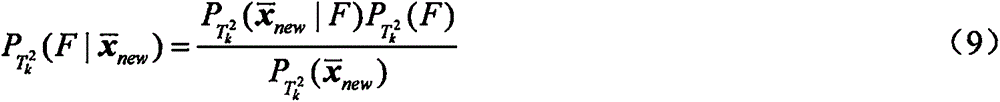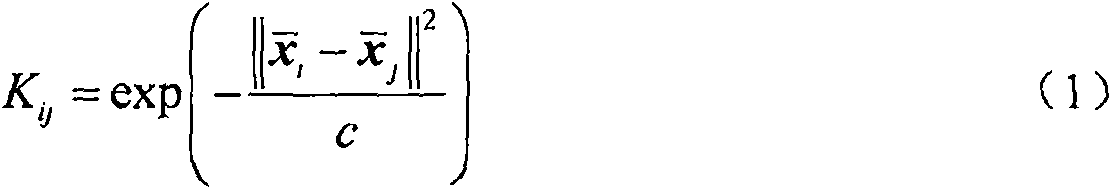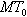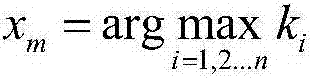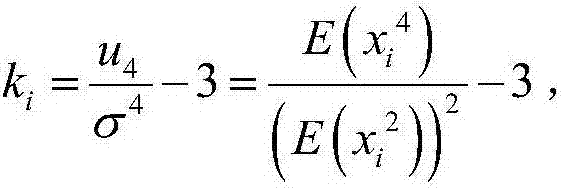Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
53 results about "Non-Gaussianity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, a non-Gaussianity is the correction that modifies the expected Gaussian function estimate for the measurement of a physical quantity. In physical cosmology, the fluctuations of the cosmic microwave background are known to be approximately Gaussian, both theoretically as well as experimentally. However, most theories predict some level of non-Gaussianity in the primordial density field. Detection of these non-Gaussian signatures will allow discrimination between various models of inflation and their alternatives.
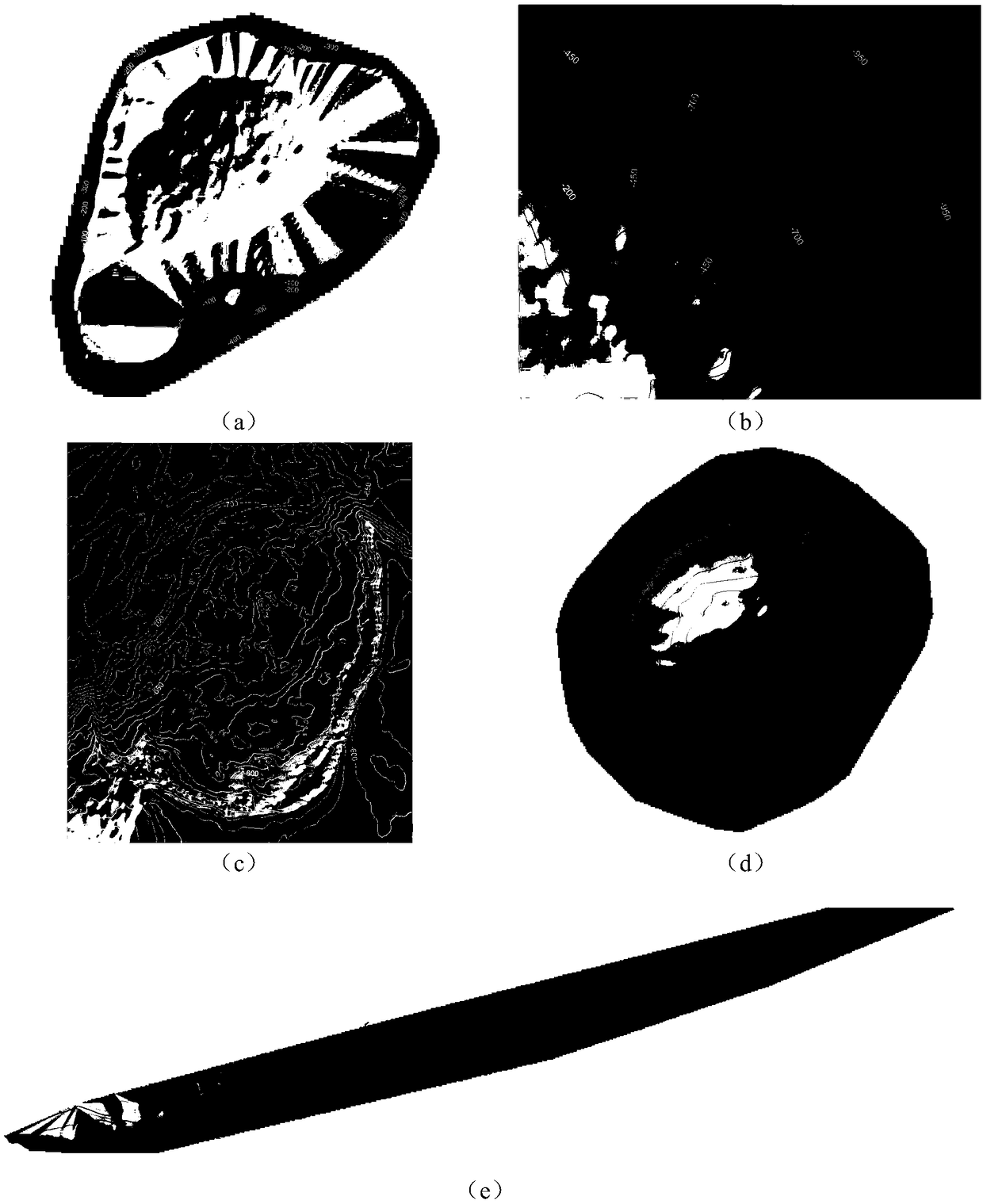
Multi-parametric analysis of snore sounds for the community screening of sleep apnea with non-gaussianity index
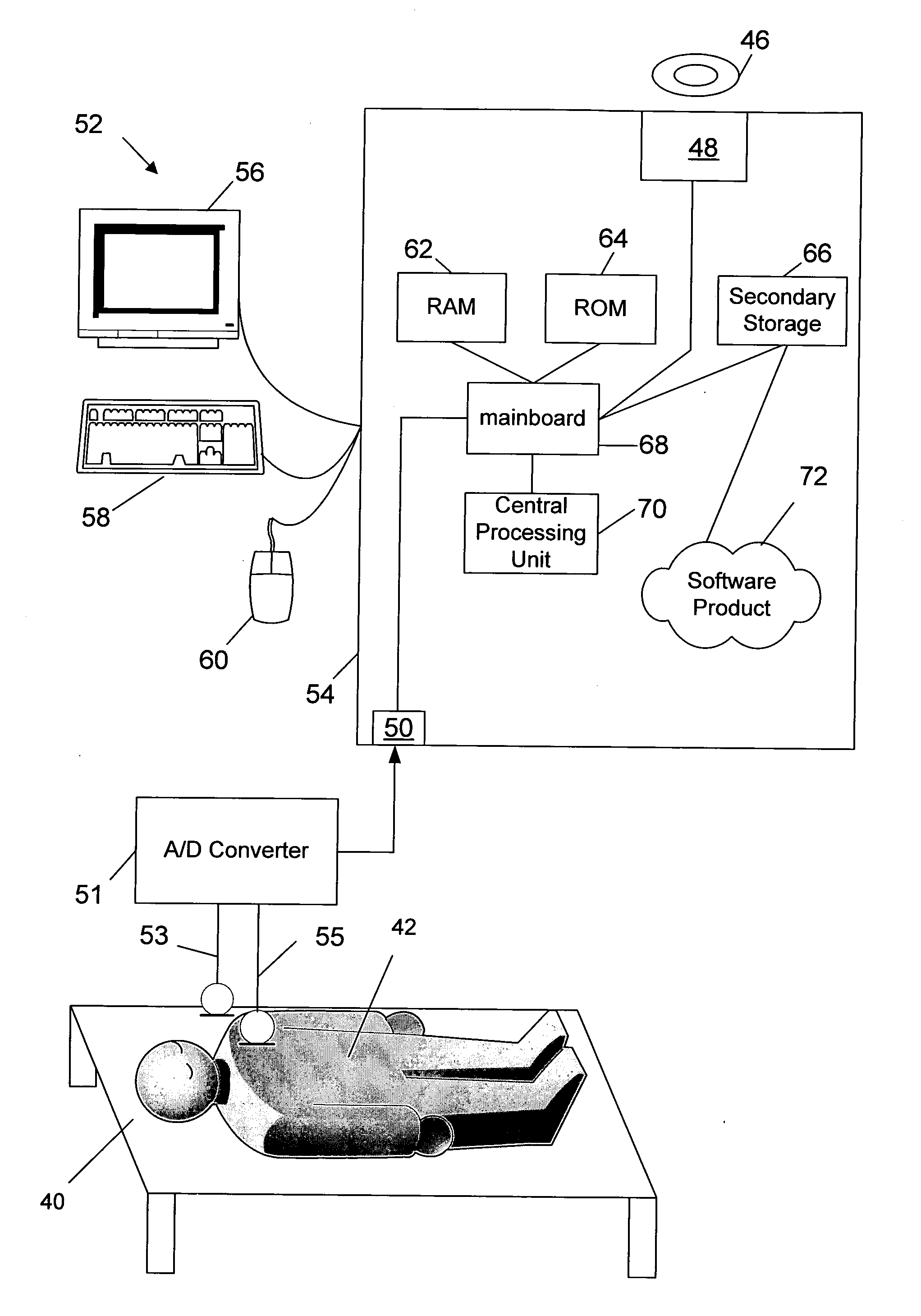
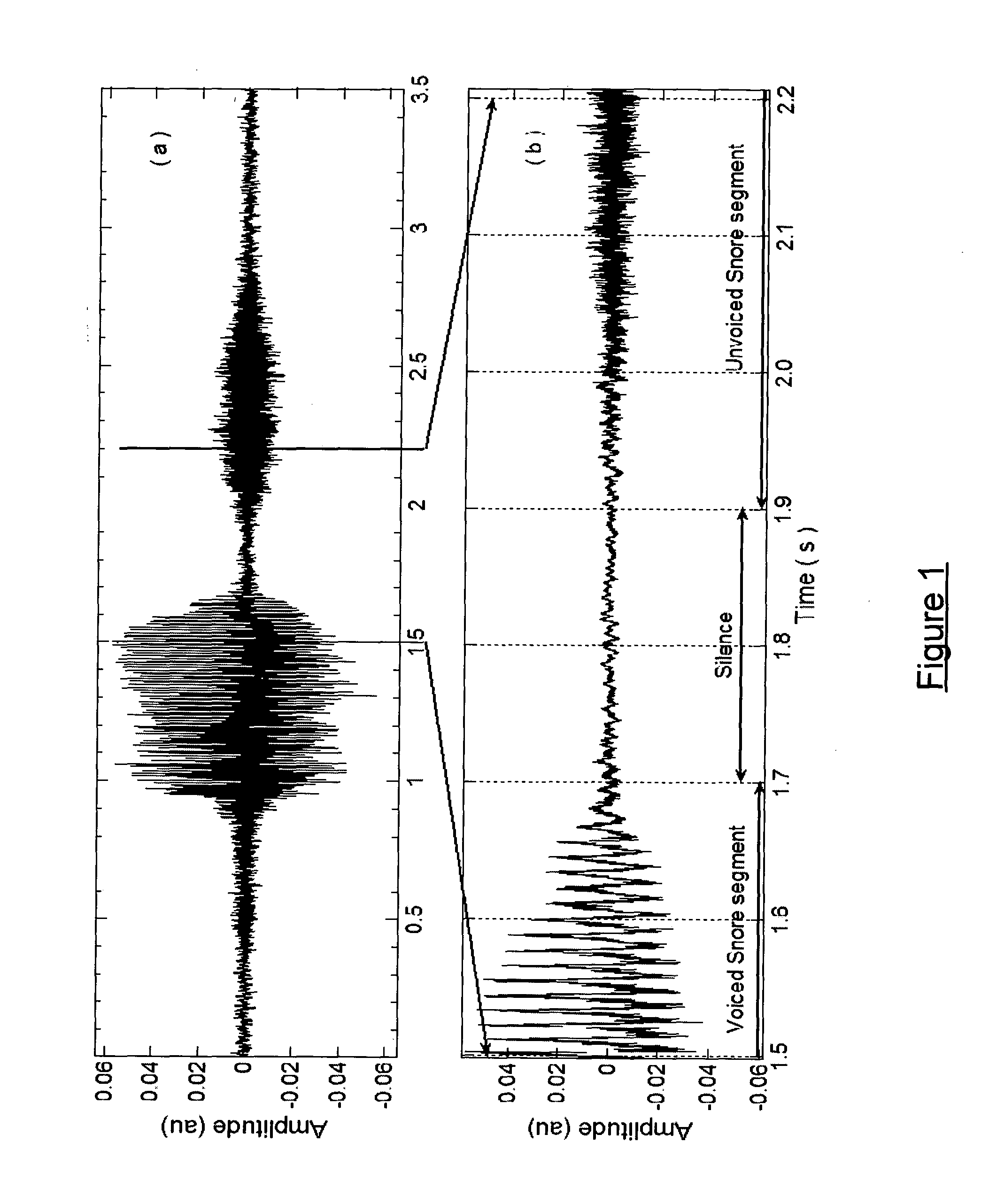
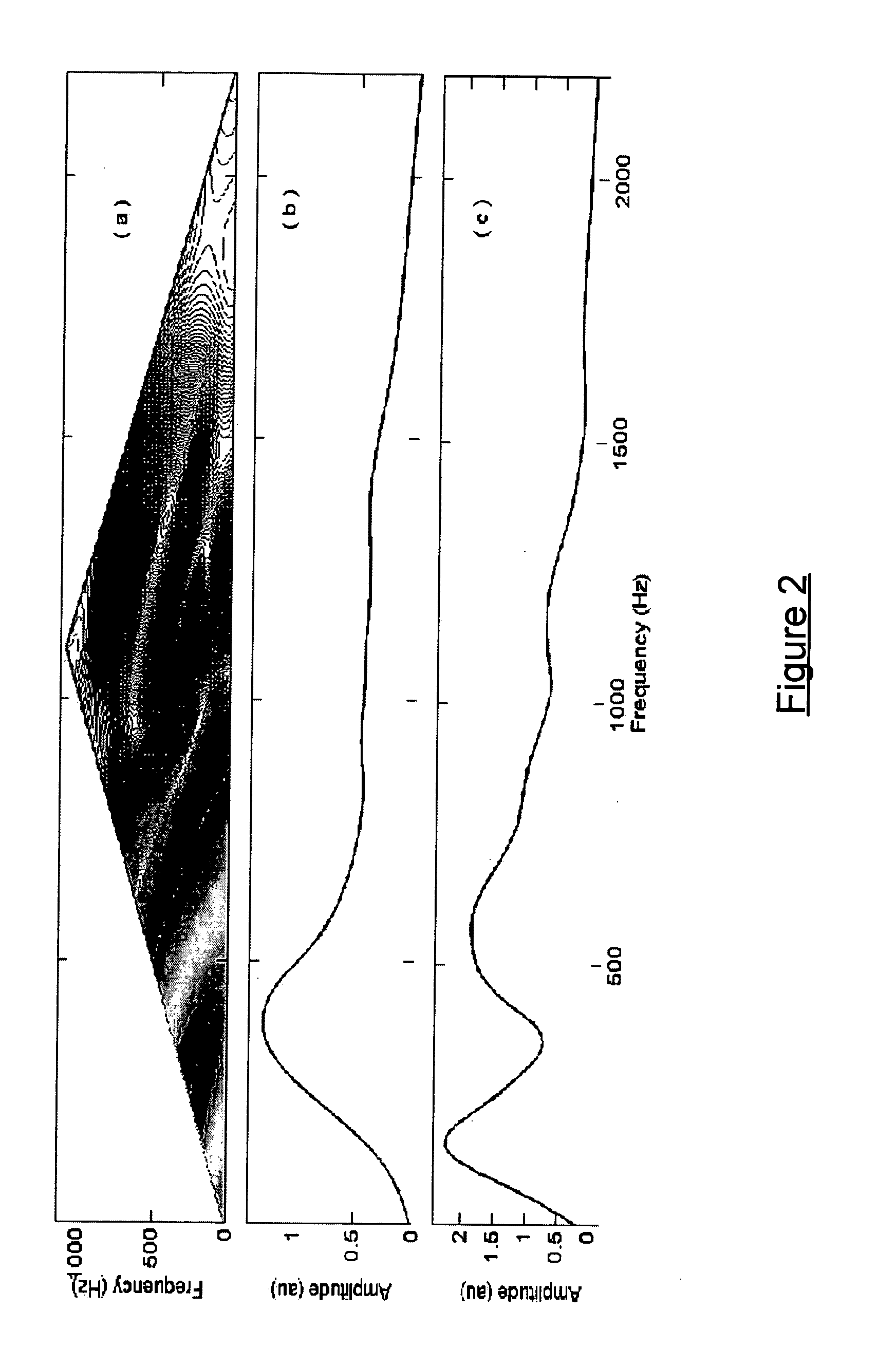
An apparatus for diagnosing sleep disorders such as OASHS from snore sounds includes a segmentation module (126) coupled to a data logger (124) to provide segments of the digitized audio signal to a Snore Segment Identifier (128). A total airways response (TAR) module (130), pitch calculator (132) and MFCC calculator (134) are each coupled to an output side of the snore segment identifier module (128). Each of these modules is respectively arranged to calculate pitch, bispectrum, diagonal slice and MFCC parameters for the snore segments received from the snore segment identifier (128). Similarly, the NGI calculator (136) produces a non-Gaussianity index for the digitized audio signal. A classification module (144) is arranged to process the calculated parameters and compare a resulting diagnosis probability to a predetermined threshold value. The results of this comparison are then indicated on video display (142), which communicates with the classification module (133) via display controller (140) and bus (145). For example, if the results of the comparison are over threshold then display (142) is driven to indicate “OS AHS is present”.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Real-time learning debutanizer soft measurement modeling method on basis of Gaussian mixture models
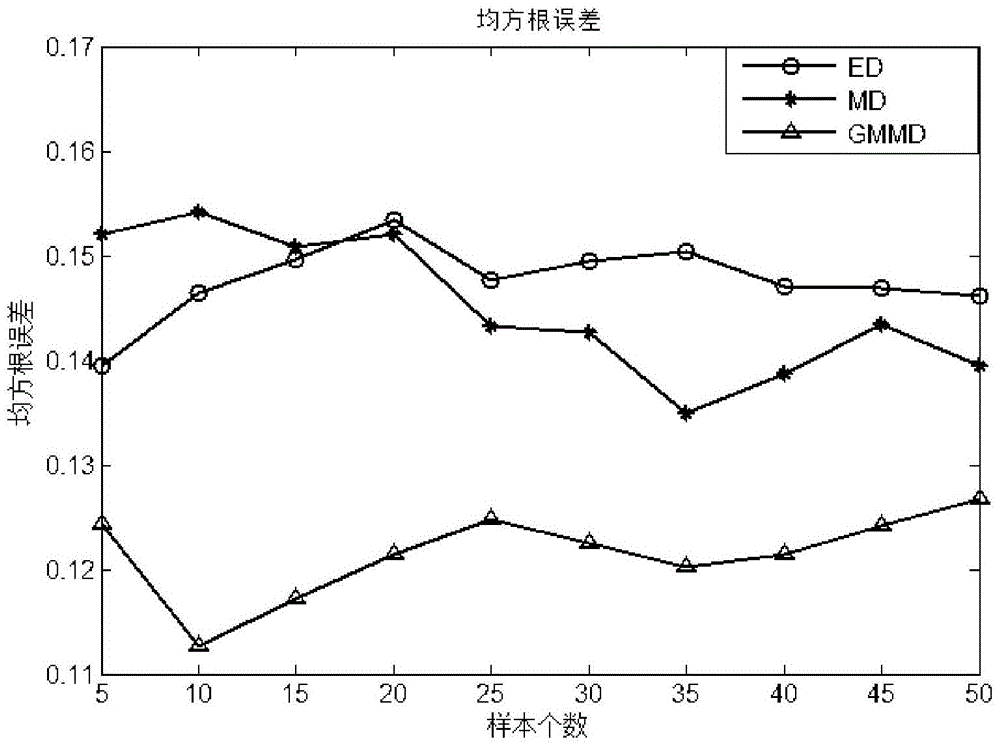
InactiveCN103927412AImprove forecast accuracyFully extractedSpecial data processing applicationsMahalanobis distanceNon-Gaussianity
The invention discloses a real-time learning debutanizer soft measurement modeling method on the basis of Gaussian mixture models (GMM). The real-time learning debutanizer soft measurement modeling method includes training process Gaussian mixture models to acquire various Gaussian component parameters and building corresponding sub-models; computing posterior probabilities of to-be-predicted samples and local Mahalanobis distances of various Gaussian components by a Bayesian process so as to obtain weighted sample similarity definition indexes; reasonably selecting similar samples by the aid of the new similarity indexes for local modeling. The posterior probabilities indicate whether the to-be-predicted samples belong to the various Gaussian components or not. The real-time learning debutanizer soft measurement modeling method has the advantages that problems of process non-Gaussianity and nonlinearity can be effectively solved, characteristics of the to-be-predicted samples can be sufficiently extracted, the similar samples can be reasonably selected for real-time learning modeling, and accordingly the real-time learning debutanizer soft measurement modeling method is favorable for improving the model prediction precision.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Course monitoring method based on non-gauss component extraction and support vector description
InactiveCN101403923AOvercome the shortcoming of easy to fall into local minimumAvoid the shortcoming of assuming a normal distributionElectric testing/monitoringData descriptionNon-Gaussianity
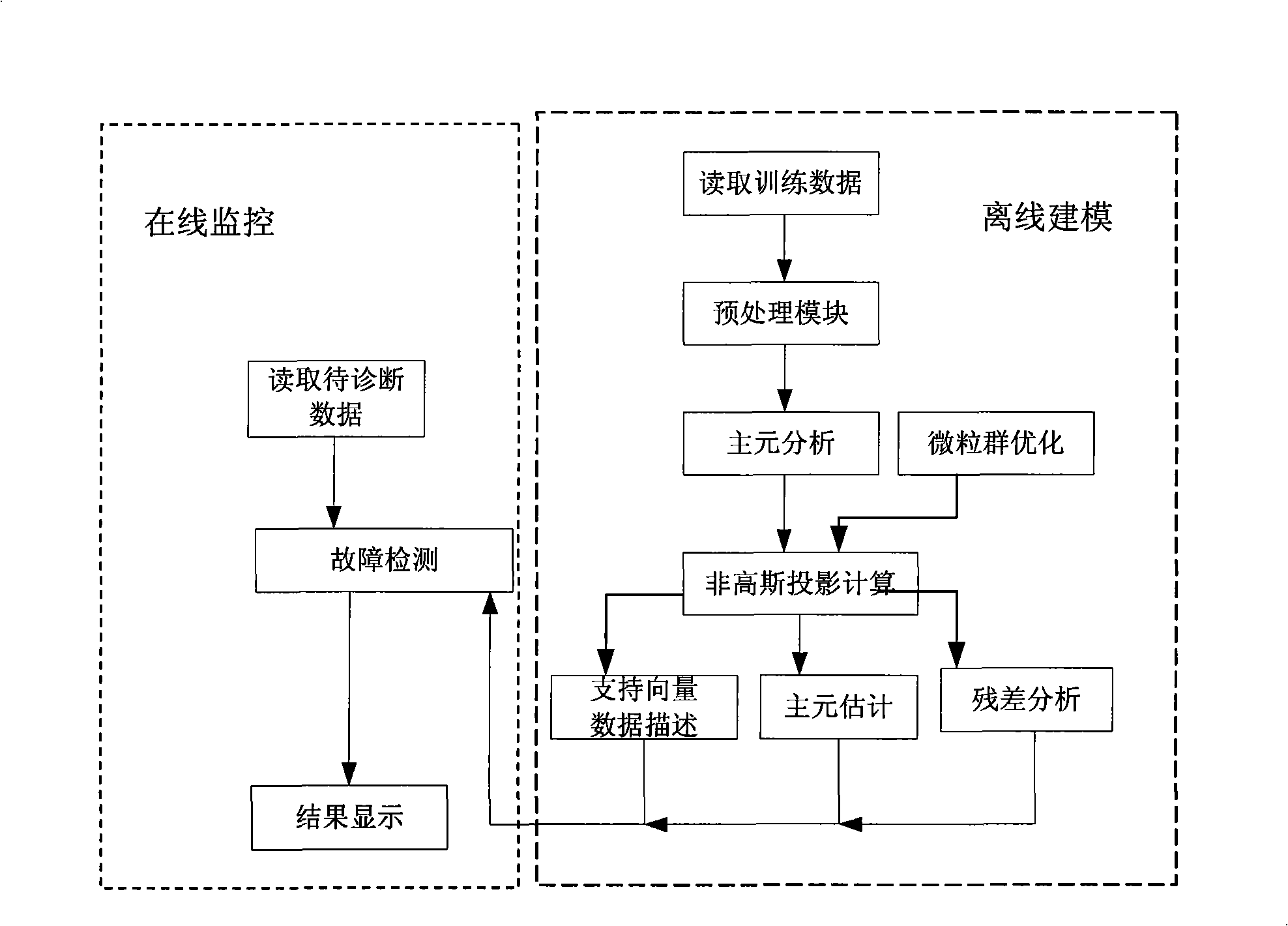
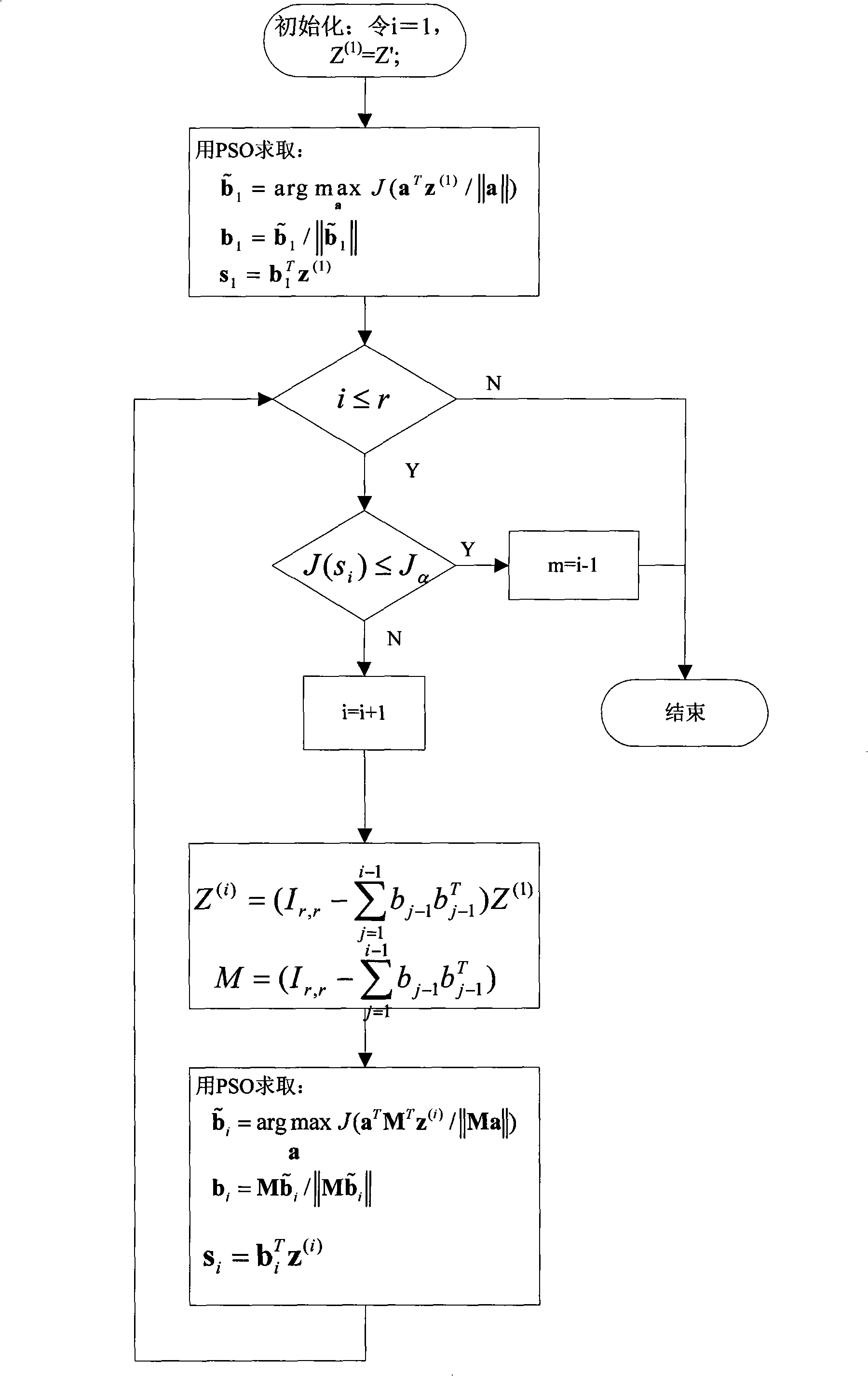
The invention discloses a process monitoring method which is based on non-Gaussian component extraction and support vector description. The method comprises the following steps: read-in of training data and data to be diagnosed, data preprocessing, establishment of a principal component analysis model, particle swarm optimization algorithm, non-Gaussian projection calculation, support vector data description, residual analysis, principal component estimation, fault detection and the model updating. By the method, the non-Gaussian components can be automatically extracted from operating data of an industrial process, thus avoiding the disadvantage that the conventional statistical process monitoring method assumes that data is subject to normal distribution, and the non-Gaussian projection algorithm based on the particle swarm optimization algorithm ensures the maximization of the non-Gaussian properties of the extracted independent components, and avoids the problem that the independent component analysis method is easy to be involved in the locally optimal solution. Compared with the conventional statistical process monitoring method, the method can find abnormity in time, effectively reduce the rate of false alarm, and obtain better monitoring effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Multi-parametric analysis of snore sounds for the community screening of sleep apnea with non-gaussianity index
