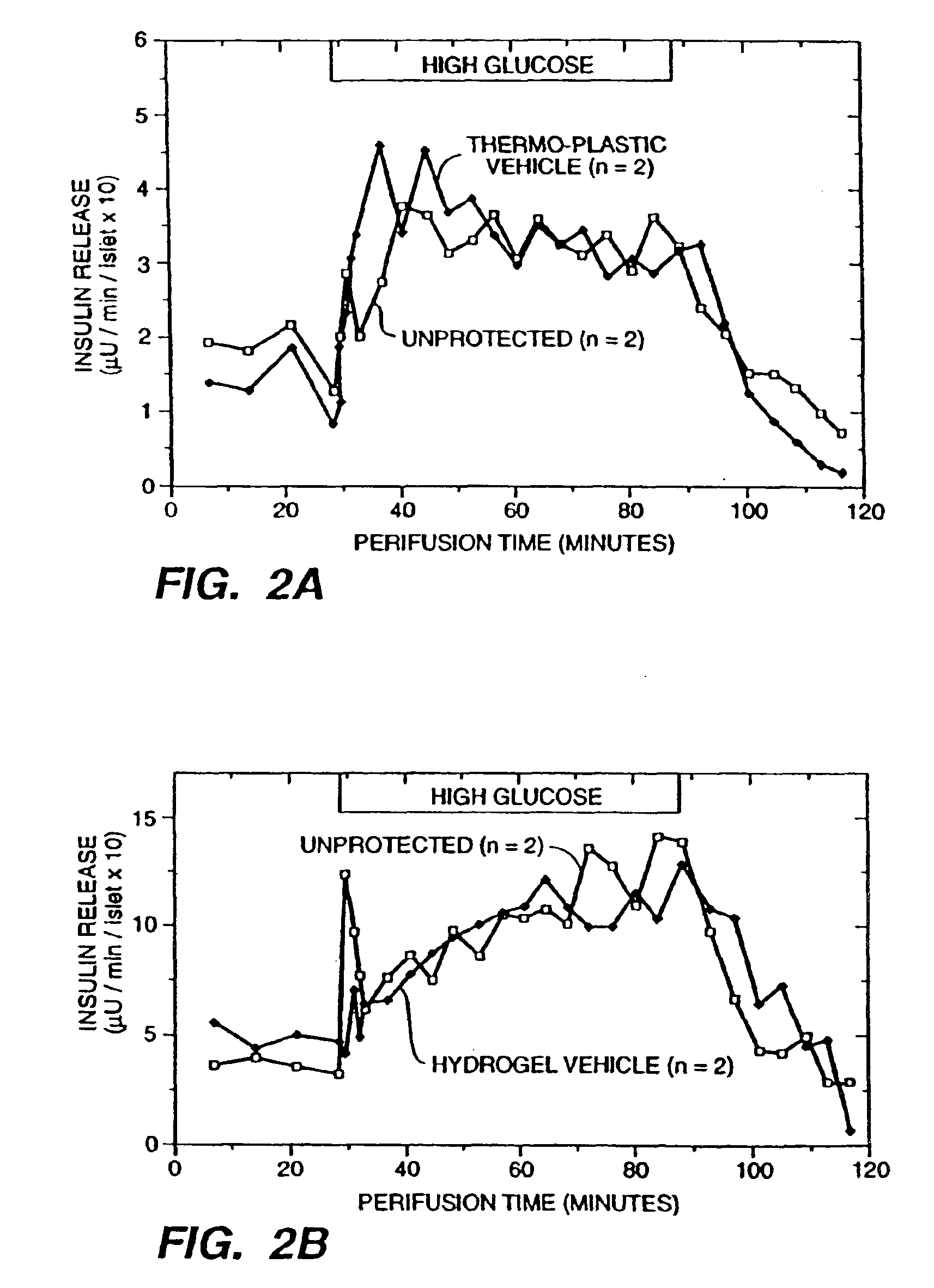
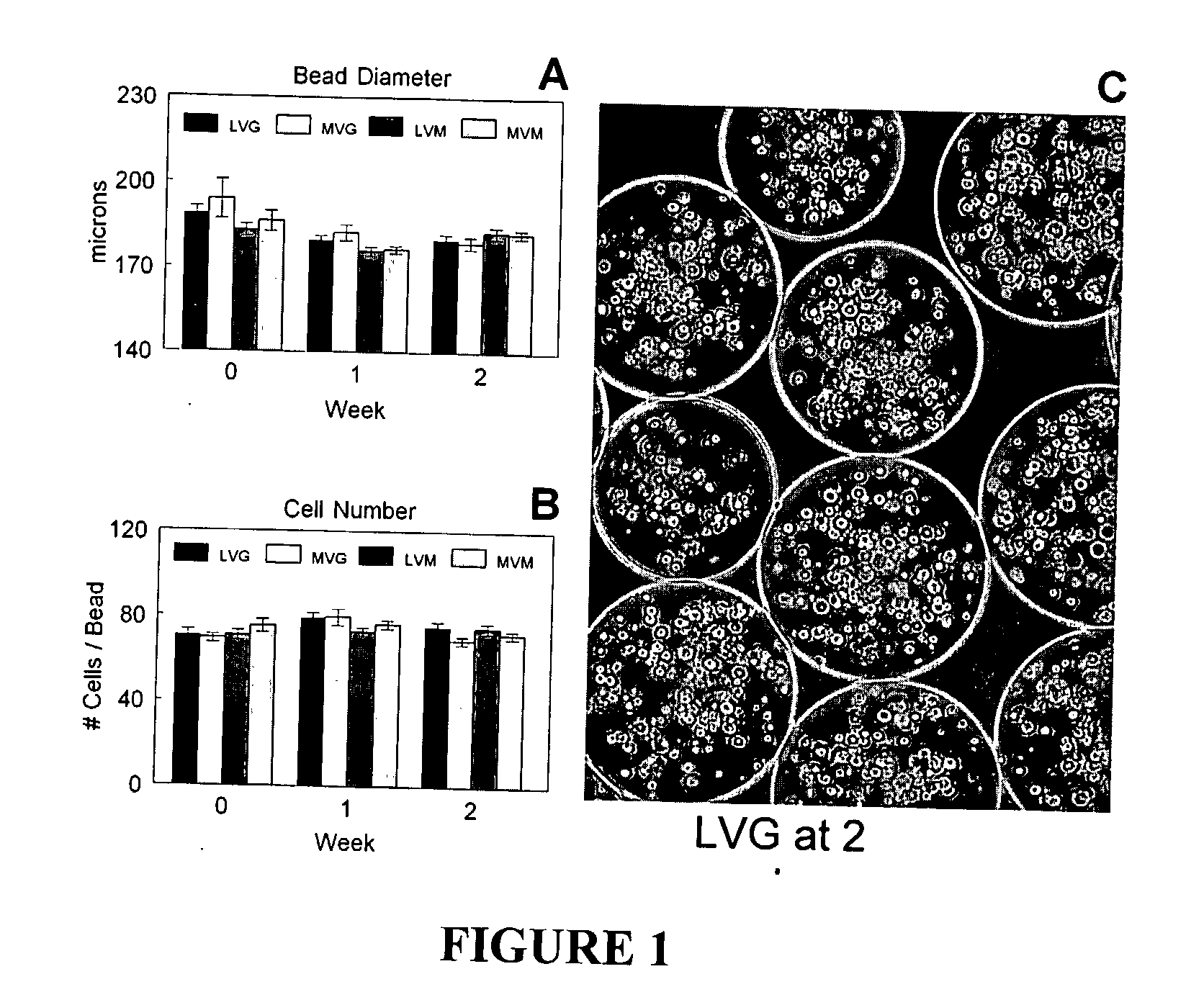
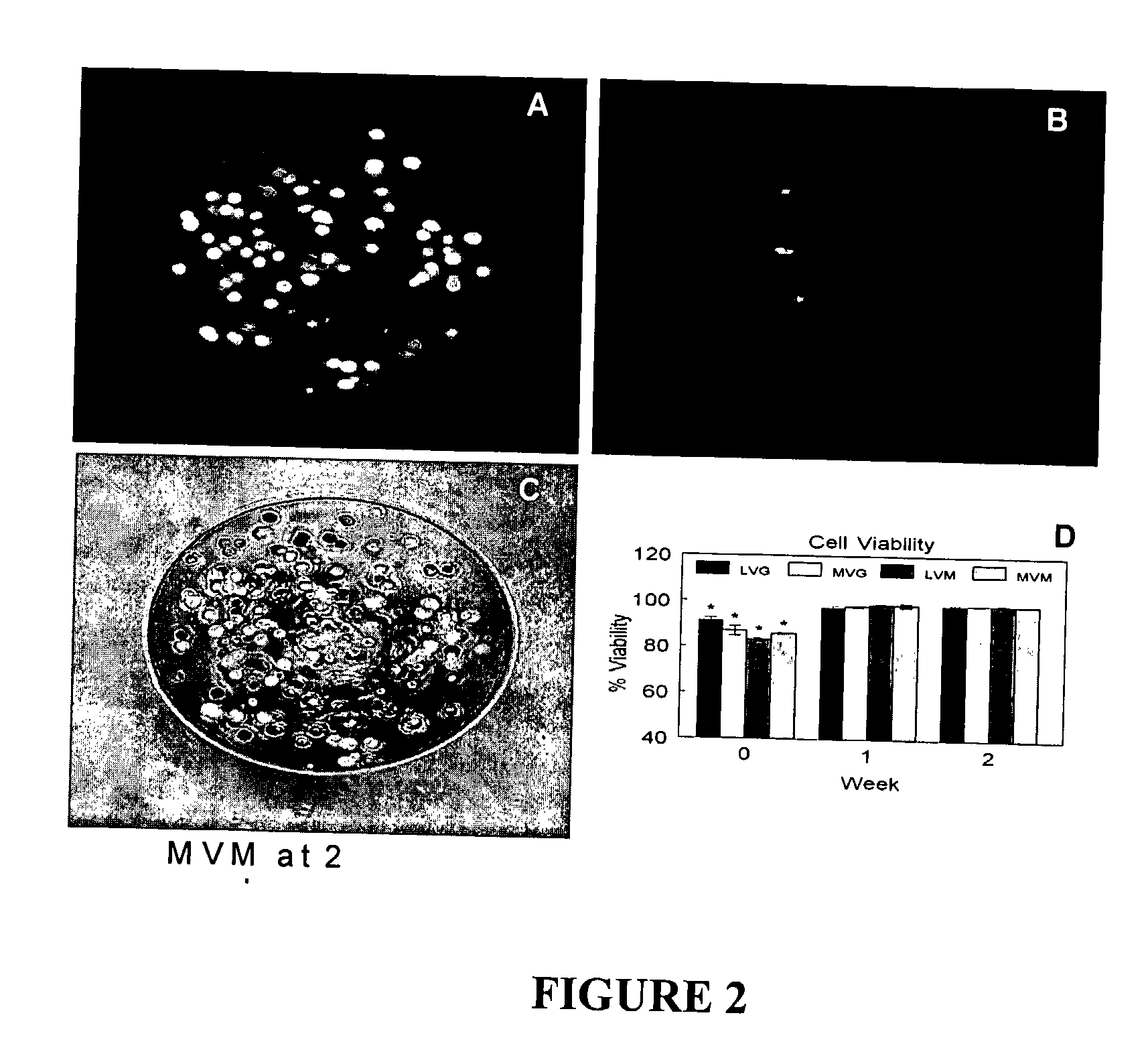
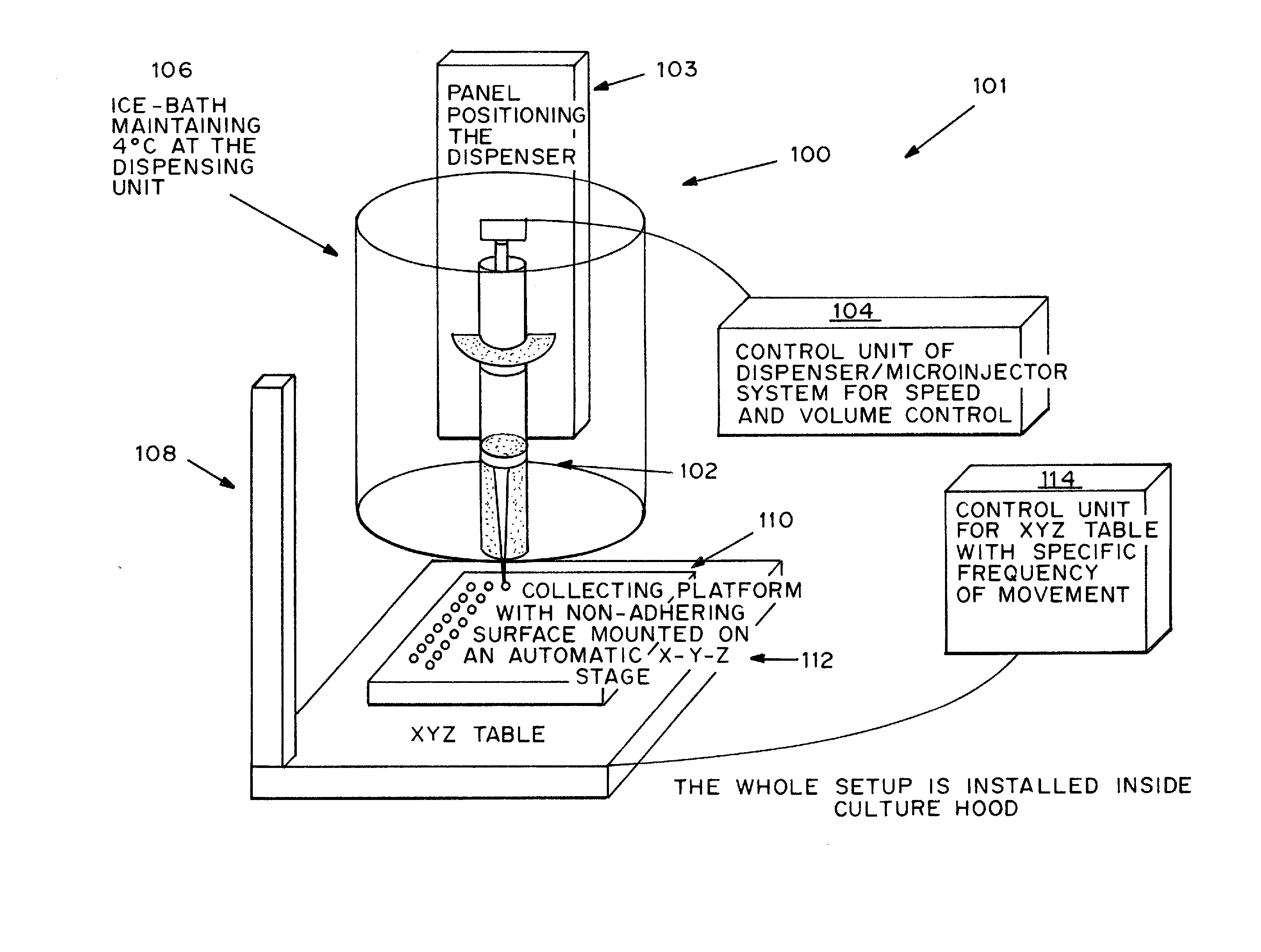
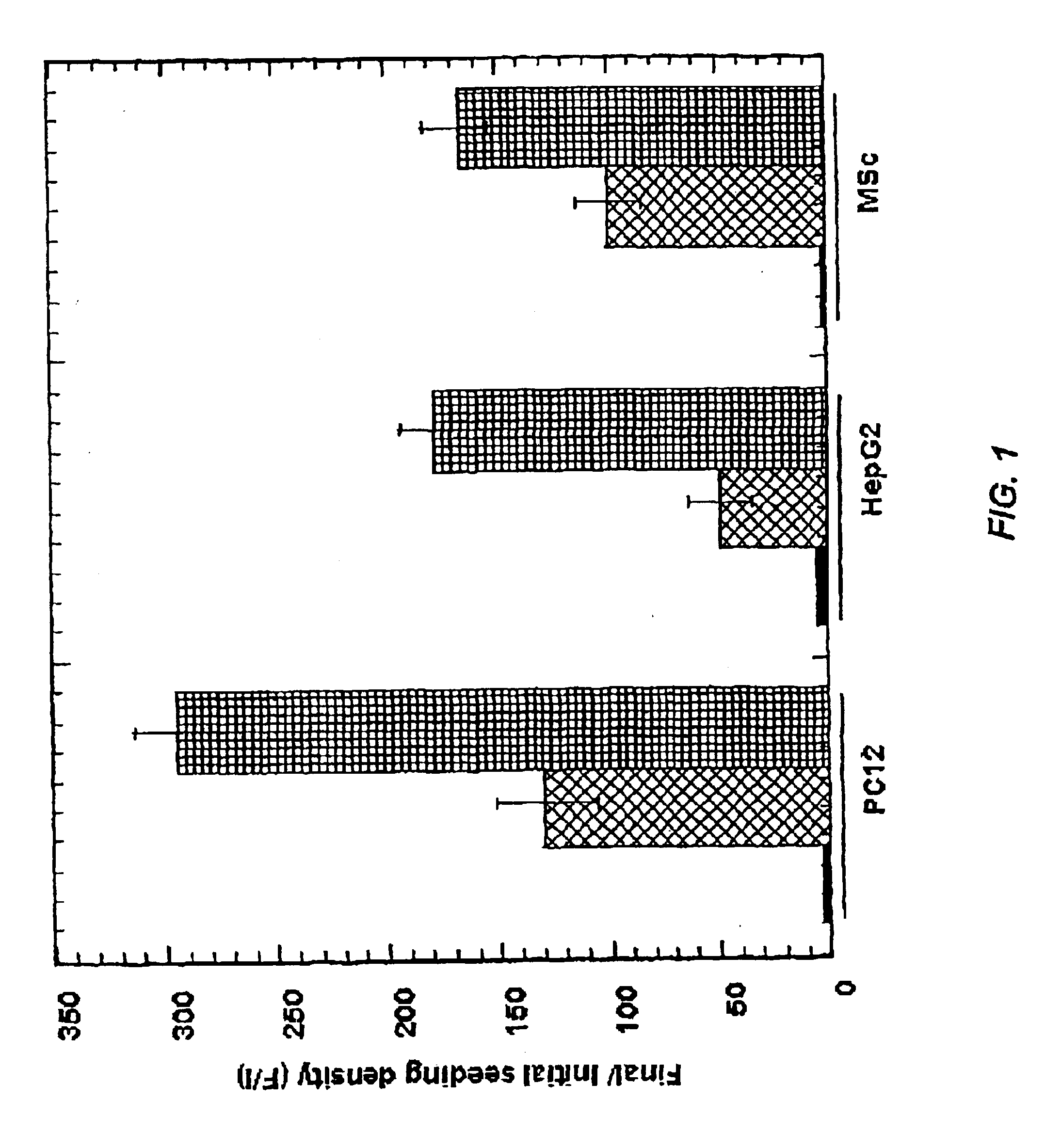
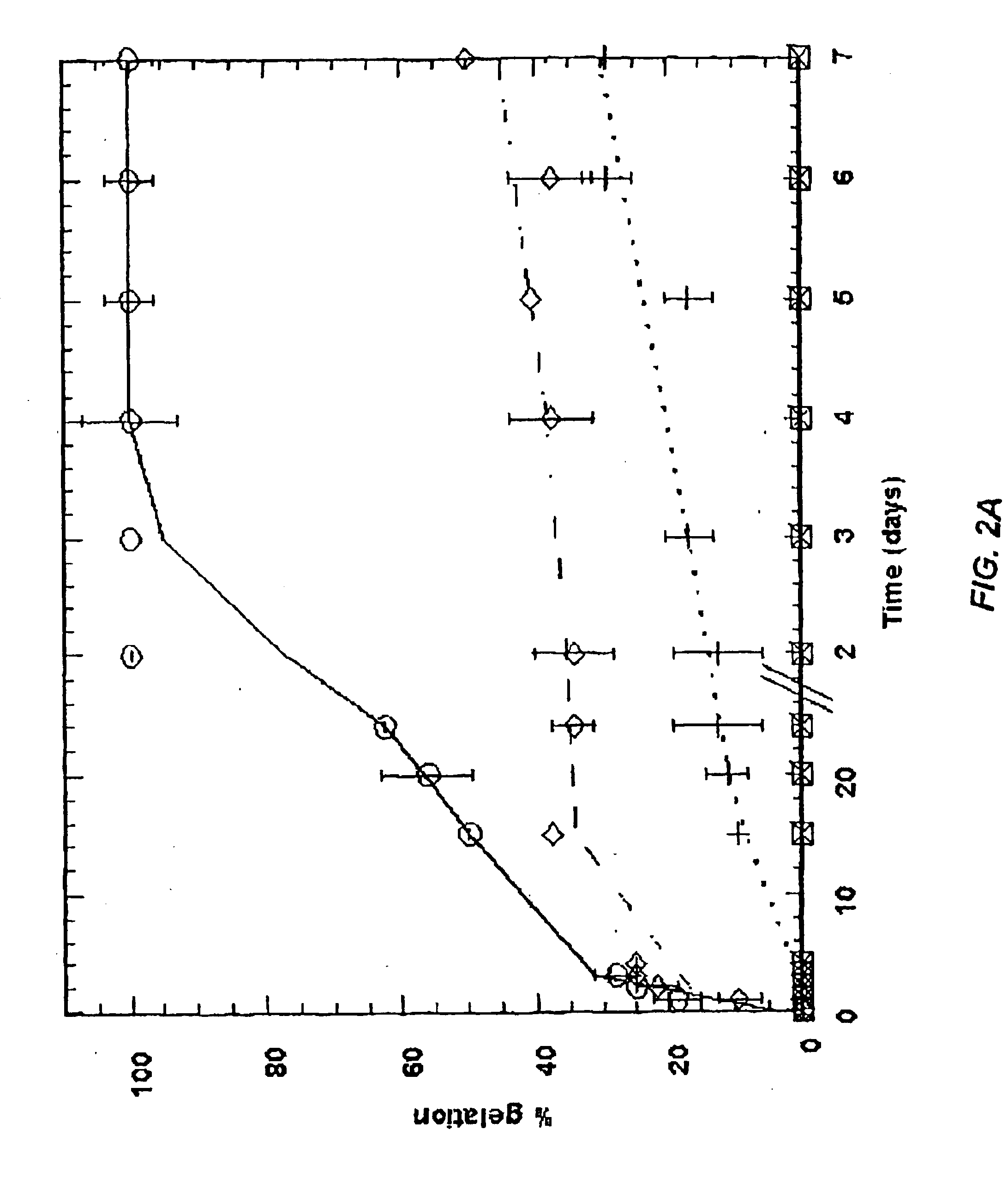
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
210results about "Cell encapsulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
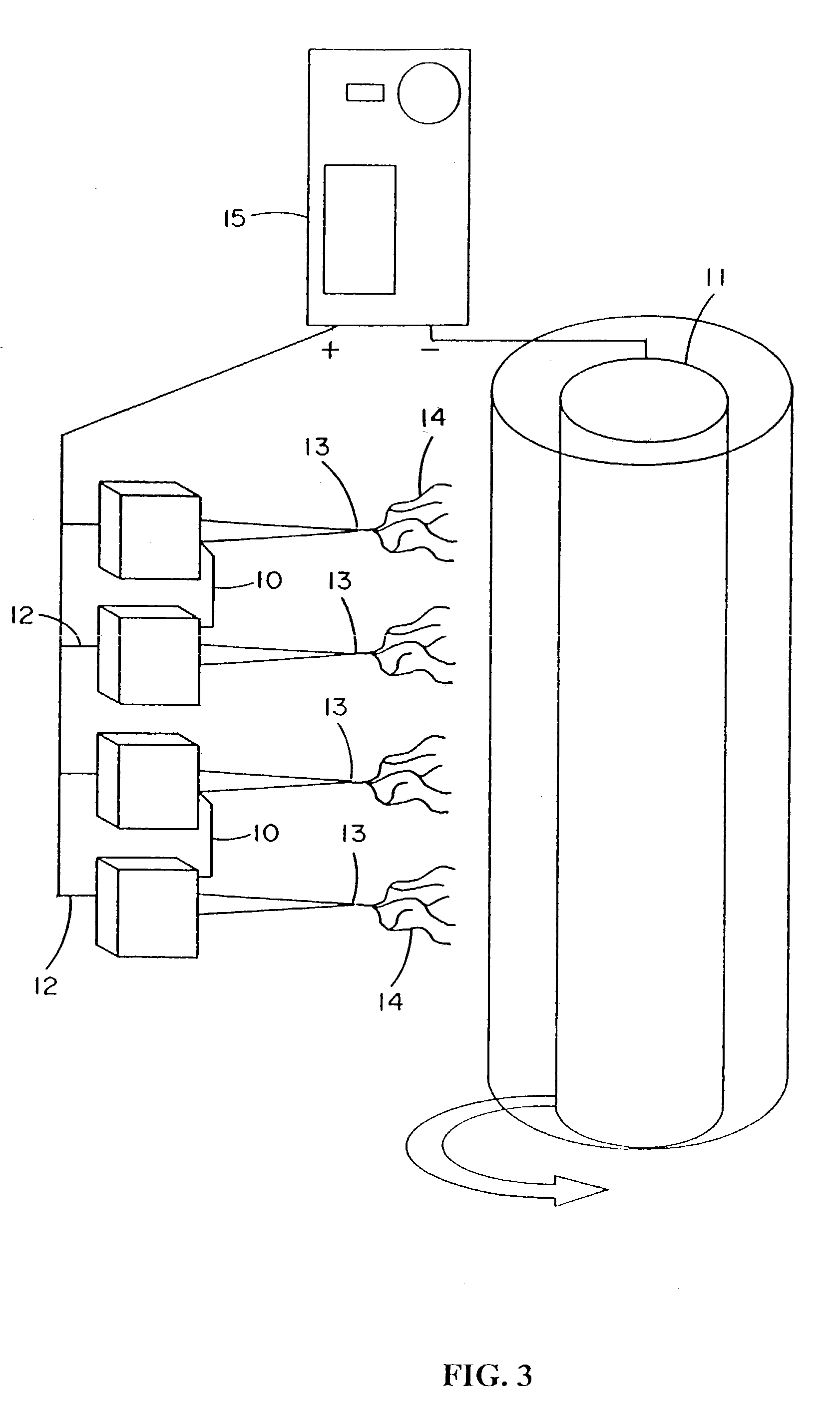
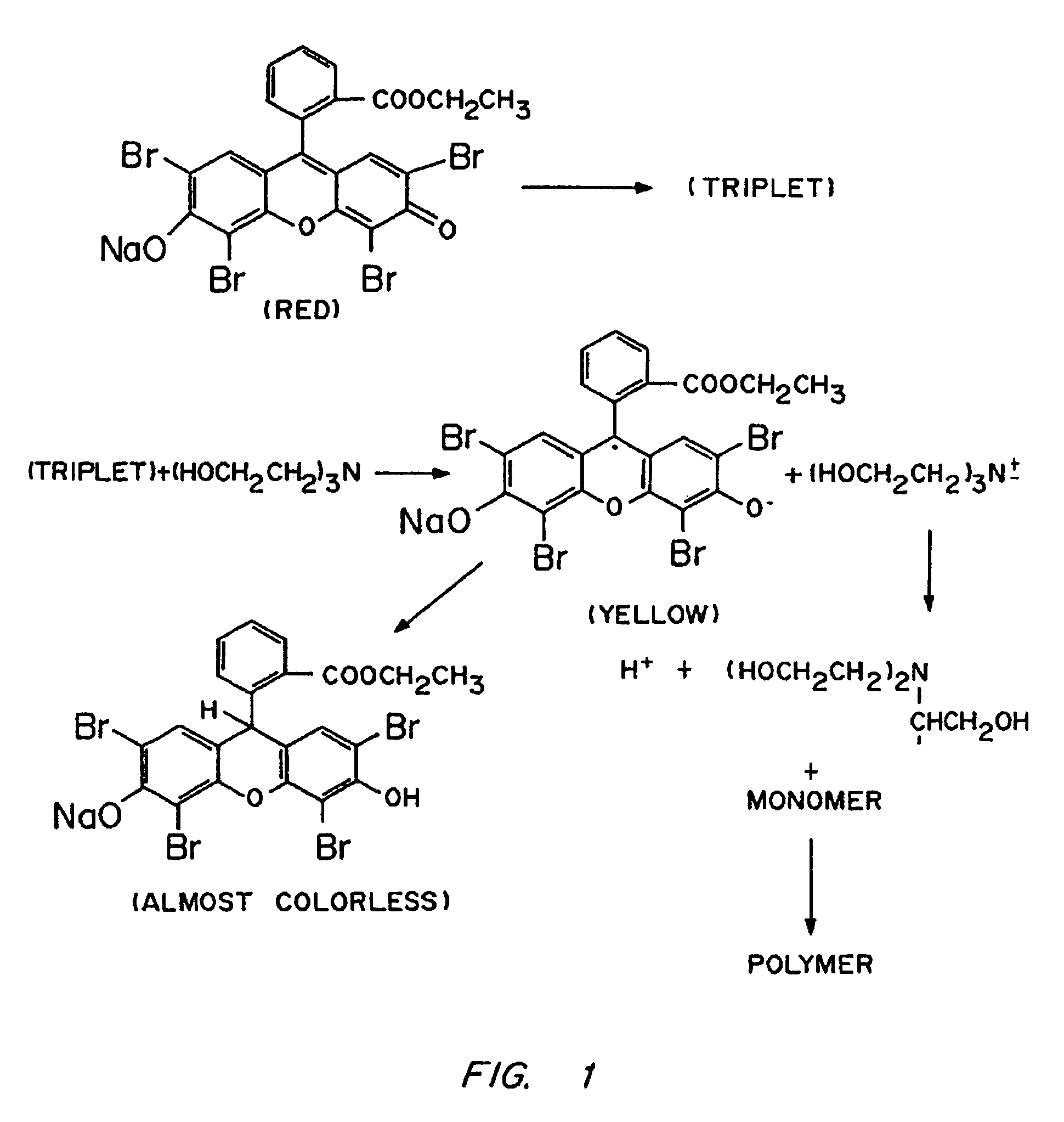
Photopolymerizable biodegradable hydrogels as tissue contacting materials and controlled-release carriers
InactiveUS6306922B1Fast gelationRapid polymerizationImmobilised enzymesPowder deliveryThermal energyUltraviolet lights
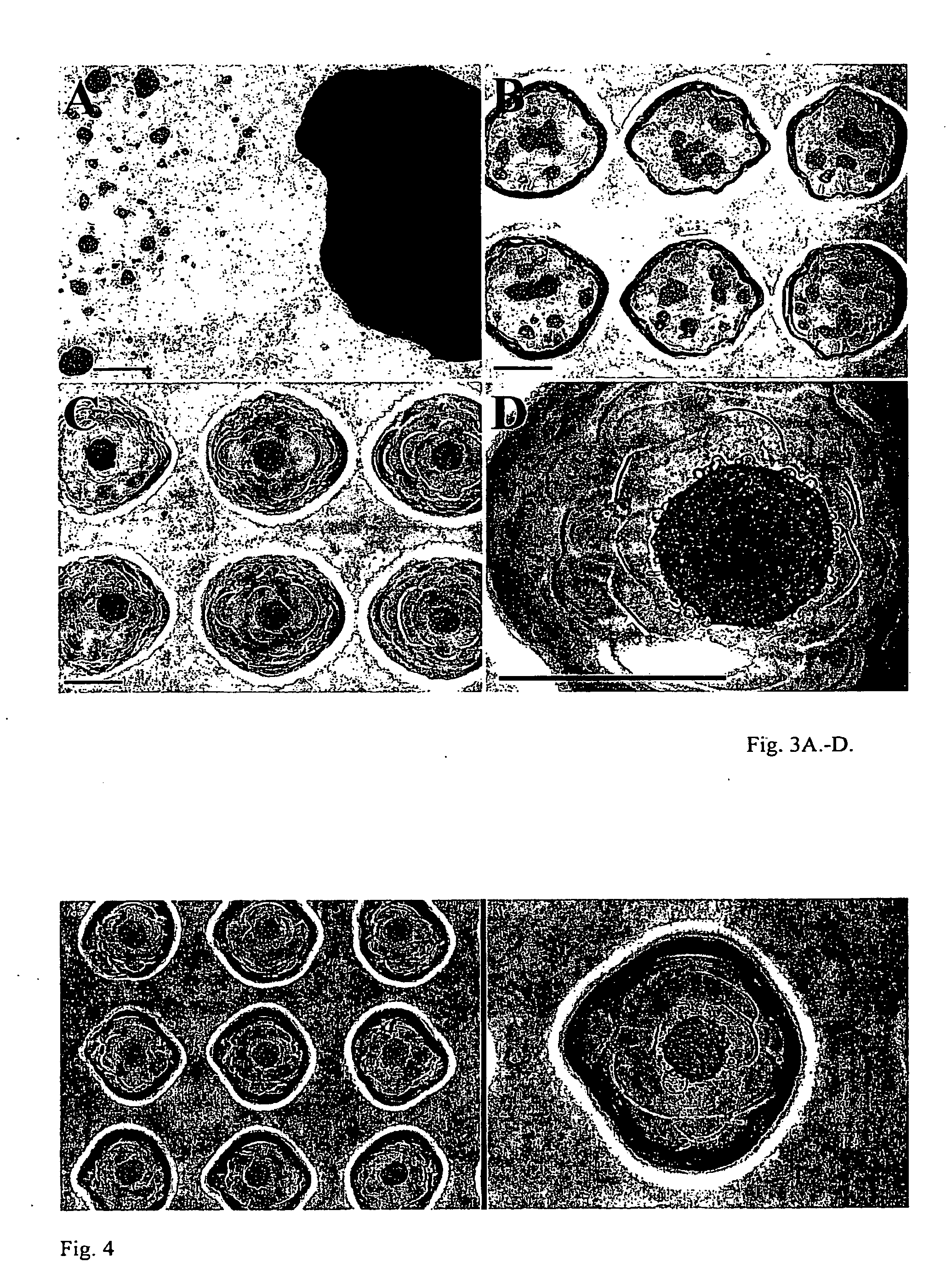
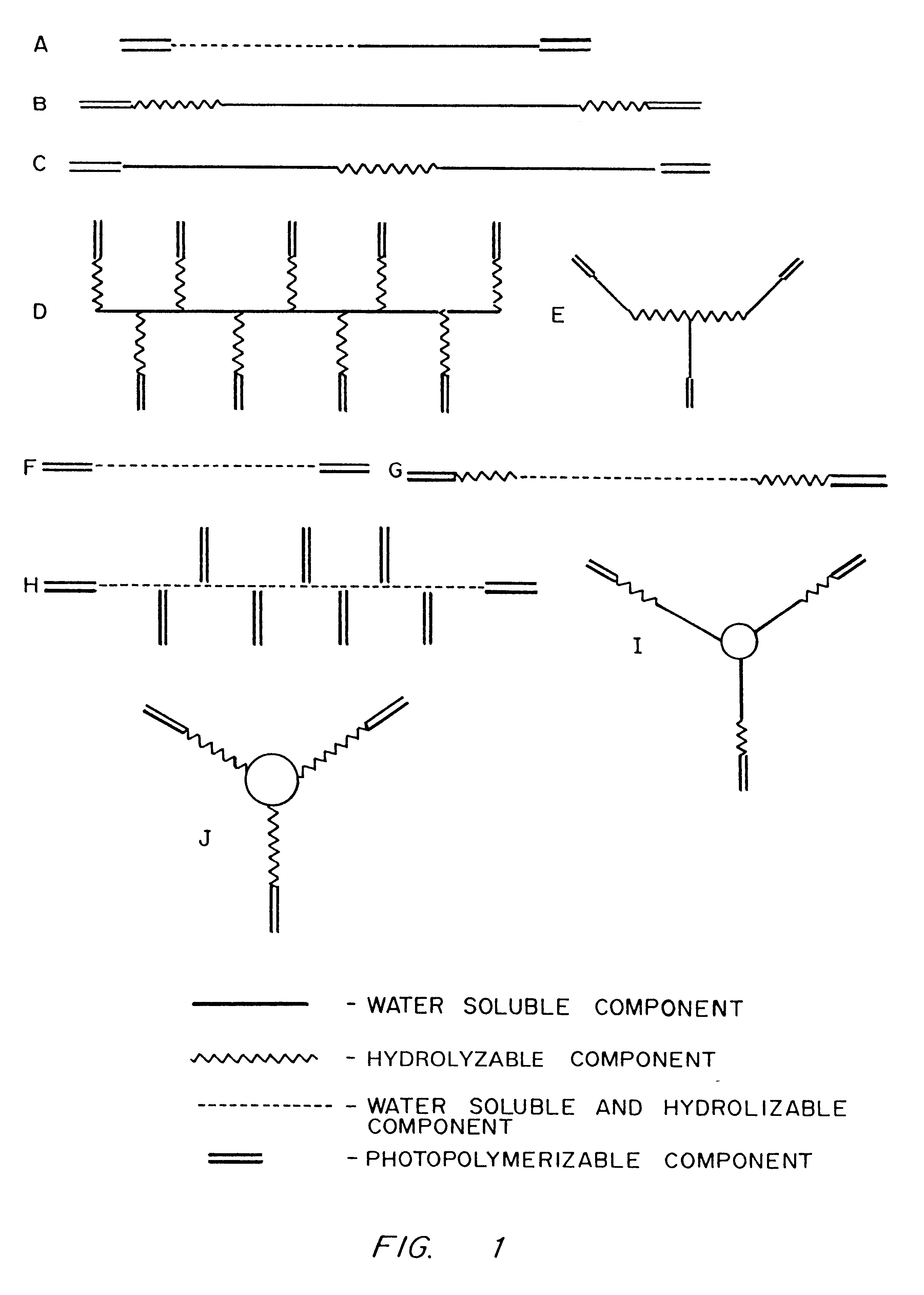
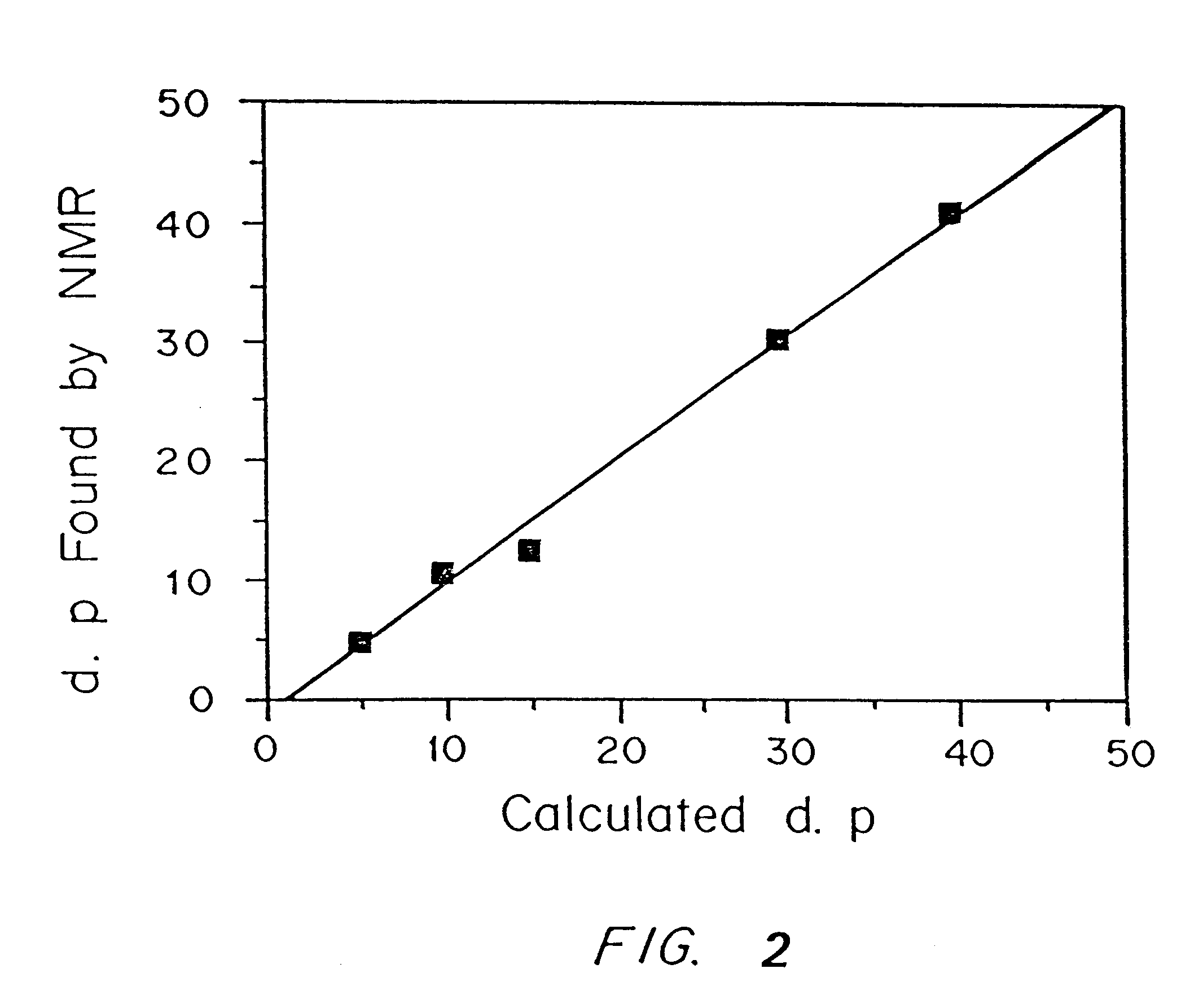
Hydrogels of polymerized and crosslinked macromers comprising hydrophilic oligomers having biodegradable monomeric or oligomeric extensions, which biodegradable extensions are terminated on free ends with end cap monomers or oligomers capable of polymerization and cross linking are described. The hydrophilic core itself may be degradable, thus combining the core and extension functions. Macromers are polymerized using free radical initiators under the influence of long wavelength ultraviolet light, visible light excitation or thermal energy. Biodegradation occurs at the linkages within the extension oligomers and results in fragments which are non-toxic and easily removed from the body. Preferred applications for the hydrogels include prevention of adhesion formation after surgical procedures, controlled release of drugs and other bioactive species, temporary protection or separation of tissue surfaces, adhering of sealing tissues together, and preventing the attachment of cells to tissue surfaces.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS
Multi-layer cell encapsulation for tissue engineering
A multi-layered microcapsule has an inner extracellular matrix and an outer shell. The inner extracellular matrix includes a first inner layer of biopolymer and a second intermediate layer of polymer that provides partial immune-protection and holds the first layer in place. The outer shell can form an exoskeleton to provide mechanical stability. Each of the individual layers can be varied to optimize mechanical stability, cell function, and immuno-protection.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
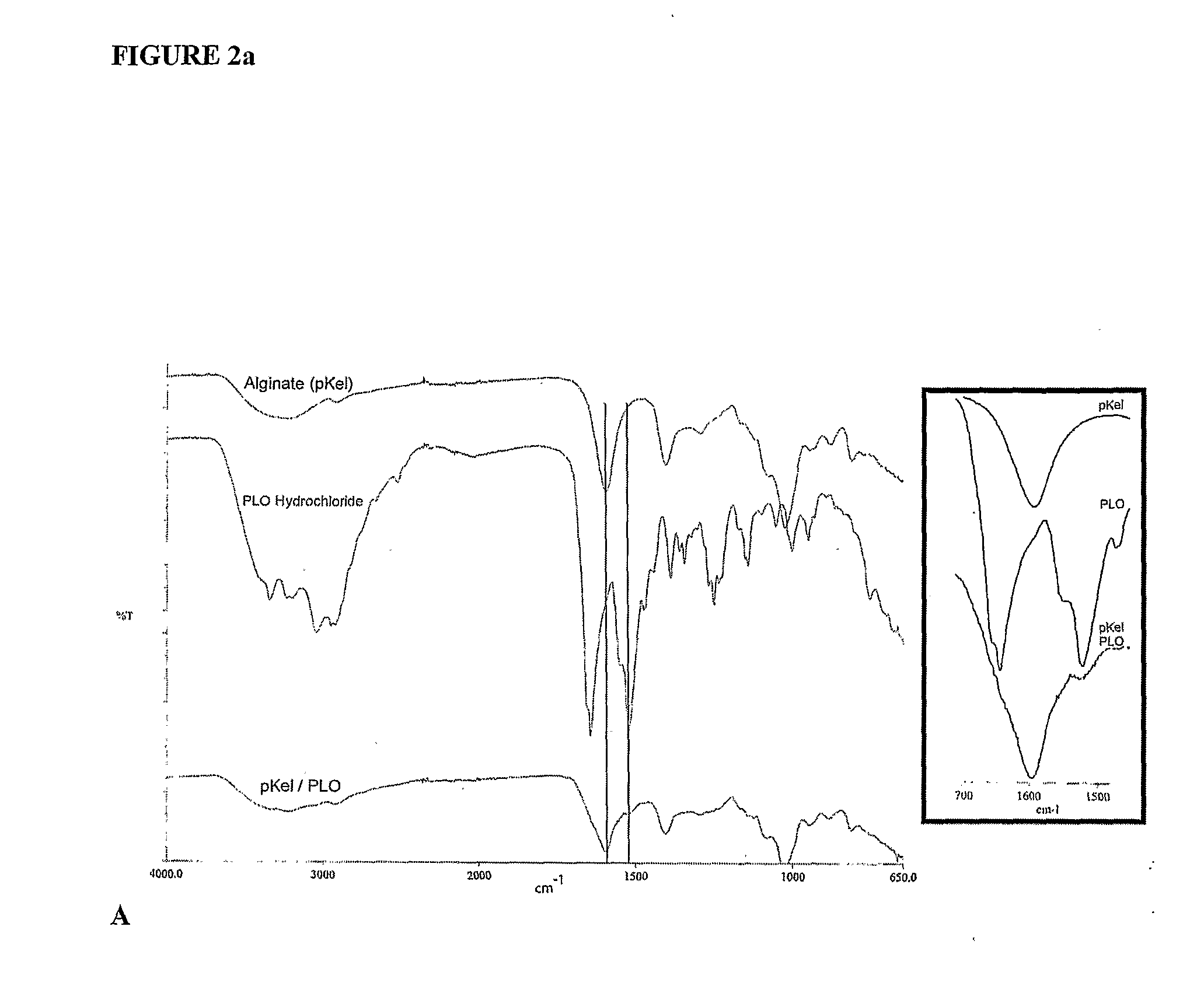
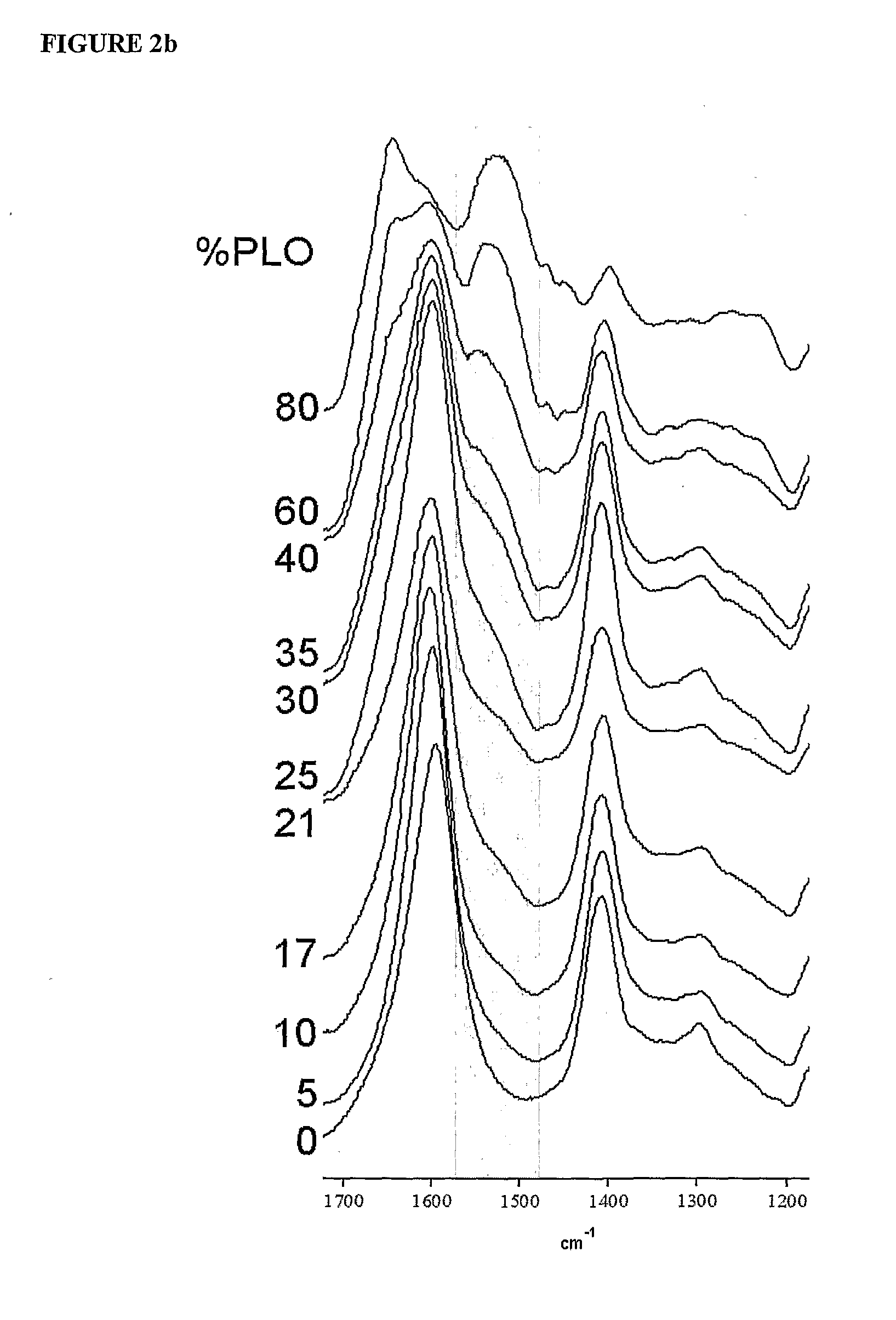
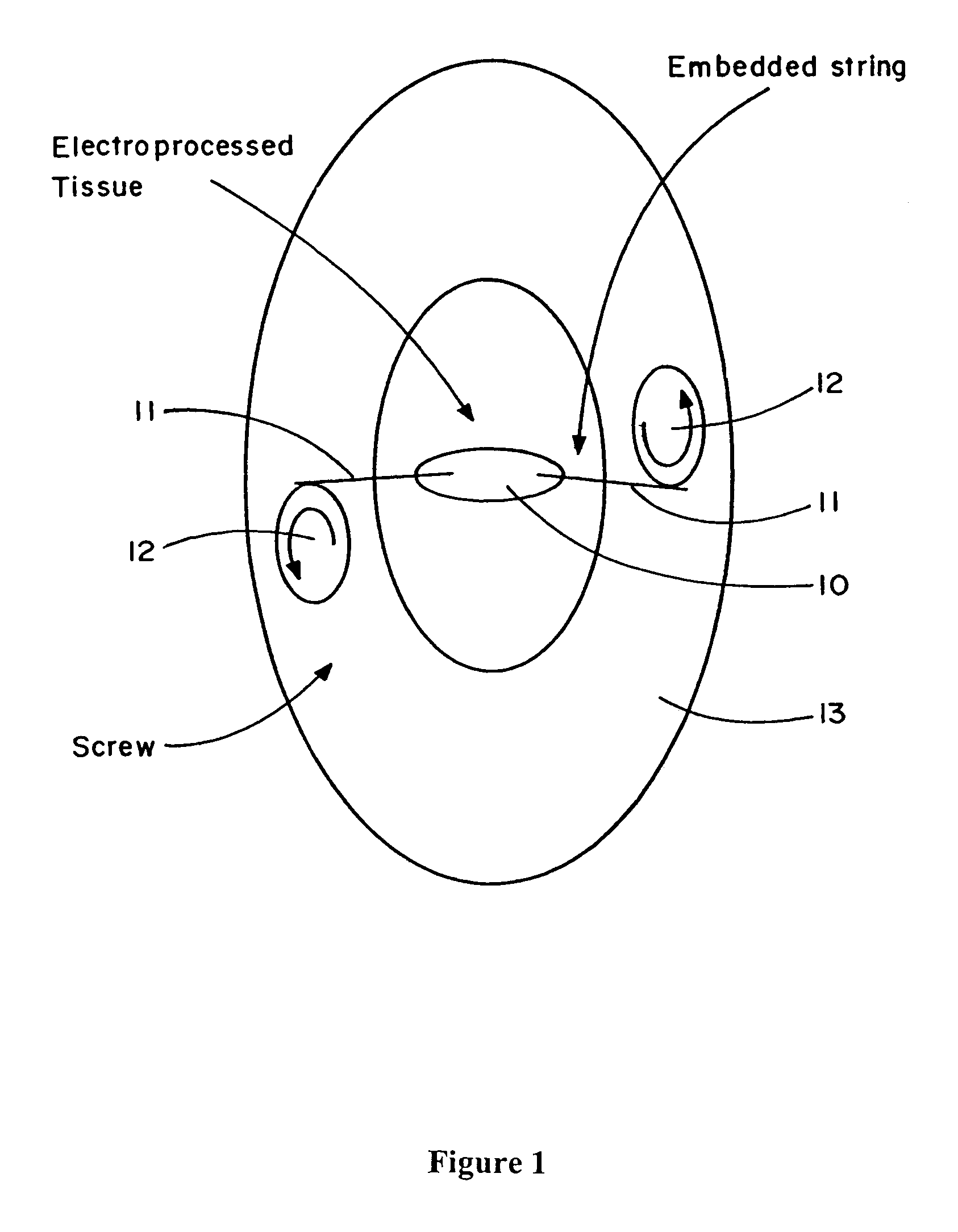
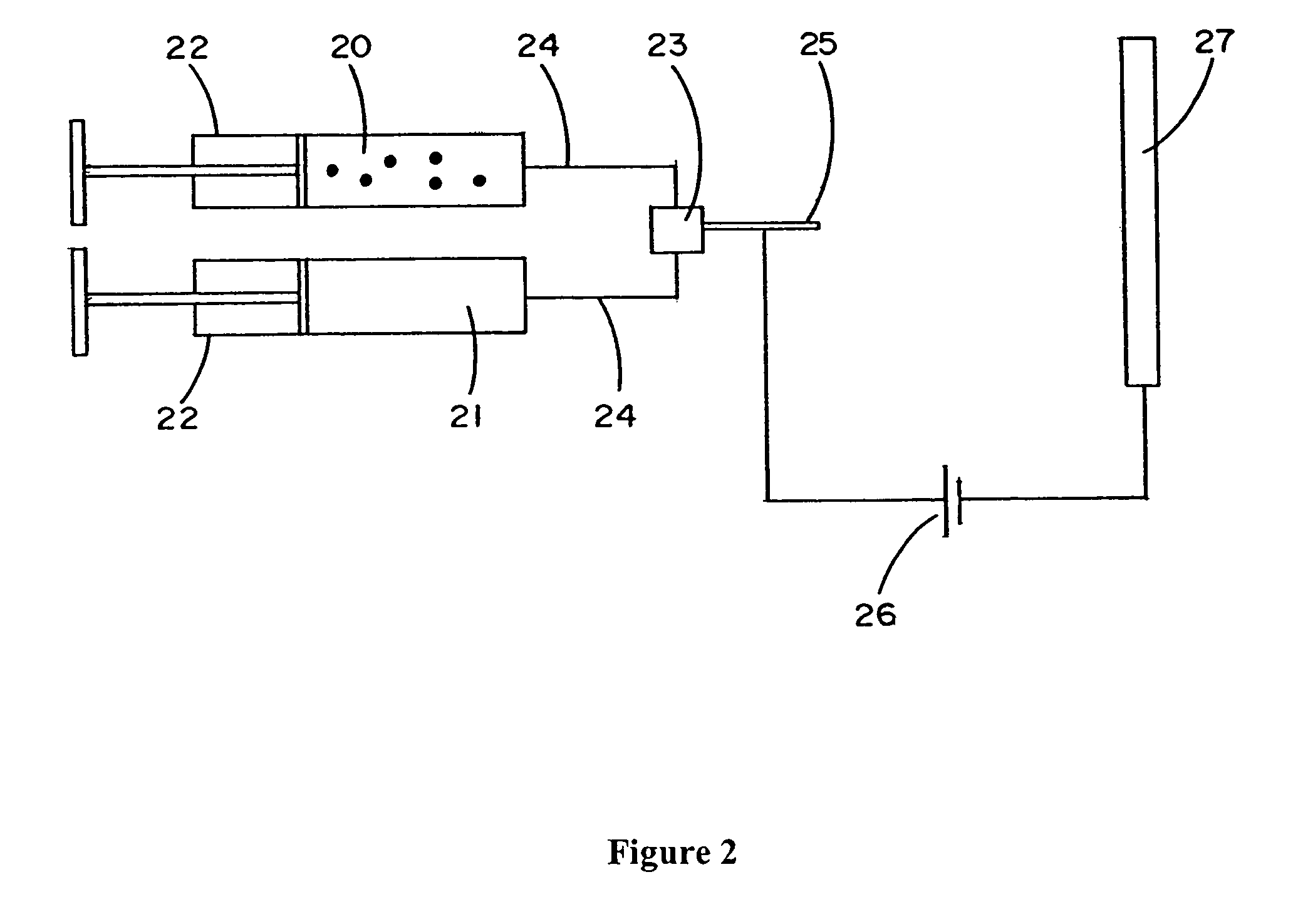
Electroprocessed collagen and tissue engineering
