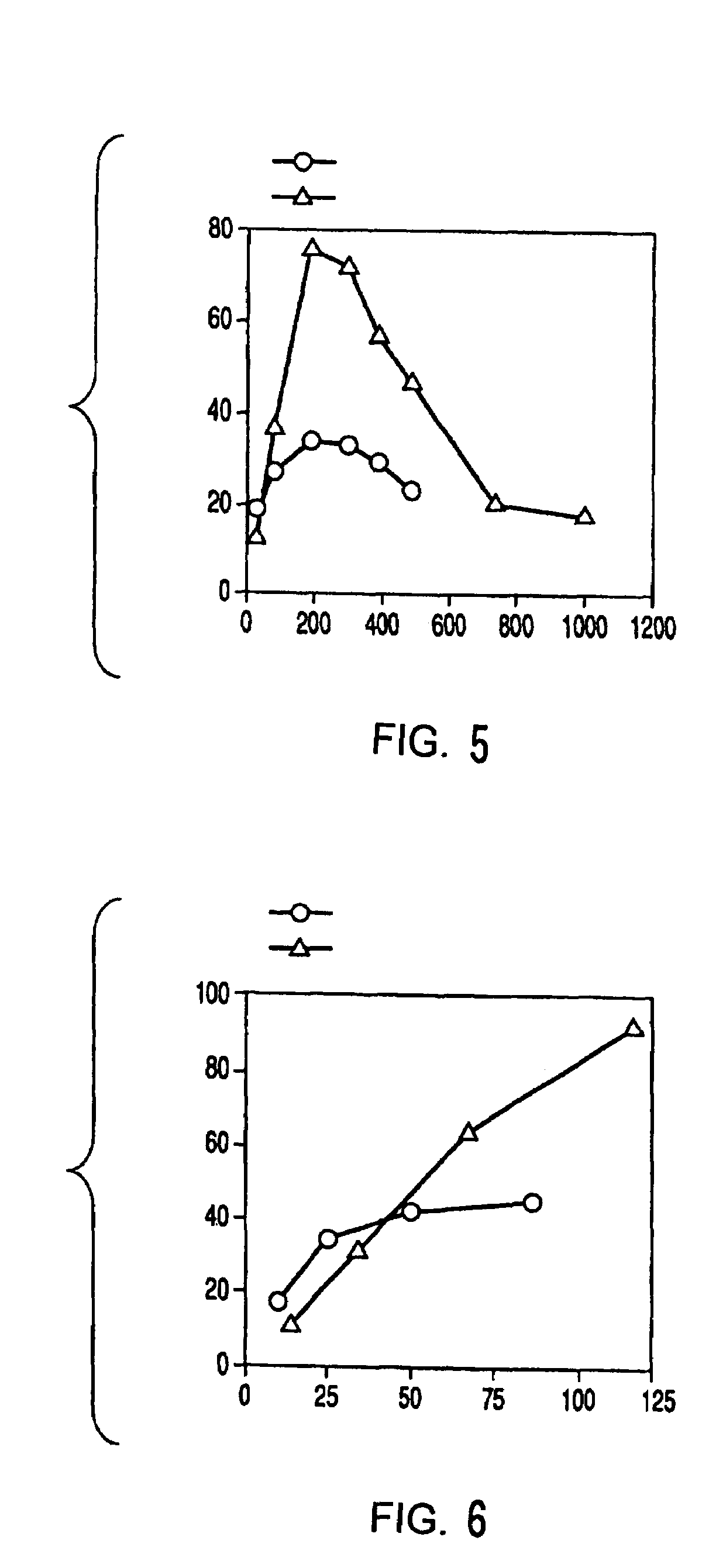
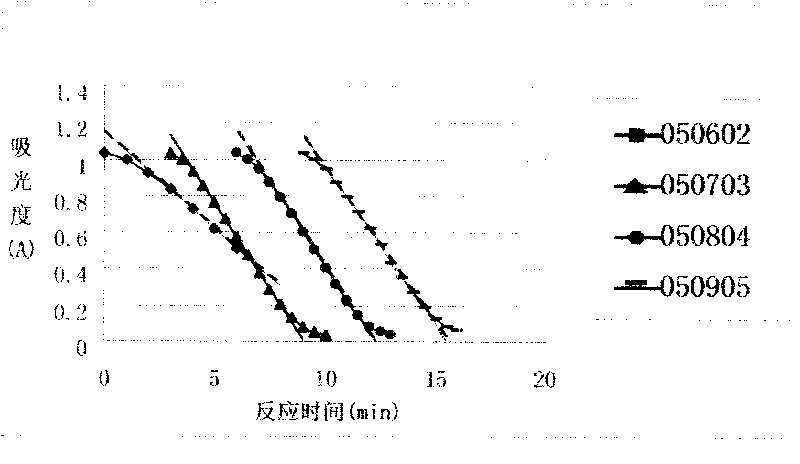
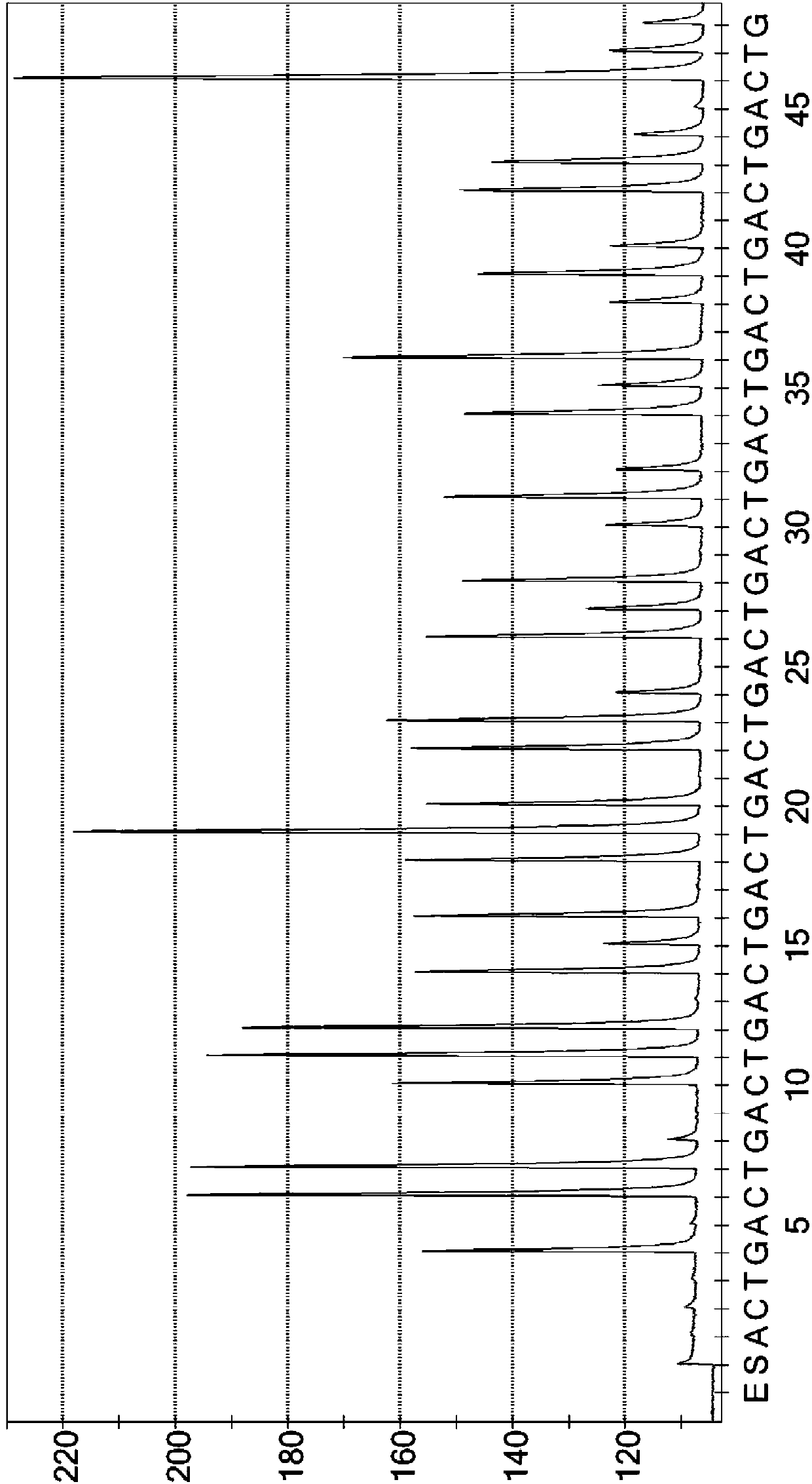
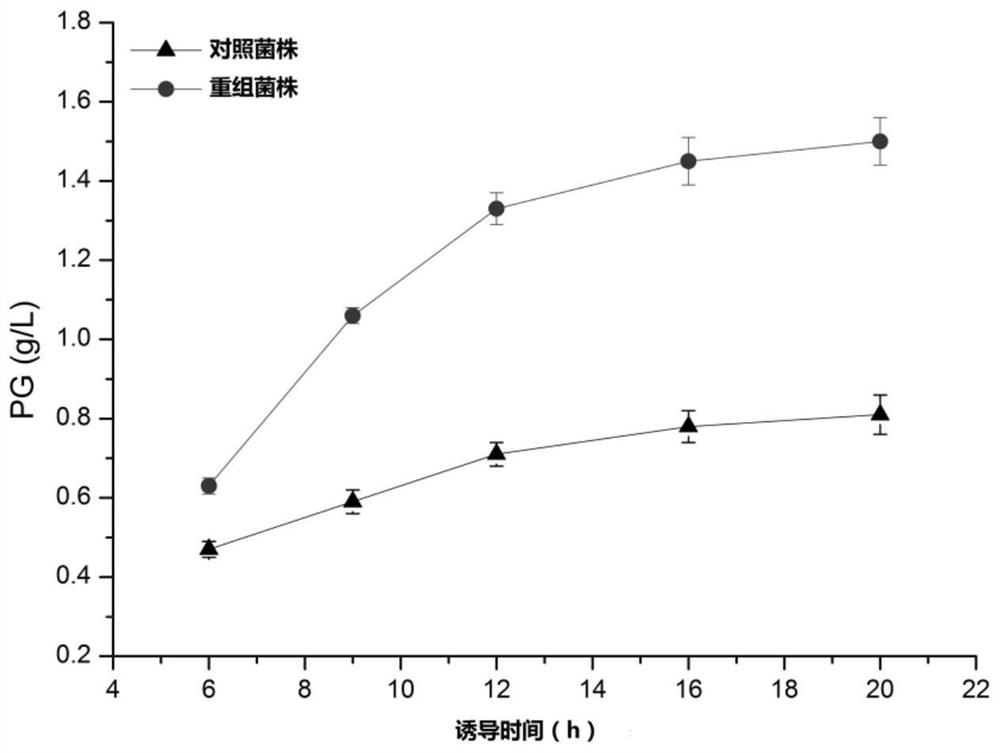
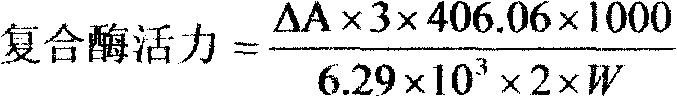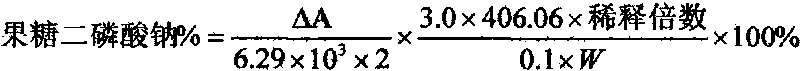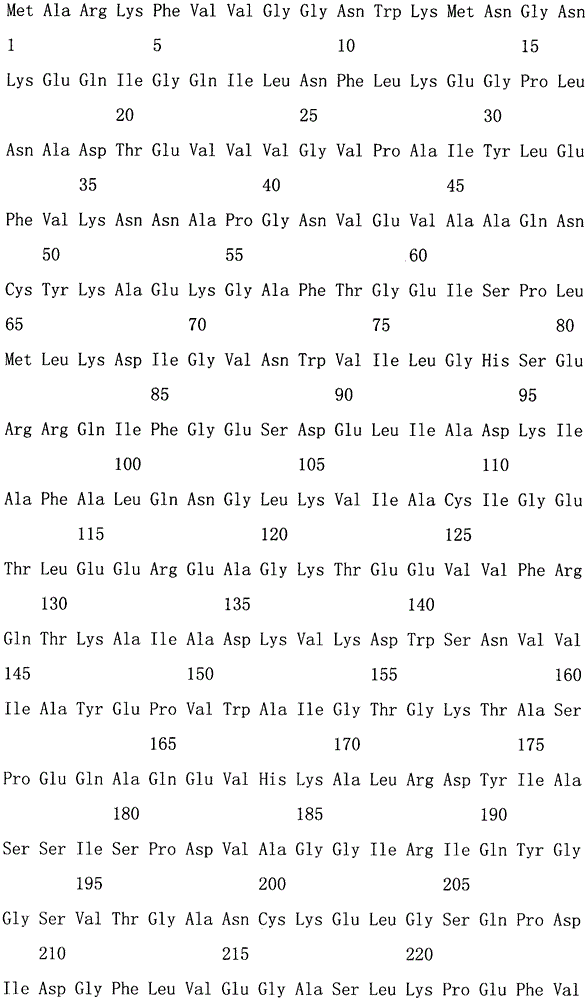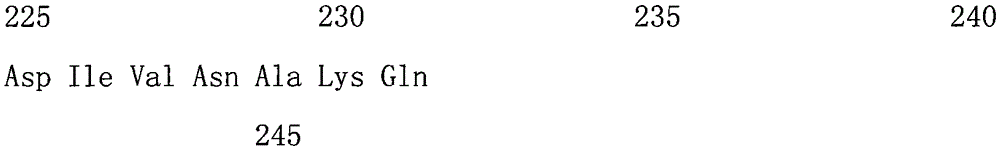Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Triose-phosphate isomerase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Triose-phosphate isomerase (TPI or TIM) is an enzyme (EC 5.3.1.1) that catalyzes the reversible interconversion of the triose phosphate isomers dihydroxyacetone phosphate and D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
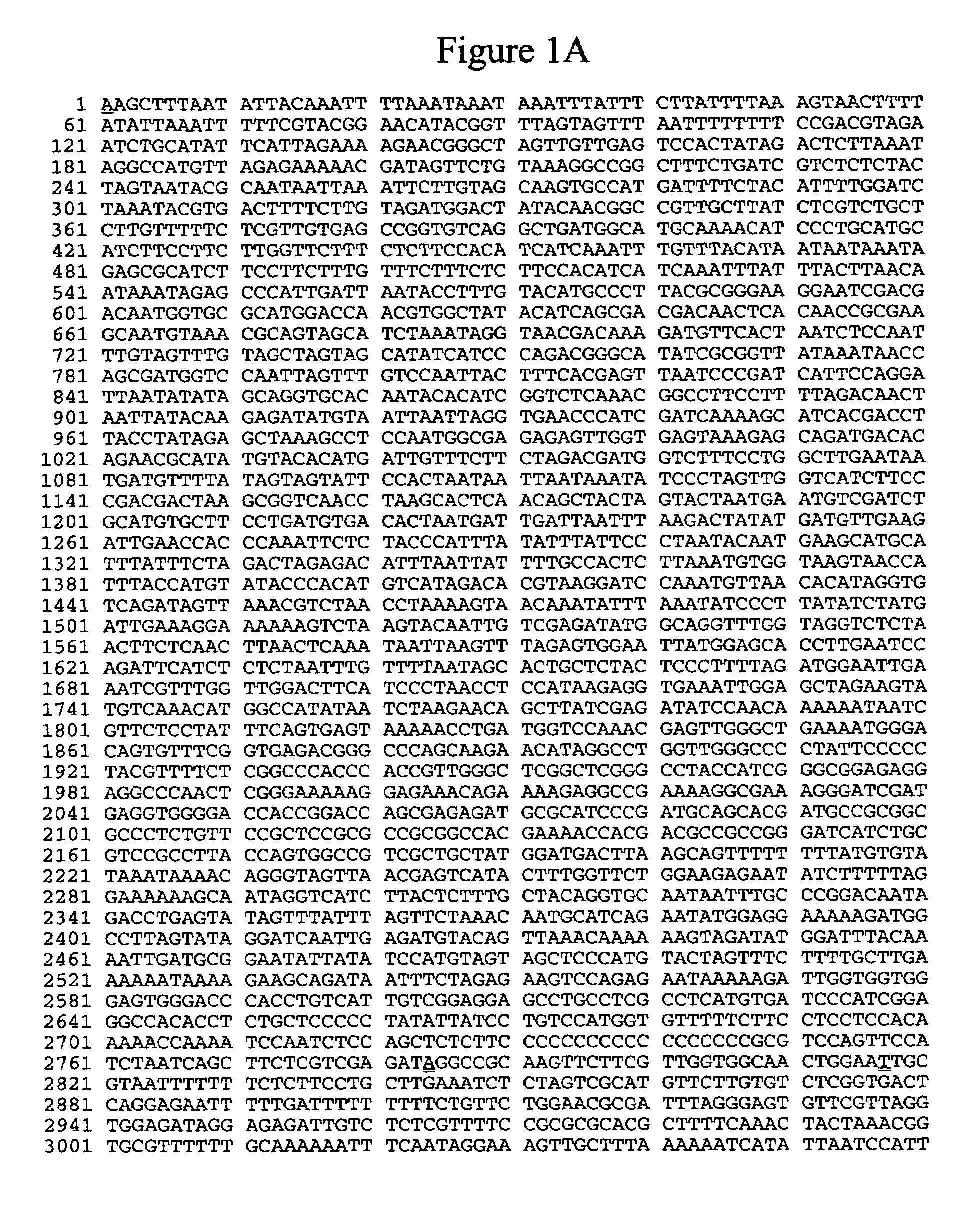
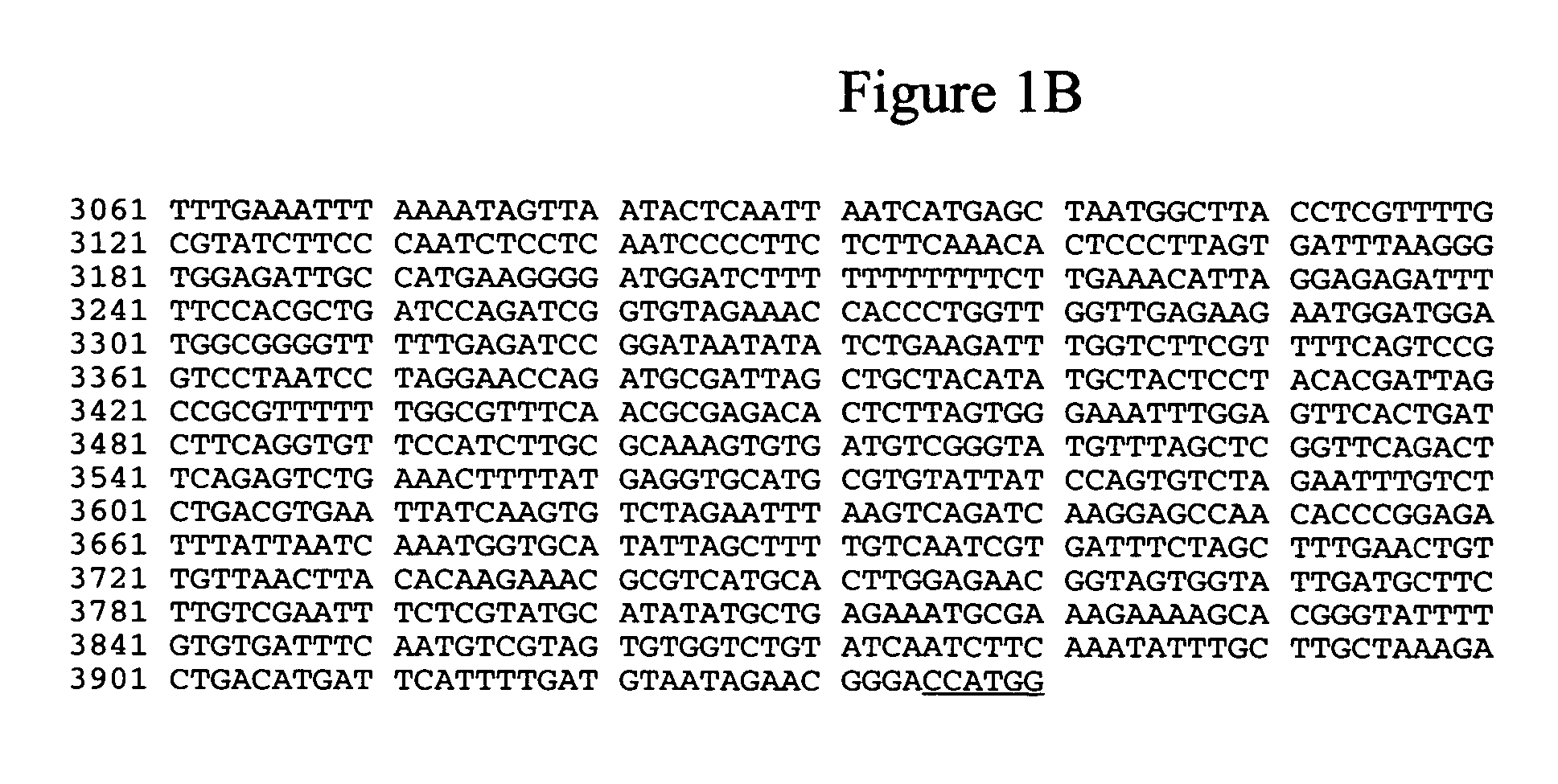
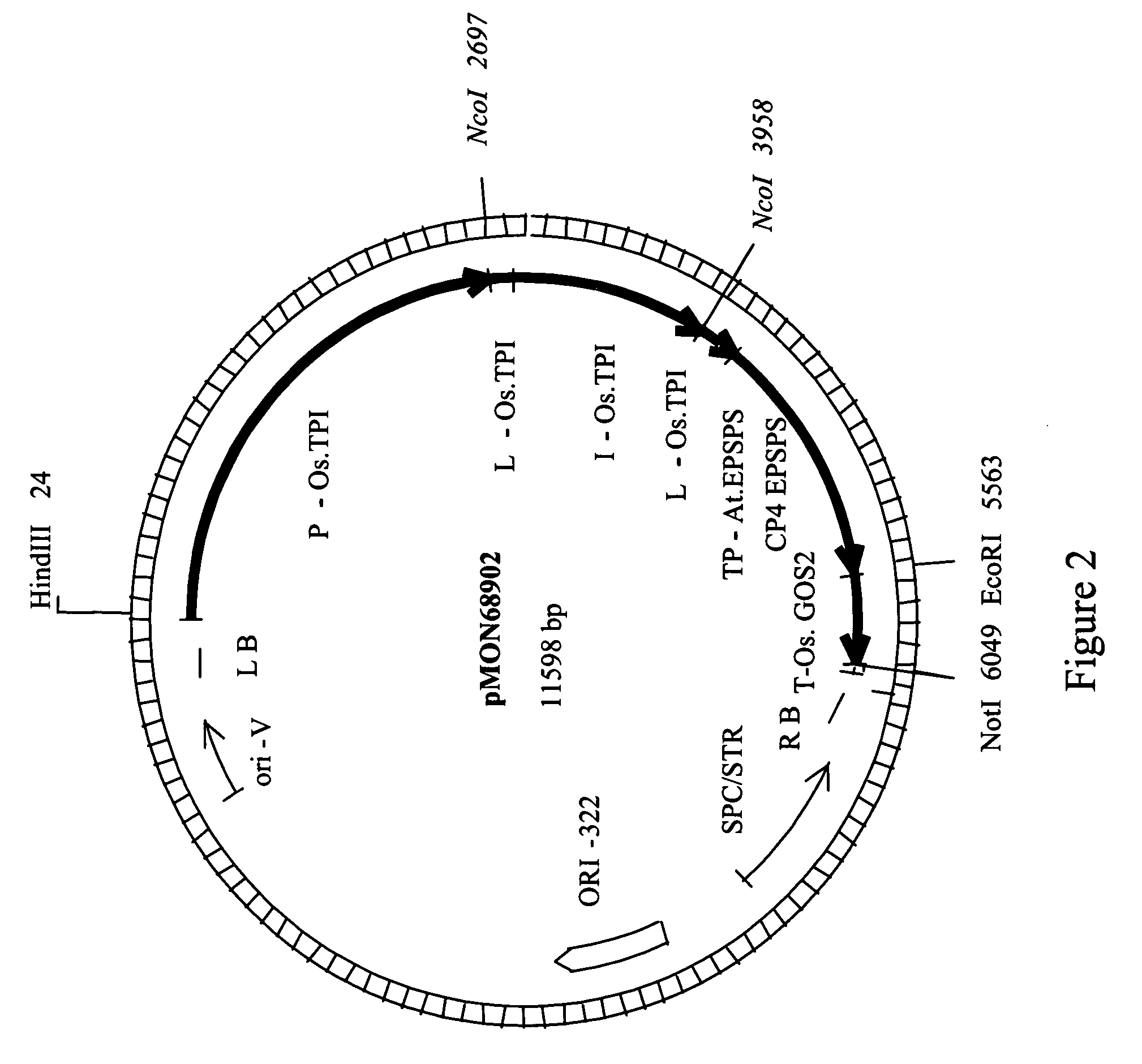
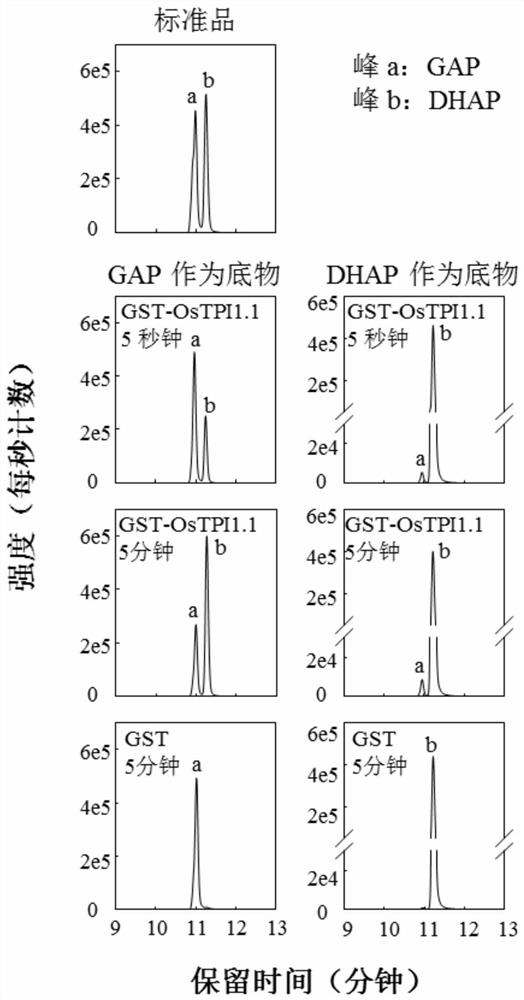
Promoter from the rice triosephosphate isomerase gene OsTPI
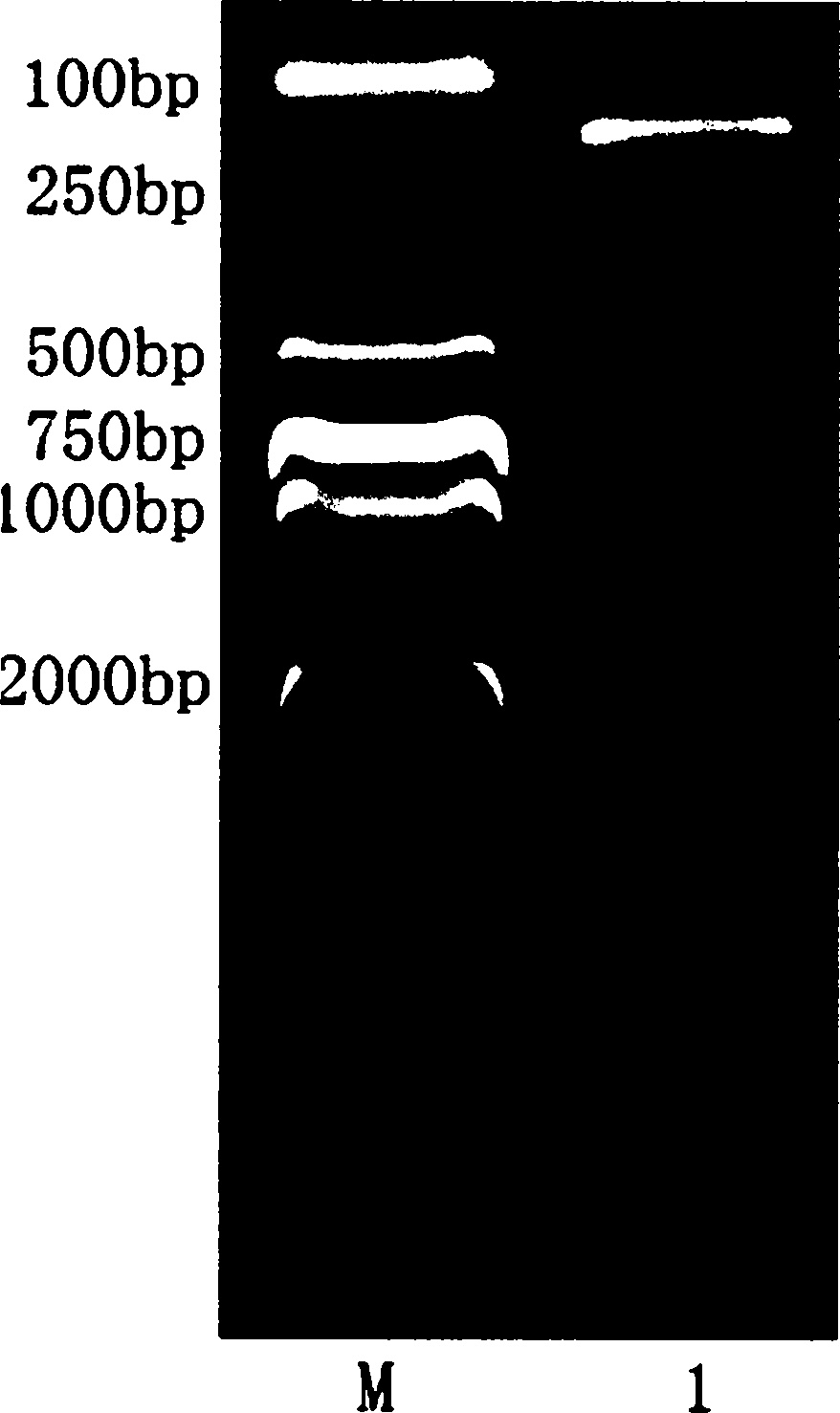
The present invention relates to polynucleotide molecules for regulating gene expression in plants. In particular, the invention relates to DNA sequences of the rice (Oryza sativa cv Nipponbare) triosephosphate isomerase (OsTPI) gene promoter that are useful for regulating gene expression of heterologous polynucleotide molecules in plants. The invention also relates to expression constructs and transgenic plants containing the heterologous polynucleotide molecules operably linked to and regulated by OsTPI DNA sequences.