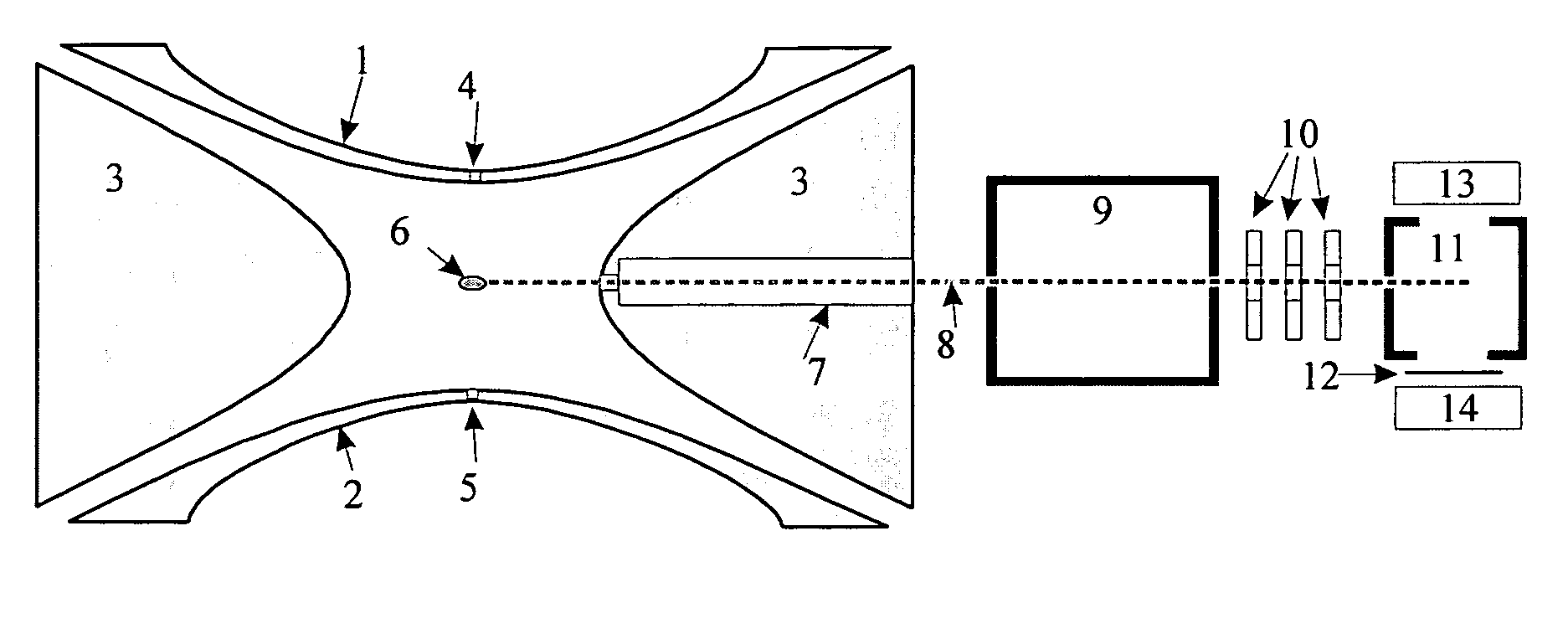
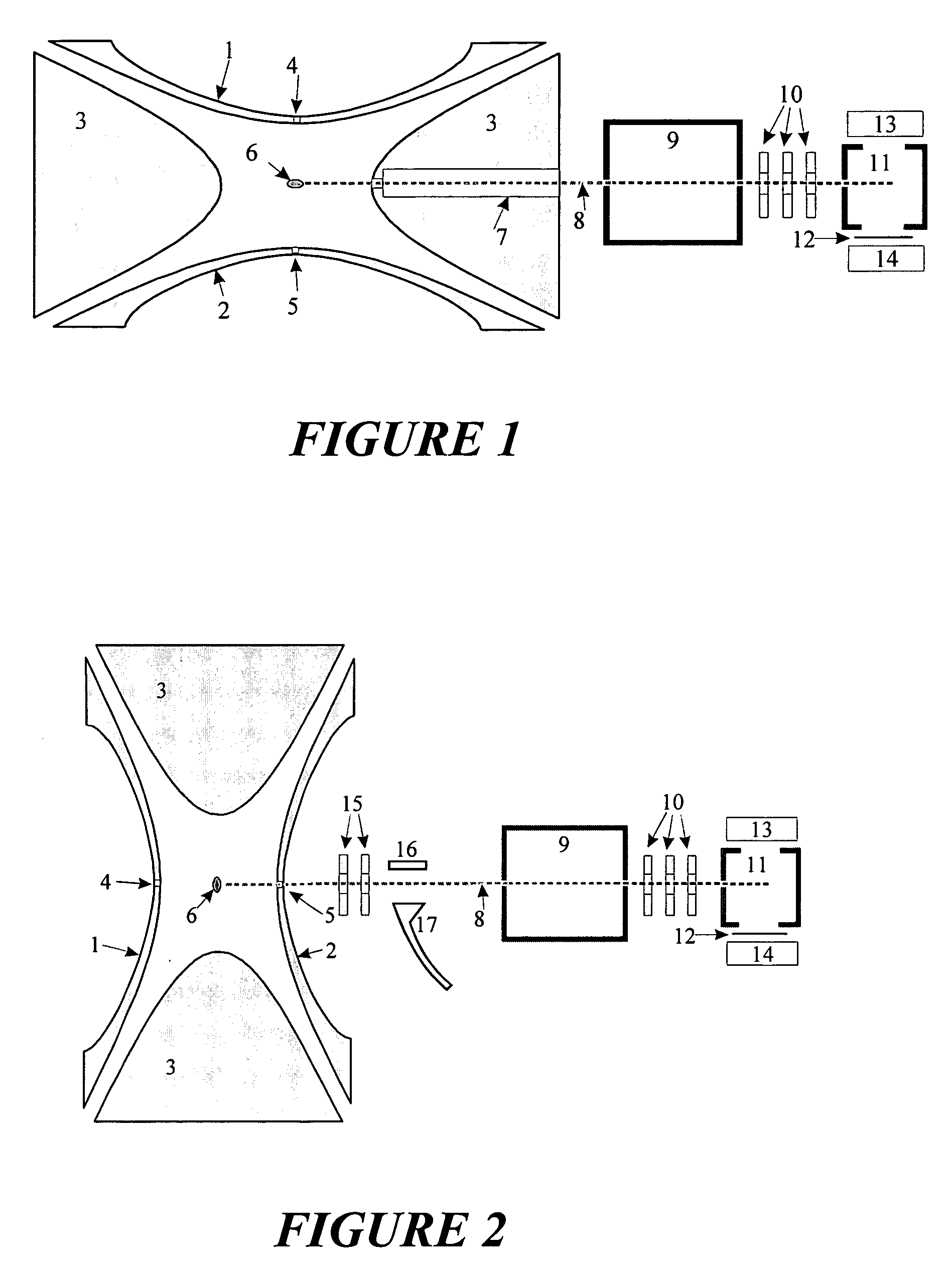
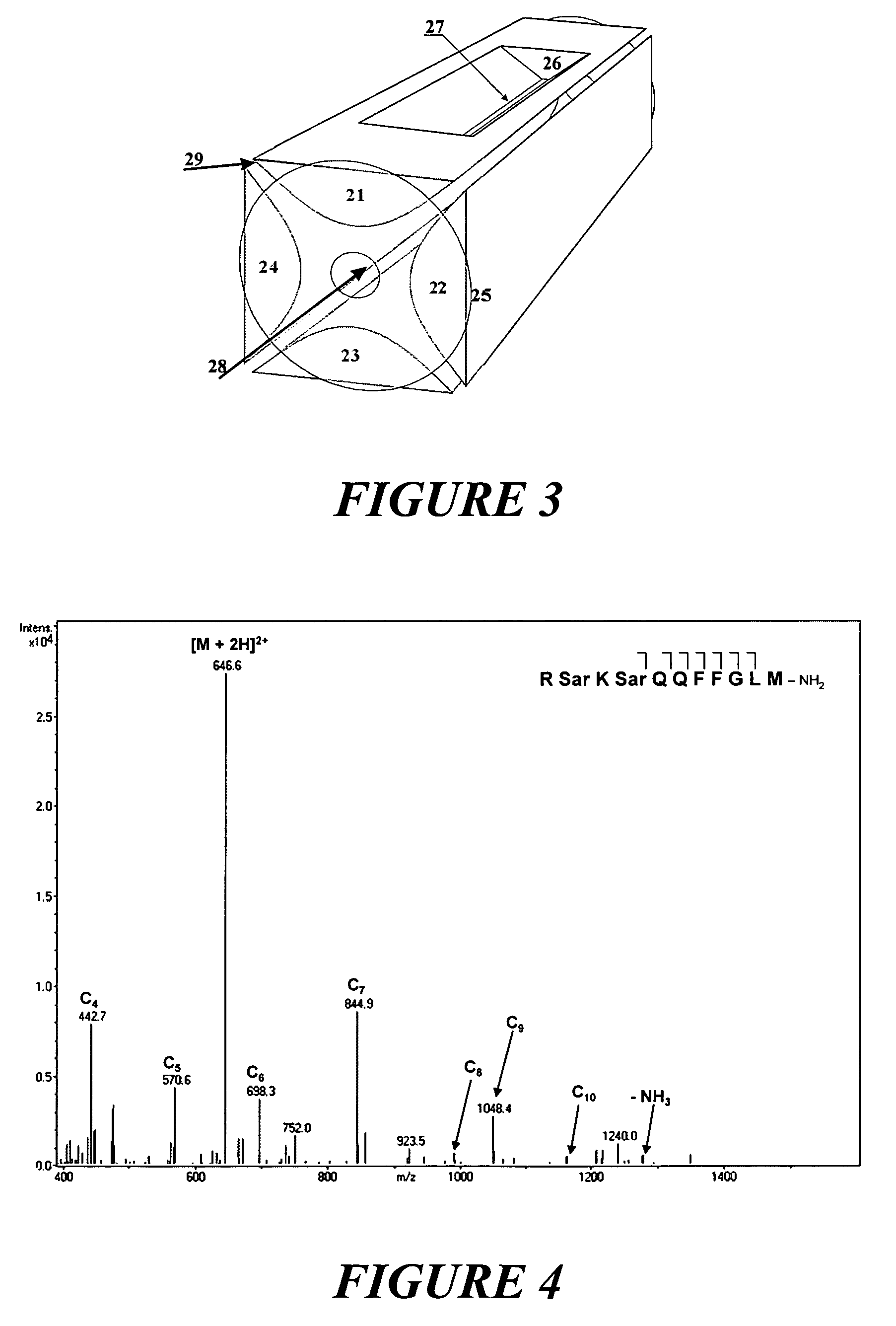
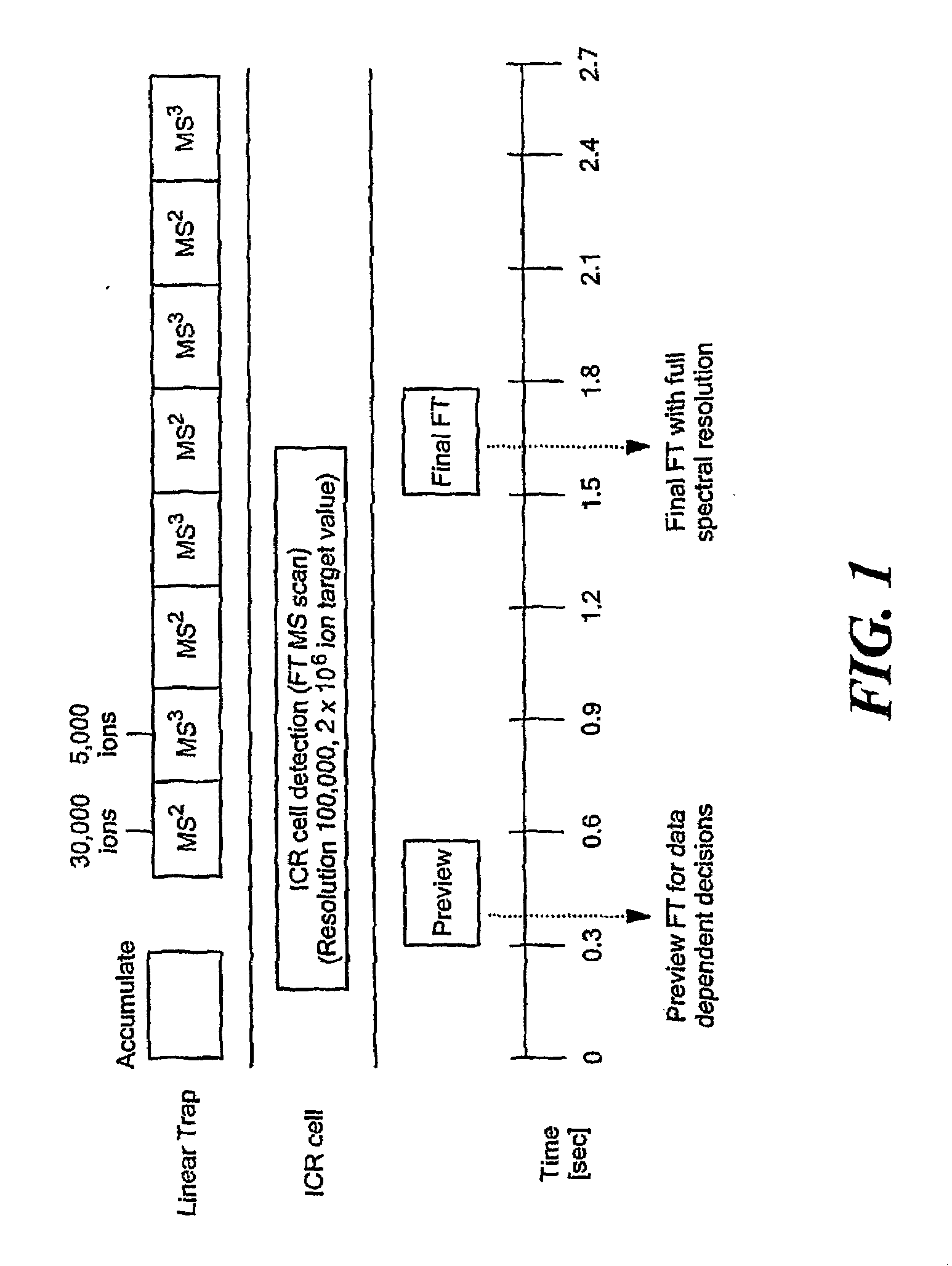
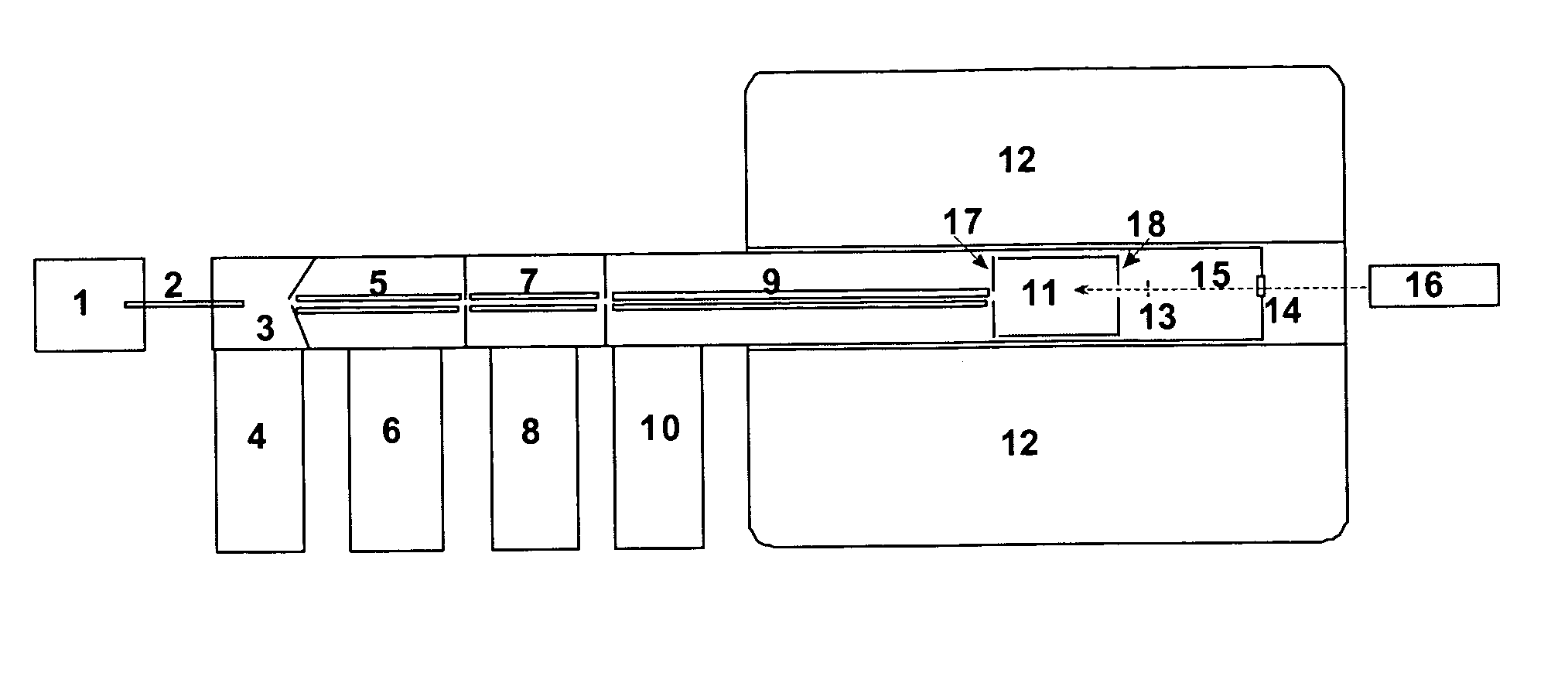
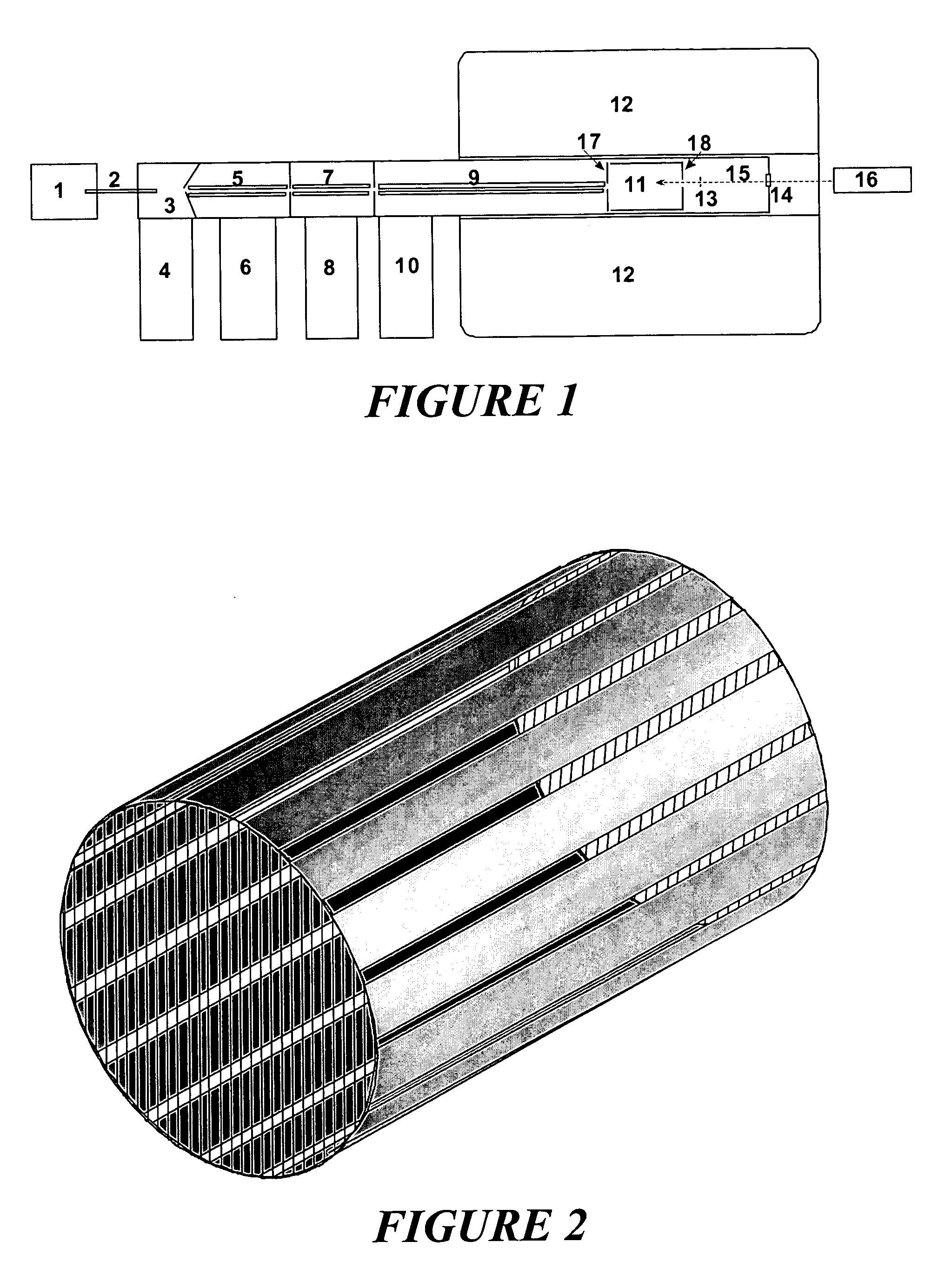
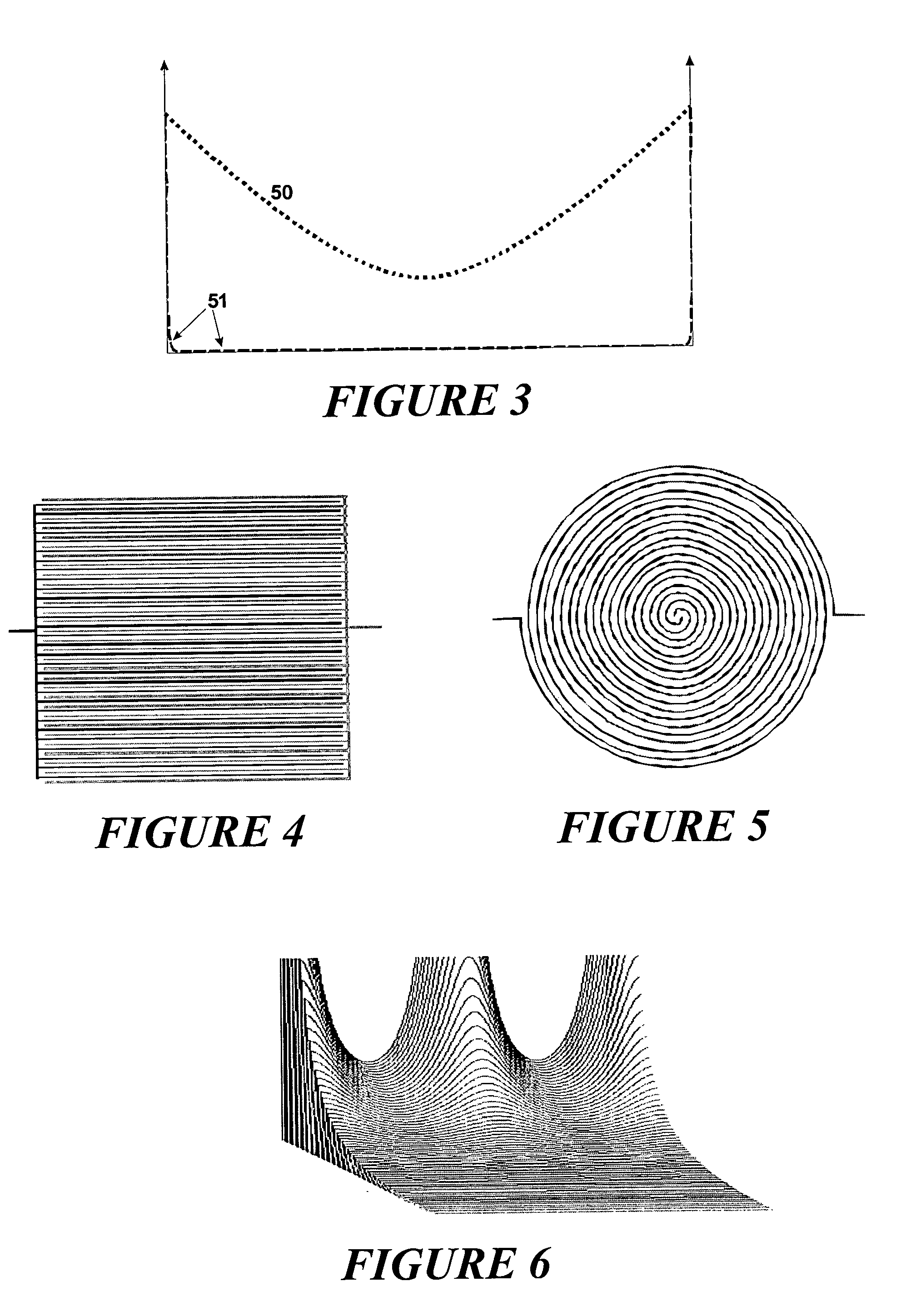
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
110 results about "Ion cyclotron resonance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
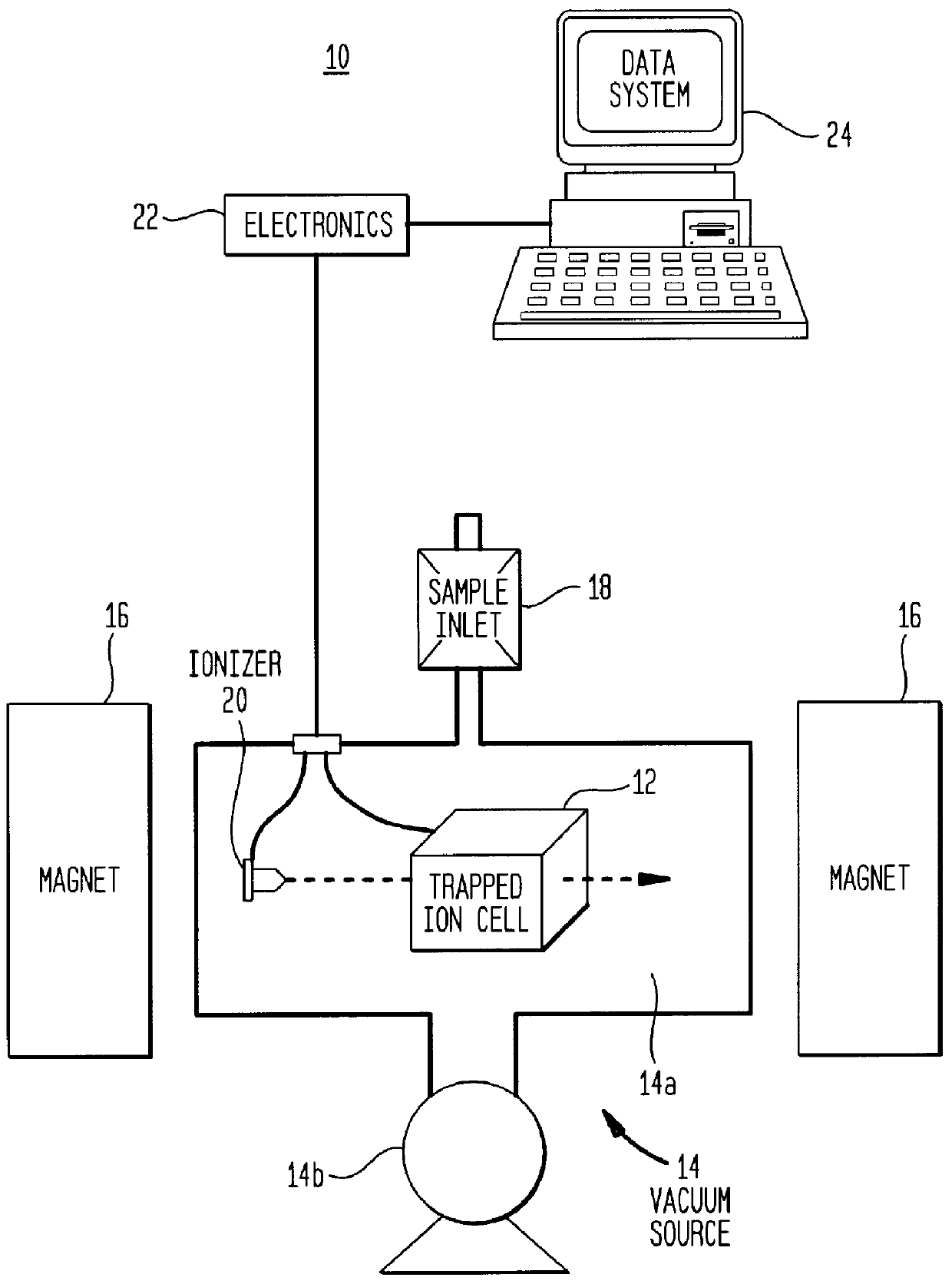
Ion cyclotron resonance is a phenomenon related to the movement of ions in a magnetic field. It is used for accelerating ions in a cyclotron, and for measuring the masses of an ionized analyte in mass spectrometry, particularly with Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometers. It can also be used to follow the kinetics of chemical reactions in a dilute gas mixture, provided these involve charged species.