InactiveUS7615373B2Monocomponent protein artificial filamentPeptide/protein ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
The invention is directed to formation and use of electroprocessed collagen, including use as an extracellular matrix and, together with cells, its use in forming engineered tissue. The engineered tissue can include the synthetic manufacture of specific organs or tissues which may be implanted into a recipient. The electroprocessed collagen may also be combined with other molecules in order to deliver substances to the site of application or implantation of the electroprocessed collagen. The collagen or collagen / cell suspension is electrodeposited onto a substrate to form tissues and organs.
Owner:ORGANOGENESIS +1
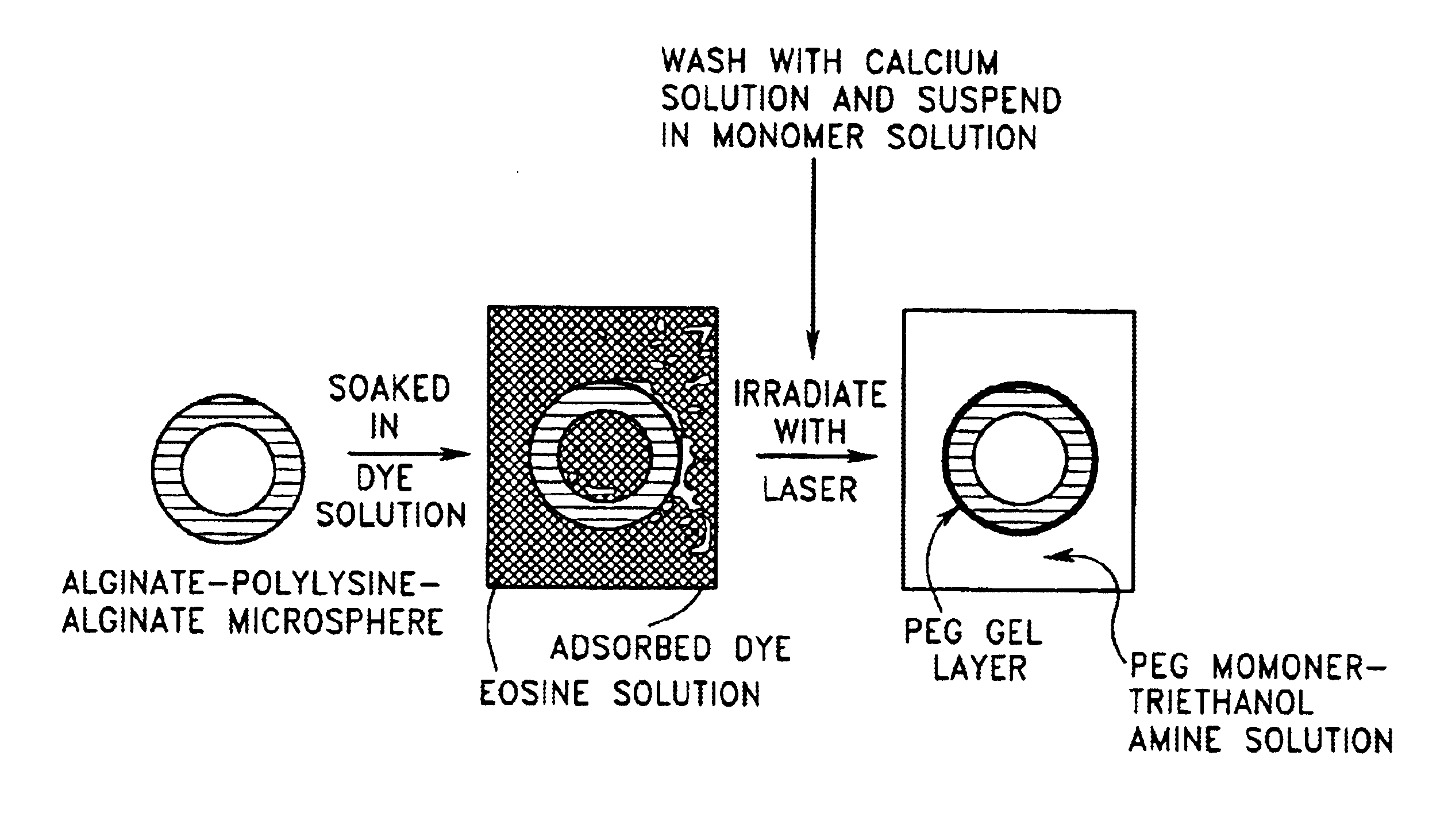
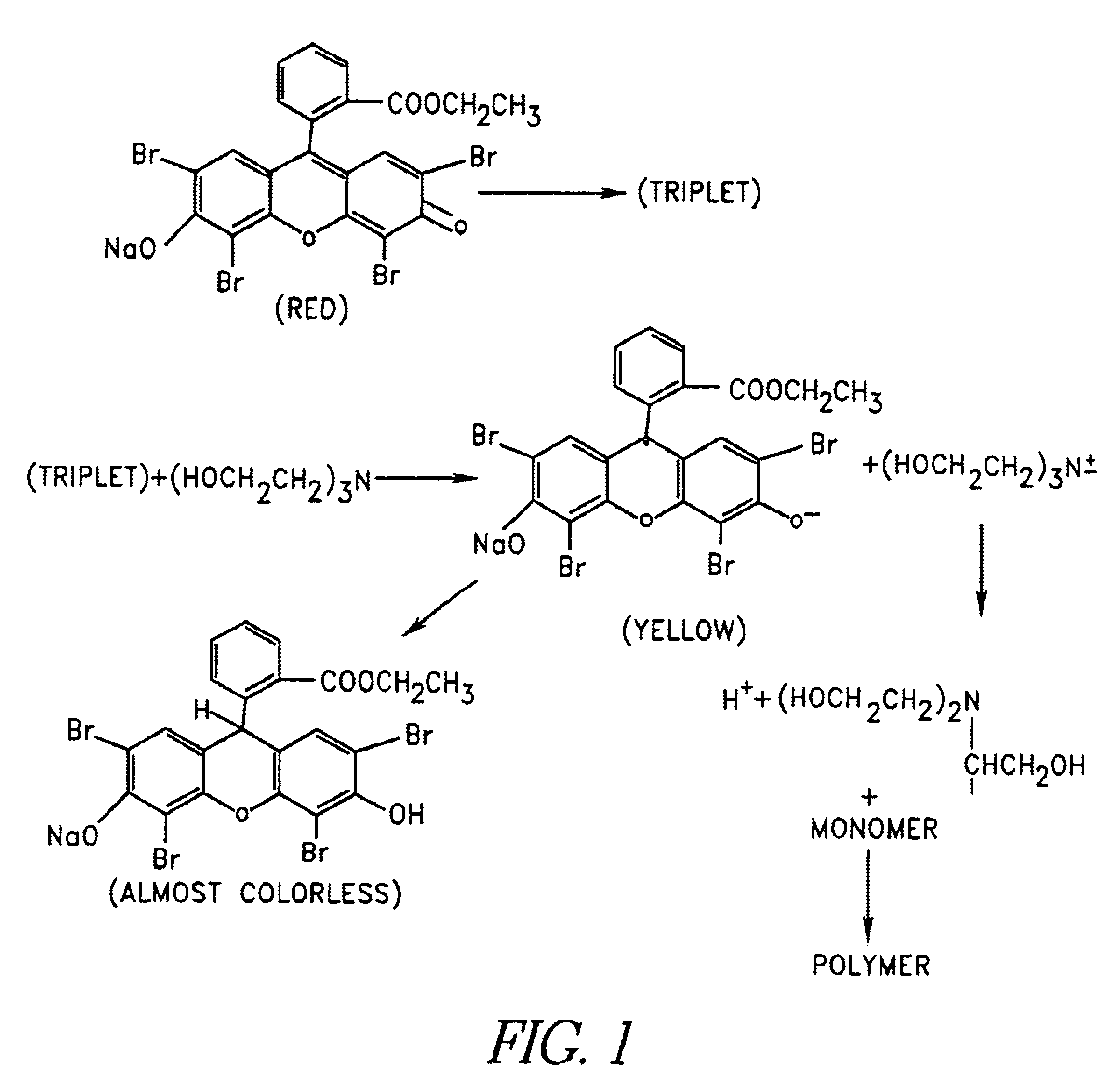
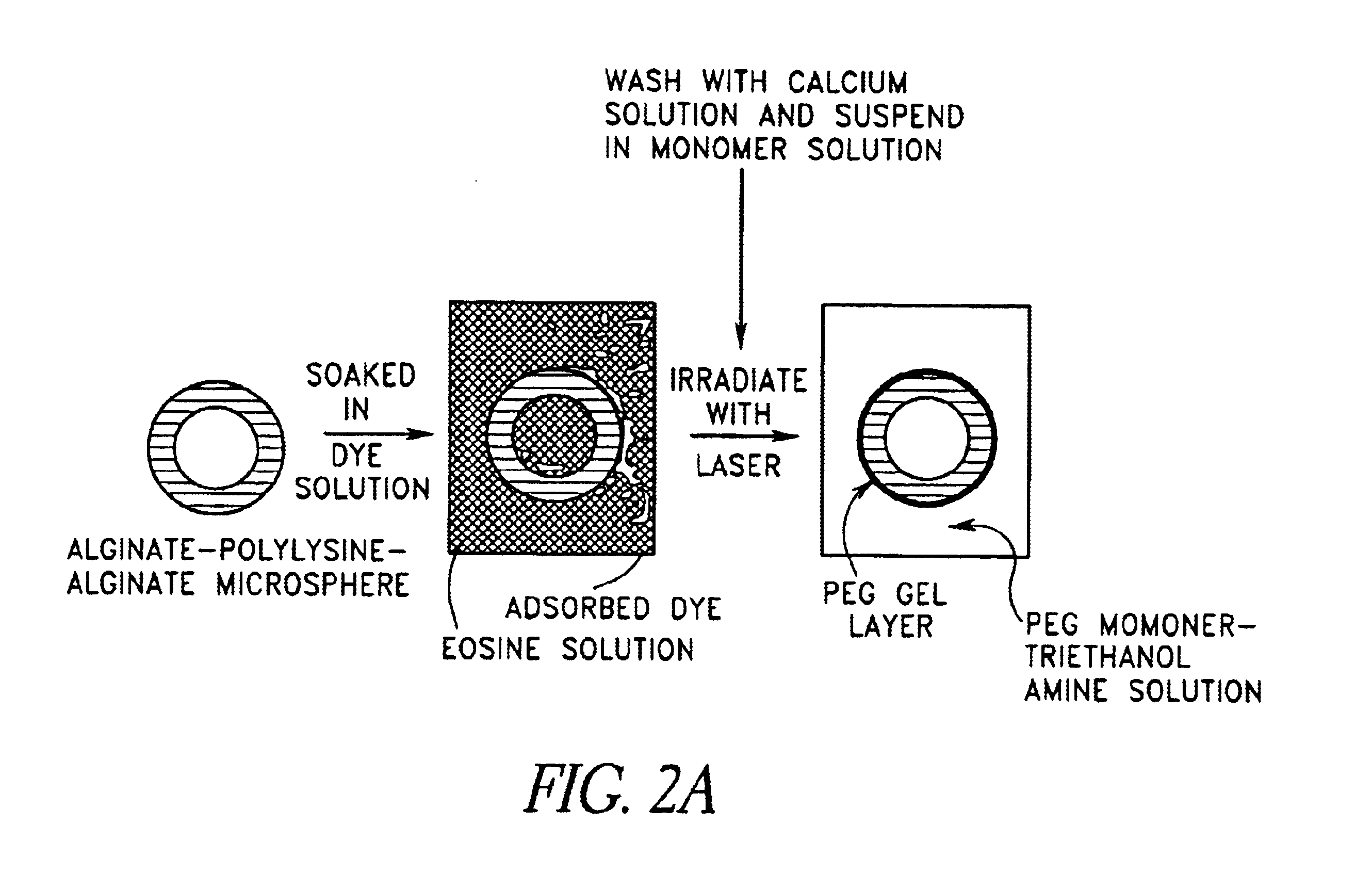
Gels for encapsulation of biological materials
InactiveUS6911227B2Efficient gluingFacilitated DiffusionImmobilised enzymesSurgical adhesivesActive matterWater soluble
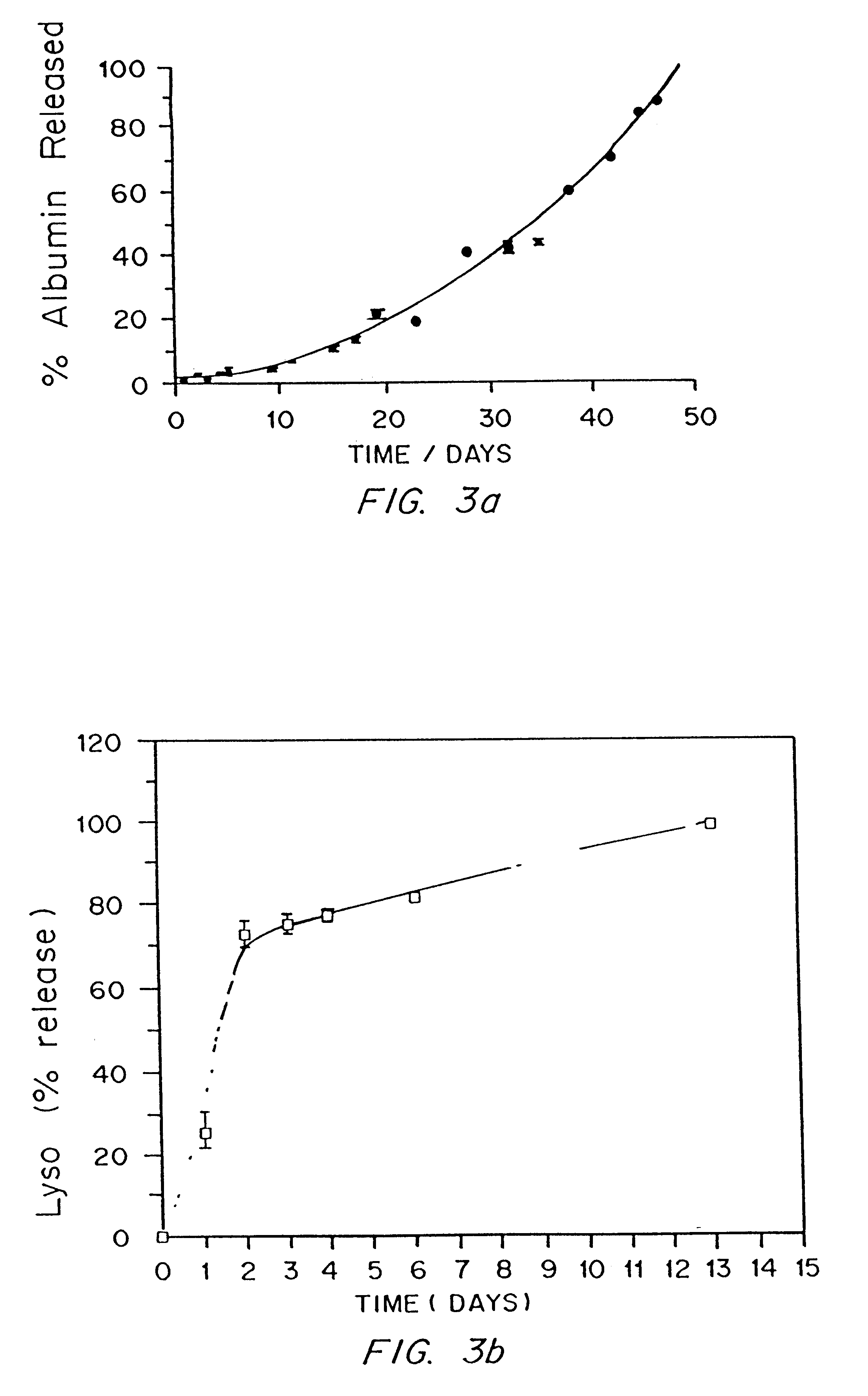
This invention provides novel methods for the formation of biocompatible membranes around biological materials using photopolymerization of water soluble molecules. The membranes can be used as a covering to encapsulate biological materials or biomedical devices, as a “glue” to cause more than one biological substance to adhere together, or as carriers for biologically active species. Several methods for forming these membranes are provided. Each of these methods utilizes a polymerization system containing water-soluble macromers, species, which are at once polymers and macromolecules capable of further polymerization. The macromers are polymerized using a photoinitiator (such as a dye), optionally a cocatalyst, optionally an accelerator, and radiation in the form of visible or long wavelength UV light. The reaction occurs either by suspension polymerization or by interfacial polymerization. The polymer membrane can be formed directly on the surface of the biological material, or it can be formed on material, which is already encapsulated.
Owner:NOVOCELL
Electroprocessed Collagen and Tissue Engineering
InactiveUS20080038352A1Powder deliveryMonocomponent protein artificial filamentCell-Extracellular MatrixMedicine
The invention is directed to formation and use of electroprocessed collagen, including use as an extracellular matrix and, together with cells, its use in forming engineered tissue. The engineered tissue can include the synthetic manufacture of specific organs or tissues which may be implanted into a recipient. The electroprocessed collagen may also be combined with other molecules in order to deliver substances to the site of application or implantation of the electroprocessed collagen. The collagen or collagen / cell suspension is electrodeposited onto a substrate to form tissues and organs.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV INTPROP FOUND INC +1
