Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
71 results about "Functional assay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Functional Assay Methods, Techniques, Protocols. Functional Assay - screening or measuring of functionally active proteins present in plasma or culture media using ELISA or other method.
Microfluidic device
InactiveUS20110003330A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTemperature controlTest channel
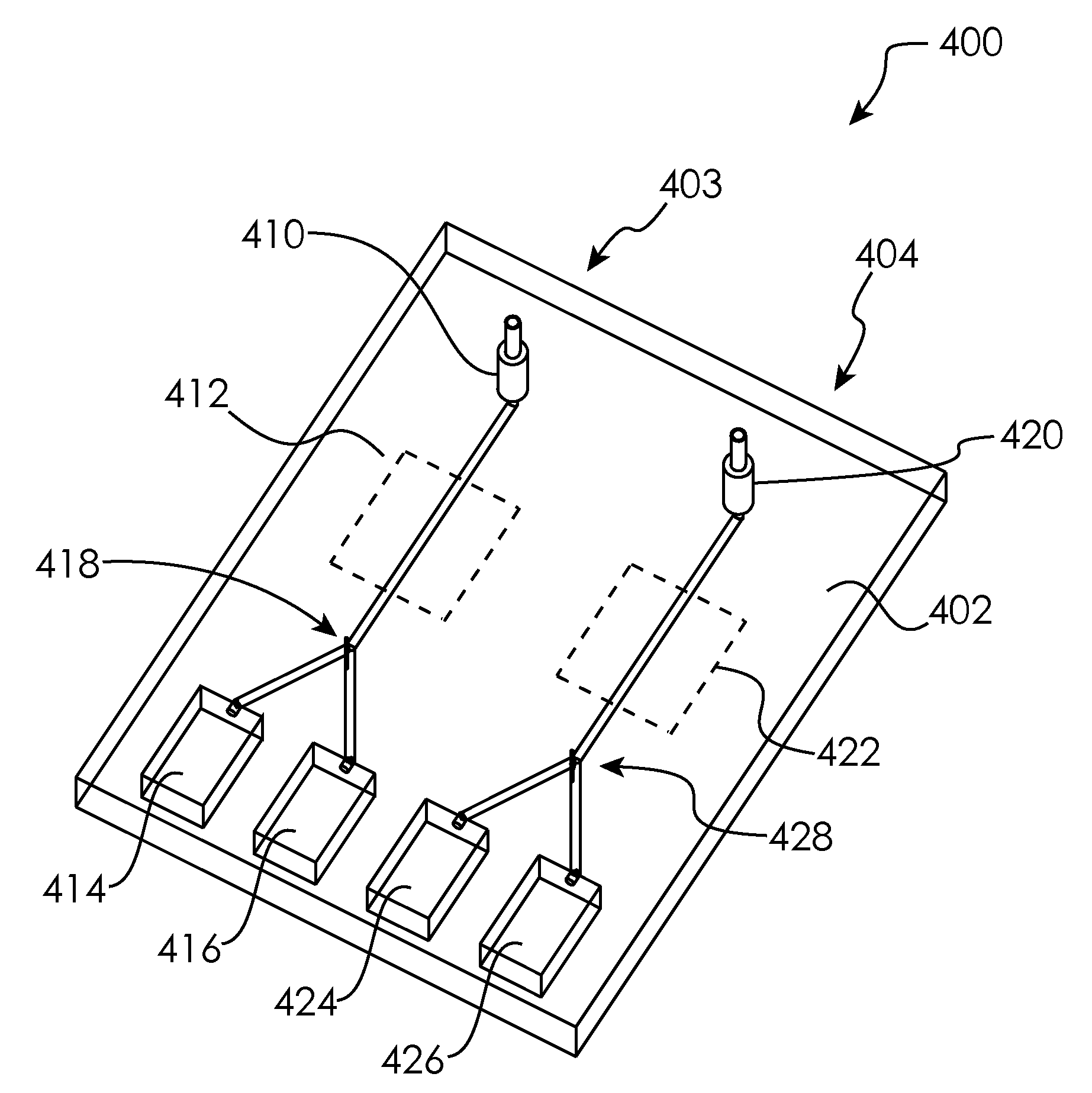
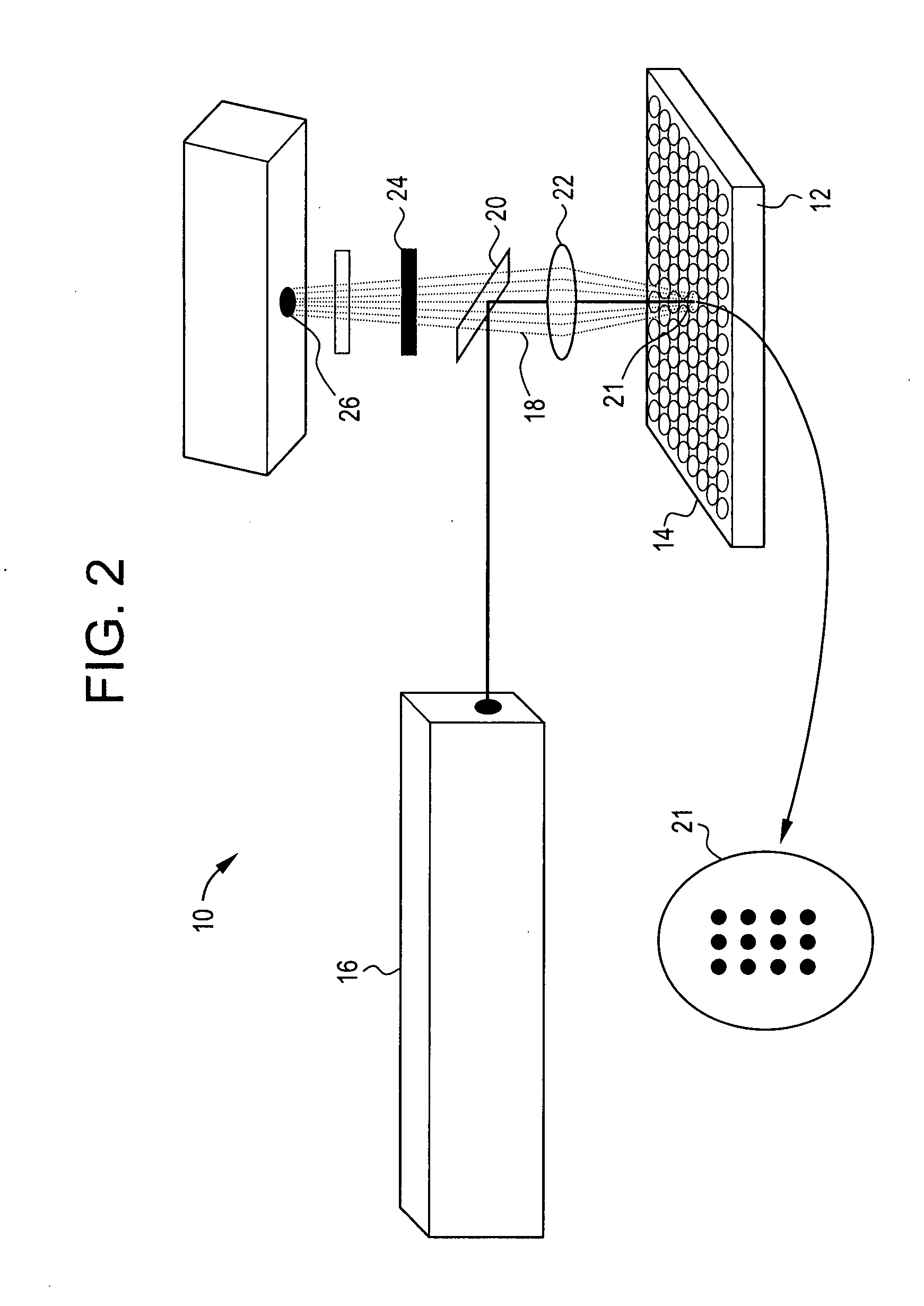
The present disclosure relates to microfluidic devices adapted for facilitating cytometry analysis of particles flowing therethrough. In certain embodiments, the microfluidic devices have onboard data storage capabilities. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have onboard anticoagulants. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have onboard test and control channels. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have integrated collection media. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have multiple onboard test channels. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have localized temperature control. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have anatomy simulating regions. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have complete assay capabilities. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have dissociable sections. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have means for performing functional assays.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Identification and isolation of acute myeloid leukemia stem cells
ActiveUS20080187950A1Microbiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsCancers diagnosisFunctional assay
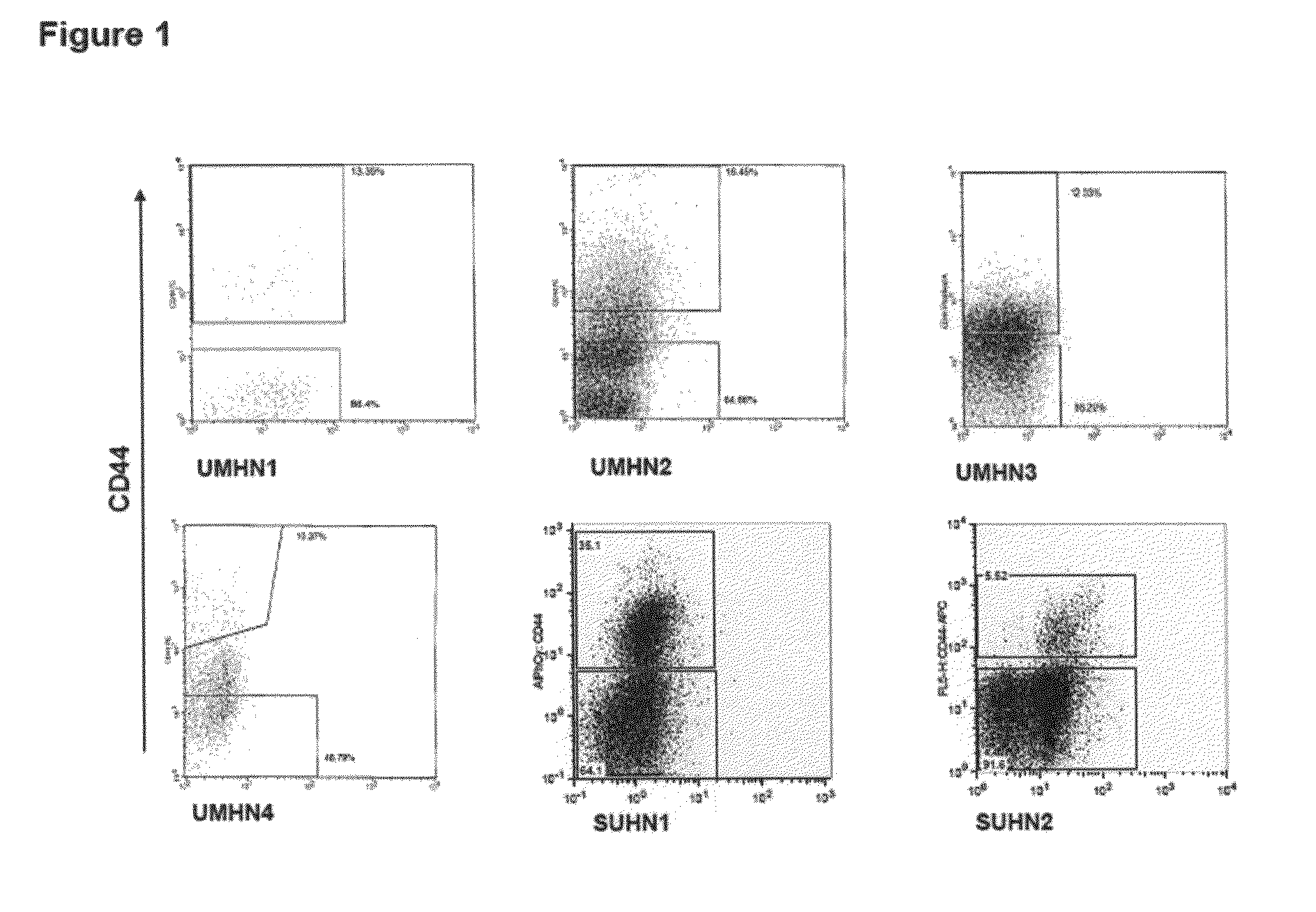
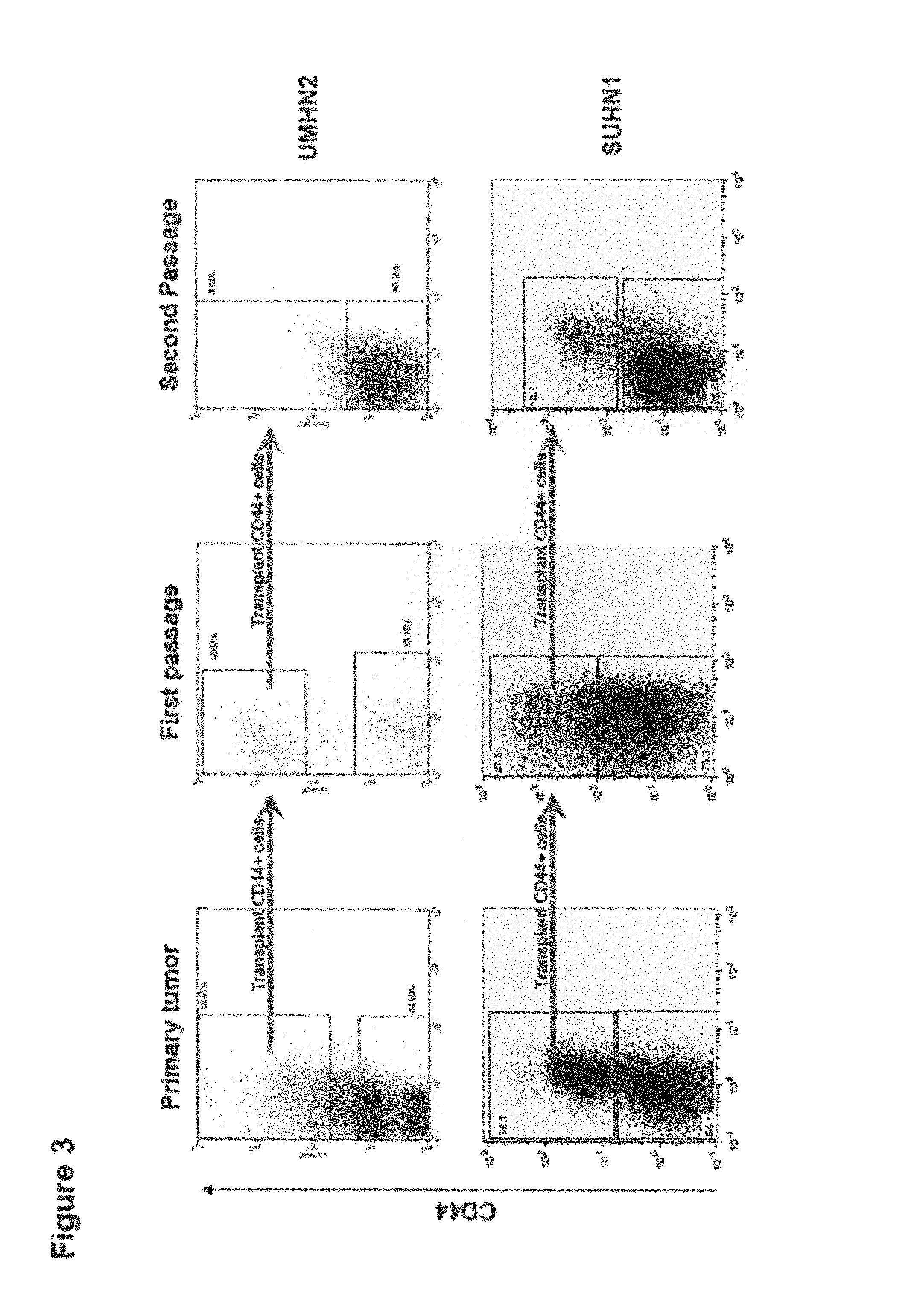
Acute myeloid leukemia stem cells (AMLSC) are identified. The cells can be prospectively isolated or identified from patient samples, and are shown to possess the unique properties of cancer stem cells in functional assays for cancer stem cell self-renewal and differentiation, and in cancer diagnosis.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Isolation and use of melanoma cancer stem cells
ActiveUS9151760B2Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementPrimary tumorFunctional assay
A set of markers for melanoma cancer stem cells are provided. The cells can be prospectively isolated or identified from primary tumor samples, and possess the unique properties of cancer stem cells in functional assays for tumor initiation, cancer stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. In addition, cancer stem cells can be used as a predictor for disease progression. The CSC have the phenotype of being positive for expression CD271.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Assay solution compositions and methods for GPCR arrays
InactiveUS20050069953A1Reduce background signalBiological material analysisBiological testingInorganic saltsFunctional assay
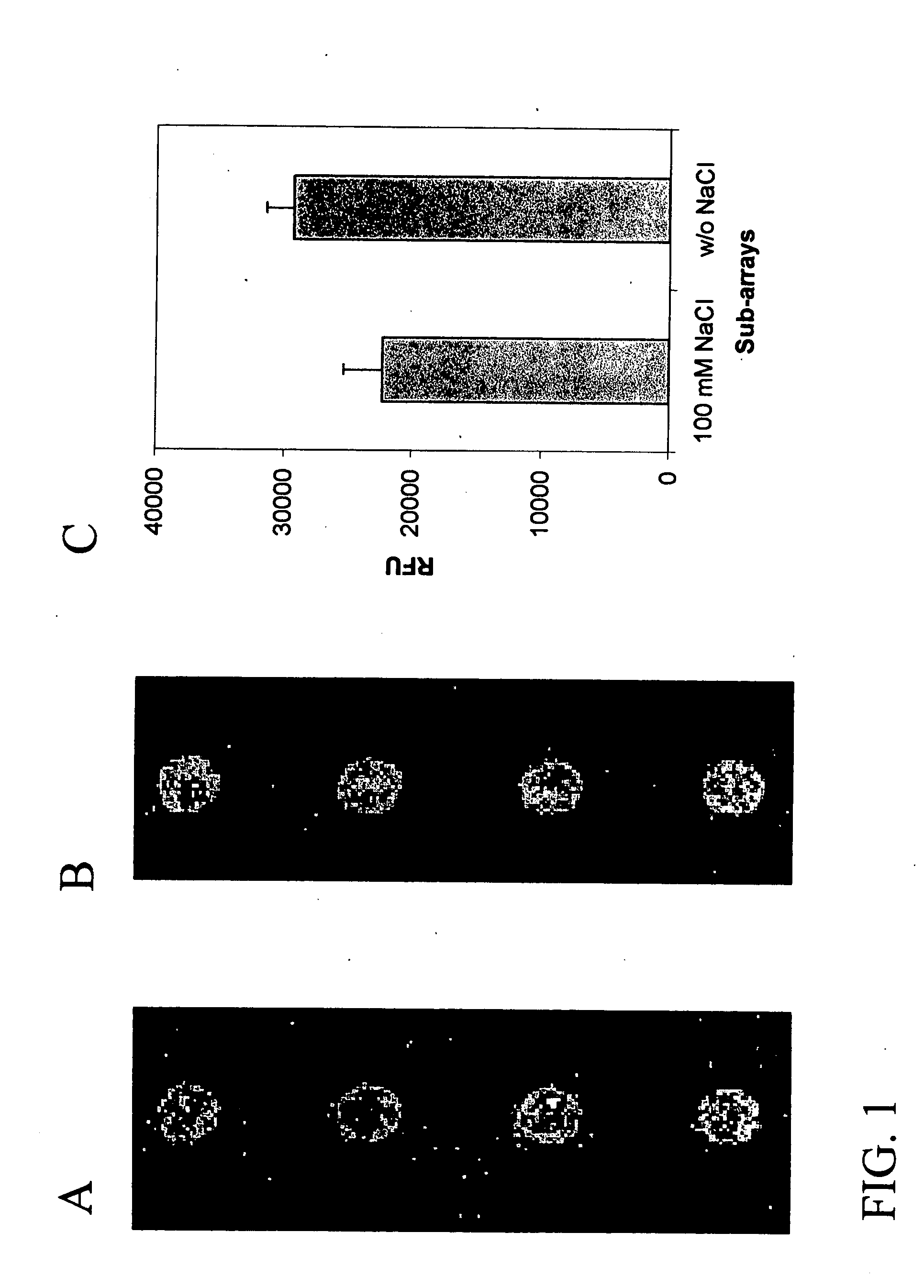
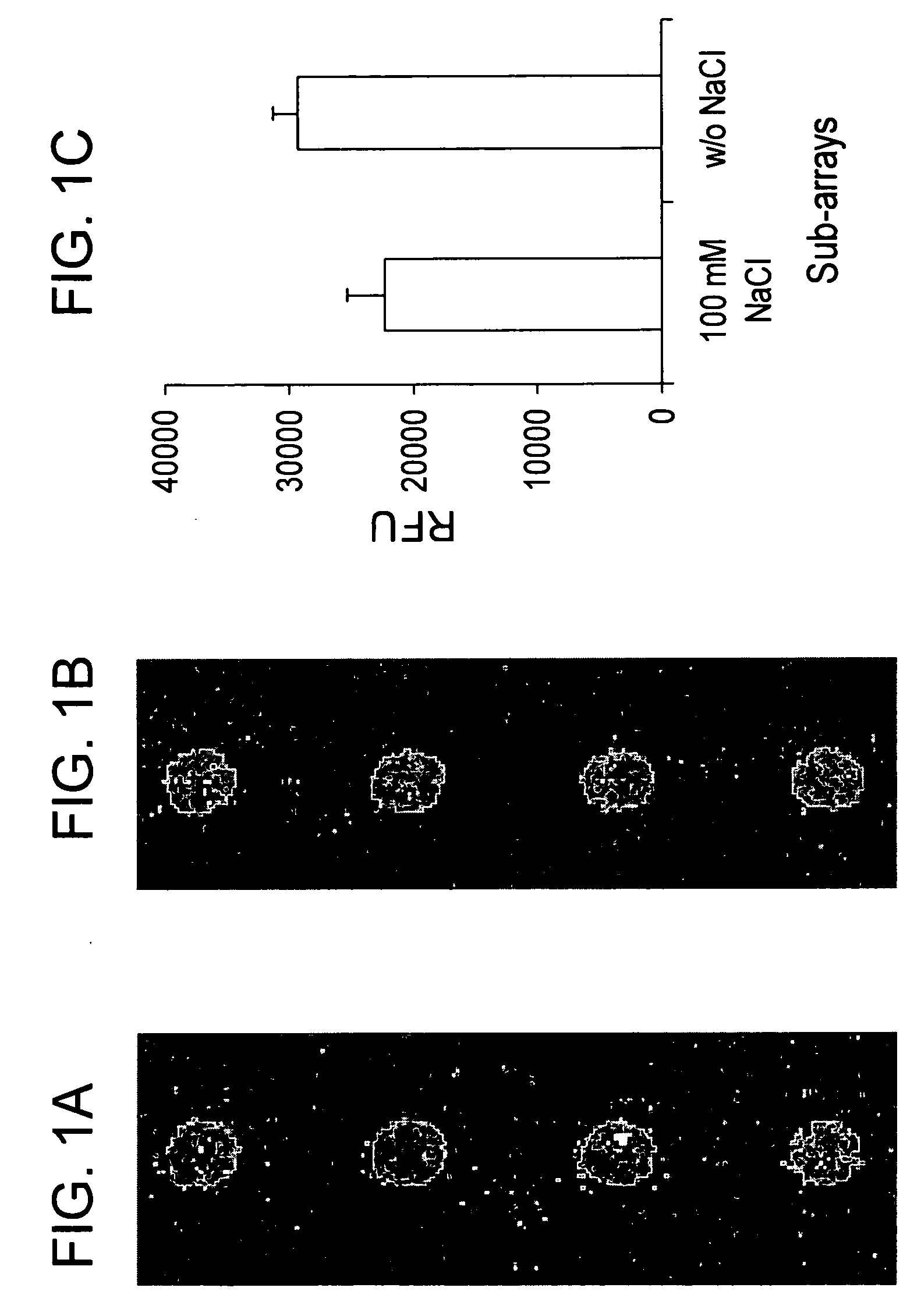
Buffered assay solutions for performing 1) binding or 2) functional assays on GPCR arrays, along with methods for their use are described. The buffered assay solution has an underlying composition having: a buffer reagent with a pH in the range of about 6.5 to about 7.9; an inorganic salt of either a monovalent or divalent species, at a concentration from about 1 mM to about 500 mM; and optionally a combination of: c) a blocker reagent at a concentration of about 0.01 wt. % to about 2 wt. % of the composition, or d) protease-inhibitor at a concentration of about 0.001 mM to about 100 mM. In an embodiment for functional assay uses, the composition is modified to also include a GTP-analogue, a guanosine 5′-diphosphate (GDP) salt, and / or an anti-oxidant reagent.
Owner:CORNING INC
Identification and isolation of transitional cell carcinoma stem cells
InactiveUS7781179B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPrimary tumorFunctional assay
Transitional cell carcinoma stem cells (TCCSC) are identified. The cells can be prospectively isolated or identified from primary tumor samples, and are shown to possess the unique properties of cancer stem cells in functional assays for cancer stem cell self-renewal and differentiation, and in cancer diagnosis.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Surface-assisted hemagglutination and hemagglutination inhibition assays
ActiveUS20110097705A1Low variabilityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSerum igeRed blood cell
