Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
100 results about "Measurement evaluation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
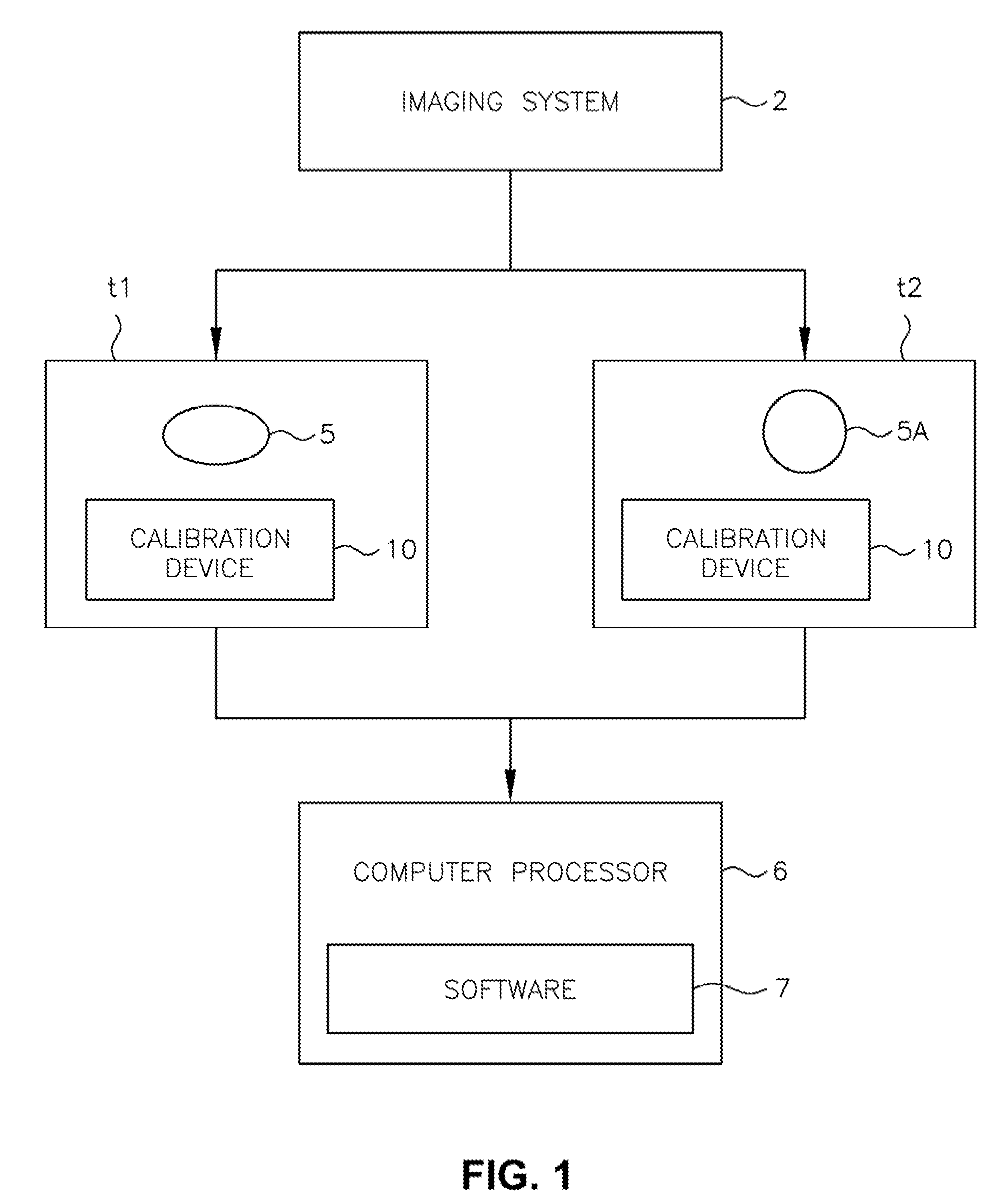
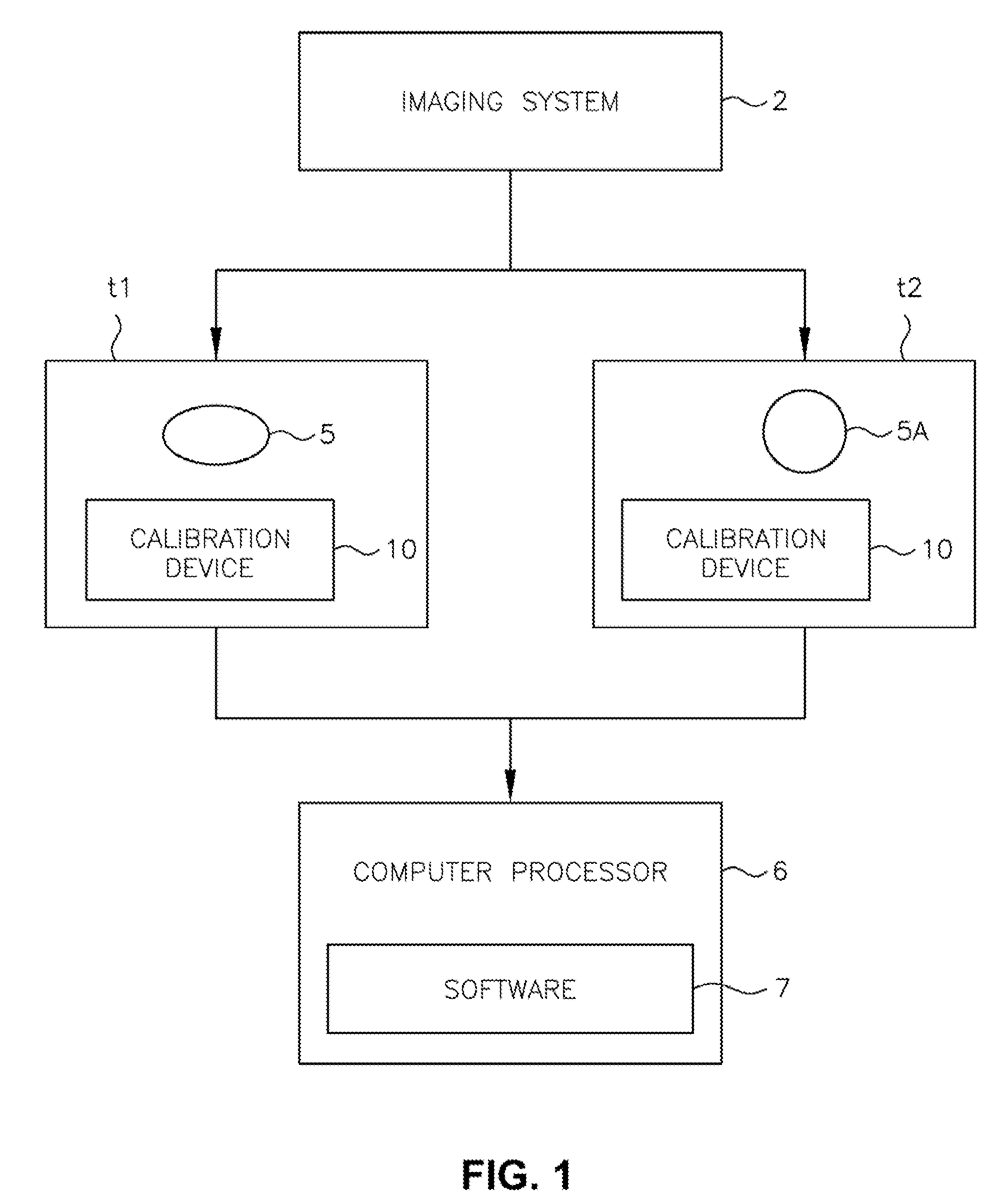
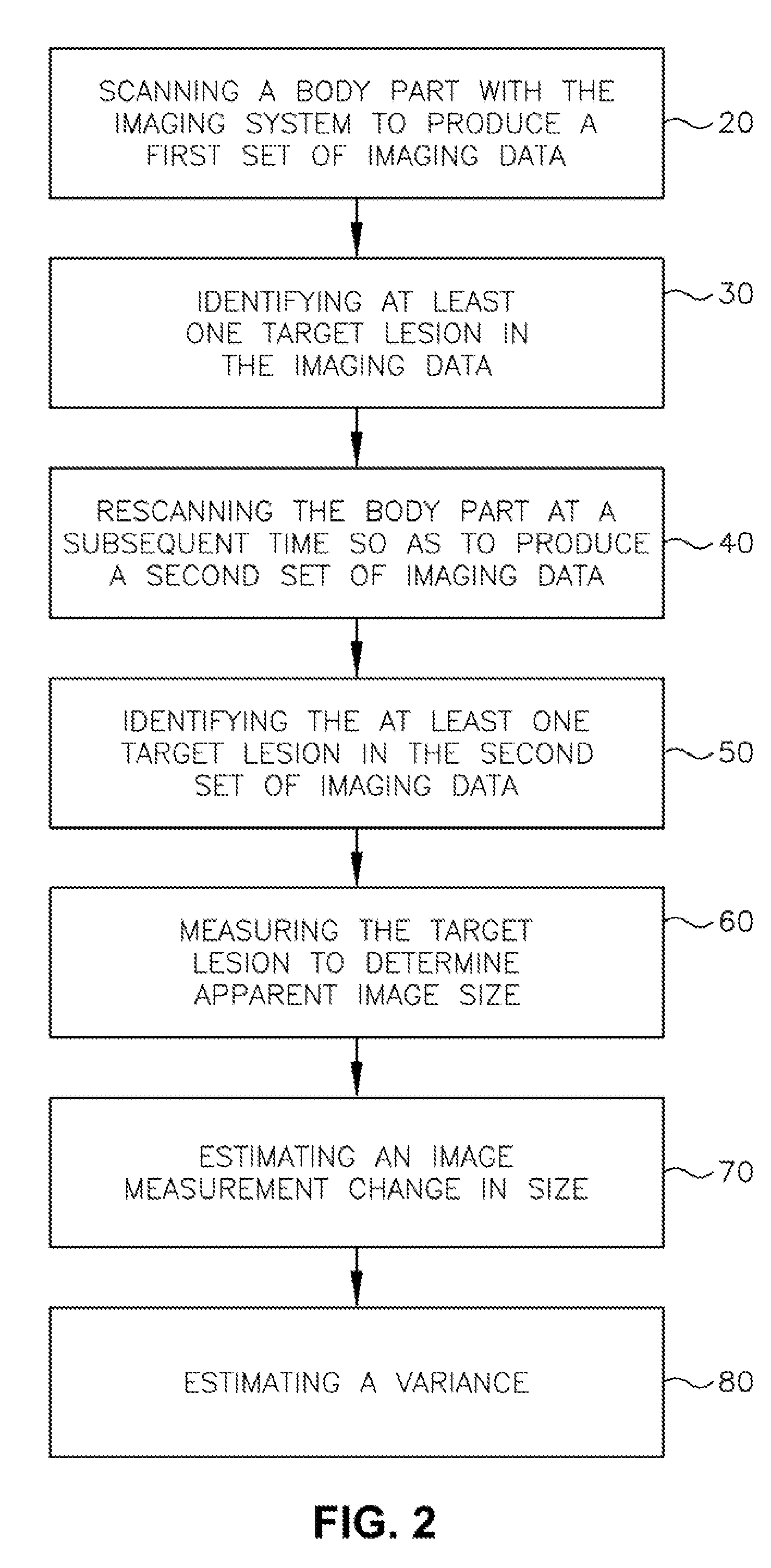
Medical imaging system for accurate measurement evaluation of changes in a target lesion
ActiveUS20070100226A1Shorten the lengthInformation can be usedImage enhancementImage analysisMeasurement evaluationMedical imaging
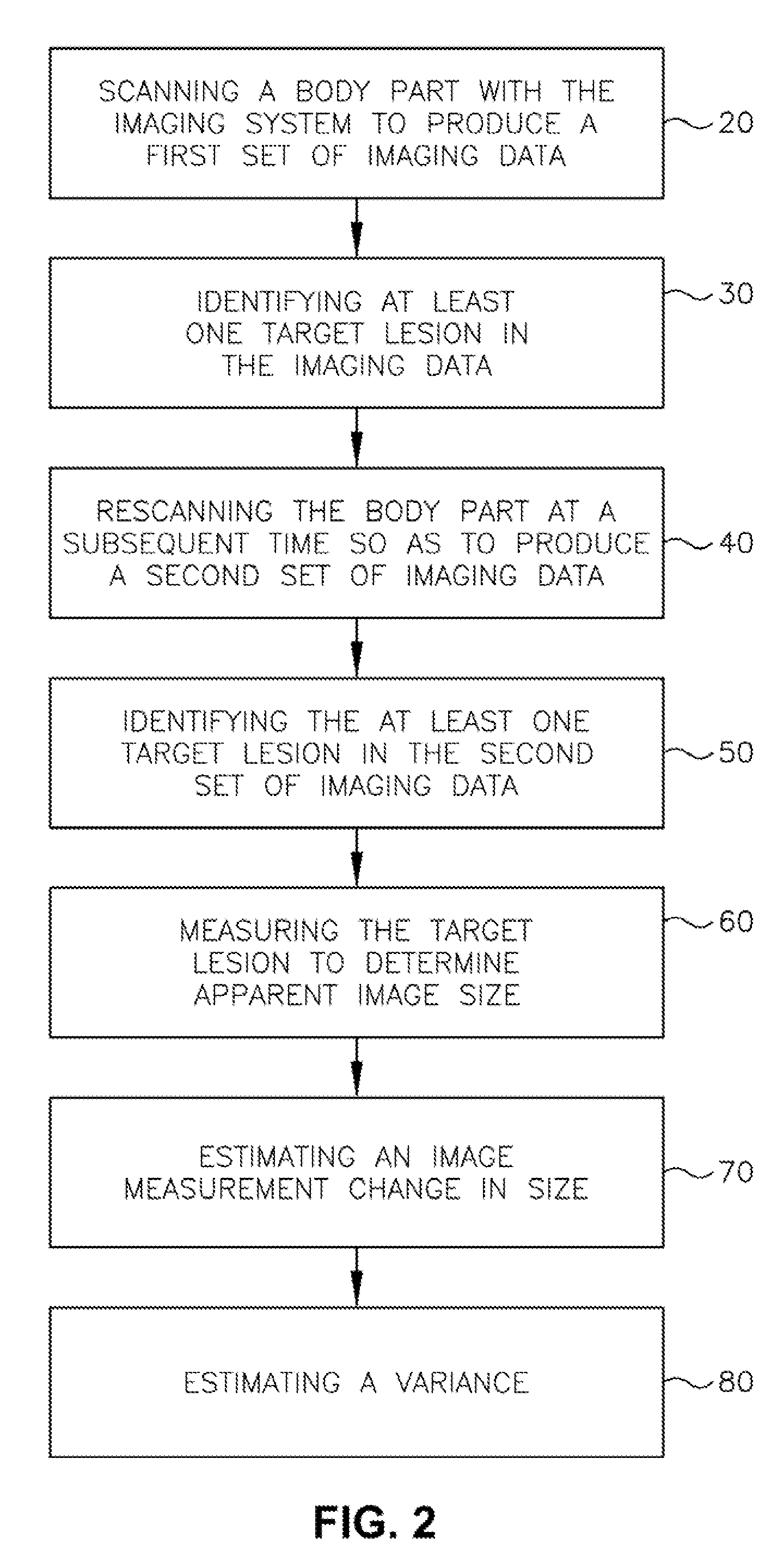
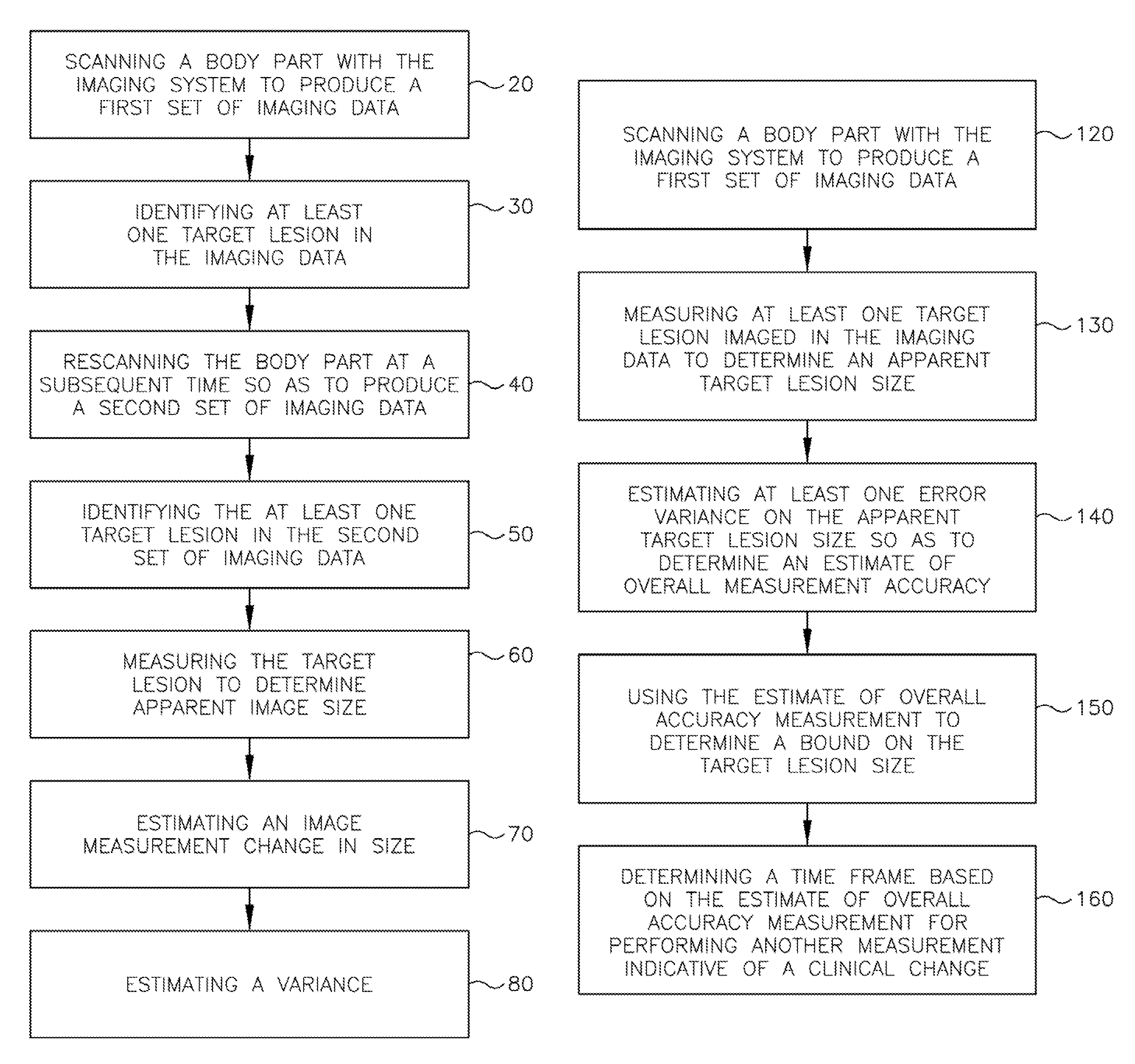
A body part is scanned to produce a first set of imaging data. A target lesion in the imaging data is identified. The body part is rescanned at a subsequent time so as to produce a second set of imaging data. The target lesion is identified in the second set of imaging data and the size of the target lesion is measured in the first and second sets of imaging data to determine two apparent image volumes corresponding to the first and second sets of imaging data. A change in size is estimated by comparing the first and second apparent lesion sizes. A variance on the change in size is estimated so as to determine a bound on the change in size measurement.
