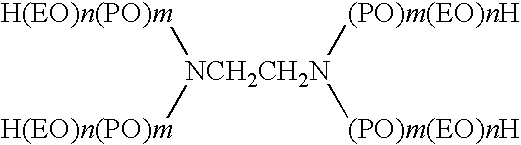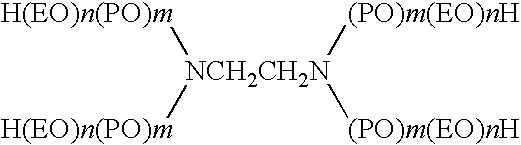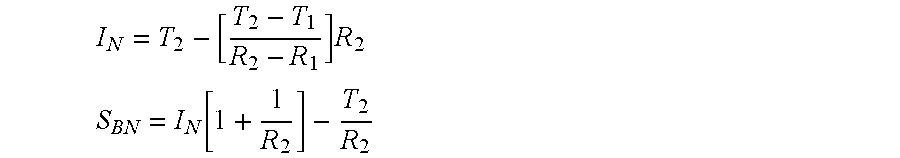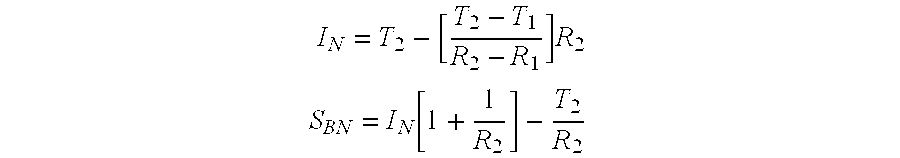Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
46 results about "Incompatible Material" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Incompatible materials. Substances that should not be stored near each other because any contact between them would cause a dangerous reaction leading to a explosion, fire, or production of hazardous new substances.
Compositions comprising cyclodextrin derivatives
A stable composition for removing unwanted molecules from a surface comprises low-degree of substitution cyclodextrin derivatives. The compositions are suitable for capturing unwanted molecules from inanimate surfaces, including fabrics, including carpets, and household surfaces such as countertops, dishes, floors, garbage cans, ceilings, walls, carpet padding, air filters, and the like, and from animate surfaces, including skin, hair, and the like. The compositions can further comprise cyclodextrin-compatible and -incompatible materials, and other optional ingredients.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
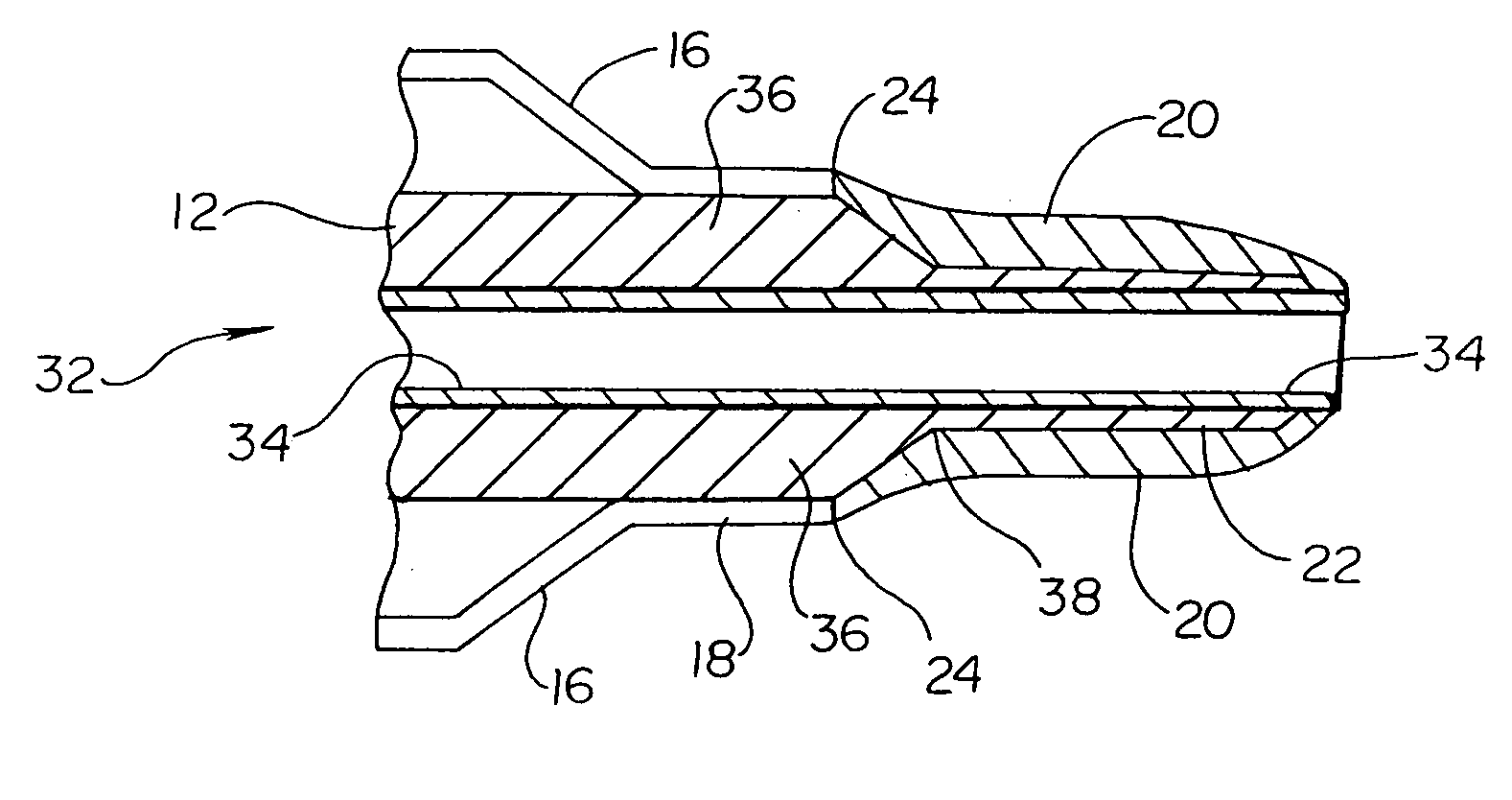
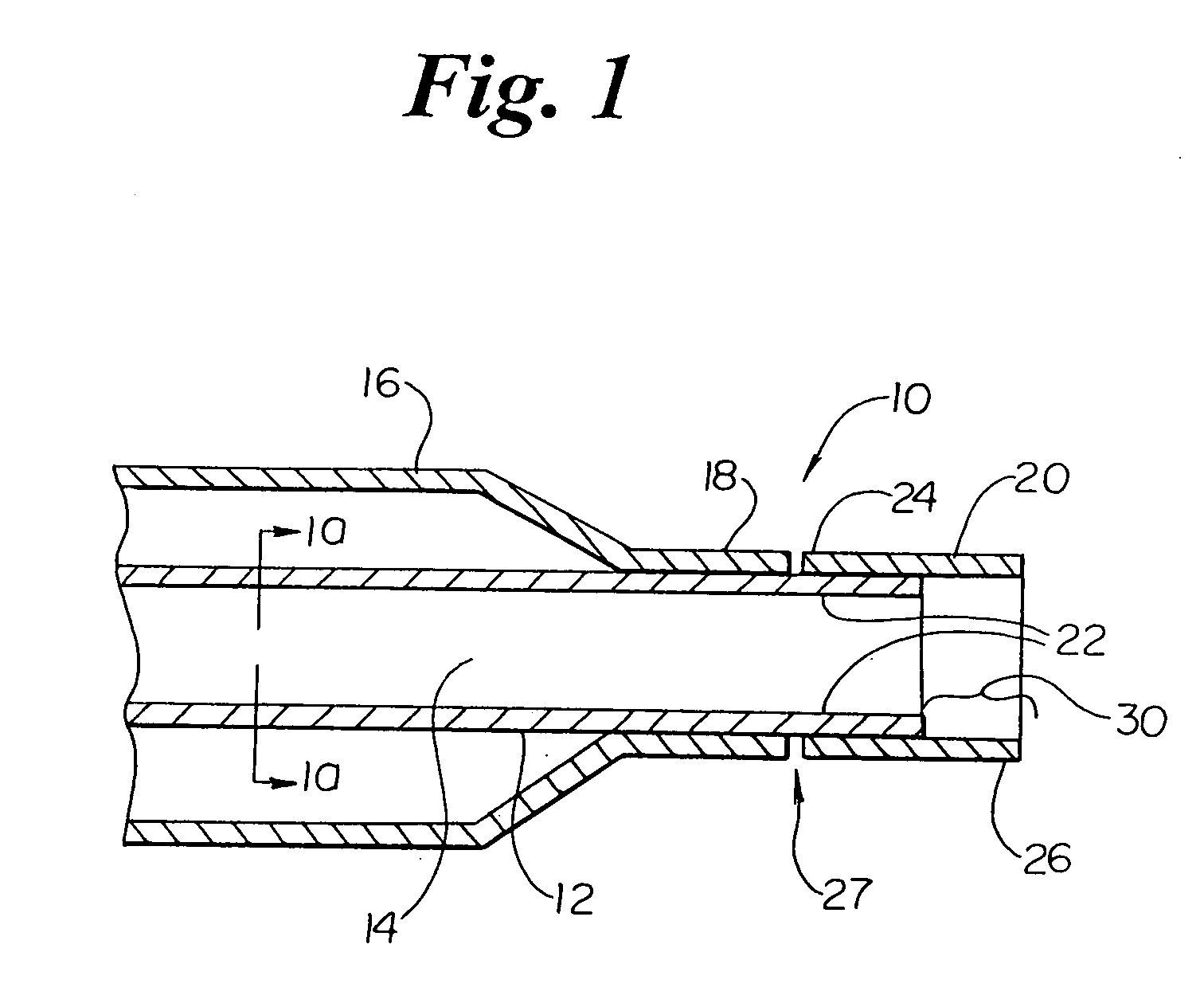
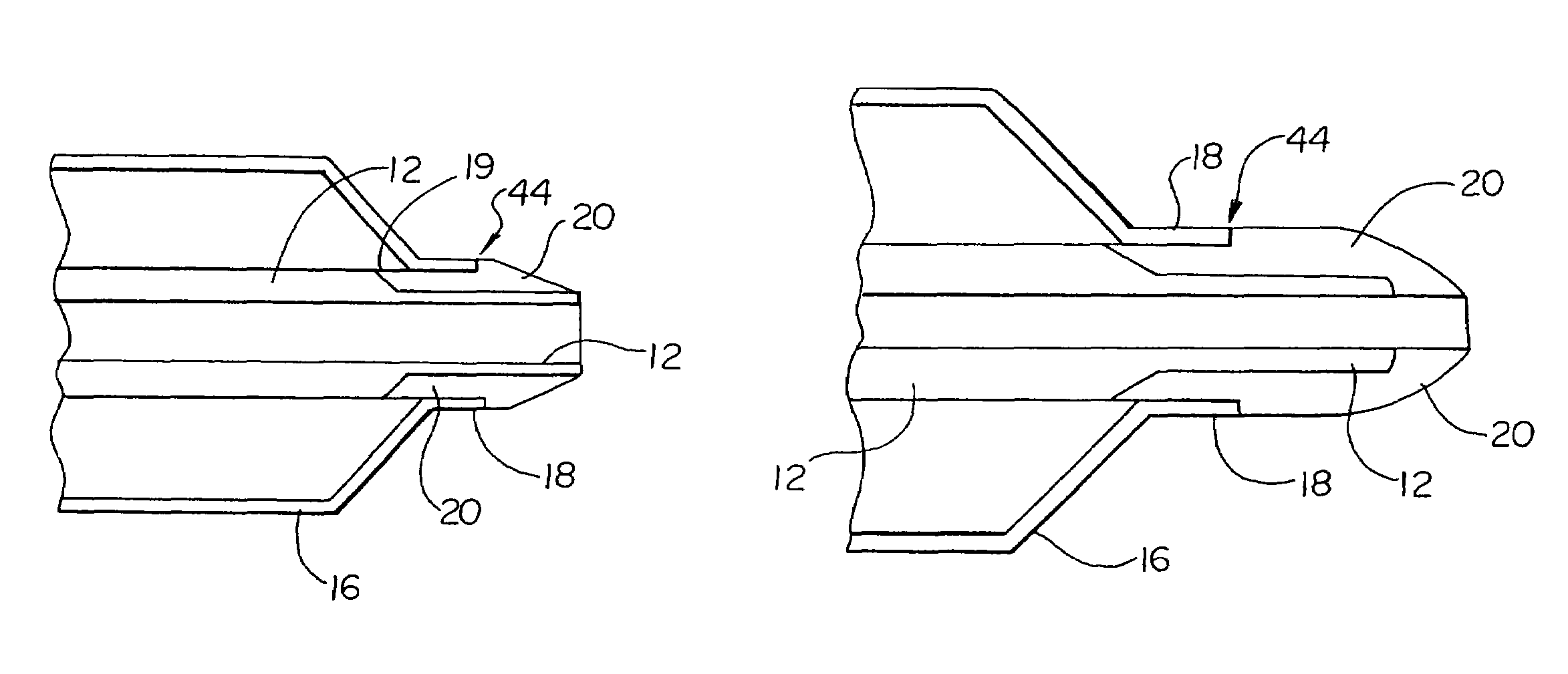
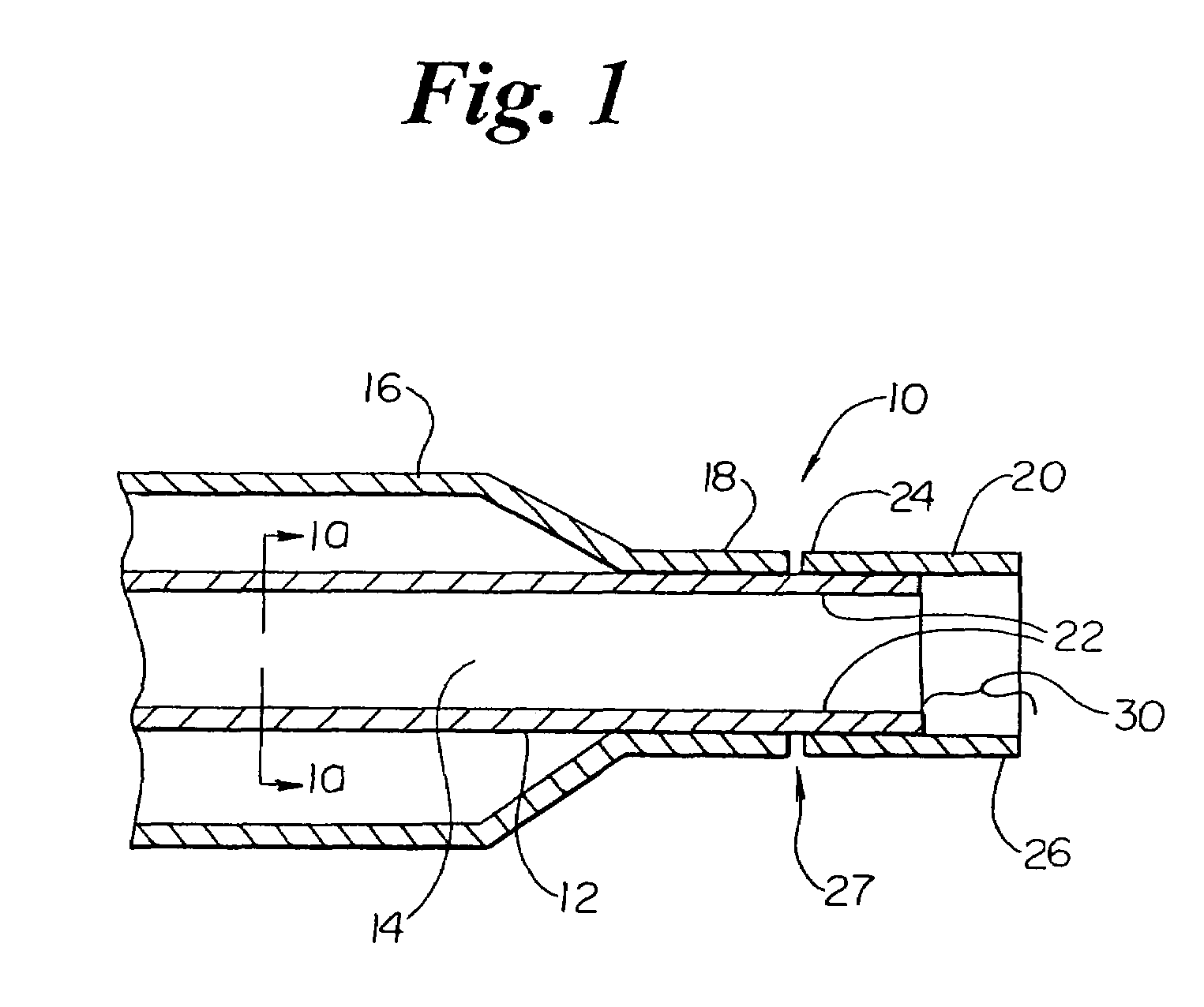
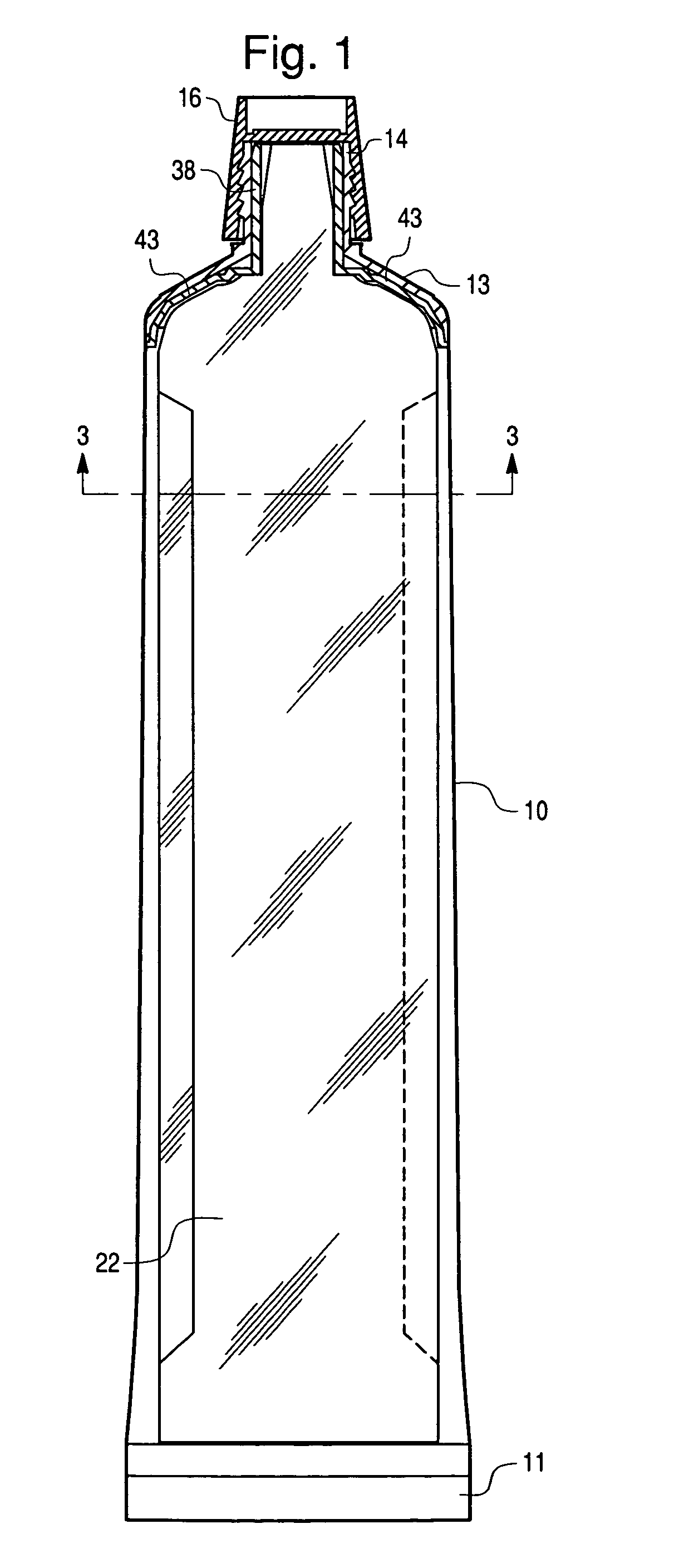
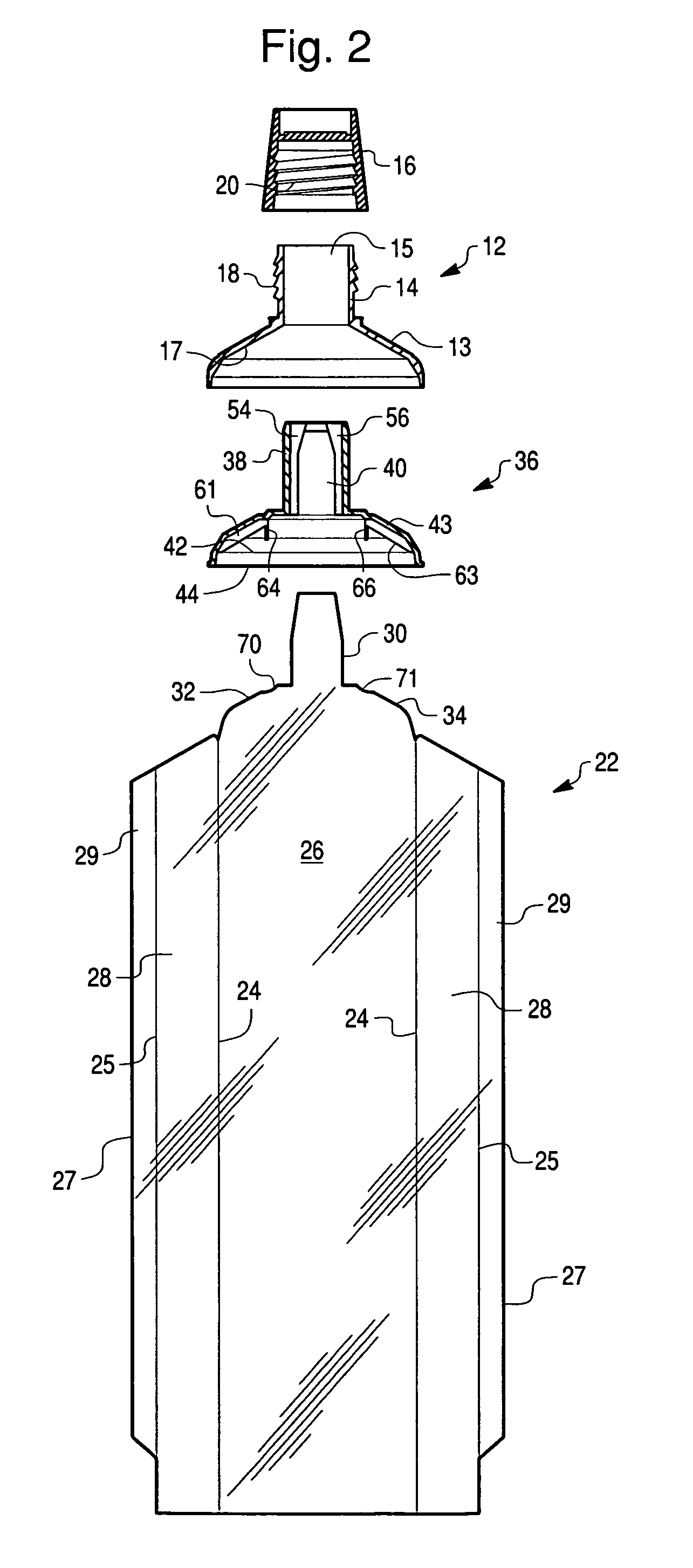
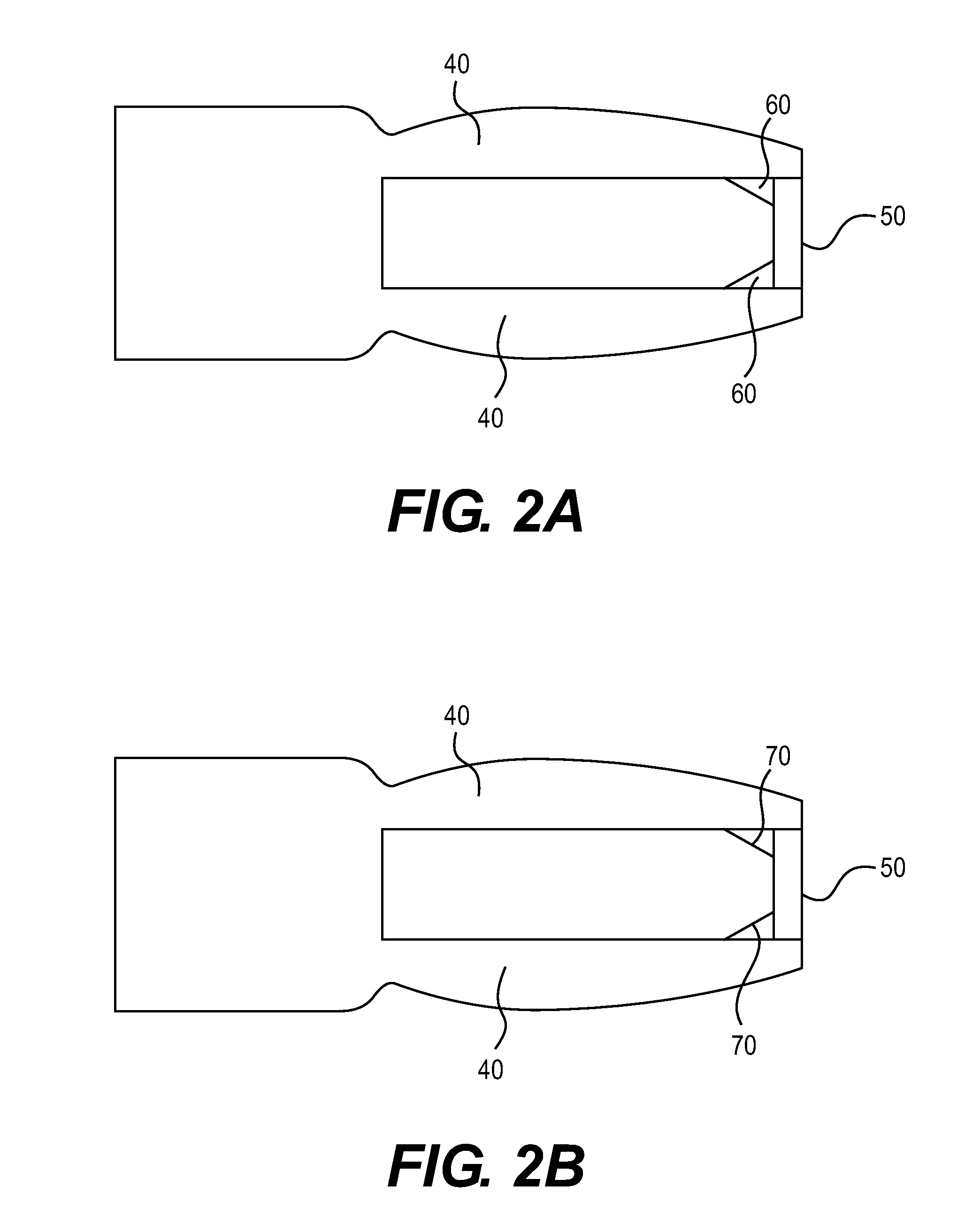
Balloon catheter tip design
InactiveUS20050131445A1Increase frictionPrevent movementStentsBalloon catheterBalloon catheterIncompatible Material
The present invention is directed to distal tip designs for catheter, wherein distal tip material is positioned about an inner shaft. The distal tip material may also be used as a tie layer for thermally bonding two incompatible materials together, such as a waist portion of a balloon to the inner shaft.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
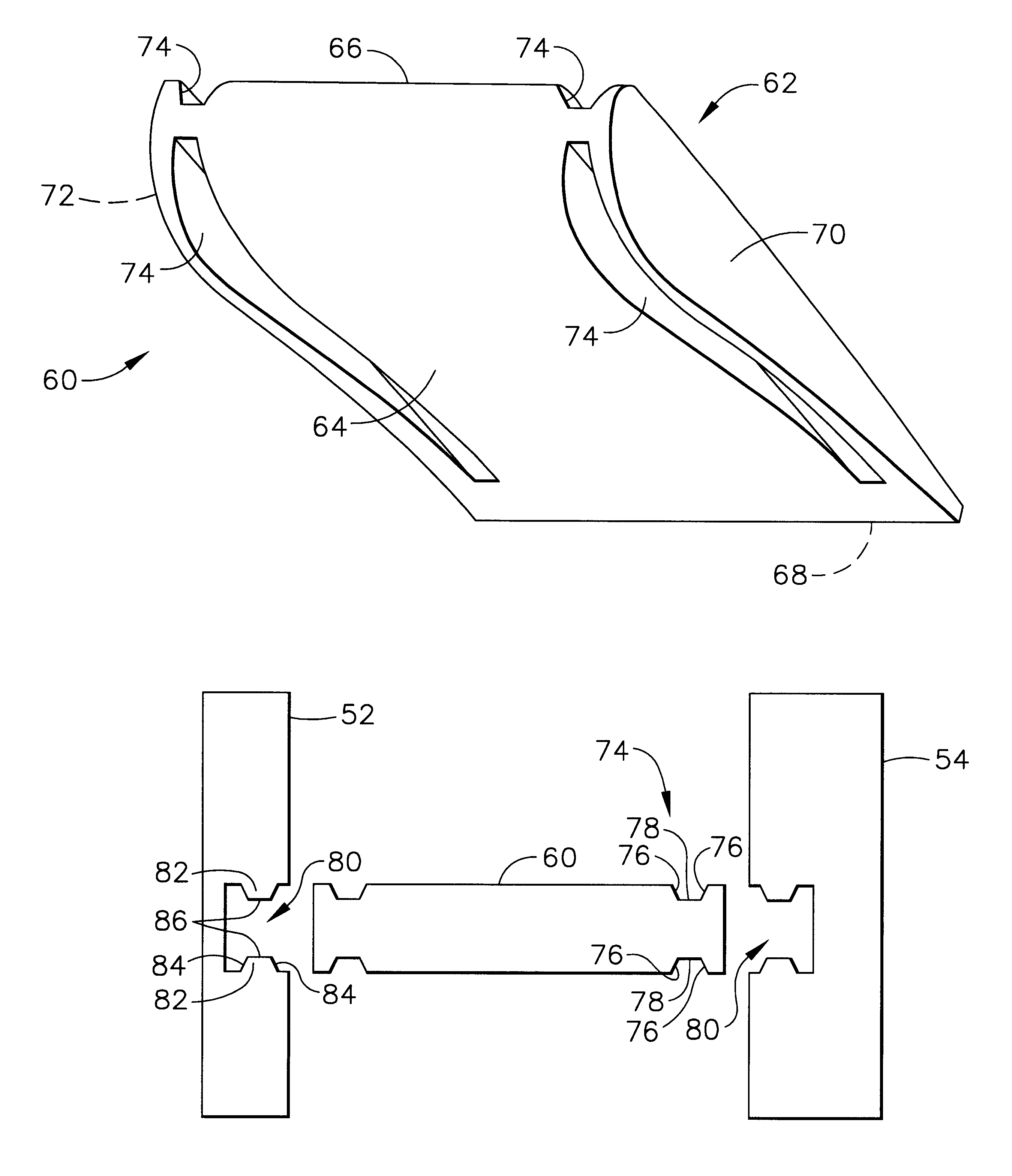
Low stress connection methodology for thermally incompatible materials
InactiveUS6409473B1Accommodates thermal growth mismatchPromote growthPump componentsBlade accessoriesLeading edgeEngineering
An assembly comprising a ceramic vane with a metal housing cast around the ends of the vane. The ceramic vane has dovetailed shaped grooves along its edges that extend from the vane's leading edge to its trailing edge. The housing is comprised of two spaced apart walls each having dovetailed protrusions for mating with the dovetail grooves in the vanes's edges. Upon the casting of the walls to the vane at least one surface of each dovetail groove comes in contact with at least one surface of the dovetail protrusion. A crushable coating is disposed between the vane's edges and the dovetail protrusions.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
