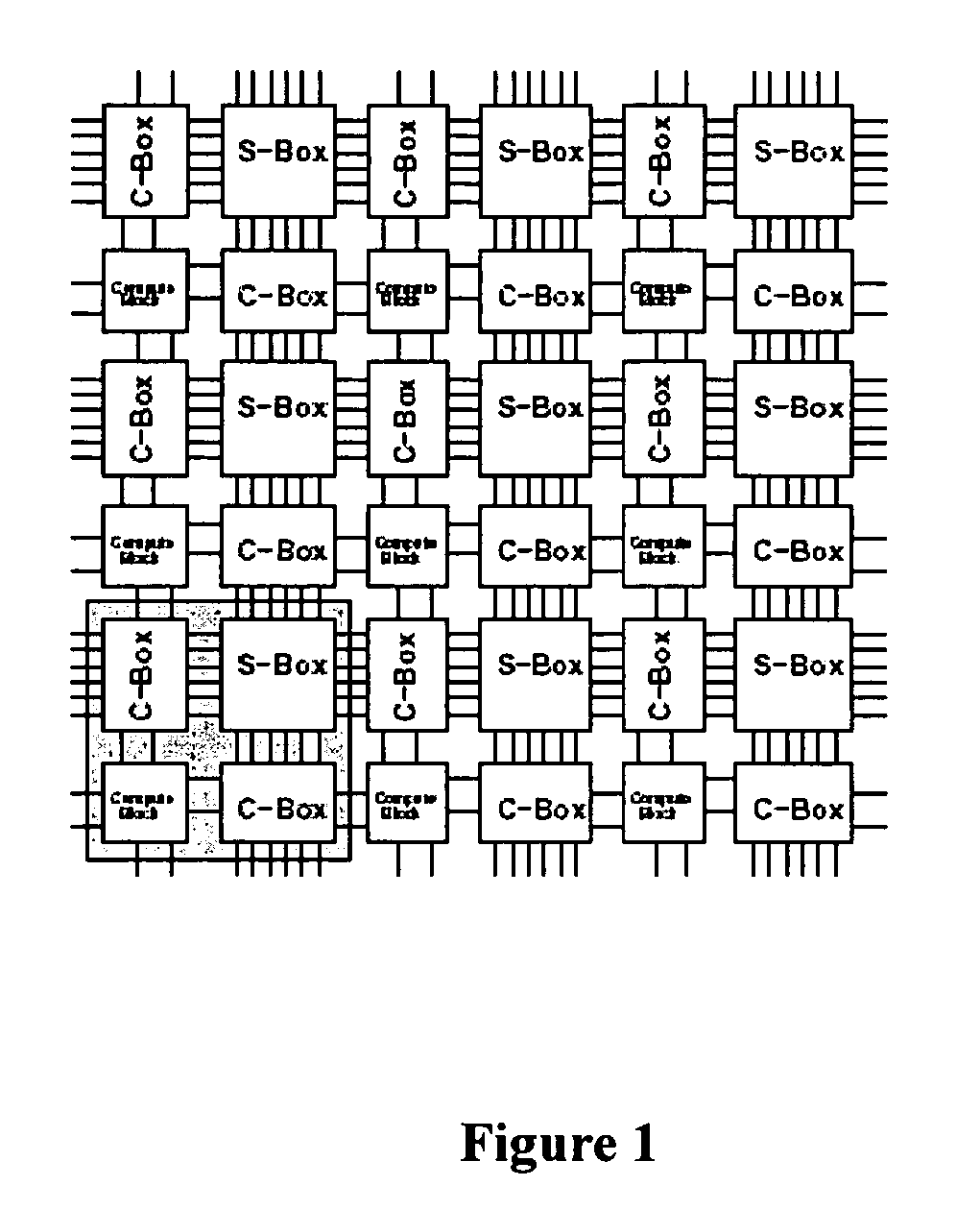
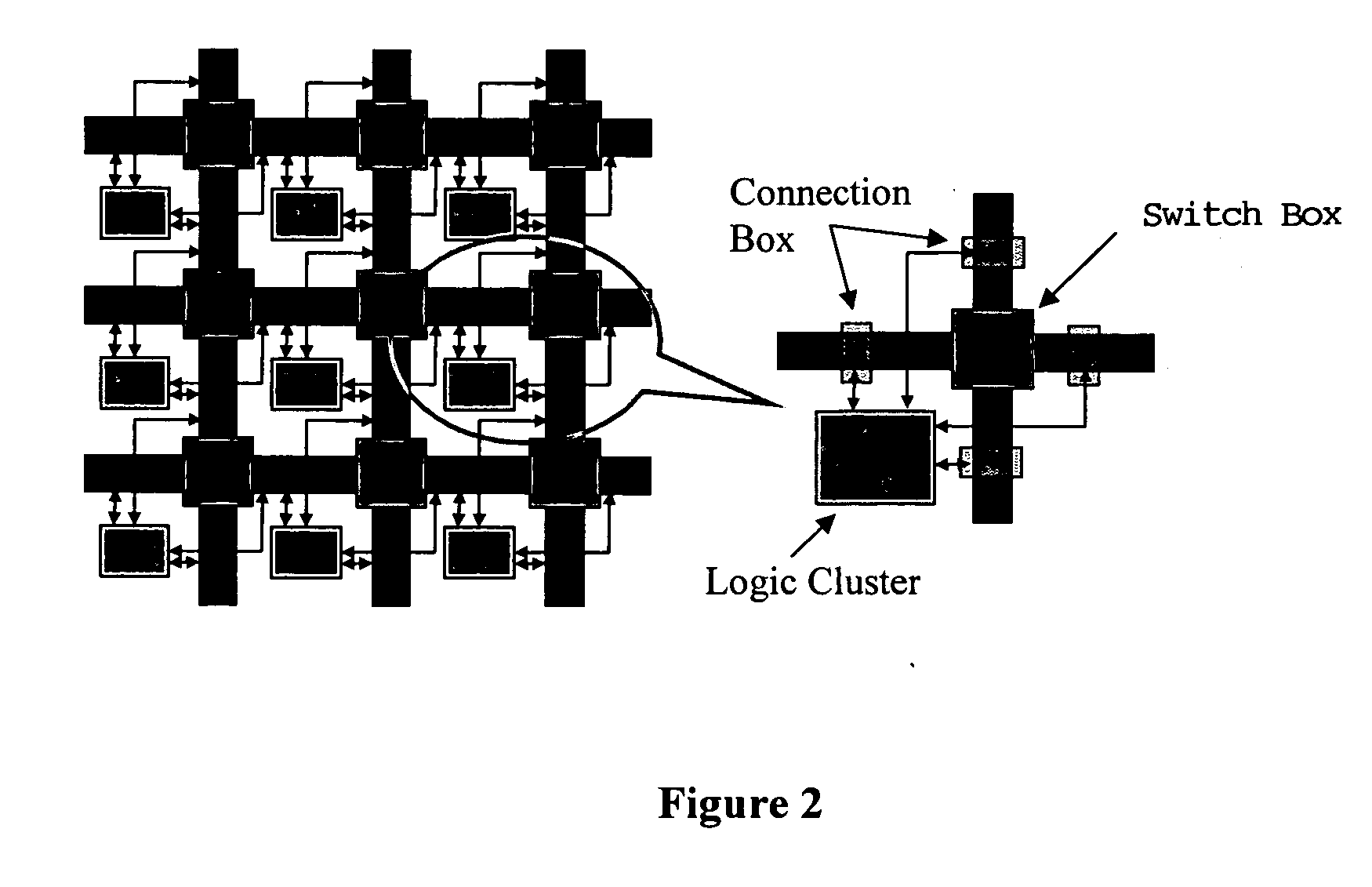
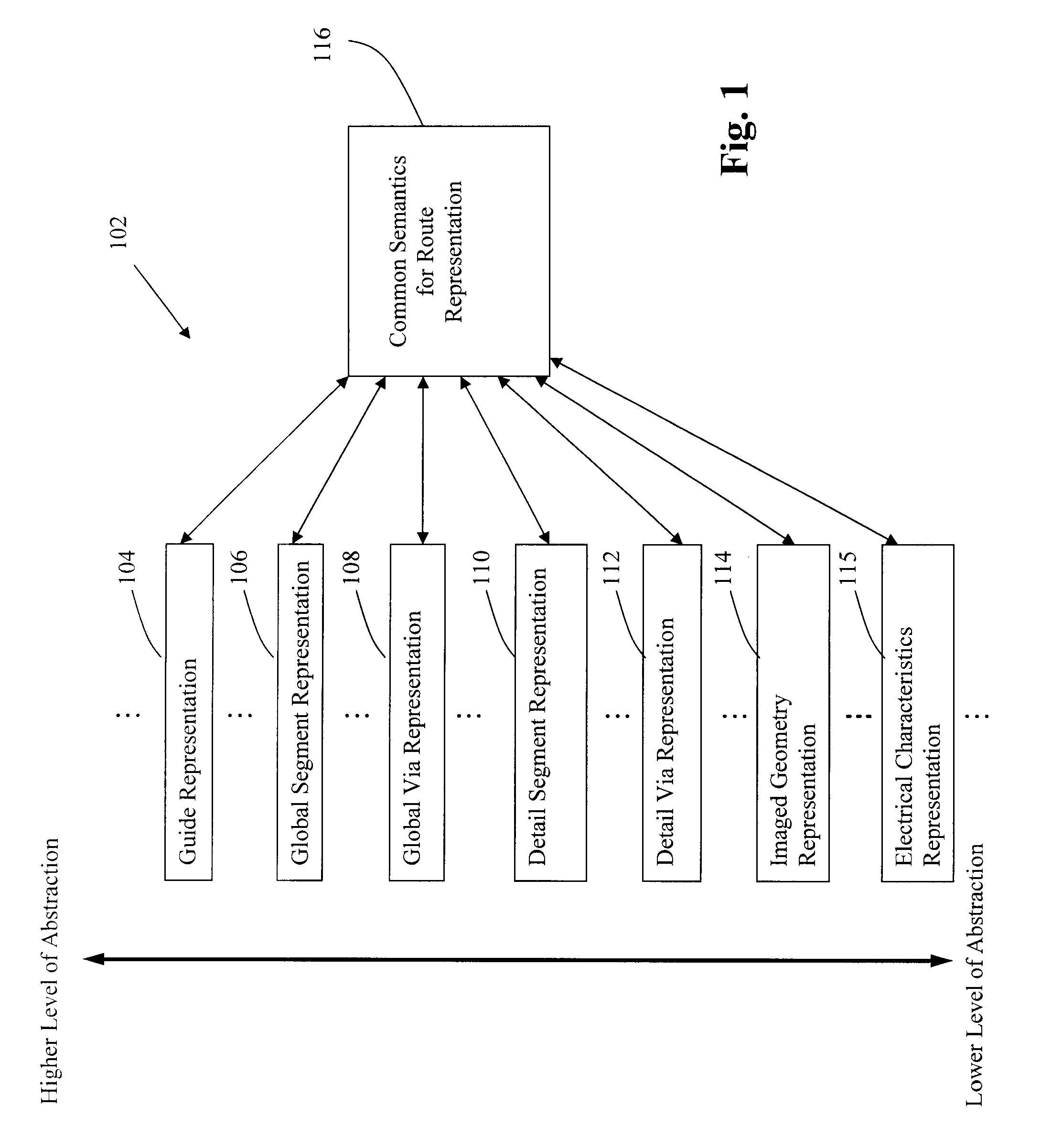
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
83 results about "Routing architecture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
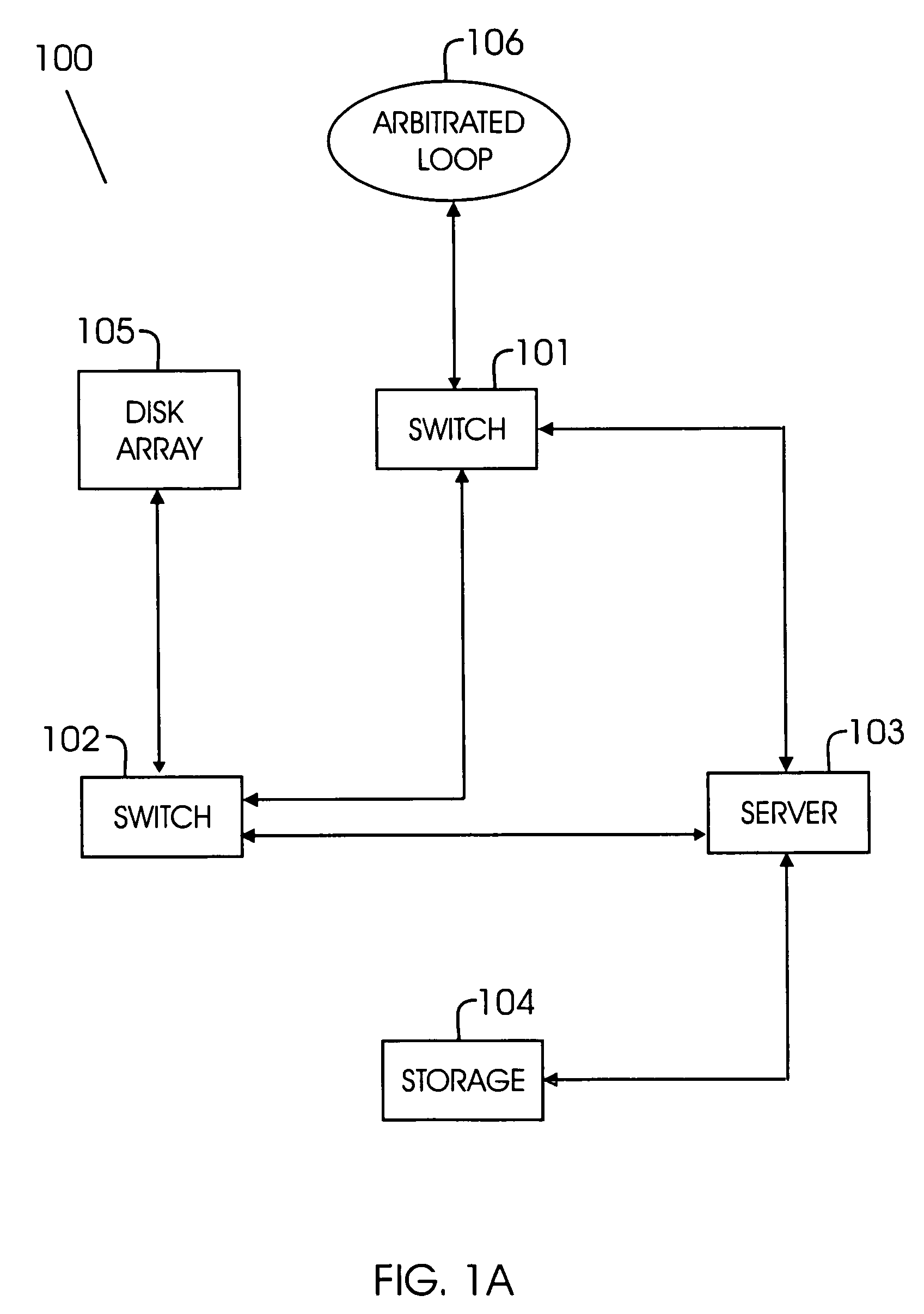
Wide-area content-based routing architecture
InactiveUS20030099237A1Easy to manageMaximum connectivityData switching by path configurationWide areaVirtualization
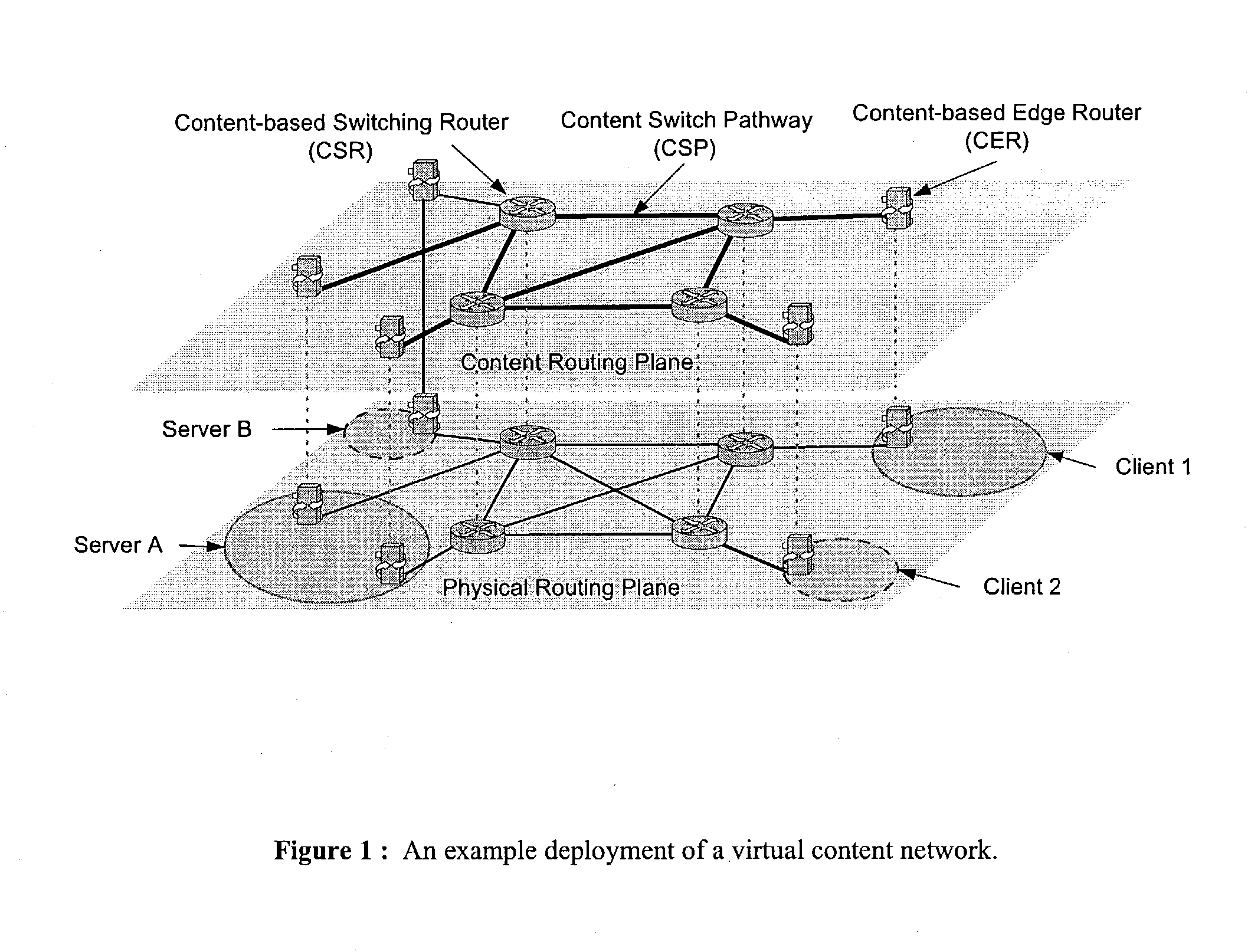
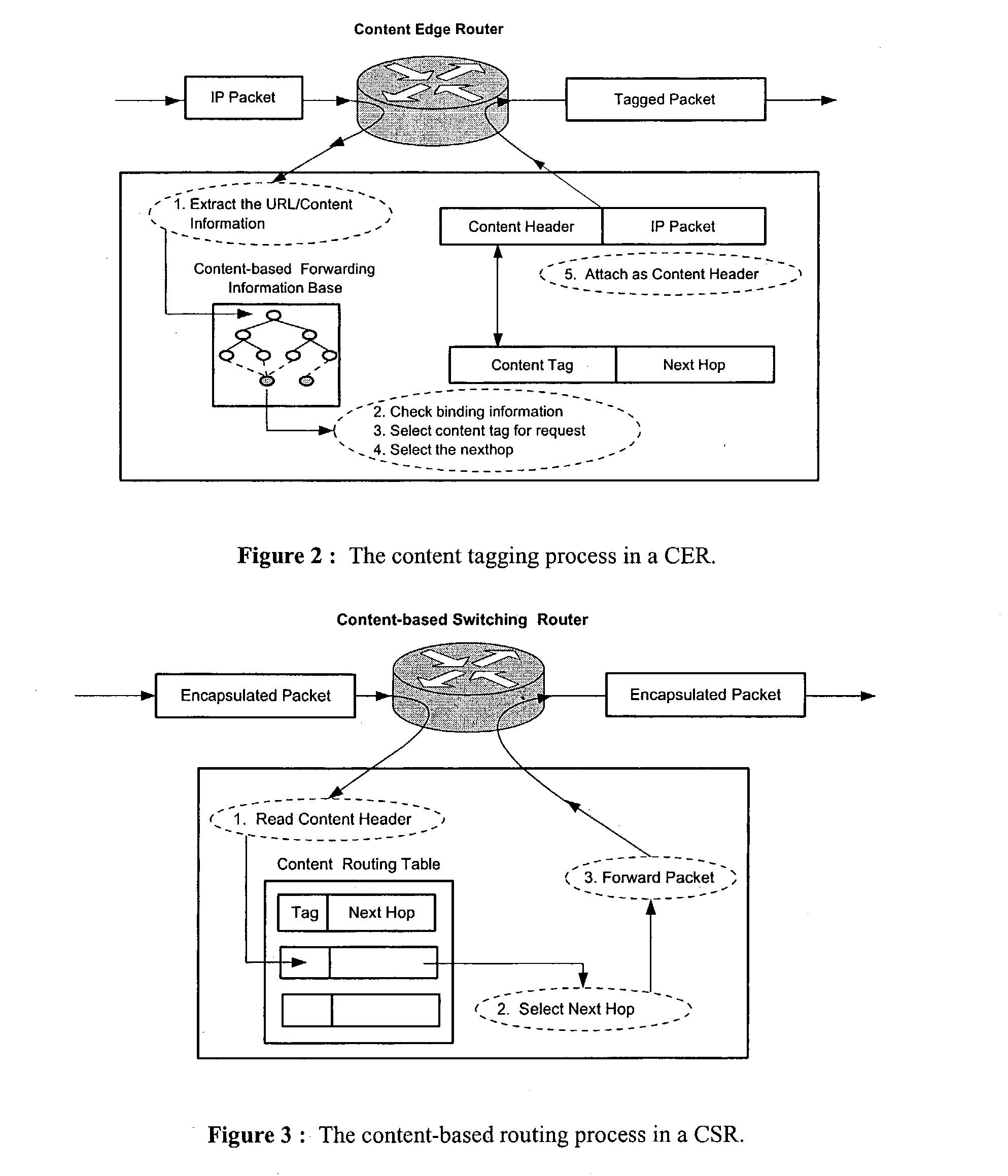
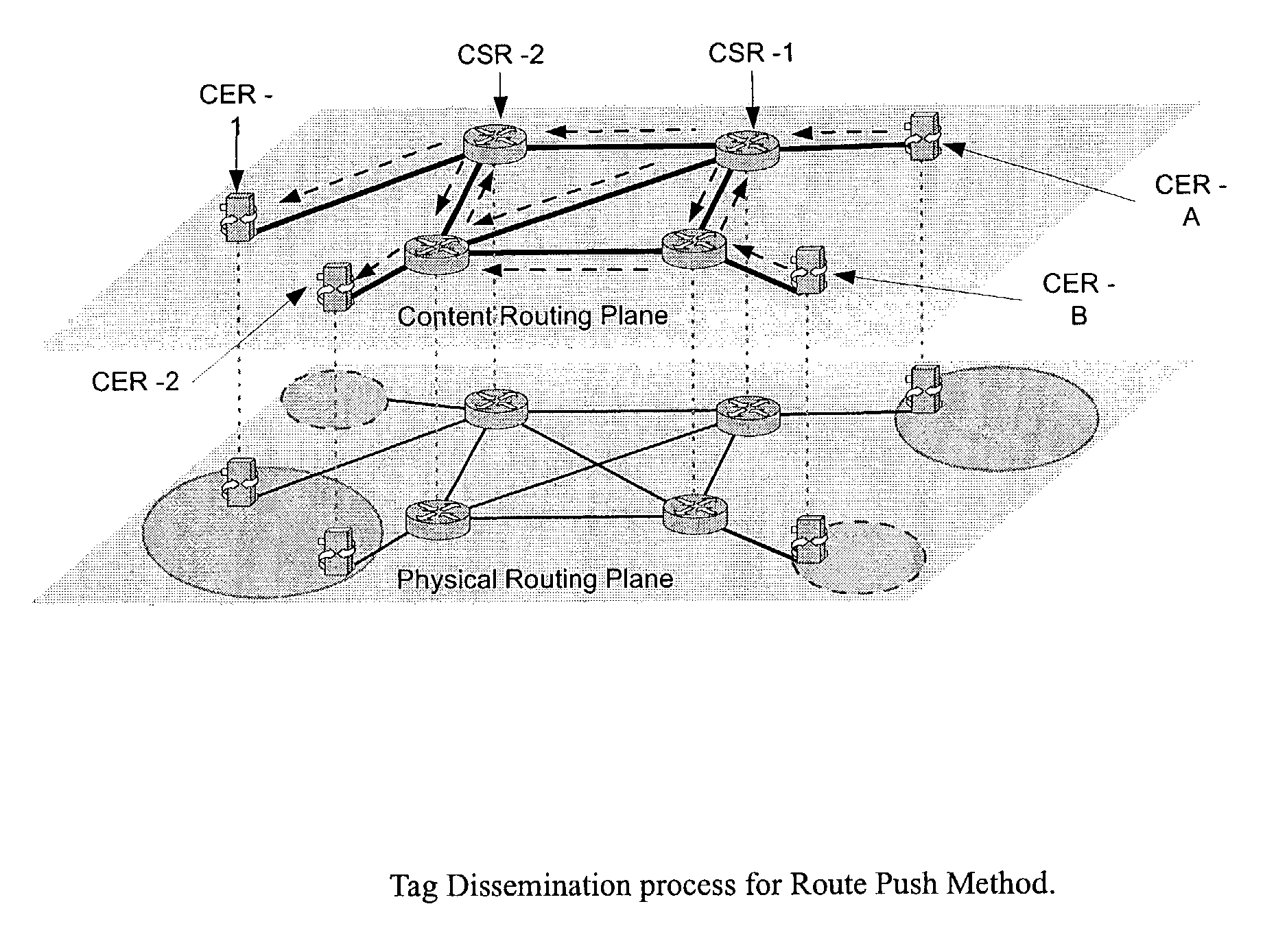
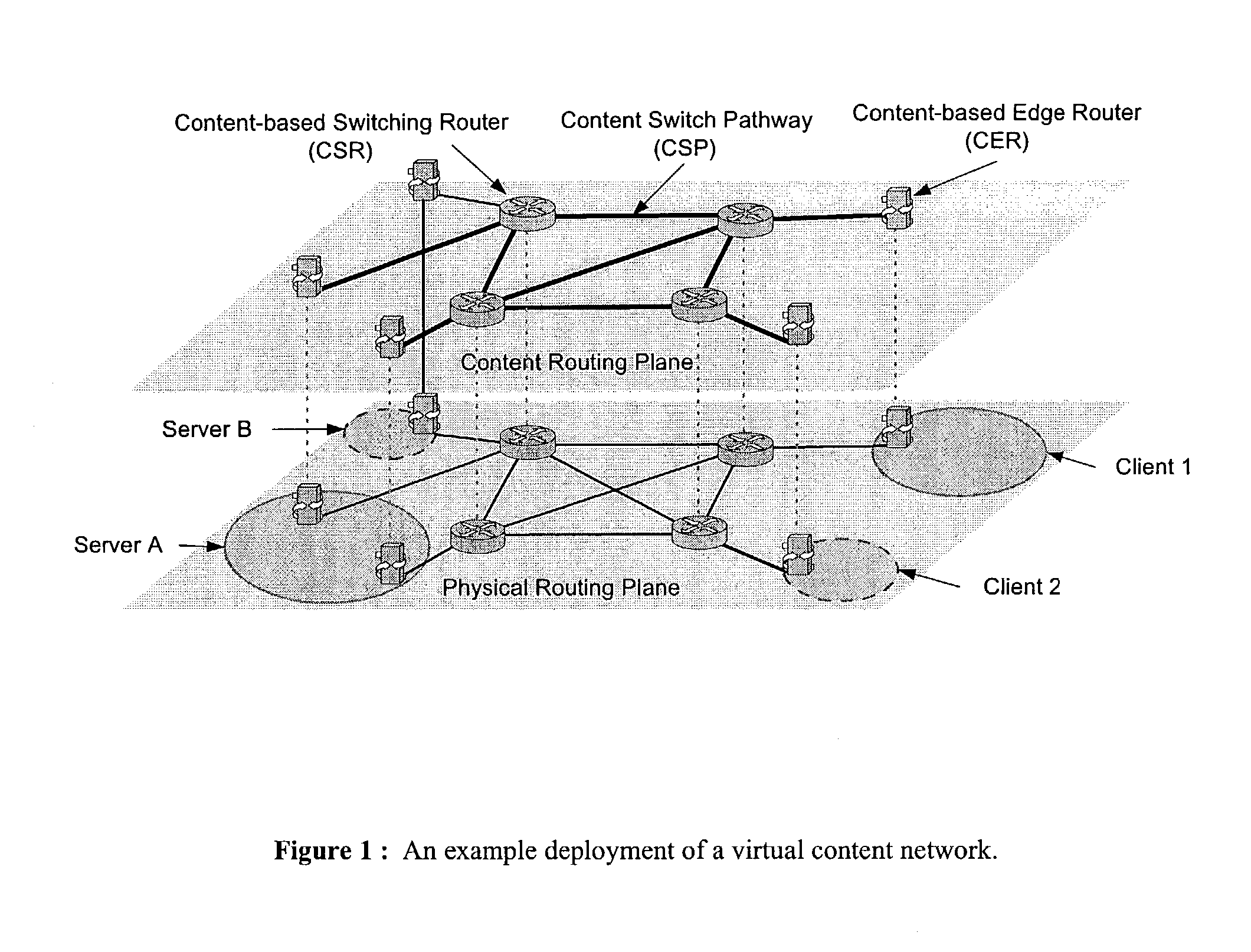
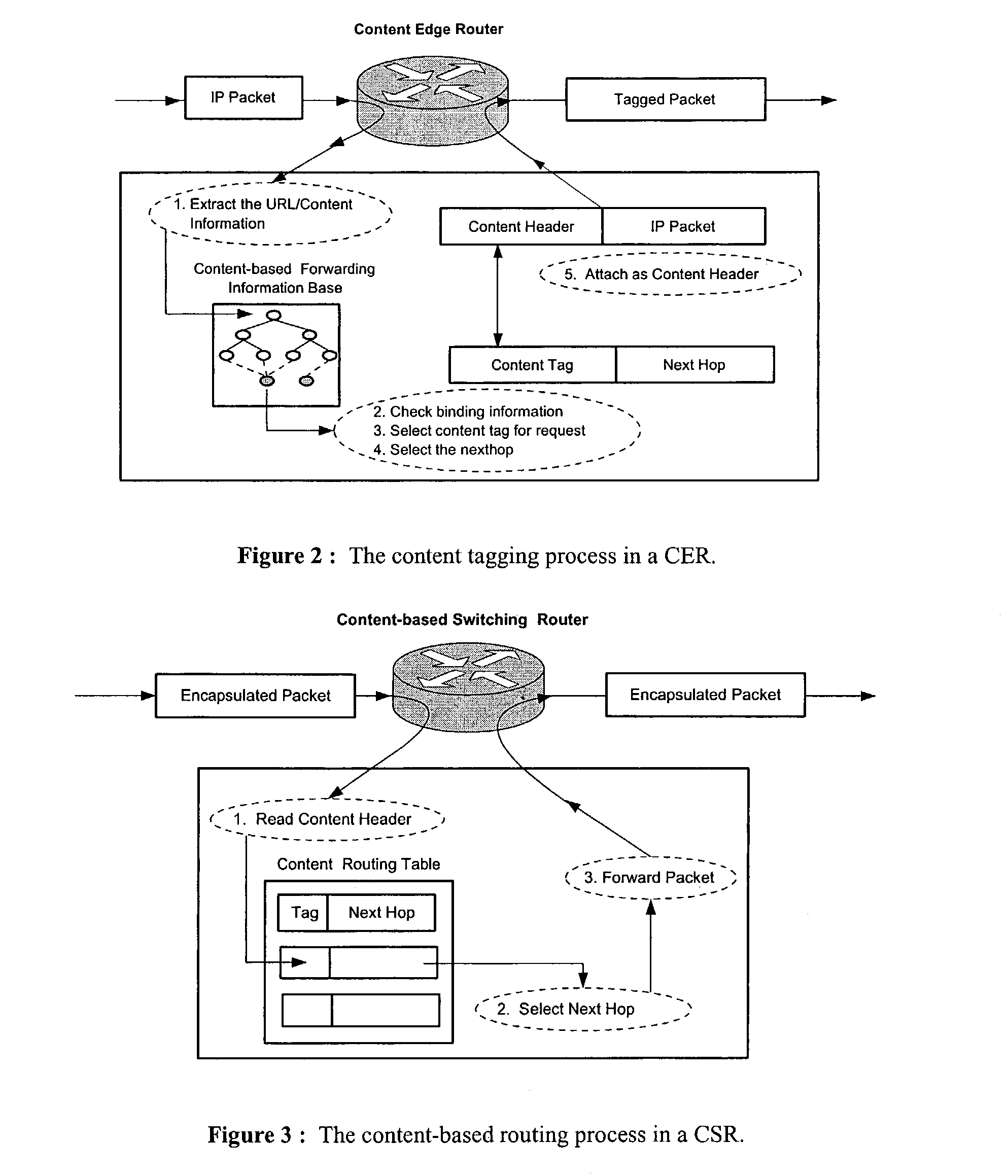
Content networking is an emerging technology, where the requests for content accesses are steered by "content routers" that examine not only the destinations but also content descriptors such as URLs and cookies. In the current deployments of content networking, "content routing" is mostly confined to selecting the most appropriate back-end server in virtualized web server clusters. This invention presents a novel content-based routing architecture that is suitable for global content networking. In this content-based routing architecture, a virtual overlay network called the "virtual content network" is superimposed over the physical network. The content network contains content routers as the nodes and "pathways" as links. The content-based routers at the edge of the content network may be either a gateway to the client domain or a gateway to the server domain whereas the interior ones correspond to the content switches dedicated for steering content requests and replies. The pathways are virtual paths along the physical network that connect the corresponding content routers. The invention is based on tagging content requests at the ingress points. The tags are designed to incorporate several different attributes of the content in the routing process. The path chosen for routing the request is the optimal path and is chosen from multiple paths leading to the replicas of the content.
