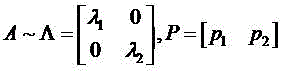Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
100 results about "Induction motor control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
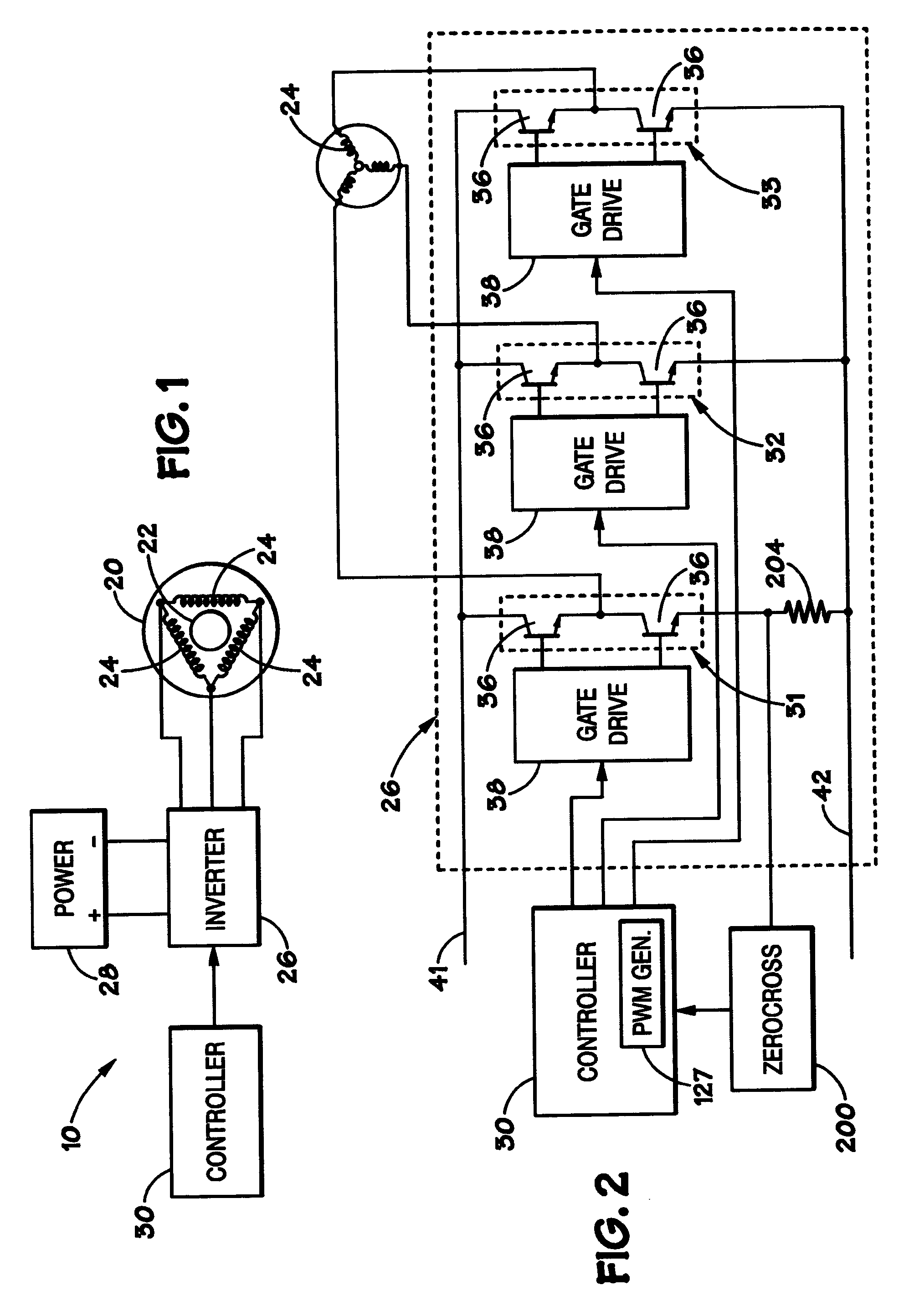
Induction motor control system
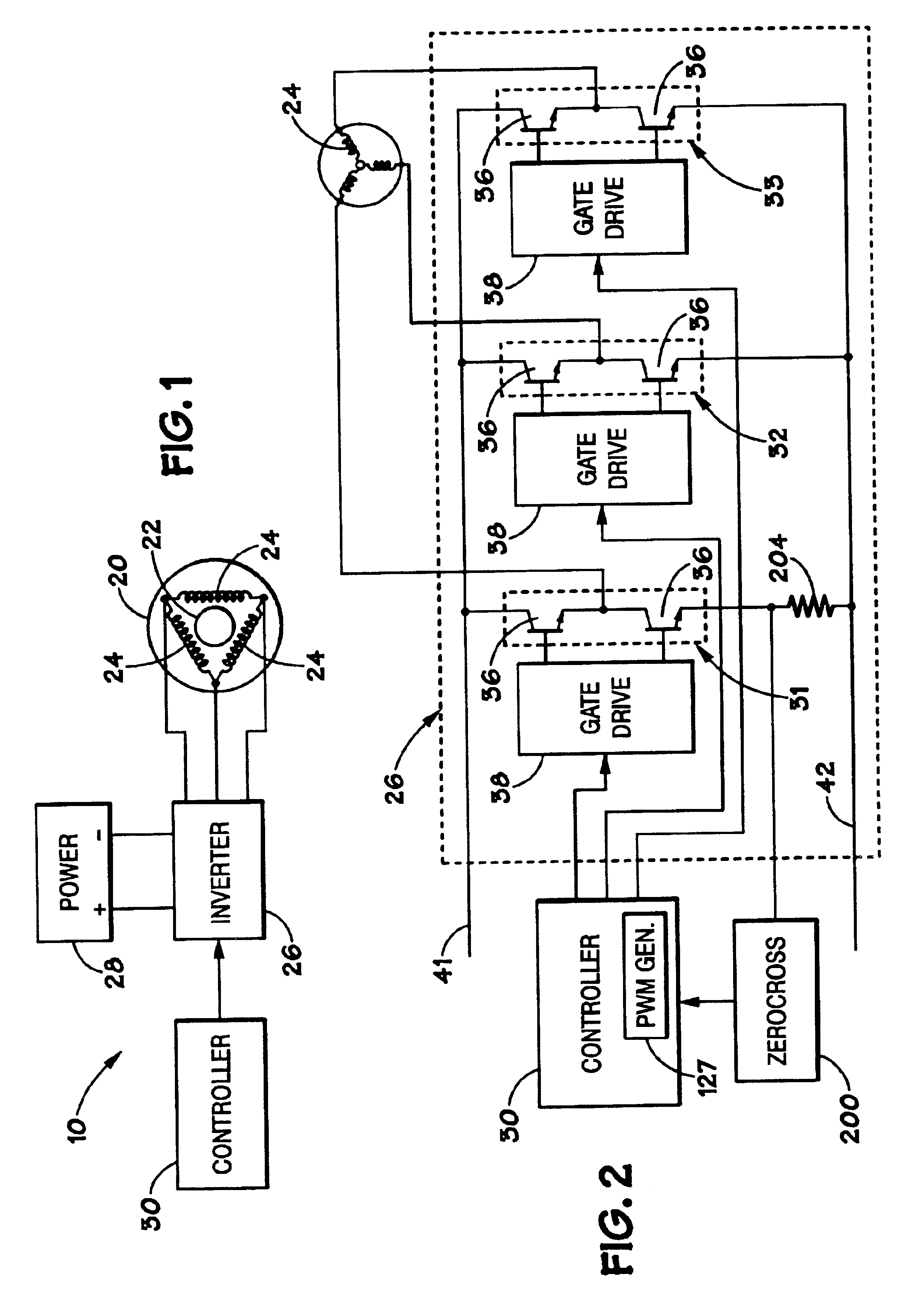
InactiveUS6828751B2Single-phase induction motor startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersPower factorInduction motor
Owner:NIDEC MOTOR CORP
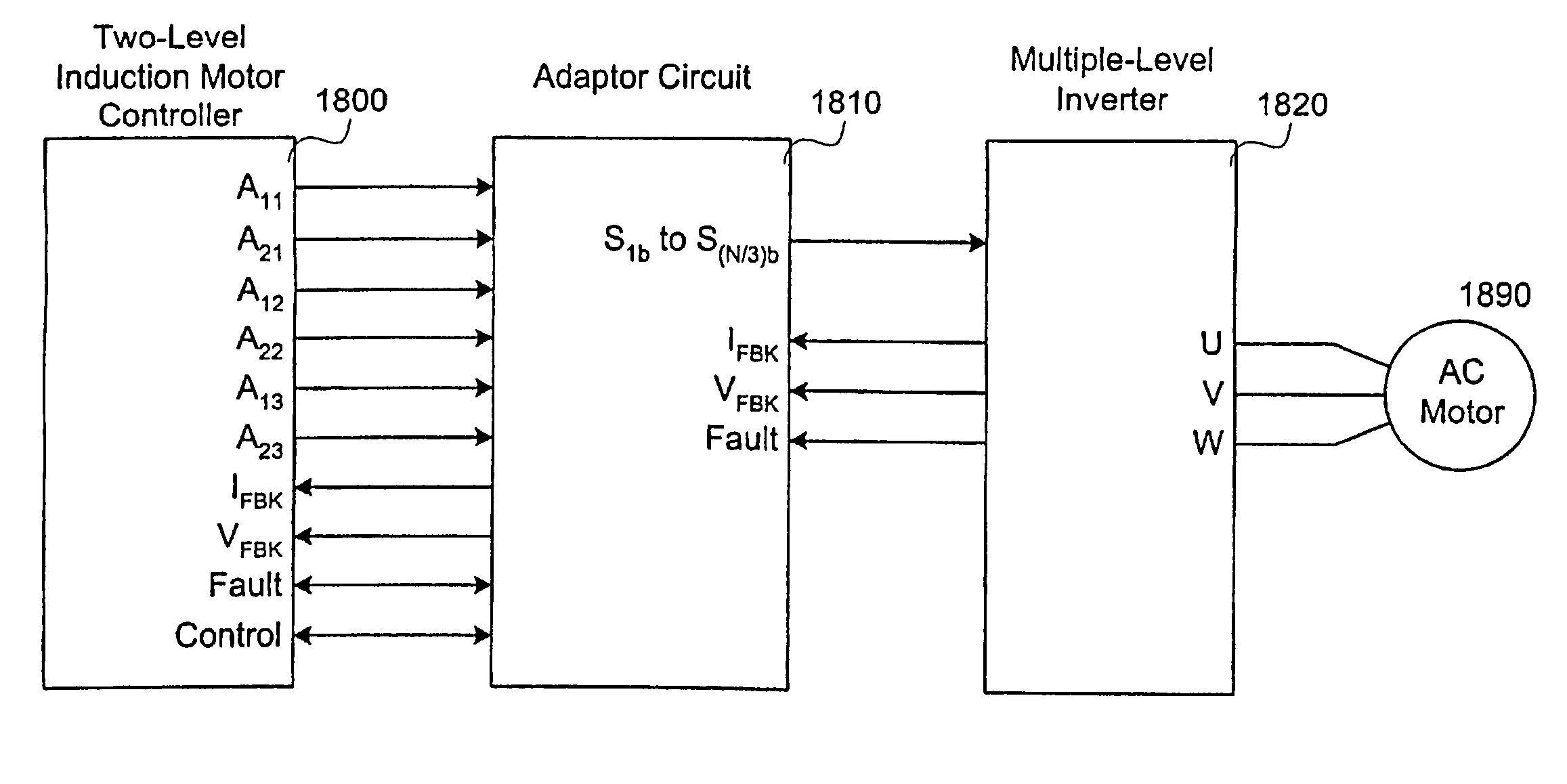
Low voltage, two-level, six-pulse induction motor controller driving a medium-to-high voltage, three-or-more-level AC drive inverter bridge
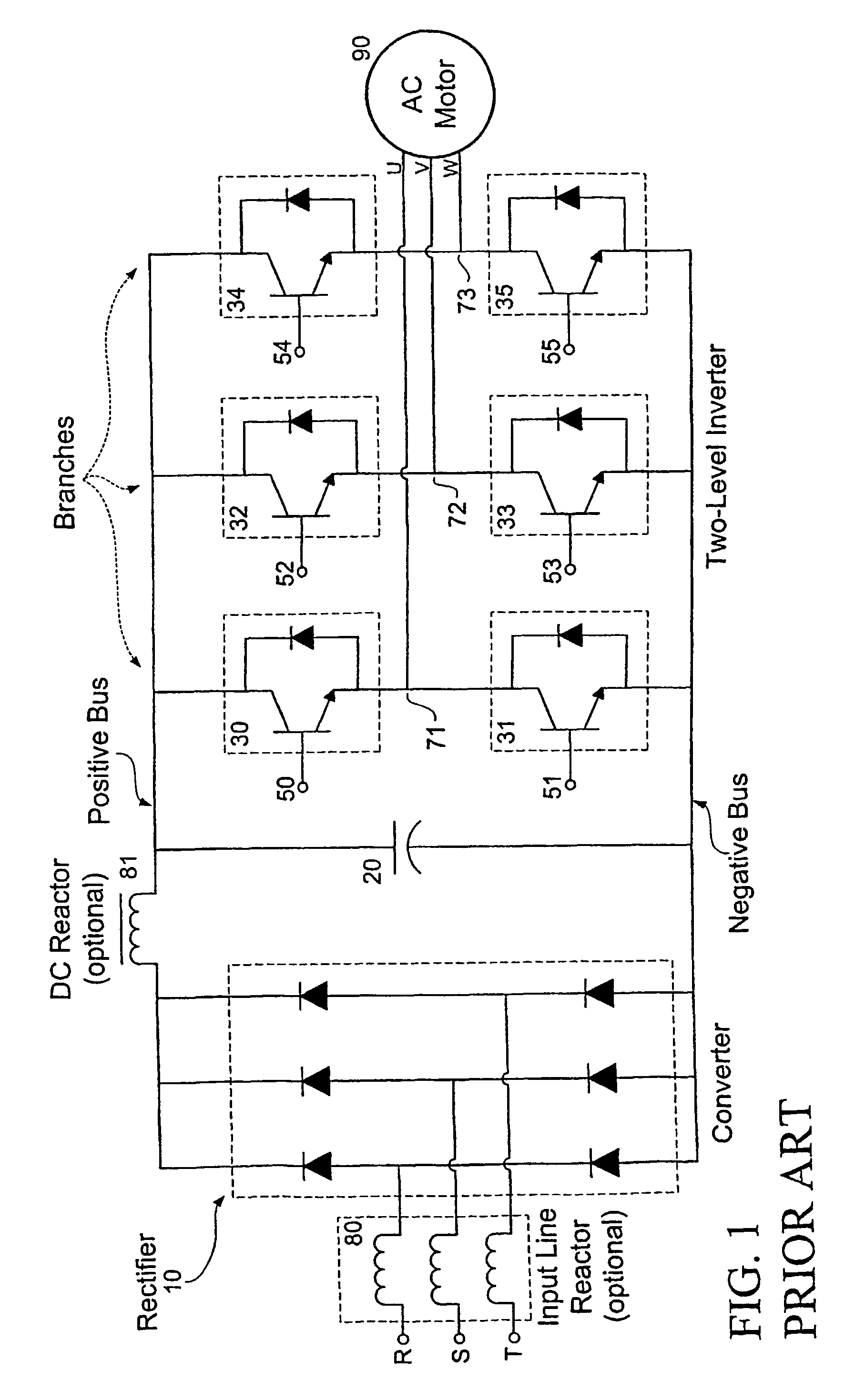
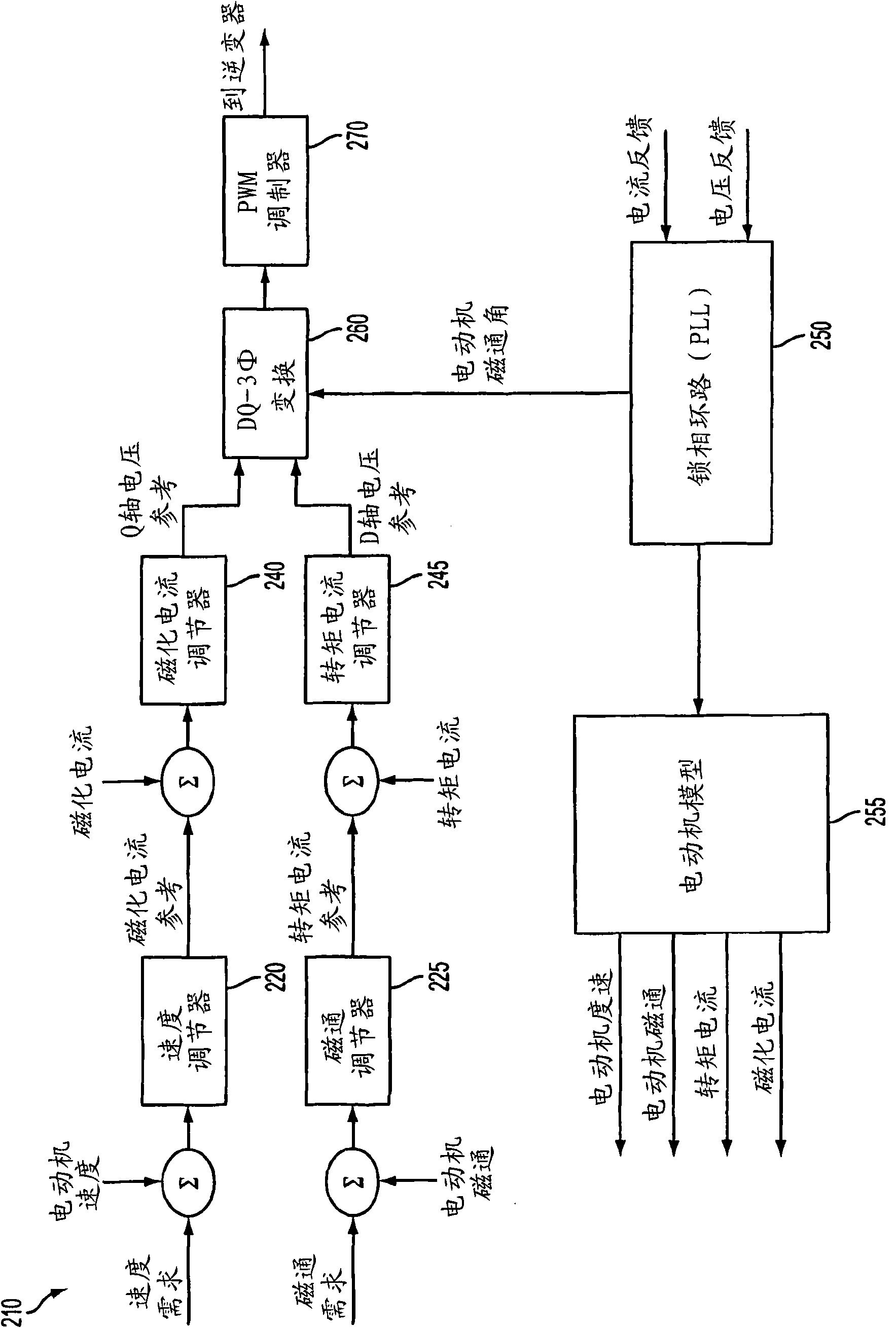
A method and circuit enabling off-the-shelf controllers designed for use with a two-level AC drive inverter bridge (1920) to drive inverter bridges with three-or-more levels. Signals from an ordinary induction motor controller or a two-level induction motor controller (2200) are used to drive the twelve-or-more switches of a three-or-more level inverter bridge (1920), as are used in medium-and-high voltage applications. The proper sequence and timing of switching for the three-or-more-level inverter bridge is based in-part upon either the output of the six pulse-width modulators, or the output of the flux and torque control device, or the voltage control device (2210), of the two-level controller (2200).
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LTD +1
Alternating current induction motor control system based on self-immunity to interference control
InactiveCN102811015AReduce the burden onImprove estimation accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsInduction motorControl system
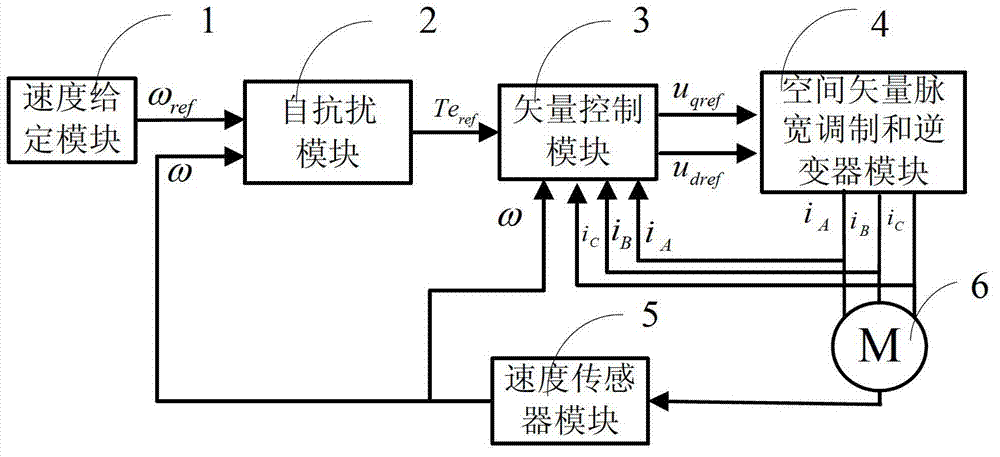
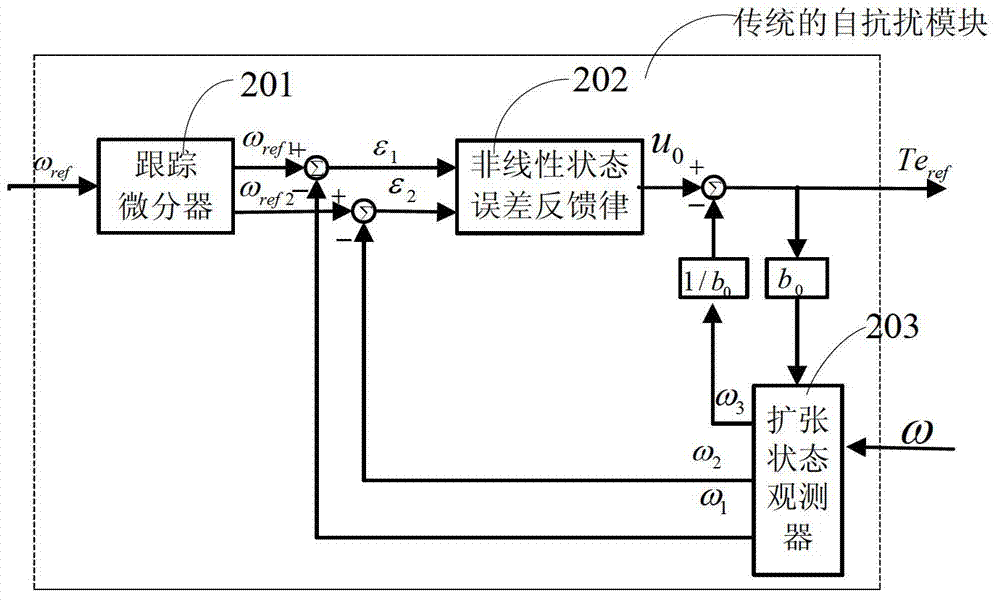
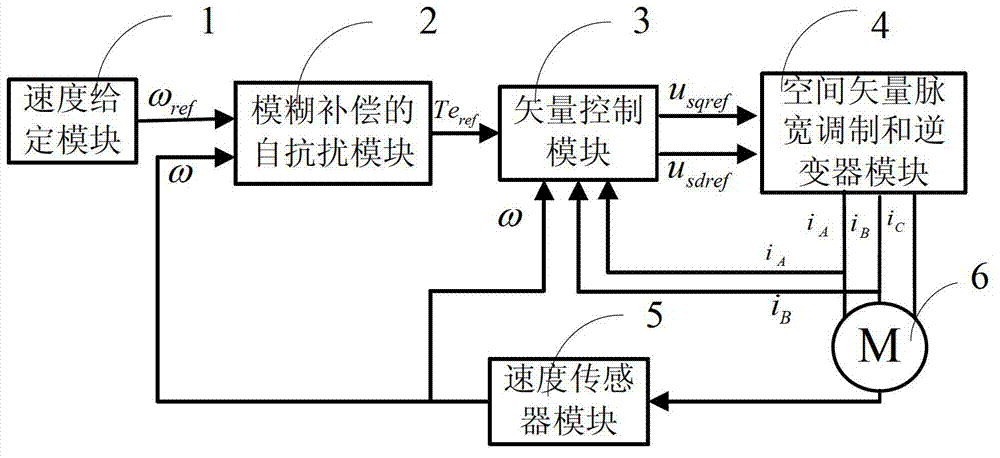
The invention discloses an alternating current induction motor control system based on a self-immunity to interference control. On basis of the prior art, according to ambiguity compensation, a known part, i.e., the ambiguity compensation sc of the rotation speed working characteristics of the alternating current induction motor is input to an expanded state observer, a sum action quantity Omega 3 of a variety of interference of an actual rotation speed Omega of the motor is an estimation of an unknown part instead of an overall rotation speed, thus burdens of the expanded state observer are relieved, meanwhile a variation scope of a parameter adapting object is enlarged, and the estimation precision of the expanded state observer is increased. By the adoption of the control system, better control effects compared with that of the alternating induction motor system based on the traditional self-immunity to interference control are obtained, the robustness and the immunity to interference are stronger, and the dynamic quality is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
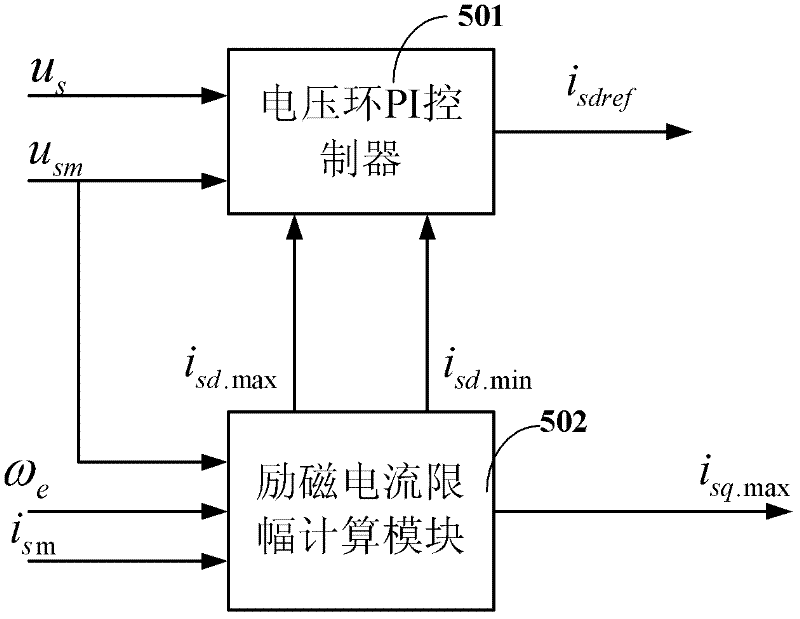
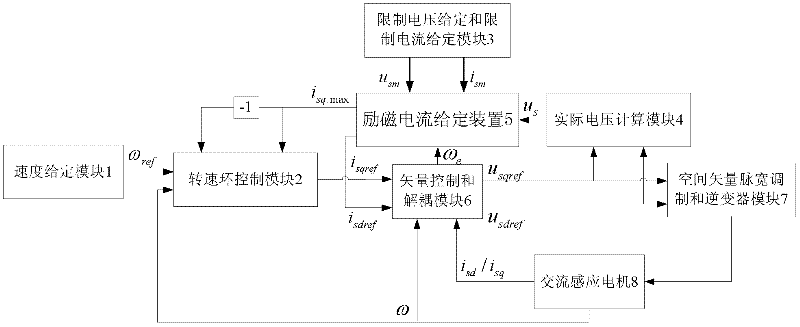
Exciting current given device of induction motor of electric vehicle
InactiveCN102403950AReduce back EMFReduce jitterElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsConstant powerVoltage vector