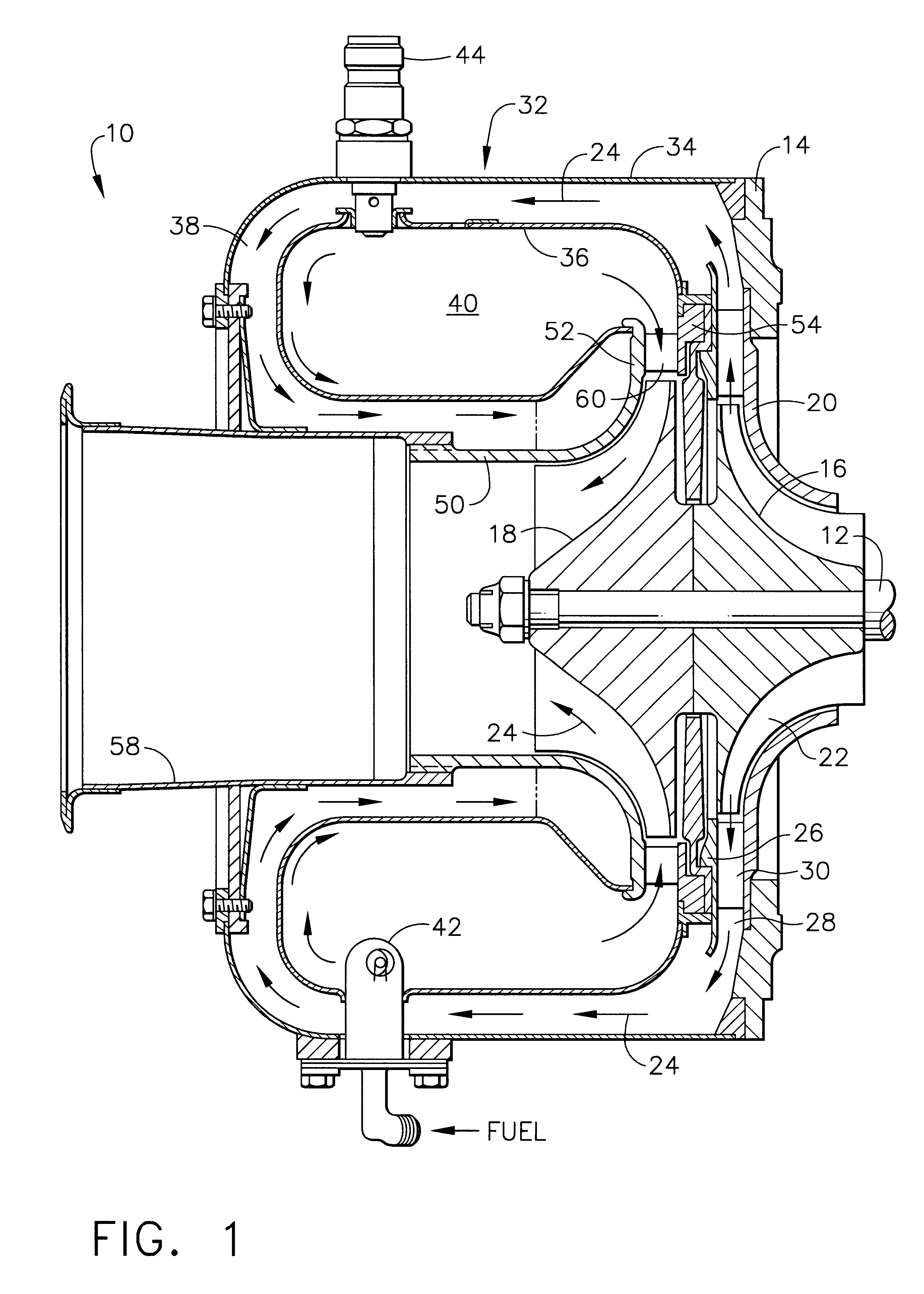
Rare gas-halogen excimer lasers with baffles
ActiveUS7257144B2Reduce pollutionExtended service lifeActive medium materialGas laser constructional detailsNoble gasLaser beams
Owner:MELA SCIENCES
Catheter distal tip
InactiveUS7575568B2Increase frictionPrevent movementStentsBalloon catheterMedicineIncompatible Material
The present invention is directed to distal tip designs for catheter, wherein distal tip material is positioned about an inner shaft. The distal tip material may also be used as a tie layer for thermally bonding two incompatible materials together, such as a waist portion of a balloon to the inner shaft.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
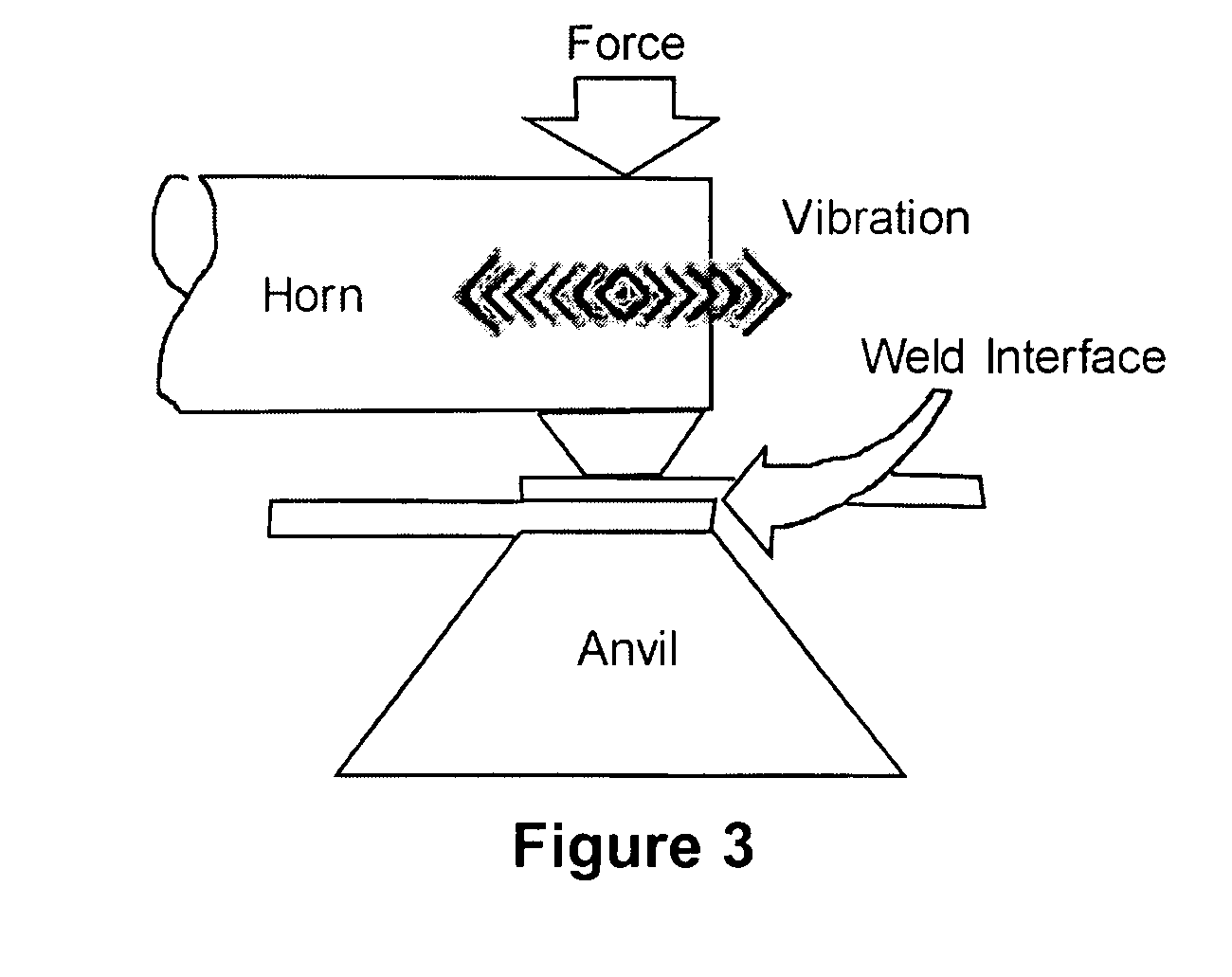
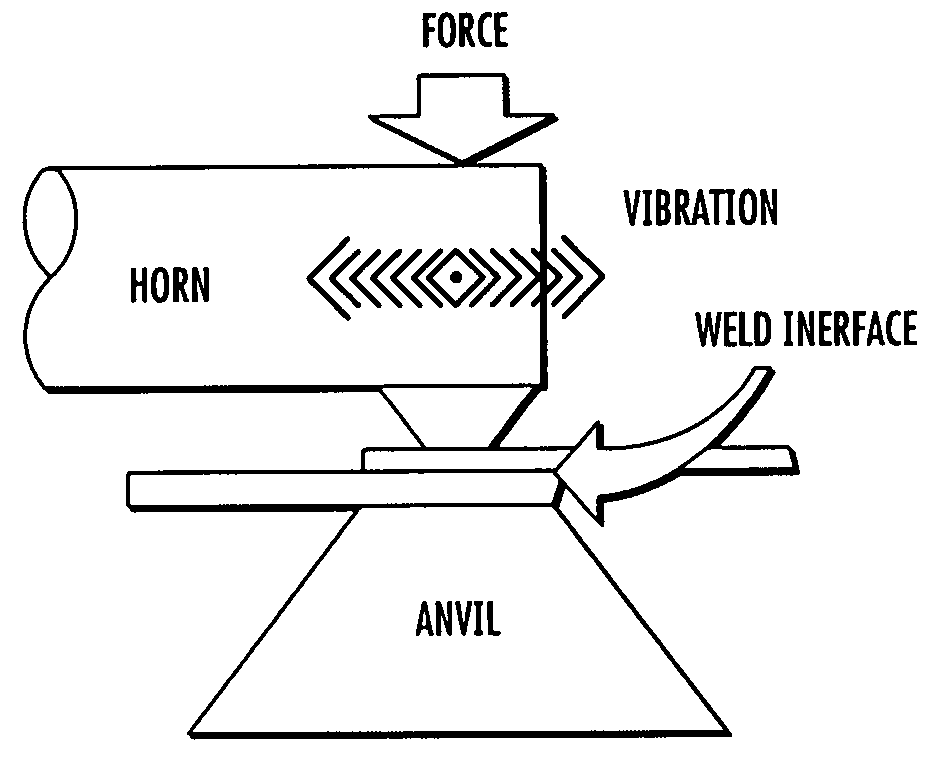
Adaptive continuous acoustic welding system for incompatible materials
InactiveUS20070257086A1Cooking-vessel materialsLamination ancillary operationsMaterial typeUltrasonic welding
A system and method are provided which enable the joining of two materials via ultrasonic welding, including materials normally considered incompatible in traditional ultrasonic welding techniques. The system permits ultrasonic welding of a first material to a second material, the second material including material types normally considered incompatible with the first material and includes an abrader for altering the surface of the material / s to be joined. A first pressure device is operative to vary the position of the abrader and thereby vary the abrasion applied to the materials. An ultrasonic source provides acoustic energy to a weld interface between the materials. A second pressure device is operative to vary the force applied to the interface between the materials while a sensor senses the weld interface temperature. A controller dynamically adjusts the acoustic energy of the ultrasonic source, the second pressure device, and at least one of the first pressure device and a temperature varying device during junction formation. The temperature varying device is operative to modify the temperature of the material / s being welded before abrasion and / or proximate the weld interface location. In this manner, the system enables a smooth, continuous junction to form at a predetermined rate.