An apparatus for diagnosing sleep disorders such as OASHS from snore sounds includes a segmentation module (126) coupled to a data logger (124) to provide segments of the digitized audio signal to a Snore Segment Identifier (128). A total airways response (TAR) module (130), pitch calculator (132), and MFCC calculator (134) are each coupled to an output side of the snore segment identifier module (128). Each of these modules is respectively arranged to calculate pitch, bispectrum, diagonal slice, and MFCC parameters for the snore segments received from the snore segment identifier (128). Similarly, the NGI calculator (136) produces a non-Gaussianity index for the digitized audio signal. A classification module (144) is arranged to process the calculated parameters and compare a resulting diagnosis probability to a predetermined threshold value. The results of this comparison are then indicated on video display (142), which communicates with the classification module (133) via display controller (140) and bus (145). For example, if the results of the comparison are over threshold then display (142) is driven to indicate “OS AHS is present.”
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Just-in-time learning soft measurement modeling method based on Bayes Gaussian mixture model
InactiveCN108804784AImprove product qualityReduce manufacturing costCharacter and pattern recognitionDesign optimisation/simulationAdditive ingredientInformation Criteria
The invention discloses a just-in-time learning soft measurement modeling method based on a Bayes Gaussian mixture model, and belongs to the field of complex industrial process modeling and soft measurement. The method is used for a time varying industrial process with nonlinearity and non-Gaussianity; through a strategy of updating localities in real time online, a Bayes information criterion isadopted to determine an optimal Gaussian ingredient number; when new test data comes, a posterior probability that the new test data belongs to each Gaussian ingredient is calcuated, a Mahalanobis distance between the new test data and training data is solved, and the posterior probability and the Mahalanobis distance are blended to serve as a similarity index; and finally, one group of data withthe highest similarity is selected from the original training sample to establish a current GPR (Gaussian Process Regression) model, and model output prediction is carried out to achieve an effect onimproving product quality and lowering production cost.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Batch process fault monitoring method based on multi-stage ICA-SVDD
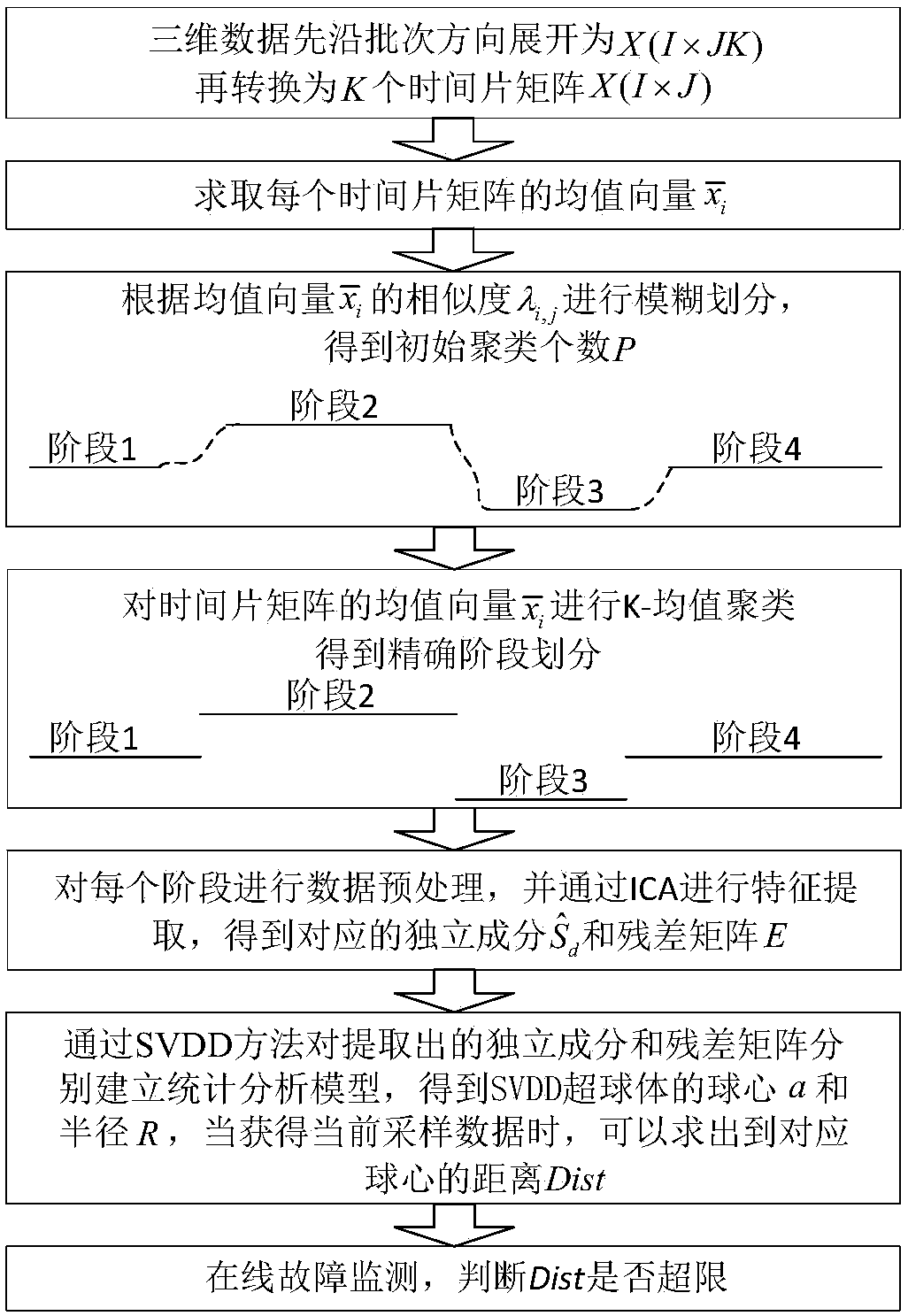
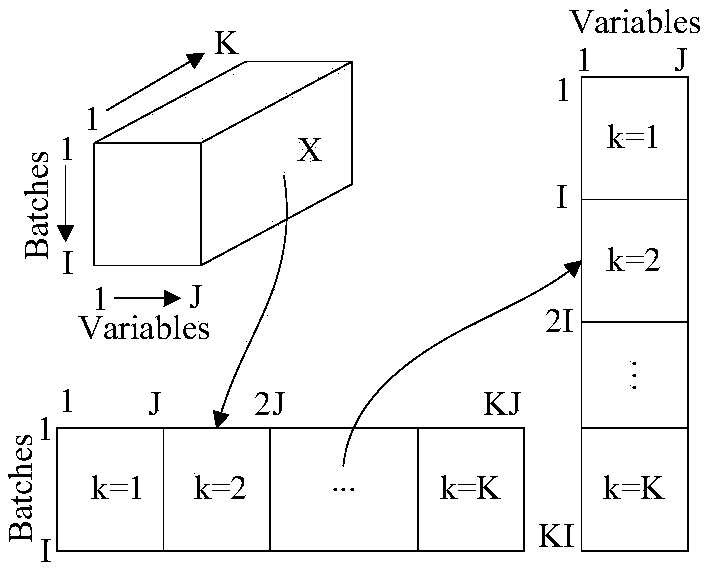
The invention discloses a batch process fault monitoring method based on multi-stage ICA-SVDD, is applied to a batch process having the complex process mechanism and multiple operation stages and aims to solve a multi-stage and data distribution non-Gauss problem existing in the batch processes. An improved stage division and fault monitoring method is employed. The method comprises steps that firstly, stage division is carried out according to similarity of each time segment and a K mean value algorithm, secondly, an independent component analysis method is utilized for each stage to extract the non-gauss characteristic information, and lastly, a support vector data description algorithm is introduced to respectively establish a statistics analysis model for independent components and the residual gauss residual error residual error space, and fault monitoring of the whole process is realized. The method is advantaged in that the method is applied to fault monitoring of the actual semiconductor etching process, and the better monitoring effect for the multi-stage batch processes is realized as proved by the result.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
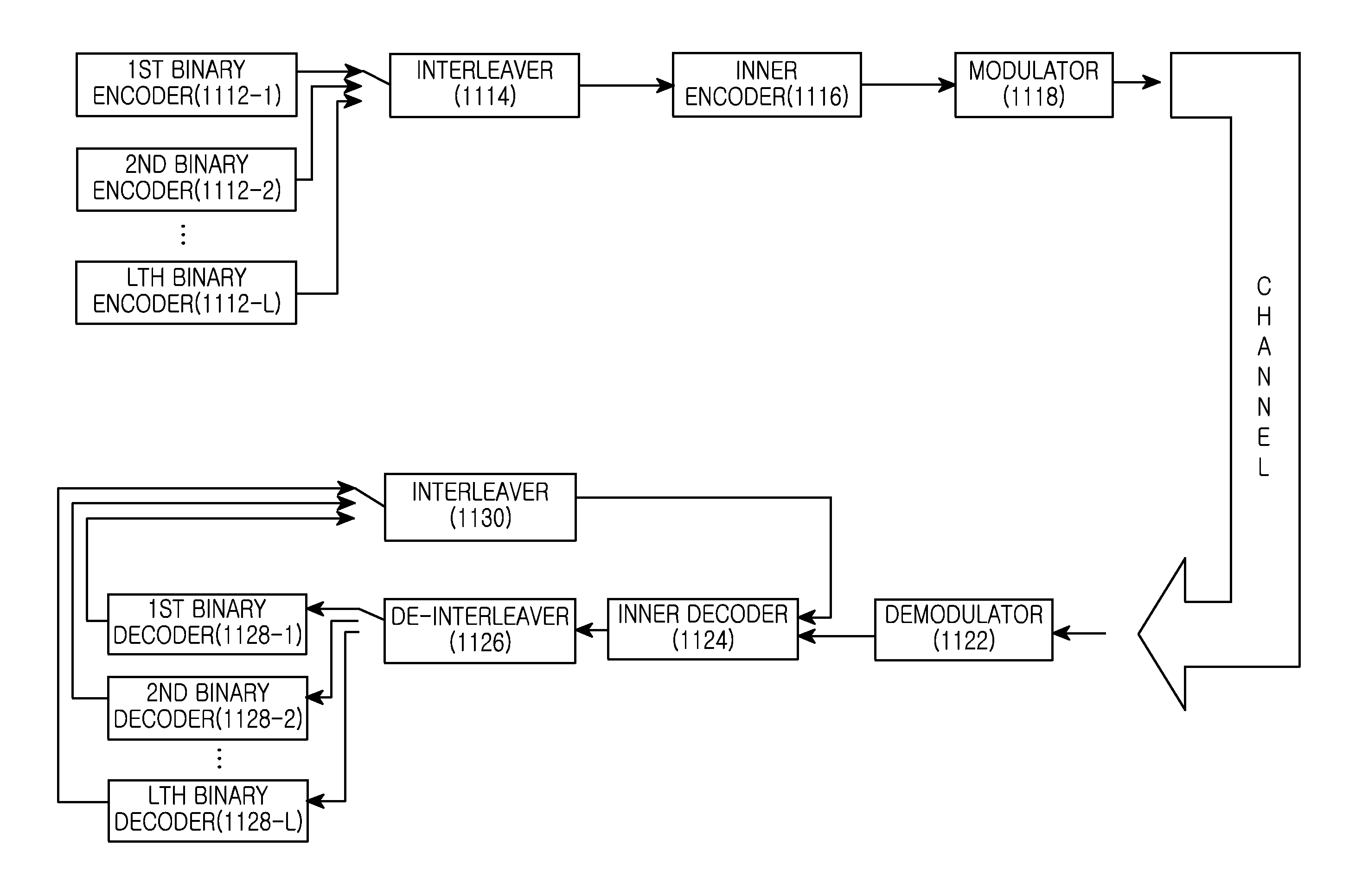
Method and apparatuses for algorithm on qam coherent optical detection
InactiveUS20140341236A1Reduce complexityPolarisation multiplex systemsModulated-carrier systemsComputation complexityPhase noise
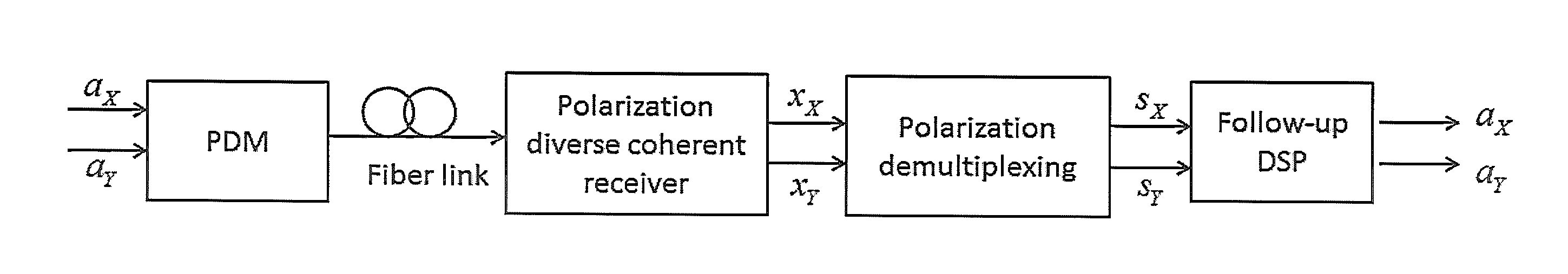
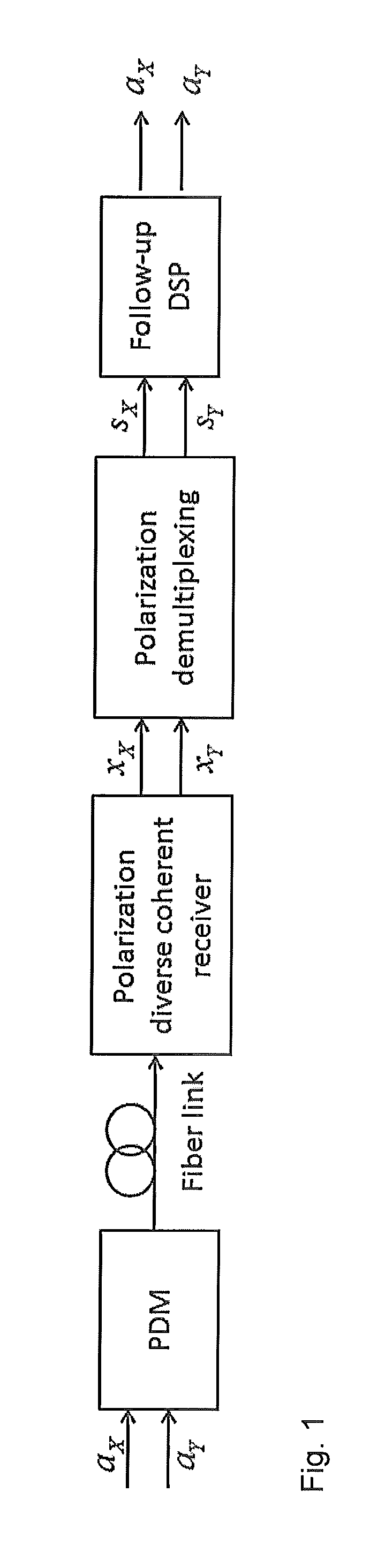
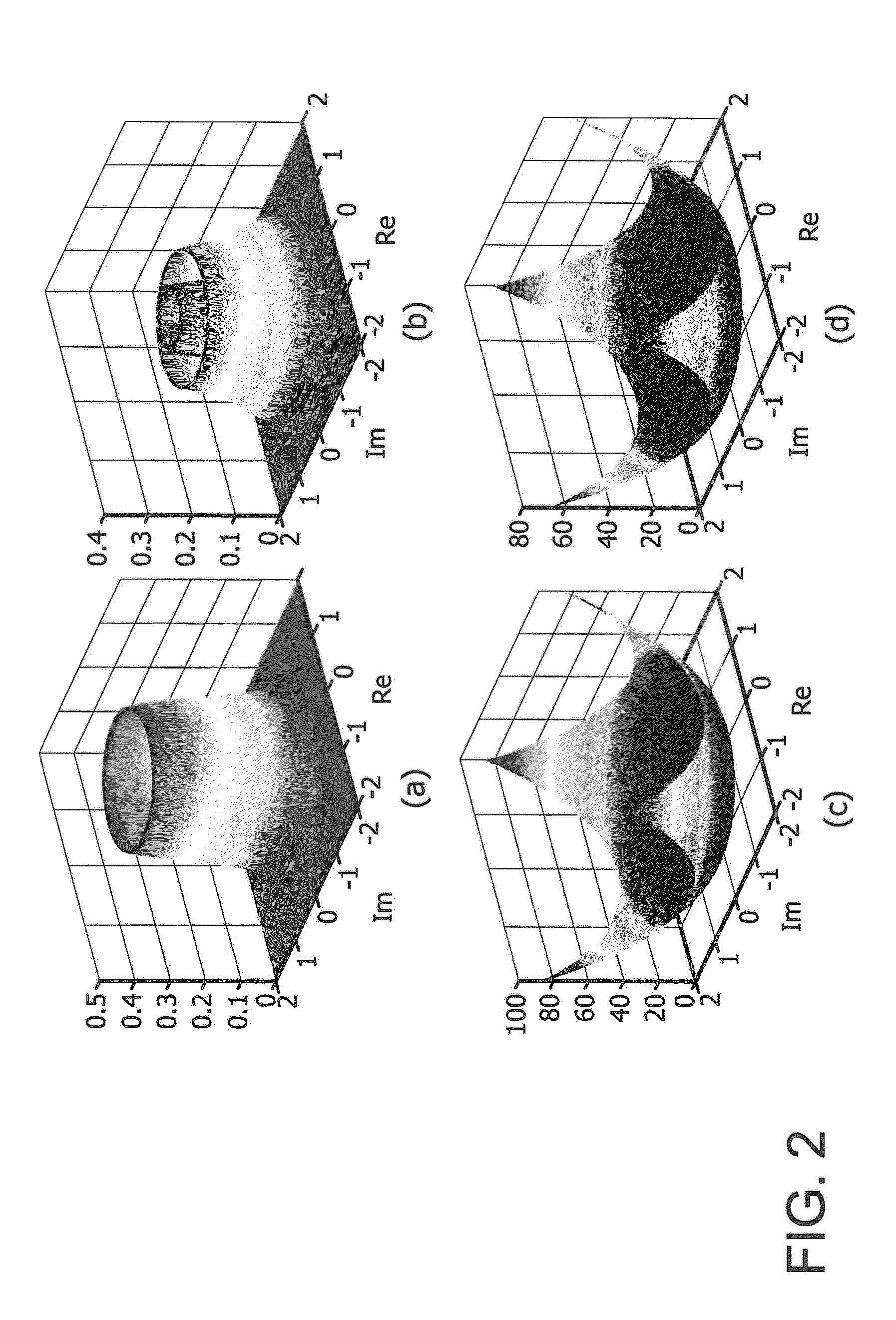
