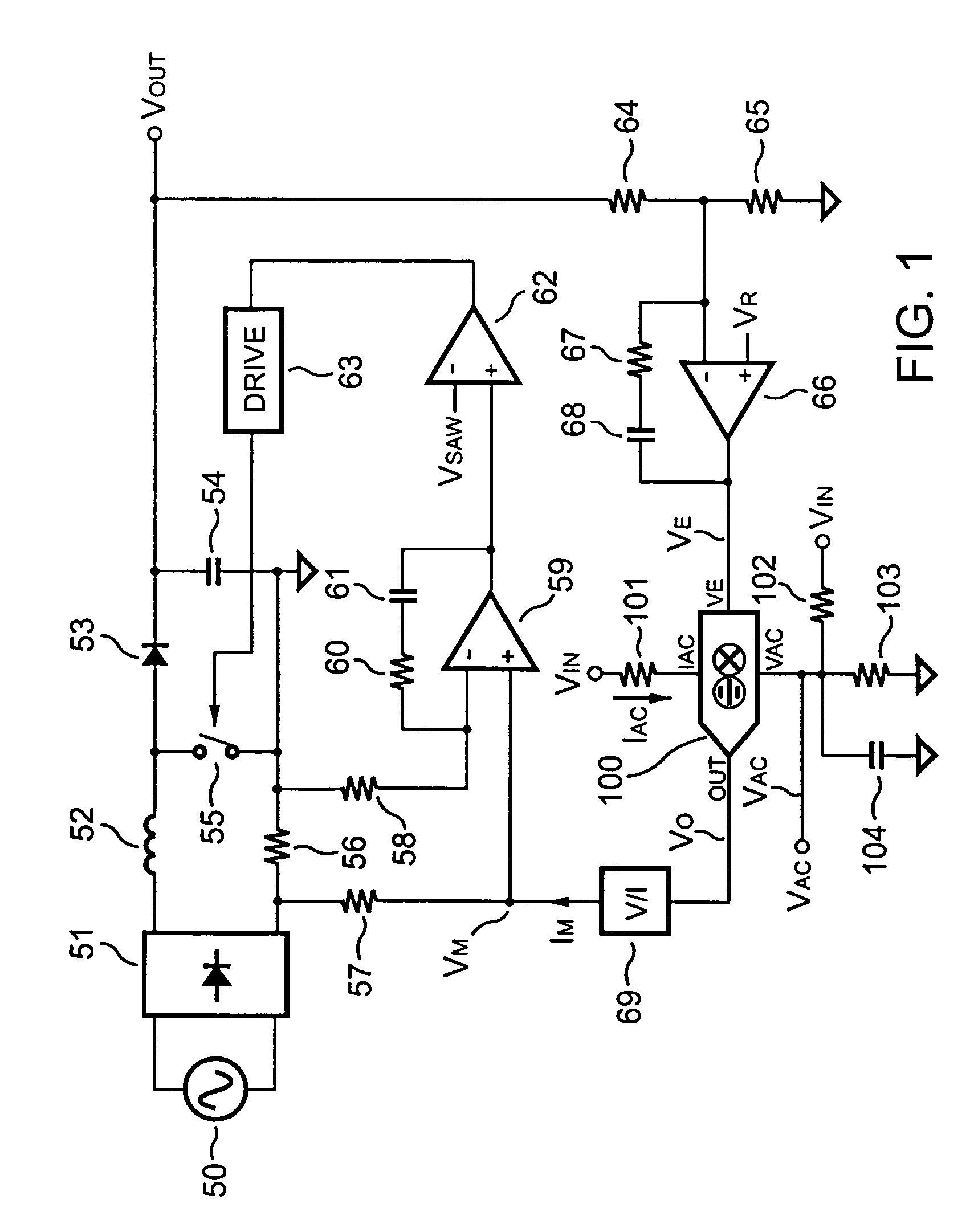
Multiplier-divider circuit for a PFC controller
ActiveUS7057440B2Small die-sizeLow costAc-dc conversion without reversalComputations using contact-making devicesCMOSAnalog multiplier
The present invention introduces an integrated analog multiplier-divider circuit. The multiplier-divider block according to the present invention is ideal for use in the power factor correction (PFC) controllers of many switch-mode power supplies. The analog multiplier-divider according to the present invention is built with CMOS devices. Because of this, it has many advantages over prior-art multiplier-dividers. One important advantage is that the die-size and the cost can be reduced. Another important advantage of the multiplier-divider according to the present invention is substantially reduced temperature dependence.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
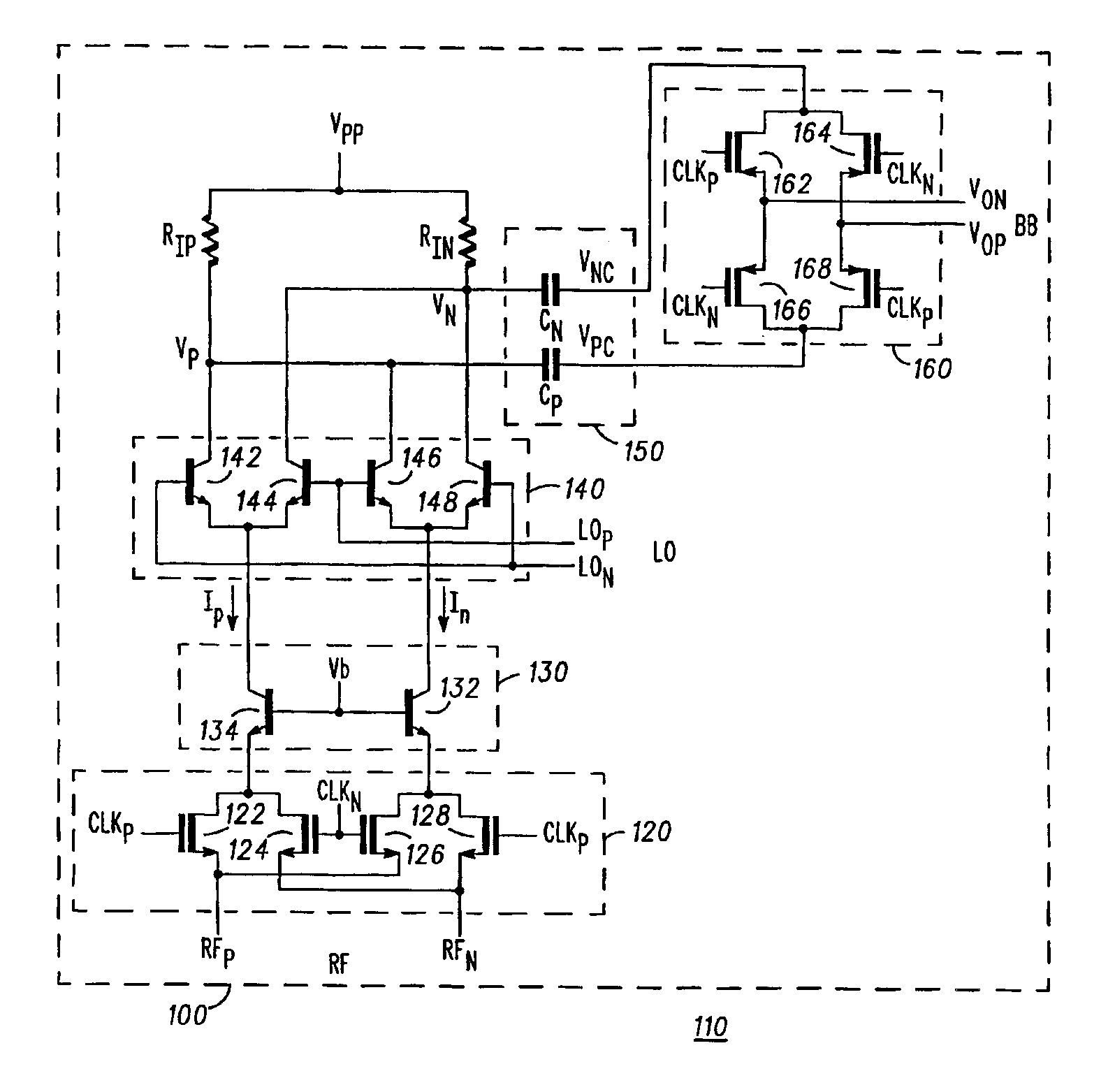
Apparatus and method for improved chopping mixer
InactiveUS6933766B2Modulation transference balanced arrangementsComputations using contact-making devicesClock rateEngineering
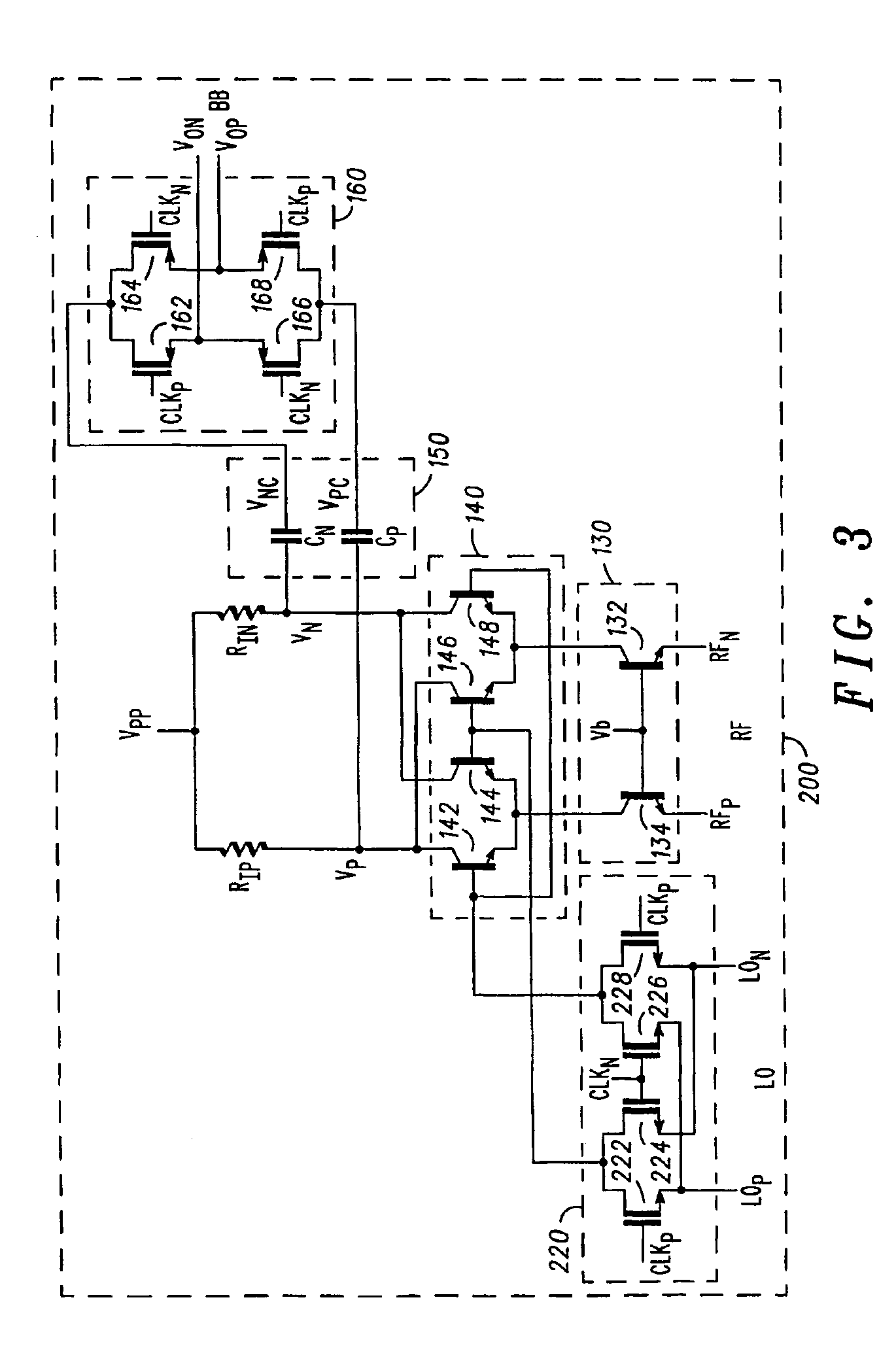
An apparatus and method for an improved chopping mixer (100) having a bipolar mixer stage (140) for mixing signals (lp, In, LOp, LOn) received thereby; an output chopping stage (160); and an AC coupling stage (150) for coupling the mixed signal to the output chopping stage. The signal prior to the chopping output stage is centered at the chopping clock frequency rather than DC. AC coupling allows removal of common mode signal in a desired frequency range. Also, the second order component present on each single ended output will also be DC blocked by the AC coupling capacitors, resulting in improved second order IP2 performance.