Hemagglutination (HA) and hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) functional assays remain important instruments of analysis of virus-cell interaction and protecting efficacy of virus-specific antibodies and sera. However, they demonstrate limited sensitivity towards many viruses, and require significant volumes of viruses, erythrocytes, sera, and antibodies. The present invention comprises new and significantly more sensitive versions of the HA and HAI assays based on observing agglutination on activated surfaces of specifically opsonized plates and ELISA plates rather than in solution. A version of the new assay that uses ELISA plates additionally allows characterizing the affinity of functional antibodies in the tested sera and fluids, which is not possible in the classical HAI assay. The methods of the present invention can also be used to improve the sensitivity of agglutination methods based on latex beads and to develop agglutination methods using target cells other than erythrocytes.
Owner:SANOFI PASTEUR VAX DESIGN
Assay solution compositions and methods for GPCR arrays
InactiveUS20060148006A1Peptide/protein ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsInorganic saltsFunctional assay
Buffered assay solutions for performing 1) binding or 2) functional assays on GPCR arrays, along with methods for their use are described. The buffered assay solution has an underlying composition having: a buffer reagent with a pH in the range of about 6.5 to about 7.9; an inorganic salt of either a monovalent or divalent species, at a concentration from about 1 mM to about 500 mM; and optionally a combination of: c) a blocker reagent at a concentration of about 0.01 wt. % to about 2 wt. % of the composition, or d) protease-inhibitor at a concentration of about 0.001 mM to about 100 mM. In an embodiment for functional assay uses, the composition is modified to also include a GTP-analogue, a guanosine 5′-diphosphate (GDP) salt, and / or an anti-oxidant reagent.
Owner:CORNING INC
In Vitro Generation of Hepatocytes from Human Embryonic Stem Cells
Differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells, such as human embryonic stem cells (hESC), into hepatocytes by in vitro methods is disclosed. The pluripotent stem cells are cultured in conditioned medium from the hepatocarcinoma cell line, HepG2. Specific growth factors and defined media may also be added to the medium for stage specific differentiation of the derived hepatocytes. Hepatocytes differentiated from human pluripotent stem cells may be characterized by fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS), immunofluorescence analysis (IF), real time polymerase reaction (RT-PCR), and functional assays. The methods disclosed herein are able to differentiate high percentages of hepatocytes from human pluripotent stem cells using the disclosed methods. These differentiated cells may exhibit polygonal shape morphology, typical of hepatocytes, and may express hepatocyte specific genes. The differentiated cells may also be positive for definitive endoderm markers and hepatic markers.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
Microfluidic device
The present disclosure relates to microfluidic devices adapted for facilitating cytometry analysis of particles flowing therethrough. In certain embodiments, the microfluidic devices have onboard data storage capabilities. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have onboard anticoagulants. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have onboard test and control channels. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have integrated collection media. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have multiple onboard test channels. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have localized temperature control. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have anatomy simulating regions. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have complete assay capabilities. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have dissociable sections. In certain other embodiments, the microfluidic devices have means for performing functional assays.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
System for high throughput GPCR functional assay
InactiveUS20080207466A1High speedImprove throughputLibrary screeningLibraries apparatusPorous substrateFunctional assay
A functional assay detection system for membrane bound proteins. The system comprises a biological array including a porous substrate having a plurality of membranes adhered thereto and a first side and a second side, a fluorescent labeling reagent configured to couple to the membrane bound proteins, a pulsed light assembly configured to excite the fluorescent labeling reagent, and a time-delayed imaging device configured to capture emitted fluorescence of the fluorescent labeling reagent. The pulsed light assembly is configured to excite the fluorescent labeling reagent from at least one of the first side and the second side of the porous substrate, and the fluorescent labeling reagent comprises a fluorophore that has an emission lifetime that is in the range of microseconds.
