Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
91 results about "Spectroscopy instrumentation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Princeton Instruments has decades of experience designing world-class spectroscopy instruments. PI has sophisticated knowledge in three key areas of spectroscopy: CCD cameras, spectrometers, and optical coatings.
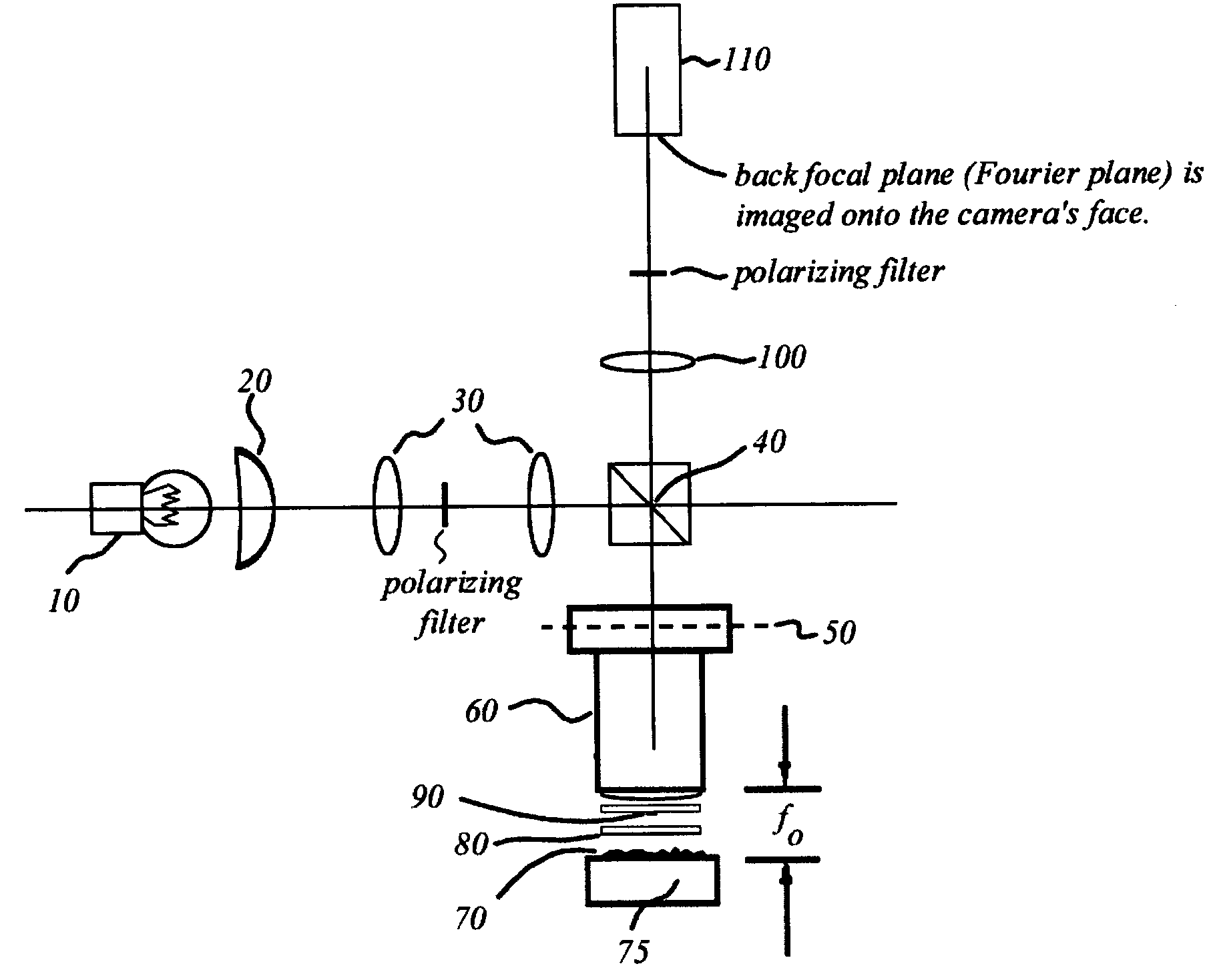
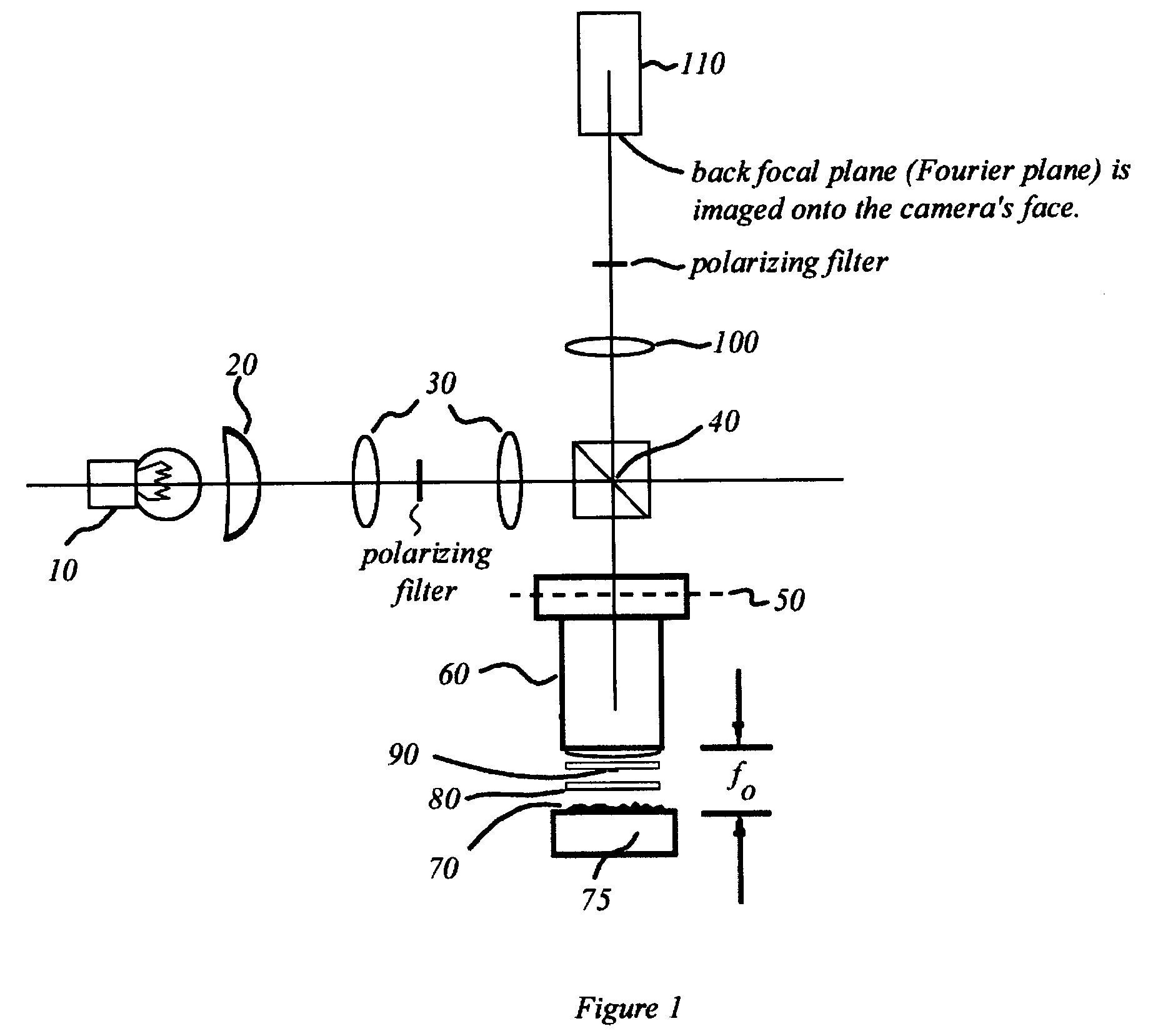
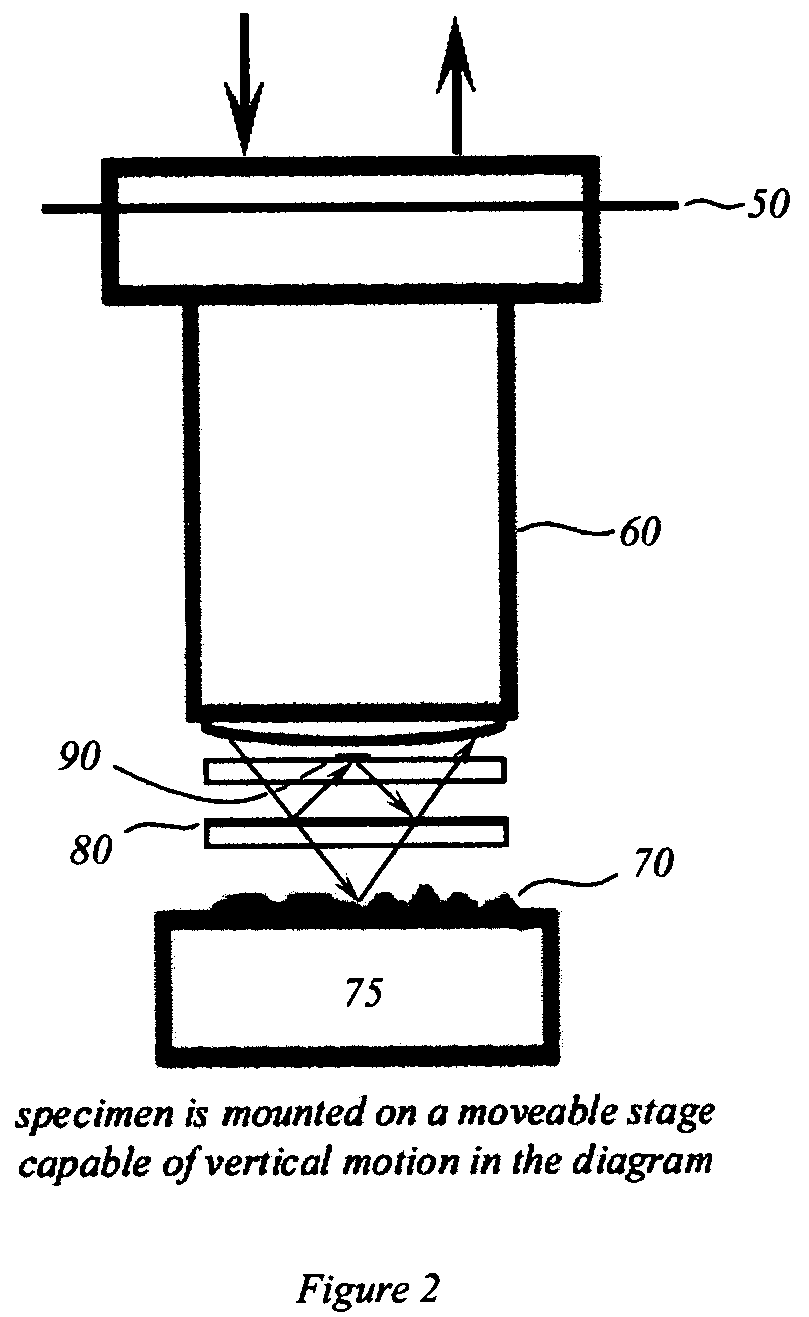
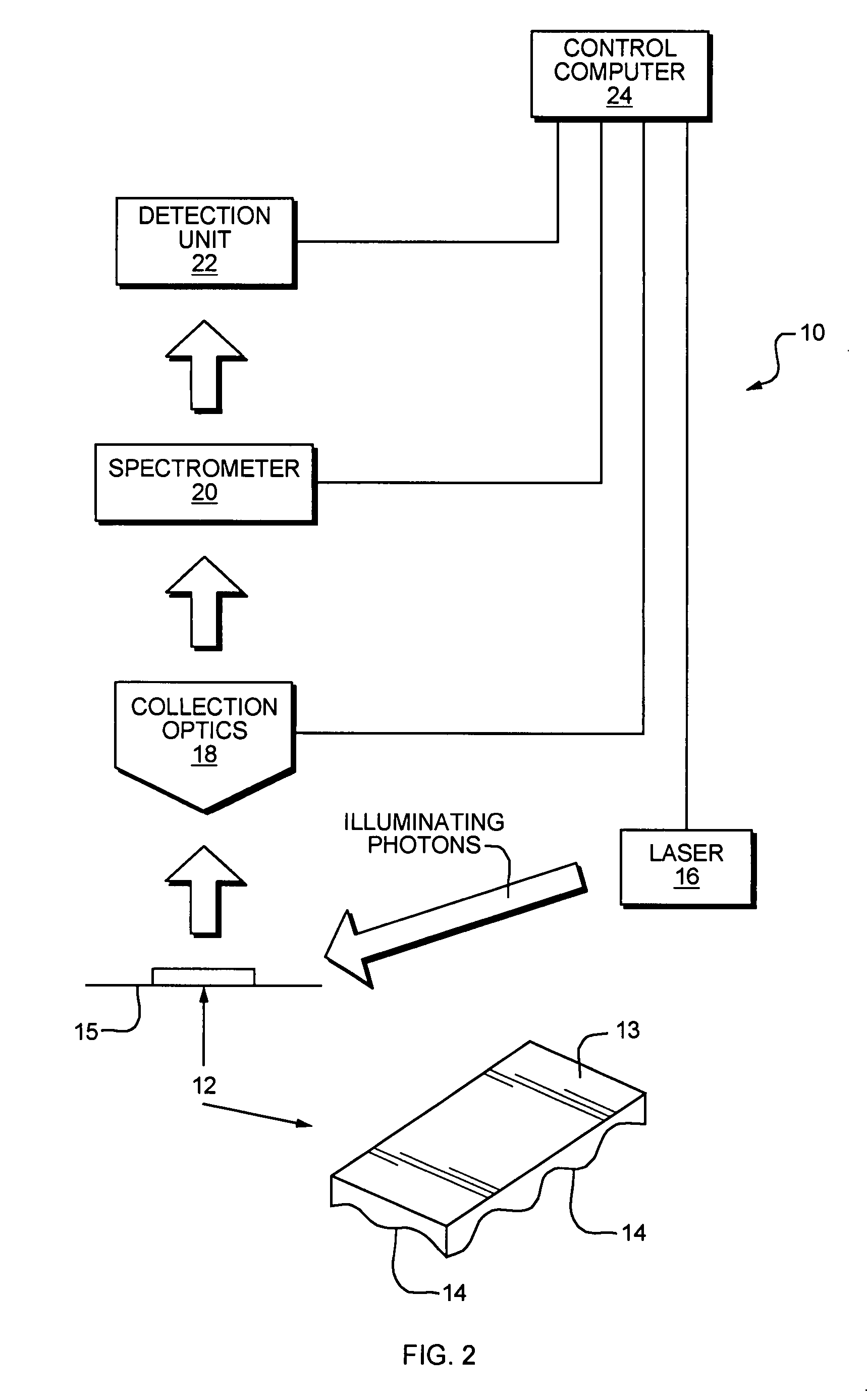
Interferometric back focal plane scatterometry with Koehler illumination
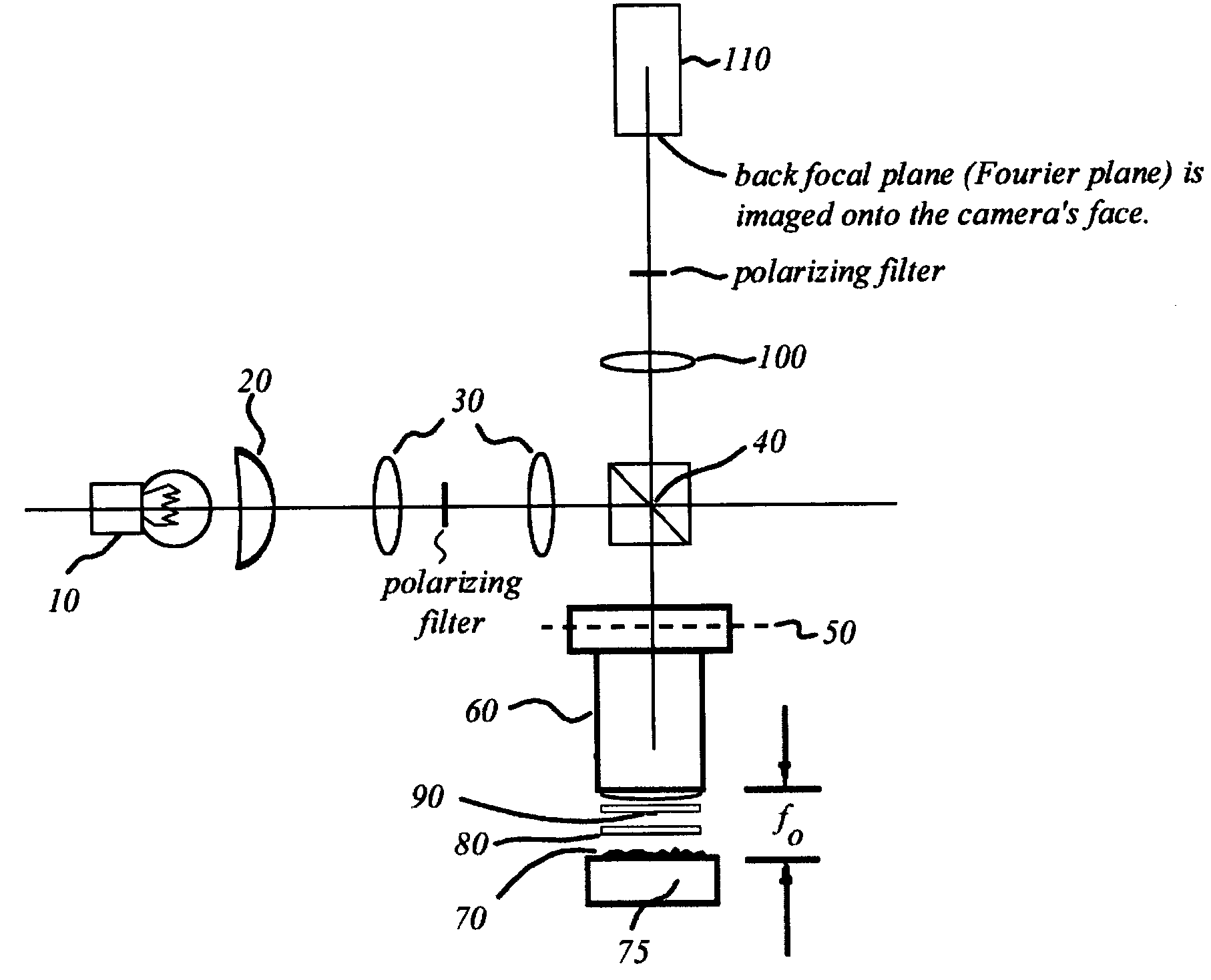
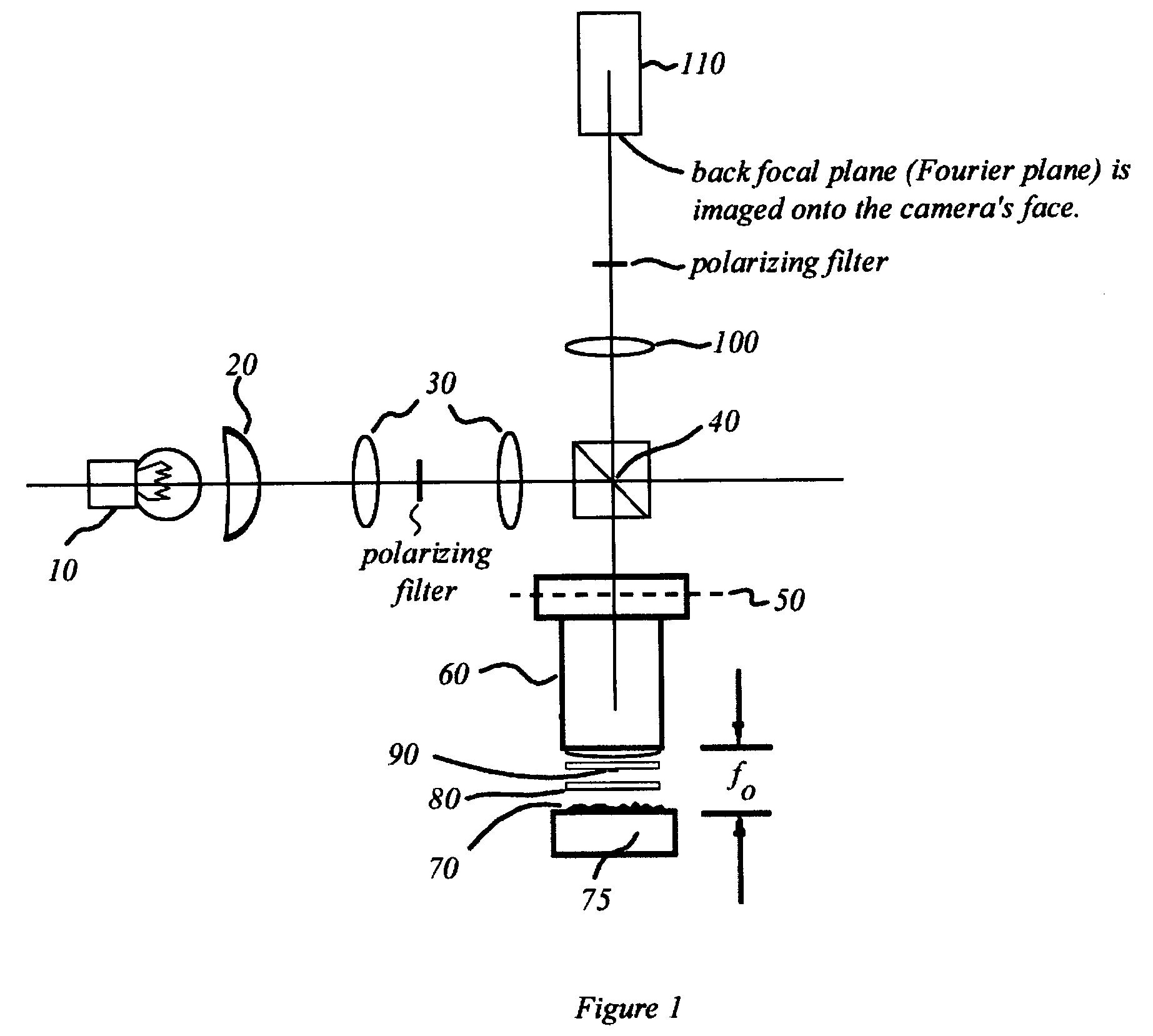
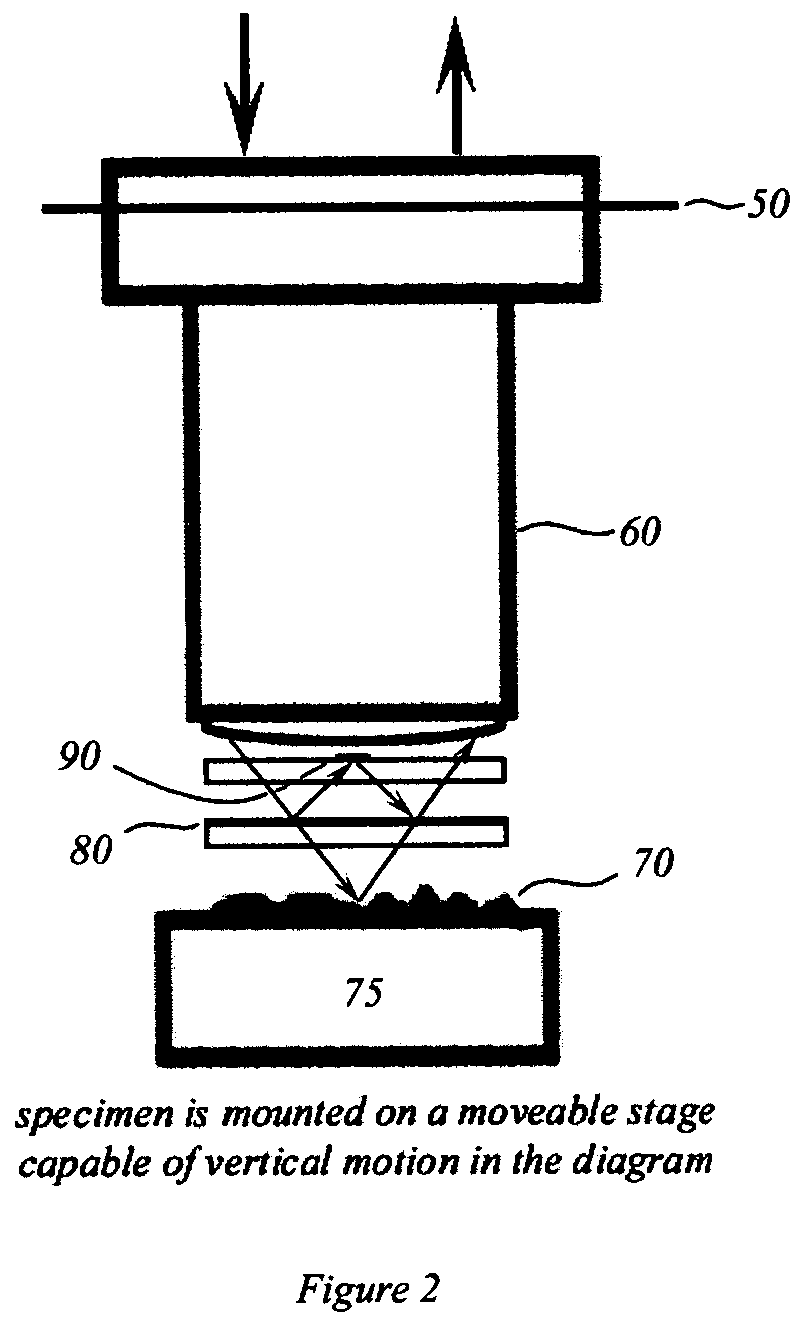
An interference spectroscopy instrument provides simultaneous measurement of specular scattering over multiple wavelengths and angles. The spectroscopy instrument includes an interference microscope illuminated by Koehler illumination and a video camera located to image the back focal plane of the microscope's objective lens while the path-length difference is varied between the reference and object paths. Multichannel Fourier analysis transforms the resultant intensity information into specular reflectivity data as a function of wavelength. This multitude of measured data provides a more sensitive scatterometry tool having superior performance in the measurement of small patterns on semiconductor devices and in measuring overlay on such devices.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
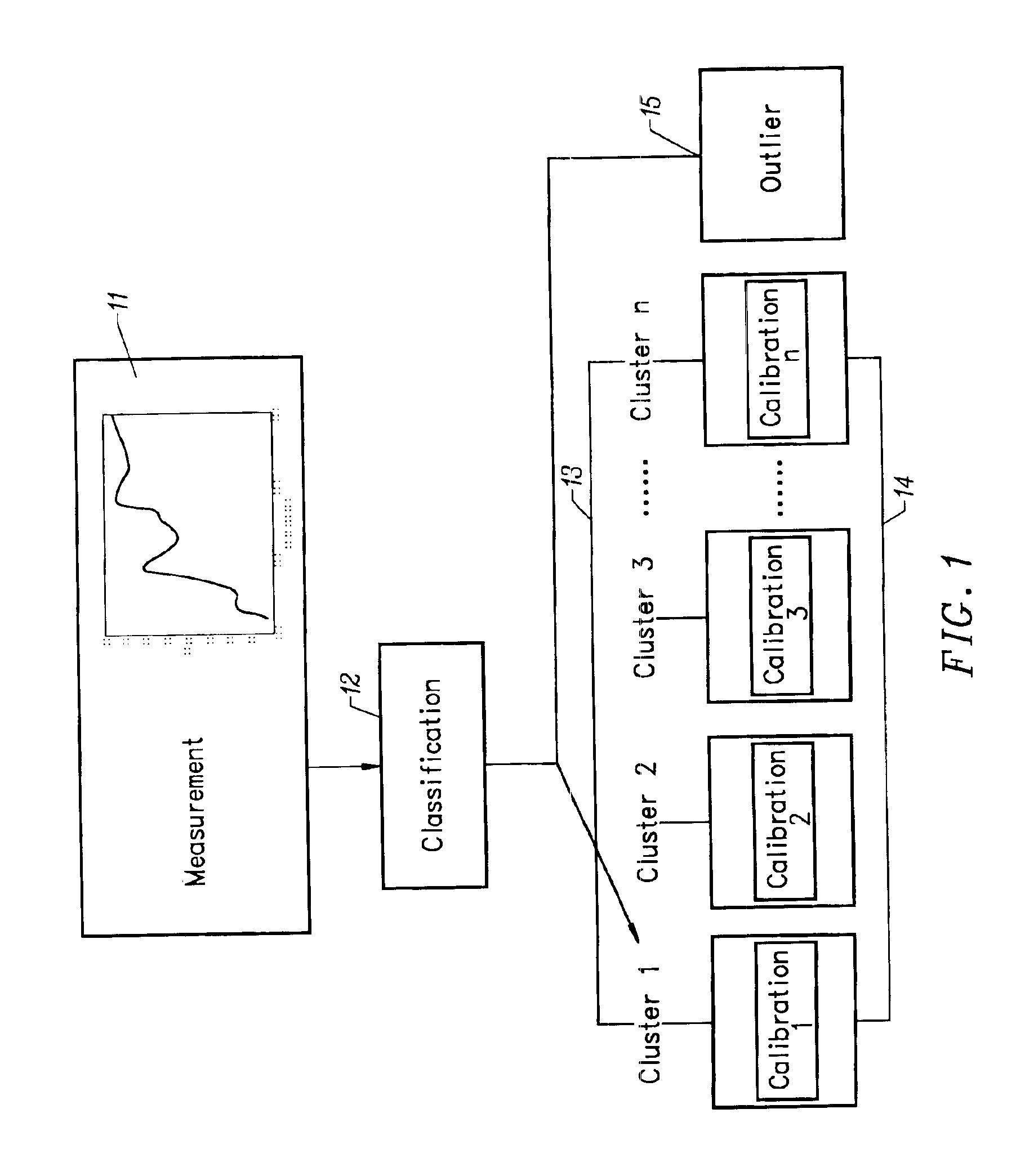
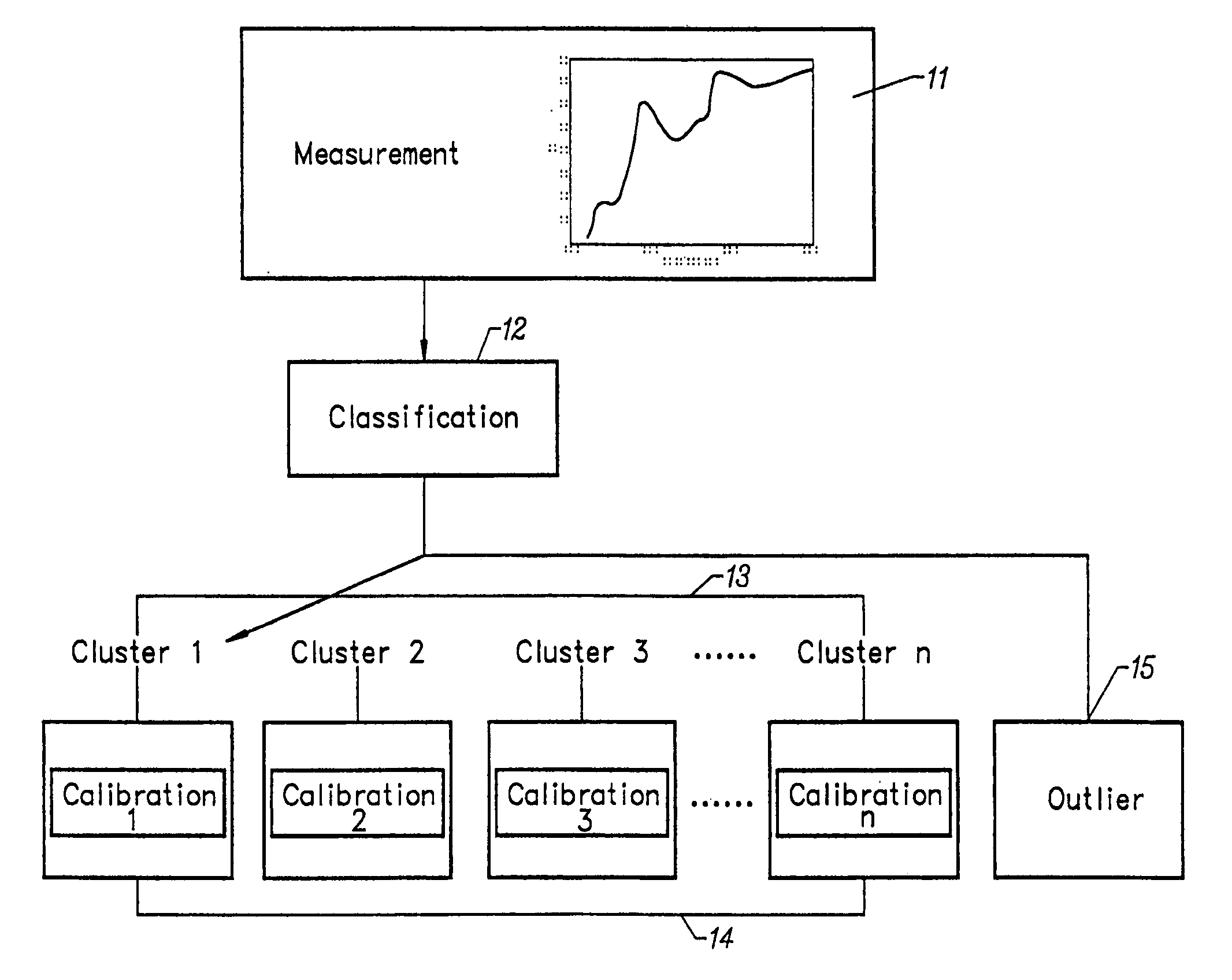
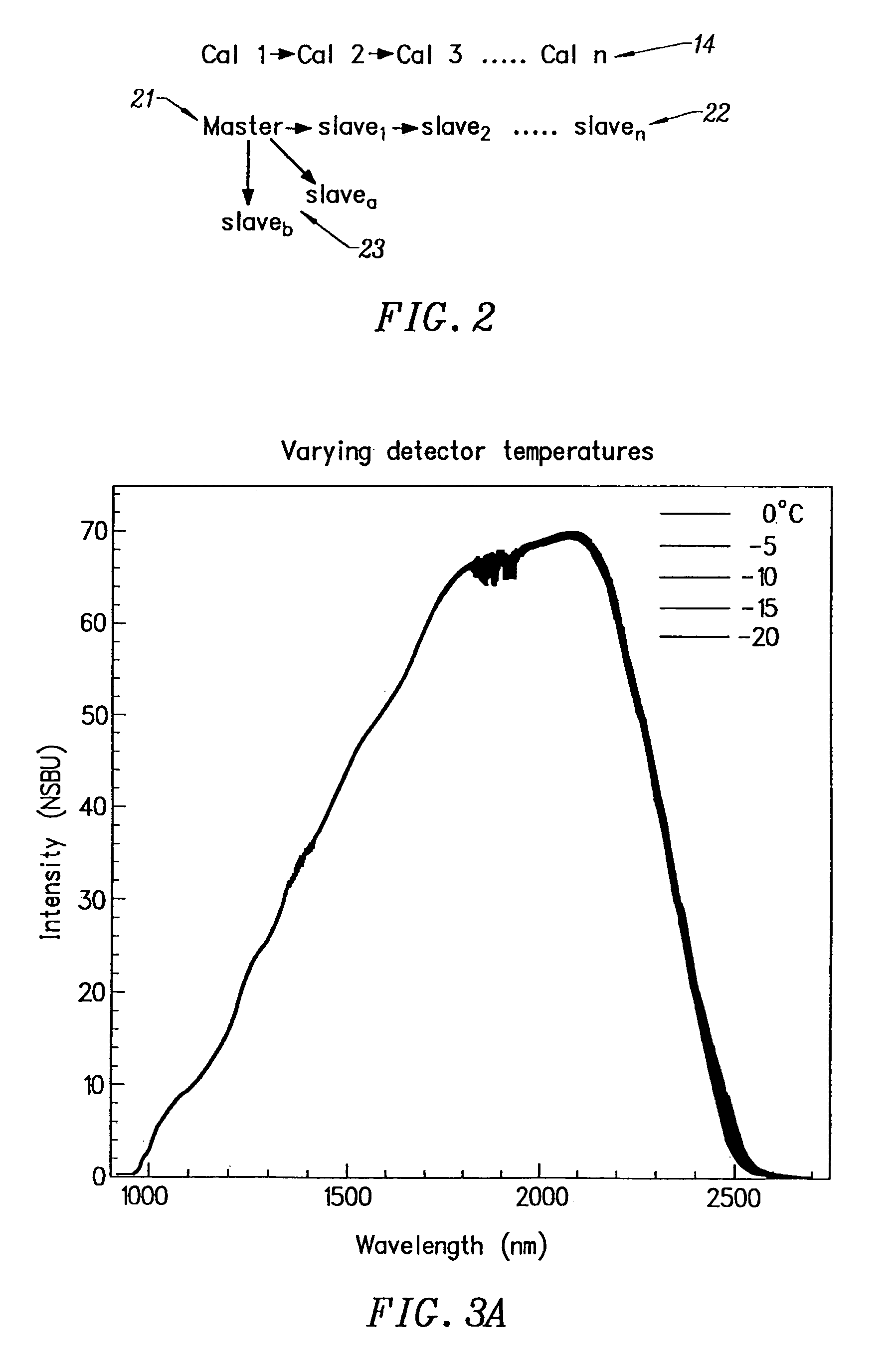
Method of characterizing spectrometer instruments and providing calibration models to compensate for instrument variation
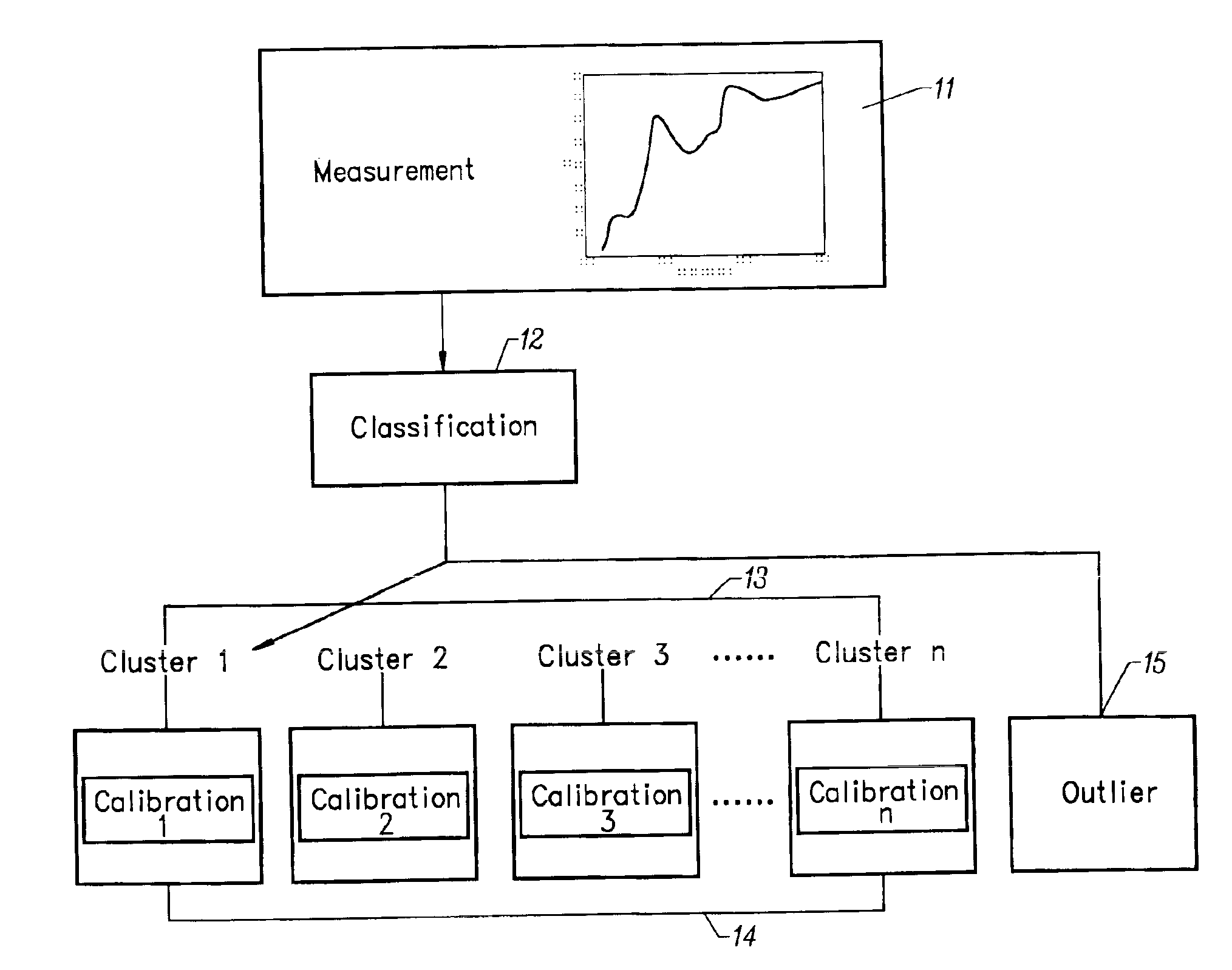
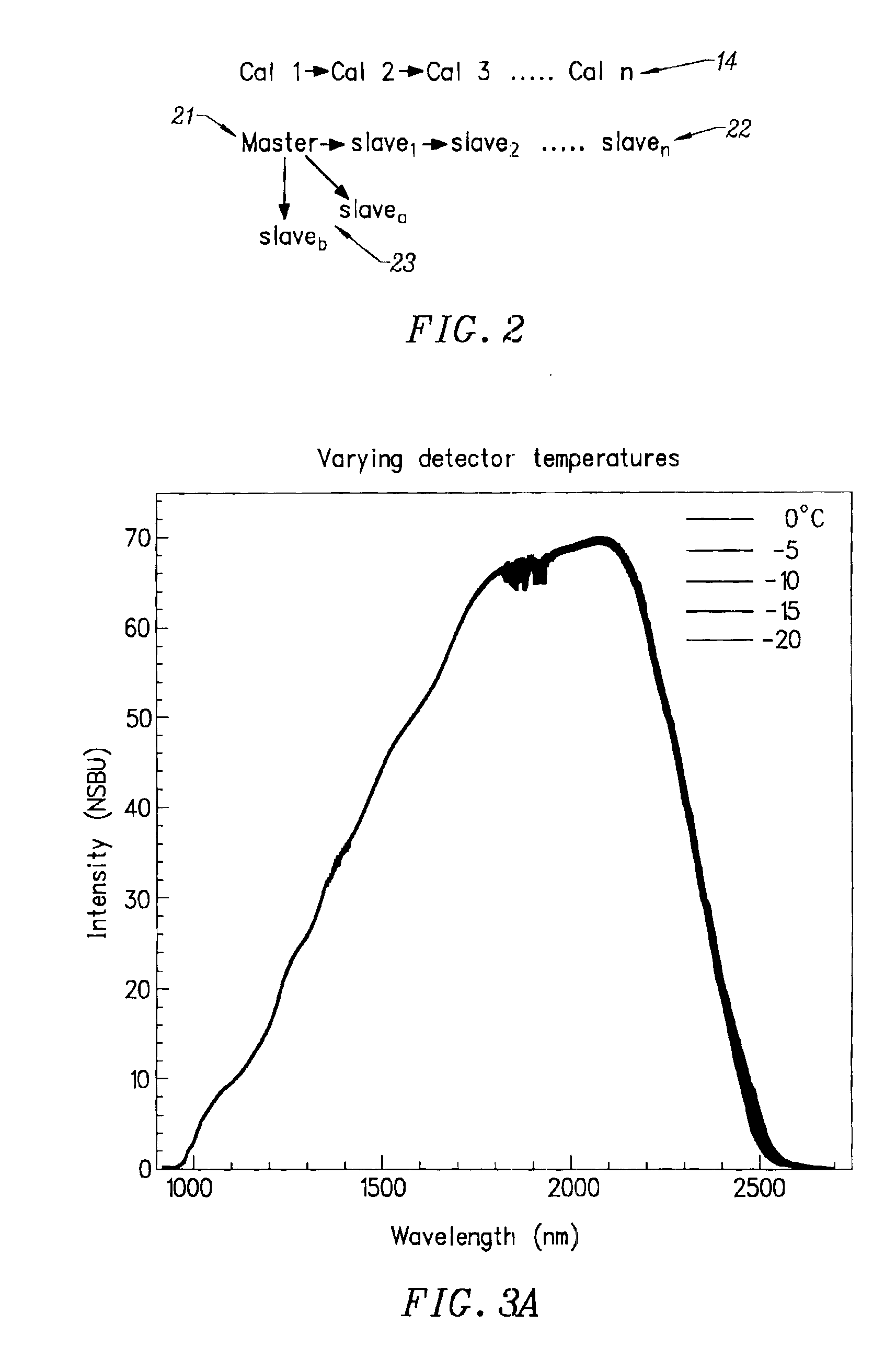
Spectrometer instruments are characterized by classifying their spectra into previously defined clusters. The spectra are mapped to the clusters and a classification is made based on similarity of extracted spectral features to one of the previously defined clusters. Calibration models for each cluster are provided to compensate for instrumental variation. Calibration models are provided either by transferring a master calibration to slave calibrations or by calculating a separate calibration for each cluster.A simplified method of calibration transfer maps clusters to each other, so that a calibration transferred between clusters models only the difference between the two clusters, substantially reducing the complexity of the model.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
