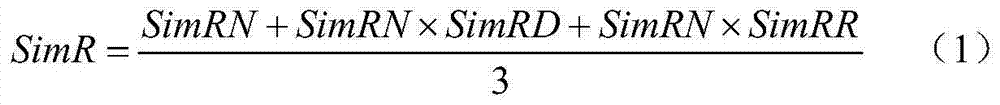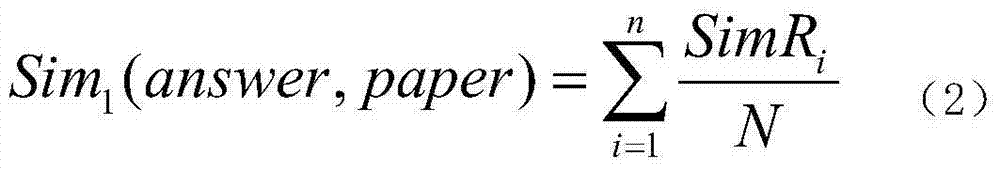Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
71 results about "Description logic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Description logics (DL) are a family of formal knowledge representation languages. Many DLs are more expressive than propositional logic but less expressive than first-order logic. In contrast to the latter, the core reasoning problems for DLs are (usually) decidable, and efficient decision procedures have been designed and implemented for these problems. There are general, spatial, temporal, spatiotemporal, and fuzzy descriptions logics, and each description logic features a different balance between DL expressivity and reasoning complexity by supporting different sets of mathematical constructors.
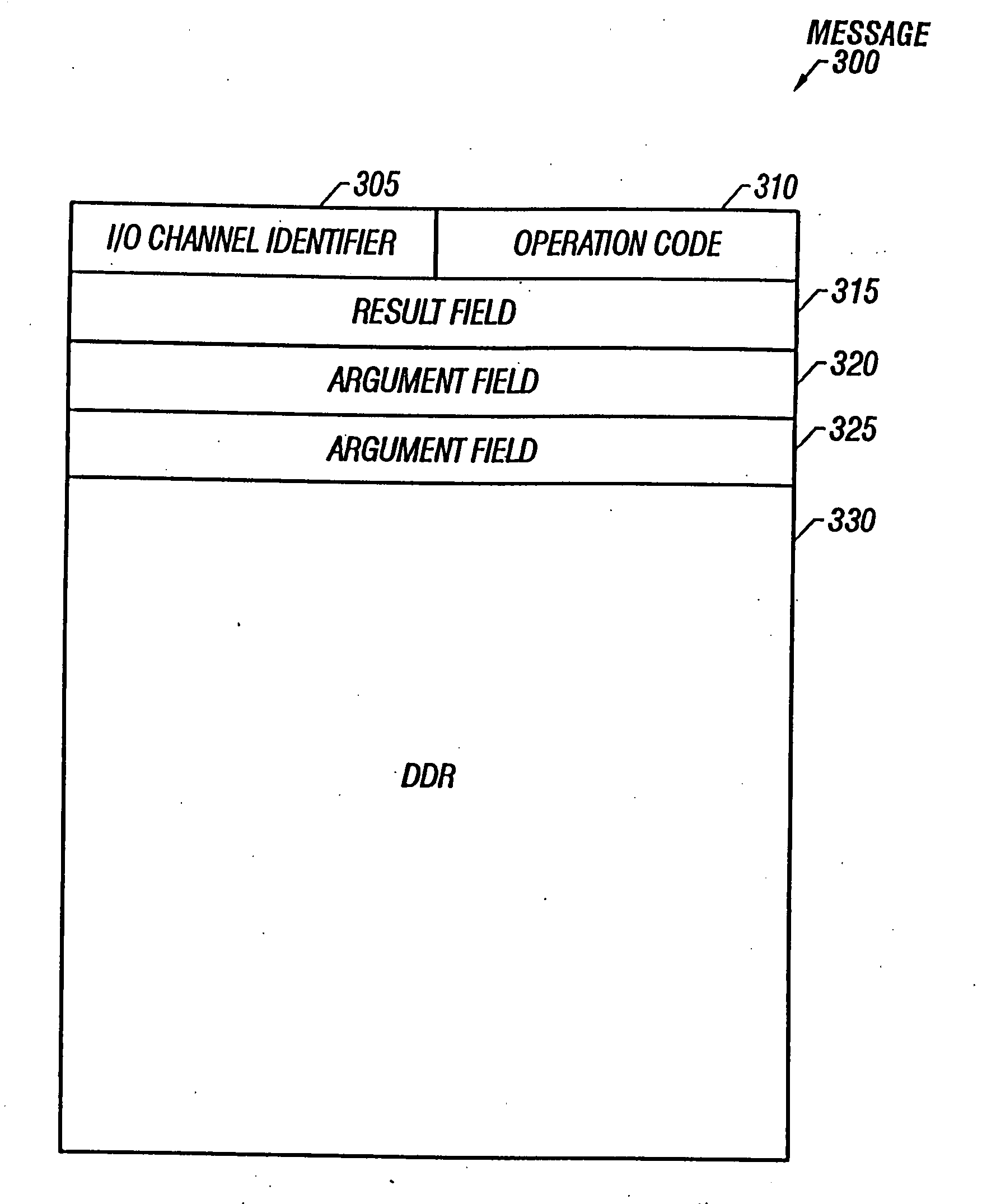
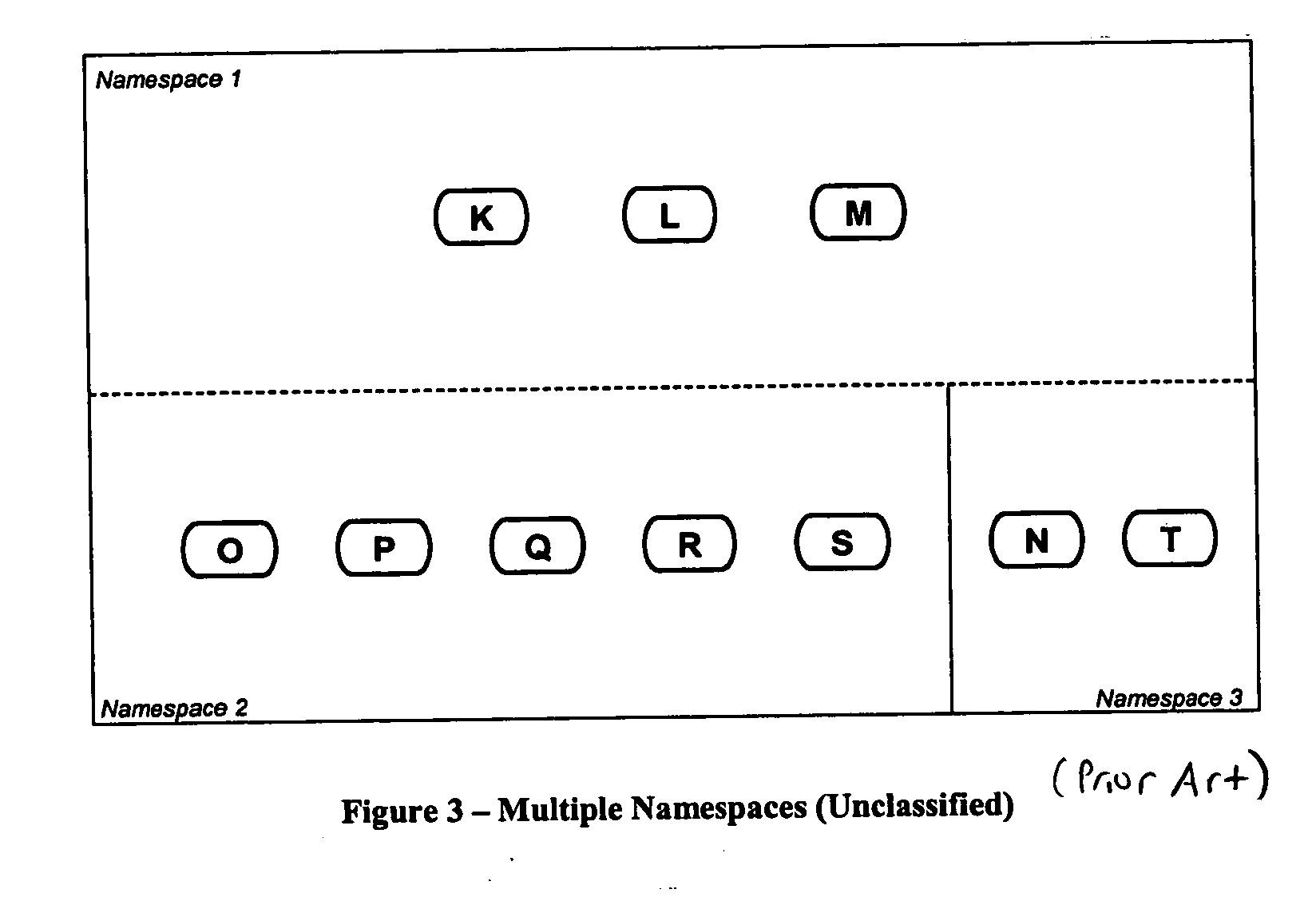
Data structure describing logical data spaces
InactiveUS20070156729A1Automatic and efficientAvoid disadvantagesData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData storingData store
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
System for knowledge acquisition
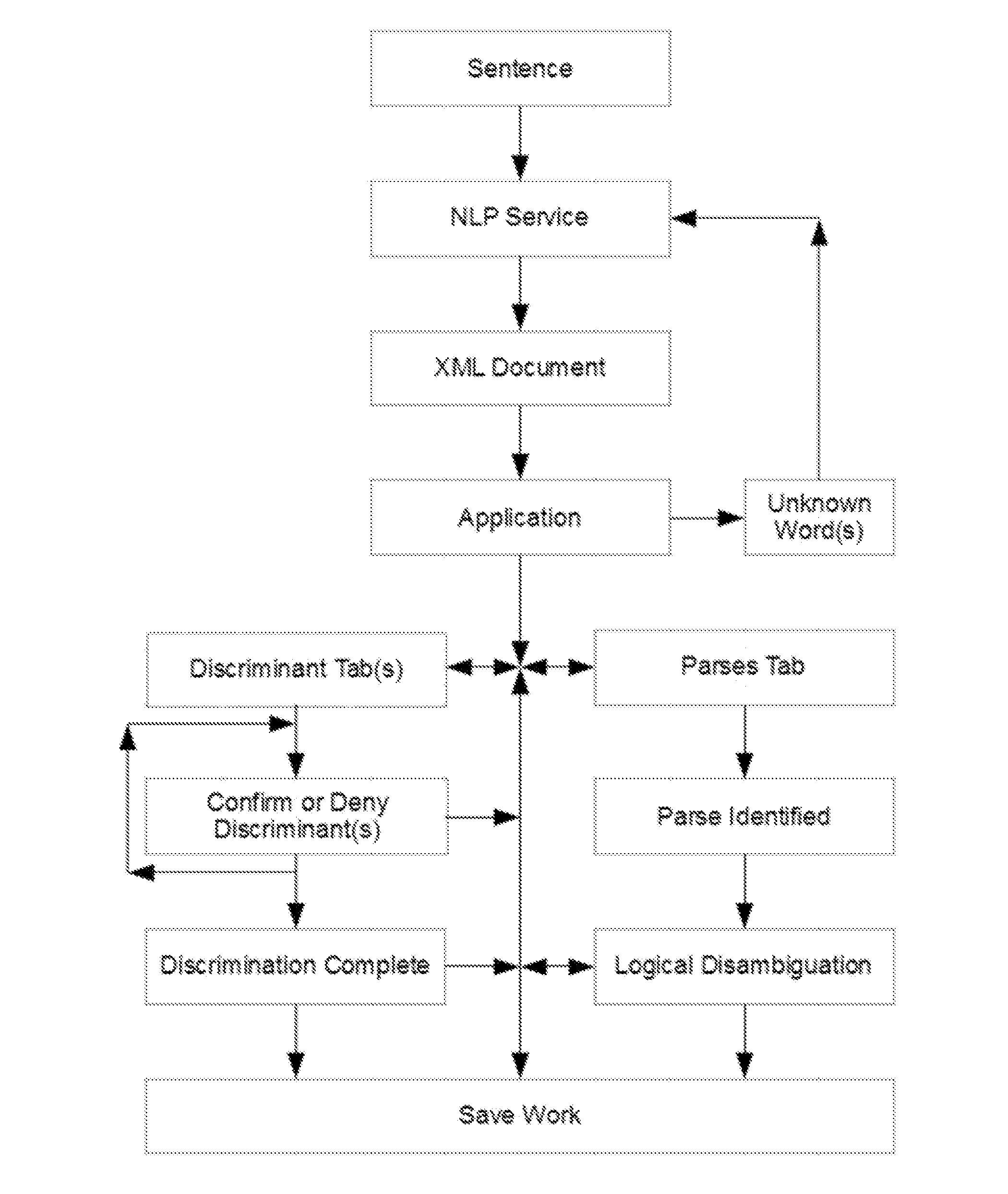
ActiveUS20160085743A1Increasing semanticIncreasing logical precisionNatural language translationSemantic analysisReasoning algorithmAmbiguity
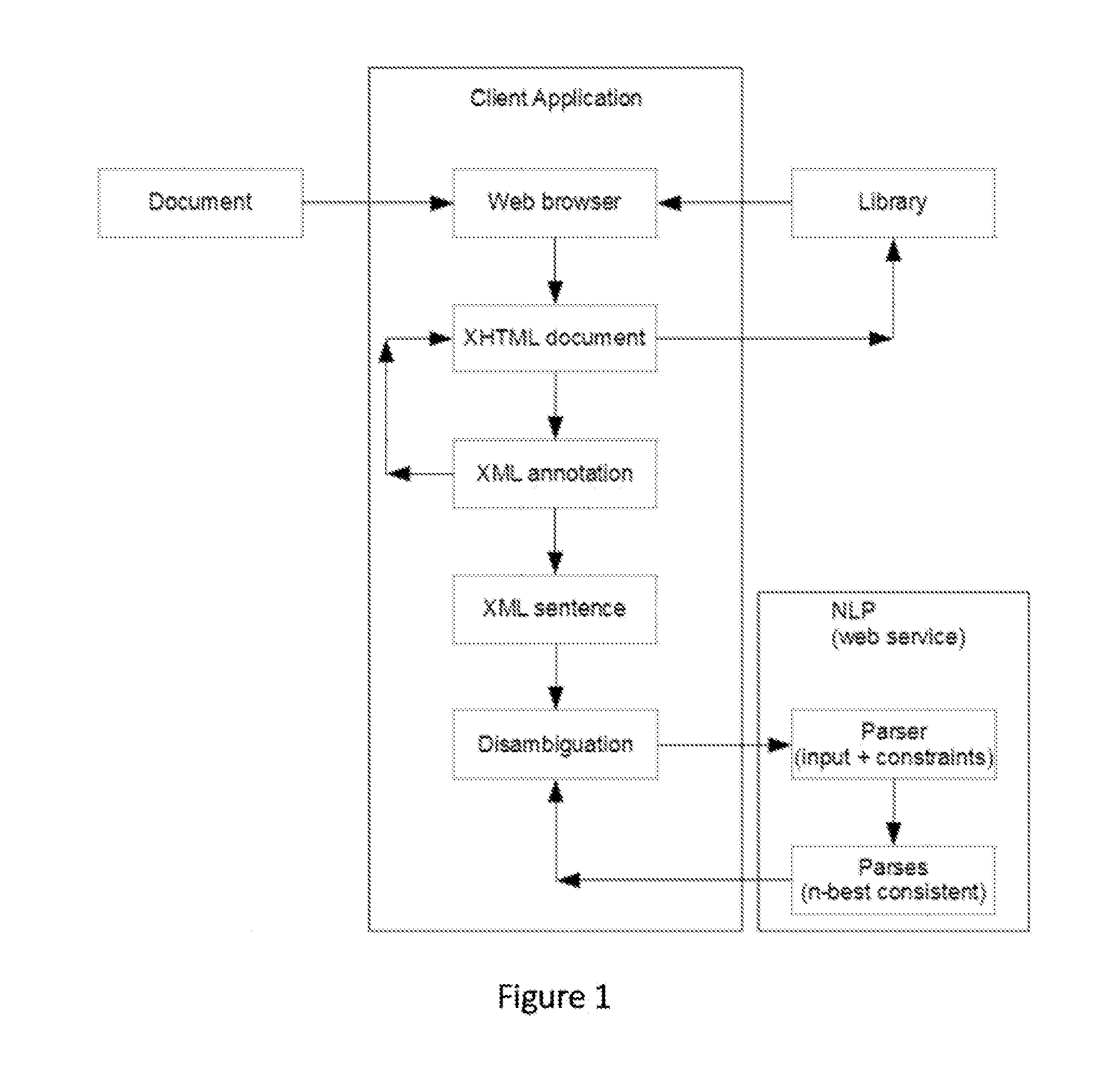
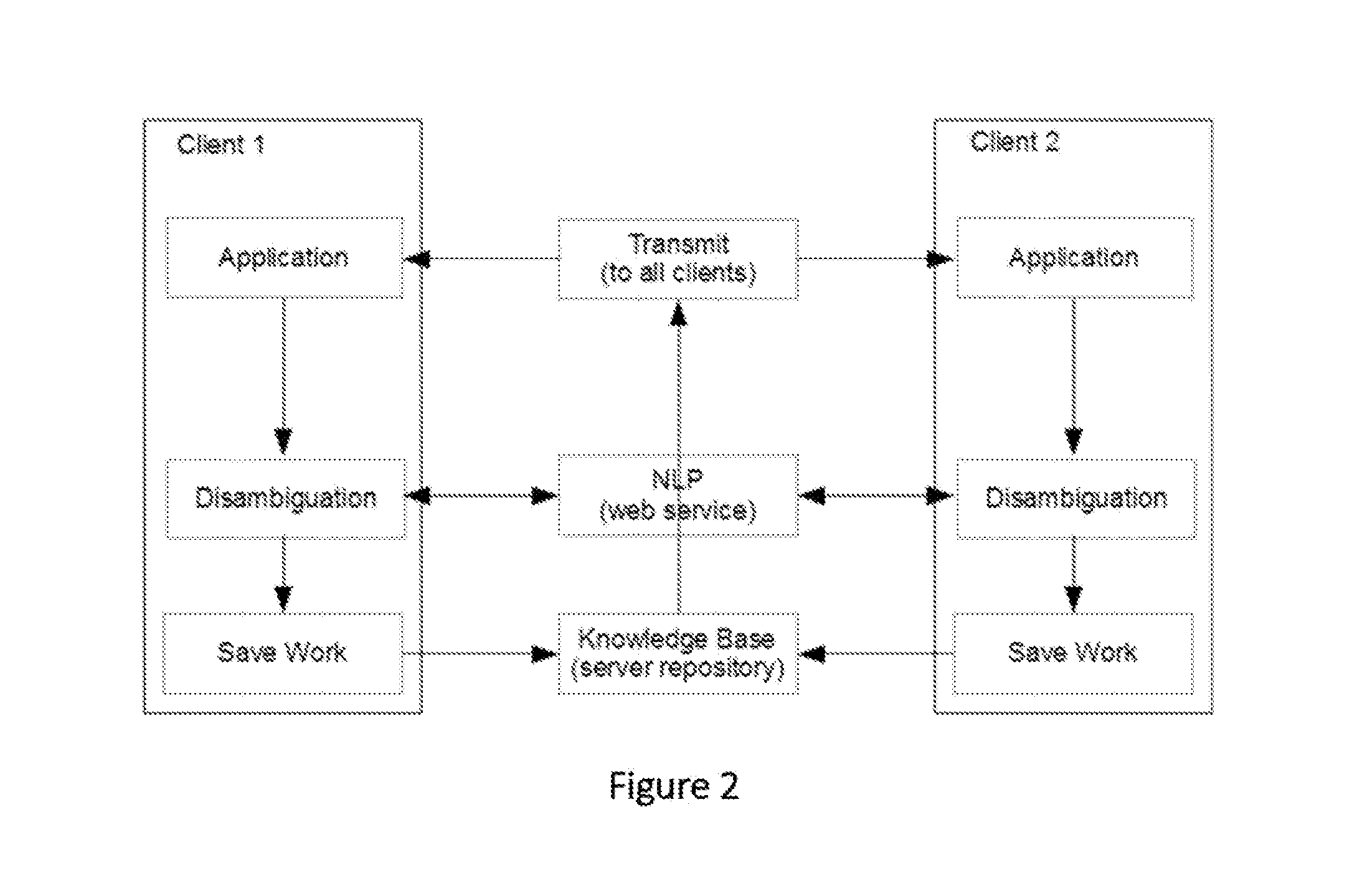
A system and method that translates sentences of natural language text into sets of axioms of formal logic that are consistent with parses resulting from NLP and acquired constraints as they accumulate. The system and method further present these axioms so as to facilitate further disambiguation of such sentences and produces axioms of formal logic suitable for processing by automated reasoning technologies, such as first-order or description logic suitable for processing by various reasoning algorithms, such as logic programs, inference engines, theorem provers, and rule-based systems.