Implantation of encapsulated biological materials for treating diseases
The present invention relates to compositions and methods of treating a disease, such as diabetes, by implanting encapsulated biological material into a patient in need of treatment. This invention provides for the placement of biocompatible coating materials around biological materials using photopolymerization while maintaining the pre-encapsulation status of the biological materials. Several methods are presented to accomplish coating several different types of biological materials. The coatings can be placed directly onto the surface of the biological materials or onto the surface of other coating materials that hold the biological materials. The components of the polymerization reactions that produce the coatings can include natural and synthetic polymers, macromers, accelerants, cocatalysts, photoinitiators, and radiation. This invention also provides methods of utilizing these encapsulated biological materials to treat different human and animal diseases or disorders by implanting them into several areas in the body including the subcutaneous site. The coating materials can be manipulated to provide different degrees of biocompatibility, protein diffusivity characteristics, strength, and biodegradability to optimize the delivery of biological materials from the encapsulated implant to the host recipient while protecting the encapsulated biological materials from destruction by the host inflammatory and immune protective mechanisms without requiring long-term anti-inflammatory or anti-immune treatment of the host.
Owner:NOVOCELL
Non-radical photochemical crosslinked hydrogel material preparation method, product and application
ActiveCN105131315APrecise and controllable time and spaceEasy to operateOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsPolymer scienceHydroxylamine
The present invention provides a non-radical photo-crosslinked hydrogel preparation method, comprising the following steps: a component A is dissolved in a biocompatible medium to obtain a solution A, component B-hydrazide, hydroxylamine or primary amine high molecular derivative is dissolved in a biocompatible medium to obtain a solution B; the solution A and the solution B are evenly mixed to obtain a hydrogel precursor solution; under illumination, aldehyde group produced by light excitation of o-nitrobenzyl in the component A of the hydrogel precursor solution is crosslinked with hydrazone, hydroxylamine or primary amine group in