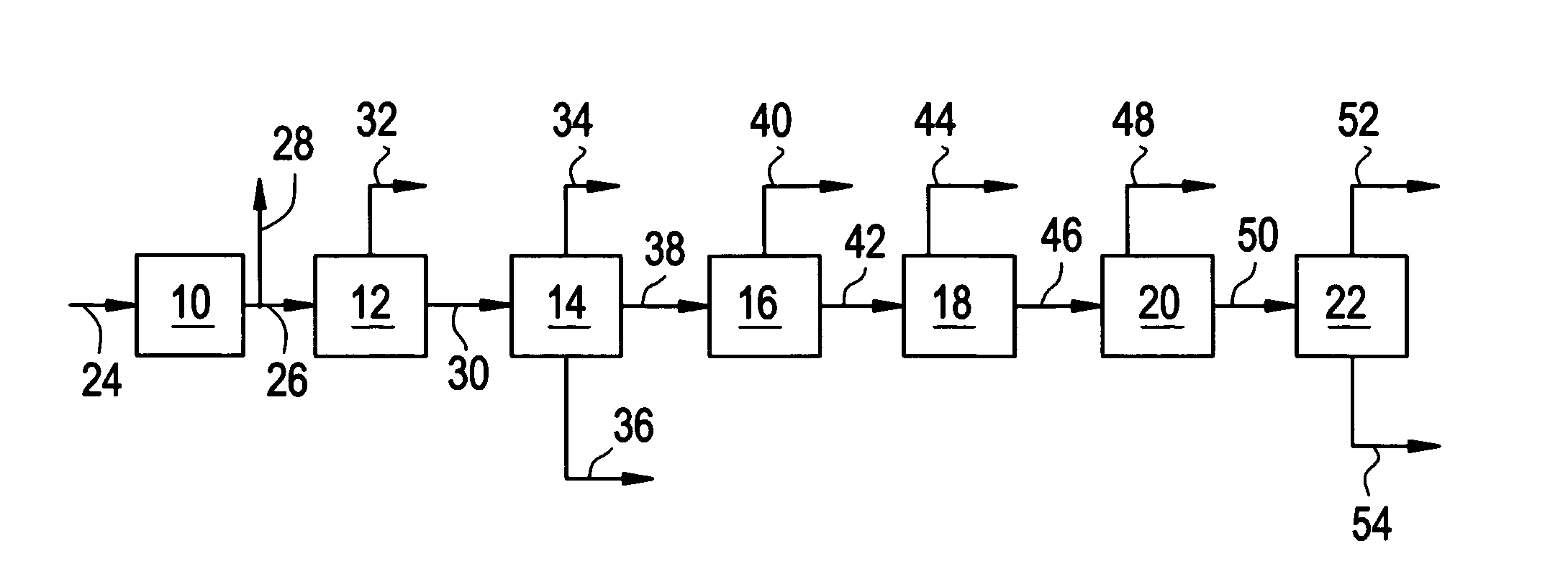
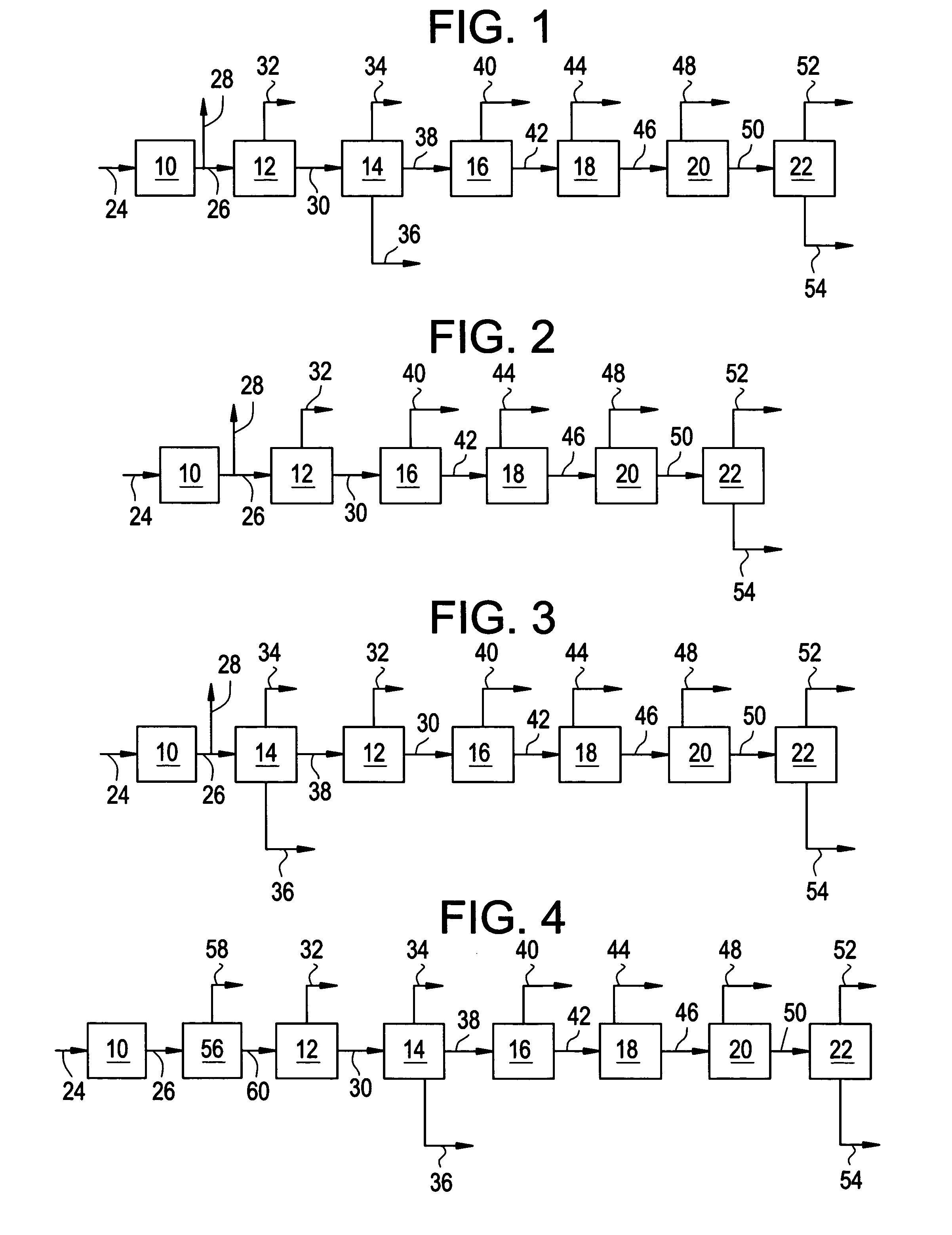
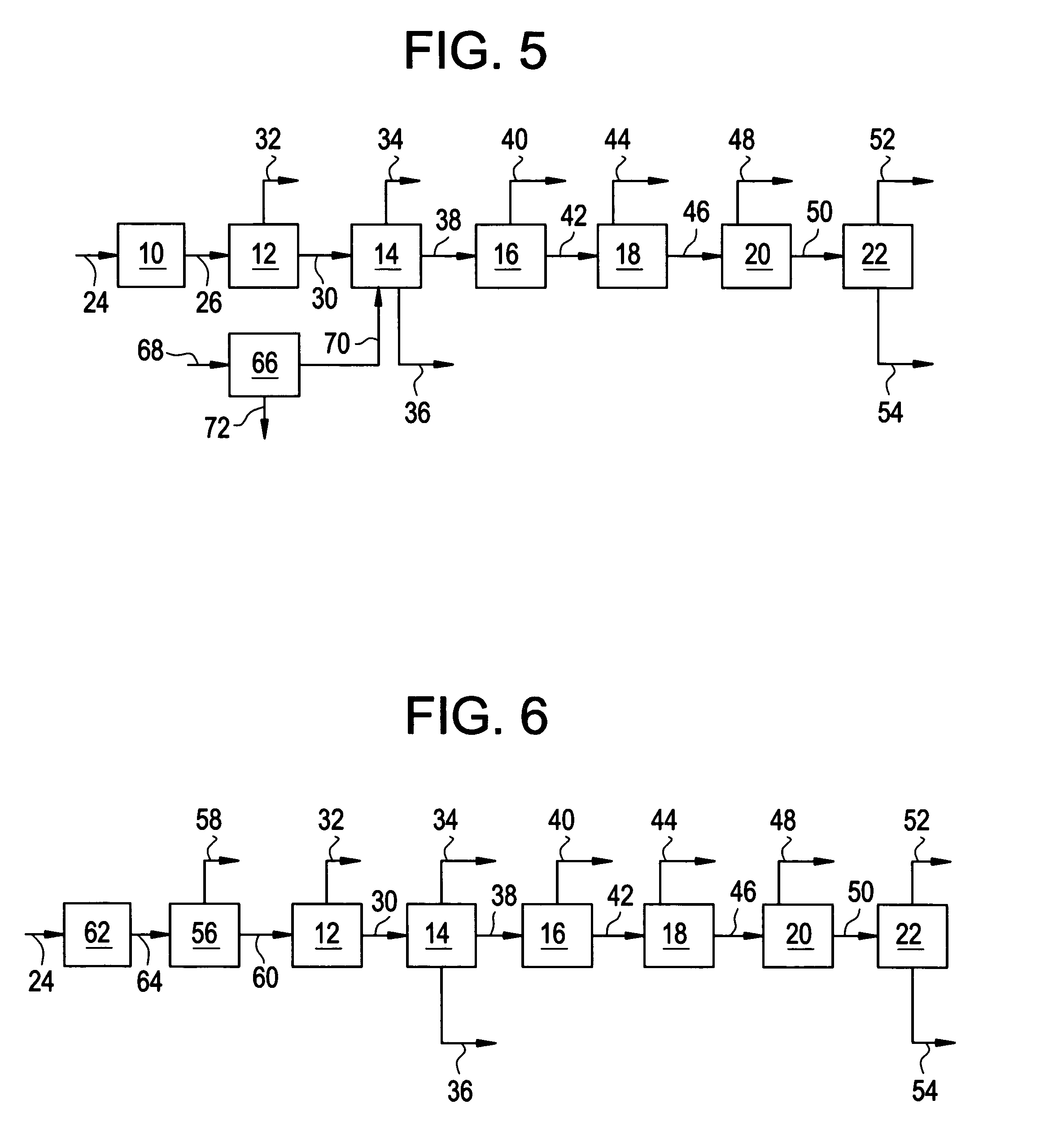
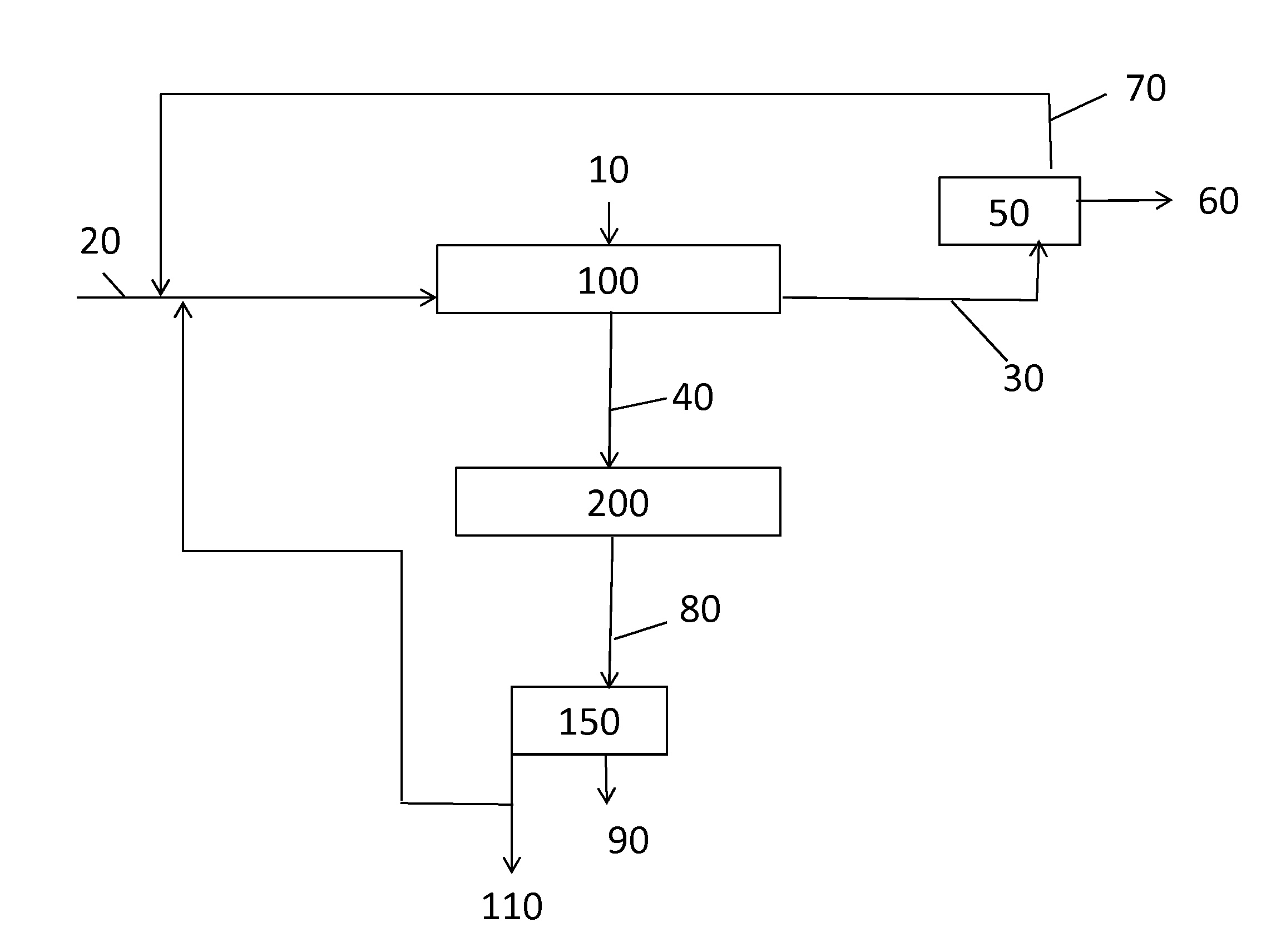
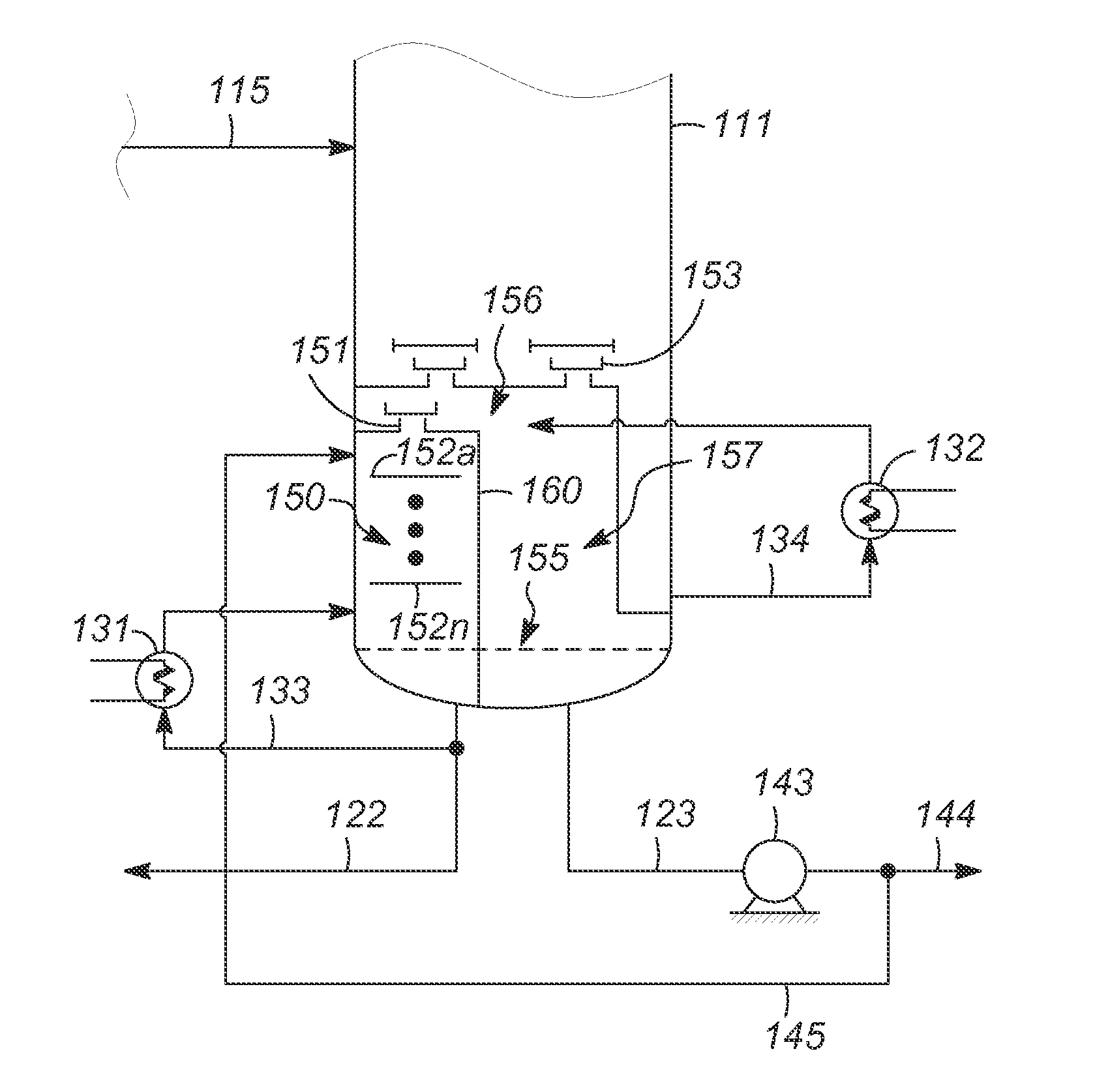
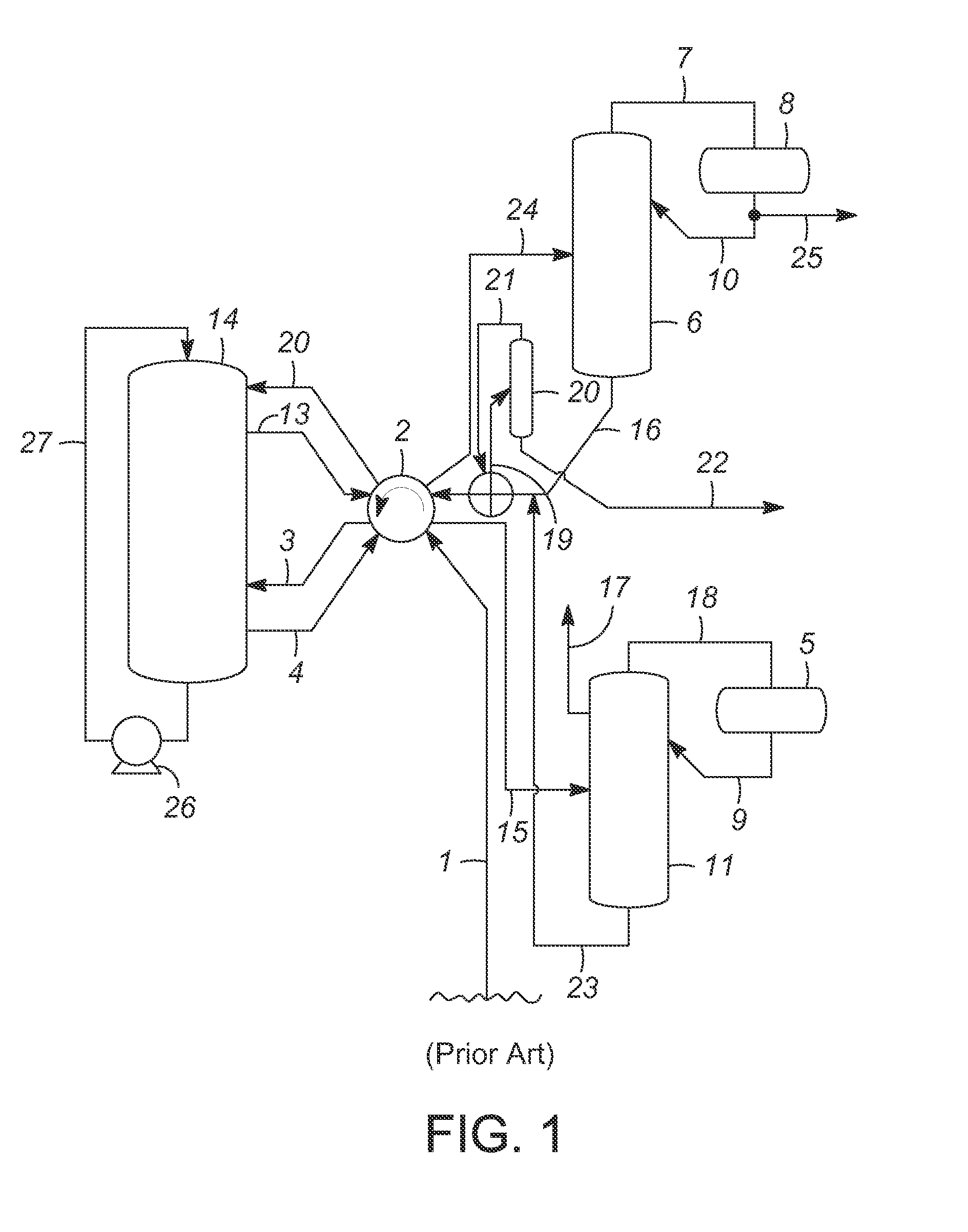
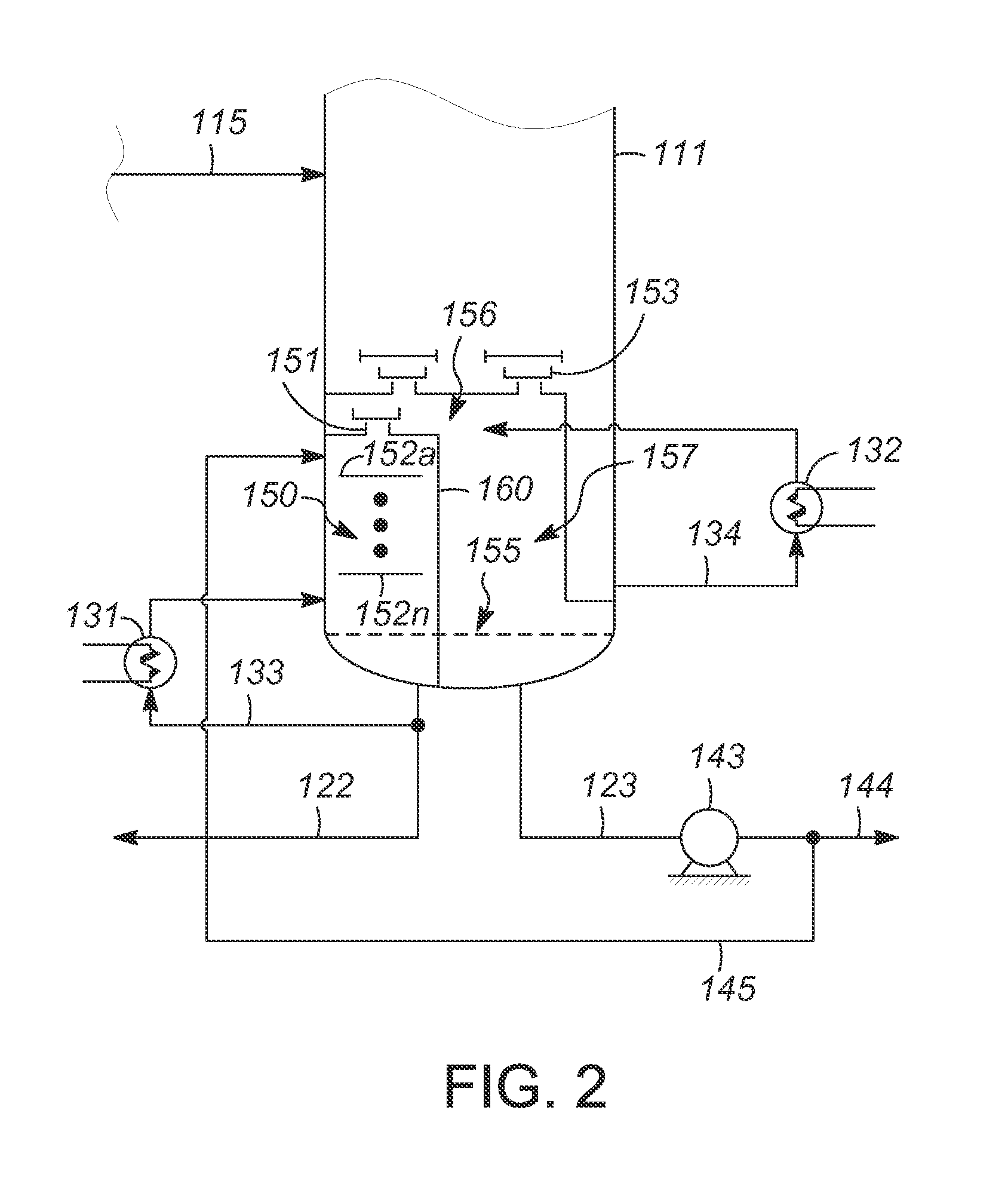
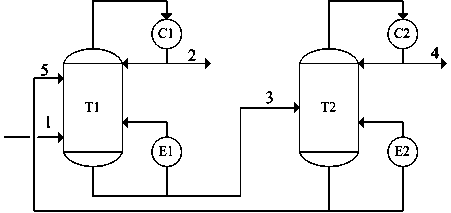
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
105results about "Azeotropic/extractive distillation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Process for generating pure benzene from reformed gasoline
InactiveUS6124514AReduce benzene contentAchieve separationThermal non-catalytic crackingCatalytic crackingBenzeneExtractive distillation
A process is disclosed for generating pure aromatic compounds from a reformed gasoline which contains aromatic compounds, olefins, diolefin, and triolefins, which comprises the steps of: (a) selectively hydrogenating the olefins, diolefins and triolefins in the reformed gasoline to obtain a mixture of hydrogenated, non-aromatic compounds and aromatic compounds; and (b) separating the aromatic compounds from the hydrogenated, non-aromatic compounds in the mixture formed during step (a) by either extractive distillation, liquid-liquid extraction or both to obtain the pure aromatic compounds.