Owner:YANKELEVITZ DAVID DR
Medical imaging system for accurate measurement evaluation of changes in a target lesion
ActiveUS7876939B2Shorten the lengthShort time intervalImage enhancementImage analysisSize measurementMeasurement evaluation
A body part is scanned to produce a first set of imaging data. A target lesion in the imaging data is identified. The body part is rescanned at a subsequent time so as to produce a second set of imaging data. The target lesion is identified in the second set of imaging data and the size of the target lesion is measured in the first and second sets of imaging data to determine two apparent image volumes corresponding to the first and second sets of imaging data. A change in size is estimated by comparing the first and second apparent lesion sizes. A variance on the change in size is estimated so as to determine a bound on the change in size measurement.
Owner:YANKELEVITZ DAVID DR
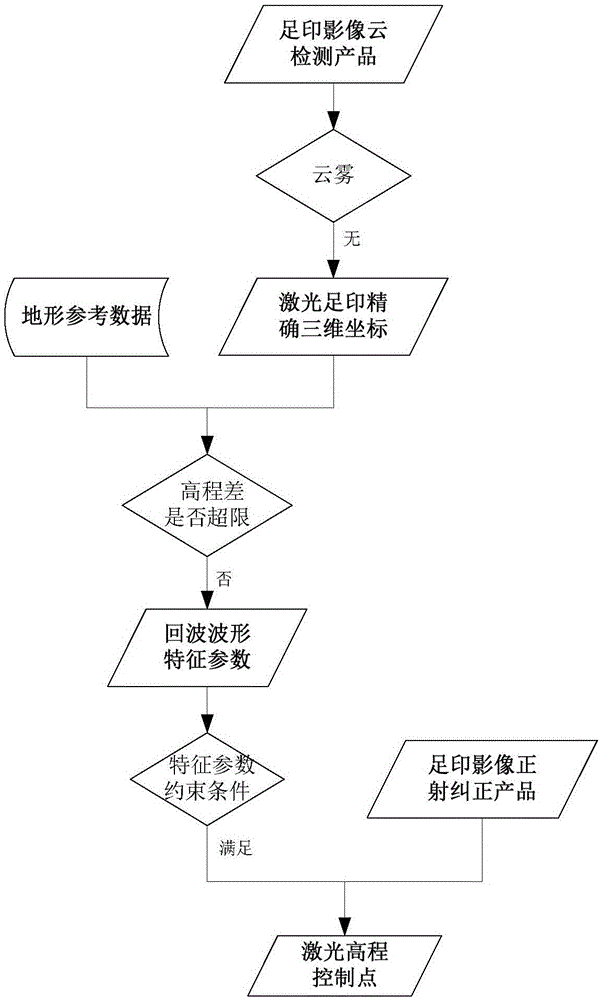
Automatic extraction method for Earth observation laser height measurement satellite elevation control points and data processing method
ActiveCN105550639AGuaranteed accuracyImprove accuracyPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryScene recognitionEarth observationPeak value
The invention relates to an automatic extraction method for Earth observation laser height measurement satellite elevation control points and a data processing method. The laser elevation control point extraction method comprises steps that an effective earth observation laser distance value measurement evaluation method is employed, determined cloudless footprint image blocks are kept, and laser elevation data of determined thin-cloud or thick-cloud footprint image blocks are removed; reflectivity Epsilon smaller than 1 of laser footprint points is taken as a screening parameter, laser footprint points of the kept footprint image blocks are screened, Epsilon=reception pulse energy / emission pulse energy, laser footprint points which have only one wave peak, have the peak value greater than the threshold, have the standard deviation sigma not greater than 3.2ns after waveform fitting are selected from an echo waveform, and parameters used for determining the threshold comprise the emission energy and a reception caliber of a laser device. Through the method, influence of clouds on laser distance measurement can be reduced, laser distance measurement precision can be guaranteed, and accuracy of the laser elevation reference data is effectively improved.
Owner:SATELLITE SURVEYING & MAPPING APPL CENTSASMAC NAT ADMINISTATION OF SURVEYING MAPPING & GEOINFORMATION OF CHINANASG
Method and apparatus for cell handoff
InactiveUS20090069012A1Accurate assessmentHandoff between cells can be more accurateNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionCommunications systemMeasurement evaluation
A method for handoff between cells in a communication system includes the network sends a cell individual offset preset for a cell in the active set relative to each of its neighboring cells respectively to a terminal; after measuring the cell in the active set and its neighboring cells, the terminal evaluates the measurement in accordance with the measurement result and the cell individual offset for the cell in the active set relative to its each neighboring cell; the terminal then submits a measurement report to the network in accordance with the measurement evaluation result; the network instructs the terminal to perform a handoff between cells in accordance with the measurement report. The invention also discloses a network controller and a terminal corresponding to the method. With the invention, the cell individual offset for a cell is set relative to its each neighboring cell so that the handoff between cells can be more accurate. As a result, user of the terminal can obtain better experience.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Filter coefficient configuration in new radio systems
ActiveUS20190058508A1Spatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringMeasurement evaluationUser equipment
Aspects of filtering coefficient configuration operations are described. Some aspects include a user equipment (UE) decoding a measurement configuration information element (IE) including a measurement quantity parameter, a reference signal (RS)-type filter configuration and at least one filter coefficient. In some aspects, the UE filters at least one of a cell measurement result and a beam measurement result, according to the measurement configuration IE. If the measurement quantity parameter indicates the cell measurement quantity, the UE can filter the cell measurement result according to the RS type filter configuration and the filter coefficient to determine a measurement evaluation input for a measurement reporting operation. If the measurement quantity parameter indicates the beam measurement quantity, the UE can filter the beam measurement result according to the RS type filter configuration and the filter coefficient to determine a beam measurement selection input for a beam measurement selection operation.
