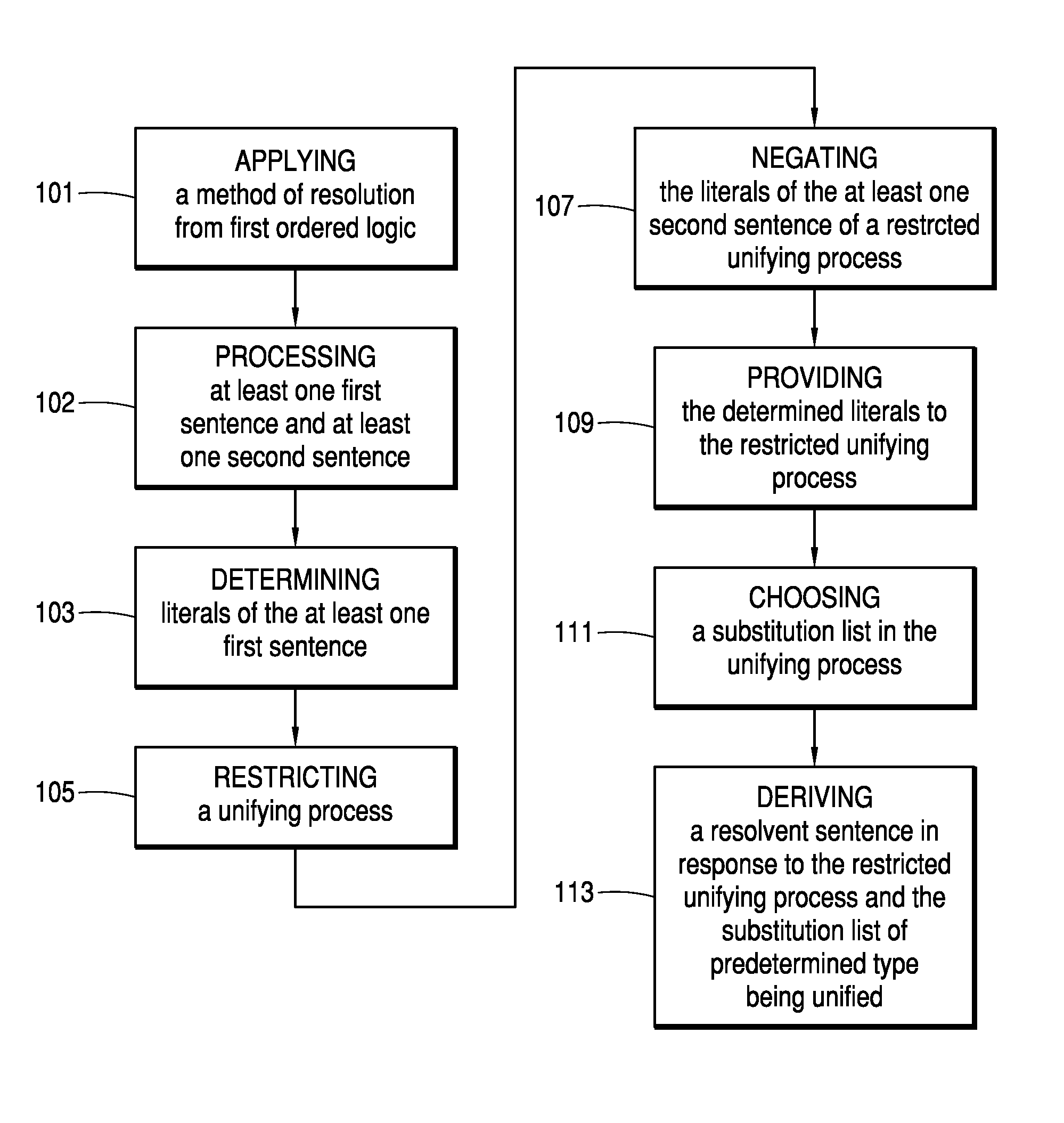
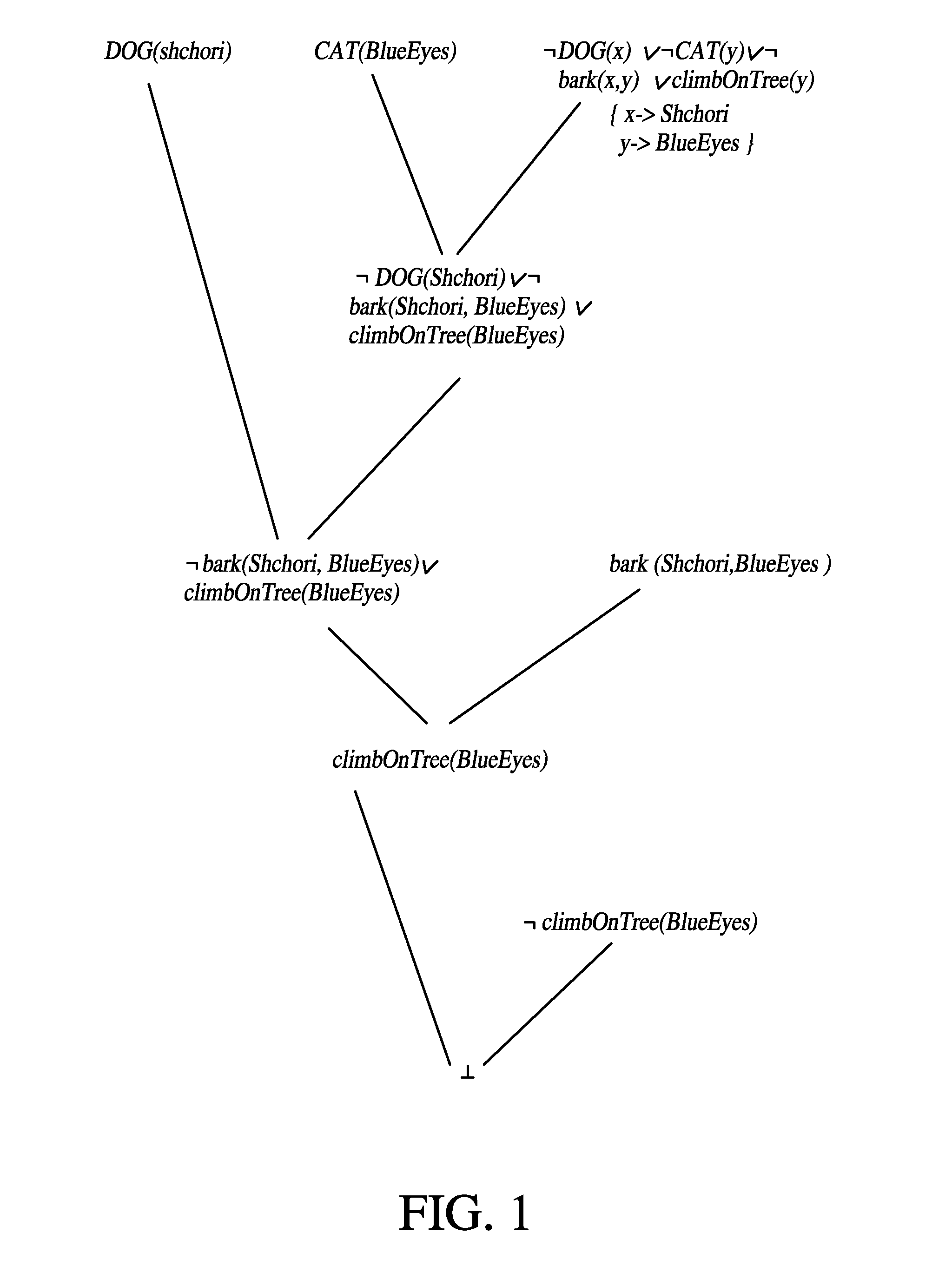
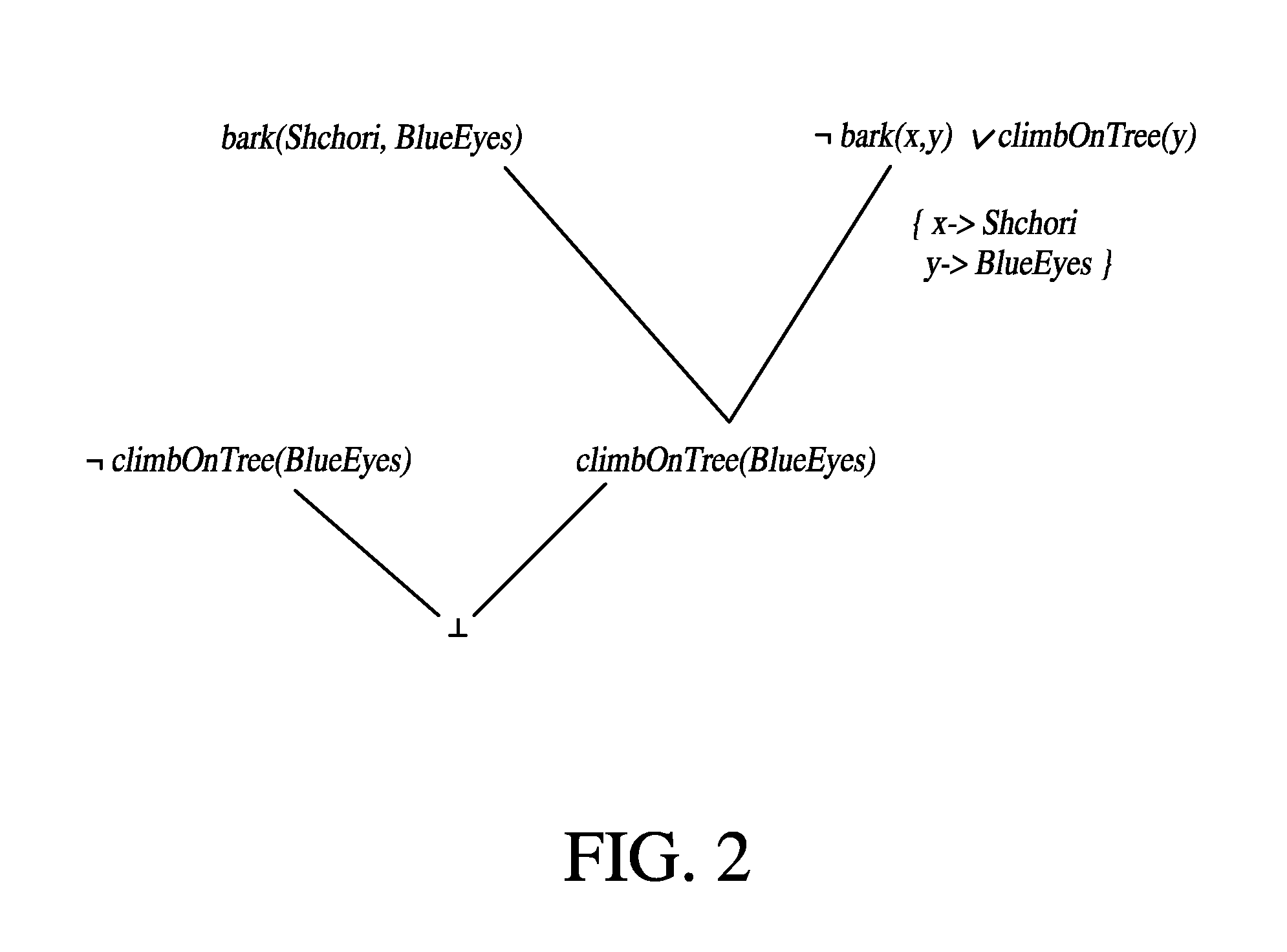
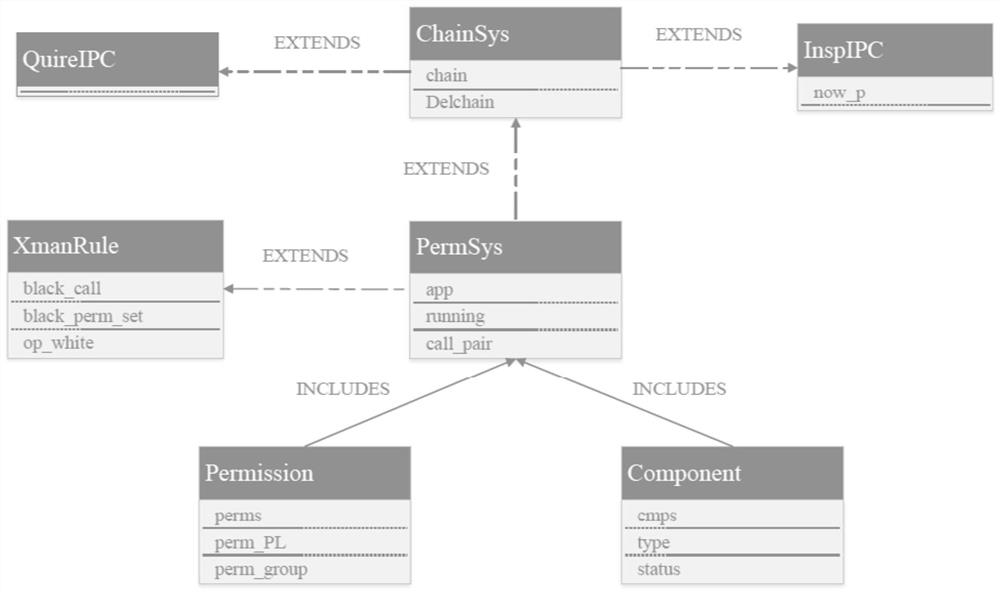
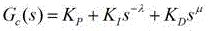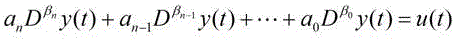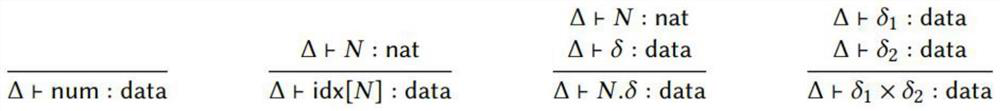Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45 results about "Theorem provers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
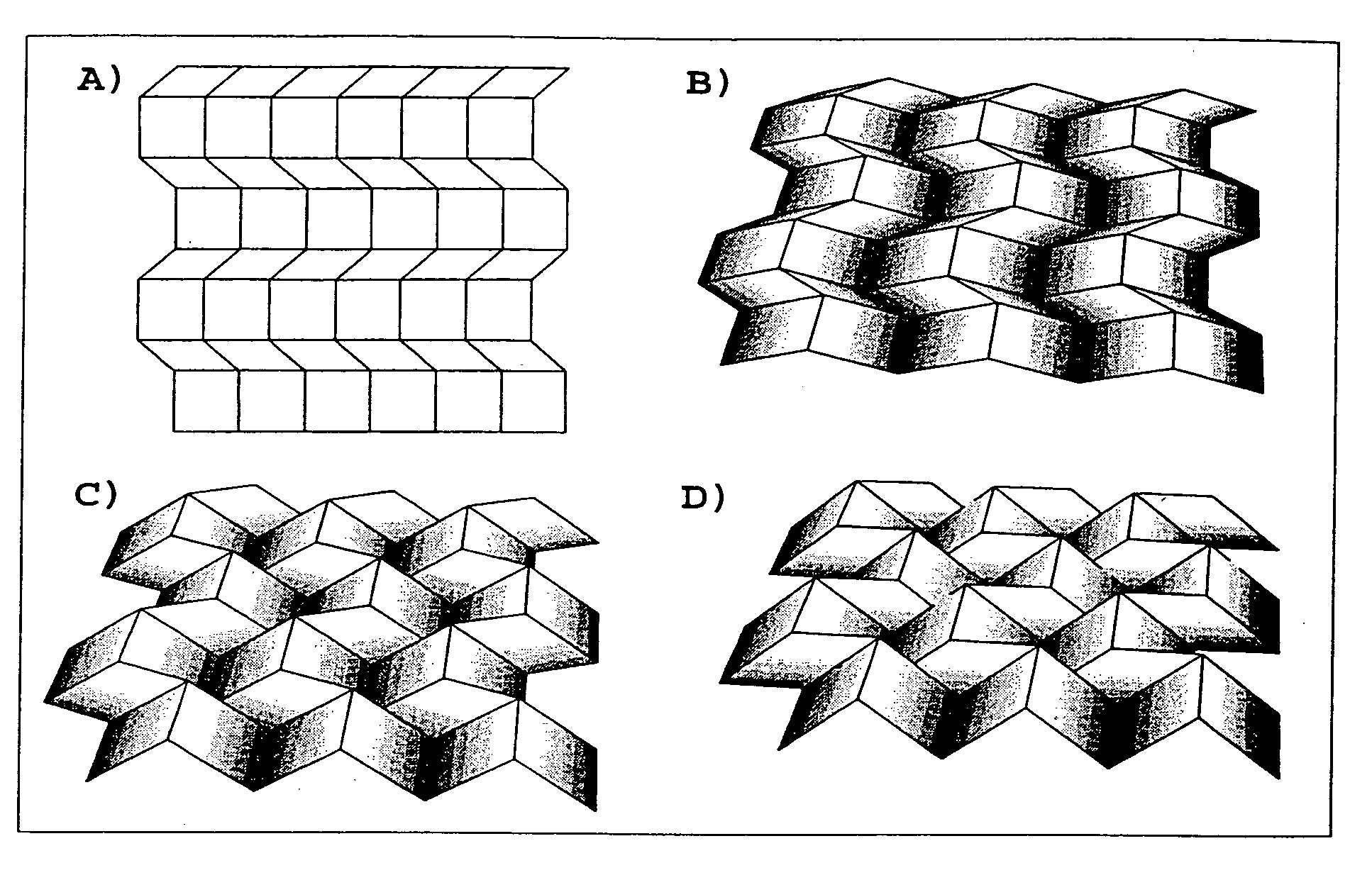
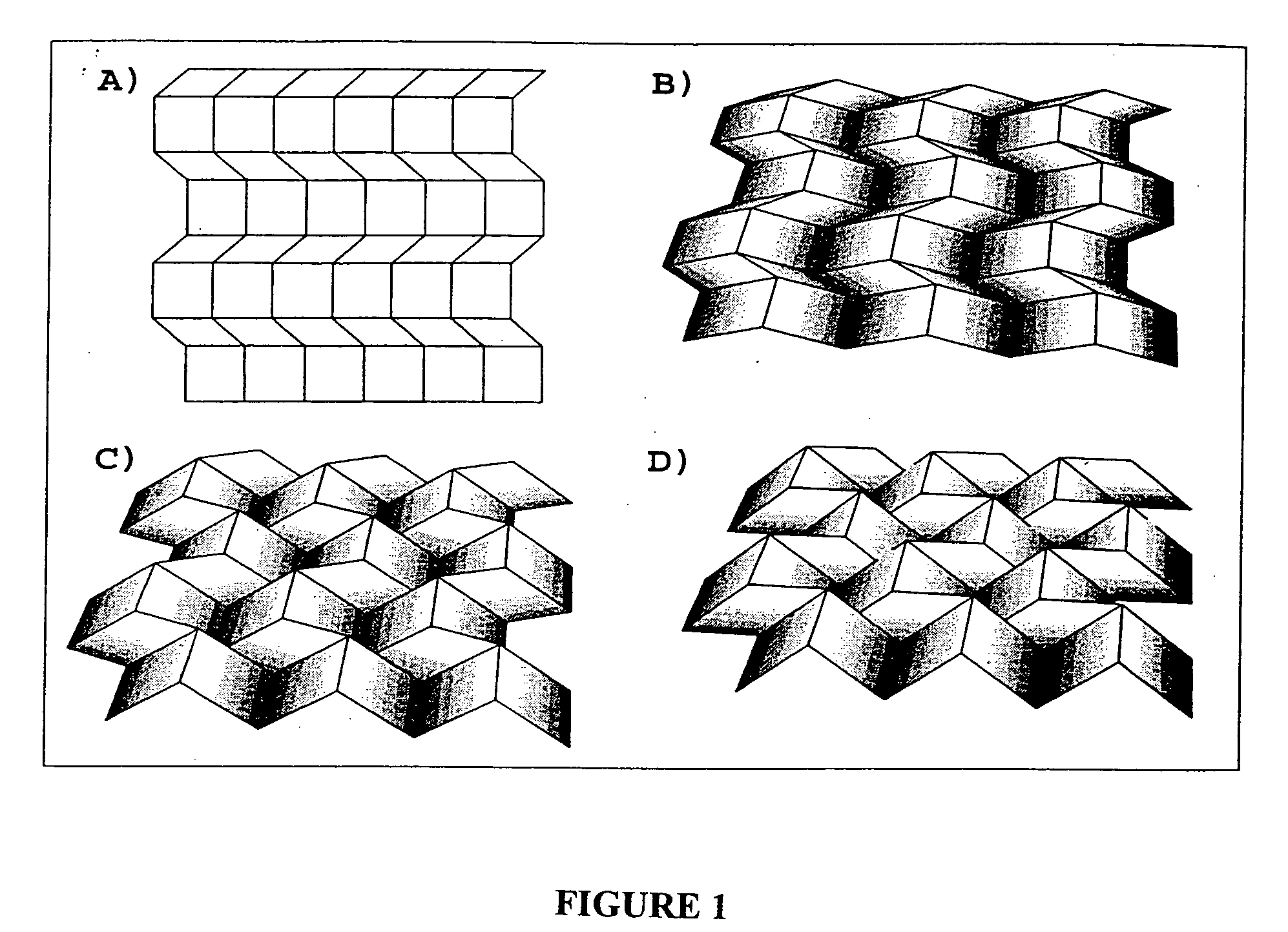
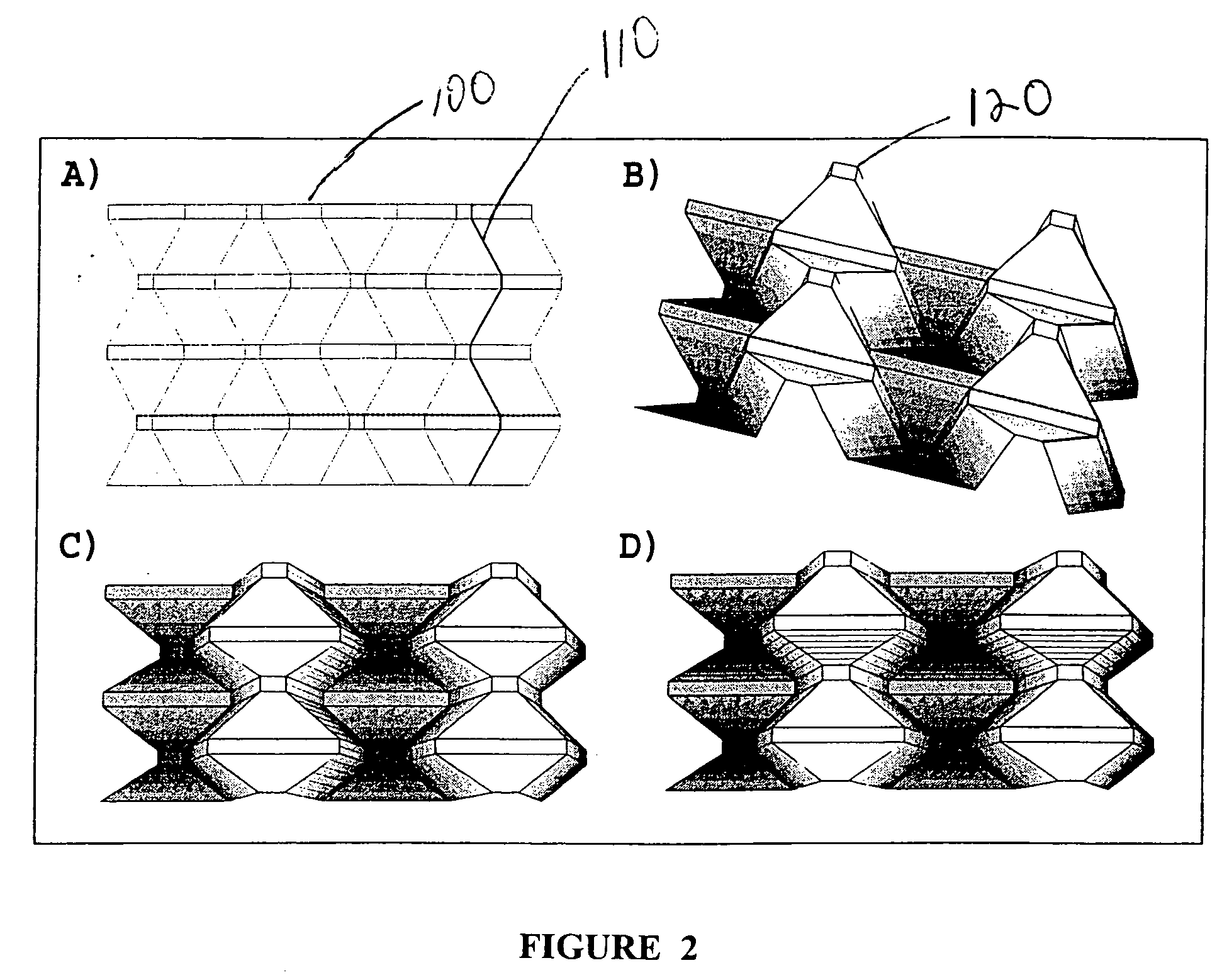
Patterning technology for folded sheet structures
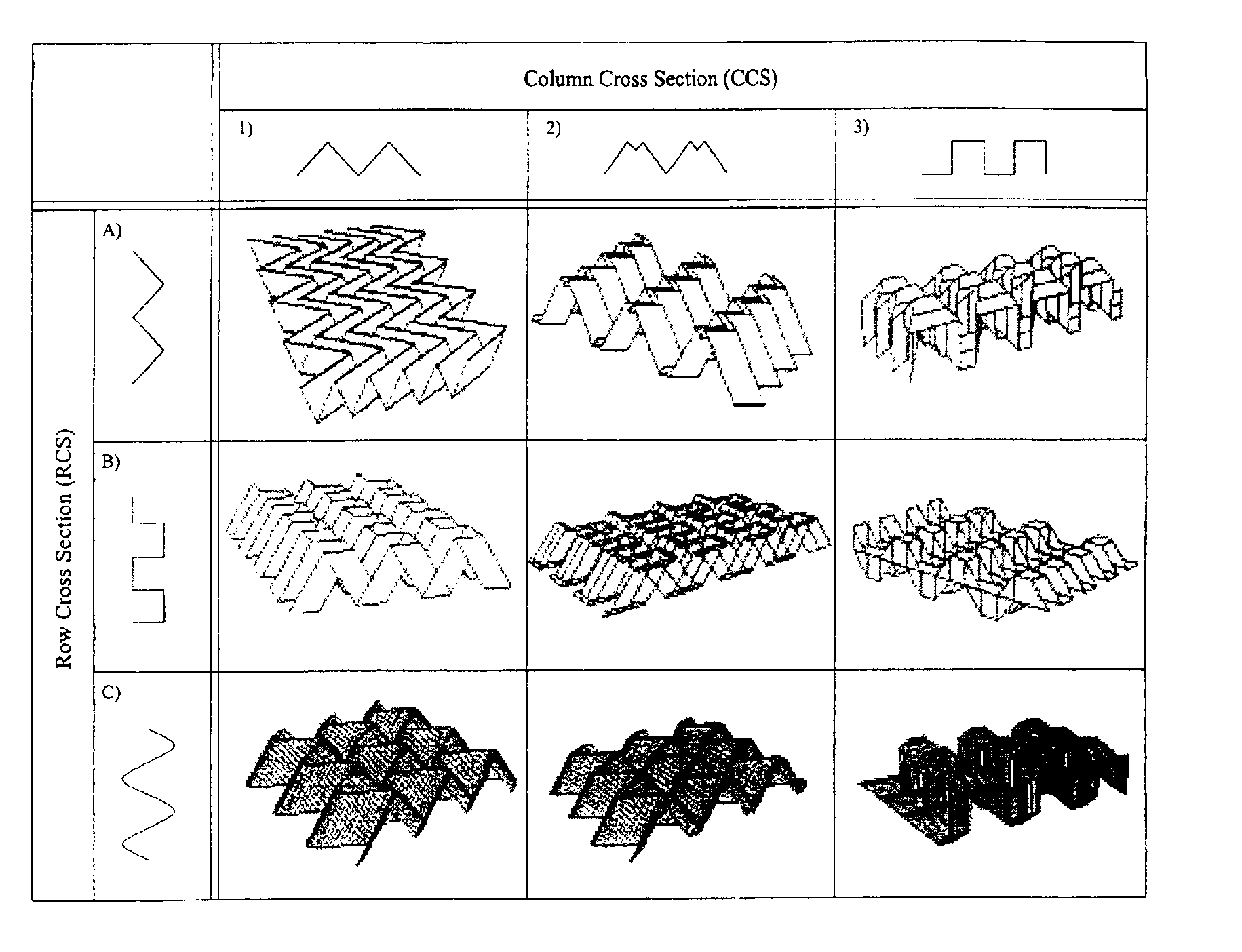
The present invention supplies practical procedures, functions or techniques for folding tessellations. Several tessellation crease pattern techniques, and the three-dimensional folded configuration are given. Additionally several new forming processes, including mathematical methods for describing the material flow are disclosed doubly-periodic folding of materials that name the doubly-periodic folded (DPF) surface, including vertices, edges, and facets, at any stage of the folding. This information is necessary for designing tooling and forming equipment, for analyzing strength and deflections of the DPFs under a variety of conditions, for modeling the physical properties of DPF laminations and composite structures, for understanding the acoustic or other wave absorption / diffusion / reflection characteristics, and for analyzing and optimizing the structure of DPFs in any other physical situation. Fundamental methods and procedures for designing and generating DPF materials include ways for defining the tessellation crease patterns, the folding process, and the three-dimensional folded configuration. The ways are mathematically sound in that they can be extended to a theorem / proof format.
