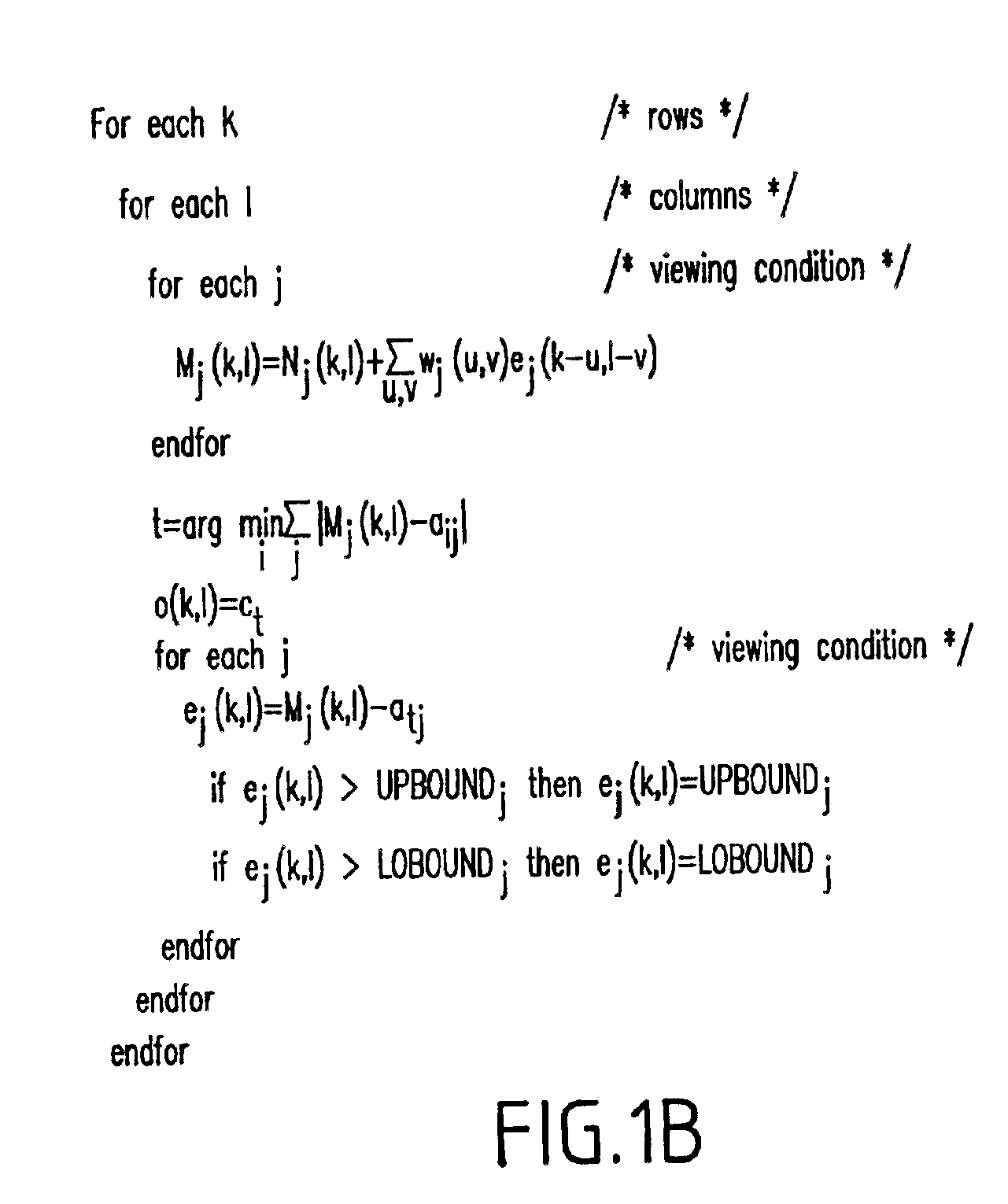Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
60results about How to "Minimizing function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Inhaler
ActiveUS8833364B2High specific evaporative capacityHigh evaporator efficiencyRespiratorsOrganic active ingredientsEngineeringInhaler
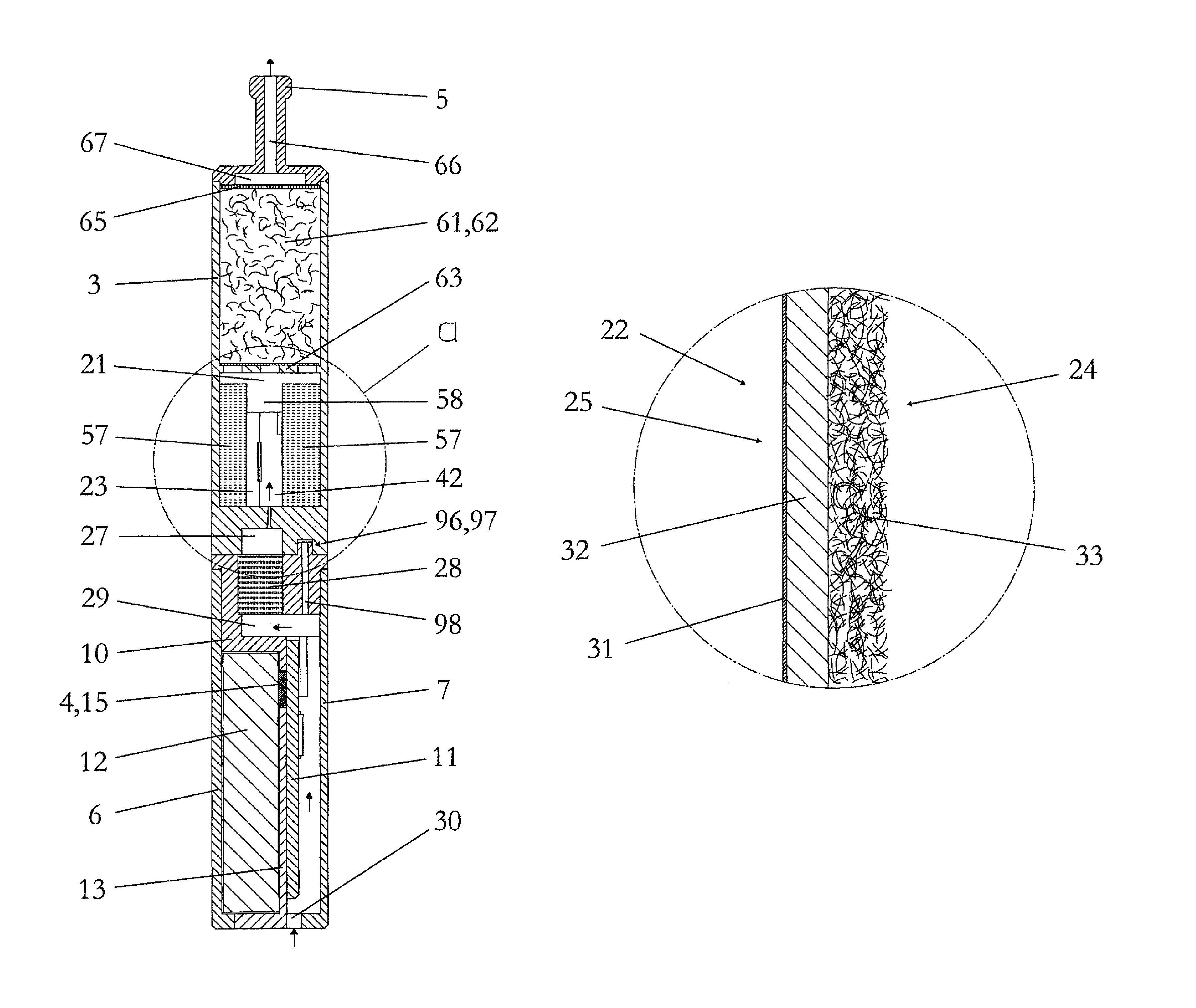
The present disclosure relates to an inhaler component for producing a steam / air mixture or / and condensation aerosol in an intermittent and inhalation- or pull-synchronous manner, the inhaler component including: a housing; a chamber arranged in the housing; an air inlet opening for the supply of air from the surroundings to the chamber; an electrical heating element for evaporating a portion of a liquid material; and a wick having a capillary structure, which wick forms a composite structure with the heating element and automatically supplies the heating element with fresh liquid material after evaporation.
Owner:NICOVENTURES TRADING LTD
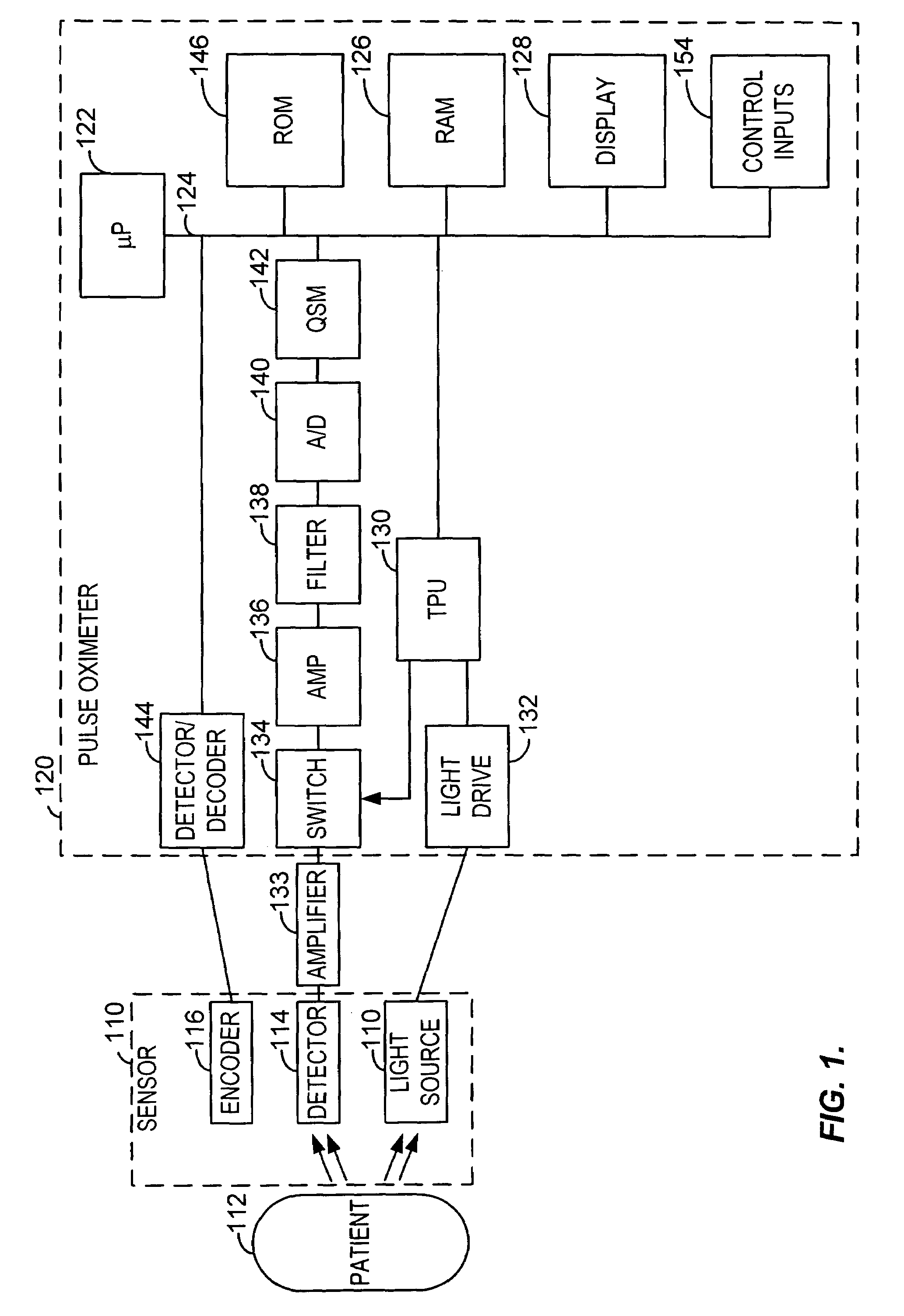
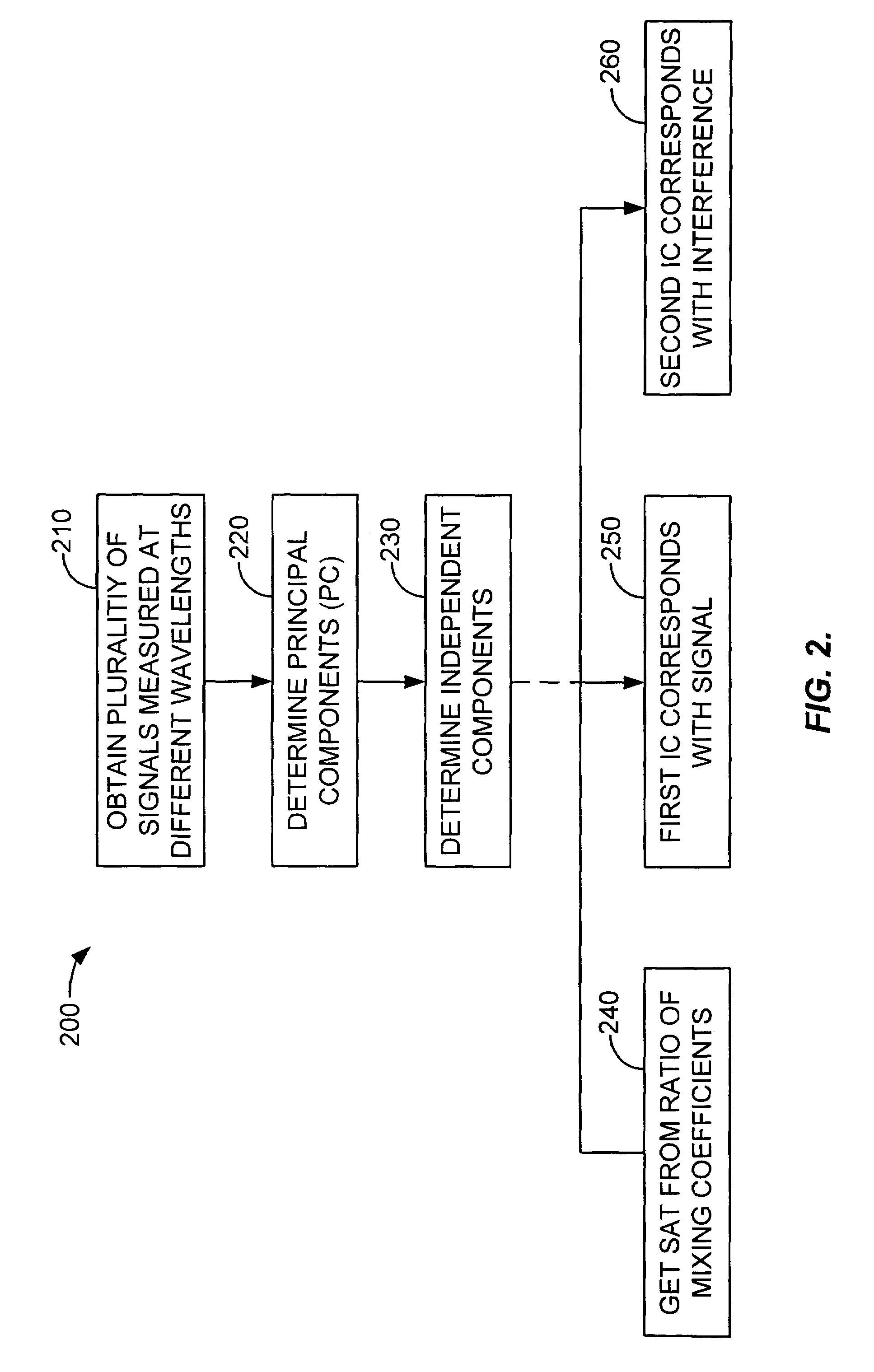
Blind source separation of pulse oximetry signals
InactiveUS7079880B2Minimize cross-correlationImprove performanceSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse ratePrincipal component analysisPulse oximetry
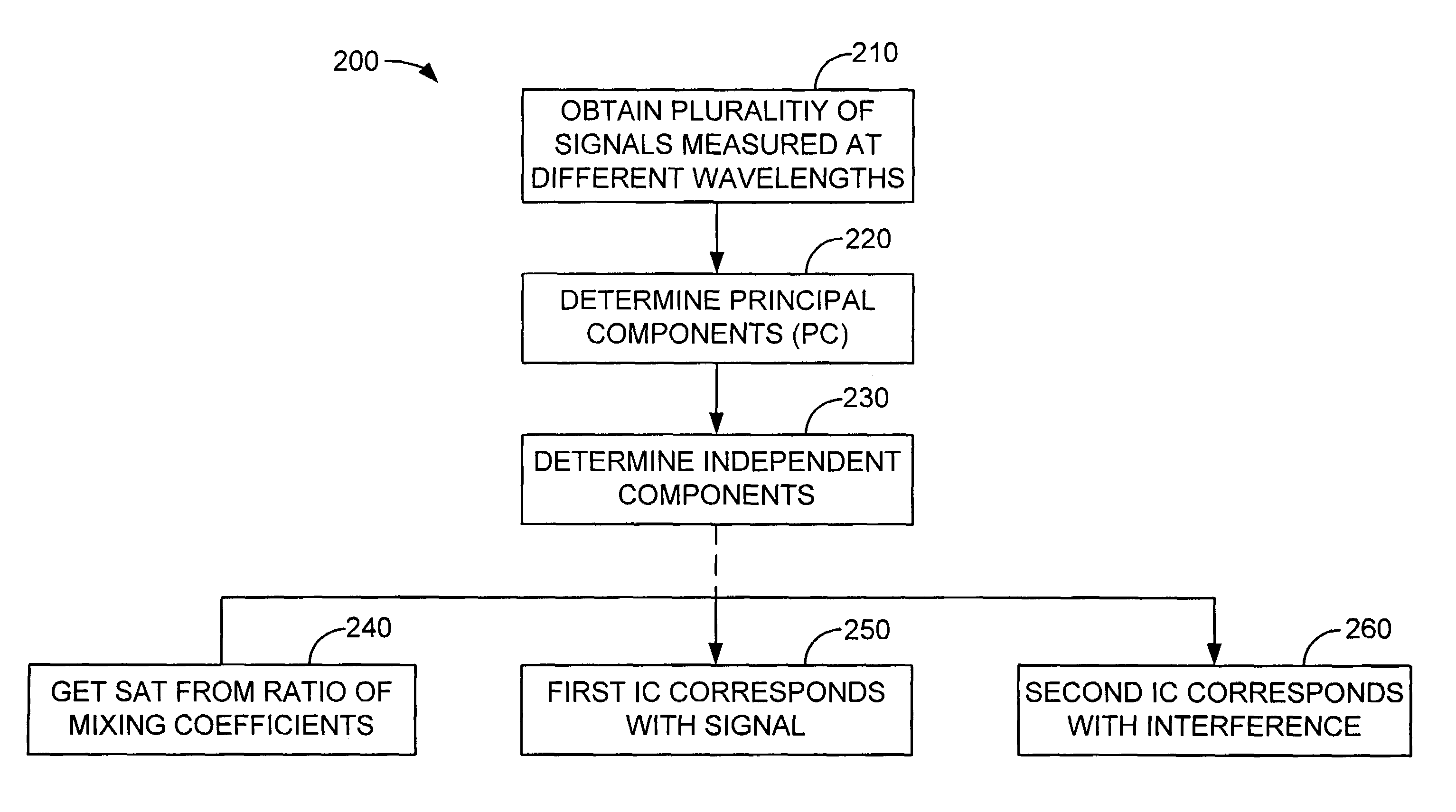