Owner:APPLE INC
Distance Measuring Device having Homogenizing Measurement Evaluation
ActiveUS20130208258A1Improve measurement reliabilityReduced measurement timeOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationMeasurement evaluationOptical measurements
A handheld measuring device for optical distance measurement includes a transmitting device, a receiving device, an evaluation device, and a homogenizing device. The transmitting device is configured to transmit periodically modulated optical measurement radiation toward a target object. The receiving device is configured to detect optical measurement radiation returning from the target object. The evaluation device is configured to receive and evaluate detection signals of the receiving device. The evaluation device comprises a plurality of accumulation devices configured to accumulate detection signals. The evaluation device conducts detection signals during a sampling time window from a plurality of sampling time windows temporally schematically changeably to an assigned accumulation device from the plurality of accumulation devices, such that the accumulation device accumulates the detection signals during the sampling time window.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Hobbing cutter abrasion test experimental platform and matched measurement evaluation method
PendingCN107687984AImprove wear resistanceSimple structureInvestigating abrasion/wear resistanceHysteresisObservational error
The invention relates to a hobbing cutter abrasion test and abrasion resistance research experimental platform and a measurement evaluation method, aiming at solving the problems that in the prior art, measurement results have hysteresis, lower in engineering guidance and large in measurement error. The hobbing cutter abrasion test and abrasion resistance research experimental platform is providedwith an abrasive box and a transmission device, wherein an output end of the transmission device is provided with a clamping element used for clamping a cutter ring of a hobbing cutter, and the cutter ring of the hobbing cutter is enabled to be positioned above the abrasive box; the clamping element comprises cutter shaft support seats arranged at the two sides, wherein the cutter shaft support seat arranged at one side is fixed at an output end of the transmission device, and the cutter shaft support seat arranged at the other side is fixed on the abrasive box; the outer ring of a cutter hubis matched with the cutter ring of the hobbing cutter, and the inner ring of the cutter hub is matched with the cutter shaft support seats; the transmission device is also provided with a sensor bracket; an eddy current sensor element is arranged on the sensor bracket and at the position corresponding to the outer side of the outer ring of the hobbing cutter. The hobbing cutter abrasion test andabrasion resistance research experimental platform and the measurement evaluation method have the advantages that measurement is carried out on the cutting basis of simulation of a working environment, and an abrasion test is effectively combined with evaluation; real-time detection is realized, the measurement accuracy is increased, and the equipment application size is wide.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY TUNNEL GROUP CO LTD +2
Textile shape retention measurement device and method
InactiveCN108333058AAvoid efficiencyAvoid errorsMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using steady bending forcesMeasurement deviceMeasurement evaluation
The invention provides a textile shape retention measurement device. The device comprises a base, a first support plate fixedly arranged on the base, a detection mechanism and a drive mechanism, wherein the detection mechanism comprises a fixed plate, a moving plate, a first elastic holder embedded in the fixed plate, a second elastic holder embedded in the moving plate and a force sensor; the fixed plate and the moving plate are parallel with each other and both perpendicular to the base; the force sensor is connected with the fixed plate and the first support plate through a first connectingpiece and a second connecting piece; the moving plate is connected with the drive mechanism; the drive mechanism can control the moving plate to move in the direction perpendicular to the moving plate. The invention also provides a textile shape retention measurement method based on mechanics. By use of the device and the method, measurement evaluation of bending crease resilience, compression resilience and tensile resilience of textile can be finished once through mechanical measurement.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Diffusion measurement evaluation method for water in oil paper of oil-immersed transformer
InactiveCN106442225AAccurate life assessmentComprehensive life assessmentDiffusion analysisEngineeringWater content
The invention discloses a diffusion measurement evaluation method for water in oil paper of an oil-immersed transformer. The diffusion measurement evaluation method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a transformer insulating paper sample; secondly, testing the mechanical strength of a polymer of an aged paper board; thirdly, establishing an extrapolation life model under the thermal aging temperature; fourthly, establishing an extrapolation life model under any thermal aging temperature and initial water content; fifthly, analyzing hot-spot temperature of a transformer winding, micro-water content in oil and real-time oil temperature data of the transformer. According to an insulation thermal aging life evaluation method of the oil paper based on a time-temperature water superimposition method, provided by the invention, accelerated aging data under high-temperature high initial water content can be extrapolated to data of low-temperature low water content under operation conditions, the defects in a traditional time-temperature superposition model can be overcome, and a more accurate and comprehensive life evaluation method is provided.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fast cell reselection method for dual-mode dual-standby terminal and terminal
The invention discloses a fast cell reselection method for a dual-mode dual-standby terminal and the dual-mode dual-standby terminal. The method comprises the following steps that: when moving to a weak signal field of a first system, the dual-mode dual-standby terminal triggers cell reselection under the first system, and simultaneously makes a request for cooperative measurement to a second system; and the second system performs measurement evaluation by utilizing a radio frequency idle time, and informs the first system of a measurement result. By the method and the terminal, the performance advantages of two radio frequency chips are fully utilized, and the dual systems cooperatively and complementarily recommend cells to realize accelerated residence.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and apparatus for cell handoff
ActiveUS20120021745A1Accurate assessmentHandoff between cells can be more accurateNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionCommunications systemMeasurement evaluation
A method for handoff between cells in a communication system includes the network sends a cell individual offset preset for a cell in the active set relative to each of its neighboring cells respectively to a terminal; after measuring the cell in the active set and its neighboring cells, the terminal evaluates the measurement in accordance with the measurement result and the cell individual offset for the cell in the active set relative to its each neighboring cell; the terminal then submits a measurement report to the network in accordance with the measurement evaluation result; the network instructs the terminal to perform a handoff between cells in accordance with the measurement report.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Electrocardiogram-signal identity recognition method based on NMF, evaluation method and device
ActiveCN109330585AStrengthen the QRS bandStrengthen the role of the QRS bandPerson identificationSensorsEcg signalIdentity recognition
The invention discloses an electrocardiogram-signal identity recognition method based on NMF, an evaluation method and a device. The electrocardiogram-signal identity recognition method based on the NMF includes the steps that electrocardiogram signals are received, serve as sample points and are preprocessed; according to the electrocardiogram signal structure, a QRS wave section is subjected tobidirectional particle size scanning, the obtained QRS wave section, a wave section before QRS and a wave section after the QRS are integrated, and the preprocessed electrocardiogram signals are reconstructed; the reconstructed electrocardiogram signals are subjected to non-negative matrix factorization, and a coefficient matrix is obtained; a sub-component of the coefficient matrix is selected with the sub-component analysis method as a final characteristic value matrix of the electrocardiogram signals; electrocardiogram-signal identity recognition is carried out through the characteristic value matrix. Through the characteristic value matrix, a homologous similarity matrix and a heterogenous similarity matrix are calculated through mahalanobis distance, the error recognition rate, the false reject rate and the equal error rate are calculated through the homologous similarity matrix and the heterogenous similarity matrix, and the recognition effect on electrocardiogram-signal identityrecognition is subjected to measurement evaluation.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Coriolis mass flowmeter
ActiveUS20110259121A1Resilience is preventedImprove permeabilityVolume meteringDirect mass flowmetersMeasurement evaluationTransducer
A Coriolis mass flowmeter (1) having at least one sensor arrangement (2), at least one transducer (3) and at least one housing (4), wherein the sensor arrangement (2) has at least one measuring tube (5) that can be excited to oscillation, at least one oscillation generator (6) and at least one oscillation sensor (7), wherein the transducer (3) at least in part has evaluation and power electronics for controlling and measurement evaluation of the sensor arrangement, wherein the sensor arrangement (2) and the transducer (3) are arranged adjacent to one another in a common volume defined by the housing (4). A Coriolis mass flowmeter of the described type, in which the physical interaction between the sensor arrangement and transducer is reduced, is realized by the provision of a thermal barrier (8) arranged at least in a space between the sensor arrangement (2) and the transducer (3).
Owner:KROHNE MESSTECHNICK GMBH & CO KG
Distance measuring device having homogenizing measurement evaluation
InactiveCN102844676AOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationObservational errorSingle-photon avalanche diode
The invention relates to a measuring device for distance measurement, in particular for optical distance measurement and, for this purpose, a specific way of evaluating detection signals. In a design according to the invention, during various partial measurements (A), (B), (C) a transmitted signal (103) is emitted in the direction of a target object, is reflected there and detected by a receiving device, which, for example, can be designed as a photon counter in the form of a SPAD (single photon avalanche diode). The phase of the transmitted signal (103) is shifted successively in relation to an unshifted signal (101) during the individual partial measurements (A), (B), (C). During sampling time windows (115, 125, 135), the detection signals are fed to associated counters (117, 127, 137). An associated of the counters (117, 127, 137) with the sampling windows (115, 125, 135) can vary between individual the partial measurements (A), (B), (C). In this way, it is possible for background light to be distributed homogeneously over all the counters (119, 127, 137), whereas the transmitted signal (103) is accumulated only in specific counters (117). Measurement errors on account of unequal time spans of the sampling time windows or on account of different measuring sensitivities within various sampling time windows can thus be minimized. Said function is performed by the homogenizing device (80) according to the invention.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Interference source positioning method, apparatus and device, and computer storage medium
PendingCN111278040AReduce adverse effectsPrecise positioningTransmission monitoringWireless communicationMeasurement evaluationData quality
The invention discloses an interference source positioning method, device and equipment and a computer storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, identifying interfered sampling points according to characteristics of external interference; secondly, calculating an average eNB antenna arrival angle based on an antenna arrival angle interval in the sampling point data, and obtaining angle information between an interference source and each interfered cell in combination with a cell actual azimuth angle in the base station configuration information; and finally, based on the idea that the intersection point density of the position of the intersection point is in direct proportion to the data quality of the intersection point position, performing data quality measurement evaluation on the target estimation position point generated by each measurement value in the two-dimensional space, determining the contribution degree of the measurement value to the interferencesource positioning result, and accurately positioning the interference source. According to the embodiment of the invention, the adverse effect of a low-quality measurement value on a positioning result can be effectively eliminated, the positioning precision of an external interference source is improved, and the utilization of measurement data achieves the unification of sufficiency and reasonability.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP SICHUAN +1
A method for evaluating the machining accuracy of building components
The invention relates to a method for detecting and evaluating the geometric accuracy of some undetermined measurement benchmarks or objects with complex shapes. It is characterized in that: select appropriate control points from the physical components and design documents respectively, and collect control data one by one, classify the data one by one, and import them into the computer, select the coordinate conversion function, and convert the physical components through the conversion function The digital model is converted to the coordinate system made by the design model, and the processing accuracy of the solid component is obtained by analyzing the difference between the data of each pair of control points one by one. The advantage of the present invention is that by adopting the method for evaluating the processing accuracy of building components of the present invention, the work of accurately evaluating the processing accuracy of building components with complex shapes can be completed.
