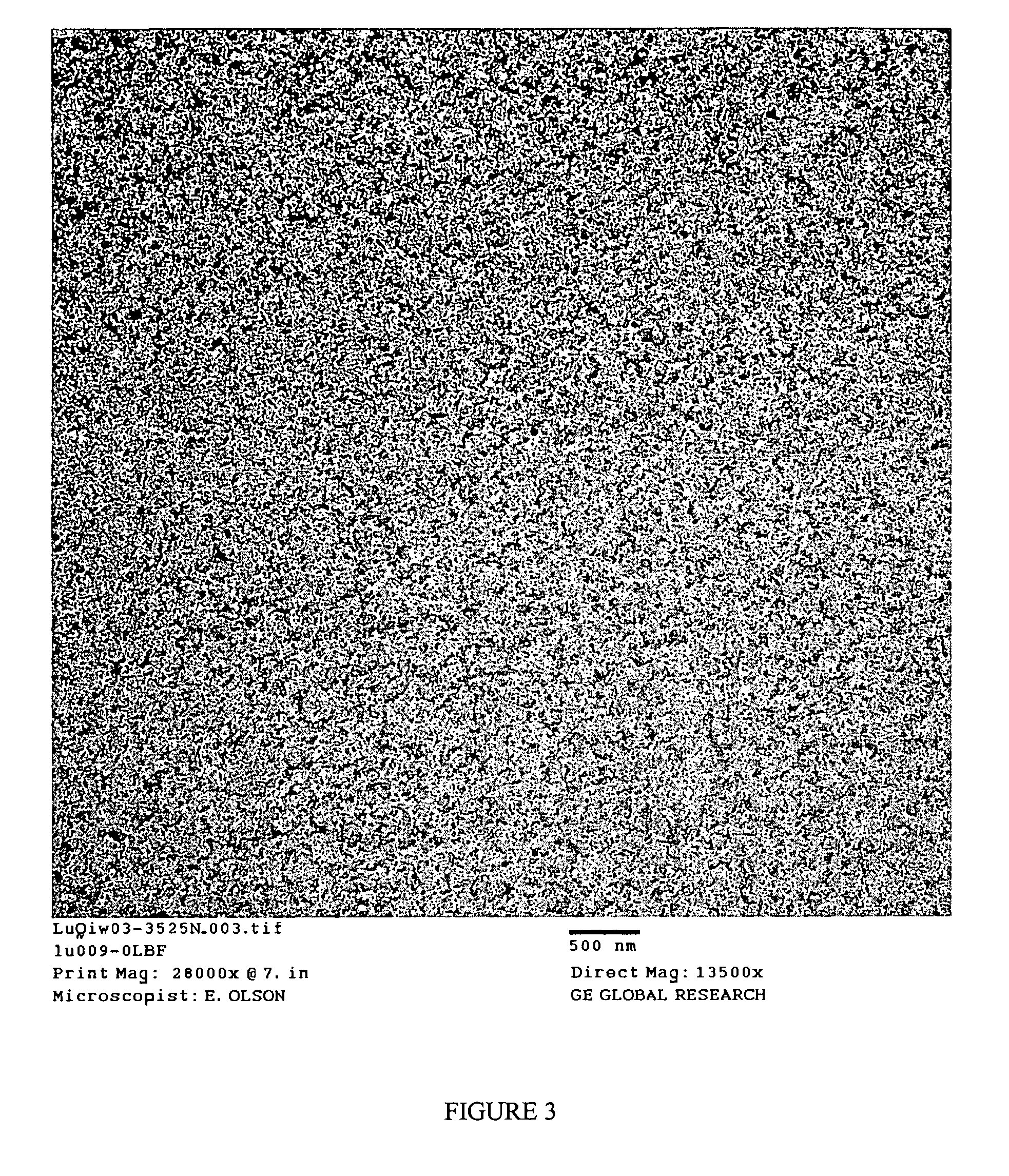
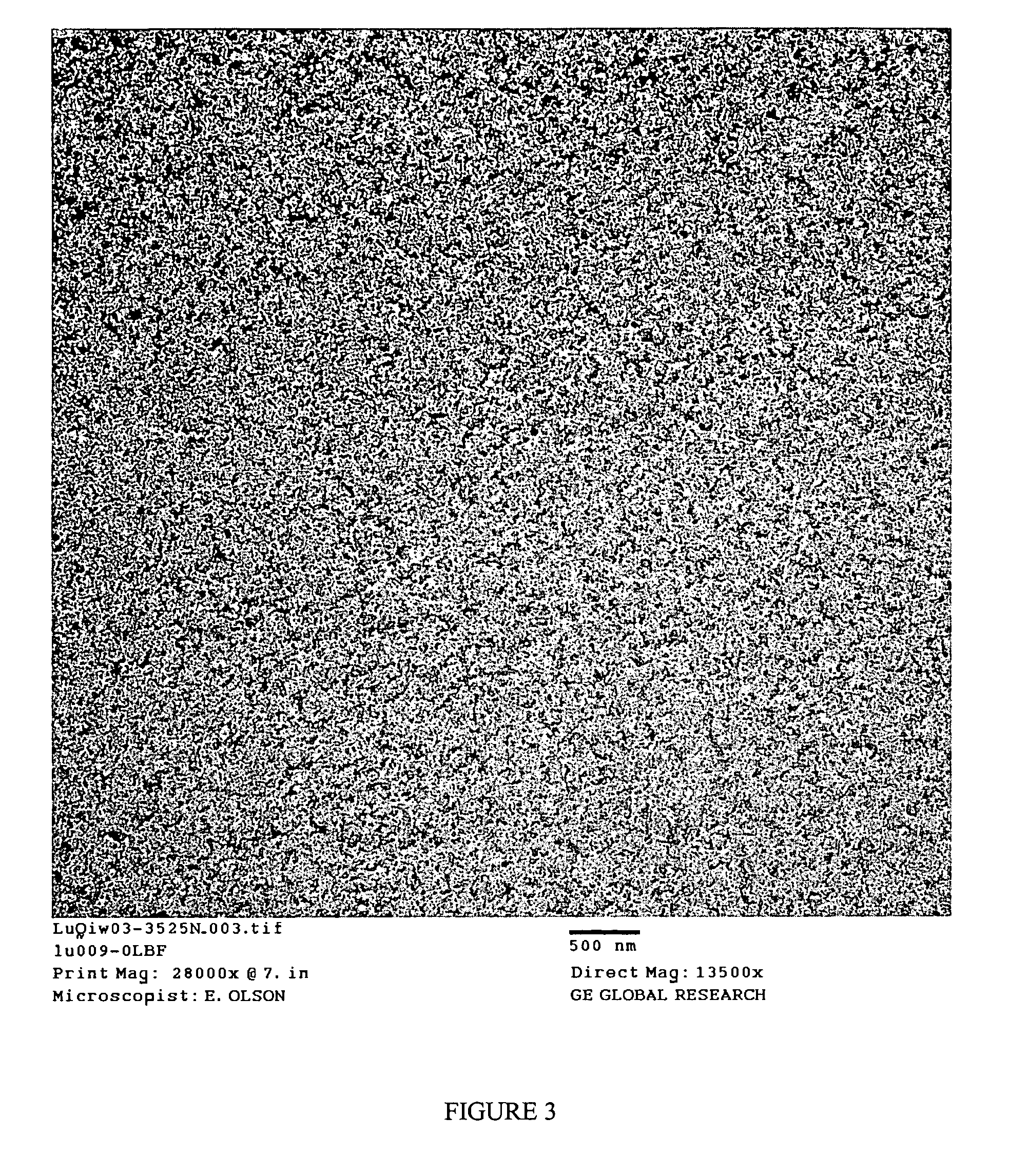
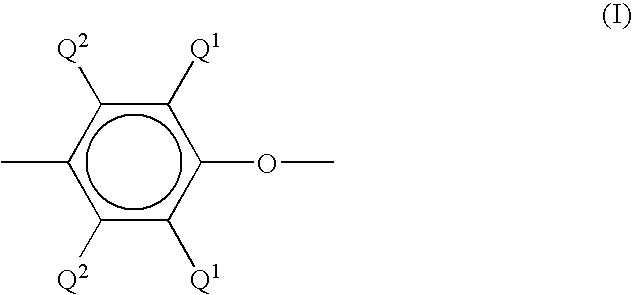
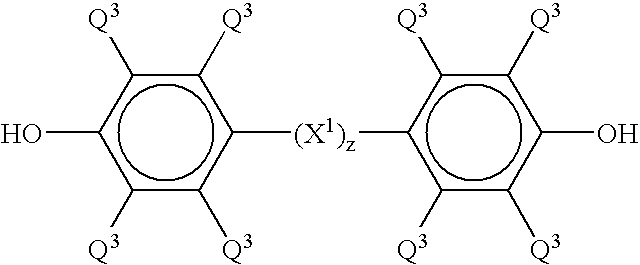
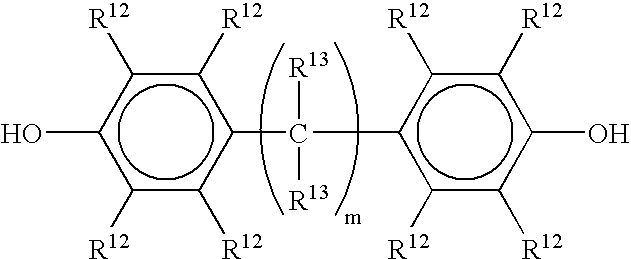
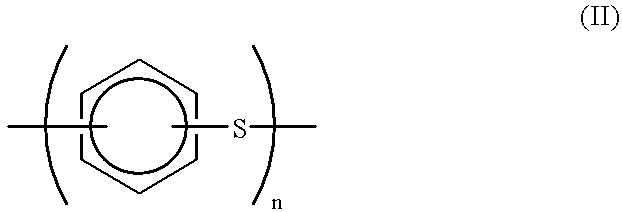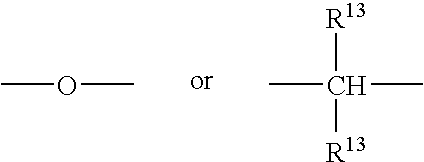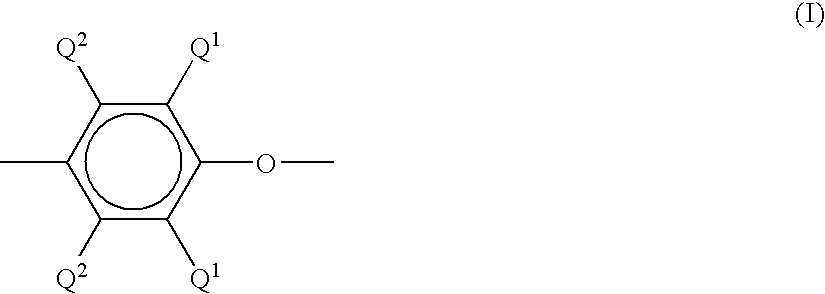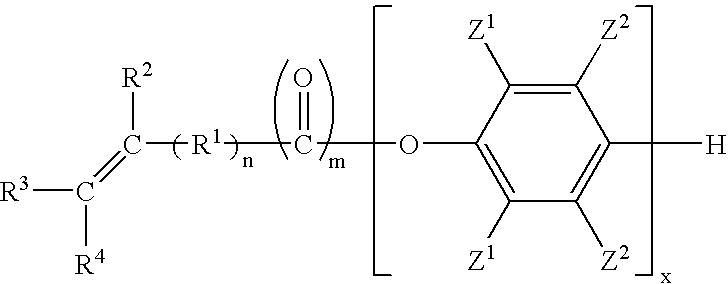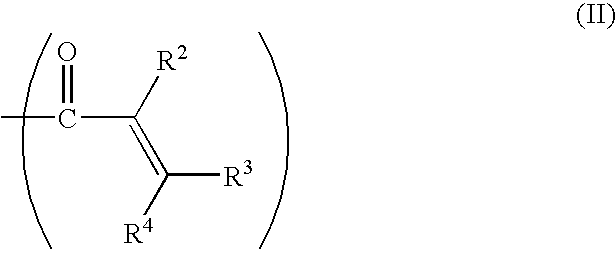Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
39 results about "Deciliters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Composite-forming method, composites formed thereby, and printed circuit boards incorporating them
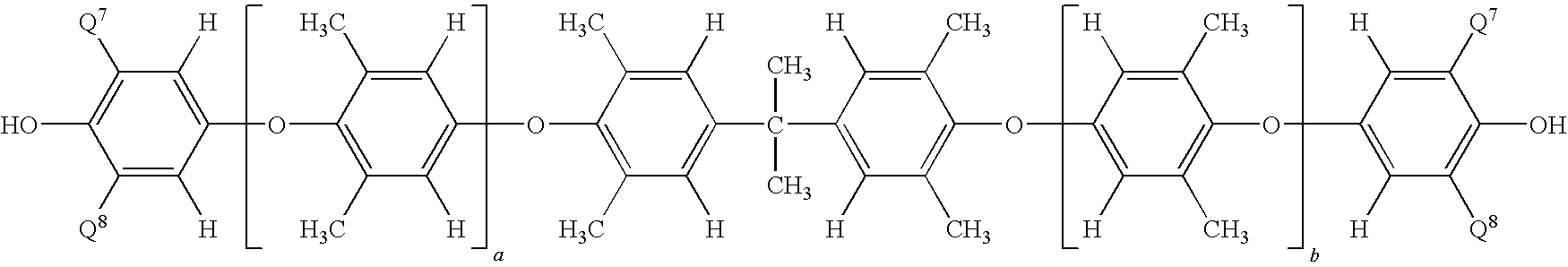
