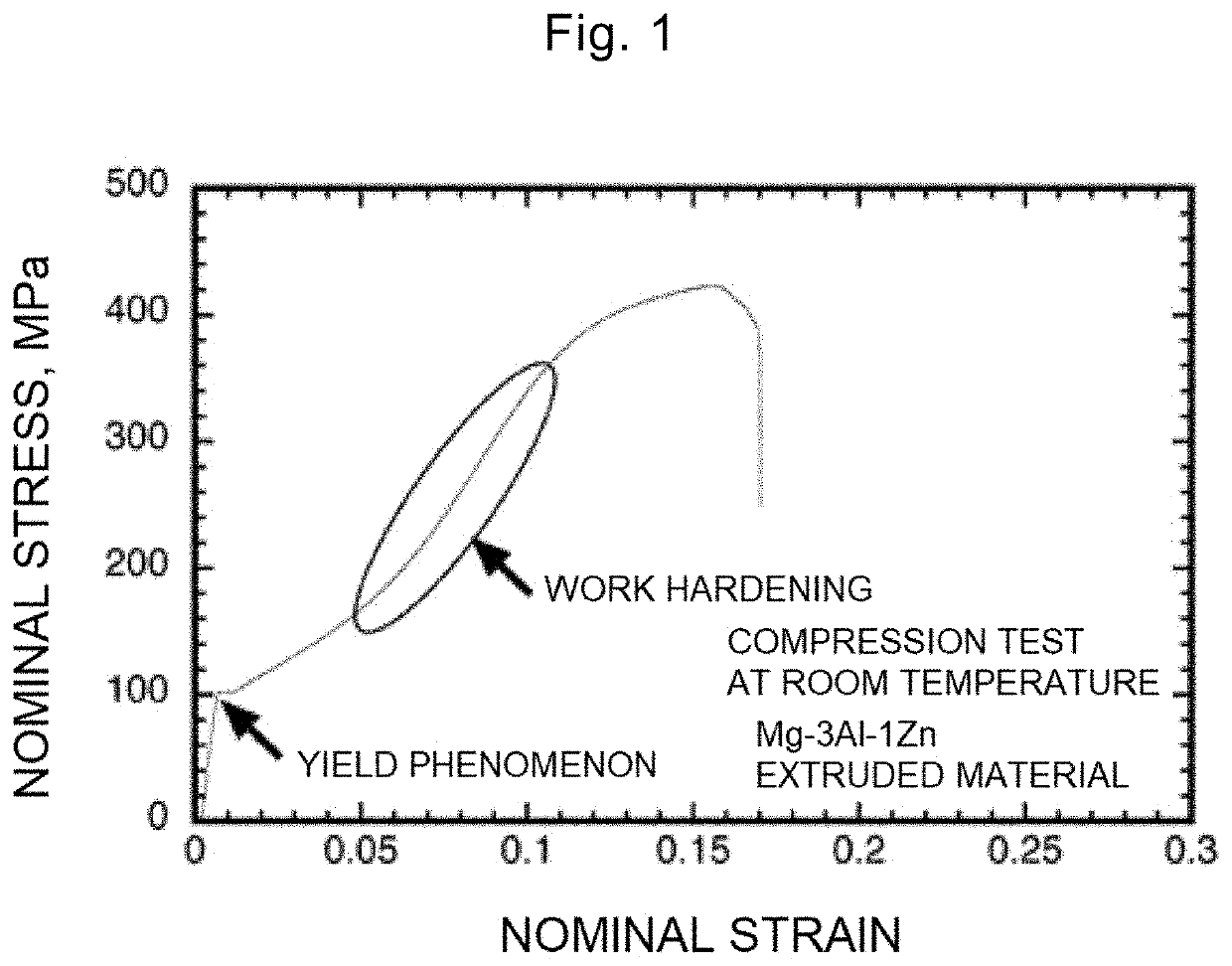
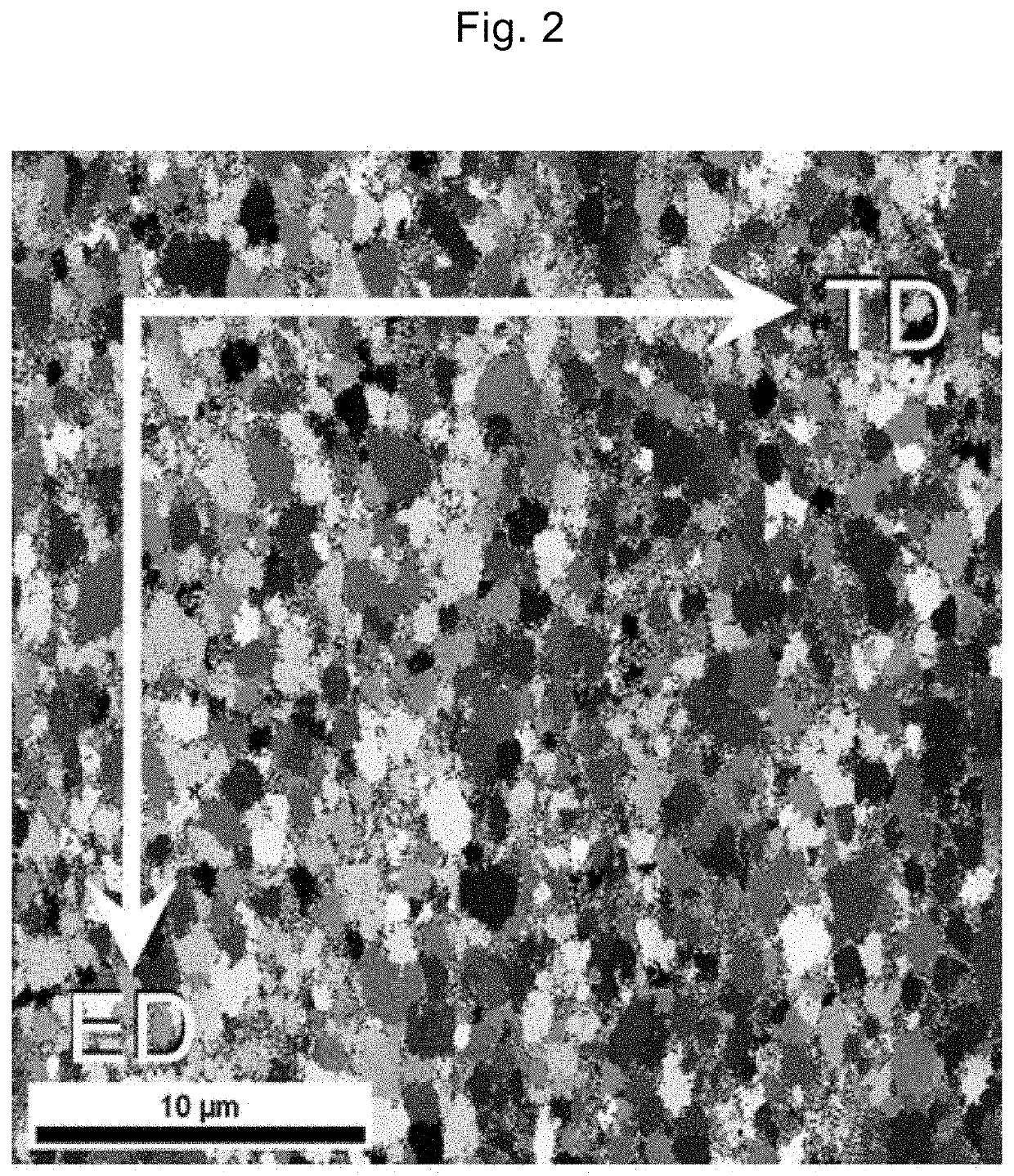
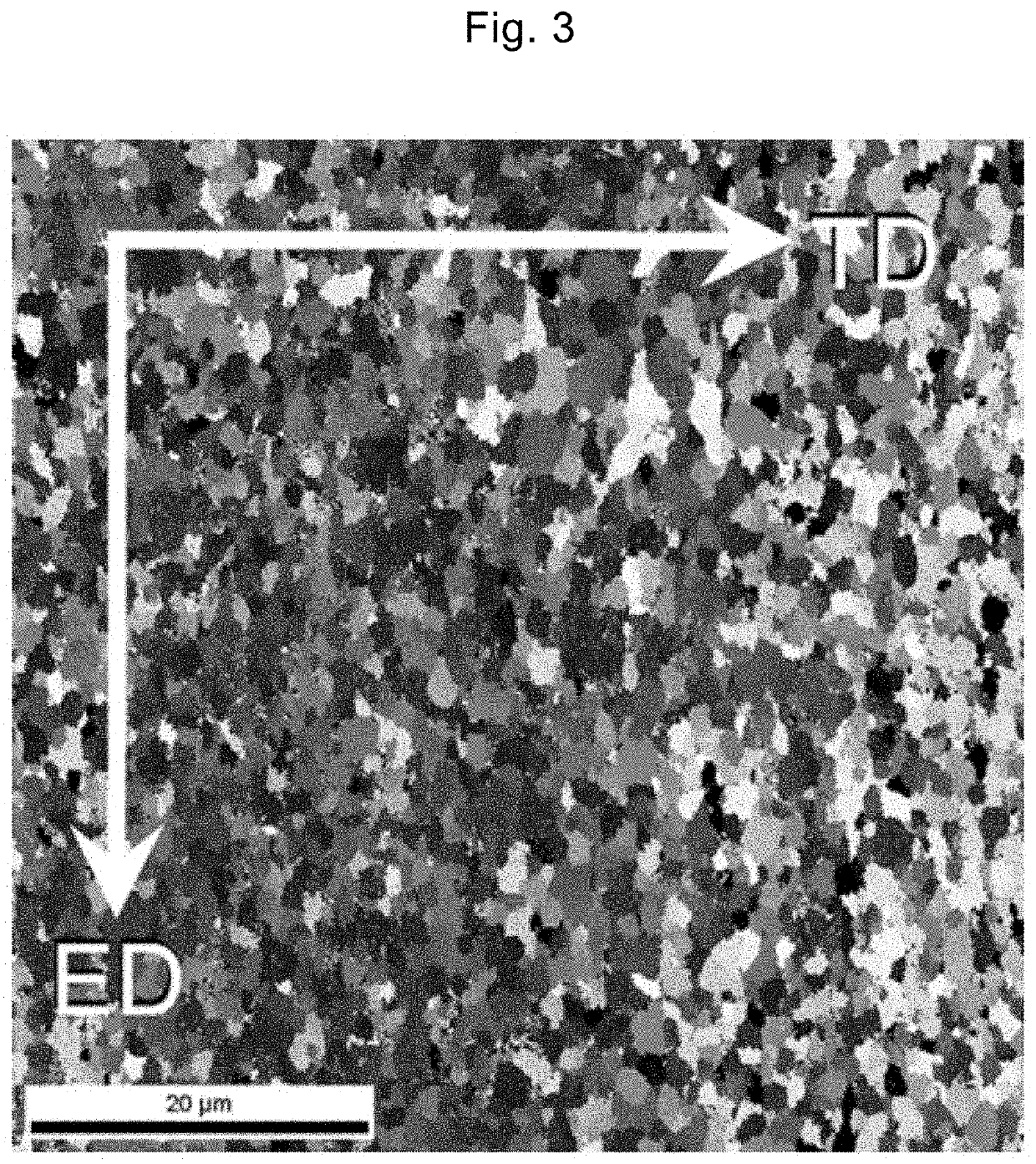
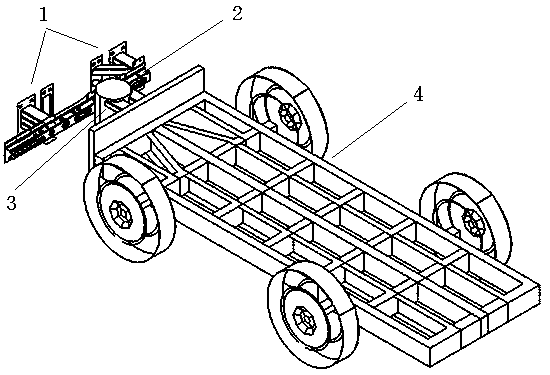
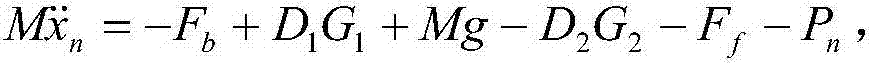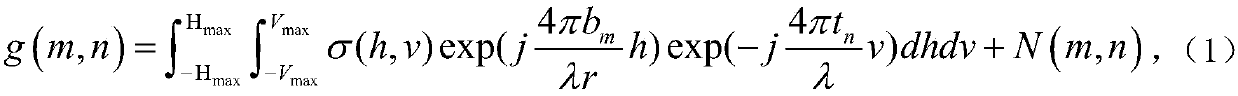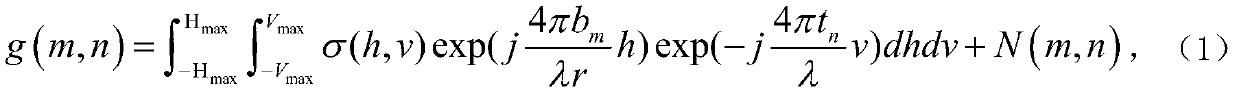Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Deformation velocity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
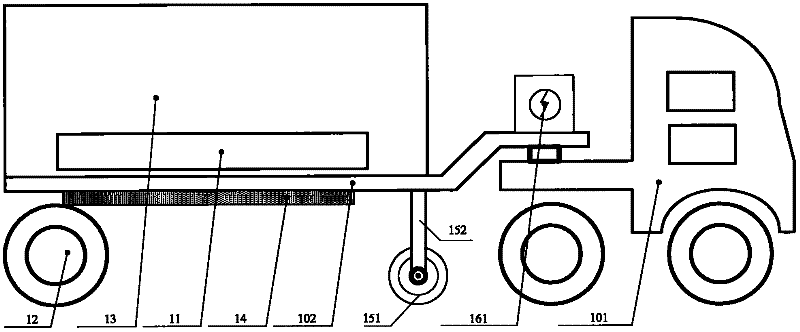
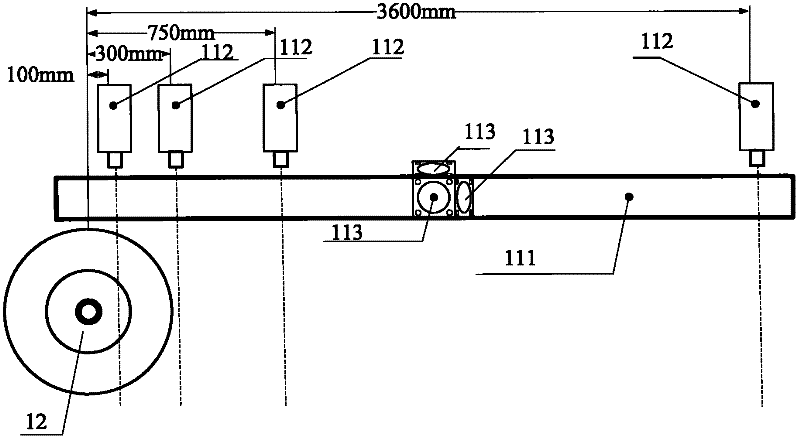
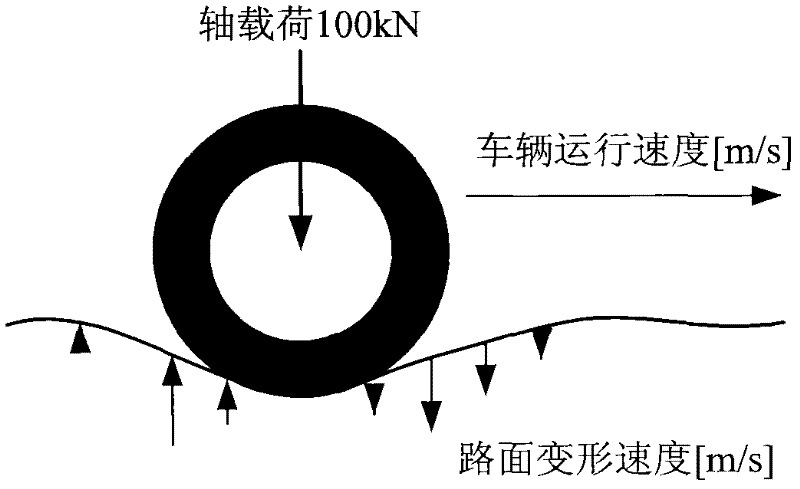
Laser dynamic deflection survey vehicle
ActiveCN102162217AFast measurementWide range of measurement speed variationUsing optical meansRoads maintainenceAccelerometerDoppler velocity
The invention provides a laser dynamic deflection survey vehicle. The survey vehicle comprises a mobile measuring table, a measuring cross beam, a running wheel, a velocity measuring wheel, an accelerometer and a data acquiring and processing device. The laser dynamic deflection survey vehicle provided by the invention has the following advantages: according to the laser Doppler velocity measurement principle and the inertia measurement principle, during the driving process of the vehicle at a normal traffic velocity (15-80km / h), a plurality of laser Doppler vibration meters arranged in the front of loading wheels of the vehicle synchronously measure the relative movement velocity of various measuring points on a road surface; the instantaneous deflection deformation velocity of the road surface is obtained through inertia compensation calculation; and a dynamic deflection value of the road surface is obtained through inversion by utilizing a road layered elastic mechanical model and used for general investigation and assessment of the bearing capacity of a road network.
Owner:WUHAN WUDA ZOYON SCI & TECH
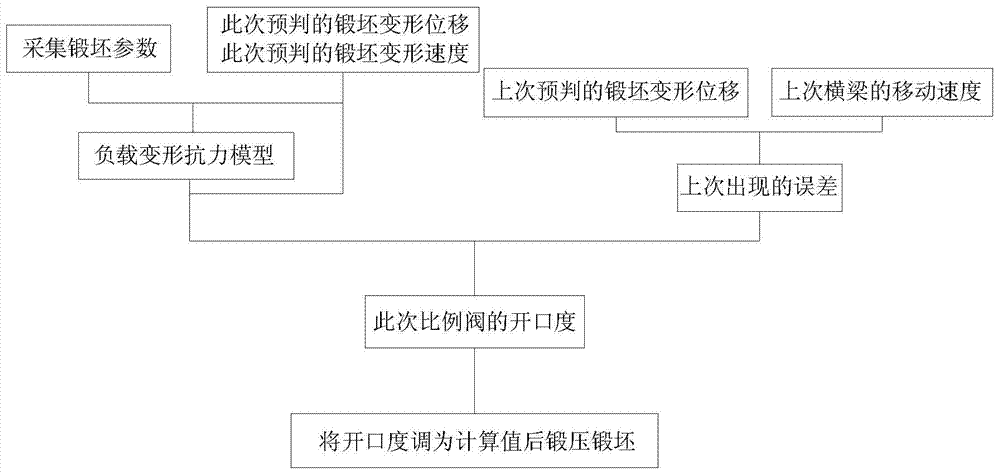
Forging press control method and control system of forging press
The invention provides a forging press control method and a control system of a forging press. The forging press control method includes steps of acquiring forging stock parameters, and calculating to obtain load deformation resistance model at the specific temperature according to the forging stock parameters, anticipated forging stock deformation displacement and forging stock deformation speed; calculating to obtain required opening degree of a proportional valve of a forging press in this forging according to the load deformation resistance model and an error appearing in the last forging process; adjusting the opening degree of the proportional valve to the calculated value and then forging the forging stock. According to the forging press control method and the control system of the forging press, forging process of a crossbeam can be frequently adjusted, the integral forging process is stable to run, and quality of forged pieces can be guaranteed.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Temperature distortion resistant magnesium alloy containing Ca and Sr
The invention provides an advanced heat-resisting deformation magnesium alloy comprising the following components by weight: Al of 6.0%-9.0%, Ca of 0.5%-3.0%, Sr of 0.05%-0.5%, Mn of 0.1%-0.8%, Mg and ineluctable foreign matters of the rest.The cost of the alloy which does not contain rare-earth elements is low. The formability range of the alloy is extended because the added elements can thin the alloy tissue substantially; and the distribution of heat-resisting phases is turned from bulky bocks or bones to fine and scattered state, which improves the formability of the alloy. The alloy which has a good plastic property and forming ability and has a large deformation temperature range is suitable for common processes of extrusion pressing, drawing, rolling and smithing and can bear bigger deflection and higher deformation velocity at one time. The alloy that can be used as the light high-strength heat-resistant structural metallic material will be widely used for high-temperature transportation piping and high-temperature load-carrying construction of aerospace, automobiles, track trains and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for preparing ultrahigh strength high toughness magnesium alloy
