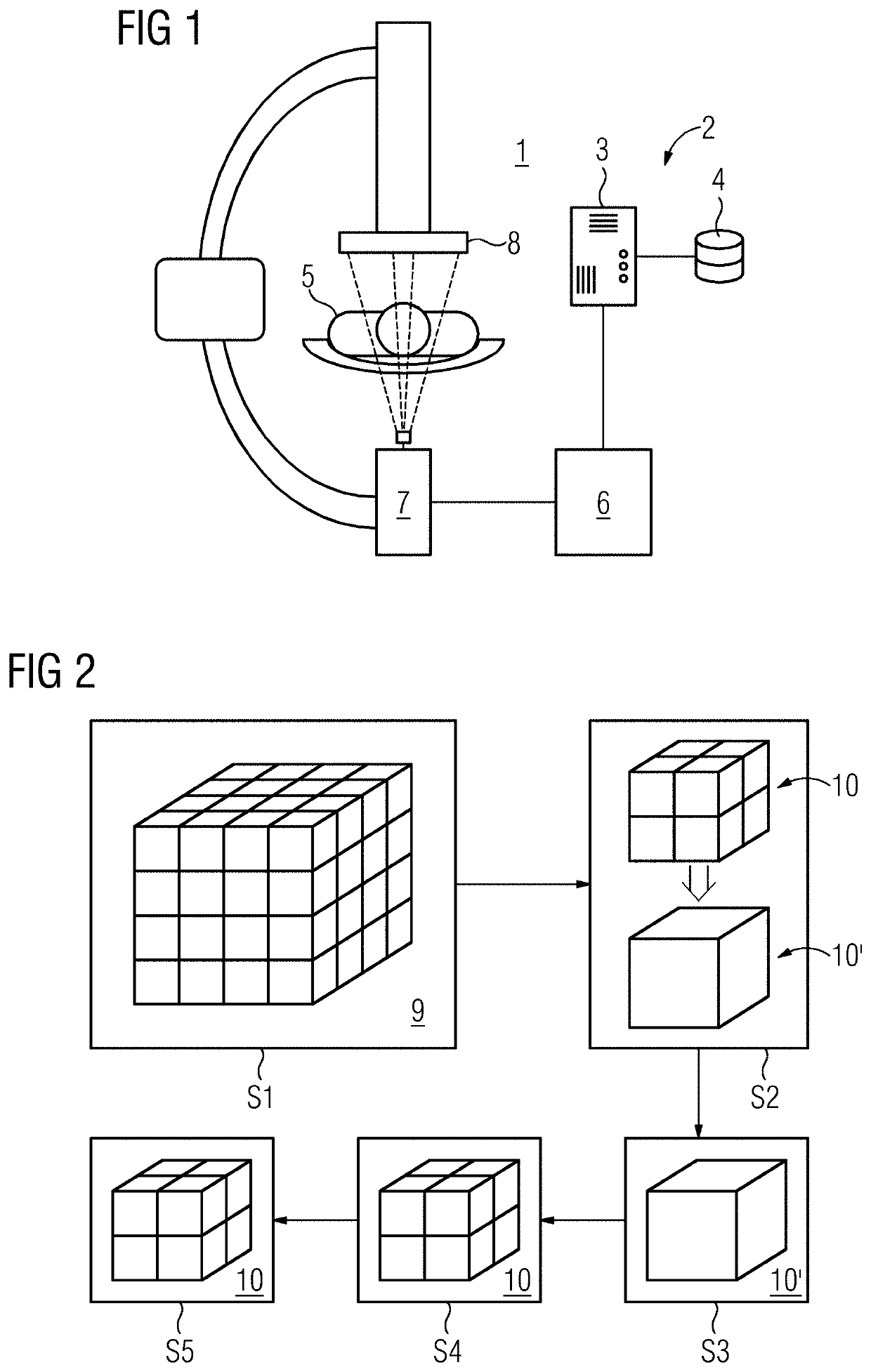
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Dose estimation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
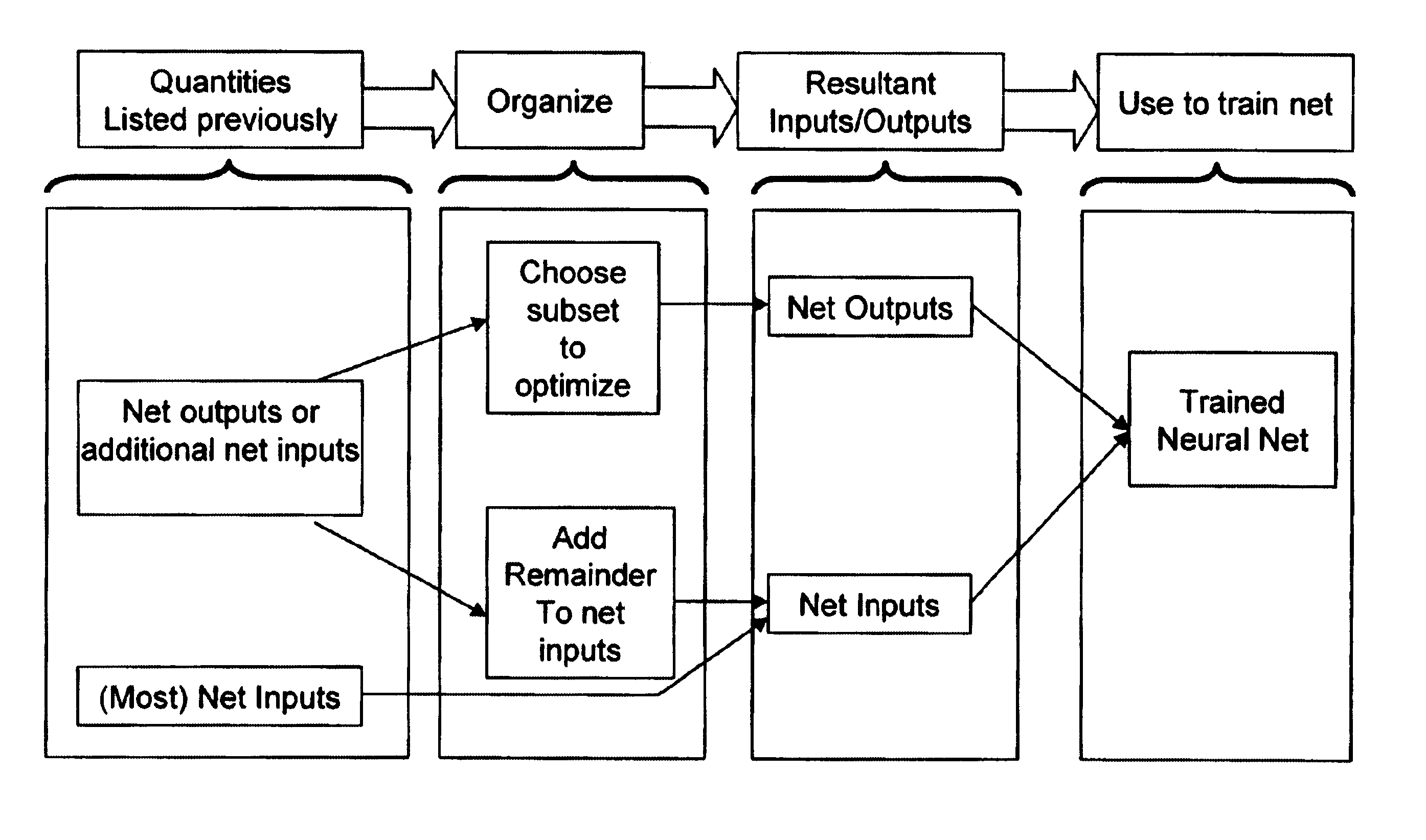
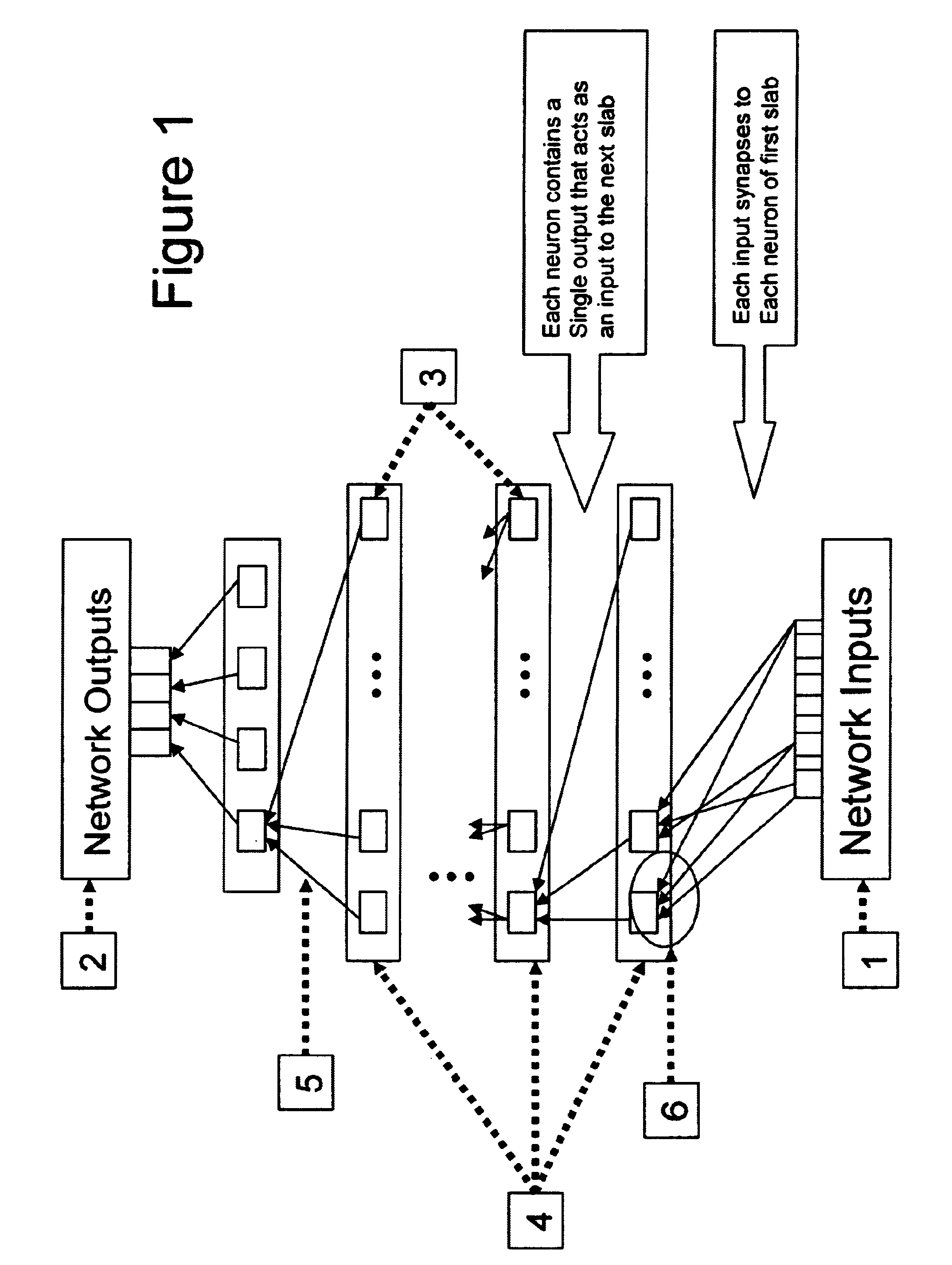
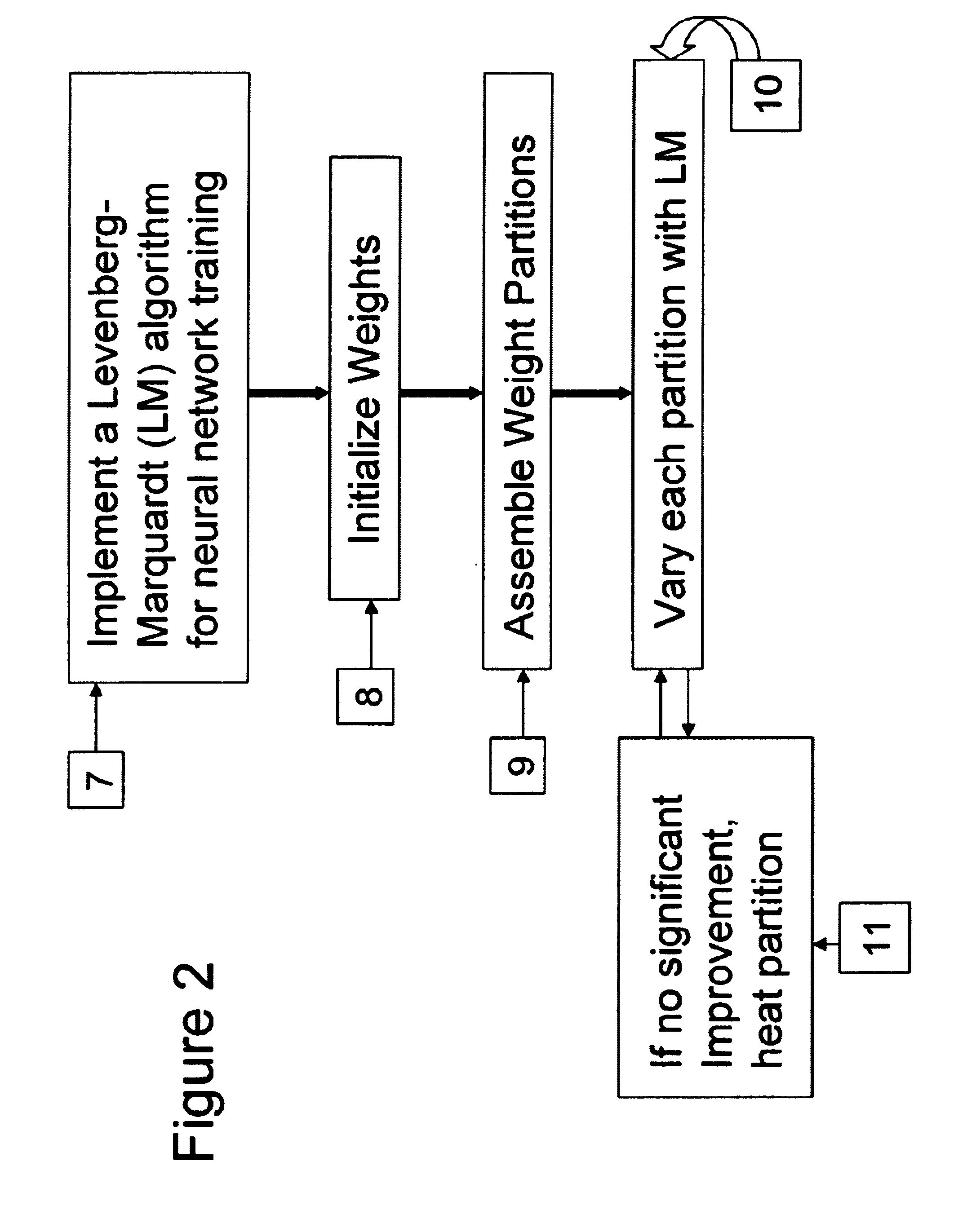
Neural network drug dosage estimation
InactiveUS6658396B1Improve accuracyGood precisionDrug and medicationsBiological neural network modelsNerve networkPatient characteristics
Neural networks are constructed (programmed), trained on historical data, and used to predict any of (1) optimal patient dosage of a single drug, (2) optimal patient dosage of one drug in respect of the patient's concurrent usage of another drug, (3a) optimal patient drug dosage in respect of diverse patient characteristics, (3b) sensitivity of recommended patient drug dosage to the patient characteristics, (4a) expected outcome versus patient drug dosage, (4b) sensitivity of the expected outcome to variant drug dosage(s), (5) expected outcome(s) from drug dosage(s) other than the projected optimal dosage. Both human and economic costs of both optimal and sub-optimal drug therapies may be extrapolated from the exercise of various optimized and trained neural networks. Heretofore little recognized sensitivities-such as, for example, patient race in the administration of psychotropic drugs-are made manifest. Individual prescribing physicians employing deviant patterns of drug therapy may be recognized. Although not intended to prescribe drugs, nor even to set prescription drug dosage, the neural networks are very sophisticated and authoritative "helps" to physicians, and to physician reviewers, in answering "what if" questions.