Owner:CORNING INC
Identification and isolation of squamous carcinoma stem cells
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
In vivo screening of protein-protein interactions with protein-fragment complementation assays
InactiveUS7855167B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein-protein complexIn vivo
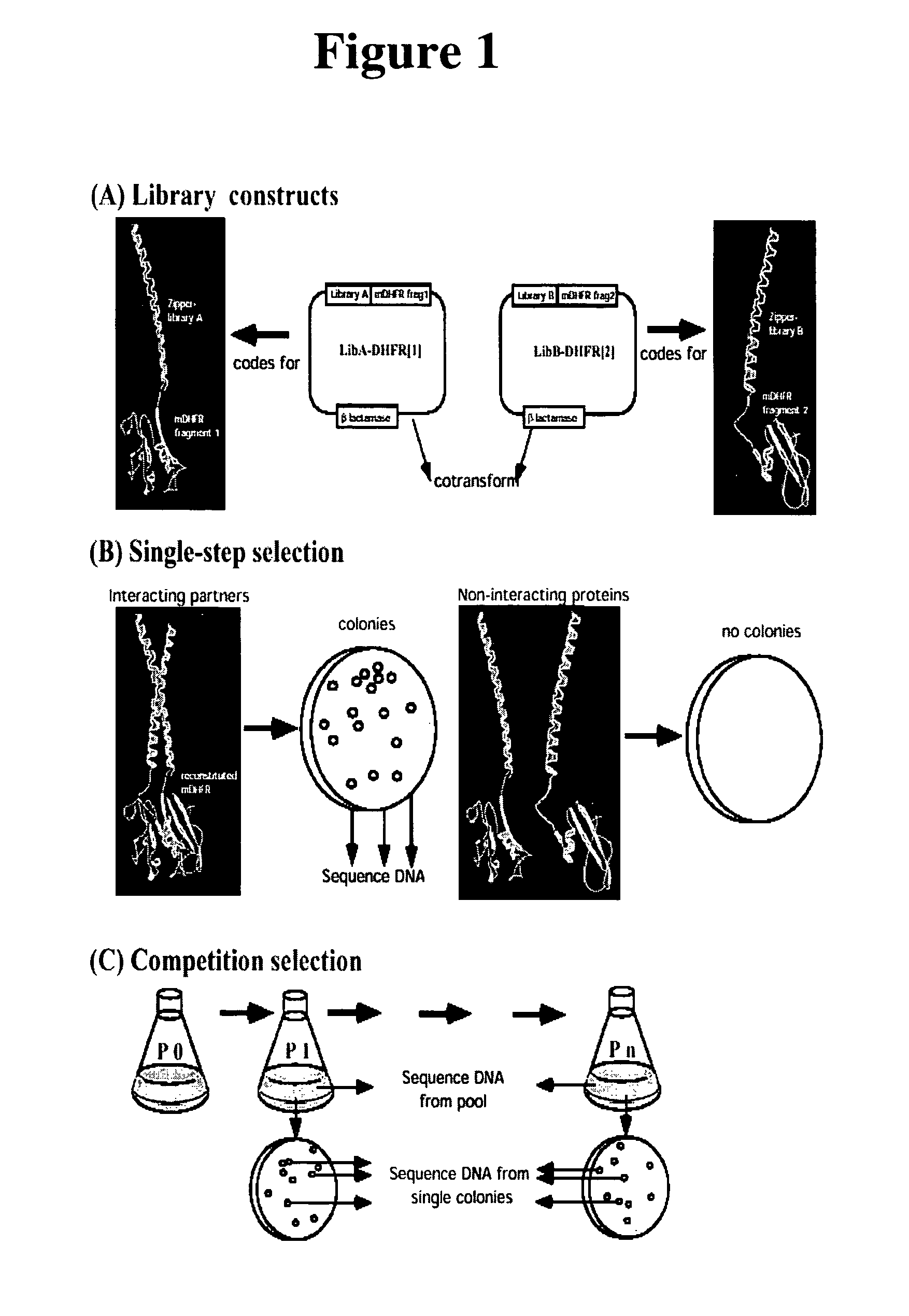
The present invention describes rapid methods to screen for biomolecular interactions in vivo based on protein fragment complementation assays (PCA). We have demonstrated an in vivo library-versus-library screening strategy that has numerous applications in the identification of novel protein-protein interactions and in directed evolution. Also we demonstrate the detection of protein-protein interactions starting with defined (full-length) cDNAs, and the concomitant generation of functional assays that provide initial validation of the cDNA products as being biologically relevant. Also, we screened a large cDNA collection using automated PCA, combined with quantitative detection of protein-protein complexes. The invention enables bait-vs.-library, library-vs.-library and defined gene screening in any type of cell or cellular context, and using a wide range of reporters and detection methods. The invention allows for identifying and validating genes involved in any cellular process and also provide assays to study effects of potential drugs, or gene knockouts on specific pathways.
Owner:EXIGEN PHARM INC
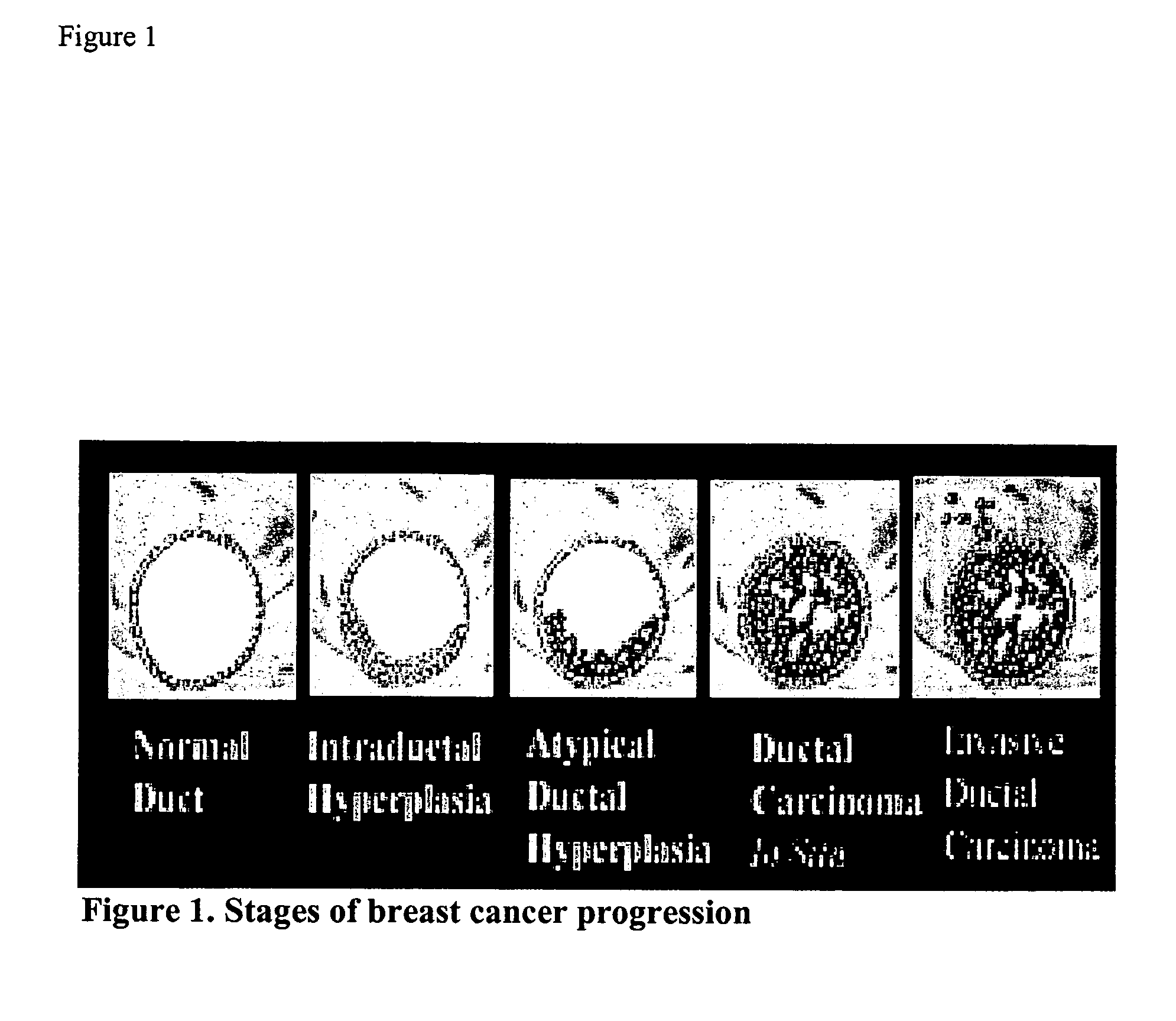
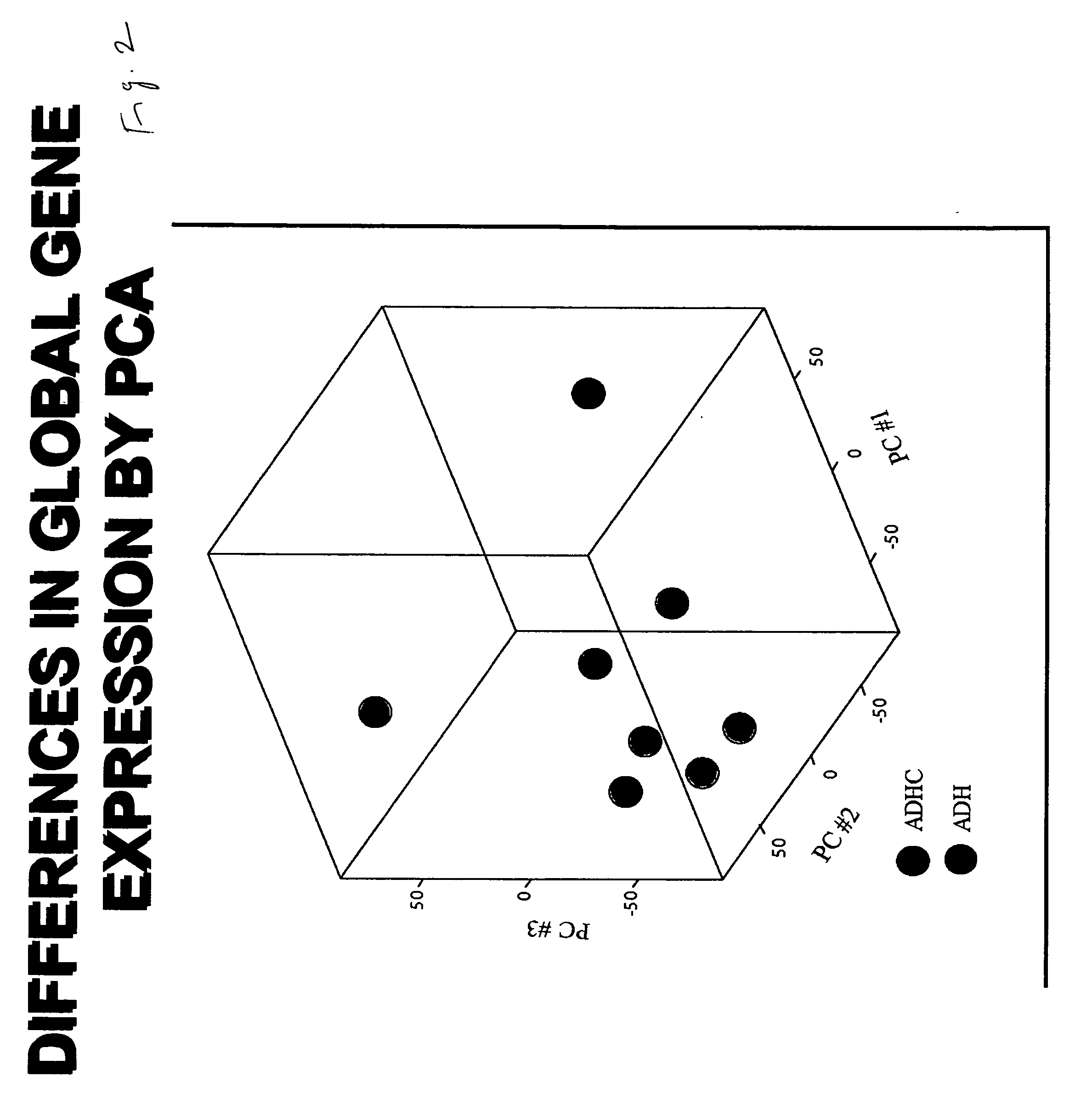
Molecular Markers that predict breast cancer development
InactiveUS20070254286A1Prevent hyperprolific conditionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisDiseaseQuantitative Real Time PCR
A number of selected genes / gene products; Application of selected genes / gene products at mRNA or protein levels either singly or in combination; Application of selected genes / gene products at mRNA levels by any of the methods such as: Northern blotting, or reverse transcription and conventional PCR, or reverse transcription and quantitative real-time PCR or gene expression micro-arrays; Application of selected genes / gene products at protein levels by either Western Blotting, or immunohistochemistry, or ELISA or functional assays or gel electrophoretic separation followed by spectroscopic identification (proteamics); Application of selected genes / gene products at peptide levels derived from proteins and spectroscopic methods of identification; Detection of a hyperproliferative condition, a precancerous condition, a predisposition to develop hyperproliferative condition or cancer by applying any one of the selected genes either singly or in combination in breast tissue, breast fluid, breast cells, blood or any other tissues or cells of a mammal; Application of selected genes either singly or in combination with others for designing molecular therapeutic drugs to treat a hyperproliferative condition, a precancerous condition, or predisposition to develop hyperproliferative condition or cancer of the breast or any other tissue of a mammal; Application of selected genes either singly or in combination with others for following up of a therapeutic treatment to a hyperproliferative condition, or precancerous condition, or predisposition to a hyperproliferative condition, or cancer, of the breast or any other tissue of a mammal; Application of selected genes either singly or in combination with others for screening of therapeutic drugs to a hyperproliferative condition, or precancerous condition, or predisposition to a hyperproliferative condition, or cancer, of the breast or any other tissue of a mammal; and Application of selected genes either singly or in combination with others for designing vaccines to prevent a hyperproliferative condition, or precancerous condition, or predisposition to a hyperproliferative condition, or cancer, of the breast or any other tissue of a mammal.