the component B in the form of respective formation of oxime and Schiff base to produce the hydrogel. The present invention also provides a kit for the hydrogel preparation, and application of the hydrogel in tissue repair, beauty and as a cell, protein or drug carrier. The tissue surface light-situ gel can be achieved by the hydrogel, in particular, wound surface in-situ thin glue formation can be achieved, and the hydrogel is especially suitable for clinical wound surface tissue repair and isolation.
Owner:上海戴云化工科技有限公司 +2
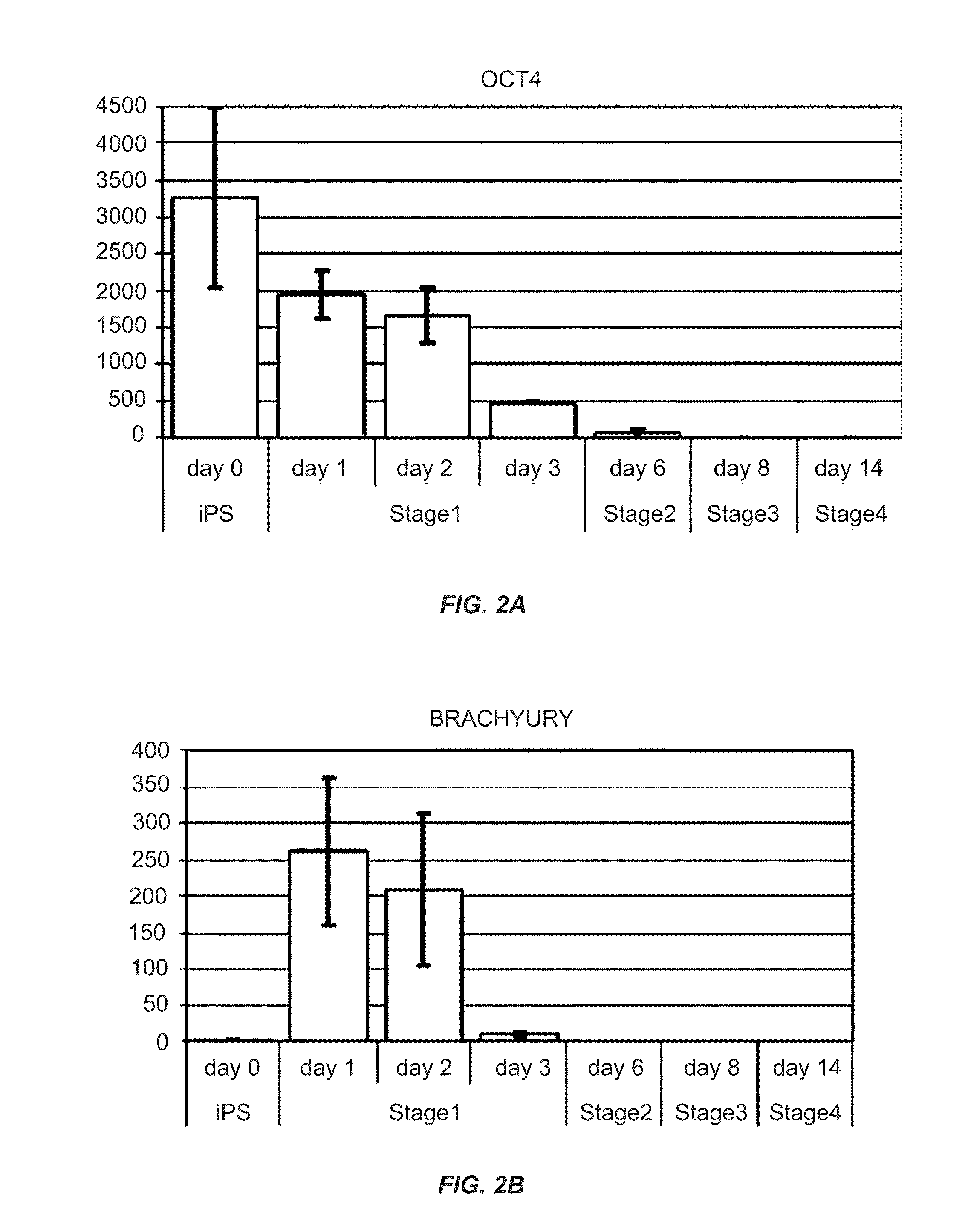
In vitro differentiation of pluripotent stem cells to pancreatic endoderm cells (PEC) and endocrine cells
A human immature endocrine cell population and methods for making an immature endocrine cell population are provided. Specifically, immature beta cells and methods for production of immature beta cells are described. Immature beta cells co-express INS and NKX6.1 and are uni-potent and thereby develop into mature beta cells when implanted in vivo. The mature beta cells in vivo are capable of producing insulin in response to glucose stimulation.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
Macroscopic scaffold containing amphiphilic peptides encapsulating cells
The invention features peptide scaffolds that are useful in the repair and replacement of various tissues. The invention also provides methods for making these scaffolds and methods for using them.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Bioprocess for the generation of cells from spheroid-forming cells
InactiveUS20030119107A1Inhibit aggregationCell culture supports/coatingTissue/virus culture apparatusHigh cellVolumetric Mass Density
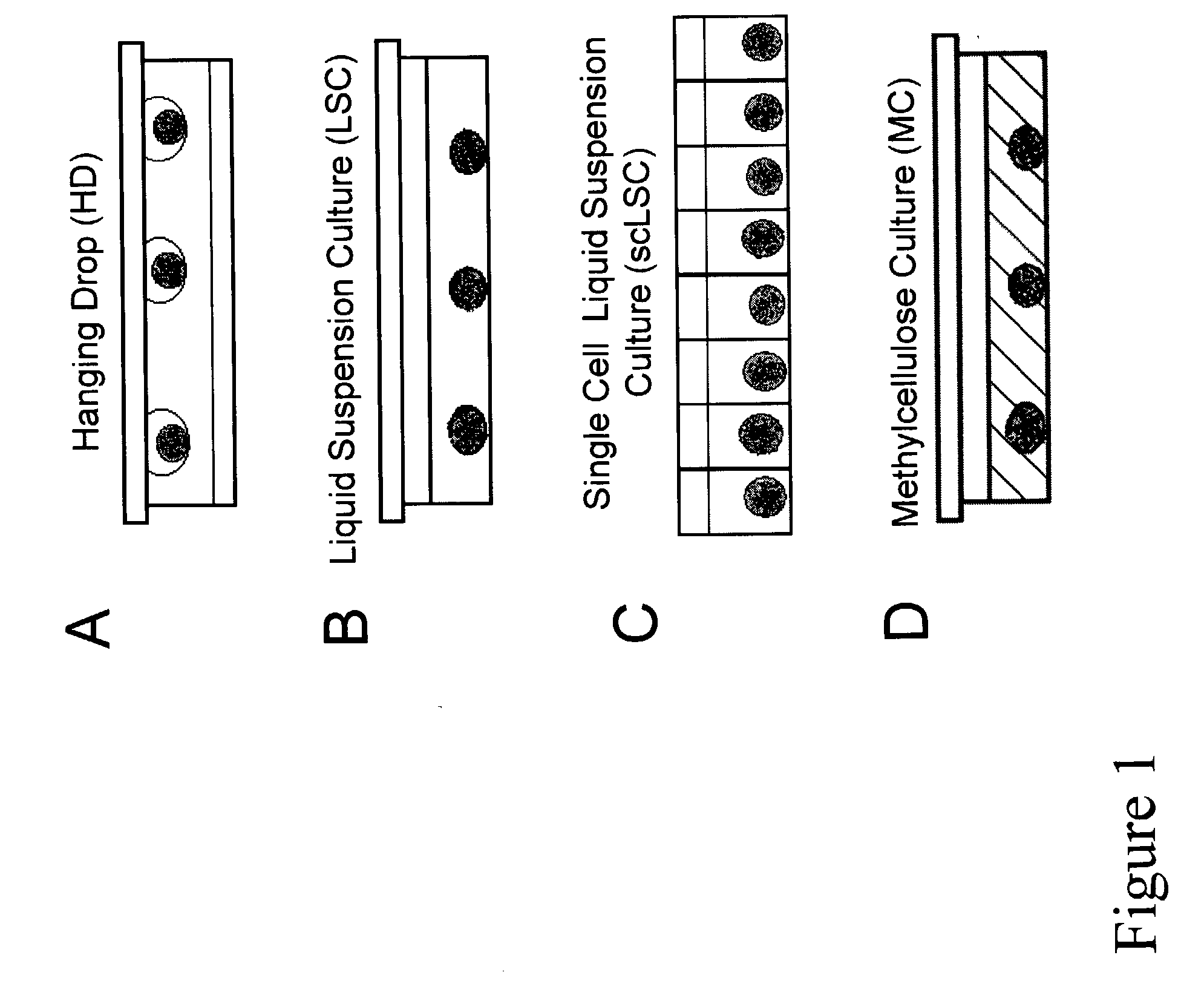
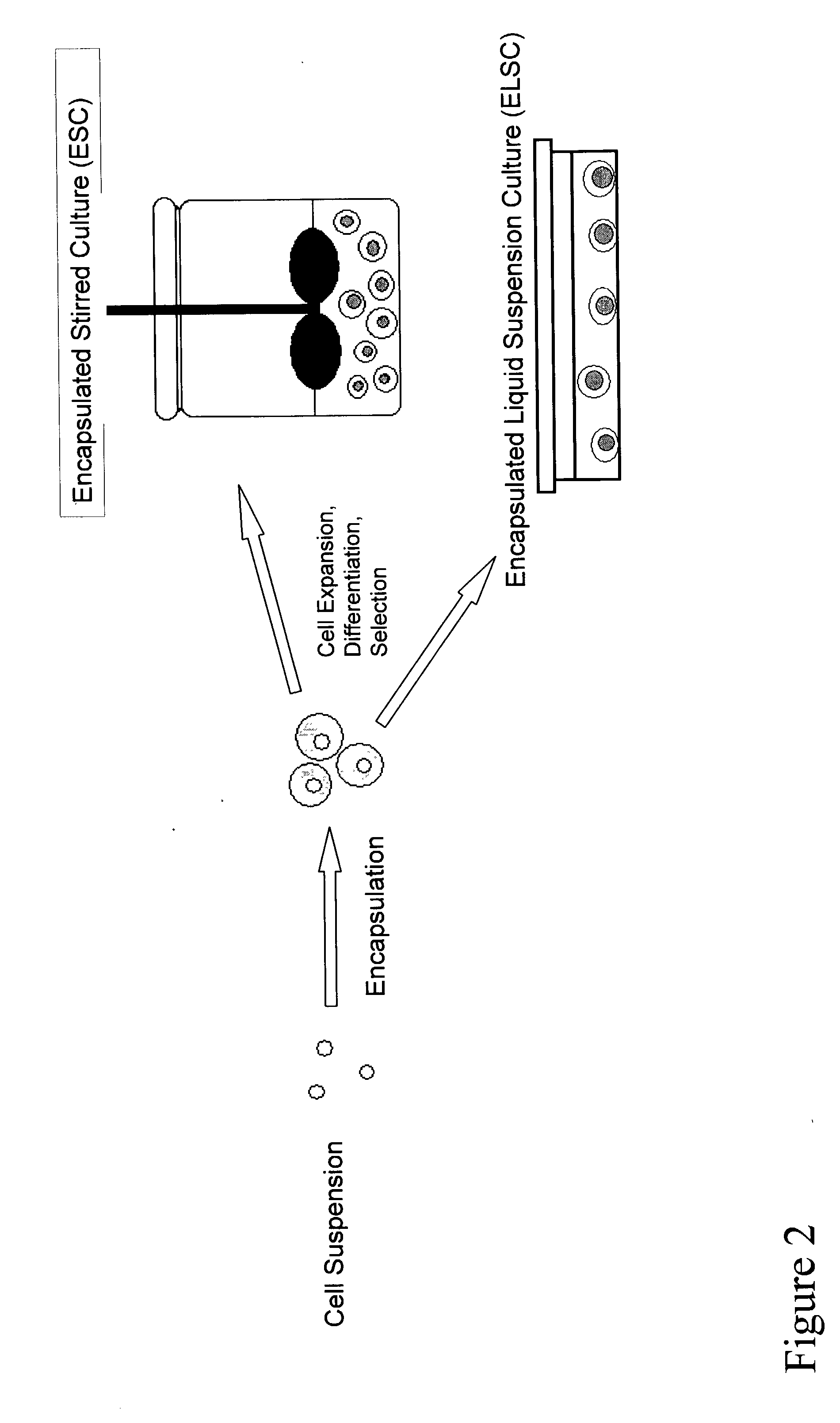
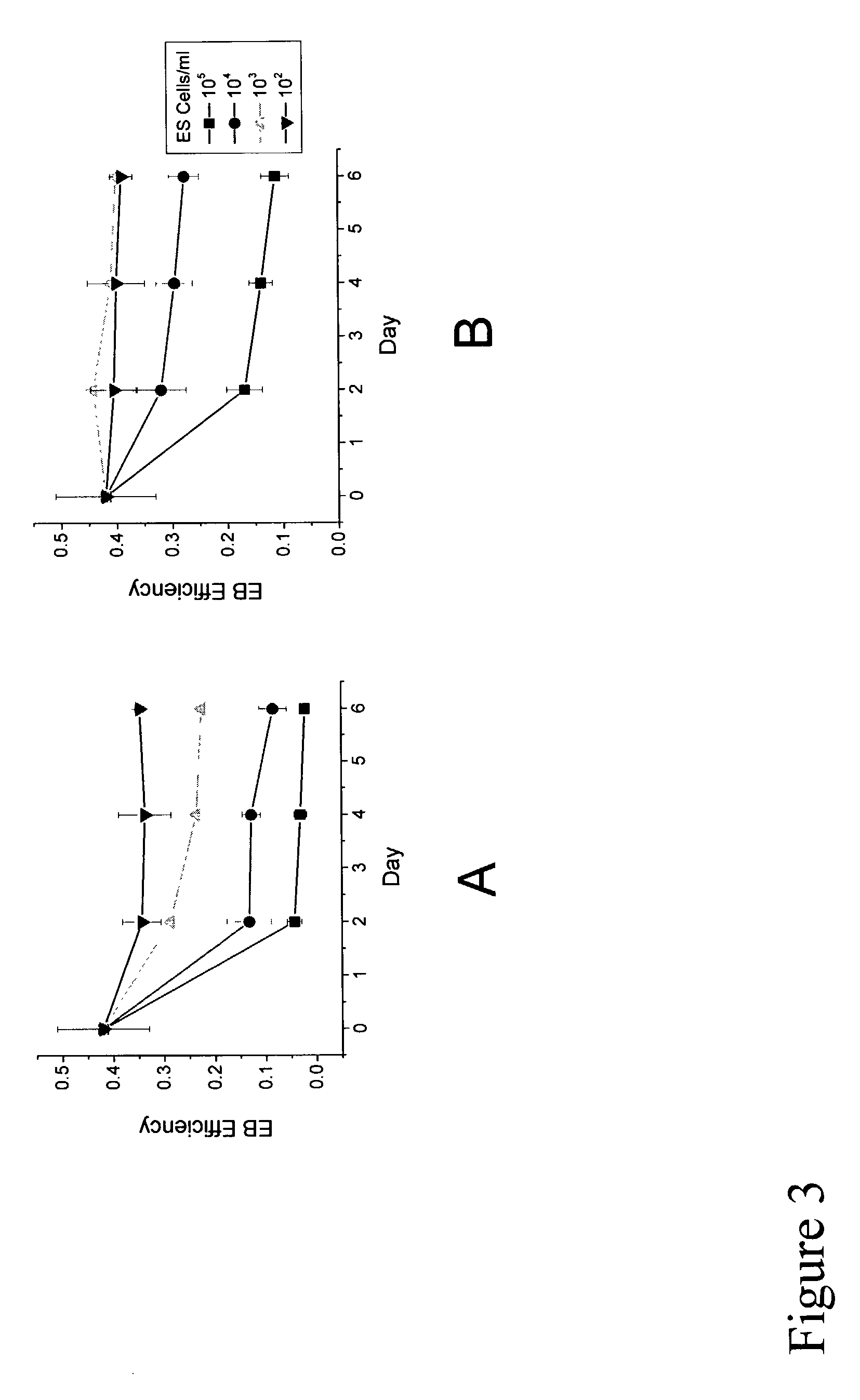
The present inventors identified aggregation of embryonic stem cells and embryoid bodies (EBs) as the cause of the difficulty in generating large numbers of the embryonic stem cells (ES) cell-derived tissues. To counter this, the invention provides a novel bioprocess where aggregation of spheroid forming cells, such as embryonic stem cells and spheroids, such as EBs is controlled, such as by encapsulation of within a matrix. As a result, EBs can be generated with high efficiency and cultured in high cell density, well-mixed systems. Well-mixed conditions facilitate measurement and control of the bulk media conditions and allow for the use of scalable bioreactor systems for clinical production of tissue. Therefore, the invention enables generation of ES cell-derived tissue on a clinical scale. The invention is also applicable to any spheroid-forming cells and other types of pluripotent cells.