Owner:PREDICTION SCI
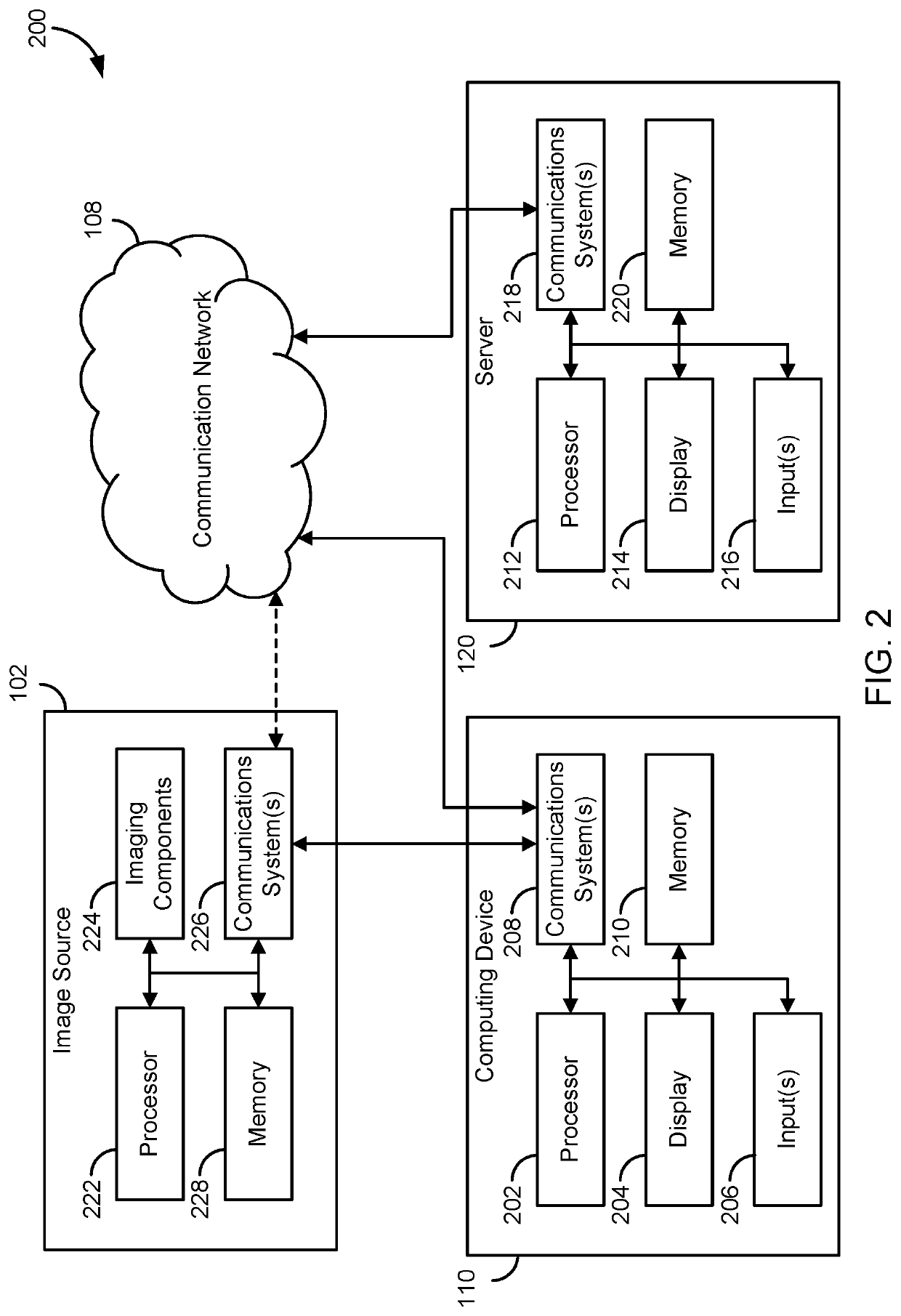
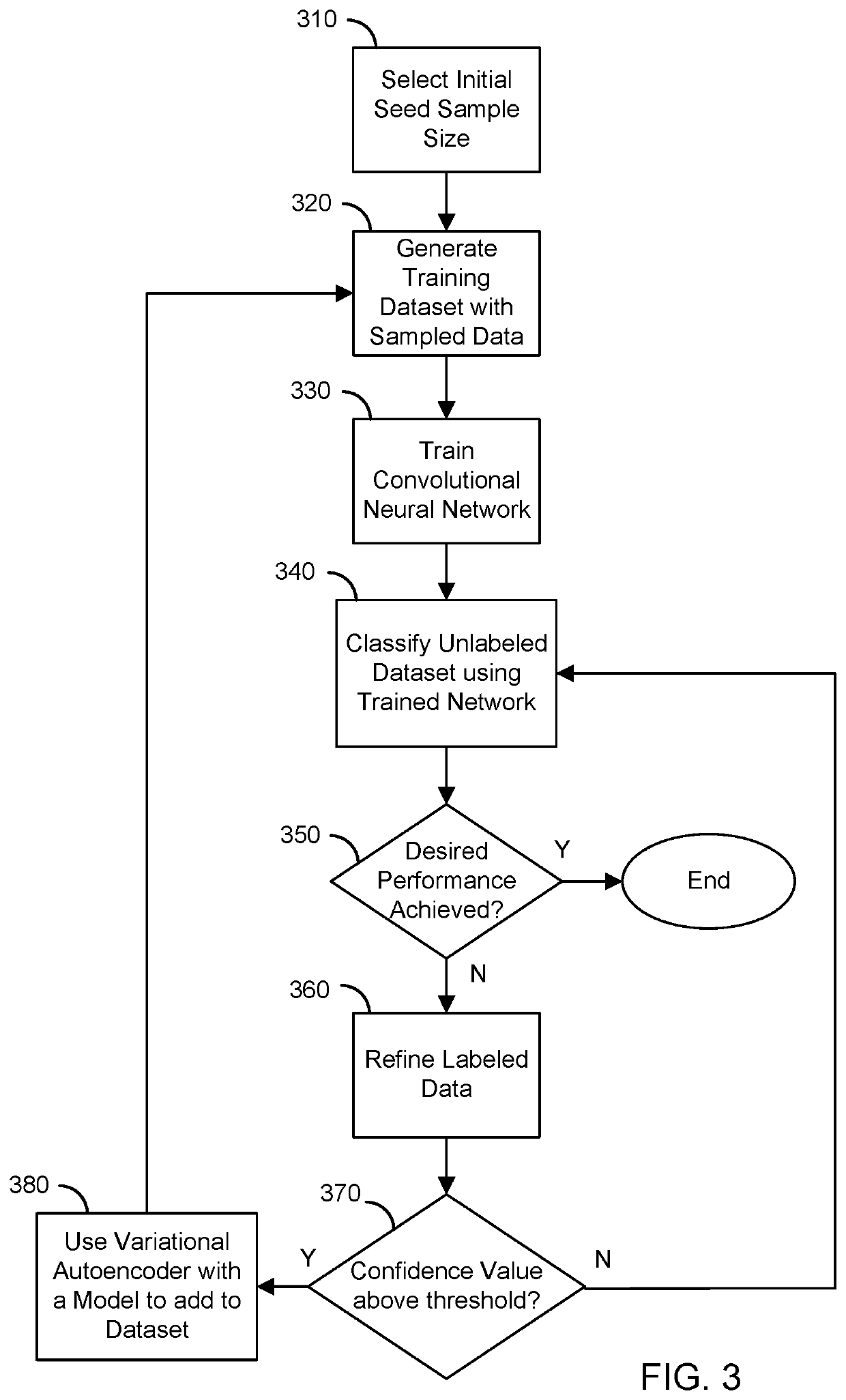
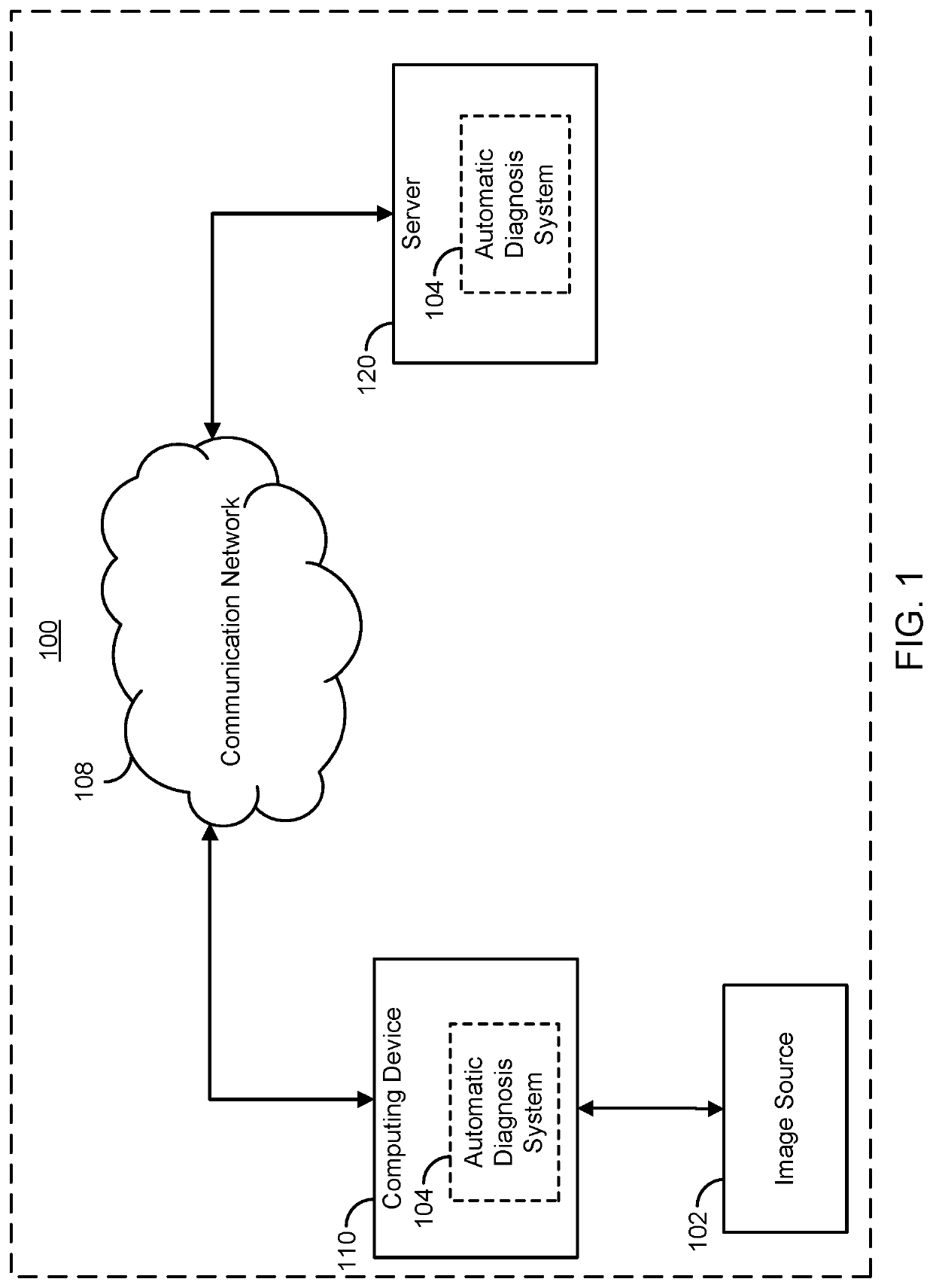
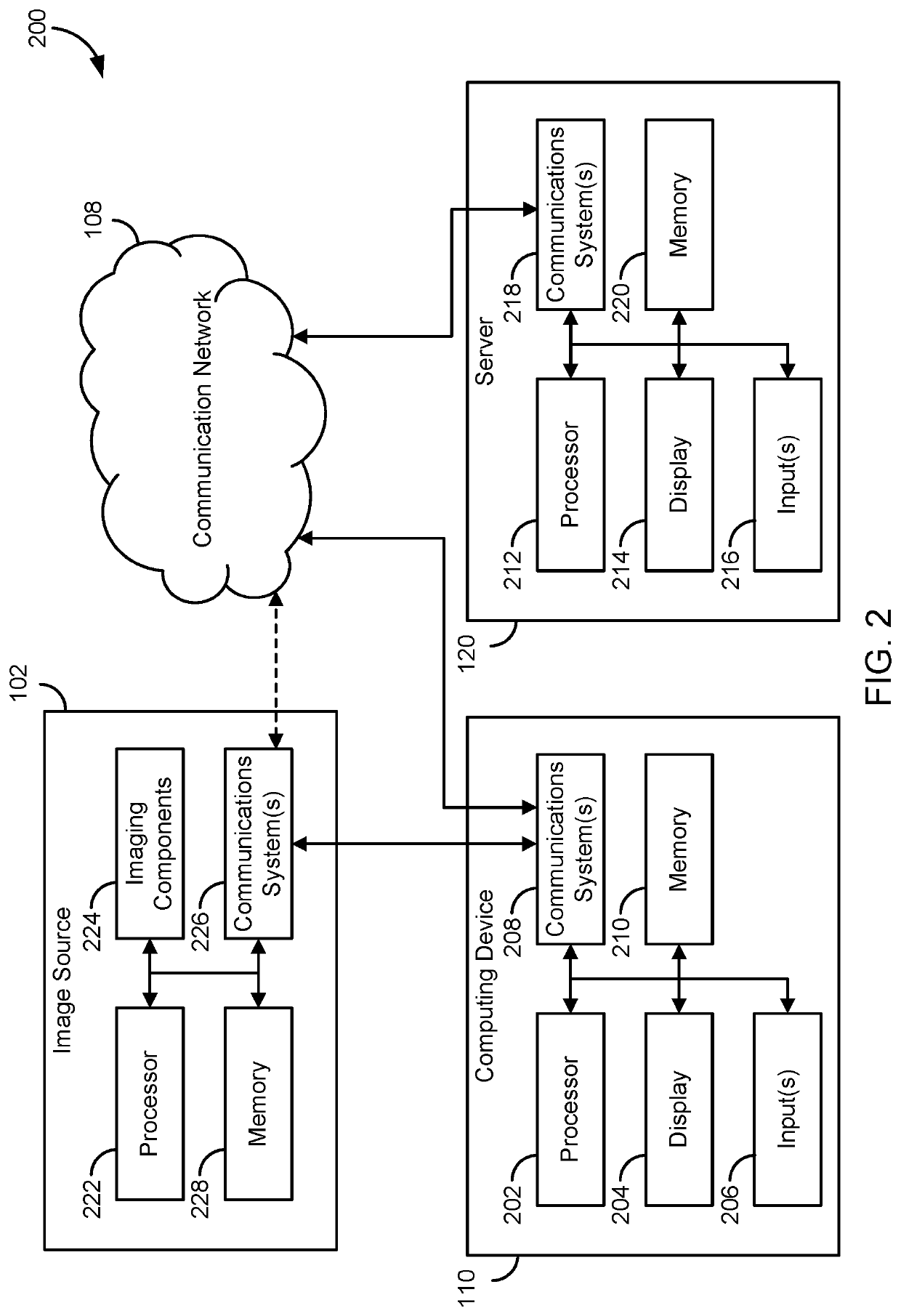
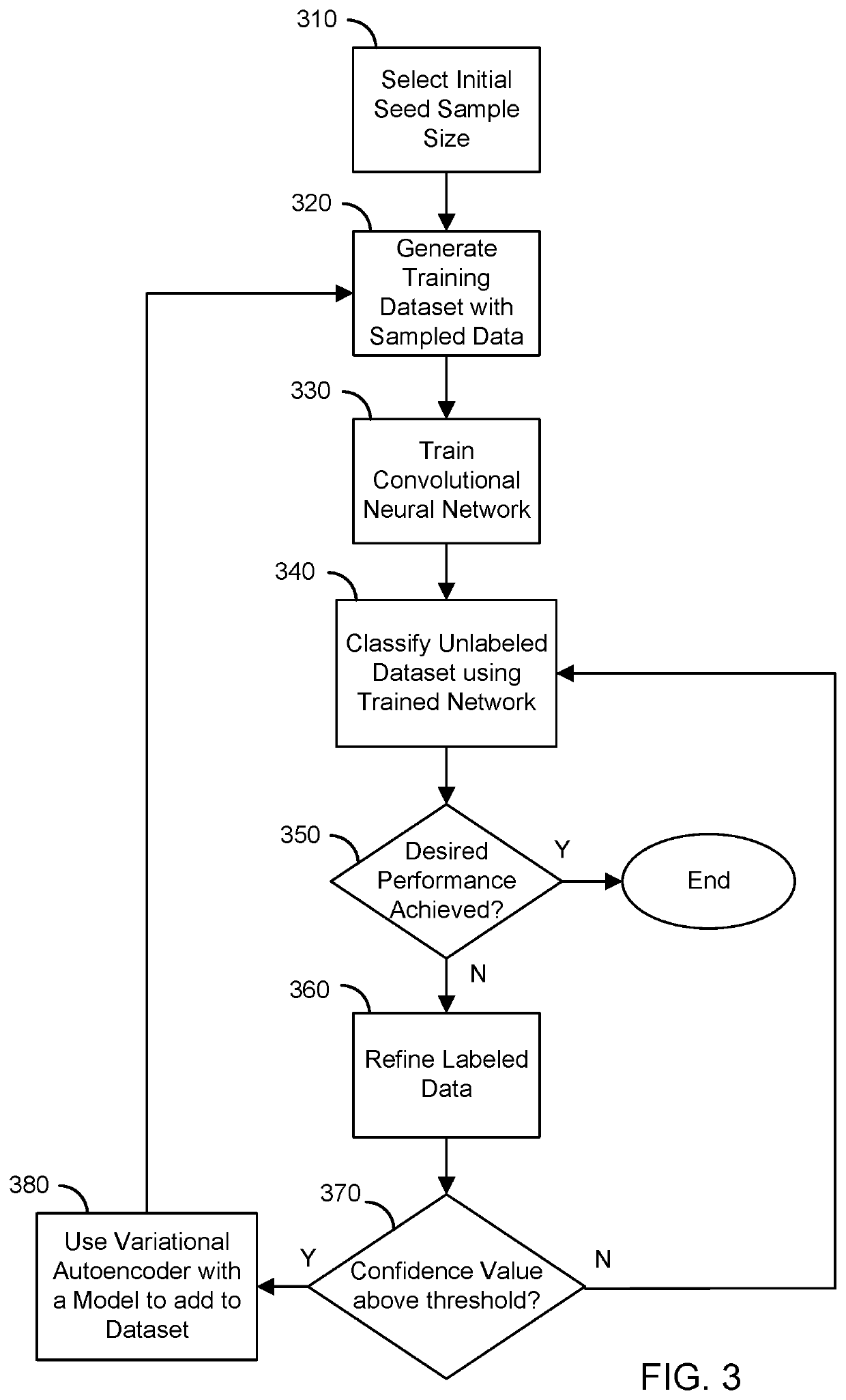
A system and method for automated labeling and annotating unstructured medical datasets
InactiveUS20200286614A1Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesCharacter and pattern recognitionData setRadiology
Supervised and unsupervised learning schemes may be used to automatically label medical images for use in deep learning applications. Large labeled datasets may be generated from a small initial training set using an iterative snowball sampling scheme. A machine learning powered automatic organ classifier for imaging datasets, such as CT datasets, with a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) followed by an organ dose calculation is also provided. This technique can be used for patient-specific organ dose estimation since the locations and sizes of organs for each patient can be calculated independently.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
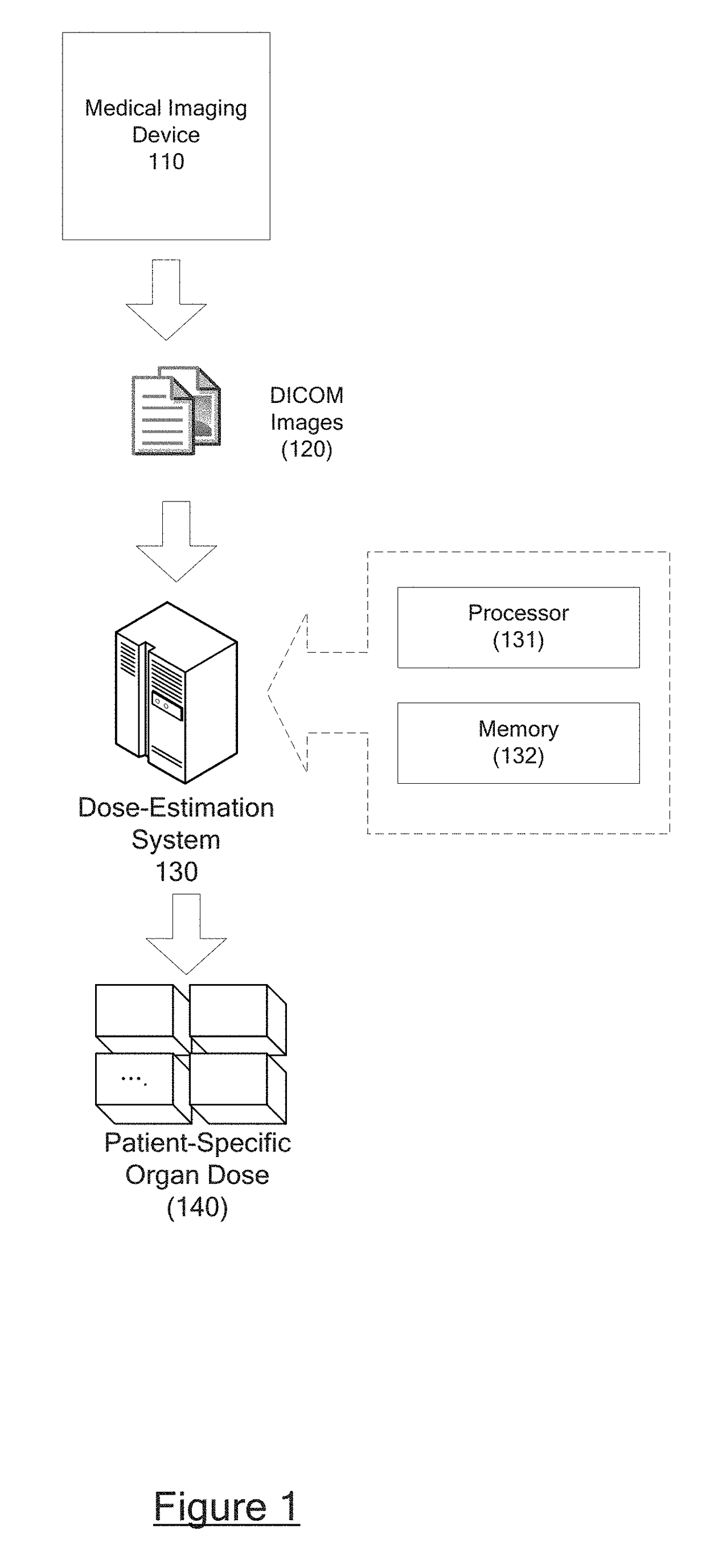
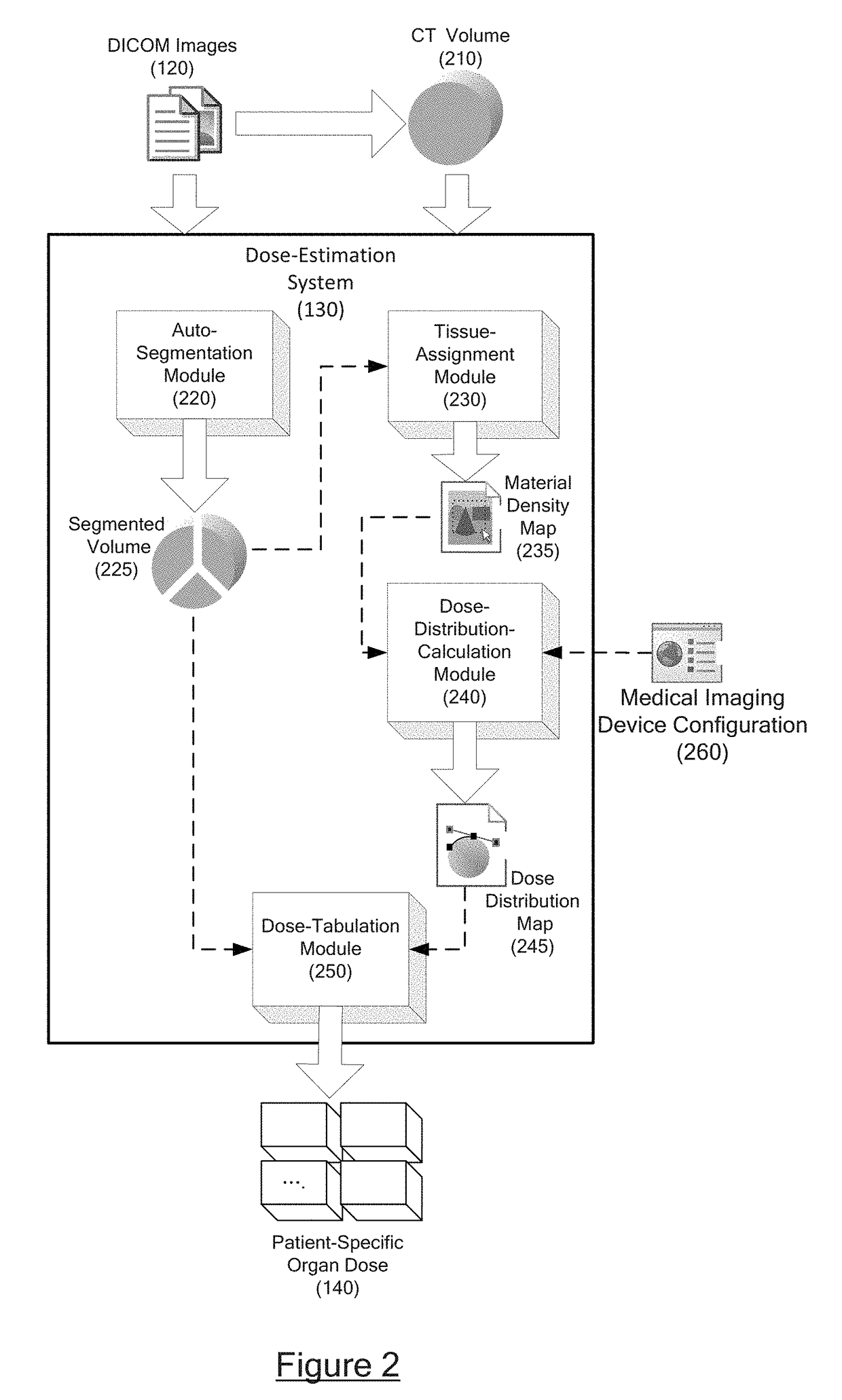
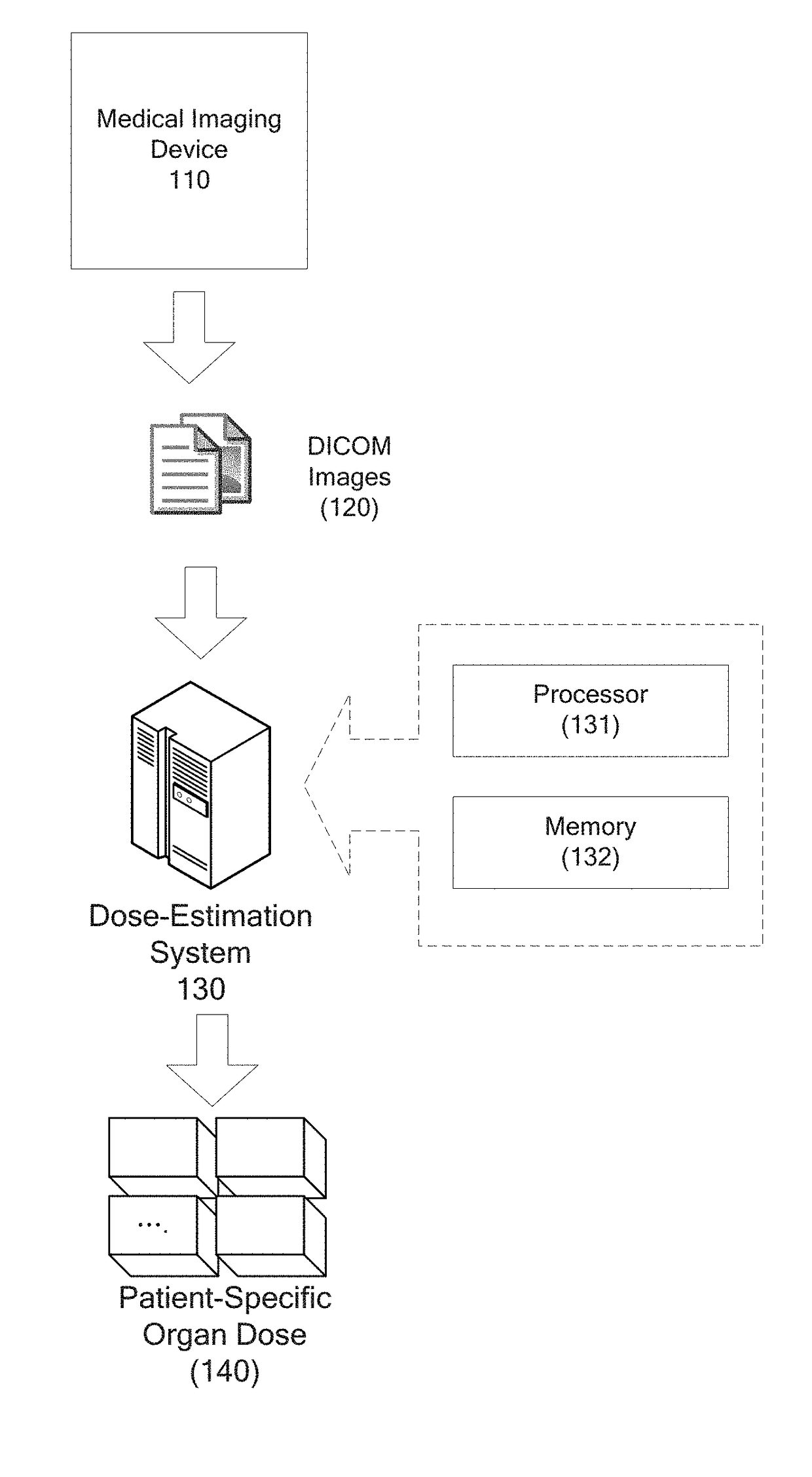
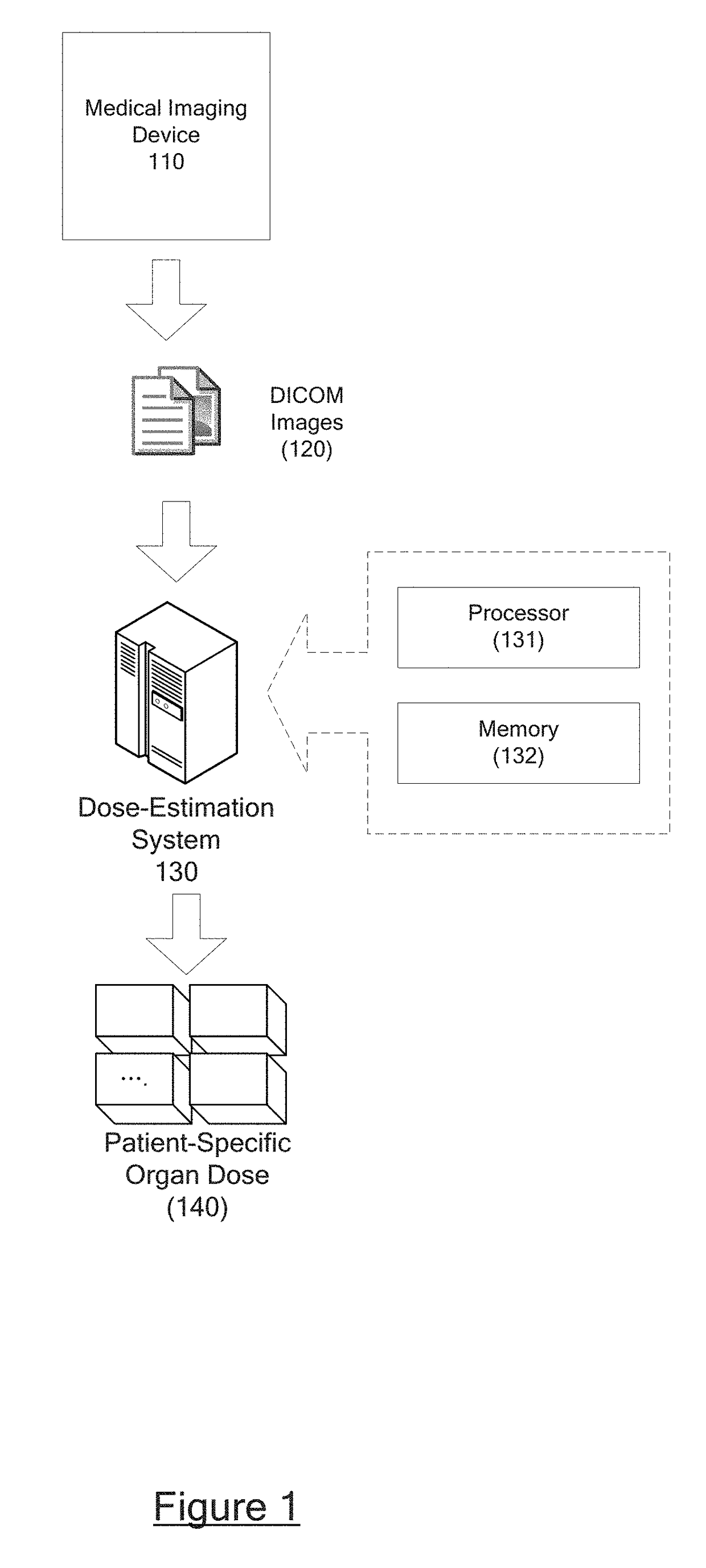
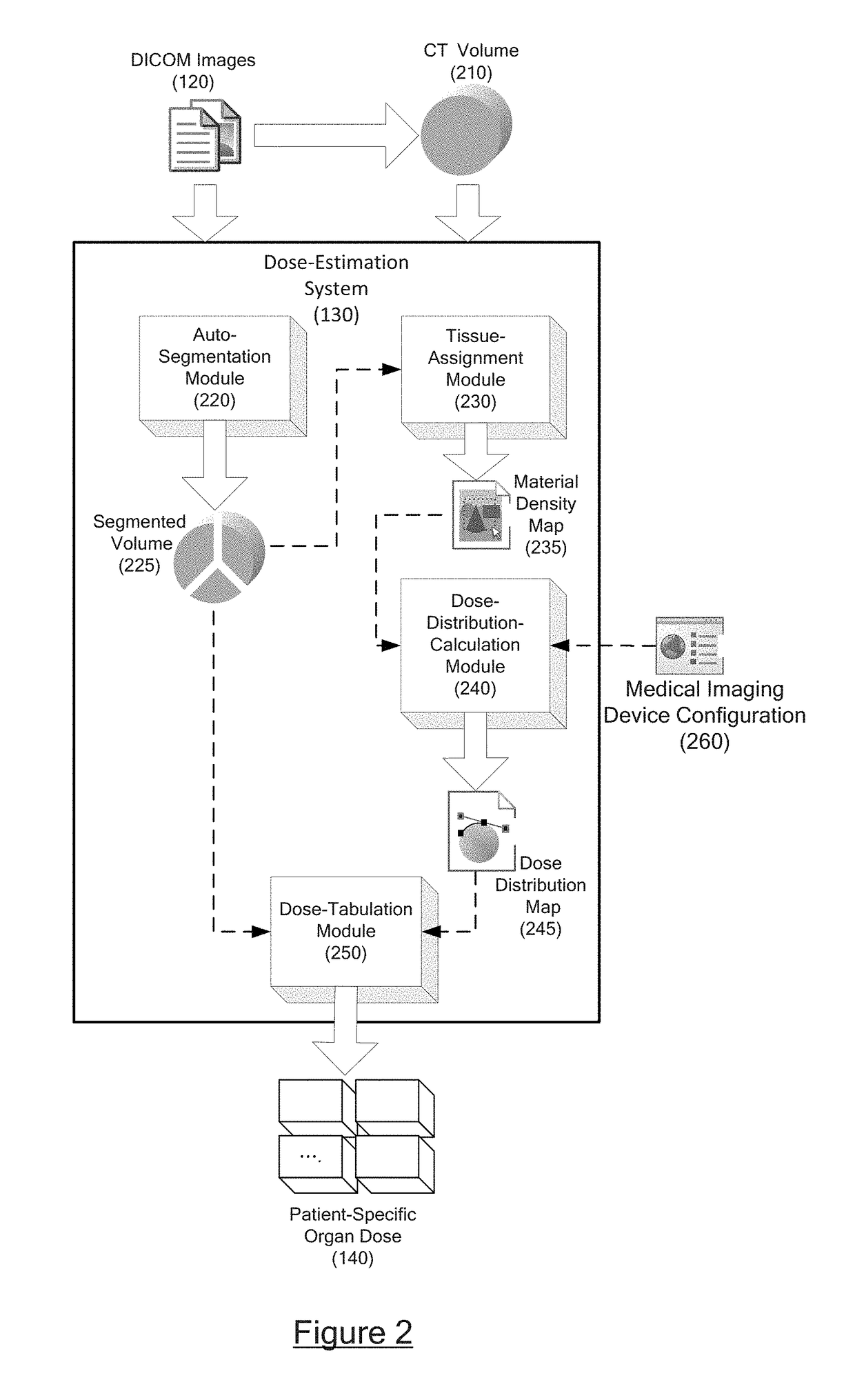
Automatic organ-dose-estimation for patient-specific computed tomography scans
In accordance with at least some embodiments of the present disclosure, a process for calculating patient-specific organ dose is presented. The process may include constructing a computed tomography (CT) volume based on CT images generated by a CT scanner. The process may include segmenting the CT volume into a plurality of organ regions, generating a material density map for the CT volume based on Hounsfield Unit (HU) values, and generating a dose distribution map for the CT volume based on the material density map by simulating particles emitting from the CT scanner and flowing through the CT volume. The process may further generate a dose value delivered to a specific organ region of the plurality of organ regions based on the dose distribution map.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
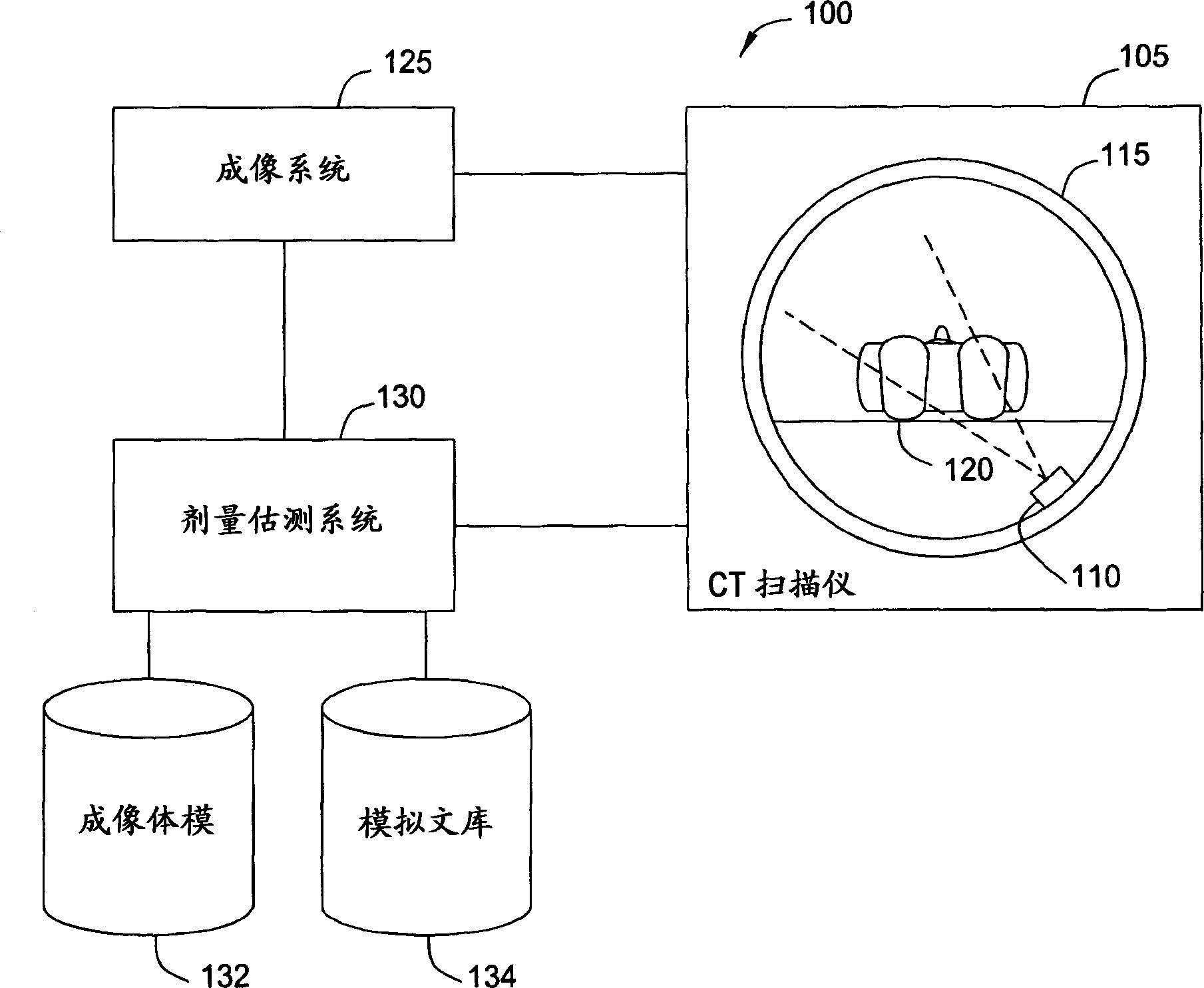
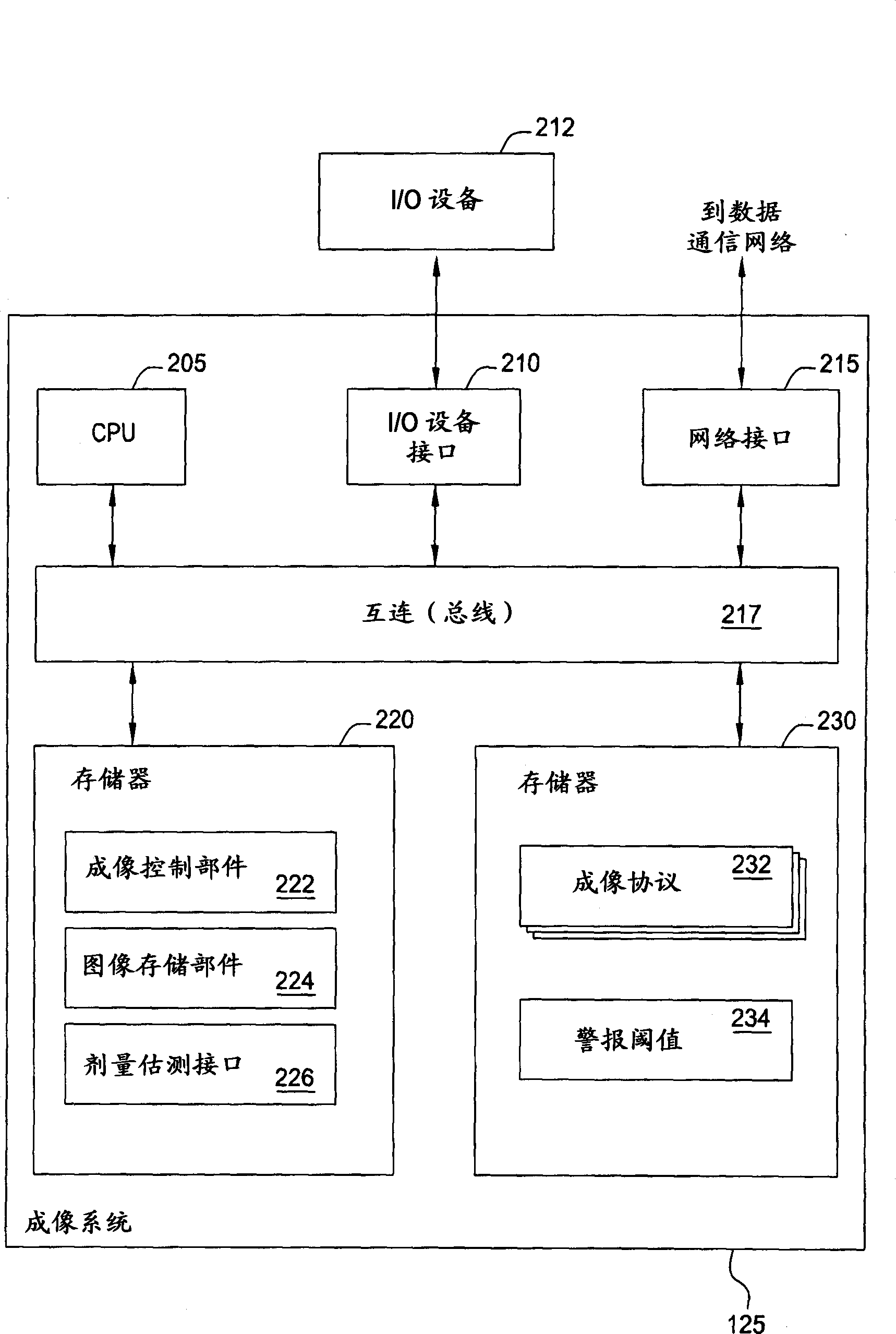
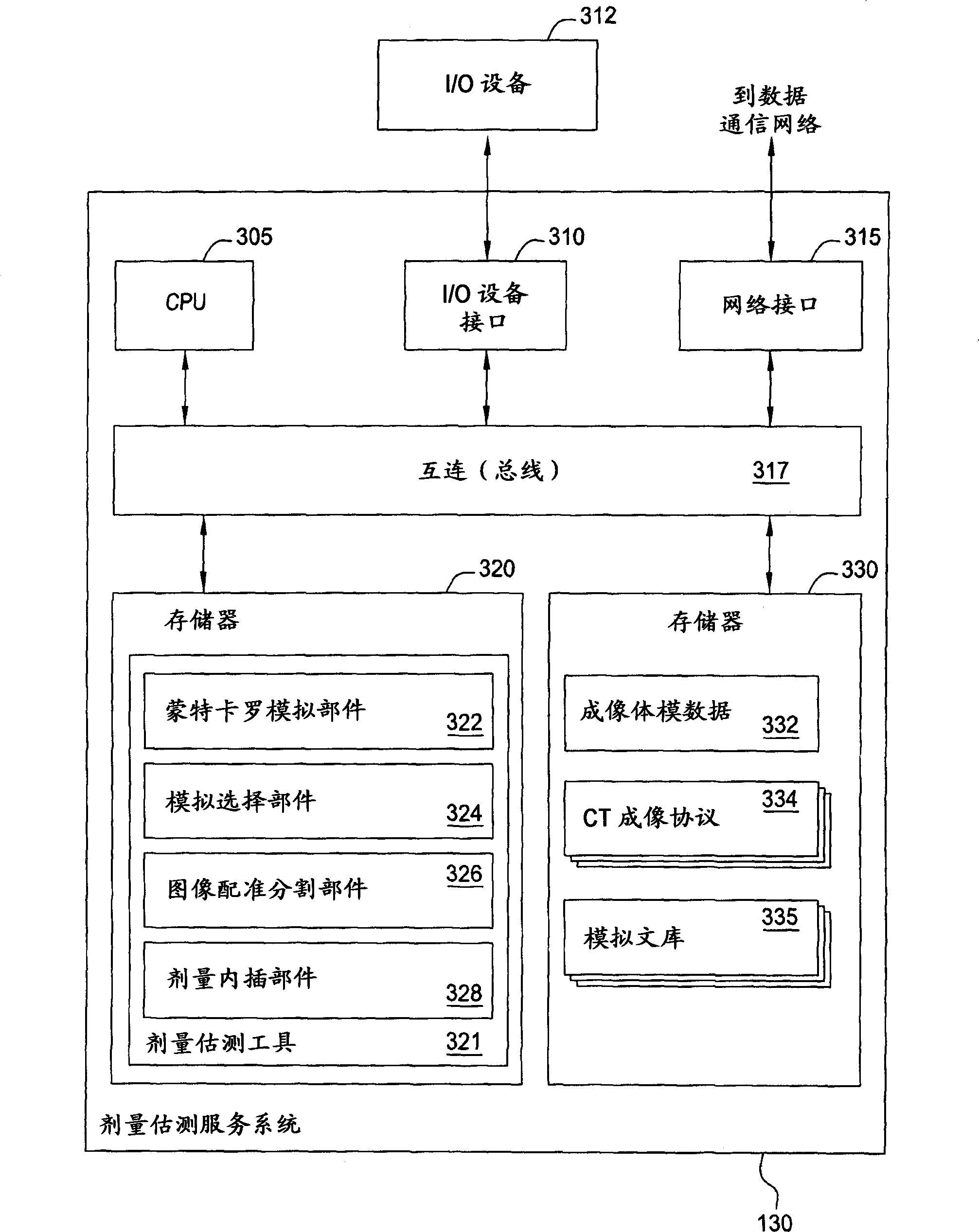
Generating a suitable model for estimating patient radiation dose resulting from medical imaging scans
Techniques are disclosed for estimating patient radiation exposure during computerized tomography (CT) scans. More specifically, embodiments of the invention provide efficient approaches for generating a suitable patient model used to make such an estimate, to approaches for estimating patient dose by interpolating the results of multiple simulations, and to approaches for a service provider to host a dose estimation service made available to multiple CT scan providers.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
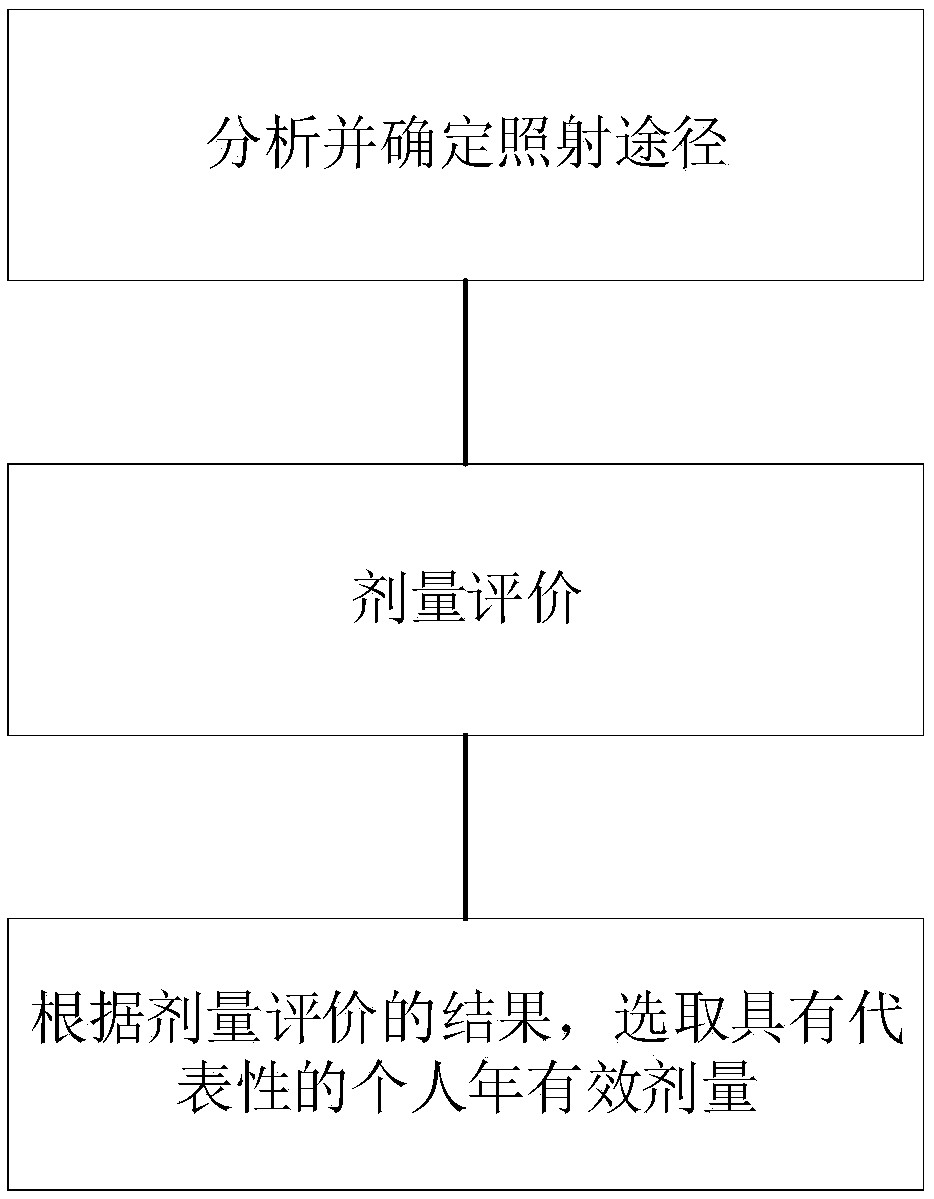
A public dose evaluation method based on a probability theory in radiation environment evaluation
The invention discloses a public dose evaluation method based on a probability theory in radiation environment evaluation. The method comprises the following steps of analyzing and determining an irradiation path, the irradiation path comprising inhaled air internal irradiation, air immersion external irradiation, surface sediment external irradiation, internal irradiation of food-in animal and plant products and dose evaluation, and selecting a representative personal annual effective dose according to the result of the dose evaluation. According to the method, in the public dose estimation process, all the public within the illuminated range are considered, a reasonable personal annual effective dose is selected as a reference dose value, the value serves as an evaluation index in radiation environment evaluation, the conservative property of the evaluation index is further enhanced, and therefore the safety of the public and the environment is guaranteed.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