Owner:APPLE INC
Tunable low noise amplifier and current-reused mixer for a low power RF application
InactiveUS6850753B2Reduce noiseReduce power consumptionModulation transference balanced arrangementsComputations using contact-making devicesEngineeringTransconductance
A radio frequency front-end receiver includes a single stage low noise amplifier connected with a resistor array and a capacitor array, and a Gilbert-type mixer connected with a PMOS transconductance stage, an inductor and a serially connected current source. The resistor array enables the adjustment of the power gain of the low noise amplifier. The capacitor array tunes the low noise amplifier so that the maximum power gain is at the desired operating frequency. The PMOS transconductance stage reduces the power consumption of the mixer. The inductor increases the impedance and the current source improves the common-mode rejection of the mixer.
Owner:MUCH IP
Circuit and method for receiving and mixing radio frequencies in a direct conversion receiver
InactiveUS7120414B2Improve linearityQuality improvementModulation transference balanced arrangementsComputations using contact-making devicesHarmonicFrequency mixer
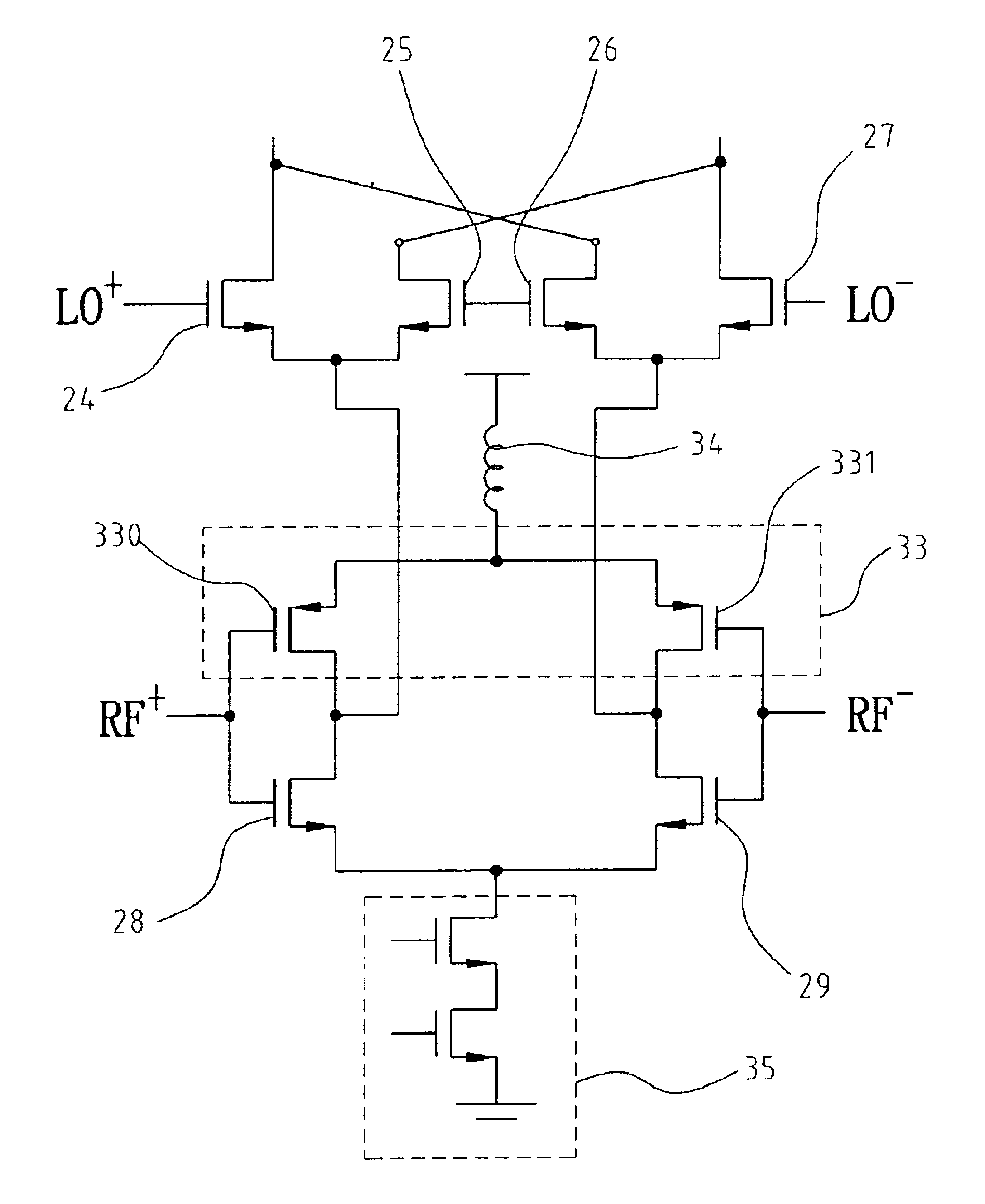
A frequency mixing circuit and a frequency mixing method. The frequency mixing circuit includes first and second differential amplifiers, a subtracter and a mixer. The first differential amplifier amplifies a first pair of input signals having a first frequency to generate a first differential signal. The second differential amplifier amplifies a second pair of input signals having the first frequency orthogonal to the first pair input signals to generate a second differential signal. The subtracter subtracts the second differential signal from the first differential signal. The mixer