Owner:BASF AG
Process for separating C5 cuts obtained from a petroleum cracking process
ActiveUS20030100809A1Improve catalytic performanceHigh activityLiquid hydrocarbon mixtures productionDistillation purification/separationAlkyneSolvent
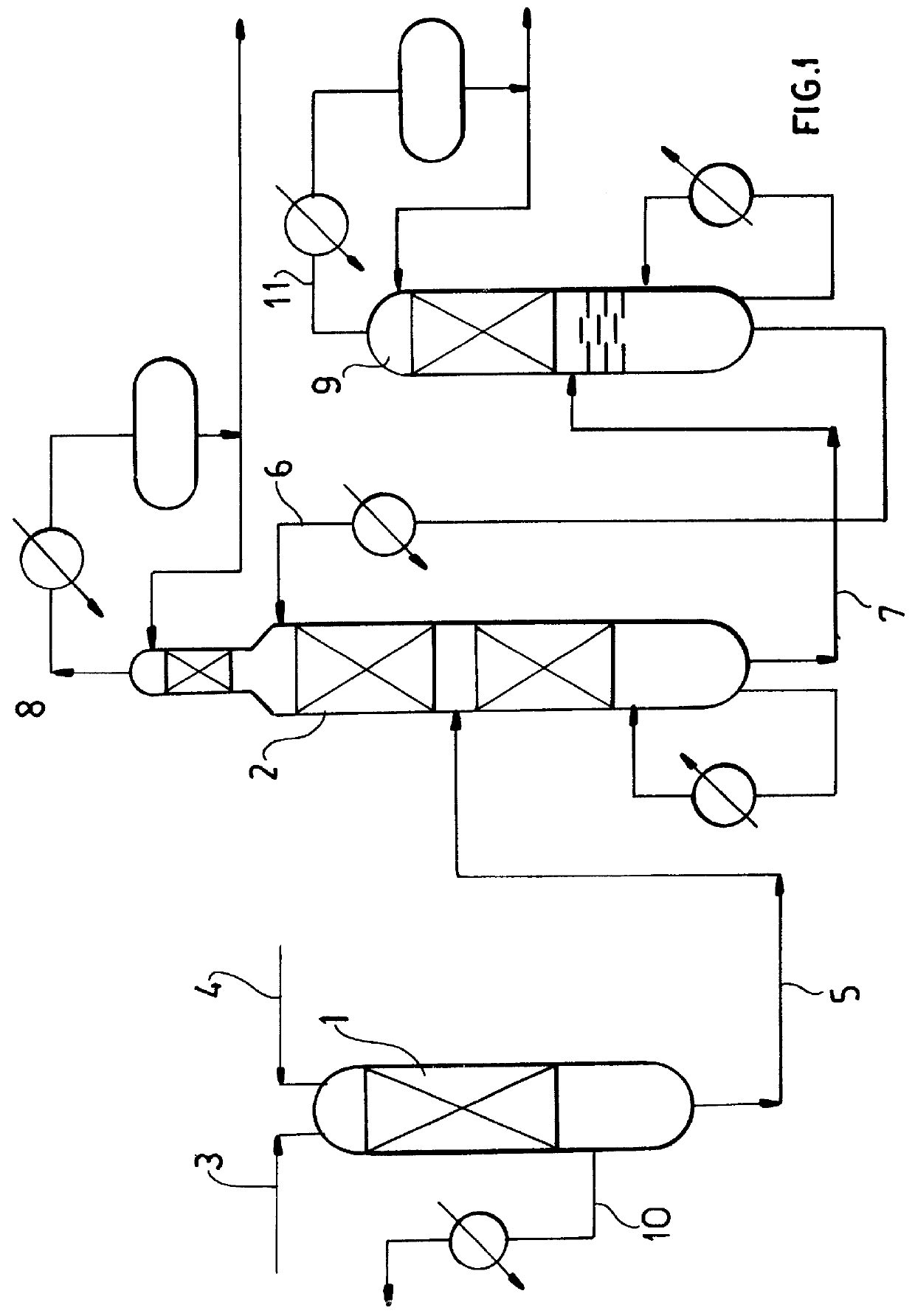
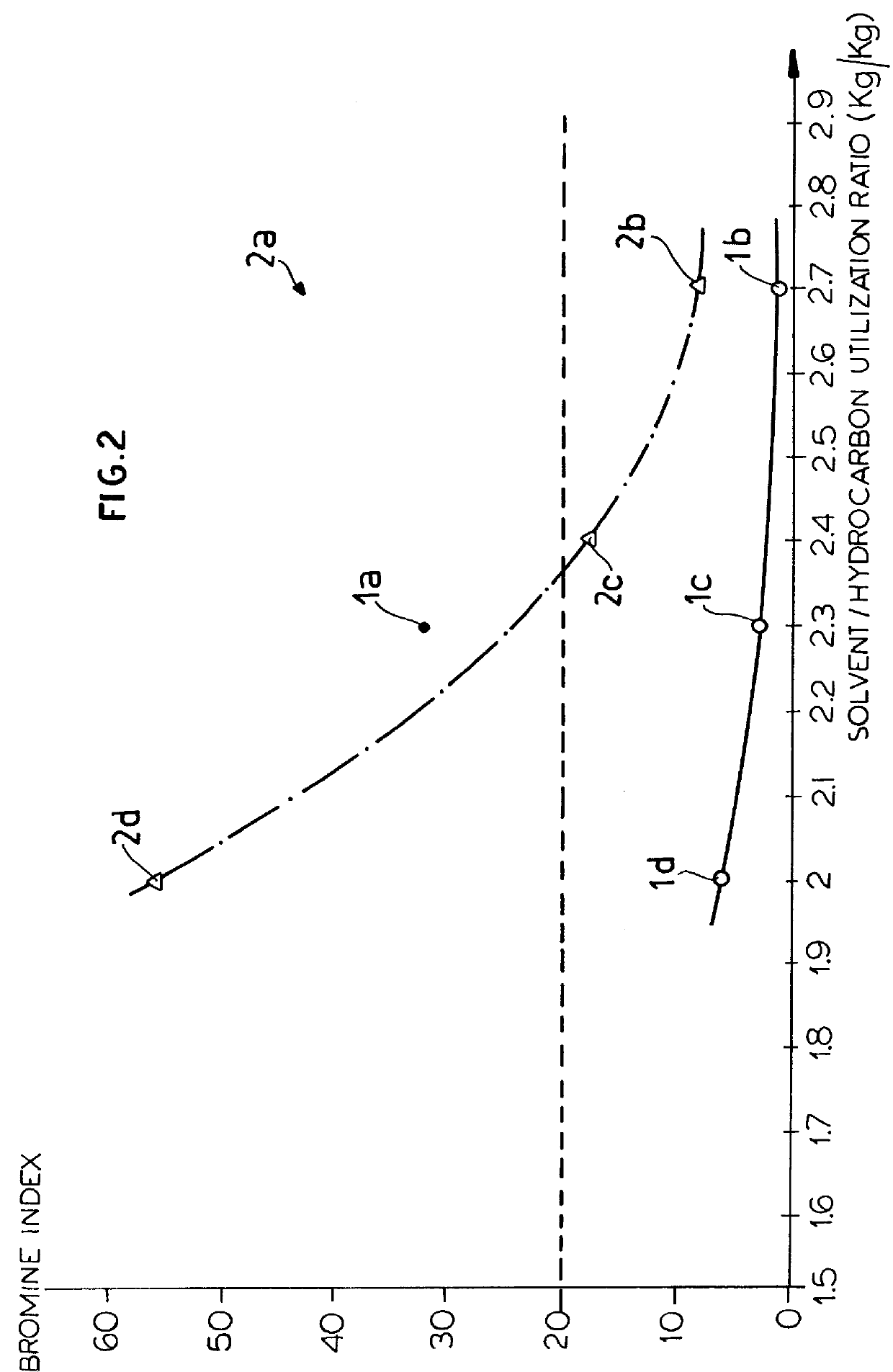
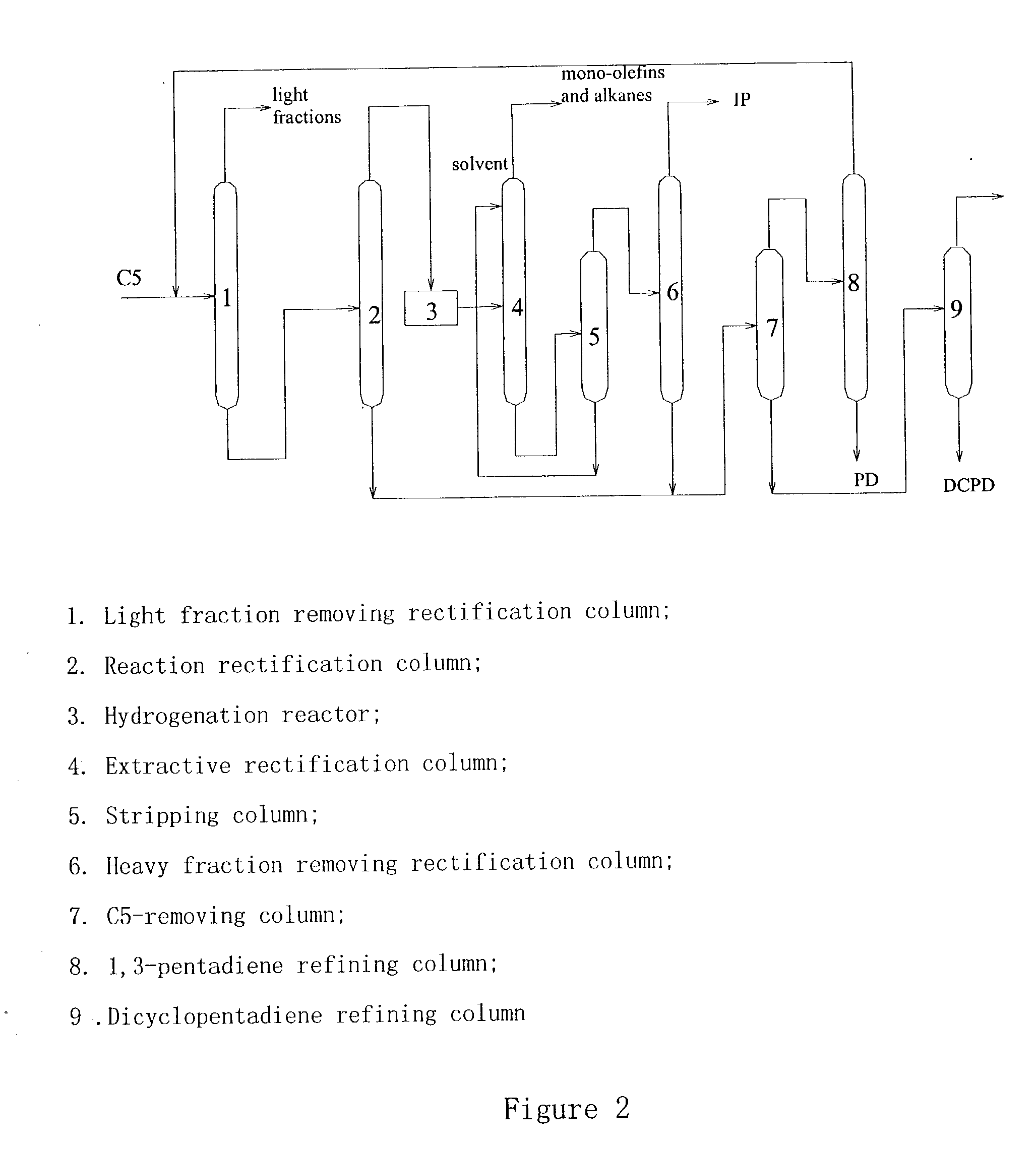
The present invention relates to a process for separating the isoprene, 1,3-pentadiene and dicyclopentadiene from a C5 cuts, comprising dimerization of the cyclopentadiene and selective catalytic hydrogenation. The second extractive rectification step can be omitted, because the alkynes are removed through selective catalytic hydrogenation prior to the extractive rectification. As a result, the solvent-recovering units can be simplified, and thus the process as a whole can be optimized. Correspondingly, the investment and energy consumption, the operation cost, and finally the production cost can be substantially reduced.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Process for increasing production of benzene from hydrocarbon mixture
ActiveUS20060287564A1Increase productivityImprove efficiencyHydrocarbon by isomerisationRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonBenzeneHydrocarbon mixtures
A process for increasing the production of benzene from a hydrocarbon mixture. A process for producing an aromatic hydrocarbon mixture and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) from a hydrocarbon mixture, and a solvent extraction process for separating and recovering polar hydrocarbons from a hydrocarbon mixture containing polar hydrocarbons (that is, aromatic hydrocarbons) and nonpolar hydrocarbons (that is, non-aromatic hydrocarbons) are integrated, thereby it is possible to increase the production of benzene.
Owner:SK INNOVATION CO LTD
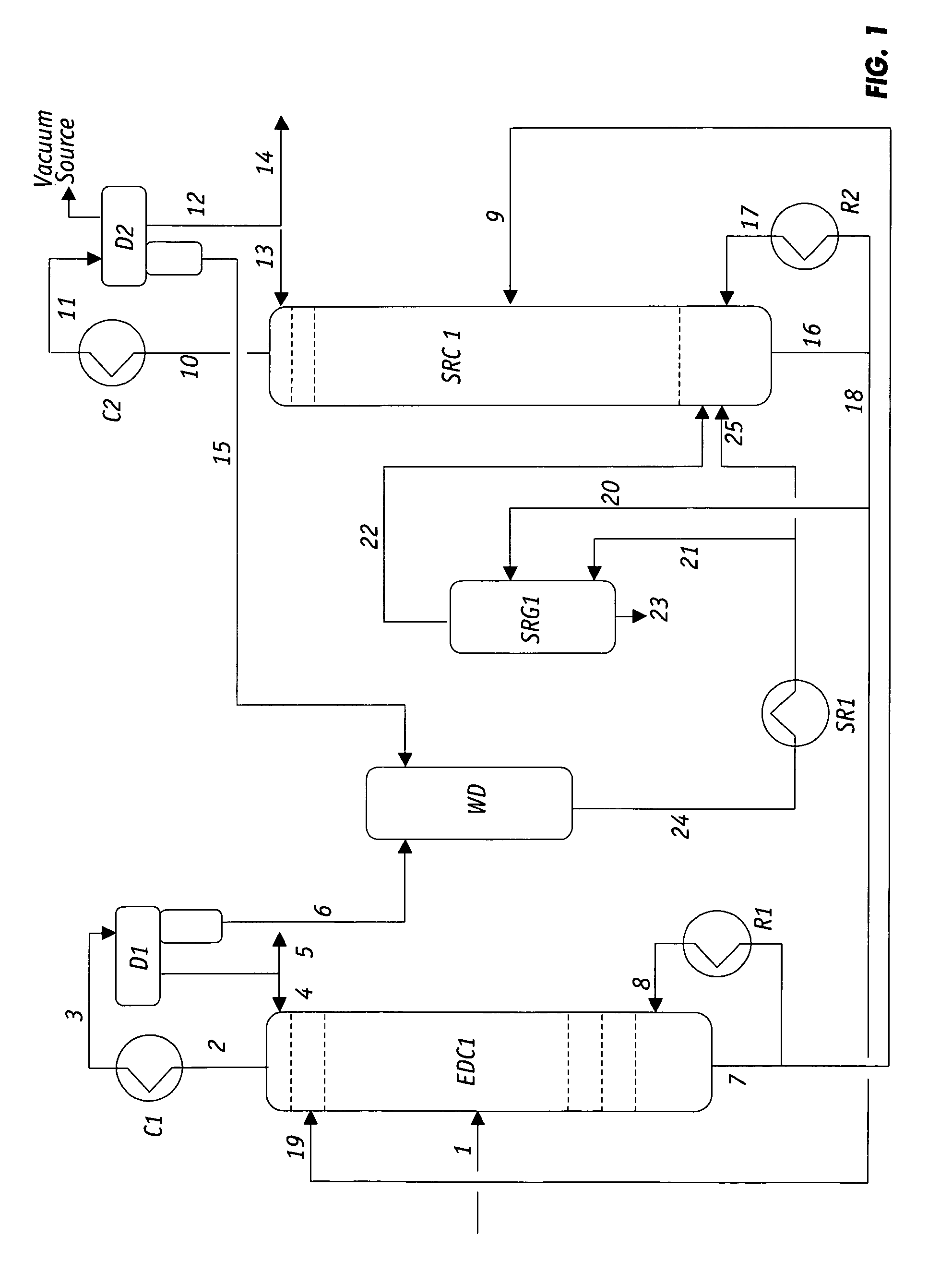
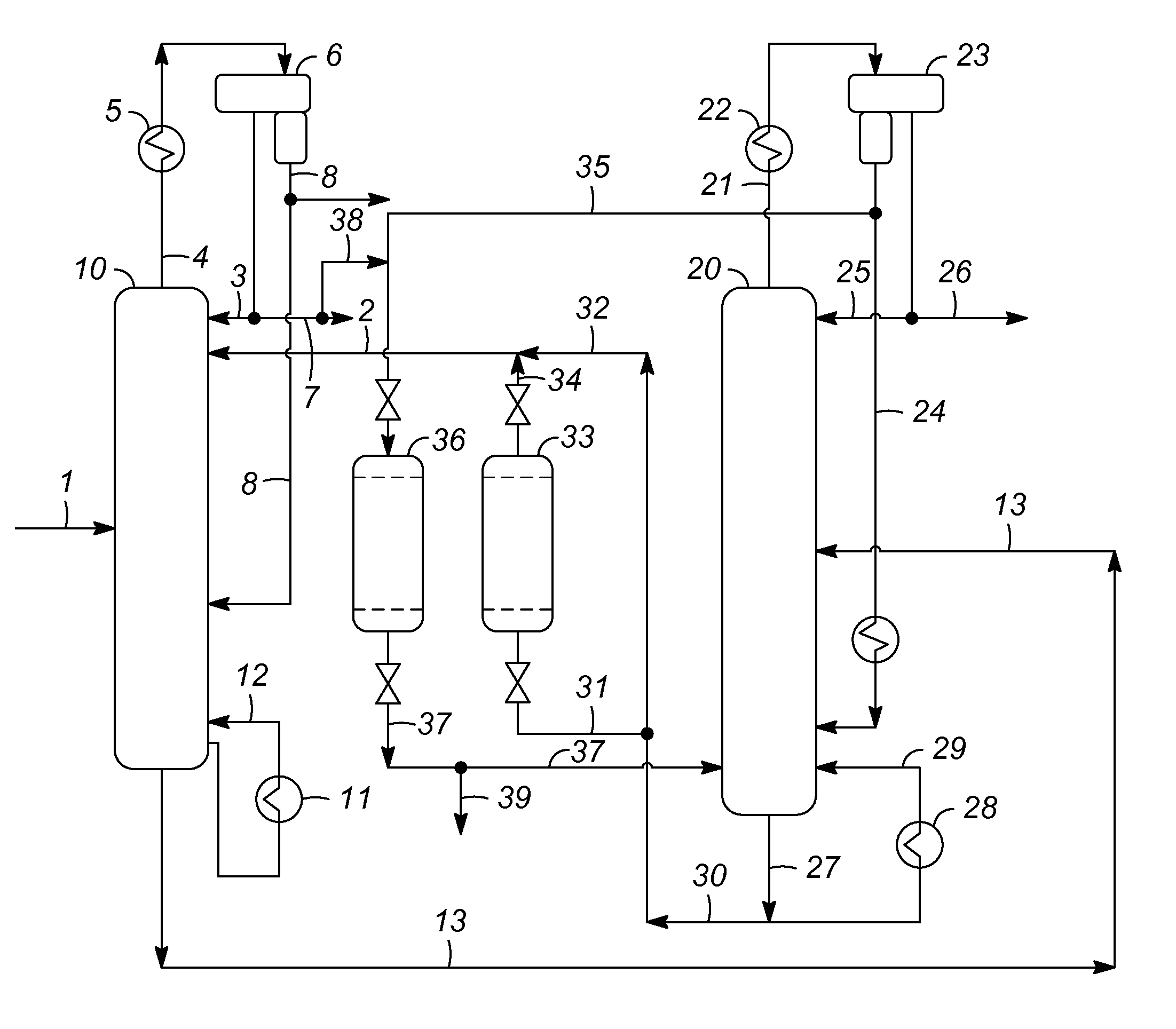
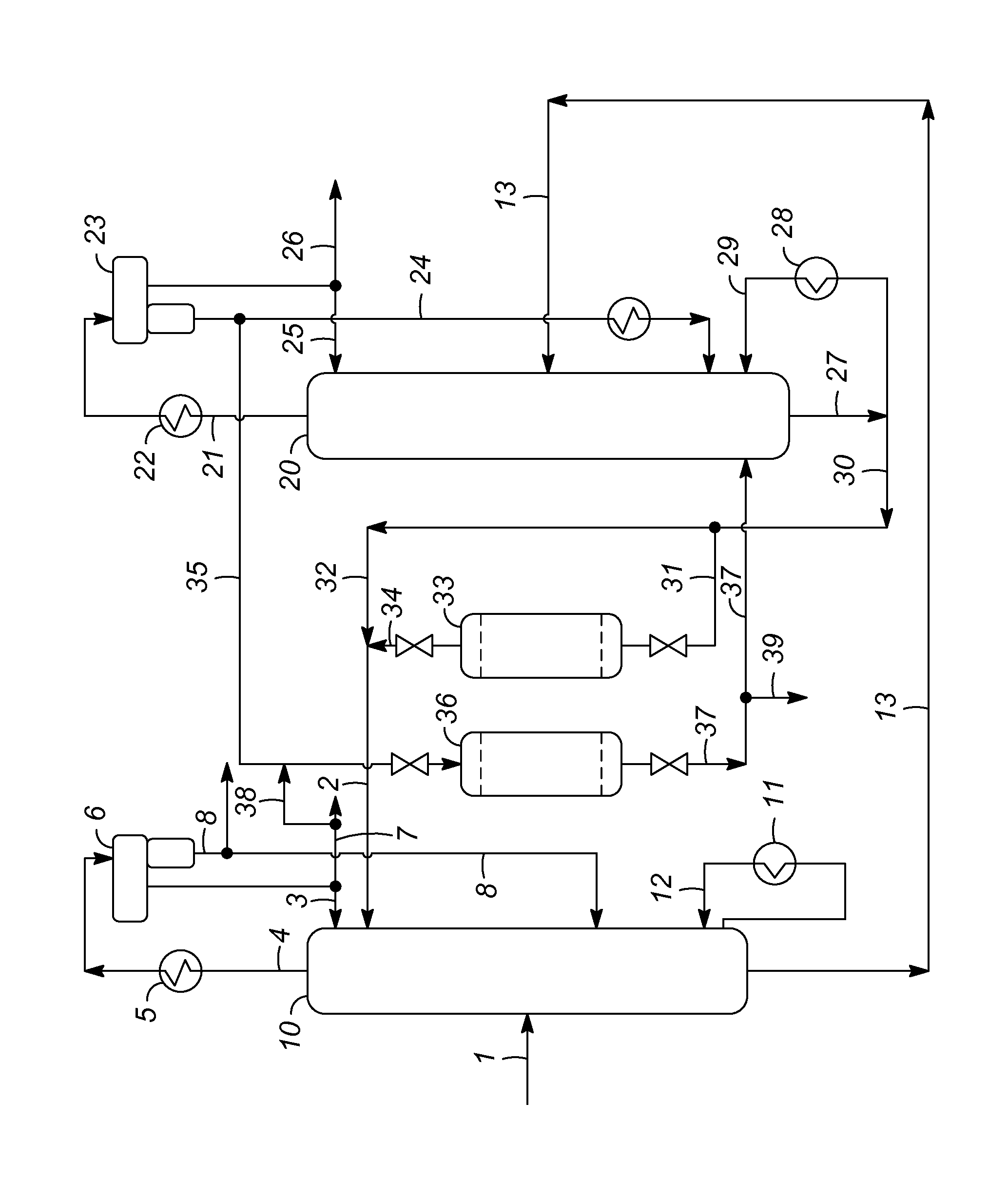
Extractive distillation process for recovering aromatics from petroleum streams
InactiveUS7666299B2Treatment with plural serial cracking stages onlyHydrocarbon oils refiningAlkaneExtractive distillation
A process for recovering polar hydrocarbons from non-polar hydrocarbons, such as aromatics from non-aromatics, naphthenes from paraffins and isoparaffins, or olefins from paraffins and isoparaffins, in feed mixtures containing at least a measurable amount of heavier hydrocarbons. This improved extractive distillation (ED) process recovers aromatic hydrocarbons including benzene, toluene, and xylenes from the C6-C8 petroleum streams containing a measurable amount of C9+ hydrocarbons. The ED process also recovers benzene and toluene from the C6-C7 petroleum streams containing a measurable amount of C8+ hydrocarbons. The ED solvent utilized to recover and purify the aromatic hydrocarbons from the petroleum stream with a heavier than intended feedstock of hydrocarbons is also regenerated and recovered.