The invention discloses an exciting current given device for an induction motor of an electric vehicle. On the basis of the prior art, the exciting current given device is additionally provided with an exciting current limiting calculation module and a limiting PI (proportional integral) control module. When the induction motor normally runs, the calculated amplitude limiting maximum value (isd.Max) of the exciting current decreases along with the increase of the real synchronous speed omega e. The exciting current isdref of a voltage loop PI controller decreases under the condition of invariable maximum voltage vector (usm). Due to the decrease of the exciting current (isdref), the counter electromotive force of the induction machine decreases, therefore, under the condition of invariable busbar voltage uDC, the induction motor can rise to a higher rotating speed. In addition, according to the exciting current given device of the induction motor of the electric vehicle, the calculation of switching points among a constant torque area, a constant power area and a constant voltage area is eliminated, so that the level jump of output exciting currents caused by the inaccurate calculation of switching points can be effectively prevented, the given value of the exiting currents can vary stably, the joggling of the induction motor control caused by the level jump of the given valueof the exciting currents is reduced, and the safety of the induction motor control is improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
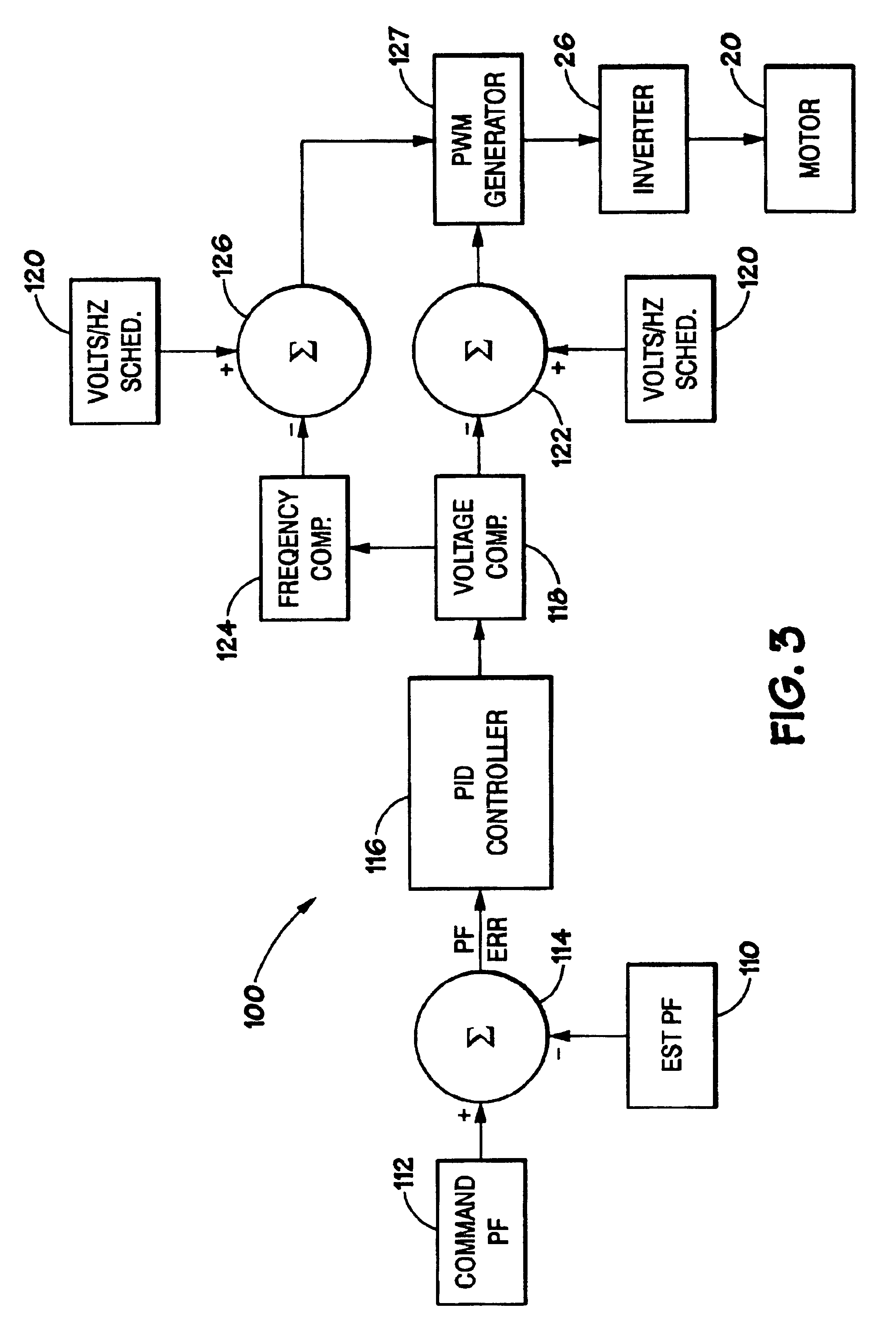
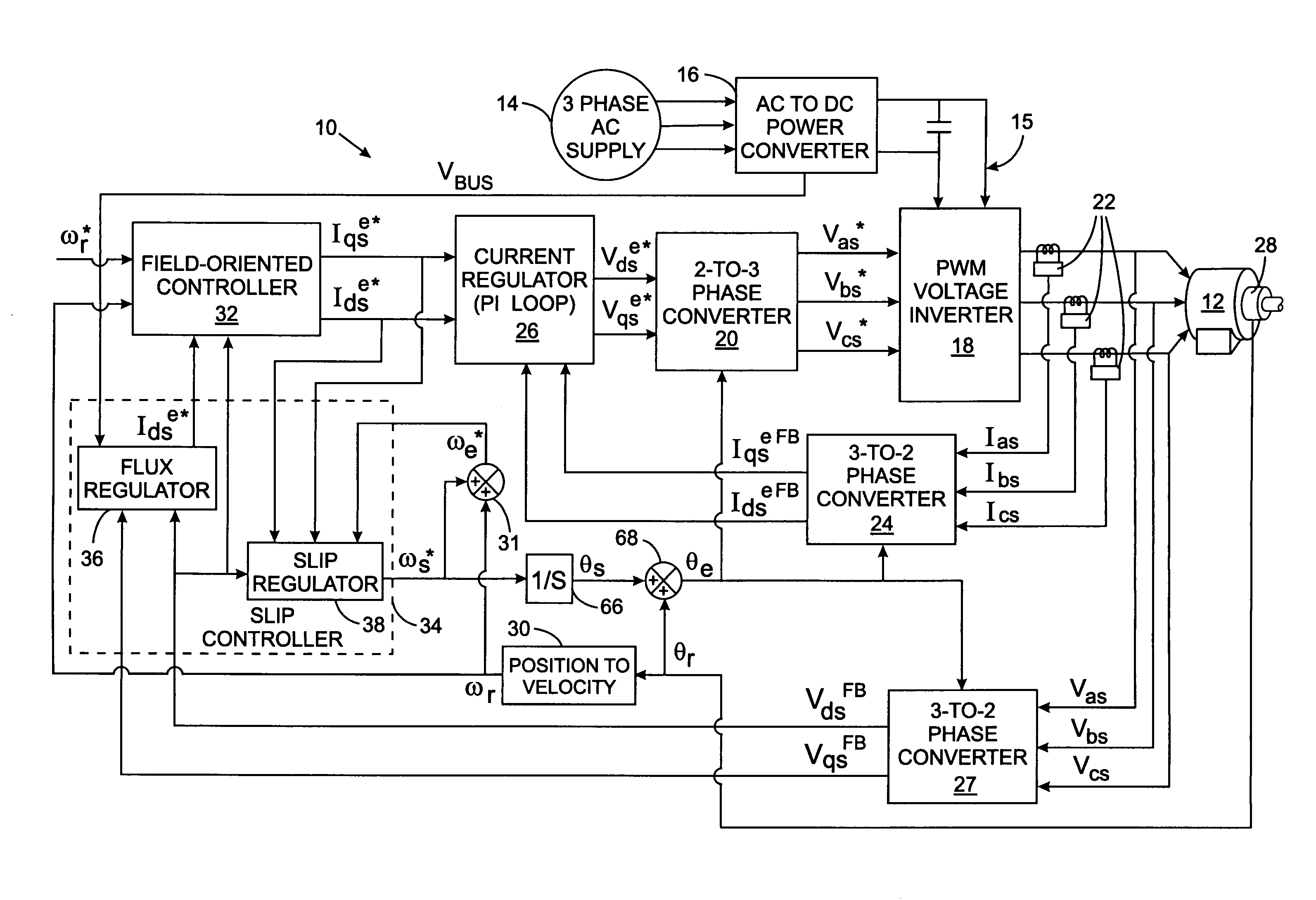
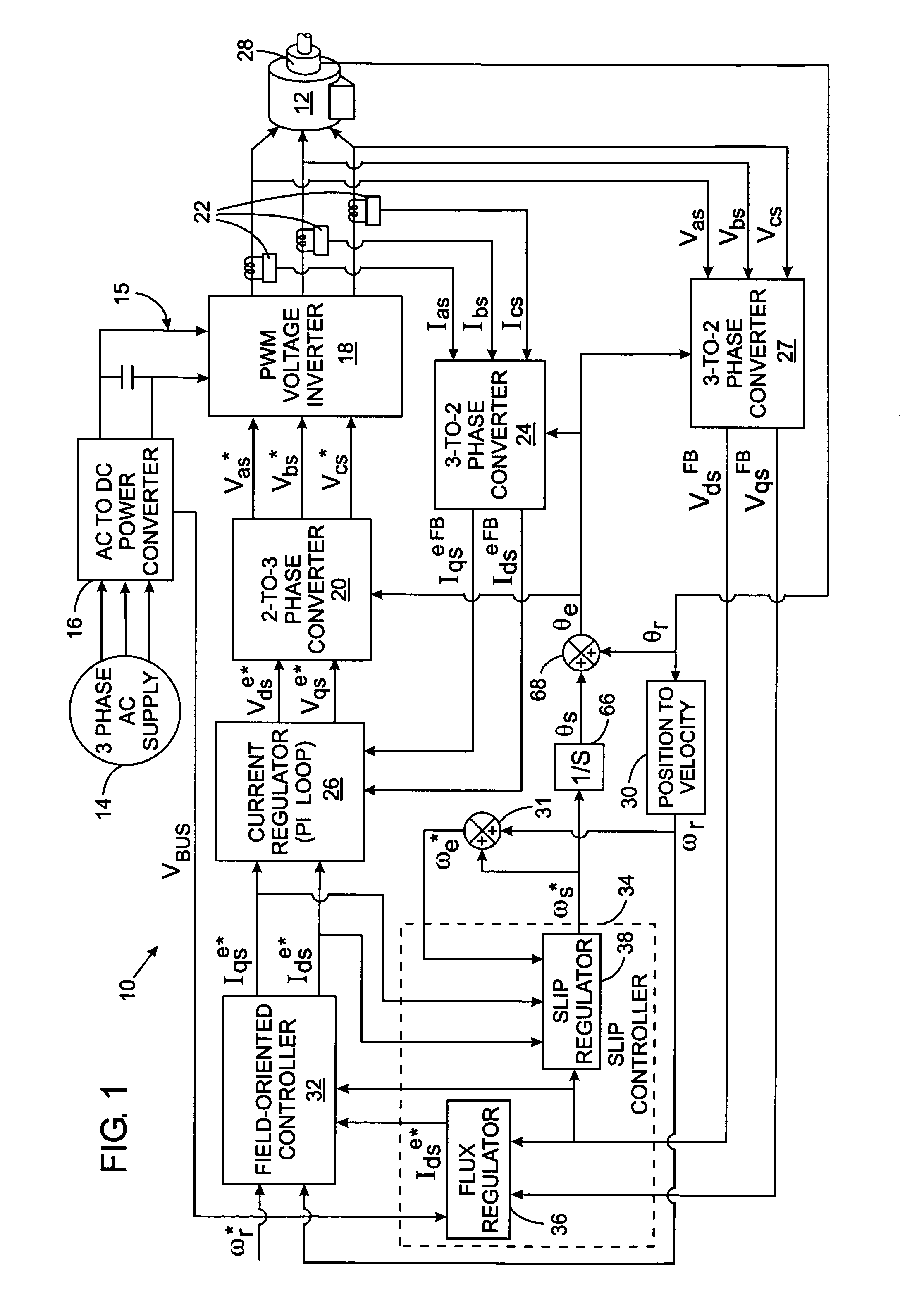
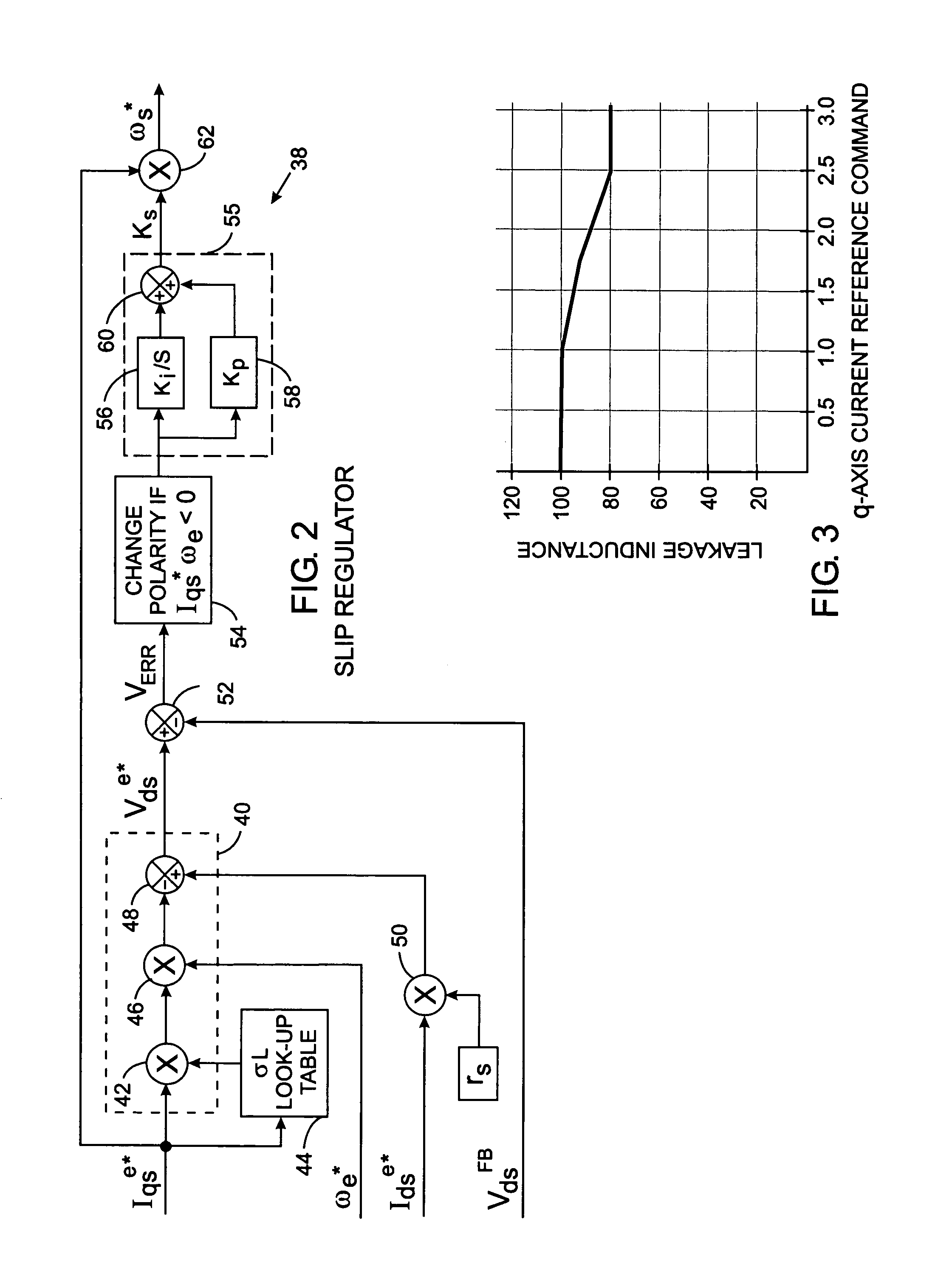
Leakage inductance saturation compensation for a slip control technique of a motor drive
ActiveUS7187155B2Single-phase induction motor startersSynchronous motors startersStator voltageControl vector
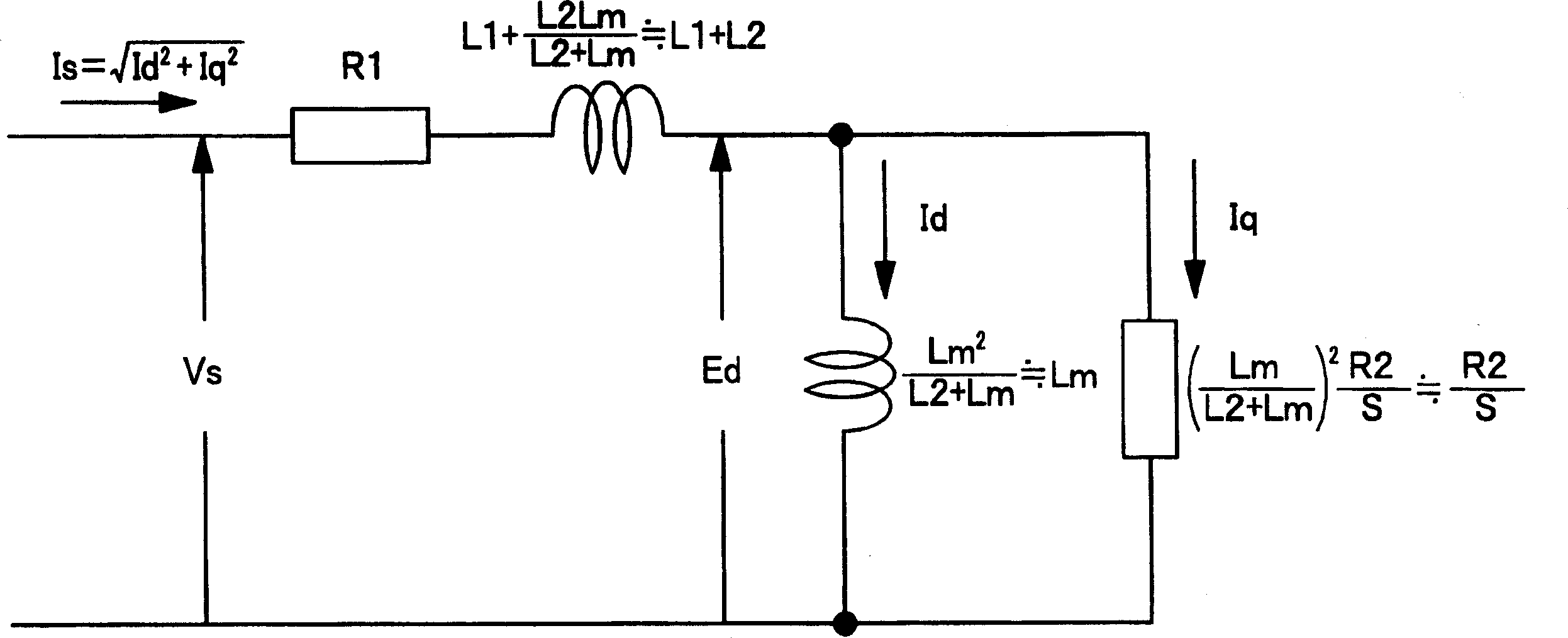
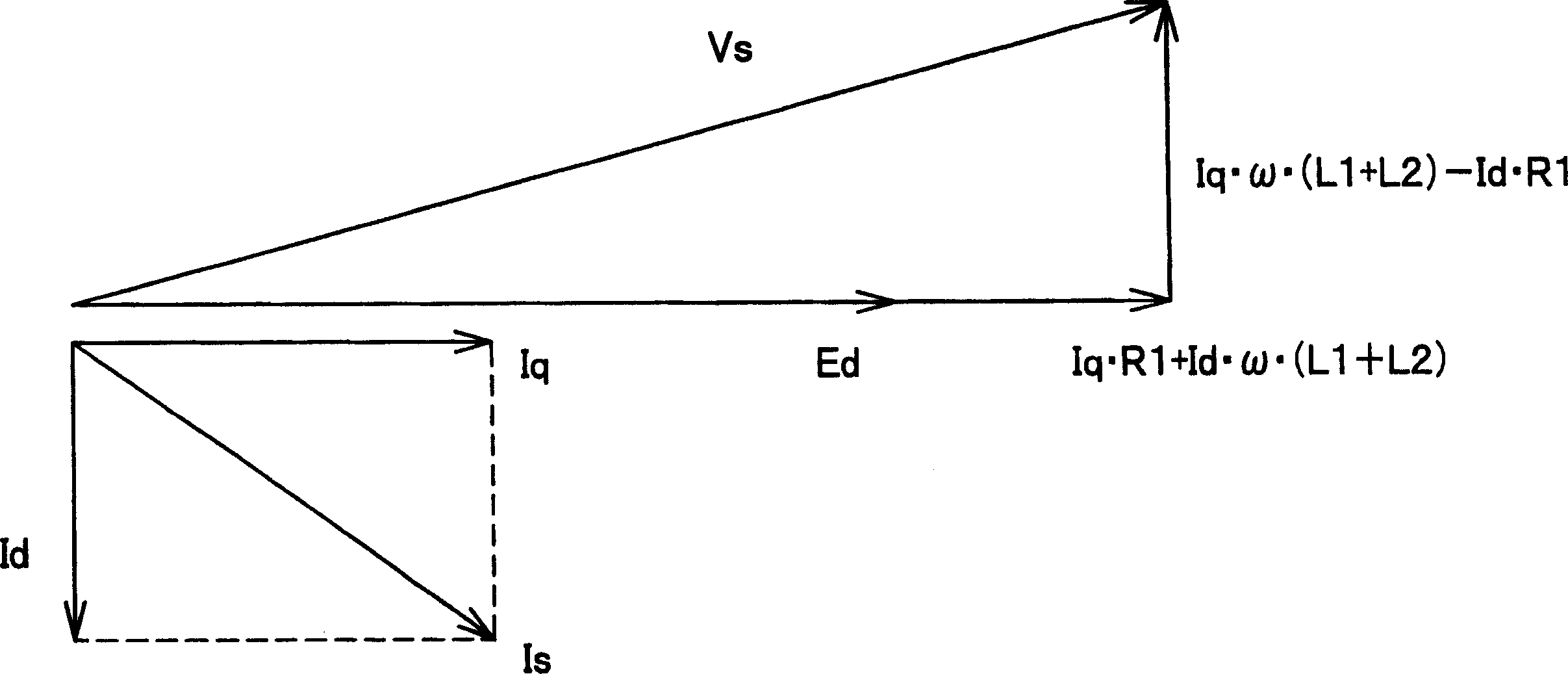
An electronic drive for vector control of an induction motor controls slip and operating frequency in response to changes in stator voltage. The drive includes a torque control loop, a flux control loop and a frequency control loop. The control is based on a commanded stator current that is resolved into a torque-producing, or q-axis, current component and a flux-producing, or d-axis, current component that are in quadrature. The frequency control loop includes slip control in which a slip frequency command is produces based on a value for the leakage inductance of the motor. The leakage inductance value dynamically varies as a function of the q-axis current reference command.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
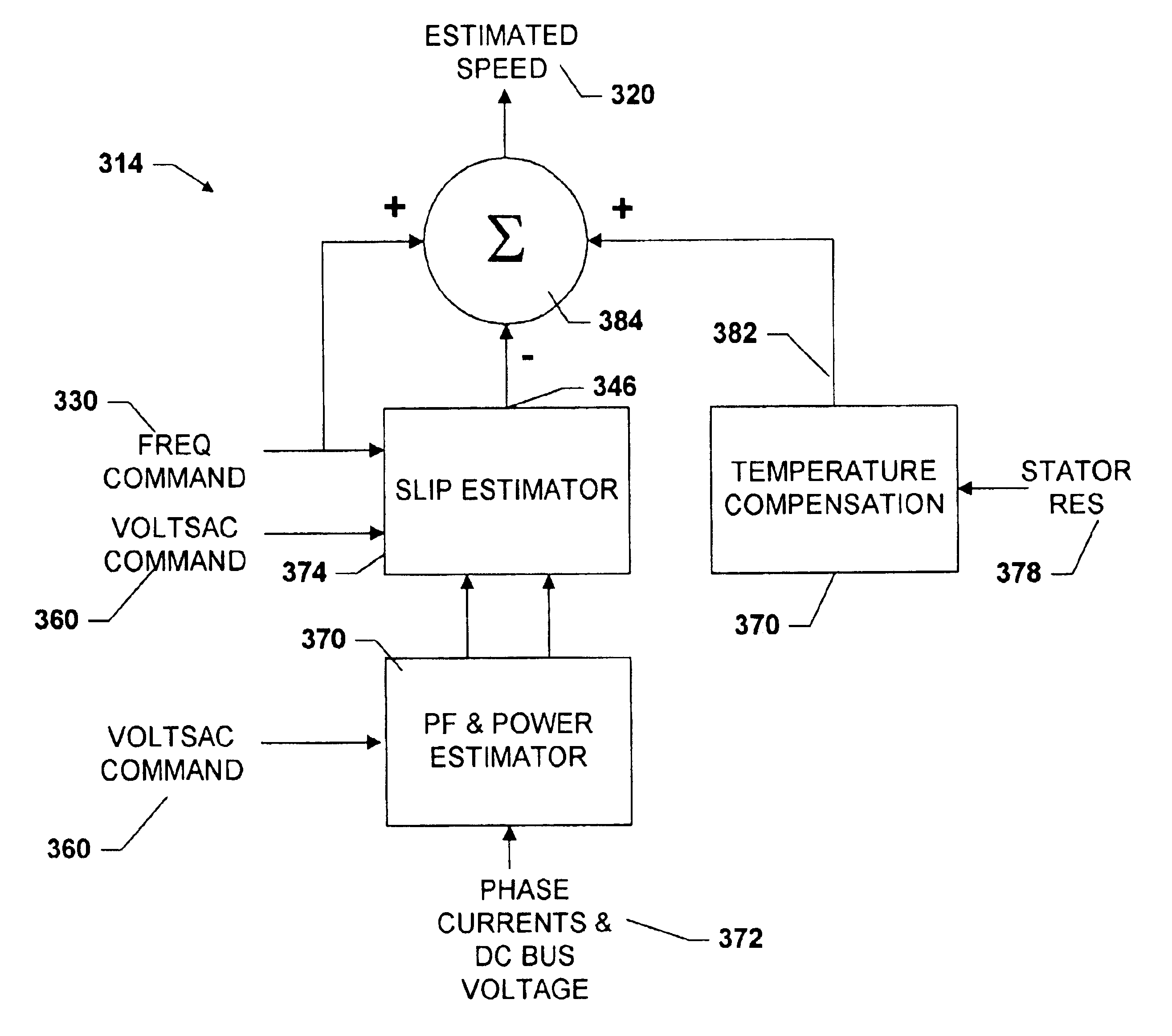
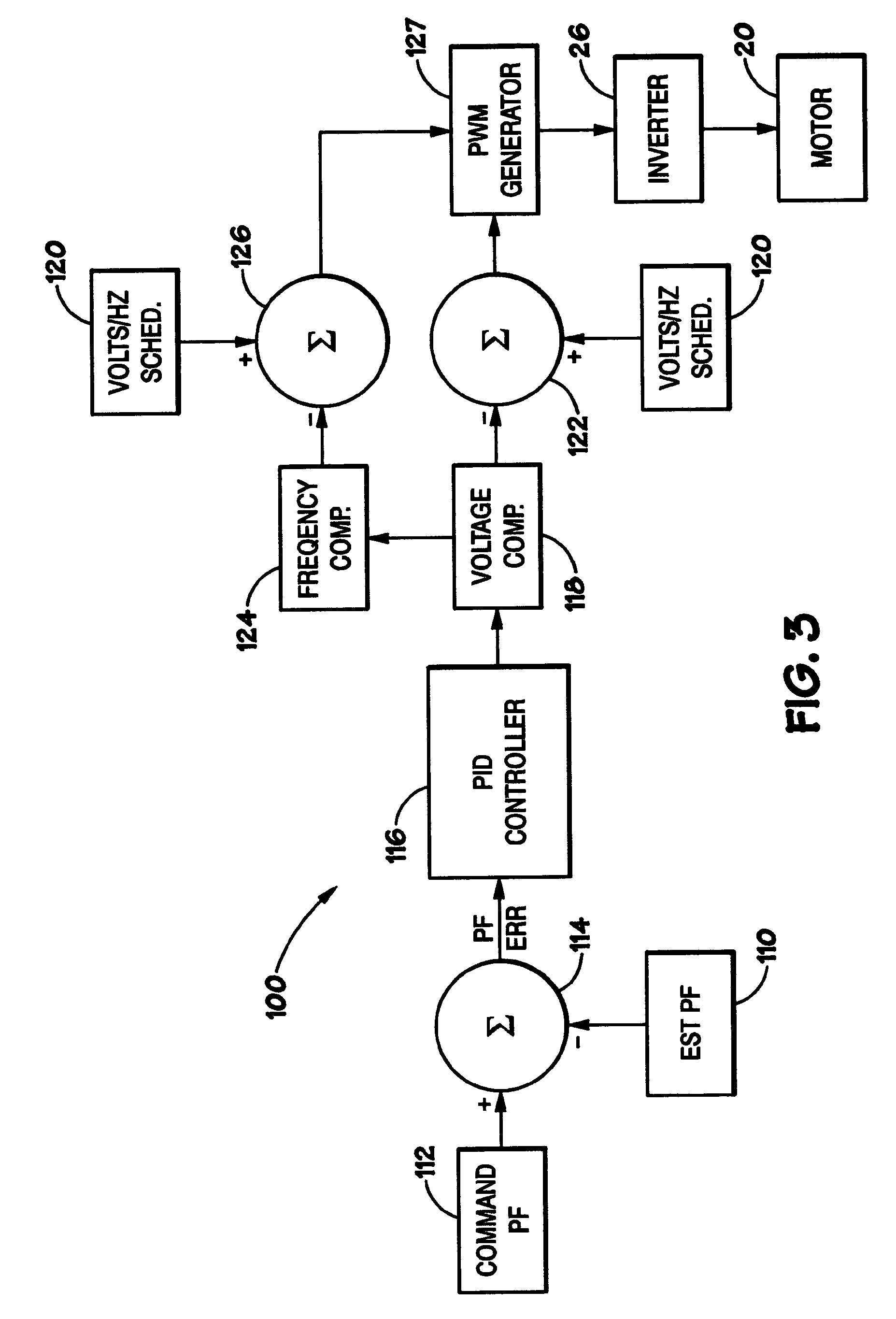
Induction motor control system
InactiveUS20040130287A1Single-phase induction motor startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersPower factorInduction motor
An induction motor drive system and method estimates a motor power factor based on the AC power output to the motor phase windings and estimates the rotor speed based on the estimated power factor. The estimated rotor speed is compared to a rotor speed command signal to generate a speed error, and the voltage and frequency input to the motor are adjusted in response to the speed error. Rotor speed is estimated based on estimated rotor slip, which is estimated based on the applied voltage, frequency, estimated power factor and estimated motor power.