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
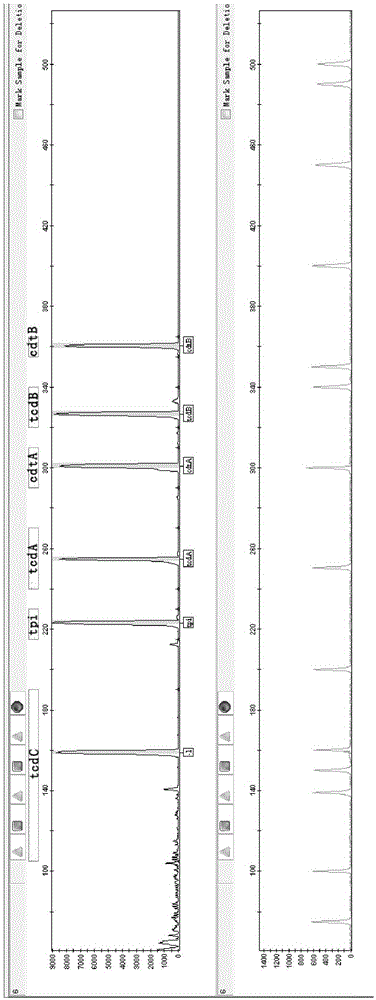
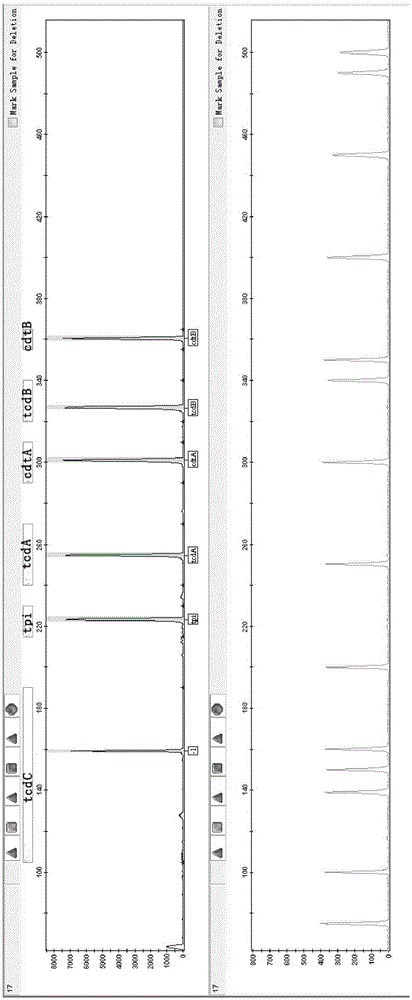
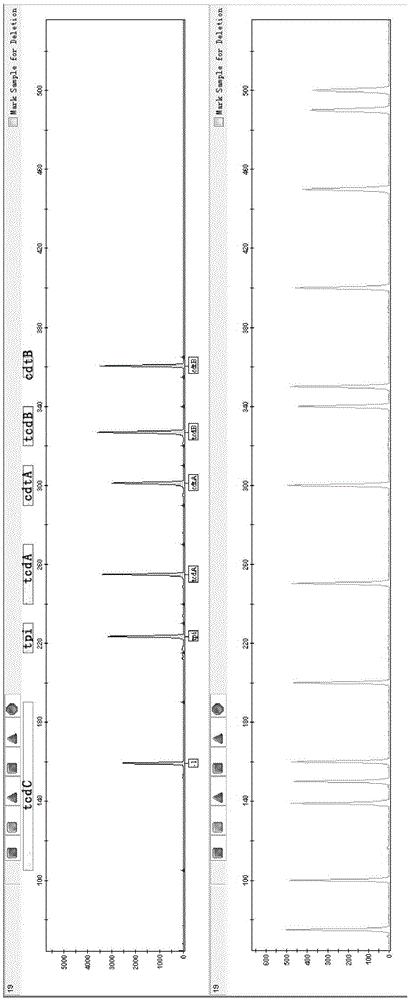
Fluorescence labeling multiplex PCR detection kit for Clostridium difficile
ActiveCN103911430AAccurate typingMicrobiological testing/measurementCapillary electrophoresisClostridium difficile toxin B
The invention provides a fluorescence labeling multiplex PCR detection kit for identification of a Clostridium difficile strain and analysis of toxin genes. The kit comprises 6 pairs of fluorescently-labeled primers used for detecting the Clostridium difficile strain. The 6 pairs of fluorescently-labeled primers comprise specific primers of specific triosephosphate-isomerase (tpi) gene, toxin A gene (tcd A), toxin B gene (tcd B), tcd C gene (tcd C), binary toxin A gene (cdt A) and binary toxin B gene (cdt B) of the Clostridium difficile strain. Amplification results are detected through capillary electrophoresis. Thus, existence of Clostridium difficile can be rapidly identified and toxin typing can be rapidly determined.