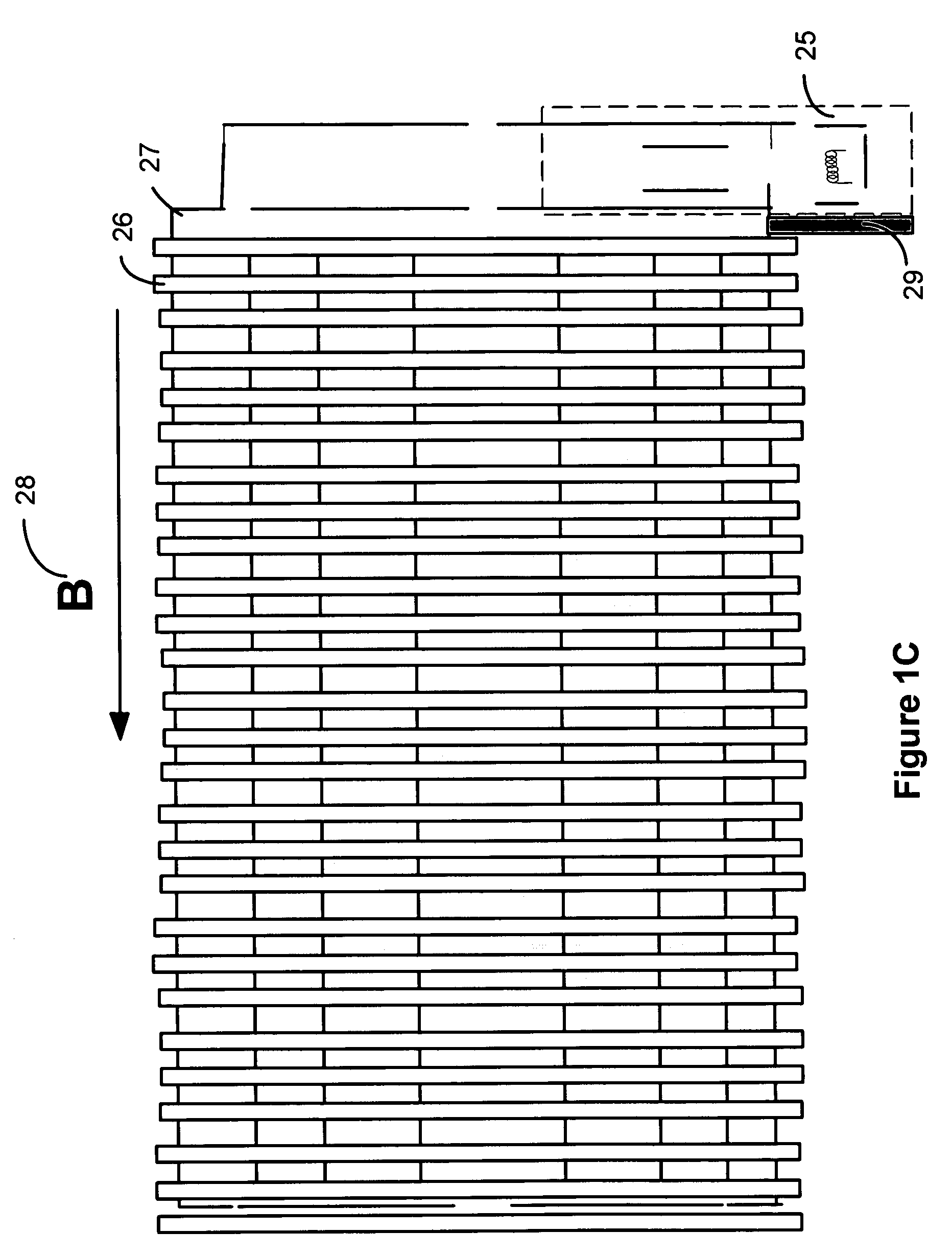
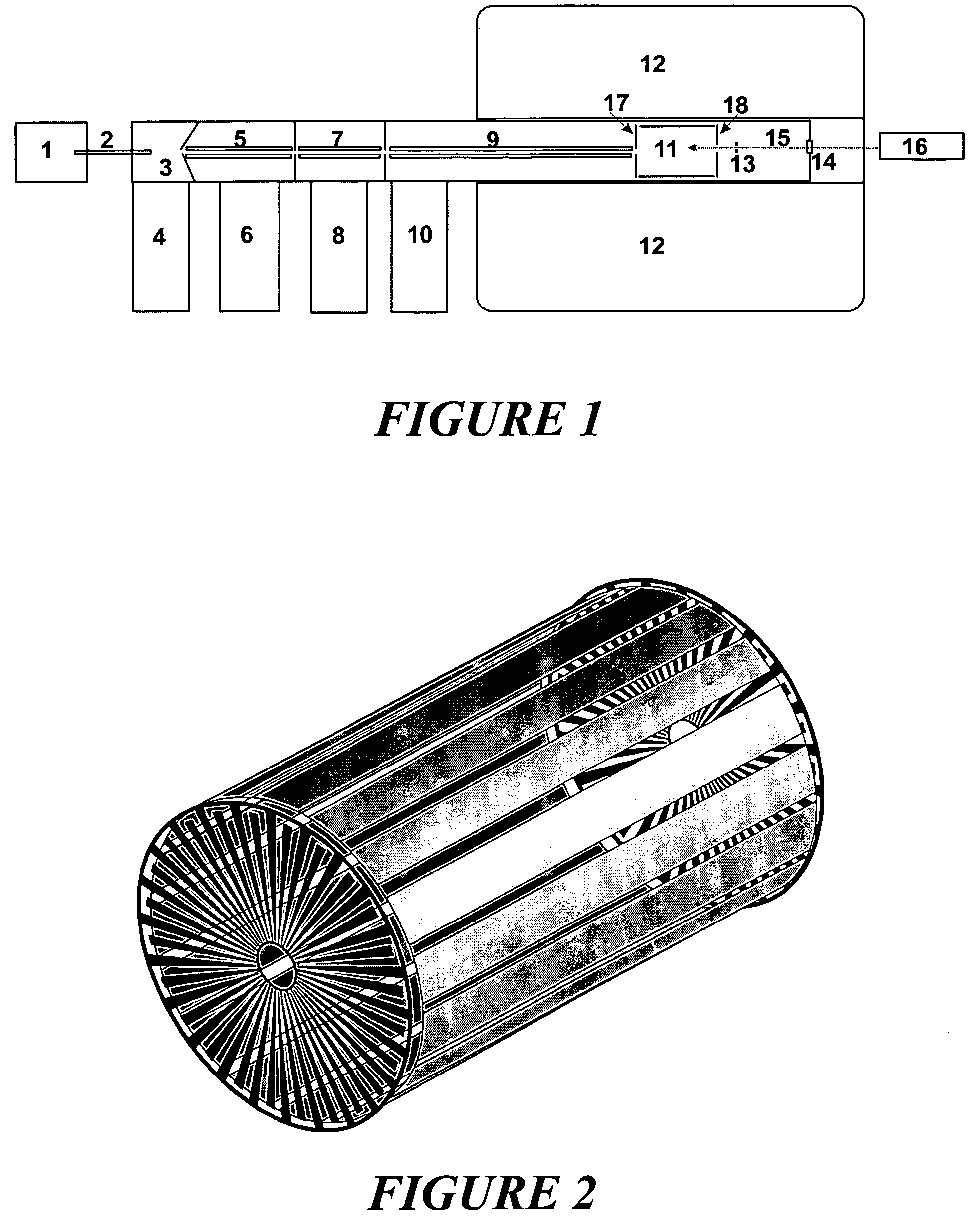
Fragmentation methods for mass spectrometry
InactiveUS6919562B1Shorten speedMinimizing velocityIsotope separationMass spectrometersMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass analyzer
Apparatus and methods are provided that enable the interaction of low-energy electrons and positrons with sample ions to facilitate electron capture dissociation (ECD) and positron capture dissociation (PCD), respectively, within multipole ion guide structures. It has recently been discovered that fragmentation of protonated ions of many biomolecules via ECD often proceeds along fragmentation pathways not accessed by other dissociation methods, leading to molecular structure information not otherwise easily obtainable. However, such analyses have been limited to expensive Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (FTICR) mass spectrometers; the implementation of ECD within commonly-used multipole ion guide structures is problematic due to the disturbing effects of RF fields within such devices. The apparatus and methods described herein successfully overcome such difficulties, and allow ECD (and PCD) to be performed within multipole ion guides, either alone, or in combination with conventional ion fragmentation methods. Therefore, improved analytical performance and functionality of mass spectrometers that utilize multipole ion guides are provided.
Owner:PERKINELMER U S LLC
Instrument for separating ions in time as functions of preselected ion mobility and ion mass
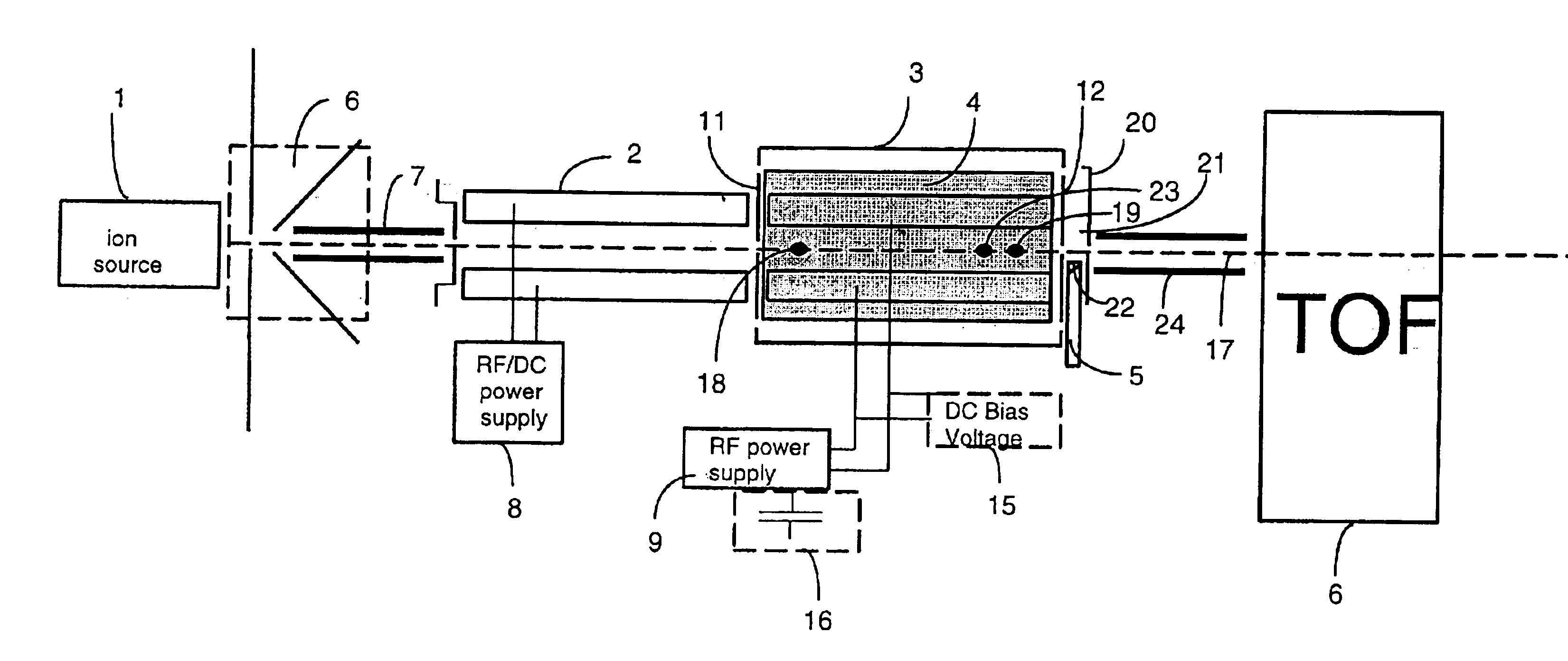
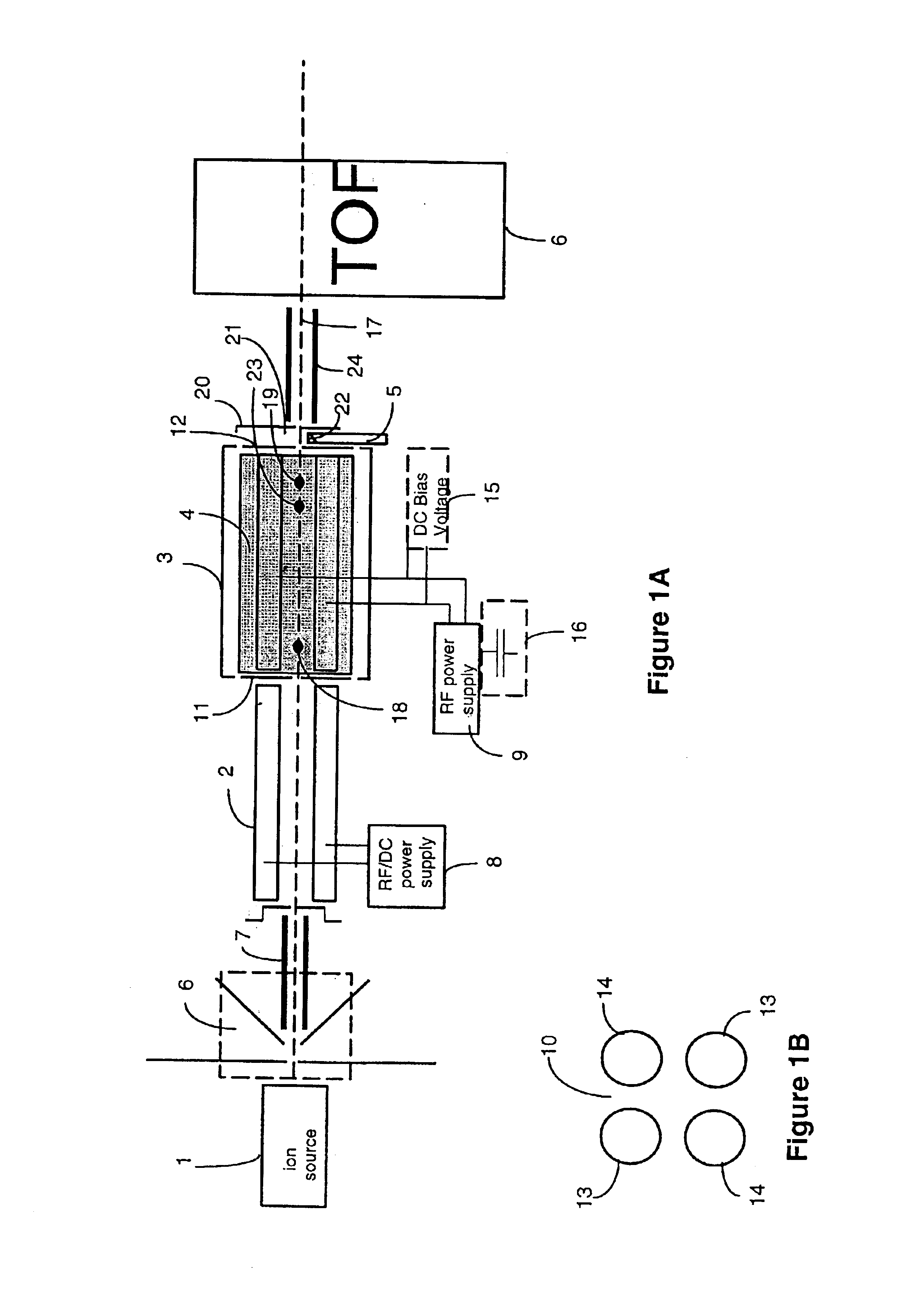
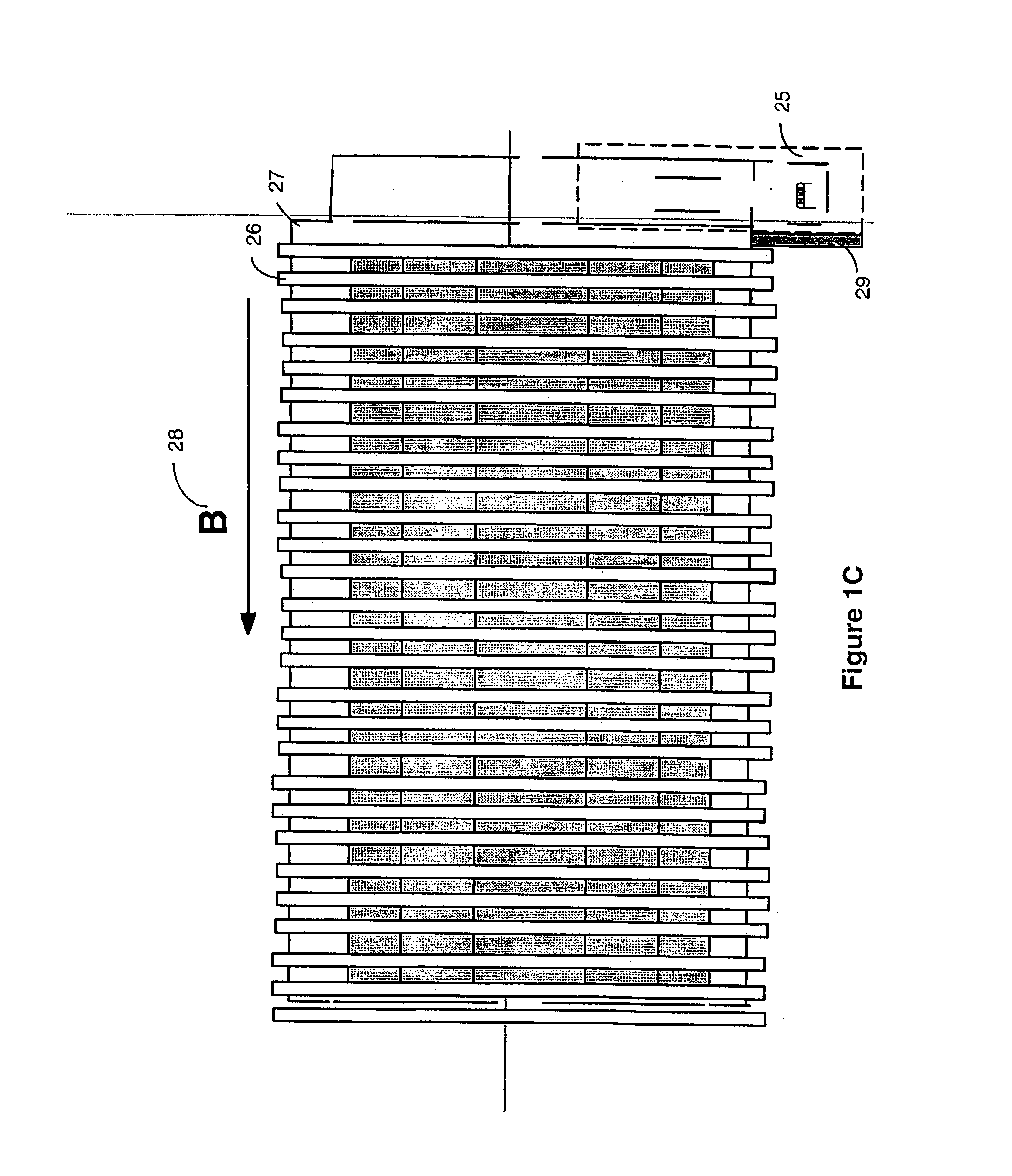
InactiveUS6960761B2Fast analysisFast sequencingTime-of-flight spectrometersIon-exchanger regenerationMass analyzerIon-mobility spectrometry
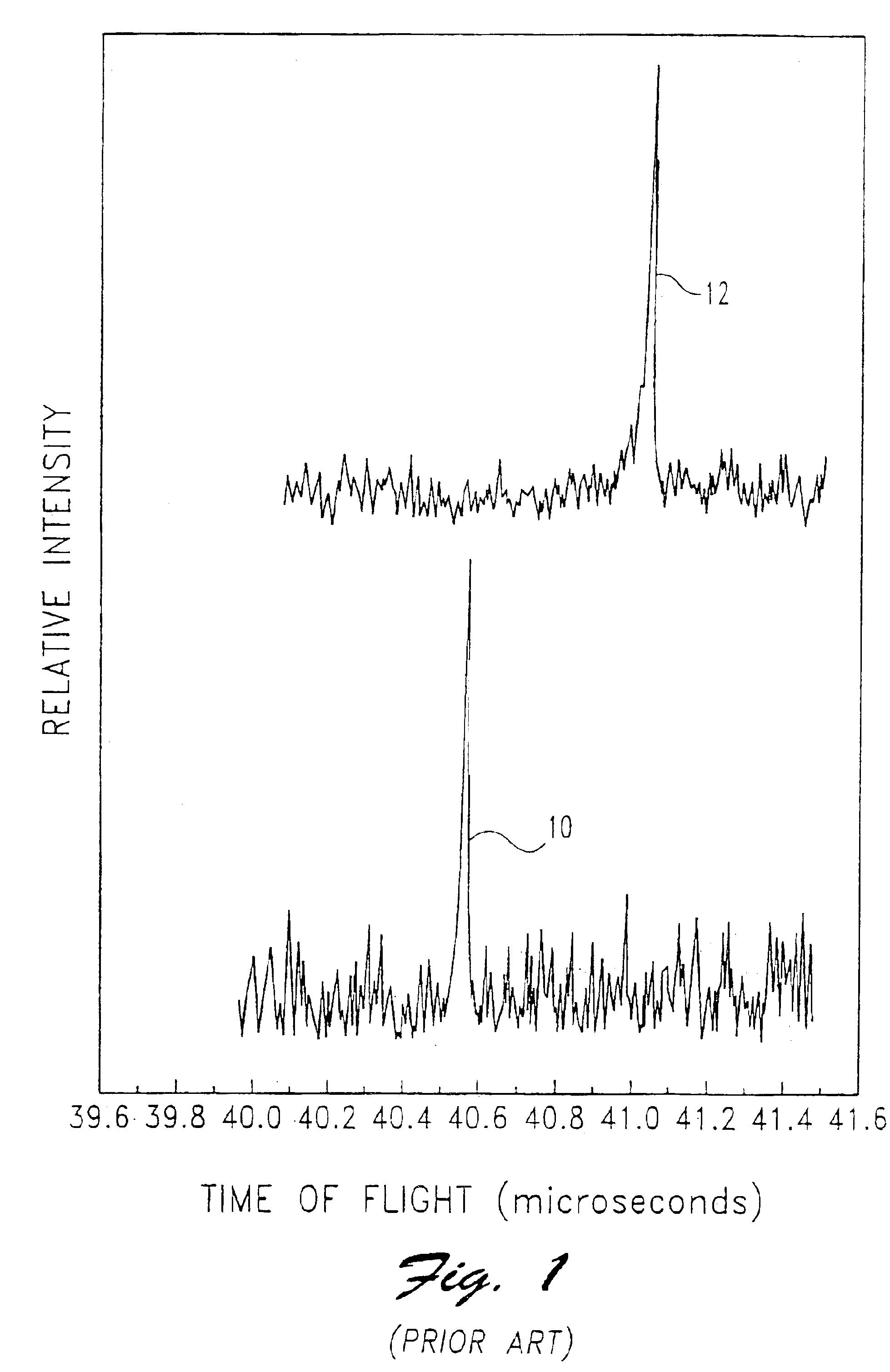
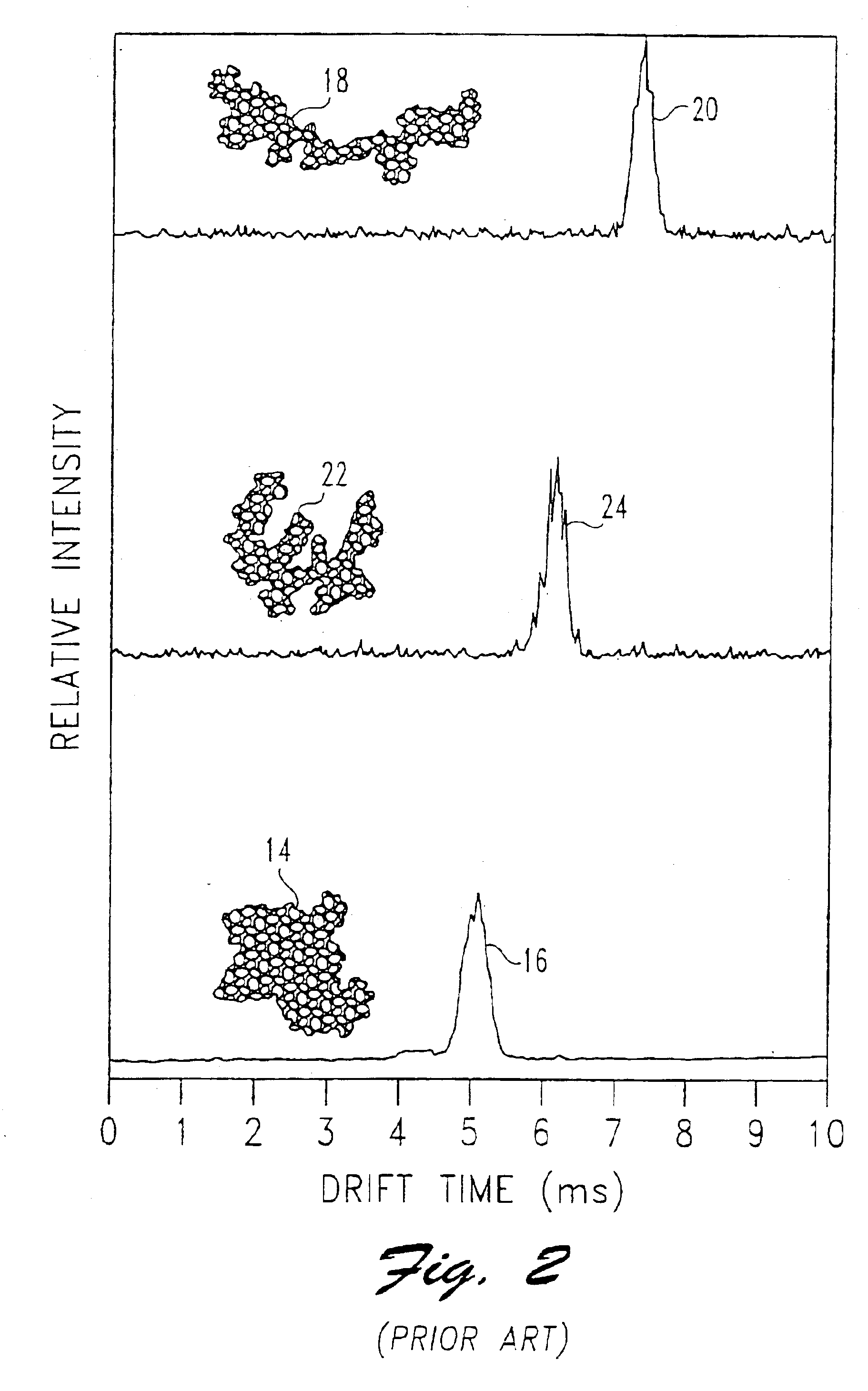
An ion separation instrument includes an ion source coupled to at least a first ion mobility spectrometer having an ion outlet coupled to a mass spectrometer. Instrumentation is further included to provide for passage to the mass spectrometer only ions defining a preselected ion mobility range. In one embodiment, the ion mobility spectrometer is provided with electronically controllable inlet and outlet gates, wherein a control circuit is operable to control actuation of the inlet and outlet gates as a function of ion drift time to thereby allow passage therethrough only of ions defining a mobility within the preselected ion mobility range. In another embodiment, an ion trap is disposed between the ion mobility spectrometer and mass spectrometer and is controlled in such a manner so as to collect a plurality of ions defining a mobility within the preselected ion mobility range prior to injection of such ions into the mass spectrometer. In yet another embodiment, an ion inlet of the ion trap may be electronically controlled relative to operation of the ion mobility spectrometer as a function of ion drift time to thereby allow passage therein only of ions defining a mobility within the preselected ion mobility range. The mass spectrometer is preferably a Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance mass spectrometer, and the resulting ion separation instrument may further include therein various combinations of ion fragmentation, ion mass filtering, ion trap, charge neutralization and / or mass reaction instrumentation.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Fragmentation methods for mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7049584B1Control outflowReduce stressIsotope separationMass spectrometersMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryElectron-capture dissociation
Owner:PERKINELMER U S LLC
Tandem mass spectrometry method
ActiveUS6924478B1Shorten analysis timeHigh sensitivityStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersIon trap mass spectrometryMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
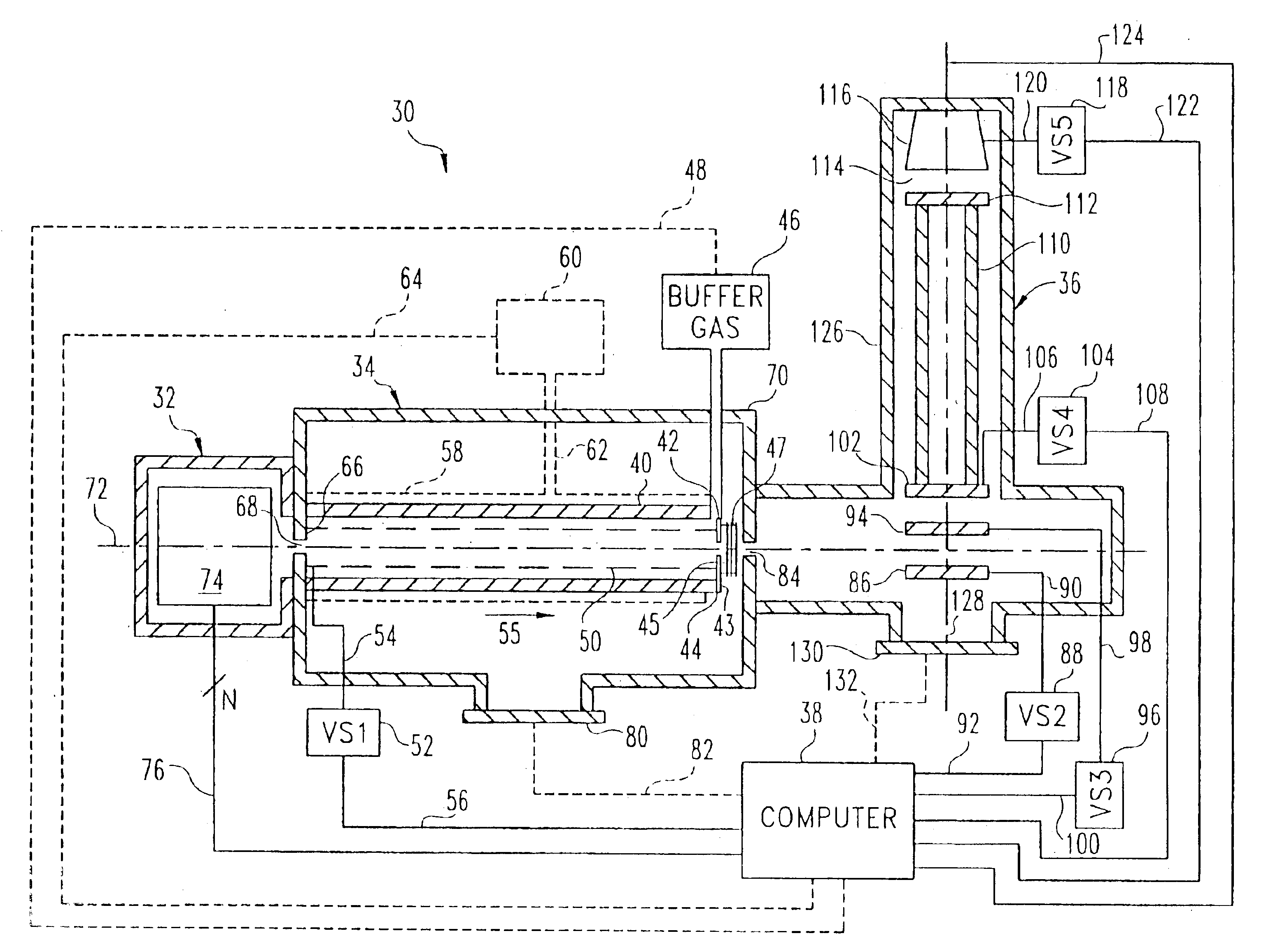
Multiply charged ions are trapped and accumulated in a spatially limited region before being injected into an ion trap mass spectrometer such as a Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer (FTICR MS). In the ion trap electron capture dissociation (ECD) and vibrational excitation dissociation are sequentially applied on ions of the same ion ensemble. The first dissociation process does not fragment all primary ions. Following the detection of the dissociation products, the primary ions that remain undissociated undergo the vibrational excitation and again, a part of them dissociate, and the fragments are detected. Thus, the same ion ensemble is used for two fragmentation processes. During these processes, further ions generated in the external ion source are accumulated in the spatially limited region for subsequent analyses.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Ion fragmentation by reaction with neutral particles
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for the fragmentation of large molecules, especially biopolymers. The invention consists in reacting analyte ions with excited or radical neutral particles, whereby, at least in the case of bombardment of analyte ions with helium atoms from an FAB generator, a new type of fragmentation occurs which strongly resembles fragmentation by electron capture (ECD). The reactions may be performed in magnetic ion traps (ion cyclotron resonance cells, ICR), in RF ion traps according to Wolfgang Paul, in RF ion guides, or in free beams of analyte ions or neutral particles.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Slotted antenna waveguide plasma source
InactiveUS7305935B1Improve scalabilityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingWaveguideIon implantation
A high density plasma generated by microwave injection using a windowless electrodeless rectangular slotted antenna waveguide plasma source has been demonstrated. Plasma probe measurements indicate that the source could be applicable for low power ion thruster applications, ion implantation, and related applications. This slotted antenna plasma source invention operates on the principle of electron cyclotron resonance (ECR). It employs no window and it is completely electrodeless and therefore its operation lifetime is long, being limited only by either the microwave generator itself or charged particle extraction grids if used. The high density plasma source can also be used to extract an electron beam that can be used as a plasma cathode neutralizer for ion source beam neutralization applications.