A method and apparatus for the application of Blind Source Separation (BSS), specifically independent Component Analysis (ICA) to mixture signals obtained by a pulse oximeter sensor. In pulse oximetry, the signals measured at different wavelengths represent the mixture signals, while the plethysmographic signal, motion artifact, respiratory artifact and instrumental noise represent the source components. The BSS is carried out by a two-step method including an ICA. In the first step, the method uses Principal Component Analysis (PCA) as a preprocessing step, and the Principal Components are then used to derive sat and the Independent Components, where the Independent Components are determined in a second step. In one embodiment, the independent components are obtained by high-order decorrelation of the principal components, achieved by maximizing the sum of the squares of the higher-order cumulants of the plurality of mixture signals.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
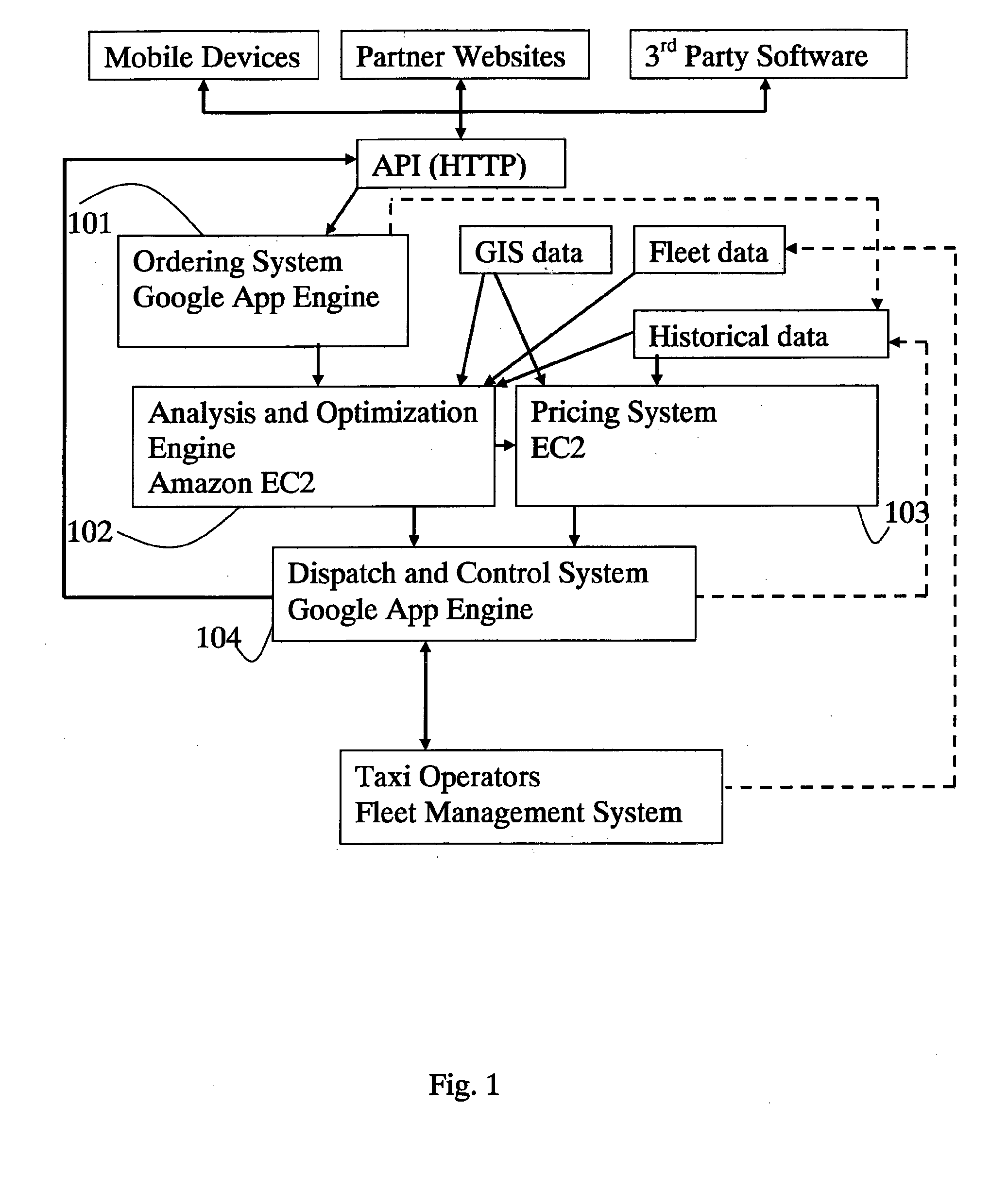
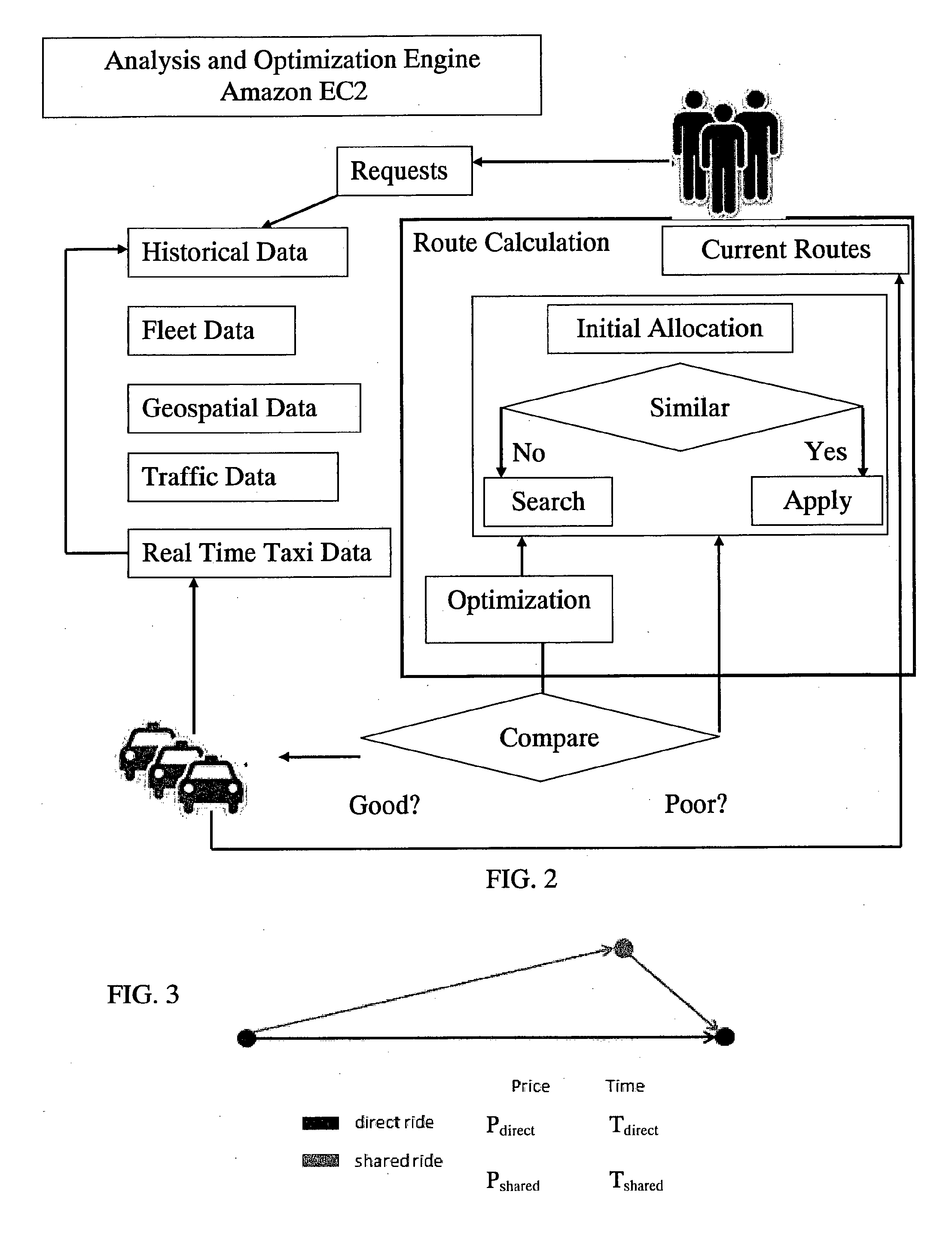
Public transport optimization
InactiveUS20130024249A1Minimize metric functionMinimizing functionInstruments for road network navigationTicket-issuing apparatusMultiple pointComputer science
A system and method for real time dispatching of vehicles taking into account multiple point to point transport requests and conditions including desired ride conditions, traffic, and infrastructure. Analysis of these factors is using suitable algorithms in order to determine optimal routes.