Owner:江苏安科华捷生物科技有限公司
Chassis system for ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) regeneration and application
The invention provides a chassis system for ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) regeneration and application. The chassis system for ATP regeneration comprises the following five enzymes: alpha-glucan phosphorylase, glucophosphomutase, phosphoglucose Isomerase, phosphoketolase and acetokinase. In addition, the chassis system can further comprise the following seven enzymes: transaldolase, transketolase,ribose-5-phosphate isomerase, ribulose-3 epimerase, triosephosphate isomerase, fructose-bisphosphate aldolase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. The chassis system can be coupled to an enzymic catalyticreaction needing ATP, utilizes starch or maltodextrin as energy, is not added with any coenzyme, can efficiently regenerate the ATP at low cost through a one-pot reaction and is an economical, highlyefficient, stable and sustainable ATP regeneration system.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Recombinant bacterium for producing acetylacetone and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN110791467AAchieve biosynthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliMethylglyoxal synthase
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium for producing acetylacetone and a construction method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The recombinant bacterium is obtained by taking Escherichia coli as a starting strain, introducing a gene encoding an acetylacetone lyase, a gene encoding a methylglyoxal synthase, and a gene encoding triose phosphate isomerase into the Escherichia coli. With this recombinant bacterium, biosynthesis of acetylacetone is achieved for the first time. The recombinant bacterium can synthesize acetylacetone by usingglucose as the sole carbon source, and can obtain 53 mg / L of acetylacetone by fermentation for 48 hours.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Yeast for dietary therapy of diabetes and construction method thereof
InactiveCN101824388AReduce biological activityImprove bioavailabilityFungiMetabolism disorderYeast chromosomeRestriction site
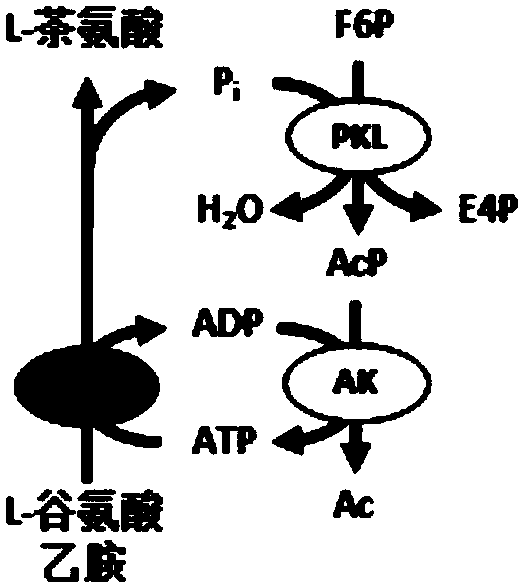
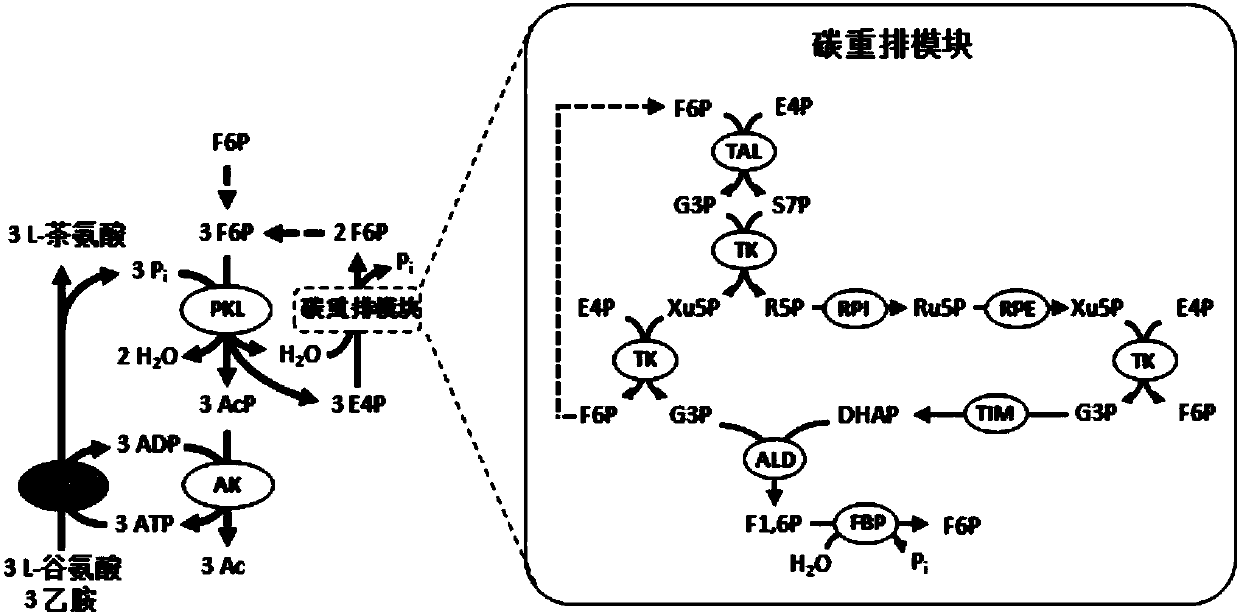
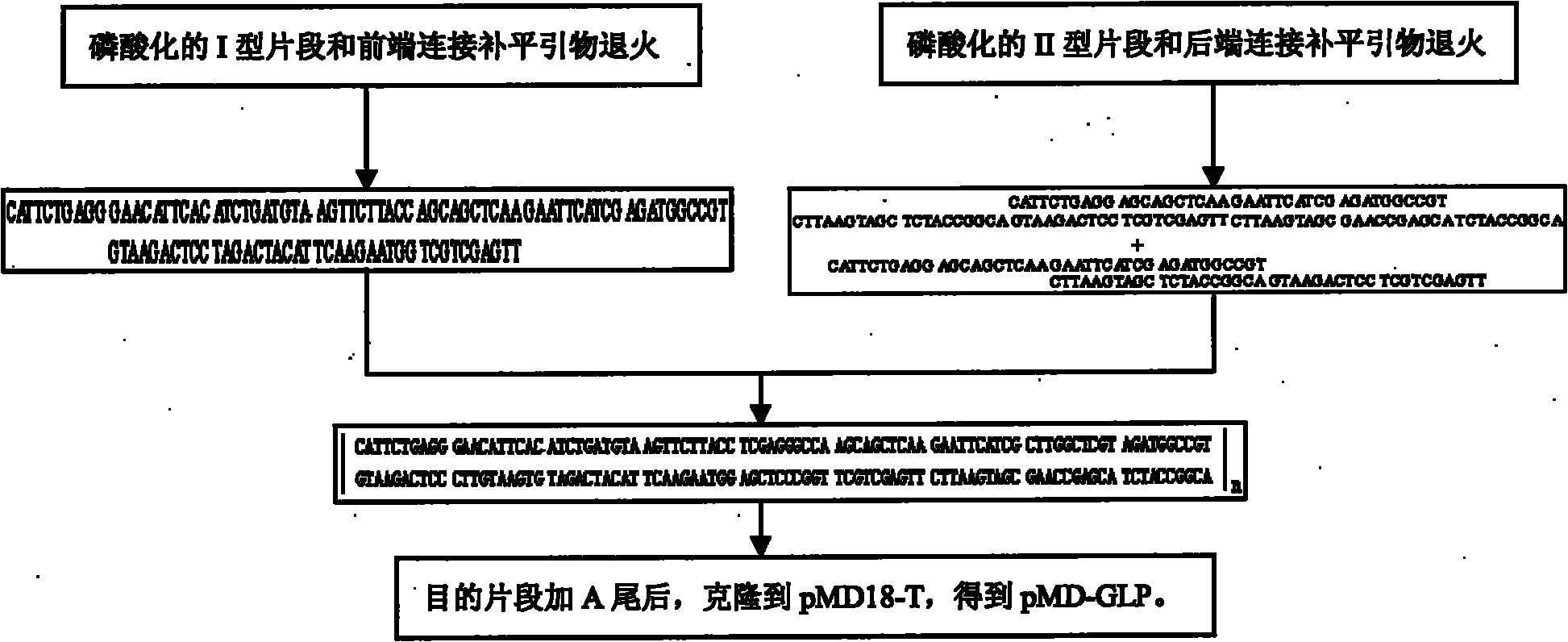
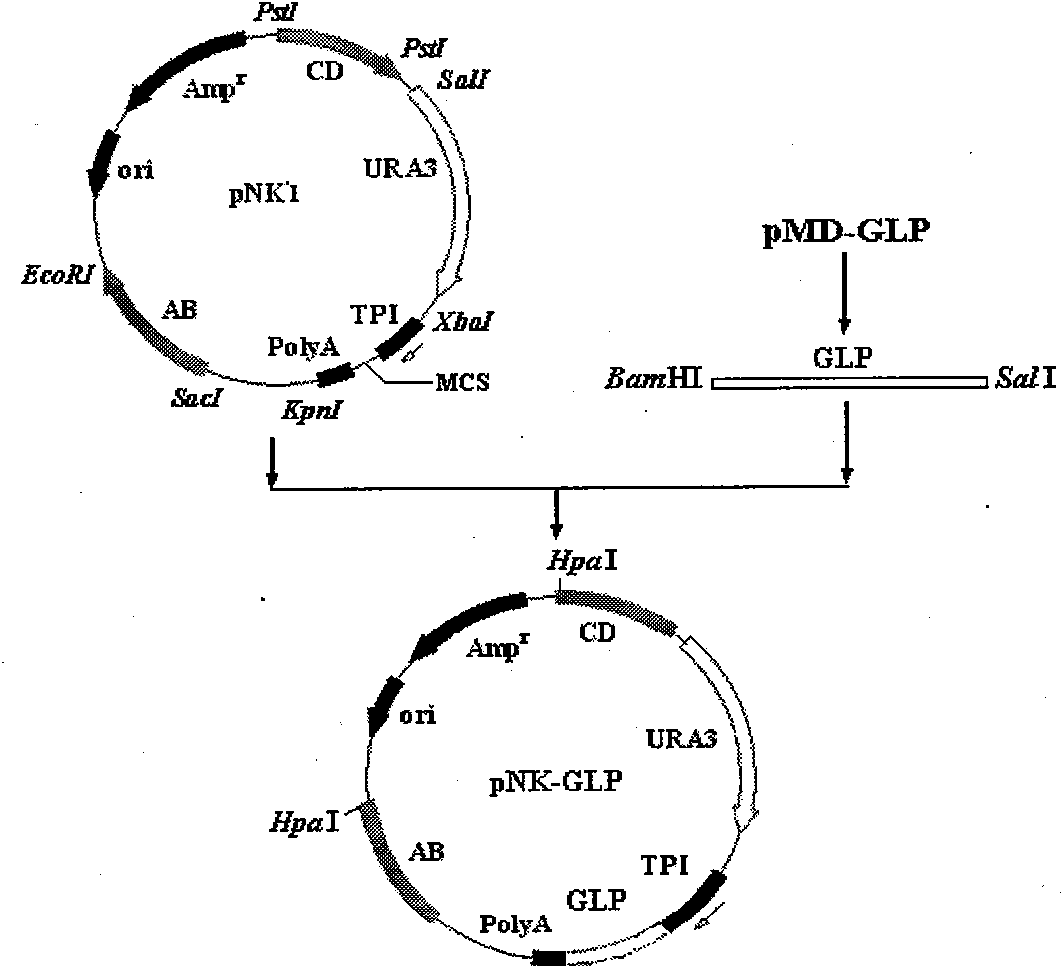
The invention describes a yeast for the dietary therapy of diabetes and a construction method thereof. A saccharomyces cerevisiae genome DNA as a template is used for amplifying two sections of rDNA sequences; pYX212 as a template is used for amplifying a nutritional marker gene URA3 and an expression cassette segment driven by a triosephosphate isomerase promoter; the four amplified products are respectively cloned at corresponding loci of pUC18, and thereby an integrating vector pNK1 is obtained. A DNA synthesization point mutation technique is then utilized to remove the restriction sites of dipeptidase VI and trypsin in the natural GLP-1 molecule, so that type I primer segments, type II primer segments and left and right connected filling primer segments are synthesized, and a ten-repeat tandem rolGLP-1 sequence is obtained by the method of step-by-step annealing and one-step connection, and is cloned in the pNK1, so that pNK-GLP is obtained. The pNK-GLP is then linearized, saccharomyces cerevisiae BJ2407 is transformed, and after screening, recombinant yeast SG2 is obtained. Because the rolGLP-1 gene is integrated in yeast chromosome, the recombinant strain can stably and efficiently express the characteristics of the rolGLP-1 and reduce the blood sugar level of a rat with hyperglycaemia, and can be used in the development of yeast biomedicine for treating diabetes.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Construction and application of heat-resistant yeast engineering bacteria capable of producing glycerine under high temperature aerobiotic condition
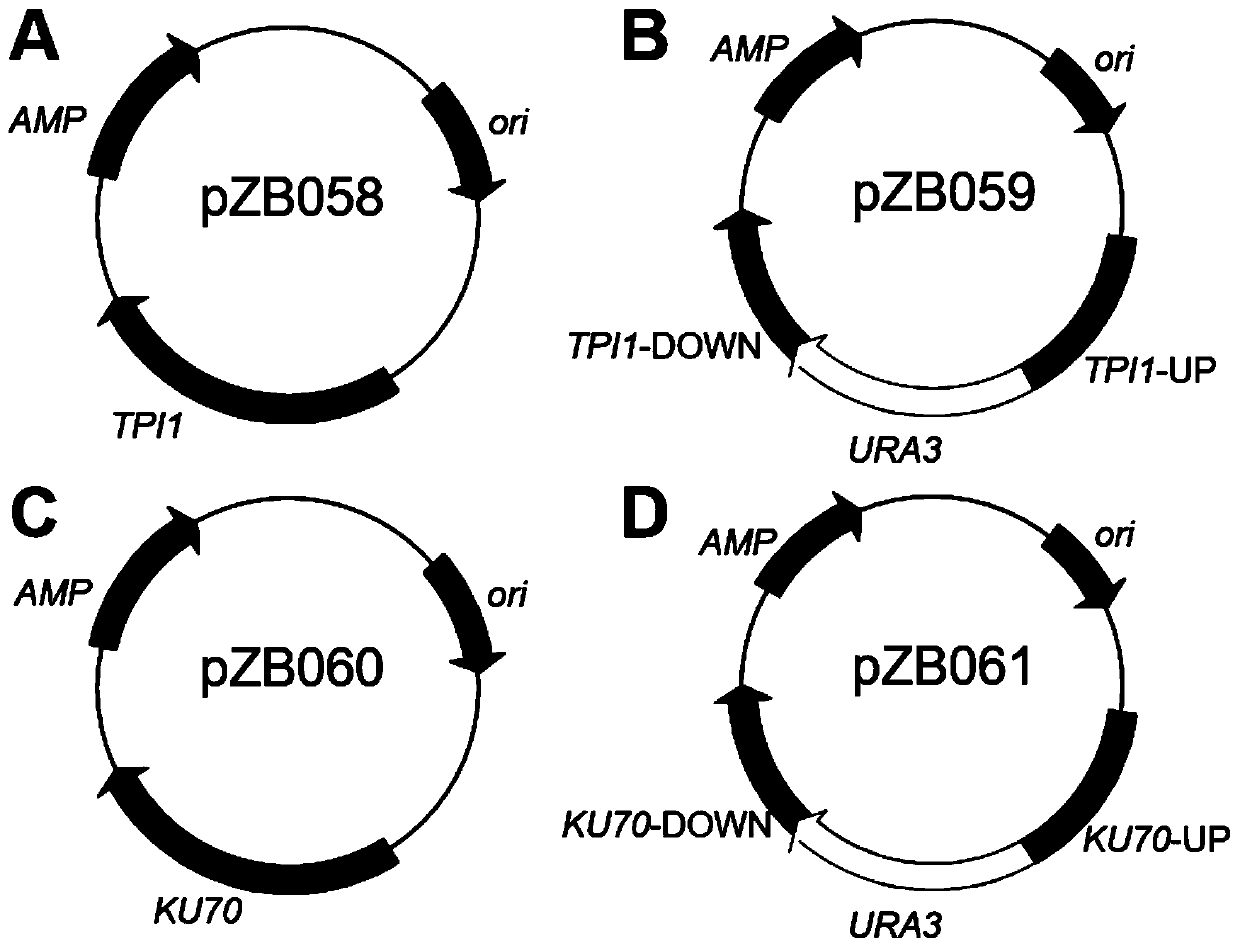
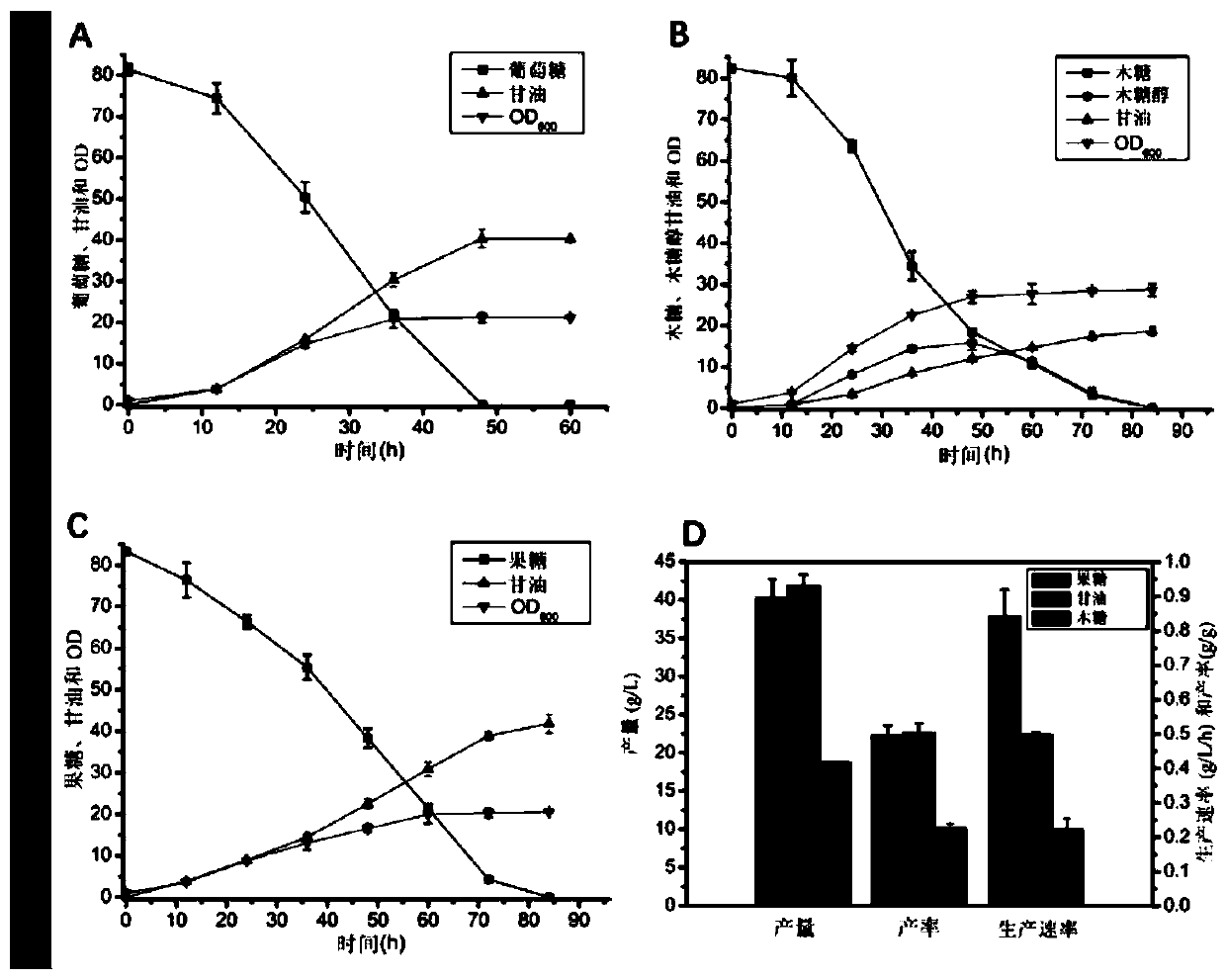
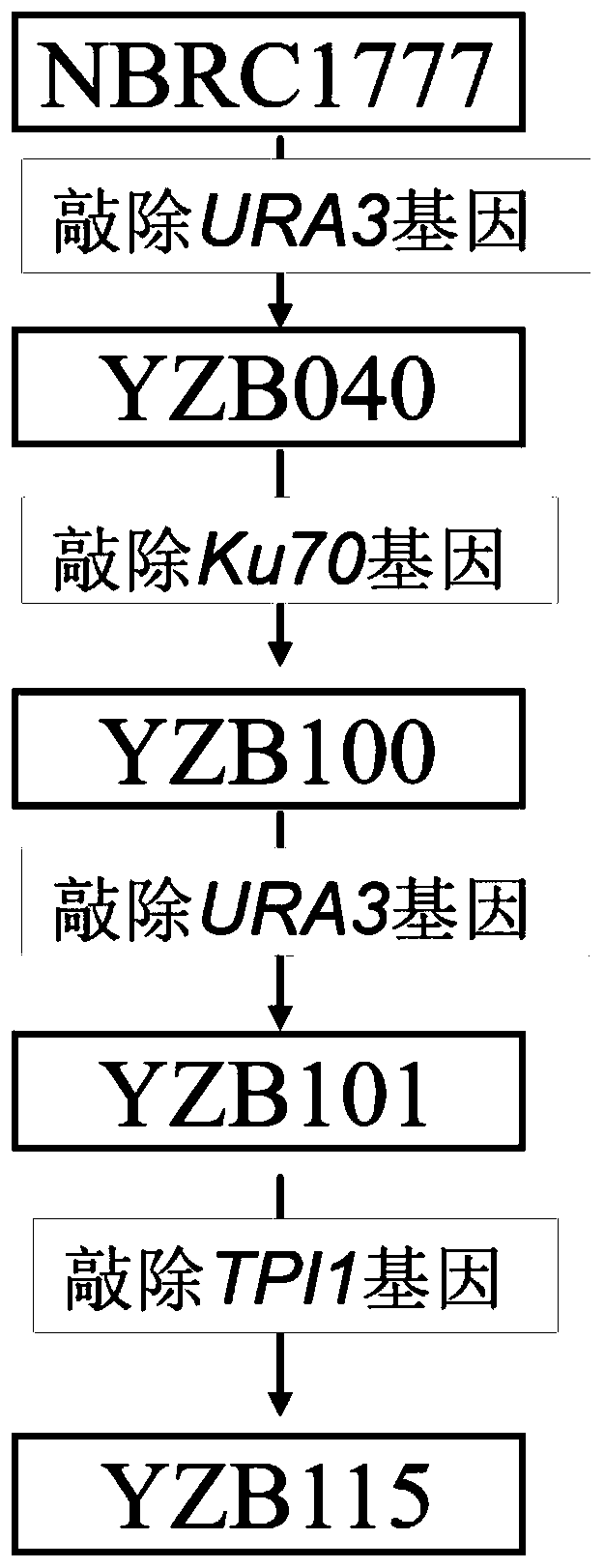
The invention discloses construction and application of heat-resistant yeast engineering bacteria capable of producing glycerine under high temperature aerobiotic condition. A heat-resistant kluyveromyces marxianus is used as a platform, methods of genetic engineering, metabolic engineering and the like are utilized, a strain having triose phosphate isomerase (TPI1) deletion is constructed, and the constructed strain has the capacity of efficiently producing the glycerine through efficient utilization of glucose, levulose and xylose under the high temperature aerobiotic condition. The obtainedkluyveromyces marxianus strain YZB115 produces 40.32 g / L glycerine through 80g / L glucose, produces 41.84 g / L glycerine through 80g / L levulose and 18.64g / L glycerine through 80g / L xylose under the aerobiotic condition of 42 DEG C, the production rates are respectively 0.84g / L / h, 0.50g / L / h and 0.22g / L / h, the yields are respectively 0.50g / g, 0.50g / g and 0.23g / g, in the fermentation process of the constructed engineering strain, a by-product namely ethanol is not produced, and xylitol is not accumulated when the operation of producing the glycerine through fermentation of xylose is ended.