Owner:TELECOMM RES LAB
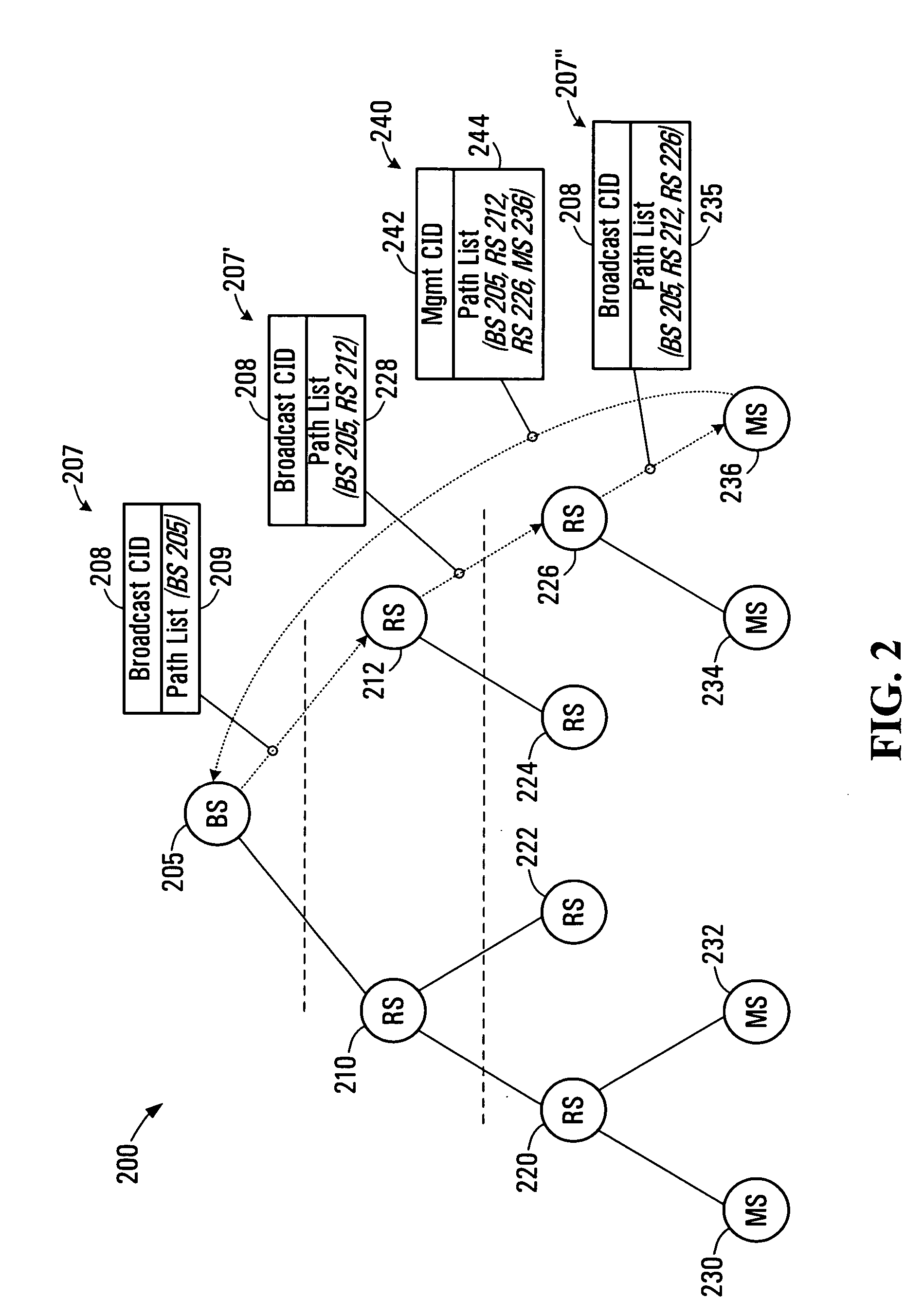
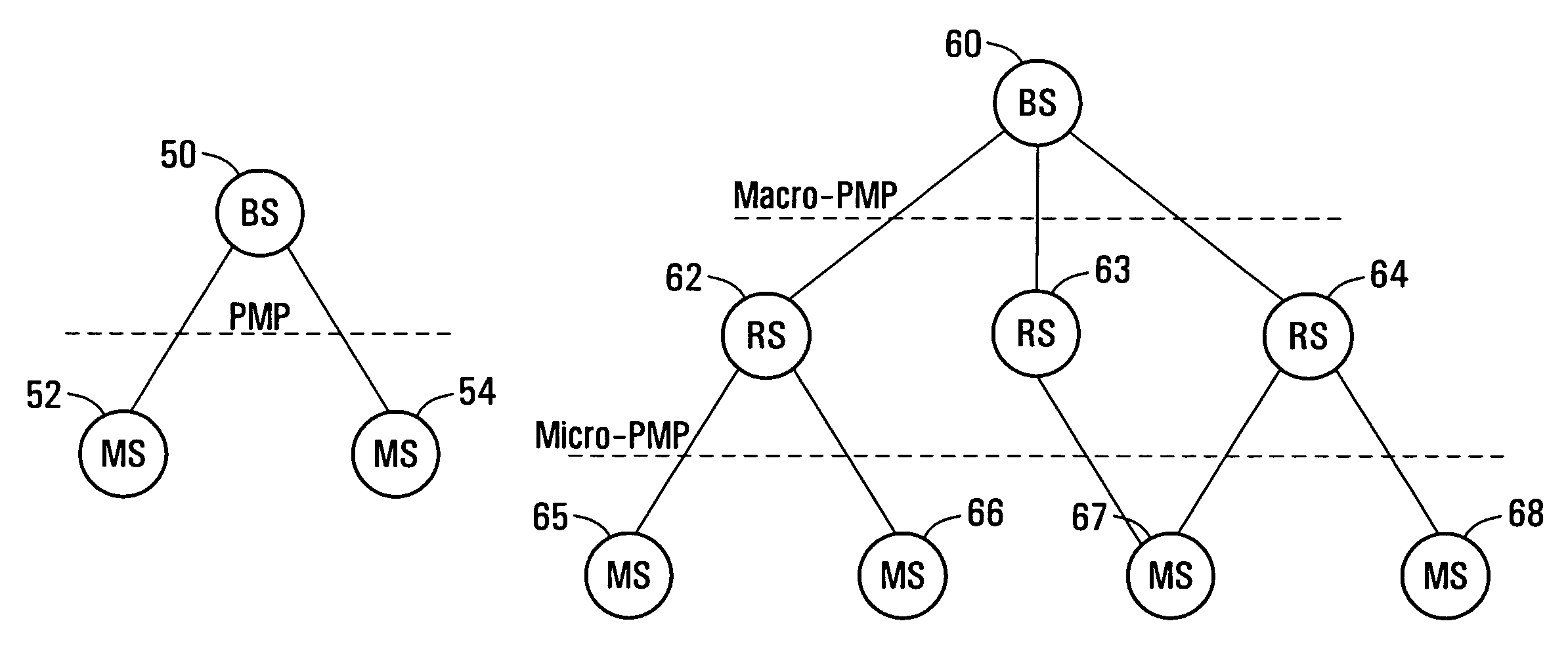
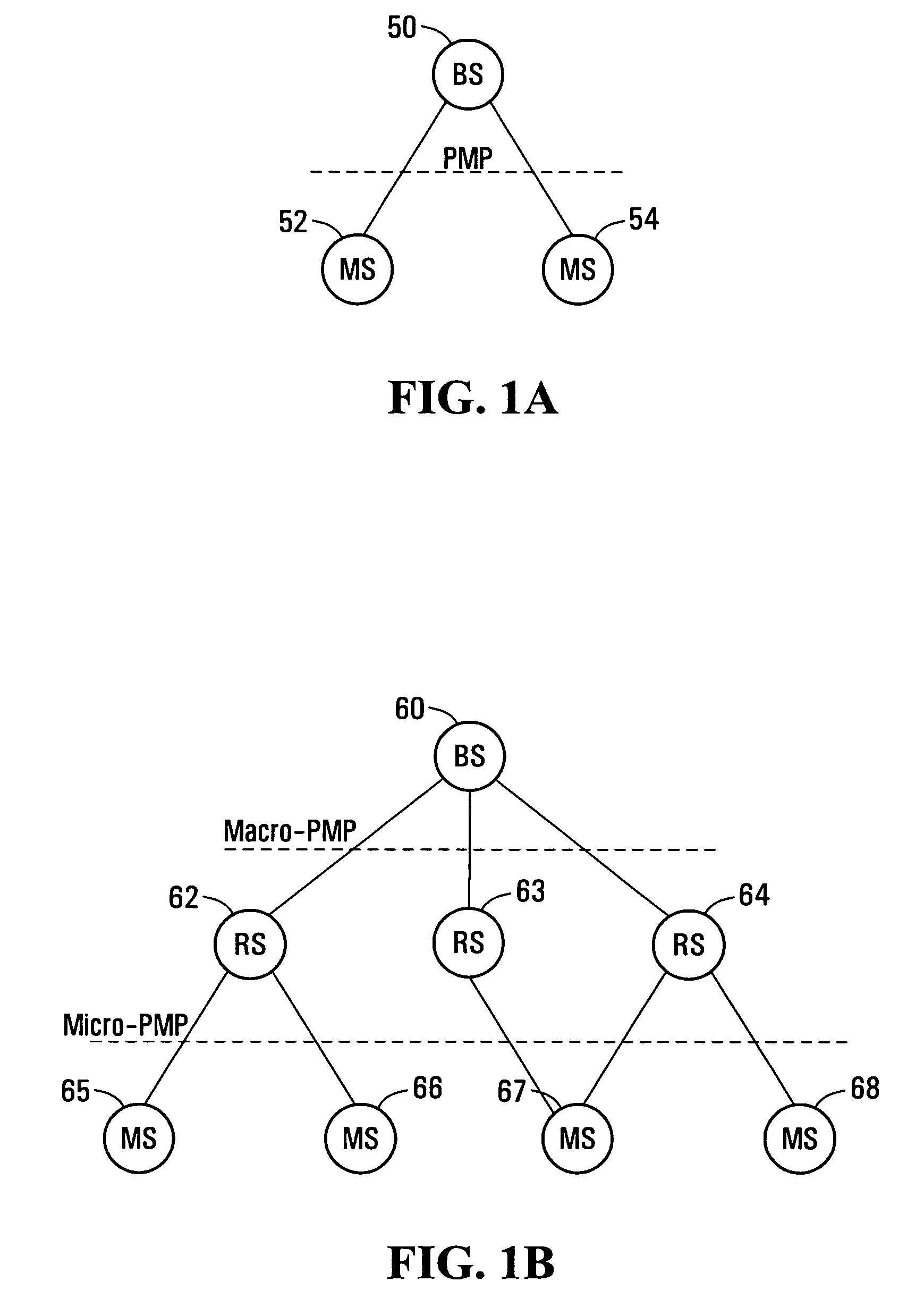
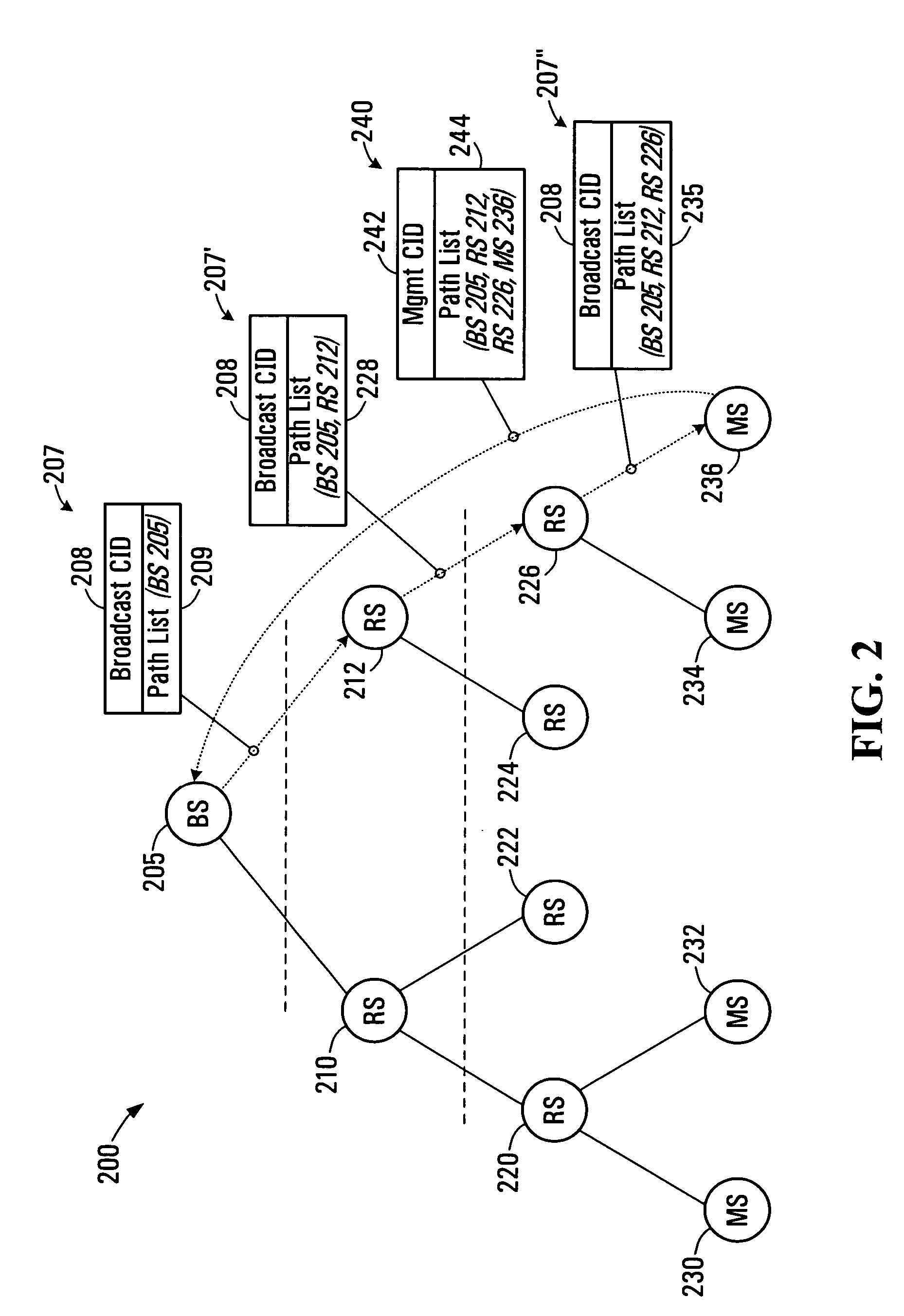
Methods and systems for a wireless routing architecture and protocol
ActiveUS20070097945A1Short pathTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationMobile stationIEEE 802
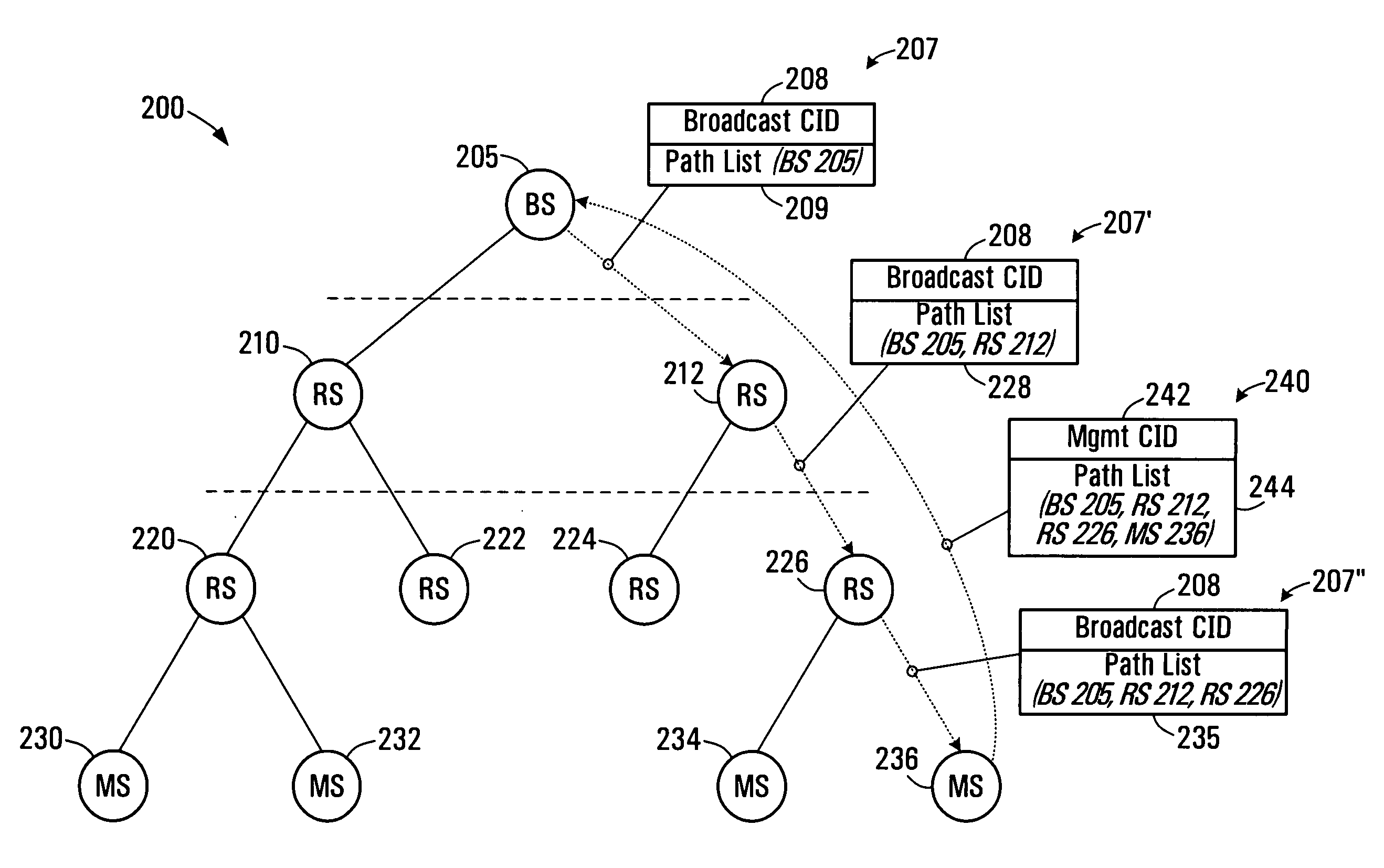
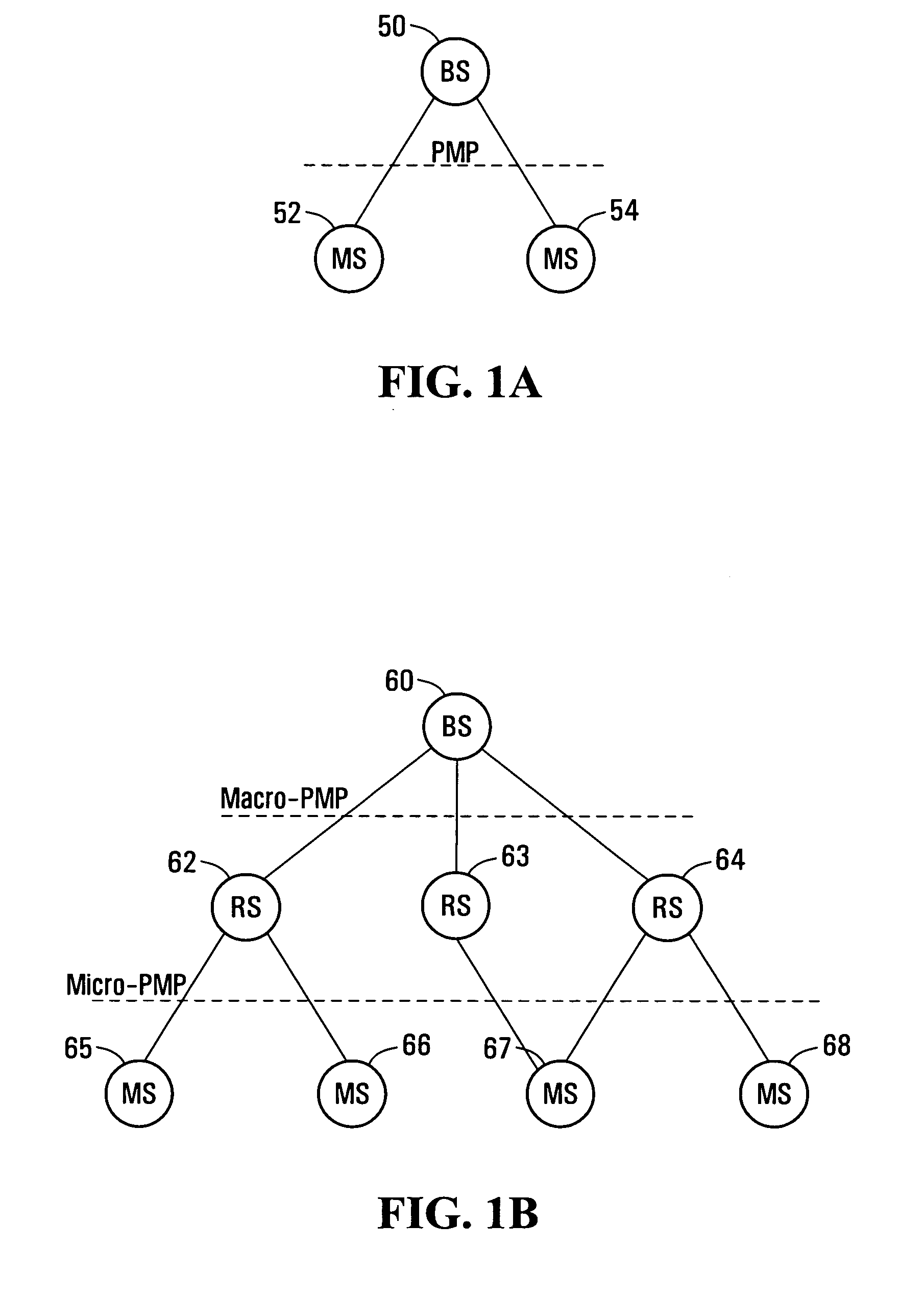
The present invention provides a method for generating routing paths in a multi-hop network. The multi-hop network includes a base station, at least one relay station, and at least one non-relay mobile station. The routing paths are paths between the base station and the at least one non-relay mobile station via the at least one relay station. The base station broadcasts a path discovery message (PDM) including a path list with a starting point of the path list being the base station. Each of the relay stations receives the PDM and updates the PDM by adding their own respective node identifier to the path list and broadcasting the updated PDM. The PDMs eventually reach the non-relay mobile station. The non-relay mobile stations reply to the base station by sending the base station the updated path list between the base station and the non-relay mobile station. In some embodiments the base station or the at least one non-relay mobile station acting as a source node sends a dynamic service (DSx) message including an end-to-end path list to an end of path destination. The relay stations use the path list to forward the message between the source node and the end of path destination. In some implementations the multi-hop network operates in a manner that is consistent with any one of: IEEE 802.16, IEEE 802.16d, and IEEE 802.16e.
Owner:APPLE INC
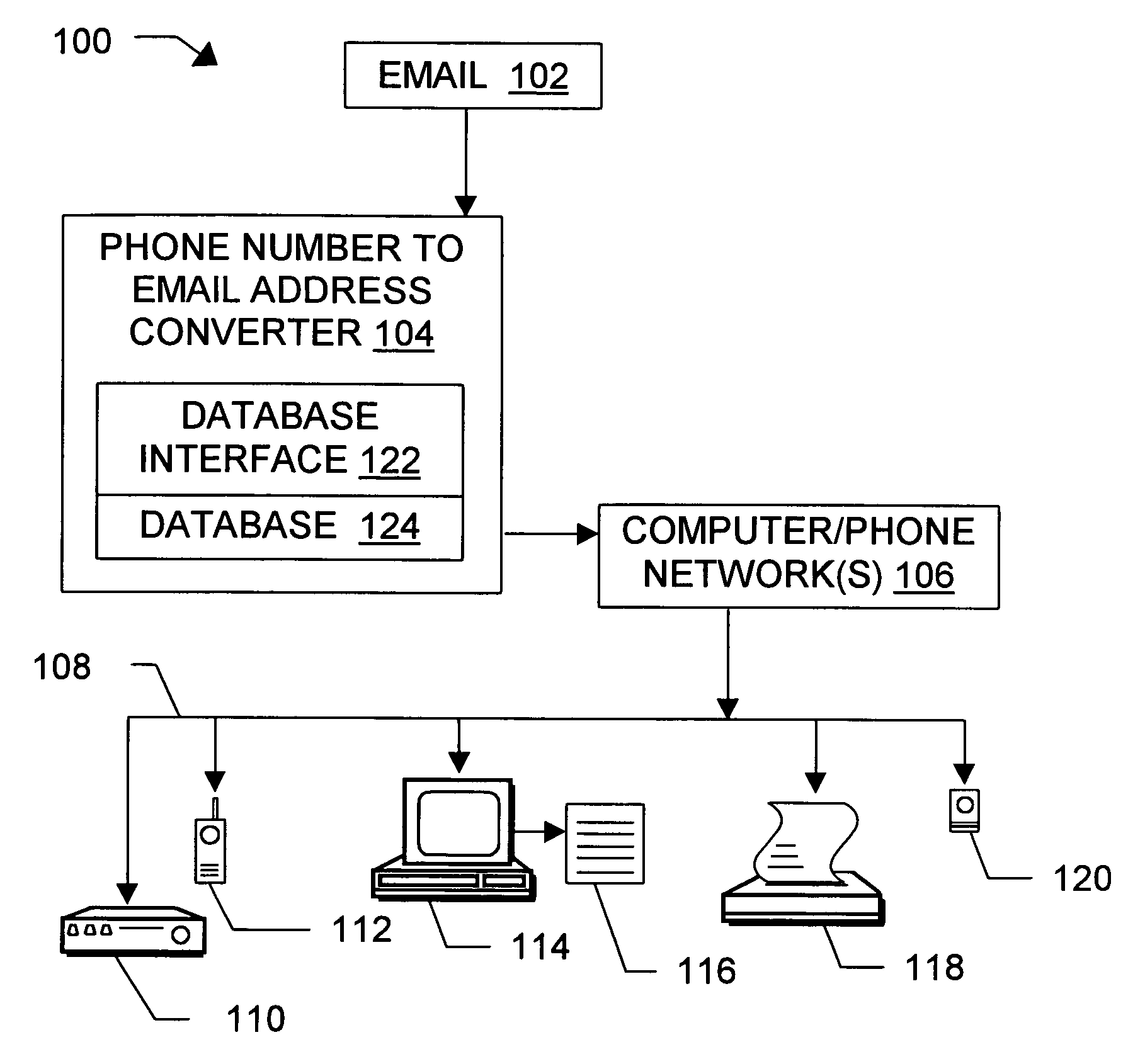
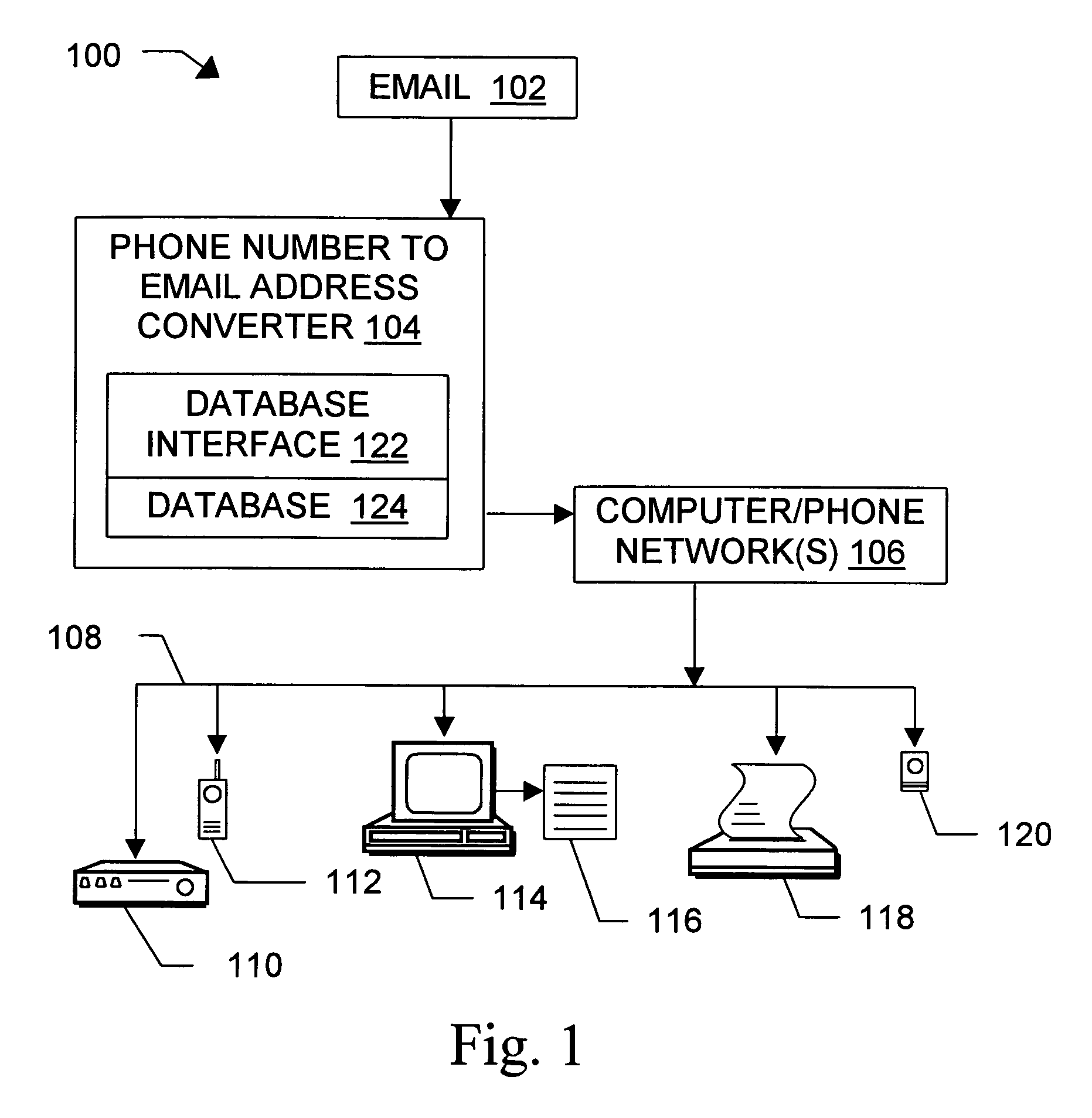
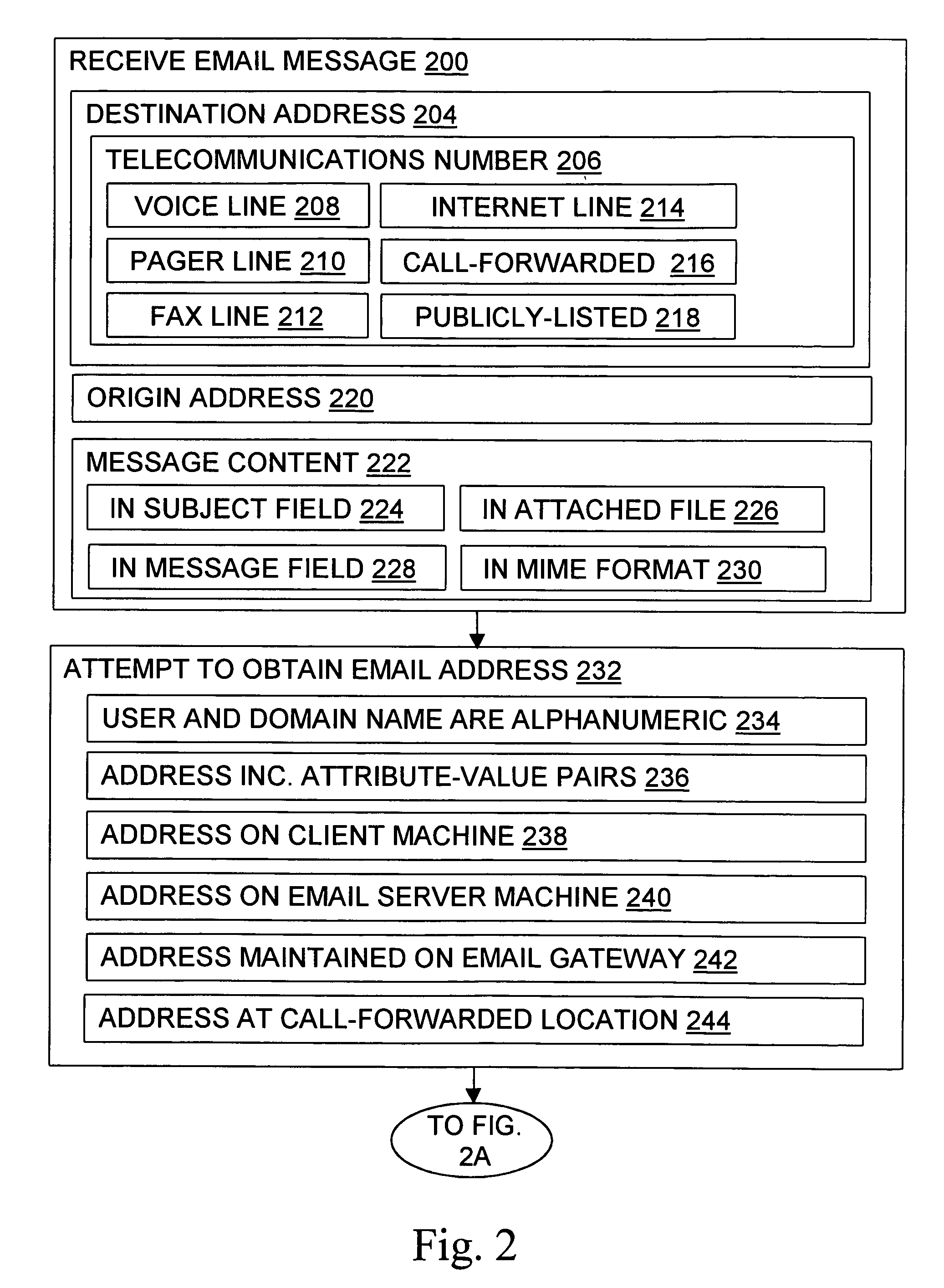
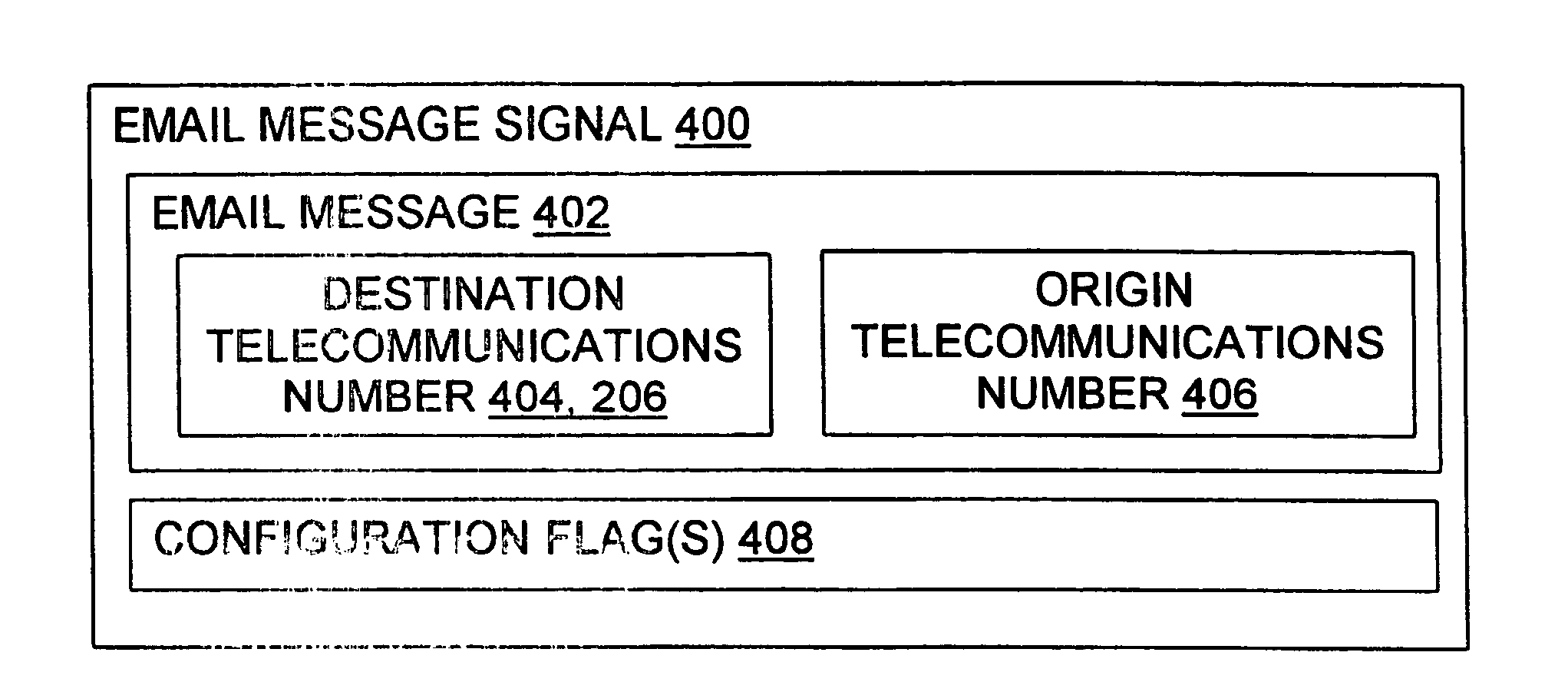
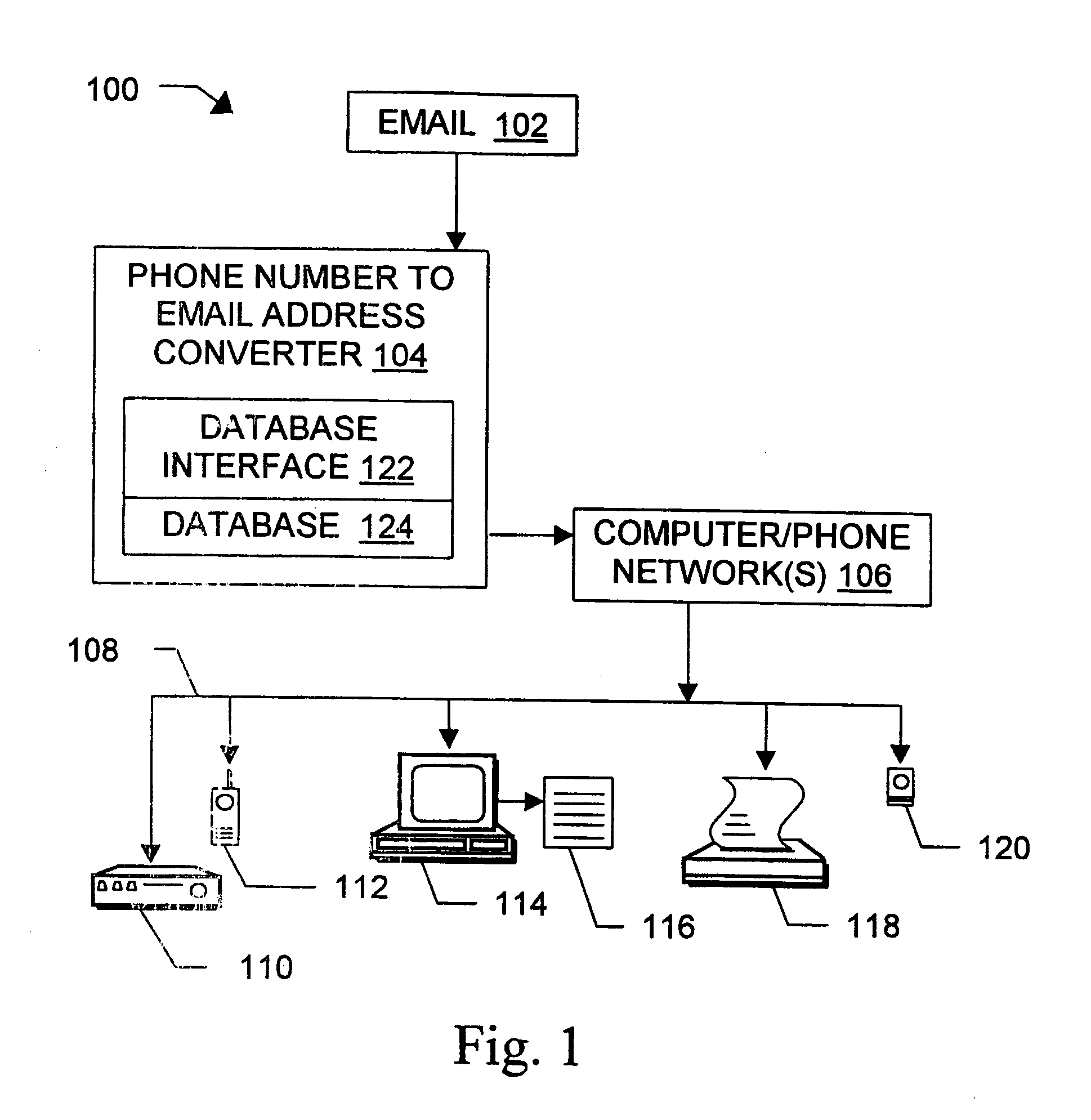
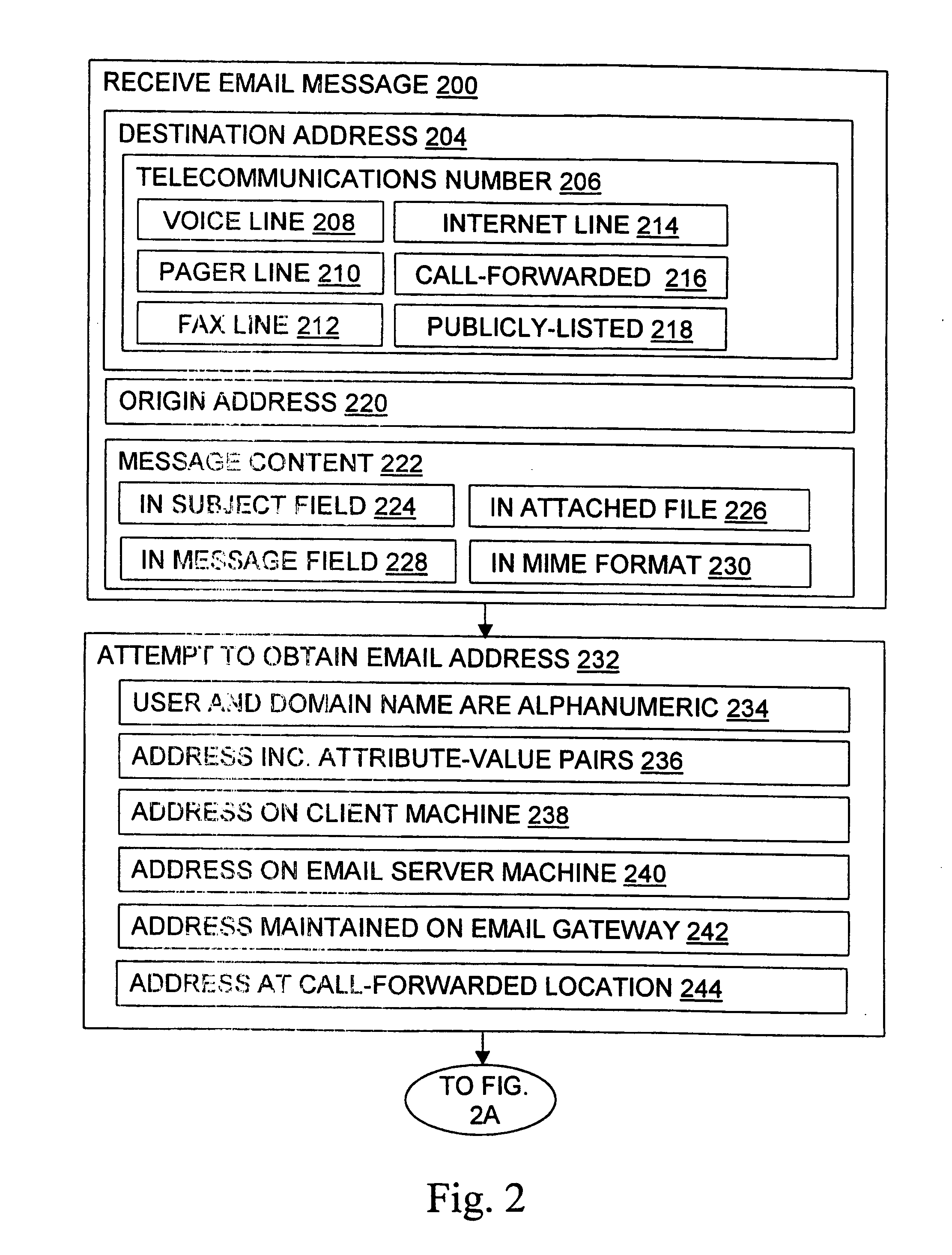
Message routing
InactiveUS6981023B1Easy to getRemove the burdenInterconnection arrangementsPublic key for secure communicationEmail addressSelective calling
Methods, devices, signals, and systems are provided in a message routing architecture which provides improved capabilities for integrating “digital” communication through email messages with “analog” communication through voice and / or fax or pager messages. Email can be addressed using nothing more than a standard telephone or fax number. If the registered owner of the telephone or fax number has a corresponding email address, then the invention converts the telephone or fax number to the email address for delivery and uses standard email delivery systems to deliver the message. If no conventional delivery email address is known, or if the message sender or recipient specify multiple delivery modes, then the email message content is transformed into voice, pager and / or fax content and delivered to the recipient using the telephone or fax number which was specified as the email address. Familiar telecommunications services such as call forwarding and selective call blocking can also be used with messages that originate as email. The invention also supports use of telecommunications numbers as indexes into databases which contain public key certificates, to make it unnecessary for a proposed message recipient to provide its public key expressly in advance to each particular proposed message originator.
Owner:HAMILTON MICHAEL +1