Owner:FOLDSTAR INC
System for knowledge acquisition
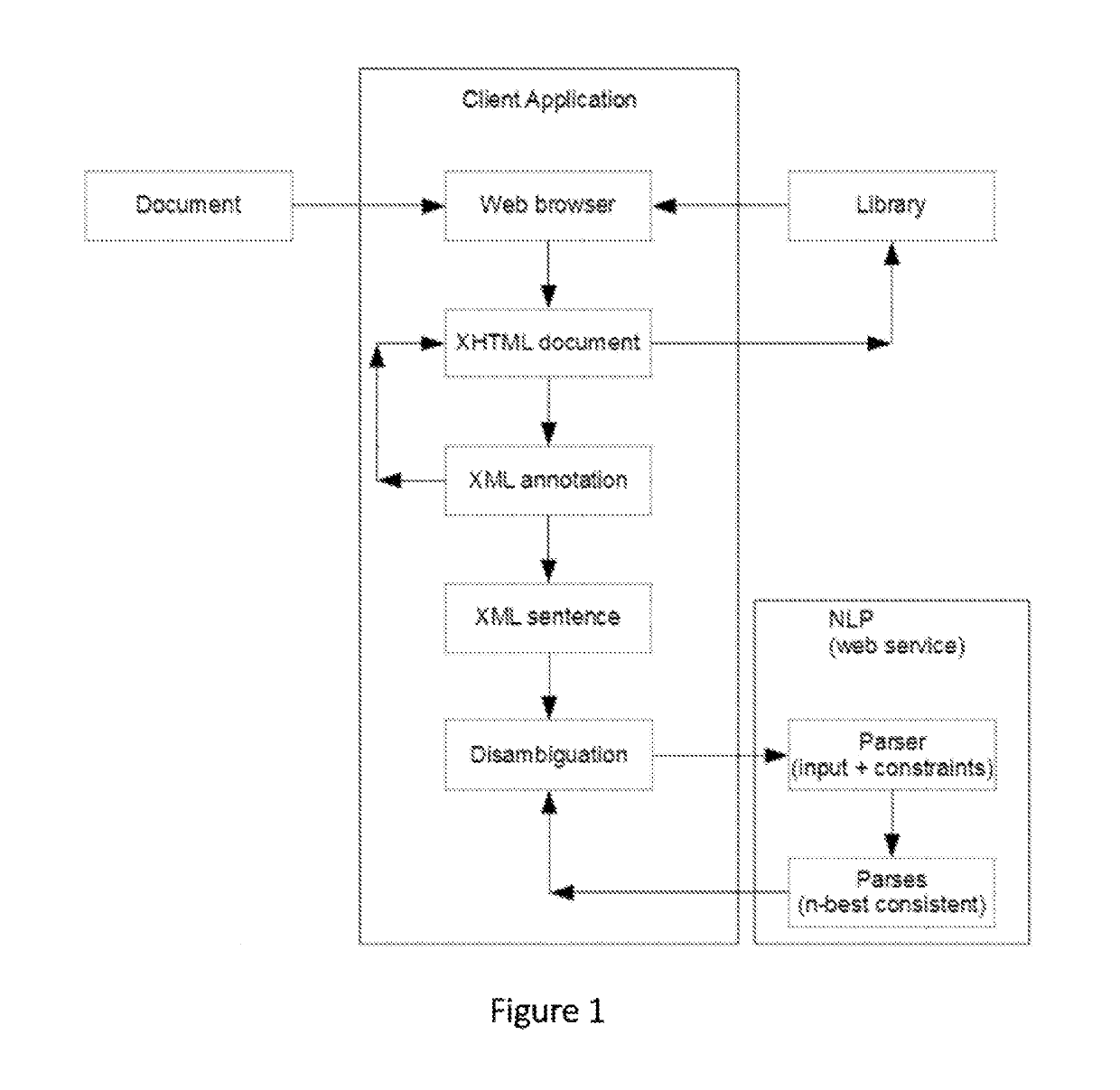
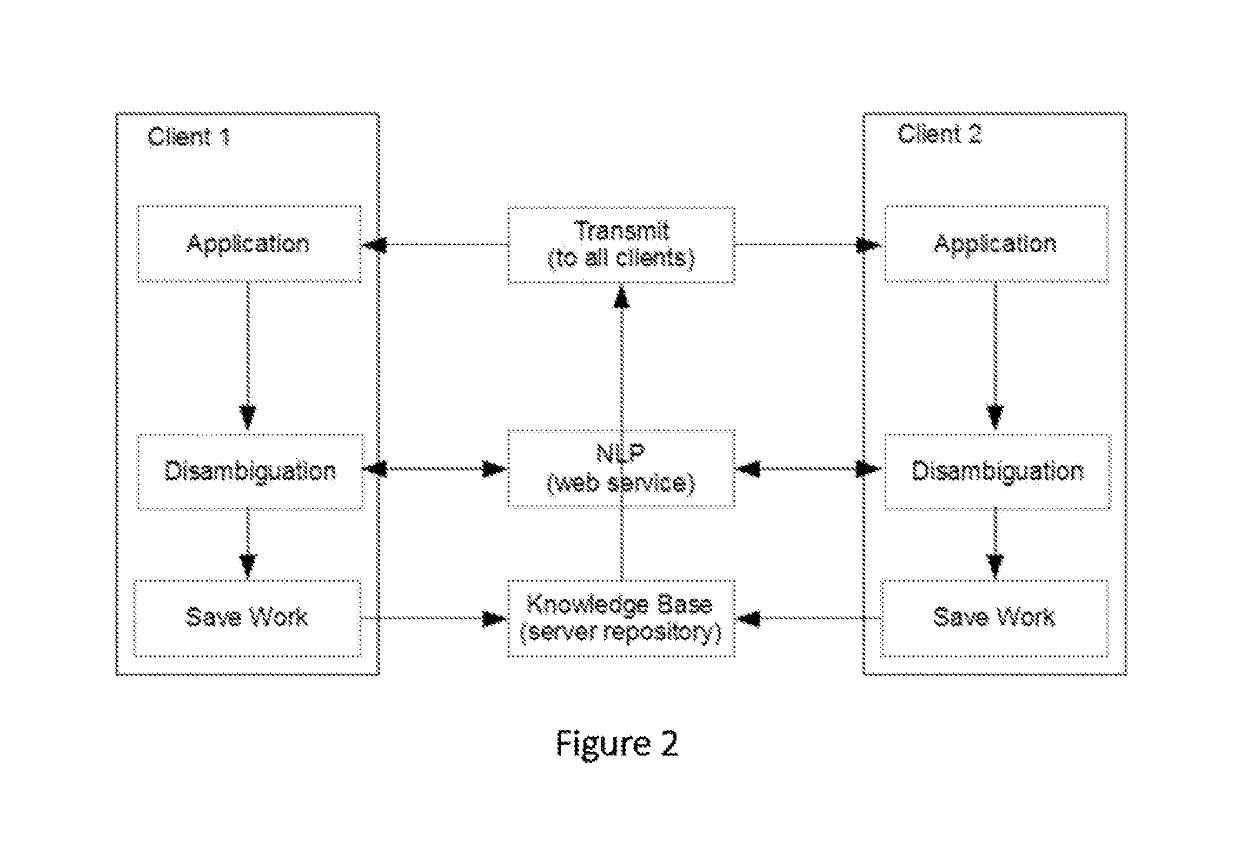
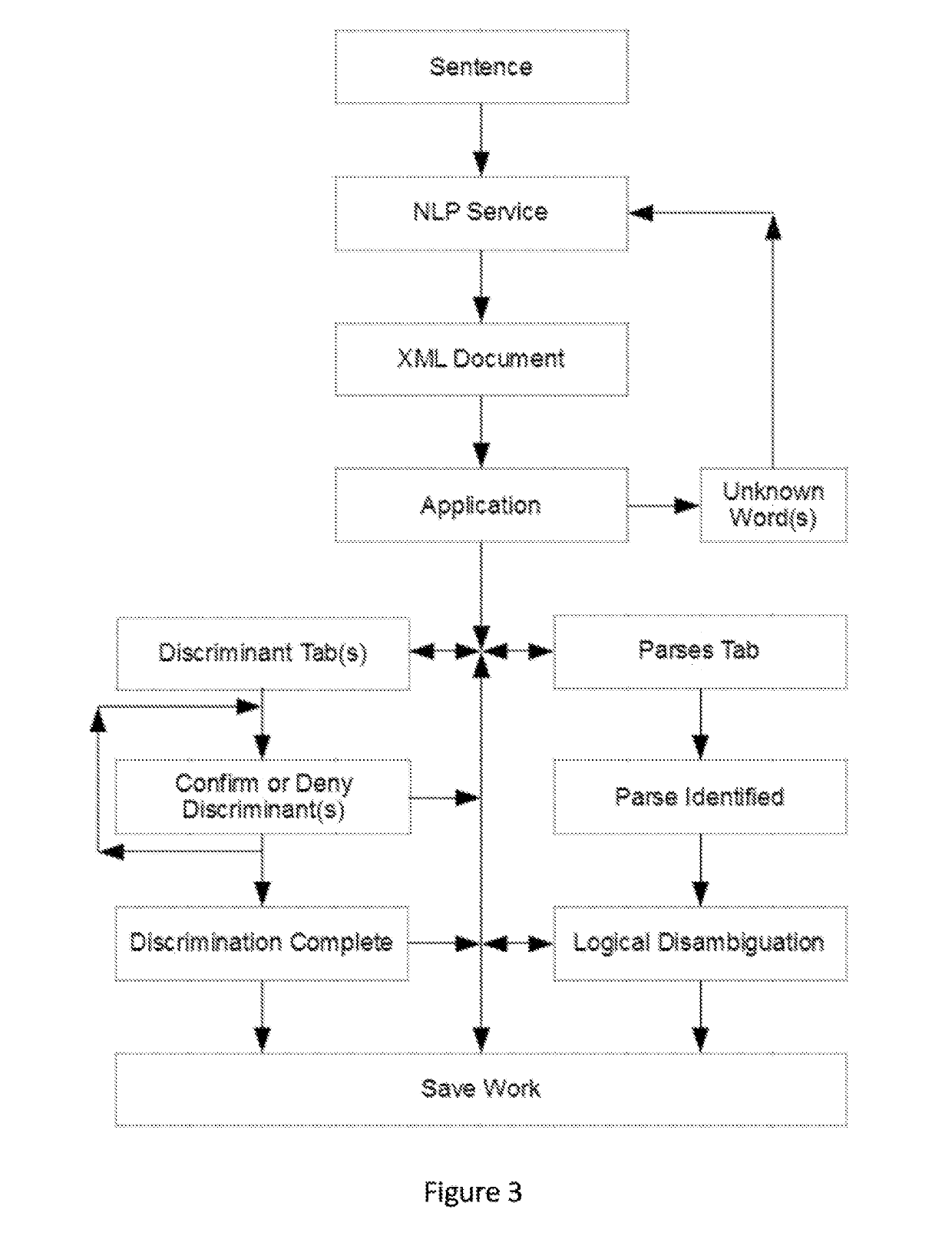
ActiveUS20160085743A1Increasing semanticIncreasing logical precisionNatural language translationSemantic analysisReasoning algorithmAmbiguity
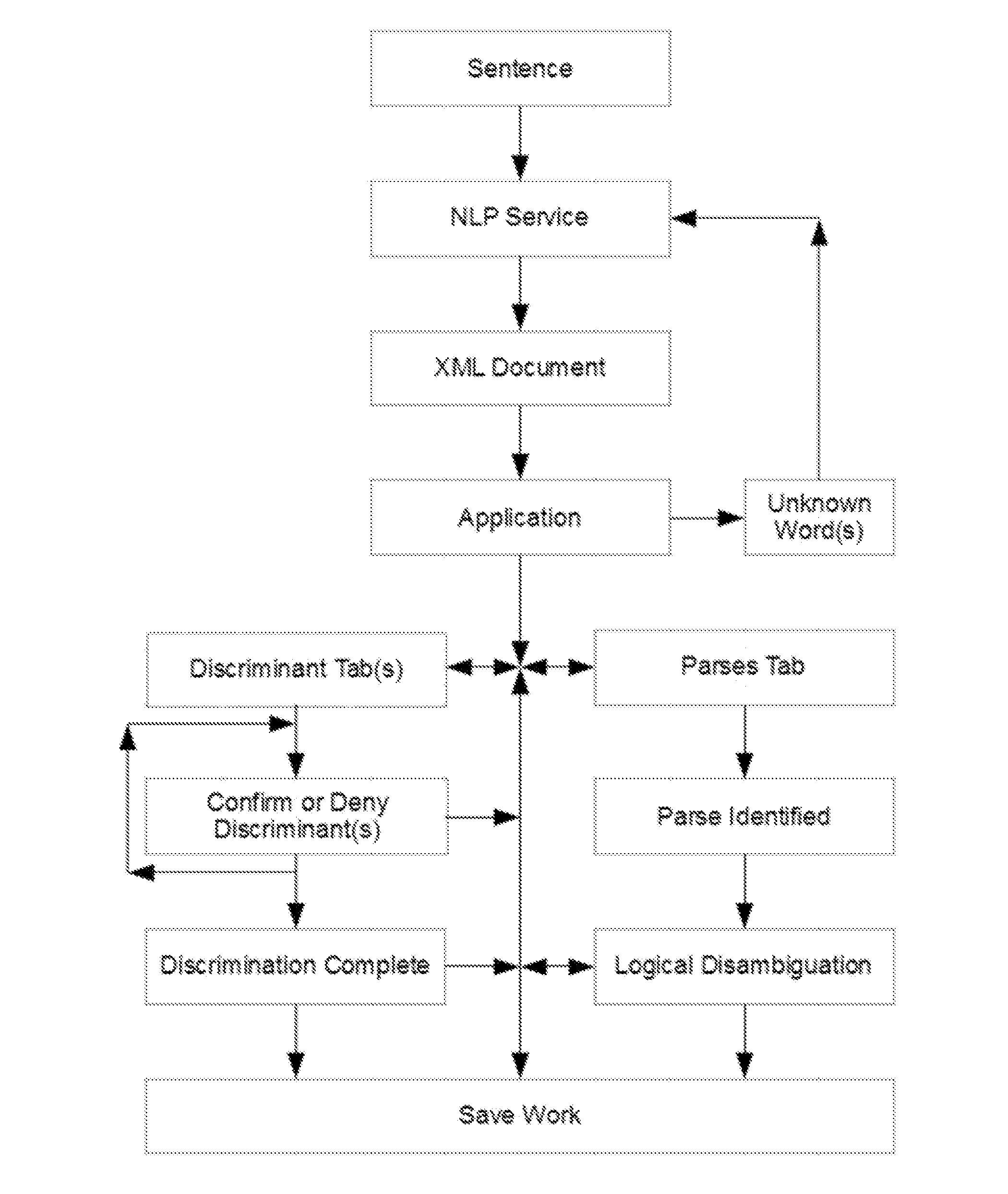
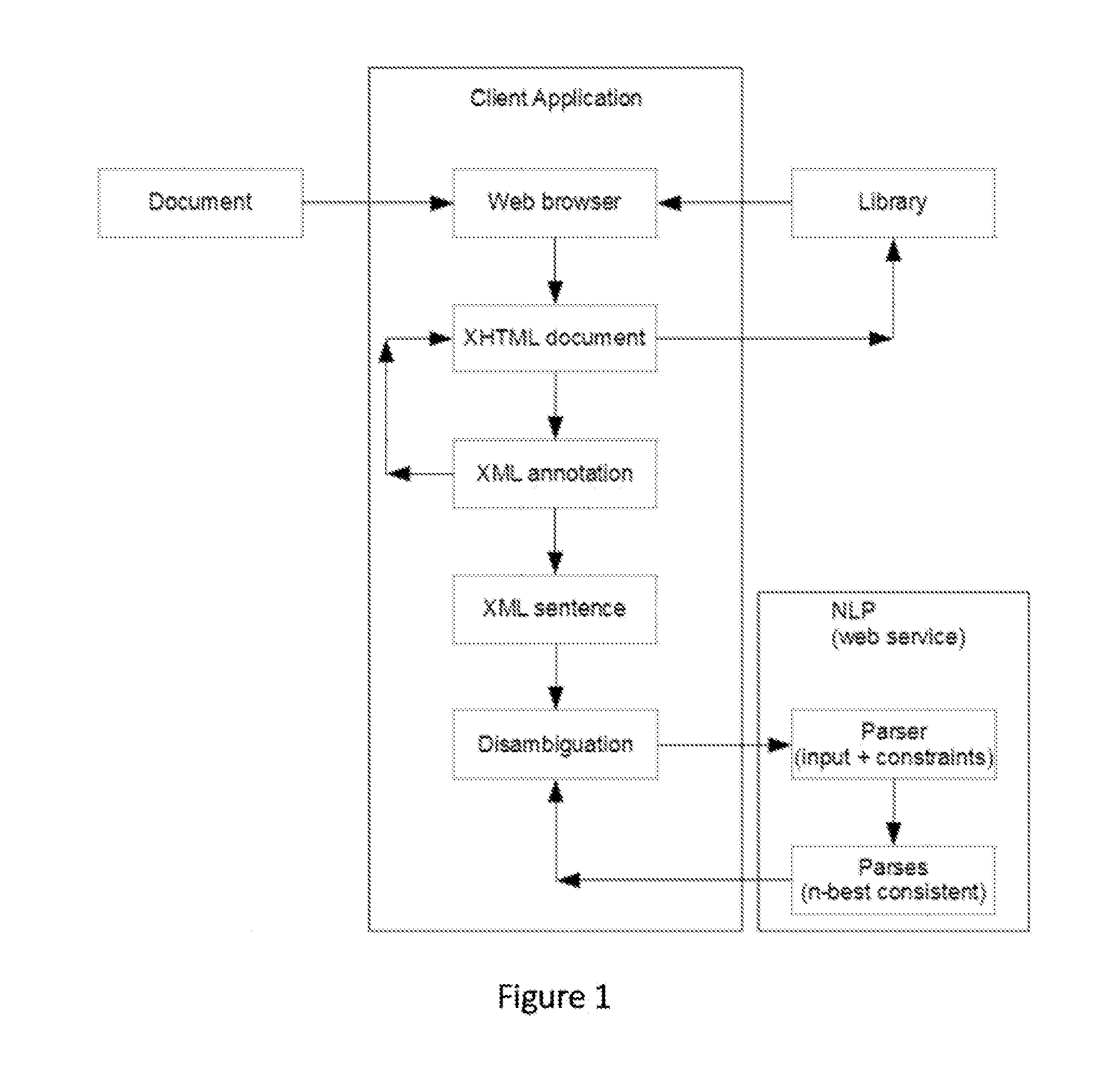
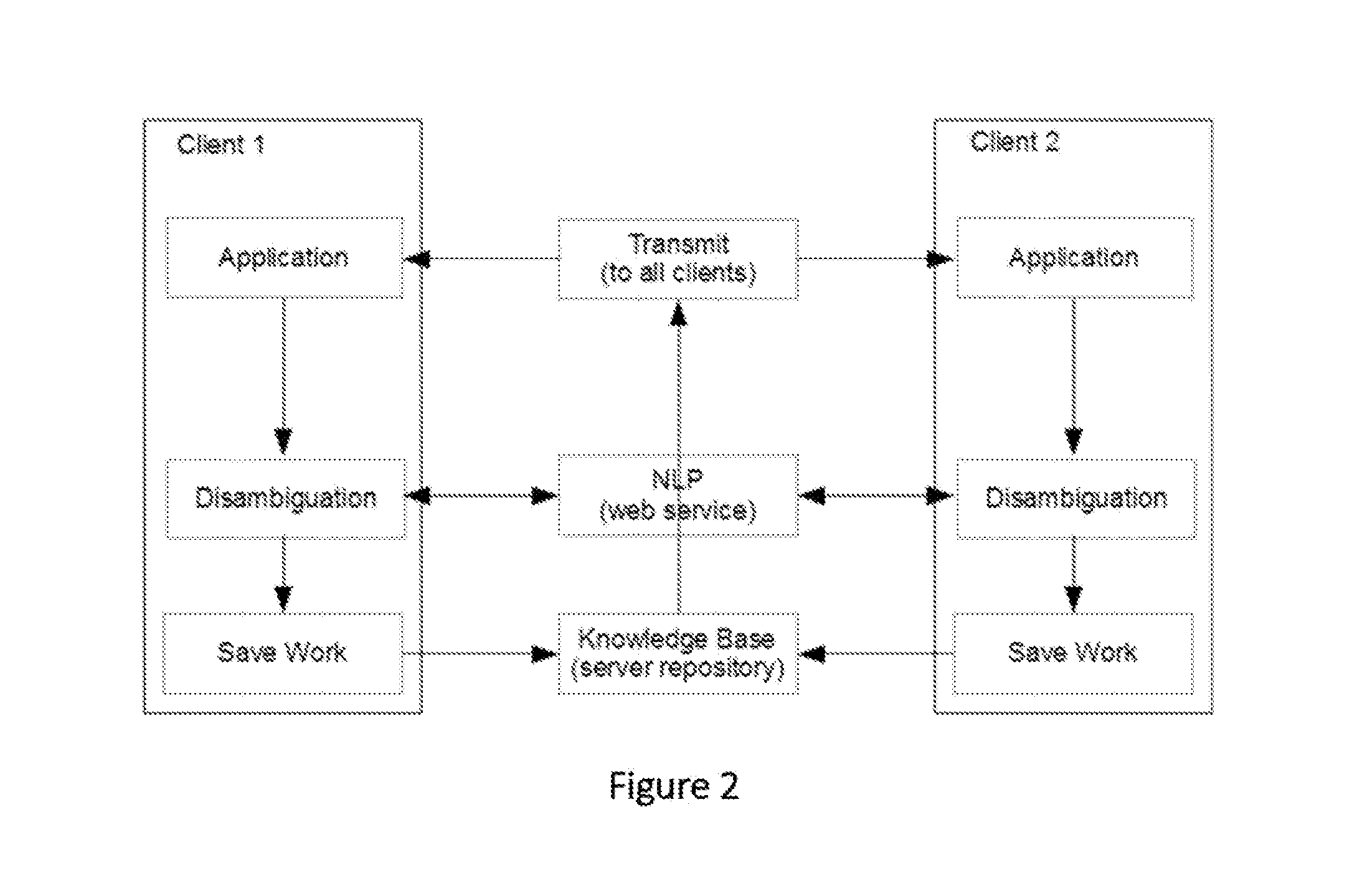
A system and method that translates sentences of natural language text into sets of axioms of formal logic that are consistent with parses resulting from NLP and acquired constraints as they accumulate. The system and method further present these axioms so as to facilitate further disambiguation of such sentences and produces axioms of formal logic suitable for processing by automated reasoning technologies, such as first-order or description logic suitable for processing by various reasoning algorithms, such as logic programs, inference engines, theorem provers, and rule-based systems.
