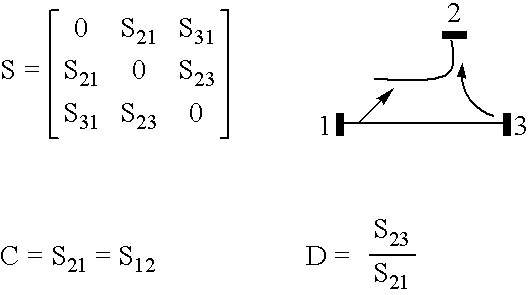Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
380results about "Ac/dc measuring bridges" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
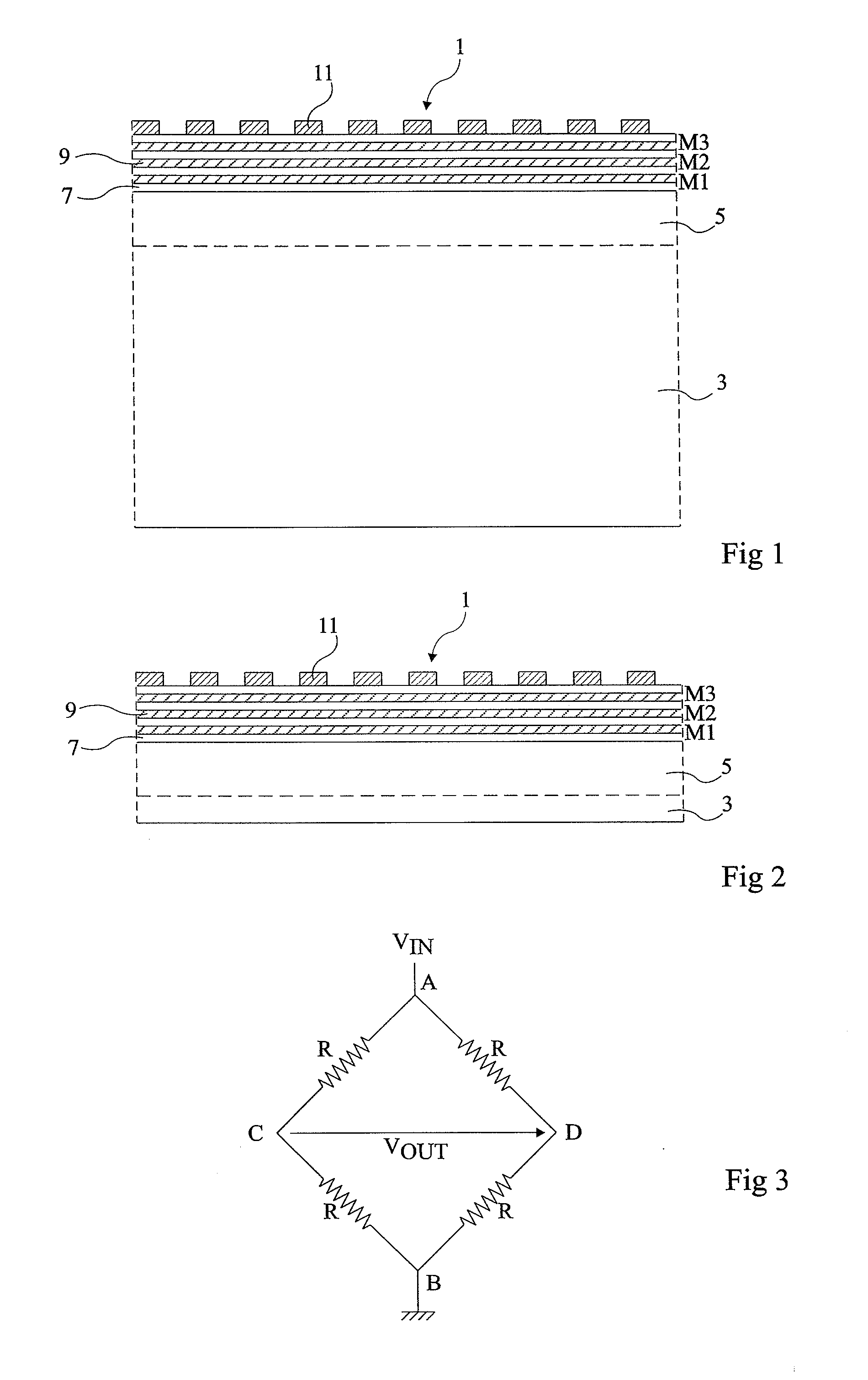
Reactive sensor modules using pade' approximant based compensation and providing module-sourced excitation
ActiveUS20050283330A1High precision measurementLow costSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsApparatus with stored calibration coefficientsEngineeringIntegrated circuit
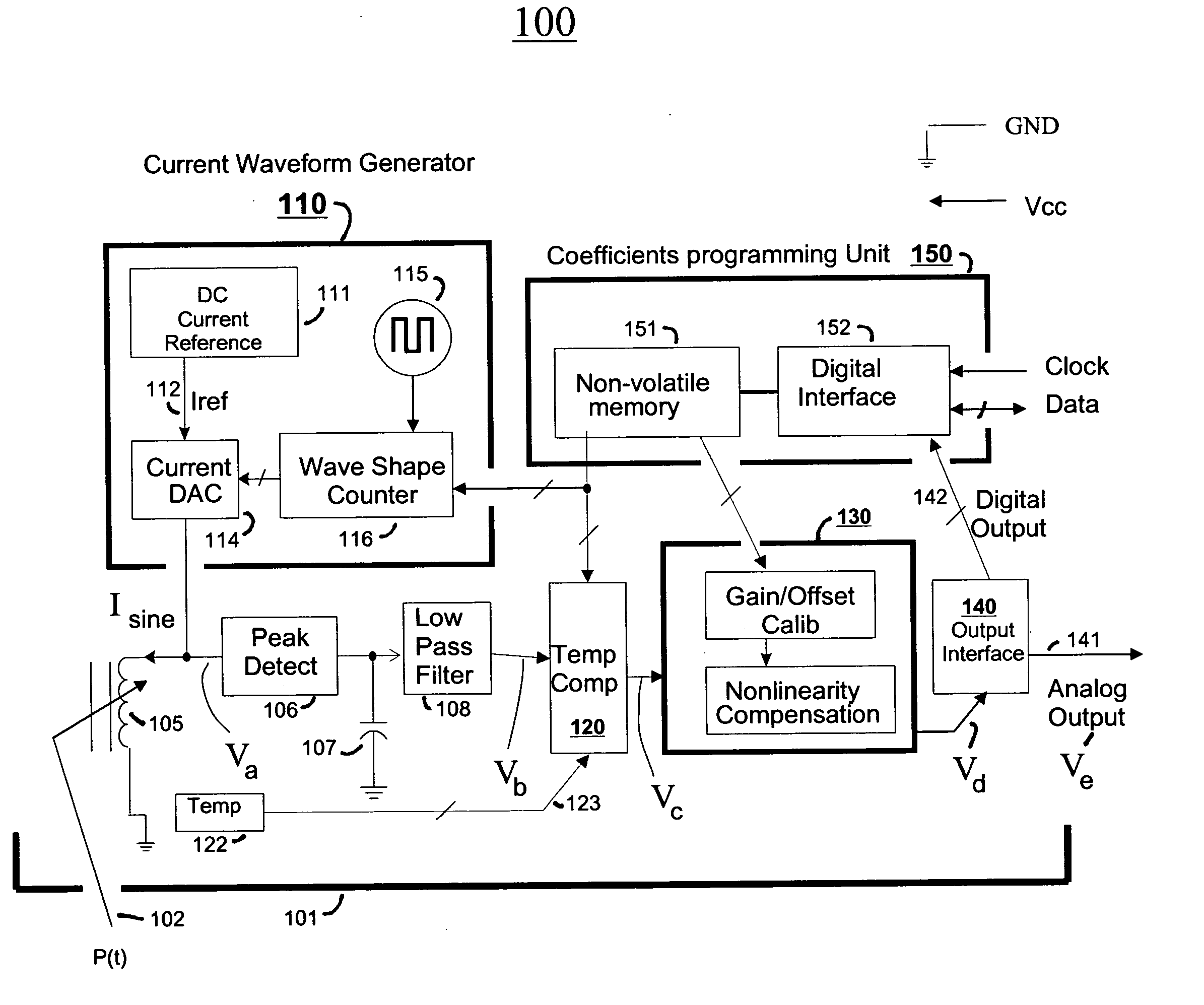
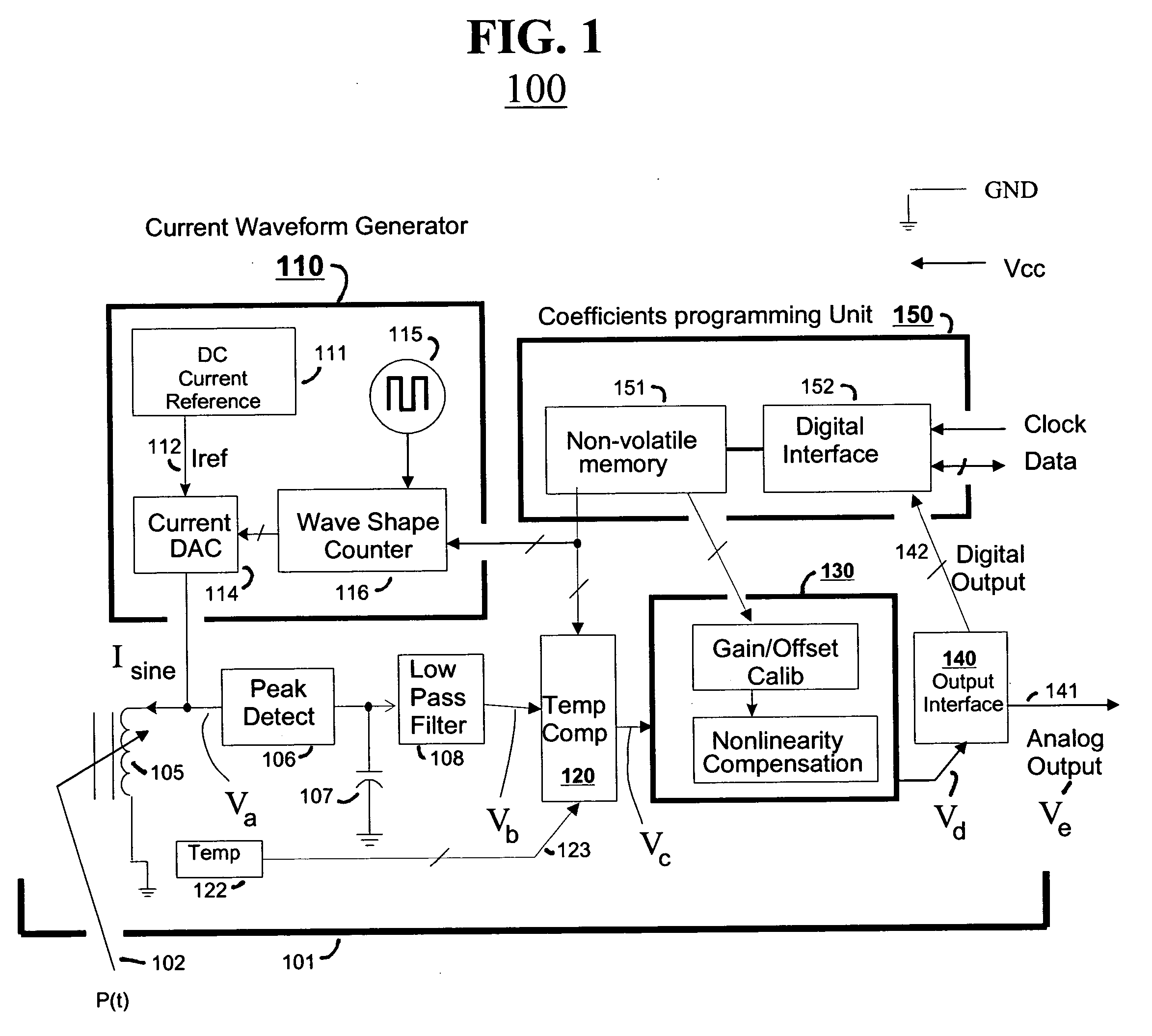
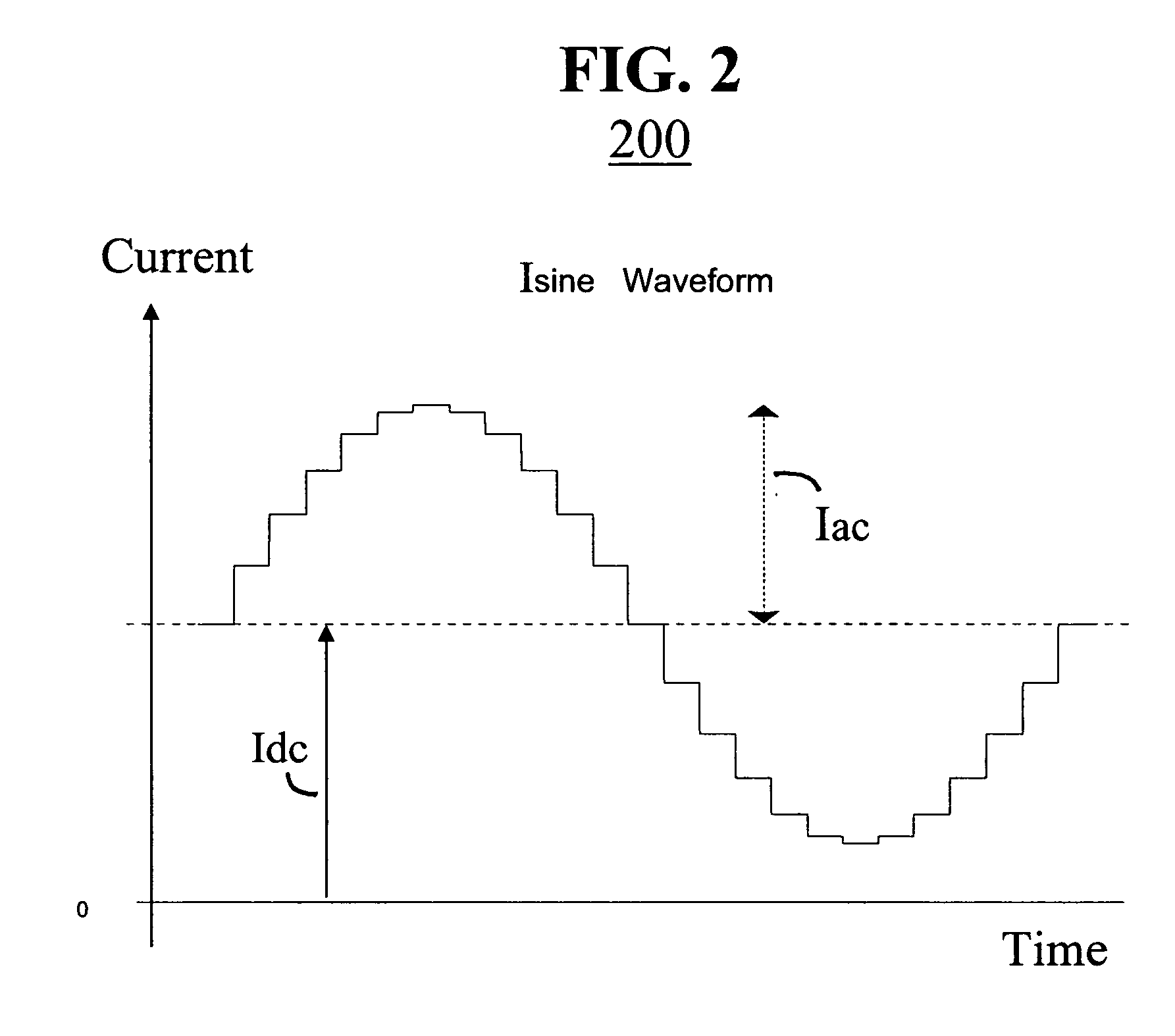
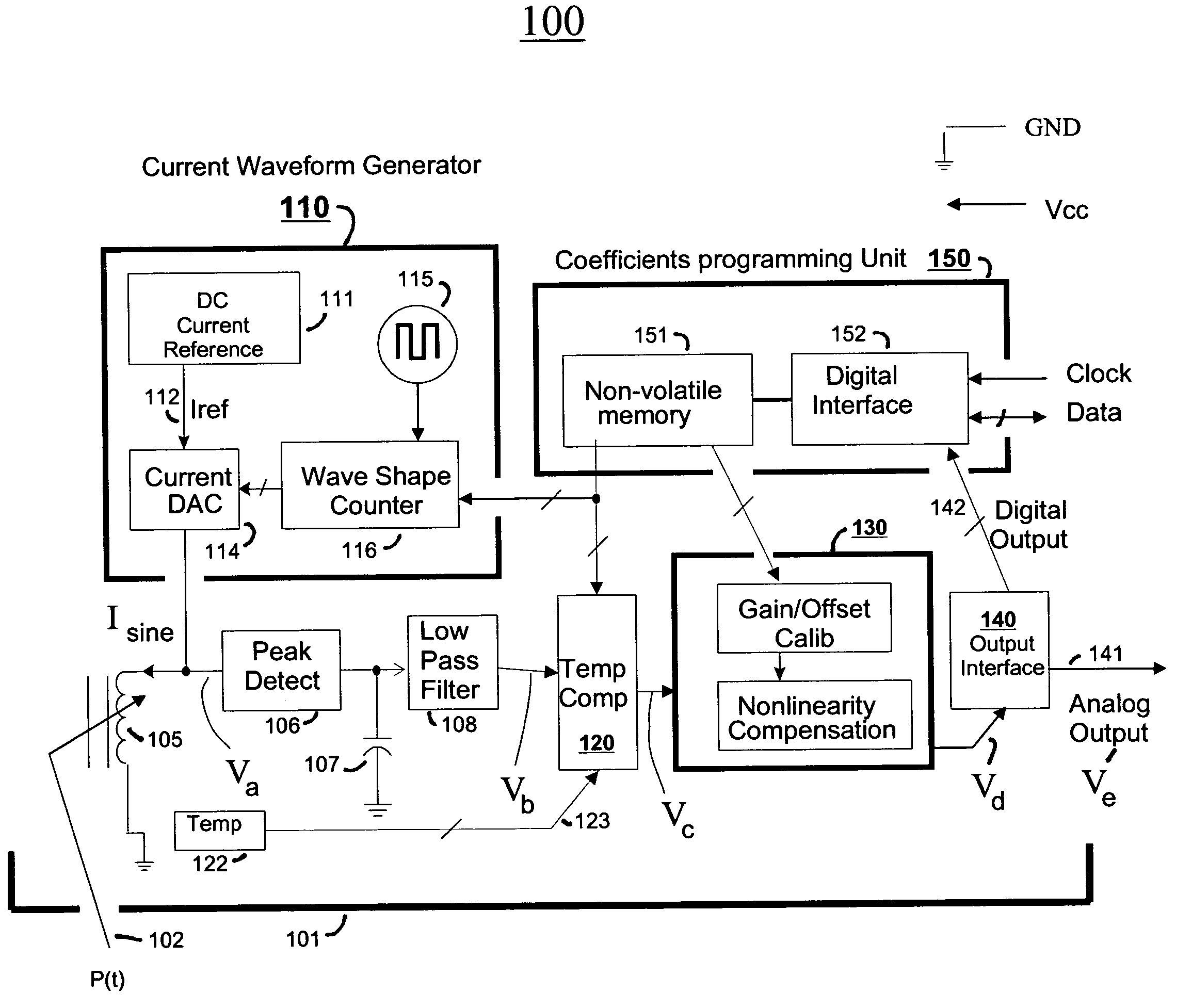
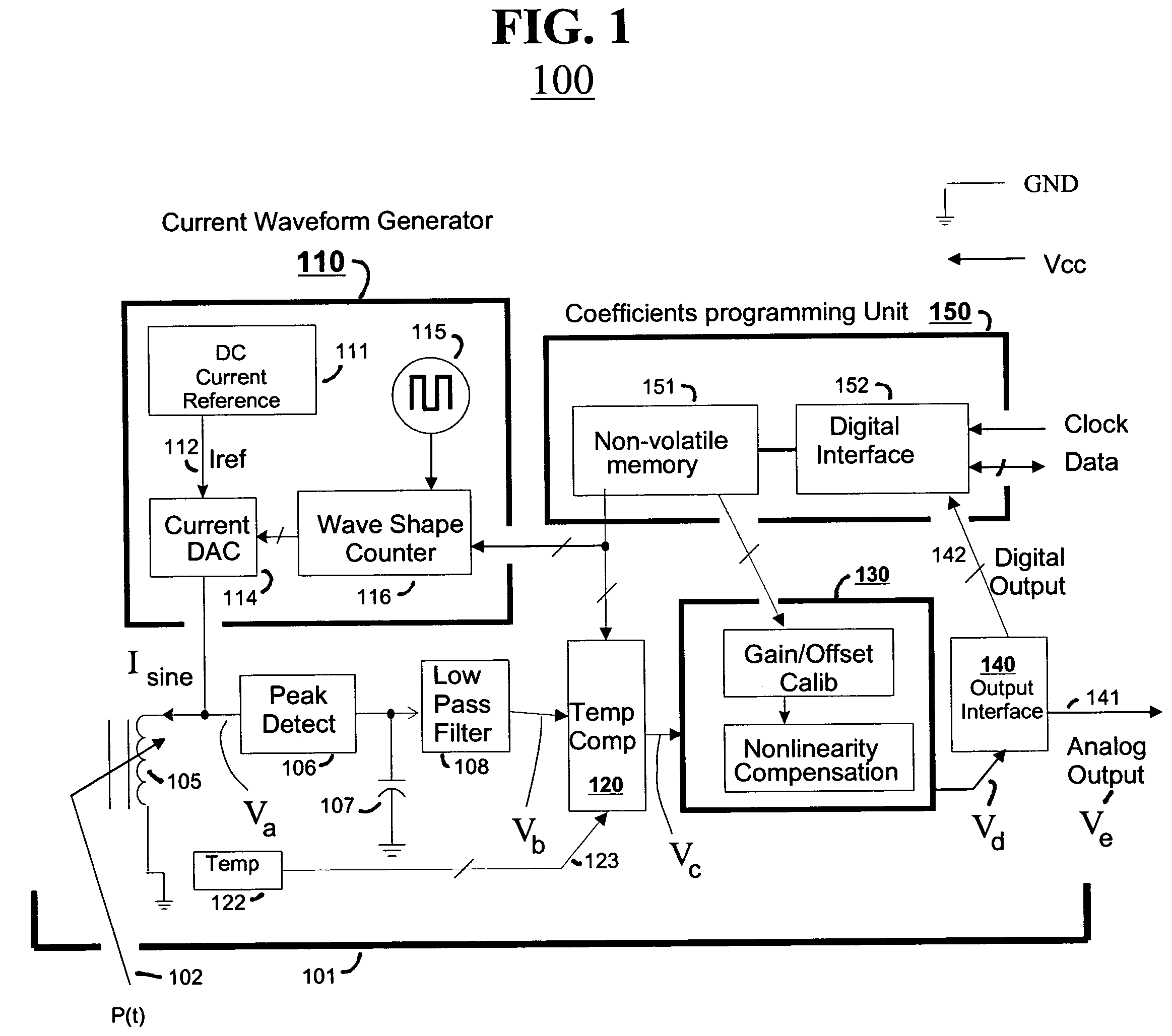
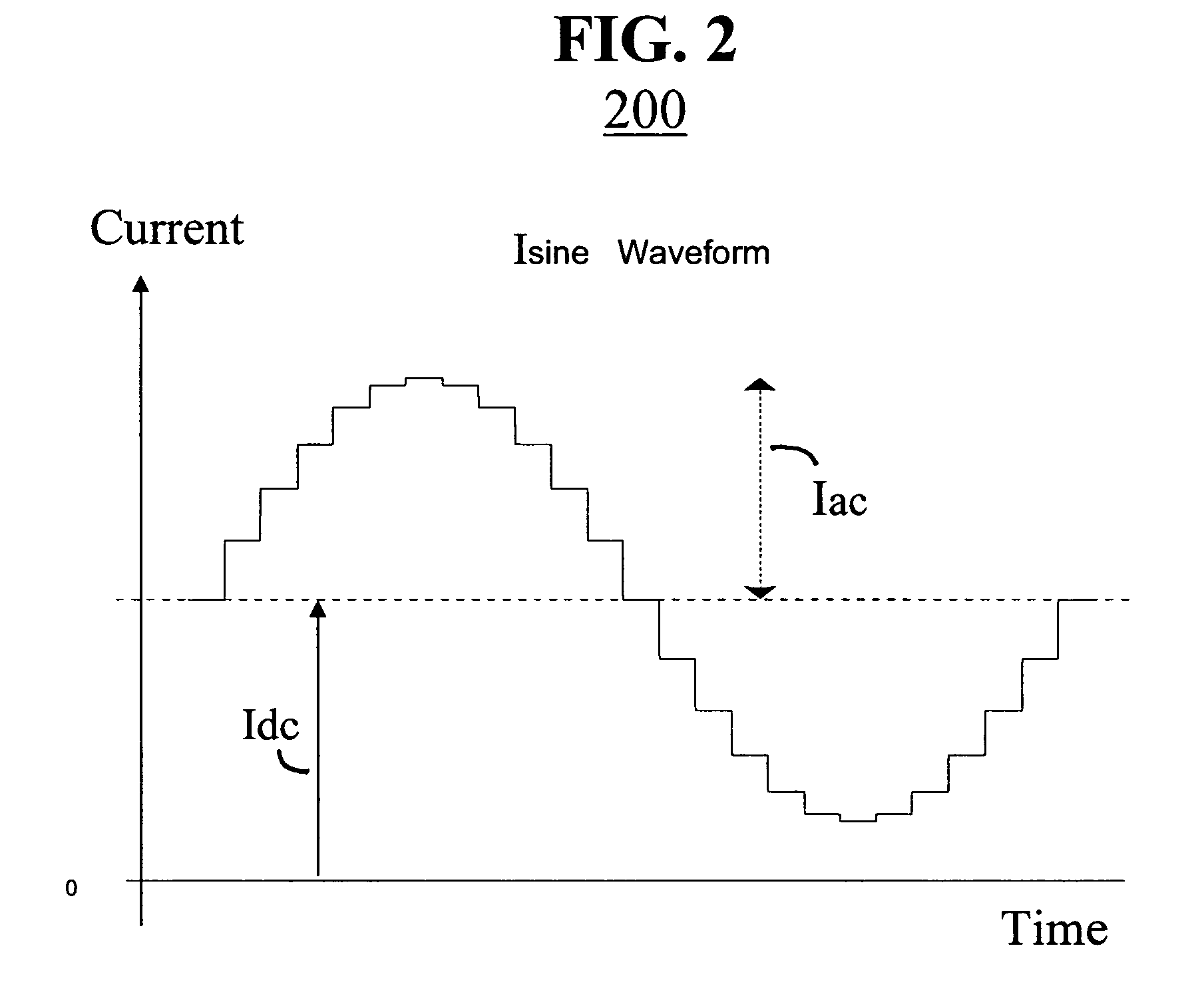
Reactive sensors typically exhibit nonlinear response to the combination of an excitational signal (e.g., sinusoidally oscillating signal) and a physical parameter under measure (e.g., position of magnetic core member). Such sensors are typically sensitive to temperature variation. Systems and methods are disclosed for compensating for the nonlinear and / or temperature dependant behavior of reactive sensors and for calibrating the post-compensation output signals relative to known samples of the physical parameter under measure (e.g., position). One class of embodiments comprises a housing containing at least part of a reactive sensor, a monolithic integrated circuit and a timing reference (e.g., an oscillator crystal). The integrated circuit includes a waveform generator for generating a sensor exciting signal, a detector for detecting the response of the sensor to the combination of the exciting signal and the under-measure physical parameter, a temperature compensating unit and a Pade' Approximant based, nonlinearity compensating unit. The temperature compensating unit and the Pade' Approximant nonlinearity compensating unit are tuned by use of digitally programmed coefficients. The coefficients calibrate the final output as well as compensating for nonlinearity and temperature sensitivity. A highly accurate measurement of the under-measure physical parameter is made possible even though each of the sensor and compensating circuitry may be relatively simple, compact, and low in cost.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC +1
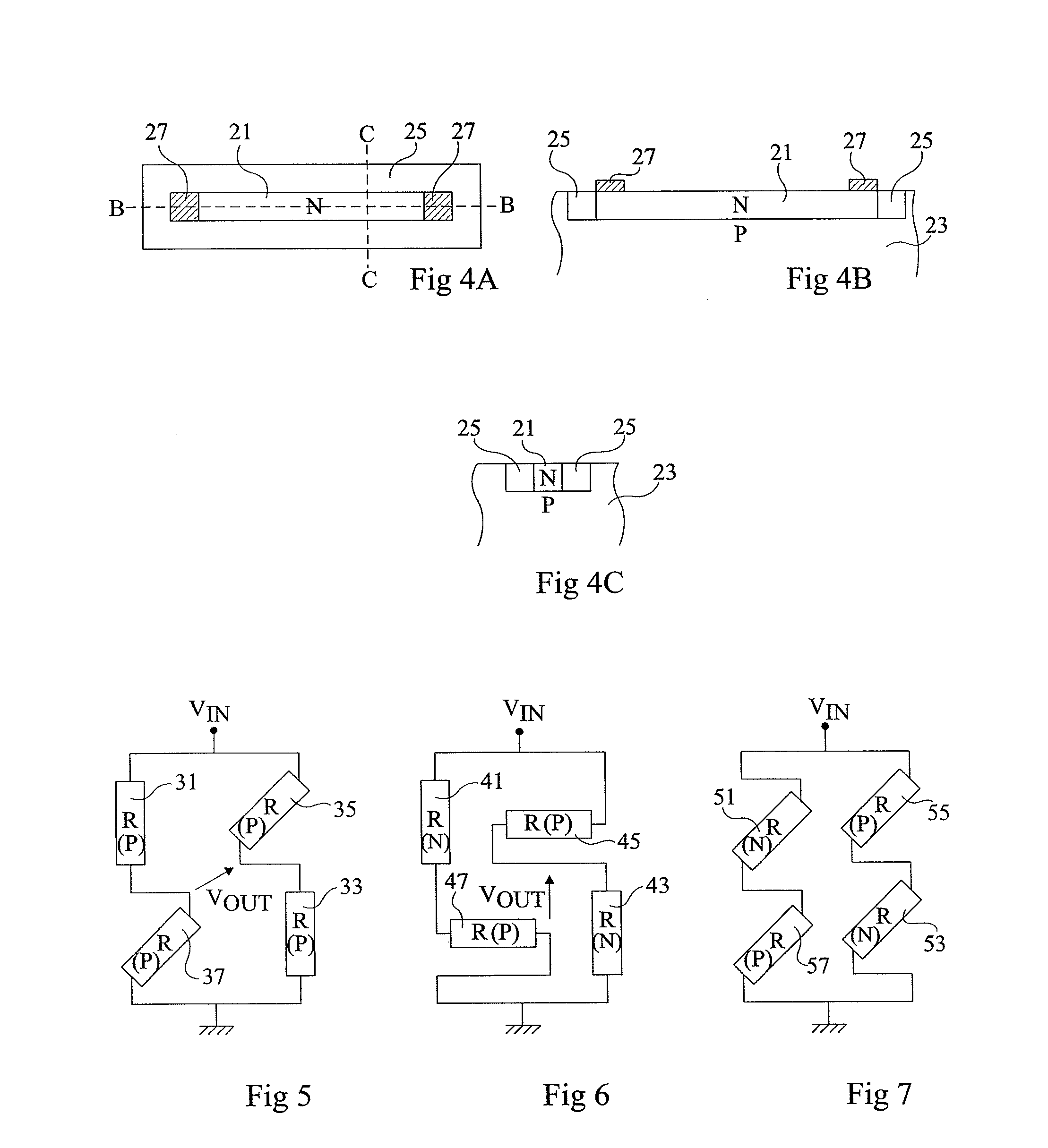
Cascode Current Sensor For Discrete Power Semiconductor Devices
InactiveUS20090039869A1Accurate detectionTransistorElectrical measurement instrument detailsMOSFETCascode
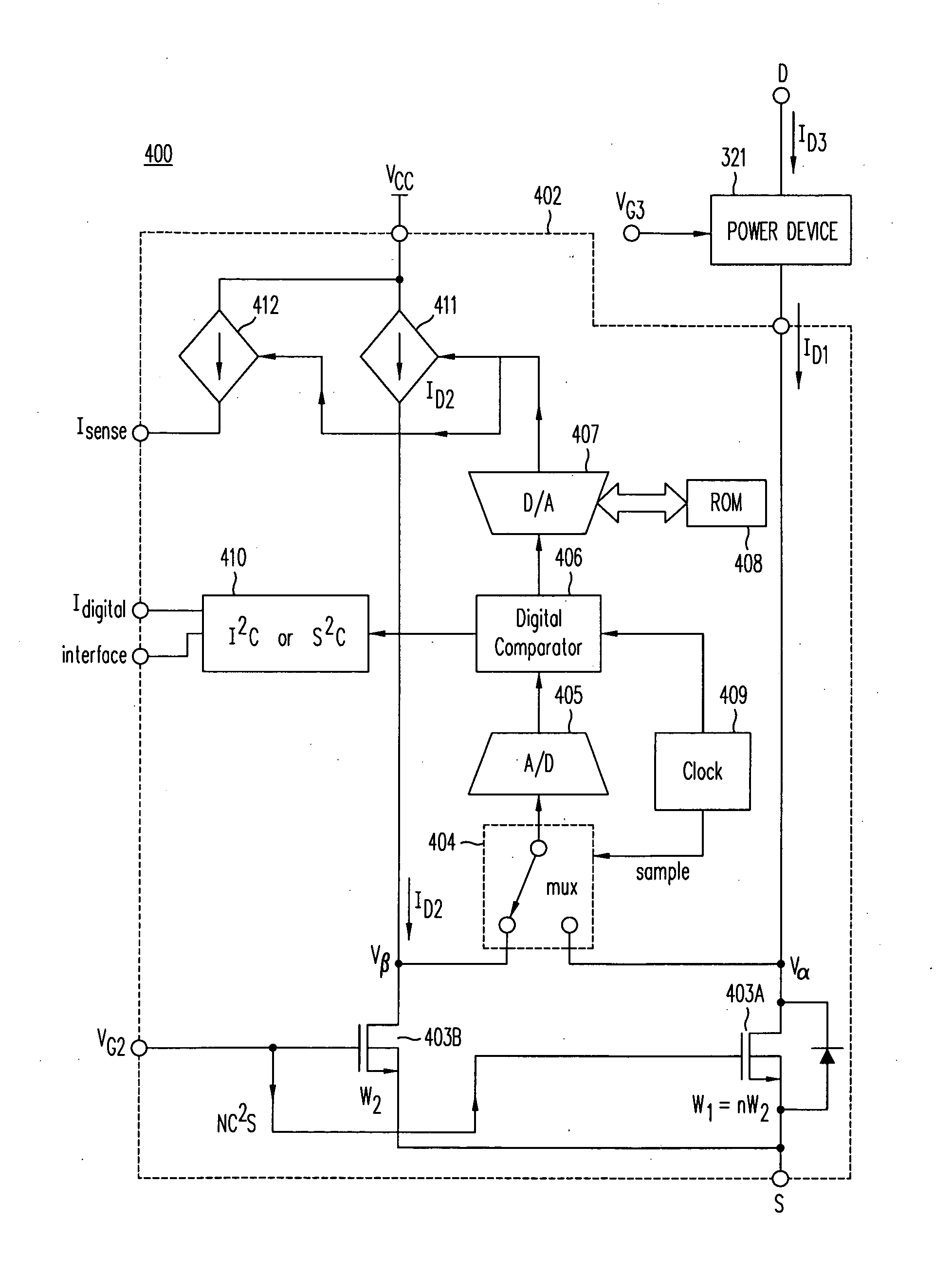
A cascode current sensor includes a main MOSFET and a sense MOSFET. The drain terminal of the main MOSFET is connected to a power device whose current is to be monitored, and the source and gate terminals of the main MOSFET are connected to the source and gate terminals, respectively, of the sense MOSFET. The drain voltages of the main and sense MOSFETs are equalized, in one embodiment by using a variable current source and negative feedback. The gate width of the main MOSFET is typically larger than the gate width of the sense MOSFET. Using the size ratio of the gate widths, the current in the main MOSFET is measured by sensing the magnitude of the current in the sense MOSFET. Inserting the relatively large MOSFET in the power circuit minimizes power loss.
Owner:ADVANCED ANALOGIC TECHNOLOGIES INCORPORATED
Sensor failure or abnormality detecting system incorporated in a physical or dynamic quantity detecting apparatus
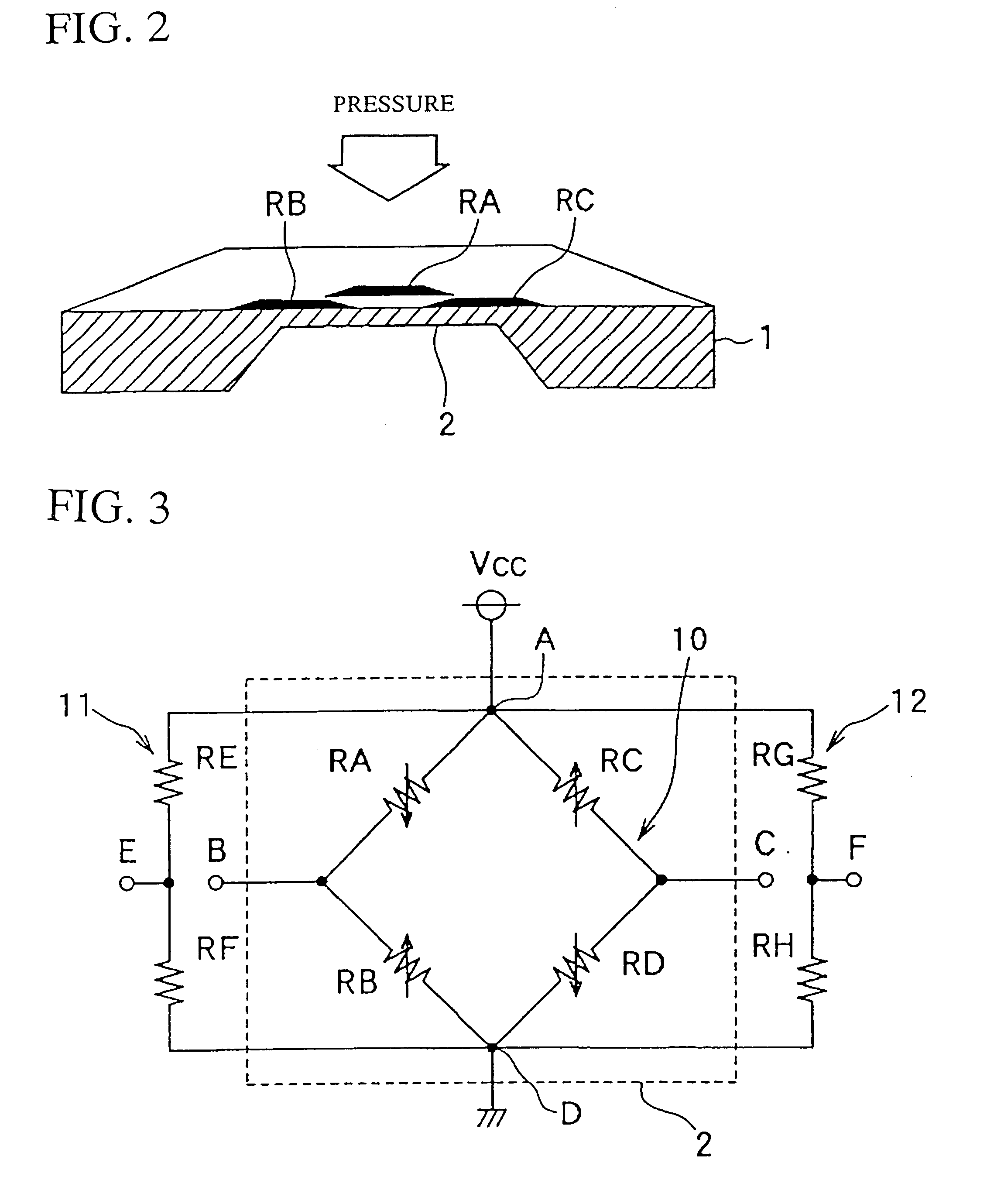