Owner:ZOHAR ZEEV EL ASHER ADIN +2
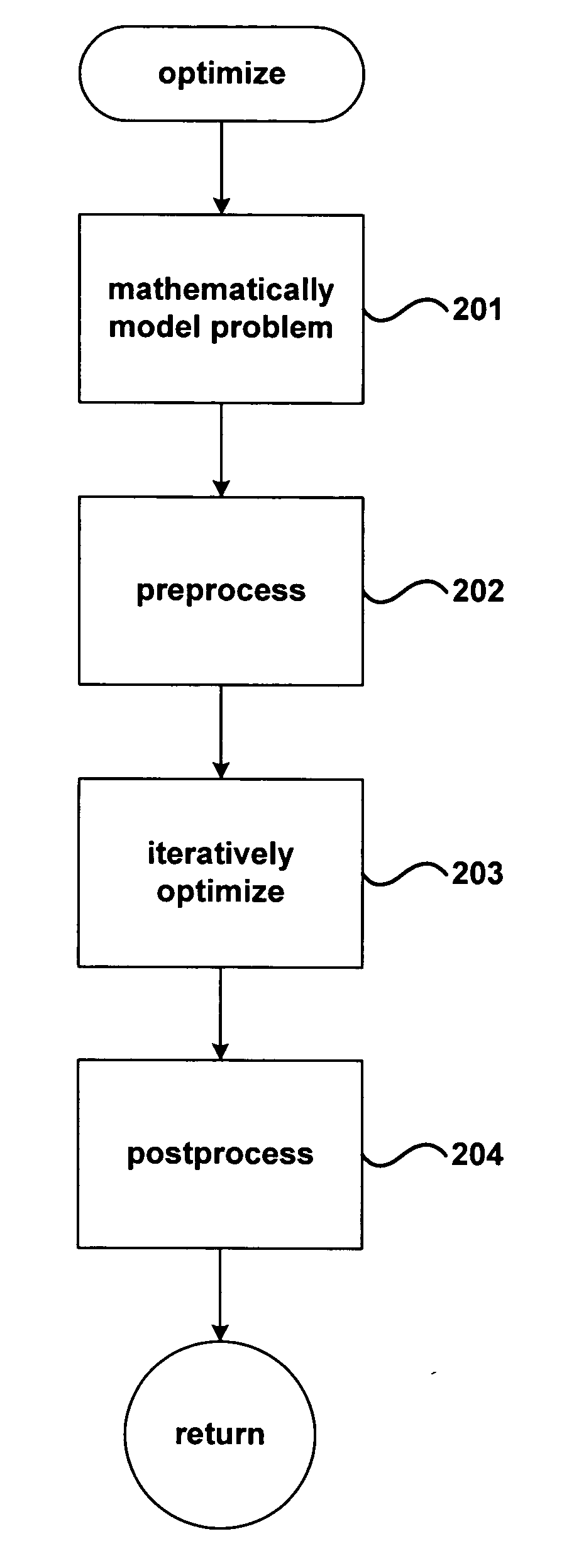
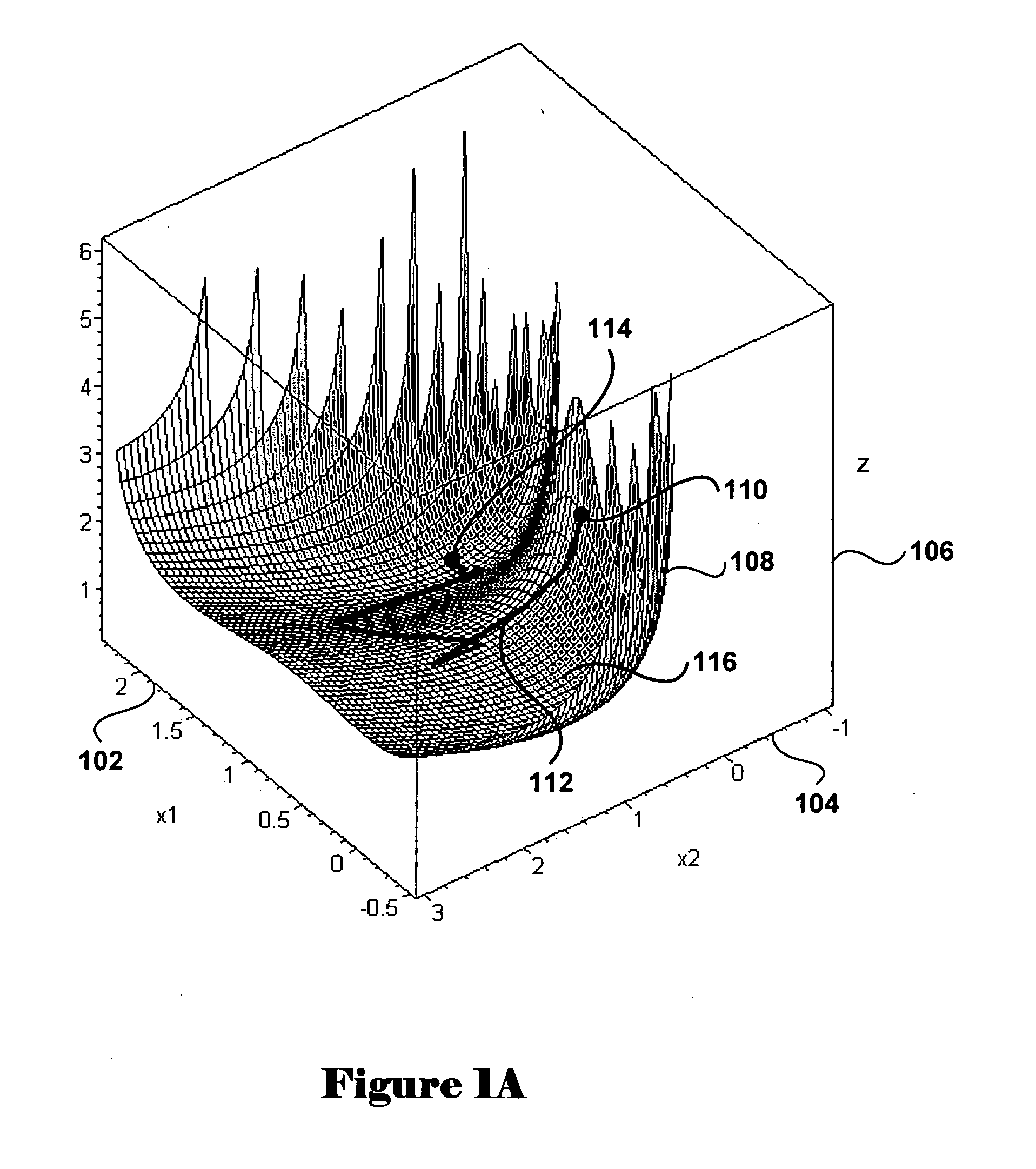
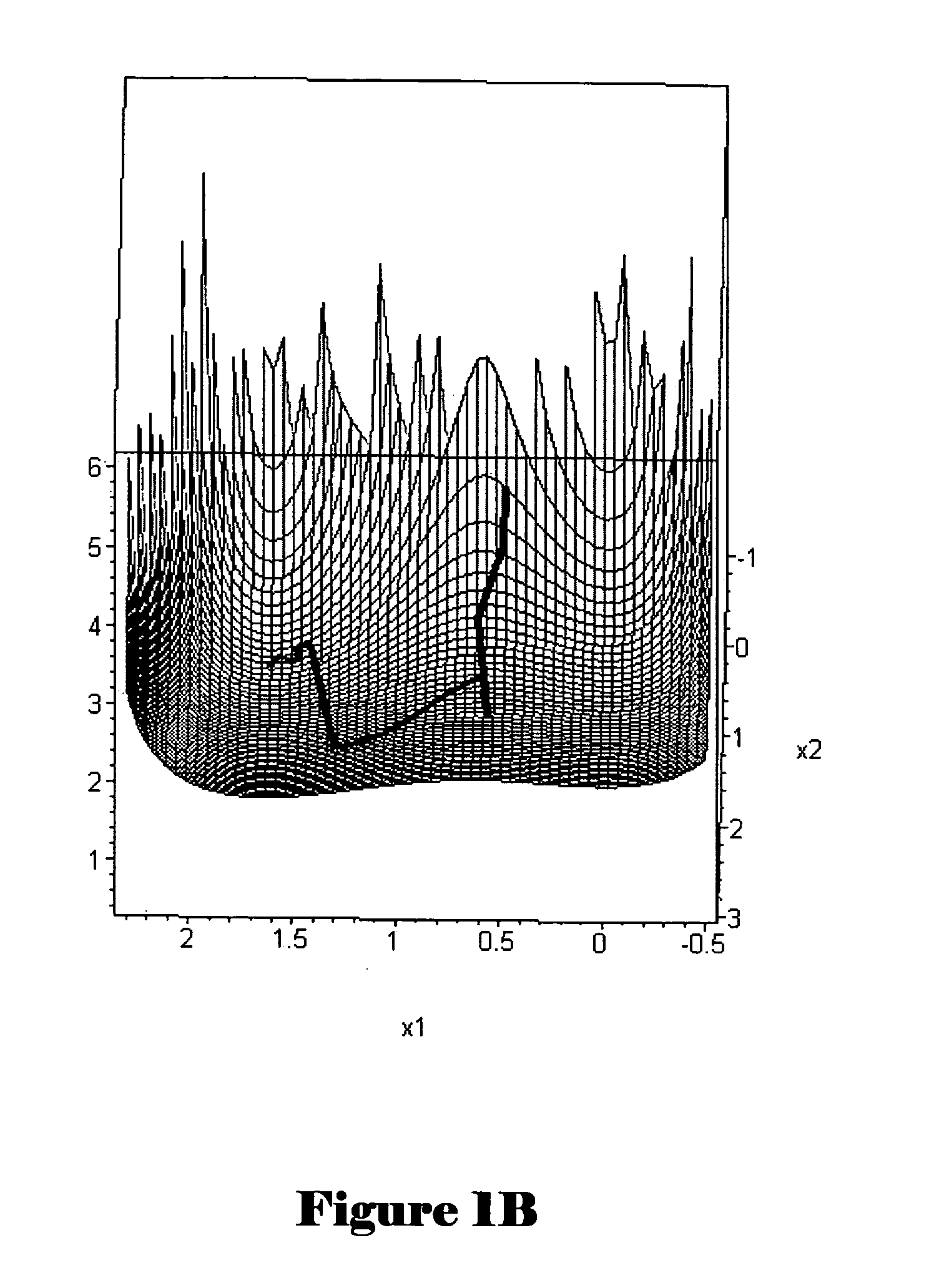
Method and system for optimization of geneal symbolically expressed problems, for continuous repair of state functions, including state functions derived from solutions to computational optimization, for generalized control of computational processes, and for hierarchical meta-control and construction of computational processes
InactiveUS20050102044A1Efficiently traverseImprove time efficiencyComplex mathematical operationsAdaptive controlDecompositionHigh dimensional
Methods and systems for finding optimal or near optimal solutions for generic optimization problems by an approach to minimizing functions over high-dimensional domains that mathematically model the optimization problems. Embodiments of the disclosed invention receive a mathematical description of a system, in symbolic form, that includes decision variables of various types, including real-number-valued, integer-valued, and Boolean-valued decision variables, and that may also include a variety of constraints on the values of the decision variables, including inequality and equality constraints. The objective function and constraints are incorporated into a global objective function. The global objective function is transformed into a system of differential equations in terms of continuous variables and parameters, so that polynomial-time methods for solving differential equations can be applied to calculate near-optimal solutions for the global objective function. Embodiments of the present invention also provide for distribution and decomposition of global-gradient-descent- field-based optimization methods, by following multiple trajectories, and local-gradient- descent-field-based optimization methods, by using multiple agents, in order to allow for parallel computation and increased computational efficiency. Various embodiments of the present invention further include approaches for relatively continuous adjustment of solutions to optimization problems in time, to respond to various events, changes in priorities, and changes in forecasts, without needing to continuously recalculate optimization solutions de novo. While many embodiments of the present invention are specifically directed to various classes of optimization problems, other embodiments of the present invention provide a more general approach for constructing complex hierarchical computational processes and for optimally or near optimally controlling general computational processes.
Owner:CLEARSIGHT SYST
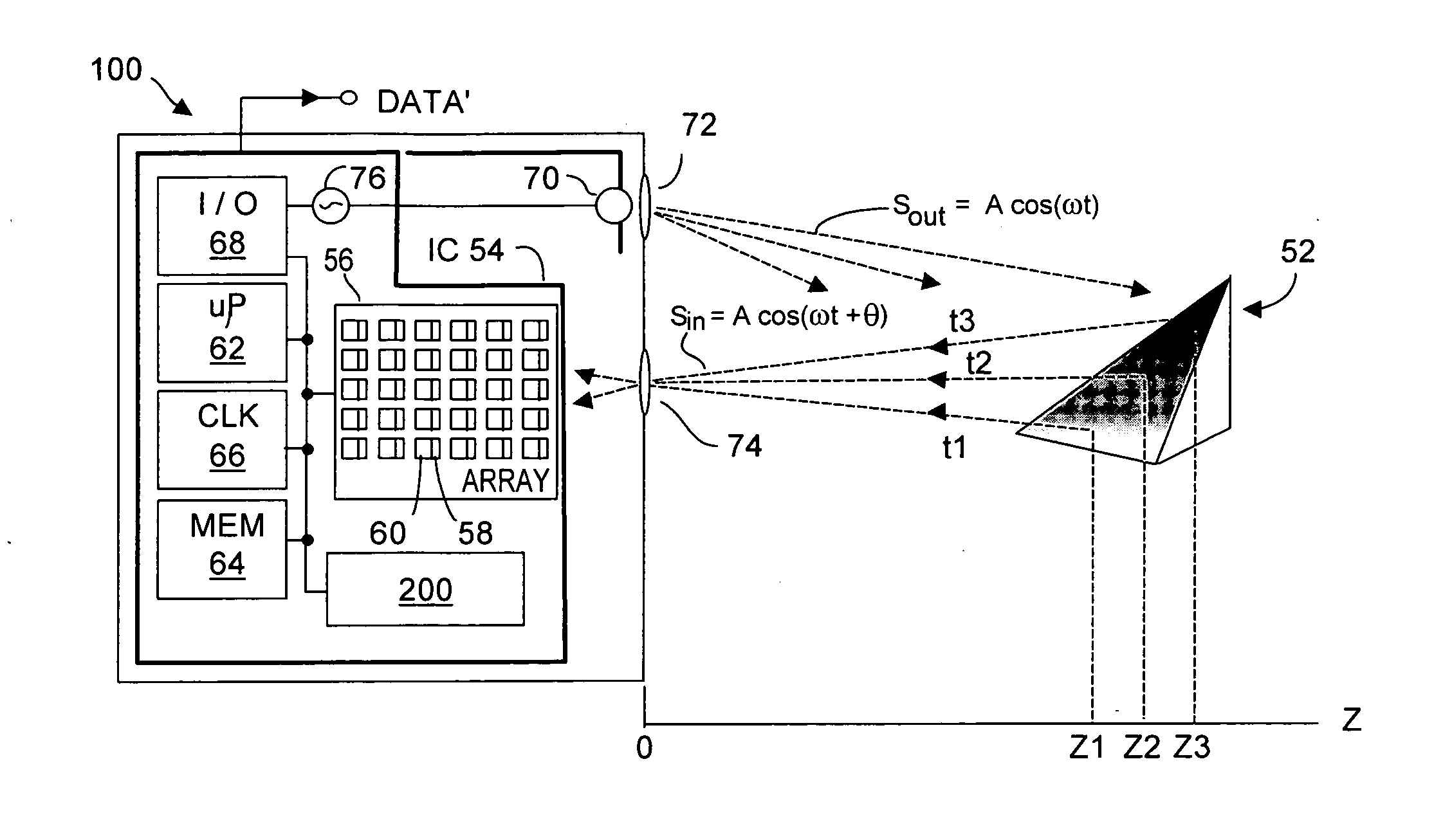
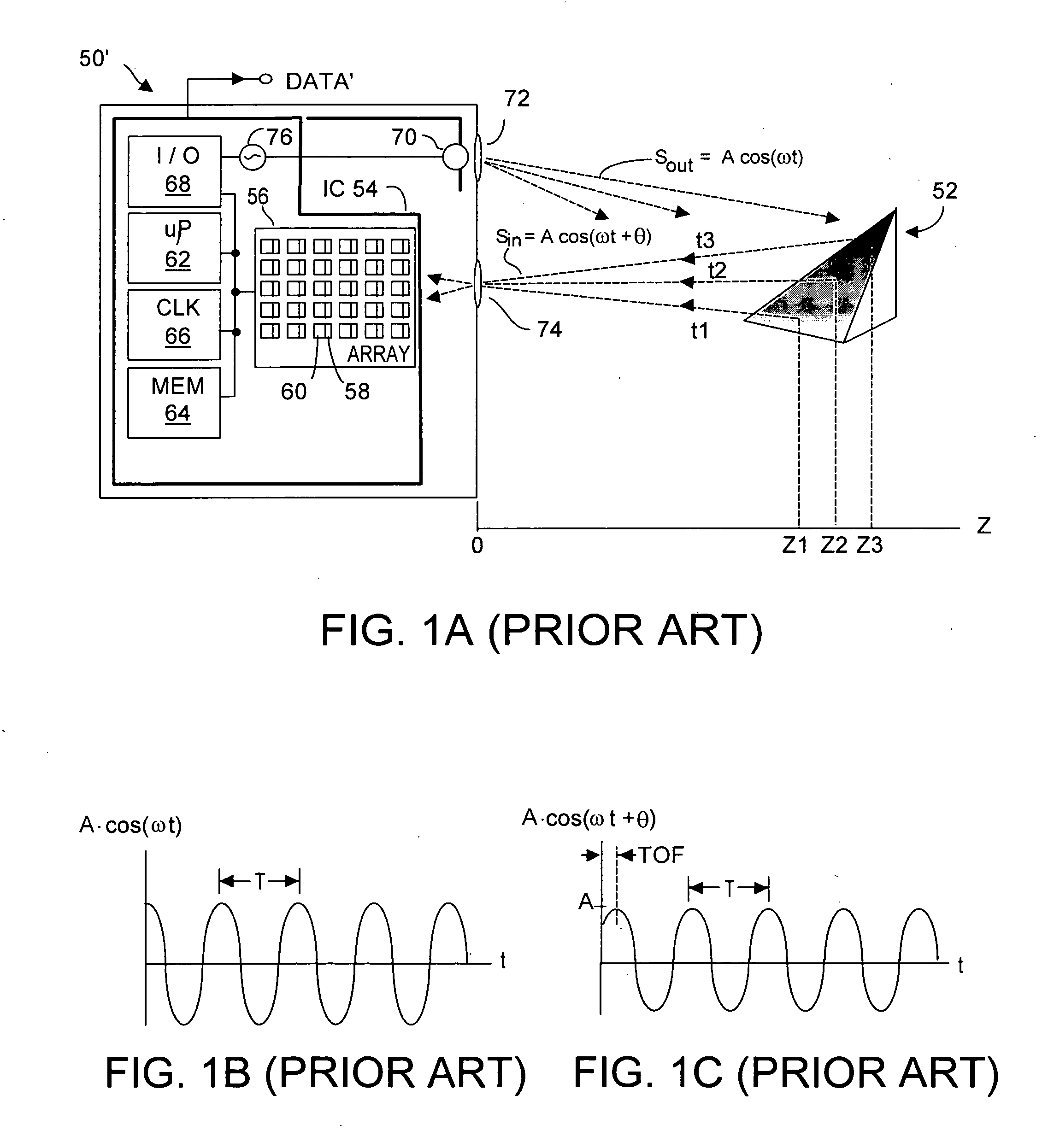
Method and system to maximize space-time resolution in a Time-of-Flight (TOF) system
ActiveUS20110292370A1Reduce depth errorReduce motion blurOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationObject motionImage resolution
Phase-based TOF systems operate with reduced depth error due to motion blur, and / or spatial blur, and / or pixel offset by intelligently determining how best to combine pixel values, and how best to compensate for individual pixel offsets. Such determination(s) may be carried out on a per pixel basis, dynamically, in real-time during TOF operation, or on archived TOF data. Offsets for individual pixels may be dynamically calculated and subtracted from the values acquired by those pixels Individual pixel offsets may be calculated for example by combining data acquired by the same pixel at two acquisitions, 180° out of phase with respect to each other. Calculated offsets may be averaged, or on a per pixel basis, and if target object motion is detected, one or more offset calculations can be discarded rather than averaged to reduce motion blur. Offsets acquired a priori during a TOF system calibration procedure may be used.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
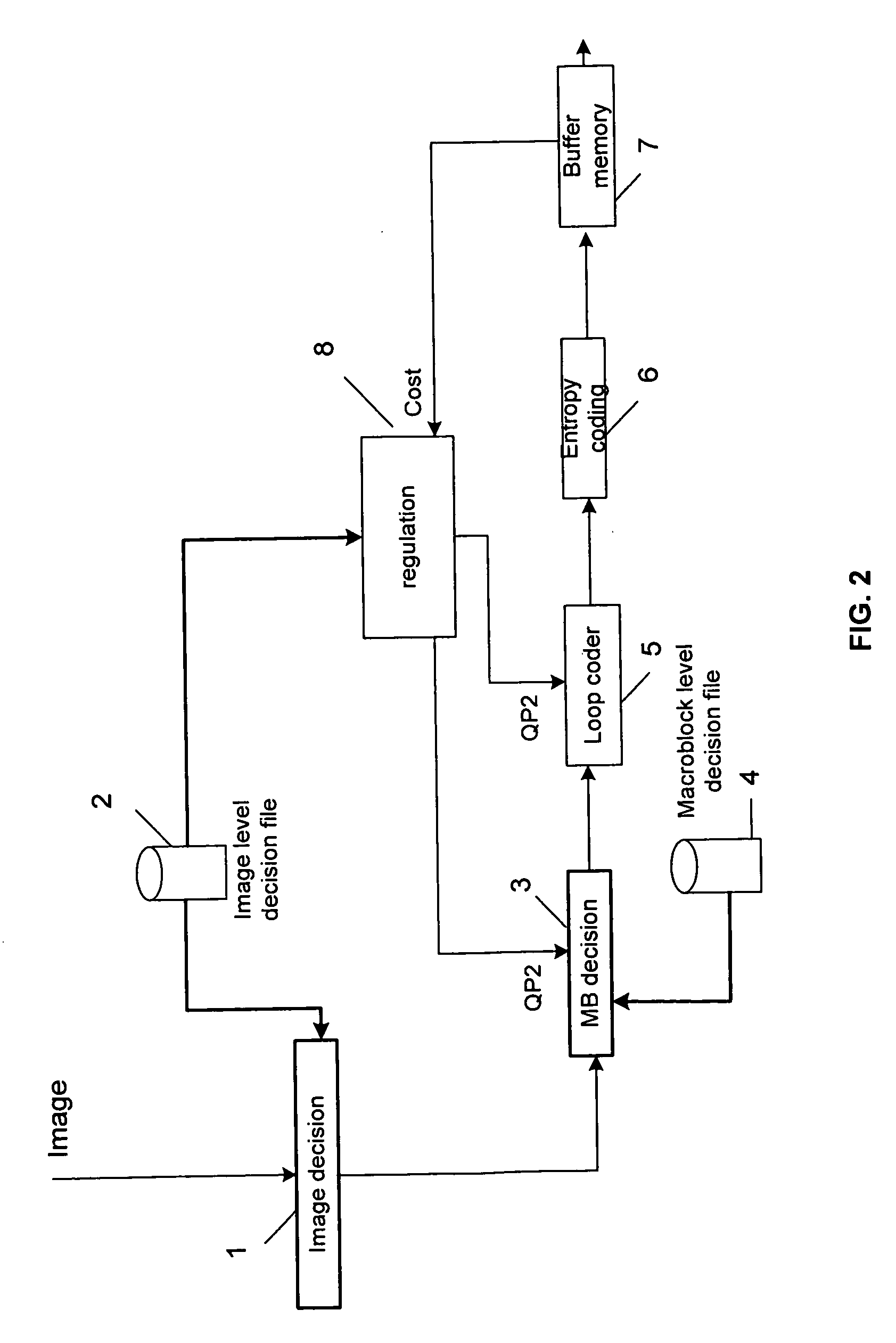
Macroblock-based dual-pass coding method
InactiveUS20100303148A1Minimise bitrate-distortion functionImprove coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionData compressionComputer architecture
