Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
199results about "Amplification control device circuits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
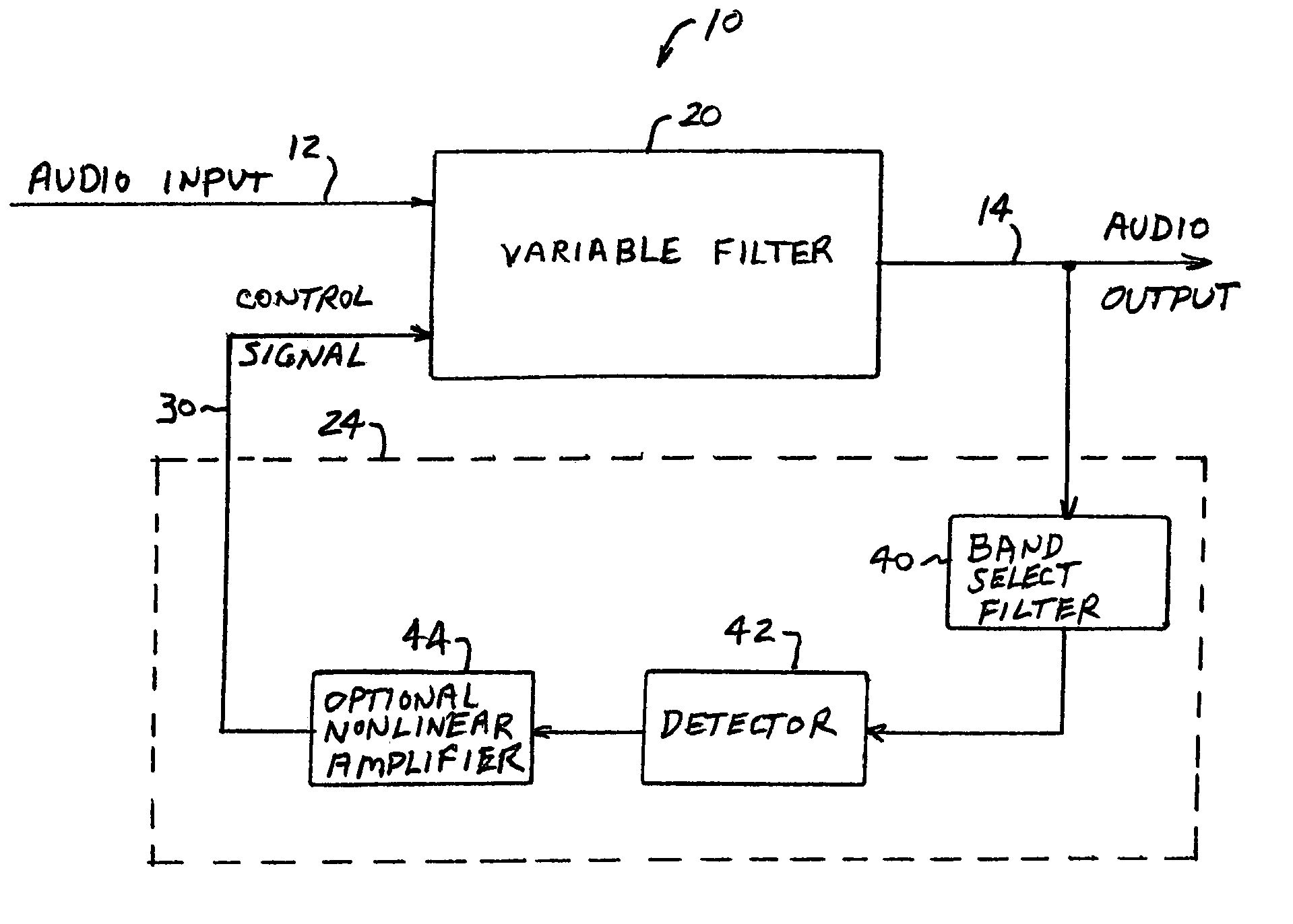
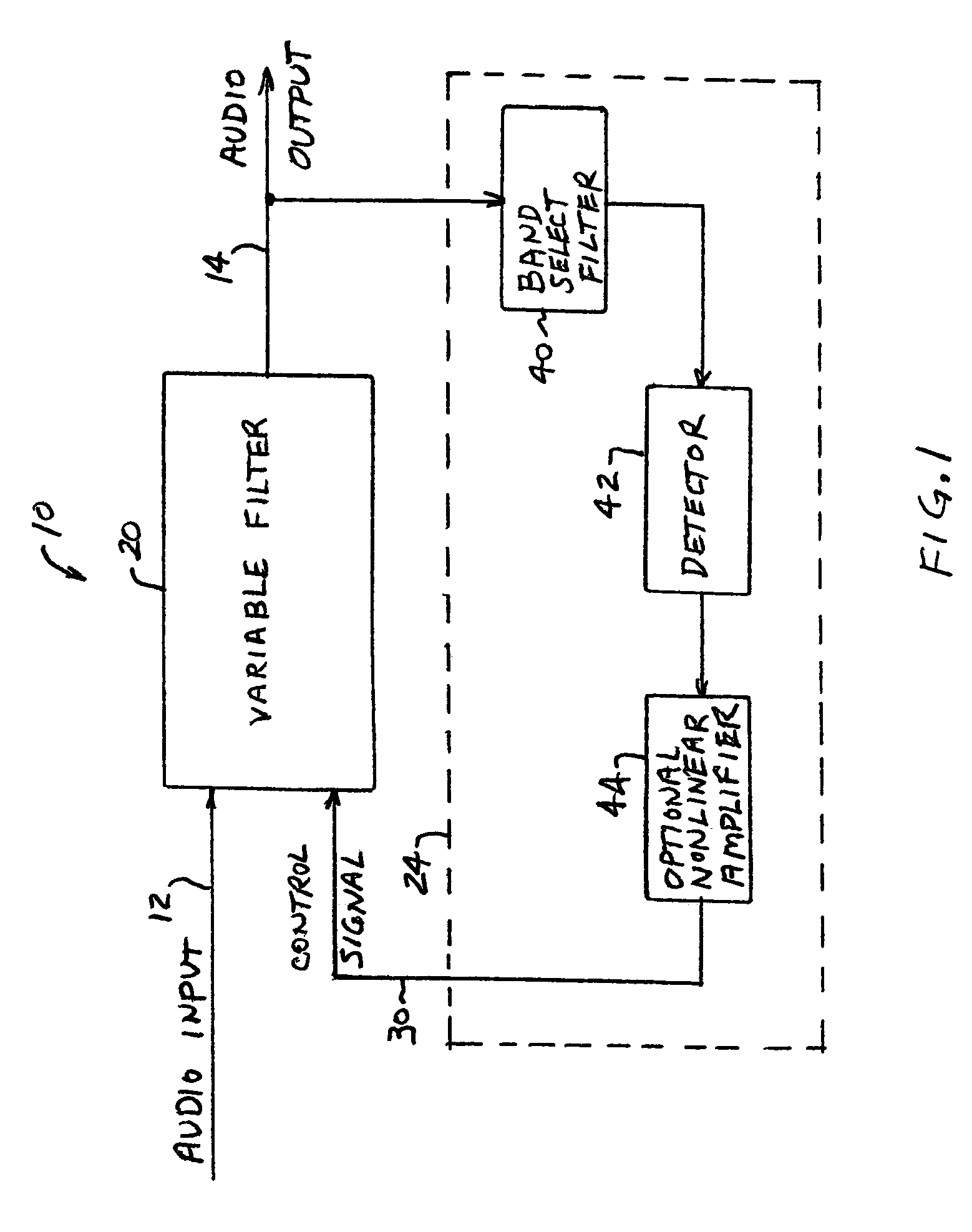
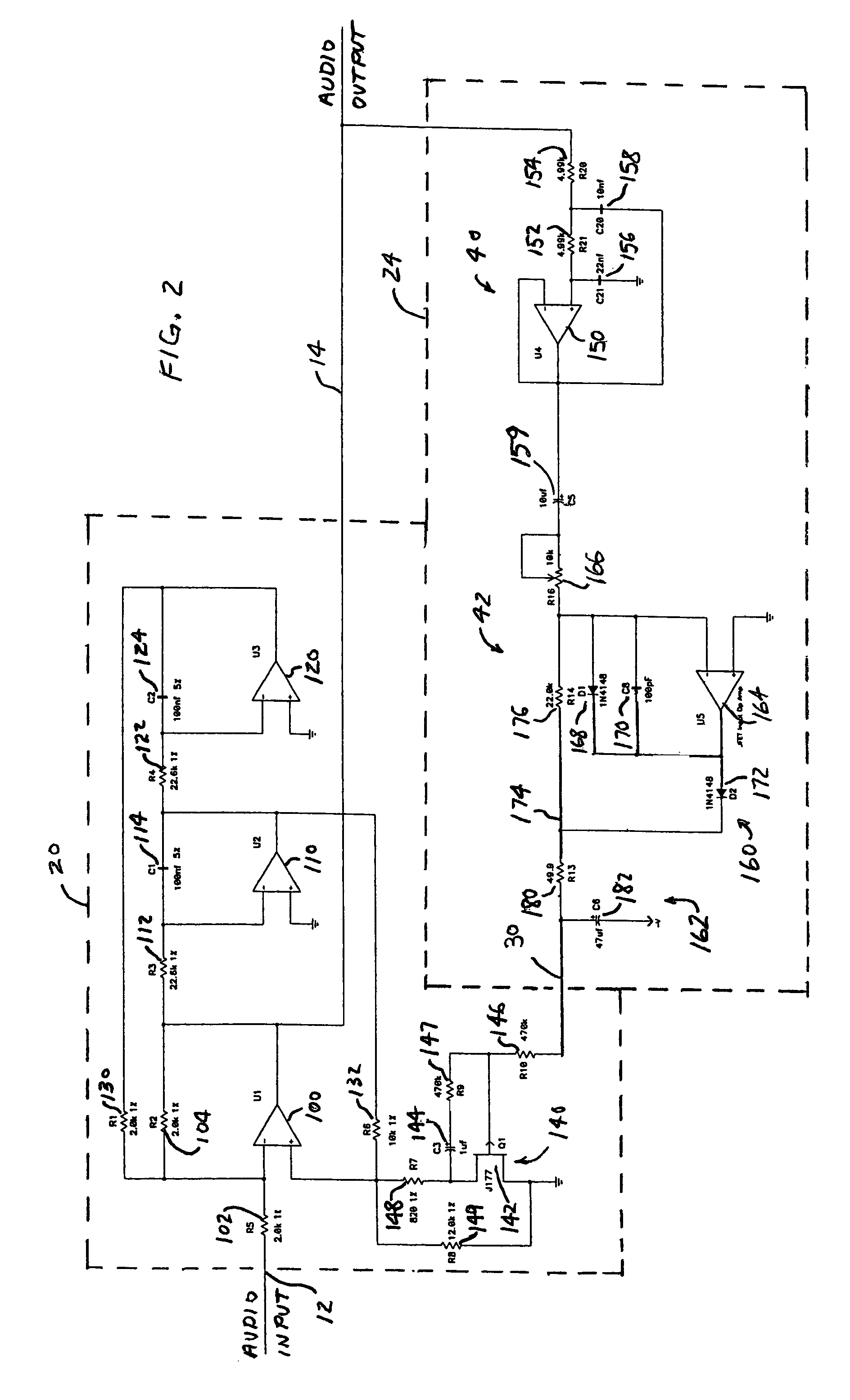
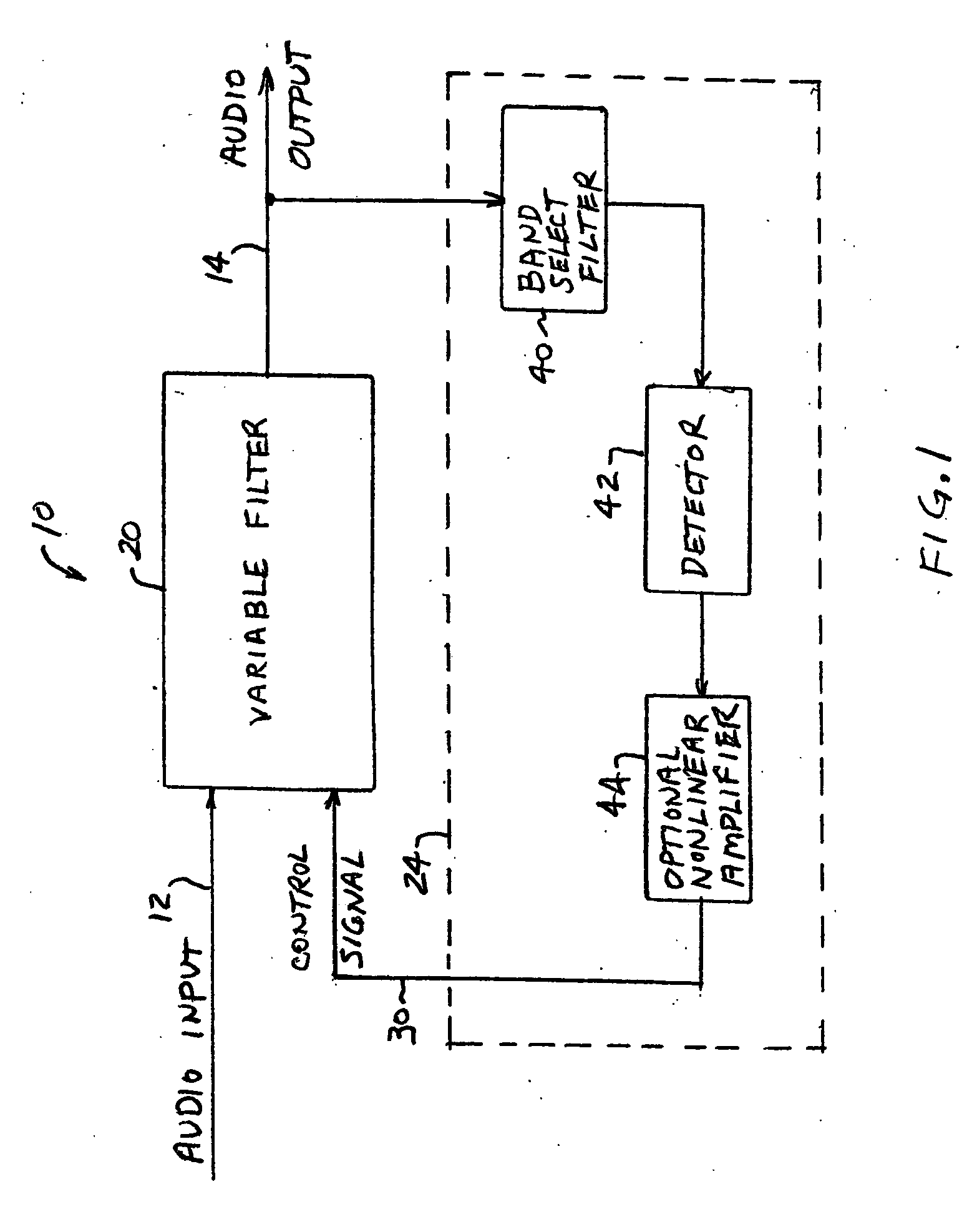
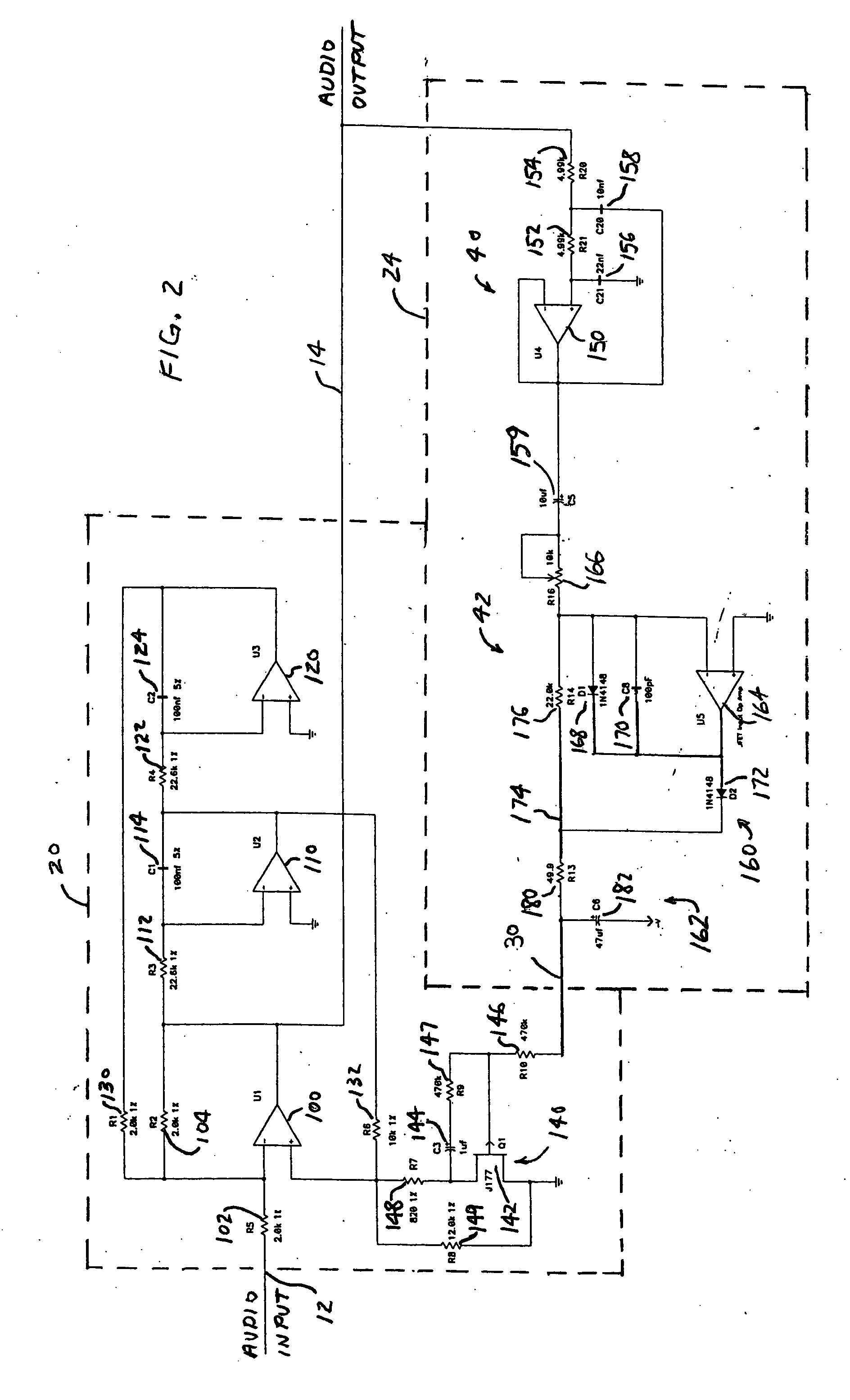
Dynamic bass boost apparatus and method
ActiveUS7171010B2Digital/coded signal combination controlTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsLow-pass filterControl signal
Audio processing methods and apparatus are provided for at least partially compensating for the Fletcher-Munson effect. An audio processor includes a variable filter receiving an input signal and providing a filtered output signal, the variable filter having a fixed cutoff frequency and a quality factor that is controllable in response to a control signal, and a control circuit configured to detect a signal level representative of input signal level in a selected band and to generate the control signal in response to the detected signal level. The control circuit may include a low-pass band select filter and a detector for detecting a signal level in the band selected by the low-pass filter and for generating the control signal.