Owner:SWCE
Adaptive continuous acoustic welding system for incompatible materials
InactiveUS7771551B2Cooking-vessel materialsLamination ancillary operationsMaterial typeJunction formation
A system and method are provided which enable the joining of two materials via ultrasonic welding, including materials normally considered incompatible in traditional ultrasonic welding techniques. The system permits ultrasonic welding of a first material to a second material, the second material including material types normally considered incompatible with the first material and includes an abrader for altering the surface of the material / s to be joined. A first pressure device is operative to vary the position of the abrader and thereby vary the abrasion applied to the materials. An ultrasonic source provides acoustic energy to a weld interface between the materials. A second pressure device is operative to vary the force applied to the interface between the materials while a sensor senses the weld interface temperature. A controller dynamically adjusts the acoustic energy of the ultrasonic source, the second pressure device, and at least one of the first pressure device and a temperature varying device during junction formation. The temperature varying device is operative to modify the temperature of the material / s being welded before abrasion and / or proximate the weld interface location. In this manner, the system enables a smooth, continuous junction to form at a predetermined rate.
Owner:SWCE
Polymer articles with Polymer layer containing incompatible material unevenly distributed and surface-roughened tape or sheet comprising the polymer articles
InactiveUS20090169817A1Improve adhesionRestricts distributionAdhesive articlesSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer scienceTotal thickness
Disclosed is a polymer article having a multilayer structure including a polymer layer and a monomer-absorptive layer that is arranged on the polymer layer and is capable of absorbing at least one of monomer components constituting the polymer. The polymer layer is a polymer layer containing an unevenly distributed immiscible material that is immiscible with the polymer and is enriched at an interface, or in the vicinity thereof, opposite to the monomer-absorptive layer. The polymer article preferably further includes a cover film arranged on the polymer layer on a side opposite to the monomer-absorptive layer. The vicinity of the interface opposite to the monomer-absorptive layer is preferably a region ranging from the interface opposite to the monomer-absorptive layer in a thickness direction to 50% or less of the total thickness of the polymer layer.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
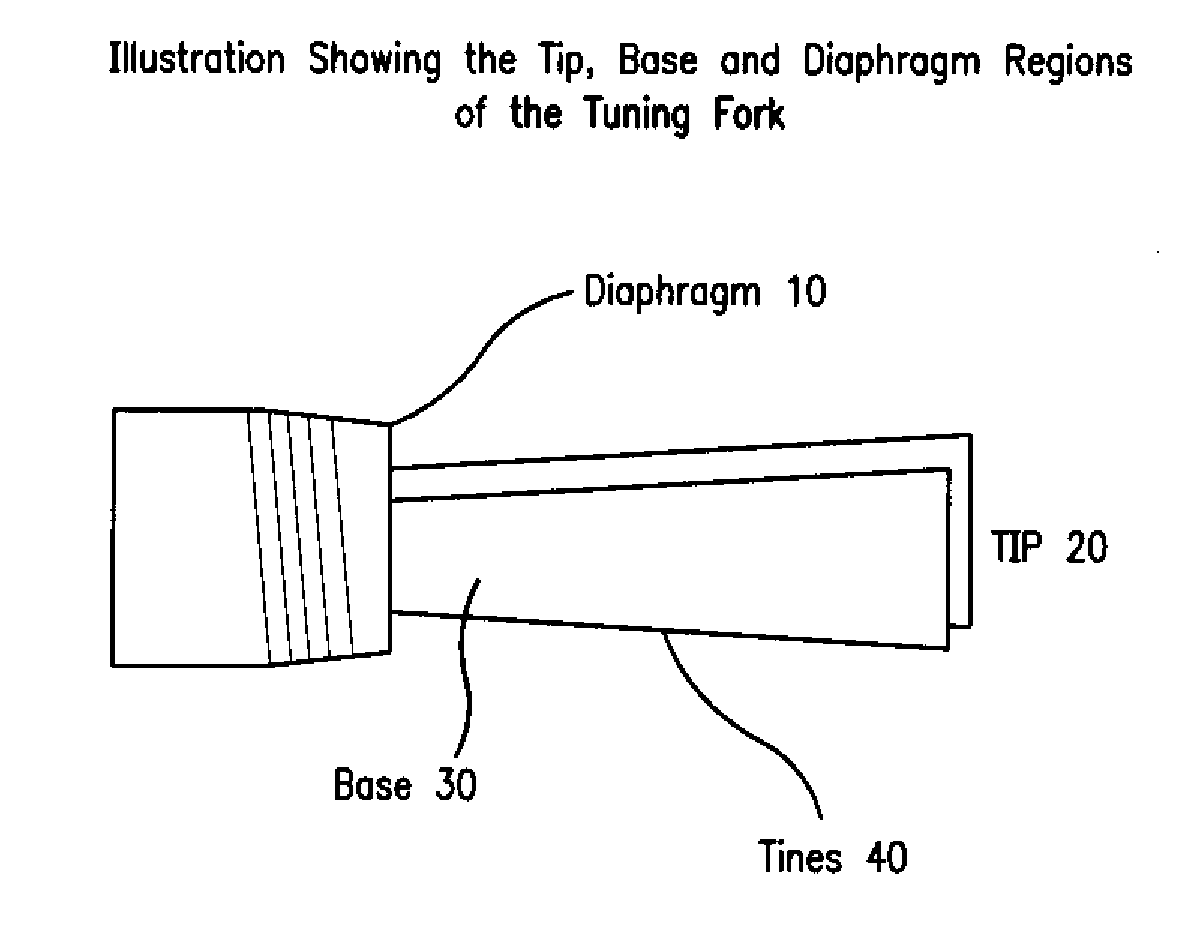
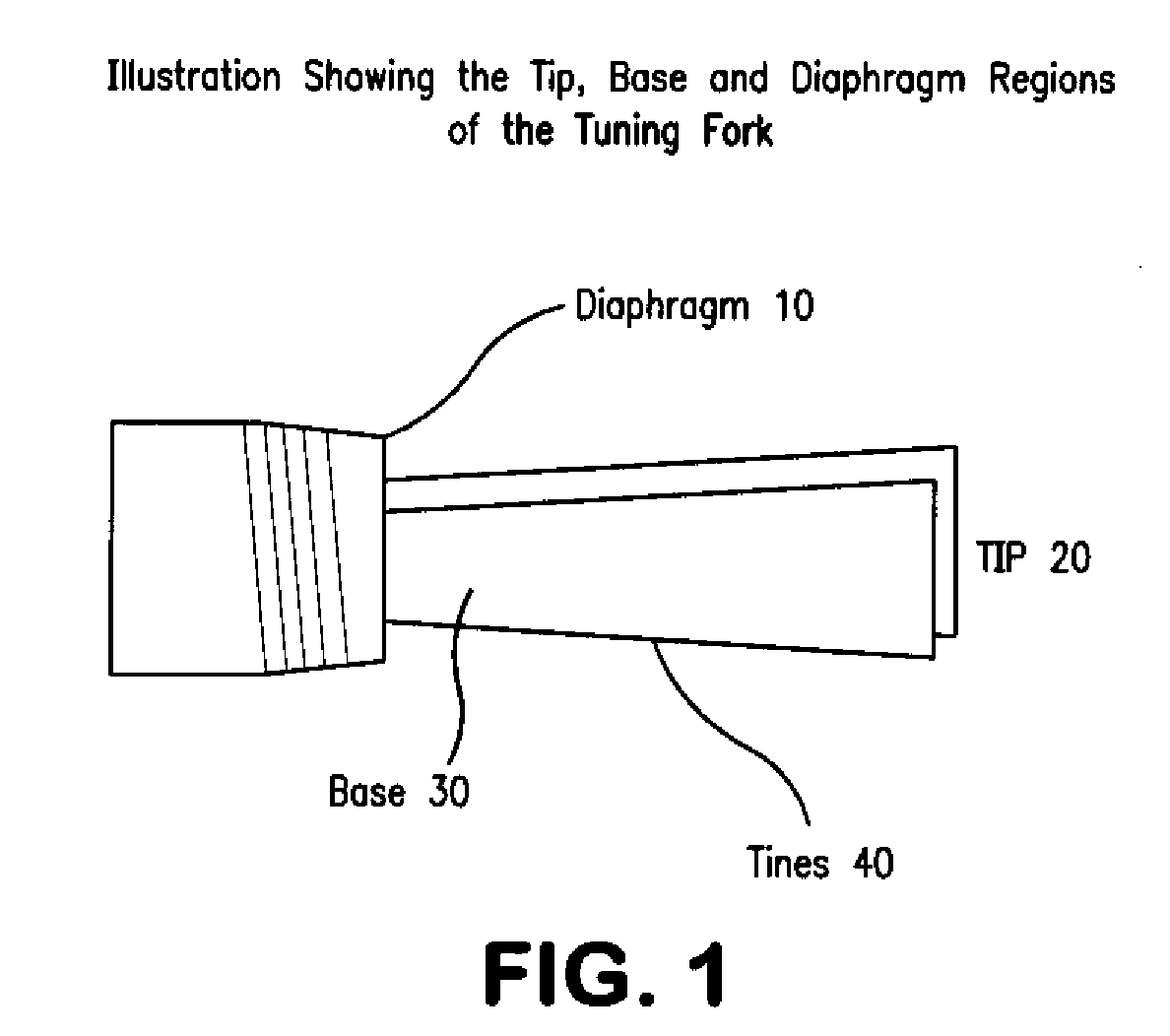
Tuning Fork Oscillator Activated or Deactivated by a Predetermined Condition
InactiveUS20100275689A1Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTuning forkForeign matter
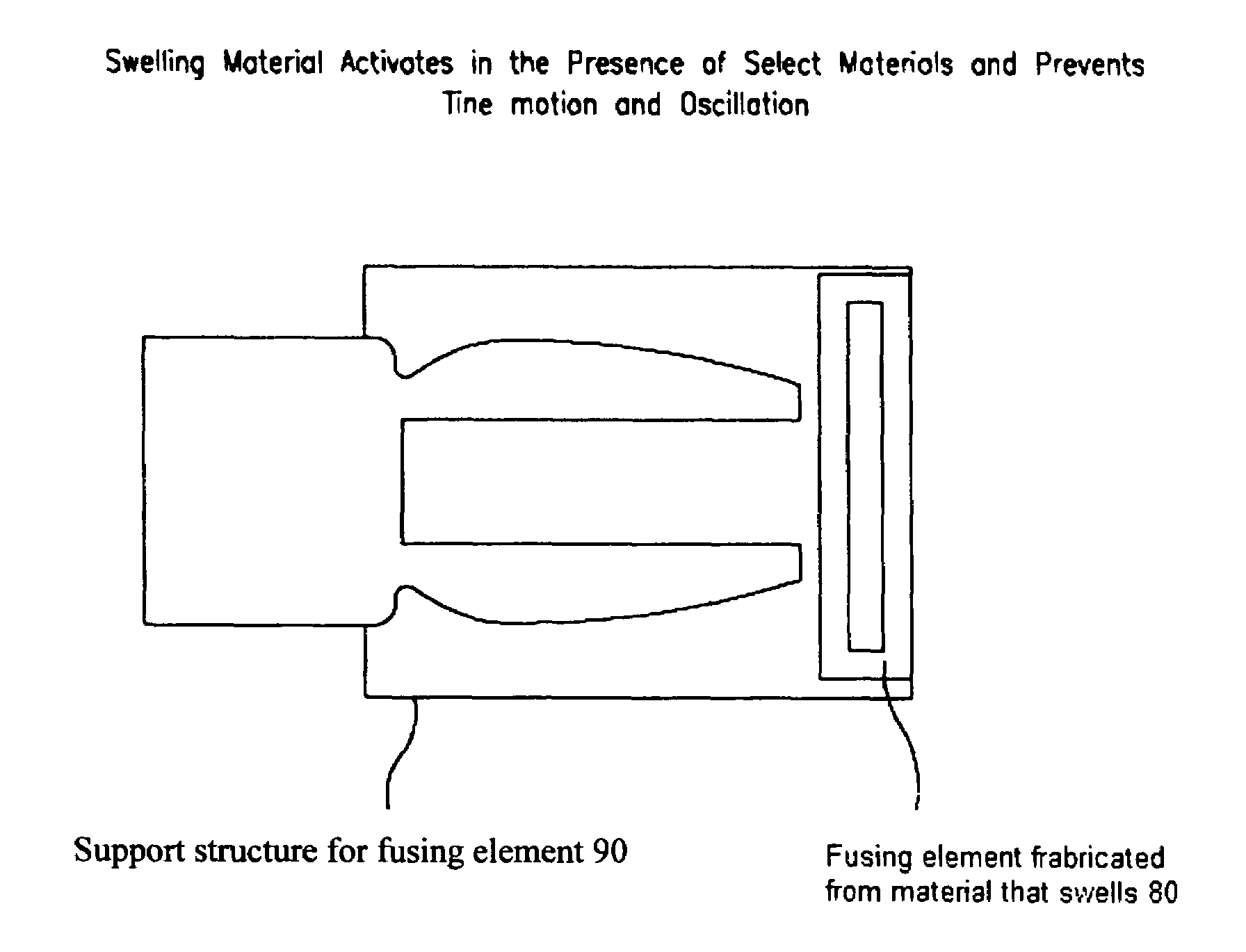
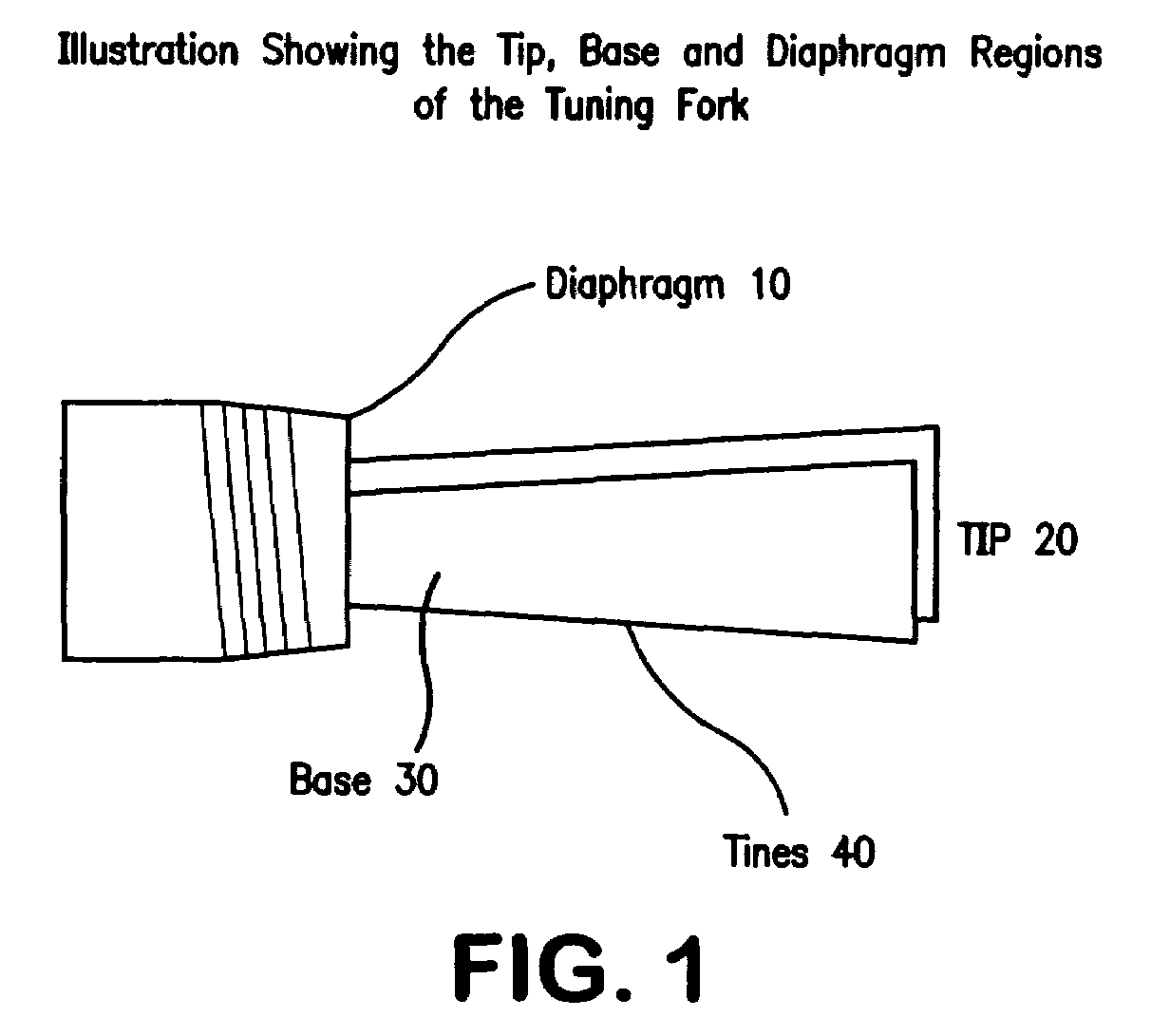
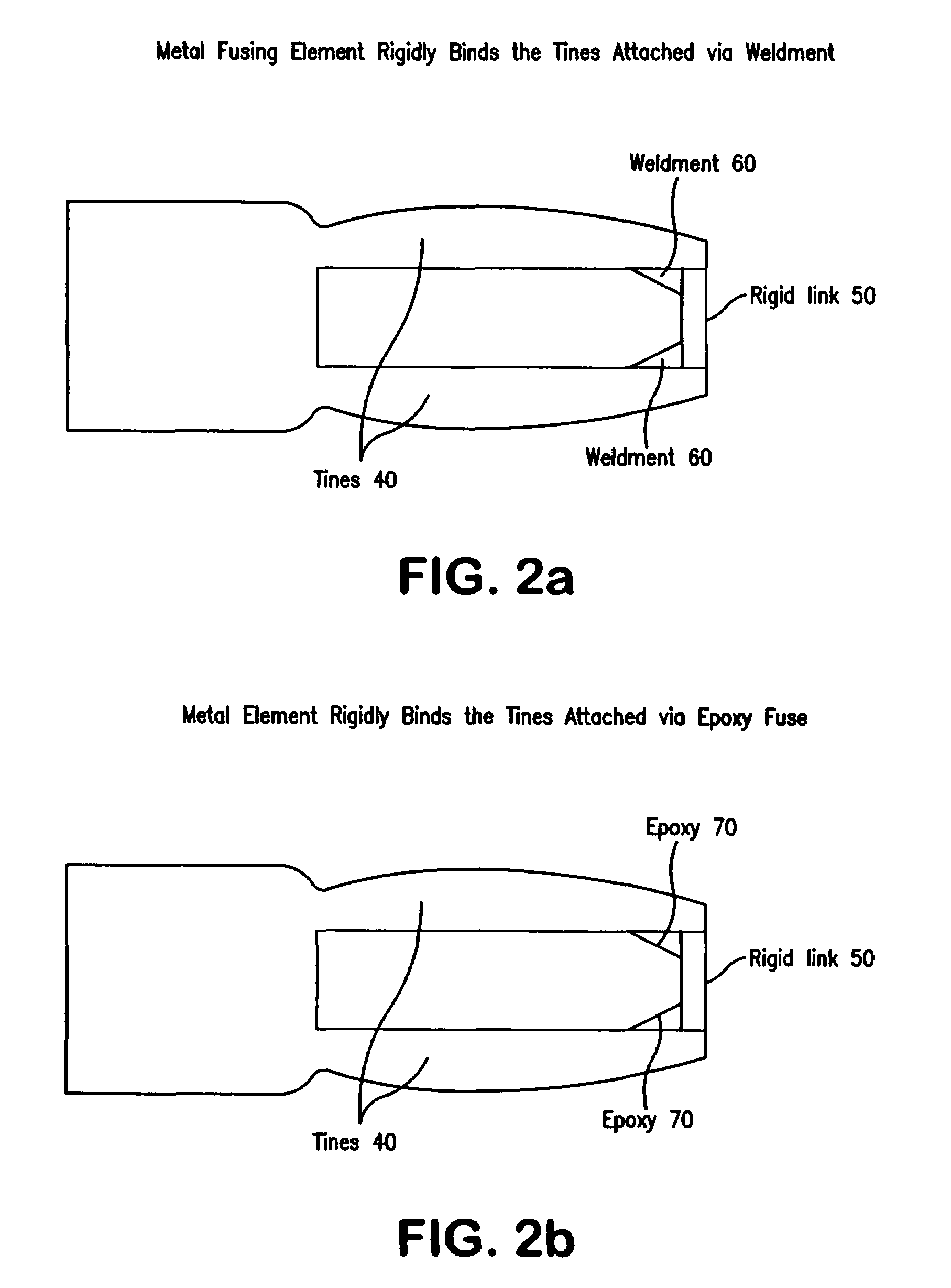
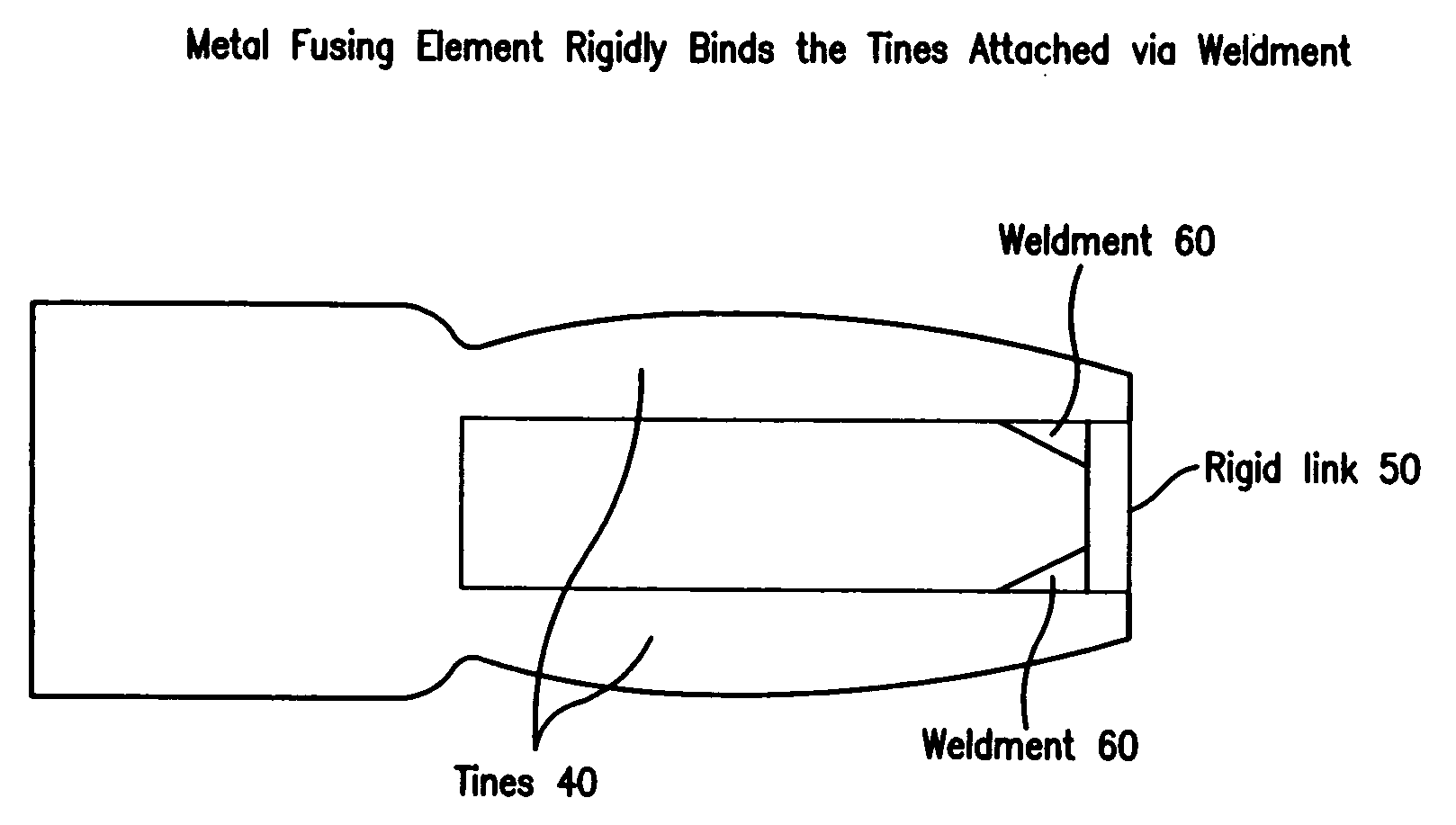
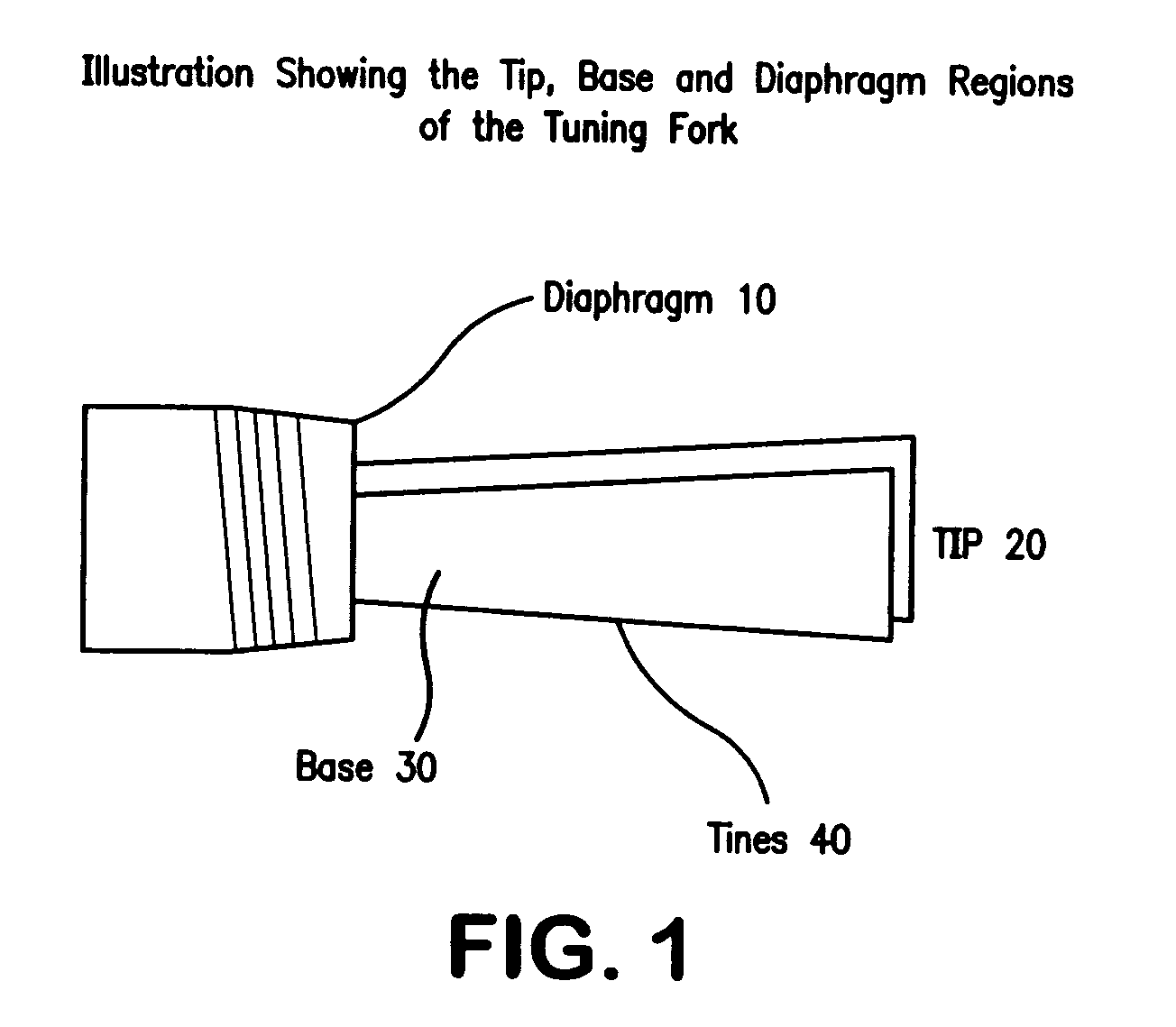