A system and method for automated labeling and annotating unstructured medical datasets
Supervised and unsupervised learning schemes may be used to automatically label medical images for use in deep learning applications. Large labeled datasets may be generated from a small initial training set using an iterative snowball sampling scheme. A machine learning powered automatic organ classifier for imaging datasets, such as CT datasets, with a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) followed by an organ dose calculation is also provided. This technique can be used for patient-specific organ dose estimation since the locations and sizes of organs for each patient can be calculated independently.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
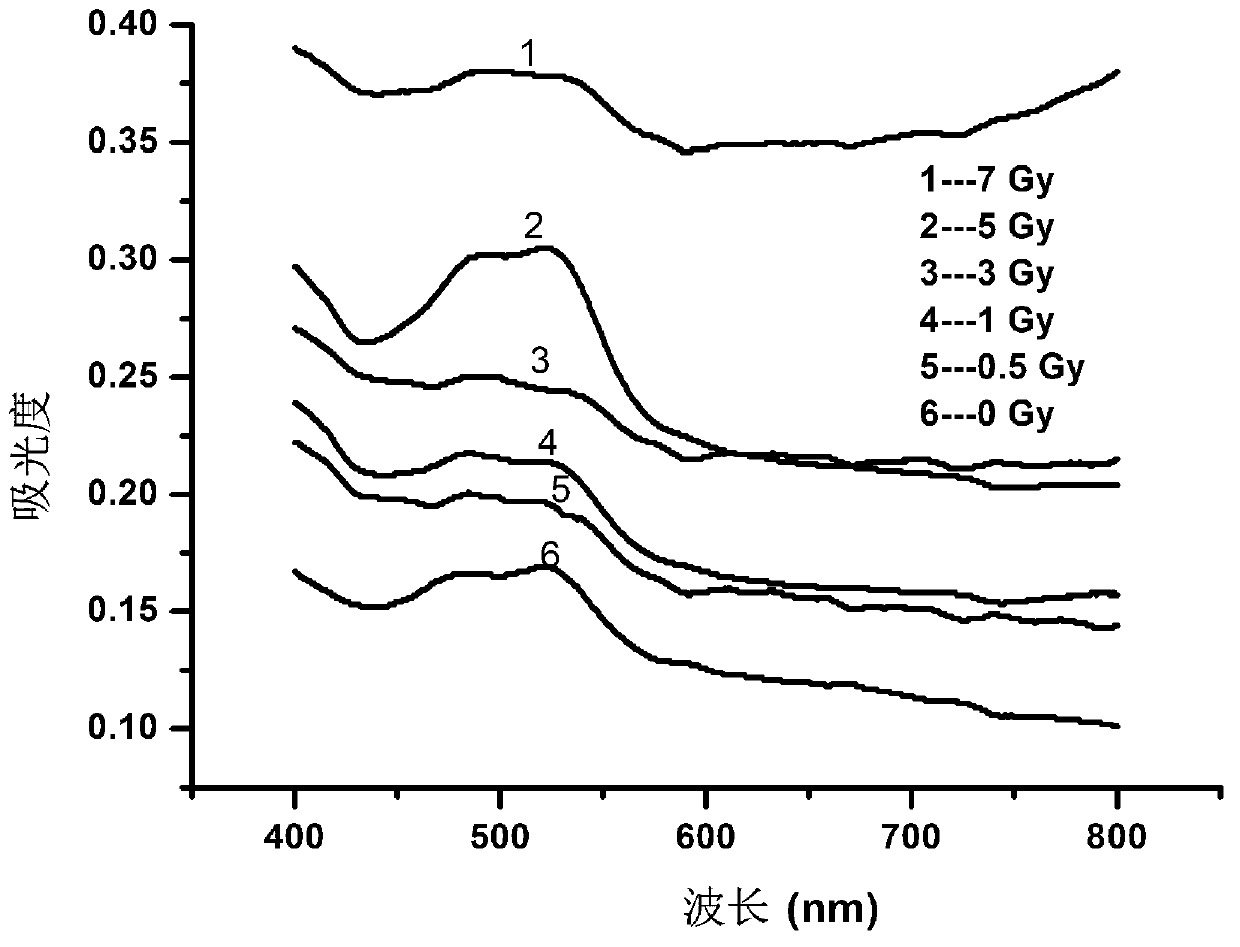
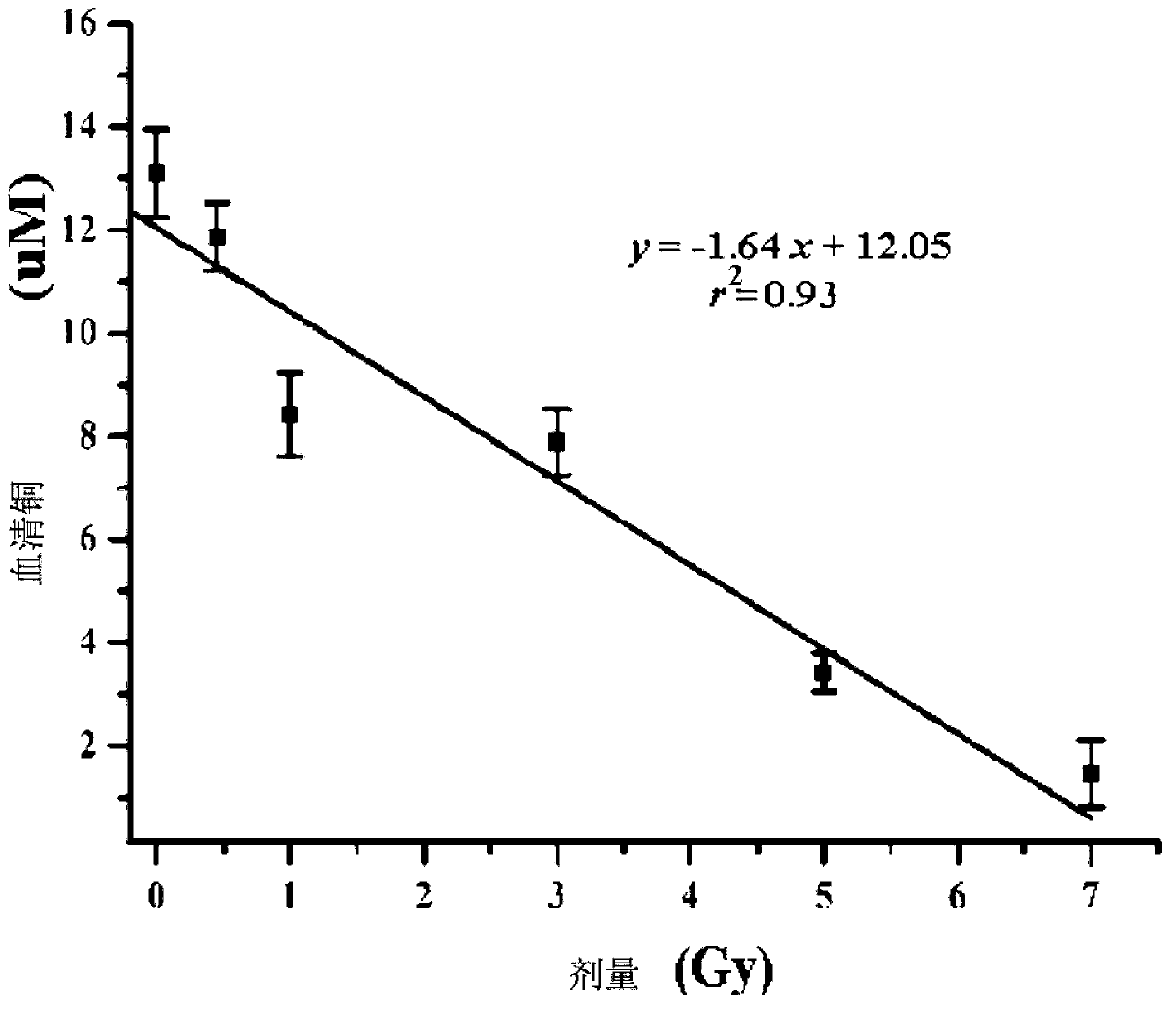
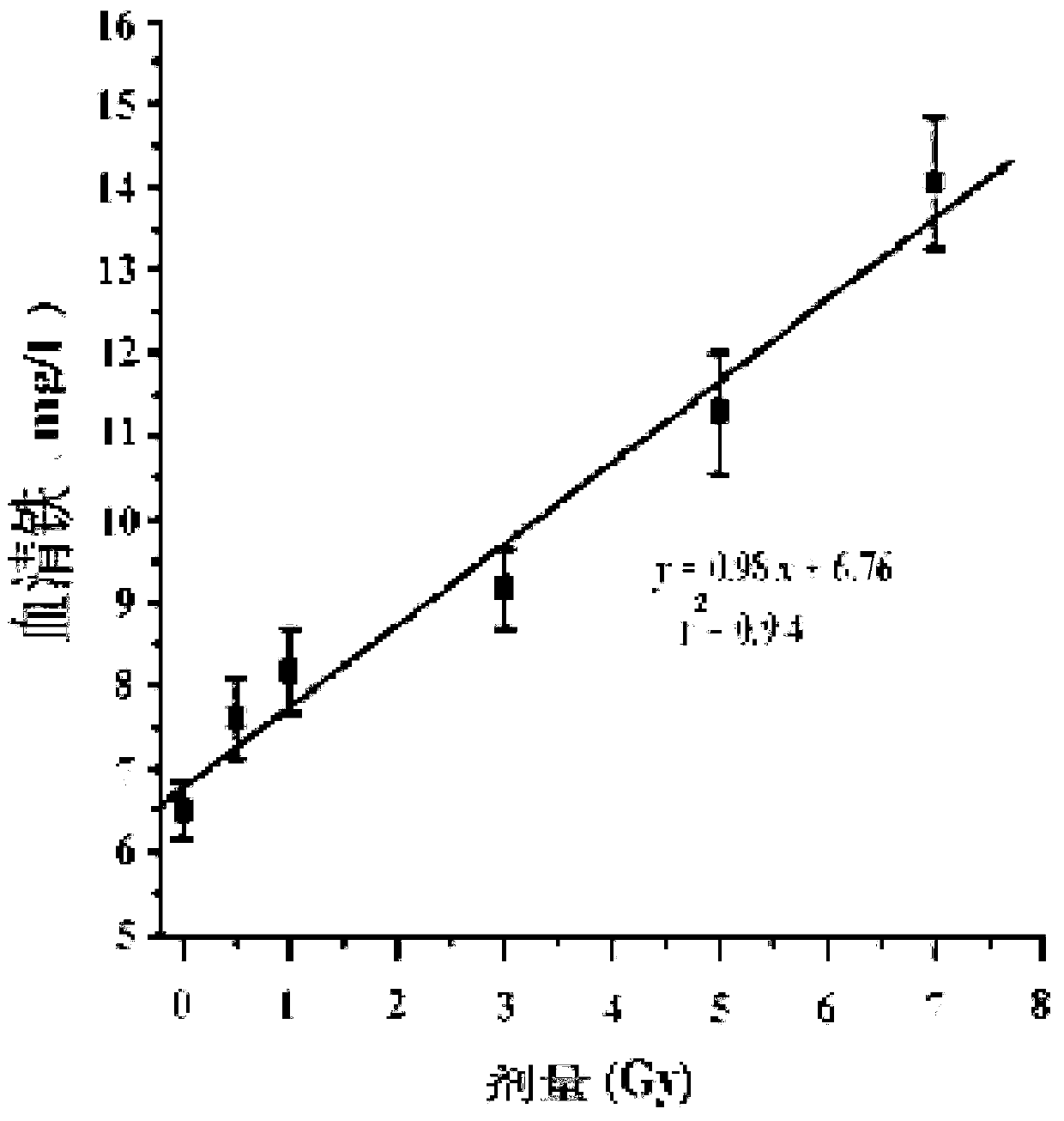
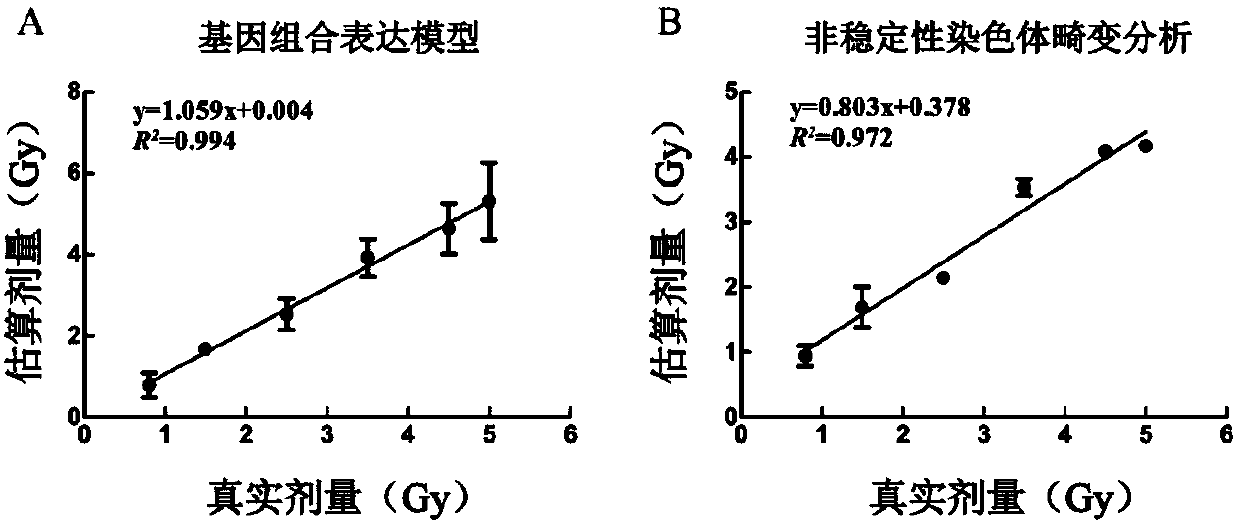
Radiation biological dose estimation method based on serum iron/serum copper
InactiveCN103267972AAccurate estimateSave time estimatingDosimetersColor/spectral properties measurementsSerum ironDosimeter
The invention belongs to the field of radiation biological dose meters, and particularly relates to a characteristic project estimation technique using serum iron and serum copper as a marker. The technique includes the steps of measuring the concentration of the serum iron and the concentration of the serum copper of a radiated mouse respectively by using a 2-(5-bromine-2-pyridine azobenzene)-5-2-diethylaminophenol (5-Br-PADAP) spectrophotometric method, calculating the ratio of the serum iron and the serum copper, and then establishing a dose-response curve between the serum iron / serum copper and a radiation dose. According to the established dose-response curve, the dose response range of the biological dose estimation technique is 0.5-7Gy, operation and index analysis are convenient, information of the radiation dose can be acquired in 30 minutes, and the requirement for biological dose reconstruction can be met. Due to the fact that the technique has the advantages that the dose response is good, detection is convenient and mass detection can be carried out, the technique has broad application prospects in biological dose estimation for nuclear radiation accidents or professional radiated workers.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
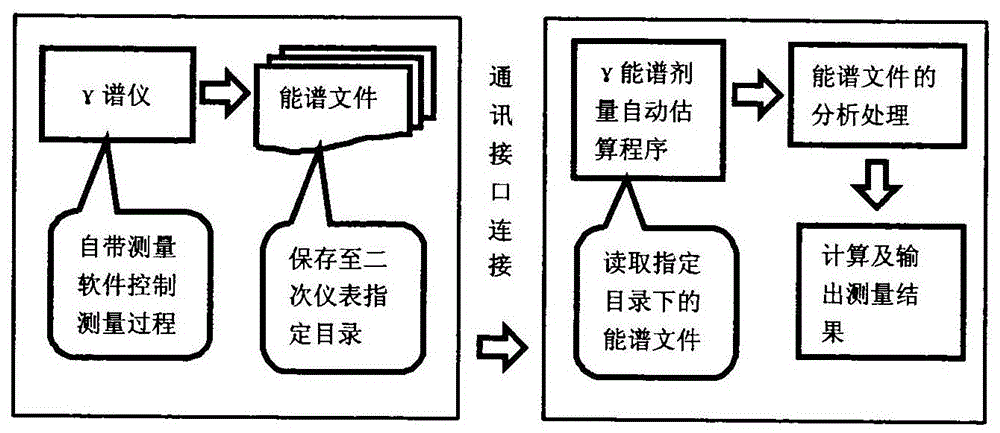
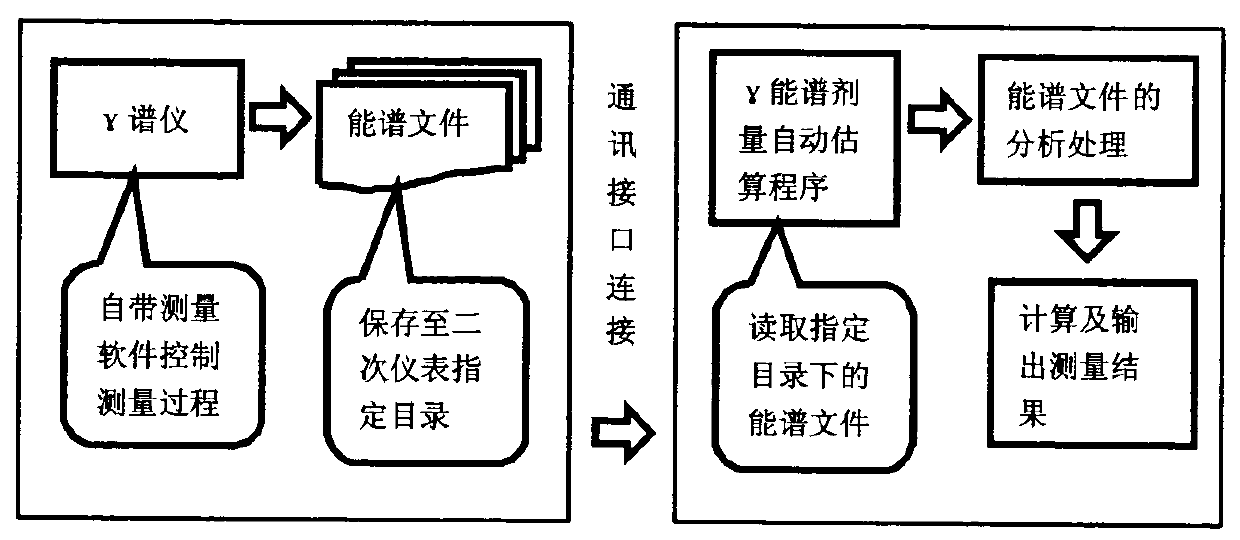
Gamma energy spectrum dose automatic measuring device and measuring method
ActiveCN106443750ARealize automatic measurementFunction increaseDosimetersCommunication interfaceAutomatic control
The invention provides a gamma energy spectrum dose automatic measuring device and a measuring method. The measuring device comprises a gamma spectrometer and secondary instrument. The gamma spectrometer and the secondary instrument are connected through a communication interface. The secondary instrument comprises a computer provided with a gamma energy spectrum dose automatic estimation program, a printer and a mobile power supply. The computer is connected with the printer and the mobile power supply through a communication interface. The gamma energy spectrum dose automatic measuring method which uses the gamma energy spectrum dose automatic measuring device comprises the steps that gamma energy spectrum is measured by the gamma spectrometer, and the measurement software of the