Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
90 results about "Pass transistor logic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
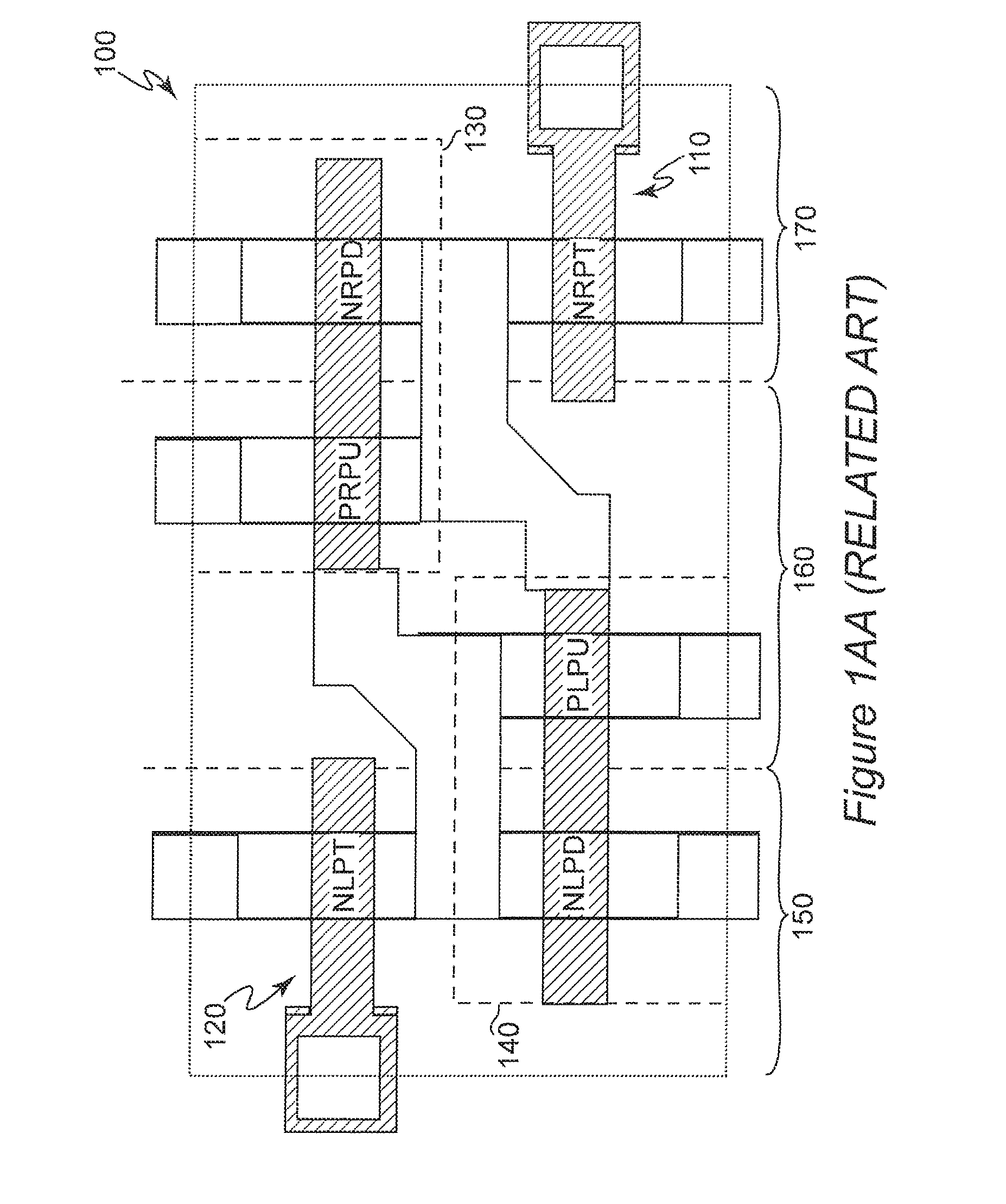
In electronics, pass transistor logic (PTL) describes several logic families used in the design of integrated circuits. It reduces the count of transistors used to make different logic gates, by eliminating redundant transistors. Transistors are used as switches to pass logic levels between nodes of a circuit, instead of as switches connected directly to supply voltages. This reduces the number of active devices, but has the disadvantage that the difference of the voltage between high and low logic levels decreases at each stage. Each transistor in series is less saturated at its output than at its input. If several devices are chained in series in a logic path, a conventionally constructed gate may be required to restore the signal voltage to the full value. By contrast, conventional CMOS logic switches transistors so the output connects to one of the power supply rails, so logic voltage levels in a sequential chain do not decrease. Simulation of circuits may be required to ensure adequate performance.
Logic circuit utilizing pass transistors and logic gate
InactiveUS6084437ATransistorReliability increasing modificationsCmos logic circuitsLogical operations
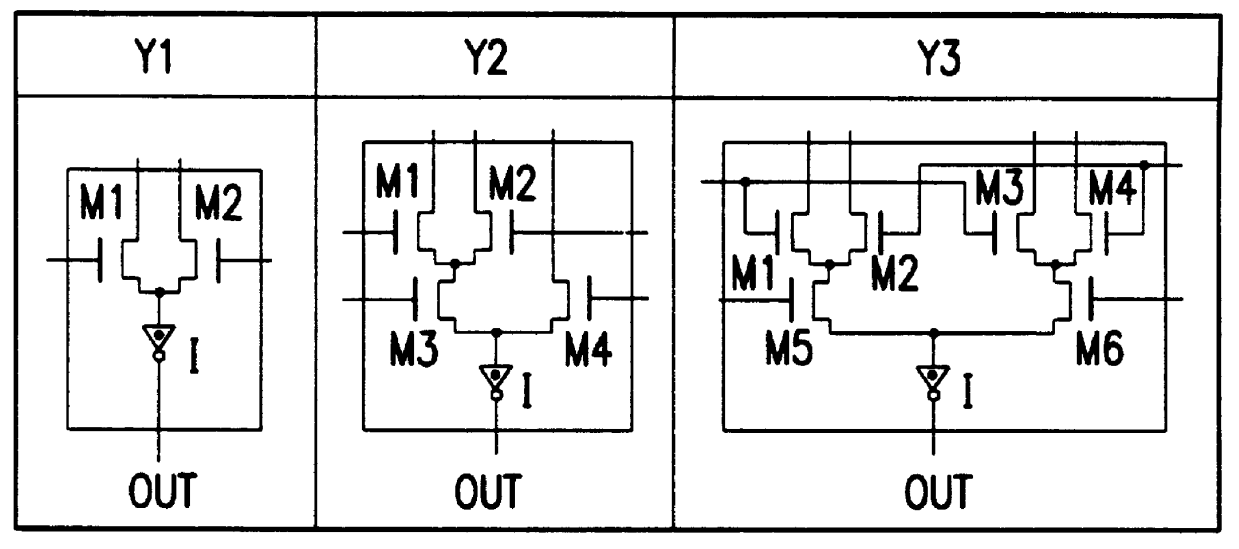
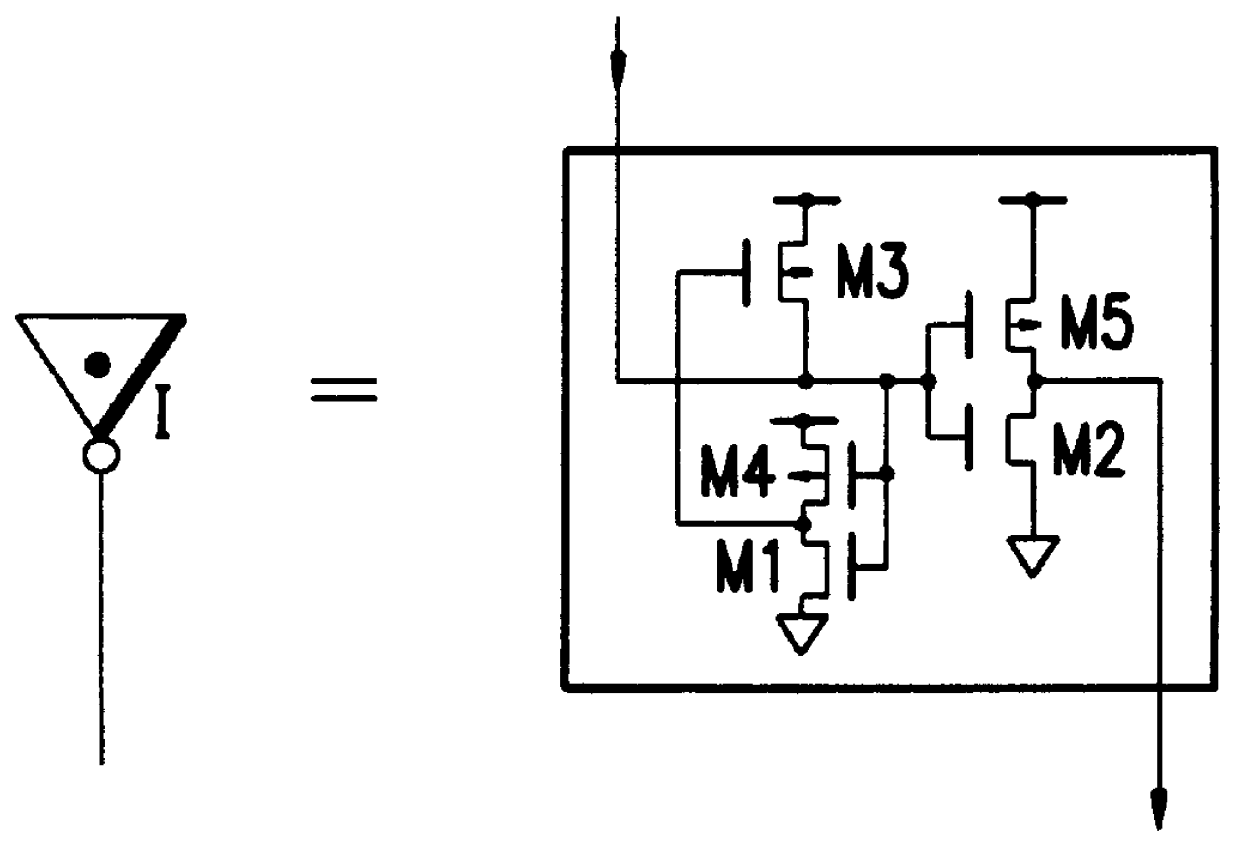
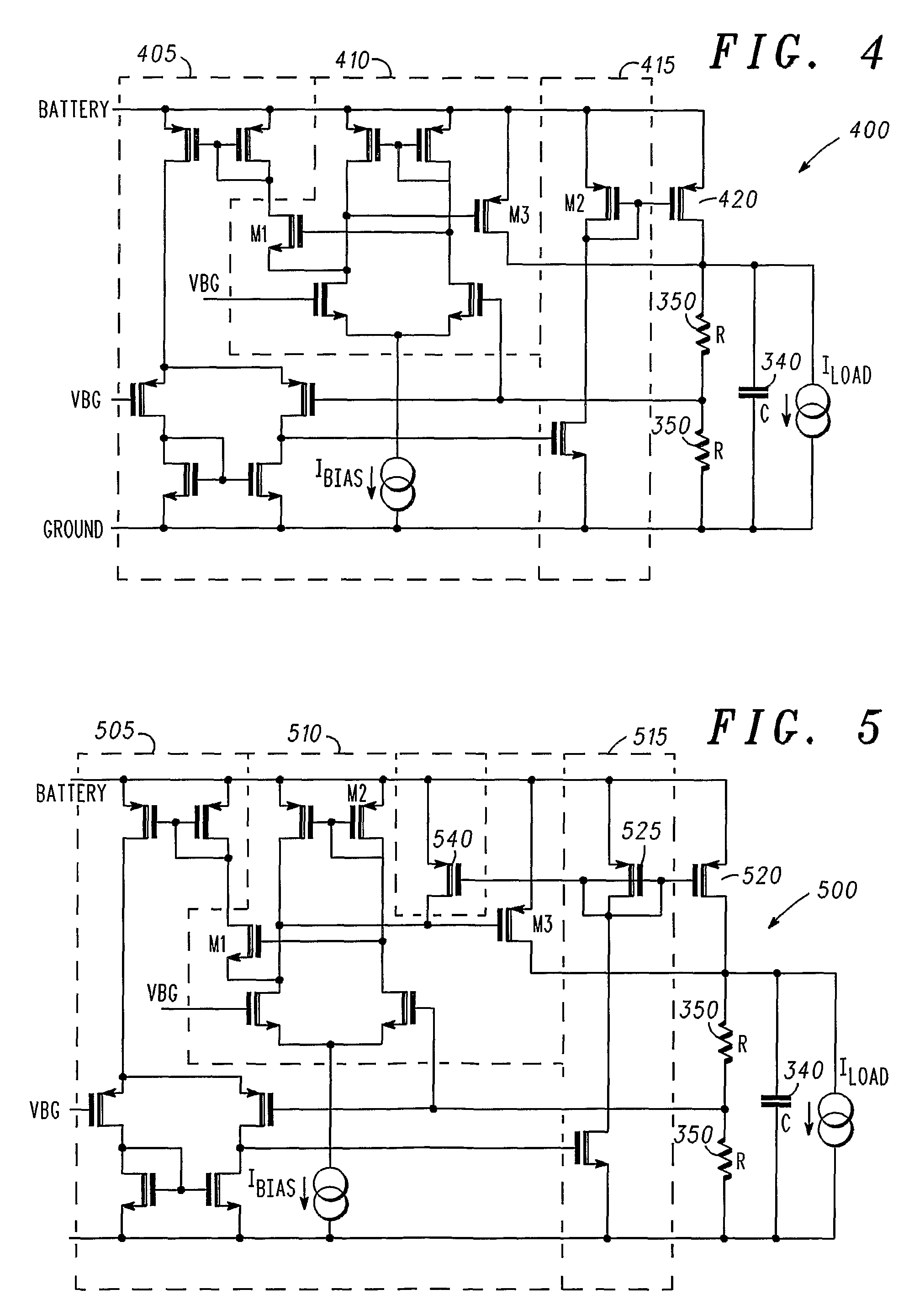
A logic circuit combines a plurality of pass-transistor logic trees and a multiple-input logic gate for receiving intermediate logic signals from the respective pass-transistor logic trees, and can express a complex logical operation while decreasing the number of stages in pass-transistor logic trees and improving operation speed. Even a logical operation that cannot