mixes the subtracted signal with a first and second pairs of drive signals having a second frequency orthogonal to each other, in a sub-harmonic double balanced mixing mode, so that the mixer generates a pair of output signals orthogonal to each other without secondary harmonics.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
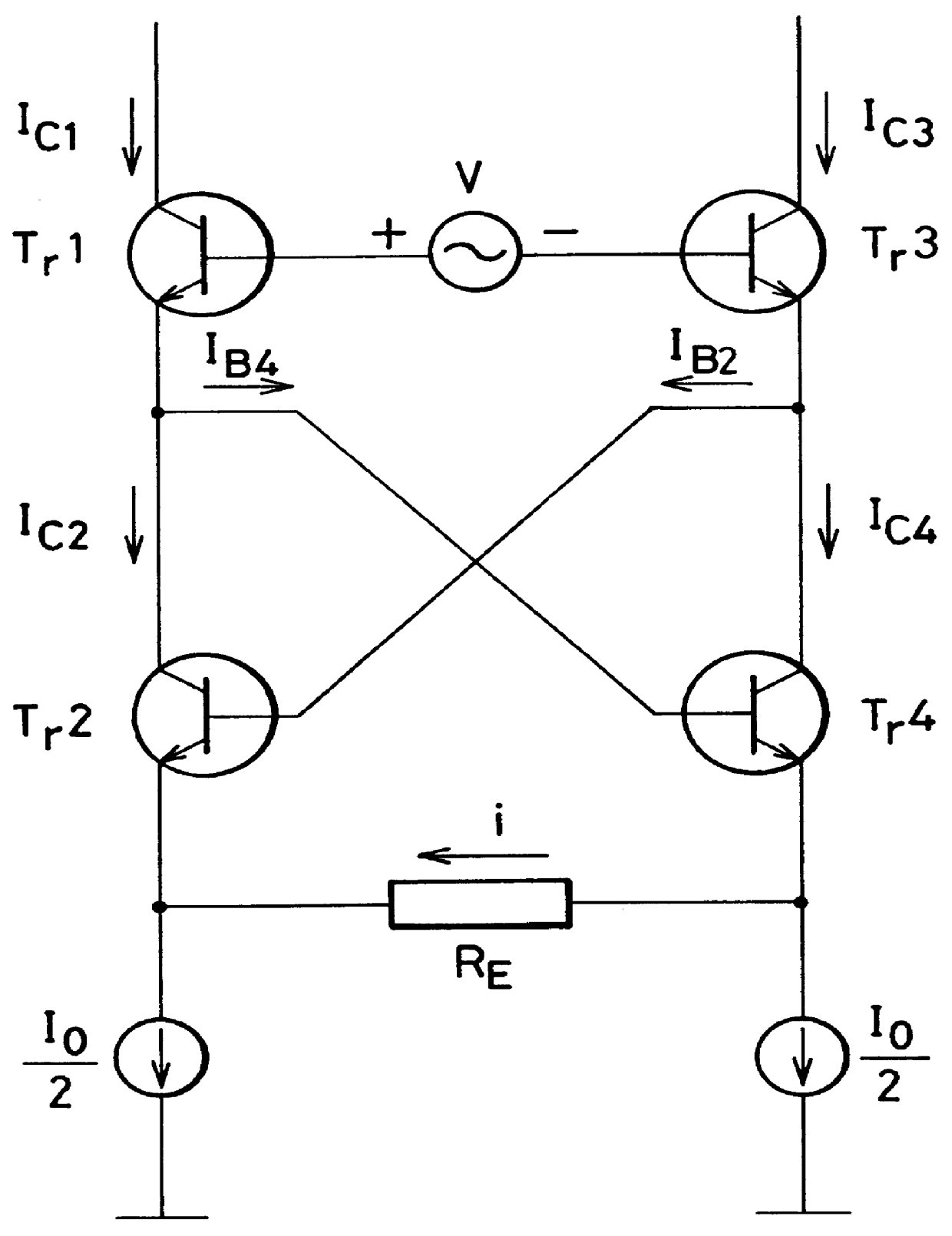
Balanced circuit arrangement and method for linearizing such an arrangement
InactiveUS7031687B2Improve balanceImprove performanceModulation transference balanced arrangementsComputations using contact-making devicesBalanced circuitLinearization
The present invention relates to a balanced circuit arrangement and methods for linearizing and calibrating such a circuit arrangement wherein linearization is obtained by introducing a load imbalance between the output branches of the balanced circuit arrangement. Thus, a controllable extraneous imbalance is created between the output loads of the balanced circuit arrangement to thereby obtain a linearization by means of even-order non-linearity.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
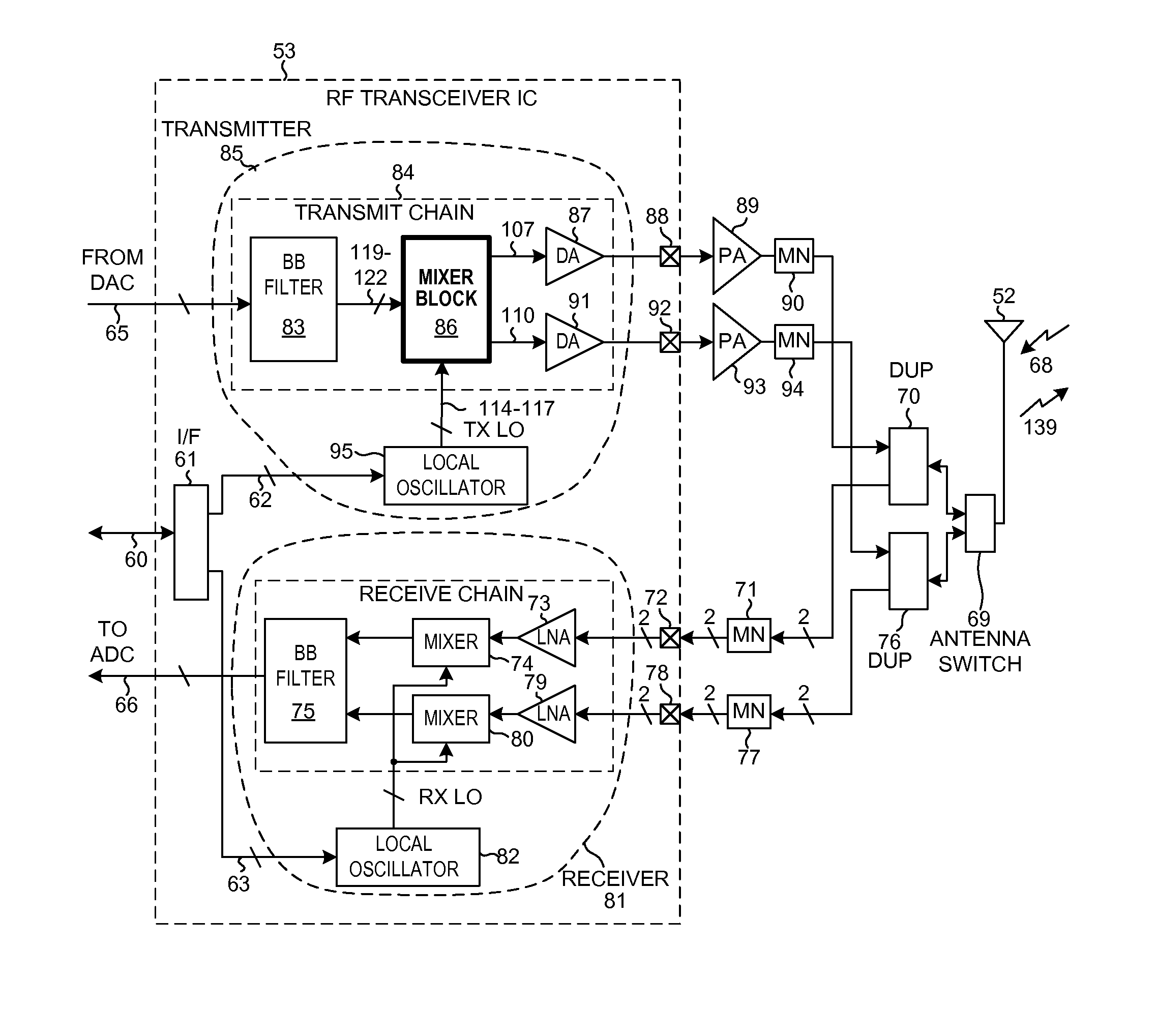
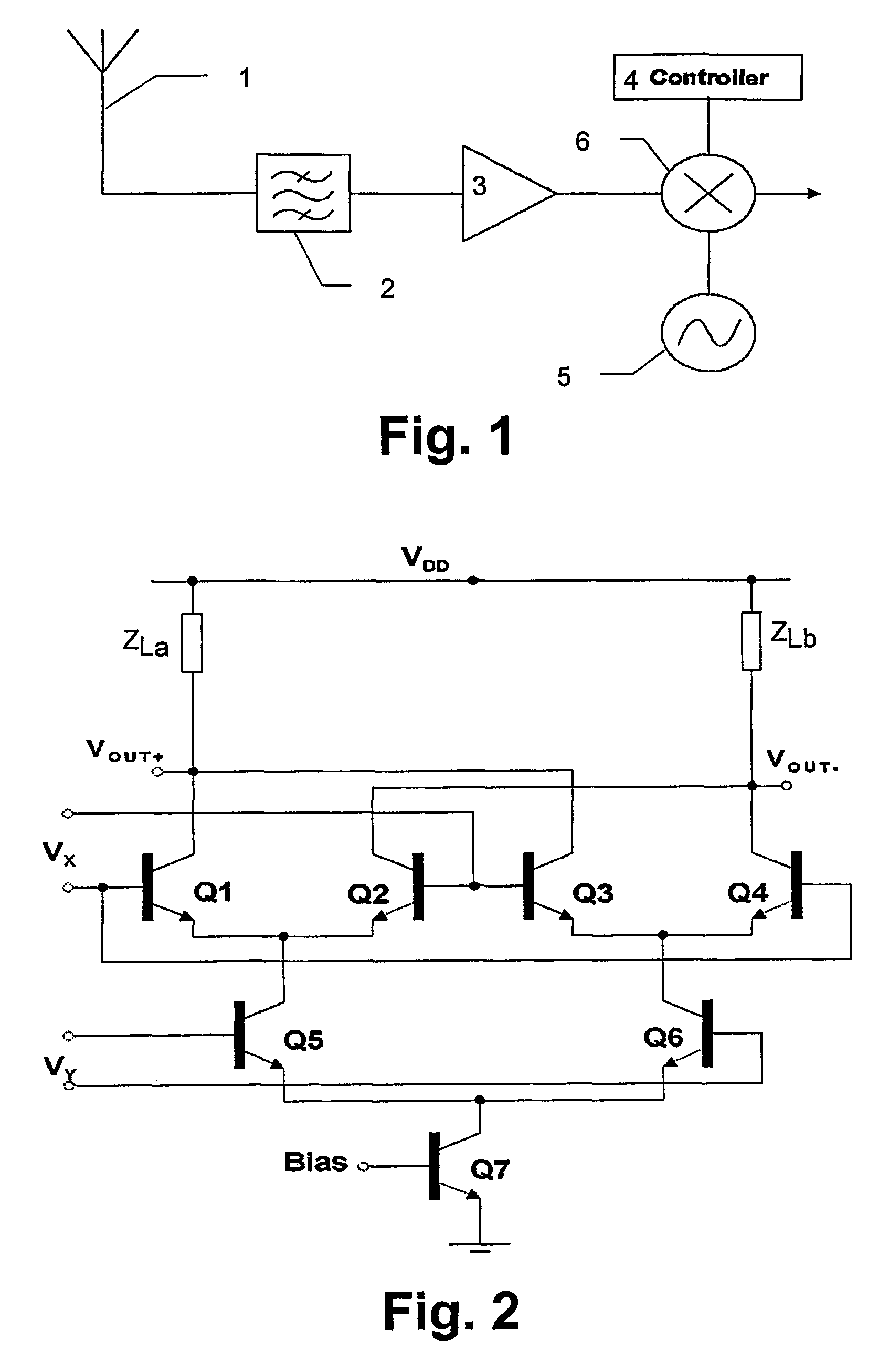
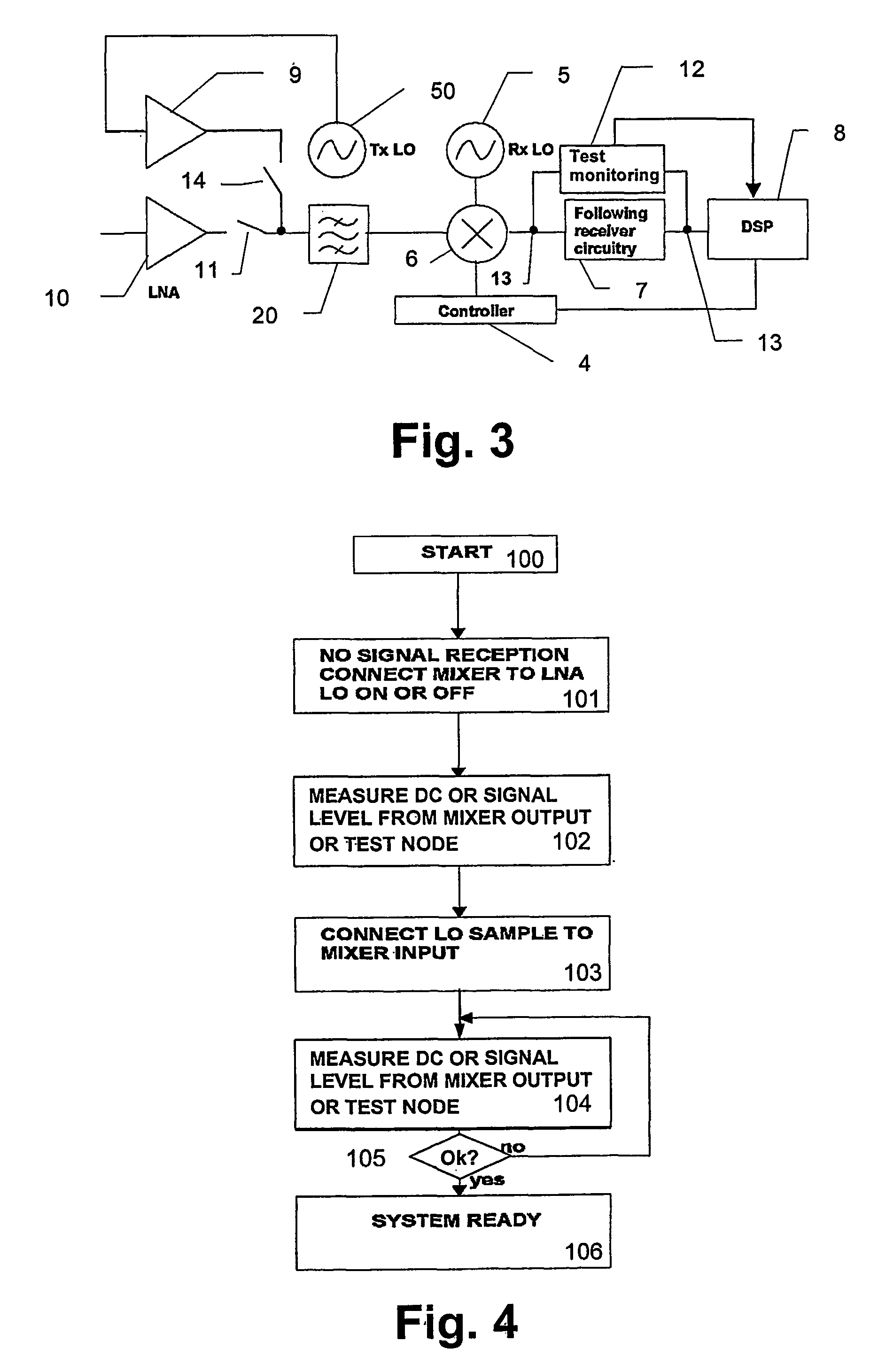
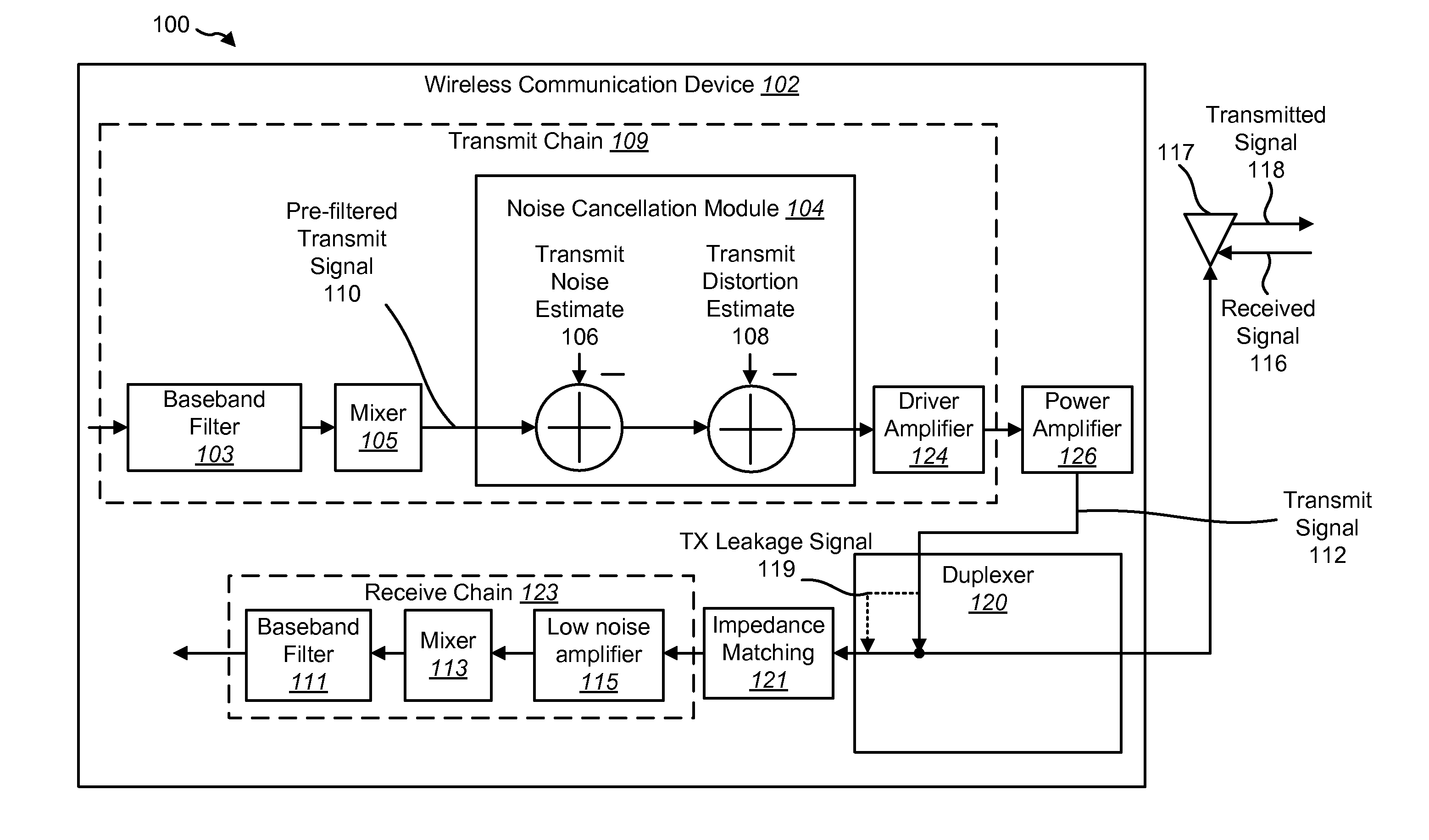
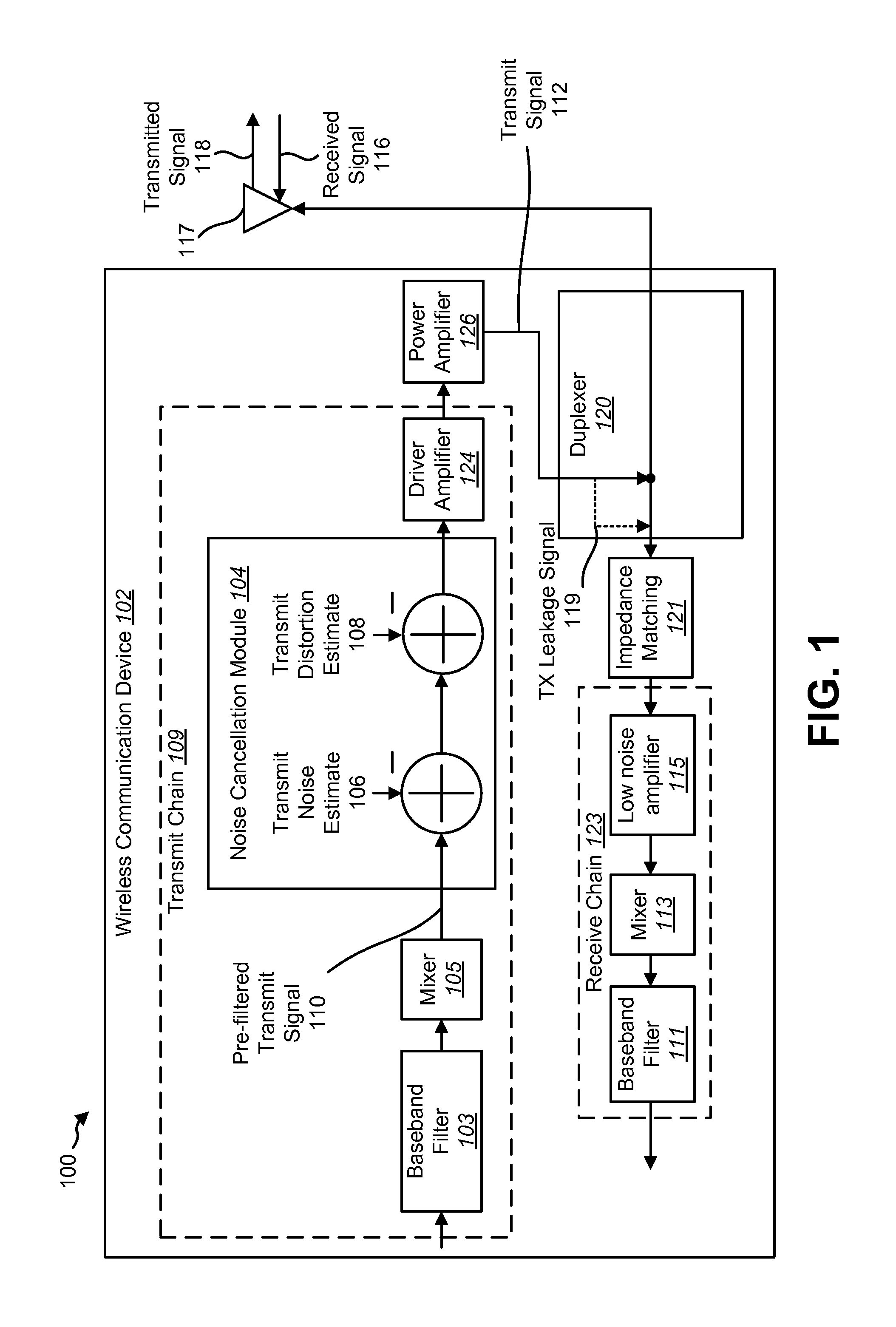
Dual-loop transmit noise cancellation
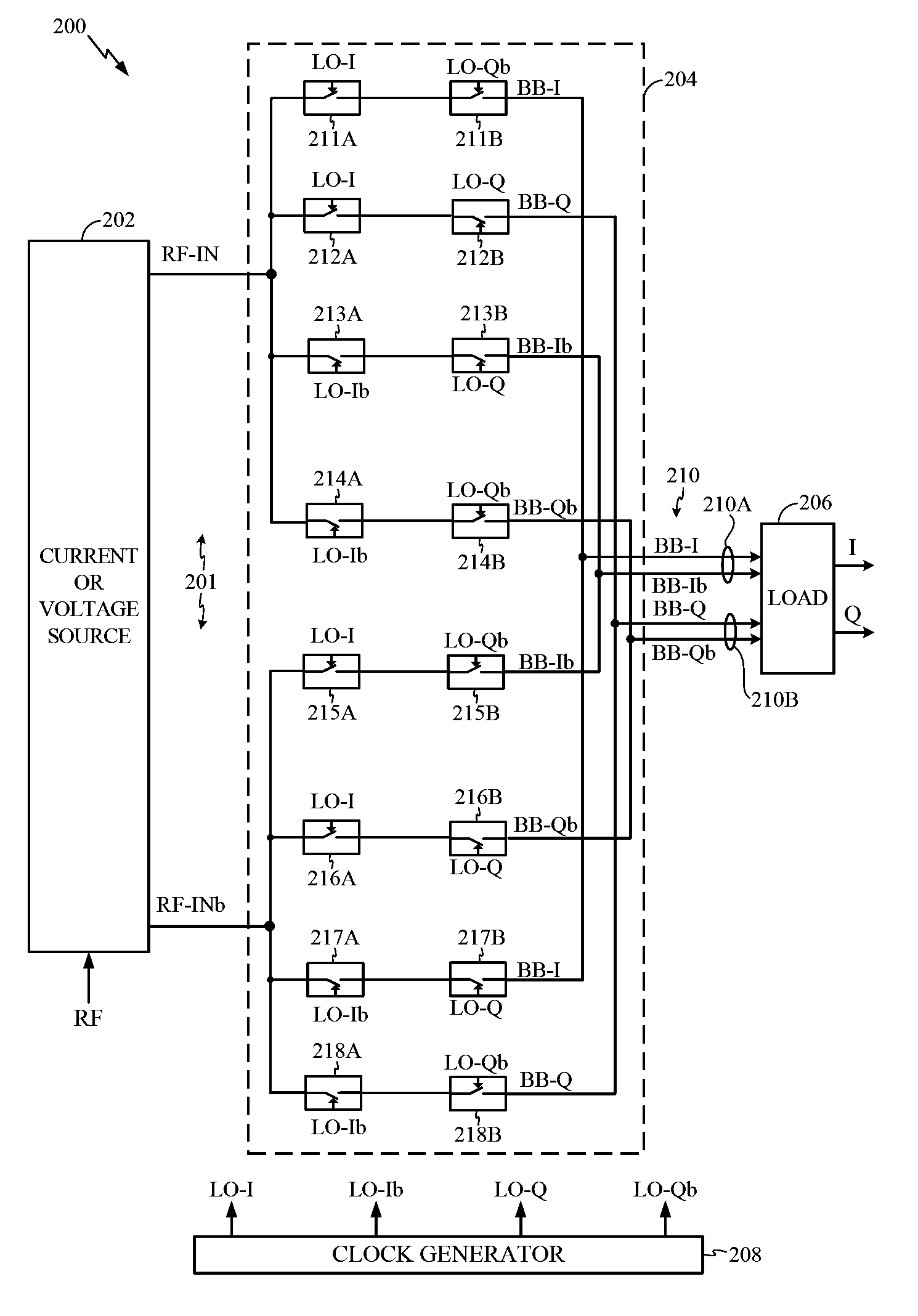
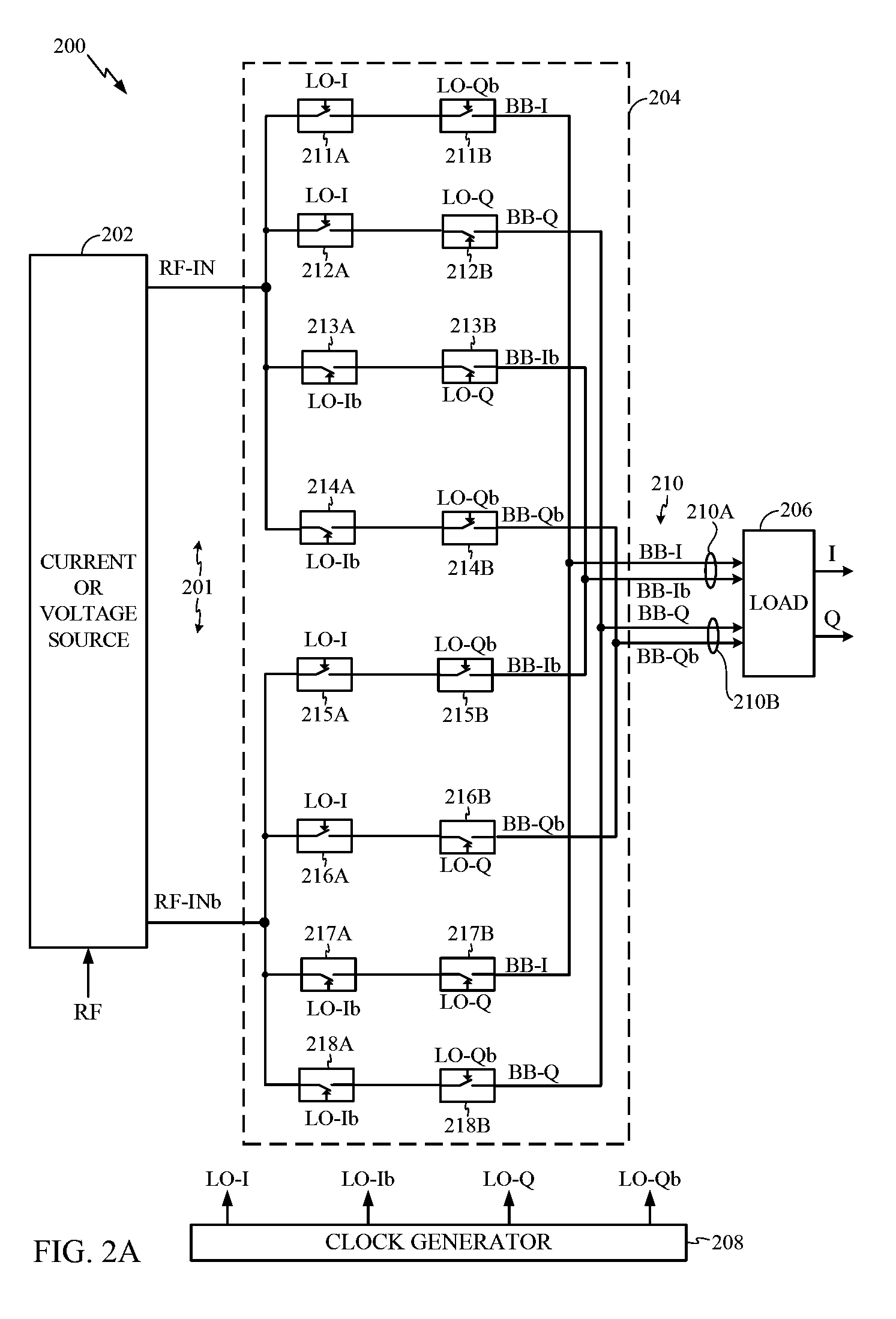
ActiveUS20110158346A1Eliminates transmission noiseRemove distortionComputations using contact-making devicesComputing operations for multiplication/divisionEngineeringFilter bank