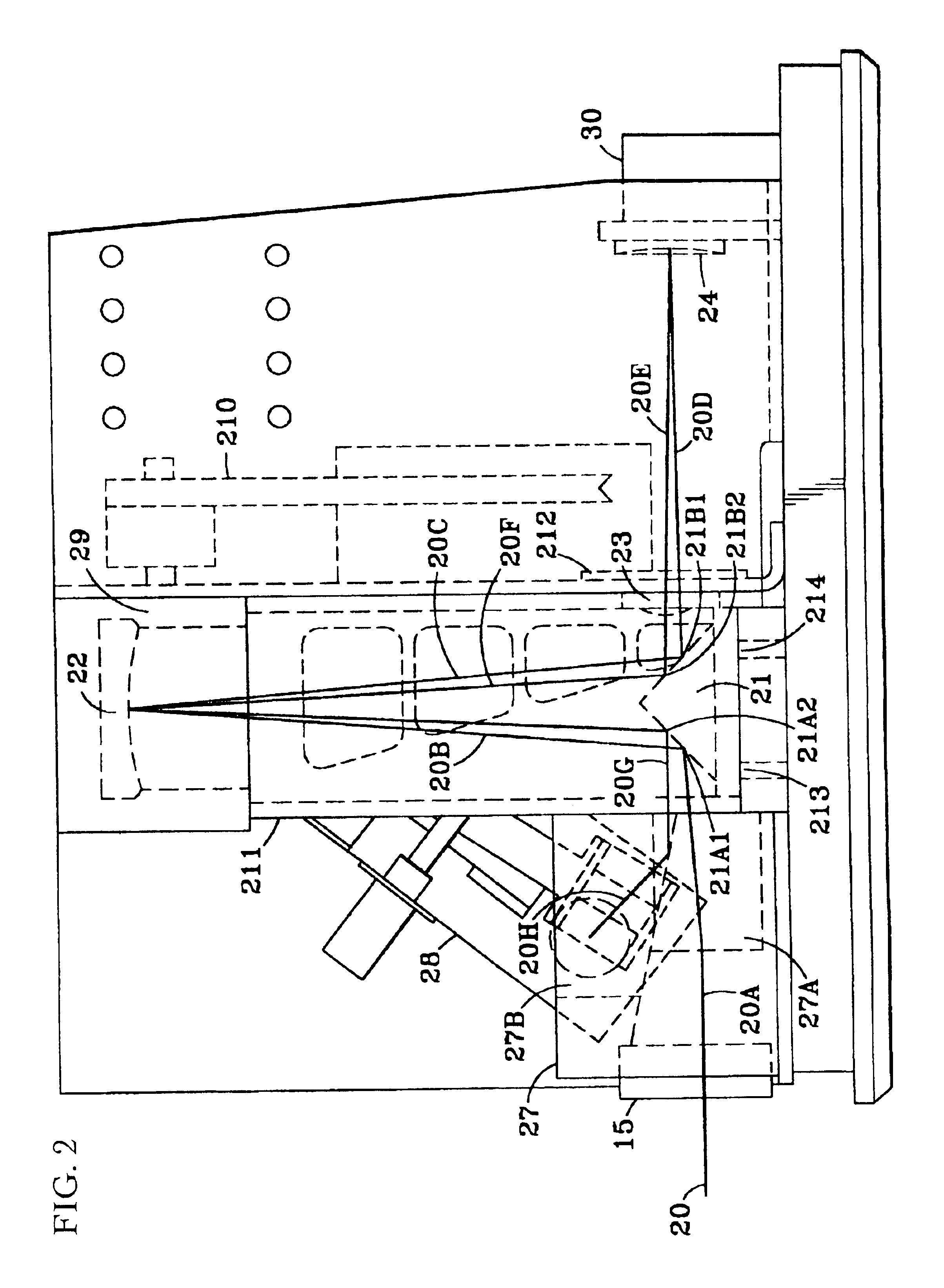
Spectral instrument using multiple non-interfering optical beam paths and elements for use therewith
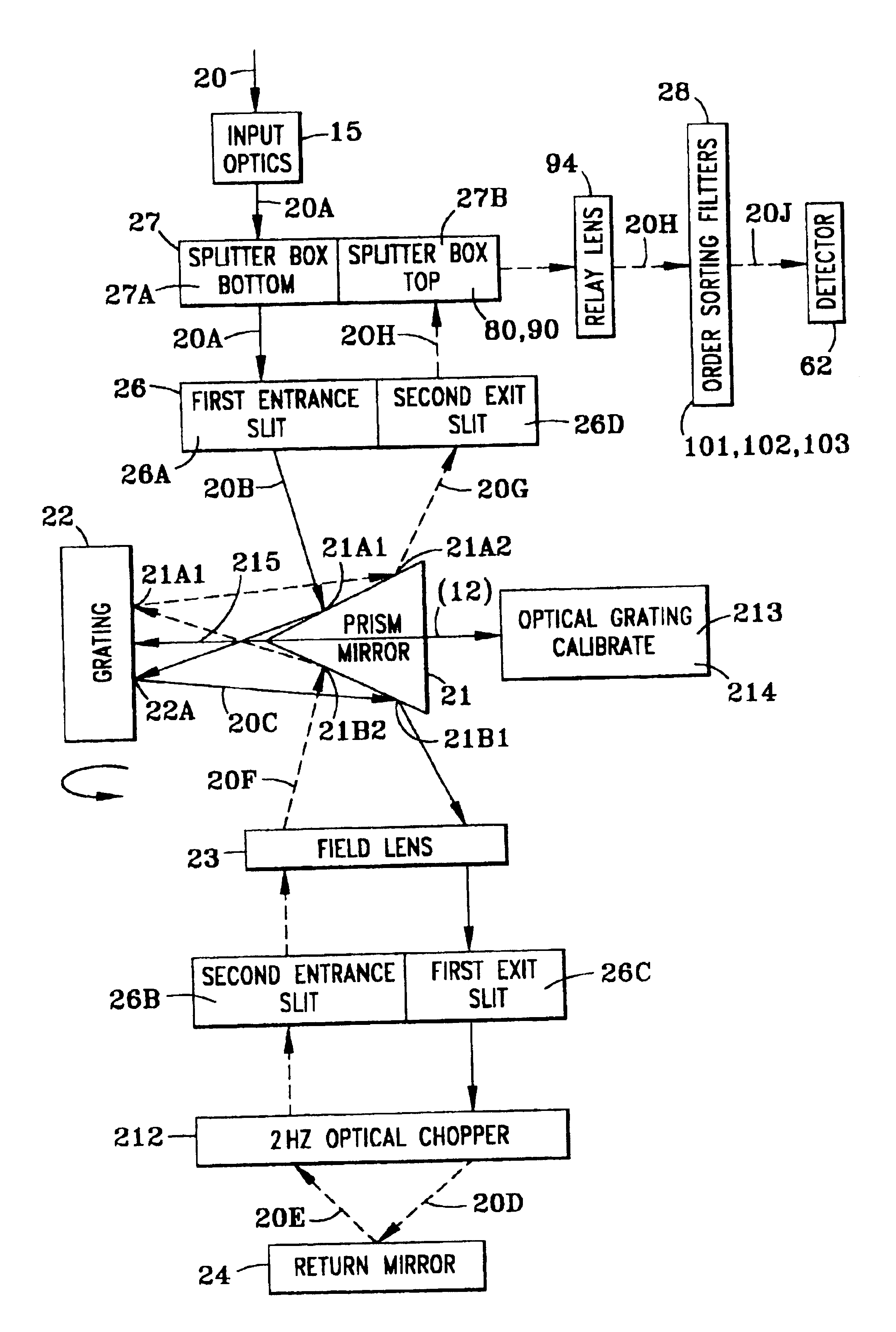
InactiveUS6714298B2Good dispersionReduce dispersionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationAngle of incidencePrism
A spectrometer, or a spectral instrument using multiple non-interfering optical beam paths and special optical elements. The special optical elements for use with the instrument are used for directing the optical beam and / or altering the form of the beam. The instrument has the potential, depending upon the totality of the optical components incorporated into the instrument, to be a monochromator, a spectroradiometer, a spectrophotometer and a spectral source. The spectral instrument may further be a part of the spectral system. The system may include the spectral instrument, a power module and means for remote control of the instrument. Such remote control may be by use of a personal computer or a control system dedicated to the control, measurement and analysis of the collected information. The multiple non-interfering beam paths are created using specially designed optical elements such as a diffraction grating, a splitter box, a zero back-lash drive system for movement of the grating element. The orientation of and a physical / spatial relationship between the field lenses, slits, return mirror, reflecting prism, turning lenses all define the multiple, preferably two paths. Particularly, there is a double pass through the grating to increase dispersion, reduce scatter while maintaining a perfect temperature independent spectral match for the second pass. Using the same grating twice reduces scatter by about a factor of 1000, increases the dispersion by a factor of two, and eliminates any temperature-related mechanical spectral drift which often is present with two separate monochromators. Because of the specially designed grating structure, the grating can cause the concurrent diffraction of a plurality of incident optical beams, each of which beams have different angles of incidence and different angles of reflection. The path of the incident and the reflected beam to and from the grating is "off-axis". That is, the beams going to and from the grating do not use the optical axis of the grating structure.
