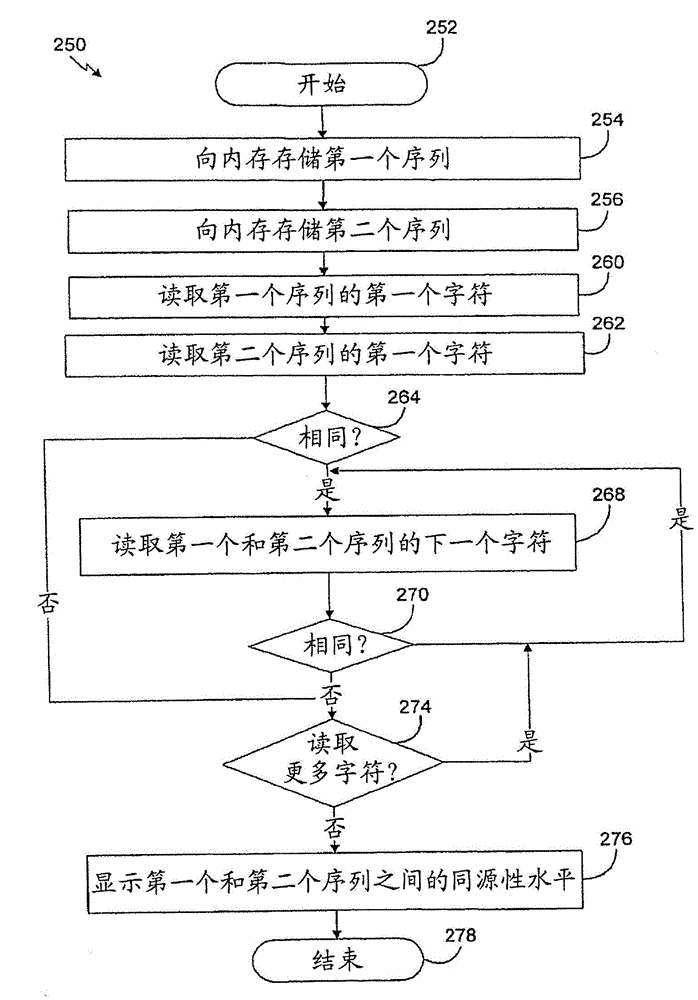
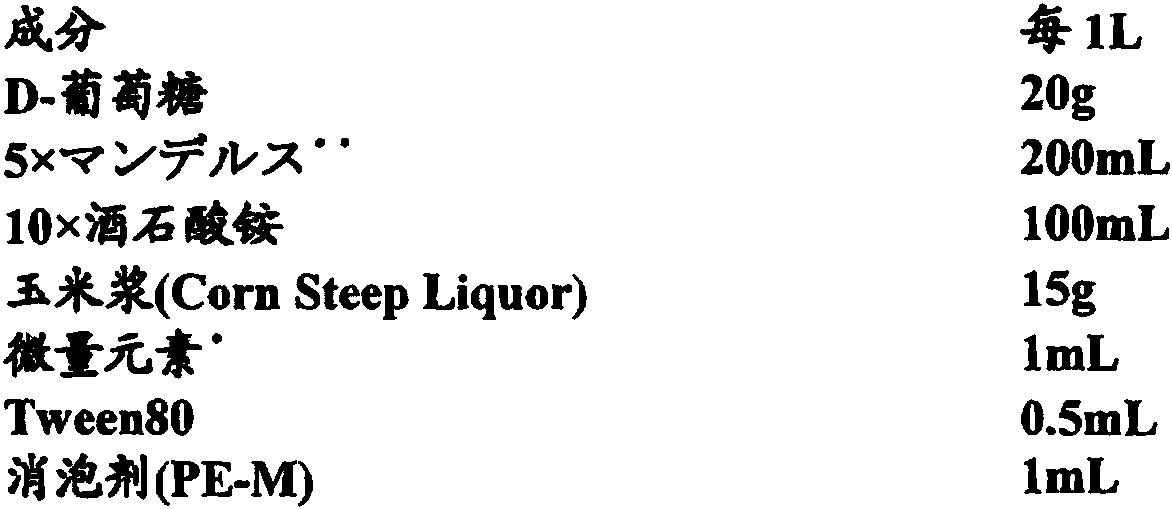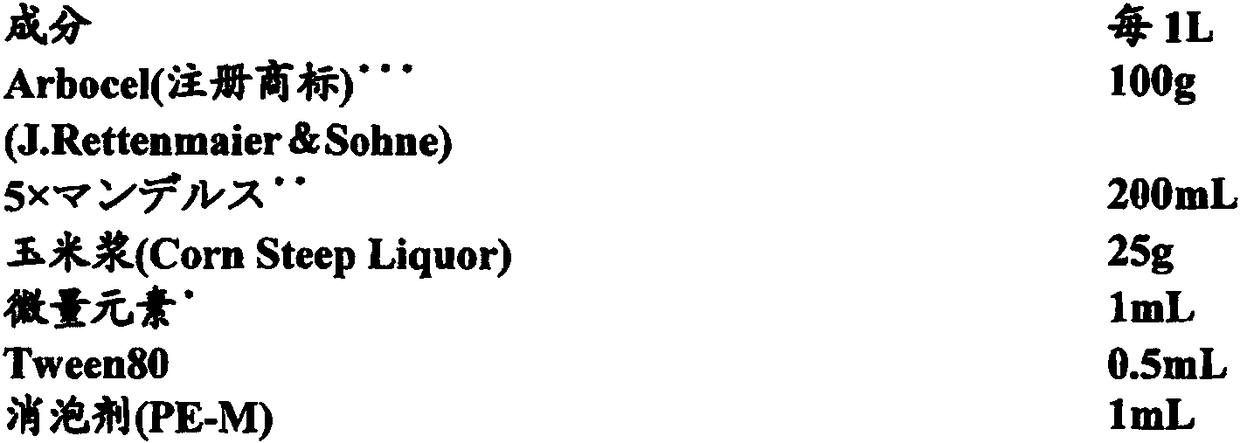Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
60 results about "Xylosidases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
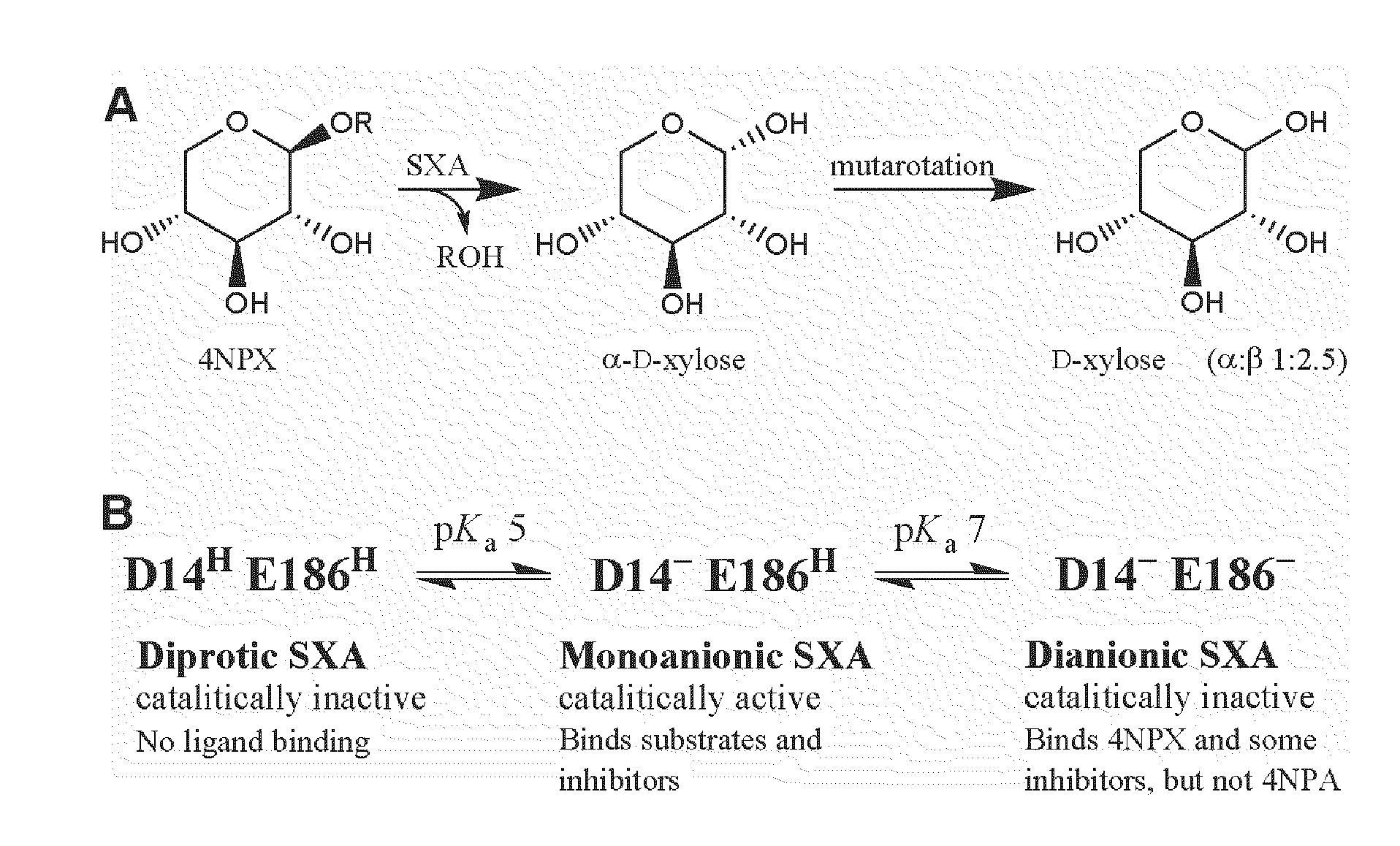
A group of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of alpha- or beta-xylosidic linkages. EC 3.2.1.8 catalyzes the endo-hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-D-xylosidic linkages; EC 3.2.1.32 catalyzes the endo-hydrolysis of 1,3-beta-D-xylosidic linkages; EC 3.2.1.37 catalyzes the exo-hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-D-linkages from the non-reducing termini of xylans; and EC 3.2.1.72 catalyzes the exo-hydrolysis of 1,3-beta-D-linkages from the non-reducing termini of xylans. Other xylosidases have been identified that catalyze the hydrolysis of alpha-xylosidic bonds.
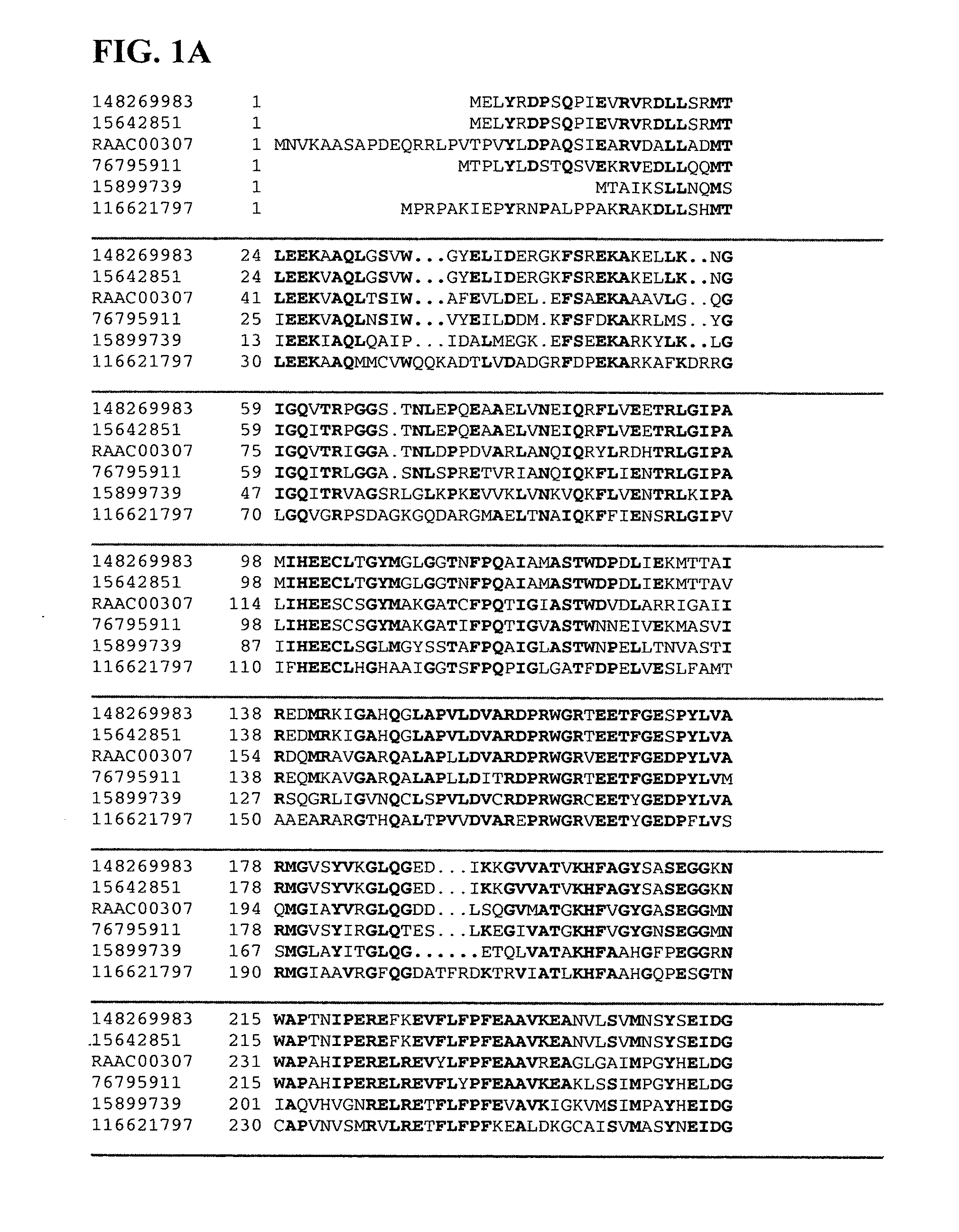
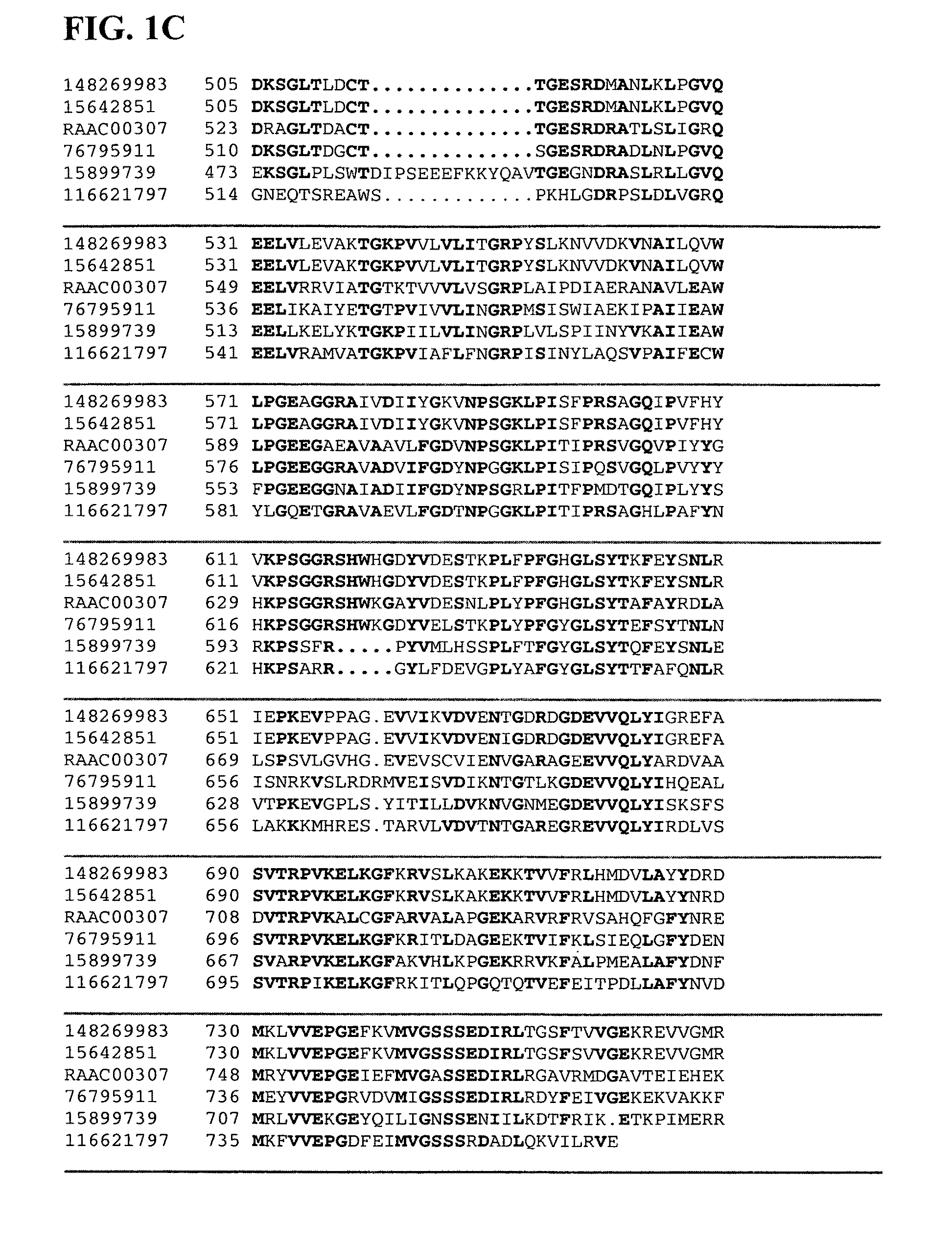
Thermal and acid tolerant beta xylosidases, arabinofuranosidases, genes encoding, related organisms, and methods
ActiveUS20100311110A1Decreasing proteolysisAllow stabilizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementXylanNucleic acid sequencing