Owner:NASA
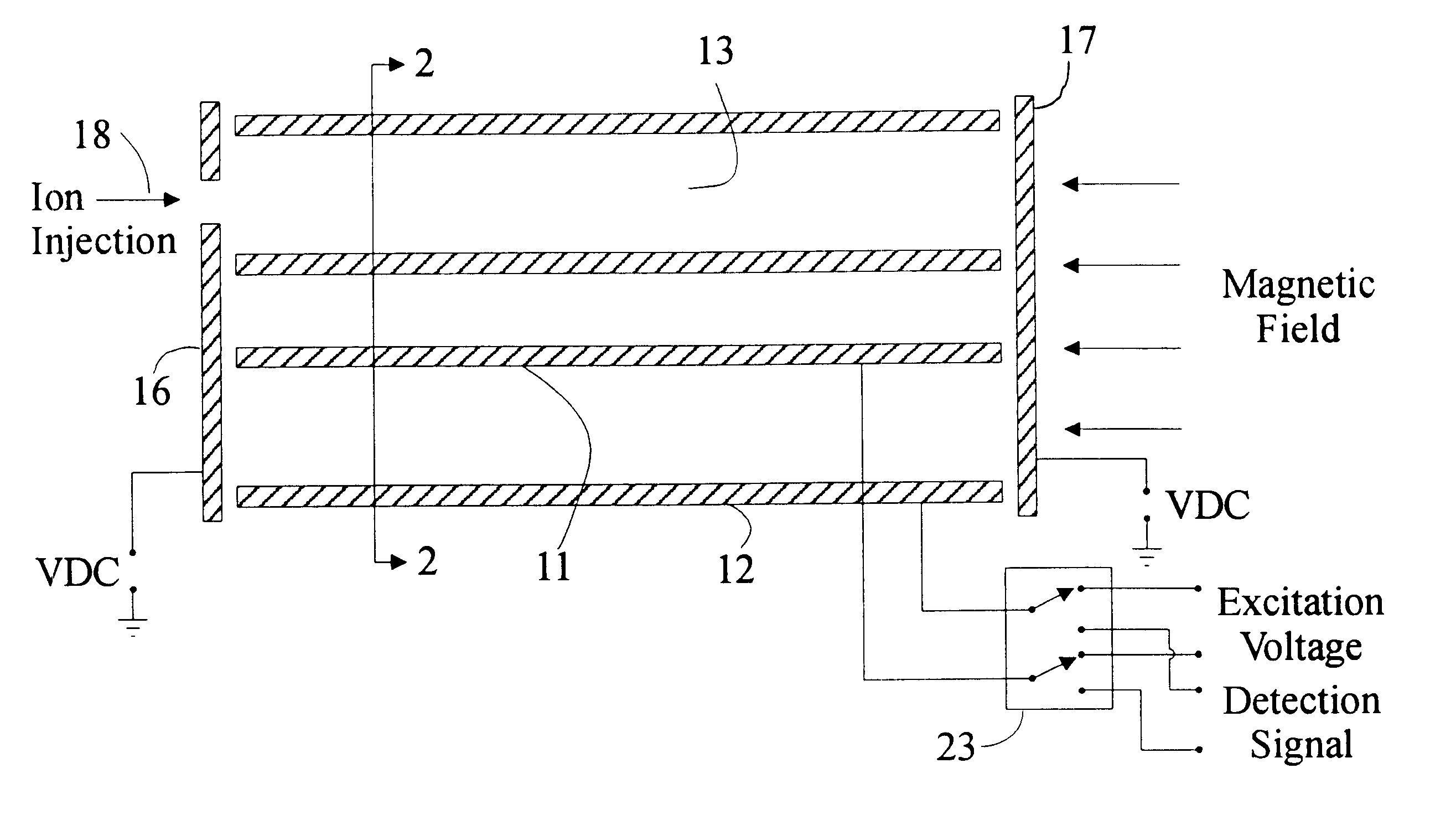
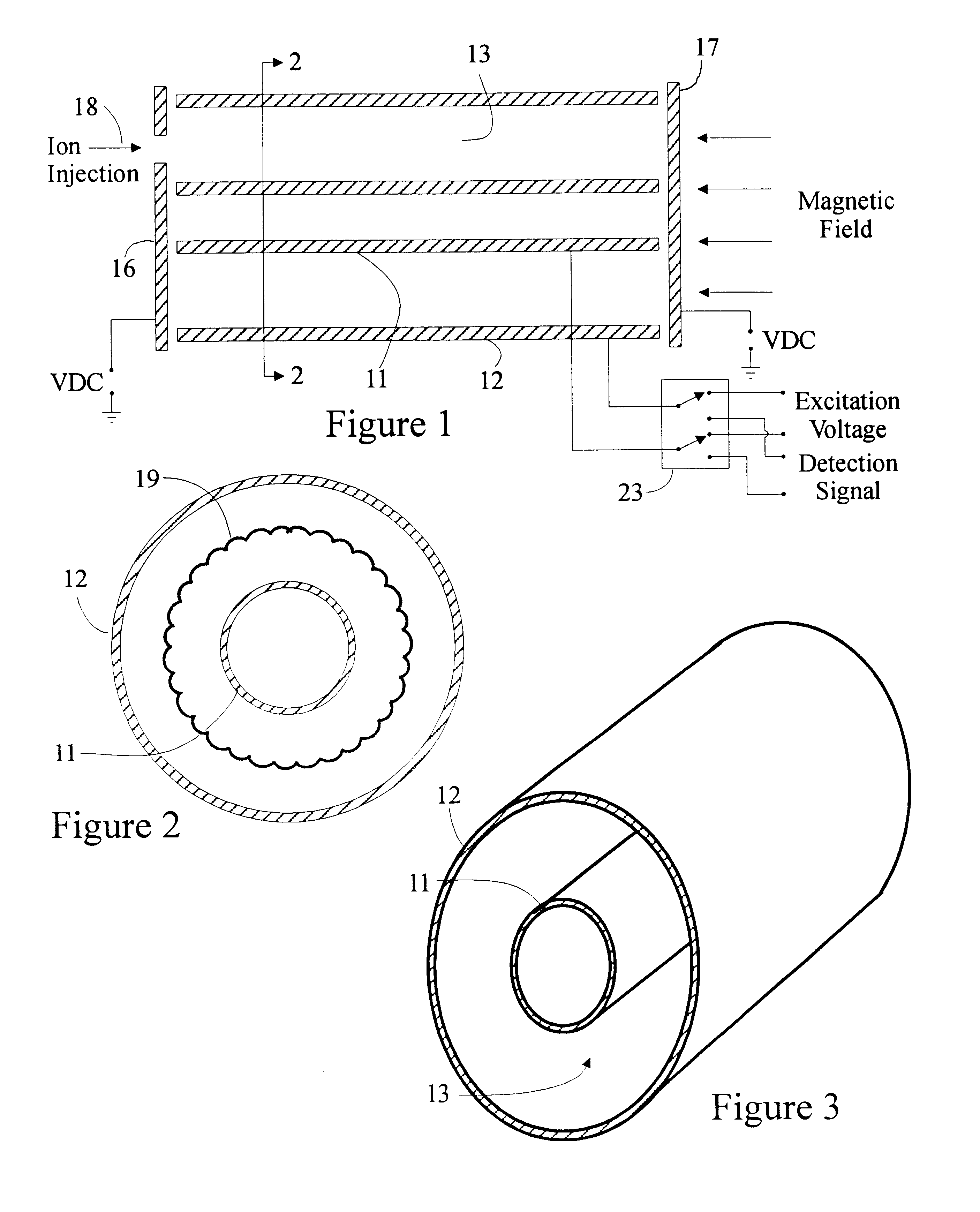
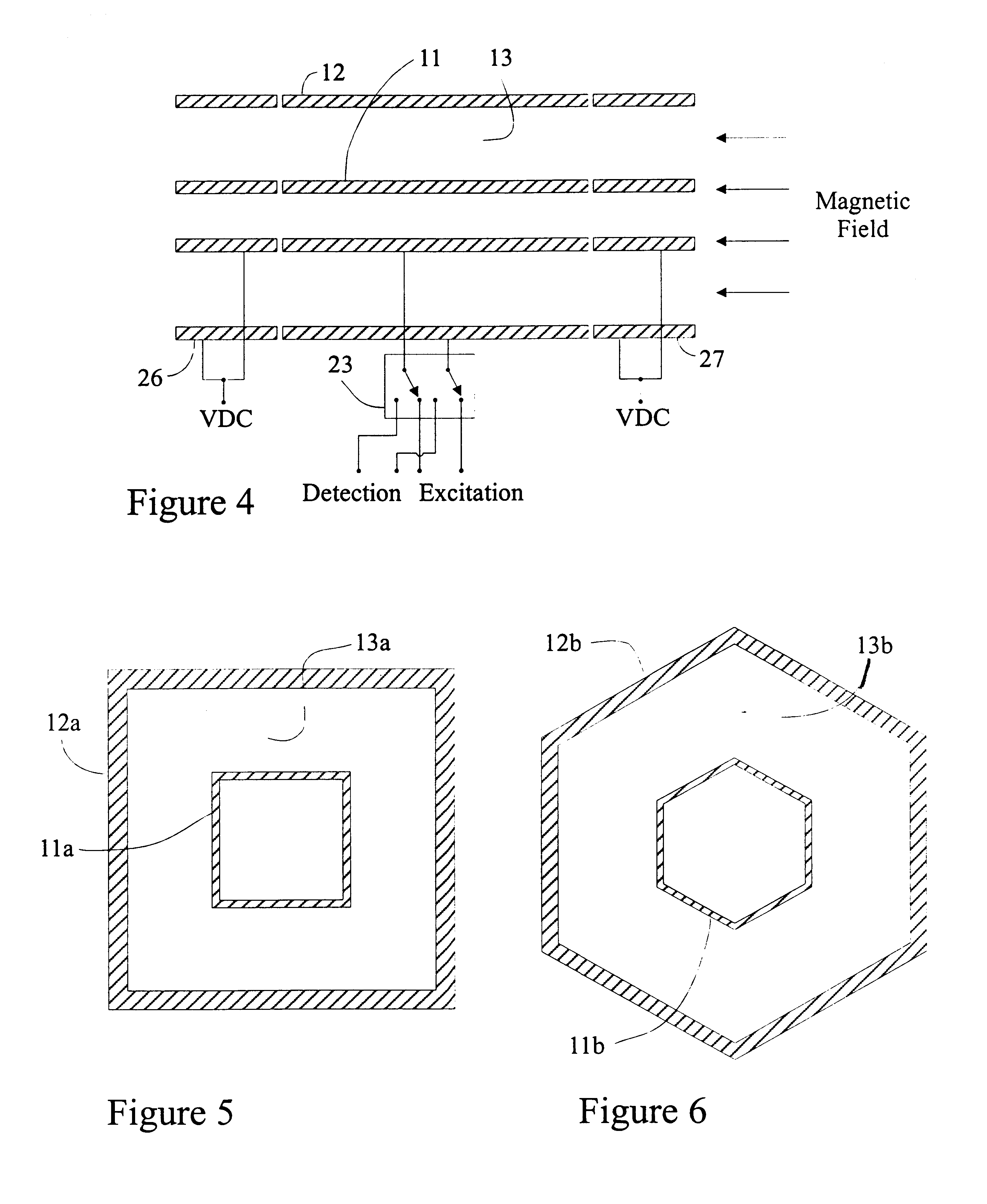
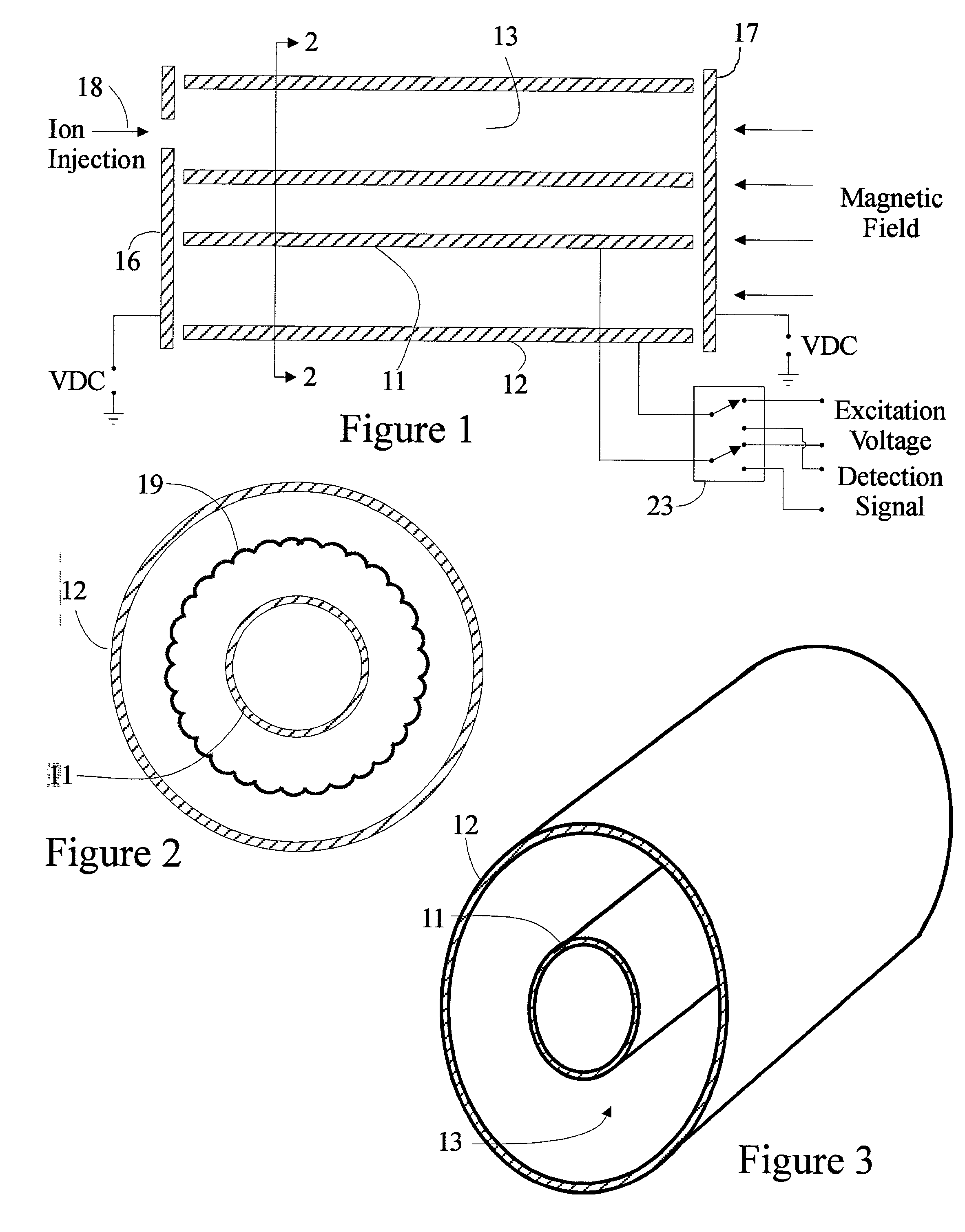
Measuring methods for ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometers
ActiveUS20060226357A1Easy to detectIncrease the number ofMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIsotope separationTrappingElectrical polarity
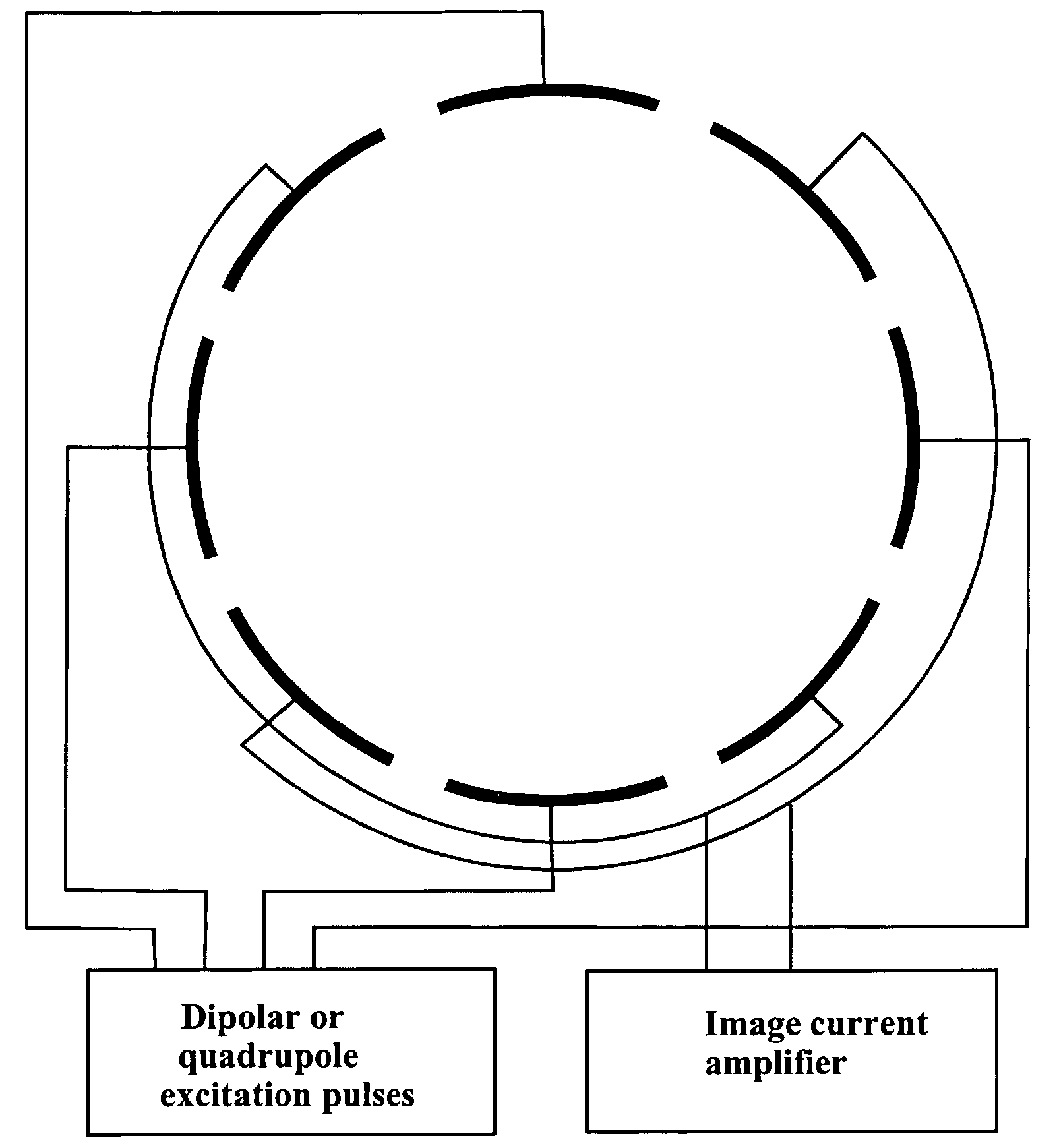
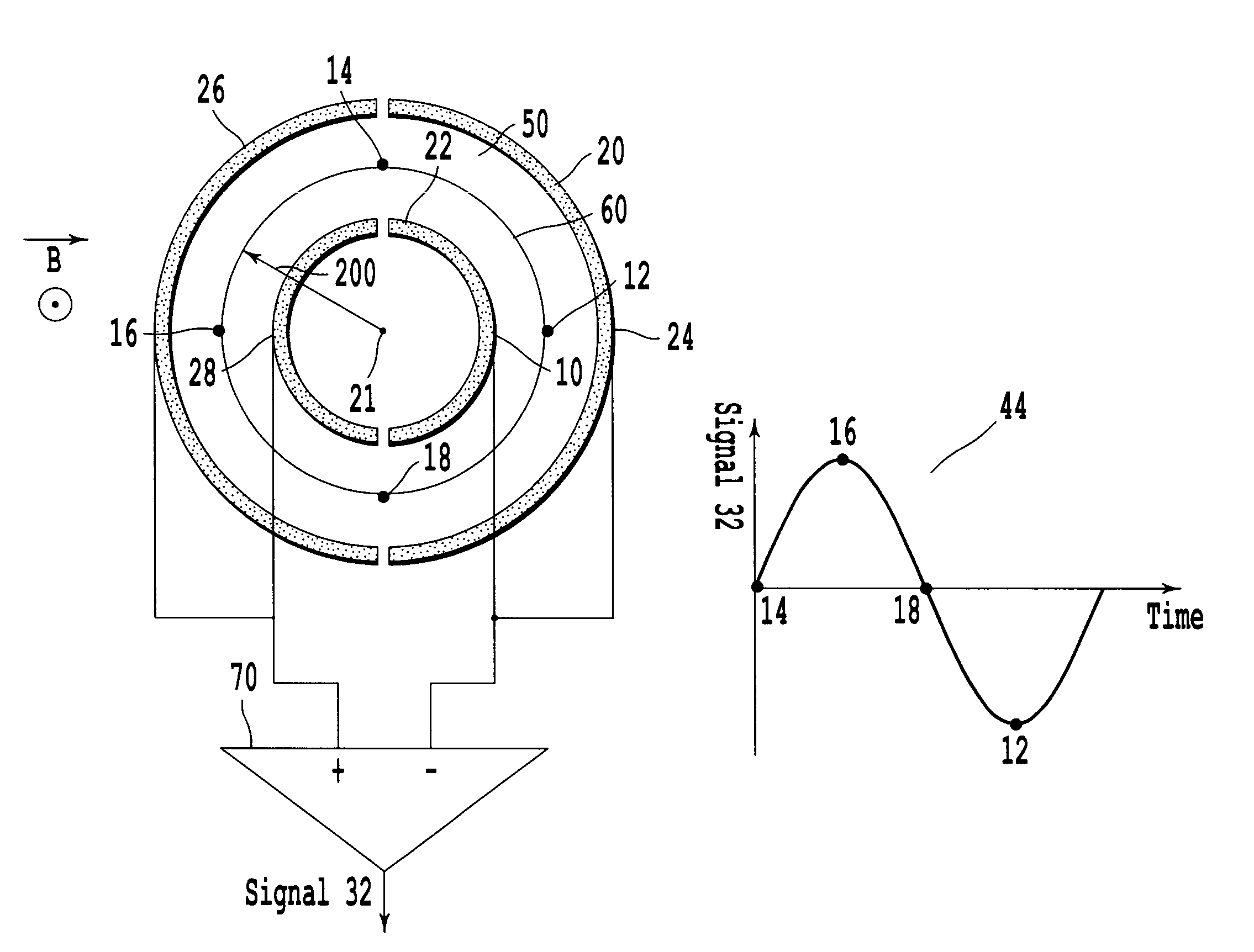
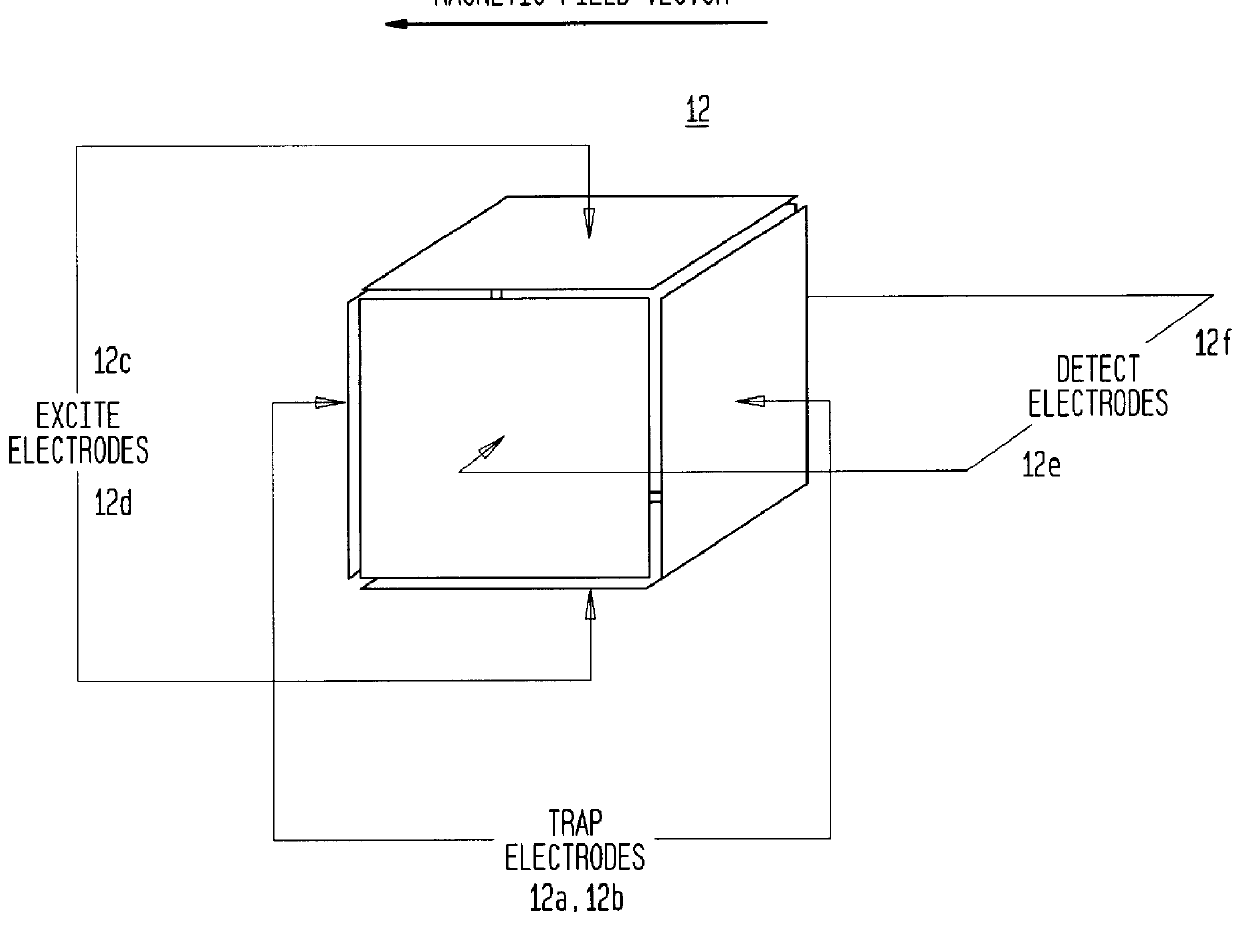
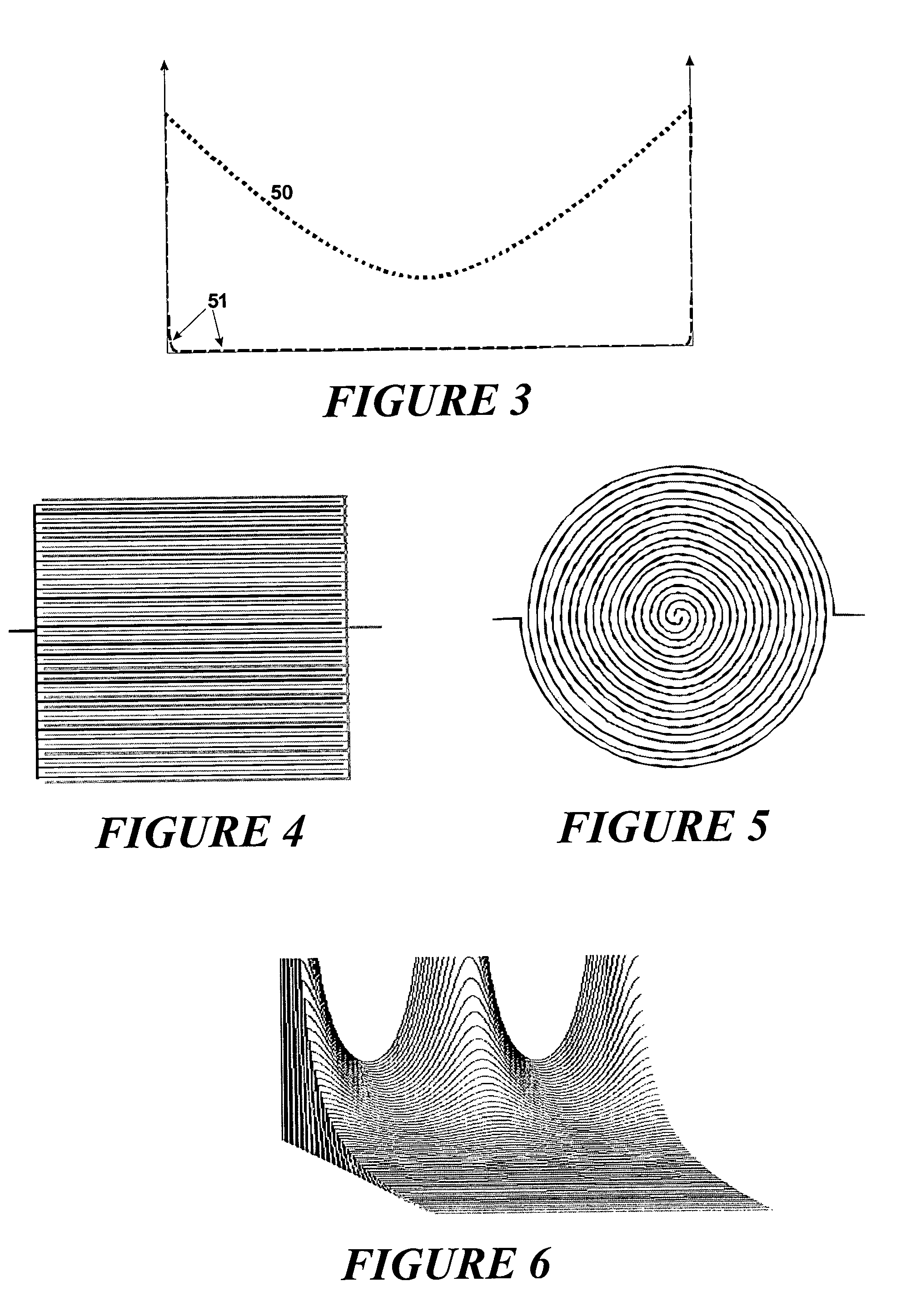
The invention relates to measuring methods and corresponding measuring cells for ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometers (FTMS). The invention provides measuring methods with measuring cells, the ends of which each incorporate a large number of trapping electrodes, DC voltages of opposite polarities being applied across adjacent electrodes. For orbiting ions this builds up a repelling pseudopotential, which holds the ions in the measuring cell by reflection. This facilitates measurement of the image currents without the disturbing influence of RF voltages
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Instrument for separating ions in time as functions of preselected ion mobility and ion mass
InactiveUS7077944B2Rapid analysis and sequencingTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMass analyzerIon-mobility spectrometry
An ion separation instrument includes an ion source coupled to at least a first ion mobility spectrometer having an ion outlet coupled to a mass spectrometer. Instrumentation is further included to provide for passage to the mass spectrometer only ions defining a preselected ion mobility range. In one embodiment, the ion mobility spectrometer is provided with electronically controllable inlet and outlet gates, wherein a control circuit is operable to control actuation of the inlet and outlet gates as a function of ion drift time to thereby allow passage therethrough only of ions defining a mobility within the preselected ion mobility range. In another embodiment, an ion trap is disposed between the ion mobility spectrometer and mass spectrometer and is controlled in such a manner so as to collect a plurality of ions defining a mobility within the preselected ion mobility range prior to injection of such ions into the mass spectrometer. In yet another embodiment, an ion inlet of the ion trap may be electronically controlled relative to operation of the ion mobility spectrometer as a function of ion drift time to thereby allow passage therein only of ions defining a mobility within the preselected ion mobility range. The mass spectrometer is preferably a Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance mass spectrometer, and the resulting ion separation instrument may further include therein various combinations of ion fragmentation, ion mass filtering, ion trap, charge neutralization and / or mass reaction instrumentation.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
Measuring methods for ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometers
ActiveUS7495211B2Easy to detectSmall diameterMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIsotope separationTrappingElectrical polarity
The invention relates to measuring methods and corresponding measuring cells for ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometers (FTMS). The invention provides measuring methods with measuring cells, the ends of which each incorporate a large number of trapping electrodes, DC voltages of opposite polarities being applied across adjacent electrodes. For orbiting ions this builds up a repelling pseudopotential, which holds the ions in the measuring cell by reflection. This facilitates measurement of the image currents without the disturbing influence of RF voltages.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Estimation of ion cyclotron resonance parameters in fourier transform mass spectrometry