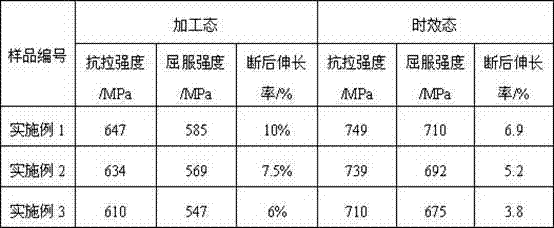
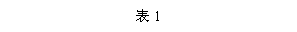
The invention relates to a preparation method for ultrahigh strength high toughness magnesium alloy. The ultrahigh strength high toughness magnesium alloy comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 6-13% of gadolinium, 2-6% of yttrium, 0.3-0.8% of zirconium, and the balance of magnesium and inevitable impurities. The magnesium alloy billets are subjected to powerful thermal deformation, and then the magnesium alloy subjected to thermal deformation is subjected to rapid warm deformation at 110-150 DEG C, wherein the deformation force is 1-4KN, the deformation speed is 15-24mm / s, and the total deformation is 10-40%. The magnesium alloy is subjected to aging heat treatment after rapid warm deformation at 140-250 DEG C for 23-38 hours. The alloy subjected to warm deformation at room temperature has a strength of extension of 610-647 MPa, the yield strength of 547-585 MPa, the percentage elongation after fracture of 6-10%. The aging state alloy at room temperature has the strength of extension of 710-749 MPa, the yield strength of 675-710 MPa, and percentage elongation after fracture of 3.8-6.9 %.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Magnesium alloy compositely forming method
InactiveCN101214600AReliable workmanshipEasy to operateExtrusion control devicesEnergy consumptionMagnesium alloy
A magnesium alloy compound forming method belongs to the processing field of magnesium alloy which is characterized in that the invention heats a cast acquired by a casting method for 350 to 425 DEG C and simultaneously heats an extruding die to 232 to 425 DEG C and then maintains temperature for 25 to 120mins; then extrudes a performing extruding proximate matter with a two-dimensional characteristic of the cast by an extruding speed of 1.2 to 12m / min; cutting a mould pressing blank material with a same volume as the cast, heats the mould pressing blank to 290to 400 degrees and maintains the temperature for 25 to 120mins after a die is heated to 232 to 400 degrees, finally carries through one-time mould pressing by a deformation speed of 2 to 200mm / s to acquire a final product. The magnesium alloy cast produced by the invention can meet not only meet the requirement for shape of the product, but also improve the comprehensive performance of the magnesium alloy cast and can simultaneously lead the comprehensive performance of the product to be more uniformly. The invention has the advantages of reliable technical quality, high efficiency, little energy consumption, high quality and high technical yield. The invention is suitable for batch productions on the structural component products with extruding and mould pressing characteristics.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
High field high-temperature compression test device and method of solid materials
InactiveCN101762427AAc-dc conversion without reversalMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesData acquisitionEngineering
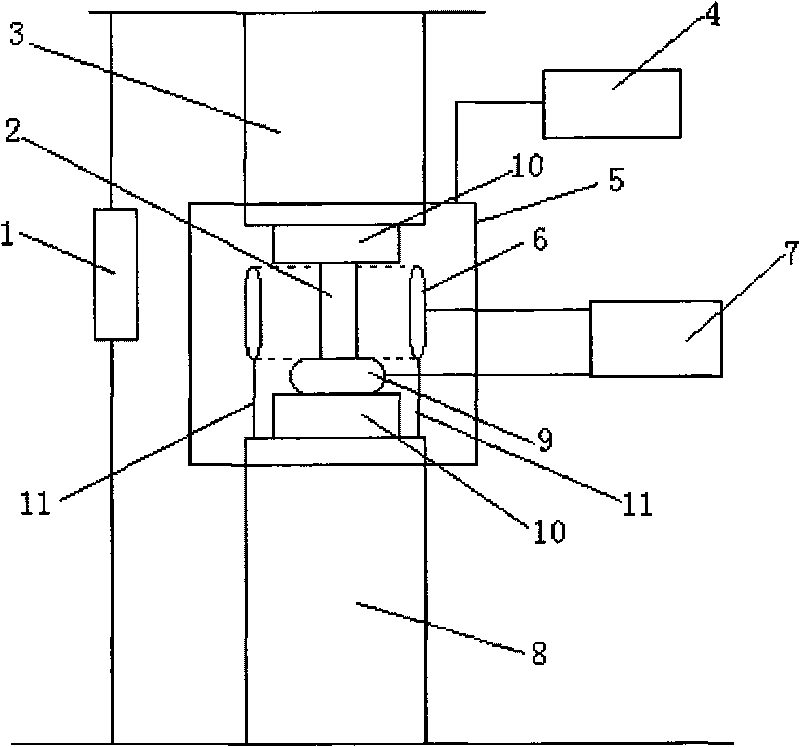
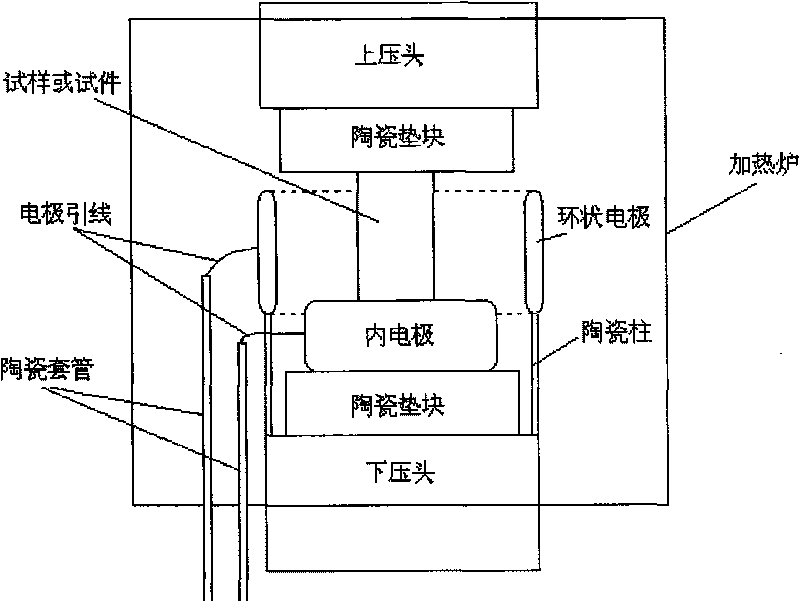
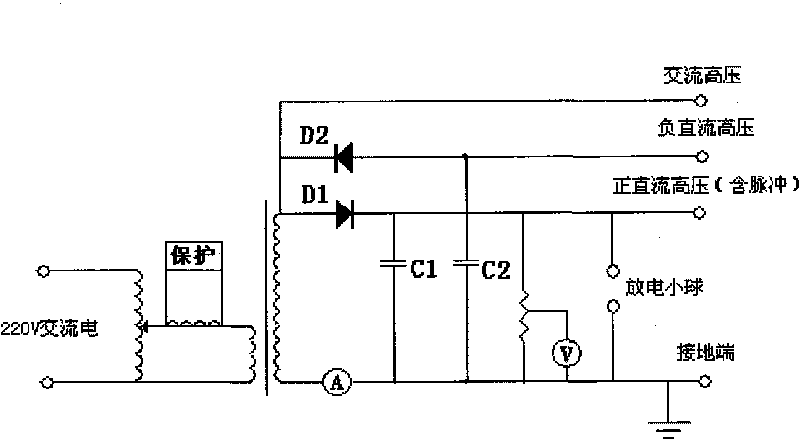
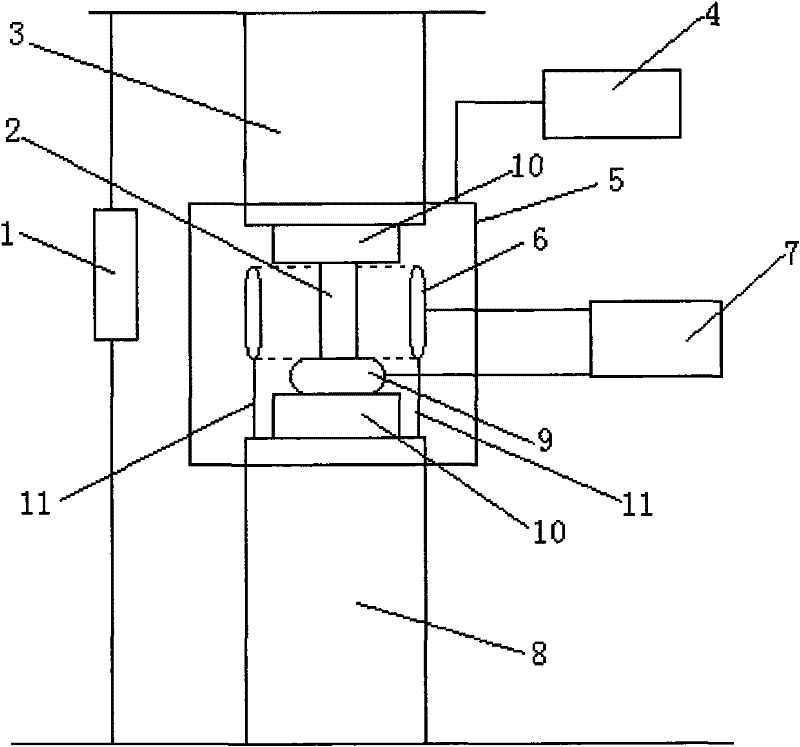
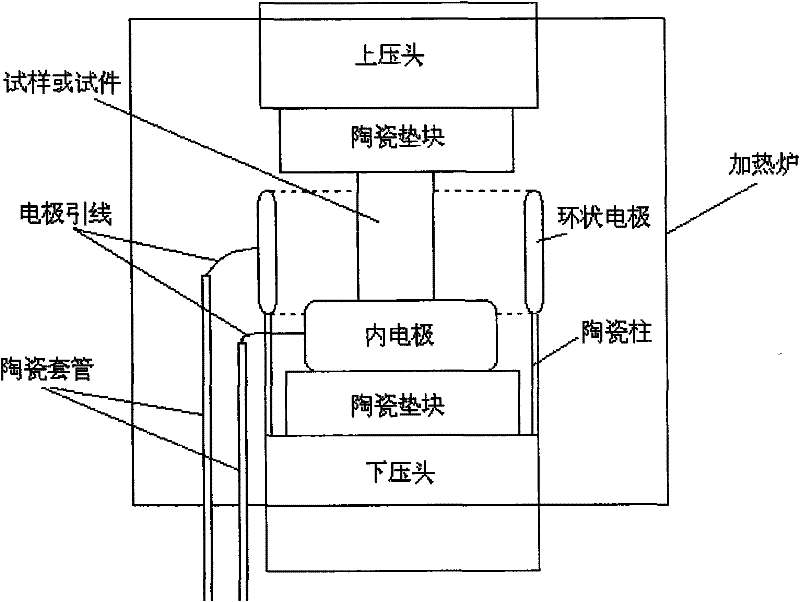
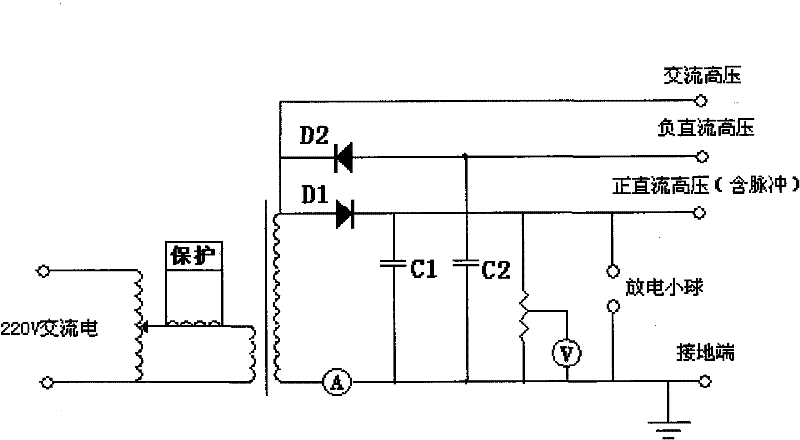