be expressed efficiently by a known or conventional pass-transistor logic circuit can be expressed efficiently with performance higher than that of a known CMOS logic circuit. Furthermore, when a static feedthrough current of the multiple-input logic gate is suppressed, power consumption can be reduced. In some embodiments, since circuitry for suppressing a static feedthrough current of the multiple-input logic gate is arranged so that a probability of occurrence of logical collision with a preceding stage will decrease or will be nil, power consumption can further be reduced.
Owner:KAWASAKI MICROELECTRONICS
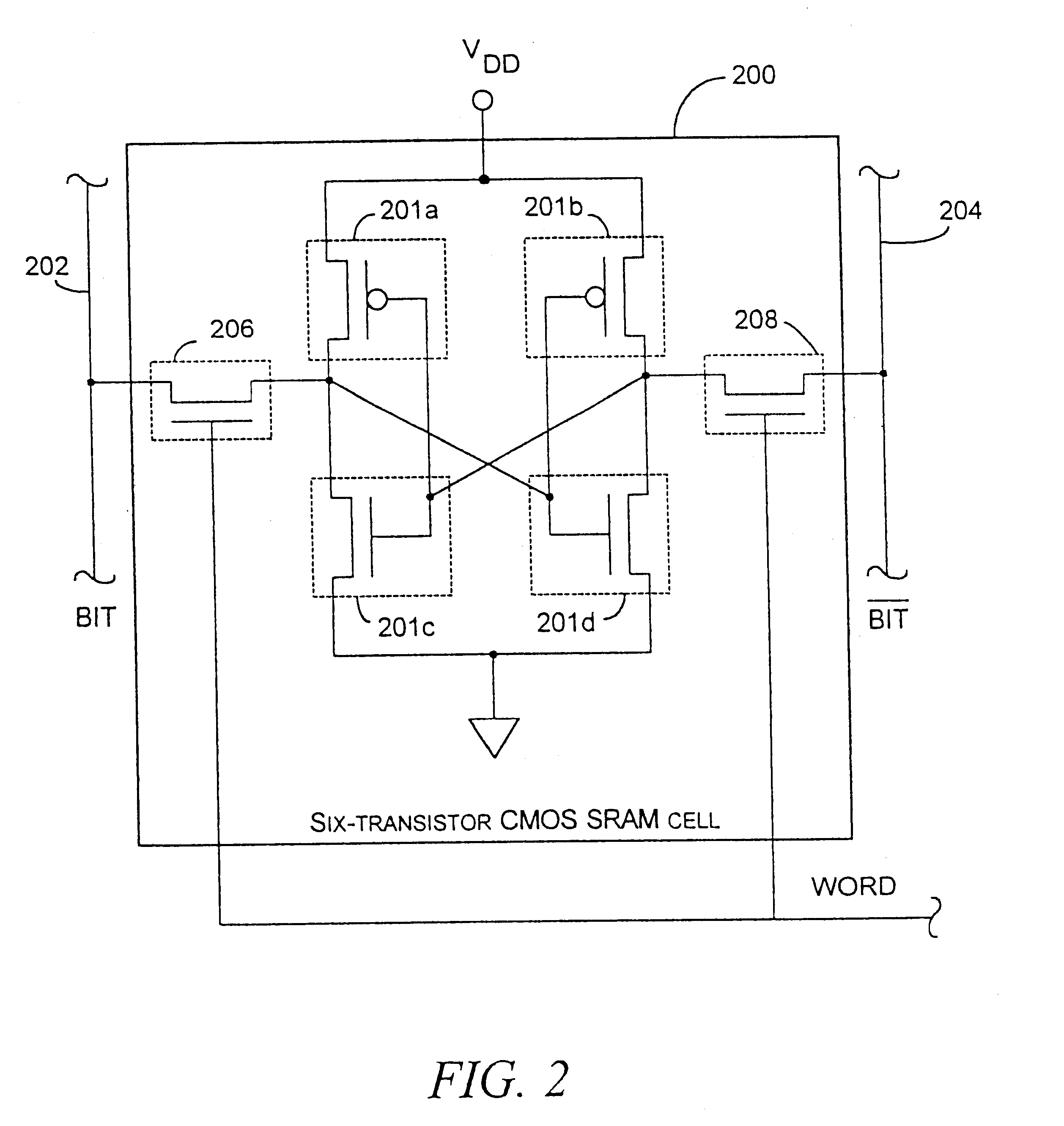
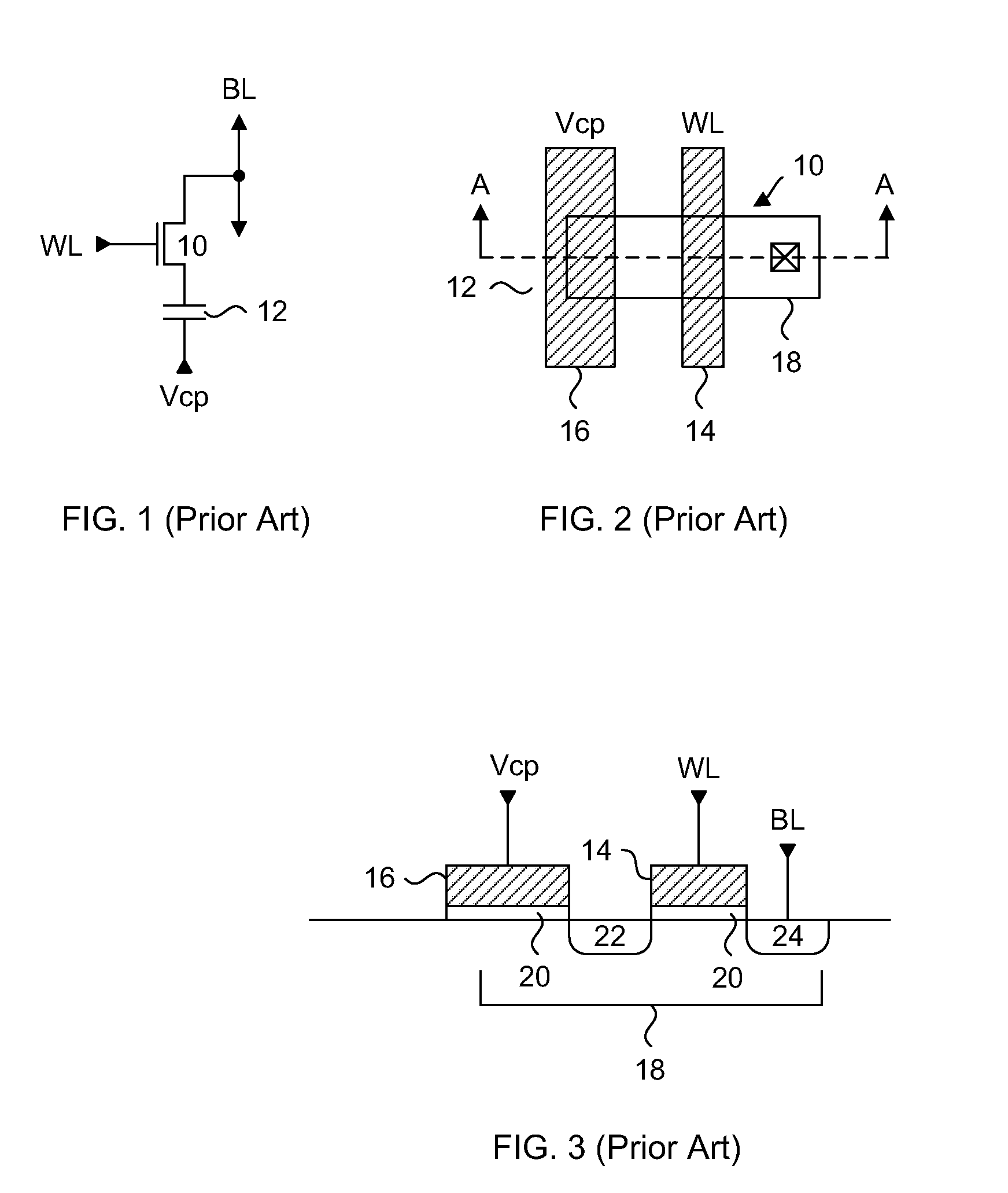
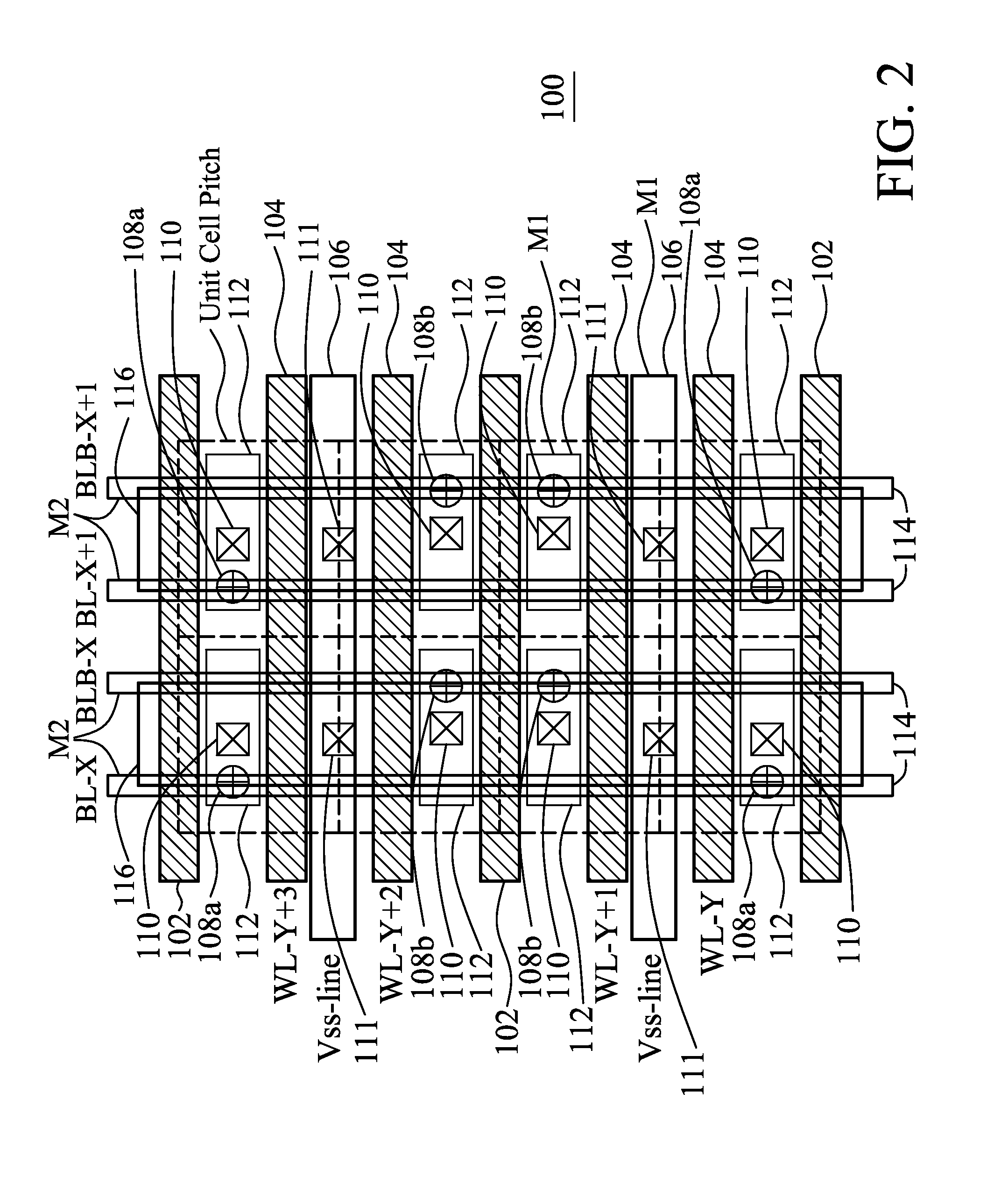
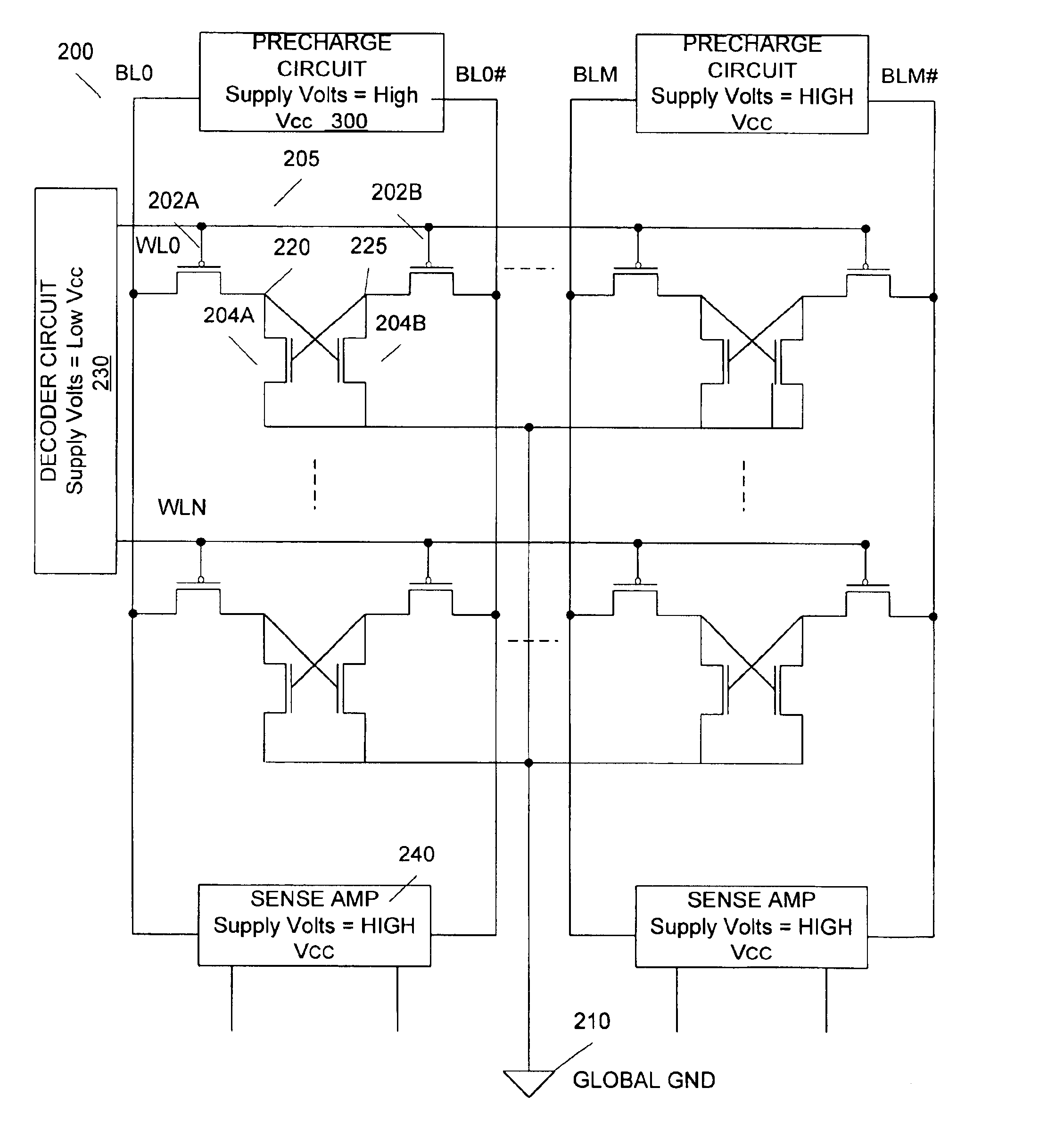
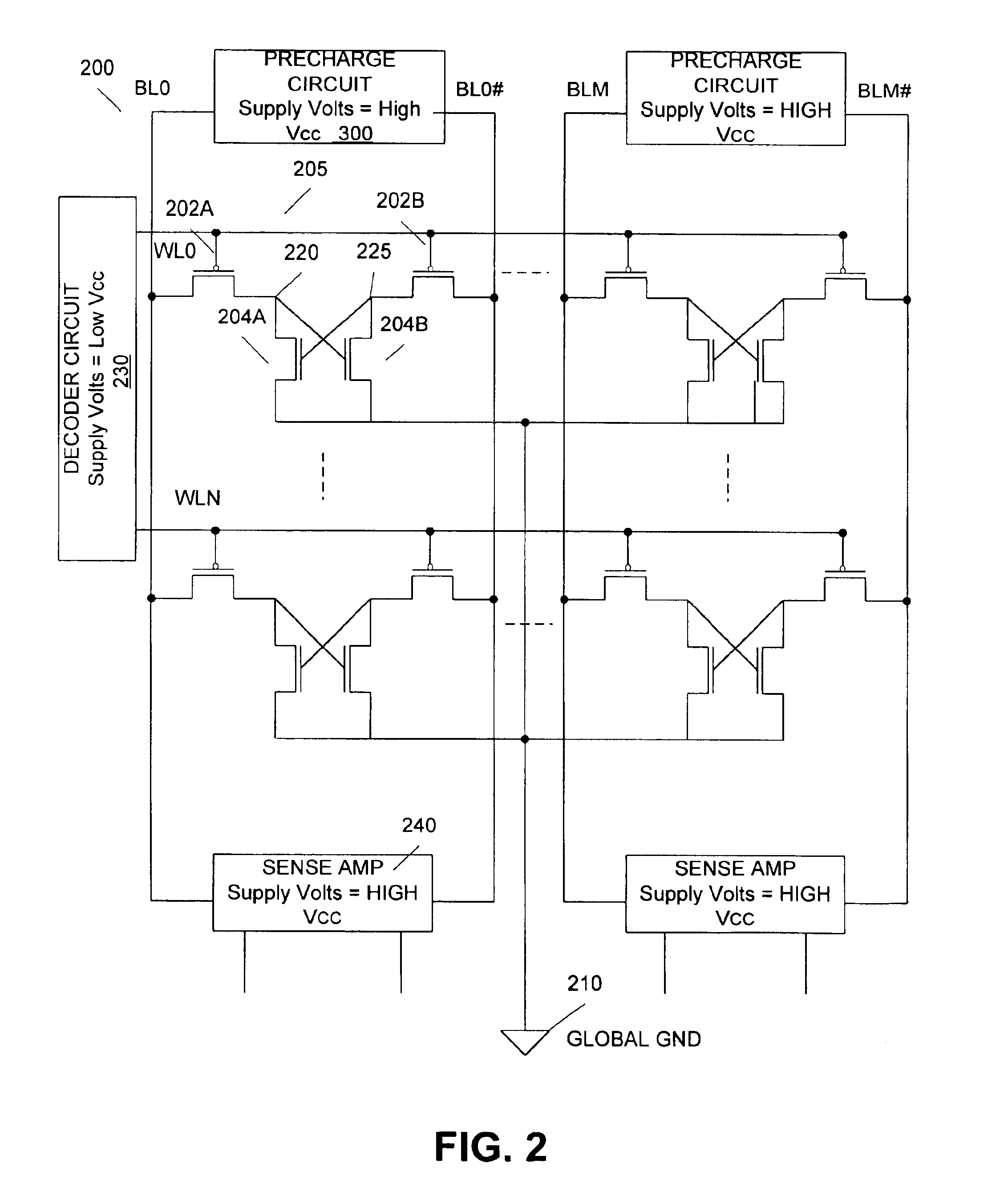
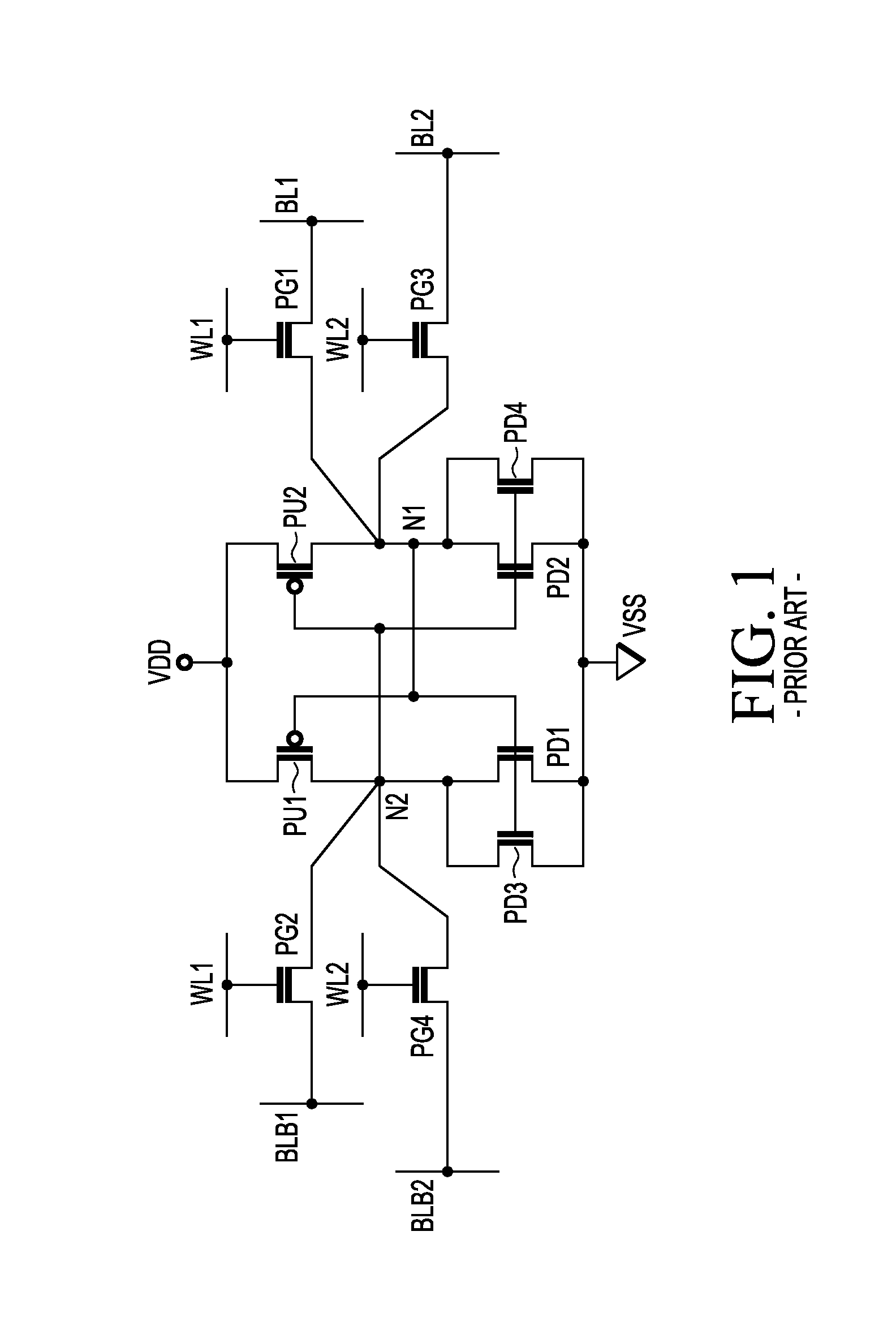
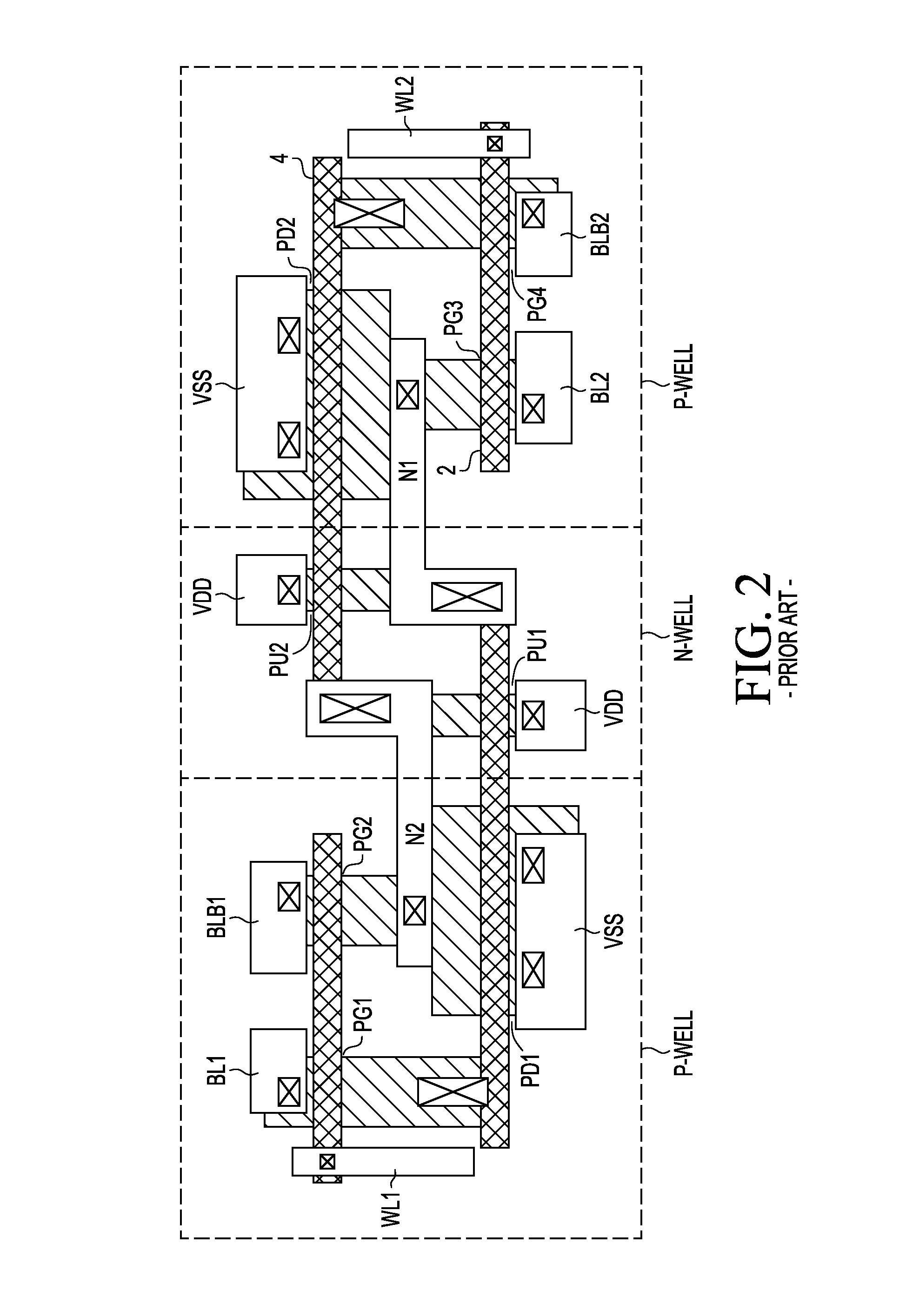
SRAM cell with common bit line and source line standby voltage
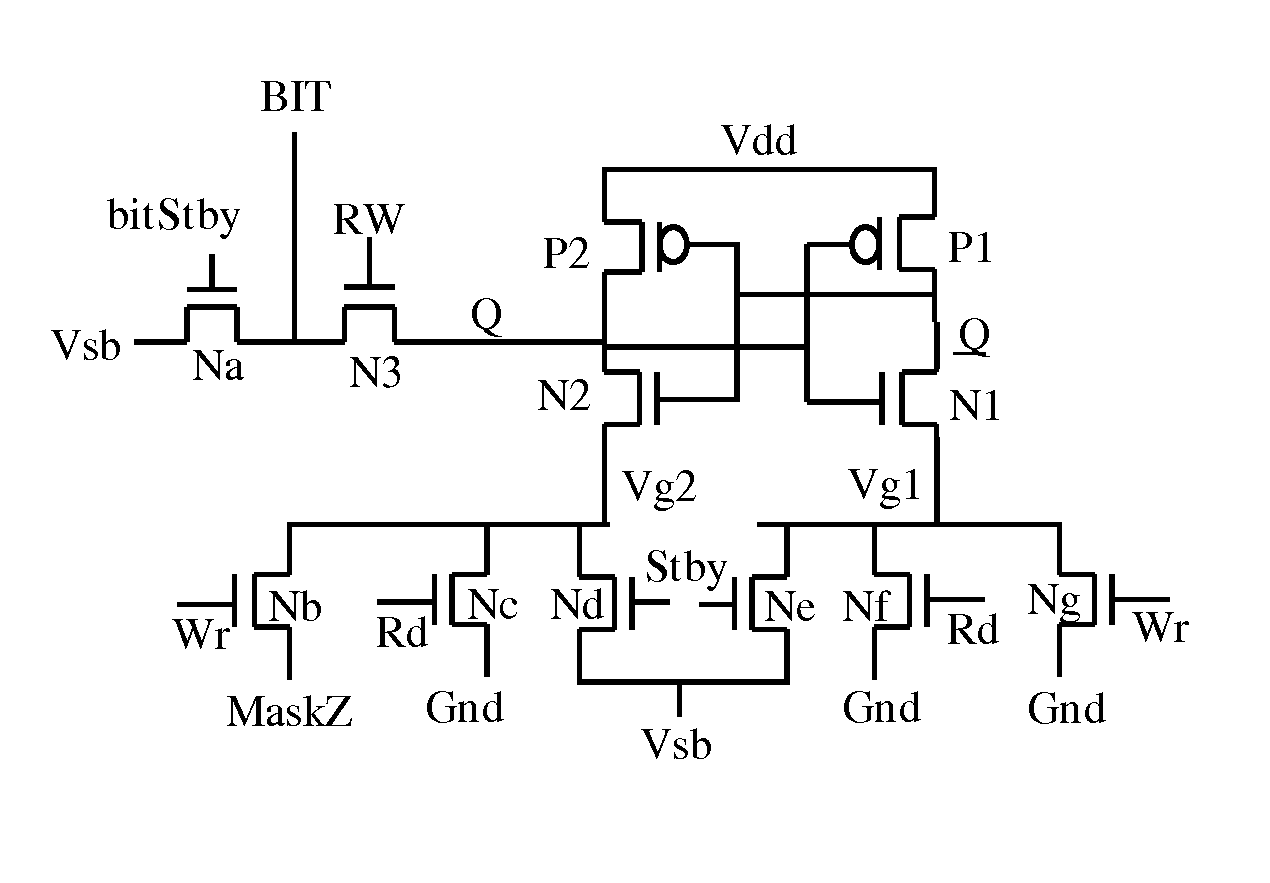
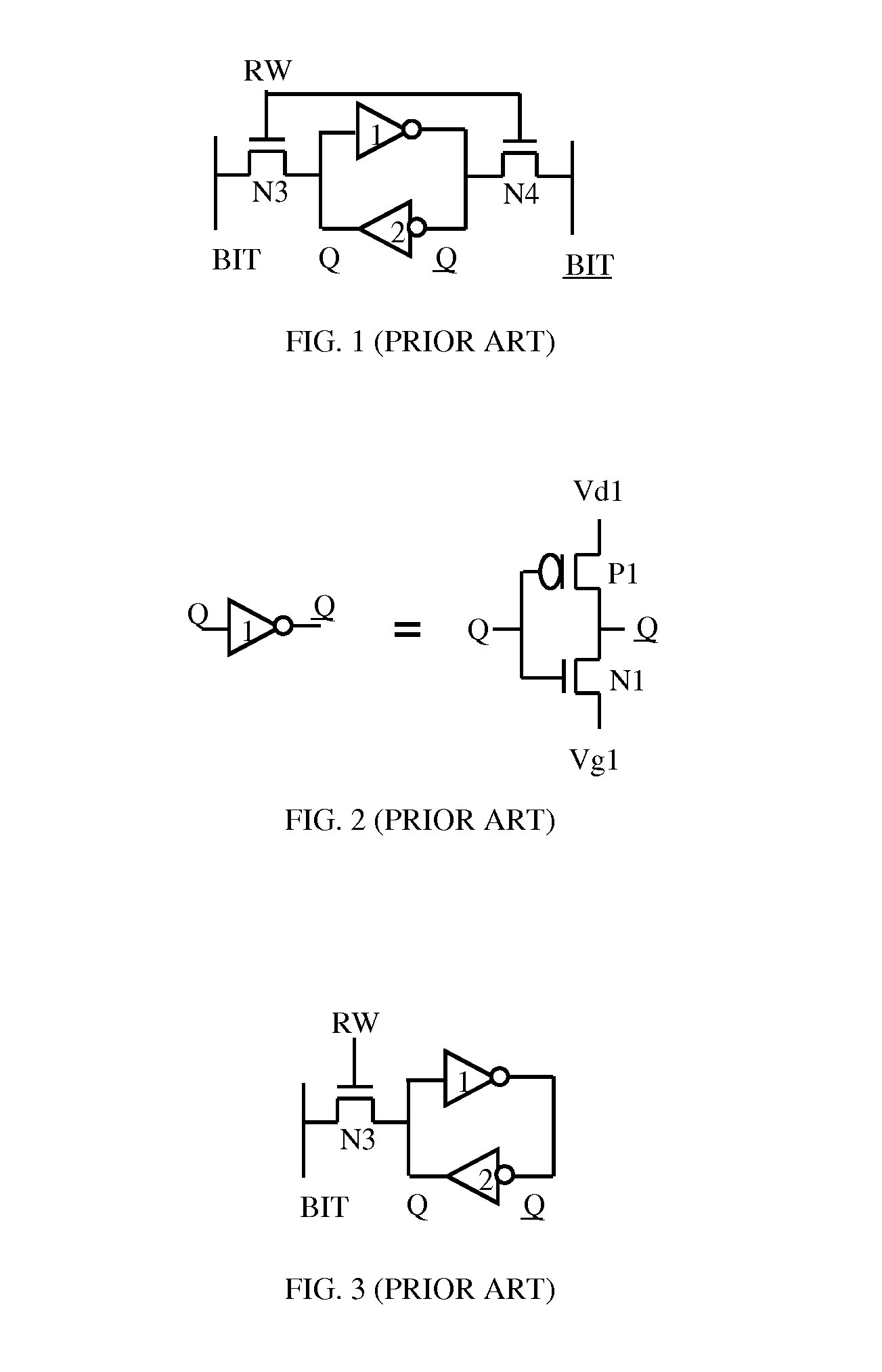
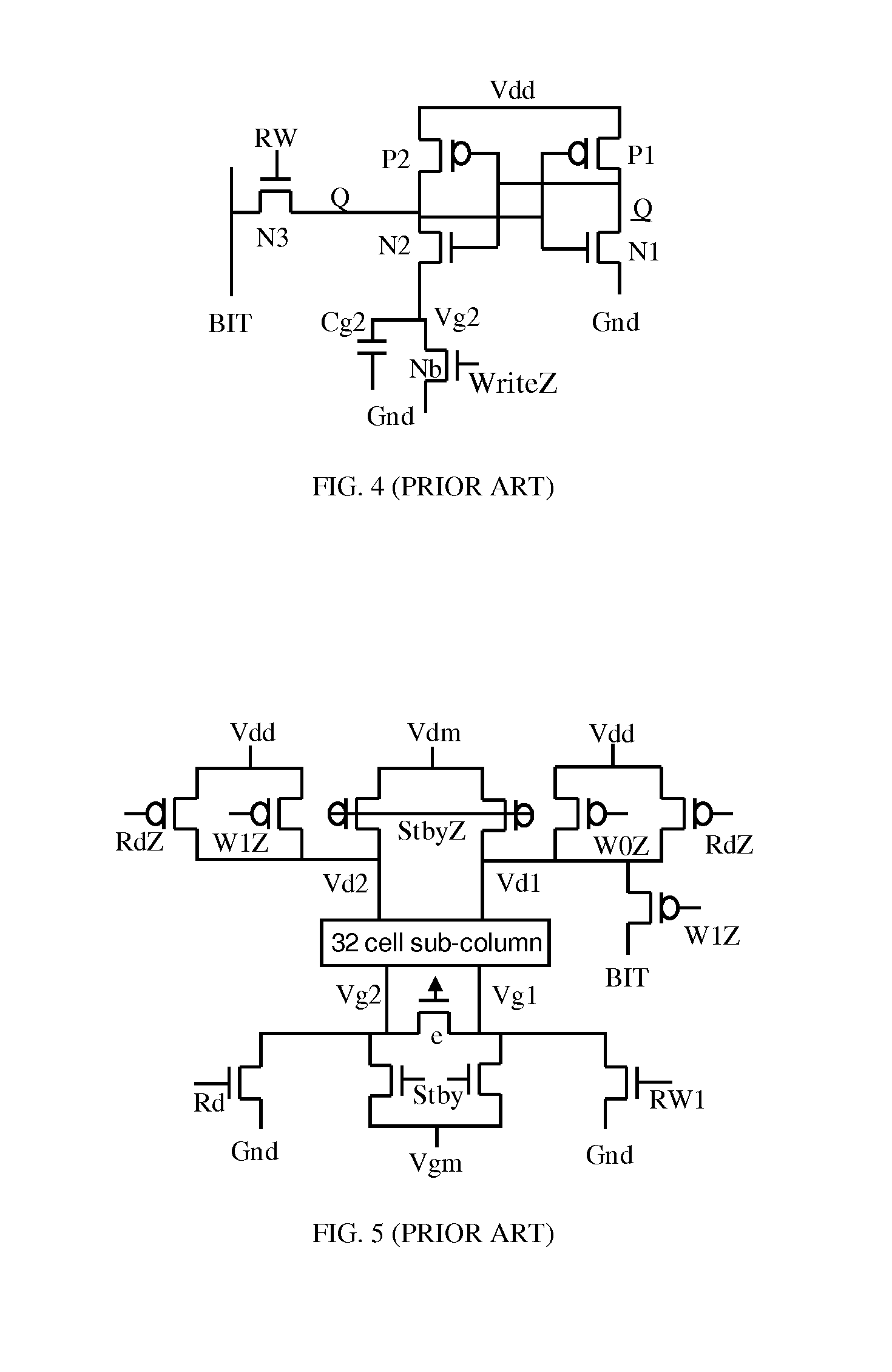
A high threshold five transistor SRAM bit cell with cross-coupled inverters has a single BIT line, a common logic 1 supply voltage, and two logic 0 virtual ground source voltages. The BIT line is coupled to the bit cell by a pass transistor. When BIT line and virtual ground lines are not otherwise being used, they are connected to a common standby voltage that substantially lowers bit cell standby leakage. Writing is performed by driving a data signal through the pass transistor and is facilitated by creating a voltage differential on the virtual ground lines. Reading is also performed through the pass transistor wherein the BIT line is initially at the standby voltage, and is then driven lower or higher depending upon the data value stored in the bit cell.