Owner:HALEY PAUL V
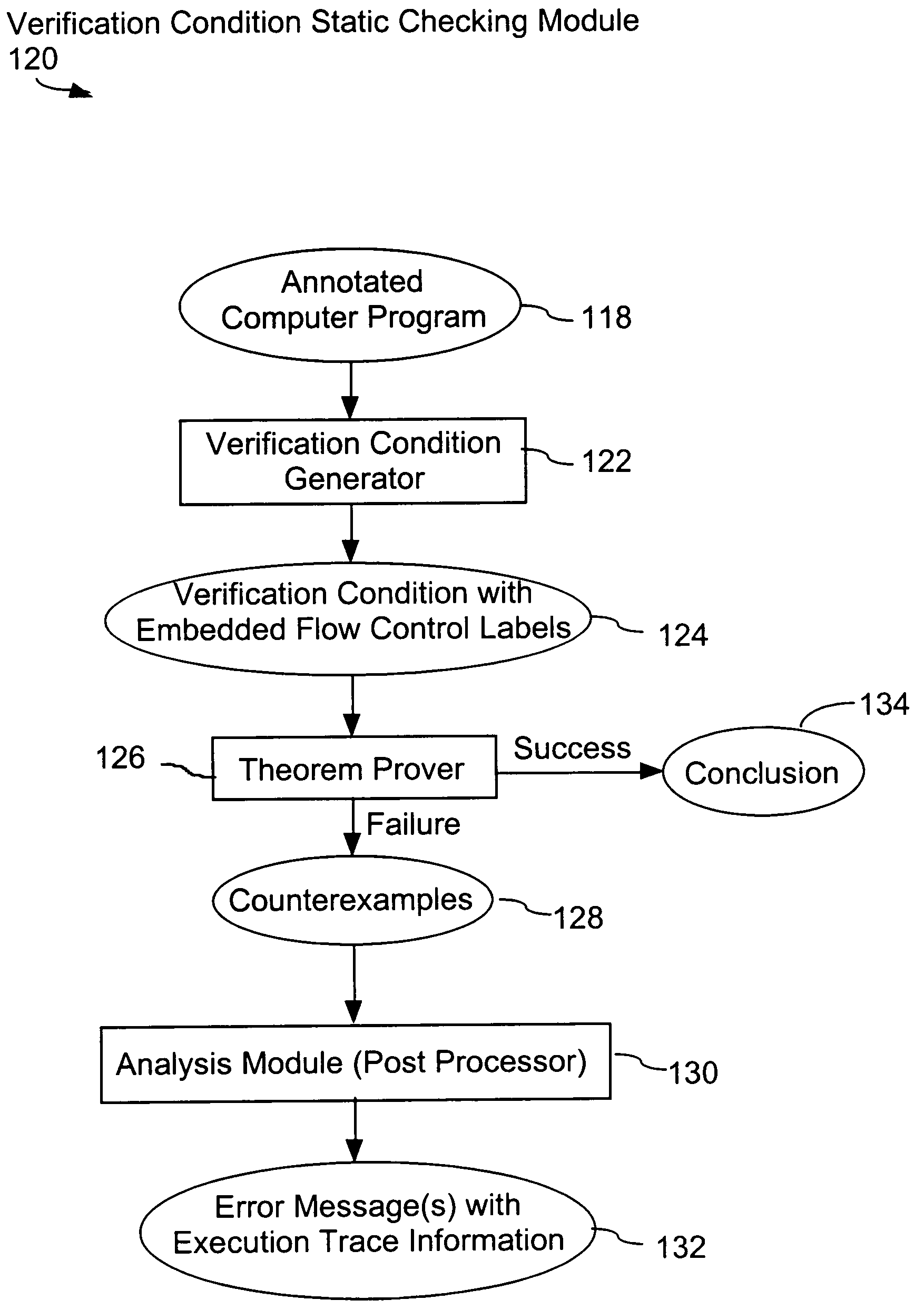
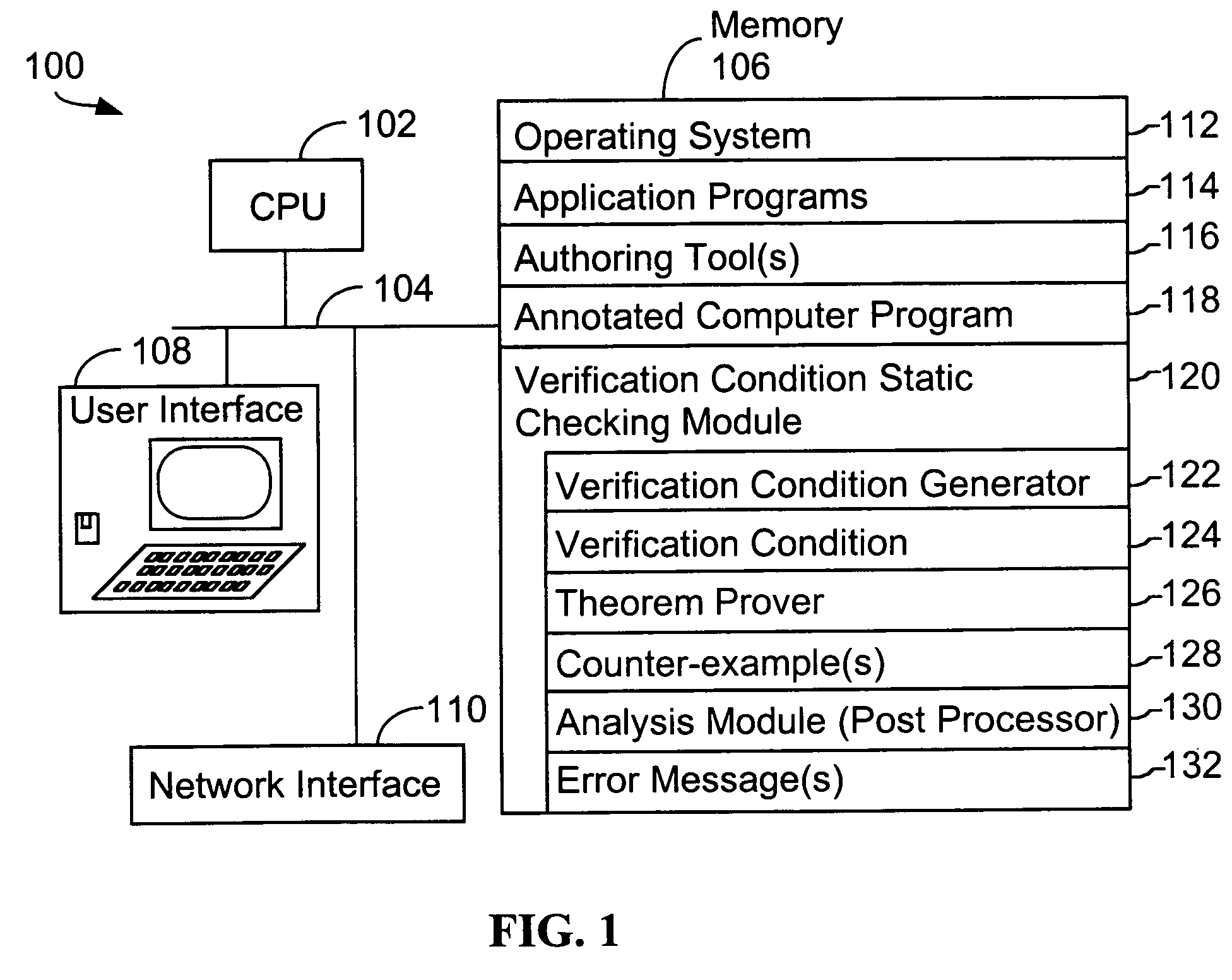
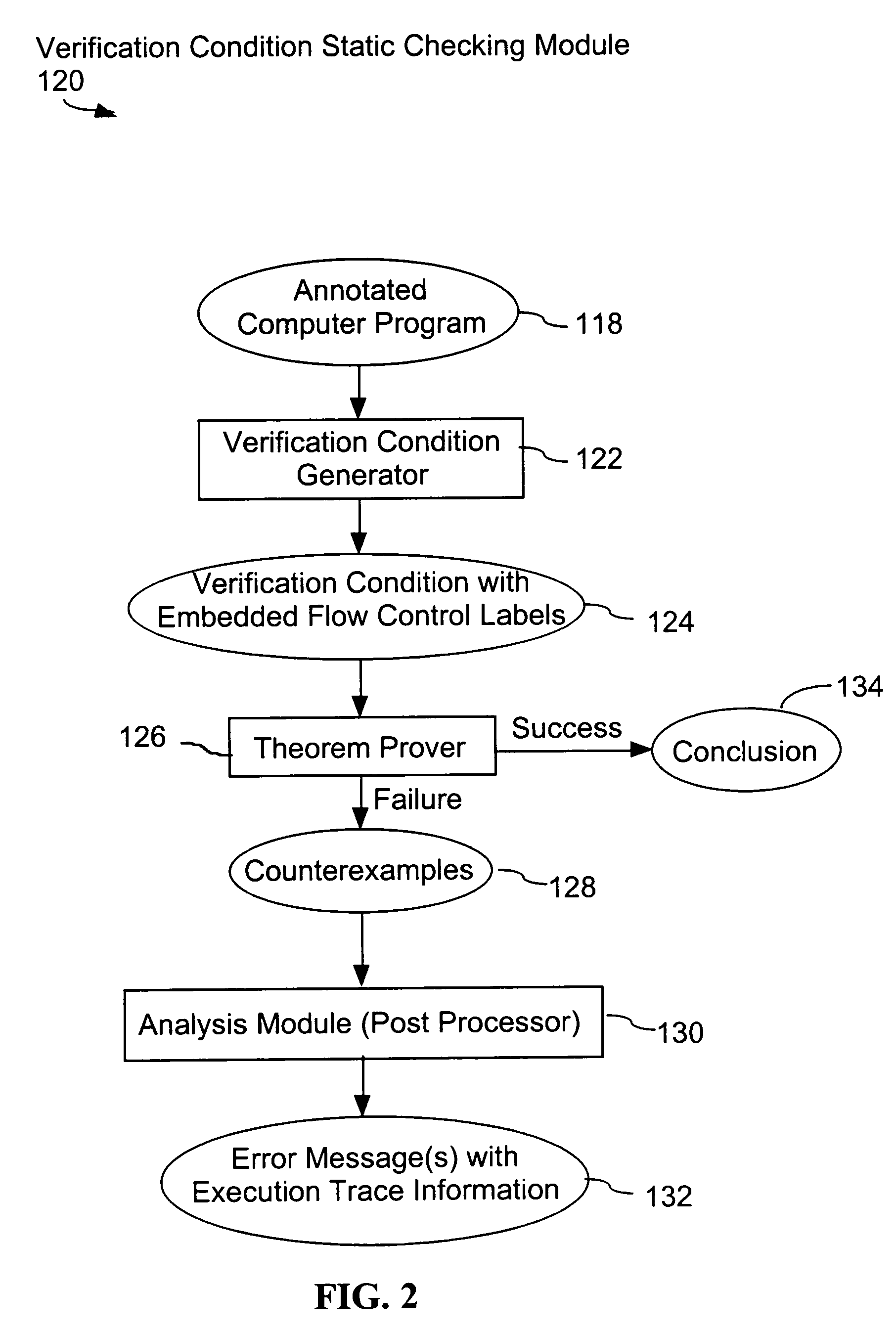
System and method for verifying computer program correctness and providing recoverable execution trace information
In a system for statically analyzing a specified computer, a verification condition generator converts the program into a logical equation, called a verification condition, and inserts program flow control labels into the sub-equations of the verification condition. The flow control labels identify conditional branch points in the specified computer program. A theorem prover is applied to the logical equation to determine truth of the logical equation, and when the truth of the logical equation cannot be proved, the theorem prover generates at least one counter-example identifying one of the conditions, one or more variable values inconsistent with that condition, and any of the flow control labels for conditional branch points of the program associated with the identified variable values. A post processing module converts each counter-example into an error message that includes a program trace when the counter-example identifies one or more of the flow control labels.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
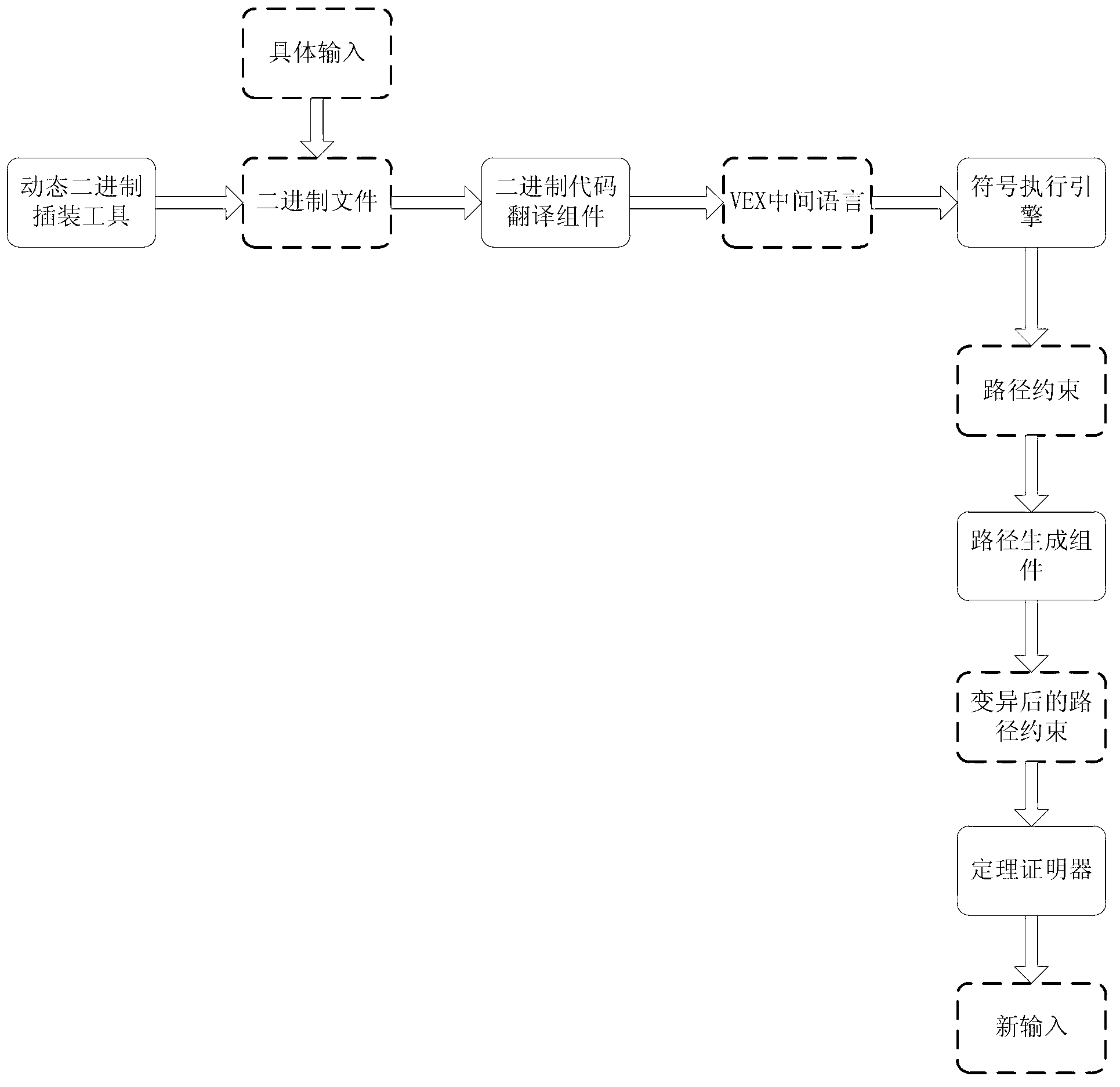
Generation method of dynamic binary code test case
InactiveCN102799529AImprove path coverageSoftware testing/debuggingAlgorithmTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a generation method of a dynamic binary code test case. The generation method comprises the following steps: a dynamic binary insertion tool is achieved to collect the context information including a register, a memory, a thread, system invoking, base loading and the like in the execution process of the binary code, transmitting such information into a binary code translation assembly, converting the information into an intermediate language, carrying out symbol execution on the intermediate language, disseminating symbol input, and collecting a path constraint depending on the input. And then, inputting the path constraint into a path generation assembly, providing a new in-step branch-path mutation algorithm and a strategy, generating new path constraints as much as possible after each symbol execution, using a theorem prover to solve the new path constraint, obtaining the new input satisfying the path constraint, transmitting the new input to the binary code to carry out specific execution for one time, obtaining new path constraints from the new execution in continuously circular manner, generating new inputs, and improving the cover ratio of the binary code.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
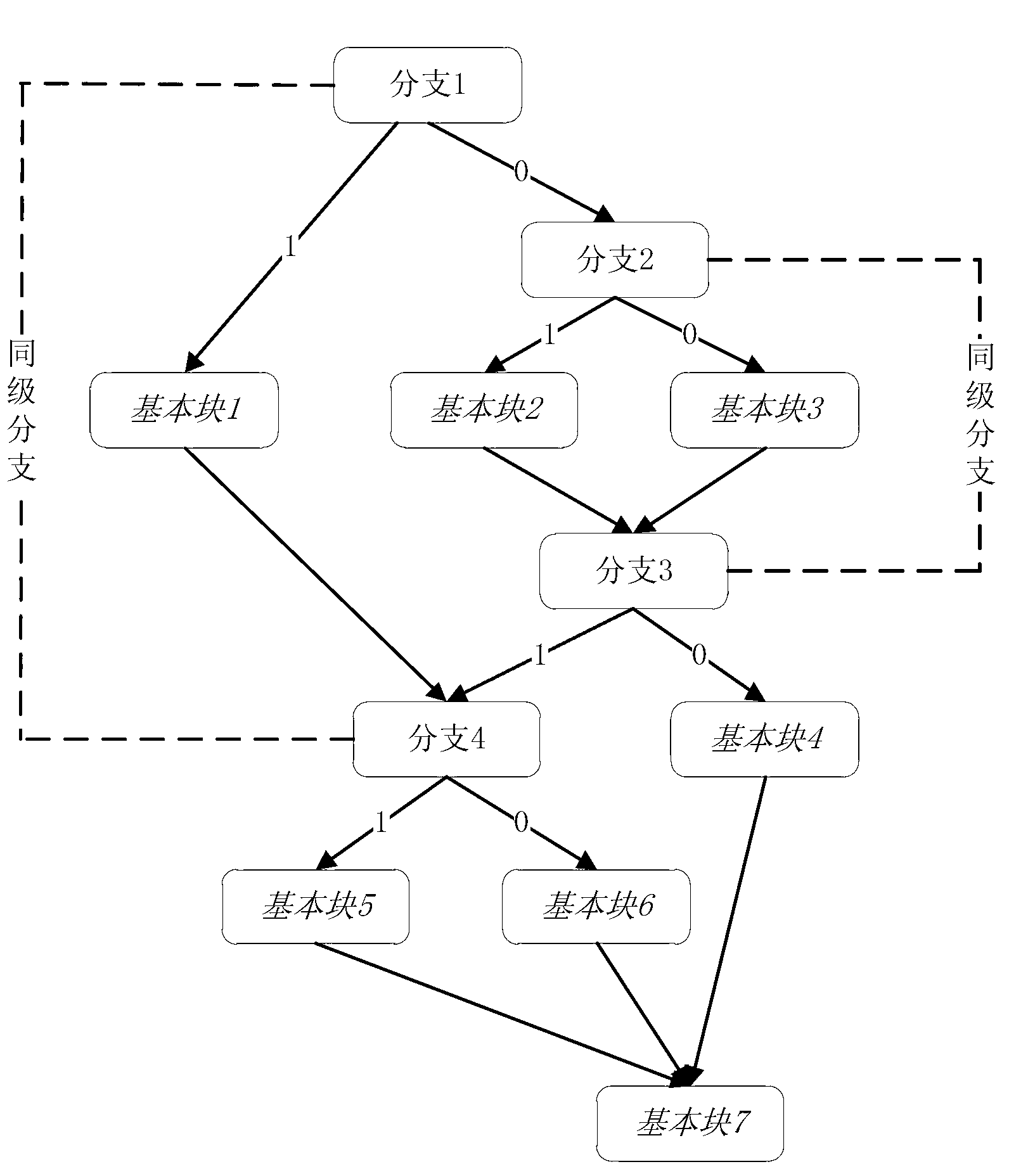
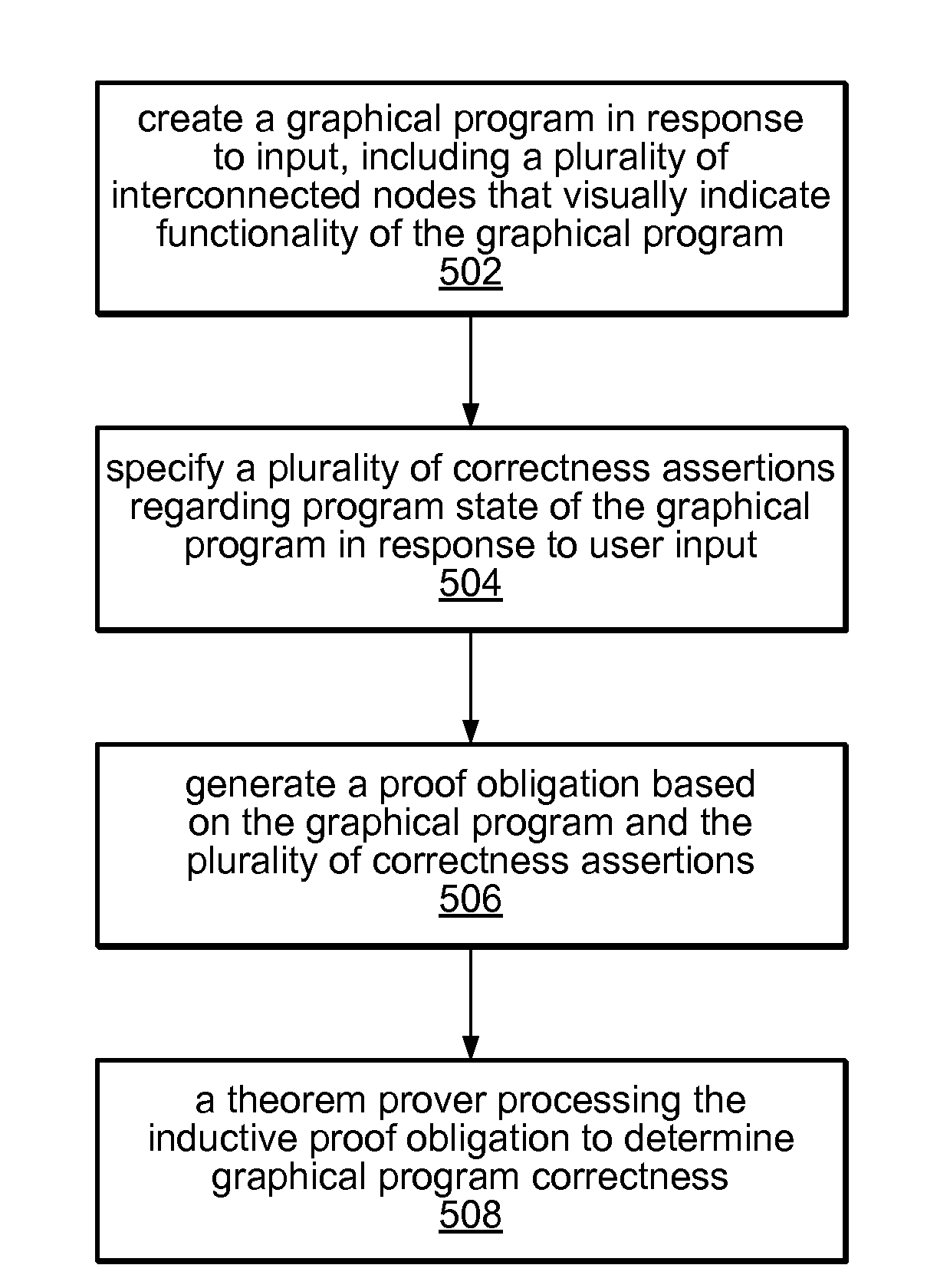
Formal Verification of Graphical Programs
InactiveUS20090064111A1Error detection/correctionVisual/graphical programmingObject levelHuman language