Owner:SHANGHAI MECHANIZED CONSTR GRP
Unified characterization method for characteristic lines of gear three-dimensional error
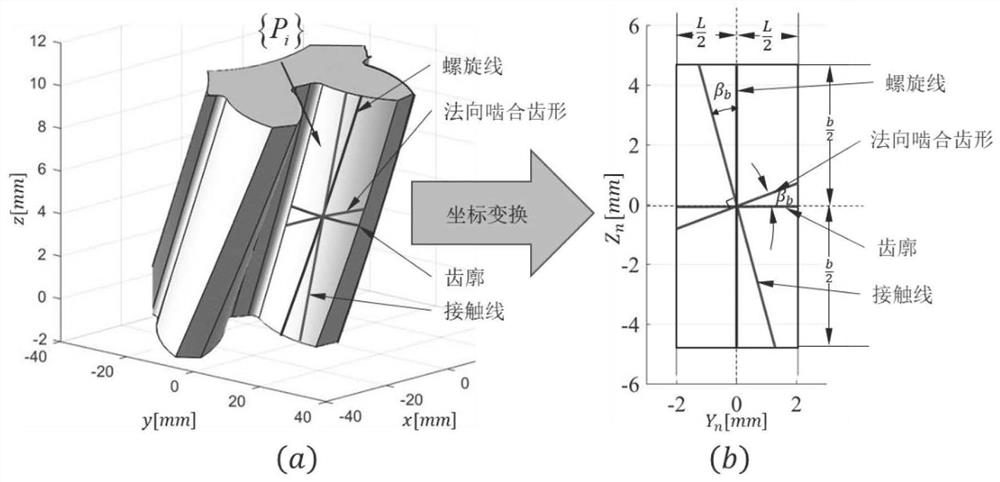
ActiveCN112903288AAchieving Unified Mathematical RepresentationComprehensive measurement and evaluation resultsMachine part testingInvoluteMeasurement evaluation
The invention discloses a uniform characterization method for a characteristic line of a gear three-dimensional error, wherein the method comprises the steps: building a relation between a coordinate system on a gear and a coordinate system of a meshing surface; giving out an equation of a gear characteristic line under a gear coordinate system under a meshing surface coordinate system, wherein an involute is a section line of a tooth surface cut by an end plane, a contact line is an intersection line of a base circle tangent plane and the tooth surface, the normal meshing tooth form is a track of an instantaneous contact point generated on the tooth surface when two tooth surfaces are meshed in spiral gear transmission, and the spiral line is the intersecting line of the gear axis coaxial cylindrical surface and the tooth surface; then two-dimensionally representing the three-dimensional measurement error on the tooth surface, and analyzing the curves to obtain that four characteristic lines on the tooth surface are all straight lines in a meshing surface coordinate system, thereby realizing unified mathematical representation of each characteristic line in the meshing surface coordinate system; finally, giving out the method for extracting a tooth profile deviation curve, a spiral line deviation curve, a contact line deviation curve and a normal meshing tooth profile deviation curve on a tooth surface along a meshing normal direction under a meshing plane coordinate system and evaluating the deviations. According to the method, four characteristic curves at any position on the tooth surface are extracted based on a large amount of tooth surface measurement data and are comprehensively evaluated, and the measurement evaluation result is more comprehensive.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Weight loss measurement evaluation method and device based on internet
InactiveCN105919553AConvenient and accurate evaluationAvoid operabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsThe InternetMeasurement evaluation
The invention discloses a weight loss measurement evaluation method and device based on the internet. The method includes: receiving human body weight data measured by an electronic balance, comparing the human body weight data and the received human body weight before the current measurement, and calculating variation of the human body weight; receiving the human body motion time and the human body motion intensity which are detected by a motion sensor and / or input by a man, and calculating corresponding energy consumption according to the human body motion time and the human body motion intensity; and evaluating a weight loss effect according to the variation of the human body weight and the energy consumption. According to the method, the variation of the human body weight and the corresponding energy consumption of the human body detected by the motion sensor are acquired, the weight loss effect can be evaluated through correlation between the variation of the human body weight and the energy consumption, and then the troubles that operations is complex due to nutrition absorbing information recorded or input by a man, and the weight loss process and the weight loss effect are difficult to monitor can be avoided.
Owner:HUNAN JIANCHENG INFORMATION TECH
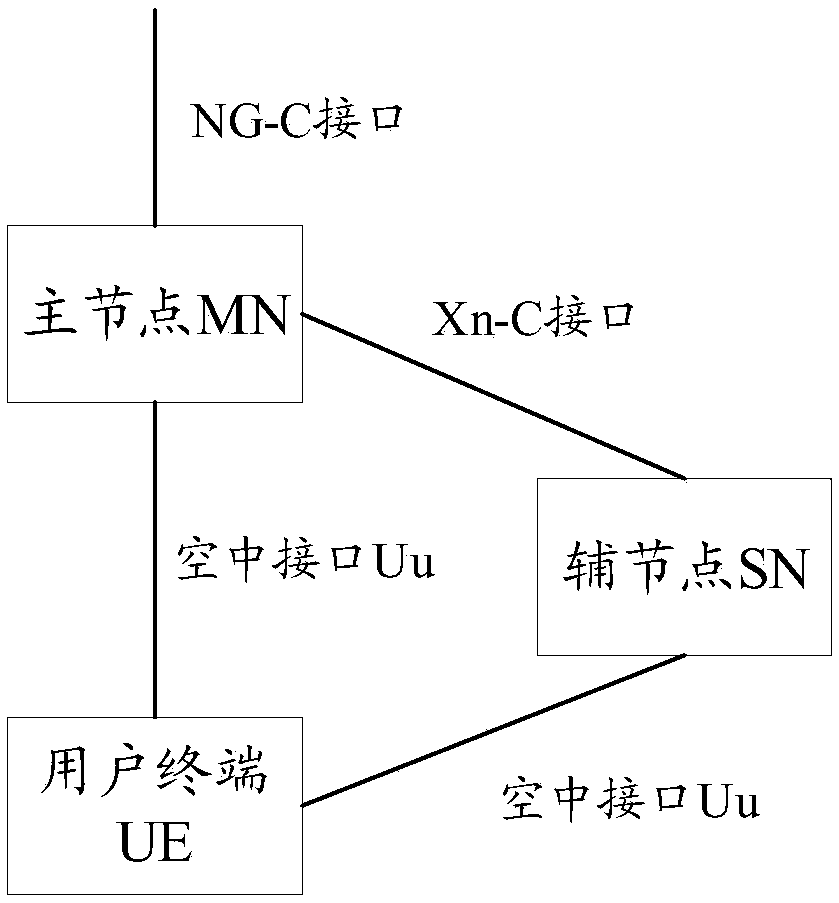
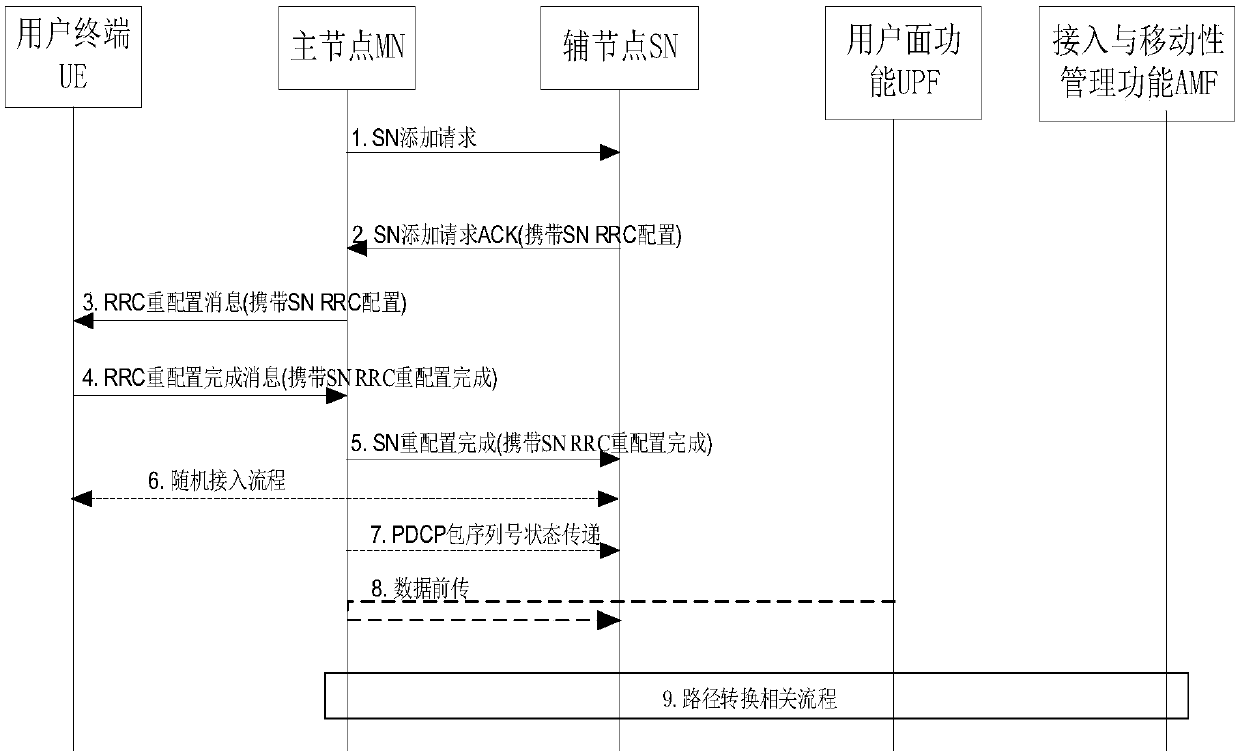
Secondary node adding/replacing method and equipment based on double/multi-connection
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
Measurement method and user equipment
ActiveCN102131206AReduce reportingSave air interface resourcesTransmission path divisionWireless communicationTelecommunicationsCarrier signal
The embodiment of the invention provides a measurement method and user equipment. The measurement method comprises the following steps of: receiving indication information sent by network-side equipment, wherein the indication information indicates a member carrier unallocated to the user equipment in a carrier aggregation cell where the user equipment is located; and performing measurement evaluation and reporting of a measurement report on the member carrier unallocated to the user equipment, indicated by the indication information, in a mode different from the mode of performing the measurement evaluation and the reporting of the measurement report on a neighbour cell of the carrier aggregation cell where the user equipment is located. By the measurement method and the user equipment provided by the embodiment of the invention, differential treatment for the member carrier unallocated to the user equipment in the carrier aggregation cell where the user equipment is located in the process of measurement is realized, the reporting of the measurement report for the member carrier unallocated to the user equipment in the same carrier aggregation cell is reduced, and null interface resources for sending the measurement report are saved.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
On-site measurement method and system for composite material mould molded surface accuracy of antenna reflector
ActiveCN110006339AImprove processing efficiencyImprove machining accuracyUsing optical meansPoint cloudMeasurement evaluation
The invention discloses an on-site measurement method and system for the composite material mould molded surface accuracy of an antenna reflector, and is used for measuring the molded surface accuracyin the machining process of the carbon fiber composite material mould of the antenna reflector. On the basis of the quick acquisition and analysis of the measurement data of a laser tracker and a robot integrated measurement system, the method and the system solve a transportation problem between the processing and the detection of the composite material mould by aiming at the defects in the prior art that the transportation frequency of the composite material mould is high and measurement accuracy is greatly affected by machine tool axial system errors in a measurement process, meanwhile, measurement equipment independent of the machine tool is used for enabling the measurement evaluation of the composite material mould molded surface to be objective and real, and the problem that point-to-point contact measurement wastes long time is solved through the efficient and automatic sampling of the point cloud of the paraboloid molded surface of the mould.