Owner:HOBSON RICHARD FREDERIC +1
DRAM memory cell and array having pass transistors with surrounding gate
InactiveUS6207985B1Easy to controlAdvantageous charge storage capabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesDram memorySilicon
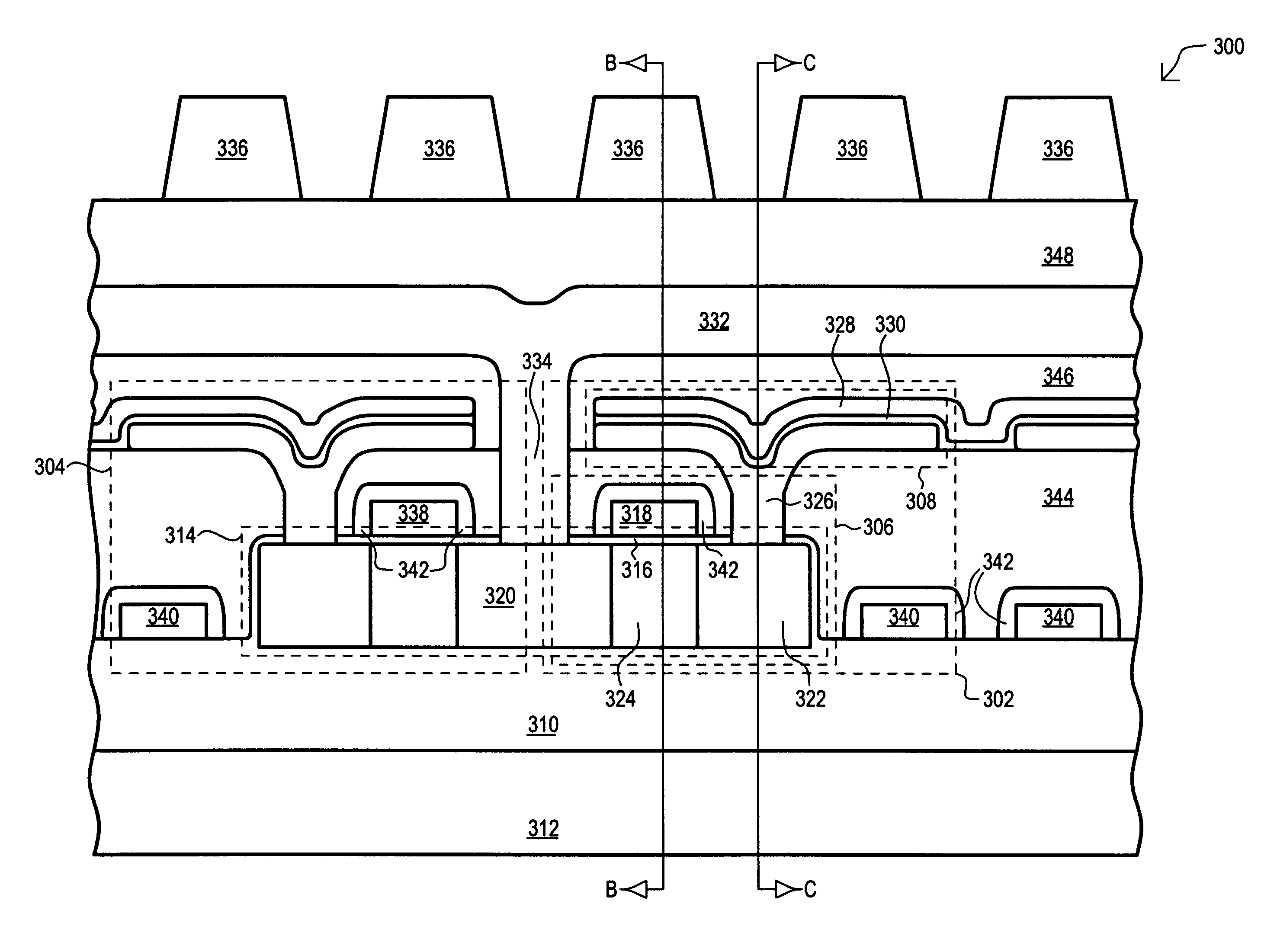
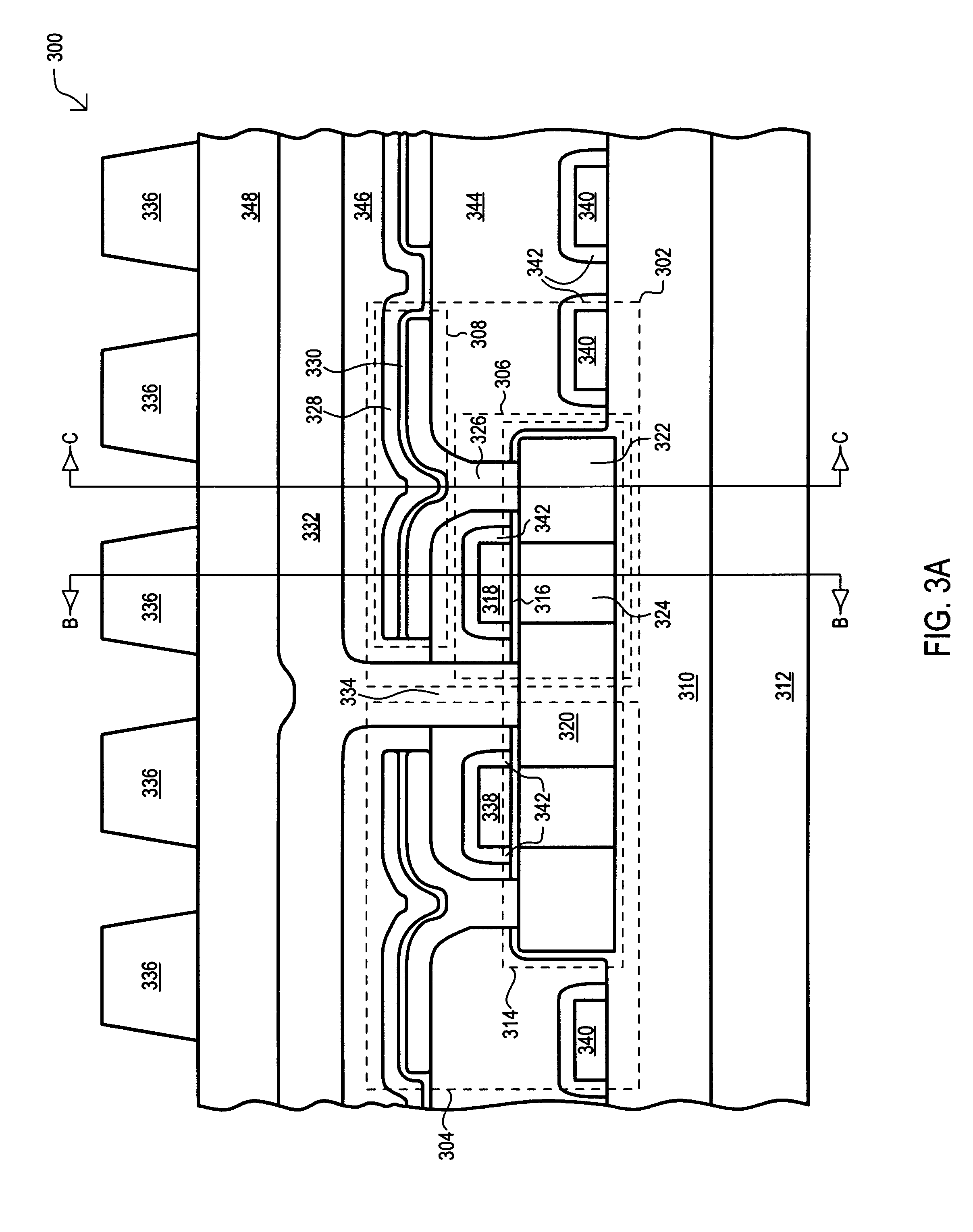
A dynamic random access memory (DRAM) cell and associated array are disclosed. In a first embodiment, the DRAM (300) includes a storage capacitor (308) and a pass transistor (306). The pass transistor (306) is formed within a silicon mesa (314), and includes a source region (320), a drain region (322), and a channel region (324) that extends in a length direction between the source region (320) and drain region (322). When viewed with respect to a width direction, the channel region (324) has a narrower width than that of the source region (320) and drain region (322). Further, the channel region (324) has a top surface and opposing side surfaces. A surrounding gate (318) is disposed around the channel region (324), adjacent to the top and side surfaces, and separated therefrom by a gate insulating layer (316). Due to the reduced channel region width and surrounding gate (318), greater control of the operation of the pass transistor (302) is provided, including an off state with reduced source-to-drain leakage.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Low vt antifuse device
ActiveUS20090250726A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh voltage transistorsProcess manufacturing
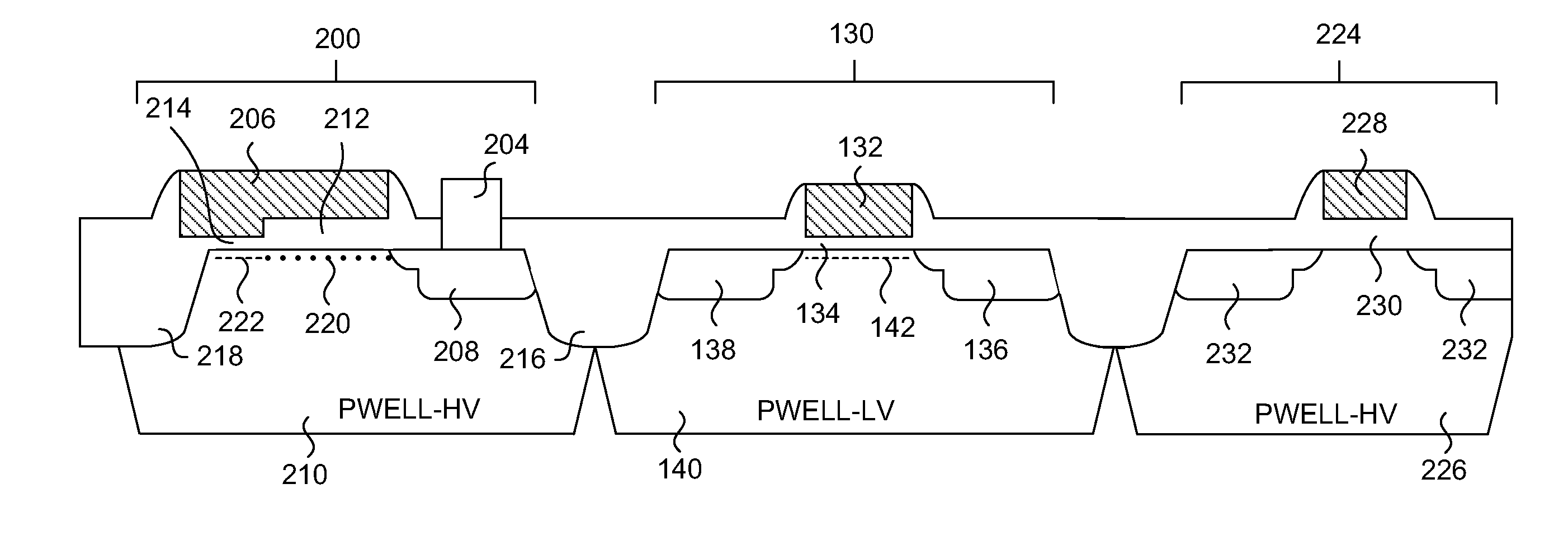
A one time programmable memory cell having an anti-fuse device with a low threshold voltage independent of core circuit process manufacturing technology is presented. A two transistor memory cell having a pass transistor and an anti-fuse device, or a single transistor memory cell having a dual thickness gate oxide, are formed in a high voltage well that is formed for high voltage transistors. The threshold voltage of the anti-fuse device differs from the threshold voltages of any transistor in the core circuits of the memory device, but has a gate oxide thickness that is the same as a transistor in the core circuits. The pass transistor has a threshold voltage that differs from the threshold voltages of any transistor in the core circuits, and has a gate oxide thickness that differs from any transistor in the core circuits. The threshold voltage of the anti-fuse device is lowered by omitting some or all of the threshold adjustment implants that is used for high voltage transistors fabricated in the I / O circuits.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
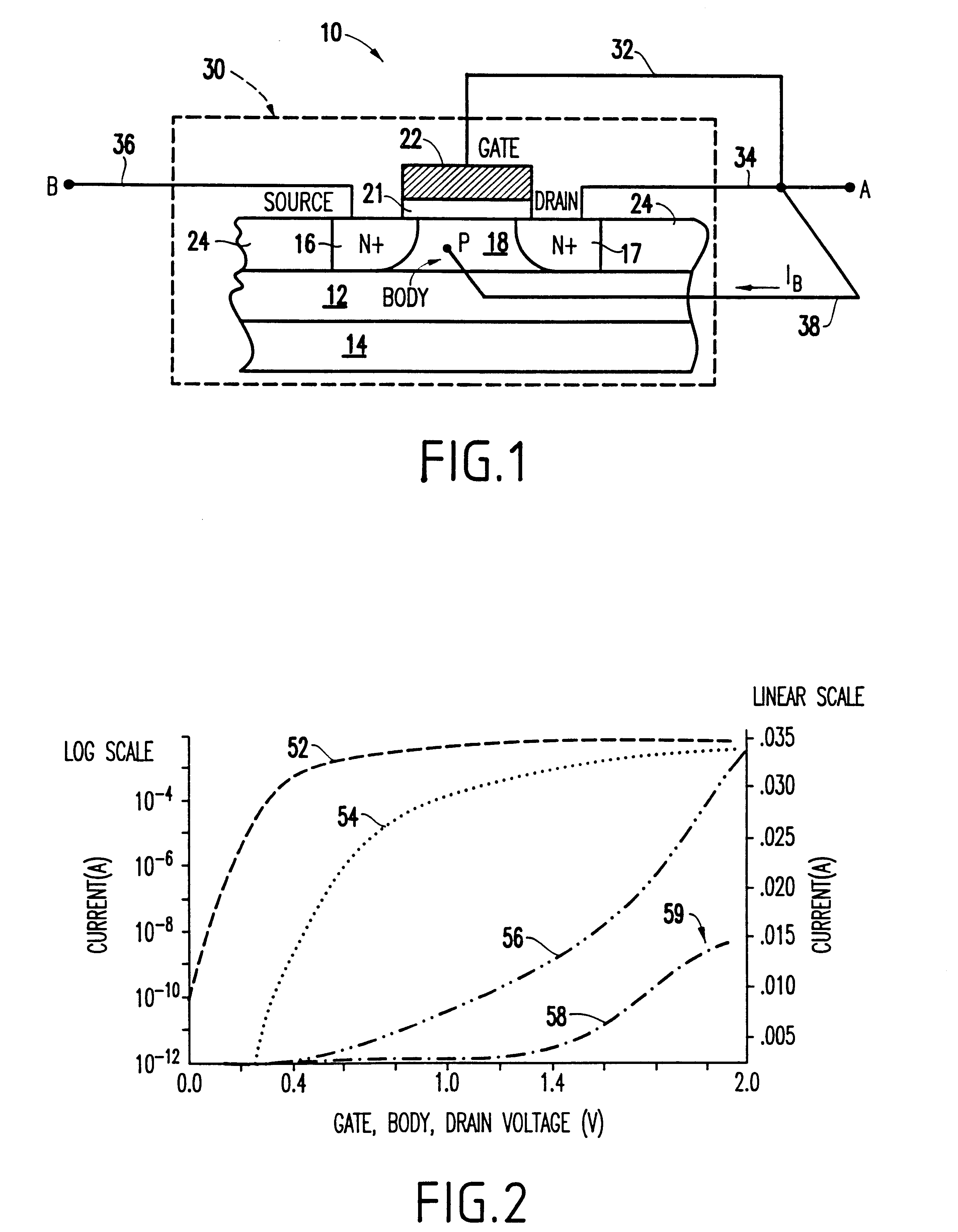
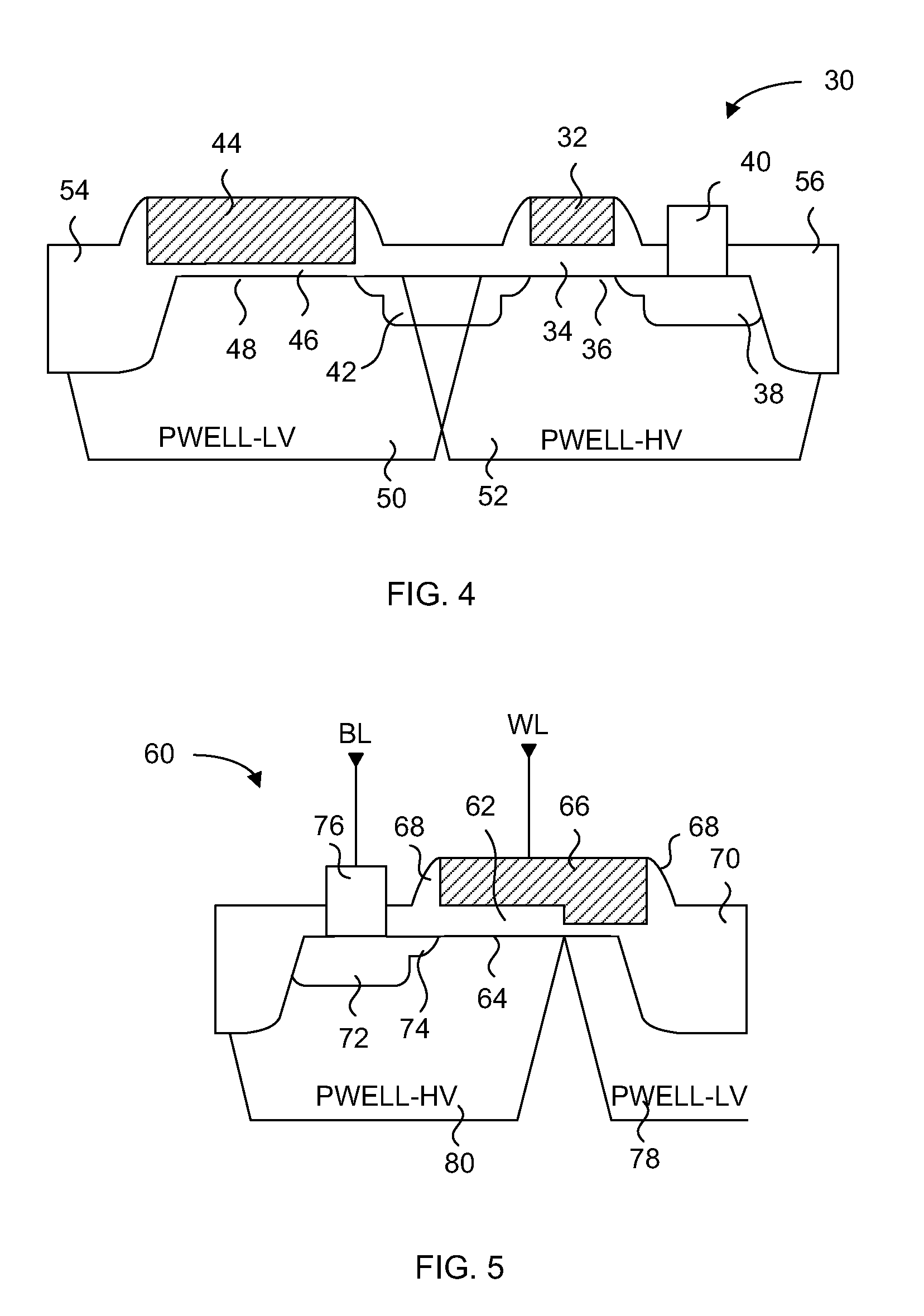
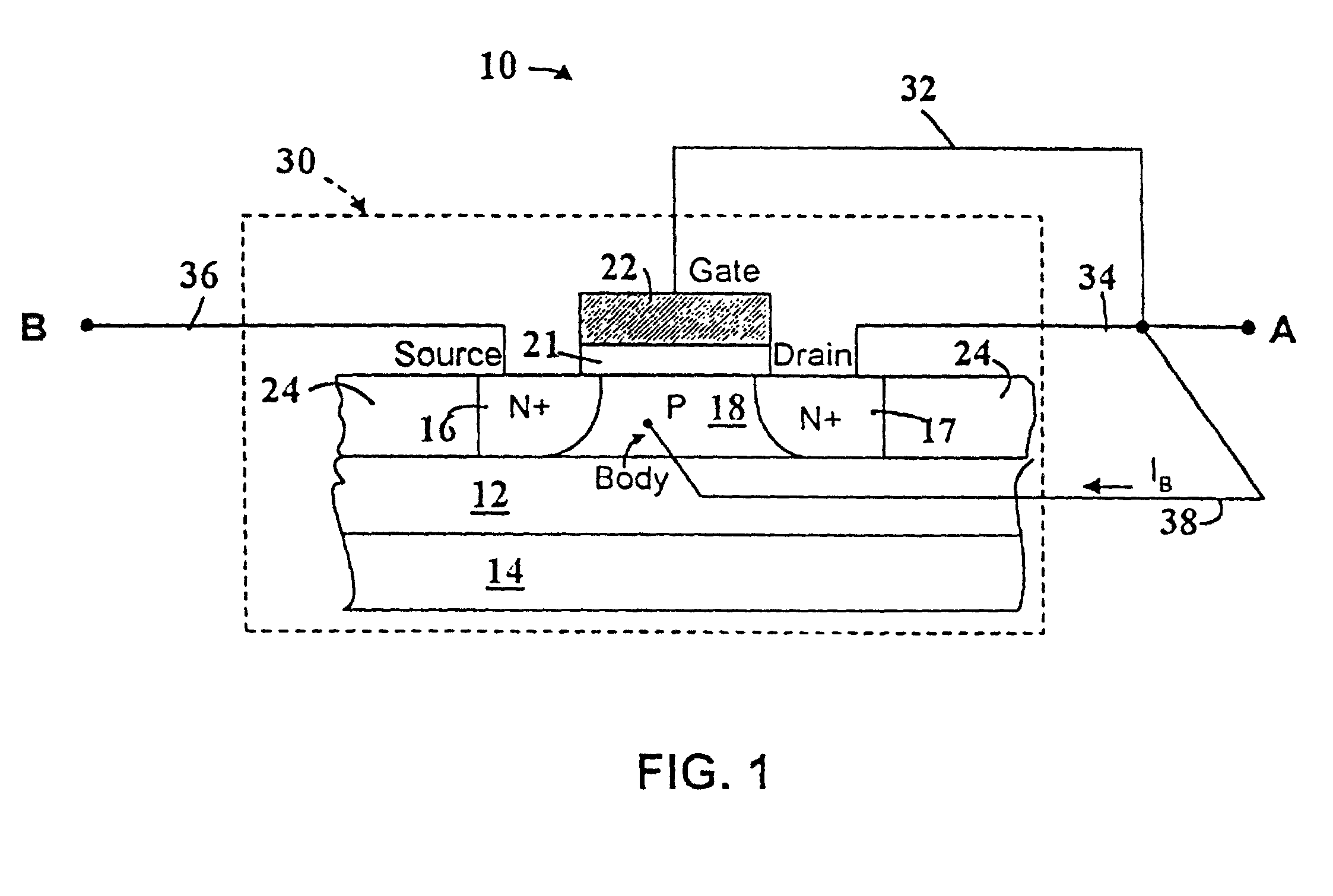
SOI voltage-tolerant body-coupled pass transistor
A method and device for A pass transistor device which includes a source; a drain opposite the source, a body between the source and the drain, and a circuit control network connected between the drain and the source, wherein the circuit control network controls a potential voltage of the body and provides overvoltage protection to the pass transistor.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
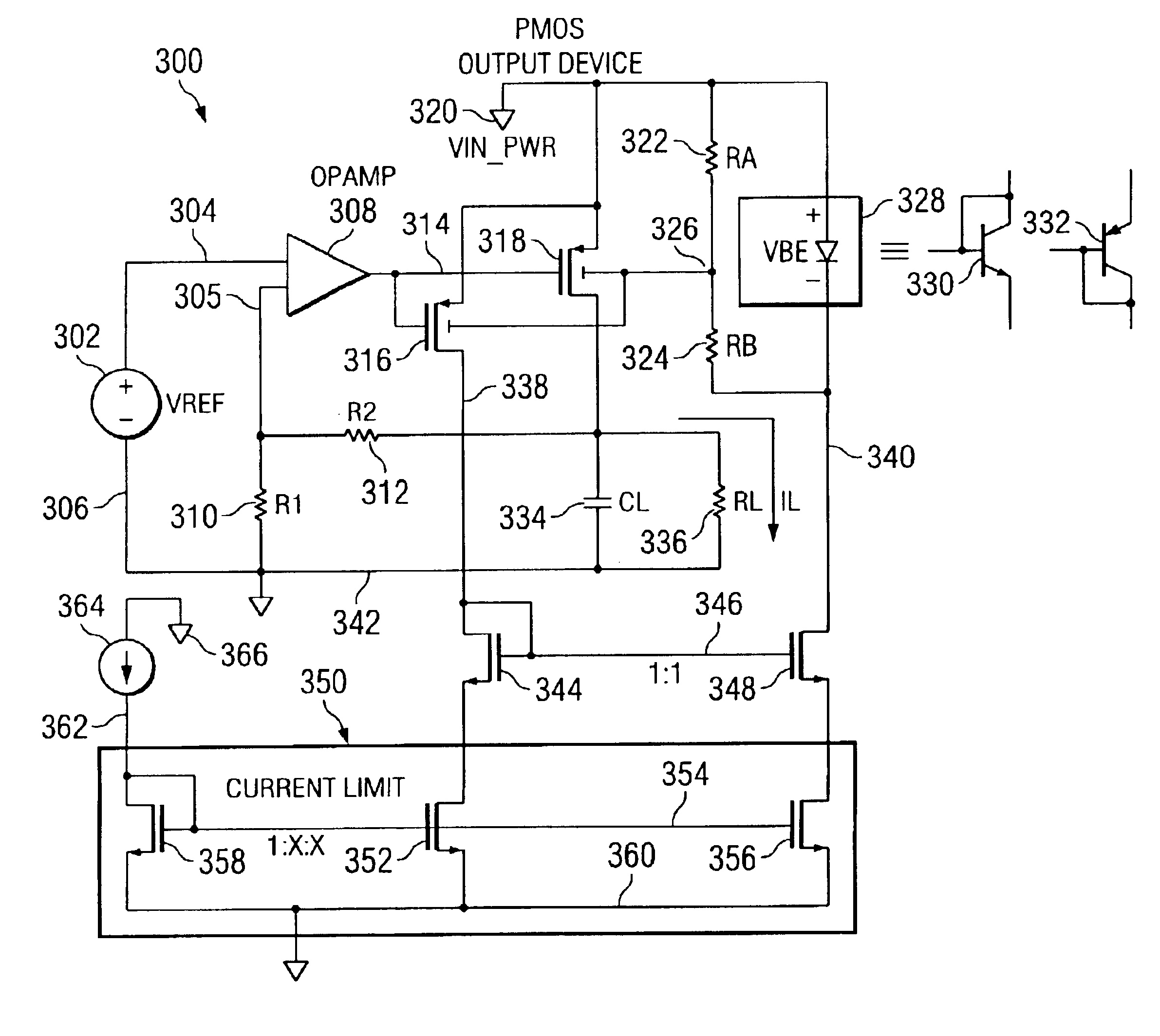
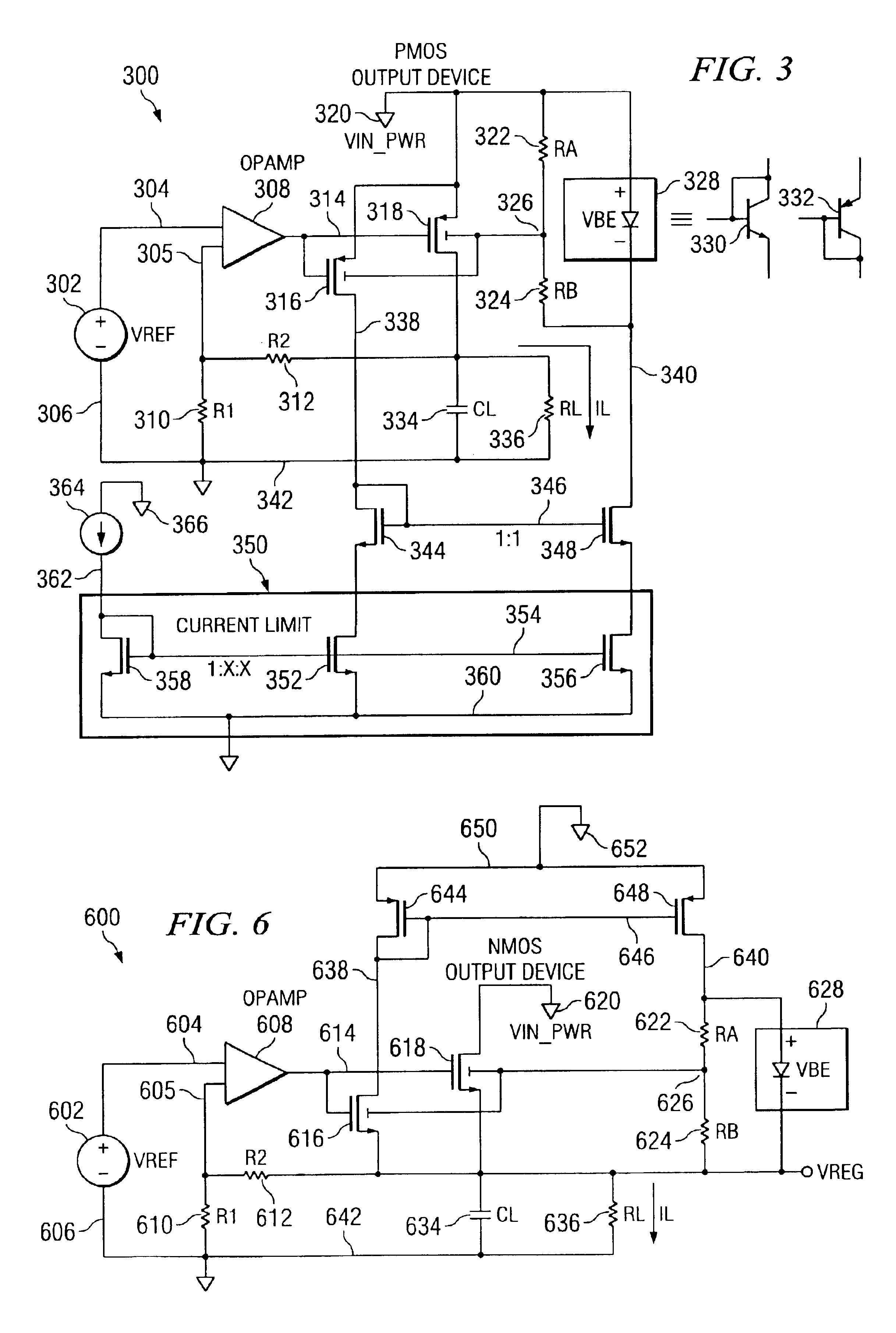
Integrated LDO with Variable Resistive Load
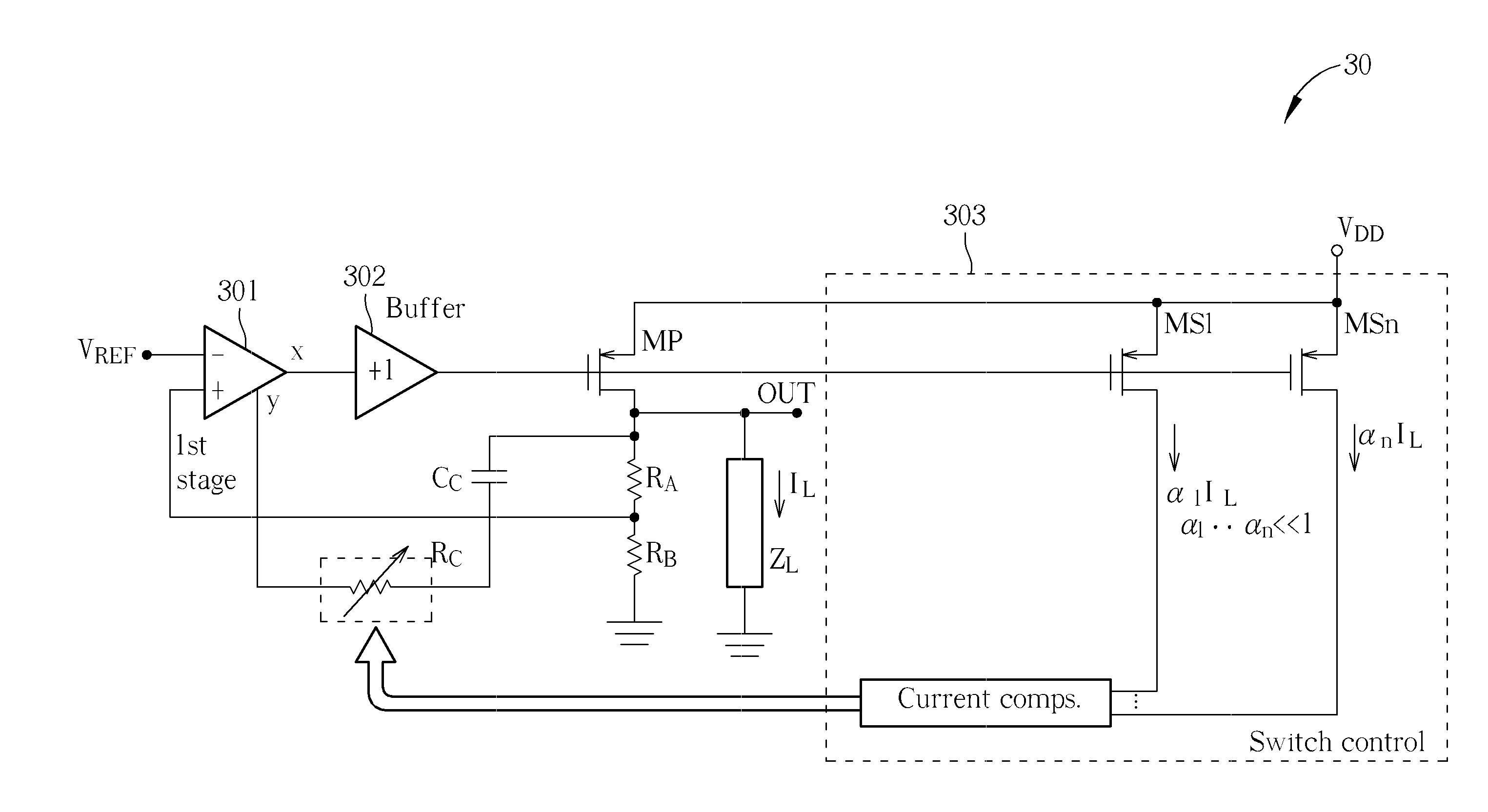
ActiveUS20100066320A1Low dropout (LDO)Electric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceAudio power amplifier
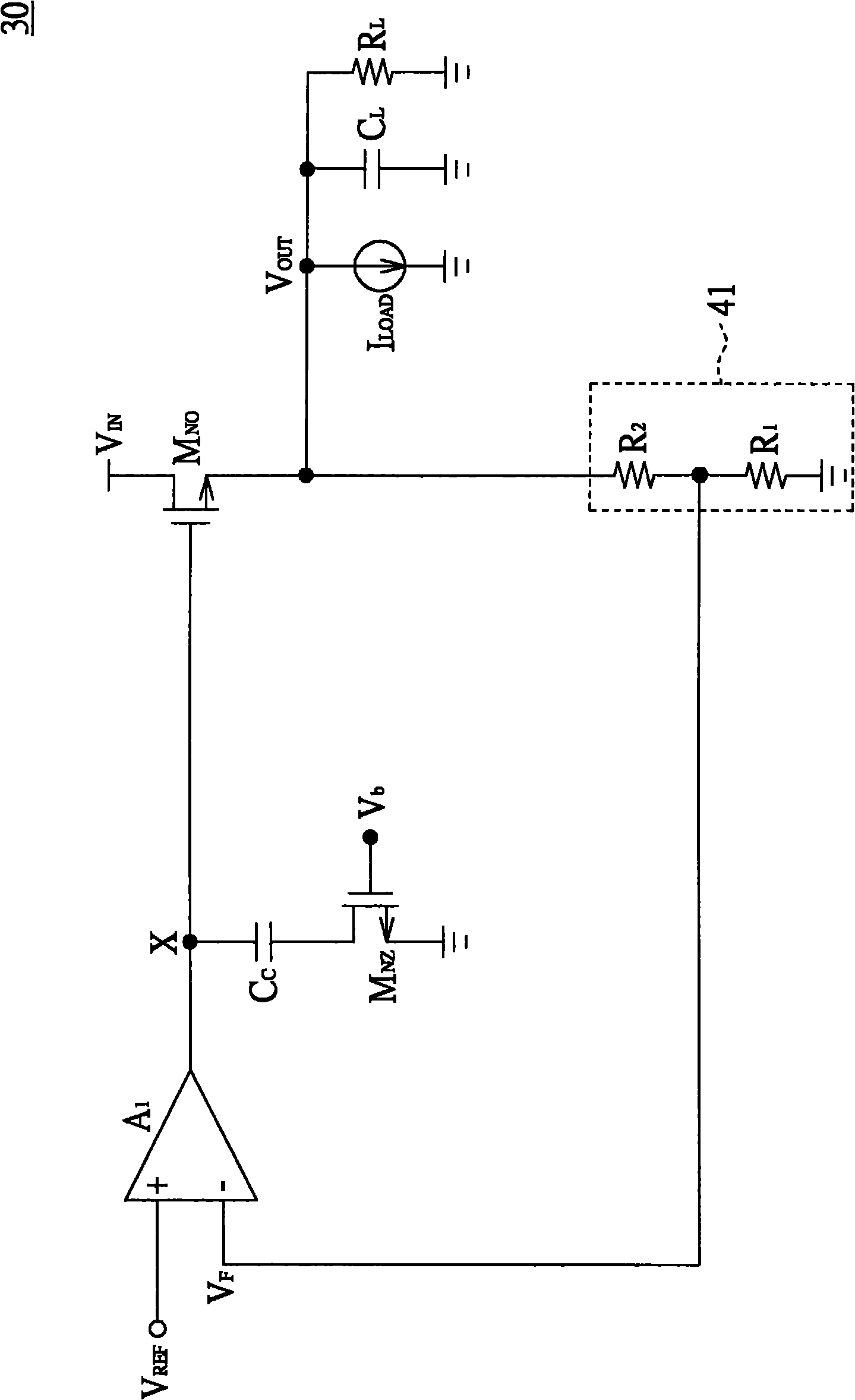
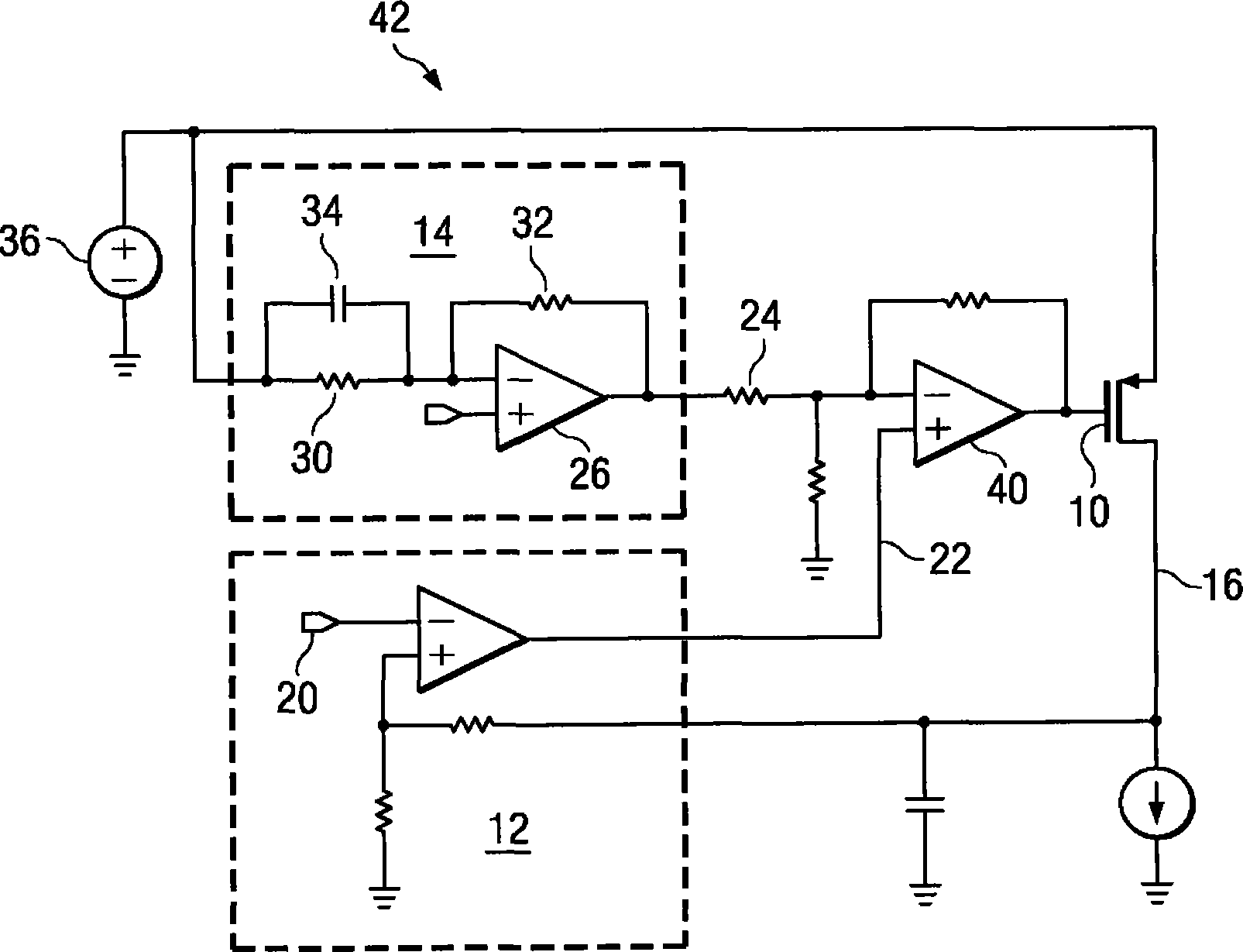
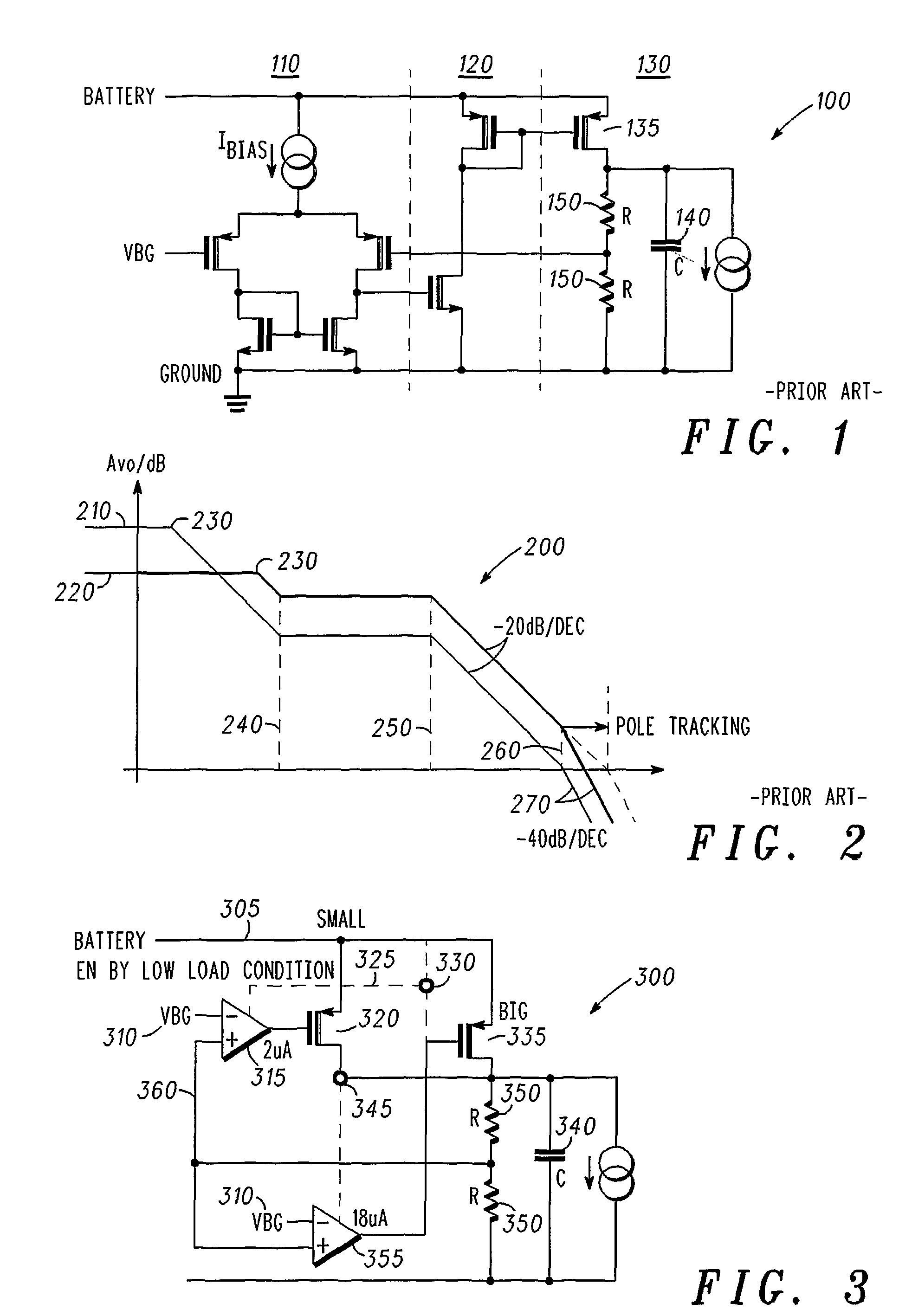
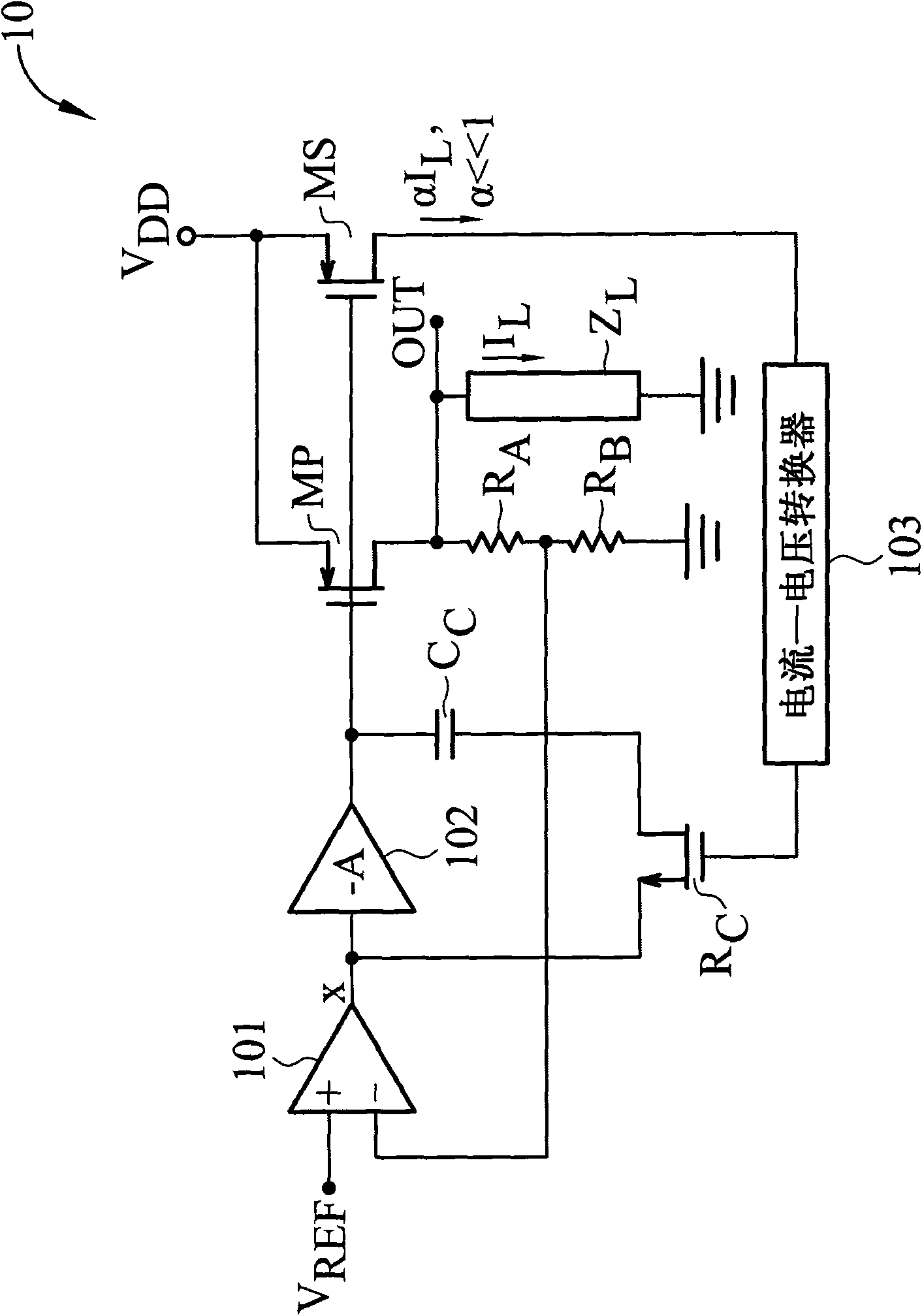
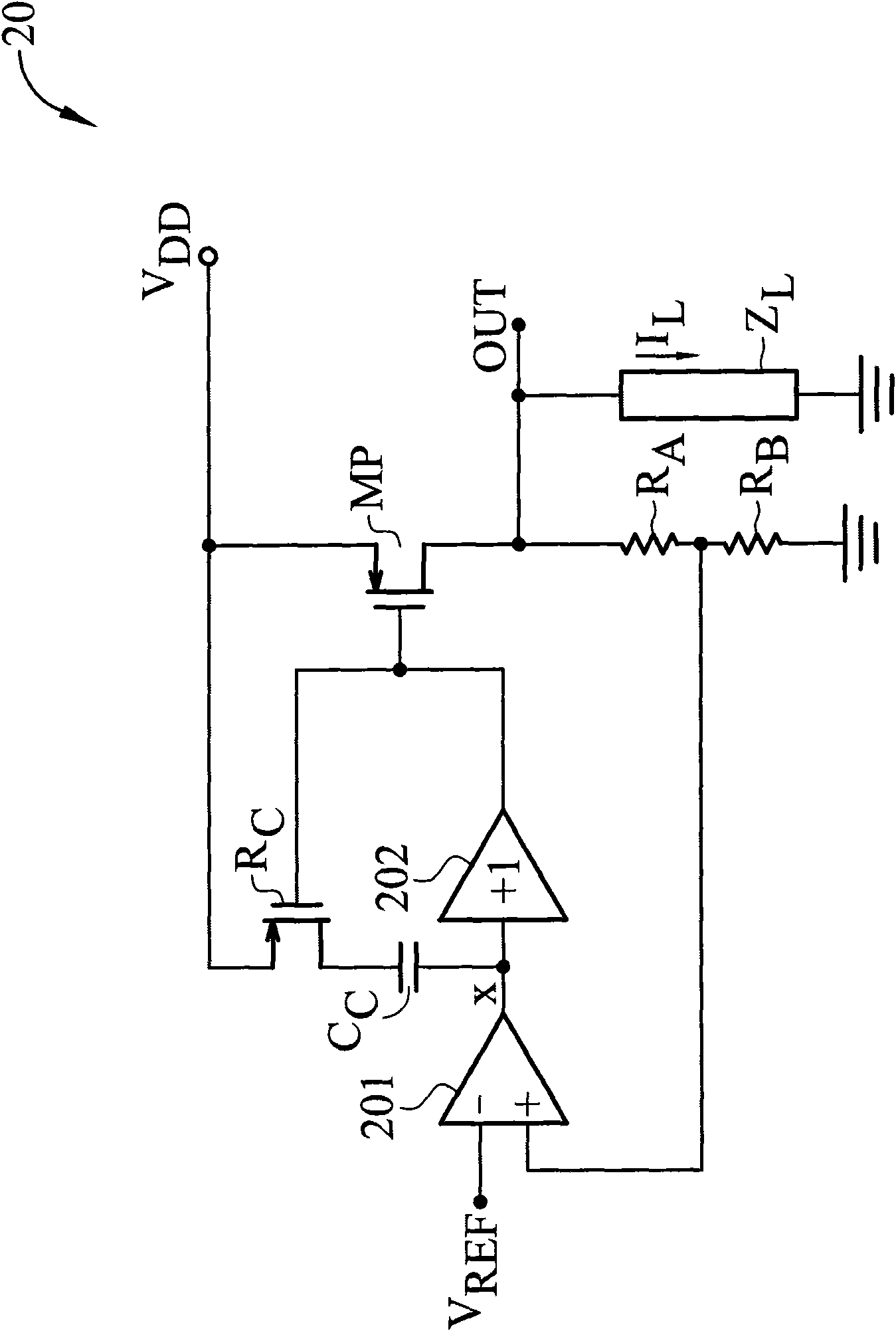
To provide adequate compensation for a wide range of output loads, a low dropout (LDO) regulator has an amplifier, a pass transistor, a voltage divider, a compensation network, and a control circuit. The amplifier outputs a comparison result according to a reference signal and a feedback signal. The pass transistor generates an output current based on the comparison result of the amplifier. The voltage divider generates the feedback signal according to the output current. The compensation network couples the output of the pass transistor to a low-impedance node of the amplifier, and has a compensation capacitor and a variable resistor coupled to the compensation capacitor. The control circuit is coupled to the input of the pass transistor and to the variable resistor for controlling resistance of the variable resistor according to the output current of the pass transistor.