Owner:RYER DAMOND V
Method of characterizing spectrometer instruments and providing calibration models to compensate for instrument variation
Spectrometer instruments are characterized by classifying their spectra into previously defined clusters. The spectra are mapped to the clusters and a classification is made based on similarity of extracted spectral features to one of the previously defined clusters. Calibration models for each cluster are provided to compensate for instrumental variation. Calibration models are provided either by transferring a master calibration to slave calibrations or by calculating a separate calibration for each cluster. In one embodiment, a simplified method of calibration transfer maps clusters to each other, so that a calibration transferred between clusters models only the difference between the two clusters, substantially reducing the complexity of the model.
Owner:GLT ACQUISITION
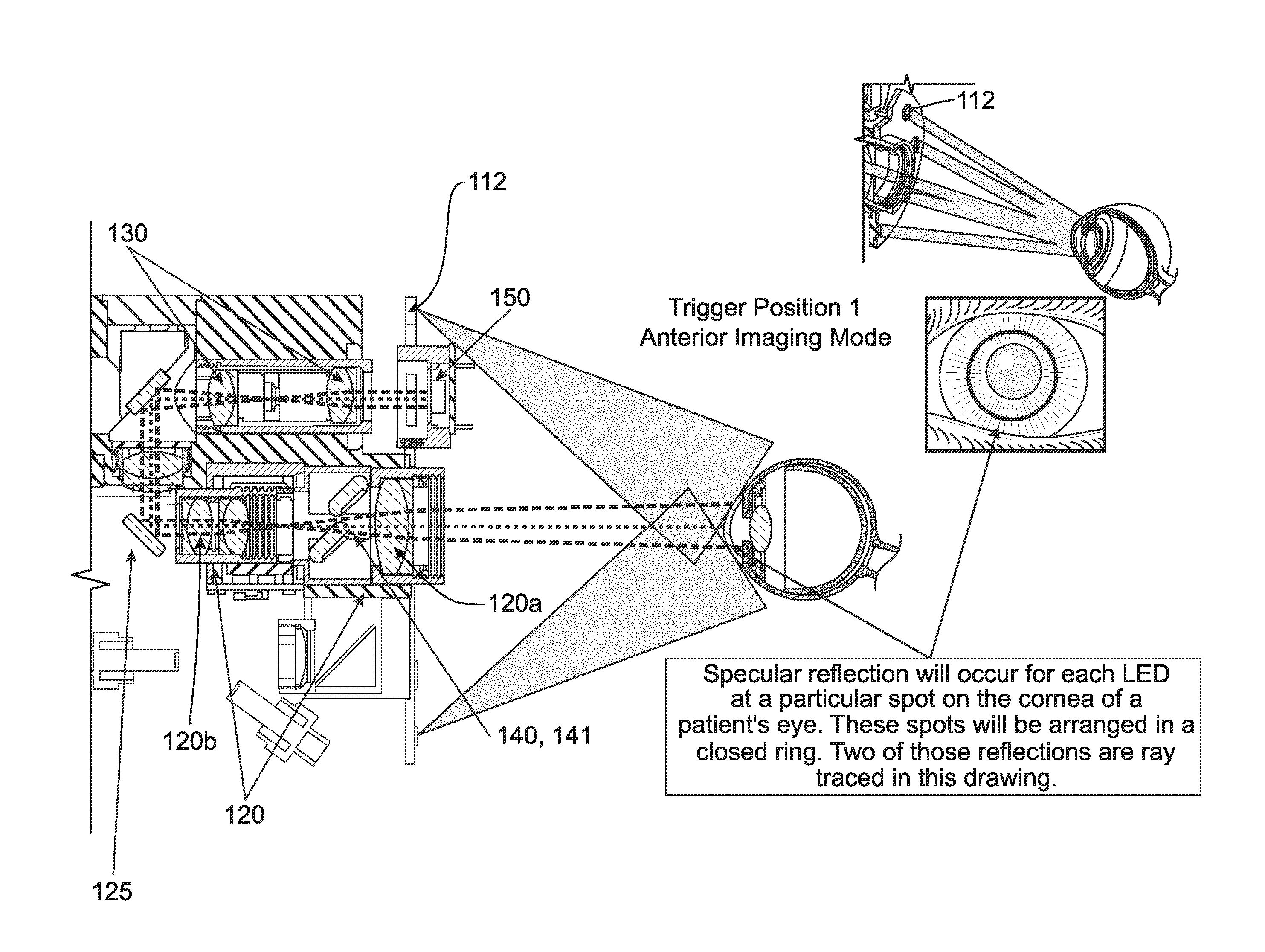
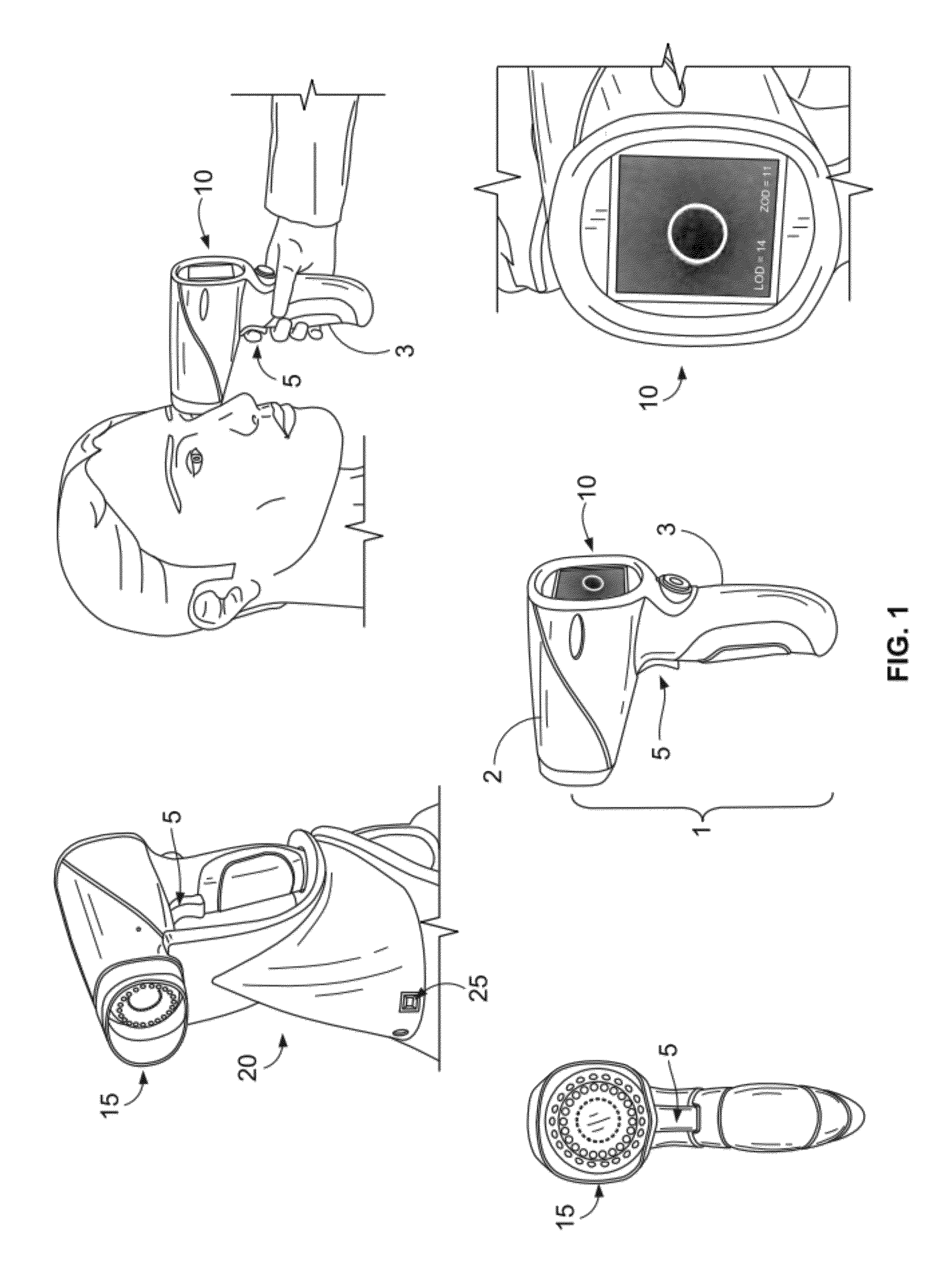
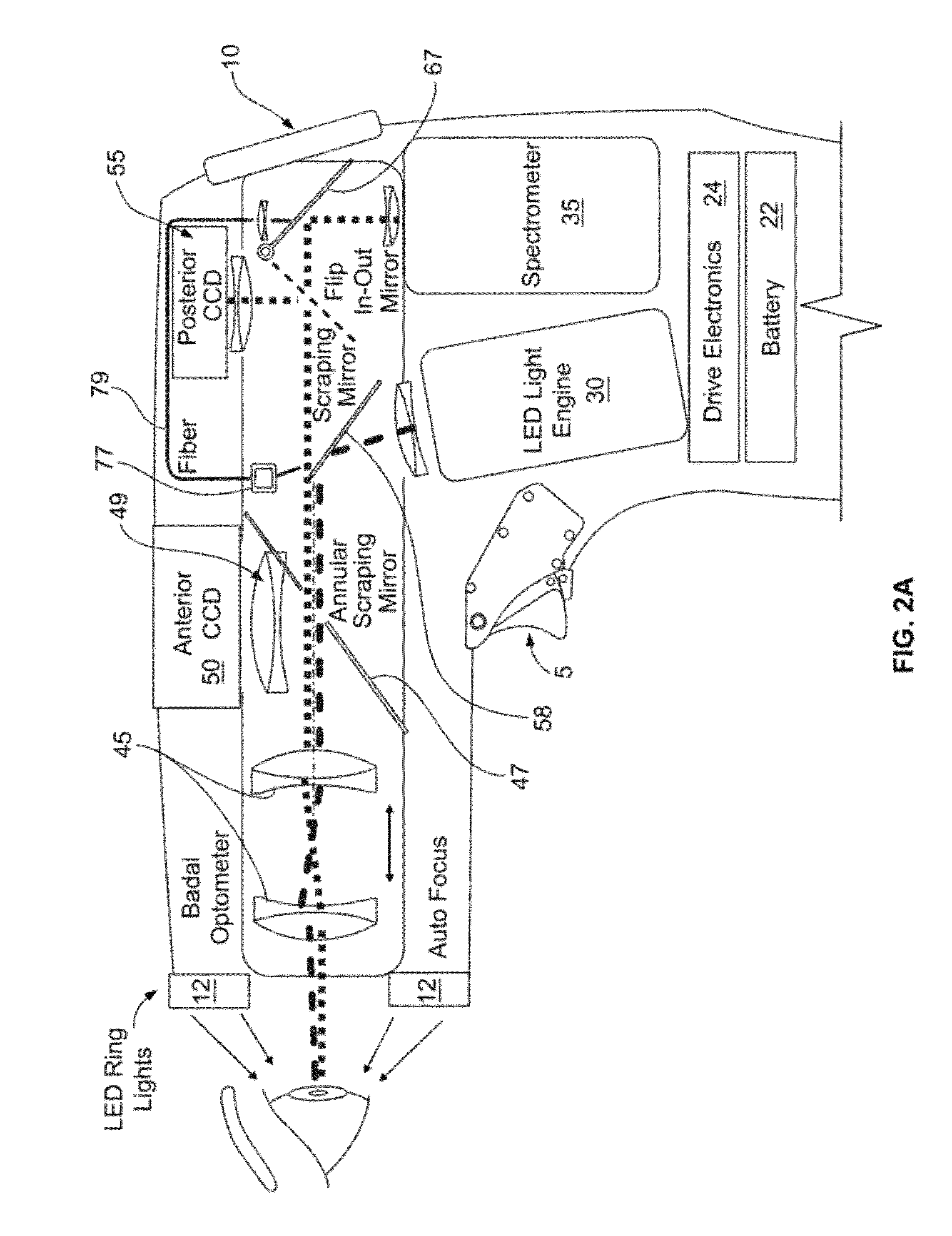
Handheld reflectometer for measuring macular pigment
ActiveUS20120092619A1Short time intervalReduce relative motionOthalmoscopesDocking stationMedical record
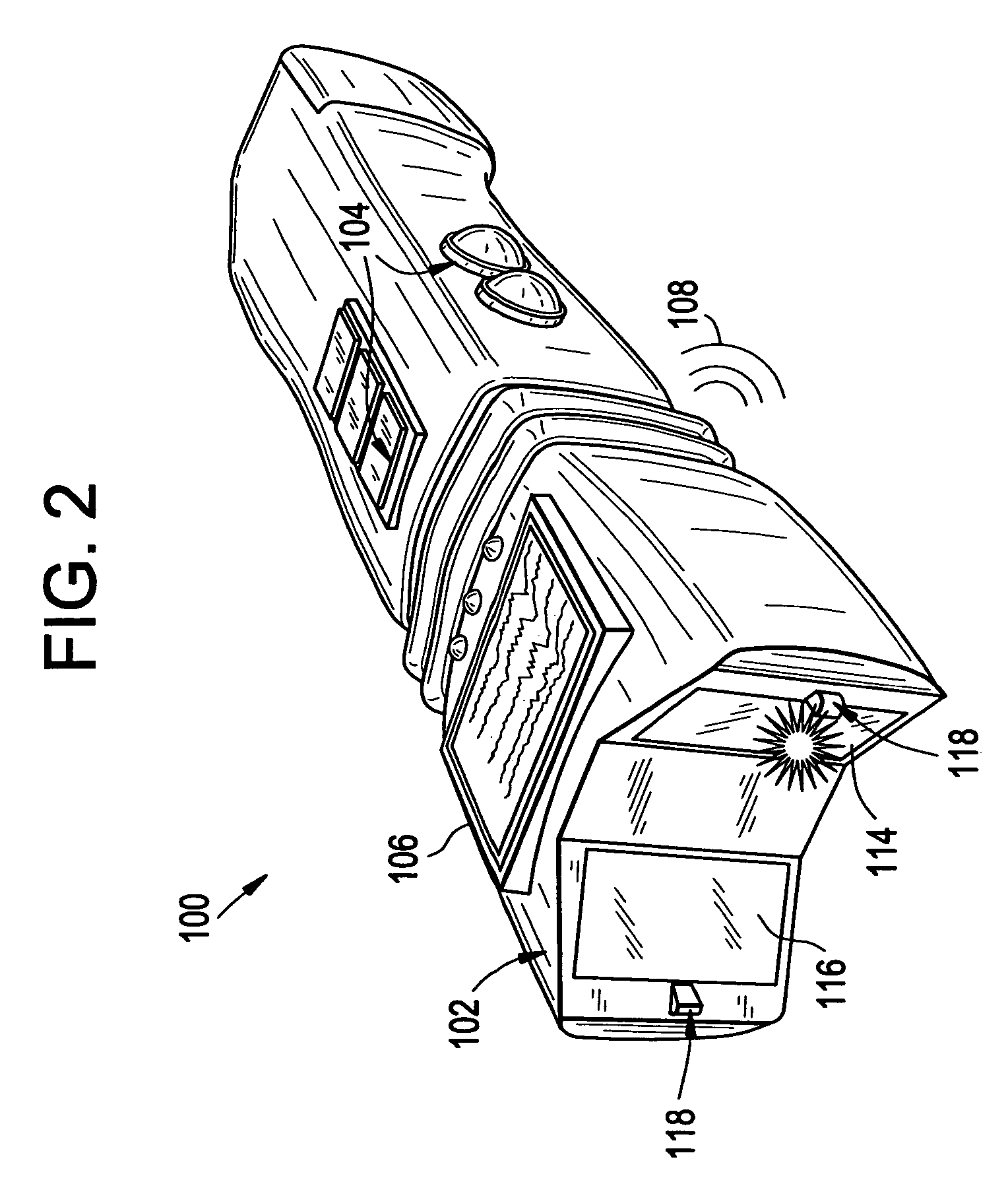
A macular pigment reflectometer is handheld, light, and portable. It can be provided as a part of a self-contained system. The self-contained system includes a docking station in which the macular pigment reflectometer is placed between uses. The docking station is used to recharge the battery of the handheld macular pigment reflectometer. The docking station also has one or more types of communication ports, such as one for a wired or wireless internet connection, through which the handheld macular pigment reflectometer can communicate with a computer or an electronic medical records system. The instrument operates in a pulsed operating mode wherein relative instrument-to-eye motion is reduced and, preferably, nearly eliminated. The handheld macular pigment reflectometer contains an on-board spectrometer which is designed to capture spectra in very short intervals of time. A trigger on the instrument allows for a rapid, intuitive, and sequential alignment followed by rapid data gathering.