Owner:SILBIOTECH
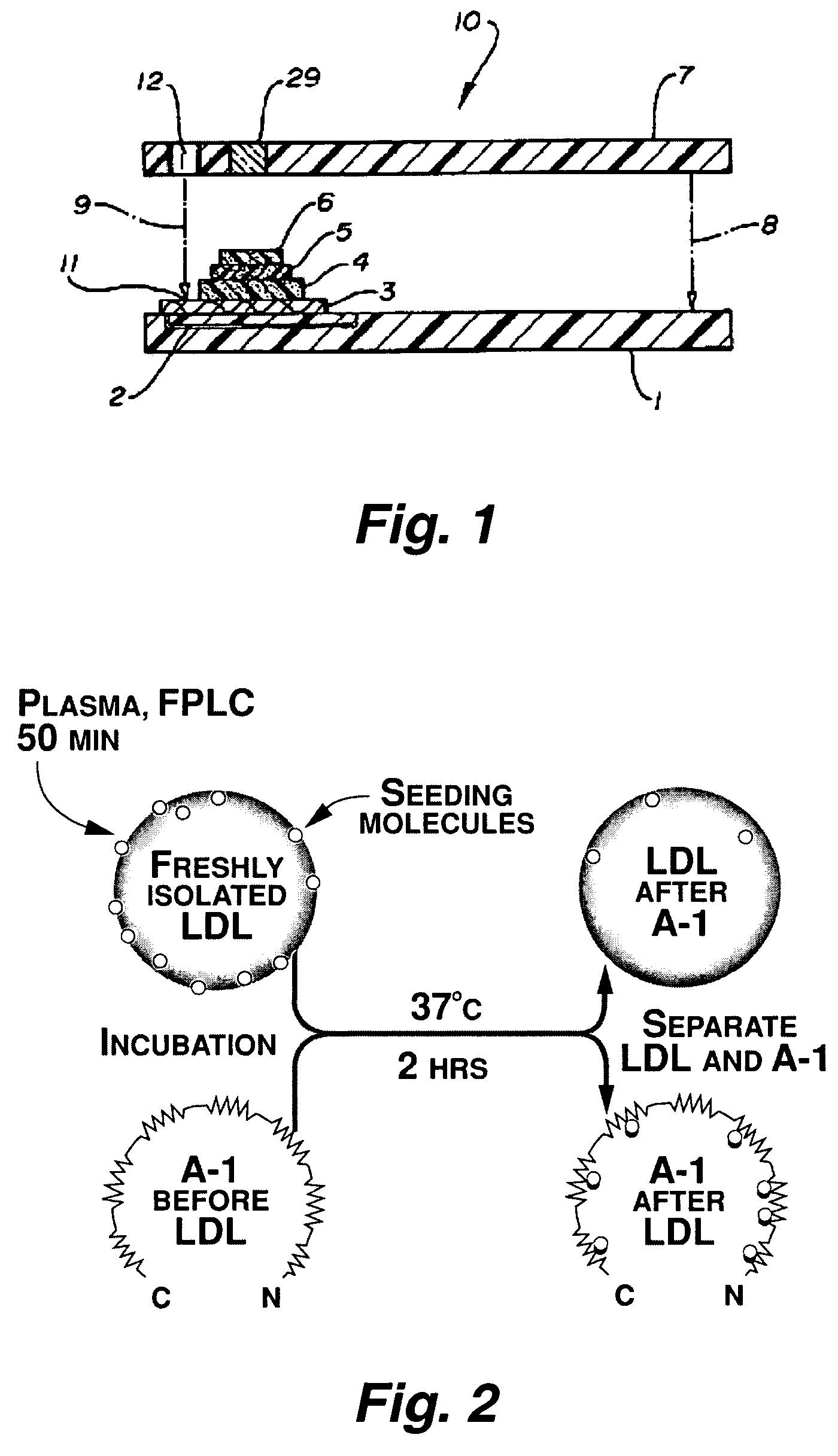
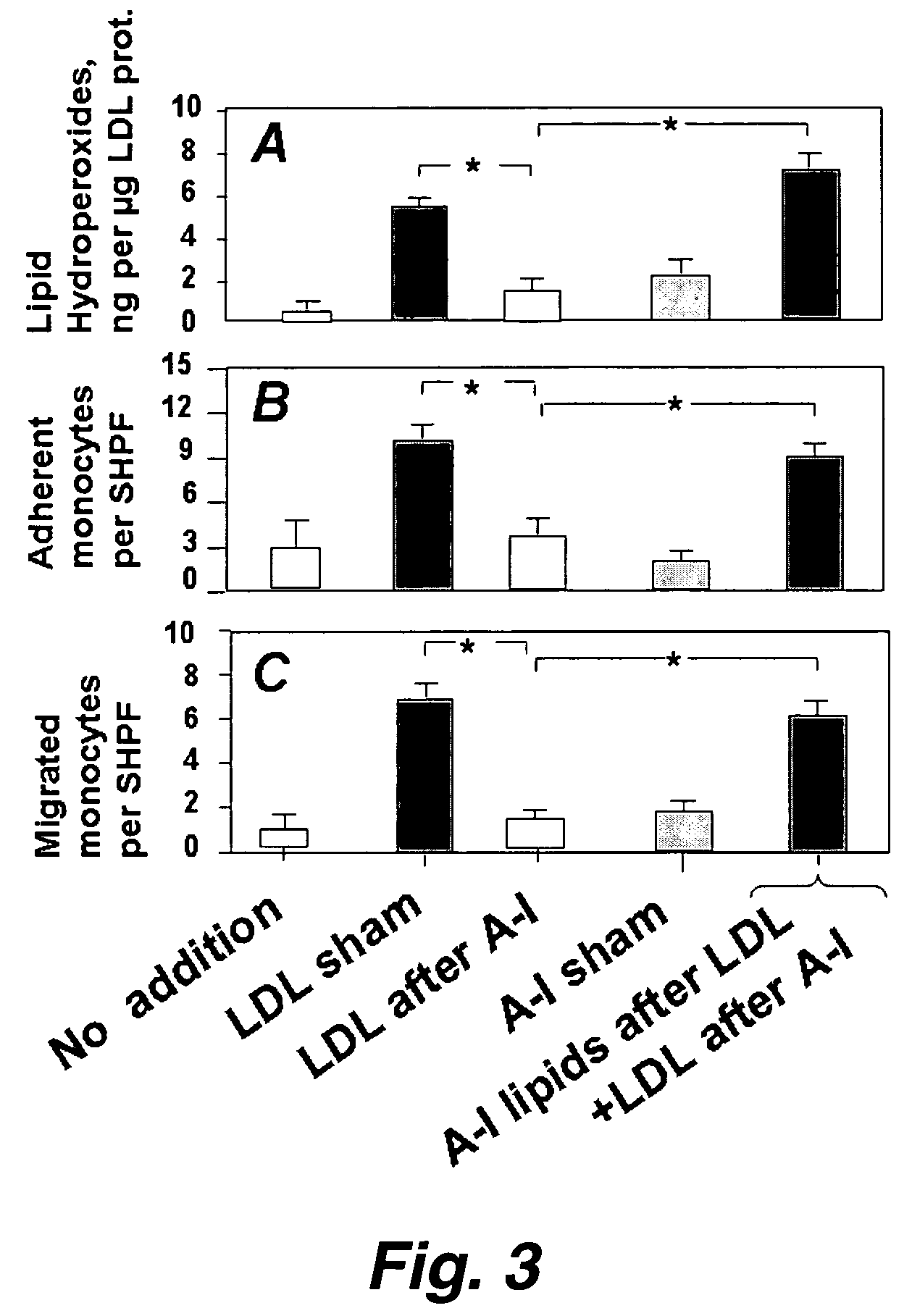
Functional assay of high-density lipoprotein
InactiveUS7250304B2Prevent oxidationReduce inflammationComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementLipid formationFunctional assay
This invention provides novel assays that are prognostic and / or diagnostic for atherosclerosis or risk of atherosclerosis. It was discovered that high density lipoprotein (HDL) or components thereof can prevent the oxidation of lipids (e.g., lipids present in LDLs) and can also repair (reduce) already oxidized lipids and thereby reduce the inflammatory response associated with and characteristic of atherosclerotic plaque formation. Moreover it was a discovery of this invention that individuals vary in the ability of their HDL to afford such protection. Thus an assay of HDL protective and / or repair activity provides a highly effective assay for risk of atherosclerosis and its associated pathologies and such assays are provided herein.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
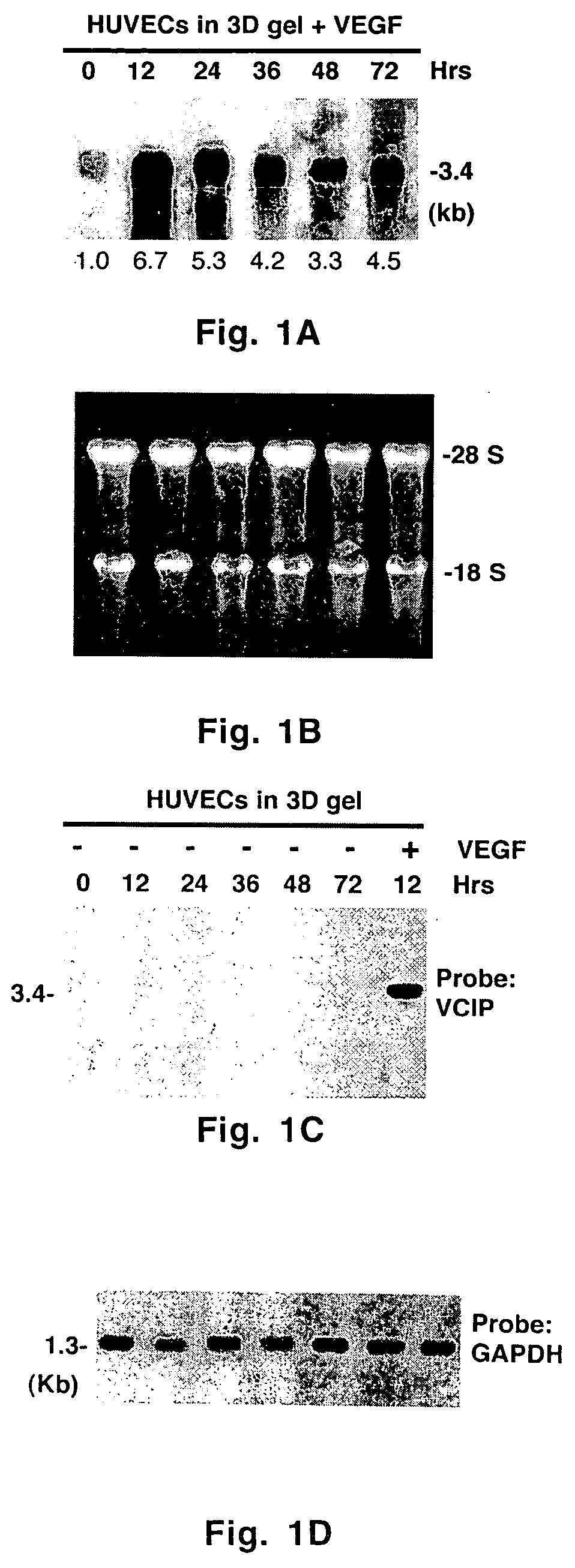
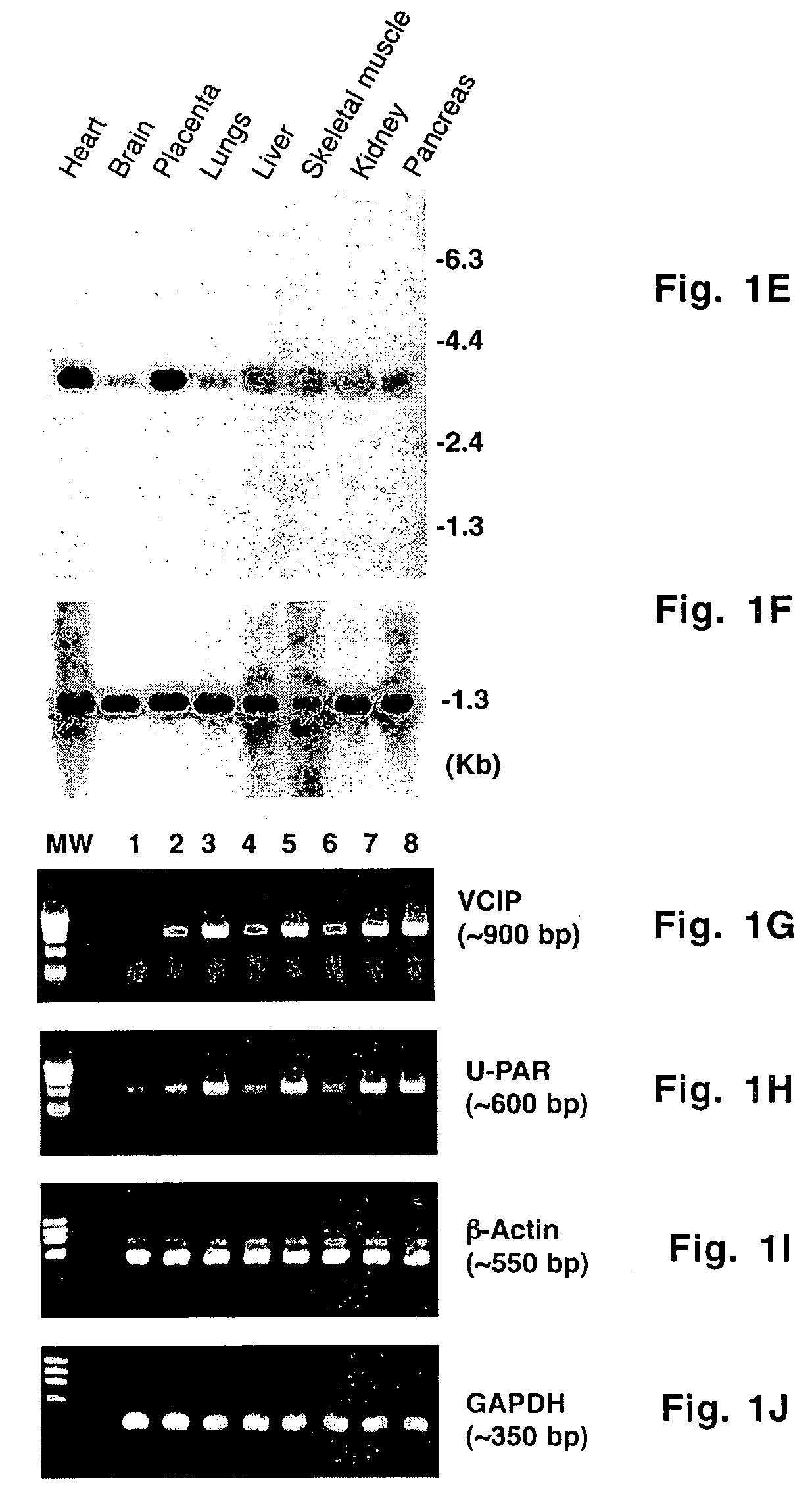
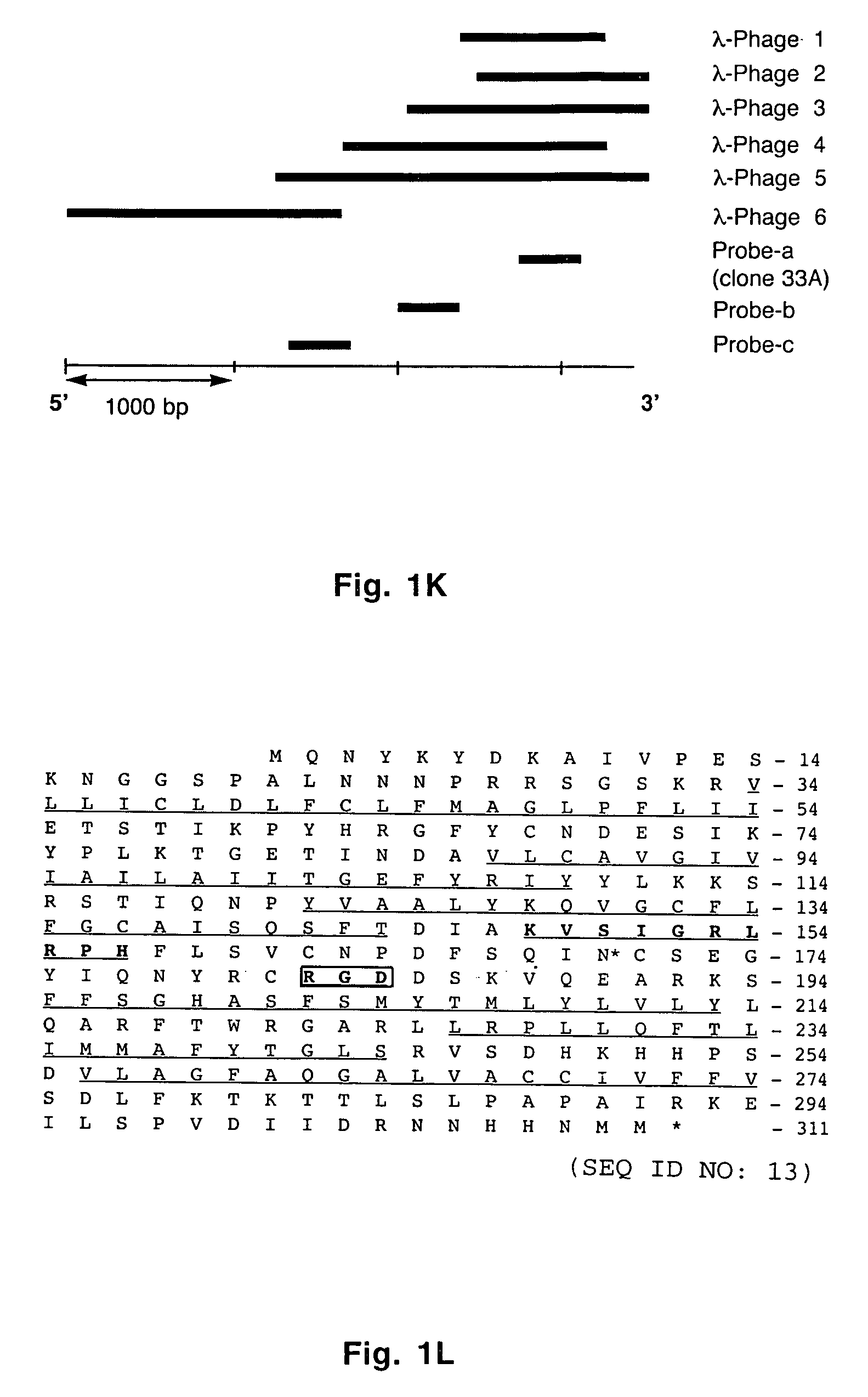
Uses of vascular endothelial growth factor and type I collagen inducible protein (VCIP)
InactiveUS20050002904A1Easy adhesionEasy to spreadBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCell–cell interactionIntegrin ligand
Vascular endothelial growth factor and type I collagen inducible protein (VCIP), also known as phosphatidic acid phosphatase 2b (PAP2b), was identified in a functional assay of angiogenesis. Previously, VCIP was not known to function as an integrin ligand. The present invention discloses VCIP-derived peptides and proteins act as integrin ligands. Since VCIP-derived peptides or proteins are capable of inhibiting specific cell-cell interactions, such inhibitors of cell-cell interactions would be useful for developing novel therapeutic approaches to treat diseases where these interactions have clear pathological consequences. For example, VCIP / PAP2b can be a novel target for anti-angiogenic, anti-cancer and anti-metastatic therapy.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Screening assay to identify correctors of protein trafficking defects
InactiveUS20110009351A1Significant differenceLimited effectivenessBiocideMetabolism disorderDiseaseClinical settings
The present invention relates to a novel assay or screen for identifying compounds with potential therapeutic value for the treatment of protein trafficking diseases such as Cystic Fibrosis (CF) and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (NDI). The usual approach involves expressing the mutant form of the gene in cells and assaying function in a multiwell format when cells are exposed to libraries of compounds. Although such functional assays are useful, they do not directly test the ability of a compound to correct defective trafficking of the protein. To address this a novel corrector screening assay for CF has been developed in which the appearance of the mutant protein at the cell surface is measured as the assay output. This assay was used to screen more than 3100 compounds. This novel screening approach to protein trafficking diseases is robust and general, and may enable the selection of molecules that can be translated rapidly to a clinical setting.