gamma spectrometer can automatically control the measurement process; the communication interface of the gamma spectrometer is used to automatically save an energy spectrum file into the secondary instrument; the gamma energy spectrum dose automatic estimation program in the secondary instrument is turned on, wherein the program can automatically read and analyze the gamma energy spectrum file to acquire gamma energy spectrum information; and finally gamma energy spectrum dose automatic measuring is realized according to a dose result calculated by the gamma energy spectrum dose estimation program.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
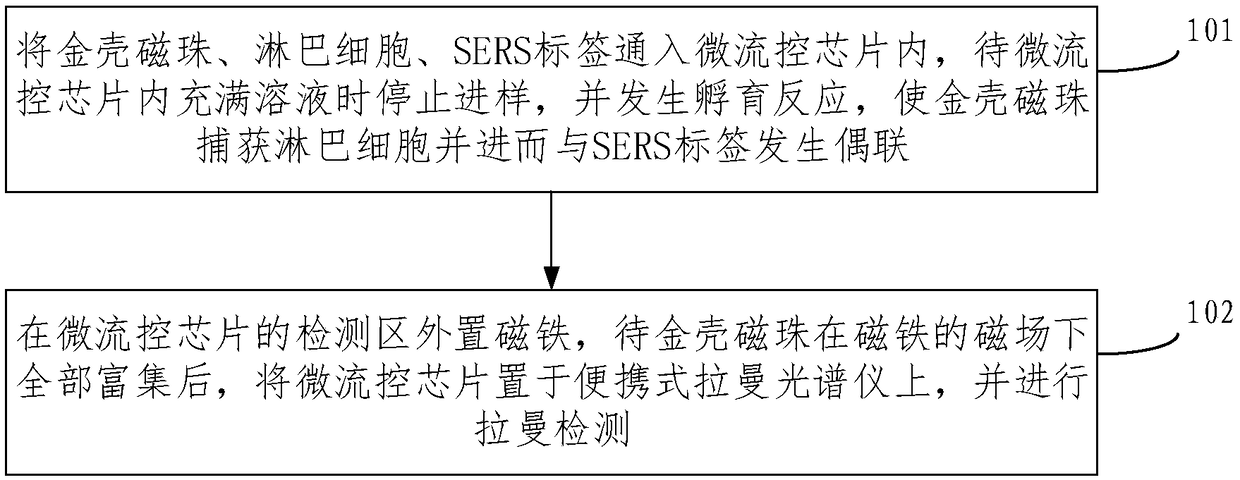
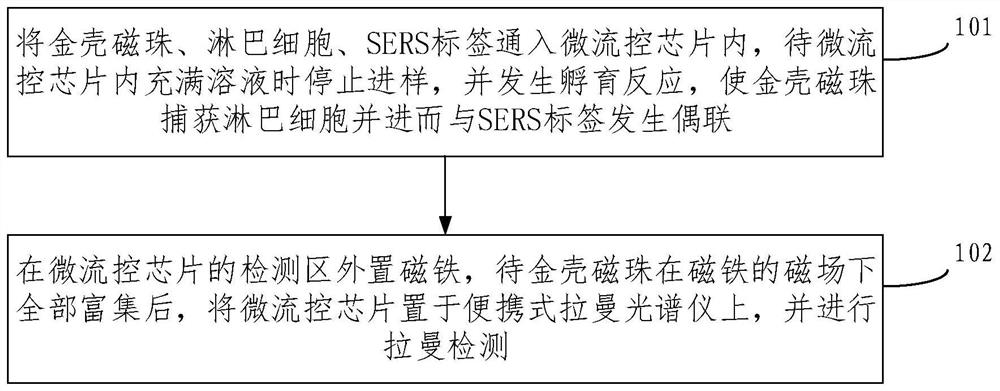
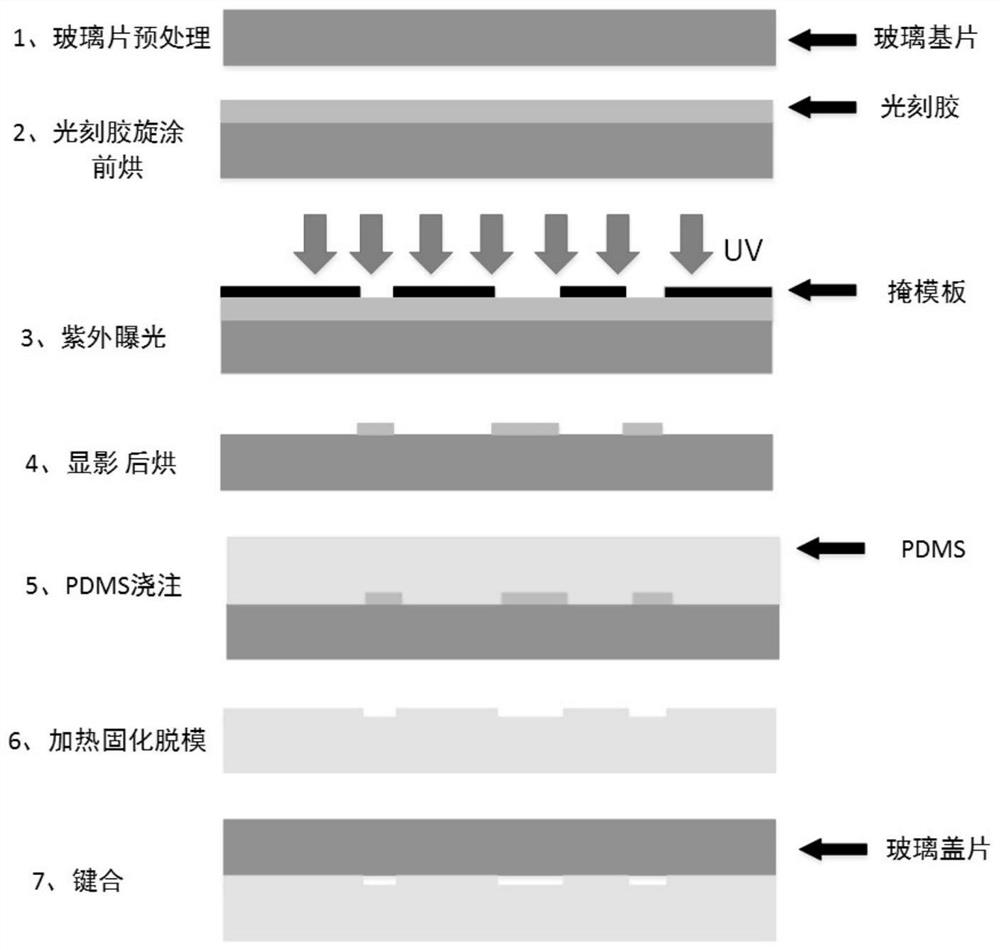
Lymphocyte irradiation damage SERS detection method
The embodiment of the invention provides a lymphocyte irradiation damage SERS detection method and belongs to the technical field of irradiation biological dose estimation. The method comprises the following steps that gold shell magnetic balls, lymphocytes and an SERS label are introduced into a micro-fluidic chip, and sample introduction is stopped and incubation reaction is generated after themicro-fluidic chip is fully filled with a solution, so that the gold shell magnetic balls capture the lymphocytes and thus generate coupling with the SERS label; and a magnet is arranged at the external of a detection region of the micro-fluidic chip, and the micro-fluidic chip is put on a portable raman spectrometer for raman detection after the gold shell magnetic balls are all enriched under amagnetic field of the magnet. According to the method, by preparing the micro-fluidic chip based on a gold shell magnetic ball raman substrate, the micro-fluidic chip has relatively high SERS performance compared with the traditional micro-fluidic chip, has the advantages of detection integration, automation, miniaturization and the like and overcomes the problems of complexity in step, relativelylarge interference with human factors, incapability in portability, efficacy losing of nano particles and the like of the traditional detection method.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
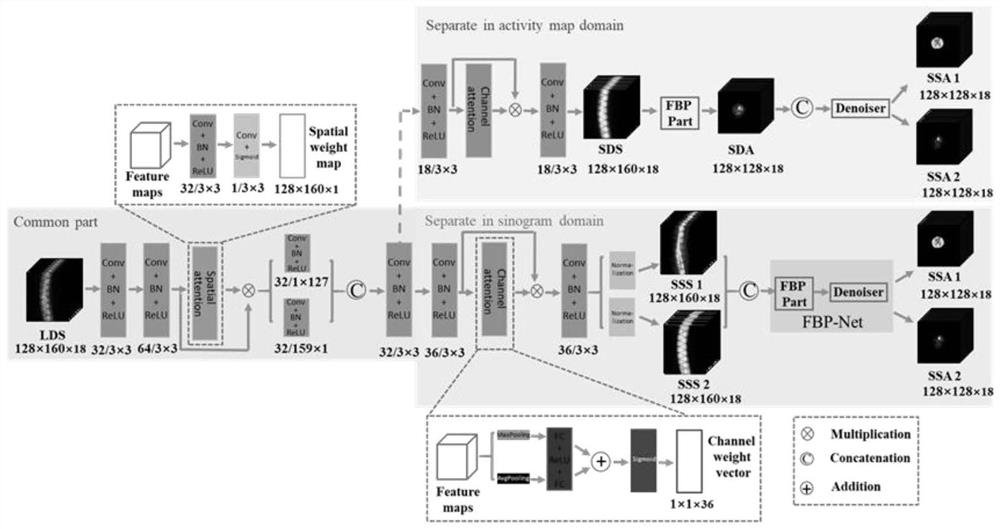
Low-dose double-tracer PET reconstruction method based on attention mechanism
ActiveCN113160347AAchieve separationVerify robustnessReconstruction from projectionNeural architecturesFeature extractionReconstruction method
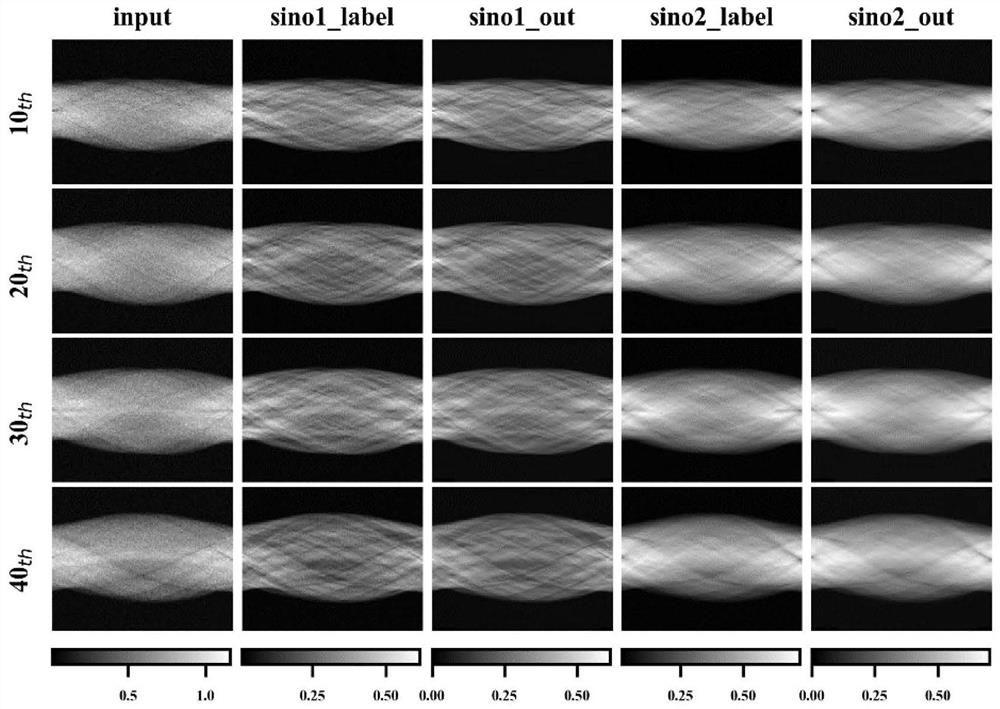
The invention discloses a low-dose double-tracer PET (positron emission tomography) reconstruction method based on an attention mechanism, namely, a low-dose double-tracer PET image reconstruction problem is solved by utilizing a convolutional network model based on the attention mechanism, and standard dose estimation and double-tracer PET signal separation are realized in a sinogram. According to the method, by means of a powerful feature extraction tool of deep learning, a single tracer PET image of a standard dose can be reconstructed from a low-dose double-tracer PET sinogram, and the method has robustness for individual differences, tracer combinations and sampling protocols.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Deep learning method for medical image low-dose estimation
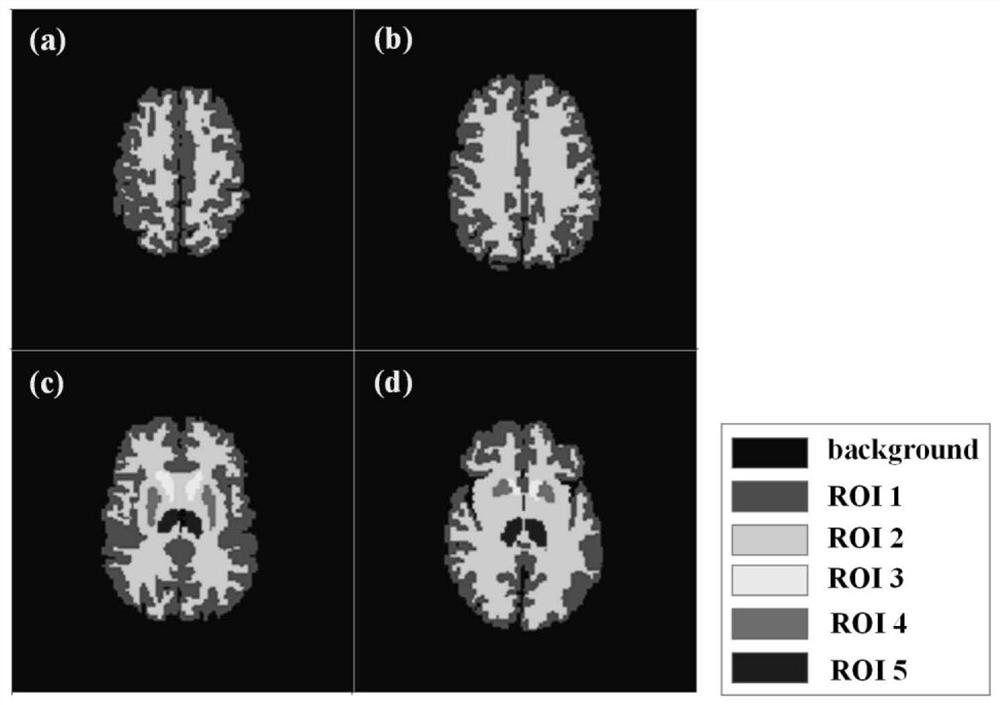
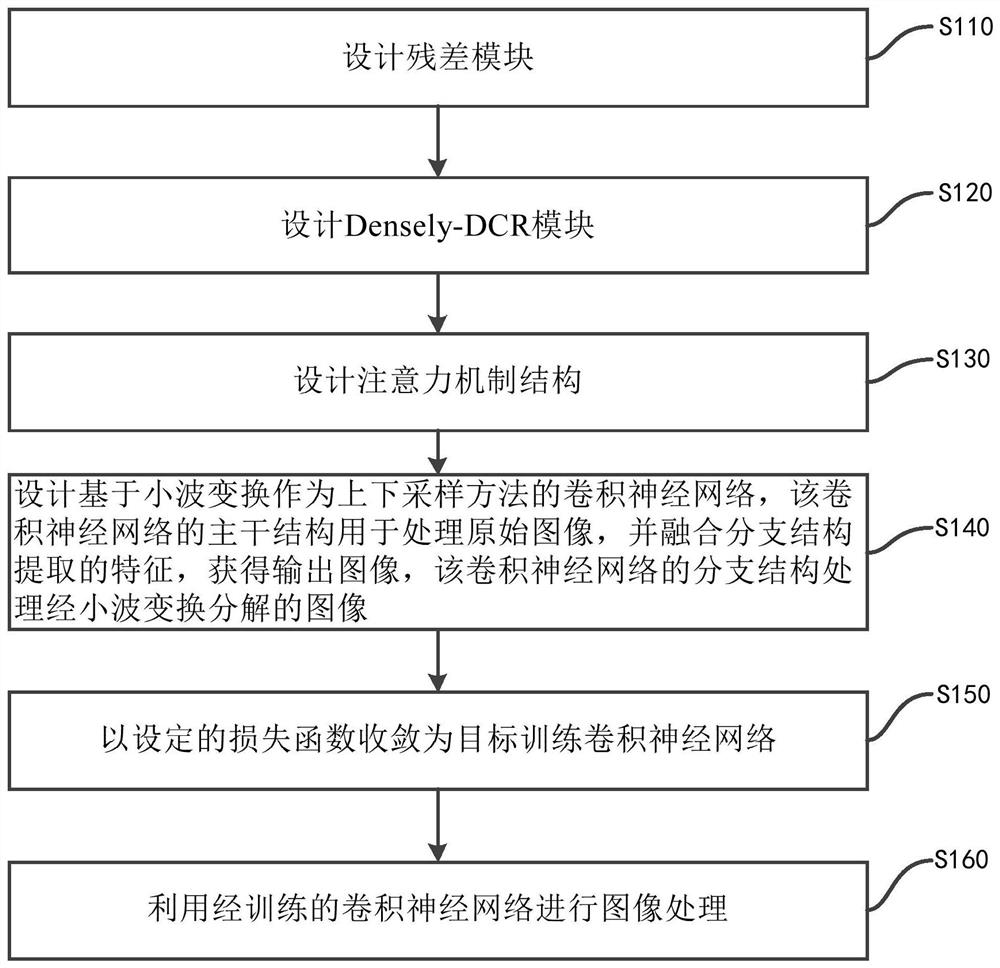
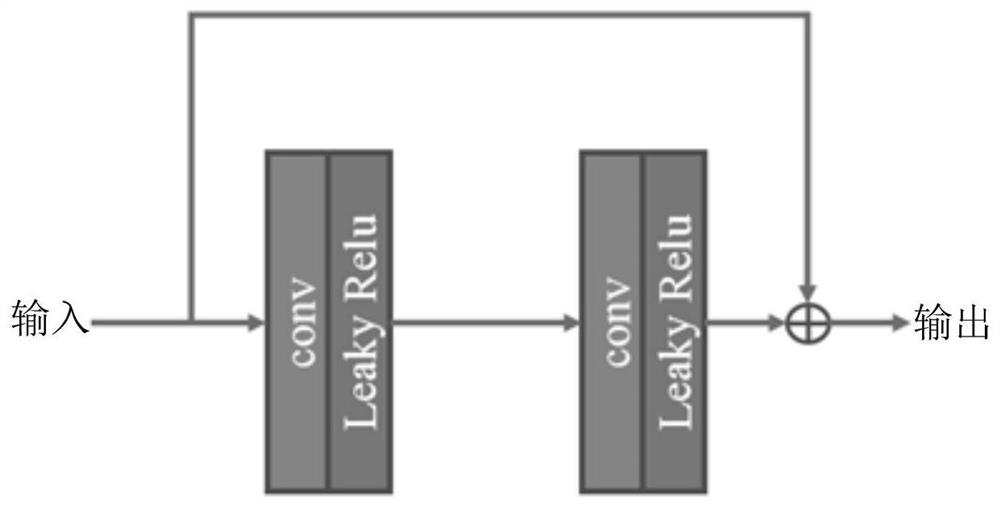
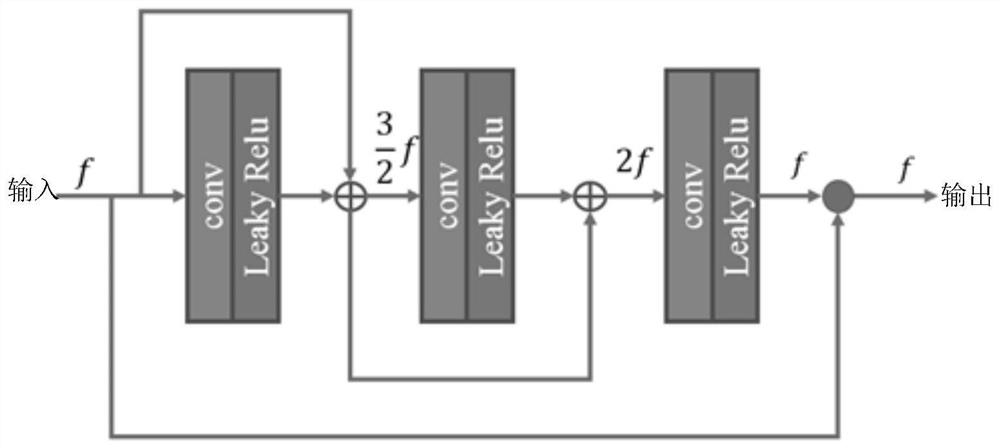
ActiveCN113053496AImprove generalization abilityImprove peak signal-to-noise ratioInternal combustion piston enginesMedical imagesDose estimationNeural network nn