A transmitter circuit is described. The transmitter circuit includes a first local oscillator that generates a first frequency equal to a duplex frequency. The transmitter circuit also includes a second local oscillator that generates a second frequency equal to a receive frequency. The transmitter circuit further includes a first mixer that combines the first frequency with a first input signal. The transmitter circuit also includes a first feedback loop. The first feedback loop includes a second mixer that combines the second frequency with a transmit signal and a first filter and a first adder that combines an output of the first mixer with an output of the first filter. The transmitter circuit also includes a third local oscillator that generates a third frequency equal to the receive frequency. The transmitter circuit further includes a third mixer that combines the third frequency with an output of the first adder.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
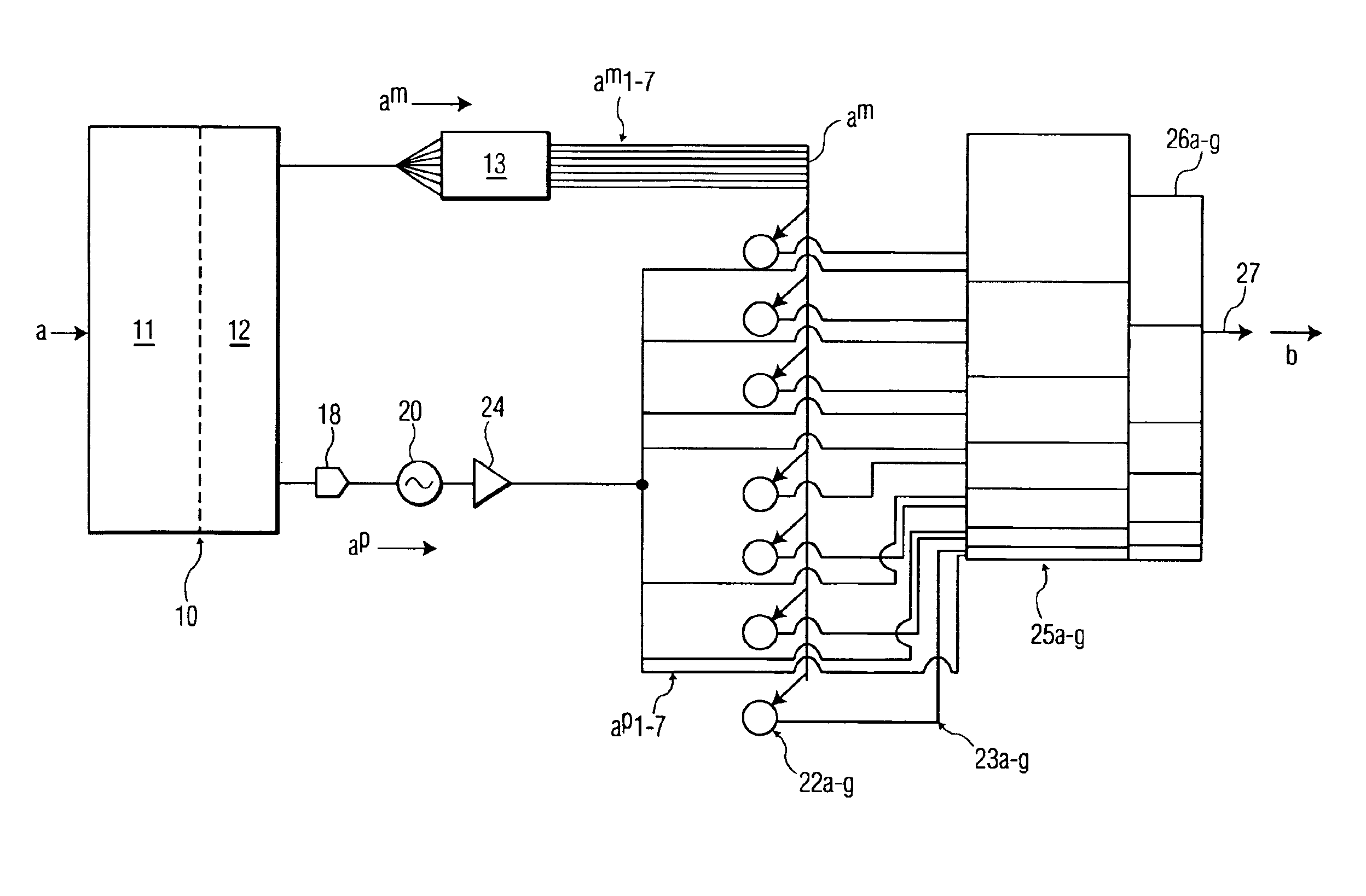
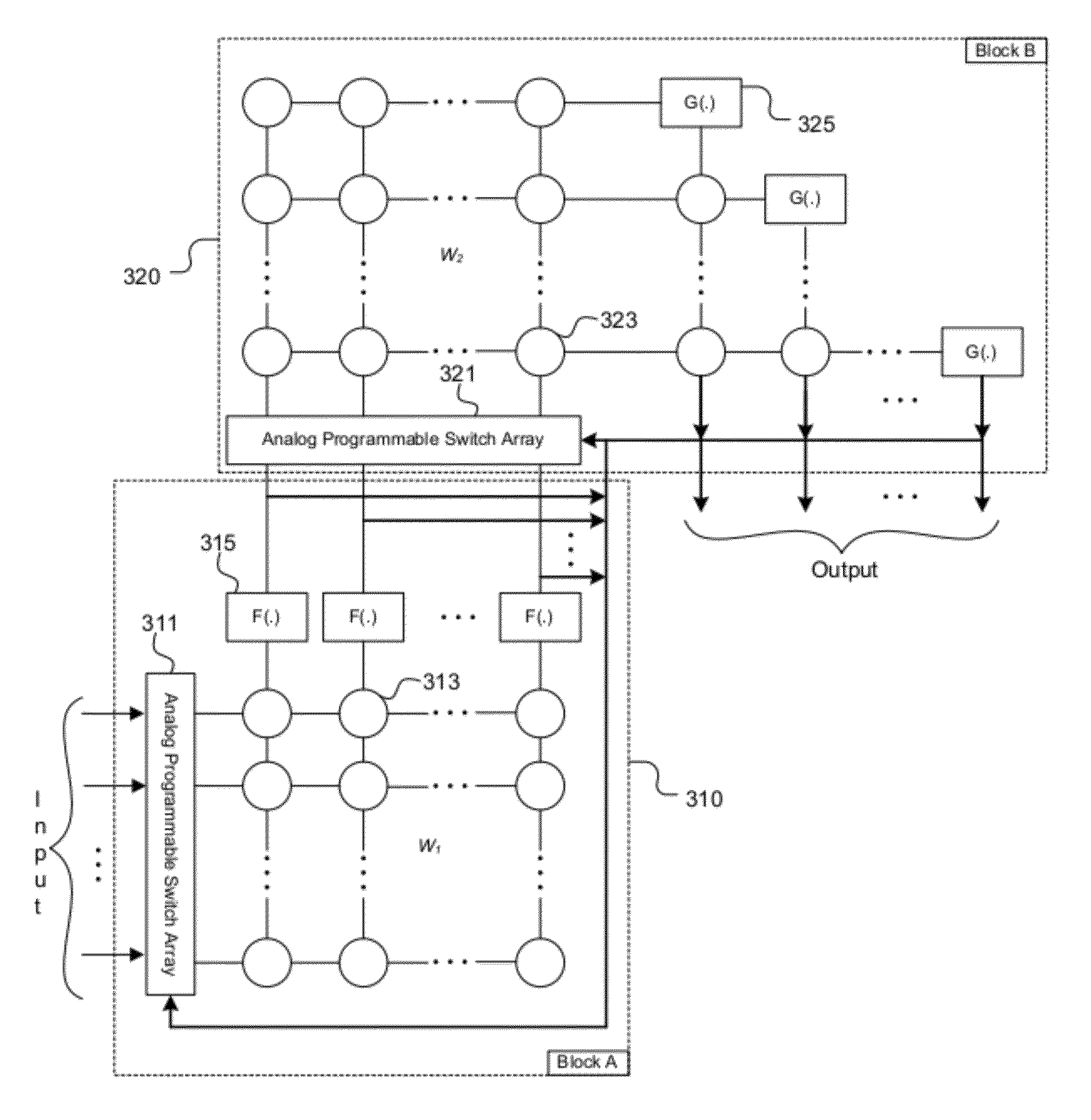
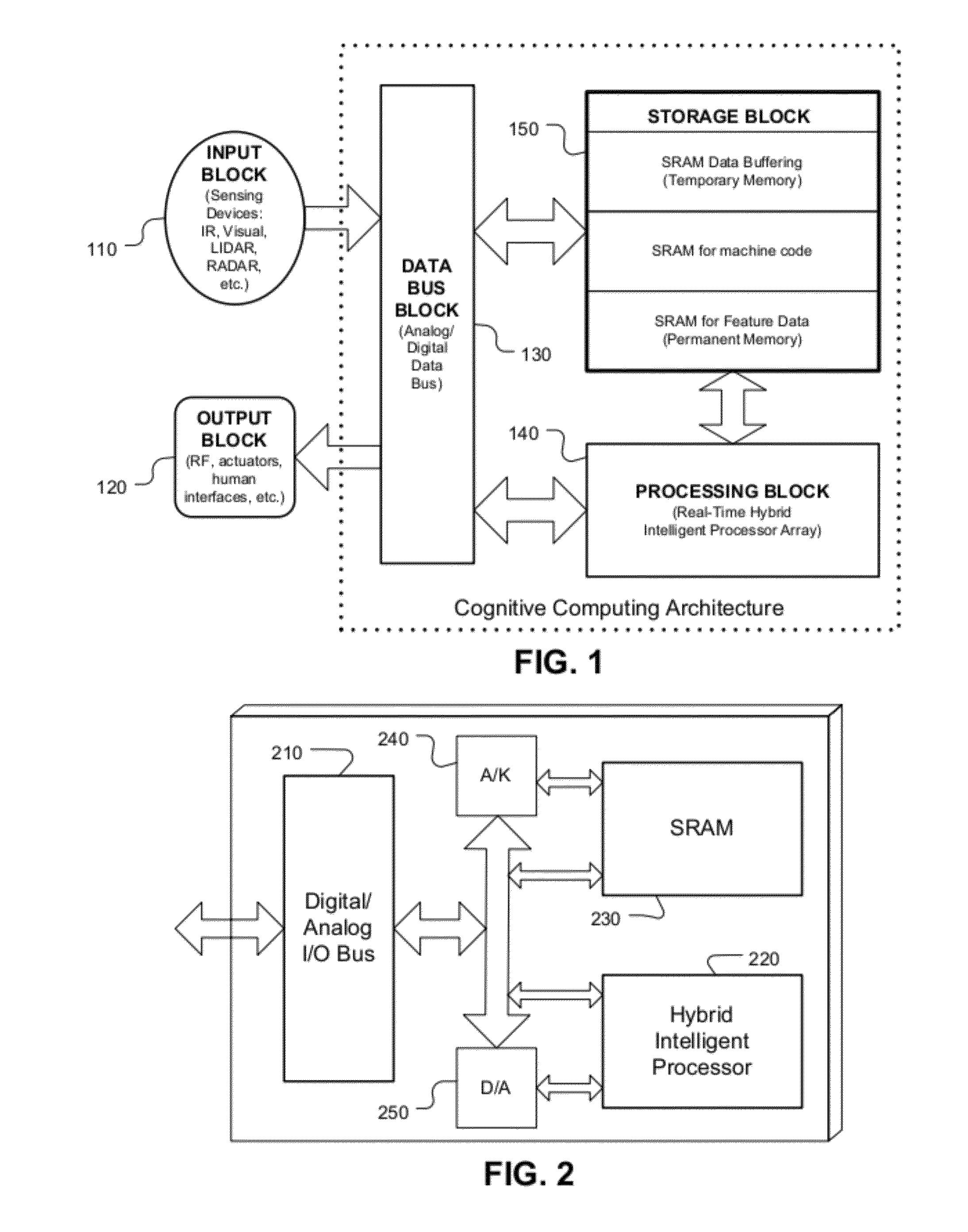
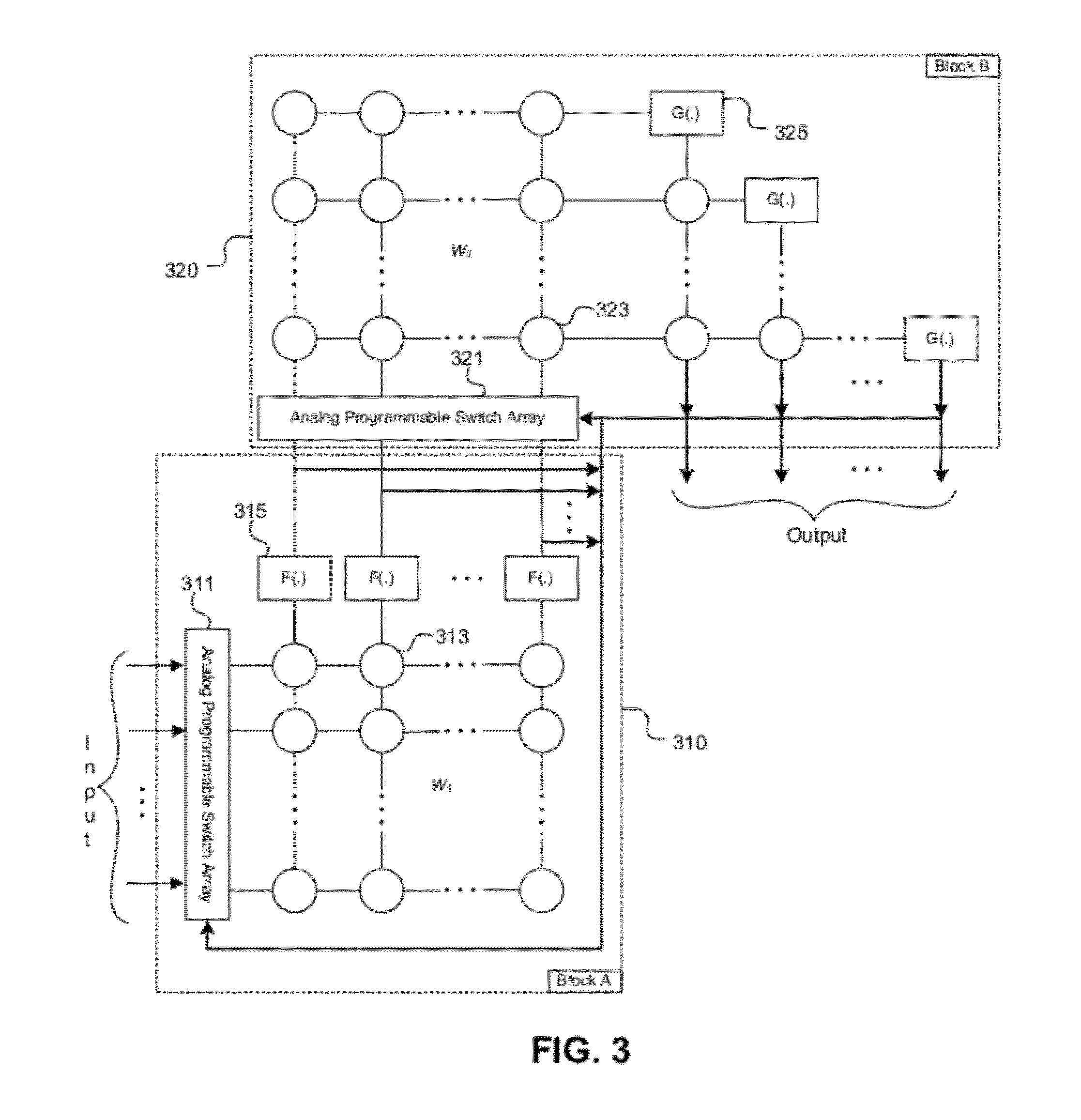
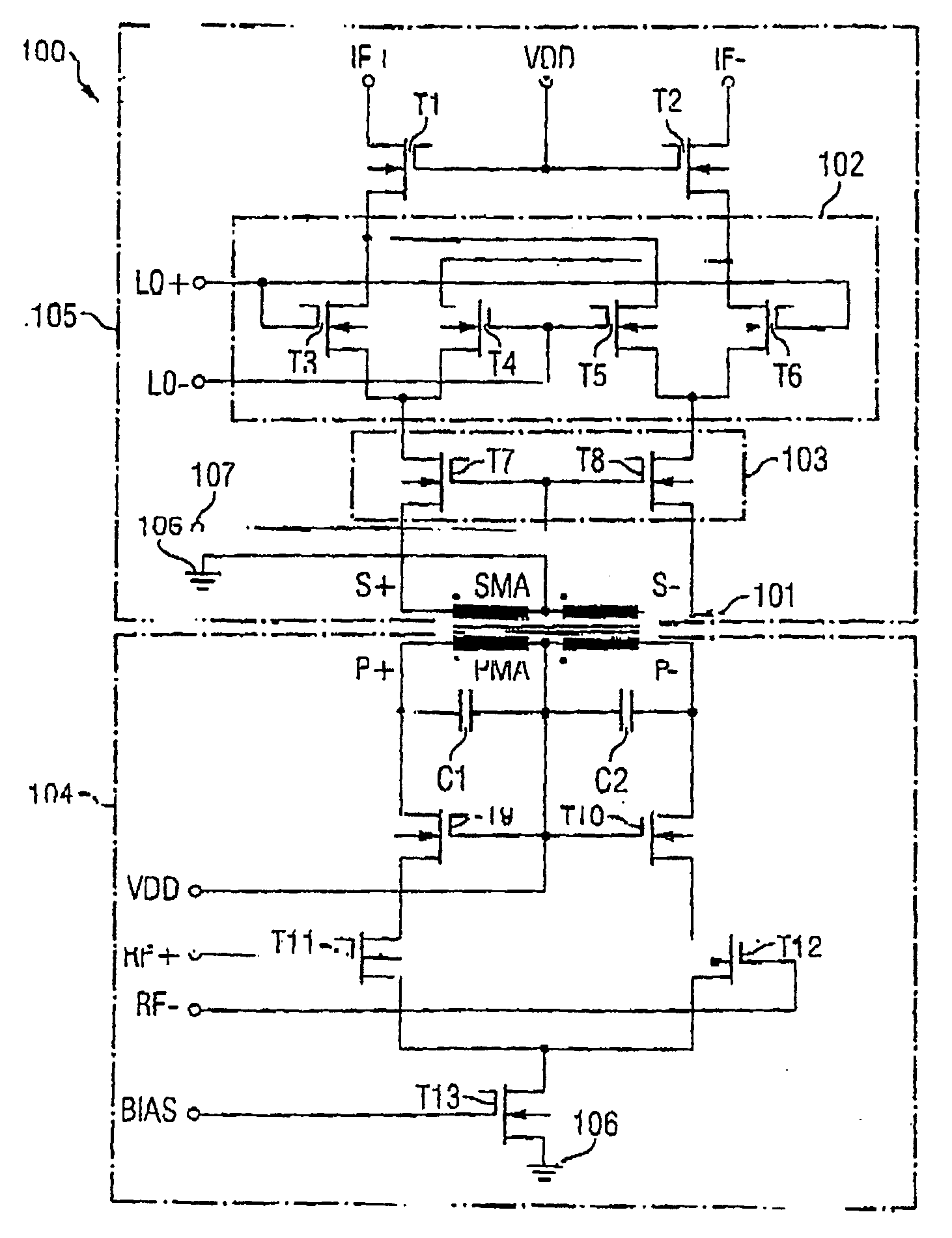
System and method for cognitive processing for data fusion
ActiveUS20120136913A1Computing operations for multiplication/divisionDigital storageAdaptive learningStatic random-access memory
A system and method for cognitive processing of sensor data. A processor array receiving analog sensor data and having programmable interconnects, multiplication weights, and filters provides for adaptive learning in real-time. A static random access memory contains the programmable data for the processor array and the stored data is modified to provide for adaptive learning.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
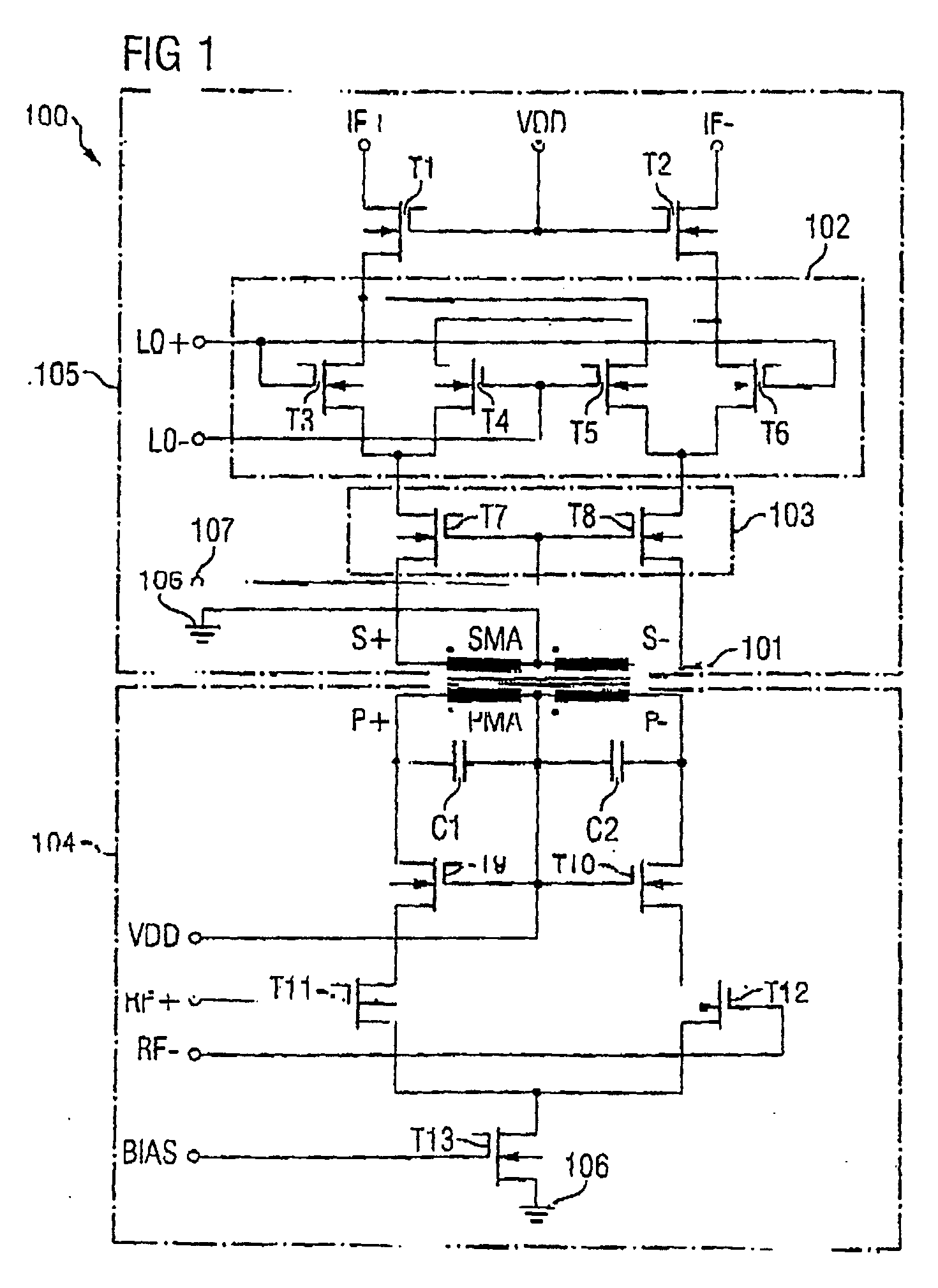
Integrated circuit having a mixer circuit
ActiveUS20050118979A1Reduce stepsLow working voltageModulation transference balanced arrangementsComputations using contact-making devicesTransformerIntermediate frequency