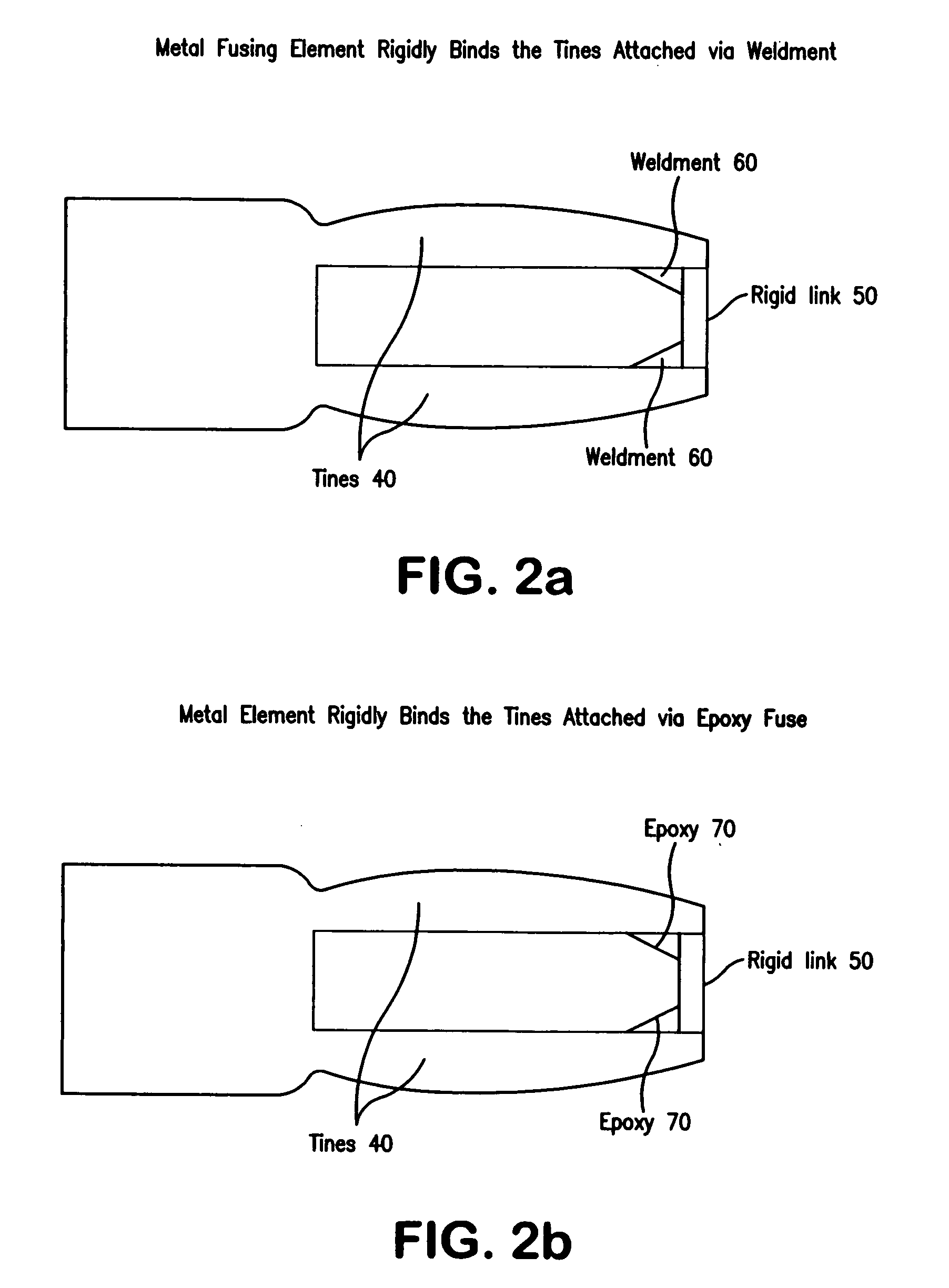
The present invention is a tuning fork oscillator for detection and measurement of corrosive or foreign materials. The elements include a means for mechanical excitation, and a mechanical oscillator, wherein said mechanical oscillator has a resonant frequency, f, and a quality factor, Q. A fuse fixed to the oscillator to change oscillator amplitude to or from essentially zero to resonance amplitude. In a preferred embodiment, the tuning fork has one region compatible with the service fluid and the other region is incompatible with the service fluid or other contaminant. The sensor alarms when a measured amount of the incompatible material has been removed or deposited.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Compositions comprising cyclodextrin
A stable composition for removing unwanted molecules from a surface comprises functionally-available cyclodextrin, cyclodextrin-compatible surfactant, and cyclodextrin-incompatible surfactant. The compositions are suitable for capturing unwanted molecules from inanimate surfaces, including fabrics, including carpets, and hard surfaces including countertops, dishes, floors, garbage cans, ceilings, walls, carpet padding, air filters, and the like, and from animate surfaces, including skin, hair, and the like. The compositions can further comprise other cyclodextrin-compatible and -incompatible materials and other optional ingredients.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Mechanical oscillator activated or deactivated by a predetermined condition
InactiveUS7721605B2Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTuning forkWorking fluid
The present invention is a mechanical oscillator for detection and measurement of corrosive foreign materials. The elements include a mechanical oscillator that is mechanically excited, wherein the mechanical oscillator has a resonant frequency, f, and a quality factor, Q. A fuse fixed to the oscillator to change oscillator amplitude to and from essentially zero to resonance amplitude. In a preferred embodiment, the mechanical oscillator has the shape of a tuning fork where one region is compatible with the service fluid and the other region is incompatible with the service fluid or other contaminant. The sensor alarms when a measured amount of the incompatible material has been removed or the physical strength of the material has been compromised.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Toothpaste tube
ActiveUS7044333B2Improve sealingPortable flexible containersFlexible containersToothpasteCapital cost
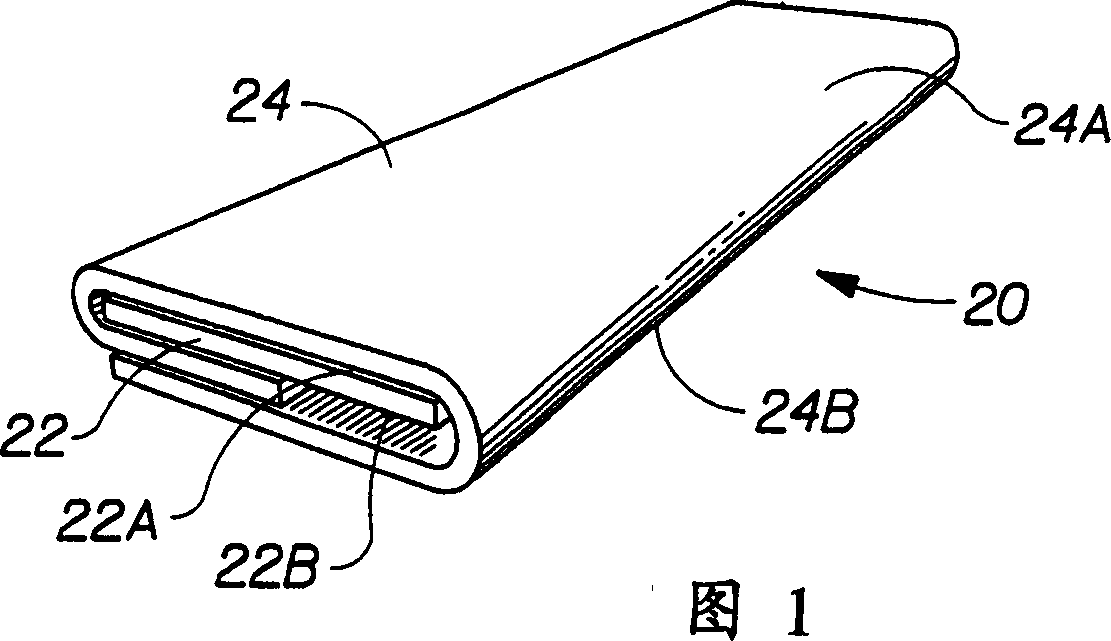
The present invention relates to plural compartment assemblies in which materials are stored in at least two separate compartments until the compartments are opened for use. More particularly, the invention relates to a dispensing tube whereby the utilization of a novel insert, a conventional dispensing tube can be divided into separate and discrete compartments at a low capital cost. The resulting dispensing assembly provides for dispensing more than one material from the same tube and even more particularly co-dispensing predetermined proportions of incompatible materials simultaneously and effectively.