Owner:OCULAR PROGNOSTICS
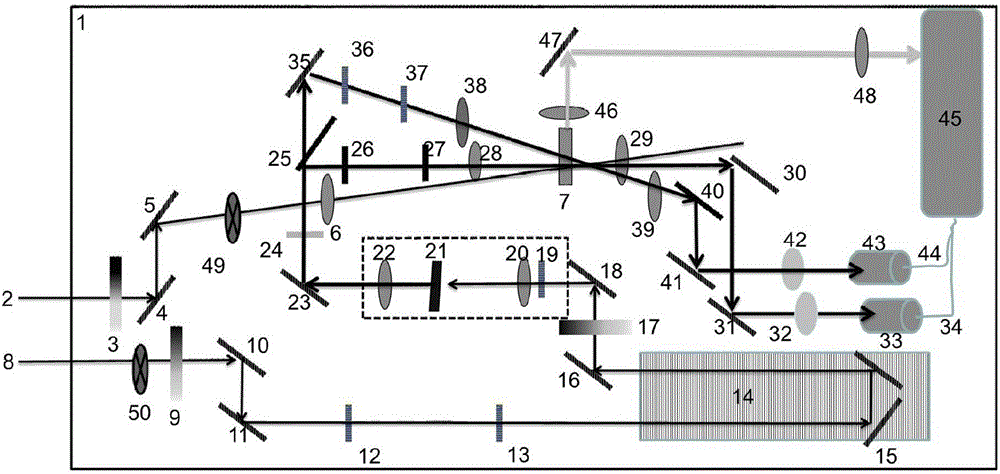
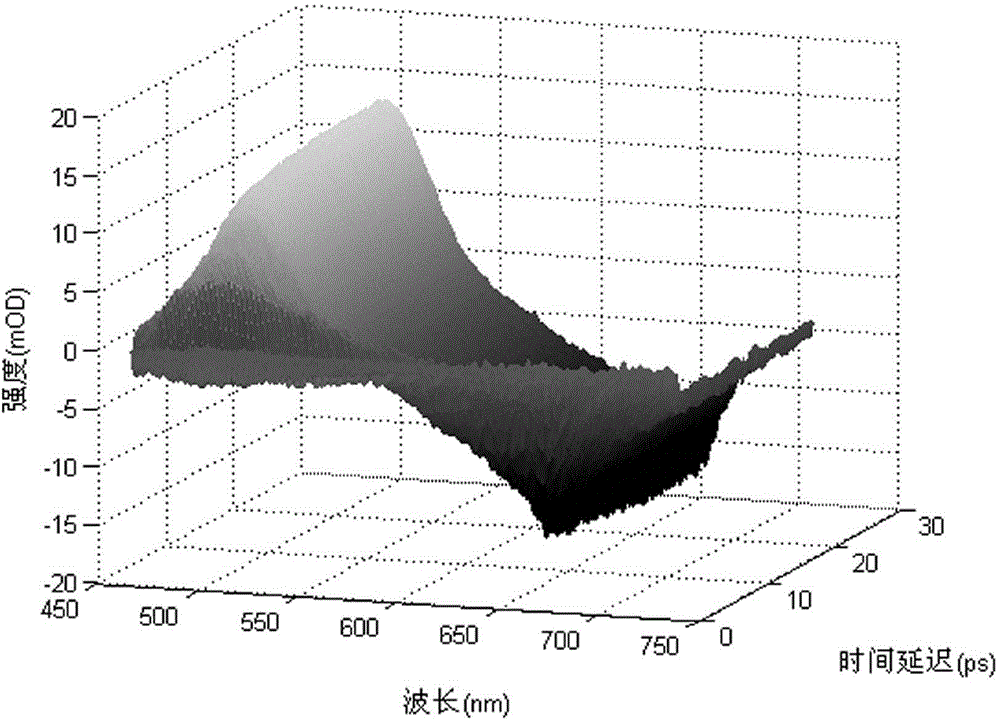
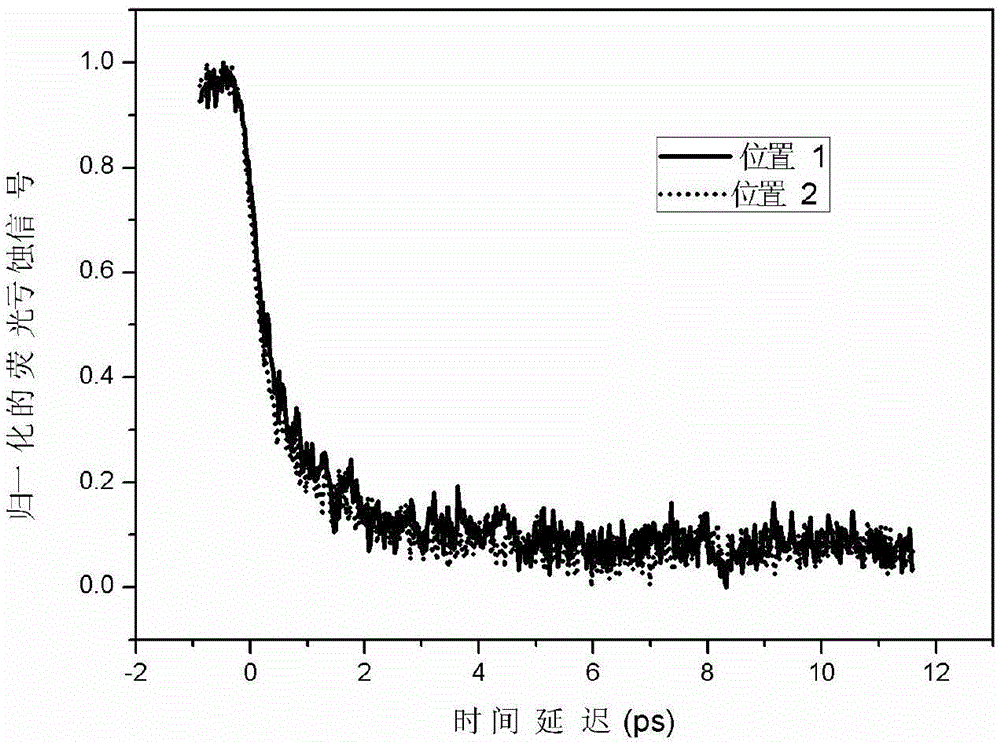
Modularized femtosecond time-resolved transient absorption and fluorescence depletion two-in-one spectrometer
ActiveCN104422519ASkilledEasy to moveEmission spectroscopyAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyNonlinear optical crystalFluorescence
The invention relates to a time-resolved spectrum measurement instrument, in particular to a modularized femtosecond time-resolved transient absorption and fluorescence depletion two-in-one spectrometer. The modularized femtosecond time-resolved transient absorption and fluorescence depletion two-in-one spectrometer comprises an instrument optical flat, a pumping light path system and a probing light path system consisting of a plane mirror, a convex lens, a light diaphragm, a light filter, a time delay line, nonlinear optical crystals and a sample system, and also comprises a spectrum detection system. Since the spectrometer uses the optical flat as a bottom plate and various optical components, the modularization of the instrument is realized and the instrument can be moved on the whole; since a femtosecond time-resolved transient absorption spectrometer and a femtosecond time-resolved fluorescence depletion spectrometer are integrated into one, working personnel can conveniently conduct adjustment and the spectrometer can be widely popularized and used.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG IND TECH RES INST CO LTD DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
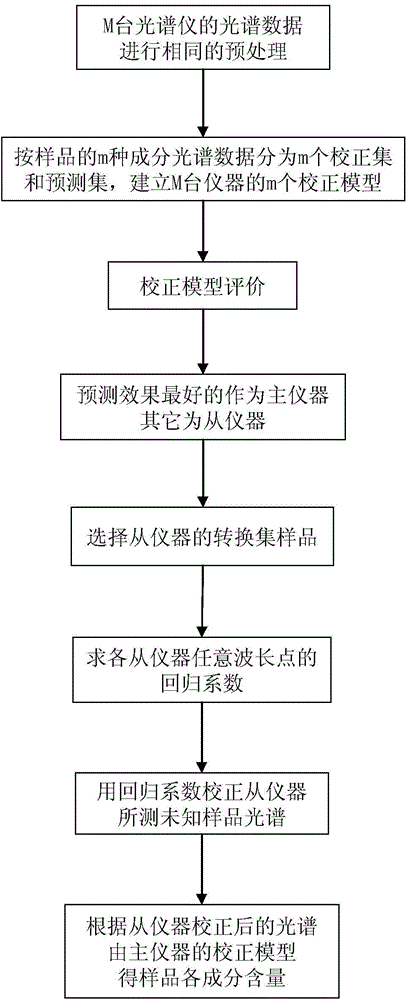
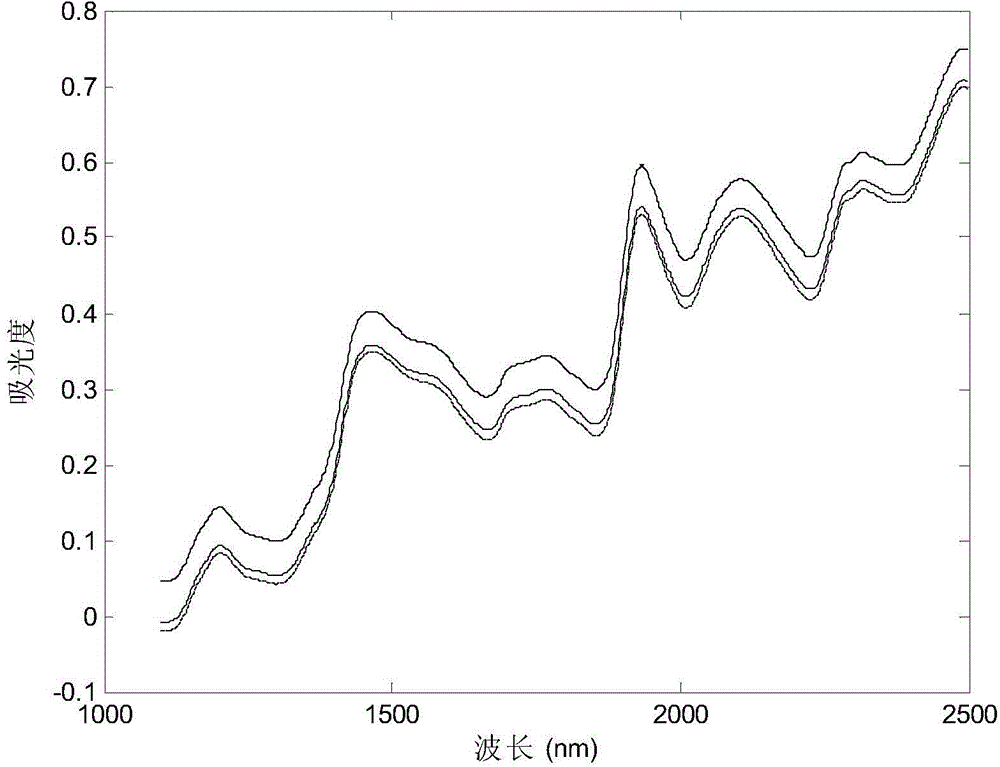
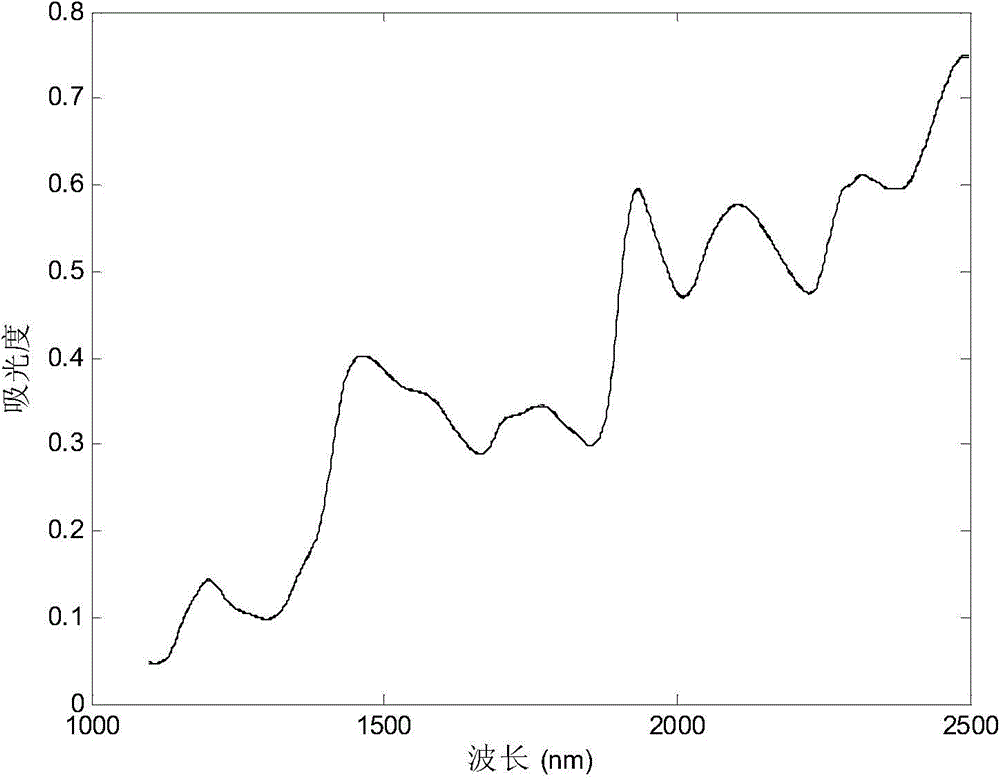
Spectral model transmission method based on unary linear regression
The invention discloses a spectral model transmission method based on unary linear regression. The spectral model transmission method mainly comprises the steps of I. performing the identical preprocessing on sample spectrums of M spectrometers; II. classifying spectrum data into m correction sets and forecasting sets according to m kinds of components of samples, and respectively constructing m correction models on the M spectrometers; III. evaluating the correction models; IV. selecting the spectrometer with the best forecasting effect as a main instruments and the other spectrometers as auxiliary instruments; and V. selecting optimal samples for all the auxiliary instruments from a correction set of the main instrument, determining samples in conversion sets of all the auxiliary instruments according to the sequence numbers, calculating regression coefficients through the unary linear regression, correcting spectrums of the auxiliary instruments, and substituting the regression coefficients into the correction model of the main instrument to obtain a sample component content result. According to the method, the difference of the different instruments is effectively eliminated; the correction model constructed on the main instrument can be shared on the multiple auxiliary instruments; the analysis test workload is reduced, and the cost of the model construction is saved; furthermore, the number of calculated parameters is small, the models are simple, and the forecasting accuracy is relatively high.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Interference scatterometer
An interference spectroscopy instrument provides simultaneous measurement of specular scattering over multiple wavelengths and angles. The spectroscopy instrument includes an interference microscope illuminated by Koehler illumination and a video camera located to image the back focal plane of the microscope's objective lens while the path-length difference is varied between the reference and object paths. Multichannel Fourier analysis transforms the resultant intensity information into specular reflectivity data as a function of wavelength. This multitude of measured data provides a more sensitive scatterometry tool having superior performance in the measurement of small patterns on semiconductor devices and in measuring overlay on such devices.
Owner:ZYGO CORPORATION
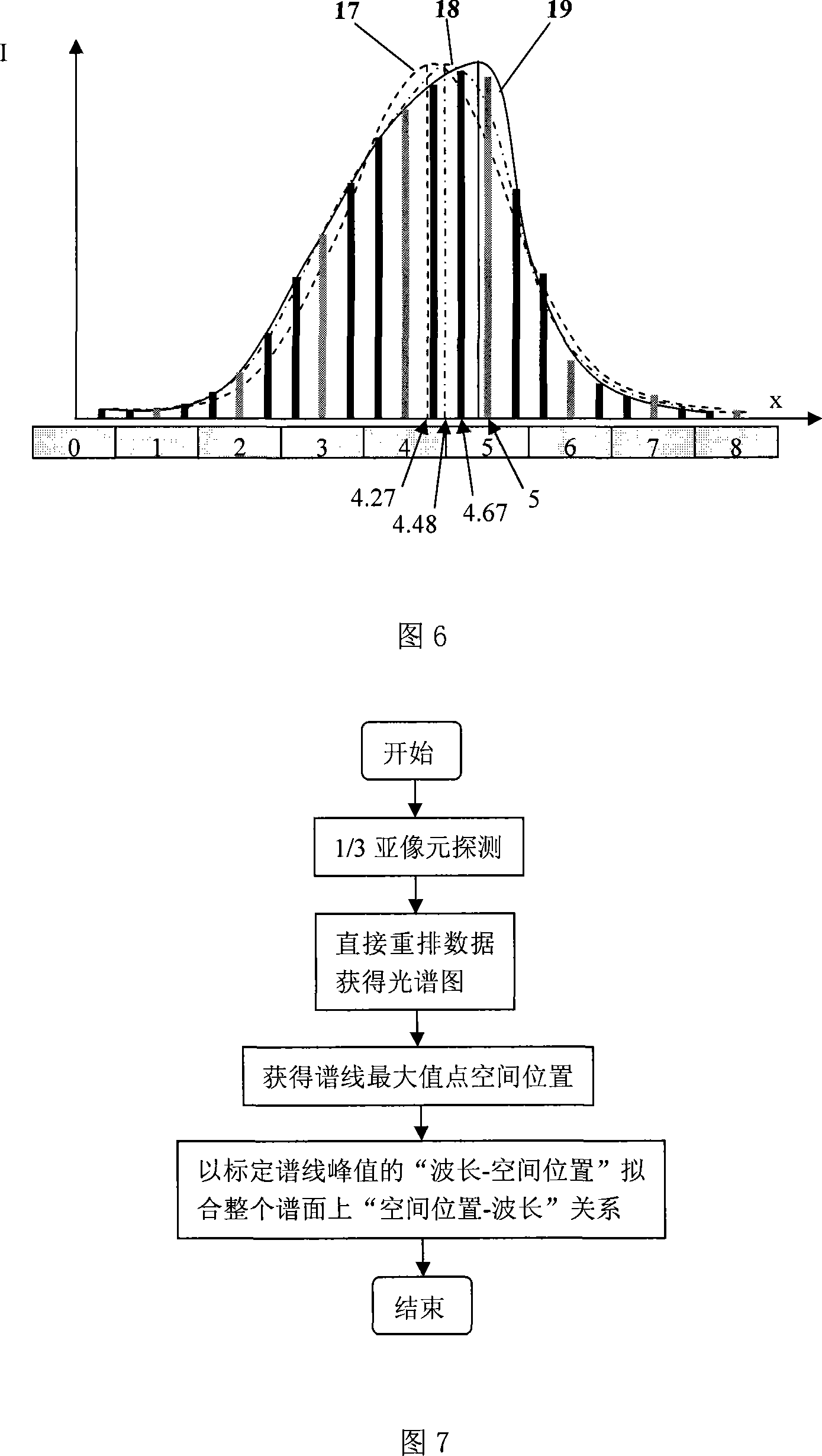
Wavelength calibration method of optical spectrum instruments
InactiveCN101158599AIncrease sampling rateHigh-resolutionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSpectral patternImage resolution
A wavelength calibration method of spectral instrumentation mainly relating to wave length calibration method adopting spectral instrumentation of array detector pertains to the filed of wave length calibration technology of spectral instrumentation. The spectral instrumentation of the method adopts array detectors and lighting source of linear spectra, spatial locations of every spectrum peak of the lighting source are acquired from the spectrogram output from the instrumentation, and the 'spatial location - wave-length relationship' on the power spectrum is fitted by according these spectrum peak wavelength and the corresponding spatial locations thereof, thus corresponding wavelength of every pixel of the detector is confirmed, the spatial locations of every spectrum peak of the lighting source is acquired through processes as following: sub-pixel detecting; sub-pixel reestablishing; spectrum peak spatial locations acquiring. The sub-pixel detecting of the invention increases sampling ratio of spectrogram, spectrogram with improved resolution in acquired; the comprehensive applications of sub-pixel detecting, sub-pixel reestablishing and spectrum contour fitting further increases the wavelength accuracy of spectral instrumentation with array detectors step by step. The invention has prominent effect.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Spectroscopic instrument and process for spectral analysis
InactiveCN104040308AInterferometric spectrometrySpectrum generation using refracting elementsFtir spectraSpectral analysis
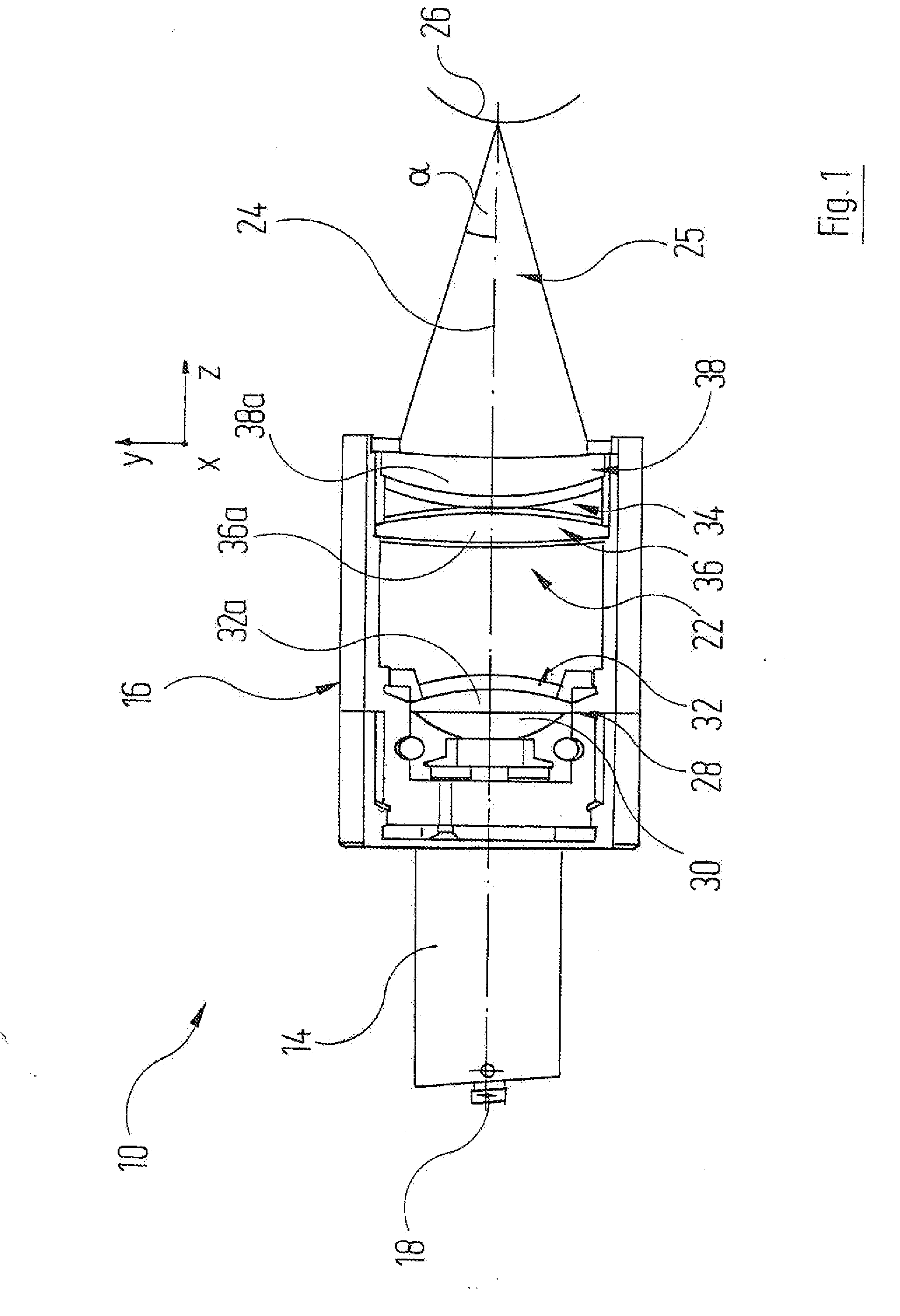
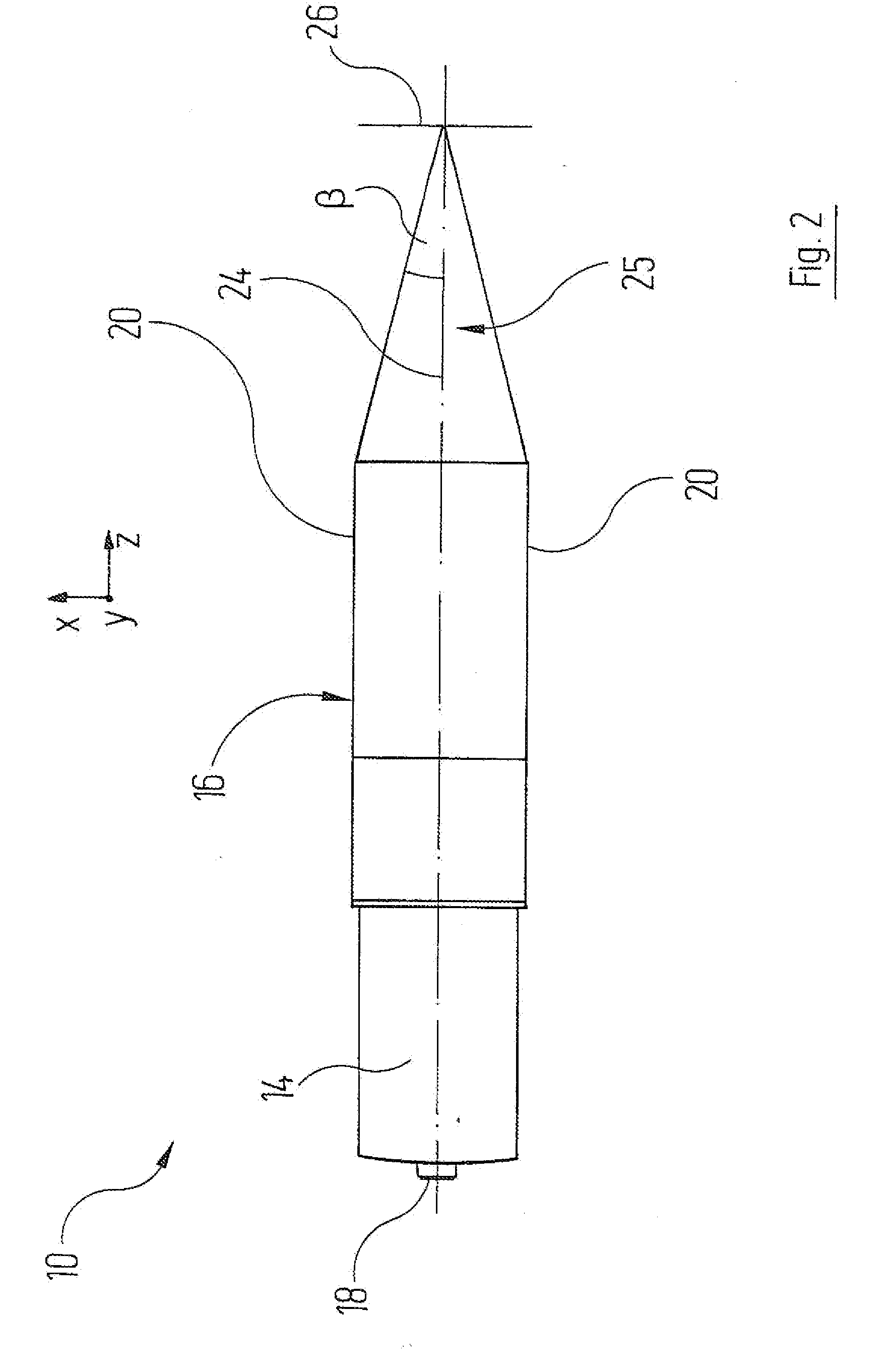
A spectroscopic instrument (38) includes a first optical component (48) for spatial spectral splitting of a polychromatic beam of light (46) impinging onto the first optical component (48), an objective (50), which routes various spectral regions (B1, B2, B3) of the split beam of light (46a, 46b, 46c) onto differing spatial regions (52a, 52b, 52c), and a sensor (54), situated downstream of the objective (50) in the beam path of the beam of light (46a, 46b, 46c), with a plurality of light-sensitive sensor elements (54a, 54b, 54c). The sensor elements (54a, 54b, 54c) are arranged in the beam path of the split beam of light 46a, 46b, 46c in such a manner that each sensor element (54a, 54b, 54c) registers the intensity of a spectral sector (A1, A2, A3) of the beam of light (46) and the medians (Mk1, Mk2, Mk3) of the spectral sectors (A1, A2, A3) are situated equidistant from one another in the k-space, where (k) denotes the wavenumber.