Owner:HUAIBEI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
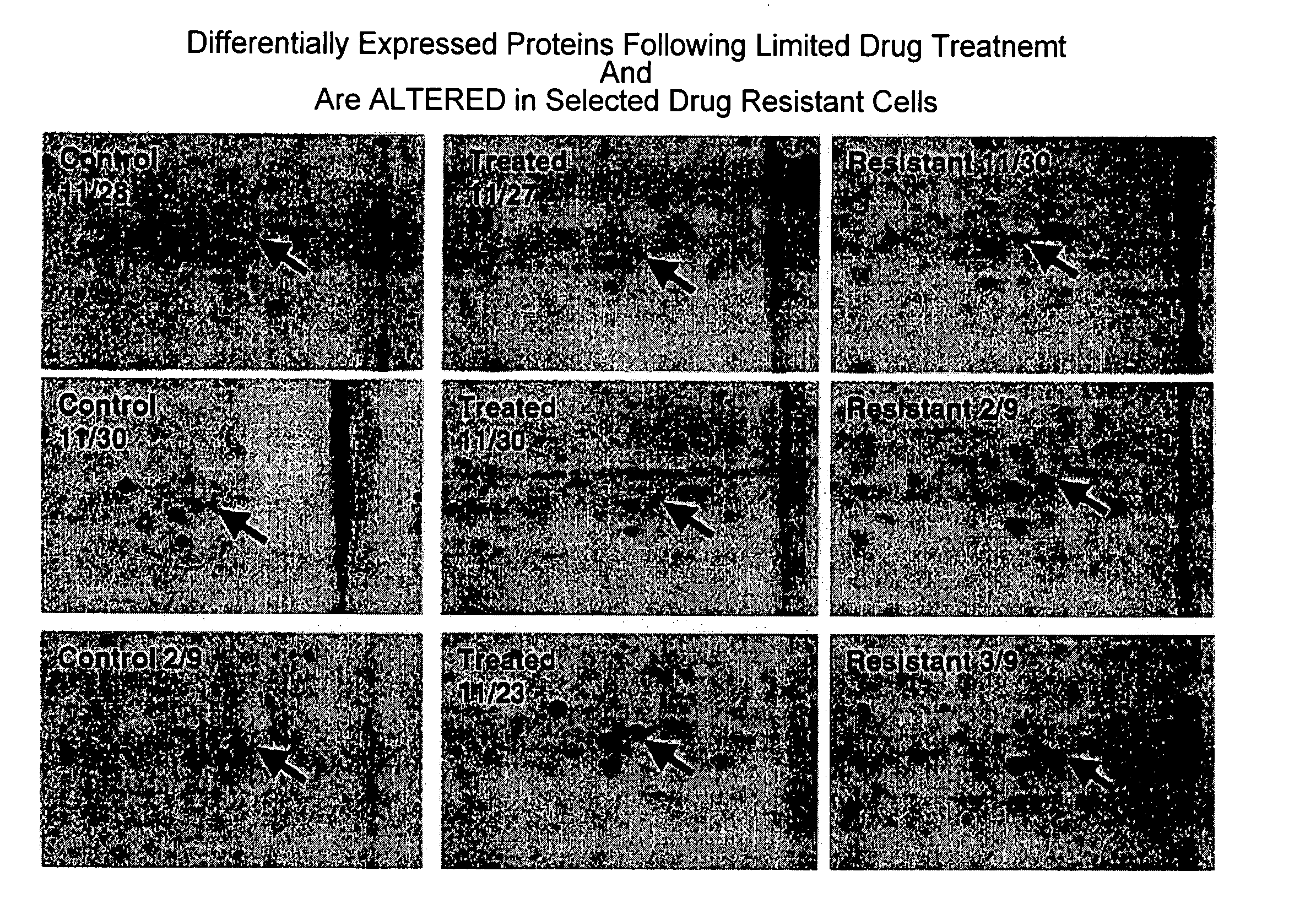
Triosephosphate isomerase directed diagnostics and therapeutics for multidrug resistant neoplastic disease
InactiveUS7358042B2Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseTriosephosphate isomerase
Disclosed are methods for detecting neoplastic or damaged cells and for detecting multidrug resistance in neoplastic or damaged cells by detecting an increase in the cellular expression of a triosephosphate isomerase (TPI) protein in a multidrug resistant neoplastic or damaged cells as compared to the level of expression of the triosephosphate isomerase protein in a normal cell.
Owner:AURELIUM BIOPHARMA
Triosephosphate isomerase directed diagnostics and therapeutics for multidrug resistant neoplastic disease
InactiveUS20050026231A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDiseaseAbnormal tissue growth
Owner:AURELIUM BIOPHARMA
Method for detecting giardia by pyrosequencing technology
ActiveCN103103276AFacilitate the establishment of standardized operating proceduresImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFood borneWater quality
The invention discloses a method for detecting giardia by a pyrosequencing technology, belonging to the technical field of detection of food-borne parasites. The method comprises the following steps of: designing a specificity primer and a pyrosequencing primer according to triose phosphate isomerase (tim) of the giardia; then extracting desoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of a sample to be detected, and performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification by the specificity primer with a tim gene; detecting an amplified product by agarose