Owner:BOSTON ACOUSTICS INC
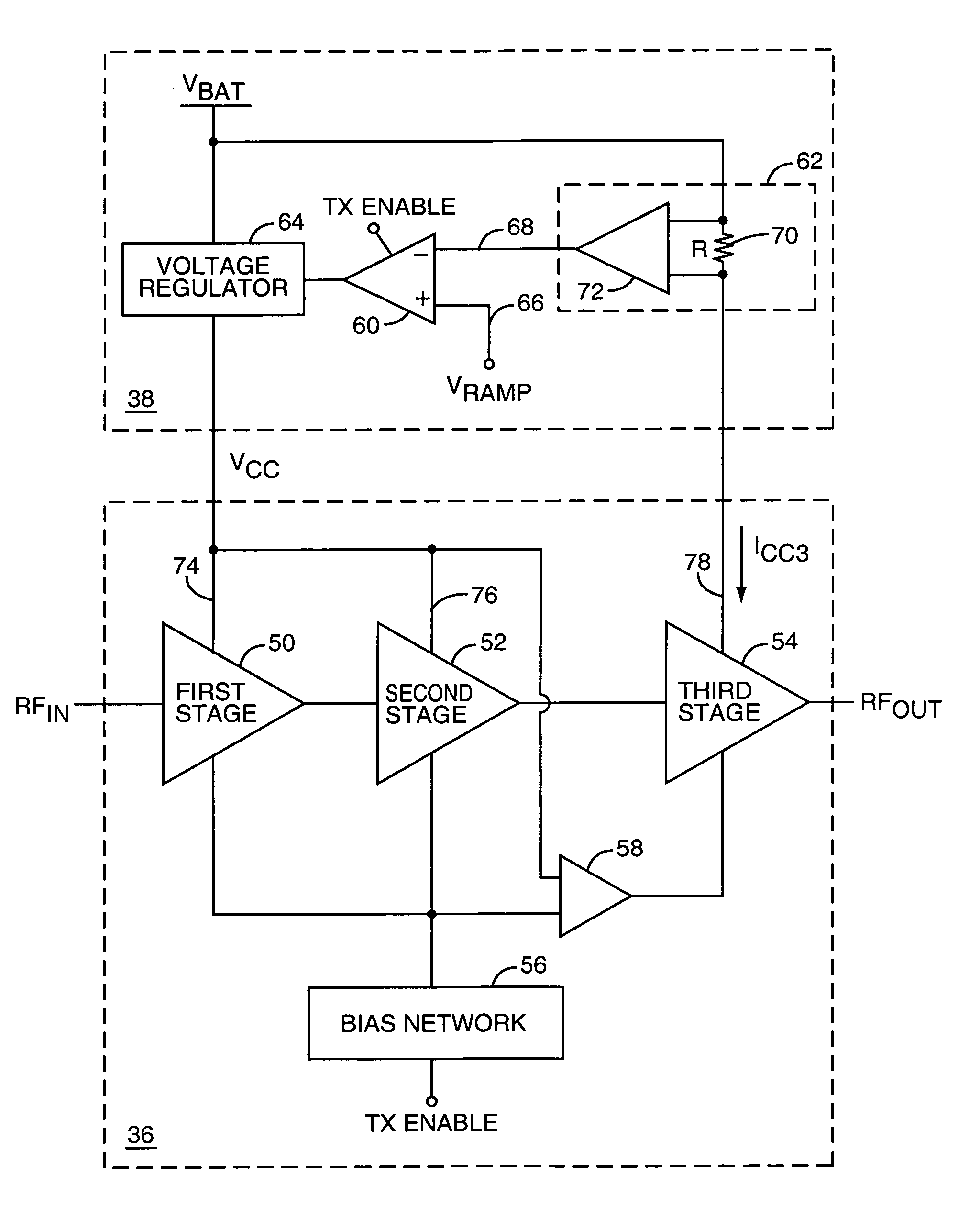
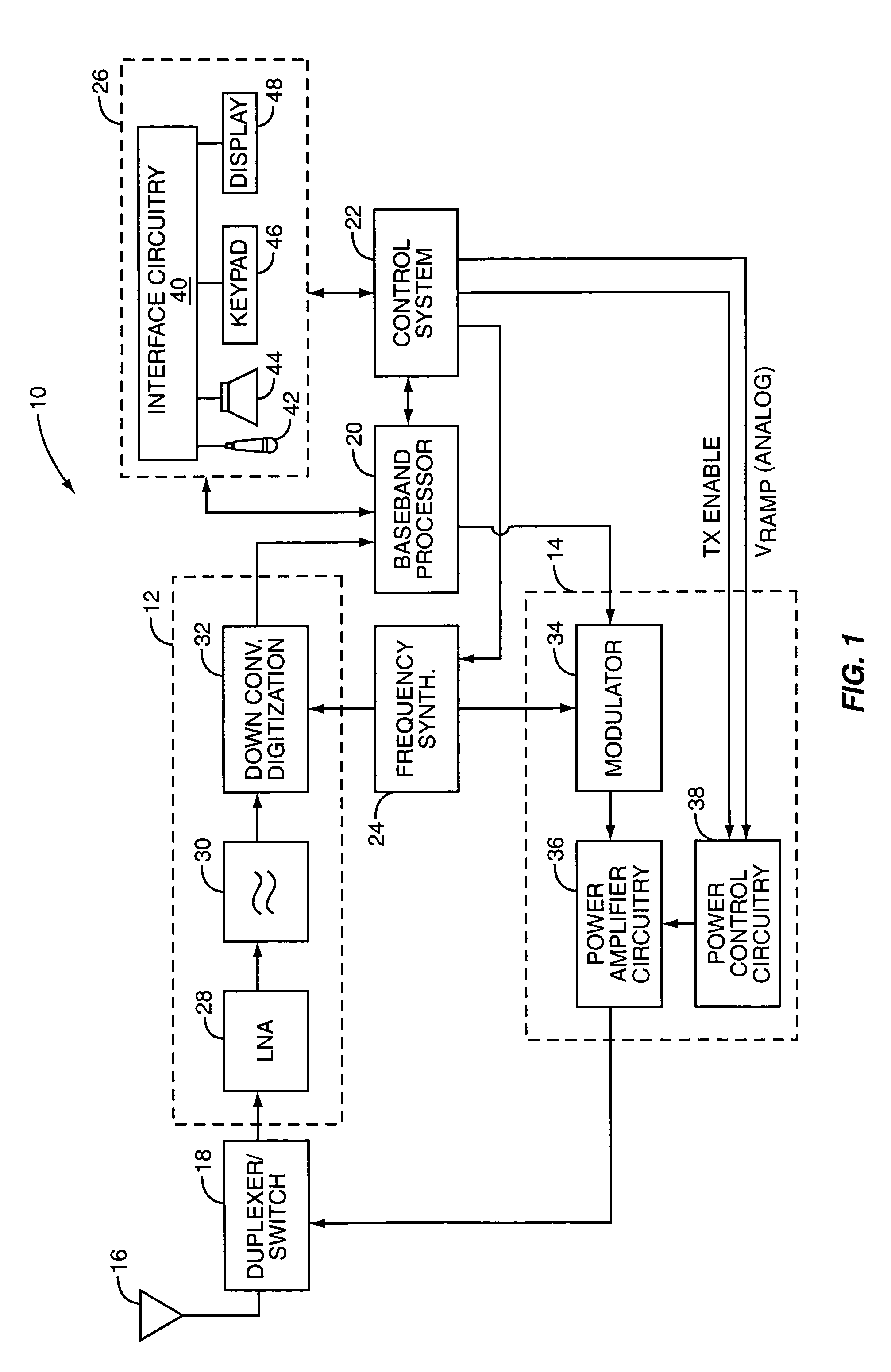
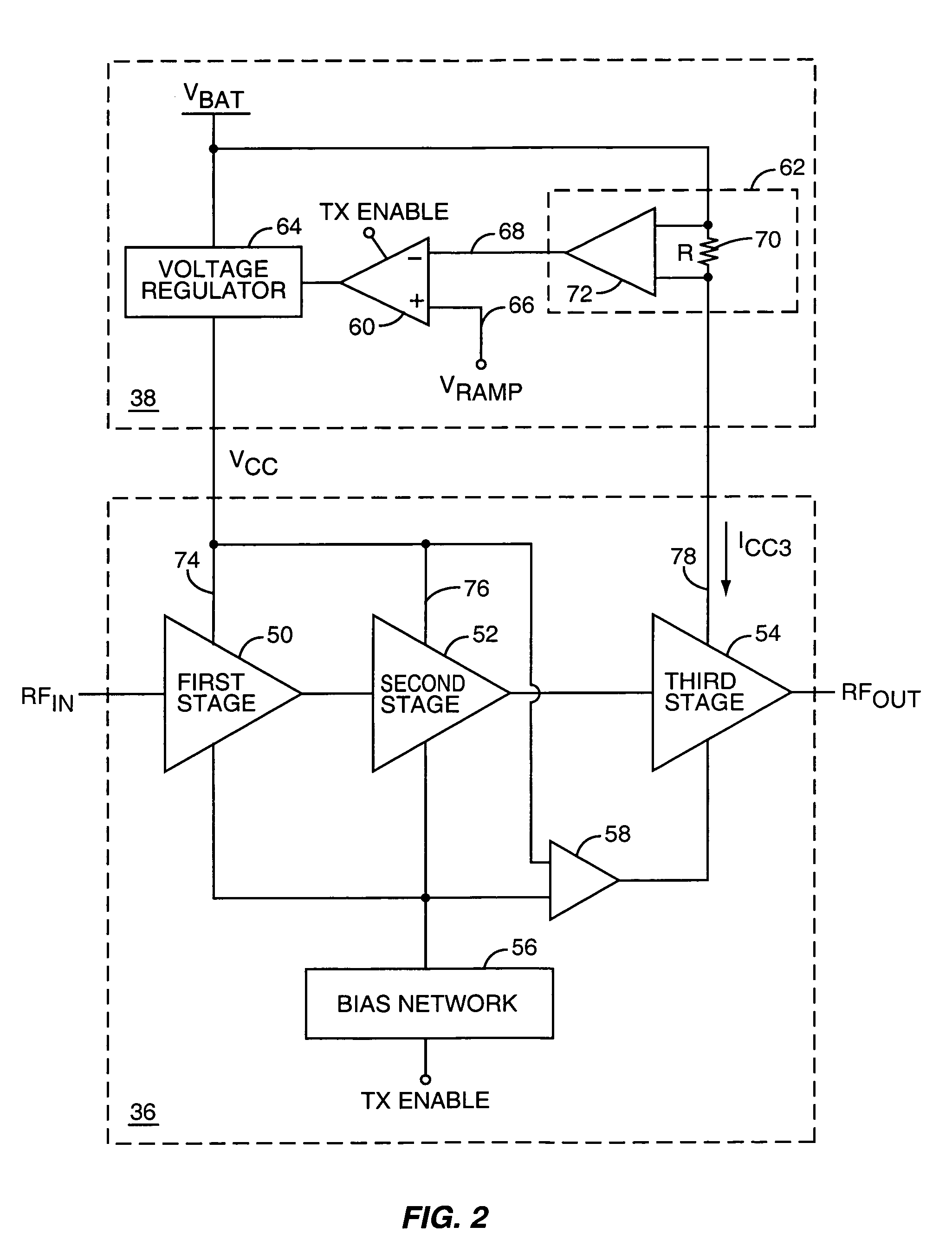
Power amplifier control technique for enhanced efficiency
ActiveUS7193459B1High gainImprove PAEPush-pull amplifiersPhase-splittersPower-added efficiencyAudio power amplifier
A power amplifier configuration including power amplifier circuitry and power control circuitry and having improved Power Added Efficiency (PAE) is provided. The power amplifier circuitry includes one or more input amplifier stages in series with a final amplifier stage. The power control circuitry provides a variable supply voltage to the input amplifier stages based on an adjustable power control signal. The final amplifier stage is powered by a fixed supply voltage. In operation, as output power of the power amplifier is reduced from its highest power level, the variable supply voltage is reduced. Accordingly, RF power of an amplified signal provided to the final amplifier stage from the input amplifier stages decreases, and the final amplifier stage transitions from saturation to linear operation, thereby increasing the gain of the final amplifier stage. Thus, a desired output level can be maintained while operating at lower current levels.
Owner:QORVO US INC
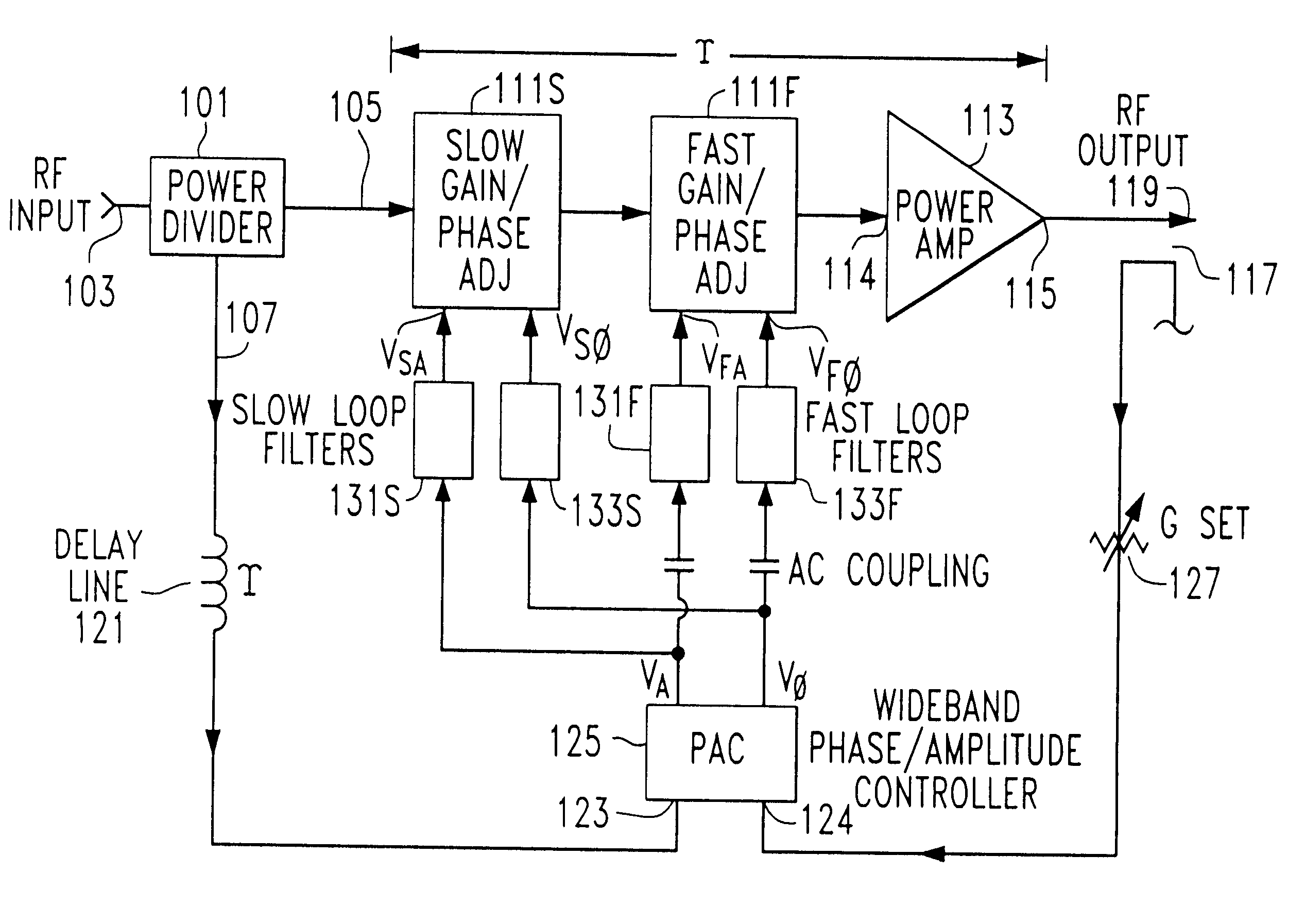
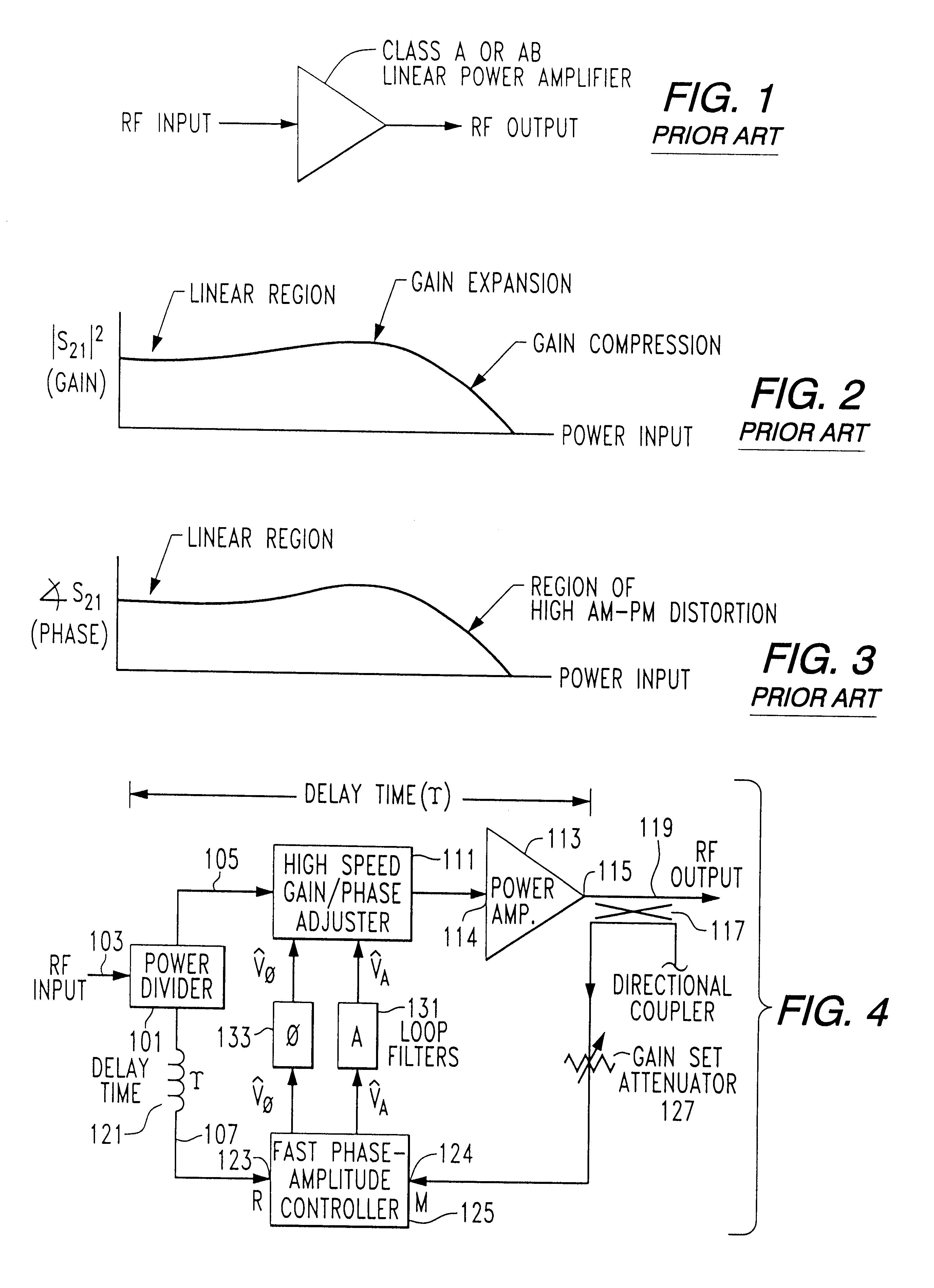
Polar envelope correction mechanism for enhancing linearity of RF/microwave power amplifier
InactiveUSRE37407E1Modest bandwidthImprove linearityAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectric devicesPhase distortionAudio power amplifier
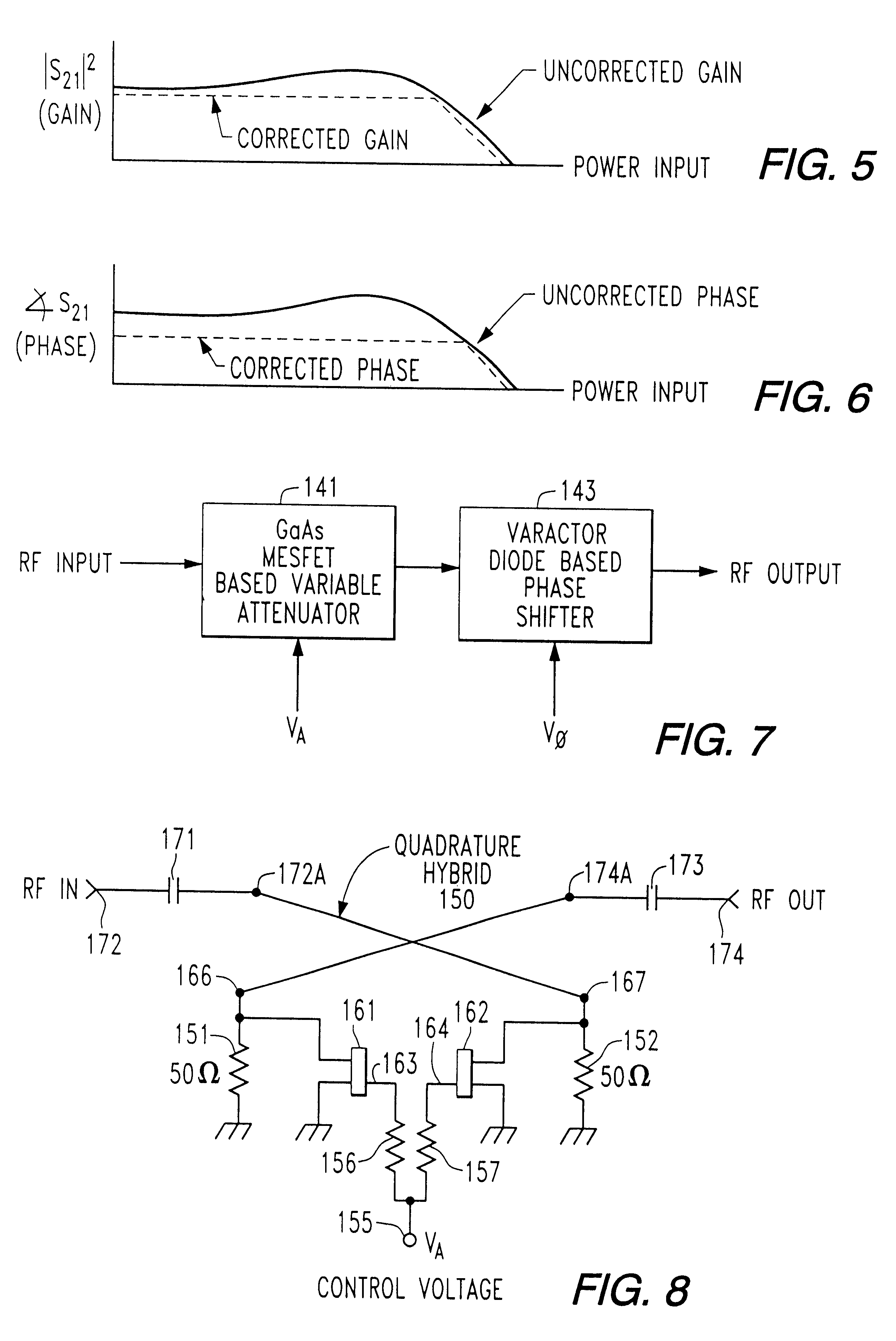
Linearity of an RF / microwave power amplifier is enhanced by an amplitude and phase distortion correction mechanism based upon signal envelope feedback, that operates directly on the RF signal passing through the power amplifier. A phase-amplitude controller responds to changes in gain and phase through the RF / microwave power amplifier signal path caused by changes in RF input power, DC power supply voltages, time, temperature and other variables, and controls the operation of a gain and phase adjustment circuit, so as to maintain constant gain and transmission phase through the RF / microwave power amplifier.