Integrated circuit including a mixer circuit, which has a first circuit section, a second circuit section, and a transformer. The first circuit section has two radiofrequency terminals. The second circuit section has two reference oscillator terminals, an active mixer unit with a signal-amplifying unit, and two intermediate frequency terminals. The active mixer unit and the signal-amplifying unit have a common current path. The transformer directly electrically decouples the two radiofrequency terminals from the active mixer unit, and couples the first circuit section and the second circuit section together such that each of the two circuit sections is separately supplied with a full operating voltage of the integrated circuit. The integrated circuit may additionally include a second transformer connected between the active mixer unit and the two intermediate frequency terminals.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Current mode differential transmission method and system for transmitting three units of data using four signal lines
InactiveUS7508881B2Reduce in quantityChannel dividing arrangementsComputations using contact-making devicesDifferential transmissionEngineering
Provided are a current mode differential transmission method and system for differentially transmitting three units of data using four signal lines. The method includes: dividing the four signal lines 1a, 1b, 2a and 2b into two pairs of signal lines 1a / 1b and 2a / 2b, and differentially transmitting respective data (first data and second data) via the two pairs of signal lines 1a / 1b and 2a / 2b; and transmitting the other data (third data) by differentially changing common mode currents of the two pairs of signal lines 1a / 1b and 2a / 2b.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