Owner:NIDEC MOTOR CORP
Method and apparatus for control of fault-induced delayed voltage recovery (FIDVR) with photovoltaic and other inverter-based devices
ActiveUS20120049629A1Dc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsInduction motorGrowth of photovoltaics
A method of assembling a motor stall correction system includes coupling an inverter-based electric power generation device to an electric power inverter assembly. The method also includes coupling the electric power inverter assembly to at least one induction motor. The method further includes operatively coupling at least one controller to the electric power inverter assembly. The controller is programmed to transmit electric current from the inverter-based electric power generation device to the electric power inverter assembly. The controller is also programmed to transmit real current and reactive current from the electric power inverter assembly to the induction motor. The controller is further programmed to modulate the real current and the reactive current as a function of at least one of an electric power grid frequency and an electric power grid voltage.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
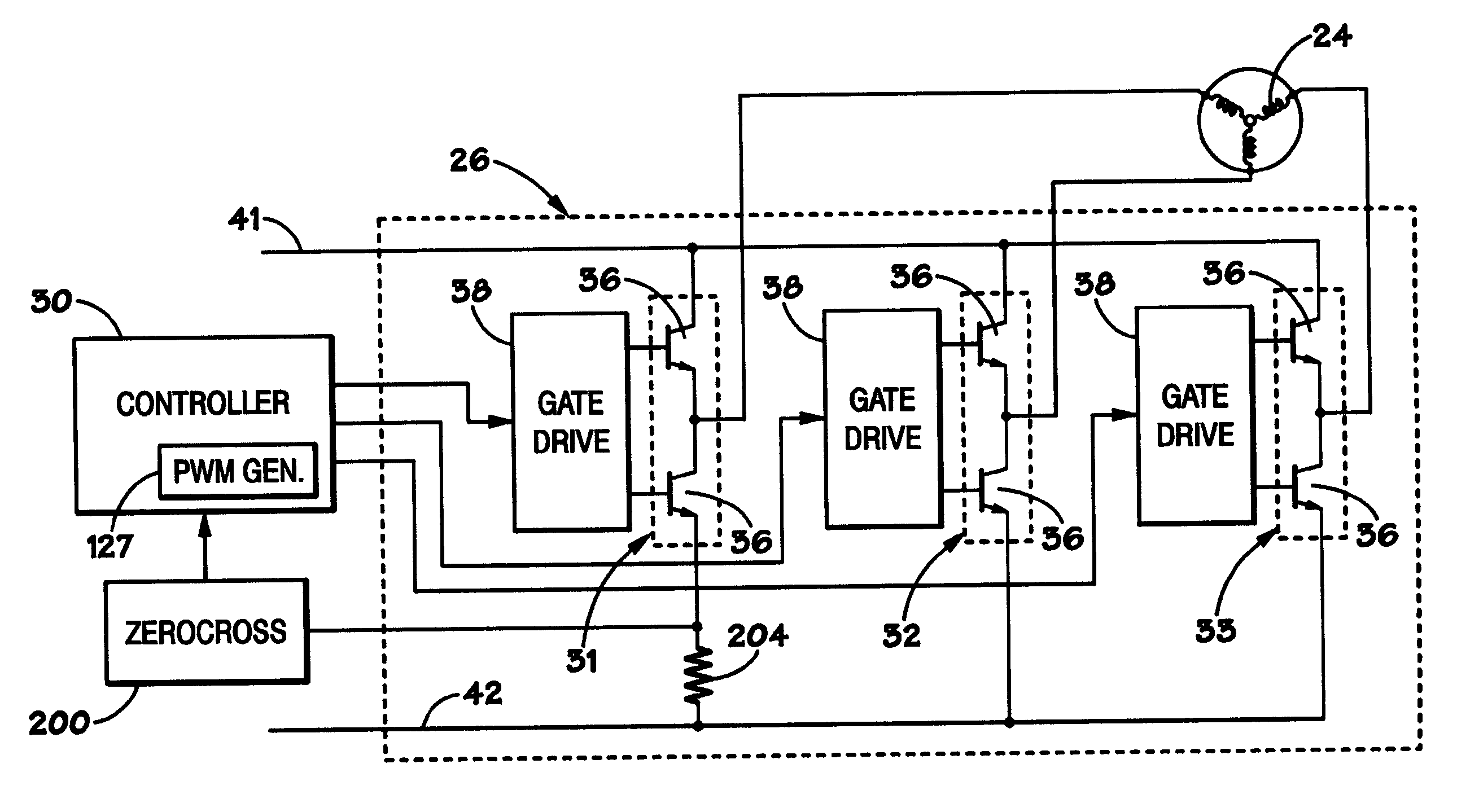
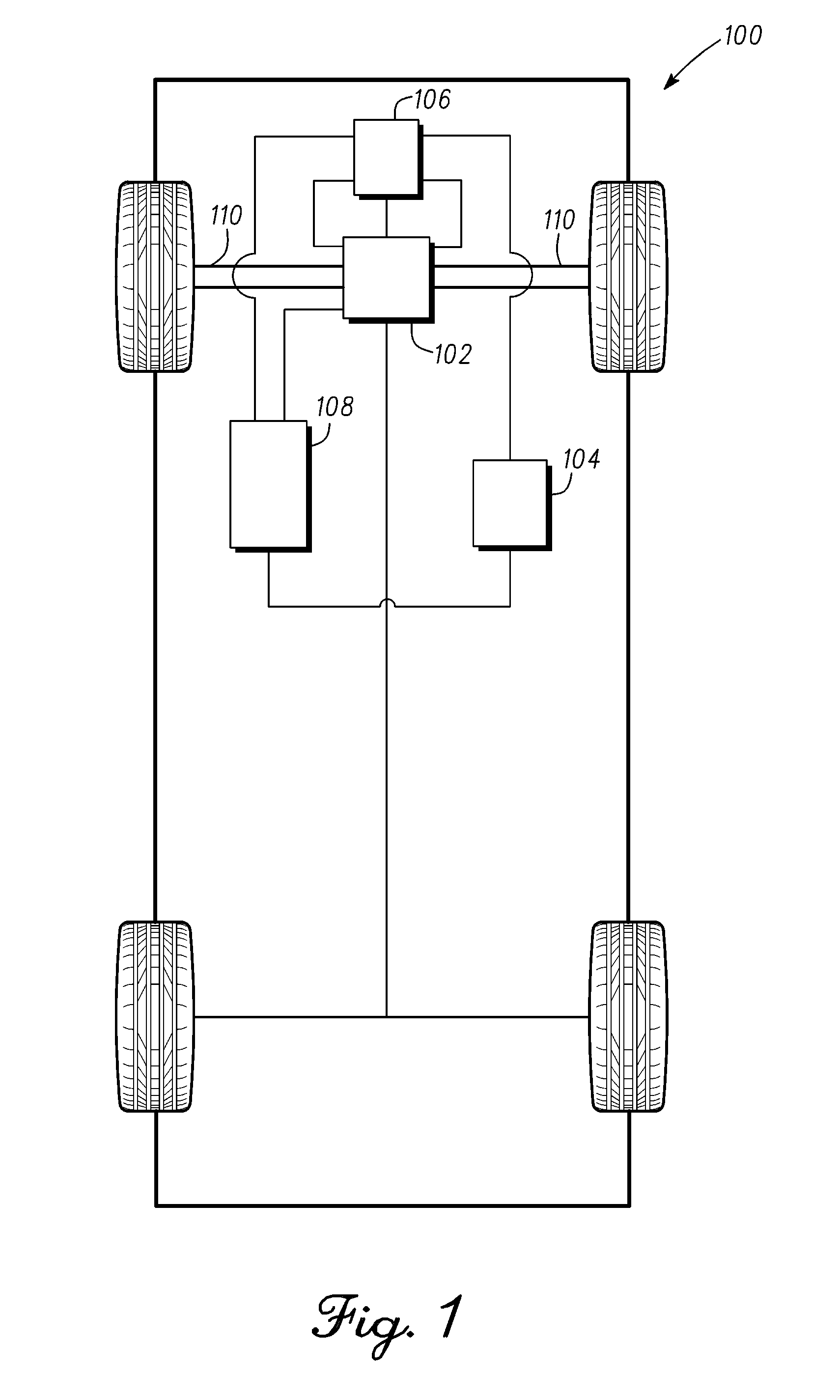
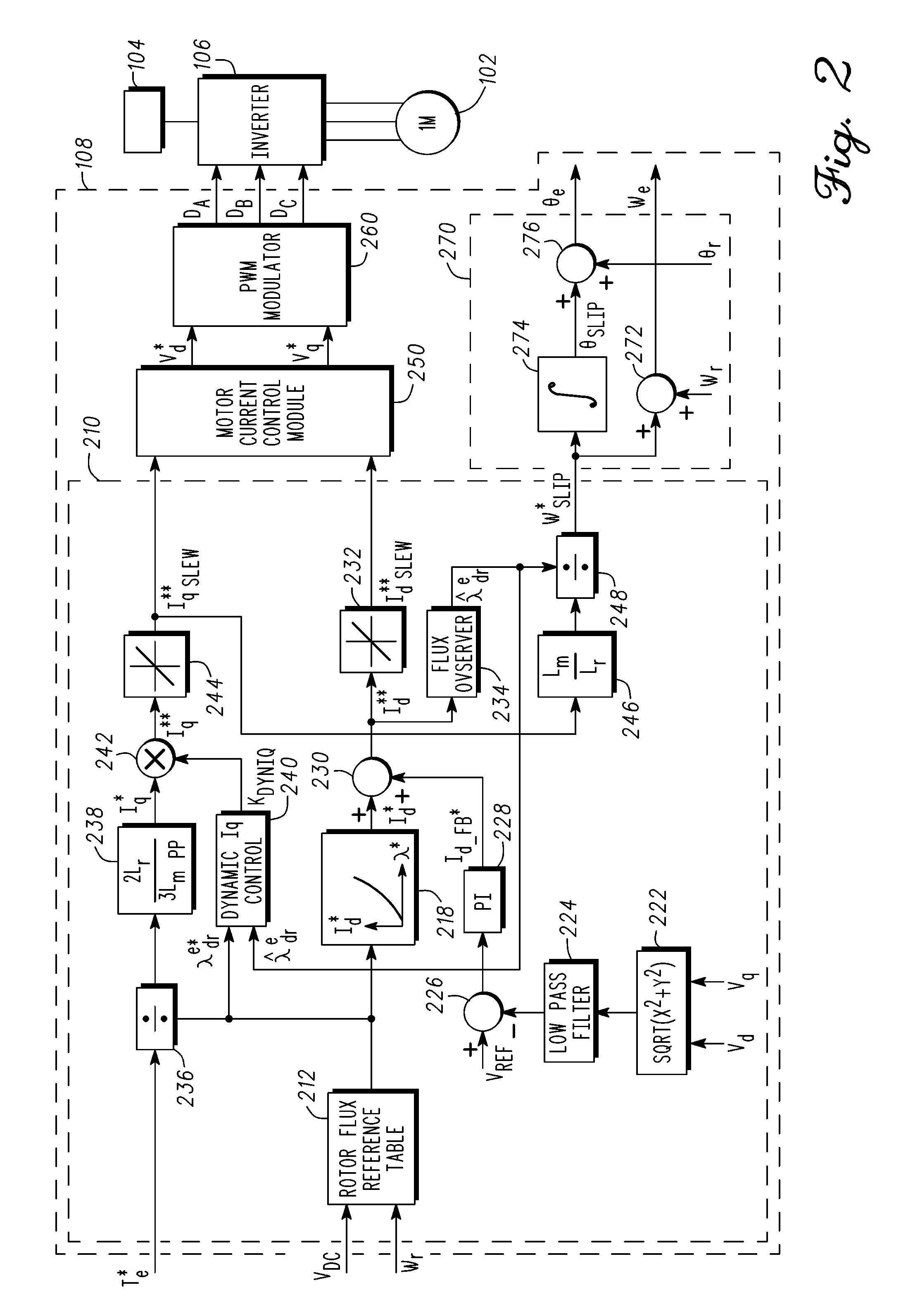
Induction motor control systems and methods
ActiveUS20110163709A1Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersControl systemControl theory
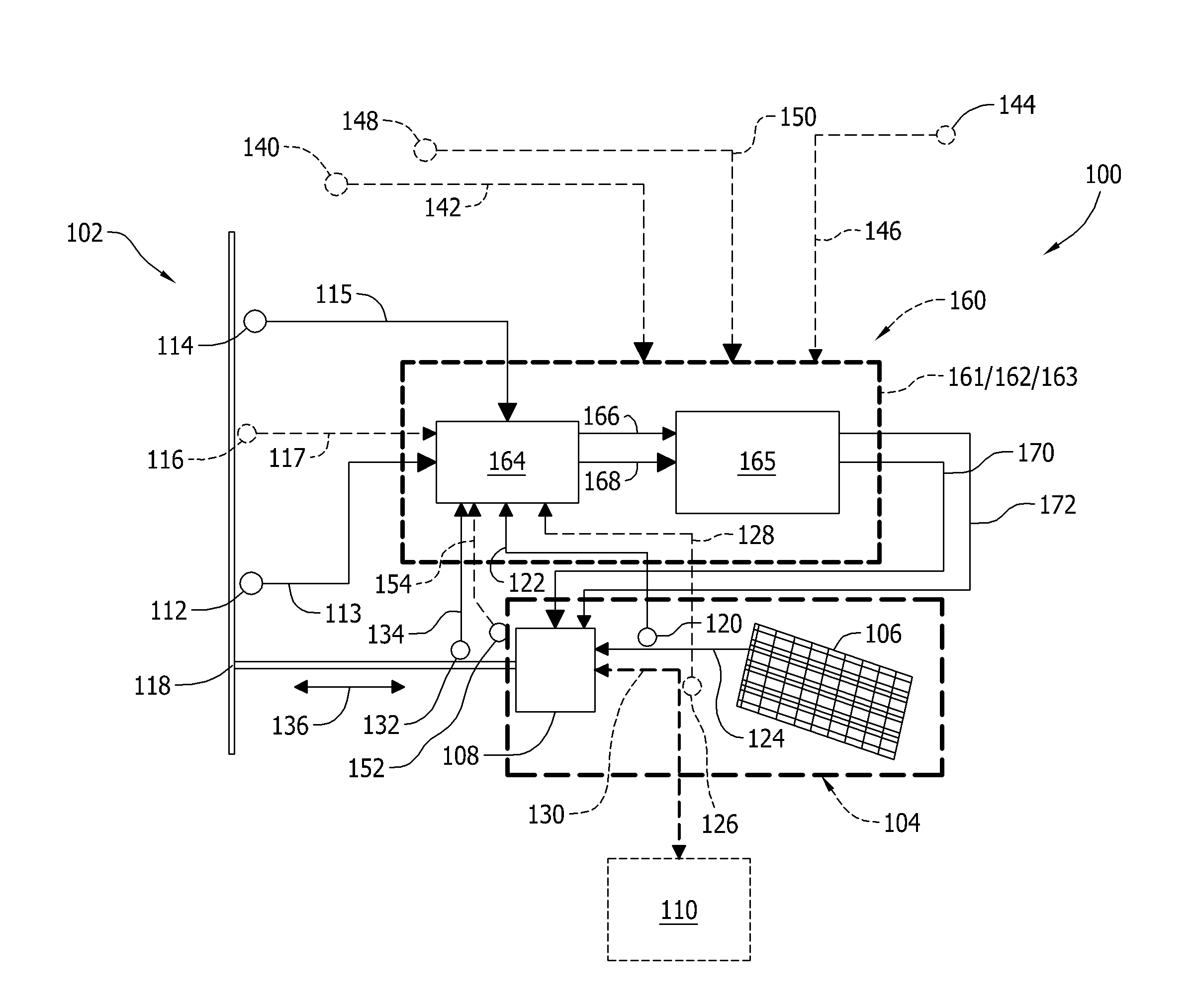
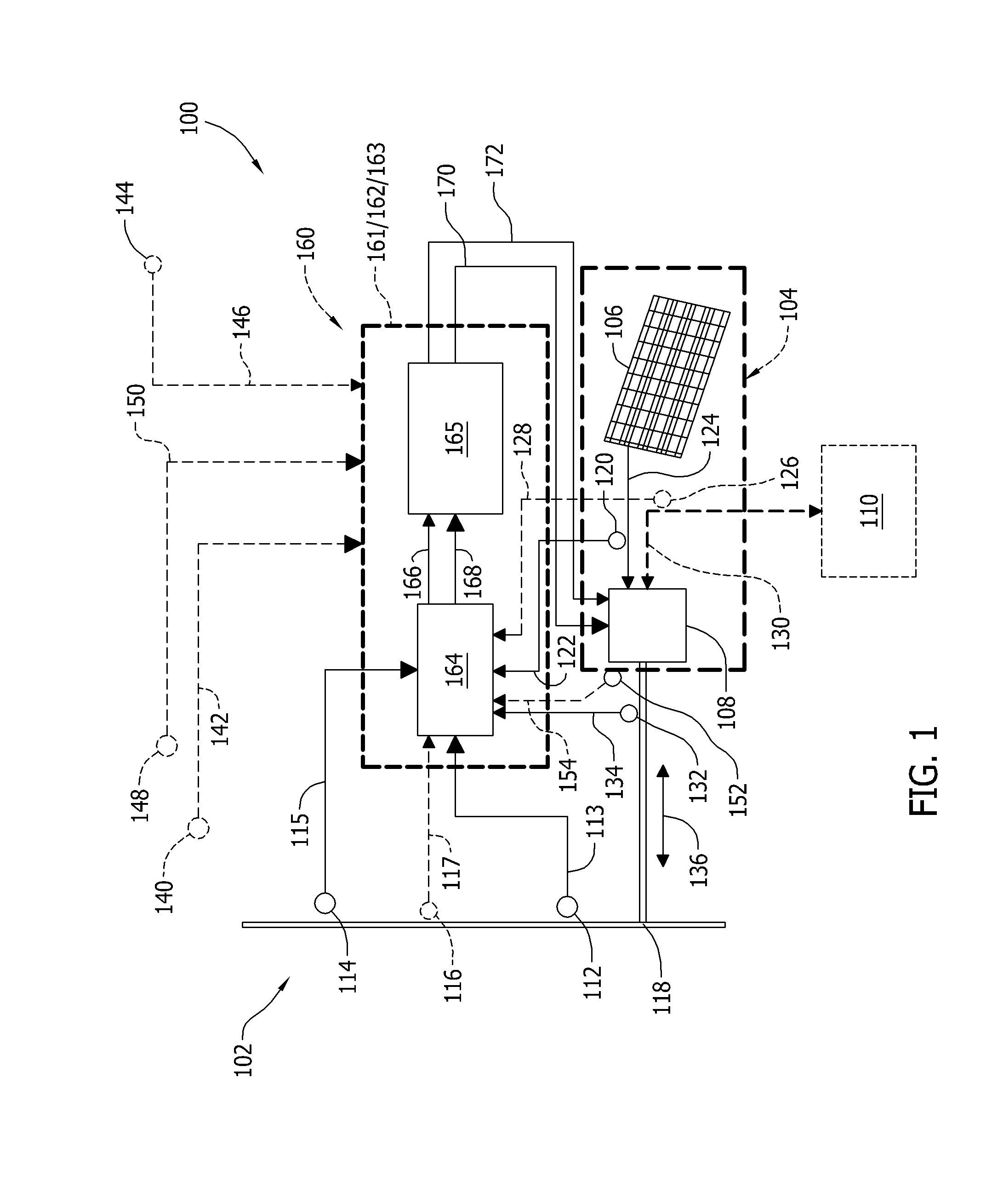
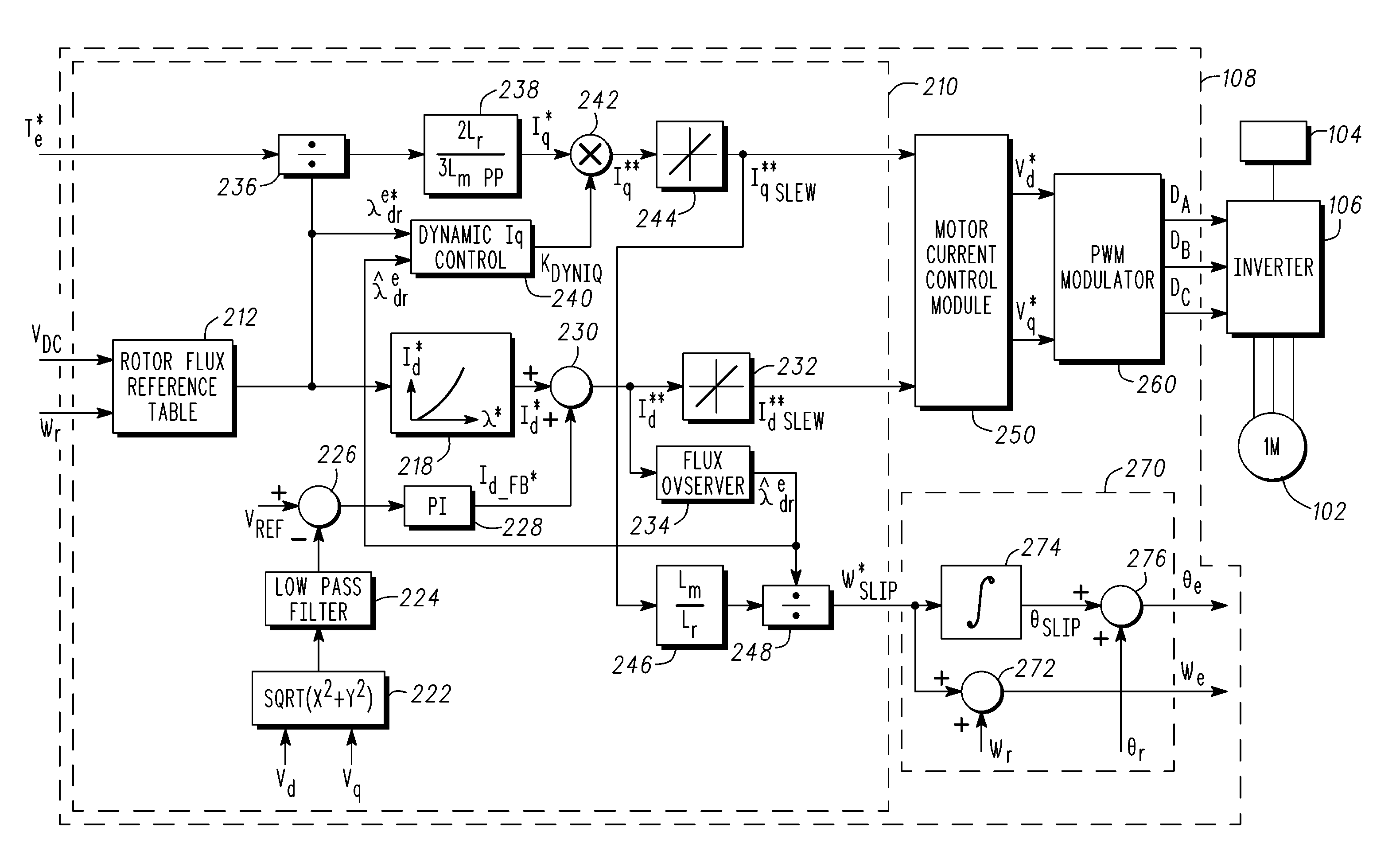
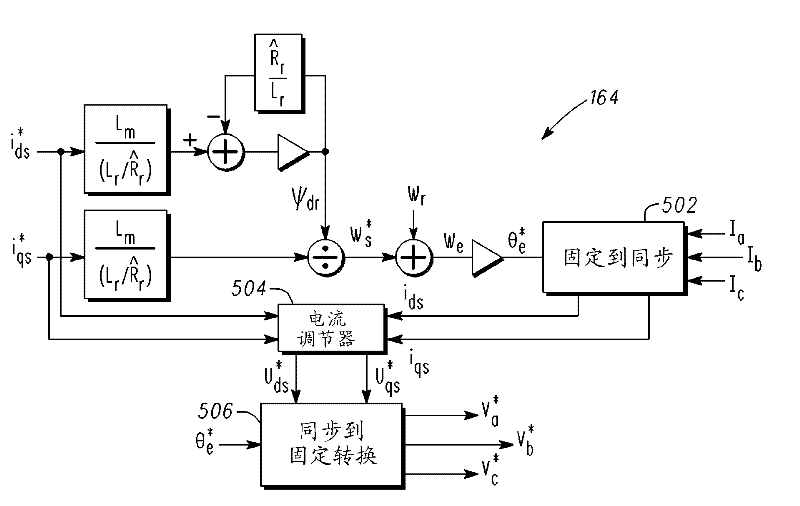
A control system is provided for an inverter assembly associated with an induction motor. The system includes a current determination module configured to generate q- and d-axis current commands based on a torque command. The current determination module is further configured to generate the q-axis current command based on an observed flux linkage and a flux linkage command. The system further includes a motor current control module coupled to the current determination module and configured to generate q- and d-axis voltage commands based on the q- and d-axis current commands generated by the current determination module and a PWM modulator coupled to the motor current control module configured to generate duty cycle signals for operating the inverter assembly based on the q- and d-axis voltage commands generated by the motor current control module.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
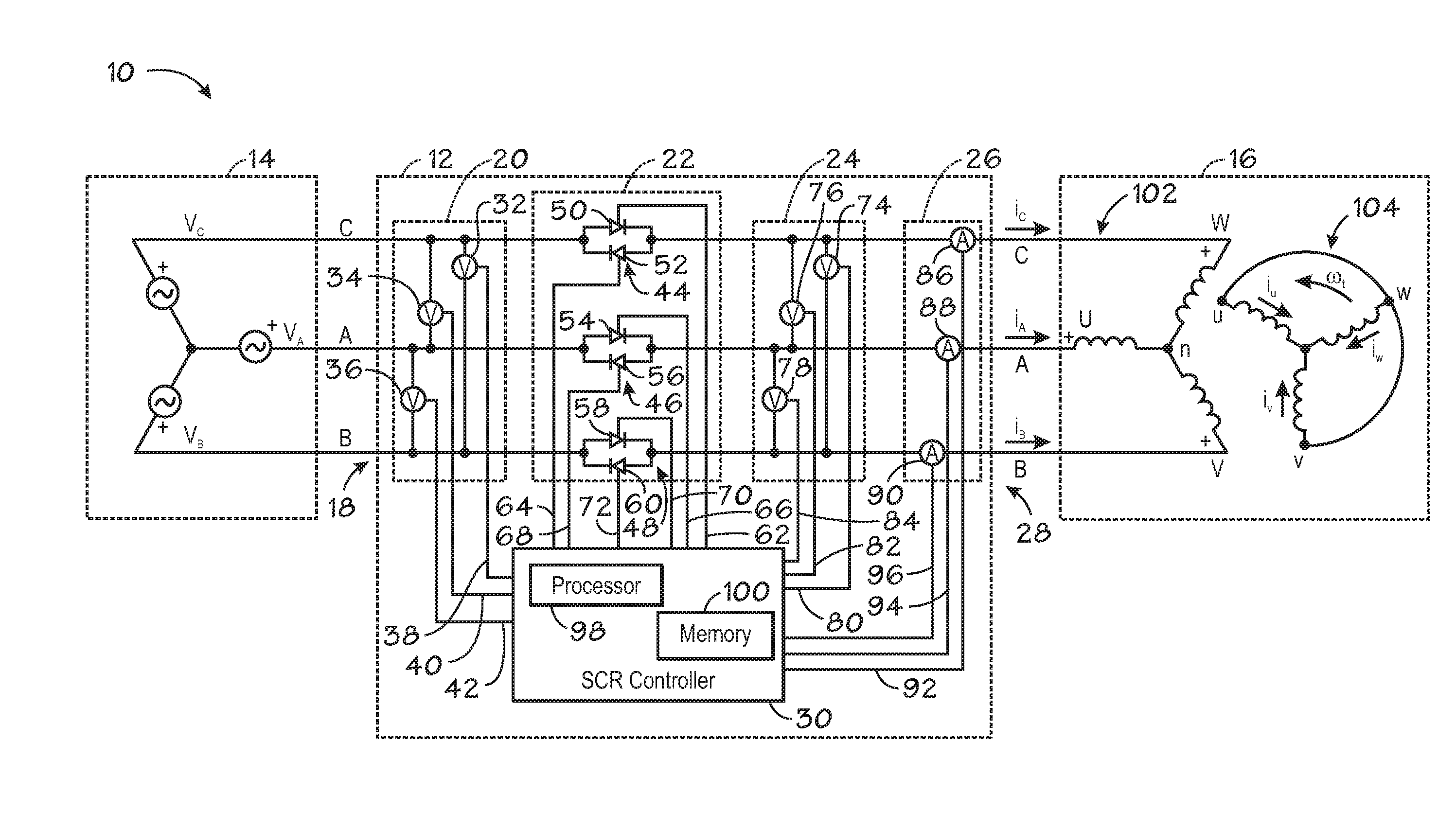
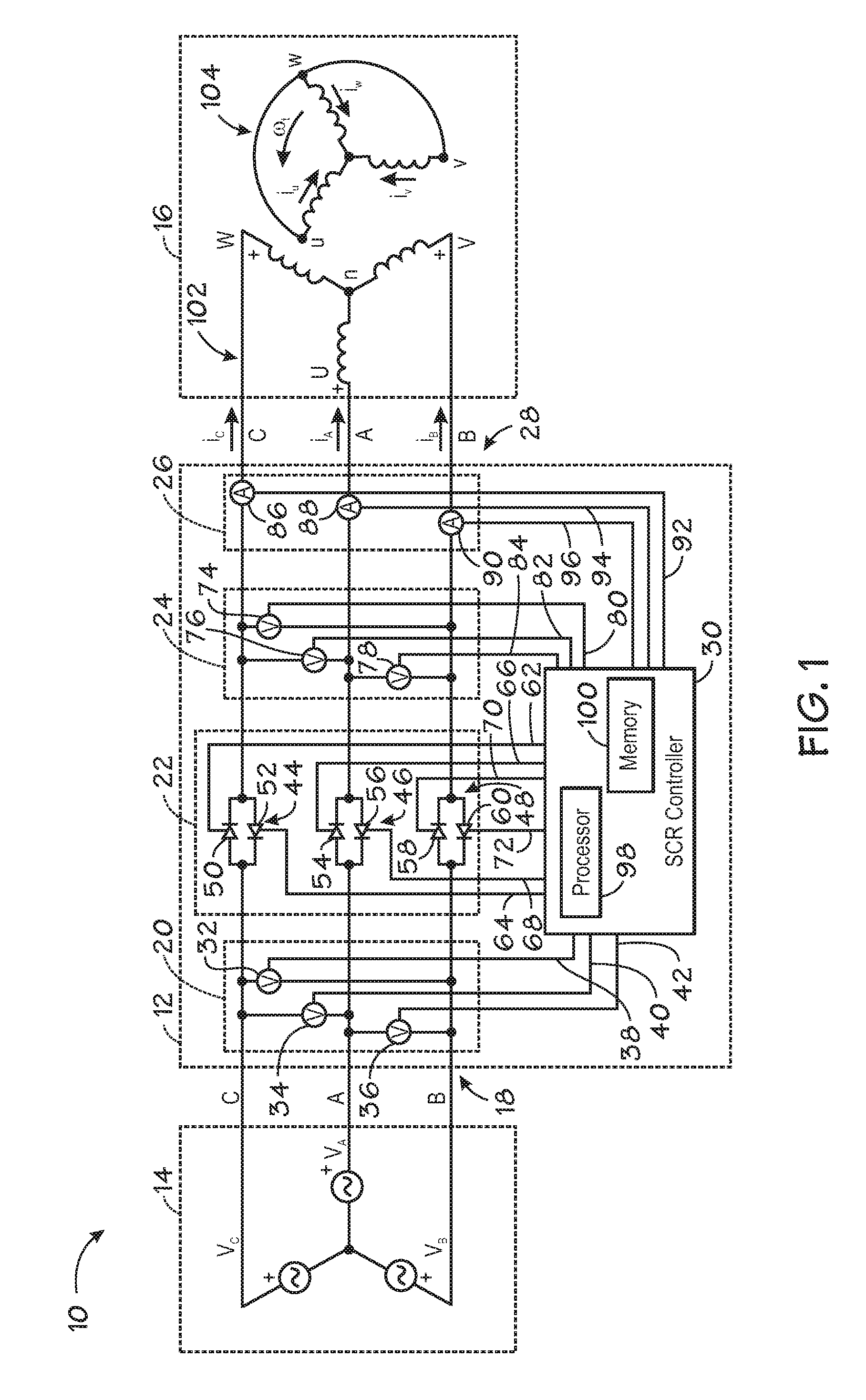
Induction motor controller
ActiveUS20080067970A1Electronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlInduction motorCurrent sensor