Owner:CHURCH & DWIGHT CO INC
Rare gas-halogen excimer lasers with baffles
ActiveUS20050175055A1Reduce pollutionExtended service lifeActive medium materialGas laser constructional detailsNoble gasLaser beams
An excimer laser comprises a gas chamber, electrodes for creating rare gas / halide molecules that disassociate and produce optical emission, and reflective surfaces that form an optical resonant cavity. The excimer laser further comprises flow control surfaces that define gas flow paths and that control the flow of gas within the chamber. Preferably such flow control surfaces direct the gases away from the laser optics. More preferably, the flow control surfaces shield the path of the laser beam, at least in the proximity of the laser optics, from contaminants in the gases. Less contaminants yields less contamination of the laser optics. As a result, the laser device becomes more reliable and useful over longer periods of time. In addition, the laser gases are preferably exposed only to compatible materials that react with the laser gases to produce stable reaction products having a low vapor pressure, so as to reduce contamination of the gases and the optics. High-purity nickel is preferred for components that are electrically conductive, and high-purity alumina is preferred for components that are non-electrically conductive. Preferably, incompatible materials are not used.
Owner:MELA SCIENCES
Mechanical oscillator activated or deactivated by a predetermined condition
InactiveUS20080314150A1Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTuning forkForeign matter
The present invention is a mechanical oscillator for detection and measurement of corrosive or foreign materials. The elements include a means for mechanical excitation, and a mechanical oscillator, wherein said mechanical oscillator has a resonant frequency, f, and a quality factor, Q. A fuse fixed to the oscillator to change oscillator amplitude to or from essentially zero to resonance amplitude. In a preferred embodiment, the mechanical oscillator has the shape of a tuning fork where one region is compatible with the service fluid and the other region is incompatible with the service fluid or other contaminant. The sensor alarms when a measured amount of the incompatible material has been removed or the physical strength of the material has been compromised.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Particles and particle gas saturated solution processes for making same
InactiveUS20130259913A1Material nanotechnologyCosmetic preparationsIncompatible MaterialSolution processed
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Polymer member having incompatible material maldistributed polymer layer and surface uneven tape or sheet made of the polymer member
InactiveCN101466540AExcellent adhesionAdhesive articlesSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer scienceTotal thickness
Disclosed is a polymer article having a multilayer structure including a polymer layer and a monomer-absorptive layer that is arranged on the polymer layer and is capable of absorbing at least one of monomer components constituting the polymer. The polymer layer is a polymer layer containing an unevenly distributed immiscible material that is immiscible with the polymer and is enriched at an interface, or in the vicinity thereof, opposite to the monomer-absorptive layer. The polymer article preferably further includes a cover film arranged on the polymer layer on a side opposite to the monomer-absorptive layer. The vicinity of the interface opposite to the monomer-absorptive layer is preferably a region ranging from the interface opposite to the monomer-absorptive layer in a thickness direction to 50% or less of the total thickness of the polymer layer.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Connecting device and connecting method of metal-and-plastic mixed thin-wall structure
PendingCN107433389AReduce weightAchieve energy saving and emission reductionLaser beam welding apparatusElectricityEngineering
The invention discloses a connecting device of a metal-and-plastic mixed thin-wall structure. The device comprises a femtosecond laser device which can emit laser beams, a four-axis movement platform which can conduct planar motion, a fixture and a computer, wherein the fixture is arranged at the top surface of the four-axis movement platform and can apply clamping acting force to edges of a metal workpiece and / or a transparent plastic workpiece, the computer is electrically connected with the femtosecond laser device and the four-axis movement platform separately, and the femtosecond laser device emits the laser beams to make the laser beams irradiate an irradiating surface of the workpiece clamped by the fixture. The invention further provides a connecting method of utilizing the connecting device of the metal-and-plastic mixed thin-wall structure. Compared with the prior art, the technical problem of welding of hetero-incompatible materials of plastic and metal is solved, and the work reliability and work efficiency of laser connection of metal and plastic are improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Method for improving hybridization success rate of sweet potato and incompatible material
InactiveCN104982328AIncrease success rateEasy to operatePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsMaterials preparationGrowth plant
The invention discloses a method for improving the hybridization success rate of sweet potato and an incompatible material. The method comprises the following steps: performing material preparation, hybridization treatment and plant growth regulator treatment; smearing the growth regulator on female parent stigmas and ovaries thereof after pollination, then continuing cultivation, and performing young embryo rescue and seedling cultivation. The method disclosed by the invention is higher in operability and high in practicability, the success rate of sweet potato inter-species incompatible hybridization can be obviously improved, and the method is also suitable for sweet potato intra-species incompatible hybridization.
Owner:SAAS BIOTECH & NUCLEAR TECH RES INST
Method to control the environment in a laser path
InactiveUS20140346157A1Low costIncrease heating capacitySurveyConstructionsLaser lightLighting spectrum
A method of controlling the environment intermediate a laser head and a targeted portion of a bore wall to remove solid material at the wall includes running an umbilical into the bore to position the head, irradiating the targeted portion of the wall using laser light, sensing a light spectrum resulting from irradiation of the solid material, comparing the sensed light spectrum to a light spectrum corresponding to favorable irradiation of the solid material, adjusting the rate of introduction of a laser-compatible material to displace laser-incompatible materials from the laser light path to obtain more favorable irradiation of the solid material. The method enable the conservation of the source of the laser-compatible material or improved irradiation of the solid material for solid removal by using the laser to cut, heat, fracture or melt the solid material.
Owner:SLD ENHANCED RECOVERY
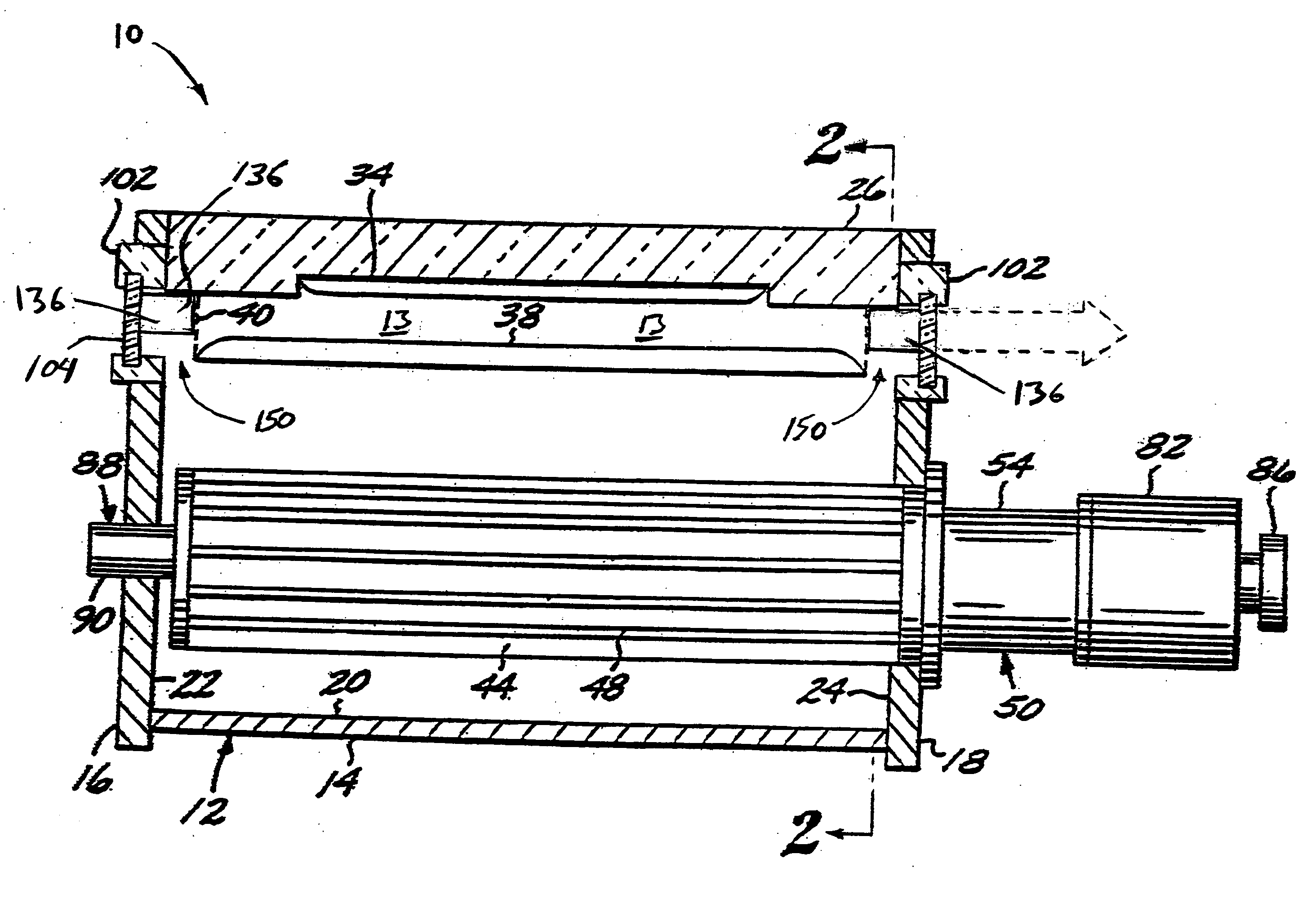
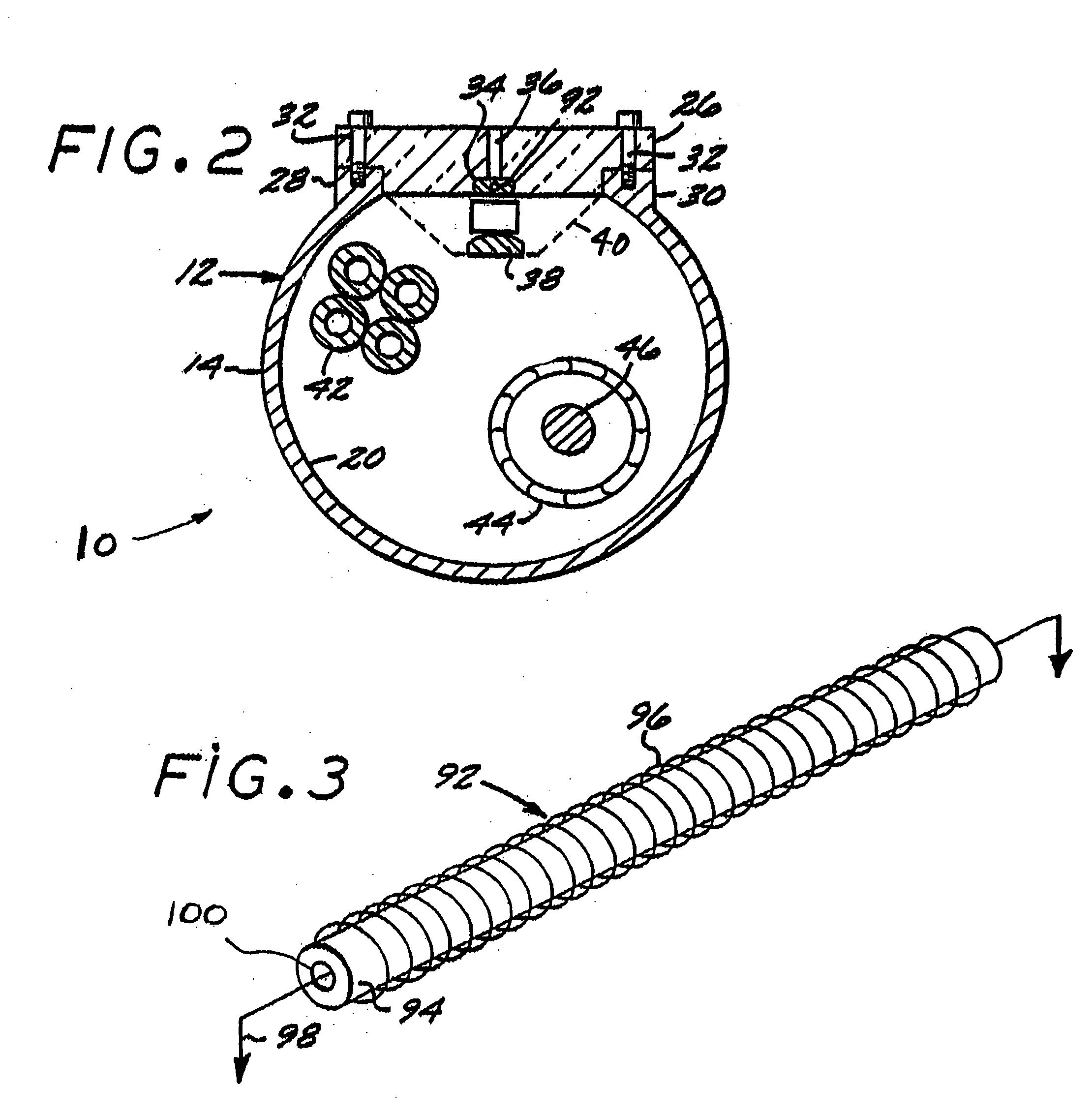
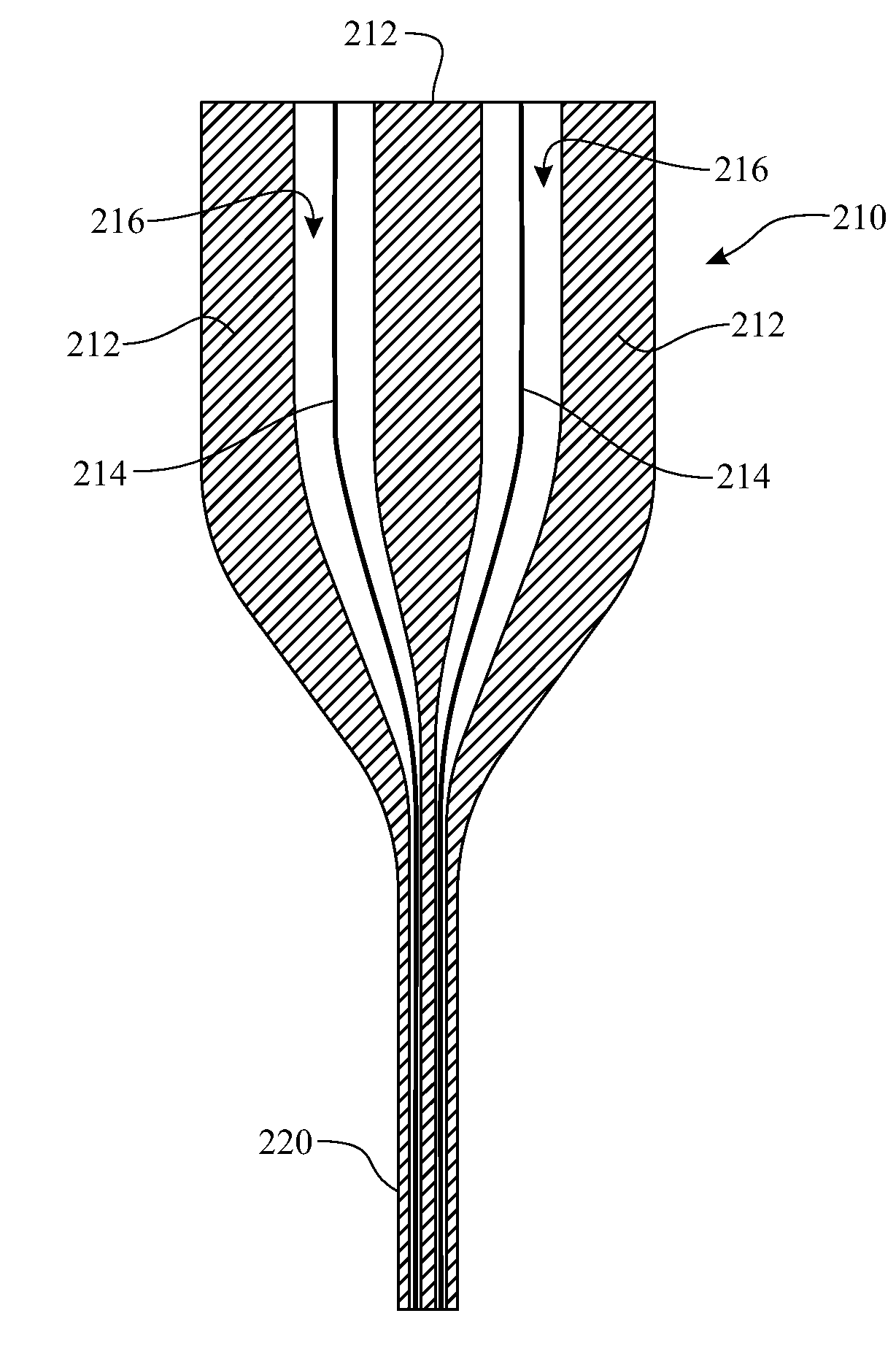
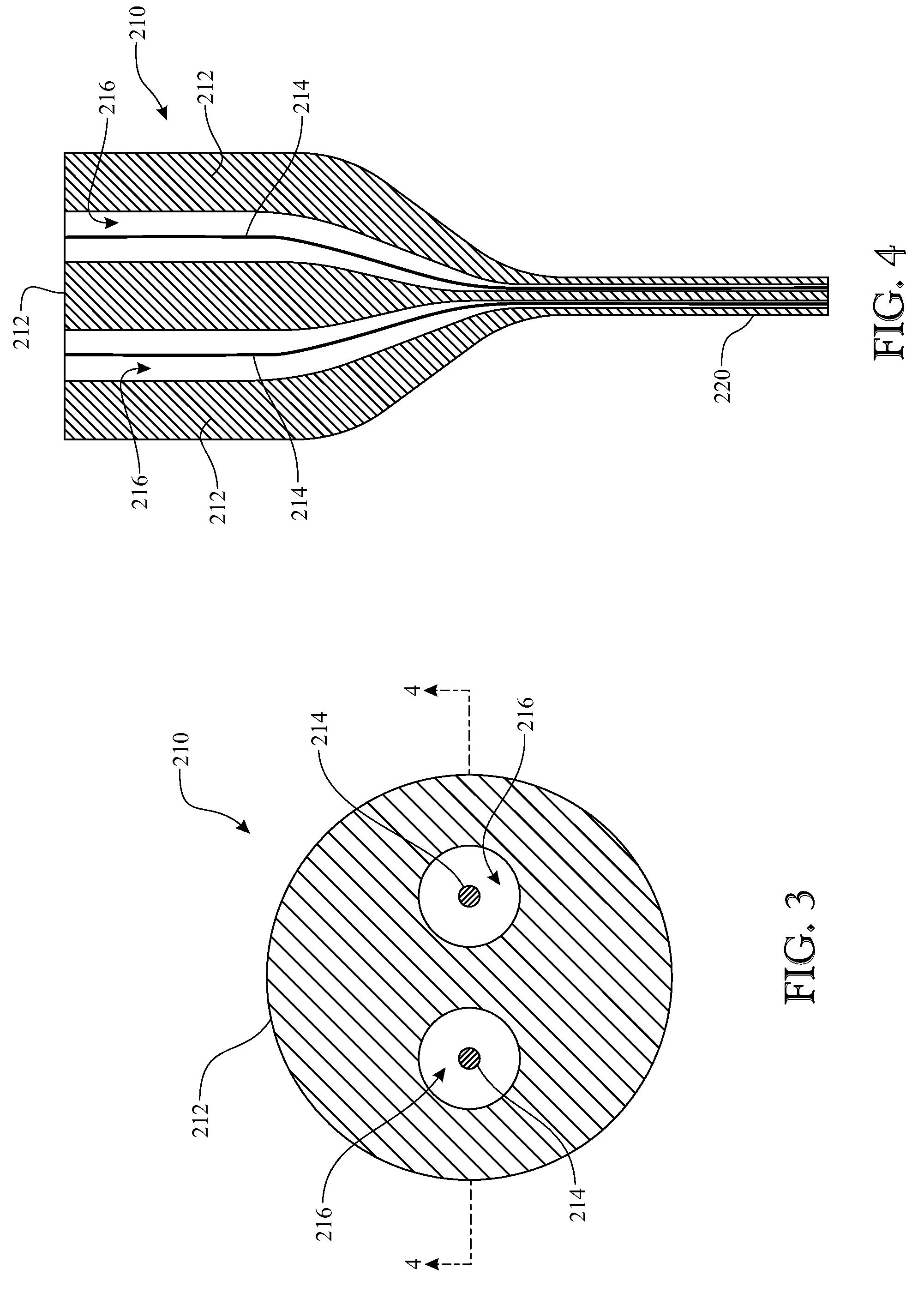
Method of co-drawing hybrid incompatible materials
A method of drawing different materials includes forming a first material into a preform body defining at least one channel extending therethrough having a first cross-sectional area. A first element formed of a second material is inserted into the channel and with the preform body creates a preform assembly. The first element has a cross-sectional area that is less than the cross-sectional area of the channel, and the second material has a higher melting temperature than the first material. The preform assembly is heated so that the first material softens and the preform assembly is drawn so that the preform body deforms at a first deformation rate to a smaller cross-sectional area and the first element substantially maintains a constant cross-sectional area throughout the drawing process. Upon completion of the drawing step, the cross-sectional area of the channel is equivalent to the cross-sectional area of the first element.