The invention relates to a high field high-temperature compression test device of solid materials, which comprises a stable high-voltage power source system used for providing various types of voltage, an electric field applying device used for making a test sample or test specimen (2) positioned in a uniform stable strong electric field, a heating and temperature control system used for ensuring the test sample or test specimen at a given temperature, and a loading and data acquiring system which loads the test sample or test specimen within the deformation velocity range of 0.02-100mm / min and can automatically detect the whole process of compression deformation. The invention can test the characteristic of high-temperature compression deformation of the materials in strong electric field environment, and related material shaping and processing technology is developed and seared on the basis, and real-time tracking, recording, data processing and display are carried out to the whole process of high-temperature compression plastic deformation. The complete set of device has the advantages of complete functions, high test precision, safety, reliability and convenient use.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel method for preparation and processing of high-performance magnesium alloy profile
ActiveCN106399884AWeaken the texture of the base surfaceGrain refinementMaterial typeUltimate tensile strength
Provided is a novel method for preparation and processing of a high-performance magnesium alloy profile. According to the method, magnesium alloy materials of the same type are subjected to plastic processing through the different-temperature hot extrusion technology, or a magnesium alloy material and a dissimilar alloy material are subjected to plastic processing through the identical-temperature / different-temperature hot extrusion technology, the extrusion speeds and the deformation speeds in the direction perpendicular to the axial direction are different due to the different temperatures or material types, then shear strain is generated on a contact interface, a basal texture weakening effect is achieved for magnesium alloy plates formed through hot extrusion, and the forming property is improved; and a grain refinement effect is achieved for magnesium alloy bars formed through hot extrusion, and the strength of the magnesium alloy bars is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
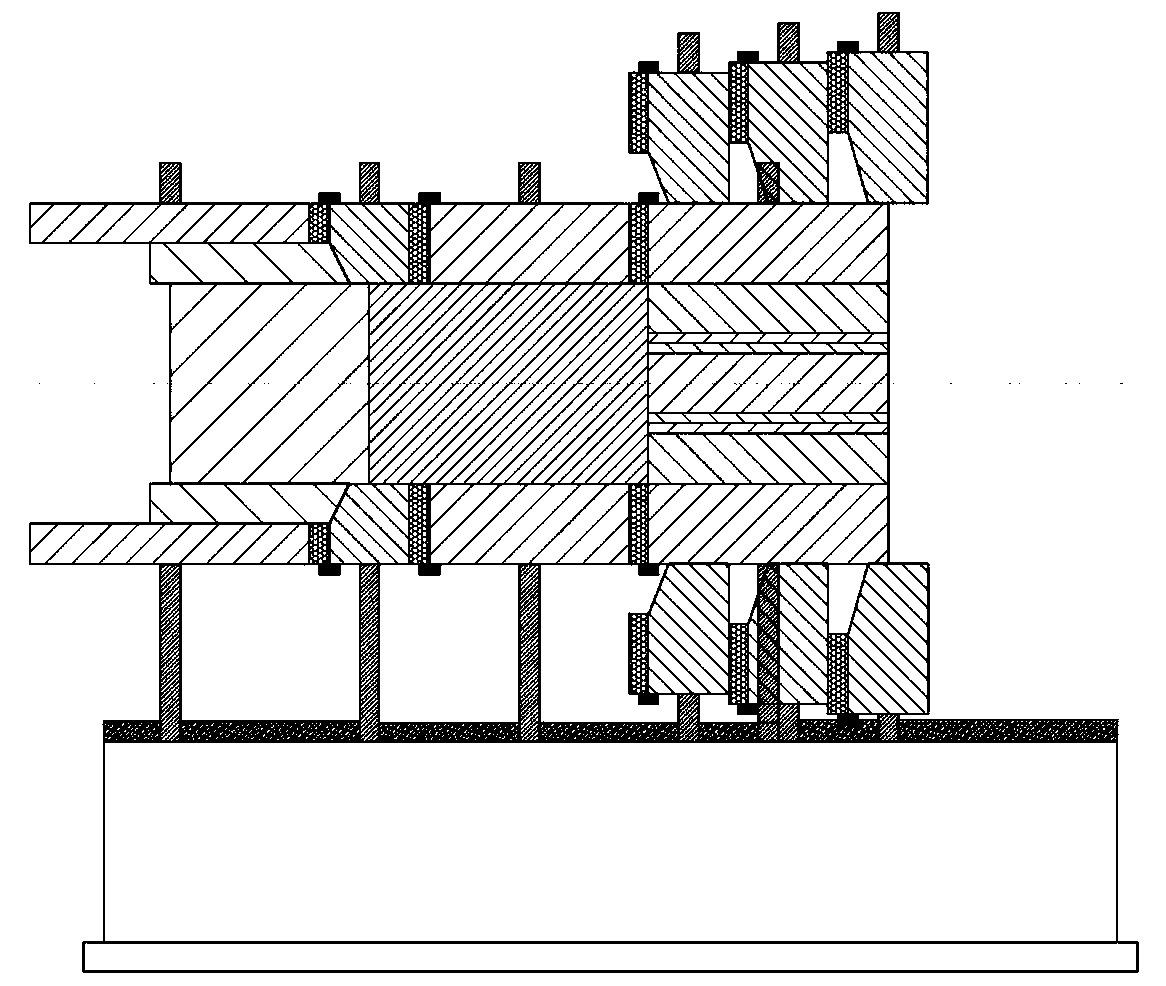
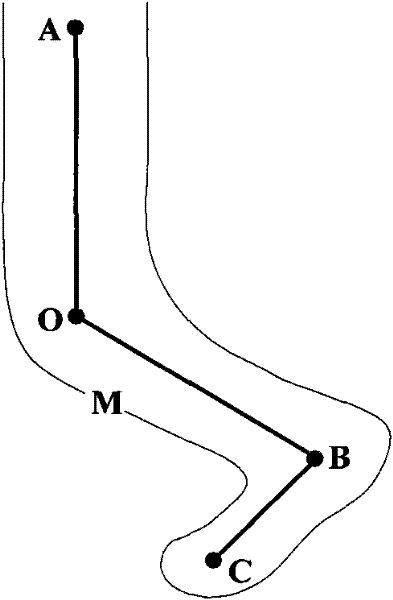
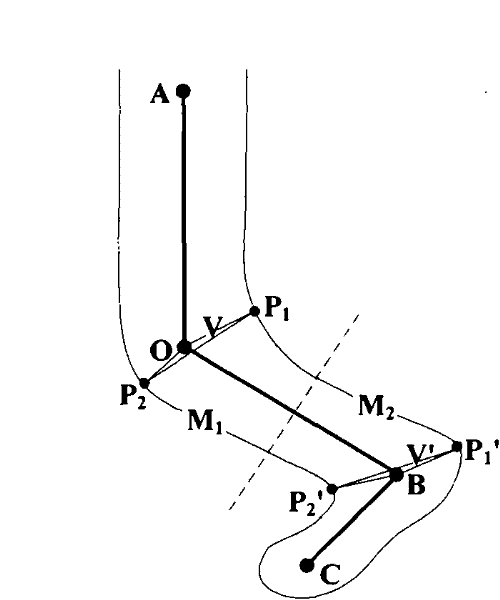
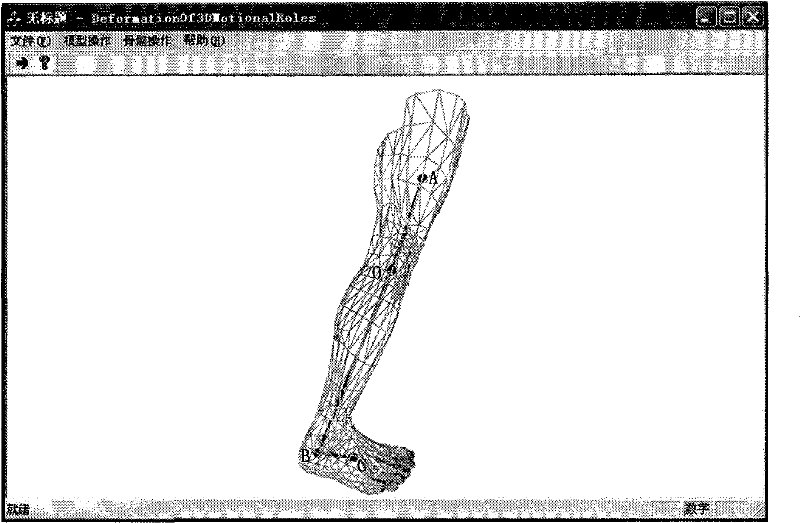
Method for carrying out segmentation on role model by utilizing grid vertexes
InactiveCN101866494AIncrease the speed of deformationQuality improvement3D-image renderingAlgorithmTorsional angle
The invention discloses a method for carrying out segmentation on role model by utilizing grid vertexes. The method comprises the steps: selecting four adjacent articulation points in a prototype, carrying out classification on the grid vertexes on the basis of a position relation of articulation points and the skeletons according to skeleton information of the role model, segmenting the role model into a plurality of local models, therefore, the method can carry out deformation on each local model to form the role model respectively, so as to improve the deformation velocity and deformation quality, acquire bending and torsional angles in a motion unit corresponding to the local model from action data and realize automatic deformation.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
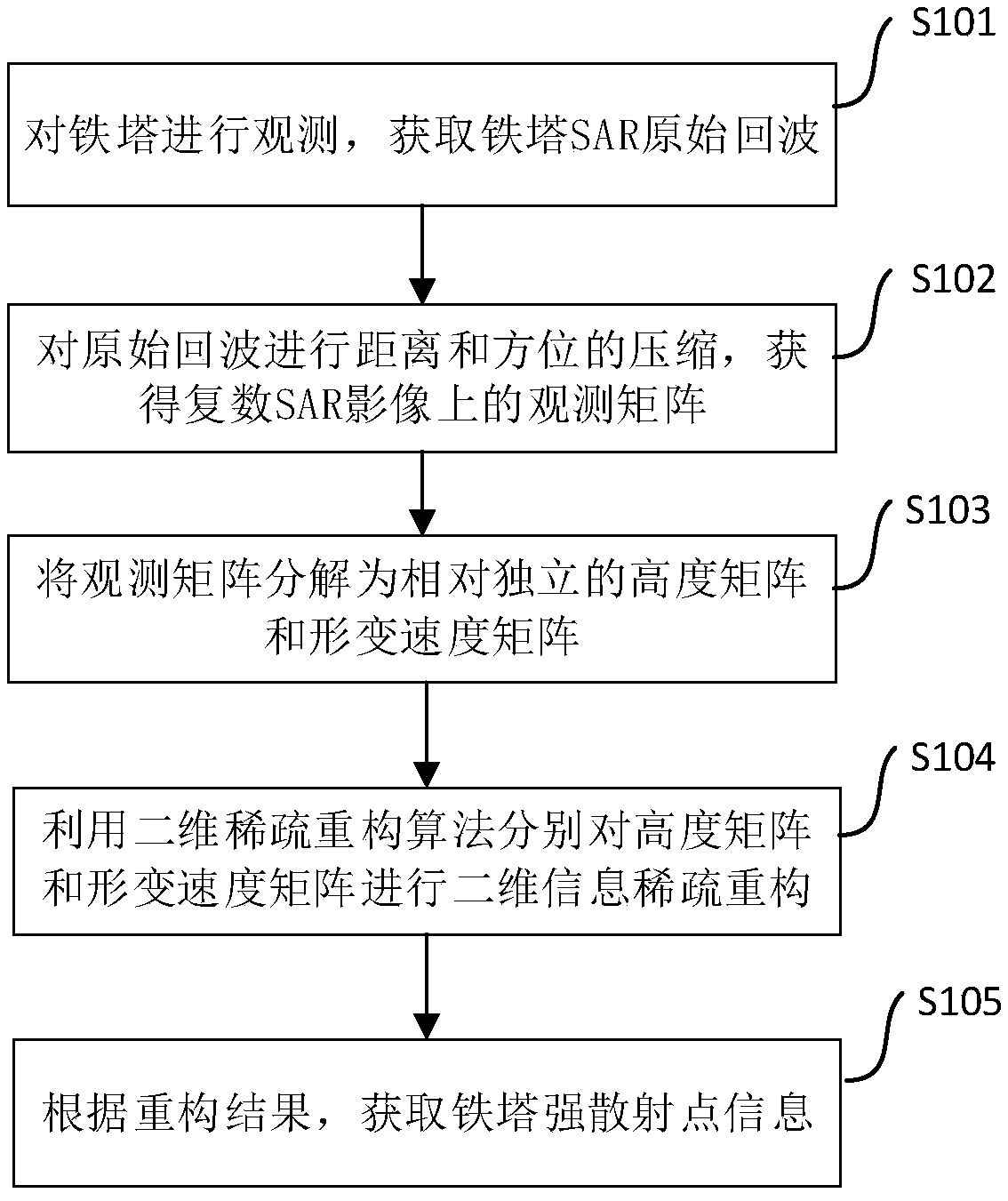
SAR differential tomography method and device
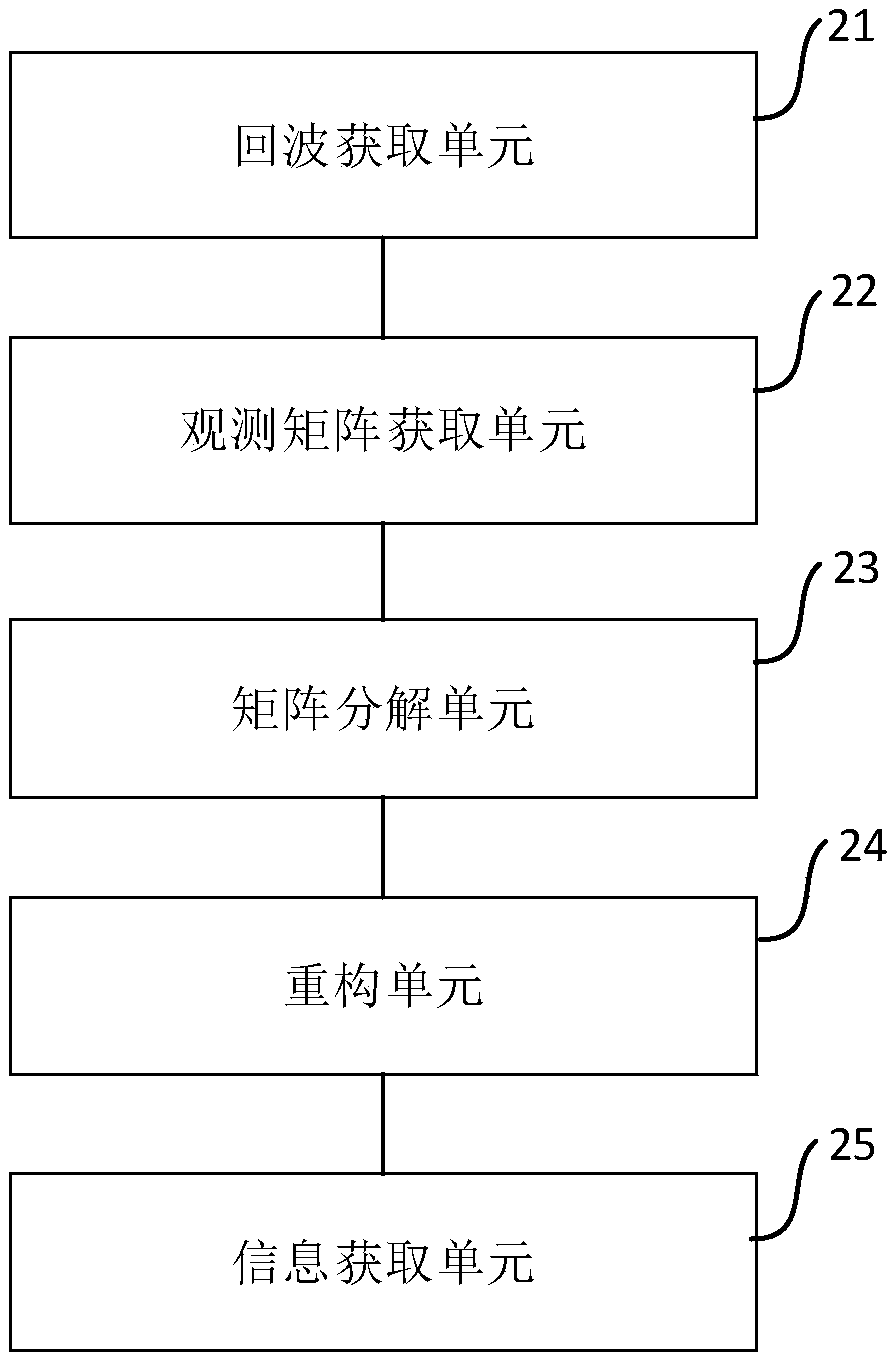
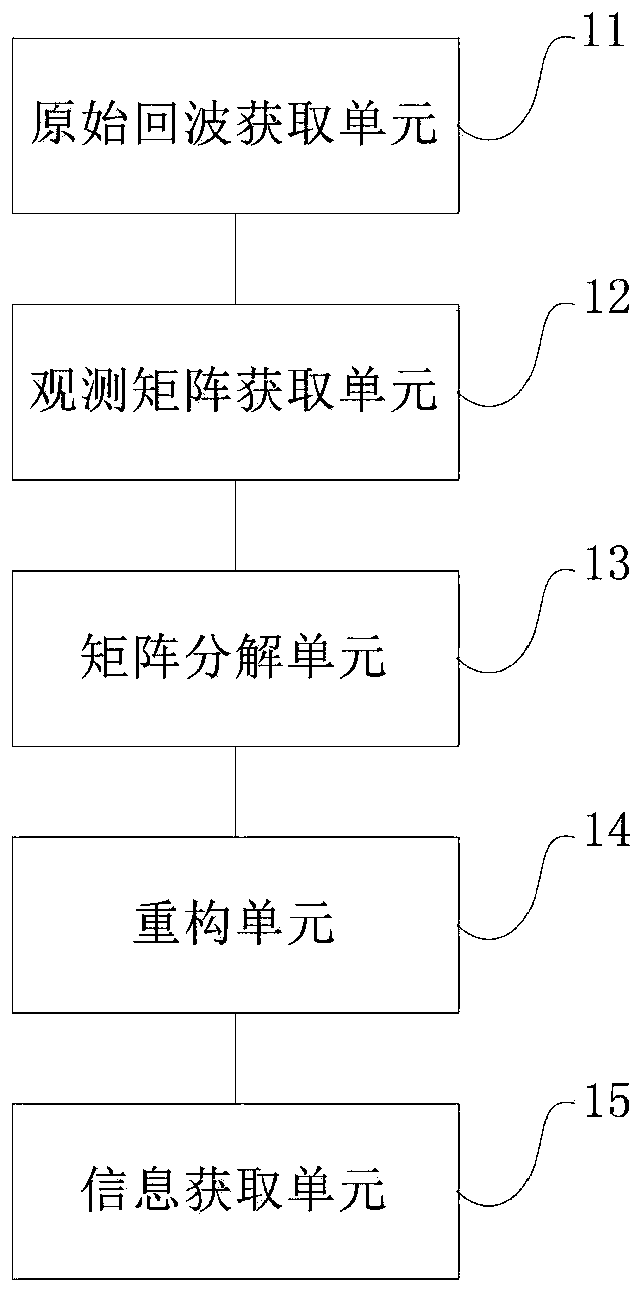
InactiveCN109521425ASolve the disadvantages of large amount of calculationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMatrix decompositionDeformation monitoring