Blind polarization demultiplexing algorithms based on complex independent component analysis (ICA) by negentropy maximization for quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) coherent optical systems are disclosed. The polarization demultiplexing is achieved by maximizing the signal's non-Gaussianity measured by the information theoretic quantity of negentropy. An adaptive gradient optimization algorithm and a Quasi-Newton algorithm with accelerated convergence are employed to maximize the negentropy. Certain approximate nonlinear functions can be substitutes for the negentropy which is strictly derived from the probability density function (PDF) of the received noisy QAM signal with phase noise, and this reduces the computational complexity. The numerical simulation and experimental results of polarization division multiplexing (PDM)-quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK) and PDM-16QAM reveal that the ICA demultiplexing algorithms are feasible and effective in coherent systems and the simplified ones can also achieve equivalent performance.
Owner:ZTE (USA) INC
Industrial fault diagnosis method and application based on self-adaption feature extraction
ActiveCN104731083AImplement fault diagnosisImprove accuracyElectric testing/monitoringFeature extractionDiagnosis methods
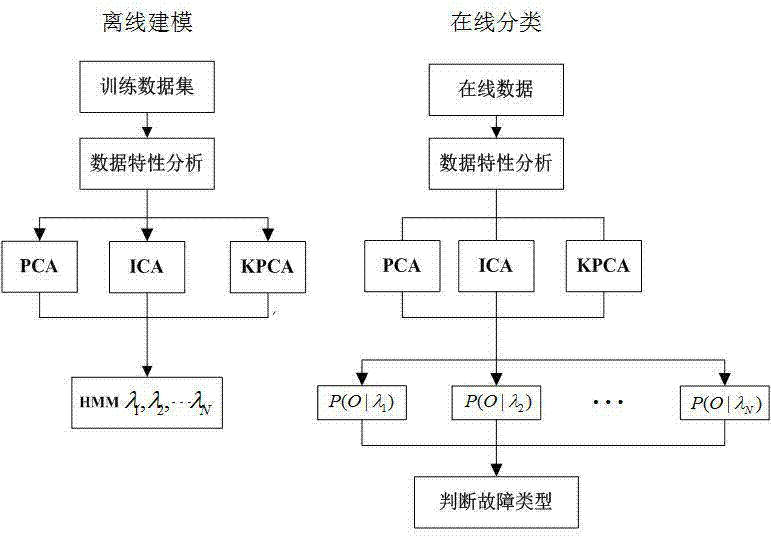
The invention discloses an industrial fault diagnosis method and application based on self-adaption feature extraction, and belongs to the technical field of industrial process monitoring and diagnosis. Firstly, data feature analysis is conducted on industrial acquisition data, and appropriate feature extraction methods are chosen according to different data features; secondly, fault classification is achieved through a Hidden Markov model method. According to the industrial fault diagnosis method and application based on the self-adaption feature extraction, the self-adaption feature extraction method is adopted specific to diversity of the industrial data with features such as linearity, nonlinearity and nongaussianity, the purpose of reserving effective information to a maximum extent is achieved, and classification of the industrial process faults is conducted through extremely strong dynamic procedure time series modeling capability and time-series pattern classification capacity of the Hidden Markov model, so that compared with other existing methods, due to the fact that the data features are adequately considered, by means of the industrial fault diagnosis method based on the self-adaption feature extraction, higher precision rate of industrial fault diagnosis is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Industrial process fault detection method based on correction type independent element analysis and Bayes probability fusion
ActiveCN106092625AImprove reliabilityImprove stabilityStructural/machines measurementIndependent elementNon-Gaussianity
The invention relates to an industrial process fault detection method based on correction type independent element analysis and Bayes probability fusion. A conventional fault detection method based on the correction type independent element analysis requires selection of a non-quadratic function to measure non-gaussianity. Different industrial process data or objects can cause a fact that enough experiential knowledge for guiding the selection of the non-quadratic function is hard to acquire in an actual application. By aiming at different non-quadratic functions, the normal data training of the industrial process is adopted to acquire different correction-type independent element models. The Bayes probability fusion method is used to integrate decision results of a plurality of fault detection models together to acquire a final probability type monitoring index. Compared with the prior art, the industrial process fault detection method is used to solve a model uncertainty problem caused by non-quadratic function diversity, and a plurality of model possibilities are fully considered, and the reliability of the fault detection models is enhanced to a great extent.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Fault detection method based on particle swam optimization kernel independent-component analysis model
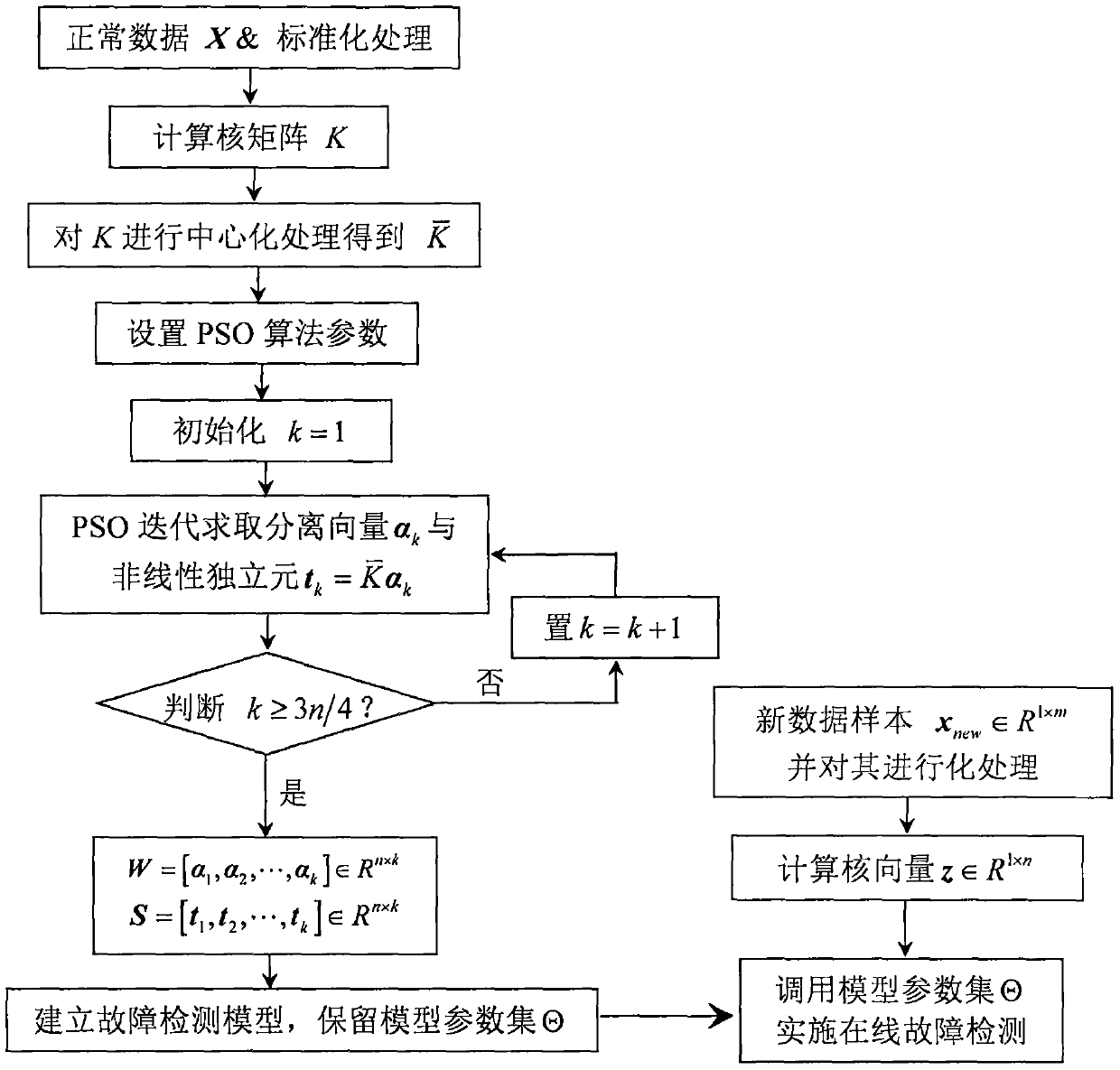
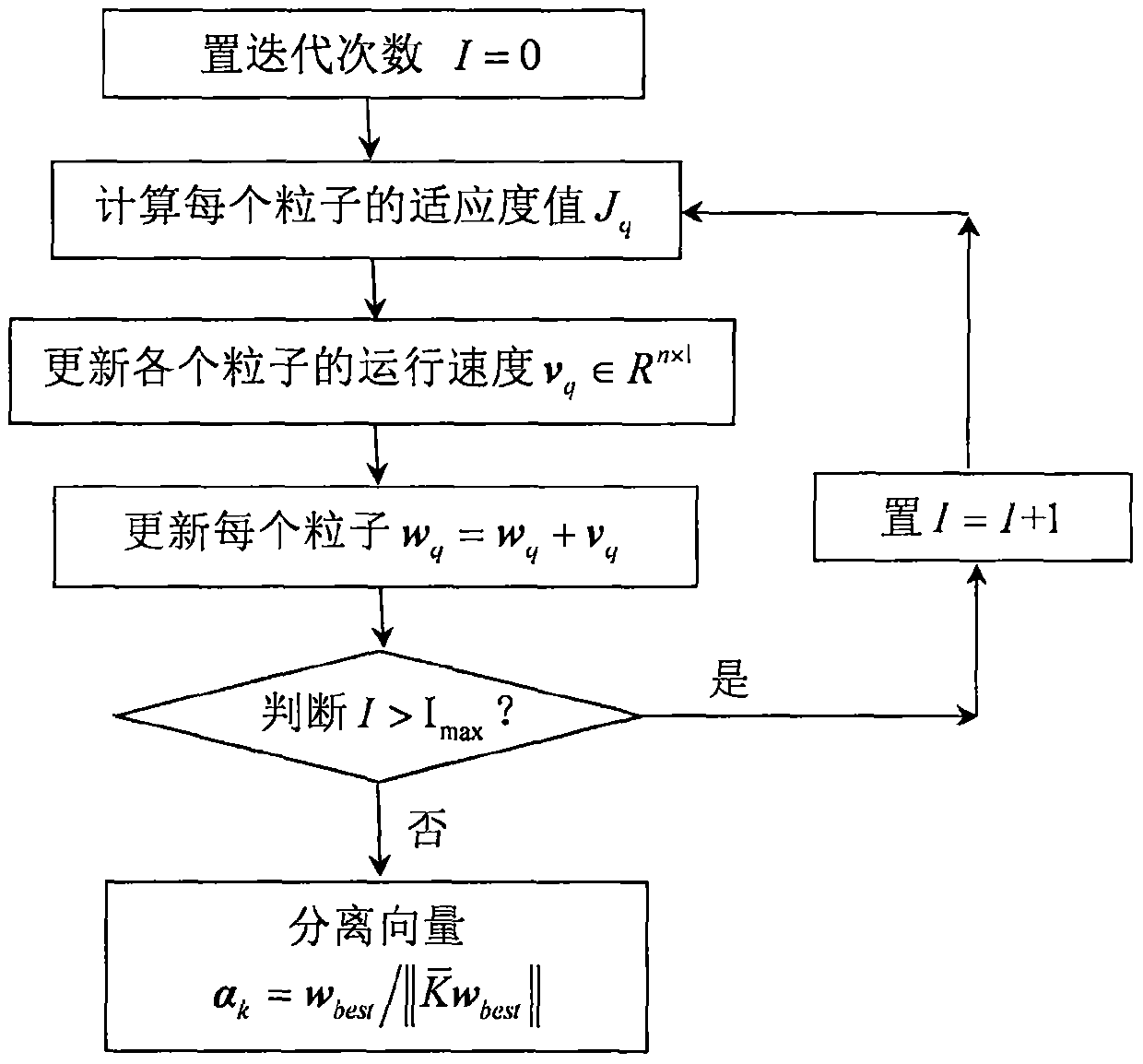
ActiveCN107065842AAvoid the bleaching processProgramme controlElectric testing/monitoringOriginal dataNon-Gaussianity
The invention discloses a fault detection method based on a particle swam optimization kernel independent-component analysis model. Kernel learning skills and a particle swam optimization algorithm are combined and used in the method, a traditional independent component analysis method is expanded into a modeling method capable of directly processing non-linear process data, and a corresponding fault detection model is established on the basis. The fault detection method specifically comprise the following steps: firstly, an original training data matrix is converted into a kernel matrix through a kernel function, and centralization processing is carried out; secondly, non-linear independent components are solved by utilizing iteration of the particle swam optimization algorithm and are ranked according to non-Gaussian sizes; and, finally, the non-linear fault detection model is established, and online fault detection is implemented. Compared with a traditional method, the method of the invention prevents a whitening pretreatment process so that a condition that original data information loses or is distorted cannot occur. Furthermore, the method of the invention is not limited to establish the fault detection module, but can be applied to other fields related to non-linear data signal source separation.