Isolated and / or purified polypeptides and nucleic acid sequences encoding polypeptides from Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius and variations thereof are provided. Further provided are methods of at least partially degrading xylotriose, xylobiose, and / or arabinofuranose-substituted xylan using isolated and / or purified polypeptides and nucleic acid sequences encoding polypeptides from Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius and variations thereof.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
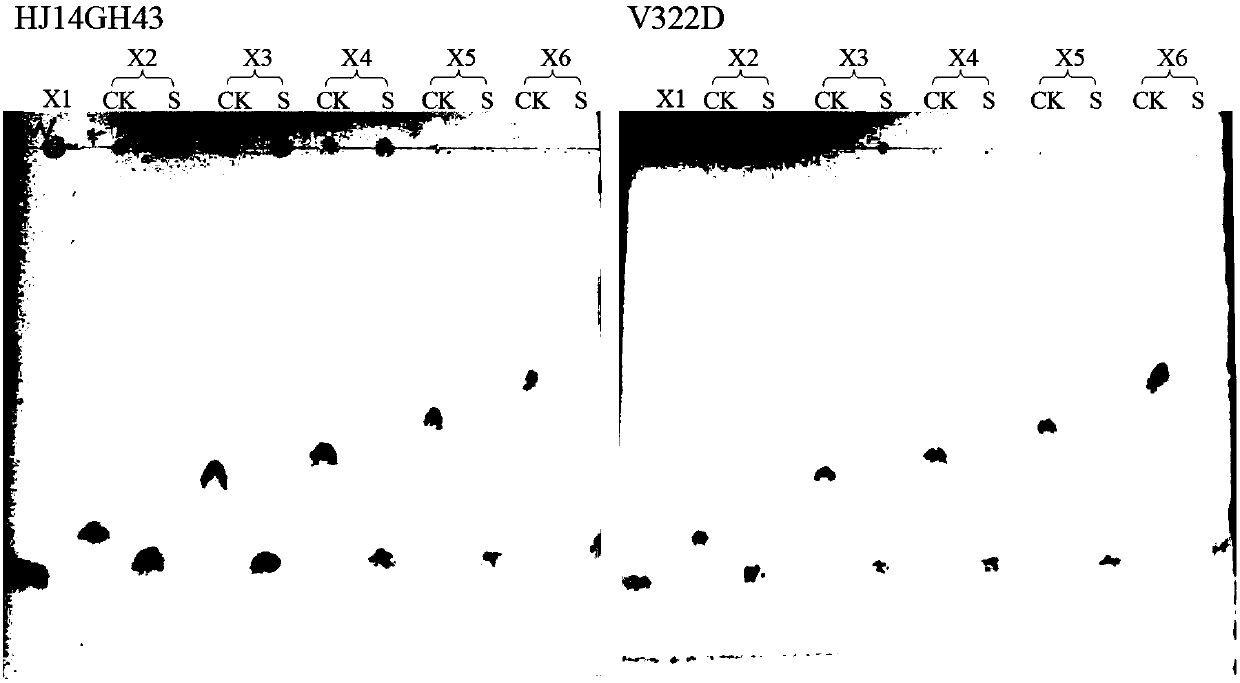
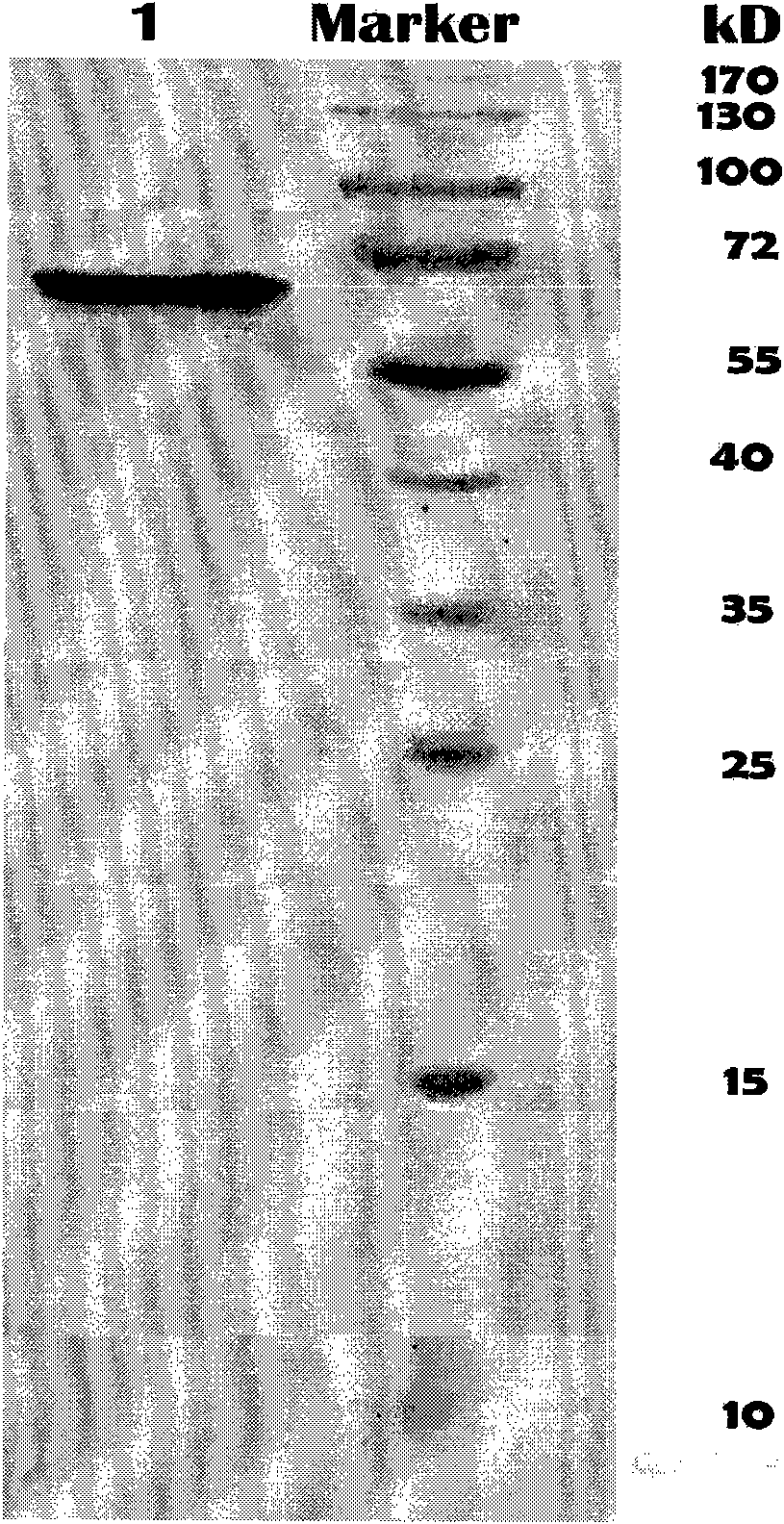
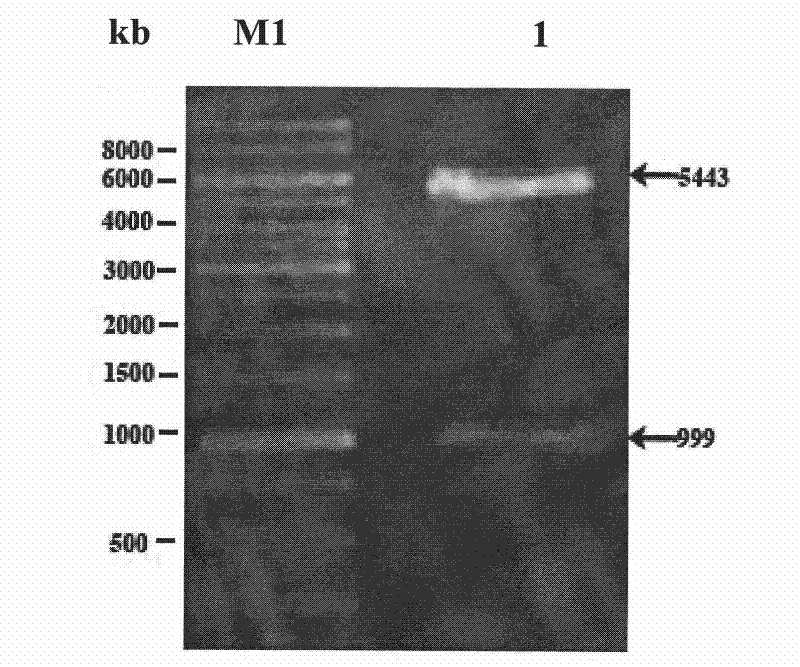
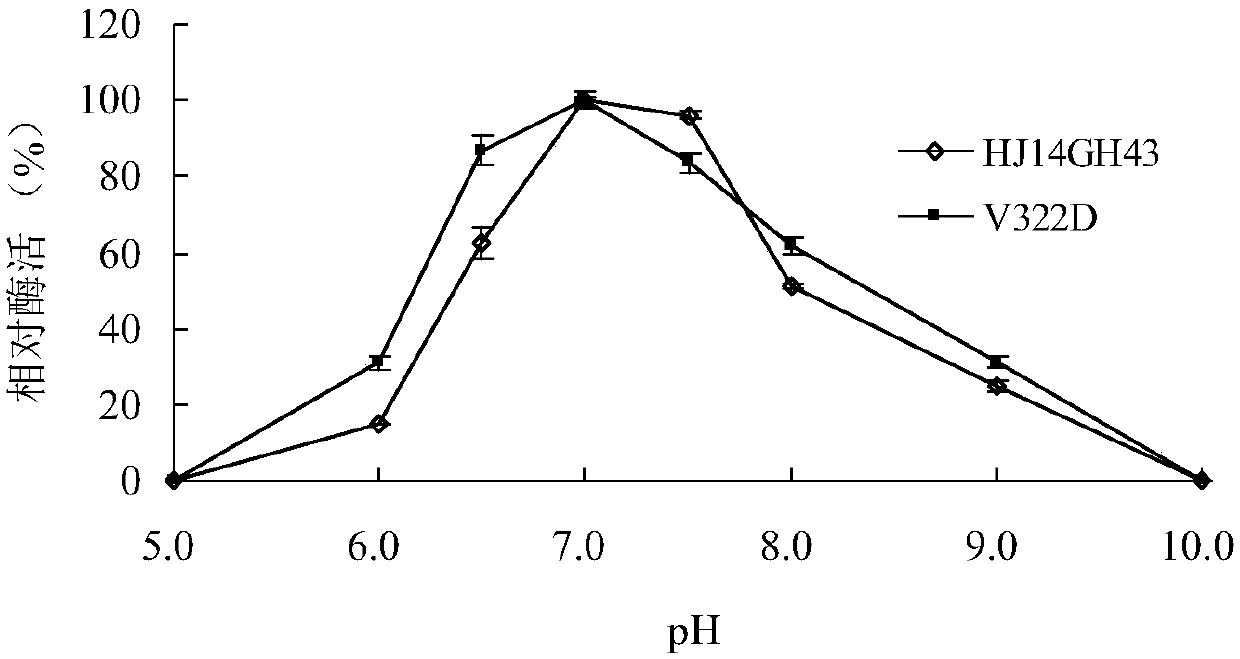
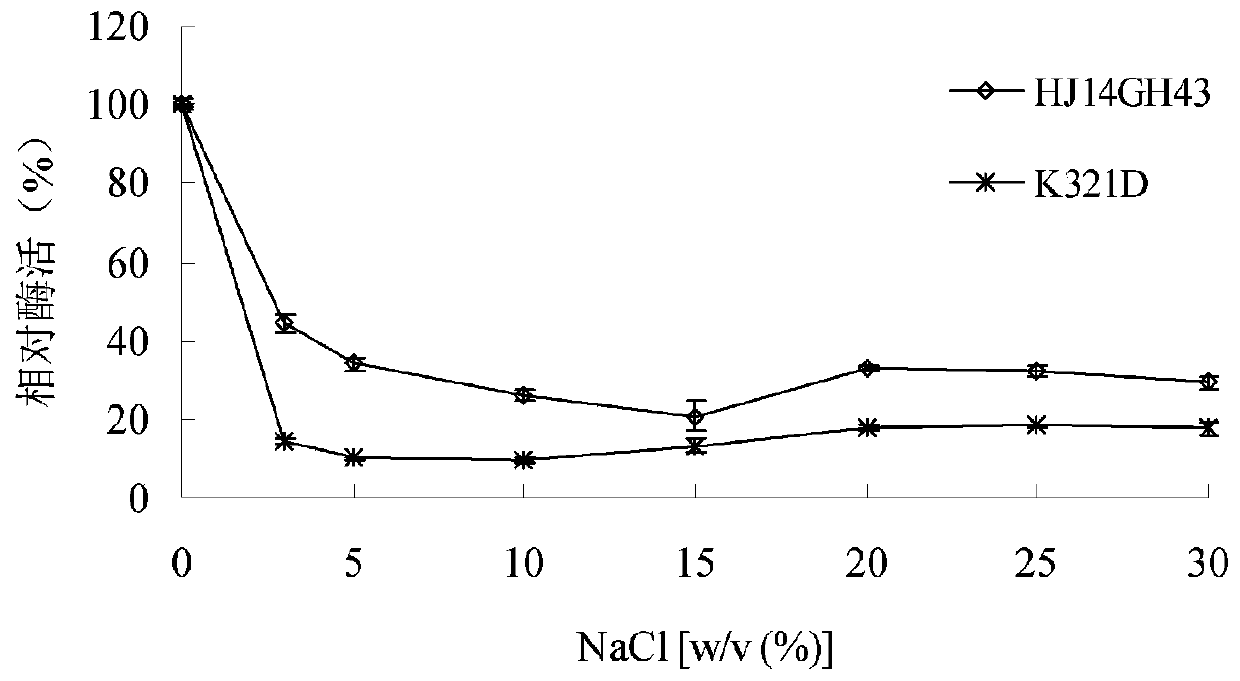
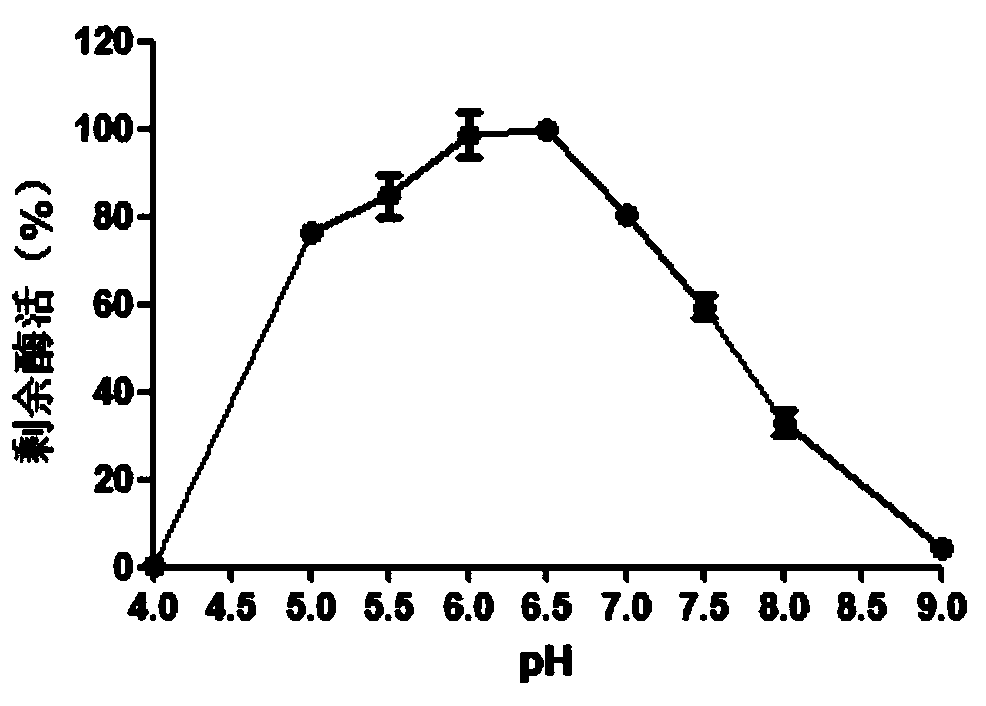
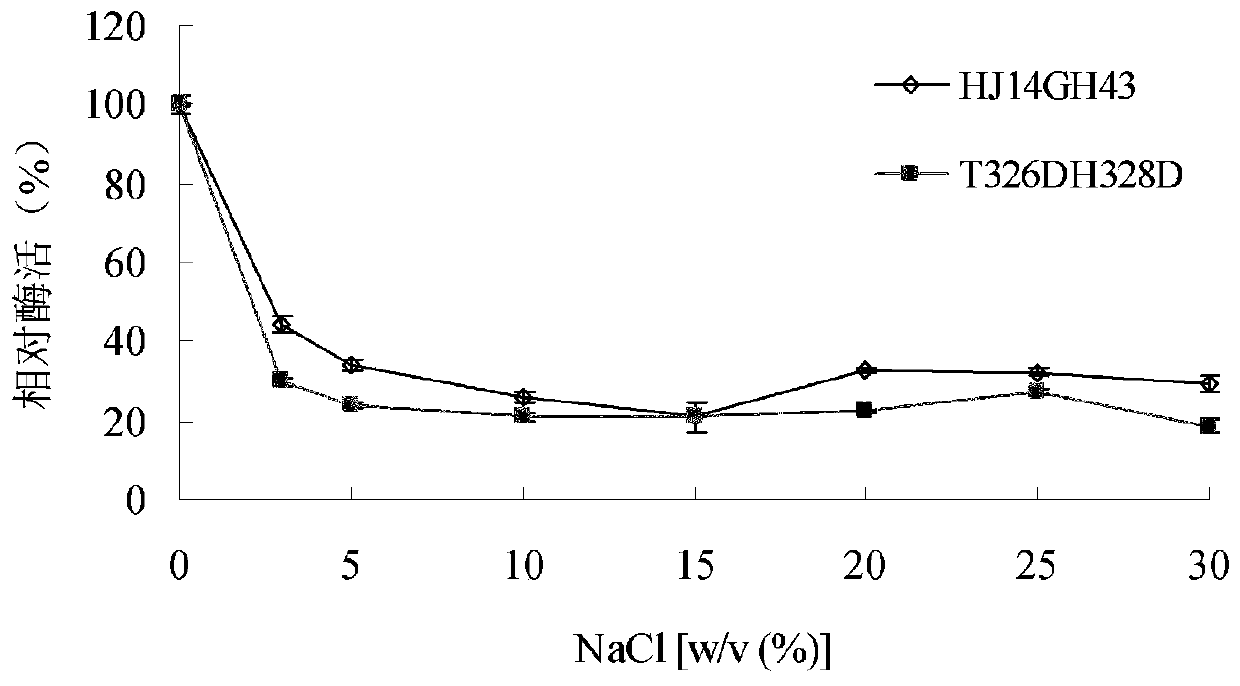
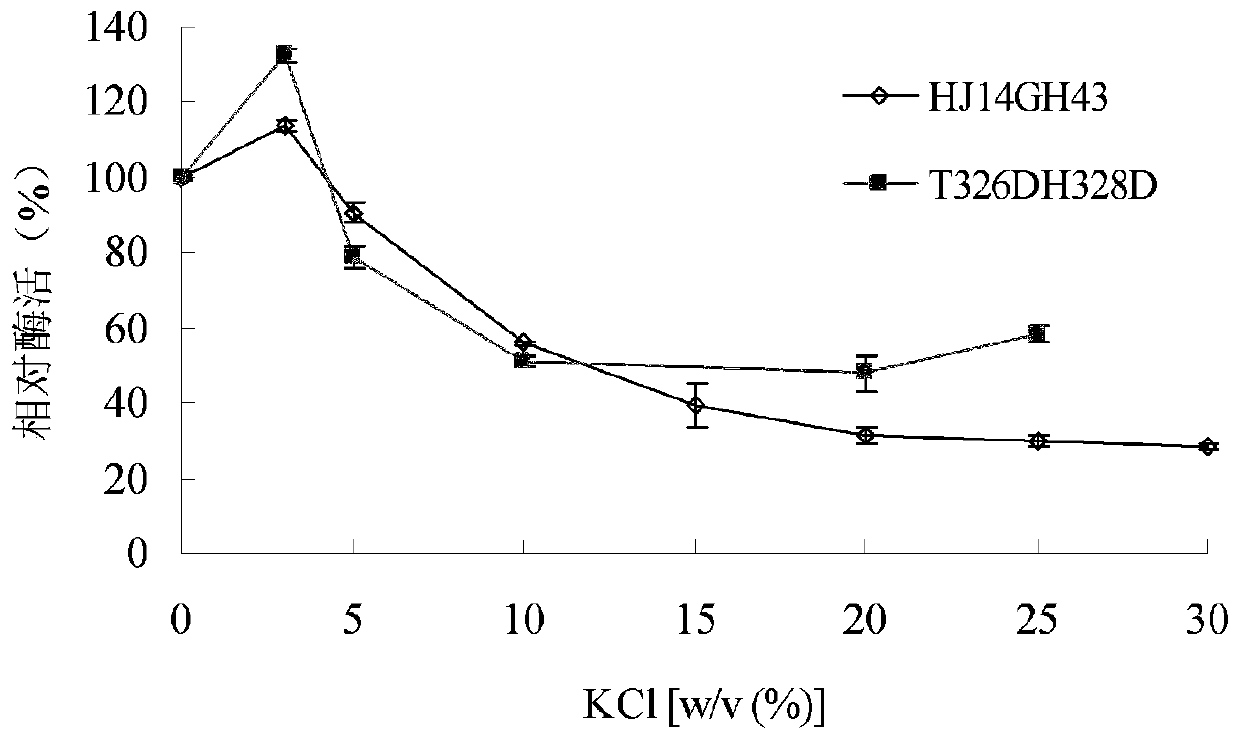
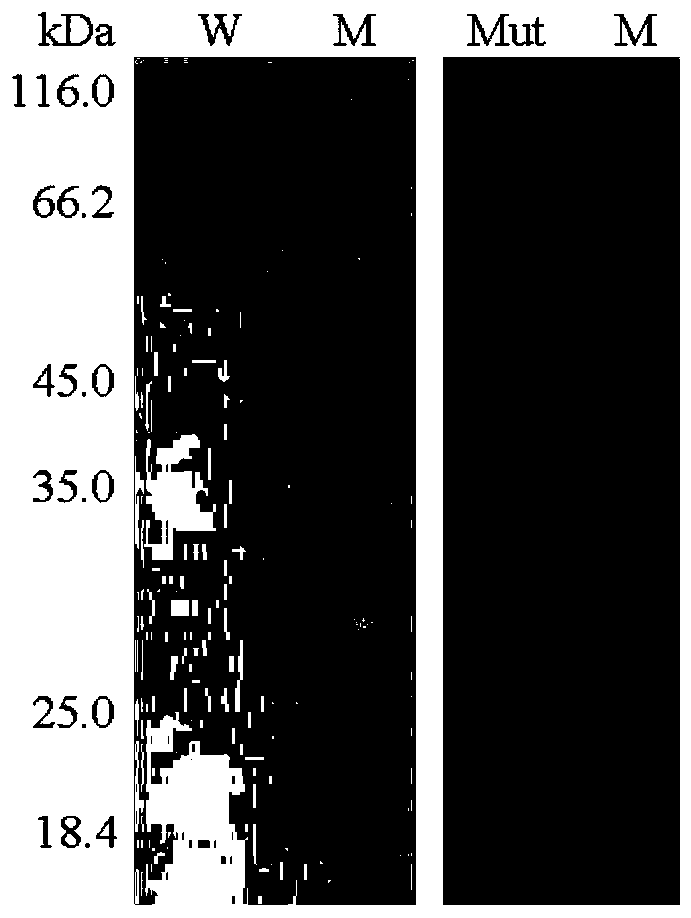
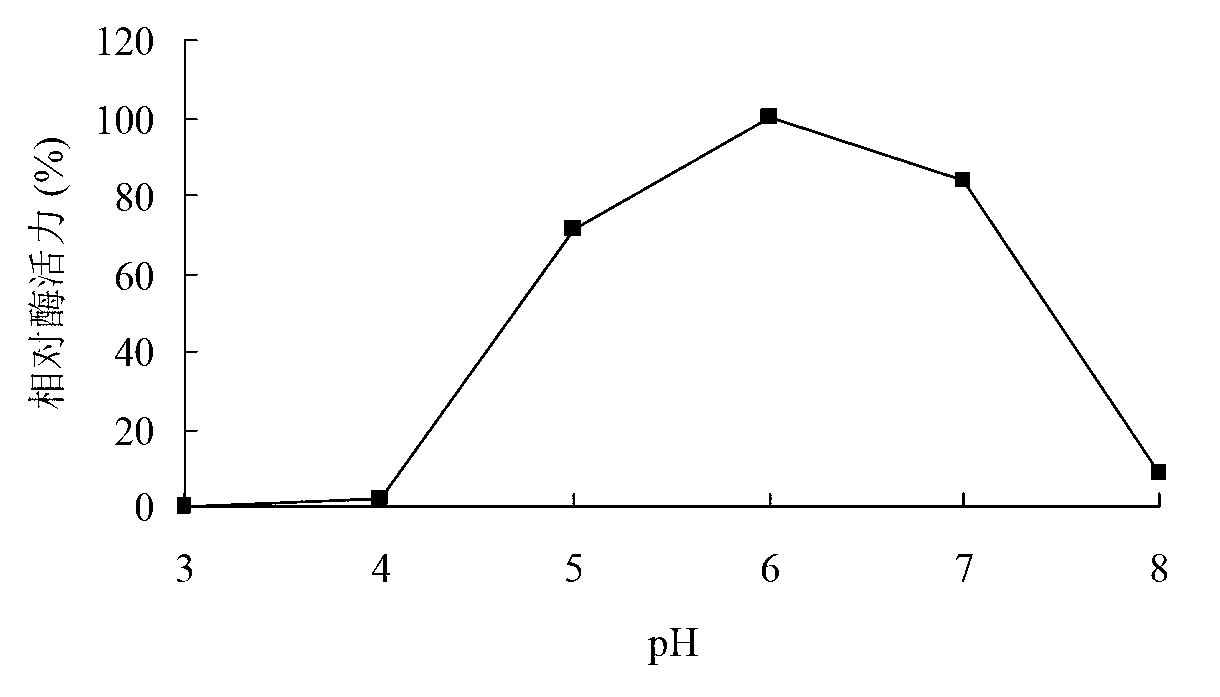
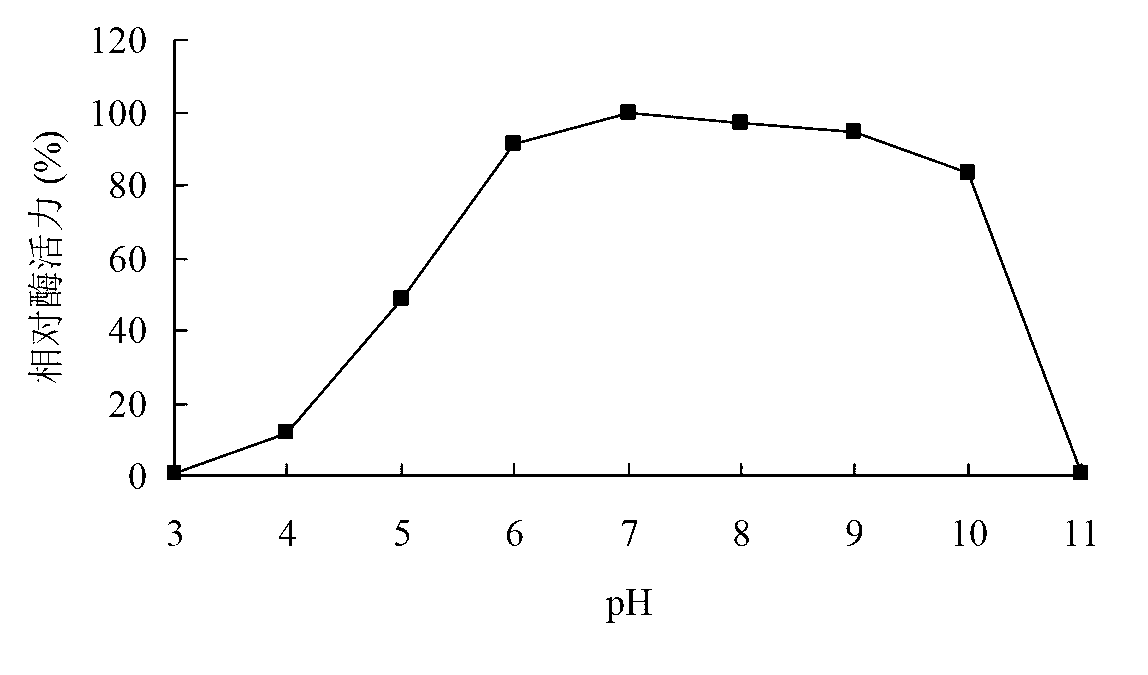
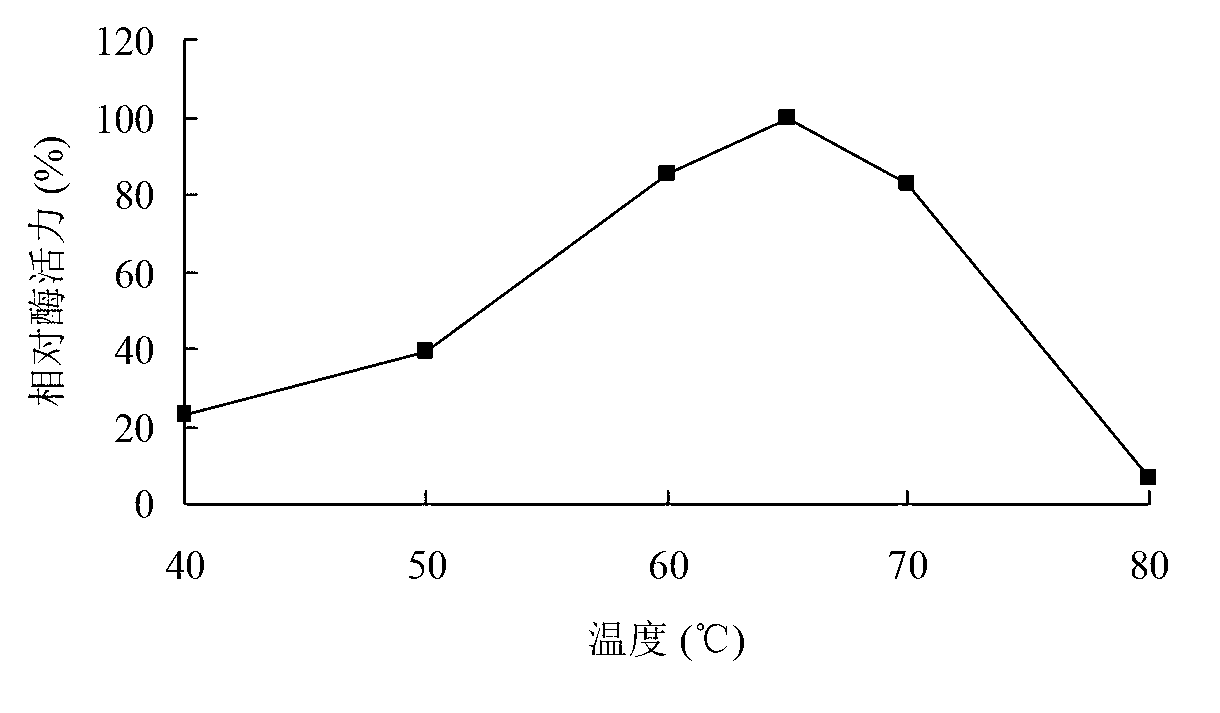
Low temperature xylosidase HJ14GH43 and salt-tolerant mutant thereof
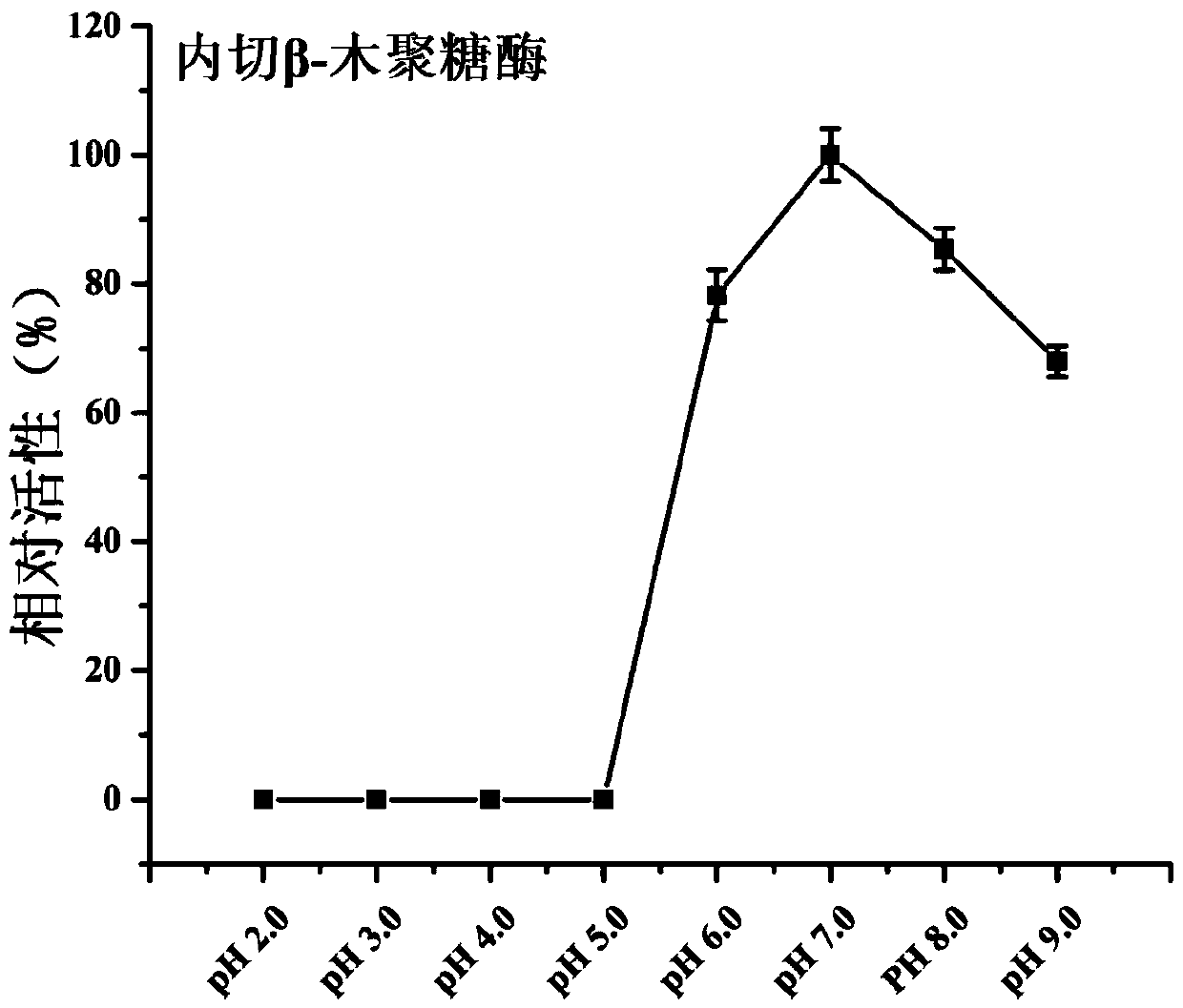
The invention discloses low temperature xylosidase HJ14GH43 and a salt-tolerant mutant thereof. The amino acid sequence of the xylosidase is as shown in SEQ ID No.1, and the nucleotide sequence of a xylosidase gene hJ14GH43 for coding xylosidase HJ14GH43 is as shown in SEQ ID No.2; the amino acid sequence of the salt-tolerant mutant is as shown in SEQ ID No.3. The optimum pH of xylosidase HJ14GH43 is 7.0, and the optimum temperature is 25 DEG C. According to the low temperature