The method comprises the following steps:during the first pass, a memorization of the M best coding modes and their coding parameters per image macroblock,during the second pass, a calculation, according to the new quantization step determined by the regulating algorithm according to the parameters memorized, among the M coding modes memorized, of the coding mode minimising the bitrate-distortion criterion, to select it,a coding according to the selected coding mode.The applications relate to the compression of data.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
Control strategy for an internal combustion engine in a hybrid vehicle
InactiveUS7110904B2Minimizing functionSimple processInternal combustion piston enginesPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
A system and method is disclosed for operating an internal combustion engine disposed in a hybrid vehicle, in which engine operation is selected to provide secondary vehicular functions, such as cabin heating, cabin cooling, and exhaust aftertreatment of exhaust components.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Modifying a design to reveal the data flow of the design in order to create a more favorable input for block placement
ActiveUS20050183054A1Minimizing wire lengthMinimizing other cost functionSpecial data processing applicationsComputer architectureAND gate
A system is employed for modifying a hierarchical description of a design to reveal the data flow of the design. The modified design provides a more favorable input for block placement. In one embodiment, the modifications includes any one of or a combination of moving hard macros to a higher level of the hierarchical description of the design, flattening modules that are bigger than a threshold, and / or flattening star blocks. Up to three clustering strategies are employed as part of the flattening process, including name-based clustering, external connection based clustering and gate clustering.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Production and preprocessing system for data mining
InactiveUS6868423B2Improve efficiencyEfficiency of transformation is promotedData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData aggregatorData mining
Disclosed is means capable of solving trouble in managing data formats and procedures and capable of carrying out advanced preprocessing more intuitively. A data aggregate to be inputted to a mining engine is converted into hierarchical unit trees, and node conditions of the hierarchical unit trees are changed, whereby the data aggregate and a data structure are subjected to dynamic conversion / edition processing. Thus, a system is constructed, in which preprocessing for data mining is unitarily managed / semi-automated.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Statistical dynamic modeling method and apparatus
InactiveUS7515155B2Minimizing functionAnimationImage generationStatistical dynamicsPattern recognition
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
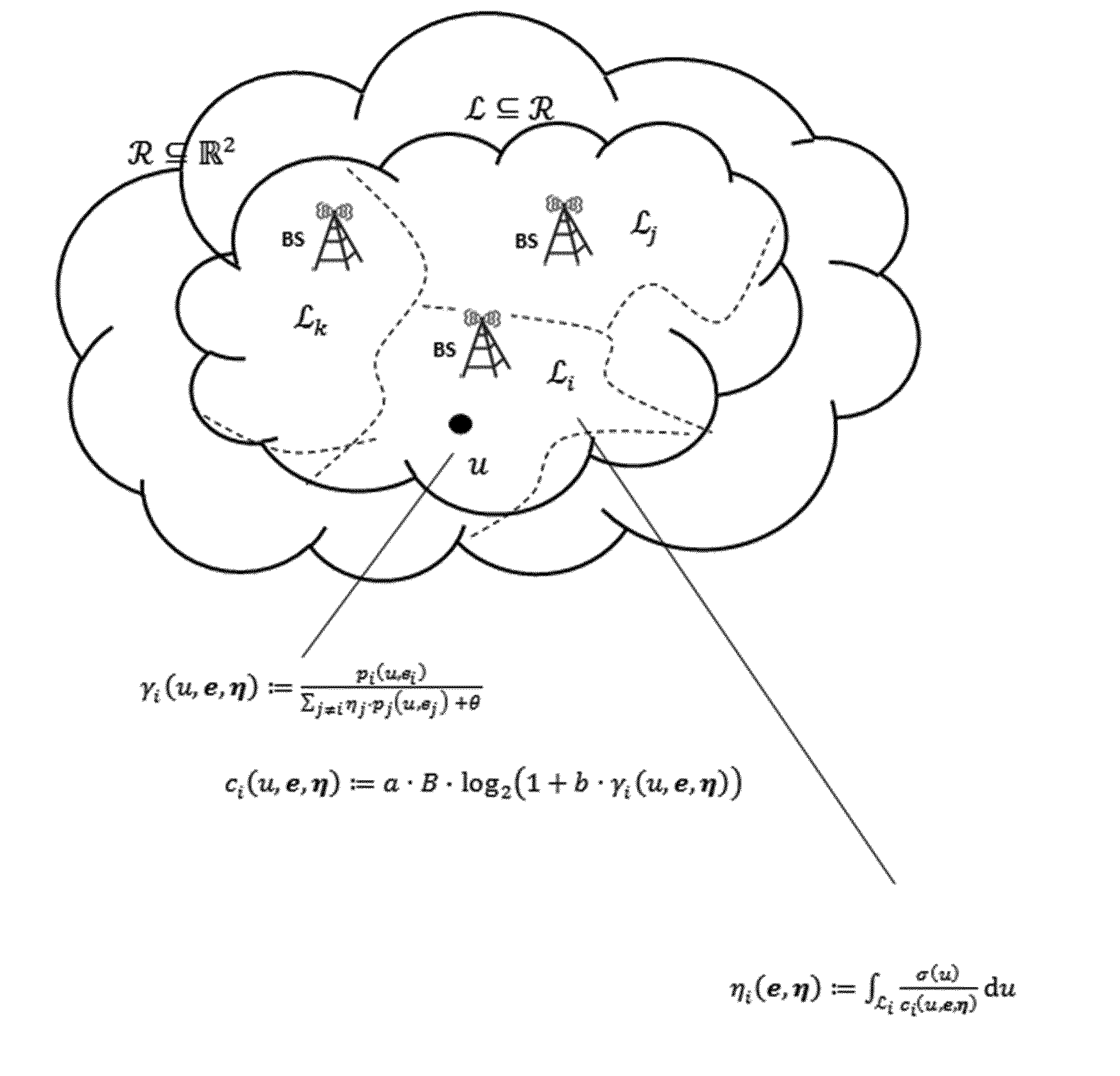
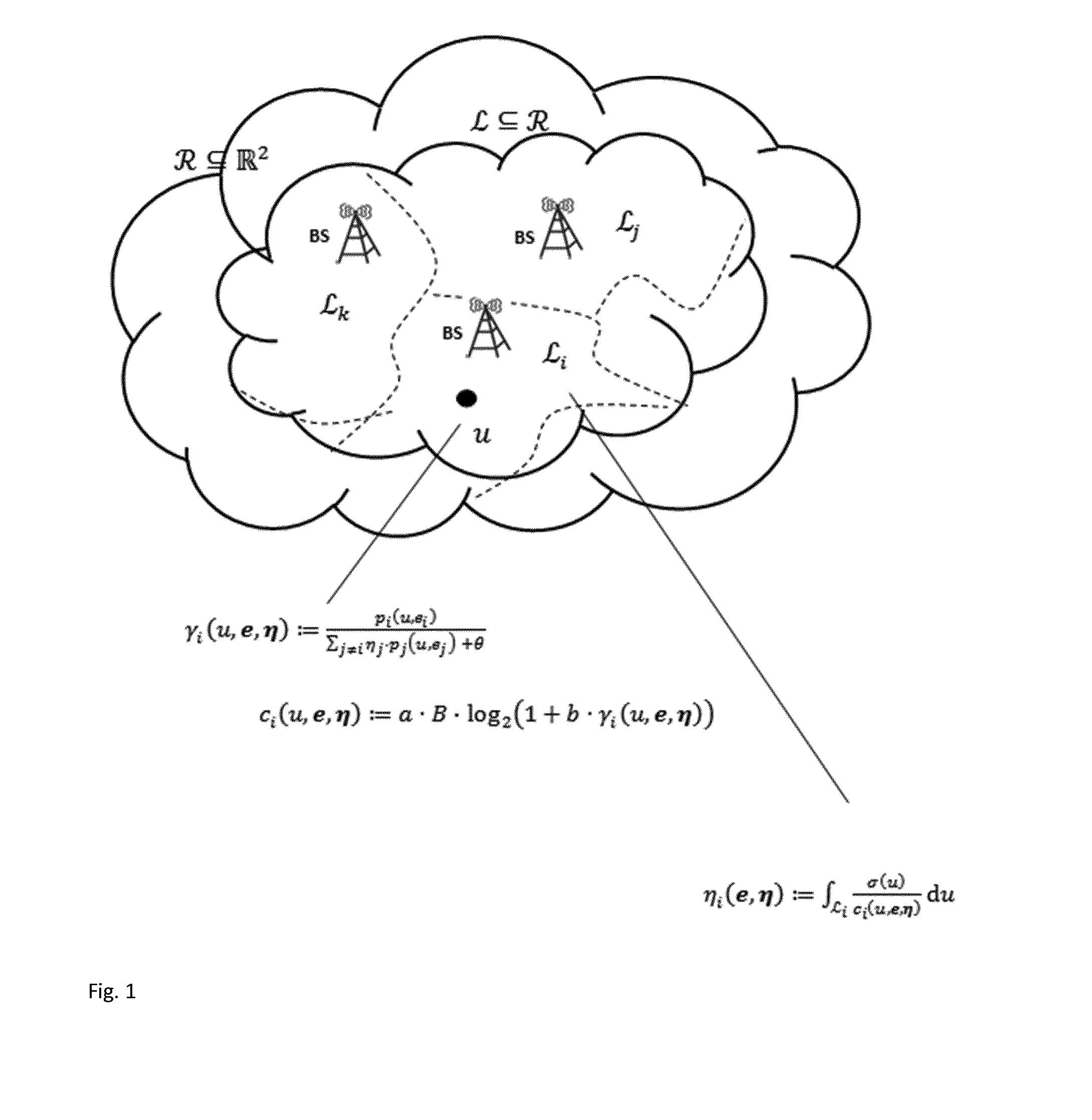
Method for joint and coordinated load balancing and coverage and capacity optimization in cellular communication networks
ActiveUS20150189533A1Load minimizationPreventsError preventionTransmission systemsCellular communication systemsCapacity optimization
The present invention relates to a method for optimizing a real cellular, wireless communication network that combines mobility load balancing (MLB) with coverage and capacity optimization (CCO) in a joint and coordinated optimization. An optimal set of physical base station parameters is determined by performing an iterative direct search. The iterative direct search comprises a partitioning strategy to jointly determine an optimal partition of the served area and an associated optimal load of each of the plurality of base stations for a current set of physical base station parameters for each direct search iteration; said partitioning strategy using an updated value of the received power of the pilot or reference signal for each the plurality of user locations associated with the current set of physical base station parameters for each direct search iteration.