InactiveUS6422088B1Detect failureFluid pressure measurement using ohmic-resistance variationForce measurementElectrical resistance and conductanceAnomaly detection
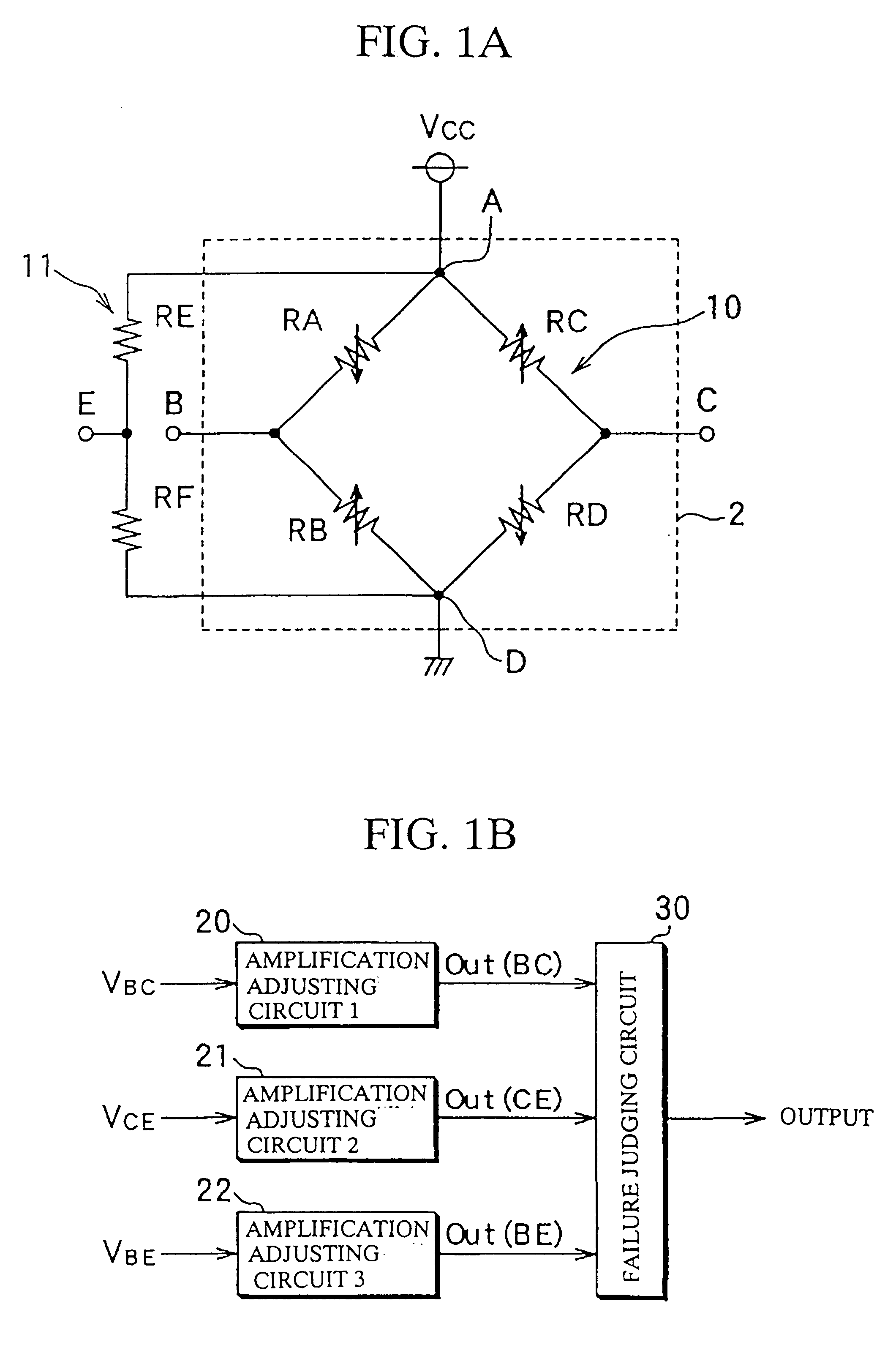
A reference voltage generating circuit is constituted by resistors RE and RF each having a resistance not influenced by an application of pressure. The reference voltage generating circuit is connected between one and the other ends of a bridge circuit. A failure judgement of the bridge circuit is performed based on a comparison of a voltage difference VBC between two midpoints B and C of the bridge circuit and voltage differences VCE and VBE between a reference voltage level of the reference voltage generating circuit and the voltage levels of two midpoints B and C.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Apparatus for employing low ohmic alloy conductors and method for simplifying current drain data retrieval
ActiveUS20130183043A1Decrease in Q-factorSmallAc-dc conversionTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsElectrical conductorData retrieval
Apparatus and method for measuring current drain and reporting power consumption using current transformer with primary windings made of low ohmic alloy, enabling the use of the secondary coil to power the sensing and reporting circuits eliminating the power wasted by AC-DC power adaptors used for the current sensors. The saving is substantial as the current sensors will not drain a current when the AC outlets are disconnected from a load or when the load is switched off. The apparatus using low ohmic alloy is extended to the structuring of terminals, including power pins, power sockets and combinations to provide a low ohmic sensing elements in AC plugs, outlets, adaptors and extension cables with multi outlets, dissipating the heat from the sensing elements by the plugs and the larger metal heat dissipation.
Owner:ELBEX VIDEO LTD
Method for monitoring alternating current discharge on a double electrode and apparatus
InactiveUS6420863B1Improve reliabilityReliable detectionElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEngineeringAlternating current
Process for monitoring an alternating-voltage discharge between the electrodes of a double electrode and an apparatus. The process includes measuring values of at least one of a discharge current and a discharge voltage for each half-wave within an alternating-voltage discharge period, determining a difference between the measured values of a second half-wave and the measured values of the first half-wave, and comparing the determined differences to specific tolerance values. When the specific tolerance values are exceeded by the determined differences, a power supply is reduced, whereby the discharge is at least briefly suppressed. The apparatus includes a double magnetron including first and second targets arranged to form a double electrode, and a power supply coupled to supply power to the first and second targets. The power supply includes a measurement unit for measuring values of at least one of discharge current and discharge voltage, such that at least one of a discharge current and a discharge voltage for each half-wave within an alternating-voltage discharge period is measured. A device for determining a difference between the measured values of a second half-wave and the measured values of the first half-wave is provided, as well as a device for comparing the determined differences to specific tolerance values, and a device for at least briefly suppressing the discharge when the specific tolerance values are exceeded by the determined differences.