Owner:INTEL CORP
High frequency power amplifier circuit and electronic component for high frequency power amplifier
ActiveUS20050083129A1Avoid short channel effectsReduce widthGain controlAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationChannel length modulationAudio power amplifier
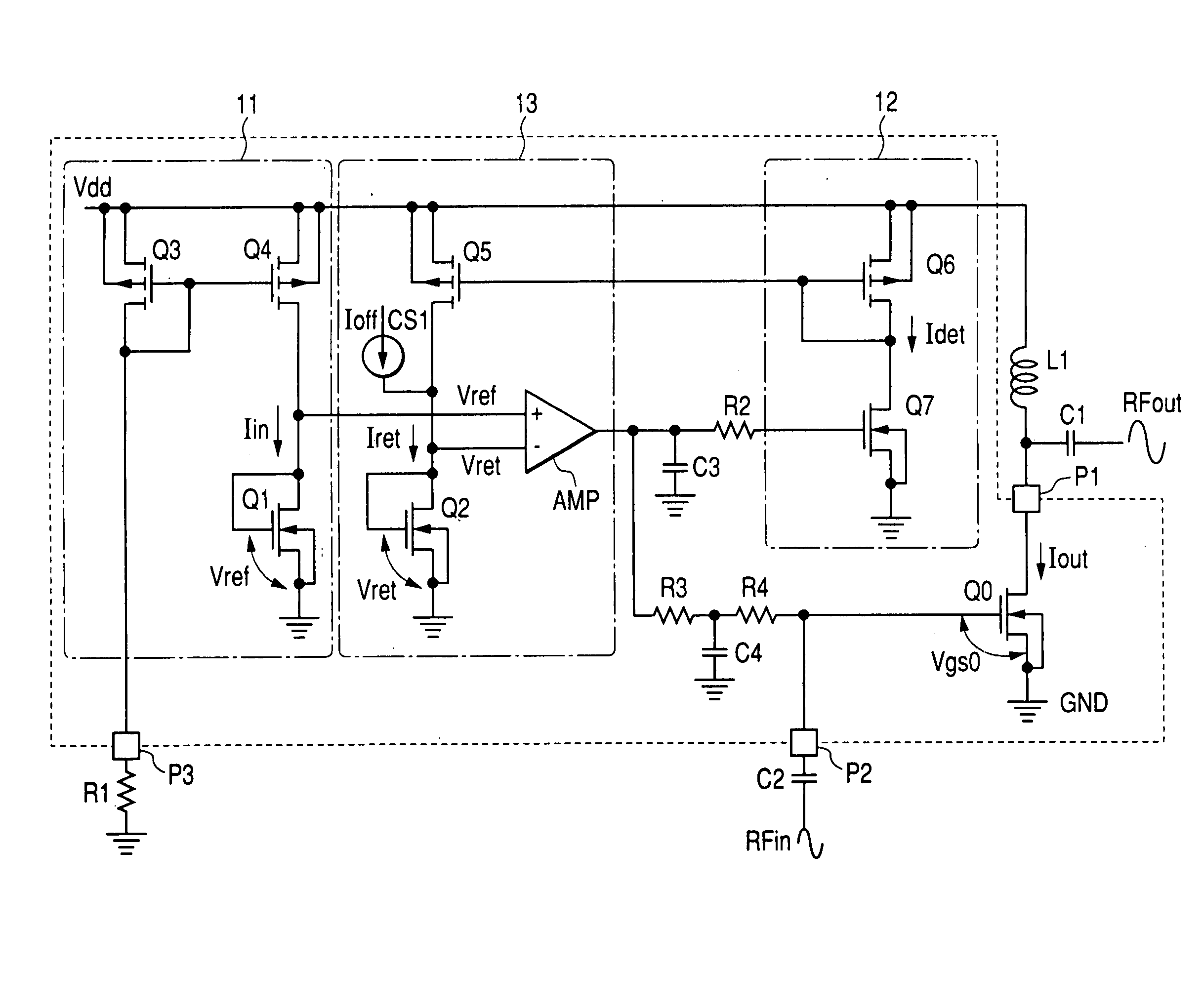
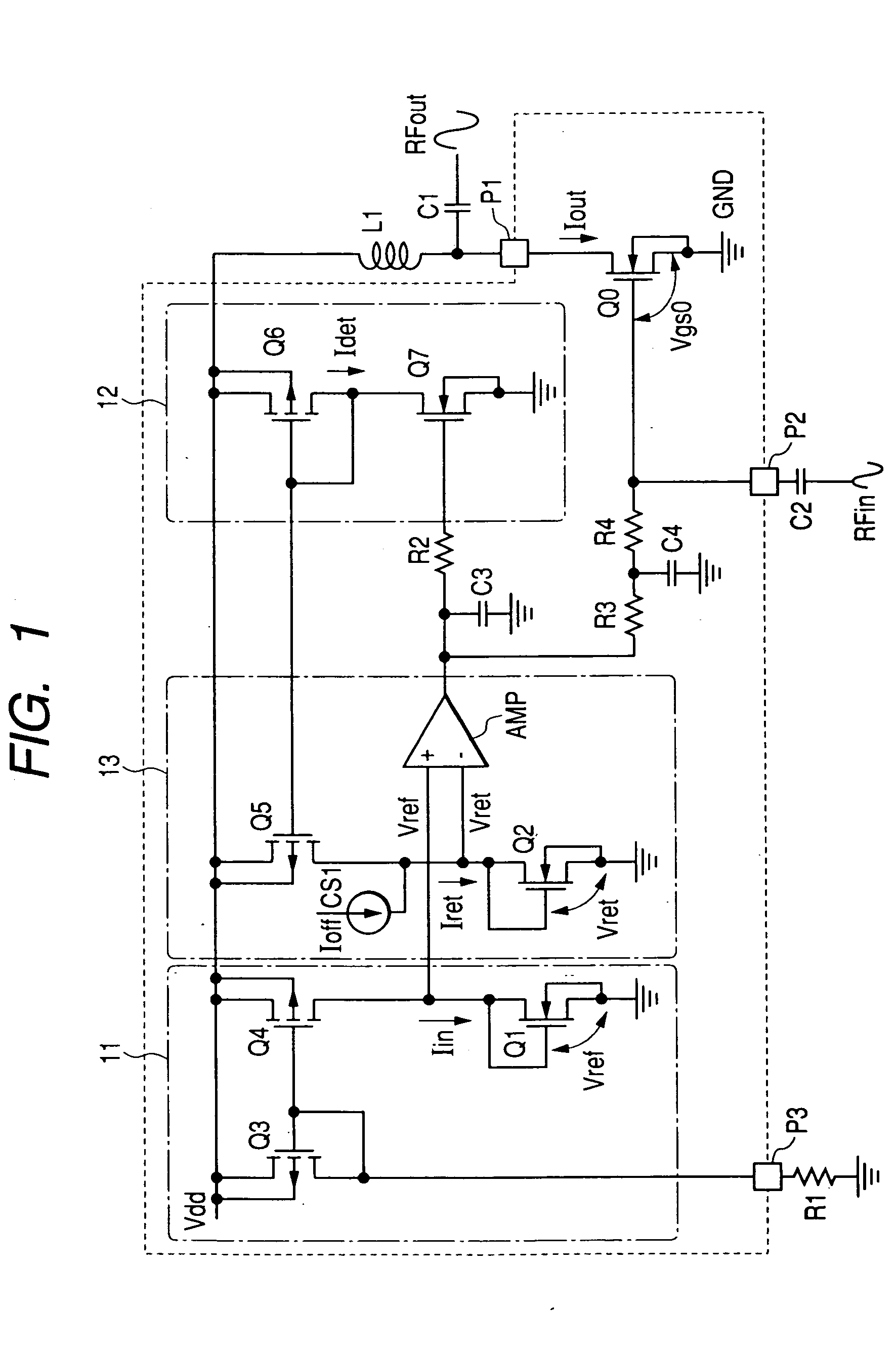
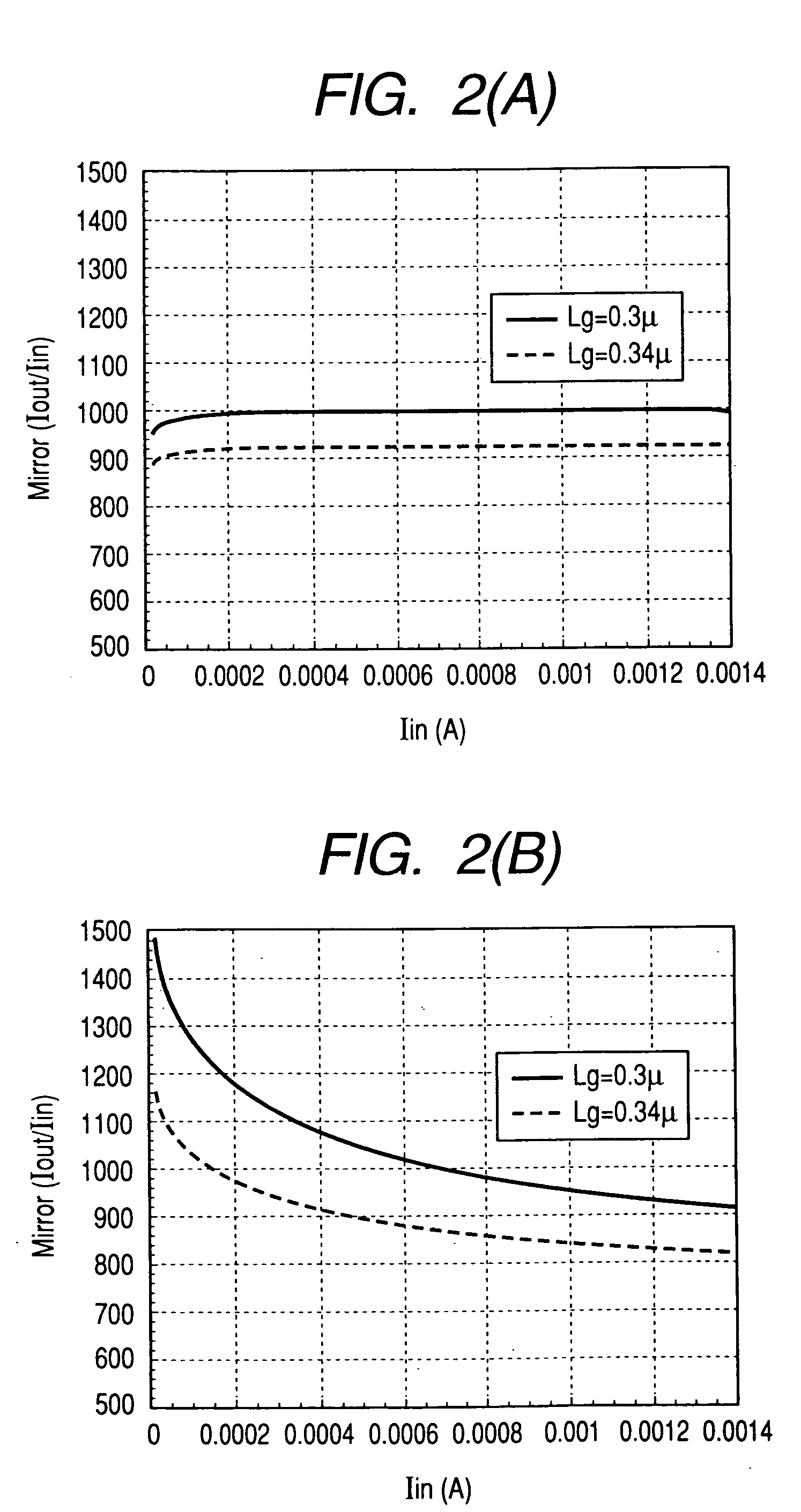
In a high frequency power amplifier circuit that supplies a bias to an amplifying FET by a current mirror method, scattering of a threshold voltage Vth due to the scattering of the channel impurity concentration of the FET, and a shift of a bias point caused by the scattering of the threshold voltage Vth and a channel length modulation coefficient λ due to a short channel effect are corrected automatically. The scattering of a high frequency power amplifying characteristic can be reduced as a result.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Broadband variable gain amplifier with high linearity and variable gain characteristic
InactiveUS6882226B2Improve linearityImprove noise figureNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
A broadband variable gain amplifier with improved linearity and gain characteristic is provided. According to the present invention, the broadband variable gain amplifier comprises: an amplification unit for amplifying an input signal applied to an input terminal and outputting an amplified signal to an output terminal; and a gain control unit which is connected between the input and output terminals, and for controlling gain of said amplification unit, wherein said gain control unit comprises: a variable resistance unit whose resistance value is varied according to a control signal; and a broadband matching unit for proving an optimal impedance characteristic to the input terminal said amplification unit in a broad band, where in said variable gain resistance unit and said broadband matching unit is connected in parallel.
Owner:INTEGRANT TECH
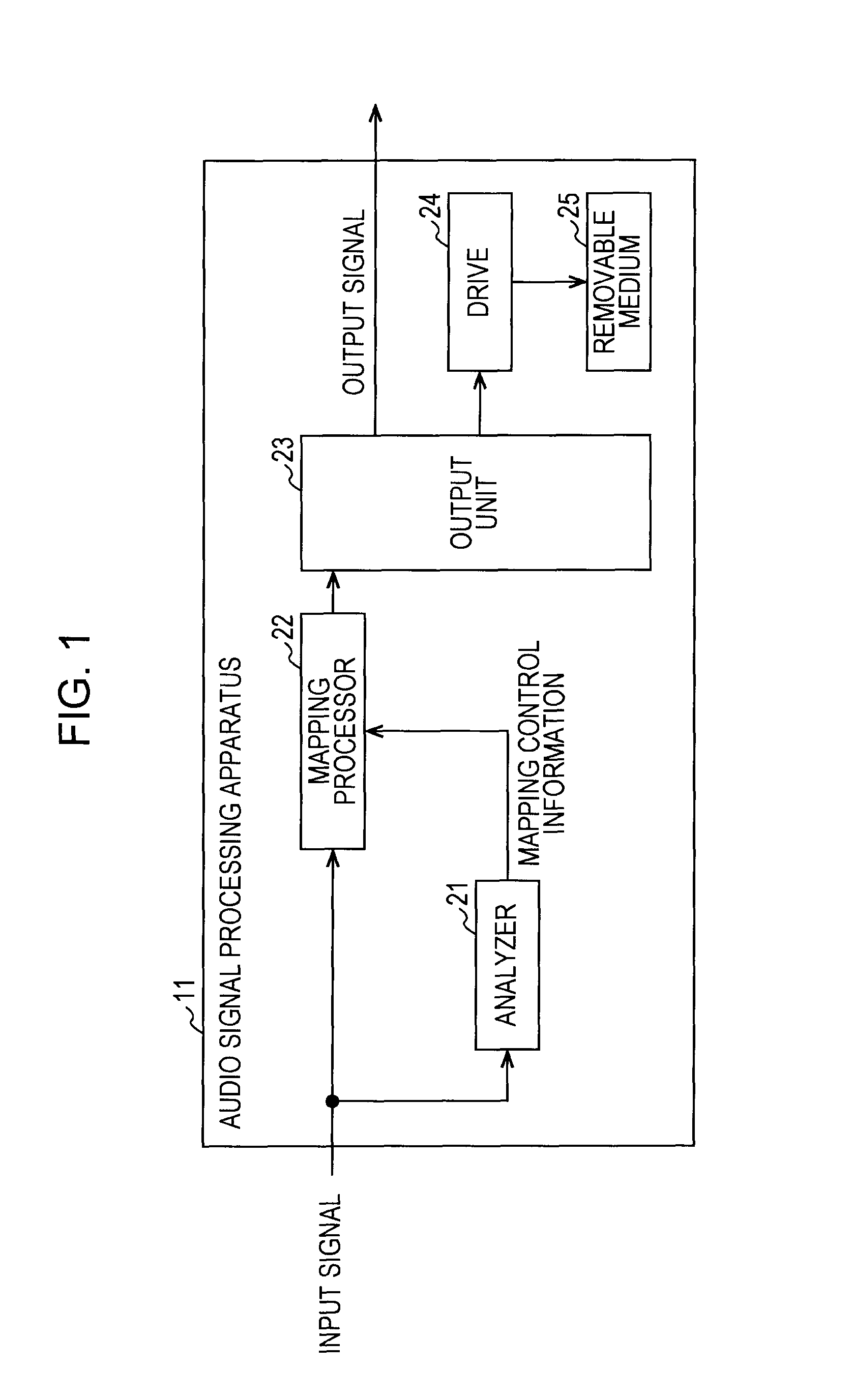
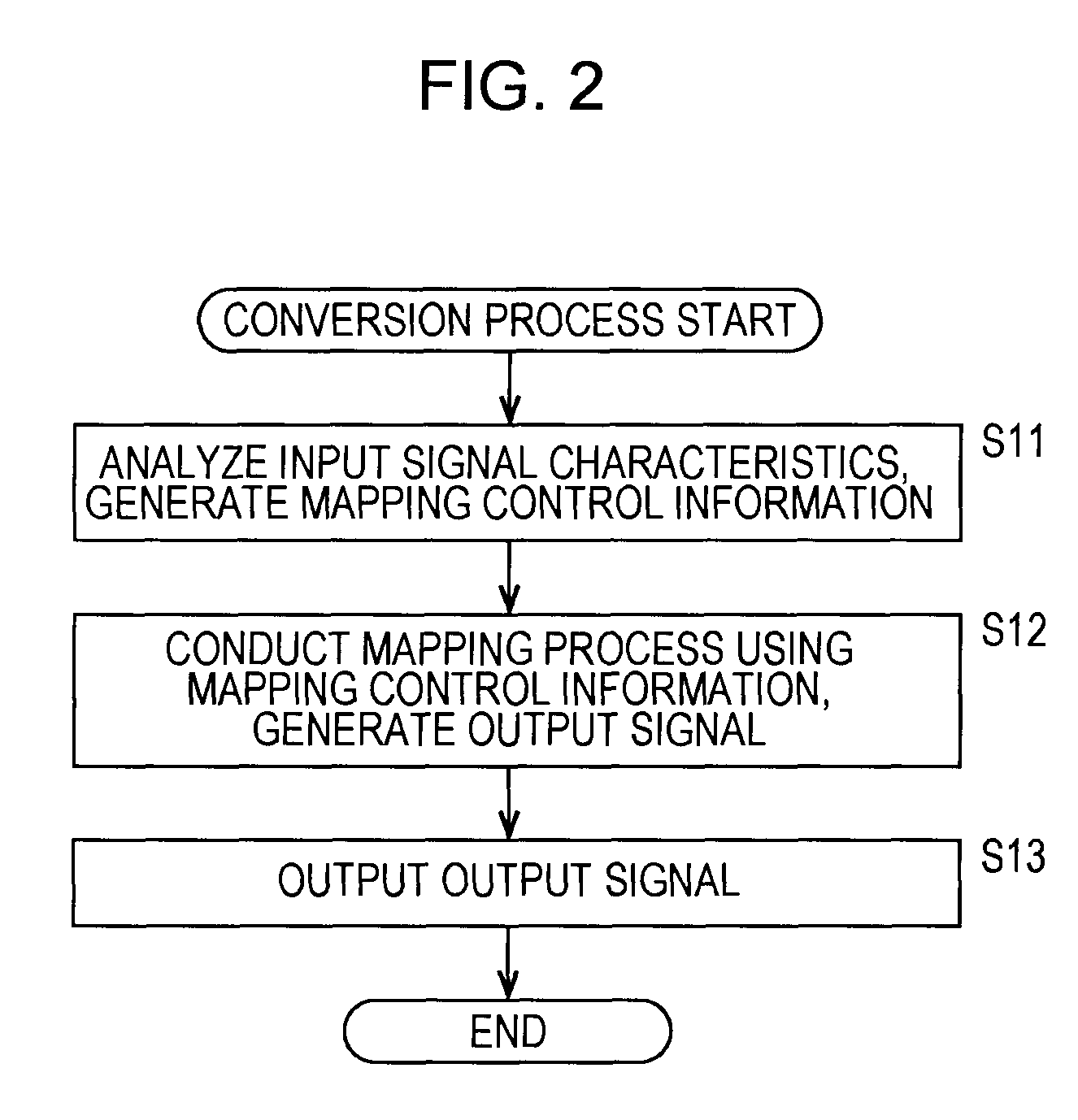
Signal processing apparatus and method, program, and data recording medium
InactiveUS8903098B2Improve the level ofMultiple-port networksError preventionData recordingComputer science
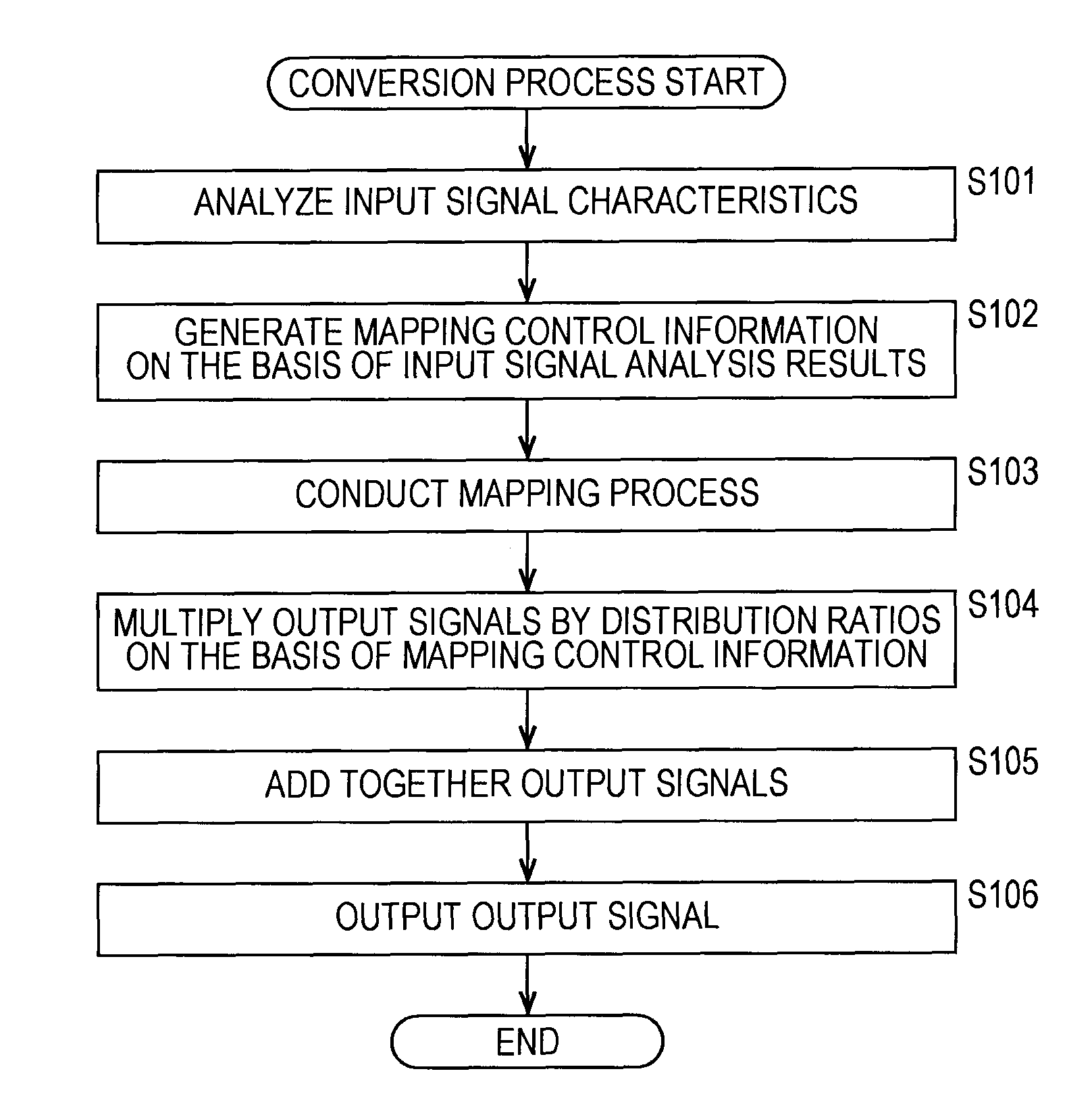
The present invention relates to a signal processing apparatus and method, a program, and a data recording medium configured such that the playback level of an audio signal can be easily and effectively enhanced without requiring prior analysis.An analyzer 21 generates mapping control information in the form of the root mean square of samples in a given segment of a supplied audio signal. A mapping processor 22 takes a nonlinear function determined by the mapping control information taken as a mapping function, and conducts amplitude conversion on a supplied audio signal using the mapping function. In this way, by conducting amplitude conversion of an audio signal using a nonlinear function that changes according to the characteristics in respective segments of an audio signal, the playback level of an audio signal can be easily and effectively enhanced without requiring prior analysis. The present invention may be applied to portable playback apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
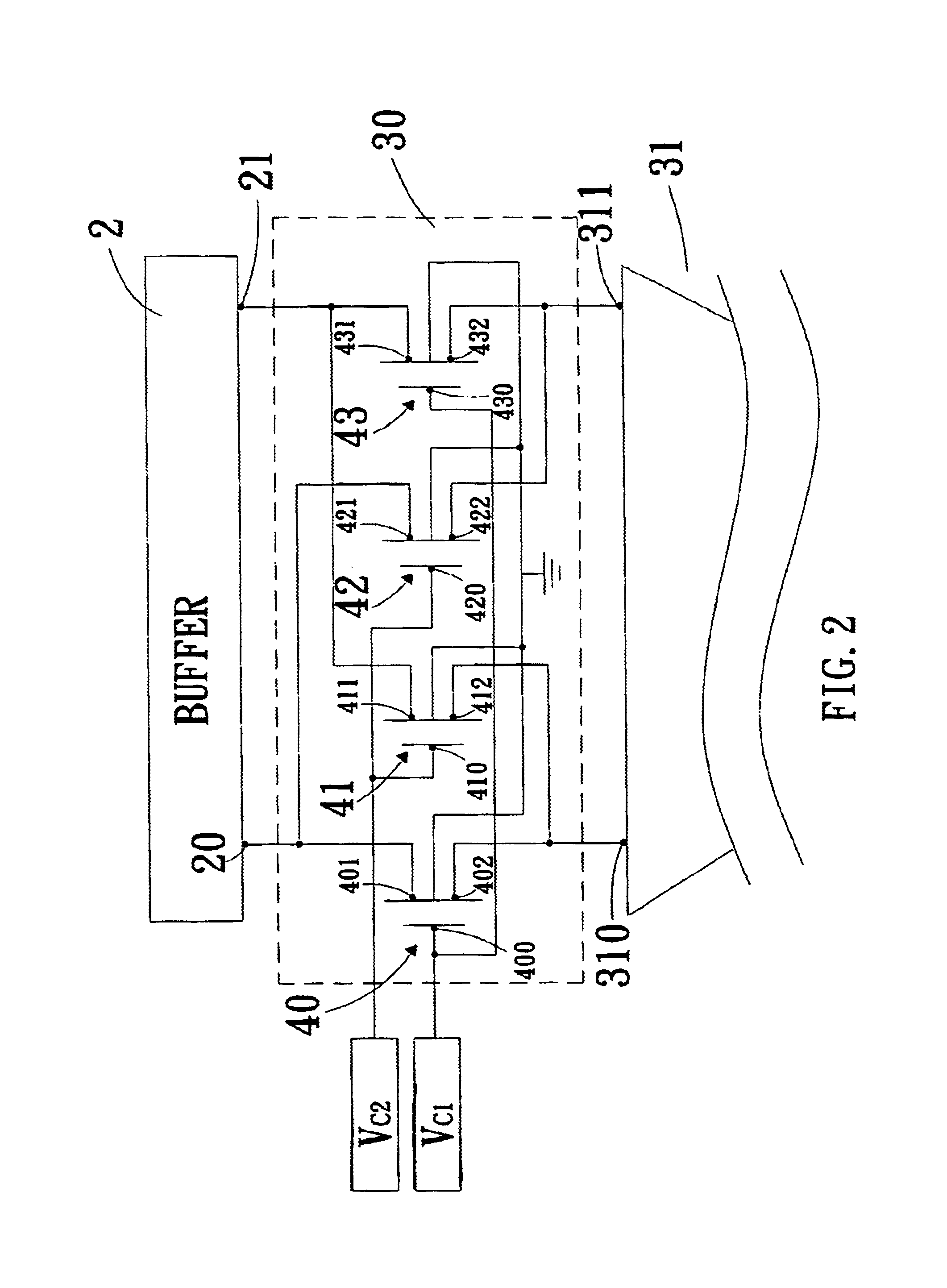
Novel VGA-CTF combination cell for 10 GB/S serial data receivers
InactiveUS20050248396A1Easy to understandGain controlDifferential amplifiersVariable-gain amplifierEngineering