Owner:FLEX OPTRONIX TECH
Process for producing a high stability desulfurized heavy oils stream
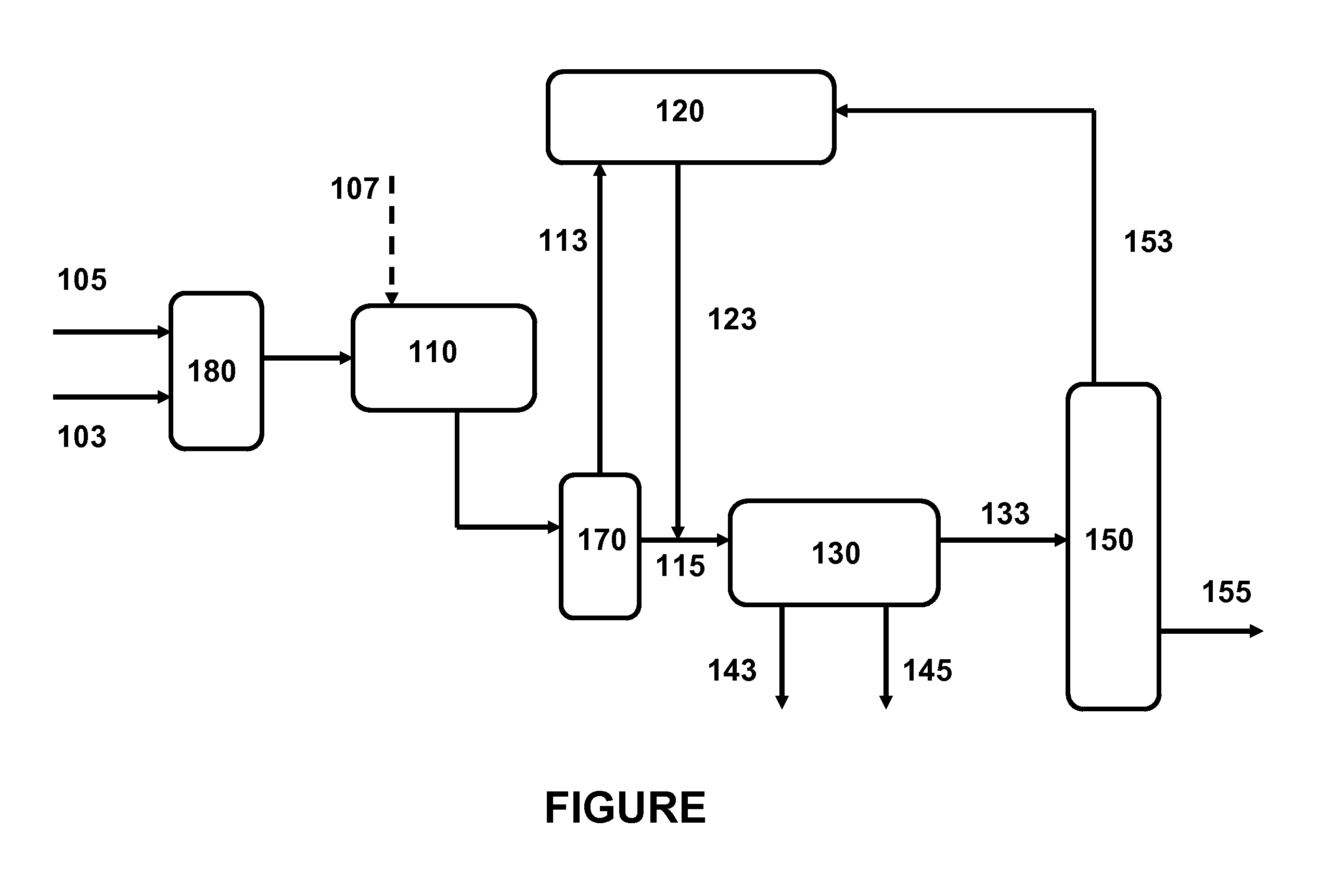
InactiveUS8613852B2Reduce the numberThermal non-catalytic crackingRefining by water treatmentSolubilityFuel oil
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Process For Joining Incompatible Materials And Materials Formed Thereby
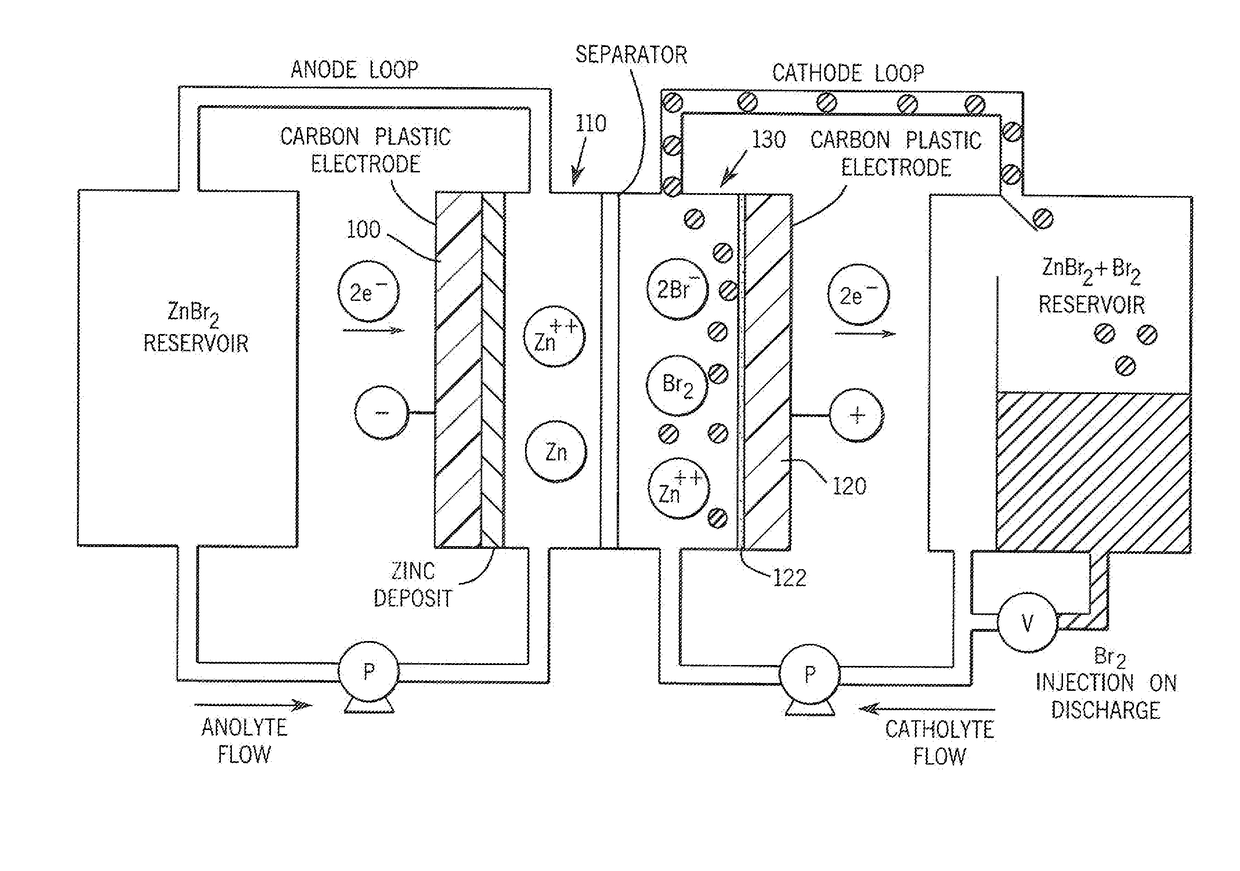
A method for joining incompatible materials is provided that includes the steps of welding a first component formed of a thermoplastic material and a second component of a porous material to one another to form a subassembly and optionally molding a third component around the subassembly. The method enables the incompatible first component and the third component to be joined to one another, such as to form an electrolyte battery flow frame around an ion exchange material and / or microporous separator material in order to form a separator for an electrolyte flow battery.
Owner:FAITH TECH INC
Tuning fork oscillator activated or deactivated by a predetermined condition
InactiveUS20130122593A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceTuning forkEngineering
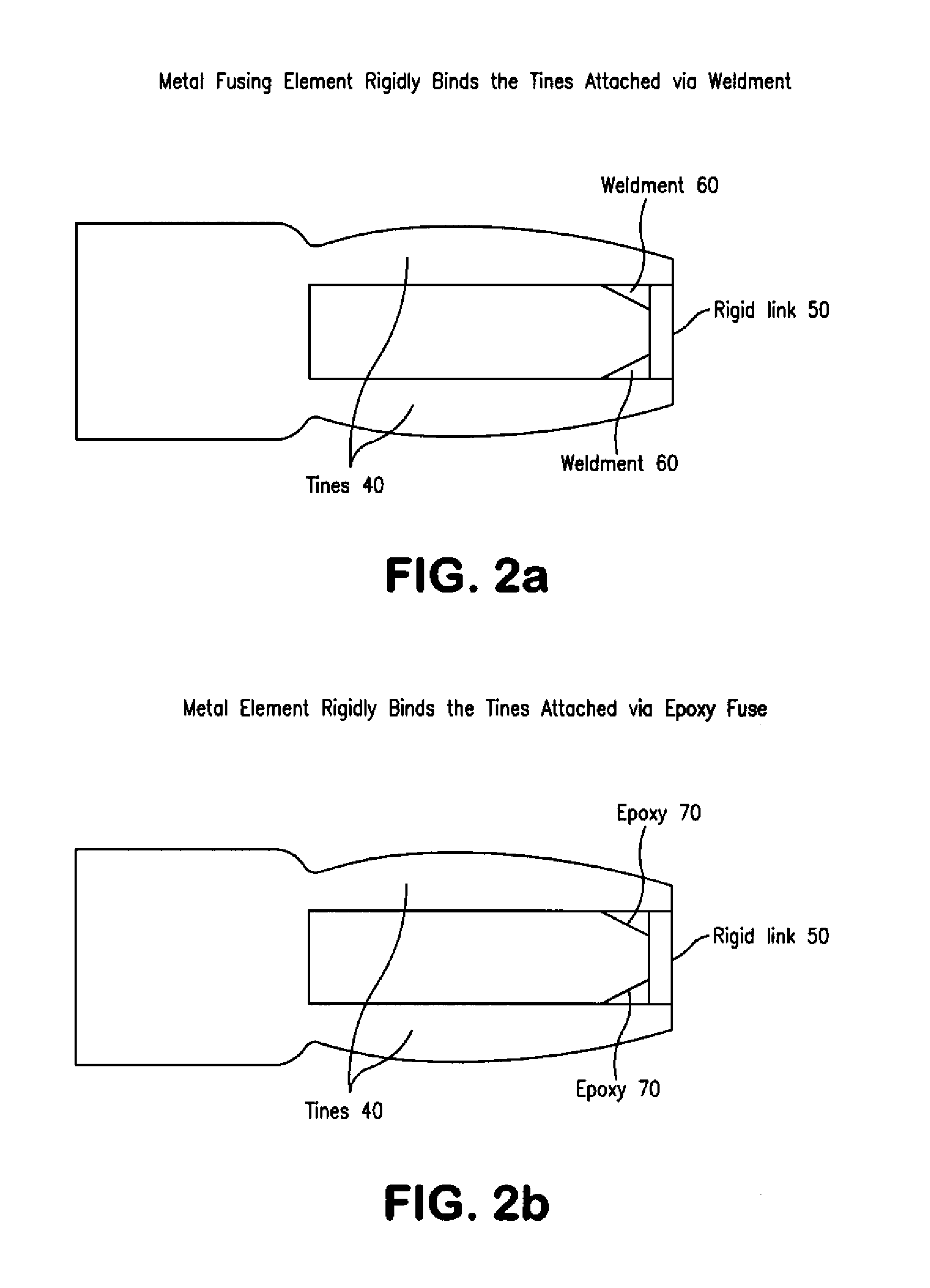
A sensor for detection and measurement of incompatible (corrosive or foreign) materials in a fluid medium. The sensor includes a tuning fork mounted on a diaphragm with tines having an amplitude and a resonant frequency. The sensor alarms when a measured amount of the incompatible material has been deposited on the sensor to form a fusing element on the tines which causes vibration of the tines to cease.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Compositions comprising cyclodextrin
A stable composition for removing unwanted molecules from a surface comprises functionally-available cyclodextrin, cyclodextrin-compatible surfactant, and cyclodextrin-incompatible surfactant. The compositions are suitable for capturing unwanted molecules from inanimate surfaces, including fabrics, including carpets, and hard surfaces including countertops, dishes, floors, garbage cans, ceilings, walls, carpet padding, air filters, and the like, and from animate surfaces, including skin, hair, and the like. The compositions can further comprise other cyclodextrin-compatible and -incompatible materials and other optional ingredients.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Process for producing a high stability desulfurized heavy oils stream
InactiveUS20110147271A1Reduce the numberThermal non-catalytic crackingRefining by water treatmentSolubilityFuel oil
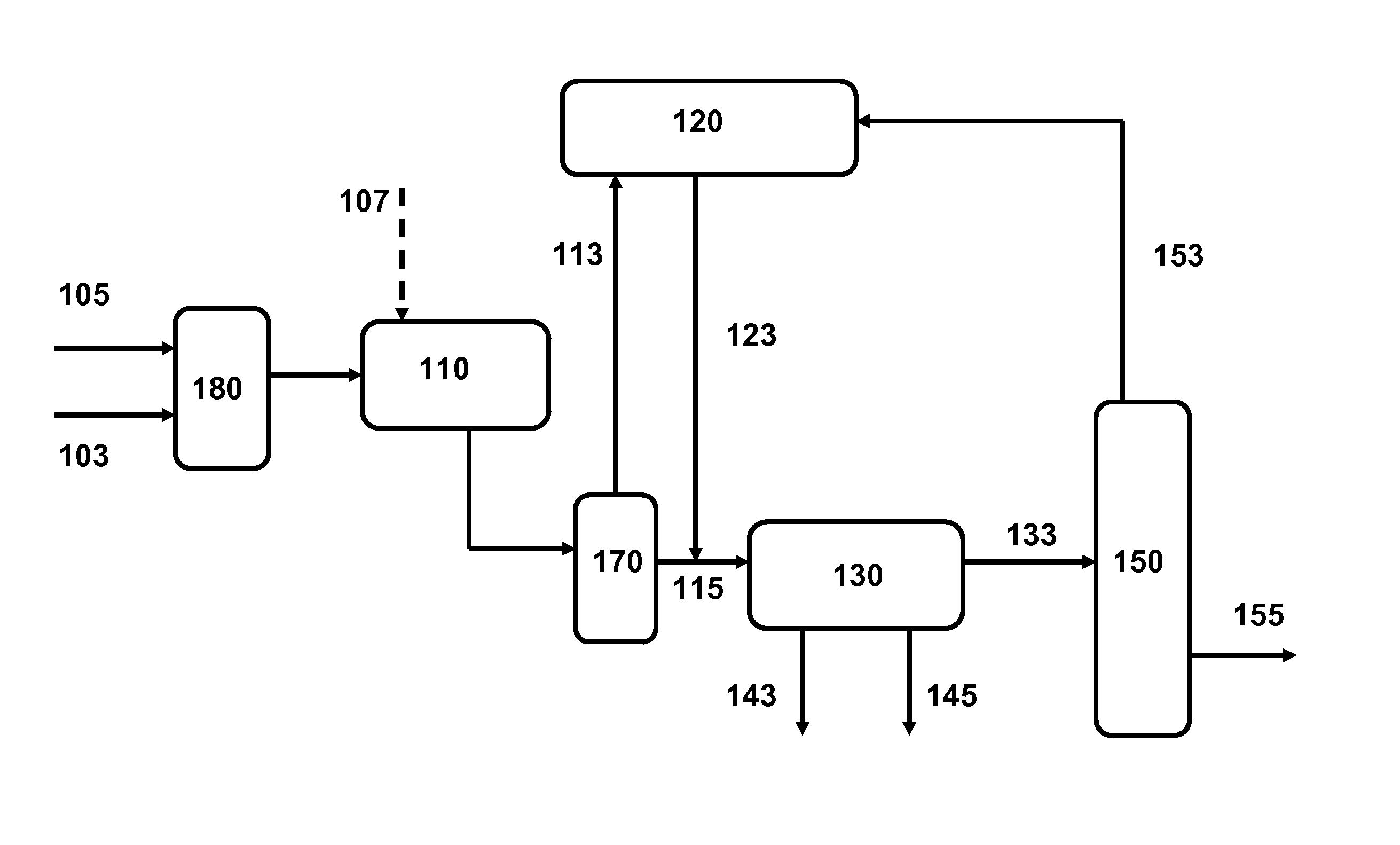
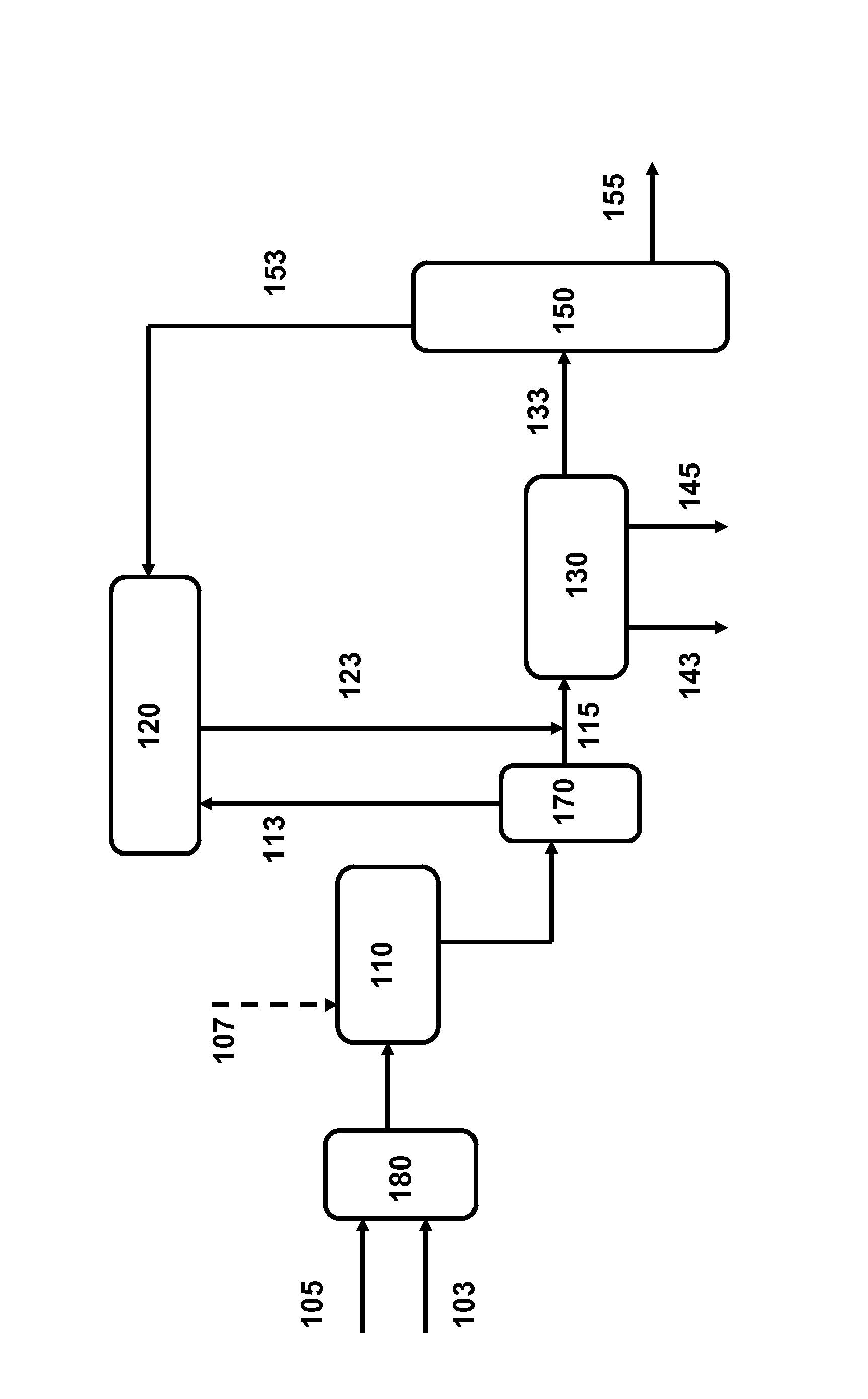
Self-compatible heavy oil streams are produced from converted and / or desulfurized fractions. In a preferred embodiment, an incompatibility stream is added to the converted and / or desulfurized stream to reduce the solubility number of the stream. After using a water wash to remove incompatible material, a lighter fraction is removed from the stream to increase the solubility number.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Breeding method for the self-incompatible line of brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis (L.) makino var. rosularis tsen et lee