Owner:HUETTINGER ELECTRONICS GMBH & CO KG
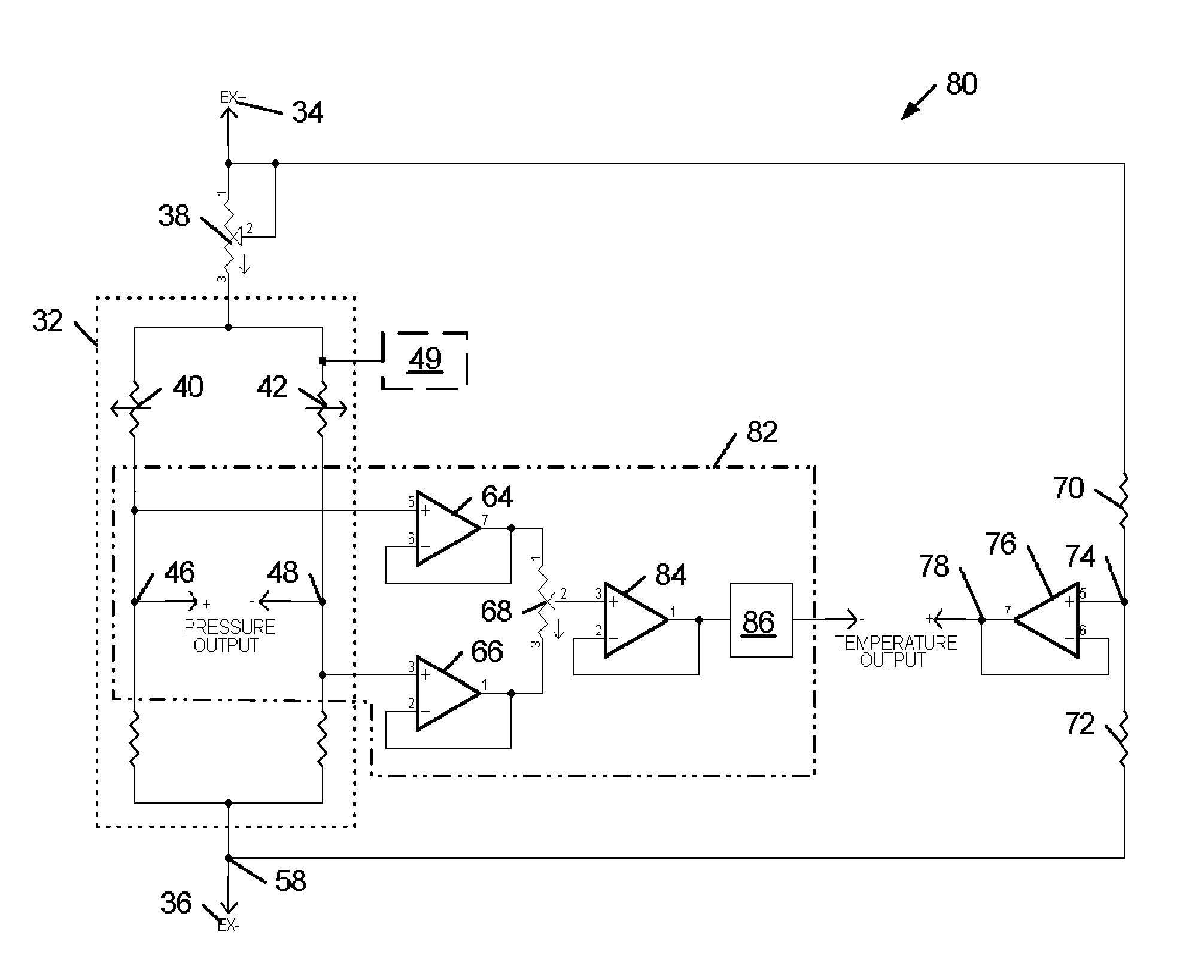
Calibration utility for non-linear measurement system
A method and system for calibrating an analog sensor used in a digital measurement system is provided. The design comprises generating a precise pressure value set at multiple calibration points and supplying said precise pressure value set to an uncalibrated pressure sensor, detecting sensor changes for the uncalibrated pressure sensor based on each precise pressure value generated, polling an actual pressure reading associated with a sensor change for the uncalibrated pressure sensor for each calibration point, and establishing a mathematical relationship between measured value readings and actual pressure for the uncalibrated sensor. Establishing the mathematical relationship converts the uncalibrated sensor to a newly calibrated sensor. A known good sensor may be employed to enhance calibration reliability.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
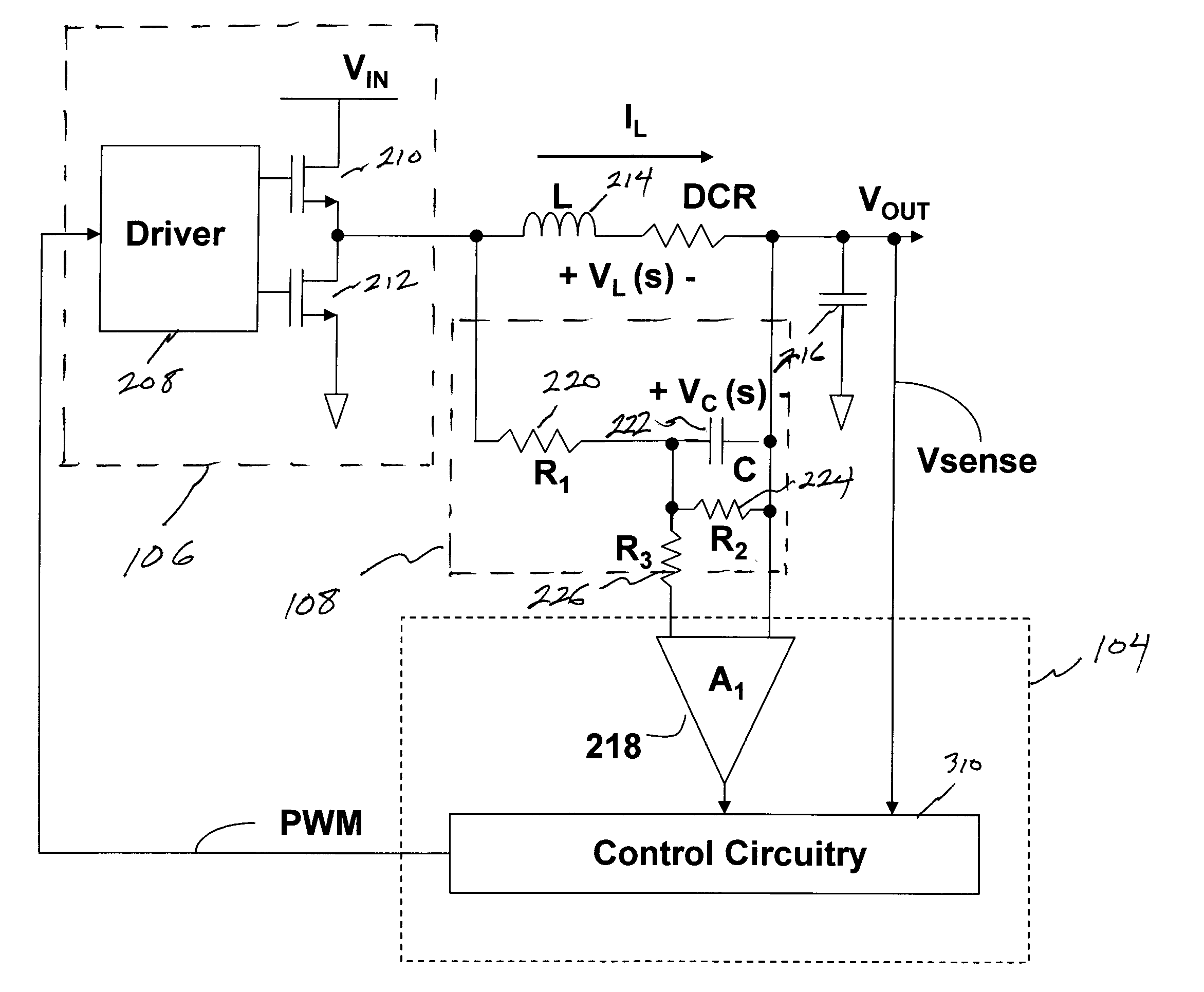
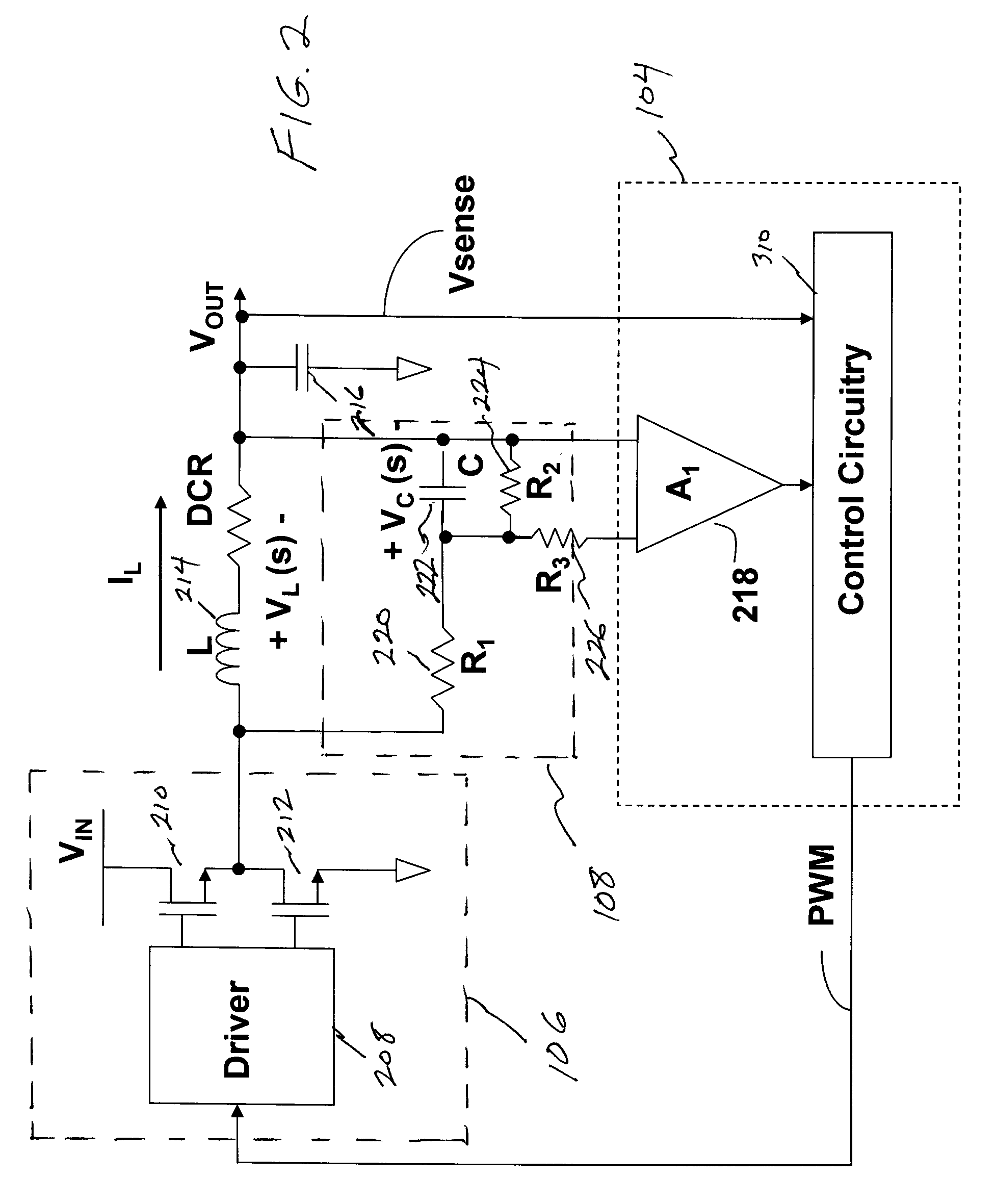
Methods and apparatus for current sensing
ActiveUS20090146643A1Current/voltage measurementElectrical measurement instrument detailsRC time constantCurrent sensor
Methods and apparatus for current sensing according to various aspects of the present invention sense the current in a circuit, such as an inductor circuit. The current sensing systems may comprise an RC element connected such that the RC time constant matches the L / R time constant of the inductor. The current sensor may be configured to generate voltages that are proportional to the instantaneous current in the inductor with scaled gain for a wide range of inductor self resistance (DCR) values.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AUSTRIA AG
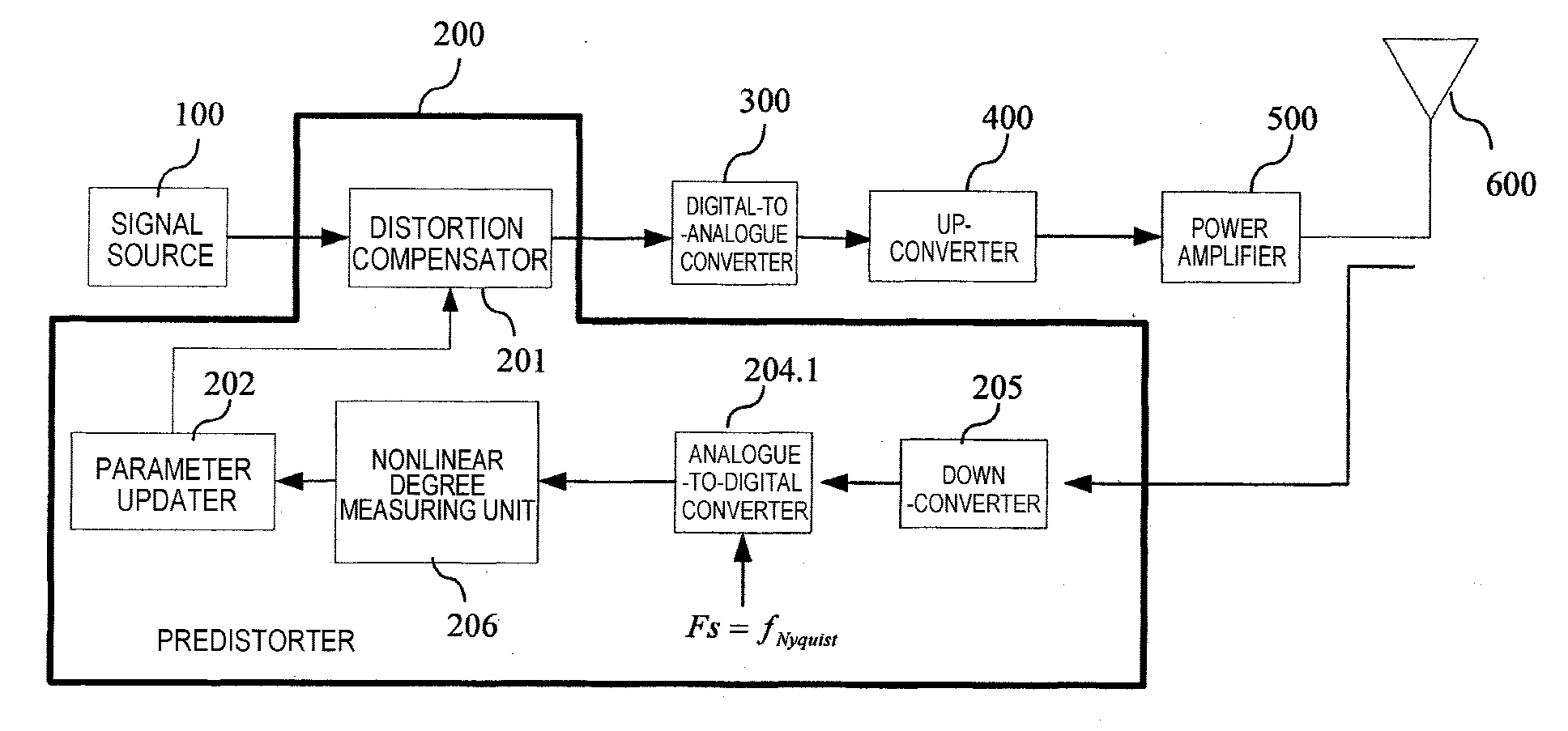
Nonlinear Degree Measuring Apparatus And Method For A Power Amplifier, Predistortion Compensation Apparatus
InactiveUS20100039100A1Low costReduce power consumptionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsCurrent/voltage measurementMeasurement deviceAudio power amplifier
This invention relates to a nonlinear degree measuring apparatus and method for a power amplifier, and a predistortion compensation apparatus. The nonlinear degree measuring apparatus comprises a delayer (304), for delaying inputted pilot frequency data; a subtracter (305), for subtracting, from the pilot frequency data delayed by the delayer, subsequently inputted pilot frequency data; a power calculating unit (306), for calculating an instantaneous power of an outputted signal from the subtracter (305); and an averager (307), for averaging the instantaneous power calculated by the power calculating unit (306) to obtain an averaged power.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Reactive sensor modules using Pade' Approximant based compensation and providing module-sourced excitation
ActiveUS7006938B2High precision measurementLow costSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsApparatus with stored calibration coefficientsIntegrated circuitNon linear response