The invention discloses an SAR differential tomography method and device. The method comprises steps that firstly, an iron tower is observed to obtain SAR original echo of the tower; secondly, the distance and the azimuth of the original echo are compressed to obtain an observation matrix of a complex SAR image; thirdly, the observation matrix is decomposed into a height matrix and a deformation velocity matrix which are relatively independent; the two-dimensional sparse reconstruction algorithm is utilized to perform two-dimensional information sparse reconstruction of the height matrix and the deformation velocity matrix respectively; and lastly, according to the reconstruction result, the strong scattering point information of the tower is obtained. The method is advantaged in that thedisadvantage of a large amount of calculation during extraction of the tower height and the deformation rate based on the sparse reconstruction method can be solved, and the practical process of the satellite remote sensing technology in transmission line tower deformation monitoring is promoted.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Deep coal seam roadway side soft coal rock anchor bar and cable supporting rationality evaluation method
ActiveCN107273636AEasy to operateEasy to implementGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationDeformation velocityRock bolt
The invention relates to a deep coal seam roadway side soft coal rock anchor bar and cable supporting rationality evaluation method. The supporting rationality can be evaluated through reflection of a constant speed stage deformation velocity coefficient value. On the basis of determining a constant speed stage deformation velocity reasonable value when the coal rock bearing capacity of different sections is exerted fully, through monitoring of soft coal rock deformation evolution characteristics along with time within a deep coal seam roadway side soft coal rock anchor bar anchorage zone and anchor cable anchorage zone and out of the anchorage zones in engineering, constant speed phase soft coal rock deformation velocity coefficients of the different sections are analyzed and the coefficients are compared with a reasonable value, thereby evaluating the rationality of anchor bar and anchor cable supporting parameters and determining the reasonable supporting parameters. The supporting reasonability can be judged in the early coal rock deformation stage, the supporting parameter adjustment can be carried out timely, and the supporting cost is minimized on the basis of ensuring the safety.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE
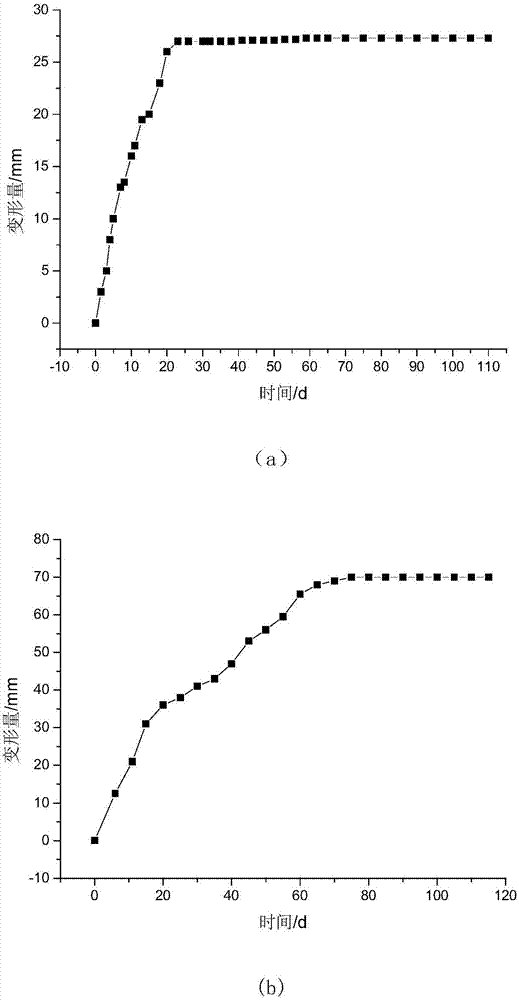
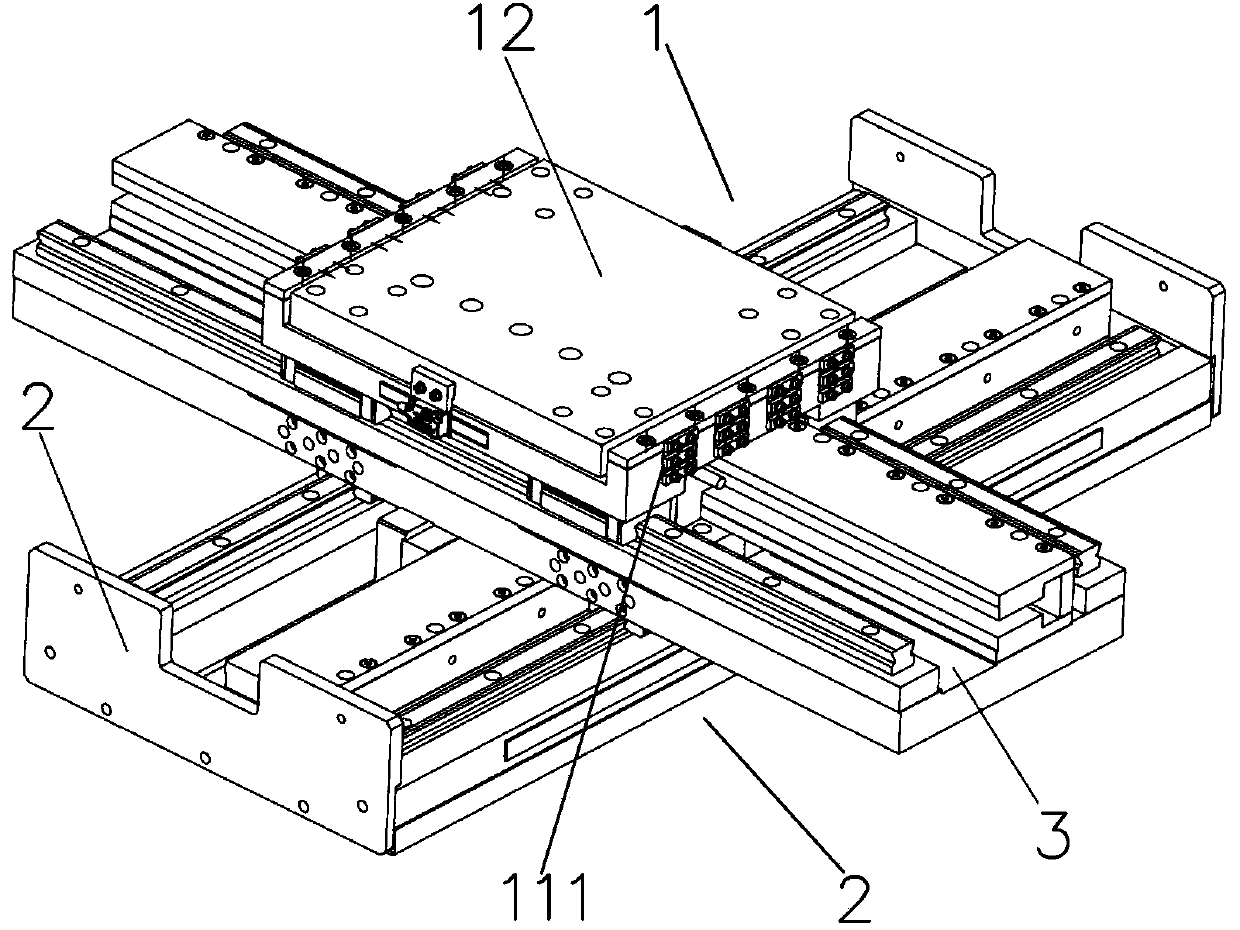
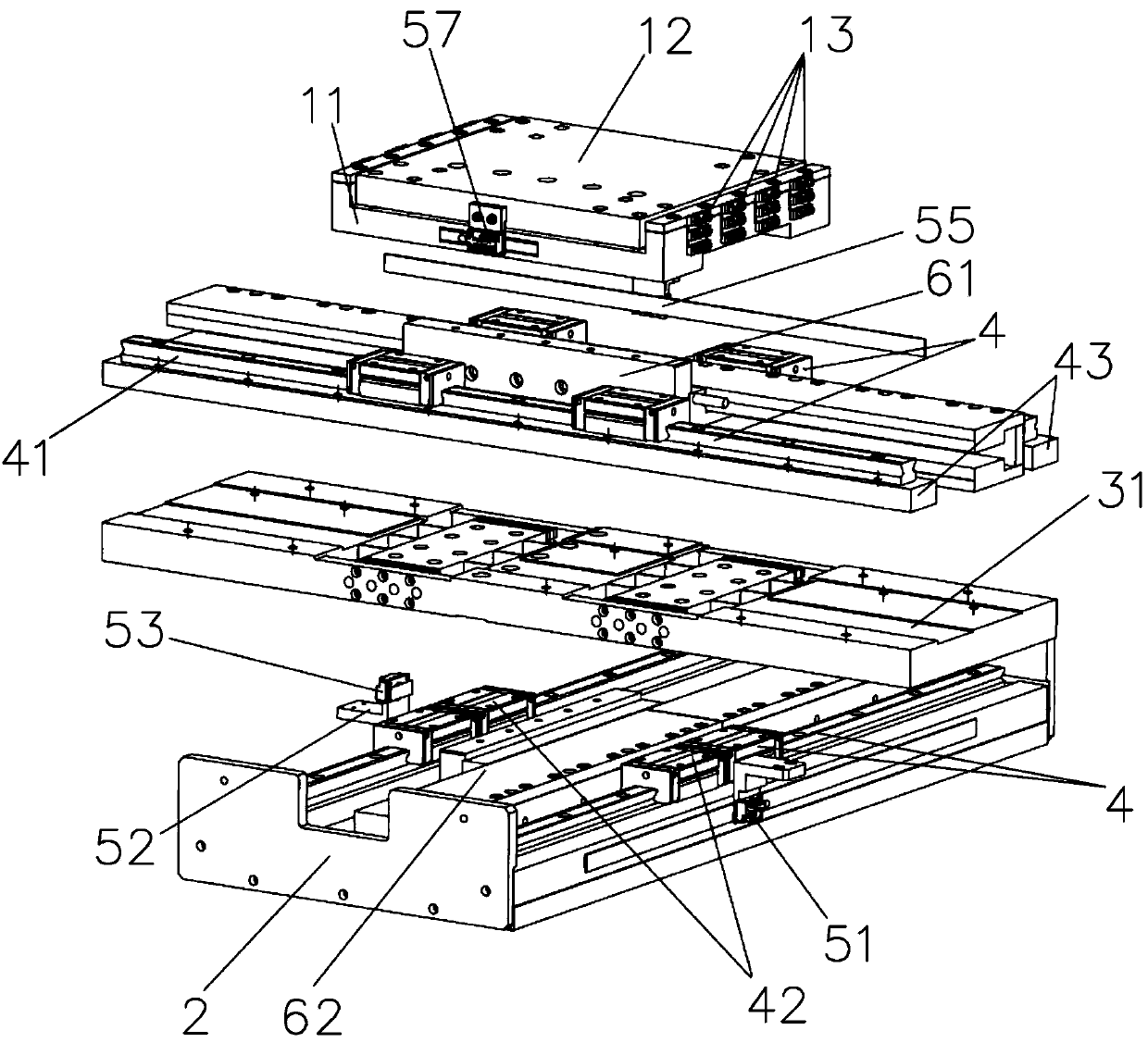
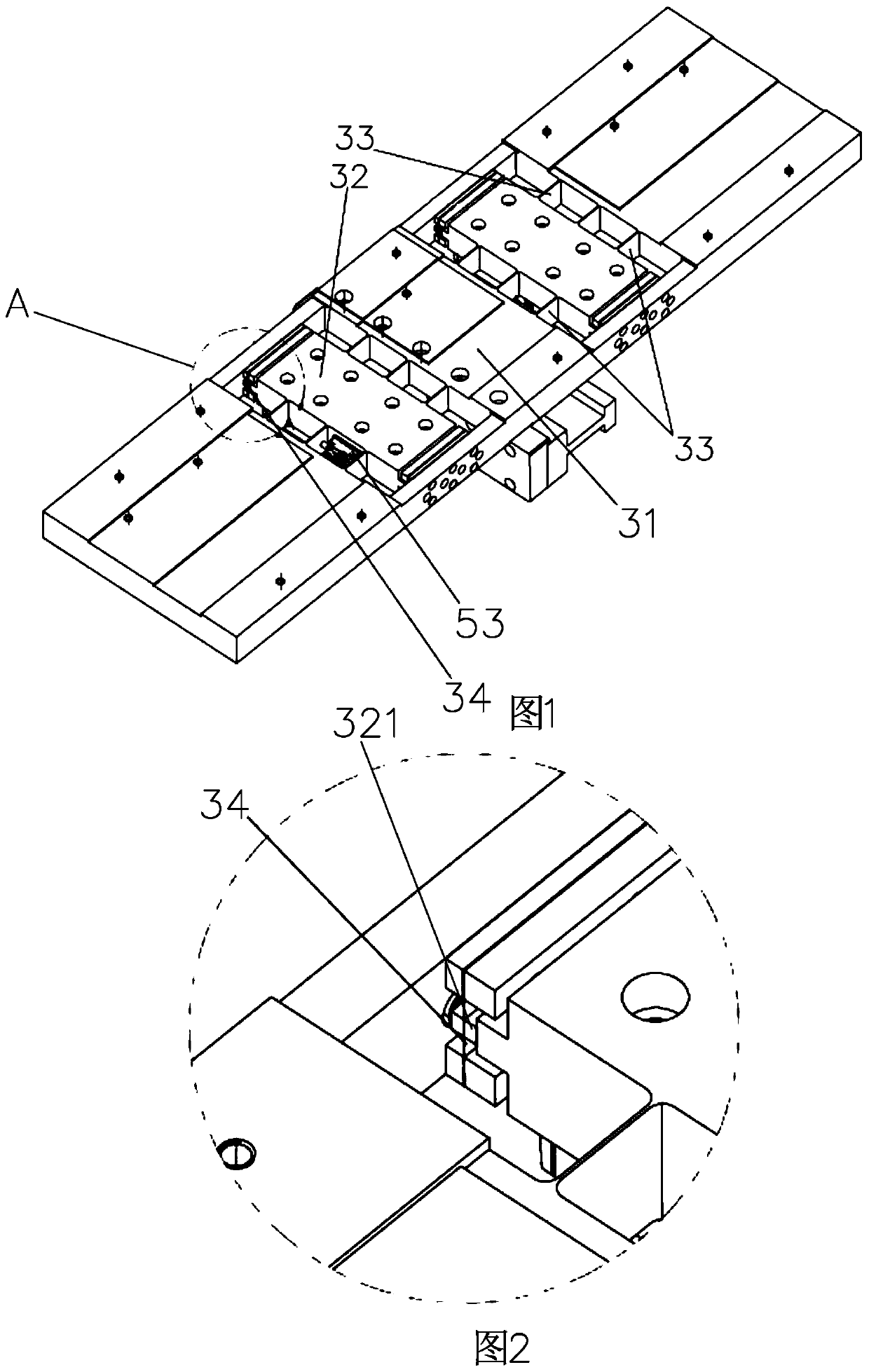
Compact rigid-flexible coupling platform connecting structure and multi-axis motion platform formed by same
The invention discloses a compact rigid-flexible coupling platform connecting structure and a multi-axis motion platform formed by same. The compact rigid-flexible coupling platform connecting structure comprises an upper platform, a lower platform, a motion detection element and a driving device, wherein an upper platform base is designed into a rigid-flexible coupling structure and is mounted ona lower platform guide rail; the driving device is mounted on the lower platform and drives the upper platform to move along the guide rail direction; the motion detection element detects the displacement or speed of an upper platform frame; and a second detection element can be selected to detect the deformation amount or deformation speed of a flexible hinge. According to the compact rigid-flexible coupling platform connecting structure, the bottom of the upper platform and the lower platform are integrated, and a middle connecting plate is omitted, so that the overall gravity center of theplatform is reduced, the structure is compact, and the Z direction is flattened; and moreover, multiple layers of platforms can be superposed, multi-degree-of-freedom motion is realized, and the required multi-degree-of-freedom high-precision motion platform is flexibly constructed. In addition, the rigid-flexible coupling connecting structure adopts the sandwich type flexible hinge, and meanwhile, no assembly error and fatigue life are guaranteed.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