An induction motor controller that may include three phase paths leading from a power input to a power output, a solid-state switching device interposed between the power input and the power output on each of the three phase paths, a voltage sensor coupled to two of the phase paths between the solid-state switching device and the power output, a current sensor on one of the phase paths, a processor communicatively coupled to the voltage sensor, the current sensor, and the solid state switching device; and a memory coupled to the processor. The processor may be configured to calculate a motor parameter based on a signal from the voltage sensor and a signal from the current sensor and store the calculated motor parameter in memory.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
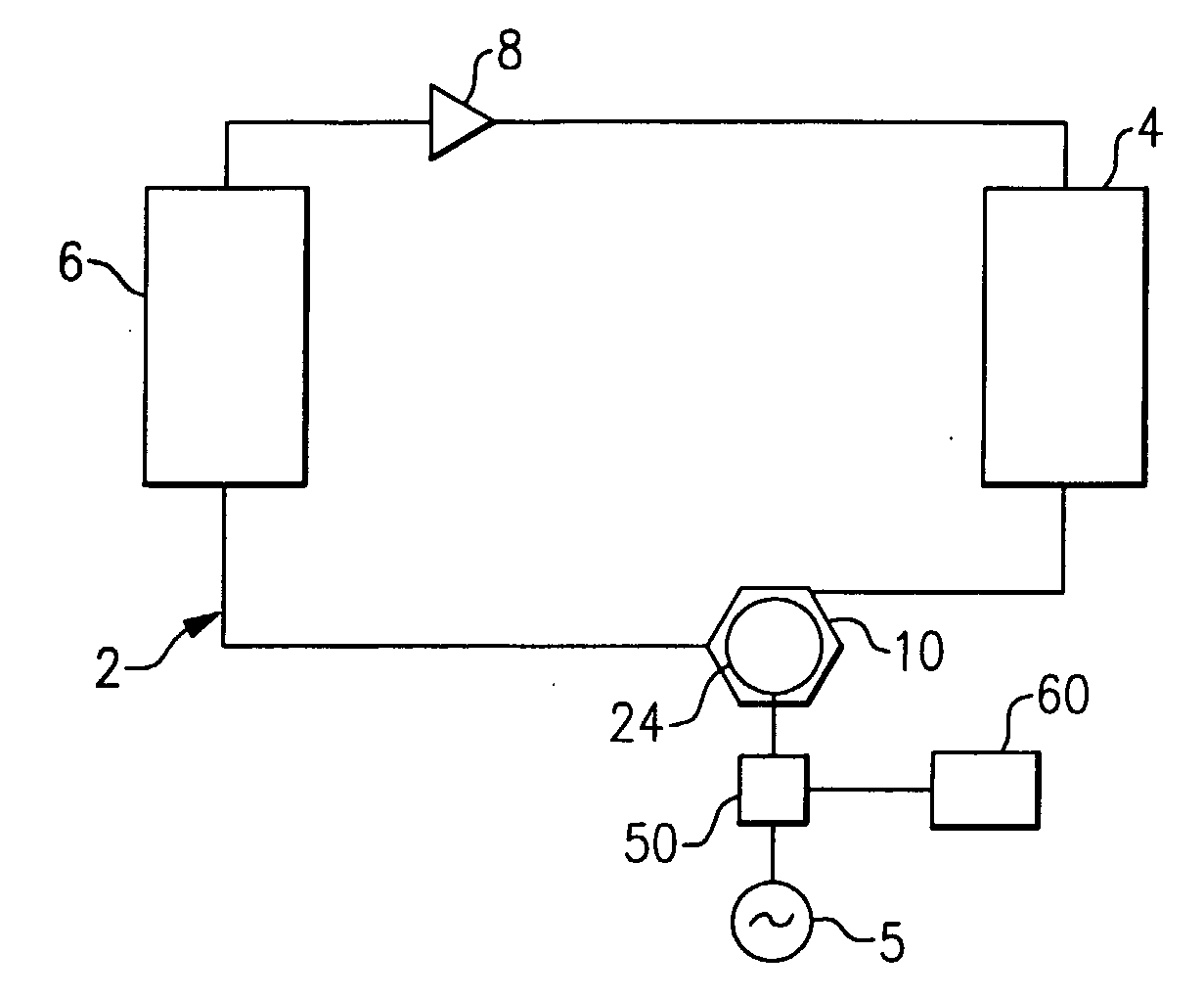
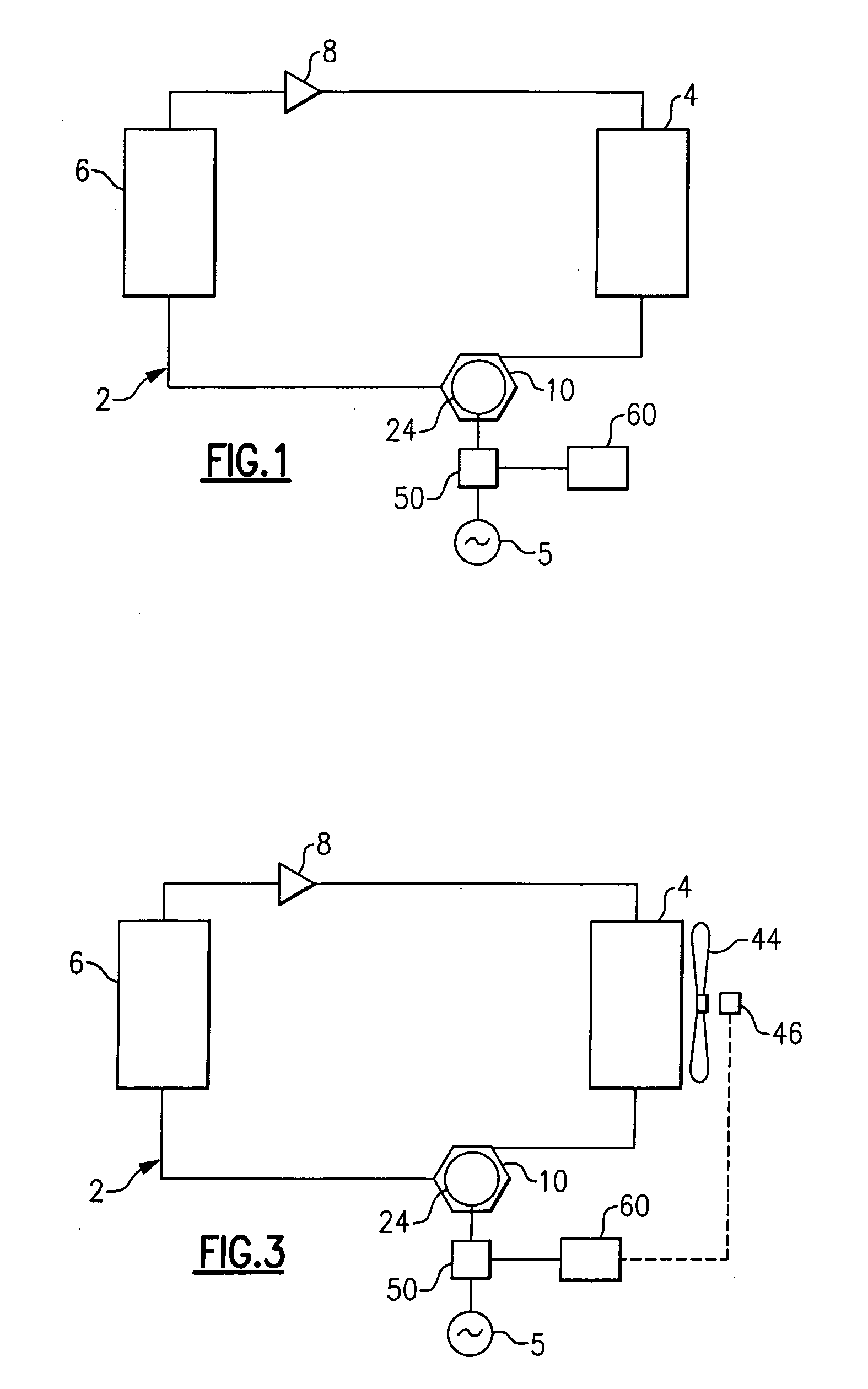
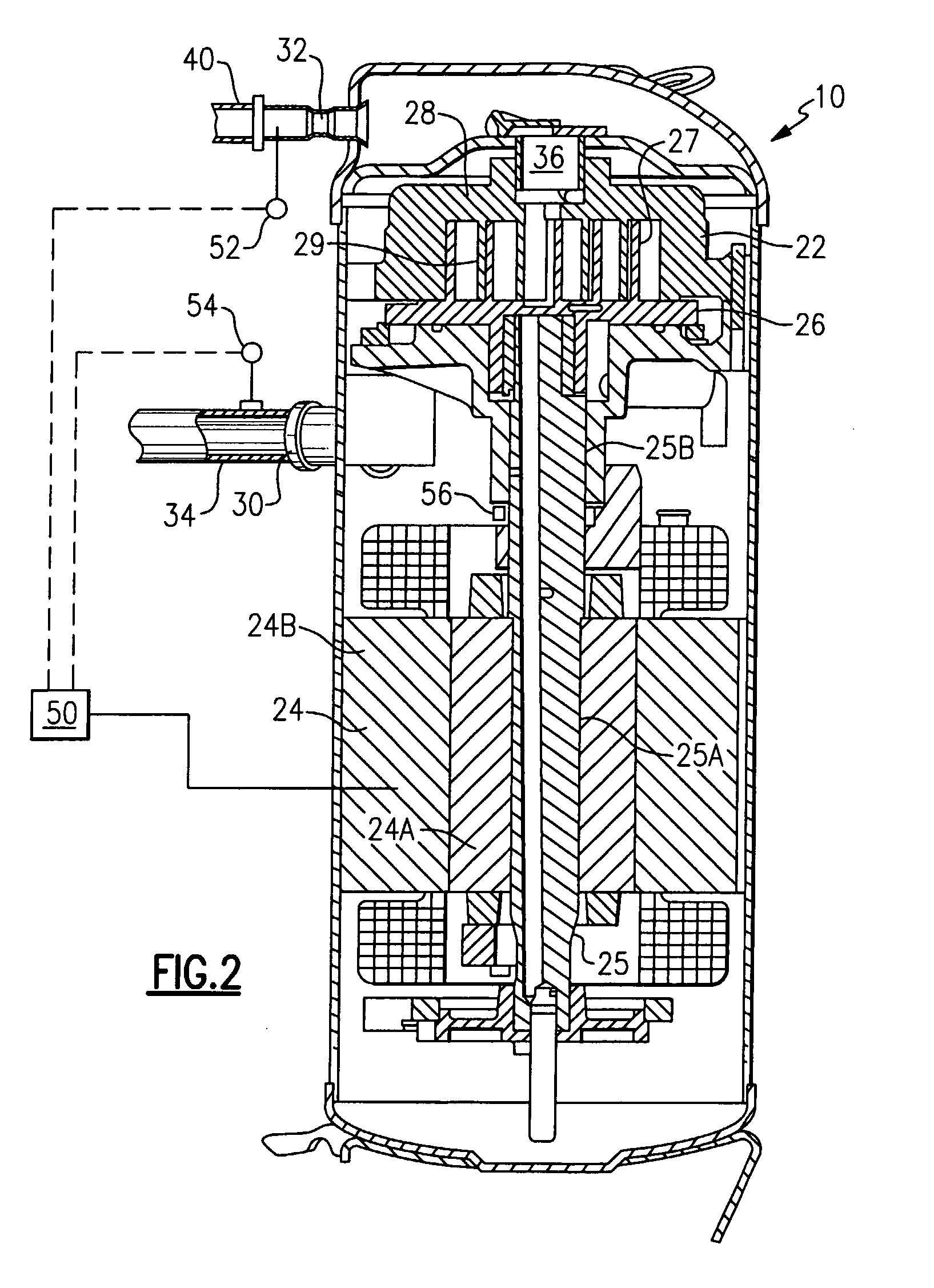
Induction Motor Control
InactiveUS20080260541A1Operation controlPump controlPositive-displacement liquid enginesElectricityInduction motor
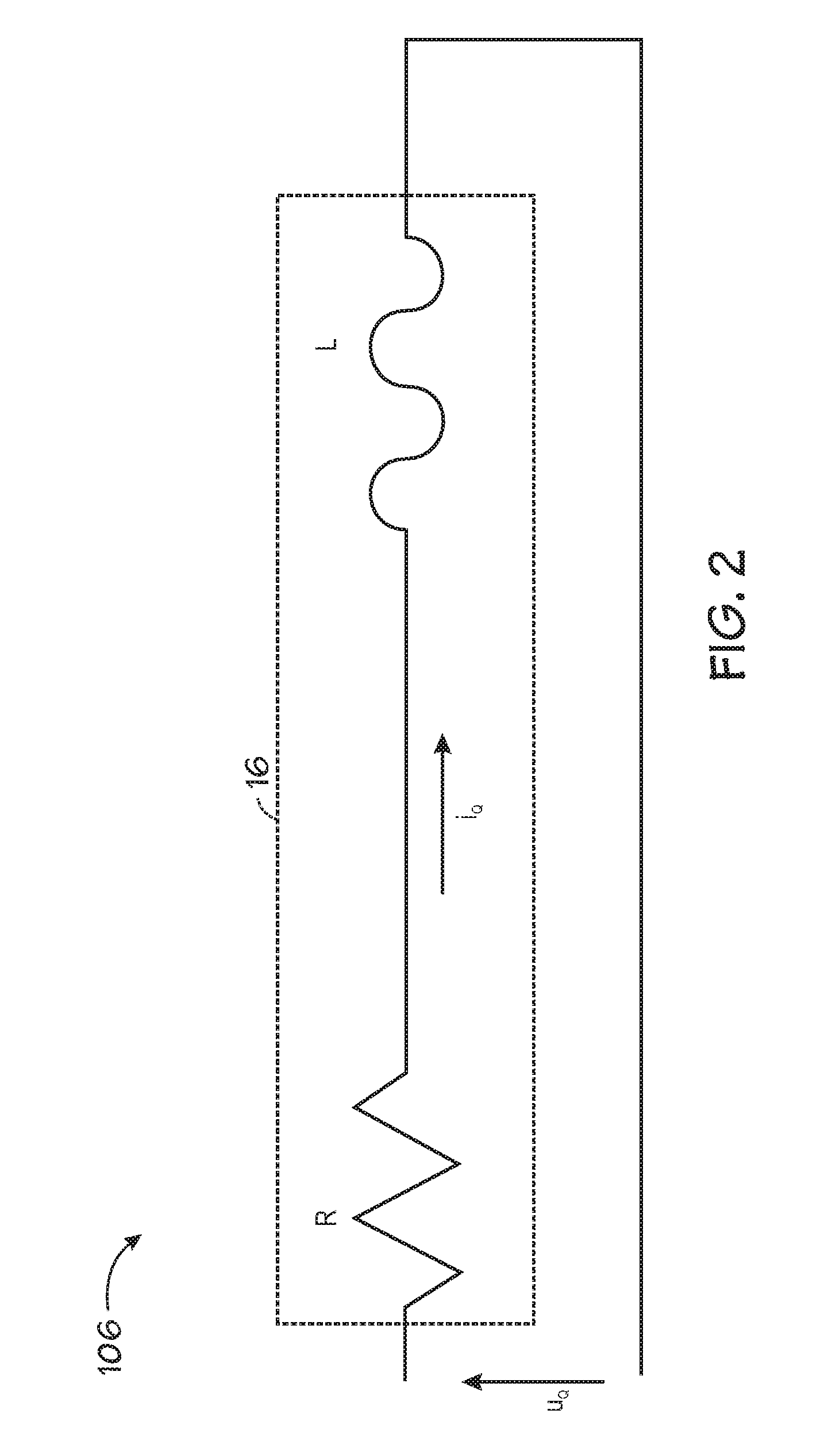
The operation of an AC induction motor 24 is controlled in response to the actual slip exhibited by the motor during operation. The slip of the motor 24 may be determined by determining the actual running speed, n, of the motor shaft 25A, measuring the line frequency, ns, of the electricity supplied to the motor, and calculating the slip, S, of the motor using the relationship: S=((ns−n) / ns)*100. If the slip is too high when compared to a predetermined maximum acceptable slip, corrective action is taken to decrease the loading on the motor. If the slip is too low when compared to a predetermined minimum acceptable slip, corrective action is taken to increase the loading on the motor. By adjusting the operation of the system by appropriately changing the load on the motor, or changing the electrical supply parameters, the actual slip exhibited by the motor 24 is returned to a value within the range between the minimum acceptable slip and the maximum acceptable slip, thereby protecting the motor and improving overall reliability.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
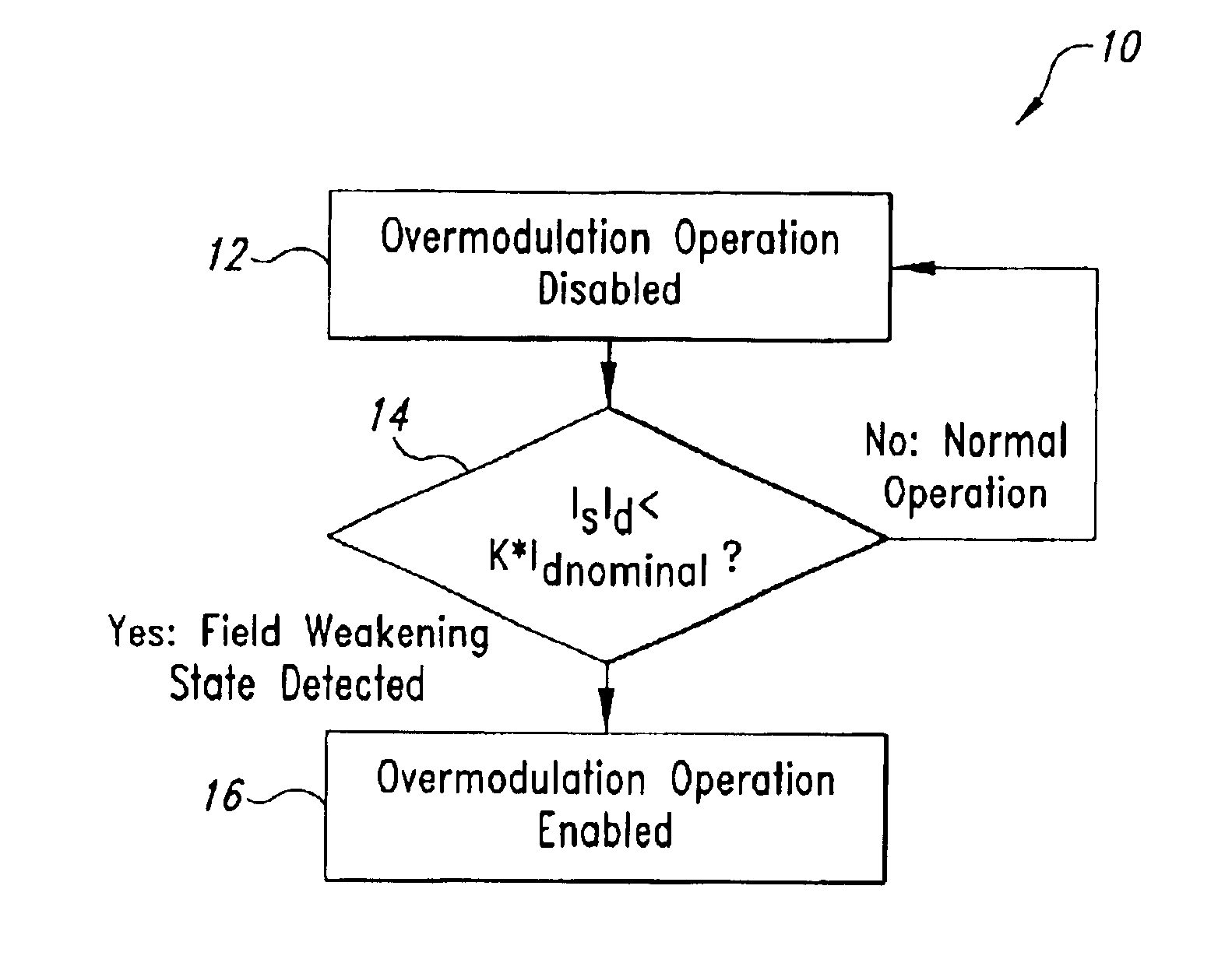
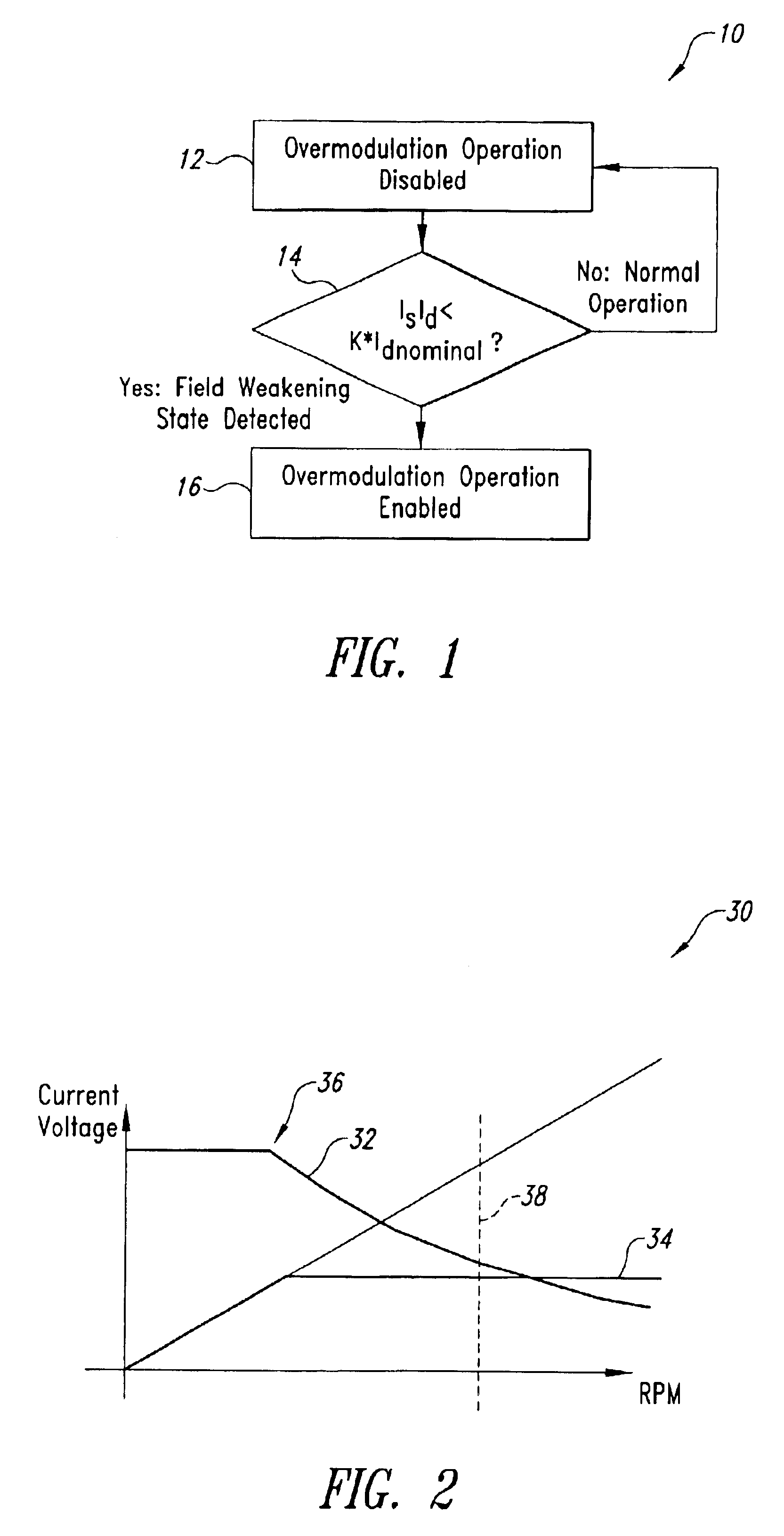
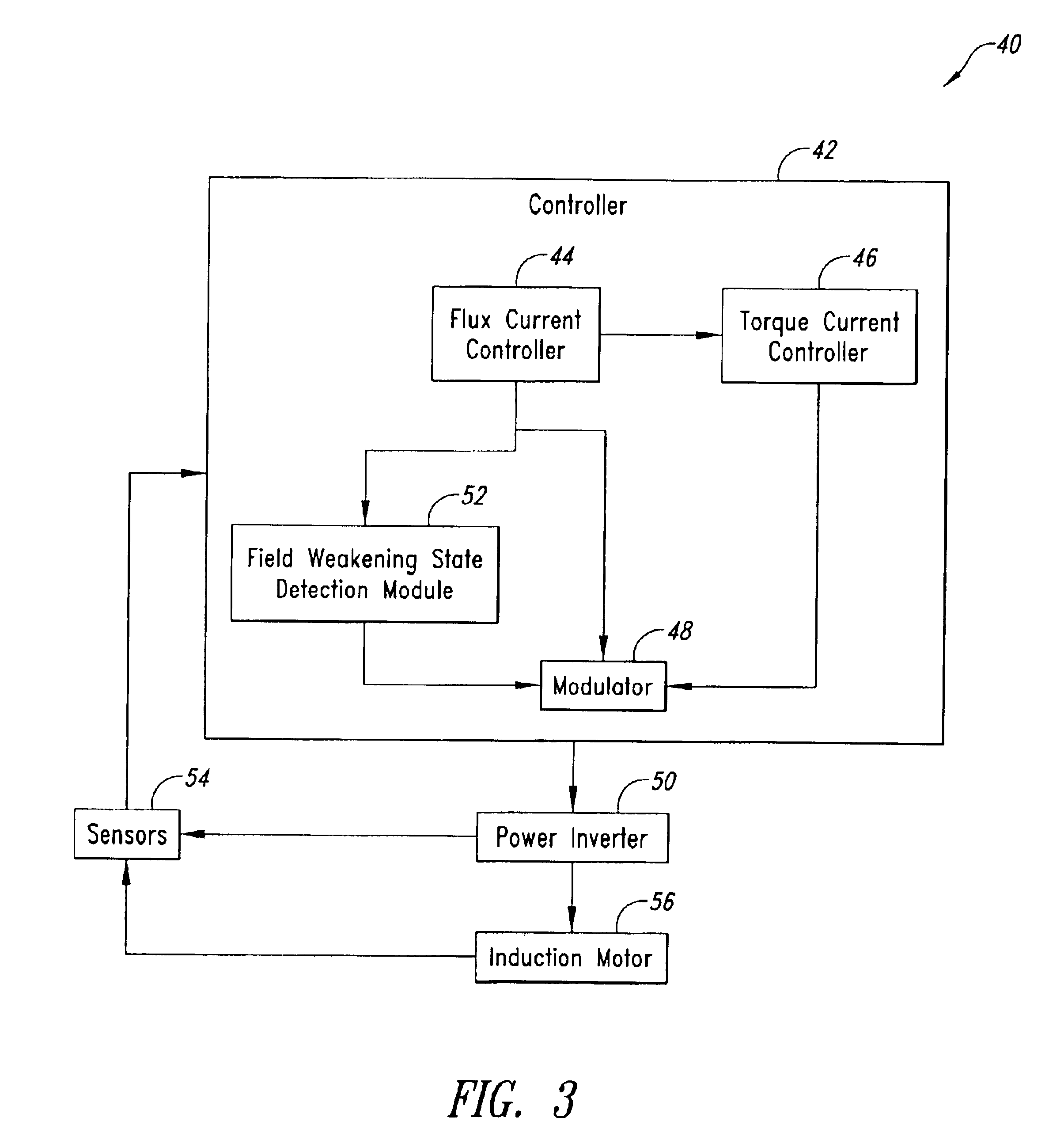
Overmodulation systems and methods for induction motor control
InactiveUS6844701B2Improve robustnessReduce generationSingle-phase induction motor startersElectronic commutation motor controlInduction motorControl theory
Systems and methods for controlling an induction motor including detecting a field weakening operation state of the motor, wherein the field weakening operation state is detected when a flux current, Id, in the motor is reduced to a predetermined fraction of its normal, non-voltage limited value. The systems and methods also including an overmodulation operation state of the motor before said field weakening operation state is detected and enabling the overmodulation operation state of the motor after said field weakening operation state is detected.