Owner:郑州优碧科技有限公司
Long-distance pipeline pressure monitoring method based on ensemble modified ICA-KRR algorithm
PendingCN108804740ARepair in timeAvoid lostPipeline systemsDesign optimisation/simulationWeight coefficientNon-Gaussianity
The invention discloses a long-distance pipeline pressure monitoring method based on an ensemble modified ICA-KRR algorithm. The method comprises the following steps: 1) constructing a long-distance pipeline pressure monitoring data matrix; 2) calculating a variable P belonging to Rm x m; 3) extracting a component matrix T=PTX; 4) whitening the extracted component matrix T to obtain a whitened result; 5) calculating a matrix S=CTZ; 6) calculating a matrix Cn; 7) calculating a separation matrix W belonging to Rd x m and a mixing matrix A belonging to Rm x d; 8) obtaining source signals of independent components, wherein the independent relationship between the source signals of the independent components is reflected by a non-Gaussian property, the non-Gaussian property is quantized by a negative entropy function, and the negative entropy function can select three non-quadratic functions; 9) constructing three kinds of component importance evaluation standards; 10) blending to form a two-layer comprehensive learning strategy; 11) forming 9 component selection models; 12) obtaining a weight coefficient w; 13) obtaining regression fault signal data y; 14) and calculating a leakage position d. The method can realize real-time monitoring and accurate positioning of the leakage position on a long-distance pipeline.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
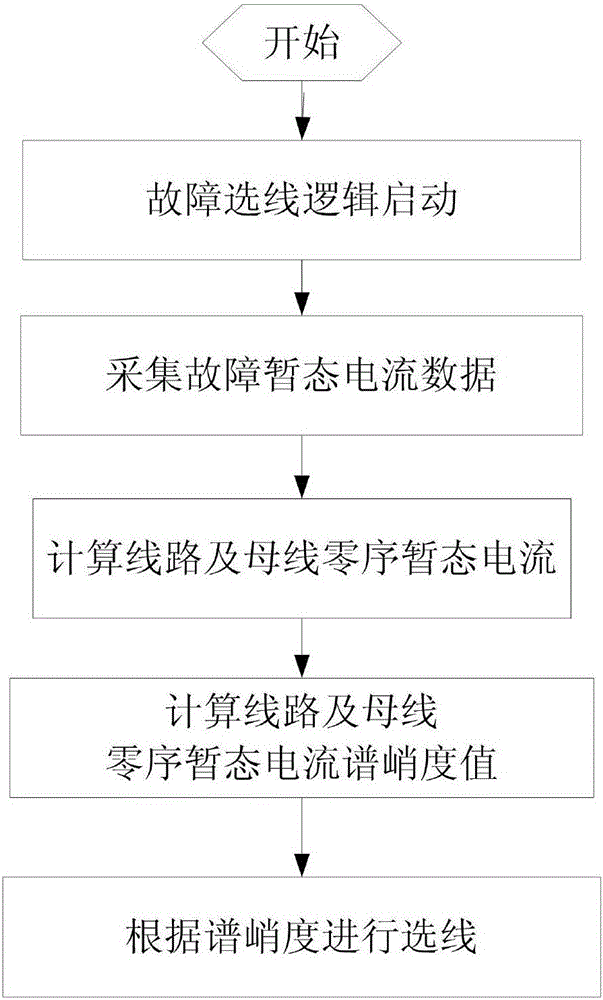
Novel small-current grounding system transient line selection method
InactiveCN106019046ALarge non-stationarityLarge non-GaussianElectrical testingElectrical resistance and conductanceTransient state
The invention discloses a novel mall-current grounding system transient line selection method, and the method comprises the following steps: starting a fault line selection logic; collecting the fault transient current data of all branch circuits on a bus; calculating zero sequence fault transient currents of the circuits and bus; calculating the spectral kurtosis of the circuits and bus; and carrying out line selection according to the spectral kurtosis of the circuits and bus. The method is very strong in anti-noise capability, and can completely inhibit white noise theoretically. When a fault angle is smaller or a grounding resistance is big, a fault transient current is smaller, thereby causing line selection through a first half wave method, an energy method, a wavelet method and other methods based on a transient component to be difficult. The method provided by the invention takes the non-stationarity and nongaussianity of signals as characteristic values for judgment, avoids the above impact, achieves the correct line selection, and improves the accuracy of line selection.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Non-Gaussian submarine landform type identification method based on multi-fractal spectrum characteristic
InactiveCN108629364AImprove recognition accuracyMultifractal spectral widthCharacter and pattern recognitionSupport vector machineOcean bottom
The invention discloses a non-Gaussian submarine landform type identification method based on a multi-fractal spectrum characteristic. The method comprises the following steps of 1) calculating depthdistribution skewness and kurtosis according to submarine depth measurement data and determining whether a landform is a non-Gaussian landform; 2) calculating the multi-fractal spectrum characteristicof the non-Gaussian landform; 3) using the multi-fractal spectrum characteristic as an original variable, and applying a factor analysis method to extract a landform factor; 4) according to the landform factor, using a support vector machine to design a landform type classifier; and 5) calculating landform depth distribution skewness and kurtosis of a landform to be identified, determining the nongaussianity of the landform, calculating the multi-fractal spectrum characteristic of the non-Gaussian landform and the landform factor, and using the designed classifier to identify a landform type.The method has advantages that the method is simple, a calculated amount is small, an identification accuracy is high, and manpower is saved and so on. The method is suitable for non-Gaussian submarine landform type identification.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA) +1
Impulsivity estimates of mixtures of the power exponential distrubutions in speech modeling
A parametric family of multivariate density functions formed by mixture models from univariate functions of the type exp(-|x|<beta>) for modeling acoustic feature vectores are used in automatic recognition of speech. The parameter beta is used to measure the non-Gaussian nature of the data. beta is estimated from the input data using a maximum likelihood criterion. There is a balance between beta and the number of data points that must be satisfied for efficient estimation.
Owner:IBM CORP
Stable output method for PPS (pulse per second) of satellite navigation receiver
ActiveCN107976700ASuppression of non-GaussianEasy to implementSatellite radio beaconingDiffusionKaiman filter