ActiveUS20090278037A1Improve correspondenceImprove accuracyCurrent/voltage measurementIsotope separationFourier transform on finite groupsMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The present invention comprises a method and system for accurate estimation of the ion cyclotron resonance (ICR) parameters in Fourier-transform mass spectrometry (FTMS / FT-ICR MS). The parameters are essential to estimating the mass to charge ratio of an ion from FT-ICR MS data, the intended purpose of the instrument. Achieving greater accuracy in the parameters assists in greater accuracy of the mass to charge ratio of an ion, and obtaining an accurate estimation of the mass to charge ratio of an ion further aides in detecting mass with sub-ppm accuracy. Estimating mass in this manner enhances identification and characterization of large molecules. The inventive method and system thereby enhances the data obtained by conventional FTMS by accurately estimating ICR parameters. Ultimately, accurate estimates of the masses of molecules and detection and characterization of molecules from FT-ICR MS data are obtained.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Ion fragmentation by reaction with neutral particles
ActiveUS20060192100A1Optical radiation measurementSugar derivativesIon trap mass spectrometryAnalyte
The invention relates to a method and apparatus for the fragmentation of large molecules, especially biopolymers. The invention consists in reacting analyte ions with excited or radical neutral particles, whereby, at least in the case of bombardment of analyte ions with helium atoms from an FAB generator, a new type of fragmentation occurs which strongly resembles fragmentation by electron capture (ECD). The reactions may be performed in magnetic ion traps (ion cyclotron resonance cells, ICR), in RF ion traps according to Wolfgang Paul, in RF ion guides, or in free beams of analyte ions or neutral particles.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
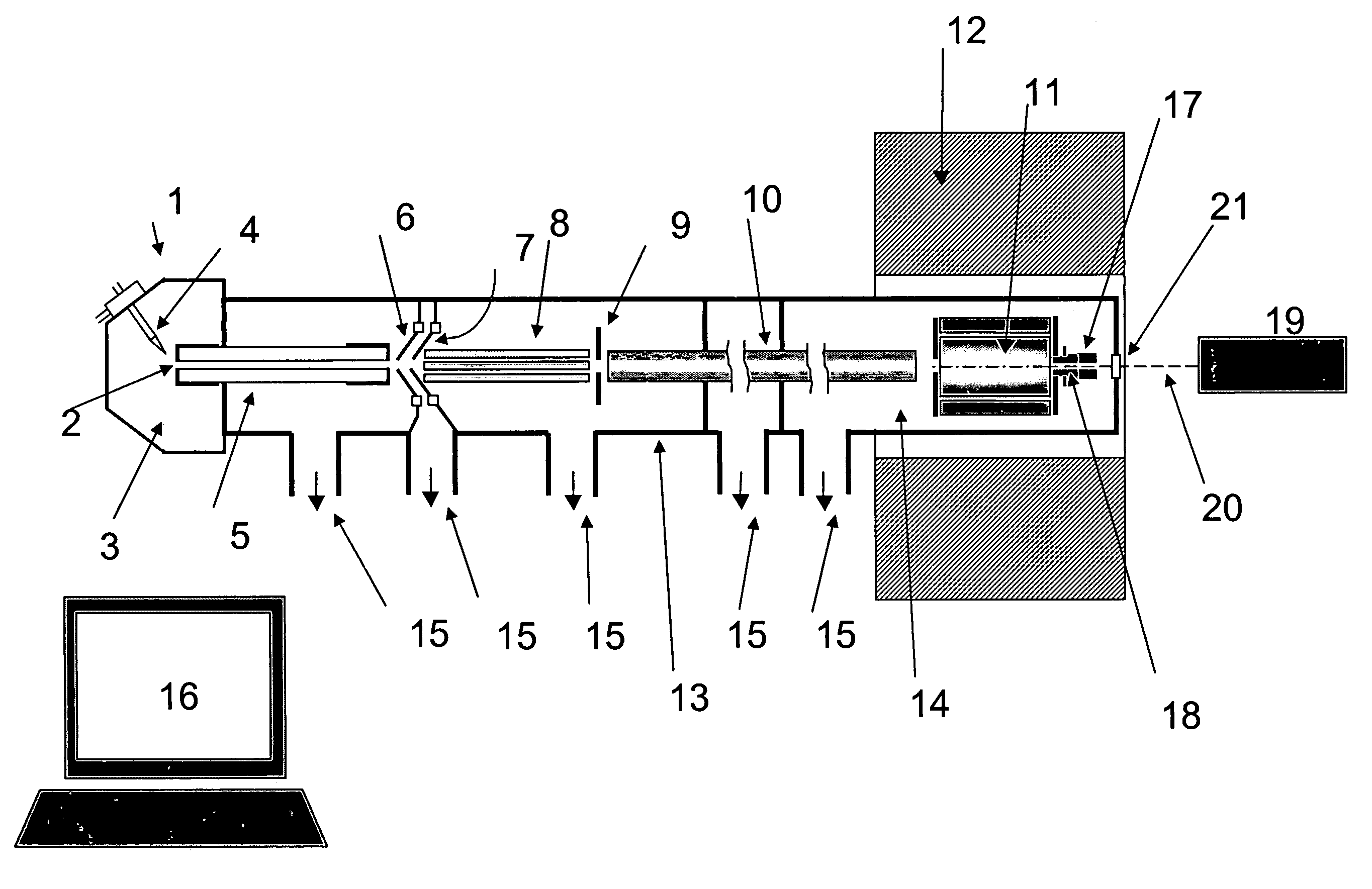
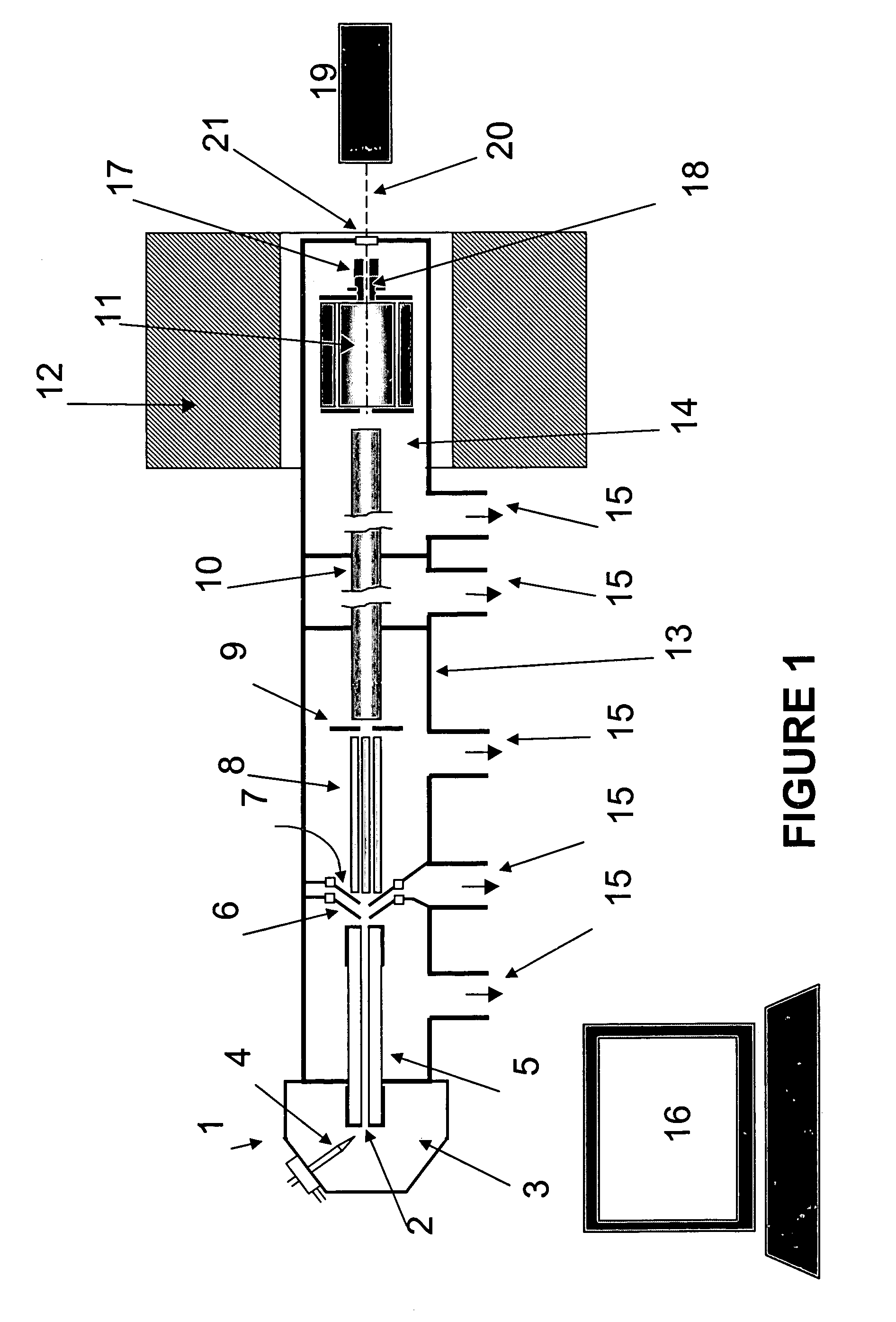
Method and apparatus for fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry
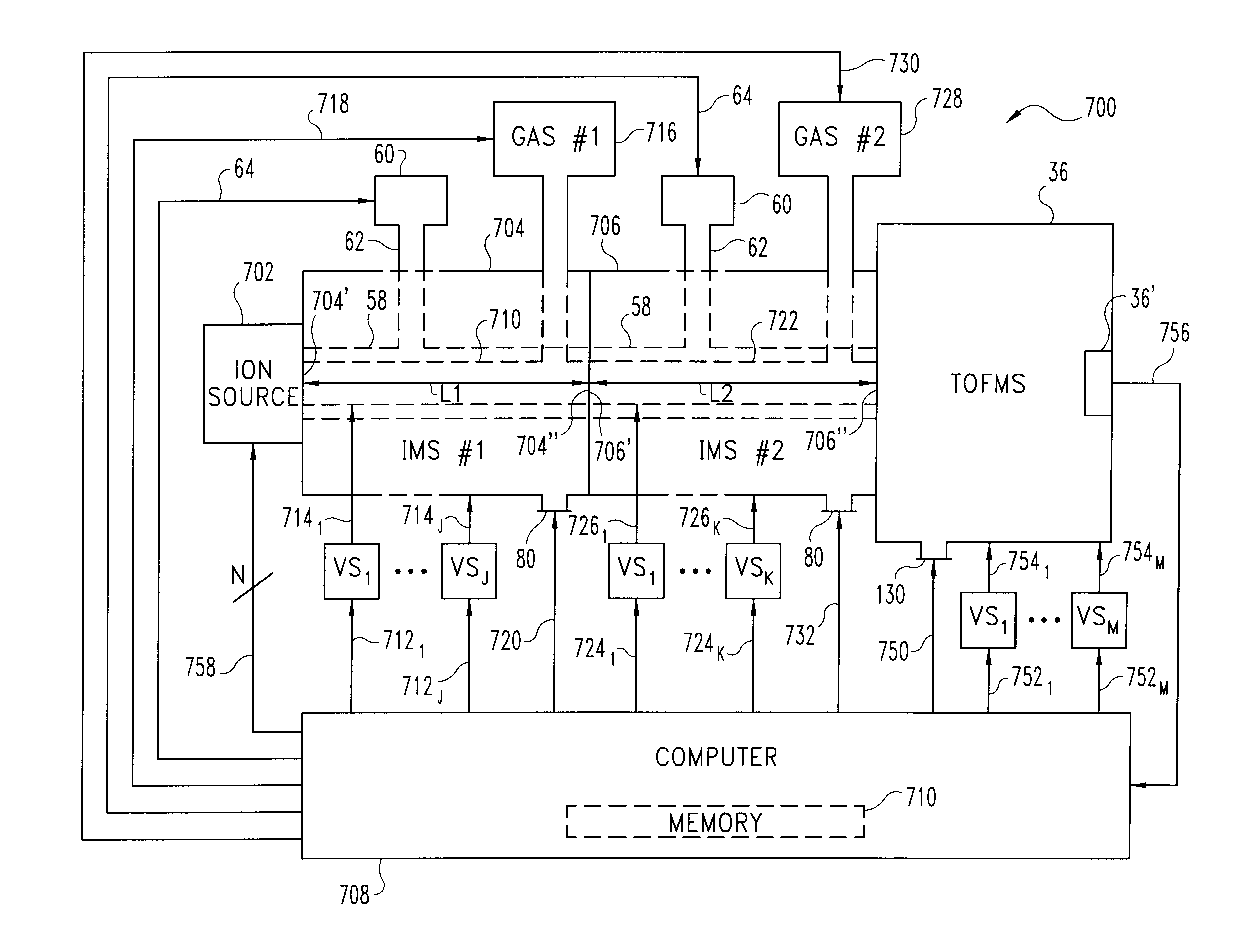
InactiveUS20090057553A1Isotope separationOmegatronsIon trap mass spectrometryMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
A novel method and apparatus for Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry (FTICR-MS). The FTICR-MS apparatus has a pre-ICR mass separation and filtering device capable of receiving ionized molecules with a plurality of mass to charge (M / Z) sub-ranges. The pre-ICR mass separation and filtering device divides the ionized molecules into a plurality of smaller packets, each of the smaller packets is within one of the M / Z sub-ranges. A magnet in the FTICR-MS apparatus provides a controlled magnetic field. A plurality of ion cyclotron resonance (ICR) cells are arranged in series in the controlled magnetic field and operate independently. An ion trapping device connects the pre-ICR mass separation and filtering device, and stores one of the plurality of smaller packets, prior to sending it to one of the plurality of ICR cells.
Owner:MED LIFE DISCOVERIES LP
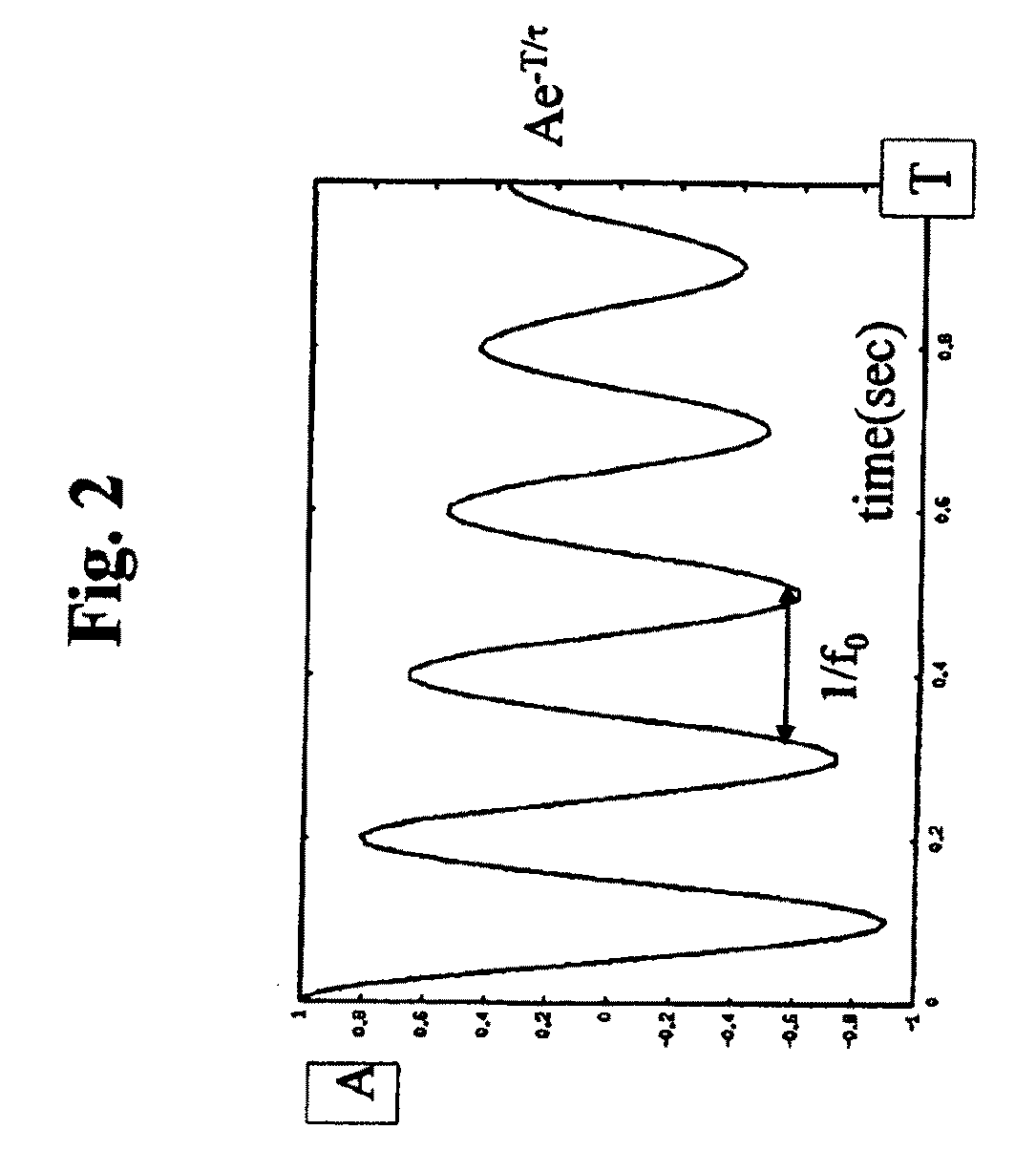
Spectral deconvolution in ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry
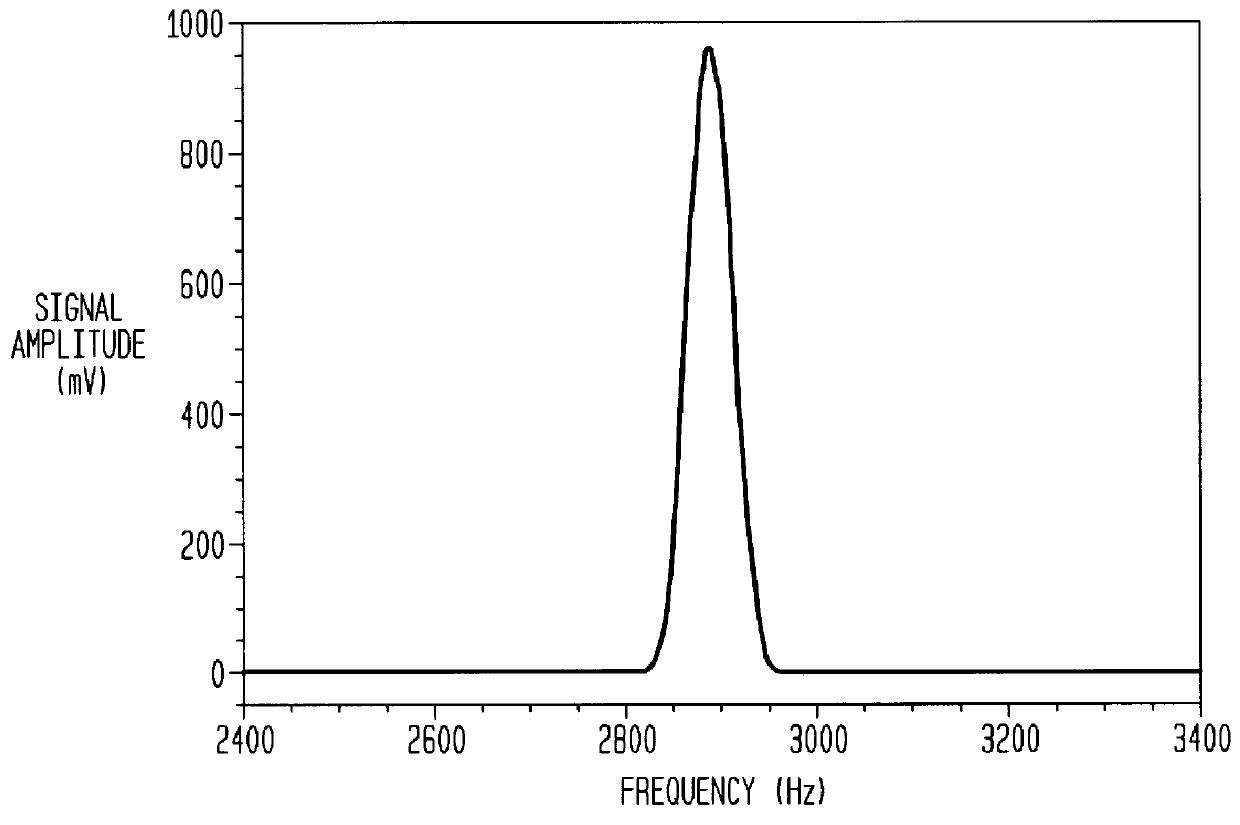
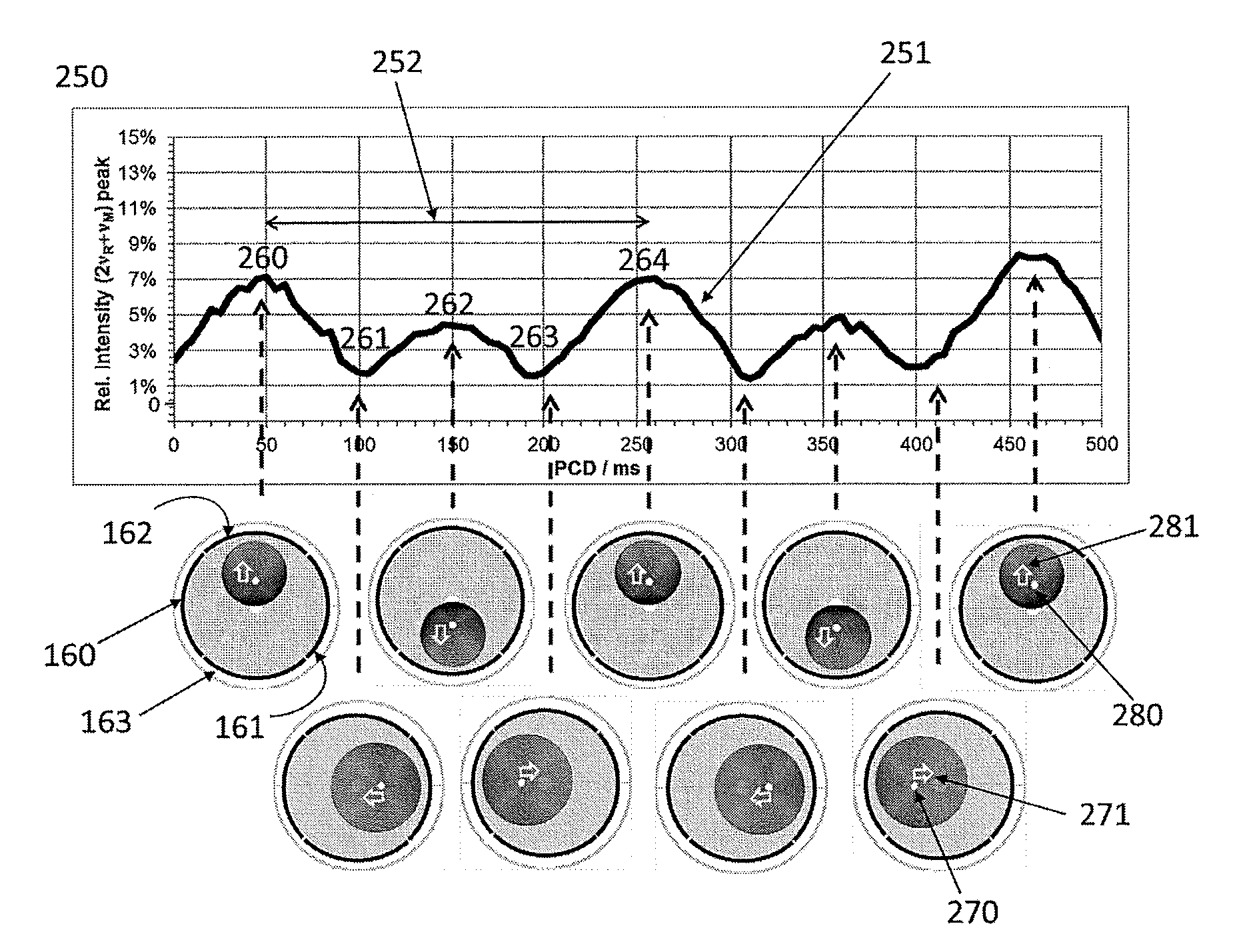
A method and system for deconvolution of a frequency spectrum obtained in an ICR mass spectrometer based on a detection of ion oscillation overtones of the M-th order (where the integer M>1). A plurality of frequency peaks is collected within the frequency spectrum corresponding respectively to oscillations of different groups of ions, and associates at least one of the frequency peaks having a frequency f and a measured amplitude A with a particular group of the ions. The method and system identify whether the frequency peak is related to one of an overtone frequency, a subharmonic frequency, a higher harmonic frequency, or a side-shifted frequency of the oscillations of the different group of ions. The method and system derive calculated amplitudes of the overtone frequency peaks associated with the groups of ions by incorporating measured amplitudes of the frequency peaks related to the subharmonic frequency, the higher harmonic frequency, or the side-shifted frequency associated with the groups of ions into the calculated amplitudes of the overtone frequency peaks. The method and system generate a deconvoluted frequency spectrum including the overtone frequency peaks associated with the different groups of ions.