Owner:WAVELIGHT GMBH
Compact, hand-held raman spectrometer microsystem on a chip
Owner:MORPHO DETECTION INC
Laser plasma spectroscopy apparatus and method for in situ depth profiling
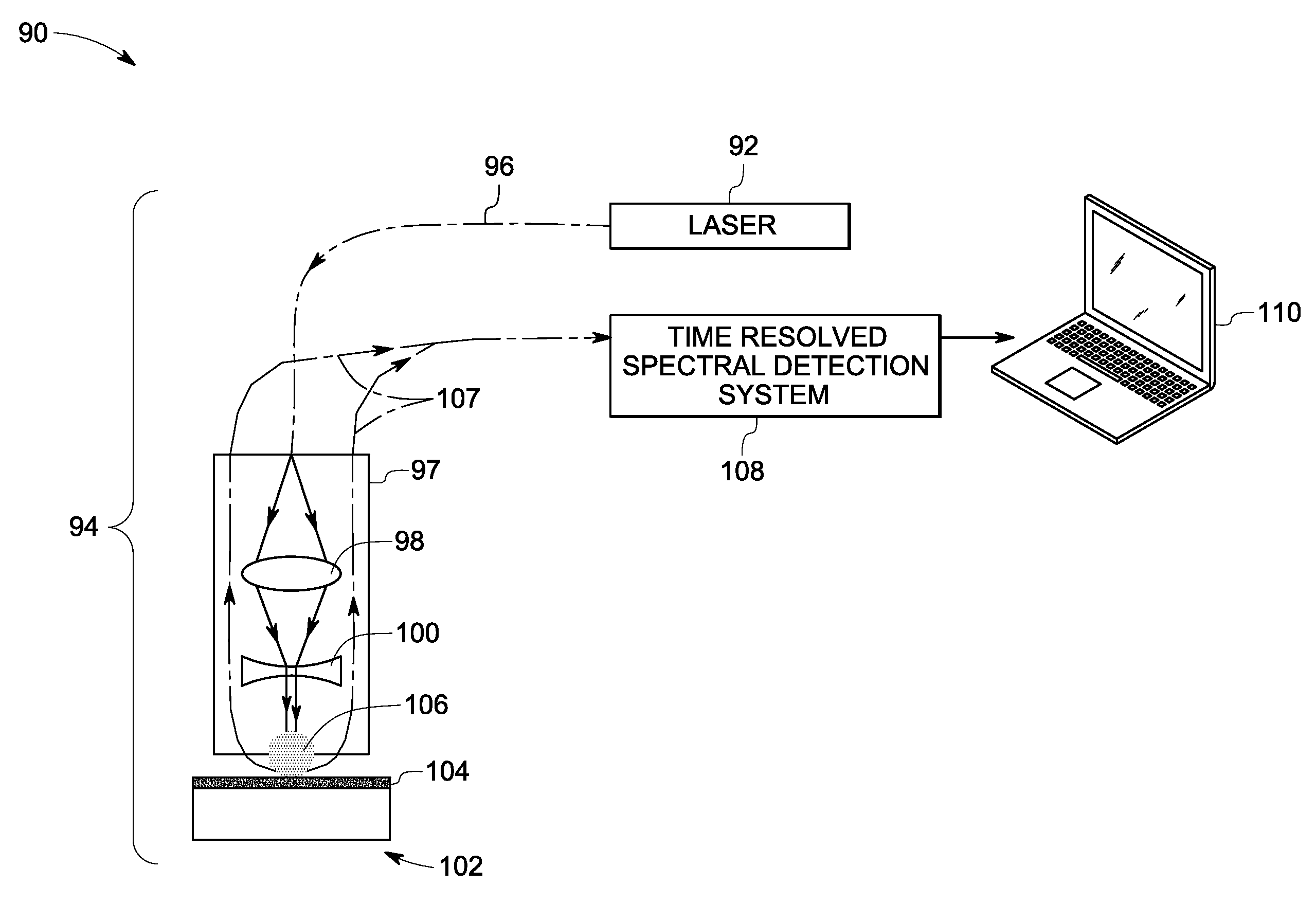
An in-situ laser plasma spectroscopy (LPS) system for automated near real-time elemental depth profiling of a target including: an optical source configured to generate an optical beam, wherein the optical beam is pulsed; an optical probe system configured to deliver the optical beam from the optical source to a surface of a target to generate an ablation plasma; a time resolved spectral detection system configured to generate time resolved spectral data from emission signals from the ablation plasma; and a data acquisition and processing system configured to acquire the time resolved spectral data to determine, in combination with predetermined calibration data, an absolute elemental concentration as a function of depth in near real-time.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
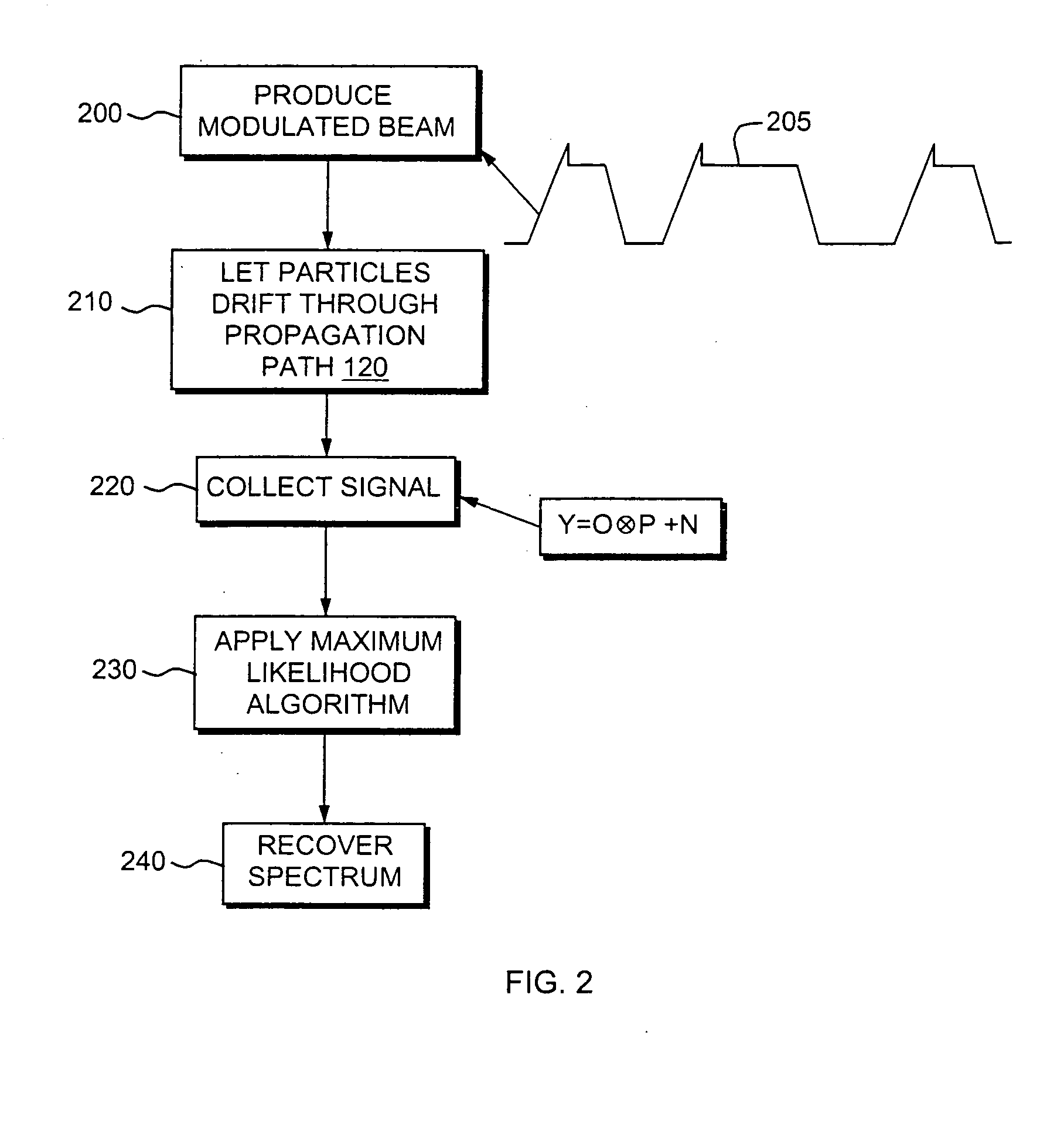
Spectroscopy instrument using broadband modulation and statistical estimation techniques to account for component artifacts
InactiveUS20050086026A1High resolutionReduce artifactsTime-of-flight spectrometersRadiation/particle handlingSpectroscopy instrumentationBroadband
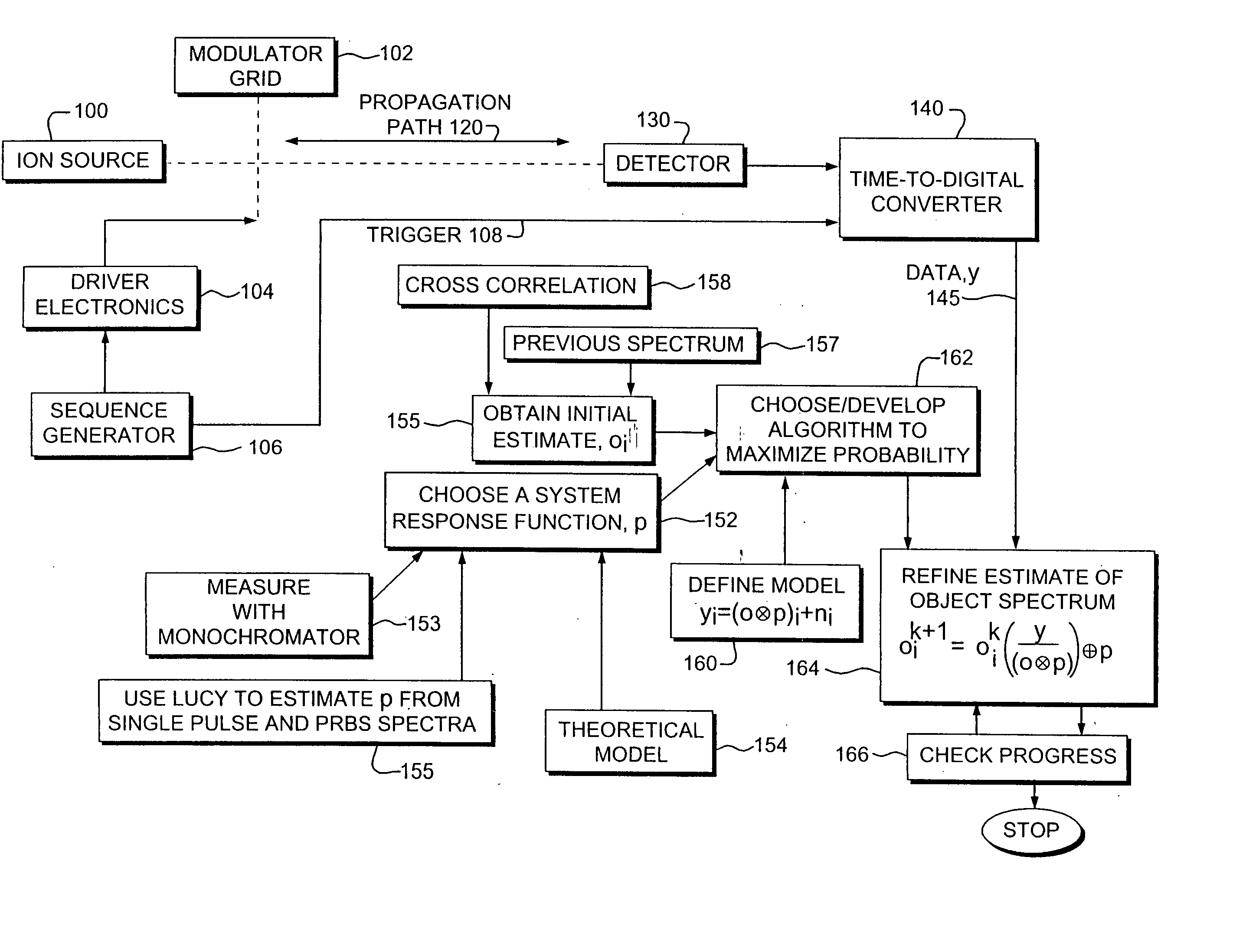
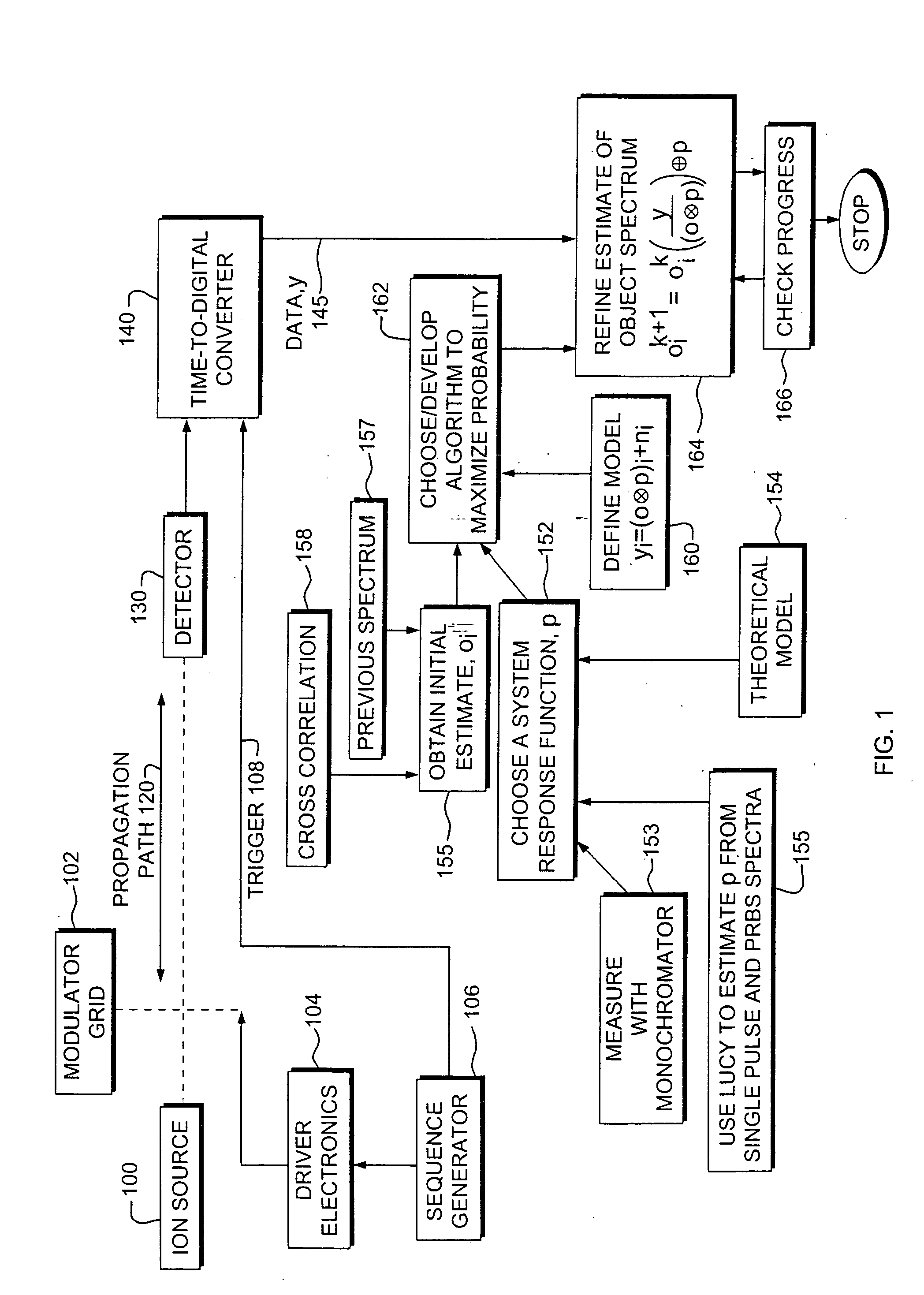
A spectroscopy instrument that uses spectra produced from random binary sequence modulated data. Statistical estimation techniques are used to achieve resolution enhancement, while properly accounting for the Poisson noise distribution and other artifacts introduced by a modulator or “chopper” or other system components. Indeed, a resolution similar to that of modern spectrometers can be achieved with a dramatic performance advantage over conventional, serial detection analyzers. Both static and dynamic behaviors are theoretically or measured experimentally accounted for in the model as determined. In one embodiment, the finite penetration of the field beyond the plane of the chopper leads to non-ideal chopper response, which is characterized in terms of an “energy corruption” effect and a lead or lag in the time at which the beam responds to the chopper potential.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MAINE +2
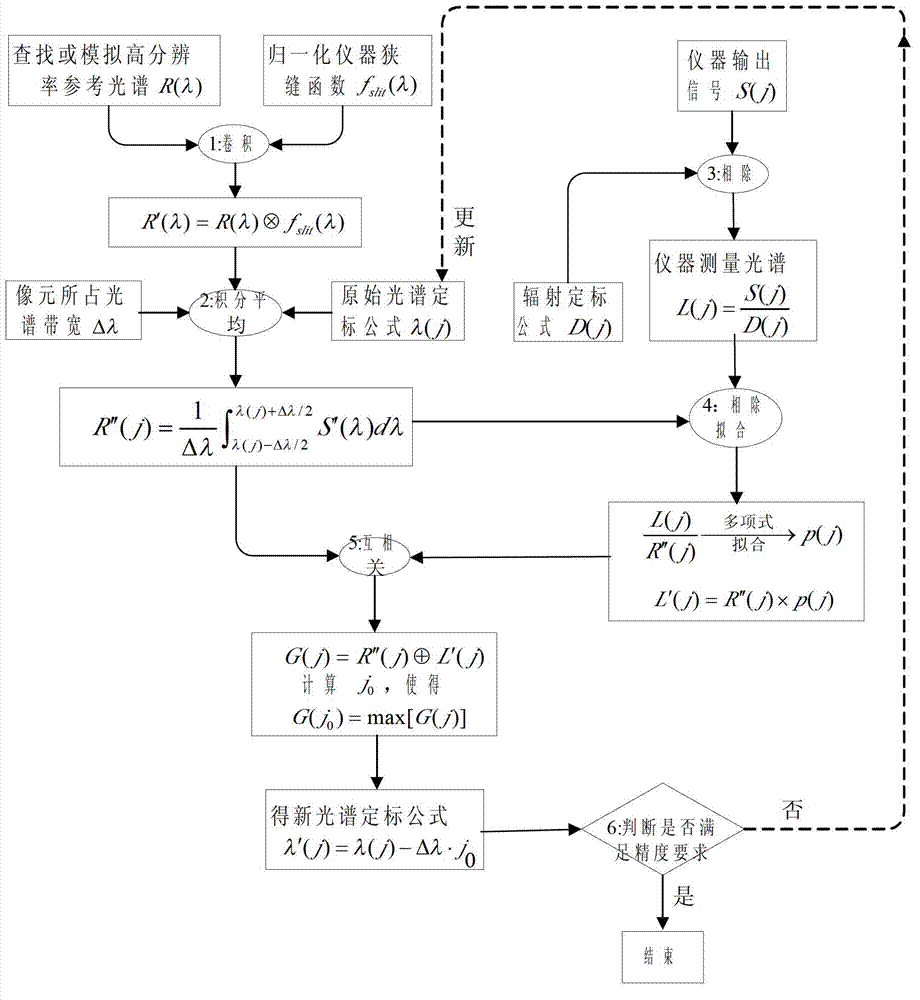
Method for calibrating ontrack high-precision optical spectrum of space remote sensing optical spectrum instrument
InactiveCN102788643AImprove calibration accuracyEliminate errorsSpectrum investigationSpectroscopy instrumentationInstrumentation
The invention relates to a method for calibrating ontrack high-precision optical spectrum of a space remote sensing optical spectrum instrument, which comprises the following steps: step I, constructing a dispersed reference spectrum R'(j); step II, carrying out amplitude approach on a measured optical spectrum L(j) of the instrument and the reference optical spectrum R'(j) to obtain the revised measured optical spectrum L'(j) of the instrument; and step III, comparing the reference optical spectrum R'(j) with the revised measured optical spectrum L'(j) to obtain offset of the instrument ontrack optical spectrum position. By virtue of the method for calibrating ontrack high-precision optical spectrum, no extra calibration device is needed to be increased; the reliability of the instrument is ensured; the continuous reference optical spectrum with high resolution is taken as the standard to avoid the disadvantages of the other ontrack optical spectrum calibrating methods that the spectral line quantity is small, and the distribution is not even; the optical spectrum calibrating precision is effectively improved, thus the reliability and the precision of the ontrack detecting data of the space remote sensing optical spectrum instrument can be ensured.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
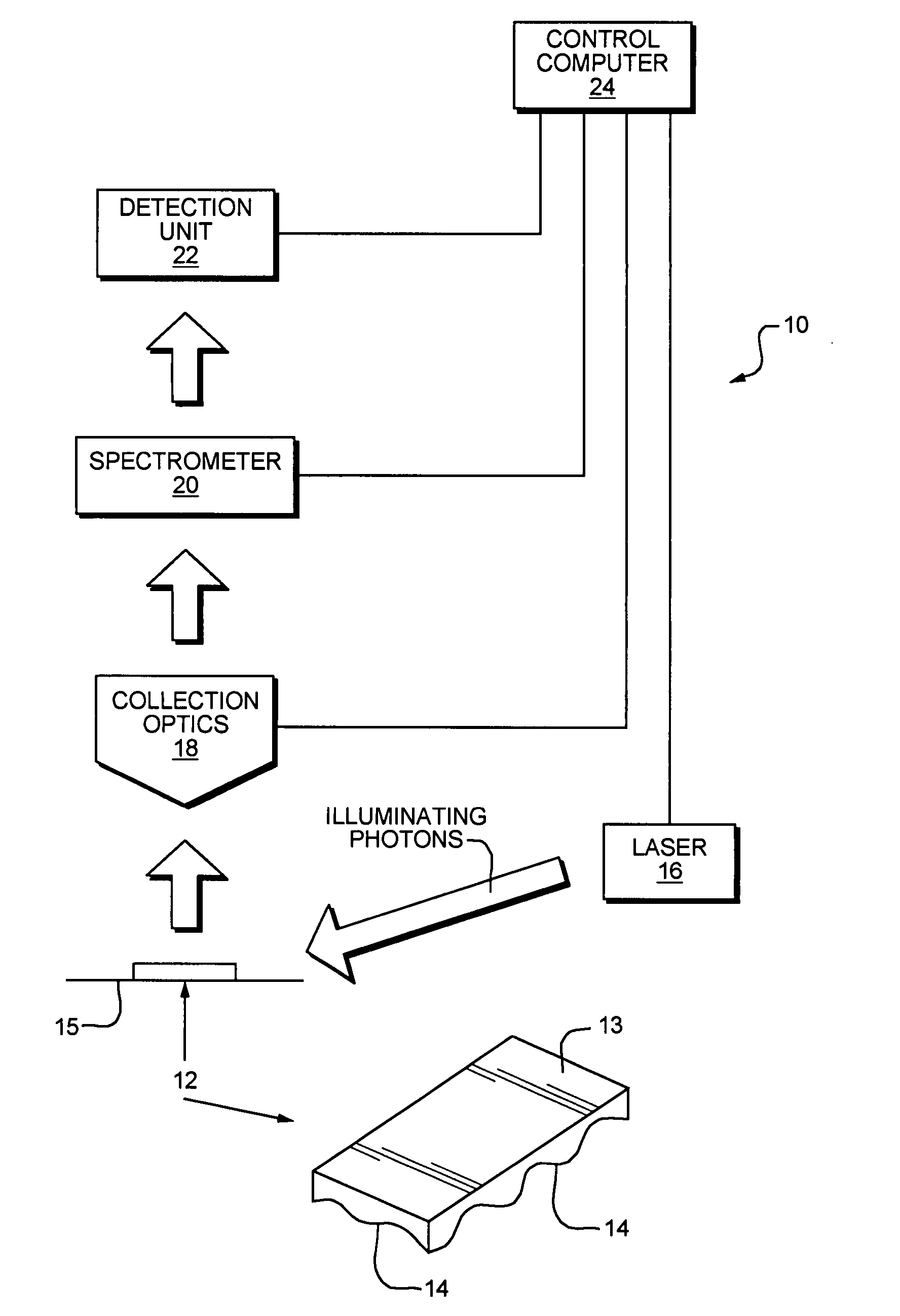
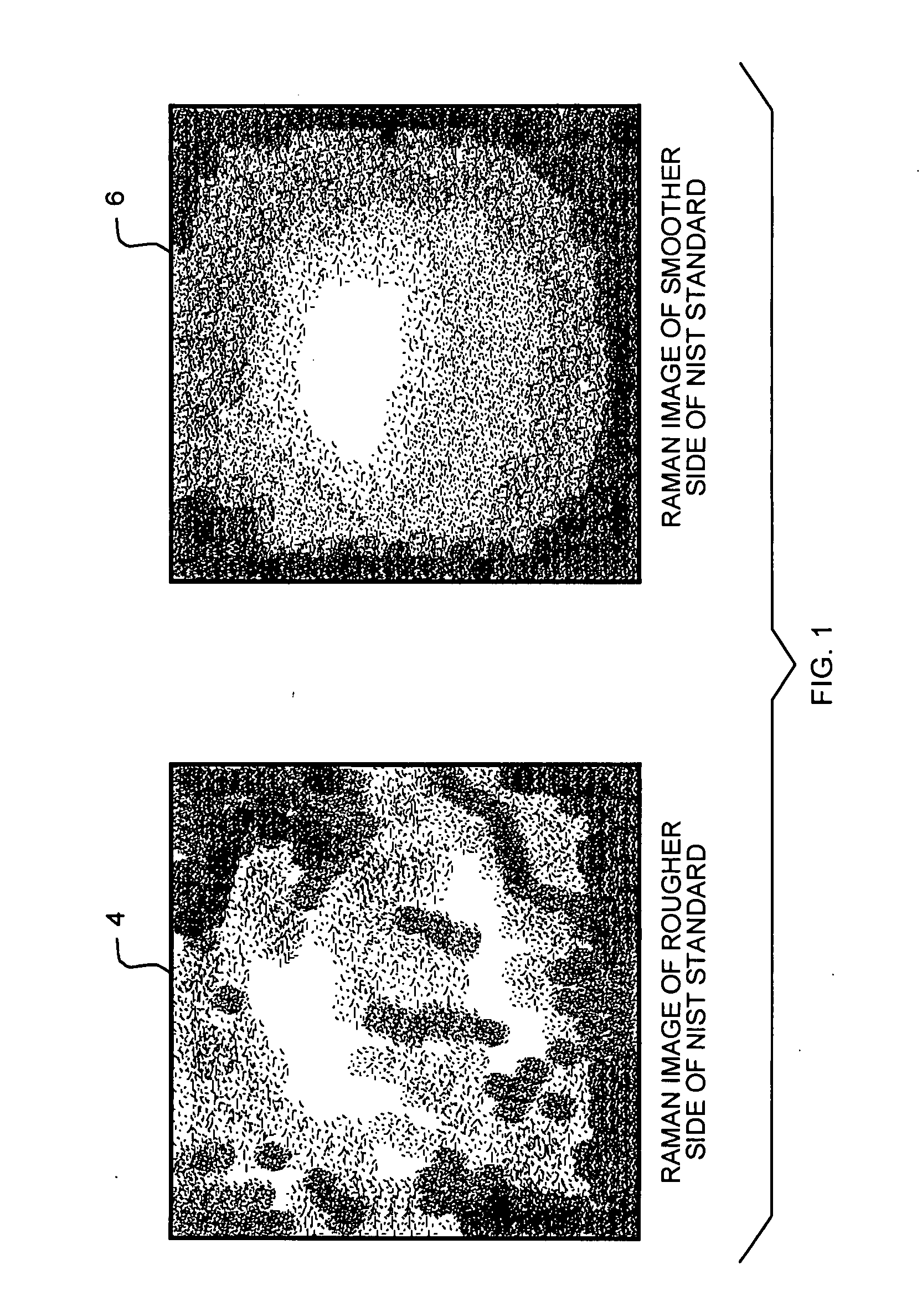