System and method for formal verification of a graphical program. A graphical program comprising a plurality of interconnected nodes is created in response to input. One or more correctness assertions regarding program state of the graphical program are specified in response to user input, and a proof obligation generated based on the graphical program and the correctness assertions, which is usable by a theorem prover to determine correctness of the graphical program. The proof obligation may be generated by compiling the graphical program to generate an object-level diagram, parsing the correctness assertions to generate an intermediate logical form of the one or more correctness assertions, and analyzing the object-level diagram, the intermediate logical form, and / or semantics of the graphical programming language in which the graphical program is written to generate the proof obligation. A theorem prover may then process the proof obligation to determine whether the graphical program is correct.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
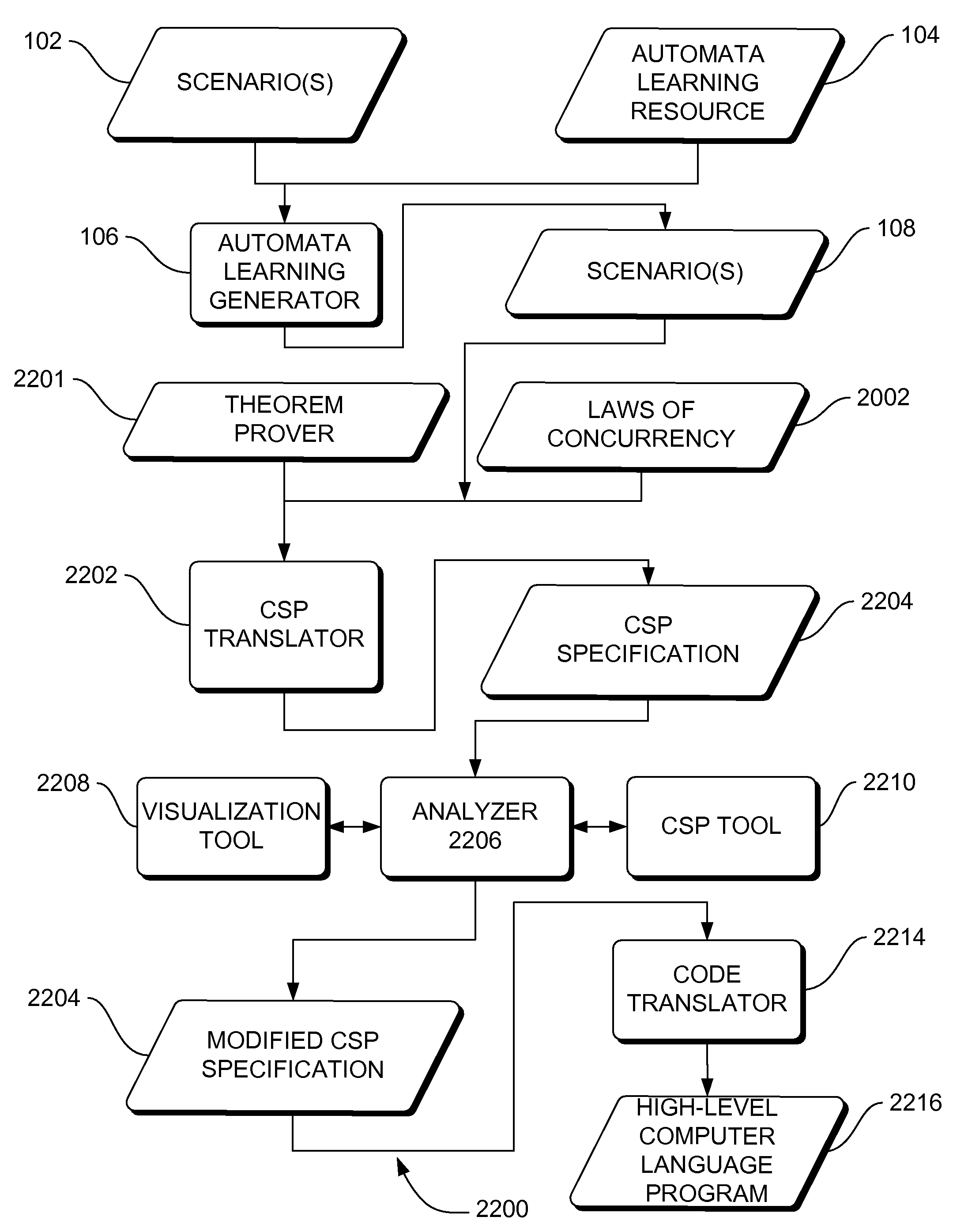
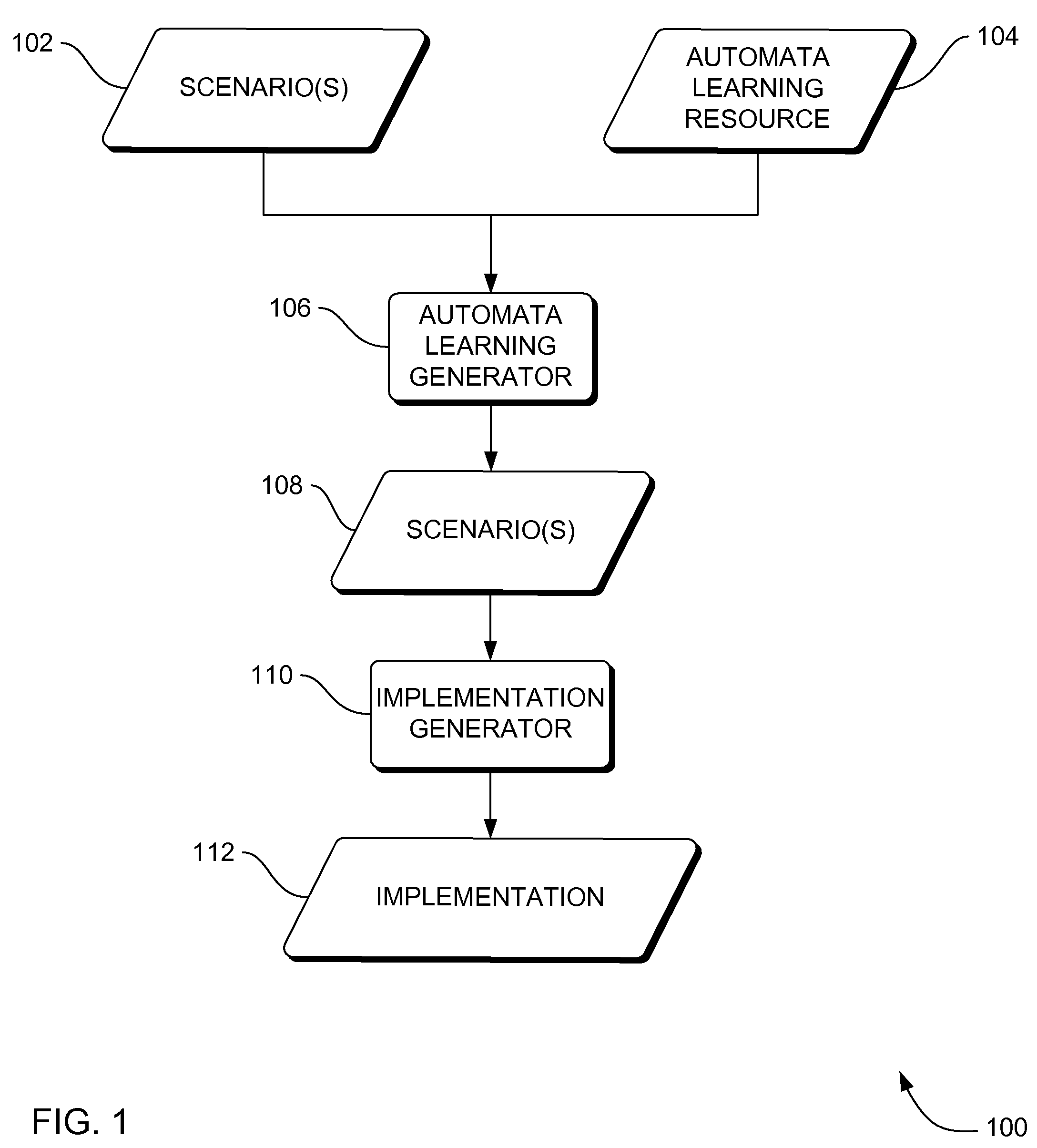
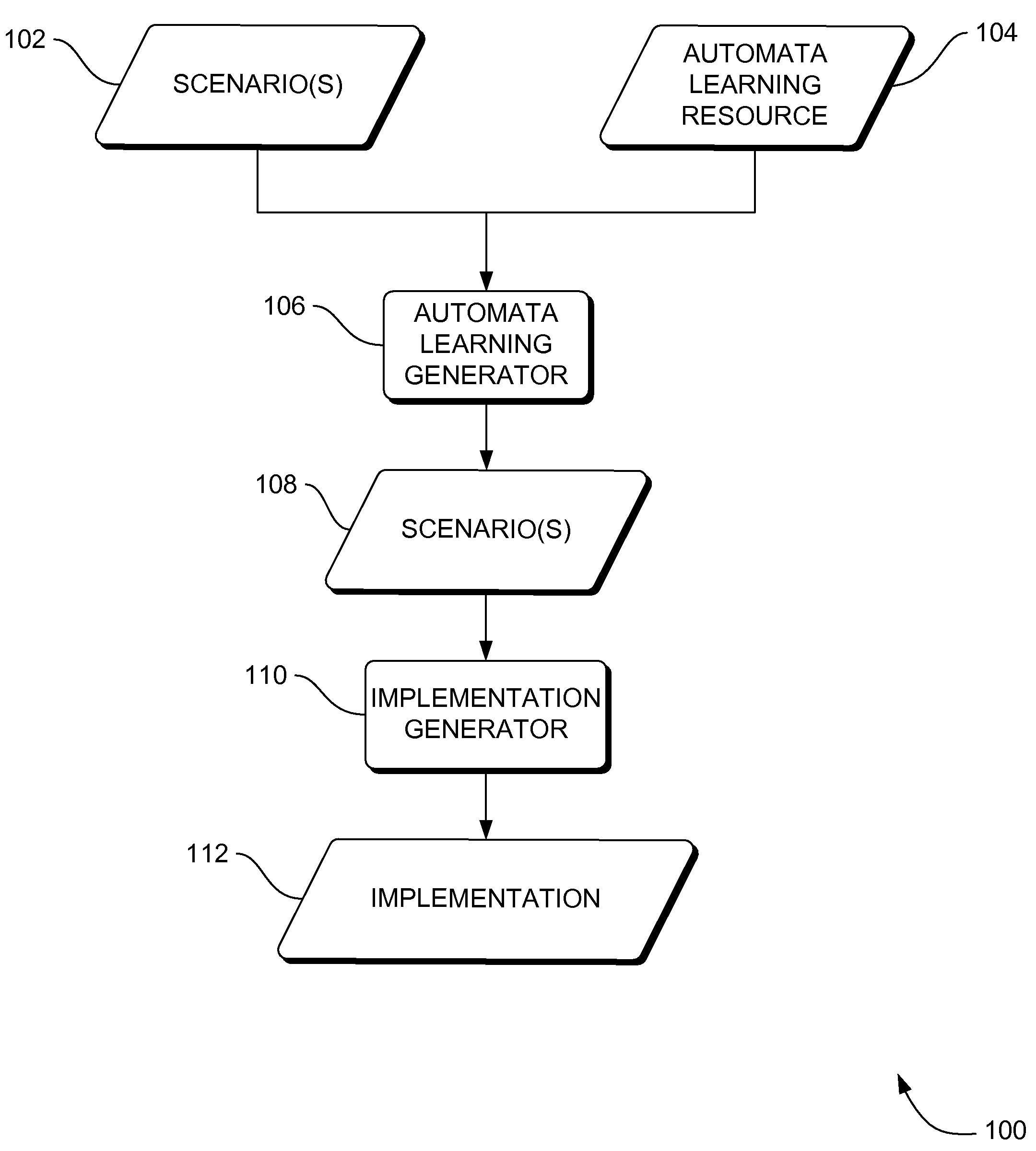
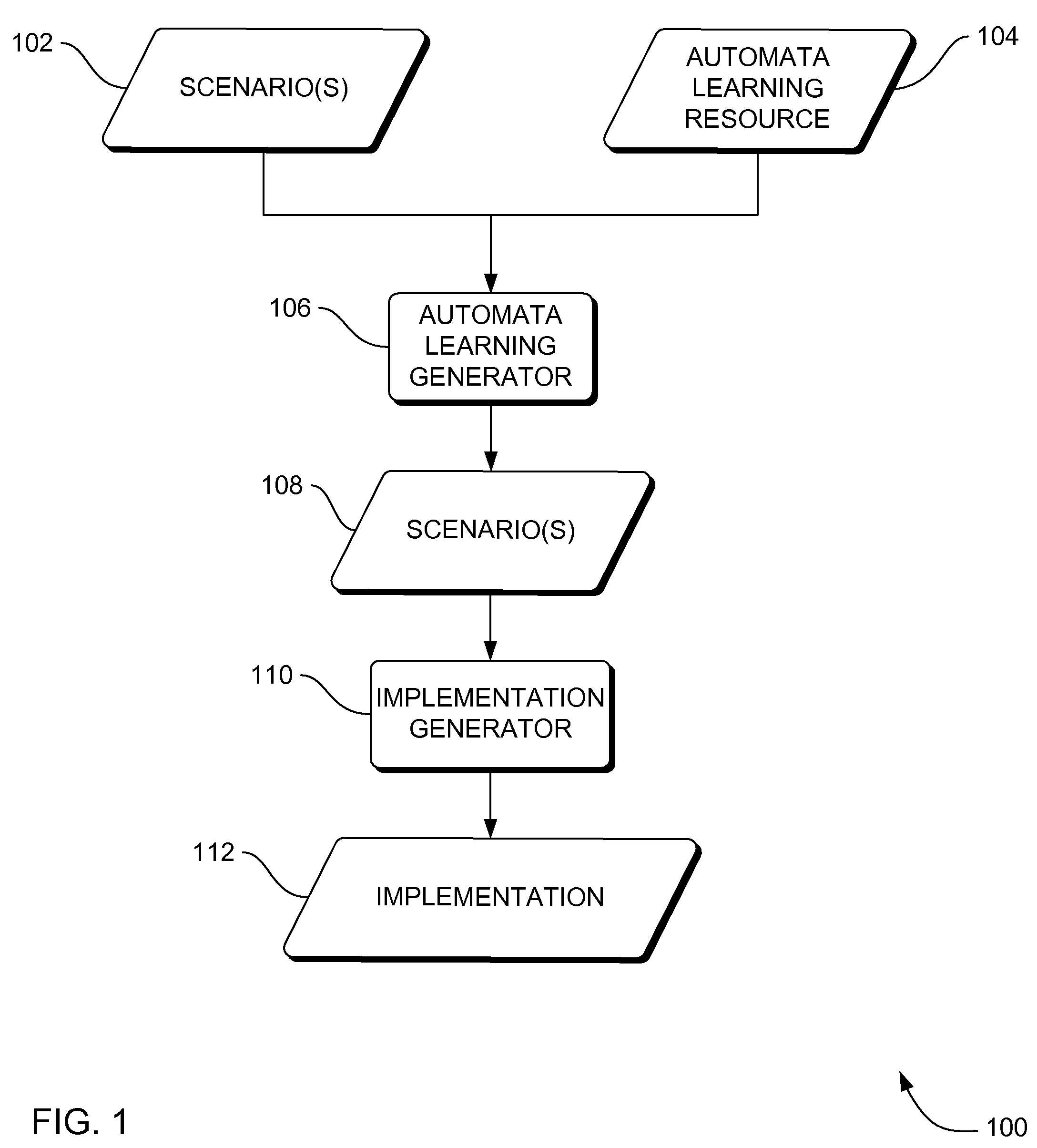
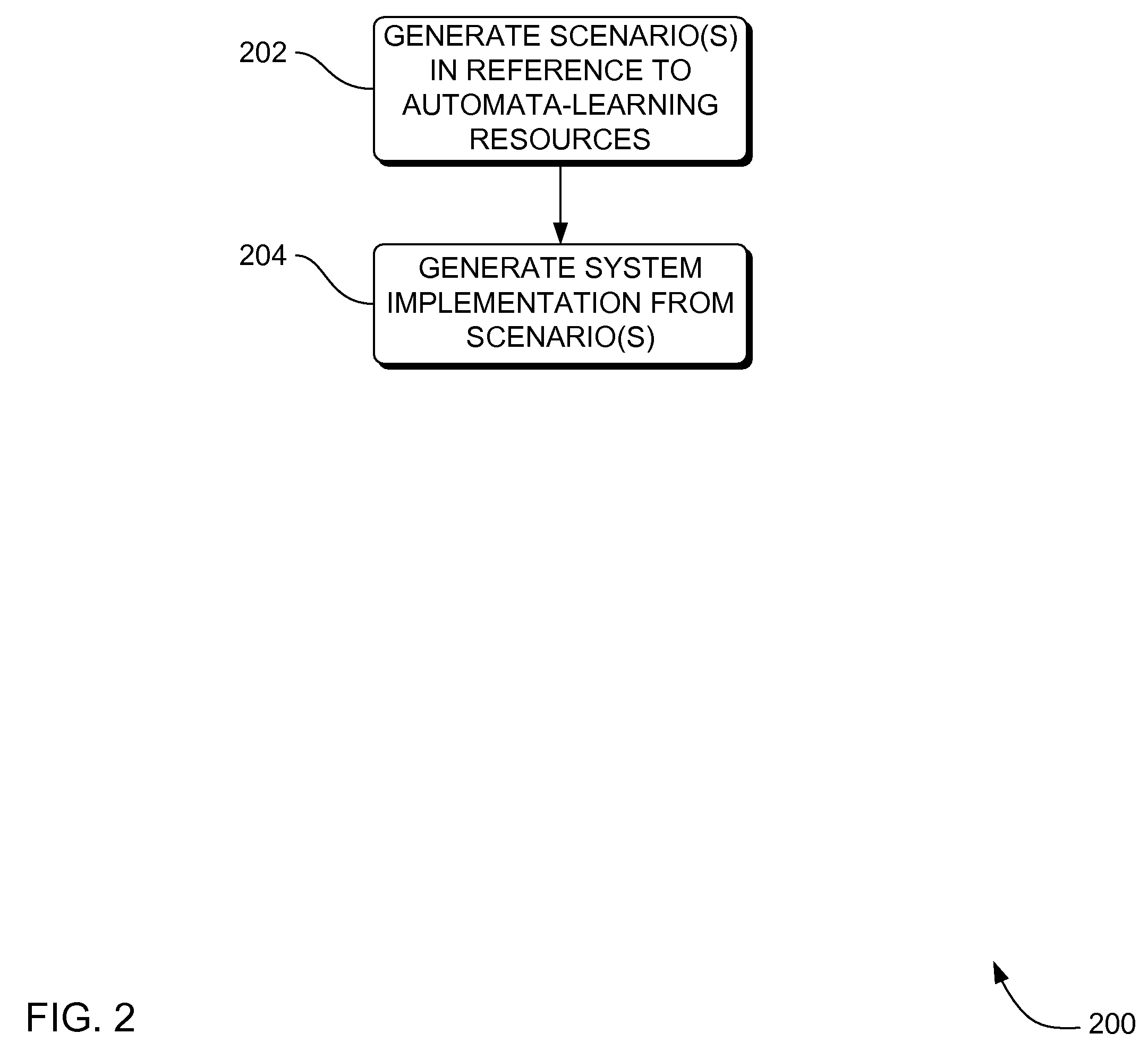
Systems, methods and apparatus for automata learning in generation of scenario-based requirements in system development
InactiveUS20070162410A1Reduce partialityKnowledge representationInference methodsAutomata learningSystem development
Systems, methods and apparatus are provided through which in some embodiments, automata learning algorithms and techniques are implemented to generate a more complete set of scenarios for requirements based programming. More specifically, a CSP-based, syntax-oriented model construction, which requires the support of a theorem prover, is complemented by model extrapolation, via automata learning. This may support the systematic completion of the requirements, the nature of the requirement being partial, which provides focus on the most prominent scenarios. This may generalize requirement skeletons by extrapolation and may indicate by way of automatically generated traces where the requirement specification is too loose and additional information is required.
Owner:STEFFEN BERNARD +4
Patterning technology for folded sheet structures
Owner:FOLDED STRUCTURES COMPANY
Automata learning algorithms and processes for providing more complete systems requirements specification by scenario generation, CSP-based syntax-oriented model construction, and R2D2C system requirements transformation
InactiveUS7668796B2Reduce partialityKnowledge representationInference methodsAutomata learningSystem requirements
Systems, methods and apparatus are provided through which in some embodiments, automata learning algorithms and techniques are implemented to generate a more complete set of scenarios for requirements based programming. More specifically, a CSP-based, syntax-oriented model construction, which requires the support of a theorem prover, is complemented by model extrapolation, via automata learning. This may support the systematic completion of the requirements, the nature of the requirement being partial, which provides focus on the most prominent scenarios. This may generalize requirement skeletons by extrapolation and may indicate by way of automatically generated traces where the requirement specification is too loose and additional information is required.