Owner:SCI & ENG SERVICES
Comprehensive Characterization Of Complex Proteins At Trace Levels
InactiveUS20080280317A1High sequence coverageHigh molecular weightElectrolysis componentsMicrobiological testing/measurementConjugated proteinData acquisition
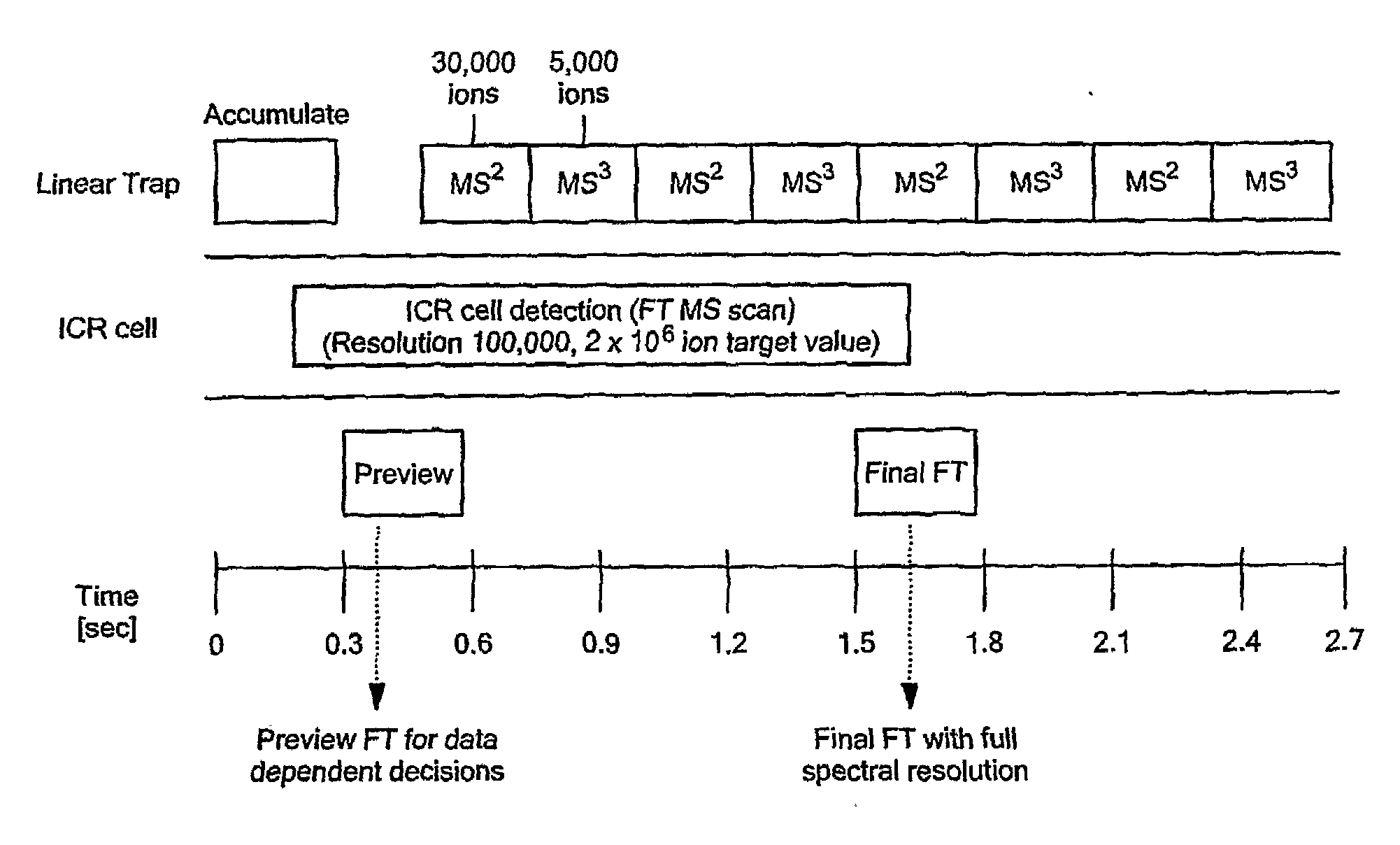
A combination of “bottom up” and “top down” MS analysis of posttranslational modifications in complex proteins is described. The method comprises digestion of the protein with an enzyme that forms larger peptide fragments than trypsin (>3000 D), performing HPLC with the fragments and applying a new data acquisition strategy using on-line coupling with e.g. LTQ-FTMS, a hybrid mass spectrometer that couples a linear ion trap with a Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (FTICR) cell. The method is applied to analysis of posttranslational modifications of protein isoforms.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
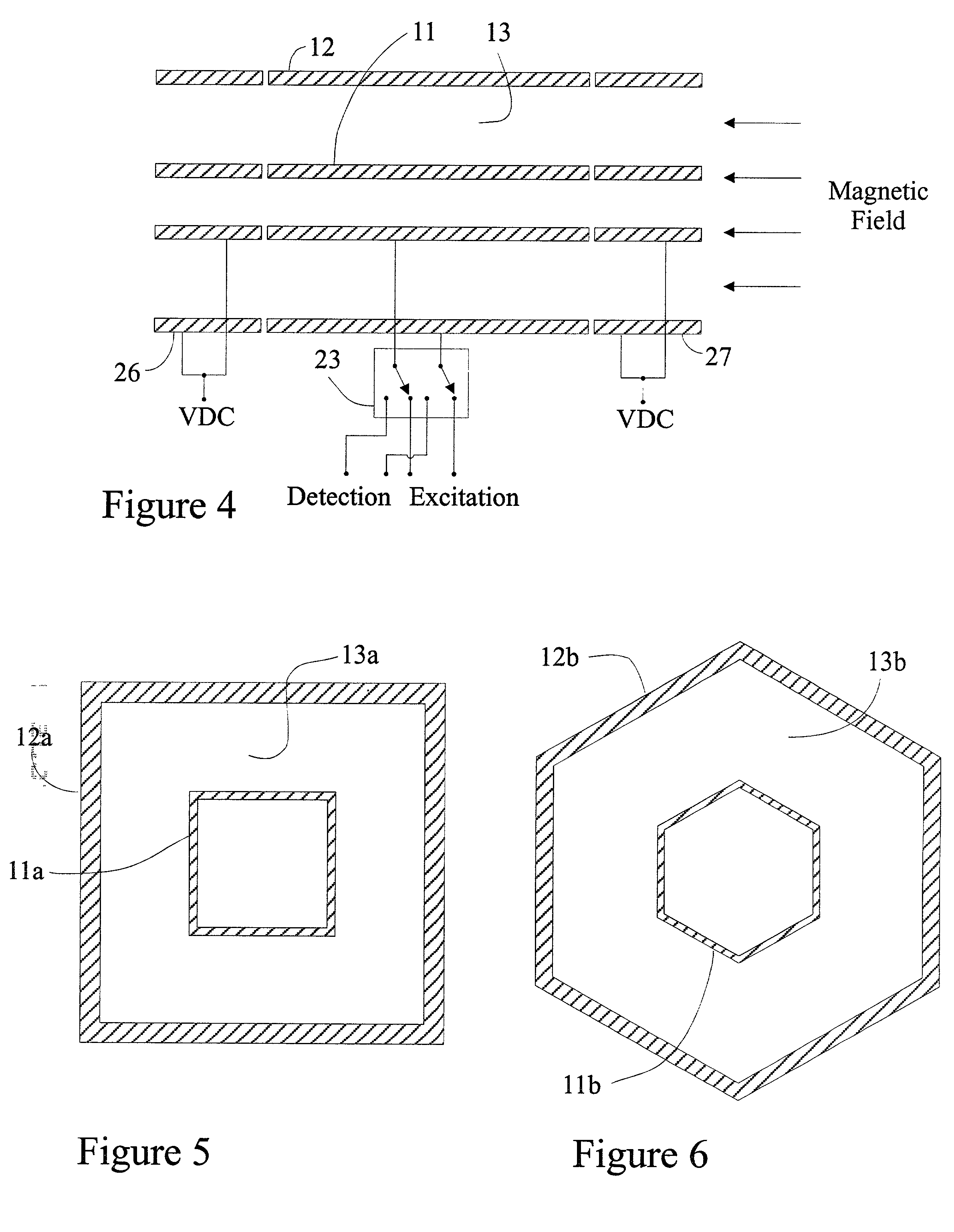
Measuring cell for ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer
ActiveUS20060027743A1Increases mass mass accuracyImprove resolution accuracyTime-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationTrappingSpectrometer
The invention relates to a measuring cell for an ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer (FTMS). The invention provides a measuring cell which, on the one hand, consists of two ion-repelling RF grids at the front ends as trapping electrodes and thus produces a pure cyclotron motion of the ions without the usually co-existing magnetron motion and, on the other hand, measures a multiplied cyclotron frequency by means of a plurality of detection electrodes, whereby either a higher mass accuracy or a shorter measuring time can be achieved.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer
ActiveUS7038200B2Easy to detectSimplifying massIon sources/gunsIsotope separationElectrical polarityStructuring element
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
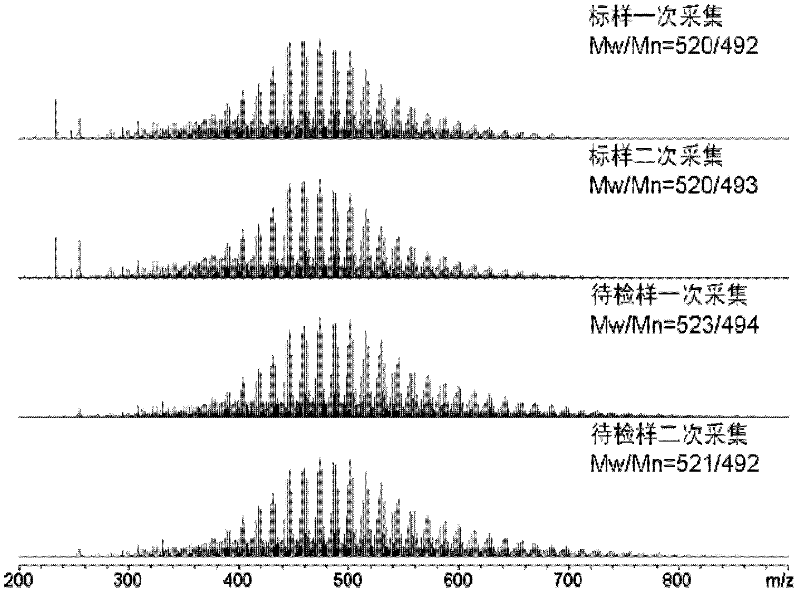
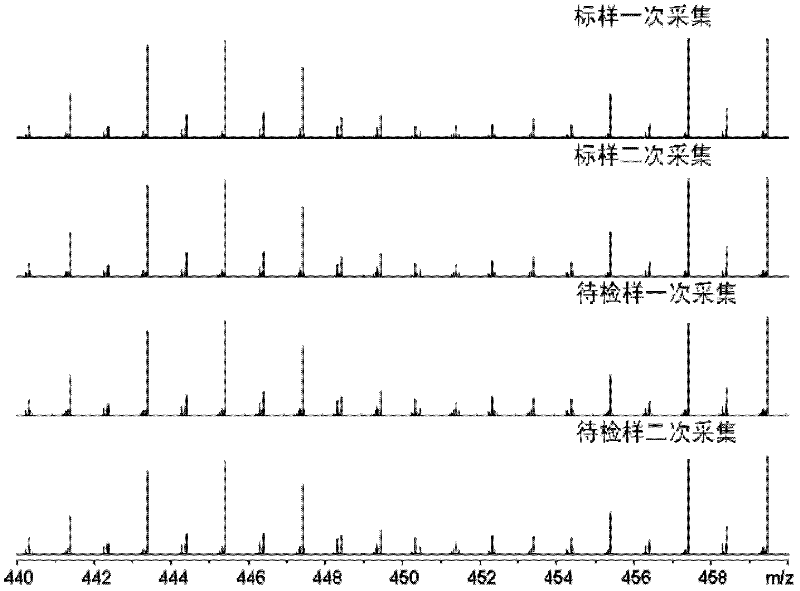
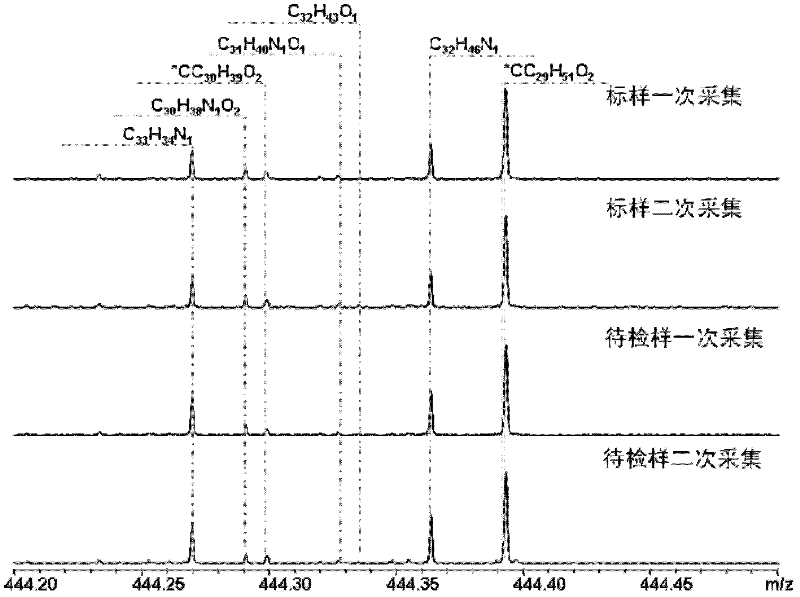
Asphalt analysis discriminating method
ActiveCN102507718AQuality improvementGuaranteed accuracyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSpectral ratioPetroleum
The invention relates to an asphalt analysis discriminating method by utilizing an electronic spray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry technology. The asphalt analysis discriminating method comprises the following steps of: (1) detecting a standard sample in an electronic spray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer to determine molecular composition, molecular weight and distributed mass spectrometric data of a polar compound in the standard sample; (2) detecting a sample to be detected in the electronic spray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer to determine the molecular composition, molecular weight and distributed mass spectrometric data of another polar compound in the sample to be detected; and (3) evaluating differences of the molecular compositions, molecular weights and distribution of the sample to be detected and the standard sample, detected in a wide band mode and a narrow band mode, by utilizing a spectral ratio method and a repeatability limit method to obtain an asphalt fingerprint identification result. Through the asphalt analysis discriminating method disclosed by the invention, the characteristics of the obtained asphalt fingerprint are remarkable and have very high representativeness and reliability; and the variety discrimination and product identification of petroleum asphalt, coal pitch, natural asphalt (consisting of rock asphalt and lake asphalt) can be realized by comparison of asphalt fingerprint mass spectrometric data of the standard sample and the sample to be detected.
Owner:RES INST OF HIGHWAY MINIST OF TRANSPORT
Method for controlling nanocrystalline graphene size in carbon film through electron cyclotron resonance (ECR) electron irradiation density
ActiveCN103938170AVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingCarbon filmElectron cyclotron resonance