Owner:MEDIATEK SINGAPORE PTE LTD SINGAPORE
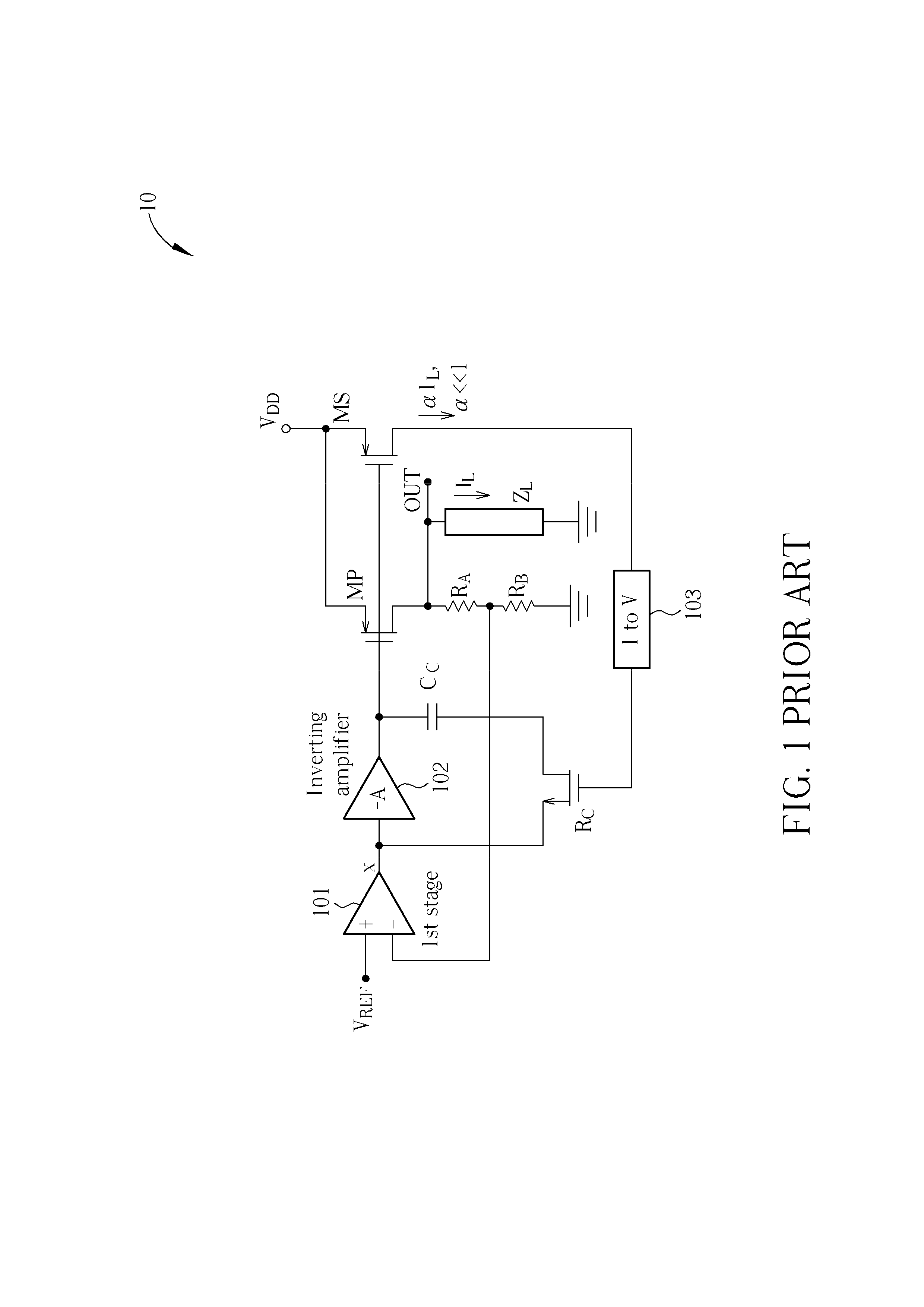
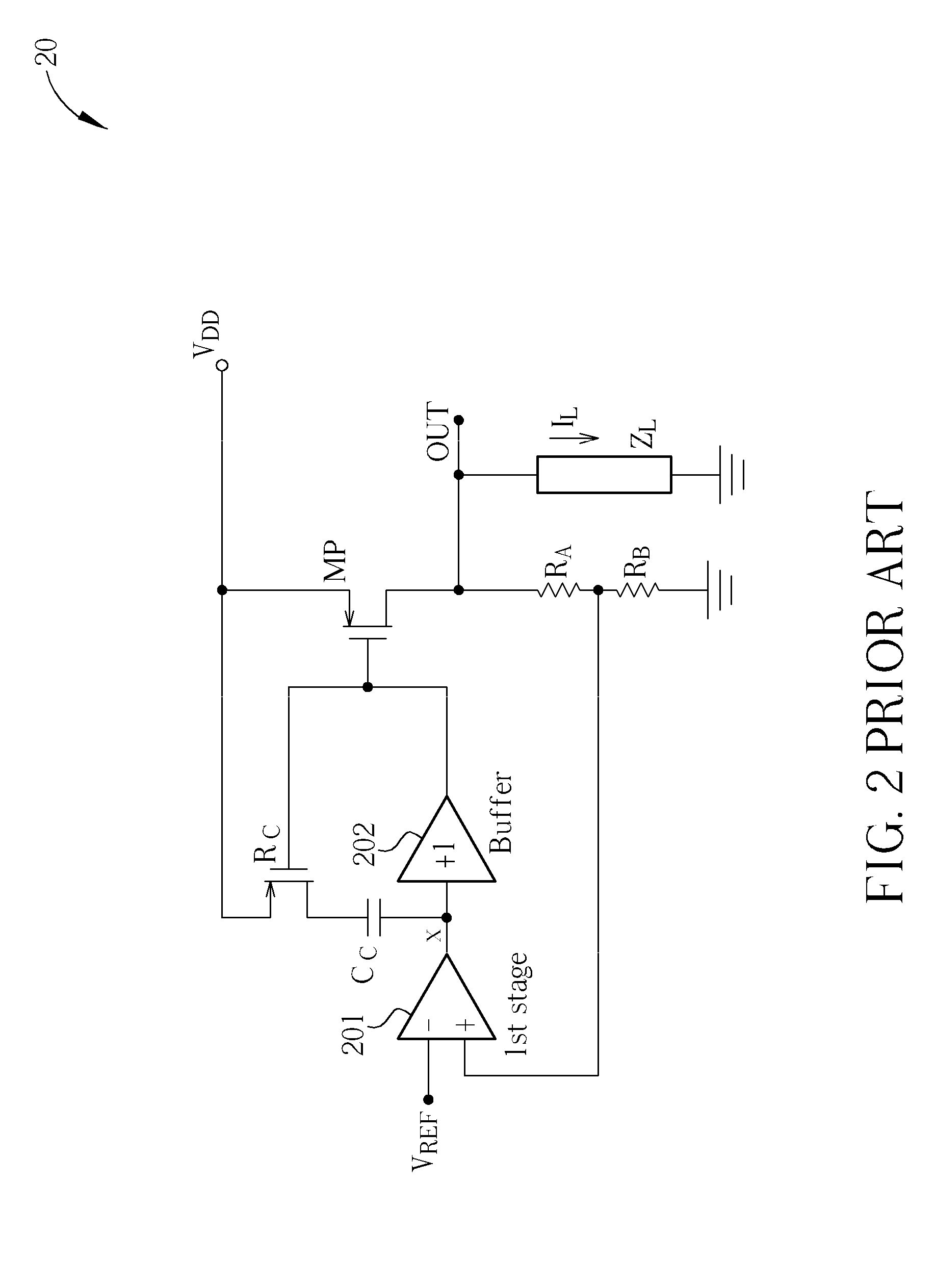
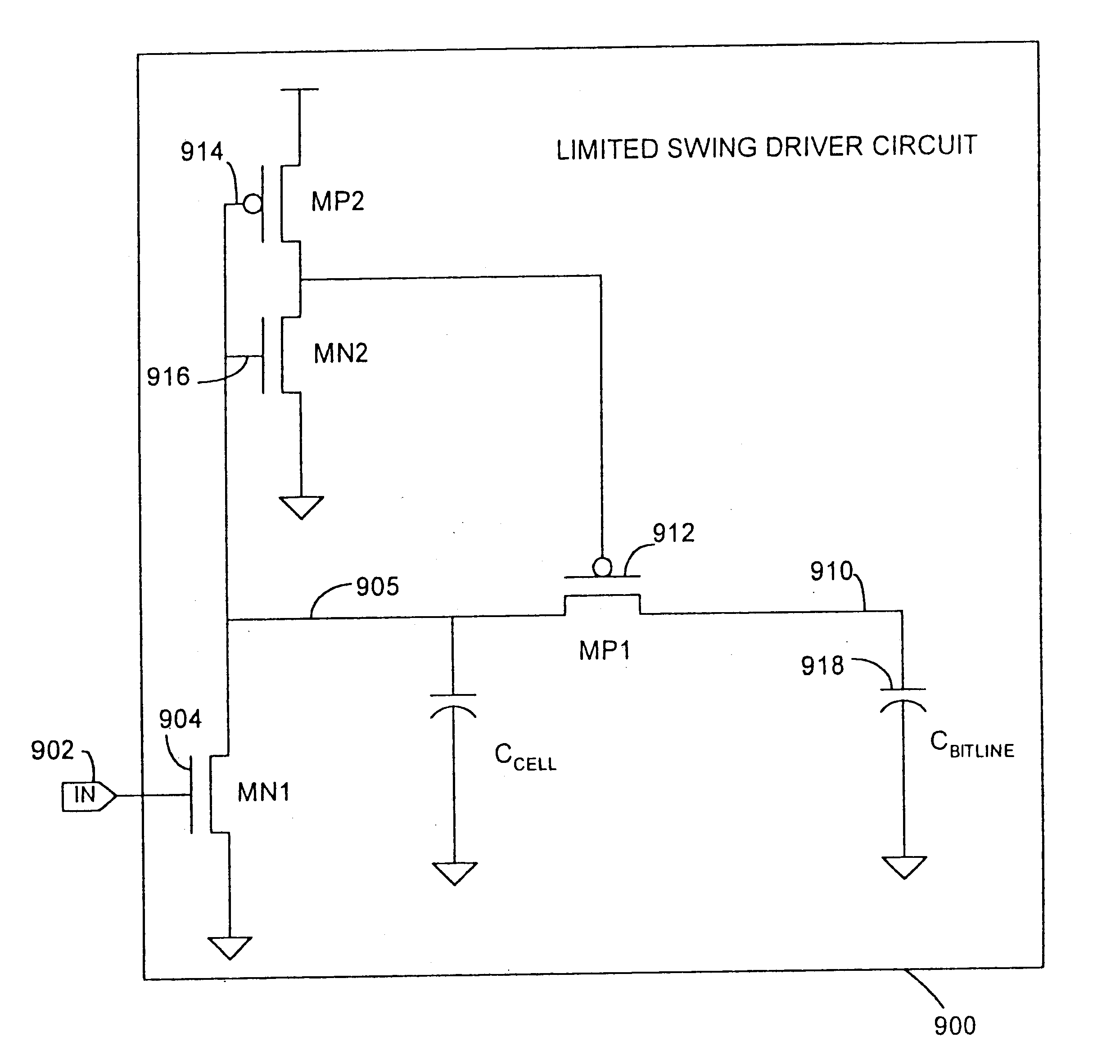
Limited swing driver circuit
A limited swing driver with a pass transistor coupled between a memory cell and an associated bitline; an inverter, its output coupled to the gate of the pass transistor, and its input coupled with the memory cell. A memory node is formed at the juncture of the inverter input and the memory cell forming a memory node. The driver also includes a discharge transistor coupled between the memory node and ground. The discharge transistor is driven by an input on the discharge transistor gate. It is preferred that the discharge transistor being programmed to produce a limited swing voltage at the memory node. It is desirable that the limited swing voltage be less than about 350 mV, and it is preferable that the limited swing voltage be between about 300 mV and about 200 mV. In addition, the limited swing voltage driver can include a tri-state output enable isolating the memory node from the bitline, particularly if the bitline is a shared or multiplexed bitline; and a self-reset circuit resetting the driver to a predetermined signal state.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
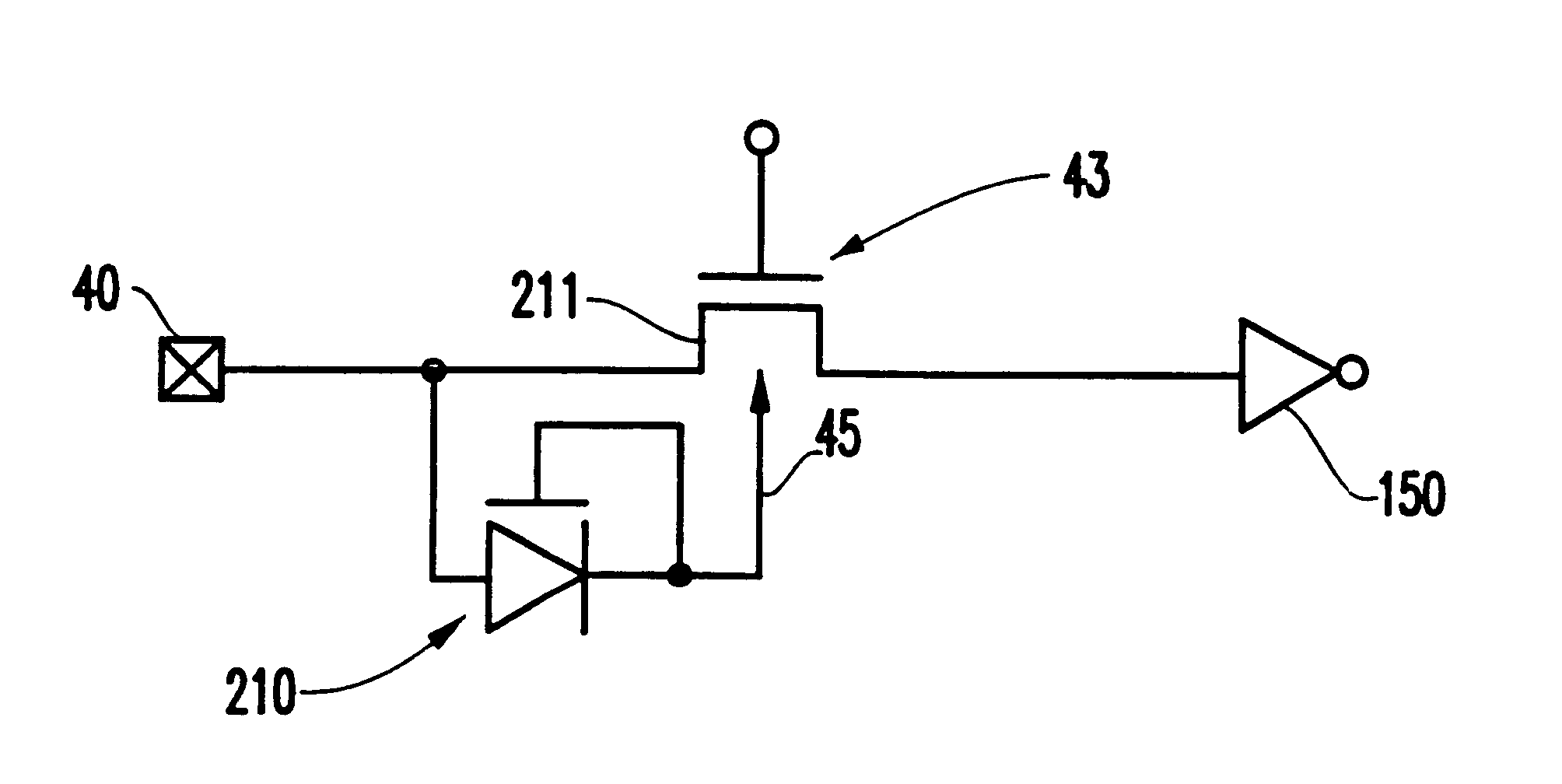
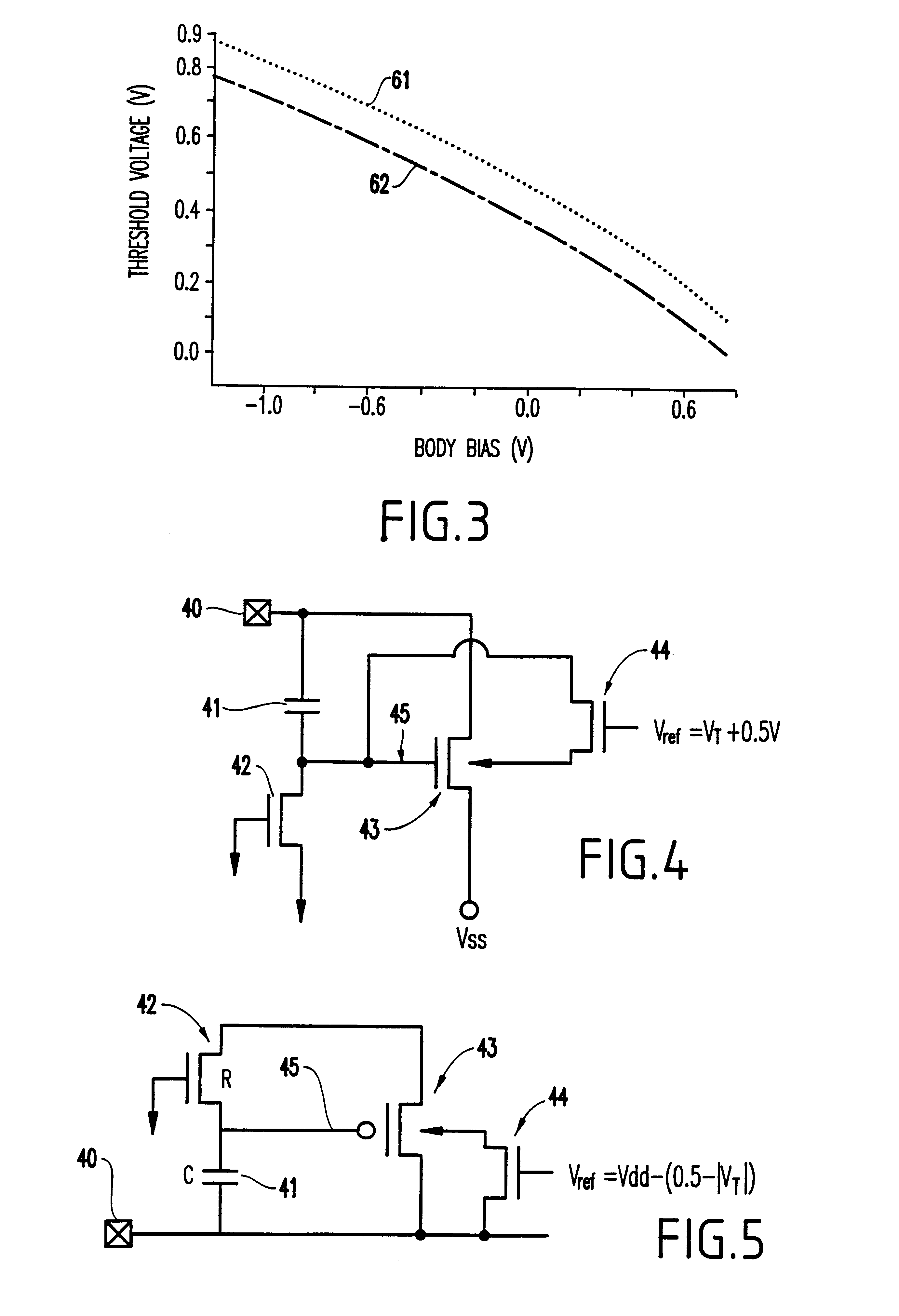
Threshold voltage adjustment for MOS devices
The Vt of an MOS transistor is lowered in response to its load current. In a LDO (low dropout) regulator, lowering the Vt of the pass transistor with load increases the level of drive that can be applied to the pass transistor thus allowing a smaller transistor to be used for the same load.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
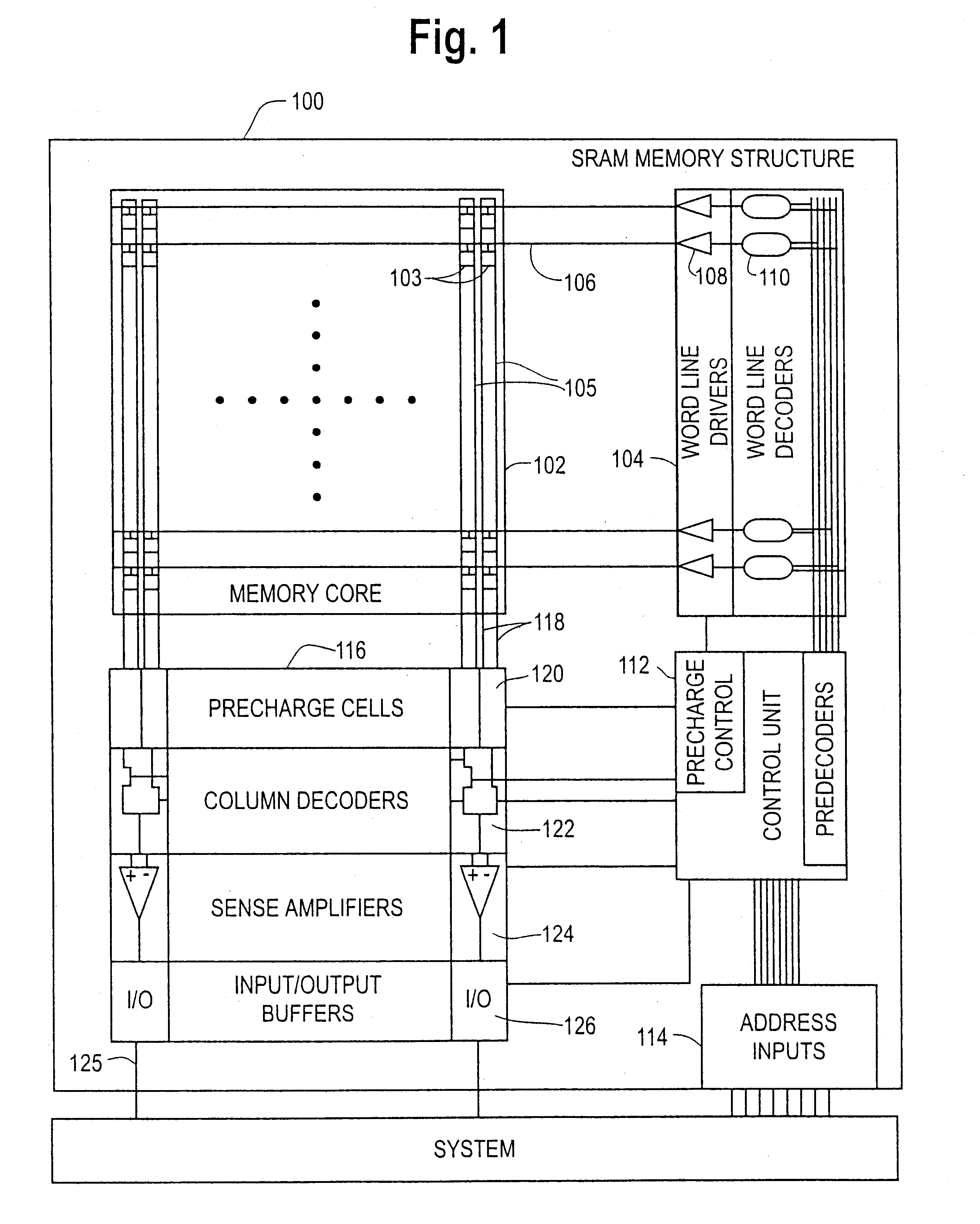
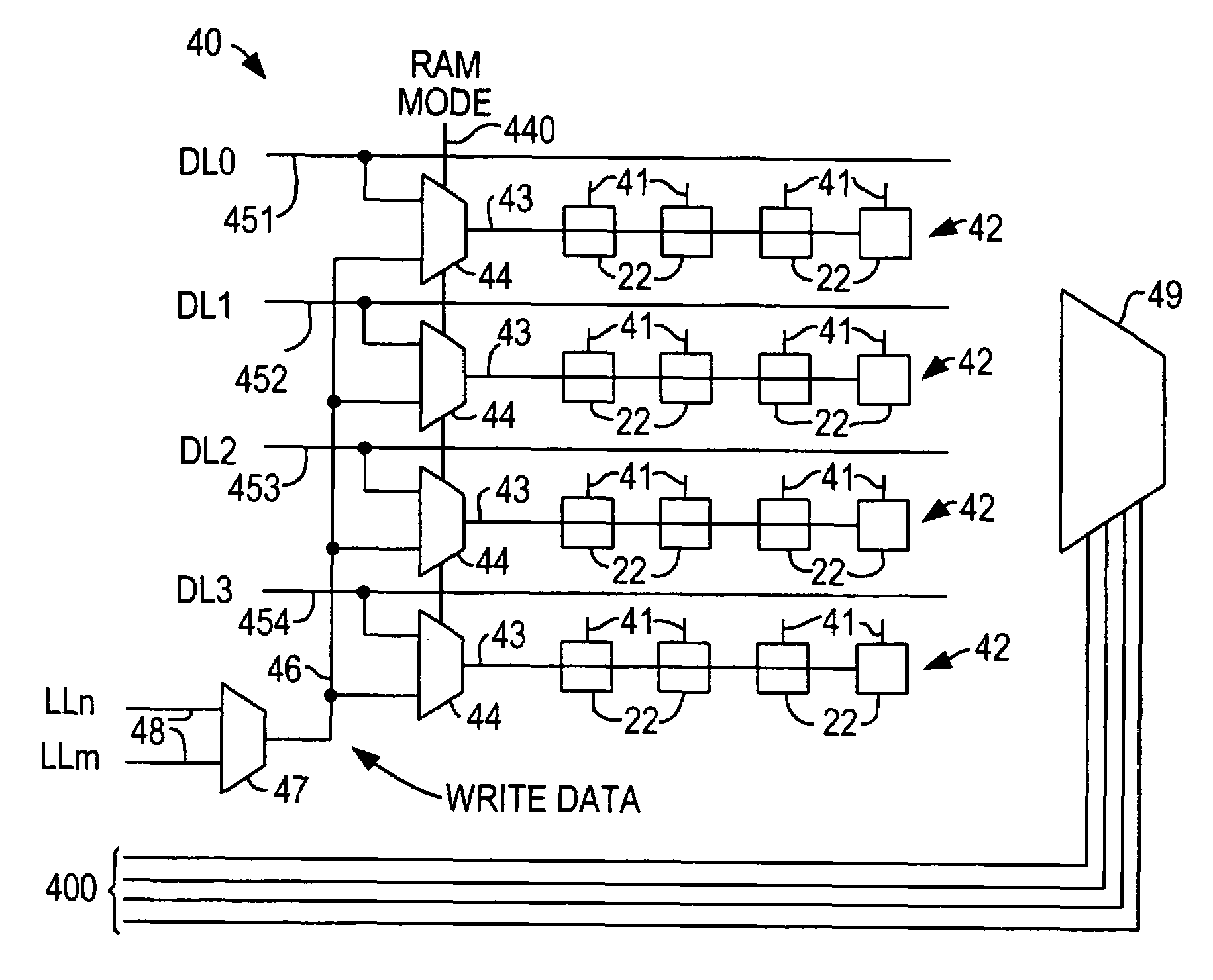
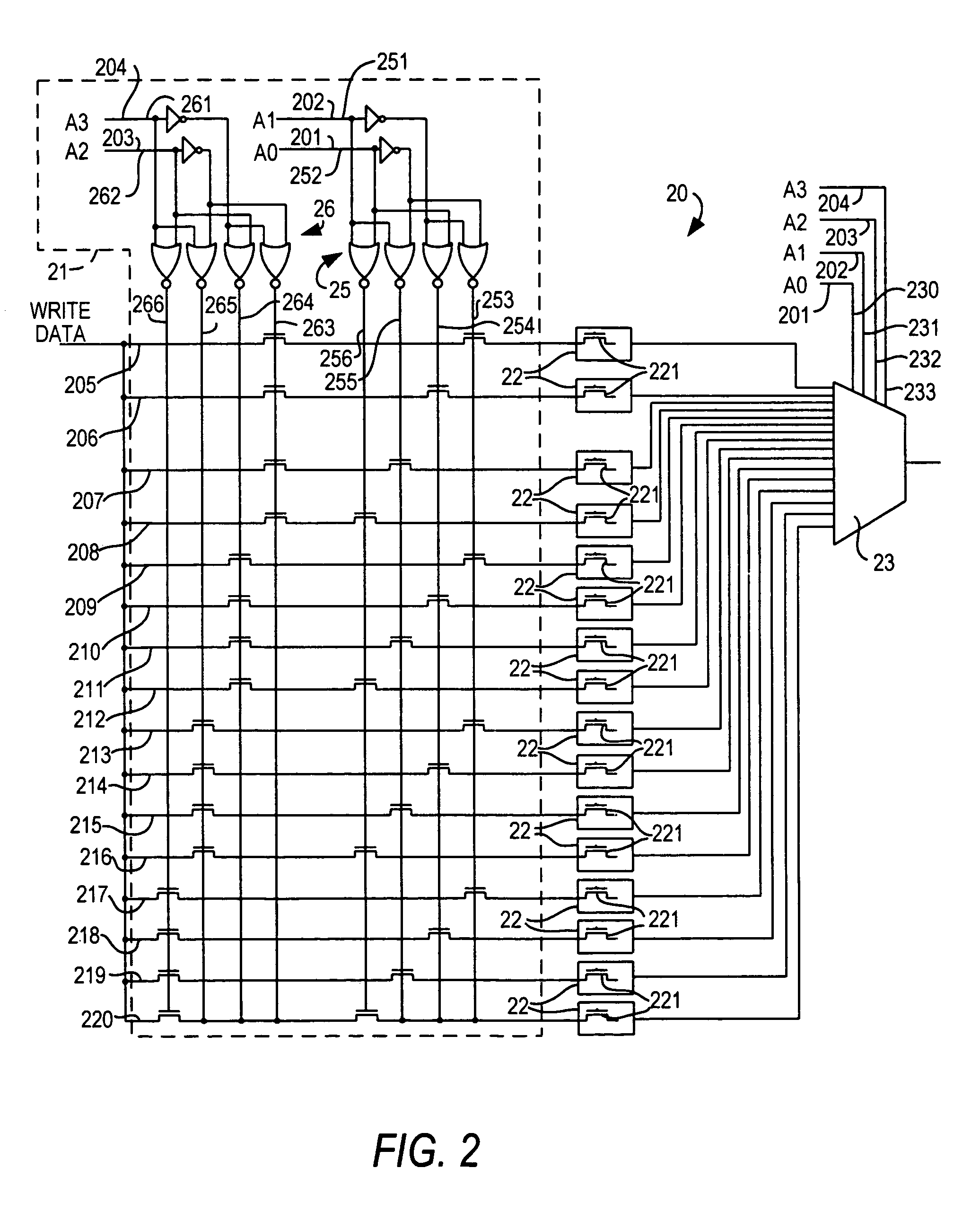
Distributed random access memory in a programmable logic device
ActiveUS7084665B1Low costEasy to switchLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsComputation using denominational number representationShift registerStatic random-access memory
Distributed random access memory in a programmable logic device uses configuration RAM bits as bits of the distributed RAM. A single write path is used to provide both configuration data and user write data. Selection circuitry, such as a multiplexer, is used to determine whether the single write path carries configuration data or user write data. In another aspect of the invention, the configuration RAM bits are used as to construct a shift register by adding pass transistors to chain the configuration RAM bits together, and clocking alternate pass transistors with two clocks 180° out of phase with one another.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Semiconductor Device, Driver IC, Display Device, and Electronic Device
ActiveUS20160071463A1Improve accuracyTransistorStatic indicating devicesMiniaturizationDisplay device
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Linear voltage regulator and current sensing circuit thereof
The invention discloses a linear voltage regulator and a current sensing circuit thereof. The linear voltage regulator comprises a pass transistor, a compensation capacitor, a variable resistor, an error amplifier and a current sensing circuit, wherein the current sensing circuit comprises a sensing transistor and a voltage lock; the sensing transistor is controlled by the error amplifier; the first end of the sensing transistor receives input voltage; the sensing transistor is used for generating a sensing current which is related to transmission current flowing through the pass transistor; the voltage lock is coupled with the second end of the pass transistor and the second end of the sensing transistor, and controls the voltage of the second end of the pass transistor to be equal to the voltage of the second end of the sensing transistor; and the voltage lock regulates the variable resistor coupled with the compensation capacitor according to the voltage of the second end of the pass transistor and the voltage of the second end of the sensing transistor.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