Wide-area content-based routing architecture
Owner:TELECOMM RES LAB
Remote parking meter auditing module
ActiveUS20080238715A1Without significantly reducing its lifetimeImprove reliabilityElectric signal transmission systemsTicket-issuing apparatusSignal routingTransceiver
A remote parking meter monitoring system is provided. The system has a plurality of radio transceivers. Each transceiver communicates with at least one other transceiver within a transceiver communication region. The transceivers are integrated to parking meters. A separate aggregate point has a transceiver and a communication network that is connected to a computer. The aggregate point communicates with at least one proximal transceiver and communicates to the computer through the network. The system has a mesh communication arrangement, and a signal routing architecture, where the information is communicated along any path of adjacent communication regions. The computer is able to communicate information through the network to the aggregate point, and the aggregate point transceiver sends the information to the proximal transceiver. The information is communicated to any one of the transceivers in the mesh using the routing architecture by communicating the signal through any path between adjacent communication regions.
Owner:STREETLINE TECH LLC
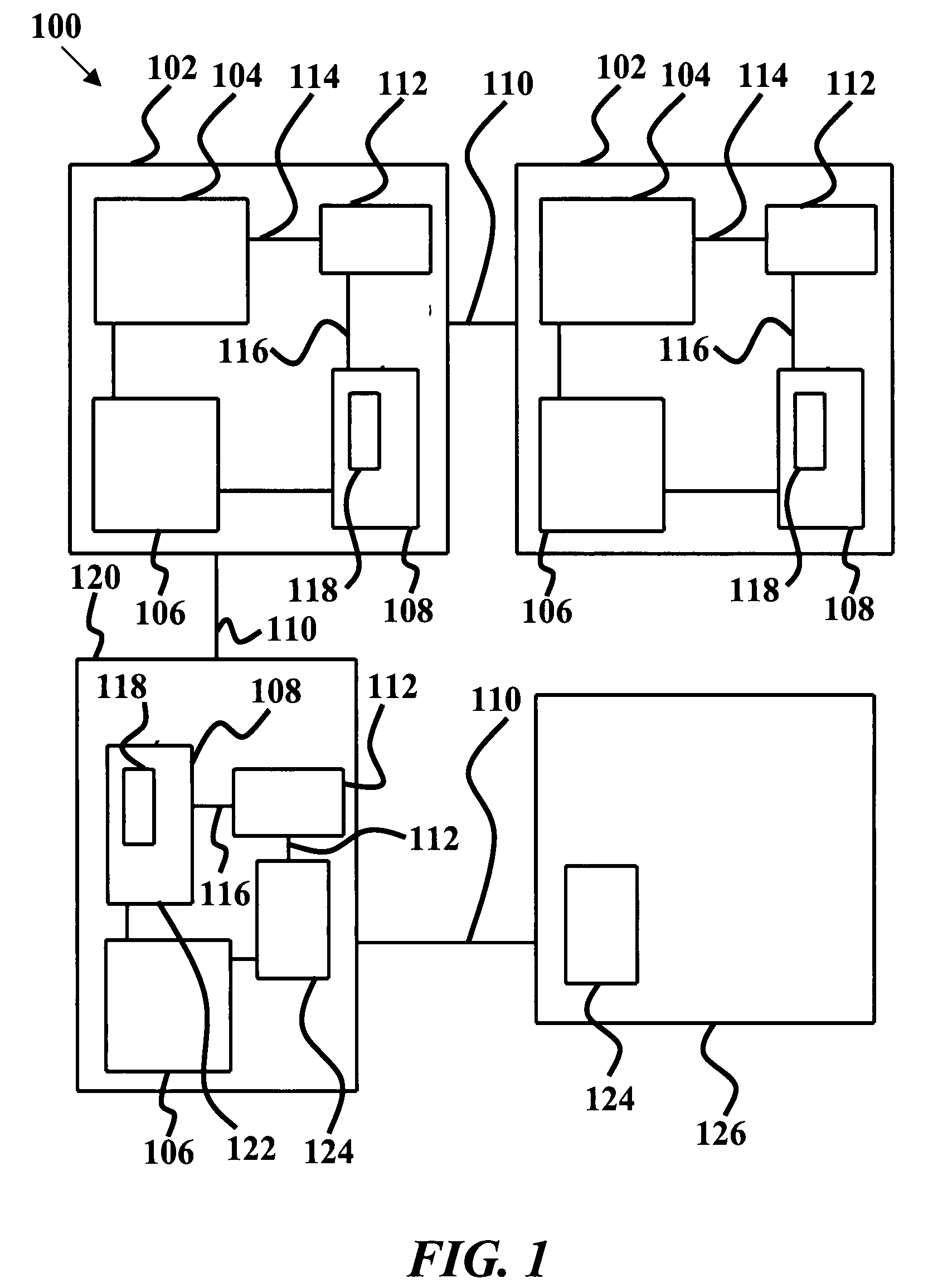
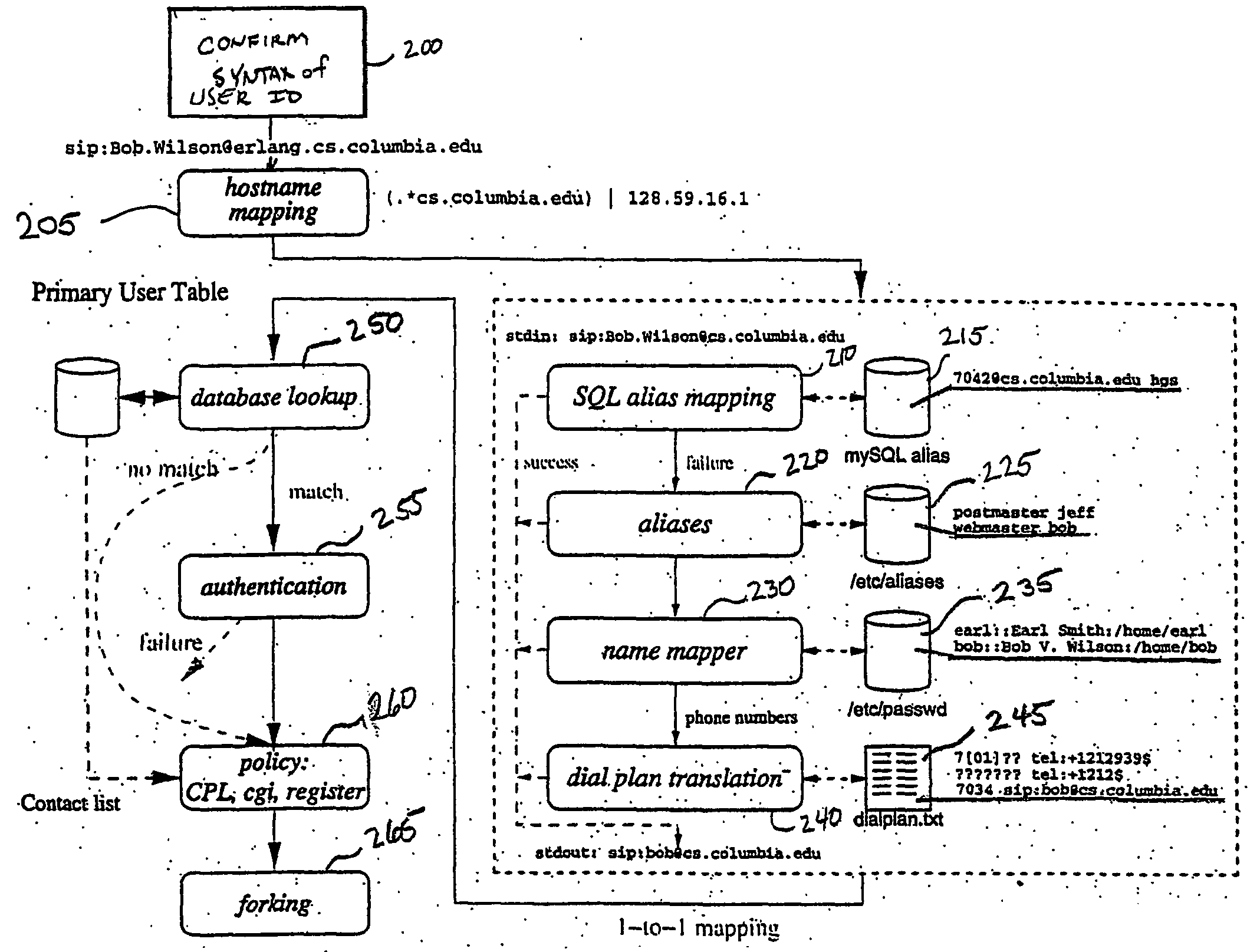
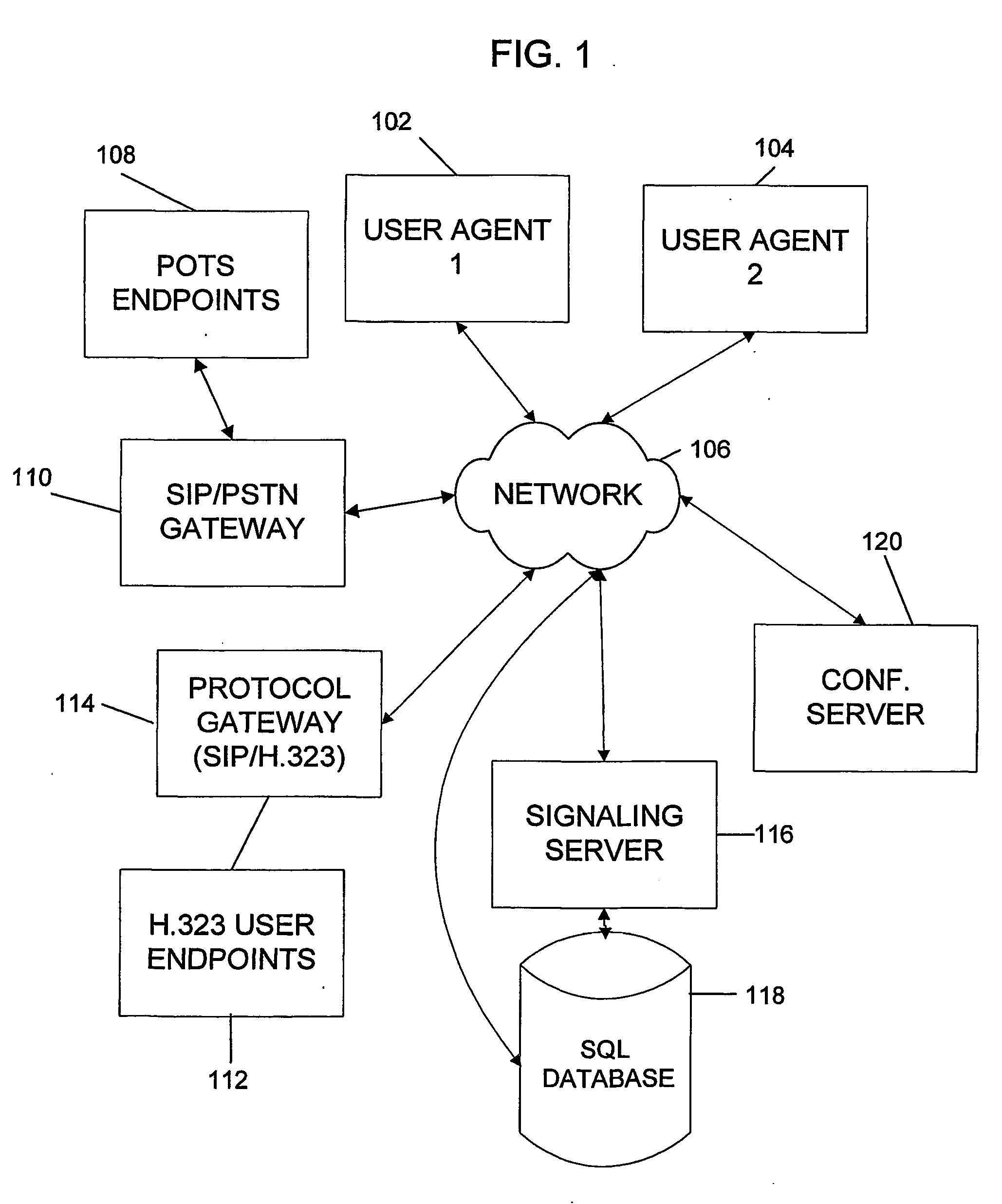
System and method for call routing in an ip telephony network
A method of processing a call request to a callee in a network telephony system is provided which includes mapping a hostname portion of a callee address to a canonical form of the hostname and determining a canonical form of a username portion of a callee address. The canonical form of the user identity of the callee is then used as an index to a user database to retrieve a callee database record. The callee database record is then used to determine call routing based on the retrieved callee database record, such as user location, preferences and policy data stored in the record. The method is generally performed by a signaling server in the network, such as a SIP proxy server. The signaling server can also provide security features such as caller authentication. A scalable signaling and routing architecture is also provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
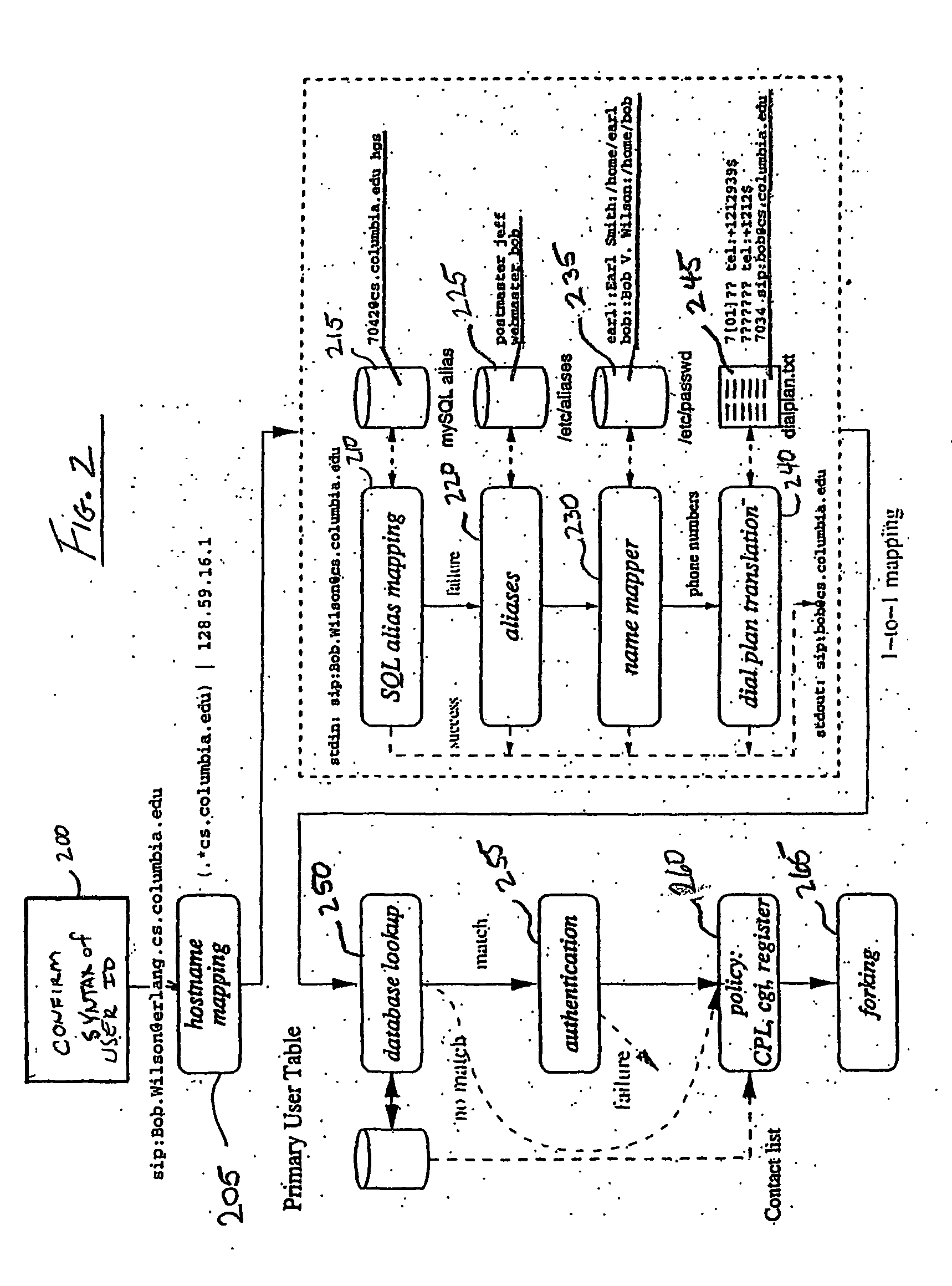
Routing architecture including a compute plane configured for high-speed processing of packets to provide application layer support
ActiveUS6970943B1Without impacting forwarding performanceAvoid negatively impacting performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksProtocol ApplicationDistributed computing
The present invention provides a routing architecture including a control plane, a compute plane, and a forward plane. The forward plane provides traditional forwarding of packets to the next-hop address, along with any necessary header manipulation, while the control plane configures the forward plane and the compute plane for desired operation. The compute plane is configured for high-speed processing of packets to provide application level support, including manipulating application data in the payload of the packets during routing. The forward plane preferably implements forwarding rules using filters sufficient to forward a received packet to the next-hop address, to the compute plane for application processing, or to the control plane to facilitate control or configuration.