Owner:STEFFEN BERNARD +4
CPS (Cyber Physical Systems) adaptability verification method based on Hybrid UML (Unified Modeling Language) and theorem proving
InactiveCN102426521AReduce difficultyReduce development riskSpecific program execution arrangementsValidation methodsSemantics
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
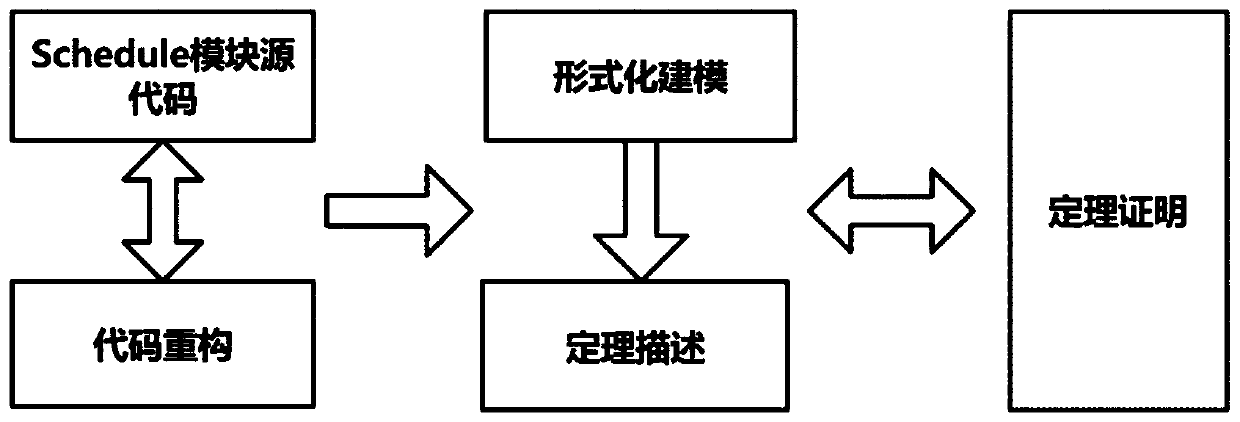
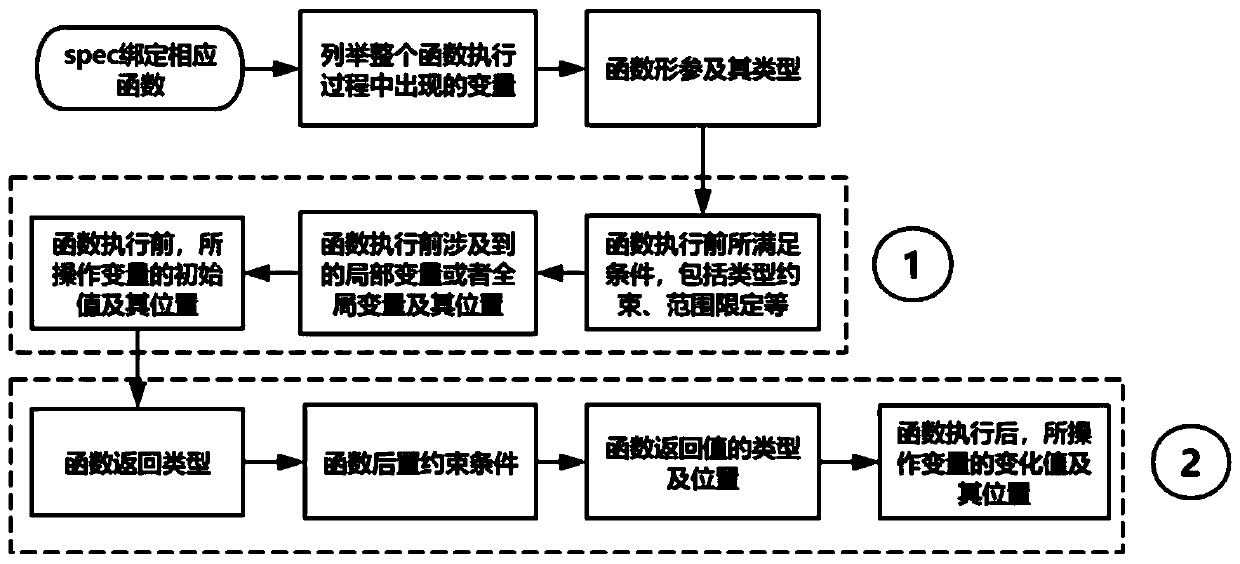
Theorem proving-based formal verification method
InactiveCN110989997AVerified conclusions are credibleProgramming languages/paradigmsOperational systemValidation methods
The invention discloses a theorem proving-based formal verification method. The method is applied to the field of secure operating systems. The invention aims to solve the security problem of an existing operating system. The theorem proving-based formal verification method comprises the following steps that: source codes are reconstructed; formal modeling is conducted on a function; theorem description is conducted on the function; and finally, formal certification is conducted. According to the method of the invention, the semi-automatic proving of human-computer interaction is adopted; by means of an isomorphic relationship between a type system and logic, a proof constructing process is converted into a program writing process; proof correctness check is changed into a type check problem; although a large amount of manual labor is needed to construct the proof, the method provided by the invention does not need to sacrifice the expression ability of protocols and codes, particularly logic with very strong expression ability can be used in a program to realize representation; the proof itself has display representation in a machine; the correctness of the proof itself can be automatically checked; and a verified conclusion is more credible.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
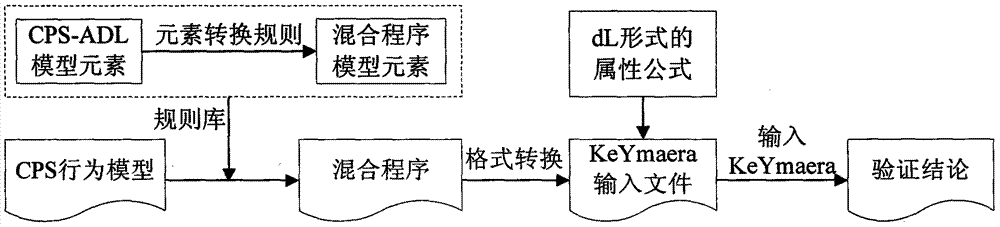
CPS (cyber physical system) modeling and verifying method based on conversion from CPS-ADL (architecture description language) model into hybrid program
InactiveCN103699743AImplement the rules for conversionSpecial data processing applicationsArchitecture description languageValidation methods
The invention discloses a CPS (cyber physical system) modeling and verifying method based on conversion from a CPS-ADL (architecture description language) model into a hybrid program. The method is mainly used for modeling a CPS and verifying attributes. The method is characterized in that a CPS is modeled on a CPS-ADL platform by the aid of an E-HYSDEL (expanded-hybrid system description language); a formalized definition HPM (hybrid program model) of an HP (hybrid program) model is given, and conversion rules among the CPS-ADL model elements and HP model elements are established when model conversion consistency is met; model description codes of a specific CPS are automatically converted into the hybrid program based on the conversion rules; input files of a KeYmaera are generated by the aid of the hybrid program and a dynamic differential logic description system attribute formula according to an input format of the KeYmaera of a theorem prover; the input files are opened in the KeYmaera to perform reasoning and verifying. The method and the mechanism based on conversion from the CPS-ADL model into the HP are elaborated, and the rules of conversion from the CPS-ADL model elements into the HP model elements are realized.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Local sensitive program analysis method based on abstract syntax tree and theorem proof
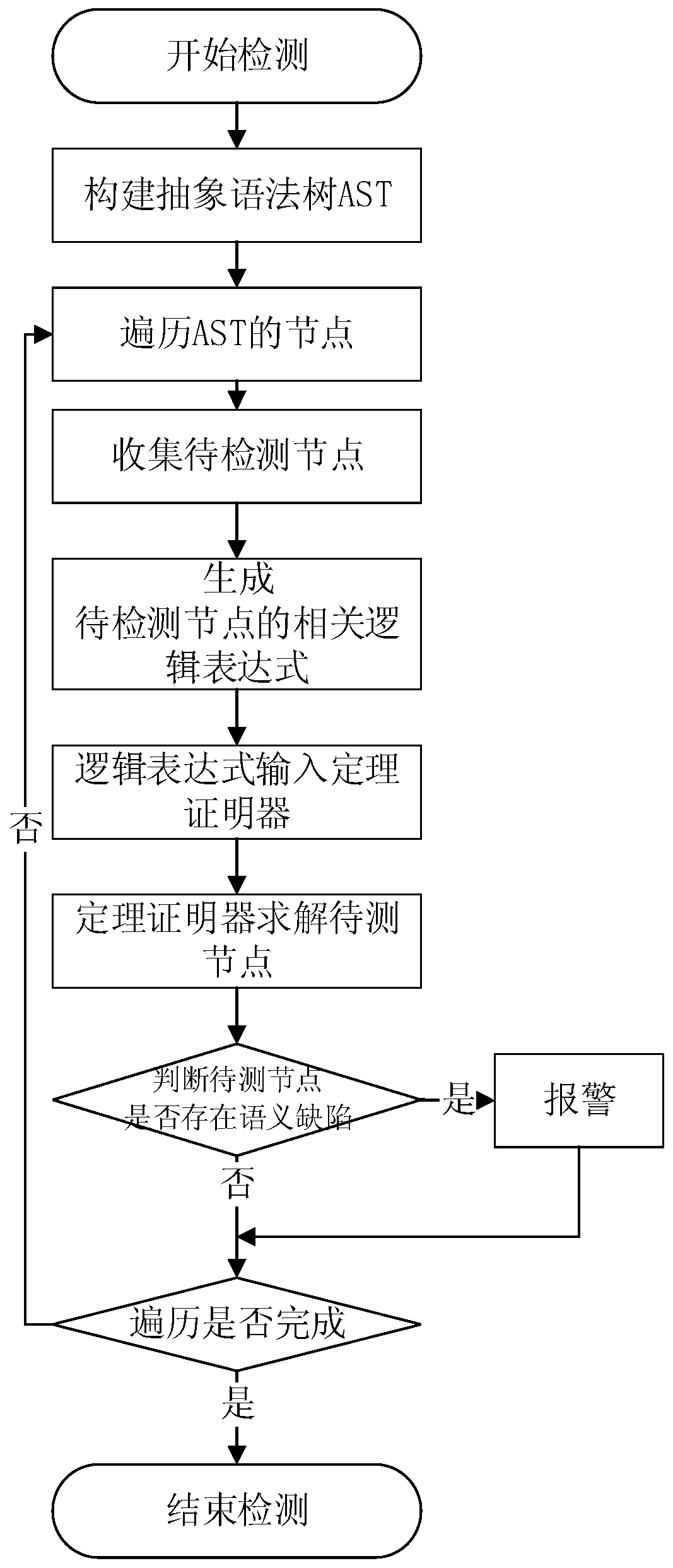
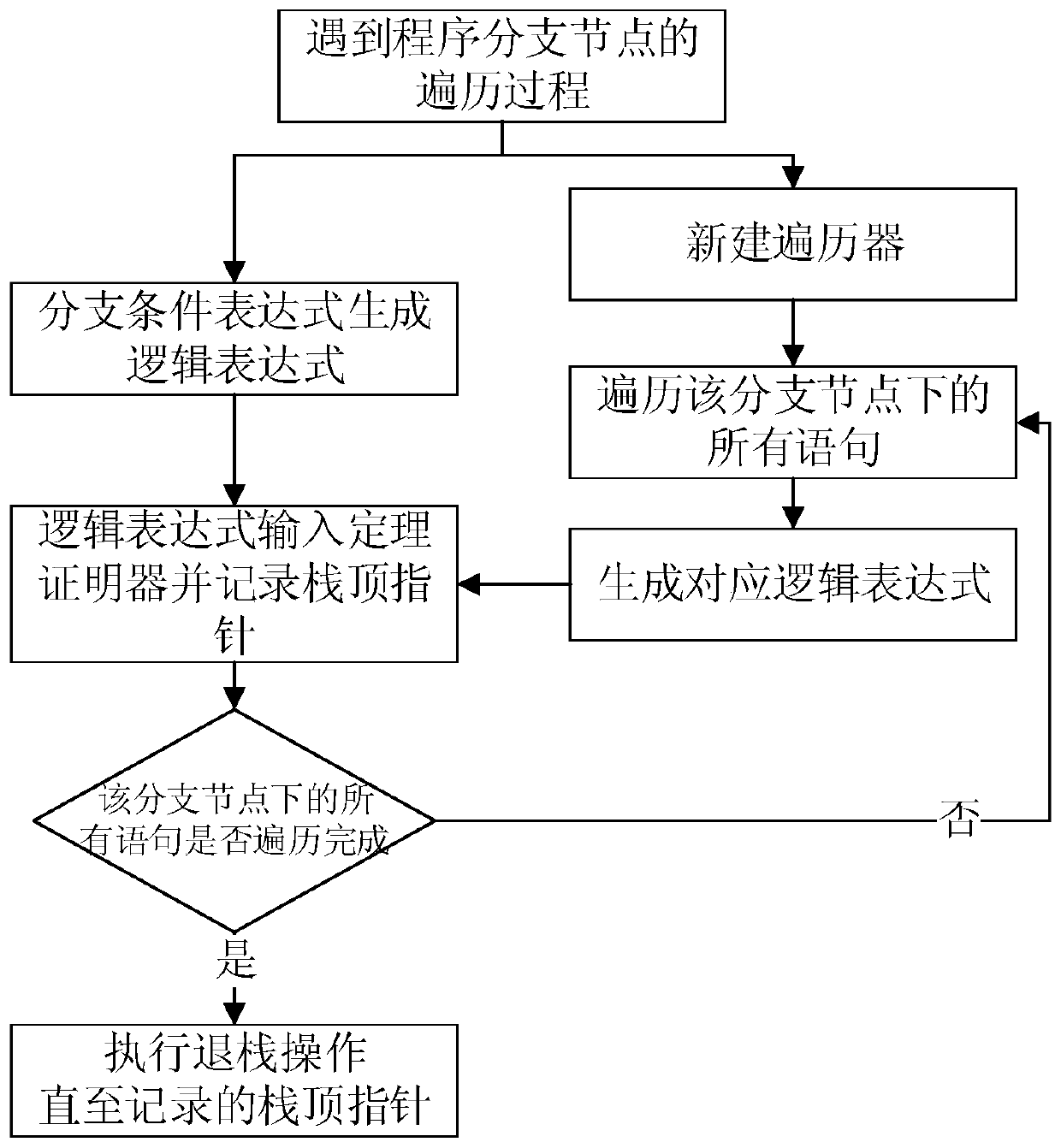
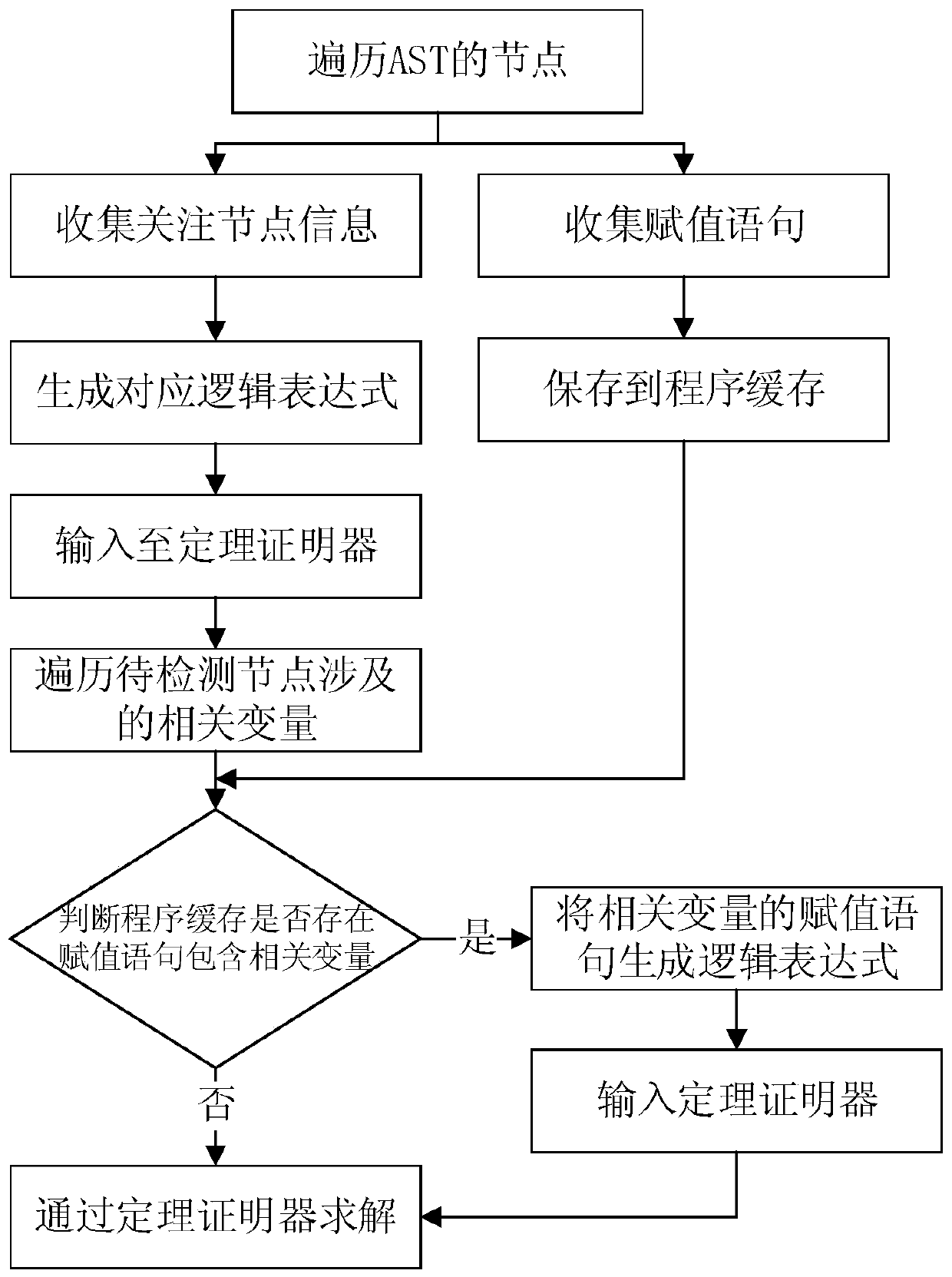
ActiveCN110879708ARealize detectionAvoid inefficiencyPlatform integrity maintainanceEnergy efficient computingPathPingSyntax error
The invention discloses a local sensitive program analysis method based on an abstract syntax tree and theorem proof. The local sensitive program analysis method comprises the steps of constructing the abstract syntax tree AST without syntax errors for program codes; traversing an abstract syntax tree AST of the program code, collecting a to-be-detected node and related nodes of the to-be-detectednode, forming a related logic expression of the to-be-detected node according to the to-be-detected node and related node information, and inputting the related logic expression into a theorem prover; and the theorem prover solves the to-be-detected node through the logic expression, and if an abnormal condition exists in the solved to-be-detected node value, judging that the program has a semantic defect. According to the method, by collecting the local context and the local path information of the program node, some wrong alarms are avoided, the usability is improved, semantic defect detection of the program code is achieved, and the problem that a traditional symbolic execution tool is long in time consumption for analyzing the code due to path explosion is solved.