Owner:VITESCO TECH USA LLC
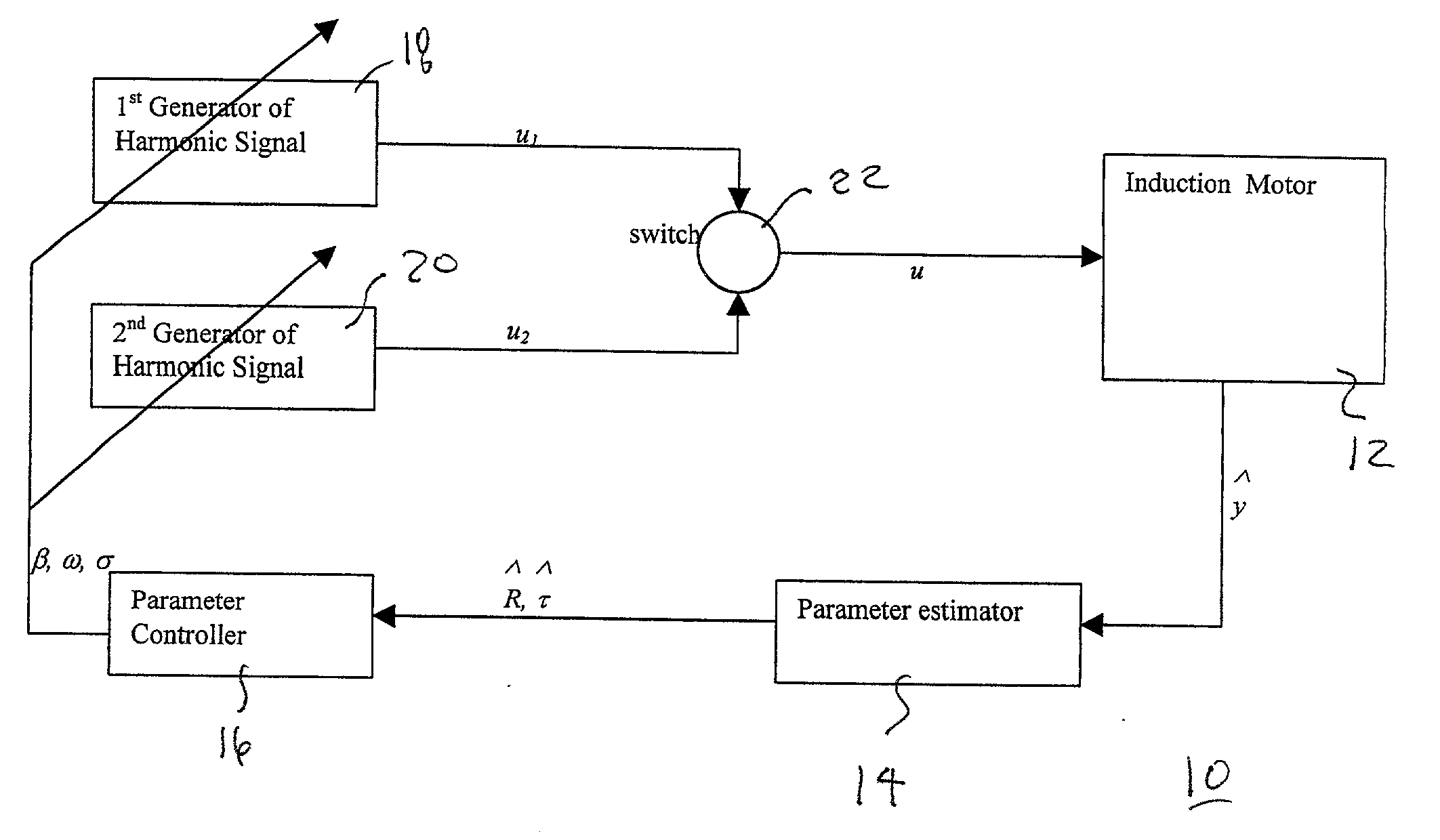
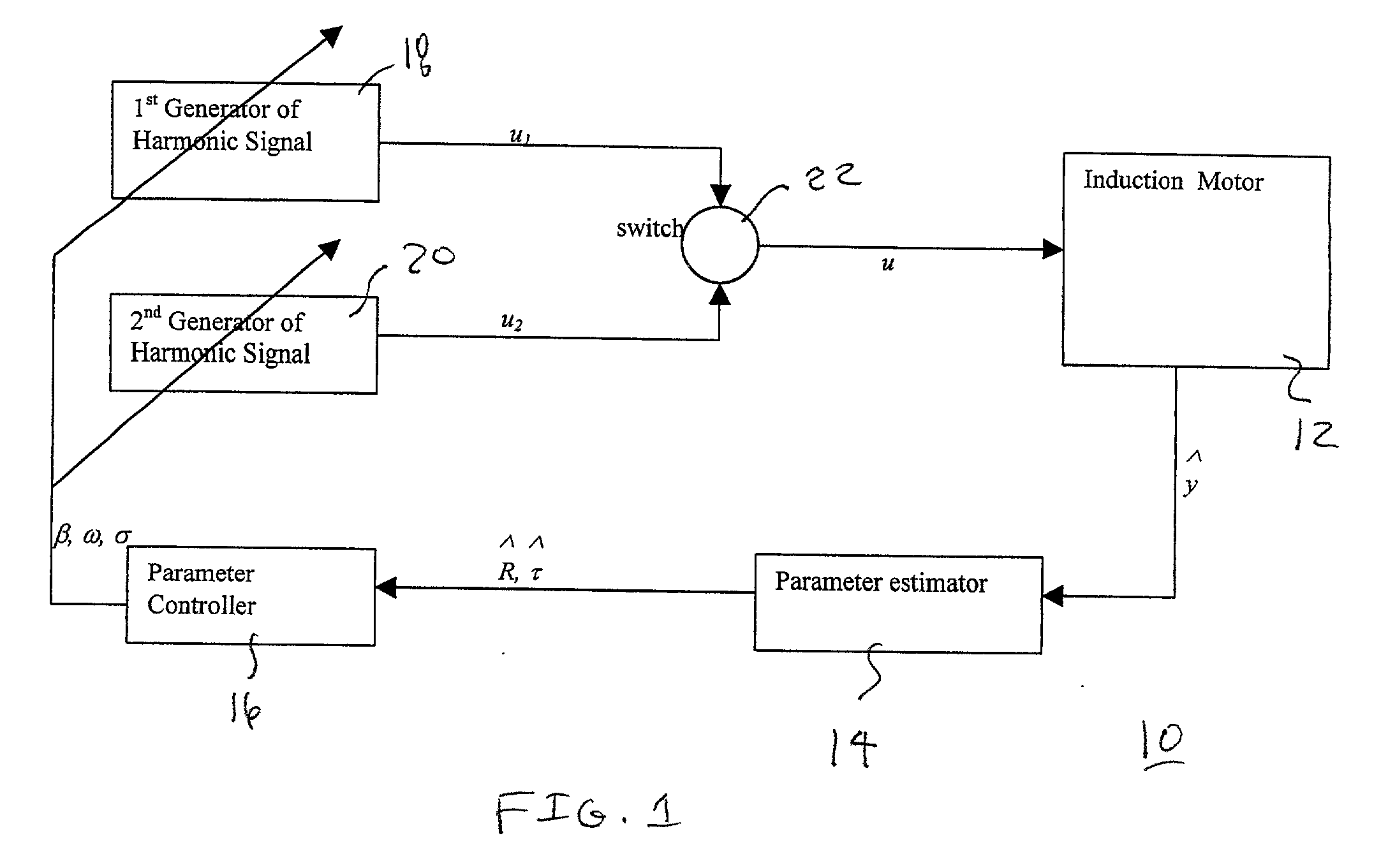
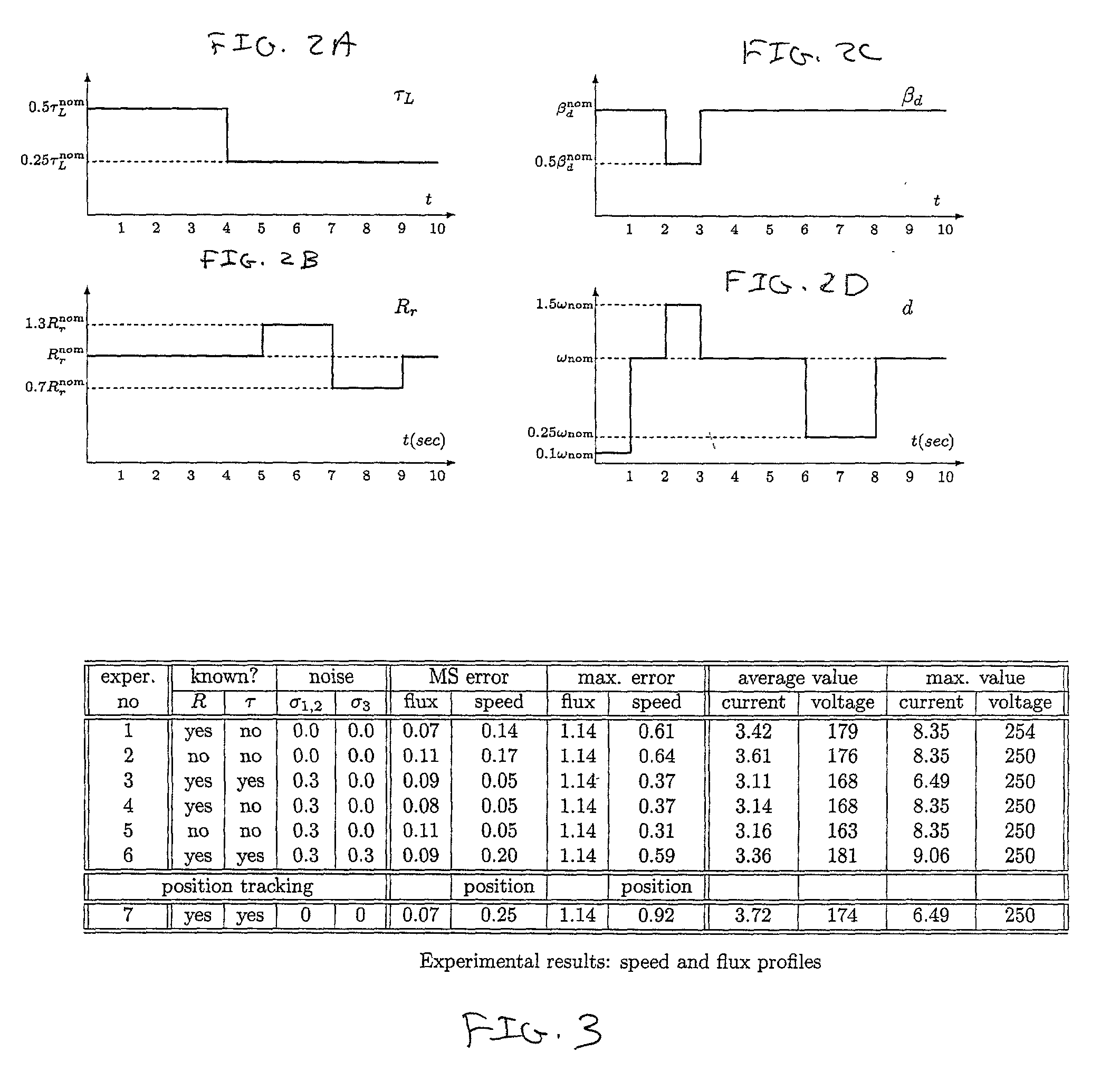
Discrete-time system and method for induction motor control
InactiveUS20020053894A1Single-phase induction motor startersElectronic commutation motor controlControl signalLoad torque
A simple and robust discrete-time induction motor control technique employs a control algorithm that estimates load torque and rotor resistance from the measured rotor velocity of the motor to be controlled. The estimates of load torque and rotor resistance are employed to generate periodic estimates of parameters that are employed to control first and second harmonic signal generators. A switch controls which of the signal generators supplies a control signal to the motor at any given moment. The two signal generators work in turn such that while one produces the motor control signal, the other one is being readjusted to the new set of parameters by the parameter controller. The control method can be considered as a generalization and modification of Field Oriented Control. In a "non-adaptive" modification, it ensures global exponential stability of a closed-loop system, if at least local stabilization of the system by static control is possible, for given parameter estimates. In an adaptive version, it provides identification and global exponential stabilization of the system.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY
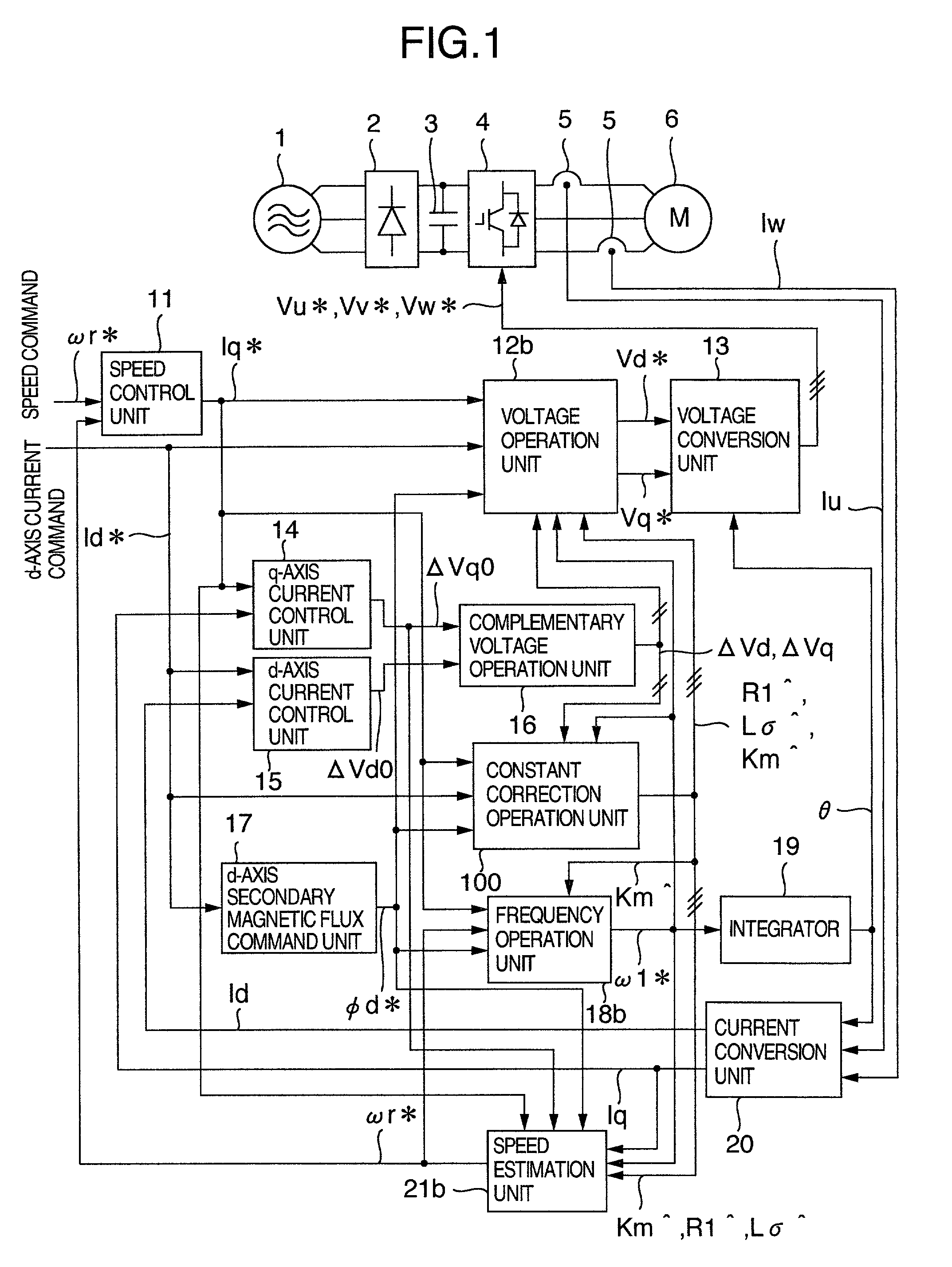
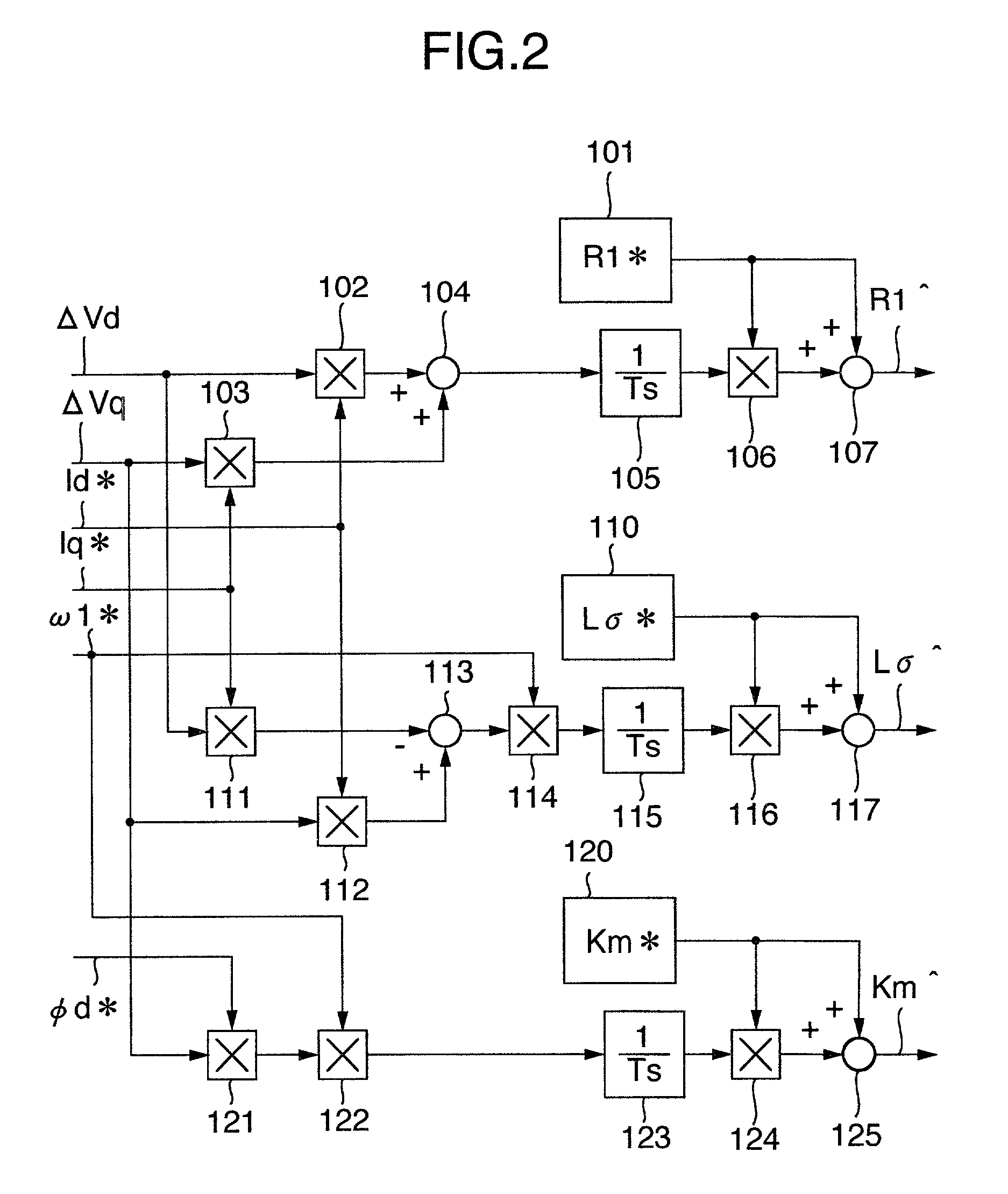
Control apparatus of induction motor
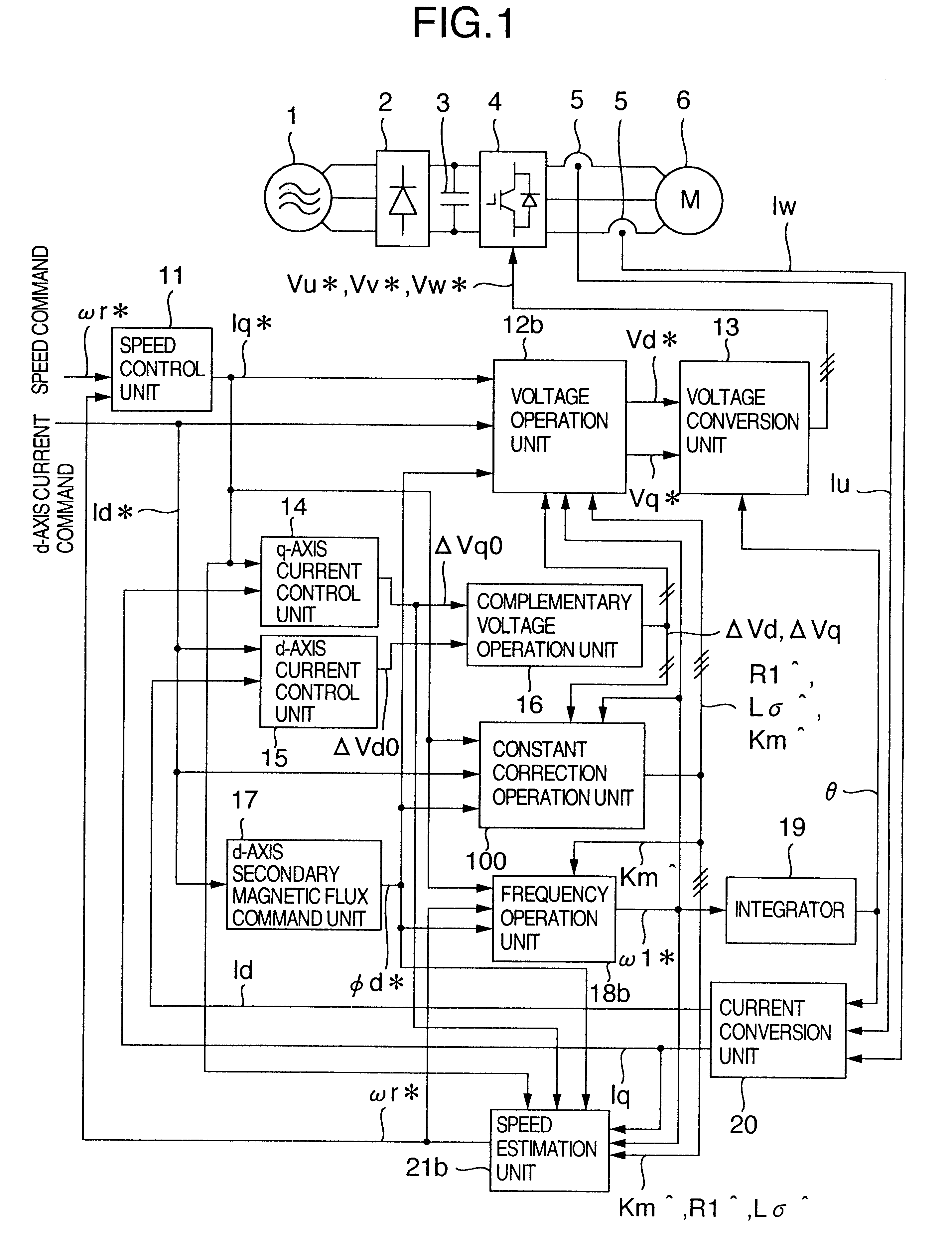
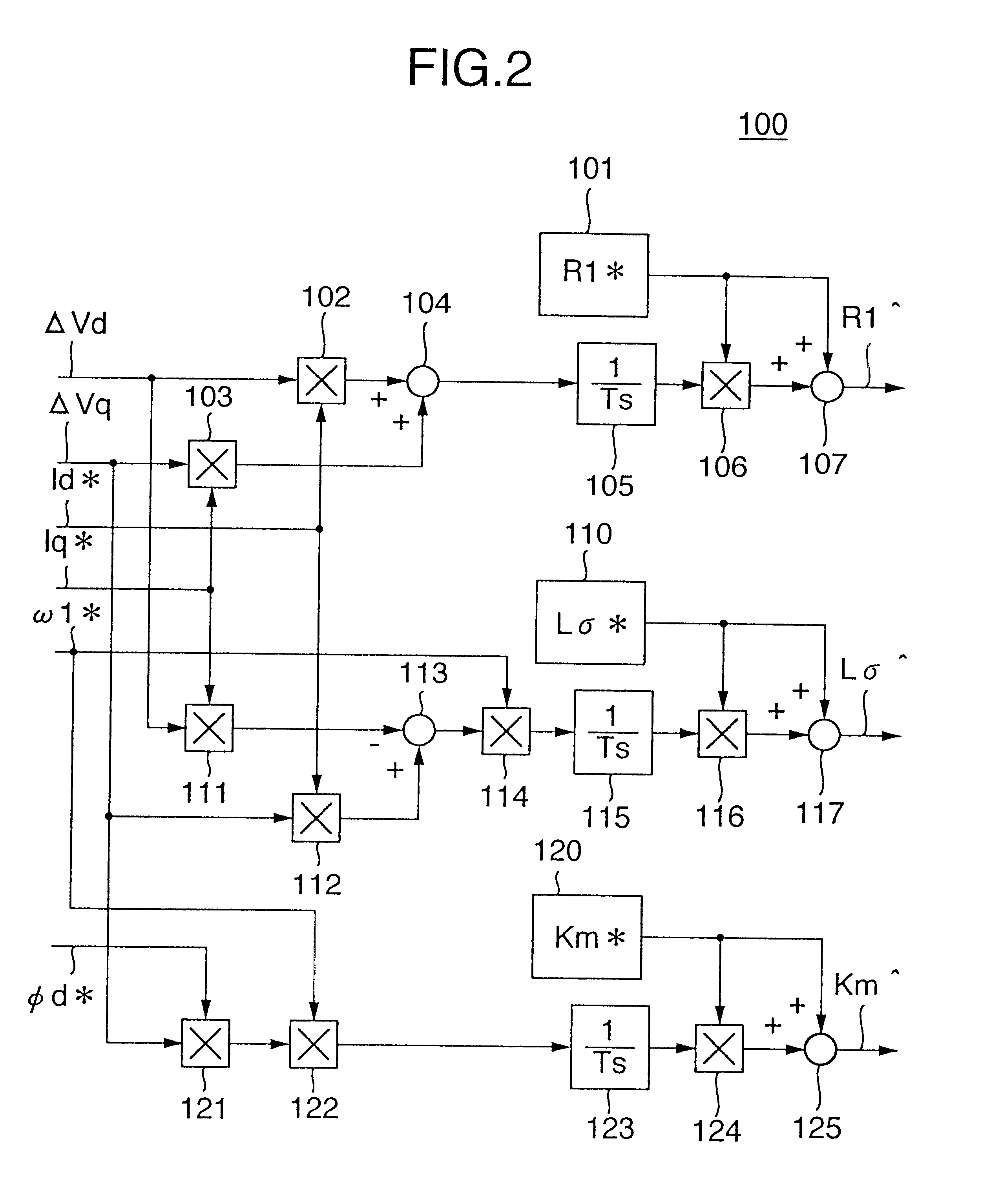
InactiveUS20010026140A1Suppress deterioration of control performanceSingle-phase induction motor startersDC motor speed/torque controlElectrical resistance and conductanceInduction motor
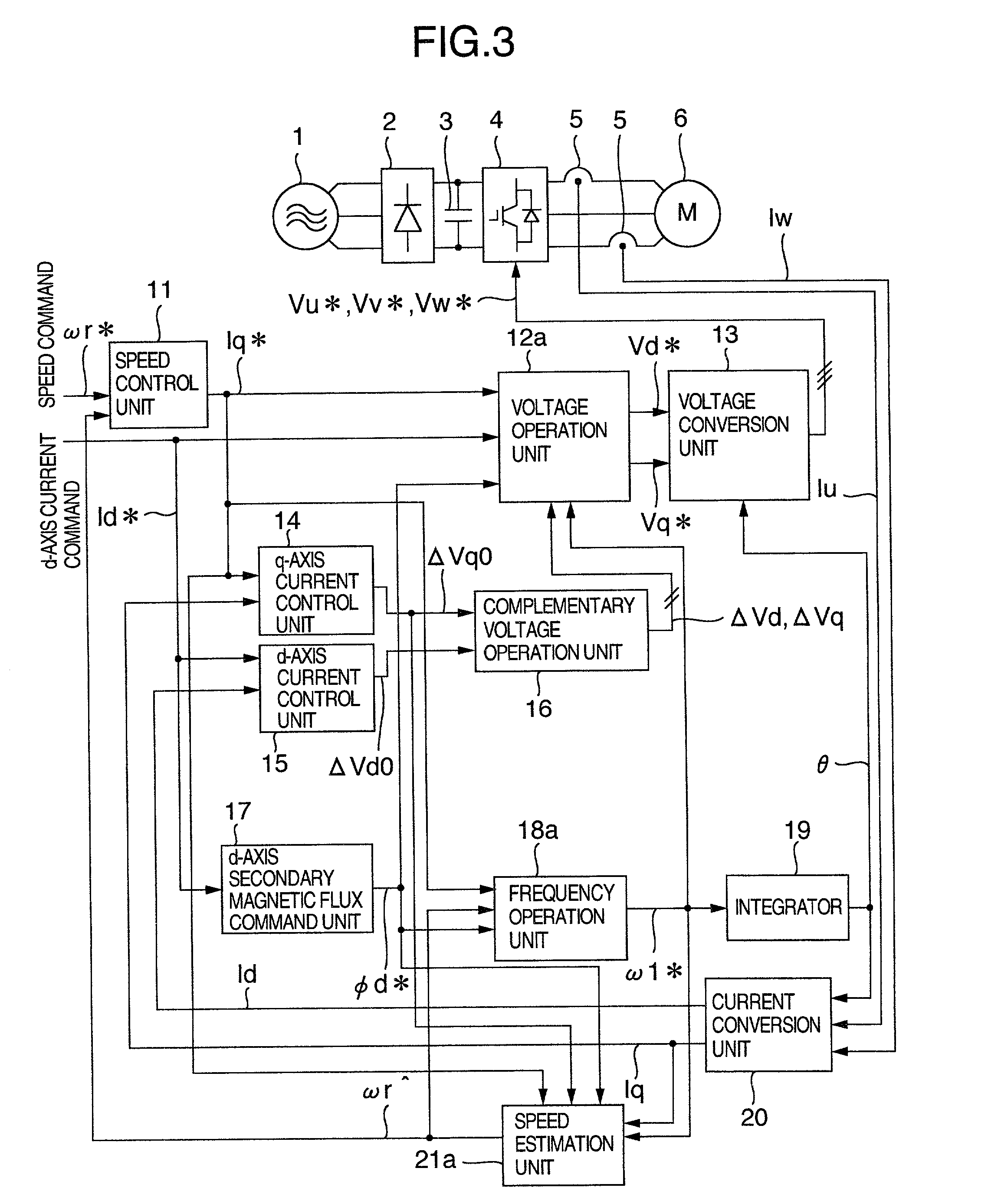
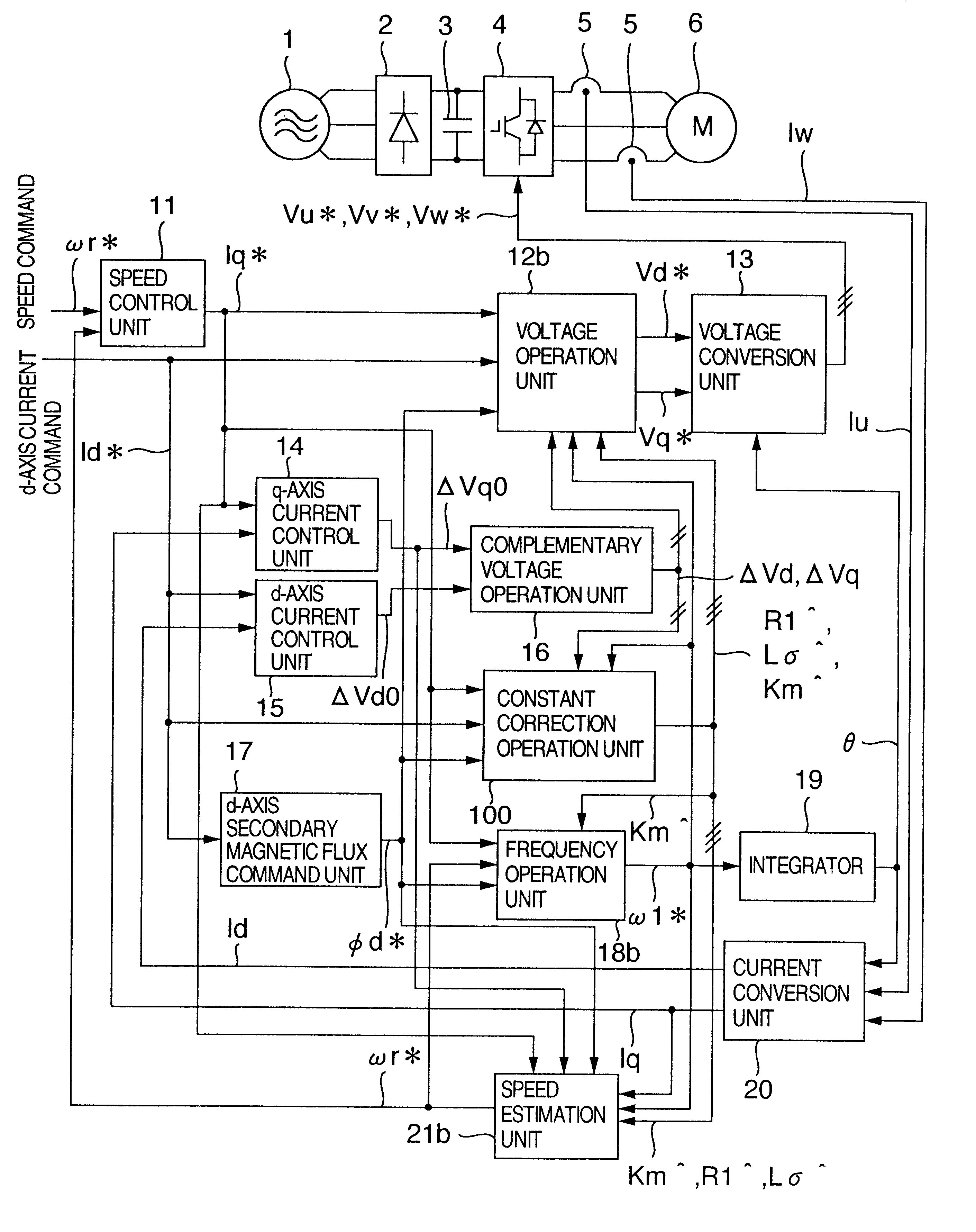
An induction motor control apparatus includes a first constant correction unit for correcting primary resistance based on quantity obtained by multiplying quantity of a voltage command from a frequency voltage control unit by the output of a correction unit, the quantity of the voltage command being a result of partial differentiation with the primary resistance; a second constant correction unit for correcting the inductance based on quantity obtained by multiplying quantity of the voltage command, the quantity of the voltage command being a result of partial differentiation with the inductance; and a third constant correction unit for correcting the inductance ratio based on quantity obtained by multiplying quantity of the voltage command, the quantity of the voltage command being a result of partial differentiation with the inductance ratio, suppressing the deterioration of control performance caused by the setting errors.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Speed sensorless vector control method for induction motor
InactiveCN103227604AReduce dependenceIncrease dynamicsElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsClosed loopInduction motor control
The invention discloses a speed sensorless vector control method for an induction motor, which comprises the followings steps: performing flux linkage control: setting an instruction value of field current and performing closed-loop control of the field current; performing coordinate transformation: transforming the detected stator current value of the induction motor into a field current component and a torque current component of the motor; performing speed control to obtain synchronous angular frequency; performing flux linkage evaluation to obtain the position of a rotor flux linkage; performing torque voltage calculation to obtain the instruction value of the torque voltage; and performing coordinate transformation: transforming the instruction value of exciting voltage and the instruction value of the torque voltage into a three-phase static coordinate, performing corresponding pulse-width modulation, and driving a power inverter unit to generate three-phase alternating voltage to drive the induction motor to operate. According to an experimental result, a speed sensorless induction motor control system has good dynamic performance, and is fast in current response under sudden load increase and decrease conditions, strong in loading capacity in the whole speed regulation range, small in parameter dependence, stable, reliable, and strong in robustness.