Owner:BEIJING SATELLITE MFG FACTORY
Radio link management method and device
The invention provides a radio link management method and device. The method comprises the steps of receiving a radio resource management RRM measurement parameter issued by a base station through radio resource control RRC signaling; carrying out RRM measurement on a plurality of or all beams managed by a transmit receive point TRP of a target beamforming BF distribution base station according tothe RRM measurement parameter, thereby obtaining an RRM measurement result; and jointly evaluating the RRM measurement result based on the plurality of or all beams, and switching from the TRP of a source BF distribution base station to the TRP of the target BF distribution base station or additionally adding the TRP of the target BF distribution base station according to an evaluation result. Through application of the method and the device, the problem that in related technologies, the terminal mobility performance is relatively low due to the fact that radio resource control measurement evaluation is carried out and mobile switching between beamforming base stations is carried out by taking a single beam as granularity is solved, thereby achieving the effect of improving the terminal mobility performance.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method for scene matching region selection and reference image optimization of image matching system
ActiveCN106709501AMeasure quality in real timeAchieve matchabilityImage enhancementImage analysisFeature vectorRegion selection
The invention relates to a method for scene matching region selection and reference image optimization of an image matching system, which comprises the steps of performing initialized blocking on a remote sensing satellite image, extracting edge features of each region according to an edge feature extraction algorithm, and screening block regions with centralized edge gradient points; calculating the autocorrelation degree of each region by using a repetition pattern index measurement method, sorting the regions from small to large according to an intracorrelation index, and outputting an optimal candidate region; building a spatial feature vector of a reference image of the candidate region by adopting a spatial distribution description method; building a scene matchability measurement evaluation index set, analyzing the relevance between the evaluation index set and the matching probability, and outputting a matching performance evaluation index set; and statistically analyzing matched and correlated aspects of the reference image and the satellite image, and optimizing the reference image according to a reference image optimization method. High matching performance and high reliability are realized by using the optimized reference image when the matching system operates in an unknown environment, and the image matching system is guaranteed to complete a task successfully.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
UE triggering based measurement optimization method and device in mobile scenes
ActiveCN108574955AReduce power consumptionGood energy saving effectPower managementHigh level techniquesMeasurement evaluationEngineering
The invention discloses a UE triggering based measurement optimization method and device in mobile scenes. The method includes the following steps: receiving terminal UE measurement characteristic determination parameters broadcast by a base station and measurement frequency factors corresponding to different measurement characteristics, wherein the UE measurement characteristic determination parameters include parameters characterizing wireless quality changes in wireless environment of UE; determining the measurement characteristics of the UE according to the UE measurement characteristic determination parameters, wherein the measurement characteristics include the degree of the wireless quality changes in the wireless environment of the UE; determining the measurement frequency factorscorresponding to the measurement characteristics; and modifying a predefined measurement interval reference value and a measurement evaluation interval reference value by using the measurement frequency factors to obtain the measurement interval and the measurement evaluation interval of the UE. The determination method for wireless quality measurement interval and measurement evaluation intervalcan save power consumption of UE to the greatest extent and improve the energy saving effect of UE in a NB-IoT system.
Owner:ZTE CORP
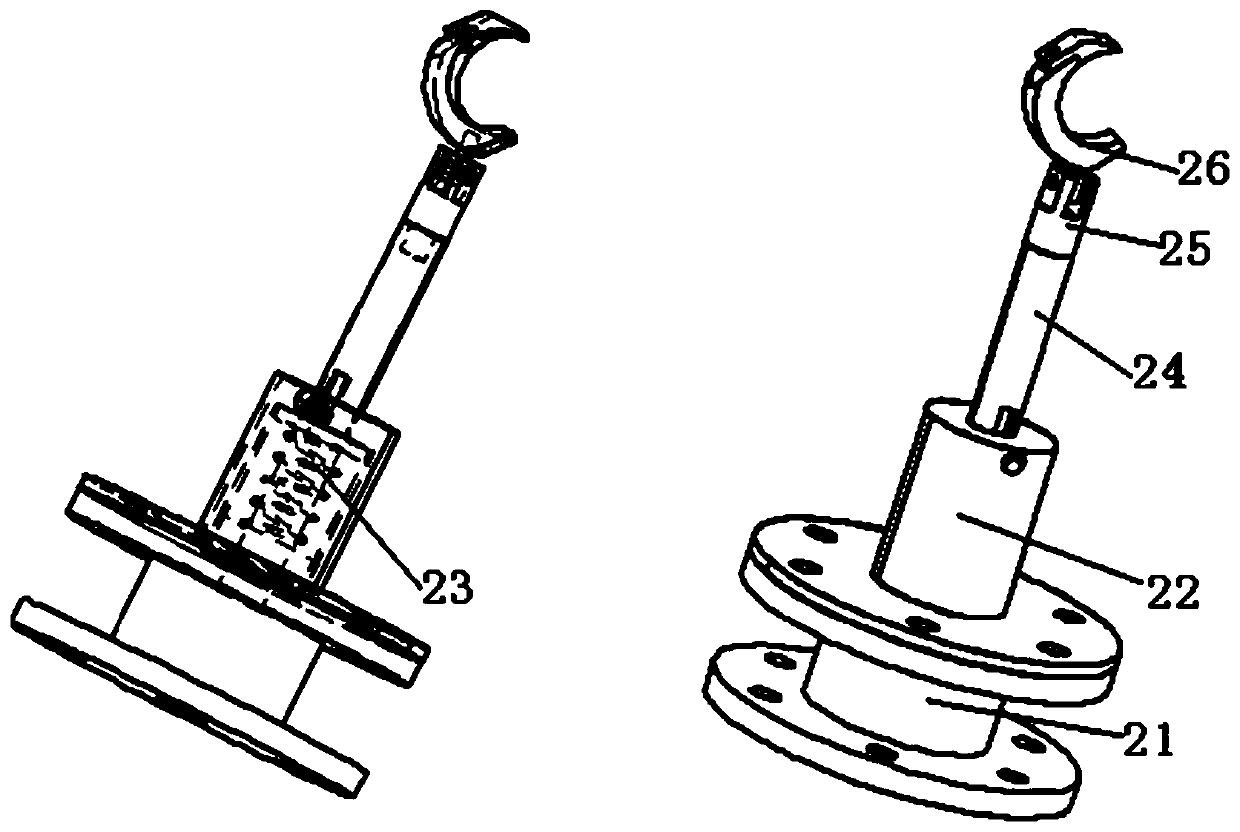
Method for detecting relative angle of small circular hole of revolving body thin-walled part
The invention discloses a method for detecting the relative angle of a small circular hole of a revolving body thin-walled part. The method comprises the steps of adjusting the measurement reference,specifically, enabling the revolving body thin-walled part to be vertically placed on a measurement platform, enabling a measurement rod to extend into a measured small hole and be concentric with themeasured small hole, and enabling the normal direction of the measured small hole to be consistent with the X axis of measurement equipment; establishing a first theoretical plane, specifically, establishing a vertical reference plane of the small hole C by taking the central axial direction of a reference cylinder A as a reference direction; establishing a first coordinate system, specifically,taking the small hole C as a space circle for measurement, taking a top surface B of the revolving body part as a first axial Z-direction constraint plane, jointly projecting circle center points of the space circles extracted by the reference cylinder A and the small hole C onto the first axial Z-direction constraint plane, connecting the circle center of the projection of the reference cylinderA with the circle center point of the small hole C, and performing second axial constraint; establishing a second coordinate system, specifically, performing coordinate system rotation according to aninitial angle marked by the drawing to obtain the second coordinate system; establishing other theoretical planes; and conducting measurement evaluation.