gel electrophoresis, if an amplified section is 165bp in length, preparing a pyrosequencing single-chain template, and performing pyrosequencing reaction; and finally, judging whether the sample contains the giardia according to a PCR amplification result and a pyrosequencing result. The method is suitable for quick detection and confirmation for the giardia and can be widely applied to water quality monitoring in an environment, oocyst detection in a human body and confirmation of protozoons of the type in import and export trades.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT SHANDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
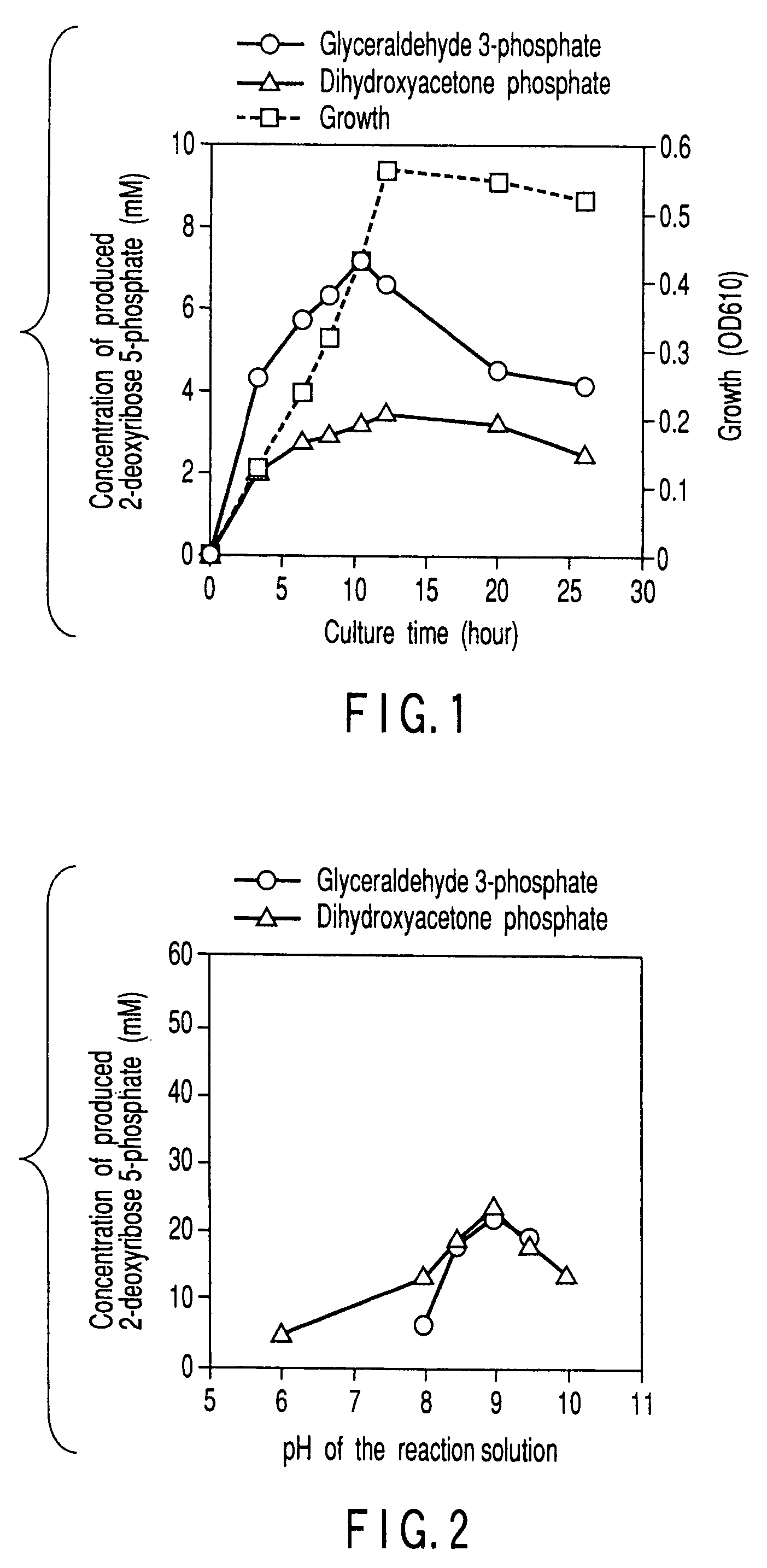
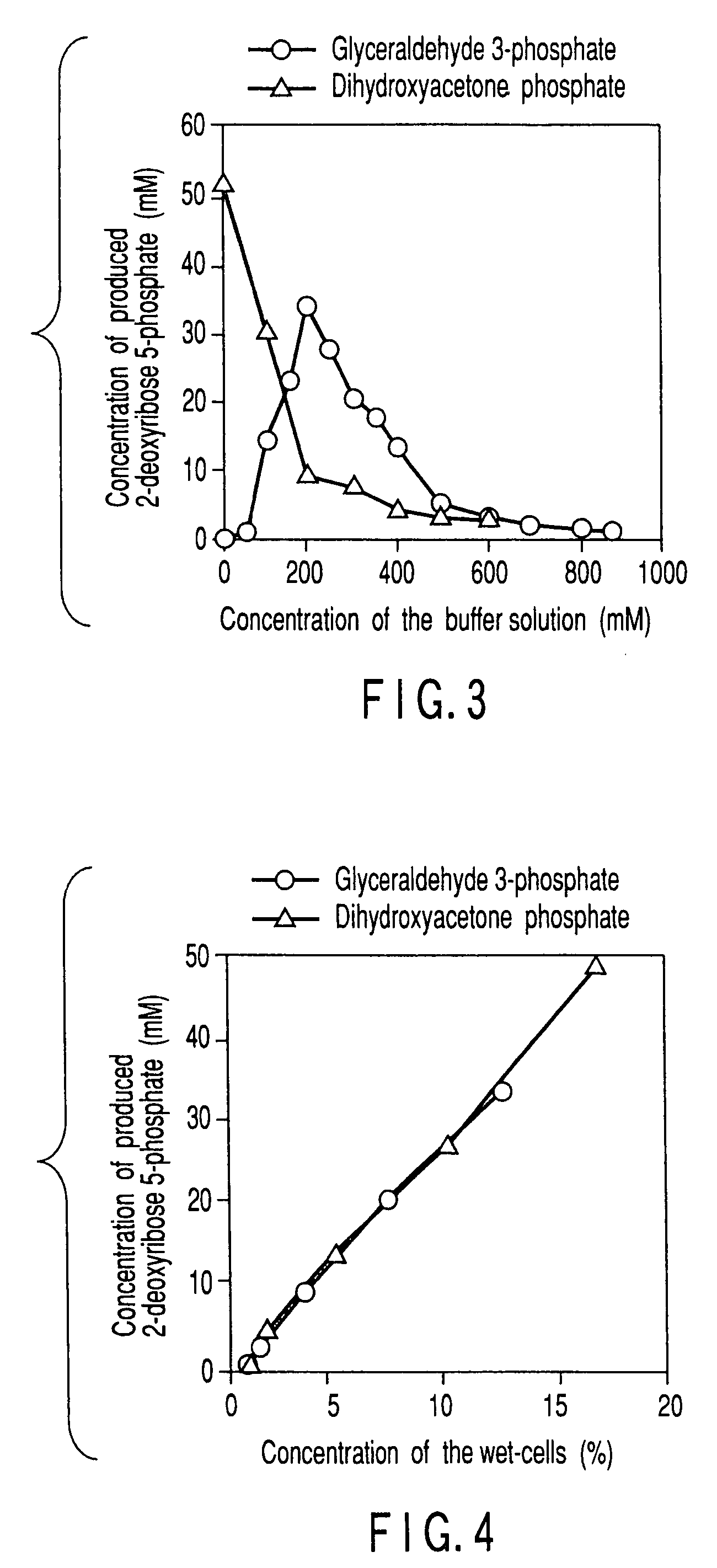
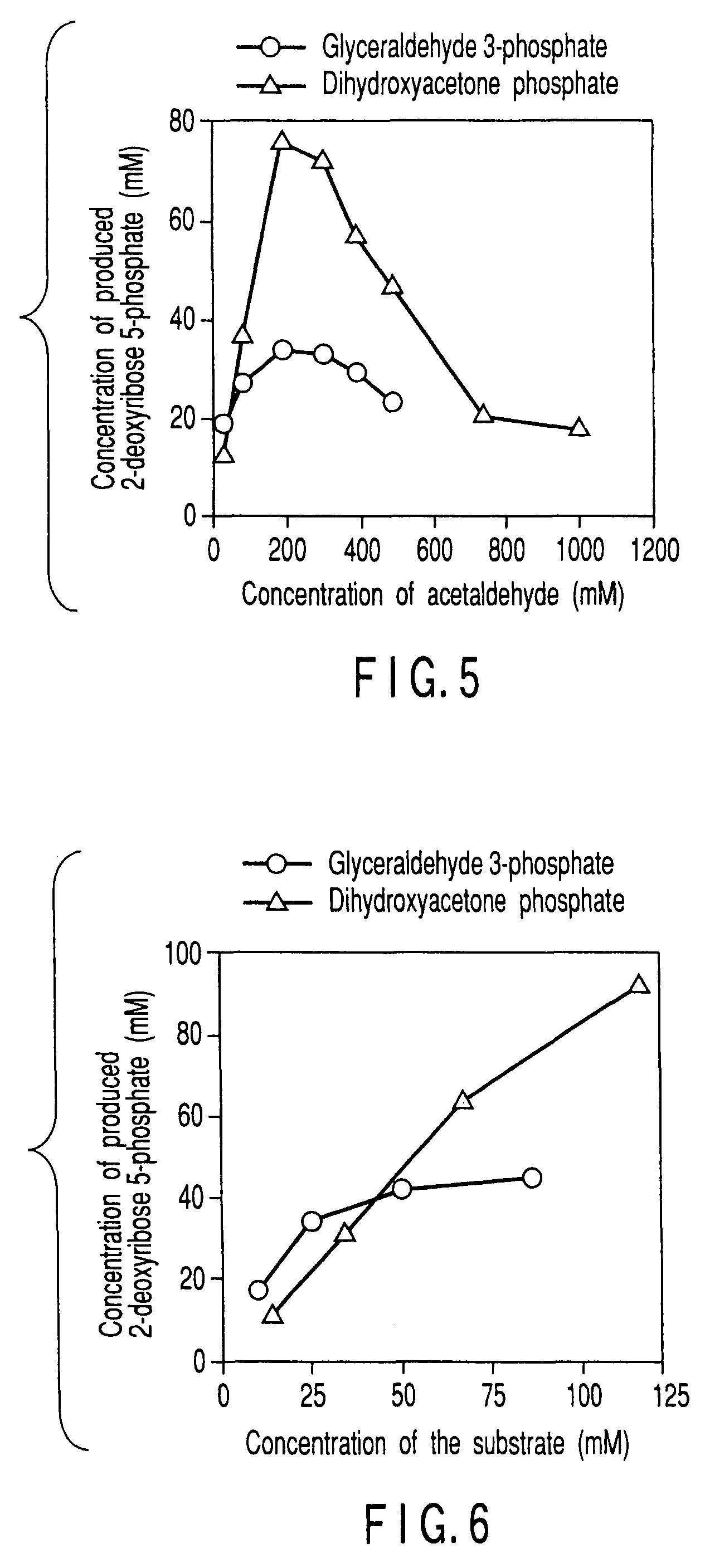
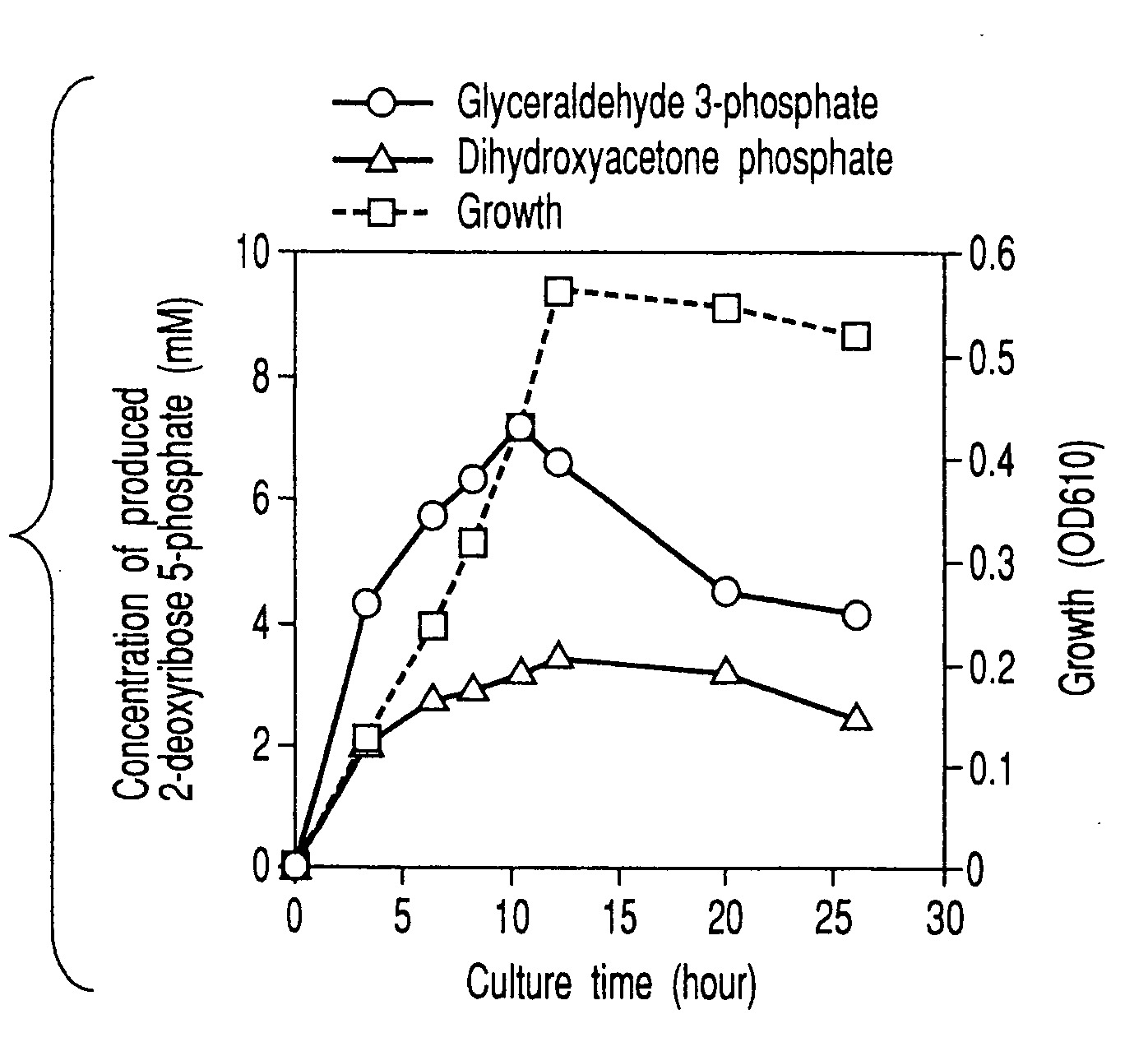
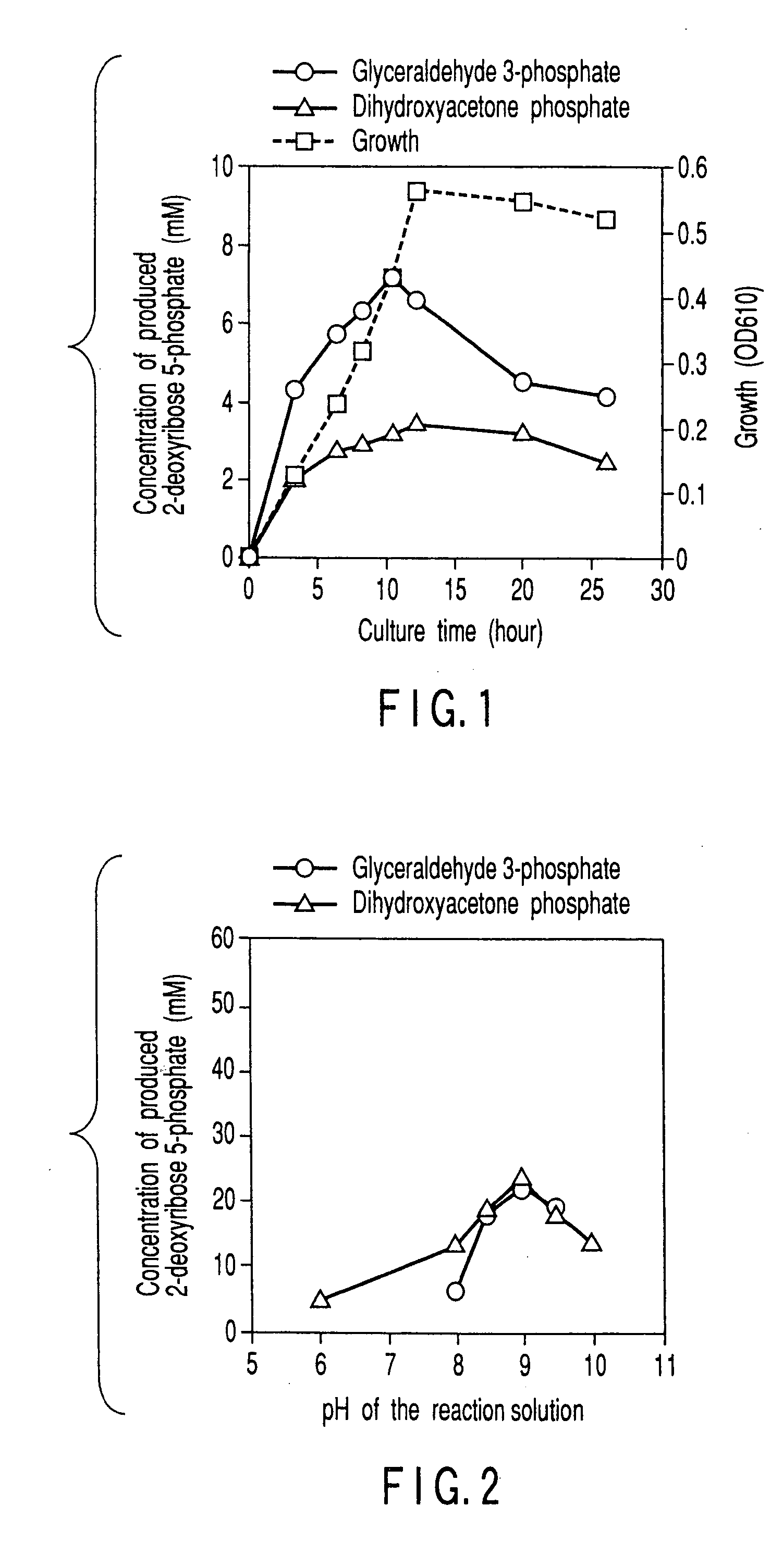
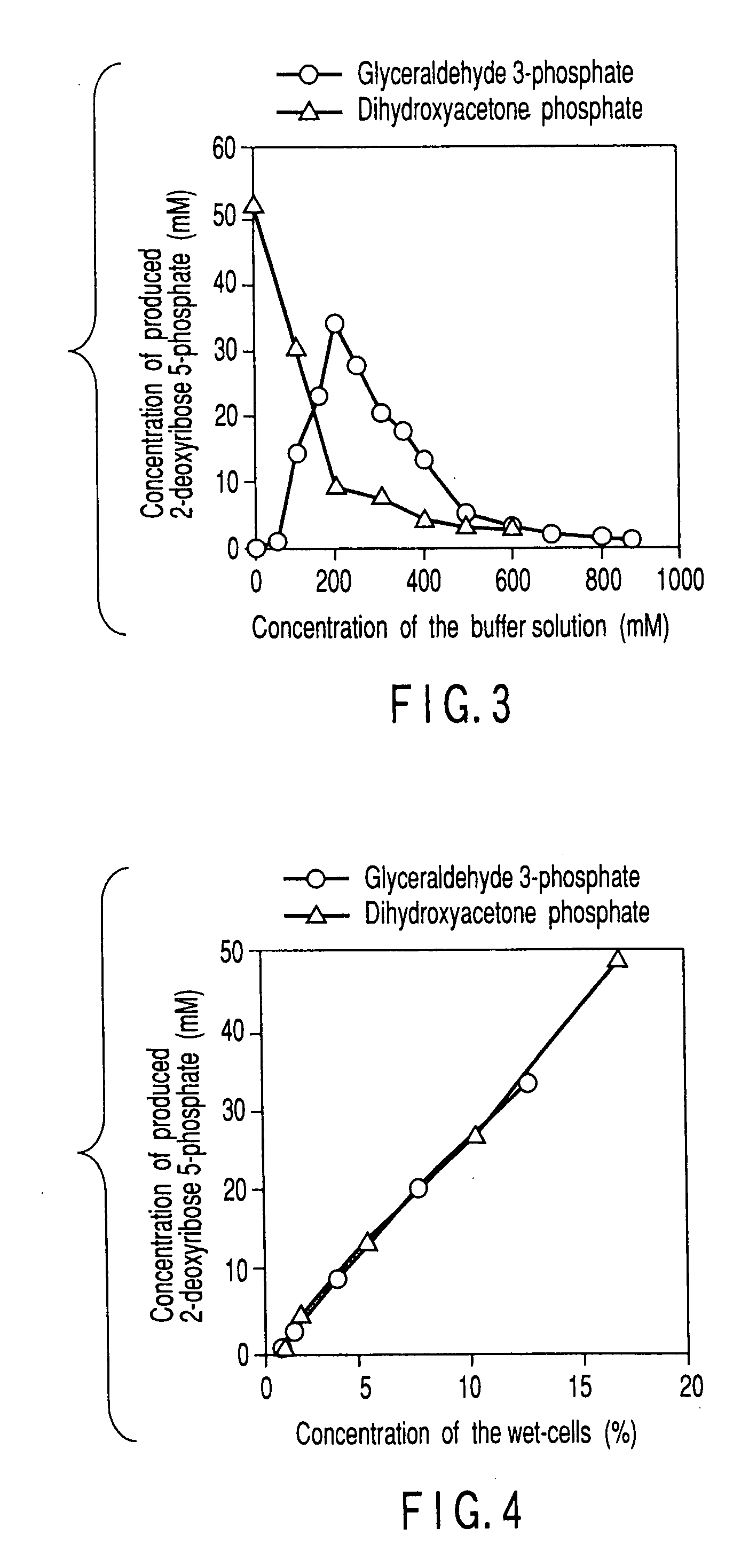
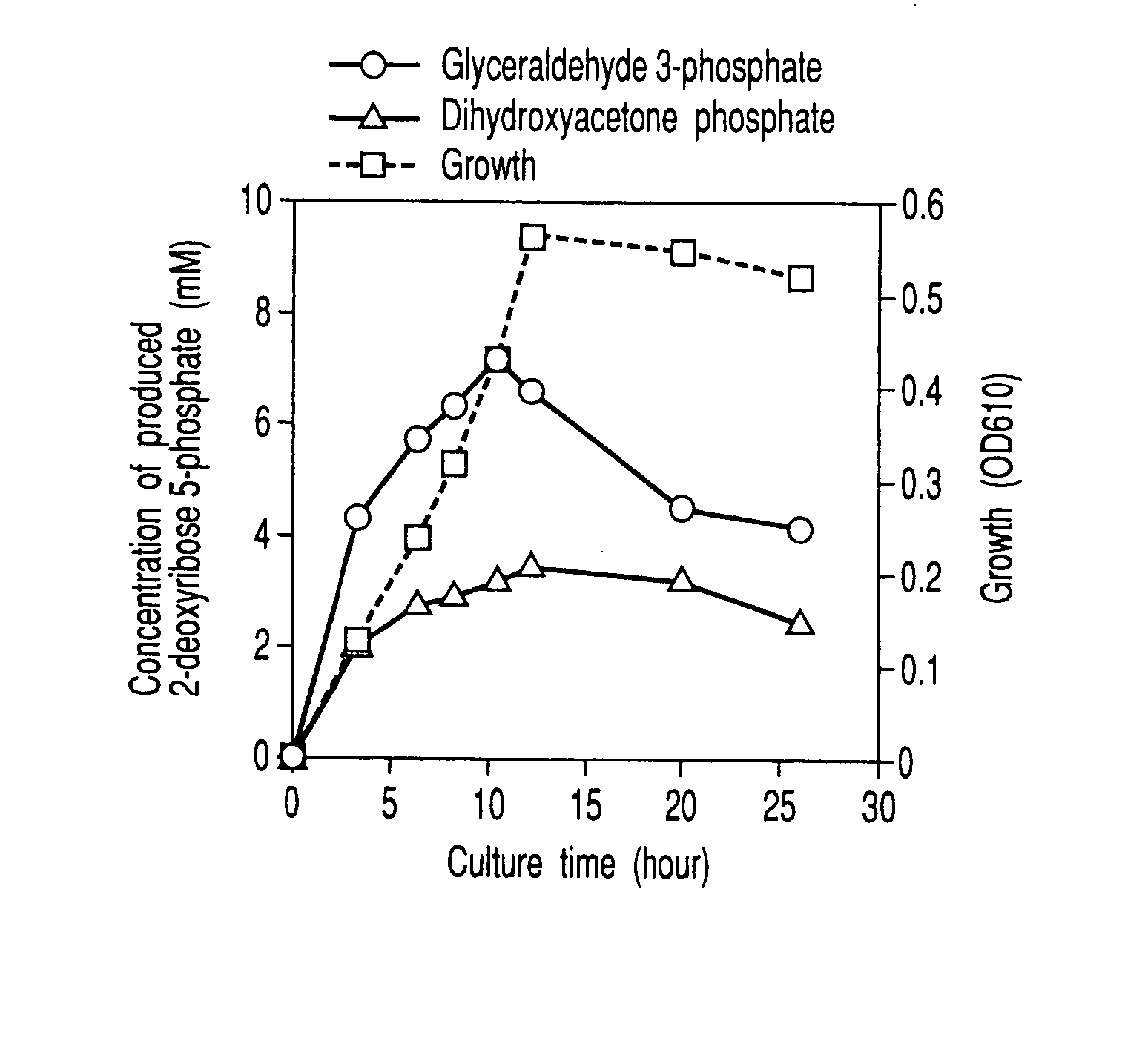
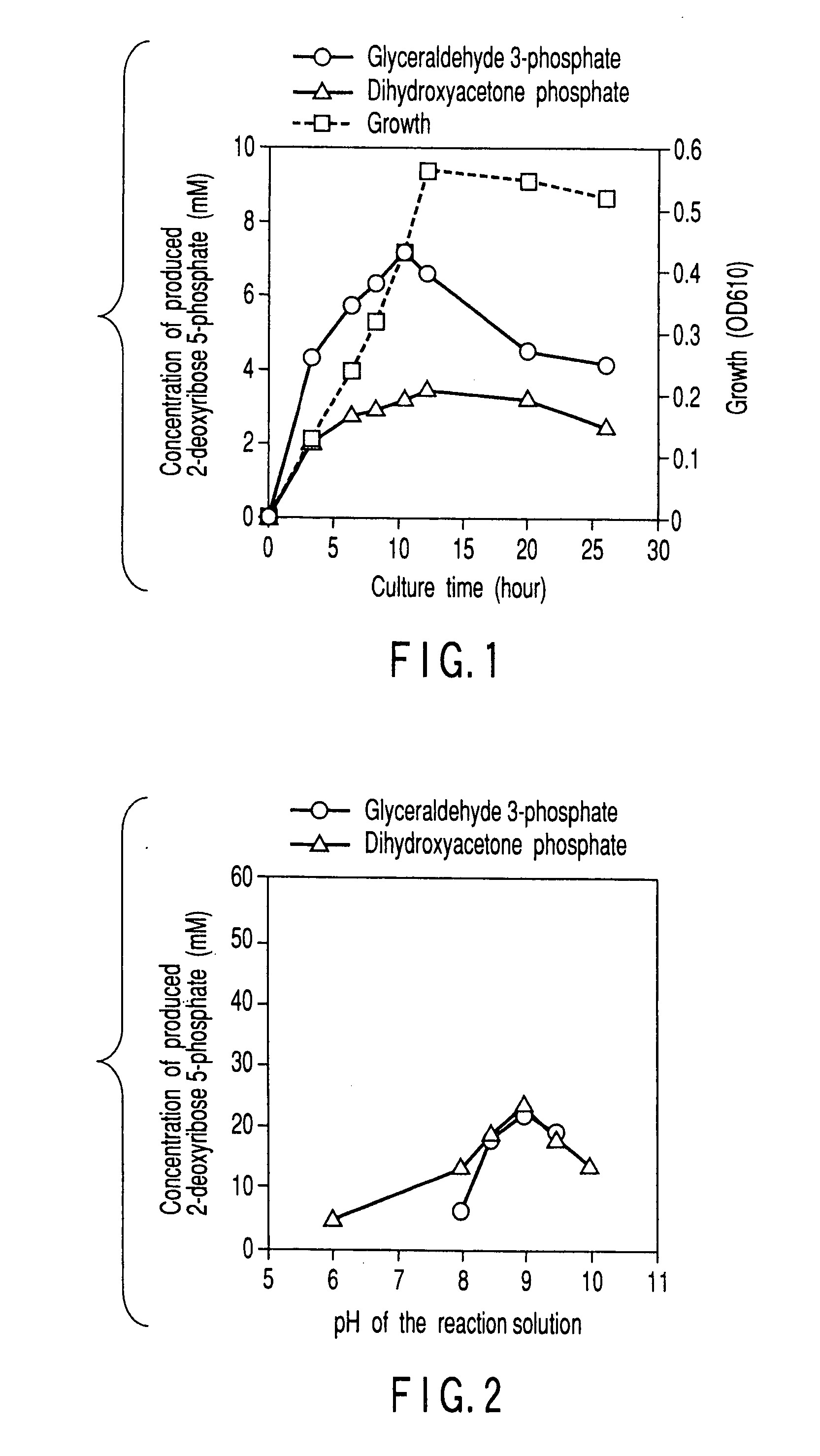
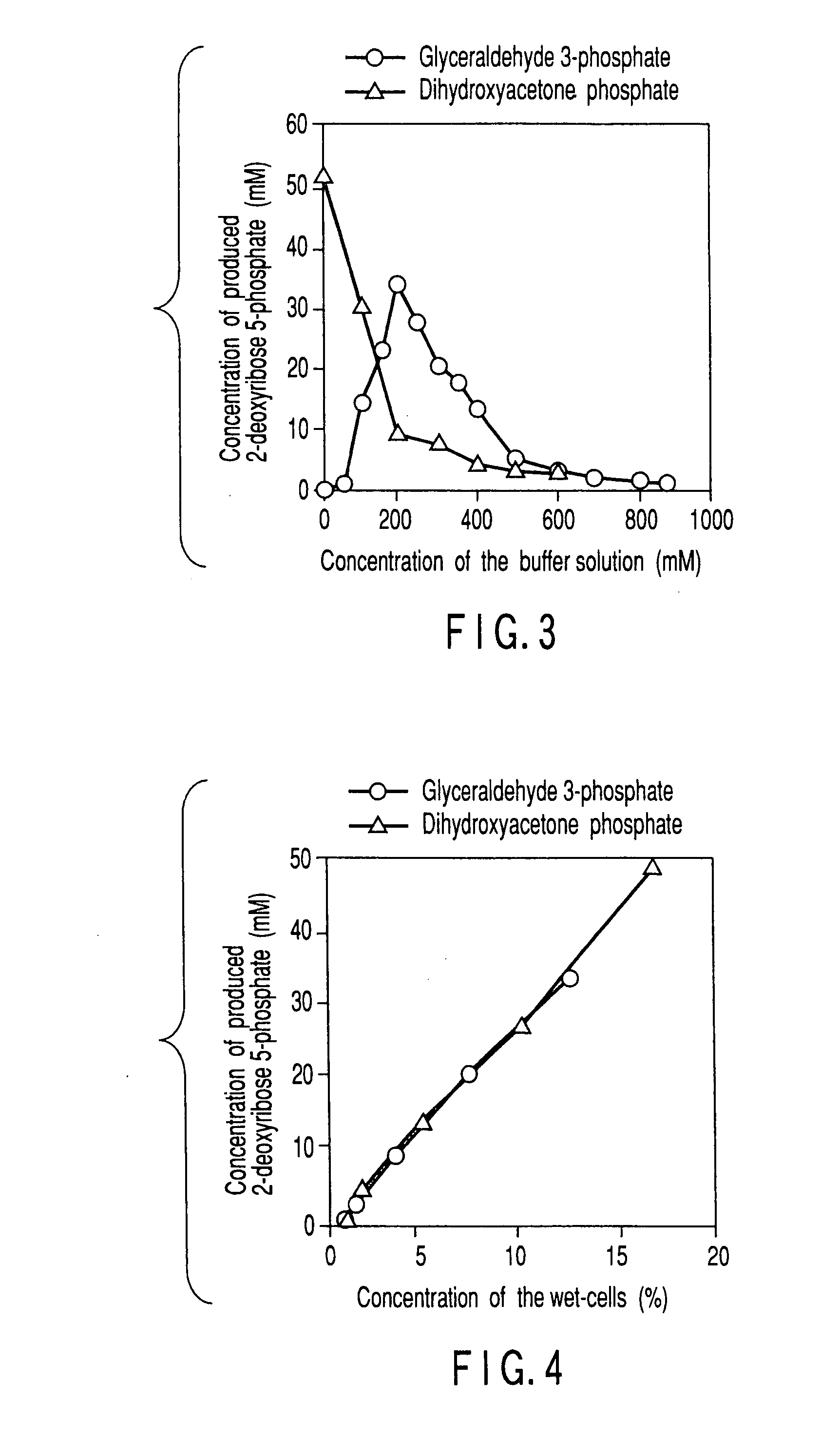
Method of preparing 2-deoxyribose 5-phosphate
The present invention discloses a method of preparing 2-deoxyribose 5-phosphate by reacting glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and acetaldehyde in the presence of either a microorganism itself which contains 2-deoxyribose-5-phosphate aldolase but substantially no phosphatase or the enzyme derived from the microorganism. The present invention also discloses a method of preparing 2-deoxyribose 5-phosphate by reacting dihydroxyacetone phosphate and acetaldehyde in the presence of either a microorganism itself which contains 2-deoxyribose-5-phosphate aldolase and triose-phosphate isomerase but substantially no phosphatase or the enzymes derived from the microorganism.