An input processing circuit includes a first and second input transistors for receiving a differential pair of first and second input signals, respectively. At least one resistor is coupled between first terminals of the first and second input transistors. The input processing circuit includes a variable gain amplifier (VGA) circuit. At least one first transistor has a gate terminal, and is coupled between the first terminals of the first and second input transistors. At least one second transistor has a gate terminal, and is coupled between the first terminals of the first and second input transistors. A gate switch is coupled to the gate terminal of the at least one second transistor. The at least one first transistor and the at least one second transistor adjust a gain of the input processing circuit in response to a control voltage. The control voltage is applied to the gate terminal of the at least one first transistor, and the control voltage is applied to the gate terminal of the at least one second transistor through the gate switch.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Gain amplifier with DC offset cancellation circuit
ActiveUS6903593B2Shorten convergence timePulse automatic controlComputing operation arrangementsNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
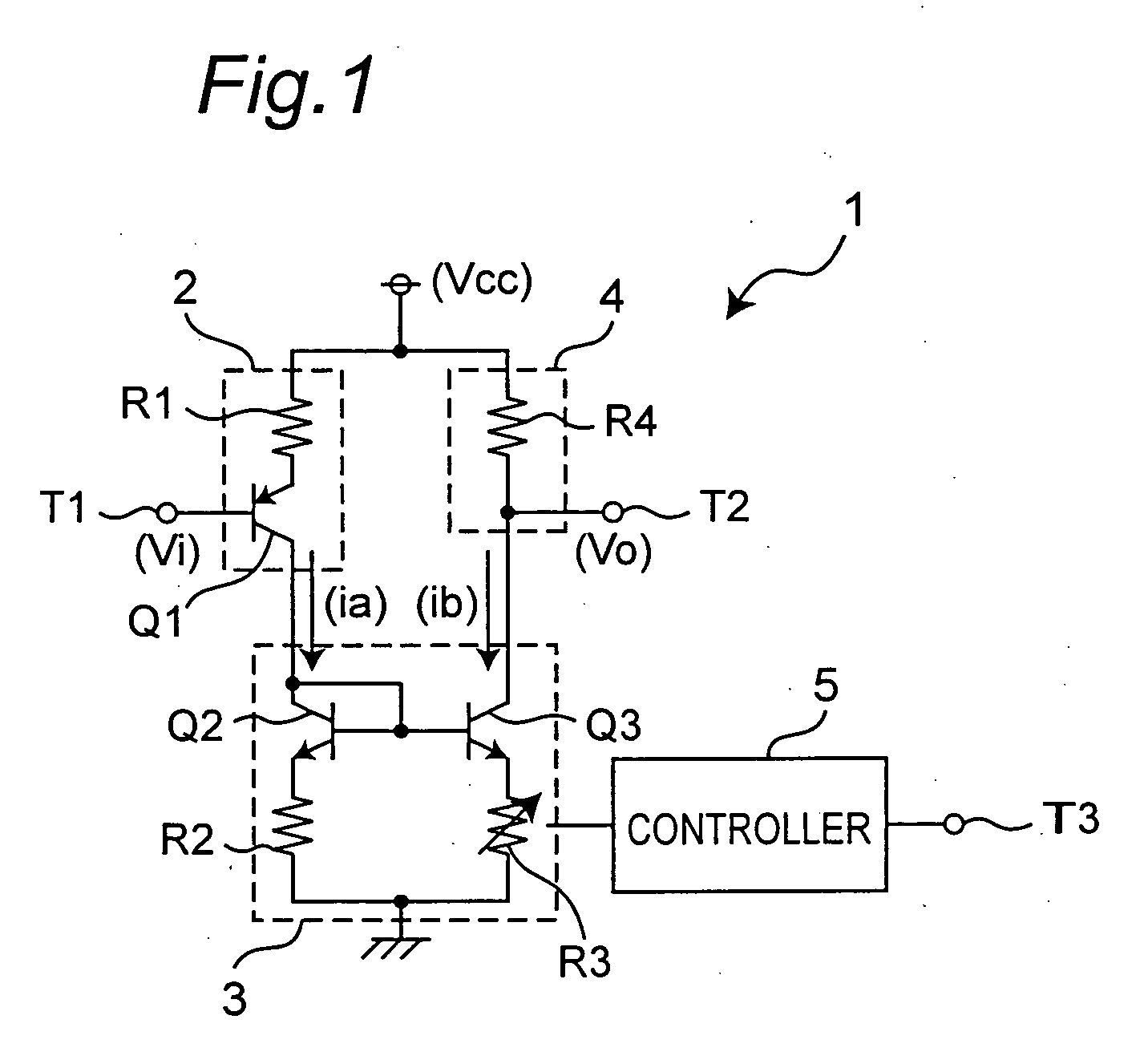
A DC offset cancellation circuit employs multiple feedback factors for canceling DC offset by increasing convergence time. The DC offset cancellation circuit features an active low-pass analogue filter including a variable resistor, an amplifier, a capacitor pair and a comparator, the amplifier being coupled to an output of the variable resistor. Negative feedback is provided from the output of the variable resistor to the input signal source, the capacitor pair is coupled to the amplifier, one input of the comparator is coupled to an output of the amplifier, and a second input of the comparator is coupled to a reference voltage source such that a comparison signal is output by the comparator to the variable resistor after comparing the negative feedback signal with a reference voltage.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
VGA-CTF combination cell for 10 Gb/s serial data receivers
An input processing circuit includes a first and second input transistors for receiving a differential pair of first and second input signals, respectively. At least one resistor is coupled between first terminals of the first and second input transistors. The input processing circuit includes a variable gain amplifier (VGA) circuit. At least one first transistor has a gate terminal, and is coupled between the first terminals of the first and second input transistors. At least one second transistor has a gate terminal, and is coupled between the first terminals of the first and second input transistors. A gate switch is coupled to the gate terminal of the at least one second transistor. The at least one first transistor and the at least one second transistor adjust a gain of the input processing circuit in response to a control voltage. The control voltage is applied to the gate terminal of the at least one first transistor, and the control voltage is applied to the gate terminal of the at least one second transistor through the gate switch.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
High frequency power amplifier circuit and electronic component for high frequency power amplifier
ActiveUS7304539B2Avoid short channel effectsReduce widthGain controlAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationChannel length modulationHigh frequency power
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
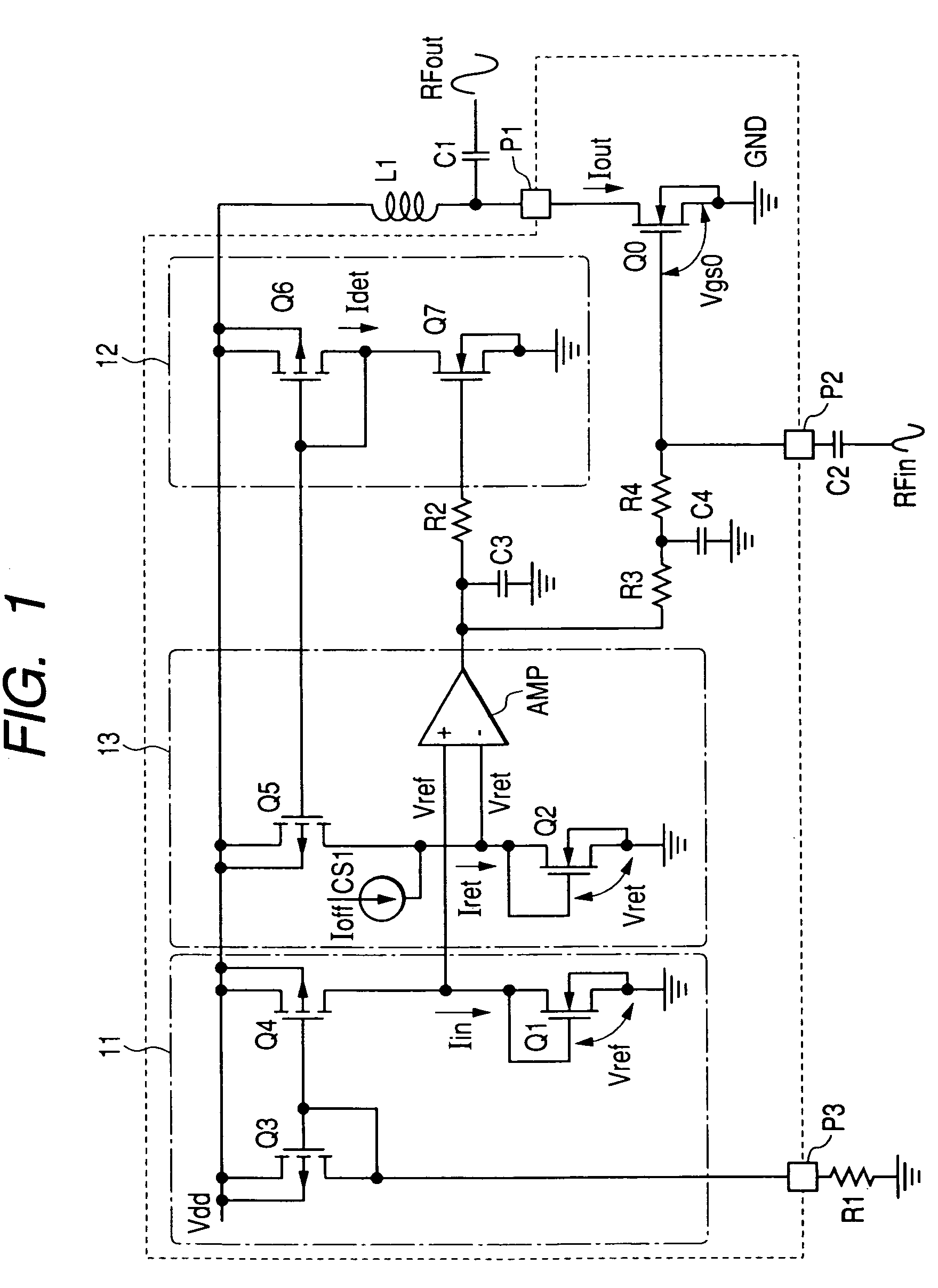
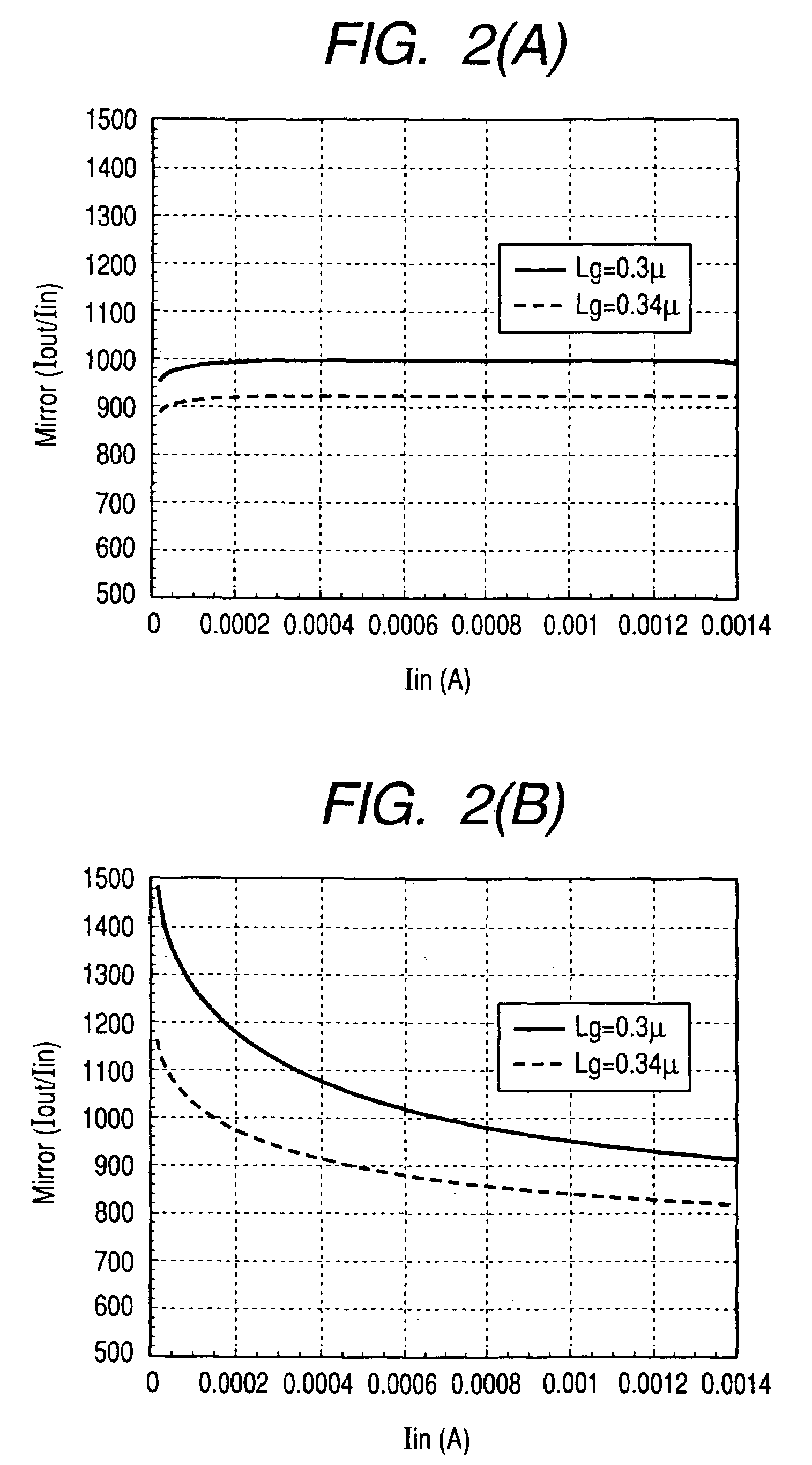
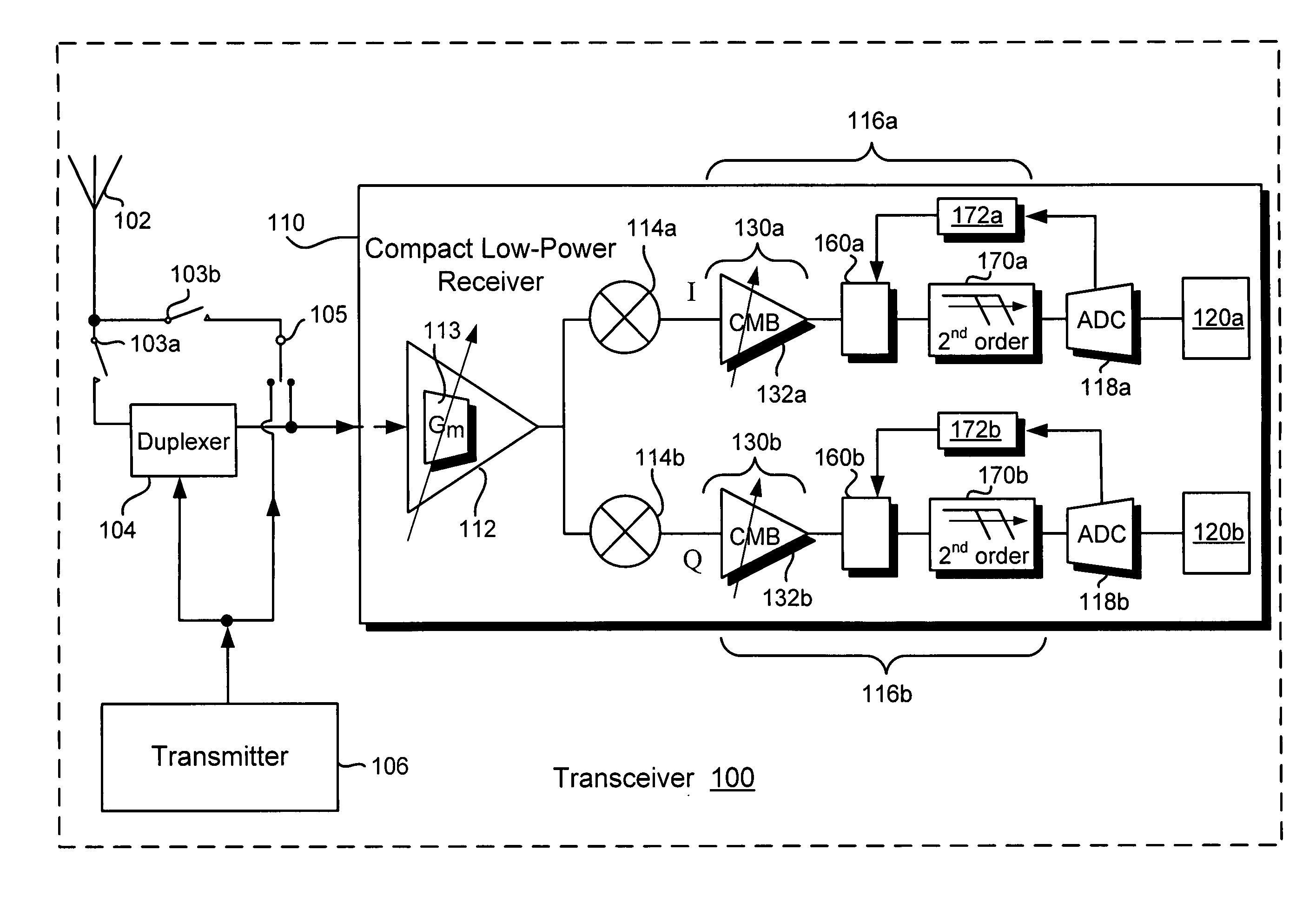
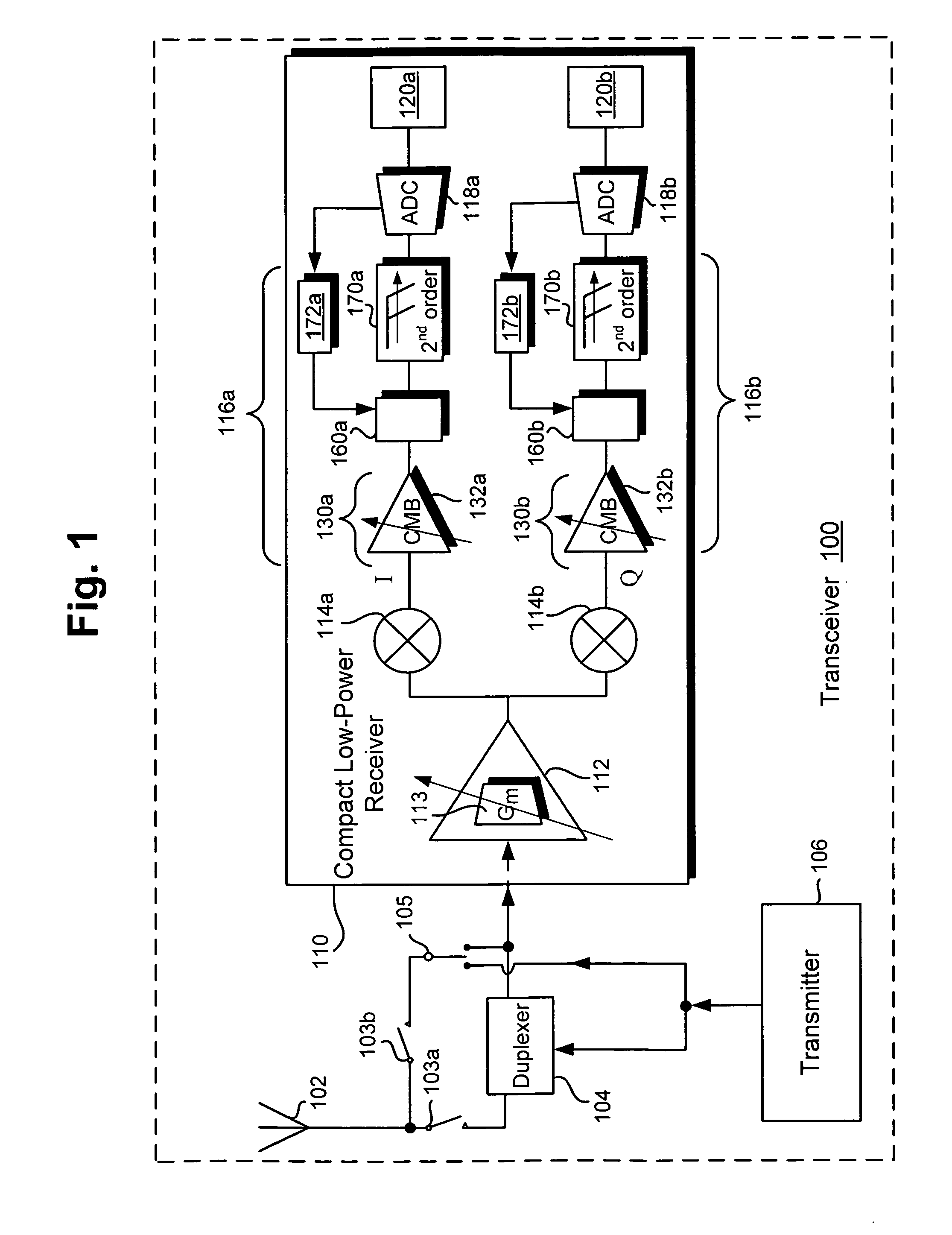
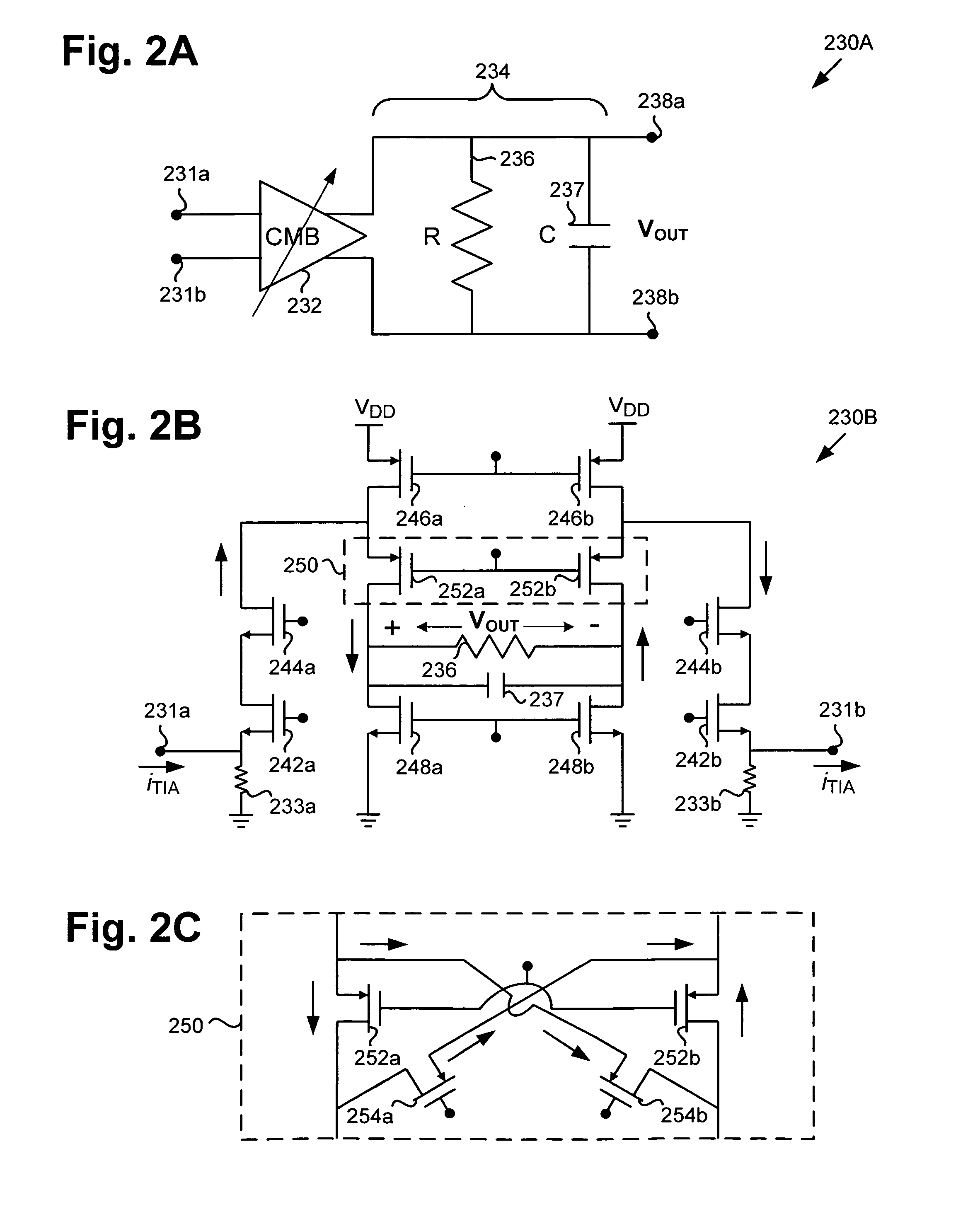
Compact low-power receiver including transimpedance amplifier, digitally controlled interface circuit, and low pass filter