The invention discloses a stable output method for the PPS (pulse per second) of a satellite navigation receiver, and the method comprises the steps that an FPGA maintains a local PPS according to thefrequency of a local rubidium atomic clock and records the PPS outputted by a general satellite navigation receiver, and a TDC measures the time interval between the PPS outputted by the receiver andthe local PPS; the FPGA transmits a measurement result to a DSP, and the DSP carries out the limited memory Kalman filtering, estimates the position of an ideal second in real time and outputs the parameter of the ideal second through a numerical control delay line, wherein the position of the ideal second is converted into a control parameter of the numerical control delay line in the DSP; the FPGA outputs configuration parameters according to the parameter of the ideal second, adjusts the final second output through the numerical control delay line, and completes the stabilizing of the PPS.The structure of a system is easier to implement, is suitable for a general receiver, and is lower in cost. The output precision of the PPS is higher than 3ns (RMS) through testing after 6h synchronization. The method employs the limited memory Kalman filter, and effectively inhibits the system diffusion caused by the non-gaussianity of a model.
Owner:武汉华中天纬测控有限公司
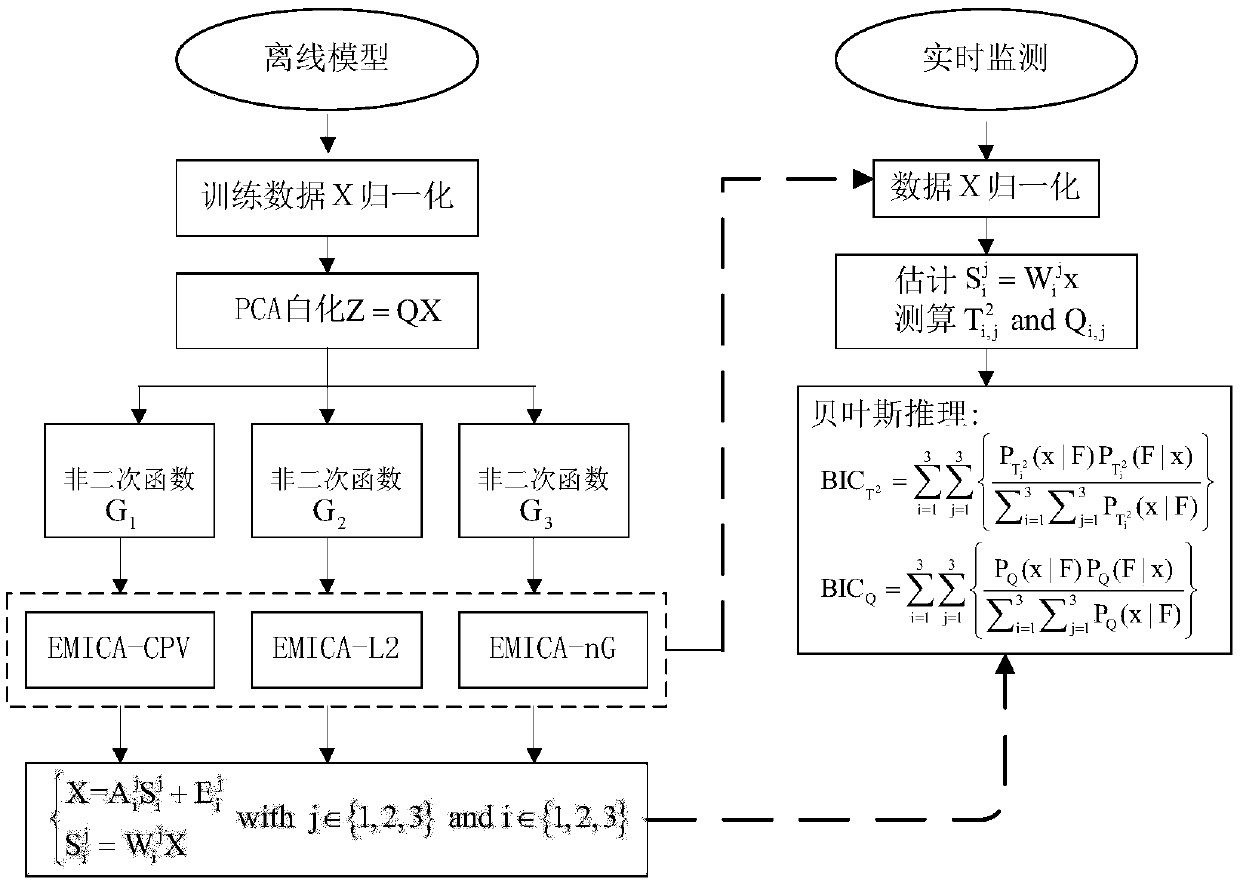
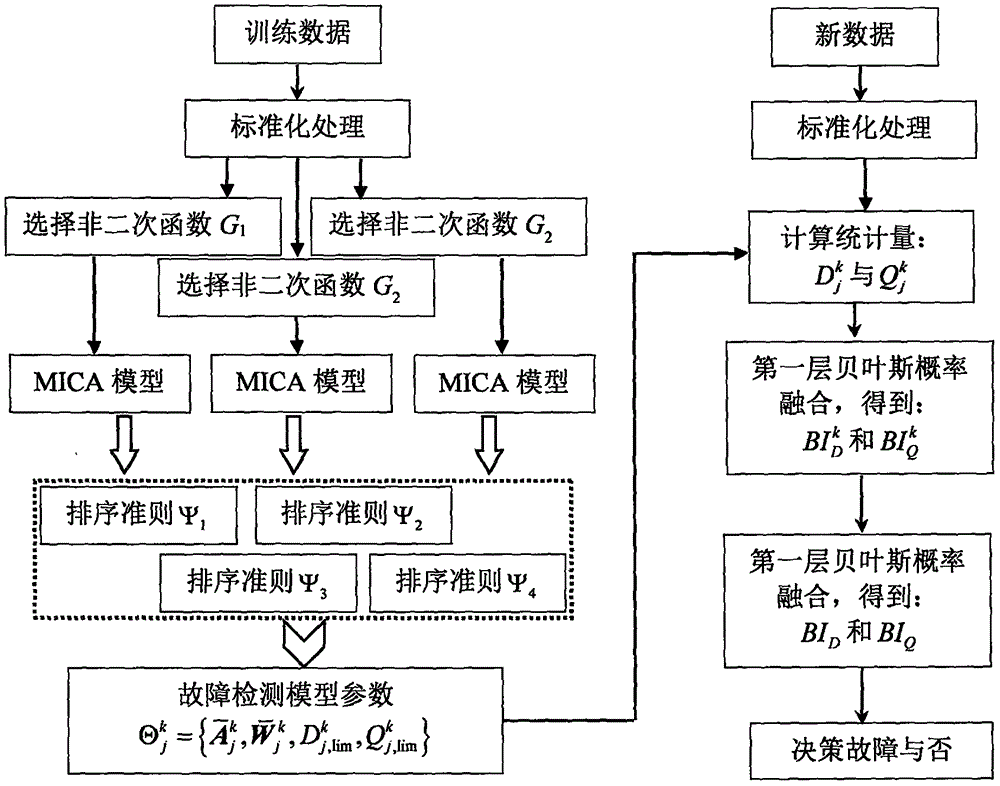
Double-layer integrated type industrial process fault detection method based on modified independent component analysis (MICA)
ActiveCN106054859AImprove general performanceImprove reliabilityElectric testing/monitoringNon-GaussianityIndependent component analysis
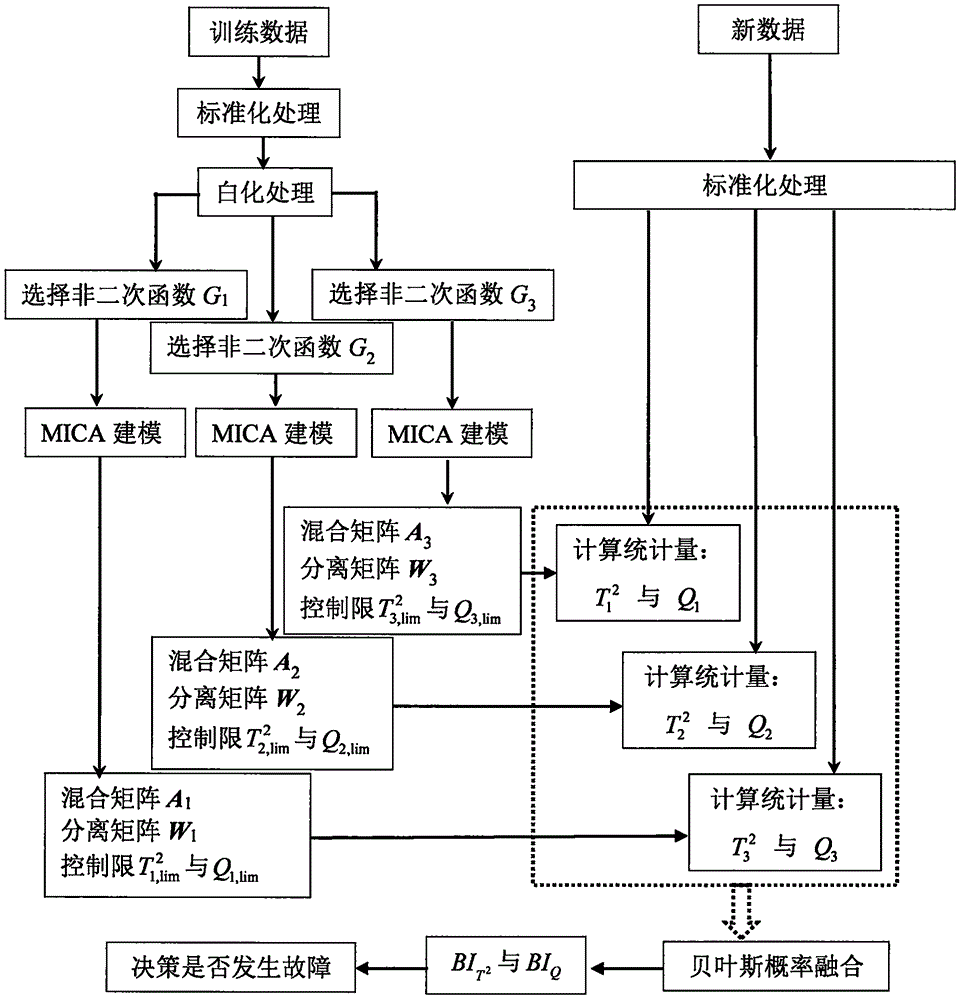
The invention relates to a double-layer integrated type industrial process fault detection method based on modified independent component analysis. The double-layer integrated type industrial process fault detection method mainly solves two problems which are unavoidable in the establishment process of non-Gaussian process fault models: one is how to determine non-quadratic functions so as to measure magnitude of non-Gaussianity, the other is how to select important independent components to establish the models. The double-layer integrated type industrial process fault detection method comprises the steps of: firstly, utilizing all selection possibilities to establish a plurality of MICA fault detection models in sequence; secondly, monitoring the same process data by means of the plurality of MICA fault detection models; and finally, adopting a double-layer Bayesian probability fusion method to integrate different fault detection results into one result, so as to facilitate the final fault decision-making. The double-layer integrated type industrial process fault detection method provided by the invention can minimize the fault missing report rate caused by the wrong selection of the non-quadratic functions or ranking criteria, and greatly improves the reliability and applicability of the corresponding fault detection models.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
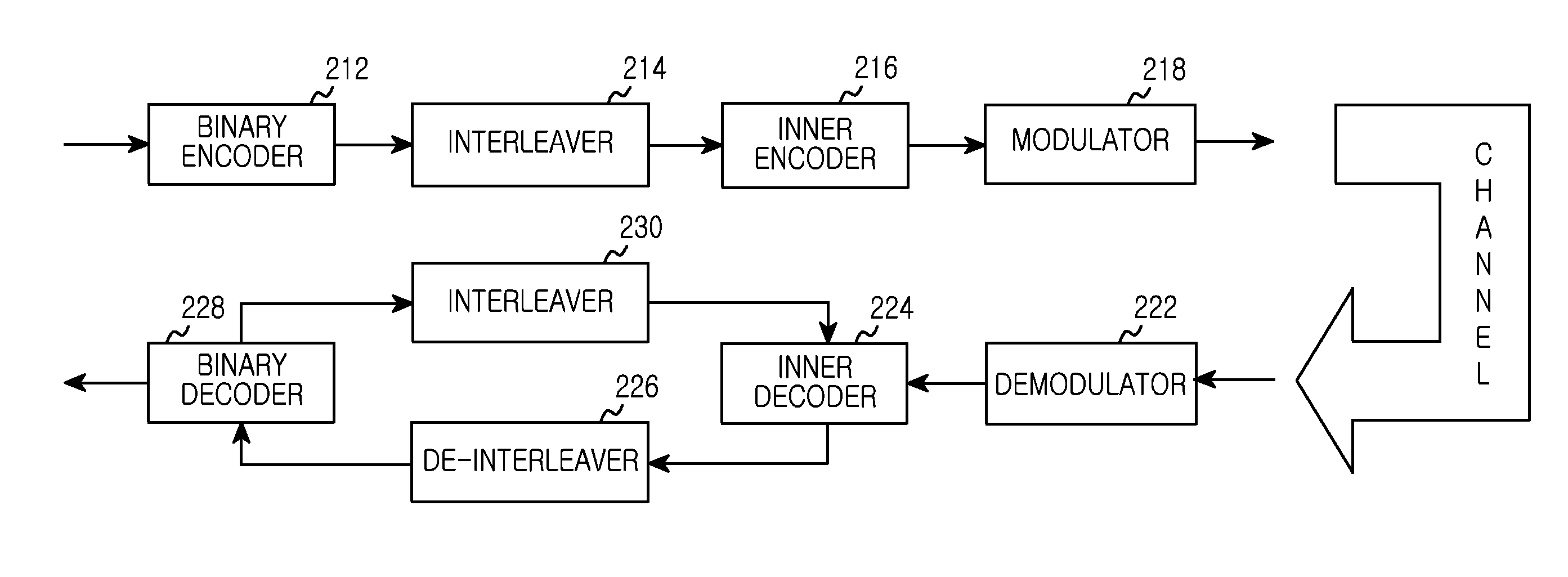
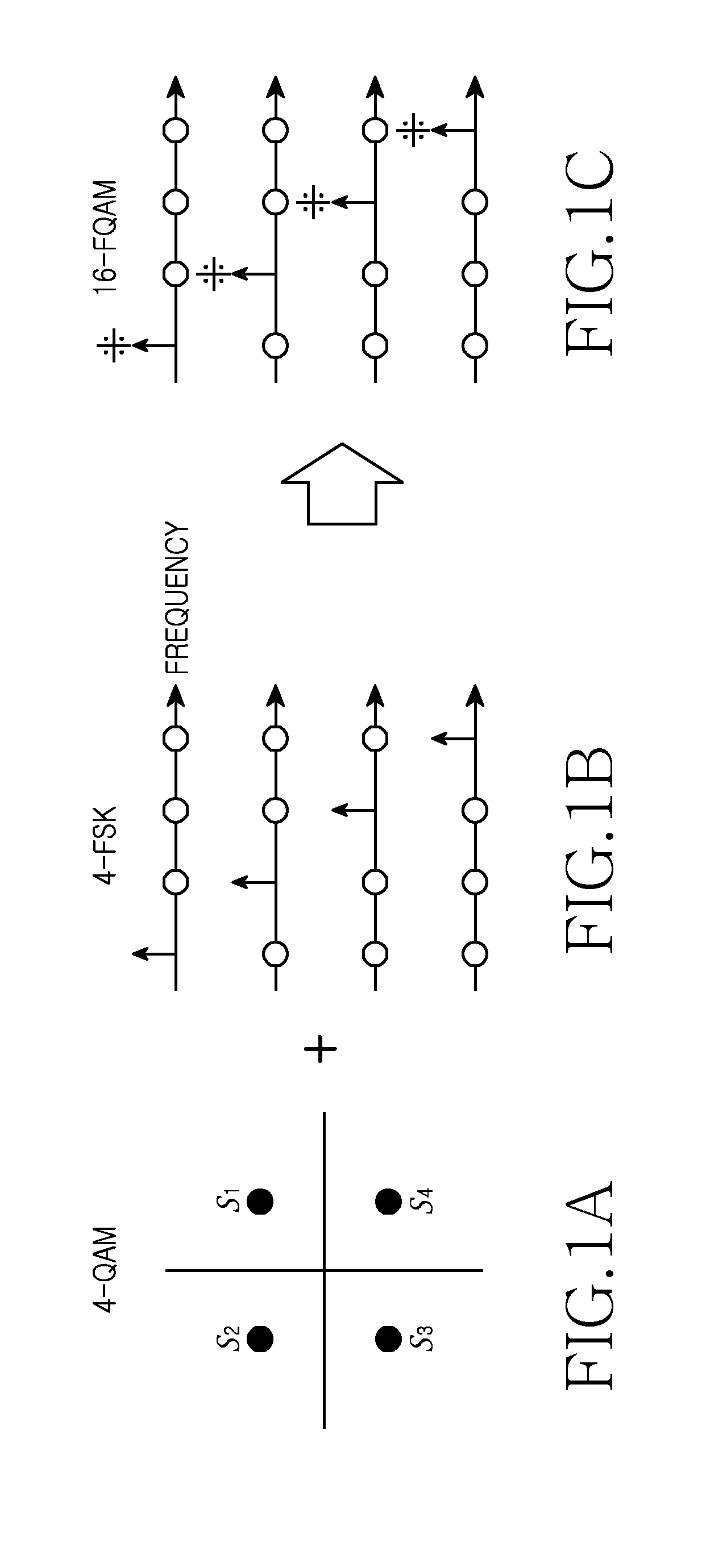
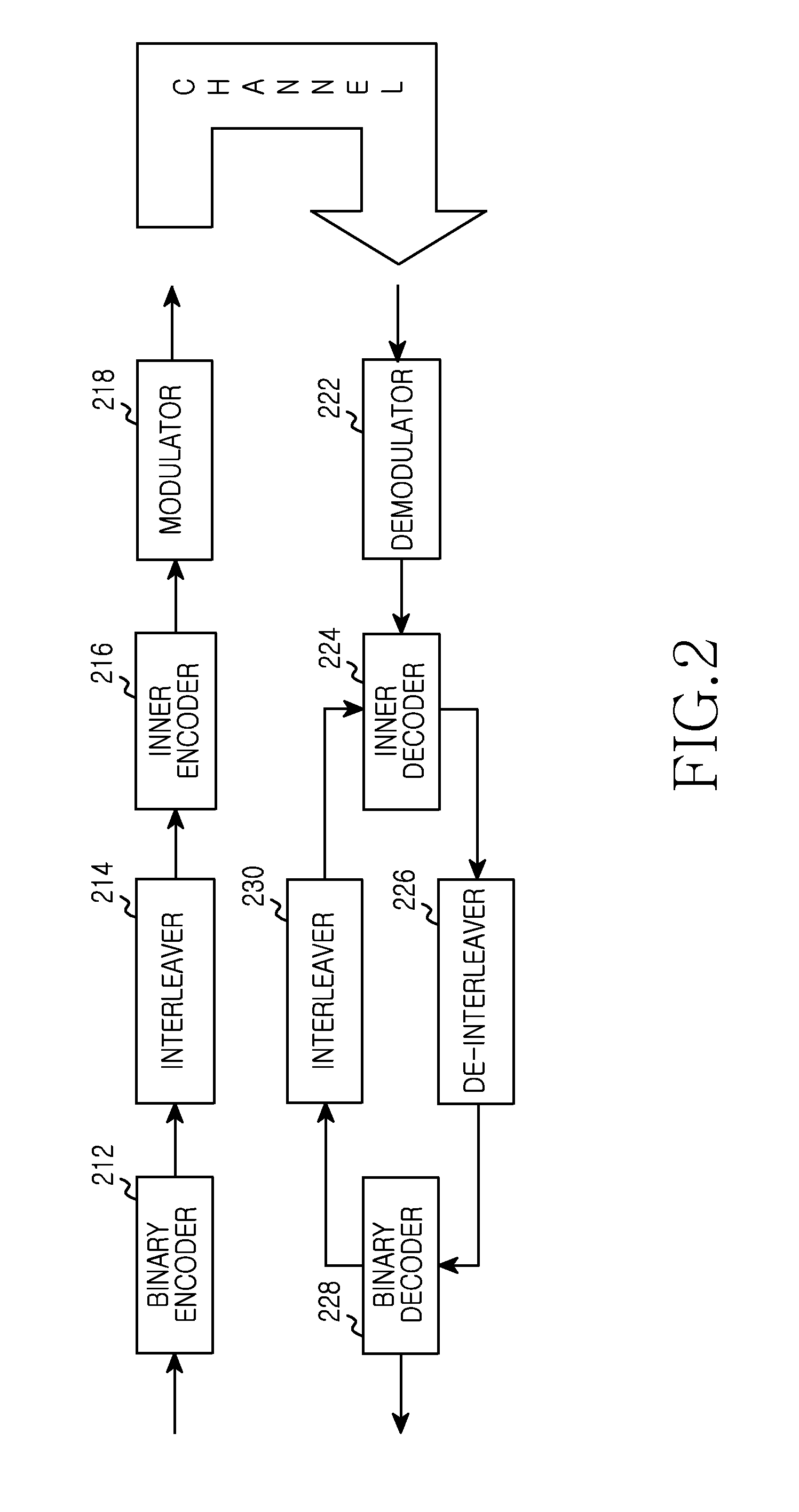
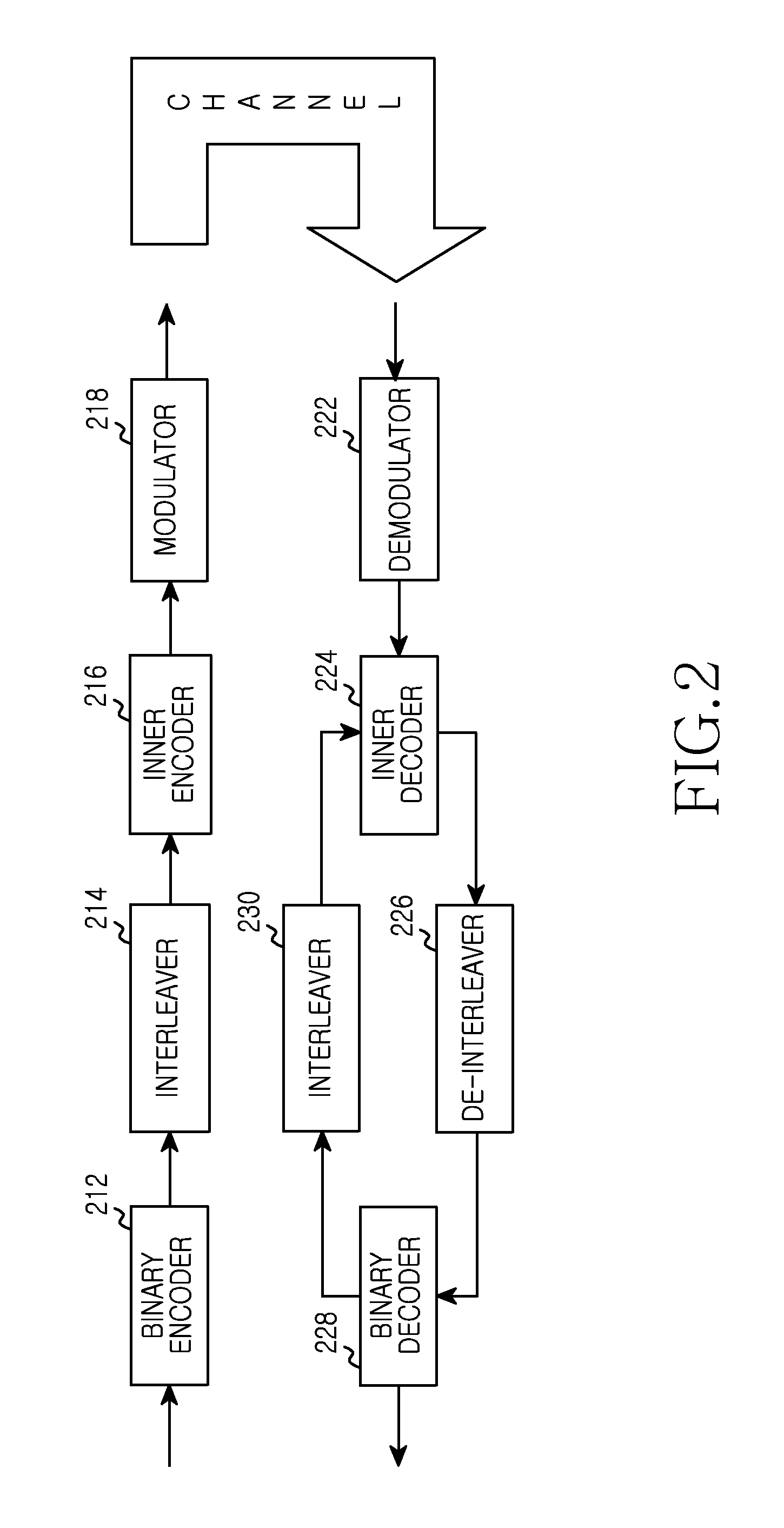
Apparatus and method for adaptively selecting channel code based on non-gaussianity of channel in wireless communication system
InactiveUS20150222472A1Efficient executionError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorError correction/detection using concatenated codesCommunications systemNon-Gaussianity
A method and apparatus are provided for adaptive channel code selection according to a non-Gaussianity of a channel in a wireless communication system. A method includes receiving channel feedback information from a receiving node; selecting, based on the channel feedback information, a channel code among a plurality of channels code having different degree distributions of repetition codes; and encoding transmission data based on the selected channel code.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
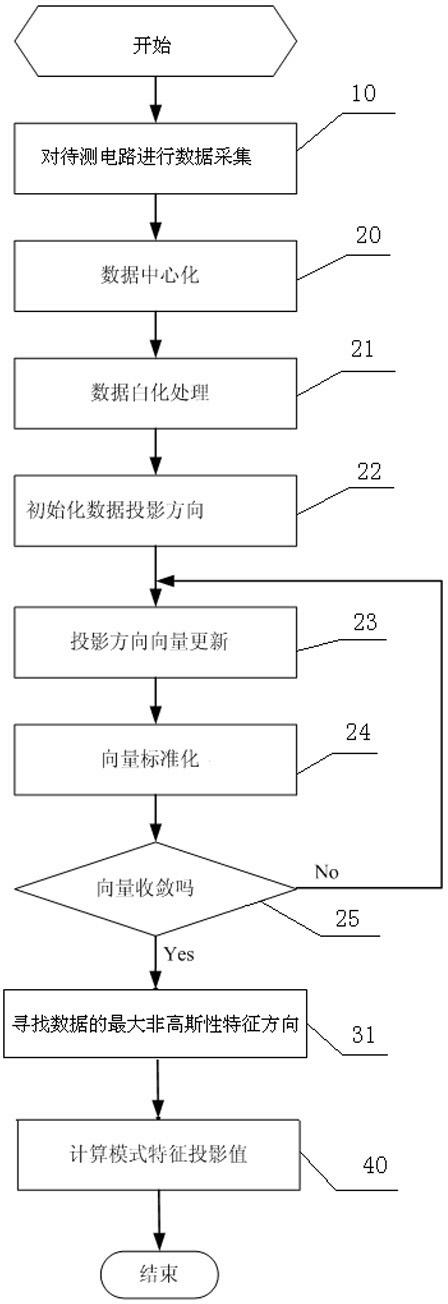
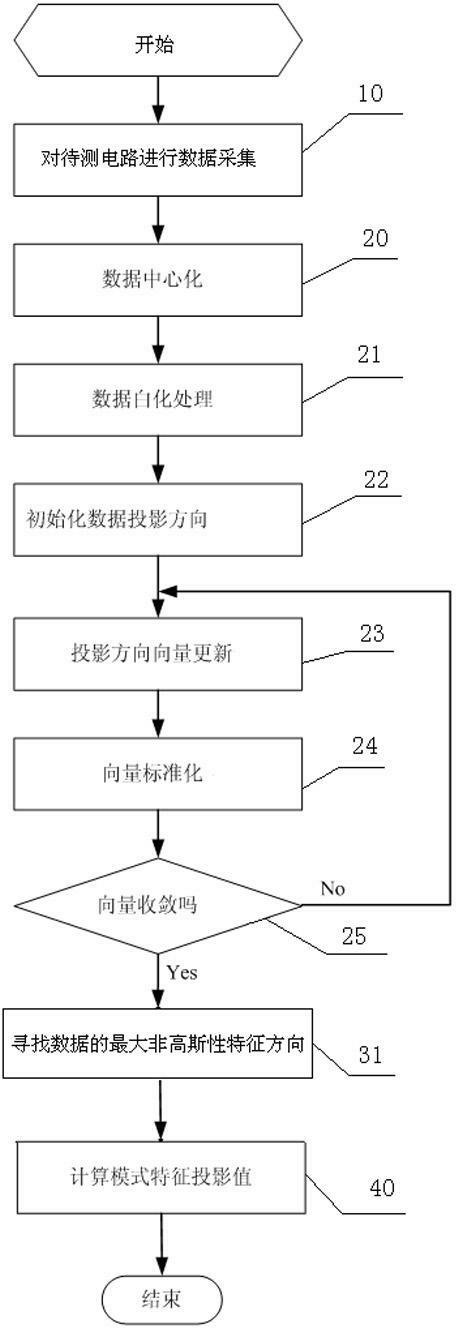
Analog circuit failure diagnosing method
InactiveCN102323535AEasy to implementReduce false positive rateAnalog circuit testingProperty distributionSystems design
The invention discloses an analog circuit failure diagnosing method which comprises the following steps of: 1, acquiring data, i.e., acquiring test variables, acquiring voltage or current variables at two or more testable nodes of a circuit to be tested; 2, testing that a maximum information entropy of the variables approaches a characteristic direction vector; 3, searching a maximum non Gaussian property characteristic direction vector of the test variables; and 4, calculating projection values of the test variables at the maximum non guassian property characteristic direction vector. The invention has the advantages of simpleness in realization and low false rate, solves the problem of performance reduction or failure of a system designed by observation variables on the basis of Gaussian property assumption, and is especially suitable for non Gaussian property distribution conditions.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Wireless communication system frequency spectrum sensing method based on non-gaussianity measure
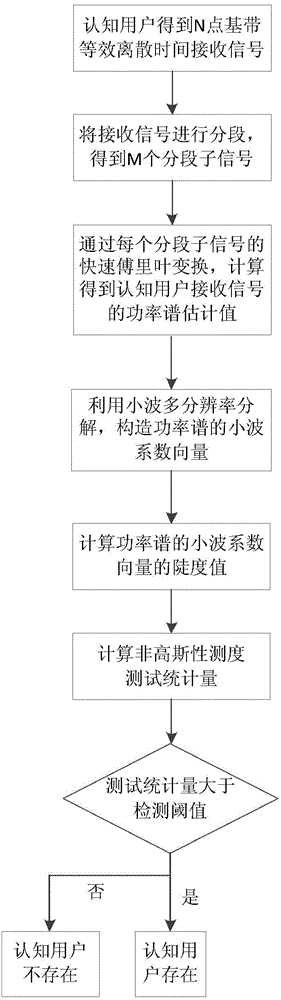
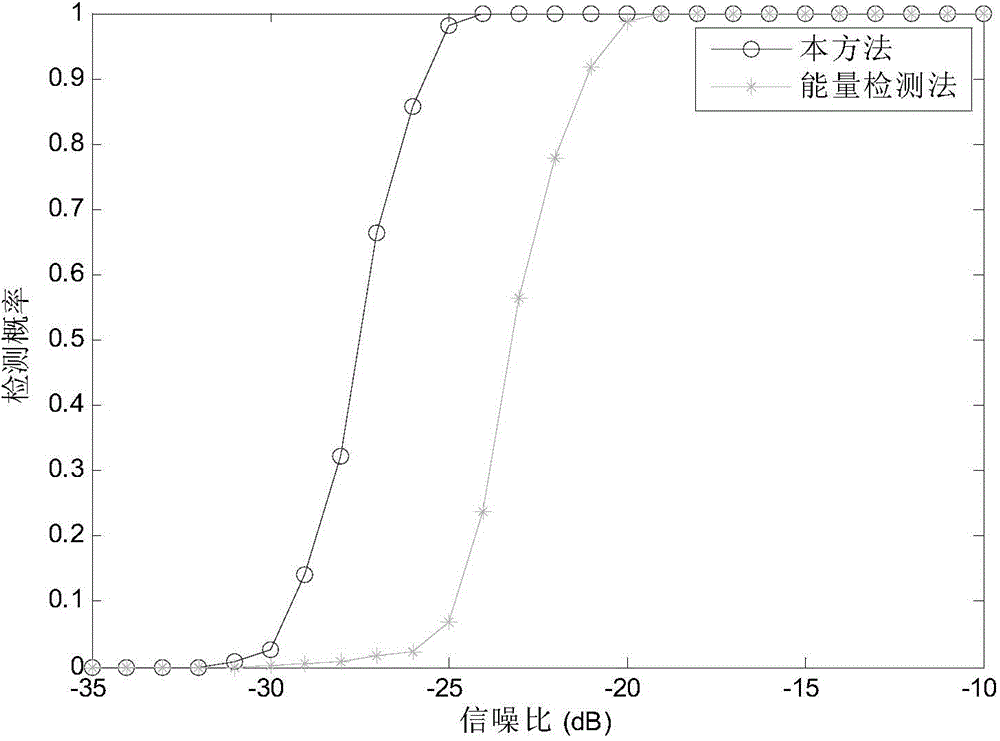
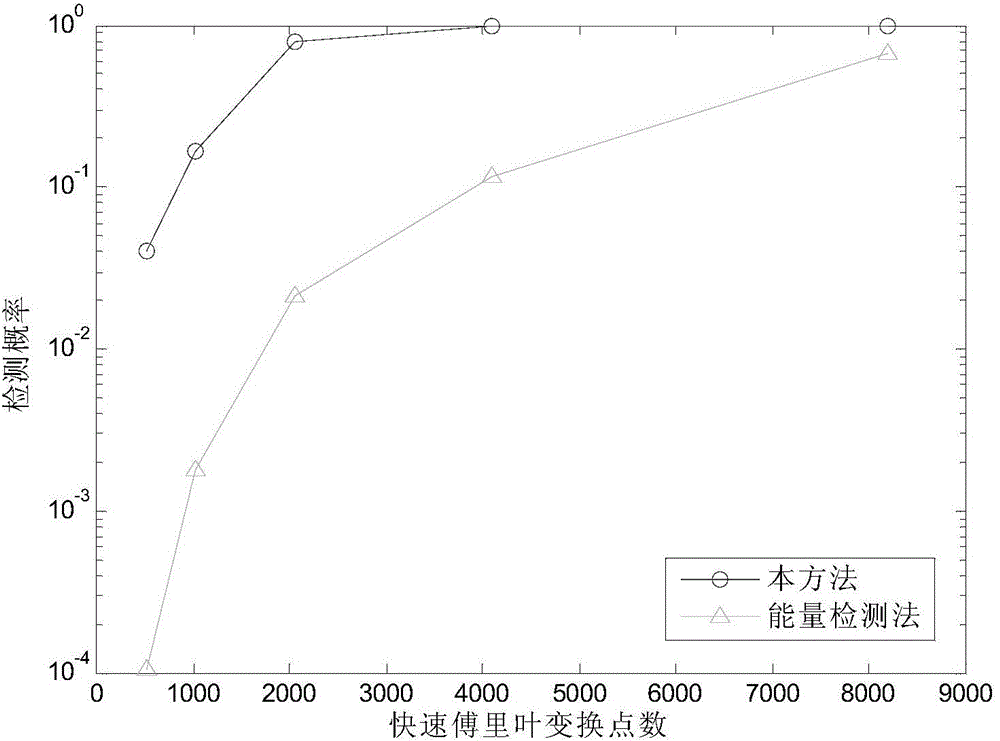
ActiveCN104363065AImplement Spectrum DetectionEfficient detectionTransmission monitoringCognitive userFrequency spectrum