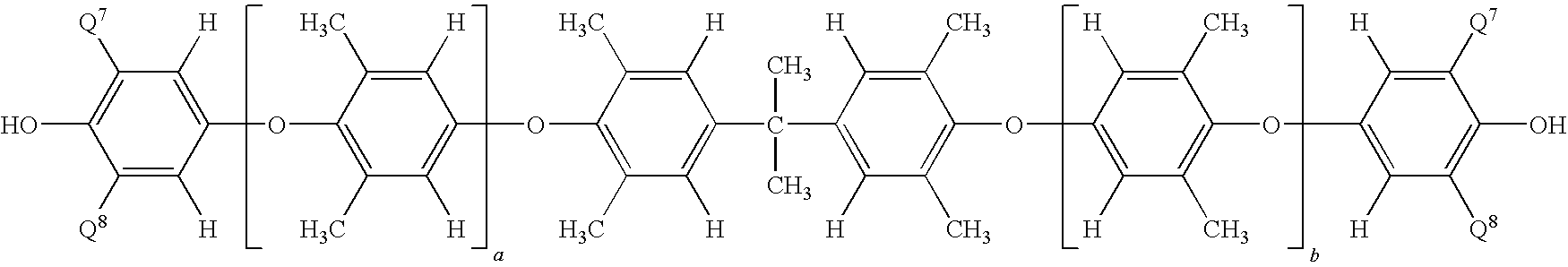
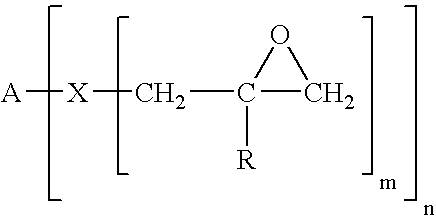
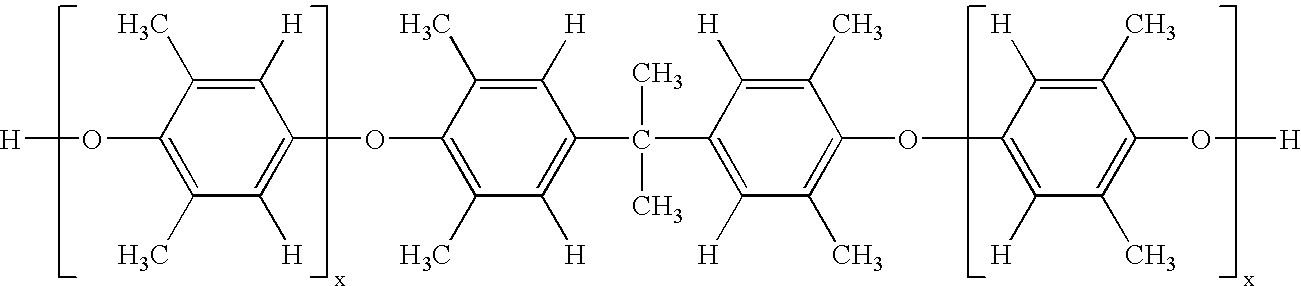
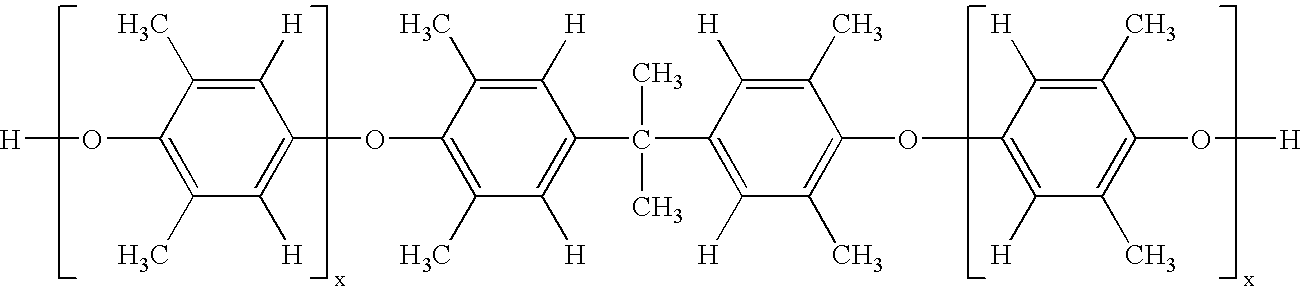
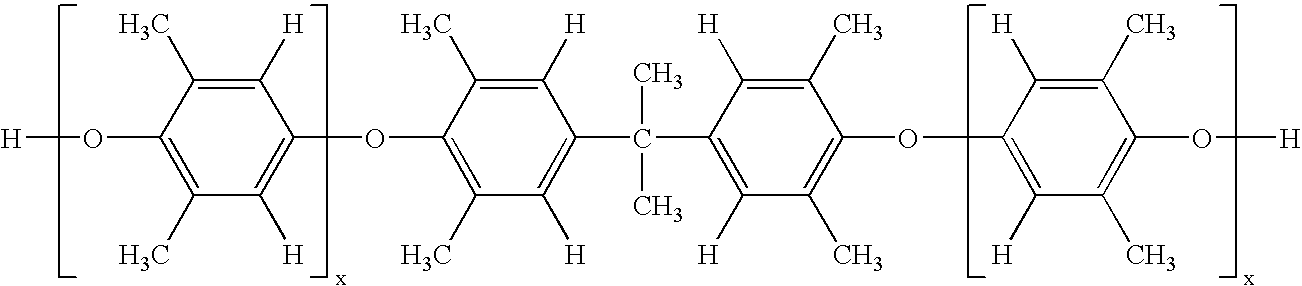
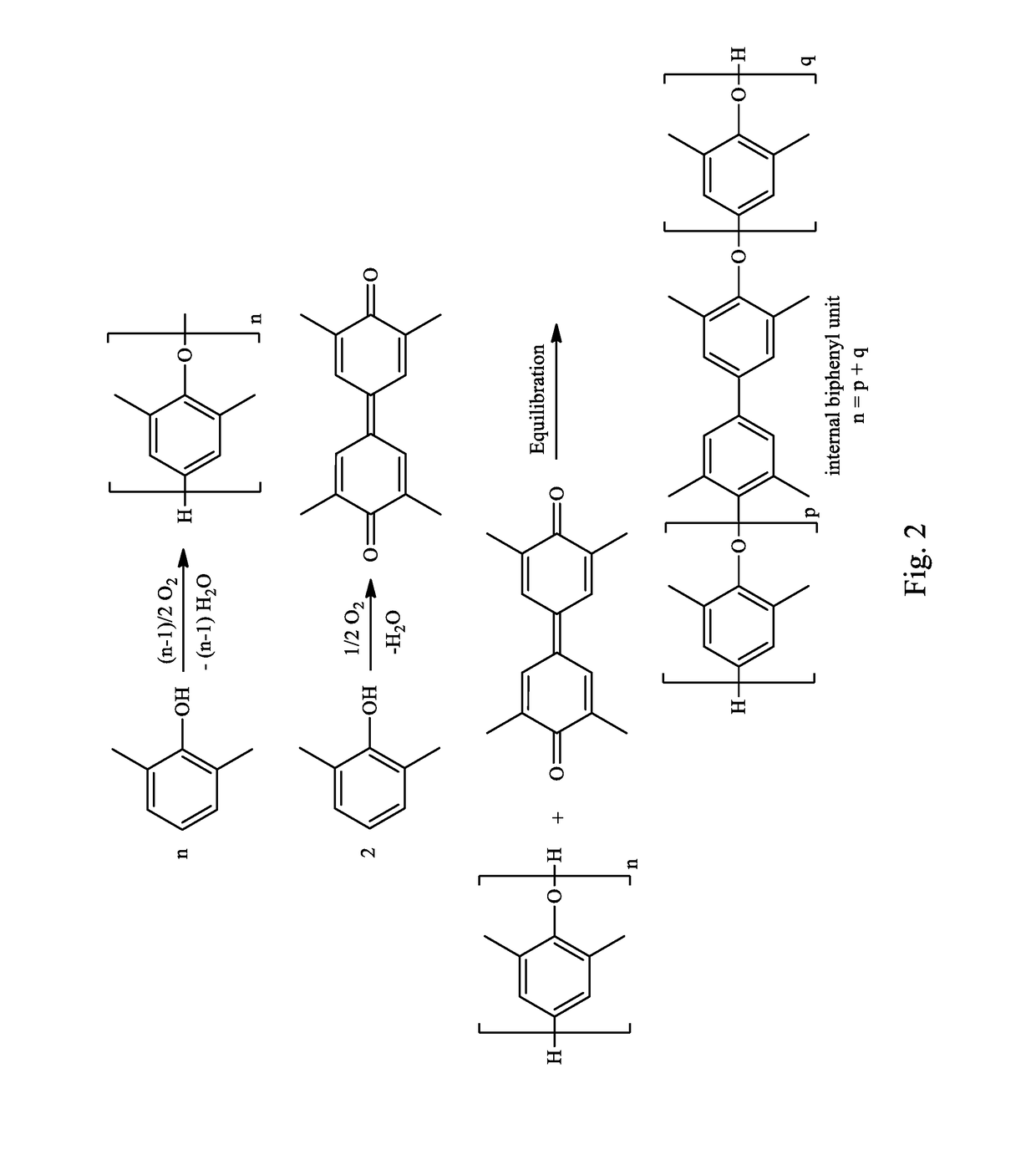
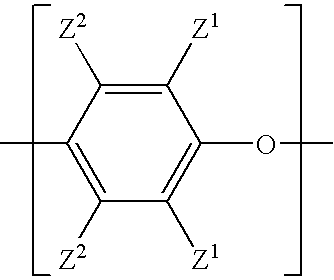
A composite-forming process includes impregnating a reinforcing structure with a curable composition at a temperature of about 10 to about 40° C. The curable composition includes specific amounts of an epoxy resin, a poly(arylene ether), a solvent, and a curing promoter. The poly(arylene ether) includes, on average, about 1.6 to about 2.4 phenolic