According to one embodiment, a compact low-power receiver comprises first and second analog circuits connected by a digitally controlled interface circuit. The first analog circuit has a first direct-current (DC) offset and a first common mode voltage at an output, and the second analog circuit has a second DC offset and a second common mode voltage at an input. The digitally controlled interface circuit connects the output to the input, and is configured to match the first and second DC offsets and to match the first and second common mode voltages. In one embodiment, the first analog circuit is a variable gain control transimpedance amplifier (TIA) implemented using a current mode buffer, the second analog circuit is a second-order adjustable low-pass filter, whereby a three-pole adjustable low-pass filter in the compact low-power receiver is effectively produced.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
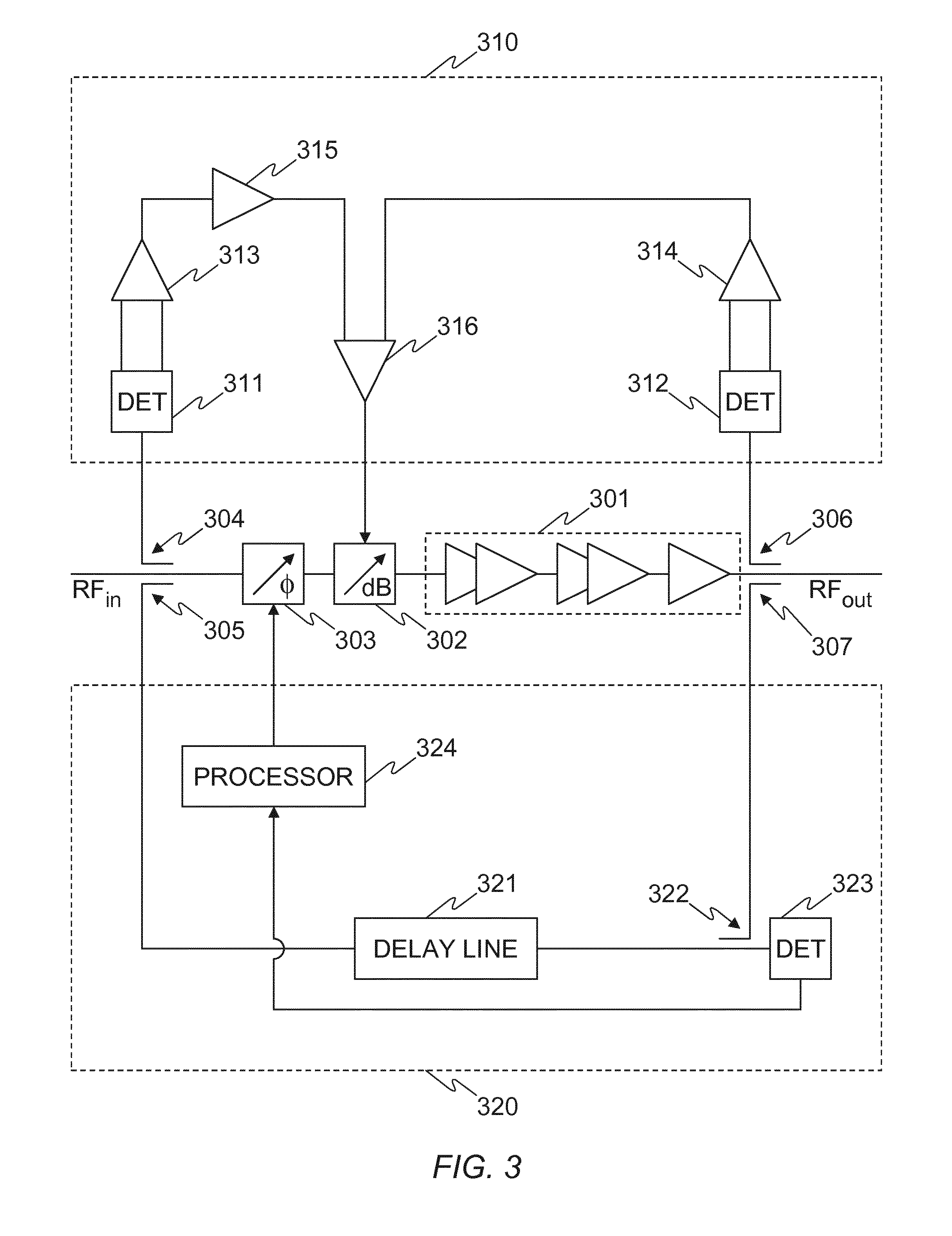
Control system for a power amplifier
ActiveUS20150054582A1Minimise measured powerMinimize powerAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierPhase difference
An apparatus for controlling the gain and phase of an input signal input to a power amplifier comprises a gain control loop configured to control the gain of the input signal based on power levels of the input signal and an amplified signal output by the power amplifier, to obtain a predetermined gain of the amplified signal, and a phase control loop configured to obtain an error signal related to a phase difference between a first signal derived from the input and a second signal derived from the amplified signal, and control the phase based on the error signal, to obtain a predetermined phase of the amplified signal. The phase control loop delays the first signal, such that the delayed first signal and the second signal used to obtain the error signal correspond to the same part of the input signal. The apparatus may be included in a satellite.
Owner:ASTRIUM GMBH
AGC circuit providing control of output signal amplitude and of output signal DC level
An AGC circuit suitable for applications such as an optical receiving apparatus includes a differential amplification adjustment circuit section for operating on a pair of input signals to produce a corresponding pair of complementary controlled output signals having a fixed amplitude, a peak detector for detecting a peak value of at least one of the controlled output signals, a DC monitoring circuit for detecting the DC level of at least one of the controlled output signals, and an amplitude fixing control circuit for deriving a value of voltage difference between the peak value and DC level and for generating an amplitude control signal based on comparing the voltage difference with a reference voltage. The differential amplification adjustment circuit section applies a degree of amplification that is determined by the amplitude control signal, to thereby perform feedback control of the output signal amplitude. The AGC circuit can further be configured to control the DC levels of the controlled output signals, so that both DC level and amplitude of the controlled output signals are held constant against changes in DC level and amplitude of the input signals.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Dynamic bass boost apparatus and method
ActiveUS20050058303A1Eliminate the effects ofDigital/coded signal combination controlTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsControl signalLow-pass filter
Audio processing methods and apparatus are provided for at least partially compensating for the Fletcher-Munson effect. An audio processor includes a variable filter receiving an input signal and providing a filtered output signal, the variable filter having a fixed cutoff frequency and a quality factor that is controllable in response to a control signal, and a control circuit configured to detect a signal level representative of input signal level in a selected band and to generate the control signal in response to the detected signal level. The control circuit may include a low-pass band select filter and a detector for detecting a signal level in the band selected by the low-pass filter and for generating the control signal.