ActiveCN104472343AOvercoming technical problems in breeding selectionReduce blindnessPlant genotype modificationBrassicaSelfing
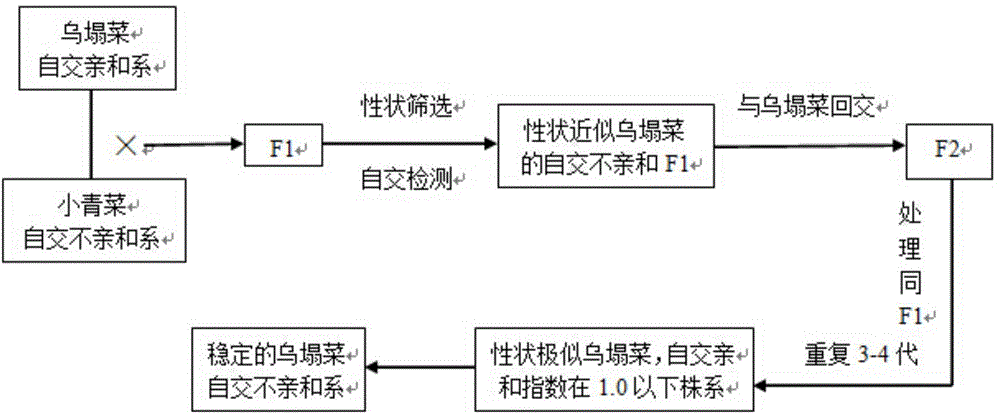
The invention discloses a breeding method for the self-incompatible line of brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis (L.) makino var. rosularis tsen et lee. The breeding method comprises the steps of by adopting the self-incompatible line of the brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis (L.) makino var. rosularis tsen et lee as a recurrent parent, and adopting the self-incompatible line of brassica chinensis as a transferring-in source, and carrying out back cross on filial generations and the recurrent parent for a plurality of generations so as to obtain the stable self-incompatible line of the brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis (L.) makino var. rosularis tsen et lee. The breeding method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the generations are screened by utilizing the brassica chinensis which has extremely-close genetic relationship with the brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis (L.) makino var. rosularis tsen et lee and has rich self-incompatible materials as the transferring-in source of the self-incompatible line and combining selfing segregation, so that the purpose of breeding the self-incompatible line of the brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis (L.) makino var. rosularis tsen et lee in a high-efficiency and fast manner is achieved; compared with the conventional method, the breeding method has the advantages that the working blindness is greatly alleviated, the time and the labor are saved, simultaneously the parent-material source is wide and the technical problem of difficult variety breeding for the self-incompatible line of the brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis (L.) makino var. rosularis tsen et lee is overcome.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
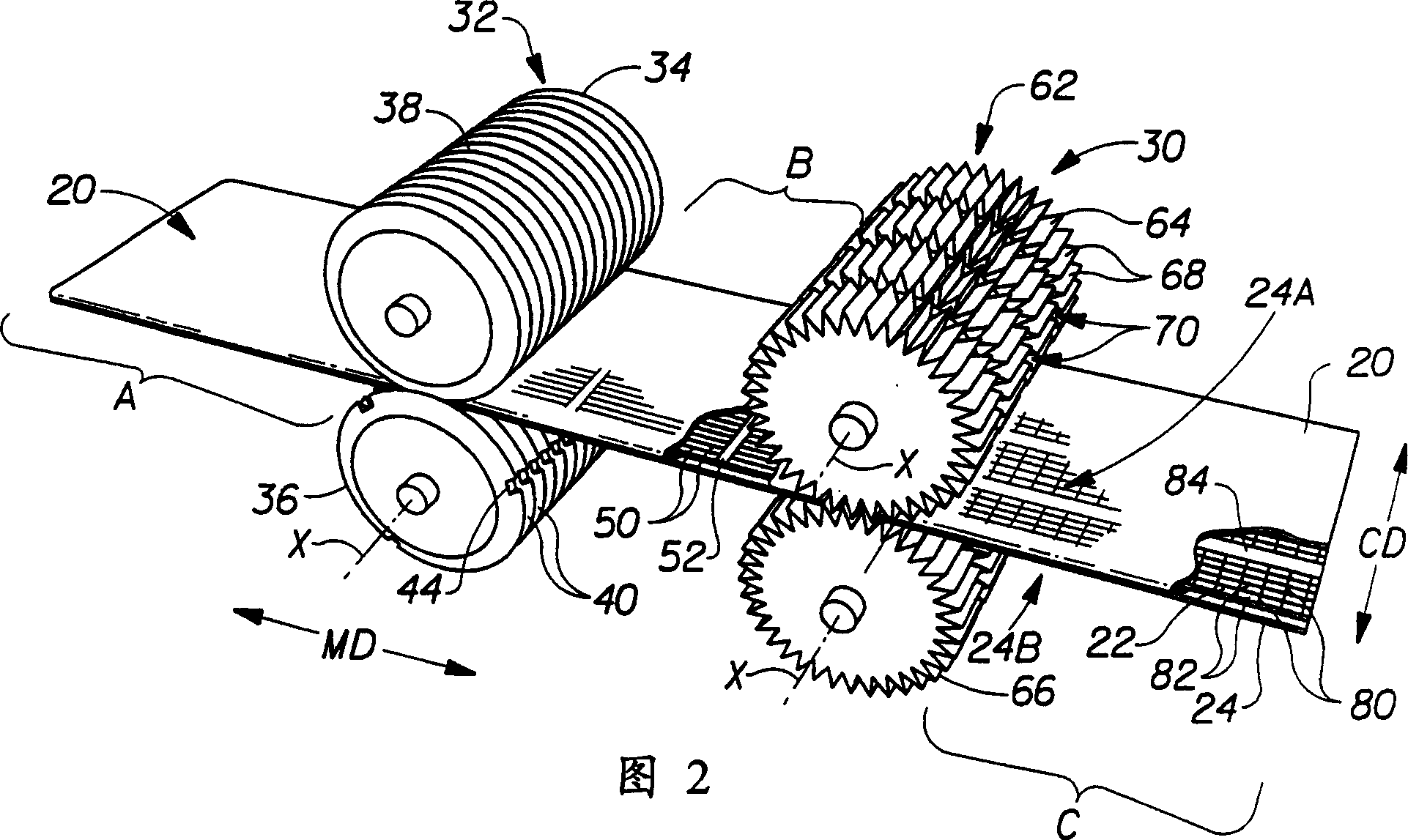
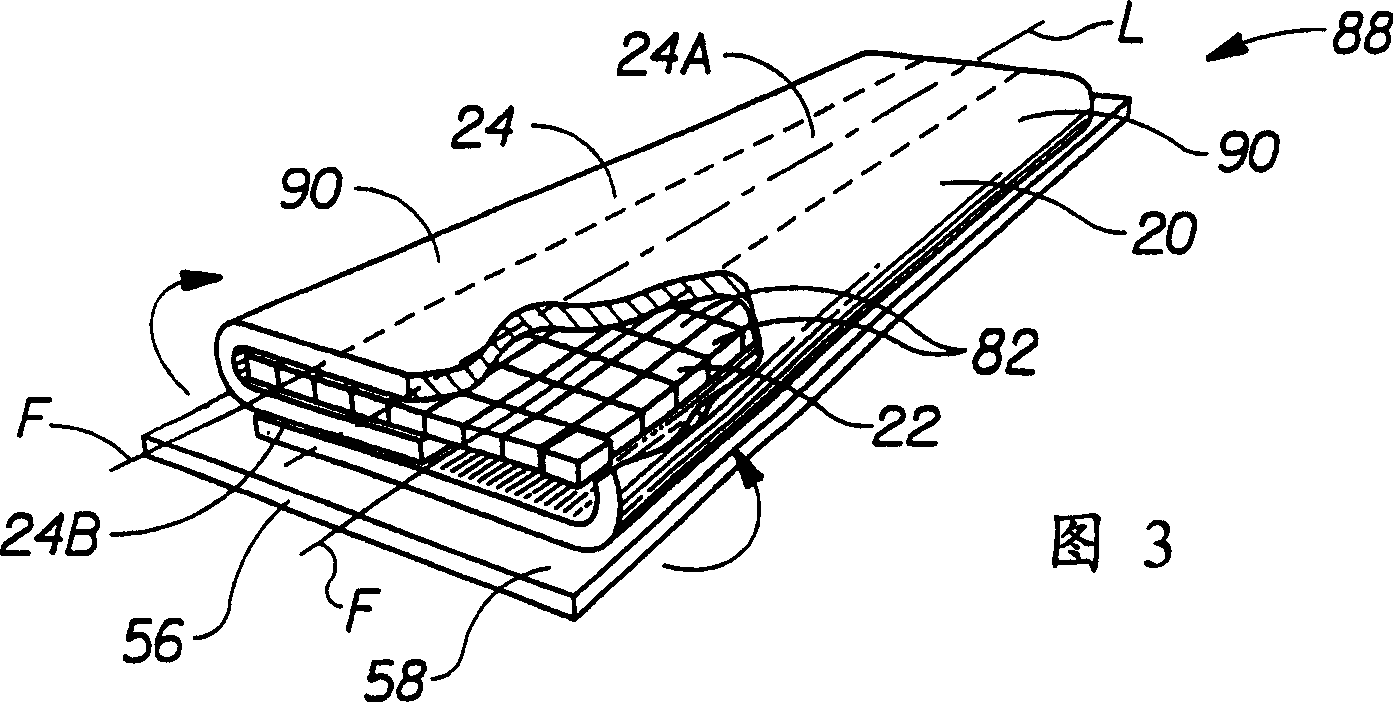
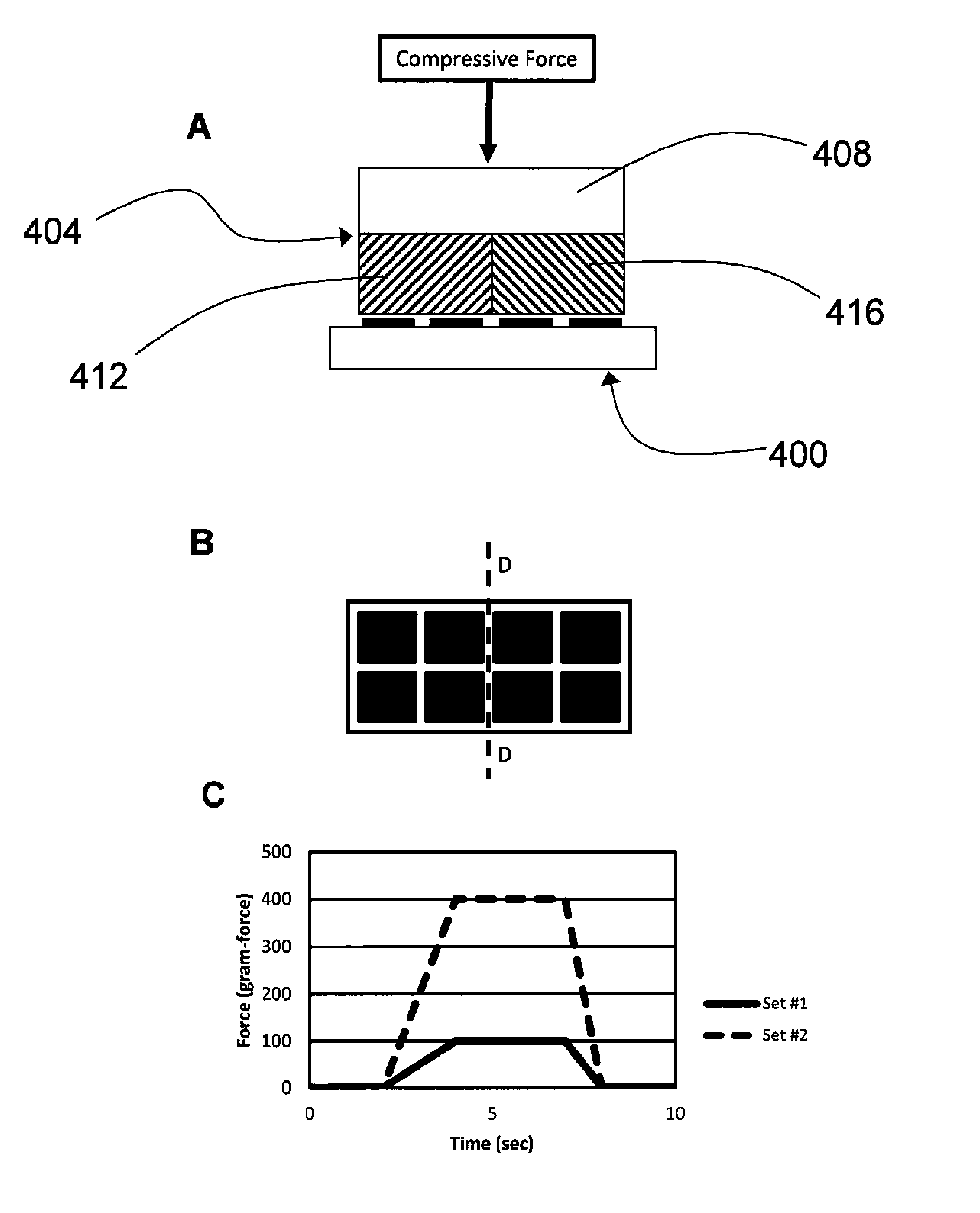
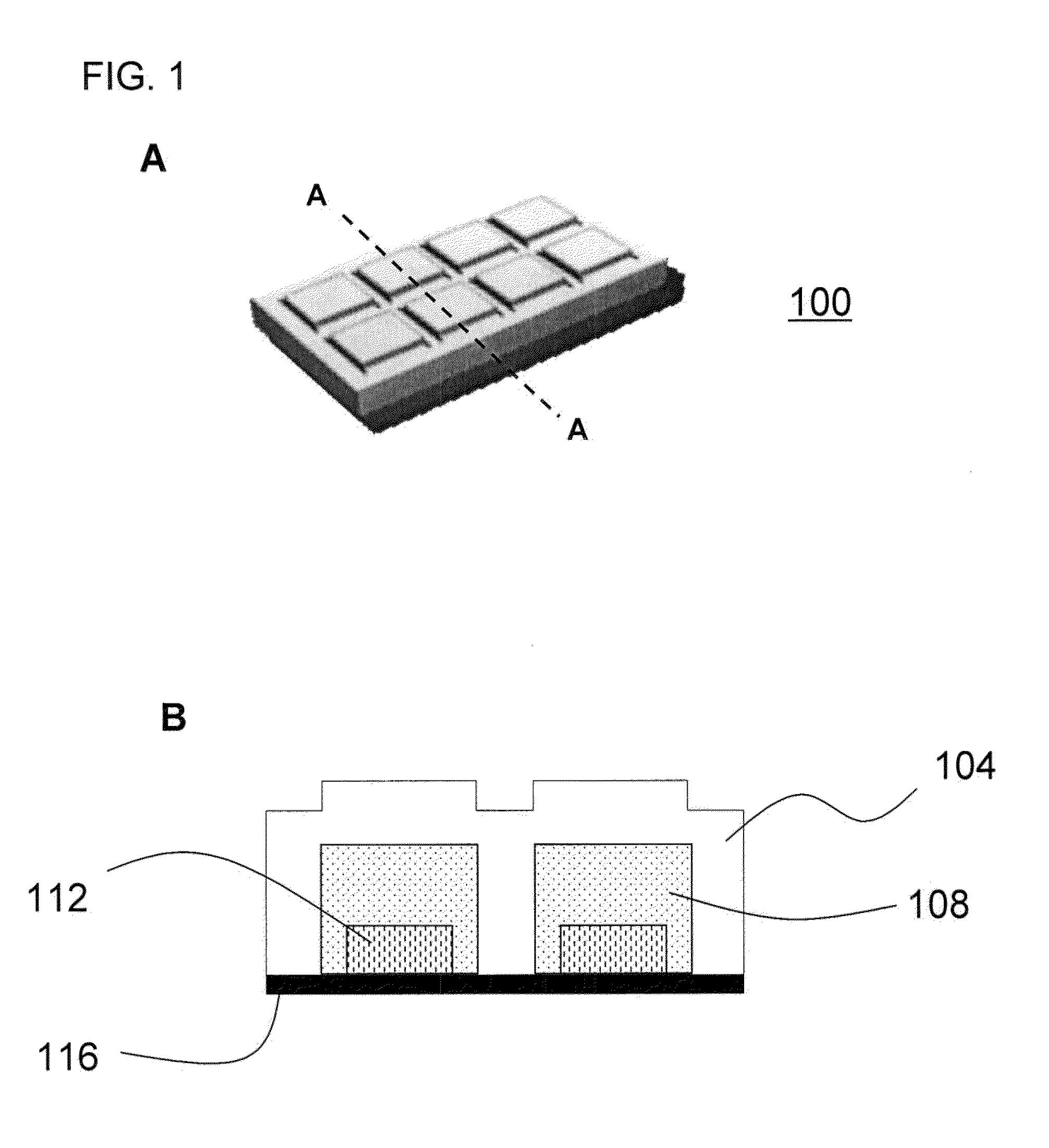
Methods of bonding materials, especially materials used in absorbent articles
Methods of bonding materials used in the manufacture of articles, including, but not limited to, absorbent articles such as sanitary napkins, pantiliners, tampons, absorbent interlabial devices, diapers, incontinence devices, wipes, and the like are disclosed. There are numerous aspects of the disclosed methods. In one aspect, the method involves bonding through incompatible materials during the process of making a composite structure comprising several materials. In another aspect, improvements are made that allow the method to be used to bond through relatively thick materials (e.g., materials having a thickness of greater than or equal to about 4 mm). In another aspect, the methods are provided with the ability to create a virtually unlimited number of bonding patterns in the materials to be bonded. In still another aspect, the methods of bonding utilize a compression step to improve bond formation. In still another aspect, methods of bonding that utilize a step of slitting a material through which the bonds are made are disclosed.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