Reactive sensors typically exhibit nonlinear response to temperature variation. Systems and methods are disclosed for compensating for the nonlinear and / or temperature dependent behavior of reactive sensors and for calibrating the post-compensation output signals relative to known samples of the physical parameter under measure. One call of embodiments includes a housing containing at least part of a reactive sensor, a monolithic integrated circuit and a timing reference. The integrated circuit includes a waveform generator for generating a sensor exciting signal, a detector for detecting the response of the sensor to the combination of the exciting signal and the under-measure physical parameter, a temperature compensating unit and the Pade Approximant nonlinearity compensating unit are tuned by use of digitally programmed coefficients. The coefficients calibrate the final output as well as compensating for nonlinearity and temperature sensitivity.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC +1
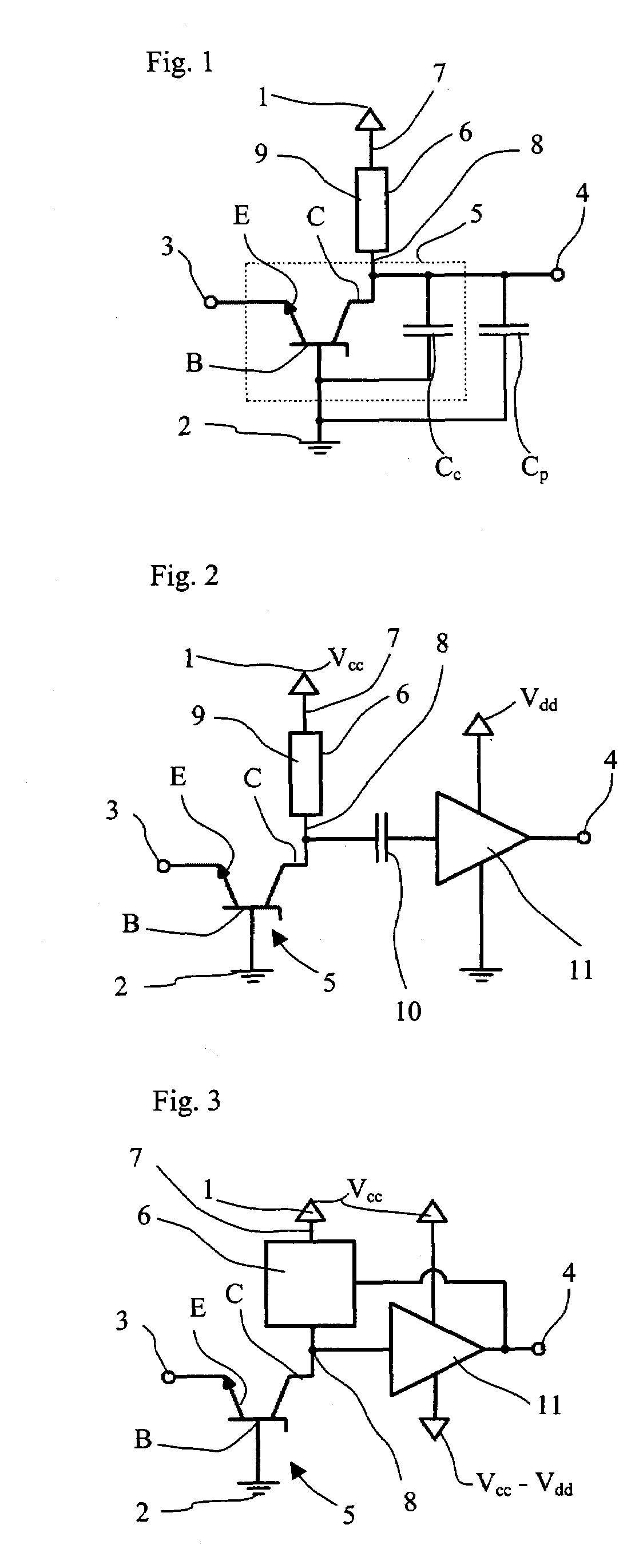
Position indicator
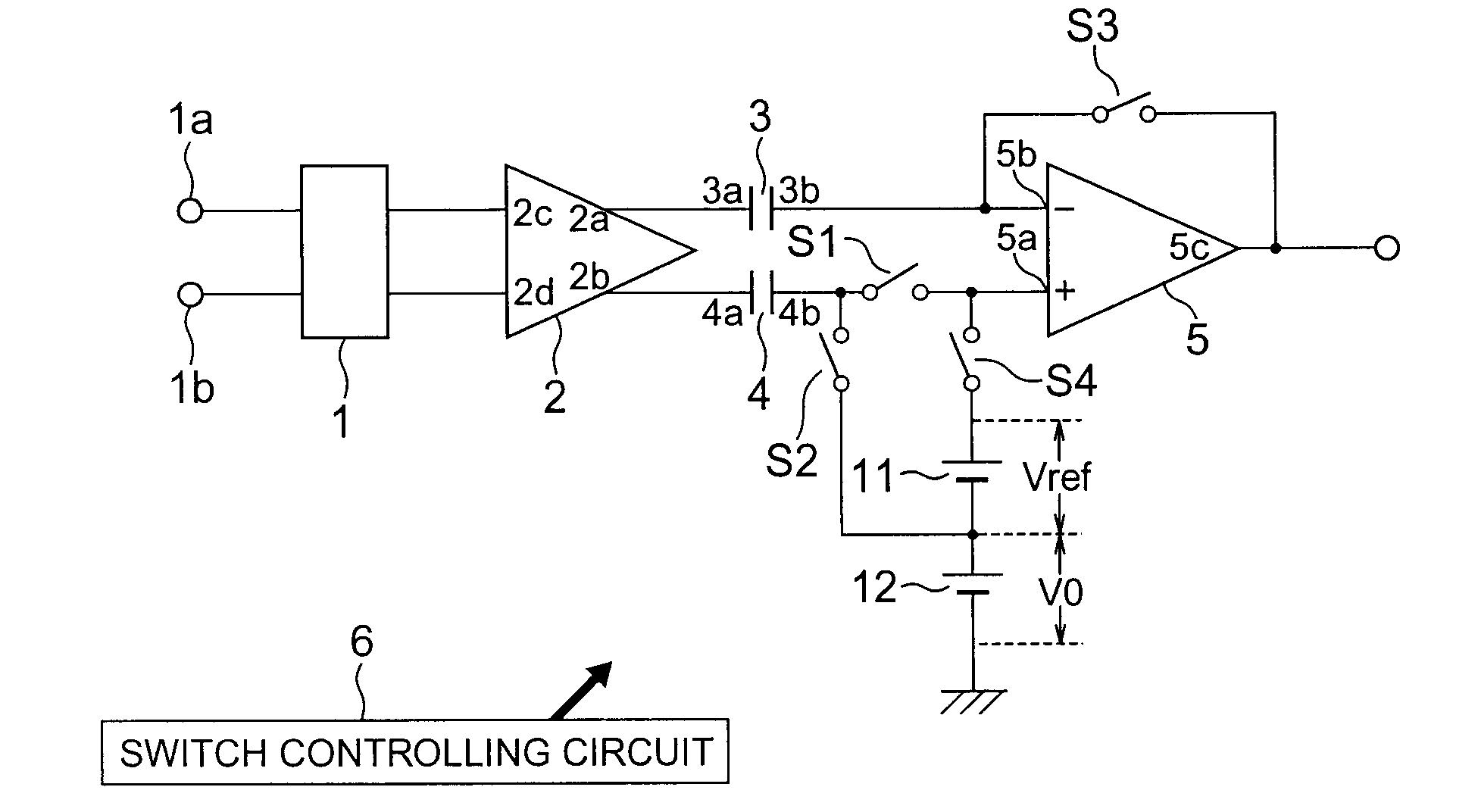
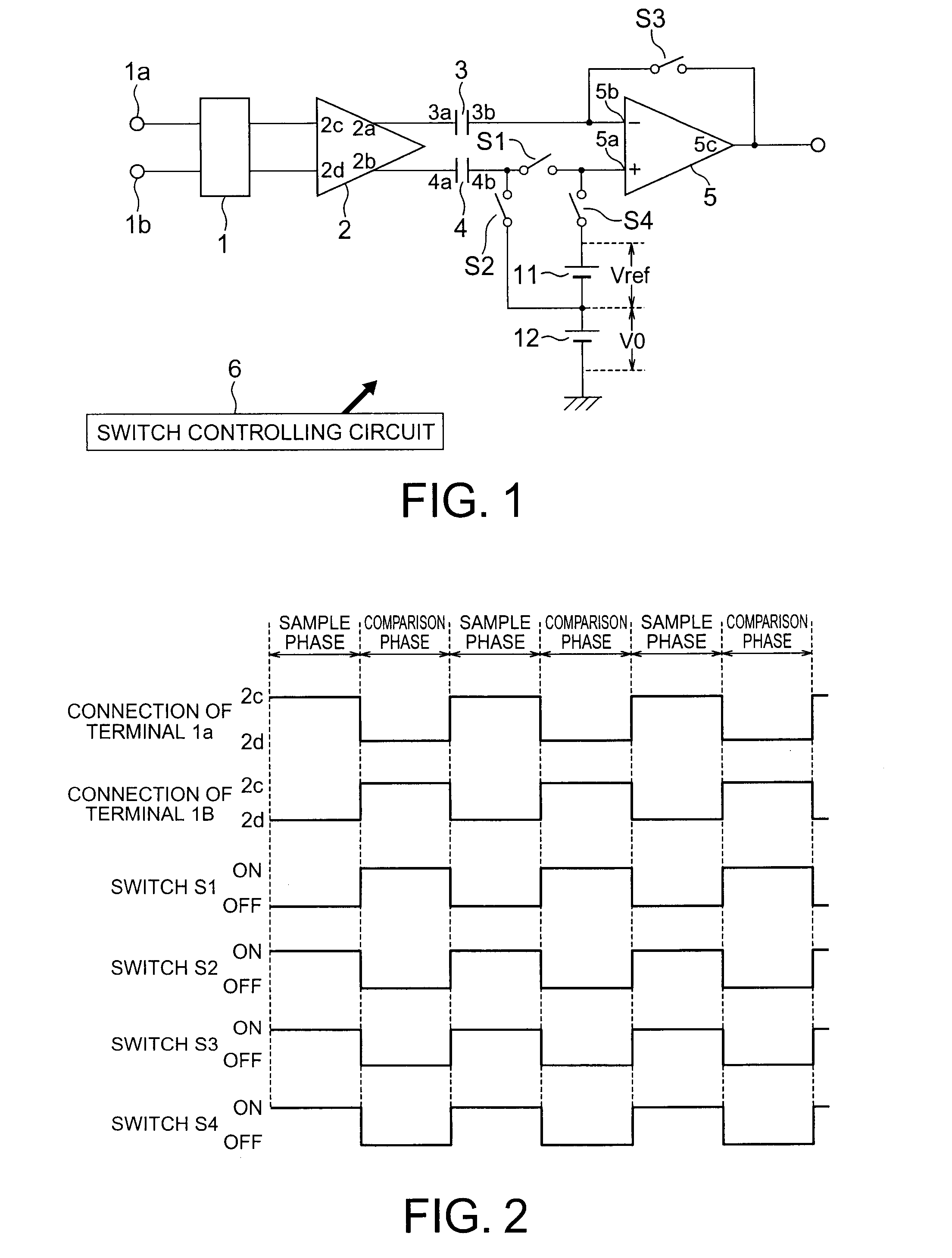
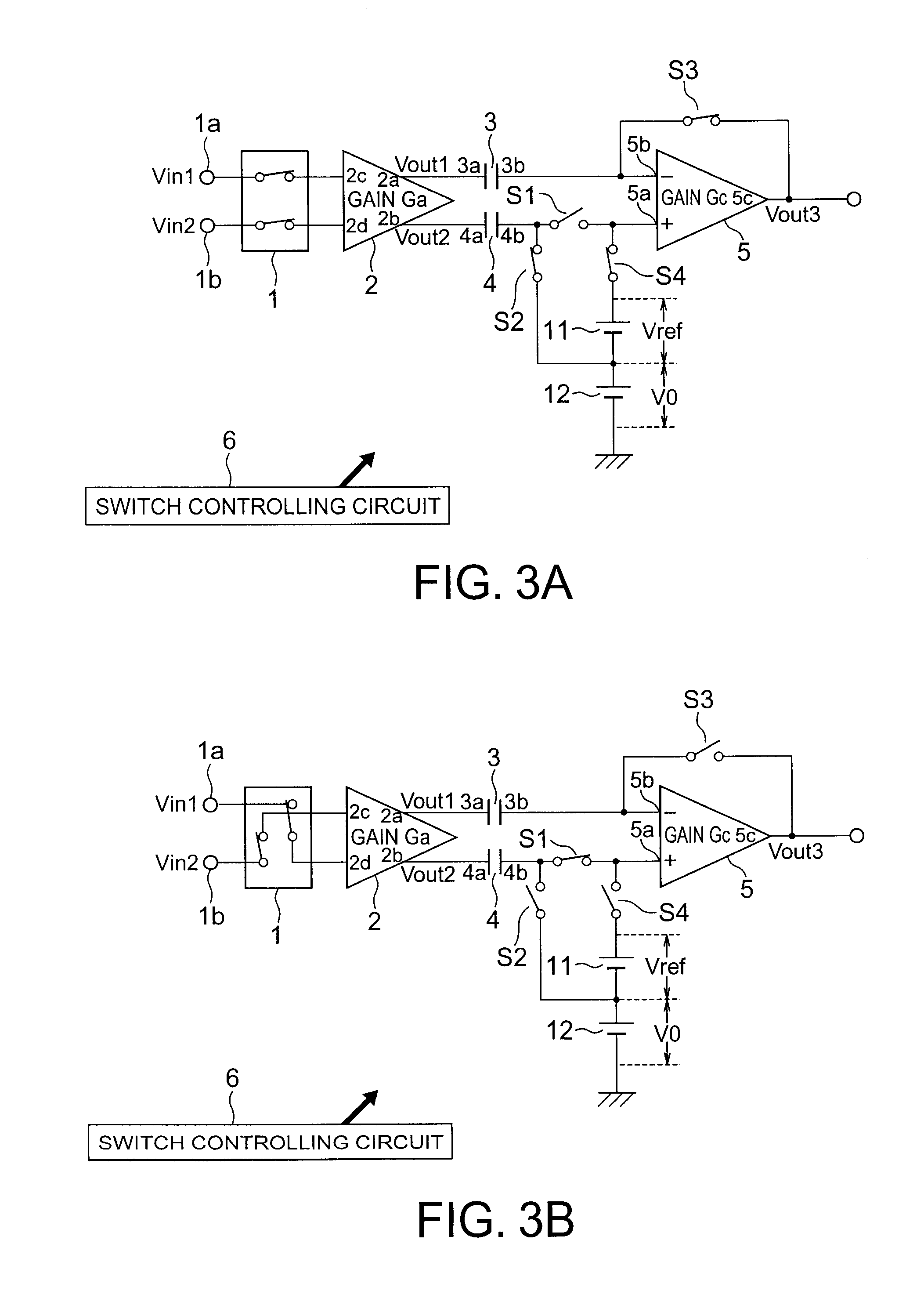
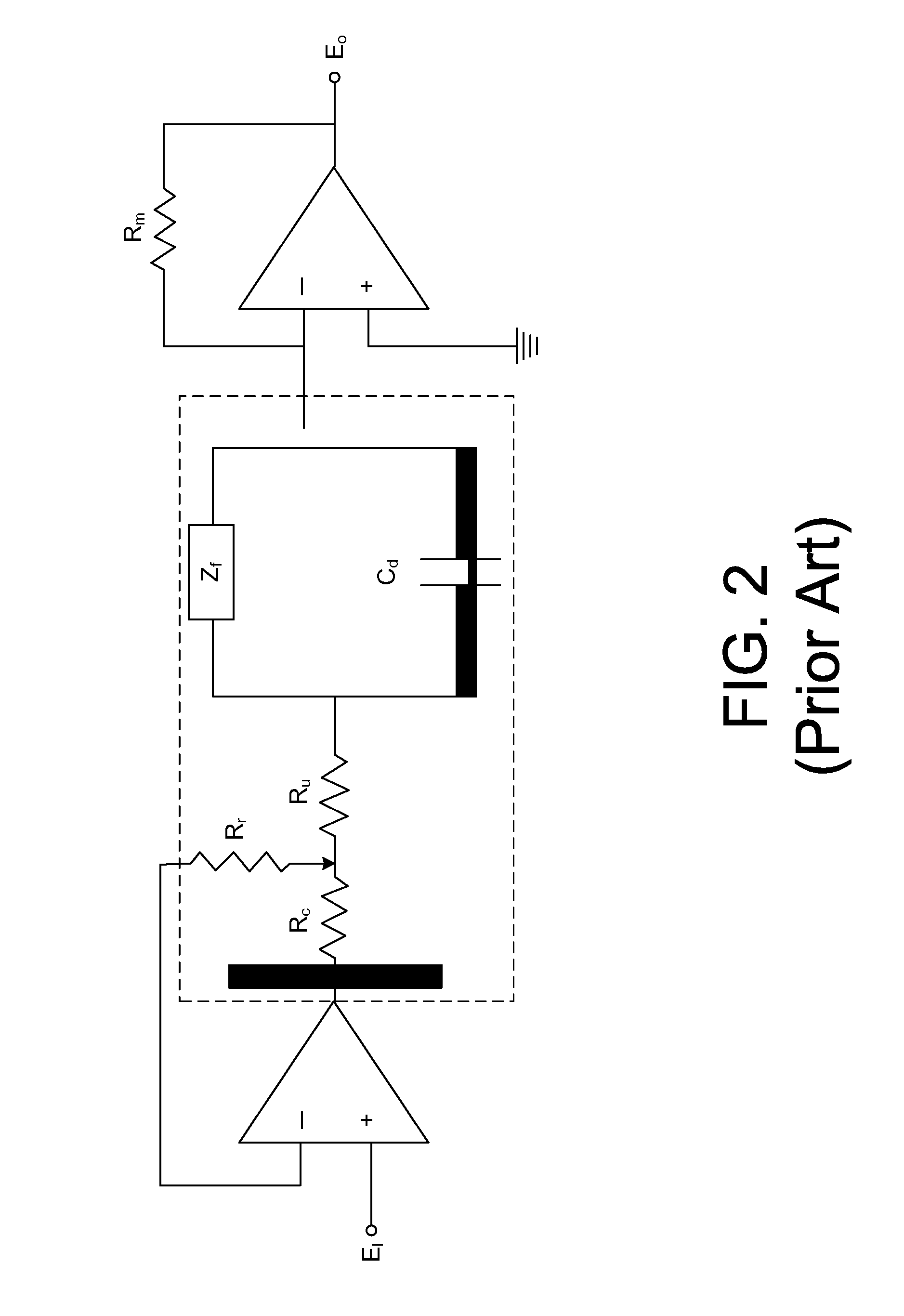
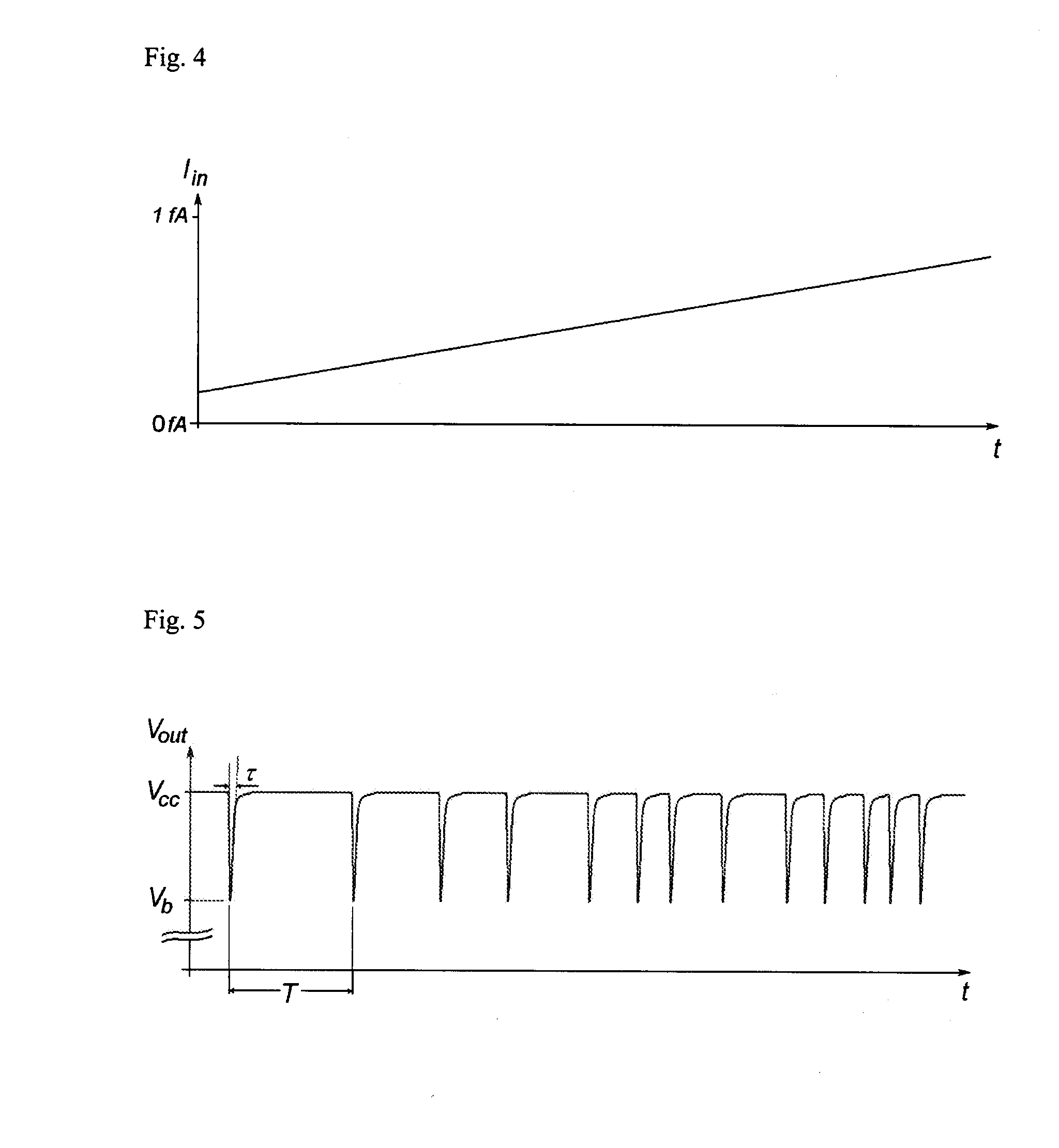
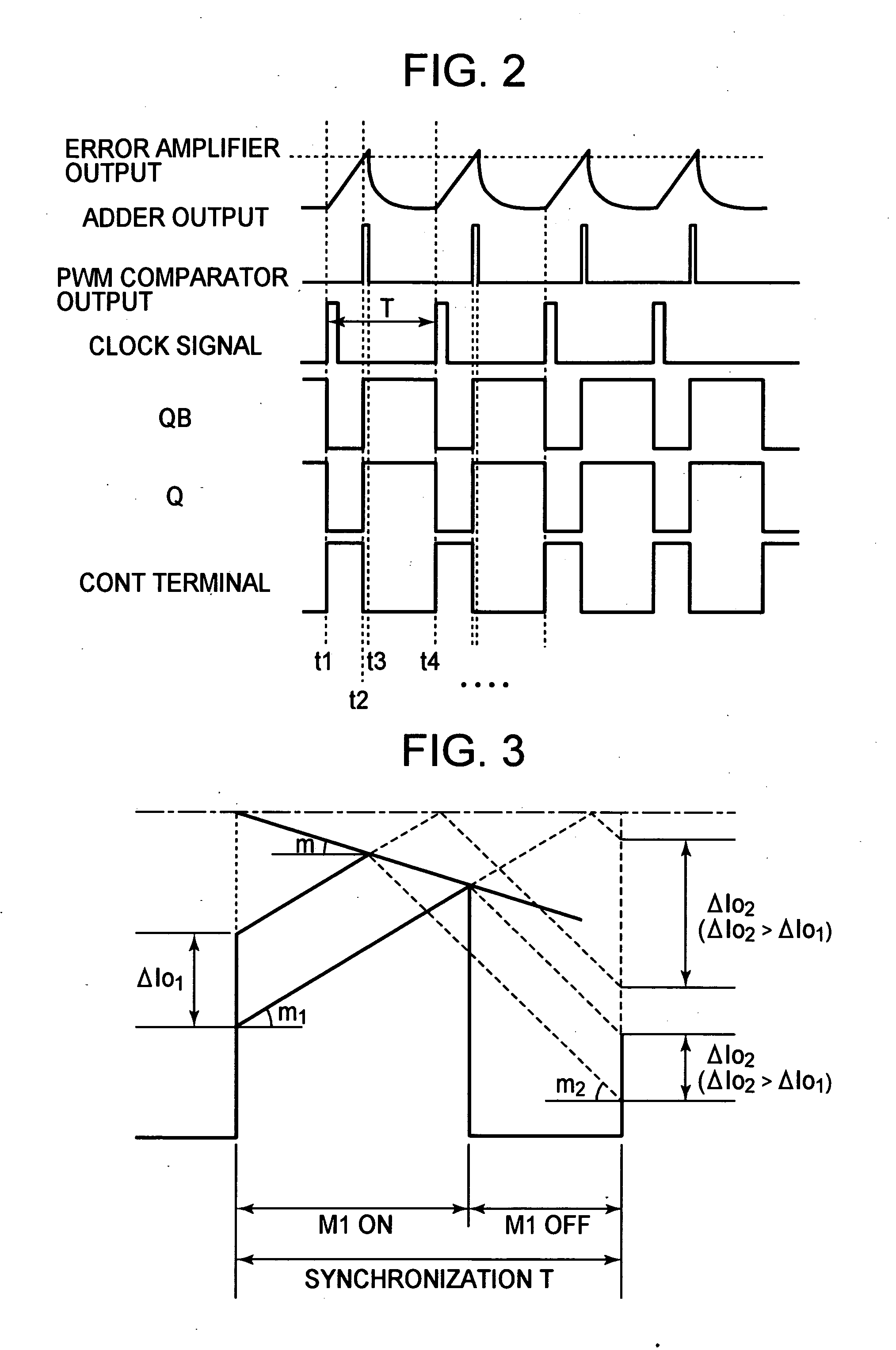
ActiveUS20090065268A1Quick checkHigh resolutionTransmission systemsAc/dc measuring bridgesHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
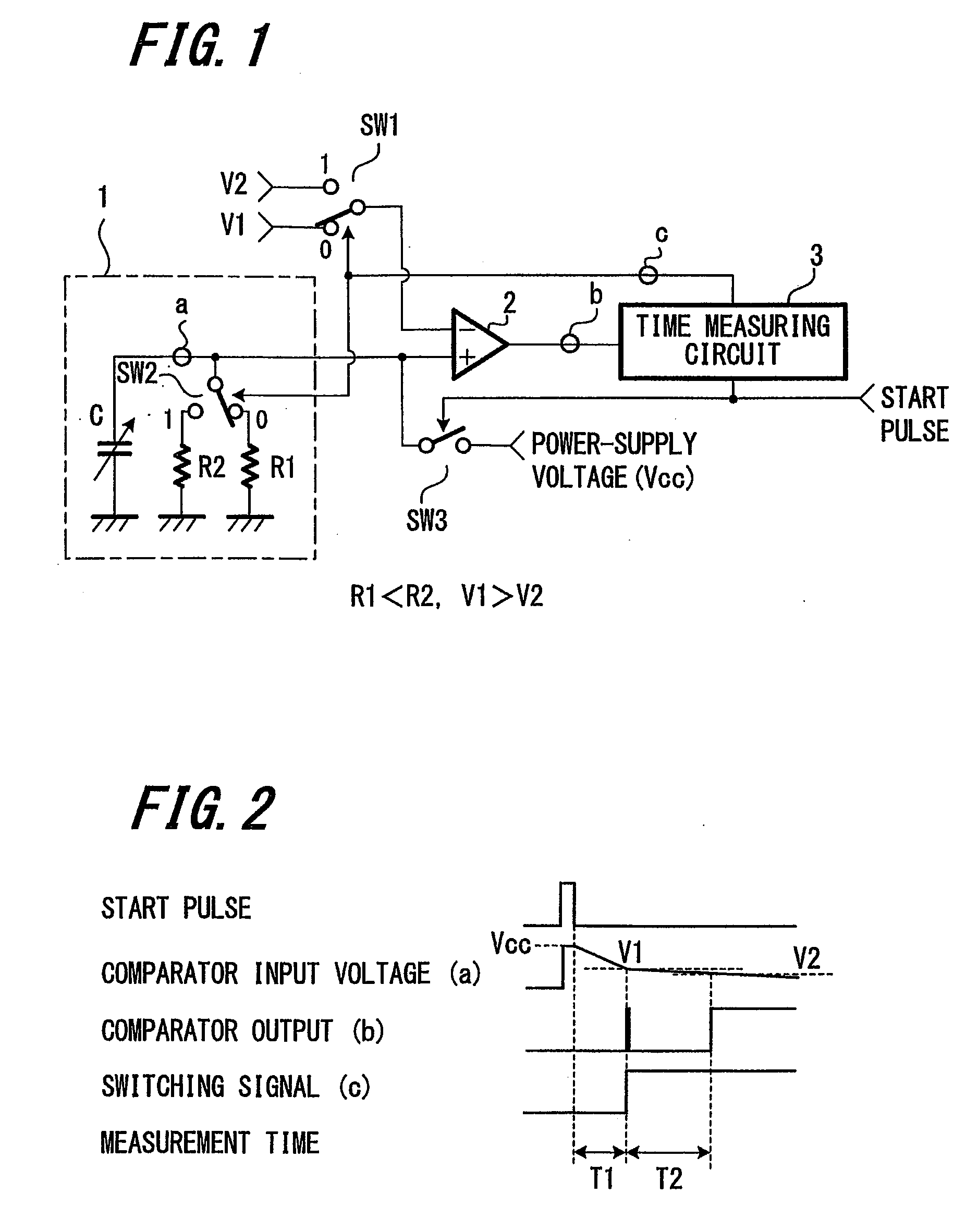
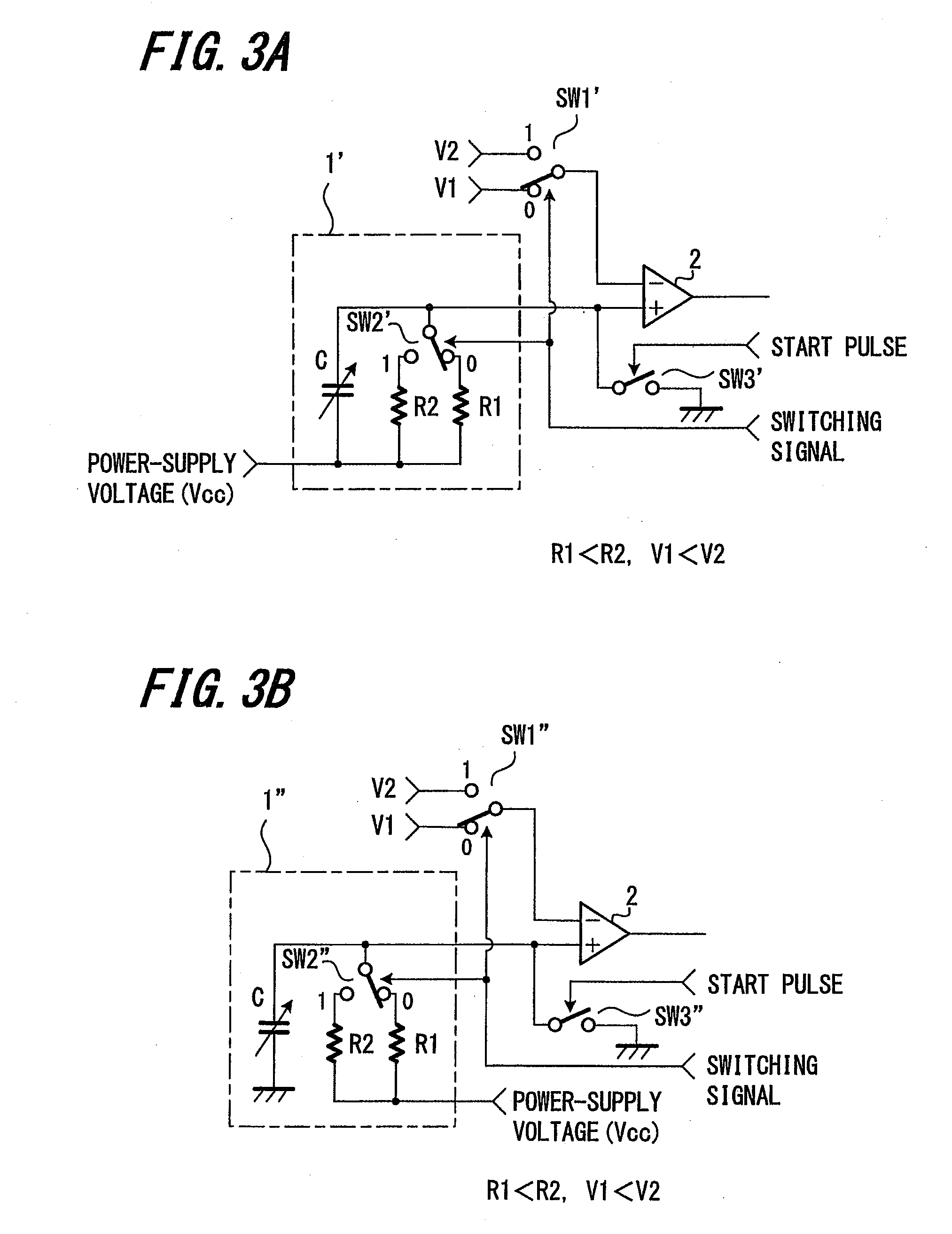
When a start pulse is supplied, a time-constant circuit (1) is charged to a voltage Vcc, and charge in a variable capacitor (C) is discharged through a resistor (R1). Upon the voltage (a) of the variable capacitor (C) reaching a preset reference voltage V1, a signal (b) is output from a comparator (2). In response to the signal (b), a time measuring circuit (3) stores a measured time period as a time period “T1”, and at the same time a switching signal (c) is output. The switching signal (c) switches the reference voltage V1 to a reference voltage V2, which is slightly lower than the reference voltage V1, and further switches the resistor R1 to a resistor R2, which has higher resistance than the resistor R1. Upon the voltage (a) of the variable capacitor (C) reaching the reference voltage V2, the signal (b) is output from the comparator 2. In response to the signal (b), the time measuring circuit (3) stores a measured time period as a time period “T2”.
Owner:WACOM CO LTD
Voltage detecting apparatus and line voltage detecting apparatus
InactiveUS20090319210A1Quick changeExpand the scope of detectionElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingElectricityVoltage converter
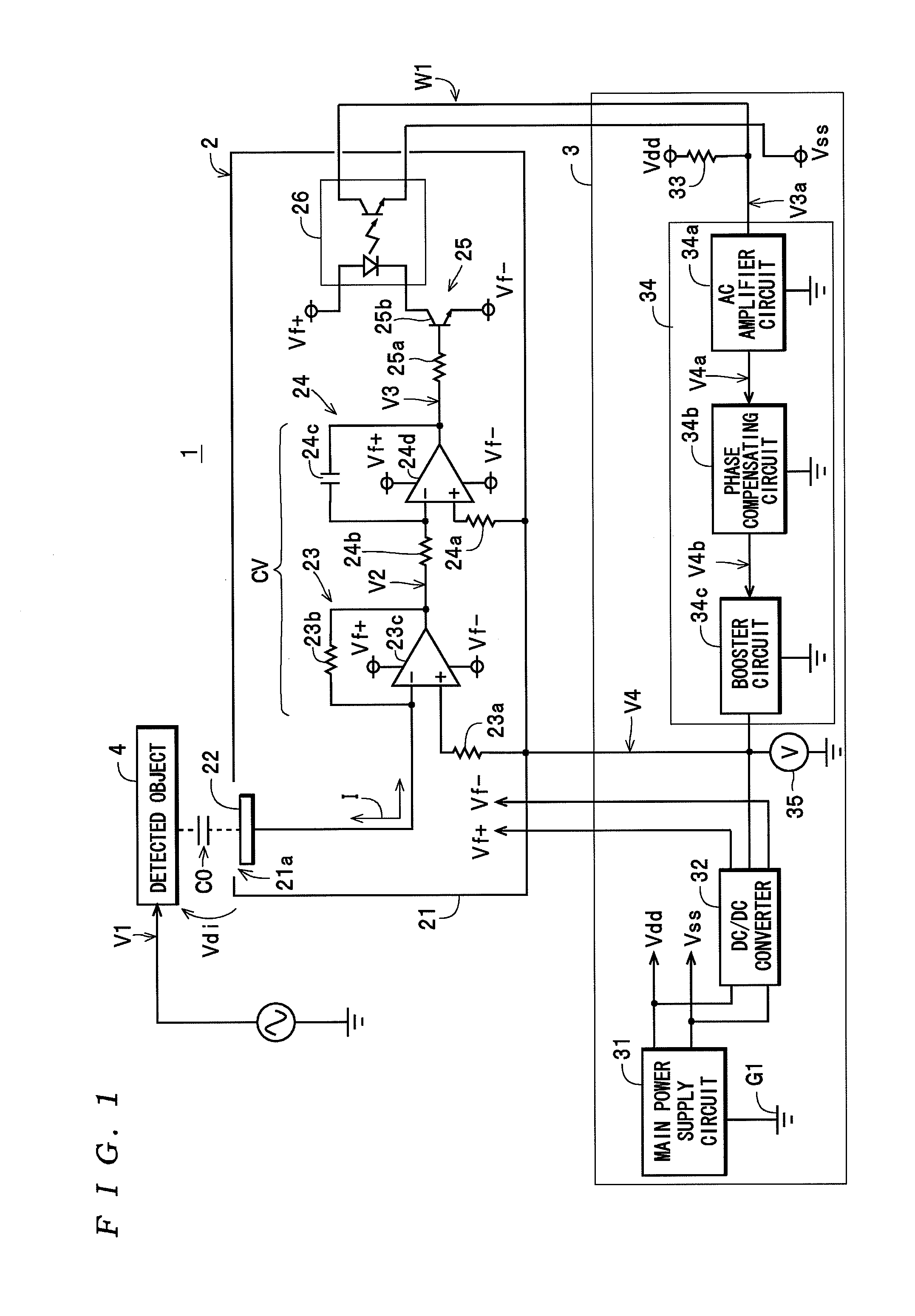
A voltage detector that detects an AC voltage in an object includes: an electrode disposed facing the object; a current-to-voltage converter that has a first input set at a reference voltage and a second input connected to the electrode and converts a detection current, which corresponds to a potential difference between the detected AC voltage and the reference voltage on a path including the electrode and a feedback circuit connected to the second input, to a detection signal; an integrating circuit that integrates the detection signal and outputs an integrated signal whose amplitude changes in accordance with the potential difference; an insulating circuit that inputs the detection signal or the integrated signal, and outputs the signal so as to be electrically insulated from the input; and a voltage generating circuit that generates the reference voltage by amplifying a signal based on the integrated signal to reduce the potential difference.