The invention discloses a deep learning method for medical image low-dose estimation. The method comprises the steps that wavelet transform is used for decomposing a low-dose original image to obtain multiple layers of decomposed images, and each layer of decomposed image comprises multiple sub-band images with different view angle characteristics corresponding to the original image; the multiple layers of decomposed images and the original image are input into a convolutional neural network for training, a mapping relation from a low-dose original image to a standard-dose image is learned through decomposition and reconstruction, the convolutional neural network comprises a trunk structure and a plurality of branch structures, the trunk structure takes the original image as input, and the plurality of branch structures respectively take the corresponding decomposed images of each layer as input. According to the method, the wavelet transform is combined with the convolutional neural network, so that the image detail information is enhanced while the image peak signal-to-noise ratio, the structural similarity and the contrast signal-to-noise ratio are improved.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED MEDICAL DEVICES SHENZHEN
A dose estimation method and system based on maximum food consumption of residents
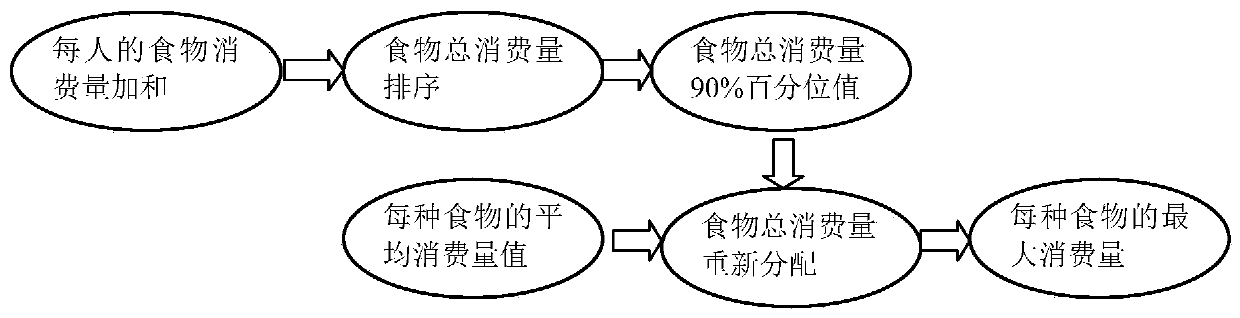
ActiveCN109738929AReasonable maximum consumptionImprove the accuracy of environmental assessmentDosimetersNuclear powerDose estimation
The invention discloses a dose estimation method and system based on maximum food consumption of residents. The method comprises the following steps: S1) carrying out diet survey on the residents within a preset radius range of a nuclear power station to obtain weekly consumption for various foods of the residents, and calculating annual consumption for various foods of the residents; S2) rankingthe annual food consumption of individuals in an ascending order, then, taking the annual food consumption of a person ranked in the 90% percentile, and reallocating the annual food consumption of theindividuals according to share of average consumption of each kind of food to obtain annual maximum consumption of each kind of food; and S3) substituting the annual maximum consumption of each kindof food into an internal irradiation dose calculation formula to obtain internal irradiation dose of each resident, and calculating the total dose of the nuclear power plant to the residents accordingto the internal irradiation dose. The provided method and system calculate the maximum food consumption, consistent with the actual situation, of the residents by using a percentile method, thereby making the calculated resident dose more accurate.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
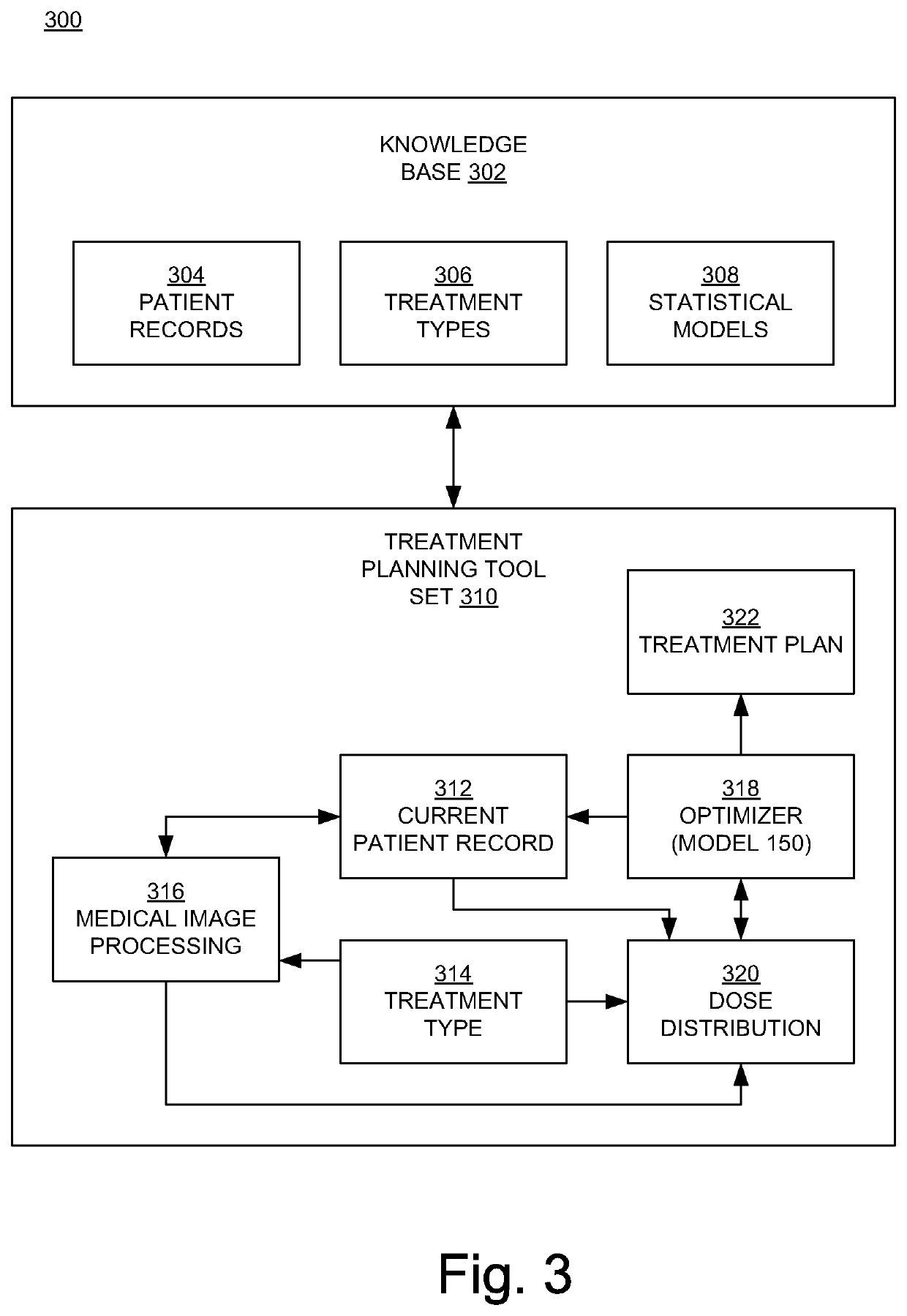
Knowledge based treatment planning corrected for biological effects
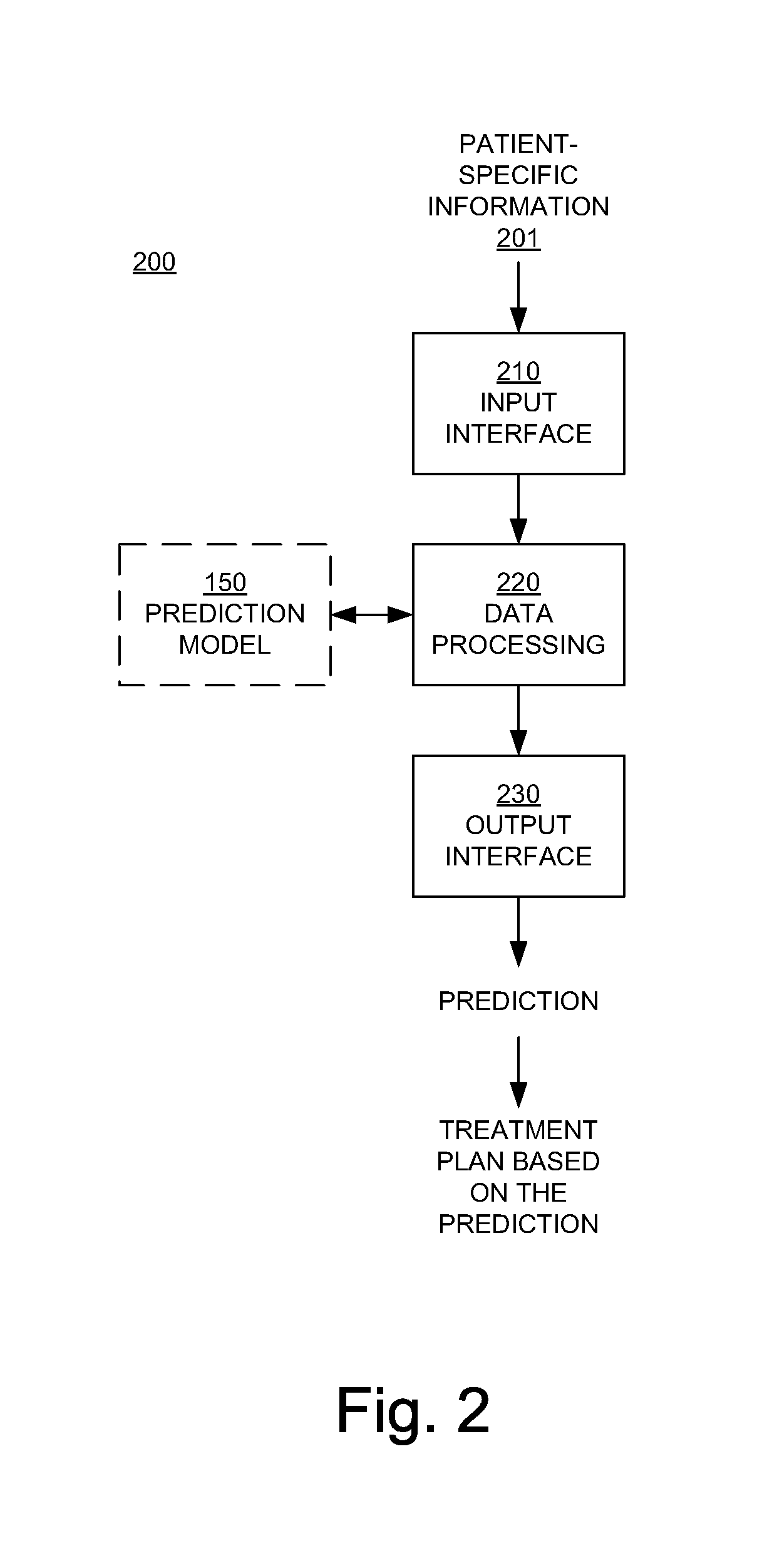
Solutions are provided herein that specifically accounts for biological effects of tissue during radiation planning (such as treatment planning). In one or more embodiments, the biological effects may be calculated by accessing a knowledge base to determine reference data comprising at least one biological characteristic corresponding to the at least one organ, predicting a biological effect for the plurality of identified structures based on the biological characteristic corresponding to the at least one organ, and generating or modifying a radiation plan based on the biological effect. By incorporating biological data and fraction dose information, dose-estimation models can be created and trained to more accurately estimate dose absorption and effectiveness. Moreover, existing estimation models may be adapted to create dose estimations that account for the biological efficiency of target structures.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