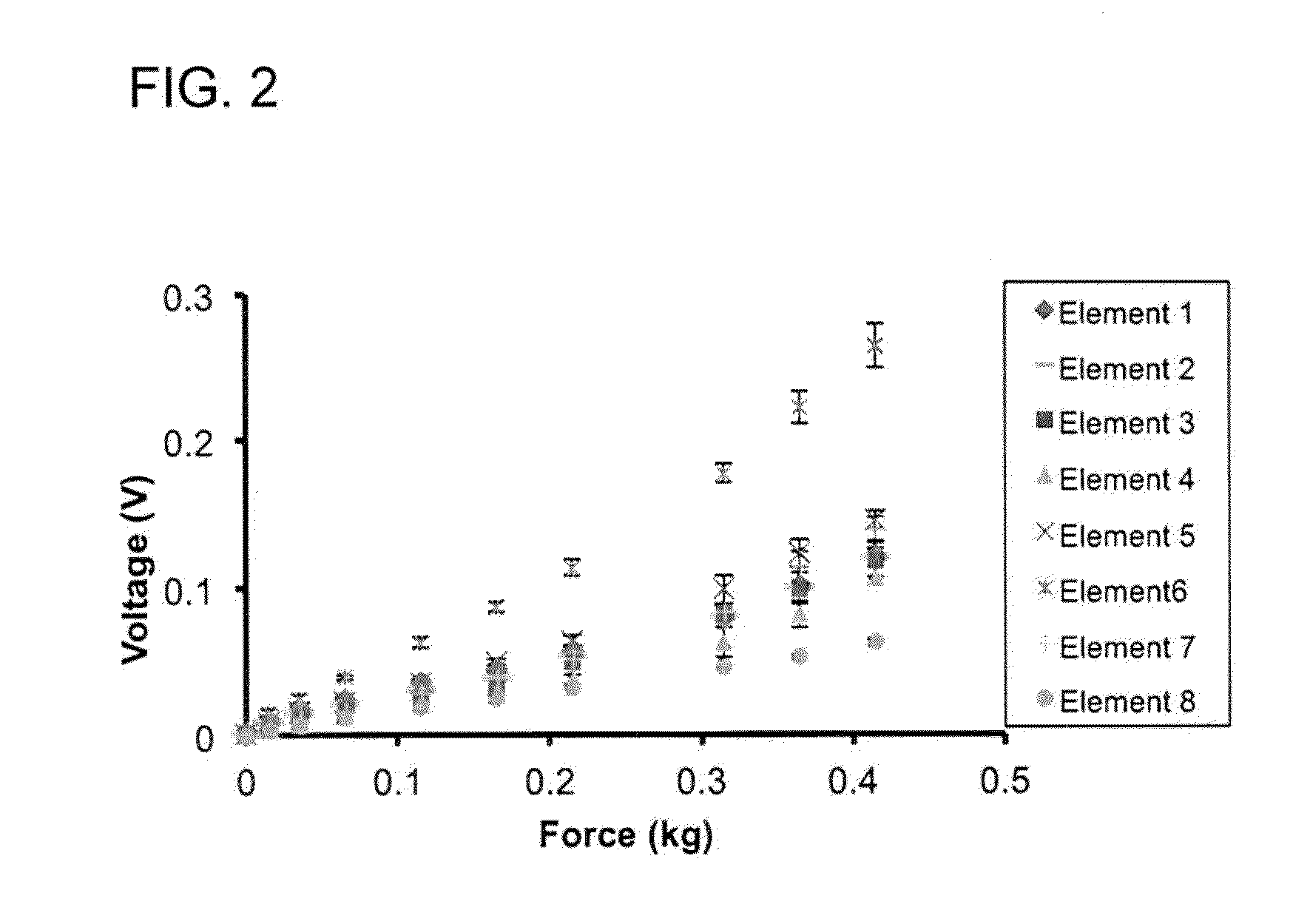
Novel Tactile Feedback System for Robotic Surgery
ActiveUS20130085511A1Accurate informationMinimal damageDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsElastomerSensor array
Apparatuses and methods for the haptic sensation of forces at a remote location. Groups of MEMS-based pressure sensors are combined into sensor arrays. In some embodiments, the pressure sensors are encased in silicone or other elastomeric substance to allow for routine use in the aqueous environment of the body. The sensor arrays may be housed in a No-compatible material (e.g., stainless steel, plastic) and may be attached to a printed circuit board to allow the electrical signal generated by the sensors to be communicated to a user. The sensor arrays may be used with faceplates that directly interact with the target tissue or object. The faceplates may be rough, smooth, serrated, or any other texture. The present apparatuses and methods are particularly well suited for robotic surgery and may be used in wherever haptic sensing of forces at a remote location is desired.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Stabilization of incompatible materials by macromolecules
InactiveUS20030036590A1Composition is stableEnhanced interactionIn situ pavingsBuilding insulationsFlocculationPolyolefin
A stable dispersion of polyethylene and other polyolefins in a continuous bituminous phase is provided by dissolving macromolecular material into the bitumen to create a potential energy barrier to coalescence and flocculation of the polymer dispersion.
Owner:LIANG ZHI ZHONG
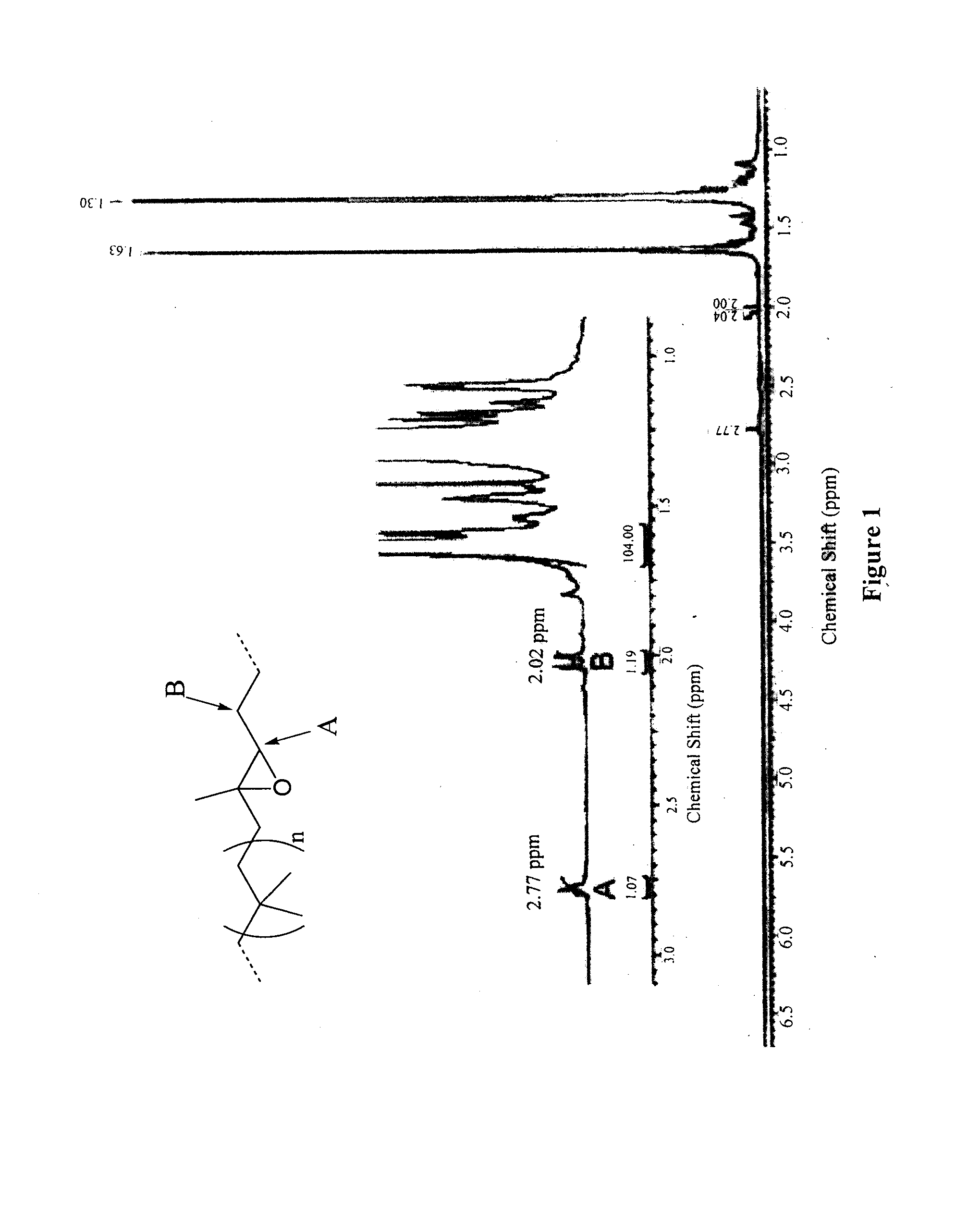
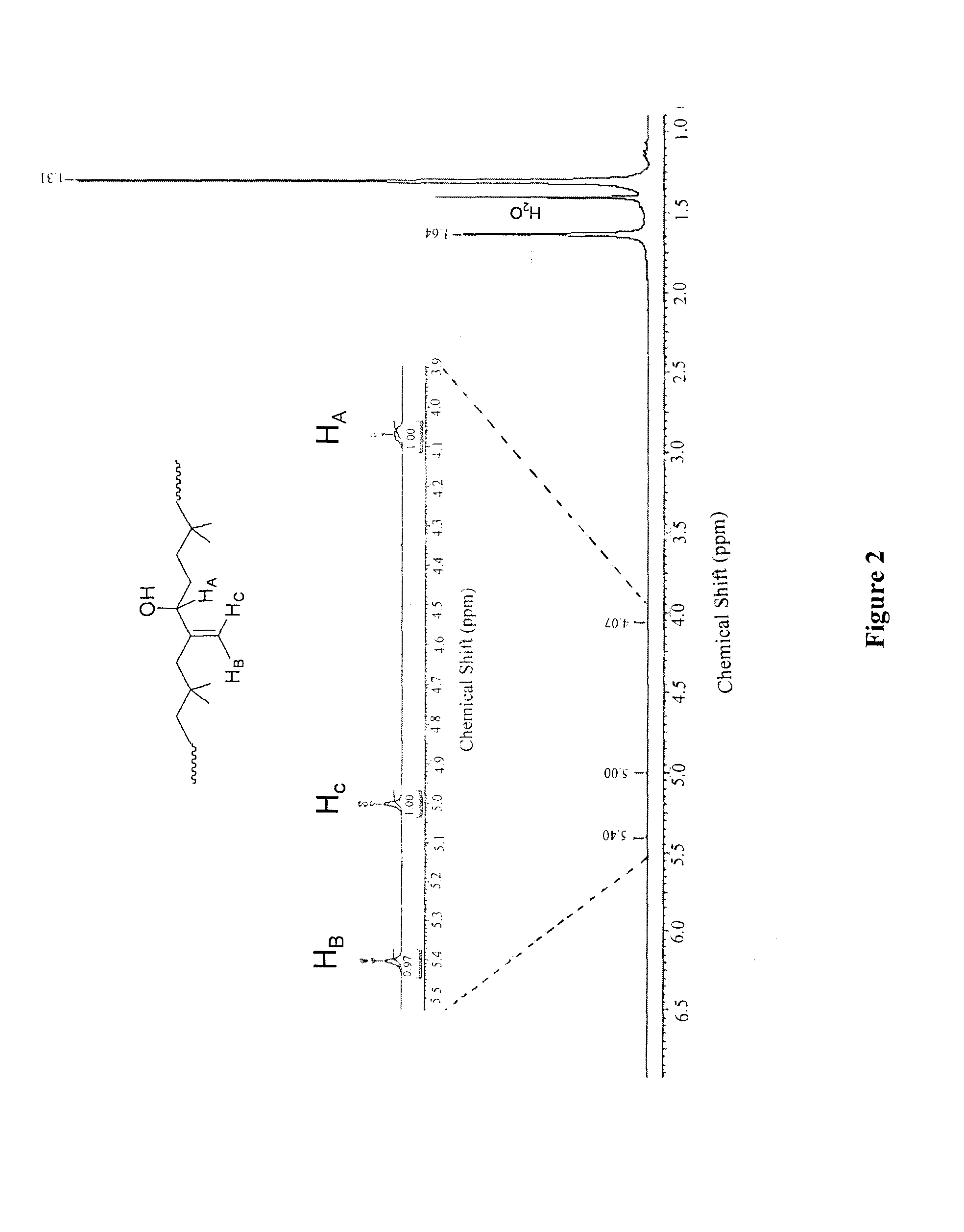
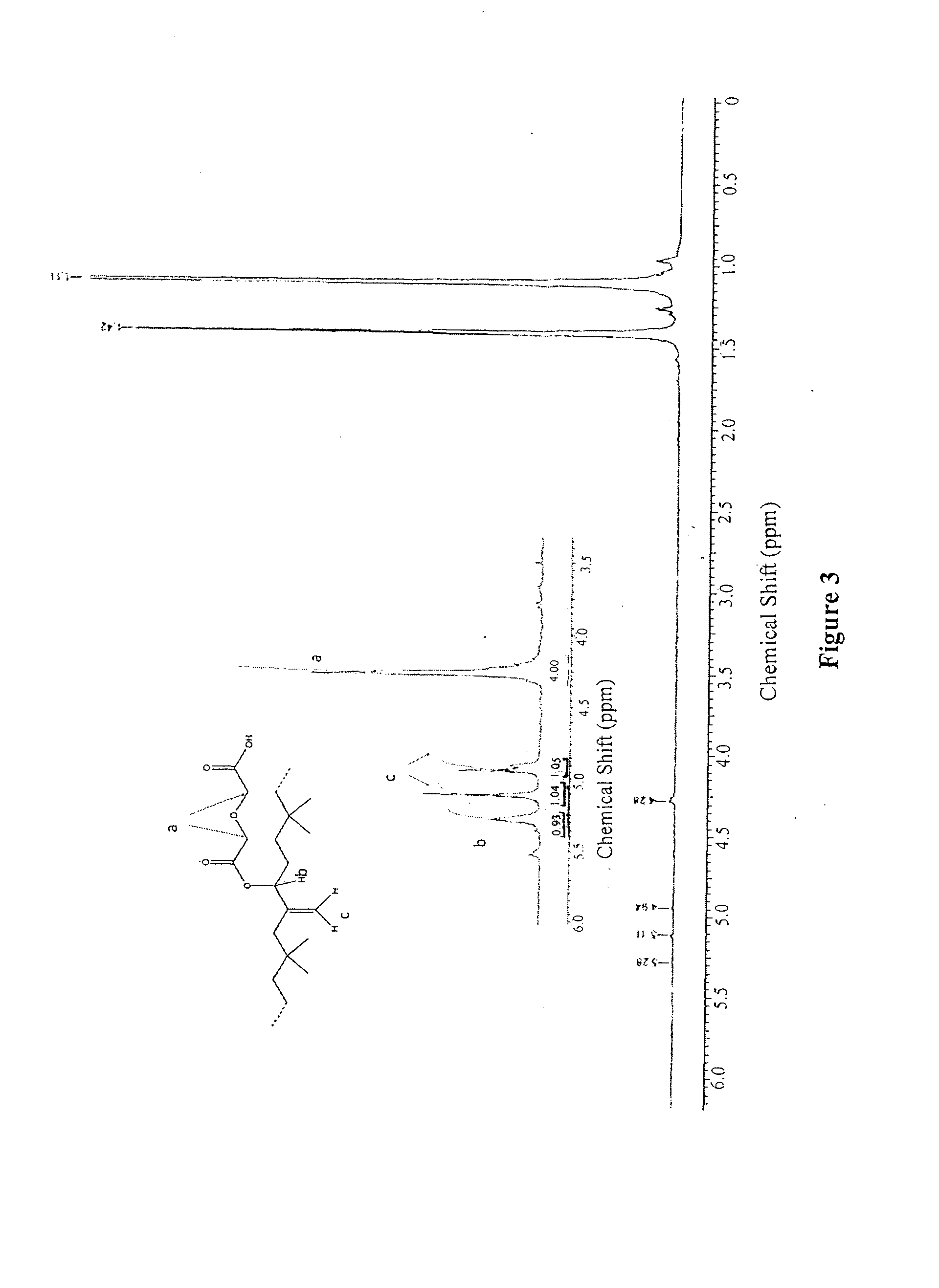
Functionalized copolymers of isoolefins and diolefins and their use as compatibilizers
InactiveUS20140004252A1Improve wettabilitySurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical containersHydrophilic polymersDouble bond
Functionalized copolymers of isoolefins and conjugated diolefins, methods of preparing said copolymers, and their use as compatibilizers are disclosed. The diolefin monomer units of the co-polymer are modified at the C—C double bond along the backbone of the copolymer to include an oxygen containing functional group such as epoxide, ester or alcohol. The functionalized copolymers improve the wettabilty of a non-hydrophilic surface towards hydrophilic polymer and allows for the formation of homogenous layers of the hydrophilic polymers. In particular, the spreading of a hydrophilic polymer on a non-hydrophilic substrate is facilitated by applying the co-polymers as an interfacial layer between the two incompatible materials. The resulting coated substrates exhibit resistance to protein adsorption and cell growth after grafting. The co-polymers are especially suited in the coating of biomedical devices where a high degree of uniformity of the coated surface is required.
Owner:ARLANXEO SWITZERLAND SA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com