Optical Spectroscopy Instrument Response Correction
A system and method for correction of instrument response of an optical spectroscopy instrument using a Raman standard sample supplied by NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology). The smoother side of the NIST sample is placed facing a light collection optics in the spectroscopy instrument, whereas the non-smooth or rough side remains away from the light collection optics, but in contact with a platform or sample placement surface in the spectroscopy instrument. An instrument response function is determined with the NIST sample so placed. Thereafter, spectra or spectral images of target samples obtained using the spectroscopy instrument are divided by the instrument response function to correct for imperfections in the response of the optical spectroscopy instrument. The target sample spectra may be non-Raman spectra. The optical spectroscopy instrument may be a gratings-based or a tunable filter based chemical imaging system.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE CORP
Spectrum measurement method and system for improving luminous flux
ActiveCN104266755AIncrease luminous fluxHigh resolutionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationGratingLight energy
The invention provides a spectrum measurement method and system for improving luminous flux. According to the method, the width of an incidence slit in a traditional chromatic dispersion spectrograph or a traditional spectrum measurement system is increased, a set of imaging lenses for measuring zero-level spectrums is additionally arranged behind an optical grating in the traditional chromatic dispersion spectrograph or the traditional spectrum measurement system, the mathematic relation between the zero-level spectrums and one-level spectrums measured in the original spectrum measurement system is utilized, and new spectrums are obtained through calculation. The new spectrums have more light energy compared with the spectrums obtained by the traditional spectrum measurement system adopting a small slit; meanwhile, the high resolution possessed by the spectrum measurement system adopting the small slit can also be kept. The method and the system can effectively improve the luminous flux of an incidence optical spectrum instrument, and the higher spectrum resolution can be kept through mathematical calculation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
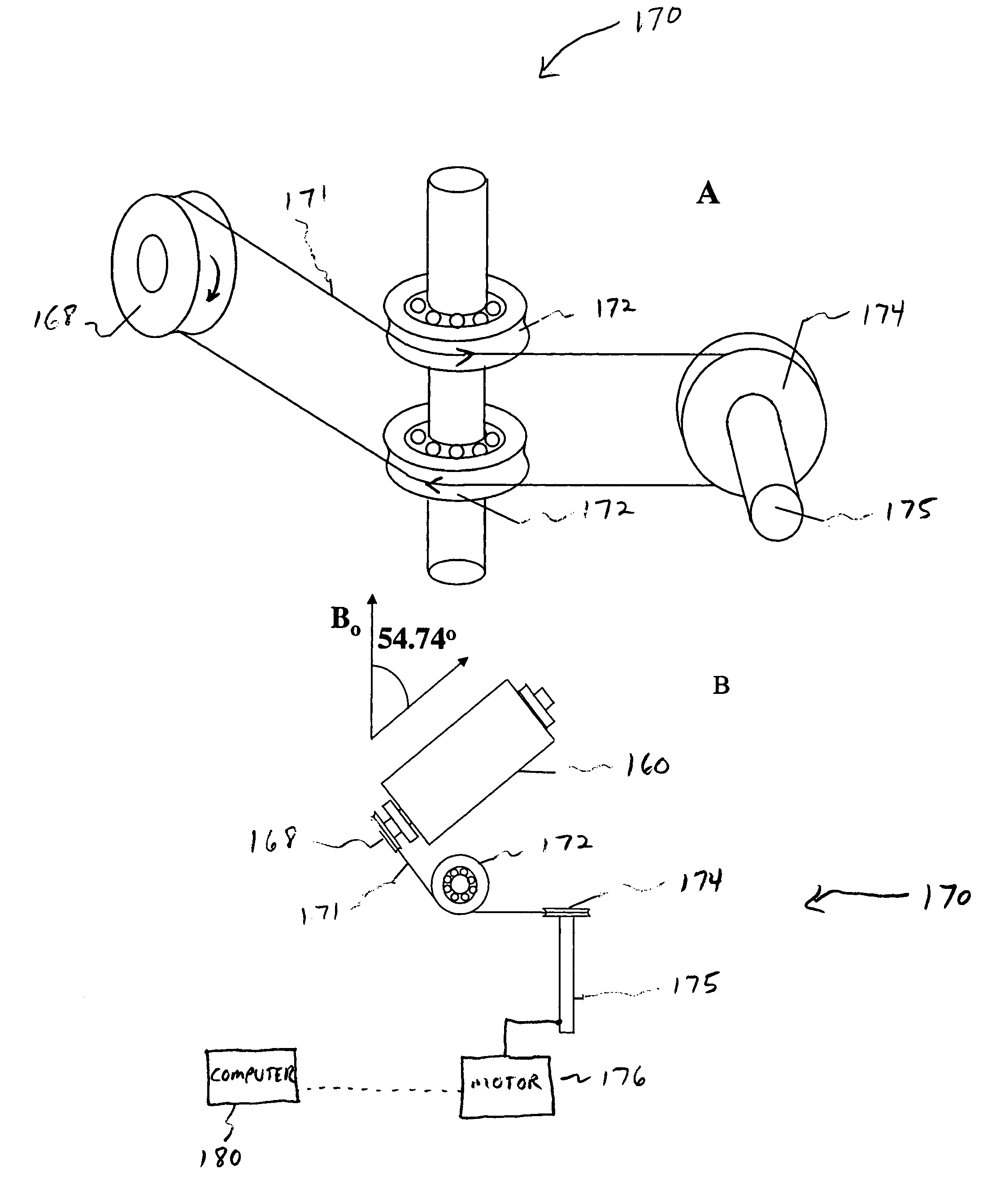
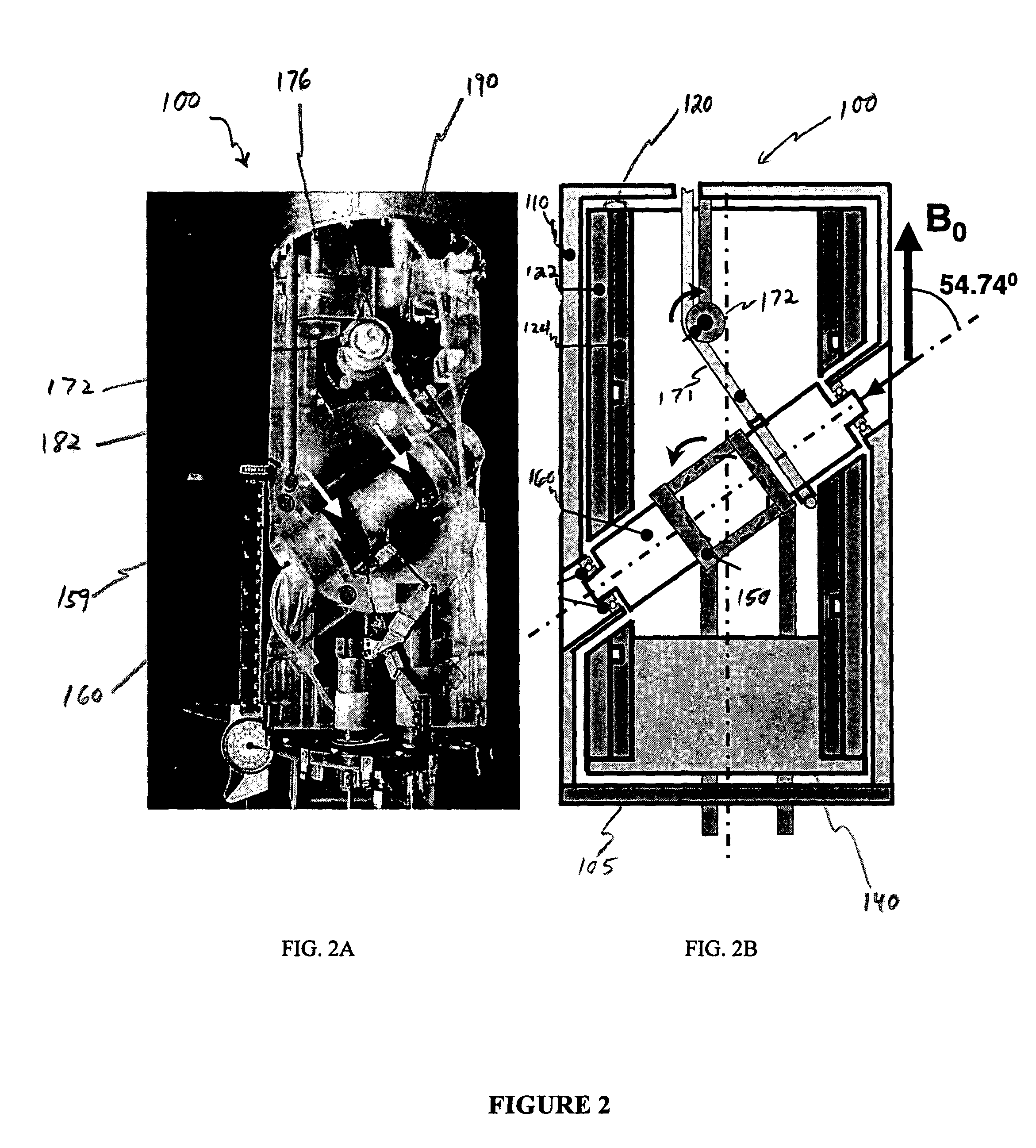
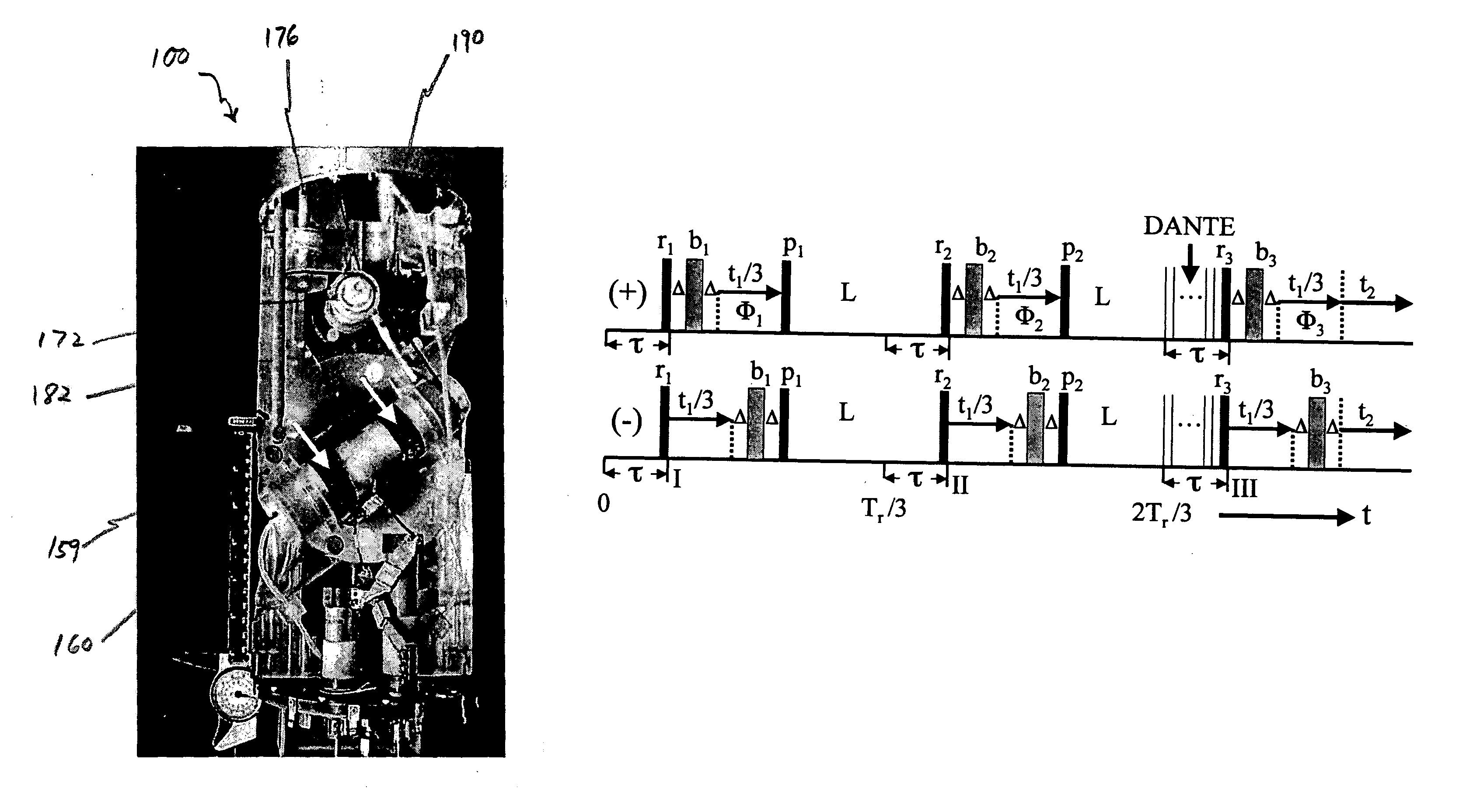
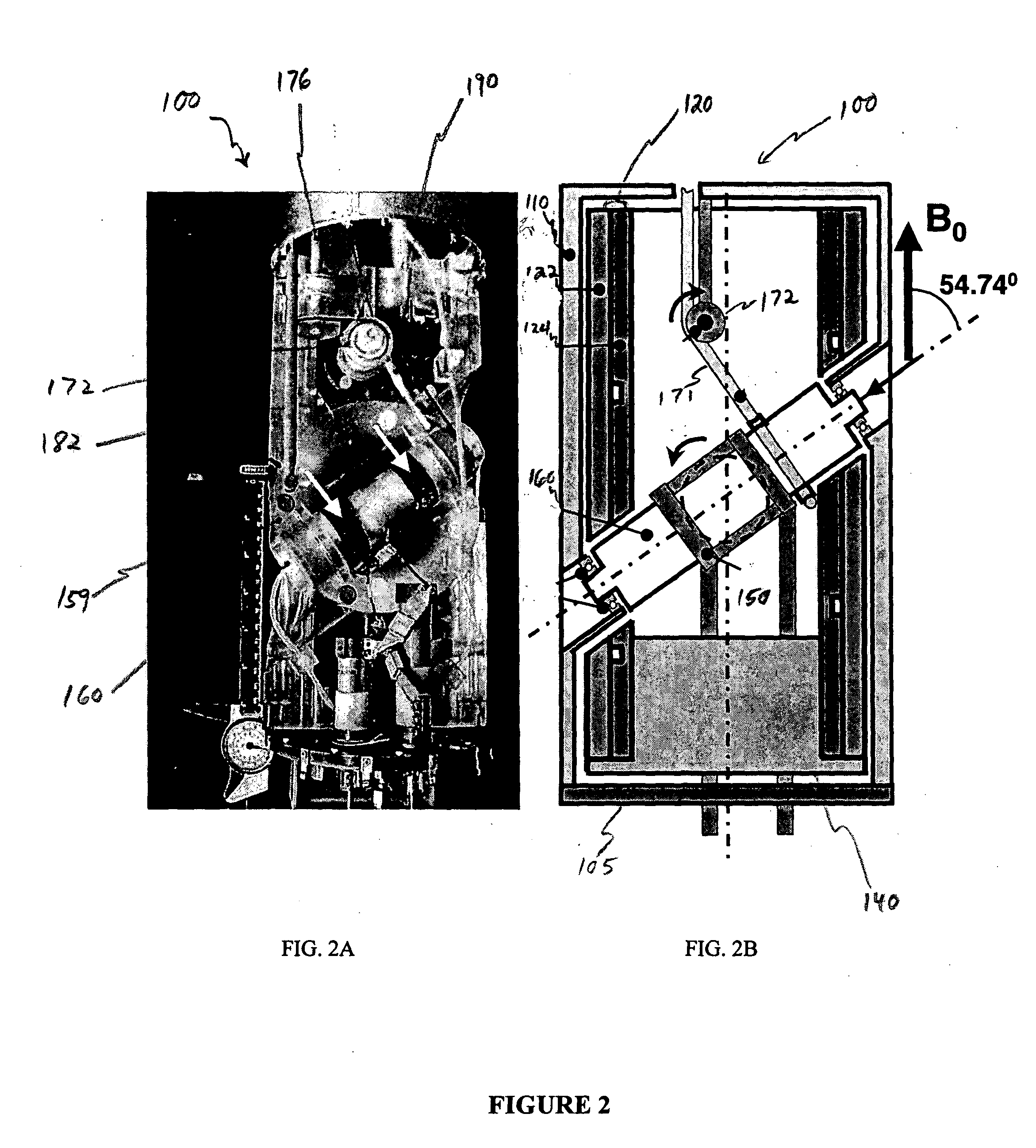
Advanced slow-magic angle spinning probe for magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy
InactiveUS6989674B2Additive manufacturing apparatusMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyMagic angle spinningMetabolite
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
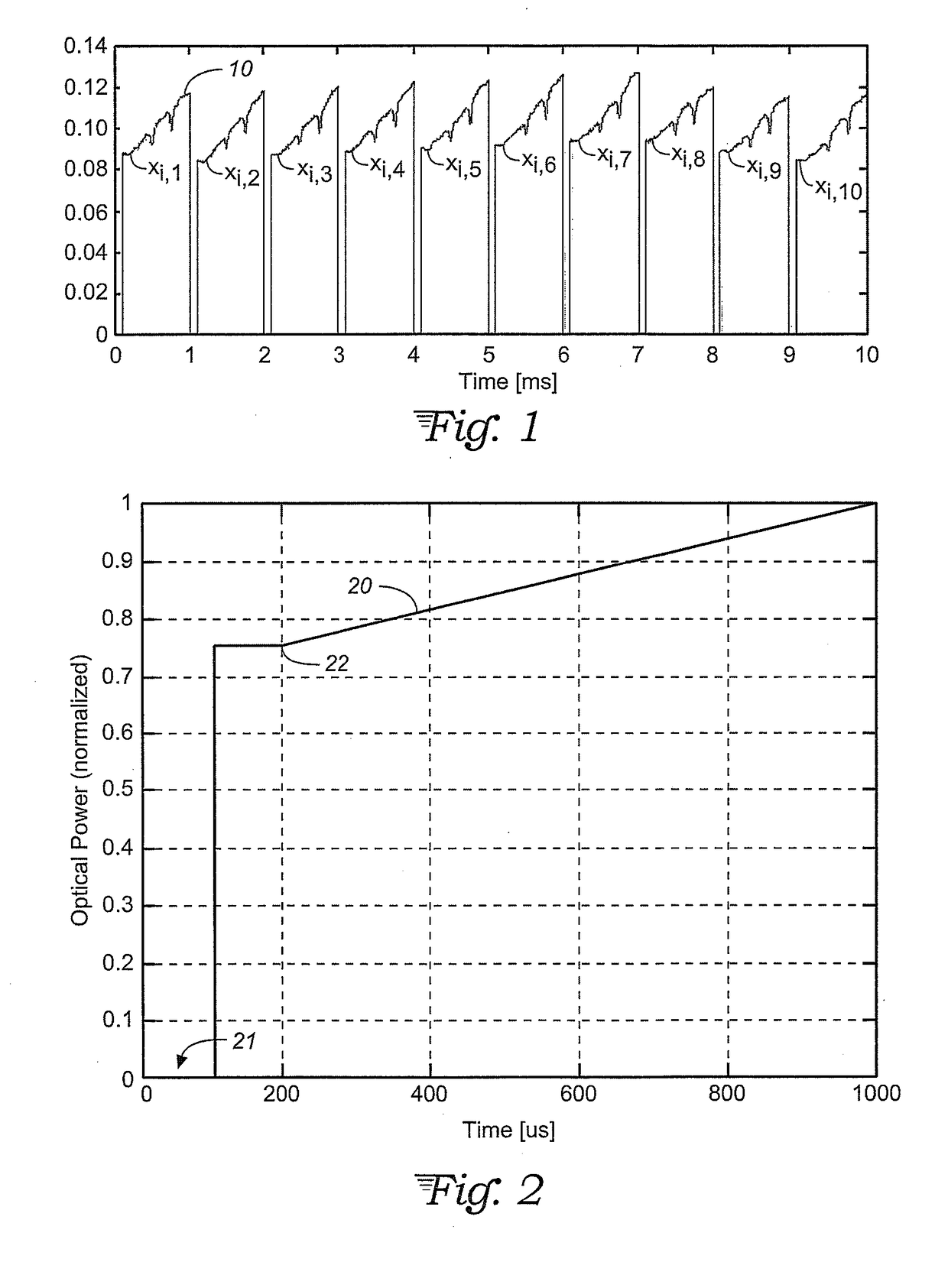
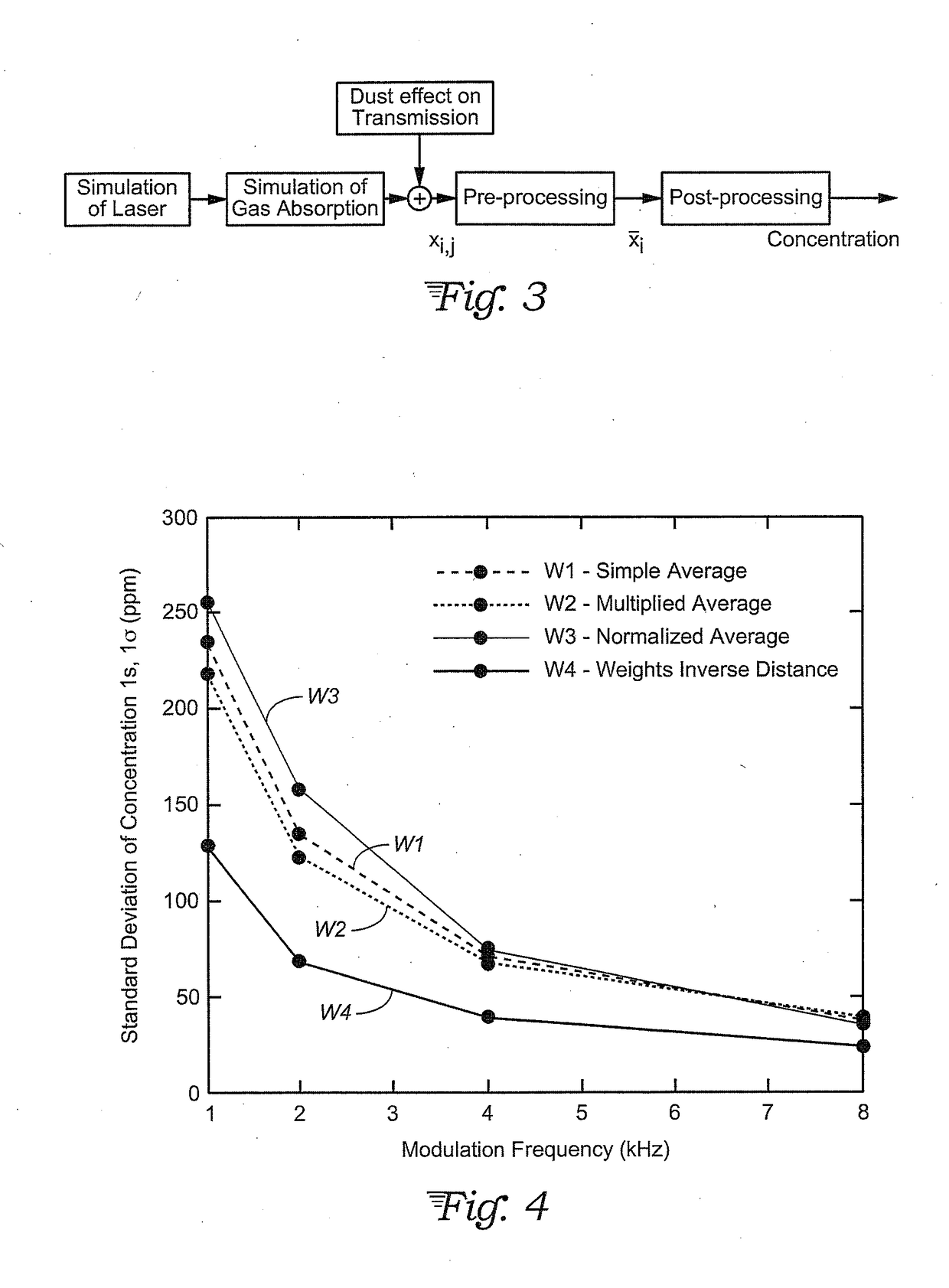
Optimal weighted averaging pre-processing schemes for laser absorption spectroscopy
ActiveUS20170212042A1Improve sensor performanceReduce measurement noiseAbsorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyColor/spectral properties measurementsPattern recognitionWeight coefficient
A method of processing raw measurement data from a tunable diode laser absorption spectroscopy (TDLAS) tool or other spectroscopic instrument is provided that determines what types of noise (electronic or process flow) are present in the measurement. Based on that determination, the noise is reduced by performing a weighted averaging using weights selected according to the dominant type of noise present, or a general case is applied to determine weights where neither noise type is dominant. The method also involves performing continuous spectroscopy measurements with the tool, with the data and weighted averaging being constantly updated. Weighting coefficients may also be adjusted based on similarity or difference between time-adjacent traces.