Owner:ACTIX
Method for estimating the pose of a ptz camera
ActiveUS20080267453A1Minimizing functionImage enhancementImage analysisReference imageIterative method
Provided is an iterative method of estimating the pose of a moving PTZ camera. The first step is to use an image registration method on a reference image and a current image to calculate a matrix that estimates the motion of sets of points corresponding to the same object in both images. Information about the absolute camera pose, embedded in the matrix obtained in the first step, is used to simultaneously recalculate both the starting positions in the reference image and the motion estimate. The recalculated starting positions and motion estimate are used to determine the pose of the camera in the current image. The current image is taken as a new reference image, a new current image is selected and the process is repeated in order to determine the pose of the camera in the new current image. The entire process is repeated until the camera stops moving.
Owner:FLIR COMML SYST
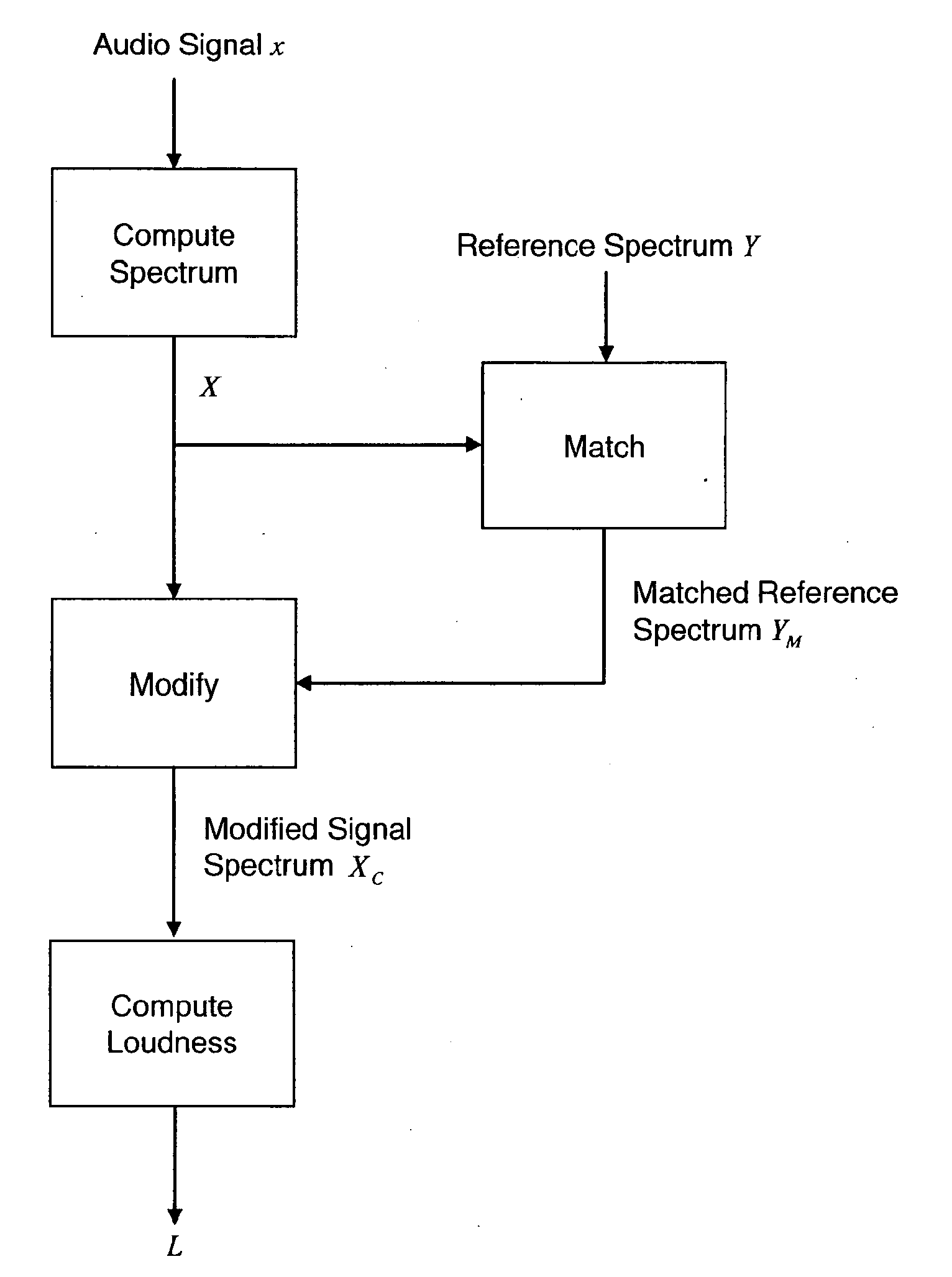
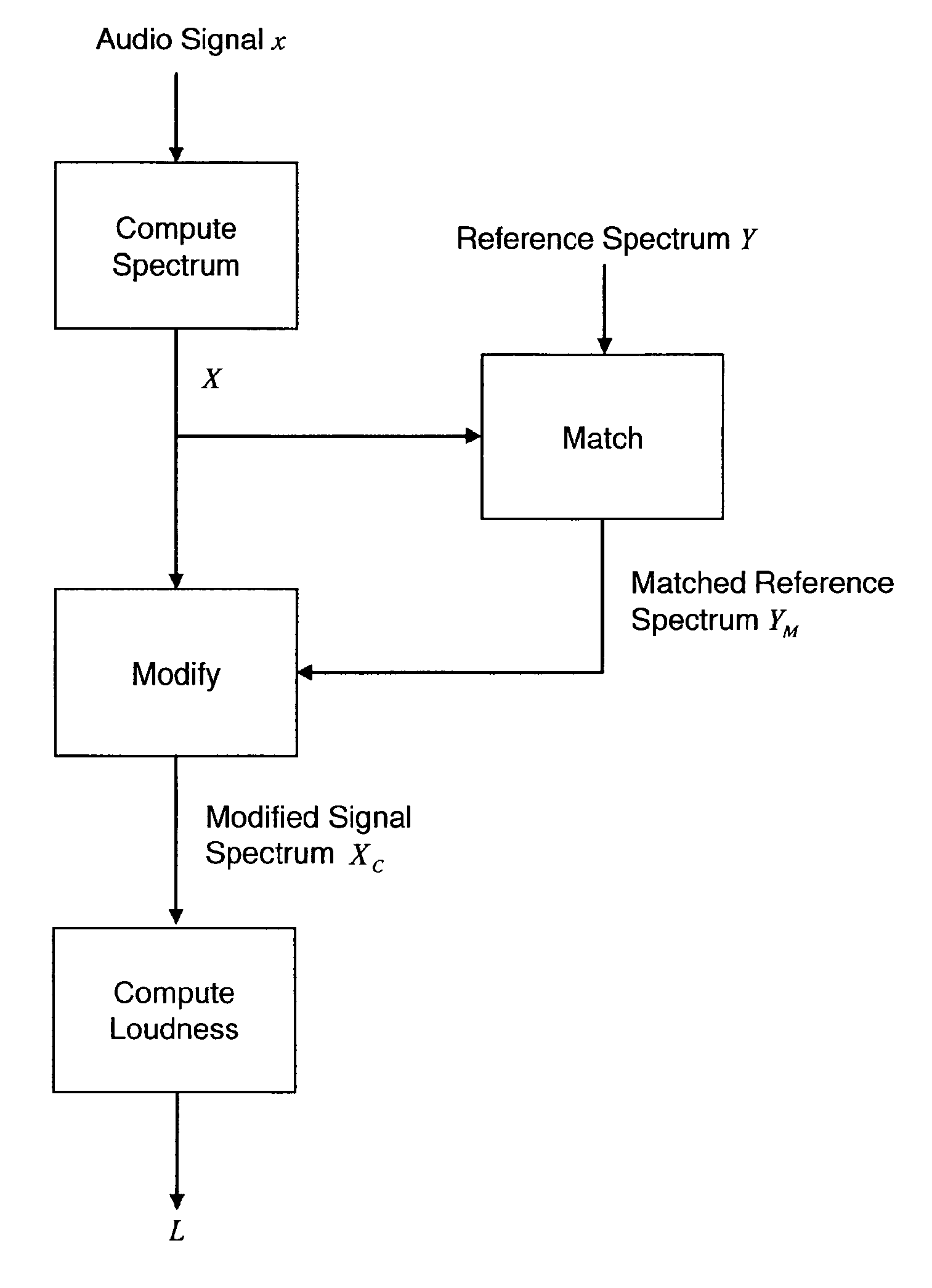
Loudness Measurement with Spectral Modifications
ActiveUS20100067709A1Minimizing functionImprove the level ofGain controlSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumSpectral representation
The perceived loudness of an audio signal is measured by modifying a spectral representation of an audio signal as a function of a reference spectral shape so that the spectral representation of the audio signal conforms more closely to the reference spectral shape, and determining the perceived loudness of the modified spectral representation of the audio signal.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
Modifying a design to reveal the data flow of the design in order to create a more favorable input for block placement
ActiveUS7269815B2Easy to placeMinimizing functionComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsComputer architectureAND gate
A system is employed for modifying a hierarchical description of a design to reveal the data flow of the design. The modified design provides a more favorable input for block placement. In one embodiment, the modifications includes any one of or a combination of moving hard macros to a higher level of the hierarchical description of the design, flattening modules that are bigger than a threshold, and / or flattening star blocks. Up to three clustering strategies are employed as part of the flattening process, including name-based clustering, external connection based clustering and gate clustering.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Dig-Cola: directed graph layout through constrained energy minimization
InactiveUS7714862B1Minimizing functionDrawing from basic elementsBreakfast cerealStress minimization
A method and system for drawing directed graphs including receiving data coordinates associated with nodes for graphing, performing a constrained stress minimization, and outputting results of the constrained stress minimization and displaying the results on a visual medium. The described method may take the form of instructions residing on a computer readable medium. The described method and system may be utilized for drawing directed graphs in a very wide range of applications ranging from gene networks, to flowcharts, to display of relational characteristics of breakfast cereal and so on.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Loudness measurement with spectral modifications
ActiveUS8213624B2Minimizing functionImprove the level ofGain controlSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumSpectral representation
The perceived loudness of an audio signal is measured by modifying a spectral representation of an audio signal as a function of a reference spectral shape so that the spectral representation of the audio signal conforms more closely to the reference spectral shape, and determining the perceived loudness of the modified spectral representation of the audio signal.