hydroxy groups per molecule, and it has a polydispersity index less than or equal to 2.2 and an intrinsic viscosity of about 0.03 to about 0.2 deciliter per gram. These characteristics substantially improve the solubility of the poly(arylene ether) in the curable composition and allow the curable composition to be formed and used at or near room temperature. Composites formed by the process and circuit boards including the composites are also described.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Functionalized poly(arylene ether) composition and method
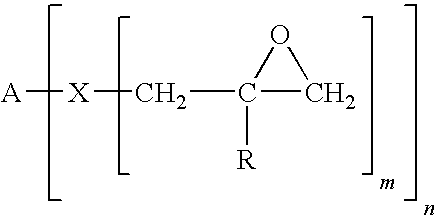
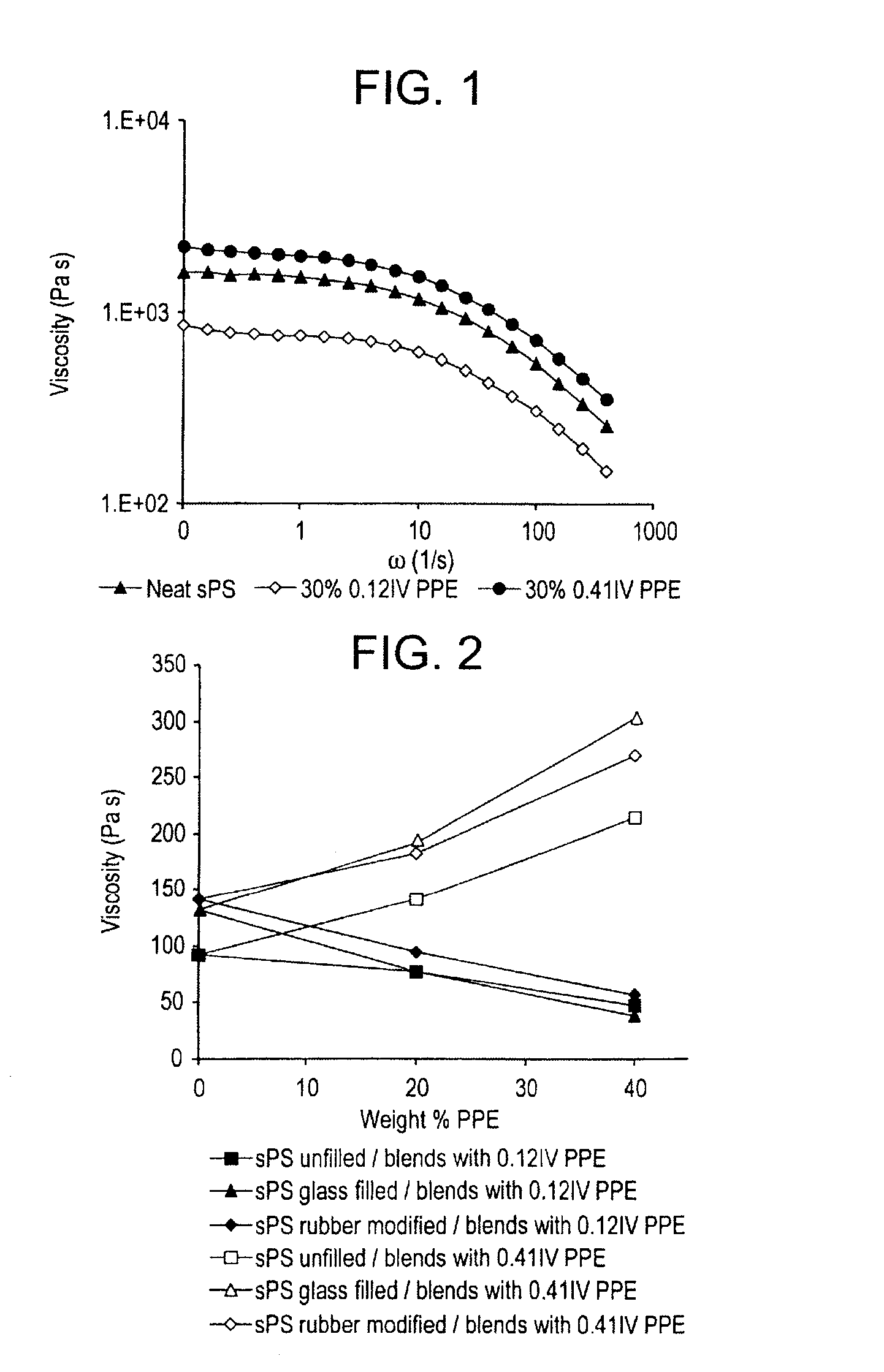