SAR differential tomography method and device
InactiveCN109828272APromote the practical processSolve the large amount of calculationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMatrix decompositionAzimuth compression
The invention discloses a SAR differential tomography method and device. An iron tower is observed by using a radar to obtain an original echo of a tower SAR; distance and azimuth compression is carried out on the original echo to obtain observation matrixes on a plurality of SAR images; the observation matrixes are decomposed into a height matrix and a deformation velocity matrix; on the basis ofa two-dimensional sparse reconstruction algorithm, two-dimensional information sparse reconstruction is carried out on the height matrix and the deformation velocity matrix respectively to obtain a reconstructed height matrix and a reconstructed deformation velocity matrix; and strong scattering point information of the tower is obtained based on the reconstructed height matrix and the reconstructed deformation velocity matrix. According to the invention, the original echo of the tower SAR is processed, the height matrix and the deformation speed matrix are reconstructed by combining the two-dimensional sparse reconstruction algorithm, and then the strong scattering point information of the tower is obtained. Therefore, a problem of the large computing load for the iron tower height and deformation rate extraction in the prior art is solved; and the practical progress of the satellite remote sensing technology in the transmission line tower deformation monitoring is promoted.
Owner:YUNNAN POWER GRID CO LTD ELECTRIC POWER RES INST
Laser dynamic deflection survey vehicle
ActiveCN102162217BFast measurementWide range of measurement speed variationUsing optical meansRoads maintainenceAccelerometerDoppler velocity
The invention provides a laser dynamic deflection survey vehicle. The survey vehicle comprises a mobile measuring table, a measuring cross beam, a running wheel, a velocity measuring wheel, an accelerometer and a data acquiring and processing device. The laser dynamic deflection survey vehicle provided by the invention has the following advantages: according to the laser Doppler velocity measurement principle and the inertia measurement principle, during the driving process of the vehicle at a normal traffic velocity (15-80km / h), a plurality of laser Doppler vibration meters arranged in the front of loading wheels of the vehicle synchronously measure the relative movement velocity of various measuring points on a road surface; the instantaneous deflection deformation velocity of the road surface is obtained through inertia compensation calculation; and a dynamic deflection value of the road surface is obtained through inversion by utilizing a road layered elastic mechanical model and used for general investigation and assessment of the bearing capacity of a road network.
Owner:WUHAN WUDA ZOYON SCI & TECH
Method for measuring critical strain of continuous casting billet corner crack propagation
ActiveCN112834339AUniversalThe testing process is simpleMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMetallurgyStructural engineering