The invention provides a wireless communication system frequency spectrum sensing method based on non-gaussianity measure, and relates to the technical field of frequency spectrum sensing. The method includes the specific steps that a corresponding base-band equivalent discrete-time signal is obtained by means of a wireless signal received by a cognitive user antenna and is sectioned, so that sectional sub signals are obtained; fast fourier transform is carried out on the sectional sub signals, and a power spectrum of the received signal is obtained through calculation; by means of a harr wavelet function, two-layer wavelet multi-resolution decomposition is carried out on the power spectrum of the signal received by the cognitive user and a wavelet coefficient vector of the power spectrum of the received signal is constructed and obtained; then a steepness value of the wavelet coefficient vector is calculated; a non-gaussianity measure testing statistical magnitude of the wavelet coefficient vector of the power spectrum of the received signal is obtained through calculation; the test statistical magnitude is compared with a detection threshold value, if the test statistical magnitude is larger than the detection threshold value, it is indicated that an authorized user signal exists and otherwise, it is indicated that an authorized user does not exist. According to the method, known noise statistic information is not needed, good frequency spectrum sensing performance is attained while a low signal-to-noise ratio is achieved, and a small-scale small-power wireless communication device can be effectively detected.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Nonlinear system state deviation evolution method based on differential algebra and Gaussian sum
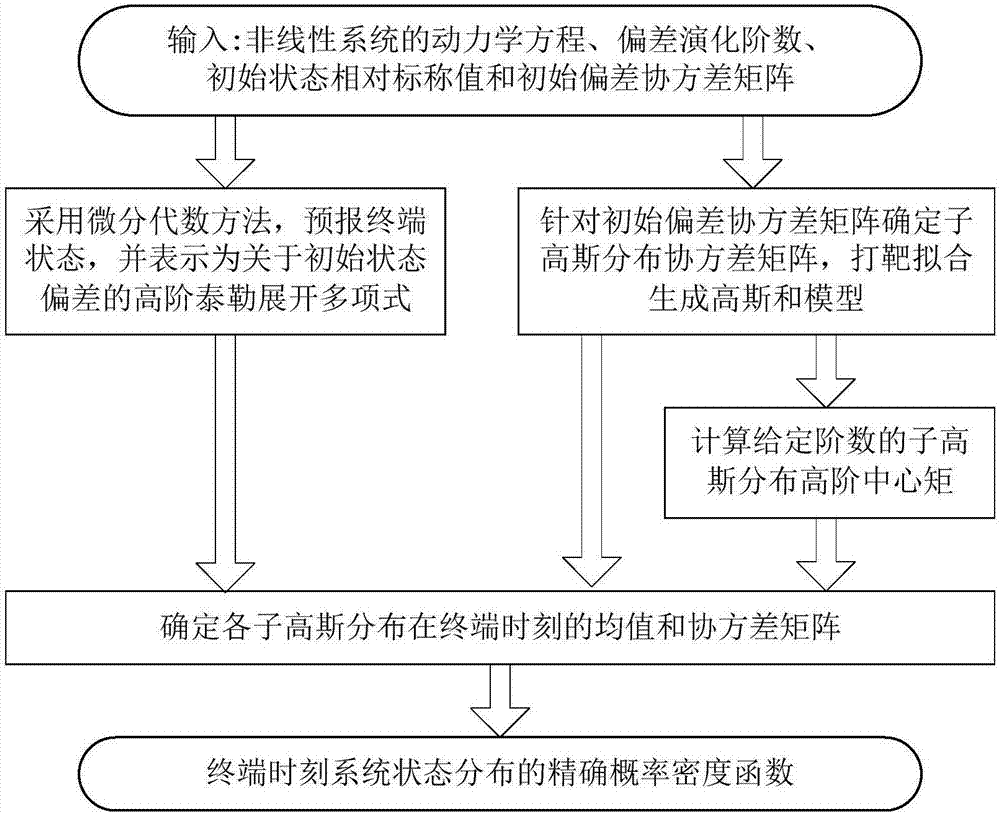
ActiveCN107402903AImprove calculation accuracyEasy to useComplex mathematical operationsNormal densityAnalytical problem
The invention discloses a nonlinear system state deviation evolution method based on differential algebra and Gaussian sum. The method includes forecasting the terminal state of a nonlinear system according to a differential algebra method, and representing it as a high-order Taylor expansion polynomial related to original-state deviation; determining a sub Gaussian distribution covariance matrix, and fitting a Gaussian sum model for each sub Gaussian distribution through shooting; calculating the high-order central moment of the sub Gaussian distributions; determining the mean value and the covariance matrix of each sub Gaussian distribution at the terminal moment, and providing a terminal-state deviation distribution probability density function in the form of the Gaussian sum. The method can be extended to any designated-order deviation evolution accuracy automatically, manual derivation of high-order partial derivatives of kinetic equations is not needed, the method is applicable to long-term forecasted nonlinear system deviation evolution analysis problems with high nonlinearity, the remarkable efficiency advantages of the method can be still maintained as compared to the Monte Carlo simulation method while deviation distribution and non-Gaussianity thereof are described accurately, and accordingly, the method has the advantages of convenience in use and high calculation accuracy.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Dynamic non-Gaussian structure monitoring data exception identification method
InactiveCN106897509ADesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsStatistical correlationPre whitening
The invention belongs to the field of civil engineering structure health monitoring, and provides a dynamic non-Gaussian structure monitoring data exception identification method. The method comprises the steps of firstly, defining past and current observation vectors for monitoring data, and performing pre-whitening on the past and current observation vectors; secondly, building a statistical correlation model for the whitened past and current observation vectors, and obtaining dynamic whitened data; thirdly, dividing the dynamic whitened data into a system-related part and a system-unrelated part, and performing independent component analysis modeling on the system-related part and the system-unrelated part; and finally, defining two statistical quantities, determining control limits of the two statistical quantities, and when the statistical quantities exceed the control limits, judging whether an exception exists in the monitoring data. The non-Gaussianity and the dynamic characteristic of the structure monitoring data are considered at the same time, so that the exception in the data can be effectively identified based on the defined statistical quantities.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Device fault detection method based on acoustic features
InactiveCN110310667AAccurate judgmentEasy to useSpeech analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionFrequency spectrumSignal classification
The invention discloses a device fault detection method based on acoustic features, and relates to the technical field of fault detection. An interference sound separation calculation method comprisesthe following steps: S11, taking kurtosis as measure of signal nongaussianity. According to the device fault detection method based on the acoustic features, a sound of a power transformation devicein working is collected through a microphone array; independent source sound signals are extracted by an interference sound separation technology based on negative entropy independent component analysis; dimensionality reduction processing is performed on sound data based on two-dimensional principal component analysis to extract main frequency spectrum feature information; the sound signals are classified based on a multi-value decision diagram to realize fault diagnosis; and finally the power device fault location based on weighted multi-signal classification is performed. The purpose of real-time on-line fault detection is achieved; the device fault type and information can be judged accurately and timely; and while the working efficiency is improved, the use by a user is facilitated.