Owner:TRAFFICK THERAPEUTICS
Parallelized sample handling
InactiveUS20160114322A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFunctional assayComputational biology
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
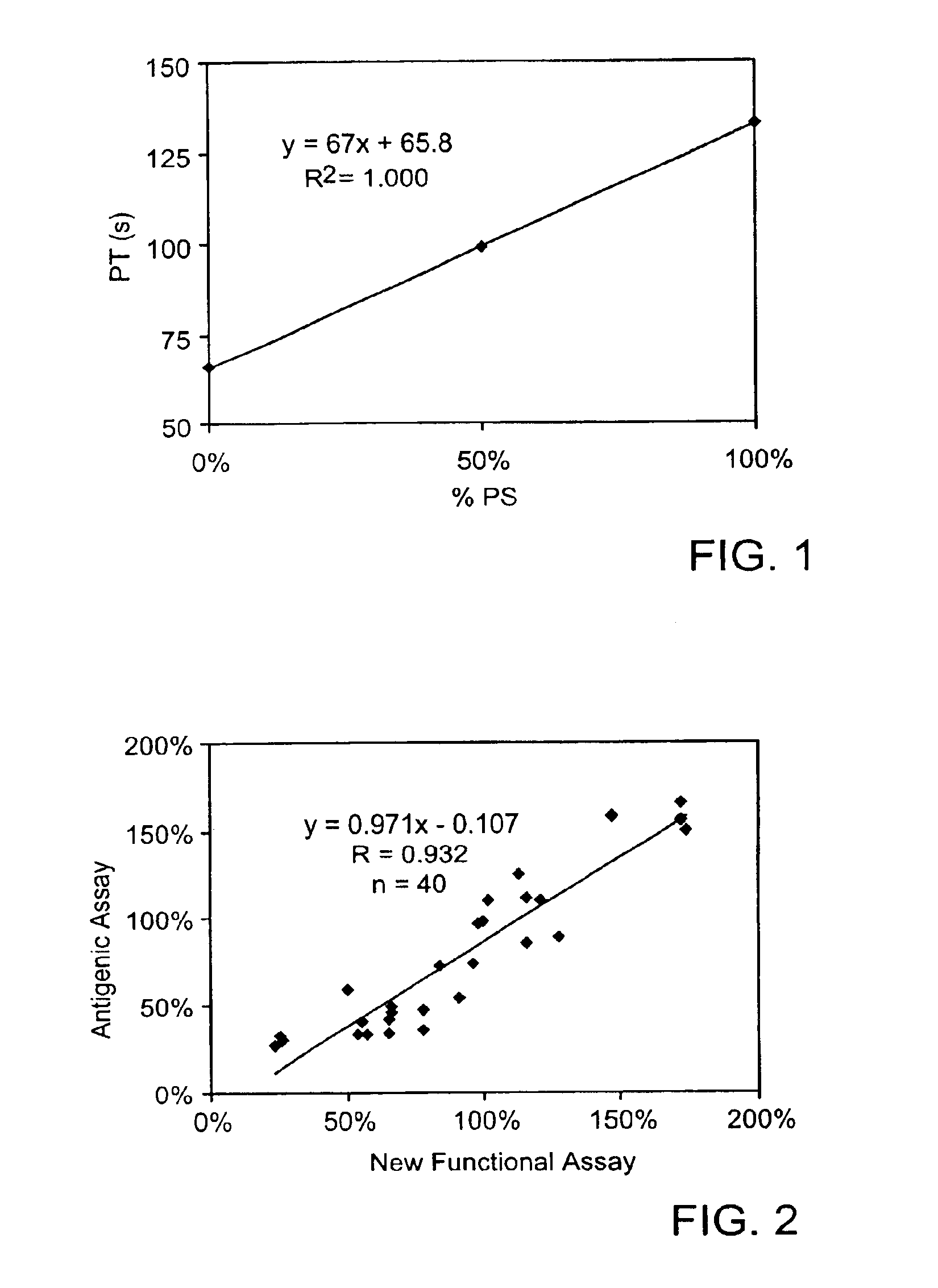
Protein S functional assay and kit therefor
The invention relates generally to a new functional protein S assay and kit that is based on the ability of endogenous protein S to prolong clotting time. In the assay procedure, a test plasma sample is diluted with protein S deficient plasma, followed by the addition of purified or recombinant tissue factor (pTF or rTF), purified natural or synthetic phospholipid (pPL or sPL) and activated protein C (APC) or protein C activator (PCA). The clotting time is then measured and compared to a standard curve or a normal control.
Owner:INSTR LAB
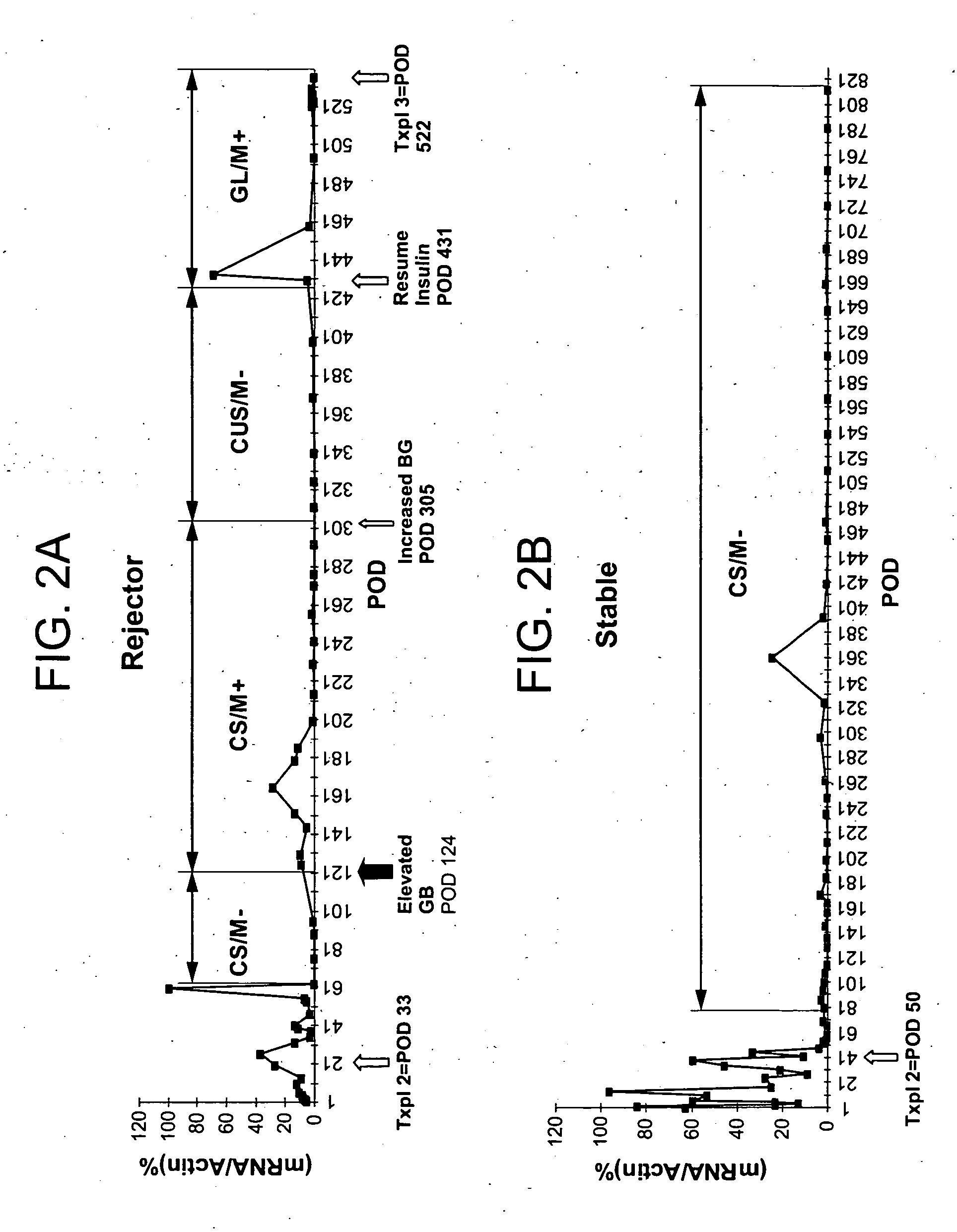
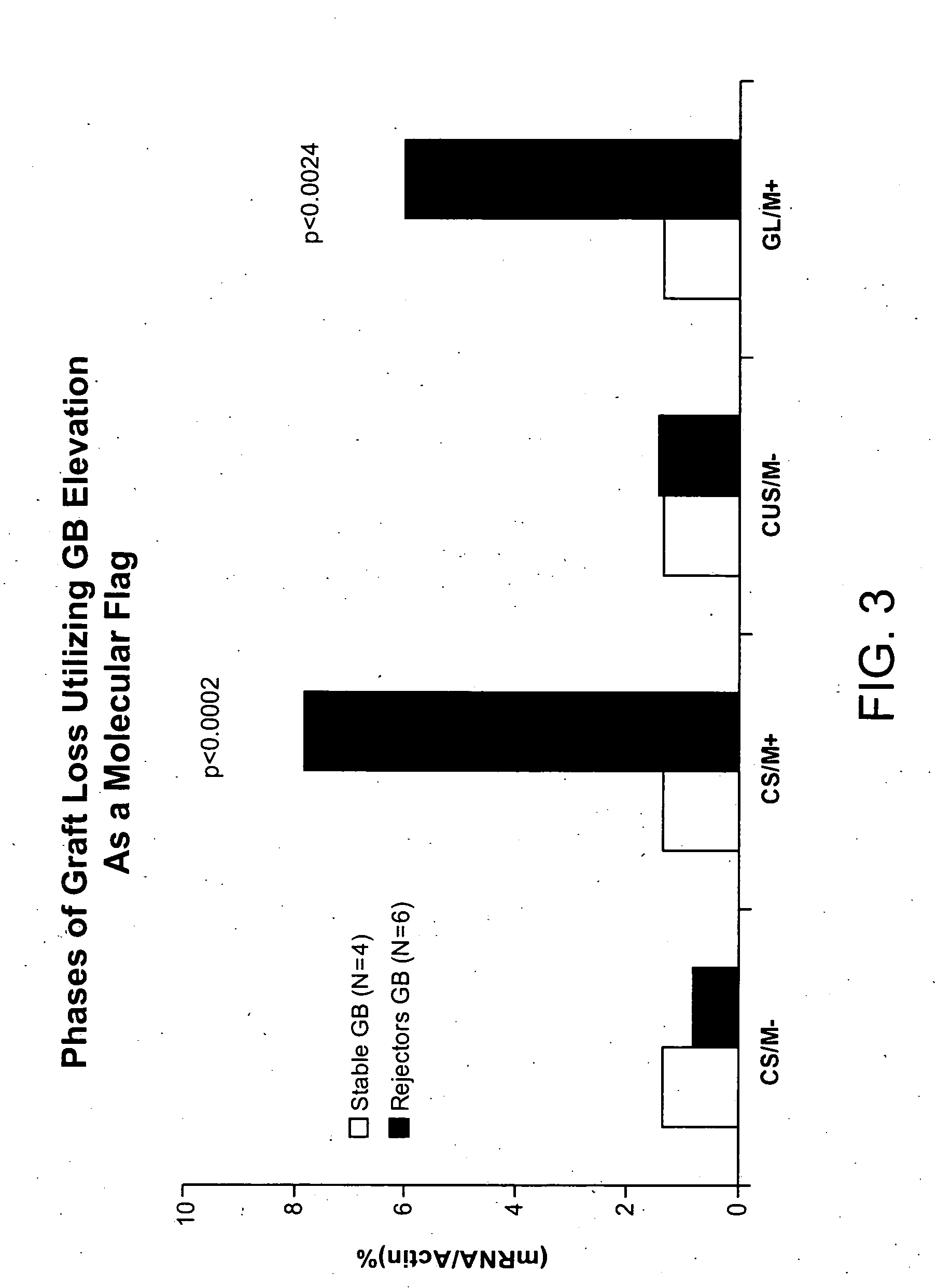
Molecular dissection of cellular responses to alloantigen or autoantigen in graft rejection and autoimmune disease
InactiveUS20060263343A1High expressionBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementAutoimmune conditionAuto antigen
An antigen-specific T-cell response to alloantigen, tissue-specific antigen (e.g., islet antigen or other autoantigens involved in autoimmune disease), or self (or host) antigen is detected at an early stage of graft rejection or recurrent autoimmunity. An increase in cytotoxic lymphocyte gene (CLG) expression in peripheral blood is a risk factor for development of deleterious immune responses, which may be confirmed by functional assays. For example, the distinction between production of regulatory or inflammatory cytokines by T cells may dissect the type of immune response which is being induced: the survival of transplanted islet cells used to treat type 1 diabetes may be monitored, loss of the transplant by graft rejection (i.e., an alloantigen target) may be distinguished from autoimmune disease (i.e., a self or host antigen target).
Owner:BECKMAN COULTER INC +1
High throughput functional genomic screening methods for osteoarthritis
InactiveUS20060188885A1Microbiological testing/measurementSkeletal disorderFunctional assayGene product
High-throughput functional screening assays are provided that identify genes and gene products that are associated with the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis (OA) in chondrocytes. In addition, genes and gene products identified by such functional assays are also provided. The genes and gene products provided herein are useful inter alia for diagnosing OA in individuals and as drug targets for identifying drugs to treat OA.