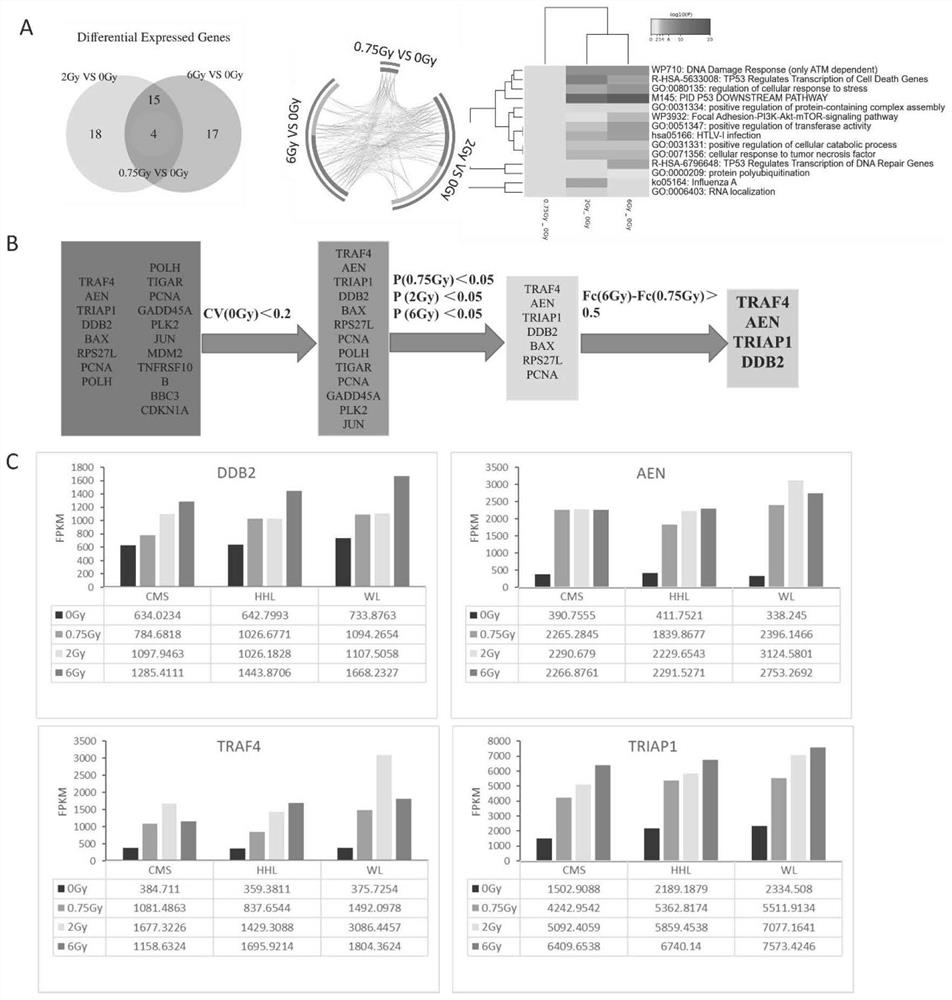
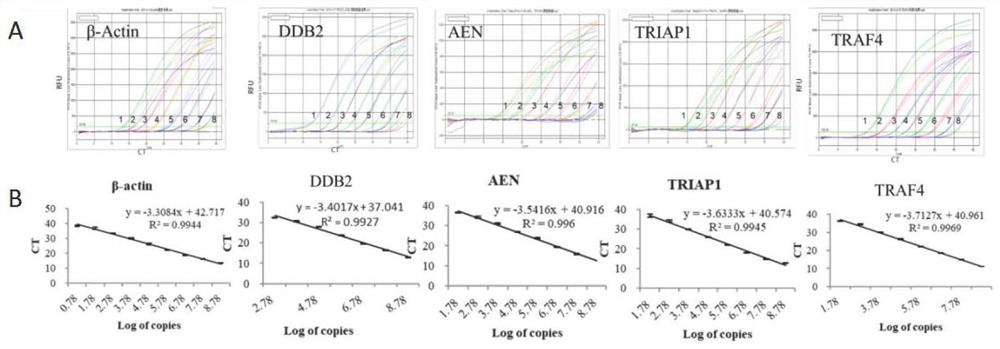
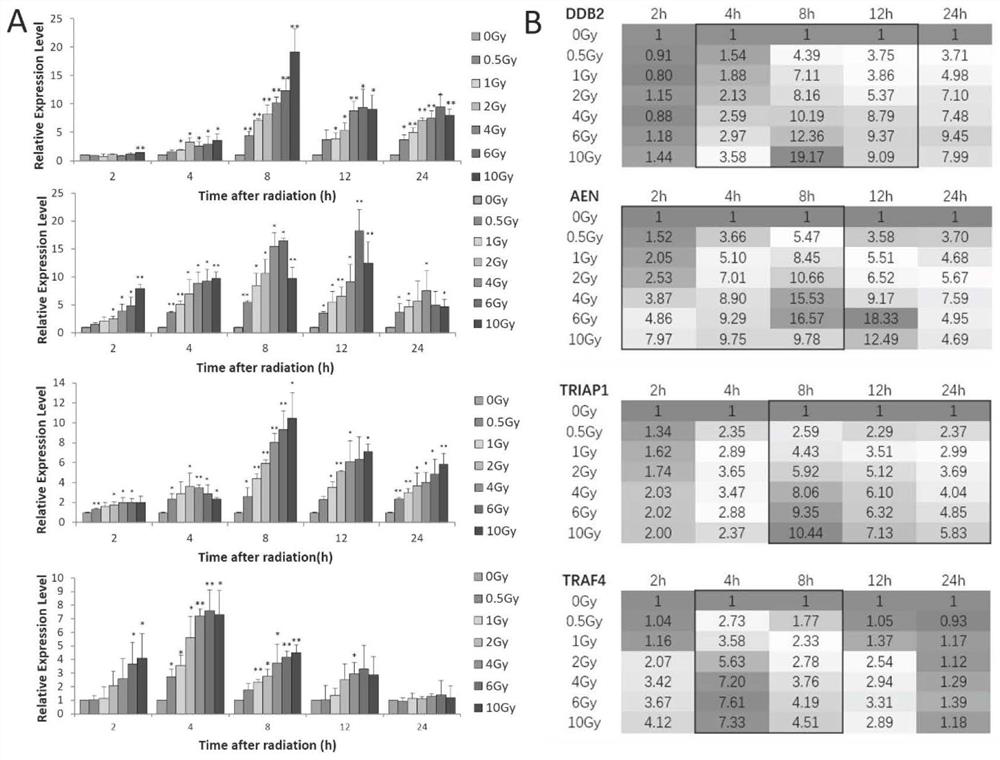
Group of markers, detection model and application thereof in radiation dose detection
InactiveCN114369655AShorten the timeImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisNuclear radiationDose estimation
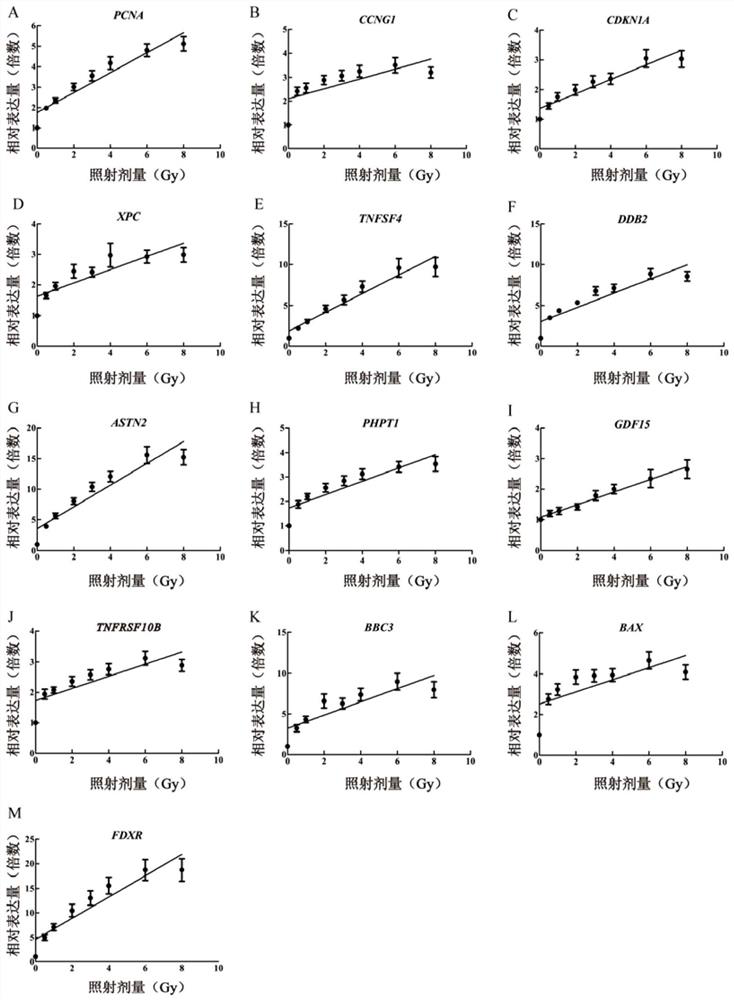
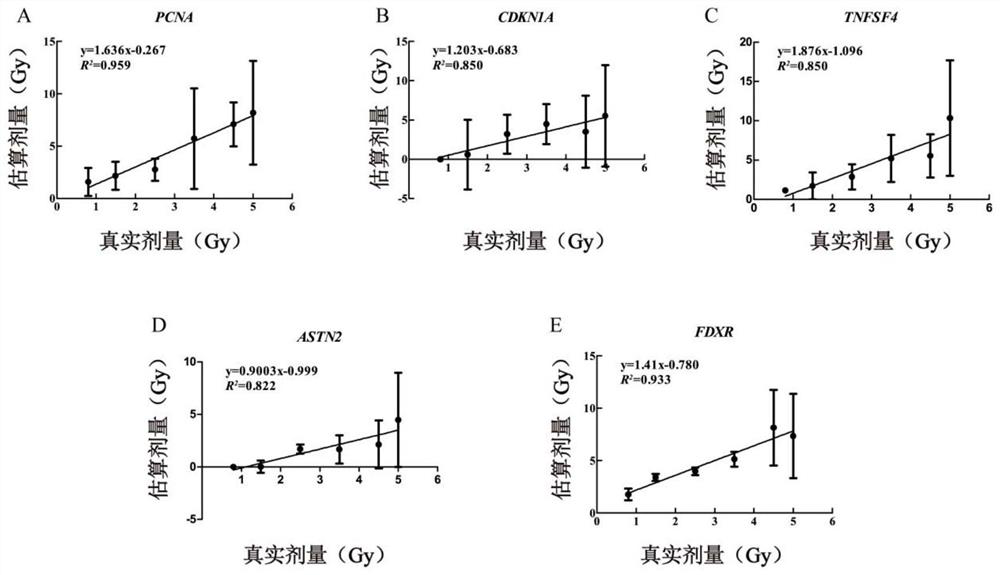
The invention discloses a group of markers, a detection model and application thereof in radiation dose detection, and belongs to the technical field of biological detection. In order to solve the problems existing in an existing radiation biological dose estimation method, based on background levels of DDB2, AEN, TRIAP1 and TRAF4 and sensitivity specificity in the early stage of radiation, a guide threshold value is given for detection of each gene at different detection time points, finally, the four genes are combined according to different change modes of the four genes in the early stage of radiation, and the radiation biological dose estimation method based on DDB2, AEN, TRIAP1 and TRAF4 is obtained. And an effective radiation early dose detection model is constructed. The model can be used for classification and dose estimation of large-batch nuclear radiation irradiated personnel within 24 hours after exposure, and a new thought and method are provided for corresponding scientific research of radiation dose.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
Estimation Method of γ-ray Irradiation Dose Based on Transcription Factor IIIA
InactiveCN106918833BExpand the scope of detectionExtended dose-response rangeChemical dosimetersDose estimationColorimetry
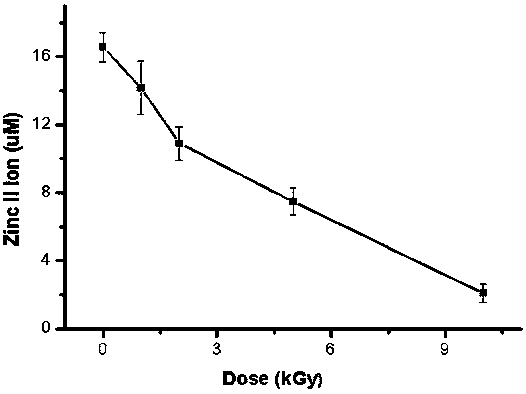
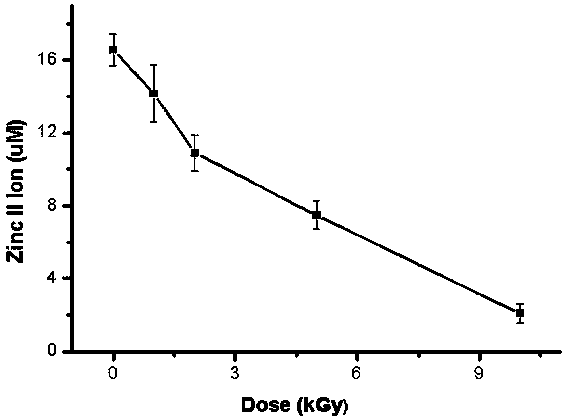
The embodiment of the invention discloses a [Gamma] ray irradiation dose estimation method based on a transcription factor IIIA, and relates to the nucleonic field. The irradiation dose is scaled through the changing of the transcription factor IIIA divalent zinc ion concentration. The [Gamma] ray irradiation dose estimation method based on the transcription factor IIIA employs the chemical colorimetry to detect the transcription factor IIIA divalent zinc ion concentration of different doses [Gamma] ray irradiation, and a dose-effect curve between the transcription factor IIIA divalent zinc ion concentration and the irradiation dose is established. According to the established dose-effect curve, a double blind method is employed to estimate the [Gamma] ray irradiation dose, the dose estimation range is wide and the operation is simple.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Application of radiation sensitive genes as radiological dosimeter
ActiveCN110195101AQuick estimateAccurate estimateMicrobiological testing/measurementPopulation sampleDosimeter
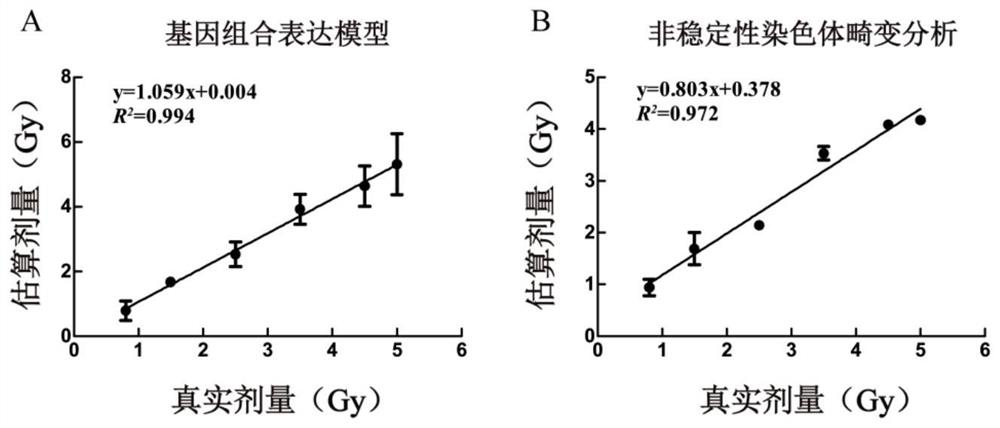
The invention relates to an application of a combination of multiple radiation sensitive genes as a radiological dosimeter in radiation dose estimation. Specifically, the invention relates to an application of a combination of 5-13 different radiation-sensitive genes as a radiological dosimeter in radiation dose estimation, a kit and a microarray used for radiation dose estimation and prepared based on the combination of 5-13 different radiation-sensitive genes, and a method for radiation dose estimation by the kit and the microarray. Compared with traditional methods including chromosome aberration analysis, the radiological dosimeter and an application method have the advantages of simplicity, rapidity and high throughput, and have high accuracy of dose estimation, and are especially suitable for radiation dose estimation of large-scale population samples in nuclear accidents and radiation accidents.