ROM cell having an isolation transistor formed between first and second pass transistors and connected between a differential bitline pair
ActiveUS8120939B2Balance performanceIncrease process marginSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesBit lineEngineering
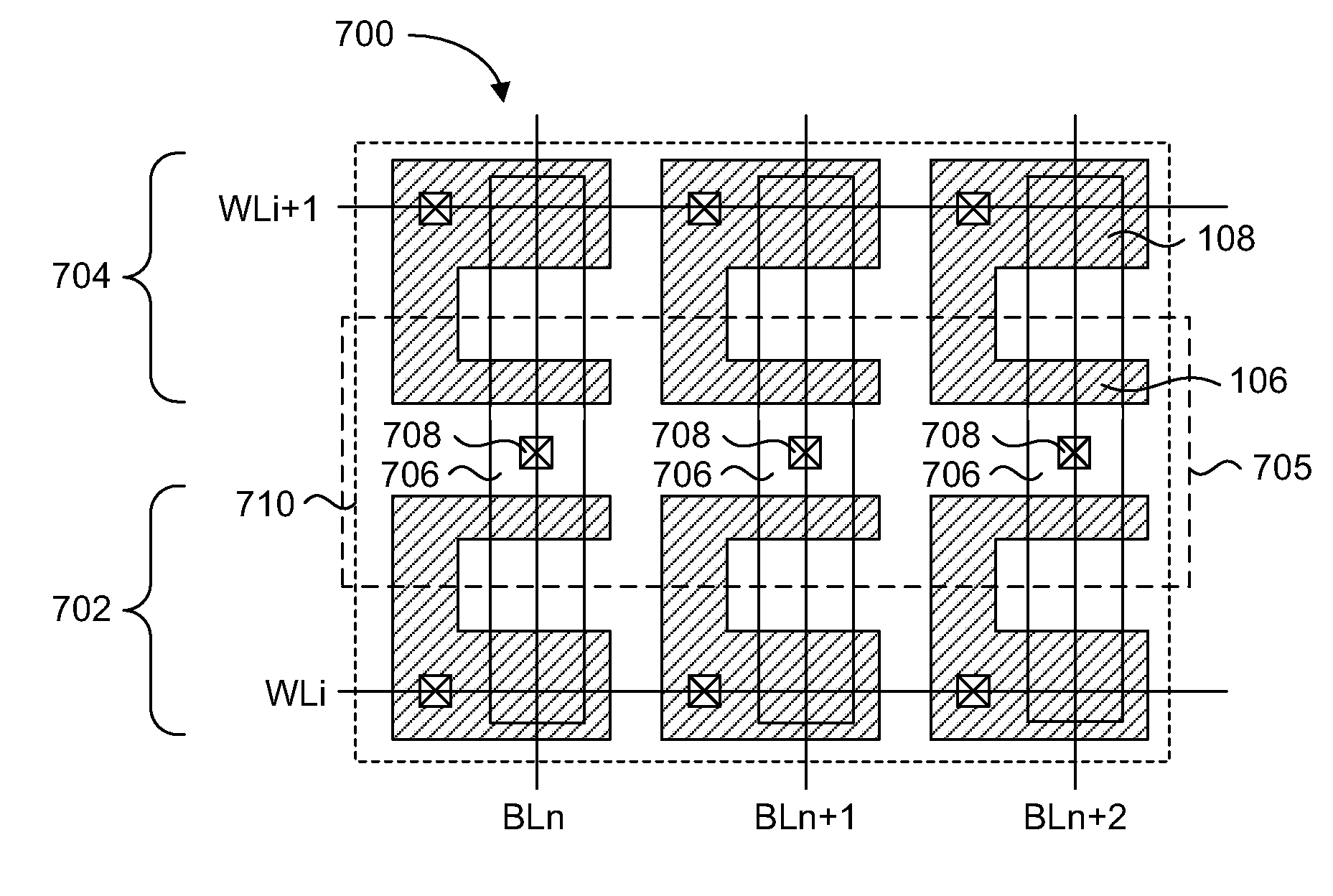
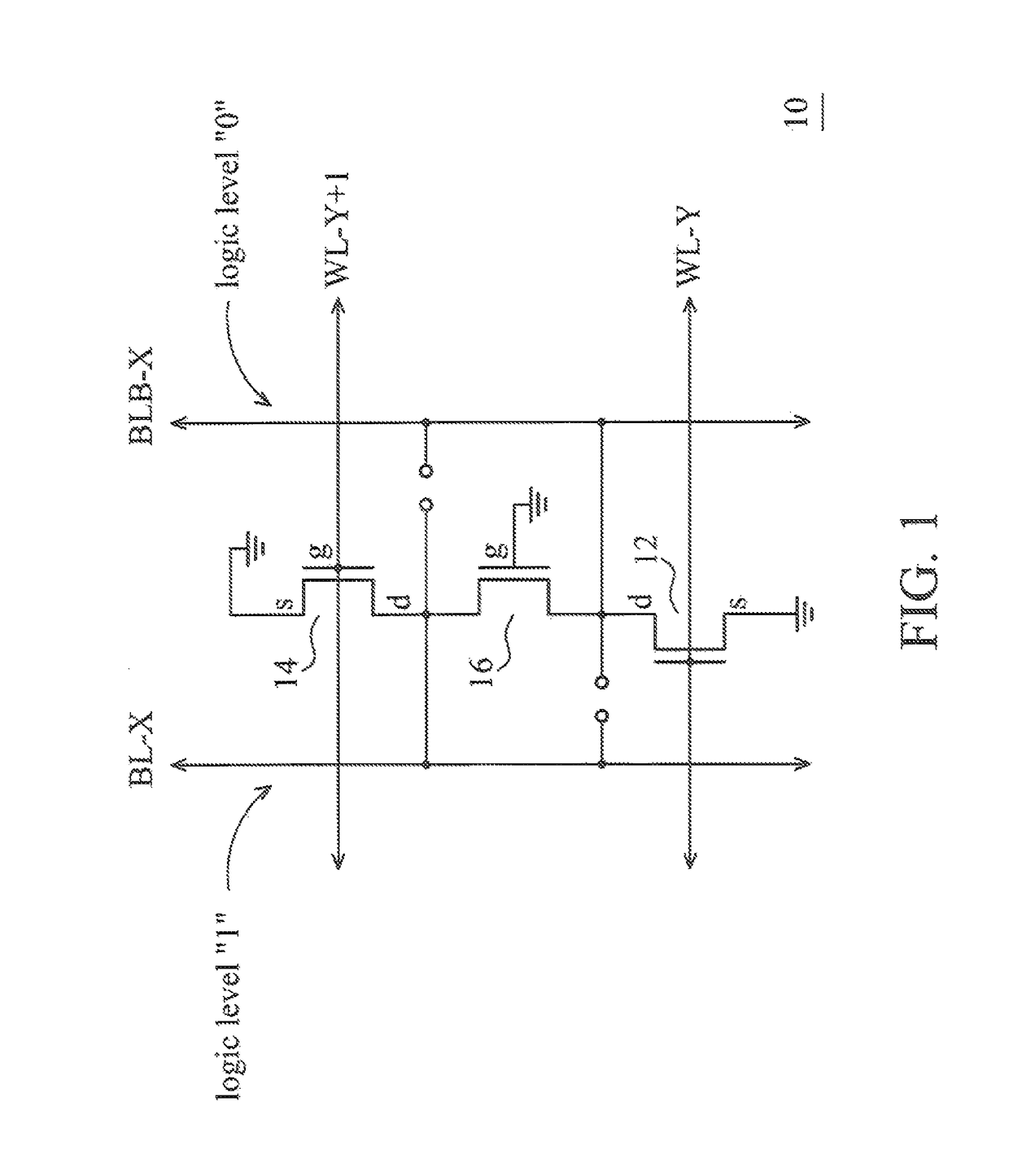
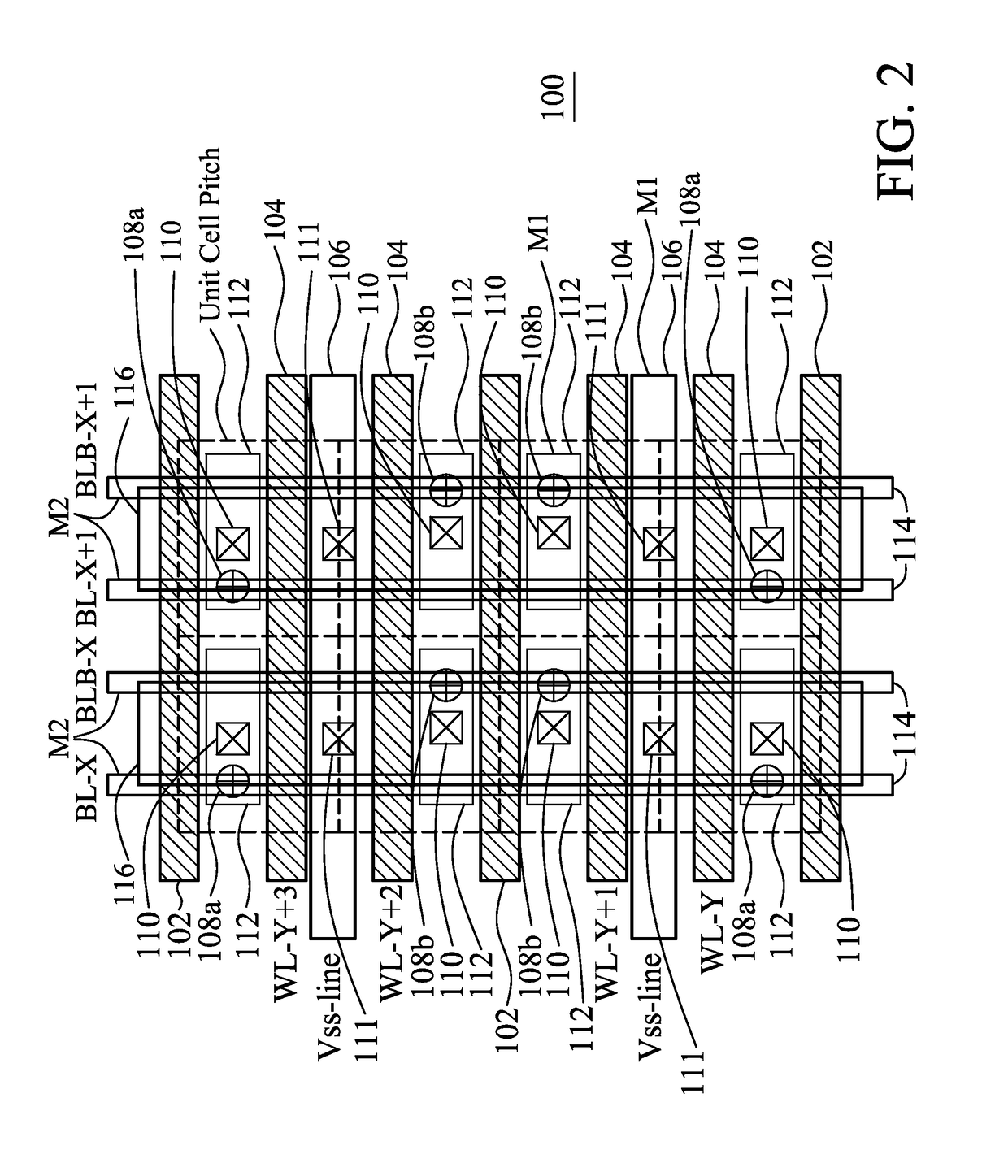
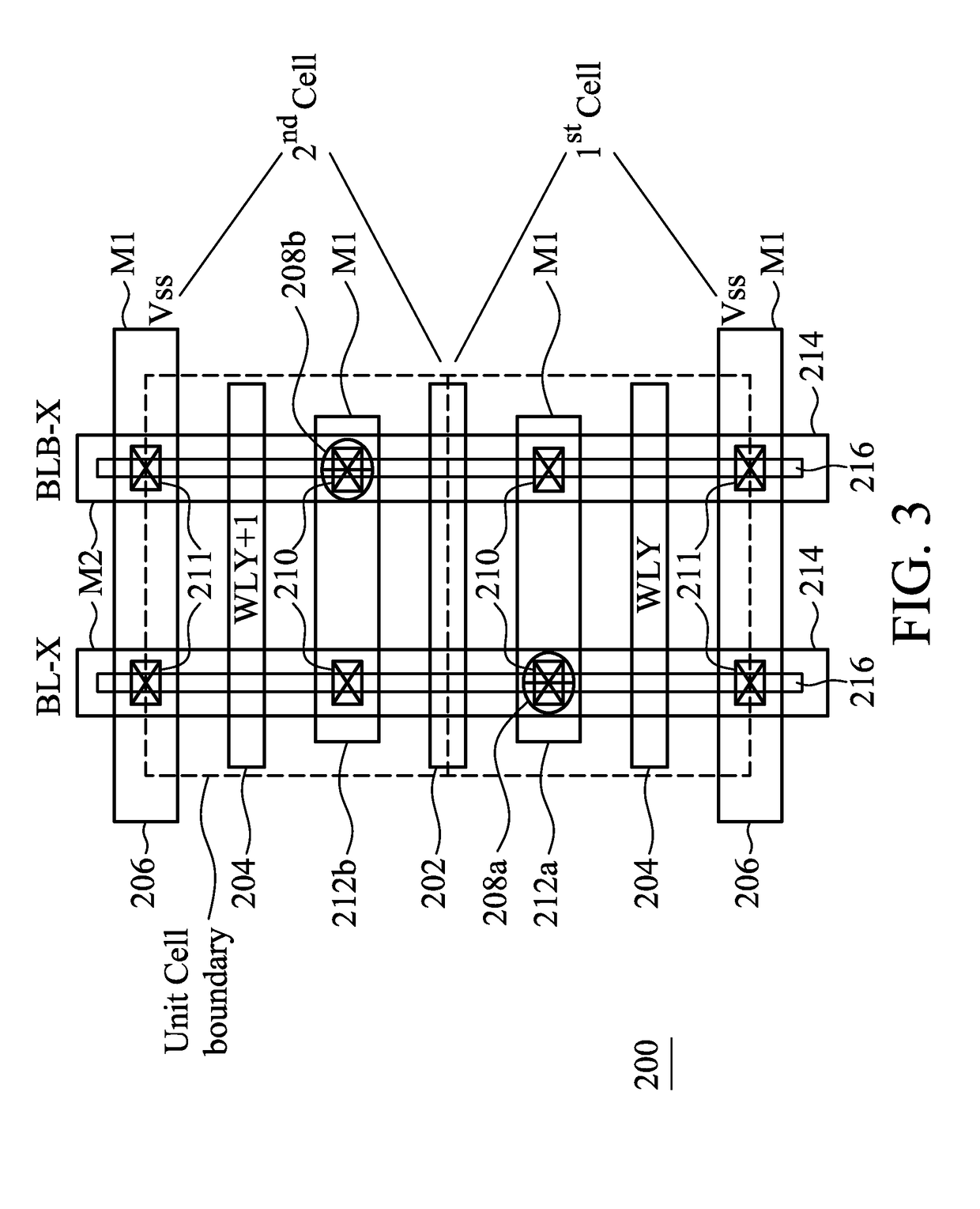
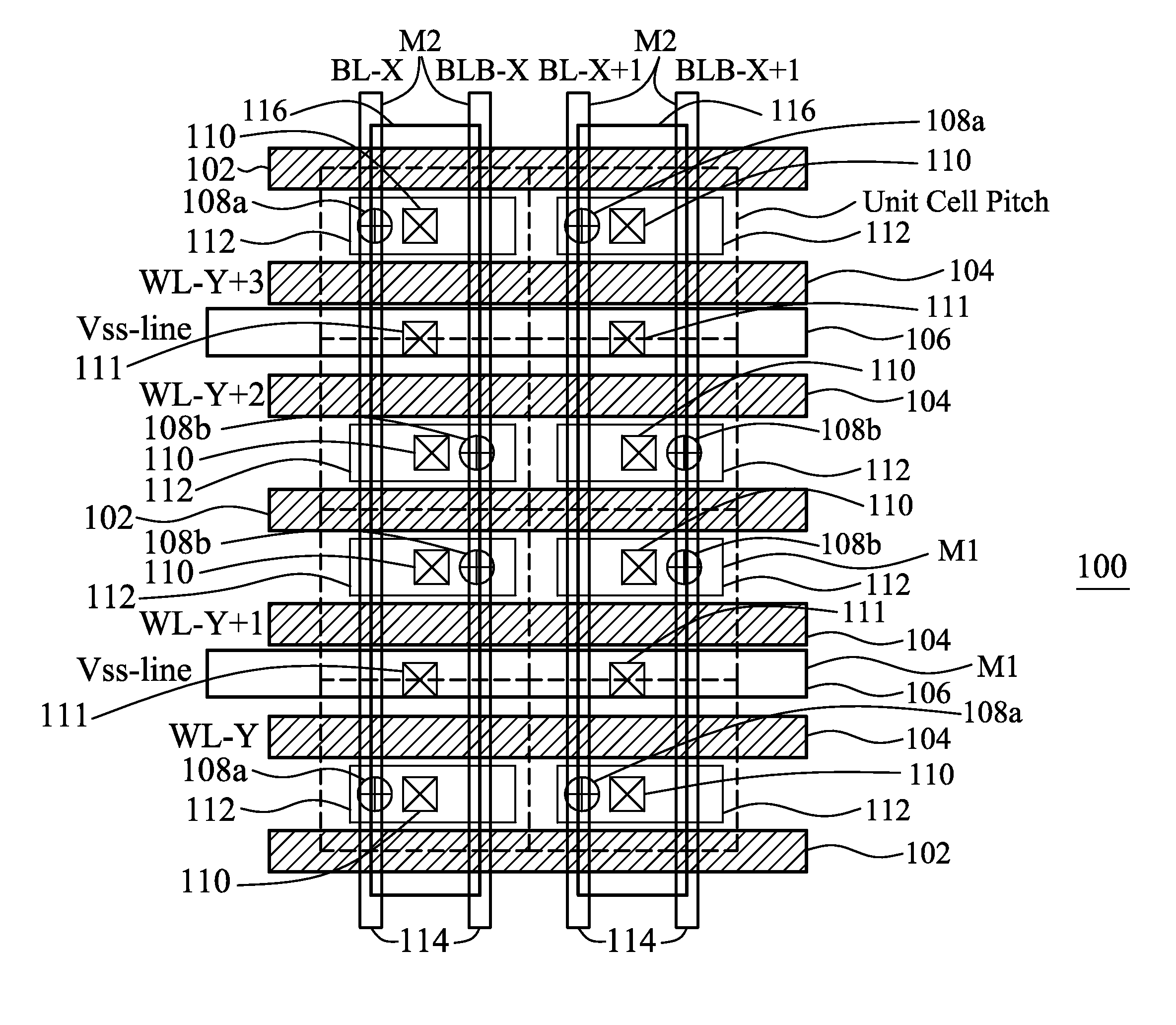
A semiconductor memory cell array includes an elongated continuous active region. First and second pass transistors are formed in the elongated continuous active region and form part of first and second adjacent memory cells, respectively, of a column of memory cells in the array. An isolation transistor is formed in the elongated continuous active region between the first and second pass transistors and biased in an off state. First and second word lines are coupled to the gates of the pass transistors for applying a reading voltage. The array includes a differential bit line pair including first and second bit lines, a first logic value being encoded into the memory cells by connecting the pass transistors to the first bit line and a second logic value being encoded into the memory cells by connecting the pass transistors to the second bit line.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
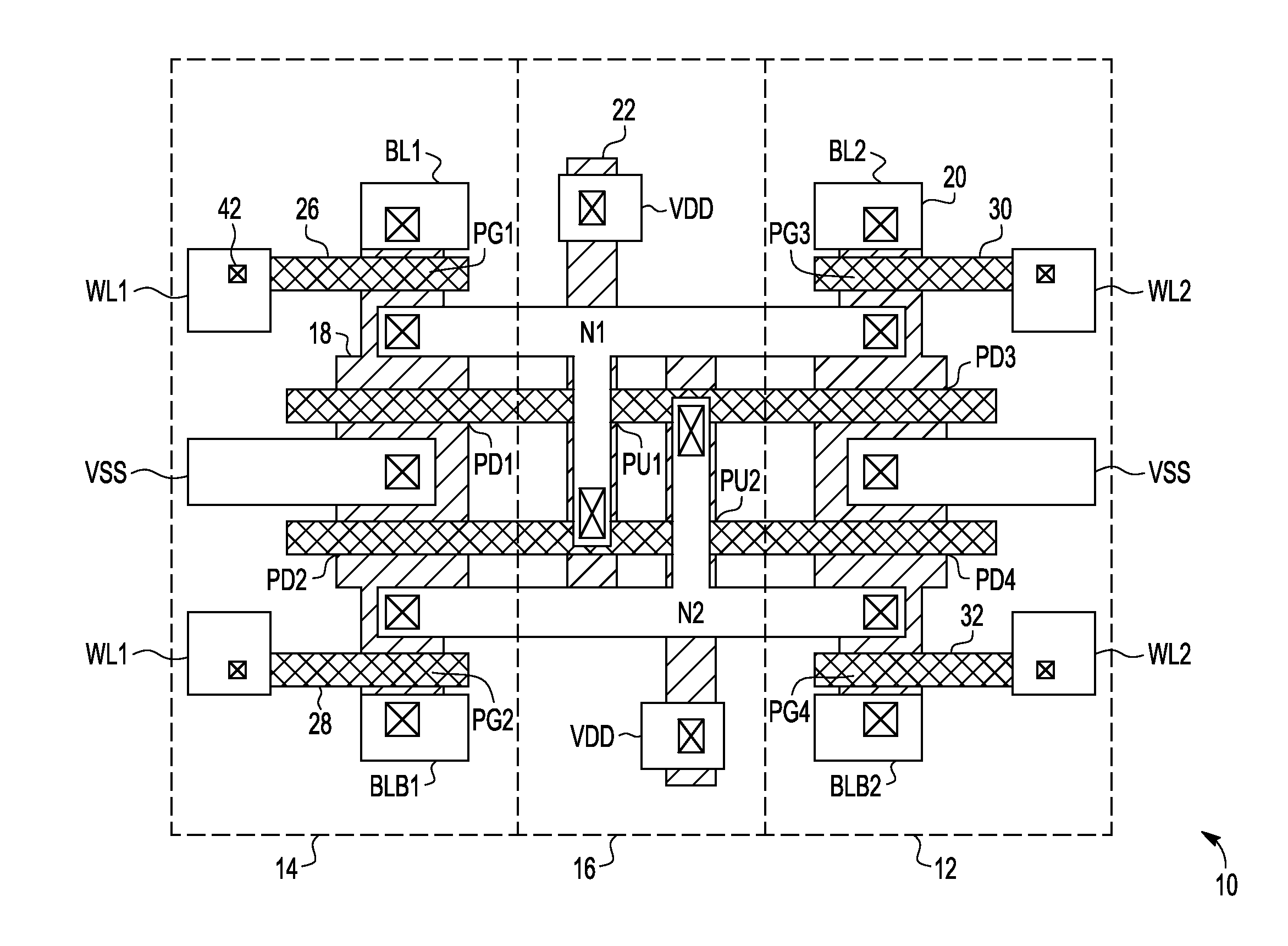
Dual port static random access memory cell layout
A dual port static random access memory cell has pull-down transistors, pull-up transistors, and pass transistors. A first active region has a first pull-down transistor coupled to a true data node, a second pull-down transistor coupled to a complementary data node; a first pass transistor coupled to the true data node, and a second pass transistor coupled to the complementary data node. A second active region has the same size and shape as the first active region and has a third pull-down transistor coupled in parallel to the first-pull down transistor, a fourth pull-down transistor coupled in parallel to the second pull-down transistor; a third pass transistor coupled to the true data node, and a fourth pass transistor coupled to the complementary data node. A first pull-up transistor and a second pull-up transistor are located between the first and second active regions.
Owner:VLSI TECH LLC
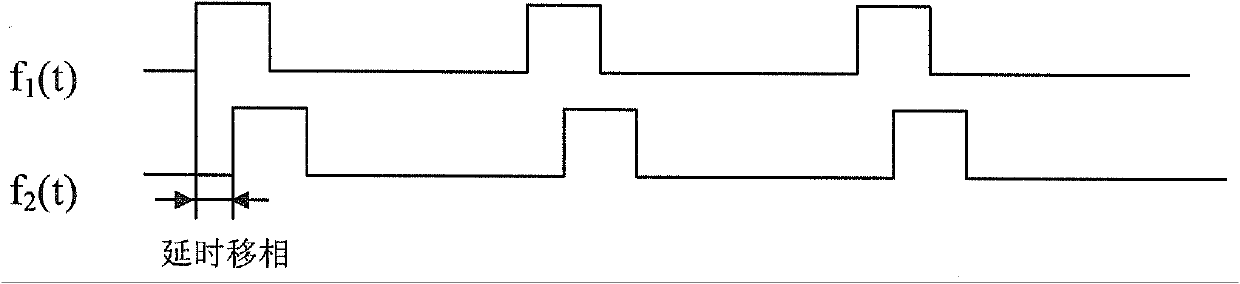
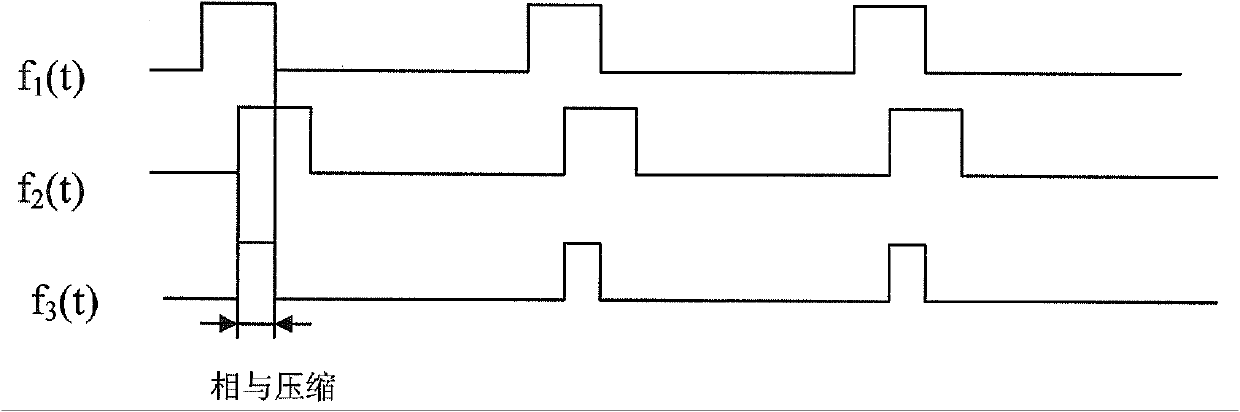
Picosecond-accuracy narrow-pulse width transistor-transistor logic (TTL) signal acquisition method based on phase shift AND operation
InactiveCN102170277AMeet Timing RequirementsImproved Pulse Width Regulation AccuracyElectric pulse generator circuitsPicosecondRange gate
The invention relates to the technical field of range gated imaging, and discloses a picosecond-accuracy narrow-pulse width transistor-transistor logic (TTL) signal acquisition method based on phase shift AND operation. The method comprises the following steps of: dividing each path of TTL pulse triggering signals comprising pulse laser triggering signals and intensified charge coupled device (ICCD) triggering signals in range gating into two paths of time sequence signals with completely identical phase and amplitude by using a multipath generator; delaying one of the divided two paths of signals by adopting a picosecond-accuracy delay line technology to produce a phase shift between the two paths of signals; and then causing the two paths of signals to pass through a logic AND gate for a logic AND operation, thereby compressing a pulse width. By the method, the phase shift between the two paths of signals is accurately controlled to obtain high-accuracy pulse width signals and higher pulse width compression accuracy, and the compressed pulse width can be close to the limit of the TTL signal, namely the order of magnitude of 1ns; and the method is applied in the field of gating application such as range gated three-dimensional imaging, underwater imaging and the like with high-accuracy time sequence requirements.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low VT antifuse device