xylosidase HJ14GH43 and the salt-tolerant mutant thereof, site-directed mutation is conducted on the basis of xylosidase HJ14GH43, valine at the 322 locus is mutated to be aspartic acid, the mutant V322D is obtained, and the activity and stability of the mutant V322D in NaCl are both improved. The HJ14GH43 and the salt-tolerant mutant thereof can be applied to food industries and aquatic feed.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Xylosidase Xyl43B with high xylose tolerance, and gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103275955AXylose tolerance is goodHigh activityFungiBacteriaThermal stabilityGenetic engineering
The invention relates to the field of the genetic engineering, and in particular relates to xylosidase Xyl43B with high xylose tolerance, and a gene and an application thereof. The invention provides xylosidase Xyl43B which is from humicola sp.L8, and an amino acid sequence of xylosidase Xyl43B is shown as SEQ ID No.1. The invention provides a coding gene xyl43B for coding xylosidase. The xylosidase has the following properties that the xylose tolerance is high (ki value is 292mM), the xylosidase is stable at the preferable condition that pH is 7.0 and between 5.5 and pH 10.0, and the preferable temperature is 50DEG C and xylosidase has good thermal stability at the temperature of 50DEG C. As a novel zymin, the xylosidase can be widely applied to the food, feed and energy industries.