Low voltage, low power differential receiver
InactiveUS6970043B2Improves low Vcc performanceReduce jitterComputations using contact-making devicesComputing operations for multiplication/divisionLow voltageLow jitter
A folded common cascode circuit with symmetric parallel signal paths from the differential inputs to a single ended output provides a low skew, low jitter, low power, high speed differential amplifier. The signal paths on either side of the differential amplifier are made equal with equal loads along each path. Pairs of complementary NMOS and PMOS transistor pairs with parallel complementary biasing current mirroring stacks on the cascode circuitry have all their gates connected together. The layout maintains symmetrical parallel signal paths and symmetrical amplification and impedance loading from differential input to output. Output inverters provide a higher drive capability.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Analog multiplier using a memristive device and method for implemening hebbian learning rules using memrisor arrays
ActiveUS20140289179A1Digital computer detailsComputing operations for multiplication/divisionBinary multiplierAlgorithm
A device, comprising: an array of cells, wherein the cells are arranged in columns and rows; wherein each cell comprises a memristive device; an interfacing circuit that is coupled to each cell of the array of cells; wherein the interfacing circuit is arranged to: receive or generate first variables and second variables; generate memristive device input signals that once provided to memristive devices of the array will cause a change in a state variable of each of the memristive devices of the cells of the array, wherein the change in the state variable of each of the memristive devices of the cells of array