Owner:HIOKI DENKI KK
Signal detecting circuit
ActiveUS20080197834A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceCurrent/voltage measurementAudio power amplifierElectrical polarity
The signal detecting circuit has a first amplifier which amplifies the supplied signals and outputs the amplified signals from first and second output terminals; a switch unit which supplies the signals to the first amplifier such that the polarity thereof is reversed between the first and second periods; a first capacitor, one end of which is connected to the first output terminal; a second capacitor, one end of which is connected to the second output terminal; a first switch, one end of which is connected to the other end of the second capacitor; a second amplifier having an inverting input terminal connected to the other end of the first capacitor, a non-inverting input terminal connected to the other end of the first switch, and an output terminal; a second switch which is connected to between the output terminal and the inverting input terminal, a third switch, one end of which is connected to the other end of the second capacitor; a fourth switch, one end of which is connected to the other end of the non-inverting input terminal; a threshold voltage source which is connected to between the other end of the third switch and the other end of the fourth switch; and a reference voltage source which is connected to either one of the other end of the third switch and the other end of the fourth switch. In the first period, the first switch is off, and the second to fourth switches are on; in the second period, the first switch is on, and the second to fourth switches are off.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
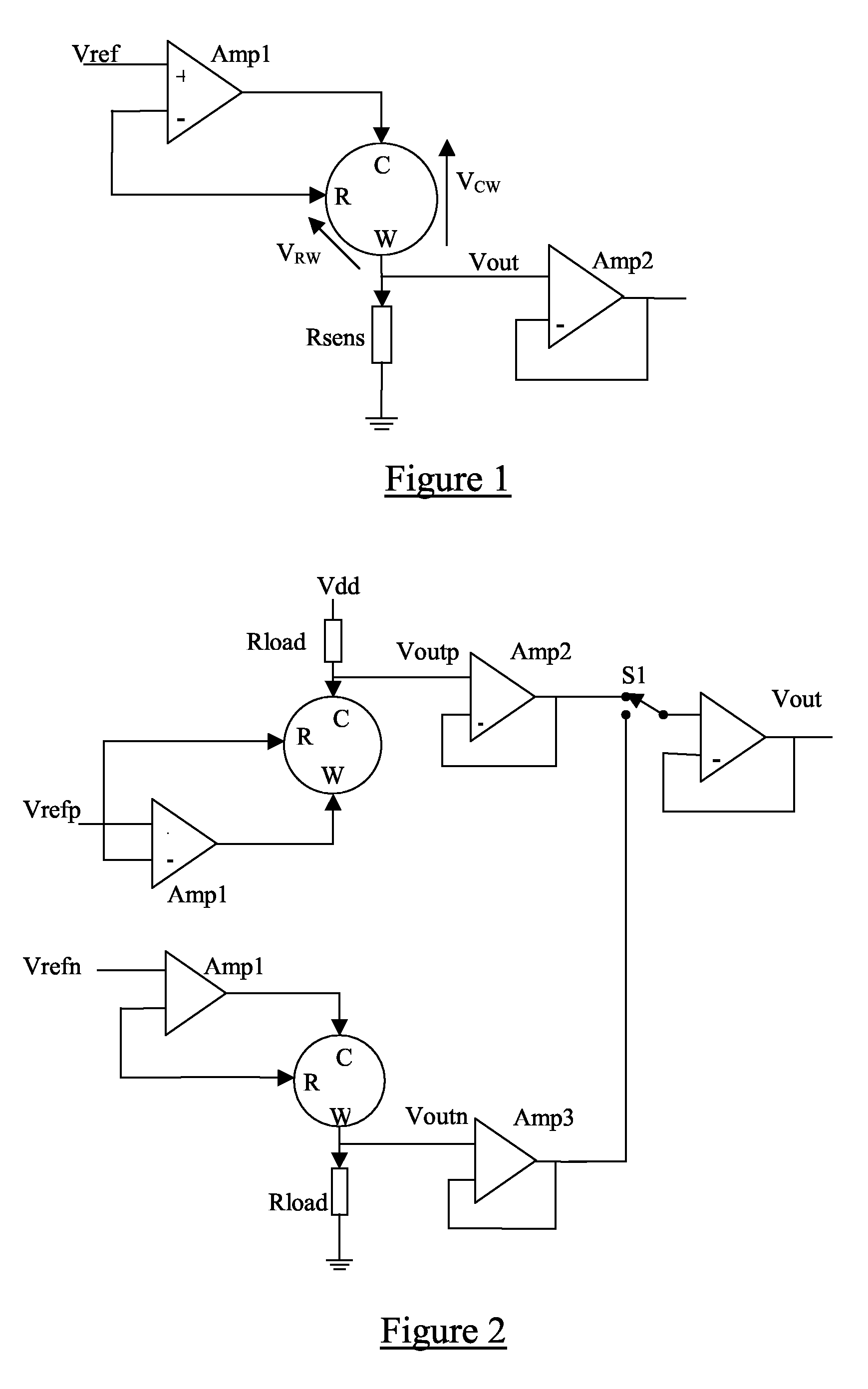
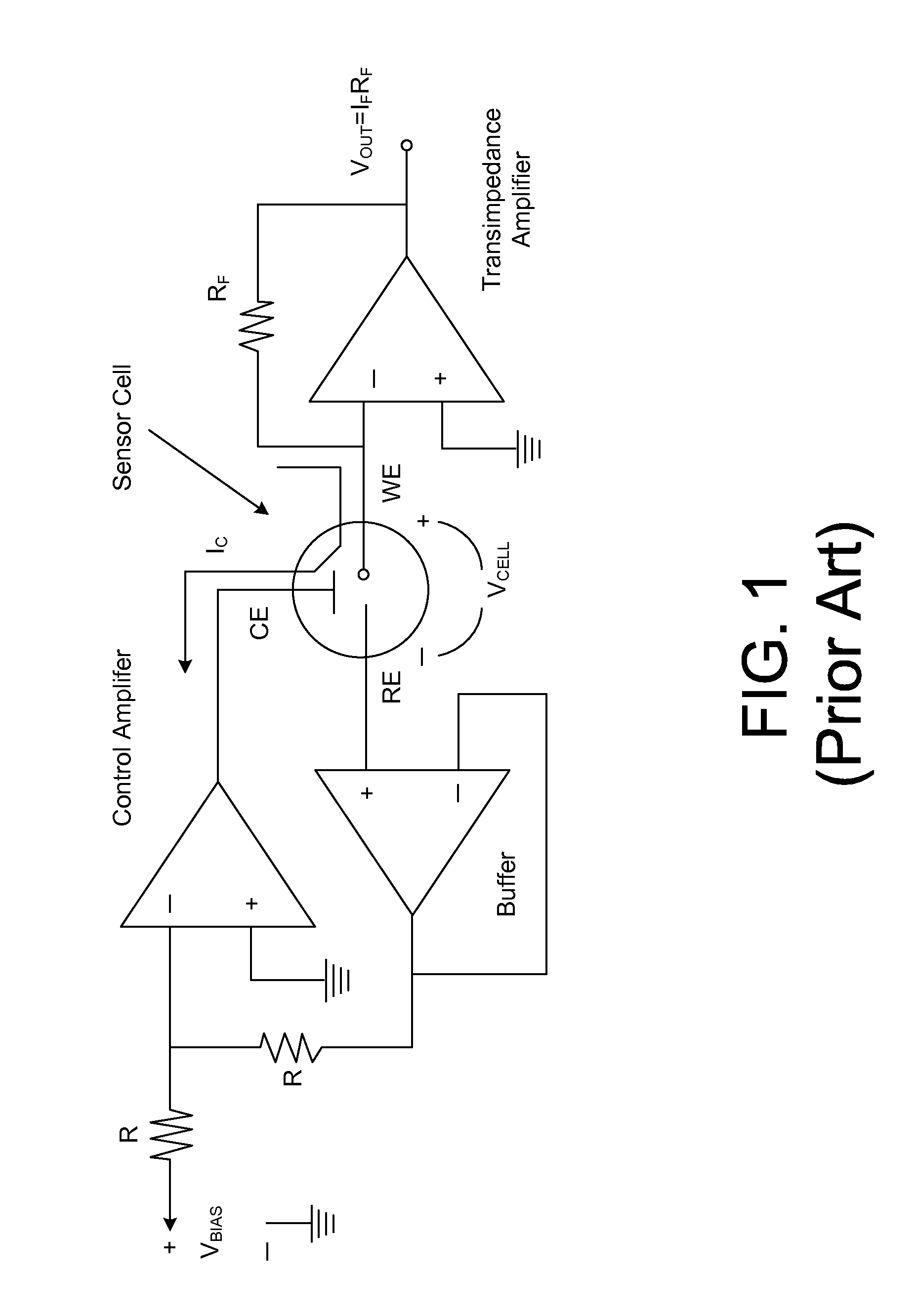
Sensor circuits
InactiveUS20090201032A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceCurrent/voltage measurementNegative feedbackAudio power amplifier
A circuit for operating an amperometric sensor having a reference electrode, a counter electrode and a work electrode. The circuit comprises an amplifier having a positive input and a negative input and an output. The positive input is coupled to a reference voltage source, and the negative input and the output are coupled together via a negative feedback loop. The circuit includes means for coupling the amperometric sensor into said negative feedback loop of the amplifier wherein, in a first configuration, the counter electrode is coupled to said output and the reference electrode is coupled to said negative input and, in a second configuration, the work electrode is coupled to said output and the reference electrode is coupled to said negative input.
Owner:TOUMAZ TECH
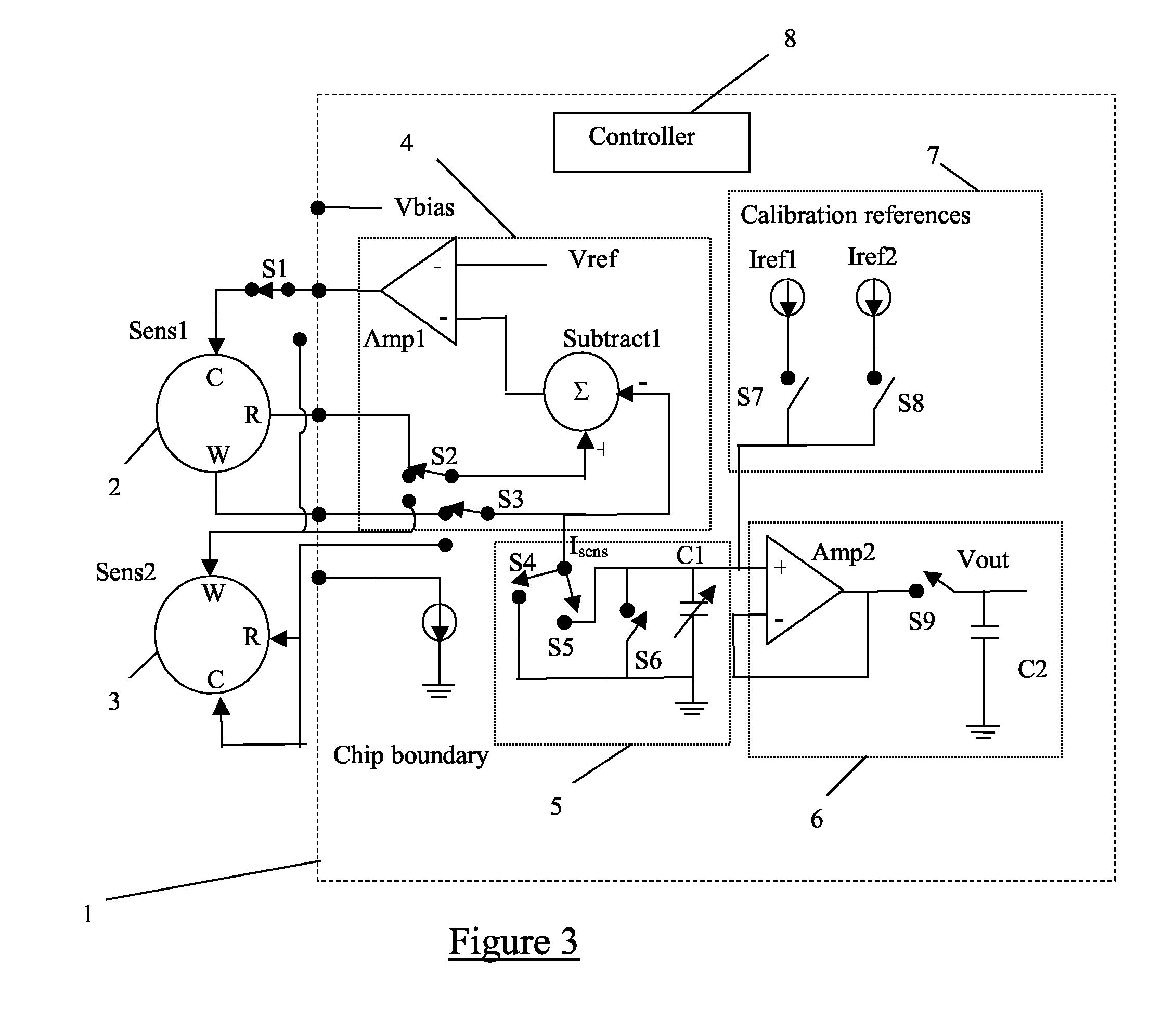
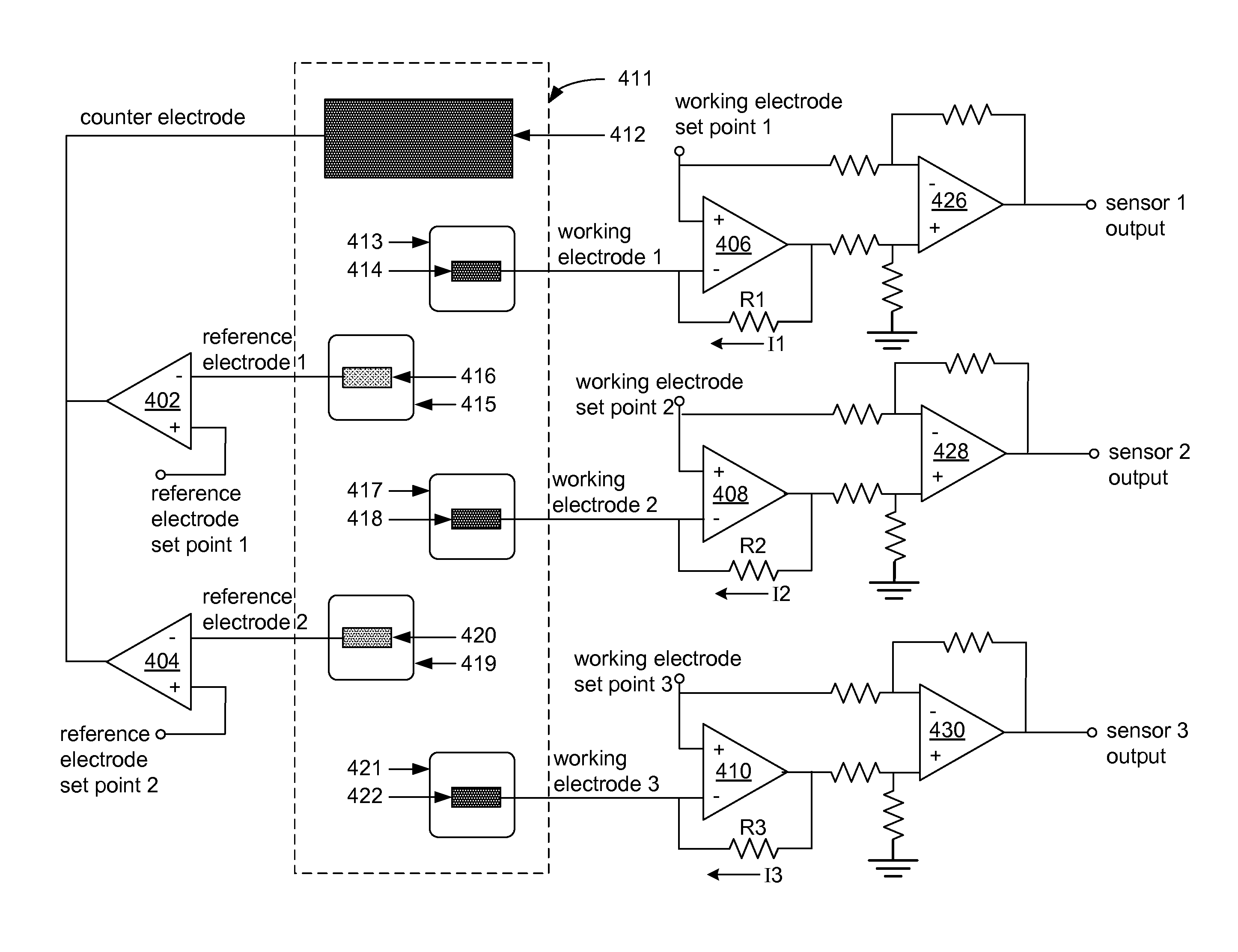
Multi-channel potentiostat for biosensor arrays
InactiveUS20110089957A1Current/voltage measurementResistance/reactance/impedenceAudio power amplifierEngineering
Arrays of biosensors are provided along with methods for operating the arrays of biosensors. The array of biosensors may include a first reference electrode that is connected to an input of a first control amplifier; a first working electrode and a second working electrode in proximity with the first reference electrode; and a counter electrode that is connected to at least an output of the first control amplifier, where the first control amplifier is operative with the counter electrode to maintain a first specified voltage between the first working electrode and the first reference electrode, and between the second working electrode and the first reference electrode. The array of biosensors optionally may further include a second reference electrode that is connected to an input of a second control amplifier, where the second control amplifier is operative with the counter electrode to maintain a second specified voltage between the first working electrode and the second reference electrode, and between the second working electrode and the second reference electrode.
Owner:DARE MB INC
Pade' approximant based compensation for integrated sensor modules and the like
InactiveUS20050256660A1Improve accuracyProgrammably adjustedResistance/reactance/impedenceMitigation of undesired influencesAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
Methods and systems using Pade′ Approximant expansion ratios provide mappings between nonlinear sensors and a more linearized output domain. In one embodiment (a) a variable gain amplifier receives a supplied input signal, the amplifier has at least a first input terminal, an output terminal, and a gain control terminal; (b) a first summer coupled to the output terminal of the variable gain amplifier adds in a first offset signal; (c) a first multiplier coupled to an output of the first summer receives a proportional feedback factor signal and correspondingly generates a multiplied feedback; (d) a second summer coupled to an output terminal of the first multiplier adds in a corresponding second offset signal; and (e) a second multiplier coupled to an output of the second summer receives a gain factor signal and generates a multiplied gain signal; where the gain control terminal of the variable gain amplifier is operatively coupled to an output terminal of the second multiplier.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
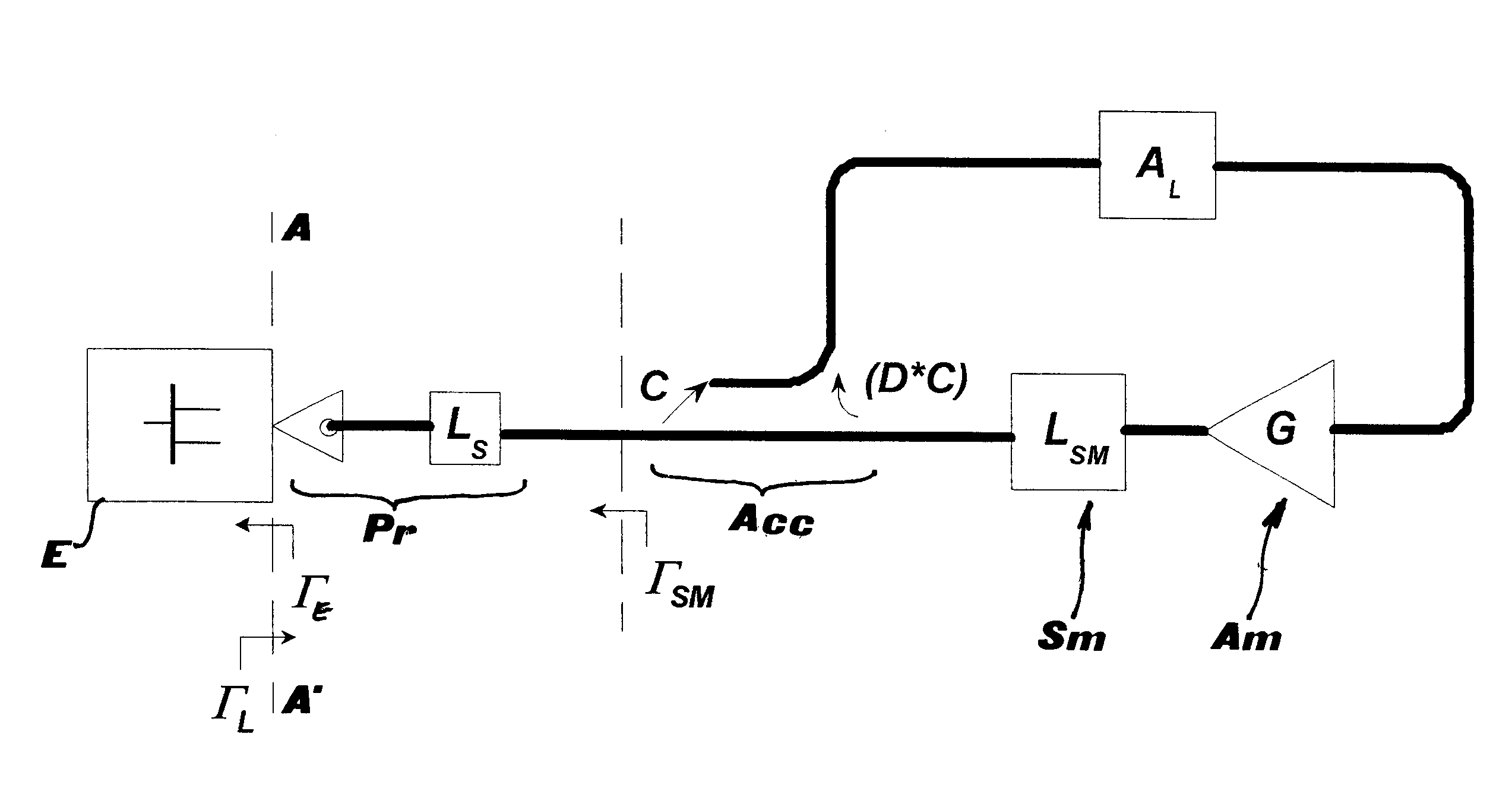
Active load or source impedance synthesis apparatus for measurement test set of microwave components and systems
InactiveUS6509743B1Resistance/reactance/impedenceCurrent/voltage measurementMeasurement testMicrowave
An active load or source impedance synthesis apparatus for experimental characterization of electronic components (E) working in the range from 500 MHz to 110 GHz, includes an active loop with at least one amplifier (Am), one magnitude and phase control system (Ra, Rs, one directional coupler (Acc) and a measurement system connected to a device under test (E), where the directional coupler (Acc) is connected after the most significant losses of the measurement system.