Owner:AVAYA MANAGEMENT LP
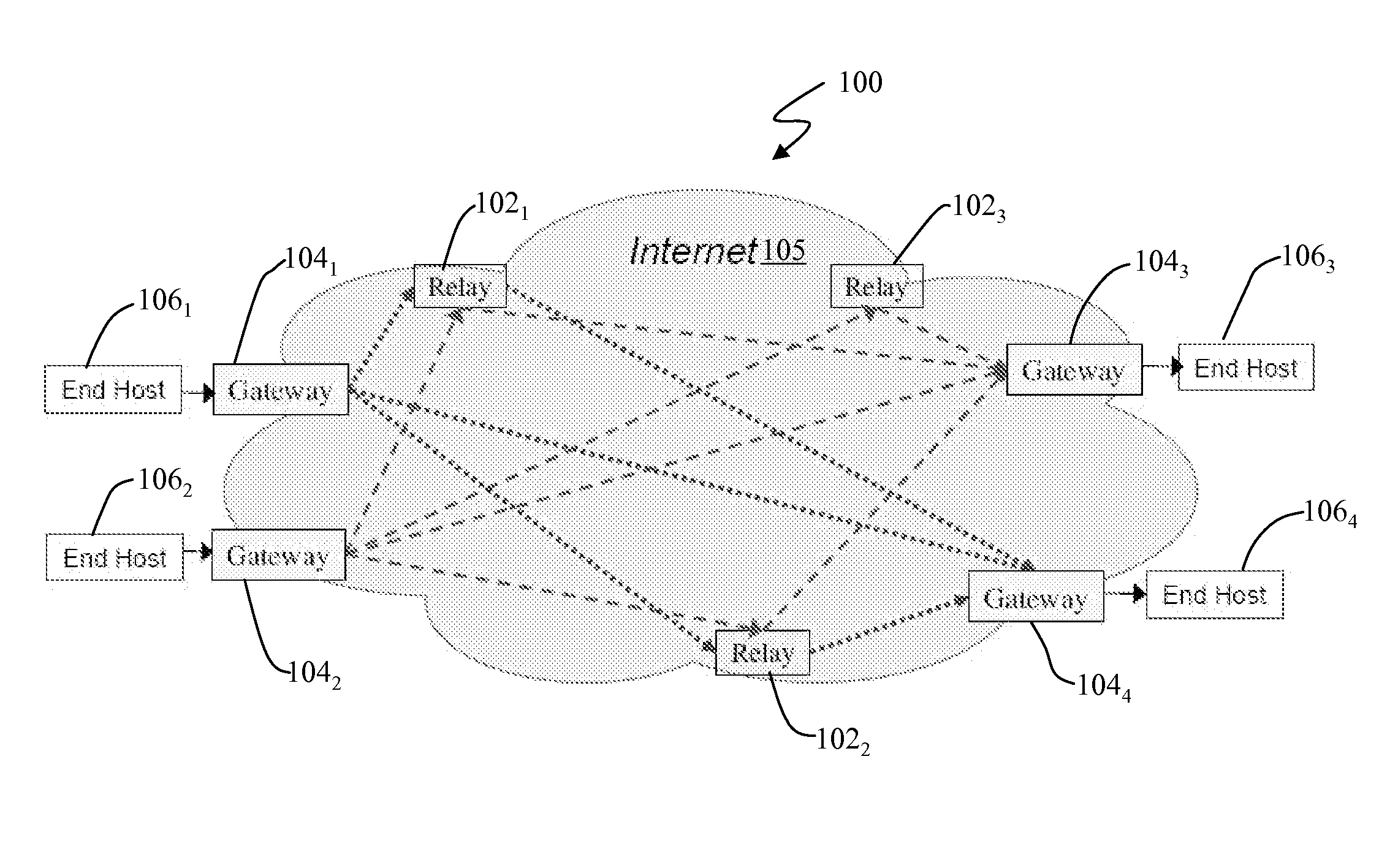
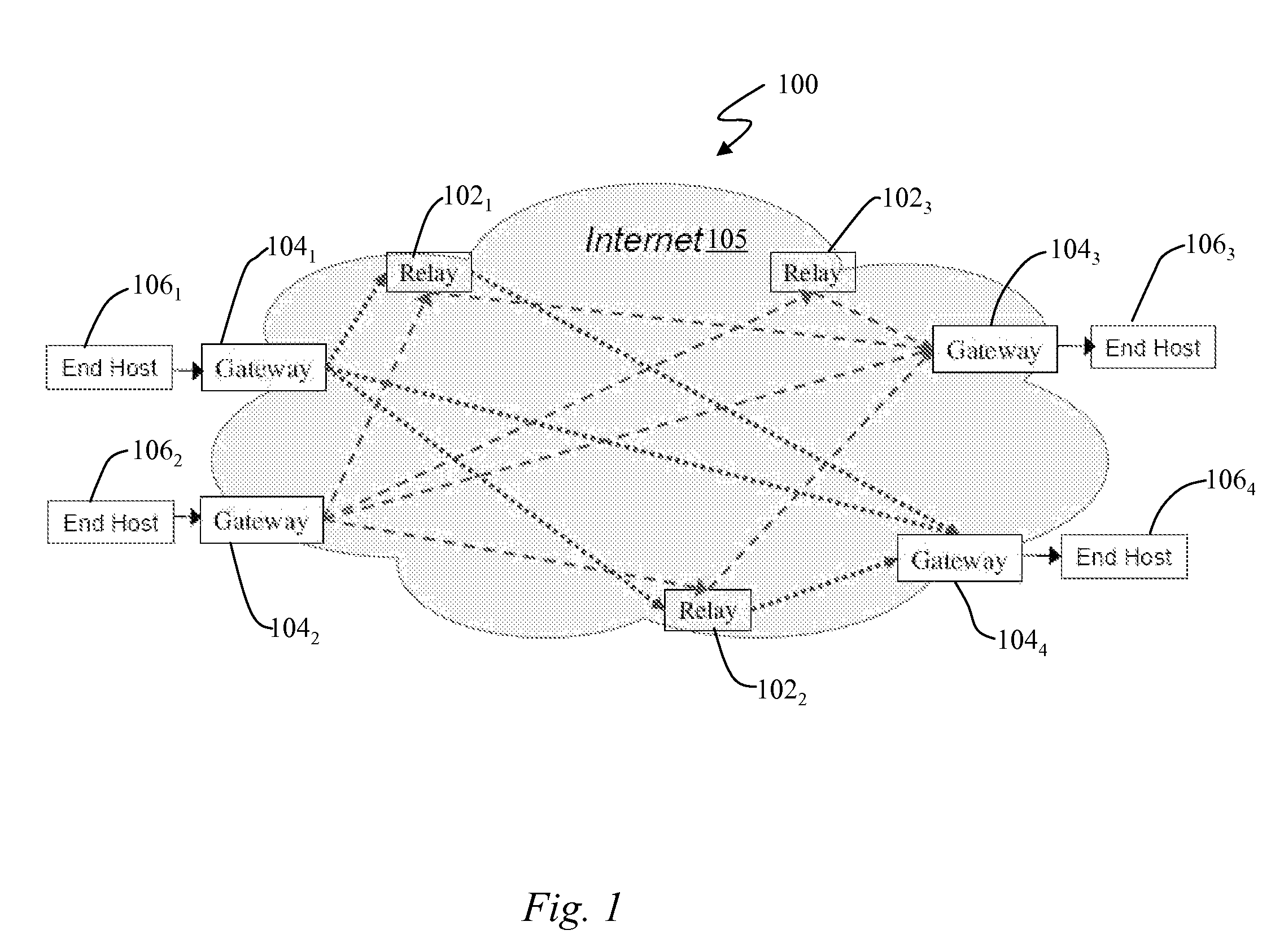
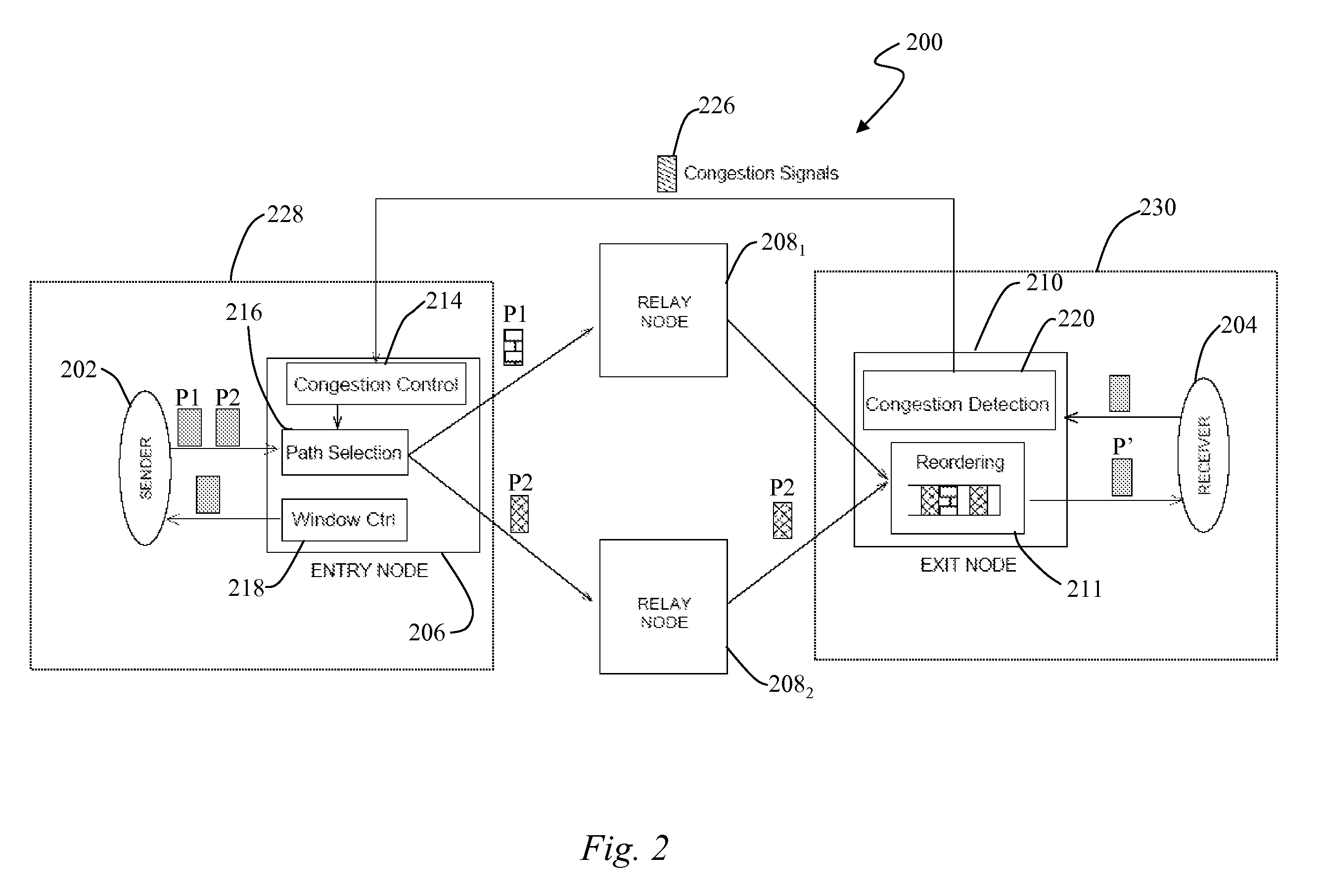
Multipath Routing Architecture for Large Data Transfers
ActiveUS20070230352A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork packetData transport
A multipath routing architecture for large data transfers is disclosed. The architecture employs an overlay network that provides diverse paths for packets from communicating end hosts to utilize as much capacity as available across multiple paths while ensuring network-wide fair allocation of resources across competing data transfers. A set of transit nodes are interposed between the end-hosts and for each end-to-end connection, a transit node can logically operate as an entry gateway, a relay or exit gateway. Packets from the sender enter the entry node and go to the exit node either directly or through one of a plurality of relay nodes. The exit node delivers the packets to the receiver. A multipath congestion control protocol is executed on the entry node to harness network capacity for large data transfers.
Owner:NEC CORP
Message routing
InactiveUS20060031364A1Interconnection arrangementsPublic key for secure communicationEmail addressSelective calling
Owner:HAMILTON MICHAEL
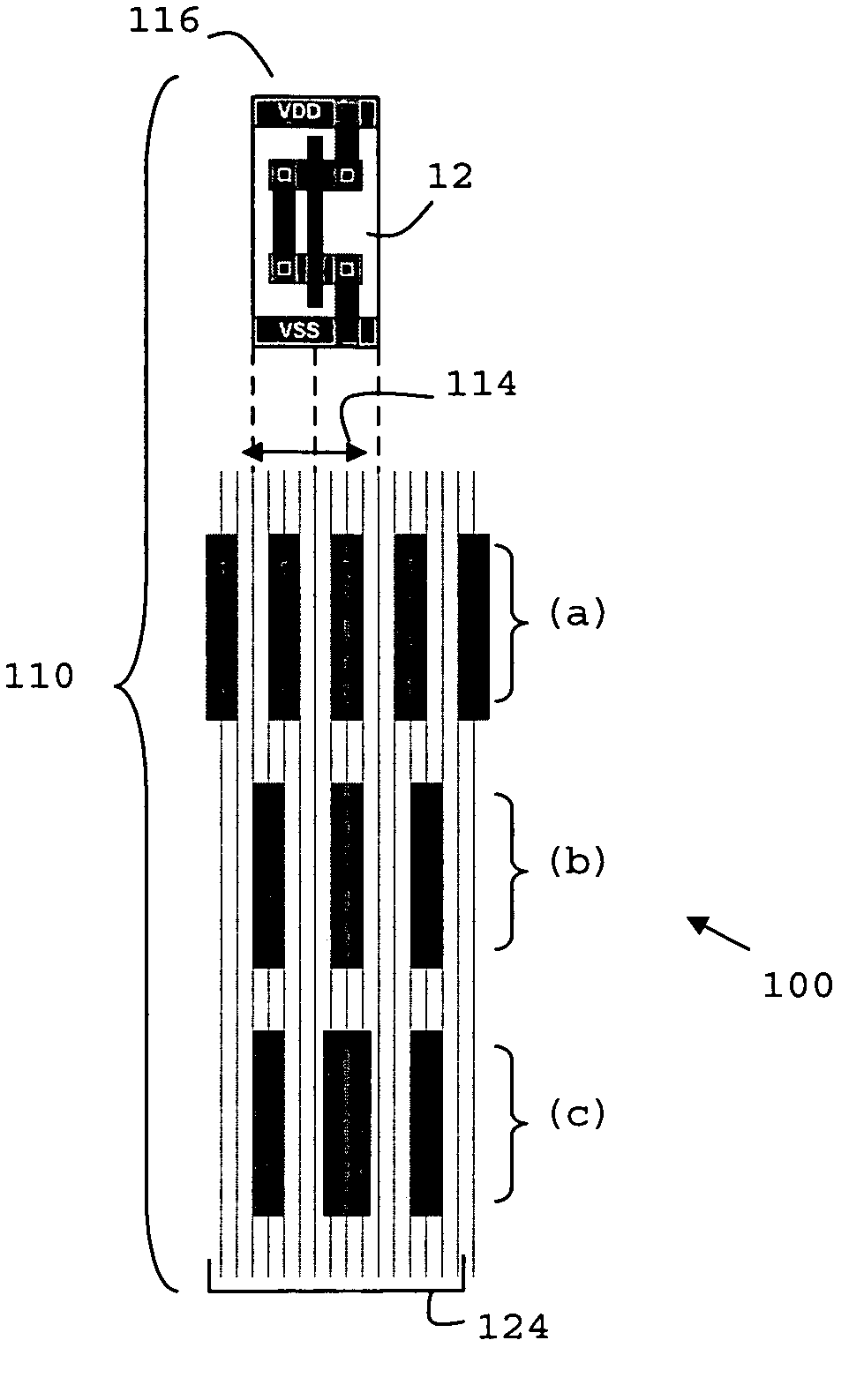
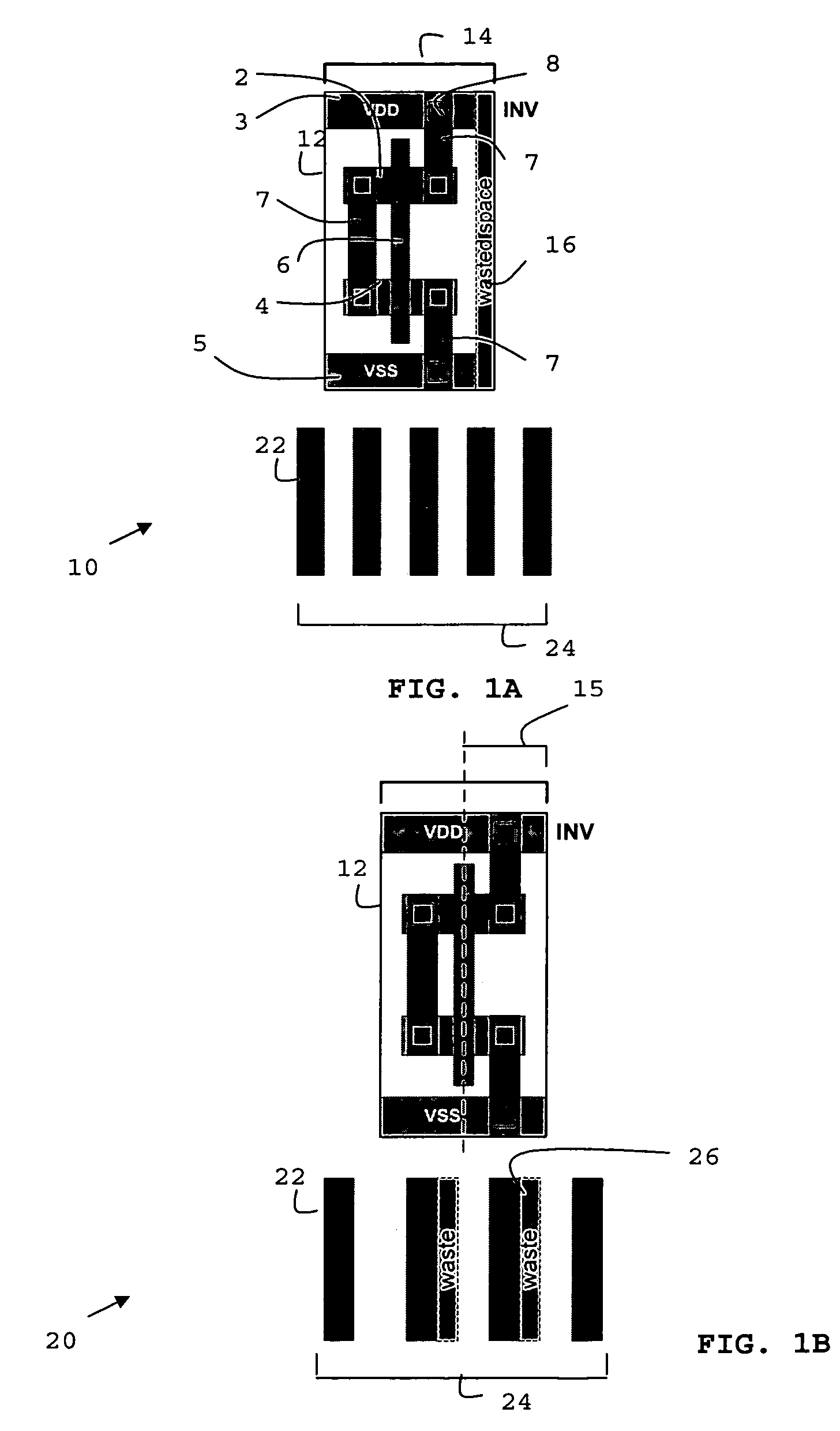
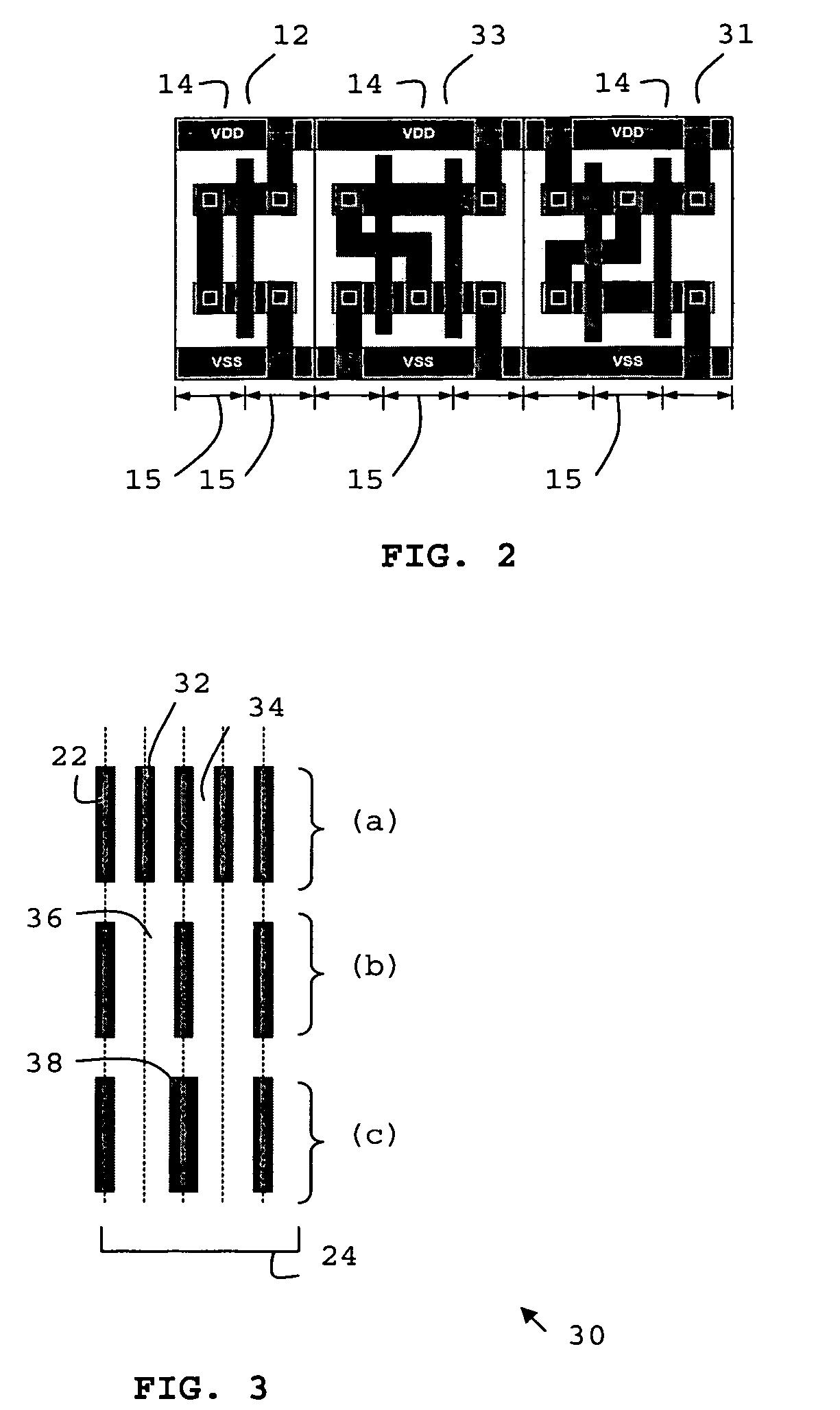
Aligned logic cell grid and interconnect routing architecture
ActiveUS20060195810A1Eliminate misalignmentCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsLogic cellAnd logic unit
A method (150) for defining an aligned logic cell grid and interconnect layout of a semiconductor integrated circuit having a logic cell (12) is disclosed. The interconnect layout is resized in accordance with a highest common denominator of an initial routing pitch (24) of the interconnect layout and a transistor pitch (14) of the logic cell. The cell grid is aligned with the resized routing pitch (124) which provides efficient routing density and transistor performance, minimises excess transistor area and wire routing waste while maximising cell packing density.
Owner:ICERA INC
Programmable logic device with redundant circuitry
InactiveUS20030072185A1Reliability increasing modificationsSolid-state devicesComputer architectureProgrammable logic device
A programmable logic device and associated method is provided with repairable regions. In one aspect, general routing interconnect lines are segmented within repairable regions. In another aspect, IO bus lines and associated circuitry are provided that accommodate redundancy in a staggered segmented architecture. In another aspect, a dedicated routing architecture between particular logic regions accommodates shifting to define and utilize repairable regions. Principles of other aspects are illustrated and described in the context of several exemplary embodiments of aspects of the invention.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Programmable logic device with redundant circuitry
InactiveUS6965249B2Reliability increasing modificationsSolid-state devicesComputer architectureProgrammable logic device
A programmable logic device and associated method is provided with repairable regions. In one aspect, general routing interconnect lines are segmented within repairable regions. In another aspect, IO bus lines and associated circuitry are provided that accommodate redundancy in a staggered segmented architecture. In another aspect, a dedicated routing architecture between particular logic regions accommodates shifting to define and utilize repairable regions. Principles of other aspects are illustrated and described in the context of several exemplary embodiments of aspects of the invention.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Methods and systems for a wireless routing architecture and protocol