Owner:HALEY PAUL V
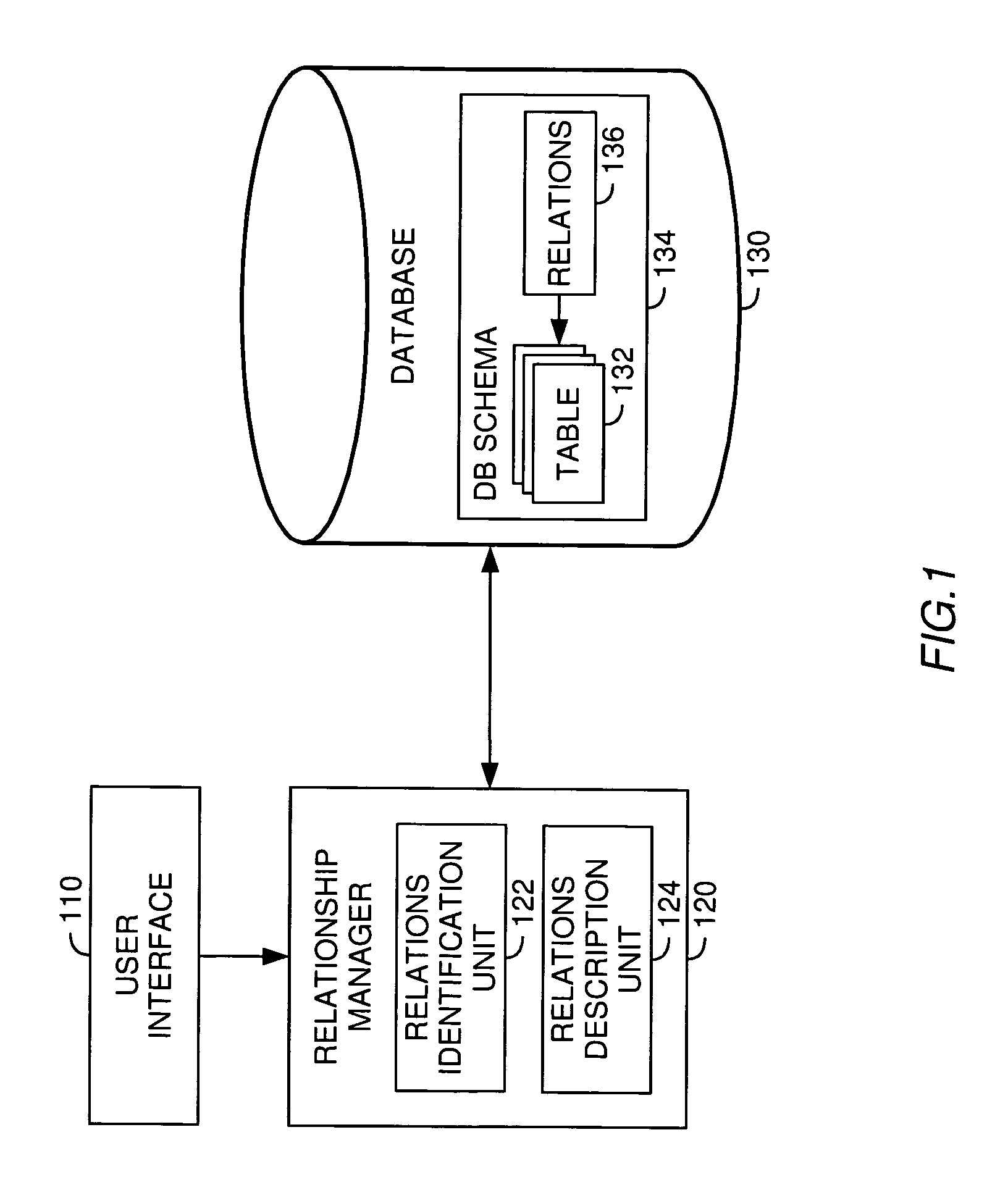
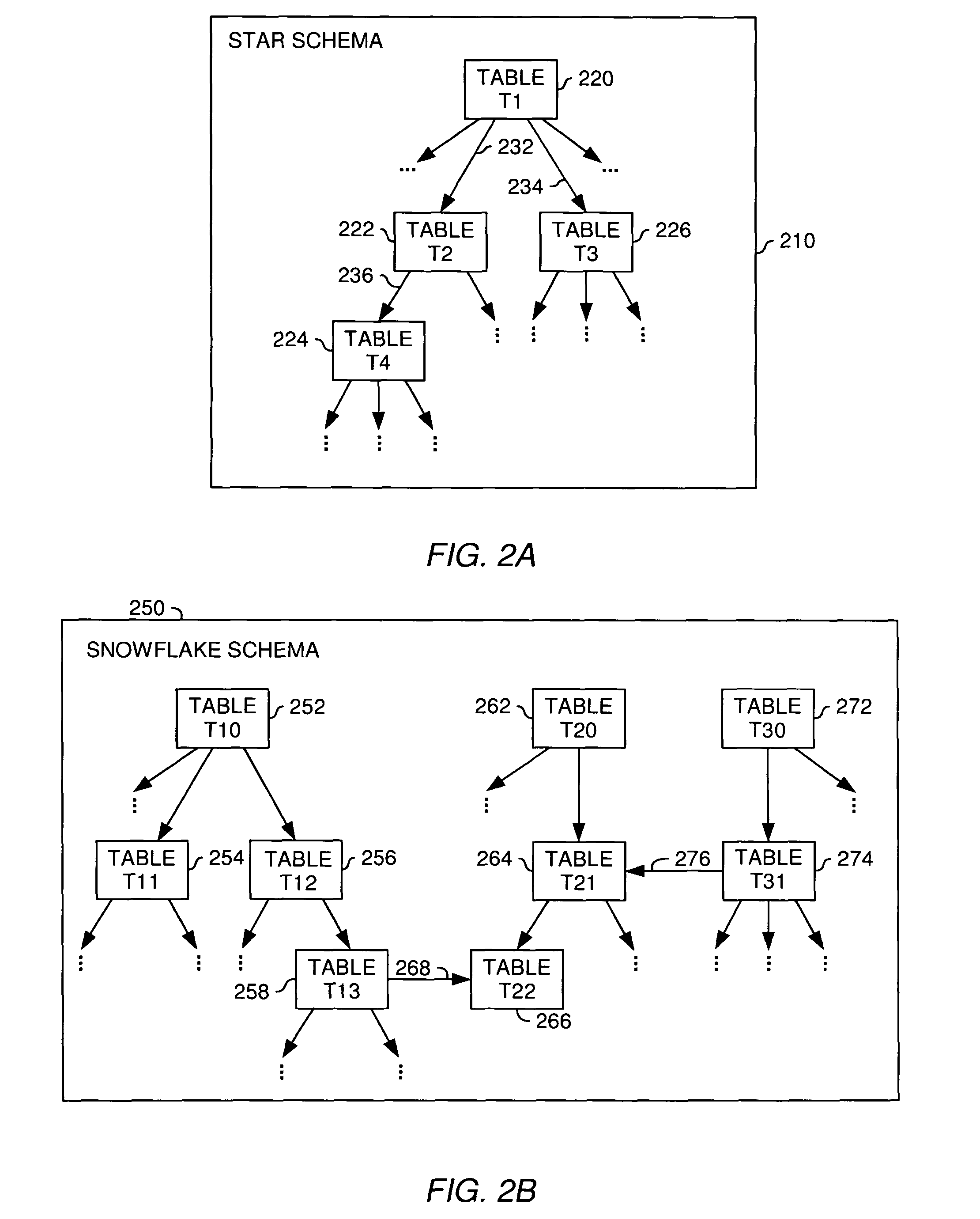
Management of relationships between database tables
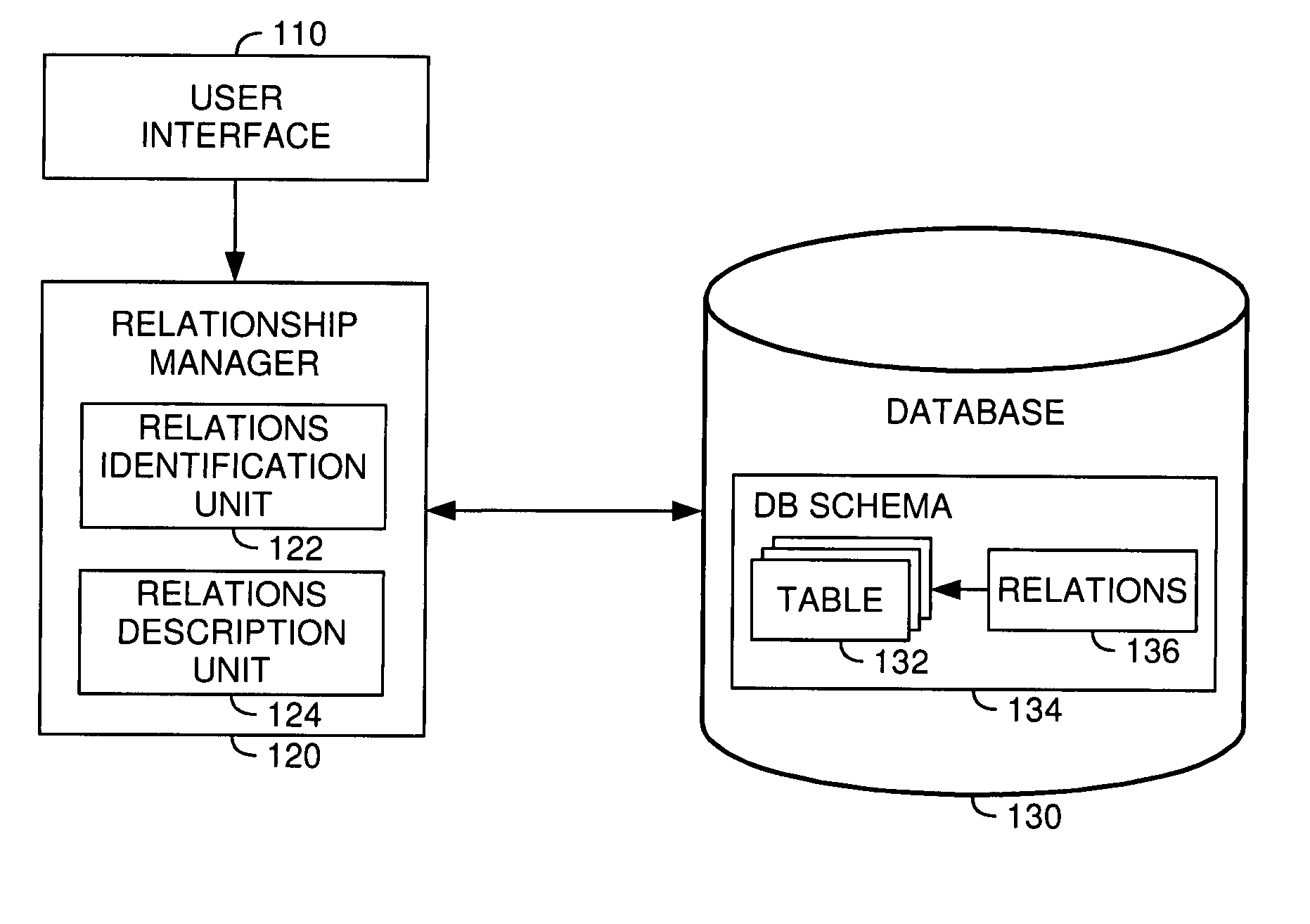
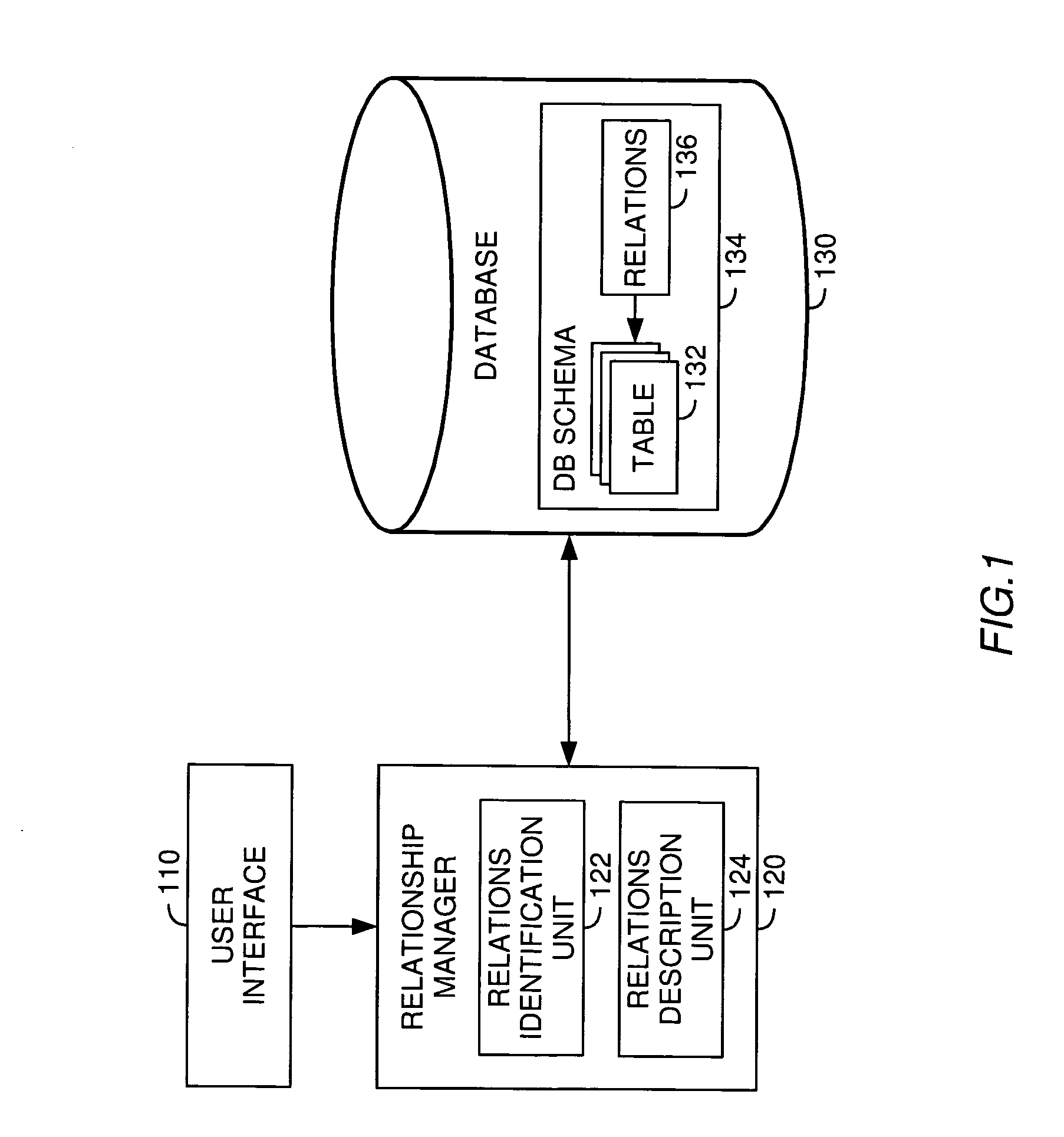
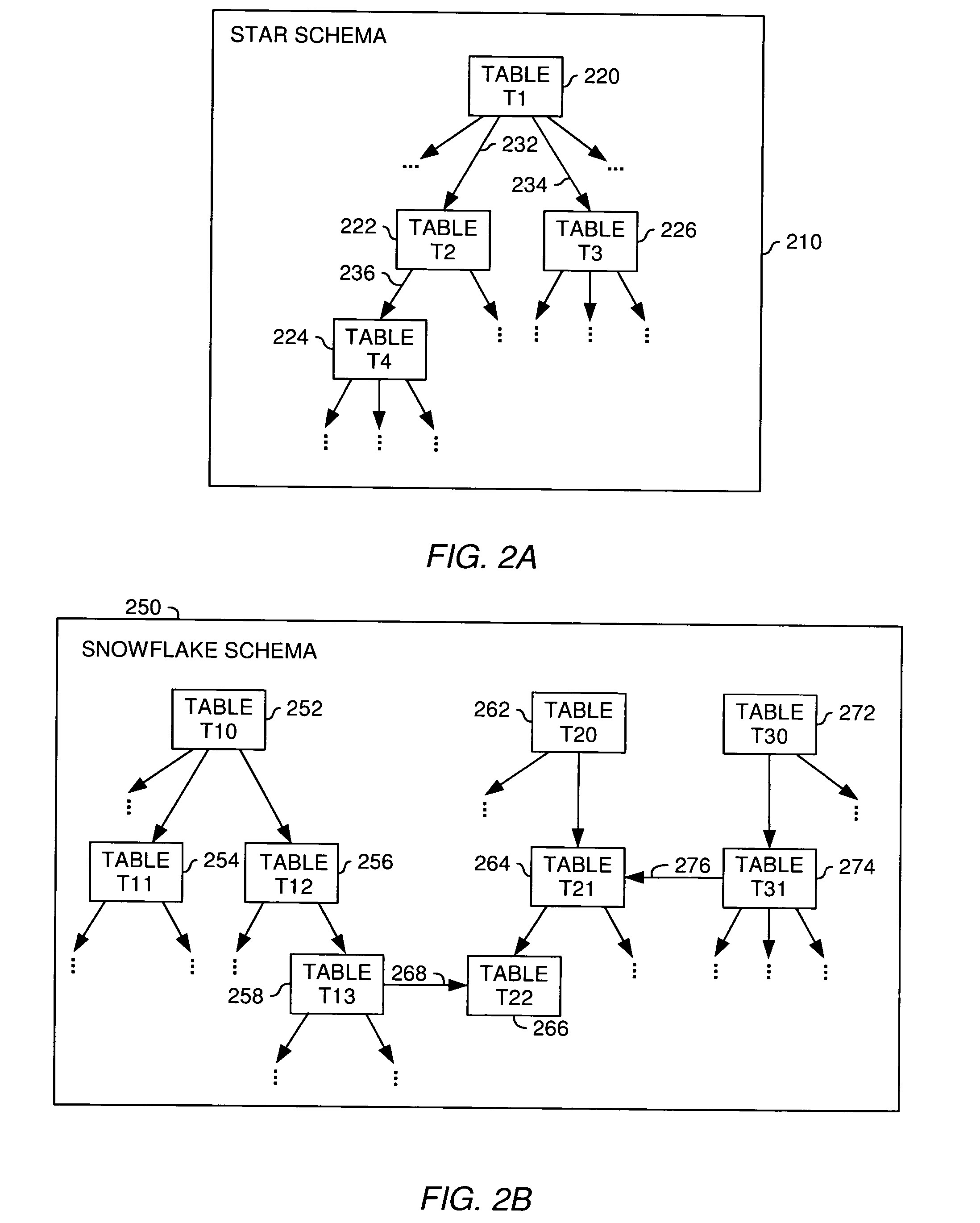
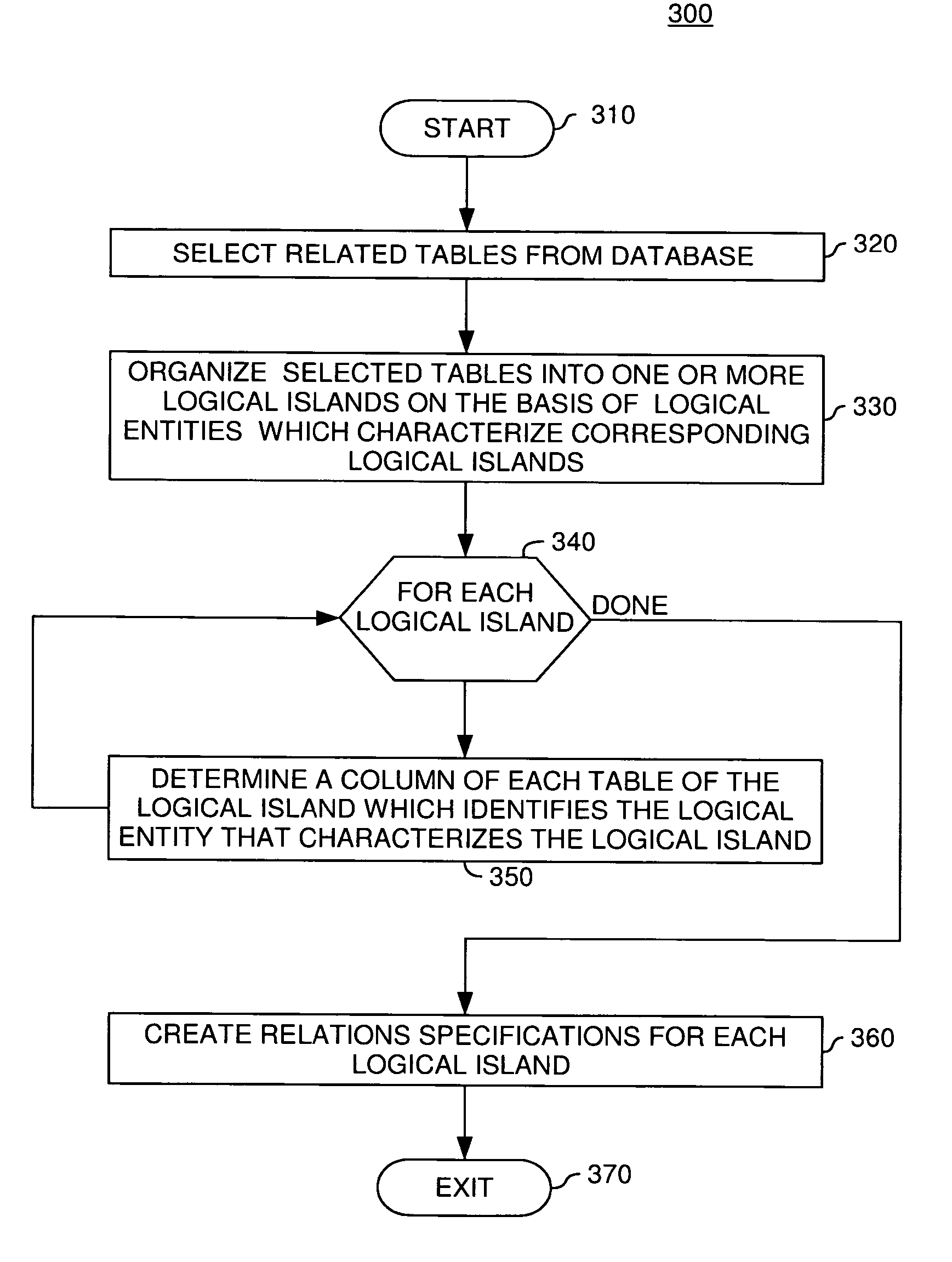
A method, system and article of manufacture for managing relationships between database tables and, more particularly, for identifying and accurately describing relationships between tables in a database. One embodiment provides a method for identifying relationships between tables in a database. The method comprises receiving user input selecting a plurality of tables from the database. The plurality of tables is organized into a logical island defining a logical unit related to a particular logical entity. The method further comprises receiving user input identifying, for each of the plurality of tables, a table column containing information that identifies the particular logical entity in the table, whereby the identified table columns of different tables define logical relationships between the different tables in the logical island. On the basis of the identified table columns, relations specifications are created which describe the logical relationships between the different tables in the logical island.
Owner:DOMO
Debugging system for gate level IC designs
ActiveUS20070174805A1Easy to understandSimplify the commissioning processSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputer architectureComputer-aided
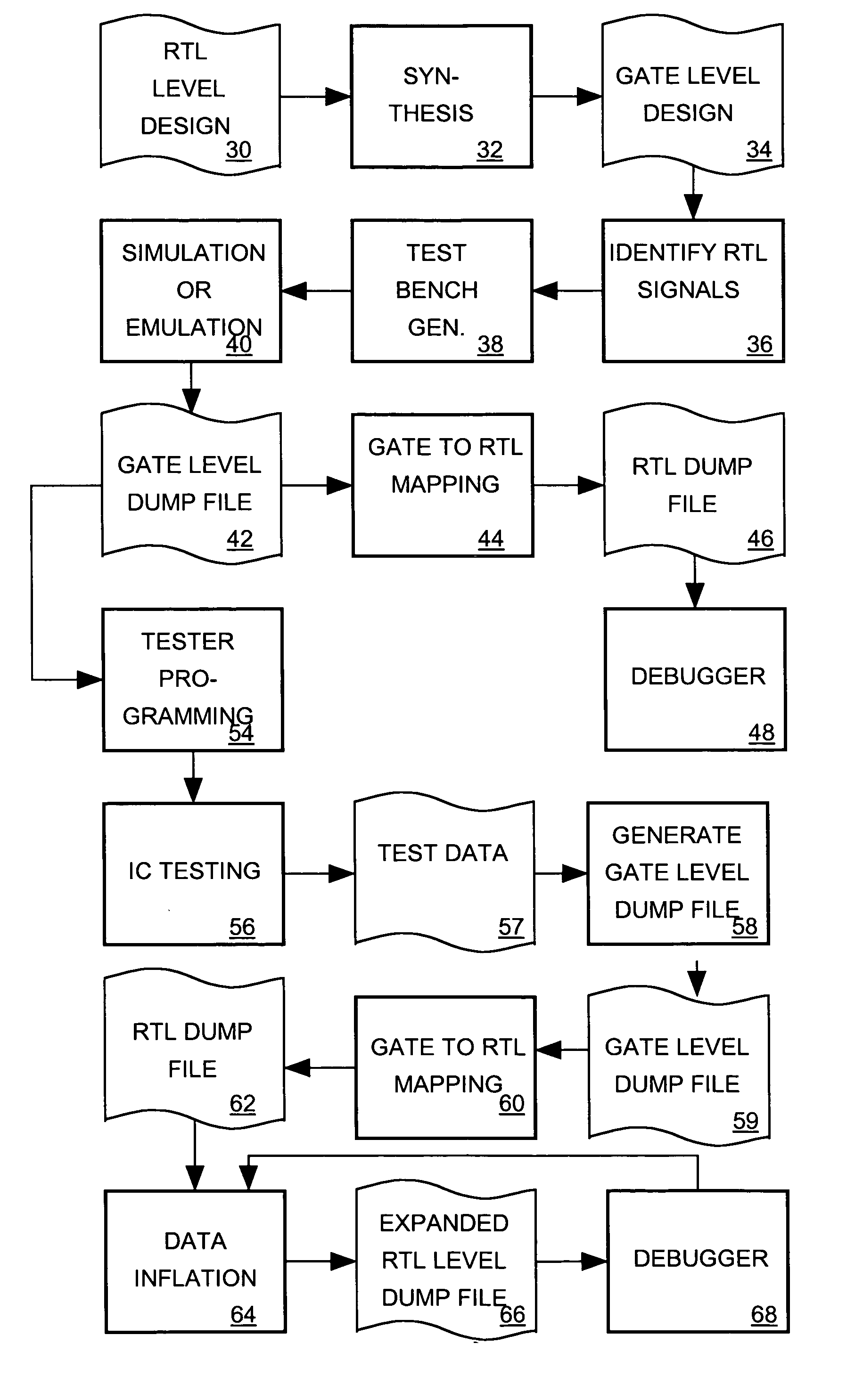
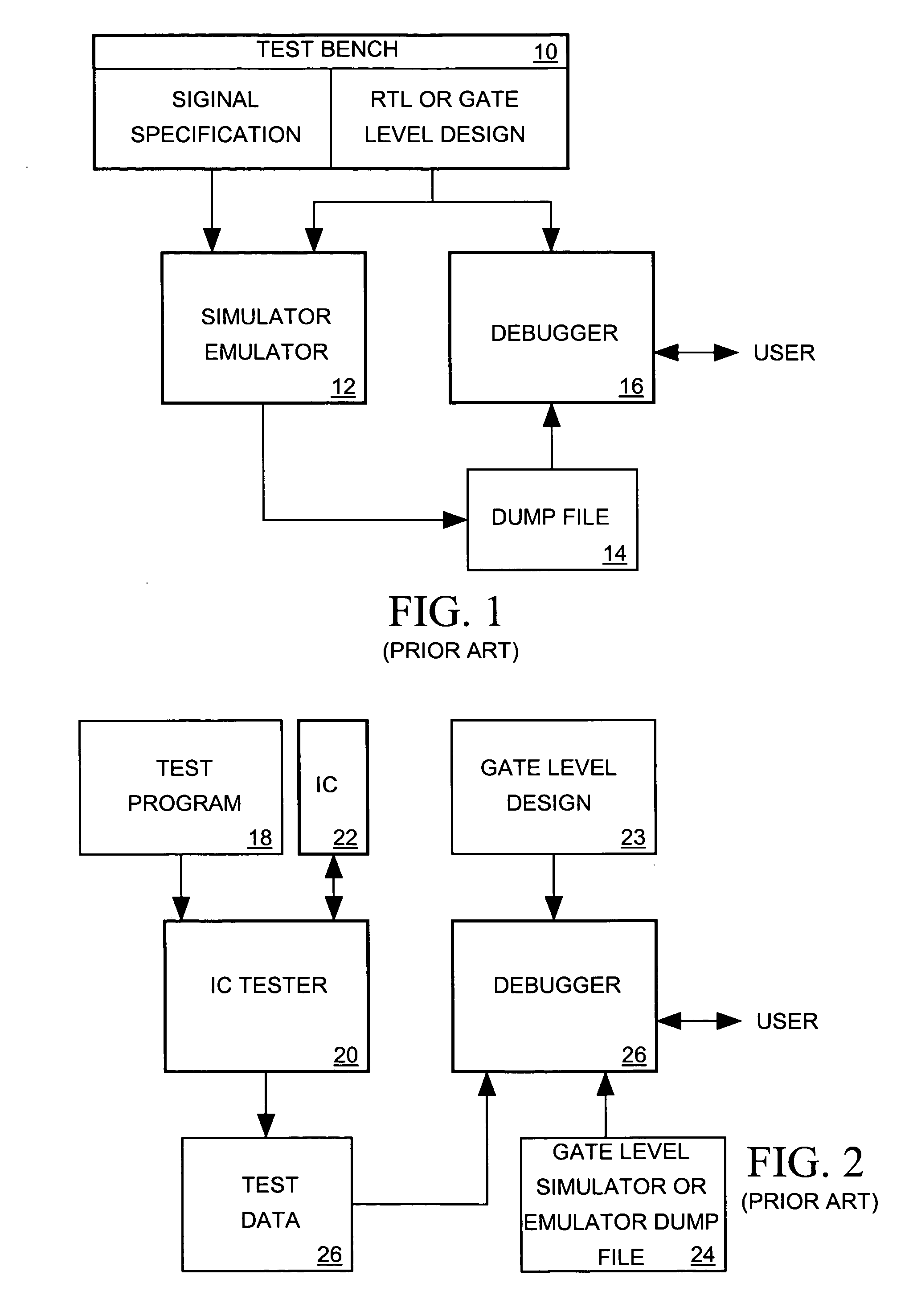
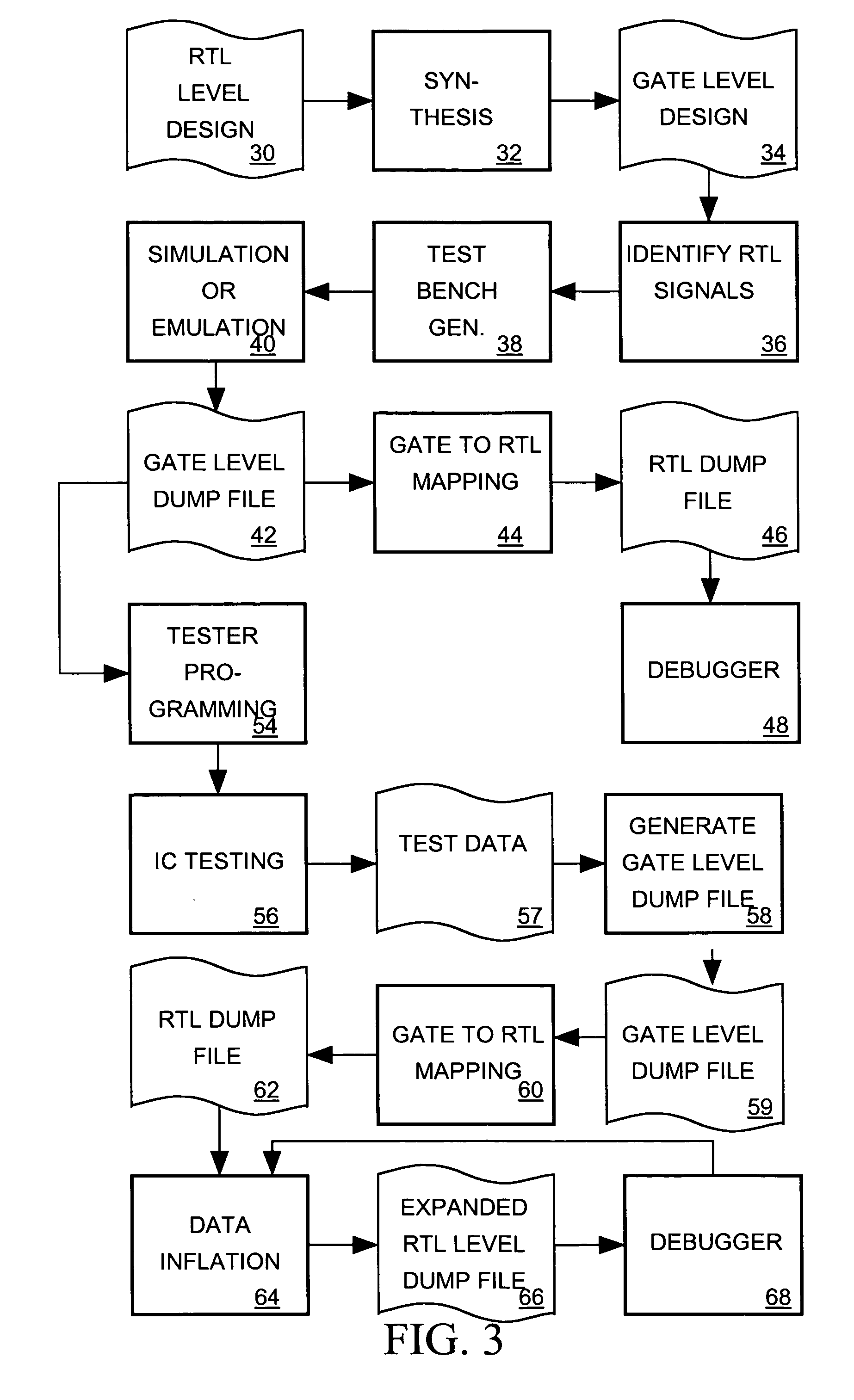
A register transfer level (RTL) IC design describing a IC as comprising a plurality of logic blocks communicating via signals and using a high level language to describe the logic blocks according to the logical relationships between signals they receive and signals they generate. A computer-aided synthesizer processes an RTL IC design to produce a gate level design for the IC describing its logic blocks as comprising instances of cells communicating via signals. A synthesizer or emulator processes the gate level design to produce a gate level dump file referencing signals of the gate level design and indicating how those signals behave in response to time-varying signals supplied as inputs to the IC. The gate level dump file is converted into an RTL dump file referencing signals of the RTL design and indicating how those signals behave. A debugger processes the RTL dump file to produce displays depicting the RTL design and behavior of signals indicated by the RTL dump file. Thus while the IC is simulated or emulated at the gate level of the design to produce waveform data for a debugger, the gate level-to-RTL dump file conversion process enables a designer debug the more familiar RTL design based on the gate level simulation or emulation results.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Physical unclonable function for security key
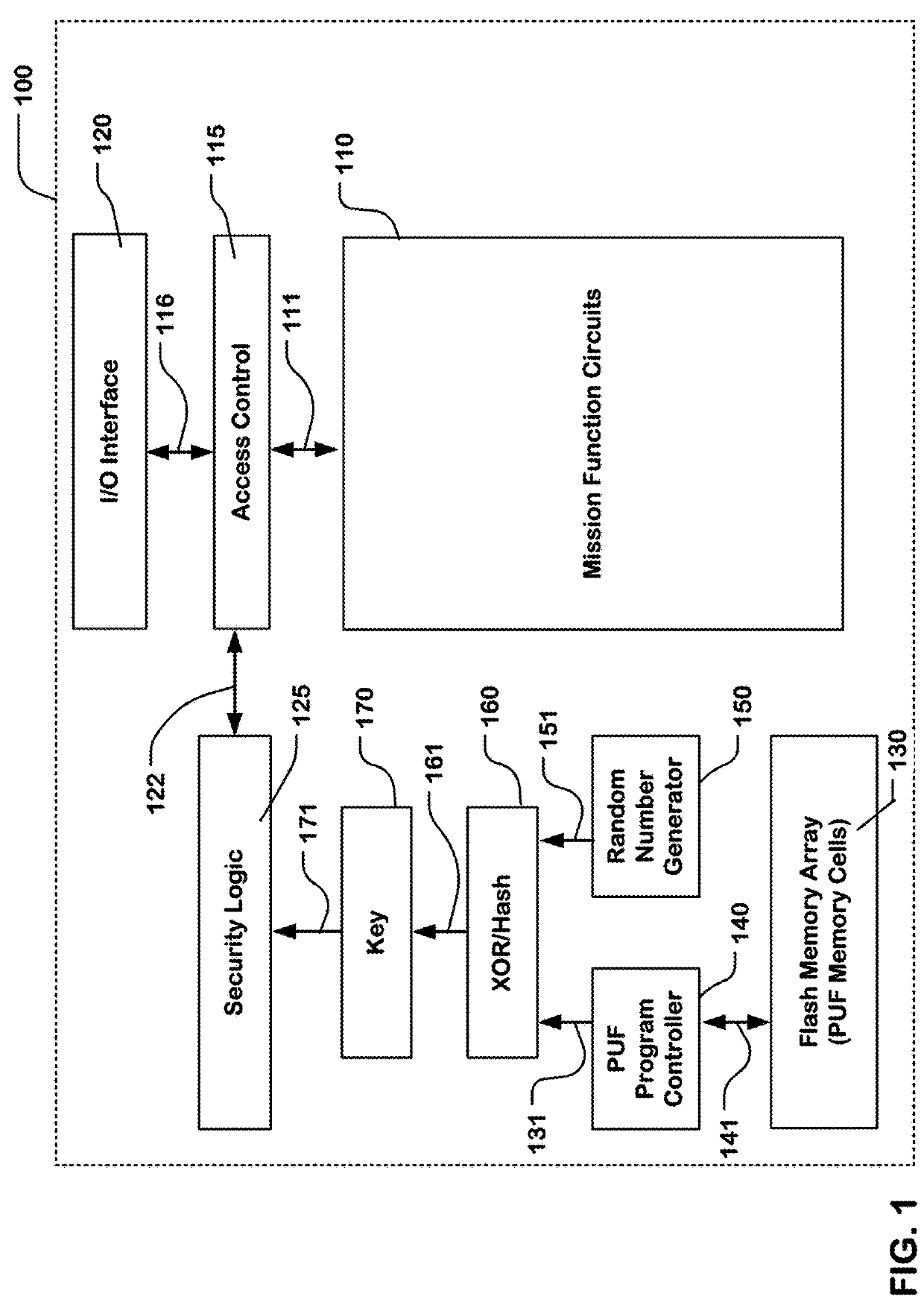
ActiveUS20180278418A1Increase entropyIncrease flexibility and reliabilityKey distribution for secure communicationPhysical unclonable functionComputer science
A system including a host and a guest device, where the guest device can be implemented on a single packaged integrated circuit or a multichip circuit and have logic to use a physical unclonable function to produce a security key. The device can include logic on the guest to provide the PUF key to the host in a secure manner. The physical unclonable function can use entropy derived from non-volatile memory cells to produce the initial key. Logic is described to disable changes to PUF data, and thereby freeze the key after it is stored in the set.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
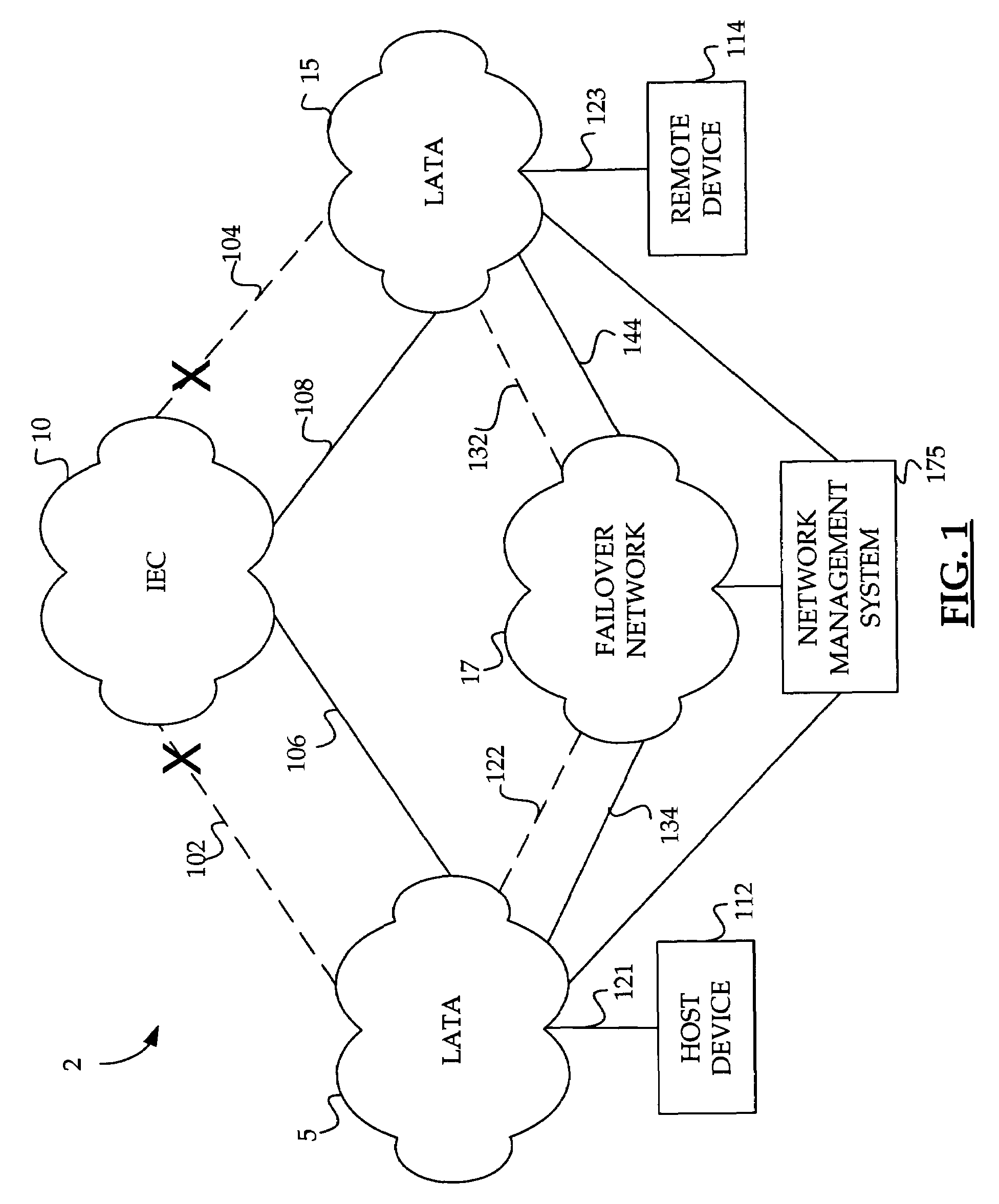
Method and system for providing a failover circuit for rerouting logical circuit data in a data network