Owner:AMT INT INC +1
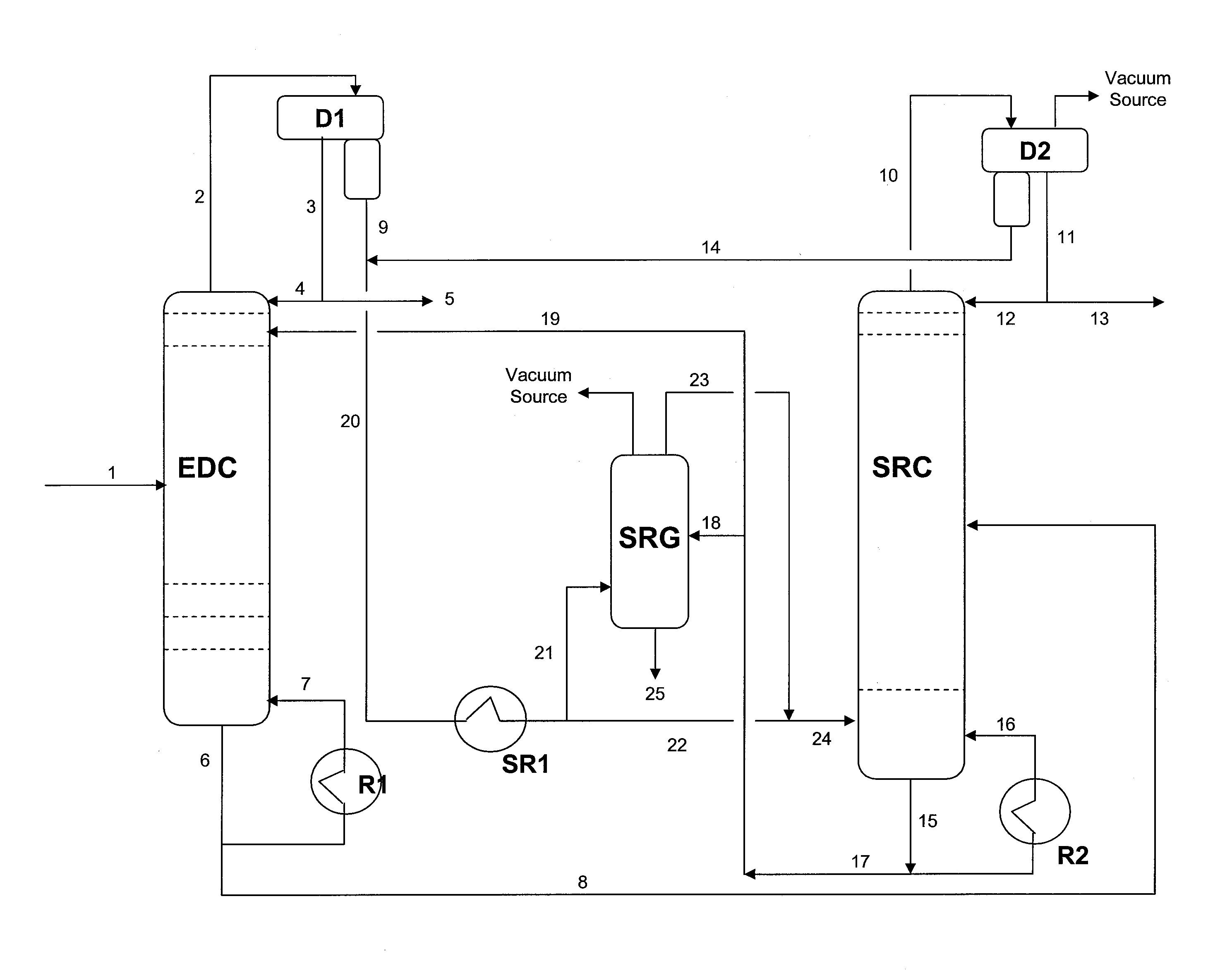
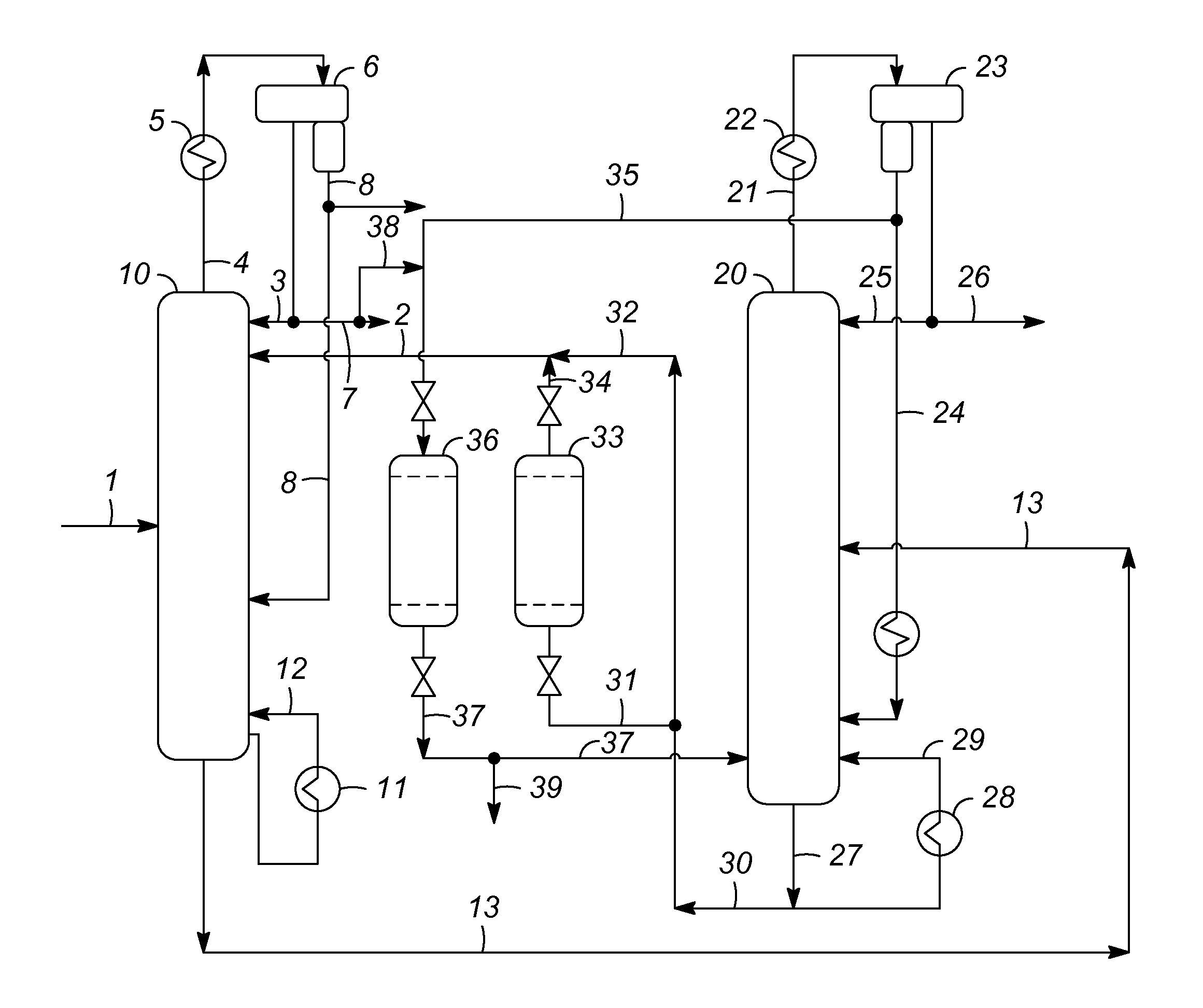
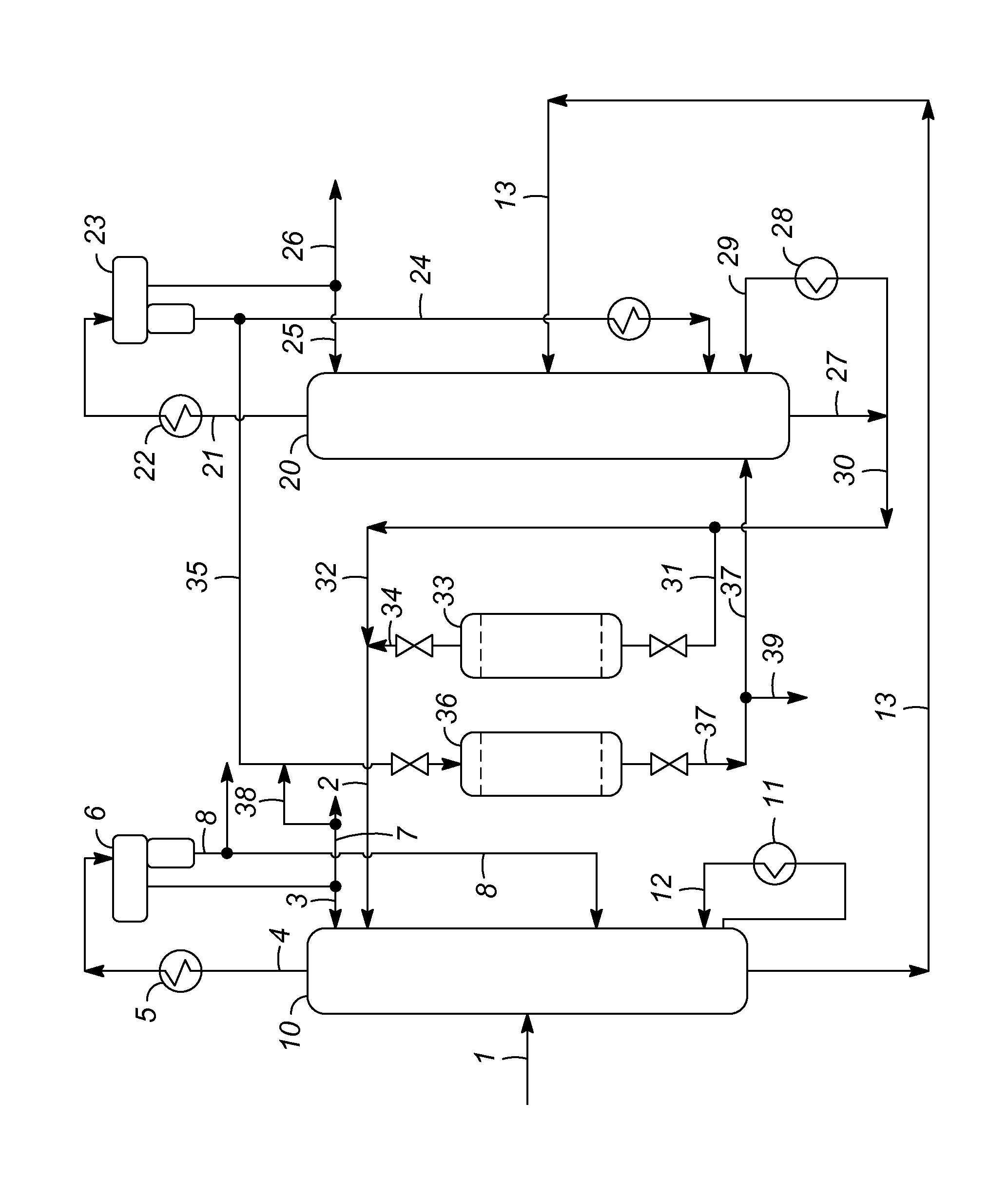
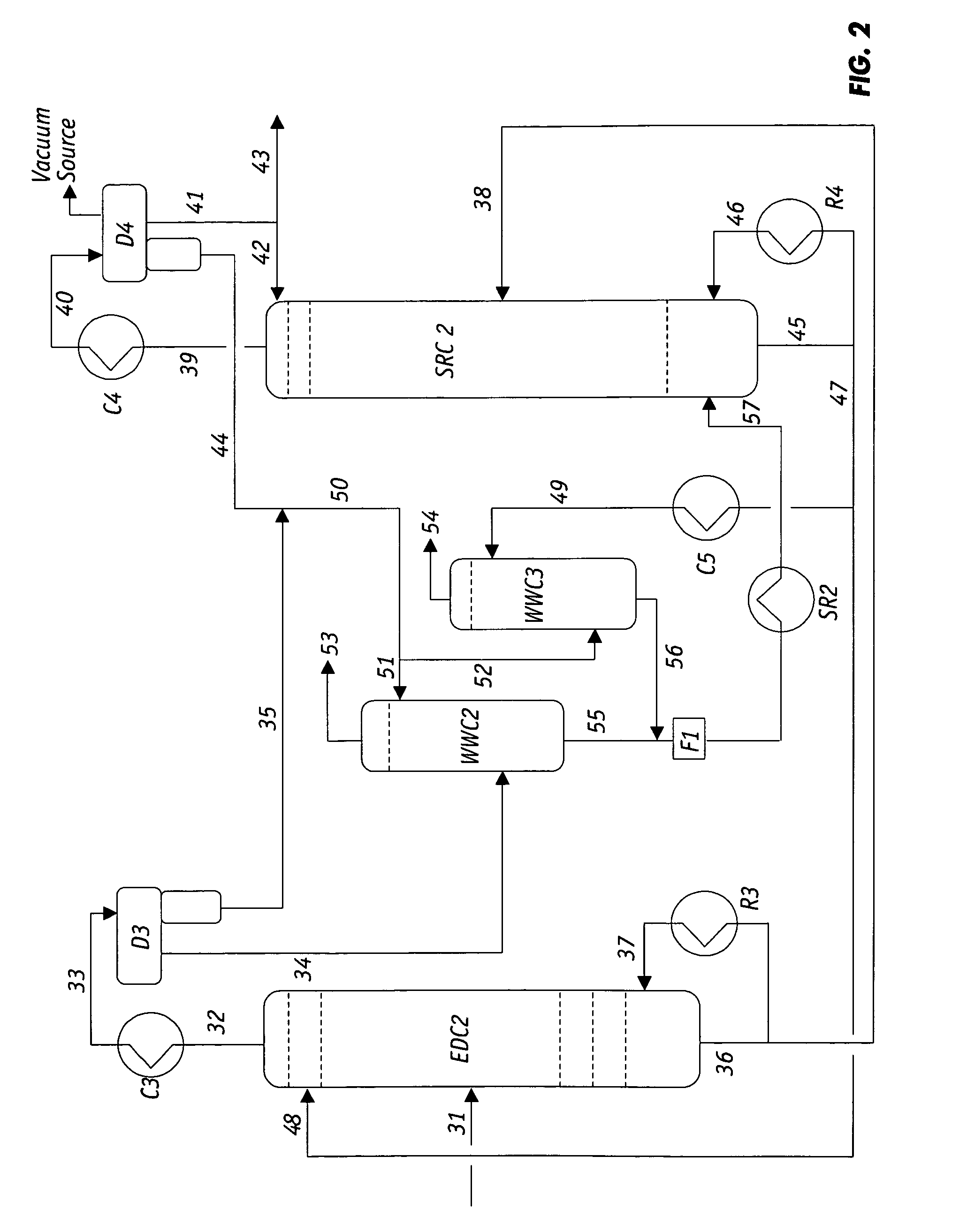
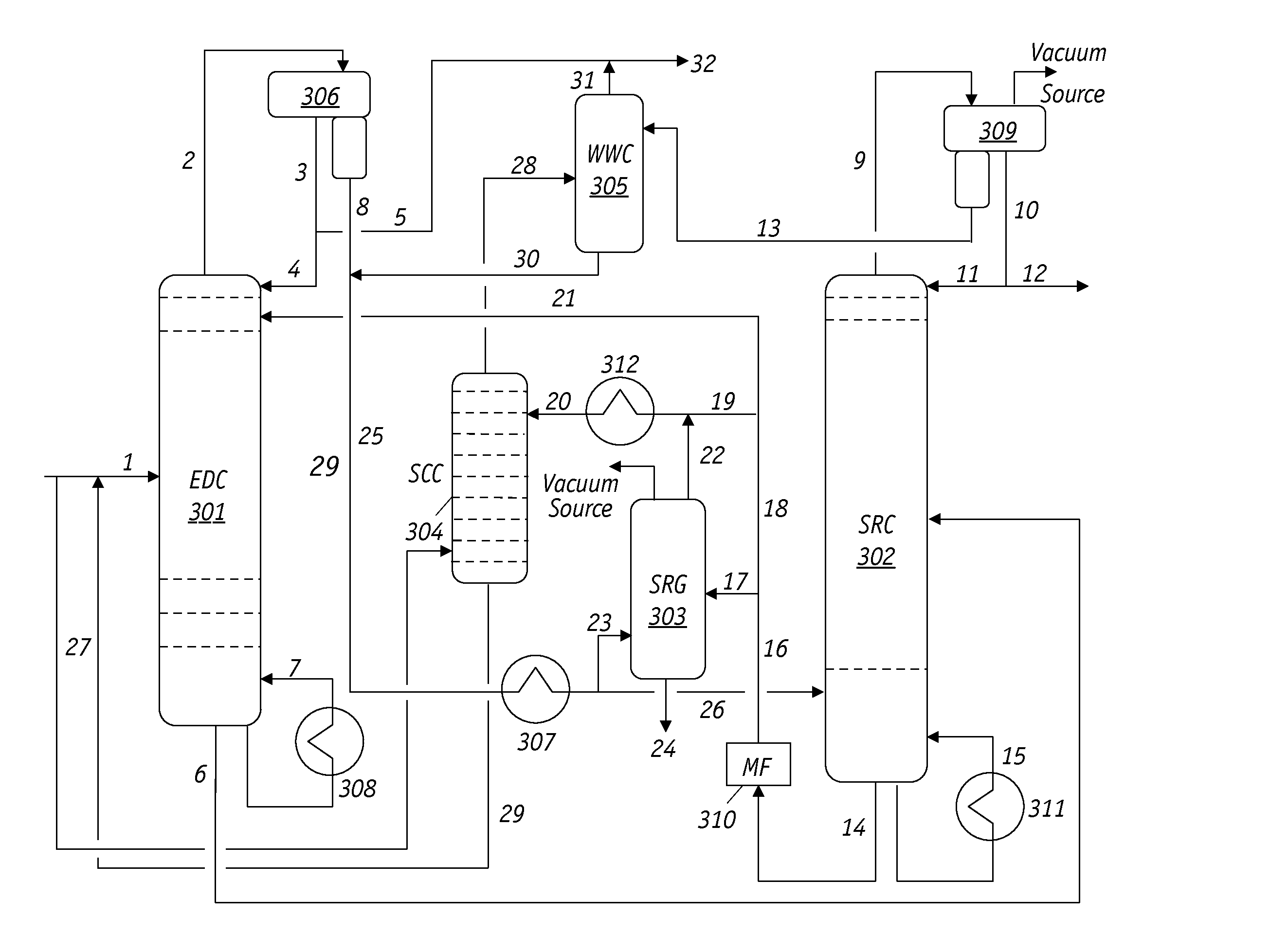
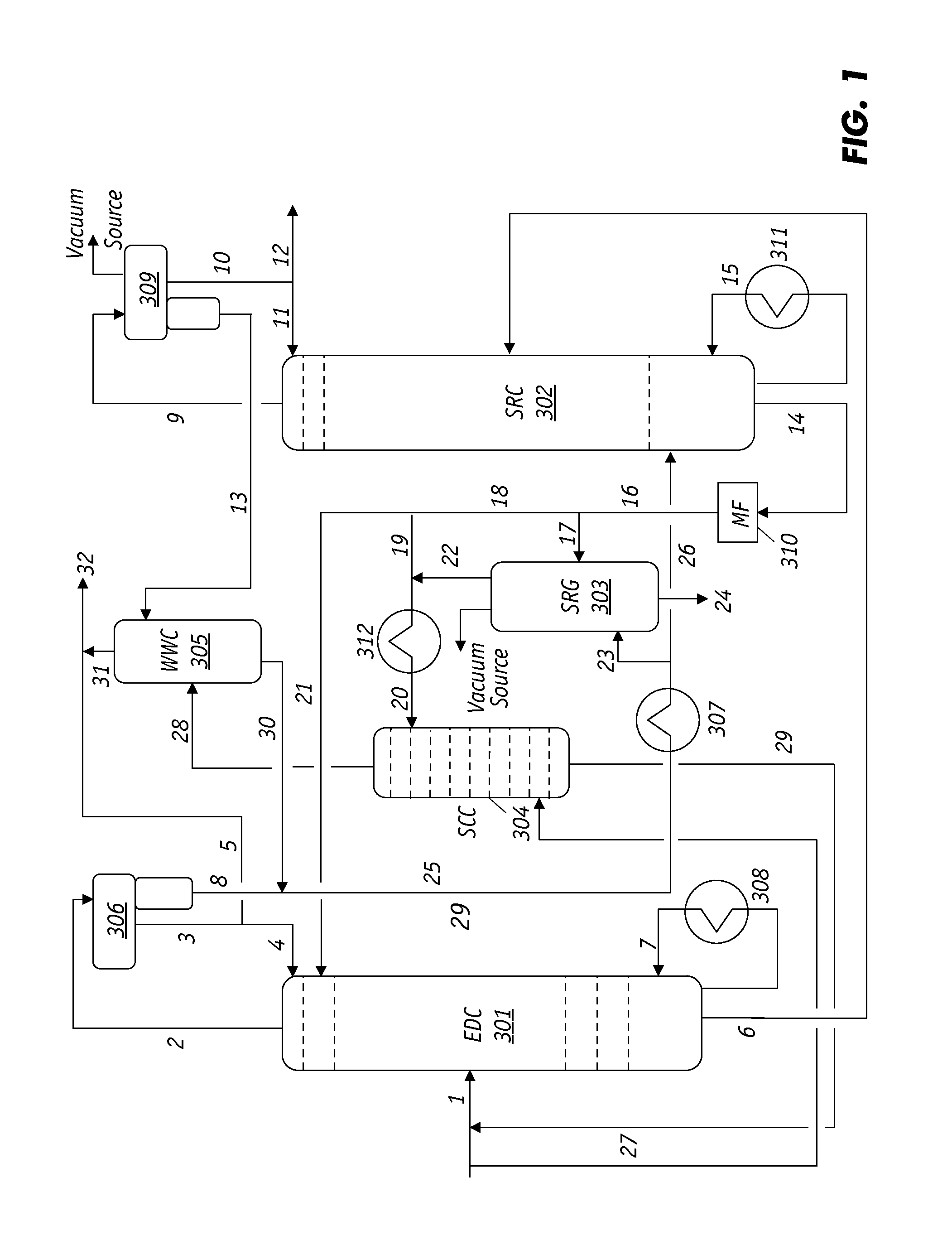
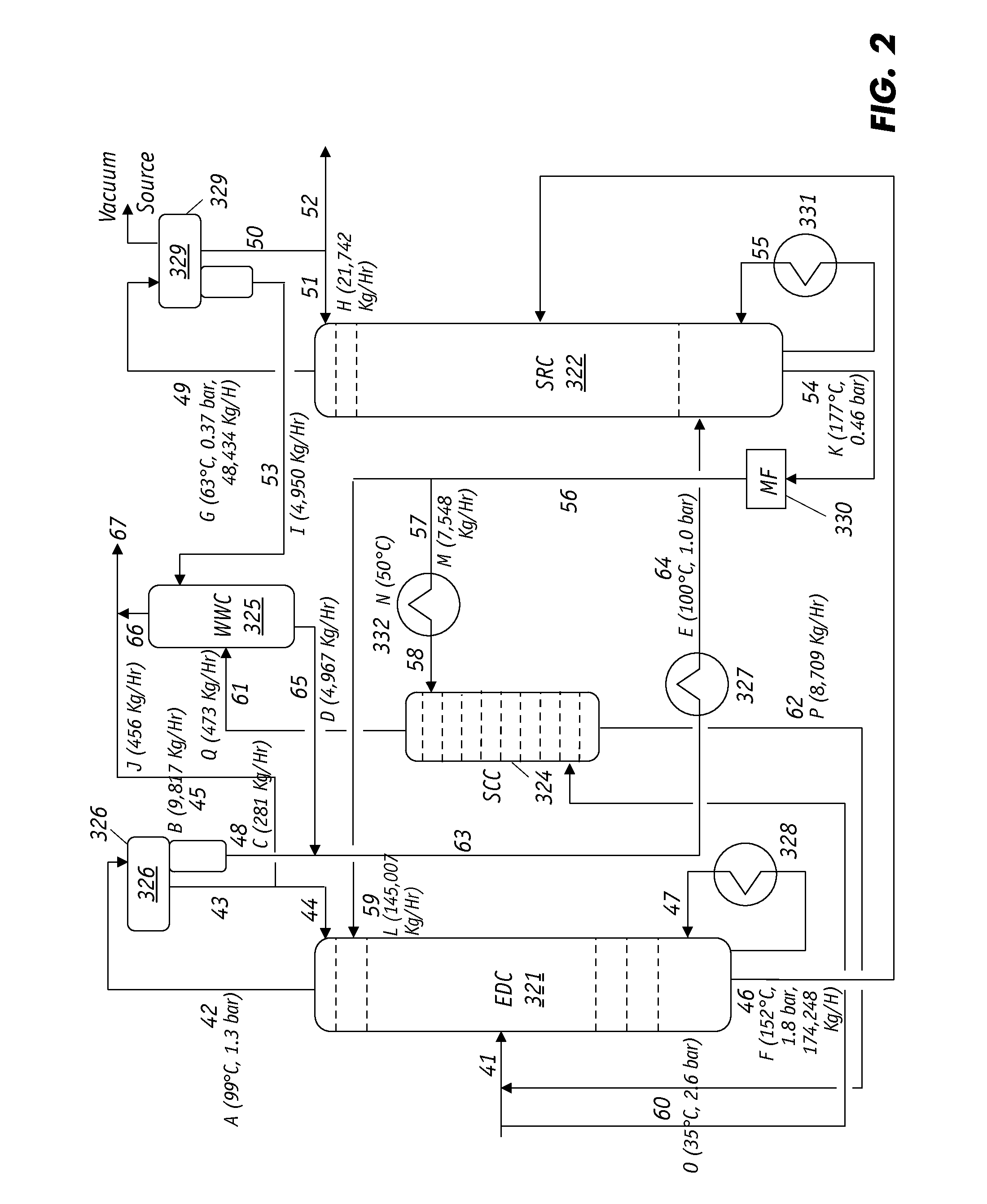
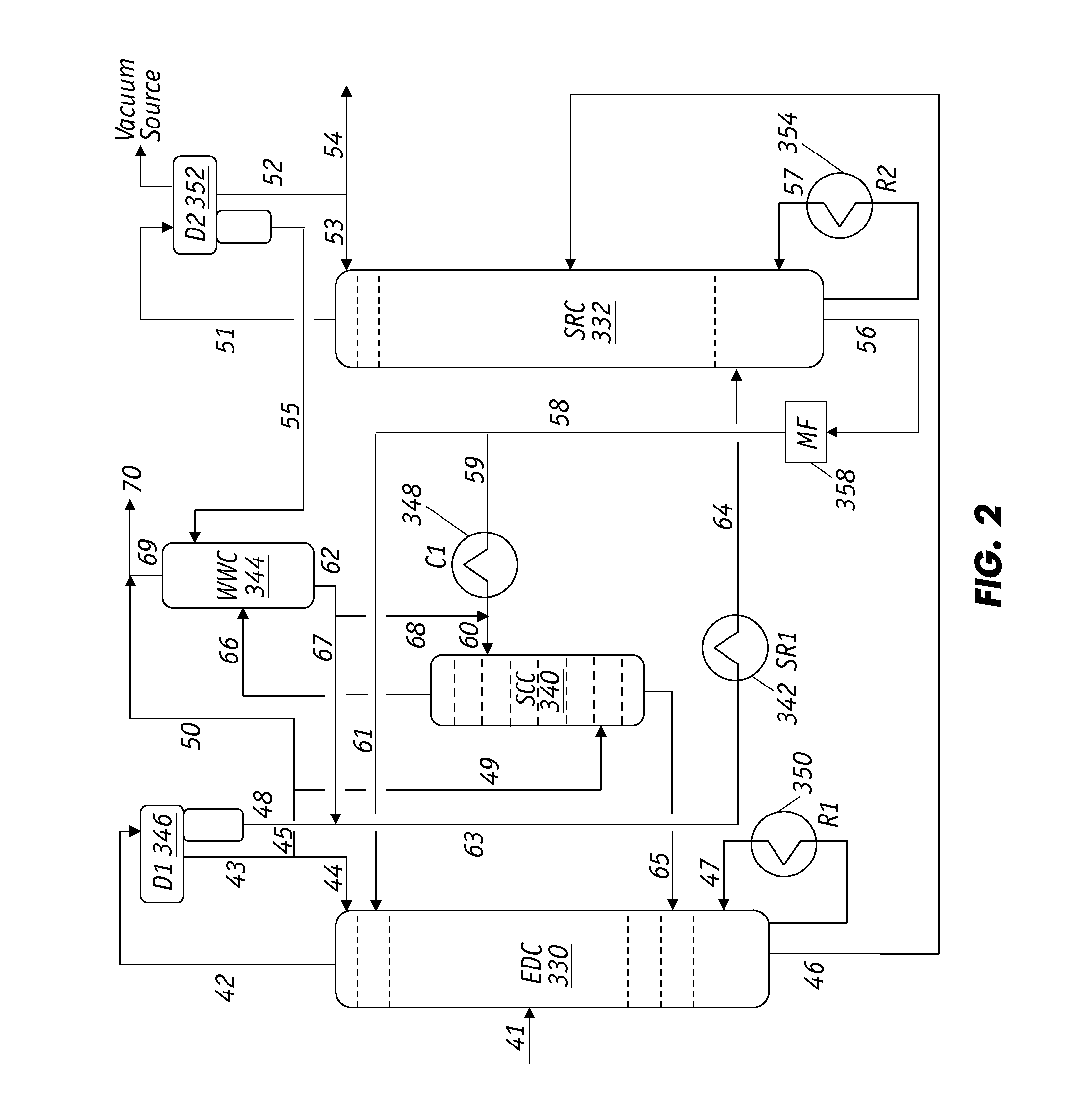
Extractive distillation processes using water-soluble extractive solvents
ActiveUS20090105514A1Reduce steam consumptionGood solvent resistanceHydrocarbon purification/separationHydrocarbonsExtractive distillationWater soluble
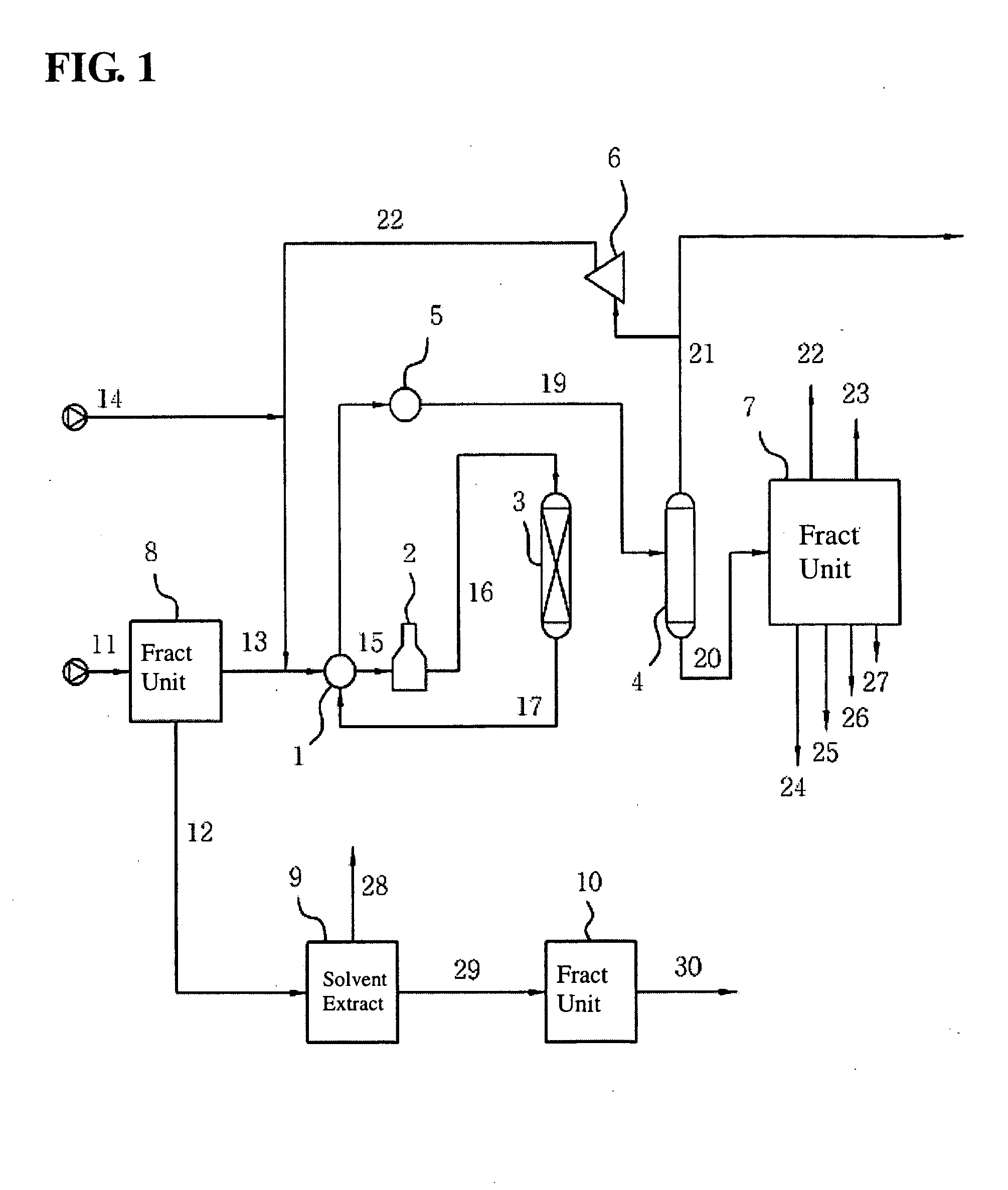
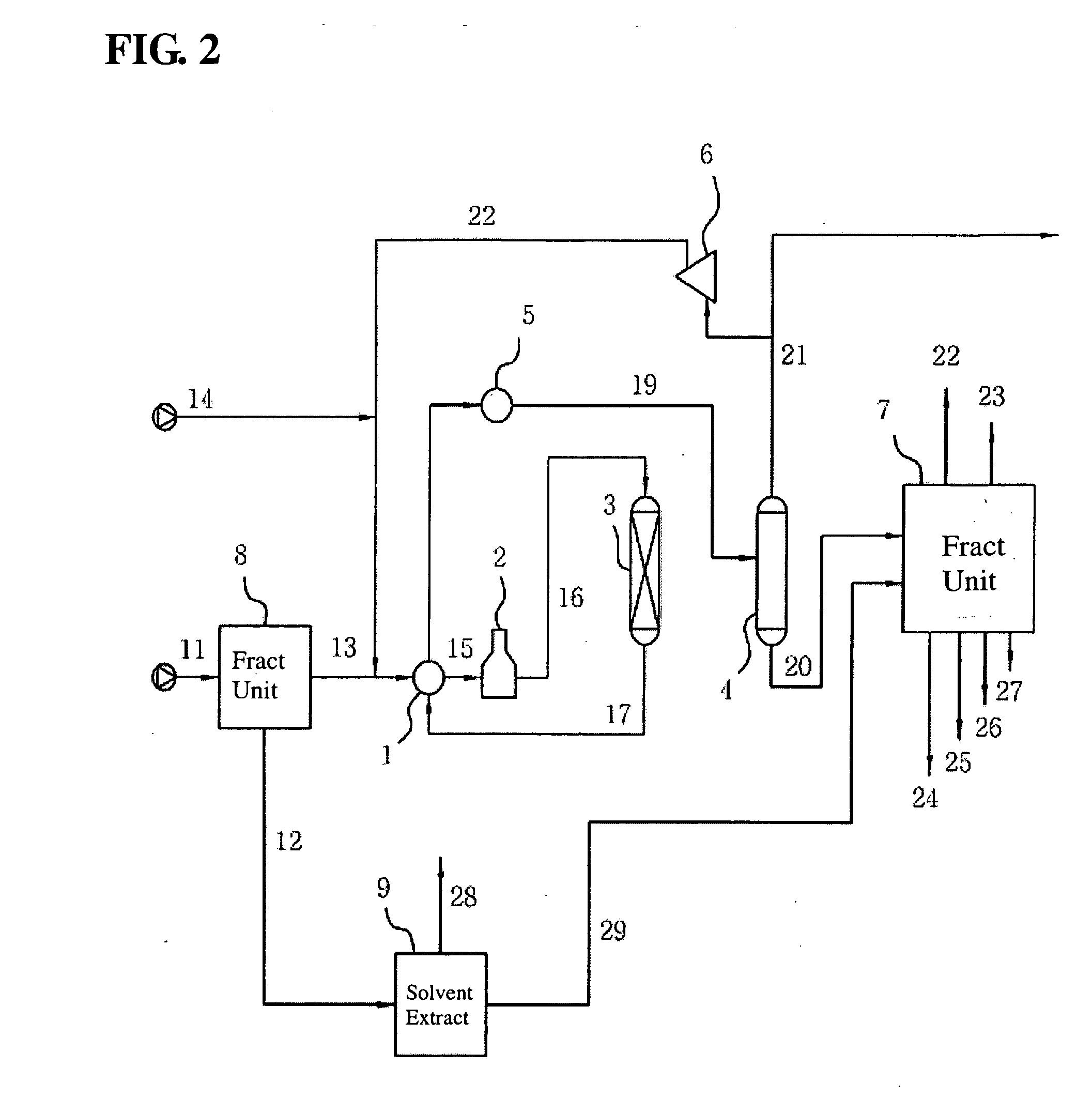
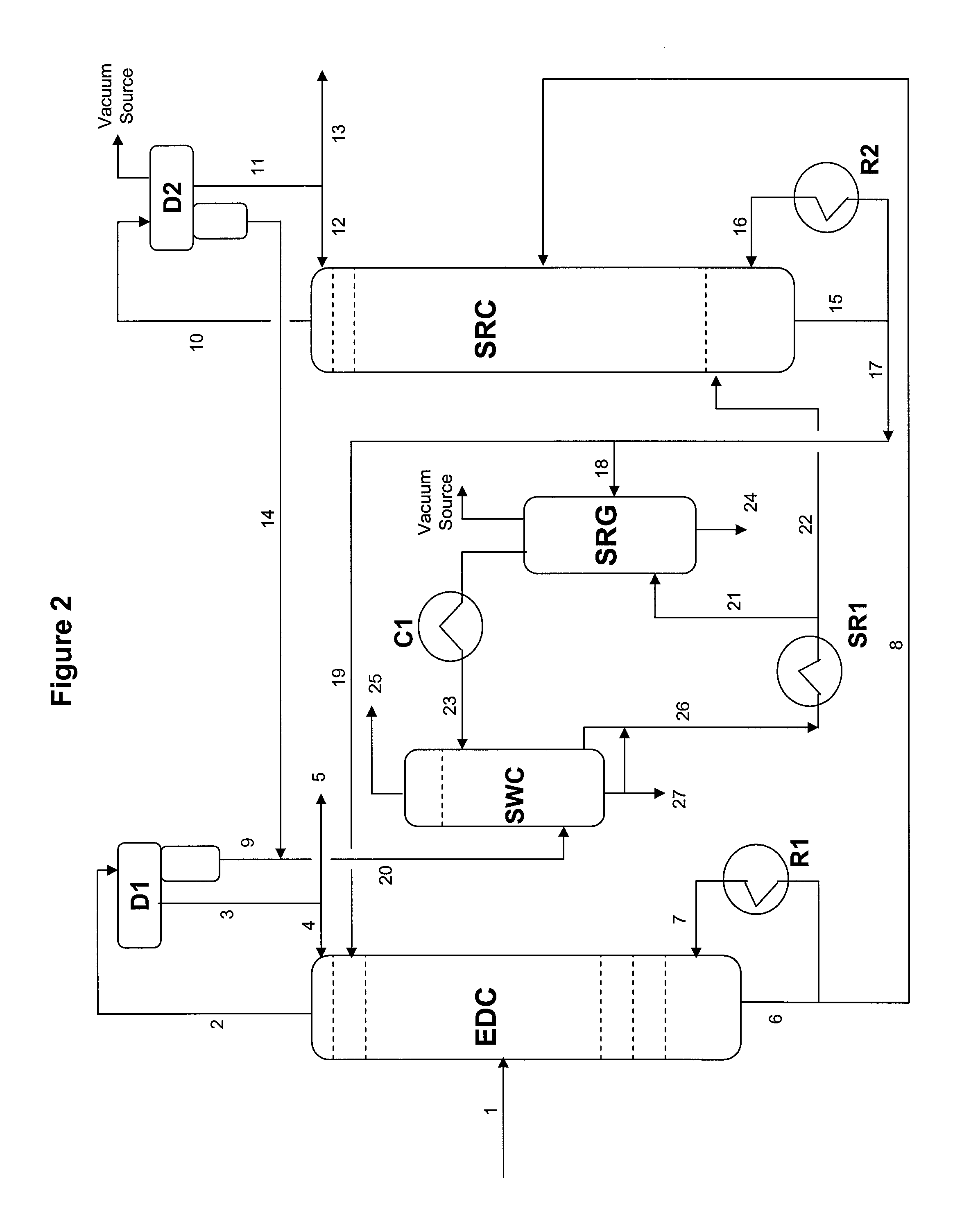
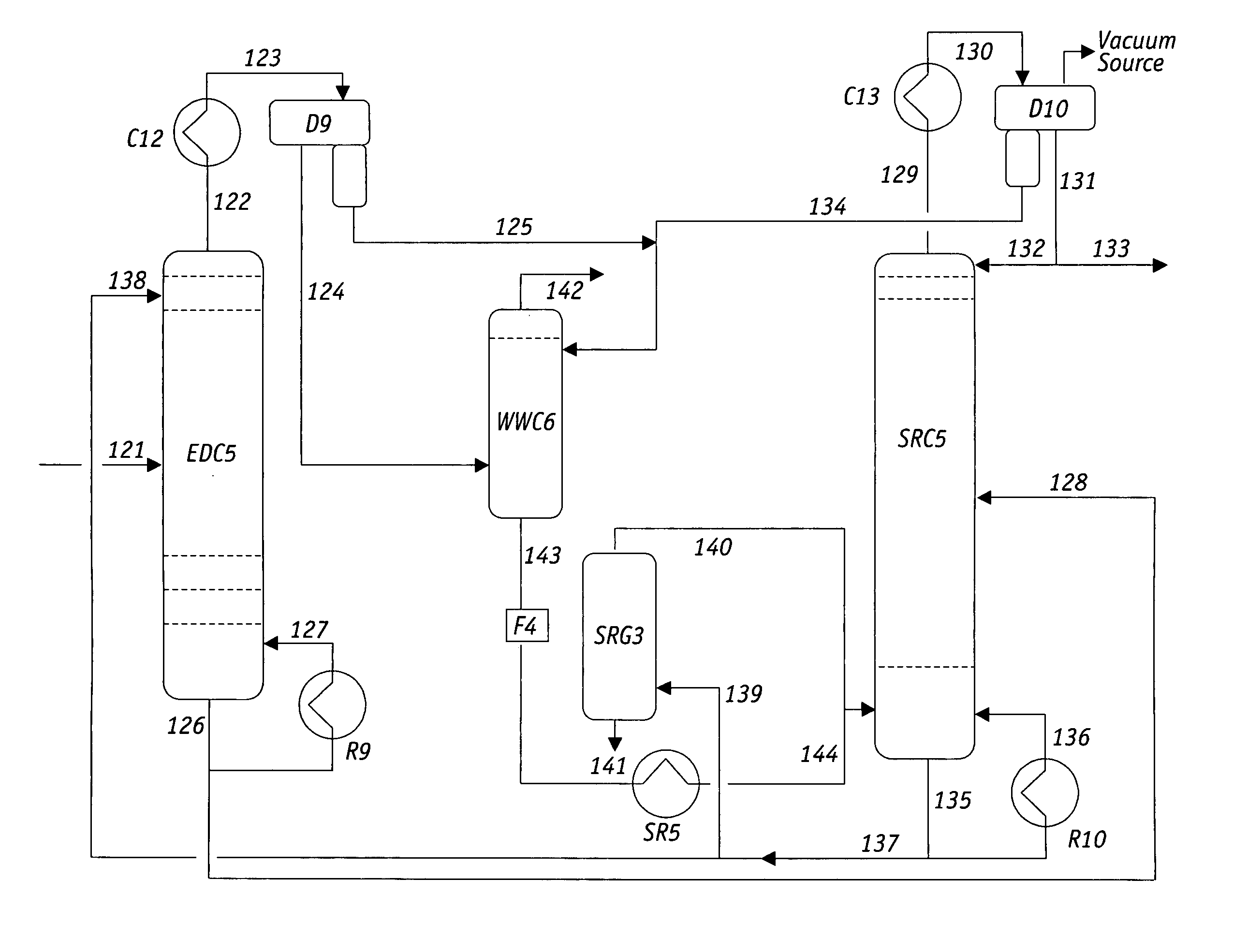
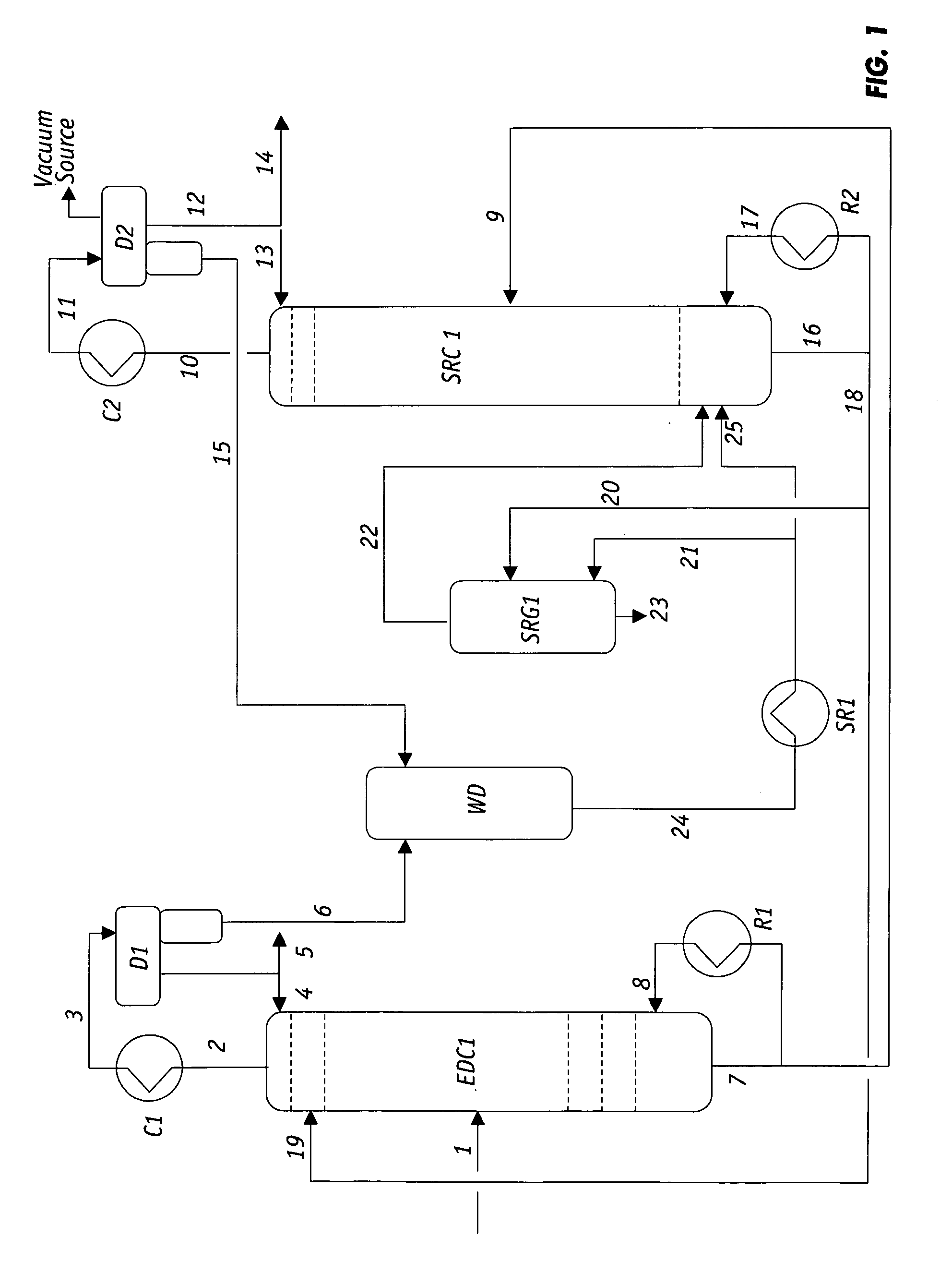
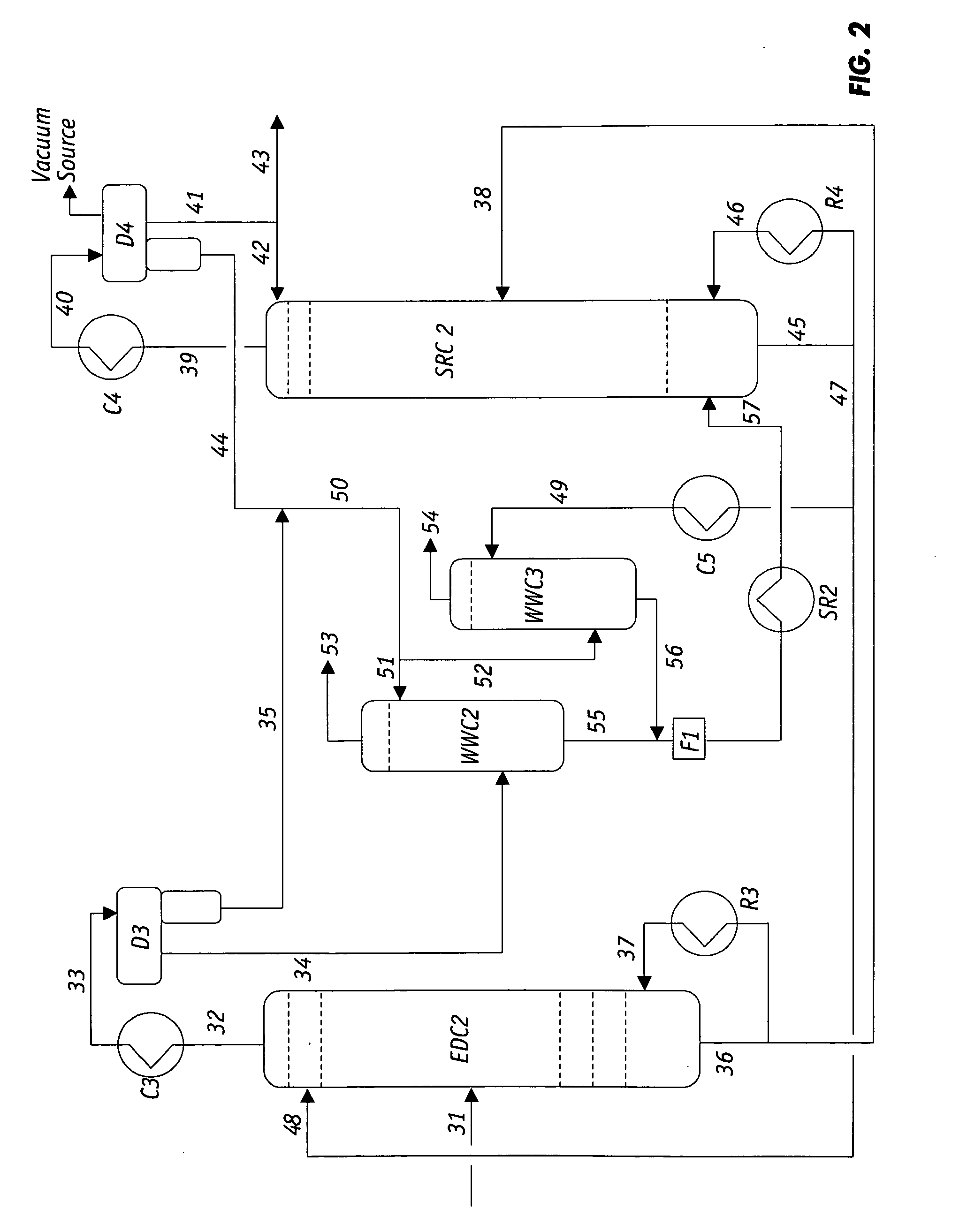
Extractive distillation processes whereby water-soluble extractive distillation (ED) solvents are regenerated and recovered employ improved operations of the extractive distillation column (EDC) so that polar hydrocarbons are recovered and purified from mixtures containing polar and less polar hydrocarbons and measurable amounts of hydrocarbons that are heavier than intended feedstock and / or polymers that are generated in the ED process. The improved process can effectively remove and recover the heavy hydrocarbons and / or remove polymer contaminants from the solvent in a closed solvent circulating loop through mild operating conditions with no additional process energy being expended. With the improved process, the overhead reflux of the EDC may be eliminated to further reduce energy consumption and to enhance the loading and performance within the upper portion of the EDC, especially when two liquid phases exists therein.
Owner:CPC CORPORATION +1
Process for separating aromatics by extractive distillation and a composite solvent used therein
InactiveUS7078580B2Improve solubilityWide boiling rangeDistillation purification/separationHydrocarbonsSulfolaneAlkalinity