ActiveUS7933236B2Short pathTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTelecommunicationsMobile station
The present invention provides a method for generating routing paths in a multi-hop network. The multi-hop network includes a base station, at least one relay station, and at least one non-relay mobile station. The routing paths are paths between the base station and the at least one non-relay mobile station via the at least one relay station. The base station broadcasts a path discovery message (PDM) including a path list with a starting point of the path list being the base station. Each of the relay stations receives the PDM and updates the PDM by adding their own respective node identifier to the path list and broadcasting the updated PDM. The PDMs eventually reach the non-relay mobile station. The non-relay mobile stations reply to the base station by sending the base station the updated path list between the base station and the non-relay mobile station. In some embodiments the base station or the at least one non-relay mobile station acting as a source node sends a dynamic service (DSx) message including an end-to-end path list to an end of path destination. The relay stations use the path list to forward the message between the source node and the end of path destination. In some implementations the multi-hop network operates in a manner that is consistent with any one of: IEEE 802.16, IEEE 802.16d, and IEEE 802.16e.
Owner:APPLE INC
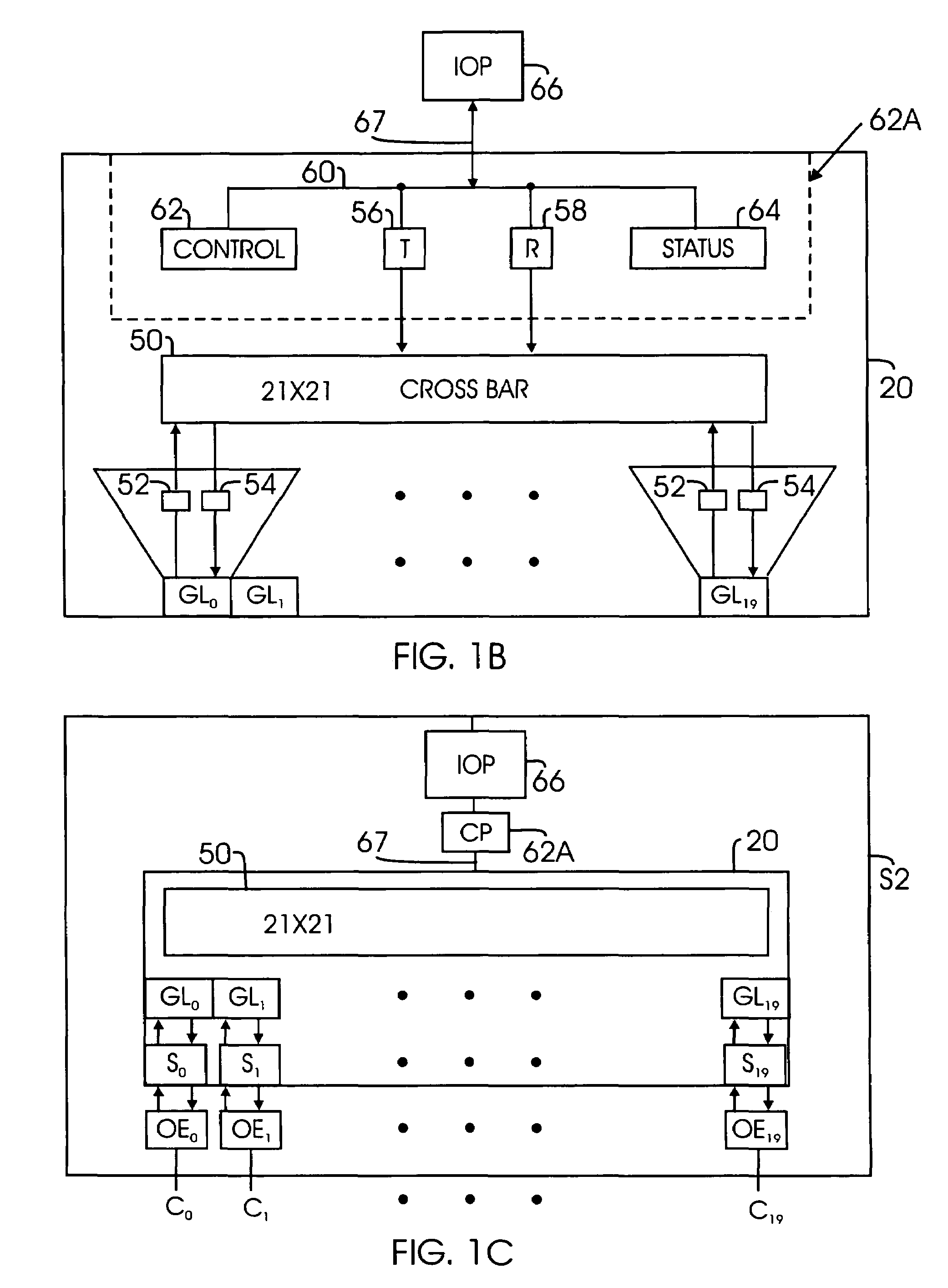
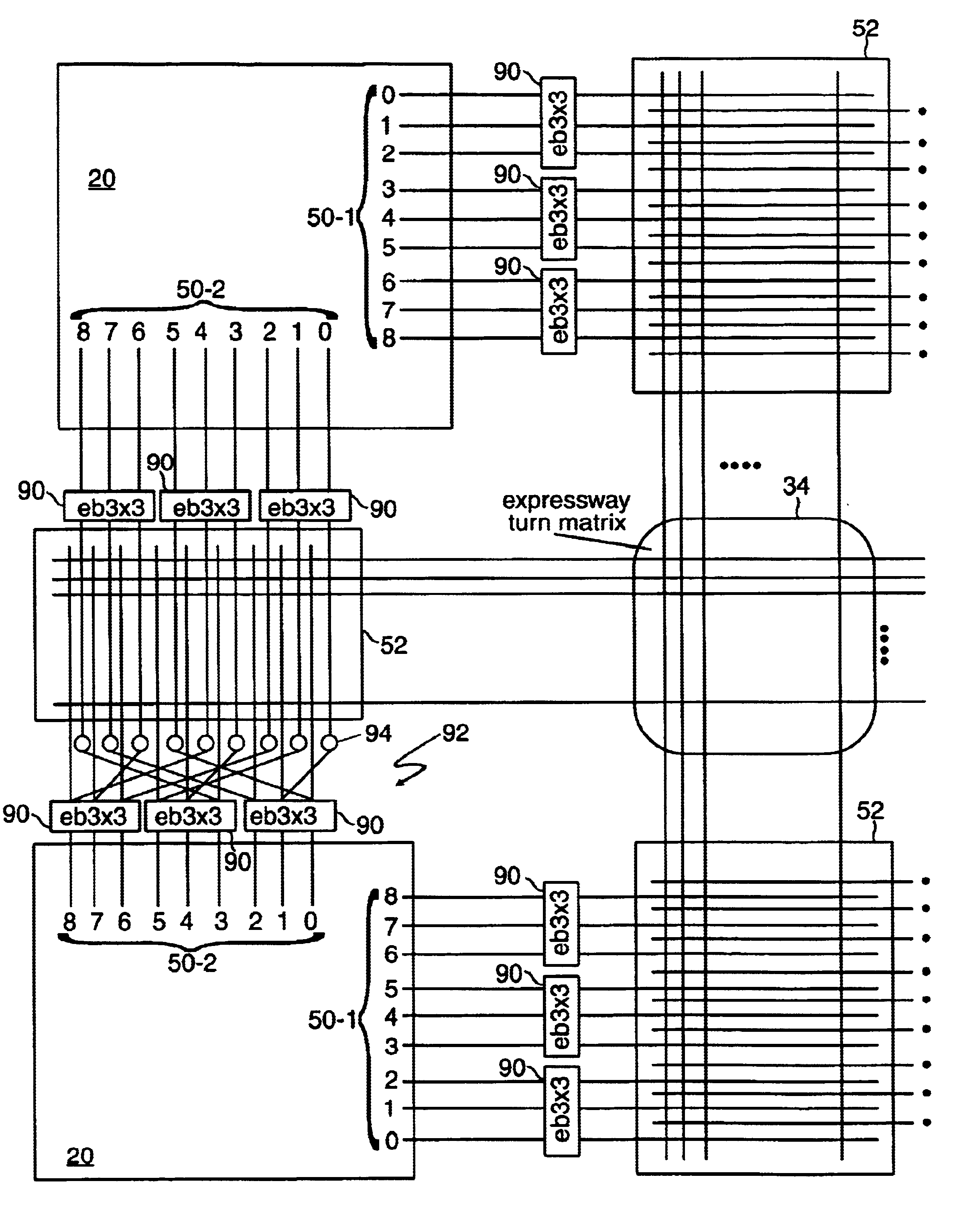
Block level routing architecture in a field programmable gate array
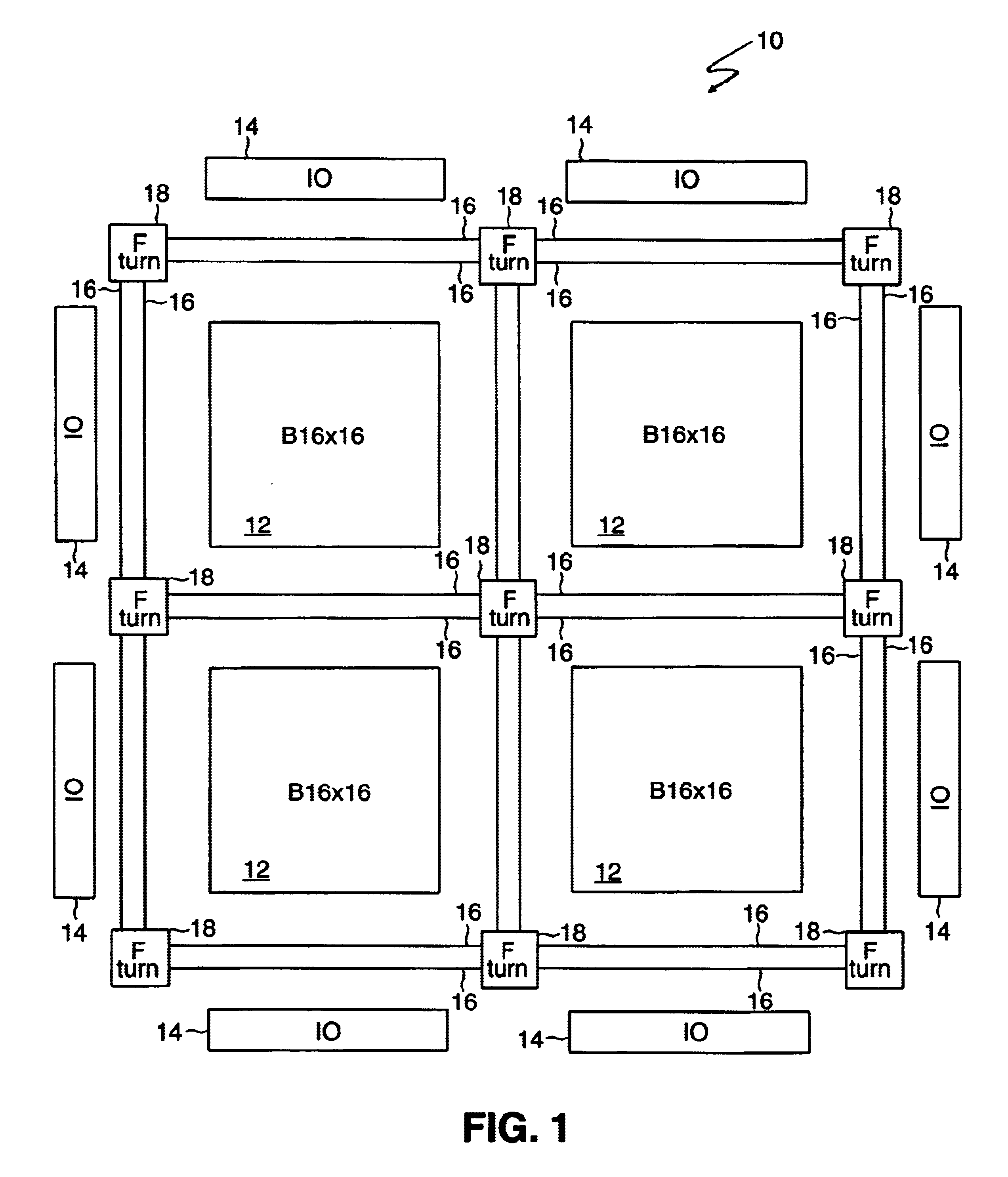
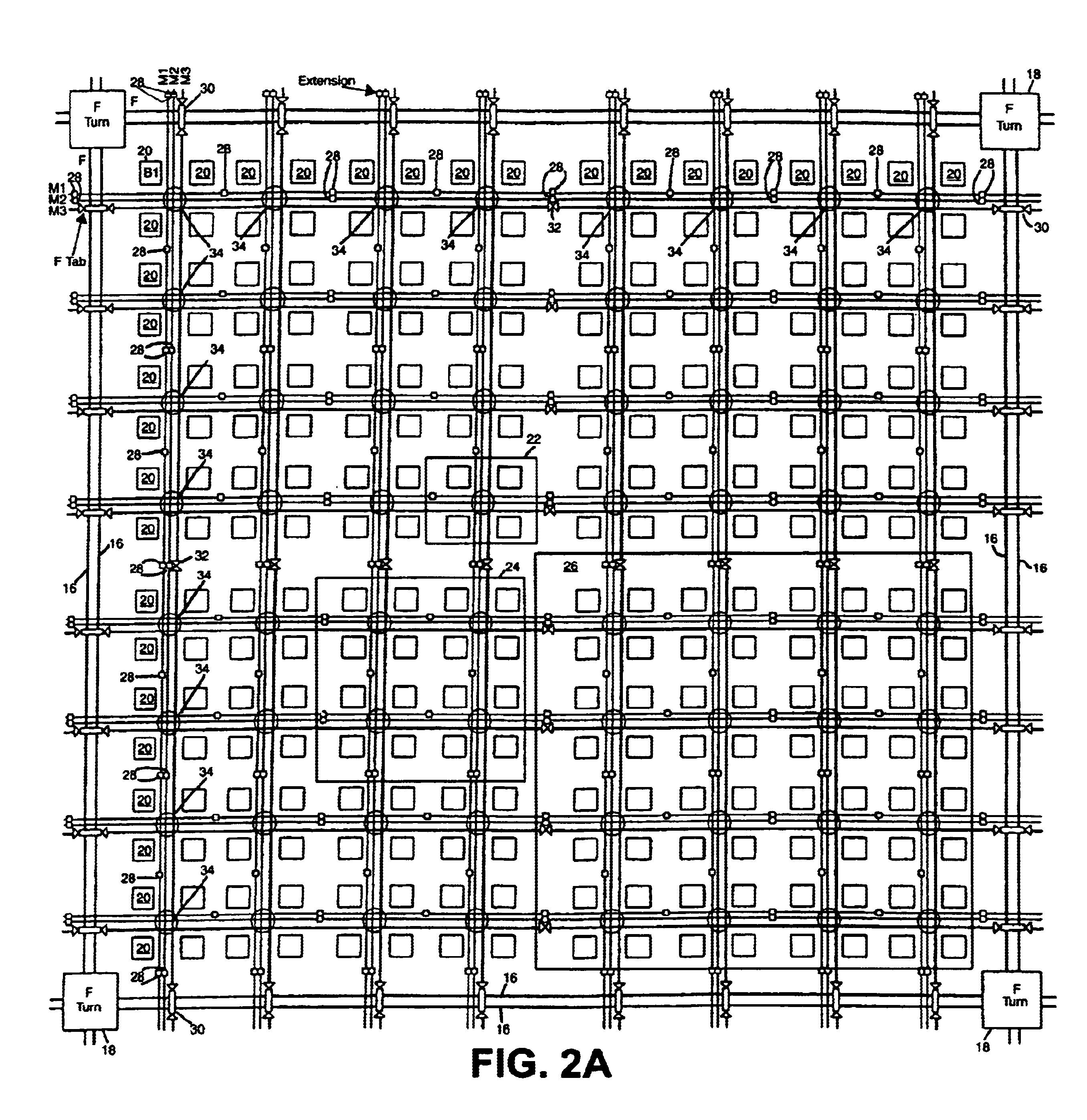
InactiveUS6567968B1Good symmetryEasy to placeSolid-state devicesSpecial data processing applicationsFpga architectureElectrical conductor
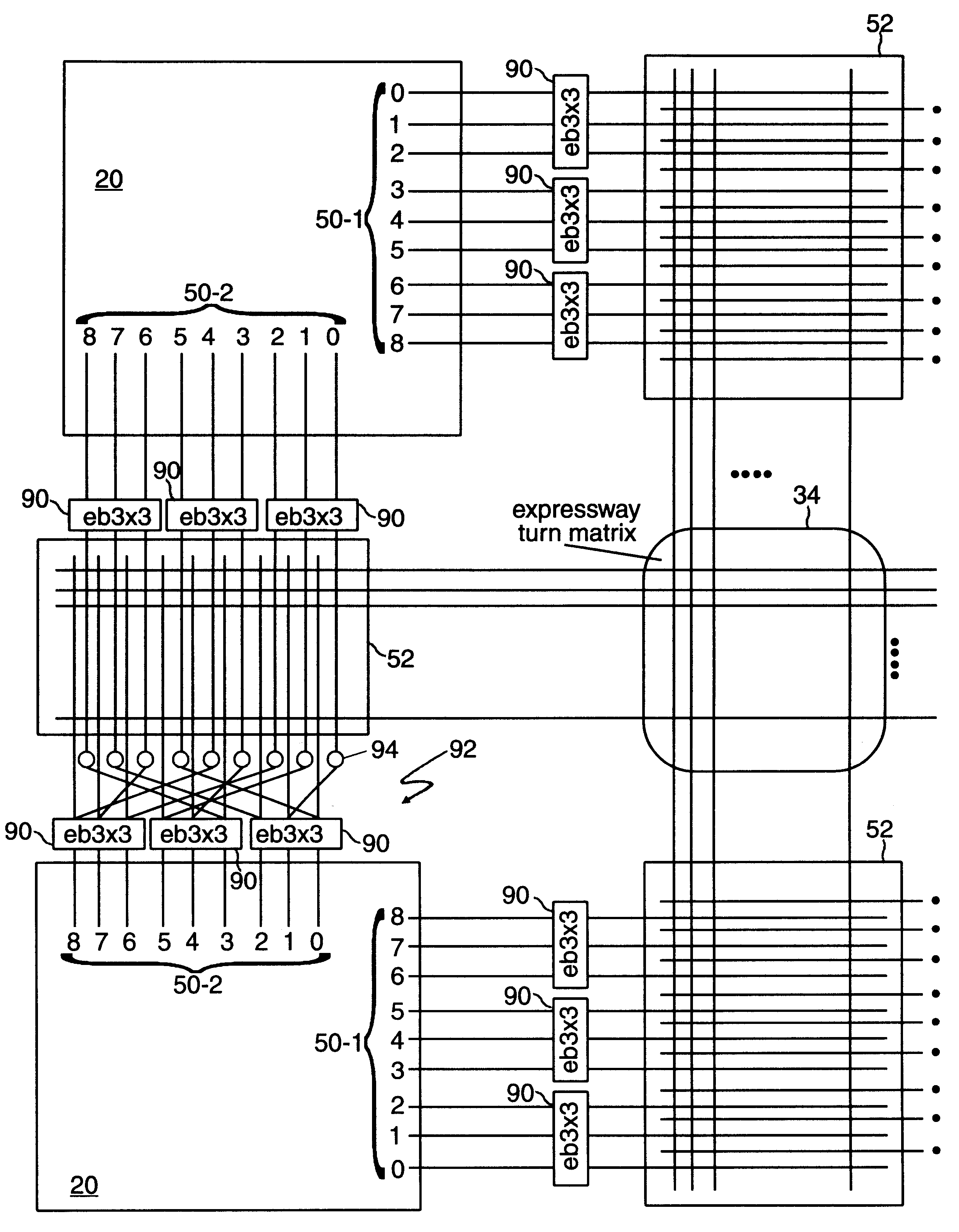
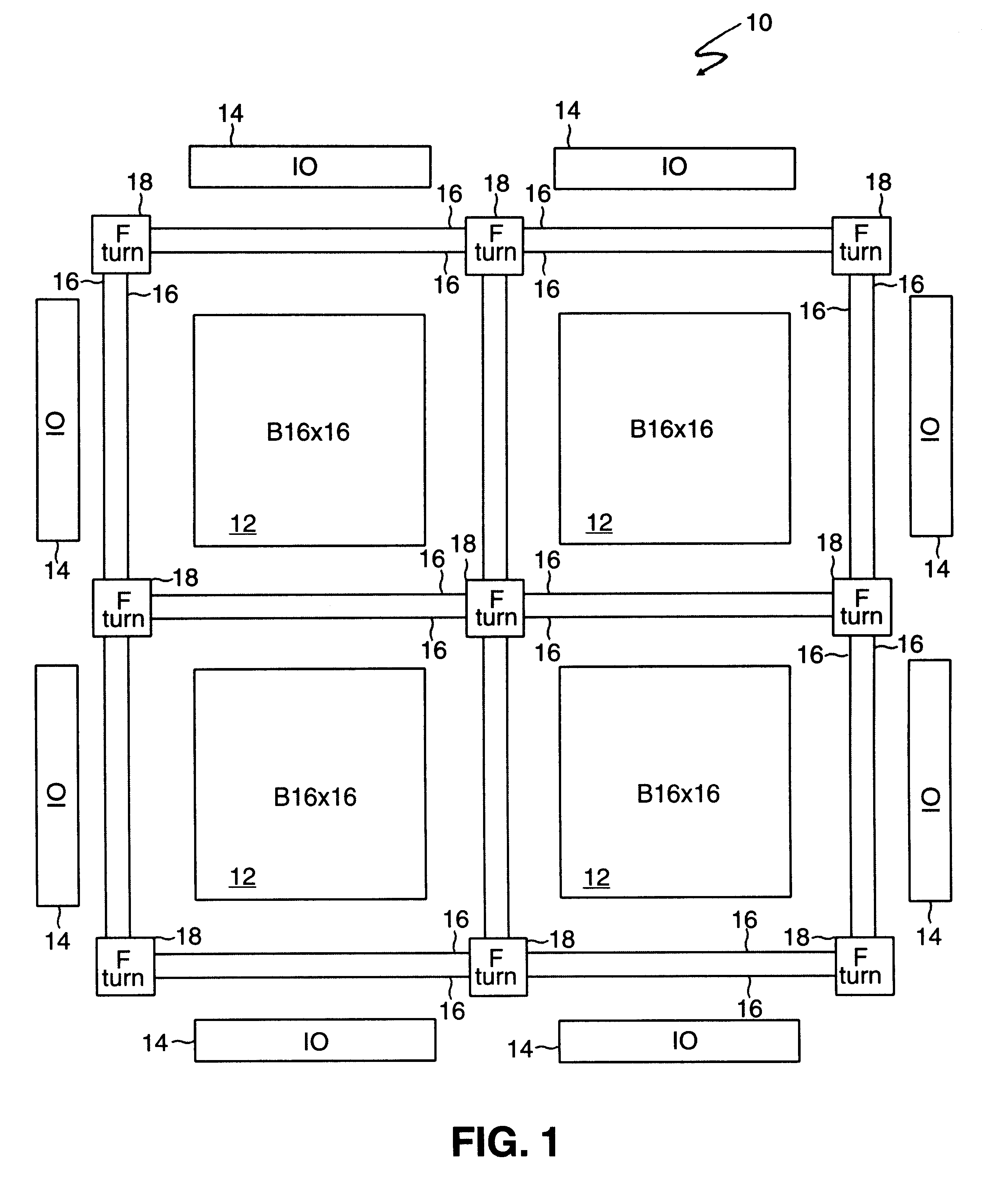
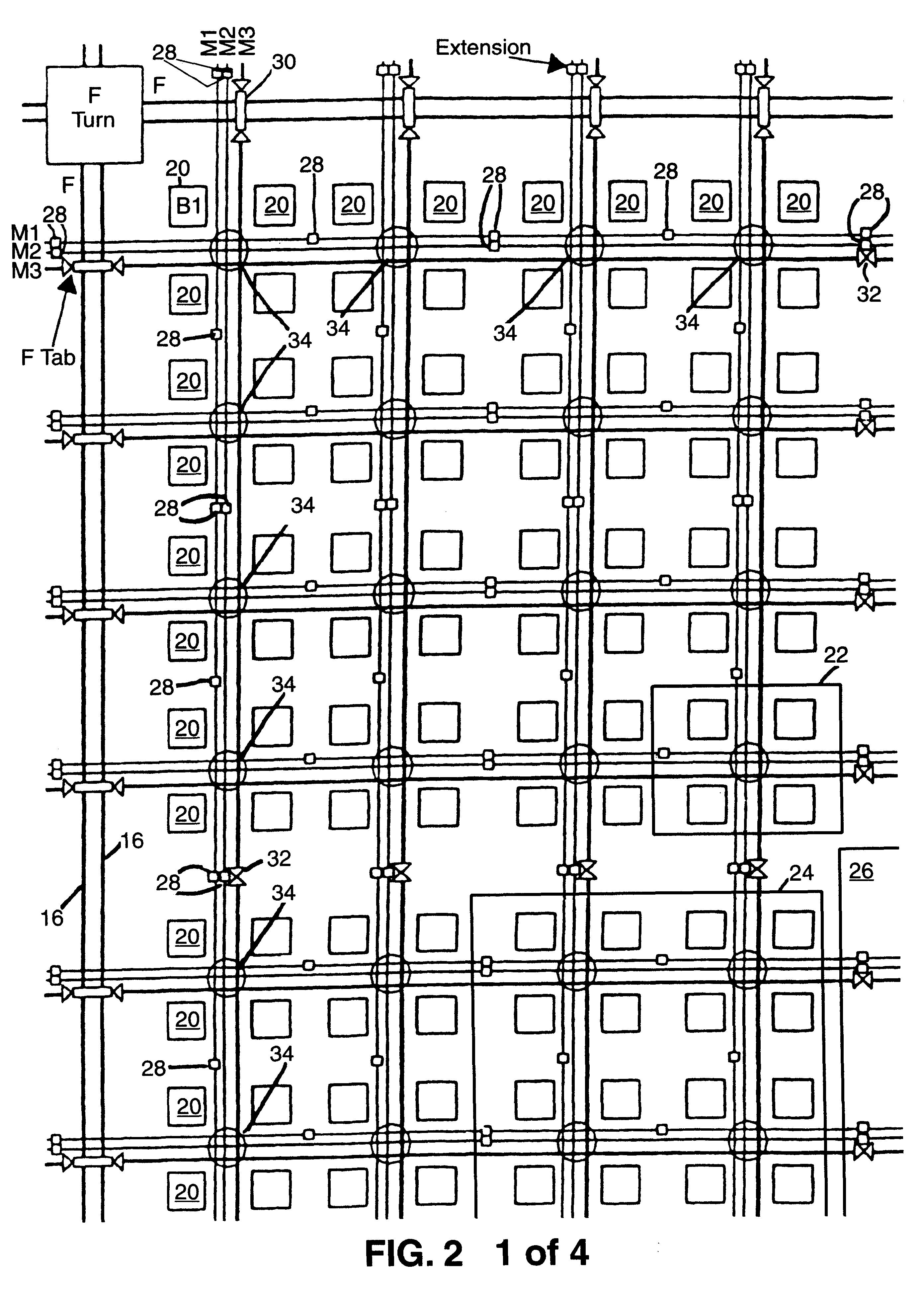
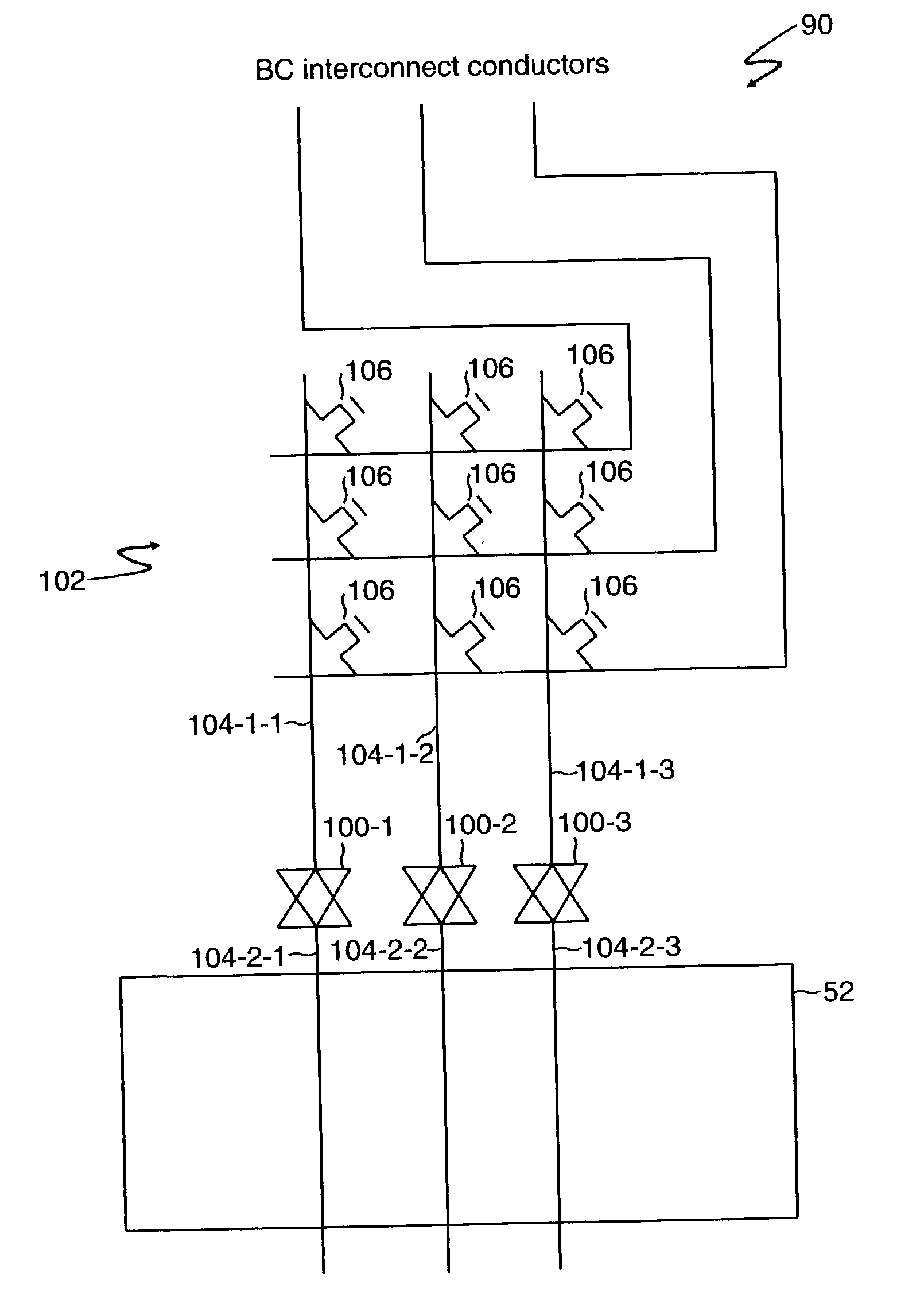
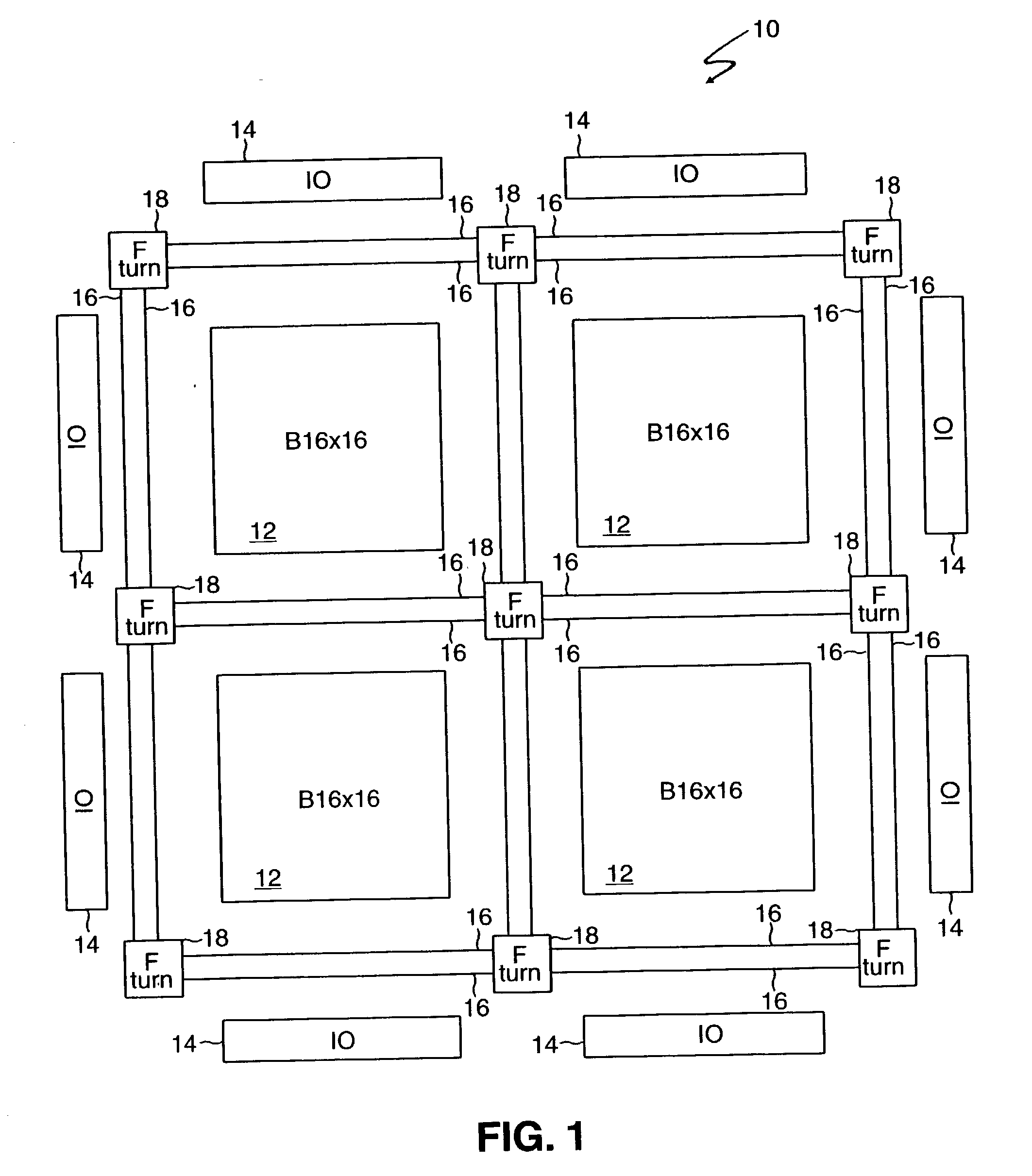
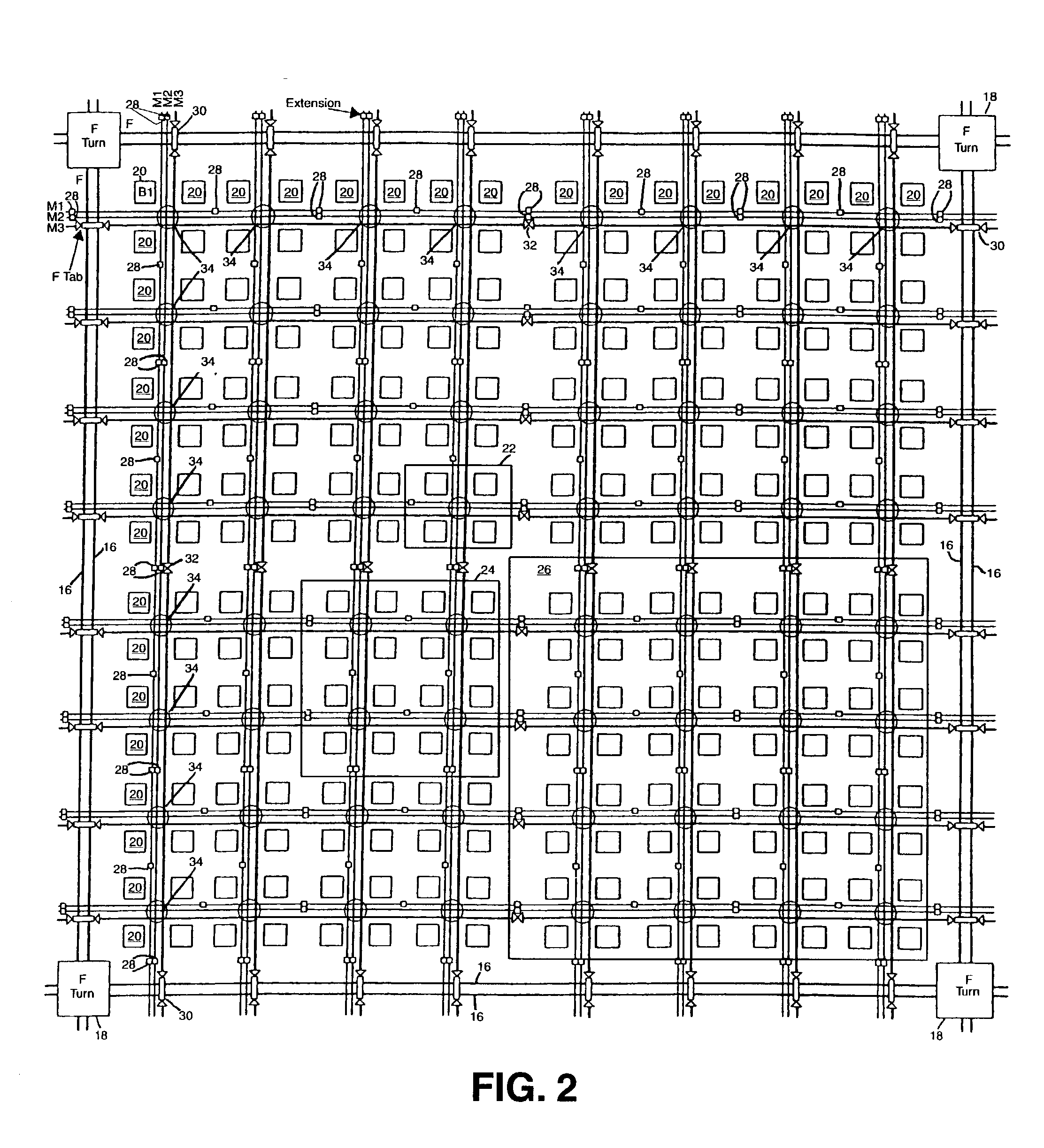
An FPGA architecture has top, middle and low levels. The top level of the architecture is an array of the B16x16 tiles arranged in a rectangular array and enclosed by I / O blocks on the periphery. On each of the four sides of a B16x16 tile, and also associated with each of the I / O blocks is a freeway routing channel. A B16x16 tile in the middle level of hierarchy is a sixteen by sixteen array of B1 blocks. The routing resources in the middle level of hierarchy are expressway routing channels M1, M2, and M3 including groups of interconnect conductors. At the lowest level of the semi-hierarchical FPGA architecture, there are block connect (BC) routing channels, local mesh (LM) routing channels, and direct connect (DC) interconnect conductors. Each BC routing channel is coupled to an expressway tab to provide access for each B1 block to the expressway routing channels M1, M2, and M3, respectively. Each BC routing channel has nine interconnect conductors which are grouped into three groups of three interconnect conductors. Each group of three interconnect conductors is connected to a first side of a Extension Block (EB) 3x3 switch matrix. A second side of each EB 3x3 switch matrix is coupled to the E-tab. Between adjacent B1 blocks, in both the horizontal and vertical directions, the leads on the second side of a first EB 3x3 switch matrix may be coupled to the leads on the second side of second EB3x3 switch matrix by BC criss-cross extension.