reflects a product of one of the first variables and one of the second variables; provide the memristive device input signals to memristive devices of the array; and receive output signals that are a function of at least products of the first variables and the second variables;
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
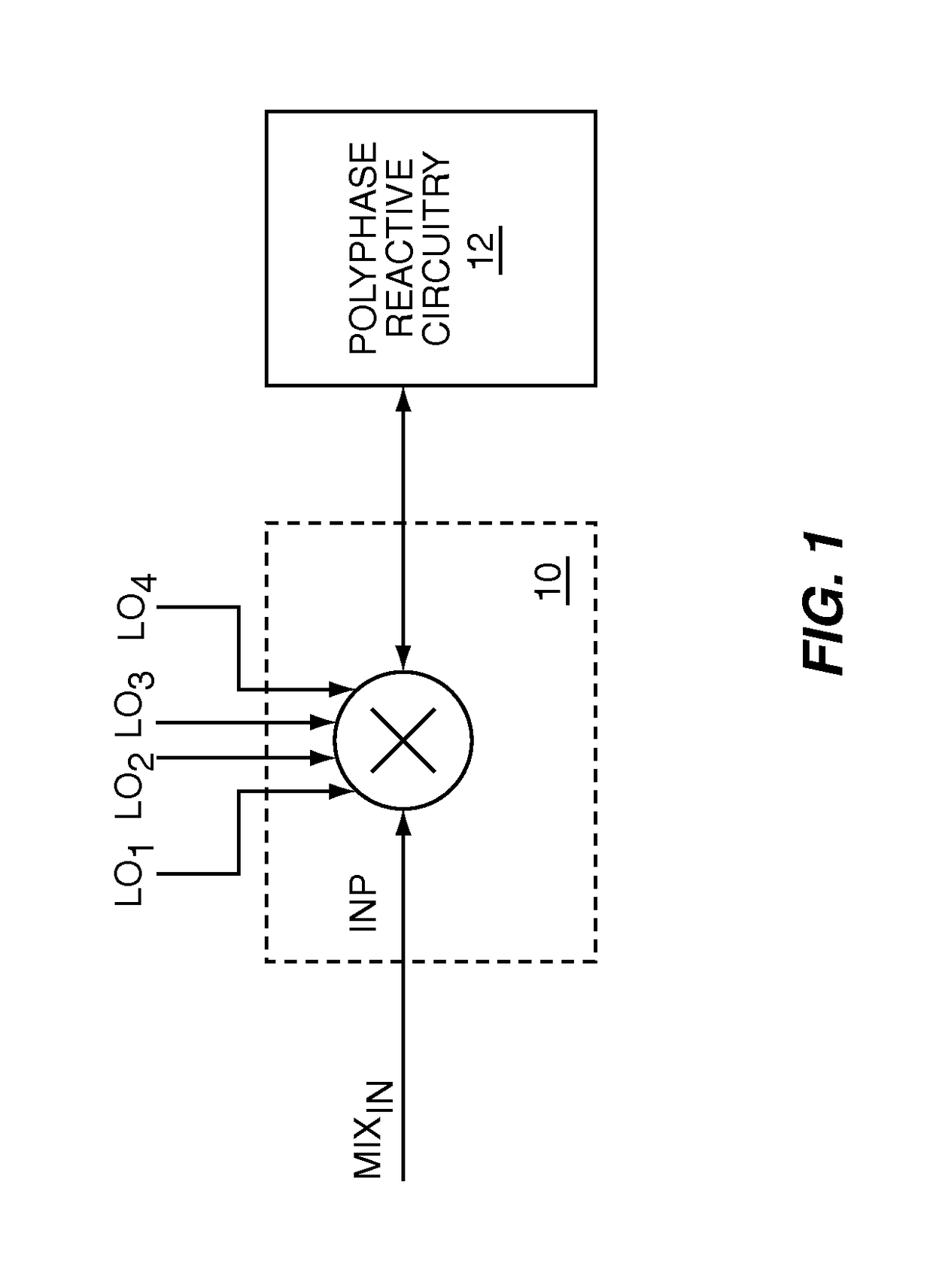
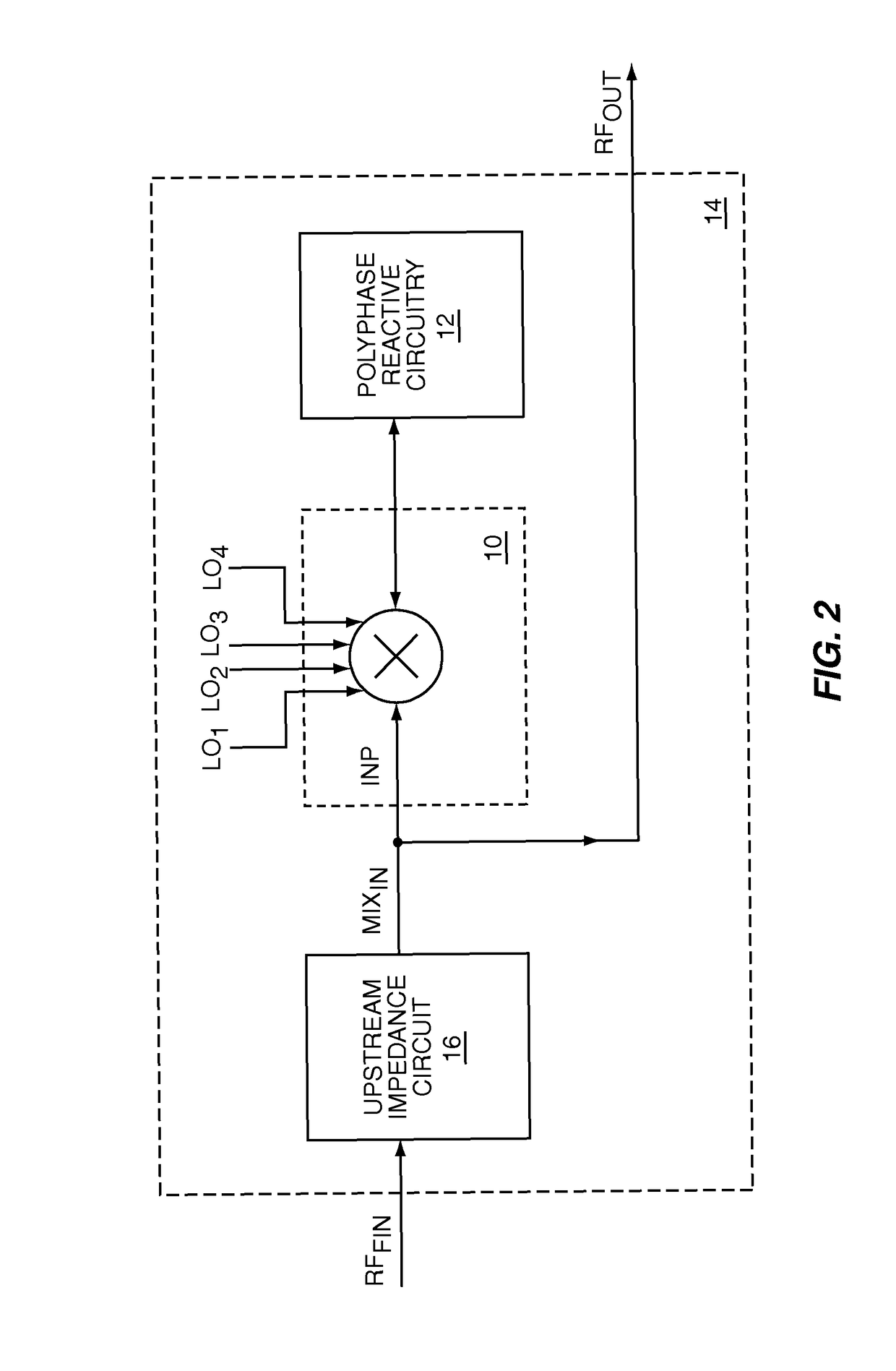
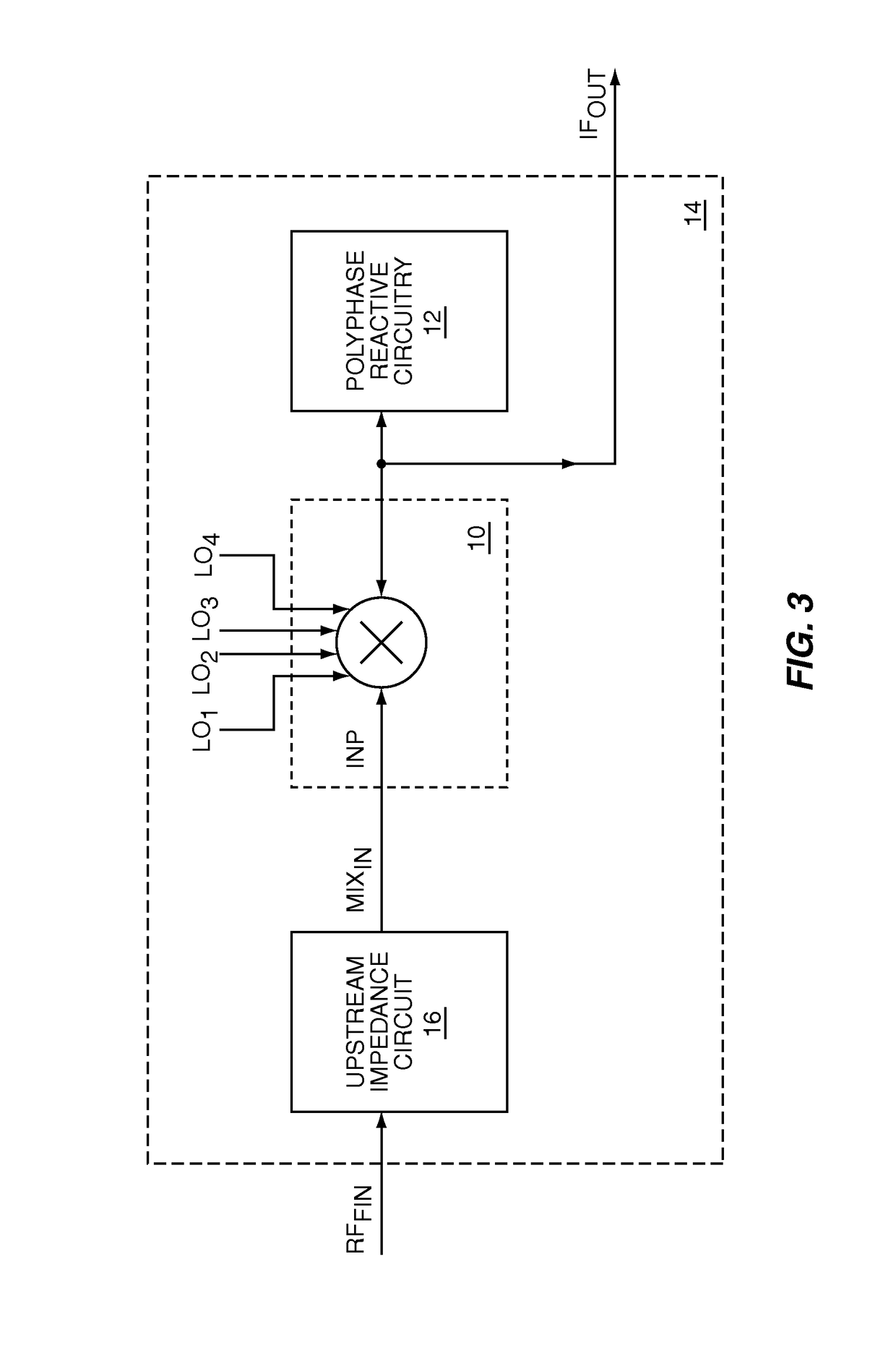
Controllable input impedance radio frequency mixer
ActiveUS8121577B1Improve receiver selectivityMaximize energy transferComputations using contact-making devicesSingle output arrangementsImpedance responseBandpass filtering
The present invention is a controllable input impedance RF mixer, which when fed from a high impedance source, such as a current source, provides a high quality factor (Q) impedance response associated with an impedance peak. The high-Q impedance response may be used as a high-Q RF bandpass filter in a receive path upstream of down conversion, which may improve receiver selectivity and replace surface acoustic wave (SAW) or other RF filters. The present invention uses polyphase reactive circuitry, such as capacitive elements, coupled to the down conversion outputs of an RF mixer. The RF mixer mixes RF input signals with local oscillator signals to translate the impedance of the polyphase reactive circuitry into the RF input impedance of the RF mixer. The RF input impedance includes at least one impedance peak. The local oscillator signals are non-overlapping to maximize the energy transferred to the polyphase reactive circuitry.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Digital delay-locked loop circuits with hierarchical delay adjustment
InactiveUS6982578B2Computations using contact-making devicesPulse automatic controlPhase differenceDigital delay locked loop