A method and system are provided for providing a failover circuit for rerouting logical circuit data in a data network. An alternate communication path is identified for routing data for a logical circuit in the data network. An inactive logical circuit is then selected in the data network for communicating the data over the alternate communication path. The inactive logical circuit is then designated as a failover circuit for rerouting the data for the logical circuit in the data network. The inactive logical circuit may be selected by selecting a currently unused logical connection in the data network for communicating the data. The inactive logical circuit may also be selected by provisioning an inactive logical circuit in the data network. The inactive logical circuit may be provisioned by sending configuration data describing a logical data path over the alternate communication path to a network device in the data network.
Owner:RAKUTEN GRP INC
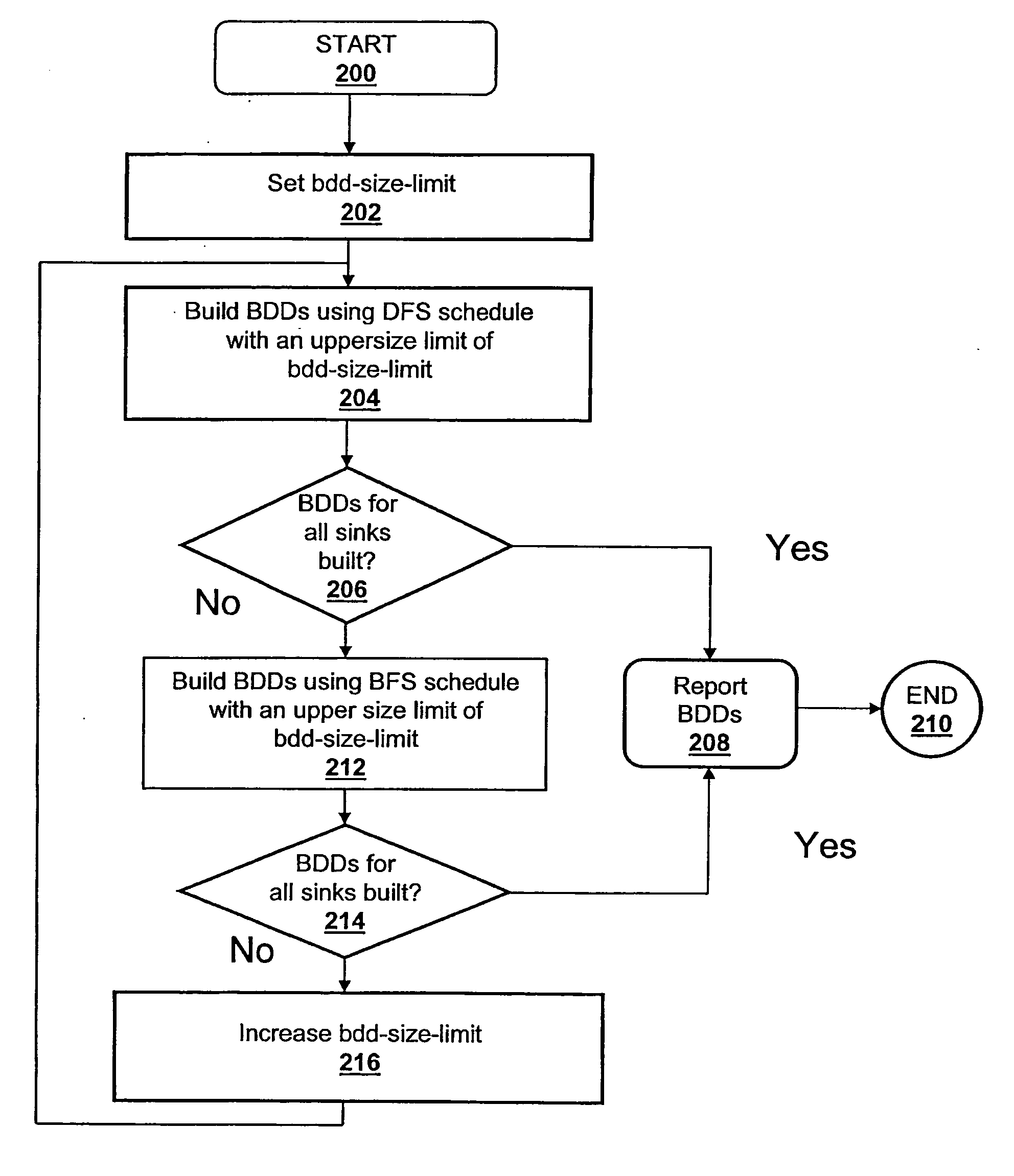
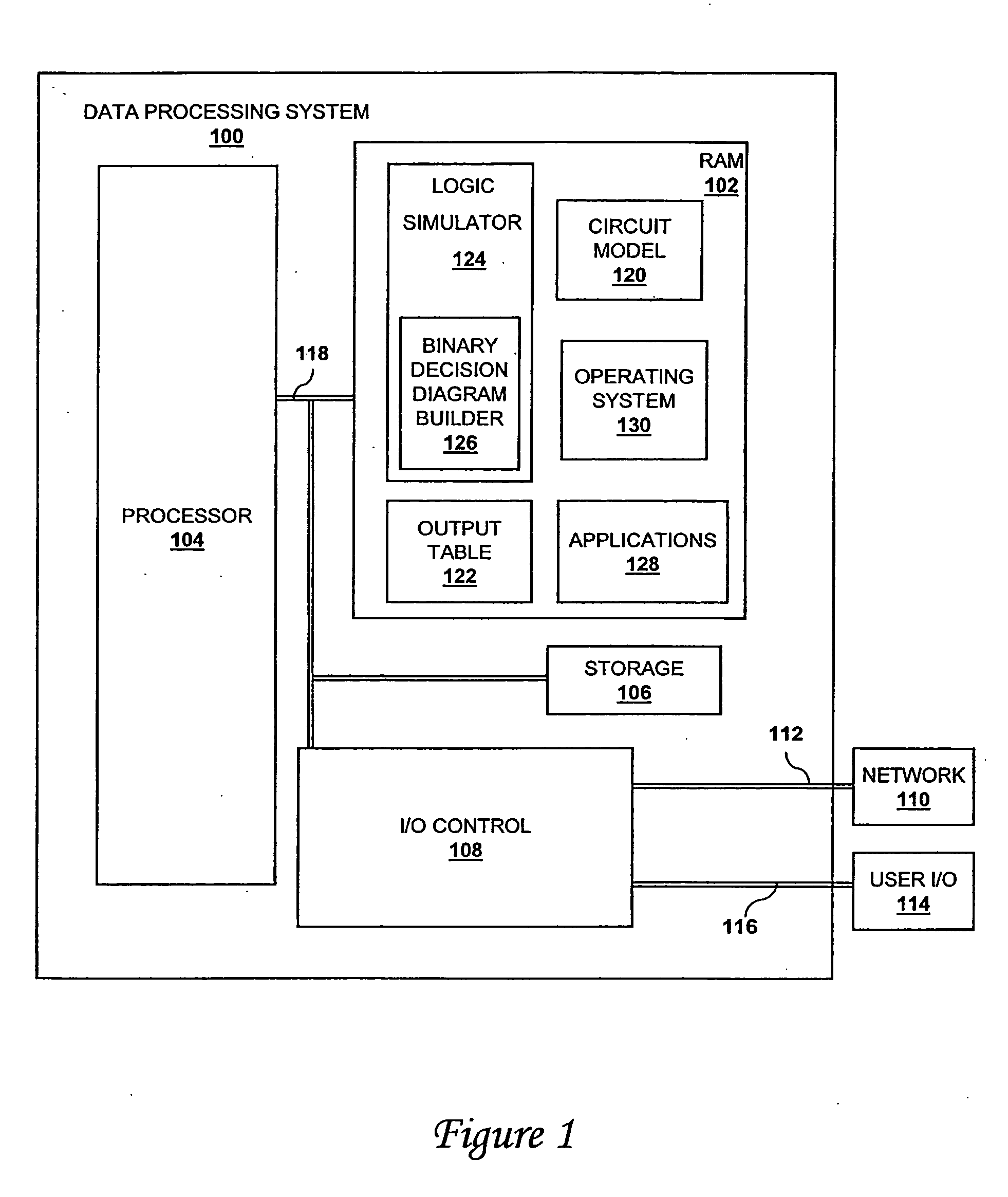
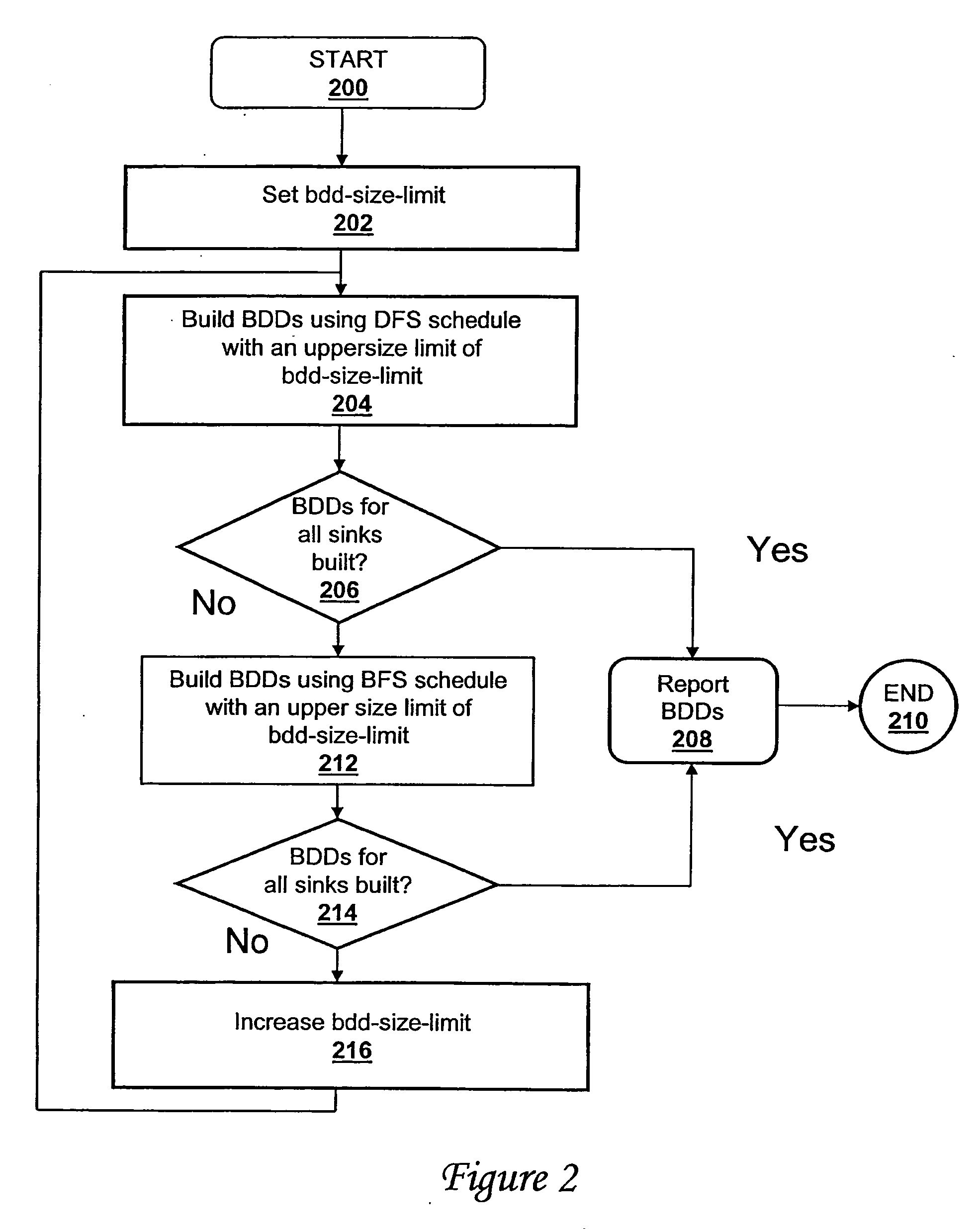
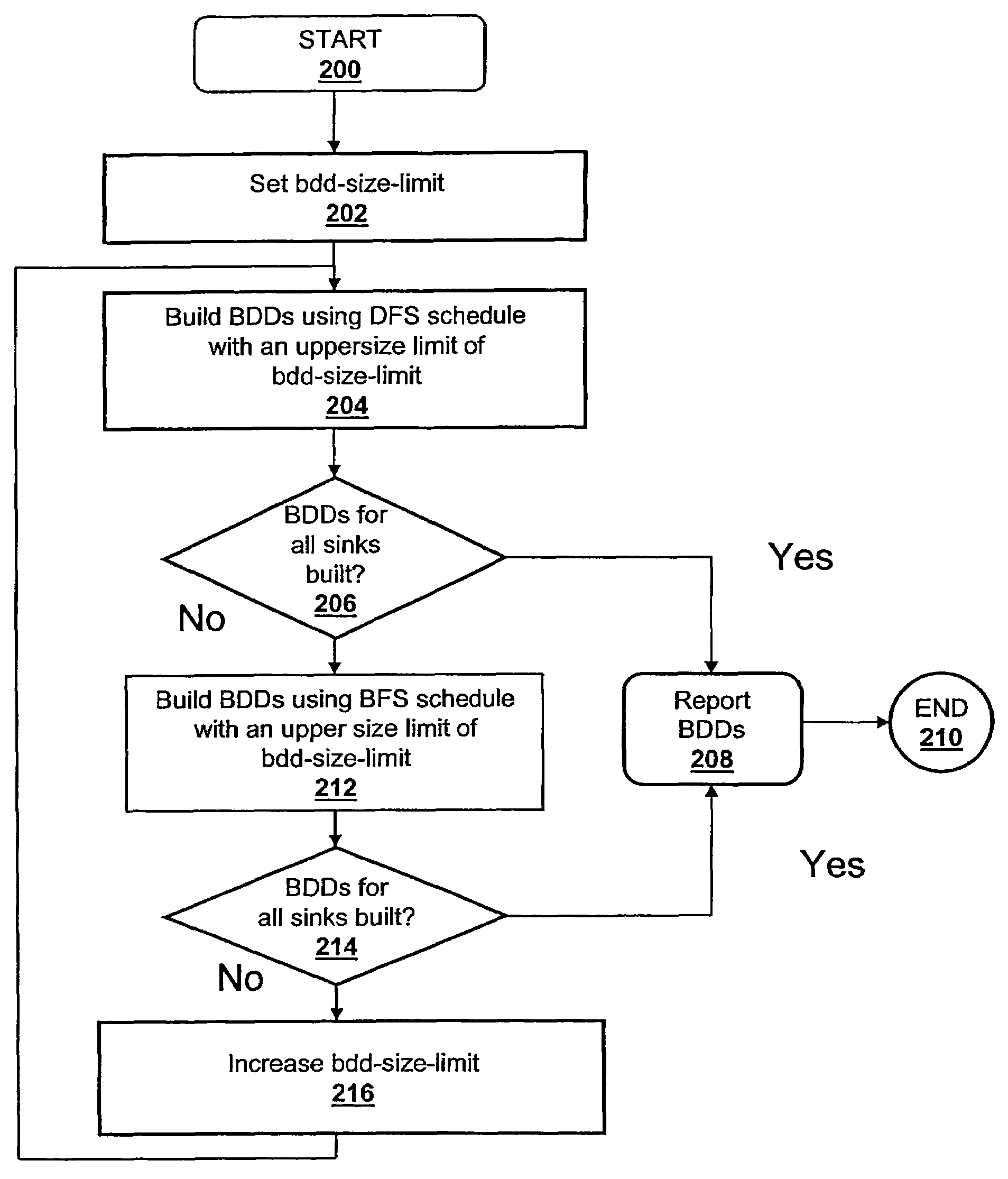
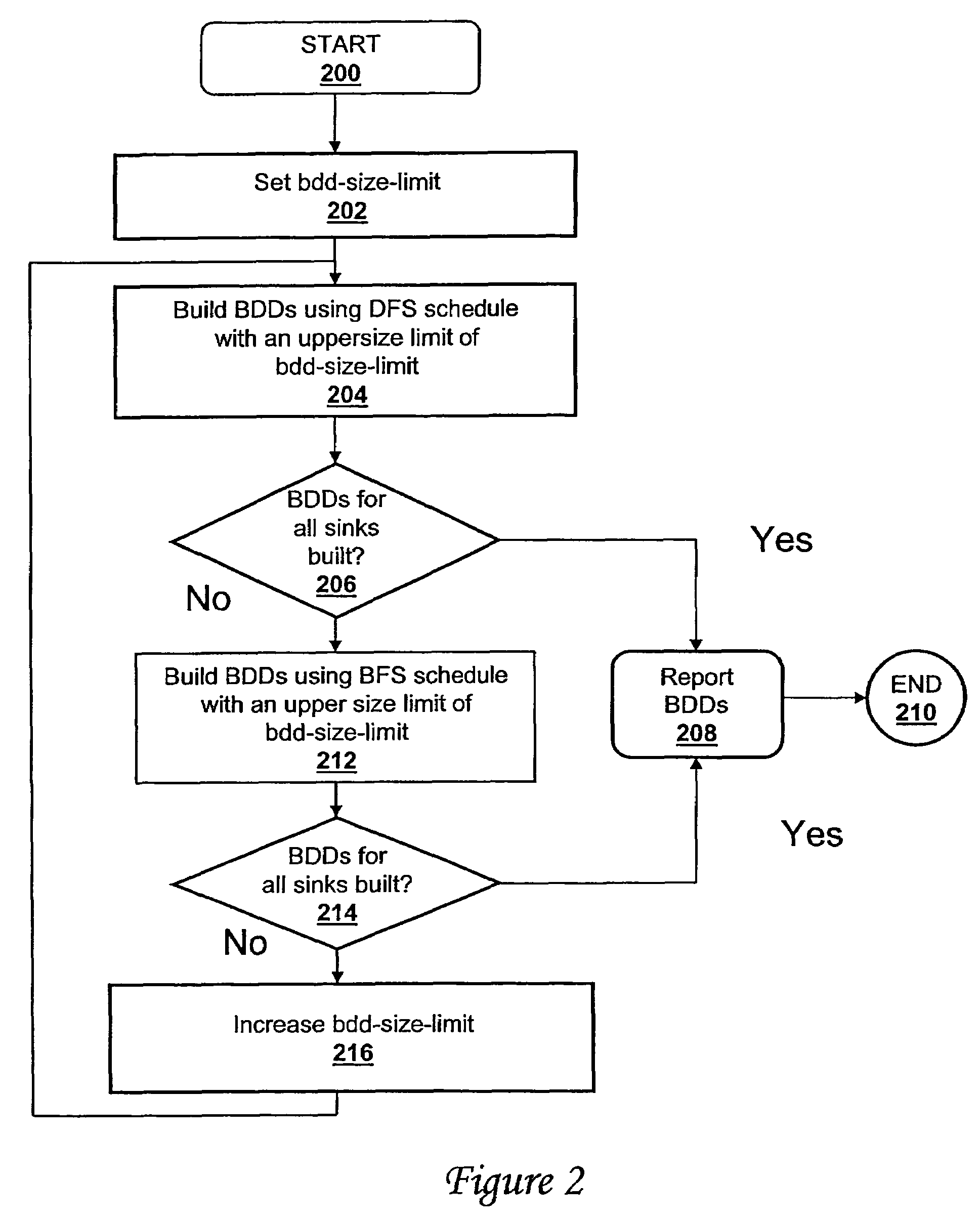
Method and system for building binary decision diagrams efficiently in a structural network representation of a digital circuit
ActiveUS20060047680A1Digital data information retrievalData processing applicationsDepth-first searchDynamic resource
A method, system and computer program product for building decision diagrams efficiently in a structural network representation of a digital circuit using a dynamic resource constrained and interleaved depth-first-search and modified breadth-first-search schedule is disclosed. The method includes setting a first size limit for a first set of one or more m-ary decision representations describing a logic function and setting a second size limit for a second set of one or more m-ary decision representations describing a logic function. The first set of m-ary decision representations of the logic function is then built with one of the set of a depth-first technique or a breadth-first technique until the first size limit is reached, and a second set of m-ary decision representations of the logic function is built with the other technique until the second size limit is reached. In response to determining that a union of first set and the second set of m-ary decision representations do not describe the logic function, the first and second size limits are increased, and the steps of building the first and second set are repeated. In response to determining that the union of the first set of m-ary decision representations and the second set of m-ary decision representations describe the logic function, the union is reported.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Chinese semantic proofreading method based on ontology consistency verification and reasoning
InactiveCN103593335AAccurately determine the cause of the errorNo ambiguitySpecial data processing applicationsLogical consistencyNatural language
A Chinese semantic proofreading method based on ontology consistency verification and reasoning includes: using the ontology learning technology to extract semantic contents from non-structural natural Chinese languages, and converting the extracted semantic contents into structural ontology forms; establishing field ontology databases, and using corresponding ontology databases according to different fields; building models integrating the formed Chinese semantic proofreading key technology, in a form of plug-in, into a grammar verifying tool or using other implementation forms such as independent Chinese semantic verification software; in the grammar verifying tool, using the consistency reasoning and verification mechanism based on description logic and contained in the ontology reasoning language to sequentially perform consistency verification and reasoning on the extracted semantic contents and correct field ontology database input into a reasoning machine according to preset orders, and labeling error labels on the Chinese semantic contents, with inconsistent logic, in the reasoning result. By the method, word-level and grammar-level Chinese proofreading can be achieved, and Chinese semantic proofreading in special fields can also be achieved.