The invention discloses a method for measuring critical strain of continuous casting billet corner crack propagation, and belongs to the technical field of continuous casting. The method comprises the following steps: sampling on a continuous casting billet, and setting reasonable notch depth and angle to prefabricate cracks; then simulating a corner temperature field of the casting blank in the continuous casting process, judging a crack sensitive area, and determining a heating schedule and a deformation speed; and finally, carrying out an in-situ tensile test in combination with the actual strain rate of the crack sensitive area, dynamically observing and analyzing the microscopic deformation morphology and fracture mechanism of the material, and recording the change condition of the metallographic structure during stretching in real time; and determining the critical strain of the corner crack propagation by combining the tensile length when the crack propagation phenomenon occurs and a stress-strain curve obtained in the test. The method for measuring the critical strain of the corner crack propagation of the continuous casting billet is more universal, is not limited by components, and is simple in test process and accurate in test result.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for continuously evaluating mechanical and microstructural properties of a metallic material, in particular steel, in a cold deformation process and related apparatus
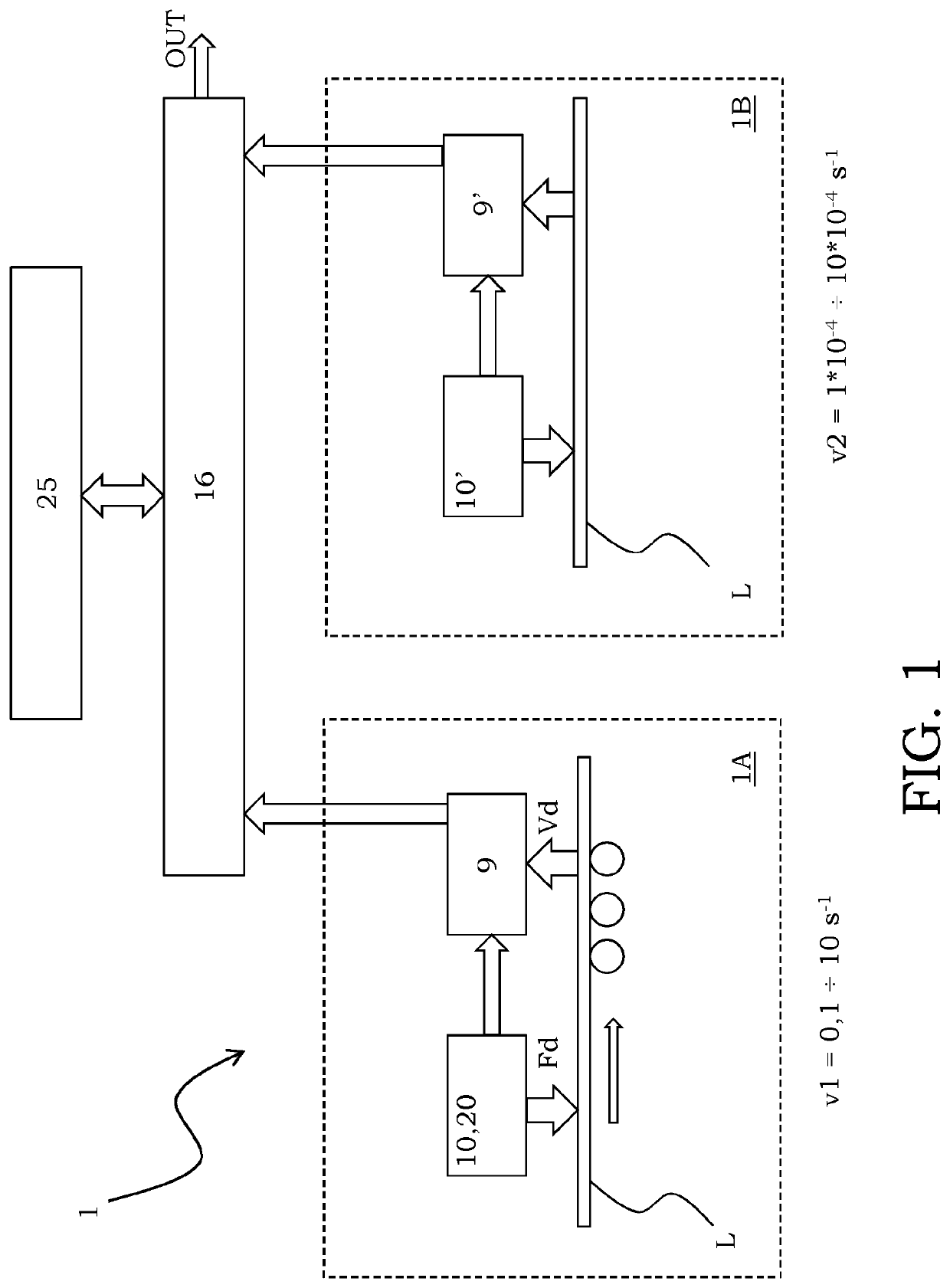
PendingUS20210096122A1Material strength using tensile/compressive forcesMaterial strength using steady bending forcesMetallic materialsThermal deformation
A method is described for continuously evaluating mechanical and micro structural properties of a rolled metallic material (L) in a cold deformation process, subjected to combinations of deformation forces selected among compression forces, traction forces and bending moment applied at low deformation speed in a range comprised between 1*10−4 and 10*10−4 s−1 which corresponds to laboratory static conditions and at high deformation speed in a range comprised between 0.1 and 10 s−1 which corresponds to dynamic pp conditions, the method comprising the step of: —measuring characteristic parameters of the cold deformation process under dynamic conditions, comprising at least one value of temperature (T), deformation (ε) and deformation speed ({acute over (ε)}) of the rolled sheet (L); characterized in that it further comprises the steps of: —calculating the traction yield strength at high deformation speed (σYD) according to equation (I), being: σc a compression strength of the rolled sheet (L) when a compression force (Fc) is applied thereon; σt a traction strength of the rolled sheet (L) when traction forces (Tin, Tout) are applied thereon;σbend a strength due to the bending of the rolled sheet (L) when a bending moment is applied thereon; and m, n, p are a first, a second and a third parameter respectively being a function of continuously-measured operating conditions of the cold deformation process and being a function of the rolled sheet (L) in terms of chemical composition and of preceding operating conditions of a hot deformation process, in terms of hot-rolling start and end temperature, winding temperature and grain size; calculating the traction yield strength at low deformation speed (σYS) according to equation (II), being: σYD the traction yield strength at high deformation speed; f a statistical optimization factor between data measured at low deformation speed and at high deformation speed; α a first characteristic parameter of the rolled sheet (L) being a function of a chemical composition of the rolled sheet (L) and of operating conditions of a hot deformation process of the rolled sheet (L); and β a second characteristic parameter of the rolled sheet (L) being a function of the cold deformation process calculated as (III), being {acute over (ε)} the deformation speed, Q an activation energy of the deformation of the rolled sheet (L) evaluated through laboratory tests, R the Boltzmann constant of ideal gases, and T the temperature of the rolled sheet (L).