Owner:安徽中科国创高可信软件有限公司
Automated verification of a type-safe operating system
InactiveUS8341602B2Verifies the safety of the kernel and applicationsSafety and correctness of the NucleusTransmissionSpecific program execution arrangementsOperational systemAutomated theorem provers
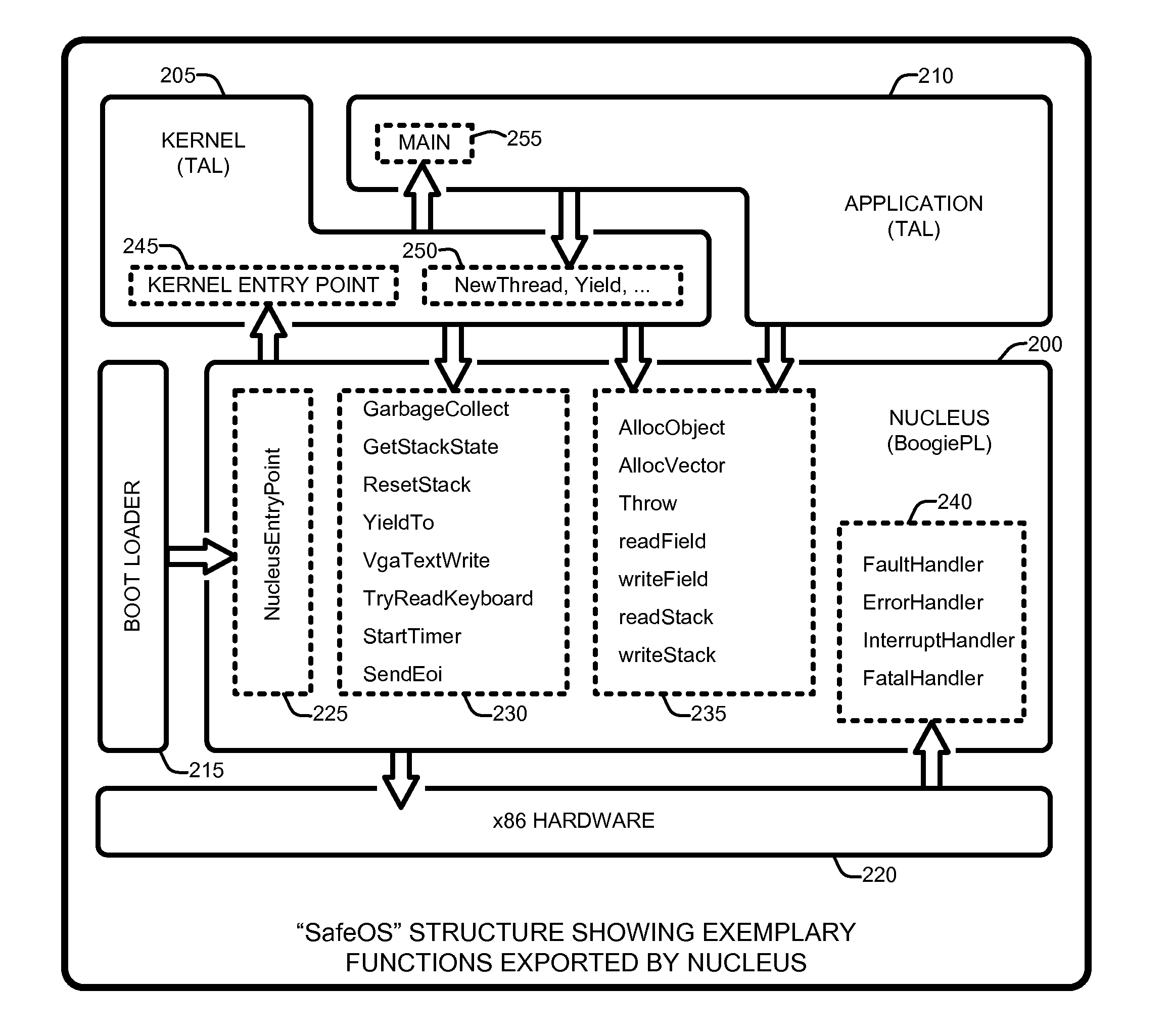
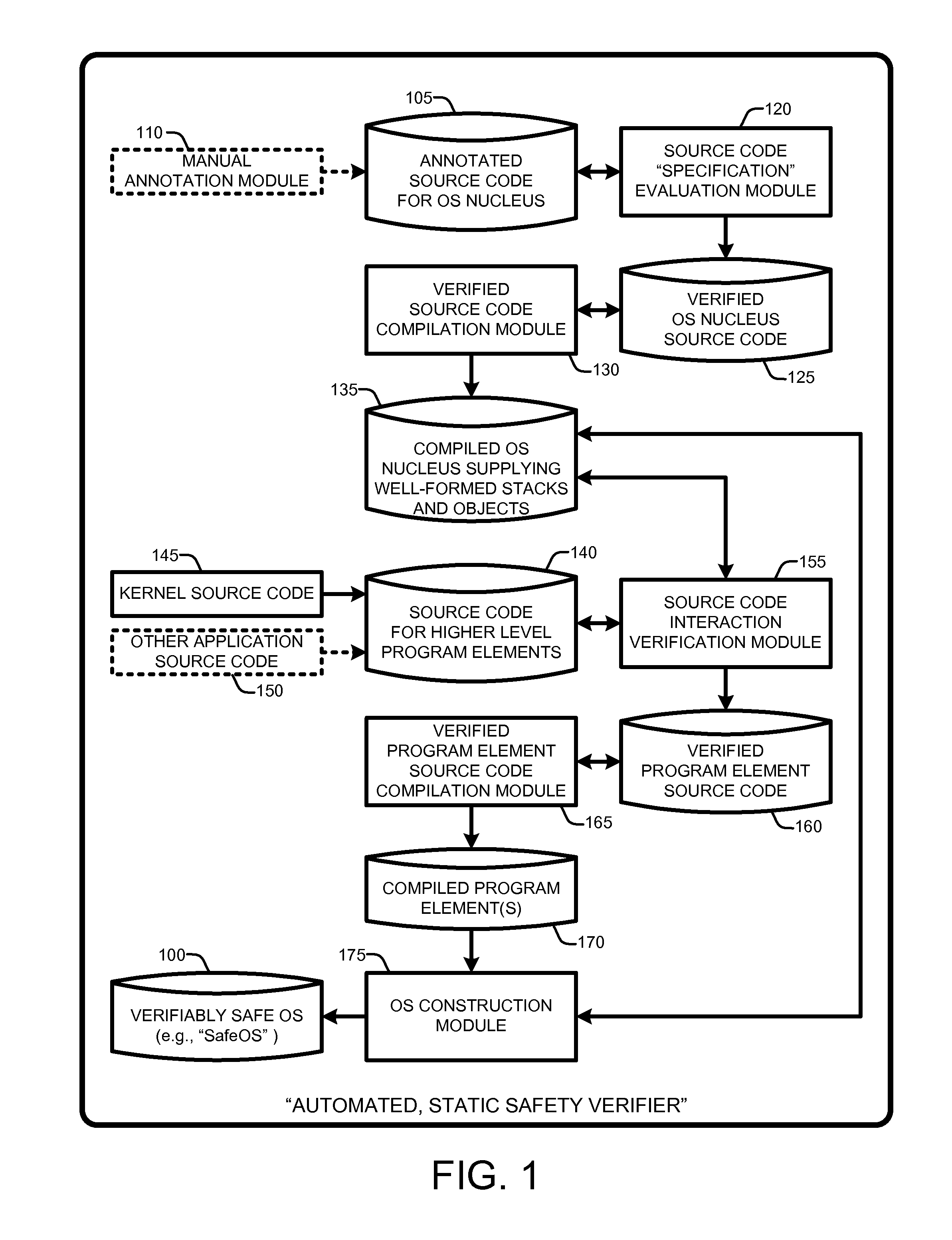
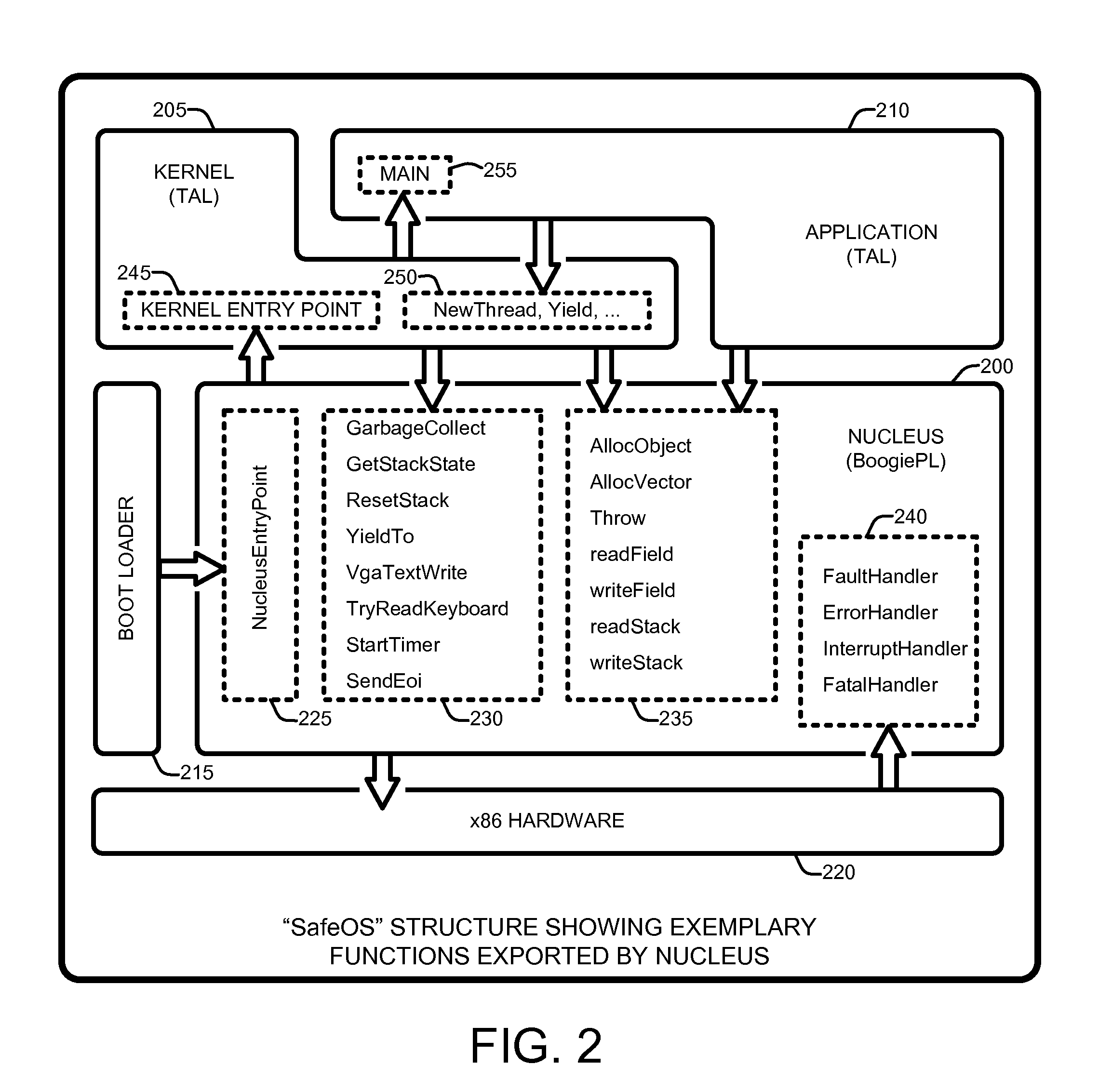
An “Automated, Static Safety Verifier” uses typed assembly language (TAL) and Hoare logic to achieve highly automated, static verification of type and memory safety of an operating system (OS). Various techniques and tools mechanically verify the safety of every assembly language instruction in the OS, run-time system, drivers, and applications, except the boot loader (which can be separately verified). The OS includes a “Nucleus” for accessing hardware and memory, a kernel that builds services running on the Nucleus, and applications that run on top of the kernel. The Nucleus, written in verified assembly language, implements allocation, garbage collection, multiple stacks, interrupt handling, and device access. The kernel, written in C# and compiled to TAL, builds higher-level services, such as preemptive threads, on top of the Nucleus. A Hoare-style verifier with automated theorem prover verifies safety and correctness of the Nucleus. A TAL checker verifies safety of the kernel and applications.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
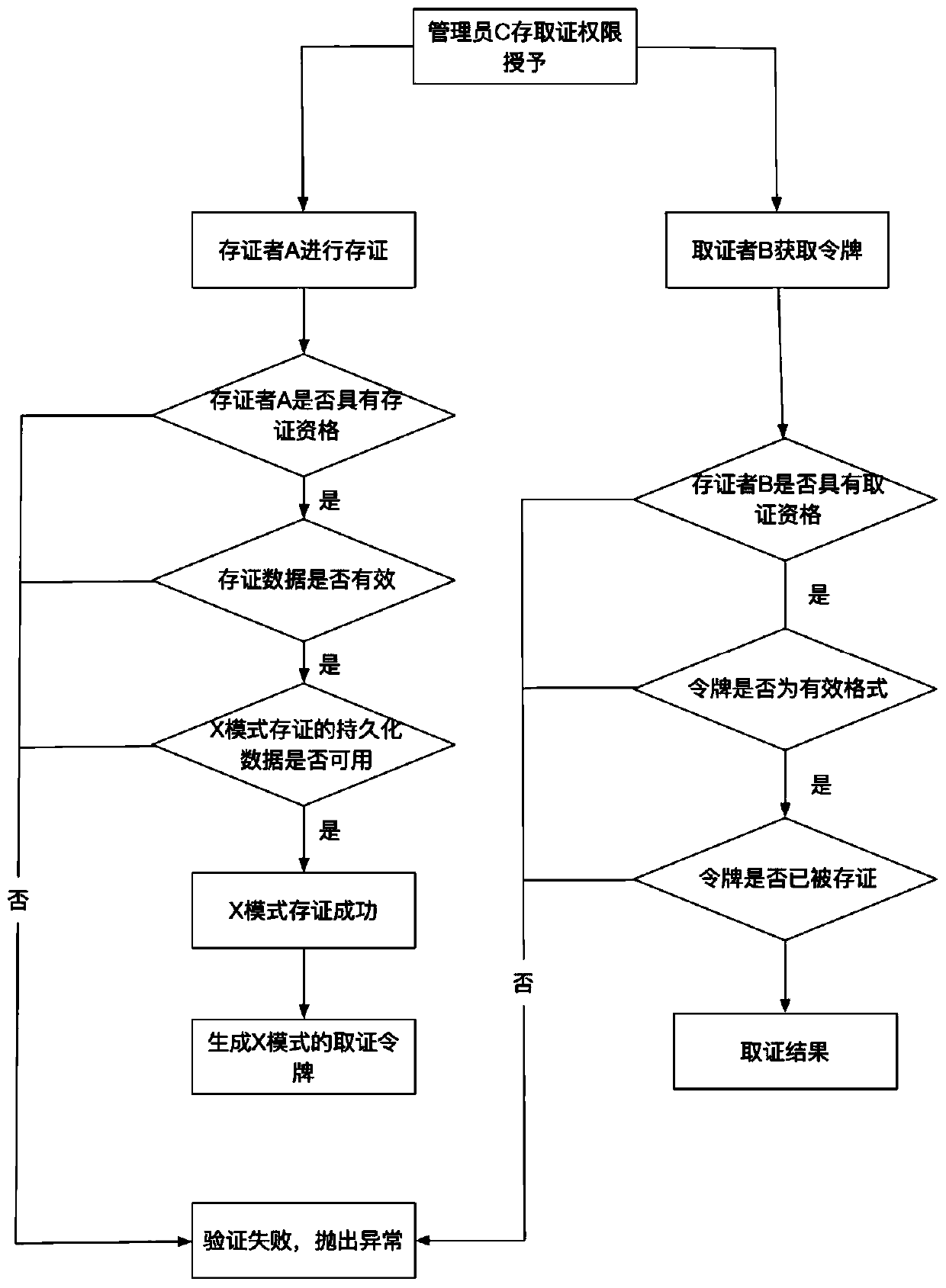
Form verification method based on blockchain evidence storage smart contract
ActiveCN110555320AImprove securityImprove reliabilityFinanceCryptography processingMathematical modelSmart contract
Owner:HANGZHOU QULIAN TECH CO LTD
Formalized verification method for stability of robot fractional order PID controller
The invention provides a method for verifying the stability of a robot fractional order PID control system by means of high-order logical theorem proving formalization method. For a robot fractional order PID controller, the method comprises the steps that a high-order logical formalized model of fractional order Laplace transformation and a high-order logical formalized model of the fractional order PID controller are established, a high-order logical formalized model of a fractional order closed-loop control system is established on this basis, and the stability of the robot fractional order PID control system is verified by means of the formalized model and theorems. According to the method, a guarantee is provided for the high reliability of the robot fractional order PID control system through formalized verification of a high-order logical theorem prover, and a firm foundation is provided for the safety of a man-machine interaction robot.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
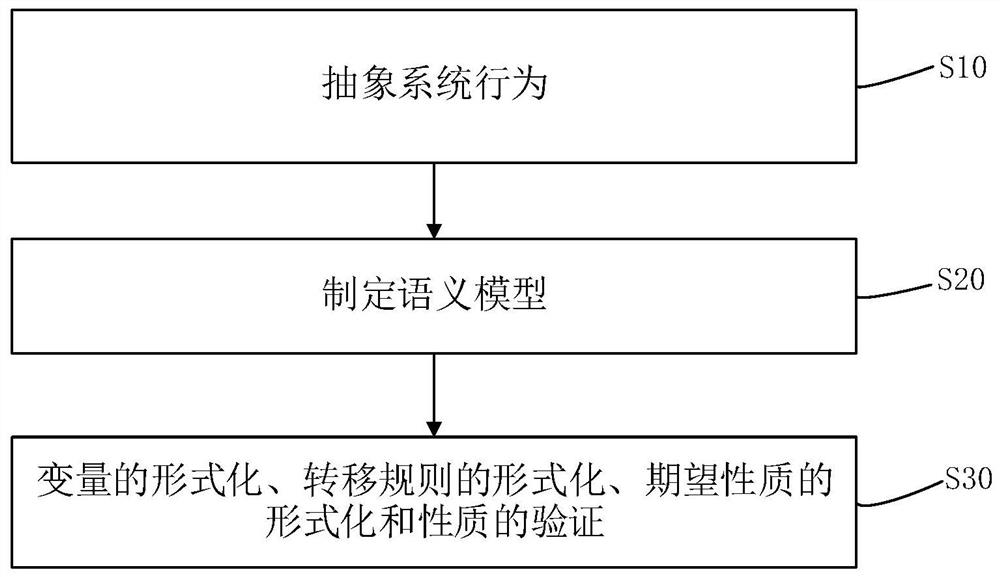
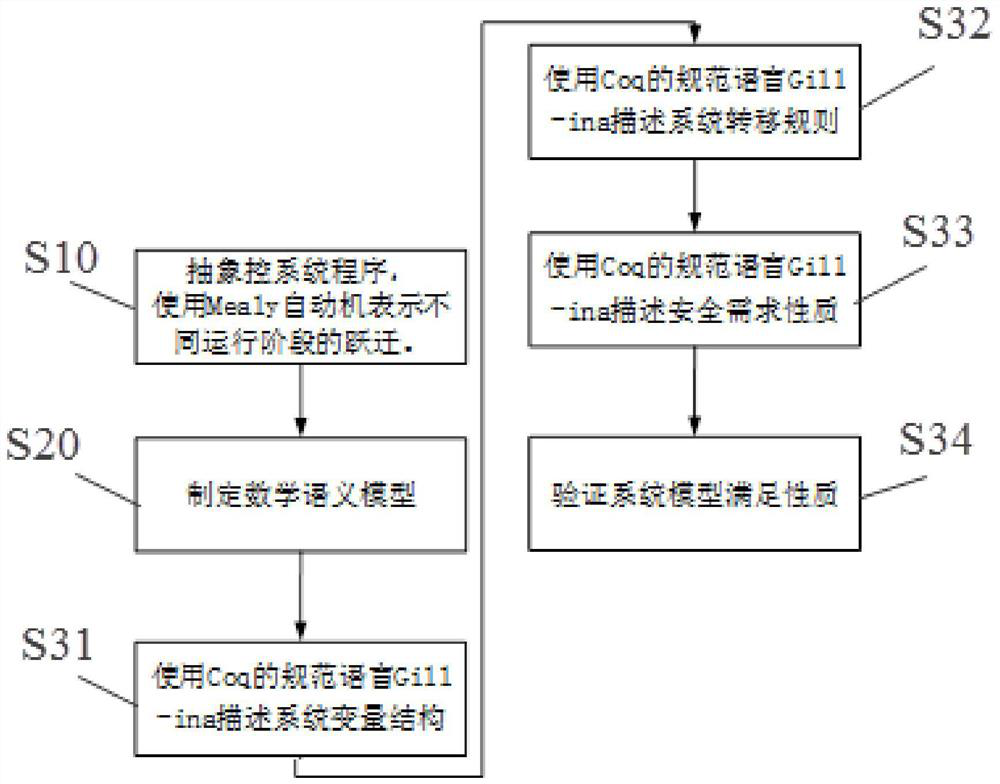
Coq-based verification method for time sequence safety of robot control system
ActiveCN112463133AProgramme-controlled manipulatorModel driven codeControl systemSoftware engineering
The invention discloses a Coq-based robot control system time sequence safety verification method. The method comprises the following steps of S10, abstracting system behaviors; s20, making a semanticmodel; and S30, carrying out formalization of variables, formalization of transfer rules, formalization of expected properties and verification of properties. According to the method, the problem ofverifying the time sequence safety of the embedded system based on the C language by utilizing the theorem prover is solved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
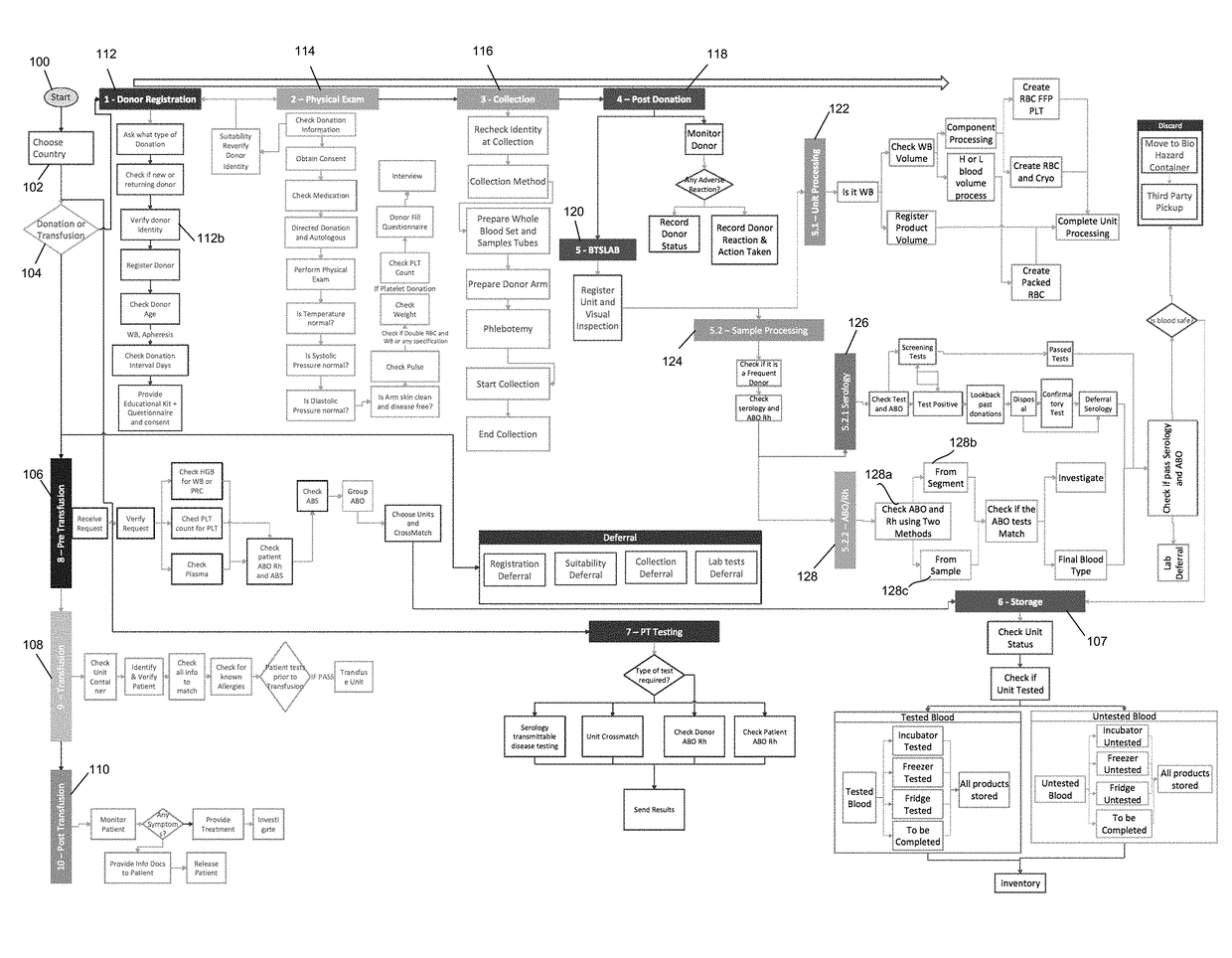
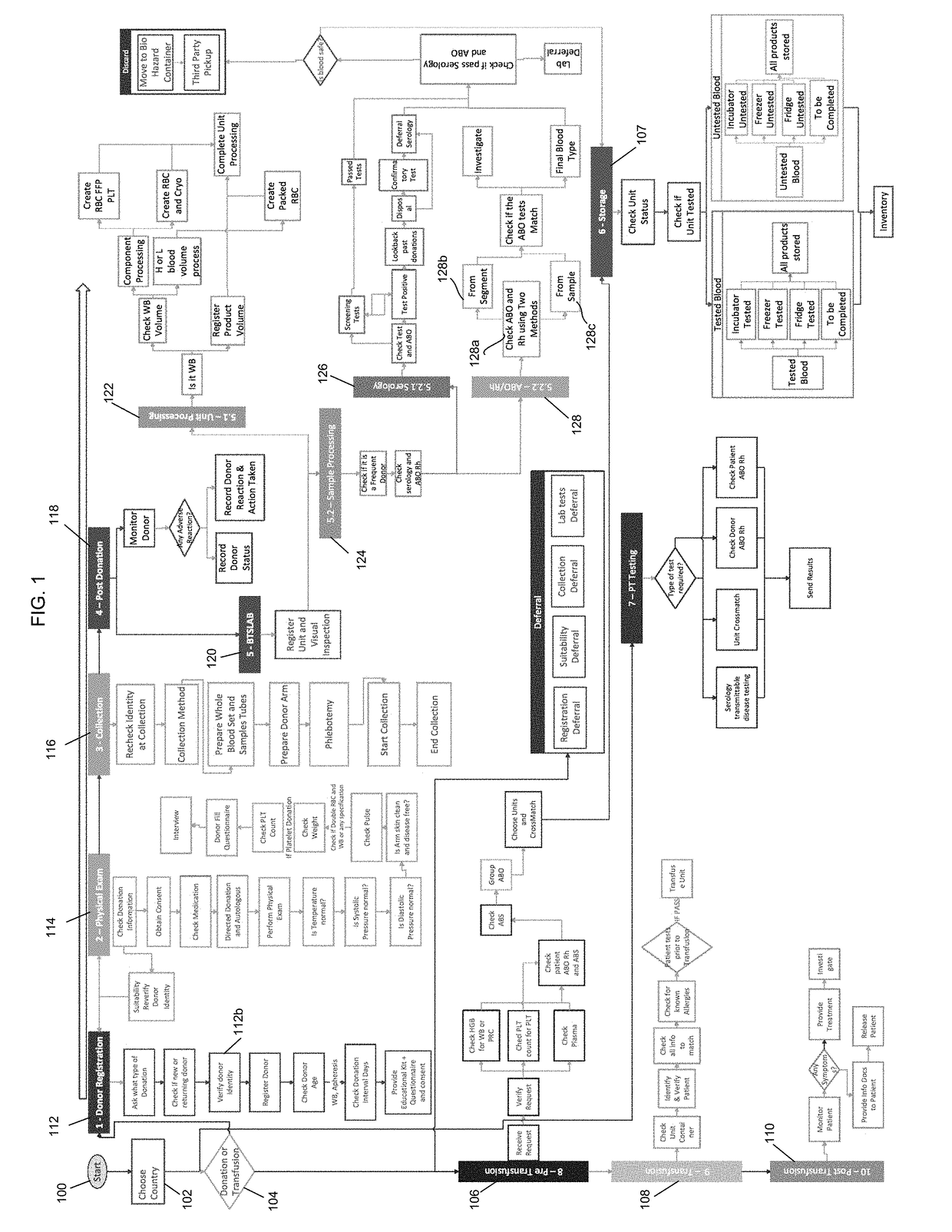
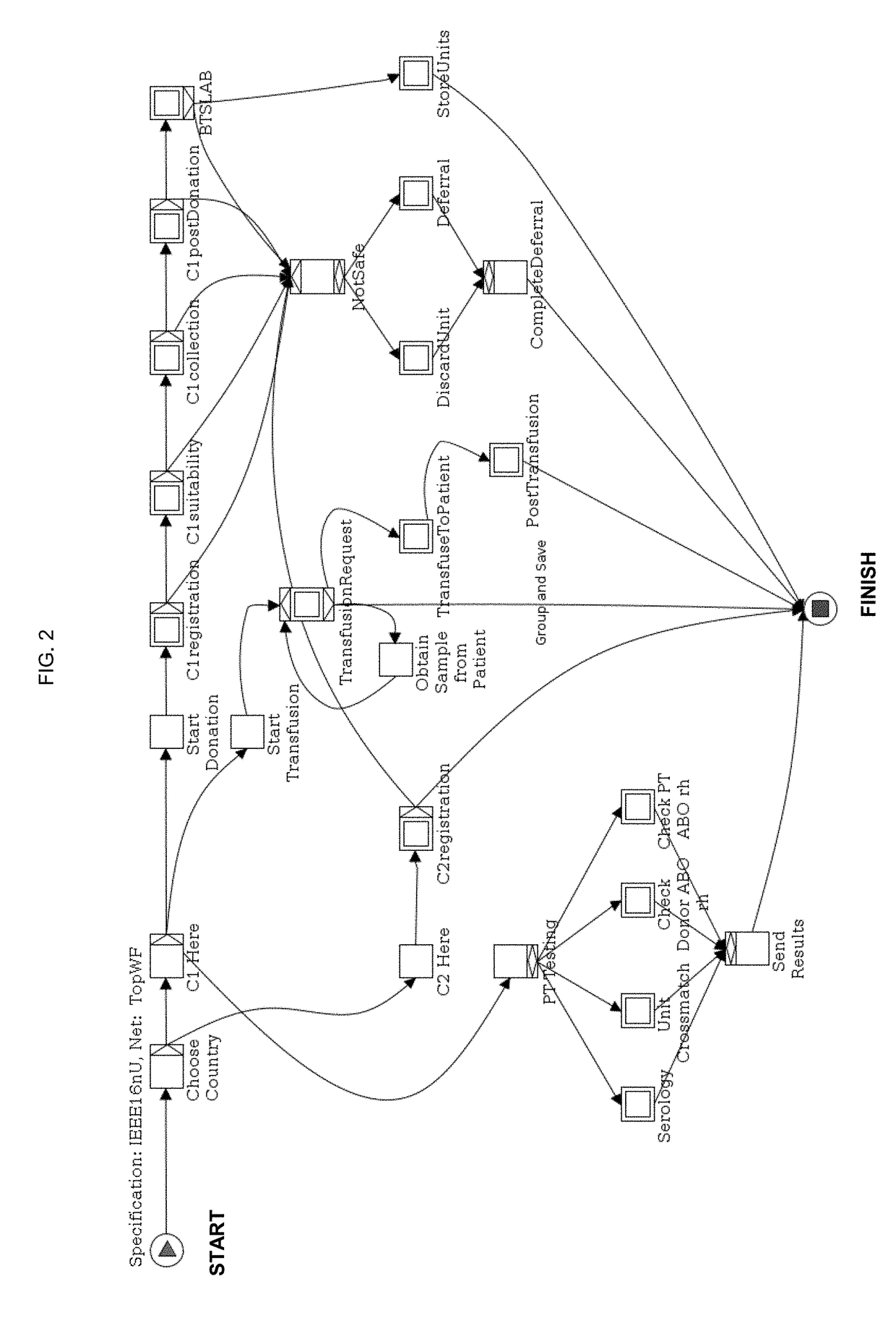
Automated system and method for blood safety workflow verification and validation
InactiveUS20180294055A1Ensure safetyHealthcare resources and facilitiesResourcesTemporal logicBlood safety
A method of using temporal logic technique to verify and validate blood safety workflows, the method includes creating a model workflow of blood supply chain process, wherein humans and machines are included as workflow constructs where involved, translating regulations governing blood safety into statements in temporal logic formula, wherein components satisfying a temporal logic formula correspond to satisfying the translated regulation, combining the translated regulations with the created blood supply chain model workflow, and validating that all translated regulations have been satisfied using a theorem prover.