Owner:姜赢
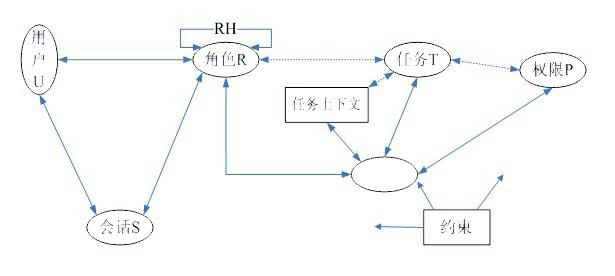
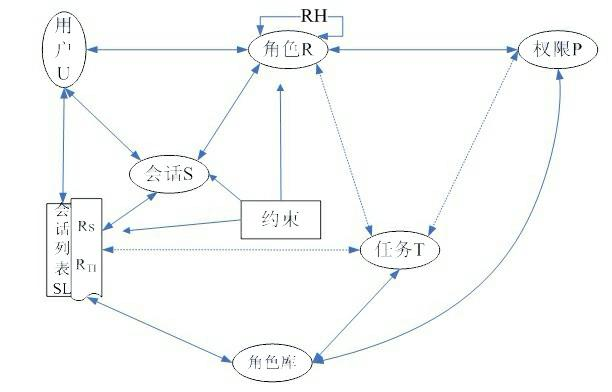
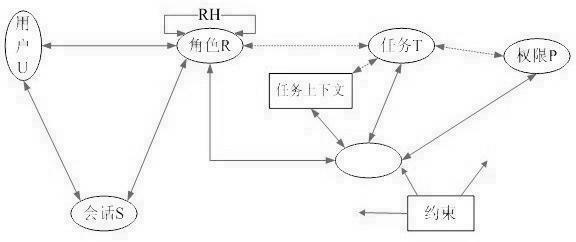
Role access control method based on dynamic description logic
ActiveCN102495985APlay a protective effectData SecurityDigital data authenticationAccess control matrixData access control
The invention discloses a role access control method based on dynamic description logic. The method is characterized in that: on the original basis of role-based access, a concept of a role library is introduced, roles are formally divided into static roles and dynamic roles, an expanded role-based access control (ERBAC) model is adopted for access control, an access control method of the ERBAC model is described by using dynamic description logic SHOIQ-DL, an SHOIQ-DL ERBAC knowledge base is established, a constraint mechanism of the roles is processed by using a method for determining the consistency of the dynamic description logic, and the constraint mechanism can be automatically processed in the access process. By adoption of the model and the method provided by the invention, data can be protected during static access control or dynamic access control of an enterprise and a network, so that the data are safer. Moreover, the method takes the dynamic description logic as the logic base, may strictly depict and reason relative knowledge in a role access control system, further realize auto treatment to the role constraint on this basis.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
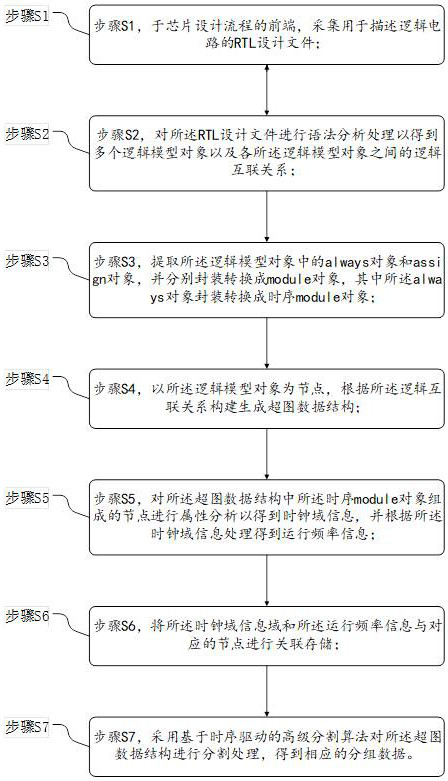
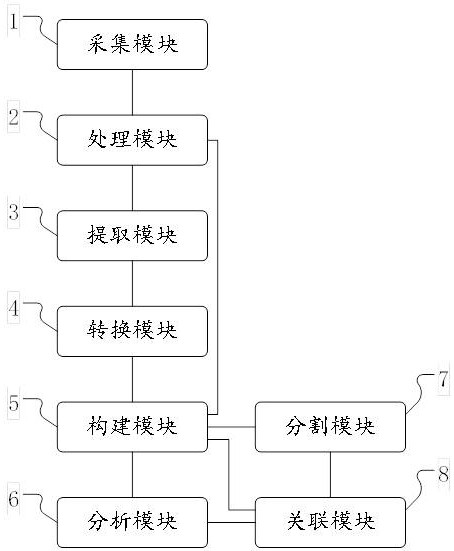
Logic design segmentation method and system
ActiveCN112257369AAccelerate the process of front-end functional verificationAccelerate time to marketCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsInformation processingSystem verification
The embodiment of the invention provides a logic design segmentation method and system, and belongs to the technical field of logic array prototype system verification, and the method specifically comprises the steps: collecting an RTL design file for describing a logic circuit; performing grammatical analysis processing on the RTL design file, extracting an always object and an assign object in the logic model object, respectively packaging, constructing and generating a hypergraph data structure, performing attribute analysis, processing according to the clock domain information to obtain operation frequency information, and performing associated storage on the clock domain information domain and the operation frequency information and corresponding nodes; and performing segmentation processing to obtain corresponding grouped data. By means of the processing scheme, other processing at the back end of the process is not affected, the segmentation duration is shortened, the segmentation efficiency is improved, meanwhile, efficient, reasonable and correct segmentation processing is conducted on the chip design logic content, the performance and efficiency of design segmentation aregreatly improved, then the process of user front-end function verification is accelerated, and the appearance of integrated circuit products is accelerated.
Owner:S2C
High-accuracy computer automatic marking method for subjective items based on domain ontology
ActiveCN104504023AGuaranteed accuracyImprove accuracyData processing applicationsNatural language data processingDegree of similarityDomain relation
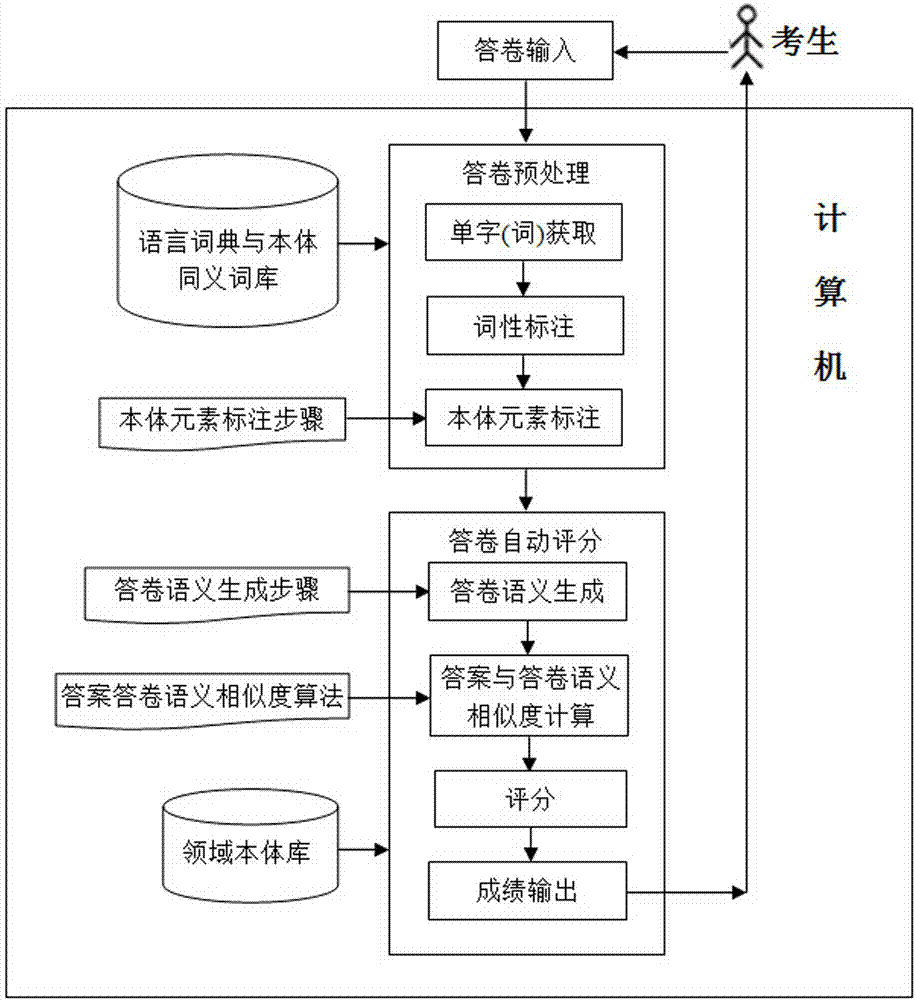
The invention discloses a high-accuracy computer automatic marking method for subjective items based on domain ontology. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, building a domain ontology structure suitable for automatically marking the subjective items, and explaining a domain relation into a sentence in a natural language for describing a domain event; secondly, building a subjective item bank structure based on the domain ontology and item description logic, requesting the items to accord with the subjective item bank structure, and then marking answer sheets of examinees according to the following steps: (1) obtaining single words and part-of-speech tagging in the answer sheet of each examinee; (2) tagging an ontology element; (3) generating an answer sheet semanteme based on the domain relation; (4) calculating based on the similarity of the answer of the domain relation and the answer sheet semanteme; (5) calculating the score of the answer sheet of the subjective items of each examinee. According to the method, the semanteme analyzing and processing flows of the natural language in each examinee answer sheet are greatly simplified; the semanteme of answer domain knowledge is relatively fully expressed; the accuracy for automatically marking the subjective items is ensured.
Owner:南京乐酷网络科技有限公司
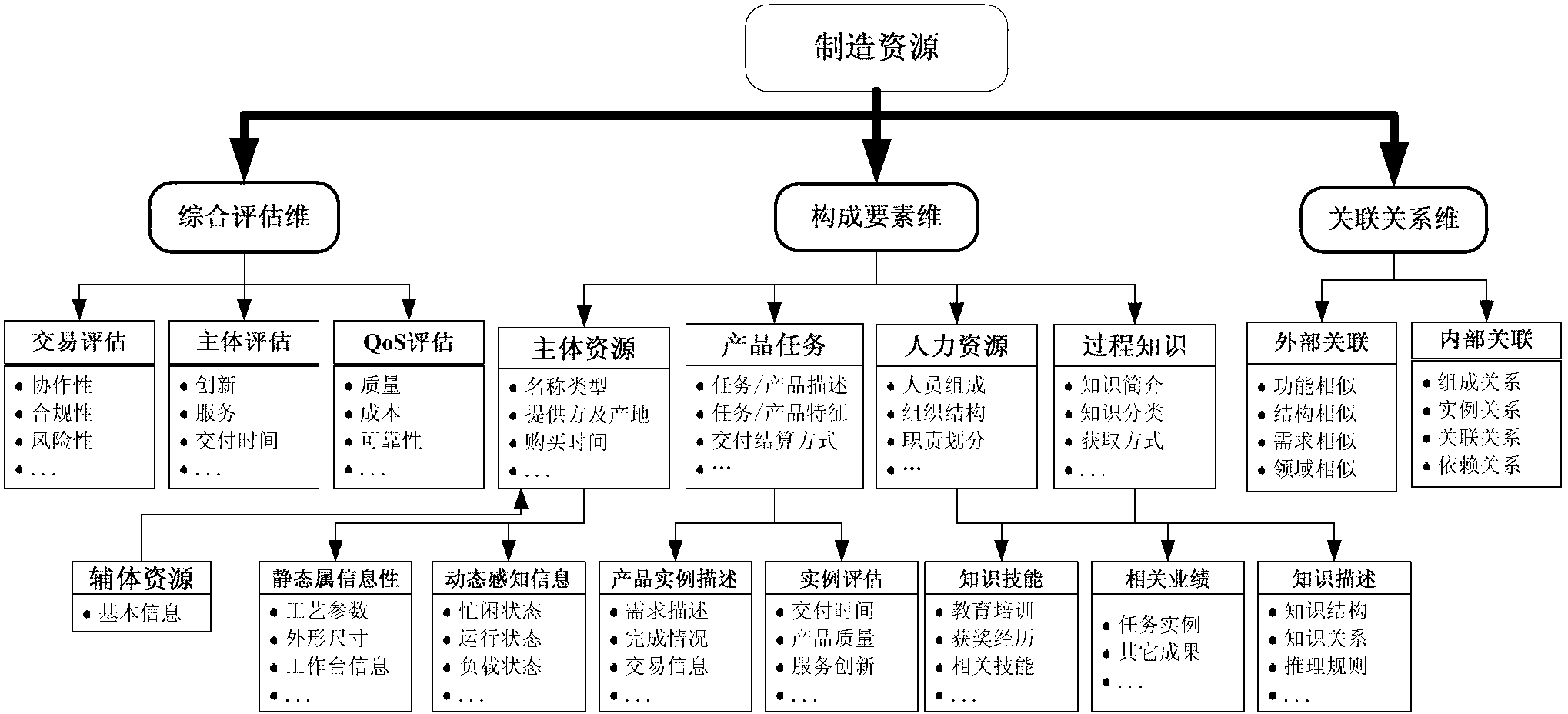
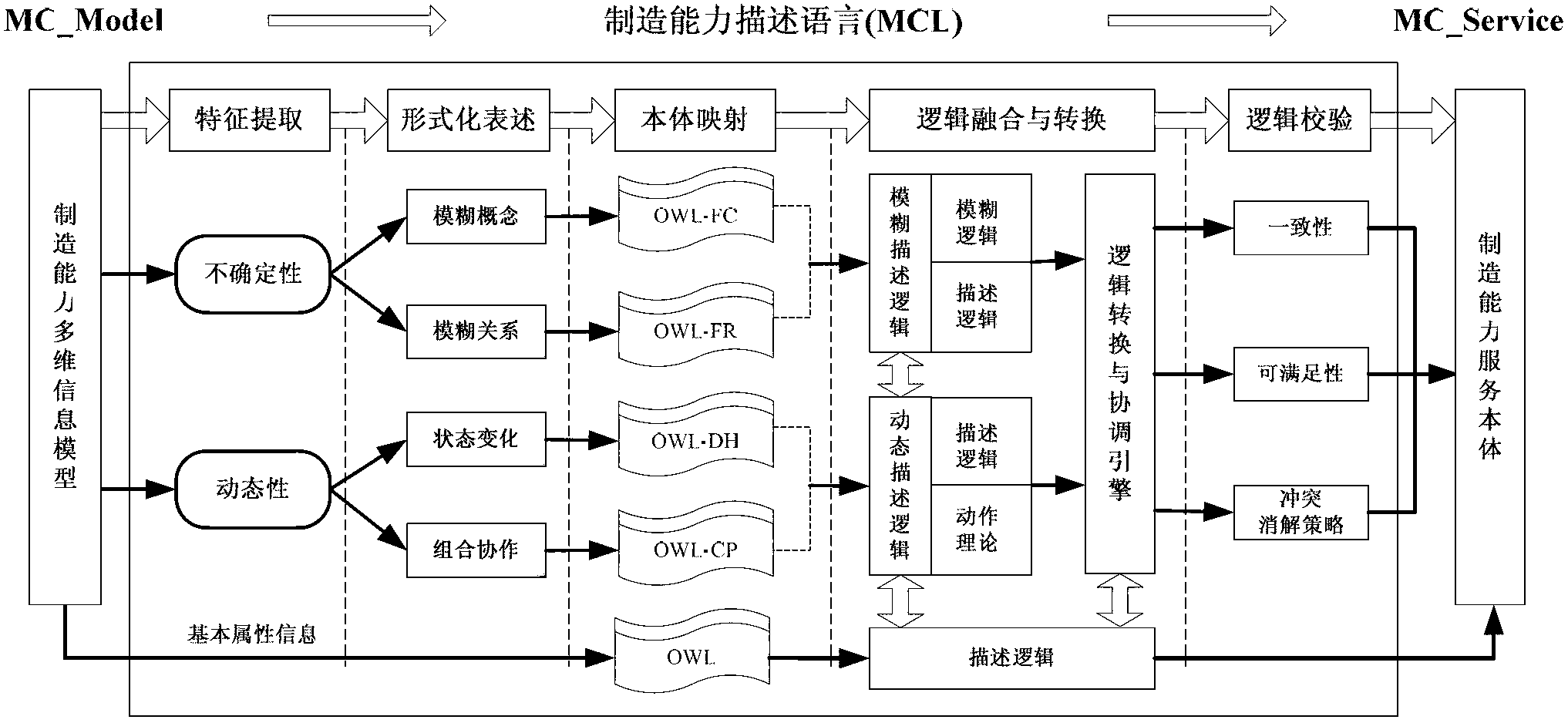
Cloud manufacturing capability description method supporting use on demand and sharing circulation of manufacturing capability
ActiveCN103020722ARealize intelligent recommendationRealize "Secondary RecommendationData processing applicationsTransmissionComputer scienceInformation model
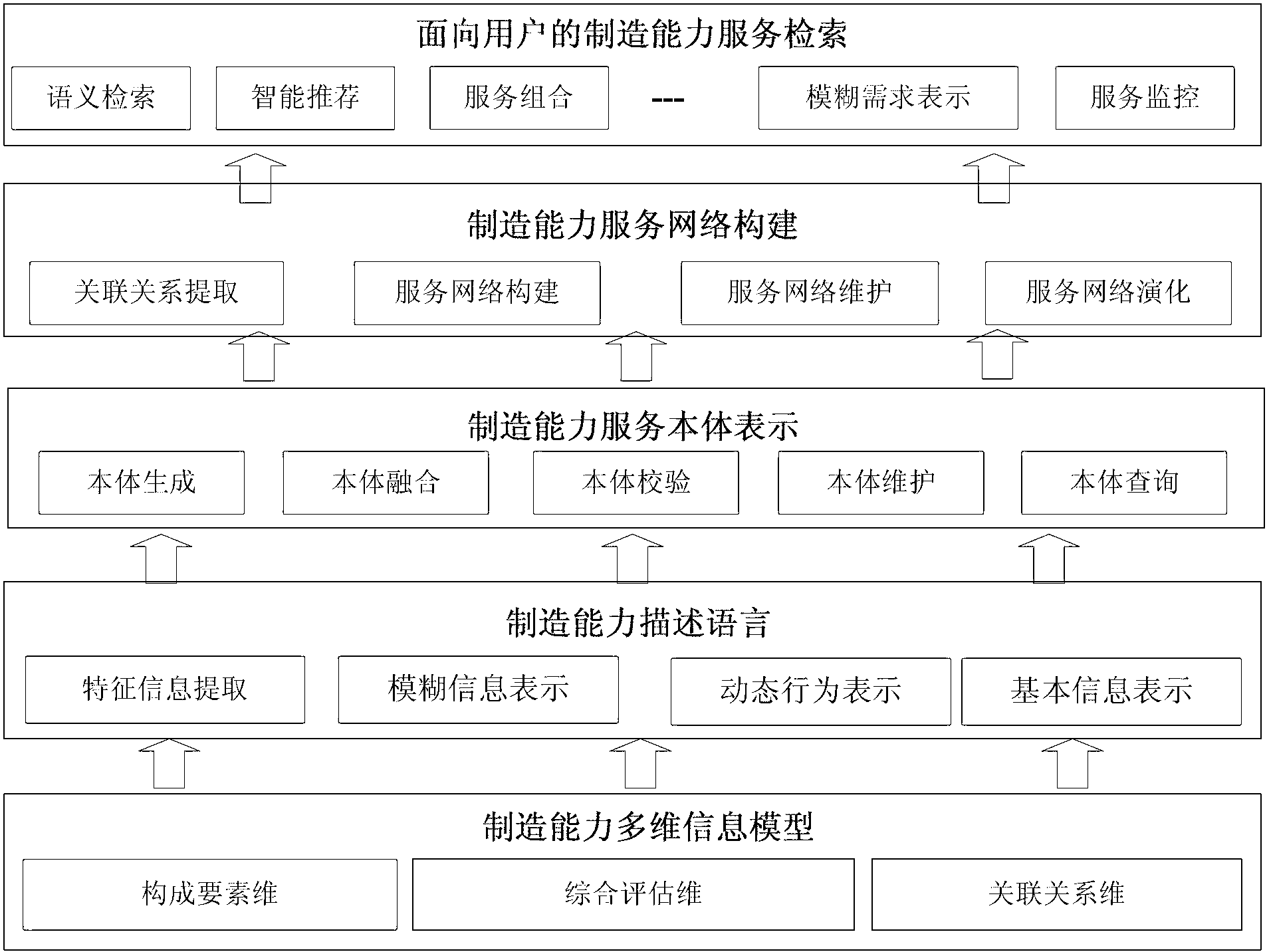
The invention provides a cloud manufacturing capability description method supporting use on demand and sharing circulation of manufacturing capability. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting and classifying fuzzy information and dynamic behavior information in a knowledge-based manufacturing capability description model (namely a multi-dimension manufacturing capability information model); formalizing a fuzzy concept and a fuzzy role relationship according to a fuzzy description logic; describing service state change and dynamic combination flow according to a dynamic description logic; and giving an intelligent search and recommendation mechanism of the manufacturing capability based on the description method. According to the cloud manufacturing capability description method, the qualitative and quantitative properties of each dimension and each level of manufacturing capability can be taken into sufficient consideration, and a knowledge-based manufacturing capability language is provided, so that manufacturing capability services are stored in a cloud manufacturing service platform in an ontology mode, and a manufacturing capability service network is formed on the basis of various relationships among the services and supports the intelligent search and the use on demand of users.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
