Method for determining intermittent pumping system through oil-well pump dynamic fullness well testing
A technology of oil well pump and fullness, which is applied in the field of well testing of rod pump oil wells, and can solve the problems of high price, difficult matching, and failure of pumping control technology to apply to oil production, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0075] In this embodiment, the test procedure and steps of the dynamic oil well pump fullness test to determine the best intermittent pumping system method are as follows Figure 8 shown. details as follows:
[0076] 1. Test the fullness of the oil well pump.
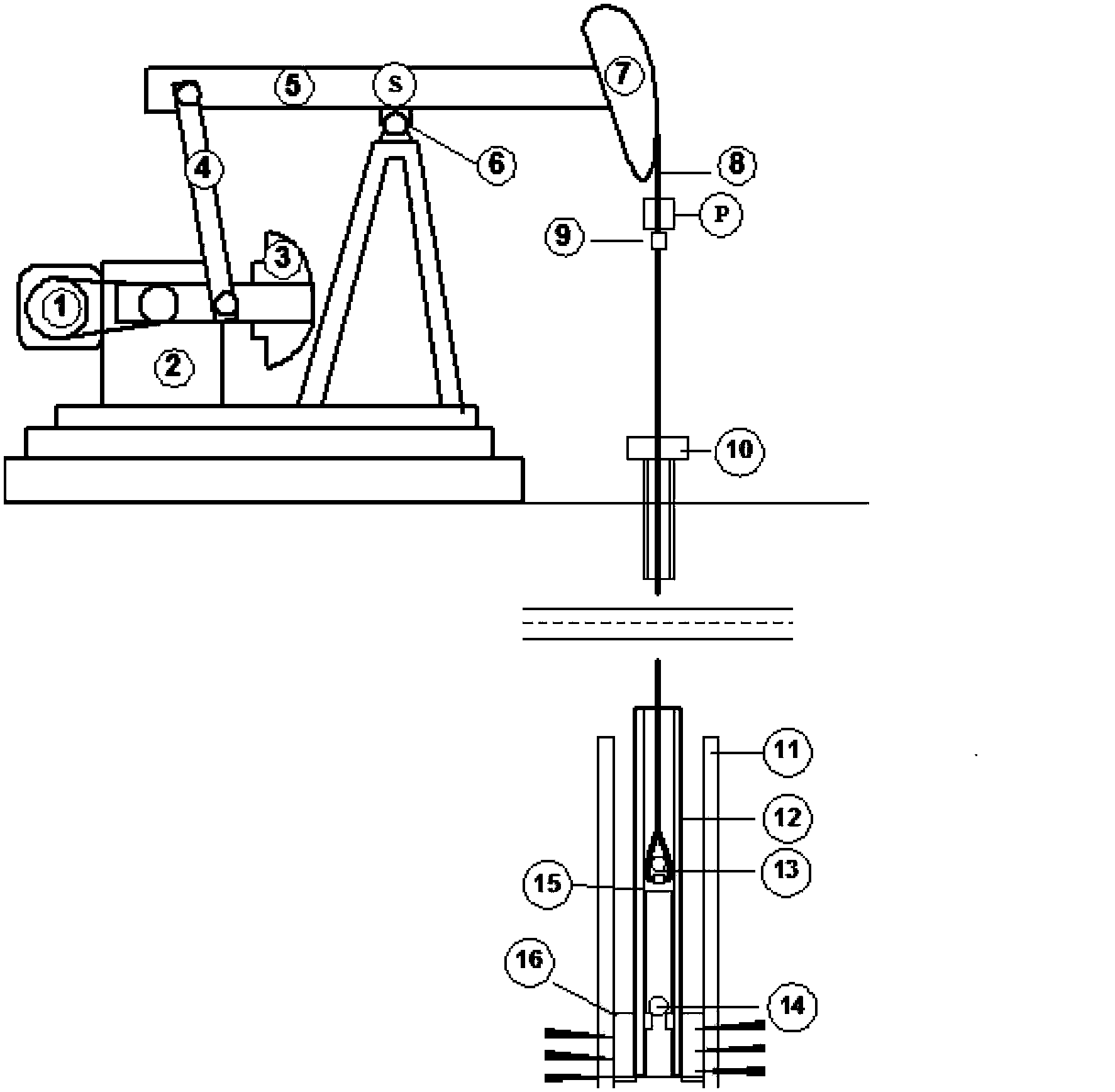
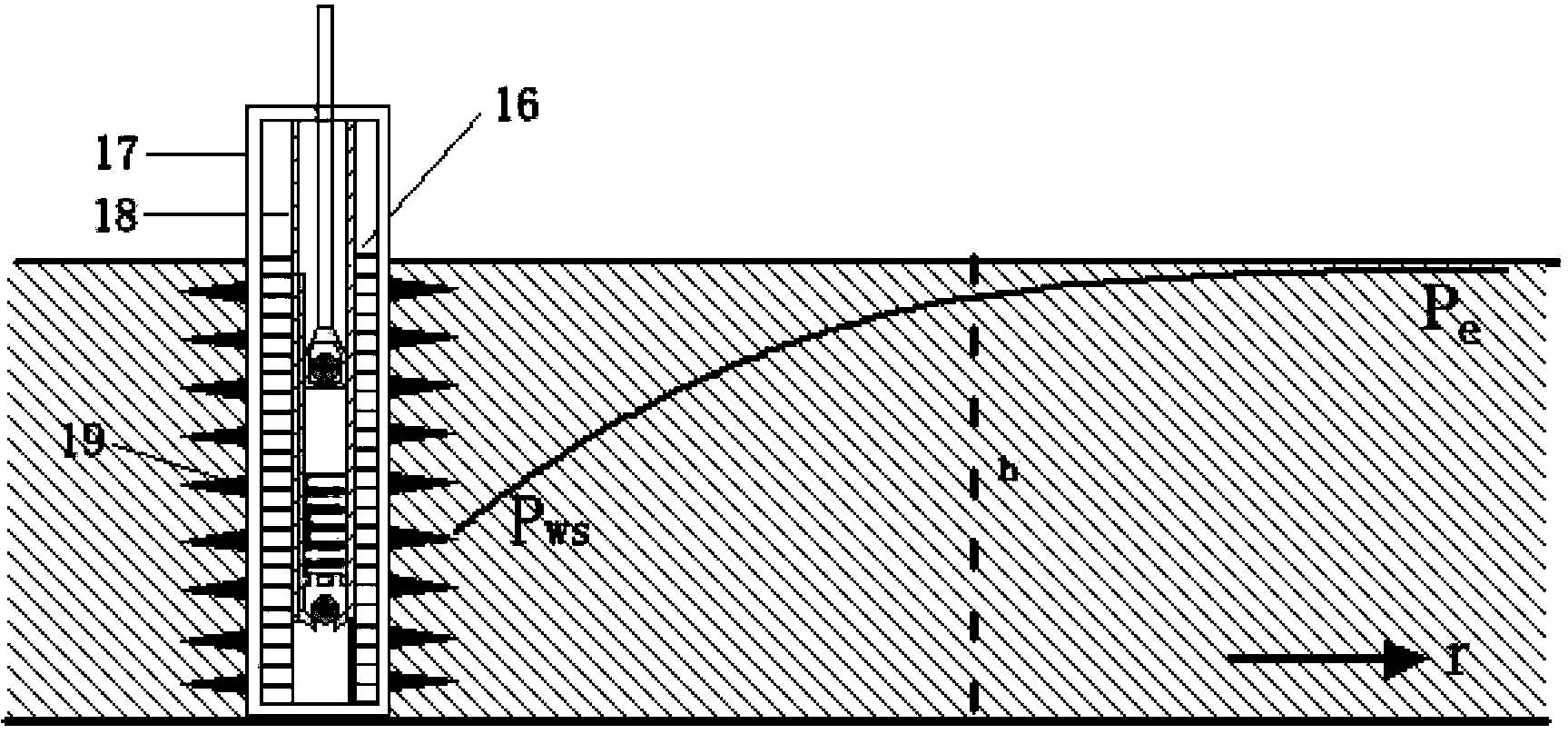
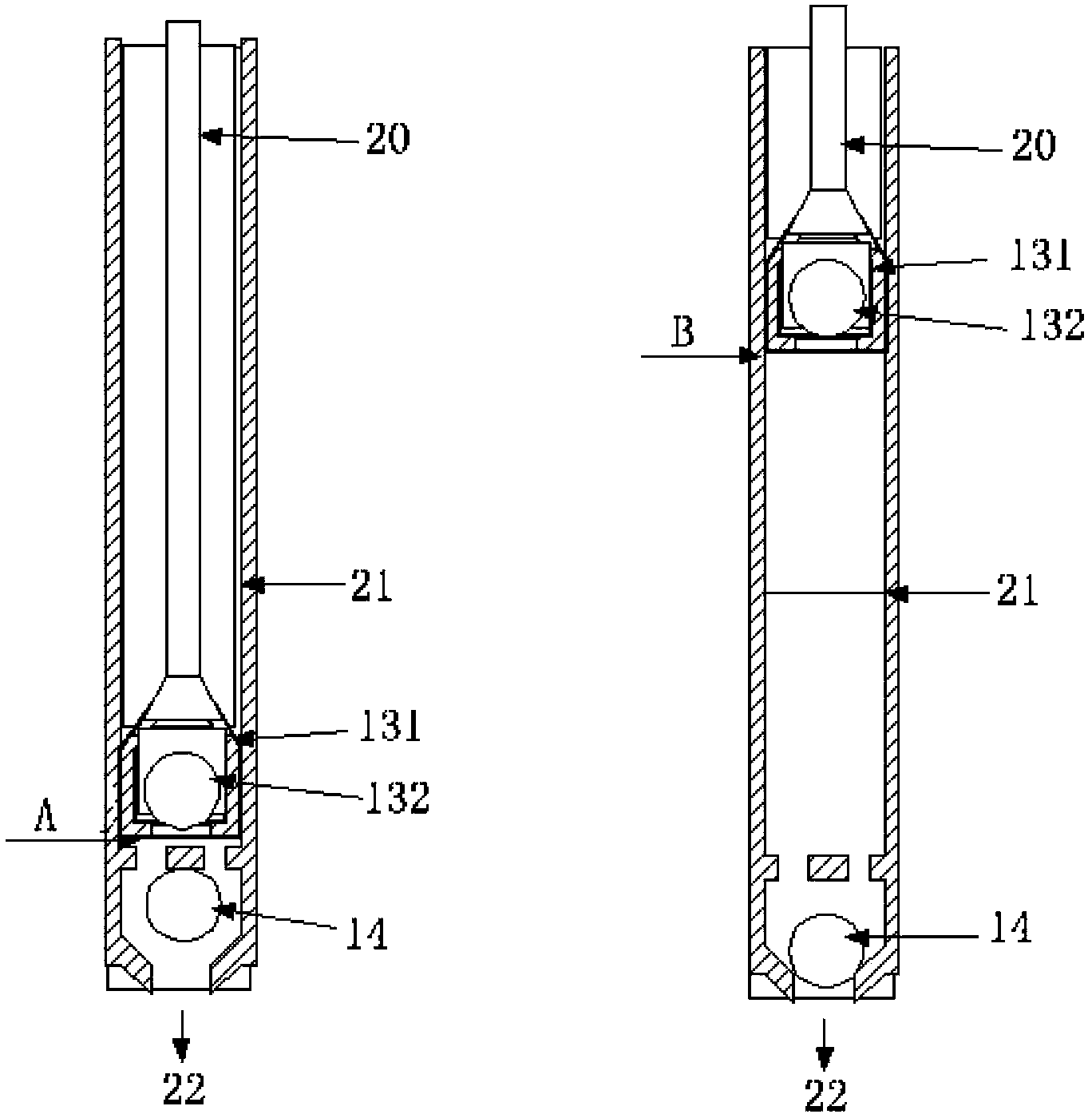
[0077] The test of the fullness of the oil pump is firstly used figure 1 The light rod load sensor on point P and the angular displacement sensor on point S in the middle measure the load-time curve and displacement-time curve. The shape of the measured curve is as Figure 5shown. In the displacement-time curve, point A is the bottom dead center, and point B is the top dead center. The load-time curve is an irregular motion curve, but there are two characteristic points on the load-time curve, namely point C and point D. Point C is when the piston moves upward from the bottom dead center until the pressure in the well pump is less than the bottom hole pressure and the opening point of the fixed valve. The positio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com