Owner:莫毓昌
Intermittent process fault monitoring method based on fourth-order moment singular value decomposition
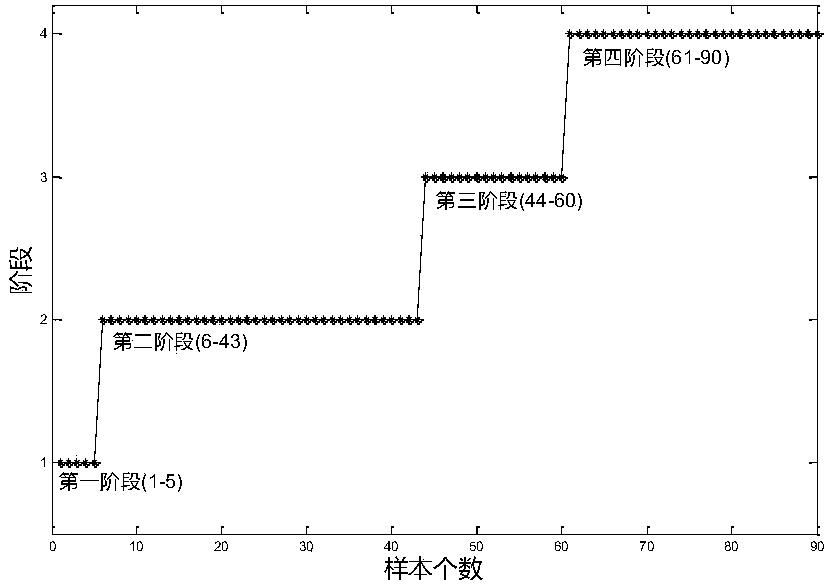
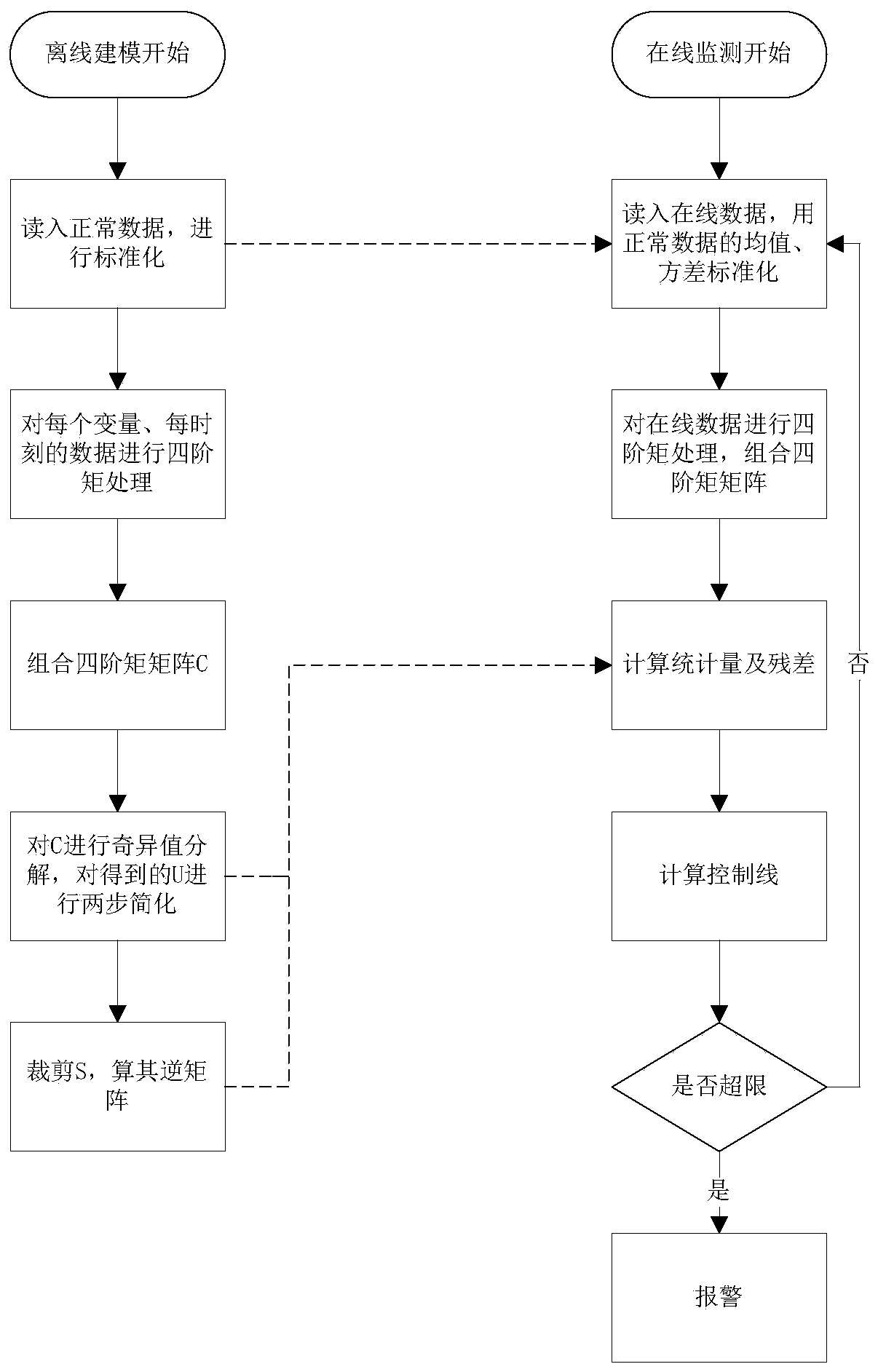
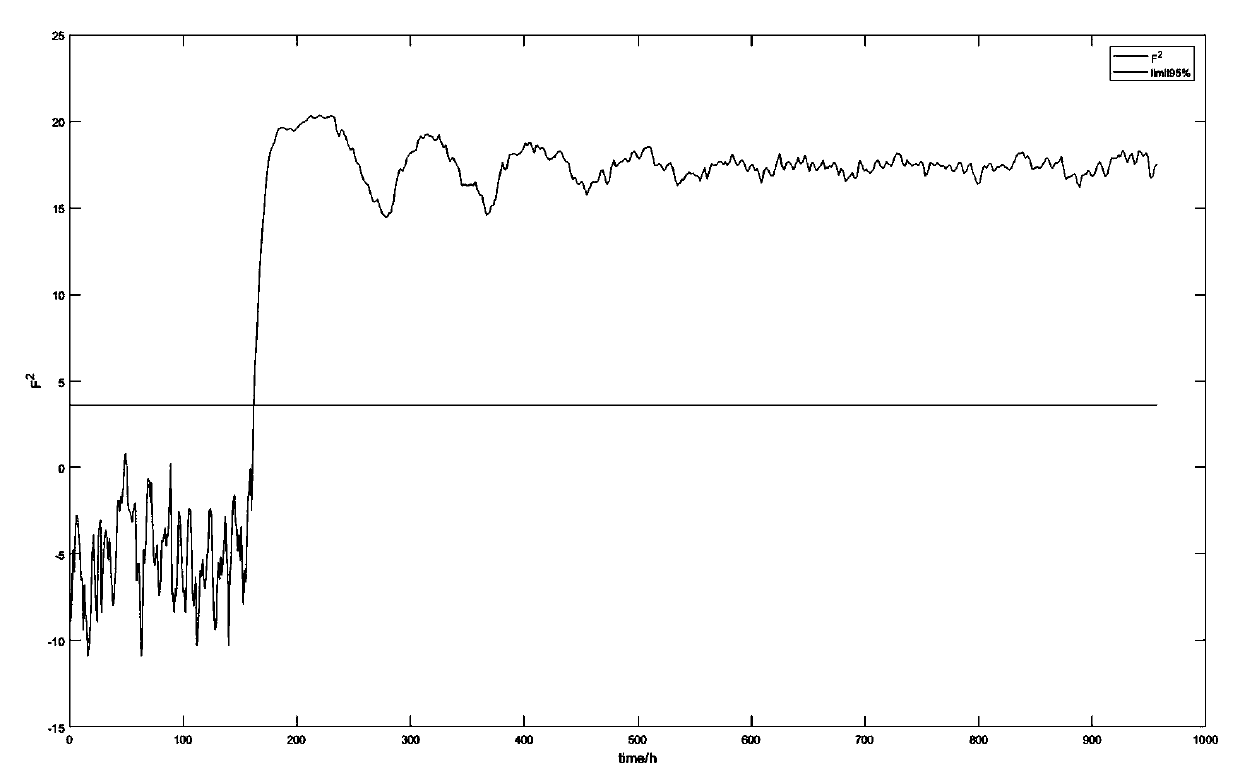
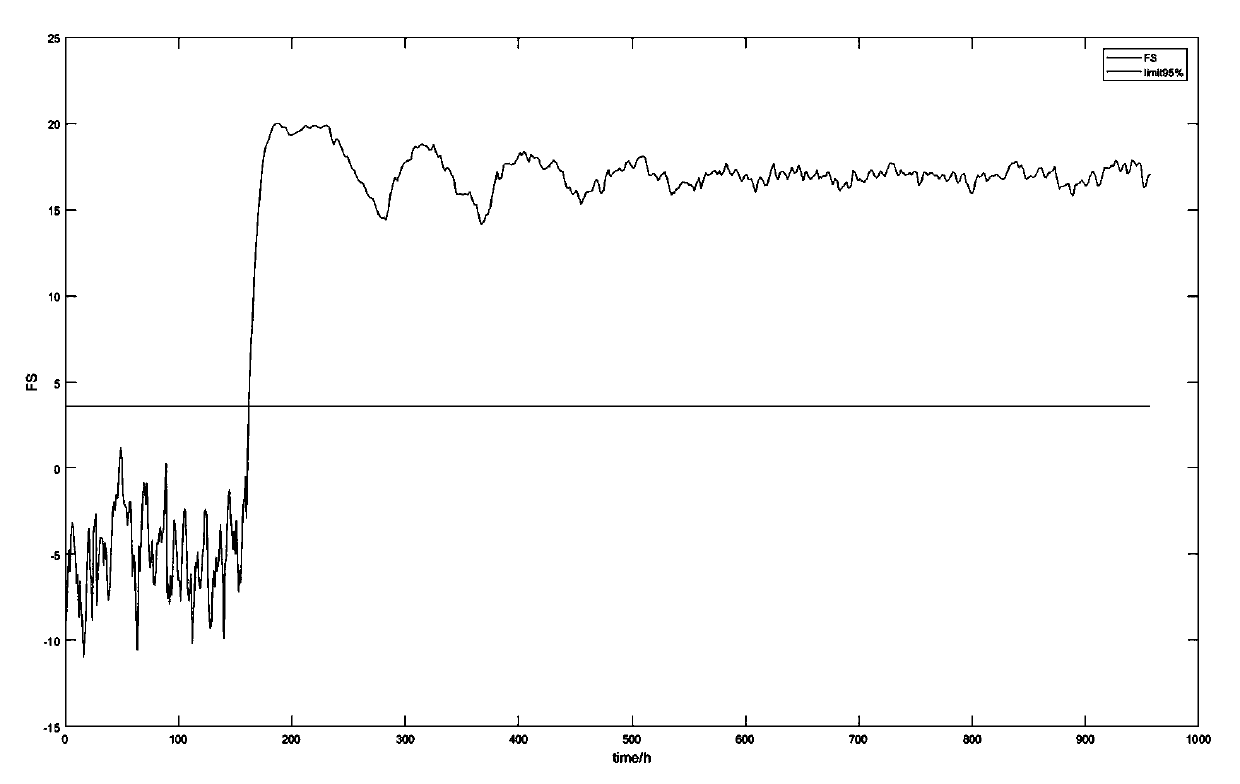
ActiveCN110297475AFully consider non-linearityFully consider the non-GaussianDesign optimisation/simulationTotal factory controlSingular value decompositionGeneration process
The invention discloses an intermittent process fault monitoring method based on fourth-order moment singular value decomposition, and is used for solving data nonlinearity and non-Gaussianity broughtby nonlinearity in an intermittent process. The method comprises two stages of "offline modeling" and "online monitoring", wherein the stage of "offline modeling" comprises the following steps that:firstly, carrying out data standardization, carrying out fourth-order moment processing, and combining fourth-order moment matrixes; and then, carrying out singular value decomposition, and simplifying the obtained matrix to make a preparation for monitoring. The stage of "online monitoring" comprises the following steps that: carrying out standardization on online data, carrying out fourth-ordermoment processing, and combining the fourth-order moment matrixes; and then, calculating a statistical amount, a residual error and a corresponding control line; and finally, using the statistical amount to monitor a generation process, and giving an alarm when faults appear. The method fully considers the nonlinearity and the non-Gaussianity of the data of the intermittent process, reduces the false alarm rate of a normal stage, reduces the false alarm rate of a fault stage, quickens response speed and has a high practical value.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
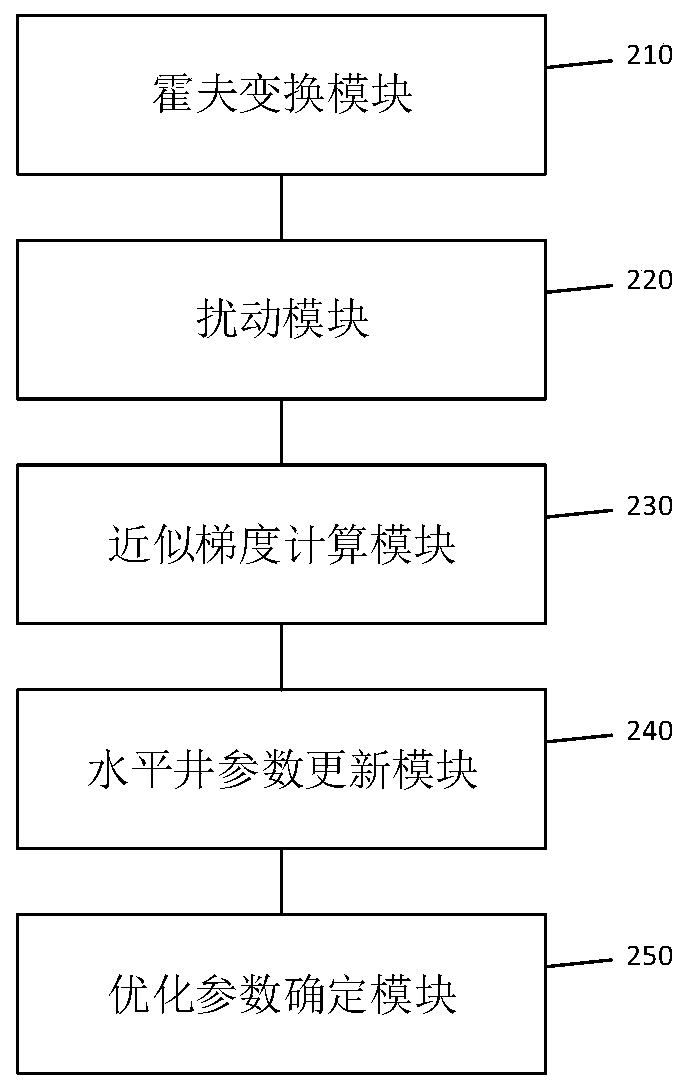
Horizontal well parameter optimization method and device
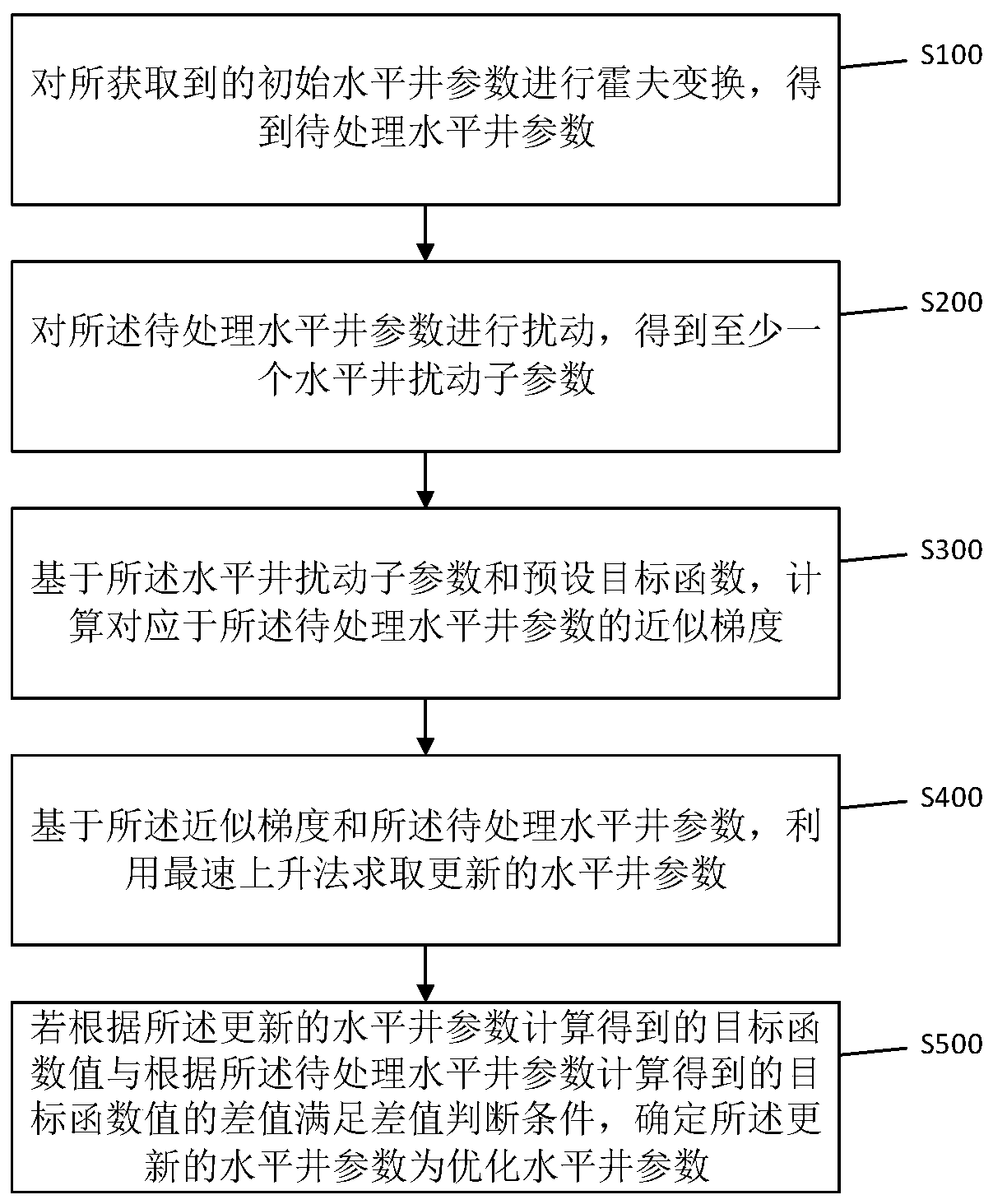
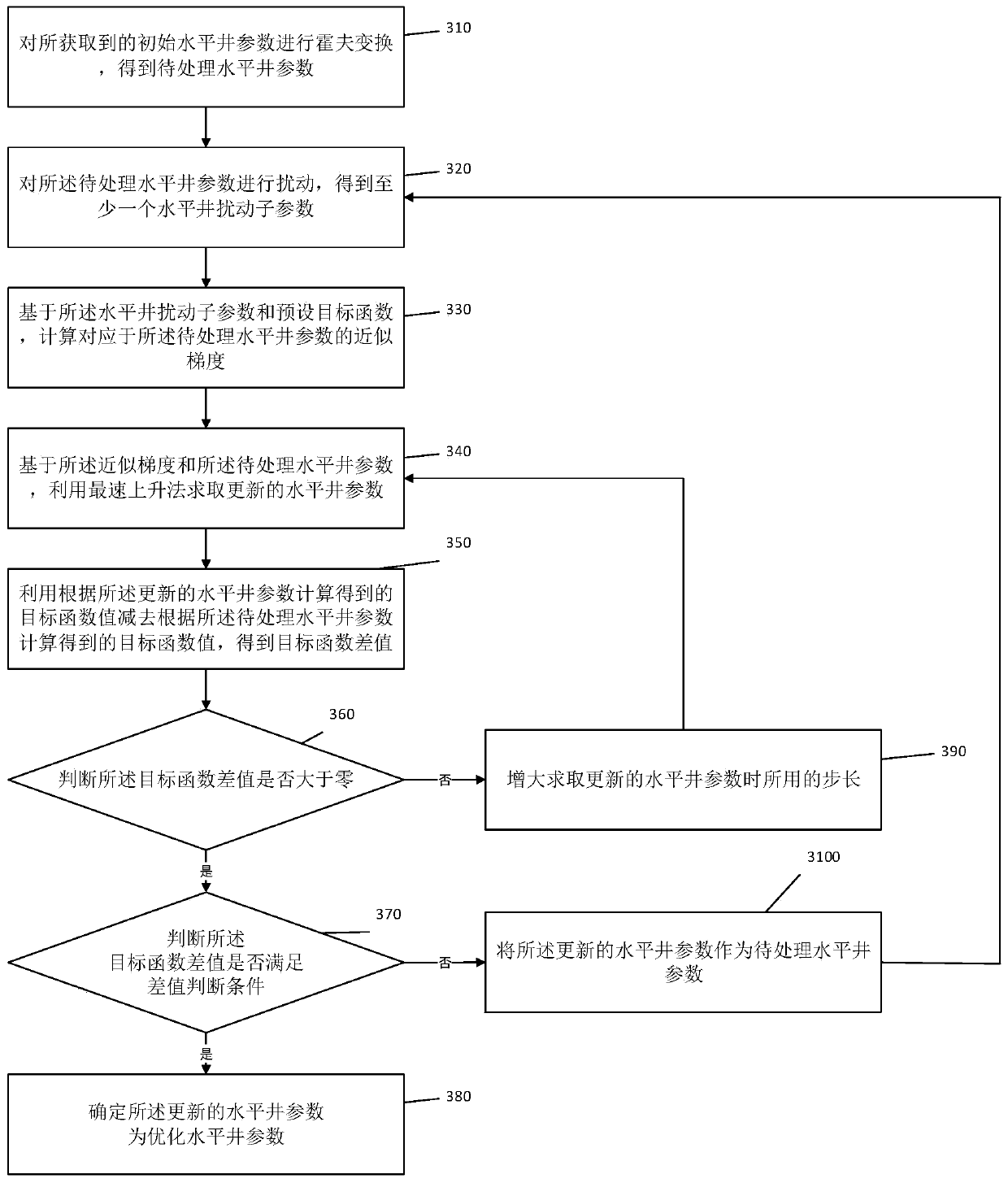
ActiveCN110490241AEasy to calculateIncrease production capacityData processing applicationsFluid removalHough transformNon-Gaussianity
The embodiment of the invention provides a horizontal well parameter optimization method and device. The method comprises: performing Hough transform on obtained initial horizontal well parameters, and obtaining horizontal well parameters to be processed; disturbing the to-be-processed horizontal well parameters to obtain at least one horizontal well disturbance sub-parameter; calculating an approximate gradient corresponding to the to-be-processed horizontal well parameter based on the horizontal well disturbance sub-parameter and a preset target function; solving updated horizontal well parameters based on the approximate gradient and the to-be-processed horizontal well parameters; and if the difference value between the target function value calculated according to the updated horizontal well parameter and the target function value calculated according to the horizontal well parameter to be processed meets the difference value judgment condition, determining the updated horizontal well parameter as an optimized horizontal well parameter. Through the embodiment of the invention, when the horizontal well parameters are optimized, the interference of the non-Gaussian property of the parameters on the calculation process can be overcome, and the horizontal well parameters can be conveniently and accurately optimized.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Apparatus and method for adaptively selecting channel code based on non-gaussianity of channel in wireless communication system
ActiveUS9036735B1Efficient executionError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorError correction/detection using concatenated codesCommunications systemNon-Gaussianity
A method and apparatus are provided for adaptive channel code selection according to a non-Gaussianity of a channel in a wireless communication system. A method includes, if a non-Gaussianity of the channel falls within a first range, encoding transmission data using a first channel code; and if the non-Gaussianity of the channel falls within a second range, encoding the transmission data using a second channel code. The first channel code and the second channel code have different degree distributions of repetition codes.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Seismic signal processing method based on improved FastICA algorithm
PendingCN107942376AReduce sensitivityFast convergenceSeismic signal processingAlgorithmNon-Gaussianity
The invention discloses a seismic signal processing method and corresponding processing system based on an improved FastICA algorithm. Through maximizing a negative entropy object function, a non-Gaussian maximum value required by observing signal linear projection is searched by using a fixed point iteration theory so as to fulfill an aim of separating signals; an iteration function is correctedby introducing correction factors improved by utilizing a gradient method, and the FastICA algorithm is optimized. According to the improved FastICA algorithm, the sensibility to an initial weight value is reduced, and the iteration times are reduced, so that the convergence speed of the algorithm is improved.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
A real-time learning soft-sensing modeling method for a butanizer based on a Gaussian mixture model