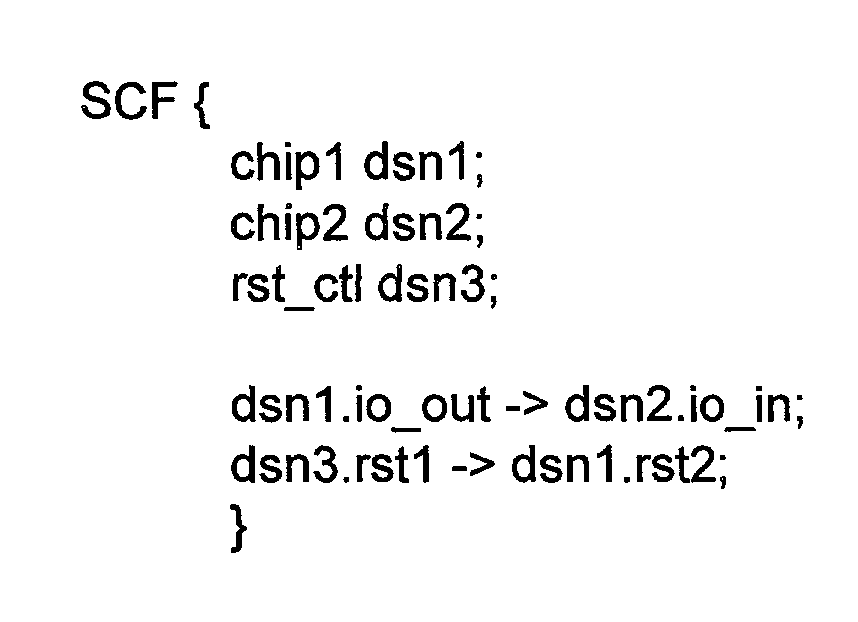
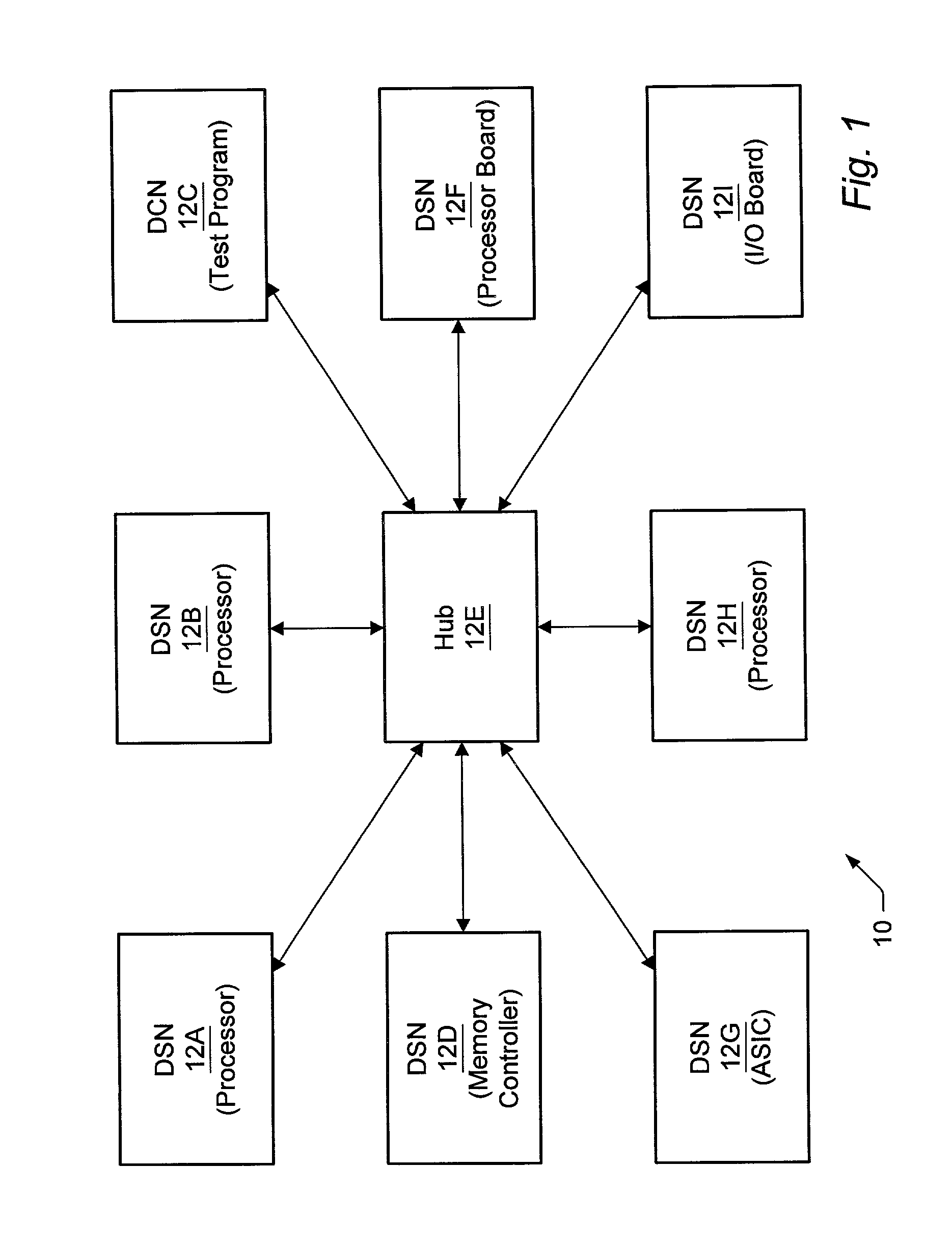
Grammar for message passing in a distributed simulation environment
InactiveUS20030093253A1Analogue computers for electric apparatusData switching networksSystem under testMessage passing
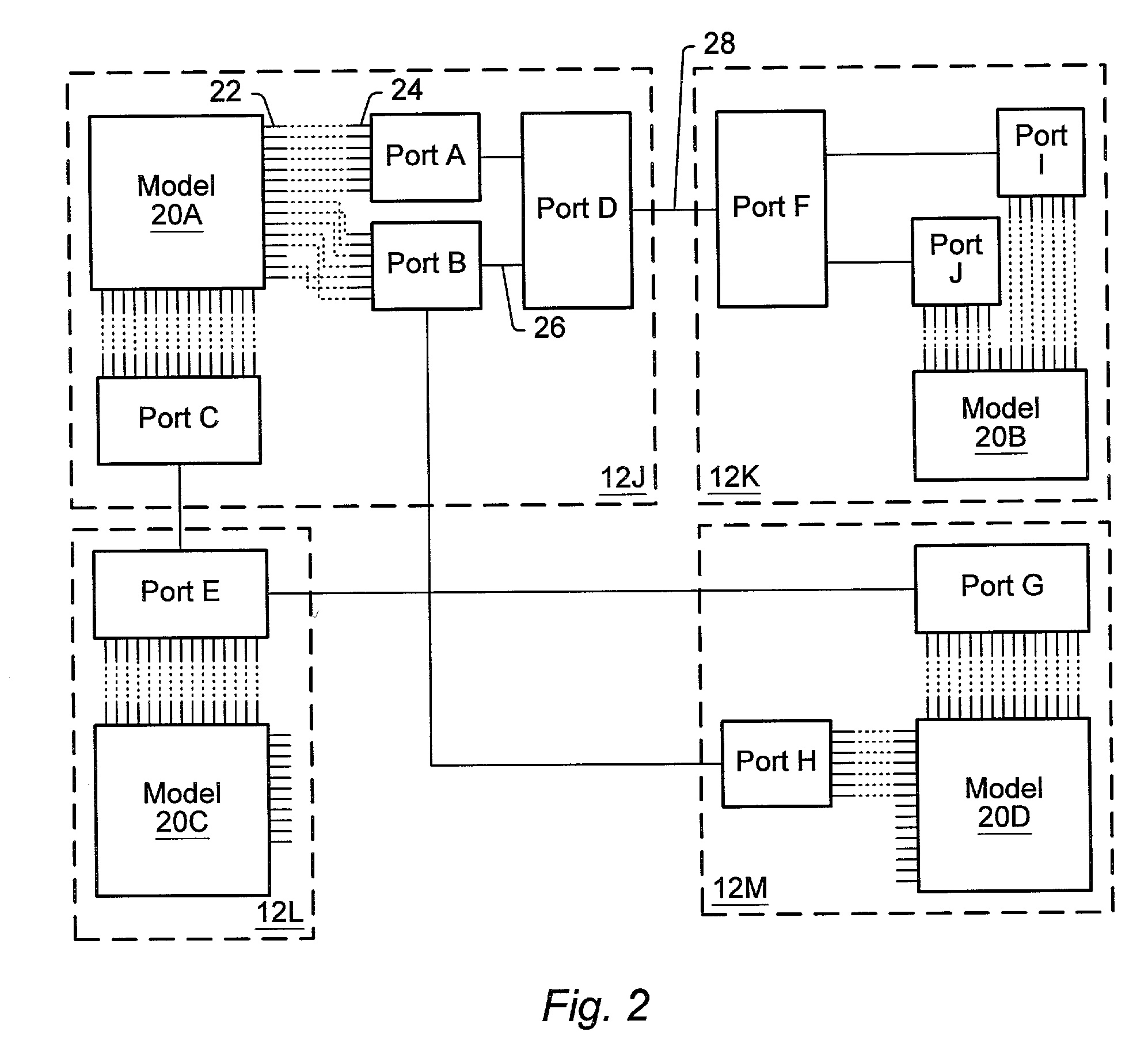
A distributed simulation system includes a plurality of nodes and a hub. Each node may simulate a portion of a system under test, or may execute a test program for the simulation. The hub may route message packets from one node to another. The message packets are formatted according to a grammar used by the distributed simulation system, which abstracts the physical signals of the system under test to logical ports. Additionally, some embodiments may include other commands, such as commands for configuring the distributed simulation system, describing the logical ports and logical signals within the logical ports, and mapping the logical signals to physical signals. A formatter program may be used in each node and the hub to format message packets for transmission, according to the grammar. A parser program may be used in each node and the hub to parse received message packets, again according to the grammar.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Business process model unification method
InactiveUS20070006132A1Fast progressQuality improvementResourcesSpecific program execution arrangementsAlgorithmSemi automatic
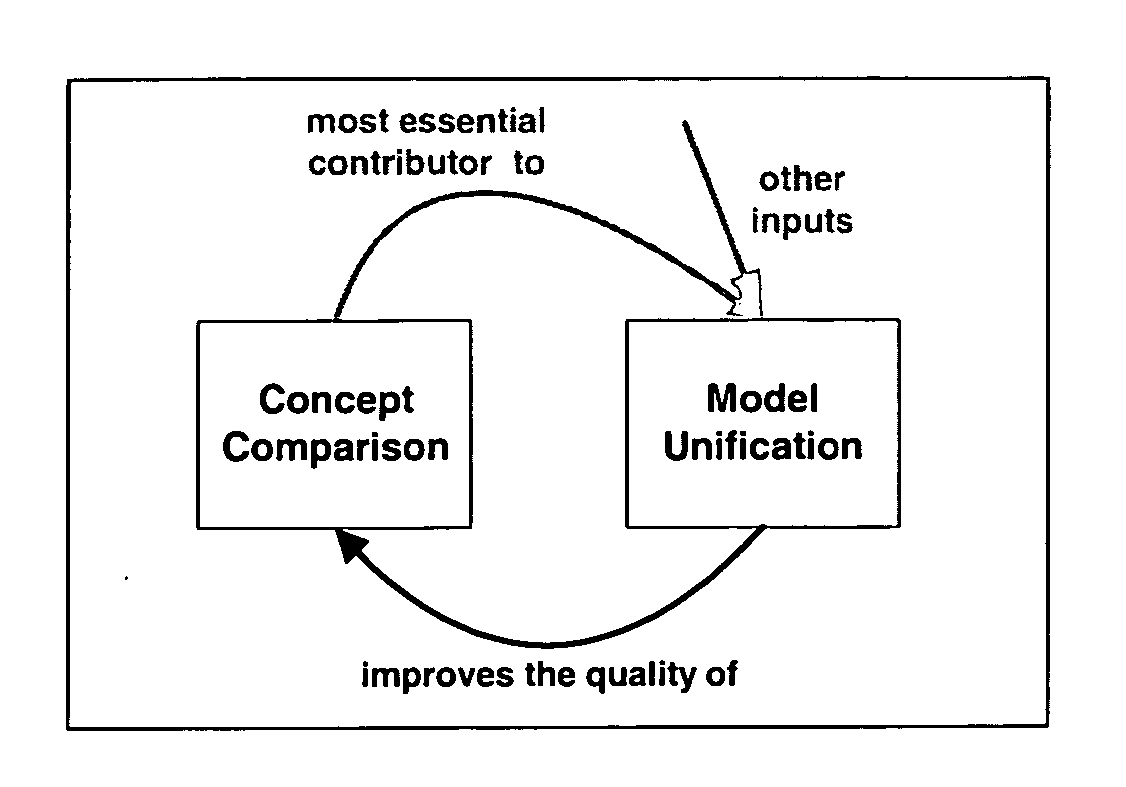
A methodology for semi-automatic unification of models of business processes permits accurate comparison of business processes across government agencies or other organizations despite heterogeneity of language and style in the original models. Input into an algorithm includes a set of models produced by different organizations that describe roughly equivalent business processes (the original models). Output includes a single integrated model in which similarities are made explicit in shared generic layers of the model, while differences are represented in organization-specific layers that inherit from the generic layers (the unified model). Internally, the system represents the original and unified models in description logic using the Web Ontology Language (OWL).
Owner:TECHTEAM GOVERNMENT SOLUTIONS
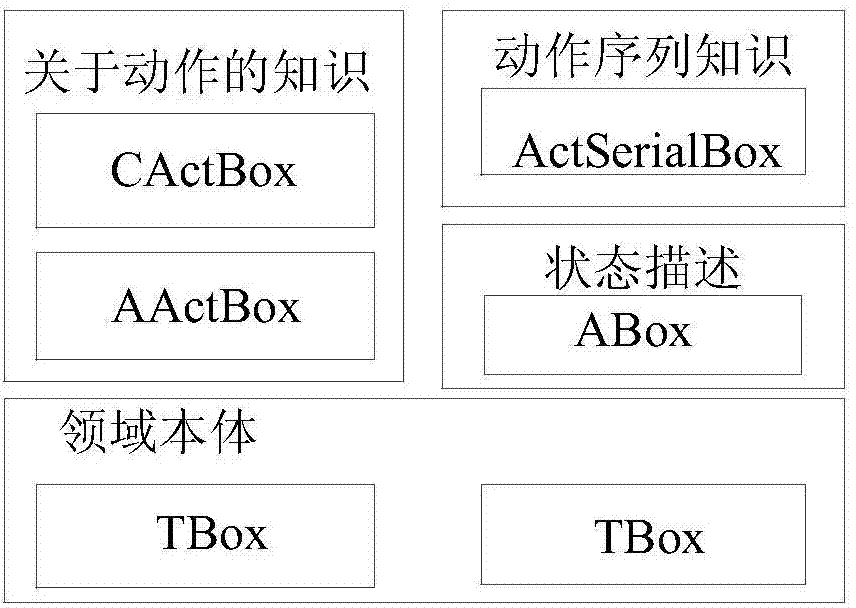
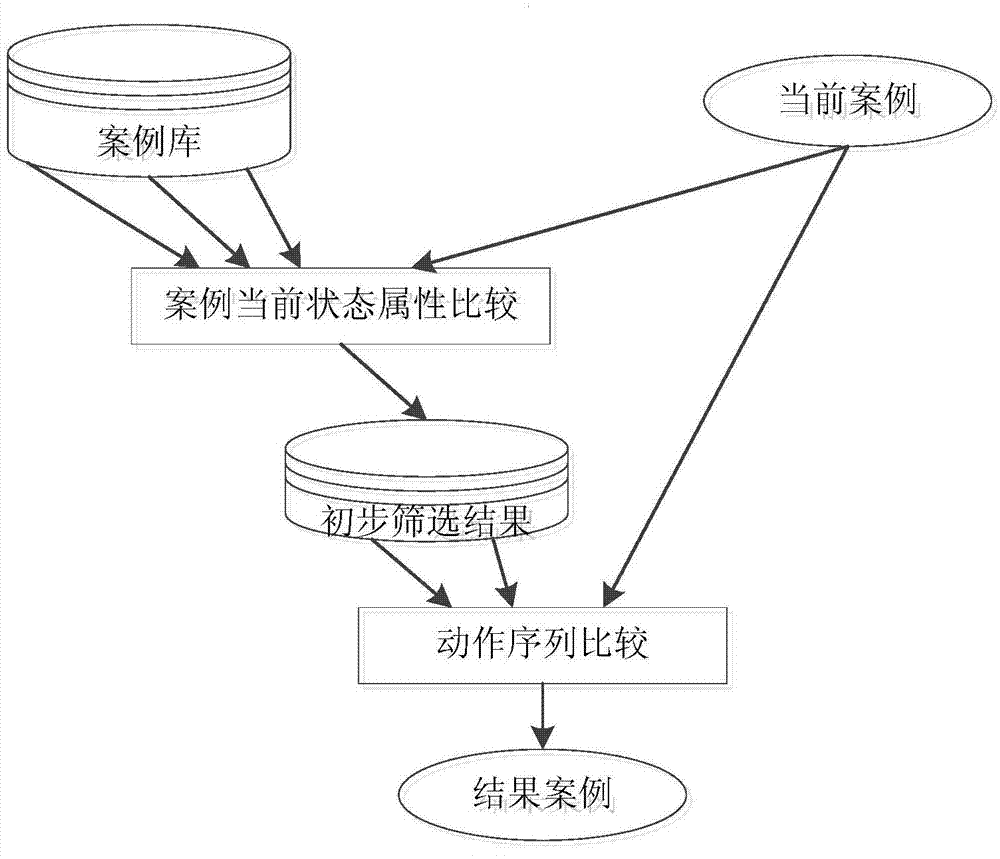
Intelligent learning method based on description logic and case-based reasoning
ActiveCN104573062AComprehensive comparisonMeet the needs of the subject of learningElectrical appliancesSpecial data processing applicationsStudy methodsLearning methods
The invention discloses an intelligent learning method based on description logic and case-based reasoning. The method comprises the steps of respectively calculating text property and data type property of the property of a case by adopting a similarity calculation method based on description logic, and giving out a preliminary result of similarity matching; building a relationship by using pheromone pheromone self-adaption updating and allocation strategy in an ant colony algorithm and case recommendation; giving out the case recommendation to learning subjects at different learning stages in the learning subjects' grades by partitioning the learning grades and problem grades of a learning subject; respectively endowing different weights to the computing results of the above methods, and comprehensively calculating the similarity among the cases; giving out a list of optimal solutions for the existing problem case in a case library through the comprehensive similarity for the selection of a learning subject. Therefore, the learner can learn from mistakes met by the learner quickly.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Method and system for building binary decision diagrams efficiently in a structural network representation of a digital circuit
ActiveUS7340473B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalDepth-first searchDynamic resource
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
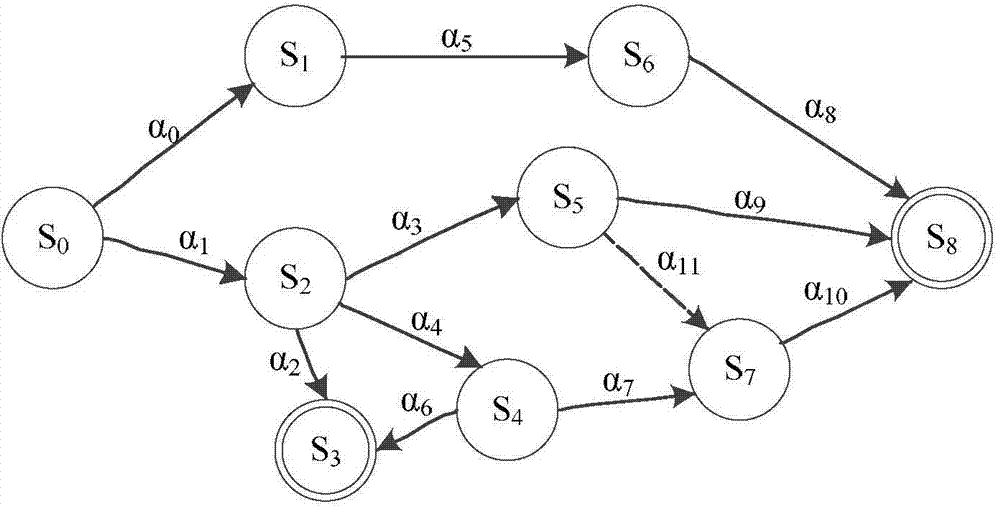
Software system fault detection method based on dynamic description logic and case-based reasoning
InactiveCN104503920AReduce complexityImprove matching efficiencySoftware testing/debuggingSoftware systemSoftware engineering
The invention discloses a software system fault detection method based on dynamic description logic and case-based reasoning. Based on states, an action theory of the dynamic description logic is adopted to describe the problem, execution of a program function module is regarded as an action changing the states, state conversion is regarded as change caused by the action, semantic information between the states is added, and the modeling complex is reduced. Fault cases are managed by combining the description capacity and reasoning capacity of the dynamic description logic and a case-based reasoning technology, and experience support for the method is provided for solution of new faults to be occurred of a system. Case retrieval matched with action sequences is added to improve the precision ratio of the case retrieval of the system faults. After faults occur in the operation process of the system and by means of the software system fault detection method, similar fault cases are found out through state switching sequences operated by software and corresponding repair measures are provided.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
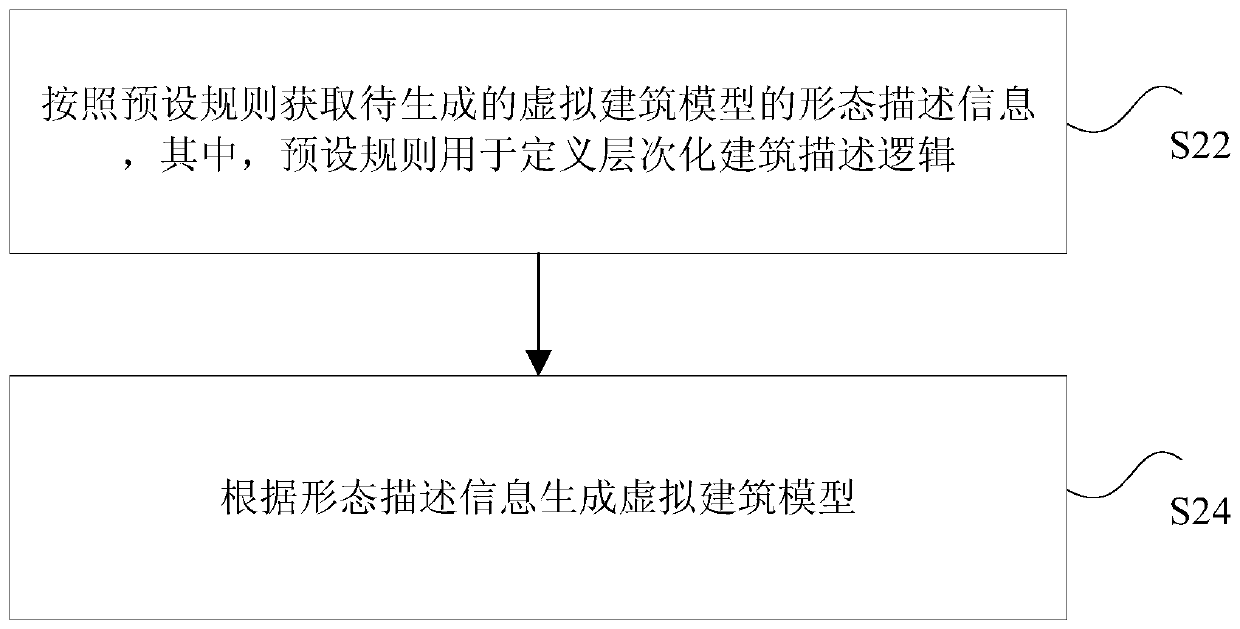
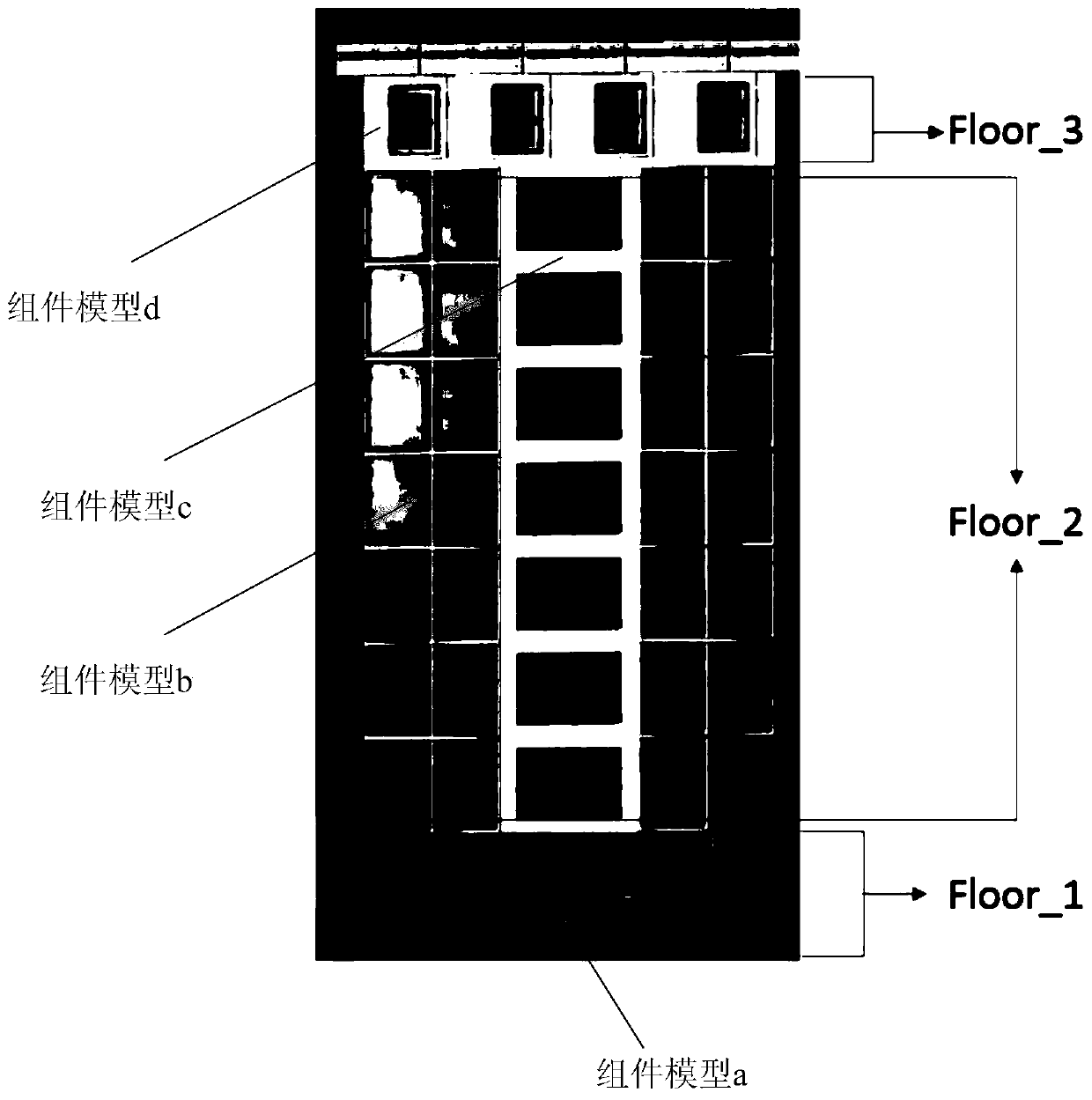
Generation method and device of virtual building model in game, processor and terminal
InactiveCN110102058AImprove manufacturing efficiencyReduce operational complexityVideo games3D modellingComputer terminalVisual perception
The invention discloses a generation method and device of a virtual building model in a game, a processor and a terminal. The method comprises the steps of obtaining morphological description information of the to-be-generated virtual building model according to a preset rule, wherein the preset rule is used for defining layering building description logic; generating the virtual building model according to the morphological description information. By means of the generation method and device of the virtual building model in the game, the processor and the terminal, the technical problems inthe prior art are solved that the operation complexity of the generation mode of the virtual building model is high, the manufacturing efficiency is low, and the visual effect of the game is monotonous.