Owner:YUKI GOSEI IND +1
Method of preparing 2-deoxyribose 5-phosphate
The present invention discloses a method of preparing 2-deoxyribose 5-phosphate by reacting glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and acetaldehyde in the presence of either a microorganism itself which contains 2-deoxyribose-5-phosphate aldolase but substantially no phosphatase or the enzyme derived from the microorganism. The present invention also discloses a method of preparing 2-deoxyribose 5-phosphate by reacting dihydroxyacetone phosphate and acetaldehyde in the presence of either a microorganism itself which contains 2-deoxyribose-5-phosphate aldolase and triose-phosphate isomerase but substantially no phosphatase or the enzymes derived from the microorganism.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG +1
Special solid complex enzyme (ALD, TIM and GDH) reagent for determining content of fructose diphosphate sodium (FDP)
ActiveCN101691566AMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesPhosphoric acidFructose 6-phosphate
Owner:张莉莉
Bovine lactoferricin peptide constitutive type yeast expression vector and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104073511ASolve the suppression effect problemEfficient and stable secretionFungiMicroorganism based processesGalactokinaseTriosephosphate isomerase
The invention discloses a bovine lactoferricin peptide constitutive type yeast expression vector and a preparation method thereof. The expression vector is obtained by introducing a bovine lactoferricin peptide gene into pYES2 plasmids and utilizing a TPI (triosephosphate isomerase) promoter to substitute a GAL1 (galactokinase 1) promoter of the pYES2 plasmids. The pYES2-TPI-LfcinB recombinant plasmids constructed by the preparation method disclosed by the invention can effectively and stably secrete bovine lactoferricin peptide without using an inducer, so that production cost and production complexity are lowered.
Owner:XINJIANG XIPU BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH +1
A kind of recombinant bacteria producing acetylacetone and its construction method and application
ActiveCN110791467BAchieve biosynthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliIsomerase
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium for producing acetylacetone and its construction method and application, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering. The recombinant bacterium uses E. The genes of aldehyde synthase and triose phosphate isomerase were introduced into Escherichia coli to obtain recombinant bacteria, and the biosynthesis of acetylacetone was realized for the first time. The recombinant bacteria constructed in the present invention can use glucose as the only carbon source to synthesize acetylacetone, and ferment for 48 hours to obtain 53 mg / L acetylacetone.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
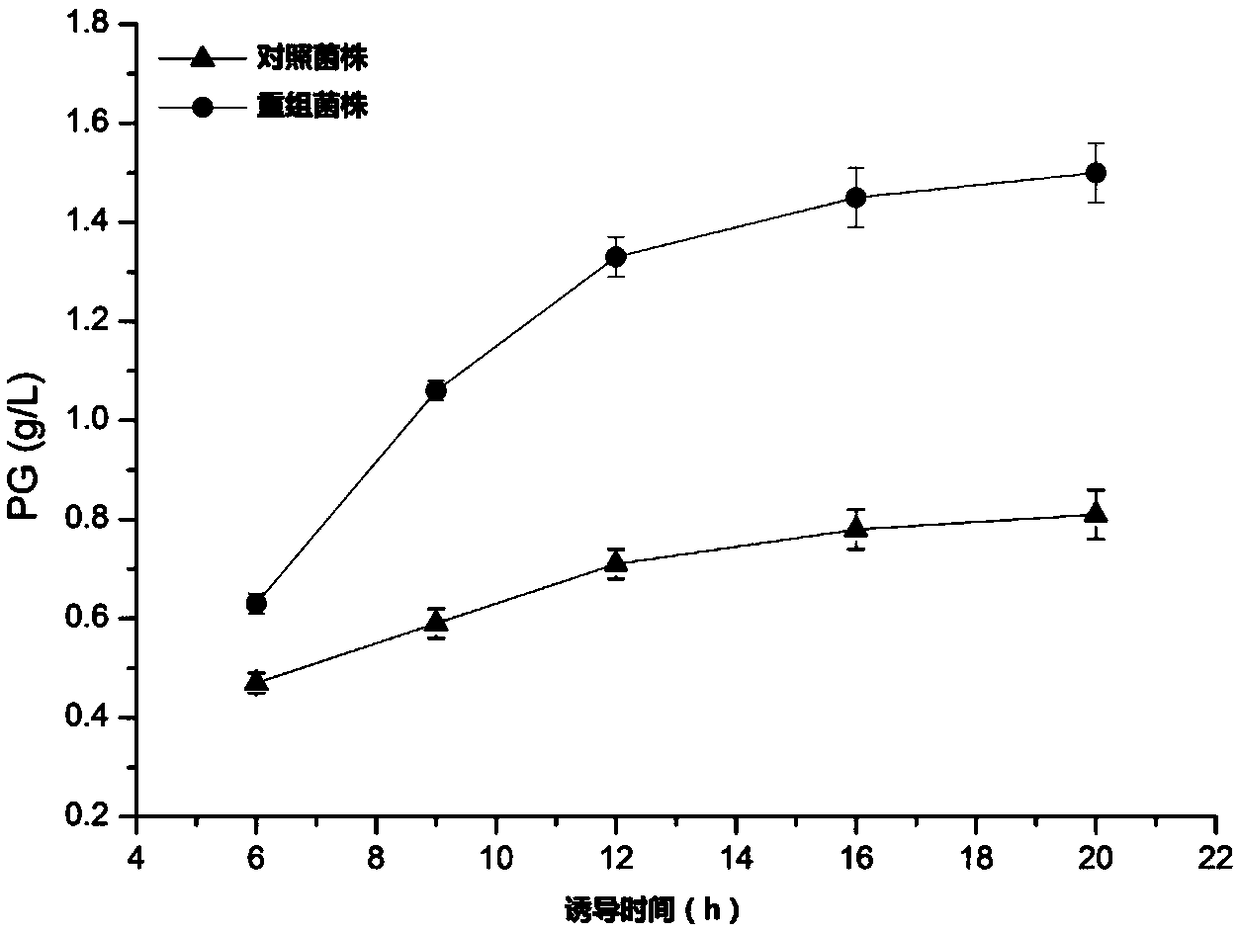
Genetically engineered bacterium for improving yield of phloroglucinol as well as construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN109439606AImprove synthesis abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTriosephosphate isomerase
The invention provides a genetically engineered bacterium for improving the yield of phloroglucinol as well as a construction method and application of the genetically engineered bacterium, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The invention provides the genetically engineered bacterium for over-expression of a triosephosphate isomerase gene tpiA, a polyketide synthase gene phlD, a multiple resistance activation factor marA and an acetyl-CoA carboxylase gene ACCase, so that the yield of the phloroglucinol synthesized by phloroglucinol producing strains is obviously improved; through shake-flask fermentation, the yield of phloroglucinol synthesized by transformed strains is 1.85 times of the yield of phloroglucinol synthesized by contrast strains. Therefore, the genetically engineered bacterium can be used for industrial production of phloroglucinol.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
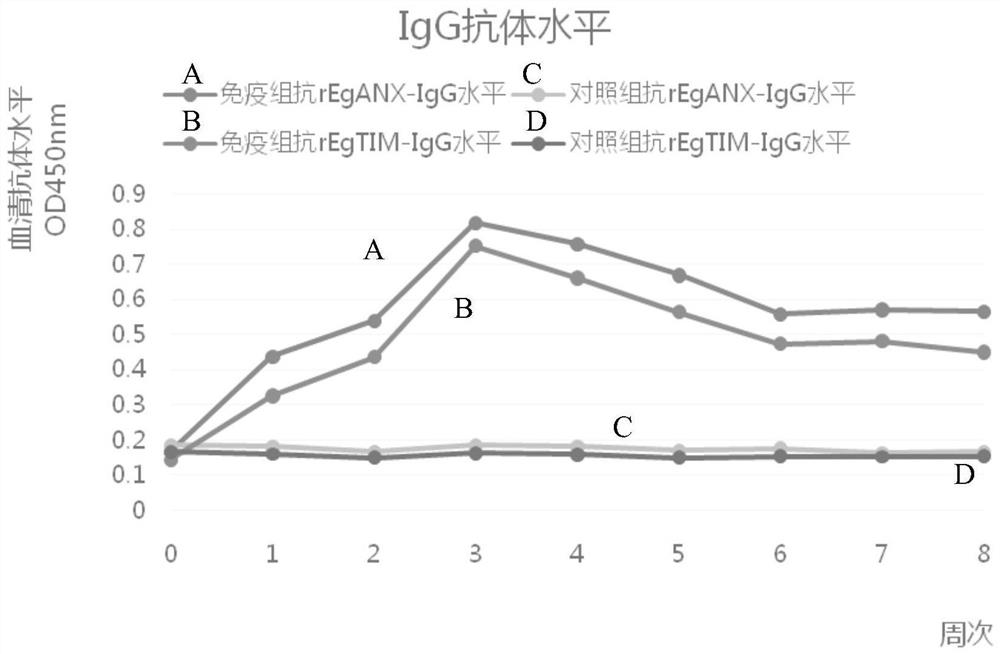
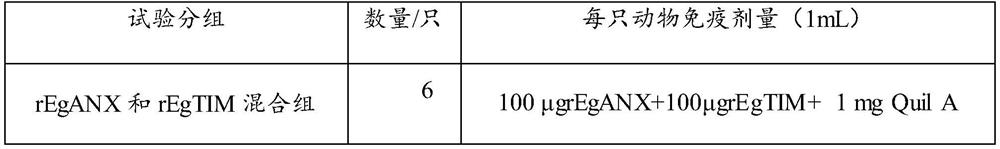
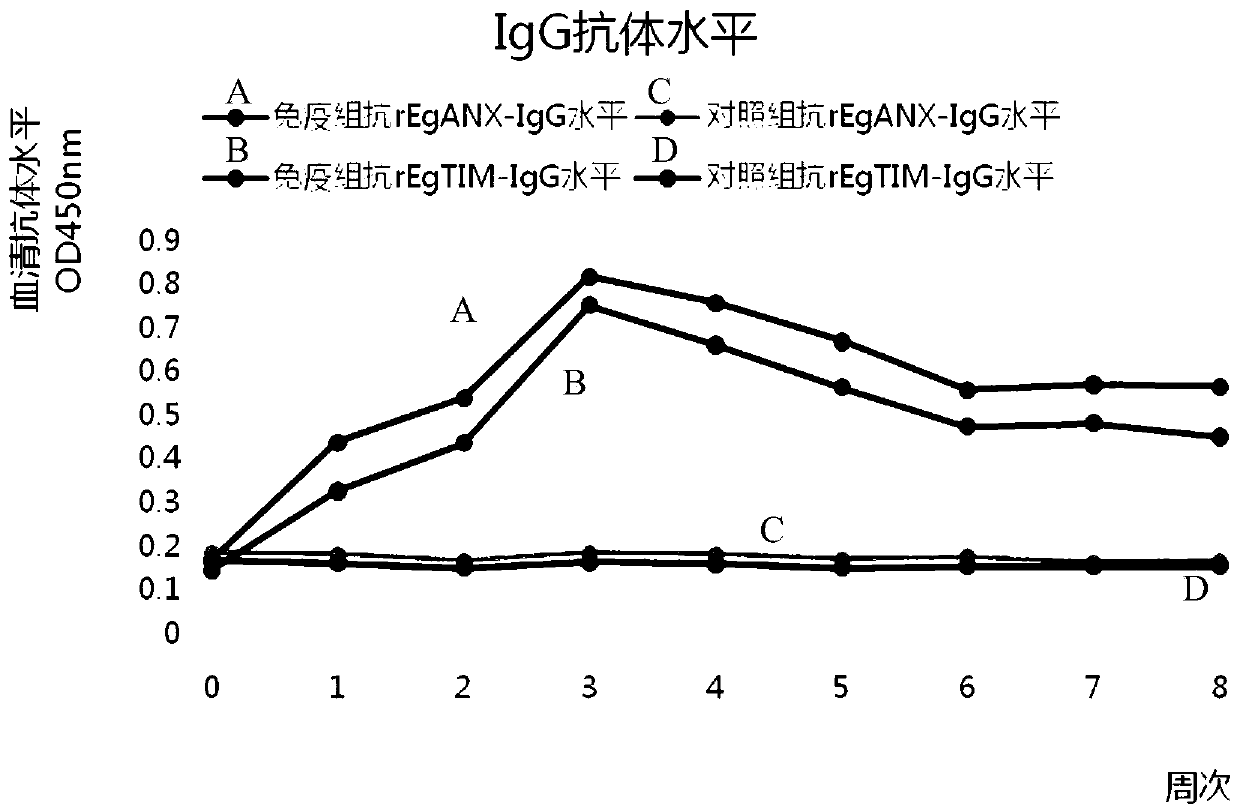
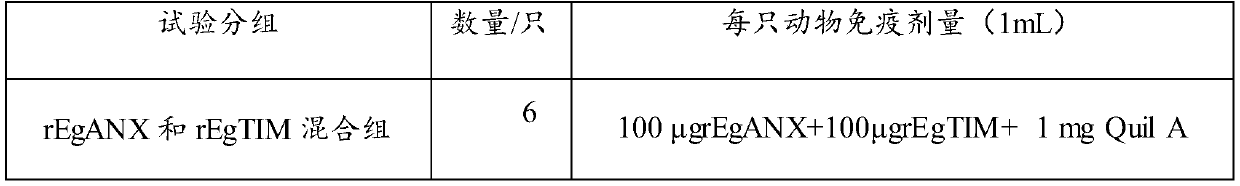
A kind of combination protein and its application
ActiveCN110655564BGood immune protectionStabilized antibodyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsOxidoreductasesIsomeraseTGE VACCINE
The invention relates to the field of a biological technology, and discloses combination protein and an application thereof. The combination protein comprises combination protein comprising echinococcus granulosus annexin EgANX and triose phosphate isomerase EgTIM or fusion protein granule echinococcus granulosus annexin EgANX and triose phosphate isomerase EgTIM. The granule echinococcus granulosus annexin EgANX and the triose phosphate isomerase EgTIM are used as antigranule echinococcus granulosus annexin for immunization experiment, and results show that two kinds of protein have good immunoprotection effects on dogs, can produce a stable antibody, and have the potential for developing a granule echinococcus vaccine for the dogs.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Leymus chinensis triosephosphate isomerase gene as well as encoding protein and application thereof
InactiveCN104975035AImprove stress resistanceIsomerasesFermentationGMO PlantsTriose-phosphate isomerase