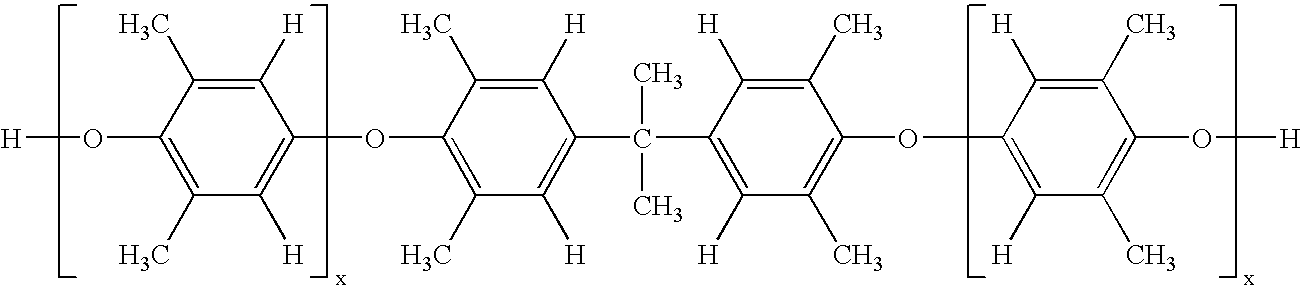
A curable composition includes an olefinically unsaturated monomer and a poly(arylene ether) having two polymerizable groups and an intrinsic viscosity of about 0.05 to about 0.30 deciliters per gram. The composition exhibits an improved combination of high flow during molding and high post-cure stiffness and impact strength. The composition is particularly useful for fabricating plastic-packaged electronic devices.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Functionalized poly(arylene ether) composition and method
A curable composition includes an olefinically unsaturated monomer and a poly(arylene ether) having two polymerizable groups and an intrinsic viscosity of about 0.05 to about 0.30 deciliters per gram. The composition exhibits an improved combination of high flow during molding and high post-cure stiffness and impact strength. The composition is particularly useful for fabricating plastic-packaged electronic devices.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Cellulose ester blends
This invention relates to a blend comprising(a) about 2% to about 98% by weight of at least one ester of cellulose comprising an alkanoyl chain having from about 1 to about 10 carbon atoms, and having at a D.S. of about 2.3 to about 3.0, and an inherent viscosity of about 0.2 to about 3.0 deciliters / gram as measured at a temperature of 25° C. for a 0.5 g sample in 100 ml of a 60 / 40 parts by weight solution of phenol / tetrachloroethane, and(b) about 98% to about 2% by weight of at least one ester of cellulose comprising an alkanoyl chain having from about 1 to about 10 carbon atoms, and having a D.S. of about 1.5 to about 2.2, and an inherent viscosity of about 0.2 to about 3.0 deciliters / gram as measured at a temperature of 25° C. for a 0.5 g sample in 100 ml of a 60 / 40 parts by weight solution of phenol / tetrachloroethane, said percentages being based on the weight of component (a) plus component (b).