Owner:HAZZAZI NOHA
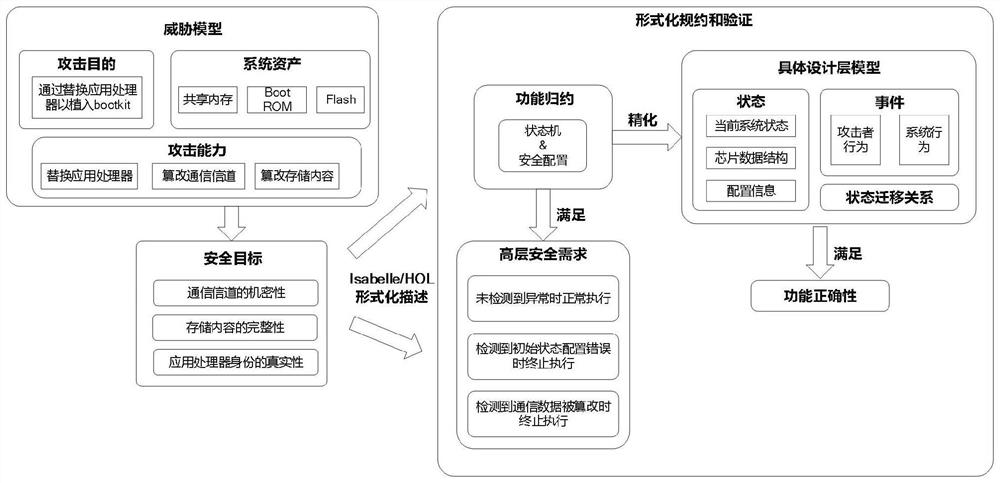
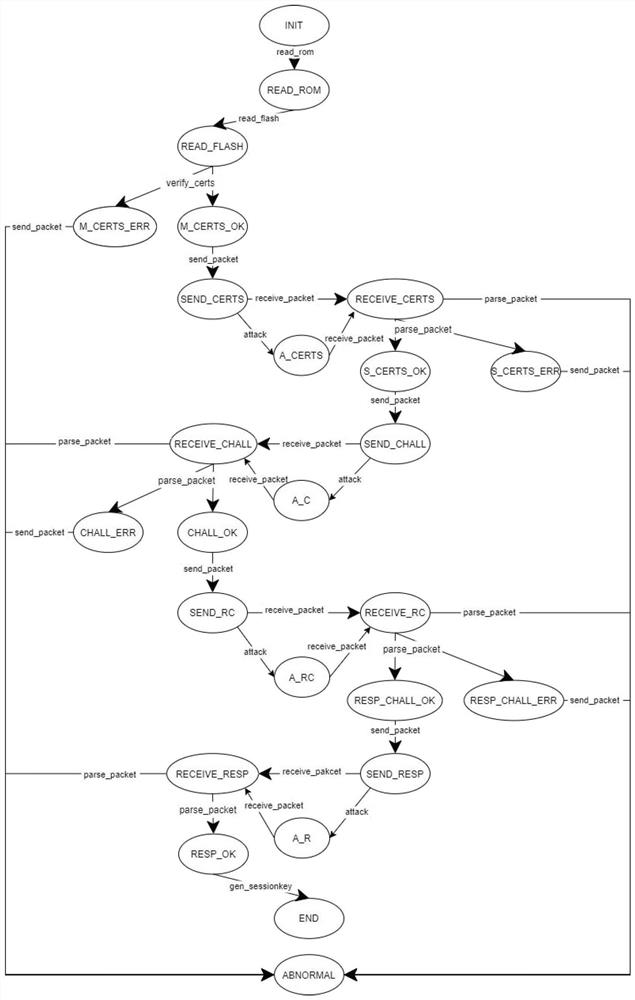
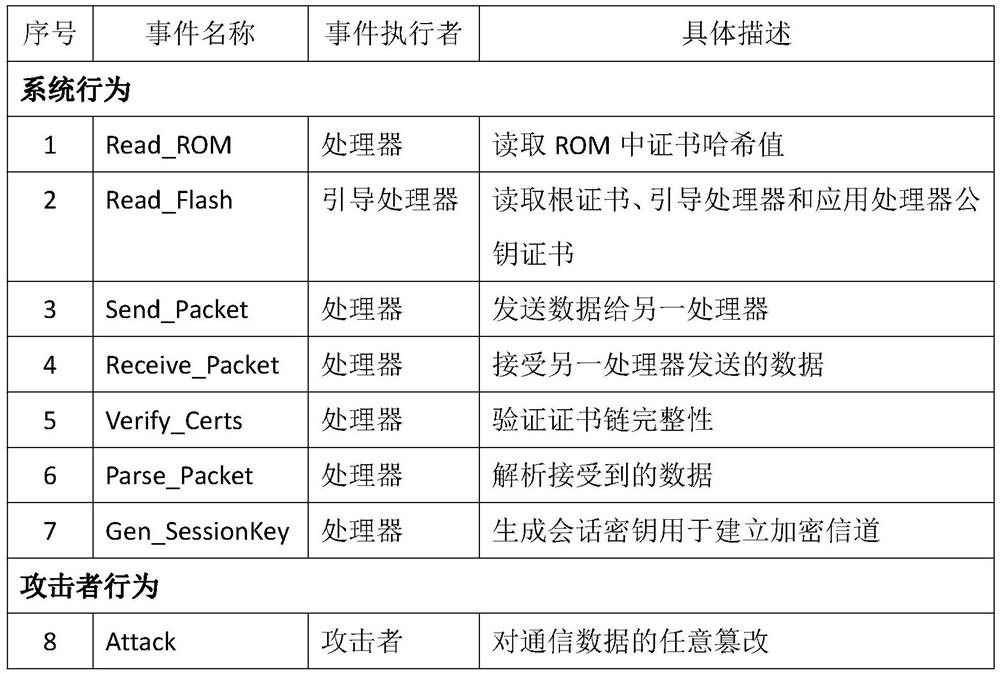
Embedded device safe starting scheme design method based on formalized verification
The invention discloses a formalized verification-based embedded device security startup scheme design method, which comprises the following steps of: based on formalized analysis and verification, analyzing a threat model to obtain a security demand, establishing a formalized model on the basis of the security demand, and finally converting the formalized model into a security startup scheme. The invention provides a solution method based on formalized verification aiming at the security problem existing in the security starting process of the embedded system equipment and ensuring the availability and security of the security starting scheme of the embedded equipment through a theorem proving method in order to solve the security problem existing in the security starting process of the embedded system equipment. The method systematically and comprehensively analyzes problems in the safe starting process, provides a specific safe starting scheme design, and provides availability and safety proof of a specific scheme by using a theorem proof method, so that threats in the safe starting process can be quickly solved, and the safety of the safe starting process is improved. And the safety and the reliability of the scheme are proved theoretically.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Internal model anti-interference control method of quad-rotor unmanned aerial vehicle system
PendingCN112764426AImprove robustnessConvergent stabilityAttitude controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsVehicle dynamicsGraph theoretic
The invention provides an unmanned aerial vehicle anti-interference control method based on an internal model control principle. A physical system of an unmanned aerial vehicle is considered. The intelligent control method comprises the steps of establishing an unmanned aerial vehicle dynamics model with external disturbance, building an external disturbance system, designing an unmanned aerial vehicle distributed control algorithm with external disturbance based on theoretical knowledge such as graph theory and convex analysis, further designing a Lyapunov function. The convergence of the designed algorithm is proved through the Lyapunov theorem, it is guaranteed that the state variables of the unmanned aerial vehicle converge to the target, finally the effectiveness and feasibility of the method are verified again through a numerical simulation example, and dynamic tracking of the unmanned aerial vehicle and formation of the unmanned aerial vehicle can be well achieved under the disturbance condition. The control precision of the unmanned aerial vehicle system is improved, and the method has certain practical value in both civil and military aspects.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Multi-agent system privacy protection and mean convergence control method
PendingCN114301666ADoS attack immunityAttack immunitySecuring communicationInformation processingComputer network
The invention discloses a privacy protection and mean convergence control method for a multi-agent system. An intelligent agent system is easy to suffer from network attacks, and meanwhile, the problem of privacy leakage of node information exists. The method comprises the following steps of: providing a distributed network node information processing mechanism based on differential privacy to ensure the privacy of initial state values of all nodes; in combination with an event trigger control method, the initial state value of the node can be protected and the mean convergence control can be achieved under the DoS attack; graph theory knowledge and strict mathematical theorem prove that conditions for realizing convergence control when the system suffers from DoS attack are analyzed. According to the method, the situation that only differential privacy and only DoS attacks are researched is overcome, the differential privacy is combined with event trigger control, it is guaranteed that the system achieves mean convergence while privacy protection is achieved, and the influence of the DoS attacks existing in the network can be immune.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
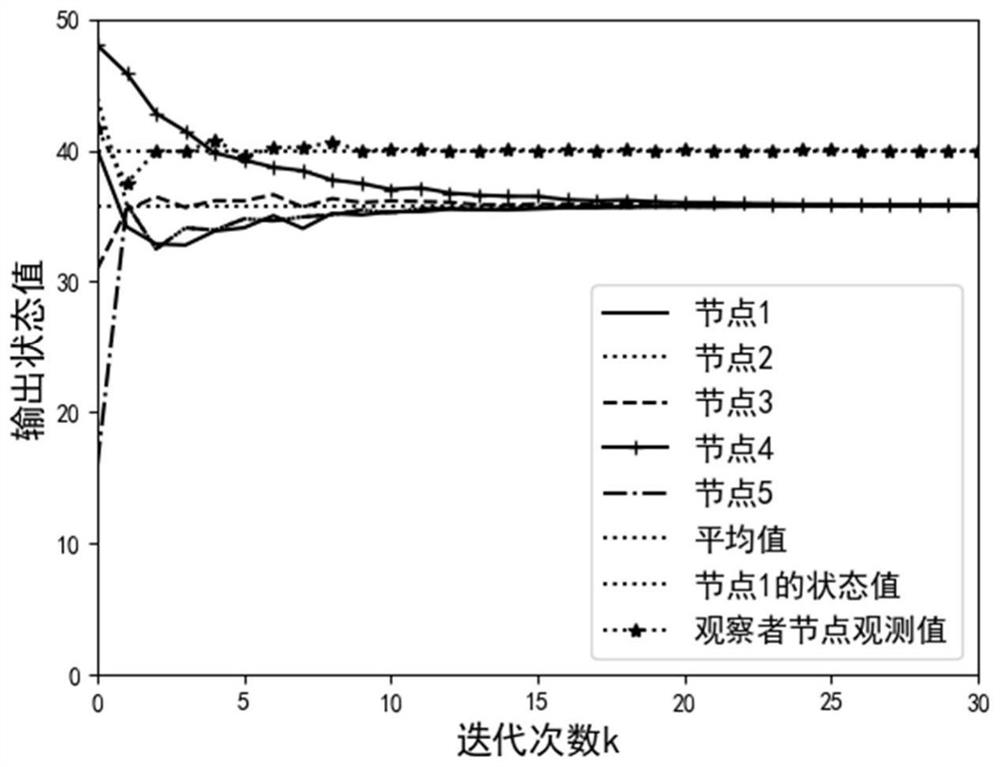
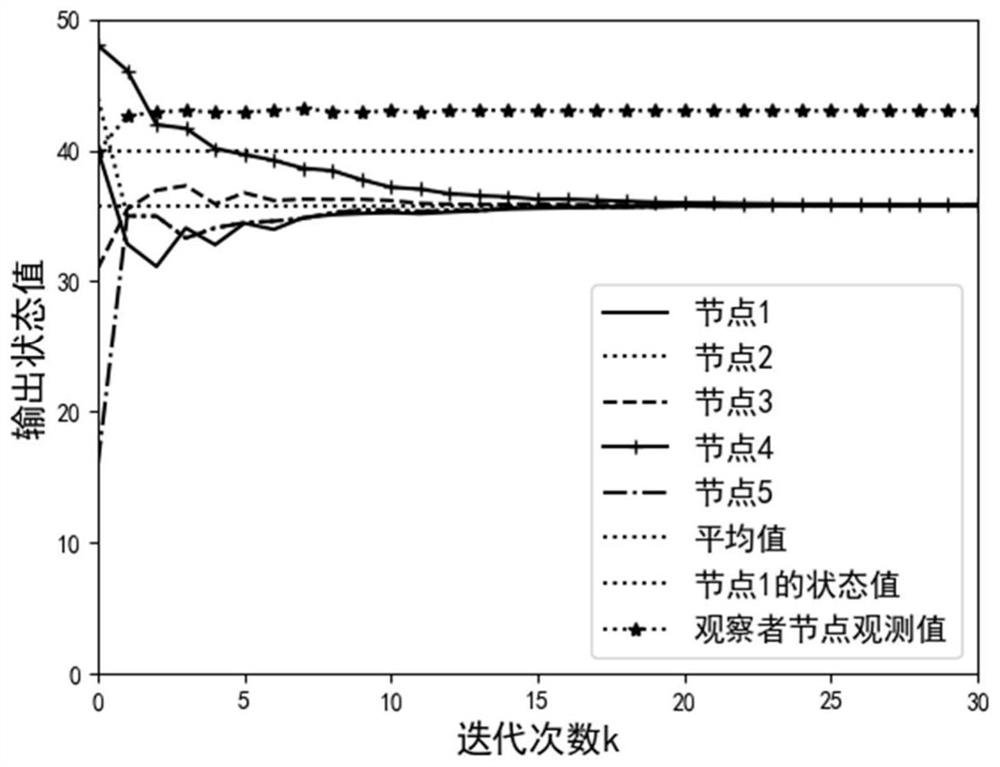
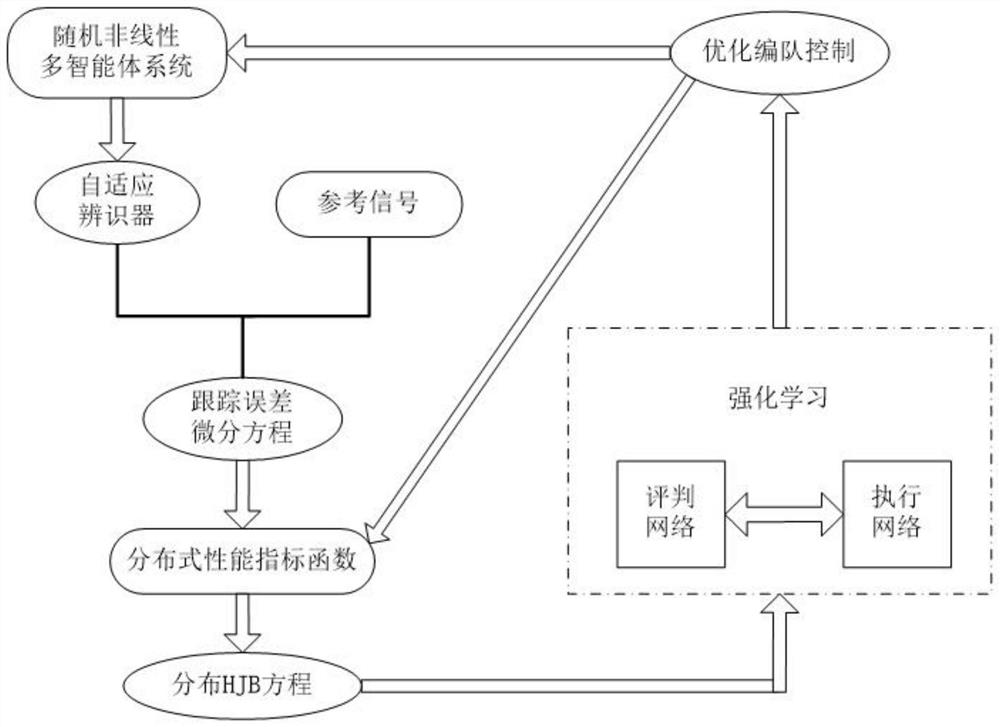
Random nonlinear multi-agent reinforcement learning optimization formation control method
InactiveCN114740710AEffective controlEase complexityTotal factory controlAdaptive controlLinear controlAlgorithm
The invention relates to the technical field of adaptive non-linear control, particularly discloses a reinforcement learning optimization formation control method for random non-linear multi-agent, and designs an adaptive identifier for estimating unknown random power based on the function approximation capability of a neural network. Then, optimization control is obtained by constructing an evaluation network and executing reinforcement learning through the network; in the invention, the reinforcement learning algorithm is obtained by executing a gradient descent method on a simple positive function, and the function is designed according to the partial derivative of an HJB equation, so that the optimal control is simpler than the traditional method, and can be more conveniently applied to a random nonlinear multi-agent system; and finally, verifying from two aspects of theorem proving and computer simulation, so that the proposed optimization method can realize an expected target.
Owner:BINZHOU UNIV
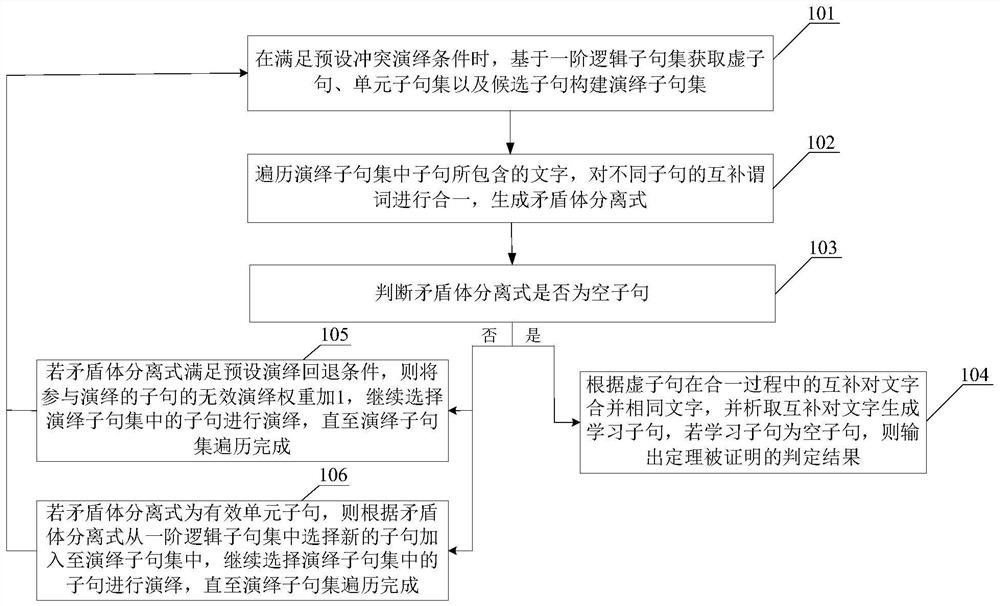
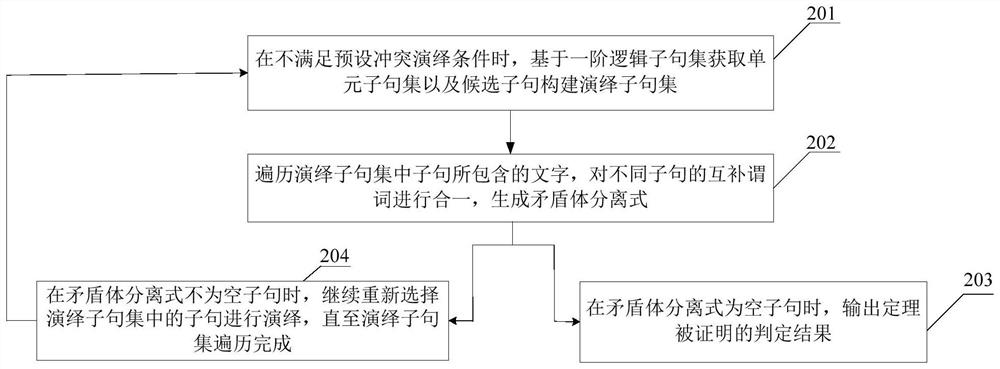
Automatic theorem proving method and device based on conflict deduction and storage medium
PendingCN113379052AEnhancing automatic theorem proving capabilities of first-order logicReduced path search spaceInference methodsFirst-order logicTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses an automatic theorem proving method and device based on conflict deduction and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: when conflict deduction conditions are met, acquiring virtual clauses, unit clause sets and candidate clauses based on a first-order logic clause set S to construct a deduction clause set Q, and performing paradox separation on the Q to obtain a separation formula R; when the R is an empty clause, performing conflict analysis to obtain a learning clause, and proving a theorem when the learning clause is an empty clause; otherwise, when the R is a unit clause and meets the limiting condition, selecting a deduced clause in the S according to the R, adding the deduced clause into the Q, and continuing to select the clause in the Q for deduction; and when the R is a non-unit clause or does not meet the limiting condition, returning to the previous deduction step, and re-selecting a clause in the Q for deduction. Through the implementation of the method, different virtual clauses are flexibly selected to simplify the deduction separation, the path search space of multivariate deduction can be effectively reduced, the deduction efficiency can be improved, and the first-order logic automatic theorem proving capability of a multivariate deduction reasoning system is enhanced.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
CPS (Cyber Physical Systems) adaptability verification method based on Hybrid UML (Unified Modeling Language) and theorem proving
InactiveCN102426521BReduce difficultyReduce development riskSpecific program execution arrangementsValidation methodsSemantics
The invention discloses a CPS (Cyber Physical Systems) adaptability verification method based on Hybrid UML (Unified Modeling Language) and theorem proving, which is mainly used for solving the problem that the formal verification method is too high in theoretical property to be popularized. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, modeling the CPS through a Hybrid UML view; transforming a Hybrid UML specification into an input-QHP (Quantitative Hybrid Program) of a theorem prover KeYmaera; in combination with the generated QHP, specifying the to-be-verified attribute in a manner of Qdl (Quantitative differential dynamic logic) formula, and then, executing automatic verification by the KeYmaera; before executing model transformation, needing to define meta models of the Hybrid UML and the QHP, while executing model transformation, firstly, eliminating the hierarchy of a top layer Mode, wherein the model obtained after transformation is named as Flat Mode, then, determining a transformation rule according to the consistency of macro semantics and meta semantics between the Flat Mode and the QHP, describing the transformation rule with the ATL (ATLAS Transformation Language), realizing the transformation from a Flat Mode model to a QHP medium model, and realizing the transformation from the QHP medium model to the QHP codes through a customized template language.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
System for knowledge acquisition
ActiveUS10452779B2Increasing semantic and logical precisionAccurately inferredNatural language translationSemantic analysisReasoning algorithmRule-based system
A system and method that translates sentences of natural language text into sets of axioms of formal logic that are consistent with parses resulting from NLP and acquired constraints as they accumulate. The system and method further present these axioms so as to facilitate further disambiguation of such sentences and produces axioms of formal logic suitable for processing by automated reasoning technologies, such as first-order or description logic suitable for processing by various reasoning algorithms, such as logic programs, inference engines, theorem provers, and rule-based systems.
