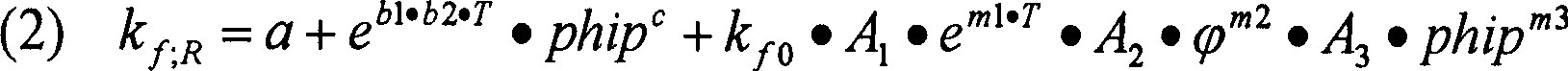Method for increasing the process stability during the hot rolling of steel or nonferrous materials
A non-ferrous, stable technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
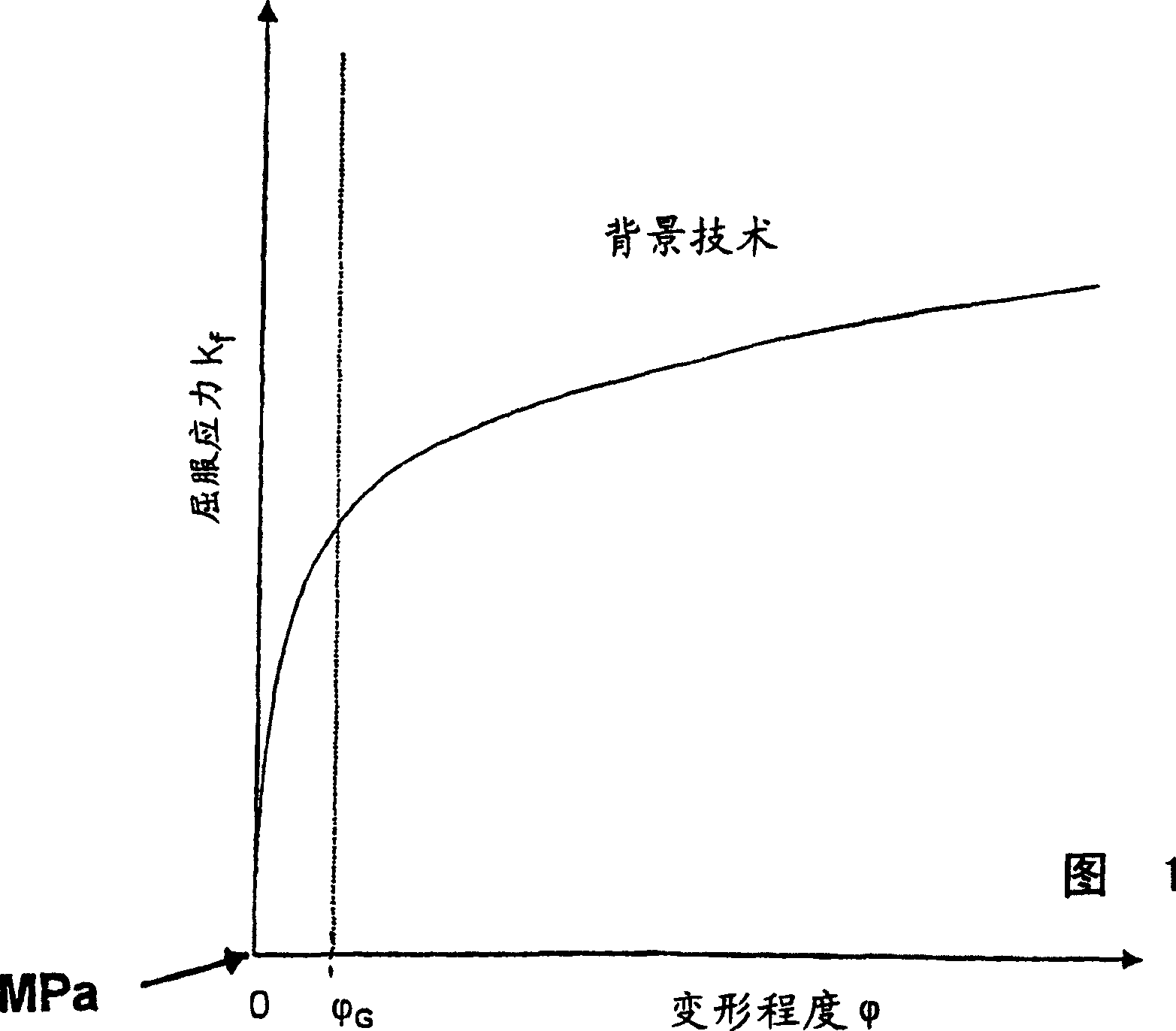
[0063] The disadvantage of the multiplicative formula (Fig. 1) for the determination of the yield stress is that the function tends towards small degrees of deformation f is 0MPa, which means that the function passes through zero, as shown in the figure.