Owner:DONGFANG HITACHI CHENGDU ELECTRICAL CONTROL EQUIP CO LTD
Control apparatus of induction motor
InactiveUS6611124B2Suppress deterioration of control performanceSingle-phase induction motor startersDC motor speed/torque controlElectrical resistance and conductanceInduction motor
An induction motor control apparatus includes a first constant correction unit for correcting primary resistance based on quantity obtained by multiplying quantity of a voltage command from a frequency voltage control unit by the output of a correction unit, the quantity of the voltage command being a result of partial differentiation with the primary resistance; a second constant correction unit for correcting the inductance based on quantity obtained by multiplying quantity of the voltage command, the quantity of the voltage command being a result of partial differentiation with the inductance; and a third constant correction unit for correcting the inductance ratio based on quantity obtained by multiplying quantity of the voltage command, the quantity of the voltage command being a result of partial differentiation with the inductance ratio, suppressing the deterioration of control performance caused by the setting errors.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
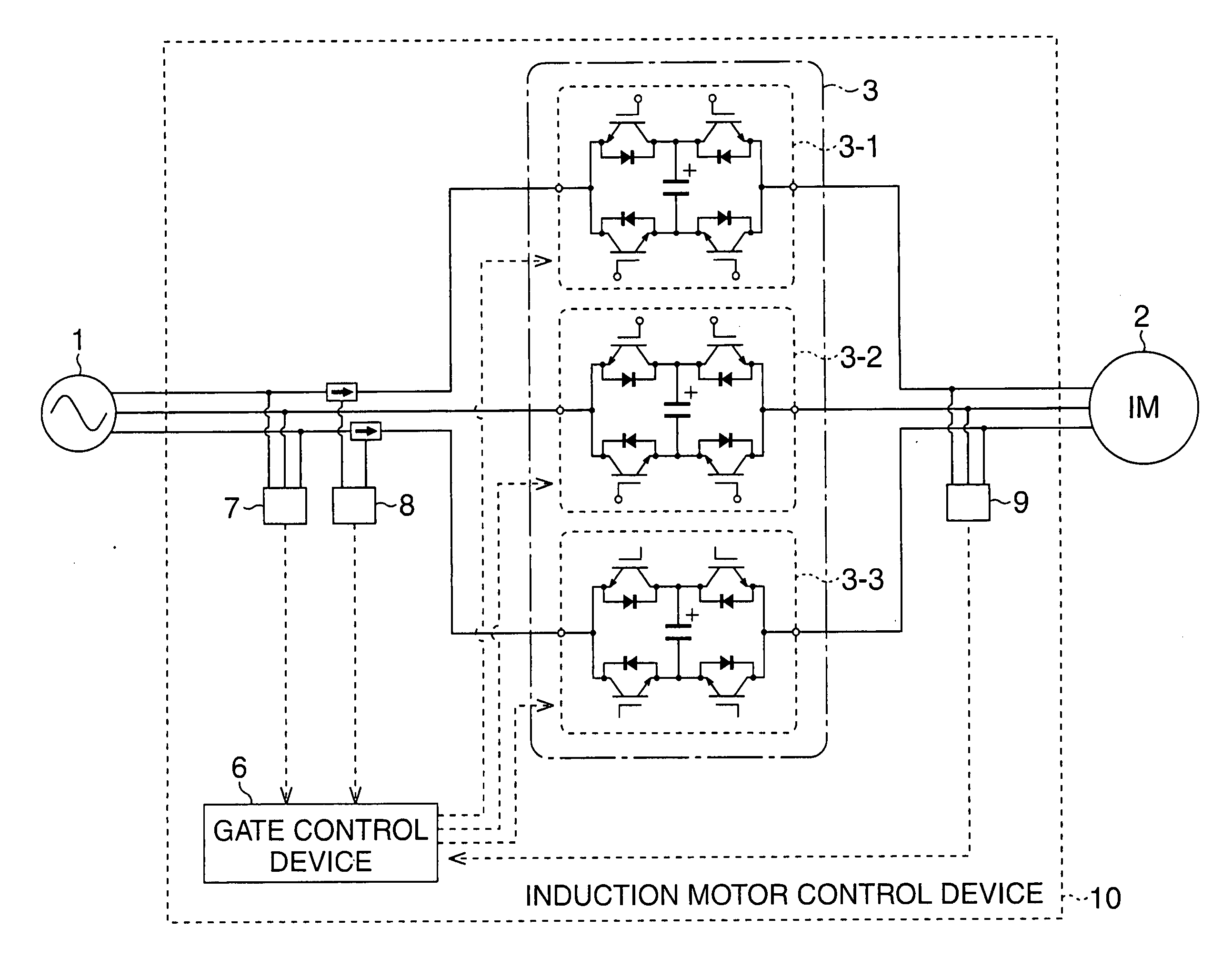
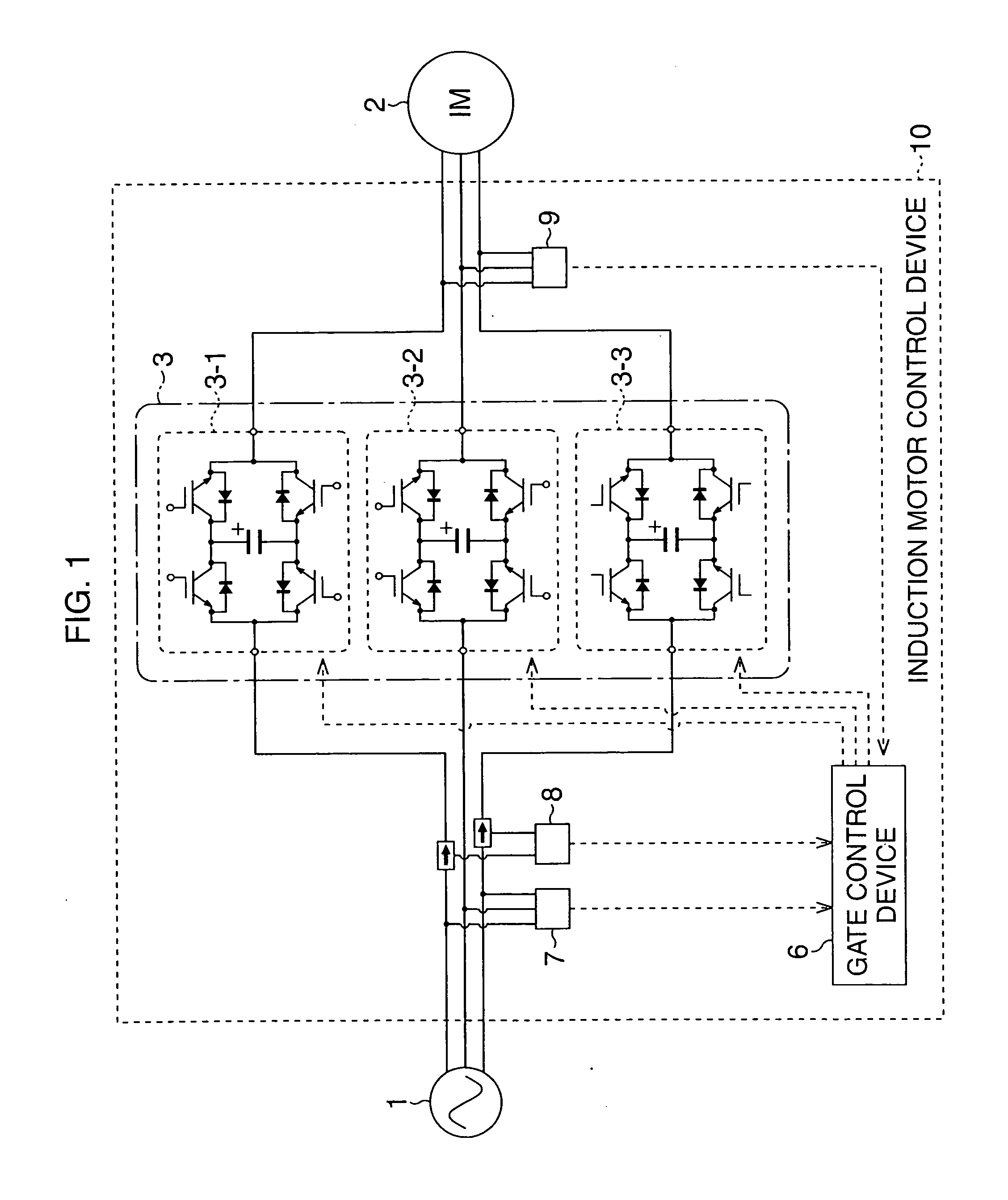
Induction motor control device and induction motor group control system
ActiveUS20120019188A1Reduce variationLimited amountMultiple ac dynamo-electric motors controlConversion without intermediate conversion to dcPower factorControl system
In an induction motor group control system, magnetic energy recovery switches (3) are connected in series to an induction motor (2) directly driven by a commercial power supply, and a plurality of induction motor control devices (10) enabling voltage control and reactive power control of the induction motor 2 are employed to control generation of reactive power so as to maximize a power factor of the entire plurality of AC loads including the induction motor or compensate variations in voltage of an AC power supply (1).
Owner:SHIMADA RYUICHI
Induction motor controller
ActiveUS7358700B2Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersInduction motorThree-phase
An induction motor controller that may include three phase paths leading from a power input to a power output, a solid-state switching device interposed between the power input and the power output on each of the three phase paths, a voltage sensor coupled to two of the phase paths between the solid-state switching device and the power output, a current sensor on one of the phase paths, a processor communicatively coupled to the voltage sensor, the current sensor, and the solid state switching device; and a memory coupled to the processor. The processor may be configured to calculate a motor parameter based on a signal from the voltage sensor and a signal from the current sensor and store the calculated motor parameter in memory.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Induction motor control device and induction motor group control system
InactiveCN102362426AReduce voltage fluctuationsControl the amount of reactive powerEfficient power electronics conversionMultiple ac dynamo-electric motors controlPower factorControl system
In an induction motor group control system, magnetic energy recovery switches (3) are connected in series to an induction motor (2) directly driven by a commercial power supply, and a plurality of induction motor control devices (10) enabling voltage control and reactive power control of the induction motor (2) are employed to control generation of reactive power so as to maximize a power factor of the entire plurality of AC loads including the induction motor or compensate variations in voltage of an AC power supply (1).
Owner:岛田隆一
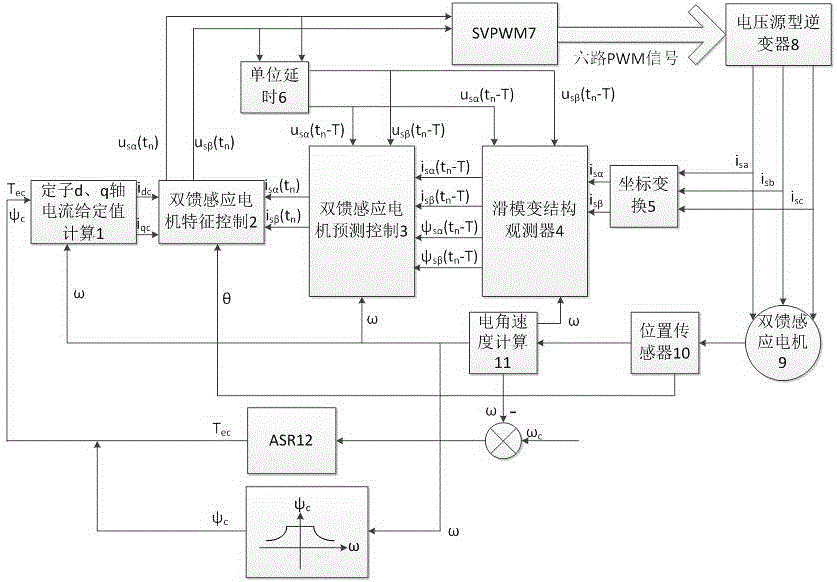
Direct characteristic control based novel double-fed induction motor control method
ActiveCN105720879AEasy to controlConvenience and correctnessElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlDiscretizationEquation of state
The invention provides a direct characteristic control based novel double-fed induction motor control technology, comprising the following steps: 1, giving a voltage equation with regards to the alpha axis and beta axis of a stator of a double-fed induction motor under a stationary frame; 2, based on the voltage equation given in the step 1 and with the currents of the alpha axis and beta axis of the stator and flux linkages of the alpha axis and beta axis of a rotor as state variables, putting forward a corresponding state equation observer; 3, designing a sliding mode variable structure observer based on the step 2 so as to observe the currents of the alpha axis and beta axis of the stator and the flux linkages of the alpha axis and beta axis of the rotor at the current state; 4, carrying out discretization based on the state equation put forward in the step 2, thus obtaining a prediction control equation, namely predicting the currents of the alpha axis and beta axis of the stator and the flux linkages of the alpha axis and beta axis of the rotor at next time; and 5, using the predicted currents of the alpha axis and beta axis of the stator and currents of the d axis and q axis of the stator, calculated according to a given torque and a given rotor flux linkage together to solve a characteristic equation to obtain the voltages of the alpha axis and beta axis of the stator and sending the voltages to SVPWM. The direct characteristic control based novel double-fed induction motor control technology can be applied to the field of wind power generation and the like.
Owner:高唐融知融智科技服务有限公司
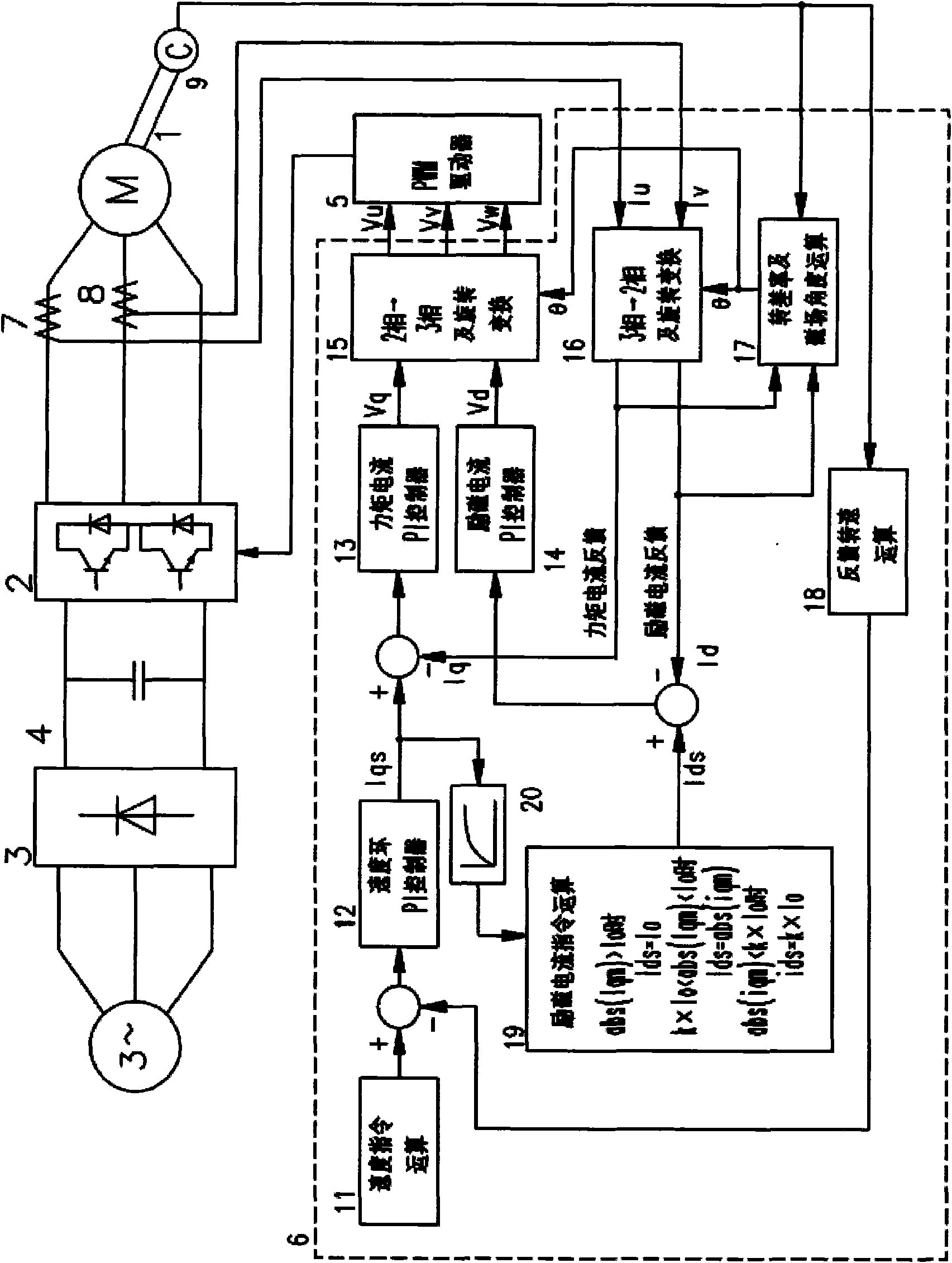
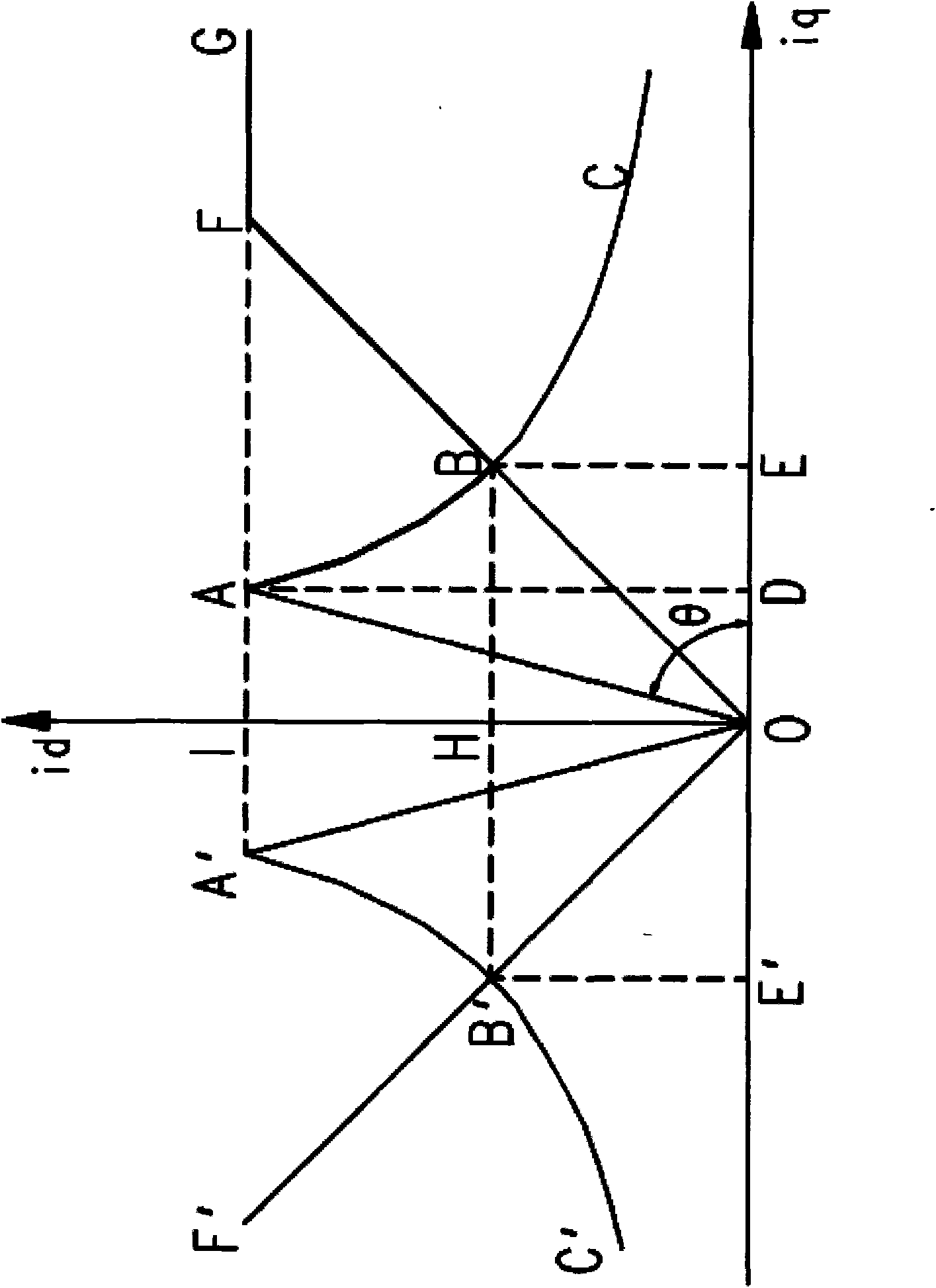
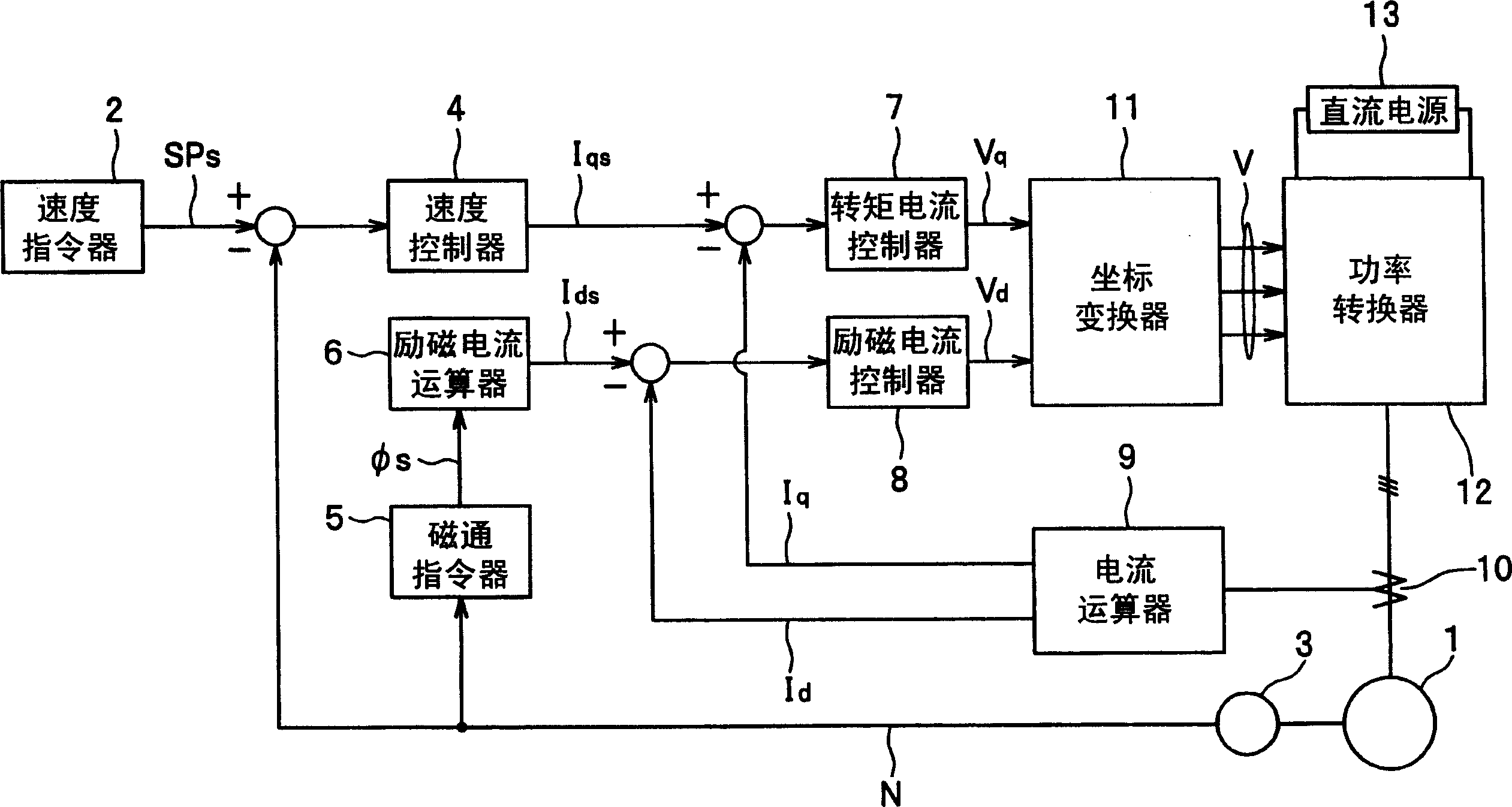
Control device of induction motor and application thereof
ActiveCN101989831ATotal current dropReduce cooling powerElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsEngineeringTotal current
The invention discloses a control device of an induction motor, comprising a tri-phase bridge rectifier, a power module, the induction motor, a current transformer, a coder, a pulse-width modulation (PWM) driver and a driving operating system, wherein the driving operation system adopts a vector control mode and comprises a filter circuit which is connected between a speed loop proportional plus integral (PI) controller and an exciting current instruction operation unit of the driving operation system and is used for filtering the moment current instruction value and inputting the filtered moment current instruction value in the exciting current instruction operation unit; and the exciting current instruction operation unit corrects the exciting current instruction value Ids of the induction motor based on the filtered moment current instruction value to lead the induction motor to have the minimum total current under the same load condition. The invention also discloses an application of the control device of the induction motor. In the invention, on the premise of not weakening the heavy load driving capacity of an escalator and a moving walk, the effect of stable operation of the motor with minimum current under a medium / light load condition is realized, thus achieving energy conservation.