Owner:DOLBY LAB LICENSING CORP
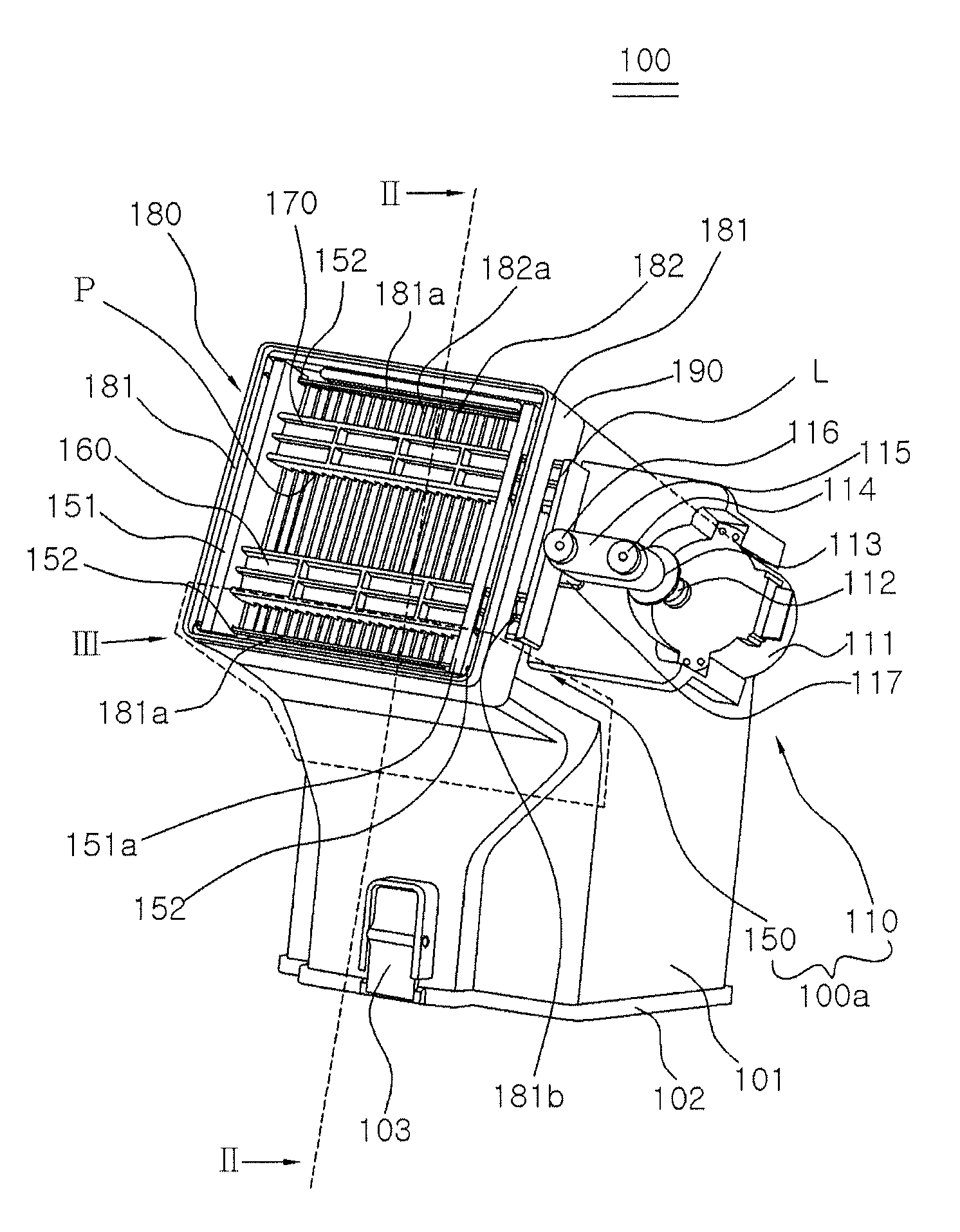
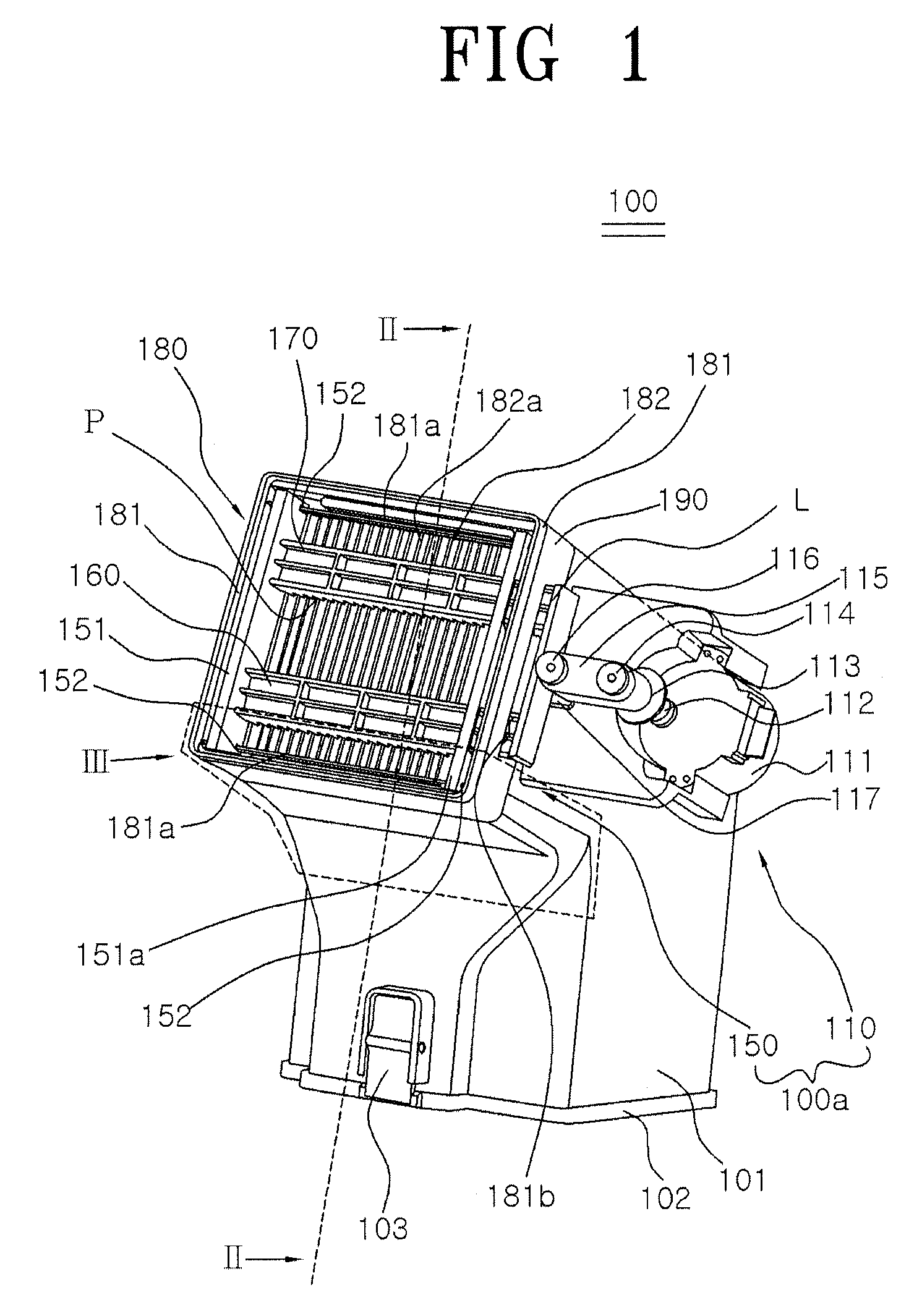
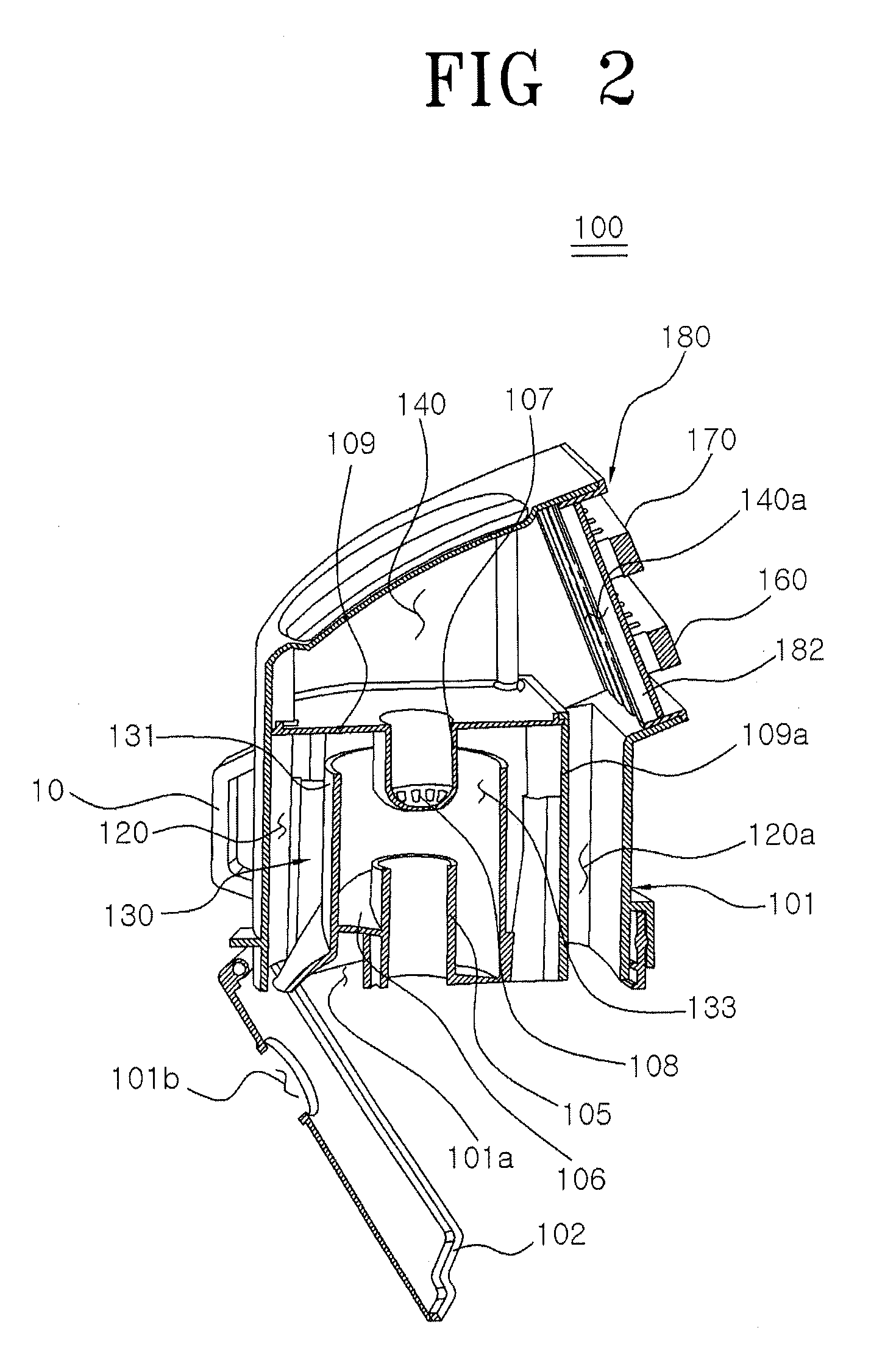
Dust collector for a vacuum cleaner having a dust removal function
ActiveUS8870988B2Volume andEffectively remove dustCleaning filter meansSuction filtersEngineeringVacuum cleaner
A dust collector includes a dust container; a centrifugal separator installed inside the dust container to separate dust from air; a filter unit installed at a discharge hole of the centrifugal separator and provided with a filter member; and a dust-removing device for dislodging dust from the filter unit. The dust-removing device includes a dust removal unit including a dust-removing member having dust-removing projections formed on an undersurface thereof, wherein the dust-removing projections move back and forth while contacting the filter unit to dislodge dust from the filter unit; and a drive unit for providing driving power to the dust removal unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
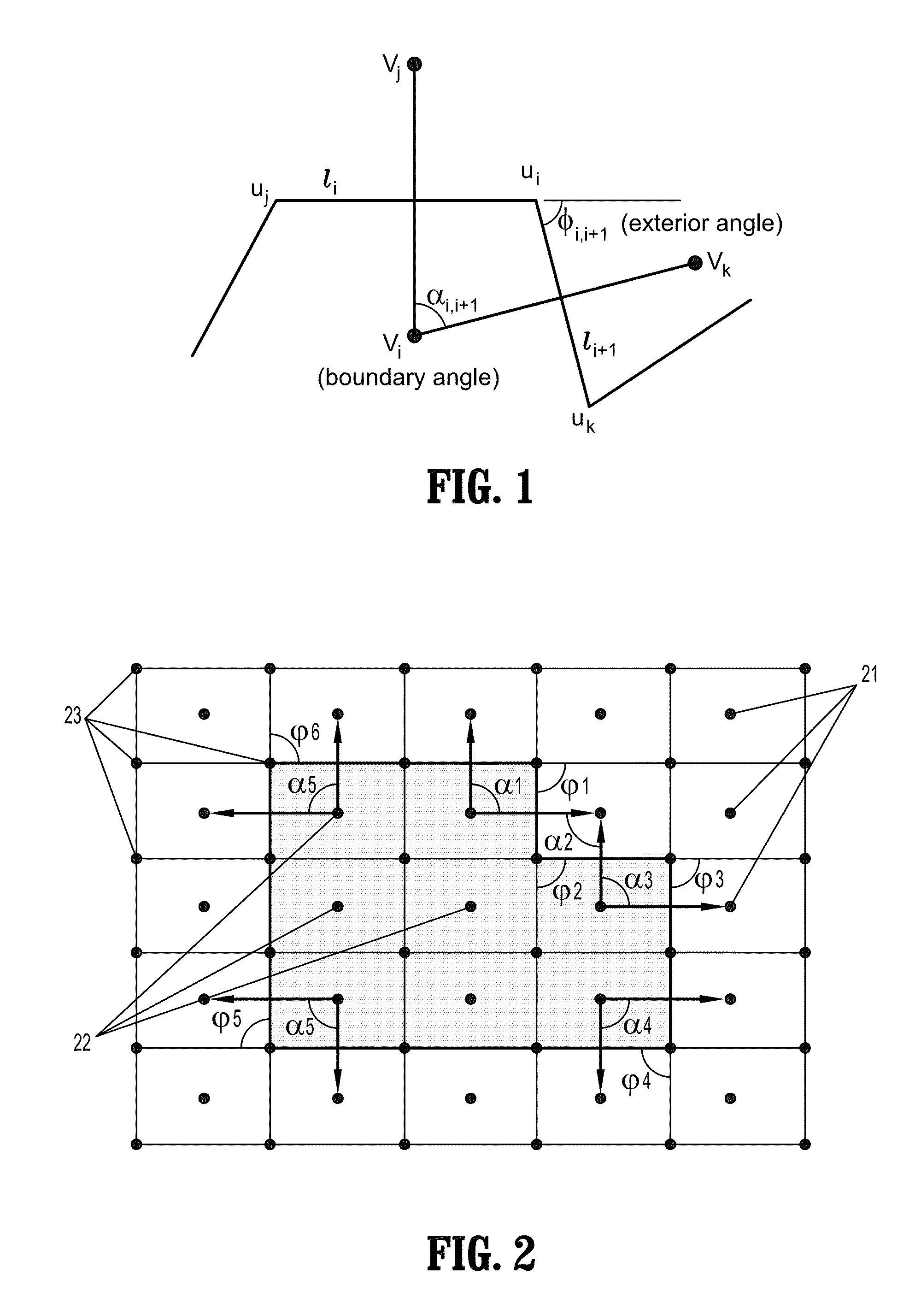
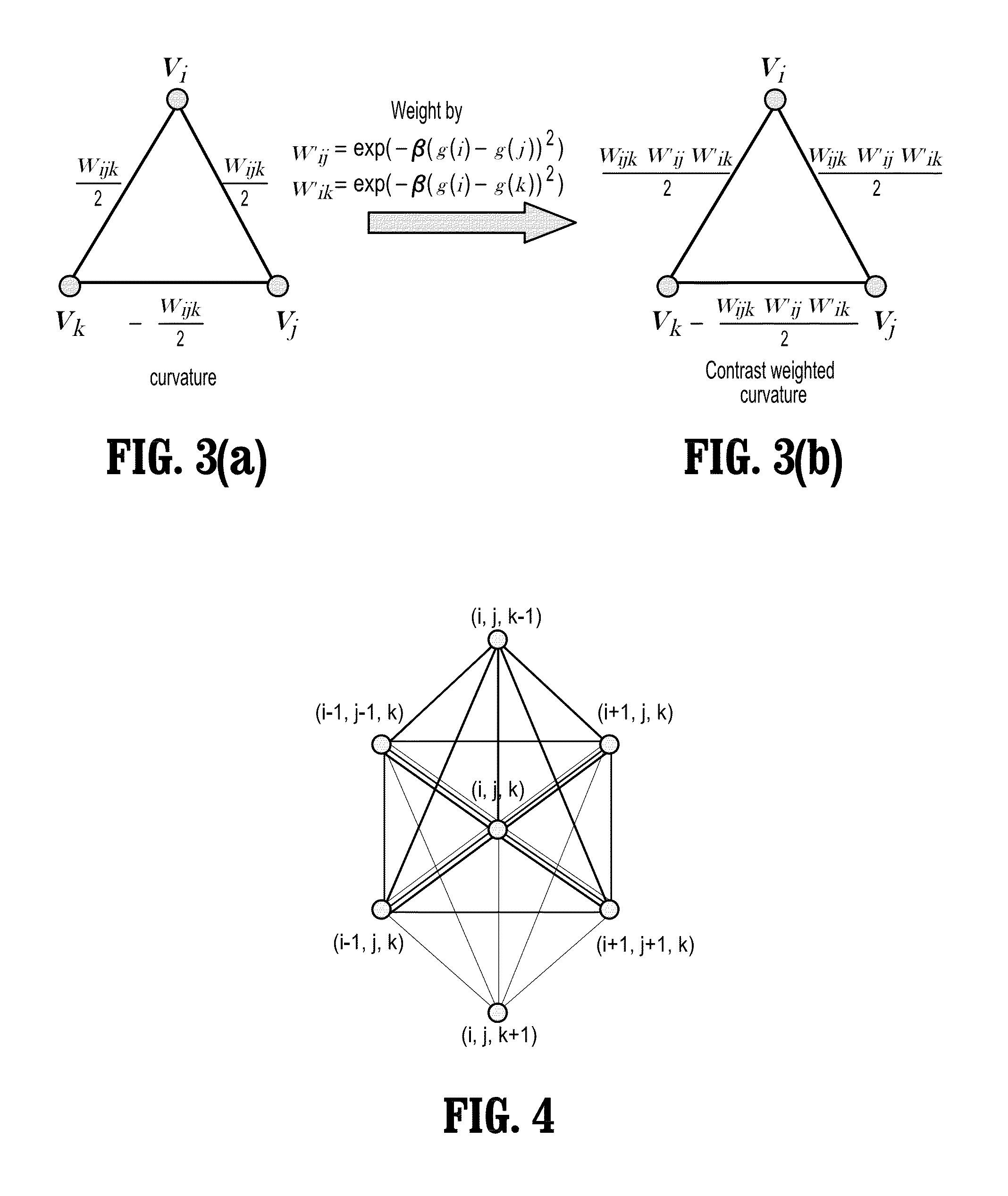
System and Method for Image Segmentation by Optimizing Weighted Curvature
ActiveUS20120314949A1High curvatureFast and robustImage enhancementImage analysisImage segmentationImage based
A method for segmenting an object in a digital image includes computing, for each point vi in the image, weights wijk of a curvature clique vivivk for each successive pair of edges eij, eik incident on point vi, decomposing each curvature clique into pairwise edge weights to form a new set of edges by adding, for all points vj, vk, an edge eij with weight wij, an edge eik with weight wik, and an edge ejk with weight wjk, where weight wij equals weight wik equals ½ wijk, and weight wjk equals −½ wijk, computing an indicator function of the points of the image indicative of whether each point belongs to an object of interest by minimizing a functional of the indicator function, and segmenting the object of interest from the image based on the value of the indicator function x at each image point.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Statistical dynamic collisions method and apparatus utilizing skin collision points to create a skin collision response
ActiveUS7307633B2Efficiently fine-tuneAccurately previewAnimationImage generationStatistical dynamicsAnimation
A method for animating soft body characters has a preparation phase followed by an animation phase. The preparation phase determines the skin deformation of a character model at skin contact points in response to impulse collisions. The skin deformation from impulse collisions are compactly represented in terms of the set of basis poses. In the animation phase, the skin impulse responses are used to create a final posed character. Regardless of the type of collision or the shape of the colliding object, the collision animation phase uses the same set of skin impulse responses. A subset of a set of skin points is selected as a set of skin collision points. A final collision response is determined from the skin collision points. The final collision response to the complete set of skin points.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
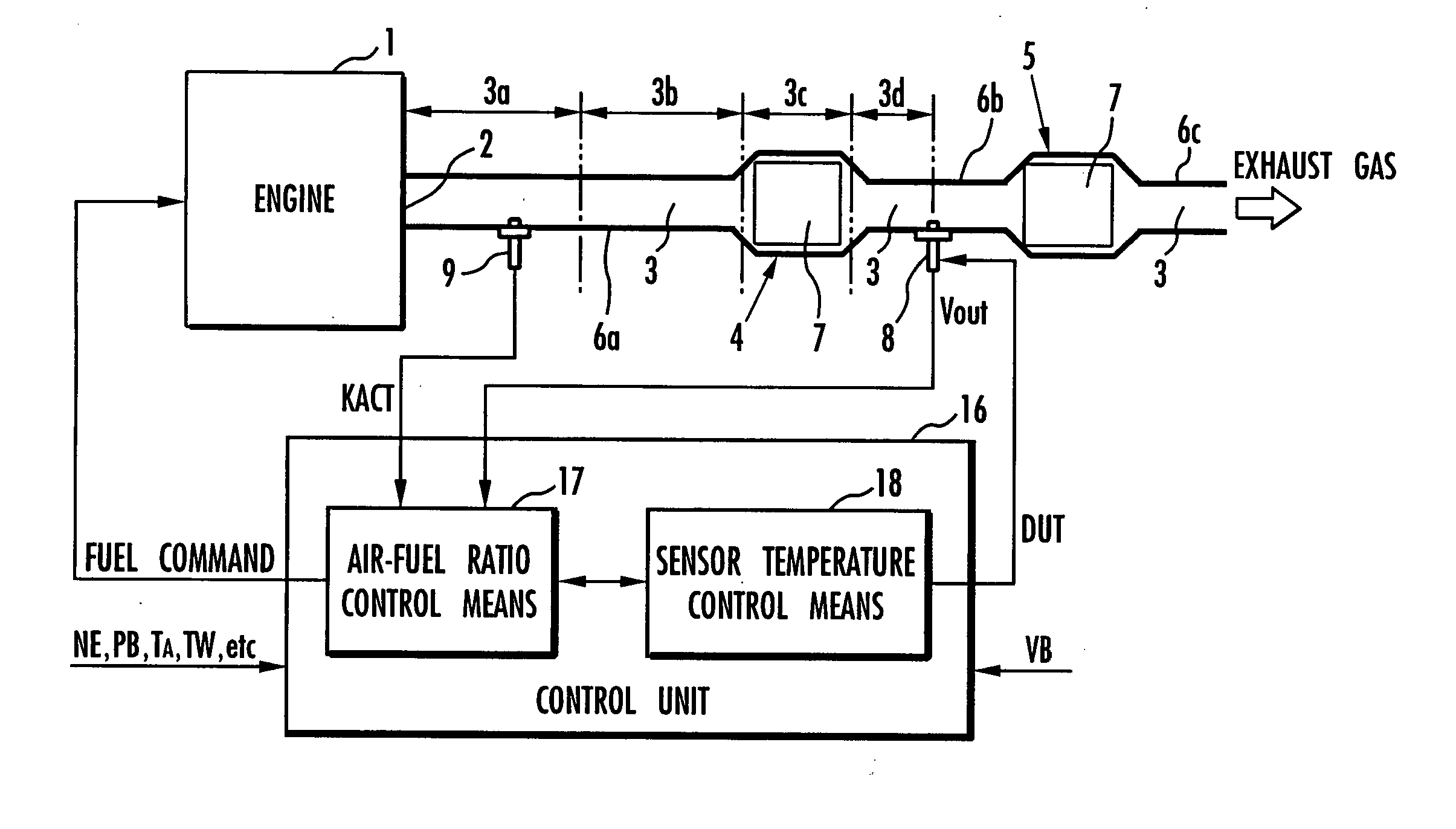
Device and method of controlling exhaust gas sensor temperature, and recording medium for exhaust gas sensor temperature control program
InactiveUS20050263397A1Stable controlMinimize changesAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlTemperature controlEngineering
A control input (DUT) for controlling a heater (13) which heats an active element (10) of an exhaust gas sensor (8) includes at least one of another component depending on the difference between temperature data of the active element (10) and a target temperature, a component depending on the target temperature, and a component depending on the temperature data of the active element (10). The control input is determined by an optimum control algorithm. A component depending on the temperature of an exhaust gas and the component depending on the target temperature are determined based on a predictive control algorithm. The temperature of the active element (10) of the exhaust gas sensor (8) is thus controlled stably at a desired temperature.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
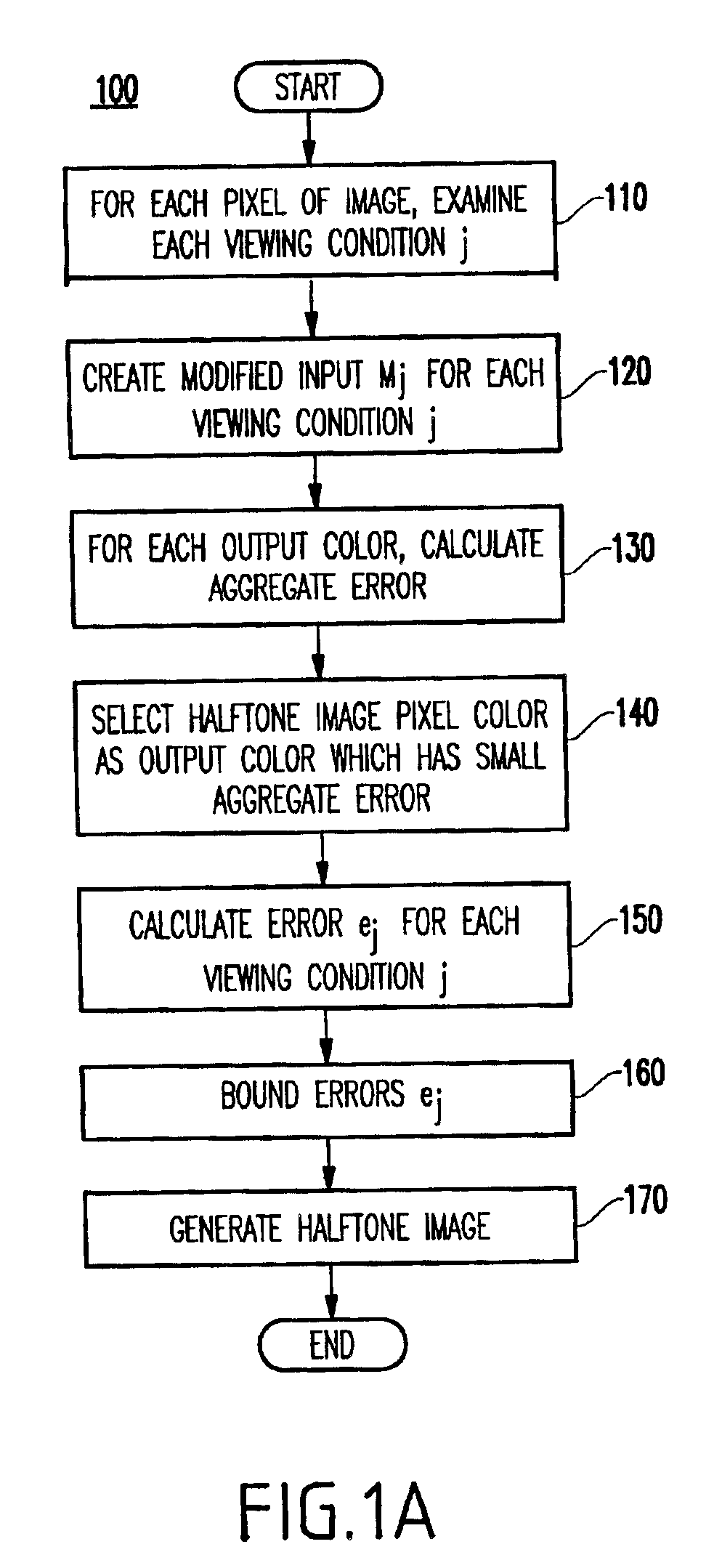
Method and system for error diffusion with a plurality of error measures
InactiveUS6870643B2Minimizing functionError minimizationDigitally marking record carriersVisual presentation using printersError diffusionComputer science
A method (and system) for producing a halftoned image, includes calculating errors corresponding to a plurality of different viewing conditions of a halftone image, and minimizing a function of the errors, such that the halftoned image appears as a different image under different viewing conditions. Alternatively, in another embodiment, the halftoned image appears as the same image under different viewing conditions.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Phantom and method for image quality assessment of a digital breast tomosynthesis system