The invention relates to a Leymus chinensis triosephosphate isomerase gene as well as an encoding protein and application thereof, relates to the field of biotechnology, and aims to solve the problem of low stress resistance of plants. The nucleotide sequence of the Leymus chinensis triosephosphate isomerase gene is shown in SEQ ID No:1. The amino acid sequence of the encoding protein of the Leymus chinensis triosephosphate isomerase gene is shown in SEQ ID No:2. The application of the Leymus chinensis triosephosphate isomerase is as follows: the Leymus chinensis triosephosphate isomerase gene is introduced to a target plant for culturing to obtain a transgenic plant with enhanced stress resistance. The expression of the LcPTI gene provided by the invention is induced by neutral salt, basic salt or PEG-simulated drought, and the LcPTI gene can participate in the response of Leymus chinensis to multiple environmental stresses, so that the stress resistance of the plant is enhanced. The introduction of the LcPTI gene to the target plant for culturing to obtain the transgenic plant with enhanced stress resistance has significance to cultivation of plant variety with enhanced stress resistance, in particular resistance to methyl-glyoxal and NaCl.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
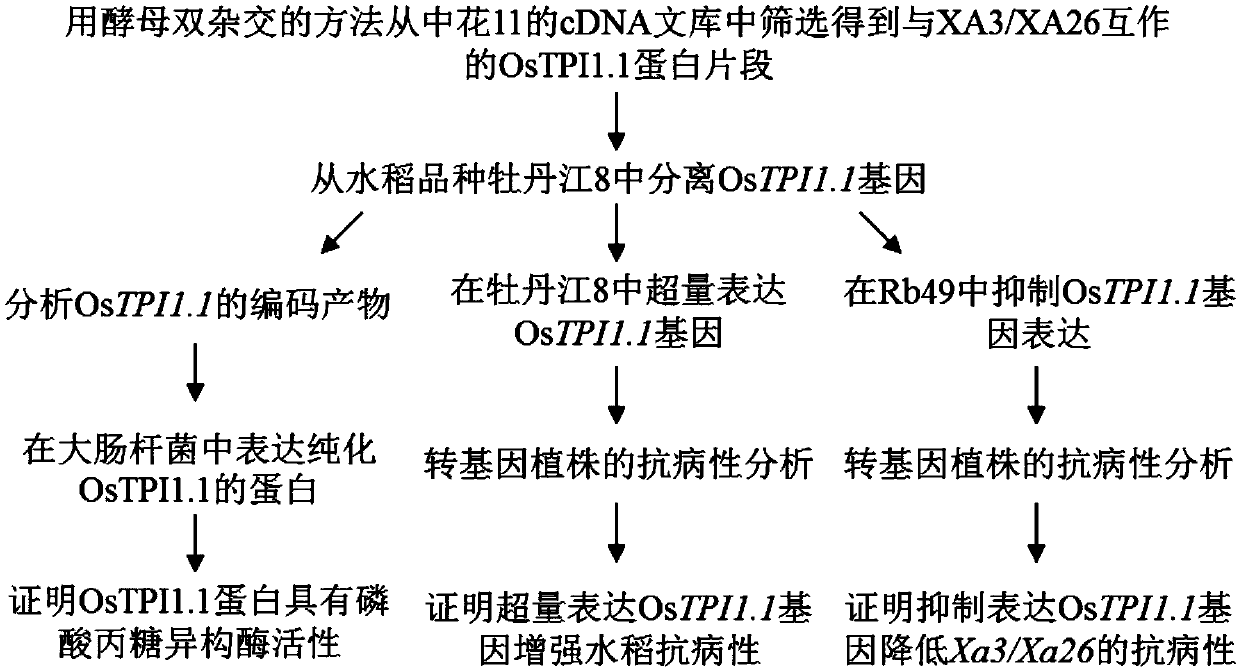
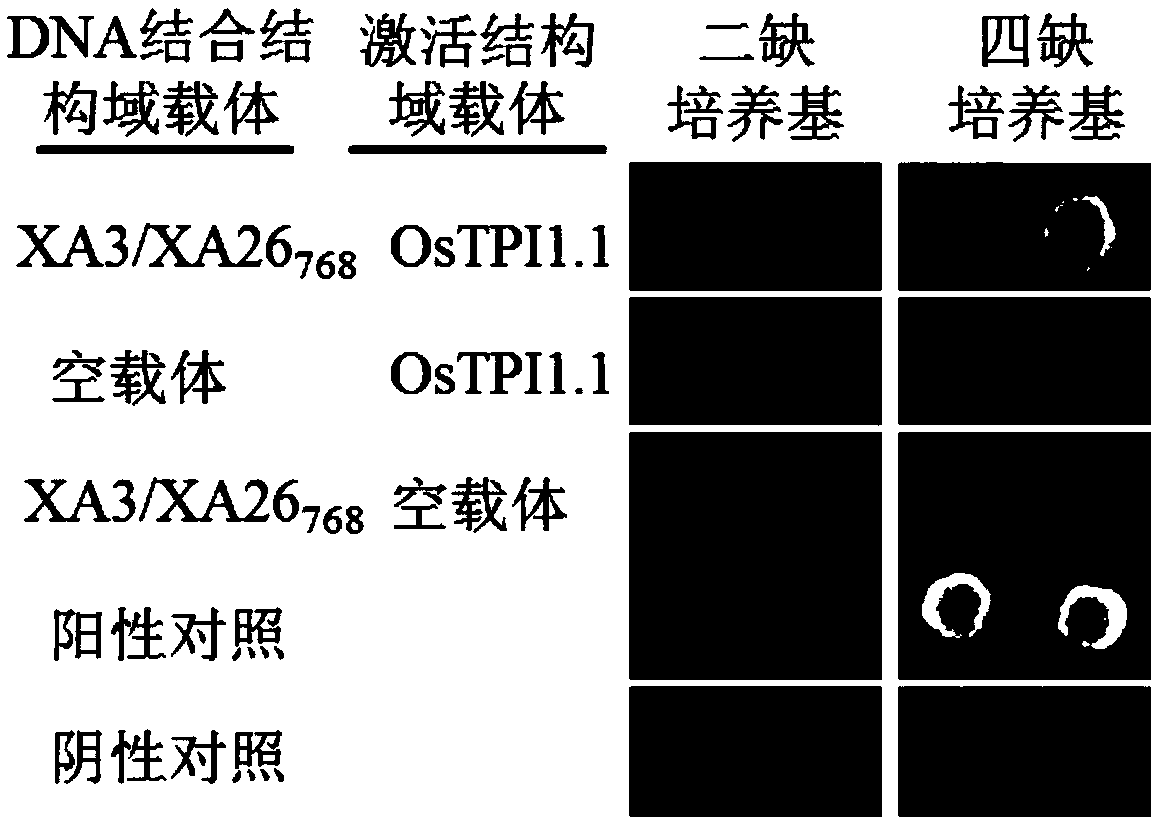
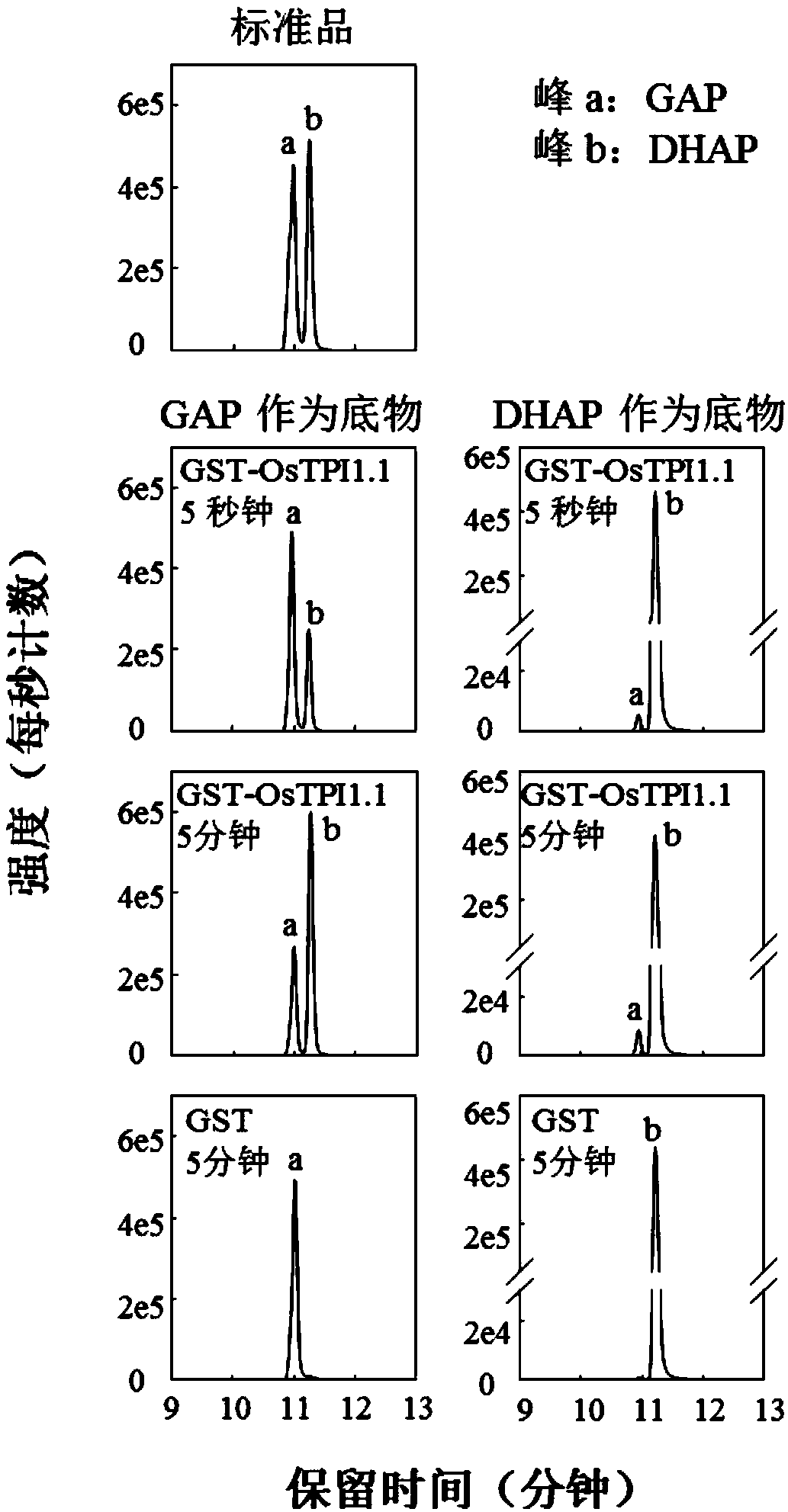
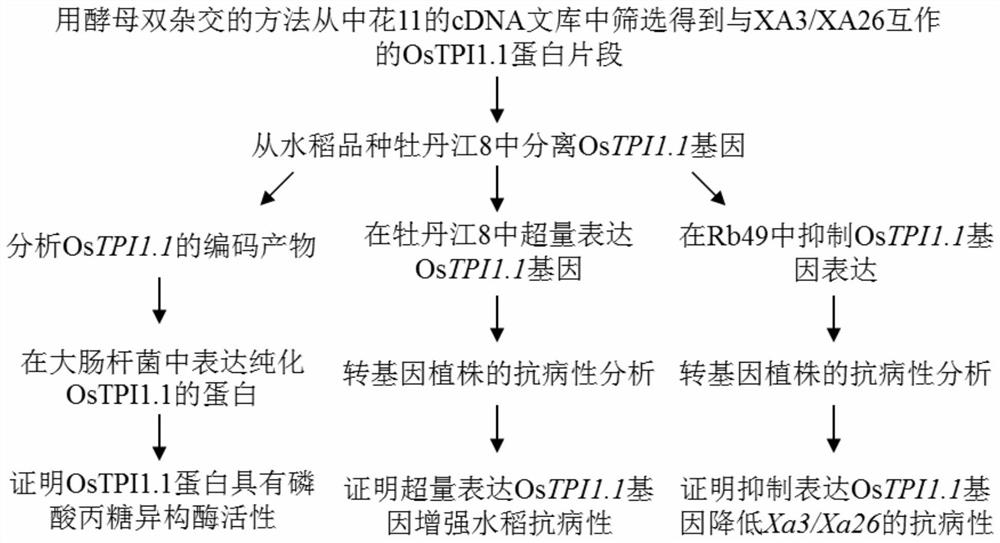
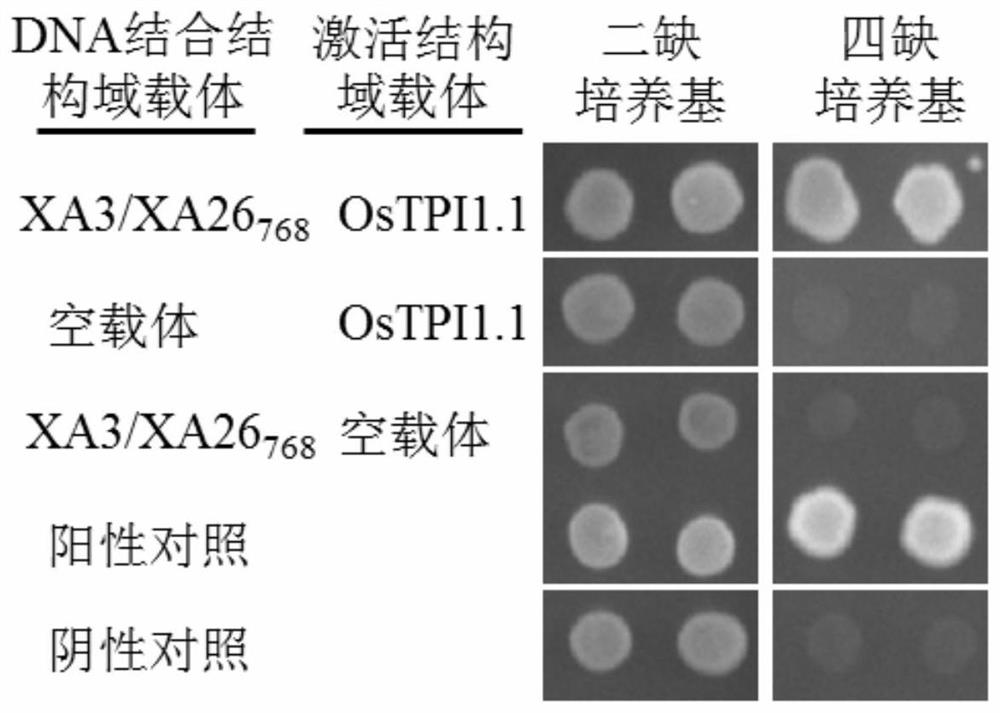
Application of rice gene OsTPI1-1 to rice disease resistance improvement
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering, and particularly relates to application of a rice gene OsTPI1-1 to rice disease resistance improvement. The gene OsTPI1-1 codesone cytoplasm TPI (triosephosphate isomerase); the nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:1 in a sequence table; and a protein sequence coded by the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:2 in thesequence table. Through the obvious expression quantity increase of the OsTPI1-1, the resistance of a converted rice plant to bacterial blight is enhanced. Under the background of a major disease-resistant gene Xa3 / Xa26, the expression quantity of the OsTPI1-1 is obviously reduced, so that the converted rice plant loses the resistance to the bacterial blight. Functional verification proves that the gene OsTPI1-1 is a positive regulation factor in the rice bacterial-blight-resistant reaction; and the disease resistance of the rice can be improved through over-expression of the gene OsTPI1-1.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
A fluorescent-labeled multiple PCR Clostridium difficile detection kit
ActiveCN103911430BAccurate typingMicrobiological testing/measurementCapillary electrophoresisFluorescence
The invention provides a fluorescence labeling multiplex PCR detection kit for identification of a Clostridium difficile strain and analysis of toxin genes. The kit comprises 6 pairs of fluorescently-labeled primers used for detecting the Clostridium difficile strain. The 6 pairs of fluorescently-labeled primers comprise specific primers of specific triosephosphate-isomerase (tpi) gene, toxin A gene (tcd A), toxin B gene (tcd B), tcd C gene (tcd C), binary toxin A gene (cdt A) and binary toxin B gene (cdt B) of the Clostridium difficile strain. Amplification results are detected through capillary electrophoresis. Thus, existence of Clostridium difficile can be rapidly identified and toxin typing can be rapidly determined.
Owner:江苏安科华捷生物科技有限公司
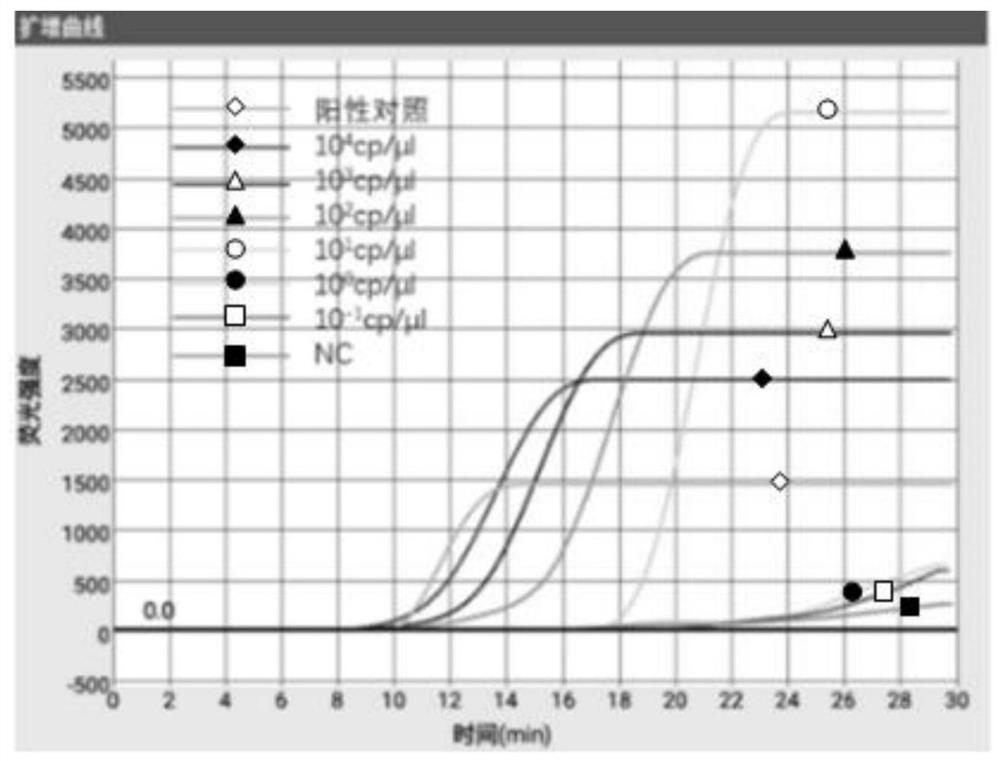
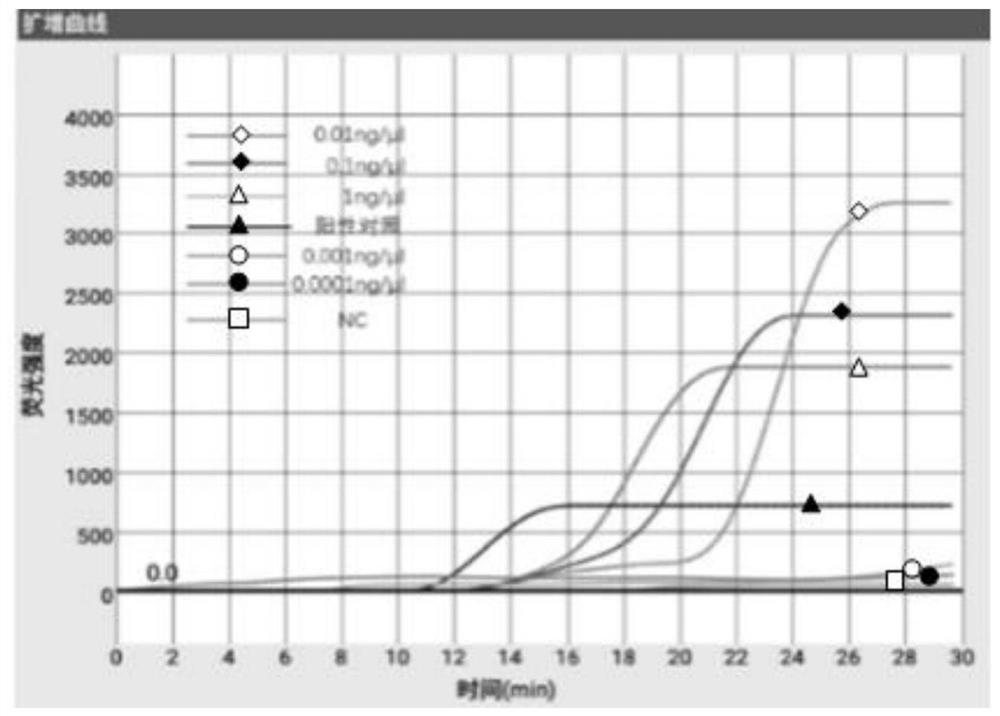
LAMP primer group for detecting giardia, kit and application
PendingCN113025739AStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesTriosephosphate isomeraseGiardia
The invention provides an LAMP (loop-mediated isothermal amplification) primer group for detecting giardia, a kit and application, and relates to the technical field of biological diagnosis and detection. The LAMP primer group disclosed by the invention is designed by taking a giardia triosephosphate isomerase (TPI) gene as a target gene. According to the primer group or the kit, amplification of giardia nucleic acid can be completed within 30 min based on the LAMP micro-fluidic chip technology, the detection sensitivity reaches 10 copies / microliter and 0.01 ng nucleic acid / microliter, and the primer group or the kit is good in giardia specificity, high in repeatability and good in stability.
Owner:INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE & OCCUPATIONAL MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY SCI
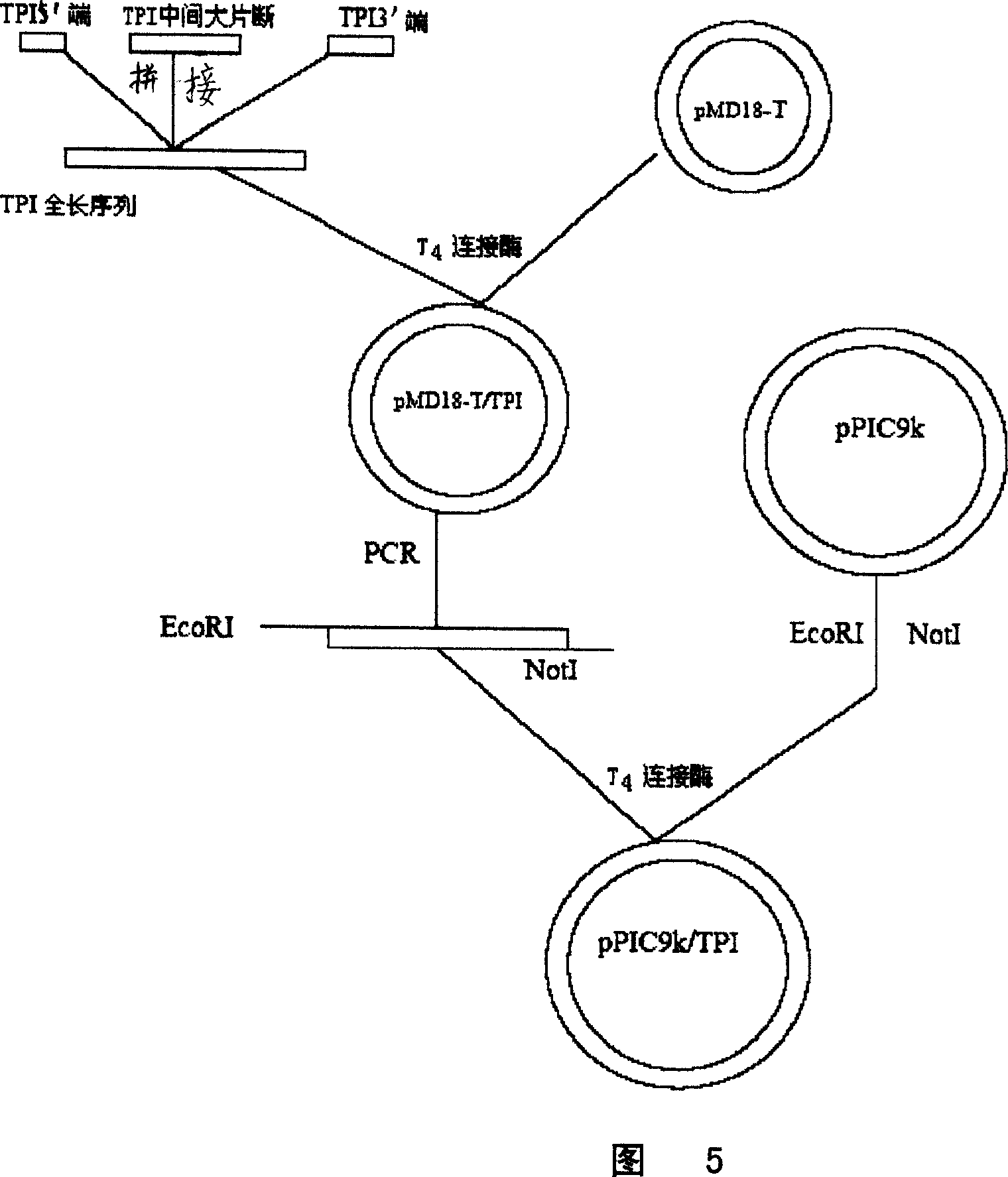
Method for producing triose phosphate isomerase
InactiveCN1978637AEasy to purifyIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisBiotechnology
The invention discloses a method to produce triosephosphate isomerase, which includes the following steps: (1) The full-length of triosephosphate isomerase gene was cloned into expression vector, and was amplified; (2) The vector was cutted with restricted enzyme to linearize, then was transformed into Pichia pastoris for expression triosephosphate isomerase; (3) The expression products were collected. The invention also disclosed the application of Pichia pastoris in the production of triosephosphate isomerase. This method is low cost and high yield. The expression level of triosephosphate isomerase in Pichia pastoris can reach up to 1200mg / l, which are several times higher than prokaryotic expression system and is easy for purification, and to facilitate application in practice.