Owner:NETEASE (HANGZHOU) NETWORK CO LTD
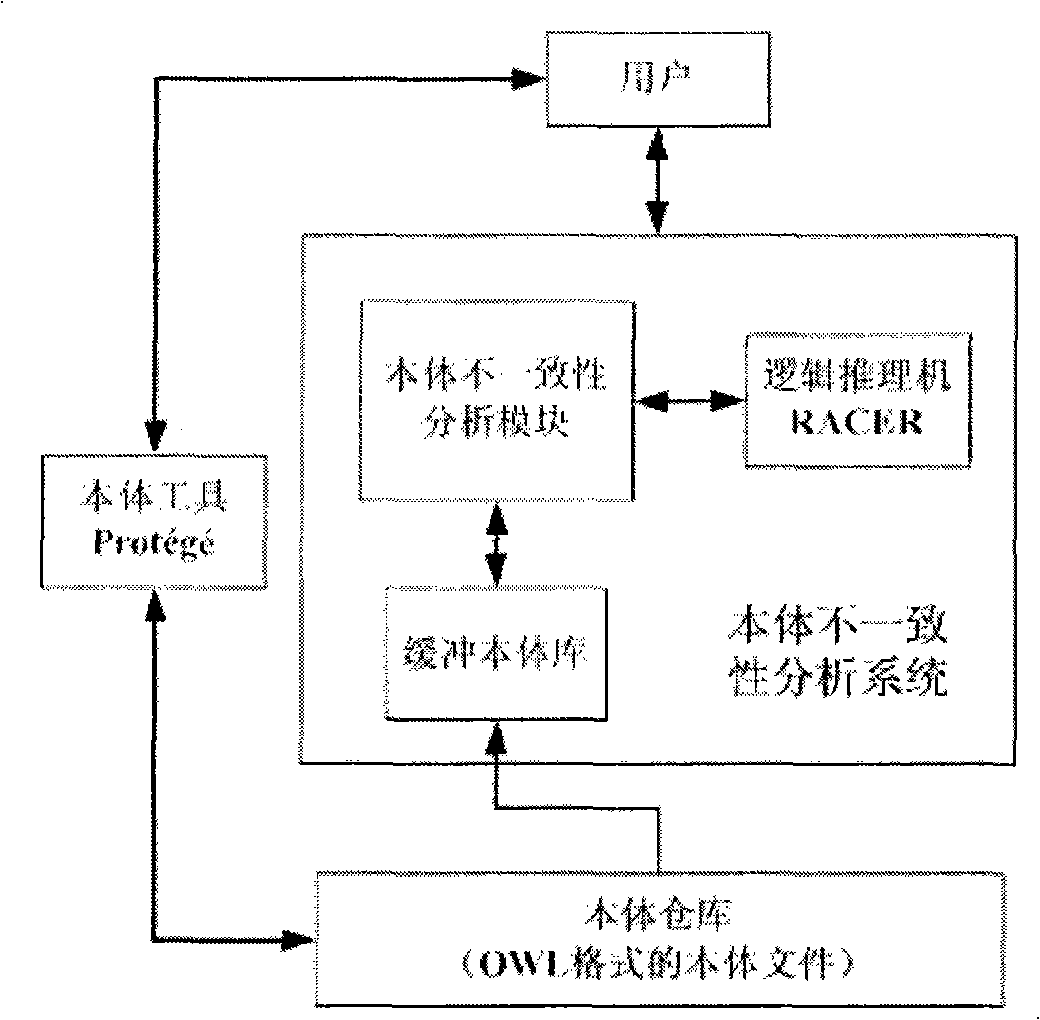
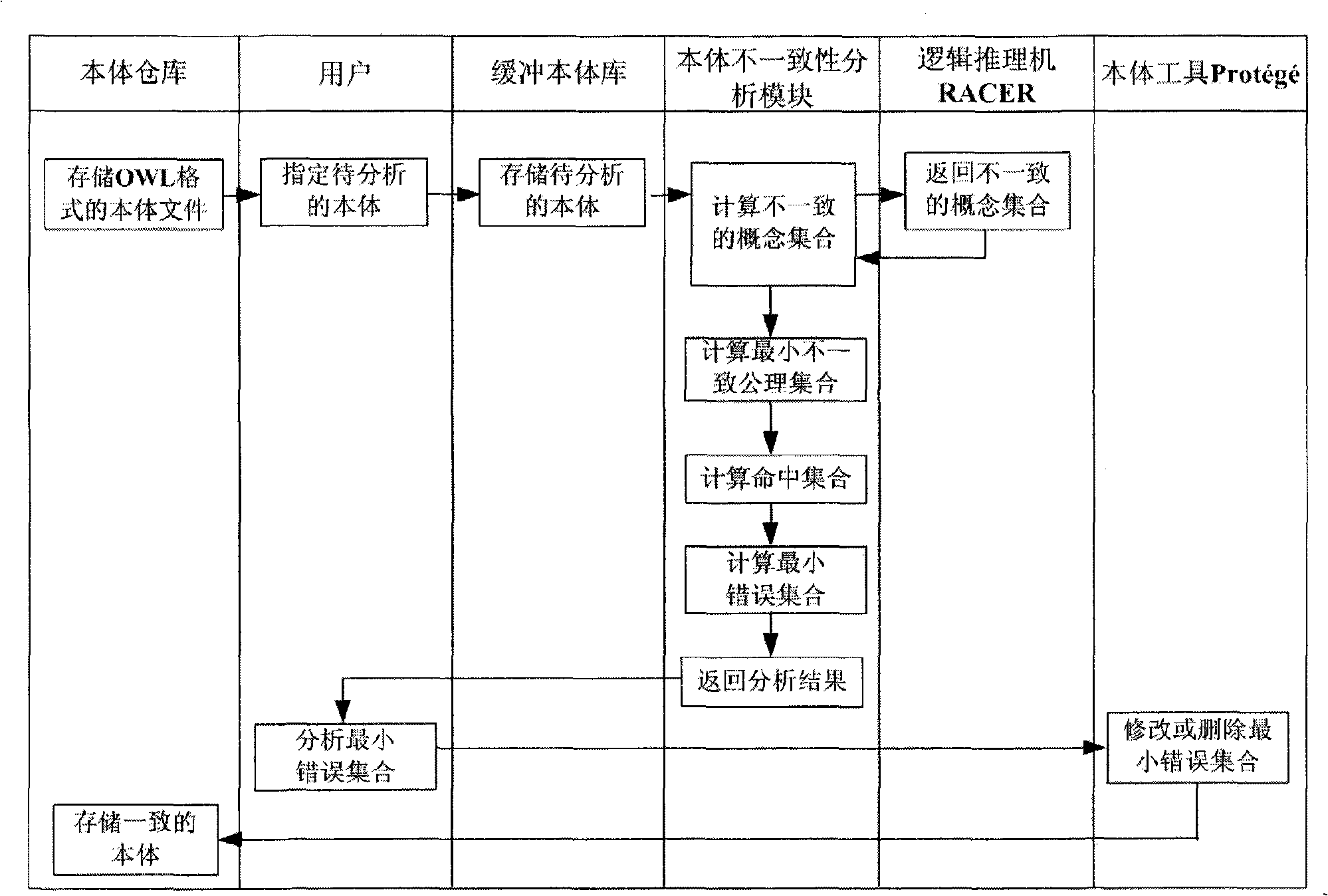
Reality inconsistency analysis method based on descriptive logic
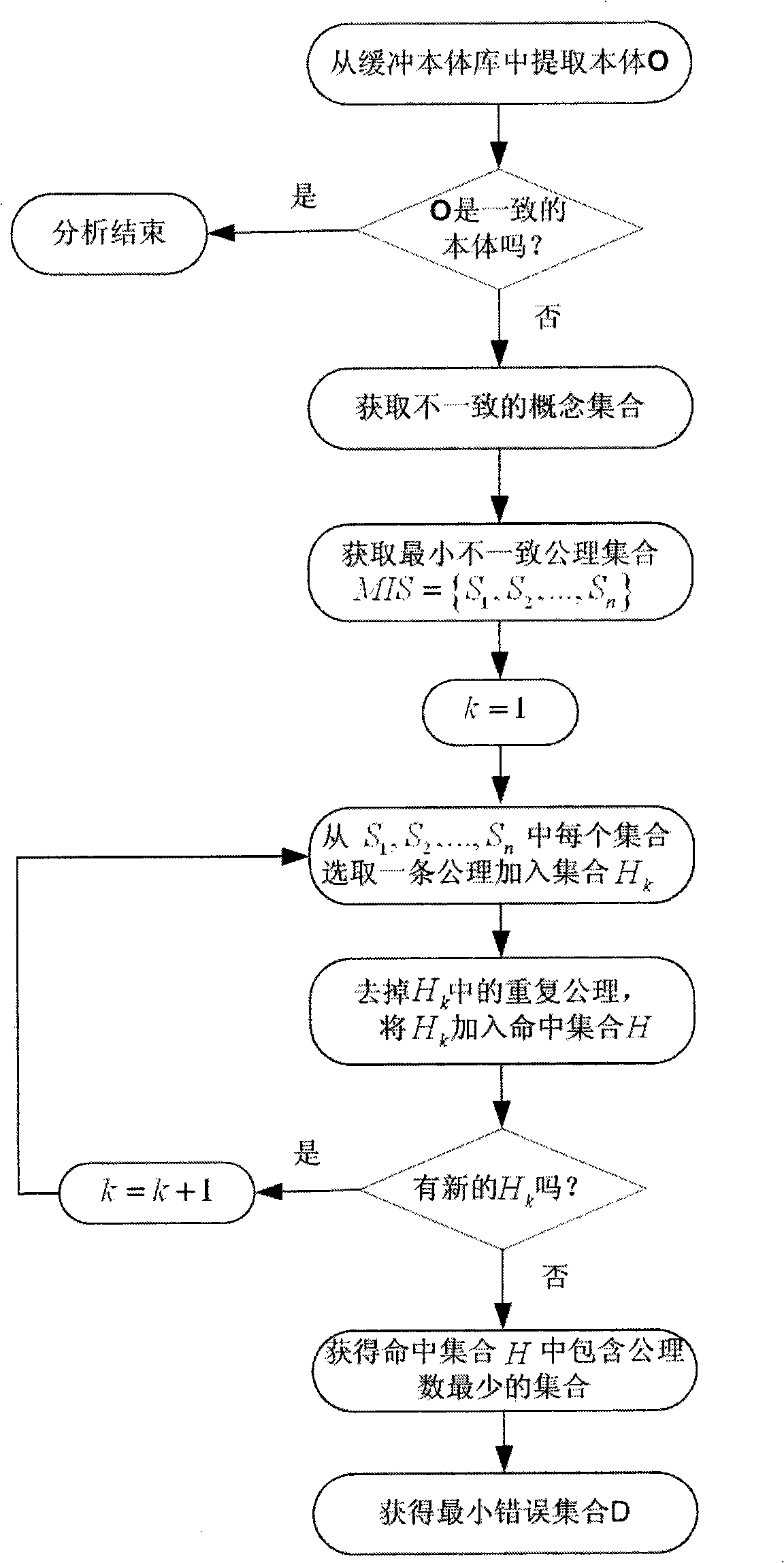
InactiveCN101266660ARestore consistencyEnsure correct understandingKnowledge representationAnalysis methodComputer science
The invention relates to a method of analysing noumenon inconsistency based on description logic, and belongs to the semantic and noumenon analysis field, which is characterized in building a noumenon warehouse, a buffering noumenon library, a noumenon inconsistency analysis module, a logic inference machine RACER and a noumenon tool Protege. The method analyses inconsistent noumenon stored in the buffering noumenon library via the noumenon inconsistency analysis module and calculates a minimum inconsistent axiomatic set and a minimum inconsistent hitting set of the noumenon to finally gain a minimum error set. The minimum error set is the root of generating the noumenon inconsistency. Deleting or modifying the minimum error set can effectively recover consistency of the noumenon. According to the invention can process to analyse for the noumenon in the situation of semantic inconsistency and find out the root of generating the noumenon inconsistency, so as to effectively recover the consistency of the noumenon.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Dynamic hierarchical integrated data accessing method capable of guaranteeing semantic correctness
InactiveCN103049555AReduce computational complexitySatisfy the need for semantic correctnessSpecial data processing applicationsComputation complexityRelational database
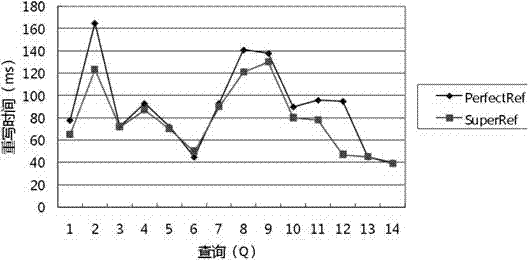
The invention discloses a dynamic hierarchical integrated data accessing method capable of guaranteeing semantic correctness and aims to solve the problem about how to provide data access with completely correct semantics under condition of integration of large-scale relation databases. The technical scheme includes that the dynamic hierarchical integrated data accessing method includes firstly, expanding to obtain a description logic subset DL-Lite, then layering the ontology TBox on the basis of the description logics, and establishing LAV (local as view) mapping and O-GAV (object-global as view) mapping between the relation database and the ontology; expanding and rewriting query request by means of SuperRef algorithm according to the T<Q> in layering of the TBox, and establishing a dynamic ABox A<Q> according to query results; and finally, refining the ABox A<Q>, and feeding back query response results. The dynamic hierarchical integrated data accessing method can provide data with the completely correct semantics for users and meet the requirement for correctness of the semantics in integrated data access. Further, calculating complexity can be reduced and expanding, query and rewriting efficiency can be improved.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
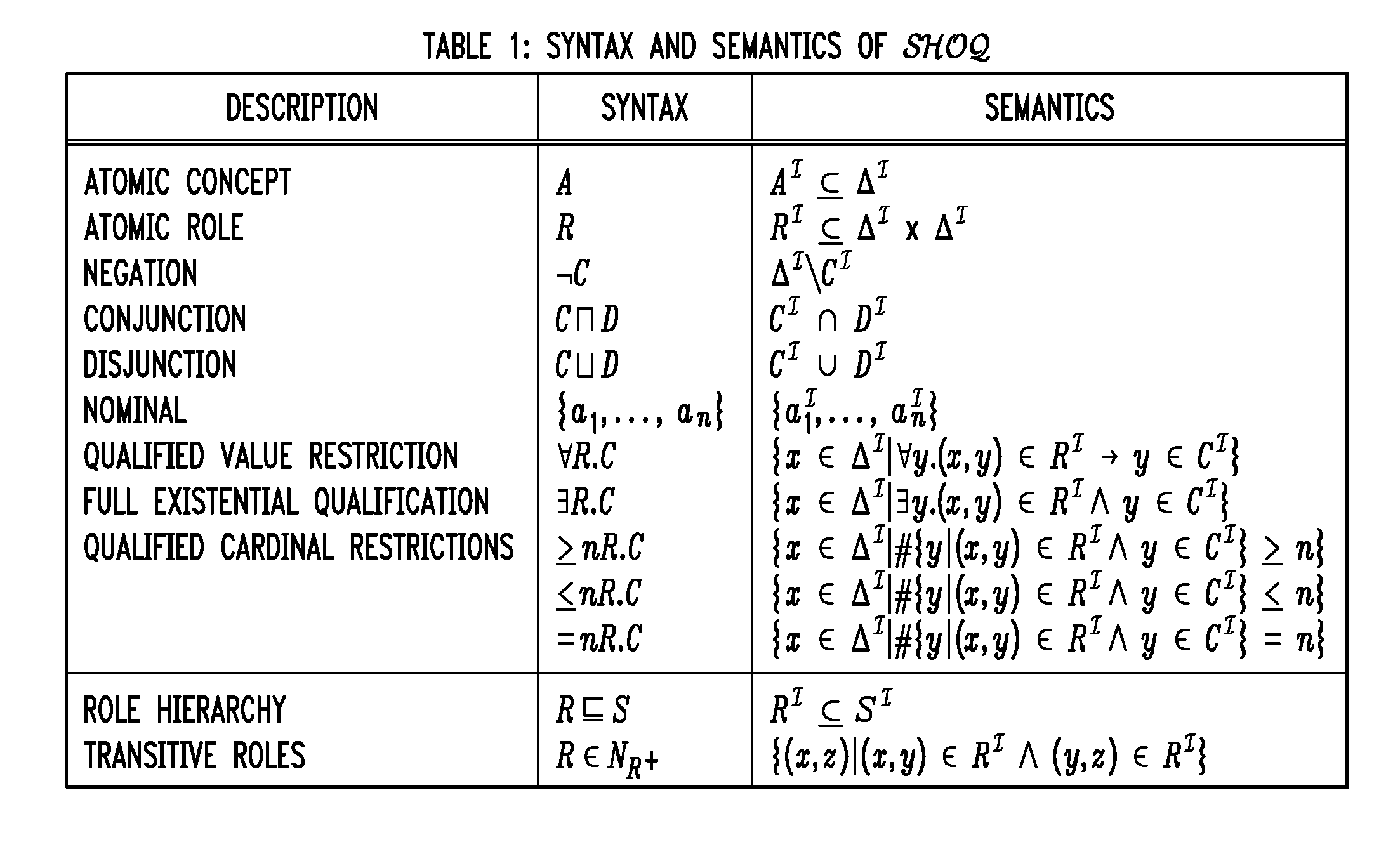
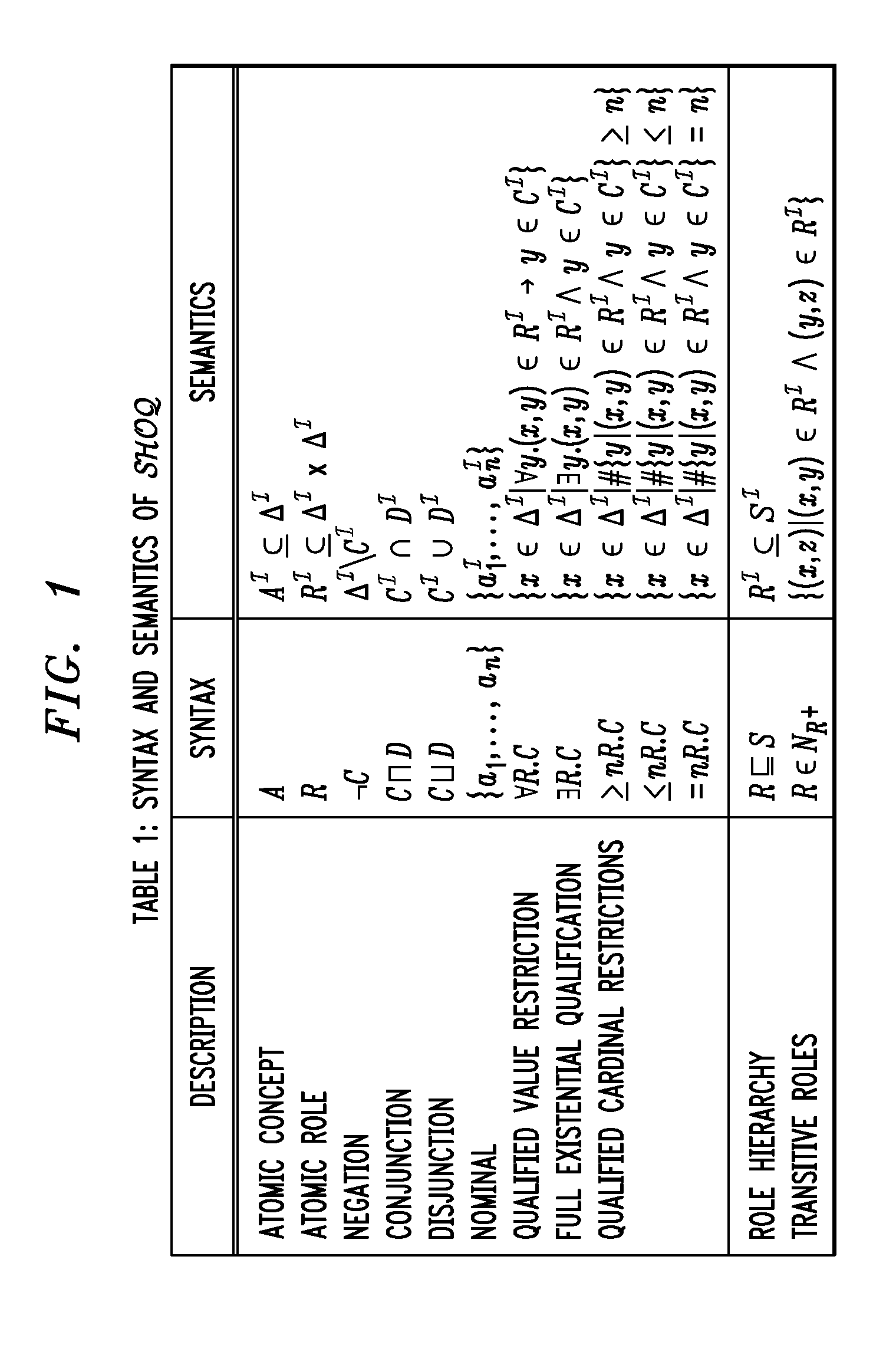
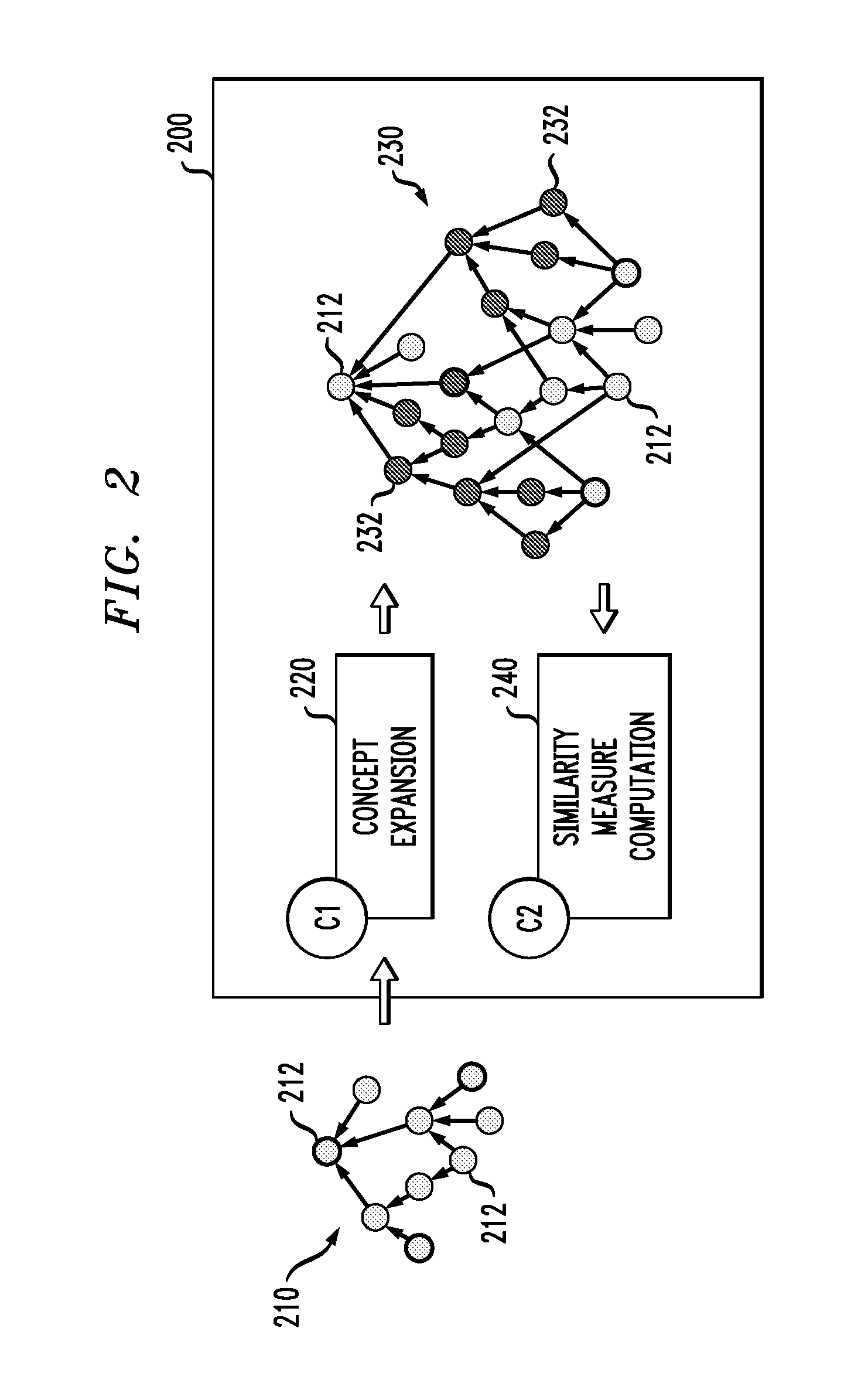
Ontological Concept Expansion for SHOQ Description Logic and the Like
In one embodiment, prior to similarity measure computation, concept expansion is applied to an original ontology to generate an expanded ontology having the original concepts plus one or more pseudo-concepts, wherein at least one original concept is defined using a hierarchy of (possibly transitive) properties. As a result, the similarity measure computation can produce results that are better than those produced using conventional techniques. In one implementation, the similarity measure computation involves combining two similarity results: a first similarity result corresponding to common semantics found in the two concepts and a second similarity result corresponding to dissimilar semantics found in the two concepts.