Owner:SHANDONG LONGKETE ENZYME PREPARATION
Glucosidase/xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102041251AHigh activityReduce complexityMicroorganism based processesEnzymesChemical industryCellulose
The invention relates to a novel beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The coding sequence of amino acid of the RuGBGX2 contains 18-755th sites of an SEQ ID NO 2 sequence. The RuGBGX2 is sourced from the rumen microorganism of yak from China, a novel coding gene of the beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 is obtained by function screening and sequencing analysis on a rumen metagenome cosmid library and a subclone library. The beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme provided by the invention can be widely applied to the degradation of cellulose and the fields such as cellulose biotransformation, chemical industry, spinning, foods, bioenergy, feed additives, medical industry and the like. By utilizing the difunctional enzyme RuGBGX2 to degrade wood fiber, the varieties of added enzymes can be reduced, and an enzymolysis process can be simplified.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Beta-xylosidase for conversion of plant cell wall carbohydrates to simple sugars
InactiveUS20090280541A1High activity and stabilityModerately high-temperaturesSugar derivativesBiofuelsHydrolysatePlant cell
Xylose-containing plant material may be hydrolyzed to xylose using a β-D-xylosidase which exhibits unexpectedly high activity. The enzyme has a kcat value for catalysis of approximately 185 sec−1 for 1,4-β-D-xylobiose (X2) when measured at a pH of 5.3 and a temperature of 25° C.; this is at least 10-fold greater than reported for other xylosidases at 25° C. and their optimal pH. The enzyme also has an isoelectric point of approximately 4.4. When reacted at a pH between about 4.5 and about 7.7, the β-D-xylosidase exhibits surprisingly high activity for hydrolyzing xylose-containing plant materials to xylose. The xylose released from plant materials may then be converted to other secondary products such as ethanol by fermentation or other reaction. This β-D-xylosidase may be used alone or in combination with other hydrolytic or xylanolytic enzymes for treatment of lignocellulosic or hemicellulosic plant materials or plant material hydrolysates or xylooligosaccharides.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Cryophilic xylosidase/arabinofuranosidase and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102051350AHigh catalytic activityBeta-D-xylosidase highFungiBacteriaCelluloseChemical industry
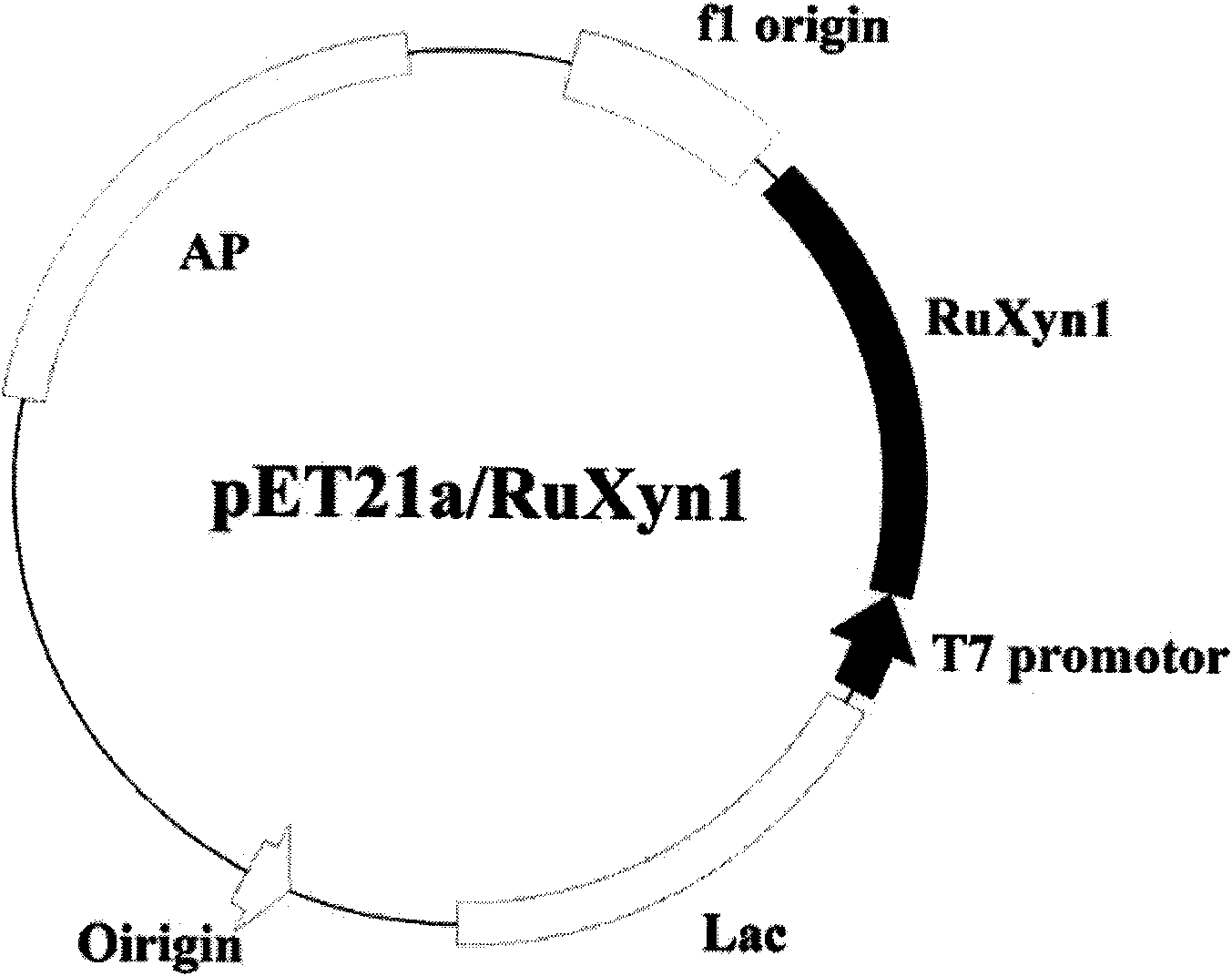
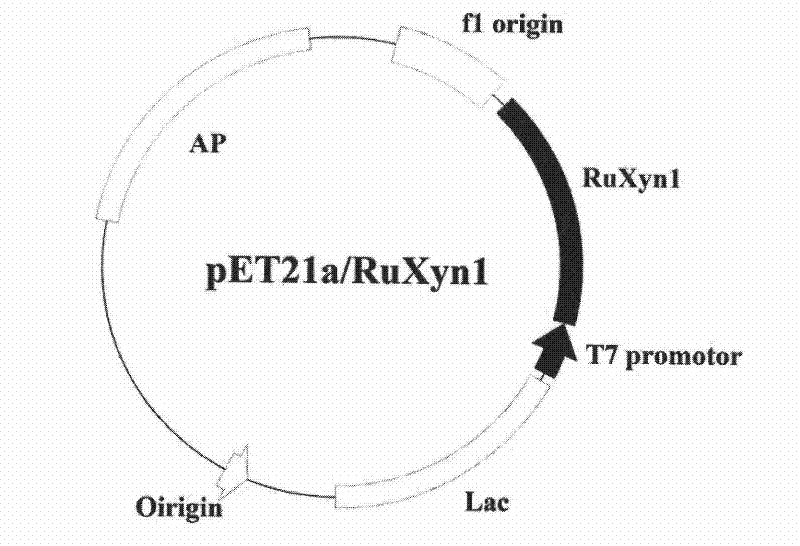
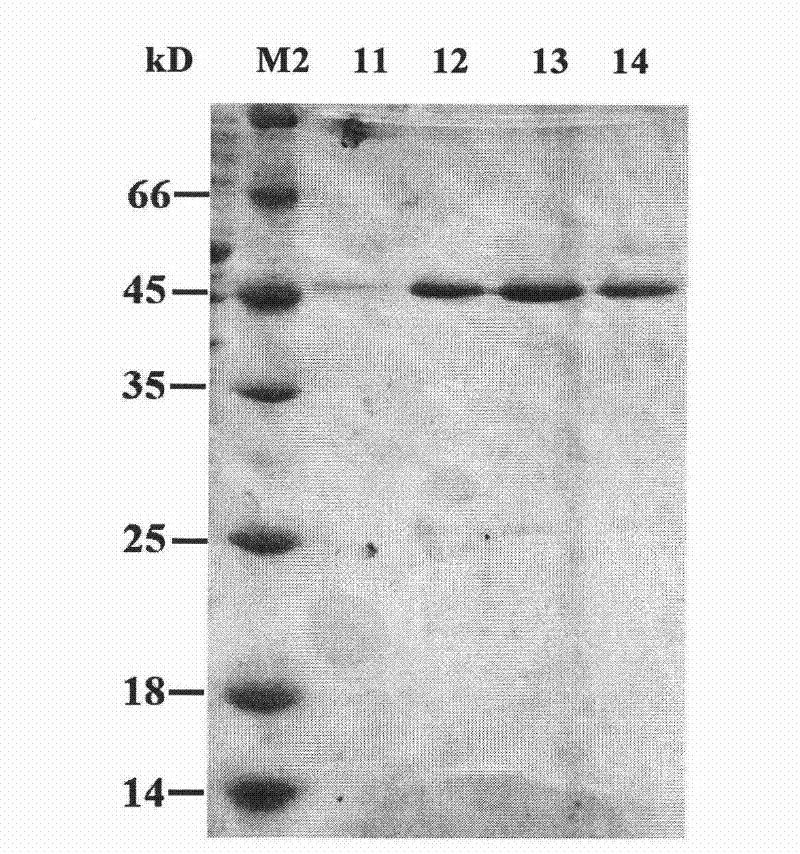
The invention belongs to the field of biological engineering and provides a novel bifunctional enzyme RuXyn1 with low-temperature resistance and activities of beta-D-xylosidase and alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase. The RuXyn1 has an amino acid coding sequence shown as SEQ ID No 2 and has a nucleotide coding sequence shown as SEQ ID No 1. The RuXyn1 can be prepared by a genetic engineering method or an artificial synthesis method. The RuXyn1 has functions of the arabinofuranosidase and the xylosidase, can keep higher activity in a low-temperature environment, and can be applied to the application fields of cellulose bioconversion, chemical industry, textiles, foods, bioenergy, feed additives, pharmaceutical industry and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Difunctional enzyme with endoglucanase/xylanase and preparation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological engineering, in particular to a difunctional enzyme RuCelA with endoglucanase / xylanase and a preparation method and application thereof. The RuCelA sources from uncultured microorganism of rumen of Chinese yaks, and has a certain activity on phosphocellulose and filter. The RuCelA not only can hydrolyze polysaccharide but also can hydrolyze trisaccharide to obtain monosaccharide; meanwhile, the RuCelA has synergistic effect with xylanase to synergetically degrade xylan; and the RuCelA can be utilized to realize mono enzymatic degradation on preprocessed lignocellulose. The difunctional enzyme RuCelA of the invention can be widely applied to cellulose degradation, comprising cellulose biotransformation, chemical industry, spinning, food, bioenergy, feed ingredients, pharmaceutical Industry and other aspects.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Beta-xylosidase and encoding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN101724615AEasy to purifyHigh recovery rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBiology
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
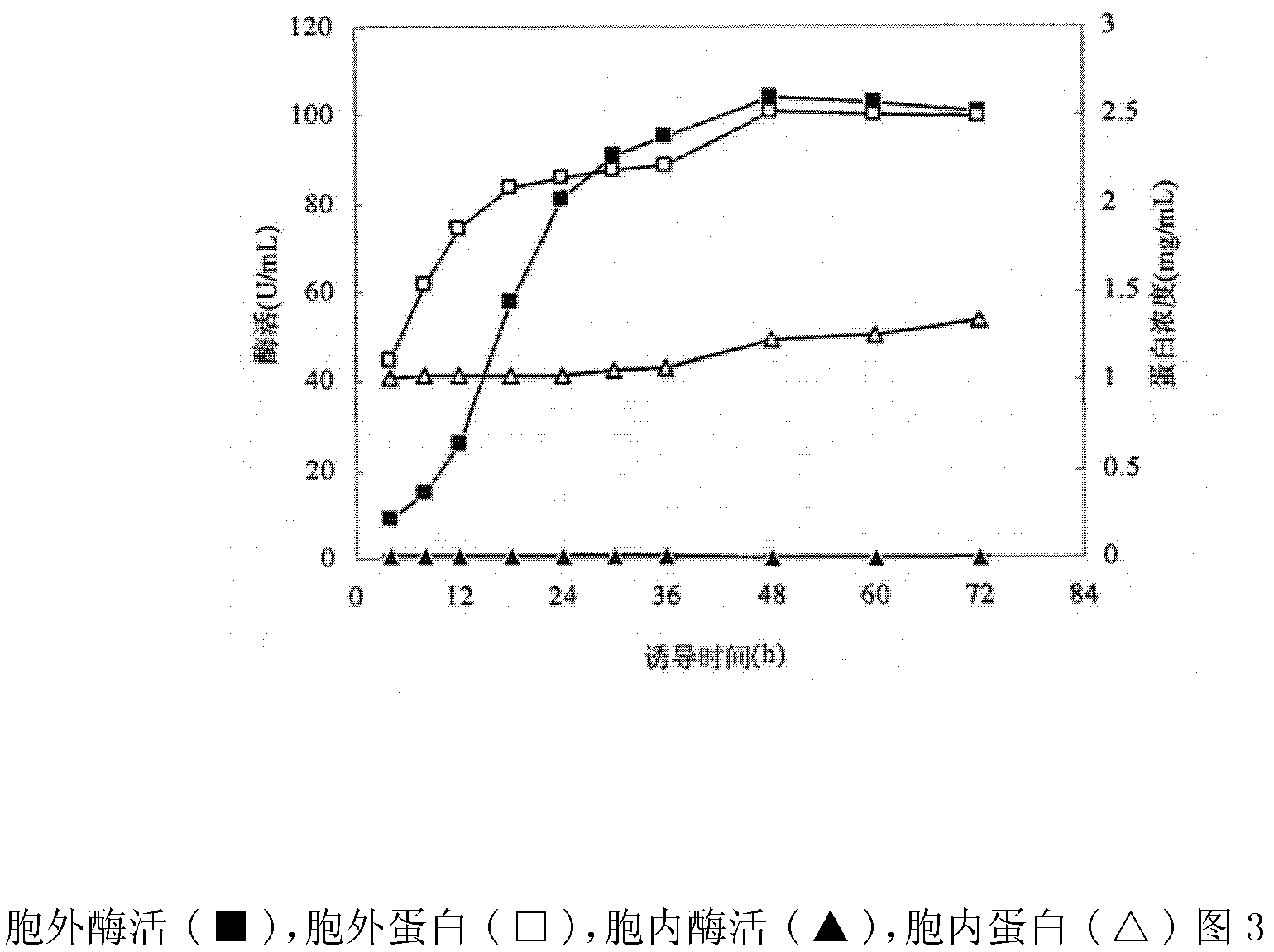
Method for producing xylanase at high yield from trichoderma reesei and application of xylanase
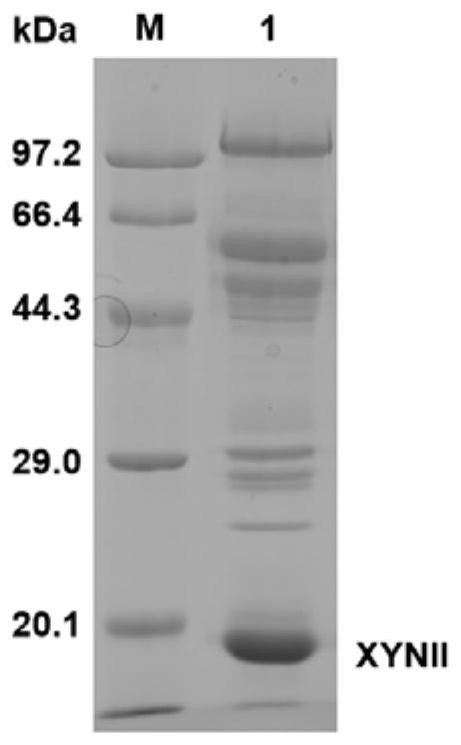
The invention discloses a method for producing xylanase at high yield from trichoderma reesei and application of the xylanase, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the invention, a transcription activator XYR1 is expressed to enhance the xylan degrading enzyme expression ability, and a transcription factor binding site on a promoter Pcbh1 is designed, so that XYR1 of constitutive expression can further activate the artificial promoter Pcbh1, and the artificial promoter Pcbh1 is used for expressing homologous xylanase XYNII to obtain recombinant trichoderma reesei. Under the cellulose induction condition, the expression quantity of the recombinant strain xylanase reaches 6410U / mL, which is 9.28 times higher than that of a parent; meanwhile, the activity of xylosidase is improved by 1.93 times and reaches 9.08 U / mL; and the recombinant strain can relieve carbon metabolism repression, soluble cheap carbon sources glucose and lactose are used as fermentation carbon sources, the activity of the extracellular xylanase of 2514 U / mL and the activity of the extracellular xylanase of 3446 U / mL can also be obtained, and meanwhile, the yield of the xylosidase is increased by 9.3 times and 2.3 times compared with that of the parent. Meanwhile, the xylanase produced with the method cooperates with commercial cellulose to perform straw saccharification, so that the saccharification efficiency can be improved by 35%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Cellulolytic enzymes, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