Owner:SHANGHAI MITSUBISHI ELEVATOR CO LTD
Control method for maximum torque current rate of induction motor
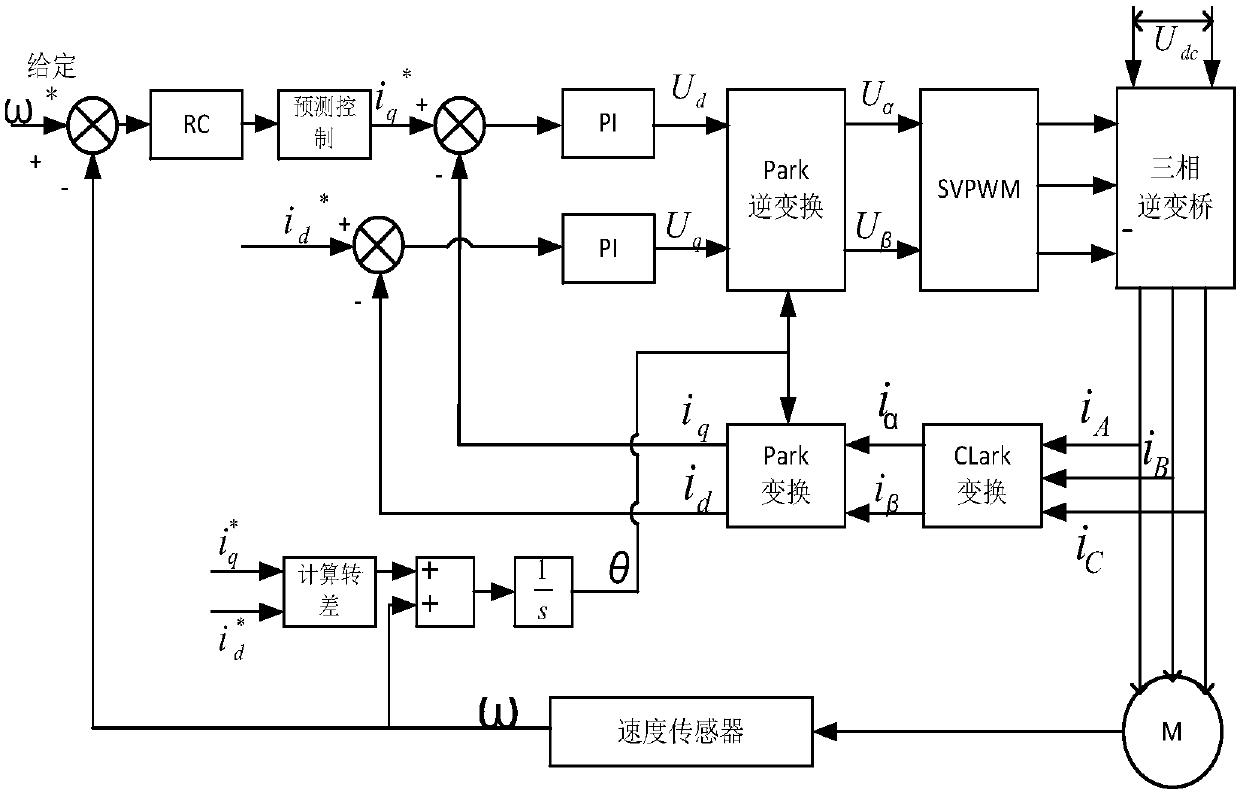
ActiveCN104135205ATaking into account efficiencyImprove operational efficiencyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsMulti inputMaximum torque
The invention discloses a control method for maximum torque current rate of an induction motor, belonging to the technical field of induction motor control. According to the control method, when the induction motor is at a working condition of light load running, PI (Proportional-Integral) and forecasting function control are combined so as to obtain a novel control method which can be applicable for a multi-input-multi-output system, control quantity output from a forecasting function controller serves as an input signal of an inverter circuit to change output voltage of an inverter, so that motor rotation speed is controlled, and tracking control on the rotation speed of the induction motor is achieved. The control method has the advantages of high control accuracy, fast tracking speed, low steady-state error and high interference resistance, the induction motor can be guaranteed to be endowed with high stability and dynamic performance, and the running efficiency of the motor at a dynamic condition can be improved.
Owner:邳州市景鹏创业投资有限公司
Methods and systems for induction motor control
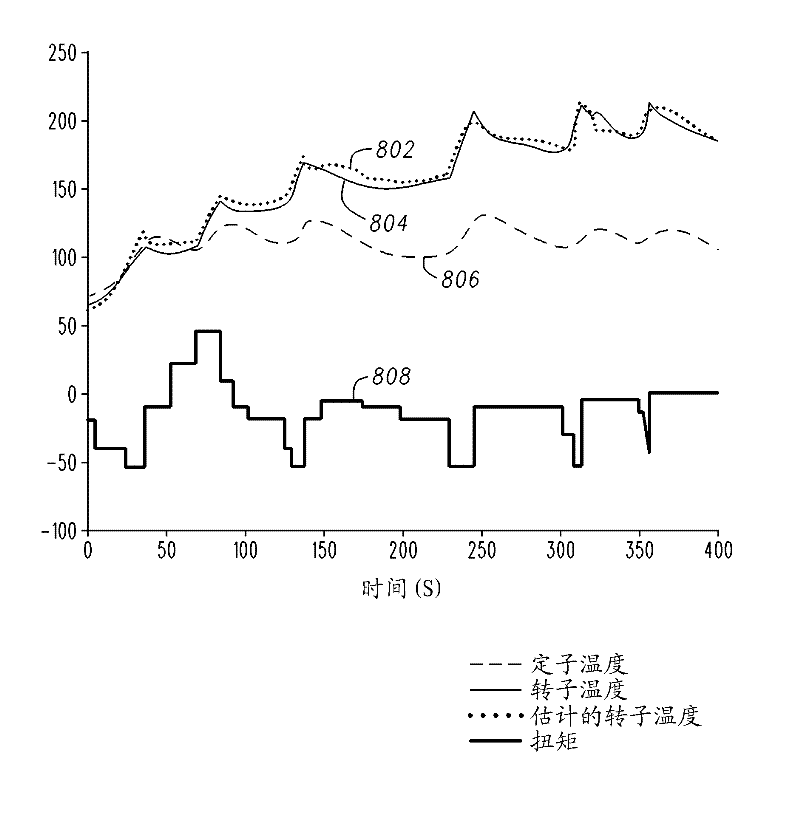
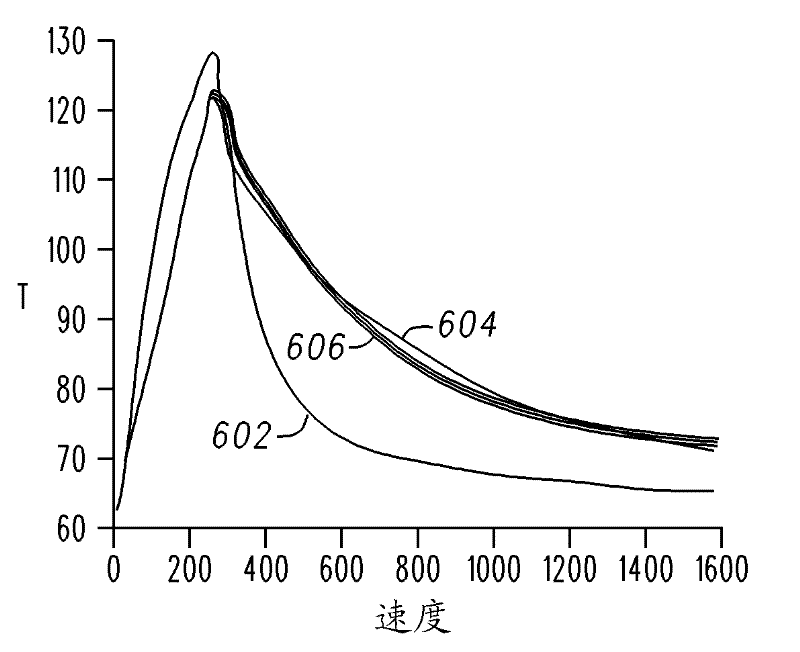
A method is provided for controlling an induction motor having a rotor. The method includes receiving a torque command; comparing the torque command to a threshold torque value; generating, with a first estimation module, a first estimated rotor resistance when the torque command is less than or equal to the threshold torque value; generating, with a second estimation module, a second estimated rotor resistance when the torque command is greater than the threshold torque value; and generating control signals for the induction motor based on the first estimated rotor resistance or the second estimated rotor resistance.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
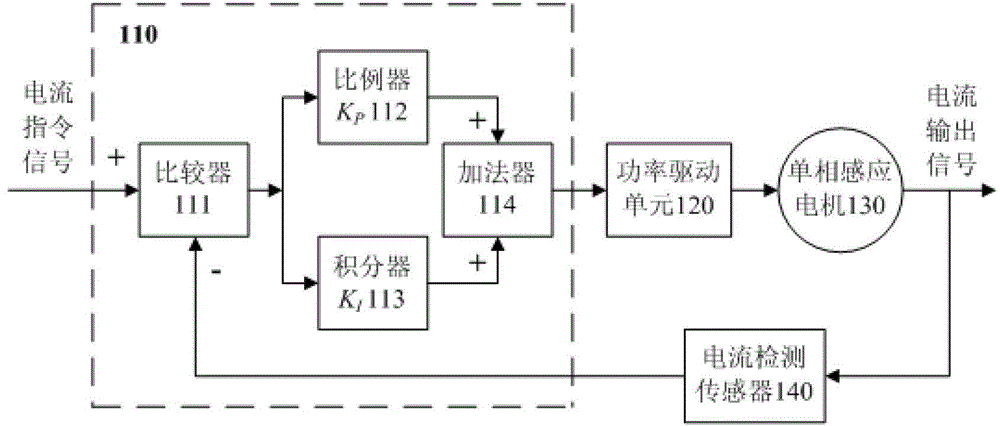
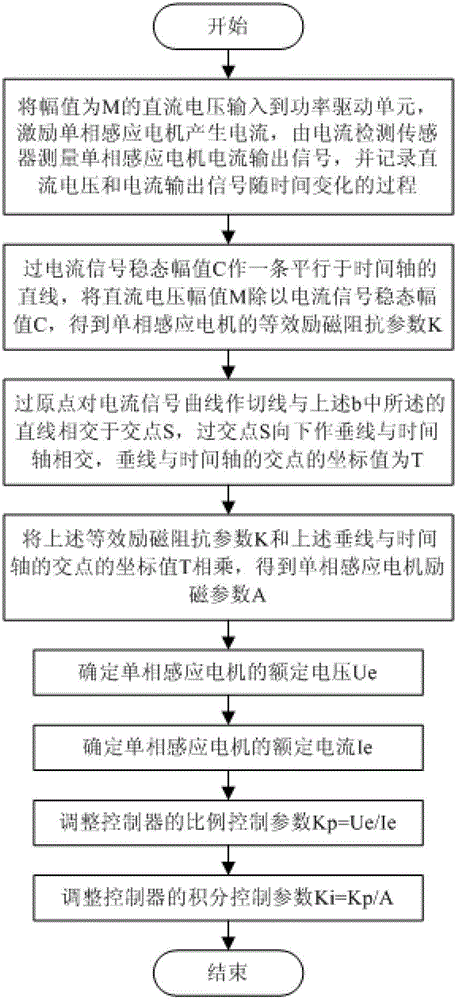
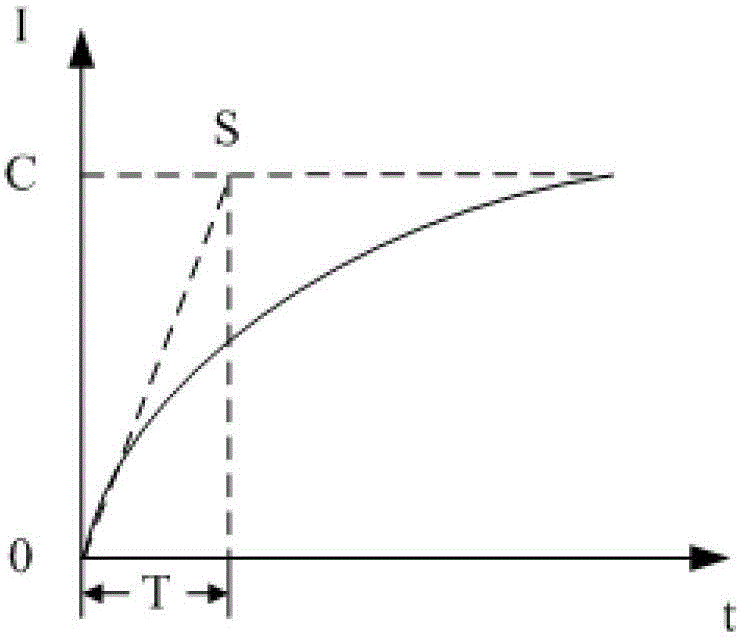
A kind of single-phase induction motor excitation current pi control method
ActiveCN103427748BCurb blindnessShorten the timeElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlProportional controlIntegrator
The invention discloses a PI (Proportional Integral) control method for exciting currents of a single-phase induction motor and belongs to the single-phase induction motor control field. A utilization system of the control method is formed by a controller, a power driving unit, a single-phase motor and a current detection sensor and the controller is formed by a comparator, a proportioner, an integrator and a summator. The PI control method for the exciting currents of the single-phase induction motor comprises firstly identifying an excitation parameter A of the single-phase induction motor and then adjusting a proportional control parameter Kp and an integral control parameter Ki of the controller. According to the PI control method for the exciting currents of the single-phase induction motor, parameters of the PI controller are regulated according to parameters of the single-phase induction motor during debugging, so that the PI controller can be adjusted purposely, parameter adjustment blindness of the PI controller is restrain, time and energy are saved, and a good current control effect is obtained.
Owner:江苏亚星波纹管有限公司
Induction motor control apparatus and induction motor control method
ActiveUS20150372628A1Torsional vibration of driveAC motor controlVector control systemsDrive wheelPower flow
An induction motor control apparatus controls an induction motor connected to drive wheels by setting a motor torque command value on the basis of vehicle information. The induction motor control apparatus calculates a first torque current command value and a first excitation current command value on the basis of the motor torque command value and estimates a rotor magnetic flux on the basis of the first excitation current command value. The induction motor control apparatus calculates a first torque command value on the basis of an estimated value of the rotor magnetic flux and the first torque current command value. Further the induction motor control apparatus calculates a second torque command value by applying filter processing to the first torque command value, a natural vibration frequency component of a drive shaft torque transmission system in a vehicle being removed in the filter processing. Then the induction motor control apparatus controls drive of the induction motor on the basis of the first excitation current command value and the second torque current command value.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Controller for induction motor
ActiveUS6879130B2Sure easySingle-phase induction motor startersElectronic commutation motor controlElectrical resistance and conductanceControl vector
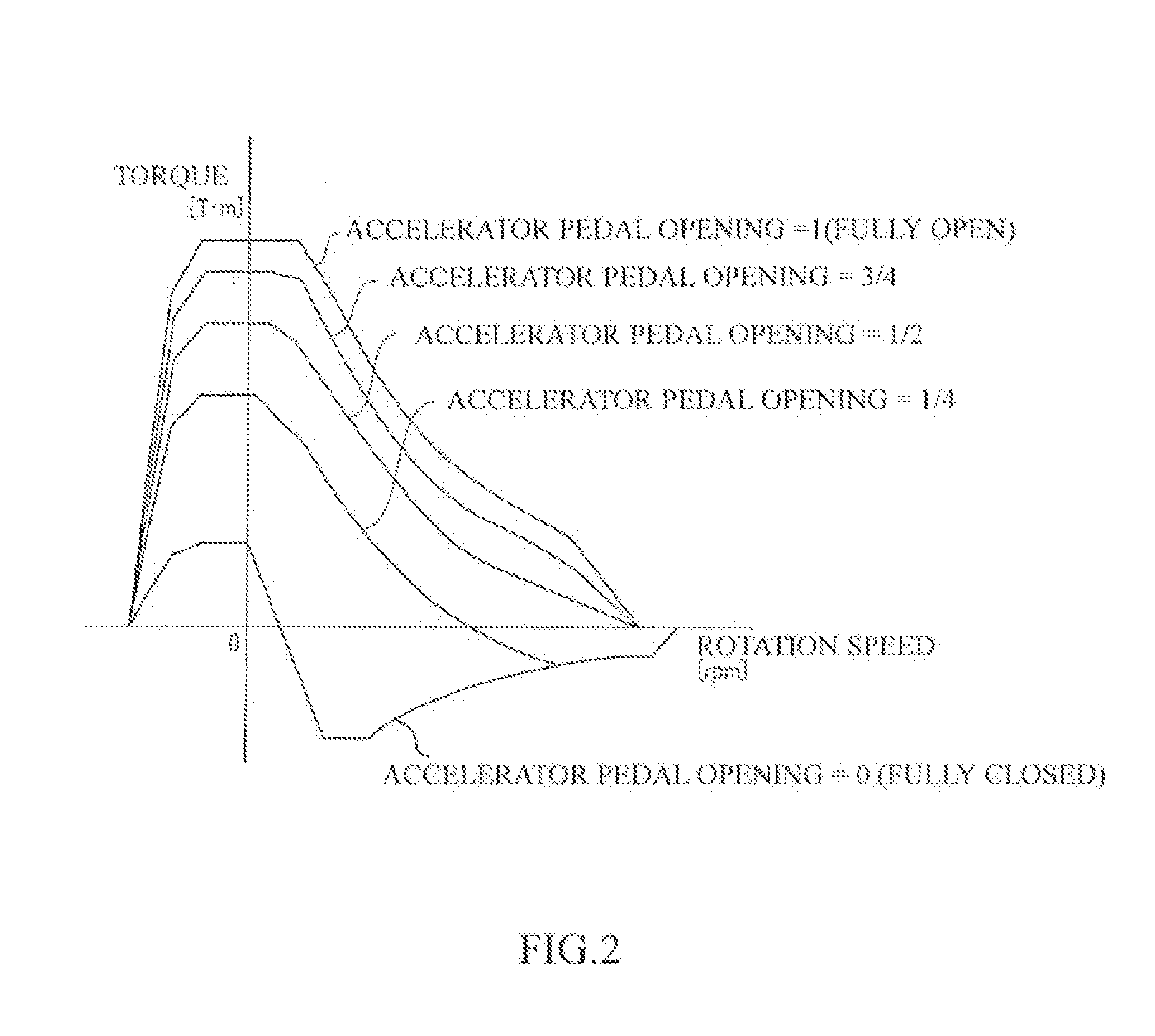
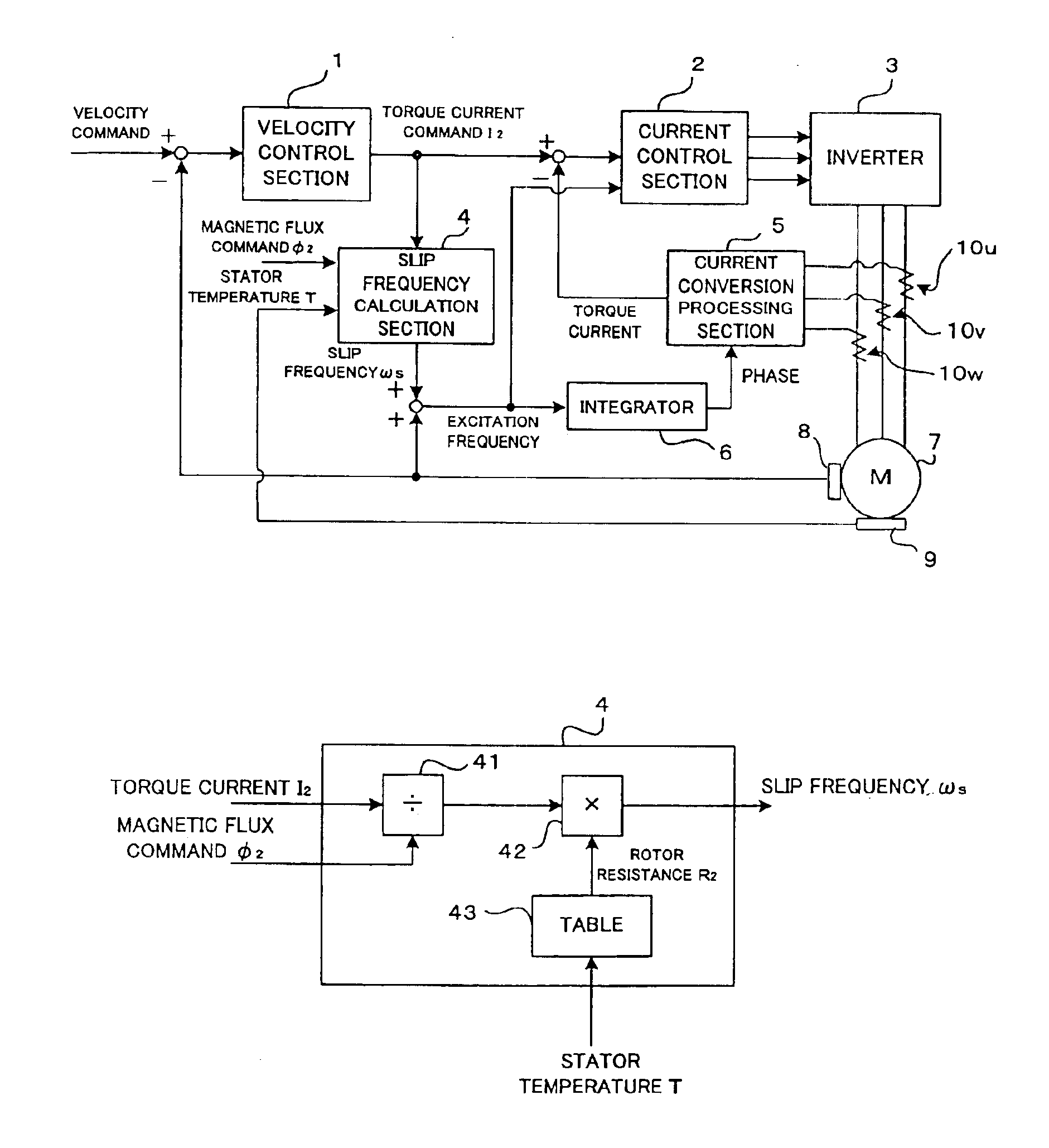
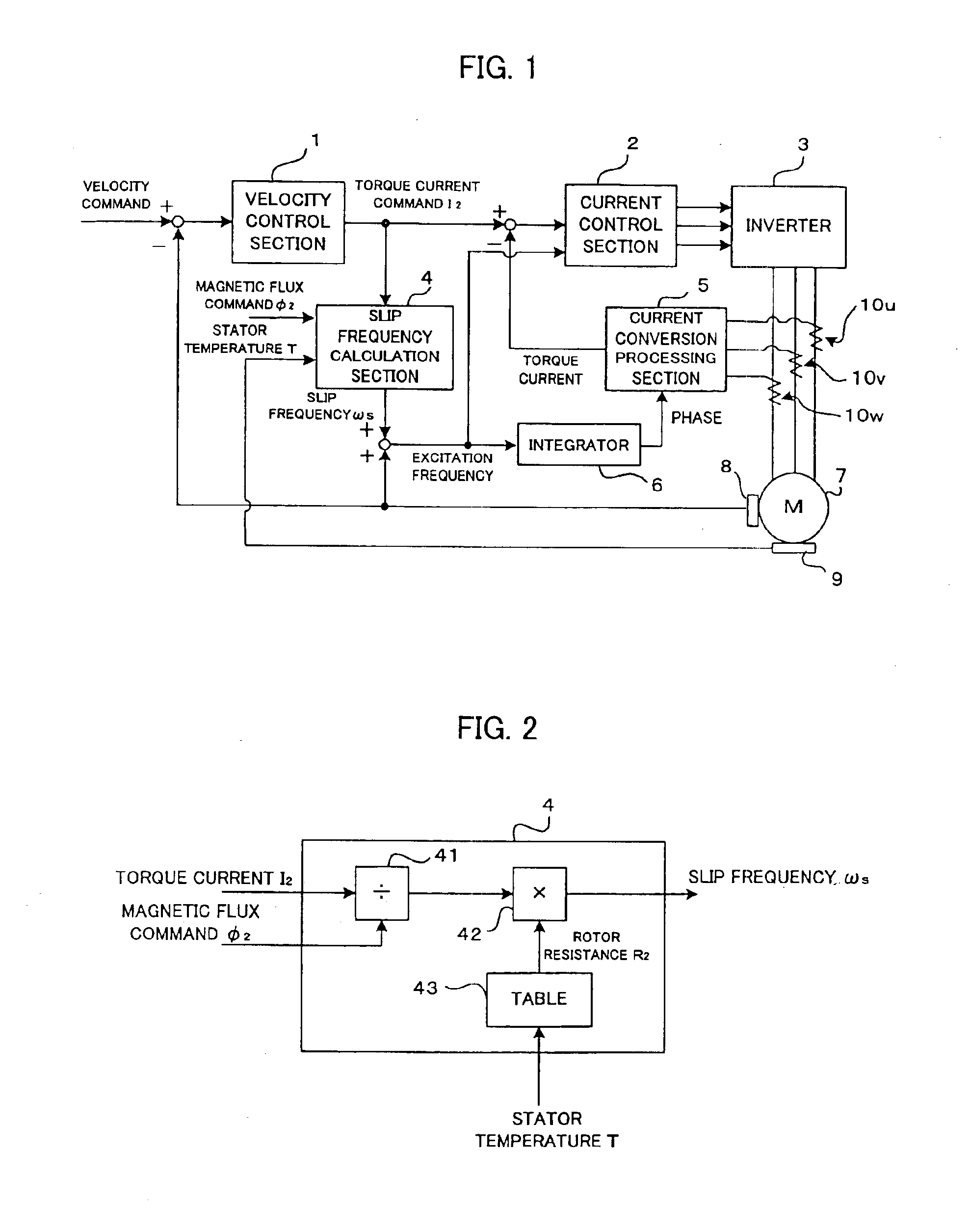
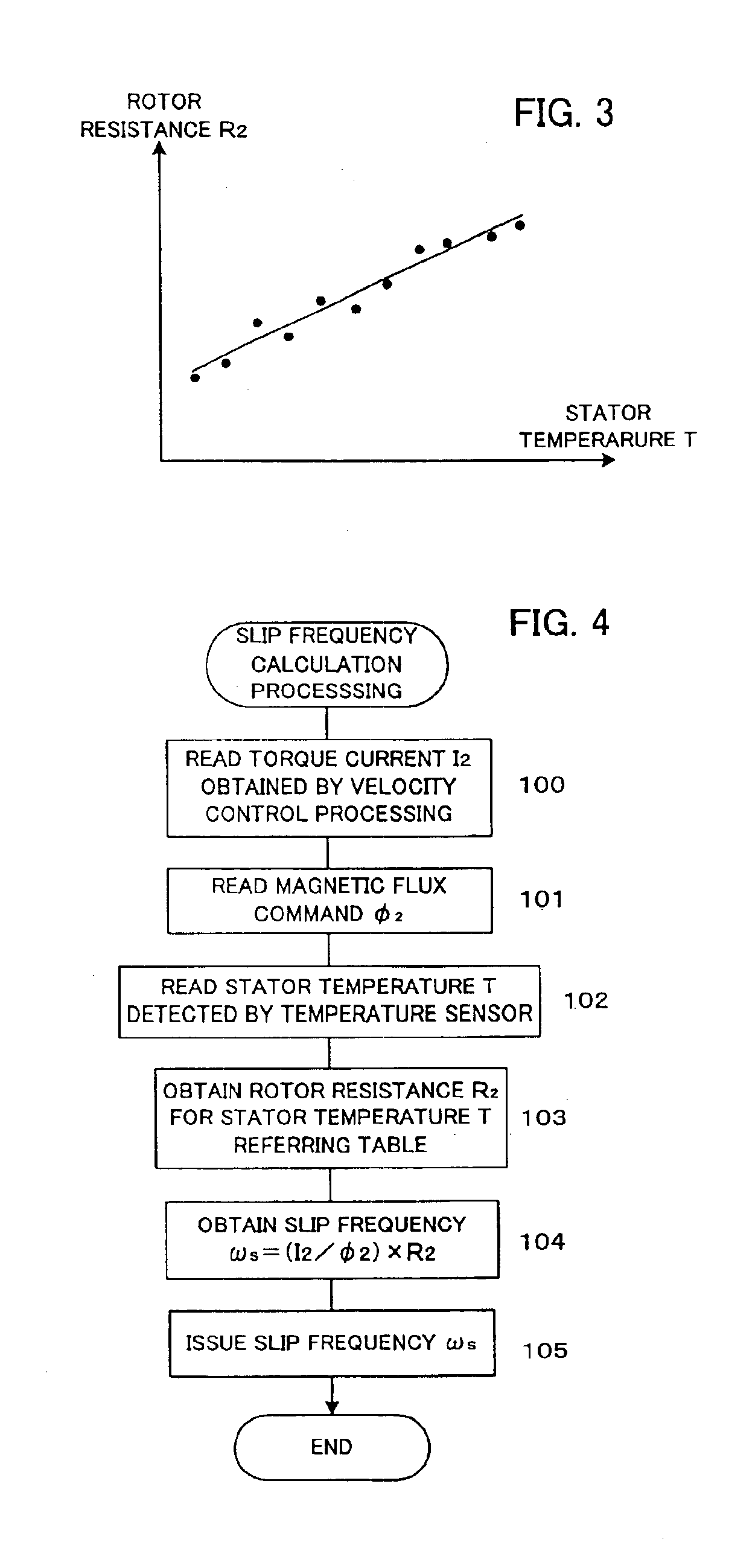
A controller for a vector control of an induction motor, which is capable of easily determining a rotor resistance for use in calculation of a slip frequency. A temperature sensor is provided for detecting a temperature of a stator. Information on relation between the rotor temperature and the rotor resistance predetermined based on measurement is stored in a table. In driving the induction motor, the rotor resistance for the stator temperature detected by the temperature sensor is read from the table. A torque command I2 is divided by a magnetic flux command Φ2 and the obtained quotient is multiplied by the read value of the rotor resistance to obtain the slip frequency ωs, so that the vector control is performed based on the obtained slip frequency ωs. The value of the rotor resistance is easily determined by simply referring the table without complicated calculation. Since the stored information on the rotor resistance are based on measured values, a more precise value of the slip frequency is obtained to realize a precise vector control of the induction motor.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Repetition and prediction control method of asynchronous motor