Owner:PIECE FUTURE PTE LTD
Method and system for multiple independent extensions of a concept taxonomy via description logic classification
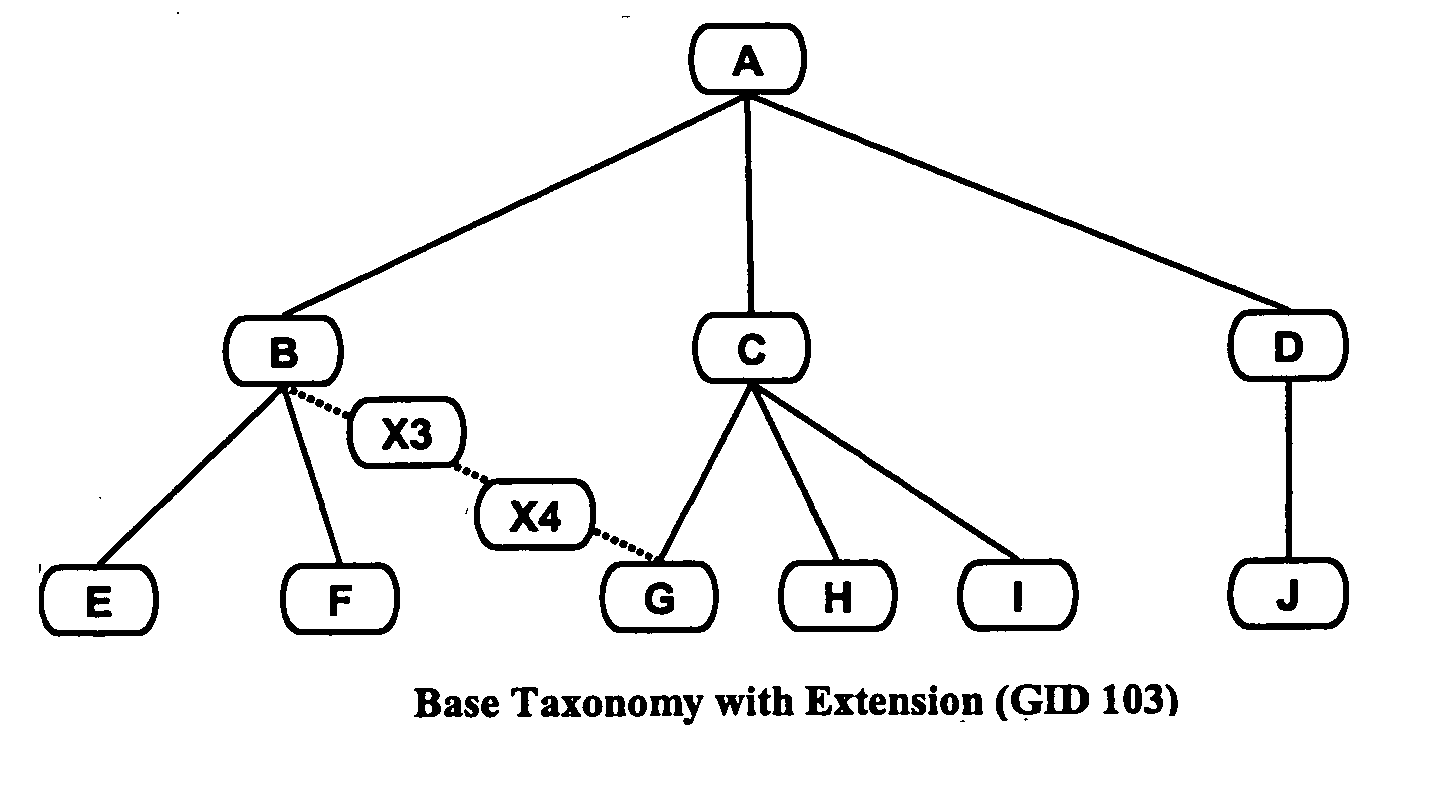
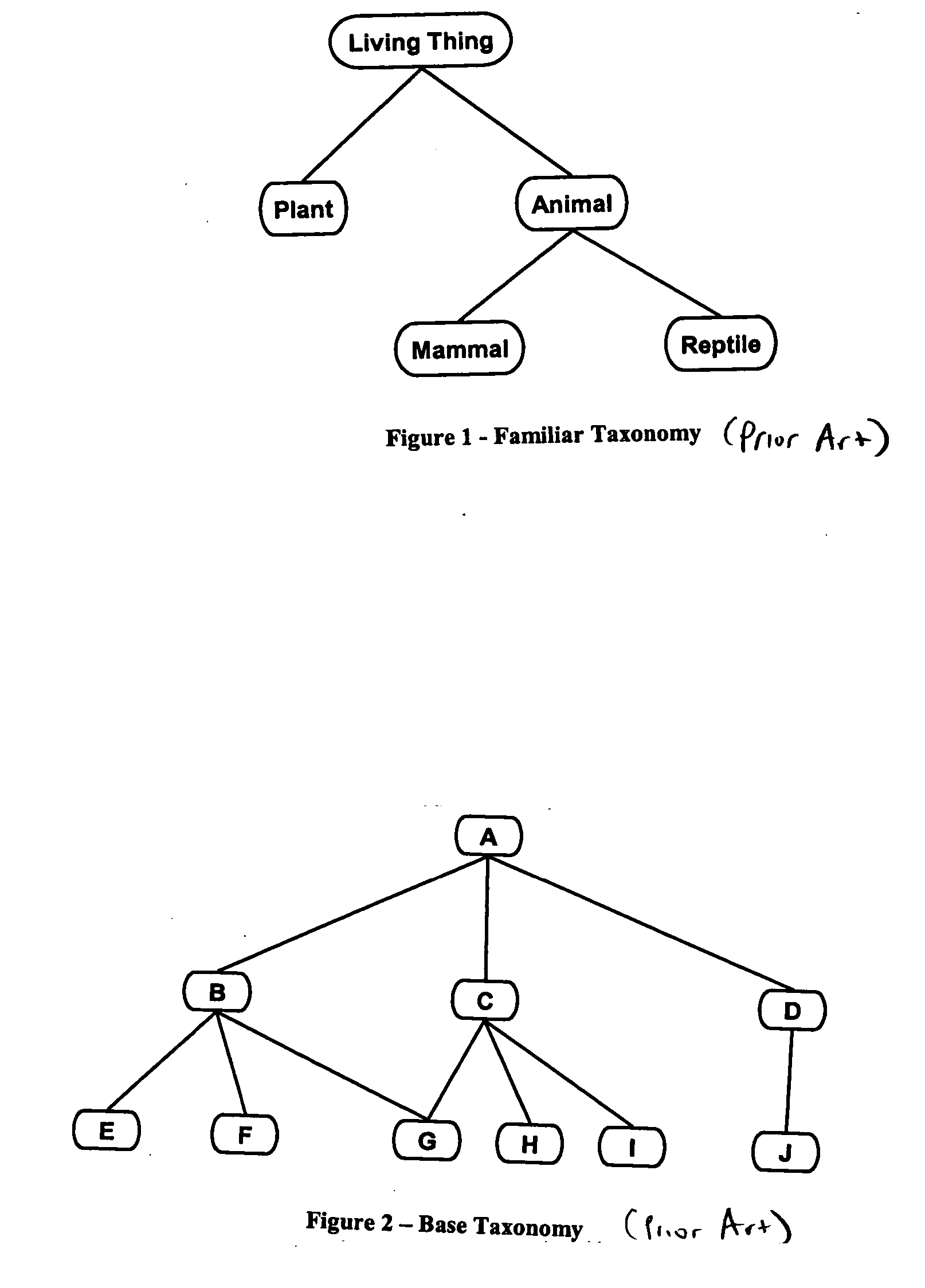
InactiveUS20070136335A1Extended efficiently and accuratelyMeet needsDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsModularityData mining
A method and system facilitating multiple independent extensions of a concept taxonomy. Separate classification operations determine how one or more distinct sets of additional concepts, each comprising an extension, fit in with the original taxonomy while leaving the original taxonomy intact and substantially without copying it. Classification results are recorded so that the original taxonomy and every extension thereof can be independently queried and retrieved on demand. This process is referred to as modular classification.
Owner:APELON
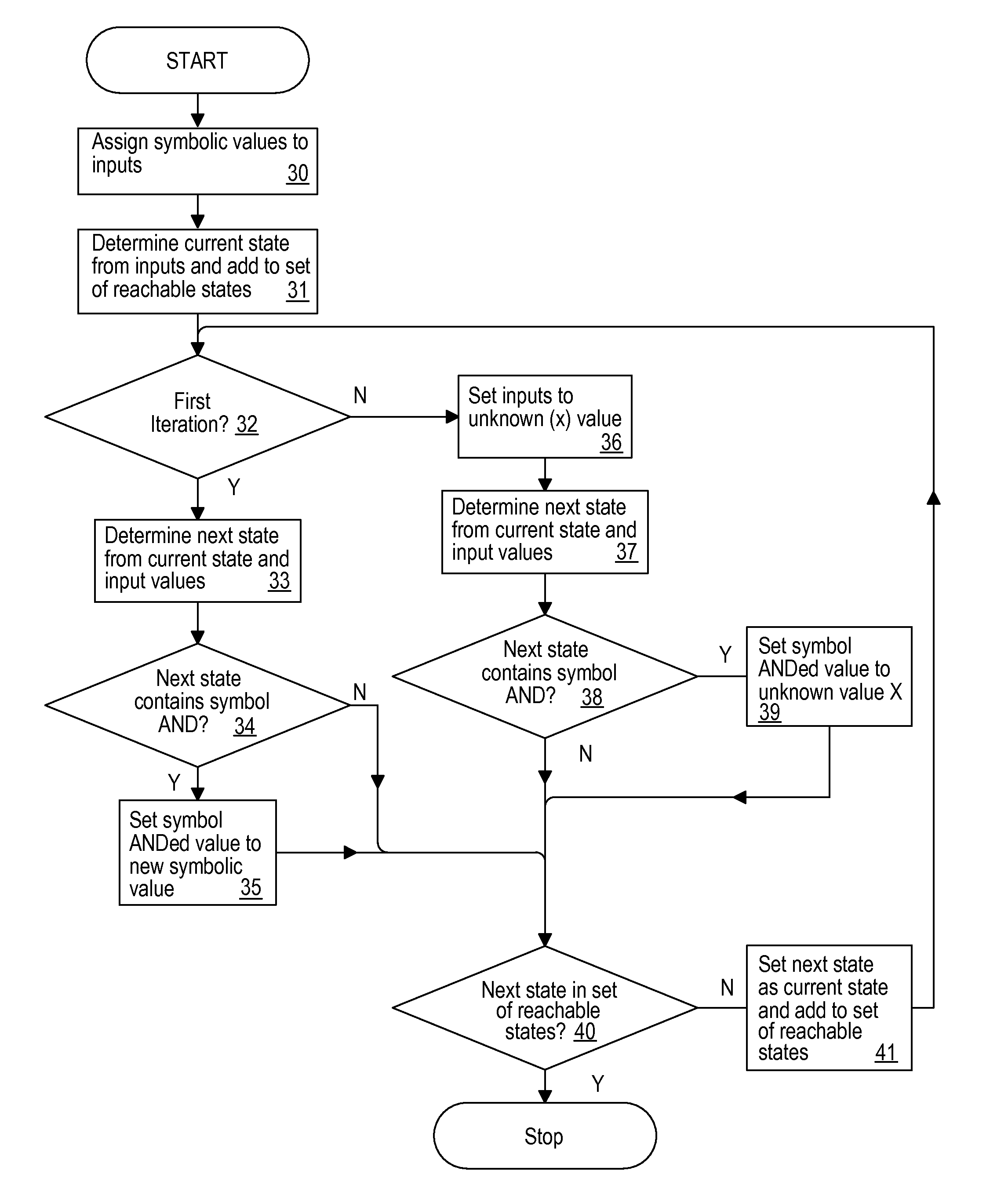
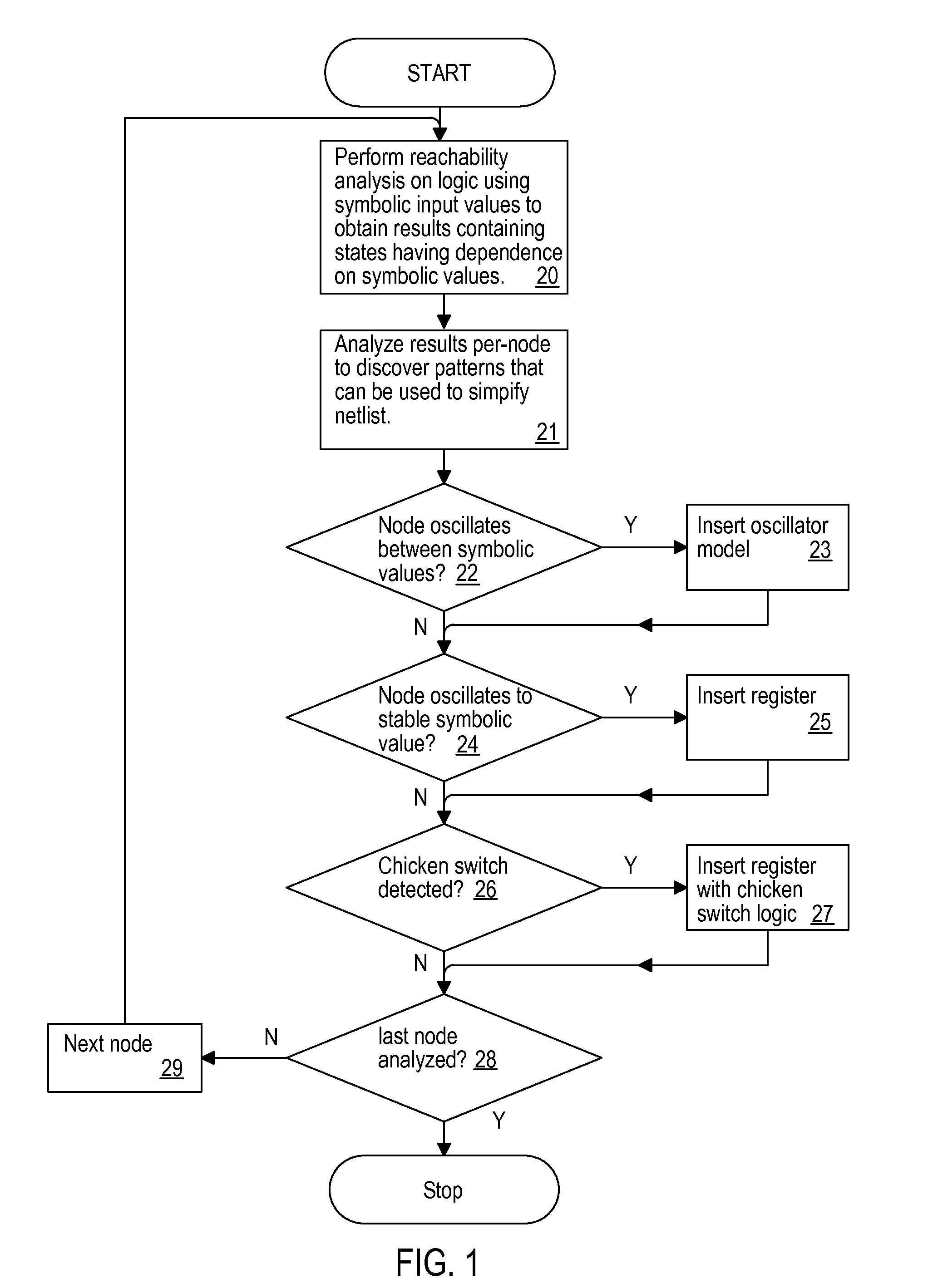
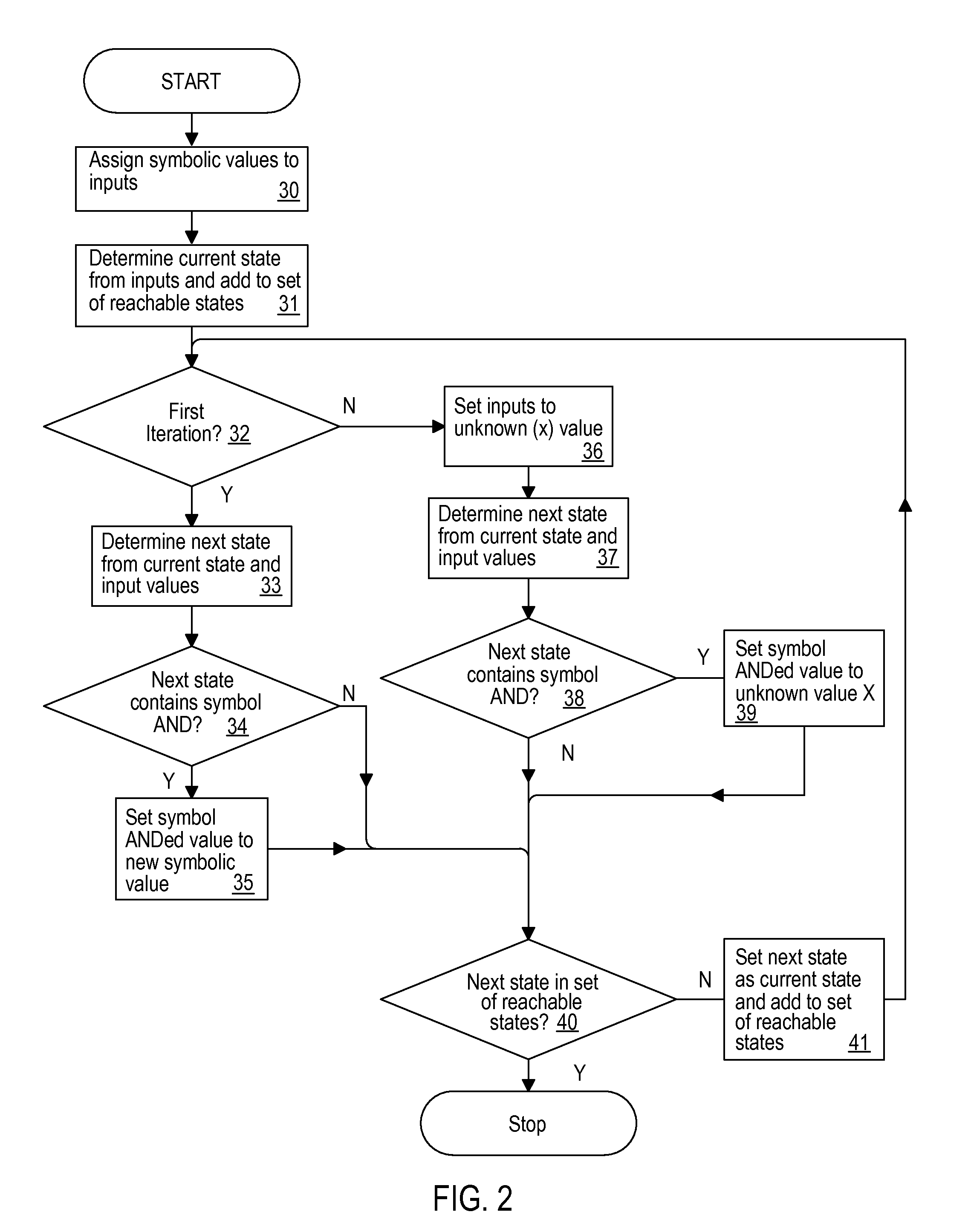
Reachability analysis by logical circuit simulation for providing output sets containing symbolic values
InactiveUS20120290282A1Simplify netlistCAD circuit designSpecial data processing applicationsReachabilitySymbol of a differential operator
A logic simulation program, method and system for obtaining a set of reachable states for a logic design that can be used to provide input to other algorithms that simplify the netlist describing the logic design or perform other types of processing, provides an efficient, compact behavior when simulating large designs. Rather than simulating using ternary input and state value representations that are restricted to true, false and unknown, the techniques of the present invention use input symbolic values that are retained in the set of reachable states retained as the output. Behaviors such as oscillators, transient values, identical signals, dependent logical states and chicken-switch determined states can be detected in the simulation results and the netlist simplified using the results of the detection.
Owner:IBM CORP
Ontology-based architectural pattern modeling method
The invention discloses an ontology-based architectural pattern modeling method. According to the method, description logic is used to perform concept modeling of an architectural pattern, a domain knowledge model is further introduced, finally a mapping relation between a high-level abstract concept and system realization is established, and therefore the model is applied to recognition of the architectural pattern. Considering extension and reuse problems of domain knowledge, the domain knowledge is organized into a netlike hierarchical structure during modeling. In the structure, a conceptmodel is at a high level, more domain knowledge is combined step by step at all lower levels to explain the high-level concept. New knowledge can be incrementally added into any node at any level andalso can be selectively reused to establish a new concept. The ontology-based architectural pattern modeling not only has the abstracting ability of concept modeling but also can utilize the domain knowledge to serve architectural pattern recognition, and therefore the automation degree and precision of architectural pattern recognition are improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Management of relationships between database tables
A method, system and article of manufacture for managing relationships between database tables and, more particularly, for identifying and accurately describing relationships between tables in a database. One embodiment provides a method for identifying relationships between tables in a database. The method comprises receiving user input selecting a plurality of tables from the database. The plurality of tables is organized into a logical island defining a logical unit related to a particular logical entity. The method further comprises receiving user input identifying, for each of the plurality of tables, a table column containing information that identifies the particular logical entity in the table, whereby the identified table columns of different tables define logical relationships between the different tables in the logical island. On the basis of the identified table columns, relations specifications are created which describe the logical relationships between the different tables in the logical island.
Owner:DOMO
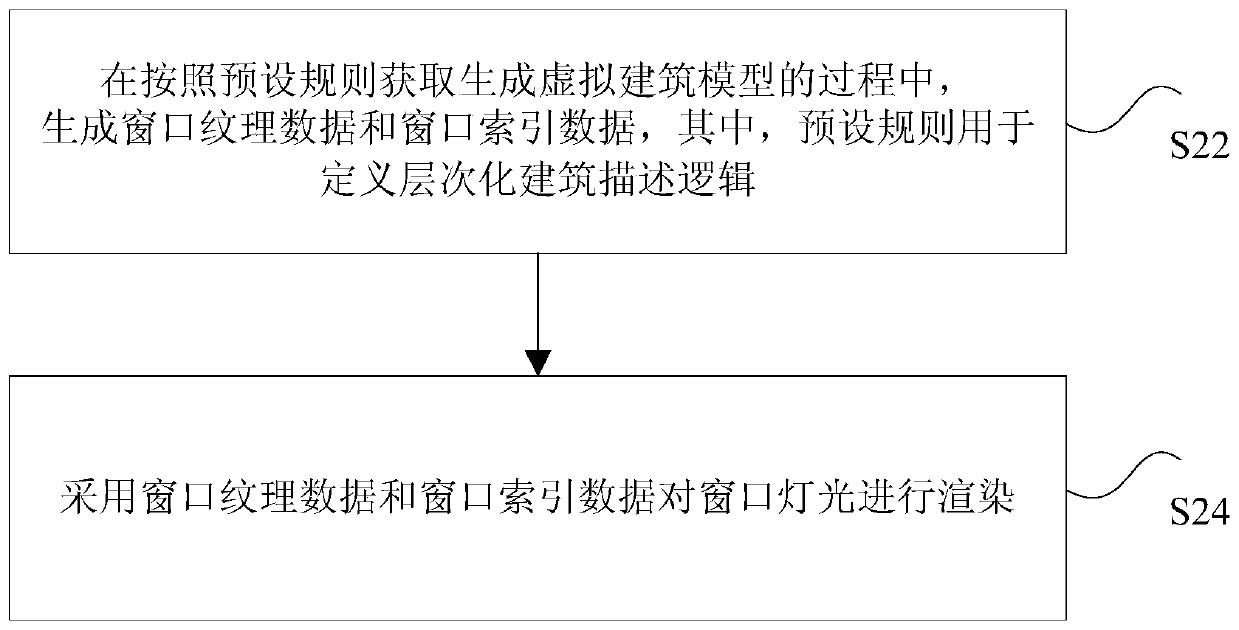
Window light control method and device of virtual building model, processor and terminal
ActiveCN110197525ARealize customizationAchieve controllabilityEnergy saving control techniques3D-image renderingComputer terminalComputer science
The invention discloses a window light control method and device of a virtual building model, a processor and a terminal. The method comprises the steps that in the process of obtaining and generatinga virtual building model according to a preset rule, window texture data and window index data are generated, and the preset rule is used for defining hierarchical building description logic; and window light is rendered by adopting the window texture data and the window index data. According to the invention, the technical problems of high operation complexity, high development cost and low development efficiency of the provided method for controlling the lighting of the virtual building model at night in the related art are solved.