Owner:BOSTON ACOUSTICS INC
Variable gain amplifier and variable gain amplifier module
ActiveUS20070126501A1Simple structureImprove featuresNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlLow-pass filterEngineering
An analog variable gain amplifier (VGA) adjusting a signal level of a mobile communication system is provided. More particularly, design of a VGA using an operational transconductance amplifier (OTA) having a wide linear input / output range is disclosed. The VGA includes two double-differential-pair OTAs and feedback resistors. A first differential input of a first double differential pair OTA receives an input signal from the forward stage, and a second differential input is negatively fed back through a differential output and a passive resistor. An input in which a first block of the connection structure and first and second differential inputs of a second double differential pair OTA are connected receives an output signal of the first block stage. The output is negatively fed back in series through a variable resistor whose resistance varies exponentially with an adjustment voltage from outside. According to the VGA, it is possible to provide a characteristic of linear variation of gain on a logarithmic scale with respect to a control voltage with a simple and inexpensive constitution. In addition, the VGA can be designed for a low pass filter having a conventional OTA used for a core circuit, and has a simple circuit structure. Therefore, the VGA is convenient for high integration and low-power design, and thus is appropriate for a terminal chip and so forth.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Linear transimpedance amplifier with wide dynamic range for high rate applications
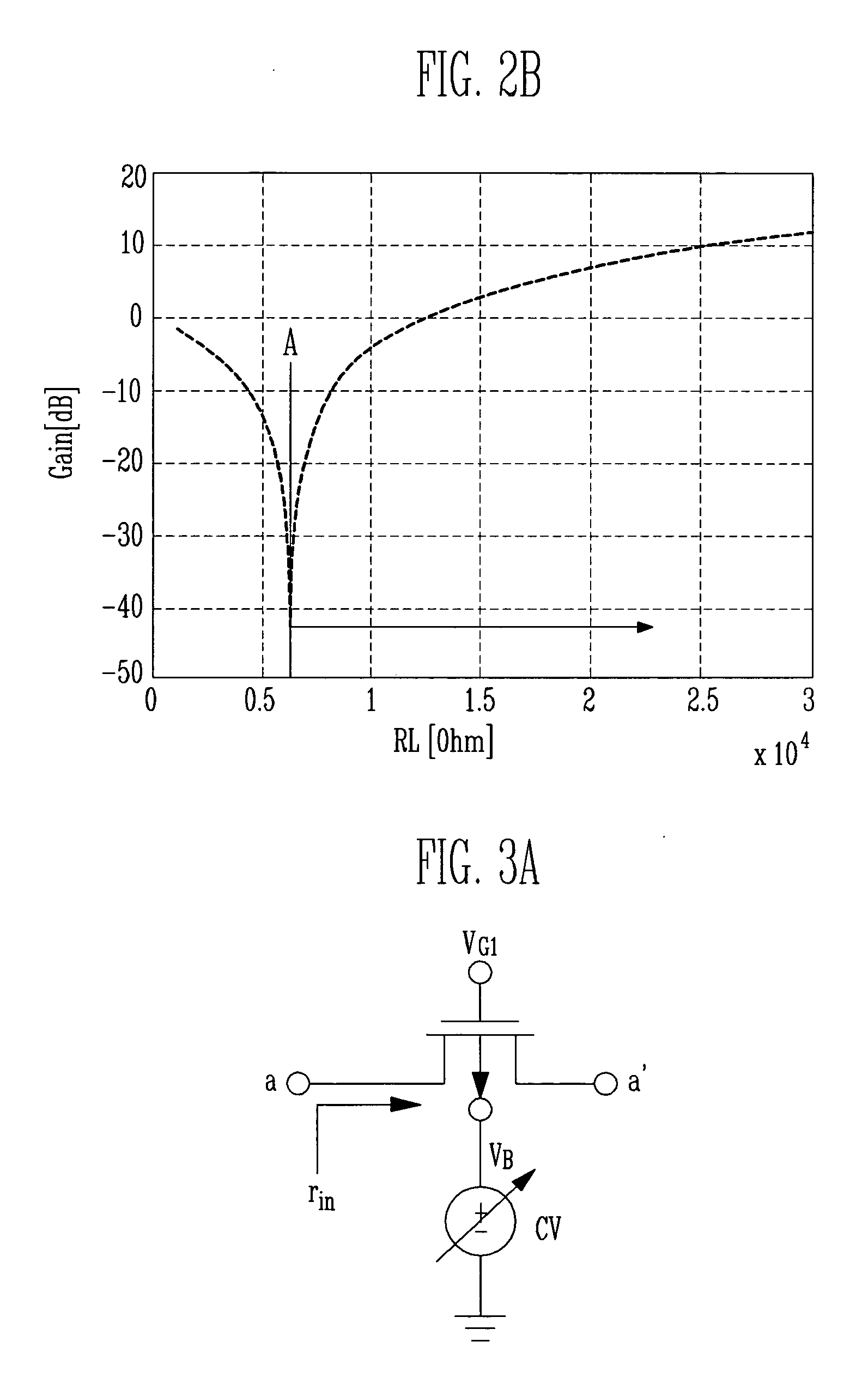
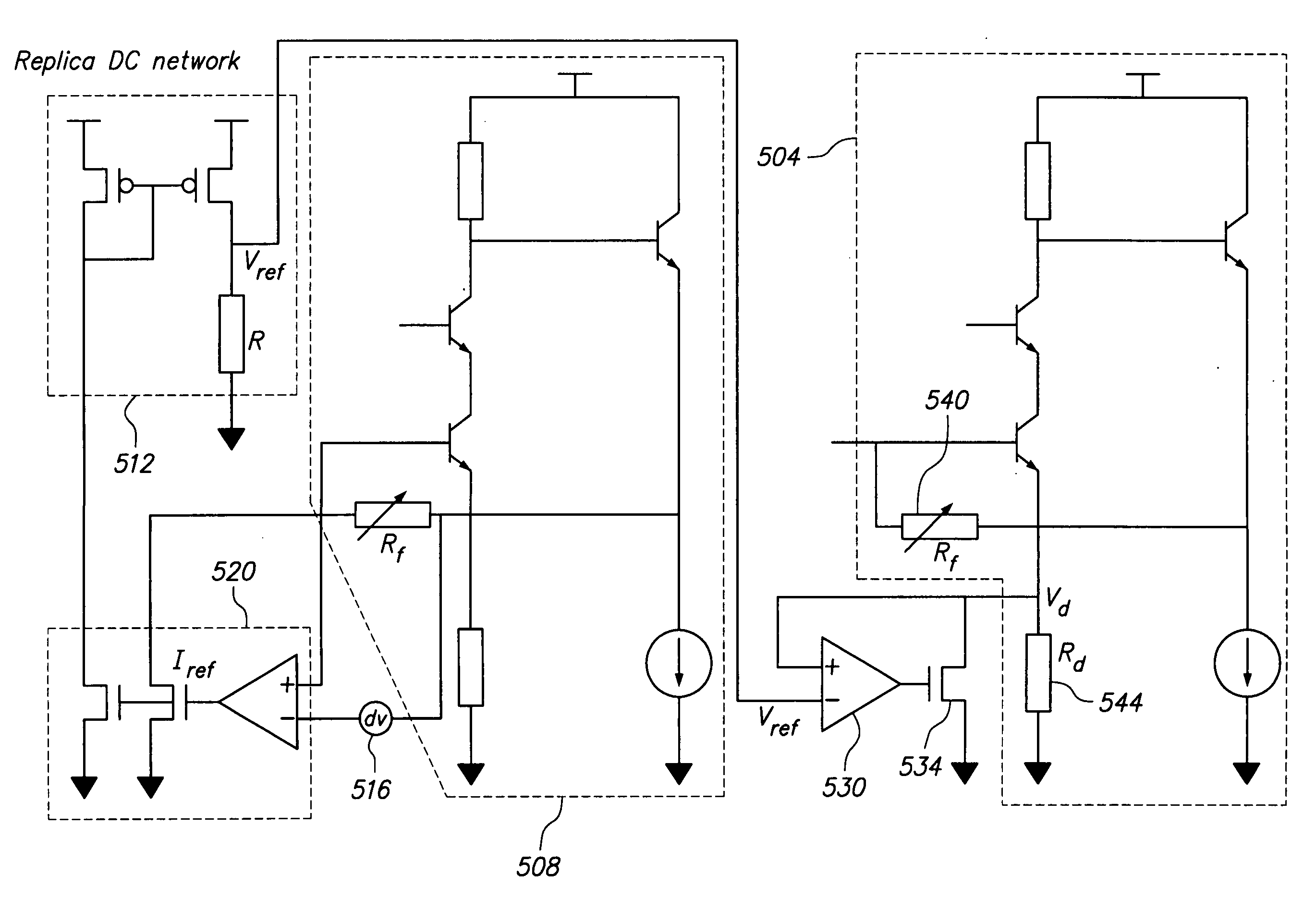
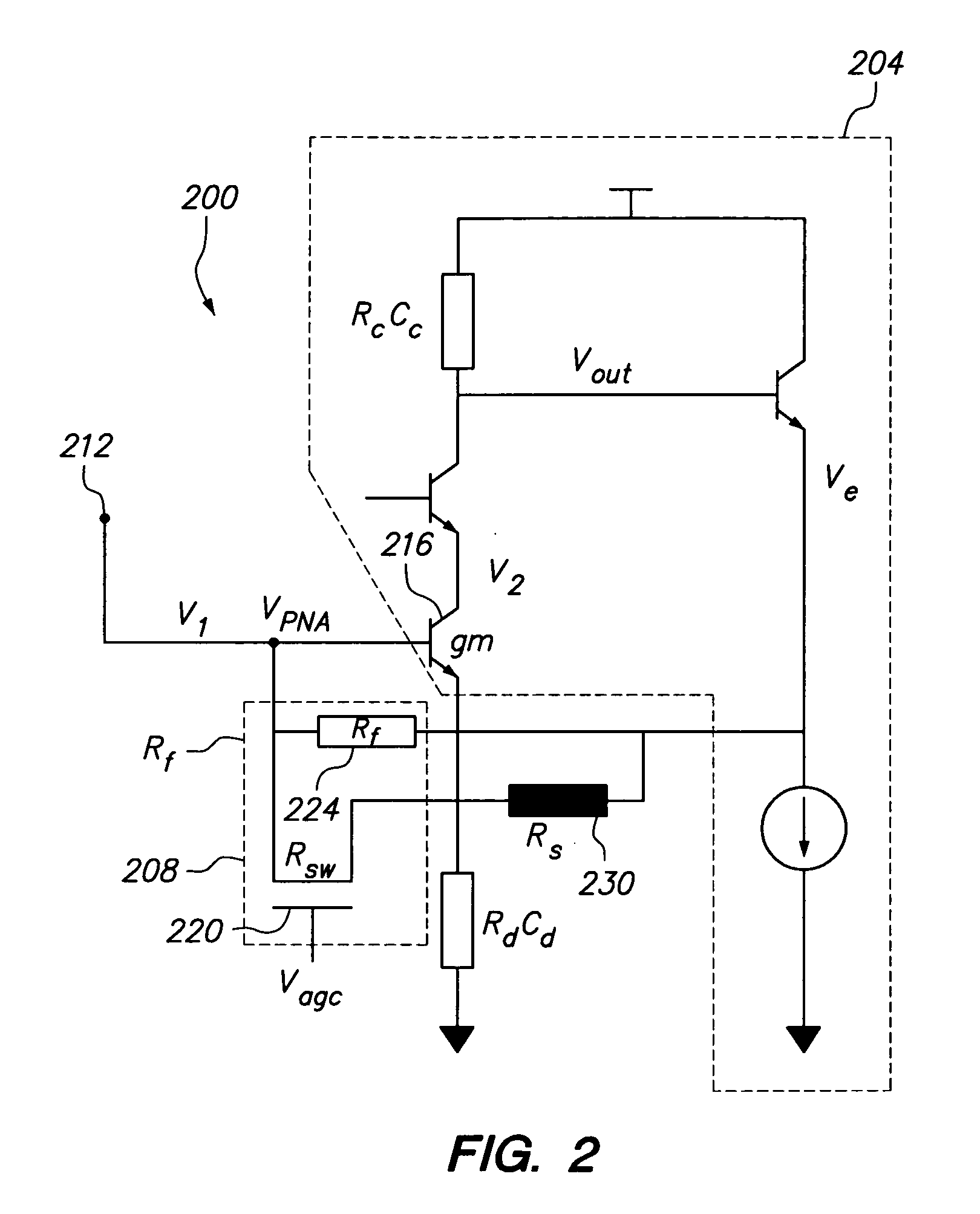
ActiveUS20100283542A1Improved performance characteristicsReduce impactNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsGain controlHigh rateAudio power amplifier
Various amplifier configurations having increased bandwidth, linearity, dynamic range, and less distortion are shown and disclosed. To increase bandwidth in a transimpedance amplifier, a replica circuit is created to replicate a degeneration resistance, or the resistance or value that relates to a feedback resistance. From the replica circuit, the replicated values are mirrored and processed to control a FET switch which modifies a degeneration resistance. The FET switch control signal is related to the feedback resistance and modifies the degeneration resistance to thereby maintain the product of the feedback resistance and the degeneration resistance as a constant. In another embodiment, a second switch controlled by an automatic gain control signal is established between a first stage amplifier and a second stage amplifier to improve dynamic range and bandwidth without degrading other amplifier specifications.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
Linearization systems and methods for variable attenuators
ActiveUS20110285481A1Gain linearity can be improvedReduce resistance variationMultiple-port networksPulse automatic controlActive componentControl engineering
Systems and methods for provided for linearization systems and methods for variable attenuators. The variable attenuators can include series transistors along a main signal path from the input to output, as well as shunt transistors. A bootstrapping body bias circuit can be used with one or of the series transistors to allow the body of a connected transistor to swing responsive to a received RF input signal. As the RF signal increases and affects the gate-to-source voltage difference of a transistor, a bootstrapping body bias circuit can adaptively adjust the threshold voltage of the connected transistor and compensate the channel resistance variation resulting from gate-to-source voltage swing. The bootstrapping body bias circuit can be implemented using passive elements, active elements, or a combination thereof.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD +1
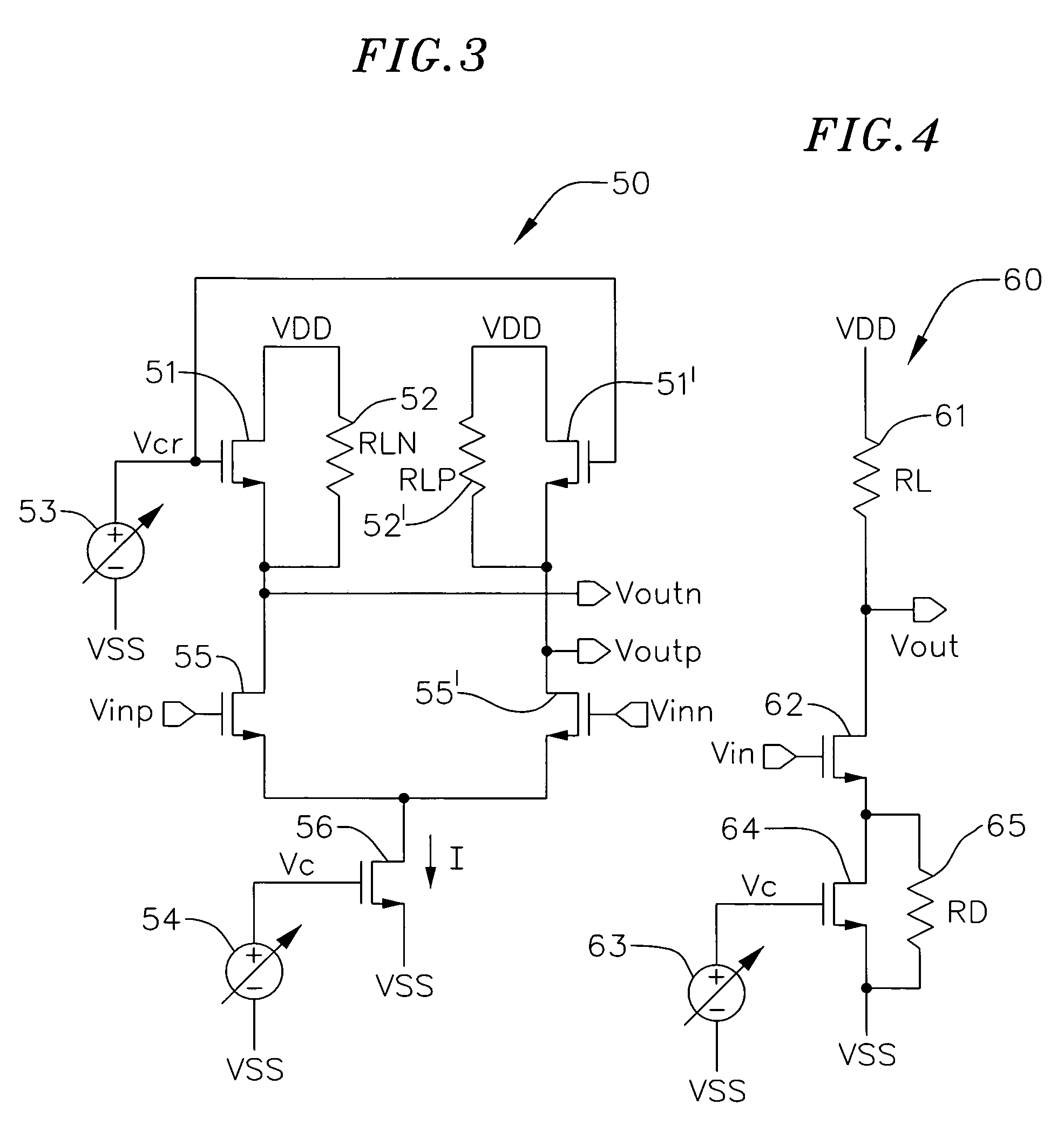
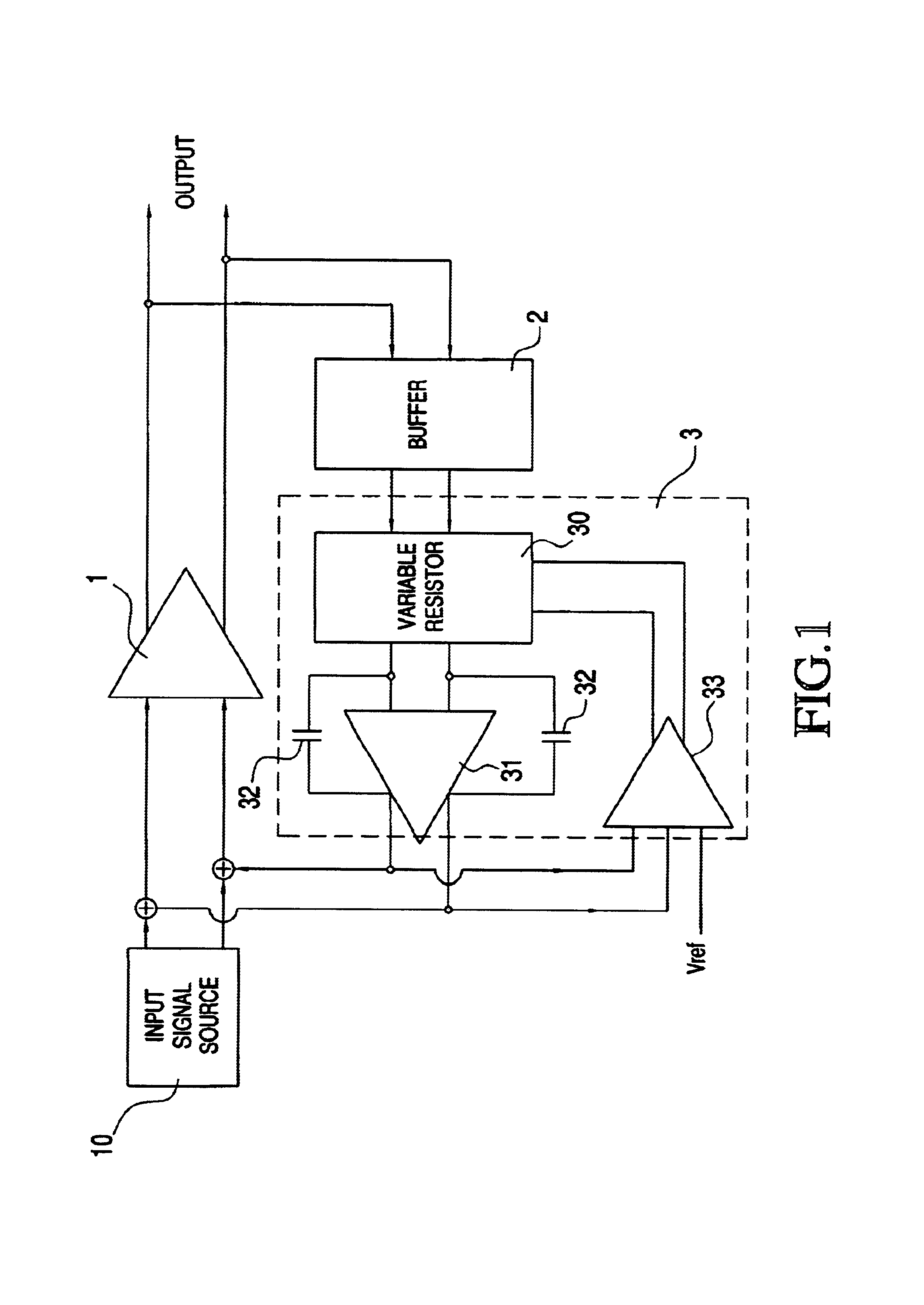
Process and temperature-independent voltage controlled attenuator and method
ActiveUS20080048751A1Pulse automatic controlAmplification control device circuitsElectrical conductorAudio power amplifier
A circuit includes a first variable resistor having a resistance which is variable in response to a resistance control signal. A resistance control circuit includes a first current source circuit for supplying a first current through a reference resistor. A second current source circuit supplies a second current through the first variable resistor. In operational amplifier has a first input coupled to a first conductor connecting the first current source to the reference resistor, a second input coupled to a second conductor connecting the current source to the first variable resistor, and an output applying the first resistance control signal to a control terminal of the first variable resistor, to force the resistance of the first variable resistor to be equal to a resistance of the reference resistor. The resistance of a second variable resistor of an attenuator is controlled in response to the resistance control signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System and method for ESD protection
InactiveUS20080174925A1Reduce areaReduce capacitanceContinuous tuning detailsPulse automatic controlCapacitanceShunt Device
An integrated receiver with channel selection and image rejection substantially implemented on a single CMOS integrated circuit is described. A receiver front end provides programmable attenuation and a programmable gain low noise amplifier. Frequency conversion circuitry advantageously uses LC filters integrated onto the substrate in conjunction with image reject mixers to provide sufficient image frequency rejection. Filter tuning and inductor Q compensation over temperature are performed on chip. The filters utilize multi track spiral inductors. The filters are tuned using local oscillators to tune a substitute filter, and frequency scaling during filter component values to those of the filter being tuned. In conjunction with filtering, frequency planning provides additional image rejection. The advantageous choice of local oscillator signal generation methods on chip is by PLL out of band local oscillation and by direct synthesis for in band local oscillator. The VCOs in the PLLs are centered using a control circuit to center the tuning capacitance range. A differential crystal oscillator is advantageously used as a frequency reference. Differential signal transmission is advantageously used throughout the receiver. ESD protection is provided by a pad ring and ESD clamping structure that maintains signal integrity. Also provided are shunts at each pin to discharge ESD build up. The shunts utilize a gate boosting structure to provide sufficient small signal RF performance, and minimal parasitic loading.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
High frequency power amplifier circuit and electronic component for high frequency power amplifier
ActiveUS20080068086A1Avoid short channel effectsReduce widthGain controlAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationChannel length modulationHigh frequency power
In a high frequency power amplifier circuit that supplies a bias to an amplifying FET by a current mirror method, scattering of a threshold voltage Vth due to the scattering of the channel impurity concentration of the FET, and a shift of a bias point caused by the scattering of the threshold voltage Vth and a channel length modulation coefficient λ due to a short channel effect are corrected automatically. The scattering of a high frequency power amplifying characteristic can be reduced as a result.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
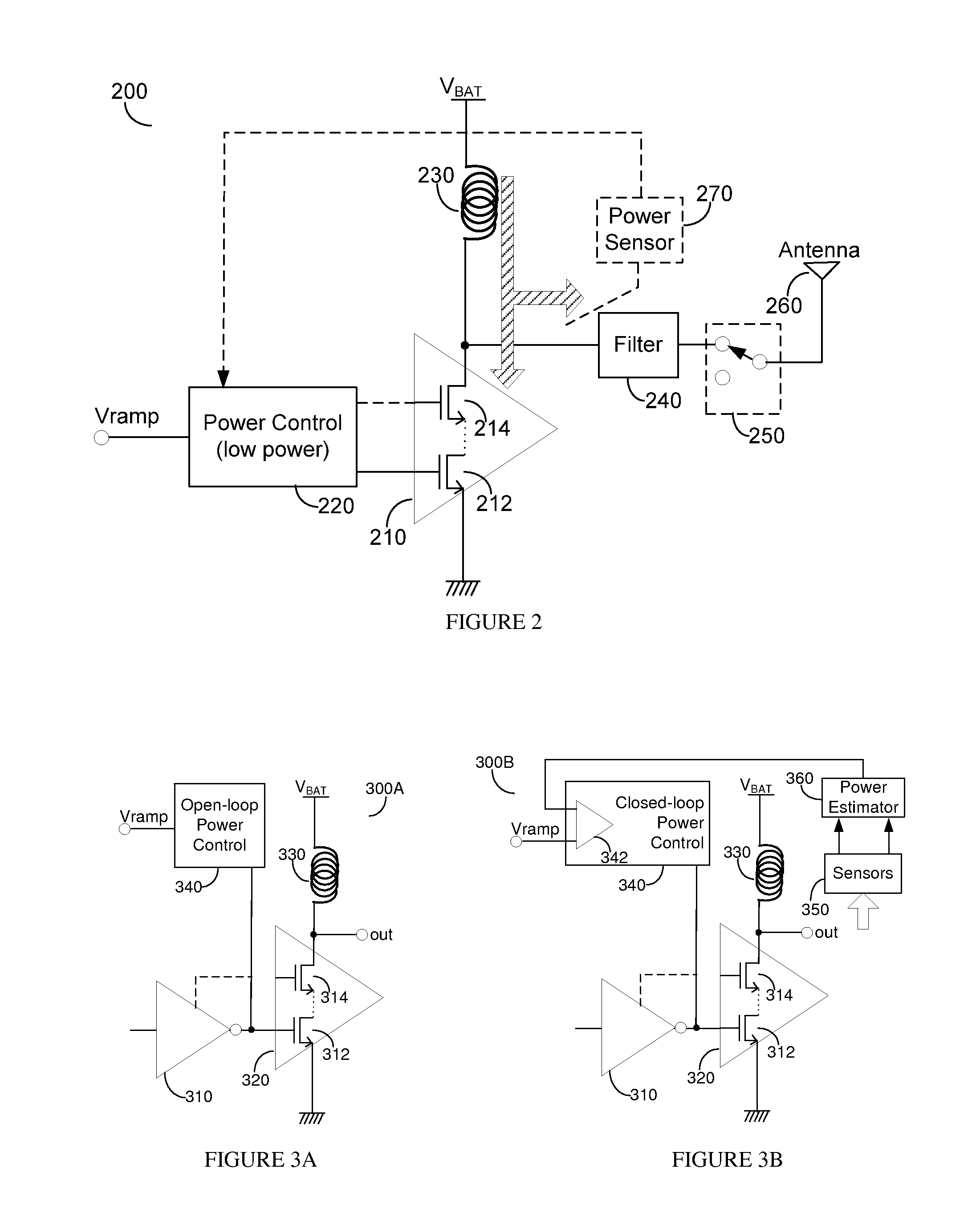
Gate-Based Output Power Level Control Power Amplifier
ActiveUS20120139635A1Gain controlAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesControl powerAudio power amplifier
A gate power control technique for a power amplifier (PA) provides practical improved efficiency at backed-off power levels. It can be applied to the main gate of the output stage of the PA, the cascode gate, or any combination thereof. Both voltage mode and current mode signal processing may be used. The gate power control can be implemented in both open-loop and closed-loop using AC and DC coupled drivers and output stages. It may further use one or more control ports in the radio frequency (RF) signal path.