ActiveUS9526471B2Minimizing functionSolve the lack of spaceRadiation diagnostics testing/calibrationTomosynthesisTomosynthesisVertical plane
Owner:THE PHANTOM LABORATORY INCORPORATED
Method and apparatus for reduction of nyquist ghosts in medical magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20070055137A1Improve phase correctionReduce generationMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringData setPhase Code
In a method and MRT apparatus for reduction of Nyquist ghosts in medical magnetic resonance imaging given the application of EPI sequences of one or more progression curves with regard to one or more characterizing quantities of the EPI echo, is determined dependent on the echo number of a readout gradient pulse train defined by pulse shape, pulse amplitude and pulse duration, an EPI measurement is implemented with a readout gradient pulse train, composed of alternating positive and negative amplitudes with under which alternating positive and negative echoes and respectively readout, and a phase coding gradient, so a phase-coded data set is acquired, the phase-coded data set is corrected on the basis of the progression curves, and is Fourier-transformed the corrected data set, to obtain an artifact-reduced (with regard to the Nyquist ghosts) image data set.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Statistical dynamic modeling method and apparatus
A method for animating soft body characters has a preparation phase followed by an animation phase. In the preparation phase, the skin deformation of the character model is determined for a set of basis poses. The skin deformation from posing is compactly represented in terms of the set of basis poses. In the animation phase, the set of basis poses and the skin mode response are used to create a final posed character. A desired character pose is projected onto the basis set to determine a set of basis weights. The basis weights are applied to the set of skin responses to create a skin pose response, and the skin pose responses is projected onto the basis set to create the posed character model.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
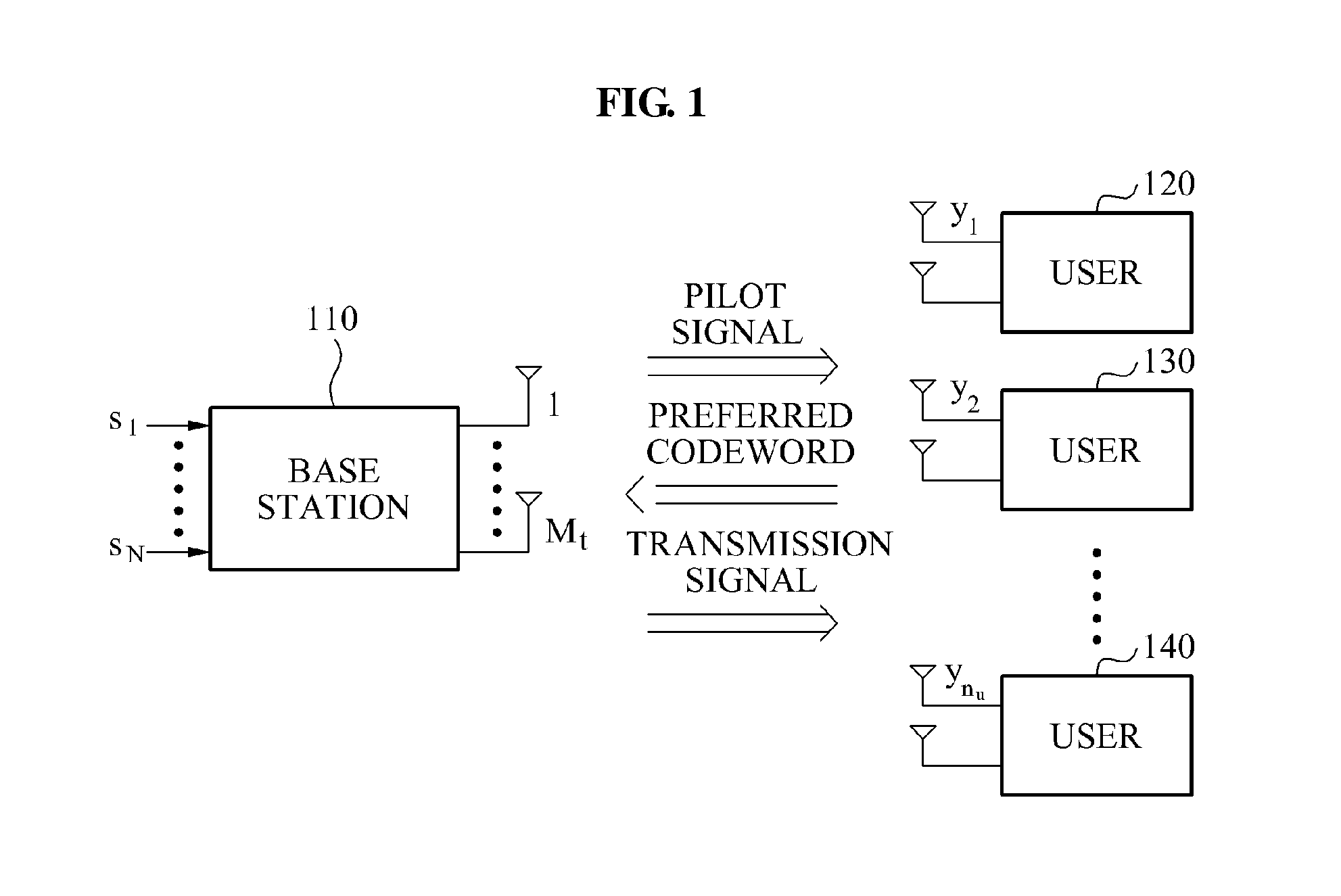
Multiple input multiple output communication system and communication method of configuring codebook
ActiveUS20110292926A1Small quantization errorImprove efficiencyRadio transmissionCommunications systemCross polarization
A multiple input multiple output (MIMO) communication system and communication method of configuring a codebook are provided. A channel may be formed between a transmitter and a receiver, and a cross-polarization discrimination value (XPD) may be detected. The XPD may vary based on a location of the transmitter and the receiver, a mobility thereof, or a peripheral environment, among other factors. The codebook may be configured based on the XPD.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
System and method for image segmentation by optimizing weighted curvature
ActiveUS8478044B2Eliminates shrinking biasAccurate captureImage enhancementImage analysisImage segmentationDigital image
A method for segmenting an object in a digital image includes computing, for each point vi in the image, weights wijk of a curvature clique vjvivk for each successive pair of edges eij, eik incident on point vi, decomposing each curvature clique into pairwise edge weights to form a new set of edges by adding, for all points vj, vk, an edge eij with weight wij, an edge eik with weight wik, and an edge ejk with weight wjk, where weight wij equals weight wik equals ½ wijk, and weight wjk equals −½ wijk, computing an indicator function of the points of the image indicative of whether each point belongs to an object of interest by minimizing a functional of the indicator function, and segmenting the object of interest from the image based on the value of the indicator function x at each image point.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Extraction Prcoess with Novel Solvent Regeneration Methods
ActiveUS20130228448A1Improve abilitiesMinimizing functionDistillation purification/separationExtraction purification/separationSolventImpurity
Solvent regeneration to recover a polar hydrocarbon (HC) selective solvent substantially free of hydrocarbons (HCs) and other impurities from a solvent-rich stream containing selective solvent, heavy HCs, and polymeric materials (PMs) generated from reactions among thermally decomposed or oxidized solvent, heavy HCs, and additives is provided. A combination of displacement agent and associated co-displacement agent squeezes out the heavy HCs and PMs from the extractive solvent within a solvent clean-up zone. Simultaneously, a filter equipped with a magnetic field is positioned in a lean solvent circulation line to remove paramagnetic contaminants. The presence of the co-displacement agent significantly enhances the capability of the displacement agent in removing the heavy HCs and PMs from the extractive solvent. As a result, the solvent regeneration system operates under milder conditions and minimizes or eliminates the need for including a high temperature, energy intensive and difficult-to-operate thermal solvent regenerator.