Owner:HALEY PAUL V
Formal description method of matrix code generation technology based on Coq
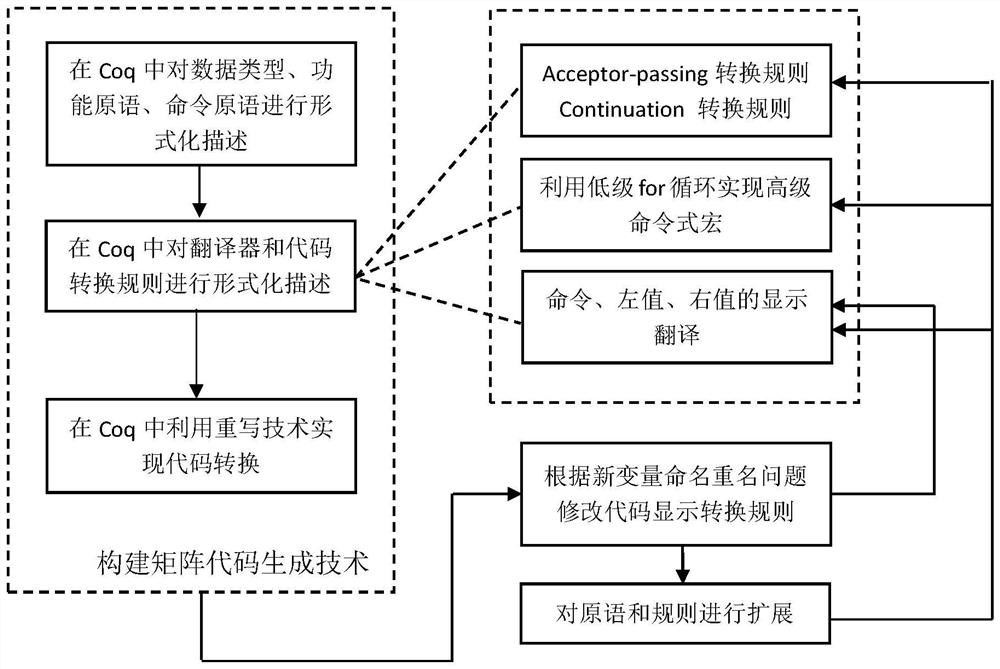
PendingCN114154114ARealize generationGenerate moreComplex mathematical operationsCreation/generation of source codeCode generationTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a formalized description method of a matrix code generation technology based on Coq, which is used for carrying out formalized description on the matrix code generation technology in a Coq theorem prover according to a DPIA principle, and perfecting and expanding the matrix code generation technology, and specifically comprises the following steps: carrying out formalized description on a data type, a function primitive and a command primitive; performing formalized description on the translator and the code conversion rule; realizing code conversion by utilizing a rewriting technology; defining a new variable name automatic generation rule, and solving the problem of variable name repetition; the primitives and rules are extended to achieve transcoding of more matrix operations. According to the method, a formalization technology is applied to a matrix code generation technology, the matrix code generation technology from a functional matrix code with an execution strategy to a parallel matrix C code is realized in a Coq theorem prover, and the problem of new variable naming repetition is solved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
A formal verification method of Laplace transform based on Coq
The invention discloses a formal verification method of Laplace transform based on Coq, which formally defines the Laplace transform in the theorem prover Coq and verifies the main properties of the Laplace transform. As that theorem prove Coq is precise and reliable, the method solves the disadvantage that the traditional method cannot accurately verify the Laplace transform. the method mainly includes the following steps: (1) The definition of Laplace transform is formalized by using the theories of differential, integral, limit, complex number and complex variable function in theorem proverCoq; (2) the formalization of the existence theorem of Laplace transform: the formalization of the existence theorem of Laplace transform; (3) The formal proof of the basic properties of Laplace transform: The linear properties, frequency shift properties, differential properties and integral properties of Laplace transform are formally proved in Coq theorem prover.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Automated many-sorted theorem prover
InactiveUS8135663B2Digital computer detailsNatural language data processingFirst-order logicComputer science
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
A B-based access control modeling and security analysis method for android
ActiveCN112100633BVerify correctnessDigital data protectionOperational systemOperating system security
The invention discloses an Android access control modeling and security analysis method based on the B method. The method uses formal language B to regulate and model the security attributes and key operations in Android access control, and verify the security through model detection. . This method provides a new method for Android access control modeling and security analysis. It formalizes the abstraction of the permission mechanism, designs the component entity abstraction machine and builds the basic model. And the extended model based on fine-grained policy, and finally analyze the security of the access control according to the theorem proof and model detection results, which provides a practical and effective way for operating system security mechanism modeling and system security proof.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
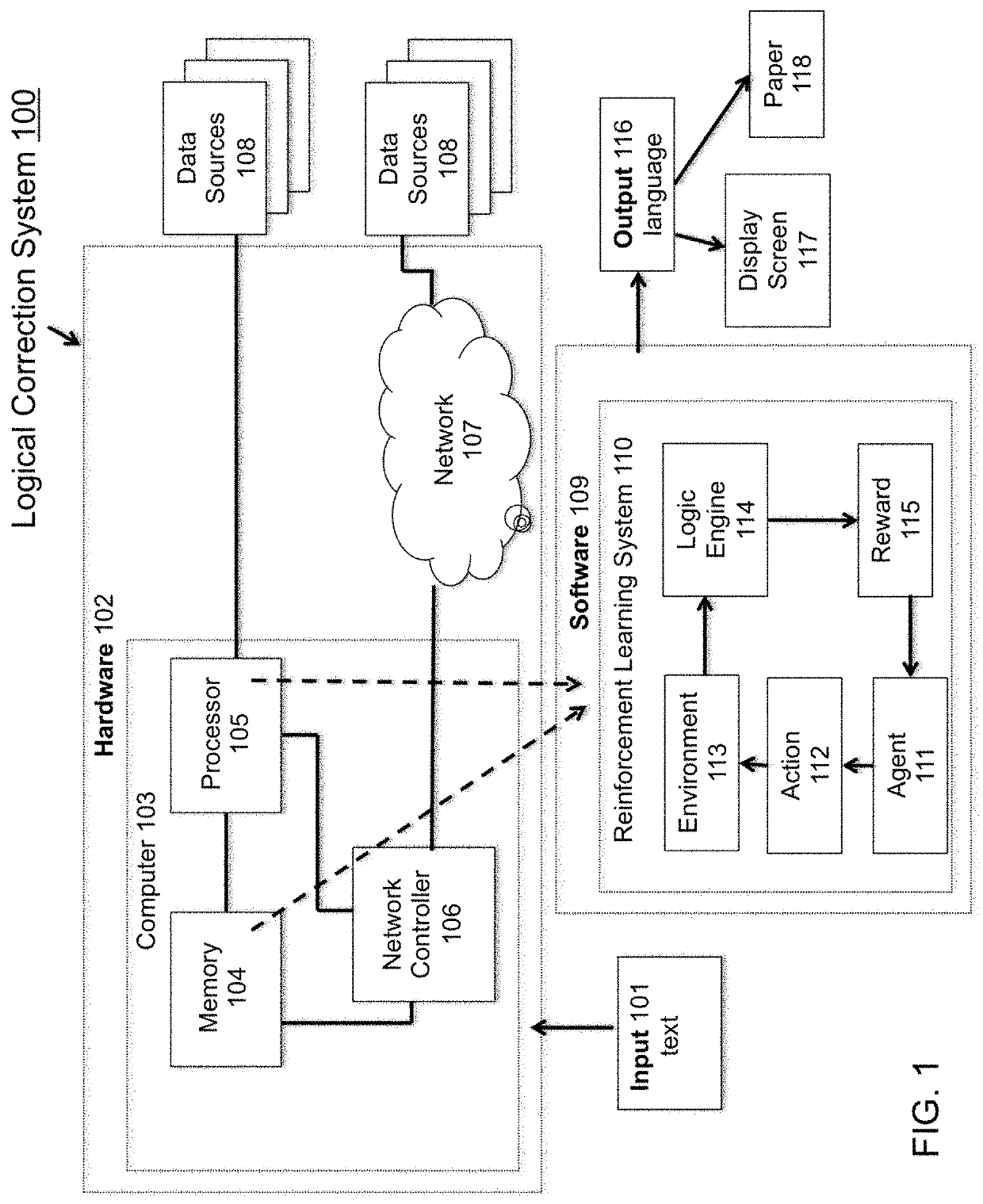
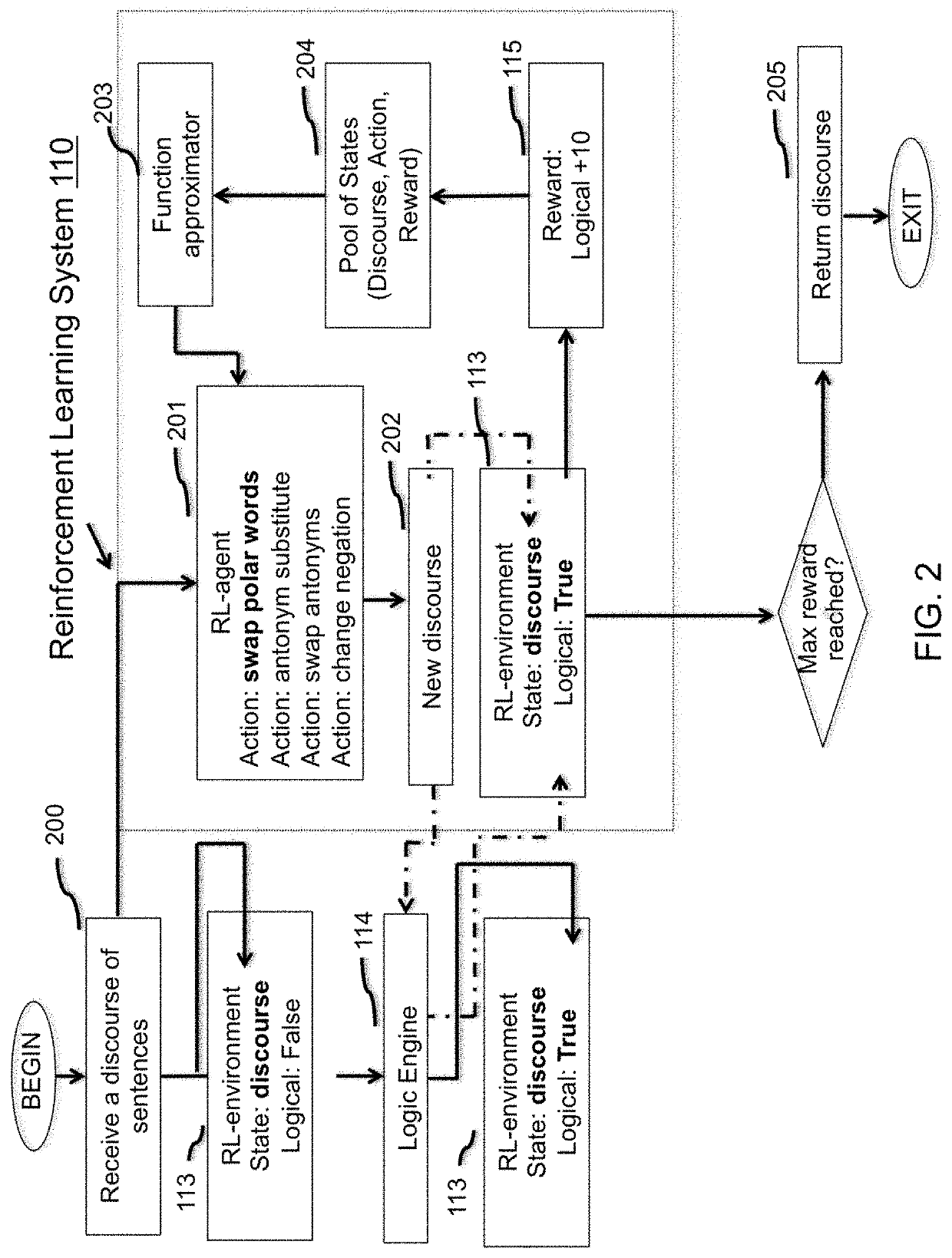
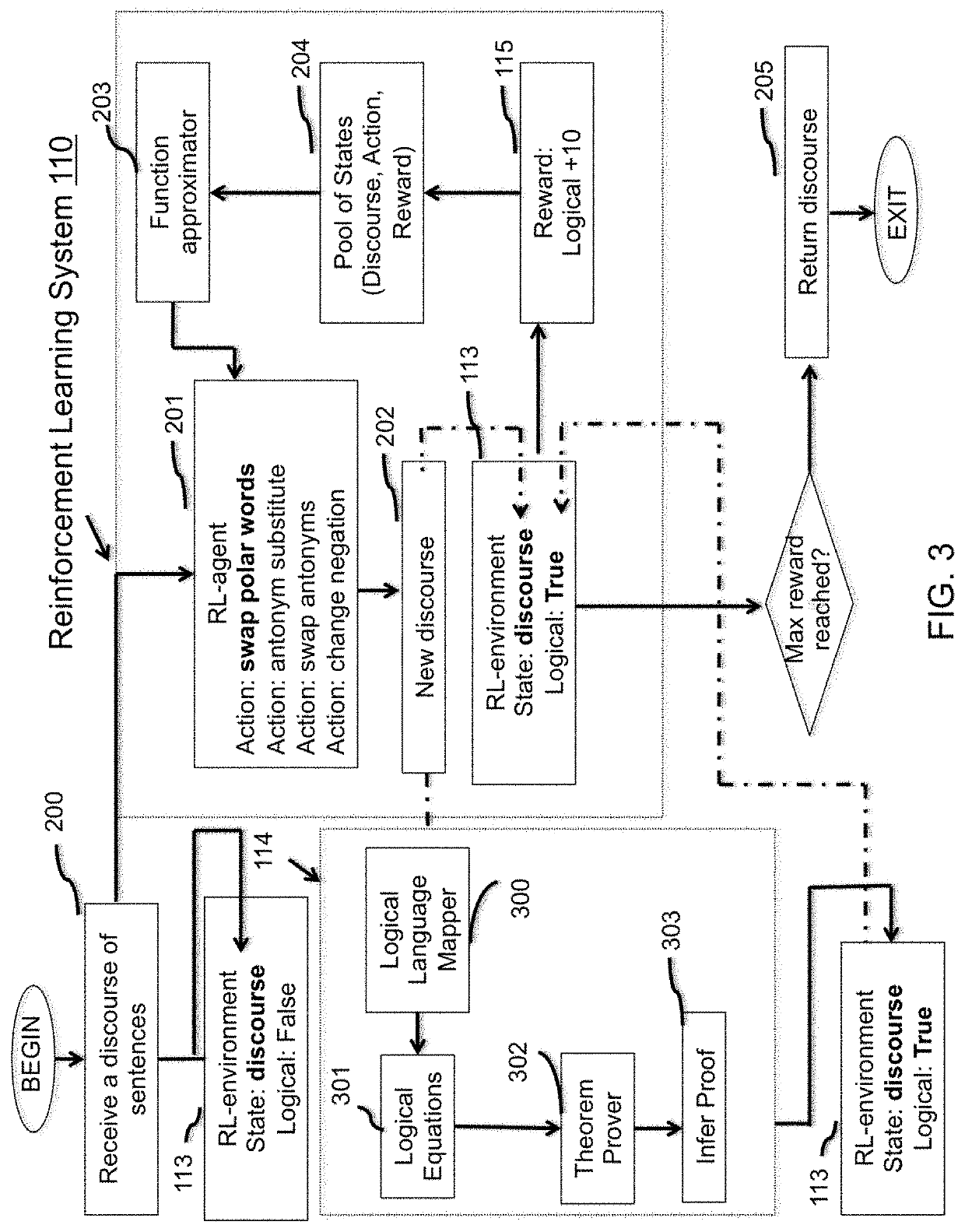
Reinforcement learning approach to approximate a mental map of formal logic
PendingUS20220036180A1Mathematical modelsNatural language data processingTheoretical computer scienceAutomated theorem provers
Methods, systems, and apparatus, including computer programs language encoded on a computer storage medium for a logic correction system whereby input text is modified to a logical state using a reinforcement learning system with a real-time logic engine. The logic engine is able to extract the symmetry of word relationships and negate relationships into formal logical equations such that an automated theorem prover can evaluate the logical state of the input text and return a positive or negative reward. The reinforcement learning agent optimizes a policy creating a conceptual understanding of the logical system, a ‘mental map’ of word relationships.
Owner:ARCHULETA MICHELLE N
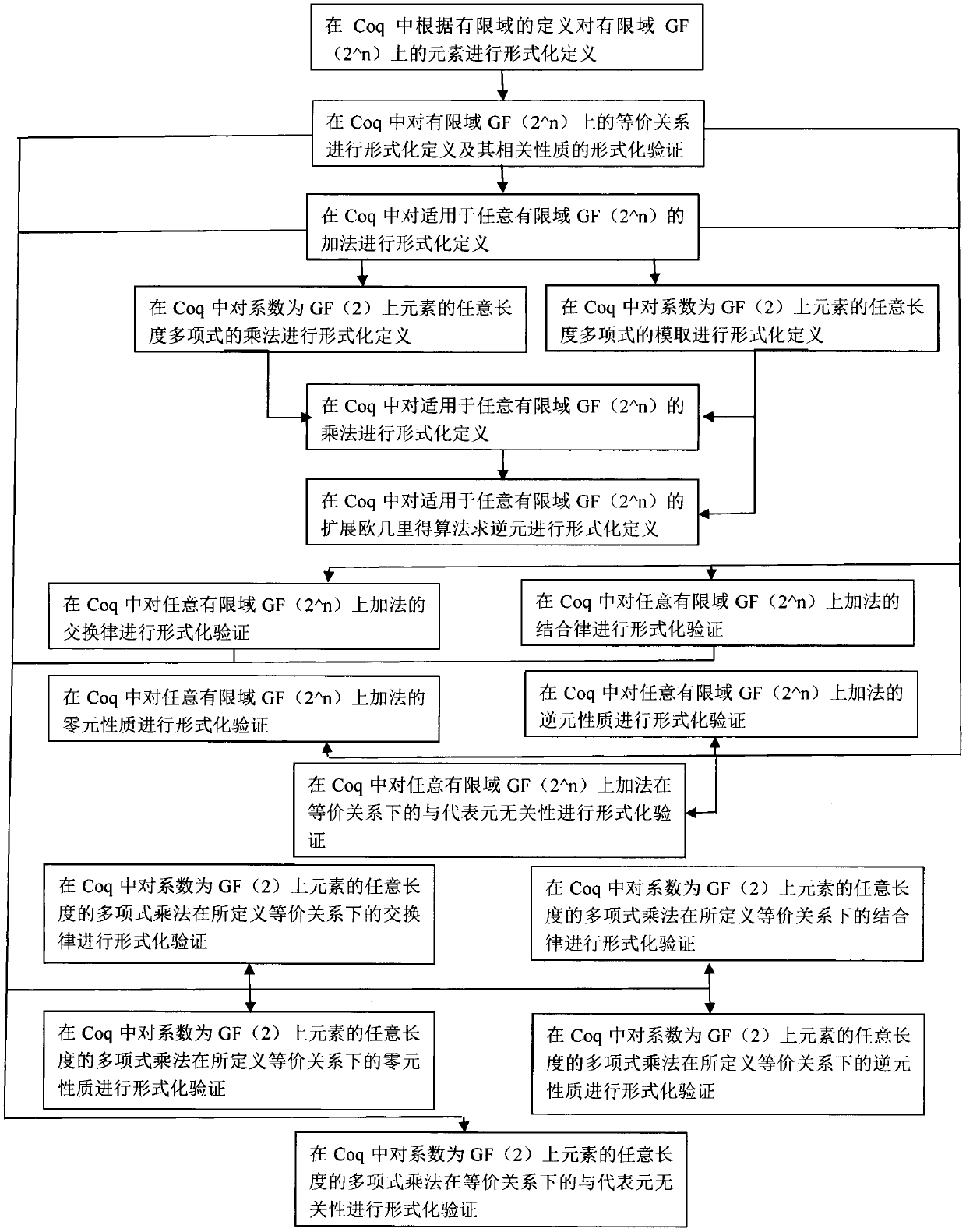
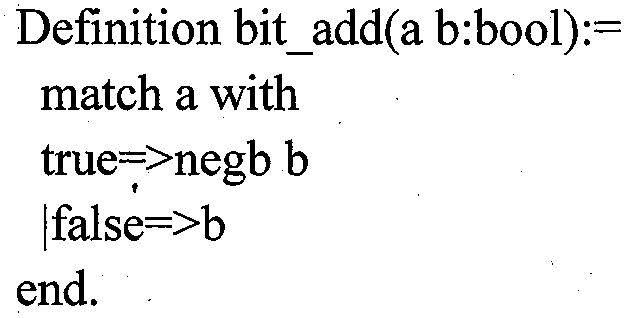
Formalized verification method of finite field GF(2 ^ n) based on Coq
InactiveCN110795337AReliableRigorousSoftware testing/debuggingComputations using residue arithmeticEngineeringMechanics
The invention discloses a finite field GF (2 ^ n) element based on a theorem prover Coq, a formal description method of operation on the finite field GF (2^n) element, and a method for carrying out formal verification on defined operation key properties. According to the invention, the strictness and reliability of the theorem prover Coq are utilized to solve the disadvantage that the previous method cannot ensure the availability of a specific operation result or a corresponding operation rule. The method mainly comprises the following steps: (1) formally defining any finite field GF(2^n) element and an operation on the GF(2^n) element in Coq, wherein the method comprises operations of addition, multiplication and multiplication inverse element solving; (2) defining an equivalence relation for judging the element equivalence of the finite field GF(2^n); (3) completing formal verification of additive properties suitable for any finite field GF(2^n) in Coq; and (4) performing formalizedverification of related properties suitable for multiplication of any finite field GF(2^n) in Coq.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com