InactiveCN103927412BImprove forecast accuracyFully extractedSpecial data processing applicationsNon-GaussianityMahalanobis distance
The invention discloses a real-time learning debutanizer soft measurement modeling method on the basis of Gaussian mixture models (GMM). The real-time learning debutanizer soft measurement modeling method includes training process Gaussian mixture models to acquire various Gaussian component parameters and building corresponding sub-models; computing posterior probabilities of to-be-predicted samples and local Mahalanobis distances of various Gaussian components by a Bayesian process so as to obtain weighted sample similarity definition indexes; reasonably selecting similar samples by the aid of the new similarity indexes for local modeling. The posterior probabilities indicate whether the to-be-predicted samples belong to the various Gaussian components or not. The real-time learning debutanizer soft measurement modeling method has the advantages that problems of process non-Gaussianity and nonlinearity can be effectively solved, characteristics of the to-be-predicted samples can be sufficiently extracted, the similar samples can be reasonably selected for real-time learning modeling, and accordingly the real-time learning debutanizer soft measurement modeling method is favorable for improving the model prediction precision.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Low-rise building enclosure member wind disaster loss analysis method considering typhoon duration effect
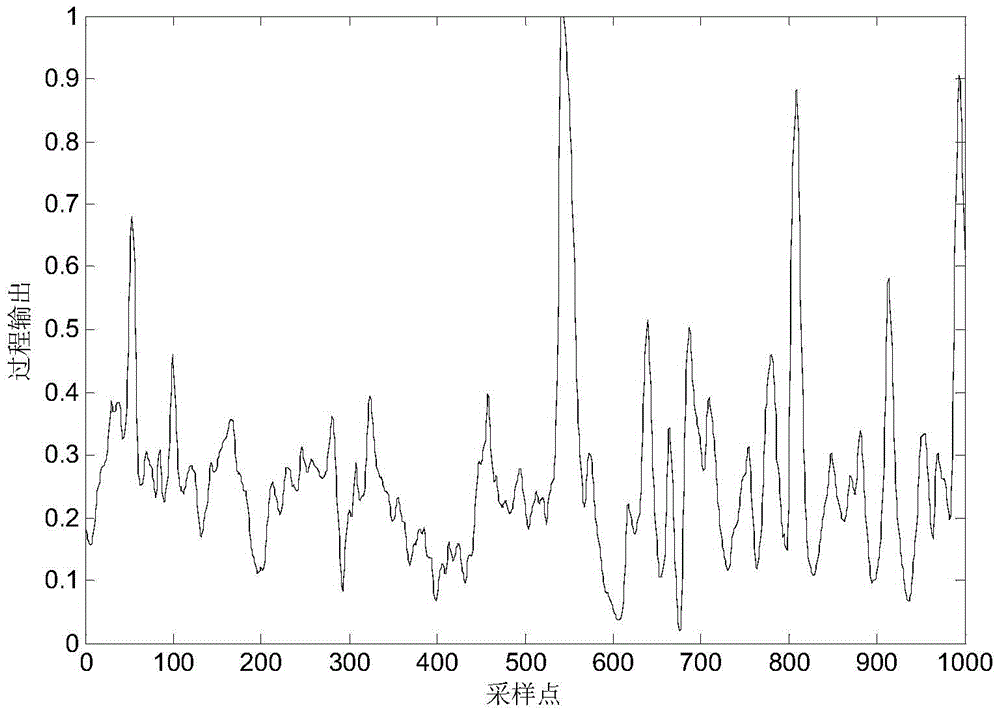
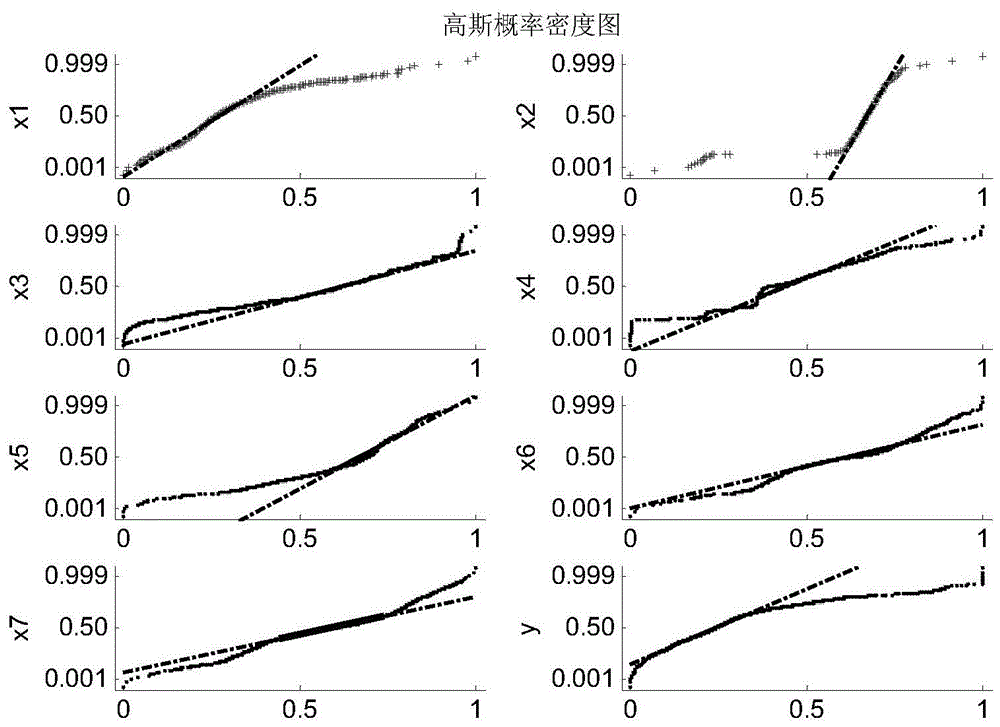
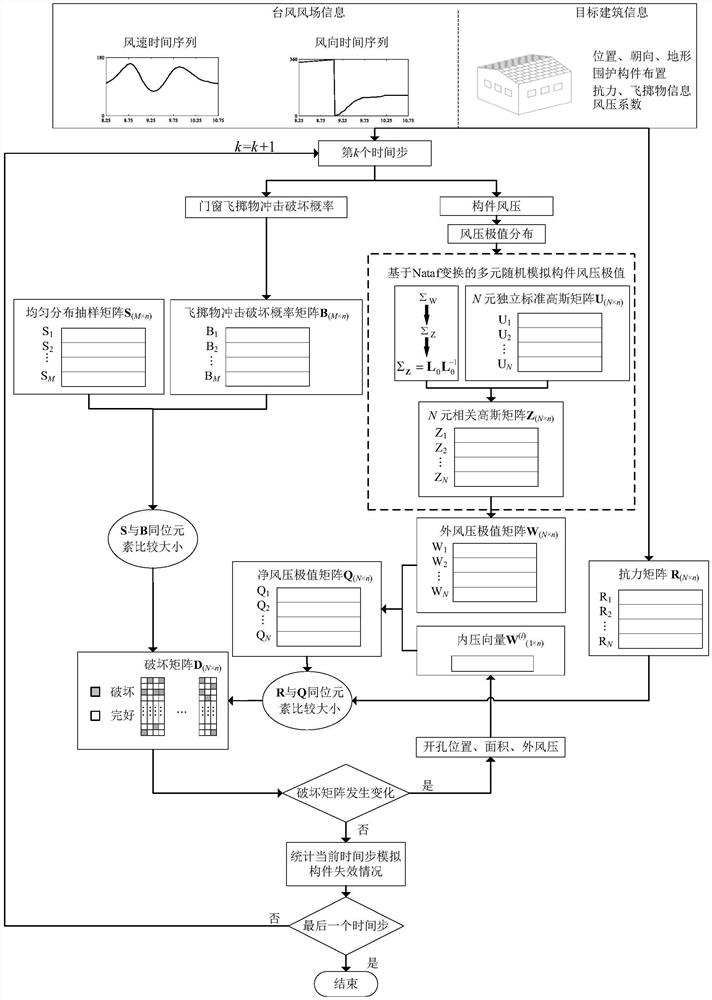
PendingCN113408932APractical assessmentResourcesComplex mathematical operationsArchitectural engineeringNon-Gaussianity
The invention discloses a low-rise building enclosure member wind disaster loss analysis method considering a typhoon duration effect. The method is used for evaluating wind-induced damage of a low-rise building enclosure structure. In the calculation process, determining the internal pressure for the current time step in combination with the house trepanning working condition; comparing the impact force of the throwing object with the impact bearing force of the throwing object to determine the damage to the window caused by the impact of the throwing object; comparing the load extreme value with the pressure bearing capacity to determine enclosure member damage caused by wind pressure; determining a new opening to update the internal pressure; carrying out damage analysis again until no new hole appears; entering the next time step until all the time steps in the typhoon duration are analyzed, and obtaining statistical values of the failure probability and the loss rate of each component in each time step. According to the invention, the time-holding effect of the typhoon is considered, meanwhile, factors such as non-Gaussian property, randomness and spatial correlation of the load of the enclosure component are considered, the loss condition in the typhoon is evaluated more practically, and the calculation efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Causal network inference method based on kurtosis
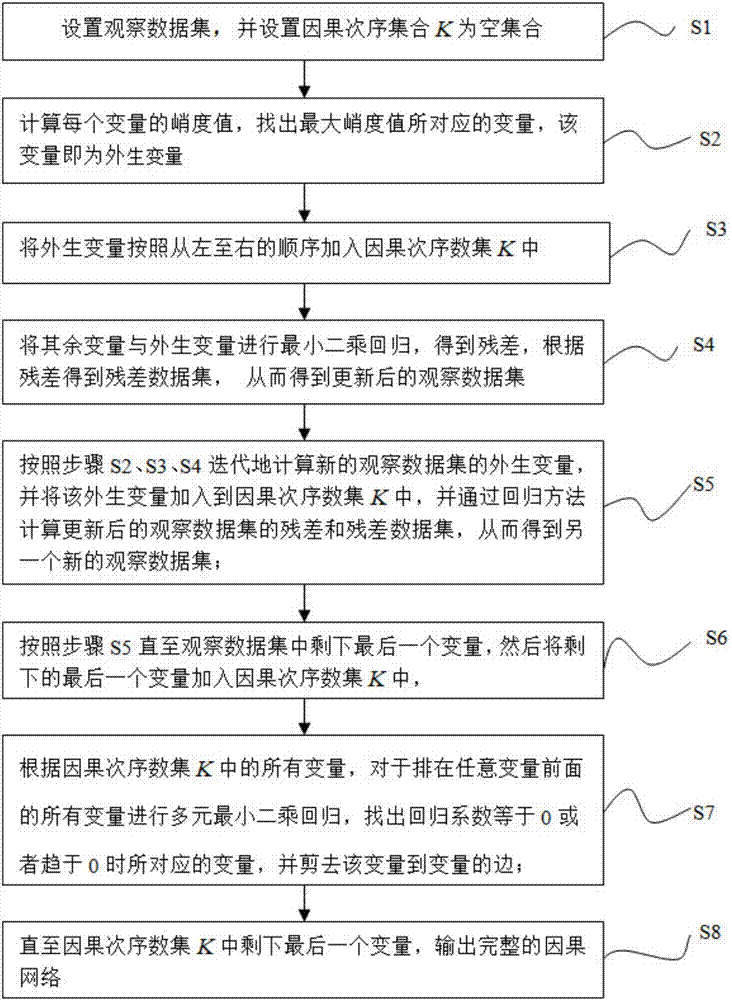
InactiveCN106874433AImprove recognition accuracyImprove recognition rateInference methodsSpecial data processing applicationsCausal orderNon-Gaussianity
The invention relates to a causal network inference method based on kurtosis. The method comprises the steps that exogenous variables are selected based on the kurtosis, a causal order is found layer by layer, and a cutting edge is tested by a cutting edge using the least square method, so that a complete causal network is output. The causal network inference method based on kurtosis is not sensitive to the degree of non-Gaussian of disturbance variables and has strong stability, can still be able to maintain a high recognition rate especially when the non-Gaussian is weak, and has low complexity, kurtosis calculation is needed for each variable itself, the method is a direct estimate way, and the causal network recognition accuracy is high.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Seismic signal Q value estimation method based on non-Gaussianity maximization
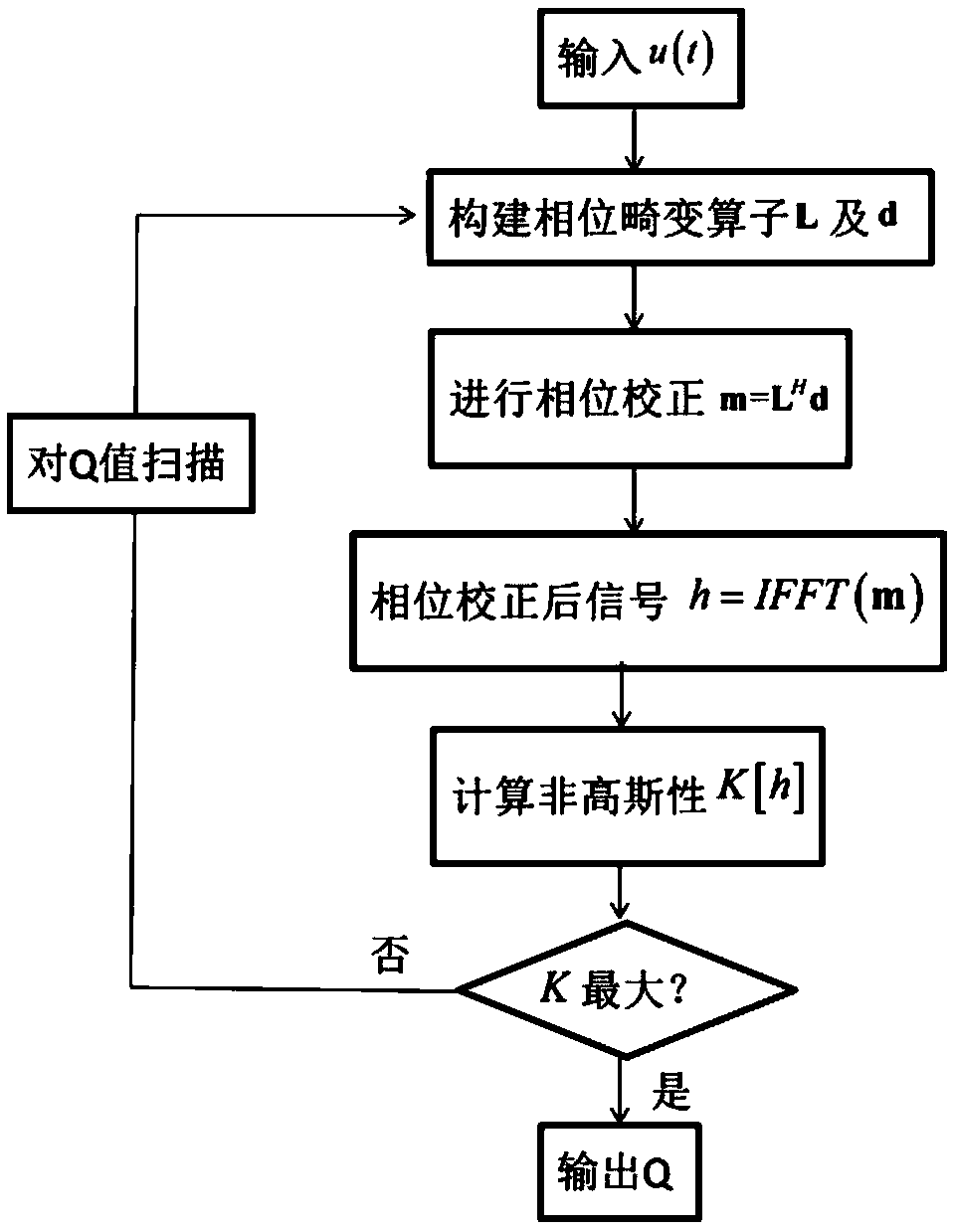
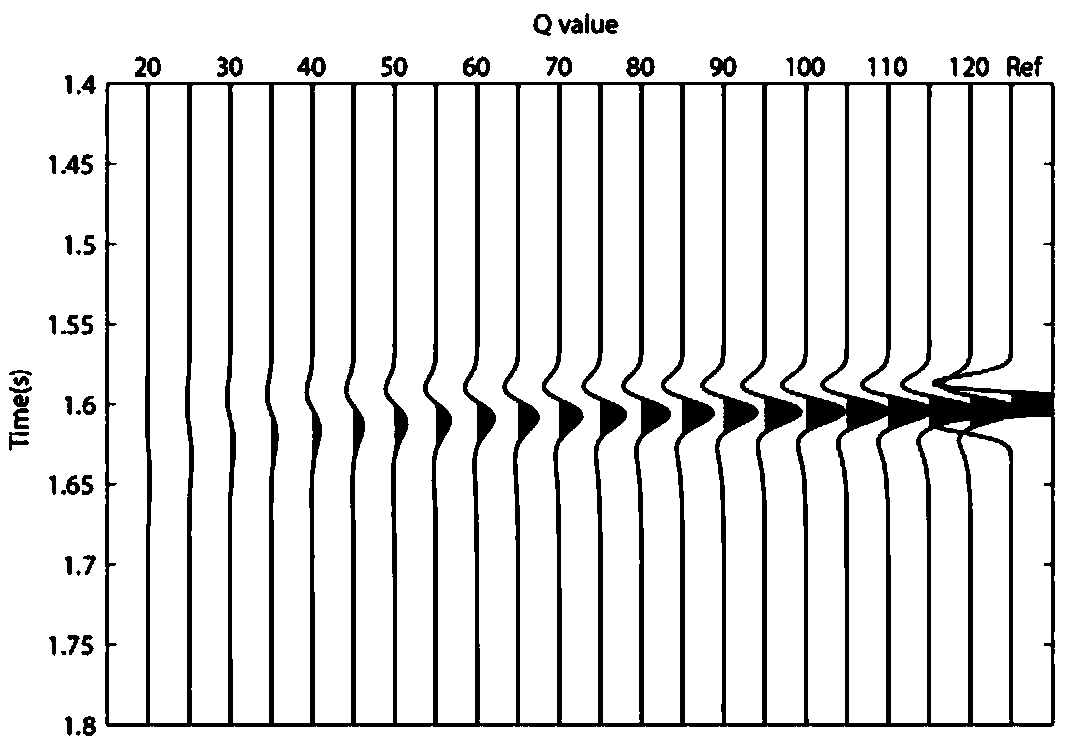
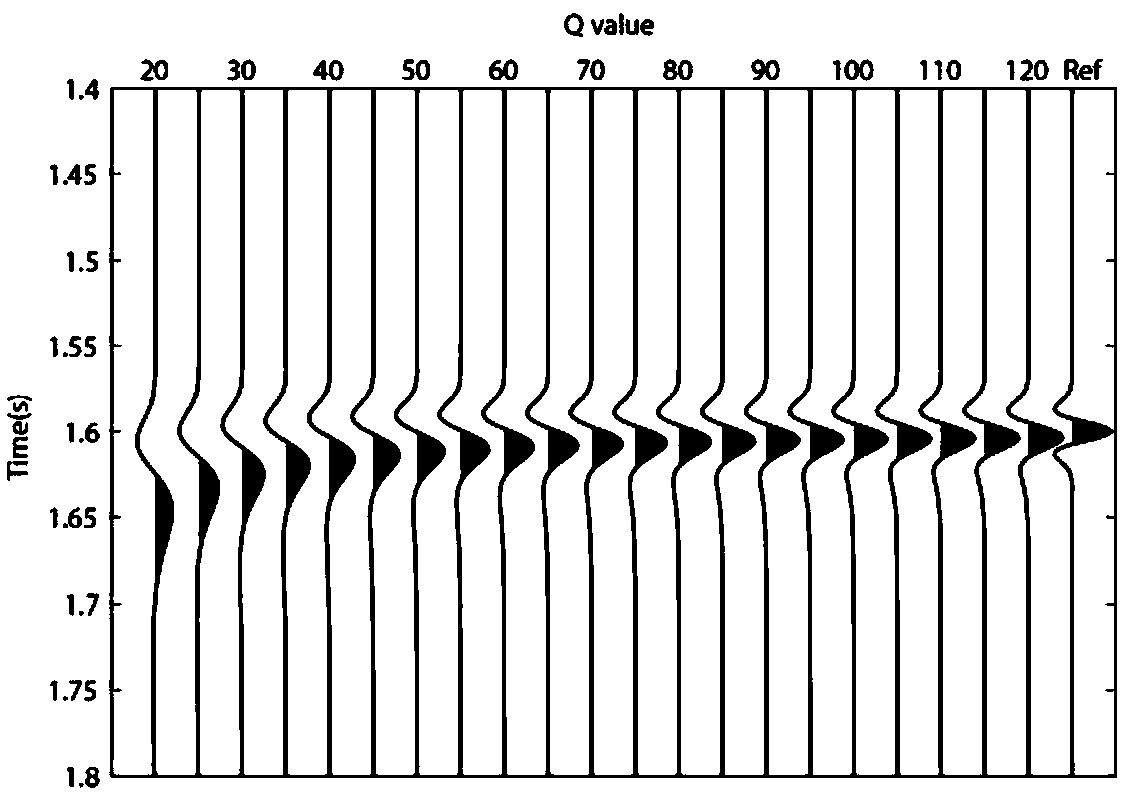
ActiveCN109239774AHas absolute stabilityAvoid instabilitySeismic signal processingNon-GaussianityWavelet
The invention relates to a seismic signal Q value estimation method based on non-Gaussianity maximization. The method comprises the following steps of S1, obtaining a seismic signal, researching a phase distortion process of the seismic signal, and analyzing a relation between the phase distortion signal and the non-Gaussianity; S2, scanning a quality factor Q value of the seismic signal, and performing phase correction; and S3, calculating the non-Gaussianity of the seismic signal after the phase correction, and when the non-Gaussianity is maximized, taking the quality factor Q value at the moment as an estimation result. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that it is not needed to assume a white noise reflection coefficient or extract a reference wavelet, only theQ value scanning needs to be subjected to the phase correction, and the accuracy of the Q value is measured by utilizing the non-Gaussianity maximization; and stable Q value distribution can be obtained, so that high-resolution seismic data processing and interpretation are facilitated.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com