The invention provides polypeptides having any cellulolytic activity, e.g., a cellulase activity, a endoglucanase, a cellobiohydrolase, a beta-glucosidase, a xylanase, a mannanse, a ss-xylosidase, an arabinofiiranosidase, and / or an oligomerase activity, polynucleotides encoding these polypeptides, and methods of making and using these polynucleotides and polypeptides. In one aspect, the invention is directed to polypeptides having any cellulolytic activity, e.g., a cellulase activity, e.g., endoglucanase, cellobiohydrolase, beta-glucosidase, xylanase, mannanse, ss-xylosidase, arabinofuranosidase, and / or oligomerase activity, including thermostable and thermotolerant activity, and polynucleotides encoding these enzymes, and making and using these polynucleotides and polypeptides. In one aspect, the invention provides polypeptides having an oligomerase activity, e.g., enzymes that convert recalcitrant soluble oligomers to fermentable sugars in the saccharification of biomass. The polypeptides of the invention can be used in a variety of pharmaceutical, agricultural, food and feed processing and industrial contexts. The invention also provides compositions or products of manufacture comprising mixtures of enzymes comprising at least one enzyme of this invention.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
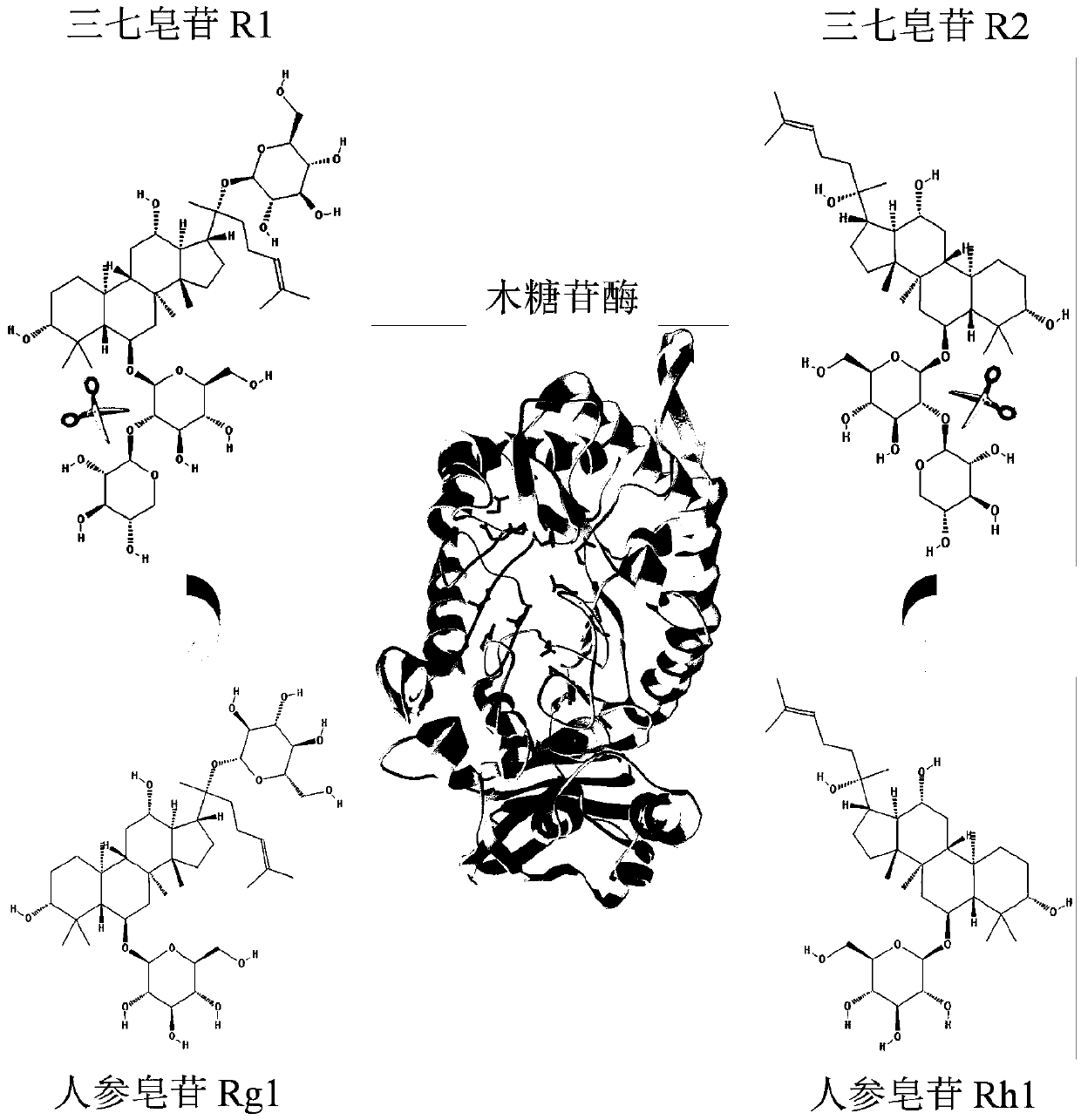
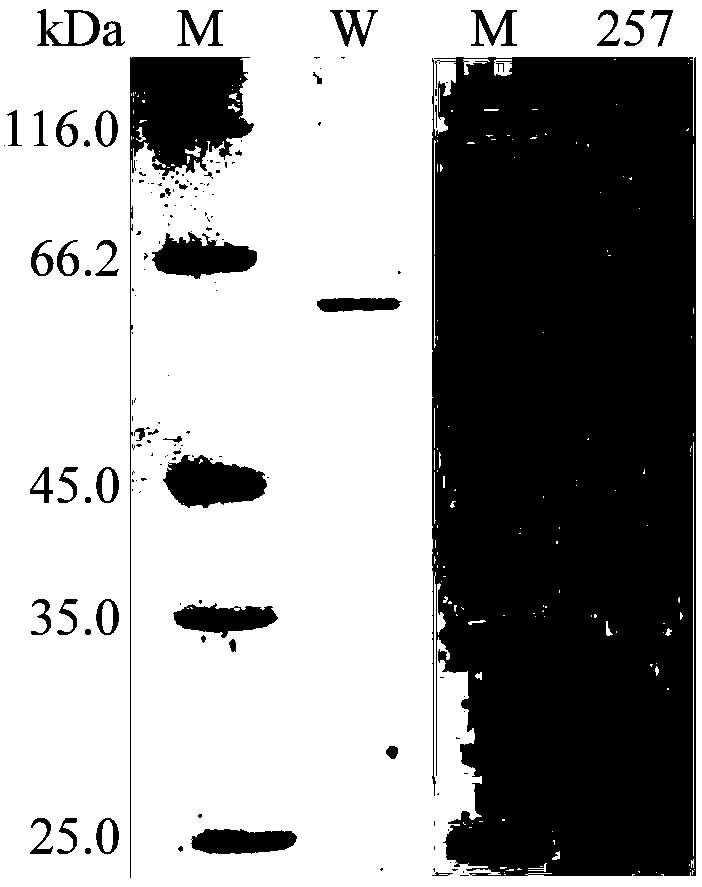
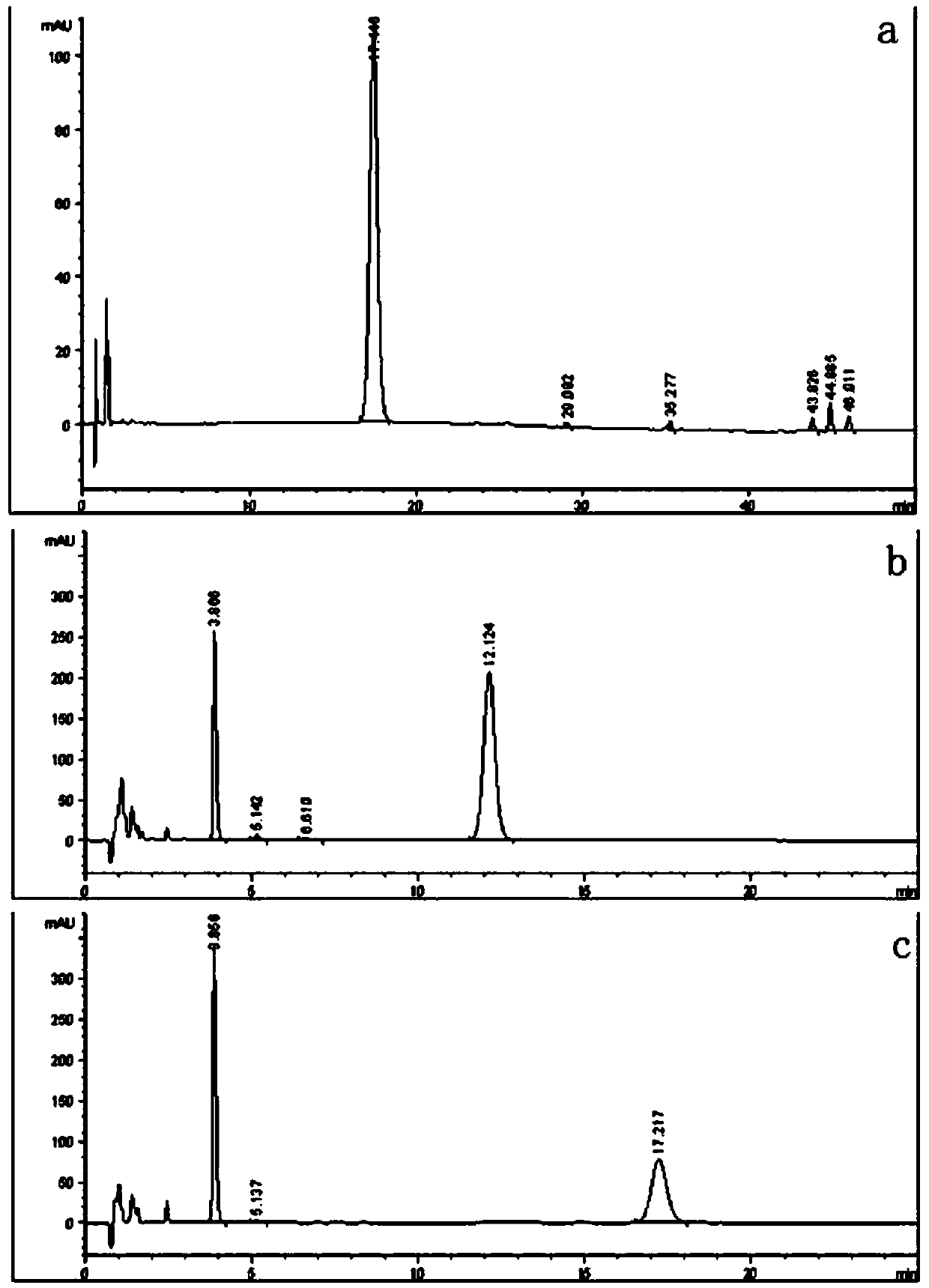
Xylosidase mutant capable of transforming notoginsenoside R1 into ginsenoside Rg1
The invention discloses a xylosidase mutant capable of transforming notoginsenoside R1 into ginsenoside Rg1, and relates to the technical field of genetic engineering and protein transformation, in particular to the xylosidase mutant MutY257T capable of transforming notoginsenoside R1 into ginsenoside Rg1, wherein the amino acid sequence of the mutant MutY257T is shown as in SEQ ID NO.1. The MutY257T can degrade the notoginsenoside R1, the product is the ginsenoside Rg1; but the mutant barely degrades notoginsenoside R2. The xylosidase mutant MutY257T can be applied to the industries like medicines and healthcare products.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
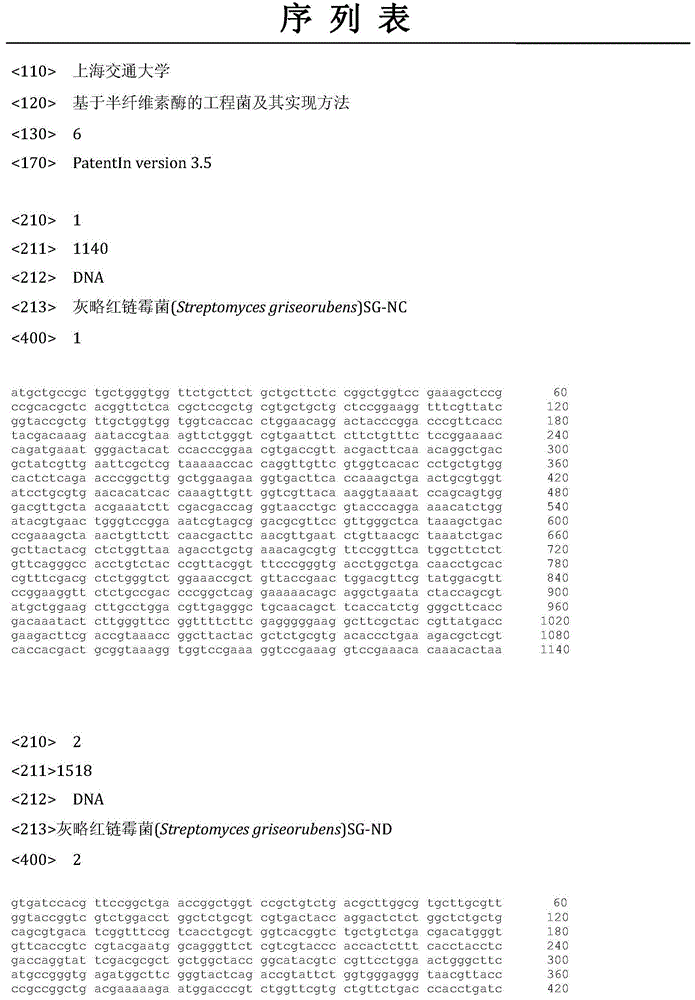
Hemicellulase-based engineering bacteria and realization method thereof
InactiveCN104152392AAchieve in vitro co-expressionHigh activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideXylanase
The invention relates to hemicellulase-based engineering bacteria in the technical field of genetic engineering and a realization method thereof. The realization method comprises the following steps: firstly, by taking a vector pUC57-XL obtained by whole gene synthesis of streptomyces griseorubens genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) as a template, performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on the vector and a primer with an enzyme cutting site to obtain a nucleotide sequence XL for coding xylanase and a nucleotide sequence XO for coding xylosidase correspondingly and respectively; secondly, connecting the gene sequences obtained by amplification to a coexpression vector pETDuet-1 in sequence, and finally recombining a coexpression vector pETDuet-XL-XO; thirdly, converting the recombinant coexpression vector to an escherichia coli expression strain so as to obtain a transgenic coexpression strain. Therefore, a large quantity of xylanase and xylosidase can be expressed and synthesized in vitro by using genetic engineering means, and finally hemicellulose can be quickly degraded in situ.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Novel beta-xylosidase and preparation thereof
ActiveCN112111472AIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBacillus licheniformisWild type
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering of enzymes, and particularly relates to a beta-xylosidase mutant with improved enzyme activity and preparation thereof. According tothe invention, a wild type beta-xylosidase gene of Bacillus pumilus is obtained through a molecular biological technology means, random mutation is carried out on the wild type beta-xylosidase gene by utilizing an error-prone PCR technology to obtain a beta-xylosidase mutant E455G and a coding gene xylm thereof, recombinant plasmids are reconstructed, efficient expression of the recombinant plasmids in Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens is realized, and high-activity beta-xylosidase is obtained through technologies such as fermentation and extraction.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
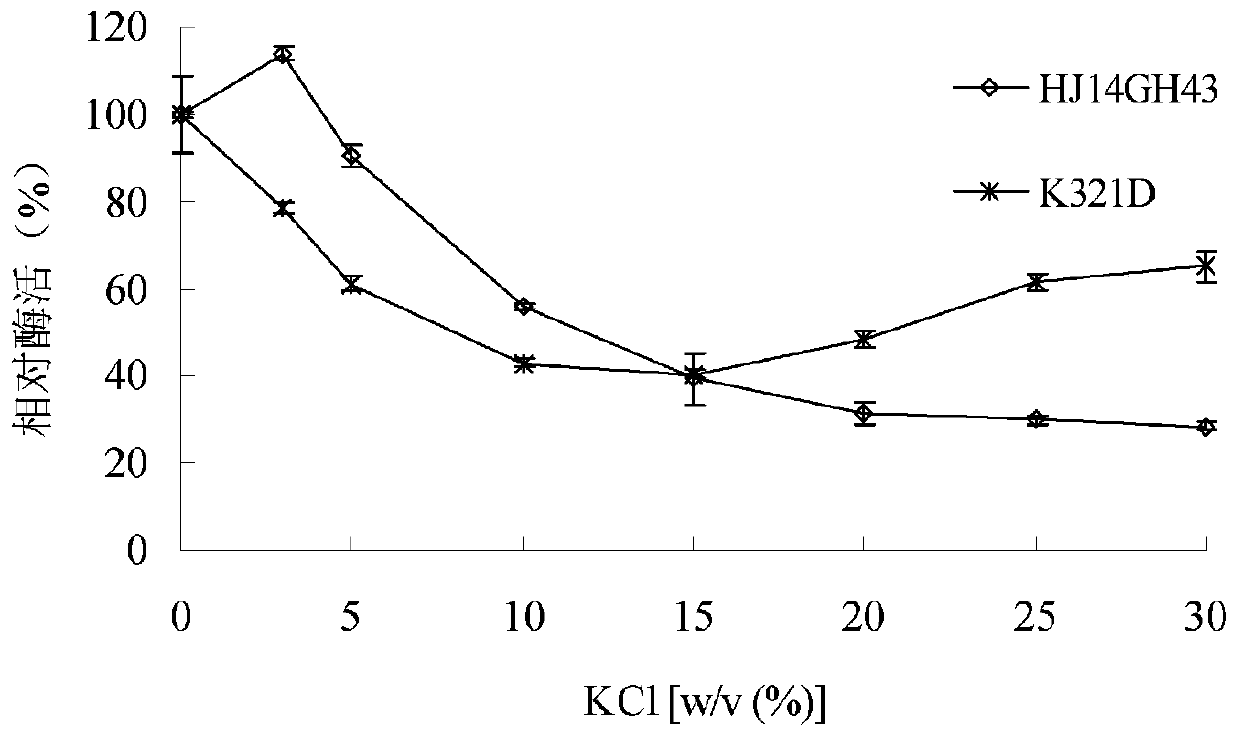
Salt-tolerant xylosidase mutant K321D as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110904075ASolve the problem of not having good stabilityImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationSewage
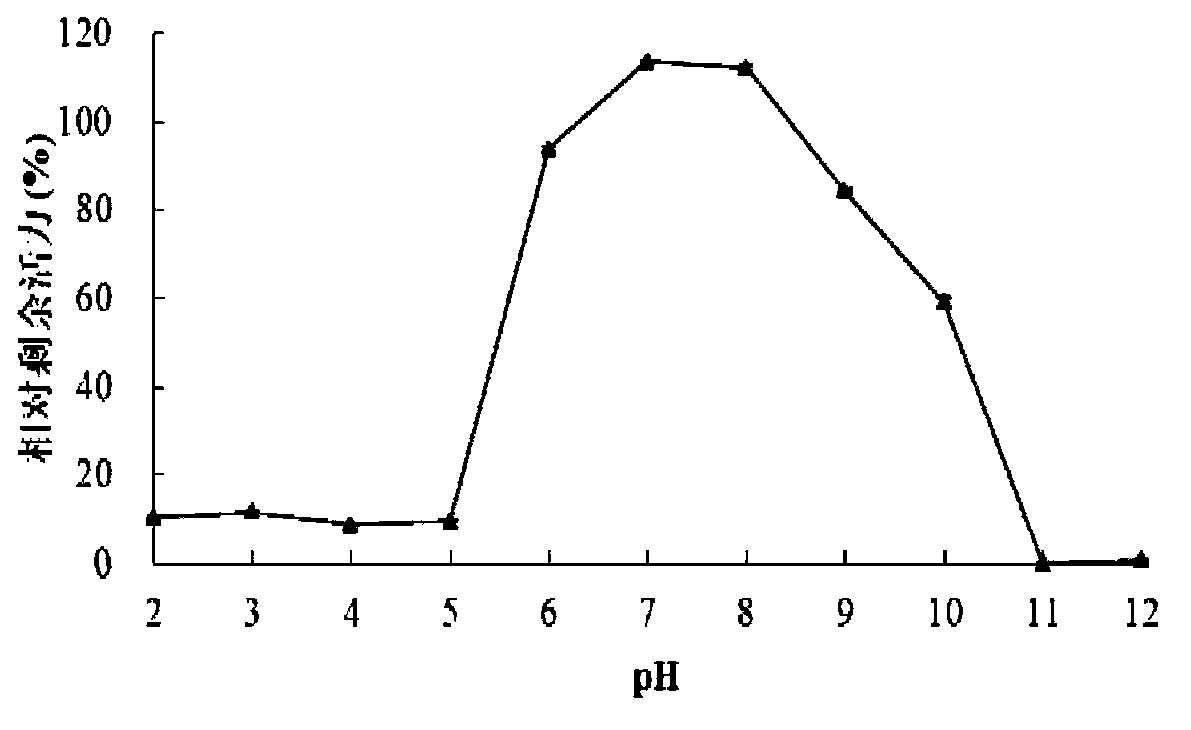
The invention discloses salt-tolerant xylosidase mutant K321D as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the mutant K321D is obtained by mutating lysine at the321st site of wild xylosidase HJ14GH43 into aspartic acid, the sequence of the mutant K321D is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the salt is not NaCl. Compared with wild enzyme HJ14GH43, the mutant has the advantages that the stability of the mutant enzyme K321D disclosed by the invention in high-concentration KCl, Na2SO4 and (NH4) 2SO4 is enhanced; the activity increased from 48% to 65% after being treated with KCl with the concentration of 20.0%-30.0%, and the activity is 93%-111% after being treated with Na2SO4 with the concentration of 10.0%-30.0%; and the activity is maintained to be higher than90% after being treated with (NH4) 2SO4 with the concentration of 20.0-30.0%; and the salt-tolerant xylosidase mutant K321D can be applied to industries such as tanning, papermaking, sewage treatmentand the like.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Milling Process
InactiveUS20150299752A1Enhance the wet milling benefit of one or more enzymesFermentationMedicineBeta-Xylosidase
Process for treating crop kernels, comprising the steps of: a) soaking kernels in water to produce soaked kernels; b) grinding the soaked kernels; c) treating the soaked kernels in the presence of an effective amount of a beta-xylosidase, wherein step c) is performed before, during or after step b).
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Cellulolytic enzymes, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
The invention provides polypeptides having any cellulolytic activity, e.g., a cellulase activity, a endoglucanase, a cellobiohydrolase, a beta-glucosidase, a xylanase, a mannanse, a beta-xylosidase, an arabinofiiranosidase, and / or an oligomerase activity, polynucleotides encoding these polypeptides, and methods of making and using these polynucleotides and polypeptides. In one aspect, the invention is directed to polypeptides having any cellulolytic activity, e.g., a cellulase activity, e.g., endoglucanase, cellobiohydrolase, beta-glucosidase, xylanase, mannanse, beta-xylosidase, arabinofuranosidase, and / or oligomerase activity, including thermostable and thermotolerant activity, and polynucleotides encoding these enzymes, and making and using these polynucleotides and polypeptides. In one aspect, the invention provides polypeptides having an oligomerase activity, e.g., enzymes that convert recalcitrant soluble oligomers to fermentable sugars in the saccharification of biomass. The polypeptides of the invention can be used in a variety of pharmaceutical, agricultural, food and feed processing and industrial contexts. The invention also provides compositions or products of manufacture comprising mixtures of enzymes comprising at least one enzyme of this invention.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Encoding gene of glycoside hydrolase for rapid hydrolysizing xylan to generate single xylose, and application of encoding gene