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Composite-forming method, composites formed thereby, and printed circuit boards incorporating them
A composite-forming process includes impregnating a reinforcing structure with a curable composition at a temperature of about 10 to about 40° C. The curable composition includes specific amounts of an epoxy resin, a poly(arylene ether), a solvent, and a curing promoter. The poly(arylene ether) includes, on average, about 1.6 to about 2.4 phenolic hydroxy groups per molecule, and it has a polydispersity index less than or equal to 2.2 and an intrinsic viscosity of about 0.03 to about 0.2 deciliter per gram. These characteristics substantially improve the solubility of the poly(arylene ether) in the curable composition and allow the curable composition to be formed and used at or near room temperature. Composites formed by the process and circuit boards including the composites are also described.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Production process for polyarylene sulfide
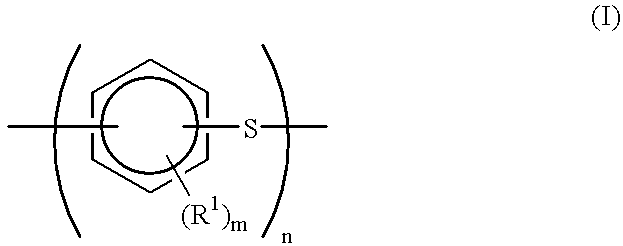
Provided is a production process for polyarylene sulfide having a high molecular weight and an excellent heat stability. It is a production process for polyarylene sulfide by reacting a dihalogenoaromatic compound with metal sulfide in a polar solvent, wherein all or a part of water required for the reaction is added on a condition that the reaction system is 100° C. or higher, whereby obtained is polyarylene sulfide which is reduced in an intrinsic viscosity [eta] by 0.05 deciliter / g or less at 206° C. when added to an N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone solvent is the polyarylene sulfide of an amount equivalent to the solvent and it is maintained at 265° C. for 8 hours.
Owner:GASOLINEEUM ENERGY CENT FOUND +1
Curable poly(arylene ether) composition and method
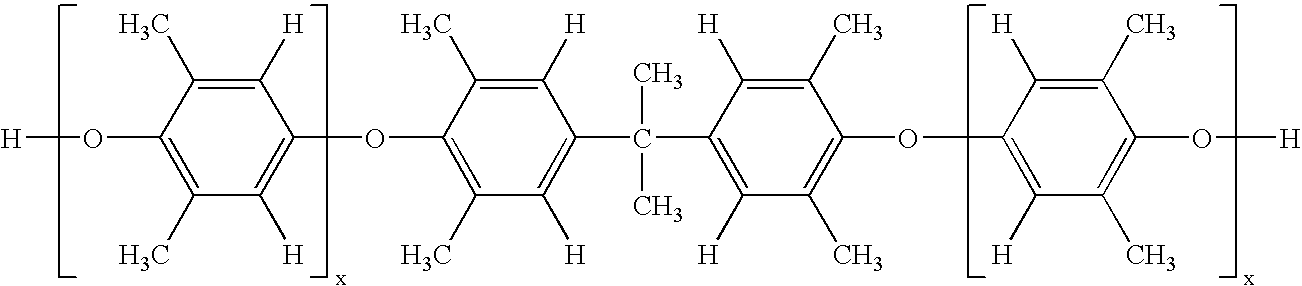
A curable composition includes an epoxy resin and a bifunctional poly(arylene ether) having an intrinsic viscosity of about 0.03 to about 0.2 deciliter per gram. After curing, the composition exhibits markedly improved impact strength relative to a corresponding composition prepared from monofunctional poly(arylene ether).