Owner:CARDION AG
Methods for embryonic stem cell culture
InactiveUS20080159994A1Assessing effectDifferentiateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSenses disorderSupport matrixScreening method
The invention relates to a method of cell culture comprising providing a pluripotent ES cell encapsulated within a support matrix to form a support matrix structure, maintaining the encapsulated cell in 3-D culture in maintenance medium, and optionally differentiating the encapsulated cell in 3-D culture in differentiation medium. The invention further relates to screening methods incorporating the use of encapsulated cells.
Owner:NOVATHERA +1
Cell Aggregation and Encapsulation Device and Method
ActiveUS20090018033A1Improve adhesionEnhanced interactionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCell adhesionAdhesion process
The invention is a cell aggregation device comprising a hydrogel substrate having at least one, preferably a plurality, of cell-repellant compartments recessed into the uppermost surface. Each compartment is composed of an upper cell suspension seeding chamber having an open uppermost portion and a bottom portion, and one, or more than one, lower cell aggregation recess connected to the bottom portion of the upper cell suspension seeding chamber by a port. The diameter of the port may be fully contiguous with the walls of the chambers and walls of the recesses, or the diameter of the port may be more narrow than the walls of the chamber but fully contiguous with the walls of the recesses or more narrow than both the walls of the chamber and the walls of the recesses. The upper cell suspension seeding chambers are formed and positioned to funnel the cells into the lower cell aggregation recesses through gravitational force. The aggregation recesses are formed and positioned to promote cellular aggregation by coalescing cells into a finite region of minimum gravitational energy, increasing intercellular contact and minimizing or preventing cell adherence to the substrate. A device for encapsulating aggregates of live cells is provided. The device comprises (i) a biocompatible, bio-sustainable substrate having a cell-encapsulating face composed of one or more biocompatible, bio-sustainable, spaced-apart, cell-encapsulating compartments extending therefrom and (ii) a coating layer composed of a biocompatible, bio-sustainable polymer that completely surrounds the substrate and the cell-encapsulating compartments. A method for making the device is also provided.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
In vitro differentiation of pluripotent stem cells to pancreatic endoderm cells (PEC) and endocrine cells
A human immature endocrine cell population and methods for making an immature endocrine cell population are provided. Specifically, immature beta cells and methods for production of immature beta cells are described. Immature beta cells co-express INS and NKX6.1 and are uni-potent and thereby develop into mature beta cells when implanted in vivo. The mature beta cells in vivo are capable of producing insulin in response to glucose stimulation.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
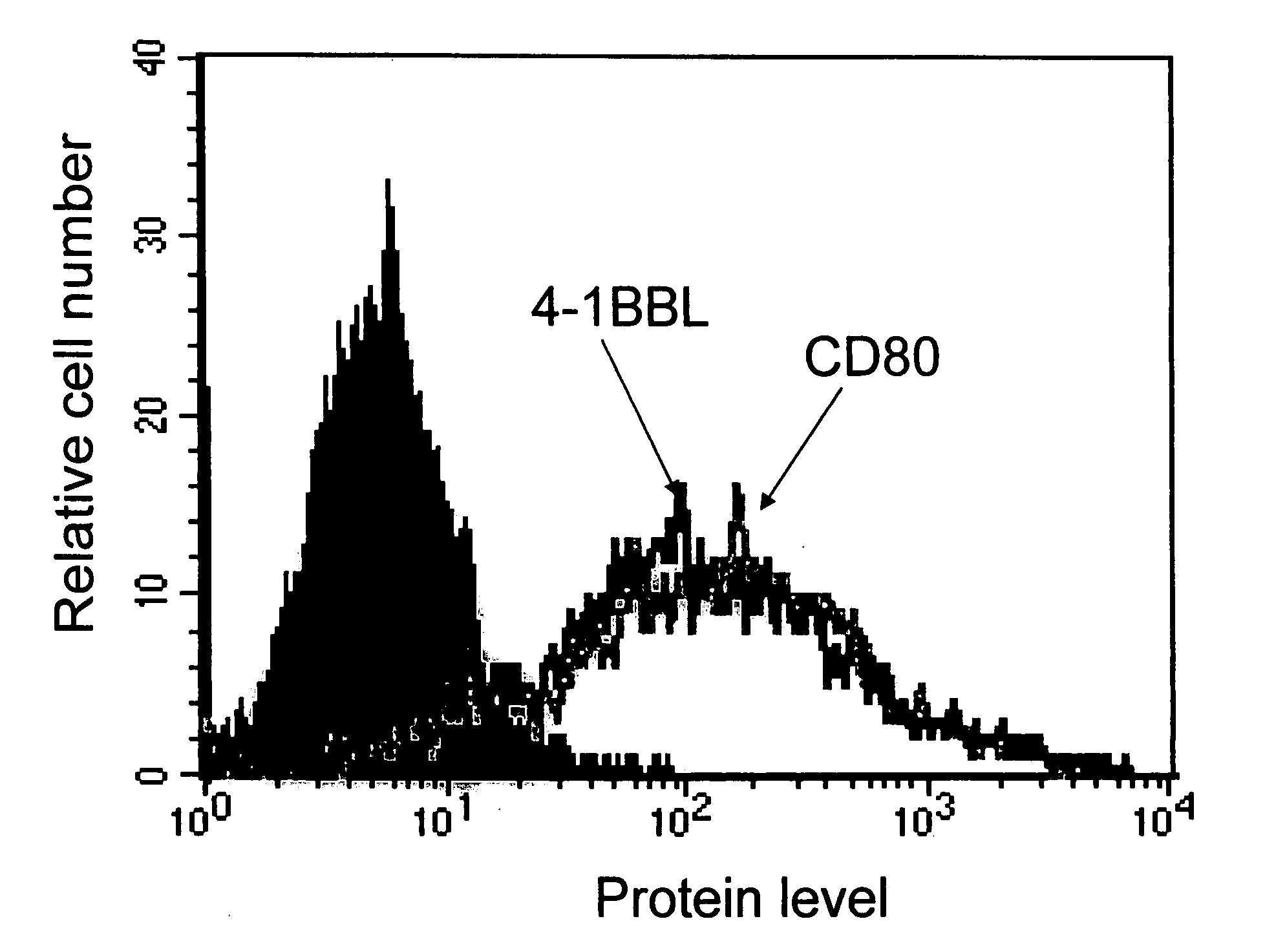
In vivo cell surface engineering
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the in vivo engineering of cell surfaces, such as tumor cell surfaces, with one or more immune co-stimulatory polypeptides. The methods, compositions and engineered cells are useful, for example, to stimulate an immune response against the cells. When the engineered cell surfaces are tumor cell surfaces, the methods, compositions and engineered cells are useful for improving a patient's immune response against the cancer and for reducing tumor size and inhibiting tumor growth.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC
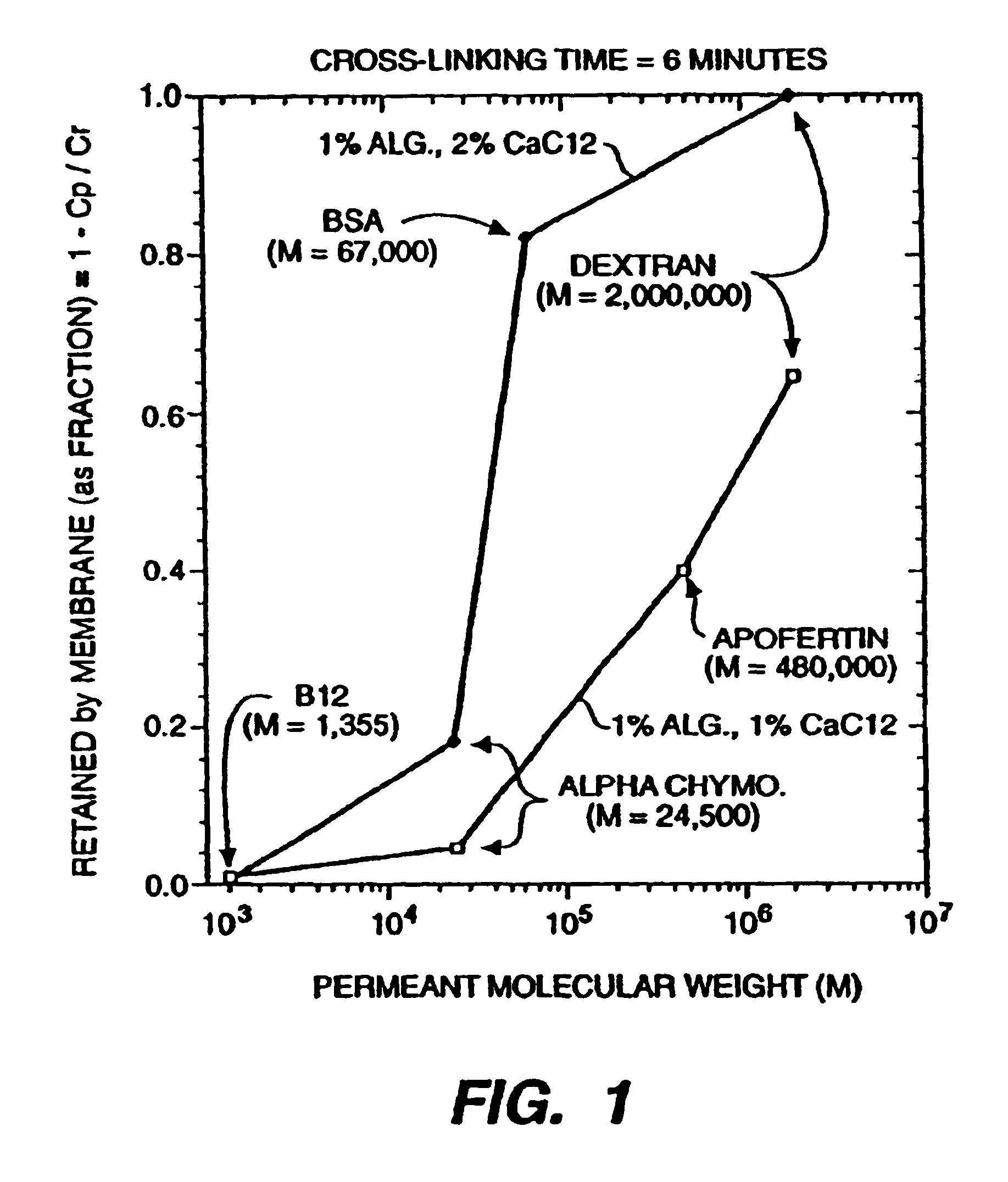
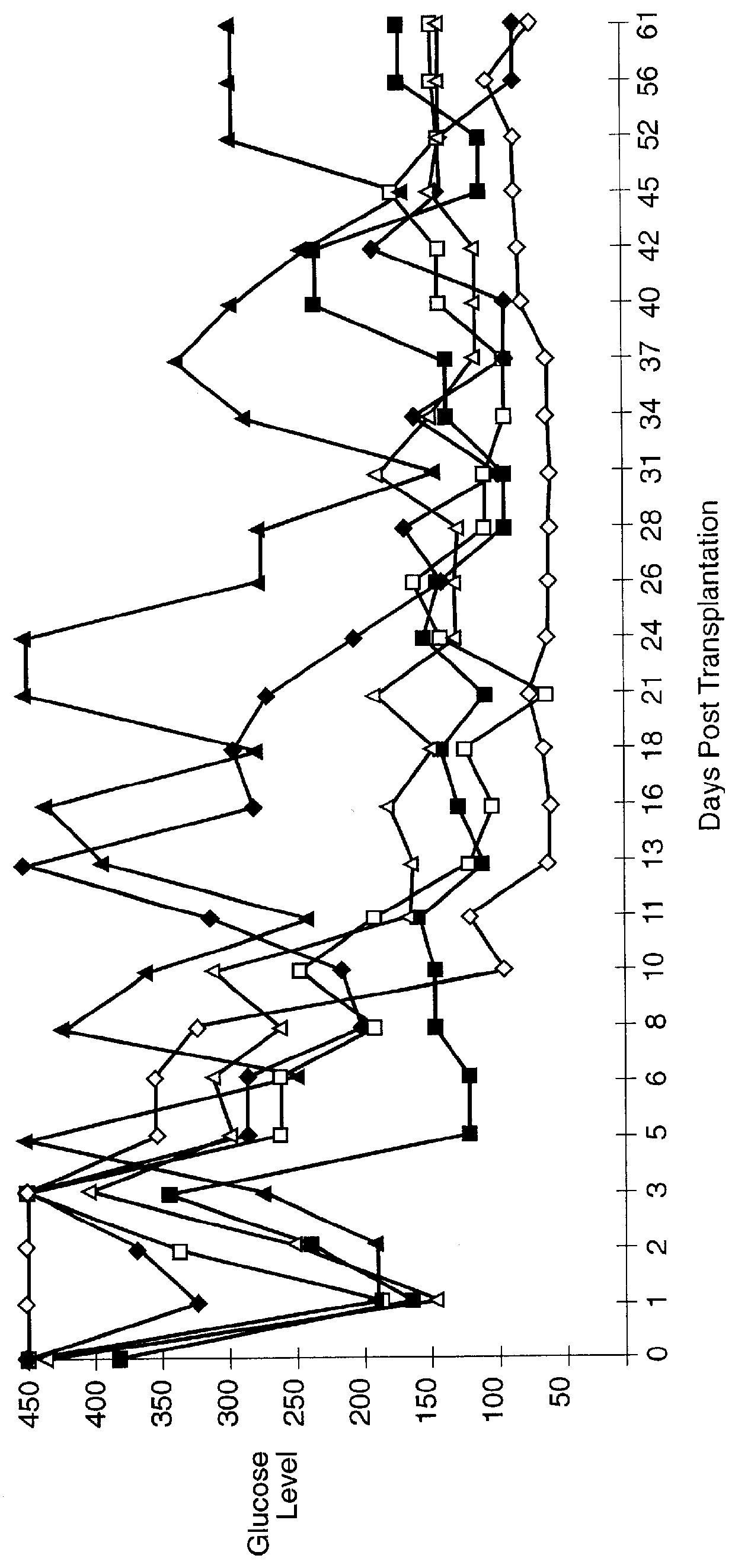
Implantable biocompatible immunoisolatory vehicle for delivery of selected therapeutic products
InactiveUS6960351B2Sufficient protectionProtection attackNervous disorderPancreatic cellsBiologyBiological product
An immunoisolatory vehicle for the implantation into an individual of cells which produce a needed product or provide a needed metabolic function. The vehicle is comprised of a core region containing isolated cells and materials sufficient to maintain the cells, and a permselective, biocompatible, peripheral region free of the isolated cells, which immunoisolates the core yet provides for the delivery of the secreted product or metabolic function to the individual. The vehicle is particularly well-suited to delivery of insulin from immunoisolated islets of Langerhans, and can also be used advantageously for delivery of high molecular weight products, such as products larger than IgG. A method of making a biocompatible, immunoisolatory implantable vehicle, consisting in a first embodiment of a coextrusion process, and in a second embodiment of a stepwise process. A method for isolating cells within a biocompatible, immunoisolatory implantable vehicle, which protects the isolated cells from attack by the immune system of an individual in whom the vehicle is implanted. A method of providing a needed biological product or metabolic function to an individual, comprising implanting into the individual an immunoisolatory vehicle containing isolated cells which produce the product or provide the metabolic function.