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, in particular to an encoding gene of glycoside hydrolase for rapid hydrolysizing xylan to generate single xylose, and application of the encoding gene. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The nucleic acid, which is provided by the invention and is shown in the SEQ ID NO. 2, can be expressed in a large amount in yeast, so that a large amount of the glycoside hydrolase Ttxy43 can be obtained; the glycoside hydrolase Ttxy43 has the activities of beta-xylosidase, endo-beta-xylanase and alpha-L-arabinofuranosidease atthe same time; in addition, the glycoside hydrolase Ttxy43 can directly degrade birch xylan so as to produce a single product xylose; compared with commercial combination of endo-beta xylanase and beta-xylosidase, the glycoside hydrolase Ttxy43 is higher in xylose yield and has a higher commercial application value.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
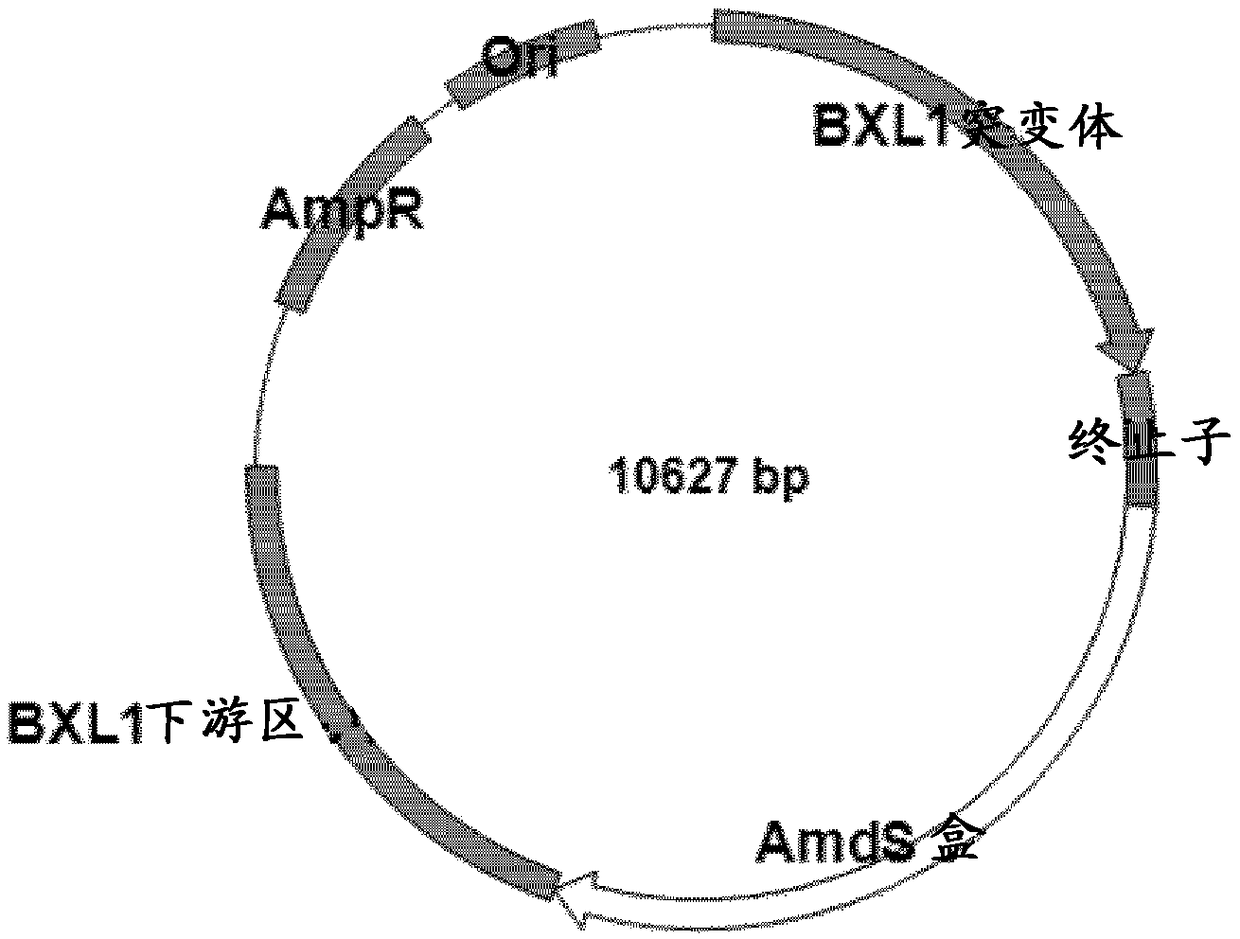
Trichoderma fungus having mutant-type bxl1 gene and method for producing xylooligosaccharide and glucose by using same
Disclosed are a novel Trichoderma reesei fungus with which xylan in a biomass is not decomposed to xylose even when a cellulase derived from a Trichoderma reesei fungus is used for the hydrolysis of acellulose-based biomass; and a method for producing glucose and xylooligosaccharide from a cellulose-containing biomass by using said Trichoderma reesei fungus. This Trichoderma fungus includes an N-terminal domain and a C-terminal domain of a beta-xylosidase 1 (BXL1) gene, wherein a Fn3-like domain is disrupted. By using this Trichoderma fungus, beta-xylosidase activity is deleted and beta-glucosidase activity is increase. Thus, xylan in a biomass is not decomposed to xylose even when a cellulose-containing biomass is hydrolyzed, and glucose and xylooligosaccharide can be produced efficiently.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
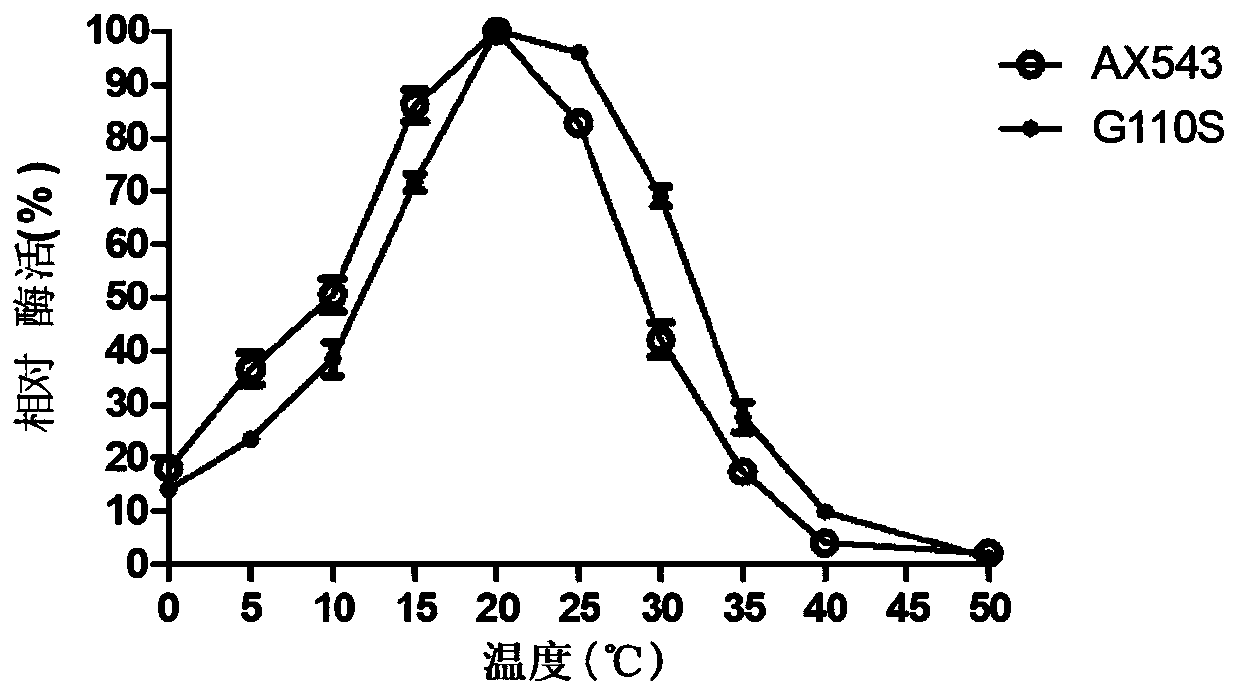
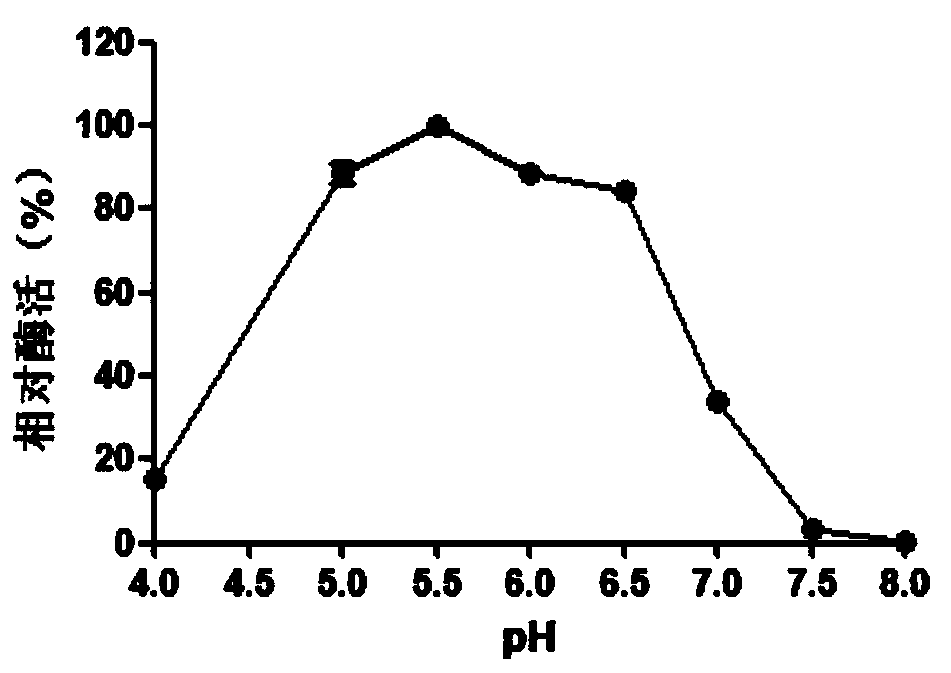
Low-temperature beta-xylosidase mutant with improved thermal stability and specific activity and encoding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN110699339AImprove thermal stabilityImprove stabilityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPapermaking
The invention relates to a low-temperature beta-xylosidase mutant with improved thermal stability and specific activity. The mutant is a low-temperature beta-xylosidase mutant G110S, and an amino acidsequence of the mutant is SEQ ID NO.1; alternatively, the mutant is a low-temperature beta-xylosidase mutant Q201R, and an amino acid sequence of the mutant is SEQ ID NO.2; and alternatively, the mutant is a low-temperature beta-xylosidase mutant loop2, and an amino acid sequence of the mutant is SEQ ID NO.3. The low-temperature beta-xylosidase mutant with improved thermal stability and specificactivity is more suitable for industrial applications, and has wider application prospects in the fields of food, feed, papermaking and the like, so that the application potential of low-temperature beta-xylosidase is expanded in food, pharmaceutical, papermaking, feed and other fields.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Xylosidase Xyl21 with high-concentration xylose, alcohol and salt tolerance as well as encoding gene and application of xylosidase Xyl21
InactiveCN110540981AImprove toleranceGood xylose toleranceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationAlcohol
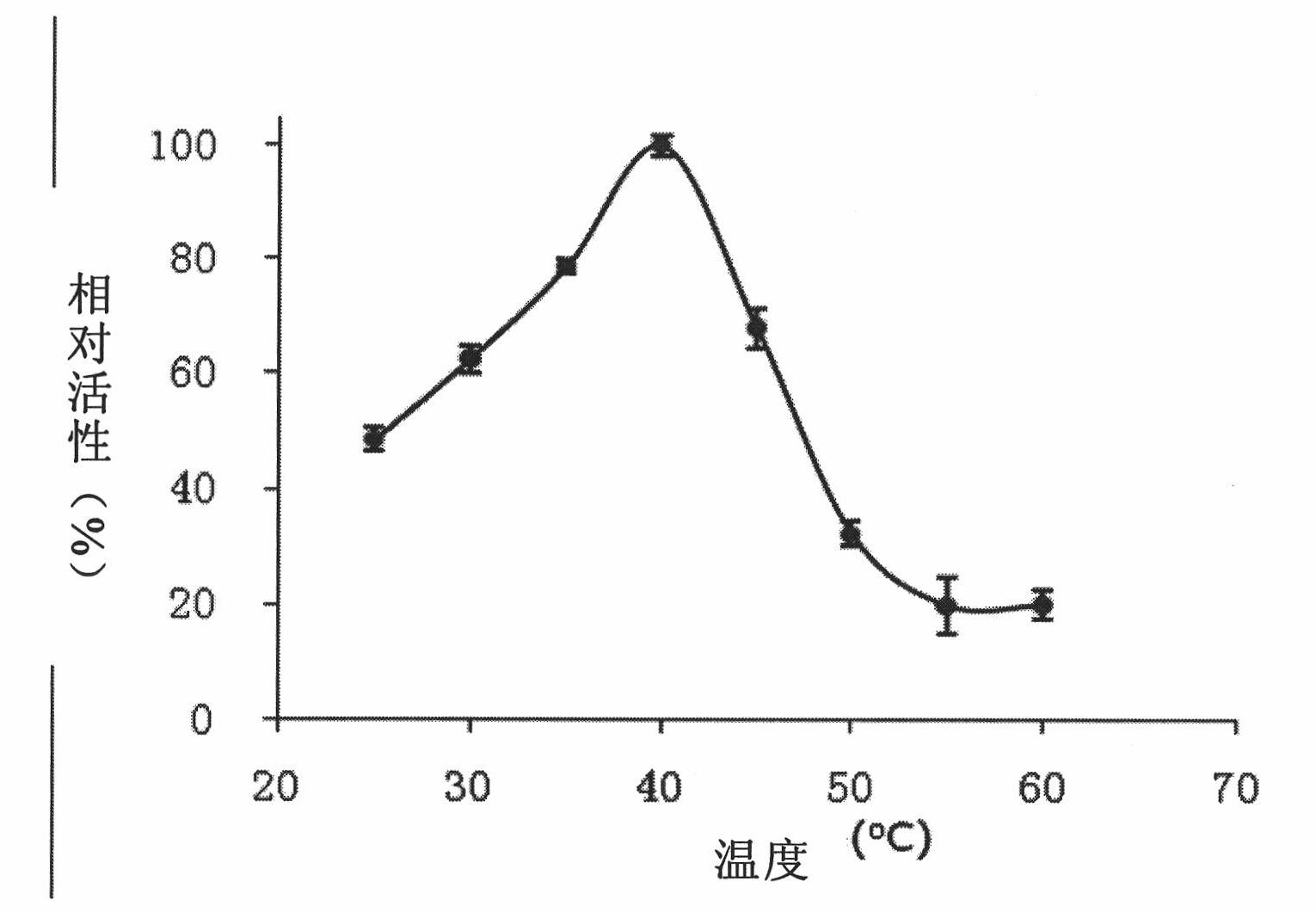
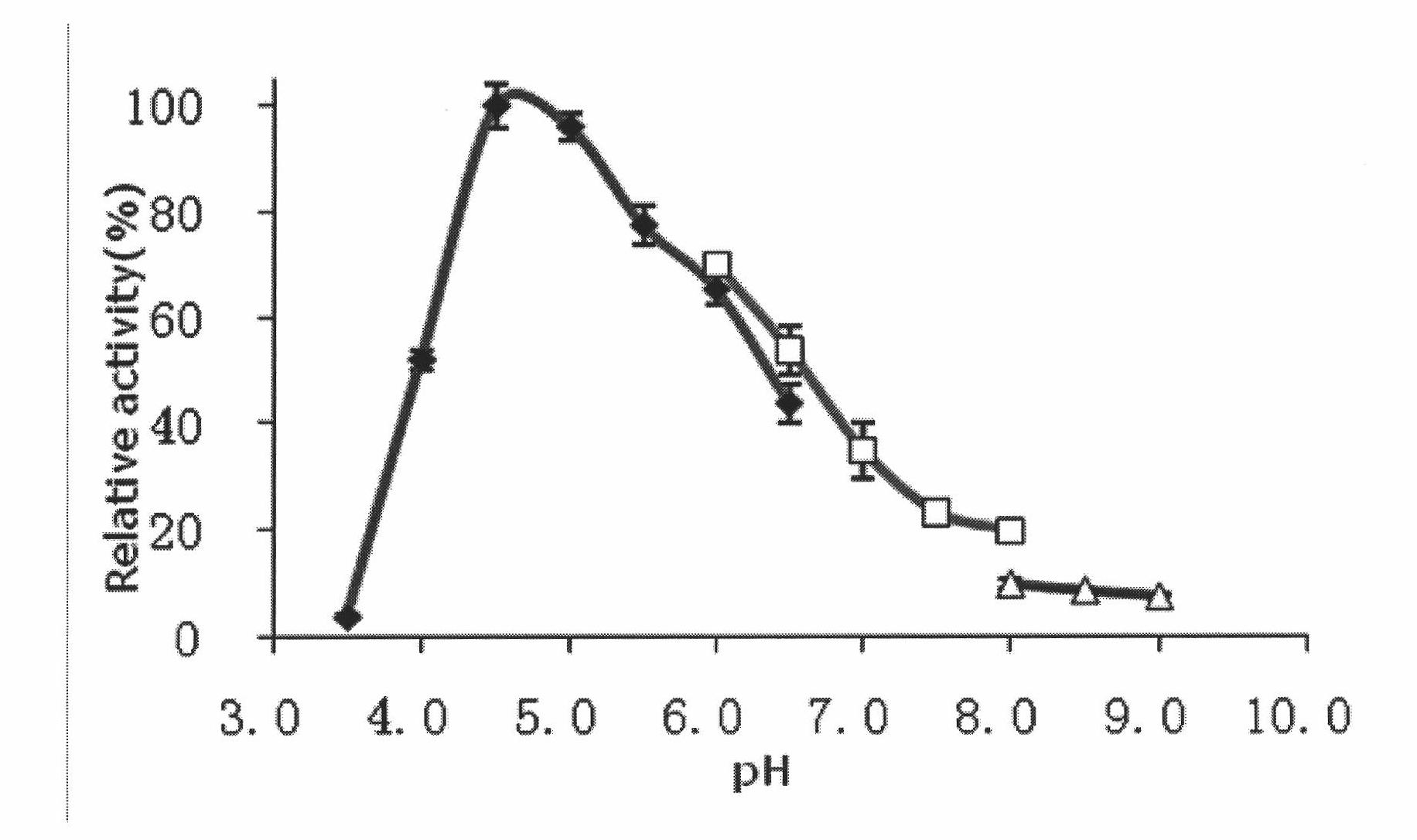
The invention relates to xylosidase Xyl21 with high-concentration xylose, alcohol and salt tolerance. An amino acid sequence of the xylosidase Xyl21 is SEQ ID NO.1. The optimum temperature of the xylosidase Xyl21 disclosed by the invention is 45 DEG C; after the xylosidase Xyl21 is treated at 45 DEG C for 1 h, the residual enzyme activity is 80%, the optimal pH is 5.5, the enzyme activity is keptat 80% or above in terms of relative enzyme activity within the pH range of 5.0-6.5, and the xylose tolerance, the ethanol tolerance and the tolerance to high-concentration salt ions are good. The xylosidase Xyl21 is novel and can tolerate high-concentration xylose, ethanol and salts, and due to the properties, the xylosidase Xyl21 serving as a novel enzyme preparation can be widely applied to industries such as energy, feed and food.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Beta-xylosidase for conversion of plant cell wall carbohydrates to simple sugars
InactiveUS7993884B2High activity and stabilityModerately high-temperaturesSugar derivativesBiofuelsHydrolysatePlant cell
Xylose-containing plant material may be hydrolyzed to xylose using a β-D-xylosidase which exhibits unexpectedly high activity. The enzyme has a kcat value for catalysis of approximately 185 sec−1 for 1,4-β-D-xylobiose (X2) when measured at a pH of 5.3 and a temperature of 25° C.; this is at least 10-fold greater than reported for other xylosidases at 25° C. and their optimal pH. The enzyme also has an isoelectric point of approximately 4.4. When reacted at a pH between about 4.5 and about 7.7, the β-D-xylosidase exhibits surprisingly high activity for hydrolyzing xylose-containing plant materials to xylose. The xylose released from plant materials may then be converted to other secondary products such as ethanol by fermentation or other reaction. This β-D-xylosidase may be used alone or in combination with other hydrolytic or xylanolytic enzymes for treatment of lignocellulosic or hemicellulosic plant materials or plant material hydrolysates or xylooligosaccharides.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
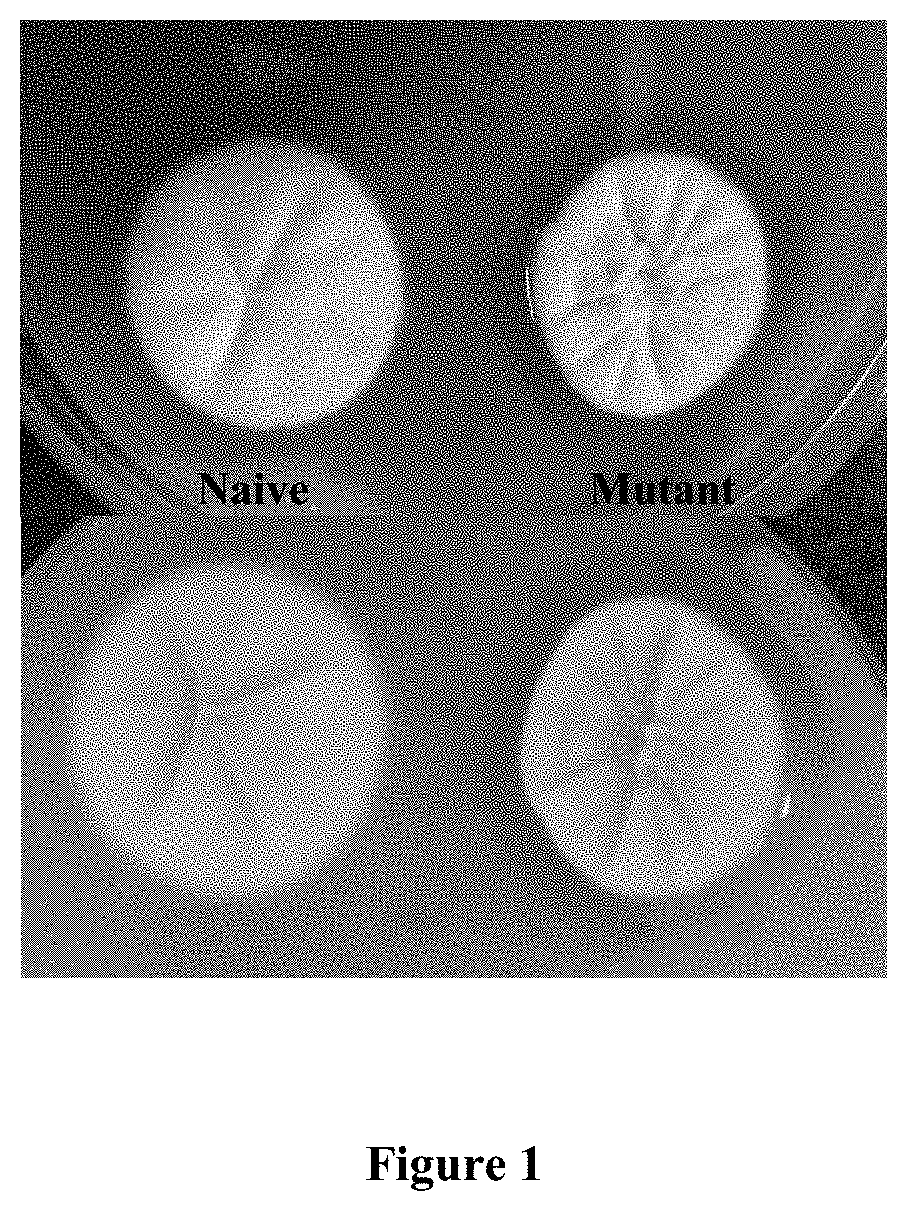
Method for preparation and screening of fungal mutant with high hydrolytic activity and catabolite derepressed character
The present invention relates to a mutant fungal strain of Penicillium funiculosum ‘MRJ-16’ characterized by the ability to produce high titer of enzyme mixture comprising FPase, CMCase, Cellobiase, β-glucosidase, endoglucanase, α-L arabinofuranosidase, β-xylosidase, xylanase, pectinase, cellobiohydrase and oxidases and produce enzymes in the presence of a catabolite repressor molecule like glucose and / or xylose. The titer of enzyme mixture produced using mutant fungal strain MRJ-16 is at least two fold higher than naive Penicillium funiculosum strain NCIM 1228, when used in a fermentation process. The mutant strain ‘MRJ-16’ with high hydrolytic activity and catabolite derepressed character is having application in the method of degrading or saccharifying biomass to produce valuable products for example-bioethanol.