Owner:ACTEL CORP
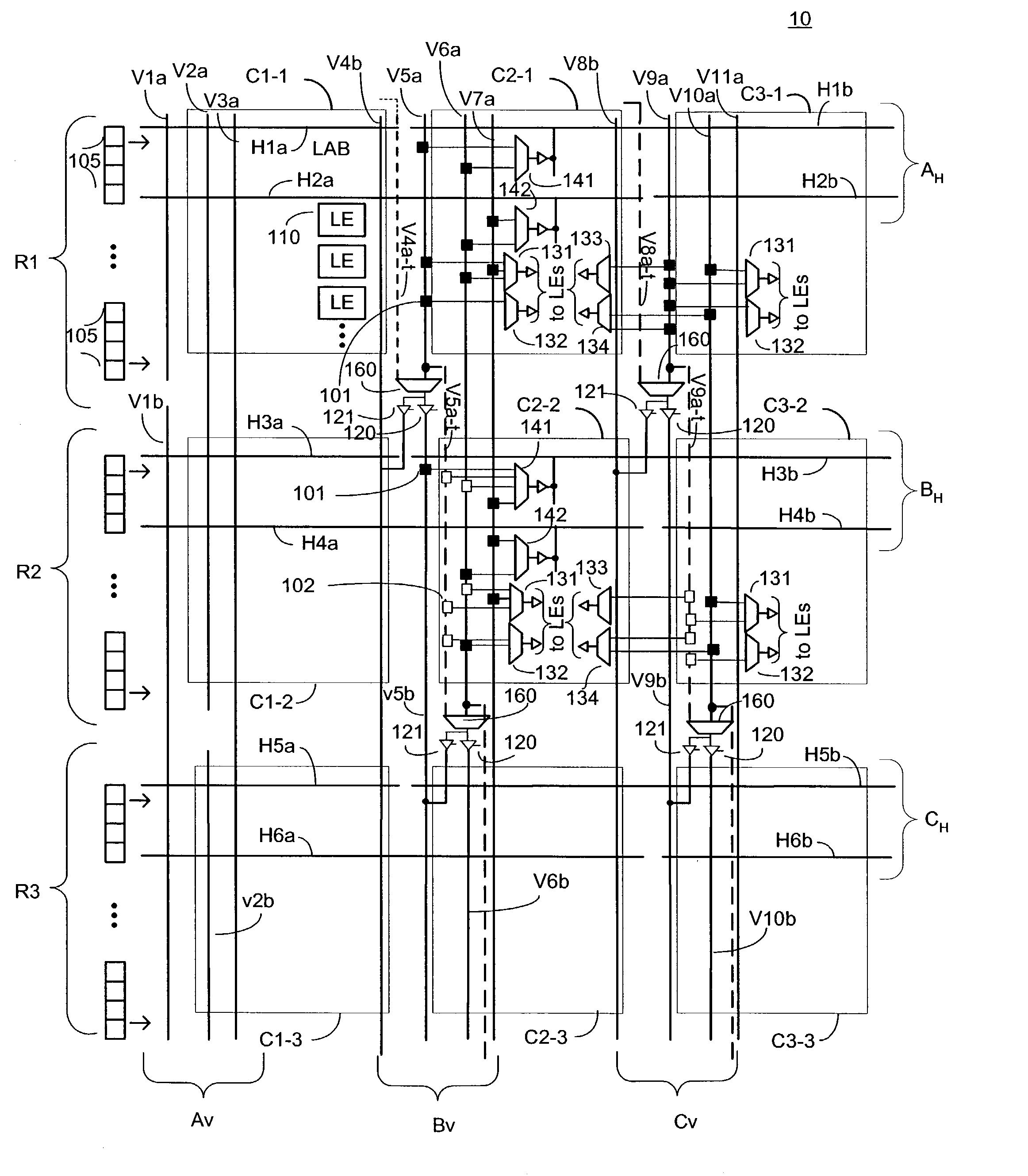
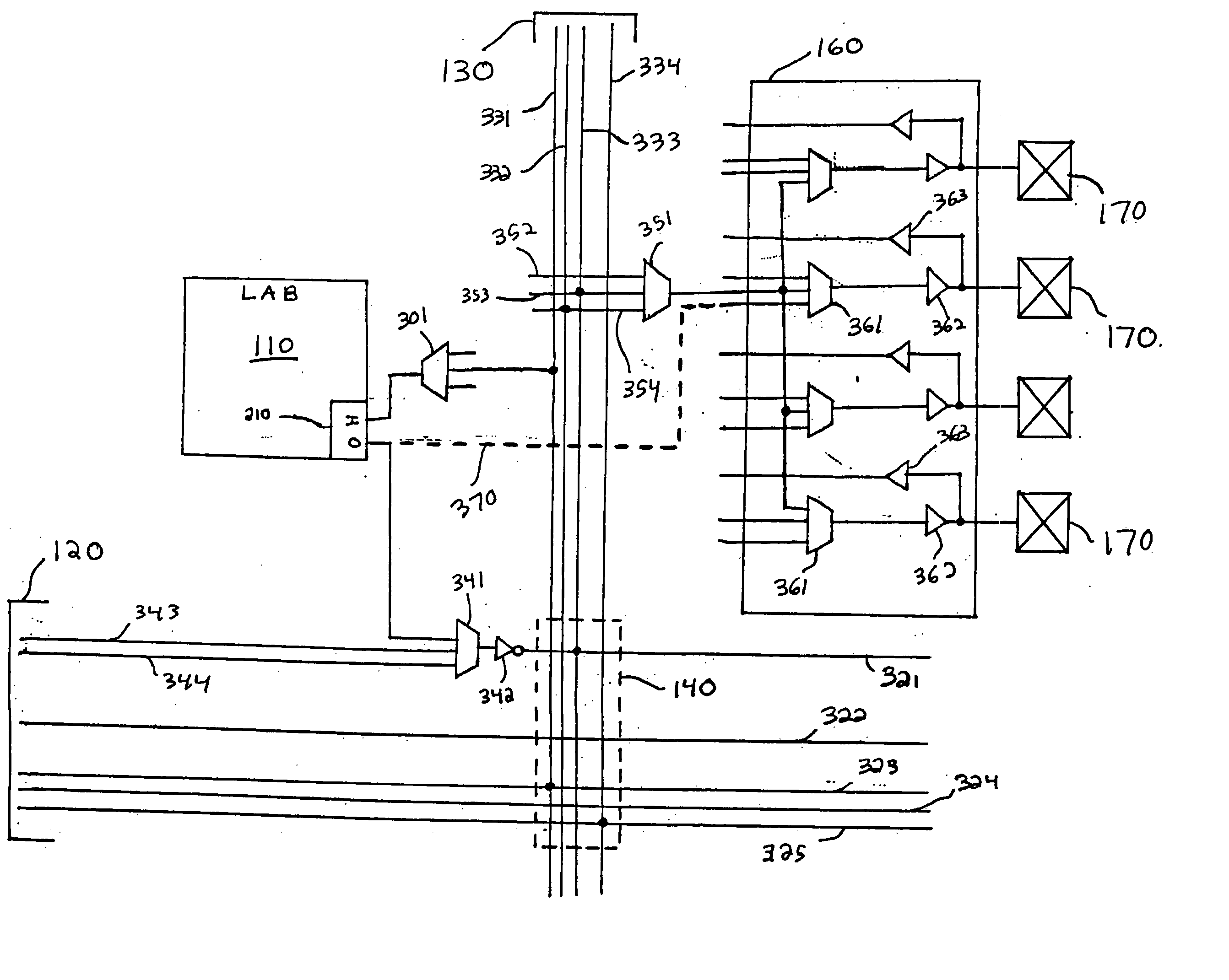
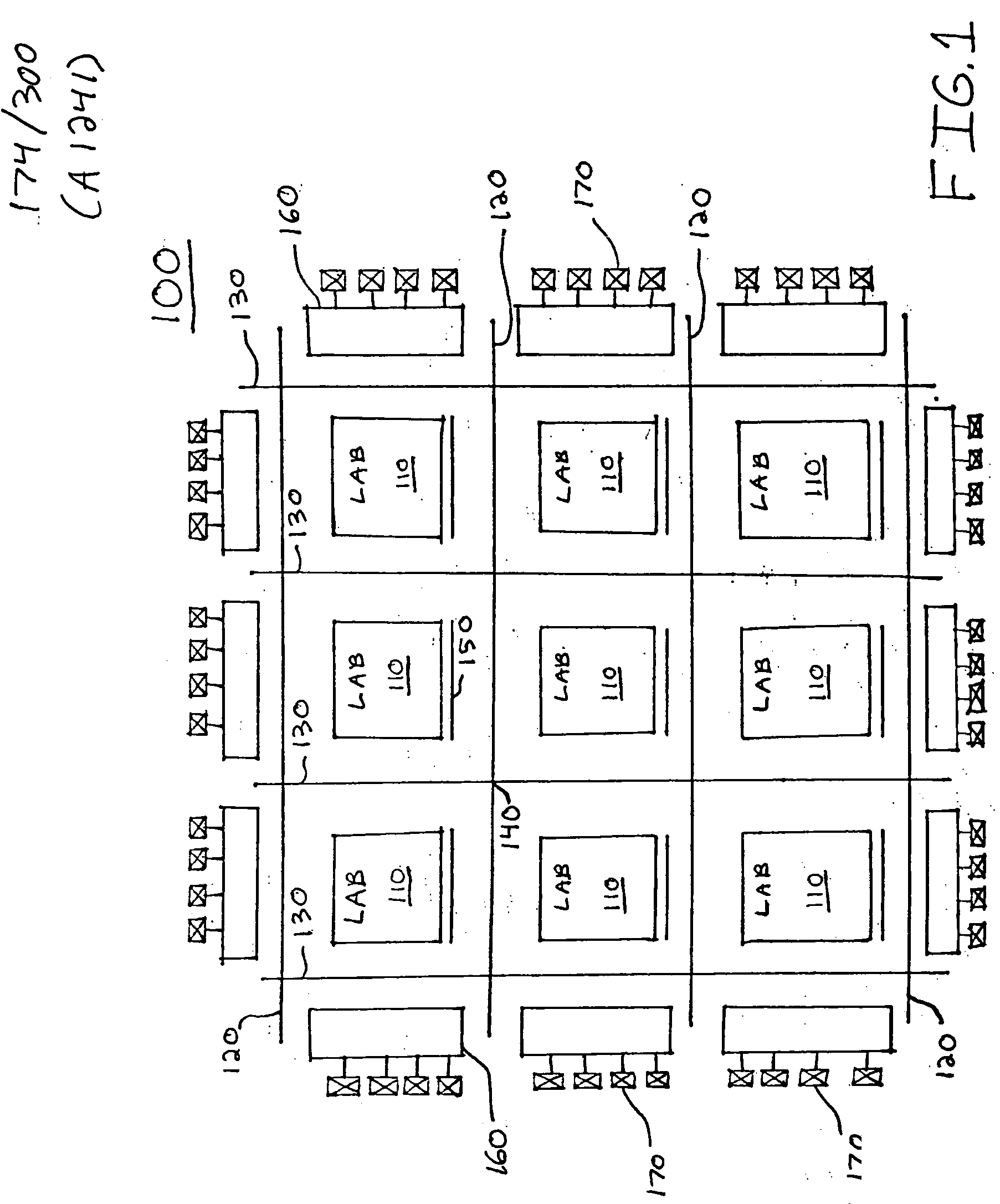
Routing architecture for a programmable logic device
InactiveUS6970014B1Solid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsProgrammable logic deviceEngineering
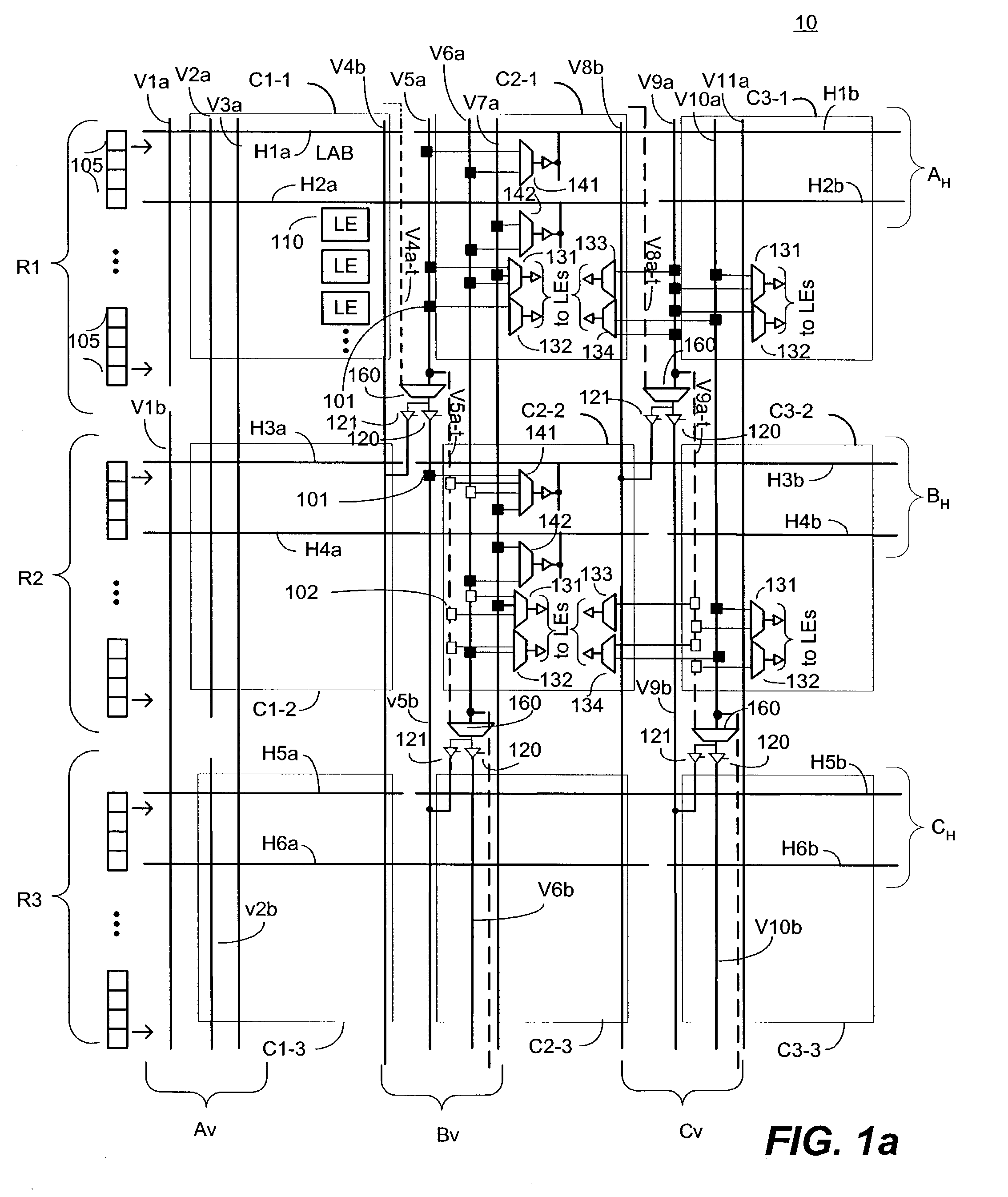
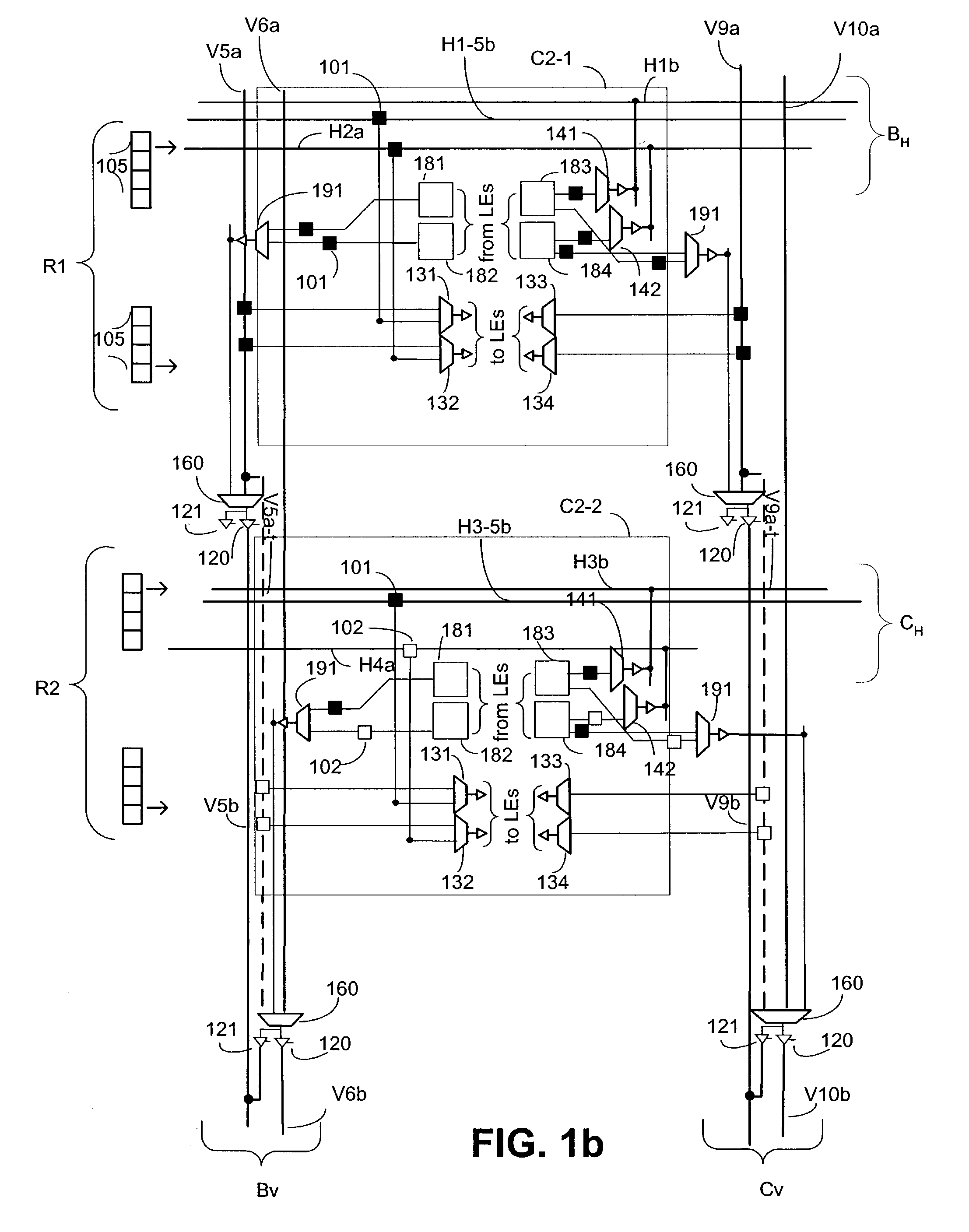
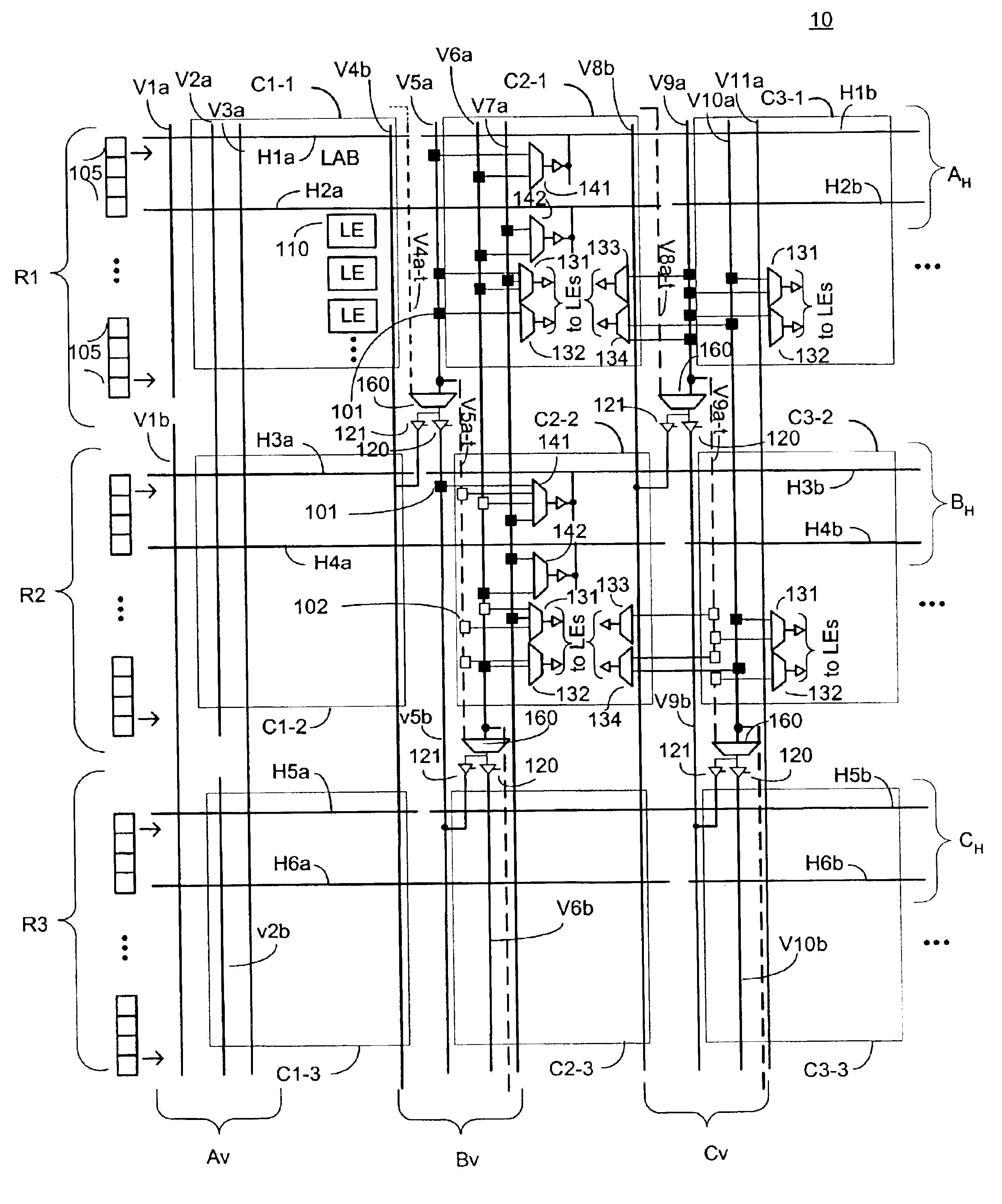
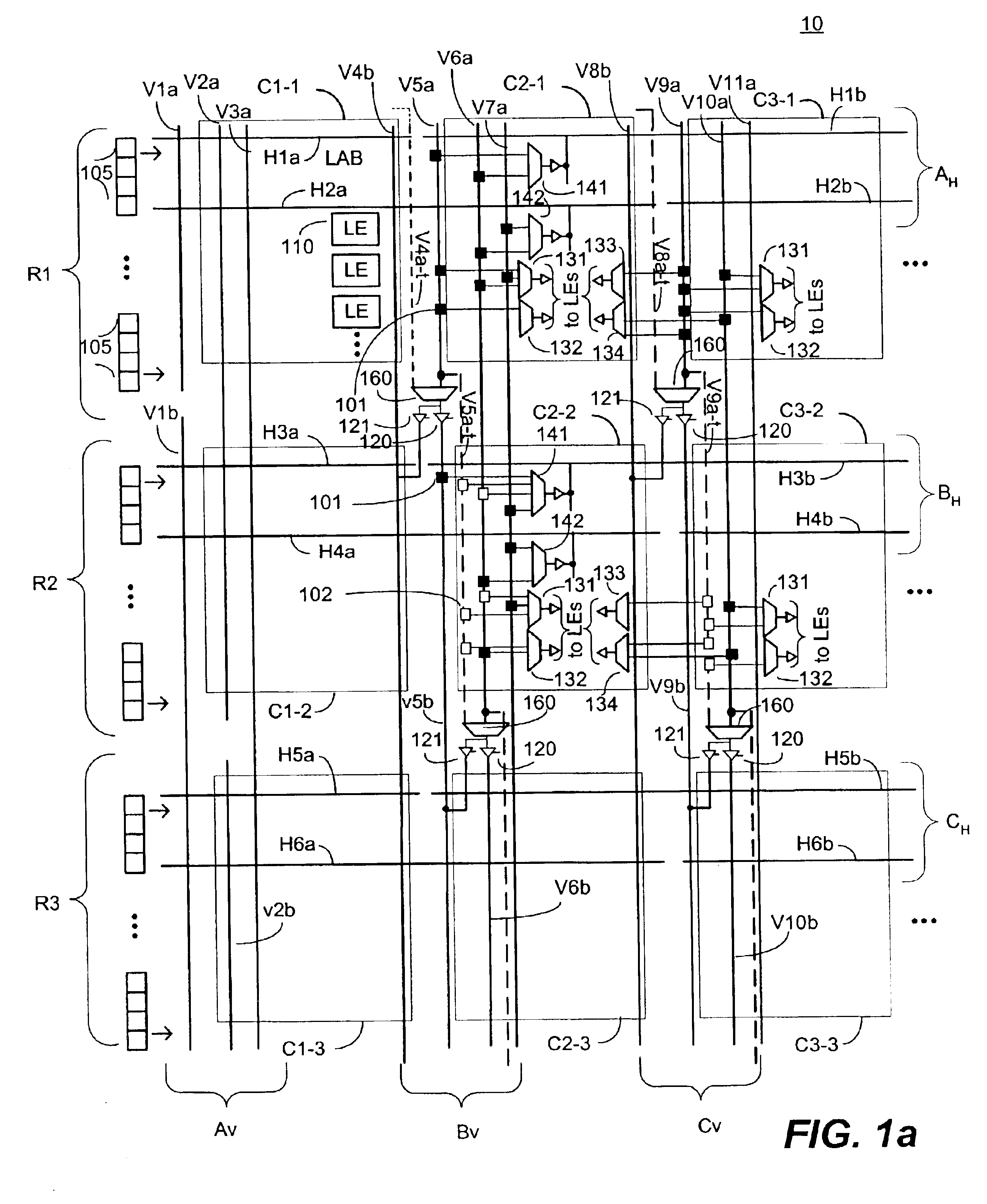
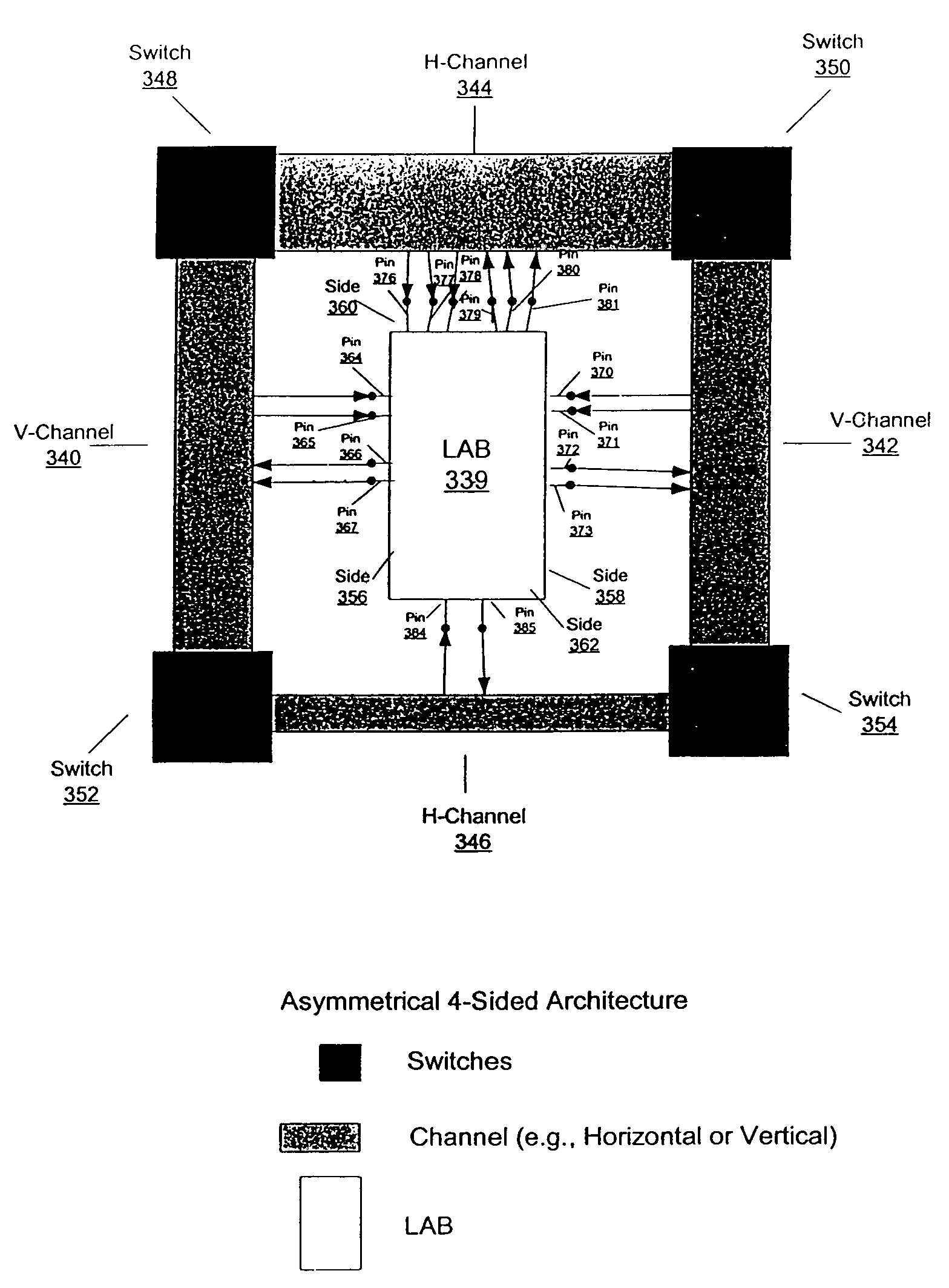
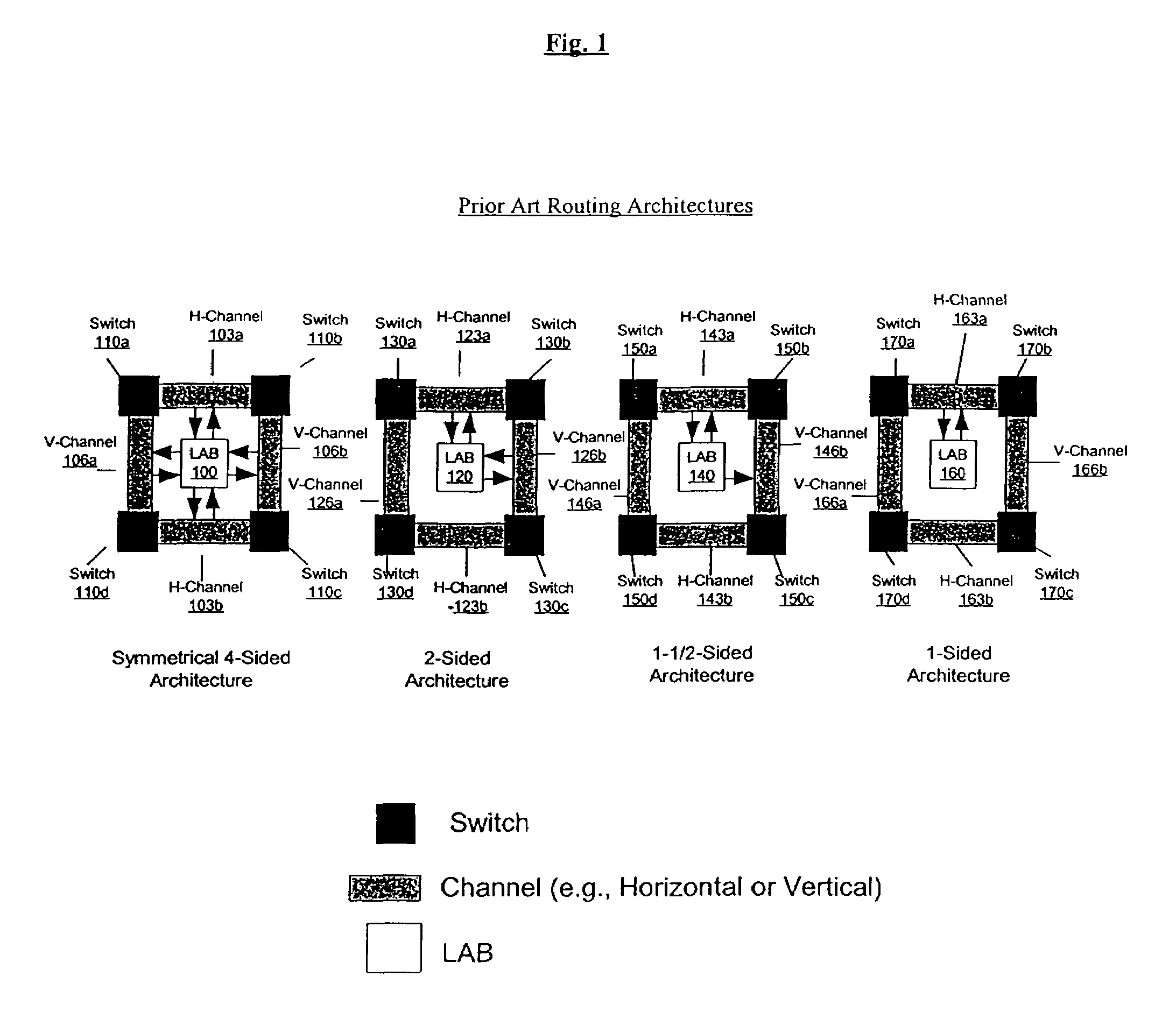
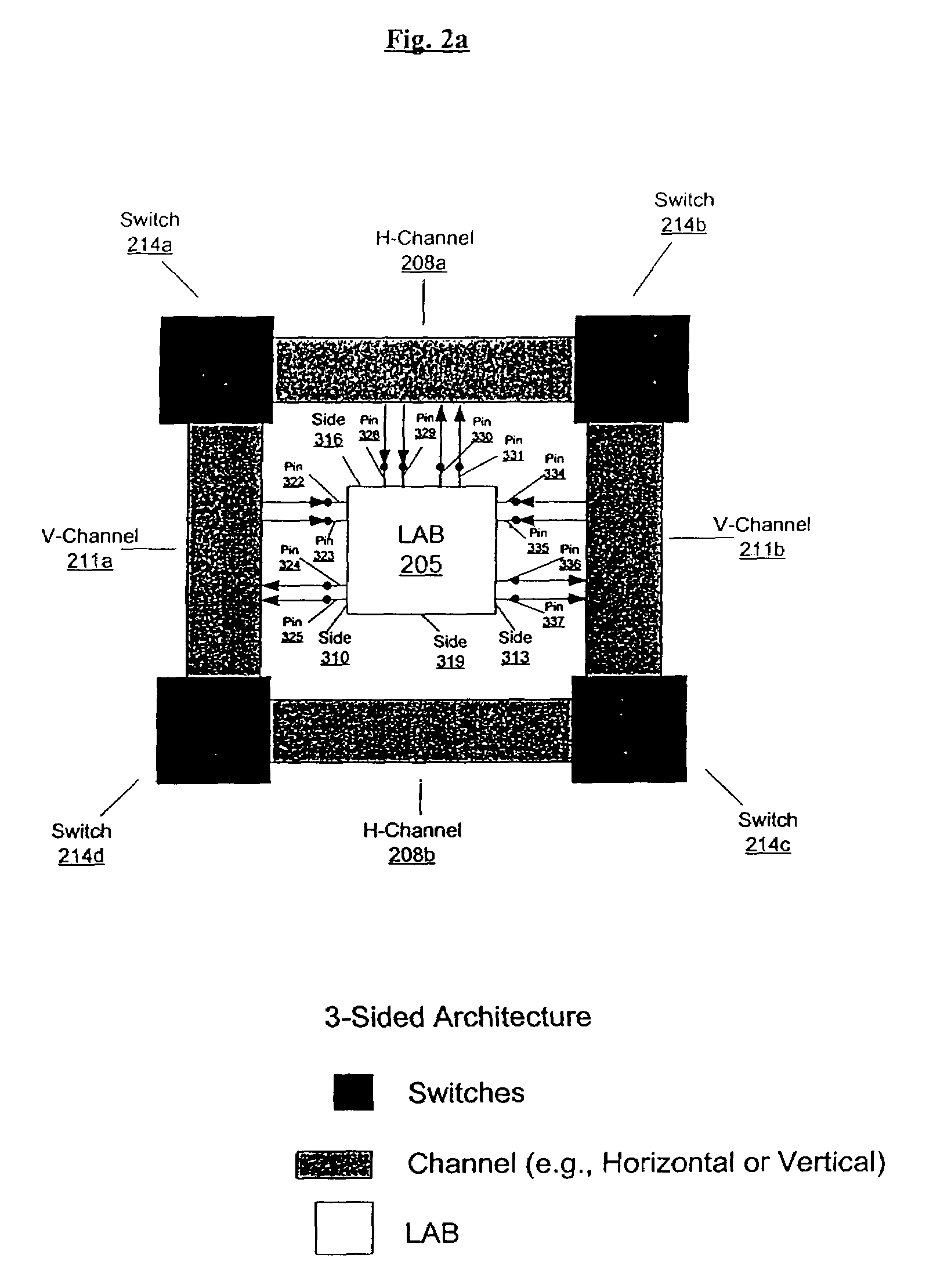
An embodiment of this invention pertains to a 3-sided routing architecture to interconnect function blocks, such as logic array blocks (“LABs”), within a programmable logic device (“PLD”). In the 3-sided routing architecture, inputs and outputs on a first side of a function block connect to a first channel, and inputs and outputs on a second side of the function block connect to a second channel where the second side is opposite the first side. Inputs and outputs on a third side of the function block connect to a third channel. A fourth channel associated with a fourth side of the function block, the fourth side opposite the third side, is coupled only to the first channel and the second channel. In one configuration, the inputs and outputs on each of the first side, the second side, and the third side have an equal number of inputs and outputs. In this configuration, each of the first channel, the second channel, and the third channel have the same width. In another configuration, the number of pins on one of the first side, the second side, or the third side differs from the number of pins on another one of those sides.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Multipath routing architecture for large data transfers
A multipath routing architecture for large data transfers is disclosed. The architecture employs an overlay network that provides diverse paths for packets from communicating end hosts to utilize as much capacity as available across multiple paths while ensuring network-wide fair allocation of resources across competing data transfers. A set of transit nodes are interposed between the end-hosts and for each end-to-end connection, a transit node can logically operate as an entry gateway, a relay or exit gateway. Packets from the sender enter the entry node and go to the exit node either directly or through one of a plurality of relay nodes. The exit node delivers the packets to the receiver. A multipath congestion control protocol is executed on the entry node to harness network capacity for large data transfers.