Owner:CHINA FIRST AUTOMOBILE
Closed subscriber group (CSG) cell reselection method and device
ActiveCN105282797AIncrease success rateReduce power consumptionWireless communicationCell IDMeasurement evaluation
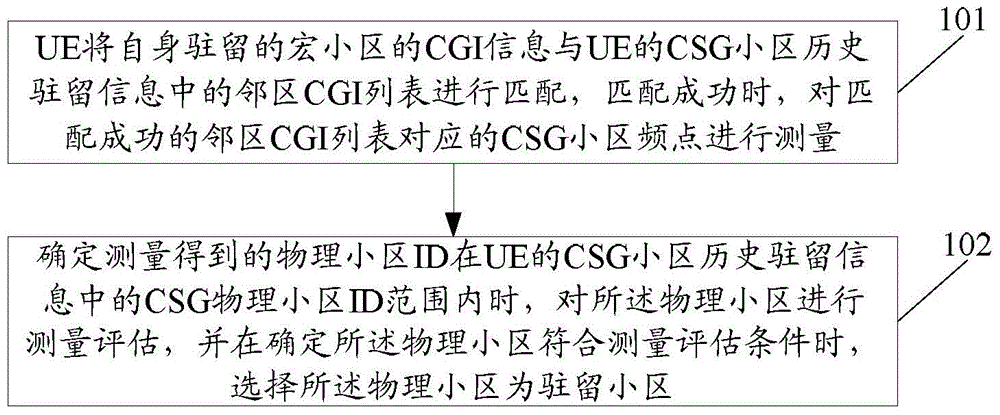
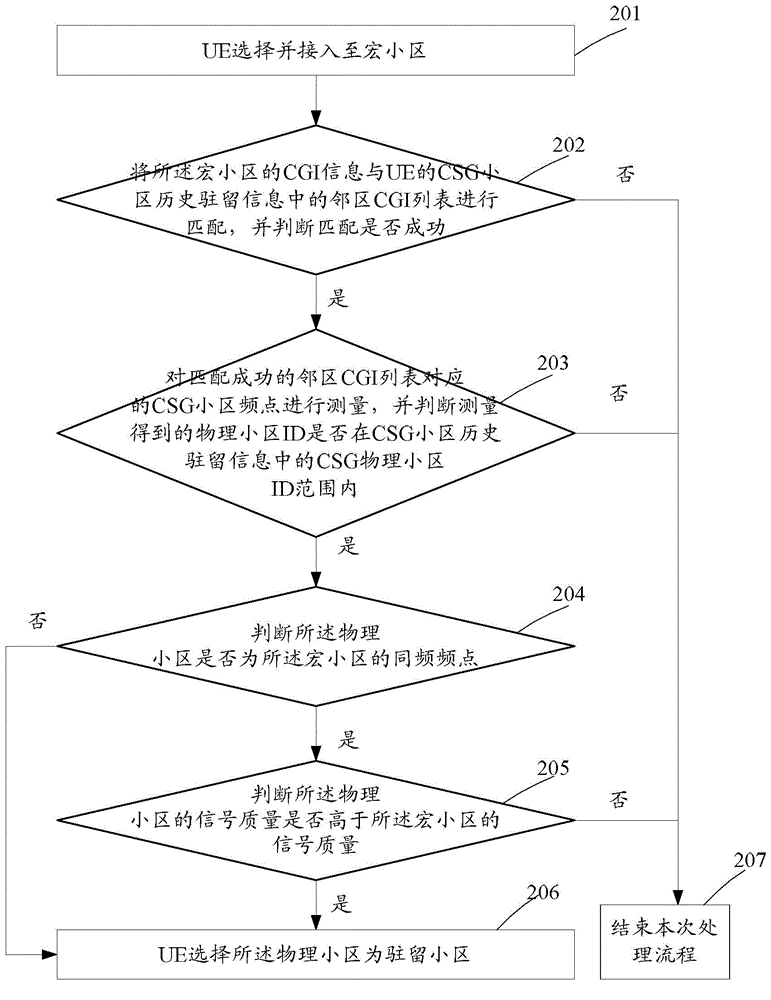
The invention discloses a closed subscriber group (CSG) cell reselection method comprising steps that UE matches the CGI information of a resident macro cell of the UE with a neighbor CGI list in the CSG cell historical resident information of the UE, and measures the CSG cell frequency points corresponding to the successfully-matched neighbor CGI list when matching succeeds; when it is determined that a measured physical cell ID is in the CSG physical cell ID range of the CSG cell historical resident information of the UE, the UE measures and evaluates the physical cell and selects the physical cell as a resident cell when it is determined that the physical cell satisfies a measurement evaluation condition. The invention also discloses a CSG cell reselection device.
Owner:SANECHIPS TECH CO LTD
Space signal continuity assessment method
InactiveCN106125100AConvenient and quick statistical determinationEase of evaluationSatellite radio beaconingDaily operationProgram planning
The invention discloses a space signal continuity assessment method. With application of the space signal continuity assessment method, an operable and easily implemented effective method is provided for space signal continuity index assessment by utilizing navigation satellite system daily maintenance data, downlink signal monitoring data and the reliability basic theory. According to the space signal continuity assessment method, firstly system daily operation interruption data and continuous health character information actually measured by a receiver are acquired, operation state sequences and actually measured health character sequences under the influence of only unplanned interruption are obtained according to analysis of the planned interruption situation of daily operation, the continuity risk of two data sources is obtained according to the theory forecast method and the actual measurement evaluation method, the continuity risk is obtained by using the actual measurement statistical method by utilizing the operation state sequences under the influence of unplanned interruption, and finally the three risk calculation results are compared so that the space signal continuity is assessed.
Owner:CHINA AEROSPACE STANDARDIZATION INST
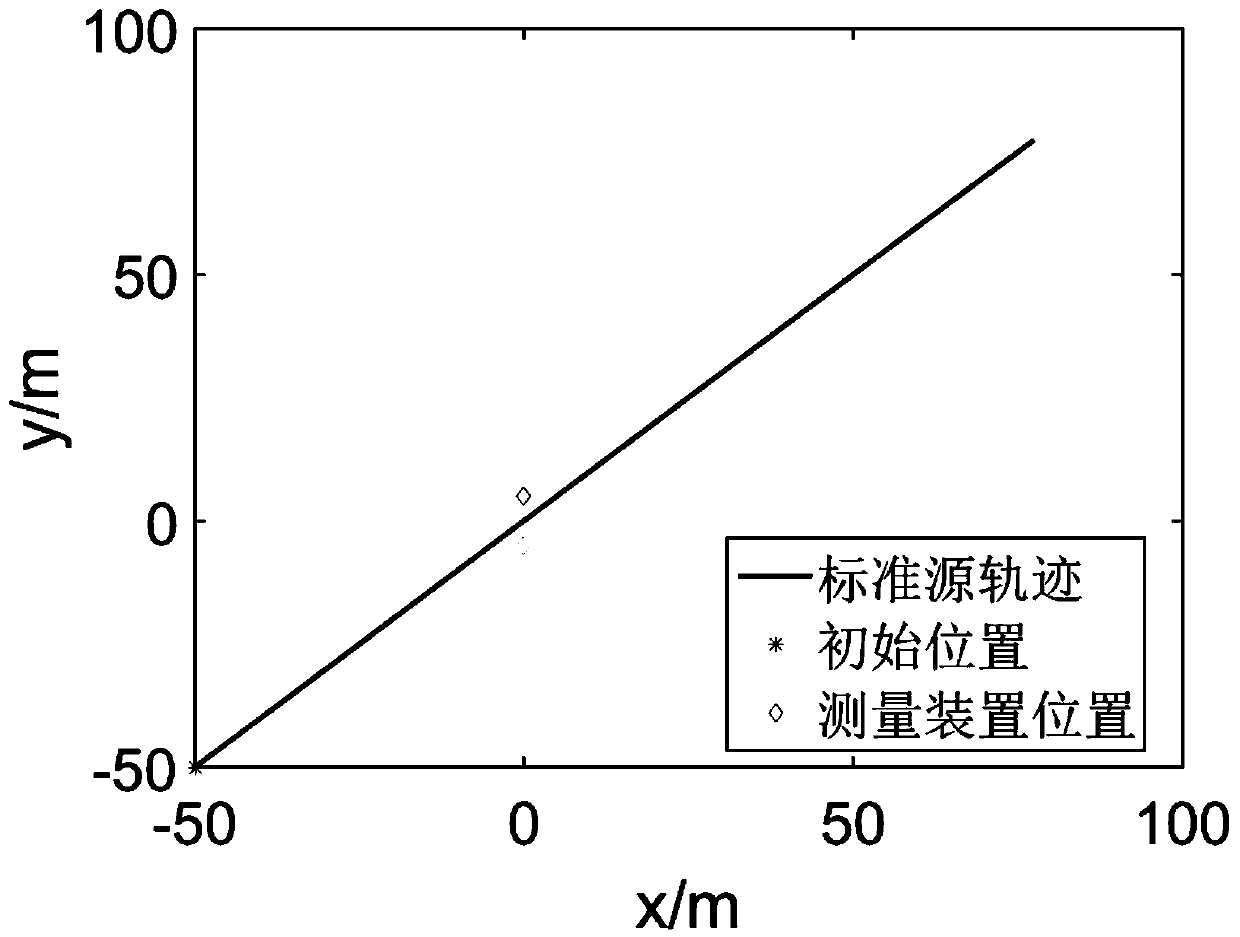
Positioning method of electric field measuring device
ActiveCN110082611ASolve the positioning problemSimple and fast operationNavigation by astronomical meansElectric/magnetic detectionElectric field sensorInterference resistance
The invention discloses a positioning method of an electric field measuring device, which comprises the following steps: firstly, building a standard current source with the functions of simulating astandard electric dipole, recording a flight path and the like; secondly, arranging an electric field measuring device; thirdly, collecting environmental background electric field data; fourthly, collecting standard source electric field data; fifthly, constructing a state space model for positioning the electric field sensor; and finally, positioning the electric field sensor by using a Kalman filtering method