The invention discloses a method for controlling nanocrystalline graphene size in a carbon film through electron cyclotron resonance (ECR) electron irradiation density. An ECR plasma processing system is utilized, the microwave power is regulated to change in a range from 160 to 400W, and change of electron irradiation density in a range from 30 to 120mA / cm<2> can be realized. The nanocrystalline graphene size in the carbon film under different electron irradiation densities is characterized by utilizing a transmission electron microscope and a Raman spectrum, and when the electron irradiation density is gradually increased from 30mA / cm<2> to 120mA / cm<2>, the average nanocrystalline graphene size is gradually increased from 1.09nm to 2.69nm. According to the control method provided in the invention, the nanocrystalline graphene size in the carbon film is conveniently and accurately controlled.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Surface plasma resonance and electron cyclotron resonance double-excitation type microwave thruster
InactiveCN106304595ASmall sizeSimple structureMachines/enginesUsing plasmaMicrowaveElectron cyclotron resonance
The invention discloses a surface plasma resonance and electron cyclotron resonance double-excitation type microwave thruster, relates to the technical field of spacecraft power, and relates to the thruster which is based on low-temperature non-equilibrium plasma, namely surface plasma, resonance and electron cyclotron resonance and is applied to a microsatellite power system for performing the tasks of satellite formation, deep space exploration and the like. The surface plasma resonance and electron cyclotron resonance double-excitation type microwave thruster is fixed into a vacuum environment through a thruster supporting frame, and comprises a permanent magnet ring, a discharge chamber, a metal antenna and a tail spraying pipe; the permanent magnet ring is mounted at the external part of the discharge chamber in a sleeving manner; the metal antenna is embedded into the interior of the discharge chamber; the permanent magnet ring is embedded into the thruster supporting frame; the tail spraying pipe is butted with an outlet of the discharge chamber. The surface plasma resonance and electron cyclotron resonance double-excitation type microwave thruster has the characteristics of being novel in structure, convenient in machining, small in size, high in stability, strong in specific impulse, long in thruster service life and the like.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
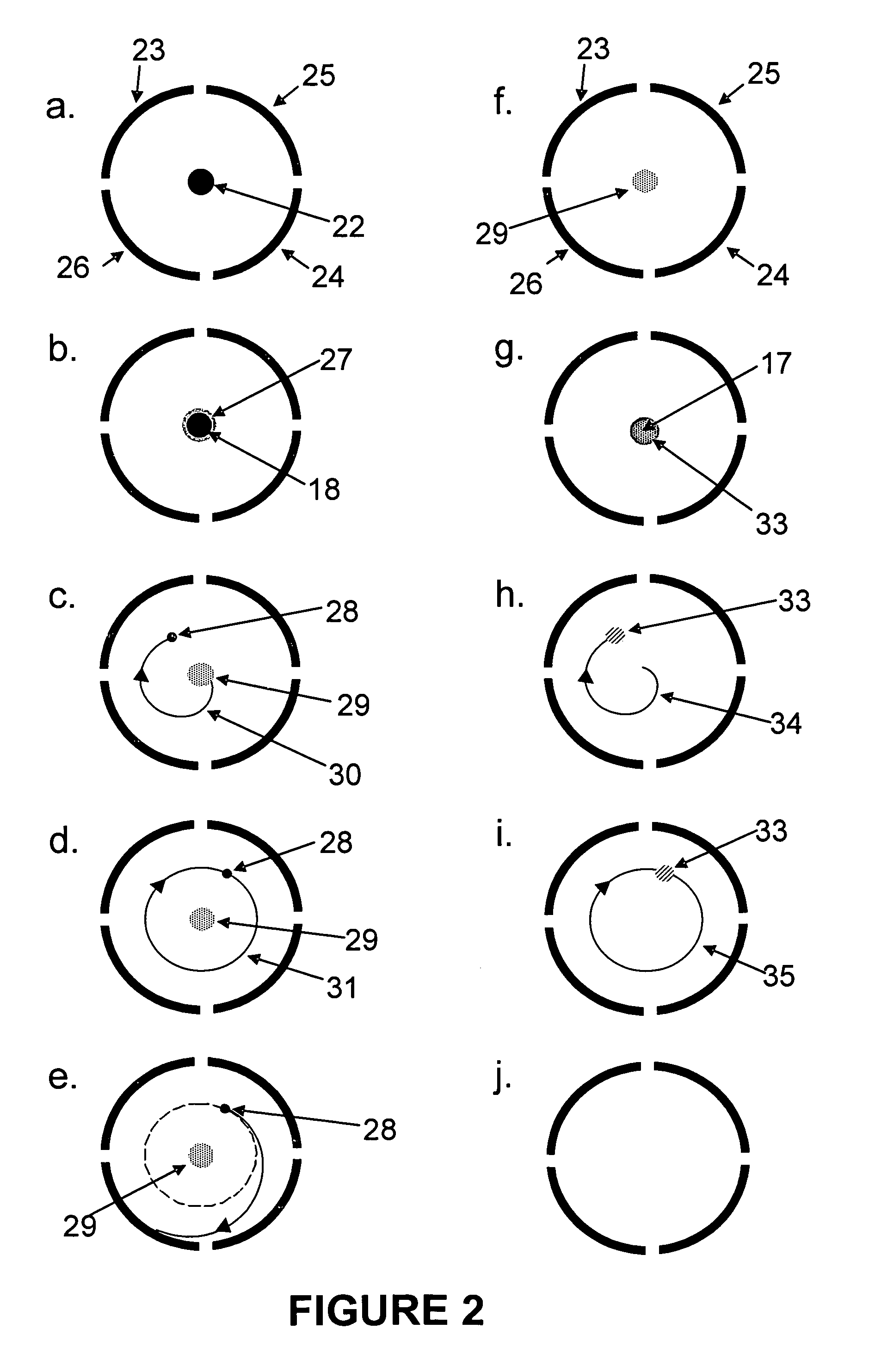
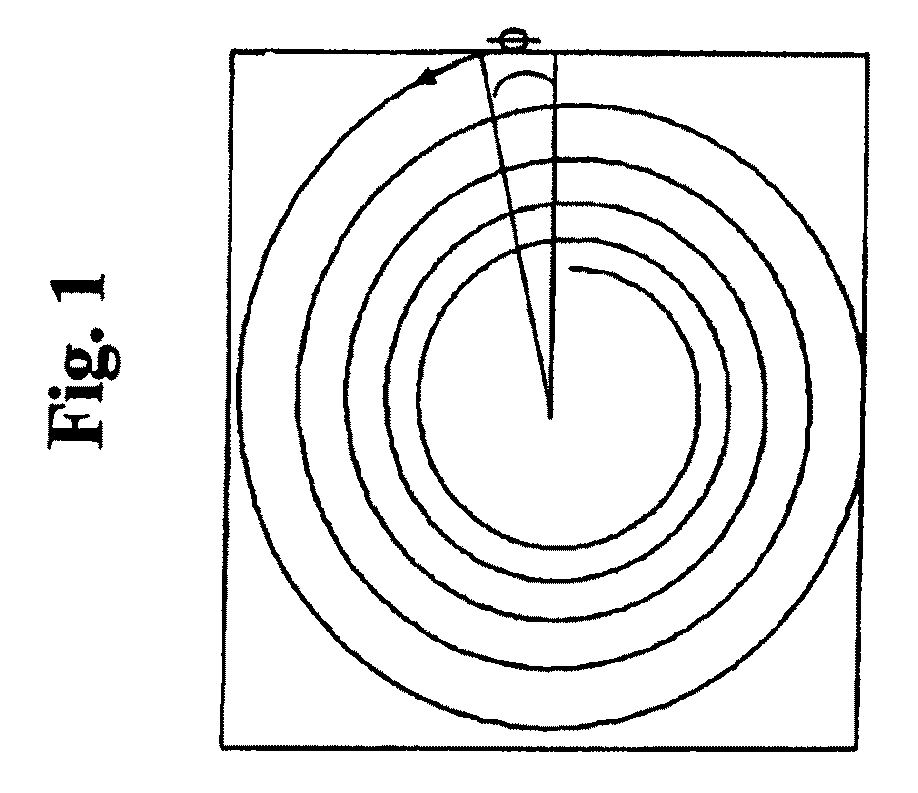
Total ion number determination in an ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer using ion magnetron resonance
The total number of ions created br obtained during an ionization or ion introduction event in a Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer are determined either by using an on-resonance experimental technique or an off-resonance experimental technique. Both techniques exploit ion magnetron motion. In the on-resonance technique the spectrometer is excited in the magnetron mode and the single resonance signal resulting from this excitation is detected to determine the total number of ions. In the off-resonance technique the magnetron mode is excited at a frequency that is near the magnetron frequency while simultaneously detecting the resulting ion motion. The off-resonance technique leaves the ion population in a state that is amenable to subsequent analysis.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
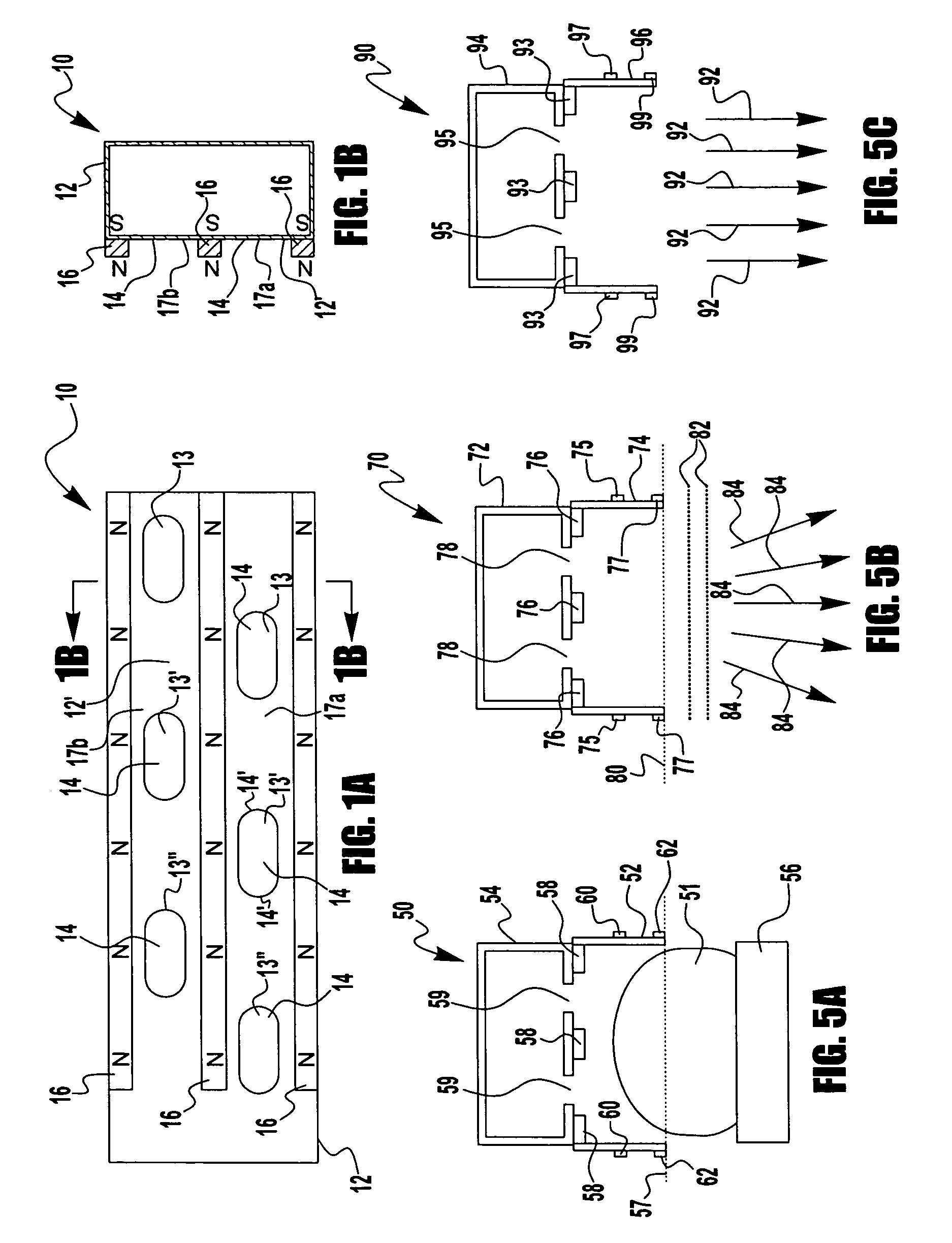
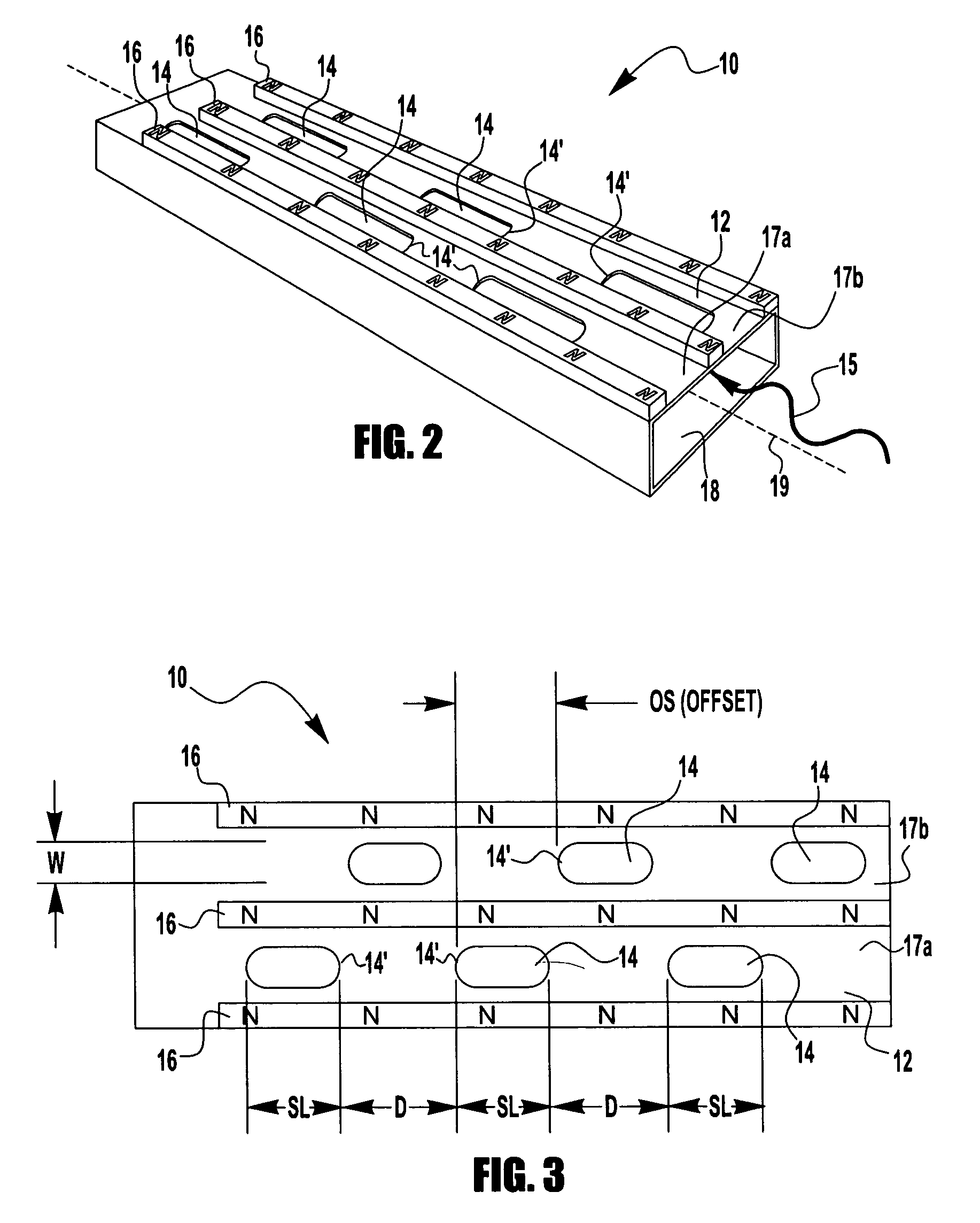
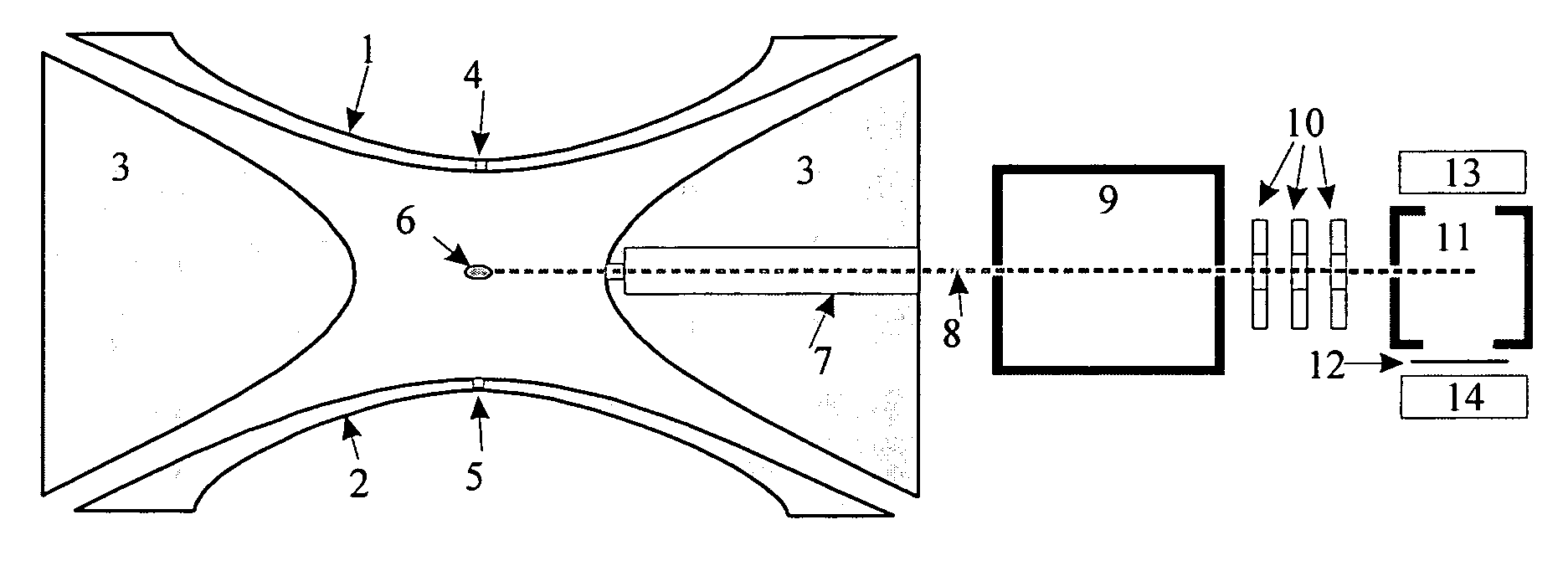
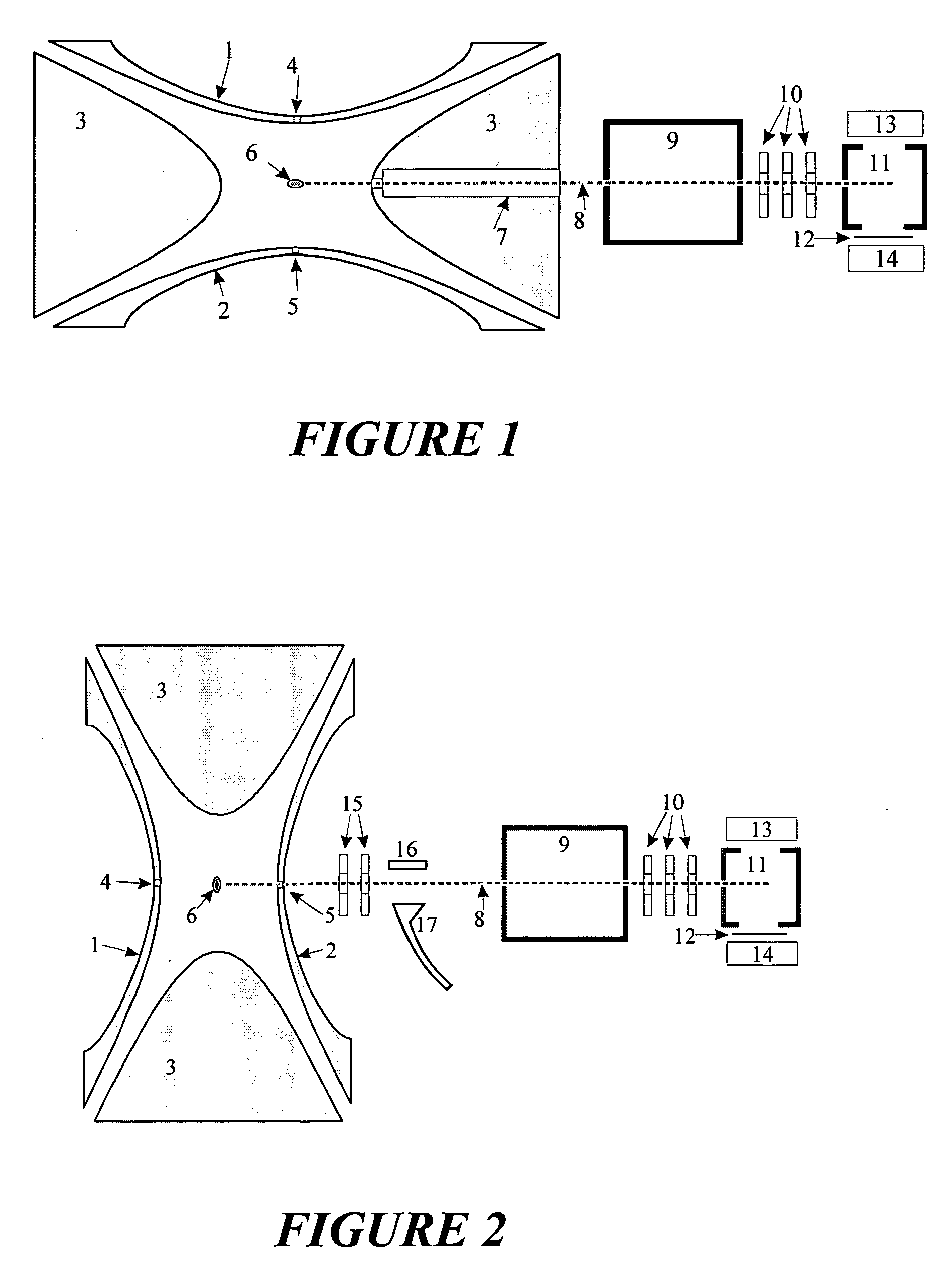
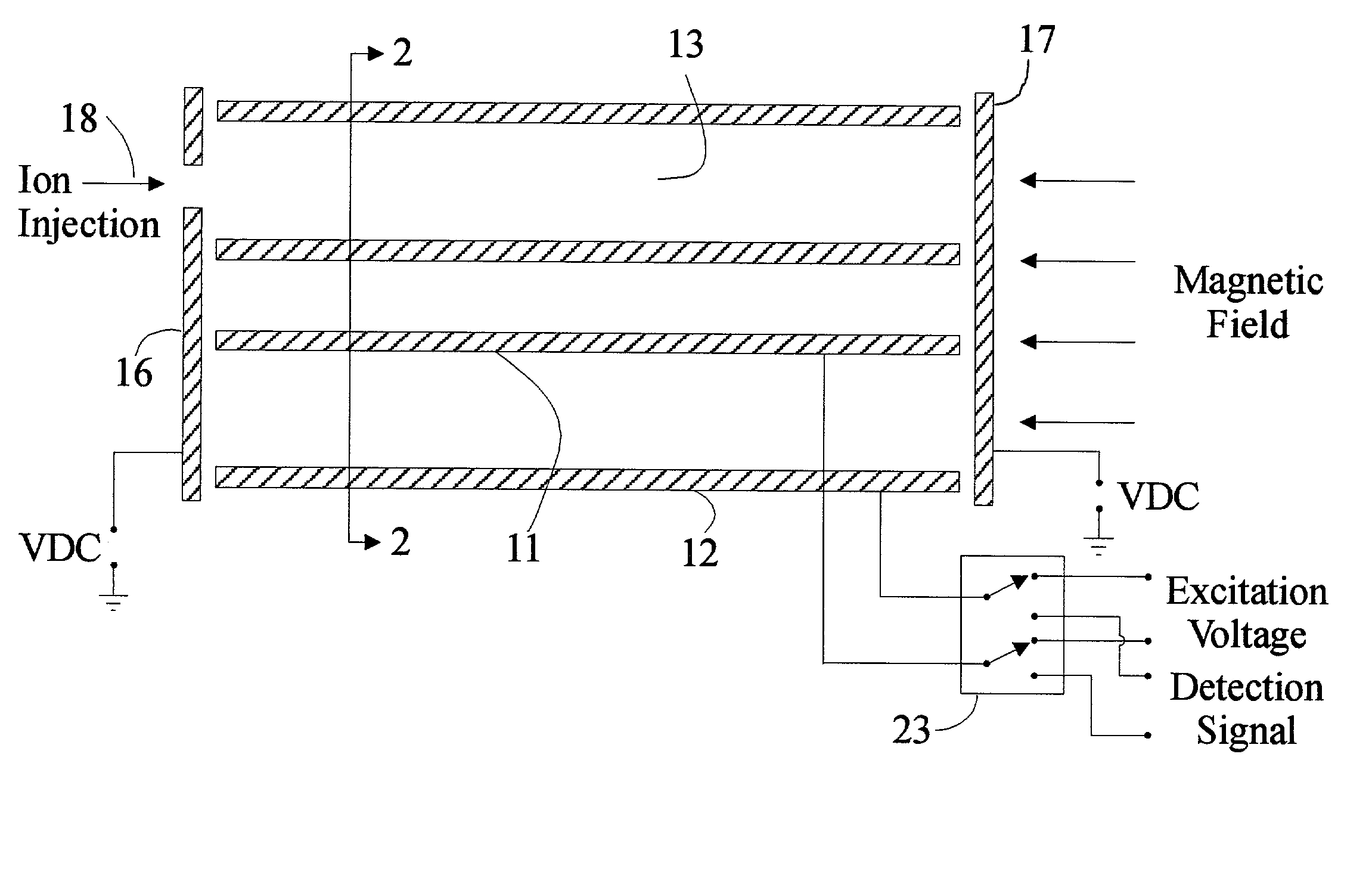
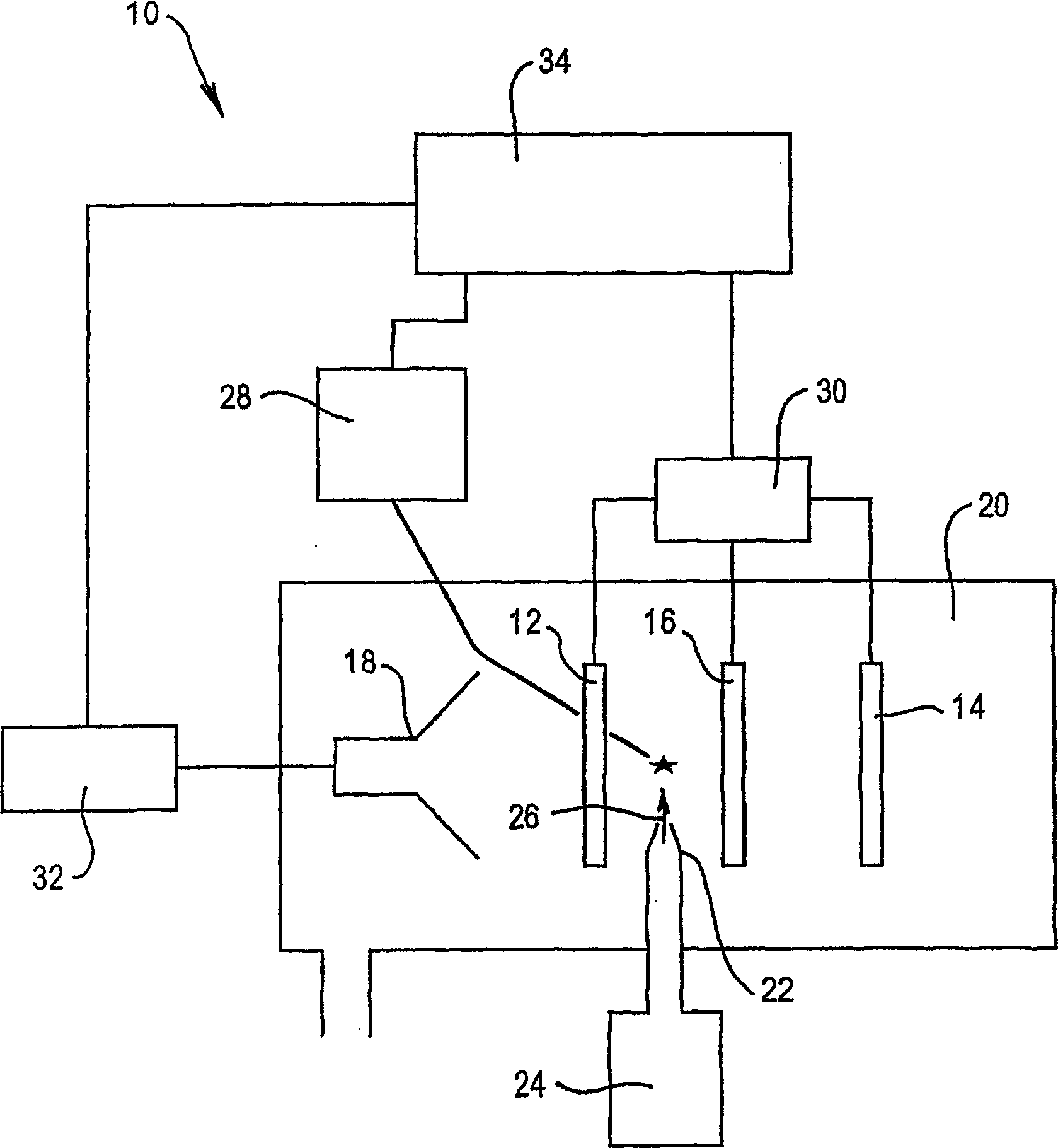
High capacity ion cyclotron resonance cell
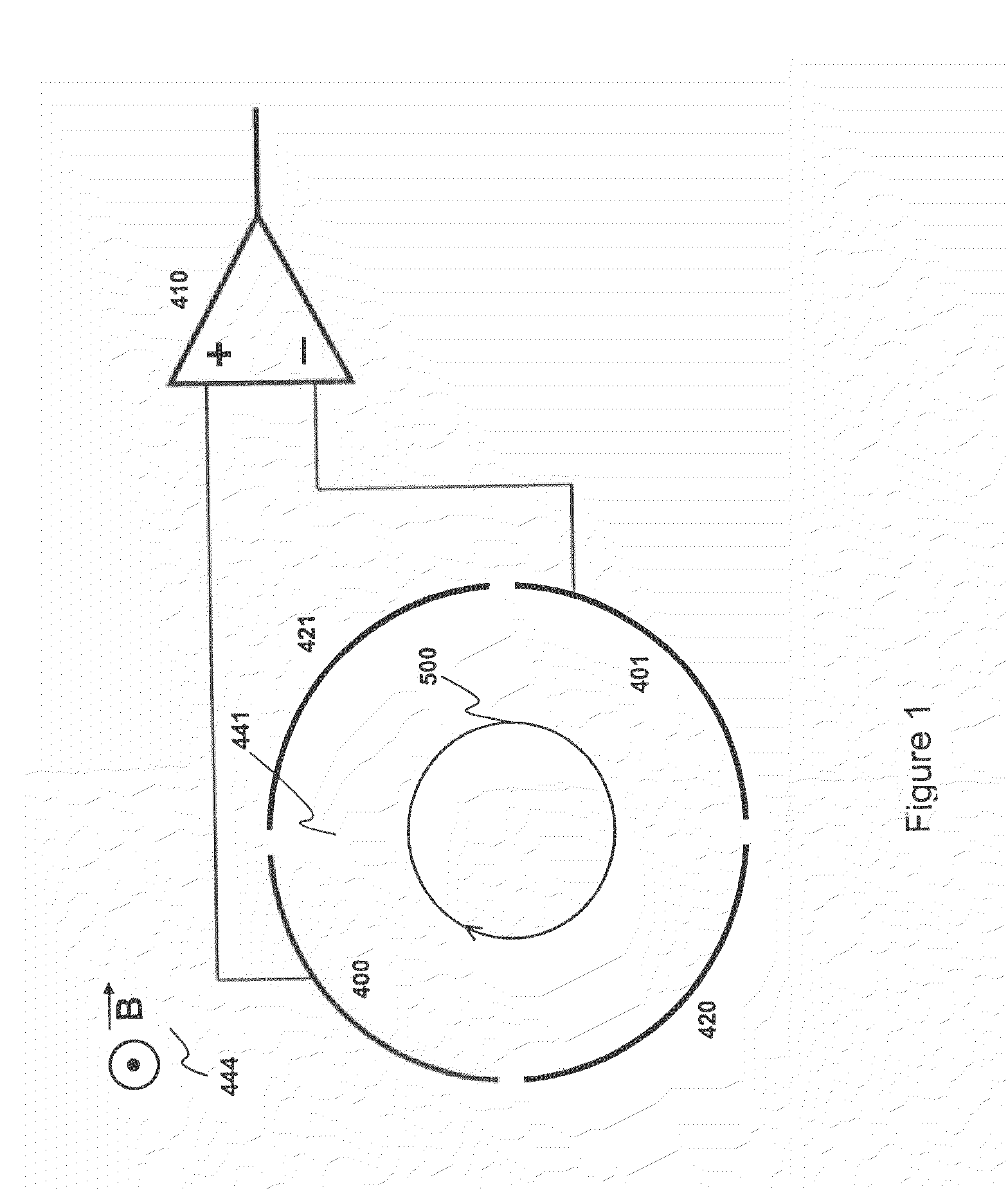
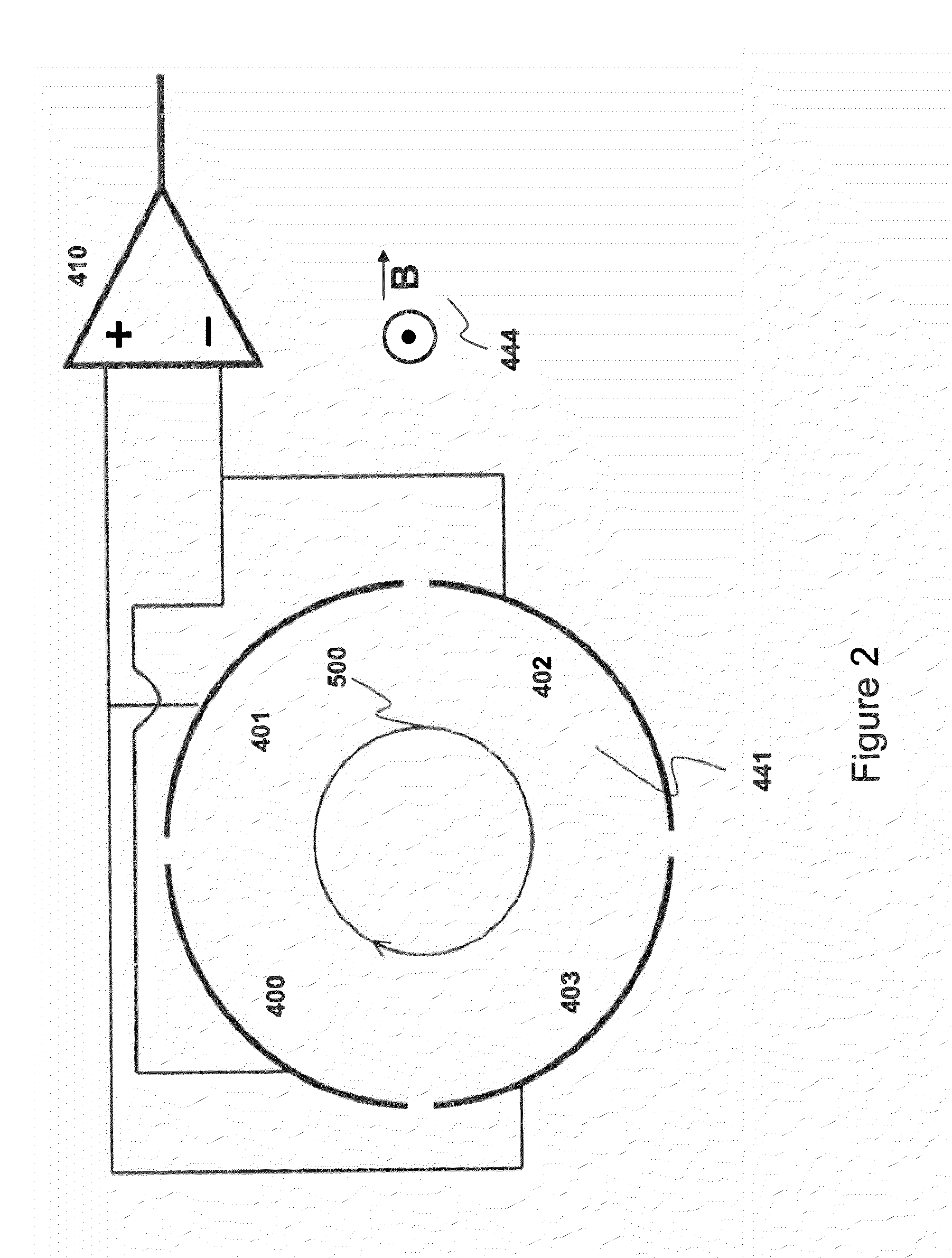
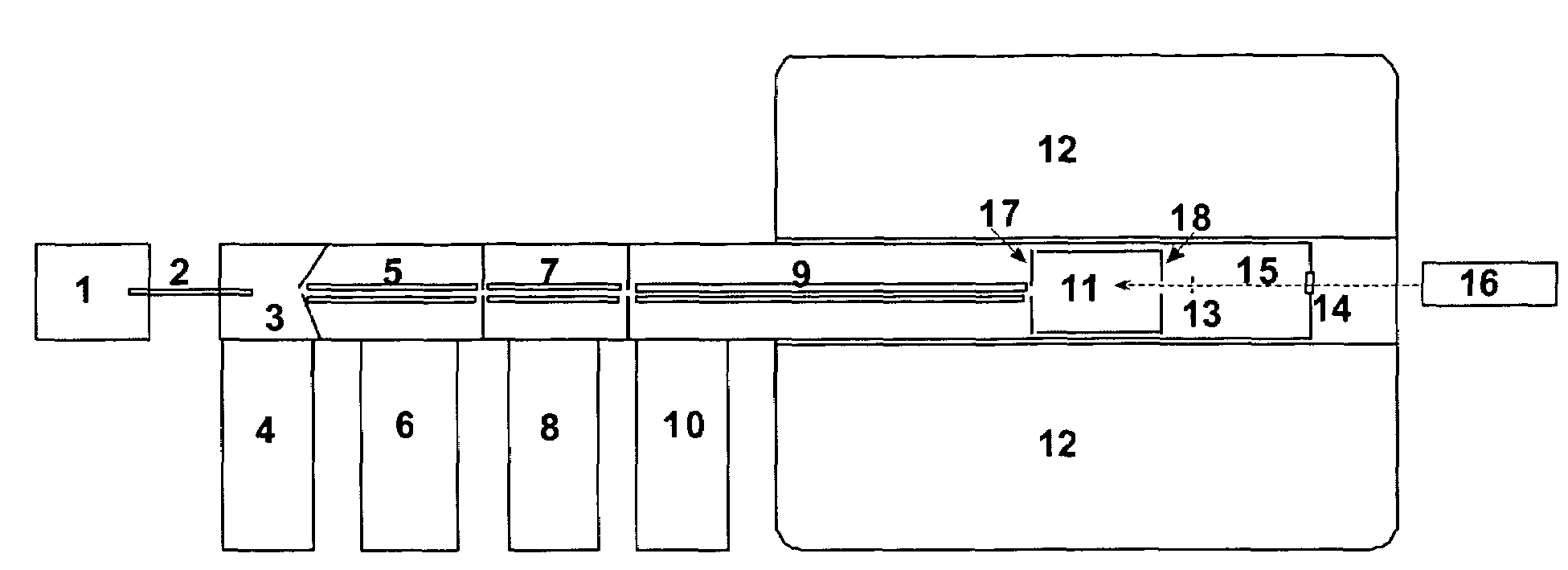
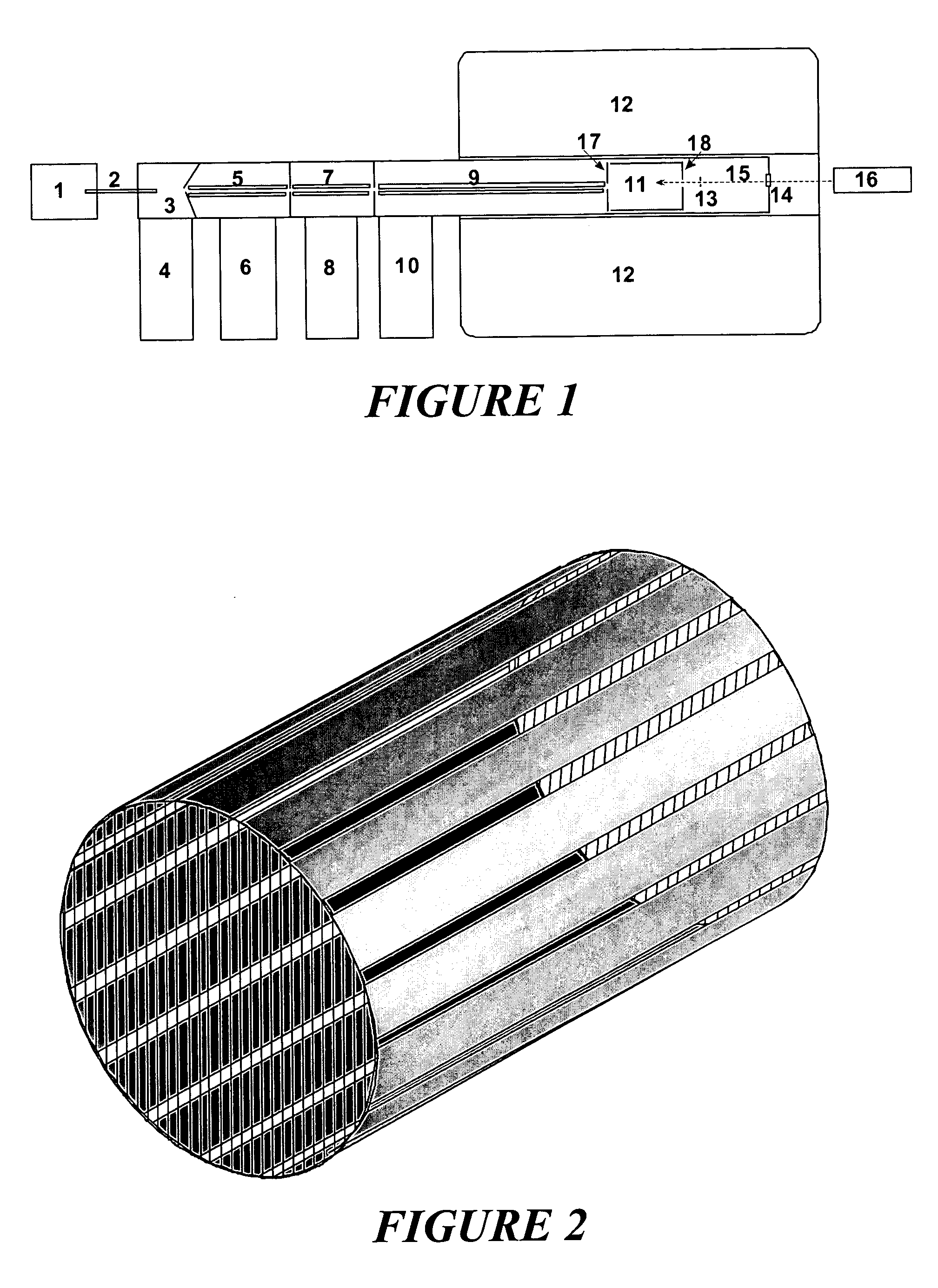
InactiveUS6573495B2Space minimizationSpatial shiftMaterial analysis by optical meansIsotope separationTrappingConcentric electrode
An ion cyclotron resonance cell having a large ion trapping volume is described. The cell includes elongated spaced concentric electrodes having a common axis in which the trapping volume is the space between the electrodes. The cell may also include trapping electrodes disposed at the ends of the elongated concentric electrodes.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