Owner:NAT INST FOR RADIOLOGICAL PROTECTION & NUCLEAR SAFETY CHINESE CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Automatic organ-dose-estimation for patient-specific computed tomography scans
In accordance with at least some embodiments of the present disclosure, a process for calculating patient-specific organ dose is presented. The process may include constructing a computed tomography (CT) volume based on CT images generated by a CT scanner. The process may include segmenting the CT volume into a plurality of organ regions, generating a material density map for the CT volume based on Hounsfield Unit (HU) values, and generating a dose distribution map for the CT volume based on the material density map by simulating particles emitting from the CT scanner and flowing through the CT volume. The process may further generate a dose value delivered to a specific organ region of the plurality of organ regions based on the dose distribution map.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Gamma energy spectrum dose automatic measuring device and measuring method
ActiveCN106443750BRealize automatic measurementFunction increaseDosimetersCommunication interfaceNuclear engineering
The invention provides a gamma energy spectrum dose automatic measuring device and a measuring method. The measuring device comprises a gamma spectrometer and secondary instrument. The gamma spectrometer and the secondary instrument are connected through a communication interface. The secondary instrument comprises a computer provided with a gamma energy spectrum dose automatic estimation program, a printer and a mobile power supply. The computer is connected with the printer and the mobile power supply through a communication interface. The gamma energy spectrum dose automatic measuring method which uses the gamma energy spectrum dose automatic measuring device comprises the steps that gamma energy spectrum is measured by the gamma spectrometer, and the measurement software of the gamma spectrometer can automatically control the measurement process; the communication interface of the gamma spectrometer is used to automatically save an energy spectrum file into the secondary instrument; the gamma energy spectrum dose automatic estimation program in the secondary instrument is turned on, wherein the program can automatically read and analyze the gamma energy spectrum file to acquire gamma energy spectrum information; and finally gamma energy spectrum dose automatic measuring is realized according to a dose result calculated by the gamma energy spectrum dose estimation program.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
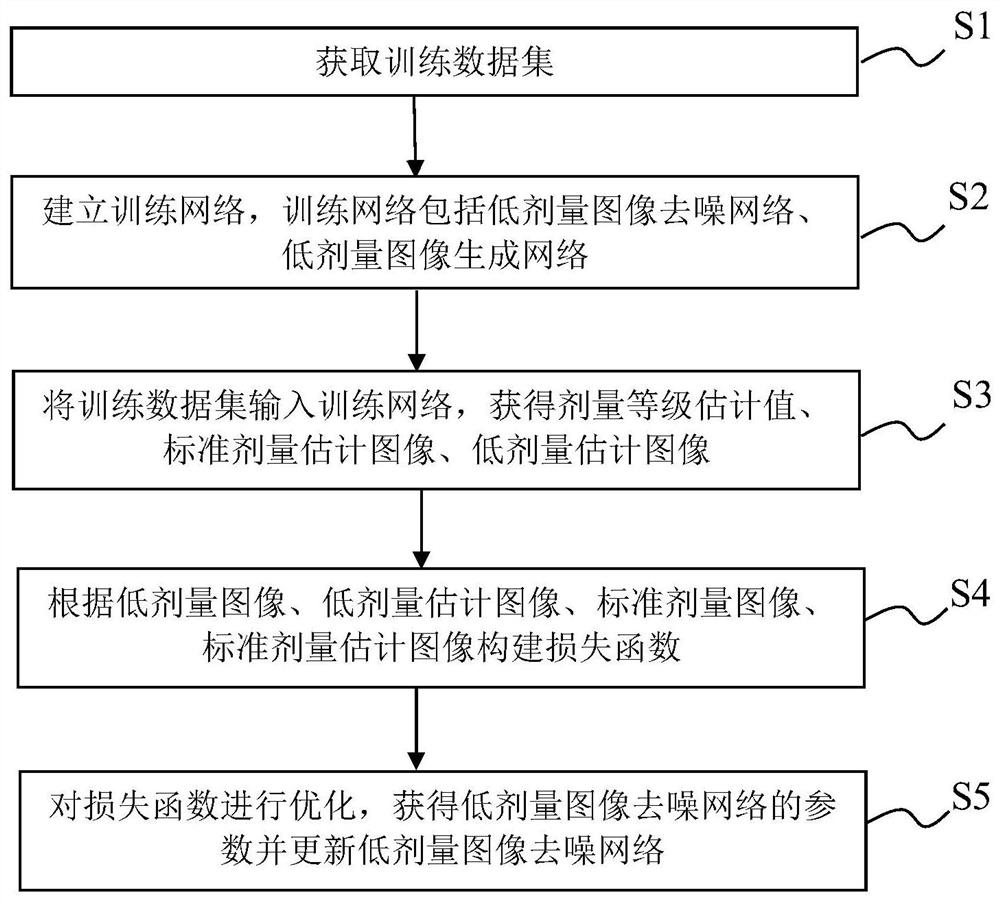
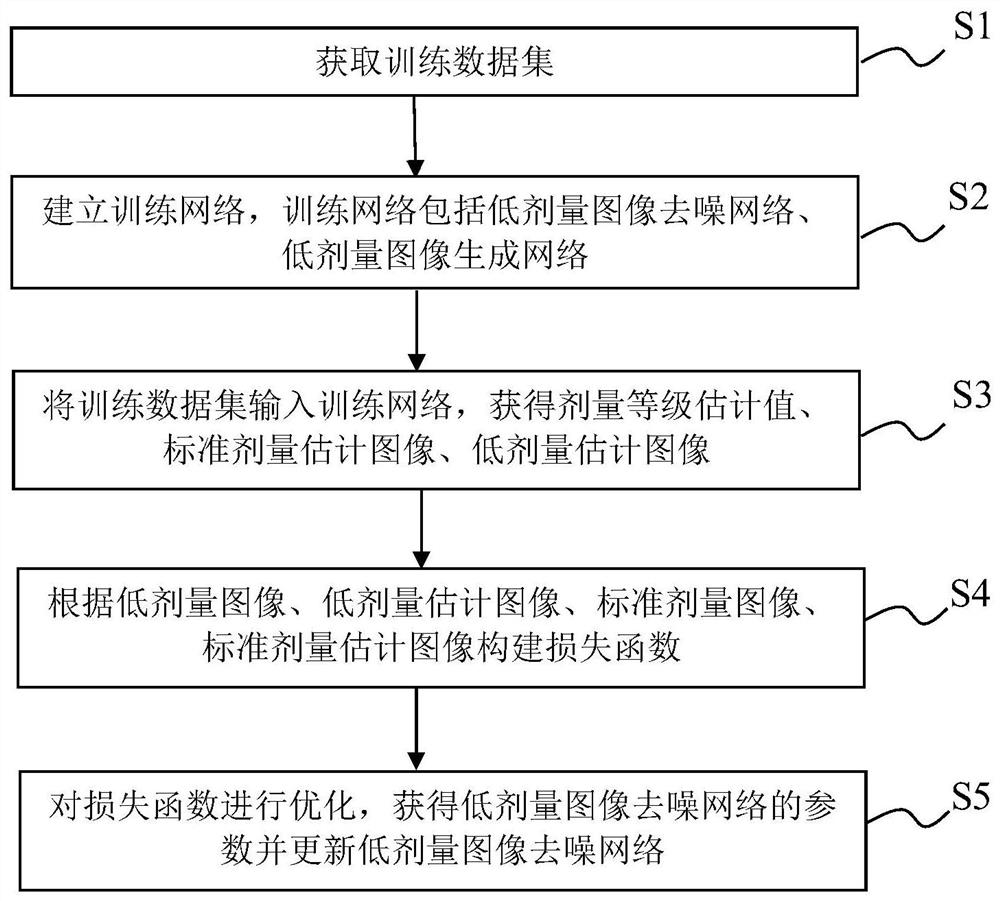
Training method of low-dose image denoising network, denoising method of low-dose image
ActiveCN112488951BImprove robustnessQuality improvementImage enhancementImage analysisImage denoisingRadiology
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Knowledge based treatment planning corrected for biological effects
Solutions are provided herein that specifically accounts for biological effects of tissue during radiation planning (such as treatment planning). In one or more embodiments, the biological effects may be calculated by accessing a knowledge base to determine reference data comprising at least one biological characteristic corresponding to the at least one organ, predicting a biological effect for the plurality of identified structures based on the biological characteristic corresponding to the at least one organ, and generating or modifying a radiation plan based on the biological effect. By incorporating biological data and fraction dose information, dose-estimation models can be created and trained to more accurately estimate dose absorption and effectiveness. Moreover, existing estimation models may be adapted to create dose estimations that account for the biological efficiency of target structures.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYST INT AG
Enamel radiation dose prediction method and system, storage medium and terminal
PendingCN114488252ANo guarantee of simplicityReduce the amount of parametersDosimetersFast Fourier transformTooth enamel
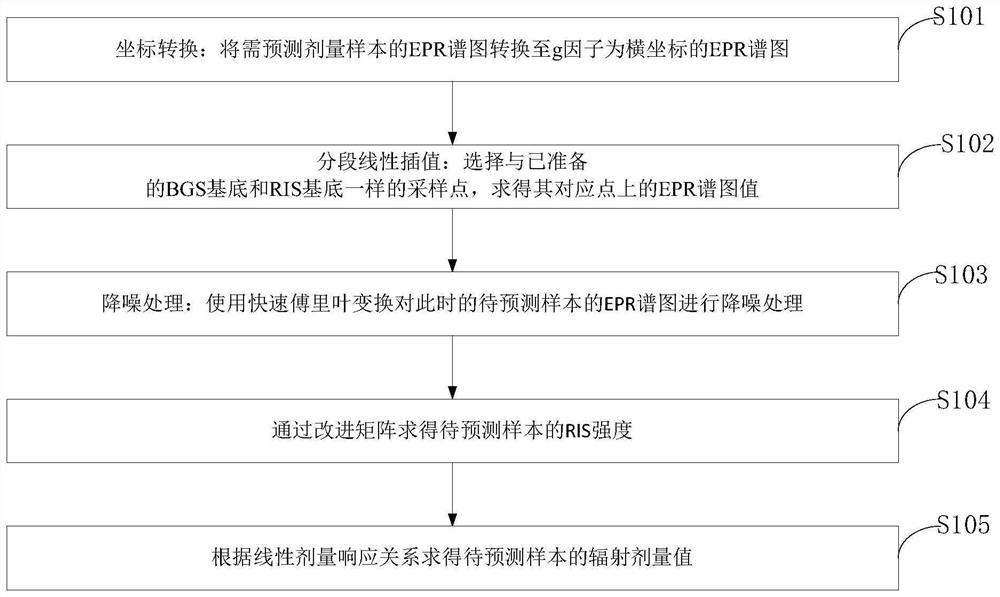
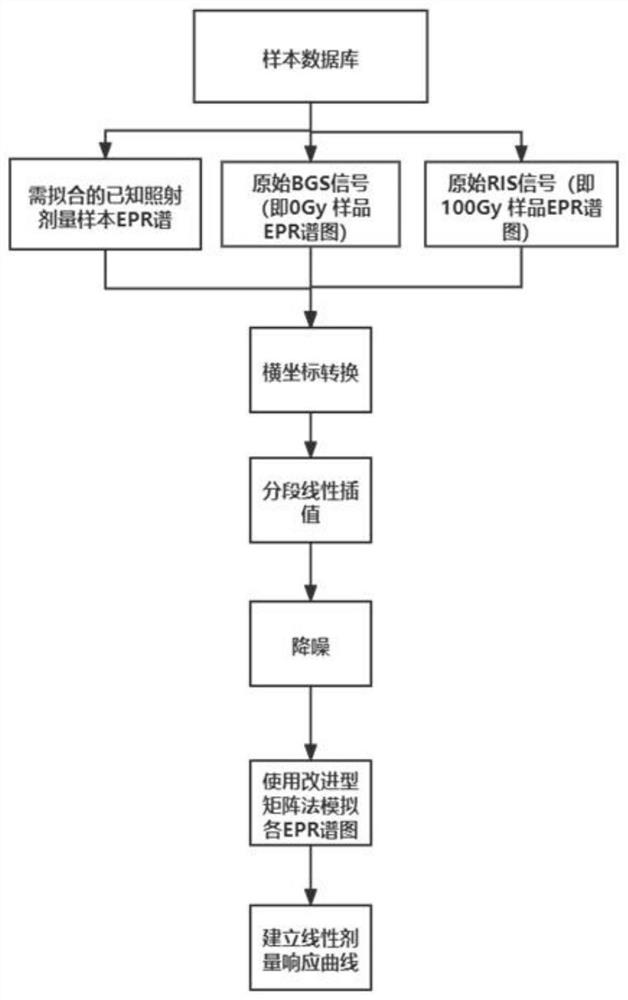
The invention belongs to the technical field of radiation dose estimation and analysis, and discloses an enamel radiation dose prediction method and system, a storage medium and a terminal. Sampling points which are the same as the prepared BGS substrate and the prepared RIS substrate are selected, and an EPR spectrogram value on a corresponding point of the to-be-predicted sample is obtained; performing noise reduction processing on the EPR spectrogram of the current to-be-predicted sample by using fast Fourier transform; solving the RIS intensity of the to-be-predicted sample through the improved matrix; and according to the linear dose response relationship, obtaining a radiation dose value of the to-be-predicted sample. According to the method, the calculated amount is equal to that of an original matrix method, new model parameters are not introduced, the number of the parameters is small, the fitting effect is good, the fitting error is smaller than 1%, EPR enamel dose estimation of a lower dose can be achieved, and in a low-dose area smaller than 0.3 Gy, the difference between the calculated irradiation dose value and a true value is smaller than or equal to 16%.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Low-dose image denoising network training method and low-dose image denoising method
ActiveCN112488951AImprove robustnessQuality improvementImage enhancementImage analysisImage denoisingRadiology
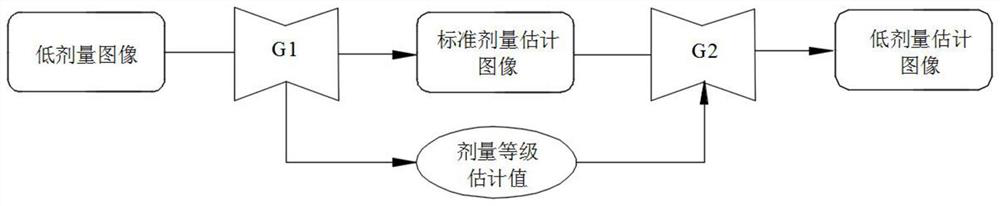
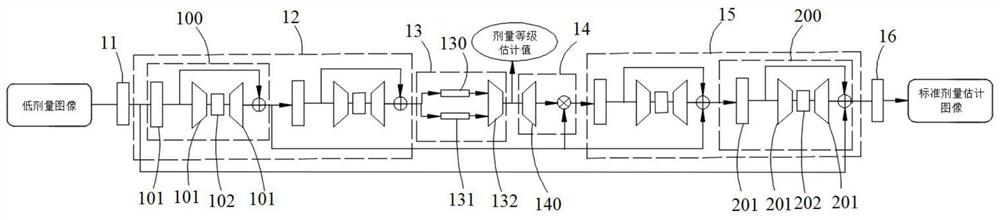
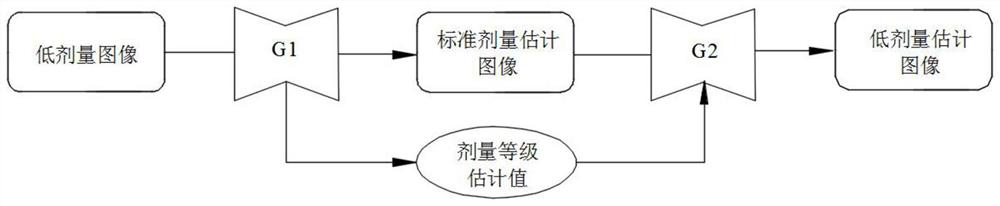
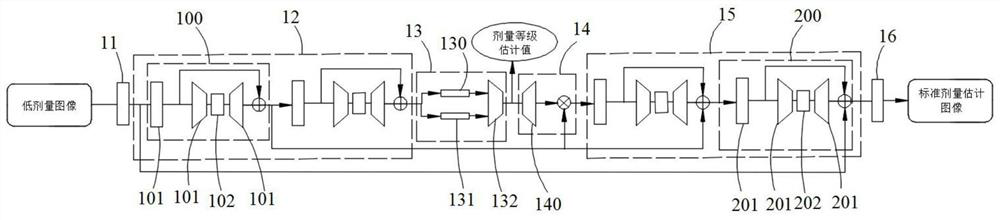
The invention provides a training method of a low-dose image denoising network, a denoising method of a low-dose image, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: employing a low-dose image denoising network for generating a dose level estimation value and a standard dose estimation image of a low-dose image according to the low-dose image, and generating alow-dose estimation image according to the standard dose estimation image and the dose level estimation value; and finally, constructing a loss function according to the low-dose image, the low-dose estimation image, the standard dose image and the standard dose estimation image, and optimizing the loss function to obtain parameters of the low-dose image denoising network, so the dose level information is fused into an image reconstruction process, and the robustness of the denoising method and the quality of the reconstructed image are improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Particle beam irradiation apparatus
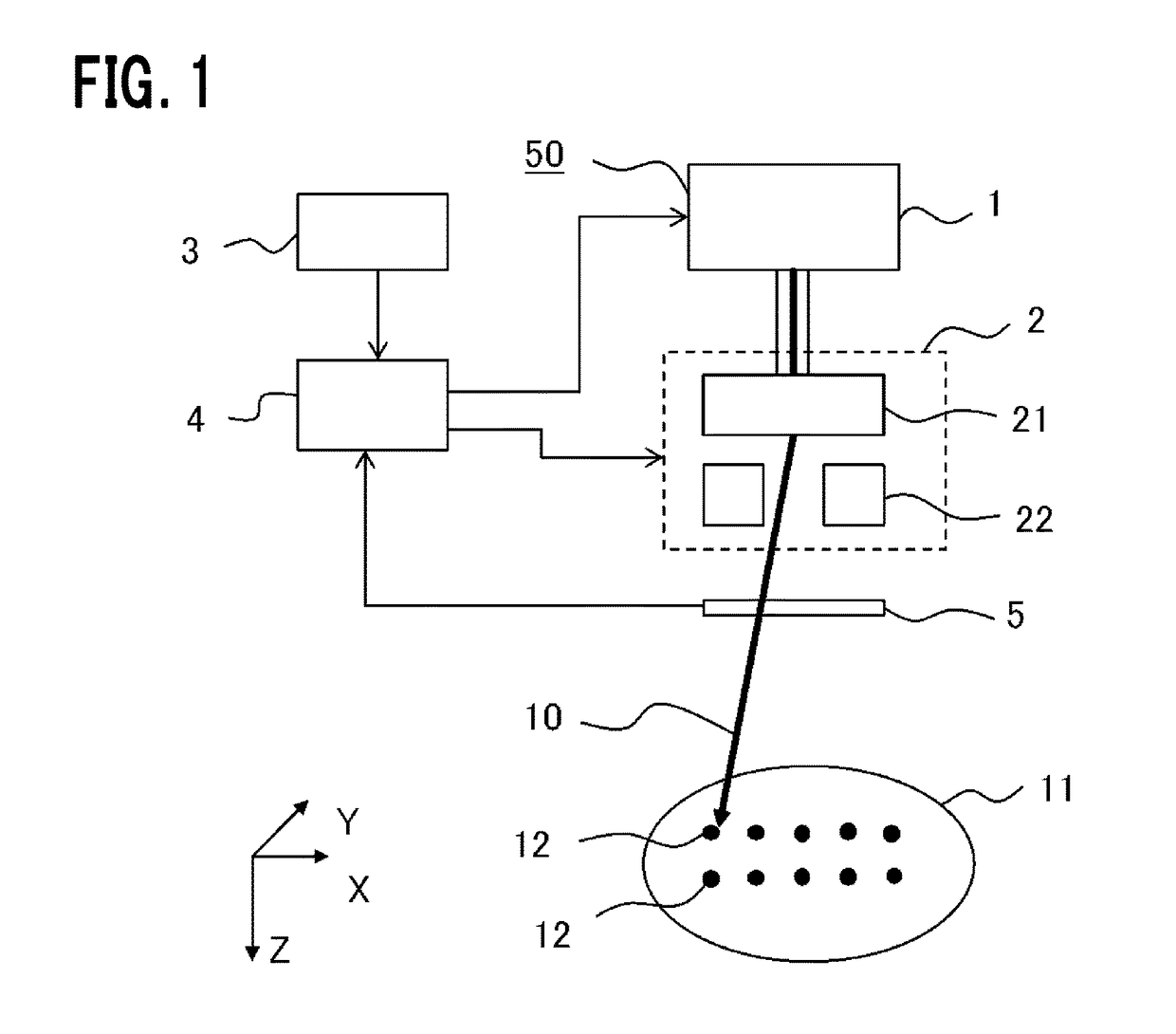
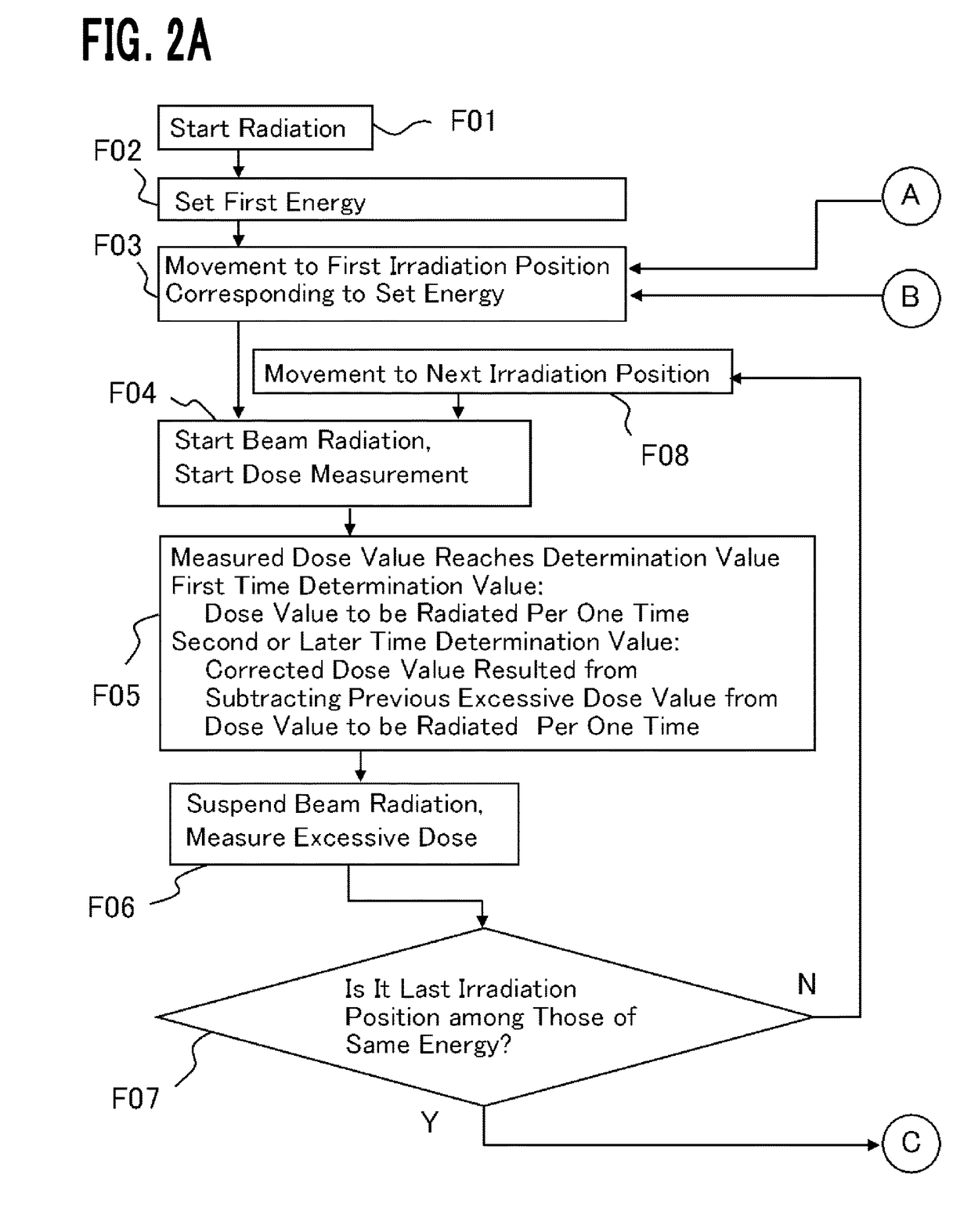
ActiveUS9889319B2Reduce the amount requiredX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyParticle beamDose estimation
A particle beam irradiation apparatus radiates a particle beam plural times per one irradiation position. A storage unit stores a dose to be radiated each of the times (divisional target dose). A dose monitor measures the dose of the particle beam radiated to the irradiation position. At the first time of radiation, a controller outputs an interruption signal when the dose measured by the dose monitor reaches the divisional target dose. The dose monitor measures a dose (excessive dose) radiated after the interruption signal is outputted until the particle beam is actually interrupted. Then, it is defined: Corrected Dose value=Divisional Target Dose−Excessive Dose Value. Instead, it may be defined: Corrected Dose value=Divisional Target Dose−Excessive Dose Estimation Value. At the second time of radiation, the controller outputs an interruption signal when the dose measured by the dose monitor reaches the corrected dose value.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
A low-dose dual-tracer PET reconstruction method based on attention mechanism
ActiveCN113160347BAchieve separationVerify robustnessReconstruction from projectionNeural architecturesFeature extractionRadiology
The invention discloses a low-dose dual-tracer PET reconstruction method based on an attention mechanism, which uses a convolutional network model based on an attention mechanism to deal with low-dose dual-tracer PET image reconstruction problems, and implements the method in a sinogram Standard dose estimation and dual-tracer PET signal separation, this method uses deep learning, a powerful feature extraction tool, to reconstruct a standard-dose single-tracer PET image from a low-dose dual-tracer PET sinogram, Robust to individual differences, tracer combinations, and sampling protocols.