This application relates to a composite solvent for separating aromatics by extractive distillation, comprising a main solvent, a solutizer and a modifier. Said solutizer is selected from any one or mixtures of any two of C8–C11 aromatics having different number of carbon atoms, the content of which is 3–39 wt %, and the number of carbon atoms of the lowest aromatic in the solutizer should be greater than that of the highest aromatic in the aromatics to be separated. When the solutizer is selected from any one of C8–C11 aromatics, the composite solvent contains 0.01–10.0 wt % of the modifier; when the solutizer is selected from mixtures of any two of C8–C11 aromatics having different number of carbon atoms, the composite solvent contains 0–10.0 wt % of the modifier. Said main solvent and modifier are independently selected from sulfolane derivatives, N-formyl morpholine, and N-methyl pyrrolidone, provided that the acidity and basicity of the modifier are opposite to those of the main solvent. When the composite solvent is used to recover aromatics by extractive distillation, it is possible to moderate the operation conditions of solvent recovery, increase the yield of aromatics, and make the separated aromatics to be neutral.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +1
Extractive distillation process for recovering aromatics from petroleum streams
The present invention relates to a process for recovering polar hydrocarbons from non-polar hydrocarbons, such as aromatics from non-aromatics, naphthenes from paraffins and isoparaffins, or olefins from paraffins and isoparaffins, in feed mixtures containing at least a measurable amount of heavier hydrocarbons. According to the invention, an improved extractive distillation (ED) process is disclosed for recovering aromatic hydrocarbons including benzene, toluene, and xylenes (BTX aromatics) from the C6-C8 petroleum streams containing at least a measurable amount of C9+ hydrocarbons.The invention also relates to an improved ED process for recovering mainly benzene and toluene from the C6-C7 petroleum streams containing at least a measurable amount of C8+ hydrocarbons. This invention is further directed toward the regeneration and recovery of the ED solvent utilized to recover and purify the aromatic hydrocarbons from the petroleum stream containing at least a measurable amount of hydrocarbons heavier than intend feedstock.