Owner:QORVO INT PTE LTD
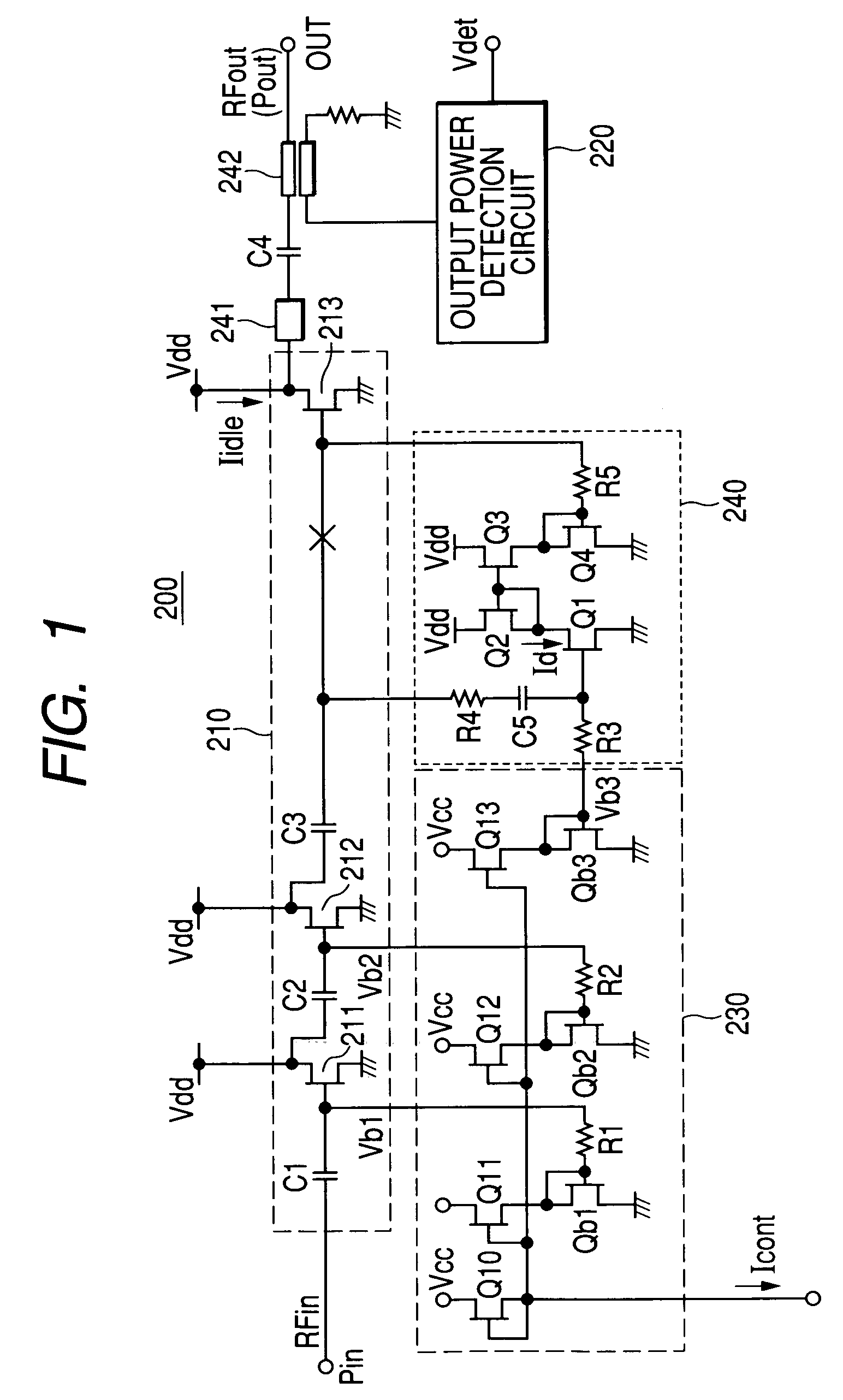
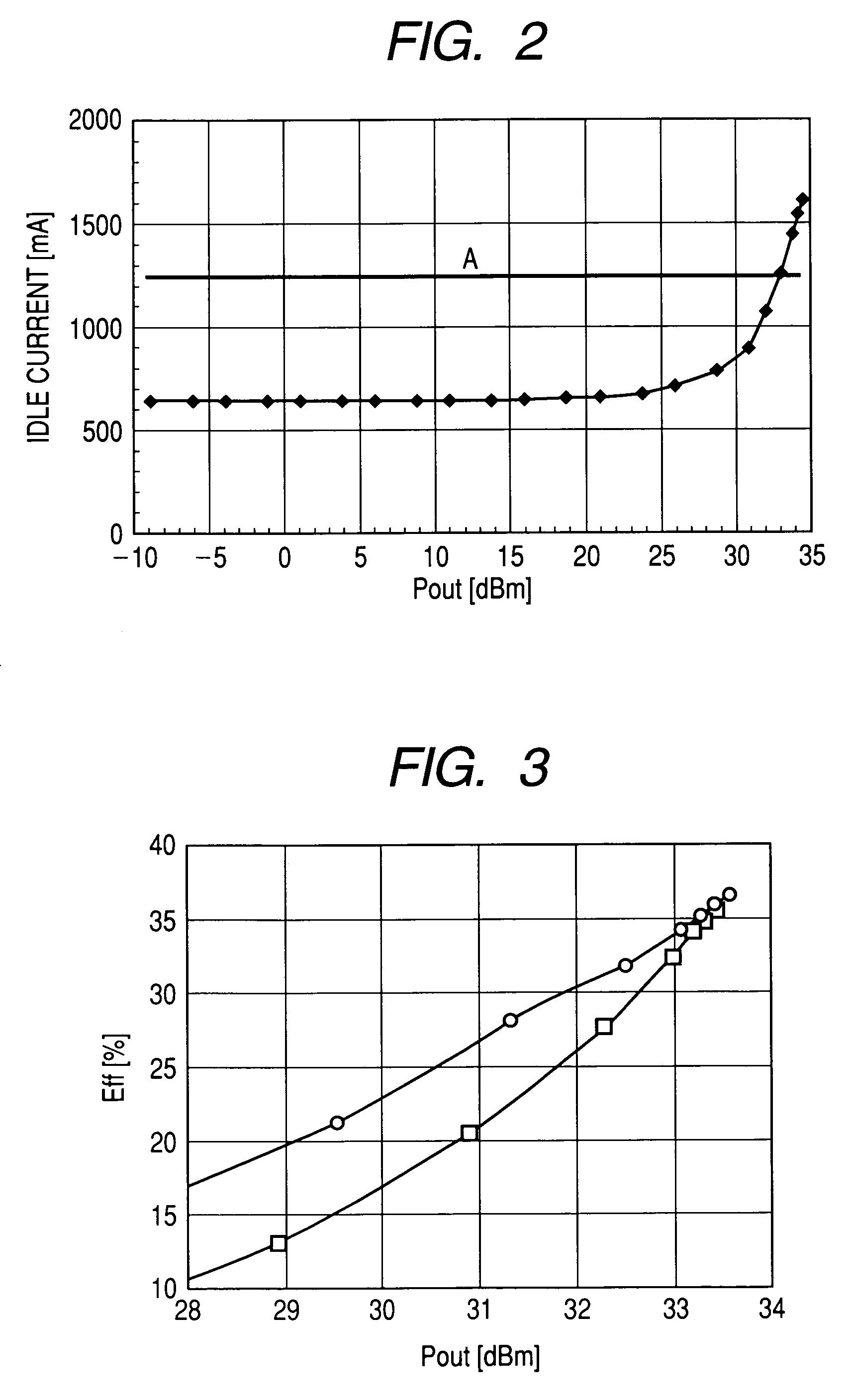
High frequency power amplifier circuit and electric component for high frequency power amplifier
ActiveUS7271662B2Prevent Waveform DistortionImprove power efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationHigh frequency powerAudio power amplifier
In a high frequency power amplifier circuit in which bias voltages are applied to the transistors for amplification by current mirroring, this invention enables preventing waveform distortion near the peak output power level by allowing sufficient idle currents to flow through the transistors for amplification, while enhancing the power efficiency in a low output power region. The power amplifier includes a detection circuit comprising a transistor for detection which receives the AC component of an input signal to the last-stage transistor for amplification at its control terminal, a current mirror circuit which mirrors current flowing through that transistor, and a current-voltage conversion means which converts current flowing in the slave side of the current mirror circuit into a voltage. In the detection circuit, a voltage from a bias circuit for generating the bias voltages for the transistors for amplification is applied to the control terminal of the transistor for detection and output of the detection circuit is applied to the control terminal of the last-stage transistor for amplification.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Variable-gain low noise amplifier
InactiveUS20110095822A1Gain controlAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceLoad circuitElectrical resistance and conductance
A highly linear variable-gain low noise amplifier is a cascode amplifier. The cascode amplifier includes a gain control circuit, a load circuit, a current steering circuit and an input circuit. The gain control circuit is used for receiving a gain adjusting voltage, thereby generating a resistance adjusting signal and a current steering control signal. The load circuit includes plural variable resistors. The resistances of the variable resistors are adjusted according to the resistance adjusting signal. The current steering circuit is connected to the load circuit through plural current paths for adjusting a current ratio between the plural current paths according to the current steering control signal. The current steering circuit has differential signal output terminals. The input circuit is connected to the current steering circuit. The input circuit has differential signal input terminals.
Owner:SUNPLUS TECH CO LTD
Controllable amplifier and the use thereof
InactiveUS20060202760A1Reduce voltageLarge signal to noise ratioAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierSignal on
A controllable amplifier amplifies a radiofrequency input signal on the basis of a control signal. A current path is formed between a supply potential connection and a reference potential connection. The current path includes an amplifier transistor and a cascode transistor, the cascode transistor being connected to the input for supplying the control signal. The output power of the amplifier is controlled using the cascode transistor, as a result of which a low power consumption is achieved in conjunction with good noise properties.
Owner:INTEL MOBILE COMM GMBH
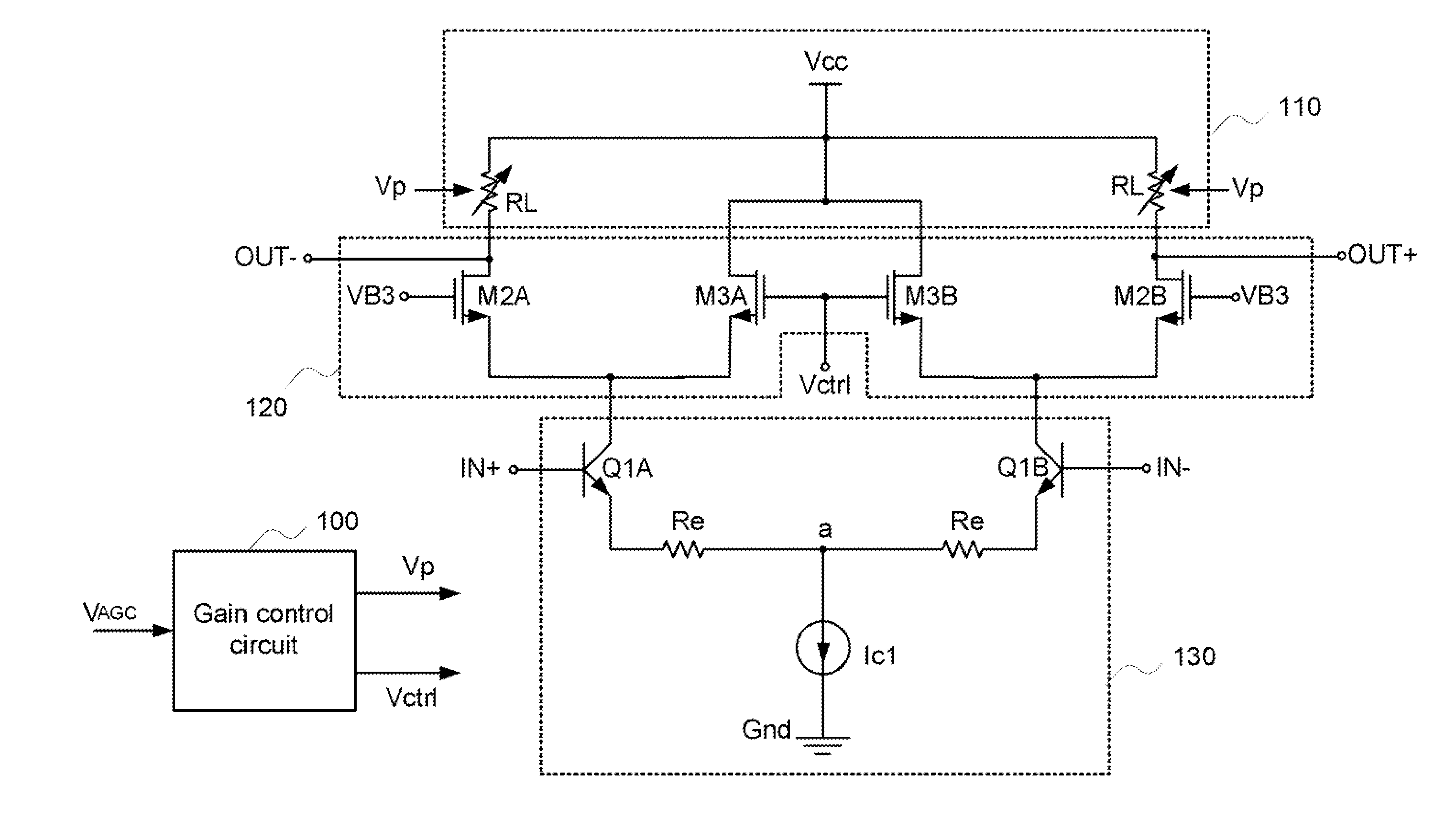
Variable gain amplifier, mixer and quadrature modulator using the same
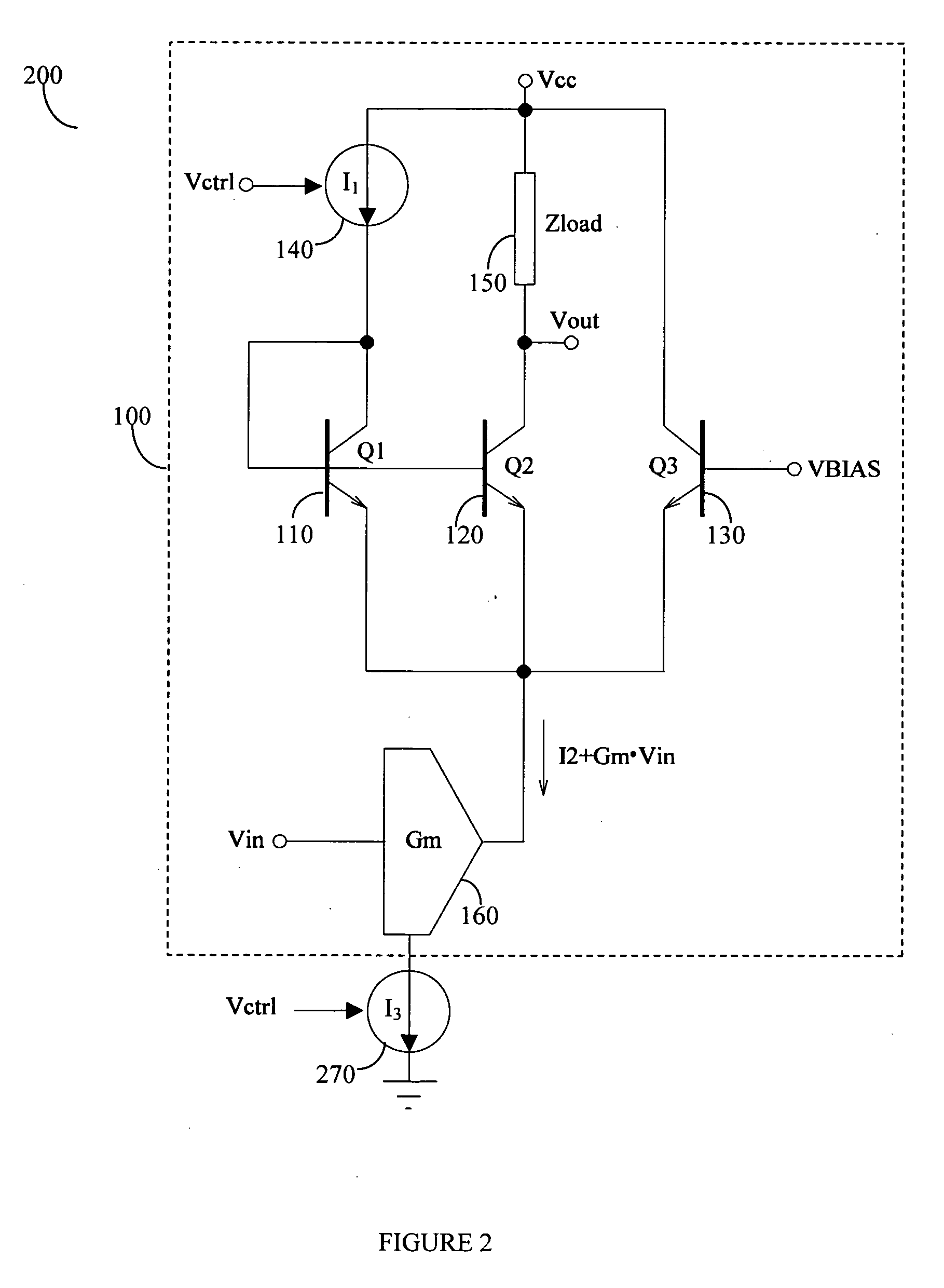
InactiveUS20060220743A1Low dissipation powerReduce distortion problemsGain controlAmplification control device circuitsVoltage converterQuadrature modulator
A variable gain amplifier includes a voltage-to-current converter for converting the input voltage to a current, a current amplifier for amplifying the current converted by the voltage-to-current converter, a current-to-voltage converter for converting the current amplified by the current amplifier into a voltage, and a controller for controlling an amplification factor of the current amplifier.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Process and temperature-independent voltage controlled attenuator and method
ActiveUS7521980B2Multiple-port networksPulse automatic controlElectrical conductorAudio power amplifier
A circuit includes a first variable resistor having a resistance which is variable in response to a resistance control signal. A resistance control circuit includes a first current source circuit for supplying a first current through a reference resistor. A second current source circuit supplies a second current through the first variable resistor. In operational amplifier has a first input coupled to a first conductor connecting the first current source to the reference resistor, a second input coupled to a second conductor connecting the current source to the first variable resistor, and an output applying the first resistance control signal to a control terminal of the first variable resistor, to force the resistance of the first variable resistor to be equal to a resistance of the reference resistor. The resistance of a second variable resistor of an attenuator is controlled in response to the resistance control signal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Gate-based output power level control power amplifier
Owner:QORVO INT PTE LTD
Linear-in-dB variable gain amplifiers with an adaptive bias current
ActiveUS20060132237A1Amplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationGain controlAdaptive biasAudio power amplifier
Linear-in-dB current-steering VGAs with an adaptive bias current operable so that as the gain of the amplifier decreases, the DC current consumption also decreases. The modified VGA circuits result in power consumption savings, which are of particular value in wireless (battery powered) applications.