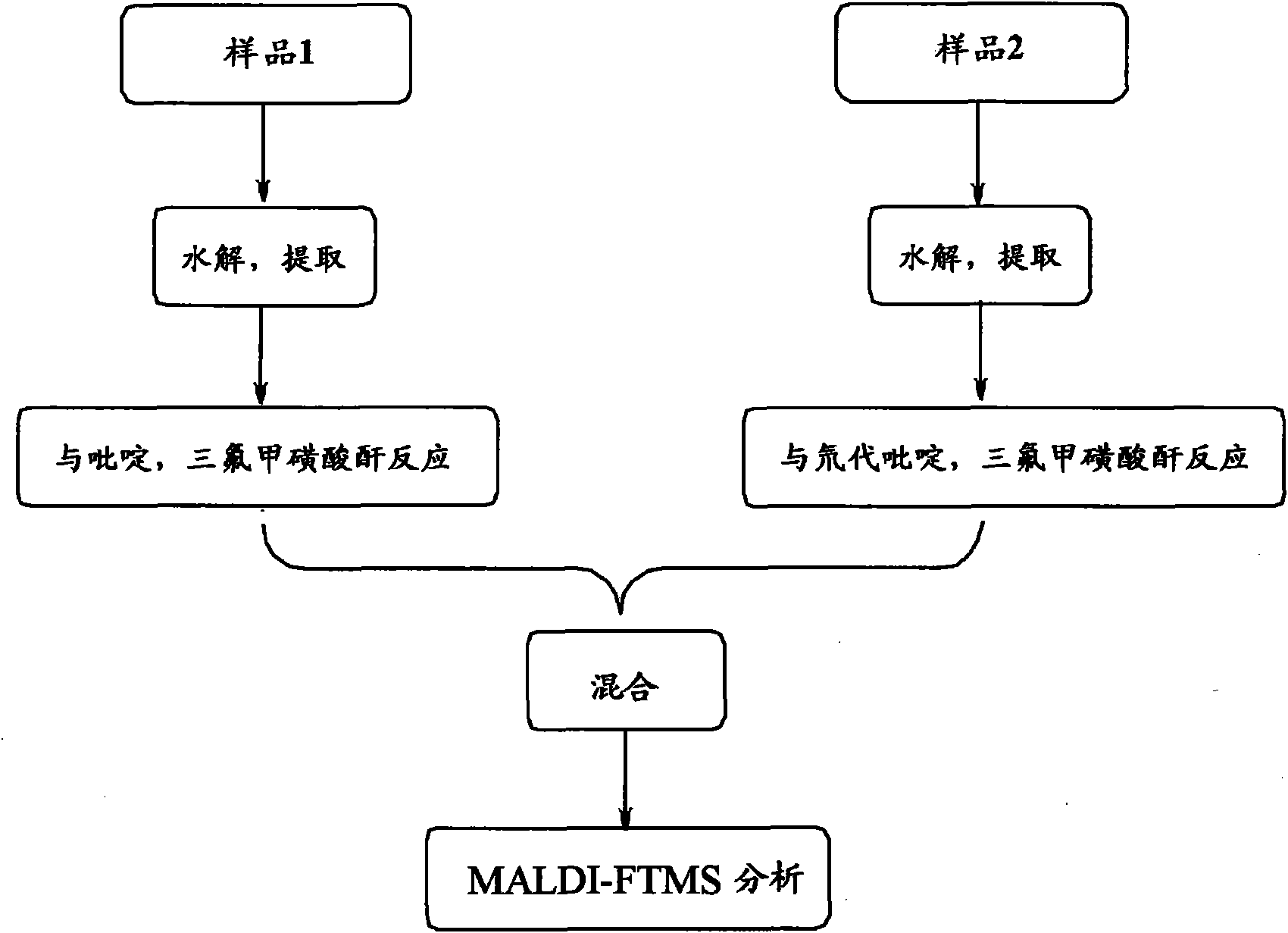
Method for analyzing biological samples by using matrix assisted laser desorption ionization-Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectra
InactiveCN102175750AImprove MS signalReduce complexityPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIsotopeDerivatization
The invention relates to a method for analyzing biological samples by using matrix assisted laser desorption ionization-Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectra (MALDI-FTMS), which is a method for analyzing alcohol compounds or / and alpha,beta-unsaturated ketone compounds in hair and urine samples qualitatively and quantitatively by combining a N-alkyl pyridine isotope derivatization method with the MALDI-FTMS. The method comprises the following steps of: performing sample preprocessing on a target analyte; reacting alcoholic hydroxyl or alpha,beta-unsaturated ketone on the target analyte with pyridine or deuterated pyridine; and performing MALDI-FTMS analysis on the marked sample solution directly. The analytical method is quick, efficient and sensitive.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Measuring cell for ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer
ActiveUS7368711B2Improve accuracyImprove resolutionTime-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationMass analyzerMass
The invention relates to a measuring cell for an ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer (FTMS). The invention provides a measuring cell which, on the one hand, consists of two ion-repelling RF grids at the front ends as trapping electrodes and thus produces a pure cyclotron motion of the ions without the usually co-existing magnetron motion and, on the other hand, measures a multiplied cyclotron frequency by means of a plurality of detection electrodes, whereby either a higher mass accuracy or a shorter measuring time can be achieved.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Apparatus and method for improving fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer signal
InactiveUS20080099672A1More stabilityIncrease powerMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingBiological activationSpectrometer
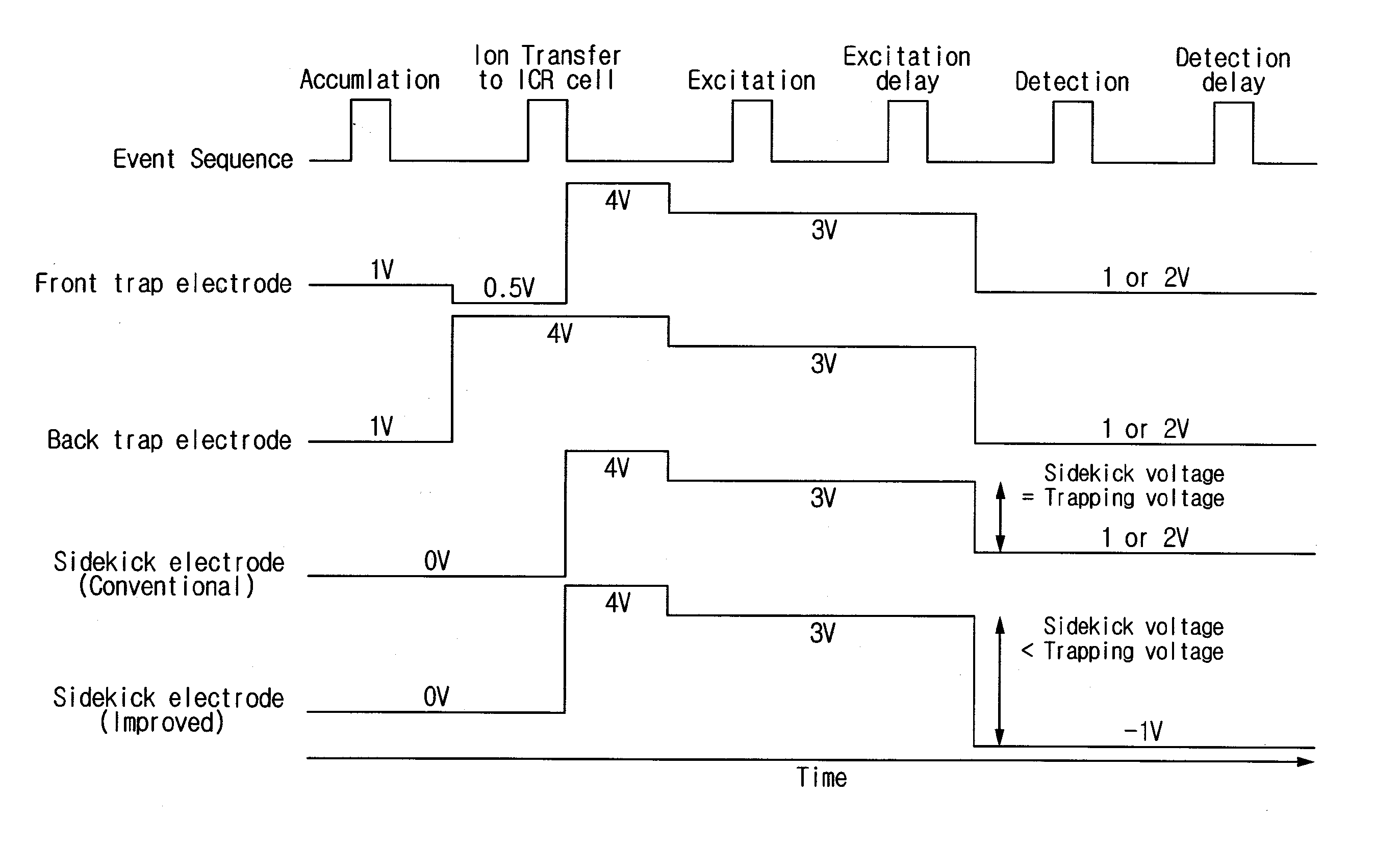
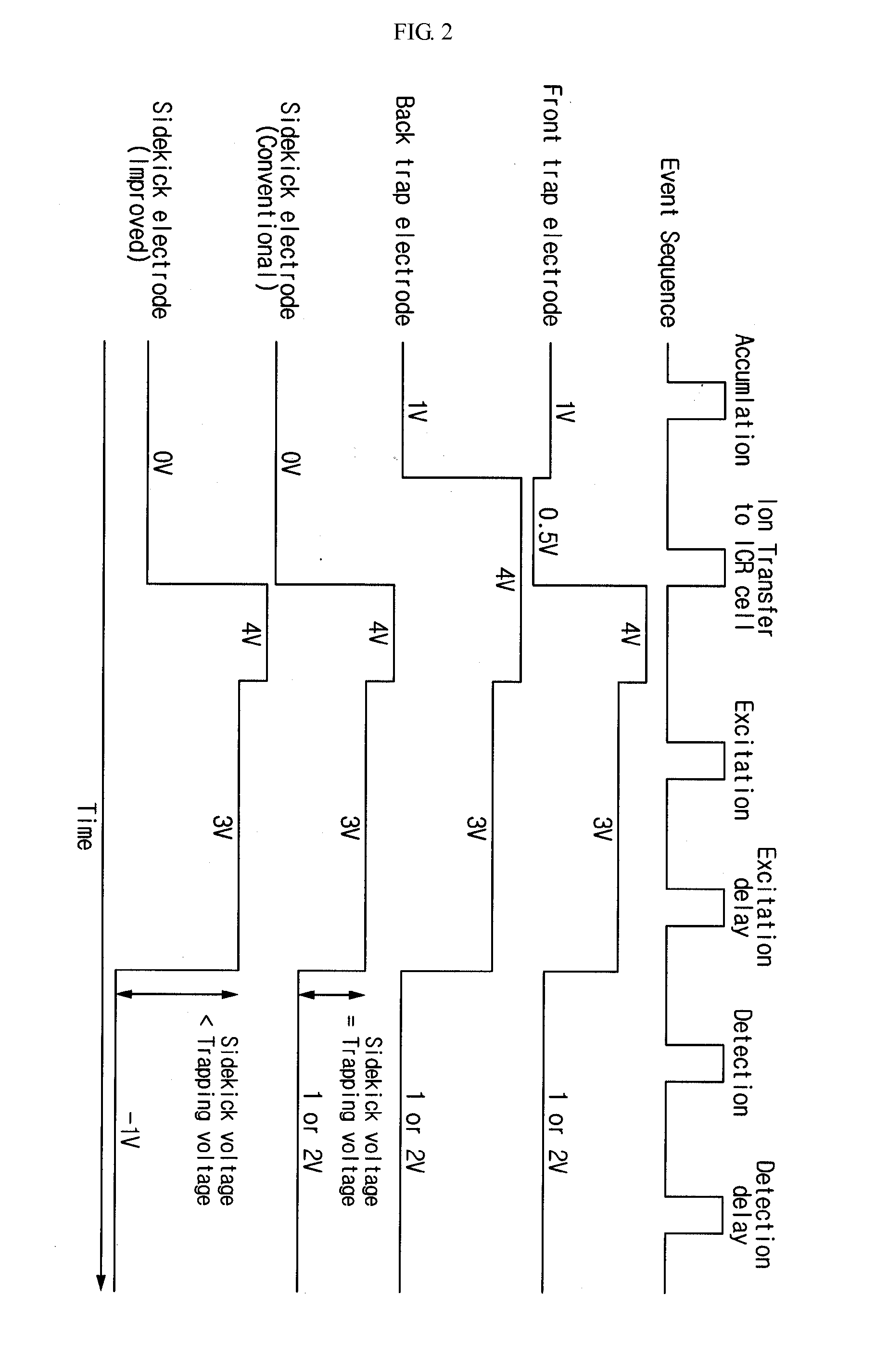
Disclosed is apparatus and method for improving the signal by changing the voltage applied to an analyzing trap of a high resolving power Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance (FT-ICR) mass spectrometer. More specifically, after the ion activation, a voltage different from that of a trap electrode is applied to an additional electrode in the center of the trap electrode, and the voltage is maintained until the end of a detection cycle. Applying the above method, the stability of the ions confined in a trap is more increased, and therefore, the detected time domain signal is being lengthened. The lengthened time domain signal results in an increase of the frequency or an improvement of the resolving power and the sensitivity of the mass-to-charge domain signal.
Owner:KOREA BASIC SCI INST
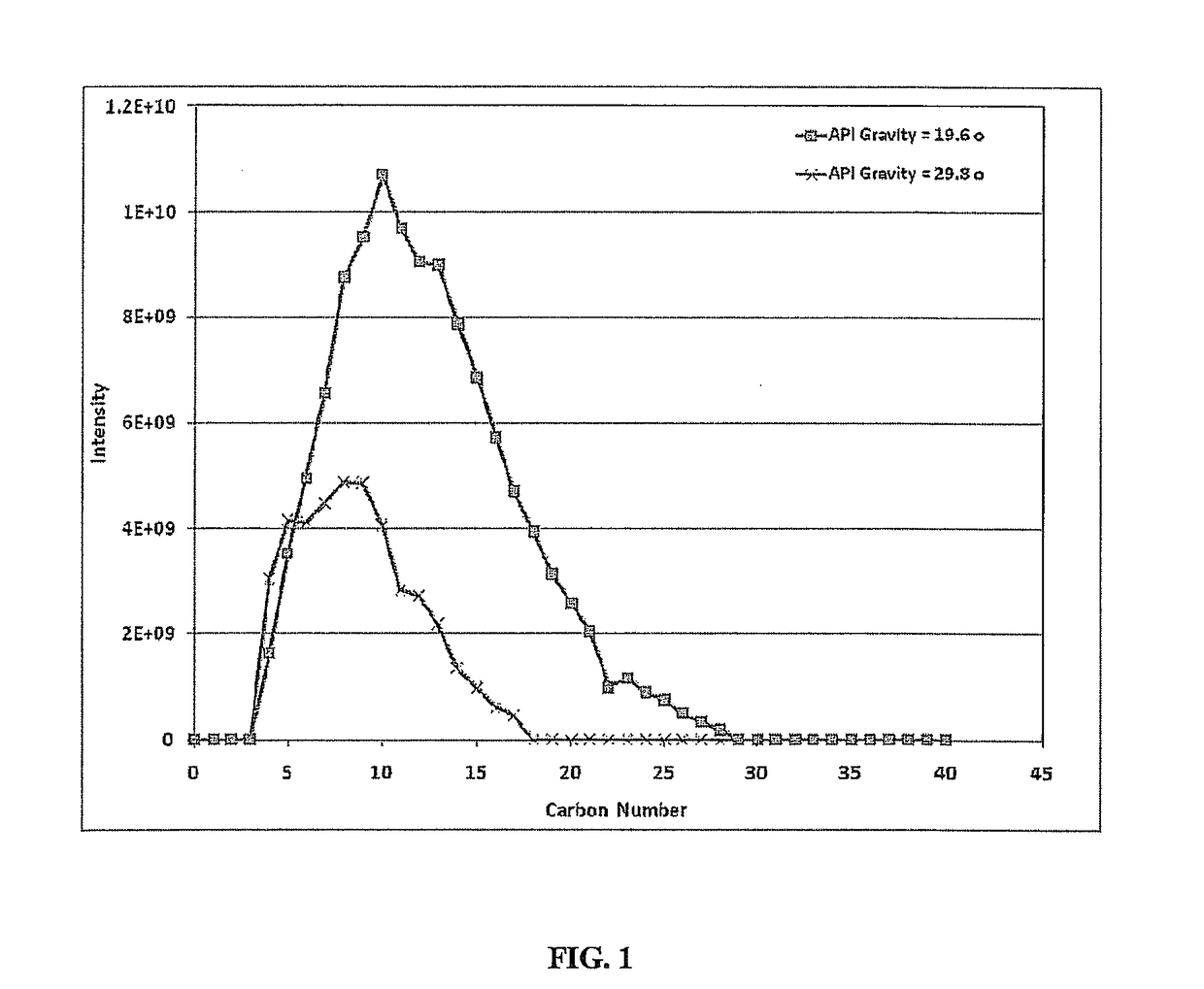
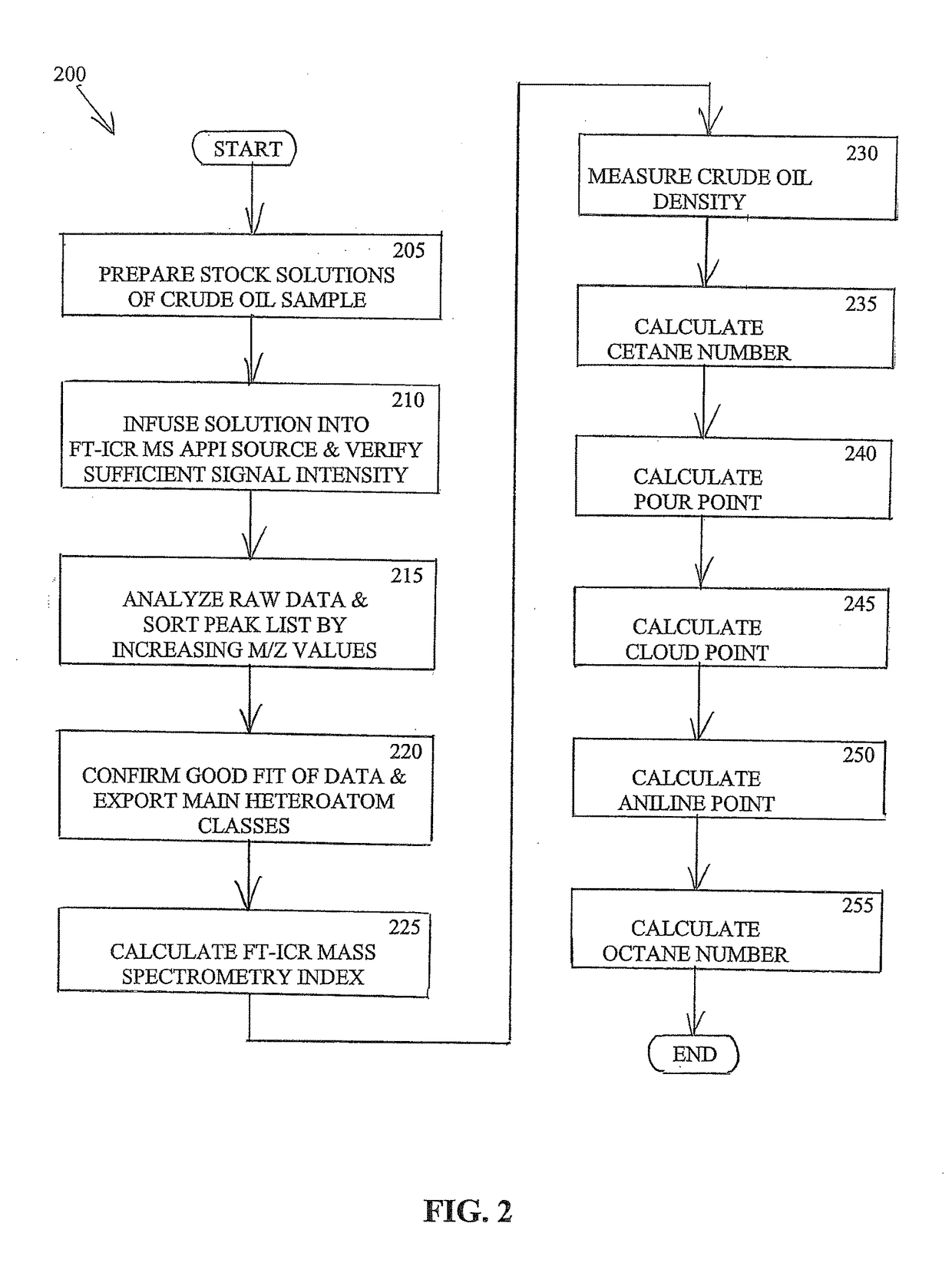
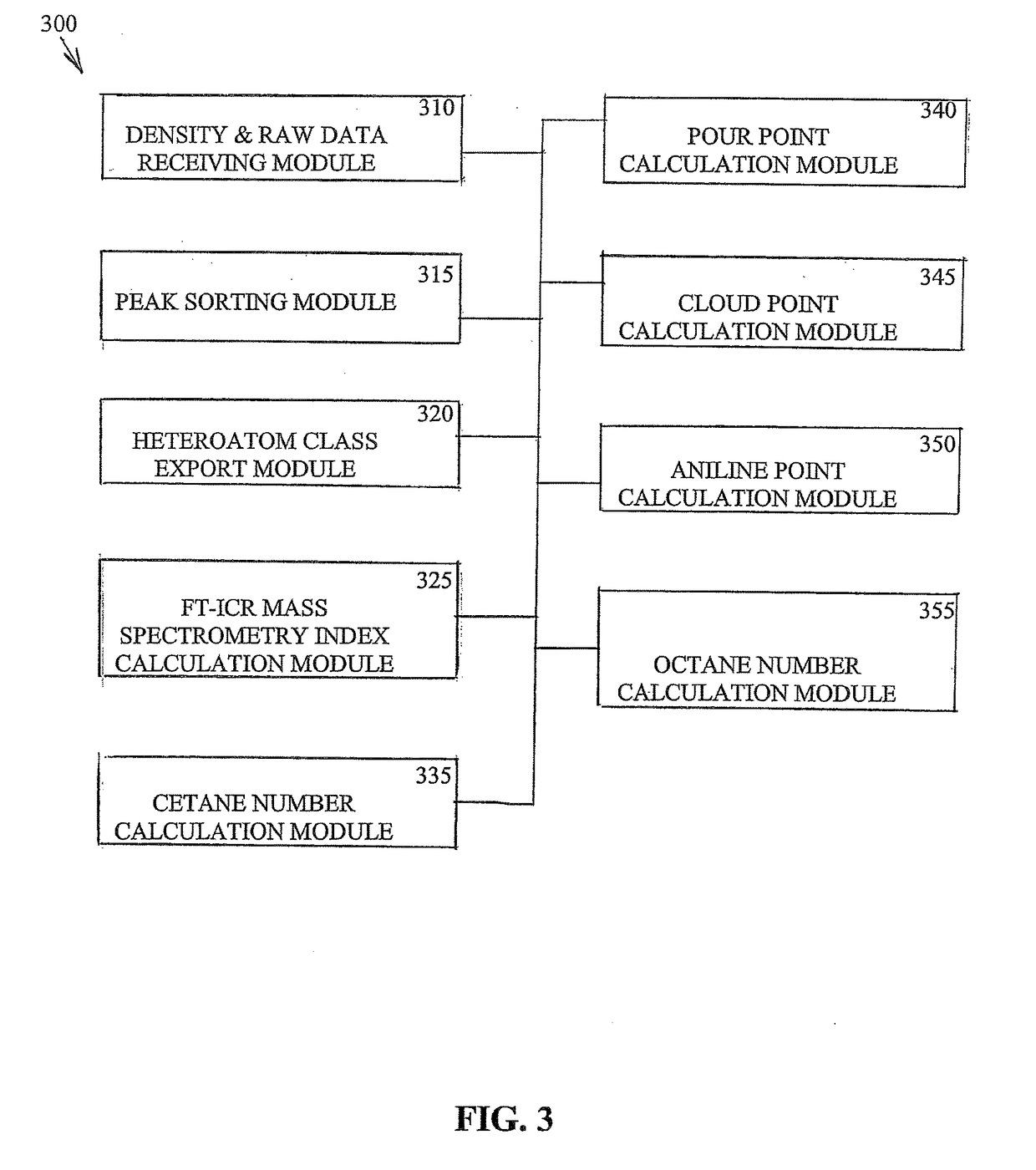
Characterization of crude oil by fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry
ActiveUS20170363602A1Provide informationImprove oil qualityChemical property predictionOmegatronsAniline pointCloud point
A system, method and computer program product are provided for calculating one or more indicative properties, e.g., one or more of the cetane number, octane number, pour point, cloud point and aniline point of oil fractions, from the density and Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry (FT-ICR MS) of a sample of an oil sample.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
High capacity ion cyclotron resonance cell
InactiveUS20020079444A1Space minimizationSpatial shiftIsotope separationOmegatronsTrappingConcentric electrode
An ion cyclotron resonance cell having a large ion trapping volume is described. The cell includes elongated spaced concentric electrodes having a common axis in which the trapping volume is the space between the electrodes. The cell may also include trapping electrodes disposed at the ends of the elongated concentric electrodes.