Owner:BROWN UNIV RES FOUND INC
Microencapsulation of Cells in Hydrogels Using Electrostatic Potentials
Compositions and methods for producing encapsulated cells having an average diameter of less than about 200 μm are provided. Methods for using the disclosed encapsulated cells are also provided
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
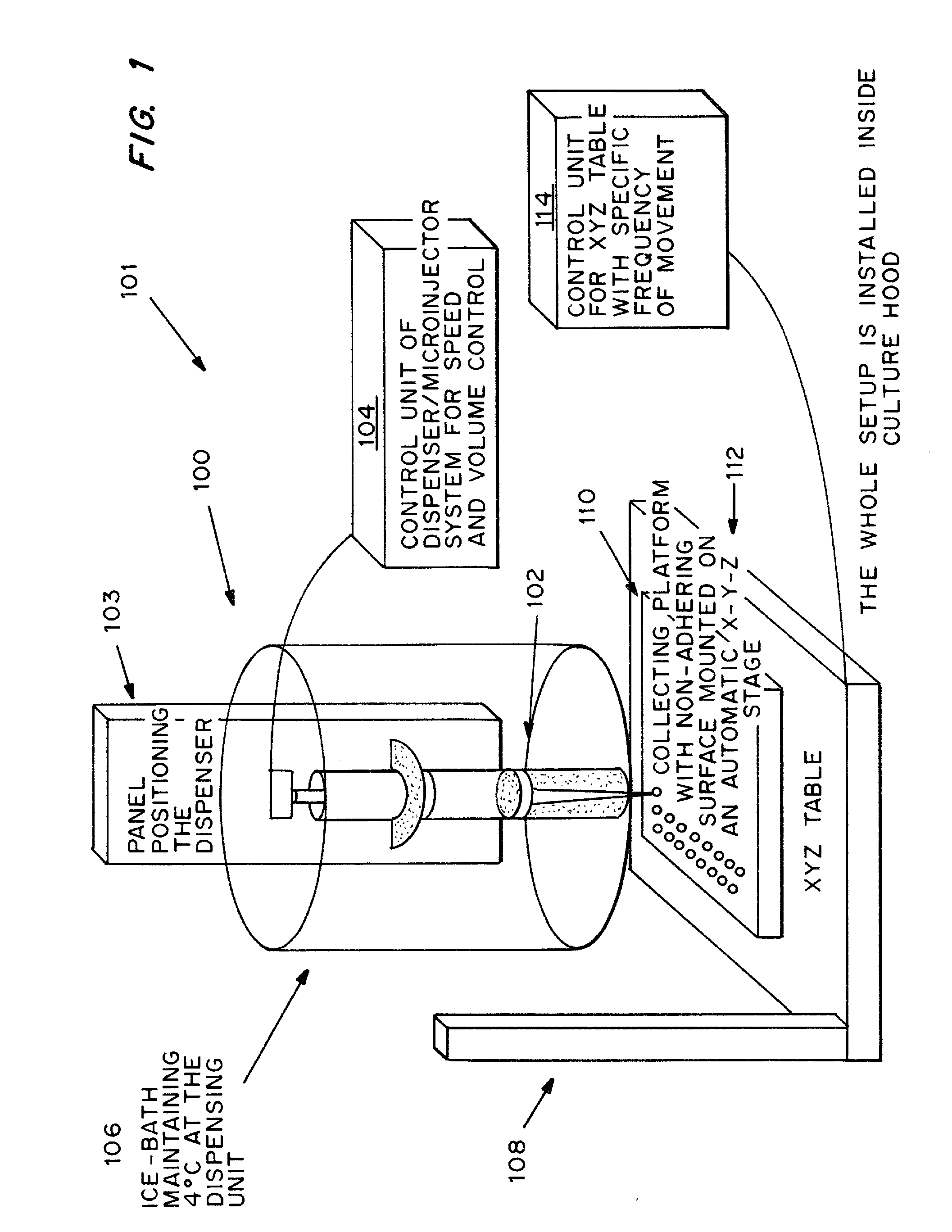
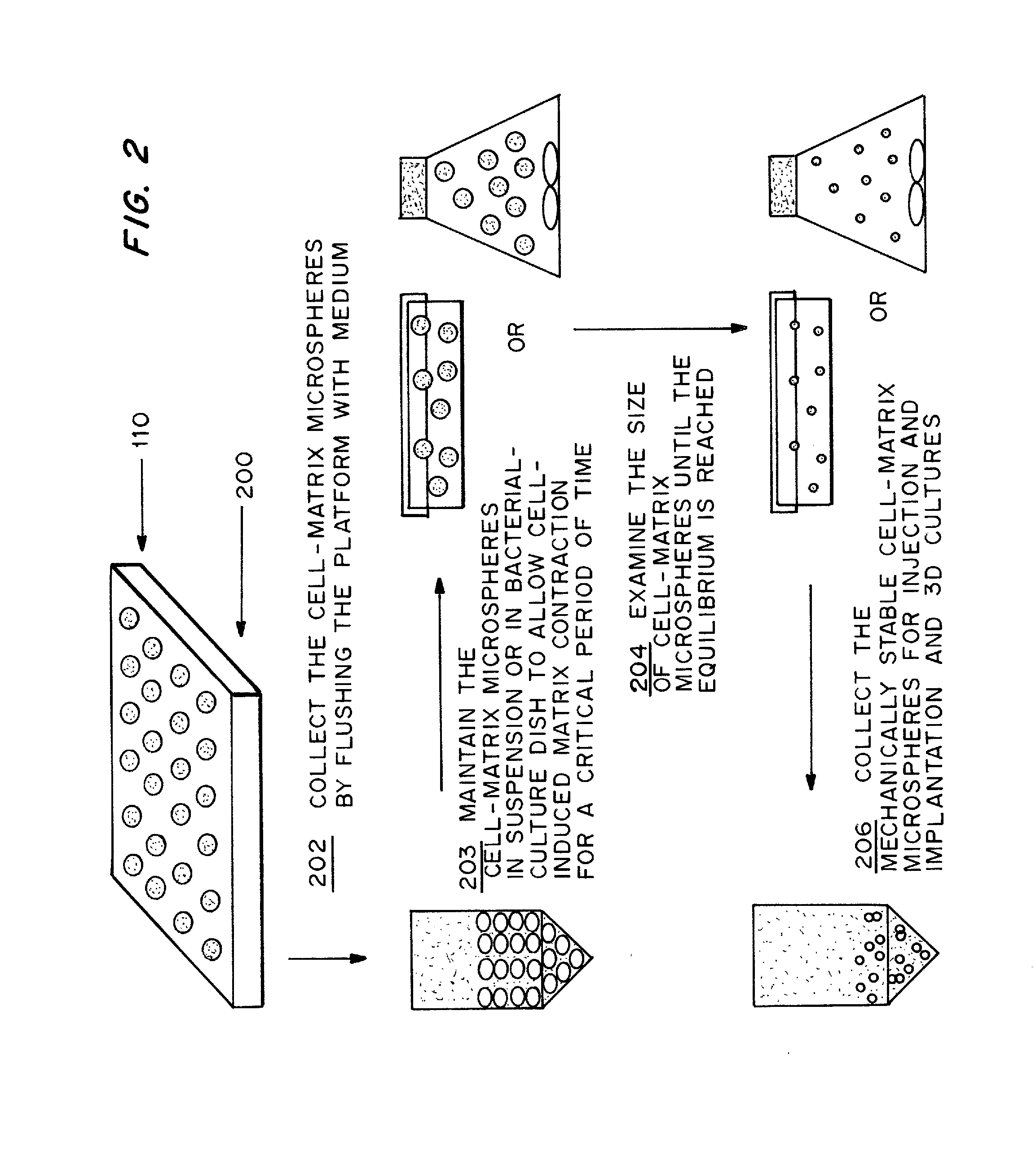
Cell-matrix microspheres, methods for preparation and applications
ActiveUS20080031858A1Increased protein productivityStable cell-matrix microspheresBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEnzymatic digestionHigh cell
A method has been developed to produce stable cell-matrix microspheres with up to 100% encapsulation efficiency and high cell viability, using matrix or biomaterial systems with poor shape and mechanical stability for applications including cell therapeutics via microinjection or surgical implantation, 3D culture for in vitro expansion without repeated cell splitting using enzymatic digestion or mechanical dissociation and for enhanced production of therapeutic biomolecules, and in vitro modeling for morphogenesis studies. The modified droplet generation method is simple and scalable and enables the production of cell-matrix microspheres when the matrix or biomaterial system used has low concentration, with slow phase transition, with poor shape and mechanical stability.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
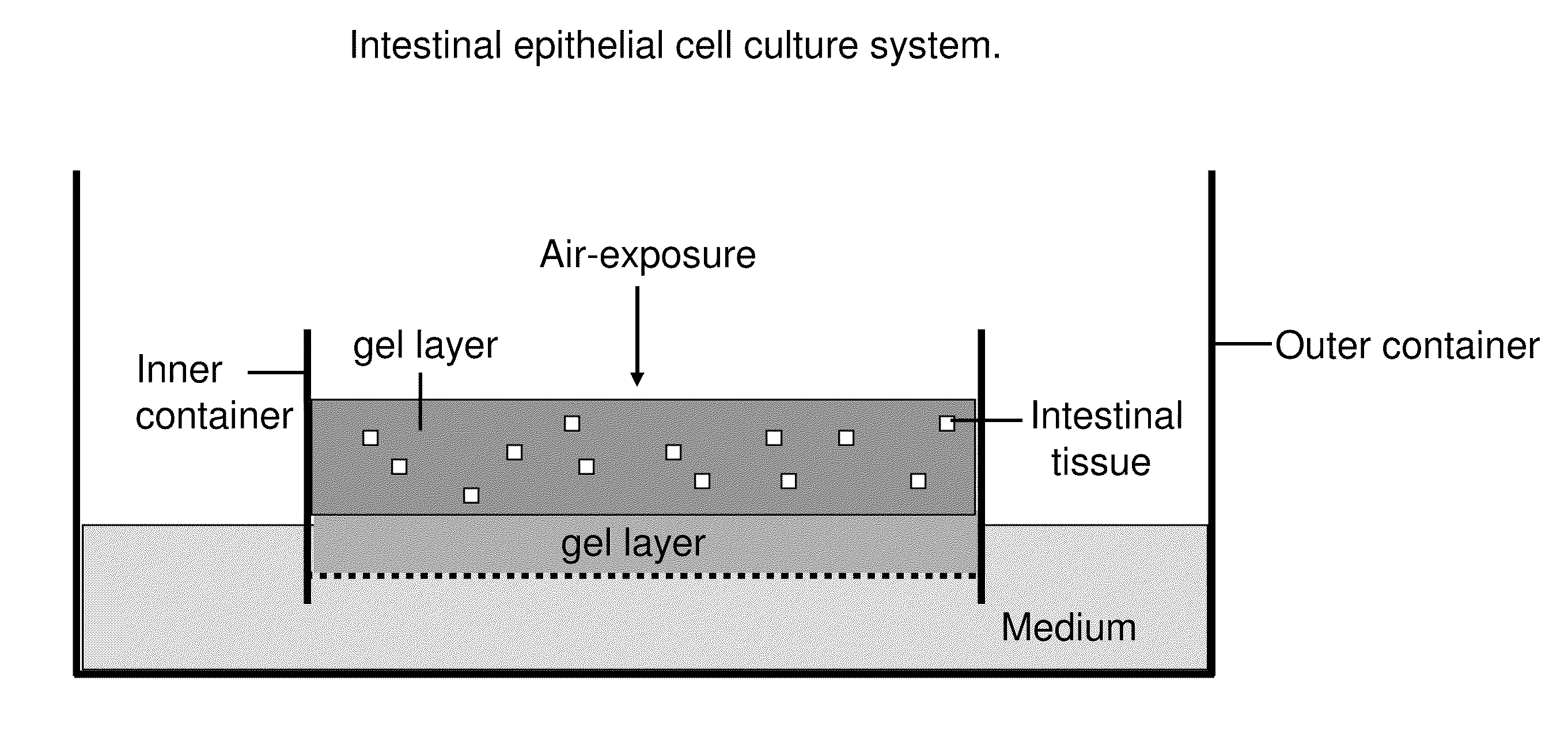
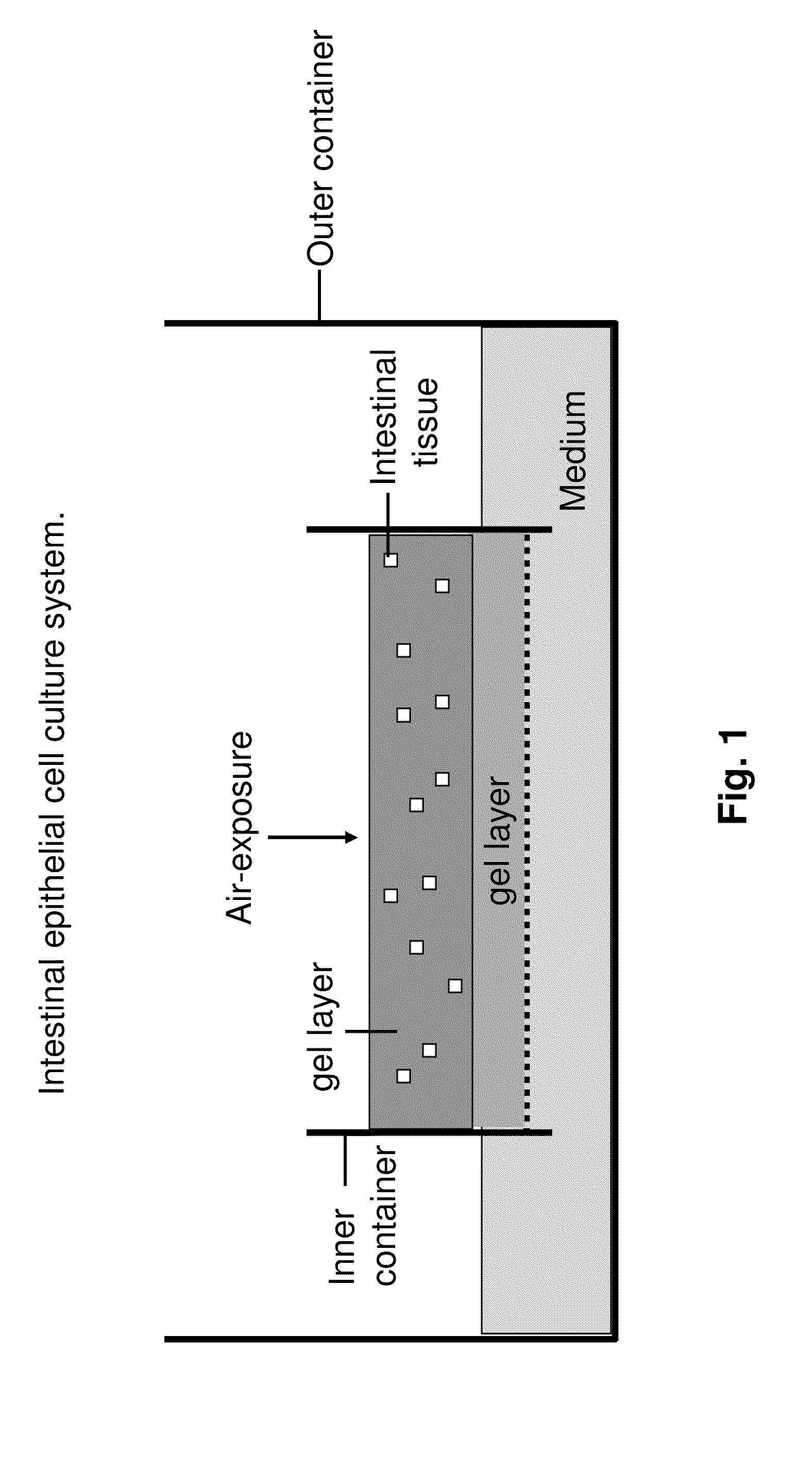
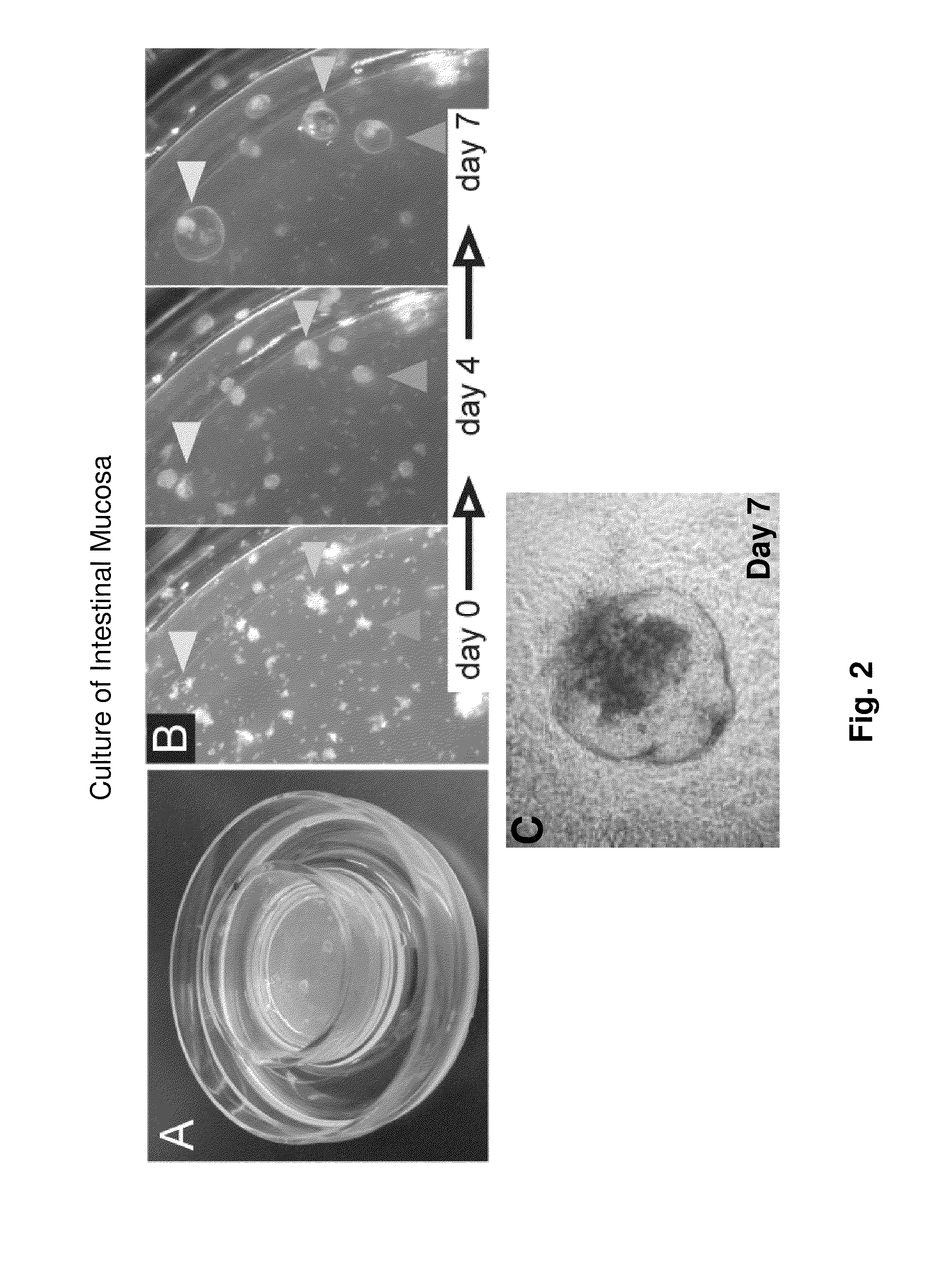
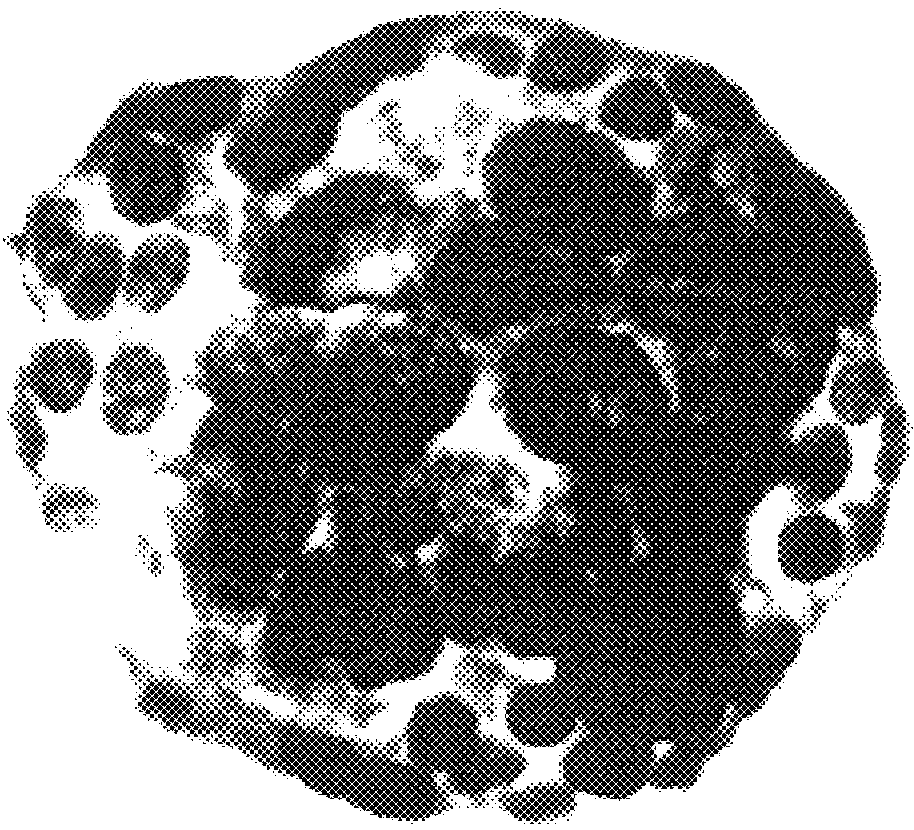
Ex Vivo Culture, Proliferation and Expansion of Intestinal Epithelium
ActiveUS20100047853A1Induce pluripotencyAlter differentiationGastrointestinal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementAir liquid interfaceMammal
Methods are provided for long term culture of mammalian intestinal cells. Cultures are initiated with fragments of mammalian intestinal tissue, which are then maintained embedded in a gel substrate that provides an air-liquid interface. Intestinal epithelium in cultures of the invention can be continuously grown for extended periods of time. Mammalian intestinal cells cultured by the methods of the invention recapitulate features of intestinal growth in vivo.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Preparation of agarose coated, solid agarose-collagen beads containing secretory cells
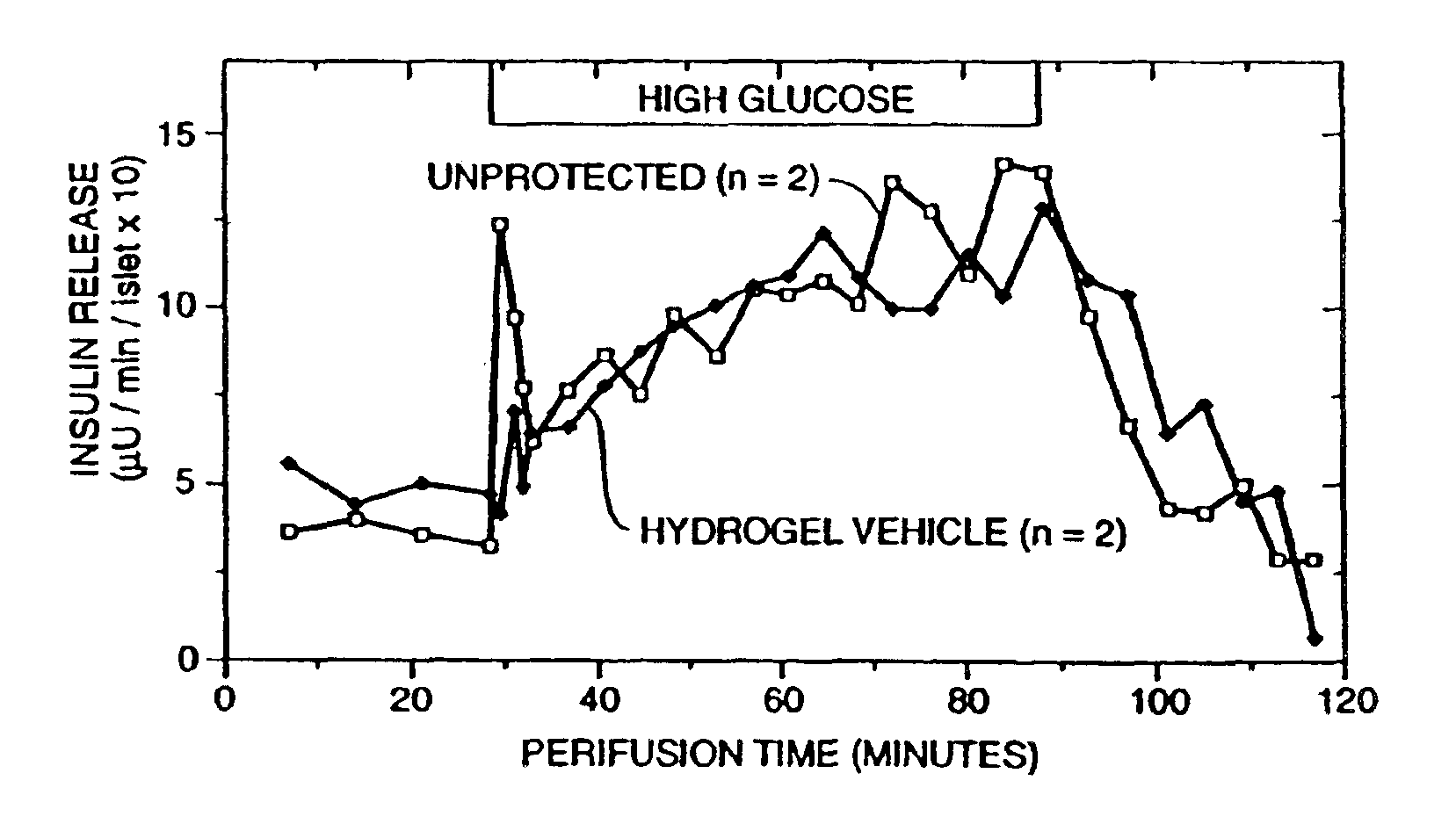
Biological agents such as secretory cells are encapsulated in a hydrophilic gel made of agarose or collagen-agarose and gelatin sponge-agarose combinations. In a preferred embodiment, semi-solid beads are formed from a suspension containing collagen, agarose and secretory cells such as pancreatic islets, the collagen is polymerized to form solid, agarose-collagen beads and the solid beads are coated with agarose. Coating is preferably by rolling the solid beads in about 5-10% agarose, contacting the rolled beads with mineral oil and washing oil from the beads. Beads containing secretory cells can be transplanted into a mammal to treat a condition caused by impaired secretory cell function.