Owner:AMT INT INC +1
Method and device for calibrating a magnetic induction tomography system
InactiveUS20110004432A1Minimized magnetic interferenceImprove image qualityMagnetic measurementsTesting/calibration apparatusTomographyMagnetic induction tomography
This invention relates to a method and device for calibrating the offset of an imaging system. The core idea of the invention is to place a reference object in the measurement chamber of the imaging system, measure the signals associated with the reference object at different points of time, calculate the merit function based on changes of the parameters representing the electromagnetic property of the reference object, and derive an optimal set of offset data that minimizes the value of the merit function for compensating the offset of the system in subsequent image reconstructions. In one embodiment, the invention uses a reference object comprising a non-conductive envelope and a cavity which can be filled with a conductive fluid and emptied, and in this way reduces the imaging interference caused by the reference object during monitoring.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
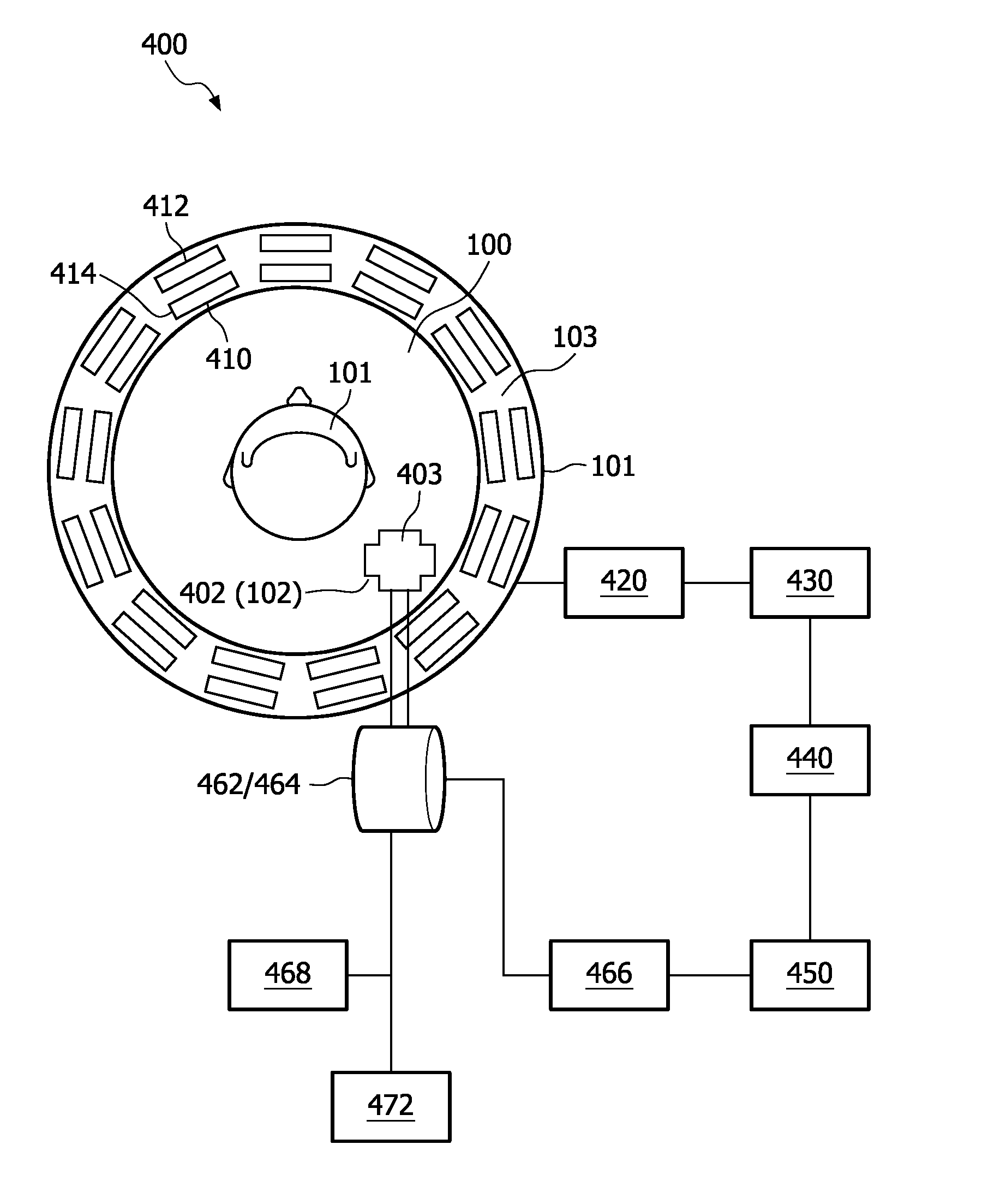
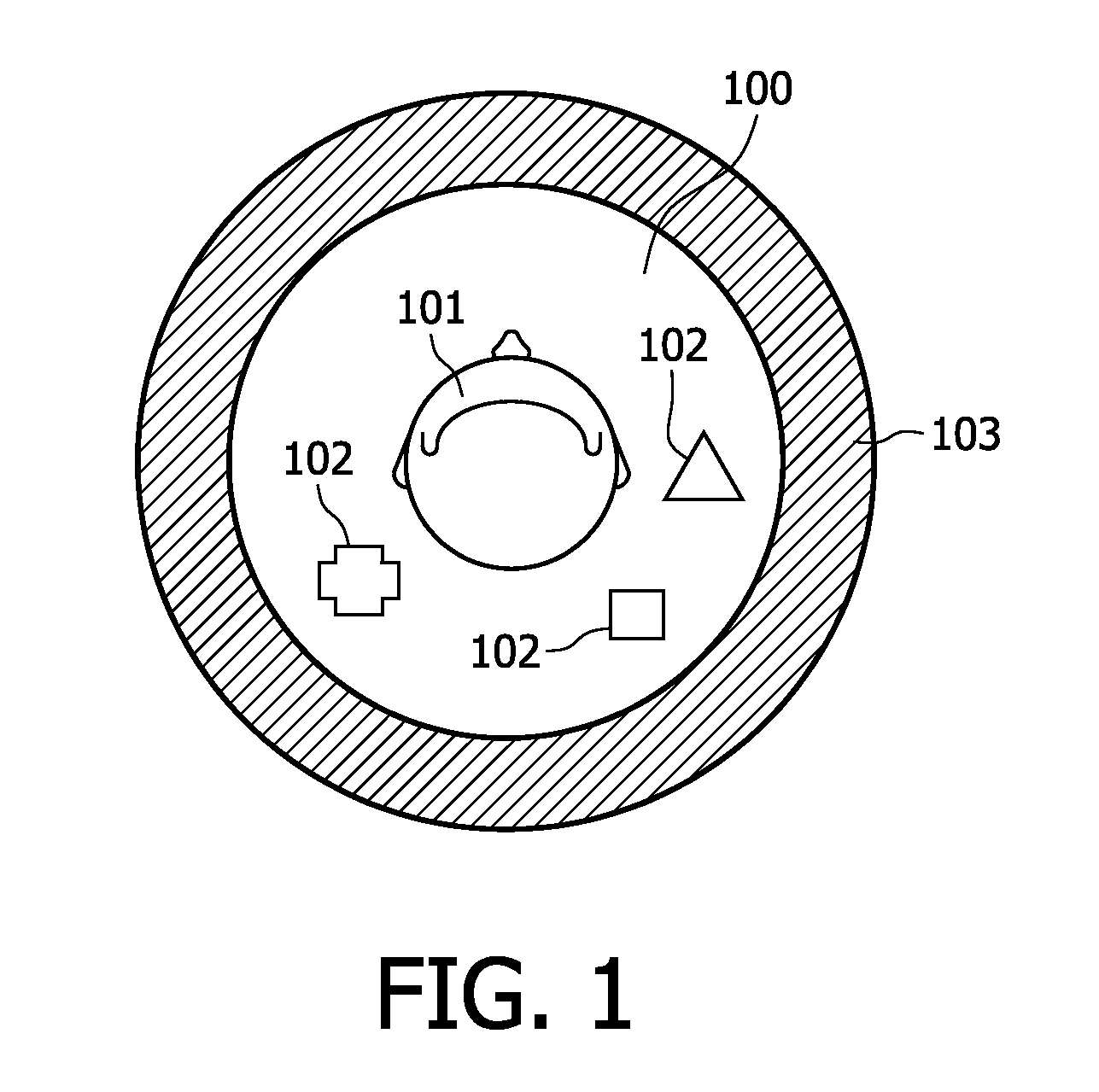
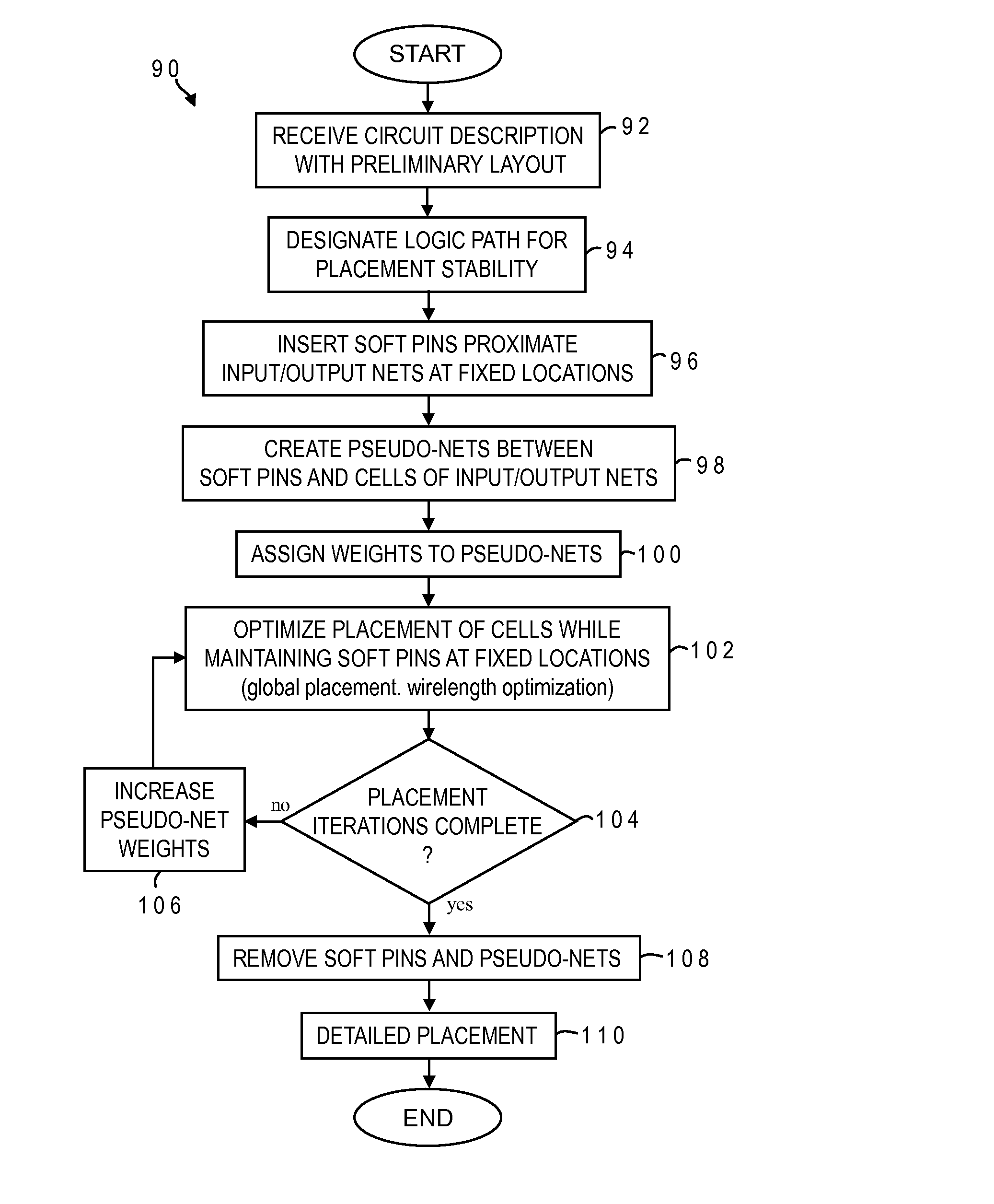
Soft pin insertion during physical design
InactiveUS20140189630A1Minimize functionIncrease weightComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsIntegrated circuitEngineering
A netlist for an integrated circuit design is constrained by virtual or “soft” pins to control or stabilize the placement of logic such as an architectural logic path. One soft pin is inserted at a fixed location proximate an input net of the path and is interconnected with the input net, and another is inserted at a fixed location proximate the output net and is interconnected with the output net. Cell placement is then optimized while maintaining the virtual pins at their fixed locations. More than two virtual pins may be inserted to bound a cluster of logic. The virtual pins may lie along the input / output nets. Pseudo-net weights are assigned to pseudo-nets formed between a cell and the virtual pins, and the pseudo-net weight can be increased for each placement iteration.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Quadrature modulation without carrier
ActiveUS7532682B1Minimizing functionImprove spectral efficiencySimultaneous amplitude and angle modulationAngle modulationQuadrature modulatorQuadrature modulation
Transmitters, receivers and associated methods are disclosed for providing phase and amplitude modulation in a carrier-less communication system (e.g., an ultra-wide band communication system). An approximate quadrature signal is provided by delaying the in-phase signal by an amount determined by various criteria, such as the bandwidths of the component signals, minimizing the mean square error between an approximate quadrature signal and the true quadrature signal, and minimizing the auto-correlation function of the in-phase signal.
Owner:OL SECURITY LIABILITY CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com