Fine tuned signal phase adjustments are provided by multiple cascaded phase mixers. Each phase mixer outputs a signal having a phase between the phases of its two input signals. With each subsequent stage of phase mixers, the signals generated by the phase mixers have a smaller phase difference, thereby providing finer delay adjustments. Multiple stages of phase mixers can be provided in digital delay-locked loop circuitry to provide additional hierarchical delay adjustment.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Quadrature radio frequency mixer with low noise and low conversion loss
ActiveUS20090174459A1Modulation transferenceComputations using contact-making devicesLow noiseSignal on
In one embodiment of the invention, a method for convolution of signals is disclosed including generating four phased half duty cycle clocks each being out of phase by a multiple of ninety degrees from the others; coupling the four phased half duty cycle clocks into a four phase half duty cycle mixer; and switching switches in the four phase half duty cycle mixer in response to the four phased half duty cycle clocks to convolve a differential input signal with the four phased half duty cycle clocks to concurrently generate a differential in-phase output signal and a differential quadrature-phase output signal on a dual differential output port.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Popular searches
Conveying record carriers Substation equipment Transmission Electrical apparatus casings/cabinets/drawers Support structures on hinges/pivots Oscillations generators Amplitude to angle modulation conversion Angle demodulation by oscillations sampling Differential amplifiers Amplification control details
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com