Owner:NETEASE (HANGZHOU) NETWORK CO LTD
Constraint solving and description logic based web service combination method
InactiveCN104750499AImprove effectivenessImprove recallSpecific program execution arrangementsService compositionDecomposition
The invention provides a constraint solving and description logic based web service combination method. The constraint solving and description logic based web service combination method comprises designing an optimization target of every fine-grained task and extracting constraint conditions of a task interface based on target task decomposition of a domain knowledge database; obtaining a combination of the fine-grained tasks through constraint solving and detecting the validity and the reasonableness of the combination through description logic, avoiding process conflicts and obtaining appropriate combined web services. According to the constraint solving and description logic based web service combination method, the web services can be effectively combined and accordingly the accuracy is significantly improved and the logic correctness of the service combination can be detected and accordingly the service combination can be reasonable and effective.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
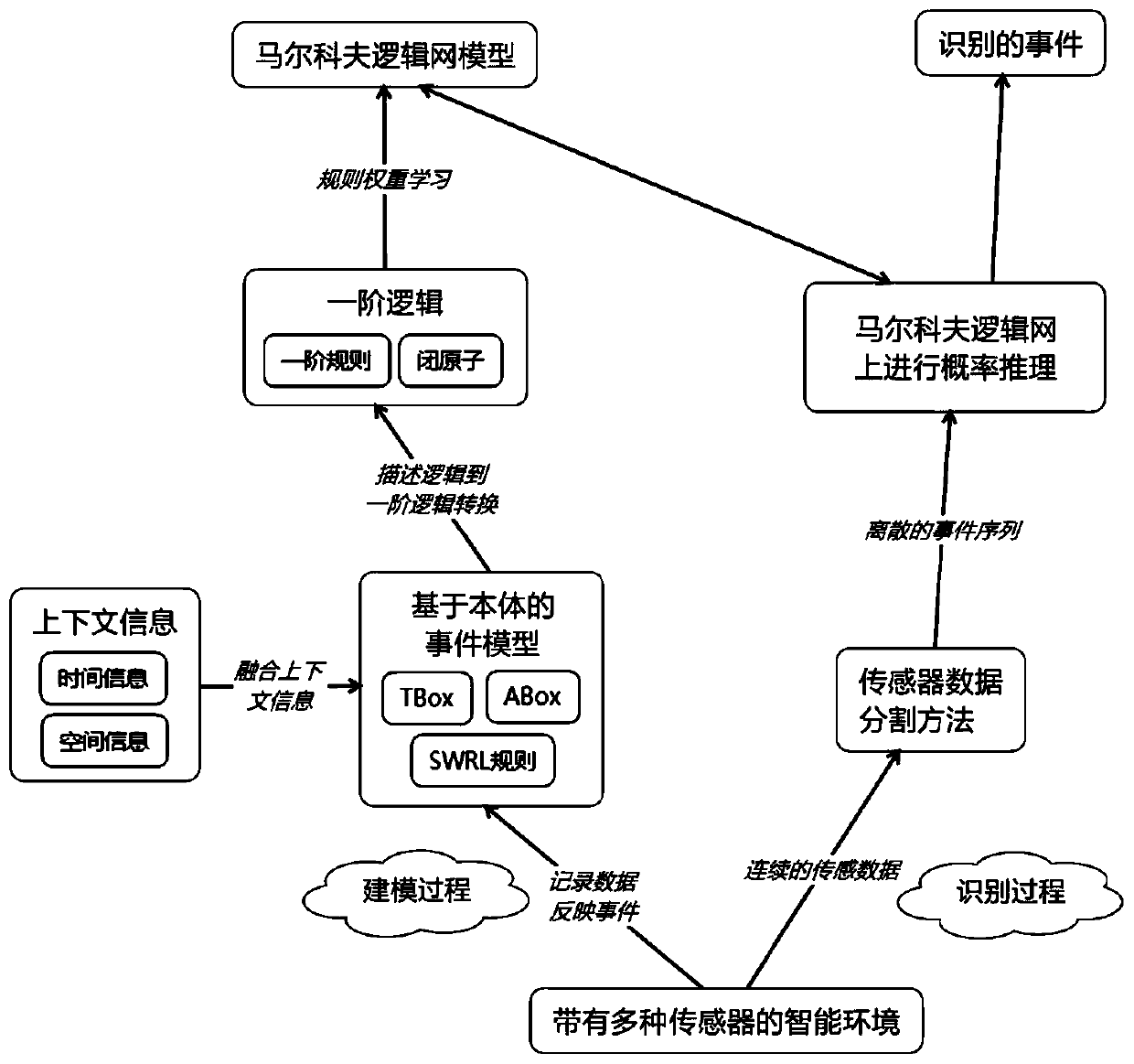
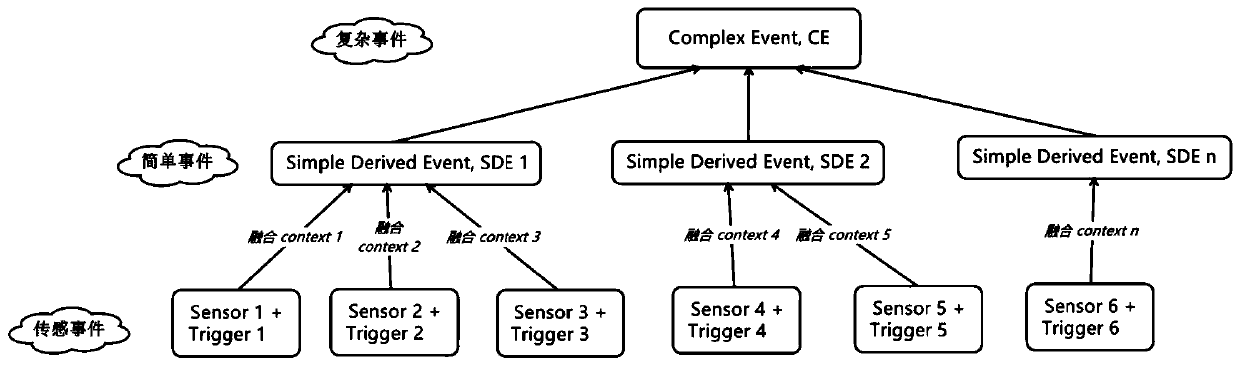
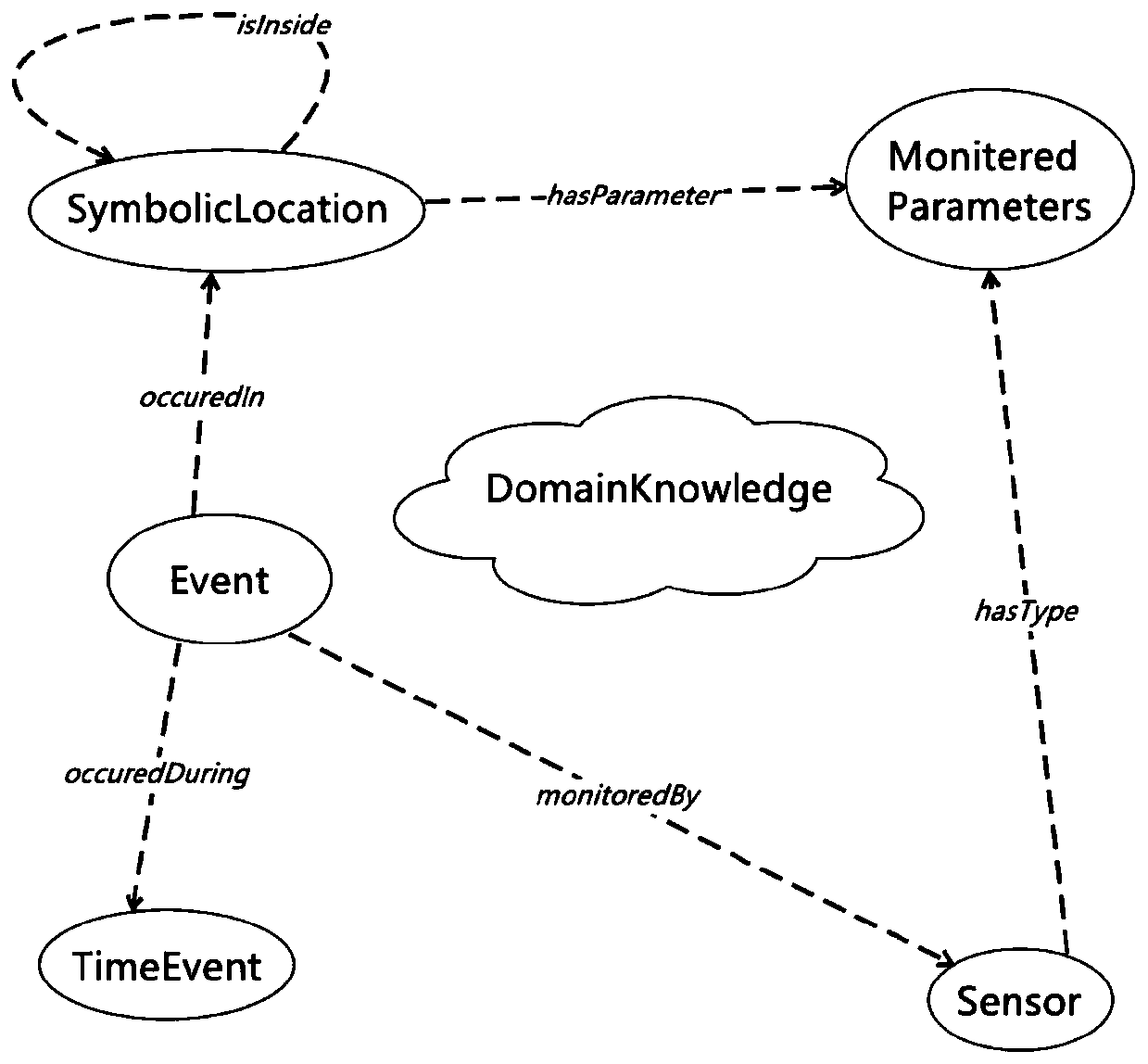
Complex event identification method based on ontology model and probability reasoning
ActiveCN110197281AEfficient integrationRemove uncertaintyMathematical modelsKnowledge representationIntelligent environmentSensing data
The invention discloses a complex event identification method based on an ontology model and probability reasoning. The complex event identification method comprises the following steps of (1) modeling a sensor and an event in an intelligent environment by using the ontology model; (2) converting the ontology model into a Markov logic network model by using the semantic attribute of the description logic; (3) segmenting the continuously generated sensor data by using a segmentation method based on a place and a fixed time interval to form an event sequence as the input of a Markov logic network model; (4) carrying out probability reasoning on the Markov logic network model, so that the events occurring in the intelligent environment are identified. According to the complex event recognition method, the advantages of a knowledge driving method and a data driving method are fused, the intelligent environment can be accurately modeled, the time constraint relation between events and the uncertainty of sensing data are effectively processed, and the identification accuracy is improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
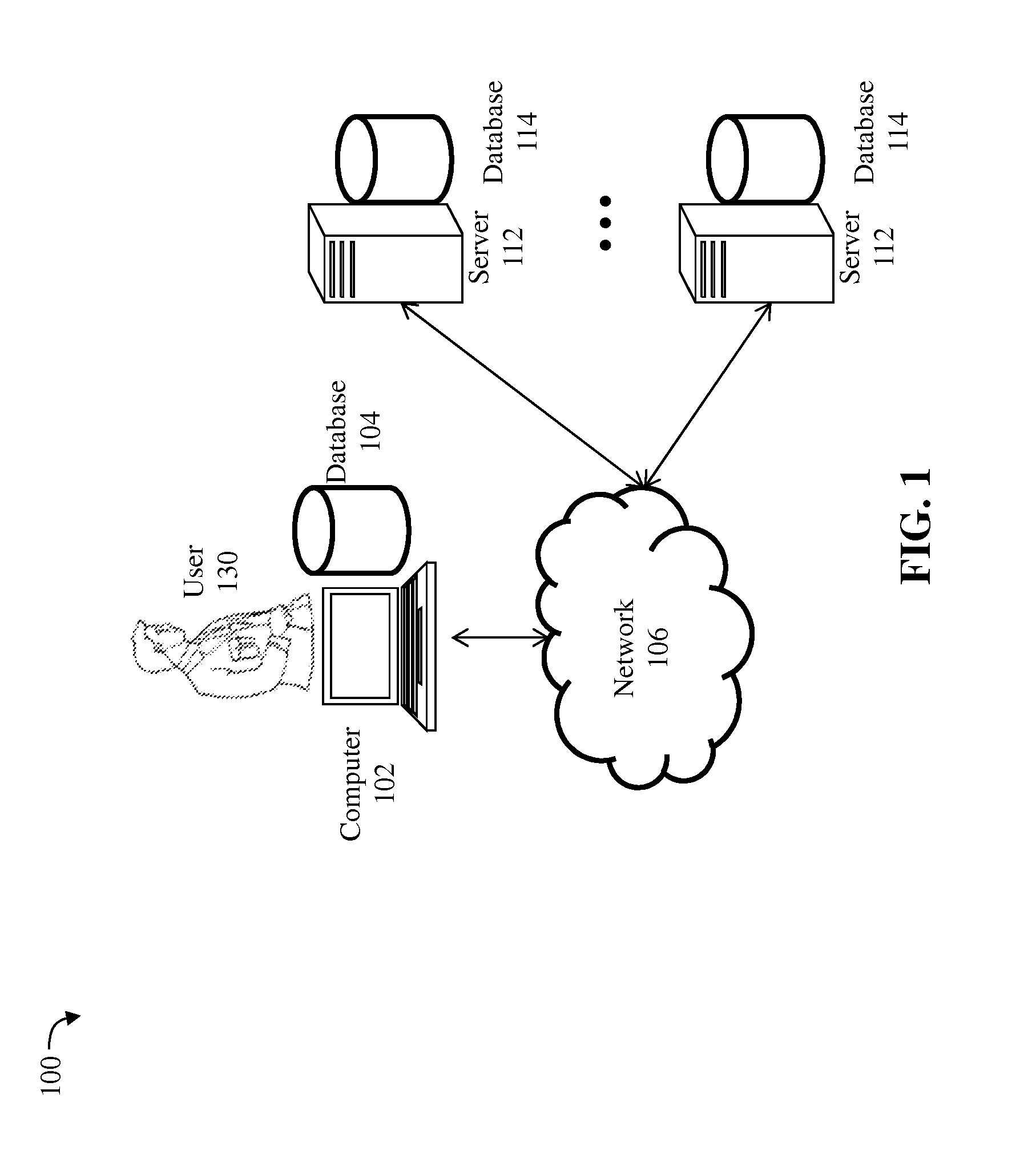
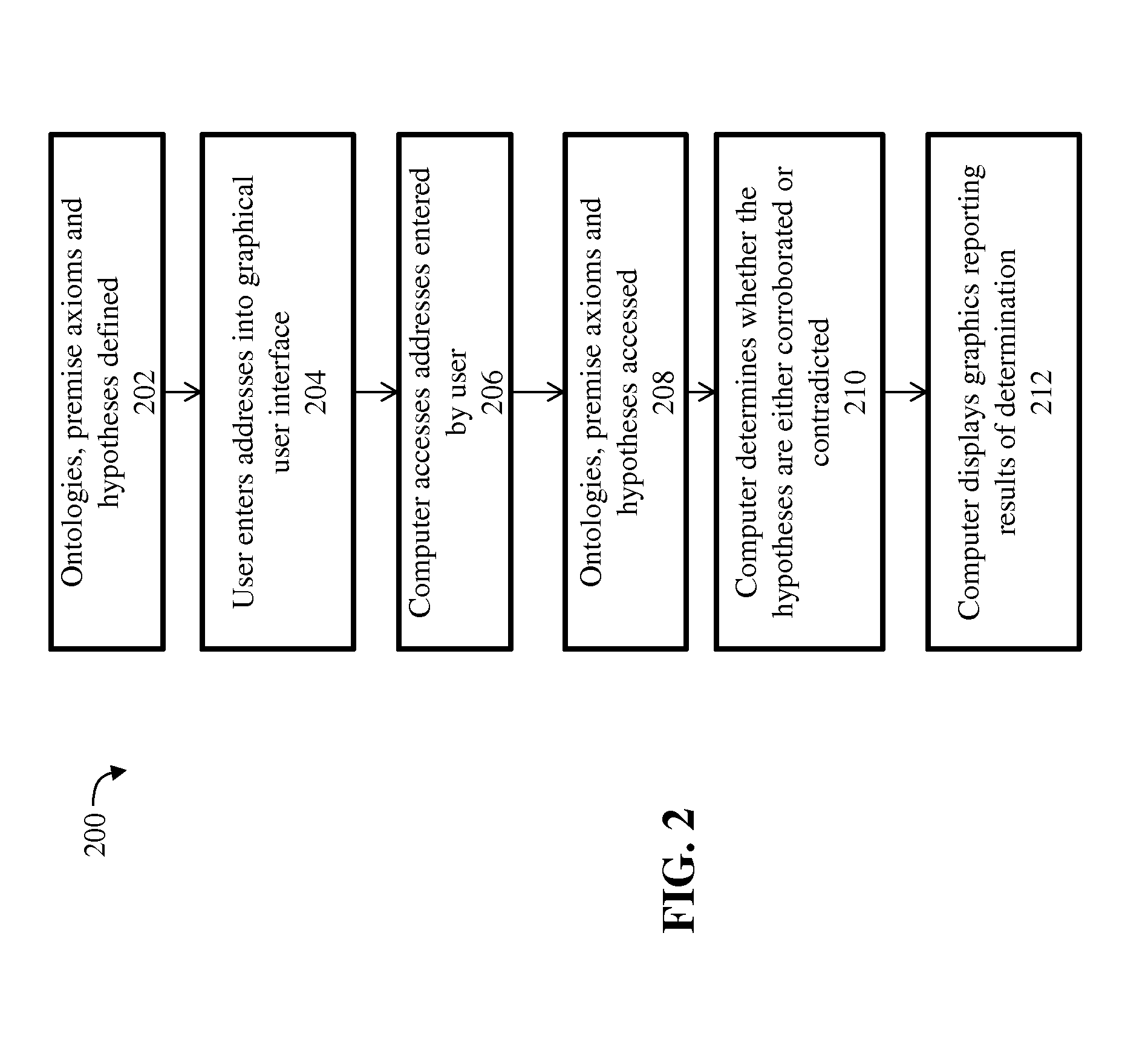
Automated verification of hypotheses using ontologies
A method on a computer for determining whether a hypothesis is verified by one or more ontologies. The method includes reading an address for a hypothesis comprised of one or more hypothesis axioms, wherein an axiom is represented in description logic form, reading an address for an ontology comprised of one or more ontology axioms and accessing the hypothesis and the ontology using the addresses that were read. The method further includes determining whether the ontology either corroborates or contradicts the hypothesis, identifying a first set of ontology axioms that corroborate the hypothesis and identifying a second set of ontology axioms that contradict the hypothesis, displaying a graphic indicating either corroboration or contradiction of the hypothesis, displaying the first set of ontology axioms together with a graphic indicating corroboration of the hypothesis and displaying the second set of ontology axioms together with a graphic indicating contradiction of the hypothesis.
Owner:INFOTECH SOFT
Apparatus and method for performing service adaptation in respect of a mobile computing device
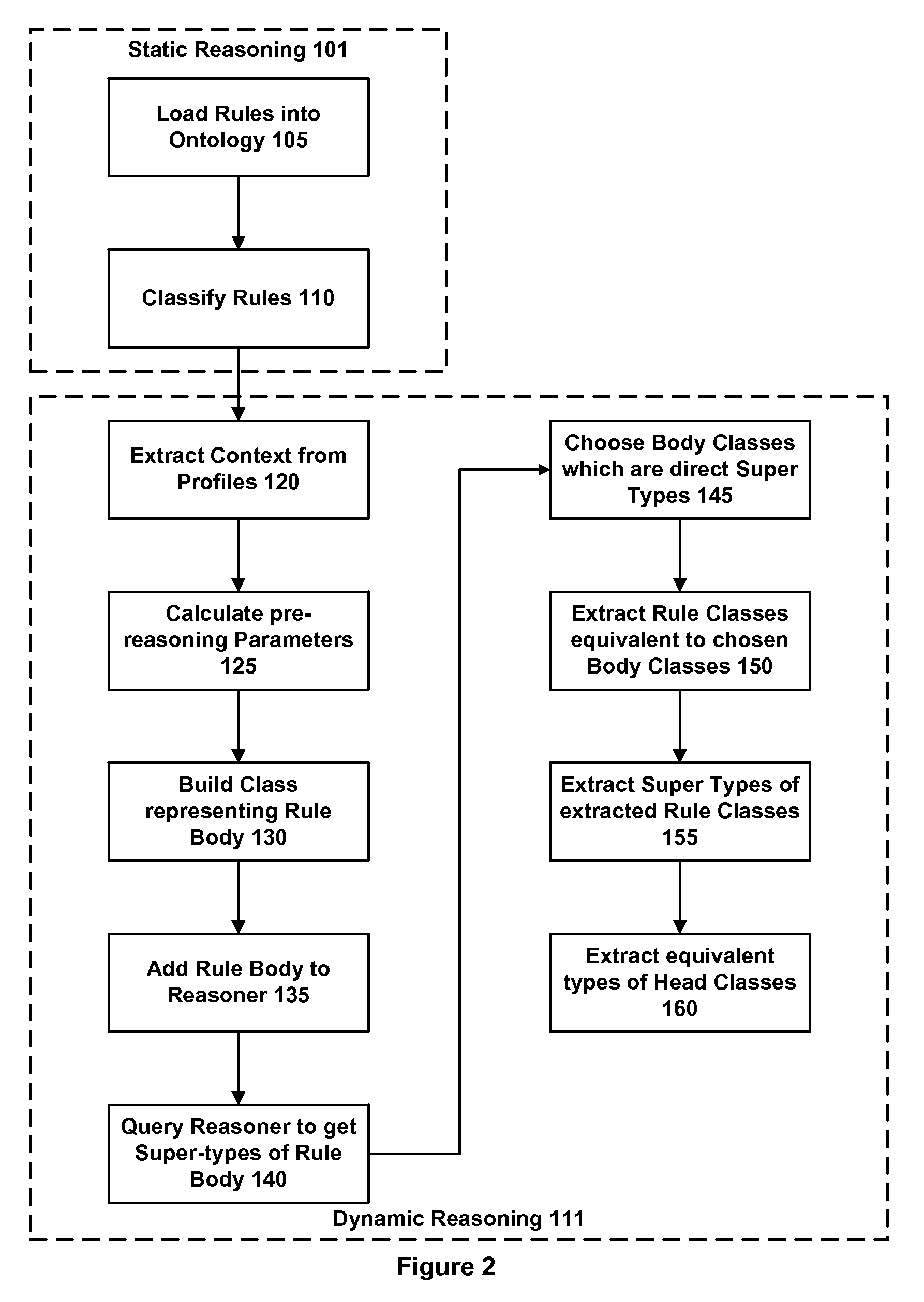
InactiveUS20100076918A1Quick responseKnowledge representationSpecial data processing applicationsService adaptationDecision taking
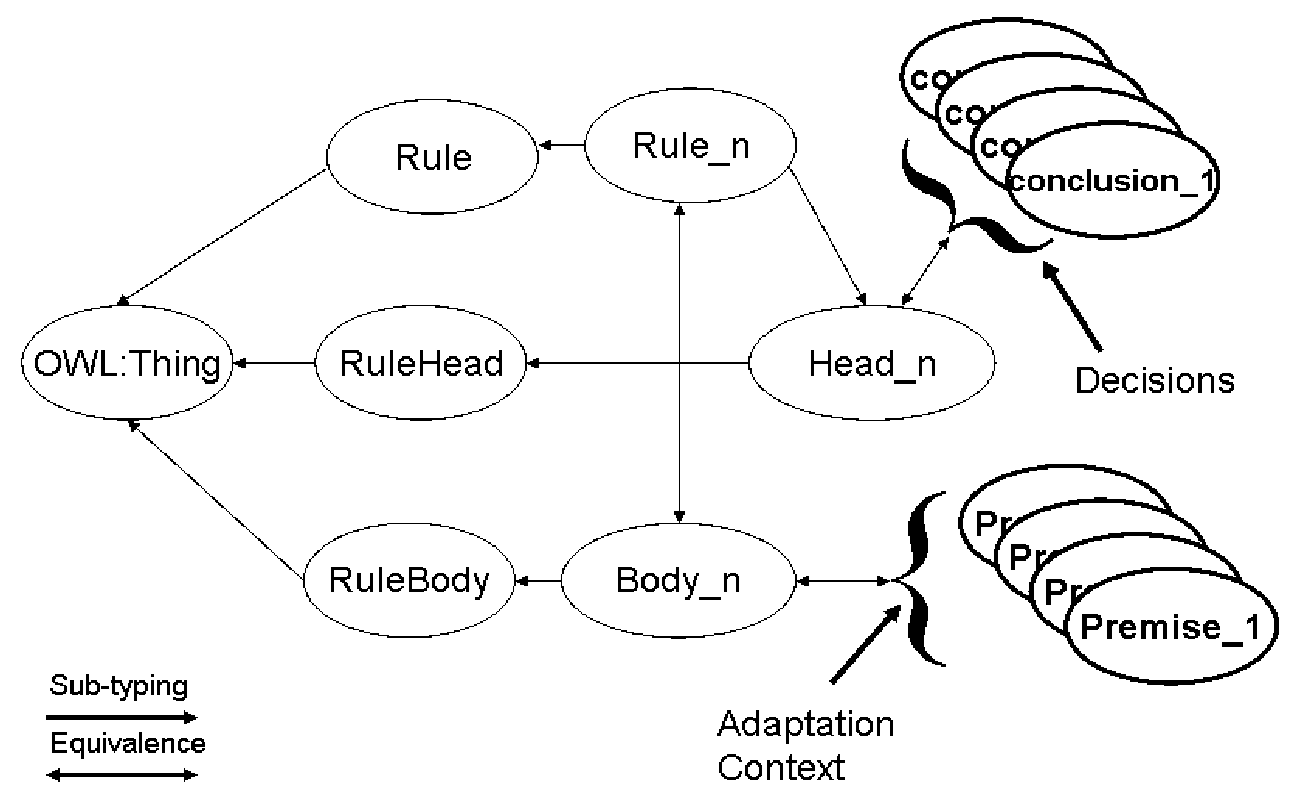
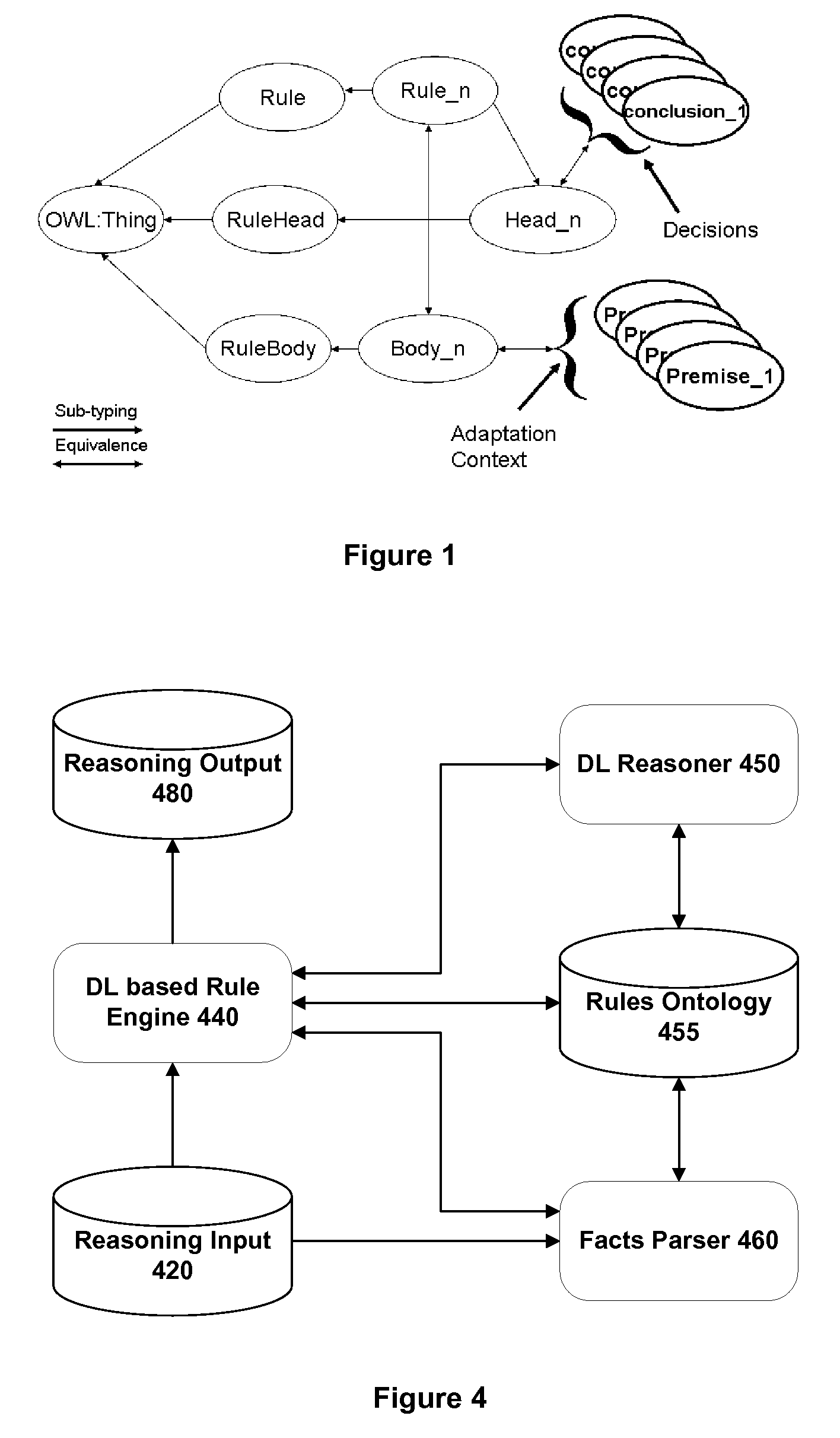
One embodiment of the invention provides a method and apparatus for performing service adaptation in respect of a mobile computing device. The method includes providing a service adaptation specification as a set of rules, where each rule comprises a rule body containing one or more premises and a rule head containing one or more conclusions that hold if said one or more premises are true. The rules are defined as classes in an ontology. The premises represent adaptation context and the conclusions represent service adaptation decisions. The method further comprises running the rules on a Description Logics reasoner in conjunction with adaptation context relating to the mobile computing device for a requested service to produce one or more service adaptation decisions. The method further comprises adapting the requested service provided to the mobile computing device in accordance with the service adaptation decisions from the description logics reasoner.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF SURREY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com