Owner:FERRERO ANDREA
Semiconductor Device For Measuring Ultra Small Electrical Currents And Small Voltages
InactiveUS20100013458A1Reduce bias voltageIncrease kinetic energyElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingSingle electronLow voltage
A semiconductor device for measuring ultra low currents down to the level of single electrons or low voltages comprises a first and a second voltage supply terminal, an input terminal for receiving an electrical current or being supplied with a voltage to be measured, a bipolar transistor having a base, an emitter and a collector, wherein a first PN junction is formed between the base and the collector and a second PN junction is formed between the base and the emitter, wherein the emitter is coupled to the input terminal and the base is coupled to the second voltage supply terminal, and wherein the first PN junction is designed for reverse biased operation as an avalanche diode, and a quenching and recharging circuit having a first terminal coupled to the first voltage supply terminal and a second terminal coupled to the collector of the bipolar transistors, the quenching and recharging circuit permitting operation of the first PN junction reverse biased above the breakdown voltage of the first PN junction.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
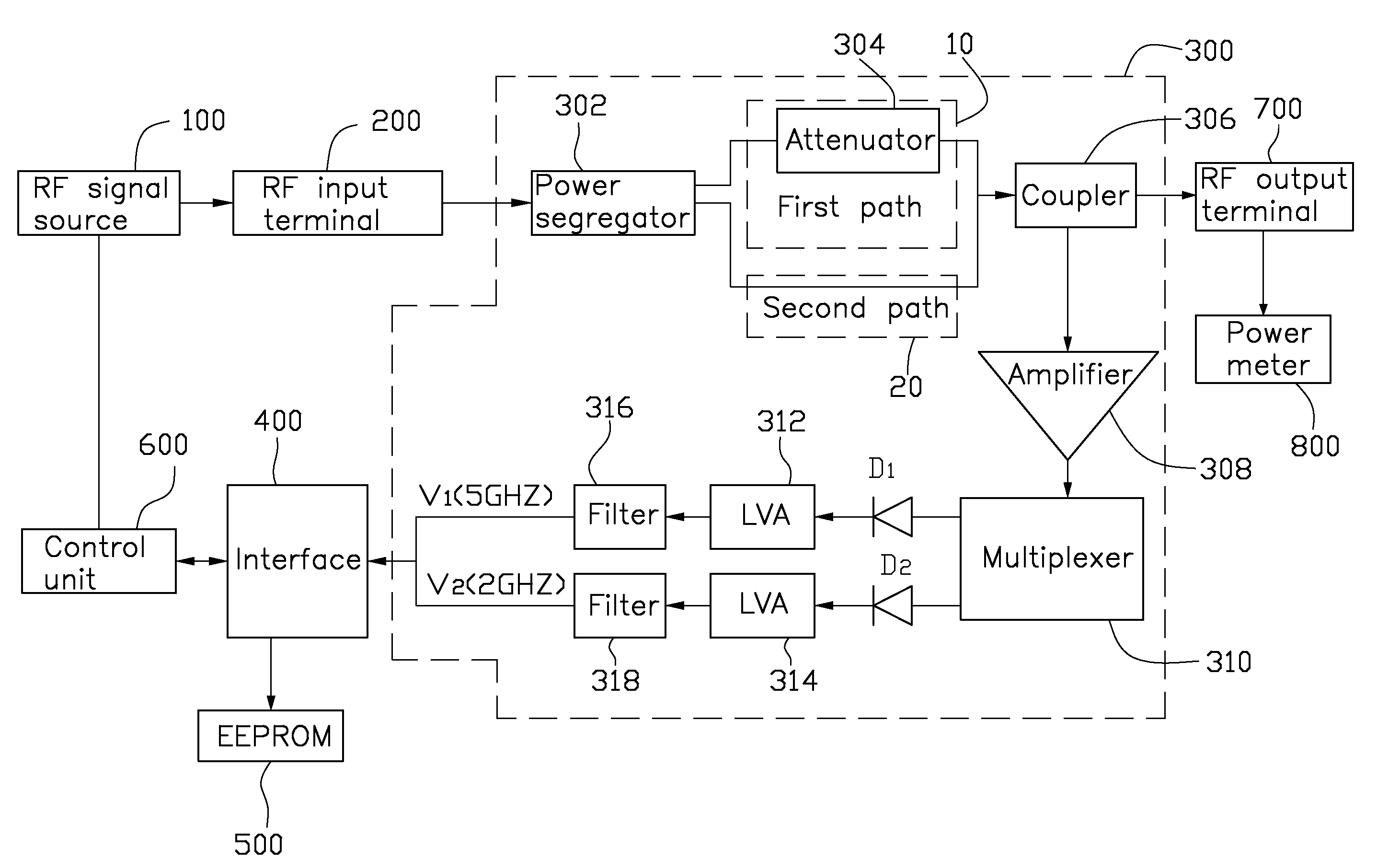
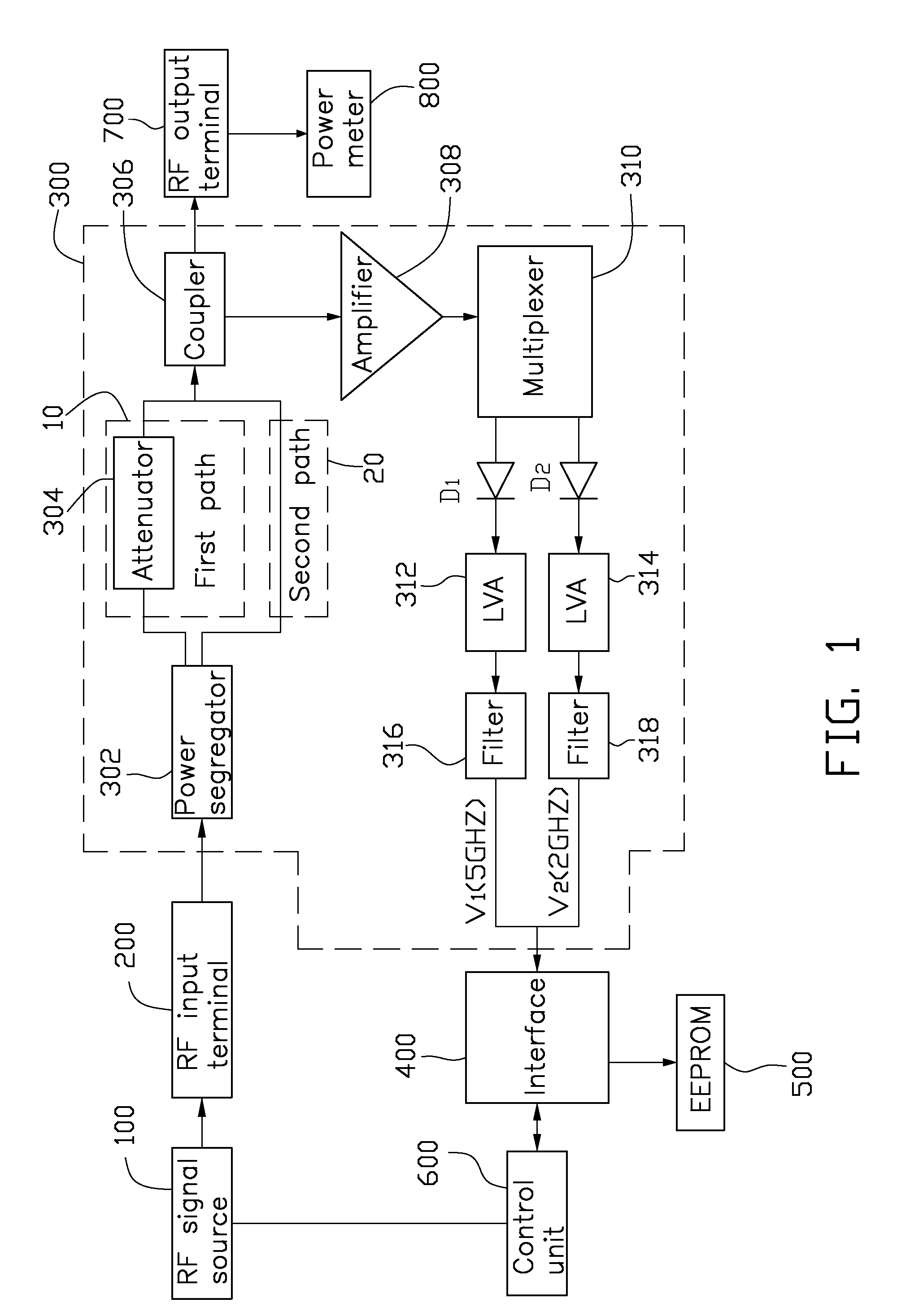
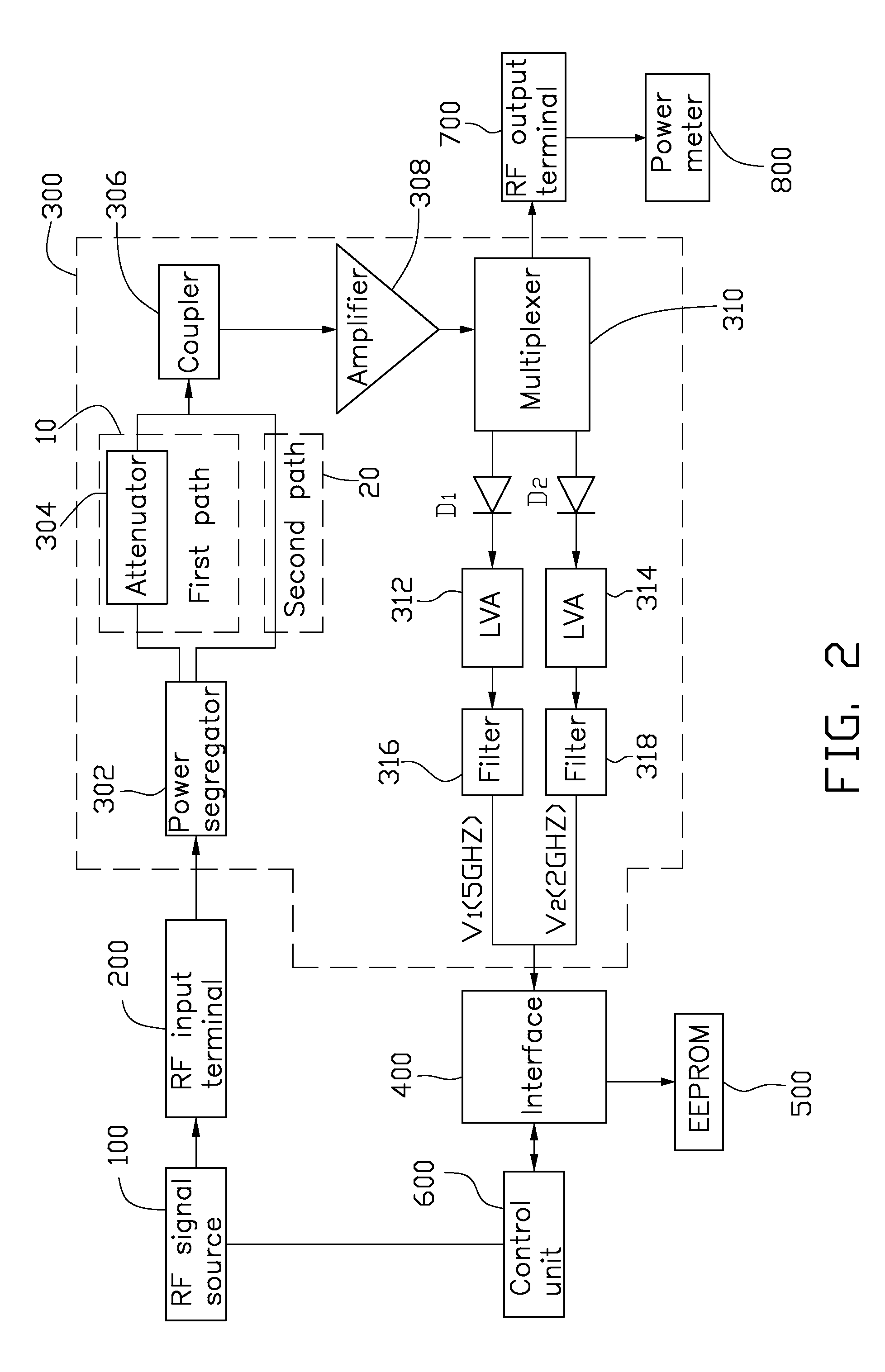
Power measurement apparatus
ActiveUS20090322313A1Wave amplification devicesCurrent/voltage measurementRadio frequency signalPower measure
A power measurement apparatus includes a radio frequency input terminal, a measurement module, an interface, a memory, and a control unit. The radio frequency input terminal is connected to a radio frequency device. The measurement module is connected to the radio frequency input terminal to convert the radio frequency signal into a voltage signal. The interface is connected to the measurement module, receiving and transmitting the voltage signal from the measurement module. The memory is connected to the interface to store a voltage-power table related to the radio frequency signal. The control unit is connected to the interface to query the voltage-power table in the memory via the interface, and obtain the power of the radio frequency device according to the voltage signal output from the measurement module.
Owner:HONG FU JIN PRECISION IND (SHENZHEN) CO LTD +1
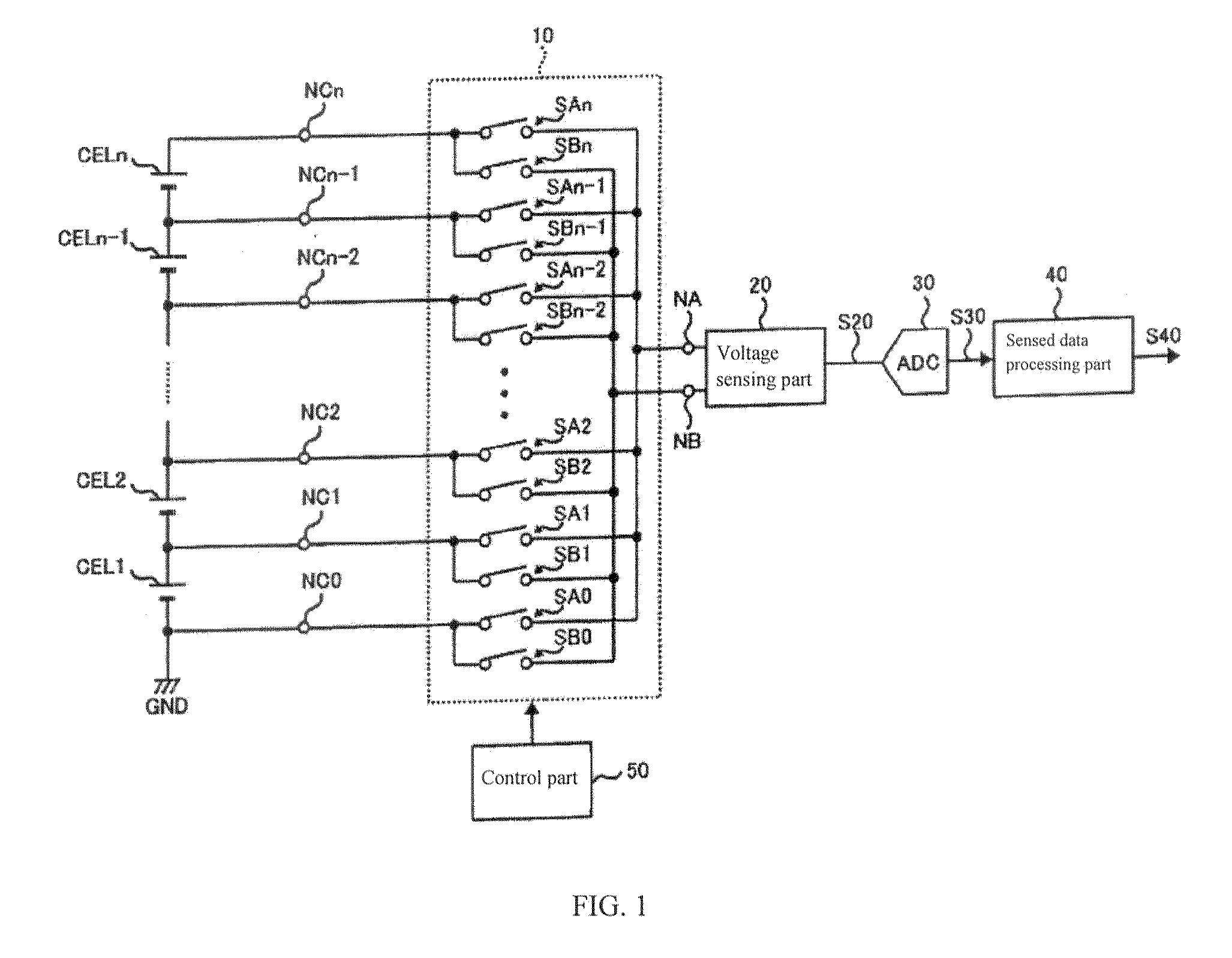
Voltage sensing device
ActiveUS20100052656A1Error componentElectrical measurement instrument detailsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSensing dataDigital data
A voltage sensing device with which high-precision voltage sensing is possible without acquiring a unique correction constant for each device. A pair of voltage input nodes NCk and NCk-1 are selected from n+1 voltage input nodes NC0-NCn in switch part 10, and the selected voltage input nodes NCk and NCk-1 are connected to inspection input nodes NA and NB. Here, voltage input nodes NCk and NCk-1 and inspection input nodes NA and NB are connected in two types of patterns of different polarity (forward connection, reverse connection) under the control of control part 50, and digital data S30 for the two sensed voltage signals S20 generated in the two types of connection patterns is input to sensed data processing part 40. With sensed data processing part 40, sensed voltage data S40 that represents the potential difference between voltage input nodes NCk and NCk-1 is generated according to the difference in the two sensed voltage signals S20.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
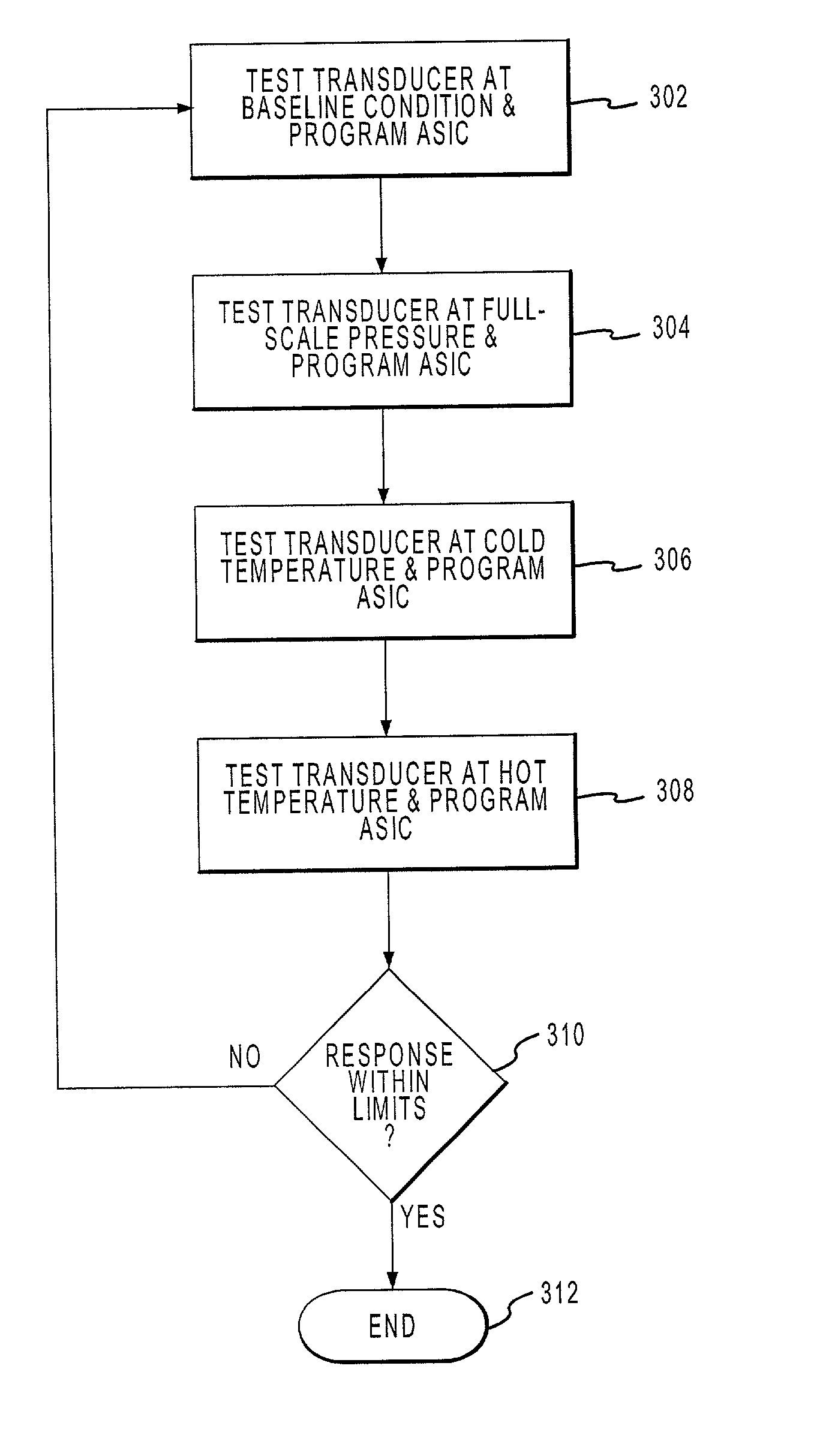
Method and apparatus for the calibration and compensation of sensors
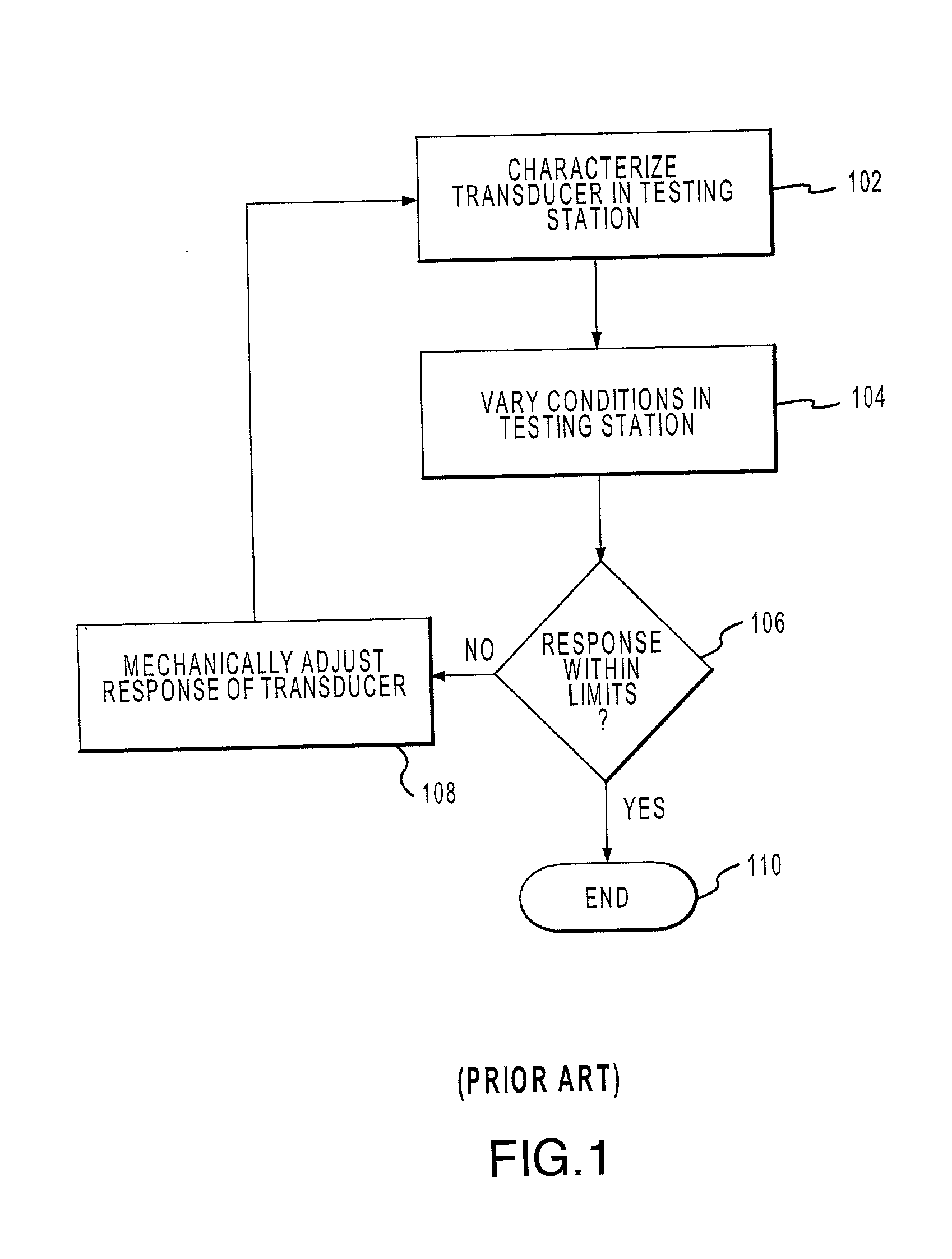
InactiveUS20020078732A1Fluid pressure measurementApparatus with stored calibration coefficientsTransducerEngineering
The present invention discloses a method of using of a programmable circuit to calibrate a transducer. The programmable circuit is coupled to or communicates with a computer and to a testing station. The computer automatically varies the conditions of the testing station and programs the programmable circuit to produce a desired response. In another embodiment, a system is presented that can be used to measure various parameters that includes a programmable that may be mounted in the same package as a sensor. Such a system may include pressure sensors that are optimized to measure very low pressures.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
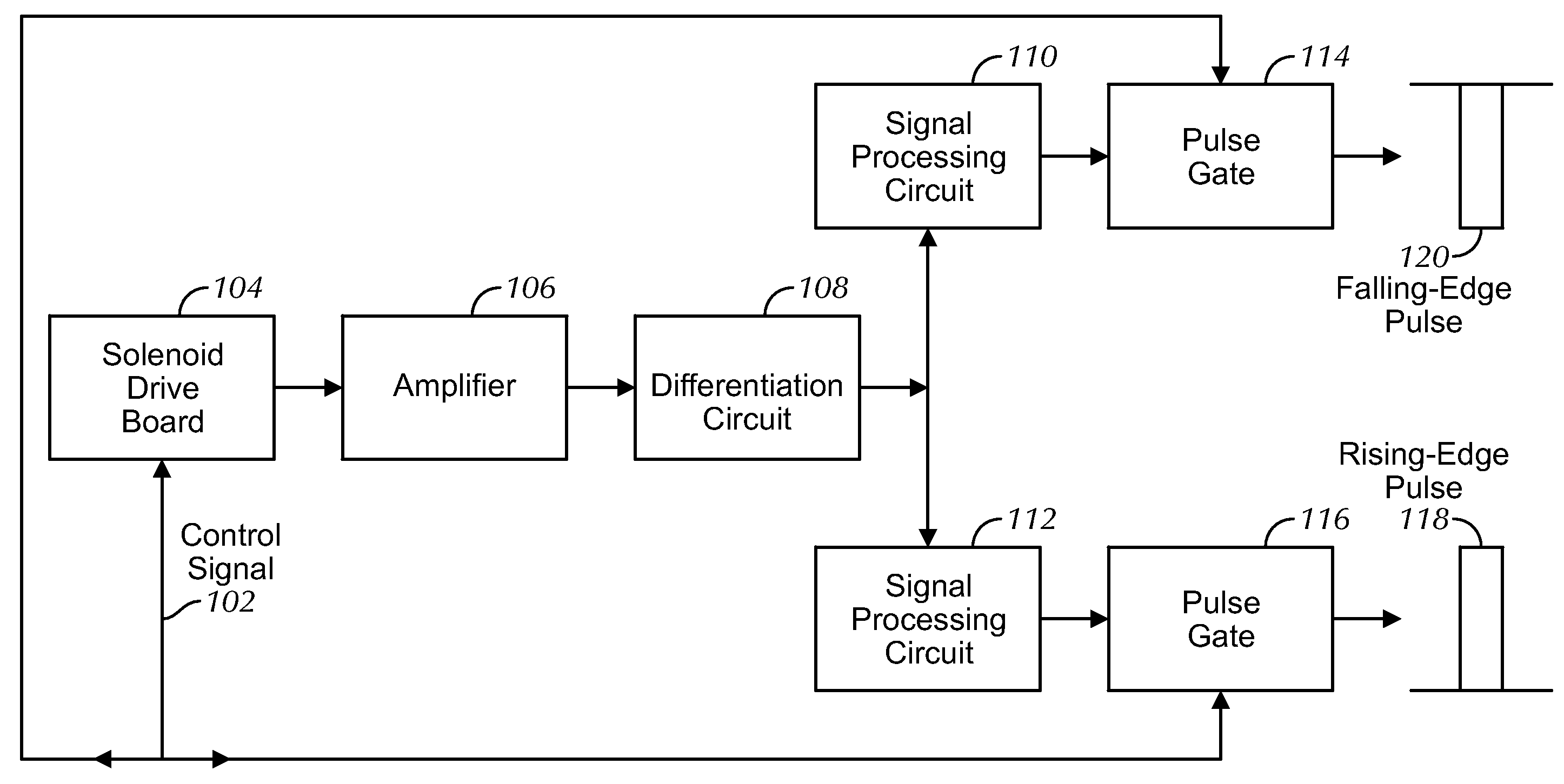
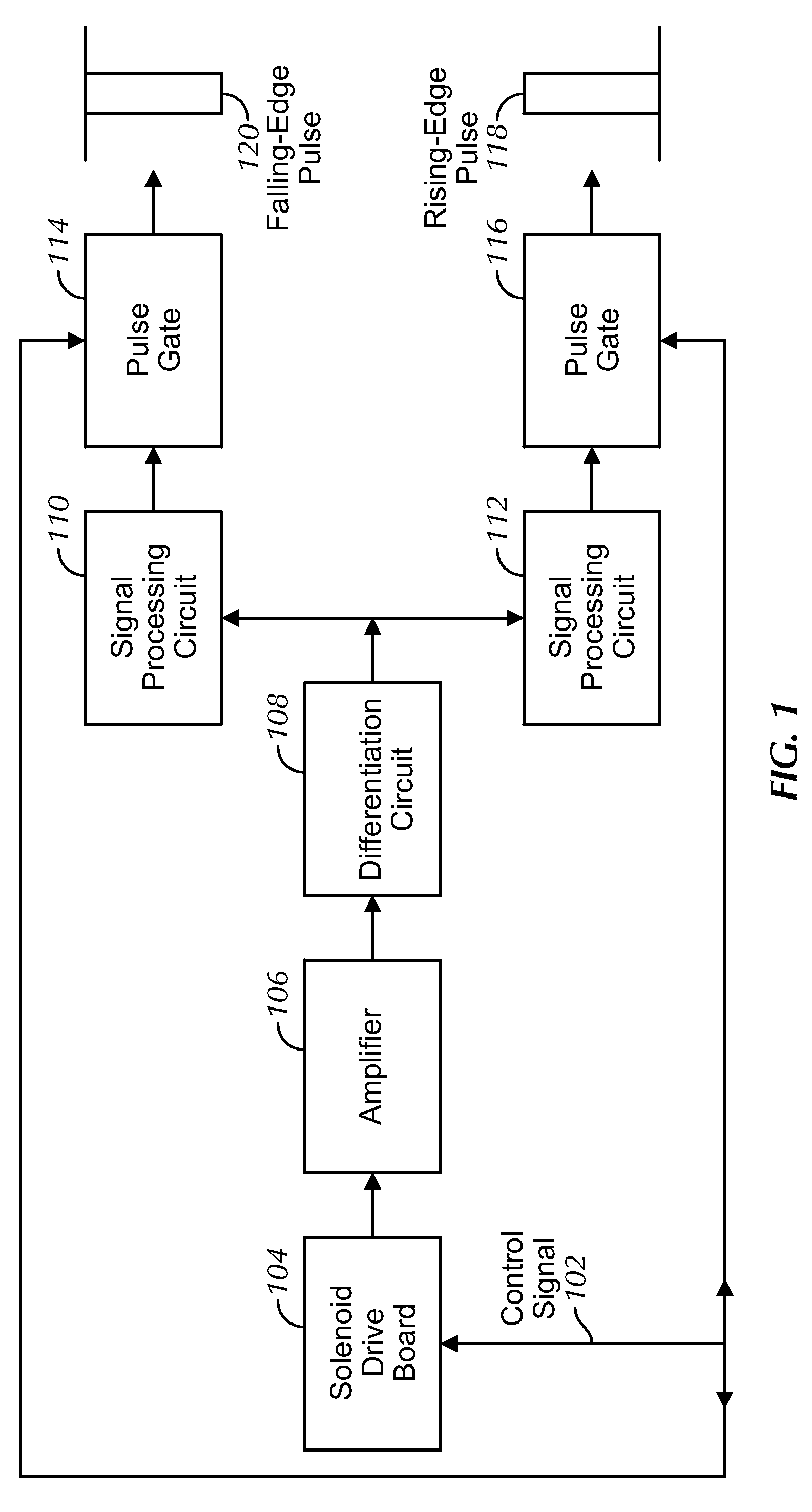
Movement detection circuit of solenoid shear seal valve on subsea pressure control system and method of detecting movement of solenoid actuator
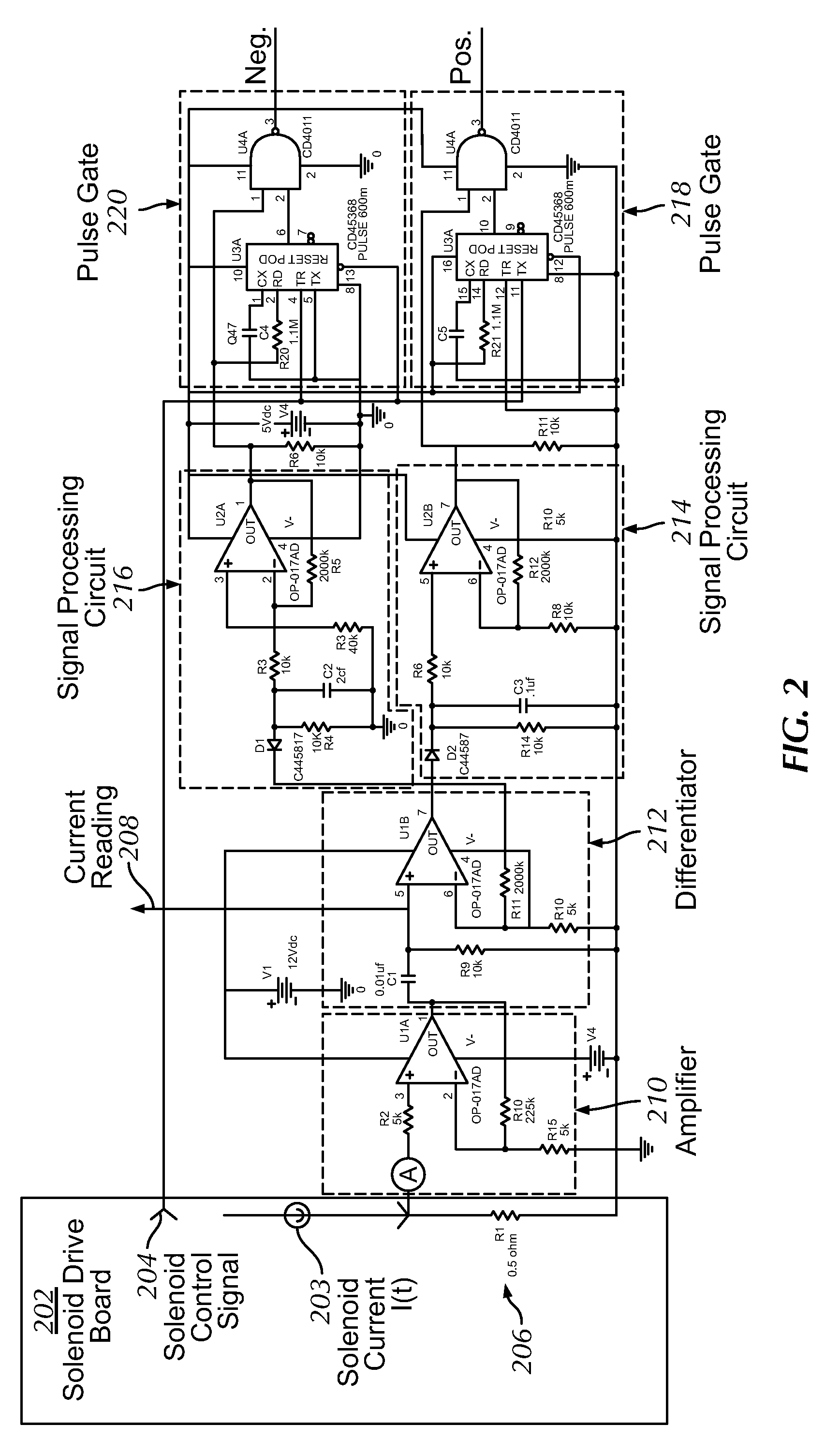
A solenoid current monitoring circuit of a solenoid actuator includes a solenoid drive board configured to receive a control signal, a sensing resistor configured to detect a current signal of a solenoid coil of the actuator resulting from the control signal, and a differentiator configured to differentiate the current signal. The solenoid current monitoring circuit detects the movement of the solenoid actuator based on a change in the differentiated current signal caused by a change in inductance of the solenoid coil.