Owner:MARCEGAGLIA CARBON STEEL SPA
Aircraft telescopic wing based on stroke amplifying mechanism
ActiveCN112407238ASimple structureEasy production and installationWing adjustmentsFlight vehicleStructural engineering
The invention discloses an aircraft telescopic wing based on a stroke amplifying mechanism, relates to the technical field of aerospace equipment and equipment, and aims at solving the problems that an existing aircraft telescopic wing is low in deformation speed and low in stability. The aircraft telescopic wing comprises a driving unit and two telescopic wing mechanisms, the two telescopic wingmechanisms are arranged back to back, each telescopic wing mechanism comprises an inner wing cover plate, an inner wing, a main rotating shaft, an outer wing, a transmission unit, a locking unit and aguide unit, the inner wing cover plate covers the upper end face of the inner wing, and the front end of the main rotating shaft is rotationally connected with the front end of the inner wing; the outer wing is arranged in the outer side of the main rotating shaft, the driving unit controls the outer wing to extend towards the outer side of the inner wing along the guide unit through the transmission unit, and the outer wing is locked through the locking unit after being unfolded in place. The aircraft telescopic wing is used for aerospace crafts.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
A Displacement Amplified Corrugated Web Damper
ActiveCN110056235BCan't give full play to energy dissipation capacityGive full play to energy dissipation capacityProtective buildings/sheltersShock proofingRelative displacementGear wheel
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
A compact rigid-flexible coupling platform connection structure and its multi-axis motion platform
The invention discloses a compact rigid-flexible coupling platform connection structure and a multi-axis motion platform formed thereof, including an upper platform, a lower platform, a motion detection element and a driving device, and the base of the upper platform is designed as a rigid-flexible coupling structure and installed on the lower layer The driving device is installed on the platform guide rail and the lower platform, and the driving device drives the upper platform to move along the direction of the guide rail; the motion detection element detects the displacement or speed of the upper platform frame, and the second detection element is optional to detect the deformation or deformation of the flexible hinge speed. The present invention integrates the bottom of the upper platform with the lower platform, eliminating the need for an intermediate connecting plate, so that the overall center of gravity of the platform is reduced, the structure is compact, and the Z direction is flatter, and multi-layer platforms can be superimposed to realize multi-degree-of-freedom movement and flexibility To build the required multi-degree-of-freedom high-precision motion platform. In addition, the rigid-flexible coupling connection structure of the present invention adopts a sandwich-type flexible hinge, while ensuring no assembly error and fatigue life.
Owner:FOSHAN HUADAO SUPER PRECISION TECH CO LTD
Energy dissipation extension arm capable of amplifying interlayer deformation and method thereof
PendingCN114562141AImprove work efficiencyAvoid damageProtective buildings/sheltersShock proofingEngineeringDamper
The invention provides an energy dissipation extending arm capable of amplifying interlayer deformation. The energy dissipation extending arm comprises a core tube, an outer frame column and an extending arm truss. The core tube and the outer frame column are connected through the outrigger truss; the outrigger truss comprises an upper chord member, a lower chord member and diagonal web members; the device is characterized by further comprising an amplification lever, the first end of the amplification lever is connected to the damper, the second end of the amplification lever is connected to one of the upper chord member and the lower chord member, the damper is connected with the other one of the upper chord member and the lower chord member, and the diagonal web member is connected with the amplification lever. The working efficiency of the damper is effectively improved by amplifying the lever effect, under the small external force effect, the deformation amount and the deformation speed are amplified through the mechanical effect to excite the damper effect, a large amount of external input energy is consumed, the damage effect of external input on a main body structure is reduced, and the structural comfort and the anti-seismic safety performance are improved; and the method has important practical significance on the development of a super high-rise structure.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN
High field high-temperature compression test device and method of solid materials
InactiveCN101762427BAc-dc conversion without reversalMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesData acquisitionEngineering
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
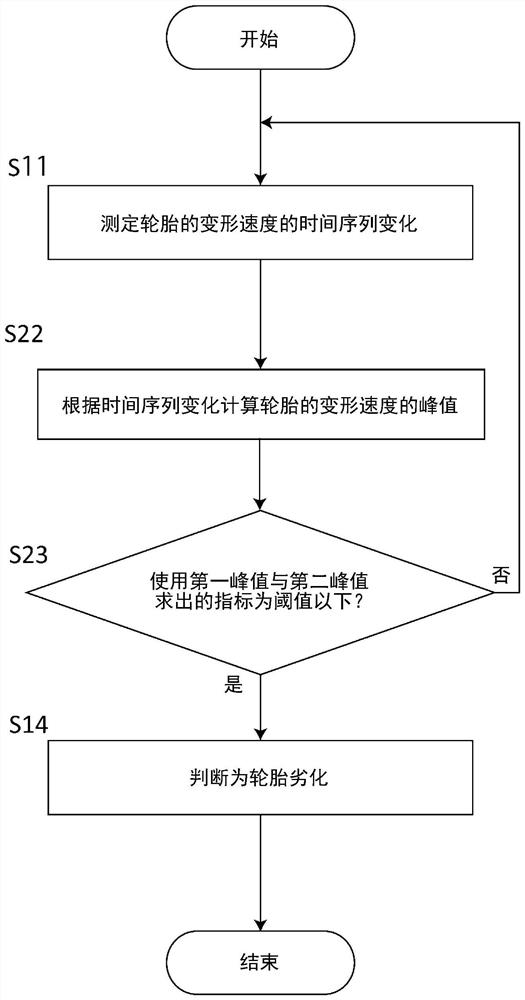
Tire degradation estimating device, and tire degradation estimating method
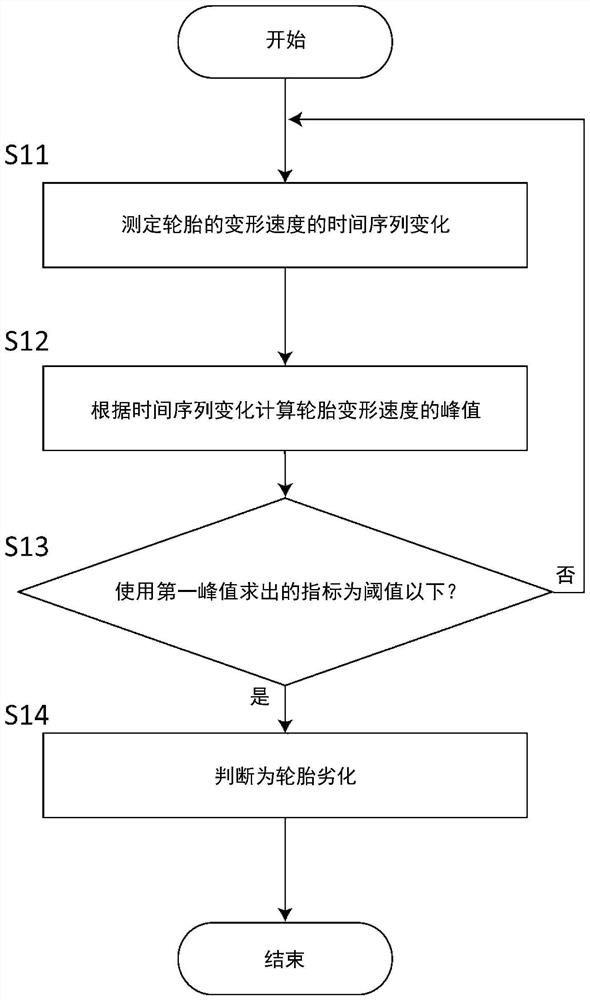
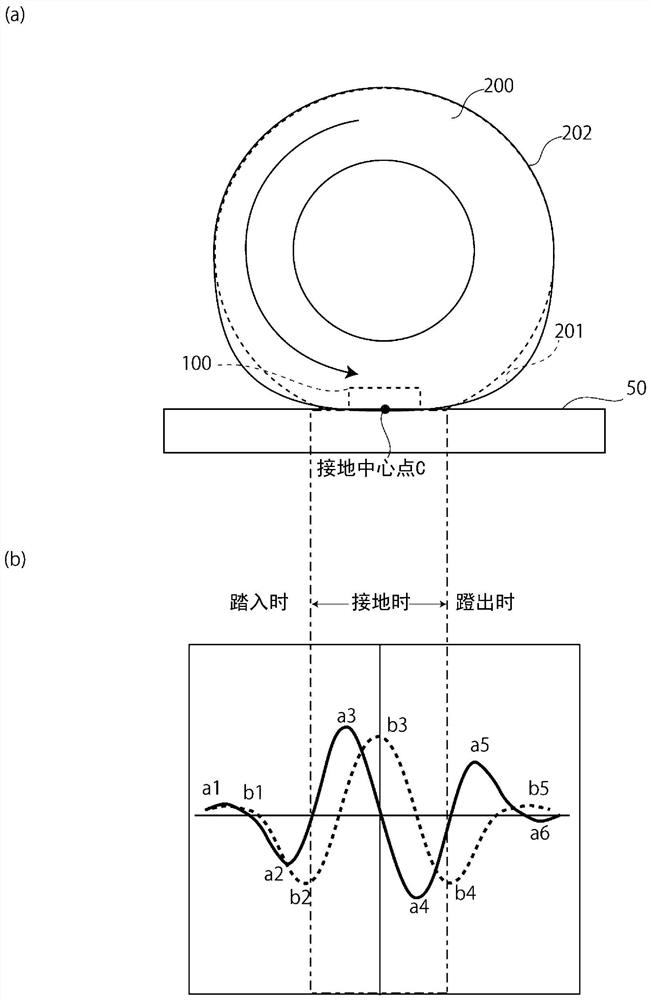
A tire degradation estimating method according to an embodiment of the present invention utilizes a tire degradation estimating device configured on the inner side surface of a tire. The method includes: a deformation speed measuring step (S11) of measuring a tire deformation speed, which is the deformation speed of the tire when the tire is rotating, and obtaining a time-series variation of the tire deformation speed; a calculating step (S12) of calculating a peak value of the tire deformation speed from the time-series variation of the tire deformation speed; and an estimating step (S13) of estimating the degree of degradation of the tire by using a first peak value, which is the peak value of the tire deformation speed before lead-in of the tire or after trail-out of the tire, in the time-series variation of the tire deformation speed. Accordingly, the degree of degradation of a tire can be estimated.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Calculation method for deformation resistance of common steel of GCr15, 60Si2Mn and 42CrMo
PendingCN111475917AComplex problems simplifiedImprove calculation accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationMetal rolling arrangementsElectric machineryDeformation velocity
The invention relates to a model for calculating the deformation resistance of common steel of GCr15, 60Si2Mn and 42CrMo. A deformation resistance and deformation degree, deformation temperature and deformation speed calculation formula are found out through deformation resistance chart regression; polynomial regression is adopted for the deformation degree influence coefficient, logarithmic regression is adopted for the deformation speed influence coefficient, logarithmic regression is adopted for the deformation speed temperature influence coefficient, the regression method simplifies complex problems, and the formula has the biggest characteristic of being high in calculation precision and can be used for checking the capacity of rollers, speed reducers and motors on a production site.
Owner:JIANGYIN XINGCHENG SPECIAL STEEL WORKS CO LTD
Wrought processed magnesium-based alloy and method for producing same
In order to improve the ductility or formability of a magnesium alloy, addition of rare earth elements or refinement of grain size is often used. However, conventional additional elements inhibit the action of grain boundary sliding for complementing plastic deformation. Therefore, it is required to search for additional elements that act to facilitate the grain boundary sliding not only at a conventional deformation speed but also in a higher speed range while maintaining a microstructure for activating non-basal dislocation. The present invention is to provide a wrought processed Mg-based alloy having excellent ductility at room temperature, which consists of 0.25 mass % or more to 9 mass % or less of Bi, and a balance of Mg and inevitable components, and is characterized by having an average grain size of an Mg parent phase after solution treatment and hot plastic working after casting of 20 μm or less.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI
A test device and method for dynamic bending resistance of automobile side pillars hitting key parts
ActiveCN107505142BReduce testing costsSimple Boundary ConstraintsVehicle shock testingCrash testRigid wall
The invention discloses a device and method for testing dynamic bending resistance performance of key parts in an automobile side post impact in order to overcome defects of large resource consumption and long development cycle caused by complete vehicle crash tests which are generally adopted in safety performance development for automobile side post impact currently. The testing device comprises a support assembly installed on a rigid wall for fixing a testing member and a collision structure applying a dynamic impact on the testing member. The device and method for testing the dynamic bending resistance performance of the collision key parts of the automobile side column can perform a dynamic impact test on the testing member installed on the support assembly through the collision structure, can simulate a bending resistance performance of the testing member under a high-speed impact, wherein the deformation speed of the testing member accords with that of the testing member in the integral automobile test, and thus can more accurately and efficiently perform an optimization design on the testing member. Furthermore, the support assembly and the collision structure are wide in universality, simple in structure, low in cost, easy to set up, easy to install and dismount, and can be repeatedly used and tested for many times.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
A powder superalloy component stage heating extrusion control device and its use method
ActiveCN108994299BImprove overall utilizationRealize the integration of solidification and controlDeformation velocitySuperalloy
The invention relates to a stage heating and extrusion controlling device for powder superalloy members and a using method. According to the using method, with the help of the deformation temperatureand pressure of stage change, the low-temperature and low-pressure curing and high-temperature and high-pressure controlling of powder materials at a time are realized. The method comprises the stepsthat firstly, powder is preliminarily cured under the conditions of lower temperature (no more than 700 DEG C) and lower pressure (no more than 500 MPa); then, the superalloy powder is completely densified by increasing the temperature (no more than 1000 DEG C) and combining plastic deformation parameters such as low extrusion ratio (no more than 2:1) and deformation speed, and a powder superalloyingot with certain deformation is obtained; and a microstructure with the grain size being 7-13 levels can be obtained by further increasing the temperature (no more than 1100 DEG C) and combining plastic deformation parameters such as larger extrusion ratio ((4:1)-(9:1)) and deformation speed. The integration of solidification-control of the powder superalloy members is achieved, the technological process is simplified, the development cycle is shortened, the material utilization rate is improved, and the manufacturing cost of the members is reduced.