ActiveUS8933492B2TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHigh voltage transistorsProcess manufacturing
A one time programmable memory cell having an anti-fuse device with a low threshold voltage independent of core circuit process manufacturing technology is presented. A two transistor memory cell having a pass transistor and an anti-fuse device, or a single transistor memory cell having a dual thickness gate oxide, are formed in a high voltage well that is formed for high voltage transistors. The threshold voltage of the anti-fuse device differs from the threshold voltages of any transistor in the core circuits of the memory device, but has a gate oxide thickness that is the same as a transistor in the core circuits. The pass transistor has a threshold voltage that differs from the threshold voltages of any transistor in the core circuits, and has a gate oxide thickness that differs from any transistor in the core circuits. The threshold voltage of the anti-fuse device is lowered by omitting some or all of the threshold adjustment implants that is used for high voltage transistors fabricated in the I / O circuits.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Soi voltage-tolerant body-coupled pass transistor
A method and device for A pass transistor device which includes a source; a drain opposite the source, a body between the source and the drain, and a circuit control network connected between the drain and the source, wherein the circuit control network controls a potential voltage of the body and provides overvoltage protection to the pass transistor.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Semiconductor integrated logic circuit device using a pass transistor
InactiveUSRE38059E1Improve output drive capabilityReduced footprintSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLogic circuitrySemiconductor
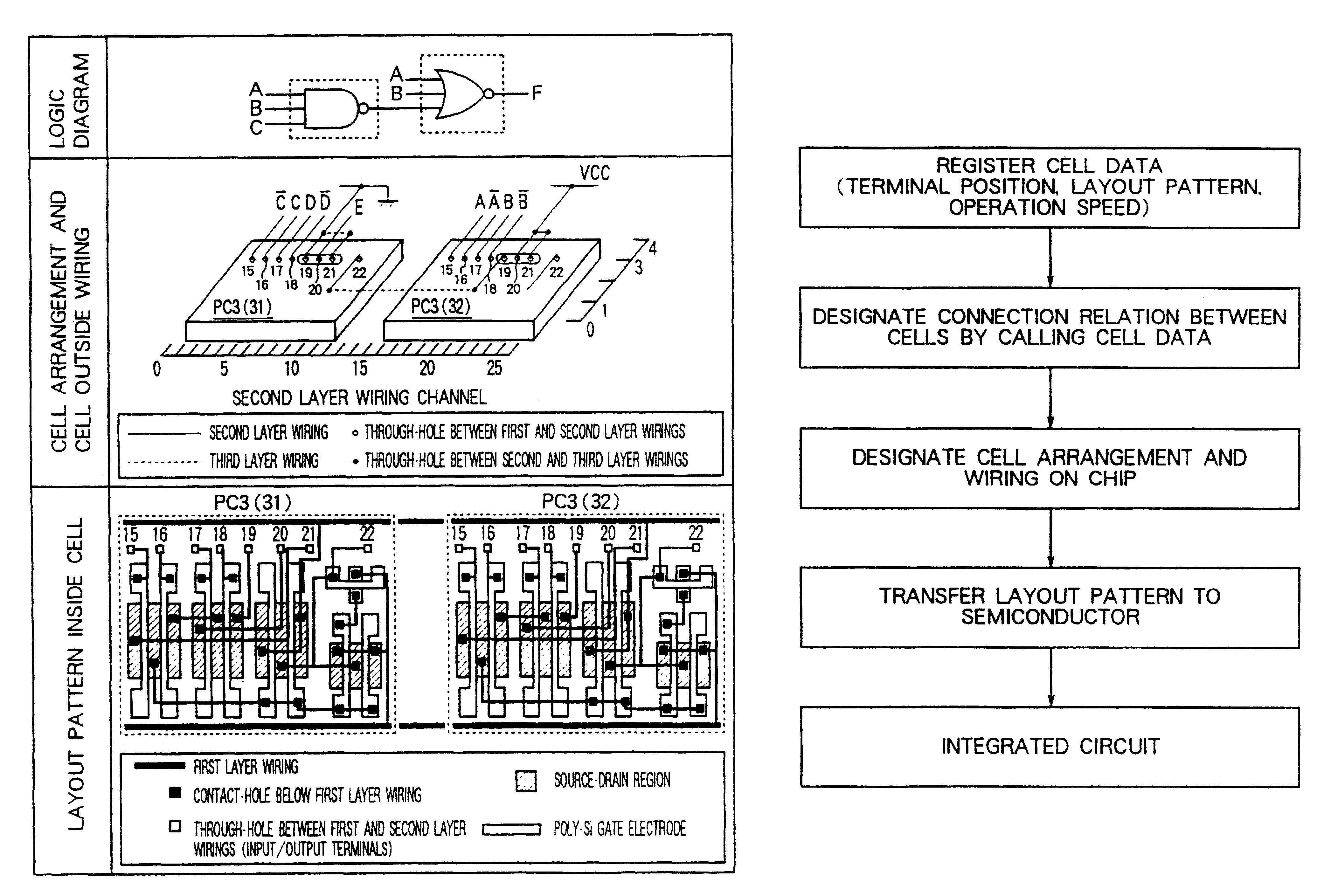
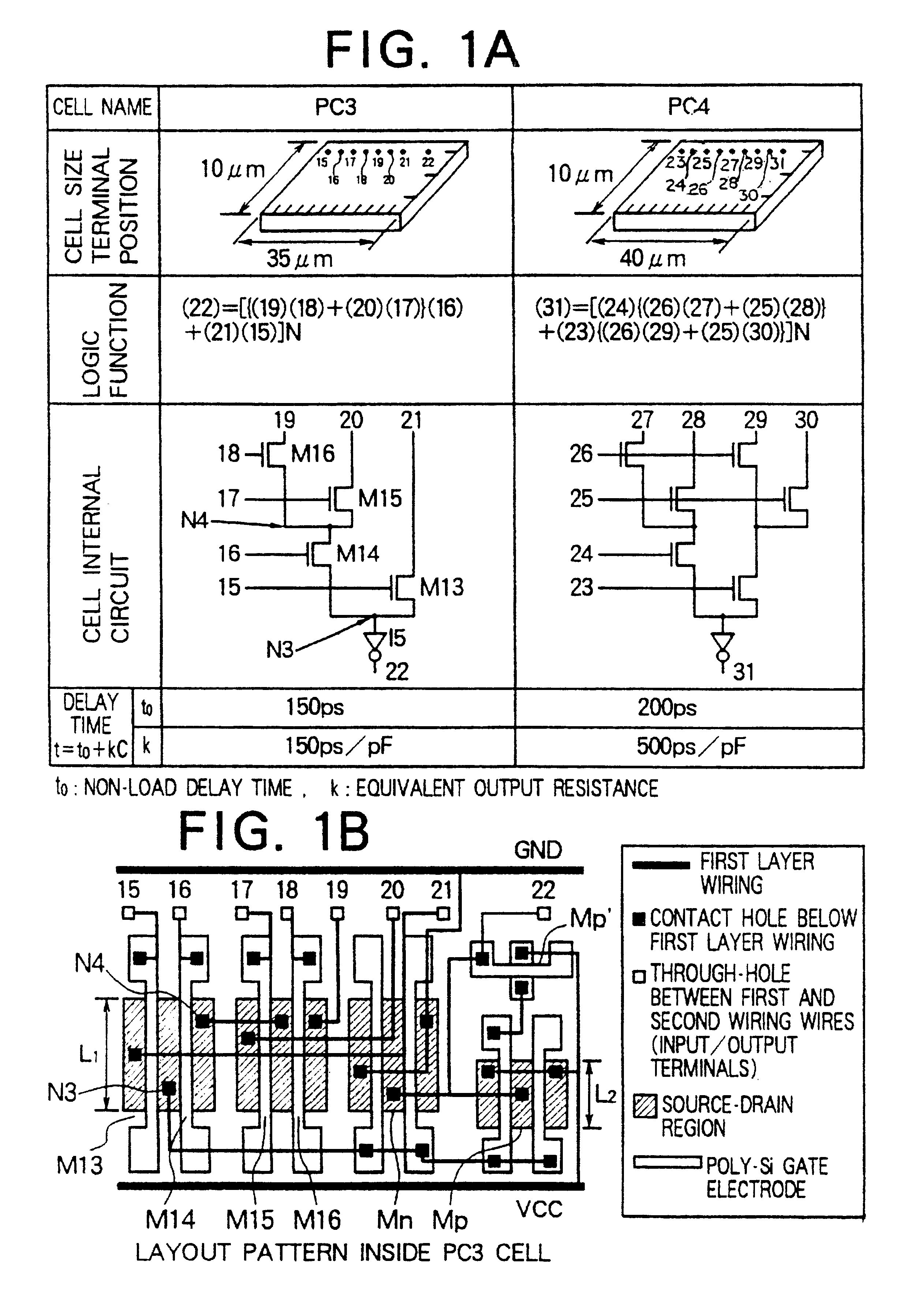
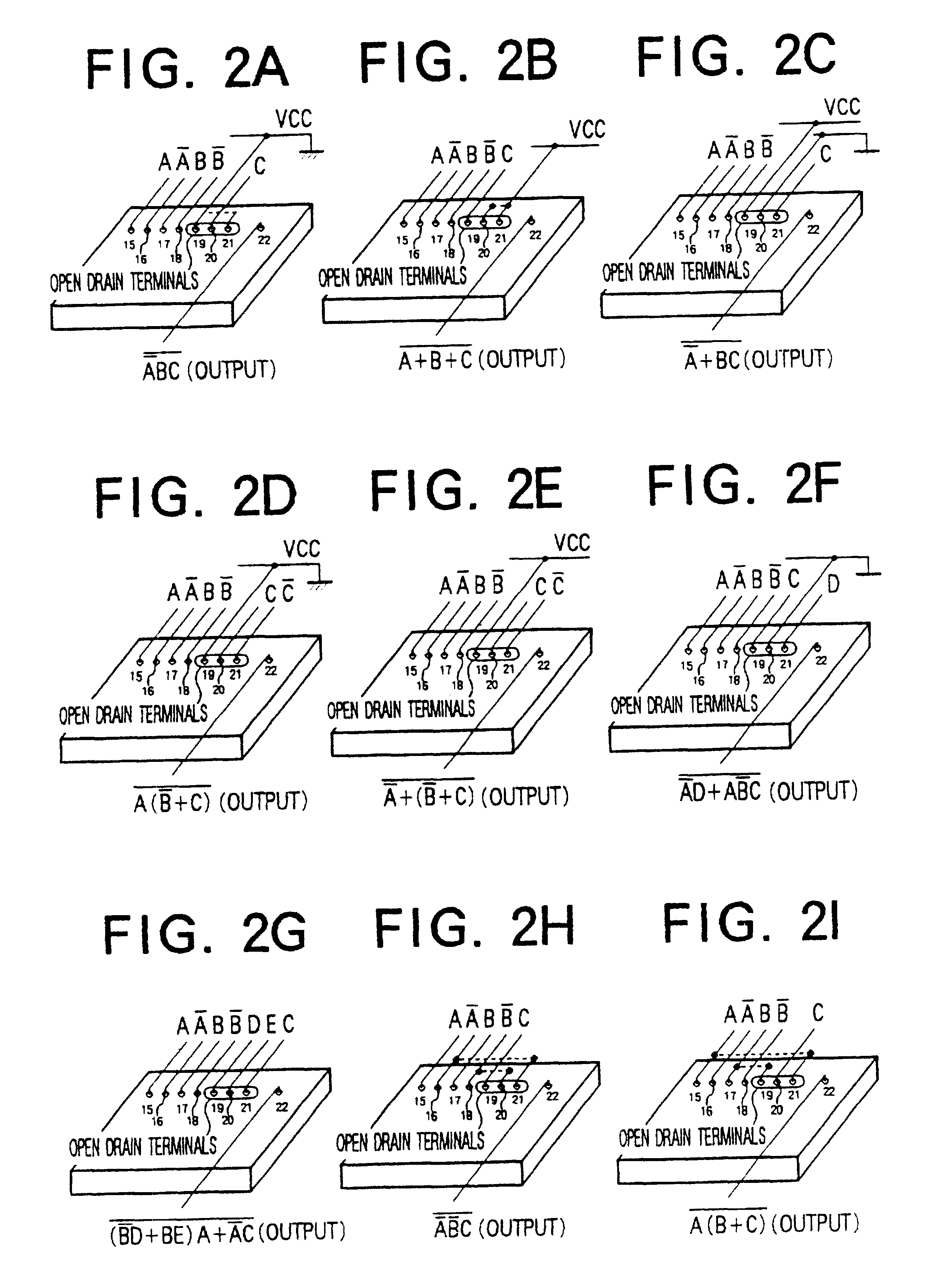
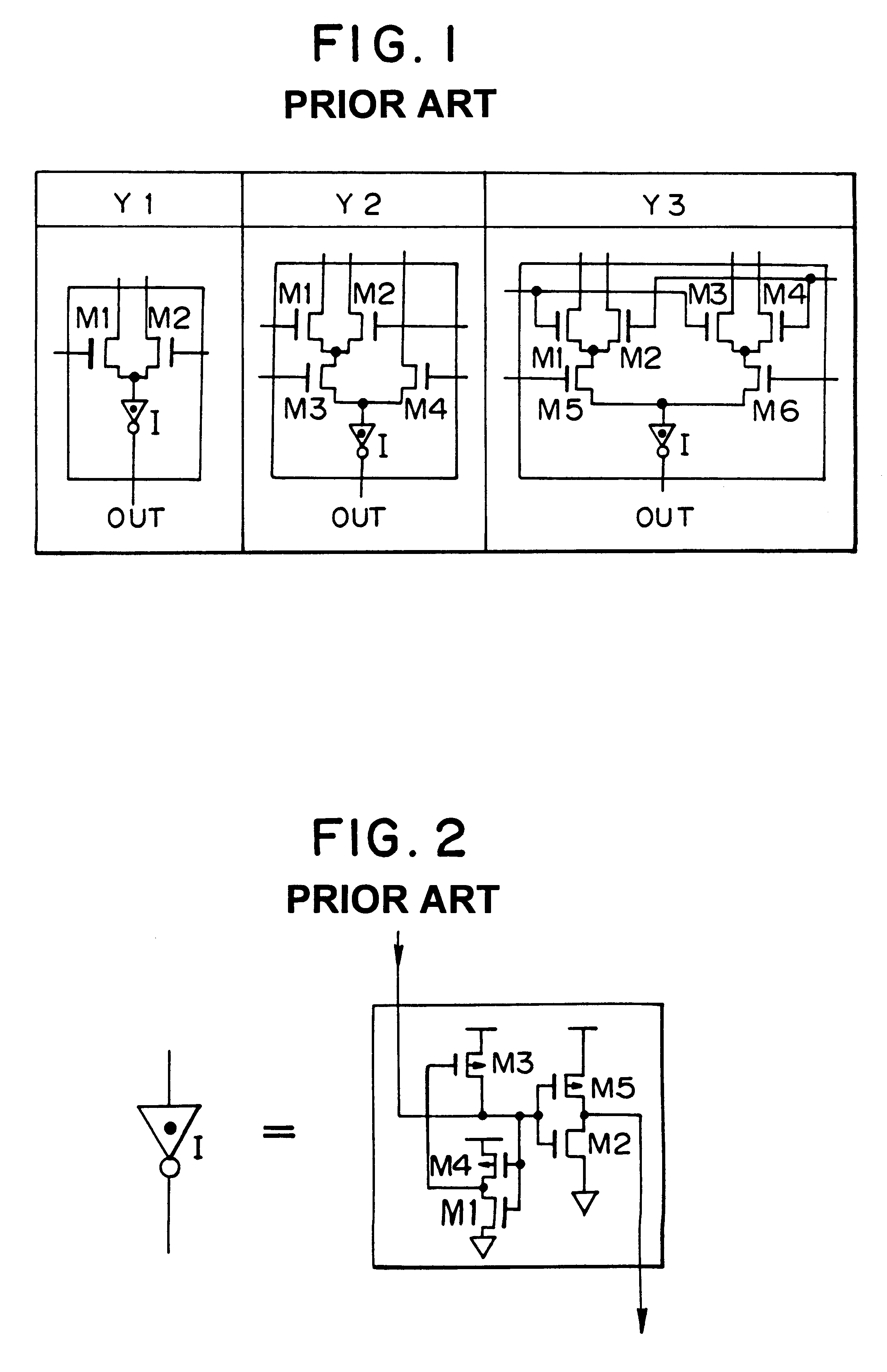
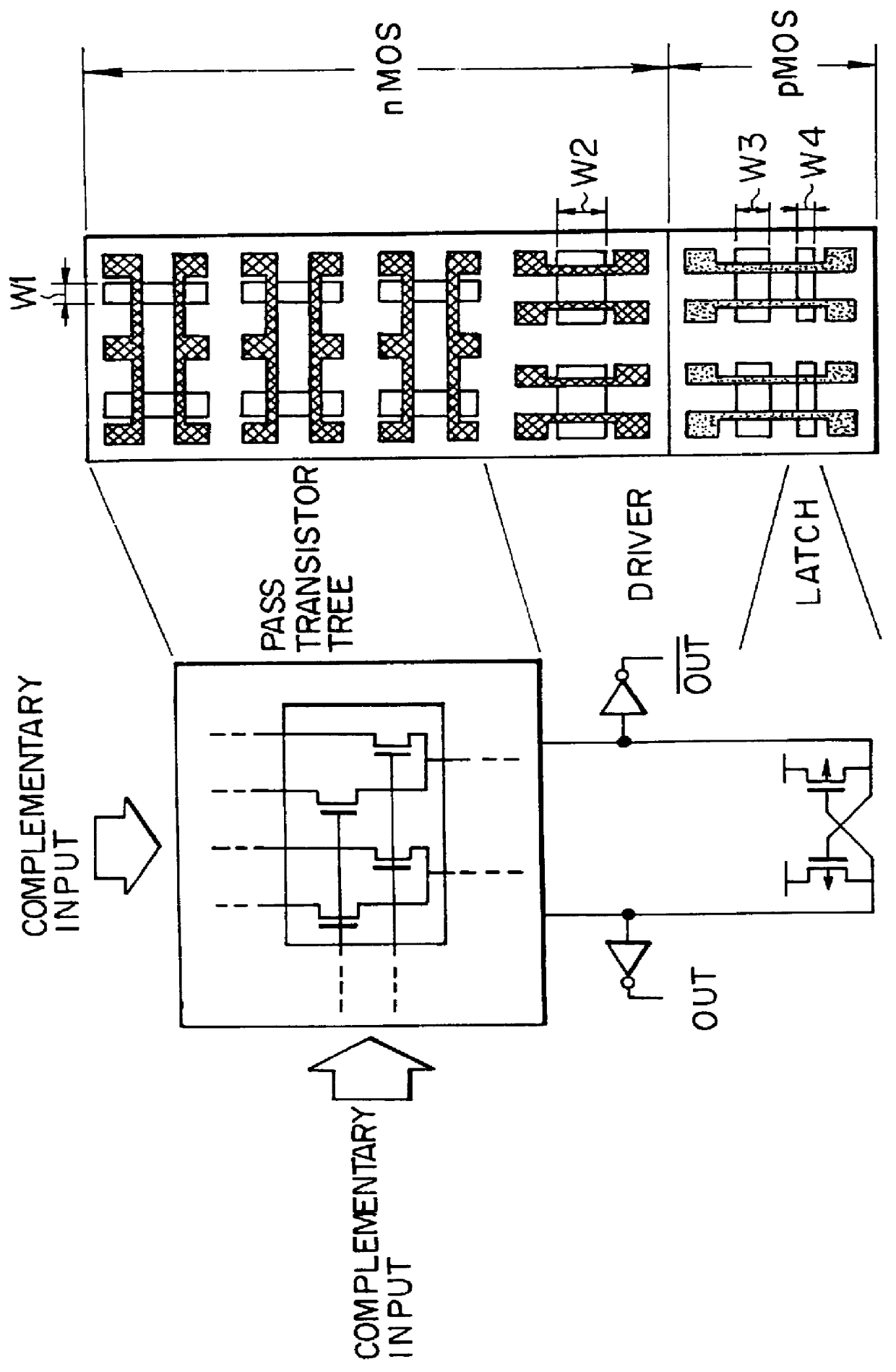
The semiconductor integrated circuit enjoys a high performance and can be produced at a low production cost and within a short time. A cell has an internal circuit connection such that an output terminal is connected to a plurality of input terminals through source-drain paths of active devices connected in the tree form, and gate electrodes of the active devices are connected to other input terminals. Two such cells having the same internal circuit connection, the same disposition of the internal circuit devices and the same disposition of the input / output terminals are disposed on the same chip, and mutually different logics can be accomplished by changing the form of application of input signals from outside the cells to the input terminals. A chip area of an integrated circuit designed by CAD using a cell library can be reduced and a high speed circuit operation can be attained. The present invention provides remarkable effect for improving performance of an ASIC, a microprocessor, etc., and for reducing the cost of production.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit capable of realizing logic functions
InactiveUS6194914B1Switching accelaration modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionGate arrayEngineering
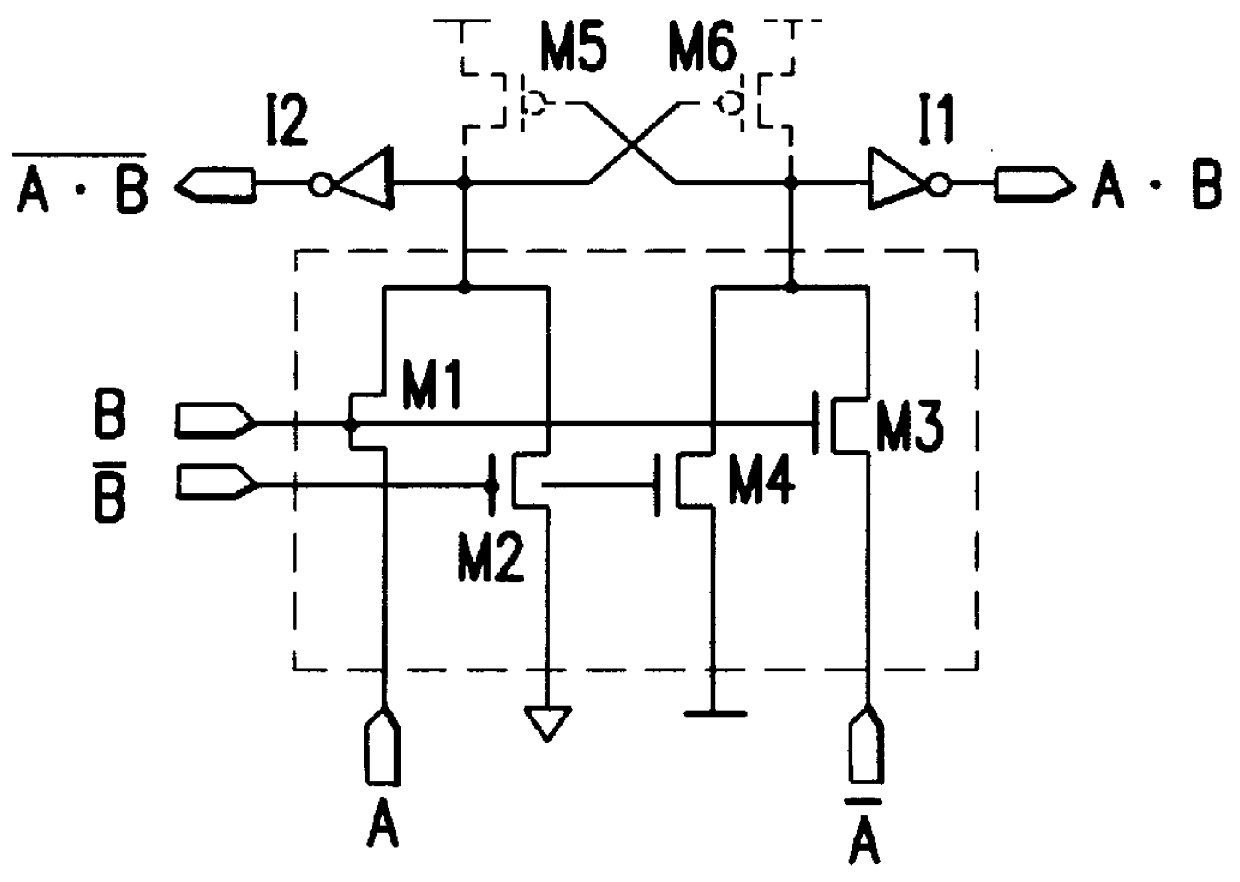
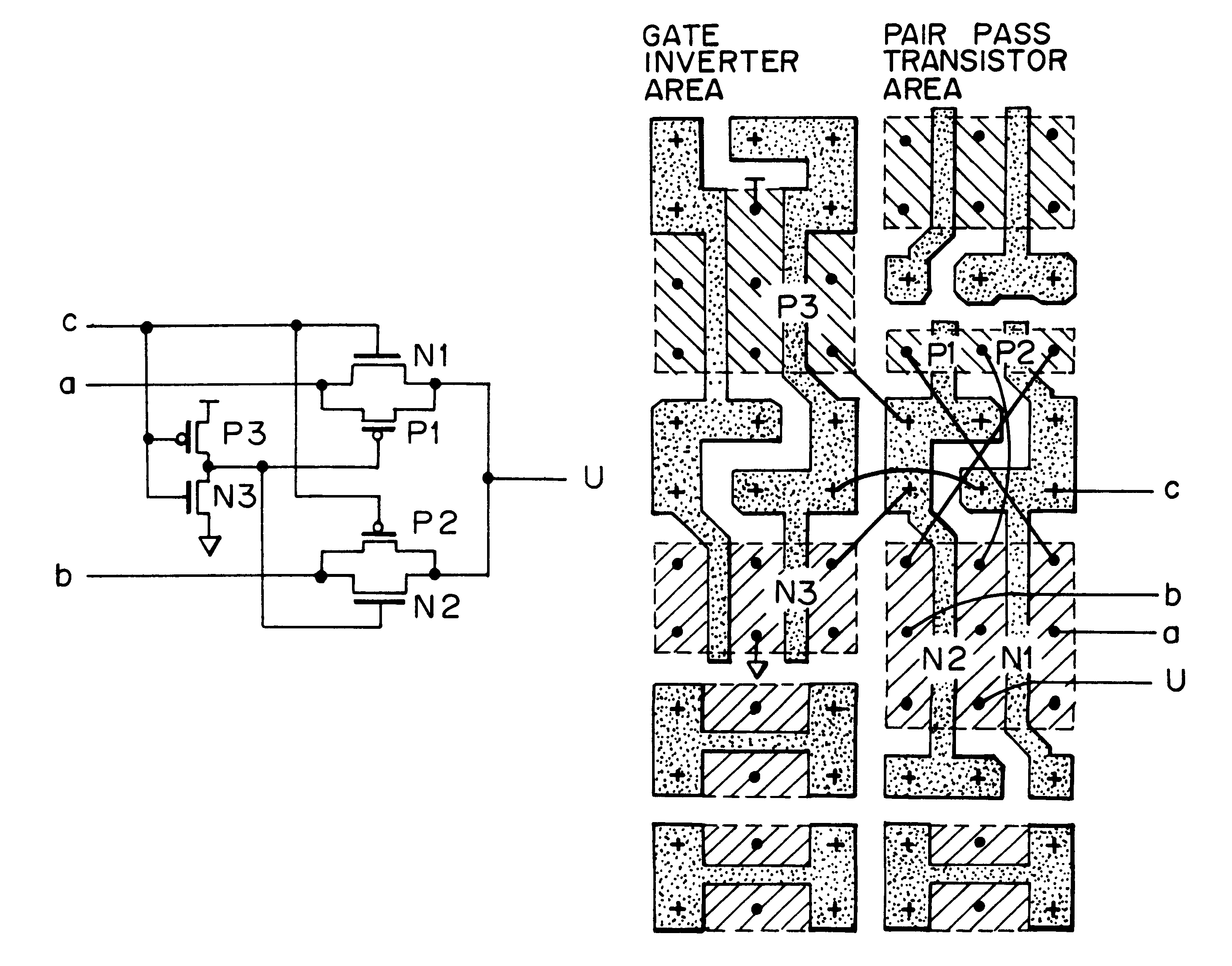
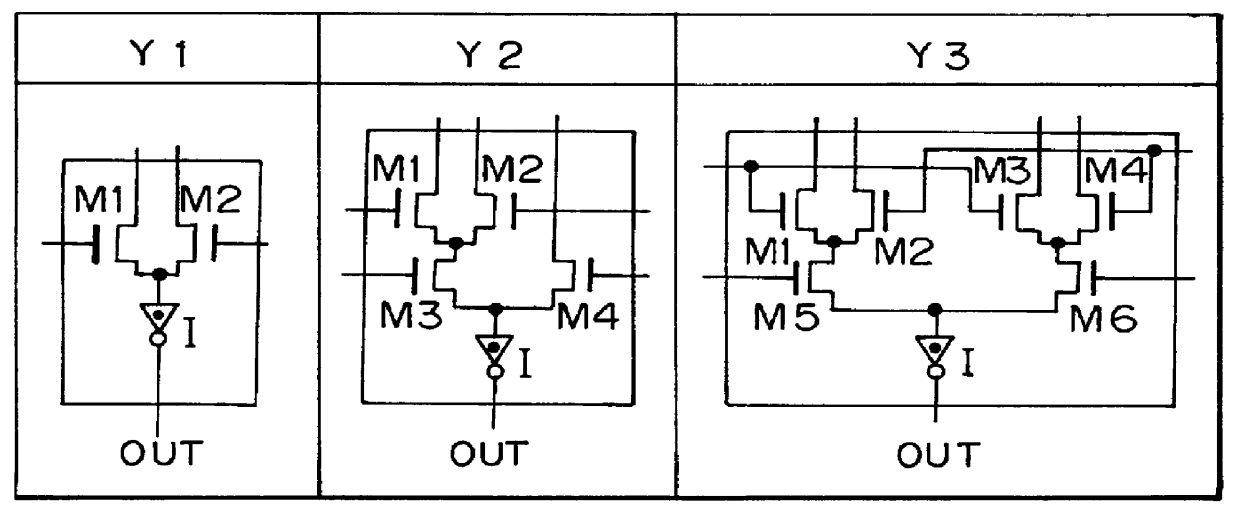
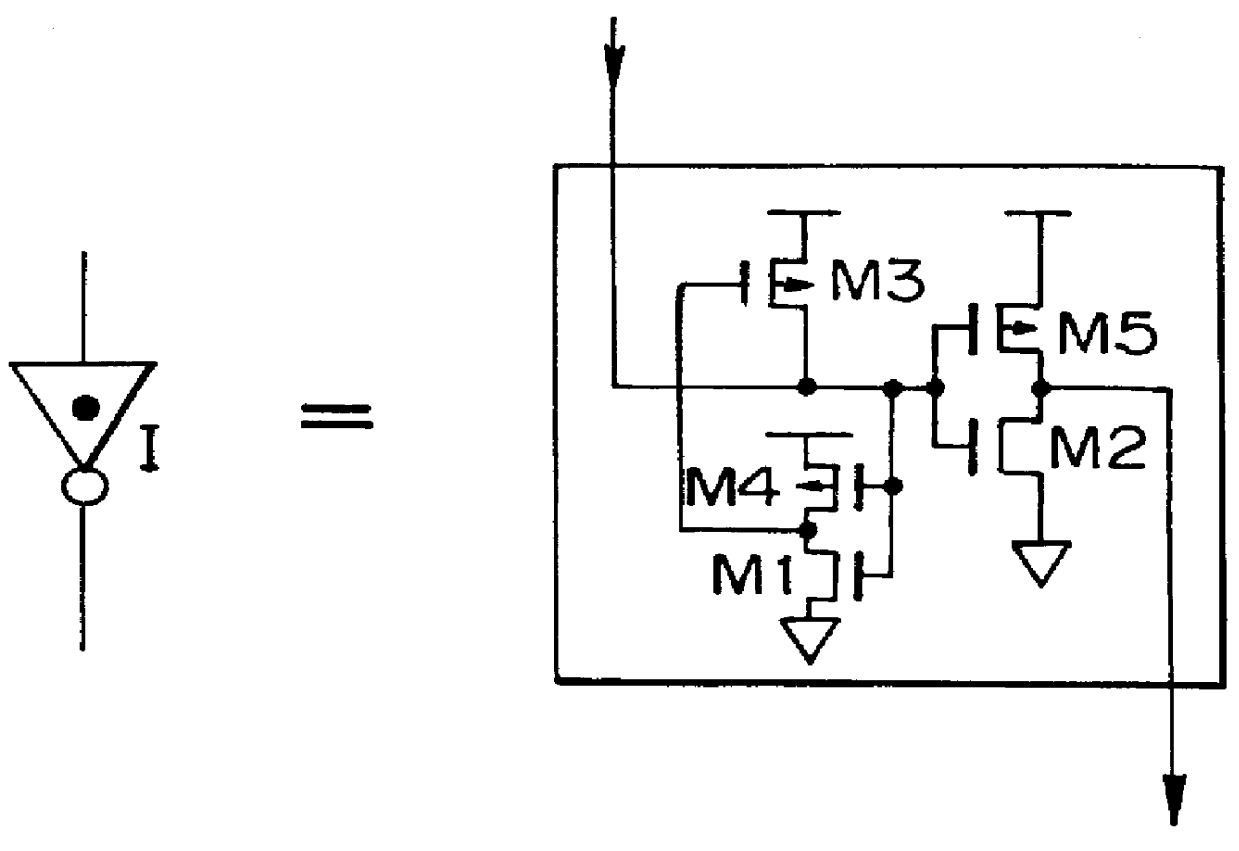