Owner:AMT INT INC +1
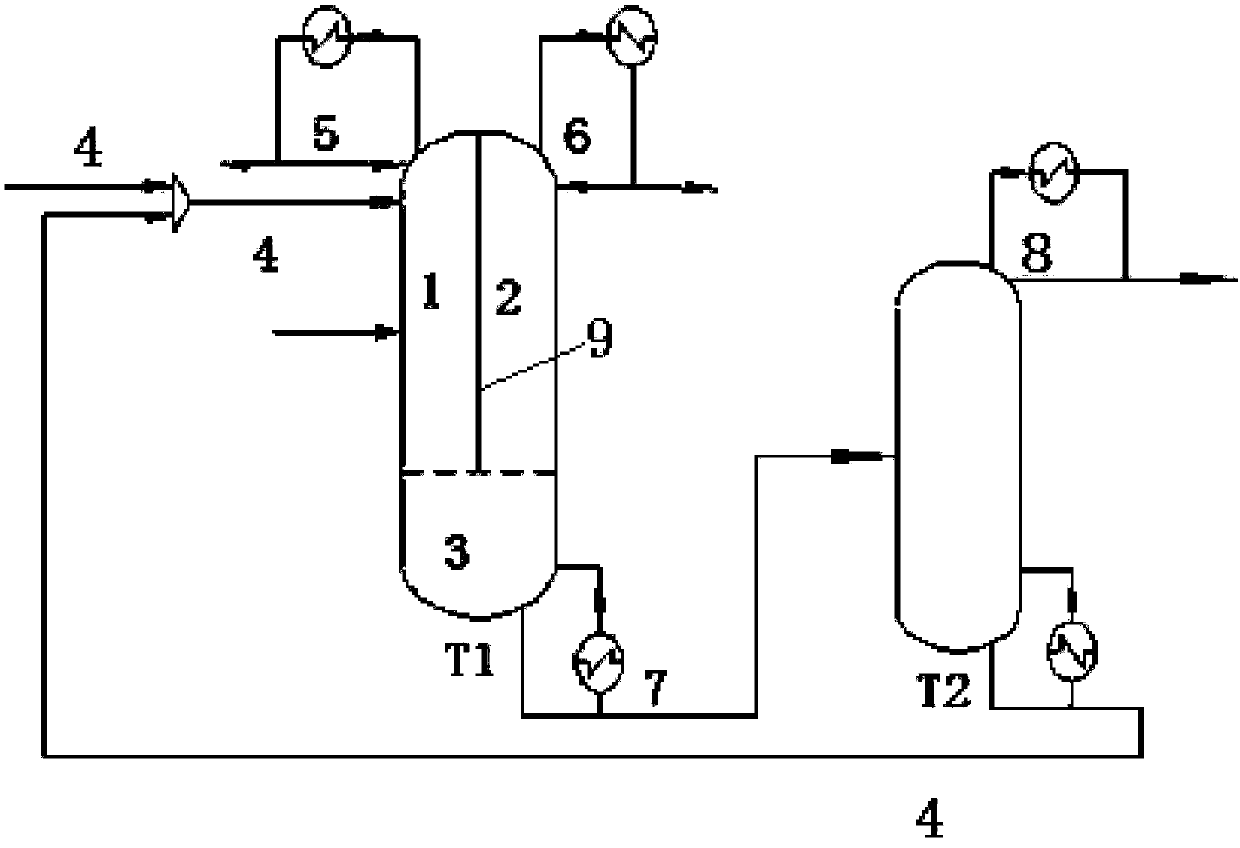
Mercury-removal process in distillation tower
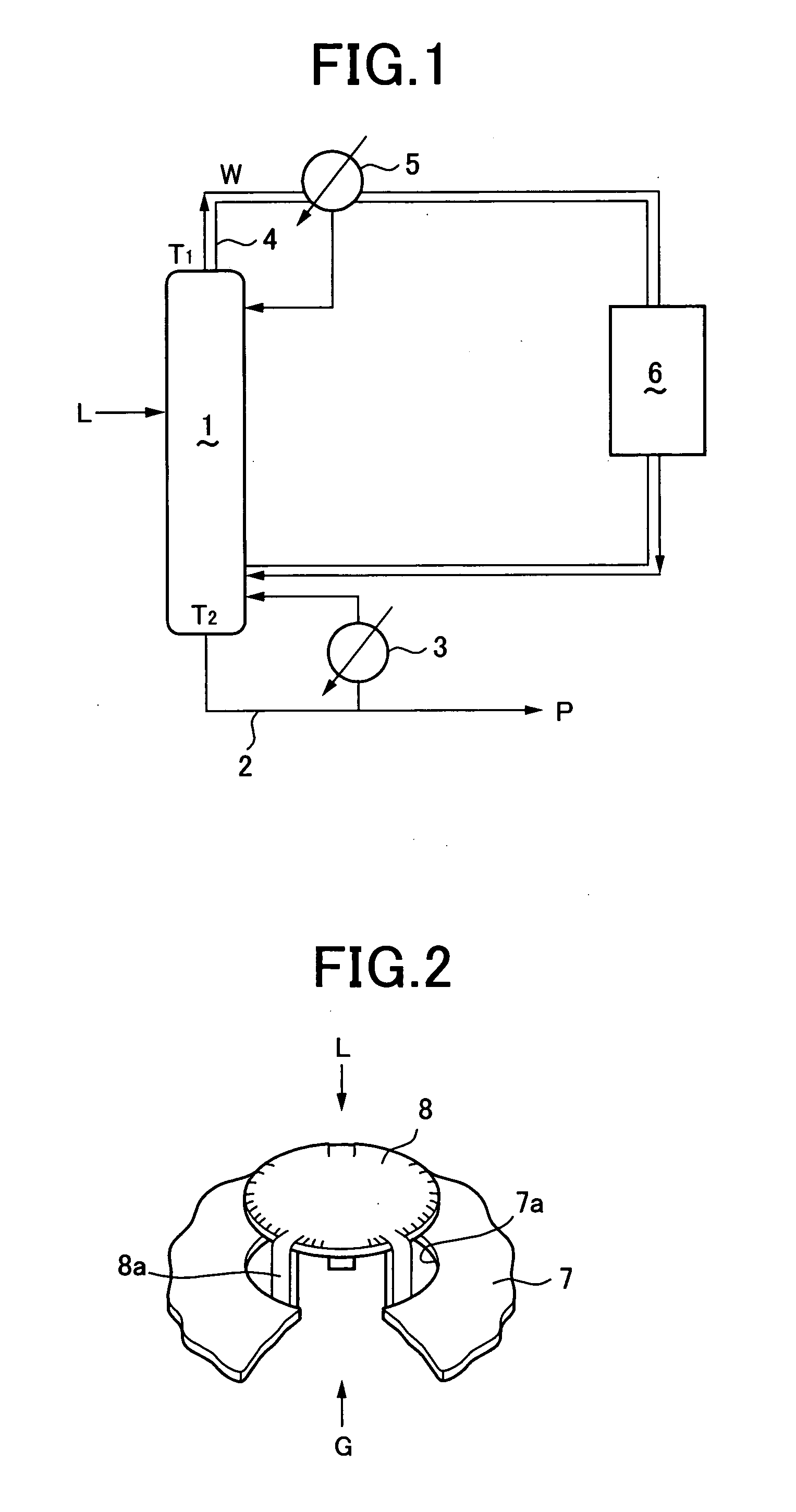
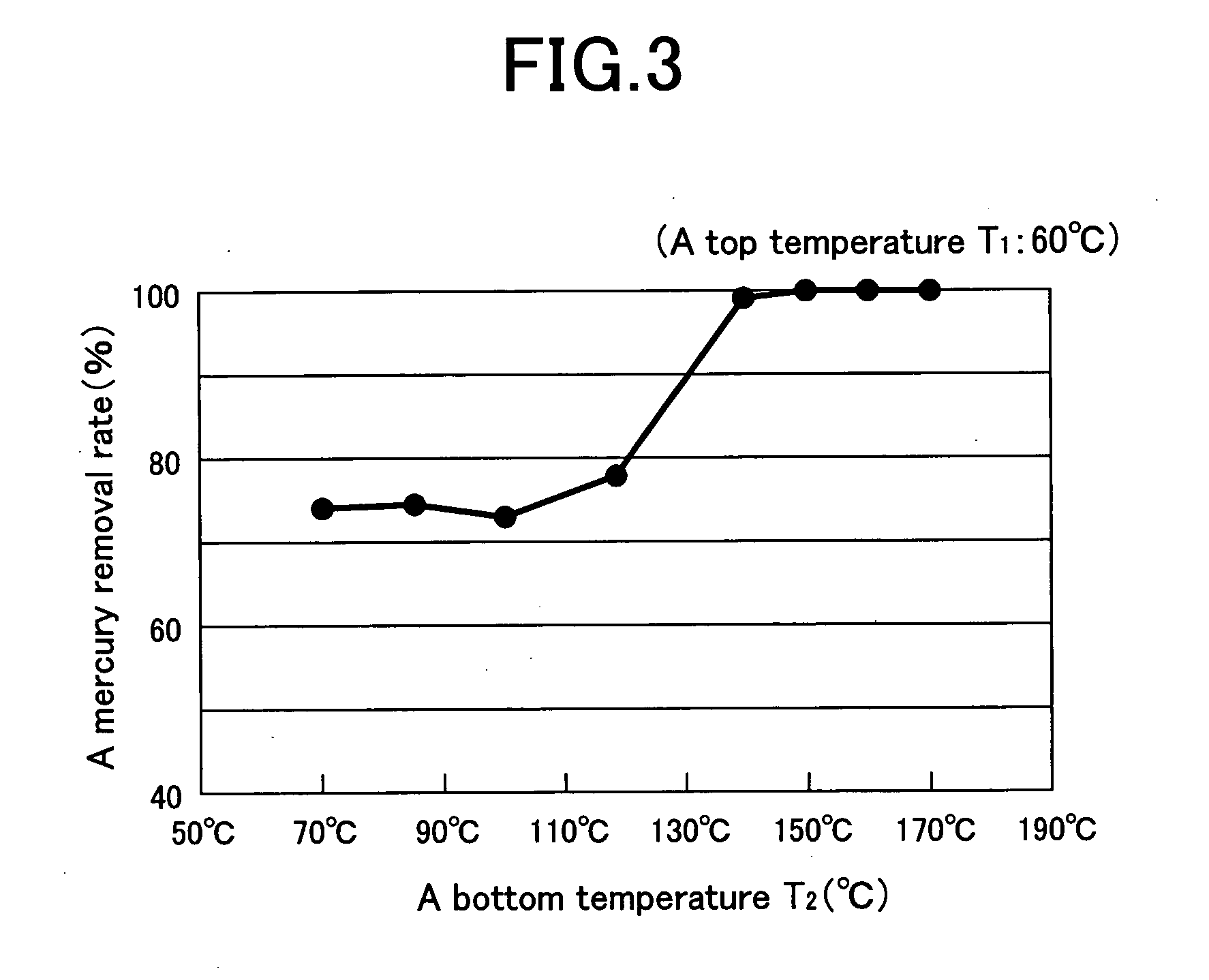
InactiveUS20050167335A1Smooth connectionEfficient and economical mercury removalSolvent extractionSpace heating and ventilationLiquid productGas phase
A top temperature T1 of a distillation tower 1 is held below a liquefying temperature of a light fraction by returning a part of an exhaust gas W, which is cooled by a condenser 5, to the upper zone of the distillation tower 1. A bottom temperature T2 is raised up to 300° C. at highest by returning a part of a liquid product P from a re-boiler 3 to a lower zone of the distillation tower 1. When a liquid hydrocarbon L comes in countercurrent contact with a stripping gas G inside the distillation tower 1 with the temperature profile that an inner temperature gradually falls down along an upward direction, mercury is efficiently transferred from the liquid L to a vapor phase without effusion of the light fraction in accompaniment with the exhaust gas W.
Owner:JAPAN PETROLEUM EXPLORATION CO LTD
Process for preparing lower olefins
InactiveUS20130172627A1Thermal non-catalytic crackingLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionMolecular sieveExtractive distillation
The invention is a process for preparing lower olefins comprising: a) steam cracking a paraffinic feedstock to obtain a cracker effluent comprising olefins and saturated and unsaturated C4 hydrocarbons; b) contacting an oxygenate feedstock with a molecular sieve-comprising catalyst, at a temperature in the range of from 350 to 1000° C. to obtain an oxygenate conversion effluent comprising olefins and saturated and unsaturated C4 hydrocarbons; c) subjecting the cracker effluent and the oxygenate conversion effluent to one or more separation steps such that an olefin product stream comprising ethylene and / or propylene, and a stream comprising saturated and unsaturated C4 hydrocarbons are obtained; and d) subjecting part of the stream comprising C4 hydrocarbons from both the cracker effluent and the oxygenate conversion effluent to extractive distillation to obtain a stream enriched in unsaturated C4 hydrocarbons and a stream enriched in saturated C4 hydrocarbons.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
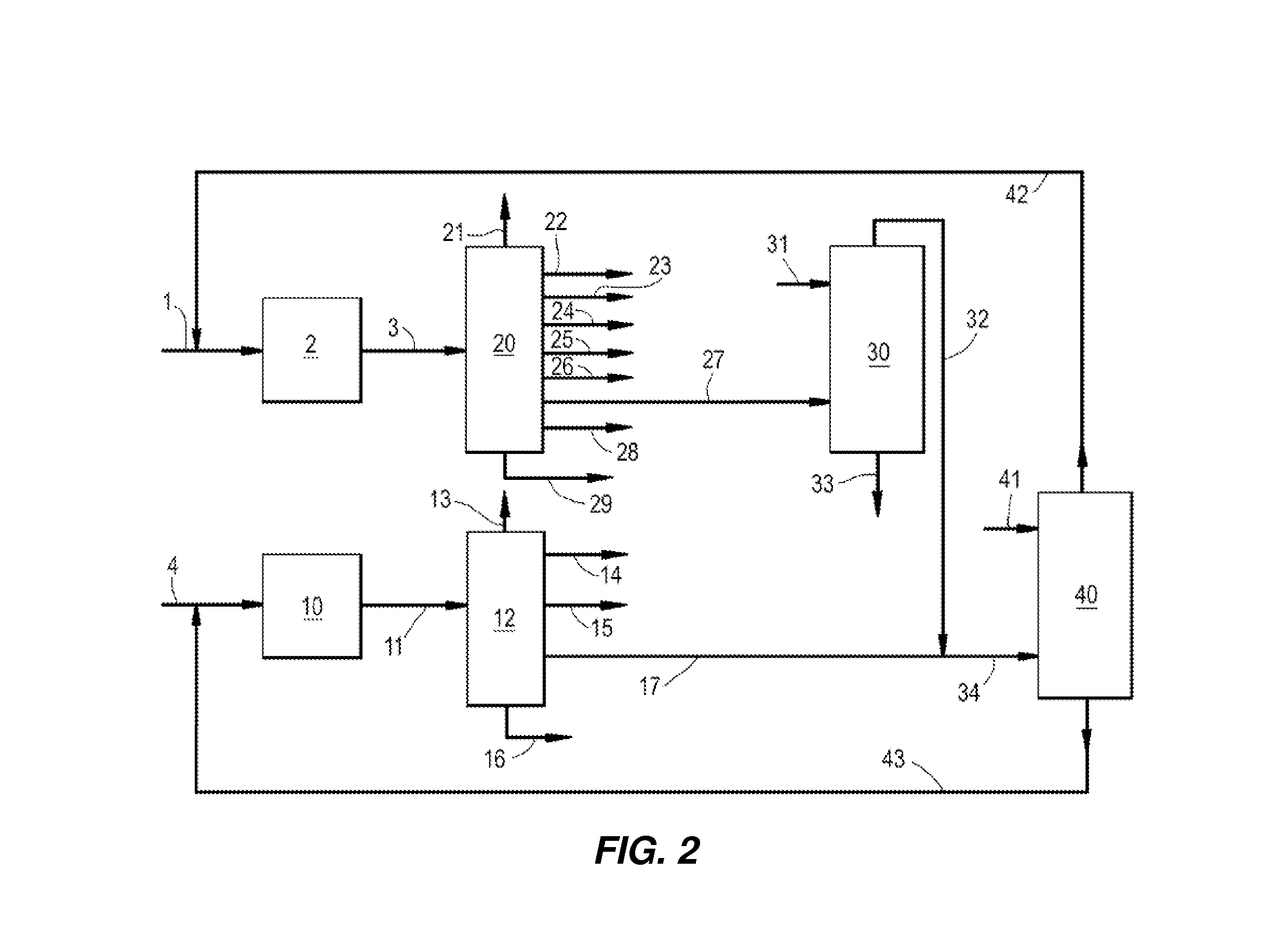
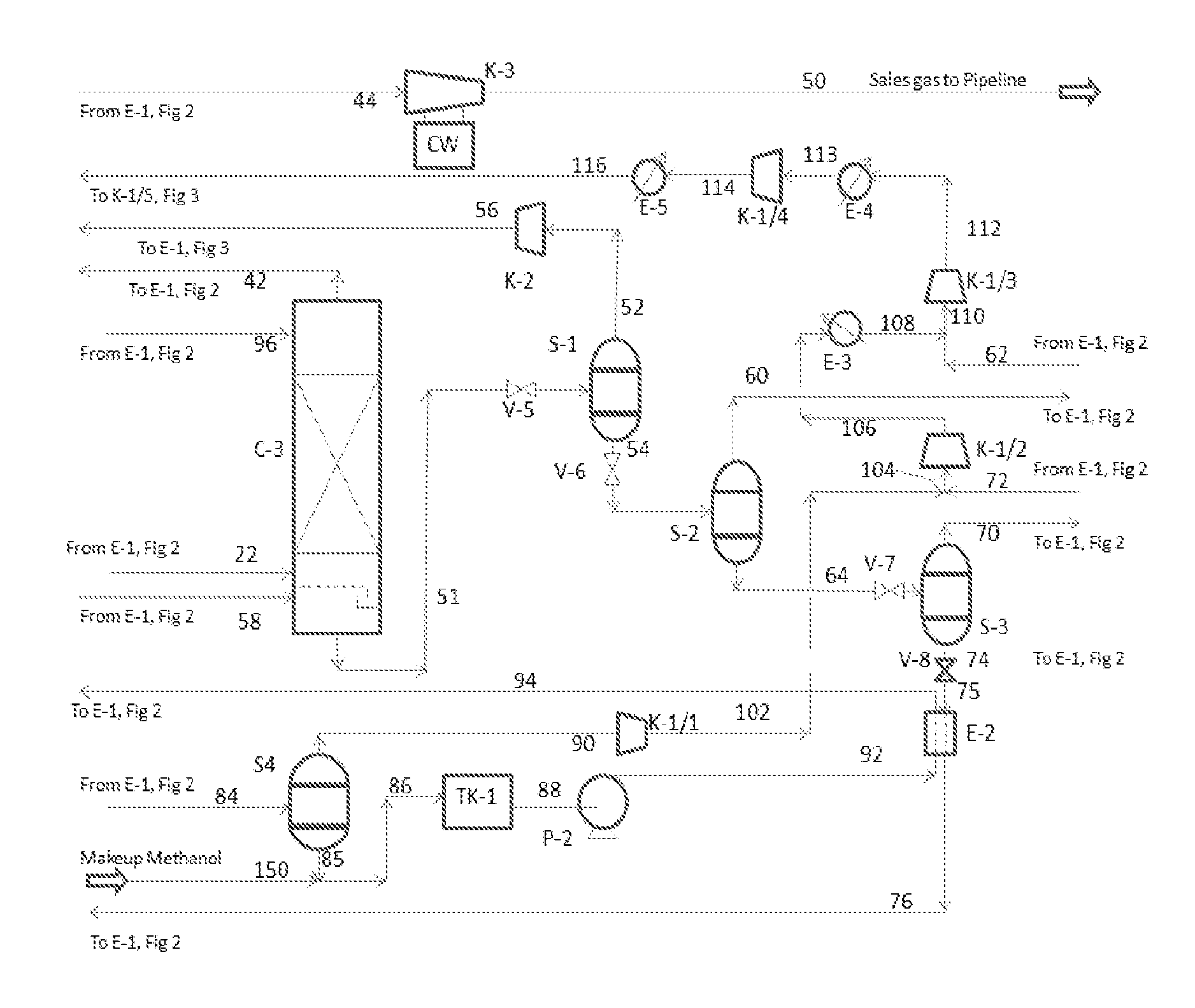
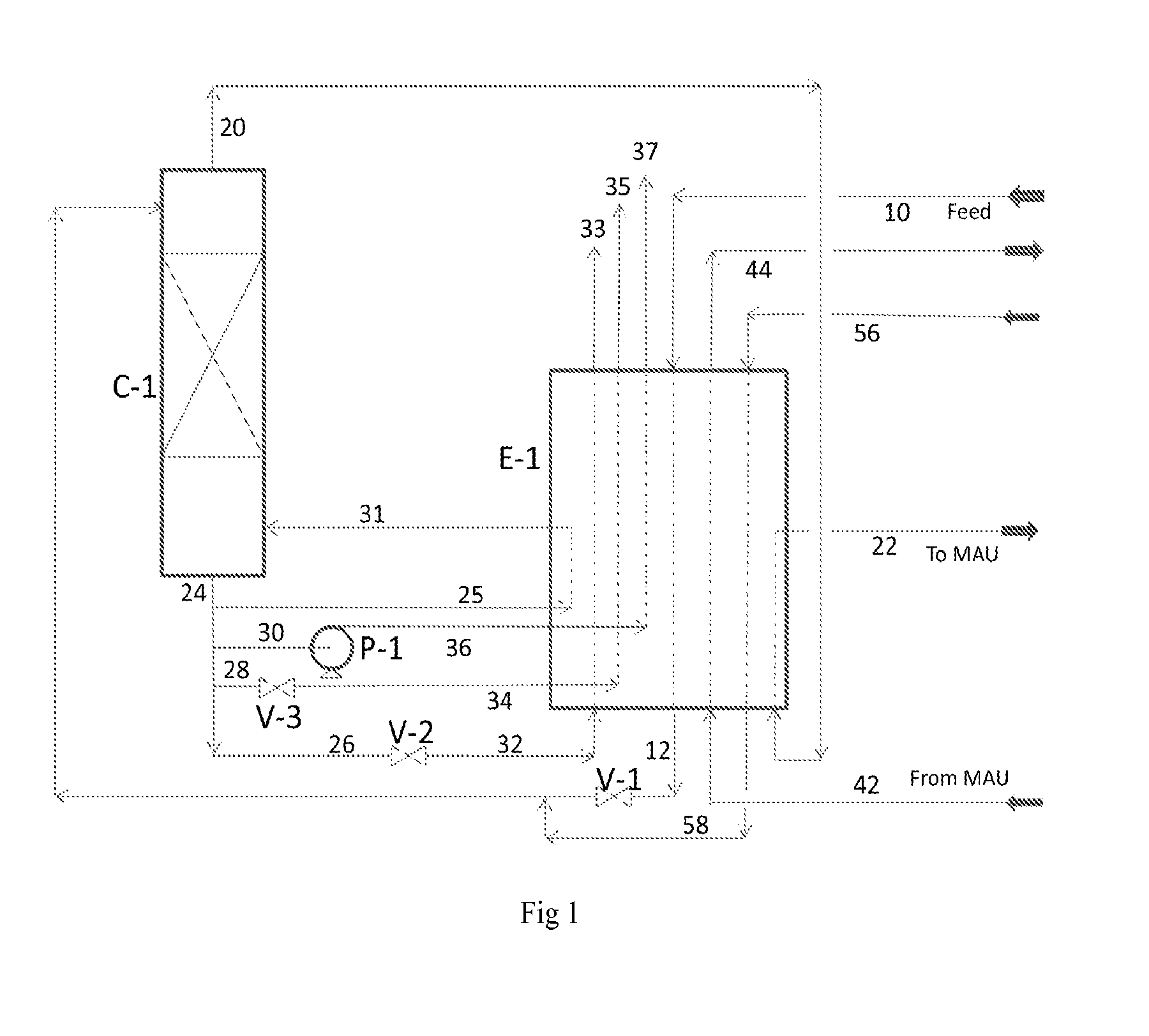
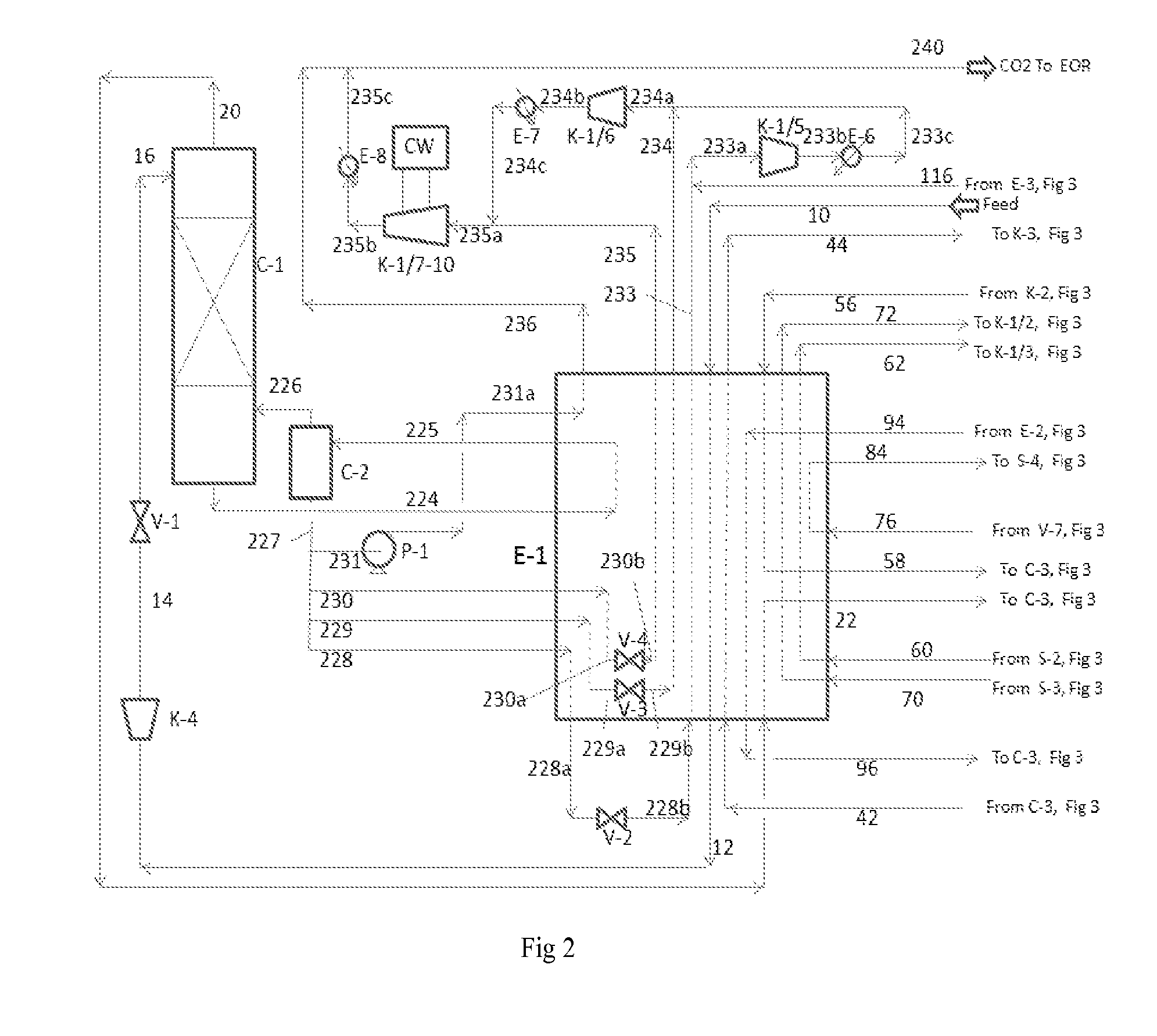
Co2 capture from co2-rich natural gas
It is described a prefractionation-physical absorption hybrid process and system for separation of a CO2-natural gas mixture containing more than 26 mol % CO2 and 0.1 mol % to 15 mol % in total one or more heavier hydrocarbons, such as ethane, propane, butanes, pentanes, and hexanes, with at least 0.0001 mol % in total one or more of pentanes and hexanes, particularly, a self-refrigerated process and system involving methanol as the absorbent.
Owner:XU JIANGUO
Process for increasing production of benzene from hydrocarbon mixture
InactiveCN101208409AHigh yieldRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonHydrocarbon oil crackingBenzeneHydrocarbon mixtures
Disclosed herein is a process for increasing the production of benzene from a hydrocarbon mixture. A process for producing an aromatic hydrocarbon mixture and LPG from a hydrocarbon mixture, and a solvent extraction process for separating and recovering polar hydrocarbons from a hydrocarbon mixture containing polar hydrocarbons (that is, aromatic hydrocarbons) and nonpolar hydrocarbons (that is, non-aromatic hydrocarbons) are integrated, thereby it is possible to increase the production of benzene.