Owner:BODIAN DALE +4
Isolation and Use of Melanoma Cancer Stem Cells
ActiveUS20120225073A1Delay is slowSufficient amountPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementPrimary tumorFunctional assay
A set of markers for melanoma cancer stem cells are provided. The cells can be prospectively isolated or identified from primary tumor samples, and possess the unique properties of cancer stem cells in functional assays for tumor initiation, cancer stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. In addition, cancer stem cells can be used as a predictor for disease progression. The CSC have the phenotype of being positive for expression CD271.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Identification and isolation of acute myeloid leukemia stem cells
ActiveUS7767410B2Microbiological testing/measurementVertebrate cellsCancers diagnosisFunctional assay
Acute myeloid leukemia stem cells (AMLSC) are identified. The cells can be prospectively isolated or identified from patient samples, and are shown to possess the unique properties of cancer stem cells in functional assays for cancer stem cell self-renewal and differentiation, and in cancer diagnosis.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
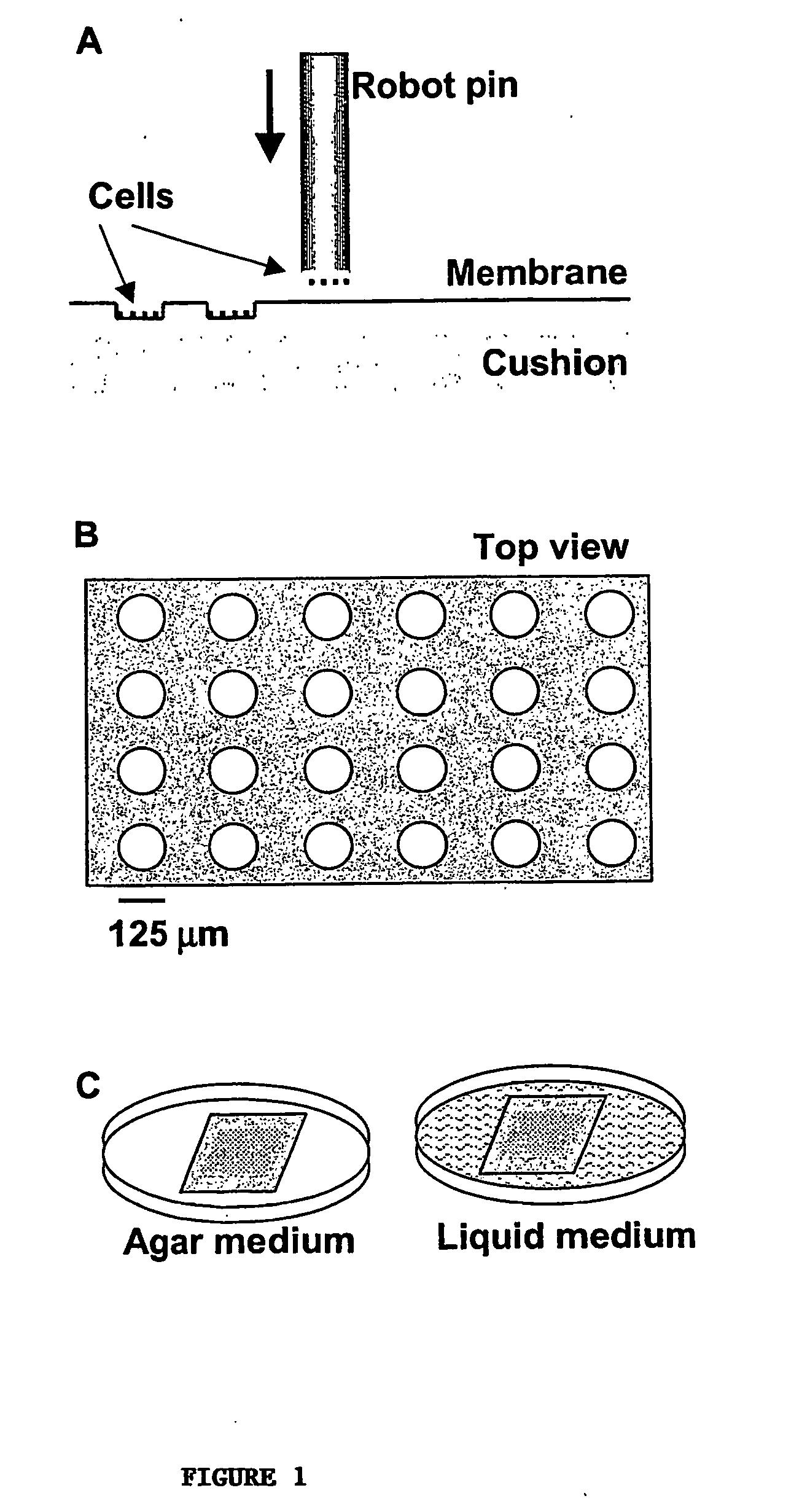
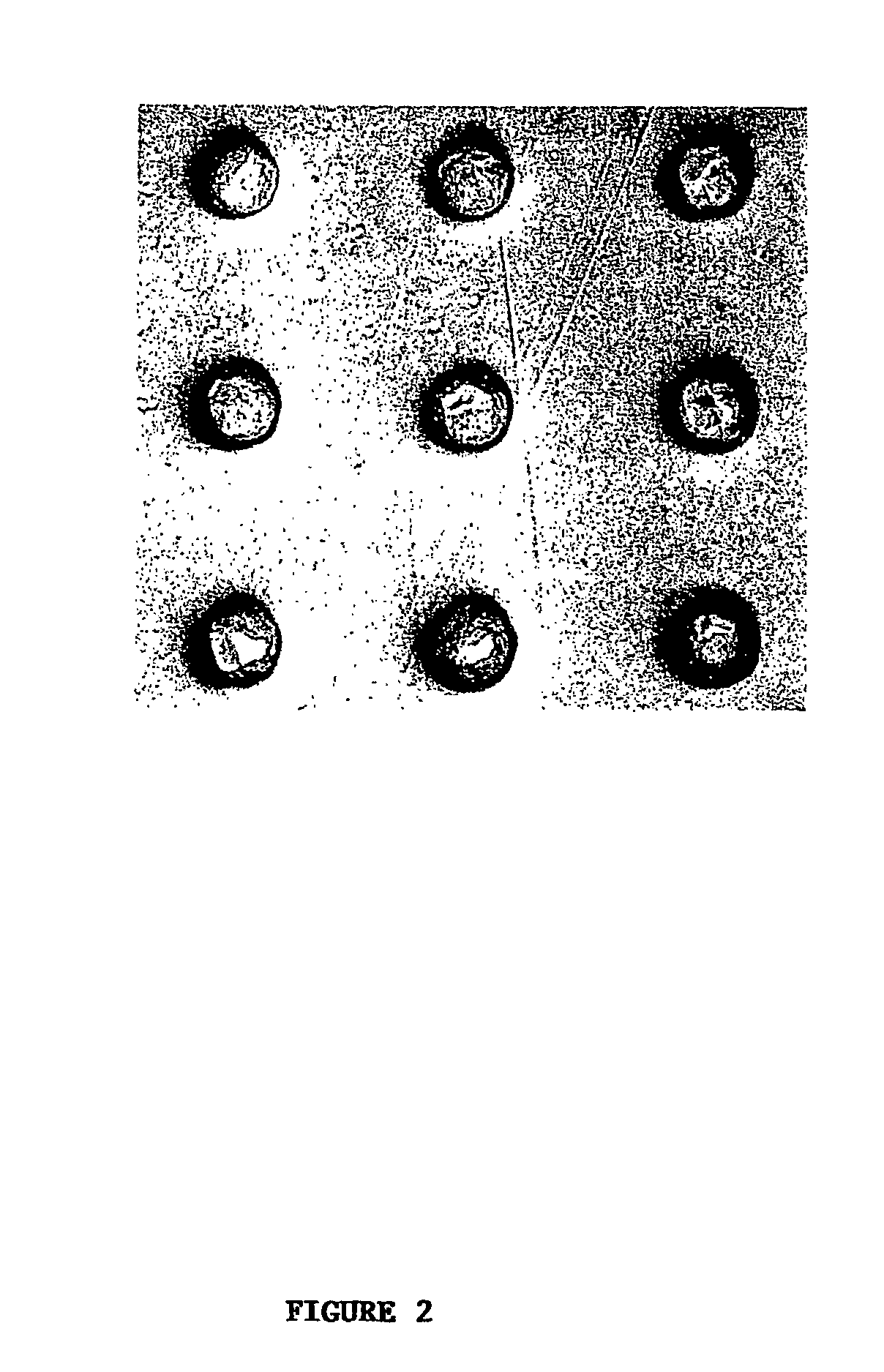
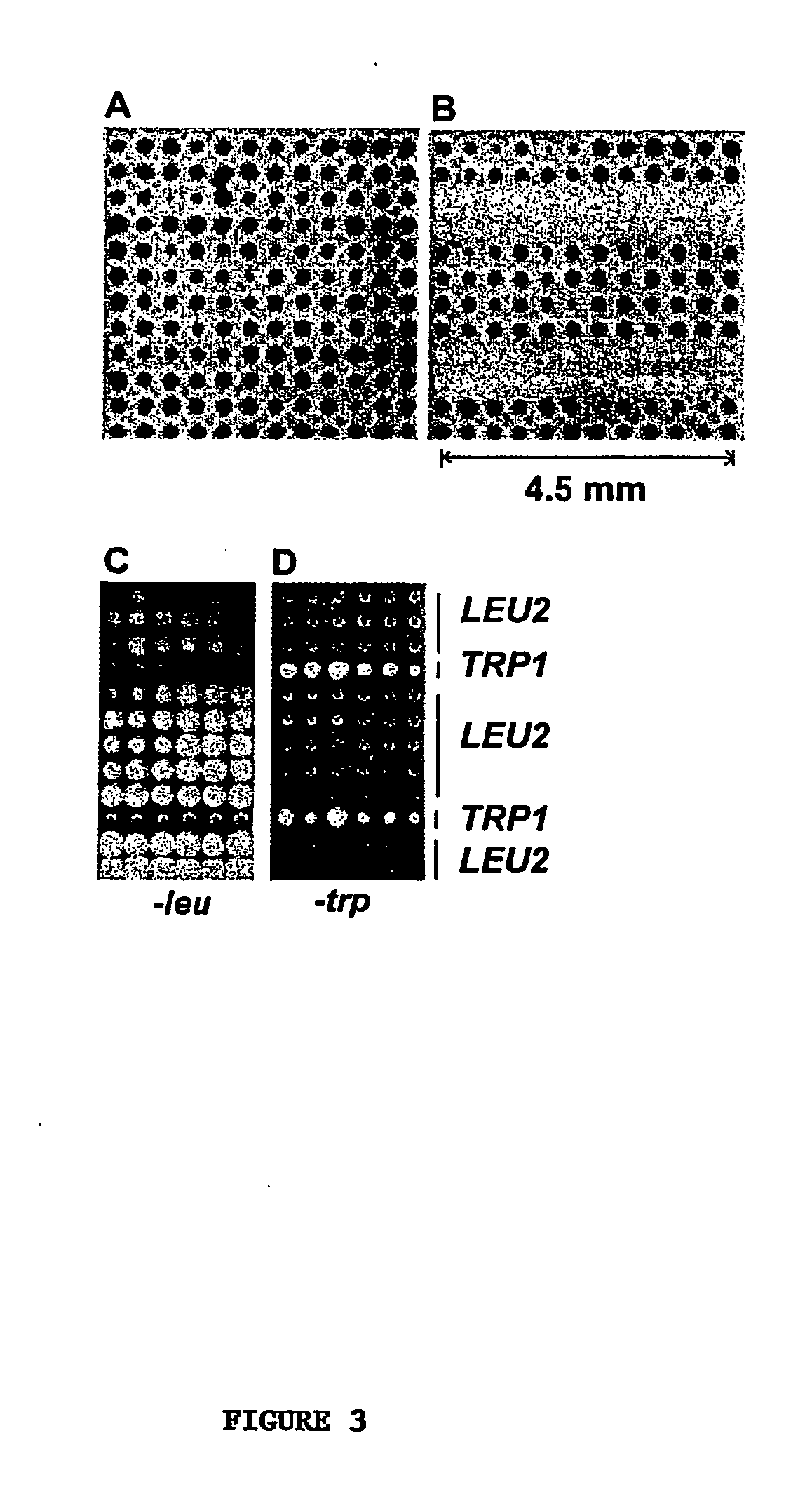
High-density cell microarrays for parallel functional determinations
InactiveUS20050014155A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh-Density MicroarrayHigh density
Disclosed are methods for generating high-density cell microarrays. The methods generally involve forming nanocraters on a permeable membrane surface and inoculating the nanocraters with cells, proteins, or other molecules. The high-density microarrazs of the invention are useful for large-scale, high throughput phenotypic determinations of gene activities.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
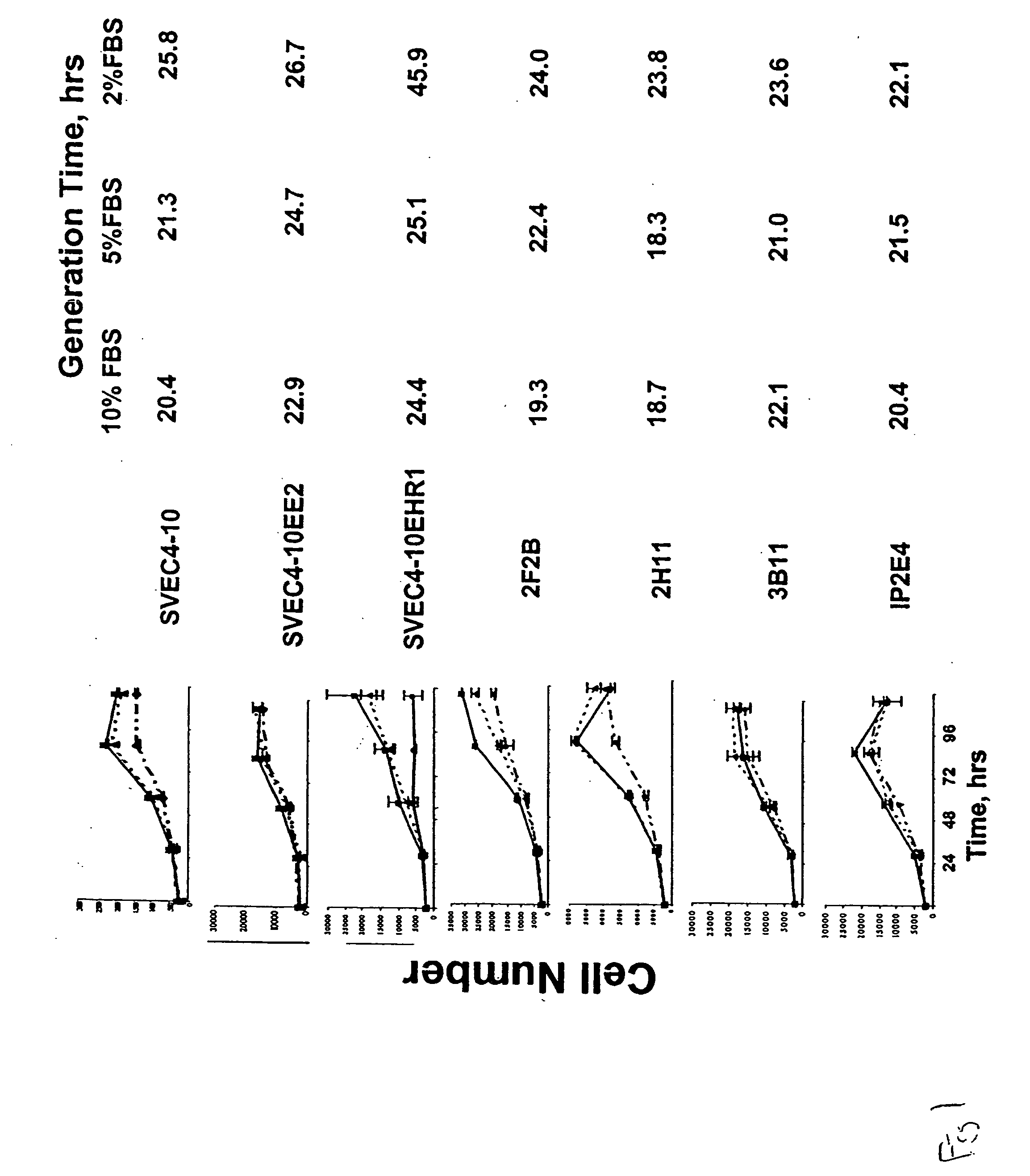
Mammalian endothelial cell model systems
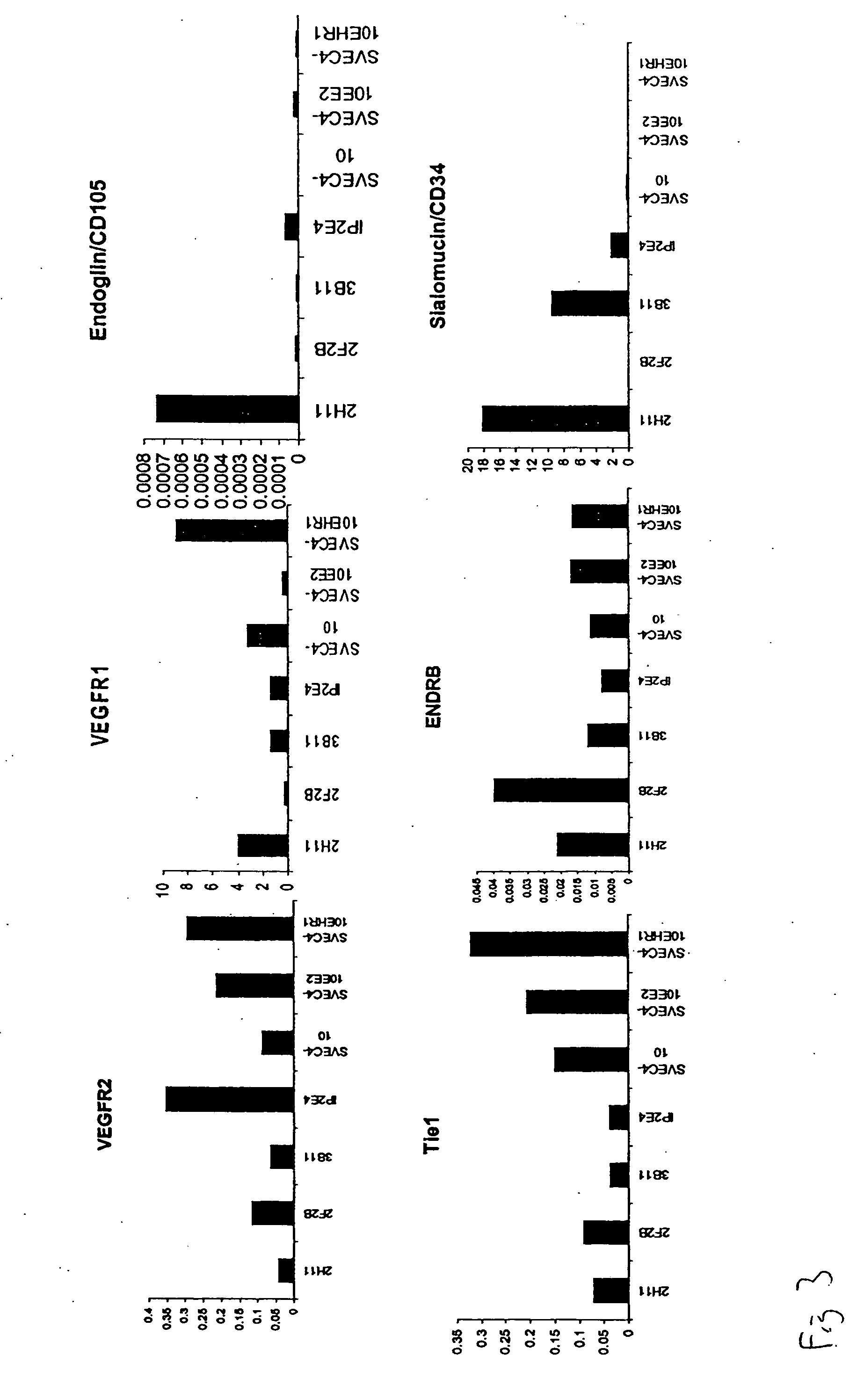
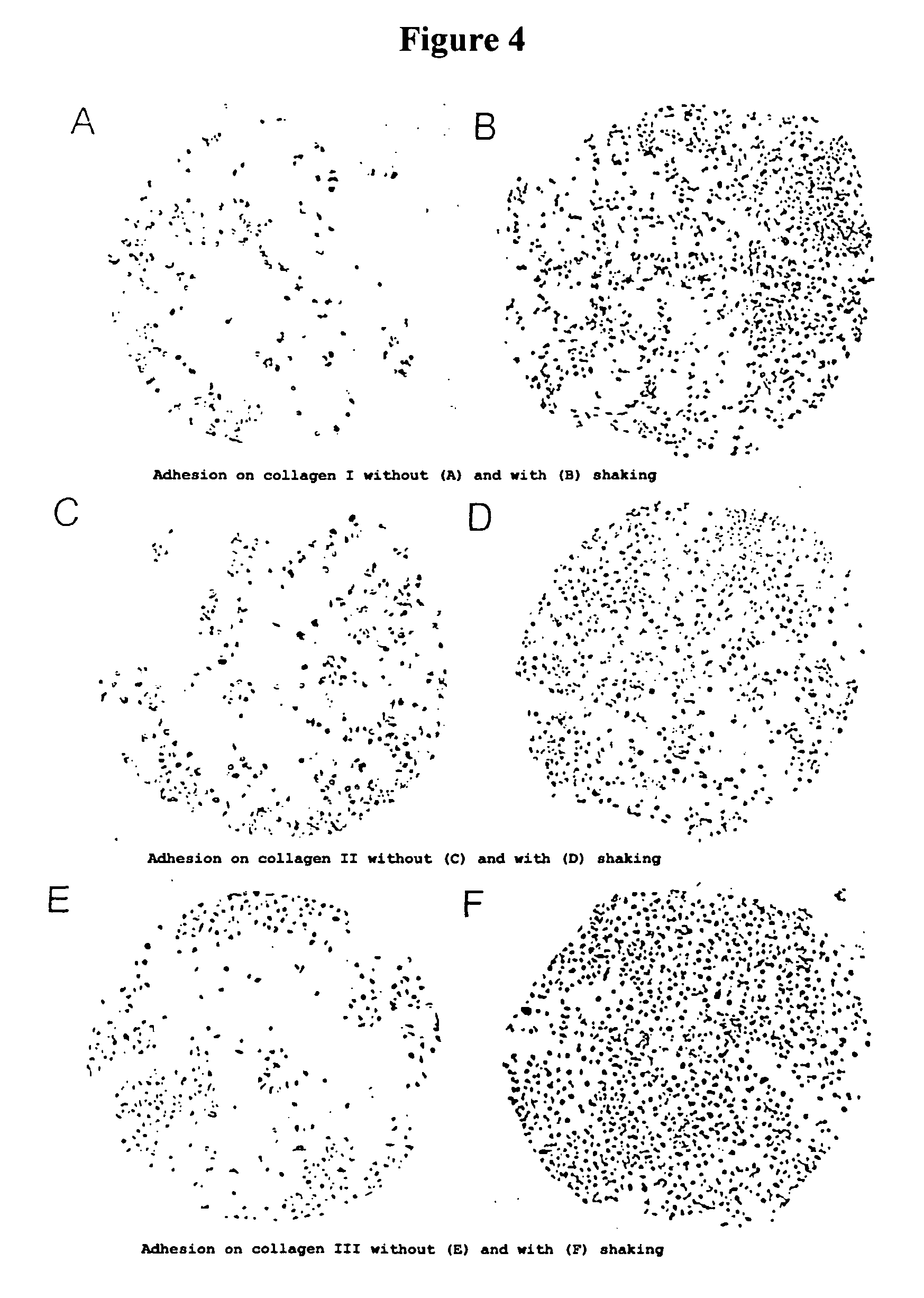
InactiveUS20050069528A1Increased formationReduce formationBiocideArtificial cell constructsAbnormal tissue growthTube formation
AC133+ / CD34+ cells isolated from human bone marrow can be stimulated with the pro-angiogenic factors VEGF, bFGF, and heparin, resulting in the generation of a population of cells that is adherent and possesses many of the same properties as mature endothelial cell types, HMVECs and HUVECs. The newly-formed, endothelial-like cells are referred as adherent endothelial precursor cells (aEPCs); these cells appear to be intermediates between haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and