Owner:HYDRIL USA DISTRIBUTION LLC
Magnetic field sensor with increased field range
ActiveUS20160313413A1Expand the measurement rangeHigh measurement sensitivityMagnetic measurementsAc/dc measuring bridgesCondensed matter physicsEarth's magnetic field
In one embodiment, a TMR field sensor utilizes existing one or more self-test current lines in a configuration to extend magnetic field measurement range without sacrificing measurement sensitivity. The self-test current lines are energized to facilitate magnetic field measurement when the measured magnetic field reaches a threshold. The magnetic field created by self-test coil opposes an external magnetic field being measured to keep the net magnetic field within a desired range where the magnetic field sensor has linear output and desired sensitivity.
Owner:EVERSPIN TECHNOLOGIES
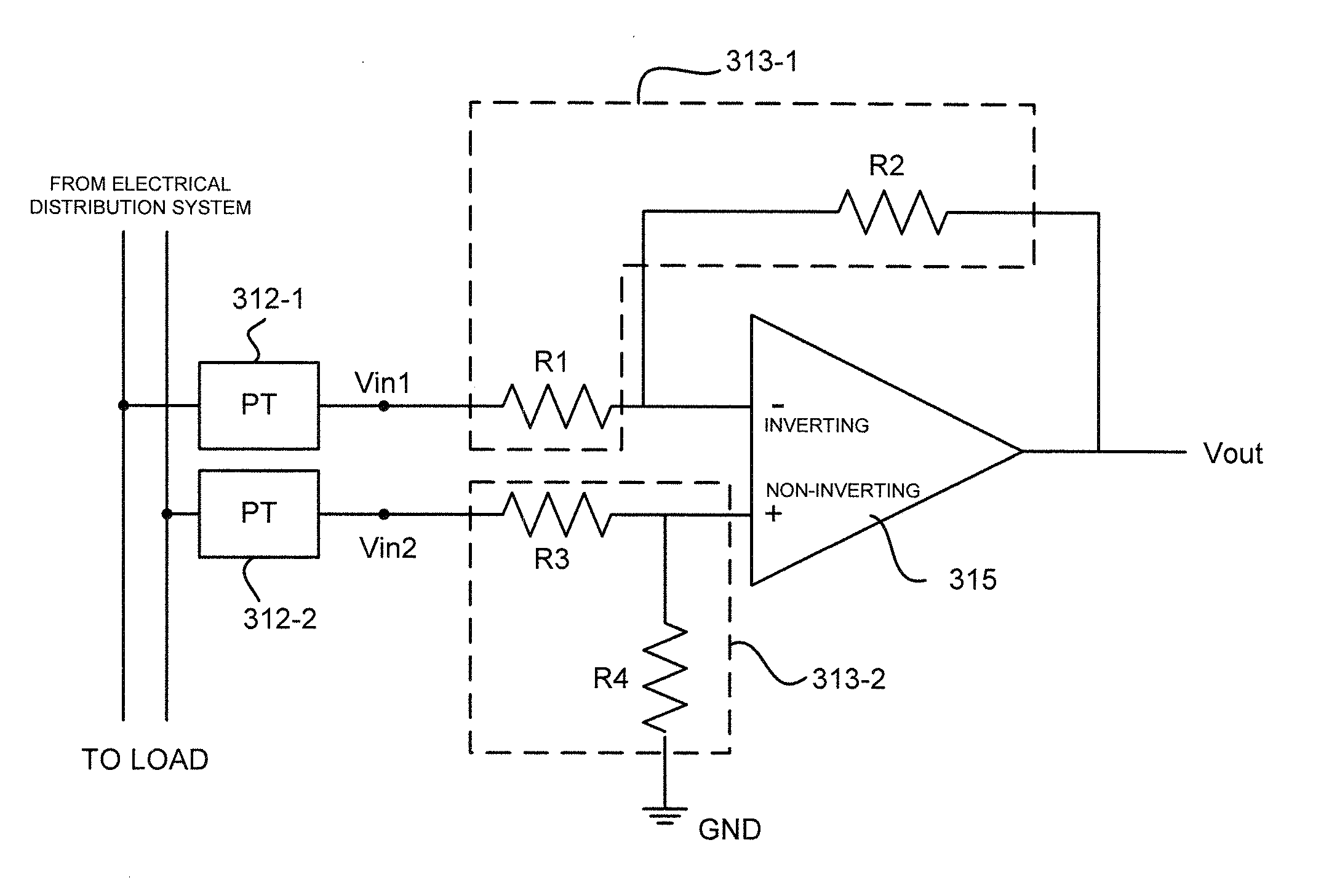
Intelligent electronic device having circuitry for highly accurate voltage sensing
ActiveUS20110260710A1Improve accuracyElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingElectric power distributionDistribution power system
An intelligent electronic device (IED), e.g., an electrical power meter having circuitry for an input voltage structure with an adjusting voltage divider, resulting in a highly accurate power measurement, is provided. The IED includes a first voltage input for receiving a sensed voltage from a first phase of an electrical distribution system, the first voltage input being coupled to a first voltage divider; a second voltage input for receiving a sensed voltage from a neutral phase of the electrical distribution system, the second voltage input being coupled to a second voltage divider; and an inverting operational amplifier (op amp) coupled to the first and second voltage inputs for providing an output proportional to the voltage of the first phase referenced to the neutral phase, wherein the first voltage divider is adjustable to match a ratio of the first voltage divider to a ratio of the second voltage divider.
Owner:ELECTRO INDUSTRIES GAUGE TECH
Current detector circuit and current mode switching regulator
InactiveUS20080218142A1Simple processReduce chip sizeDc network circuit arrangementsElectrical measurement instrument detailsCMOSDetector circuits
A current detector circuit is completely formed of CMOS transistors, and is simplified in process, and can be reduced in the chip size. The current detector circuit of the present invention generates a sense voltage that corrects a voltage for slope compensation according to a coil current in a current mode switching regulator. The current detector circuit includes: a first p-channel transistor which allows a current of 1 / N of a current which flows through a transistor that drives a coil to flow therein; a second p-channel transistor having a source connected to a drain of the first p-channel transistor; a third p-channel transistor connected to a drain of a transistor in which the coil current flows; a voltage mirror circuit having one terminal connected to a drain of the second p-channel transistor, and another terminal connected to a drain of the third p-channel transistor, in which voltages at both of the terminals are identical with each other; and a first n-channel transistor having a drain connected to the drain of the first p-channel transistor, and a source grounded through a sense resistor.
Owner:ABLIC INC
Driving device for stepping motor
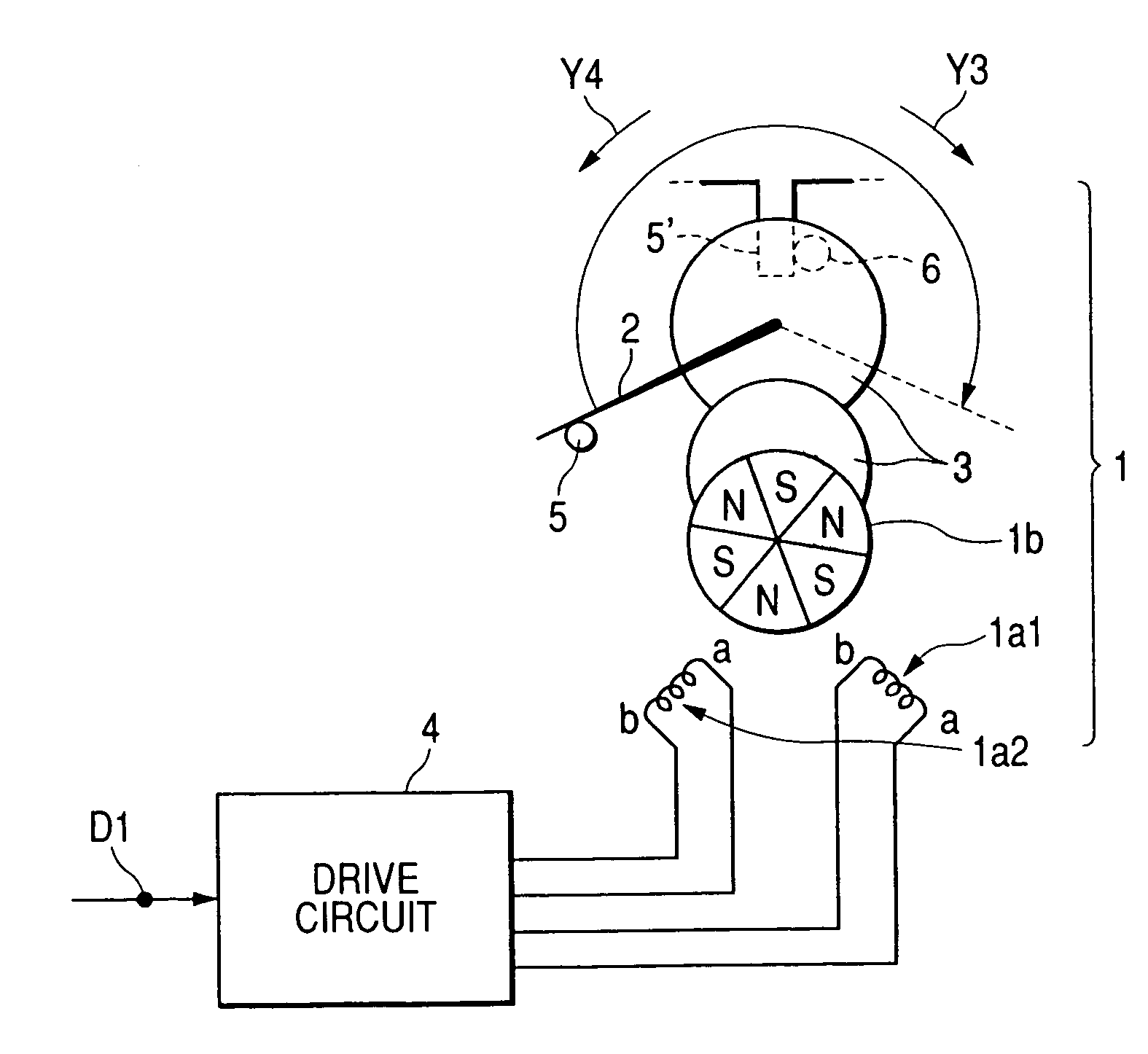
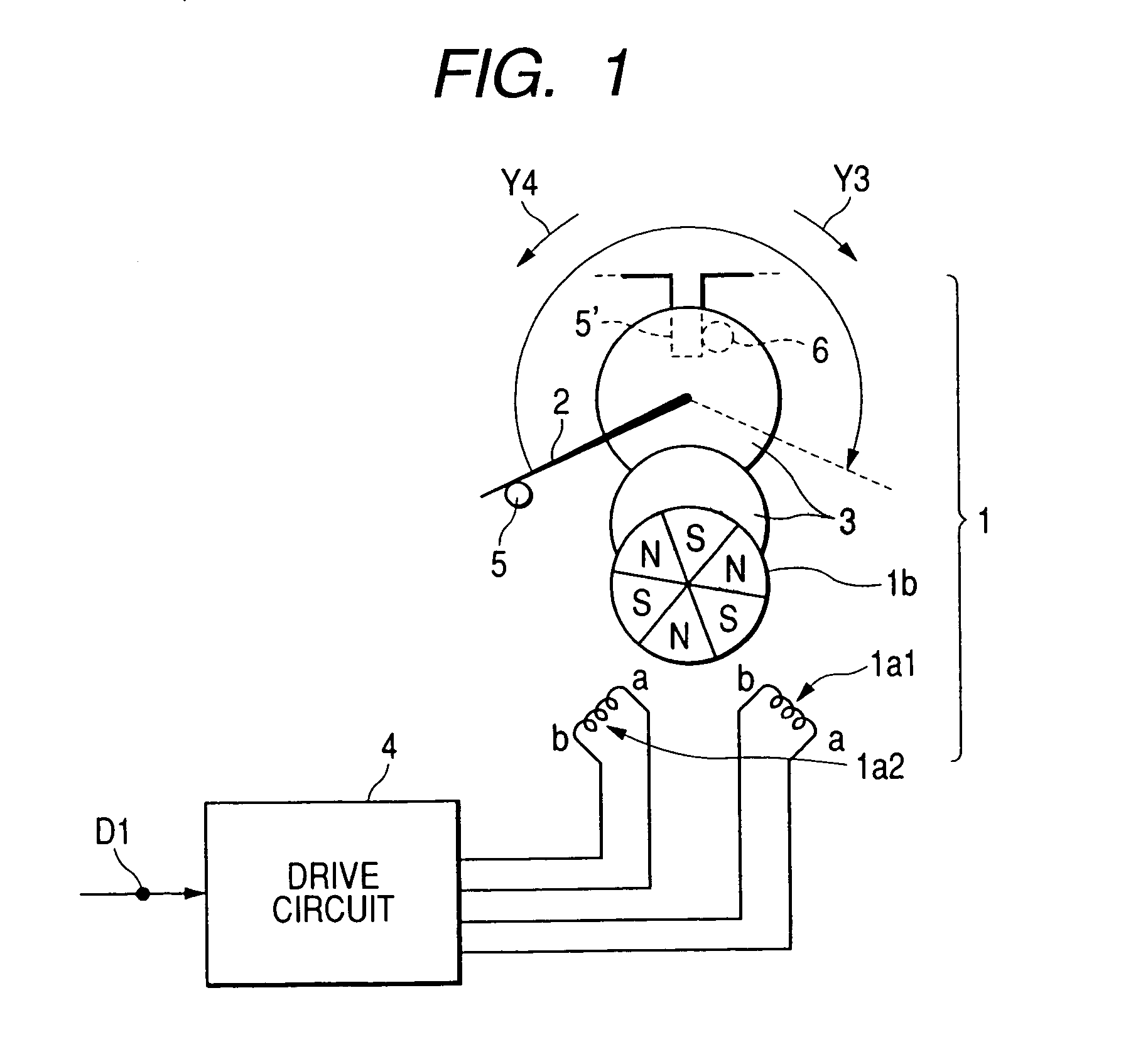
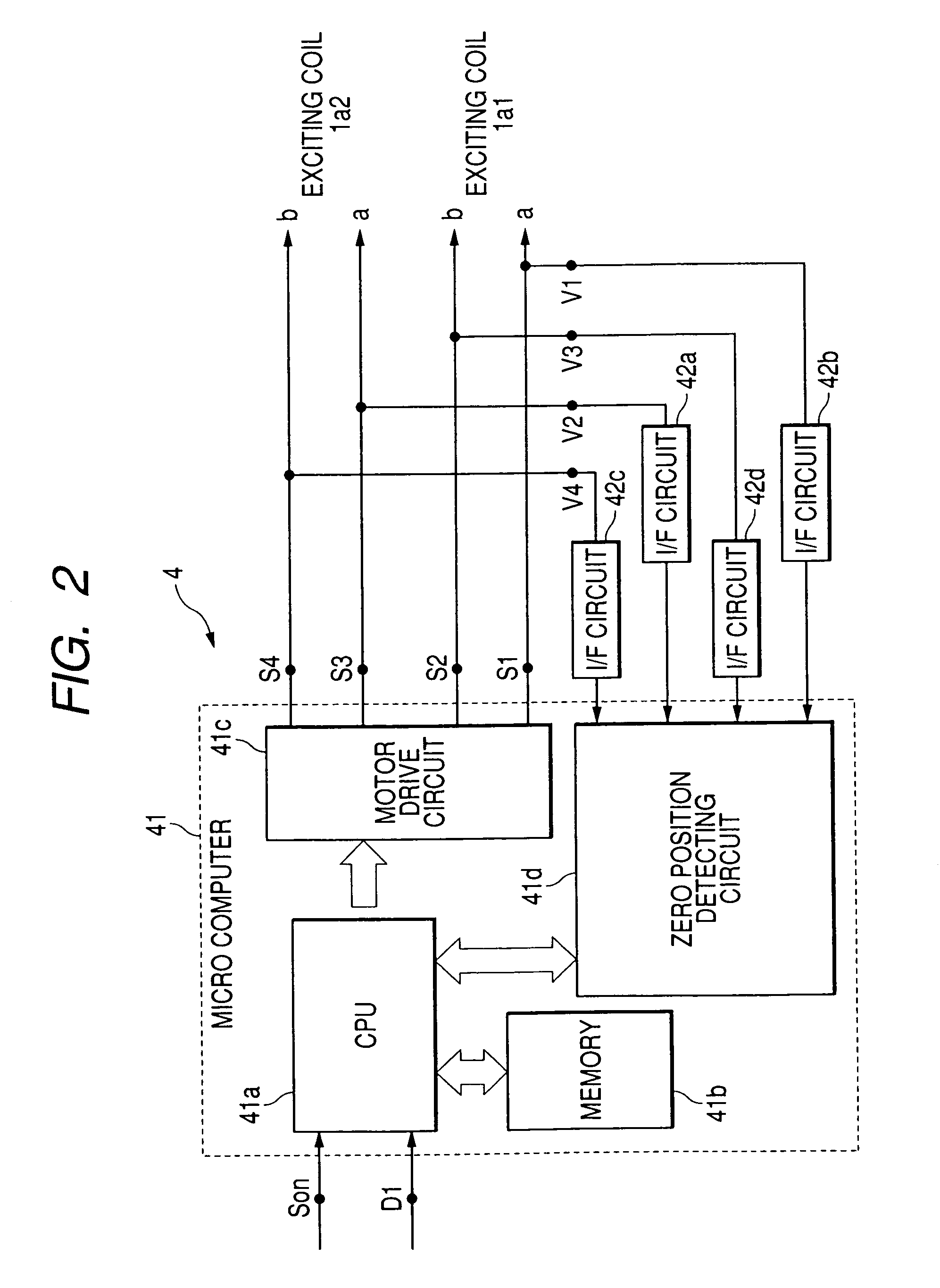
ActiveUS6956351B2Avoid it happening againErroneous detectionDC motor speed/torque controlMeasurement apparatus componentsLocation detectionEngineering
A driving device, includes a stepping motor having an exciting coil and a rotor; a driven member driven in accordance with a rotation of the rotor; a stopper mechanically stopping the driven member at a zero position; a controller controlling the state of excitation of the exciting coil; an induced voltage detector detecting an induced voltage generated by a change of magnetic flux according to the rotation of the rotor; and a zero position detector detecting a stoppage of the driven member at the zero position. The controller supplies an exciting pattern to the exciting coil at the time of processing of zero position detection. The exciting pattern includes a first exciting step for detecting the induced voltage and a second exciting step for rotation. Total periods of the first exciting step is greater than that of the second exciting step during an electrical angle 90° in the one cycle.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
Gasless calibration in metabolic gas analyzers
ActiveUS20090056409A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansGas cylinderCarbon dioxide analyzer
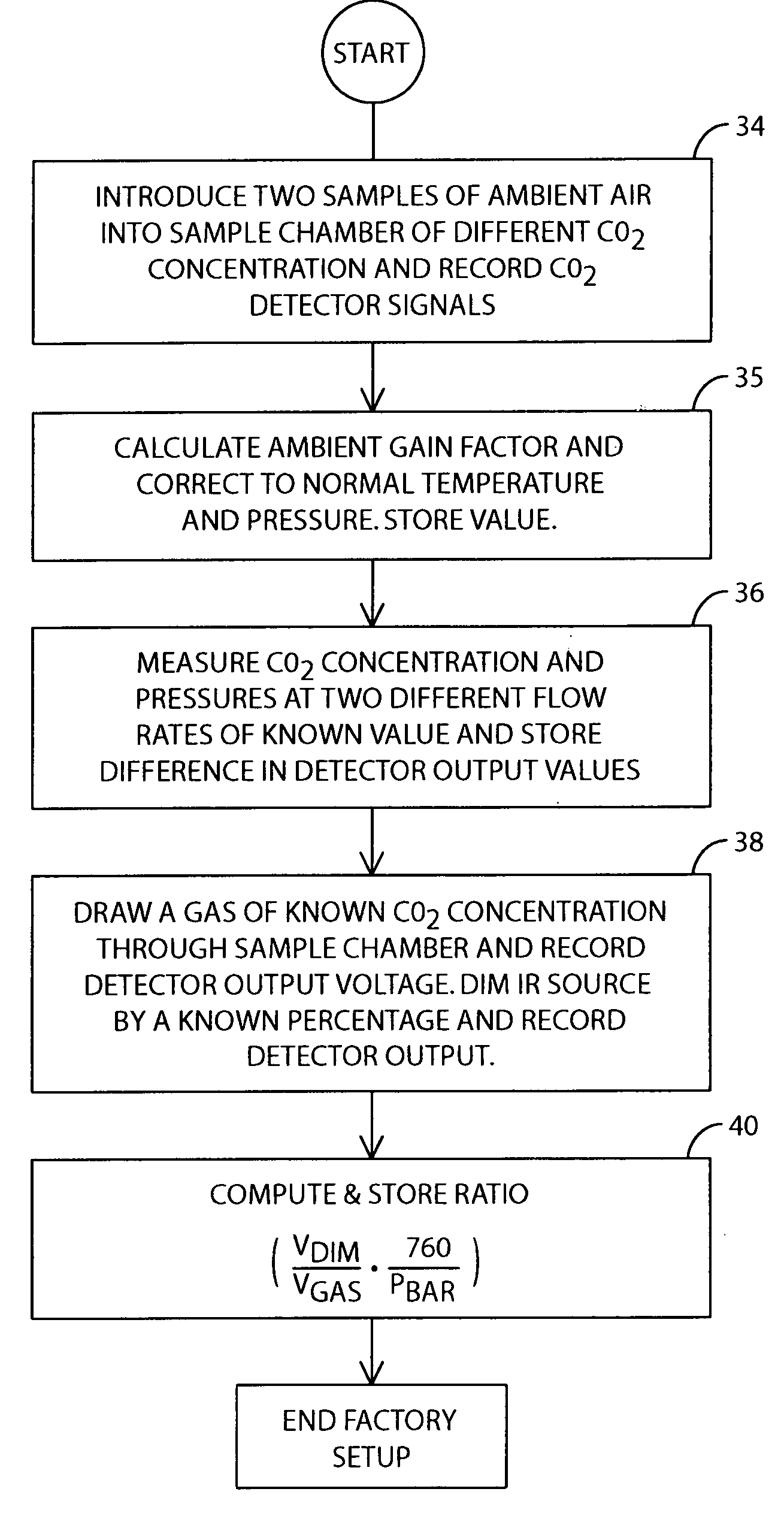
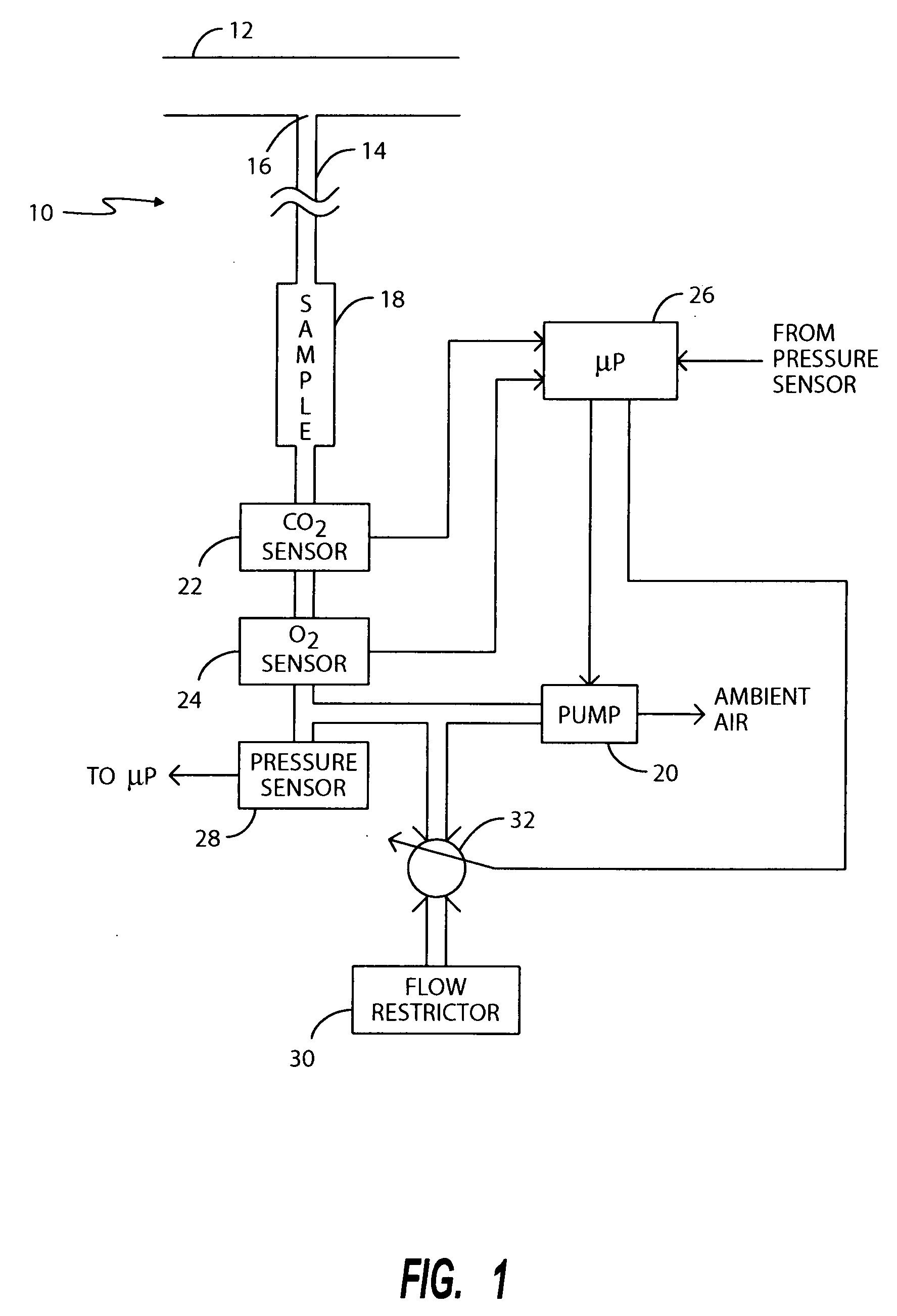
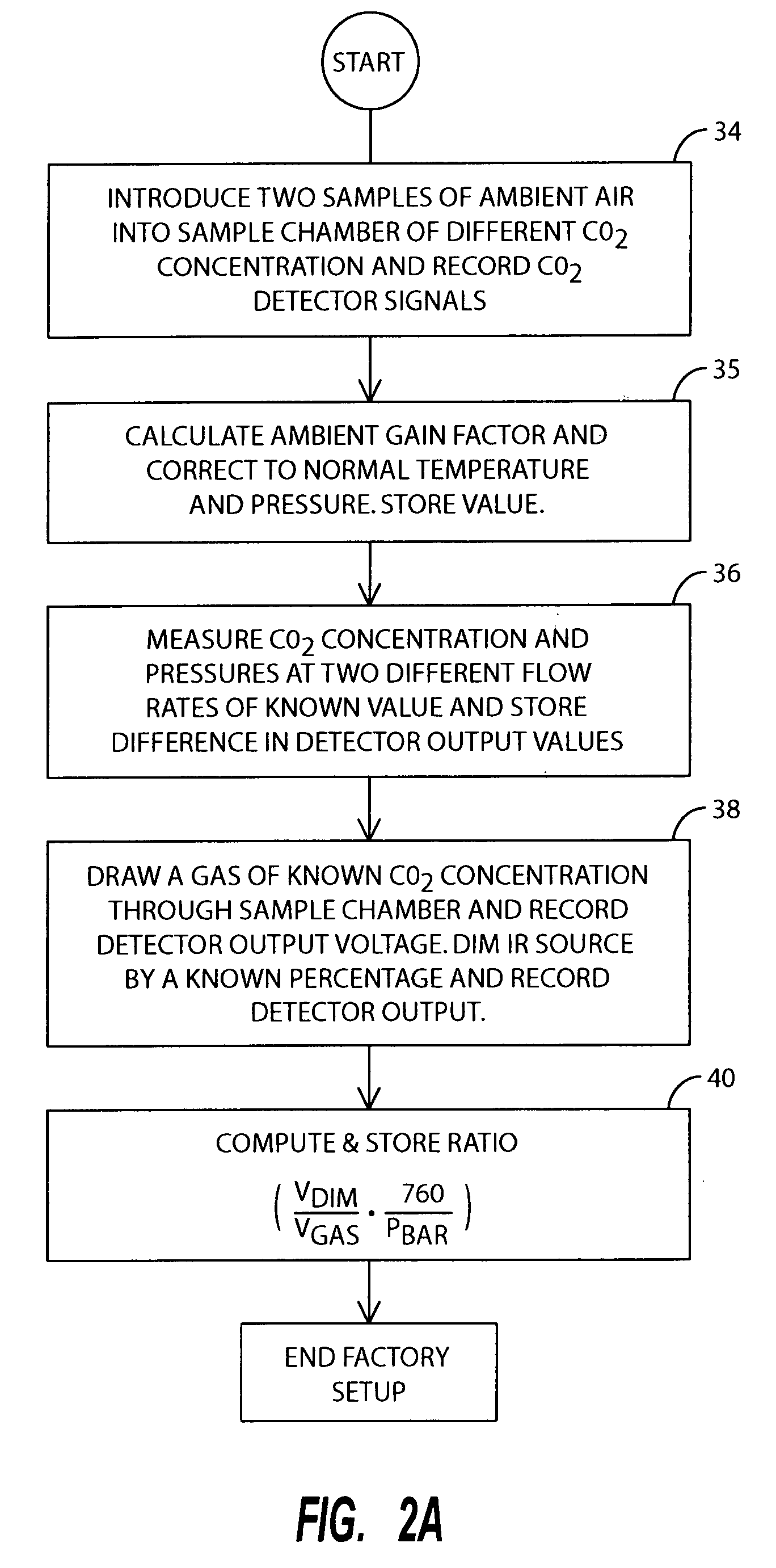