A semiconductor integrated circuit is constructed with composite pass-transistor logic circuits serving as elementary circuit units each including a plurality of pass-transistor logic trees and a multiple-input logic gate. A wide variety of logical operations, even complex opearations, can be efficiently expressed using the composite pass-transistor logic circuit, and the resultant logic circuit can operate at a high speed. Thus, the semiconductor integrated circuit of the present invention can realize various logic functions required for various users in an efficient fashion. The present invention is particularly useful when applied to a field-programmable gate array integrated circuit, since complex logical operations can be expressed in a simple and efficient fashion by the composite pass-transistor logic circuits. The gate array integrated circuit obtained in accordance with the present invention can operate at a high speed with low power consumption. The present invention also discloses a basic cell suitable for use in an integrated circuit in the form of a gate array, and more particularly, a programmable logic block for use in a field programmable gate array integrated circuit.
Owner:KAWASAKI MICROELECTRONICS
ROM cell and array structure
ActiveUS20110069527A1Balance performanceIncrease process marginSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesBit lineArray data structure
A semiconductor memory cell array includes an elongated continuous active region. First and second pass transistors are formed in the elongated continuous active region and form part of first and second adjacent memory cells, respectively, of a column of memory cells in the array. An isolation transistor is formed in the elongated continuous active region between the first and second pass transistors and biased in an off state. First and second word lines are coupled to the gates of the pass transistors for applying a reading voltage. The array includes a differential bit line pair including first and second bit lines, a first logic value being encoded into the memory cells by connecting the pass transistors to the first bit line and a second logic value being encoded into the memory cells by connecting the pass transistors to the second bit line.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Low Dropout Linear Regulator
Various embodiments of the present invention provide apparatuses and methods for regulating an output voltage. For example, an apparatus is discussed that includes a low dropout regulator having a pass transistor and an amplifier and being operable to regulate the output voltage based on a feedback signal and a feedforward signal. The apparatus also includes an auxiliary low dropout regulator having an auxiliary pass transistor and an auxiliary amplifier. The auxiliary dropout regulator is operable to generate the feedforward signal and is substantially matched with the amplifier.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Static random access memory
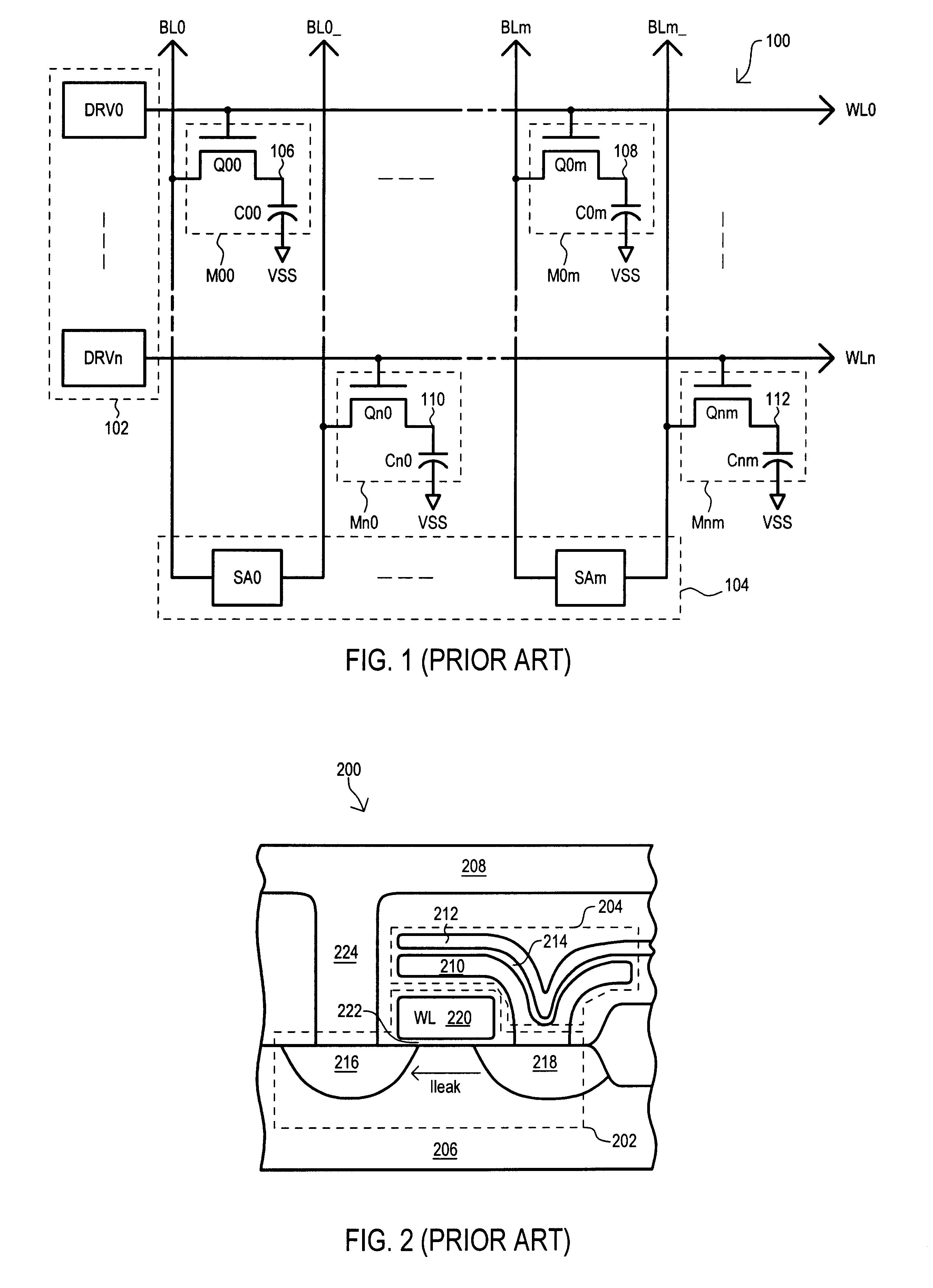
A method and apparatus for a four transistor SRAM comprising an array or block of cells. Each cell comprises a pair of pass transistors and a pair of pull-down transistors. In one embodiment of the invention, when the SRAM block is in a standby mode, the difference between the voltage at the gate and the voltage at the source of each pass transistor is greater than 0, and less than the threshold voltage of the pass transistor. In one embodiment of the invention a ground connection of the memory cell is switched such that when the SRAM block is in the standby mode, the ground connection is a virtual ground connection and when the SRAM block is in an active mode the ground connection is a global ground connection.
Owner:INTEL CORP
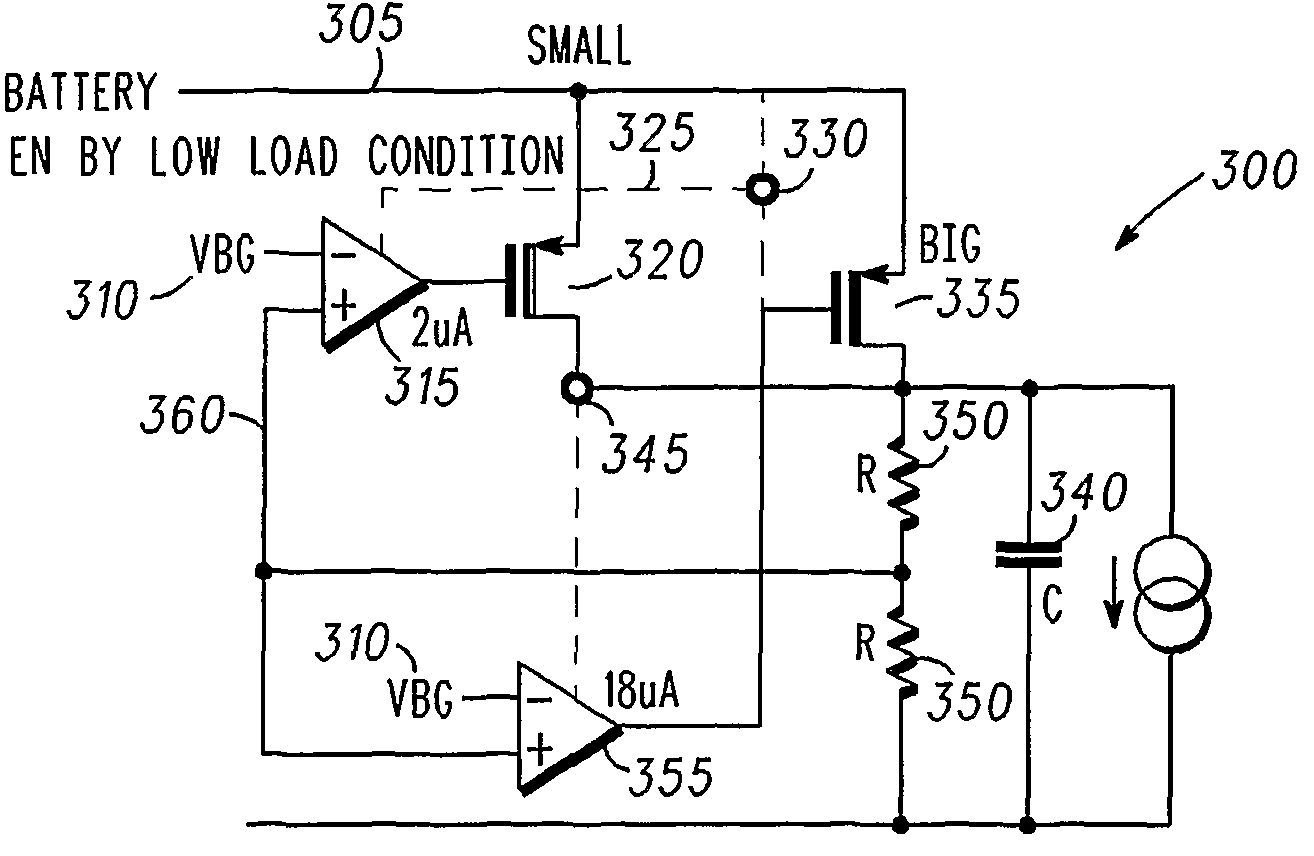
Voltage regulator with pass transistors carrying different ratios of the total load current and method of operation therefor
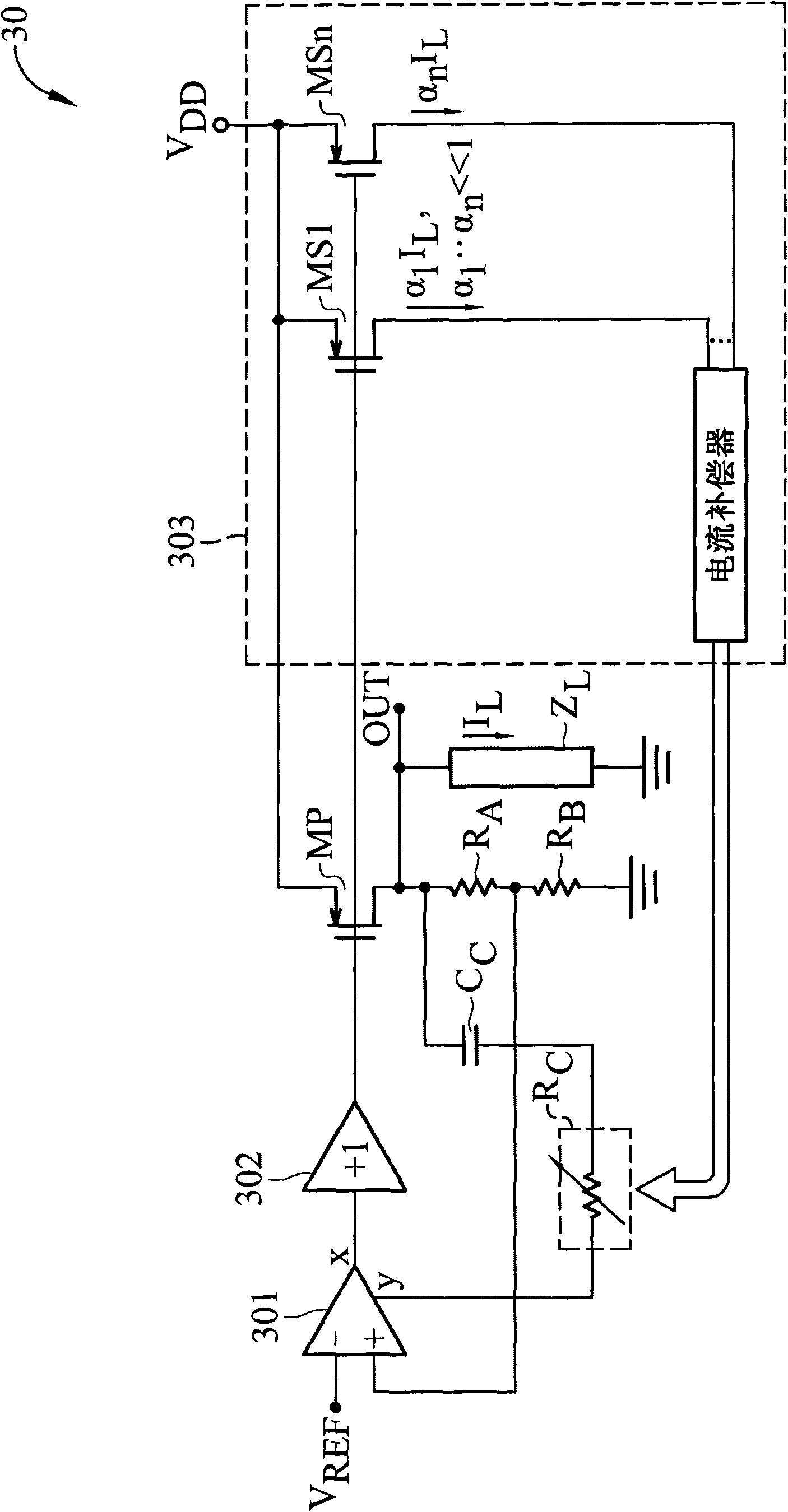
ActiveUS7821240B2Ac network voltage adjustmentElectric variable regulationLow loadVoltage regulation
A voltage regulator for providing a voltage regulated output to a load comprises a first loop and a second loop. The first loop comprises a first active device coupled to a first pass device and configured to provide a first, relatively high current output to the load. The second loop comprises a second active device coupled to a second pass device and configured to provide a second, relatively low current output to the load. This provision of two independent loops reduces the quiescent current provided by the voltage regulator under low load conditions.