mature endothelial cells. Direct comparison of aEPCs with HMVECs and HUVECs in several in vitro functional assays, such as tube formation, migration, invasion, and expression of cells surface markers, reveals differences and similarities. In a Matrigel™ matrix angiogenesis assay the aEPCs form vessels in vivo and interact with human ovarian cancer cells. Mouse cell lines that are useful models for tumor endothelial cells are identified by determining mRNA and protein expression levels of murine homologs of tumor endothelial markers. Mouse cell lines selected as models for tumor endothelial cells can be used to evaluate pro-angiogenic and anti-angiogenic factors.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Identification and isolation of transitional cell carcinoma stem cells
InactiveUS20100267079A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPrimary tumorCancers diagnosis
Transitional cell carcinoma stem cells (TCCSC) are identified. The cells can be prospectively isolated or identified from primary tumor samples, and are shown to possess the unique properties of cancer stem cells in functional assays for cancer stem cell self-renewal and differentiation, and in cancer diagnosis.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
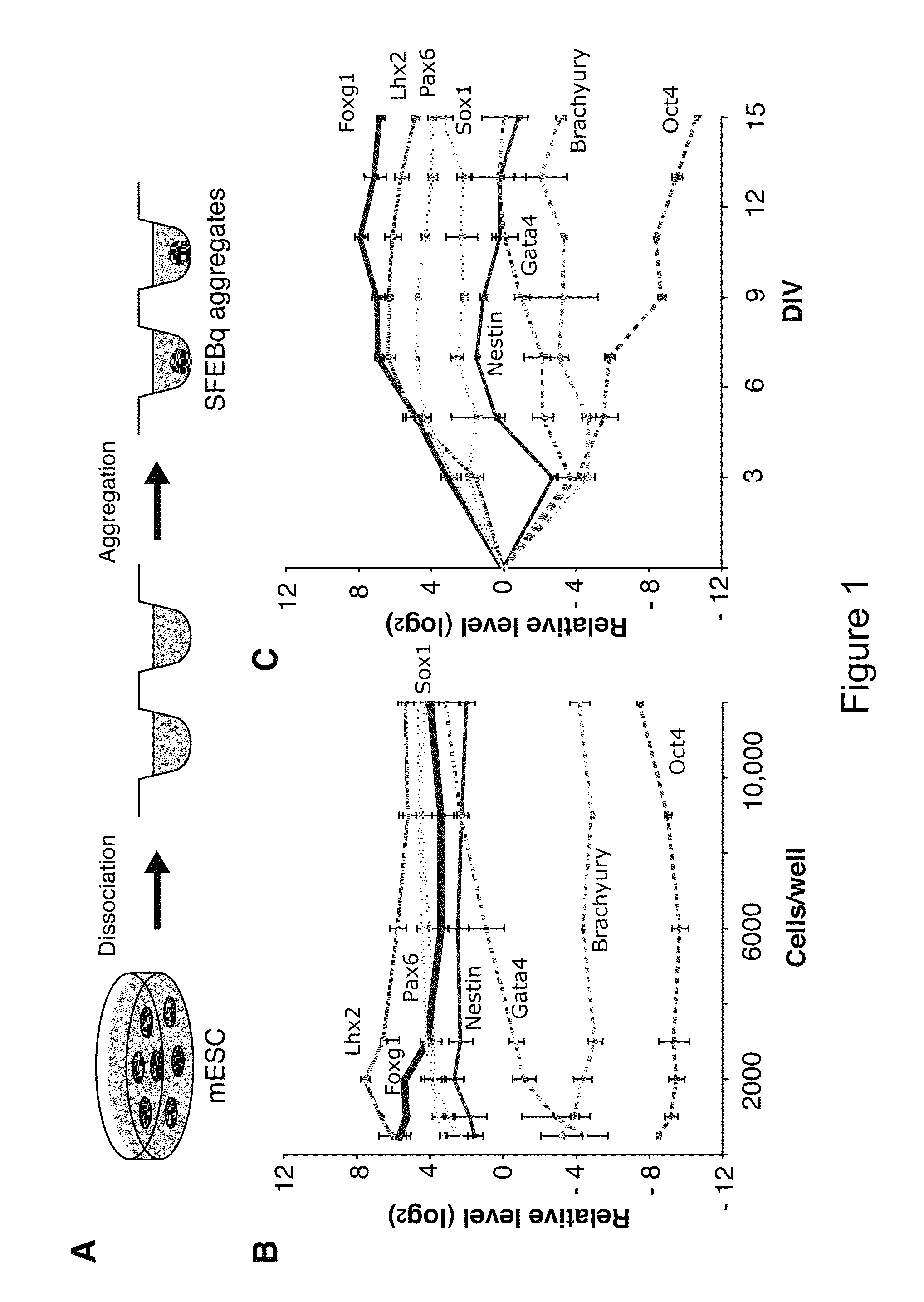
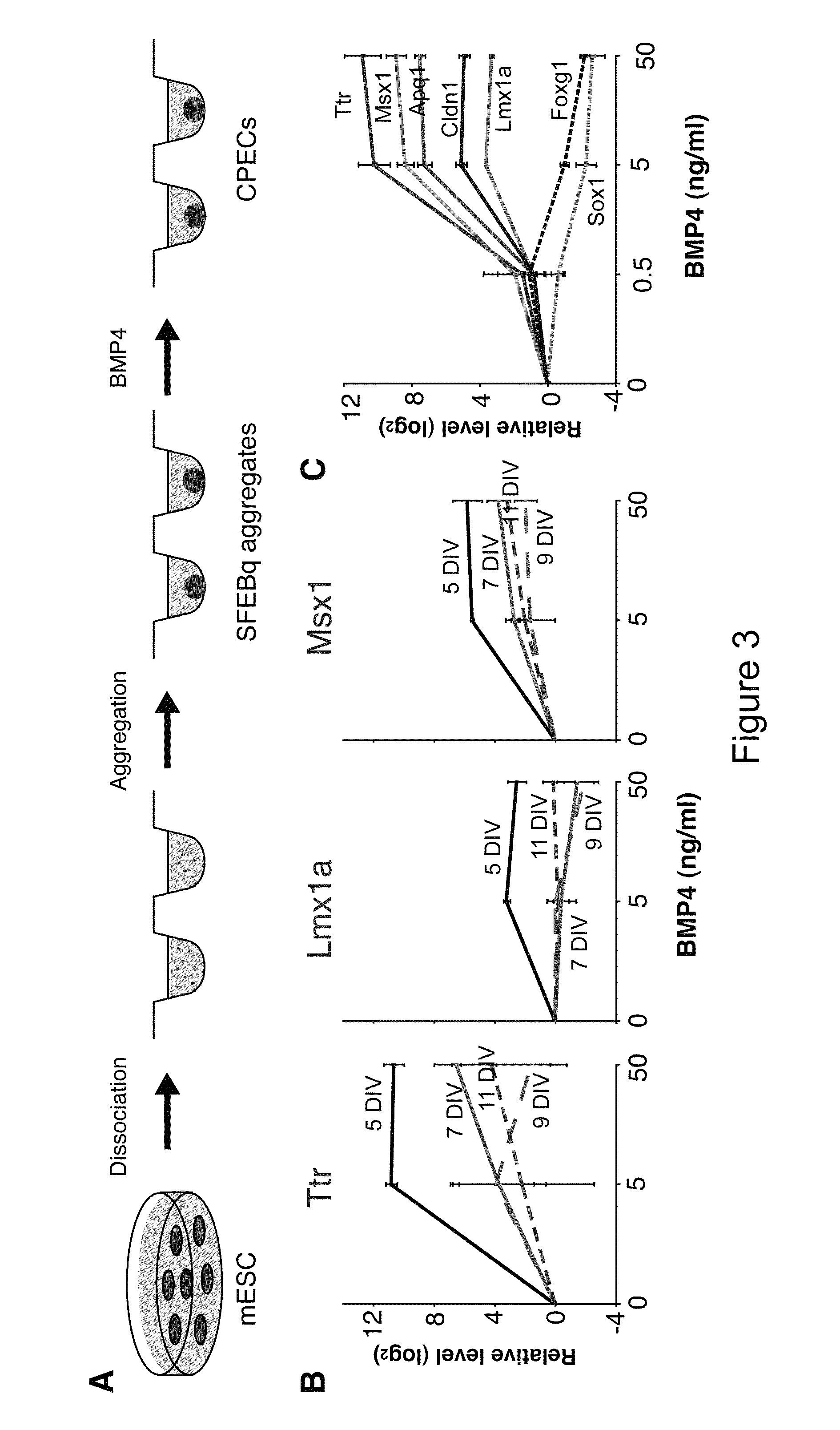
Generation of choroid plexus epithelial cells from human embryonic stem cells
Choroid plexus epithelial cells are generated in a culture medium using embryonic stem cells and adding an effective amount of bone morphogenetic protein and / or other members of the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) superfamily. Generation of such choroid plexus epithelial cells are confirmed using a combination of genetic markers, antibodies, histology inspection, functional assays, and integration into the endogenous choroid plexus in mice.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
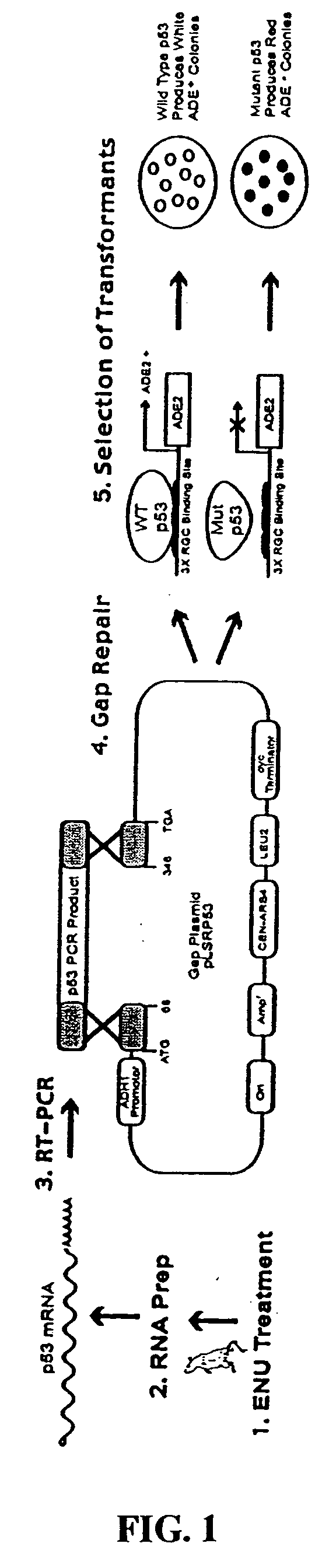
Methods of generating knock-out rodents
A method for generating knock-out rodents including rats and mice is disclosed. The method involves mutagenizing a rodent with a mutagen, obtaining progeny of the mutagenized rodent, and identifying, among the progeny, one progeny that carries a loss-of-function modification of a target gene. The preferred mutagen for generating knock-out mice and rats is N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea (ENU). The preferred screening assays for identifying a progeny of a mutagenized animal that carries a loss-of-function modification are yeast truncation assays and yeast functional assays. Knock-out rodents generated by the method of the present invention are also within the scope of the invention.
