Breeding method for the self-incompatible line of brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis (L.) makino var. rosularis tsen et lee
A Wutaicai and compatibility technology, applied in the field of breeding of self-incompatible lines of Wutaicai, can solve the problem of difficulty in obtaining self-incompatible varieties of Wutaicai, heavy workload, long cycle, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of overcoming the difficulty of breed selection, rapid selection, and wide sources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
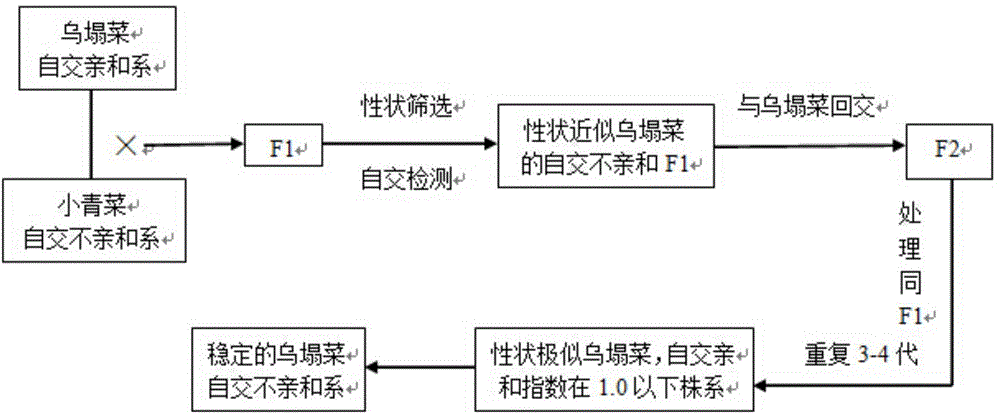
[0017] This example is the breeding method of Wutaicai S9701 self-incompatibility line, the flow chart is as attached figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0018] 1. Material preparation:
[0019] Wutaicai S9701 self-compatibility line: S9701 is an excellent self-compatibility line selected through multi-generation segregation of Wutaicai varieties in Huainan.
[0020] Xiaoqingcai Huaguan-5A self-incompatibility line: a Huaguan variety introduced from Japan, a stable Xiaoqingcai self-incompatibility line obtained after multiple generations of self-separation.
[0021] 2. Breeding steps:
[0022] (1) Using the self-compatible line of Wutaicai S9701 as the recurrent parent, and the self-incompatible line Huaguan-5A of Xiaoqingcai as the transfer source, cross-breed to obtain F1 seeds;
[0023] (2) Sowing the F1 seeds of step (1), obtaining F1 plants, screening the F1 plants whose traits are consistent with those of the recurrent parents, bagging the main infloresce...
Embodiment 2
[0030] This embodiment is the breeding method of Hefei Heixinwu self-incompatibility line, the flow chart is as attached figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0031] (1) Using Hefei Heixinwu self-compatible line as the recurrent parent, and Xiaoqingcai self-incompatible line Huaguan-5A as the transfer source, and crossed to obtain F1 seeds;
[0032] (2) Sowing the F1 seeds of step (1), obtaining F1 plants, screening the F1 plants whose traits are consistent with those of the recurrent parents, bagging the main inflorescences of all the screened F1 plants, and performing selfing at the flowering stage and selfing at the bud stage respectively, Using the affinity index method to measure its affinity, select self-incompatible F1 plants whose affinity index is less than 1 at the flowering stage and greater than 10 at the bud stage, and whose traits are consistent with those of the recurrent parent. The reincarnated parent is backcrossed to obtain F2 seeds;
[0033] (3...
Embodiment 3
[0035] In this example, the self-compatible line of Huainan black heart Aconitum is used as the recurrent parent, and the self-incompatible line of Xiaoqingcai Xiawang variety is used as the transfer source. The other steps are the same as in Example 1. The obtained F4 plant is the stable Huainan Heixinwu is a self-incompatible line.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com