Owner:NEC CORP
Field programmable gate array architecture having Clos network-based input interconnect
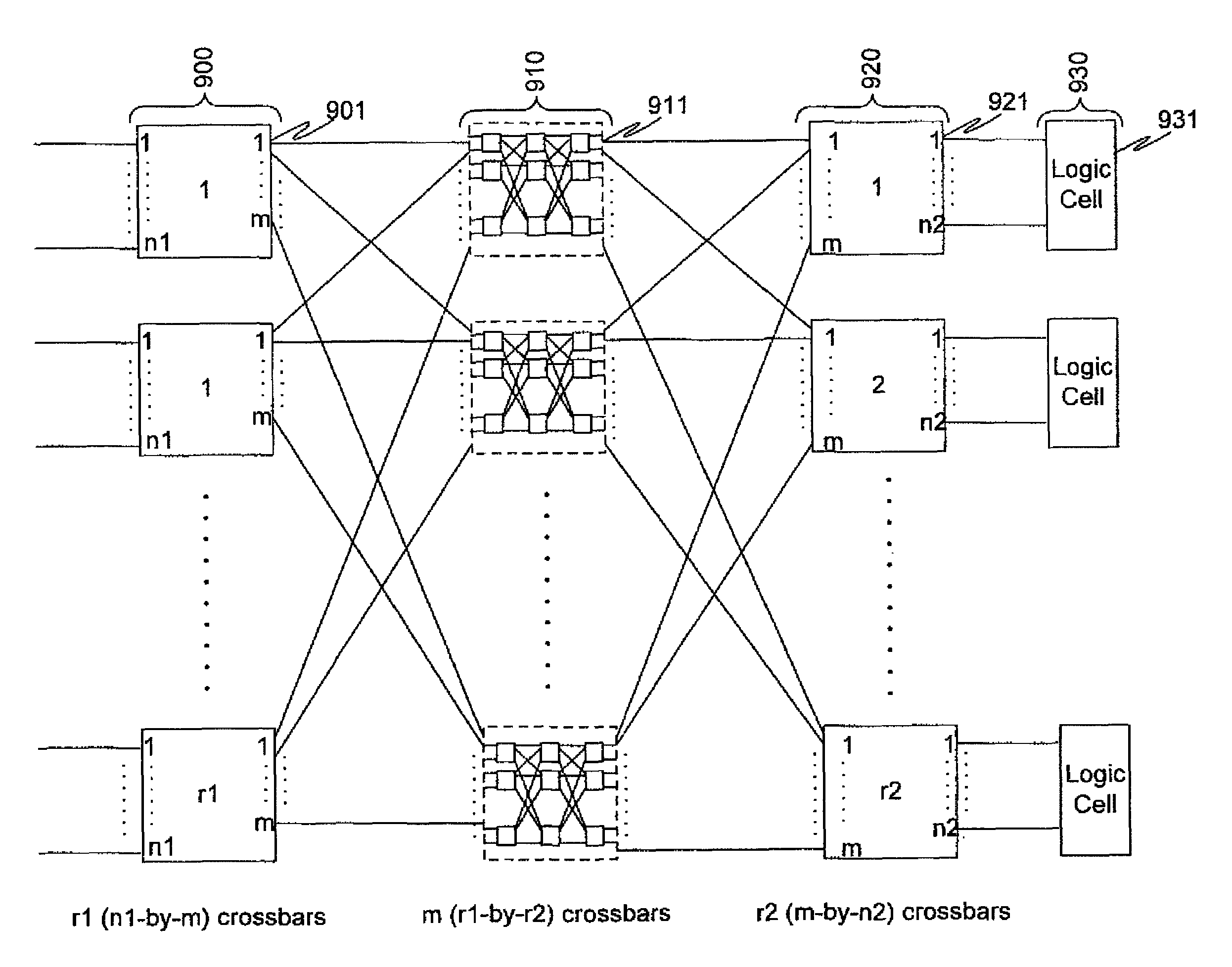
ActiveUS7924052B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsSolid-state devicesProgrammable logic deviceCluster based
A cluster internal routing network for use in a programmable logic device with a cluster-based architecture employs a Clos network-based routing architecture. The routing architecture is a multi-stage blocking architecture, where the number of inputs to the first stage exceeds the number of outputs from the first stage.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
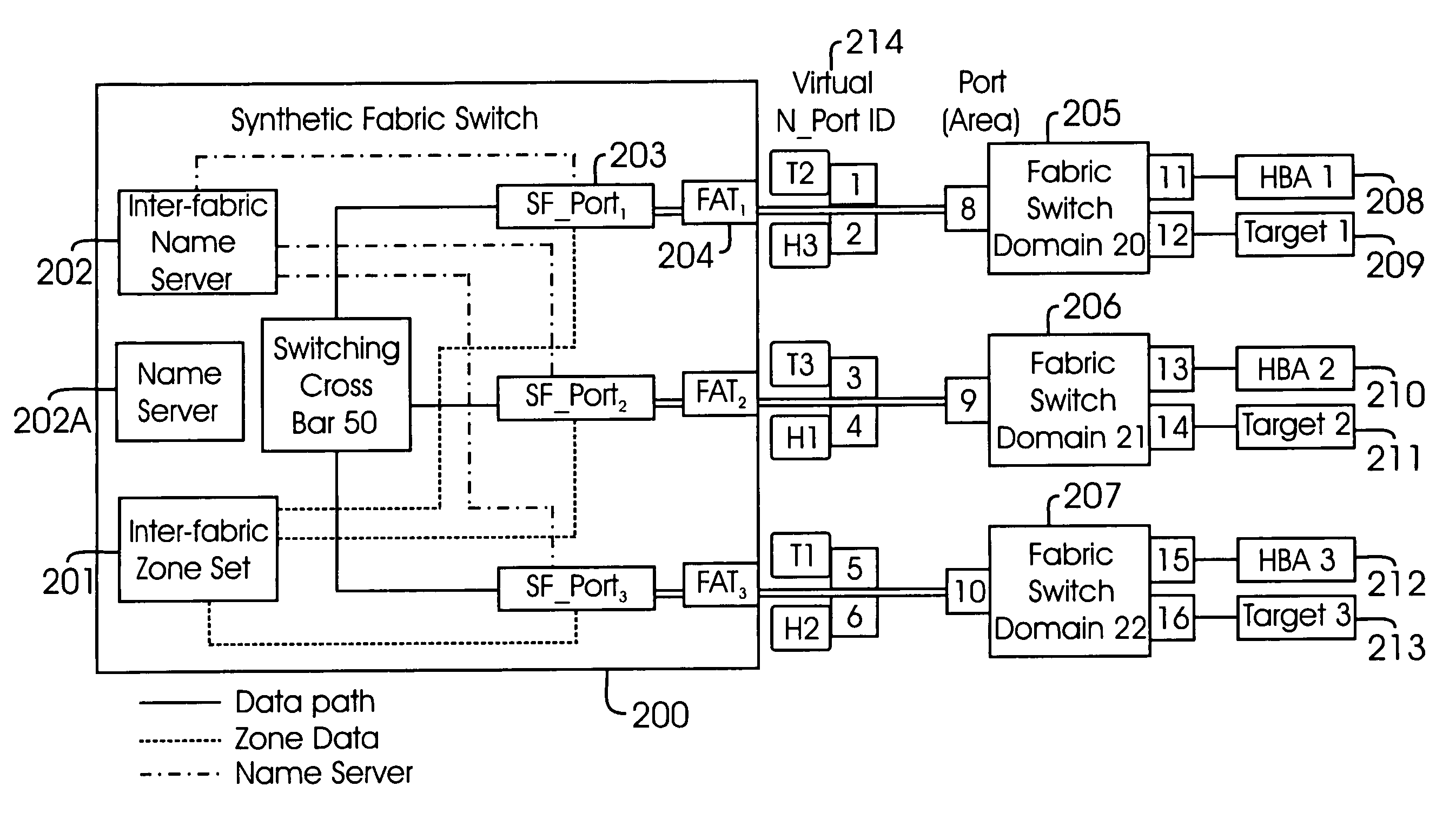
Method and system for inter-fabric routing
A Fibre Channel Switch element and method for Inter-Fabric routing is provided. The switch element includes a switch port whose worldwide port number is used in a zone set to enable Inter-Fabric frame routing without using Inter-Fabric frame headers. The method includes querying a Name Server to determine world wide port numbers of devices; storing query results in an Inter-Fabric Name Server module; extracting world wide port numbers for each switch port; registering Proxy Devices with the Name Server, wherein the Proxy Devices interface with the switch ports as if it was they were actual devices to route Inter-Fabric frames; and establishing Fabric Address Translator entries so that source identification values and destination identification values are mapped to route Inter-Fabric frames without using Inter-Fabric frame headers.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
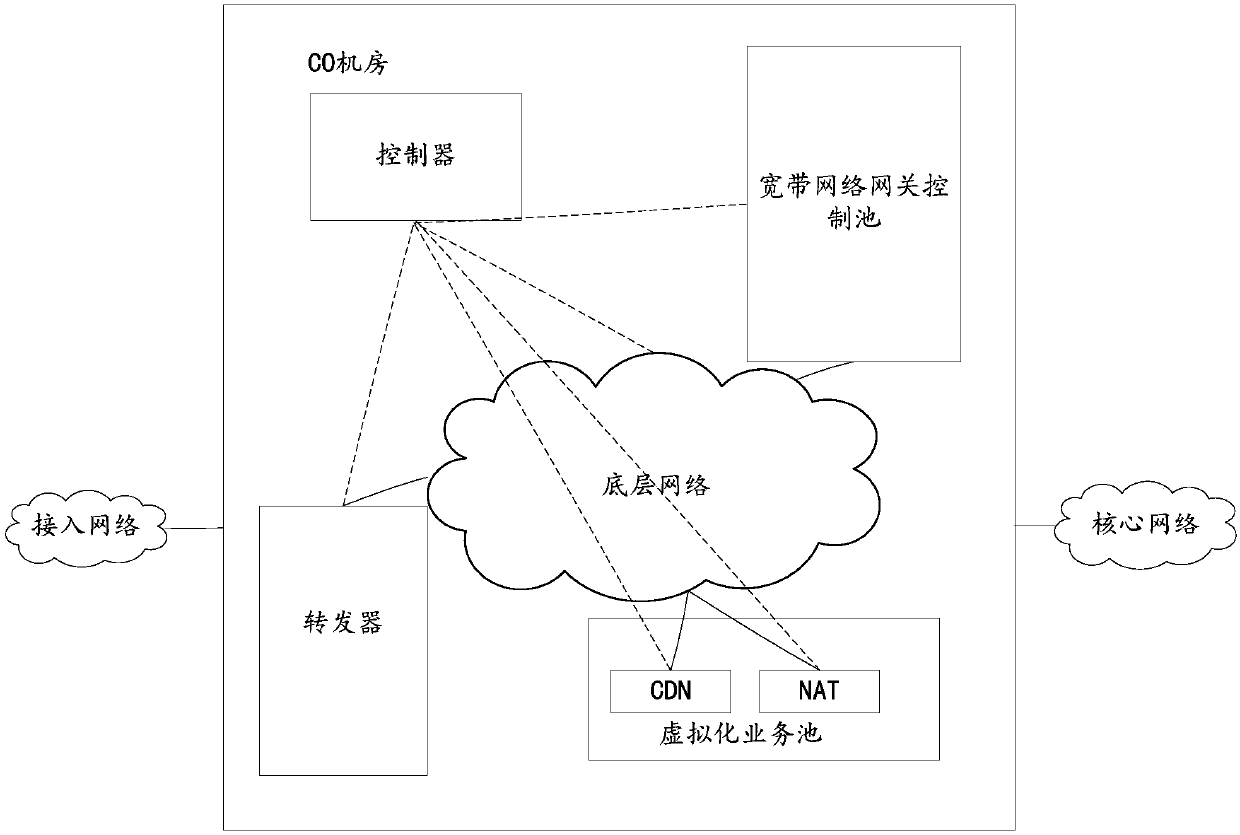
Virtual broadband remote access method and system, and controller
ActiveCN107666419AReduce energy consumptionBroadband local area networksNetworks interconnectionVirtualizationUser device
The embodiment of the invention provides a virtual broadband remote access method and system, and a controller. The method comprises: receiving a user access protocol message from a user device; selecting a broadband network gateway control pool example for the user device according to a business deployment strategy; completing access and / or authentication according to the user access protocol message and the user device, and generating a user table; and generating a user data forwarding table according to the user table; receiving a user data message, and forwarding the user data message according to the user data forwarding table. In the process of forwarding the user data message, a control function is separated, a virtualization technology is employed for realization, devices such as acontroller and the like are configured to realize forwarding of a user data message with no need for deployment of special devices or usage of special business plates on a current route architecture,and therefore the whole energy consumption is reduced and high-performance forwarding is realized.
Owner:ZTE CORP
ASIC routing architecture
InactiveUS6885043B2Well formedSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
An embodiment of the invention includes a routing architecture with a plurality of predesigned layers and a custom layer. The structure includes a plurality of parallel vertical tracks. In one layer, the tracks include a pin coupled to an input / output of an underlying function block and the track also includes a first portion of an unbroken conductive path. A second portion of the unbroken conductive path is formed under the pin in at least a second predesigned layer. In some embodiments, the second portion of the unbroken conductive path is formed in the second predesigned layer for some tracks and a third predesigned layer for other tracks. Hence, pins and unbroken conductive paths are multiplexed in a single track. In addition, the second predesigned layer further includes long horizontal conductors. When using the predesigned layers, the custom layer can be structured to provide free global routing with distinct local routing, all while using an array structure independent of routing channels and without rendering any function blocks unusable. Moreover, a structure in accordance with the invention includes conductors for clock distribution which can be used to form multiple independent clock domains. The structure is compact, yet flexible and can be customized in some embodiments with 1-2 masks.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
Interconnect structure and method in programmable devices
ActiveUS20060087342A1Easy routing predictabilityIncrease flexibilitySolid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsSignal routingRouting domain
An improved interconnect structure in programmable devices gives a new dimension to the routing architecture, where architecture is divided into various domains. It includes at least one set of input lines, each said set having predetermined number of input lines; an equal number of sets of routing lines, each said set of routing lines being connected to a corresponding set of input lines using a switch box; thereby forming domain based routing structures, each domain being disjoint with the other domain. Segregating FPGA routing resources into various independent routing domains is done; each domain providing connectivity to route a signal to a set of sinks.
Owner:MINERAL LASSEN
Method and system for implementing routing refinement and timing convergence
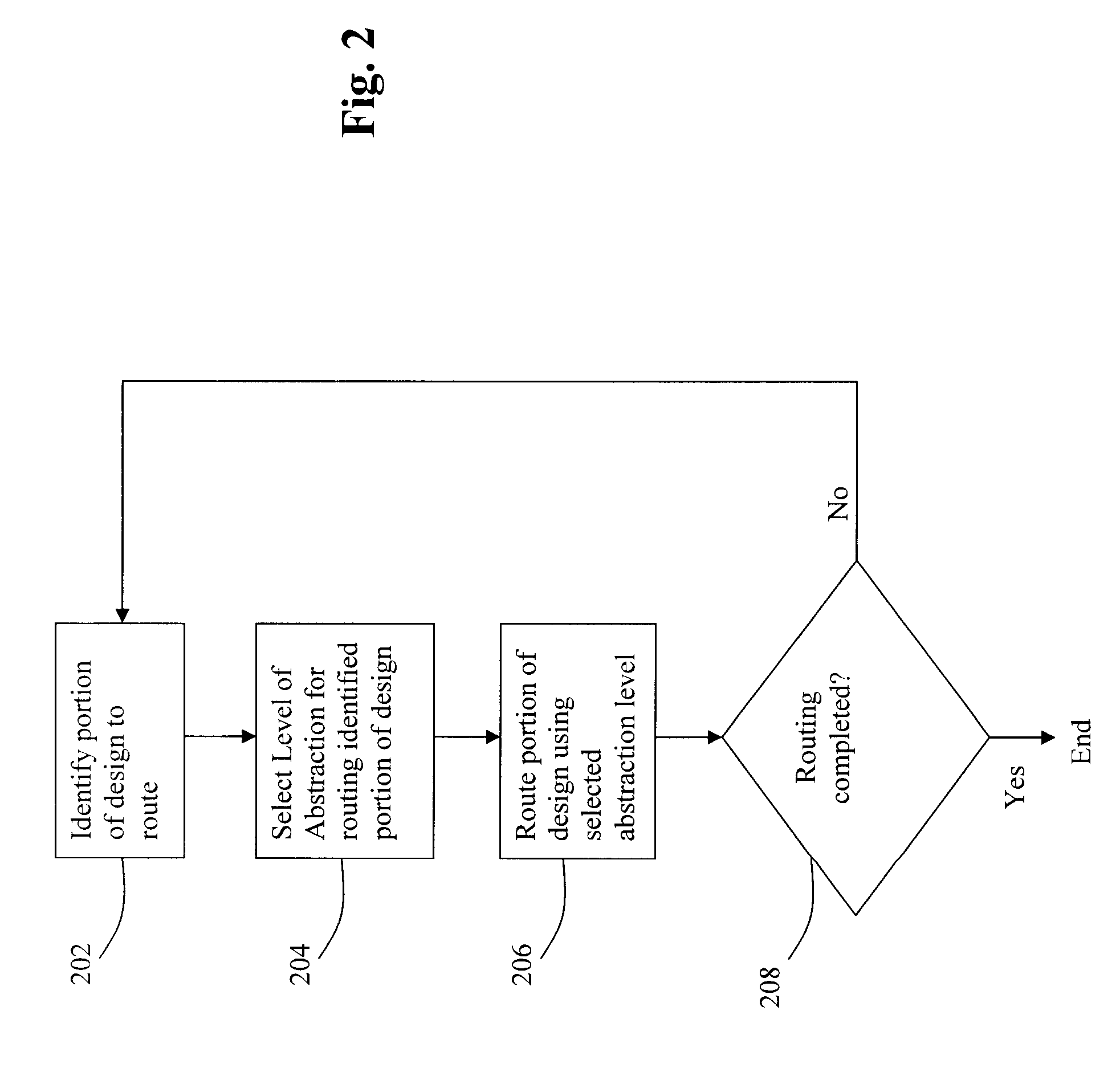
ActiveUS7657860B1Great of abstractionGreat level of detailComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsFrequency spectrumComputer architecture
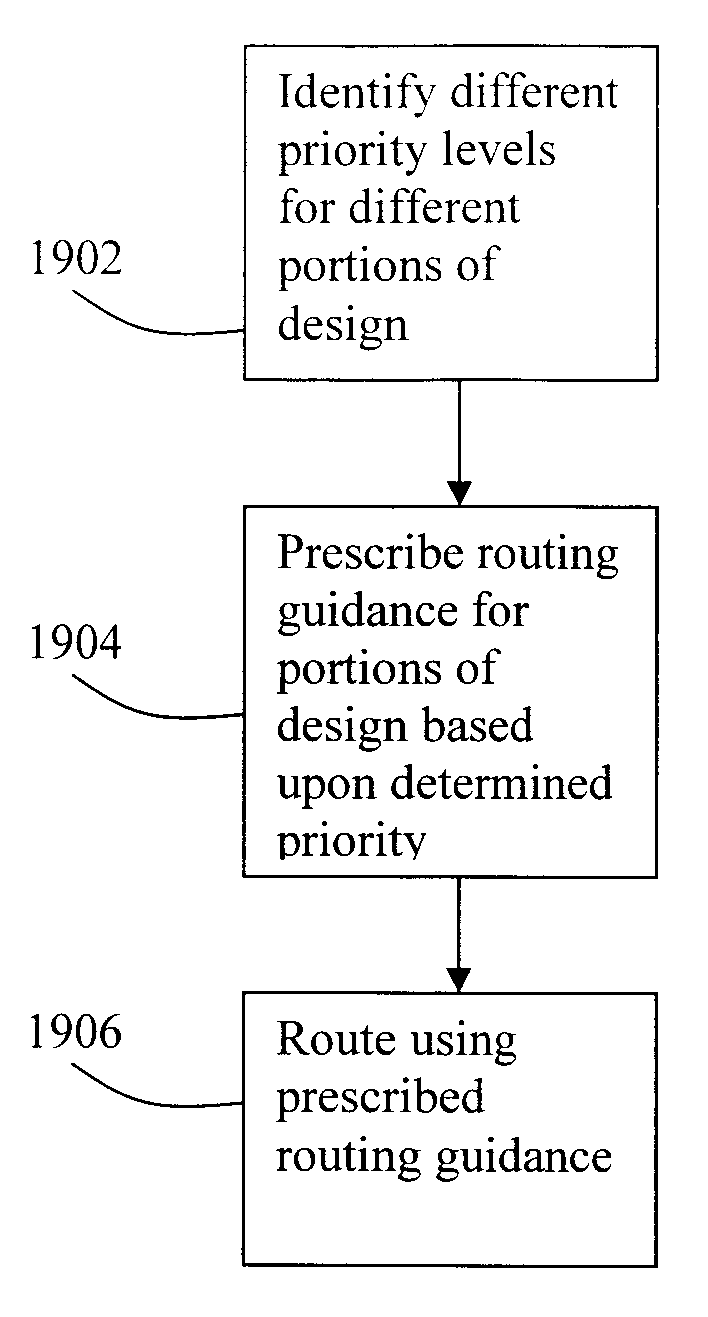
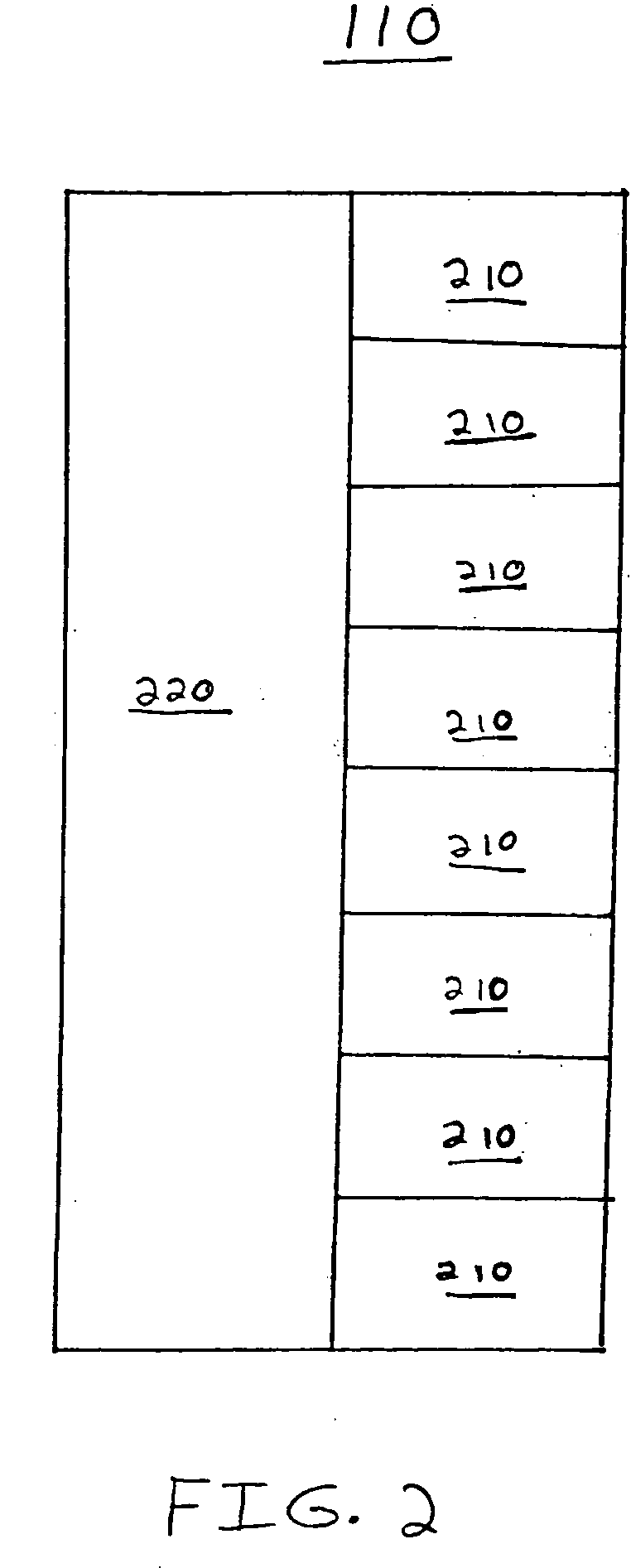
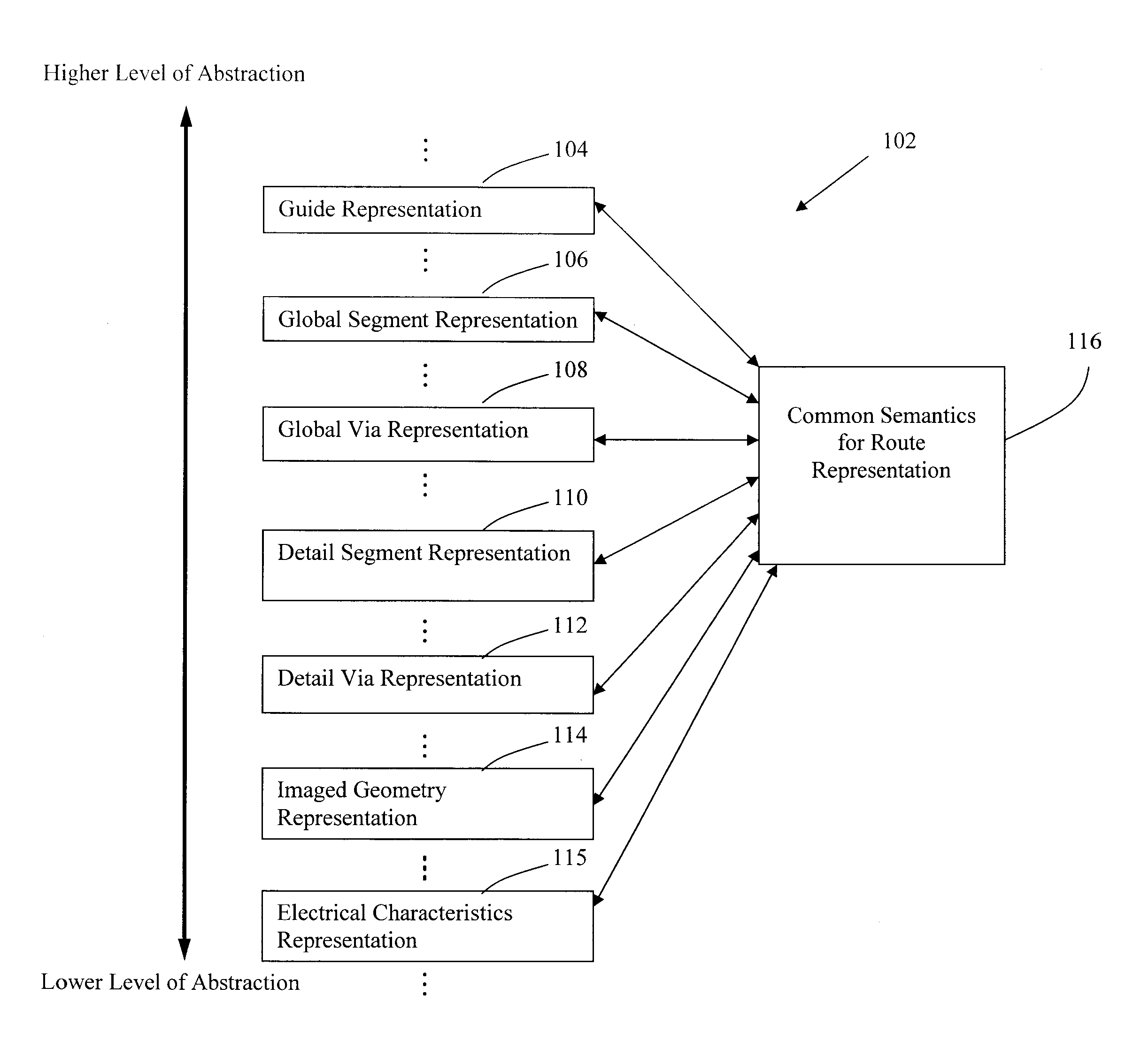
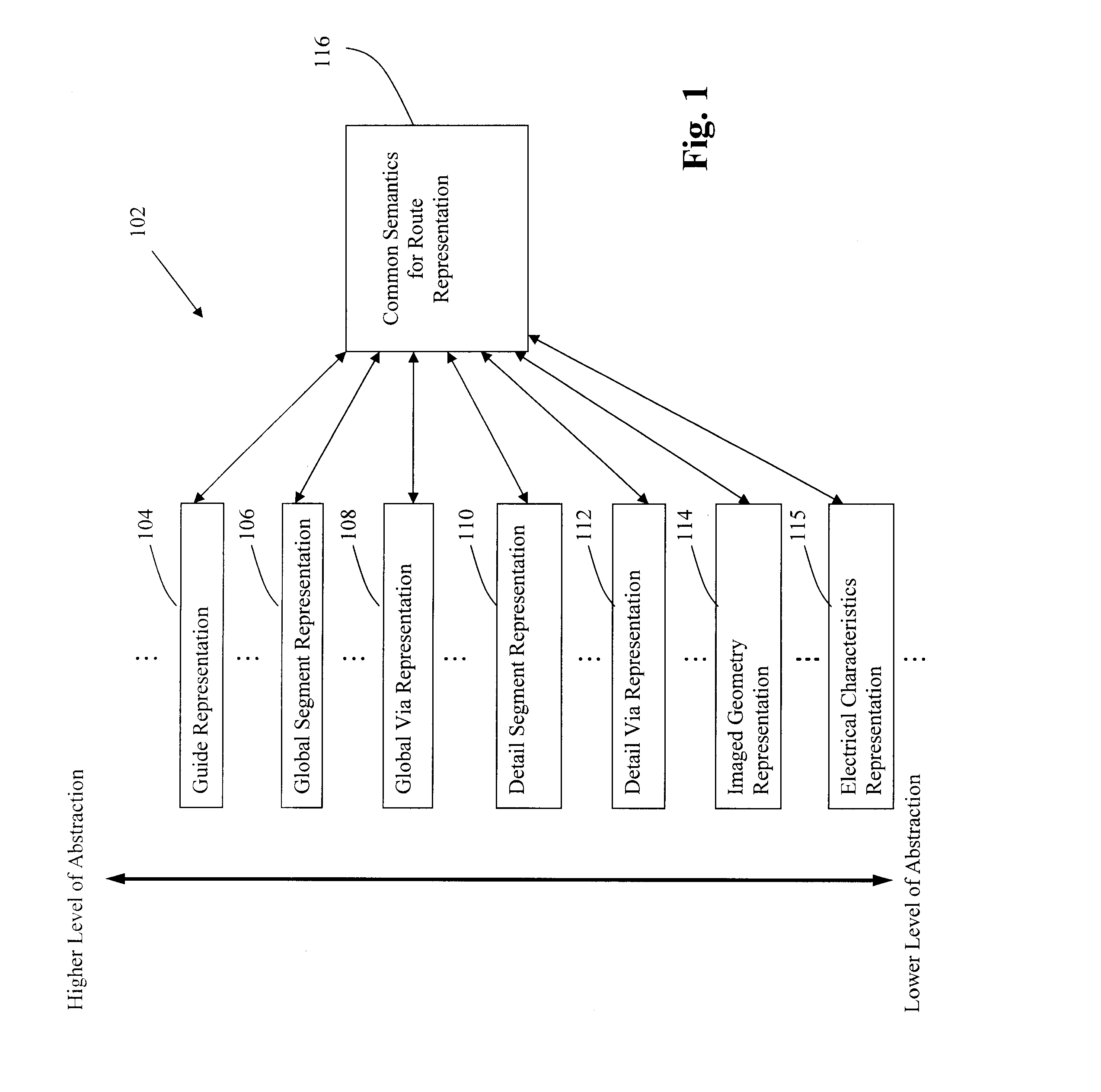
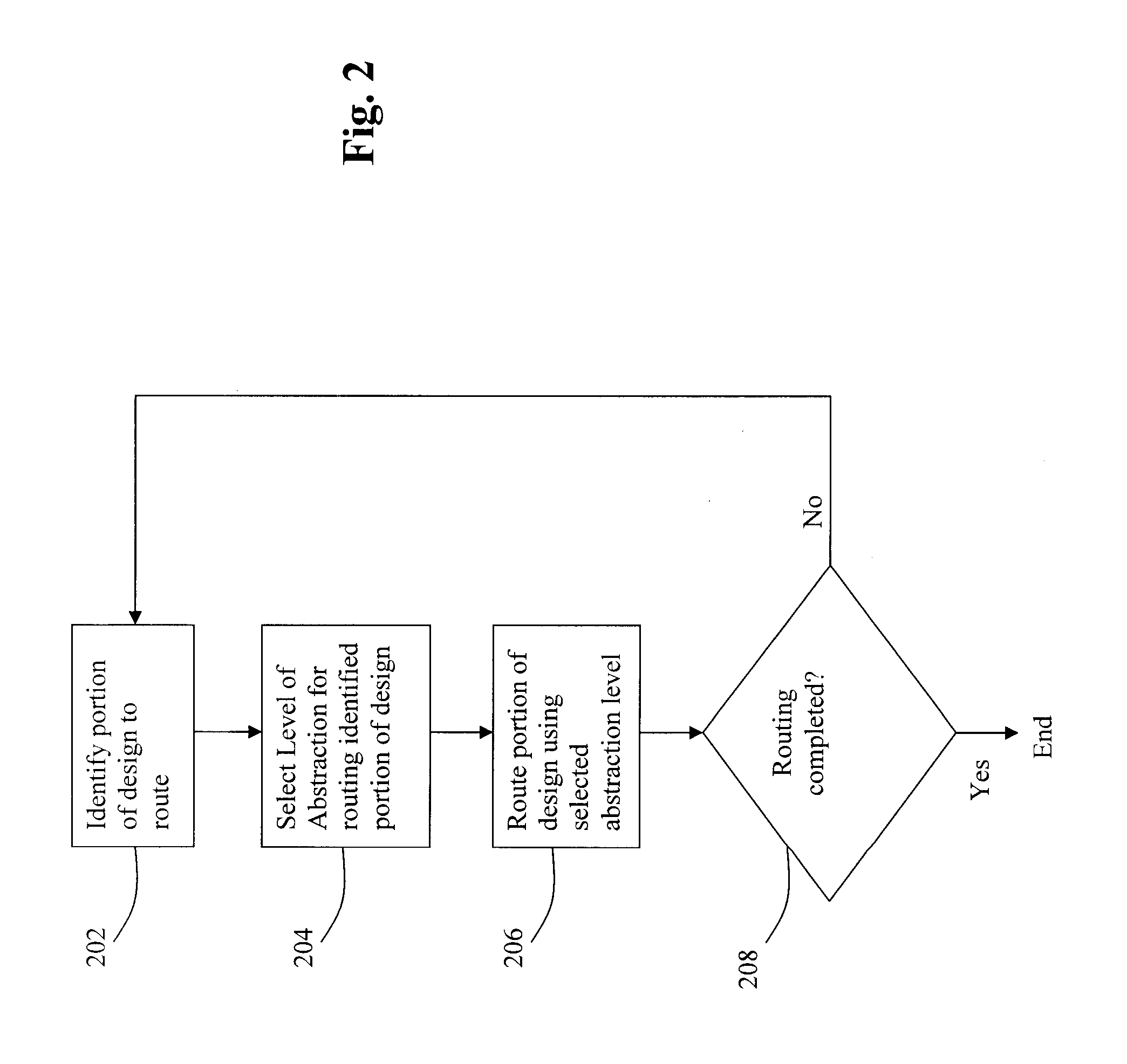
Disclosed is an improved method, system, and article of manufacture for implementing routing for an electrical circuit and chip design. A routing architecture can be represented as a spectrum of different granular routing levels. Instead of routing based upon area, routing can be performed for specific routes or portions of routes. Different types of representation or levels of abstraction for the routing can be used for the same net or route. Partial topological reconfiguration, refinement, or rip-up can be performed for a portion of the integrated circuit design, where the portion is smaller than an entire route or net. Non-uniform levels of routing activities or resources may be applied to route the design. Prioritization may be used to route certain portions of the design with greater levels of detail, abstraction, or resources than other portions of the design.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Dual path multi-mode power amplifier routing architecture
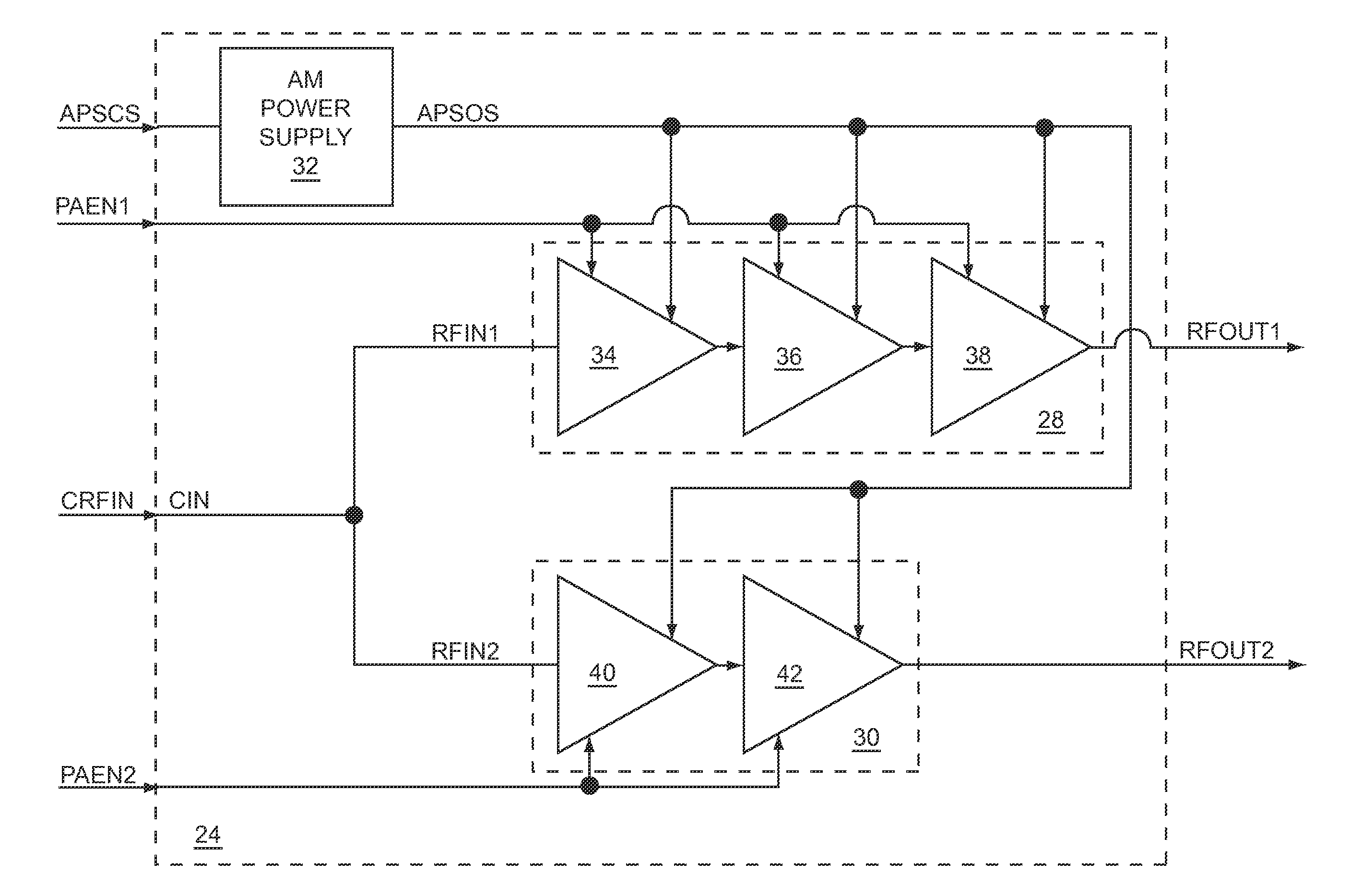
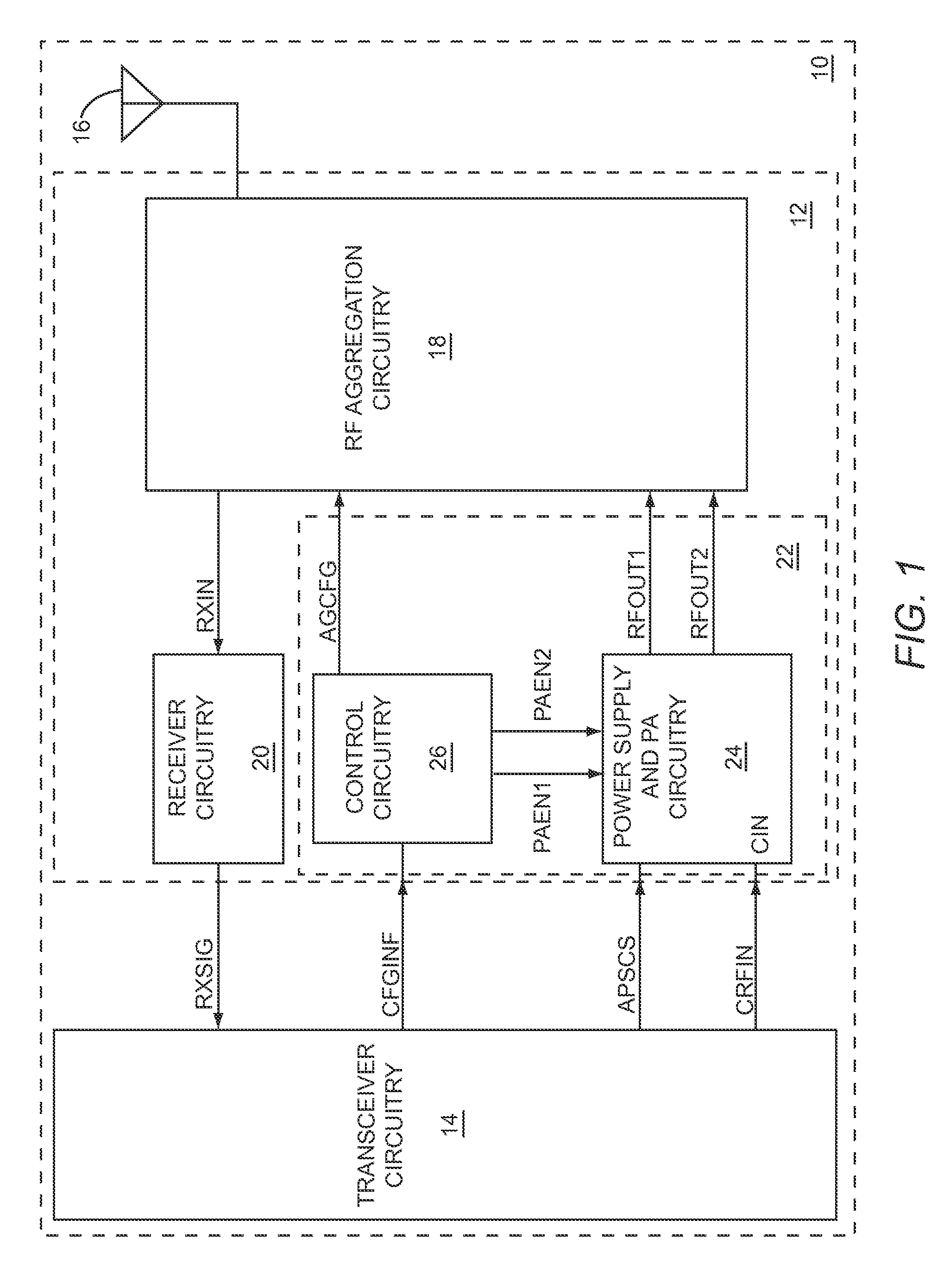
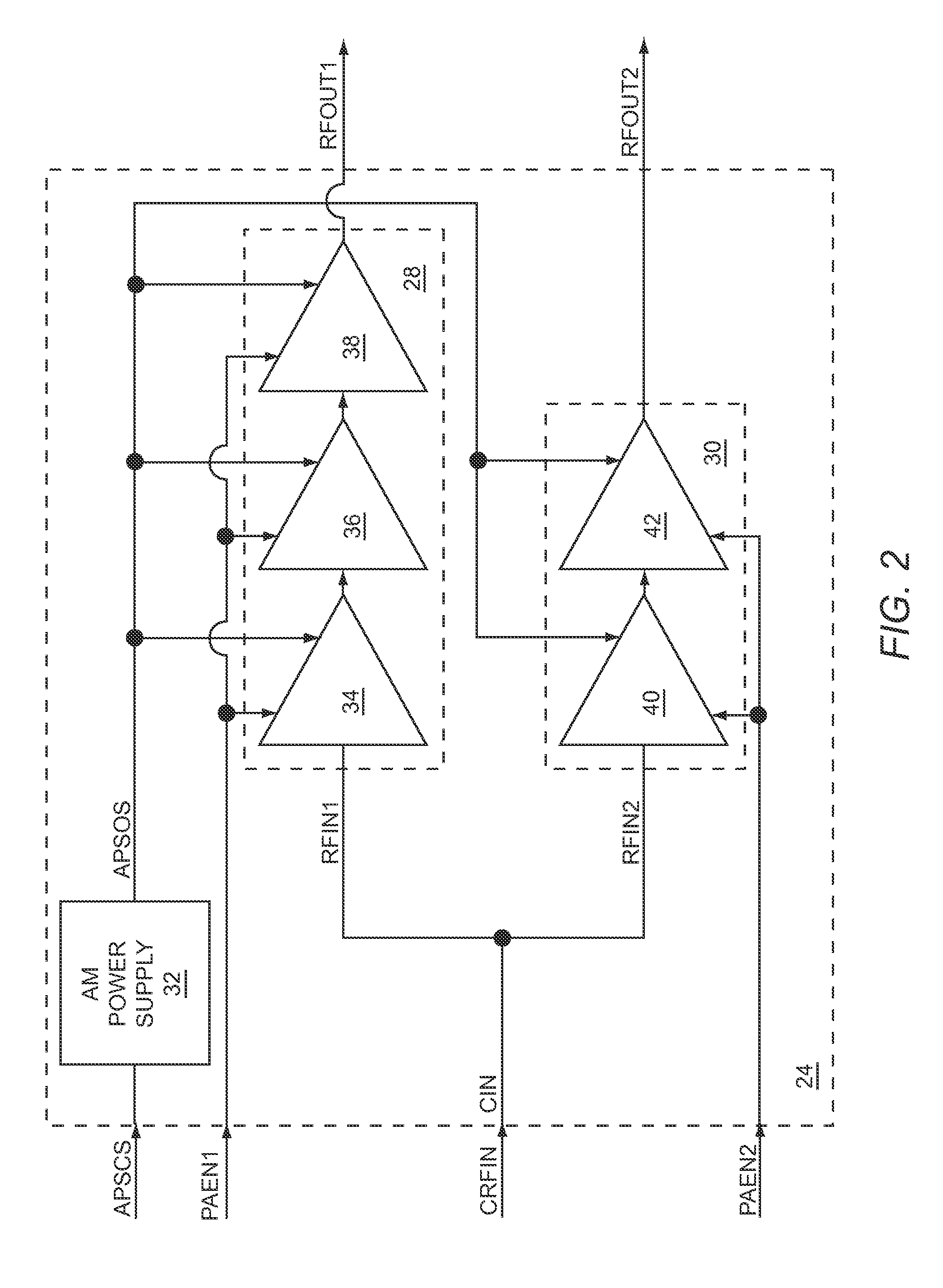
ActiveUS8417201B1Easy to shareLow costResonant long antennasSubstation equipmentOperation modeEngineering
The present disclosure relates to multi-mode RF power amplifier (PA) circuitry that may include a first PA path and a second PA path, each of which is fed from a common RF input. During a first operating mode, the first PA path receives and amplifies a first RF input signal via the common RF input, and during a second operating mode, the second PA path receives and amplifies a second RF input signal via the common RF input. To facilitate sharing of the common RF input, during the first operating mode, the second PA path is substantially de-coupled from the common RF input, and during the second operating mode, the first PA path is substantially de-coupled from the common RF input. By sharing the common RF input, size and costs of the multi-mode RF PA circuitry may be reduced.