Owner:THE ROGOSIN INST
Encapsulation system
InactiveUS20090214660A1Improve protectionReduce the degradation rateBiocideNervous disorderMedicineFunctional integrity
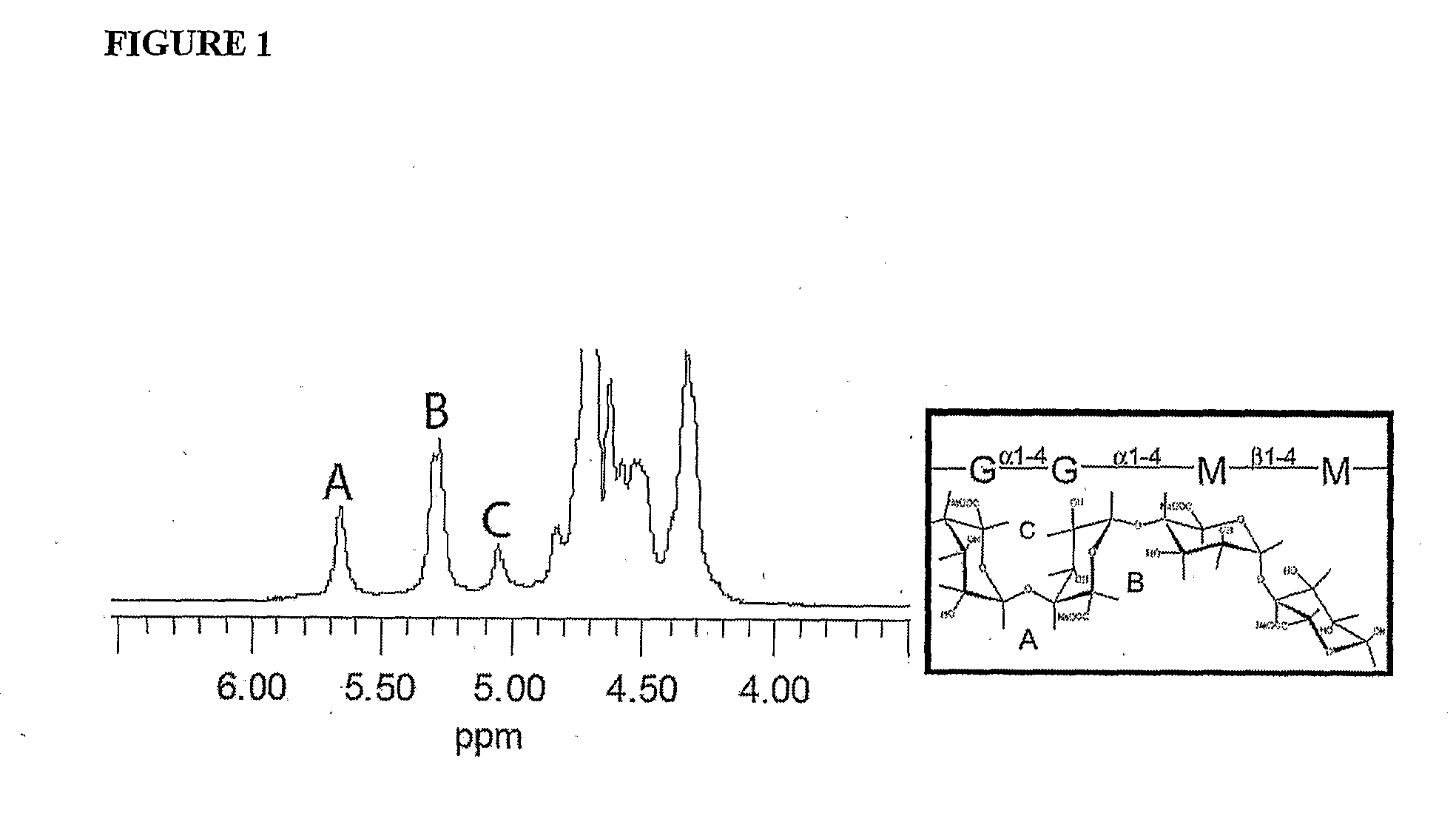
The present invention is directed to a composition comprising high mannuronic acid-containing alginate and a polycation having a polydispersity index of less than 1.5. The composition is particularly useful for making biocompatible microcapsules containing living cells for allo- or xeno-transplantation. Such microcapsules have enhanced durability and can maintain their structural and functional integrity over long periods of time compared to prior art alginate microcapsules.
Owner:LIVING CELL PRODS
Electroprocessed fibrin-based matrices and tissues
InactiveUS7759082B2Minimizing chanceCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixMedicine
The invention is directed to formation and use of electroprocessed fibrin as an extracellular matrix and, together with cells, its use in forming engineered tissue. The engineered tissue can include the synthetic manufacture of specific organs or tissues which may be implanted into a recipient. The electroprocessed fibrin may also be combined with other molecules in order to deliver the molecules to the site of application or implantation of the electroprocessed fibrin. The fibrin or fibrin / cell suspension is electrodeposited onto a substrate to form the tissues and organs.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV INTPROP FOUND INC
Modified alginates for Anti-fibrotic materials and applications
ActiveUS20160030360A1Avoid encapsulationImprove propertiesBiocideMetabolism disorderBiocompatibility TestingAnti fibrotic
Covalently modified alginate polymers, possessing enhanced biocompatibility and tailored physiochemical properties, as well as methods of making and use thereof, are disclosed herein. The covalently modified alginates are useful as a matrix for coating of any material where reduced fibrosis is desired, such as encapsulated cells for transplantation and medical devices implanted or used in the body.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Immunostimulatory compositions and methods
The invention provides conjugates comprising an immune co-stimulatory polypeptide and an antigen or infectious agent. The conjugates are useful for generating or enhancing an immune response against the antigen or infectious agent. The invention also provides immune cells modified with a conjuagte that are useful for generating or enhancing an immune response to an antigen or infectious agent. The invention also provides immunostimulatory moieties comprising an immune co-stimulatory polypeptide that are useful for stimulating an immune response. The invention also provides immunotherapy methods and methods of treating or preventing infections.
Owner:UNIV OF LOUISVILLE RES FOUND INC +1
Non-disruptive three-dimensional culture and harvest system for anchorage-dependent cells
InactiveUS20040023370A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNon destructiveCell division
A non-disruptive three-dimensional culture system allows cell growth and proliferation in three dimensions, permitting cell splitting without subjecting cells to disruptive conditions that affect cell structure and functions. An extracellular matrix provides a good environment for culturing or co-culturing anchorage-dependent cells. The cells cultured this manner can be readily used in such applications as cell transplantation, tissue engineering seeding of cells on scaffolds, and other applications that require immediate availability of functioning cells.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
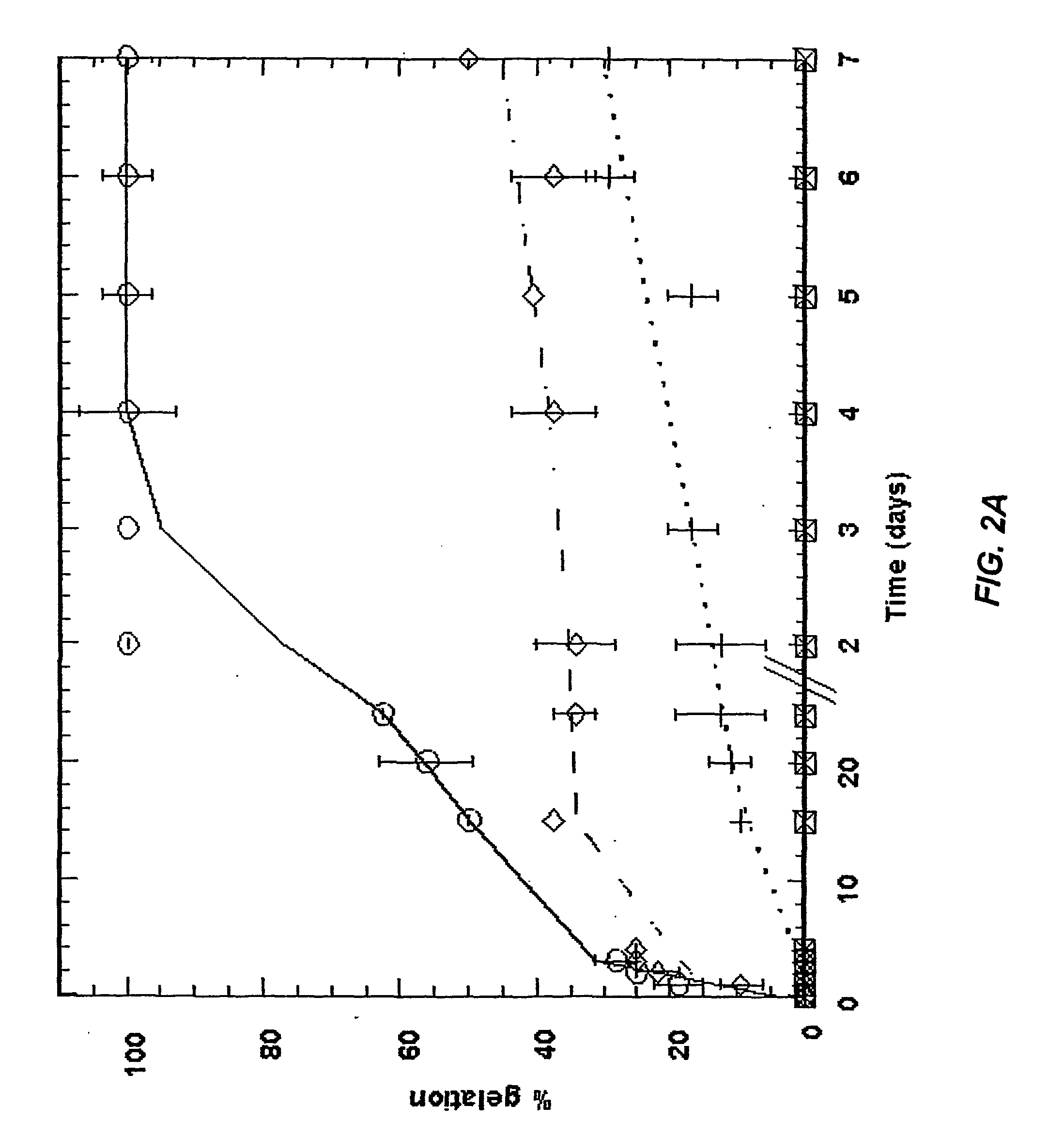
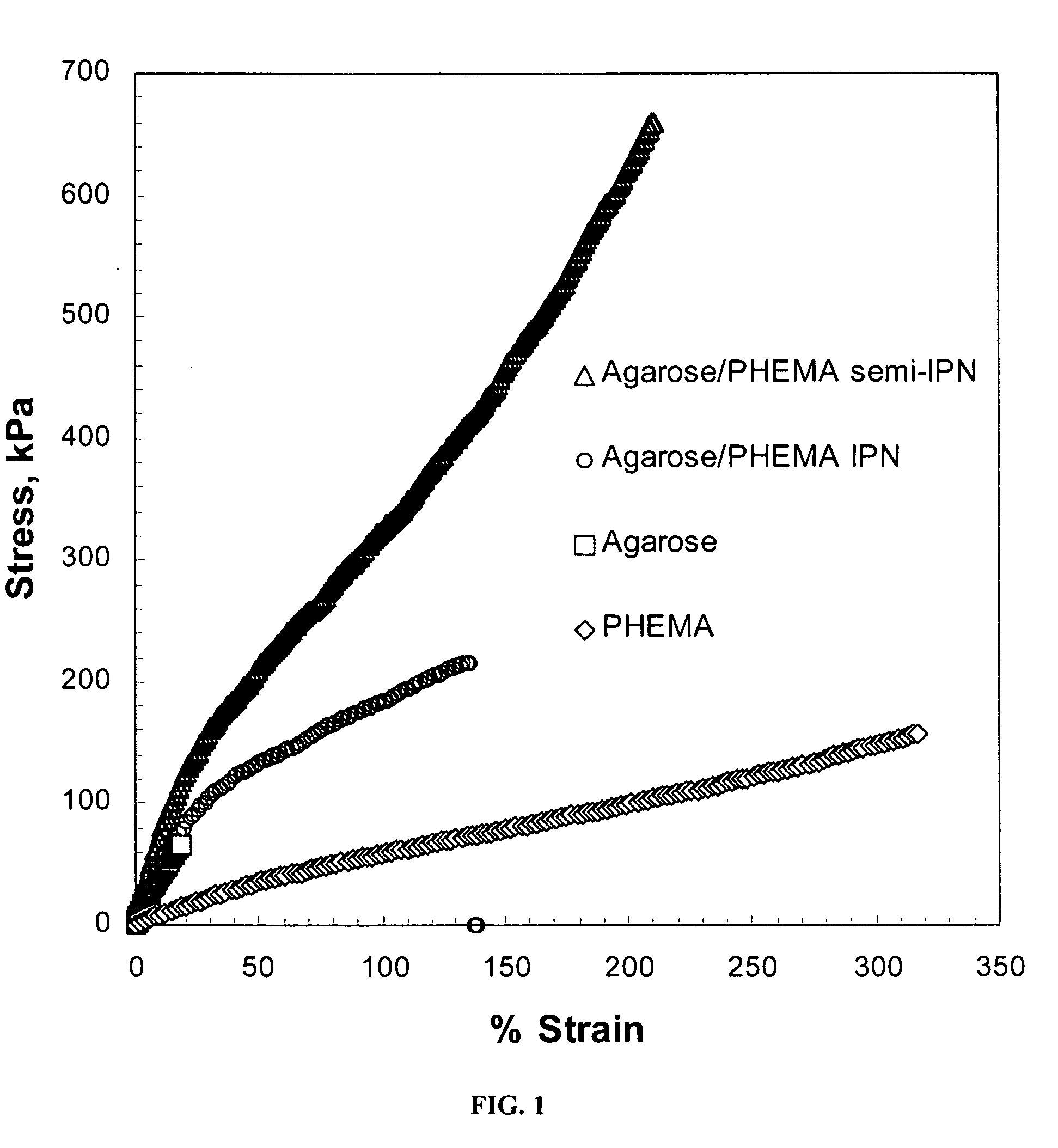
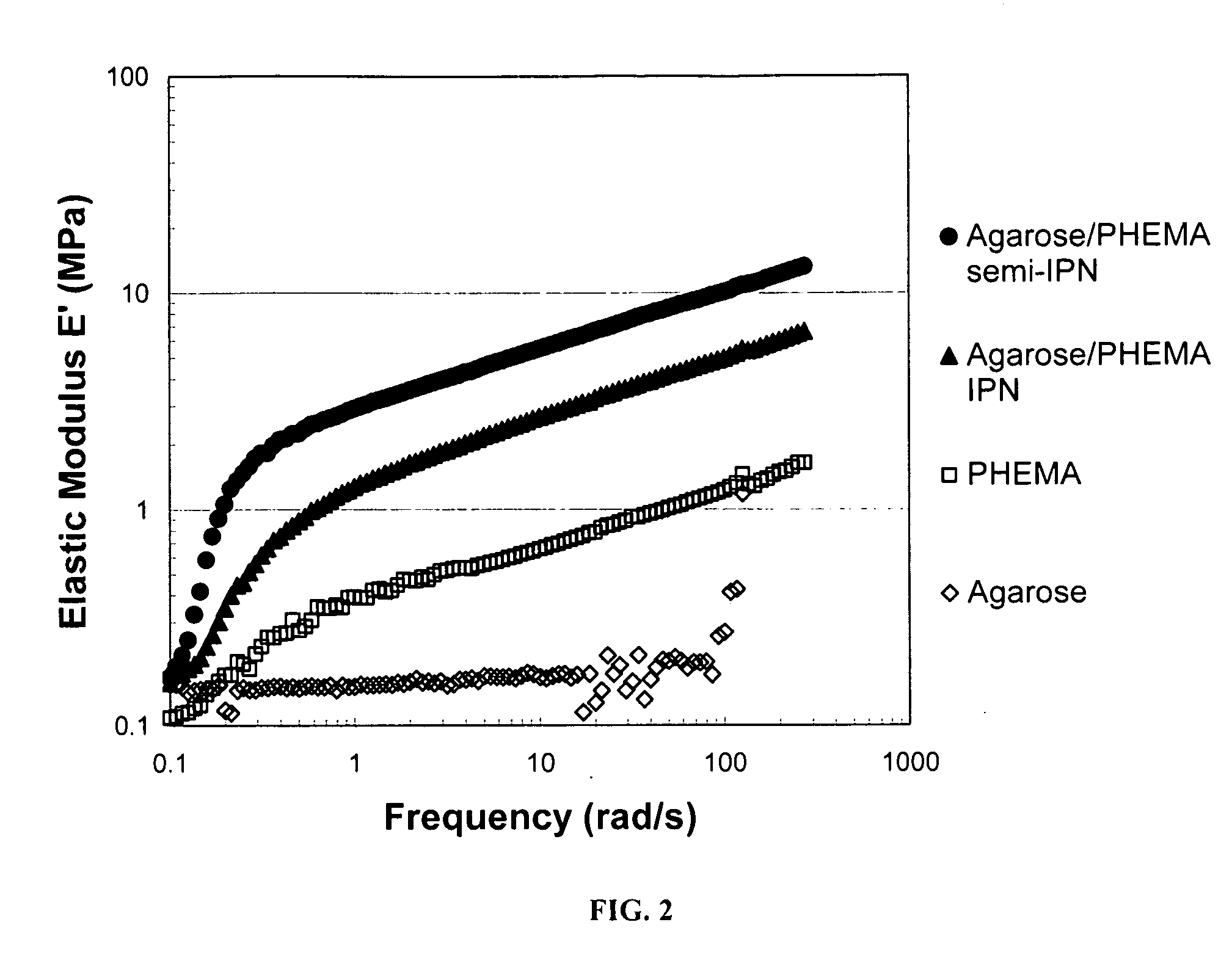
Hydrogel networks having living cells encapsulated therein
ActiveUS20090130755A1High mechanical strengthCell culture supports/coatingCultivating equipmentsCross-linkPolyethylene glycol
The present invention is directed to a hydrogel network comprised of a physically cross-linked polymer and a chemically cross-linked polymer or physically entangled copolymer containing living cells, such as chondrocytes, encapsulated therein. In a preferred aspect, the physically cross-linked polymer is selected from the group consisting of thermally gelling polysaccharides and proteins, such as agarose or gelatin, and the chemically cross-linked or physically entangled polymer is synthesized from a water-soluble vinyl monomer, either as a homopolymer or copolymer, such as polyethylene glycol diacrylate (“PEG-DA”) and 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (“HEMA”).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
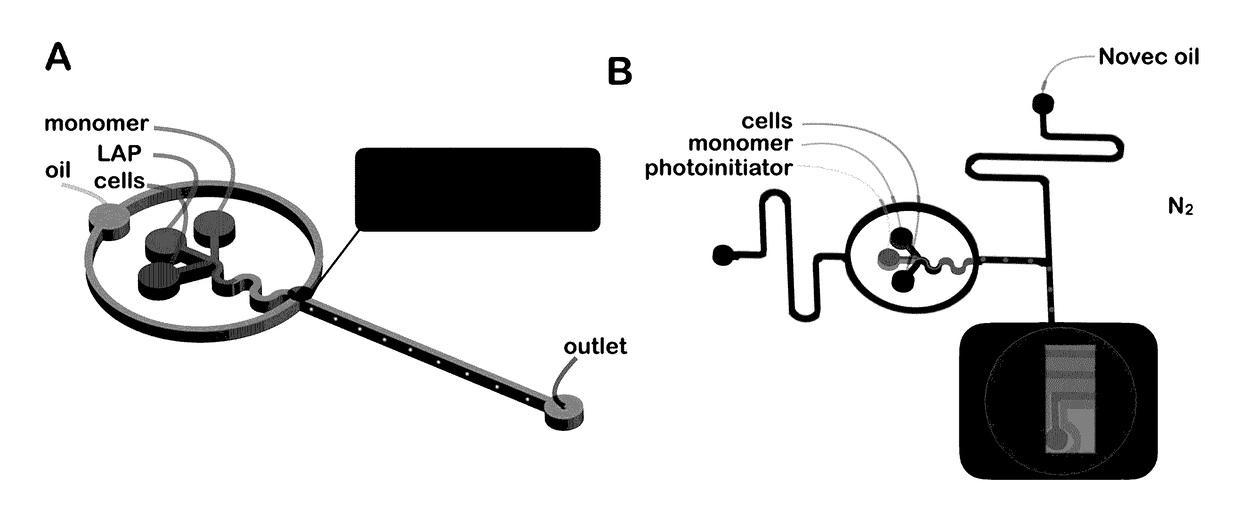
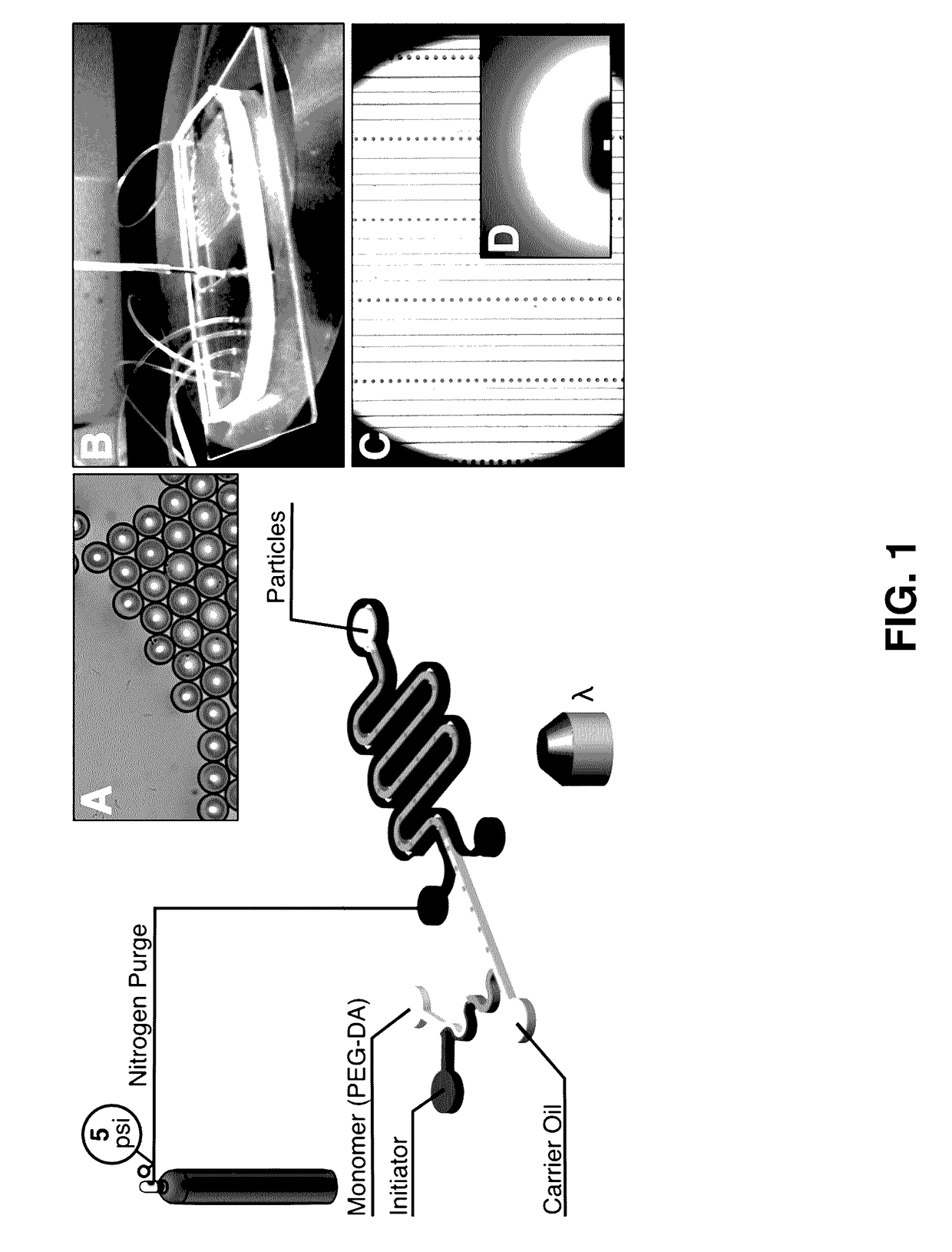
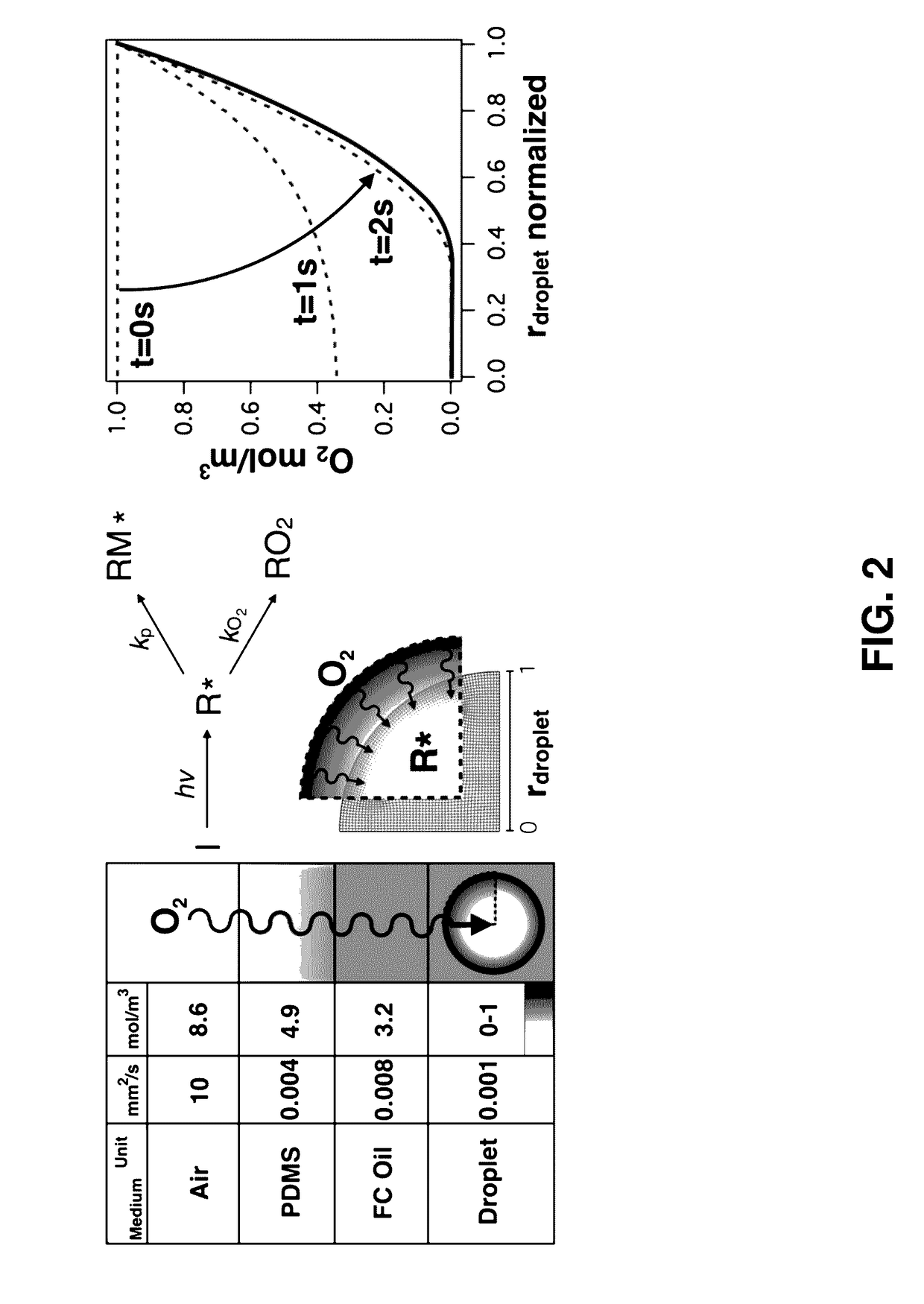
Methods of Generating Microparticles and Porous Hydrogels Using Microfluidics
PendingUS20170145169A1Ability to control the amount of oxygen presentInhibition of polymerizationFlow mixersTransportation and packagingMicrofluidicsAqueous droplet