Owner:THETA IP
Wideband variable gain amplifier with high linearity operating in switch mode
ActiveUS6919761B2Improve linearityEasy to operateGain controlAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesVariable-gain amplifierAudio power amplifier
Disclosed is a wideband variable gain amplifier with high linearity that operates in a switch mode. The variable gain amplifier includes a first amplifier unit, a second amplifier unit and a third amplifier unit. The first amplifier unit includes an amplifier, a wideband-matching element, an attenuator and first switching means. The first amplifier unit supports a high gain mode operation and a low gain mode operation. In the high gain mode, the first switching means is short-circuited and an input signal is amplified with a high gain. It is thus possible to reduce noise characteristics of the entire system by a rear stage. In the low gain mode, the first switching means is opened and the input signal is attenuated by the attenuator without an amplification operation. It is thus possible to reduce a non-linearity occurring by the rear stage of the first amplifier unit. According to another embodiment of the present invention, only the first amplifier unit can be independently used in order to amplify a signal. Furthermore, a variable gain amplifier can be implemented by connecting various combinations of the second amplifier unit and the third amplifier unit at the rear of the first amplifier unit.
Owner:INTEGRANT TECH
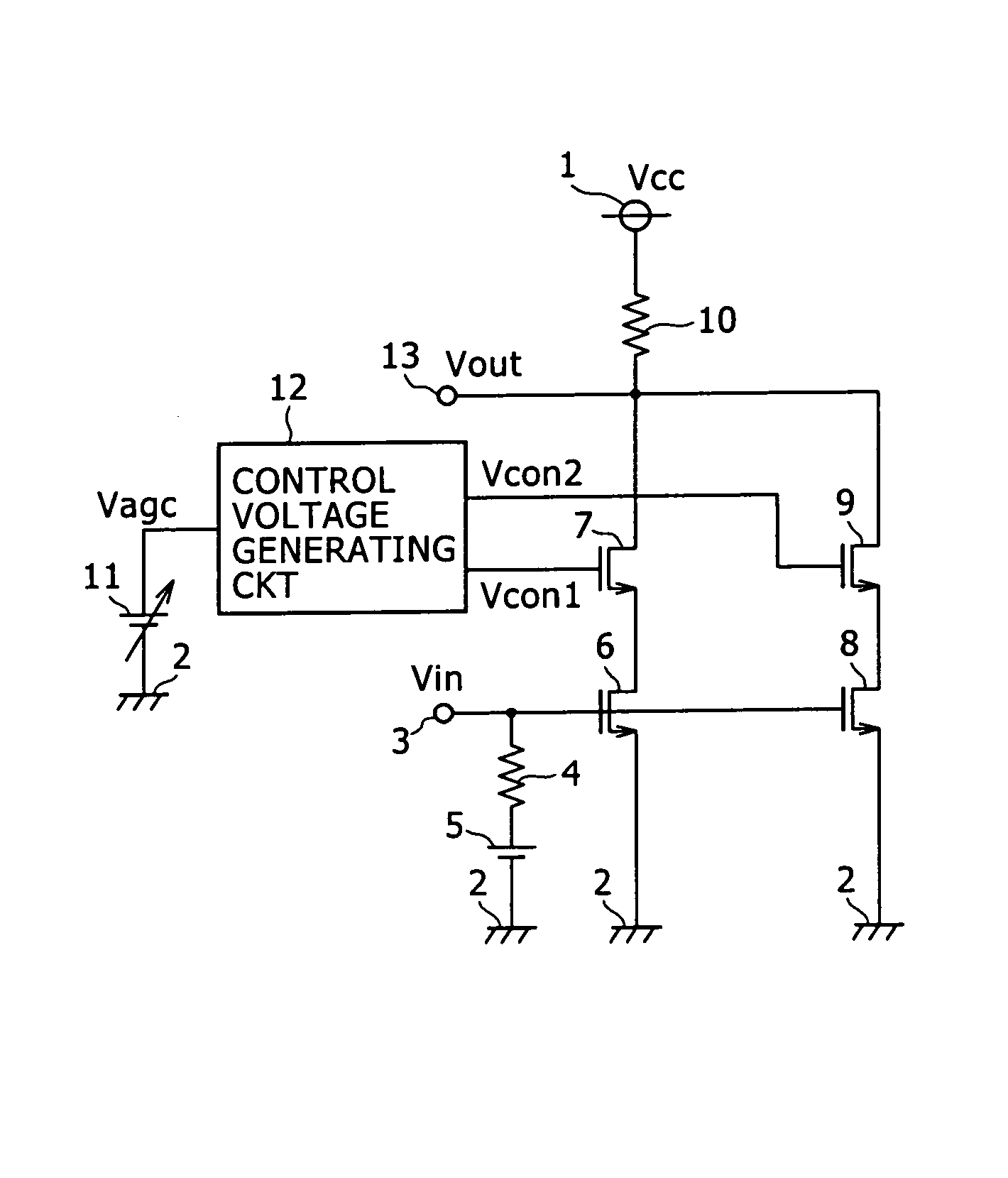
Variable-gain amplifier
InactiveUS7323937B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
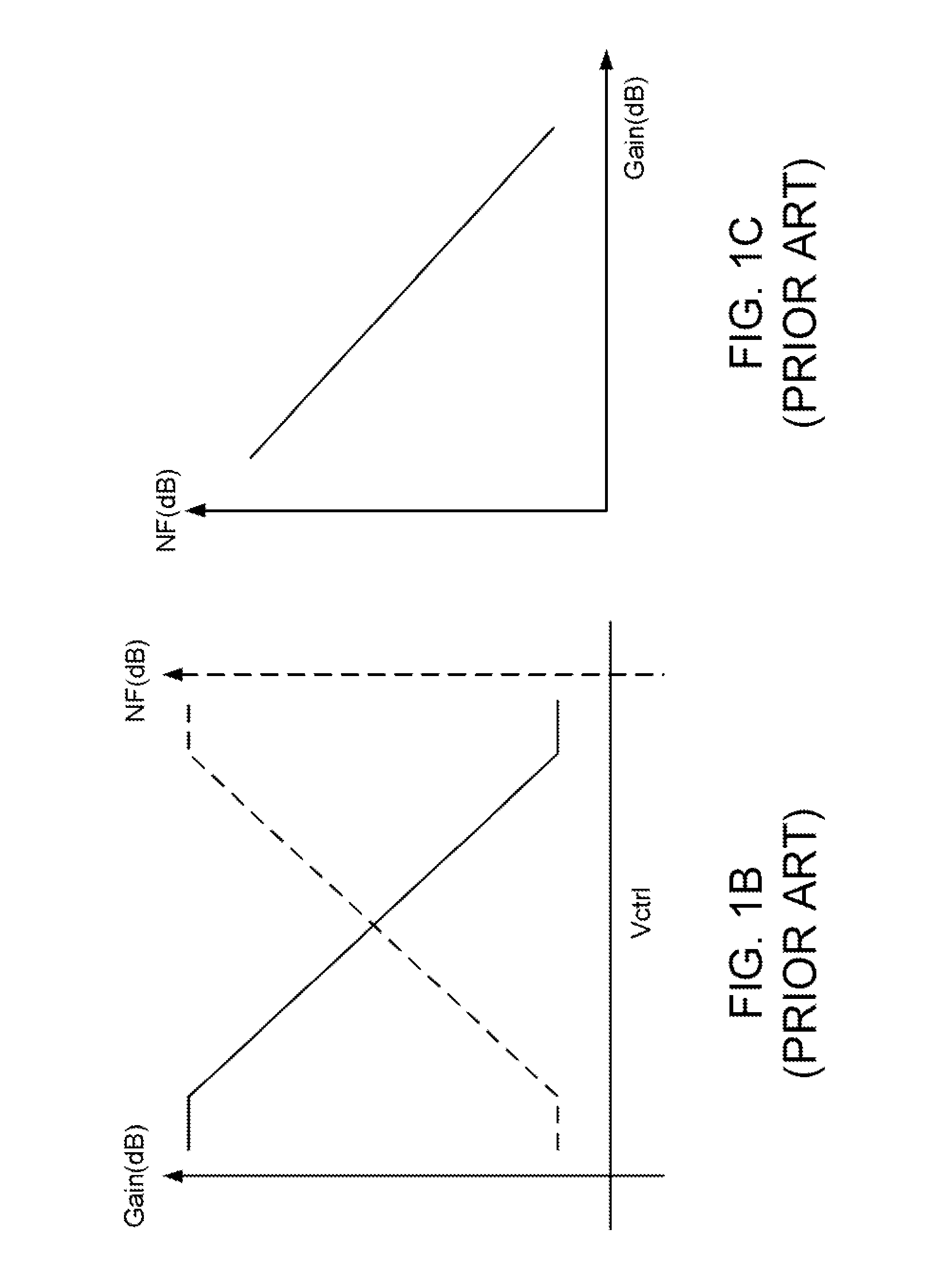
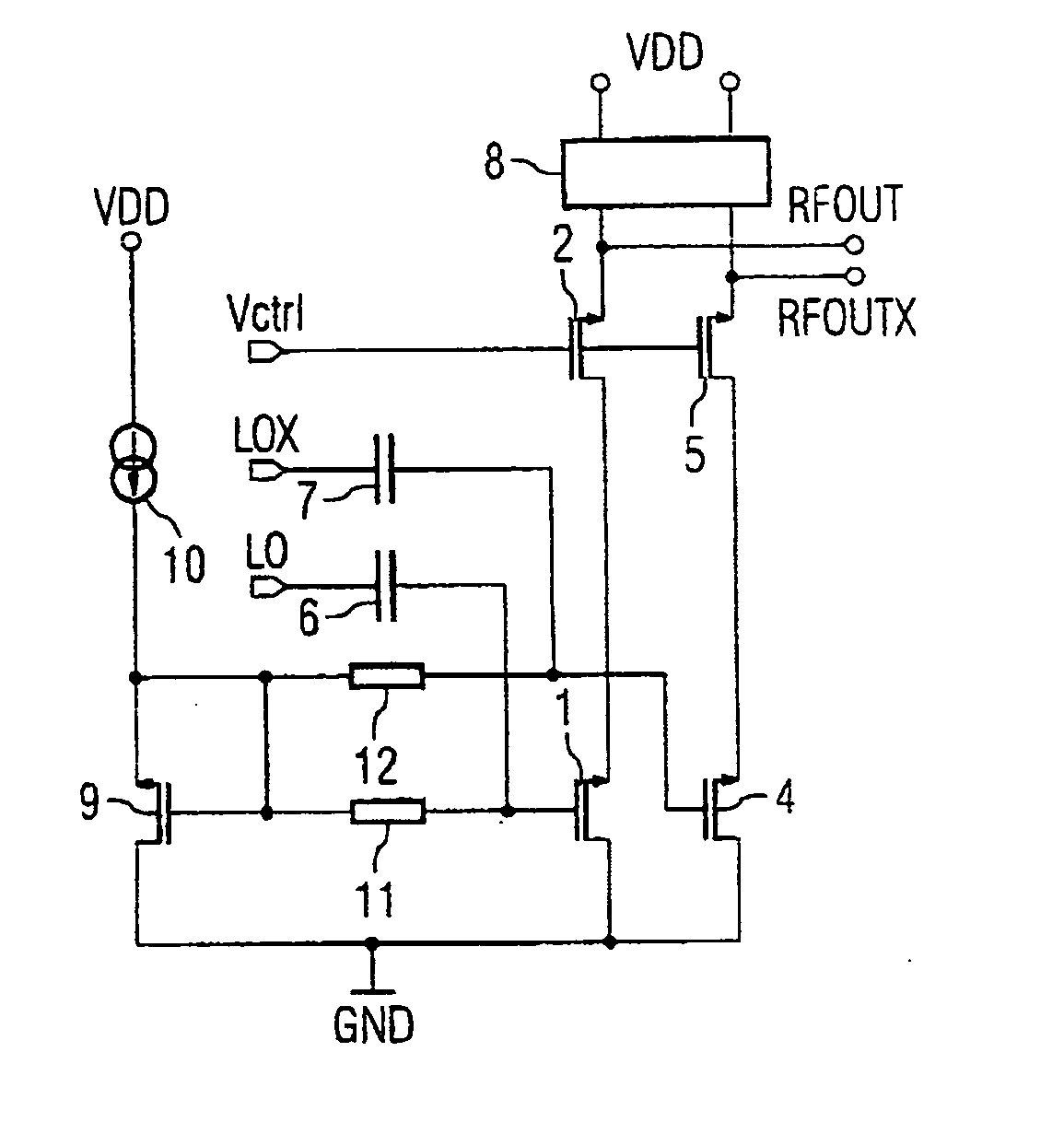
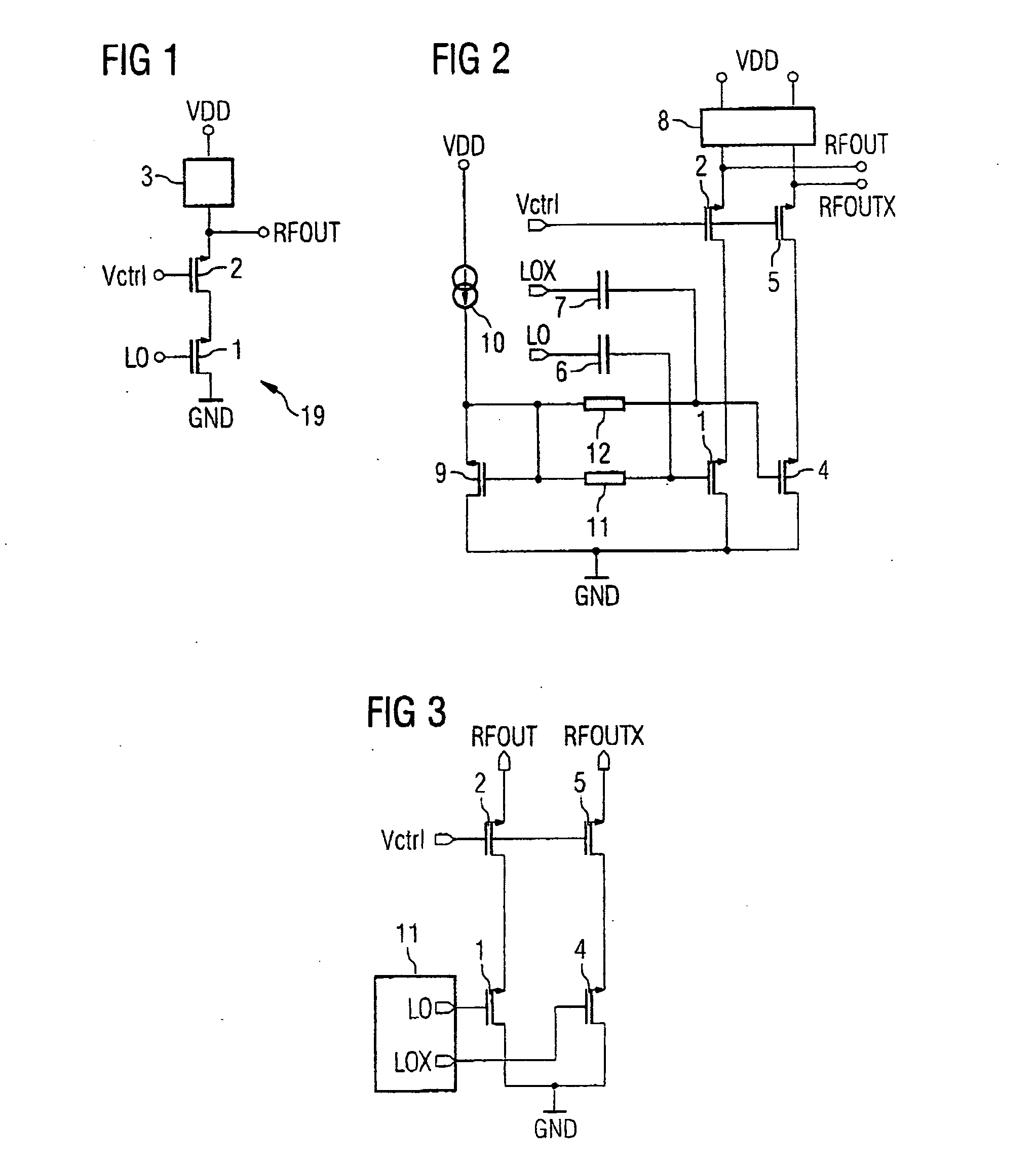
A variable-gain amplifier has distortion characteristics (IIP3) improved when the gain is attenuated without impairing characteristics with respect to a gain PG and a noise figure NF when the gain is maximum. The variable-gain amplifier has a plurality of parallel-connected dual-gate FETs having first FETs (6), (8) having gates for being supplied with an input signal and second FETs (7), (9) connected in cascade to the first FETs (6), (8), respectively. Gate control voltages (Vcon1, Vcon2) can separately be applied to the second FETs (7), (9), respectively, from voltage control means.
Owner:SONY CORP
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com