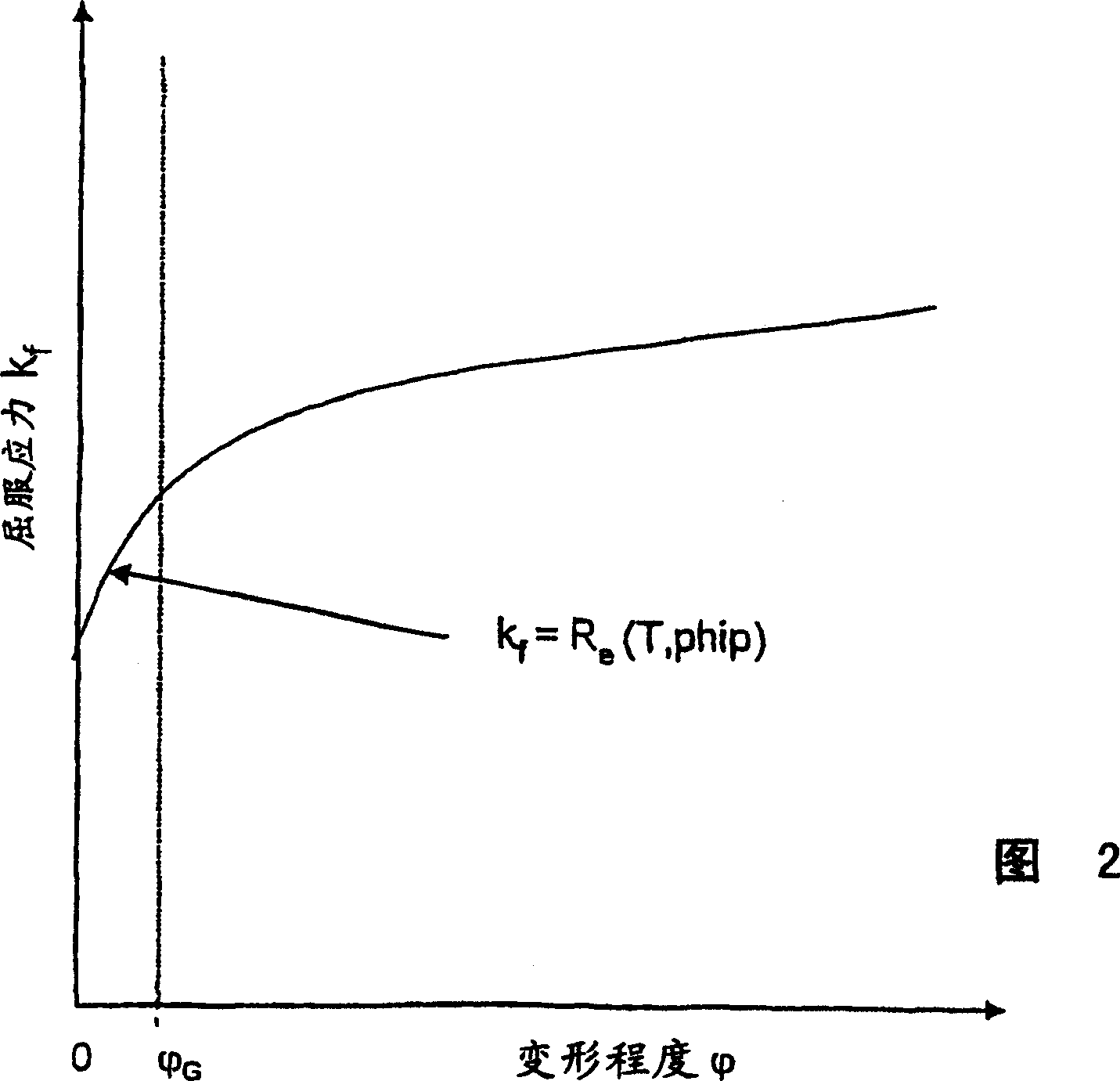
[0064] The high temperature yield limit R according to the invention depends on the deformation temperature T and the deformation speed phip e Consideration (Fig. 2) makes the method according to the invention itself towards the minimum degree of deformation to get the correct value. The starting value is the corresponding high temperature yield limit R of the material to be rolled depending on the deformation temperature T and the deformation speed phip e .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com