A method of calibrating a metabolic analyzer incorporating an oxygen analyzer and a NDIR carbon dioxide analyzer in the field that does not require the use of gas cylinders containing gases of known concentration is described. In calibrating the CO2 detector, at the time of factory setup, the detector output for a gas of a known concentration is measured and stored in the memory of the metabolic analyzer's microprocessor, as is the detector output voltage when the IR source is dimmed by a known percentage. Subsequently, in the field, CO2 levels in ambient air and cell pressure are measured at two different flow rates through the sample chamber and the IR source is again dimmed by the same percentage as had been used at the time of factory setup. Based upon the resulting readings, both the zeroing and span adjustment factors can be computed.
Owner:MEDICAL GRAPHICS CORP A CORP OF MN
Method and apparatus for current measurement using hall sensors without iron cores
A method and apparatus for current measurement using Hall sensors without iron cores, used to estimate a flowing current in an electric conducting cable are provided by the exemplary examples of the present invention. The method for current measurement using Hall sensors without iron cores includes the following step: (a) providing Hall sensors to be attached to or located near the electric conducting cable; (b) using each of the Hall sensors to measure the flux density of the magnetic field generated by the flowing current, so as to generate an output voltage according to the flux density of the magnetic field; (c) performing a statistical operation on the output voltages of the Hall sensors, so as to generate a statistical voltage; (d) estimating the flowing current in the electric conducting cable according to the statistical voltage.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Device for detecting the thinning down of the substrate of an integrated circuit chip
ActiveUS20100315108A1Overcome disadvantagesEasy to implementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringIntegrated circuit
A device for detecting the thinning down of the substrate of an integrated circuit chip, including, in the active area of the substrate, bar-shaped diffused resistors connected as a Wheatstone bridge, wherein: first opposite resistors of the bridge are oriented along a first direction; the second opposite resistors of the bridge are oriented along a second direction; and the first and second directions are such that a thinning down of the substrate causes a variation of the imbalance value of the bridge.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (ROUSSET) SAS
Methods, Devices, and Systems Which Determine a Parameter Value of an Object or an Environment From a Voltage Reading Associated With a Common Mode Signal of a Balanced Circuit
ActiveUS20140023112A1Thermometer detailsHumidity sensorsResistive sensorsElectrical resistance and conductance
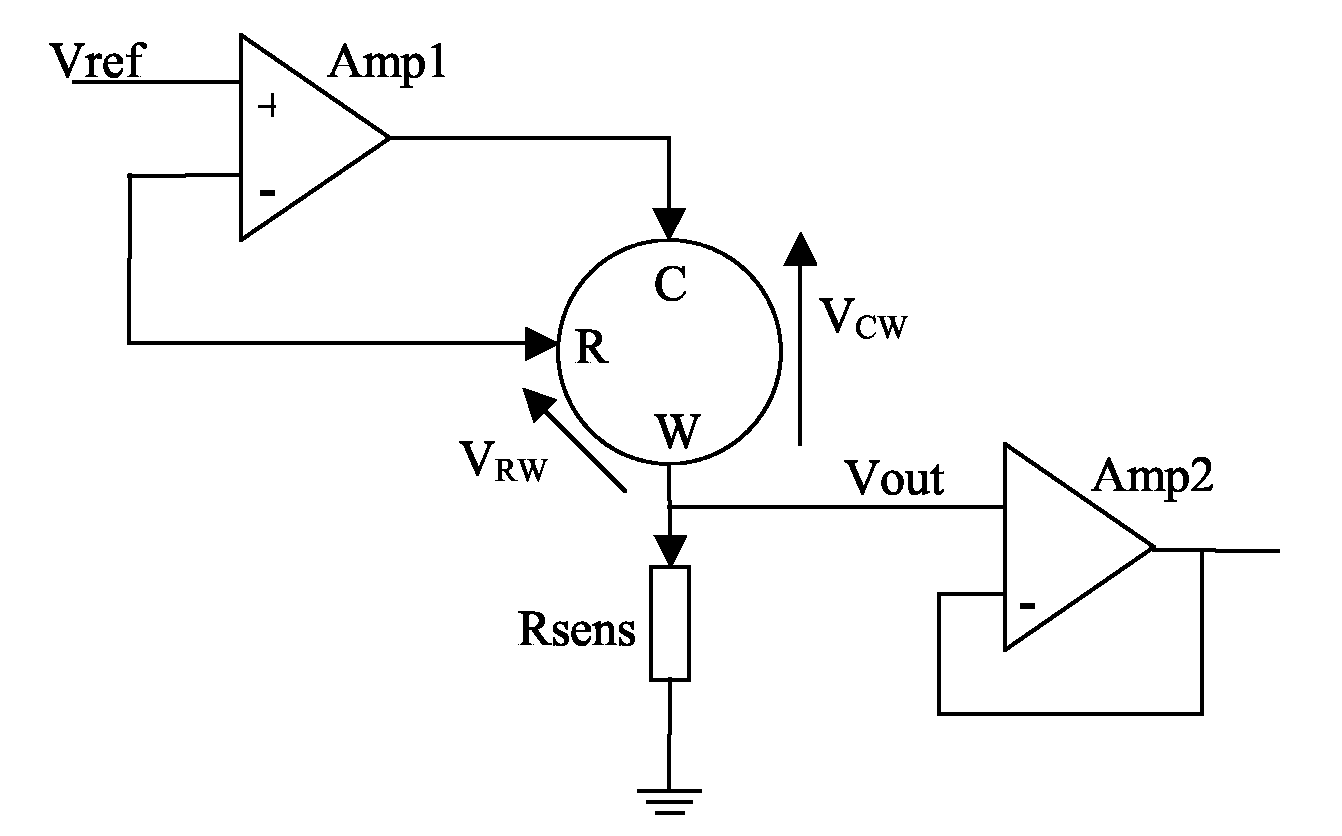
A method for determining a value of a parameter of an object or an environment includes positioning a device having a balanced circuit in or on an object or within a particular environment, wherein the balanced circuit comprises elements which are operationally sensitive to changes in a parameter of the object or the environment. The method further includes measuring a common mode signal of the balanced circuit and determining, from the common mode signal, a value of the parameter. An exemplary implementation of the method includes determining temperature using a resistive sensor having a Wheatstone bridge circuit with two variable resistors and two fixed resistors. Embodiments of systems and devices configured to employ such methods are provided, particularly medical probes, electronic signal monitoring devices, and systems employing such devices.
Owner:MILLAR INSTR
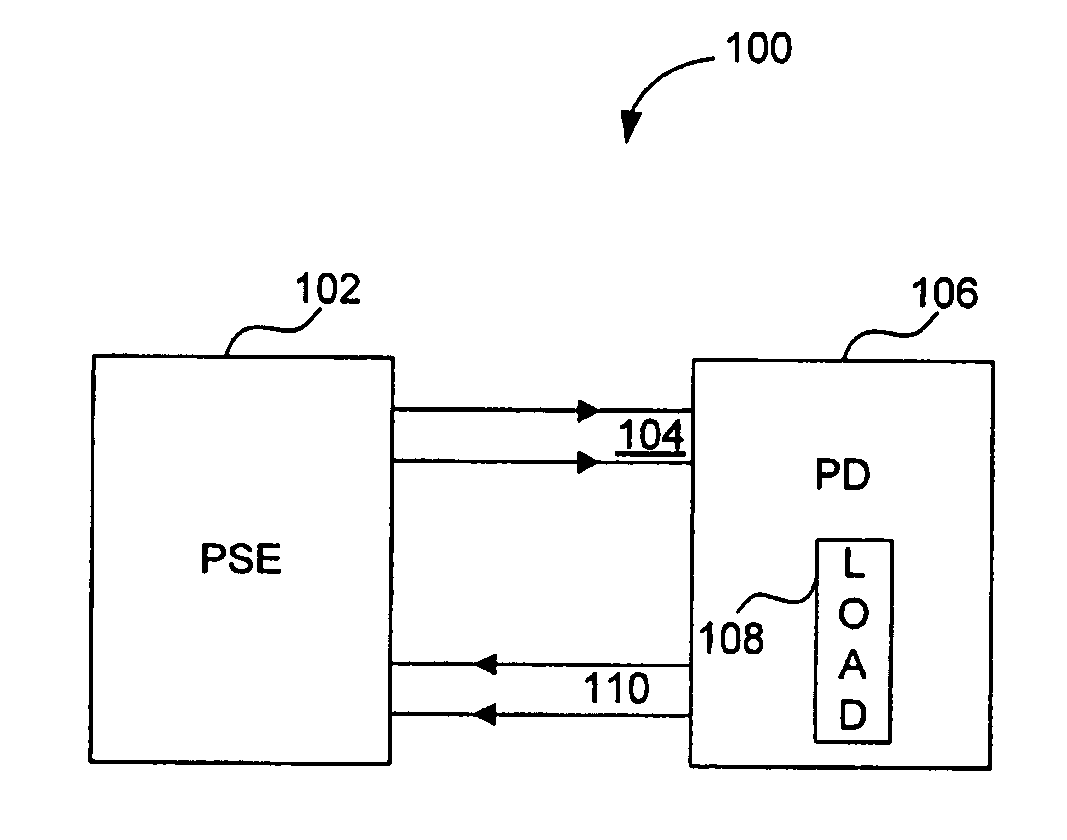
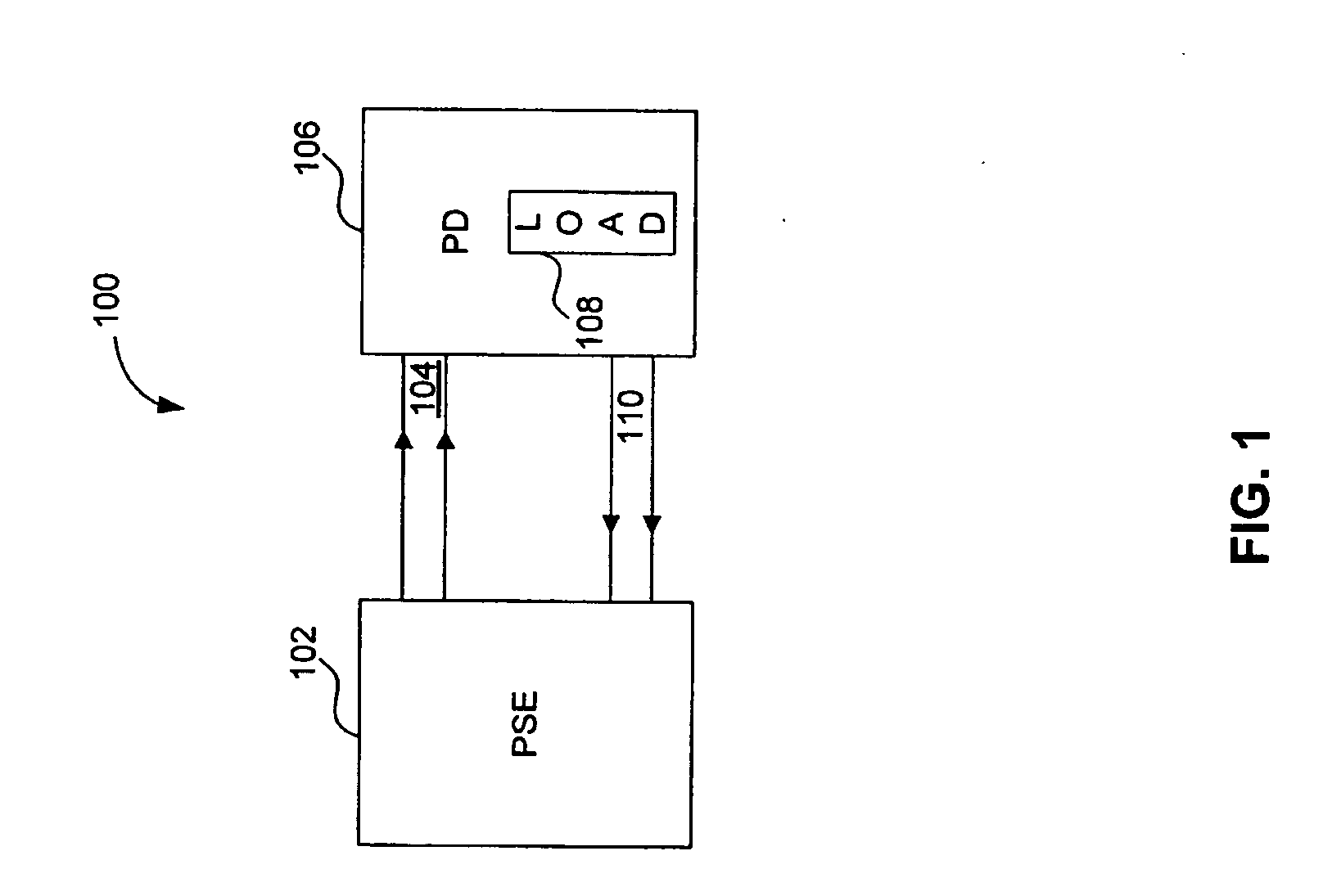
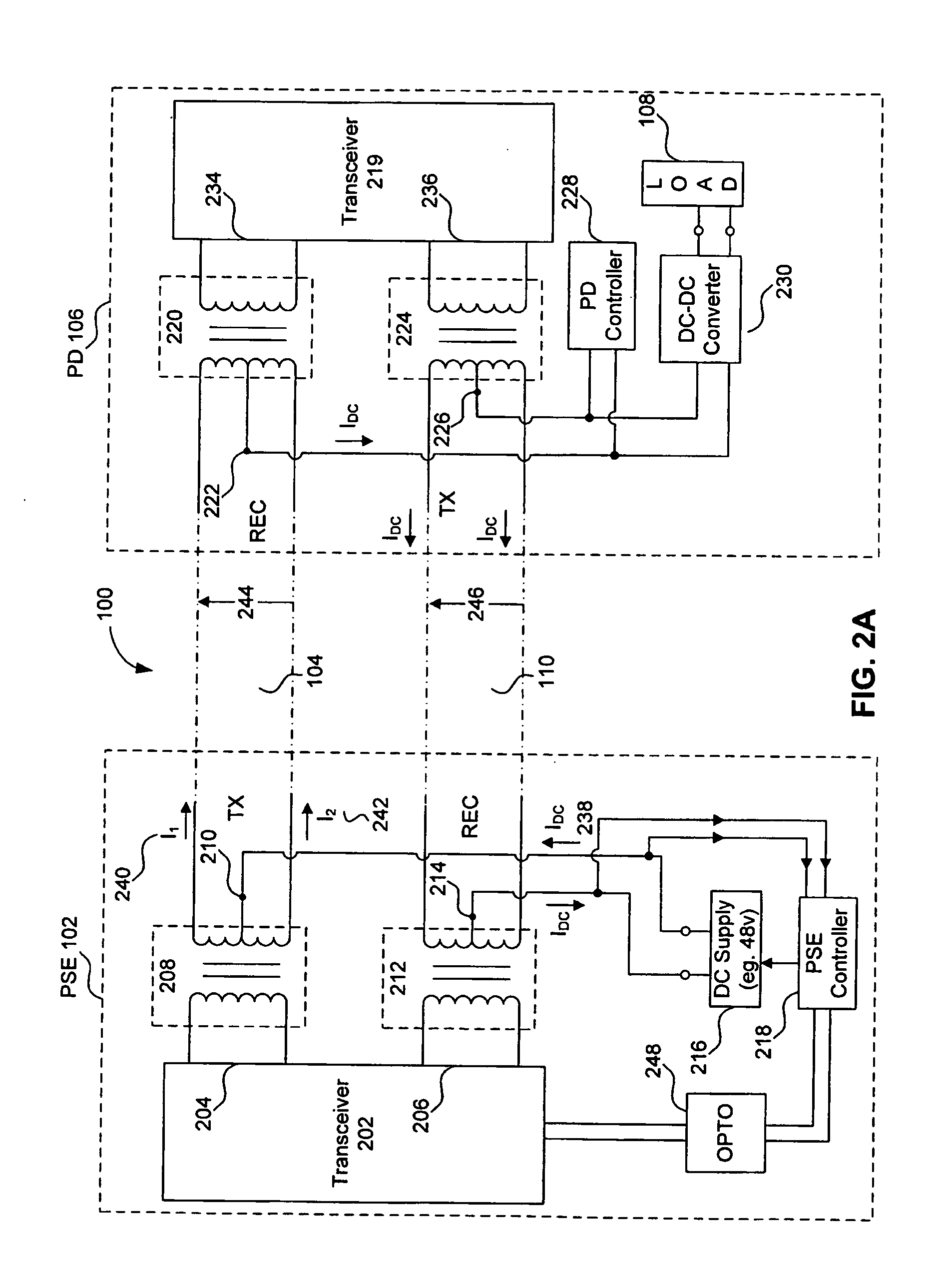
Apparatus for sensing an output current in a communications device
InactiveUS20070174527A1Multiplex communicationElectrical testingTelecommunications linkCommunication link
Power over Ethernet (PoE) communication systems provide power and data communications over the same communications link, where a power source device (PSE) provides DC power (for example, 48 volts DC) to a powered device (PD). The DC power is transmitted simultaneously over the same communications medium with the high speed data from one node to the other node. The PSE typically includes a controller that controls the DC power provided to the PD at the second node of the communications link. The PSE controller measures the voltage, current, and temperature of the outgoing and incoming DC supply lines to characterize the power requirements of the PD. The PSE controller includes a resistorless switch to measure the current. The resistorless switch includes a sense transistor and a current mirror to allowing the PSE controller to calculate the current based upon a replica current.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com