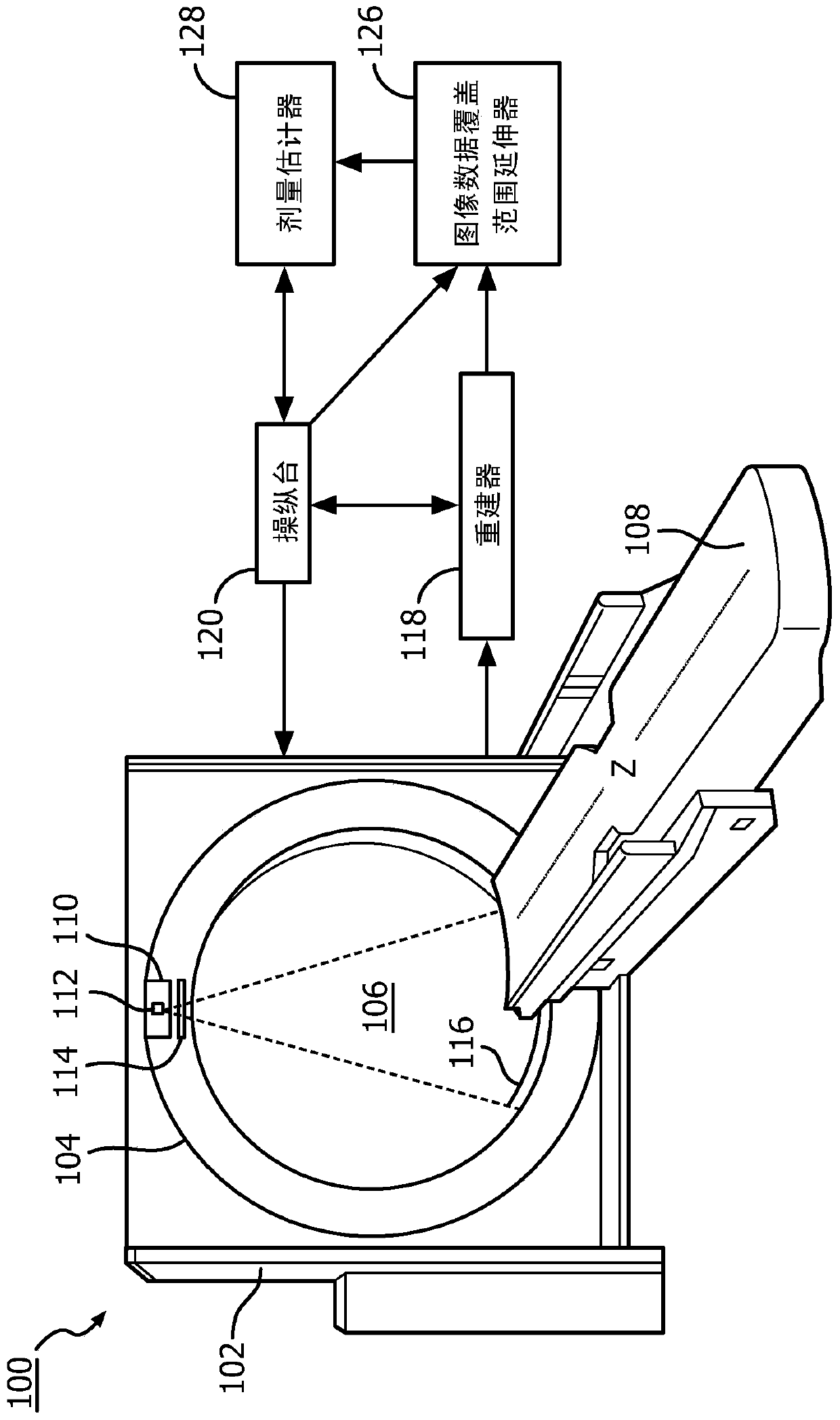
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Detection method of radiation-damaged sers in lymphocytes
An embodiment of the present invention provides a SERS detection method for lymphocyte radiation damage, which belongs to the technical field of radiation biological dose estimation. The method includes: passing gold-shell magnetic beads, lymphocytes, and SERS tags into the microfluidic chip, stopping sample injection and incubating reaction when the microfluidic chip is filled with solution, so that the gold-shell magnetic beads capture the lymphocytes and then interact with the microfluidic chip. The SERS label is coupled; a magnet is placed outside the detection area of the microfluidic chip, and after the gold-shell magnetic beads are fully enriched under the magnetic field of the magnet, the microfluidic chip is placed on a portable Raman spectrometer, and the Raman detection. By preparing a microfluidic chip based on a gold-shell magnetic bead Raman substrate, it has higher SERS performance than traditional microfluidic chips, and has the advantages of detection integration, automation, and miniaturization, which overcomes the steps of traditional detection methods. Complicated, highly disturbed by human factors, not portable, nanoparticle failure and other issues.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Application of Radiation Sensitive Gene as Radiation Biological Dosimeter
ActiveCN110195101BQuick estimateAccurate estimateMicrobiological testing/measurementPopulation sampleDosimeter
The invention relates to the application of a combination of multiple radiation sensitive genes as a radiation biological dosimeter in radiation dose estimation. Specifically, the present invention relates to the application of a combination of 5-13 different radiation-sensitive genes as a radiation biological dosimeter in radiation dose estimation, including preparing a combination of 5-13 different radiation-sensitive genes for radiation dose estimation based on the combination of the 5-13 different radiation-sensitive genes A kit for estimating dose, a microarray, and a method for estimating radiation dose using the kit and microarray. Compared with traditional methods including chromosomal aberration analysis, the radiation biological dosimeter and application method have the advantages of simplicity, rapidity, high throughput, etc., and the accuracy of dose estimation is high, especially suitable for nuclear accidents and radiation accidents. Radiation dose estimation for a range population sample.
Owner:NAT INST FOR RADIOLOGICAL PROTECTION & NUCLEAR SAFETY CHINESE CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Image data z-axis coverage extension for tissue dose estimation
ActiveCN105578963ASolve the real problemImage enhancementImpression capsDose estimationField of view
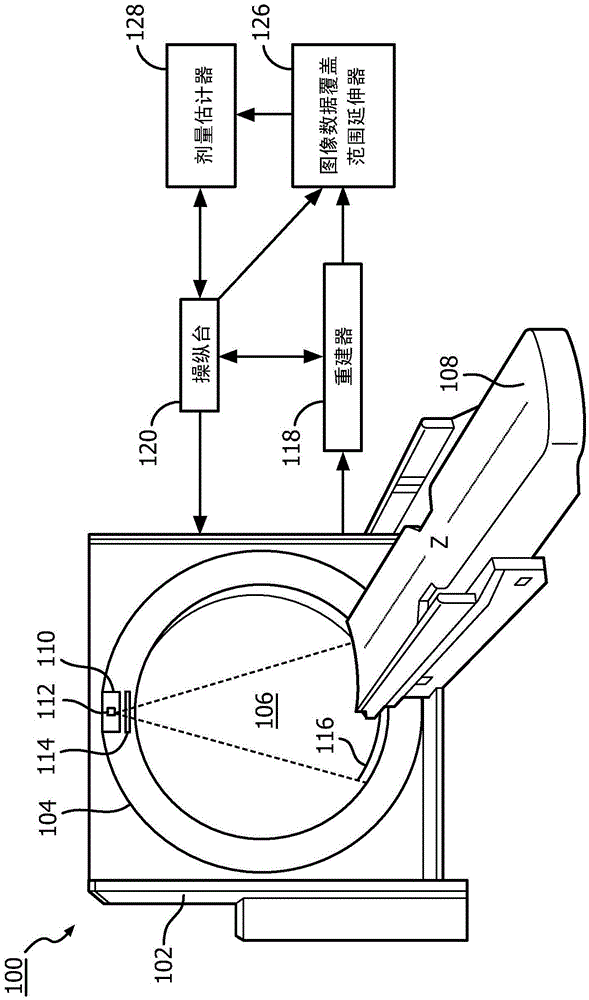
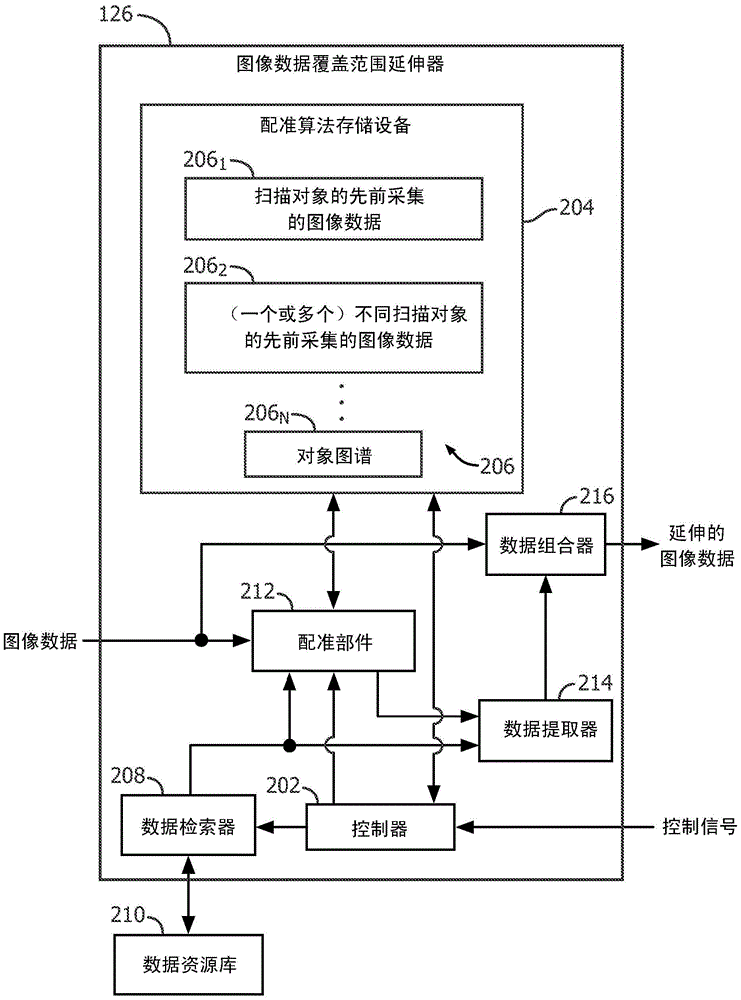
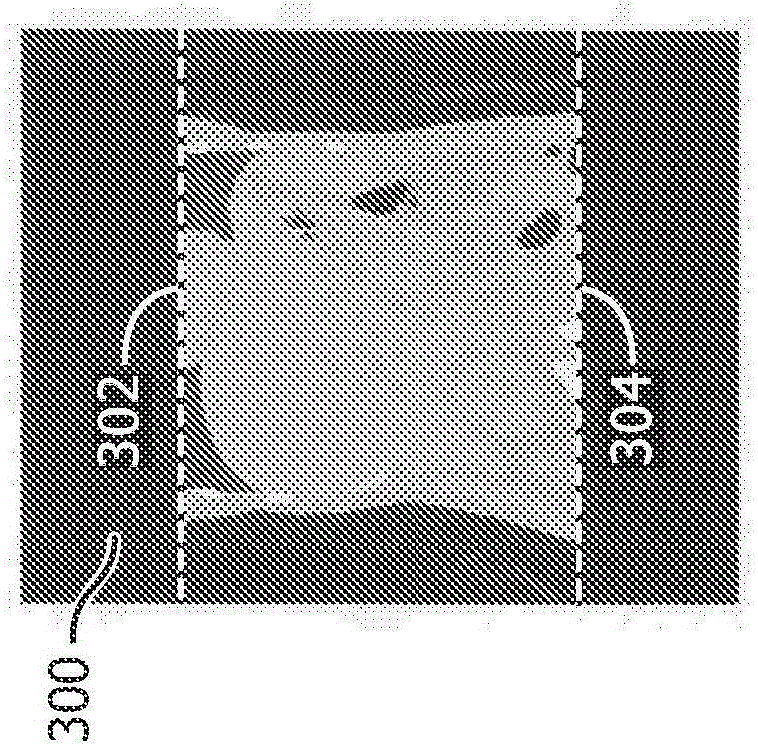
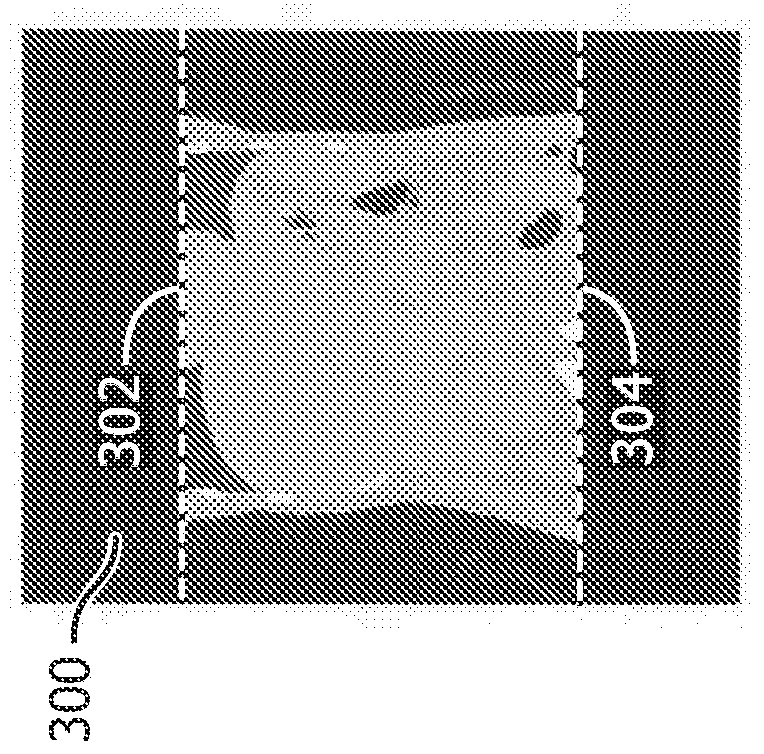
A method for extending initial image data of a subject for dose estimation includes obtaining first image data of the subject for dose calculation, wherein the first image data has a first field of view. The method further includes obtaining second image data for extending the field of view of the first image data. The second image data has a second field of view that is larger than the first field of view. The method further includes extending the first field of view based on the second image data, producing extended image data.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Extended z-axis coverage of image data for tissue dose estimation
ActiveCN105578963BSolve the real problemImage enhancementImpression capsDose estimationField of view
A method for extending initial image data of a subject for dose estimation includes obtaining first image data of the subject for dose calculation, wherein the first image data has a first field of view. The method also includes obtaining second image data for extending the field of view of the first image data. The second image data has a second field of view larger than the first field of view. The method also includes extending the first field of view based on the second image data to generate extended image data.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Nuclear emergency biological dose estimation mobile experiment platform
The invention discloses a nuclear emergency biological dose estimation mobile experiment platform which comprises a mobile chassis and an experiment cabin body, the experiment cabin body is installed on the mobile chassis, the experiment cabin body comprises a sampling room, a sterile culture room, a specimen preparation room and a film reading and biological dose estimation room which are connected in sequence, a first cabin door is arranged on the sampling room, a first workbench is installed in the sampling room, a cell culture box, a super clean bench and an ultraviolet disinfection device are installed in the sterile culture room, an experiment table, a water pool and a centrifugal machine are installed in the specimen preparation room, and a second workbench and a seat are installed in the specimen reading and biological dose estimation room. The experiment cabin body arrives at a nuclear accident place through the mobile chassis, working personnel in the sampling room carry out work such as blood sampling and information input on the detected personnel; peripheral blood lymphocytes of examinees can be cultured in the sterile culture room; chromosome specimens of peripheral blood lymphocytes for analysis can be prepared in the specimen preparation room; and analysis and evaluation of chromosome specimens can be carried out between film reading and biological dose estimation.
Owner:CHINA INST FOR RADIATION PROTECTION
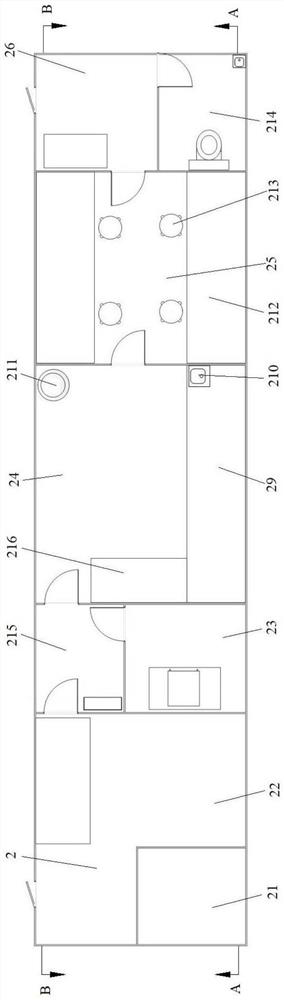
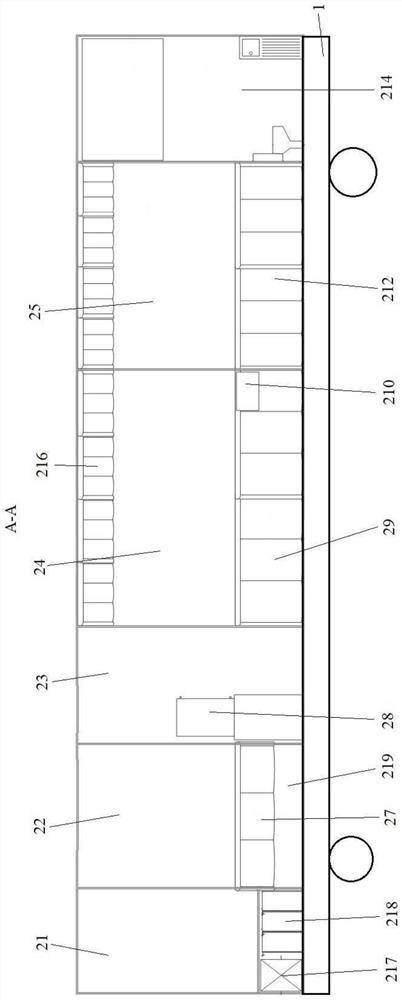
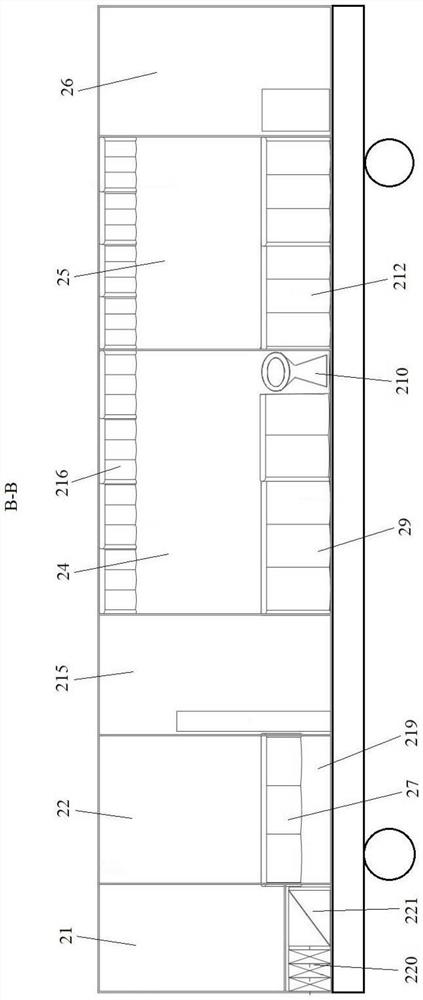
Dose estimation for the irradiation of an object
PendingUS20210353961A1Time required for the dose estimation is reducedEfficient solutionImage enhancementGeometric image transformationDose estimationIrradiation
In accordance with a method for dose estimation for the irradiation of an object, a model with a total number of spatial elements is provided on a memory element. For each spatial element, the model specifies a material composition of the object. A neighborhood material composition is determined for a neighborhood of spatial elements depending on the model by a computing unit. A radiation dose for the neighborhood with regard to an ionizing radiation is determined with aid of a simulation depending on the neighborhood material composition. A dose distribution for the object with regard to the ionizing radiation is determined based on the radiation dose for the neighborhood.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com