Owner:SK ENERGY CO LTD (KR)
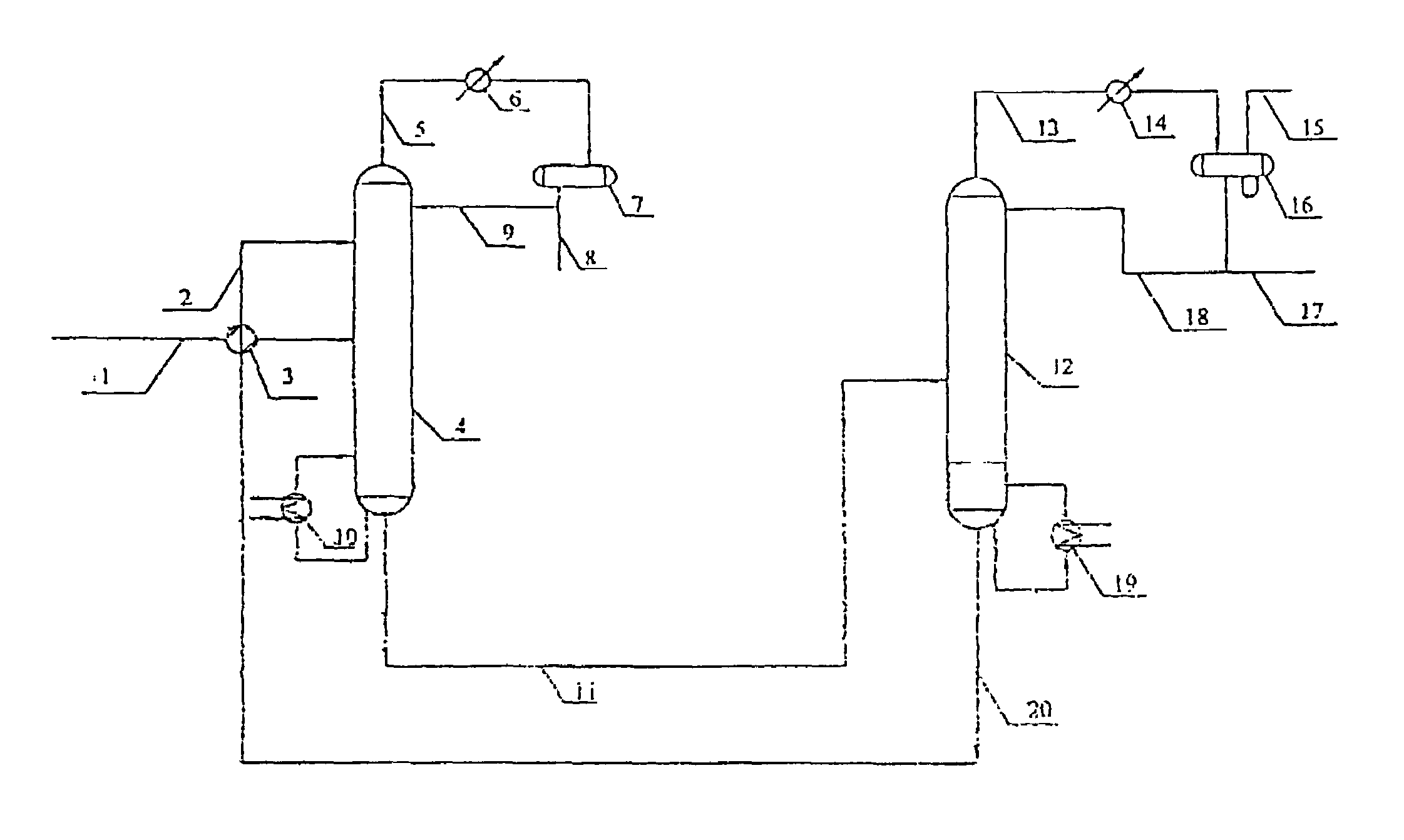
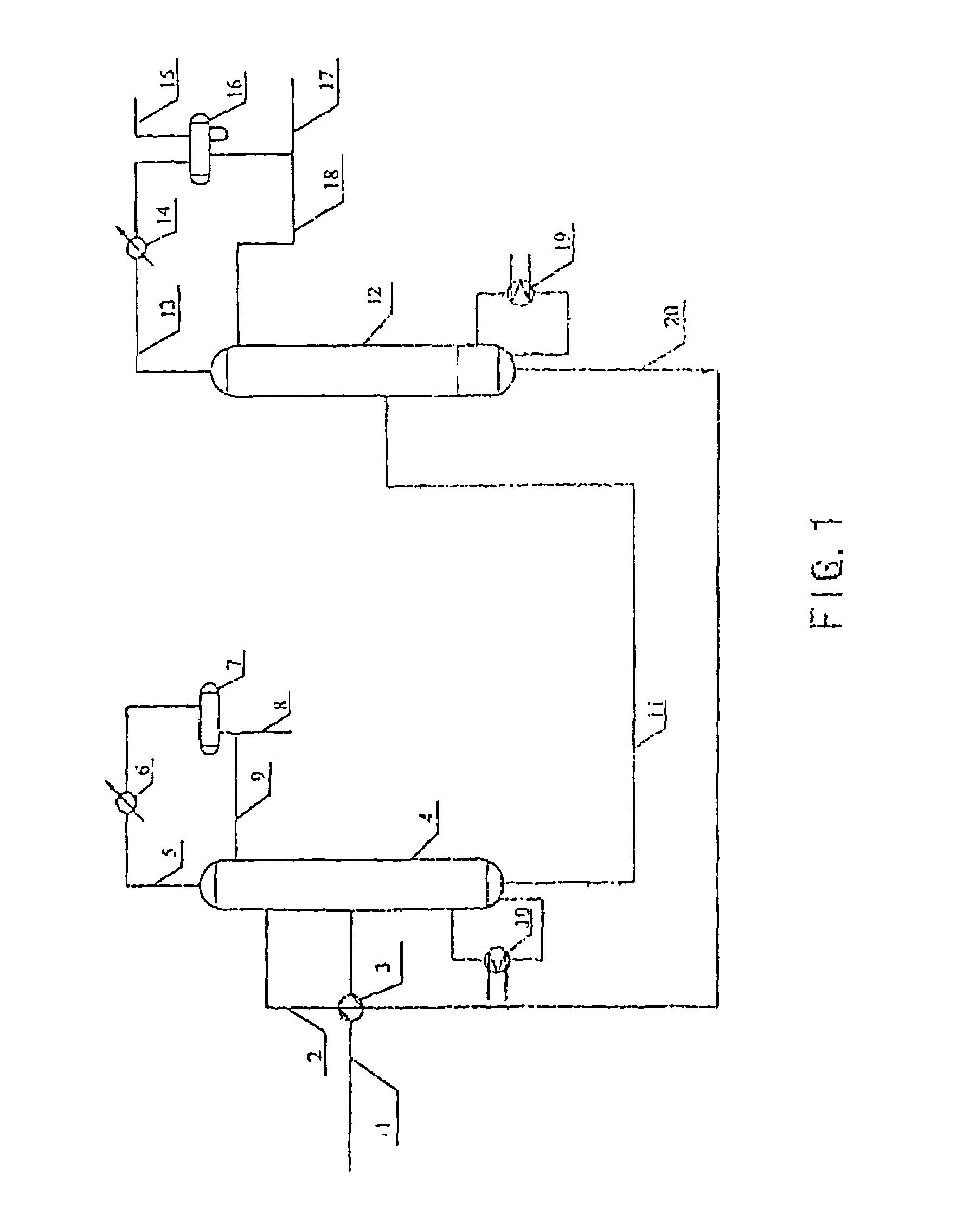
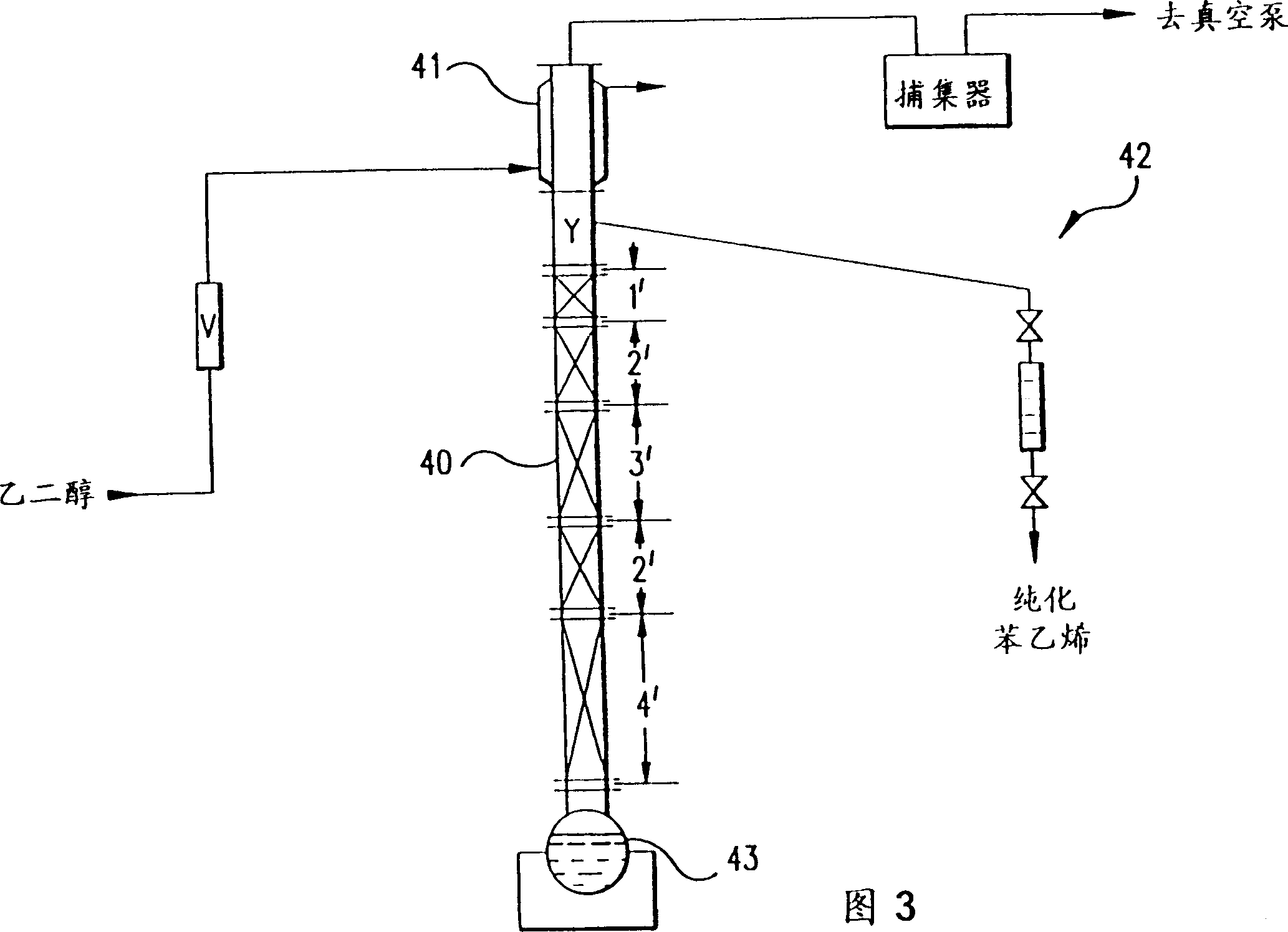
Recovery of styrene from pyrolysis gasoline by extractive distillation
InactiveCN1077560CDistillation purification/separationHydrocarbonsBoiling pointExtractive distillation
An extractive distillation process for separating at least one substituted unsaturated aromatic from a pyrolysis gasoline mixture, containing said aromatic and at least one close-boiling aromatic or non-aromatic hydrocarbon, employing a two part extractive solvent: (a) sulfolane (tetramethylene sulfone), and (b) portion consisting of water.
Owner:苏尔寿际特(北京)技术有限公司
Aromatics recovery by extractive distillation
ActiveUS20120247943A1Distillation purification/separationSolid sorbent liquid separationAlkaneExtractive distillation
The present invention relates to a process for recovering polar hydrocarbons from non-polar hydrocarbons, such as aromatics from non-aromatics, naphthenes from paraffins and isoparaffins, or olefins from paraffins and isoparaffins, in feed mixtures containing at least a measurable amount of heavier hydrocarbons. According to the invention, an improved extractive distillation (extractive-distillation) process is disclosed for recovering aromatic hydrocarbons including benzene, toluene, and xylenes from heavy (C9+) hydrocarbons. The invention also relates to an improved extractive-distillation process for recovering mainly benzene and toluene from the C6-C7 petroleum streams containing at least a measurable amount of C8+ hydrocarbons. This invention is further directed toward the regeneration and recovery of the extractive-distillation solvent utilized to recover and purify the aromatic hydrocarbons from the petroleum stream containing at least a measurable amount of hydrocarbons heavier than the intended product.
Owner:UOP LLC
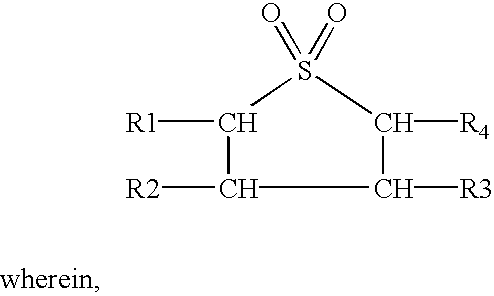
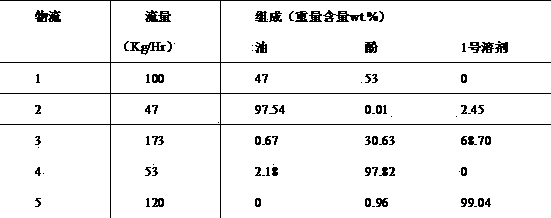
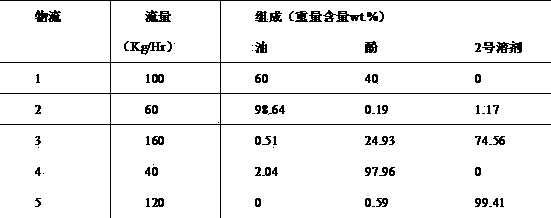
Method for extracting phenol compounds from direct coal liquefied oil through extractive distillation
ActiveCN103896739AHigh recovery rateIncrease relative volatilityOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationSulfolaneExtractive distillation
The invention relates to a method for extracting phenol compounds from direct coal liquefied oil through extractive distillation. An extractive distillation solvent (hereinafter referred to as solvent) adopted in the method is glyceryl triacetate and / or sulfolane, or a mixed solvent formed by mixing glyceryl triacetate and / or sulfolane and one or more selected from glycerol, triethanolamine, triethylene glycol, tetraethylene glycol, dimethyl sulfoxide and diethanol amine according to any proportion. The method is used for extracting phenol compounds from direct coal liquefied oil in an extraction distillation tower by using the solvent, then, a solvent flow rich in the phenol compounds enters a recovery tower and is separated, the phenol compounds discharged from the top of the recovery tower are recovered after being cooled to obtain phenol products, and the solvent is recycled after being discharged from the bottom of the recovery tower. The method has the characteristics of high product purity, low system energy consumption, no wastewater generation, no acid and alkaline waste and no corrosion to equipment.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for separating and reclaiming spent iron based catalyst and heavy hydrocarbon through Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis in slurry bed
InactiveCN1563281ASimple methodShort processLiquid hydrocarbon mixture recoveryLiquid solutions solvent extractionParaffin waxDistillation
A method for recovering waste iron-base catalyst and heavy hydrocarbon includes extracting and separating mixer of waste iron-base catalyst and heavy hydrocarbon with high liquid paraffin having initial distillation point of 210 deg.C for three to four times for achieving purpose of separating catalyst from heavy hydrocarbon. The recovered waste iron-base catalyst is to be buried underground and the recovered mixer of light liquid paraffin and heavy hydrocarbon can be directly used to produce oil product or sent back to fluid bed reactor for being reutilized as reaction media.
Owner:SYNFUELS CHINA TECH CO LTD
Extractive distillation processes using water-soluble extractive solvents
ActiveUS7871514B2Reduce amountGood solvent performanceHydrocarbon purification/separationHydrocarbonsFluid phaseExtractive distillation
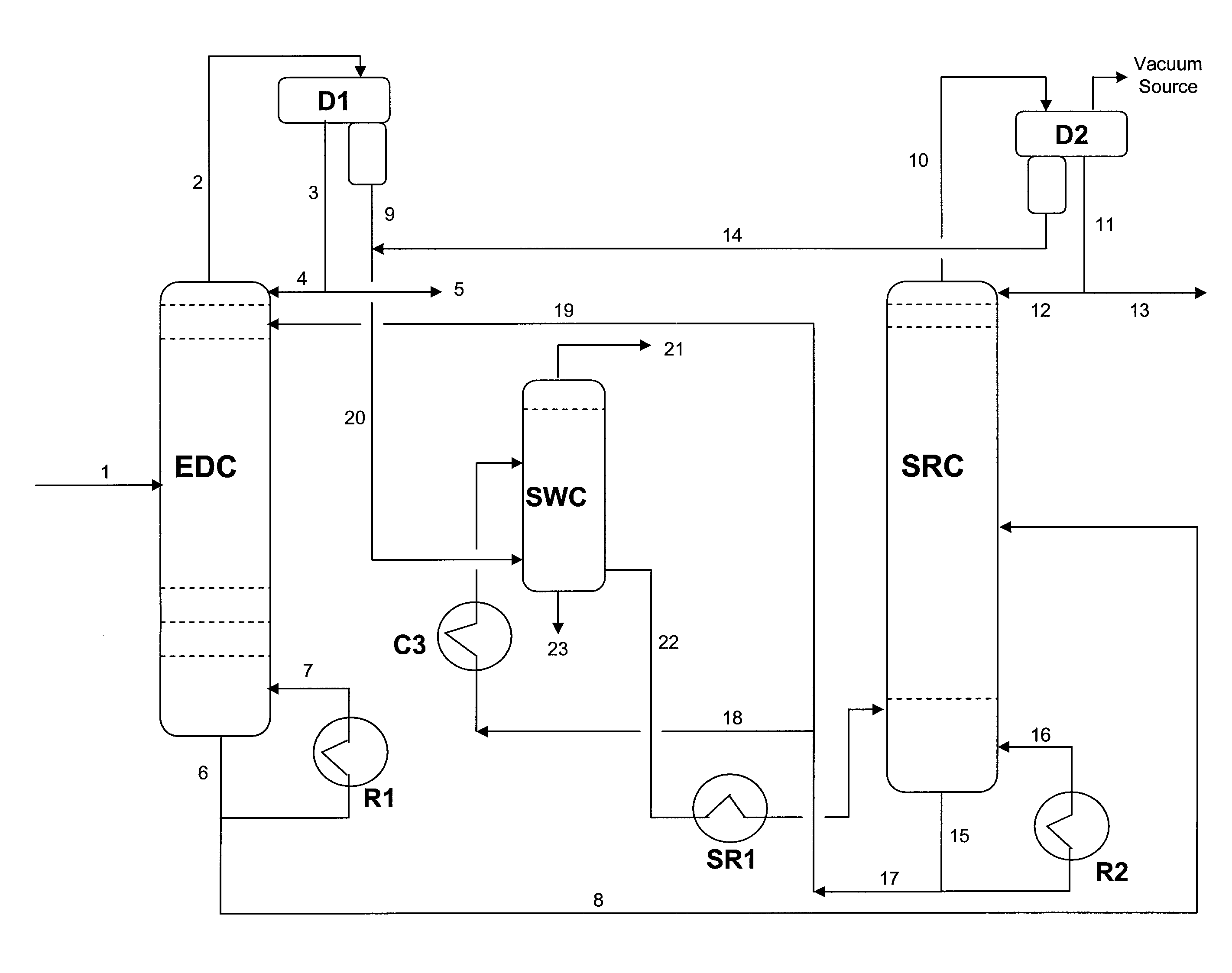
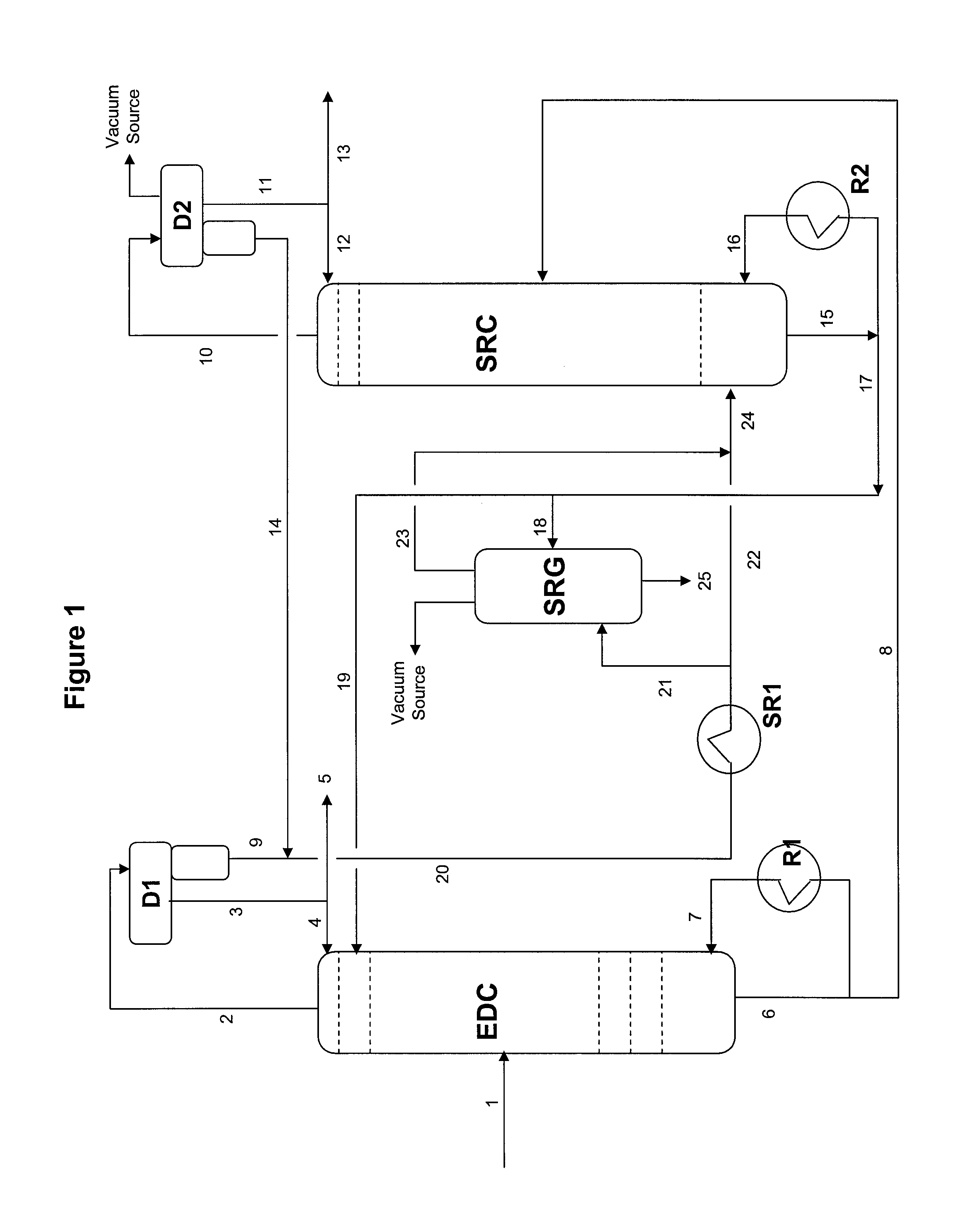
Extractive distillation processes whereby water-soluble extractive distillation (ED) solvents are regenerated and recovered employ improved operations of the extractive distillation column (EDC) so that polar hydrocarbons are recovered and purified from mixtures containing polar and less polar hydrocarbons and measurable amounts of hydrocarbons that are heavier than intended feedstock and / or polymers that are generated in the ED process. The improved process can effectively remove and recover the heavy hydrocarbons and / or remove polymer contaminants from the solvent in a closed solvent circulating loop through mild operating conditions with no additional process energy being expended. With the improved process, the overhead reflux of the EDC may be eliminated to further reduce energy consumption and to enhance the loading and performance within the upper portion of the EDC, especially when two liquid phases exists therein.
Owner:CPC CORPORATION +1
Process for increasing production of benzene from hydrocarbon mixture
ActiveUS7304195B2Increase productivityImprove productivityHydrocarbon by isomerisationRefining to change hydrocarbon structural skeletonBenzeneHydrocarbon mixtures
A process for increasing the production of benzene from a hydrocarbon mixture. A process for producing an aromatic hydrocarbon mixture and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) from a hydrocarbon mixture, and a solvent extraction process for separating and recovering polar hydrocarbons from a hydrocarbon mixture containing polar hydrocarbons (that is, aromatic hydrocarbons) and nonpolar hydrocarbons (that is, non-aromatic hydrocarbons) are integrated, thereby it is possible to increase the production of benzene.
Owner:SK INNOVATION CO LTD
Method of separating and reclaiming spent cobalt based catalyst and heavy hydrocarbon throuth Fishcher-Tropsch synthesis in slurry bed
InactiveCN1563280ASimple methodShort processLiquid hydrocarbon mixture recoveryLiquid solutions solvent extractionParaffin waxDistillation
A method for recovering cobalt-base catalyst and heavy hydrocarbon includes extracting and separating mixer of waste cobalt-base catalyst and heavy hydrocarbon with liquid paraffin having initial distillation point of 210 deg.C for three to four times, using dimethylbenzene to extract and separate for two to three times. The recovered mixer of liquid paraffin and heavy hydrocarbon can be used as reaction media in fluid bed reactor and the recovered waste cobalt-base catalyst can be directly used to recover valuable metal of cobalt.