according to the measured information such as the measured electric field signal, the track of the standard source and the like. The positioning method of the electric field measuring device is used for underwater electric field sensors, the positioning accuracy can reach 0.2 m, no equipment is required to be added on the basis of the electric field measuring device, the cost is low, the environment noise interference resistance is high, the device is not limited by the environment of a measuring area, and the positioning method of the electric field measuring device can be widely applied to the fields of ship electric field measurement evaluation, underwater positioning, geological exploration and the like.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
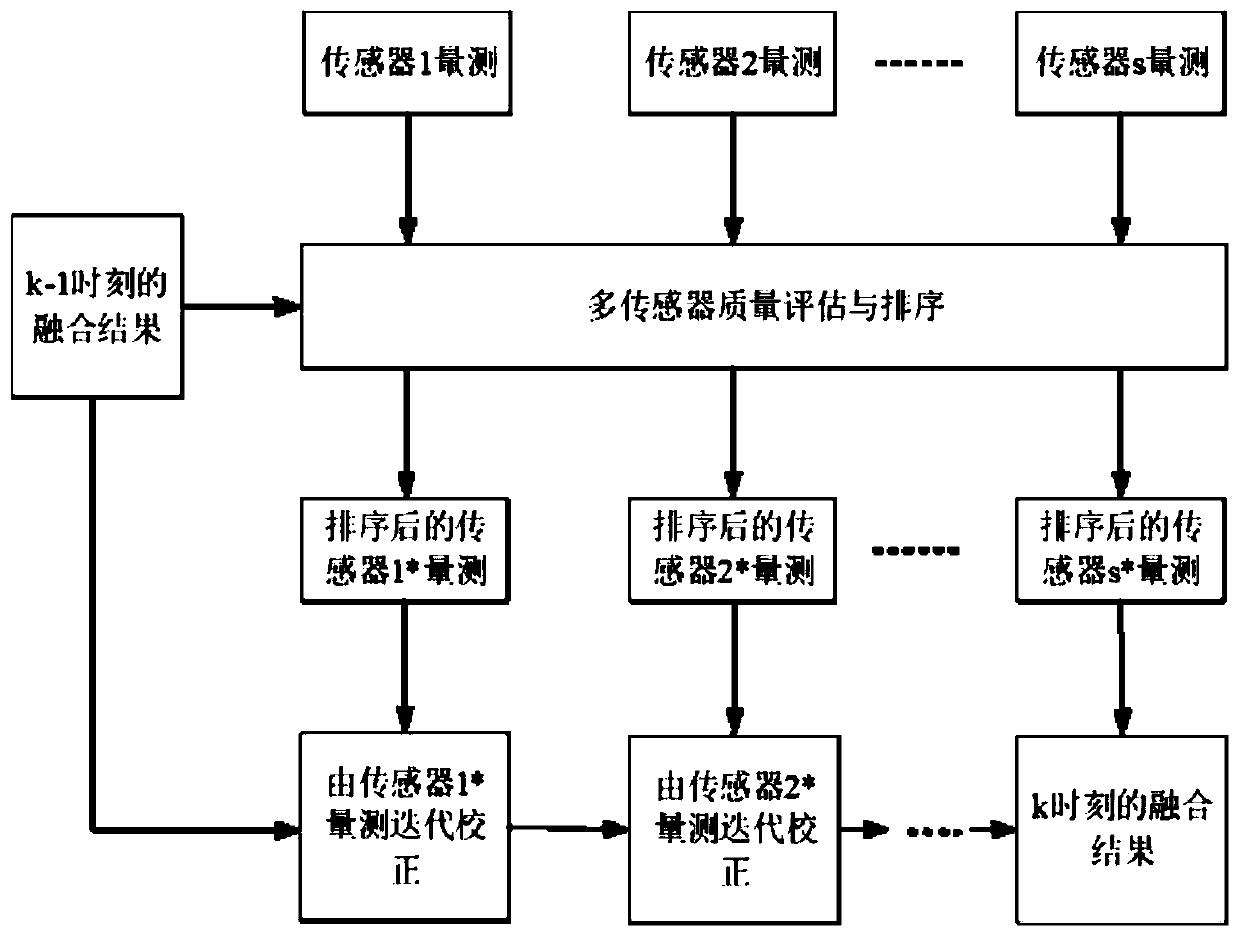
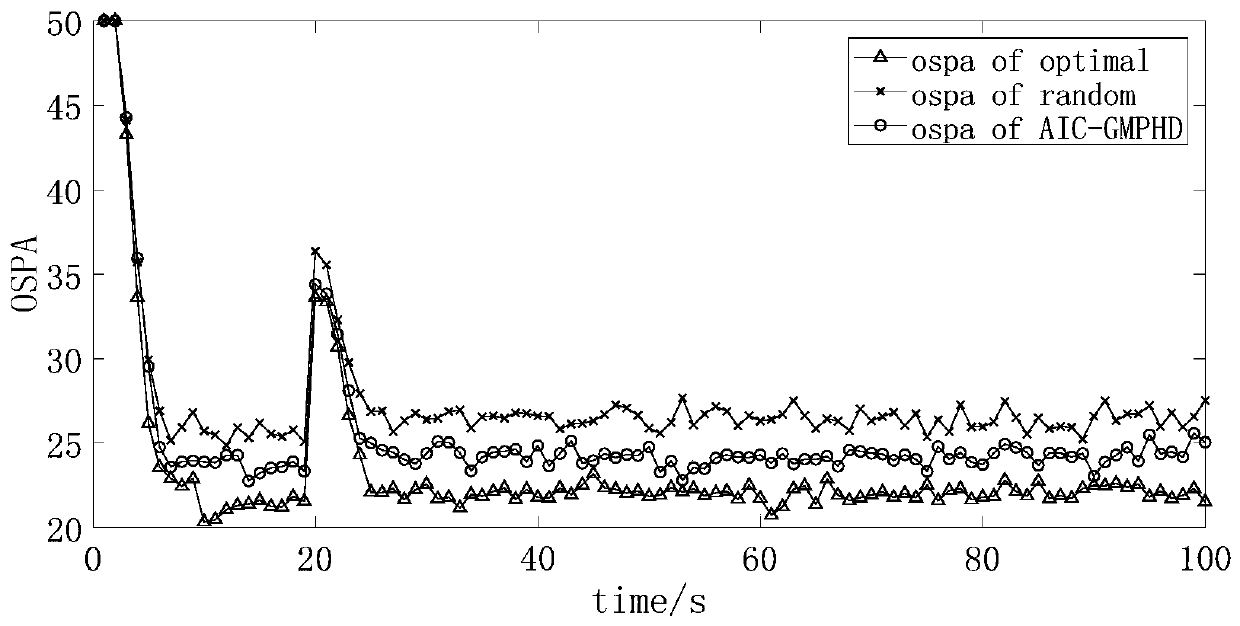
Multi-sensor GMPHD adaptive fusion method based on OSPA iteration
ActiveCN111340853AThe configuration structure is clearSmall amount of calculationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionMulti target trackingMultiple sensor
The invention discloses a multi-sensor GMPHD self-adaptive fusion method based on OSPA iteration. In order to research the influence of a fusion sequence on a fusion result, based on a measurement iteration correction multi-sensor PHD (ICMPHD) algorithm and based on an OSPA measurement evaluation index, an adaptive iterative correction multi-sensor PHD (AICMPHD) method is provided, and then a Gaussian mixture (GM) technology is introduced into the AICMPHD method to realize an AIC-GMPHD algorithm. The method is clear in configuration structure and small in calculation amount, and can be widelyapplied to the field of multi-target tracking.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Method of calibrating engine blade measuring apparatus
InactiveCN106500640AHigh measurement accuracyImprove consistencyMeasurement devicesMeasurement testMeasurement evaluation
The invention belongs to the test field of aeroengine blade measurement and relates to a method of calibrating a measuring apparatus using a standard molded surface blade. In an engine blade measurement test, the obtained measurement evaluation result by means of measuring a high-precision engine blade cannot truly reflect the precision of the engine blade totally because of the error of the blade evaluation method and the mechanical error of a measuring apparatus. The invention provides a measuring apparatus calibrating method based on a calibration standard molded surface of a blade measuring apparatus. The measuring apparatus calibrating method based on a calibration standard molded surface of a blade measuring apparatus utilizes a special calibrating apparatus. The calibrating apparatus includes a blade body and a blade tenon root, wherein the blade body is formed through normal extension of a standard cross section; the standard cross section is formed by the cross section, at any position of a stacking shaft, of a theoretical engine blade three dimensional model; an error compensation database for each parameter of the measuring apparatus is established; and error compensation for the special position space is performed on the blade measuring apparatus so as to improve the measuring precision of the engine blade.
Owner:CHINA PRECISION ENG INST FOR AIRCRAFT IND AVIC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com