Owner:THERMO FINNIGAN
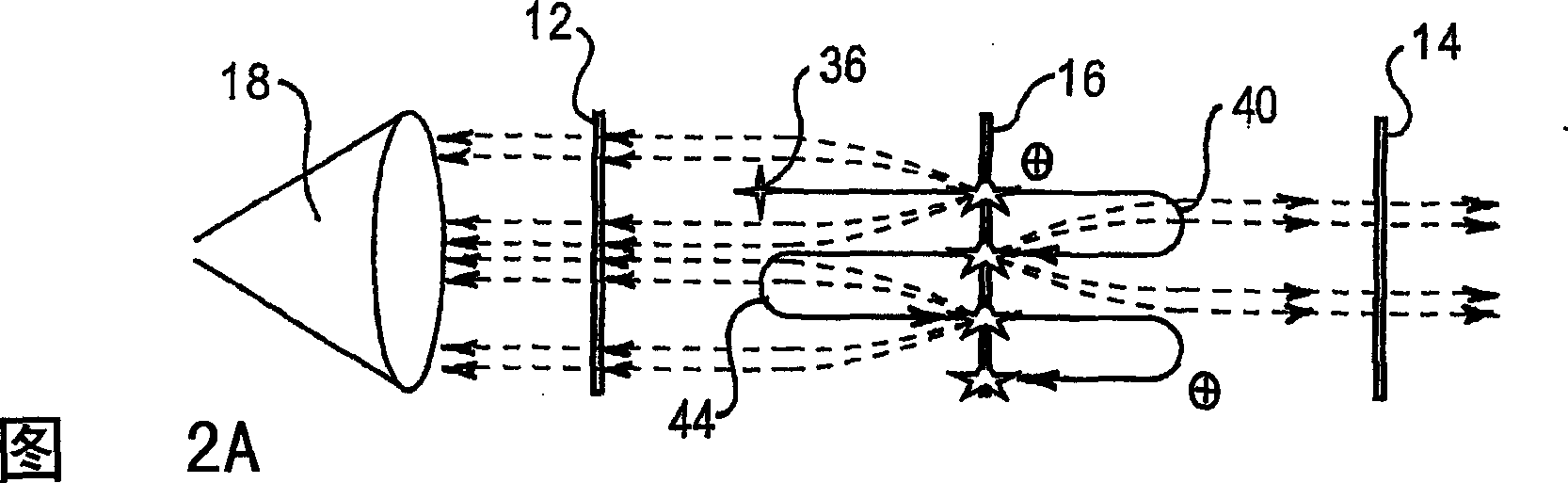
Mass spectrometer
InactiveCN1507647AImprove permeabilityGood quality resolutionStability-of-path spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsSecondary emissionMass analyzer
A new mass spectrometer (10) is described in which sample molecules (26) are ionized and caused to oscillate to and fro by reflecting electric fields established between two electrodes (12, 14) in a vacuum chamber (20). A mesh electron producing electrode (16) is located between reflector electodes (12, 14) and produces electrons by secondary emission on each pass of the oscillating ions when some of those ions strike the mesh. The secondary eldctrons are detected (18) after passage through reflector electrode (12), which is alos a mesh. The frequency of oscillation of the ions depends upon their mass and from the frequency distribution of the signals from each electron production event it is possible to identify the ions of different masses. The invention allows for a much more compact spectrometer instrument compared to a Time of flight Mass Spectrometer which is less expensive than a Fourier Transform Mass emplying ion-cyclotron resonance.
Owner:THE UNIV OF SYDNEY
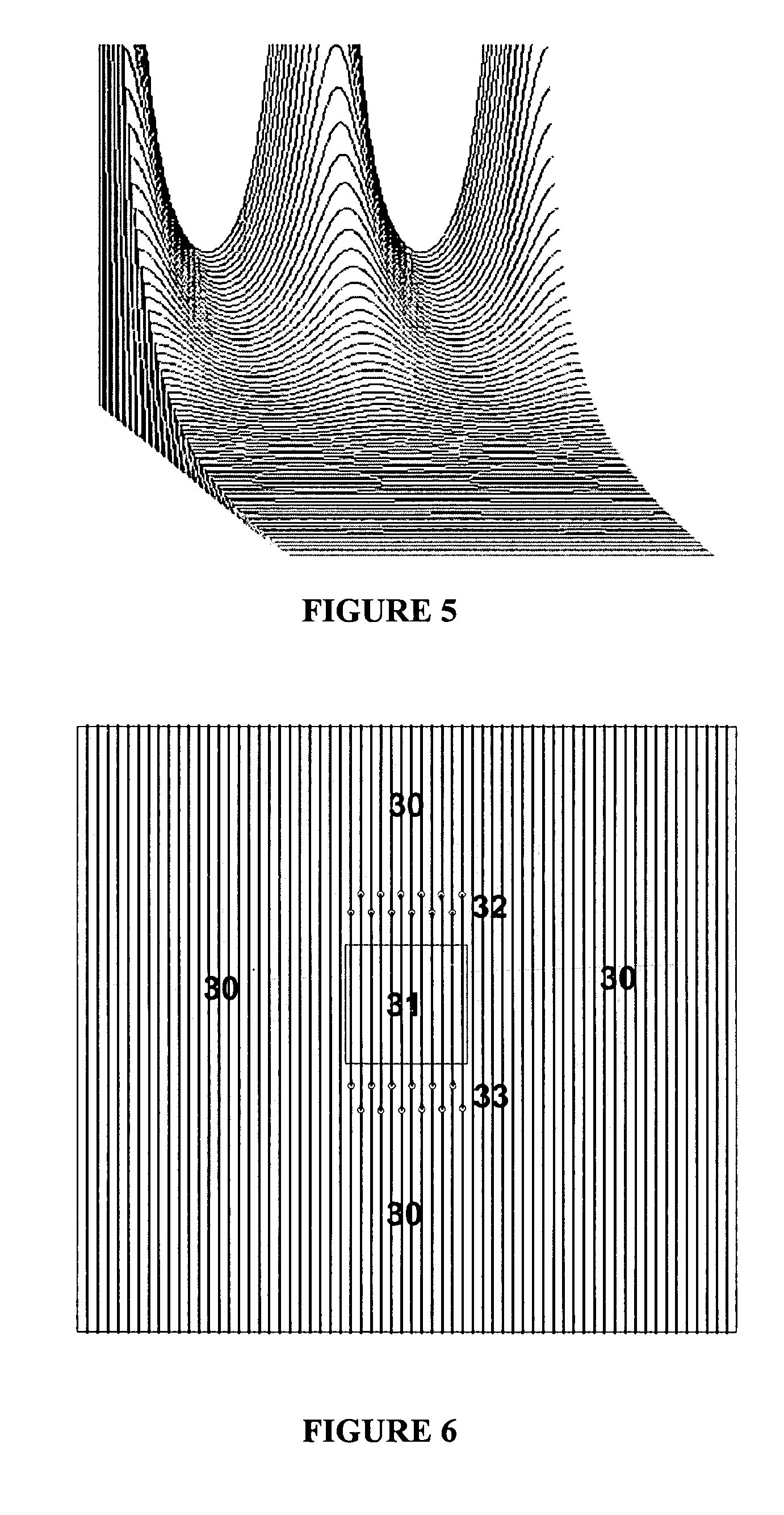
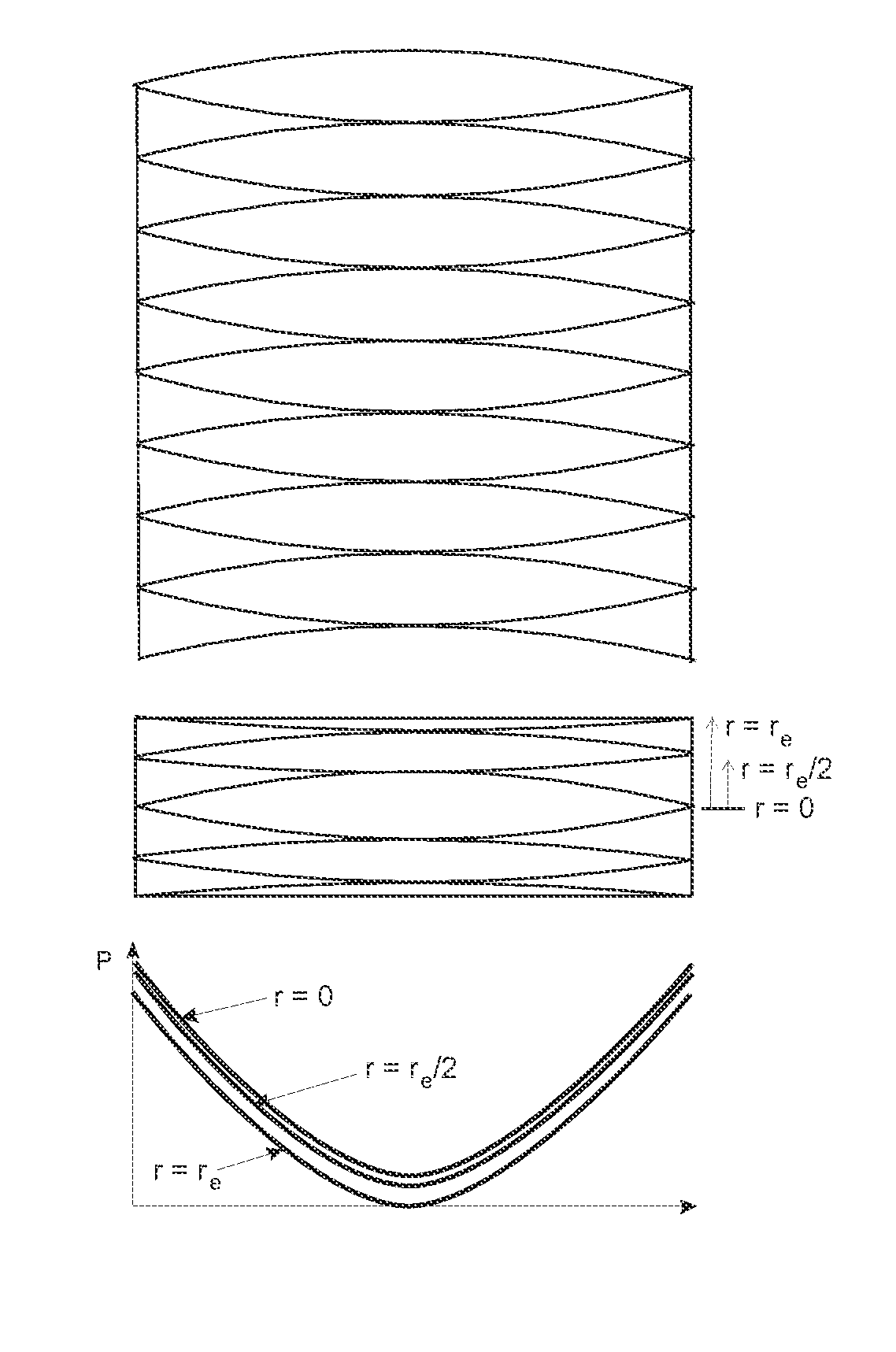
Ion cyclotron resonance measuring cells with harmonic trapping potential
ActiveUS8704173B2Isotope separationTube magnetic delectionElectrical resistance and conductanceTrapping
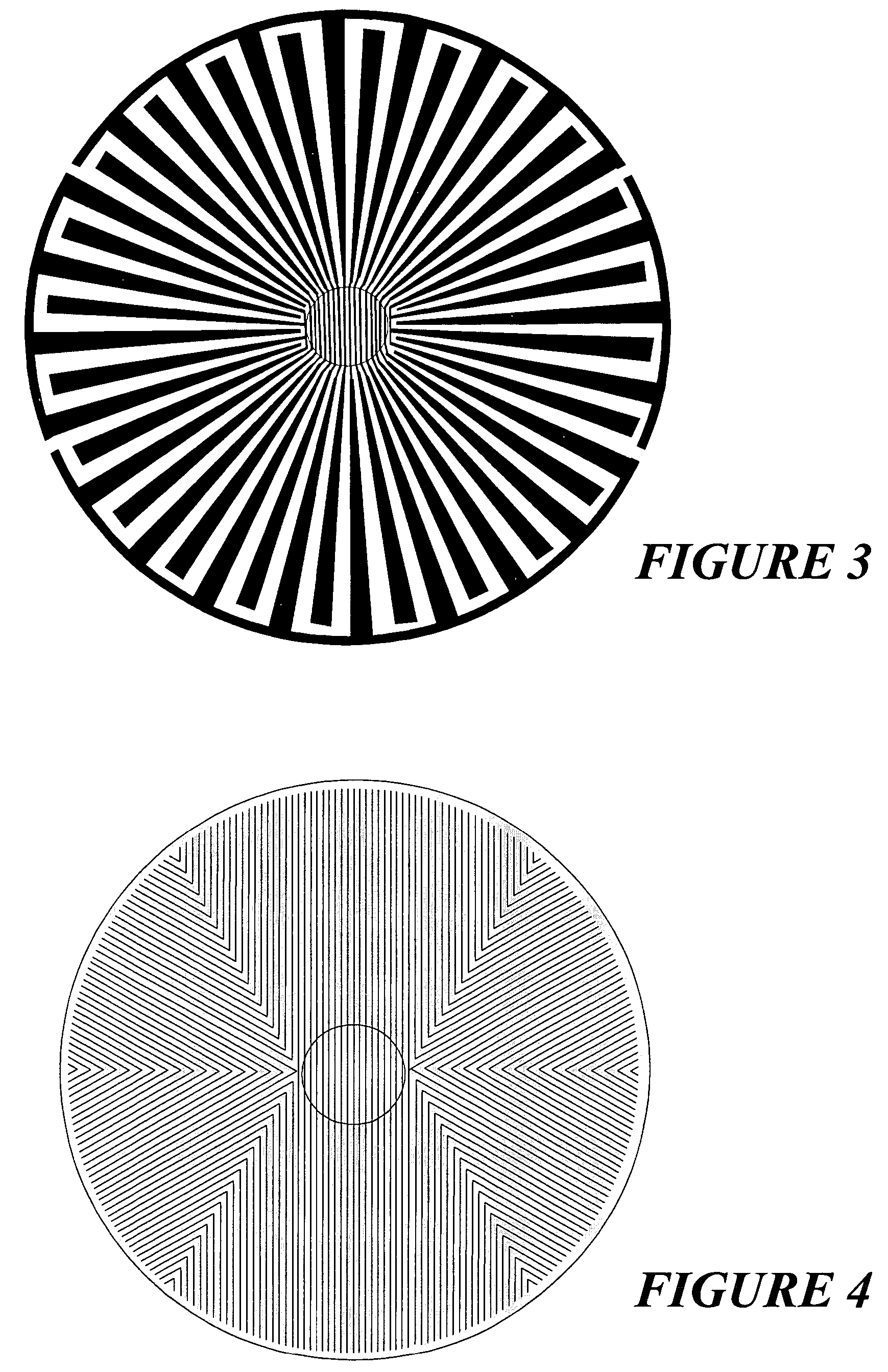
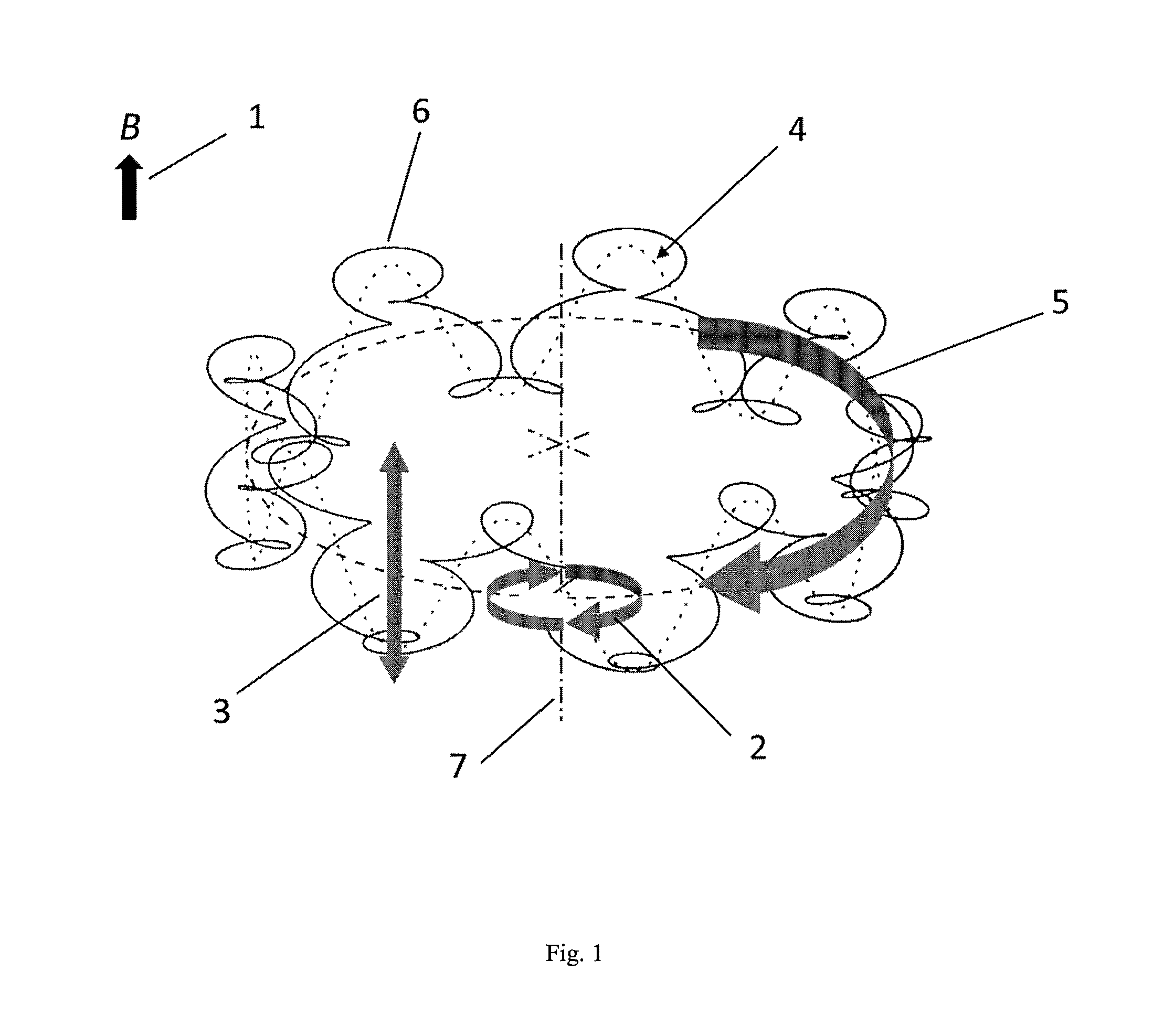
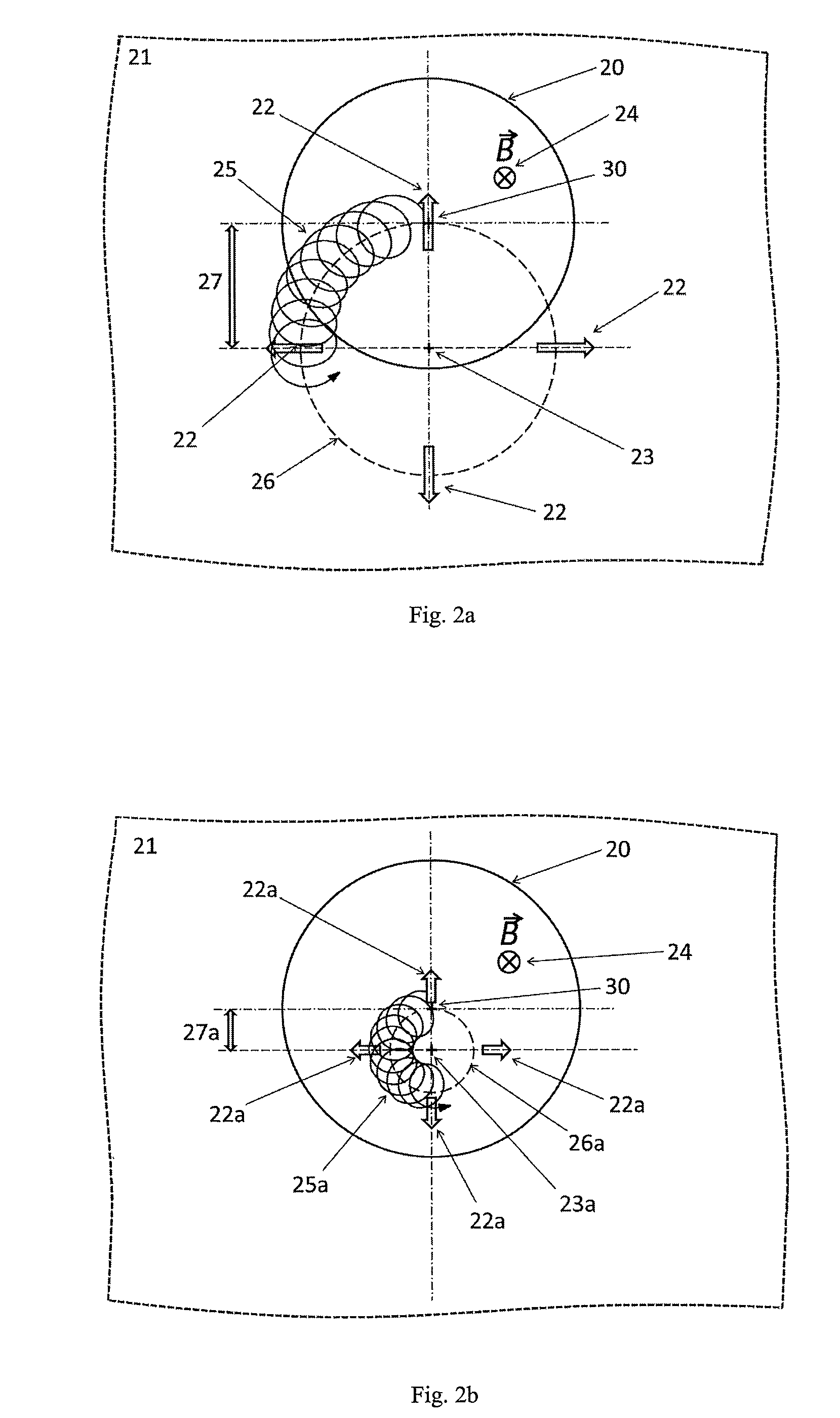
Devices and methods for the acquisition of mass spectra with very high mass resolution in ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometers include cylindrical ICR measuring cells with special electrode geometries to generate harmonic trapping potentials for orbiting ions. The sheath of the cylindrical cell is divided by longitudinal gaps into a multitude of sheath electrodes, which either have to carry layers with resistance profiles able to generate parabolic voltage profiles along the sheath electrodes, or which form sheath electrodes of varying width by parabolic gaps. Orbiting ions of a given mass m / z oscillate harmonically in an axial direction with the same frequency, independent of the radius of their orbit and their oscillation amplitude. Ideally, the cylinders are closed by endcaps with rotationally hyperbolic form, divided into partial electrodes. The ions are excited by dipolar excitation fields. The orbiting ion clouds are kept together for much longer periods than was possible hitherto.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
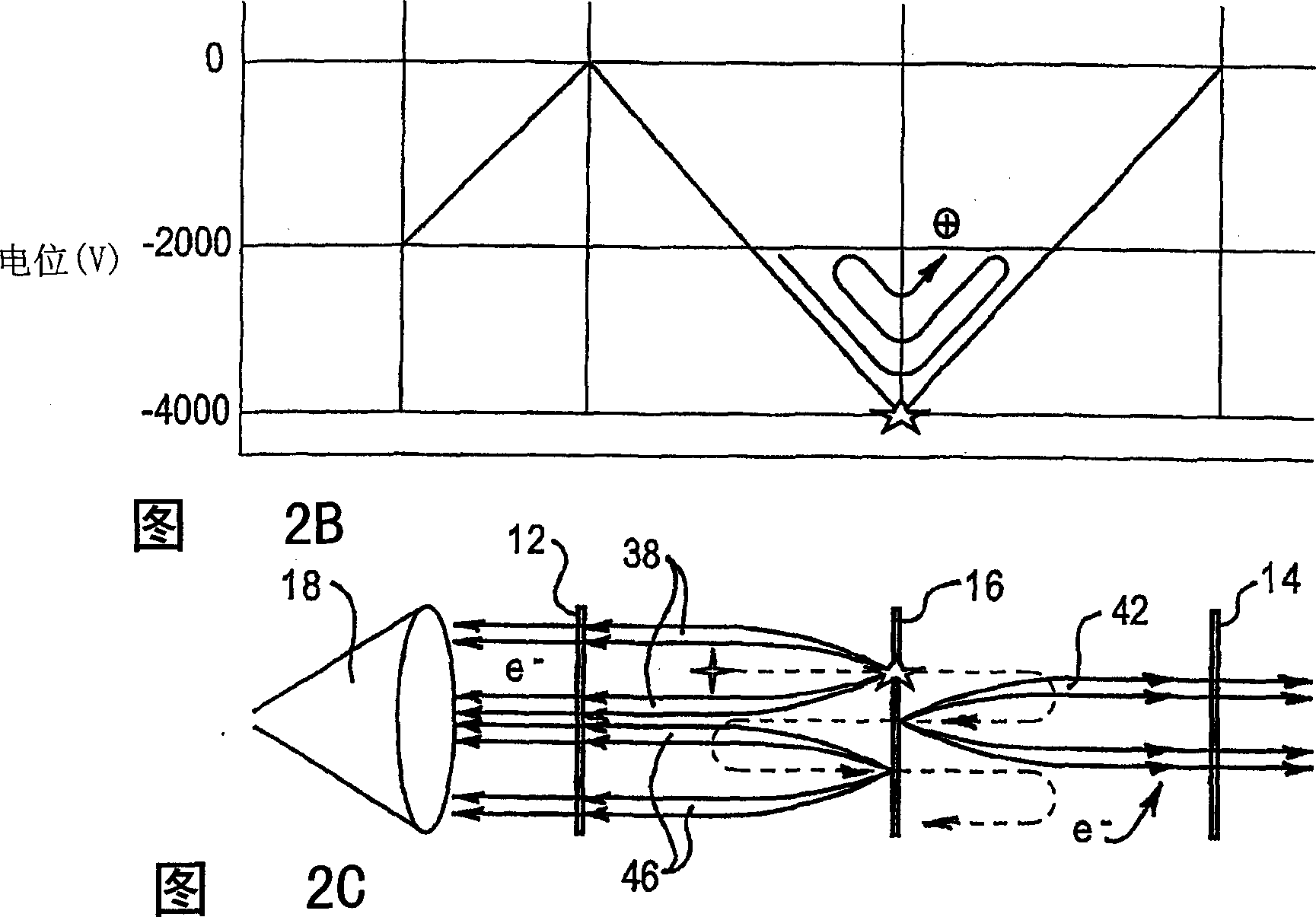
Method and apparatus for analyzing hydrocarbon streams
The present invention is a method and apparatus for identifying a mixture of particles using a Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometer (FT-ICR MS). The particles are first reacted in a charge exchange reaction within the FT-ICR MS chamber using ionic partners that are chosen to discriminate among components of the mixture based on ionization potential. Mass spectra of test runs using different ionic partners may then be compared to identify components based on information gathered about both molecular mass and ionization potential.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY & AUTOMATION INC
Correction of asymmetric electric fields in ion cyclotron resonance cells
The invention relates to a method and a device for optimization of electric fields in measurement cells of Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometers. The invention is based on the rationale that asymmetric electric fields with uniformly or non-uniformly perturbed field axes can appear in ion cyclotron resonance cells and therefore the axis of the magnetron orbit can become radially displaced. Shifted magnetron orbits negatively affect the cyclotron excitation, deteriorate the FT-ICR signal, increase the intensity of an even-numbered harmonics peak, lead to stronger side bands of the FT-ICR signal, and in extreme cases, cause loss of ions. The present invention helps in probing the shift of the magnetron motion, detecting parameters indicative of the offset of the electric field axis and / or correcting it by trimming it back to the geometric axis of the cell.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com