Owner:INDIAN OIL CORPORATION +1
Salt-tolerant xylosidase mutant T326DH328D as well as preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN110904082ASolve the problem of not having good catalytic activityImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationThreonine
The invention discloses salt-tolerant xylosidase mutant T326DH328D as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the mutant T326DH328D is obtained by mutating threonine at the 326th site and histidine at the 328th site of wild xylosidase HJ14GH43 into aspartic acid, the sequence of the mutant T326DH328D is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and the salt is not NaCl. Compared with wild enzyme HJ14GH43, the mutant T326DH328D has the advantages that the stability of the mutant enzyme T326DH328D disclosed by the invention in high-concentration Na2SO4 and (NH4) 2SO4 is enhanced; the activity is 106 to 131% after being treated with Na2SO4 with the concentration of 10.0%-30.0%; and the activity is 133 to 151% after being treated with (NH4) 2SO4 with the concentration of 15.0 to 30.0%; and the salt-tolerant xylosidase mutant T326DH328D can be applied to industries such as tanning, papermaking, sewage treatment and the like.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
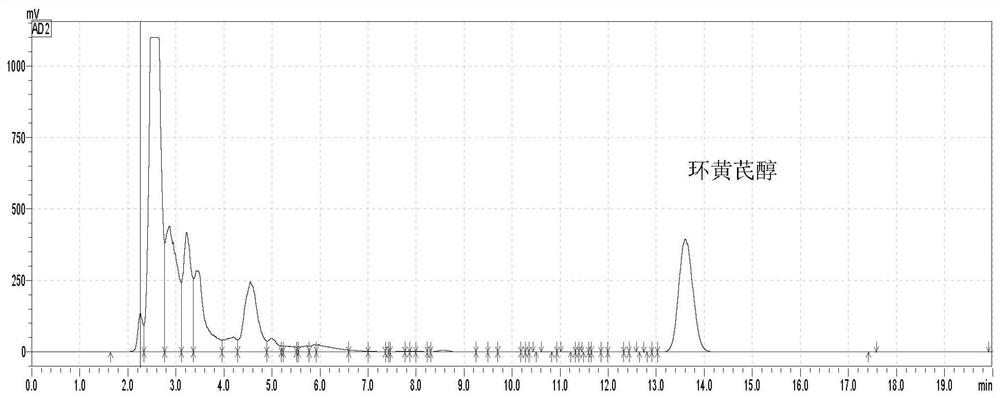
Method for preparing cycloastragenol by catalyzing astragaloside through co-immobilized double enzymes
ActiveCN111849959AReduce manufacturing costSimple processFermentationOn/in inorganic carrierAstragalosideAlglucerase
The invention belongs to the technical field of catalysis, and provides a method for preparing cycloastragenol by catalyzing astragaloside through co-immobilized double enzymes. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out a reaction among beta-glucosidase, a phosphate buffer solution, a Fe3O4 solution, a copper chloride solution and xylosidase to obtain the co-immobilized double enzymes; and carrying out a catalytic reaction by using co-immobilized double enzymes and astragaloside to obtain cycloastragenol. The method provided by the invention overcomes the problem of extractionand separation of intermediates in a process for preparing cycloastragenol by adopting a two-step reaction in the prior art, and meanwhile, the co-immobilized double enzymes can be recycled, so that the production cost is reduced, the process is simple, economic and economical, and the method is very suitable for large-scale industrial production. The conversion rate of the co-immobilized double enzymes to astragaloside basically reaches 100%, and the substrate astragaloside is completely converted into cycloastragenol. The purity of the cycloastragenol product obtained by the method can reach78.3% or above.
Owner:WEIHAI BAIHE BIOTECH +1
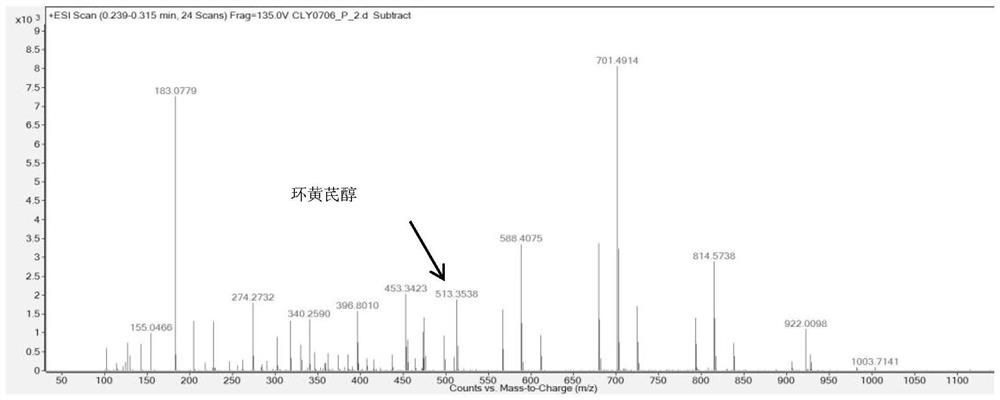
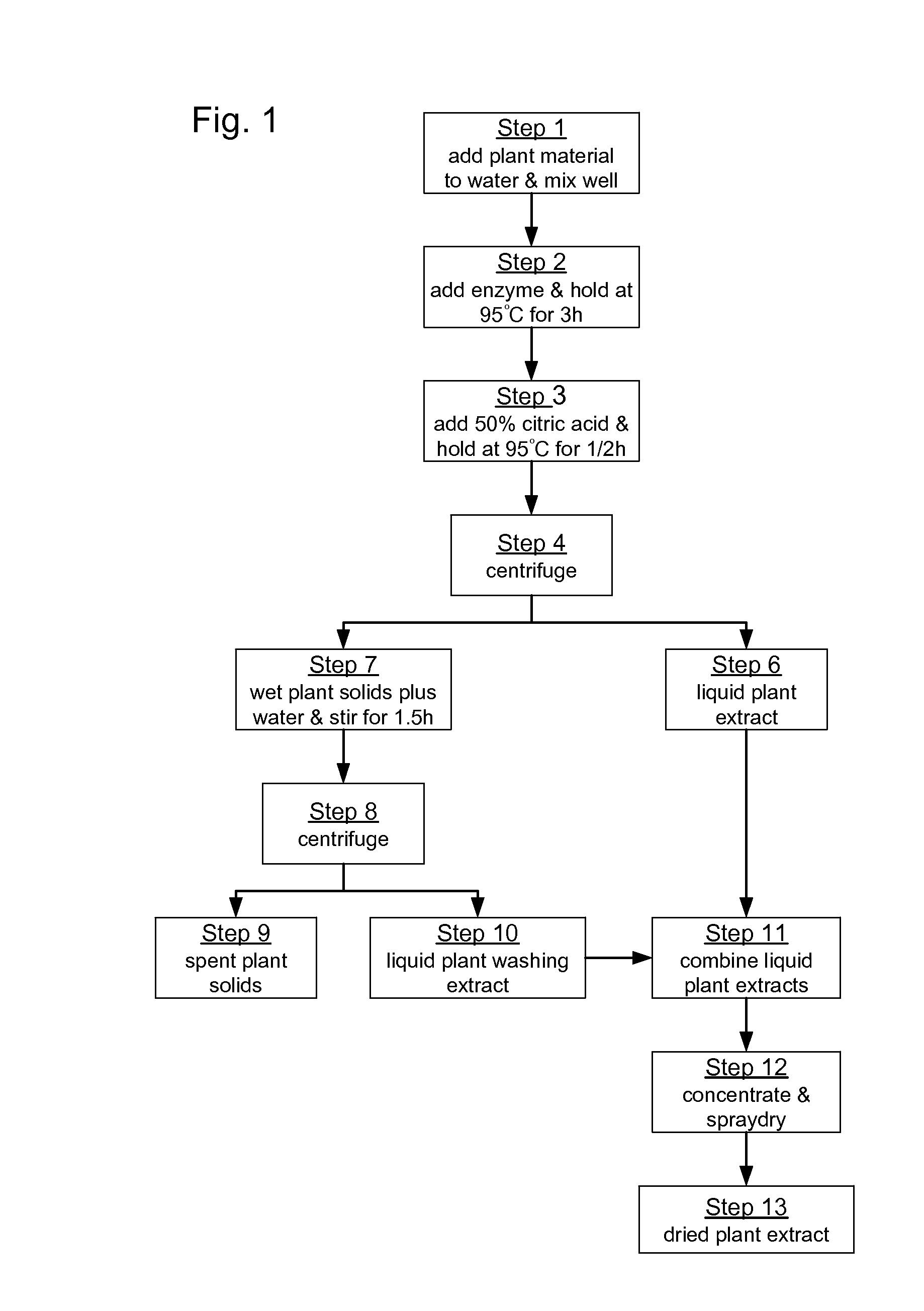
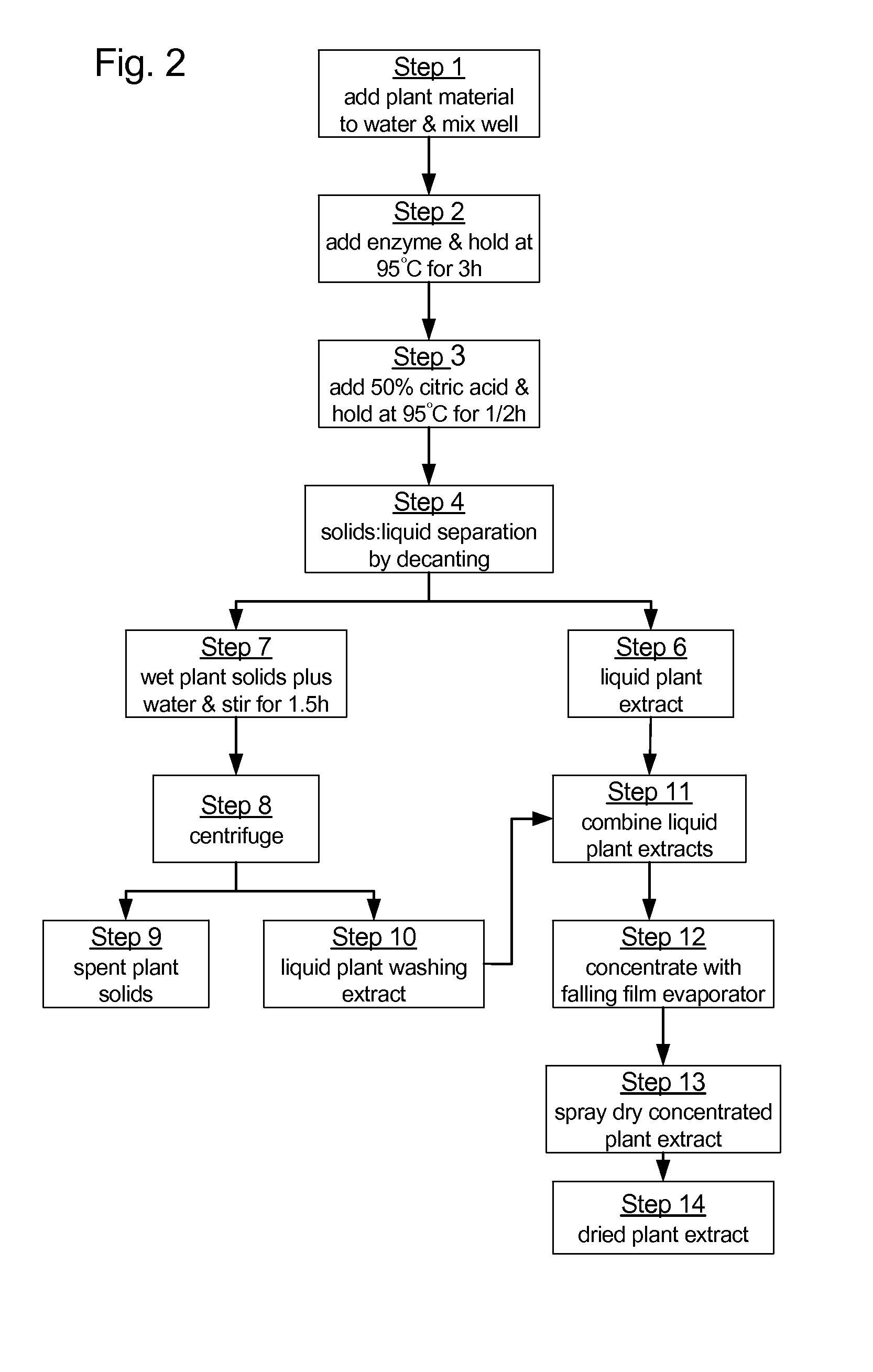
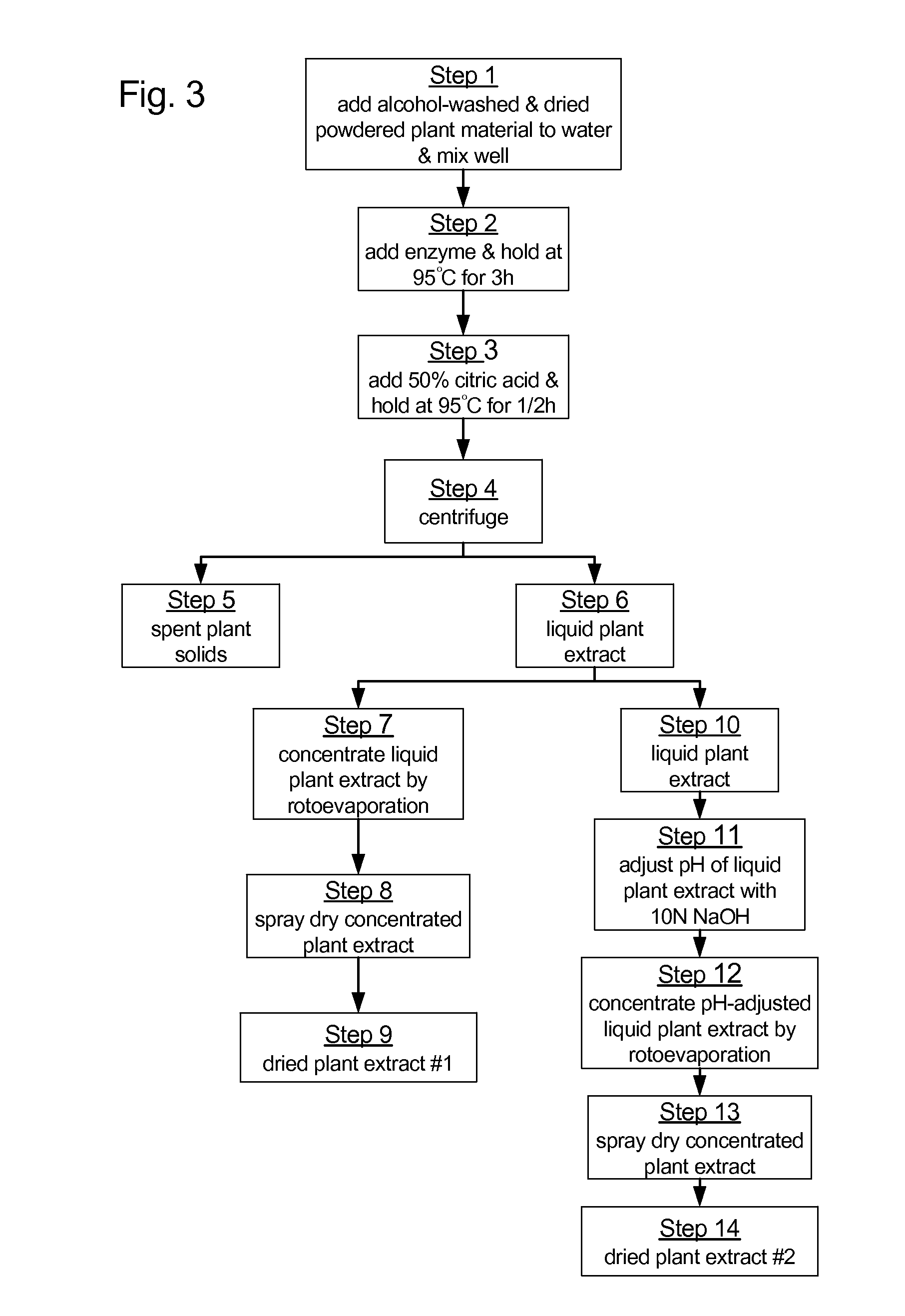
Extraction of phytochemicals by enzymatic hydrolysis
A process for extracting phytochemicals from plants. The process generally comprises controllably slurrying a selected plant material in a volume, adding a selected enzyme the slurry while it is controllably agitated, then heating the controllably agitated slurry-enzyme mixture to a temperature from the range of 40° C. to 110° C., and then maintaining the slurry-enzyme mixture at that temperature for a selected period of time. The slurry is then separated into a solids fraction and a liquids fraction that contains extracted phytochemicals. The liquids fraction is controllably de-watered to produce a fluid extract concentrate. The liquids fraction may optionally be dried to produce a dried extract concentrate. Suitable enzymes for use with this process include α-amylases, β-amylases, endo-β-1,4-glucanases, cellobiohydrolases, cellulases, hemicellulases, β-glucosidases, β-xylosidases, xylanases, pullulases, esterases and mixtures thereof.