Owner:中国农业科学院上海家畜寄生虫病研究所
Application of rice gene ostpi1-1 in improvement of rice disease resistance
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. It specifically relates to the application of the rice gene OsTPI1‑1 in the improvement of rice disease resistance. The OsTPI1-1 gene encodes a cytoplasmic triose phosphate isomerase, the nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown in the sequence listing SEQ ID NO:1, and the protein sequence encoded by the gene is shown in the sequence listing SEQ ID NO:2. The significant increase in the expression level of OsTPI1-1 enhances the resistance of the transformed rice plants to bacterial blight. The expression level of OsTPI1‑1 was significantly decreased in the background of the main disease resistance gene Xa3 / Xa26, so that the transformed rice plants lost their resistance to bacterial blight. Functional verification showed that the OsTPI1‑1 gene is a positive regulator in the rice bacterial blight resistance response, and the disease resistance of rice can be improved by overexpressing the OsTPI1‑1 gene.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Combination protein and application thereof
ActiveCN110655564AGood immune protectionStabilized antibodyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsOxidoreductasesIsomeraseTGE VACCINE
The invention relates to the field of a biological technology, and discloses combination protein and an application thereof. The combination protein comprises combination protein comprising echinococcus granulosus annexin EgANX and triose phosphate isomerase EgTIM or fusion protein granule echinococcus granulosus annexin EgANX and triose phosphate isomerase EgTIM. The granule echinococcus granulosus annexin EgANX and the triose phosphate isomerase EgTIM are used as antigranule echinococcus granulosus annexin for immunization experiment, and results show that two kinds of protein have good immunoprotection effects on dogs, can produce a stable antibody, and have the potential for developing a granule echinococcus vaccine for the dogs.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Method of preparing 2-deoxyribose 5-phosphate
InactiveUS20070298468A1High yieldBacteriaUnicellular algae2-deoxyribose 5-phosphateGlyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
The present invention discloses a method of preparing 2-deoxyribose 5-phosphate by reacting glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and acetaldehyde in the presence of either a microorganism itself which contains 2-deoxyribose-5-phosphate aldolase but substantially no phosphatase or the enzyme derived from the microorganism. The present invention also discloses a method of preparing 2-deoxyribose 5-phosphate by reacting dihydroxyacetone phosphate and acetaldehyde in the presence of either a microorganism itself which contains 2-deoxyribose-5-phosphate aldolase and triose-phosphate isomerase but substantially no phosphatase or the enzymes derived from the microorganism.
Owner:YUKI GOSEI IND +1
Preparation method of solid enzyme compound for testing content of fructose diphosphate sodium
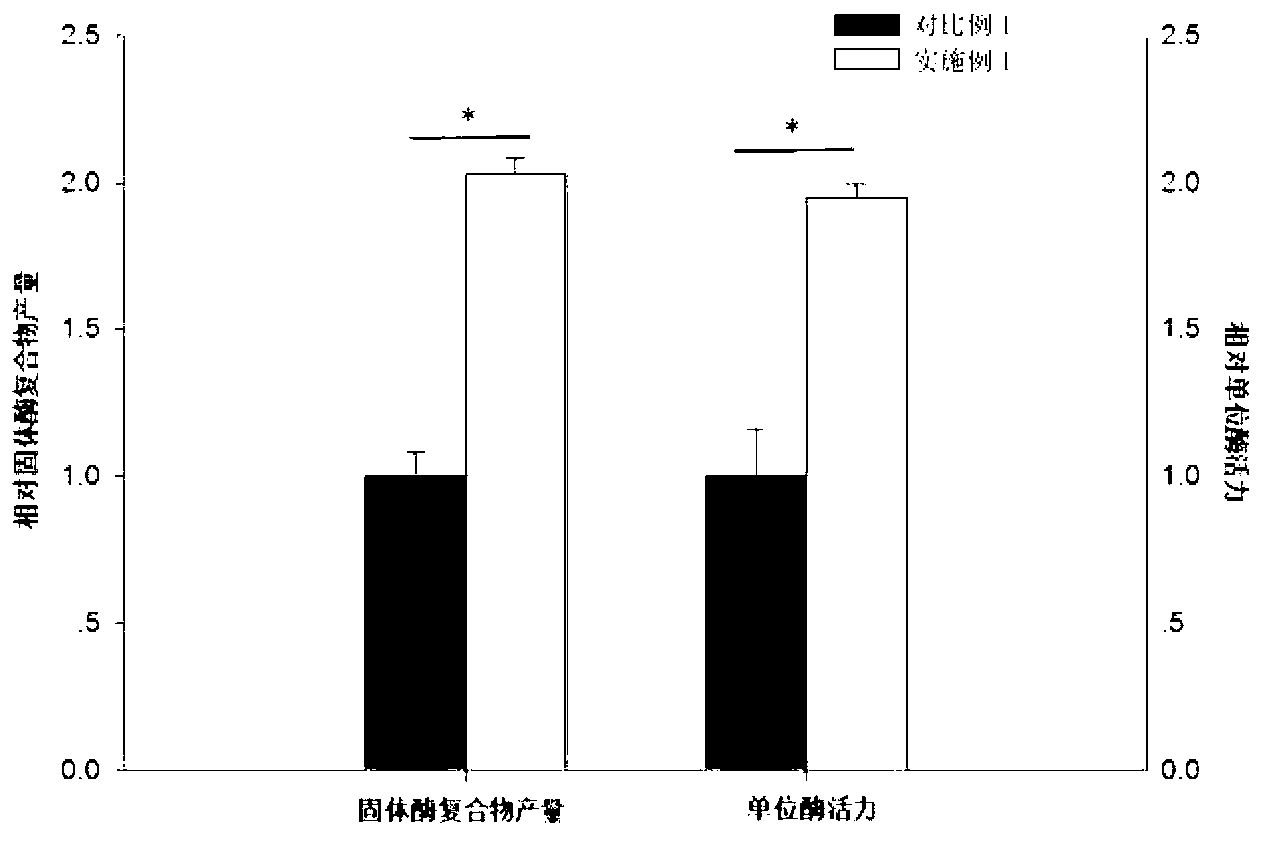
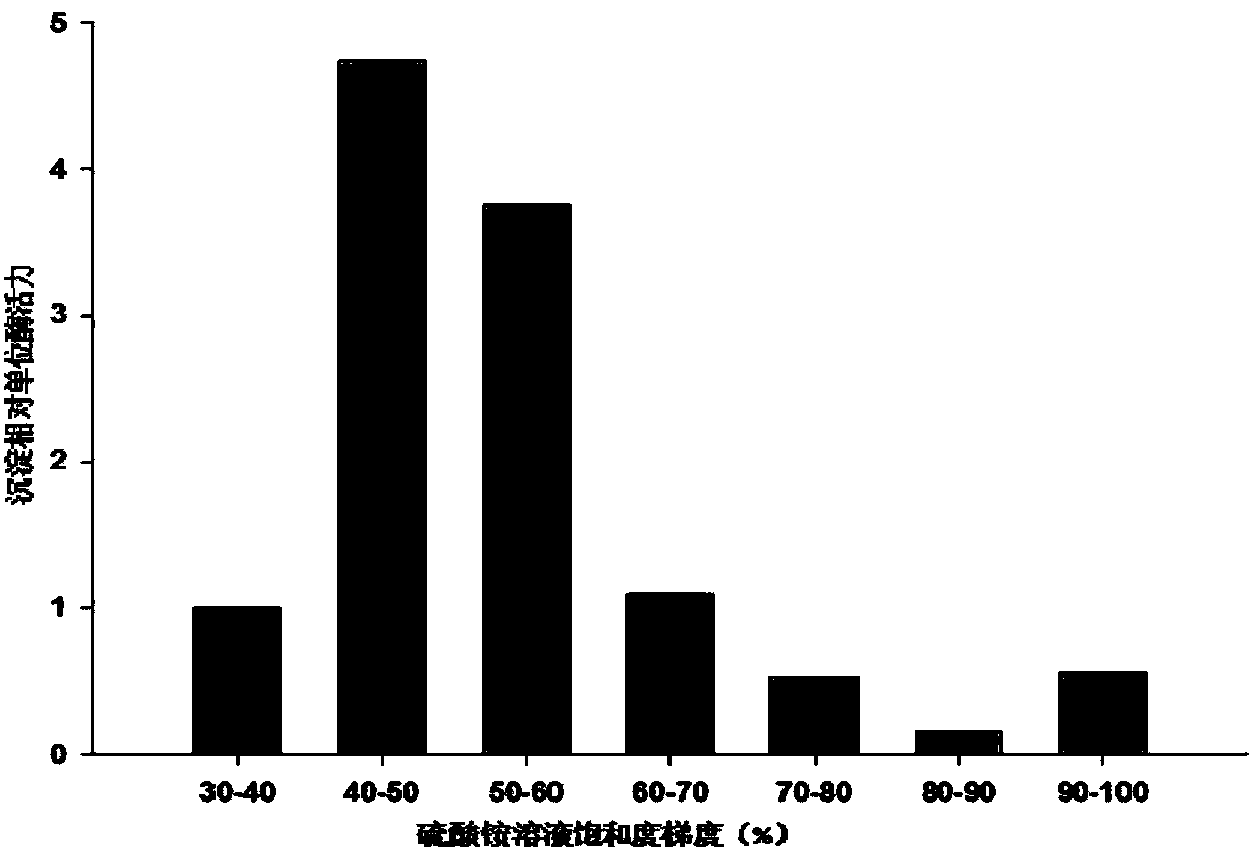
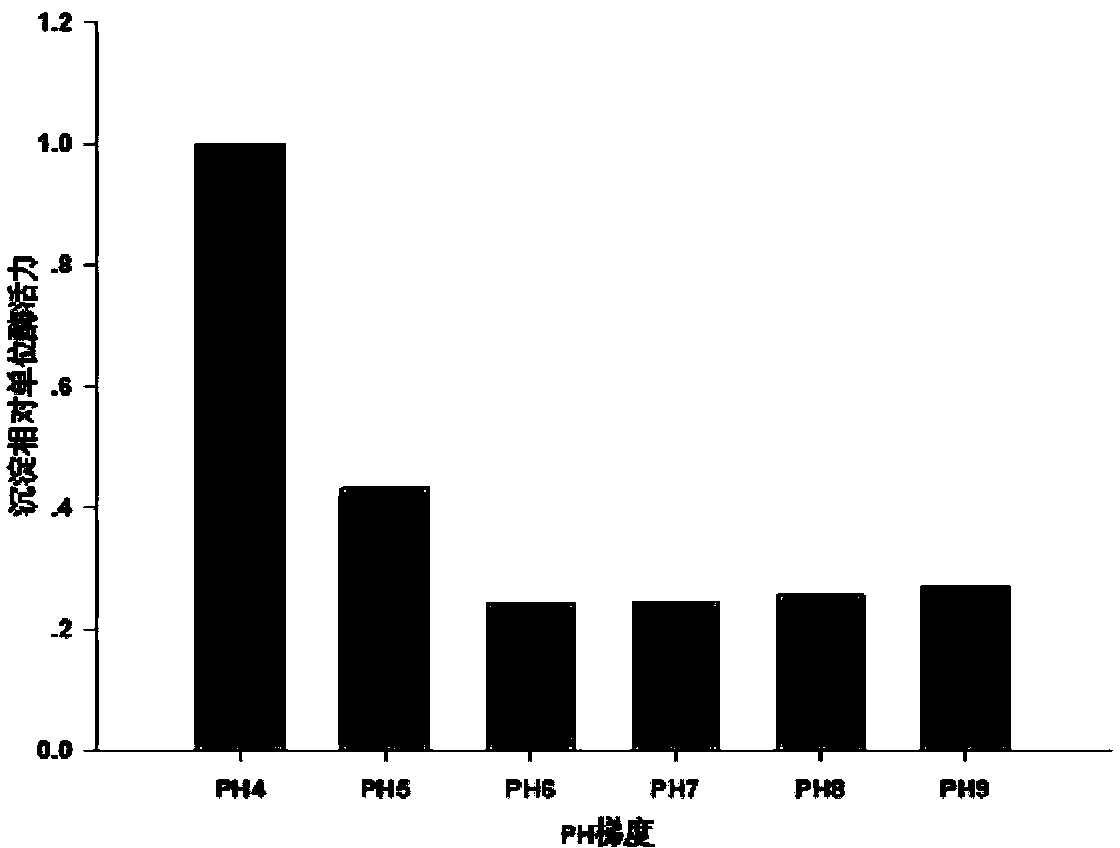
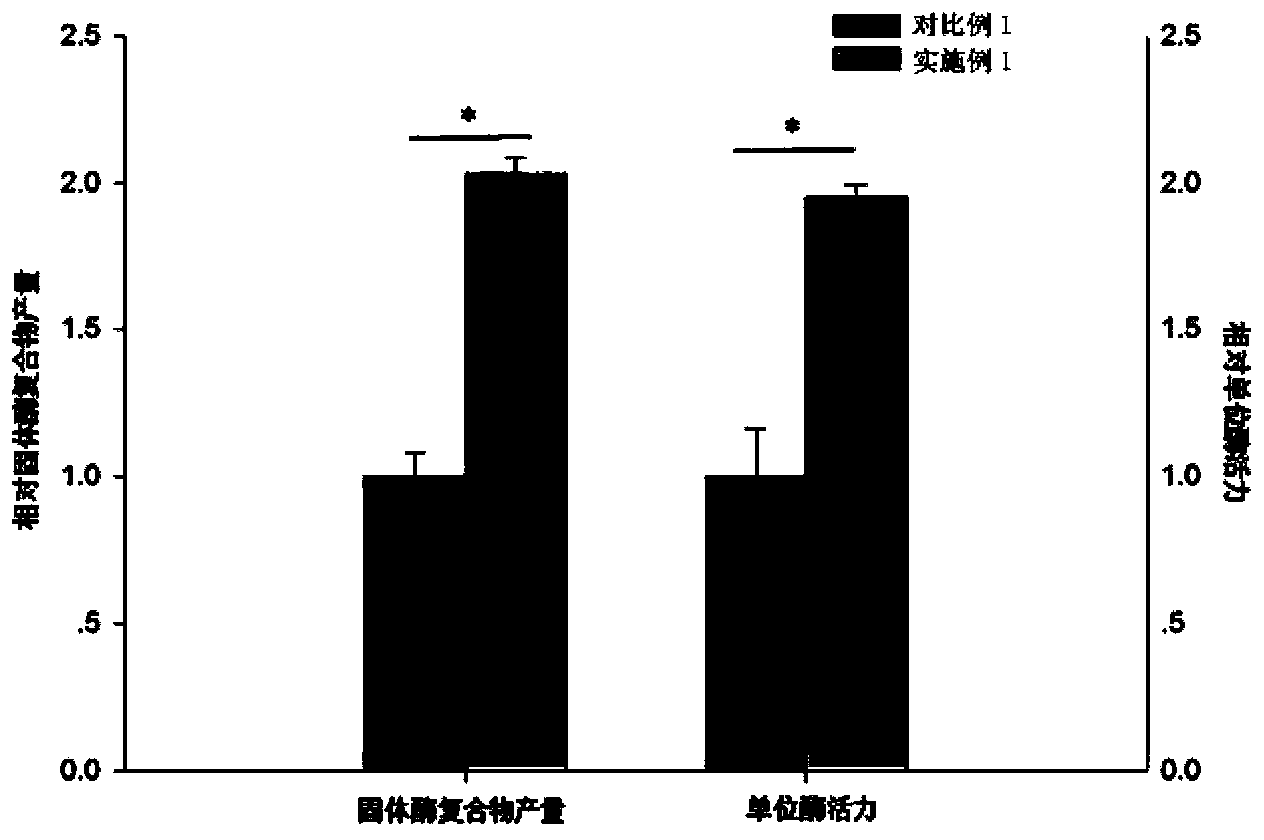
InactiveCN103173421AIncrease final yieldImprove unit enzyme activityMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesSodium phosphatesGlycerol
The invention discloses a preparation method of a solid enzyme compound for testing the content of fructose diphosphate sodium. A compound of aldolase (ALD), triosephosphate isomerase (TIM) and glycerol phosphatedehydrogenase (GDH) is extracted from rabbit meat serving as raw material through splitting and centrifuging methods, wherein the splitting method is an alkaline splitting method, and an alkaline solution with a concentration of 0.01-0.1M is added in every1mL / g of the raw material. By adopting the technical scheme, the final yield, the unit enzyme activity and the stability in volume production of the solid enzyme compound can be effectively increased.
Owner:吴海春 +1
Preparation method of solid enzyme complex for measuring sodium fructose diphosphate content
InactiveCN103173421BIncrease final yieldImprove unit enzyme activityMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesFructoseSodium phosphates
Owner:吴海春 +1
Method for detecting giardia by pyrosequencing technology
ActiveCN103103276BFacilitate the establishment of standardized operating proceduresImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFood borneWater quality
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT SHANDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
A genetically engineered bacterium for increasing phloroglucinol production and its construction method and application
ActiveCN109439606BImprove synthesis abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GenePhosphoric acid
A genetically engineered bacterium for increasing phloroglucinol production and its construction method and application belong to the technical field of genetic engineering. The invention provides a genetically engineered bacterium that overexpresses triose phosphate isomerase gene tpiA, polyketide synthase gene phlD, multiple resistance activator marA and acetyl CoA carboxylase gene ACCase, which significantly increases the The yield of phloroglucinol synthesized by the phenol-producing strain was 1.85 times that of the control strain through shake flask fermentation. The invention can be used for industrial production of phloroglucinol.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Gene full-length sequence of monochamus alternatus triosephosphate isomerase and clone method thereof
The invention relates to the field of biological gene engineering, in particular to a gene full-length sequence of monochamus alternatus triosephosphate isomerase and a clone method thereof. The clone method includes the steps that monochamus alternatus adults are used for extracting total RNA, RACE amplification is adopted to obtain a gene 3' end sequence, and the gene 3' end sequence and a constructed 5' end sequence of monochamus alternatus triosephosphate isomerase in a cDNA library are spliced to obtain the gene full-length sequence. The full length of the gene sequence is 1450 bp, the length of a gene open reading frame is 514-1257 bp, and 247 pieces of triosephosphate isomerase amino acid are encoded in total. Genes of monochamus alternatus glycolysis enzymes are supplemented, a research thought and a direction are provided for research and development of a novel schistosomiasis vaccine, and the gene full-length sequence is of great significance in immunology.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method of preparing 2-deoxyribose 5-phosphate
InactiveUS20070298467A1High yieldBacteriaUnicellular algae2-deoxyribose 5-phosphateGlyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
The present invention discloses a method of preparing 2-deoxyribose 5-phosphate by reacting glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and acetaldehyde in the presence of either a microorganism itself which contains 2-deoxyribose-5-phosphate aldolase but substantially no phosphatase or the enzyme derived from the microorganism. The present invention also discloses a method of preparing 2-deoxyribose 5-phosphate by reacting dihydroxyacetone phosphate and acetaldehyde in the presence of either a microorganism itself which contains 2-deoxyribose-5-phosphate aldolase and triose-phosphate isomerase but substantially no phosphatase or the enzymes derived from the microorganism.
Owner:YUKI GOSEI IND +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com