Owner:SYNFUELS CHINA TECH CO LTD
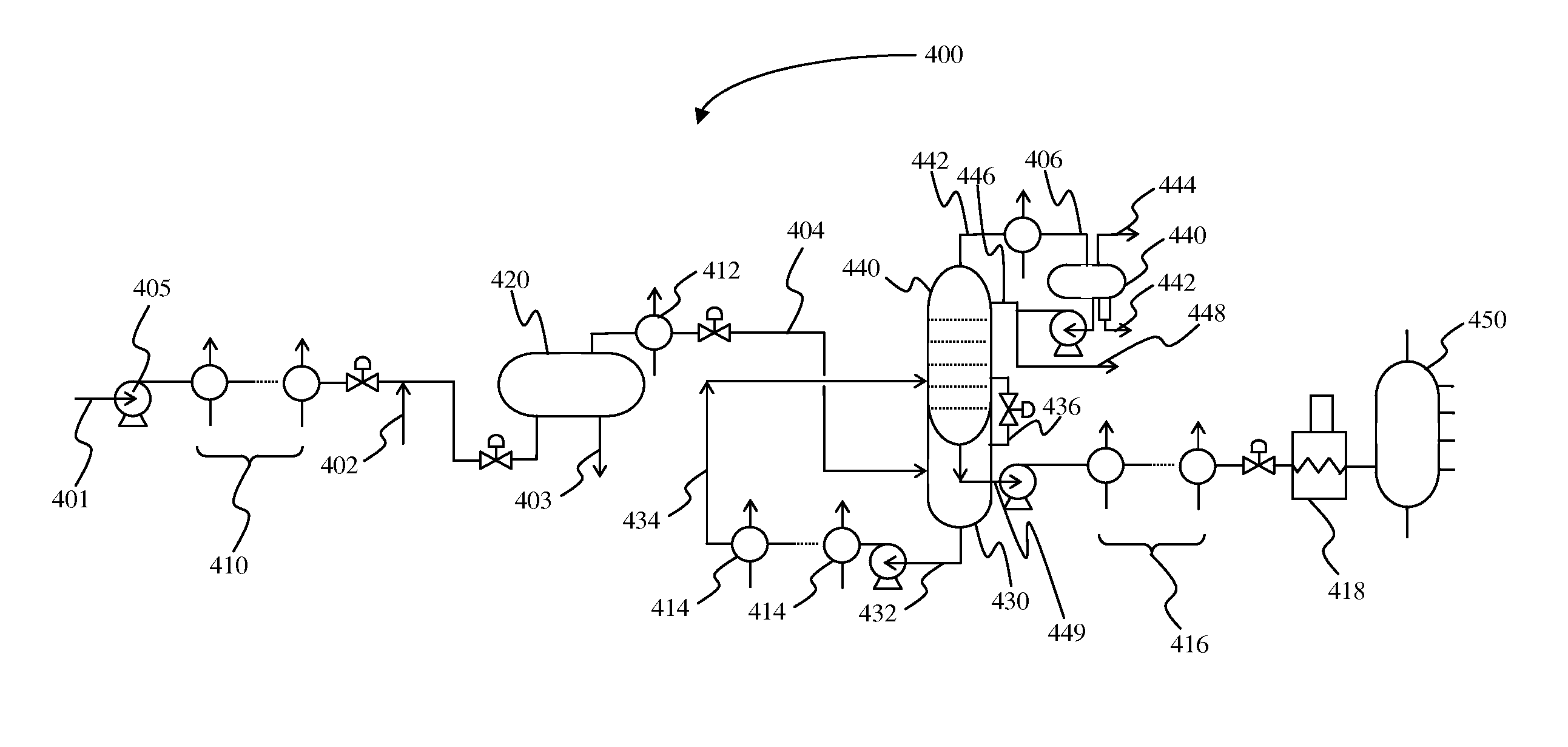
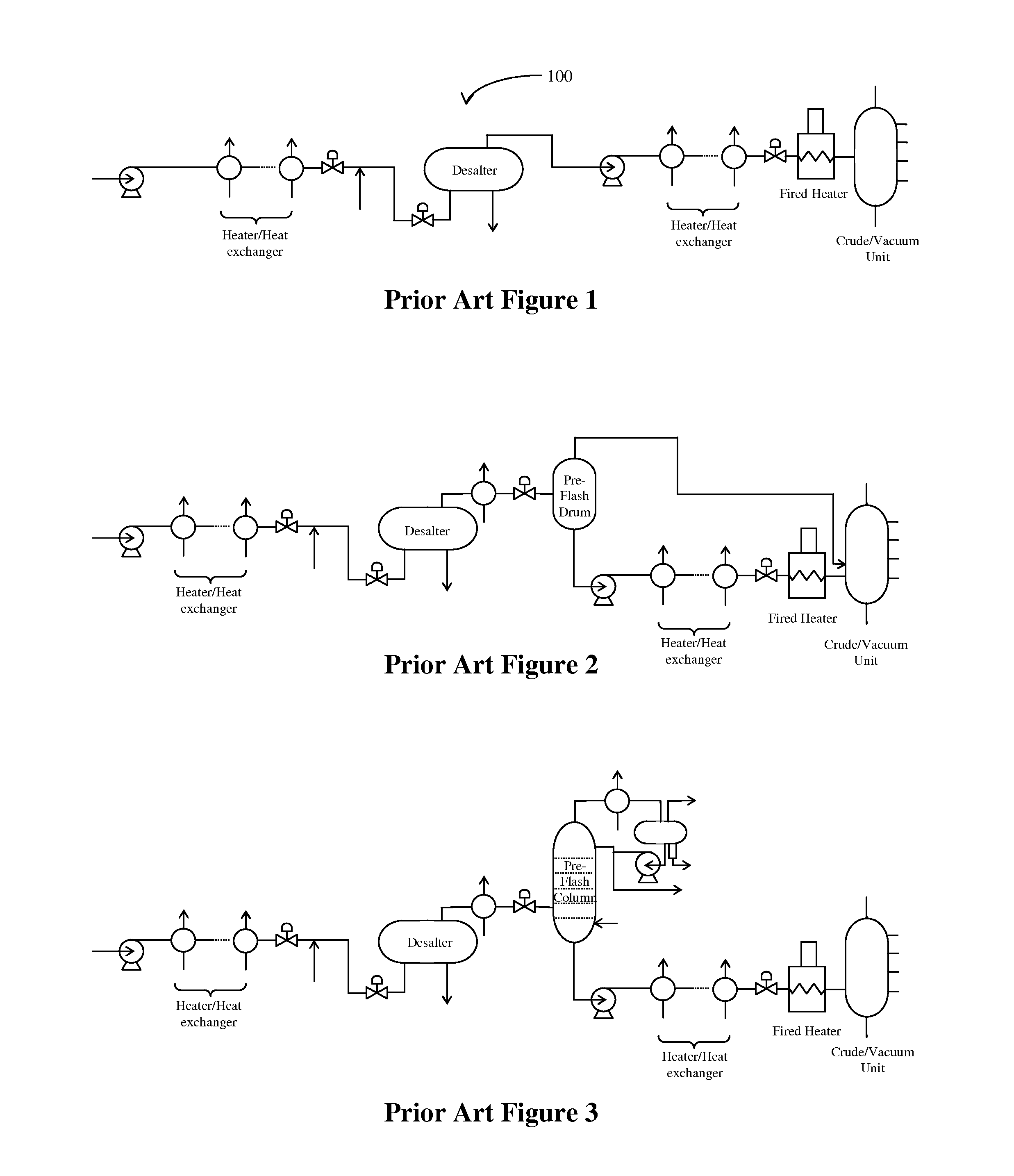
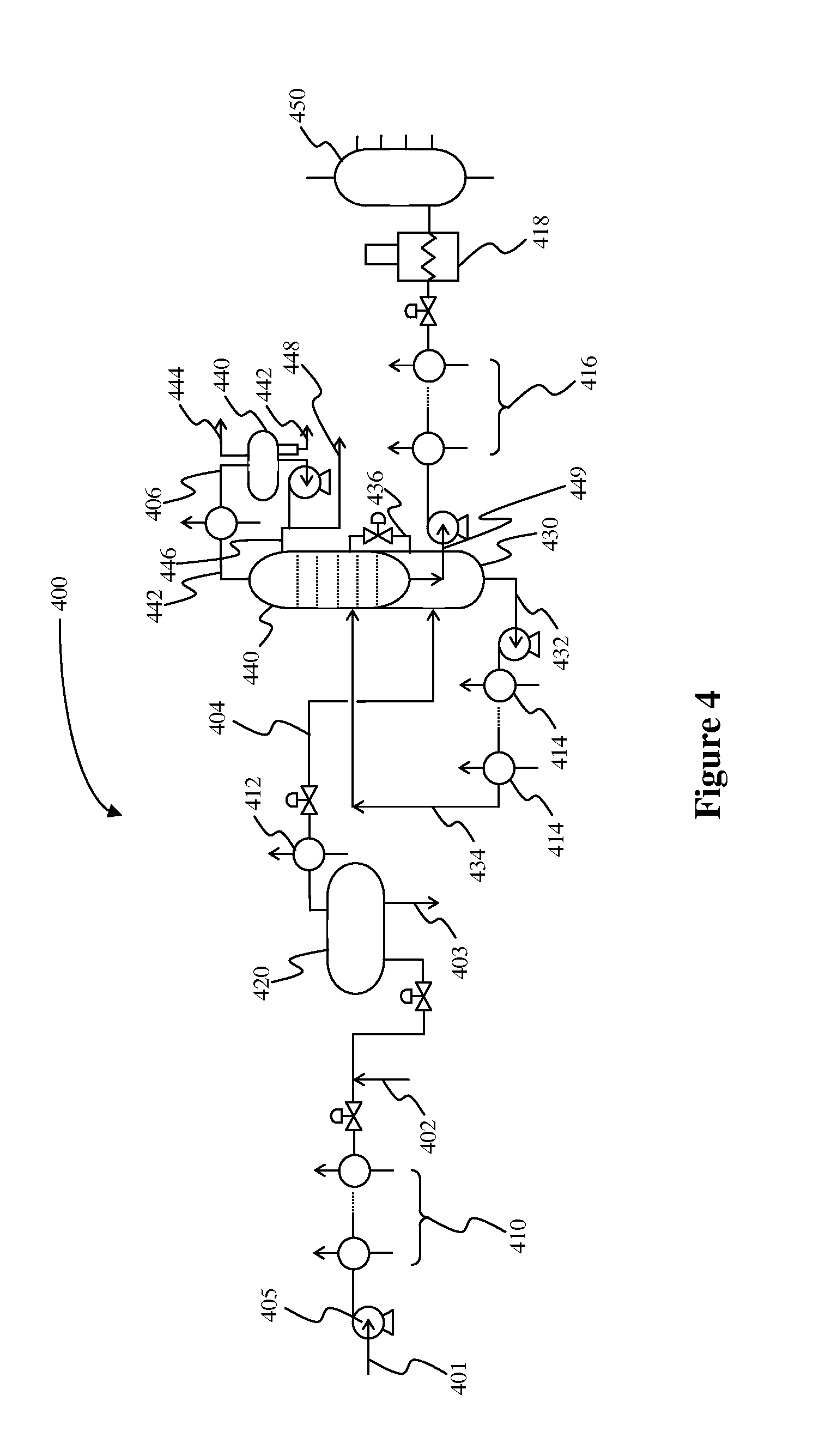
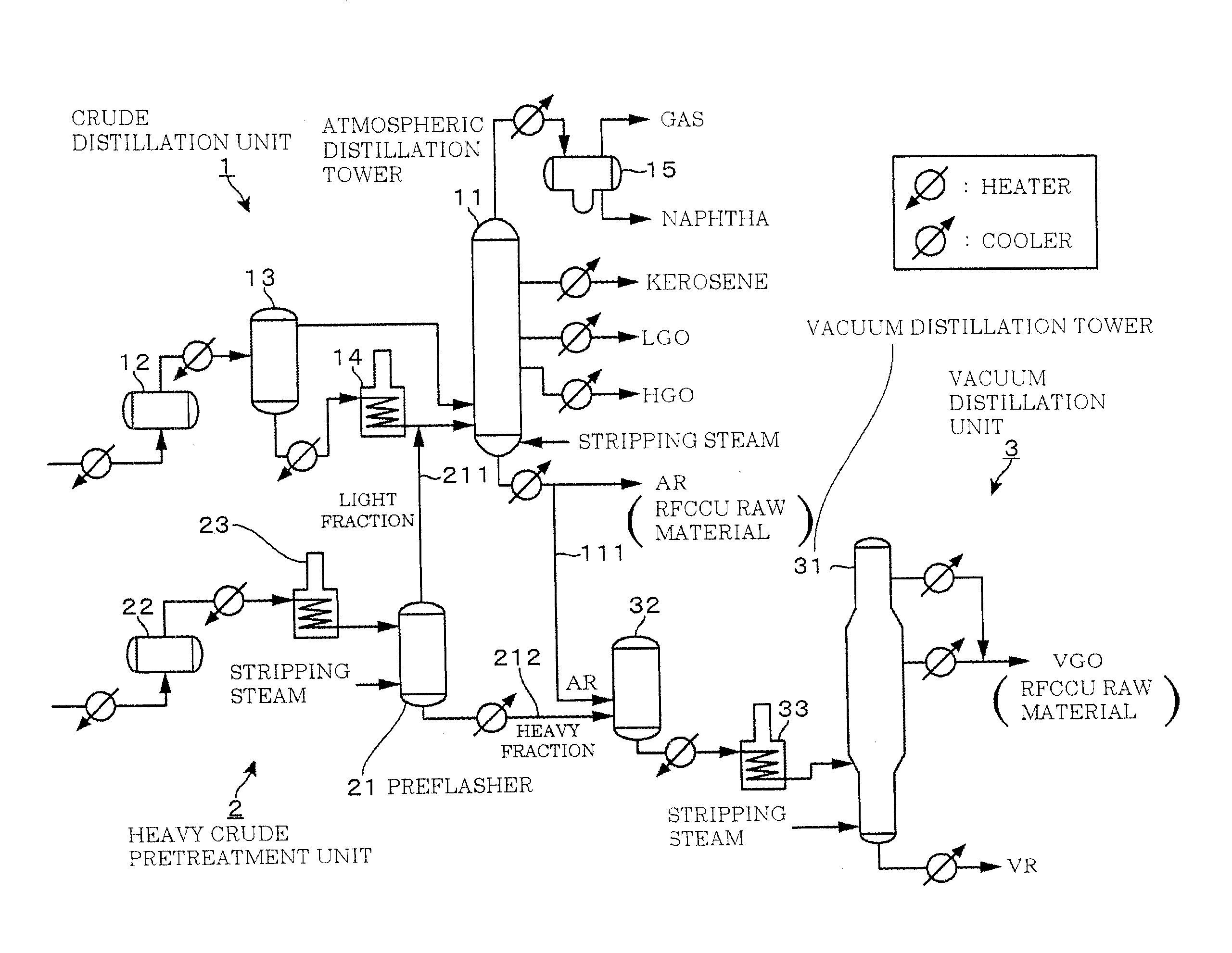
Multiple preflash and exchanger (MPEX) network system for crude and vacuum units
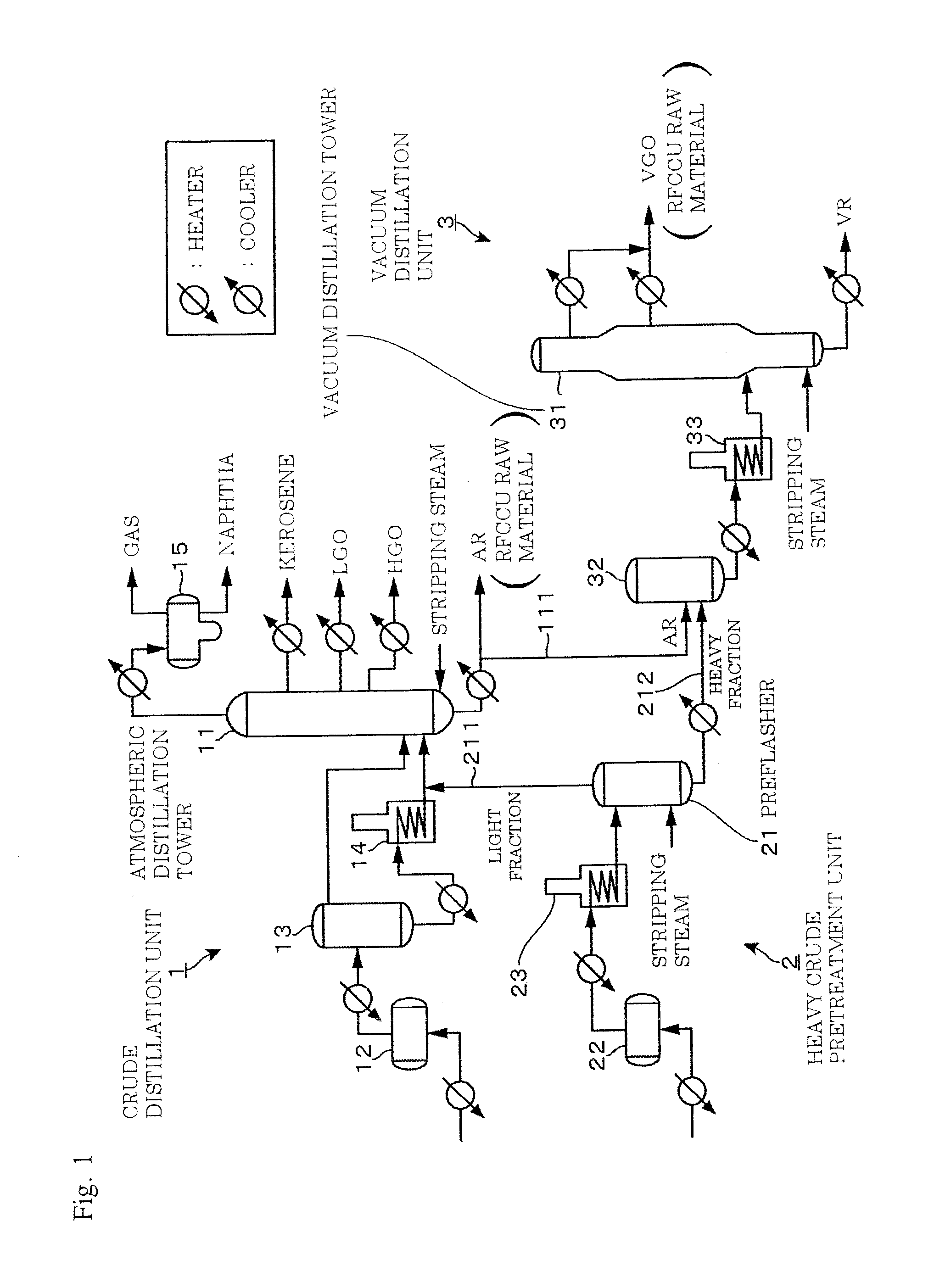
InactiveUS20140374322A1Reduce and even eliminate needPre-processing of lighter crude oil priorThermal non-catalytic crackingWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by distillationEngineeringPre treatment
Plants and methods are presented for crude feed pre-processing before feeding the crude feed into a crude unit or vacuum unit. Pre-processing is preferably achieved with a combination of a preflash drum and a preflash column that allows for high-temperature treatment of the liquids and separate vapor phase handling, which advantageously enables retrofitting existing plants to accommodate lighter crude feeds.
Owner:FLUOR TECH CORP
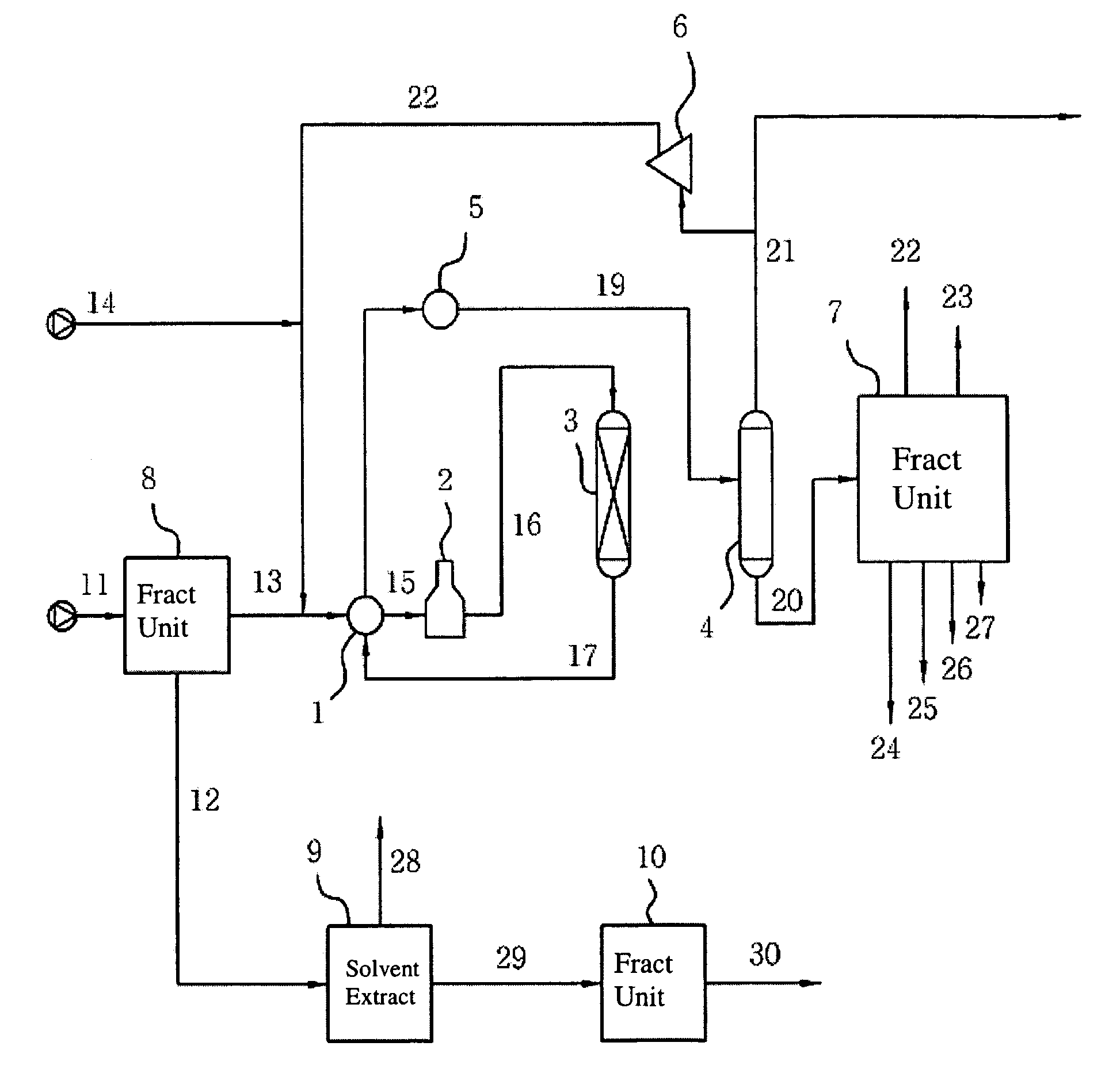
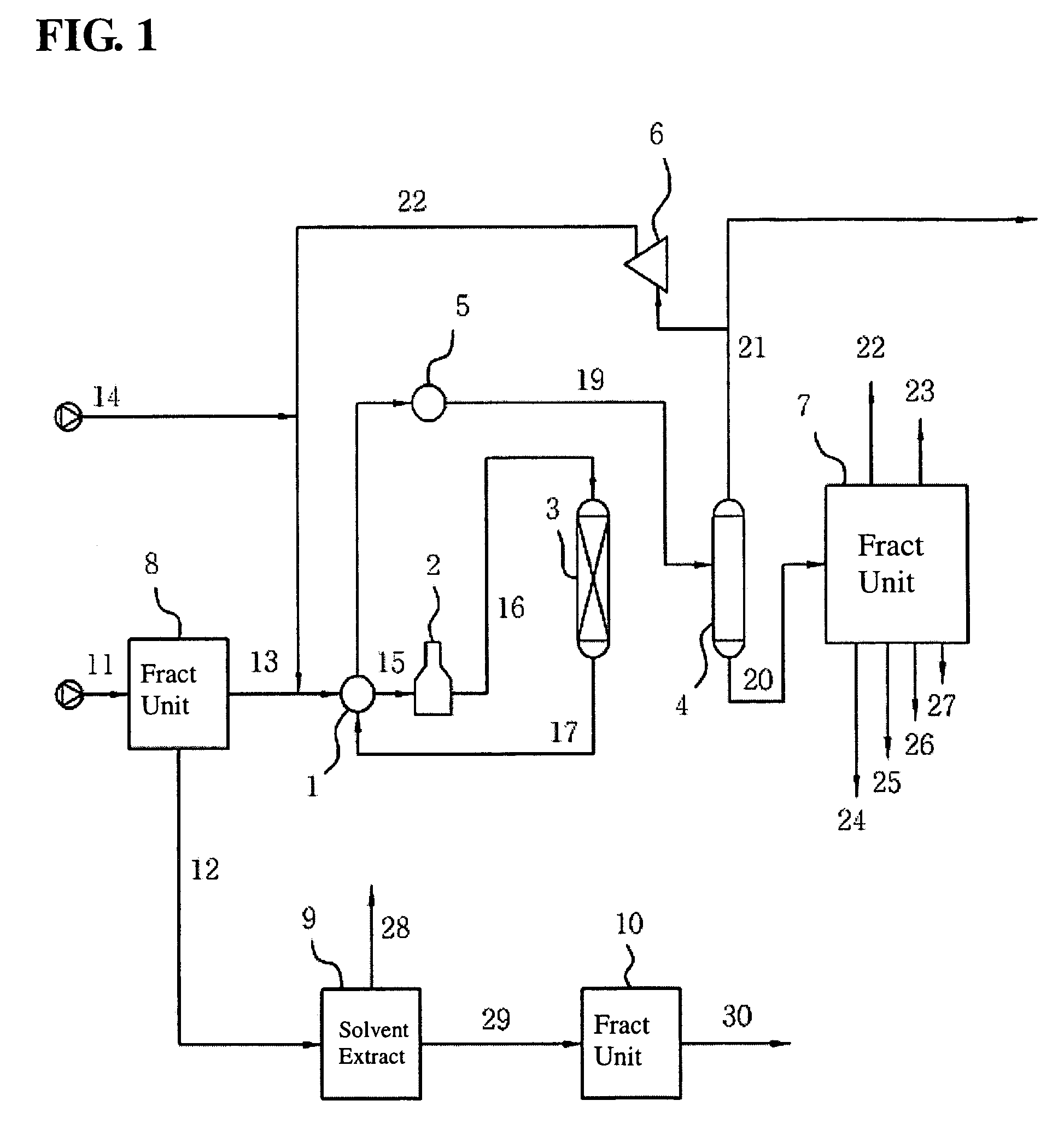
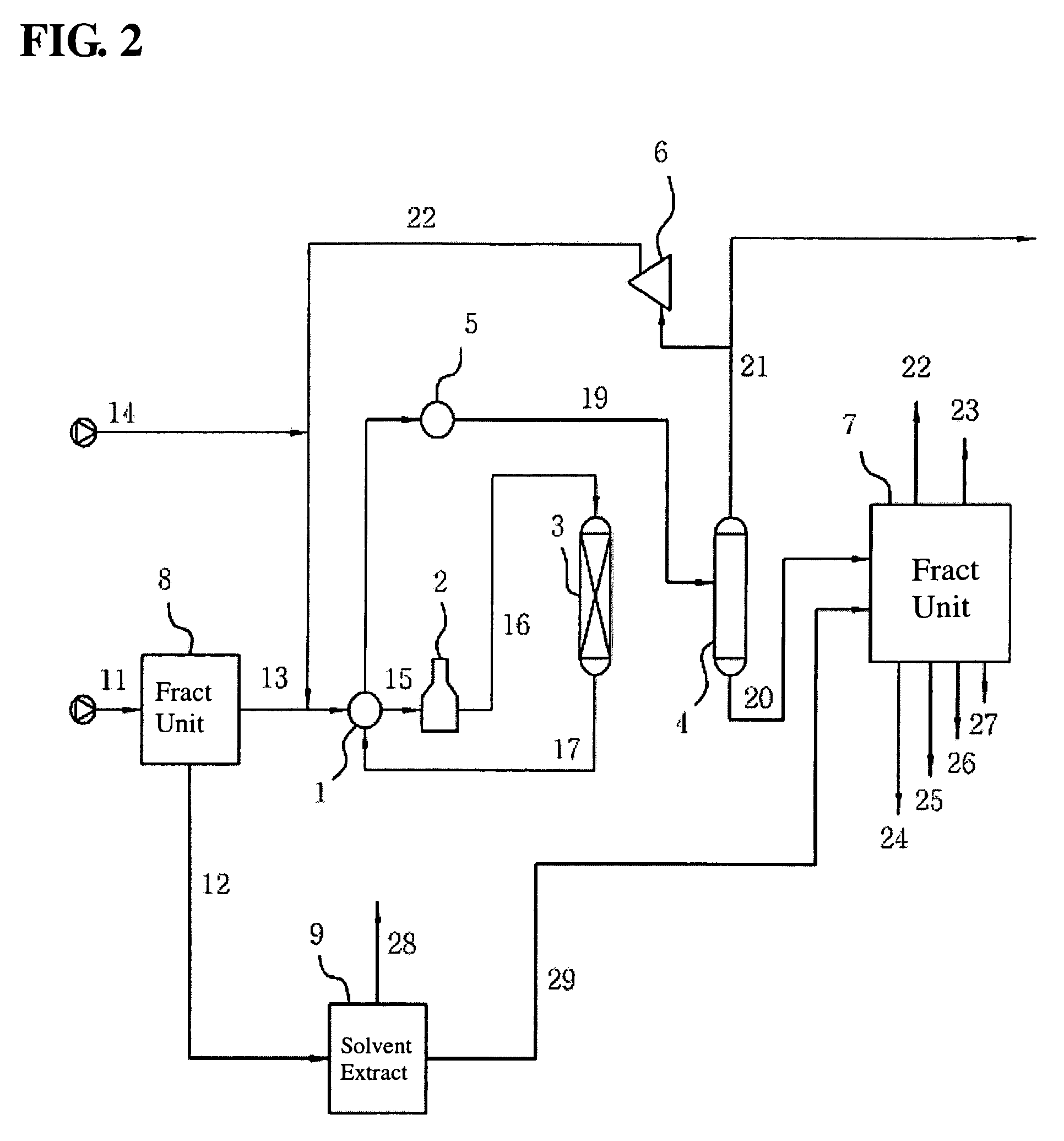
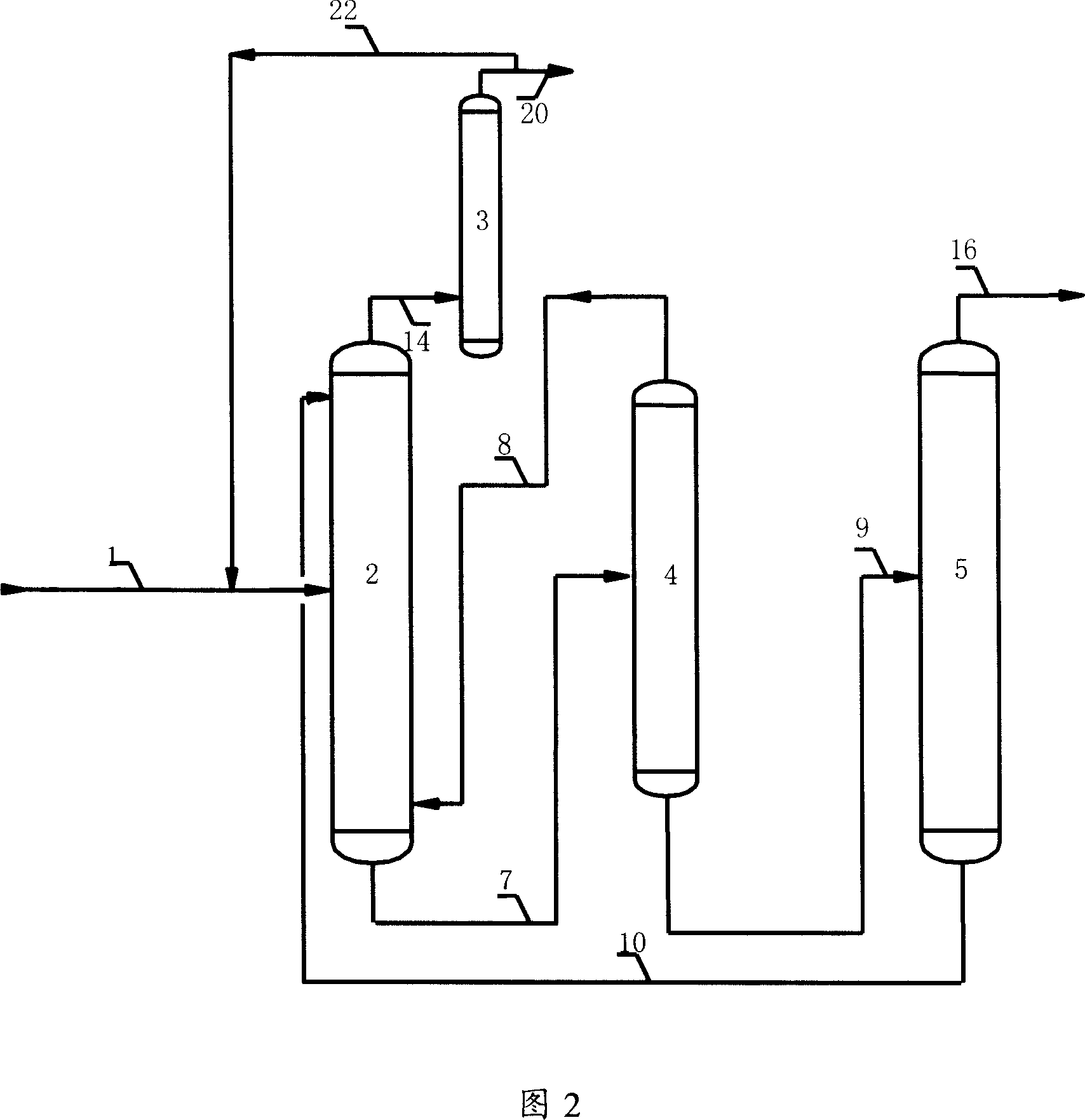
Method for recovering aromatic hydrocarbons from hydrocarbons mixture with high content of aromatic hydrocarbons
ActiveCN101081993AImprove operational efficiencyLess investmentDistillation purification/separationAzeotropic/extractive distillationHydrocarbon mixturesSolvent
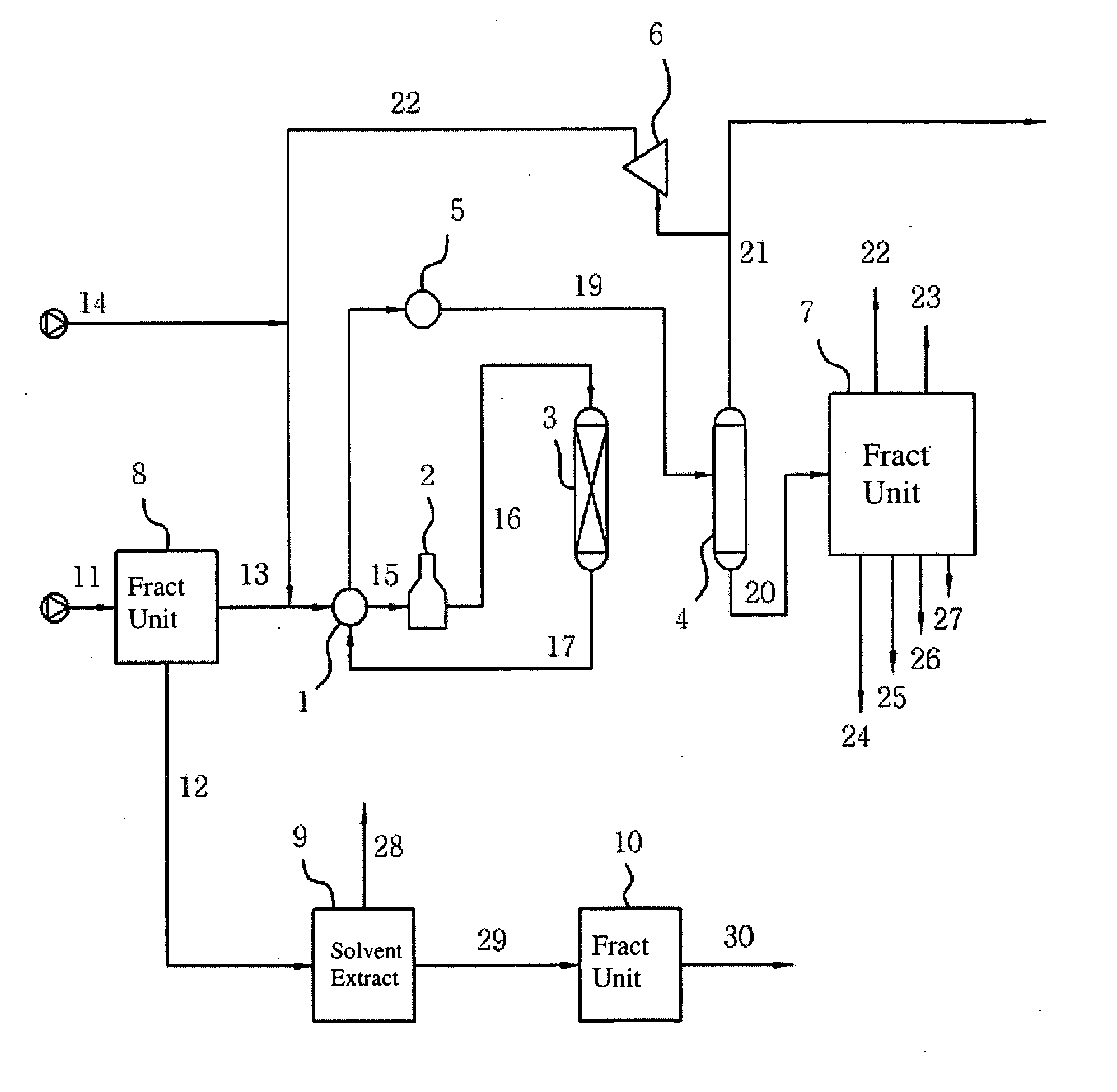
The process of recovering arene from hydrocarbon mixture with high arene content includes the following steps: separating the hydrocarbon mixture into two hydrocarbon flows; leading the first hydrocarbon flow to an solvent column for distilling extraction and exhausting the fat solvent from the bottom to a solvent recovering column; mixing the non-arene gas exhausted from the top of the solvent column with the second hydrocarbon flow and leading the mixture to a liquid-liquid extracting column, exhausting the non-arene component from the top, and steam stripping the fat solvent from the bottom of the column in a stripper and feeding the fat solvent to the solvent recovering column; separating arene from the arene selecting solvent in the solvent recovering column and obtaining arene mixture product in the top of the column; and returning the lean solvent to the liquid-liquid extracting column and the solvent column. The present invention has high arene yield and other advantages.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Regeneration of Selective Solvents for Extractive Processes
ActiveUS20130225838A1Reduce load requirementsEasy to operateSolvent extractionDistillation purification/separationBenzeneExtractive distillation
Recovering a polar hydrocarbon (HC) selective solvent substantially free of hydrocarbons (HCs) and other impurities from a lean solvent stream containing the selective solvent, measurable amounts of heavy aromatic HCs, and polymeric materials that are generated in an extractive distillation (ED) or liquid-liquid extraction (LLE) process. At least a portion of the lean solvent stream is contact in a solvent clean-up zone with a slip stream from the HC feed stream of the ED or LLE process or an external stream. The HC feed stream, such as pyrolysis gasoline or reformate, contains significant amounts of benzene and at least 50% polar (aromatic) HCs and serves as a displacement agent to remove the heavy HCs and polymeric material from the lean solvent stream. A magnetic filter can be used to remove the paramagnetic contaminants from the lean solvent.