Provided herein are methods utilizing microfluidics for the oxygen-controlled generation of microparticles and hydrogels having controlled microparticle sizes and size distributions and products from provided methods. The included methods provide the generation of microparticles by polymerizing an aqueous solution dispersed in a non-aqueous continuous phase in an oxygen-controlled environment. The process allows for control of size of the size of the aqueous droplets and, thus, control of the size of the generated microparticles which may be used in biological applications.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Gels for encapsulation of biological materials
InactiveUS7413781B2Facilitated DiffusionGood flexibilitySurgical adhesivesPeptide/protein ingredientsActive matterWater soluble
This invention provides novel methods for the formation of biocompatible membranes around biological materials using photopolymerization of water soluble molecules. The membranes can be used as a covering to encapsulate biological materials or biomedical devices, as a “glue” to cause more than one biological substance to adhere together, or as carriers for biologically active species. Several methods for forming these membranes are provided. Each of these methods utilizes a polymerization system containing water-soluble macromers, species, which are at once polymers and macromolecules capable of further polymerization. The macromers are polymerized using a photoinitiator (such as a dye), optionally a cocatalyst, optionally an accelerator, and radiation in the form of visible or long wavelength UV light. The reaction occurs either by suspension polymerization or by interfacial polymerization. The polymer membrane can be formed directly on the surface of the biological material, or it can be formed on material, which is already encapsulated.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
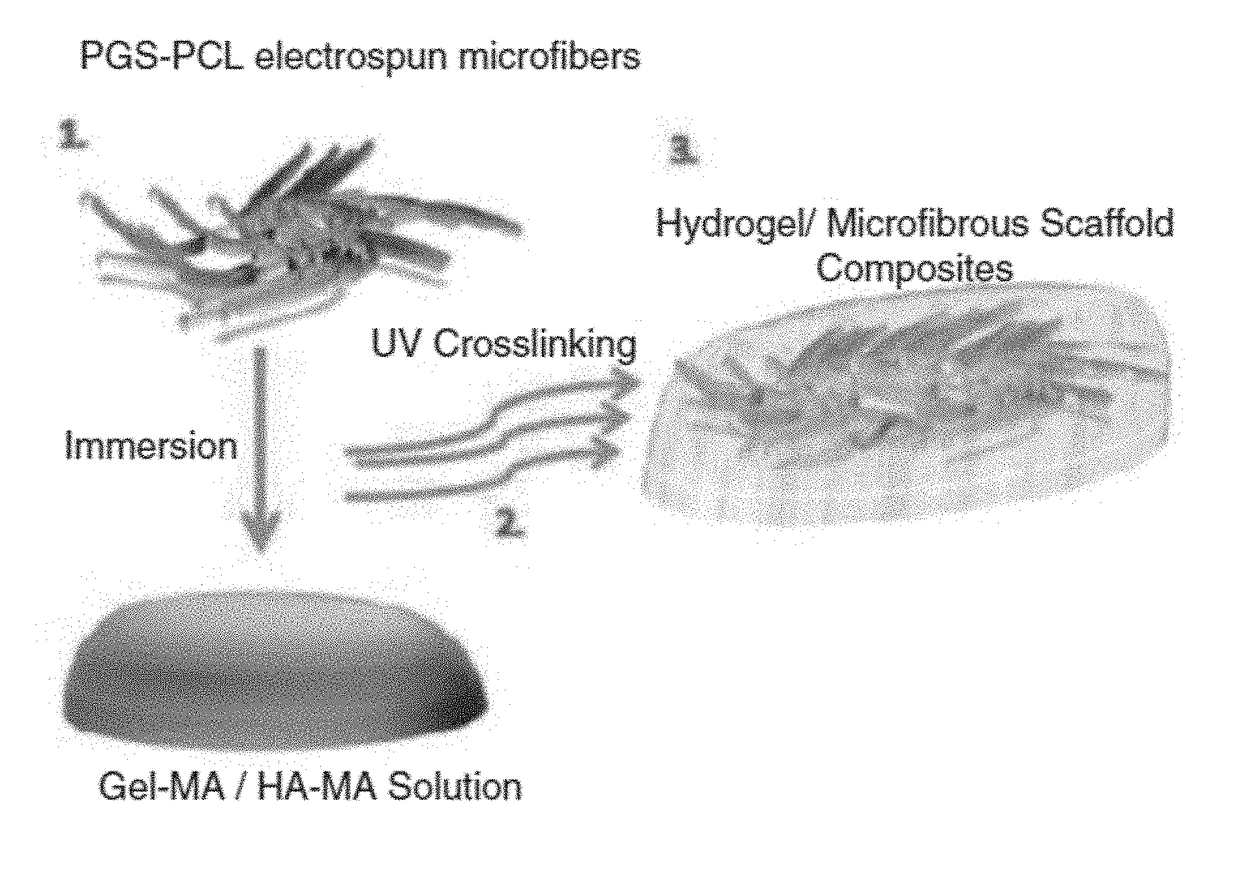
Scaffold for skin tissue engineering and a method of synthesizing thereof
ActiveUS20180117215A1Improve mechanical propertiesFacilitates penetration and imbibitionConnective tissue peptidesSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSwelling ratioGlycerol
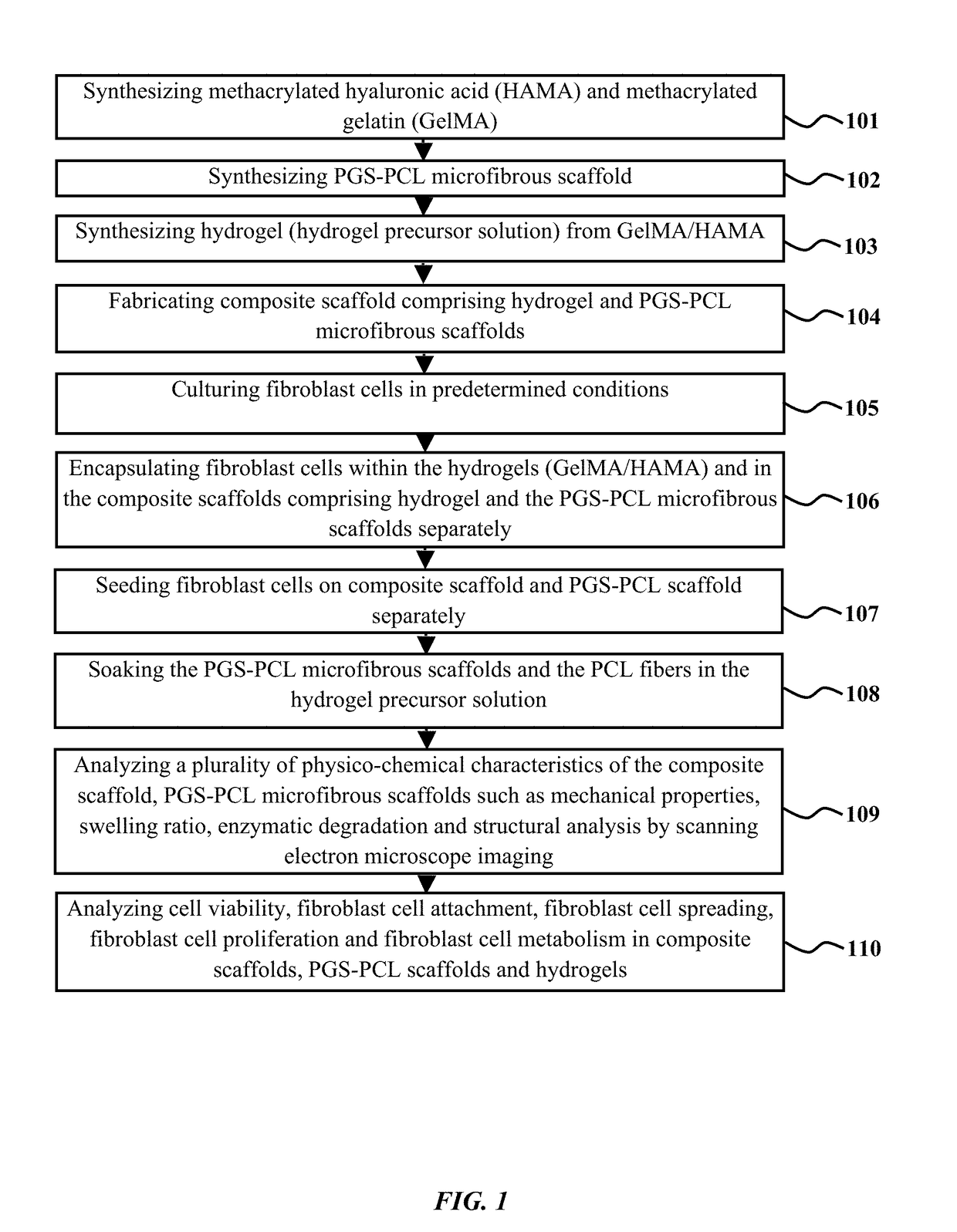
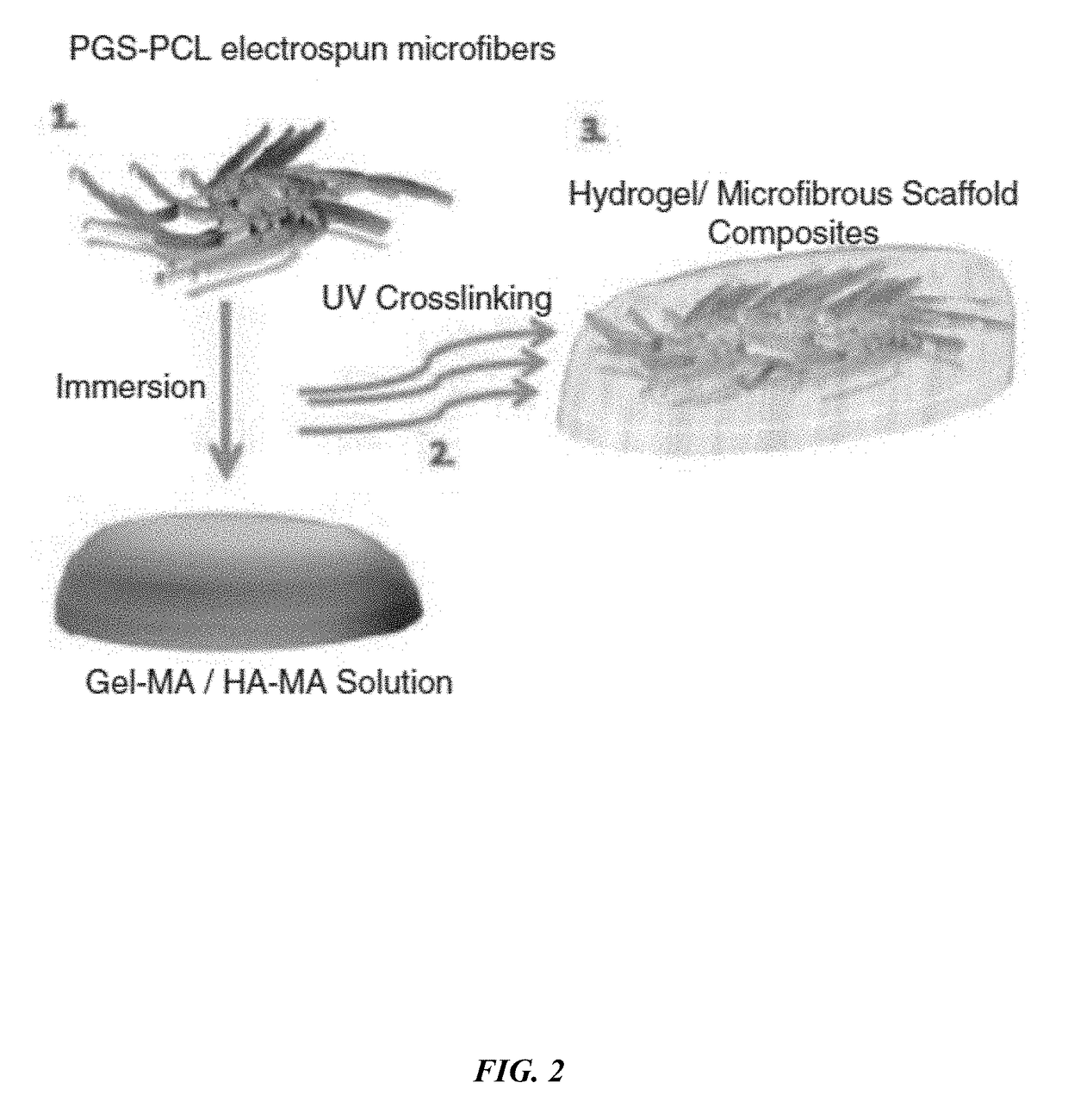
The embodiments herein disclose a method of fabricating composite scaffolds for skin tissue regeneration. The methacrylated hyaluronic acid (HAMA) and methacrylated gelatin (GelMA) are synthesized. The poly (glycerol sebacate)-poly(ε-caprolactone) (PGS-PCL) microfibrous scaffolds are synthesized. The hydrogel is synthesized. The composite scaffold comprising hydrogel and poly (glycerol sebacate)-poly(ε-caprolactone) (PGS-PCL) microfibrous scaffolds is fabricated. A plurality of physico-chemical characteristics of the composite scaffold comprising hydrogel and poly (glycerol sebacate)-poly(ε-caprolactone) (PGS-PCL) microfibrous scaffolds are analysed. The physico-chemical characteristics comprises mechanical properties, swelling ratio and enzymatic degradation and scanning electron microscope imaging. The fibroblast cells are encapsulated within the composite scaffold comprising hydrogel and poly (glycerol sebacate)-poly(ε-caprolactone) (PGS-PCL) microfibrous scaffolds and hydrogels. The fibroblast cells are seeded on composite scaffold and PGS-PCL scaffold. The fibroblast cell viability, fibroblast cell attachment, fibroblast cell spreading, fibroblast cell proliferation and fibroblast cell metabolism are analysed in composite scaffolds, PGS-PCL scaffolds and hydrogels.
Owner:ESLAMI MARYAM +2
Delivery of an organized tissue to an organism
InactiveUS20050260178A1Shortening of the organized tissue or lengtheningChange lengthBiocideGenetic material ingredientsBiological bodyMammal
A sleeve organized tissue is formed of a biocompatible structure surrounding organized tissue in at least one dimension and along a length of the tissue. In certain preferred embodiments the tissue is attached to the sleeve, subjecting the organized tissue to internal tension within the sleeve. Methods of providing organized tissue within a sleeve and delivering protein to a mammal are also disclosed.
Owner:VANDENBURGH HERMAN H
Non-disruptive three-dimensional culture and harvest system for anchorage-dependent cells
InactiveUS6905875B2Easy to useEasily brokenHepatocytesDead animal preservationCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
A non-disruptive three-dimensional culture system allows cell growth and proliferation in three dimensions, permitting cell splitting without subjecting cells to disruptive conditions that affect cell structure and functions. An extracellular matrix provides a good environment for culturing or co-culturing anchorage-dependent cells. The cells cultured this manner can be readily used in such applications as cell transplantation, tissue engineering seeding of cells on scaffolds, and other applications that require immediate availability of functioning cells.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com