Owner:QORVO US INC
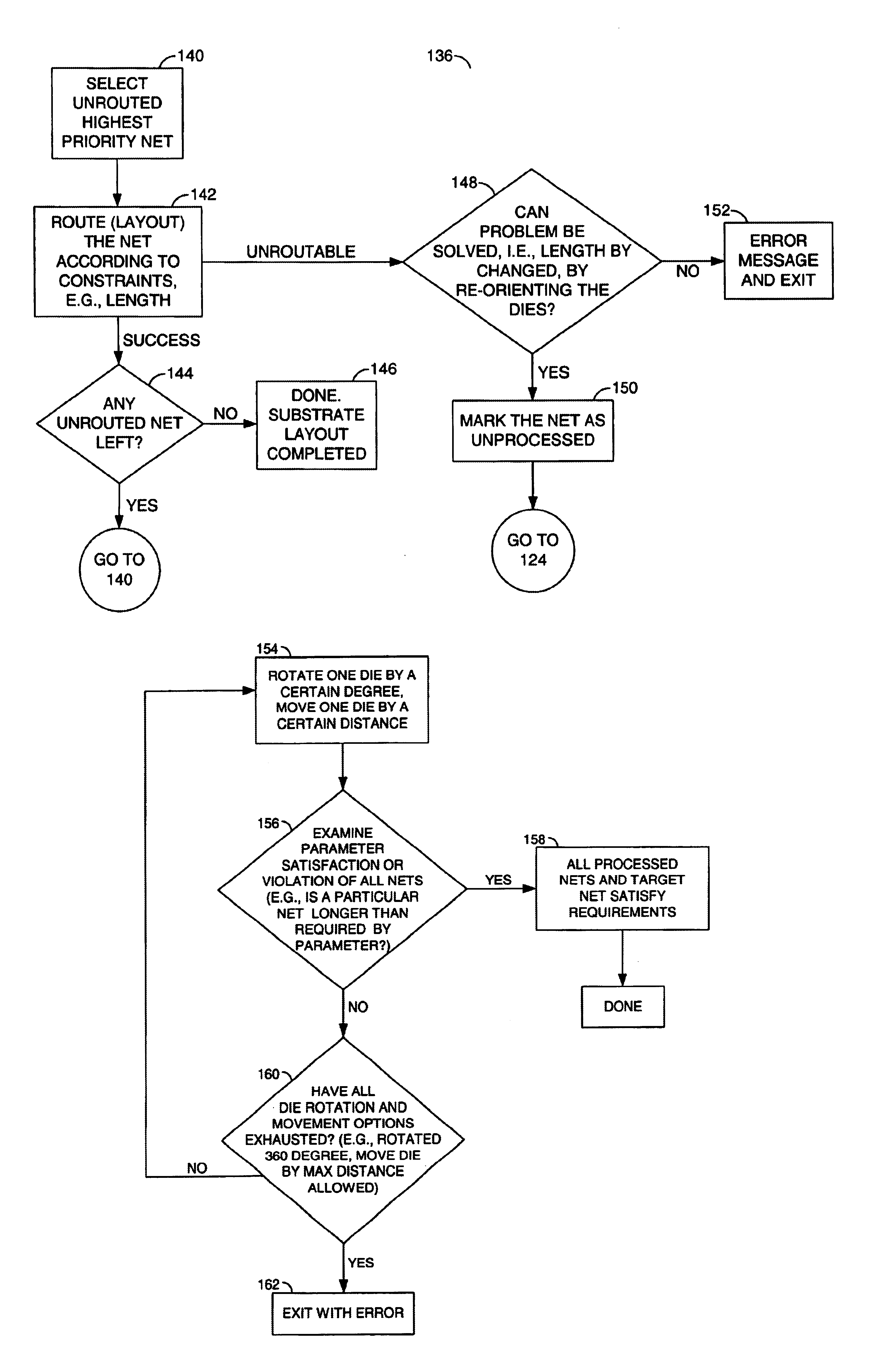
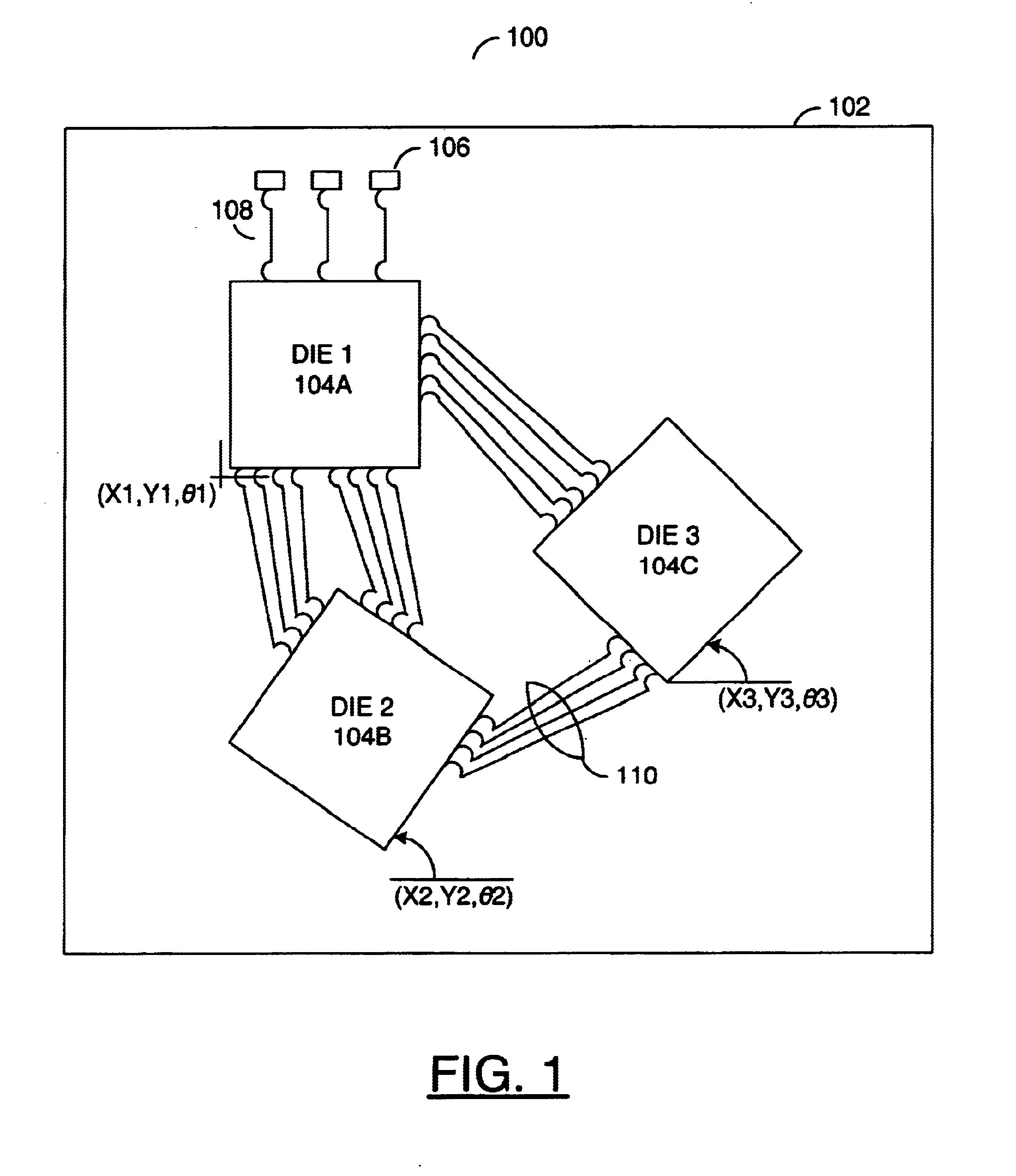
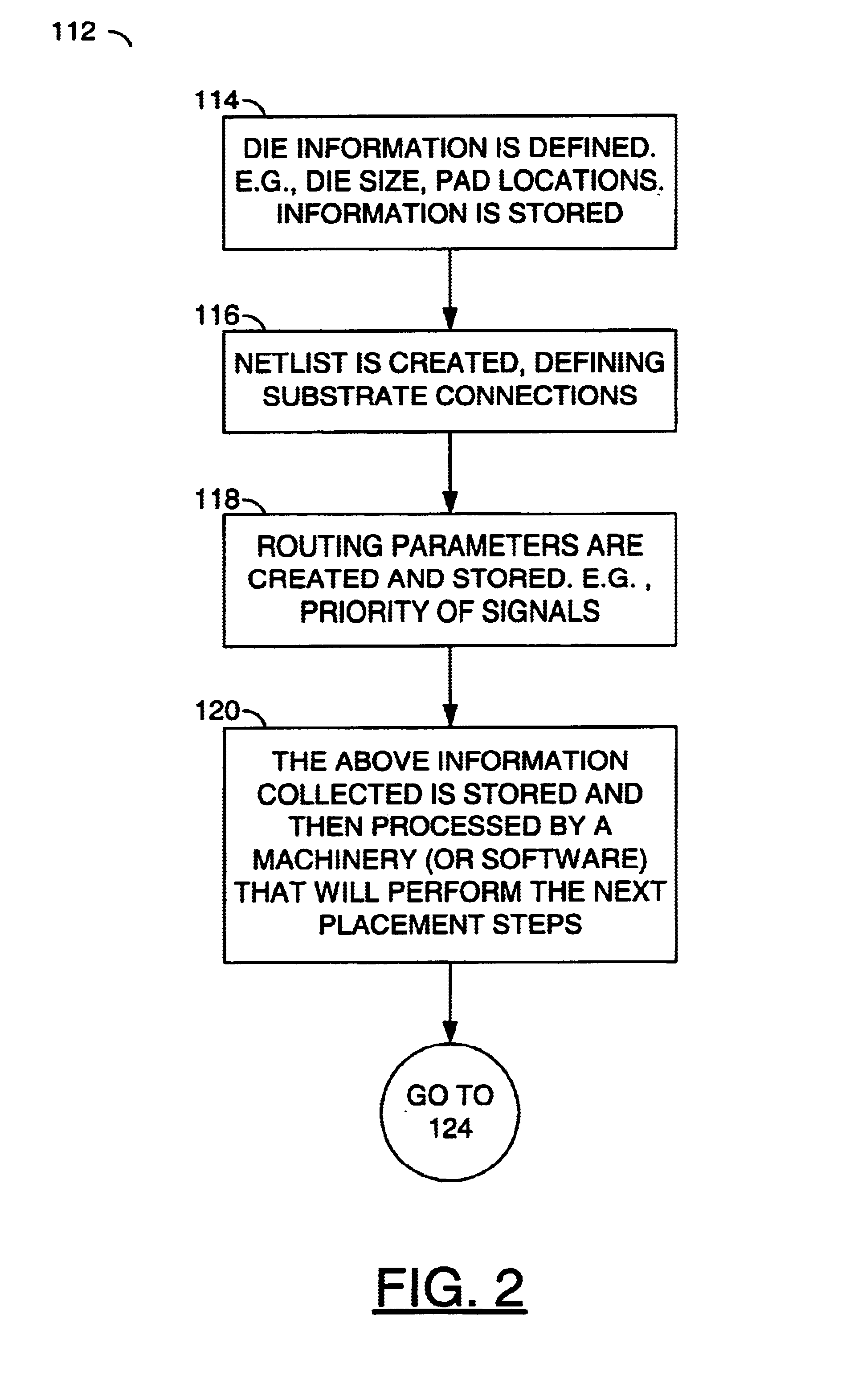
Method for determining die placement based on global routing architecture
InactiveUS6880145B1Reduce trace lengthReduces delay variationSolid-state devicesComputer aided designEngineeringExternal connection
Owner:DECA TECH INC
Block level routing architecture in a field programmable gate array
InactiveUS6898777B2Good symmetryEasy to placeSolid-state devicesSpecial data processing applicationsFpga architectureElectrical conductor
An FPGA architecture has top, middle and low levels. The top level of the architecture is an array of the B16×16 tiles arranged in a rectangular array and enclosed by I / O blocks on the periphery. On each of the four sides of a B16×16 tile, and also associated with each of the I / O blocks is a freeway routing channel. A B16×16 tile in the middle level of hierarchy is a sixteen by sixteen array of B1 blocks. The routing resources in the middle level of hierarchy are expressway routing channels M1, M2, and M3 including groups of interconnect conductors. At the lowest level of the semi-hierarchical FPGA architecture, there are block connect (BC) routing channels, local mesh (LM) routing channels, and direct connect (DC) interconnect conductors. Each BC routing channel is coupled to an expressway tab to provide access for each B1 block to the expressway routing channels M1, M2, and M3, respectively. Each BC routing channel has nine interconnect conductors which are grouped into three groups of three interconnect conductors. Each group of three interconnect conductors is connected to a first side of a Extension Block (EB) 3×3 switch matrix. A second side of each EB 3×3 switch matrix is coupled to the E-tab. Between adjacent B1 blocks, in both the horizontal and vertical directions, the leads on the second side of a first EB 3×3 switch matrix may be coupled to the leads on the second side of second EB3×3 switch matrix by BC criss-cross extension.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
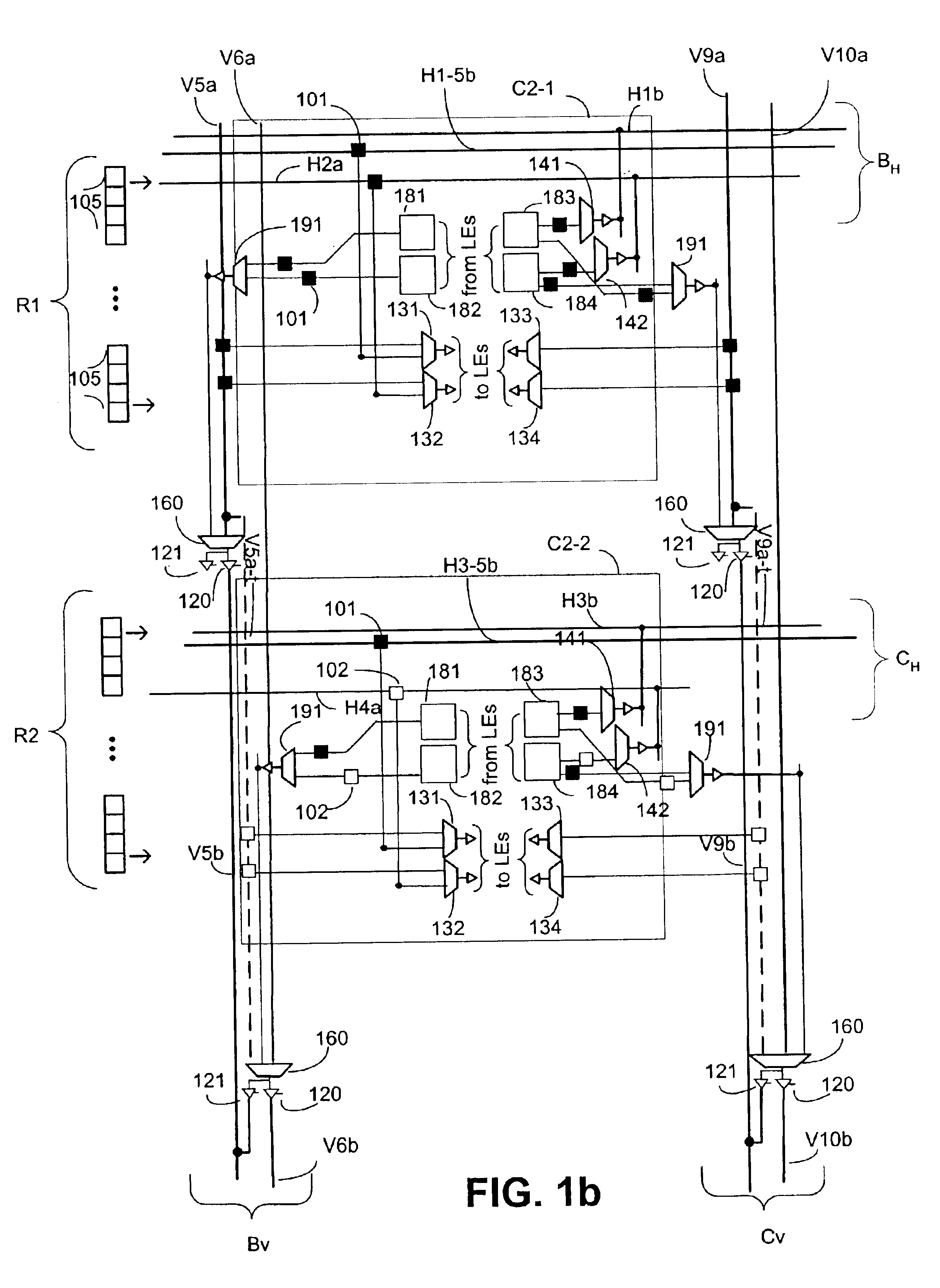
Routing architecture with high speed I/O bypass path
InactiveUS20050231236A1Quick connectionReduce delaysSolid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsElectrical conductorComputer architecture
Improved routing architectures including one or more high speed input / output (I / O) bypass paths are provided for use in, for example, programmable logic devices (PLDs) such as field programmable gate arrays (FPGAs). The output bypass paths add additional routing connections to the routing architecture, providing faster connections between the output of a logic element (LE) in the PLD and external circuitry. In one embodiment, an output bypass path is used for directly connecting the output of the LE to the input of an I / O multiplexer of an I / O block. In another embodiment, the output bypass path also bypasses the I / O multiplexer, providing a direct connection between the output of the LE and a bypass multiplexer of the I / O block. Also provided is an input bypass path which provides direct connections between an input buffer of the I / O block and an otherwise dangling conductor at the periphery of the PLD's routing architecture.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Representation, configuration, and reconfiguration of routing method and system
InactiveUS7614028B1Great of abstractionGreat level of detailComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsFrequency spectrumComputer architecture
Disclosed is an improved method, system, and article of manufacture for implementing routing for an electrical circuit and chip design. A routing architecture can be represented as a spectrum of different granular routing levels. Instead of routing based upon area, routing can be performed for specific routes or portions of routes. Different types of representation or levels of abstraction for the routing can be used for the same net or route. Partial topological reconfiguration, refinement, or rip-up can be performed for a portion of the integrated circuit design, where the portion is smaller than an entire route or net. Non-uniform levels of routing activities or resources may be applied to route the design. Prioritization may be used to route certain portions of the design with greater levels of detail, abstraction, or resources than other portions of the design.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Block level routing architecture in a field programmable gate array
InactiveUS20030121020A1Good symmetryEasy to placeSolid-state devicesSpecial data processing applicationsFpga architectureElectrical conductor
An FPGA architecture has top, middle and low levels. The top level of the architecture is an array of the B16x16 tiles arranged in a rectangular array and enclosed by I / O blocks on the periphery. On each of the four sides of a B16x16 tile, and also associated with each of the I / O blocks is a freeway routing channel. A B16x16 tile in the middle level of hierarchy is a sixteen by sixteen array of B1 blocks. The routing resources in the middle level of hierarchy are expressway routing channels M1, M2, and M3 including groups of interconnect conductors. At the lowest level of the semi-hierarchical FPGA architecture, there are block connect (BC) routing channels, local mesh (LM) routing channels, and direct connect (DC) interconnect conductors. Each BC routing channel is coupled to an expressway tab to provide access for each B1 block to the expressway routing channels M1, M2, and M3, respectively. Each BC routing channel has nine interconnect conductors which are grouped into three groups of three interconnect conductors. Each group of three interconnect conductors is connected to a first side of a Extension Block (EB) 3x3 switch matrix. A second side of each EB 3x3 switch matrix is coupled to the E-tab. Between adjacent B1 blocks, in both the horizontal and vertical directions, the leads on the second side of a first EB 3x3 switch matrix may be coupled to the leads on the second side of second EB3x3 switch matrix by BC criss-cross extension.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
Self-evolvable logic fabric
InactiveUS20130258905A1Reduce probabilityMaximize flowData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsDigital dataParallel computing
Methods and systems for achieving self-organized growth of a logic pathway. A number of hardware modules that represents a core can be configured and communicated via a packet routing architecture. Each core includes a plurality of sub-modules that interact dynamically to a growth algorithm. A flow network can be created between a sensor input and a prediction of a desired sensor input and a link can be formed between a regularity within a core and another core via a link-flow-selection process. A digital data packet can be transmitted between the cores for communicating activation of the regularity and to exchange energy. Such physically-self organized circuit fabric system interacts dynamically to a growth algorithm that takes the input to produce a desired output and continuously self-repair and / or heal if damaged.
Owner:KNOWM TECH
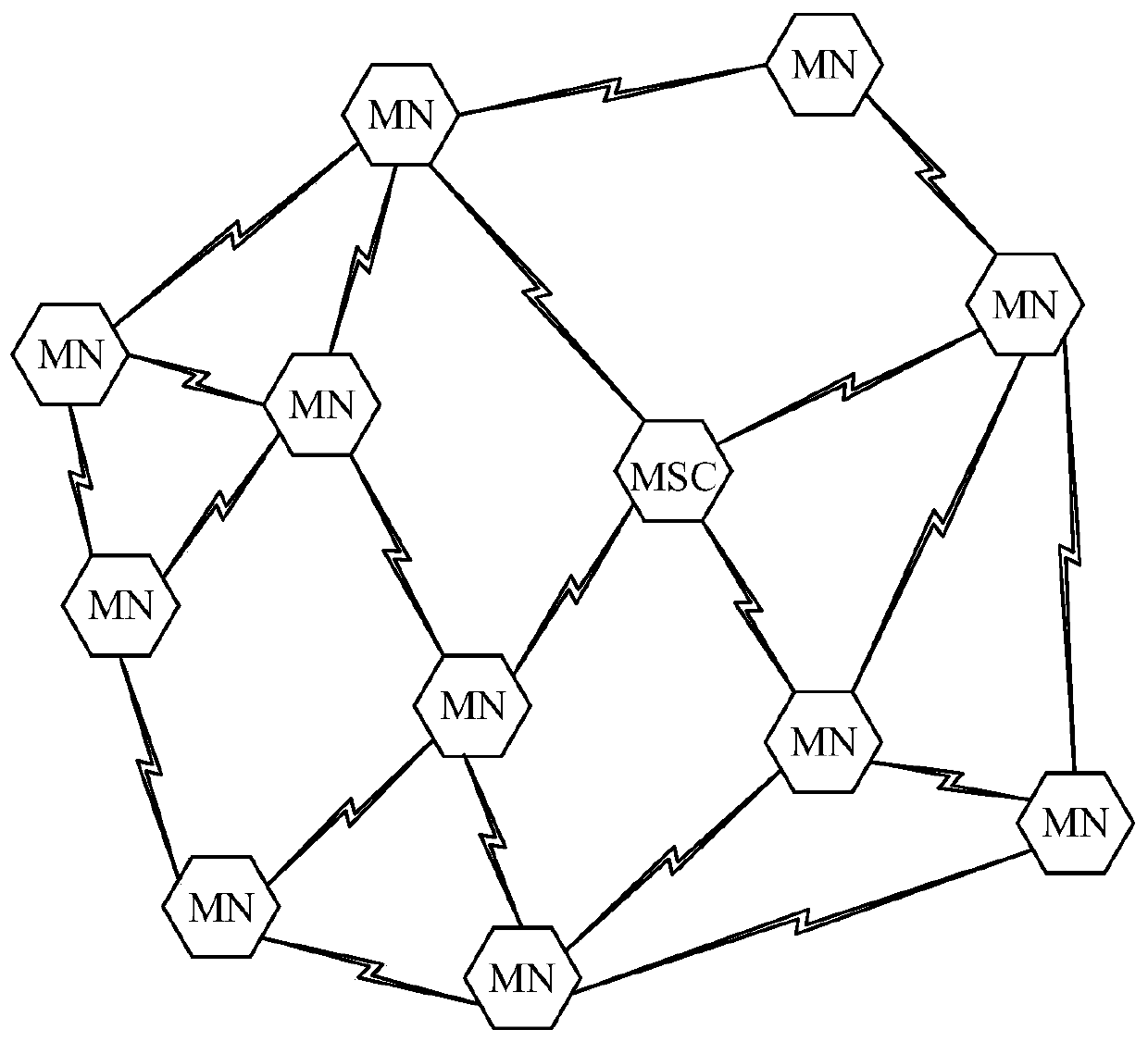
An IP-based software defined ubiquitous wireless MANET routing architecture
PendingCN110138676ASave air interface resourcesReduce sizeData switching networksAir interfaceOpenFlow
The invention discloses an IP-based software defined ubiquitous wireless MANET routing architecture, the wireless MANET routing architecture comprises three basic layers: an application plane, a control plane and a data plane, and the application plane comprises routing, data application, security, load balancing, strategy, QoS and the like, wherein the control plane comprises a control plane of amobile SDN controller MSC and a control plane of a mobile node (MN), the control plane of the mobile SDN controller MSC comprises a connection management module, a topology learning module, a forwarding management module and OpenFlow message compression and decompression, and the control plane of the mobile node MN comprises an OpenFlow message compression and decompression local adaptive controller LAC and a flow table FT, the data plane has the functions of forwarding an entered media stream according to a flow table FT rule and compressing / decompressing a packet header. According to the MANET routing system structure, position service support for tracking node positions is not needed, the size of Openflow messages is reduced through a compression and decompression method, and air interface resources of nodes are saved.
Owner:北京海泽时空科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com