Owner:AVIC BEIJING INST OF AERONAUTICAL MATERIALS
Method for carrying out segmentation on role model by utilizing grid vertexes
InactiveCN101866494BIncrease the speed of deformationQuality improvement3D modellingAlgorithmTorsional angle
The invention discloses a method for carrying out segmentation on role model by utilizing grid vertexes. The method comprises the steps: selecting four adjacent articulation points in a prototype, carrying out classification on the grid vertexes on the basis of a position relation of articulation points and the skeletons according to skeleton information of the role model, segmenting the role model into a plurality of local models, therefore, the method can carry out deformation on each local model to form the role model respectively, so as to improve the deformation velocity and deformation quality, acquire bending and torsional angles in a motion unit corresponding to the local model from action data and realize automatic deformation.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for preparing ultrahigh strength high toughness magnesium alloy
The invention relates to a preparation method for ultrahigh strength high toughness magnesium alloy. The ultrahigh strength high toughness magnesium alloy comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 6-13% of gadolinium, 2-6% of yttrium, 0.3-0.8% of zirconium, and the balance of magnesium and inevitable impurities. The magnesium alloy billets are subjected to powerful thermal deformation, and then the magnesium alloy subjected to thermal deformation is subjected to rapid warm deformation at 110-150 DEG C, wherein the deformation force is 1-4KN, the deformation speed is 15-24mm / s, and the total deformation is 10-40%. The magnesium alloy is subjected to aging heat treatment after rapid warm deformation at 140-250 DEG C for 23-38 hours. The alloy subjected to warm deformation at room temperature has a strength of extension of 610-647 MPa, the yield strength of 547-585 MPa, the percentage elongation after fracture of 6-10%. The aging state alloy at room temperature has the strength of extension of 710-749 MPa, the yield strength of 675-710 MPa, and percentage elongation after fracture of 3.8-6.9 %.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Method for increasing the process stability during the hot rolling of steel or nonferrous materials
InactiveCN100479942CGuaranteed output thicknessRoll mill control devicesMetal rolling arrangementsNonferrous metalHot rolled
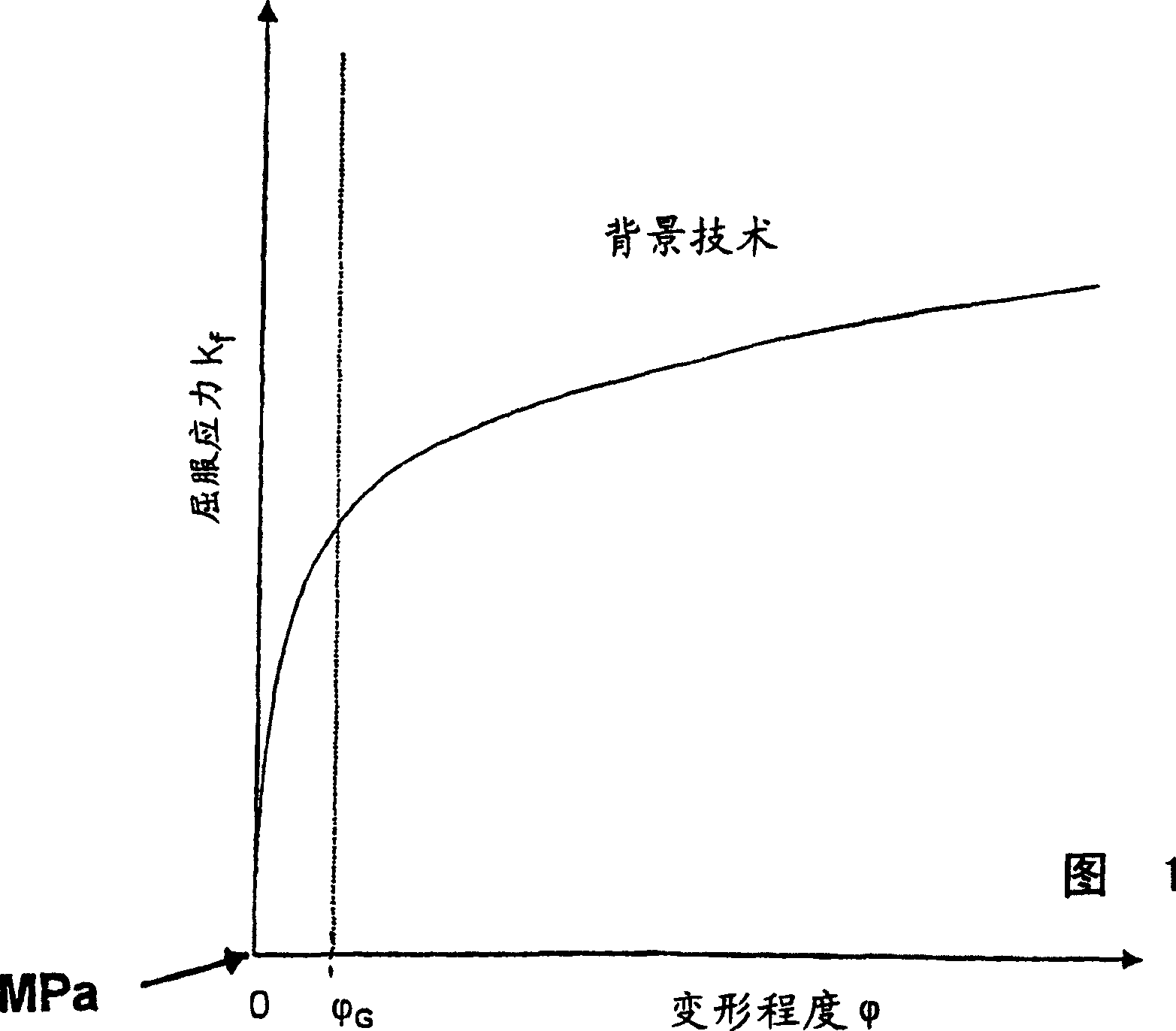
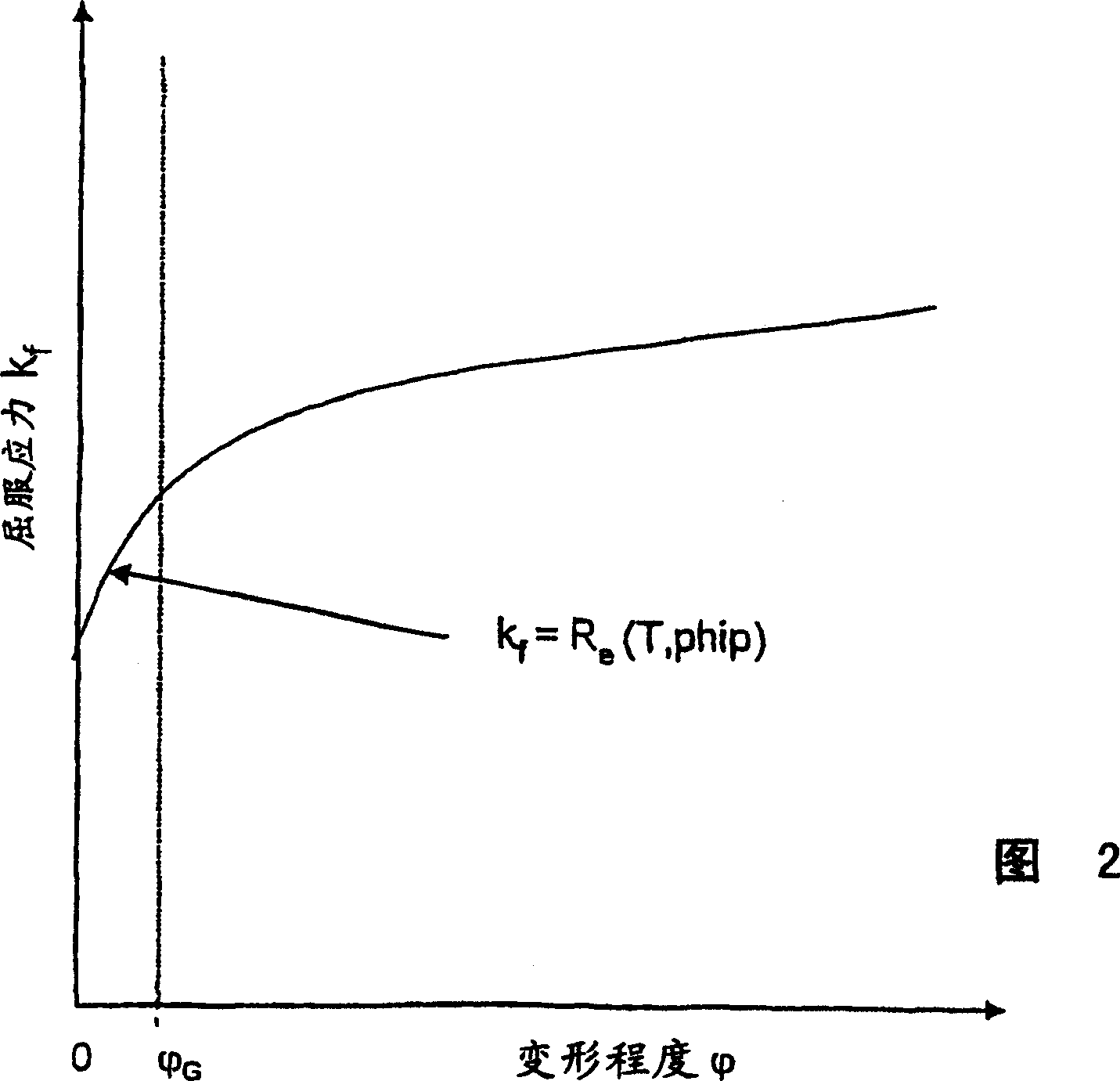
The invention relates to a method for increasing the process stability, particularly the absolute thickness precision and the installation safety during the hot rolling of steel or nonferrous materials, with small degrees of deformation (fi) or no reductions while taking the high-temperature limit of elasticity (Re) into account when calculating the set rolling force (FW) and the respective setting position (s). The process stability can be increased with regard to the precision of the yield stress (kf,R) and the set rolling force (FW) at small degrees of deformation (f) or small reductions, during which the high-temperature limit of elasticity (Re) is determined according to the deformation temperature (T) and / or the deformation speed (phip) and is integrated into the function of the yield stress (kf) for determining the set rolling force (FW) via the relation (2) ) Re= a + e . phip, in which: Re represents the high-temperature limit of elasticity; T represents the deformation temperature; phip represents the deformation speed, and; a, b, c represent coefficients.
Owner:SMS DEMAG AG
A New Method of Machining High Performance Magnesium Alloy Profiles
ActiveCN106399884BWeaken the texture of the base surfaceGrain refinementDeformation velocityUltimate tensile strength
Provided is a novel method for preparation and processing of a high-performance magnesium alloy profile. According to the method, magnesium alloy materials of the same type are subjected to plastic processing through the different-temperature hot extrusion technology, or a magnesium alloy material and a dissimilar alloy material are subjected to plastic processing through the identical-temperature / different-temperature hot extrusion technology, the extrusion speeds and the deformation speeds in the direction perpendicular to the axial direction are different due to the different temperatures or material types, then shear strain is generated on a contact interface, a basal texture weakening effect is achieved for magnesium alloy plates formed through hot extrusion, and the forming property is improved; and a grain refinement effect is achieved for magnesium alloy bars formed through hot extrusion, and the strength of the magnesium alloy bars is improved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
A method for measuring the critical strain of crack propagation in the corner of continuous casting slab
ActiveCN112834339BUniversalThe testing process is simpleMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesCrazingDeformation velocity
The invention relates to a method for measuring the critical strain of crack propagation at the corner of a continuous casting slab, which belongs to the technical field of continuous casting. The method is as follows: first take samples from the continuous casting slab, and set a reasonable notch depth and angle to prefabricate cracks. Afterwards, the temperature field at the corner of the slab in the continuous casting process is simulated, the crack sensitive area is judged, and the heating system and deformation speed are determined. Finally, an in-situ tensile test was carried out in combination with the actual strain rate in the crack-sensitive area to dynamically observe and analyze the microscopic deformation morphology and fracture mechanism of the material, and record the changes in the metallographic structure during stretching in real time. The critical strain for crack growth at the corner is determined by combining the tensile length when crack growth occurs and the stress-strain curve obtained in the test. This method provides a method for measuring the critical strain of crack propagation at the corner of the continuous casting slab, which is more universal, not limited by the composition, the test process is simple, and the test results are accurate.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com