Owner:NXP USA INC
High density six transistor finfet SRAM cell layout
InactiveUS20130140638A1Improve scalabilityImprove fidelityTransistorSolid-state devicesHigh densityStatic random-access memory
Dual orientation of finFET transistors in a static random access memory (SRAM) cell allows aggressive scaling to a minimum feature size of 15 nm and smaller using currently known masking techniques that provide good manufacturing yield. A preferred layout and embodiment features inverters formed from adjacent, parallel finFETs with a shared gate and different conductivity types developed through a double sidewall image transfer process while the preferred dimensions of the inverter finFETs and the pass transistors allow critical dimensions of all transistors to be sufficiently uniform despite the dual transistor orientation of the SRAM cell layout.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Semiconductor integrated circuit capable of realizing logic functions
InactiveUS6097221AReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionGate arrayEngineering
A semiconductor integrated circuit is constructed with composite pass-transistor logic circuits serving as elementary circuit units each including a plurality of pass-transistor logic trees and a multiple-input logic gate. A wide variety of logical operations, even complex opearations, can be efficiently expressed using the composite pass-transistor logic circuit, and the resultant logic circuit can operate at a high speed. Thus, the semiconductor integrated circuit of the present invention can realize various logic functions required for various users in an efficient fashion. The present invention is particularly useful when applied to a field-programmable gate array integrated circuit, since complex logical operations can be expressed in a simple and efficient fashion by the composite pass-transistor logic circuits. The gate array integrated circuit obtained in accordance with the present invention can operate at a high speed with low power consumption. The present invention also discloses a basic cell suitable for use in an integrated circuit in the form of a gate array, and more particularly, a programmable logic block for use in a field programmable gate array integrated circuit.
Owner:KAWASAKI MICROELECTRONICS
Highly simplified switching regulator which allows very high switching frequencies
InactiveUS8890493B2Electric signal transmission systemsBatteries circuit arrangementsVoltage regulator moduleLinear regulator
A voltage regulator circuit includes a linear voltage regulator having a pass transistor and a first feedback from an output load, and a switching regulator having a second feedback from a voltage drop across the pass transistor. The voltage regulator further includes an efficiency monitor configured to detect the voltage drop and control predetermined steps of a duty cycle of the switching regulator based on the voltage drop.
Owner:ISIK TACETTIN
High voltage switch circuit for semiconductor device
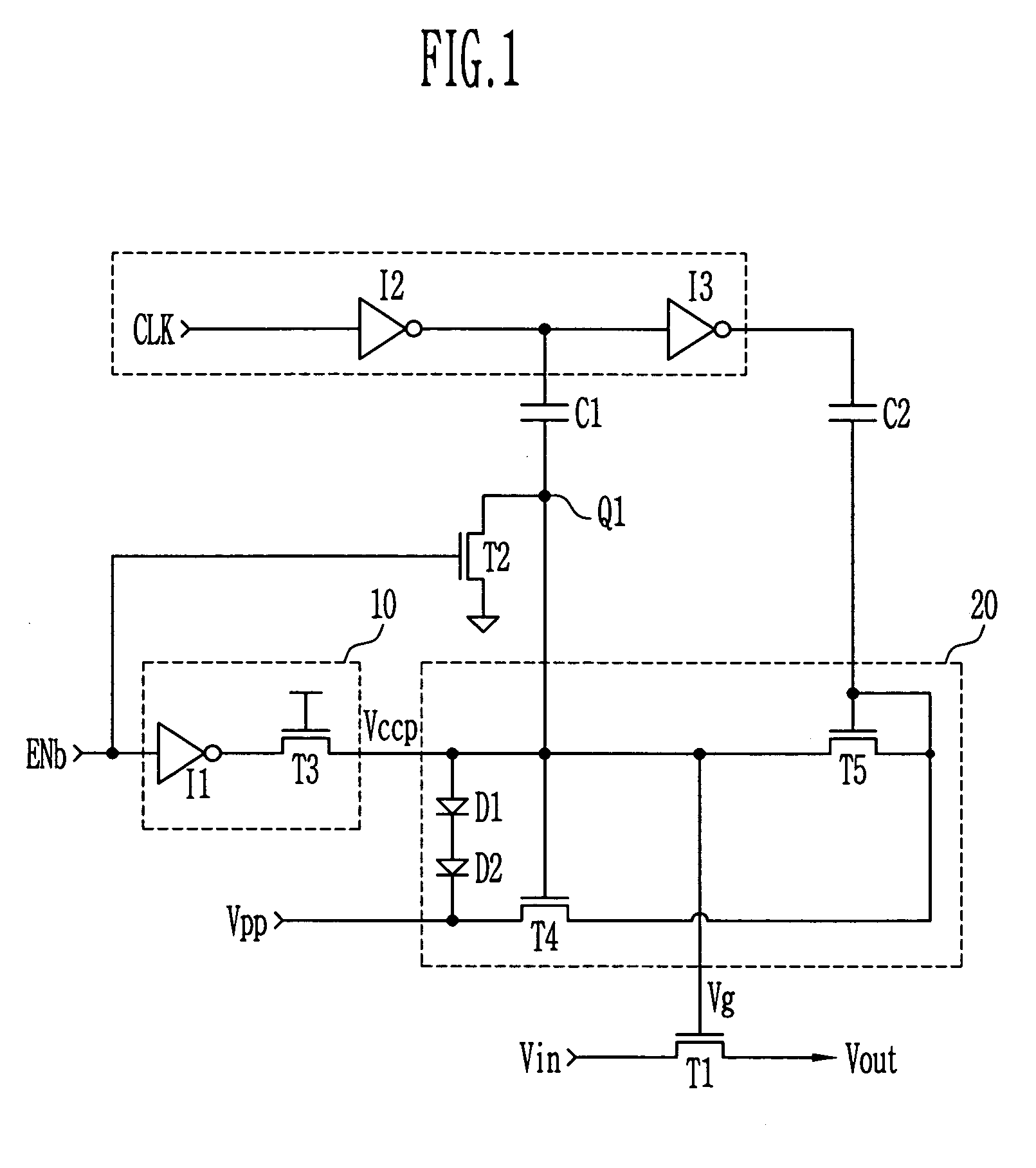
Provided is concerned with a high voltage switch circuit for a semiconductor device, which rapidly discharges a gate voltage of a pass transistor through an additional discharge transistor during inactivation of itself in the circuit structure with a positive feedback loop for transferring an internal high voltage without a voltage drop by applying an enough voltage to the gate of the pass transistor. The high voltage switch circuit prevents the internal high voltage from decreasing.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC +1
Low dropout regulator
InactiveCN101676829AGood frequency compensationAvoid craftElectric variable regulationCapacitanceManufacturing technology
The invention provides adequate compensation for a wide range of output loads, a low dropout (LDO) regulator has an amplifier, a pass transistor, a voltage divider, a compensation network, and a control circuit. The amplifier outputs a comparison result according to a reference signal and a feedback signal. The pass transistor generates an output current based on the comparison result of the amplifier. The voltage divider generates the feedback signal according to the output current. The compensation network couples the output of the pass transistor to a low-impedance node of the amplifier, and has a compensation capacitor and a variable resistor coupled to the compensation capacitor. The control circuit is coupled to the input of the pass transistor and to the variable resistor for controlling resistance of the variable resistor according to the output current of the pass transistor. The low dropout regulator provides better frequency compensation and more stable resolution and prevents the compensation effect influenced by manufacture technology and temperature.
Owner:MEDIATEK SINGAPORE PTE LTD SINGAPORE
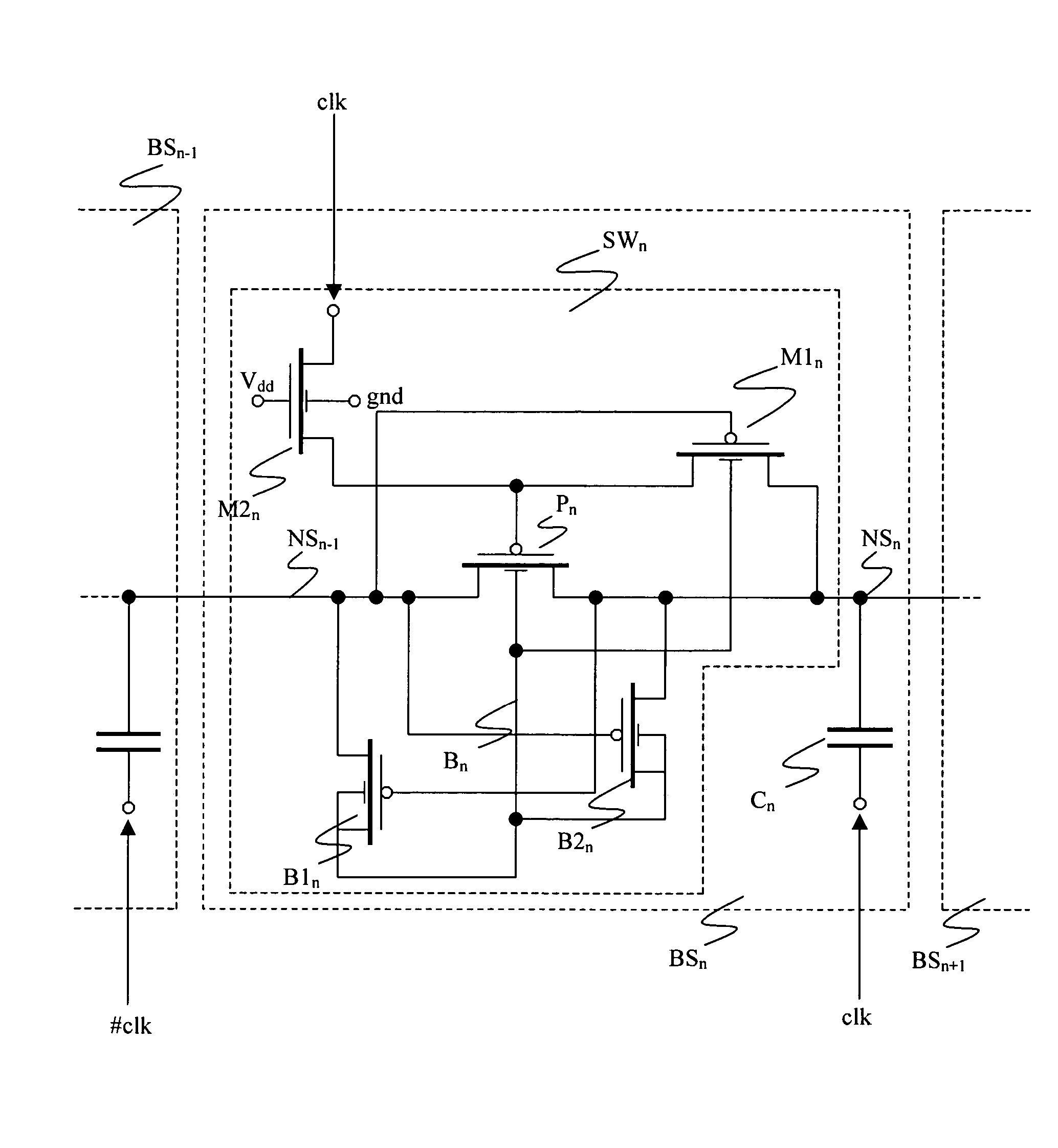
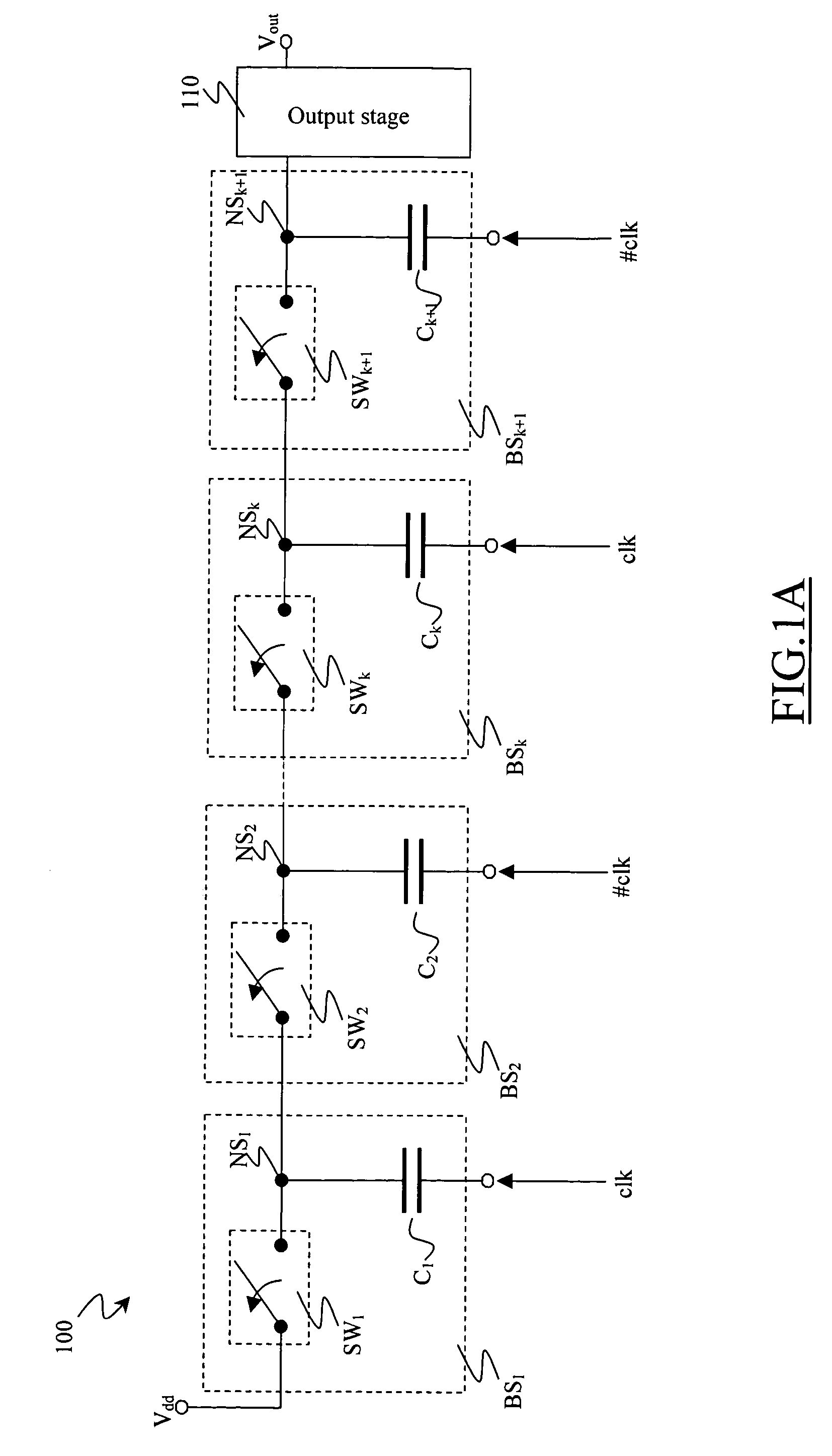
Charge pump circuit with dynamic biasing of pass transistors
A two-phase charge pump is provided that is controlled by first and second clock signals in phase-opposition. The charge pump has a sequence of cascade-connected stages. Each stage includes a capacitive element driven by one clock signal such that capacitive elements of adjacent stages are driven by different clock signals, a pass transistor that transfers electric charge to the capacitive element from the capacitive element of a previous stage, a first biasing circuit that enables the pass transistor during a first phase of the one clock signal, and a second biasing circuit that disables the pass transistor during a second phase of the one clock signal. Also provided is a two-phase charge pump having two branches that each include a sequence of such cascade-connected stages, with each stage of one branch having a corresponding stage in the other branch. A method of operating two-phase charge pumps is also provided.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Dual port static random access memory cell layout
Owner:VLSI TECH LLC
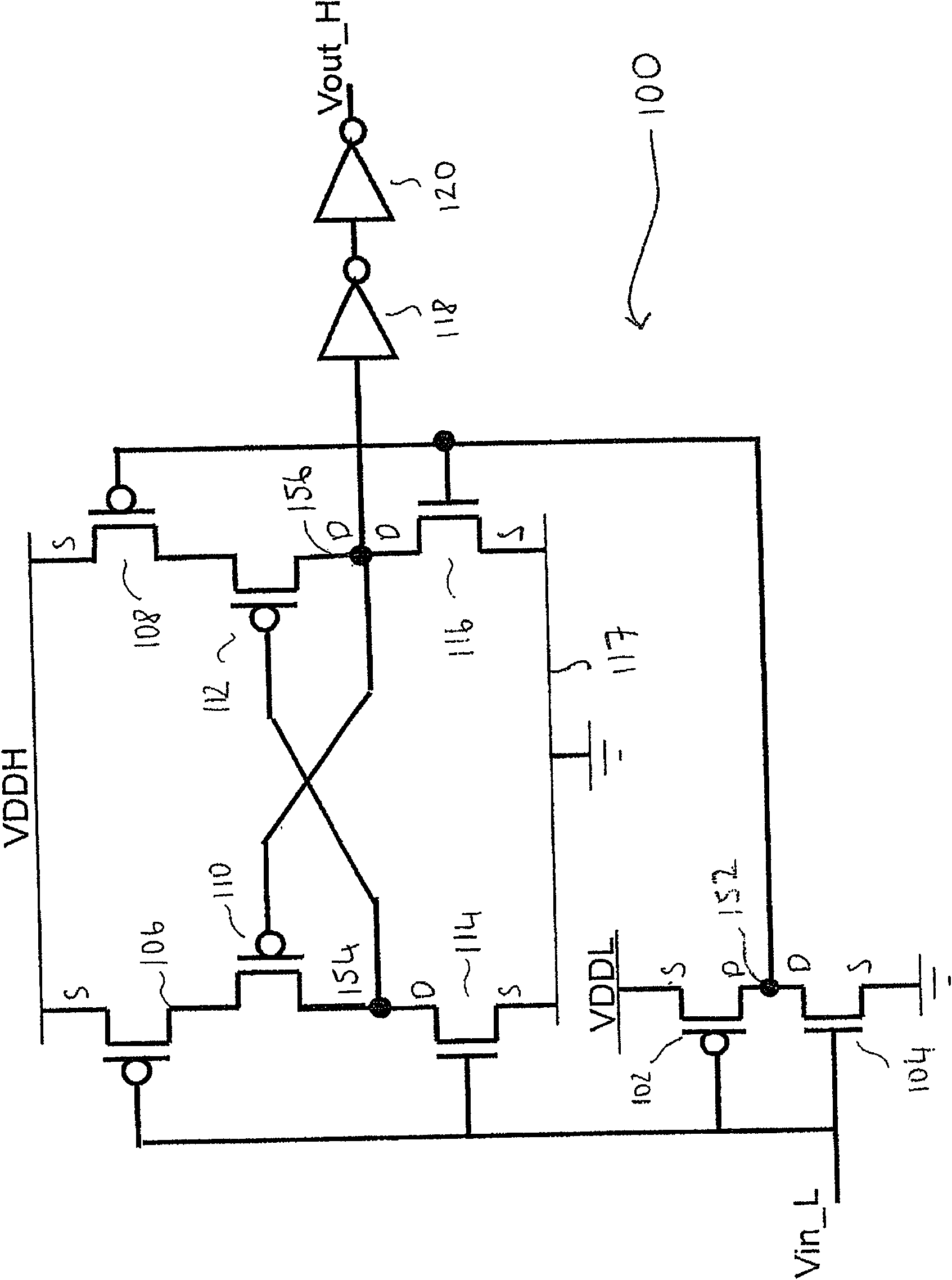
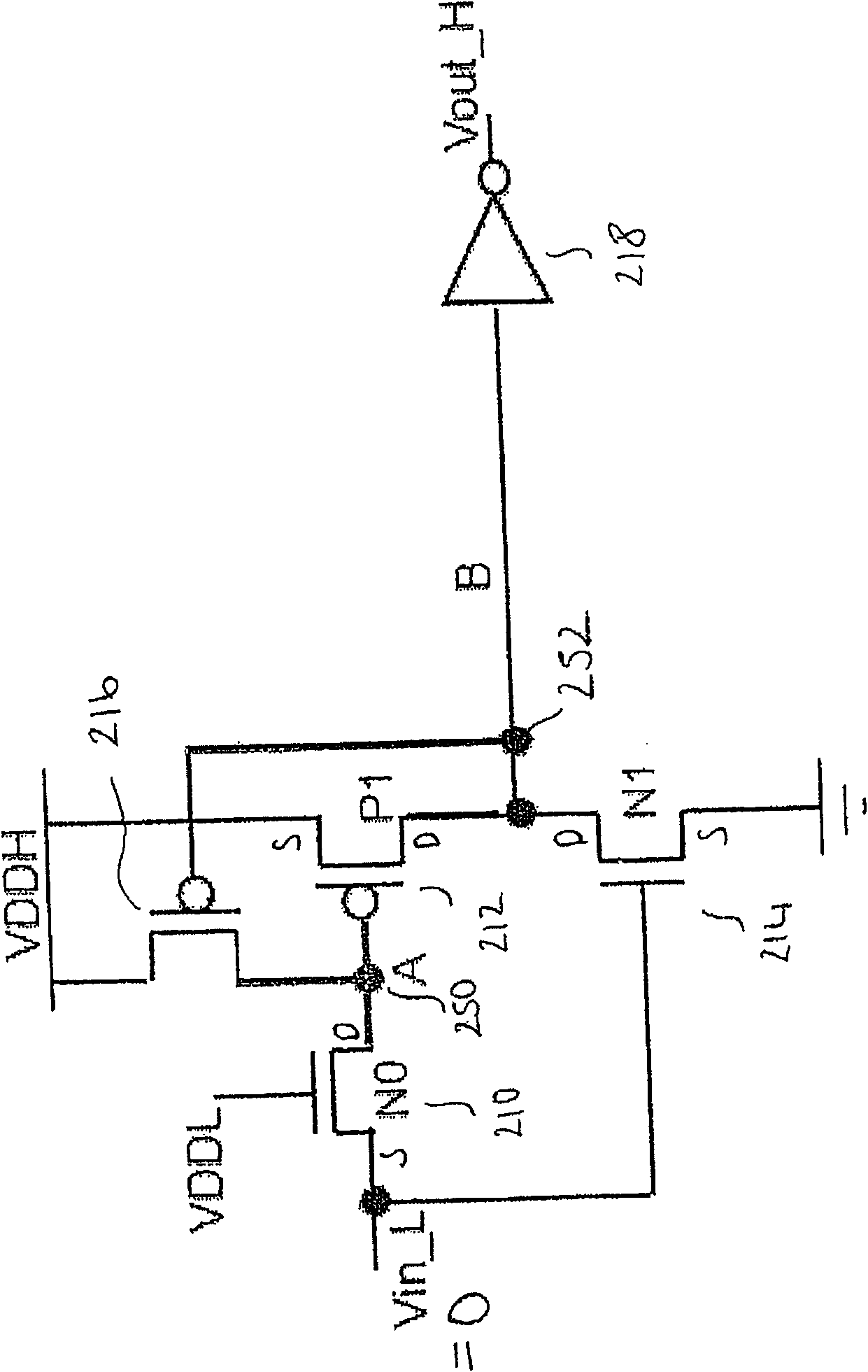
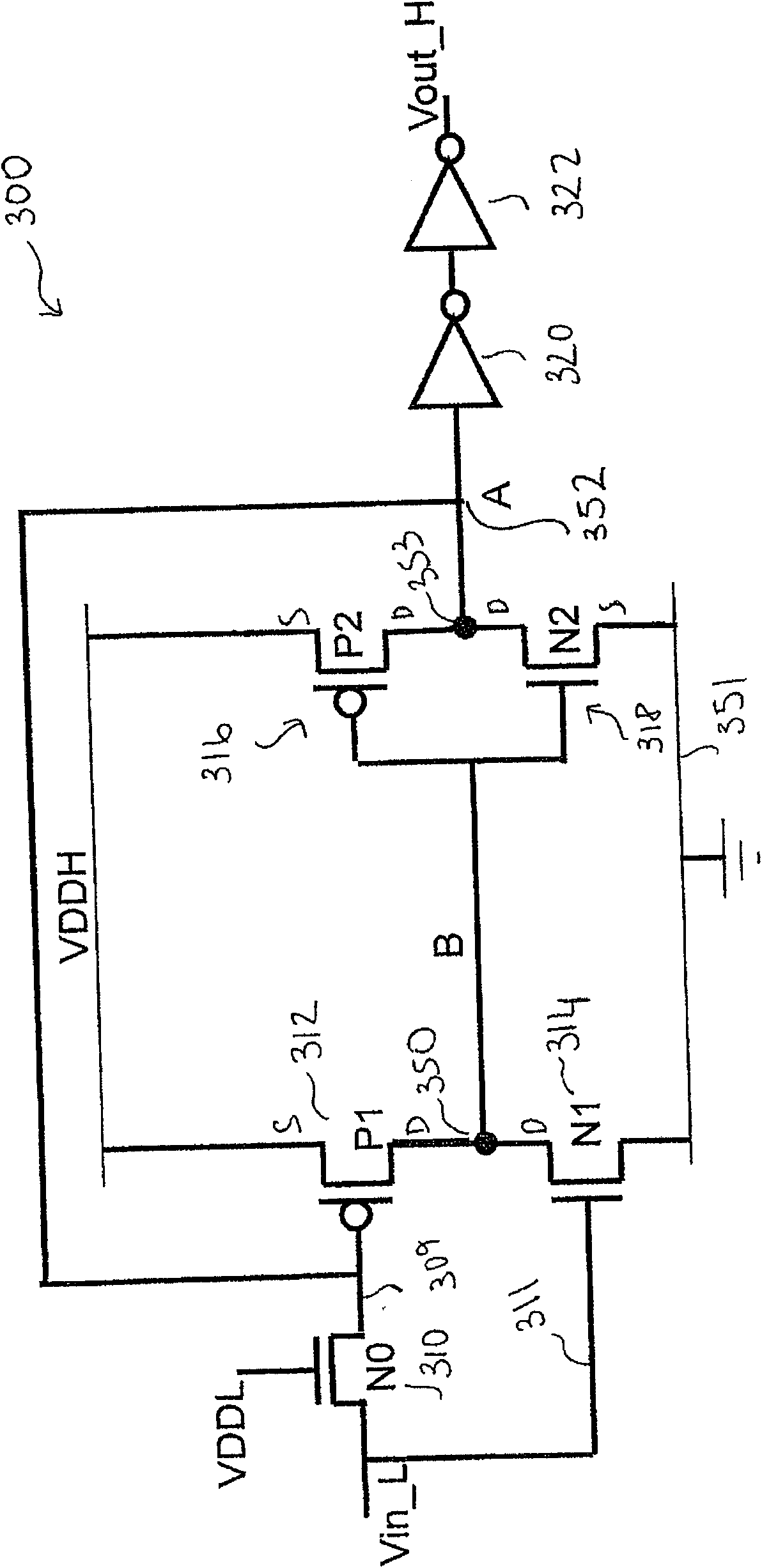
A voltage level shifter
InactiveCN101944905AElectric pulse generatorLogic circuits using dielectric elementsSignal transitionPass transistor logic
A voltage level shifter is provided for receiving an input signal from an input voltage domain and converting said signal to a shifted signal in a shifted voltage domain. The voltage level shifter has an input, switching circuitry, a pass transistor and an output. The switching circuitry is configured to isolate an output of said pass transistor from said supply voltage rail when said input voltage domain corresponds to a logical zero.
Owner:ARM LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com