Owner:ABB INC
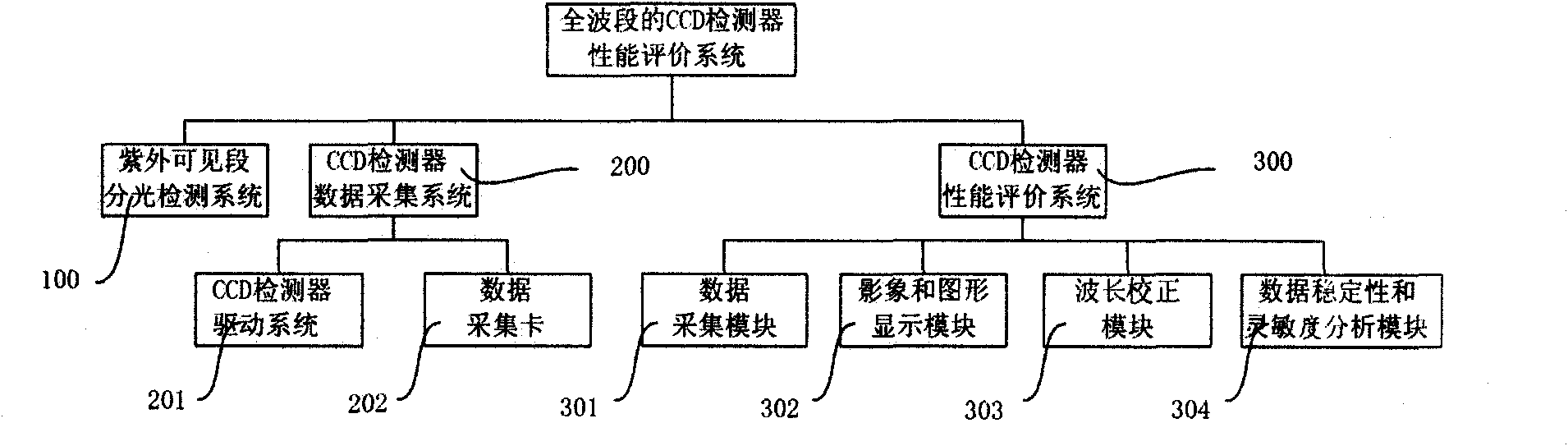
Novel full-band CCD detector performance evaluating system and method
InactiveCN102012310AMiniaturizationLightweightRadiation pyrometryTesting optical propertiesLength waveFull band
The invention discloses a novel full-band CCD detector performance evaluating system and method. The system comprises an ultraviolet visible section spectroscopic detecting system, a CCD detector data collection system, and a CCD detector performance evaluating system, wherein the ultraviolet visible section spectroscopic detecting system is connected with the CCD detector performance evaluating system through the CCD detector data collection system. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) correcting wavelengths of the system; (2) calibrating energy of the system; (3) detecting stability and sensitivity of the full-wavelength data of the CCD detector; and (4) evaluating the full-wavelength performances of the CCD detector. The invention provides the cheap, portable and fast full-band CCD detector performance evaluating system and method, thereby ensuring that the evaluation of the performances of the CCD detector is simple, fast and comprehensive and the good application of the CCD detector to the optical spectrum instrument.
Owner:SHANGHAI SPECTRUM INSTR
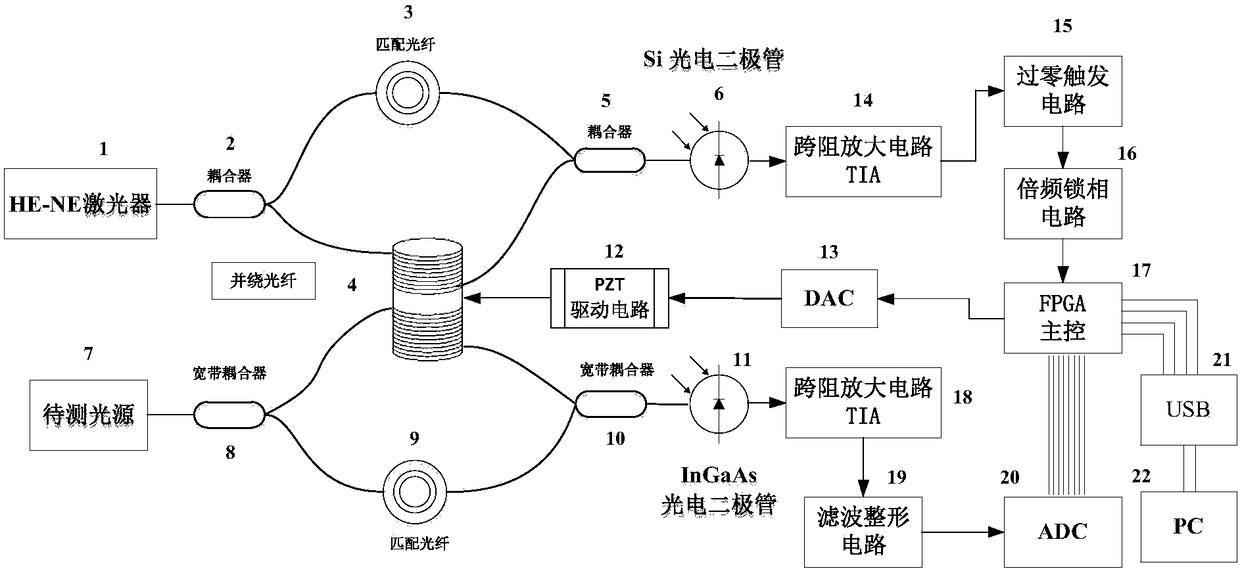
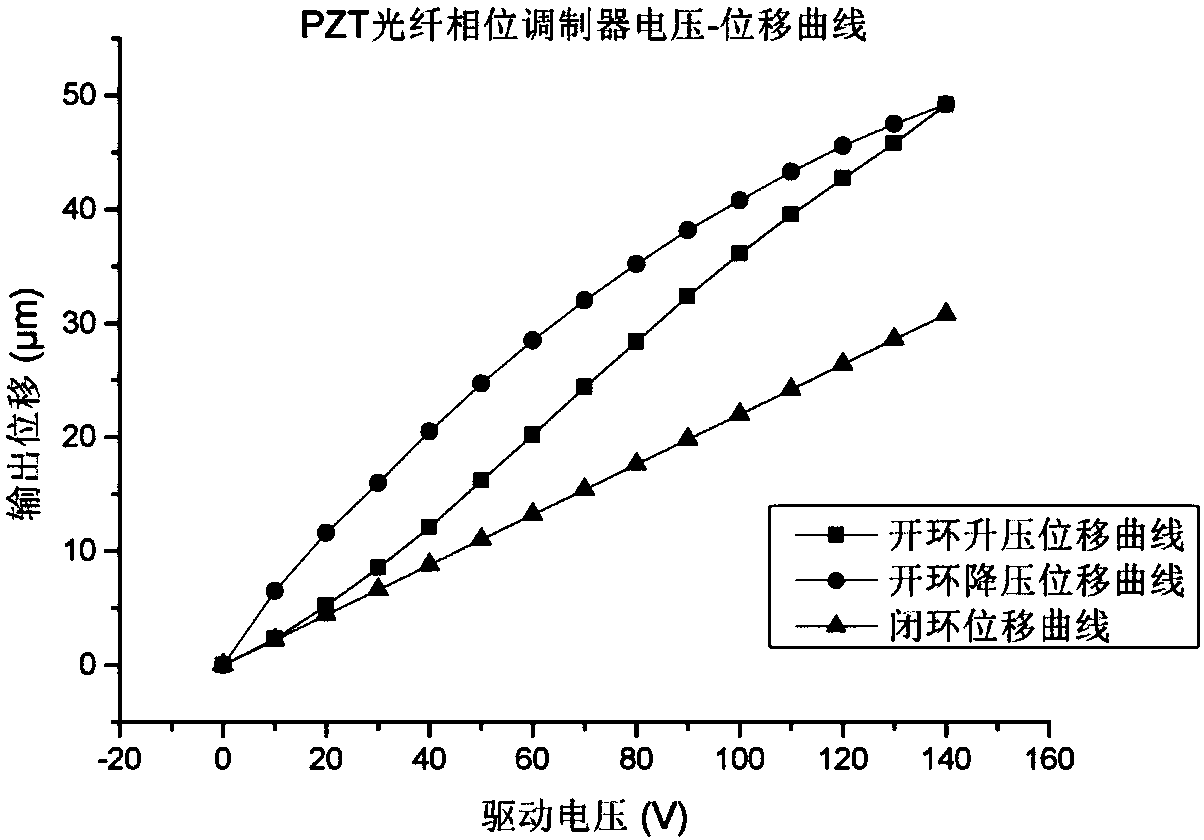
Full-fiber Fourier transform spectrometer based on PZT phase modulation real-time compensation
ActiveCN108593110ATo overcome the disadvantage of sampling errorHigh wavelength accuracyRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFiberPhysics
The invention belongs to the field of spectrum instruments, and provides a novel Full-fiber Fourier transform spectrometer, which improves the precision and the reliability of the FFTS instrument, eliminates noise and artifacts, and has the characteristics of miniaturization, portability and the like. The technical solution adopted by the invention is a full-fiber Fourier transform spectrometer based on the PZT phase modulation real-time compensation, and the structure is as follows : the sensing arms of the two optical fiber interferometers are wound on the same optical fiber phase modulatorPZT, so that the two optical fiber interferometers are fully synchronized and consistent; the test light enters one input end of the broadband coupler WIC1 through a coupling lens, and is divided intotwo bundles of 50:50 through the coupler WIC1, one bundle of fibers wound by the piezoelectric ceramic phase modulator in parallel, and the other bundle passing through the arm length matching fiber., respectively, enters the input end of the wideband coupler WIC2, and forms interference fringes at its output end after passing through the wideband coupler WIC2. The full-fiber Fourier transform spectrometer based on PZT phase modulation real-time compensation is mainly applied to the field of spectrum detection.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Device and method for the contactless measurement of at least one curved surface
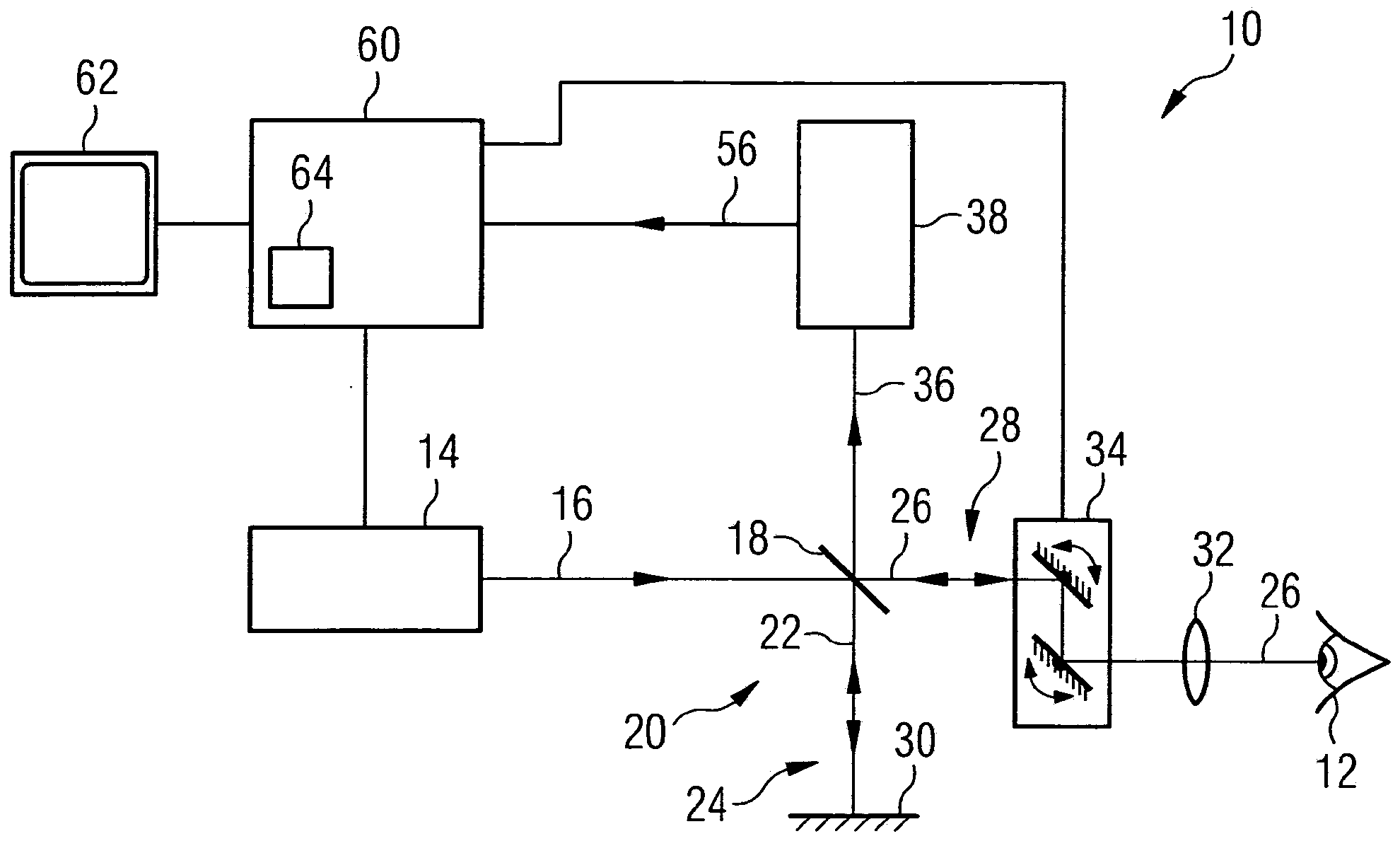
InactiveUS20070242279A1Maintain good propertiesIncreased sensitivityUsing optical meansEngineeringWavelength
A device and a method for the contactless measurement of at least one curved surface. The device comprises at least one light source for generating light with a continuous spectrum, and a light exit face assigned to the light source. It furthermore has at least one measurement head having an optical imaging system with chromatic aberration for imaging the light exit face into wavelength-dependent focal planes, and an optical spectral instrument by which it is possible to record the spectral intensity distribution of light which is directed through the optical system onto the surface to be measured and is reflected therefrom. The device is furthermore equipped with an evaluation unit by which a distance between the optical system and the surface can be assigned to each wavelength at which the intensity distribution recorded by the optical spectral instrument has a local maximum. The surface to be measured is plane in one space direction. The optical axis of the optical system is perpendicular to the surface in this space direction. Furthermore, the width of the optical system is reduced perpendicularly to its optical axis in this space direction.