Owner:AMT INT INC +1
Process for removing at least benzene from hydrocarbon streams
A method of removing at least benzene from a hydrocarbon stream comprises concentrating aromatics in the hydrocarbon stream by passing the hydrocarbon stream through a membrane unit having at least one membrane to produce a permeate stream and a retentate stream, wherein the permeate stream is aromatics rich relative to the hydrocarbon stream; and extracting aromatics after concentrating using a selective aromatics extraction solvent in an extraction unit to produce an extract stream, wherein the extract stream is aromatics rich relative to the permeate stream.
Owner:BL TECH INC
Process for converting bio-oil
ActiveUS20140256965A1Reduce acidityImprove stabilityOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationHeating oilAlcohol
Disclosed is a process for converting bio-oil, wherein the process includes the steps, where a feedstock including bio-oil selected from bio-oils, any fractions of bio-oils and any combinations thereof is subjected to azeotropic distillation with at least one alcohol to yield a liquid component, and subjecting the liquid component to alcoholysis whereby converted bio-oil is obtained. The invention also relates to the use of converted bio-oil, obtainable by the process, as heating oil, as starting material in processes for producing fuels, fuel components, fine chemicals, chemical building-blocks, and solvents.
Owner:UPM-KYMMENE OYJ
Extraction Prcoess with Novel Solvent Regeneration Methods
ActiveUS20130228448A1Improve abilitiesMinimizing functionDistillation purification/separationExtraction purification/separationSolventImpurity
Solvent regeneration to recover a polar hydrocarbon (HC) selective solvent substantially free of hydrocarbons (HCs) and other impurities from a solvent-rich stream containing selective solvent, heavy HCs, and polymeric materials (PMs) generated from reactions among thermally decomposed or oxidized solvent, heavy HCs, and additives is provided. A combination of displacement agent and associated co-displacement agent squeezes out the heavy HCs and PMs from the extractive solvent within a solvent clean-up zone. Simultaneously, a filter equipped with a magnetic field is positioned in a lean solvent circulation line to remove paramagnetic contaminants. The presence of the co-displacement agent significantly enhances the capability of the displacement agent in removing the heavy HCs and PMs from the extractive solvent. As a result, the solvent regeneration system operates under milder conditions and minimizes or eliminates the need for including a high temperature, energy intensive and difficult-to-operate thermal solvent regenerator.
Owner:AMT INT INC +1
Aromatics recovery by extractive distillation
ActiveUS8552247B2Distillation purification/separationSolid sorbent liquid separationAlkaneExtractive distillation
The present invention relates to a process for recovering polar hydrocarbons from non-polar hydrocarbons, such as aromatics from non-aromatics, naphthenes from paraffins and isoparaffins, or olefins from paraffins and isoparaffins, in feed mixtures containing at least a measurable amount of heavier hydrocarbons. According to the invention, an improved extractive distillation (extractive-distillation) process is disclosed for recovering aromatic hydrocarbons including benzene, toluene, and xylenes from heavy (C9+) hydrocarbons. The invention also relates to an improved extractive-distillation process for recovering mainly benzene and toluene from the C6-C7 petroleum streams containing at least a measurable amount of C8+ hydrocarbons. This invention is further directed toward the regeneration and recovery of the extractive-distillation solvent utilized to recover and purify the aromatic hydrocarbons from the petroleum stream containing at least a measurable amount of hydrocarbons heavier than the intended product.
Owner:UOP LLC
Method of operating crude treatment system
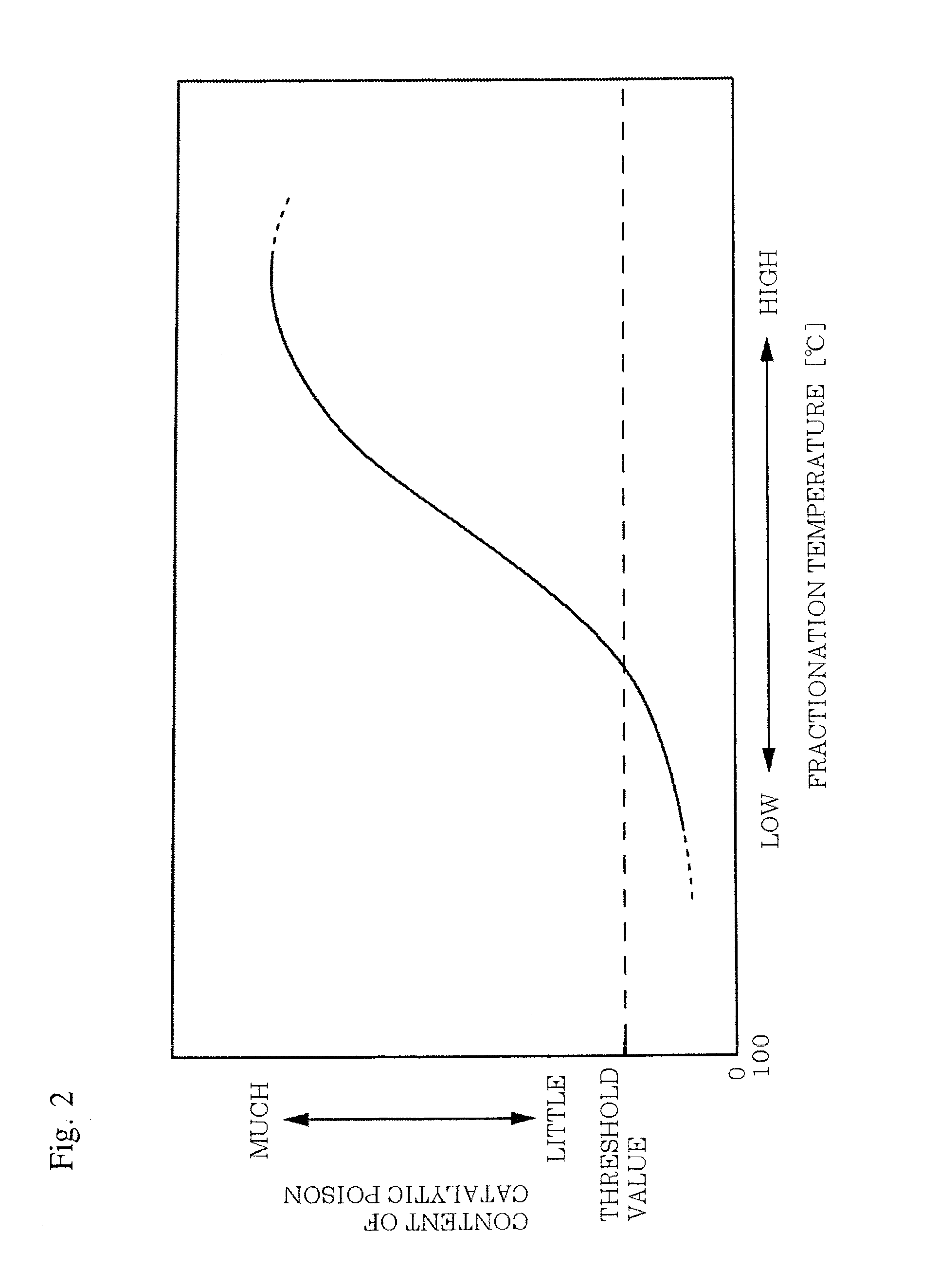
InactiveUS20150275100A1Catalyst content reductionReduce contentCatalytic crackingHydrocarbon oils refiningFractionating columnTower
Crude containing a comparatively large content of nickel, vanadium, or carbon residue is treated so as to supply a raw material to a downstream catalytic cracking process, A primary distillation tower fractionates first crude into a residue fraction partly used as raw oil of a catalytic cracking process and other fractions. A secondary distillation tower fractionates second crude containing a larger content of a catalytic poison with respect to catalysts used in the catalytic cracking process than the first crude into a light fraction included in a distillation temperature range of the other fractions and a heavy fraction as a rest thereof. A light fraction supply line supplies the light fraction to the primary distillation tower so as to be treated in the primary distillation tower.
Owner:JGC CORP
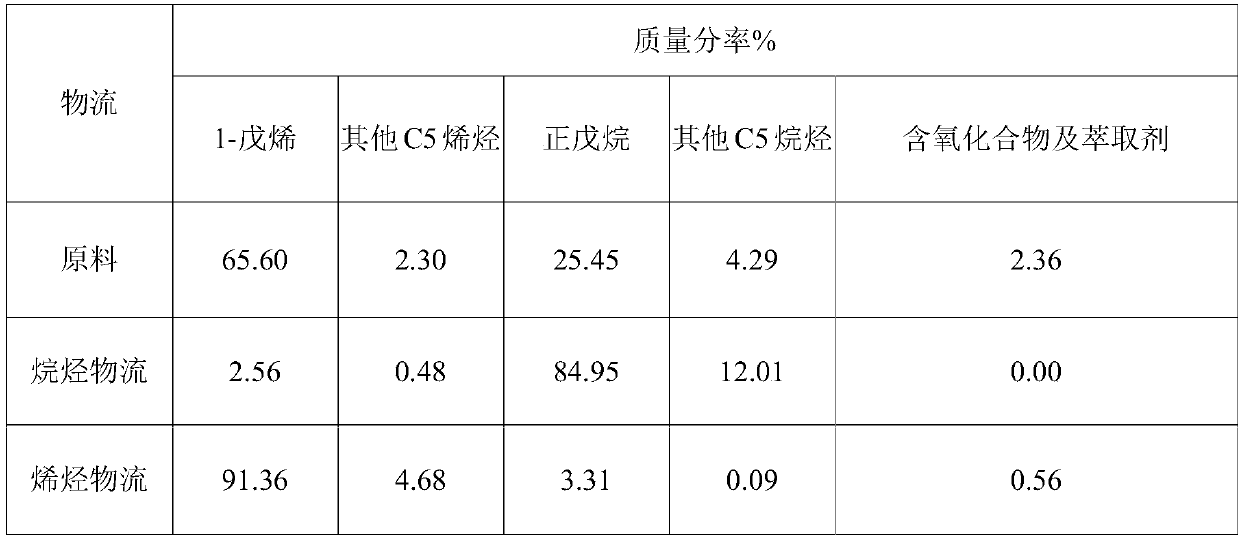
Device and method for separating olefin from Fischer-Tropsch synthetic oil
InactiveCN109652111AProcess directlySimple processDistillation purification/separationAzeotropic/extractive distillationAlkaneEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a device and a method for separating olefin from Fischer-Tropsch synthetic oil. The device combines a partition wall tower and an extractive rectification technology, a partition plate is arranged in the partition wall tower, the partition wall tower is divided into an extractive fraction part, a rectification part and a public stripping part, and the extractive fraction part is used for extracting alkane; the side line rectification section is used for extracting olefin, and the public stripping section is used for extracting the mixture of oxygen-containing compound and extractant, thereby realizing the purpose that alkane, olefin and oxygen-containing compound can be simultaneously separated from the cut Fischer-Tropsch synthetic oil in a partition tower, and caneffectively reduce the problems of high equipment cost and high operation cost when olefin is separated from the Fischer-Tropsch synthetic oil fraction, thereby improving the economic benefit of theoil product.
Owner:BEIJING SJ ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION & NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
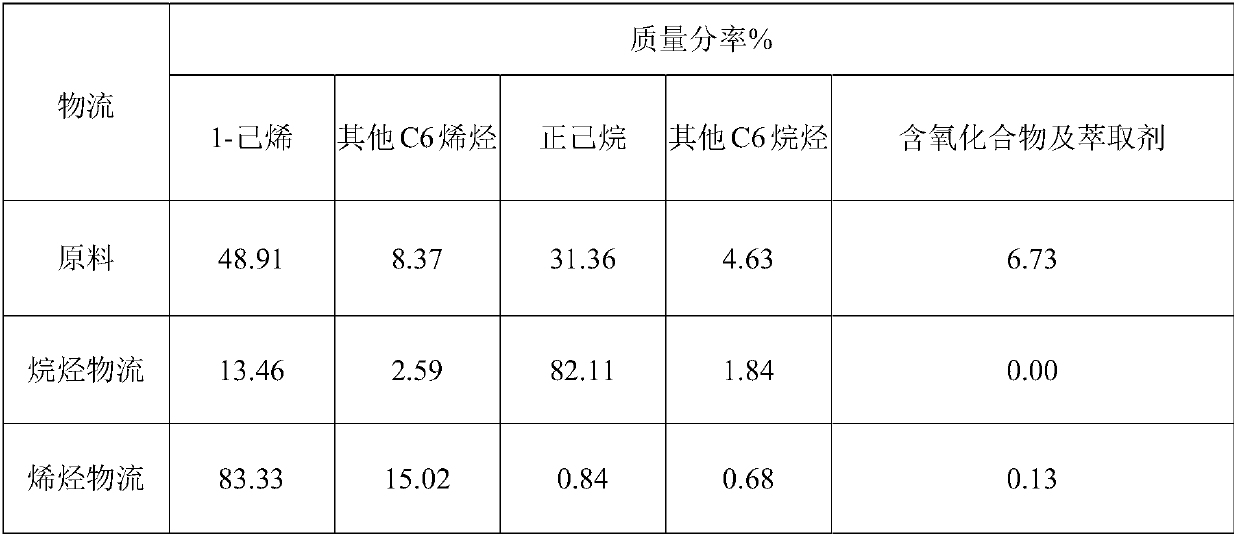
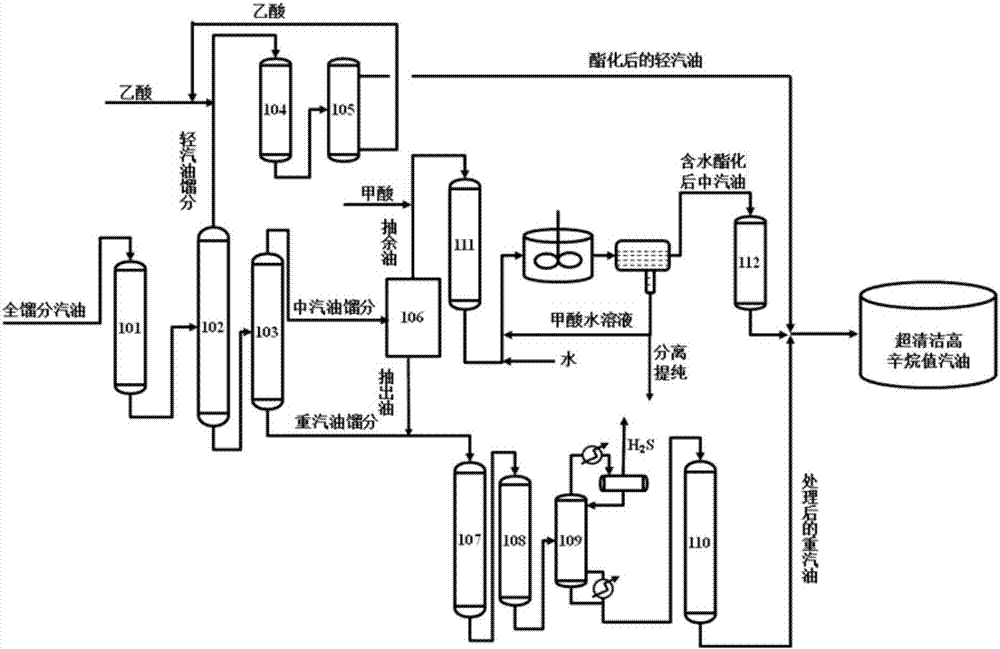
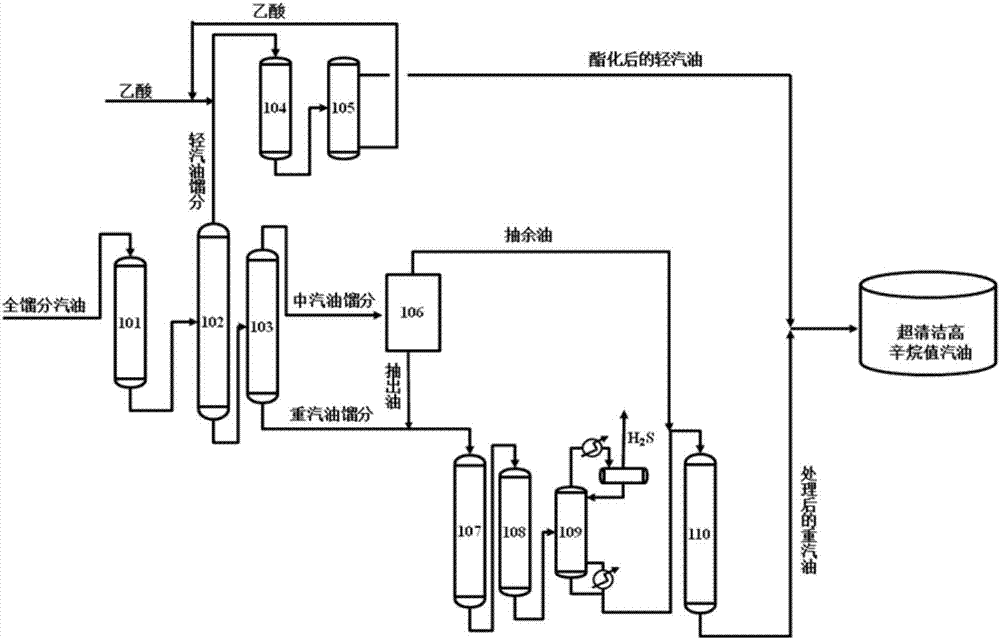
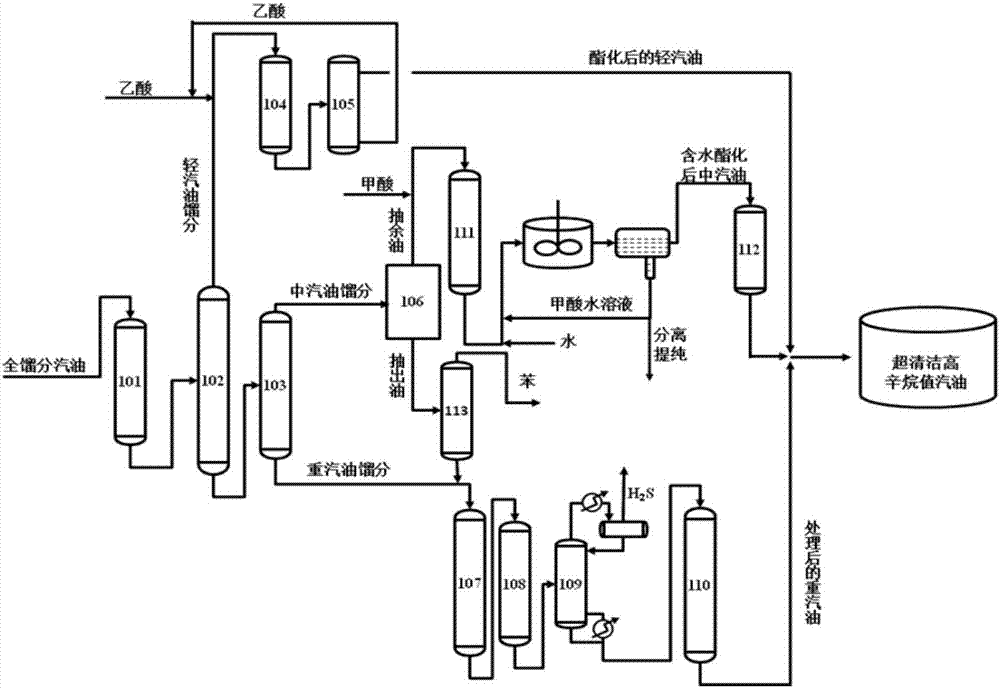
Production method and production system of super-clean high-octane number gasoline
ActiveCN107488464AMaintain or boost octaneAvoid generatingLiquid carbonaceous fuelsTreatment with hydrotreatment processesIsomerizationExtractive distillation
The invention provides a production method and a production system of a super-clean high-octane number gasoline. The production method comprises: carrying out a directional sulfur transfer reaction on full-distillate gasoline, and cutting the obtained oil products to obtain light gasoline distillate, medium gasoline distillate, and heavy gasoline distillate; carrying out an esterification reaction on the light gasoline distillate to obtain esterified light gasoline; obtaining raffinate oil and extract oil from the medium gasoline distillate through an extraction distillation system; carrying out an esterification reaction on the raffinate oil to obtain esterified medium gasoline; mixing the heavy gasoline distillate and the extract oil to obtain mixed oil, and sequentially carrying out a first-stage hydrodesulfurization reaction, a second-stage hydrodesulfurization reaction, H2S removing and a hydrocarbon isomerization / aromatization reaction to obtain treated heavy gasoline; and blending the esterified light gasoline, the esterified medium gasoline and the treated heavy gasoline to obtain clean gasoline. According to the present invention, the method is particularly suitable for high-sulfur and high-olefin catalytic cracking gasoline, and can maintain or increase the octane number of gasoline while performs ultra-deep desulfurization.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Split-shell raffinate columns and methods for use in continuous adsorptive separation processes
InactiveUS20140179975A1Well formedDistillation purification/separationHydrocarbonsChemistrySeparation process
A split-shell column includes a raffinate column portion for separating a raffinate material from a desorbent material and a desorbent rerun column portion for separating heavy contaminants from the desorbent material. A feed to the desorbent rerun column portion is provided from the desorbent material in the raffinate column. The desorbent rerun column portion occupies a portion of a lower end of the split-shell column and is thermally separated from the raffinate column portion.
Owner:UOP LLC
Method for extracting phenol compounds from direct coal liquefied oil through extractive distillation
ActiveCN103896739BHigh recovery rateIncrease relative volatilityOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationSulfolaneExtractive distillation
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com