ActiveCN108365785AImprove dynamic performanceImprove suppression propertiesElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsStable stateComputer science
The invention discloses a repetition and prediction control method of an asynchronous motor, a repetition control system is designed in the speed ring, and prediction design is designed on the basis of repetition control. Advantages of repetition control are used to realized a higher stable-state precision; but the control system has modeling errors caused by factors as parameter change and external interference due to phase lag of repetition control, and a mathematic model Gn(s) of a control object cannot represent a practical object G(s) accurately. Prediction control is designed on the basis of repetition control, so that instant performance is realized, modeling errors can be compensated, the dynamic performance of the control system can be further improved, the control system has a higher inhibition characteristic for external interference via the control strategy, and requirement for high performance of an induction motor control system can be met.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
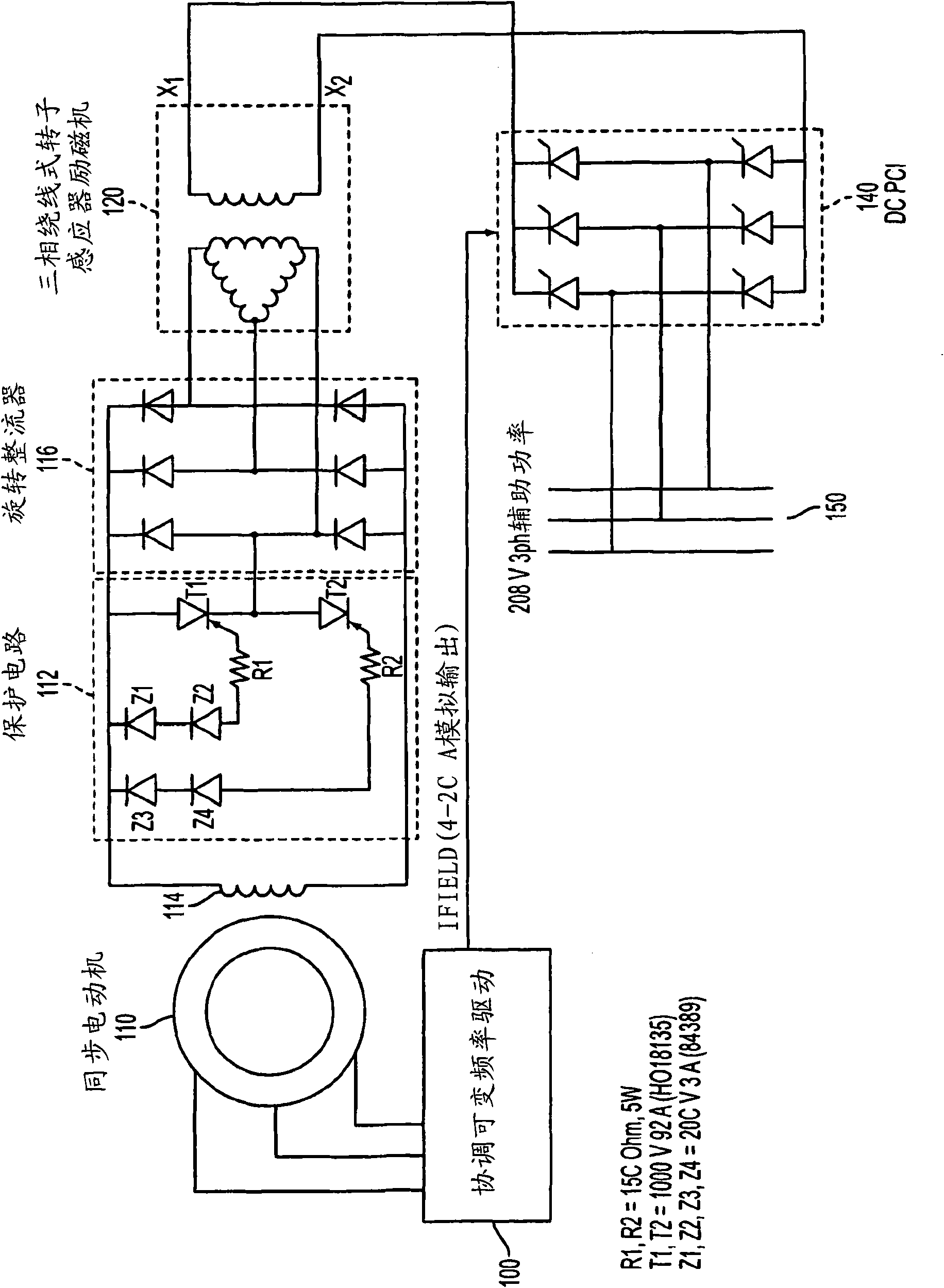
Method of starting a synchronous motor with a brushless DC exciter
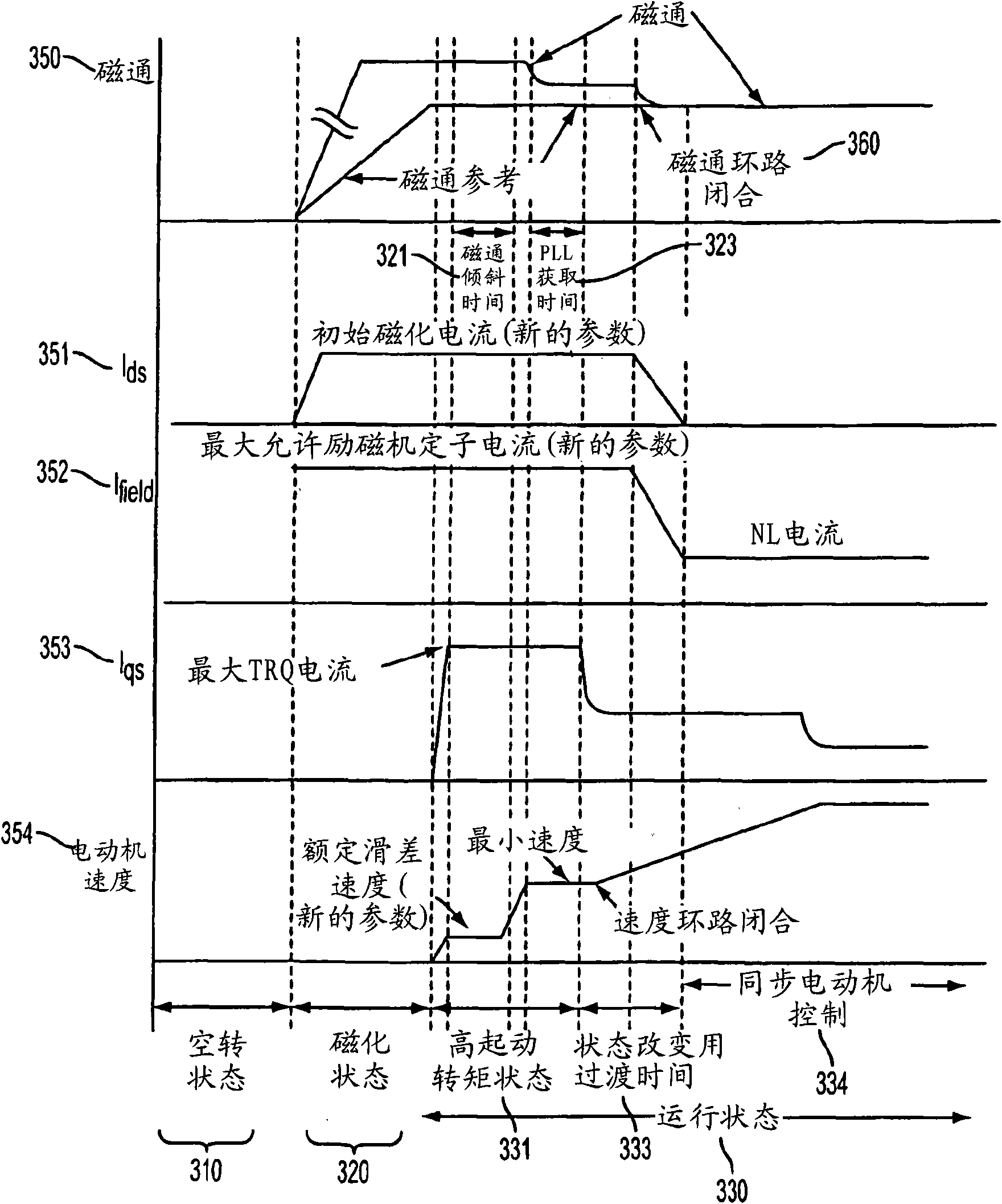
A starting method and system for a motor where the motor may be started as an induction motor by applying a magnetizing current to build flux through the stator, with the field current set at the maximum permissible exciter stator current (i.e., the current that will cause rated no-load current in the main field at the transition speed). The motor stator currents will be maintained at a value that allows the motor to generate sufficient breakaway torque to overcome any stiction. At a specific transition speed or after a period of time, the drive will initiate a transition from induction motor control to synchronous motor control by removing the initial magnetizing current, and a field current is then applied to the motor through the DC exciter. Once this transition is completed, the drive may ramp up to the desired speed demand.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Control process and control device of induction motor ind. appts.
InactiveCN1728542AHigh outputElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl vectorInduction motor
The invention aims at obtaining a high output above the rated output of an induction motor. When the magnetic field flux of the induction motor (1) is in a strong magnetic field flux status, according to an induction motor control method of carrying out the vector control of magnetic field weakening control, the magnetic field weakening control is carried out in case that the rotating speed N of the induction motor (1) is higher than a rated rotating speed. Furthermore, during carrying out the magnetic field weakening control, the magnetic field flux is changed to enable the internal inducted electromotive force of the induction motor (1) is larger than the rated rotating speed. In addition, after the magnetic field weakening control is started, the magnetic field flux is weakened according to the rise of the rotating speed N to enable the terminal voltage of the induction motor (1) not to exceed a crest voltage during a maximal overload.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Induction motor control
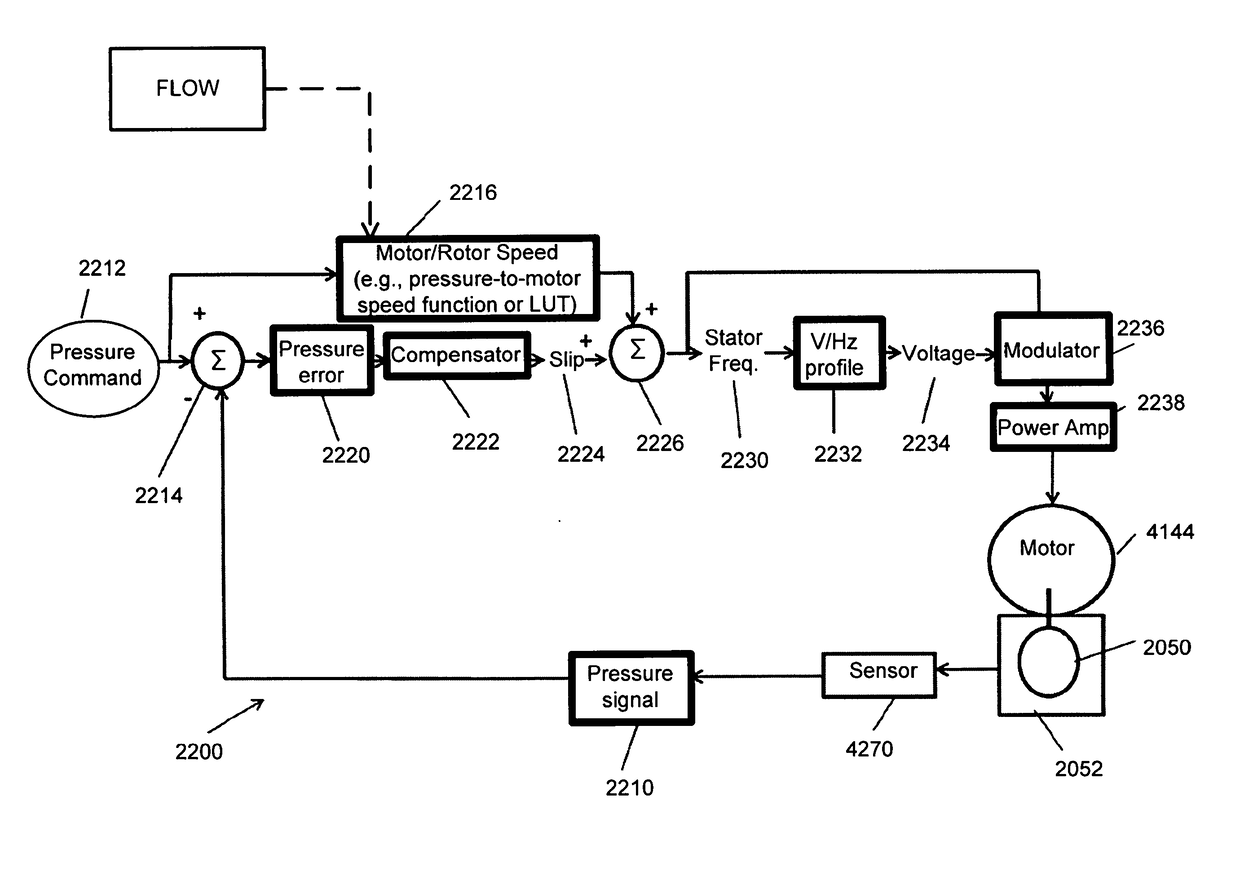
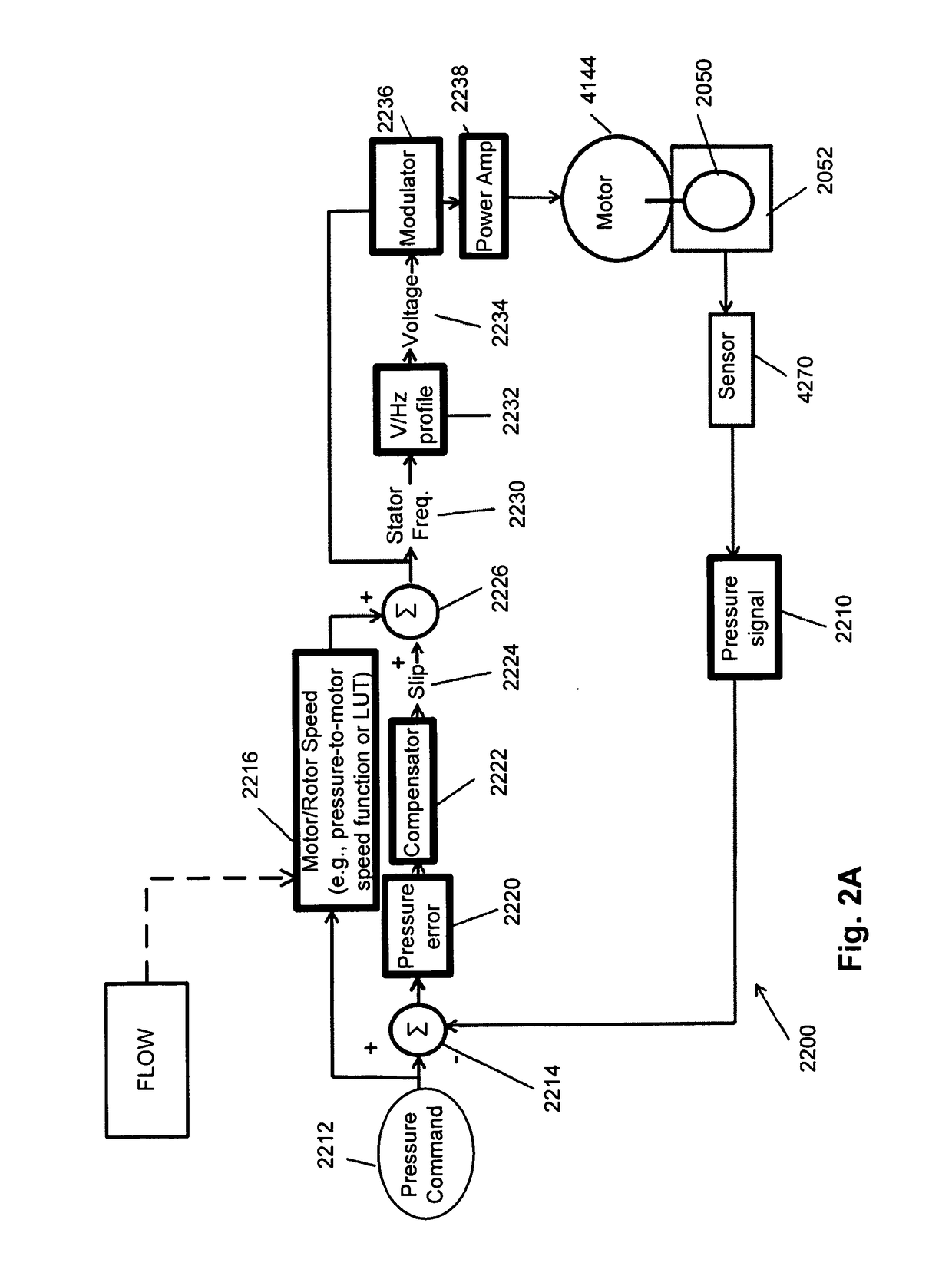
A method of a control system (2200) controls an inductance motor in a blower including an impeller and volute using a pressure compensation control system. The control system may be implemented in a respiratory pressure therapy device. The control system may include a sensor configured to provide a pressure signal indicative of the pressure of a flow of fluid produced by the blower. A measured pressure may be compared to a set pressure to determine a pressure error. A slip frequency may be adjusted as a function of the pressure error in an attempt to eliminate or minimise the pressure error.
Owner:RESMED MOTOR TECH
Induction motor controller
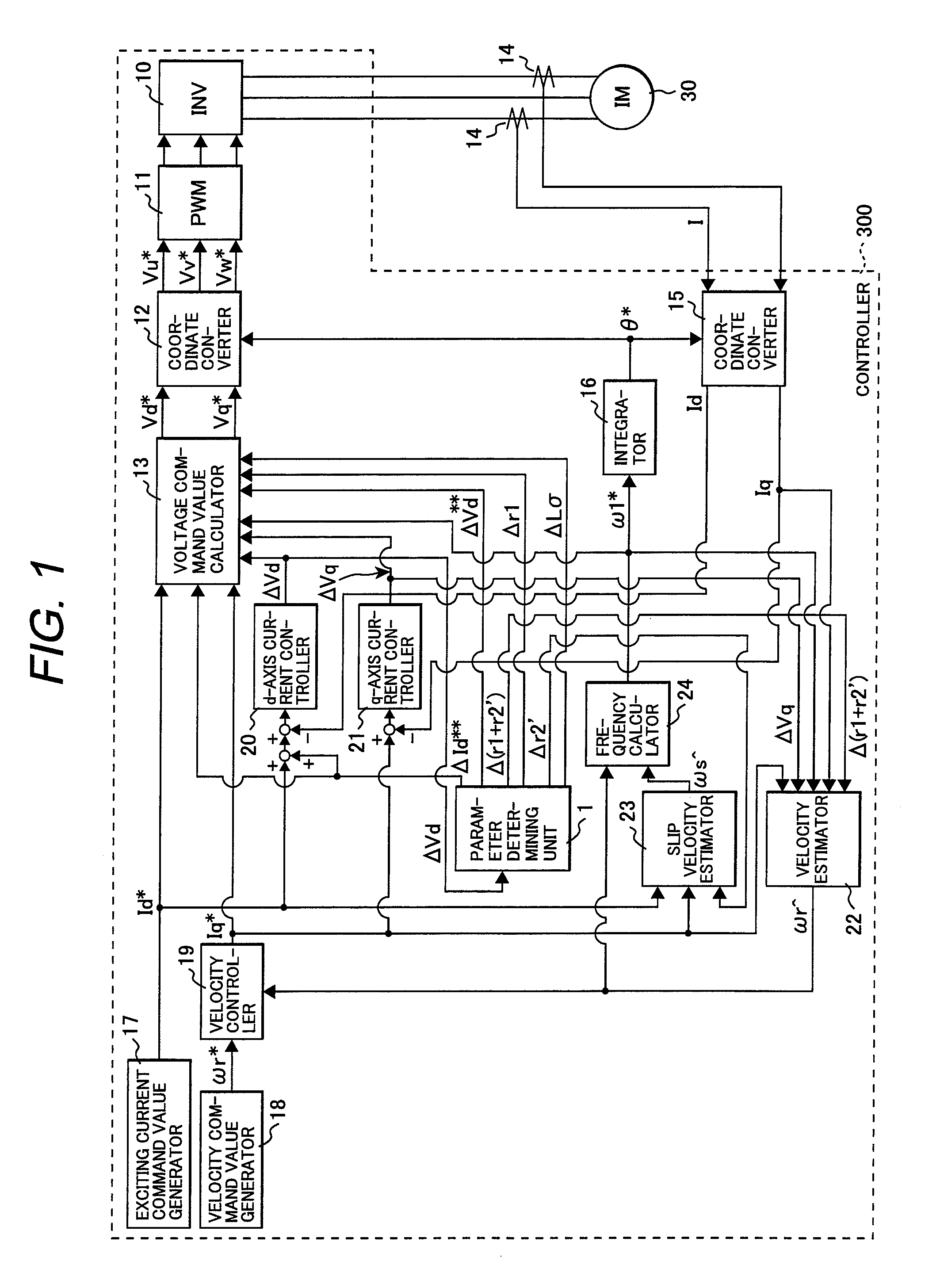
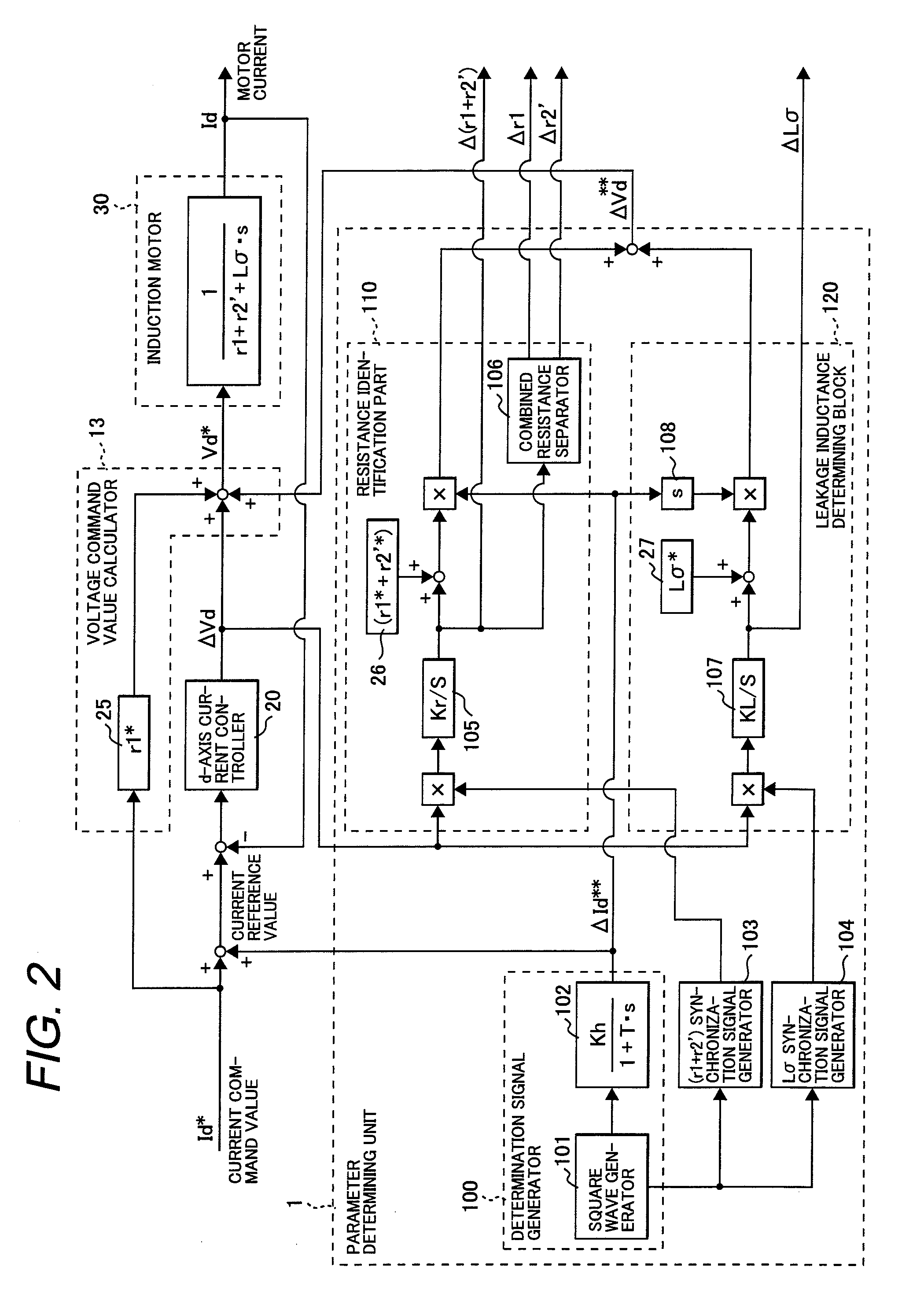
InactiveUS20080169783A1Improve controllabilityReduced controllabilitySingle-phase induction motor startersVector control systemsInduction motor controlControl parameters
The present invention provides an induction motor controller which includes: a circuit for generating a d-axis current reference signal from a d-axis current command value and a periodically varying periodic signal; a d-axis current controller for controlling a d-axis motor current flowing through an induction motor to be controlled to match the d-axis current reference signal; parameter determining means for calculating and determining a motor parameter of the induction motor based on a deviation of the d-axis motor current from the d-axis current reference signal, and controlling a voltage applied to the induction motor using a compensation voltage calculated from the calculated and determined motor parameter, in which a control parameter for controlling the induction motor is set based on the calculated and determined motor parameter.
Owner:HITACHI IND EQUIP SYST CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com