Owner:PRECITEC OPTRONIK GMBH
Integrated micro cavity-based spectral detection chip and reconstruction method
InactiveCN110031098ACapable of spectral resolutionFast preparationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationBeam splittingImage resolution
The invention discloses an integrated micro cavity-based spectral detection chip and a reconstruction method. According to the spectral detection chip, a multichannel integrated beam splitting structure is made on a common array detector chip through a nano imprinting technology and a coating technology, so that the responses, to incident light, of different pixels on the original detector chip are different; and a spectral reconstruction method is utilized to restore a sample spectrum. The spectral detection chip integrates the beam splitting and detection, so that the detector has spectral resolution ability, and a chip-level spectral instrument is realized; and the spectral detection chip has the advantages of being small in volume, low in cost, high in resolution and convenient to make, and has an important application value in the field of spectral analysis.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Advanced slow-magic angle spinning probe for magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy
InactiveUS20050035766A1Additive manufacturing apparatusMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyMagic angle spinningMetabolite
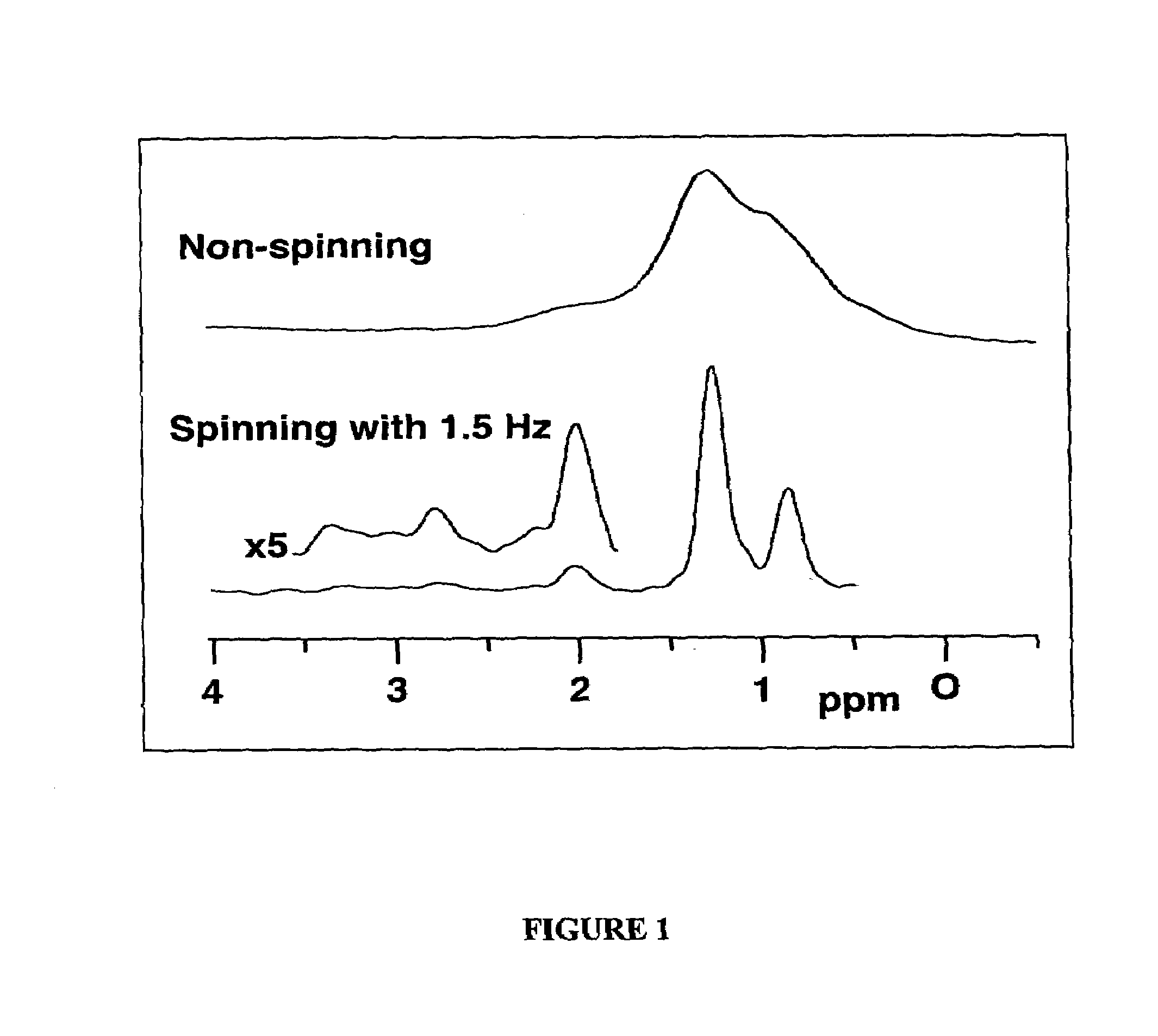
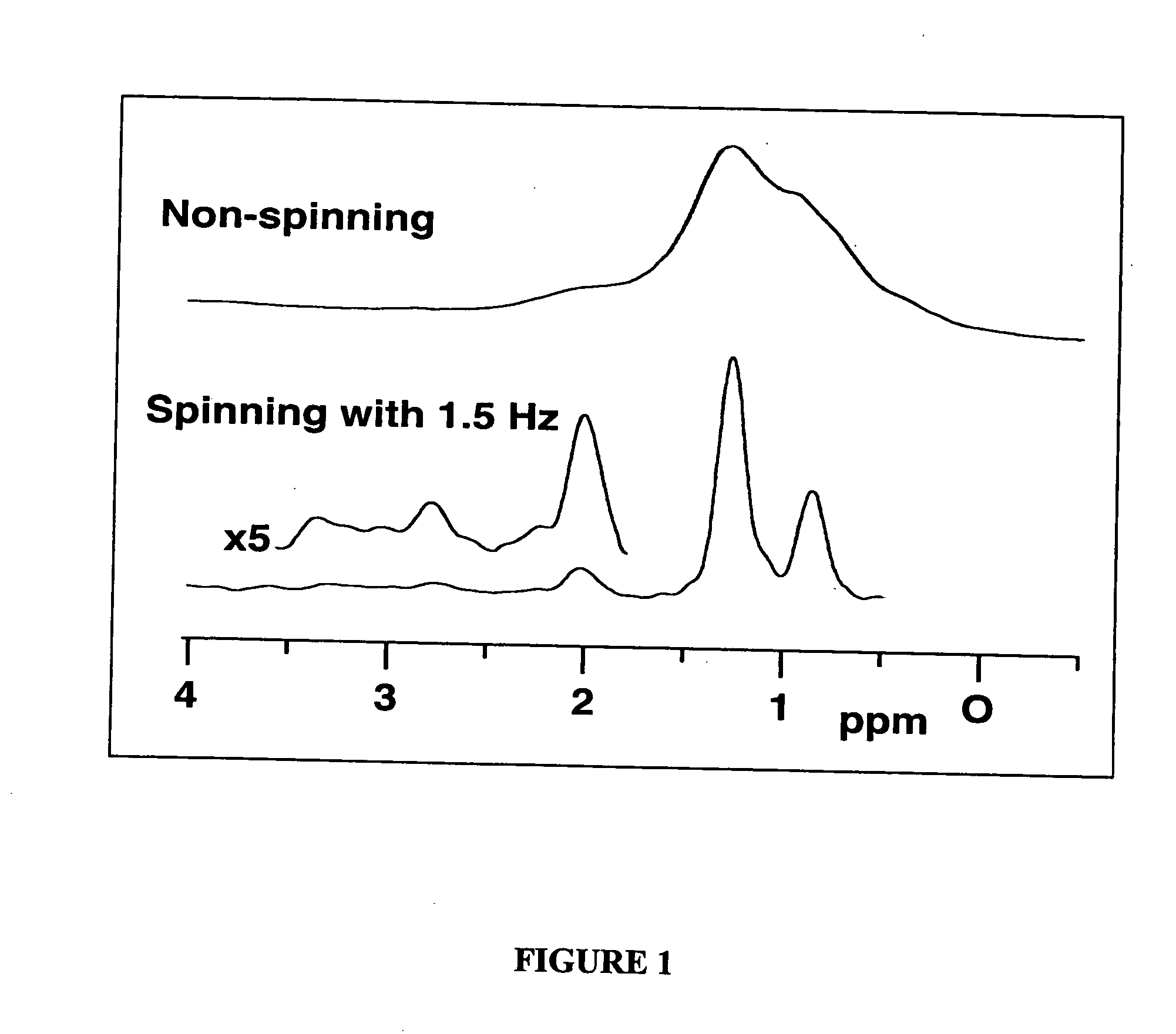
The present invention relates to a probe and processes useful for magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy instruments. More particularly, the invention relates to a MR probe and processes for obtaining resolution enhancements of fluid objects, including live specimens, using an ultra-slow (magic angle) spinning (MAS) of the specimen combined with a modified phase-corrected magic angle turning (PHORMAT) pulse sequence. Proton NMR spectra were measured of the torso and the top part of the belly of a female BALBc mouse in a 2 T field, while spinning the animal at a speed of 1.5 Hz. Results show that even in this relatively low field with PHORMAT, an isotropic spectrum is obtained with line widths that are a factor 4.6 smaller than those obtained in a stationary mouse. Resolution of 1H NMR metabolite spectra are thus significantly enhanced. Results indicate that PHORMAT has the potential to significantly increase the utility of 1H NMR spectroscopy for in vivo biochemical, biomedical and / or medical applications involving large-sized biological objects such as mice, rats and even humans within a hospital setting. For small-sized objects, including biological objects, such as excised tissues, organs, live bacterial cells, and biofilms, use of PASS at a spinning rate of 30 Hz and above is preferred.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Light damage measurement instrument based on relationship between pupil size and ambient brightness
InactiveCN102175315AThe measured data conform toThe measured data is more in line with the actual situationSpectrum investigationPhotometryControl signalMeasurement precision
The invention relates to a light damage measurement instrument based on the relationship between pupil size and ambient brightness, which consists of a light source, a field diaphragm, a control table, an illuminance probe, a controllable diaphragm, an integrating sphere, a spectrometer and a computer, wherein the light source, the field diaphragm and the integrating sphere are positioned on the control table respectively, the controllable diaphragm is connected with the integrating sphere which is connected with the spectrometer, the spectrometer is connected with the computer which is connected with the illuminance probe and the controllable diaphragm, the illuminance probe sends illuminance to the computer in the form of electric signal, the computer converts the illuminance value to a brightness value by means of computation, determines the size of pupil in human eyes under relevent situations according to the brightness level of the brightness value, and sends a control signal to change the size of the controllable diaphragm, afterwards, brightness is measured and finally, relevant spectrum data and brightness are obtained in the computer. The instrument effectively simulates the quantity of light entering pupil under different brightness levels through the controllable diaphragm; the data derived from measurement accords better with actual situation. Measurement precision can be effectually improved by the integrating sphere instead of using a portable optical spectrum instrument directly. Direct brightness measurement is replaced by the use of the illuminance probe for measurement.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Technique for preparing miniaturized radiometer of ultraviolet spectrum for experimentation of high-altitude balloon
InactiveCN1687721ASolve high and low temperatureSolve high vacuumRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationGratingRadiometer
The invention belongs to the spectrum instrument technology field and is the facture of mini ultraviolet spectrum radiator of upper air balloon experiment: connect the photic components of the photic system to the framework and fix them with the shell; the wavelength revolving lead-screw, the nut and the sway bar can scan in 180nm-400nm range; the linear expansion coefficients of the raster framework, the nut, the sway bar, the lead-screw and the shell are matched; the silica gel seals the space between the detector and the detector shell and in the high-pressure source. The invention solves the problem of the traditional device, can bear the low temperature condition and ensure the wavelength precision.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Snapshot imaging spectrometer based on miniature imaging lens array and stepped phase reflector
ActiveCN108180992AFast detectionRealize multi-channel snapshot interferometric imagingRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationBeam splitterParallel imaging
The invention discloses a snapshot imaging spectrometer based on a miniature imaging lens array and a stepped phase reflector, relates to the technical field of infrared imaging spectrum detectors, and solves problems of the real-time obtaining of a three-dimensional data cube and the miniaturization of an imaging spectrometer. The imaging spectrometer comprises a collimating mirror, the miniatureimaging lens array, a beam splitter, a lateral stepped phase reflector, a longitudinal stepped phase reflector, a relay imaging mirror, and an area array detector. The miniature imaging lens array isused for the multiple imaging of a target scene, and the imaging spectrometer which is used for the distributed phase modulation of multiple image fields through the stepped phase reflectors is employed. Through the light field coupling of a parallel imaging channel formed by the miniature imaging lens array and a parallel interference channel formed by the stepped phase reflectors, the imaging spectrometer achieves the multi-channel snapshot-type interference imaging of the target scene, does not need a complex movement mechanism, is small in size, is stationary, is high in stability, is high in integration degree, and is high in detection speed.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
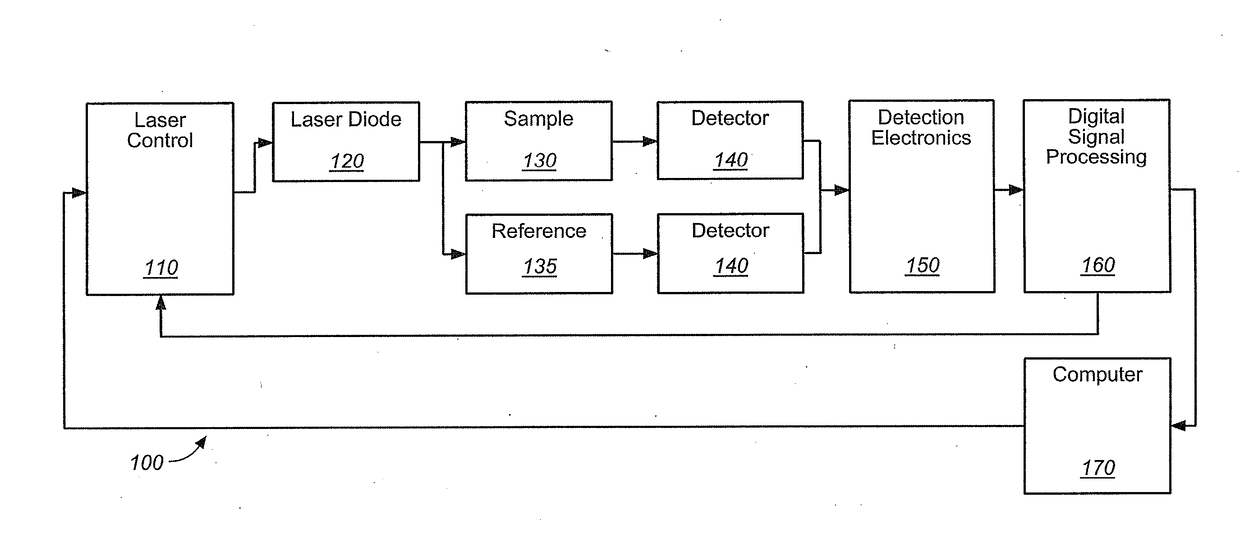
Method and system for optical spectroscopy
ActiveUS8860939B2Reduce disadvantagesOptical measurementsRadiation pyrometryQuantum-optical spectroscopyComputer module
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
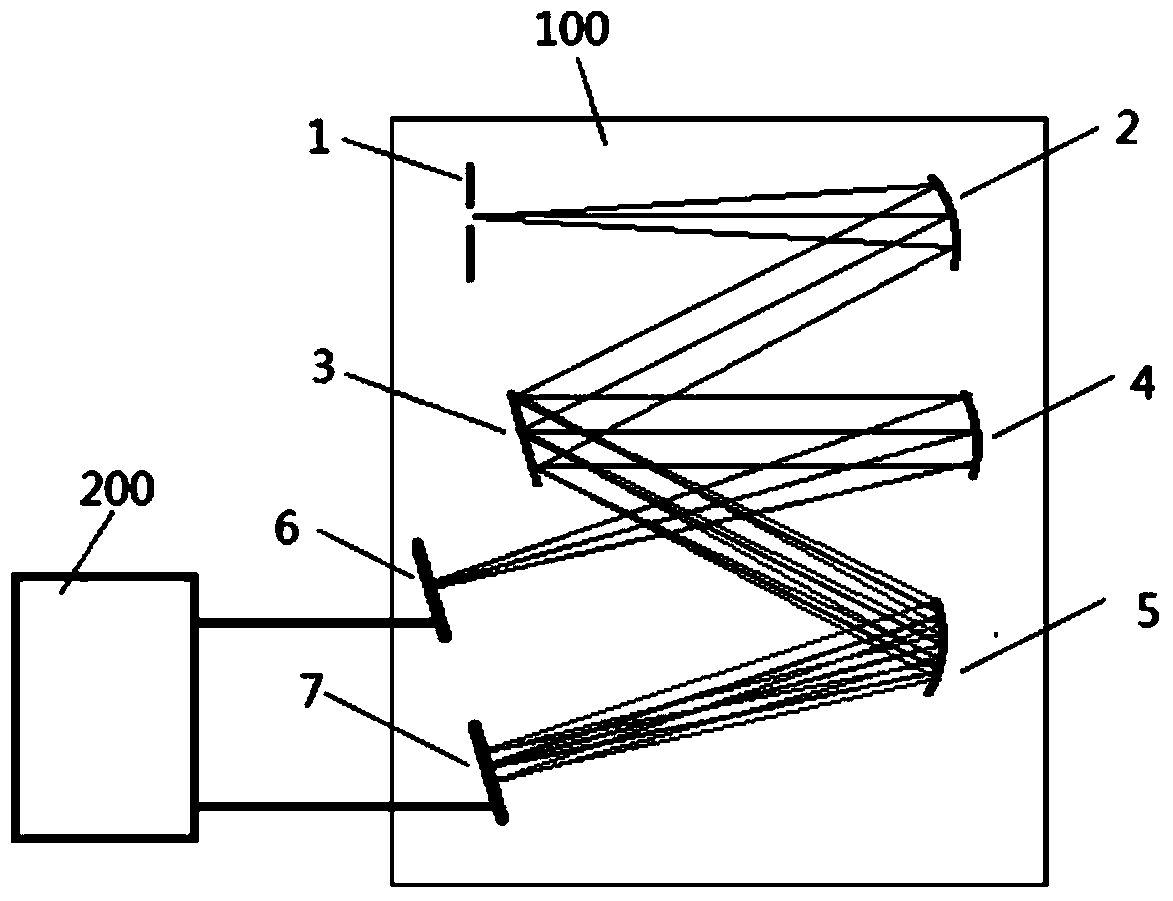
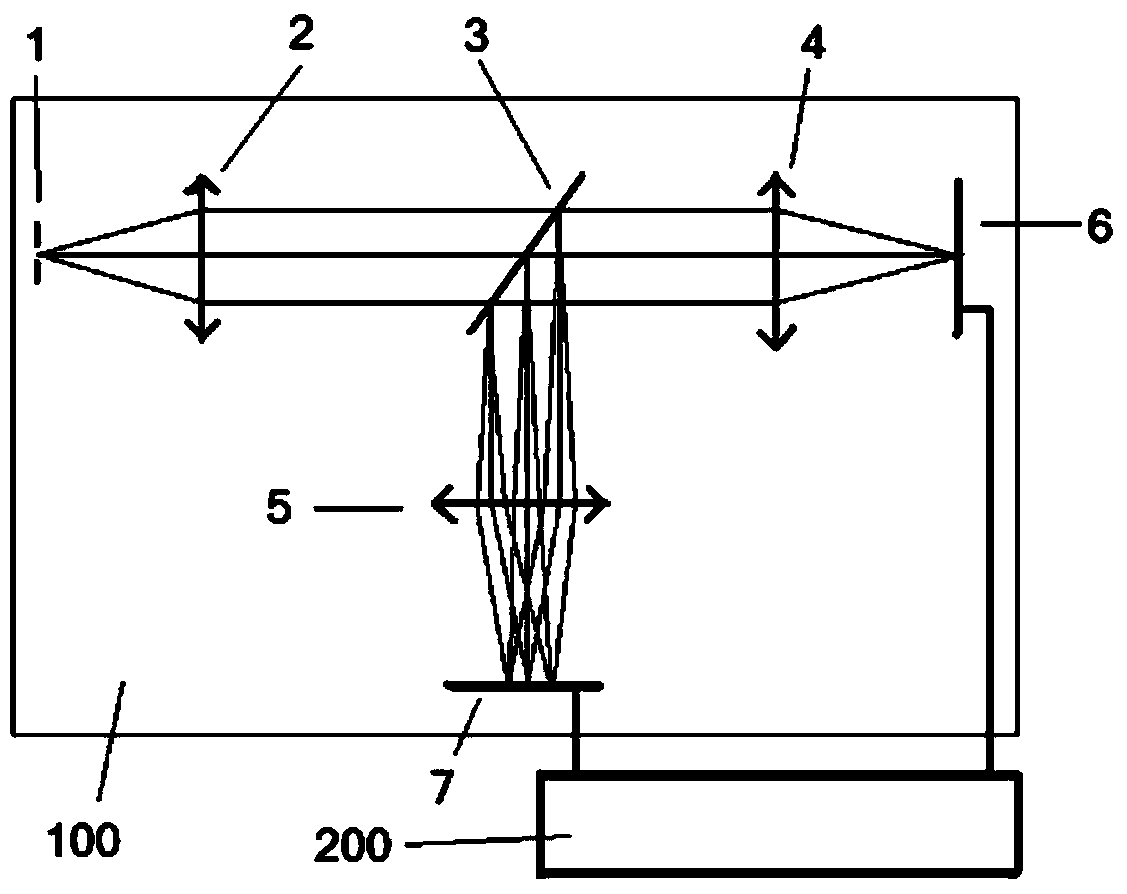
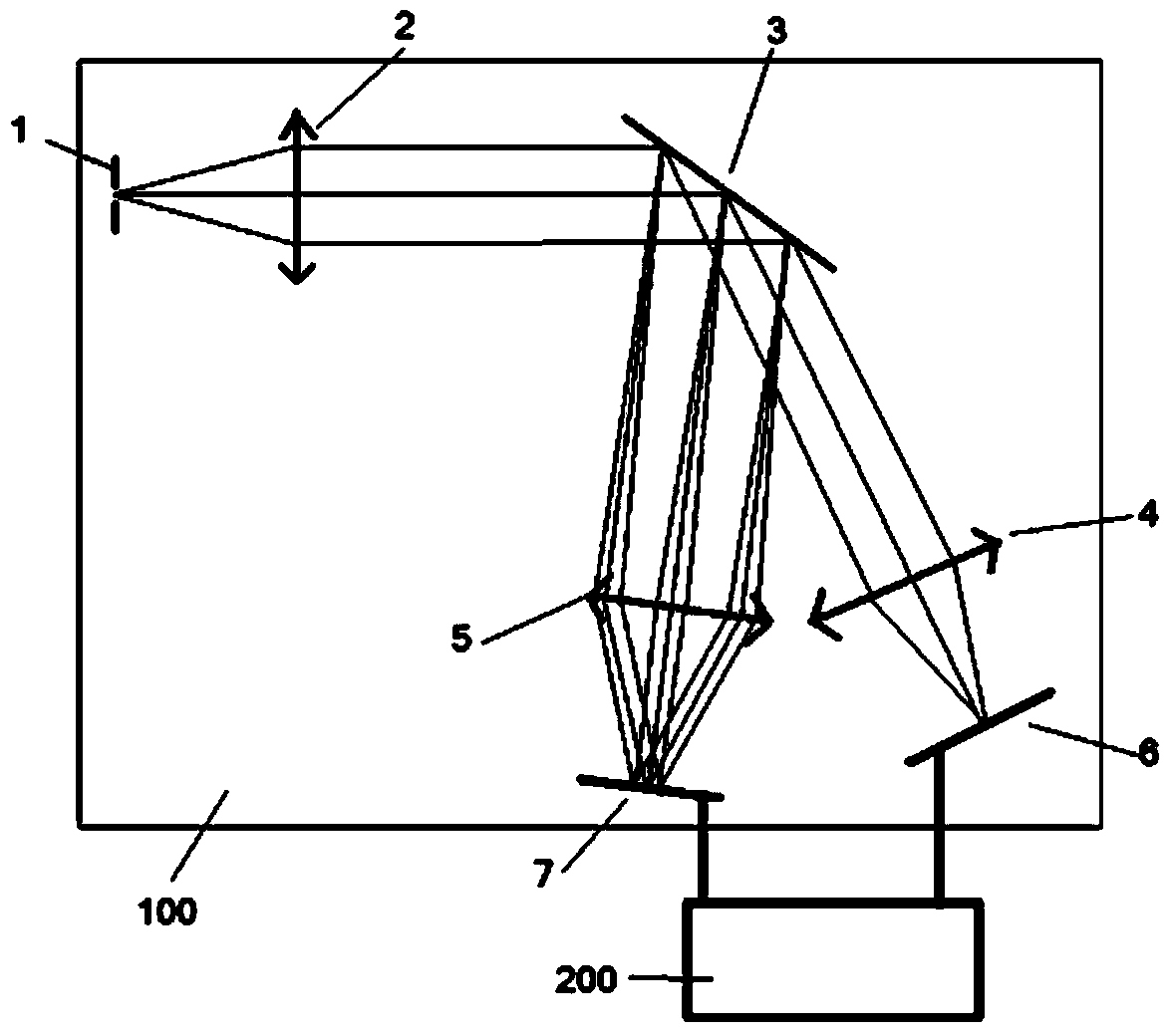
High-resolution double-grating monochromator optical path apparatus
InactiveCN106940291AImprove optical resolutionSimple structureSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsColor/spectral properties measurementsGratingMonochromator
The invention belongs to the field of spectrum measurement instruments. In order to provide a monochromator having characteristics of simple structure and small size and meeting a high resolution requirement, the technical scheme adopted by the invention is a high-resolution double-grating monochromator optical path apparatus, wherein the structure comprises an optical circulator, an optical fiber signal input port, an incident optical fiber port, a collimating and focusing lens, a grating 1, a grating 2, a grating rotation mechanism and an emergent optical fiber port, the optical fiber signal input port is connected to the first port of the optical circulator, an optical signal passes through the second port of the optical circulator, enters a free space from the incident optical fiber port, is collimated by a cemented doublet, and then irradiates on the grating 1 so as to produce first diffraction, the grating 1 diffracts the optical signal onto the grating 2 to produce second diffraction, the grating 2 diffracts the optical signal to the grating 1 according to the original path to perform third diffraction, and the third diffracted light returns to the cemented doublet according to the incident angle of the first diffraction. The high-resolution double-grating monochromator optical path apparatus of the present invention is mainly used for the design and the manufacture of spectrum measurement instruments.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Infrared polarization interference imaging spectrometer and manufacturing method
ActiveCN108180993ASimple structureHighly integratedRadiation pyrometryPolarisation spectroscopyPhotoswitchBeam splitter
The invention relates to an infrared polarization interference imaging spectrometer and a manufacturing method, and relates to the technical field of infrared spectrum detection and infrared spectrumanalysis, and solves problems that a conventional time modulation Fourier transformation infrared spectrometer is large in size and heavy because the conventional time modulation Fourier transformation infrared spectrometer employs a high-precision moving mirror drive mechanism, and also solves a problem that a spatial modulation Fourier transformation infrared spectrometer is expensive because the spatial modulation Fourier transformation infrared spectrometer employs a refrigeration-type infrared area array detector. The infrared polarization interference imaging spectrometer consists of a light source, a collimating mirror, a beam splitter, a plane reflector, an array phase reflector, a photoswitch array, a focusing mirror, and a point detector. The infrared polarization interference imaging spectrometer employs the array phase reflector for the distributed phase modulation of an incident light field, and the photoswitch array is used for the amplitude modulation of an emergent interference light field array so as to achieve a distributed-type gating and detection optical spectrum instrument. The infrared polarization interference imaging spectrometer can employ the point detector for detection, thereby further reducing the size and weight, and greatly reducing the cost.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Spectrum super-resolution method of handheld light source color illumination photometry meter
InactiveCN104236710AImprove impactGood linear relationshipSpectrum investigationObservational errorDiffusion function
The invention discloses a spectrum super-resolution method of a handheld light source color illumination photometry meter and relates to the technical field of color illumination photometry. The spectrum super-resolution method includes steps of 1) measuring and calculating spectral path point spread functions of the handheld light source color illumination photometry meter; 2) subjecting signals obtained by measuring of an optical spectrum instrument to super-resolution operation. The spectrum super-resolution method has the advantages that under a monochromater, linear relation between sampling results of the meter and measuring results of a standard instrument is improved; under the condition of different shapes of spectrums, influence on test results from response function of the meter is reduced; spectrum resolution of the meter is improved, and measuring error due to different spectral resolutions is effectively reduced.
Owner:HANGZHOU CHNSPEC TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com