Owner:POS PILOT PLANT CORP
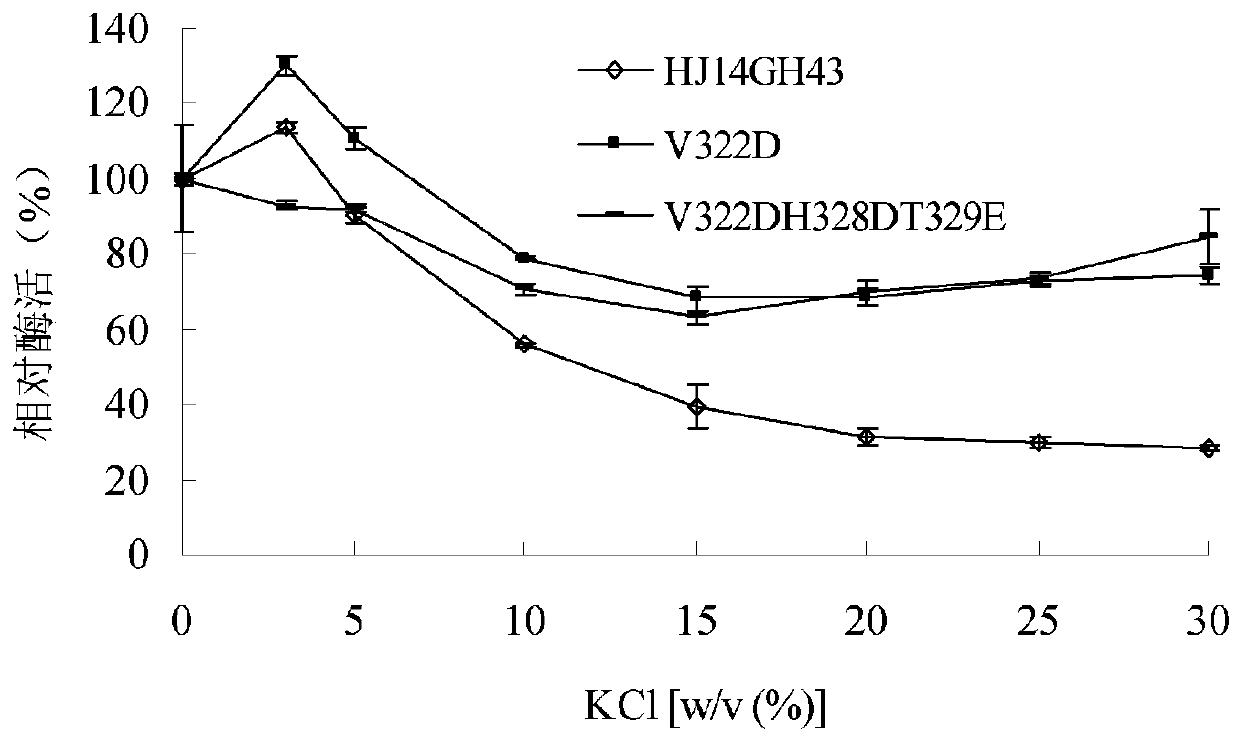
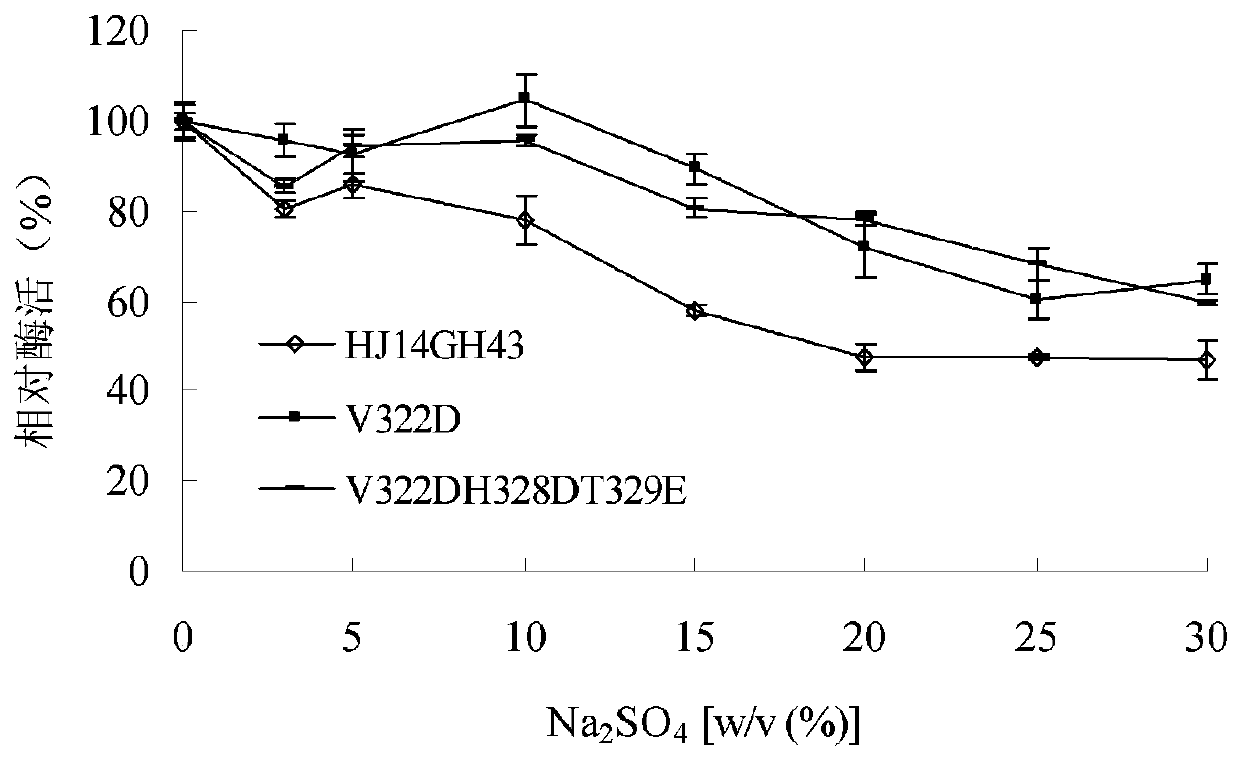
Ammonium sulfate-resistant xylosidase mutant V322DH328DT329E
ActiveCN111004789AImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGene engineeringSewage treatment
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering and protein modification, and discloses an ammonium sulfate-resistant xylosidase mutant V322DH328DT329E. The amino acid sequence of themutant V322DH328DT329E is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. After the V322DH328DT329E is treated by 15.0-30.0% (w / v) of KCl, Na2SO4 and (NH4)2SO4 for 60 minutes, the activity of the V322DH328DT329E is 63-85%,60-81% and 99-107% respectively. The ammonium sulfate-resistant xylosidase mutant V322DH328DT329E disclosed by the invention can be applied to the industries of agriculture, tanning, sewage treatmentand the like.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
High specific activity xylosidase Xyl52B8 and gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102978189AImprove thermal stabilityHigh activityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFood industry
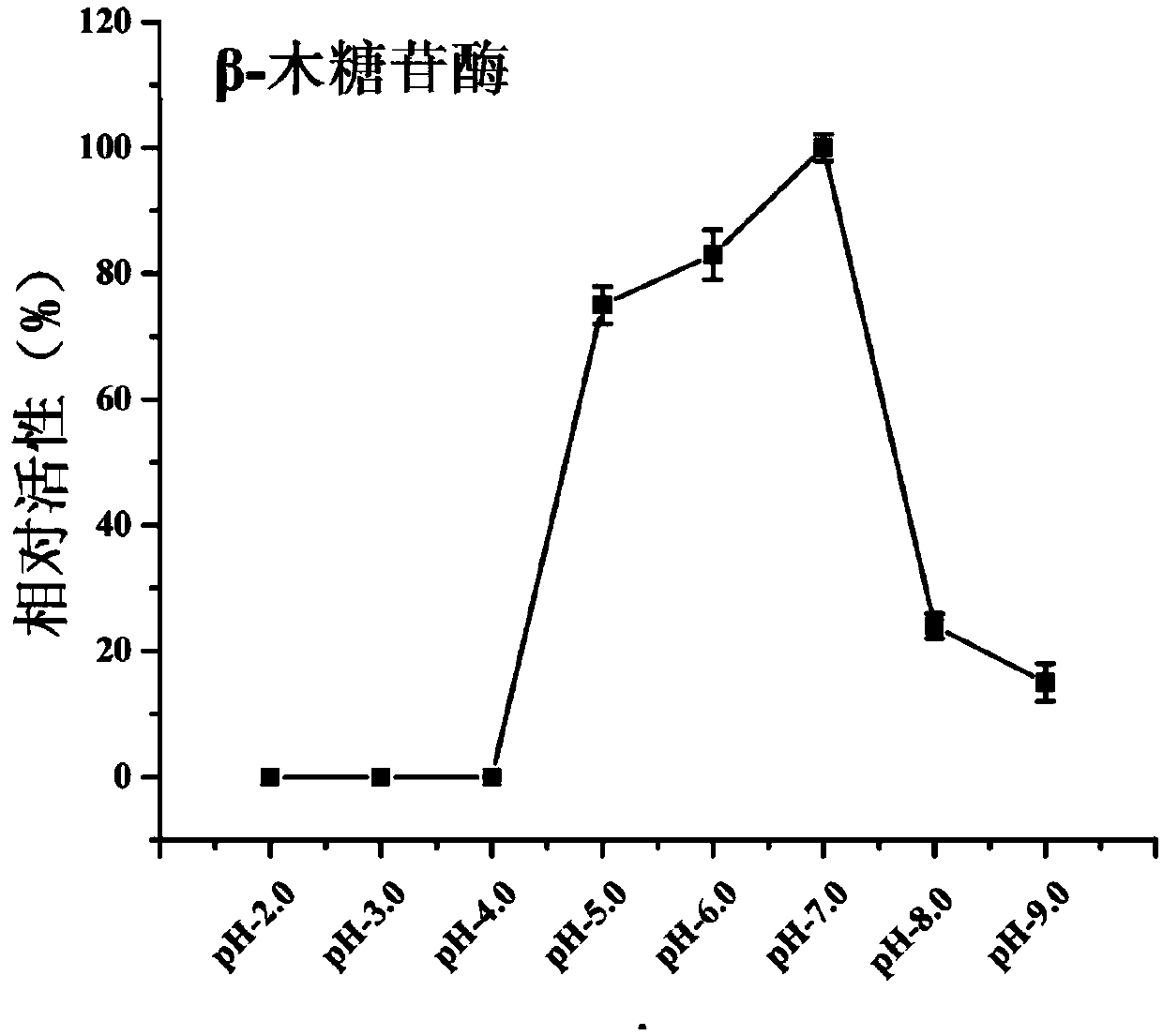
The present invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, and specifically relates to specific activity xylosidase Xyl52B8 and gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the xylosidase Xyl52B8 is shown as SEQ ID No. 1. Firstly, the technical problem to be solved by the present invention is to overcome the deficiencies in the prior art, and the invention provides novel xylosidase which has excellent nature, and is suitable for application in the feed and food industries. The optimum pH of the xylosidase of the present invention is 6.0. The xylosidase has relatively high enzyme activity at pH 5.0-7.0, and good stability of pH. The high specific activity of the xylosidase enables the application thereof in the industrial production in need of high-temperature environment.
Owner:WUHAN SUNHY BIOLOGICAL
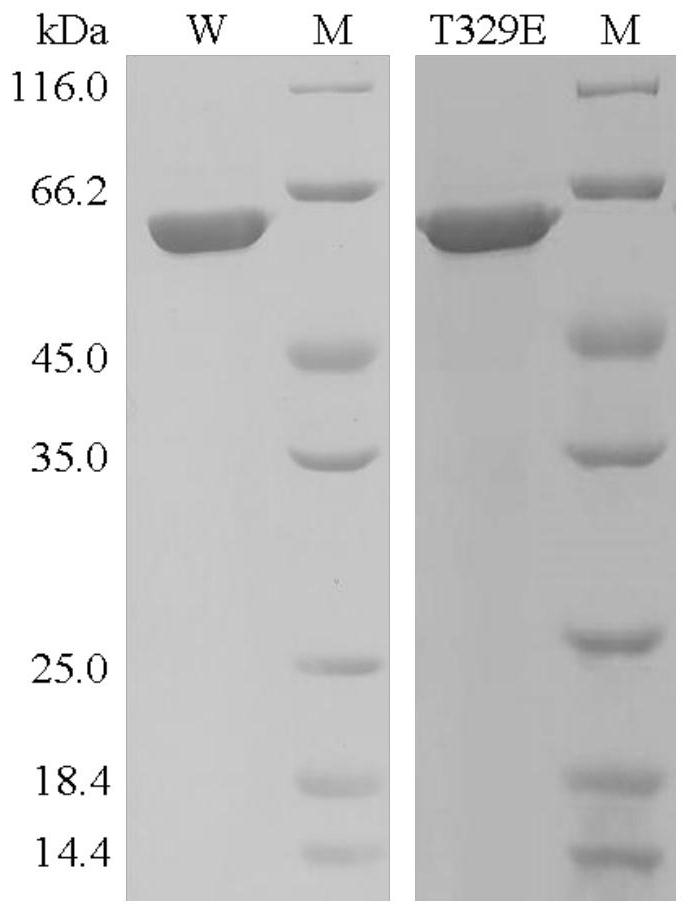
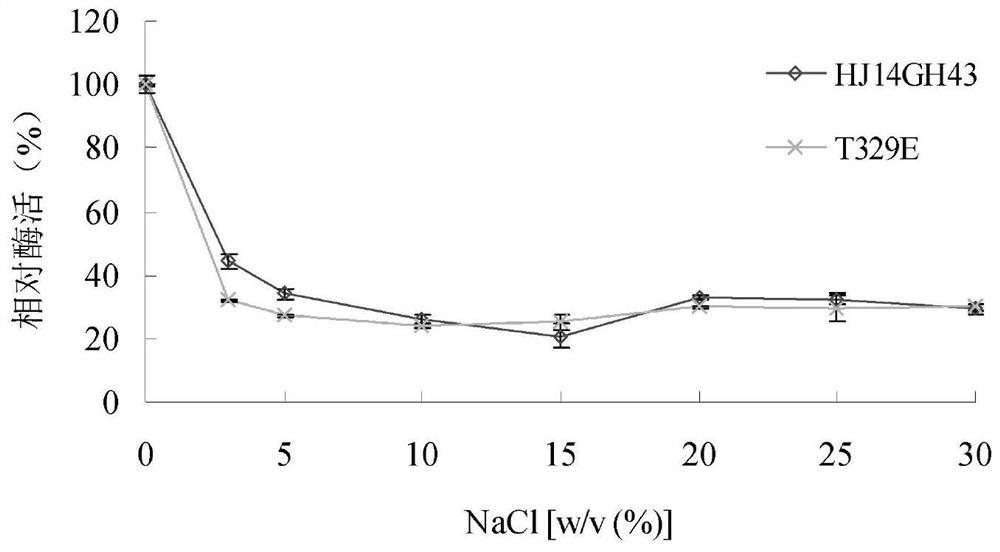
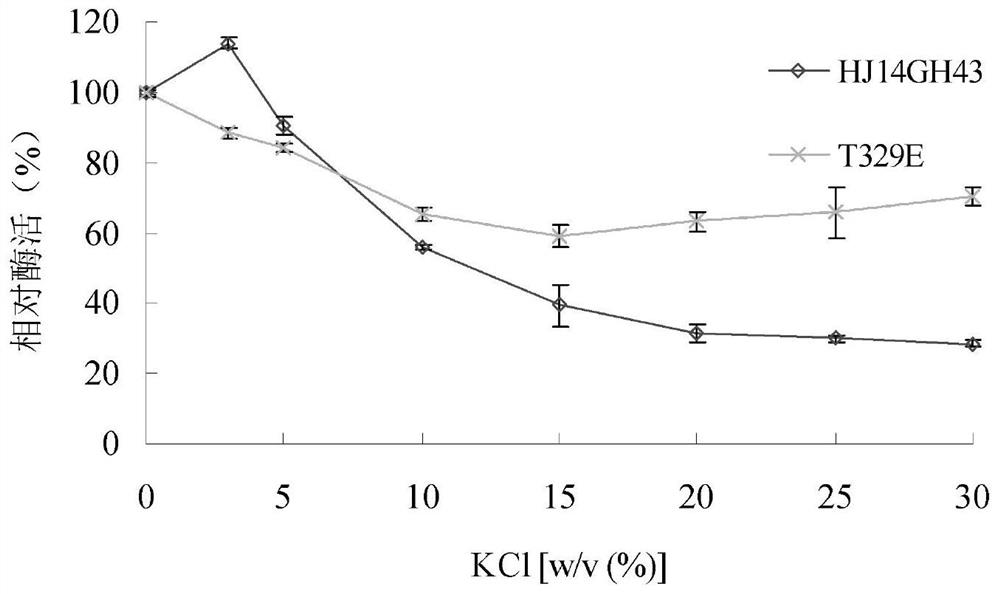
Salt-tolerant xylosidase mutant t329e and its preparation method and use
ActiveCN112342205BNo decrease in activityImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesThreonineSewage treatment
The invention discloses a salt-tolerant xylosidase mutant T329E and its preparation method and application. The amino acid sequence of the mutant T329E is obtained by mutating the threonine at position 329 of wild xylosidase HJ14GH43 into glutamic acid. Its sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the salt is not NaCl. Compared with the wild enzyme HJ14GH43, the mutant enzyme T329E of the present invention has a high concentration of KCl, Na 2 SO 4 and (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 The stability in the medium has been enhanced, after 15.0-30.0% concentration of KCl treatment, its activity remains 59-70%; after 15.0-30.0% concentration of Na 2 SO 4 After treatment, its activity remained 78-87%; after 20.0-30.0% concentration (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 After treatment, its activity is increased by about 20%, which can be applied to industries such as tanning, papermaking, and sewage treatment.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Cryophilic xylosidase/arabinofuranosidase and preparation method and application thereof
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
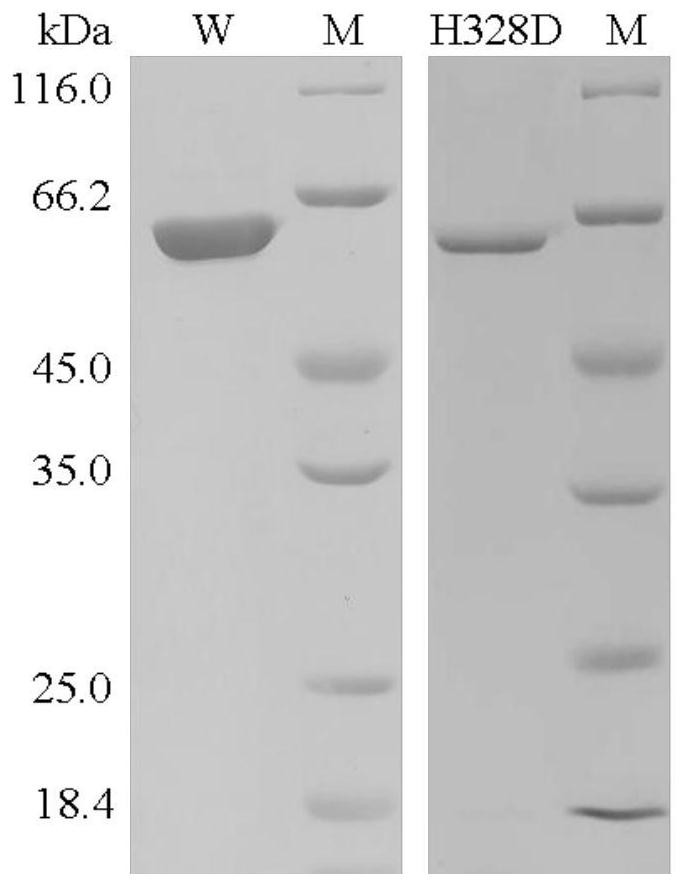
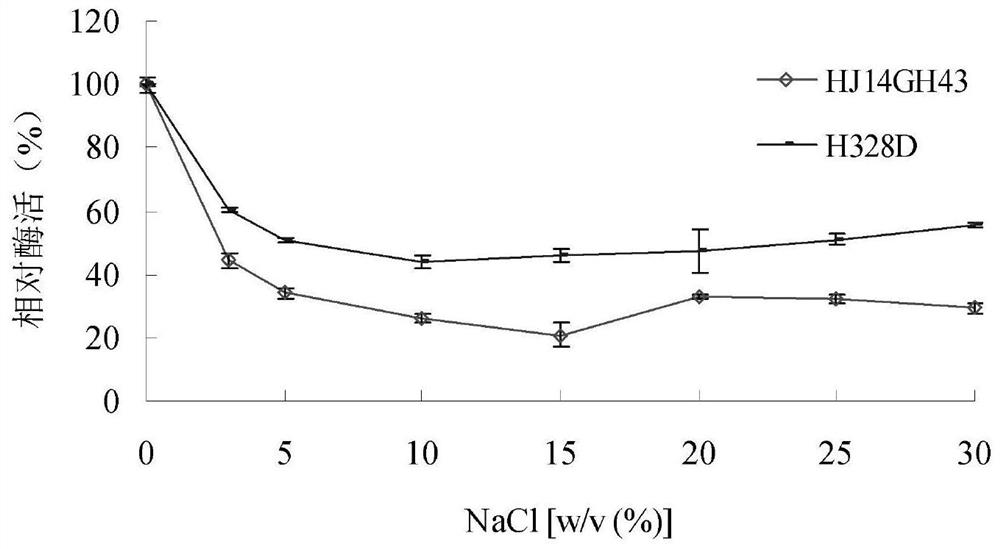
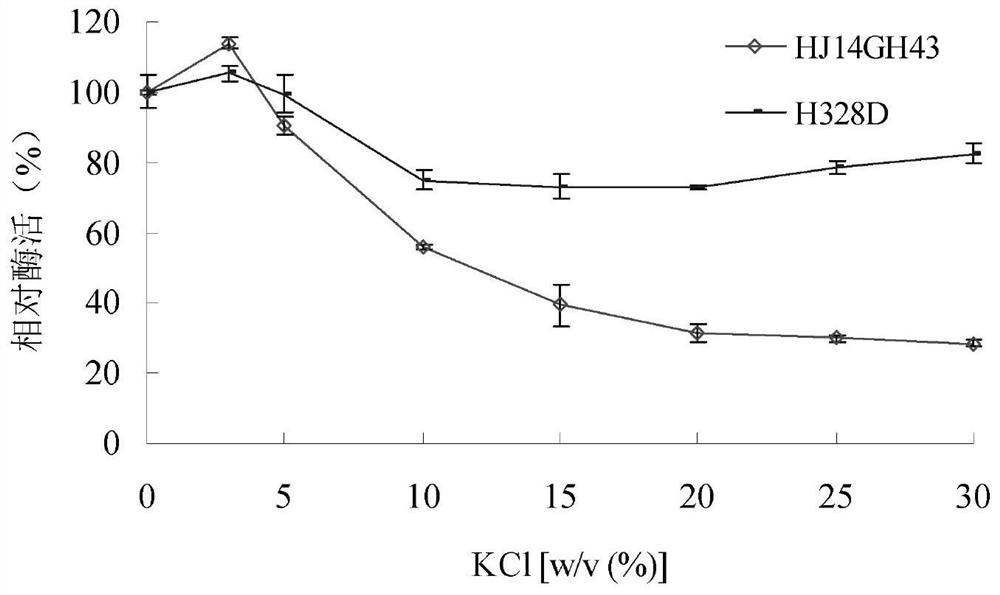
A kind of xylosidase mutant h328d resistant to sodium chloride and potassium chloride and its application
ActiveCN110862977BImprove stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSewage treatmentGenetically engineered
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering and protein transformation, and discloses a sodium chloride- and potassium chloride-resistant xylosidase mutant H328D and its application. The amino acid sequence of the mutant H328D is shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The mutant has good stability in high concentrations of NaCl and KCl. After being treated with 3.0-30.0% (w / v) NaCl for 60 minutes, the activity is 44-60%; After 60 minutes of treatment, the activity was 73-105%. The sodium chloride and potassium chloride resistant xylosidase mutant H328D of the present invention can be applied to industries such as food, agriculture, and sewage treatment.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com