Owner:GOULD MICHAEL N
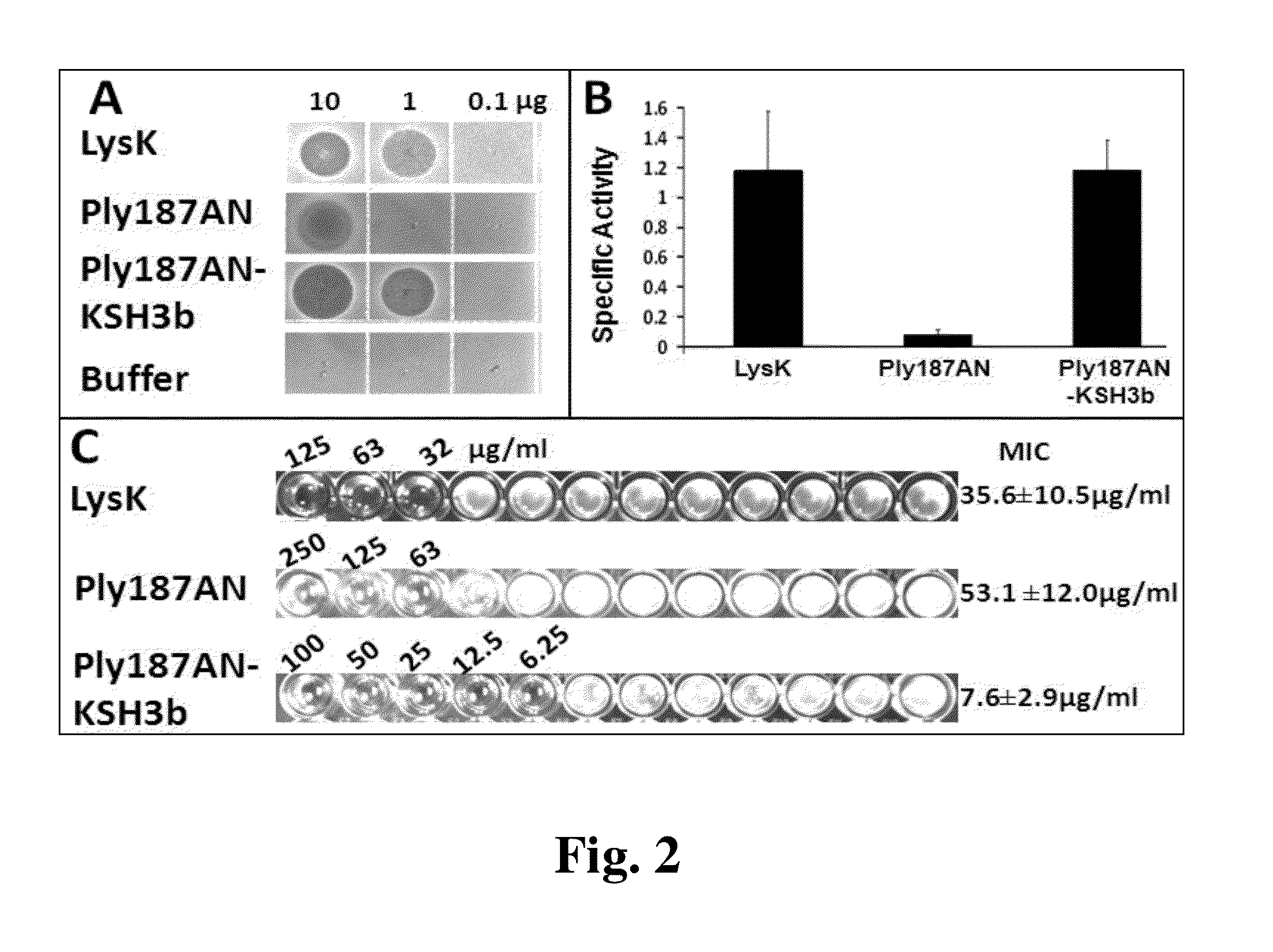
Enhanced antimicrobial lytic activity of a chimeric Ply187 endolysin
Peptidoglycan hydrolases are an effective new source of antimicrobials. A chimeric fusion protein of the Ply187 endopeptidase domain and LysK SH3b cell wall binding domain is a potent agent against Staphylococcus aureus in three functional assays.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Method and kit for performing functional tests on biological cells
InactiveUS20050214832A1Improve reliabilityGood reproducibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBiological cellMeasurement point
Owner:NMI NATURWISSENSCHAFTULCHES & MEDIZINISCHES INST AN DER UNIV TUEBINGEN
G-protein coupled receptors high-throughput functional assay
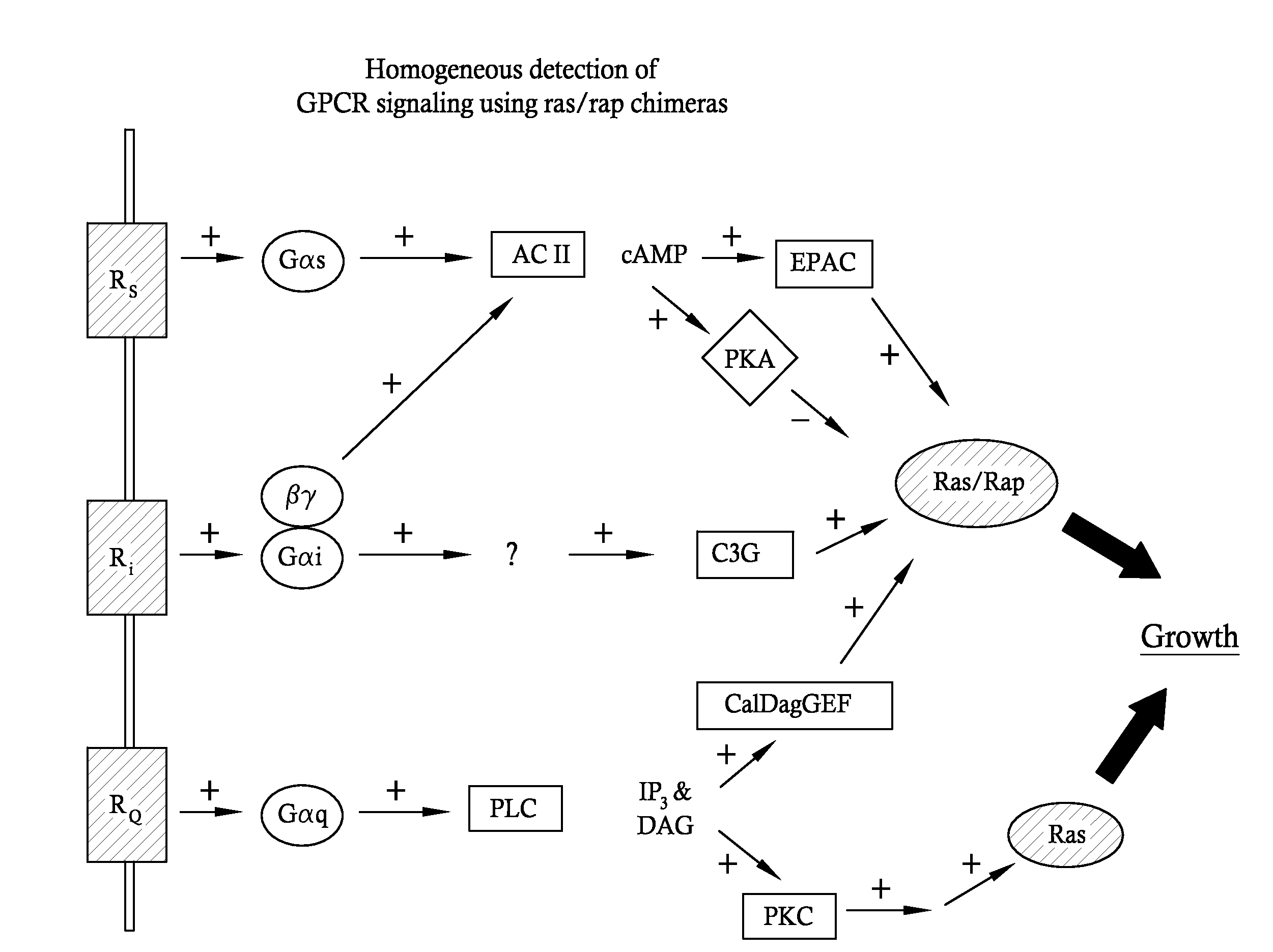
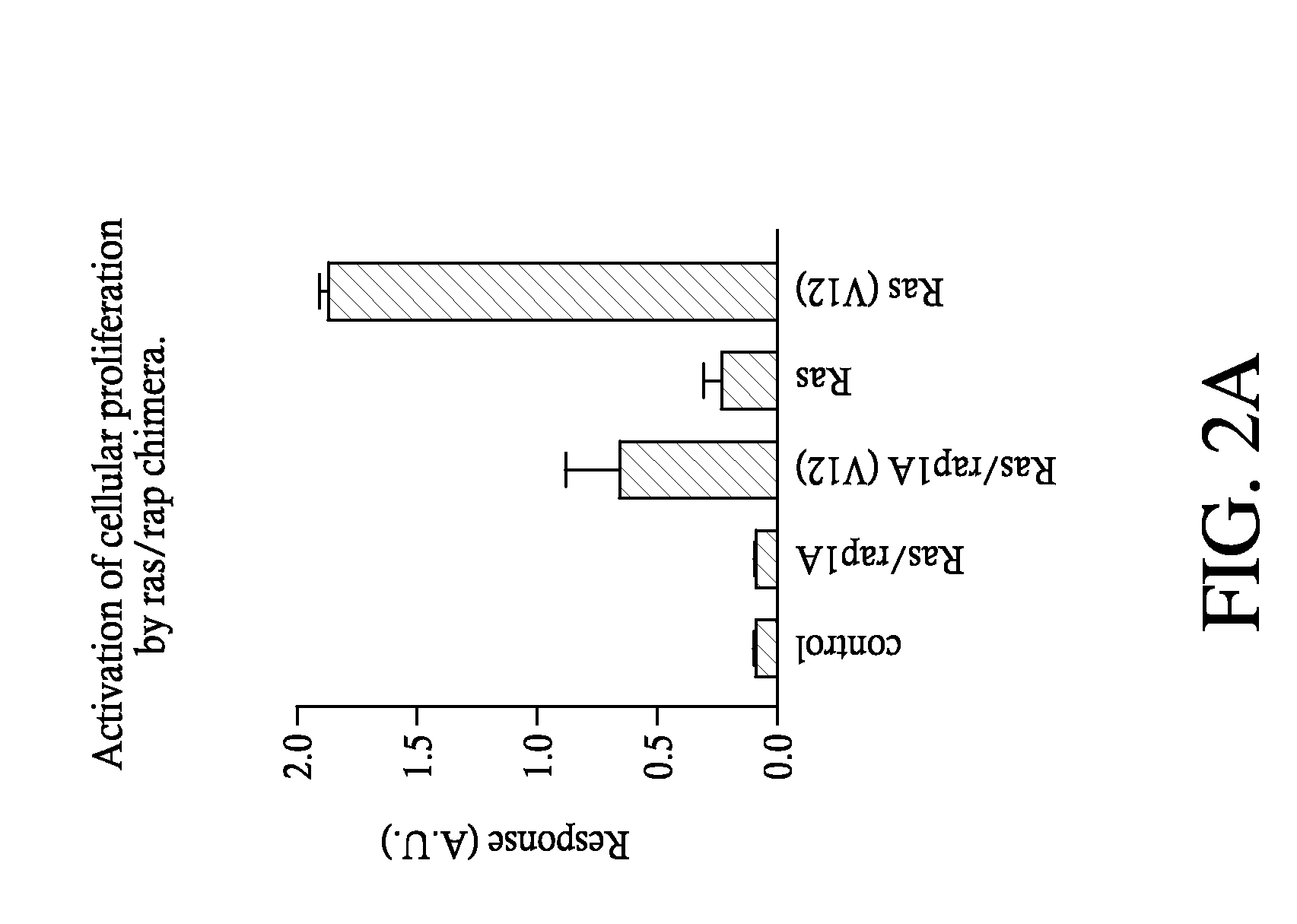
InactiveUS20080280303A1HydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementFunctional assayG protein-coupled receptor
Disclosed herein are methods for enabling or improving functional assays of G-protein coupled receptors through the use of co-expression of helper genes. In some cases, chimeras linking the regulatory domain of the rap1B protein to the effector region of the ras oncogene are used in conduction with existing functional assays for cellular proliferation. Furthermore, overexpression of other genes can further augment the enabling properties of ras / rap chimeras.
Owner:BURSTEIN ETHAN S +8
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com