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Syndiotactic polystyrene blends
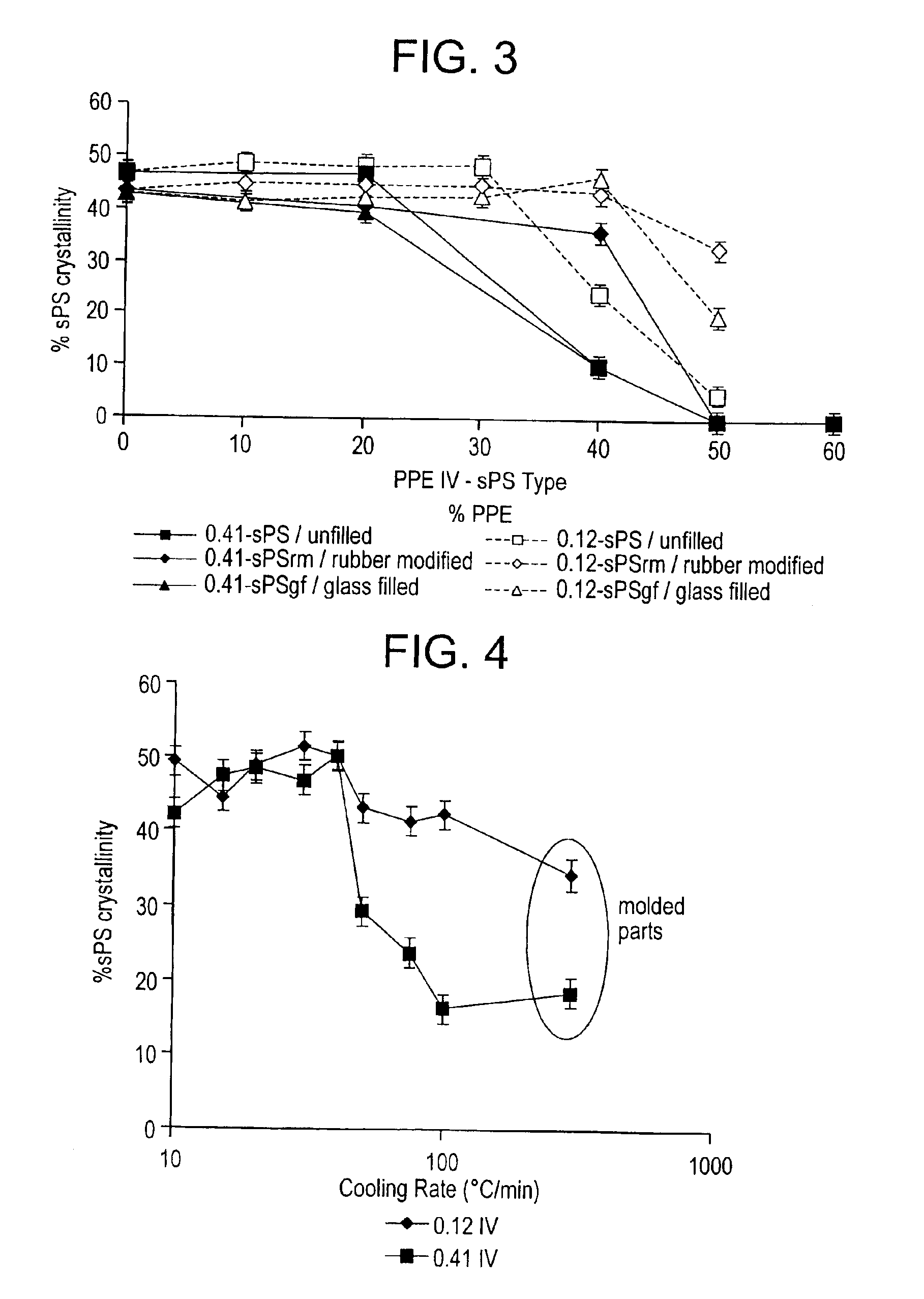
A syndiotactic polystyrene blend comprises syndiotactic polystyrene and poly(arylene ether) wherein the poly(arylene ether) has an intrinsic viscosity less than about 0.25 deciliters per gram (dl / g) when measured in chloroform at 25° C.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Varnish compositions for electrical insulation and method of using the same
A process for preparing a redistributed poly(phenylene ether), comprising reacting a poly(phenylene ether) in a reactive diluent monomer with a polyhydric phenol in the presence of a redistribution catalyst to form a composition comprising a redistributed poly(phenylene ether) in the reactive monomer diluent. The redistributed poly(phenylene ether) exhibits an intrinsic viscosity in the range of about 0.06 deciliters per gram to about 0.25 deciliters per gram, measured in chloroform at 25° C. The redistributed poly(phenylene ether) can be functionalized and admixed with unsaturated resin such as an unsaturated polyester resin or vinyl ester resin to obtain a varnish composition that, when cured, can form an electrically insulative thermoset.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Cured poly(arylene ether) composition, method, and article
A cured composition is prepared by curing a curable composition including an epoxy resin and a bifunctional poly(arylene ether) having an intrinsic viscosity of about 0.03 to about 0.2 deciliter per gram. The cured composition exhibits markedly improved impact strength relative to a corresponding composition prepared from monofunctional poly(arylene ether).
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Detection and determination of the stages of coronary artery disease
A method having clinically sufficient degree of diagnostic accuracy for detecting the presence of coronary artery disease in a human patient from the general population and for distinguishing between the stages of the disease in that patient is disclosed. The stages are, first, the non-acute stage, which is either asymptomatic coronary artery disease or stable angina, second, the acute stage known as unstable angina, and, third, the acute stage known as acute myocardial infarction. The diseased state (as opposed to the non-diseased state) is indicated by the clinically significant presence of a first marker in a sample from the patient. The presence of one of the two acute stages, unstable angina or acute myocardial infarction, is indicated by the clinically significant presence of a second marker in a sample from the patient. The presence of the more severe acute stage known as acute myocardial infarction is indicated by the clinically significant presence of a third marker in a sample from the patient. Preferably the first marker comprises OxLDL, the second marker comprises MDA-modified LDL, and the third marker is a troponin. Preferably the OxLDL and MDA-modified LDL are detected using monoclonal antibodies that can detect the presence of those markers in undiluted human plasma at concentrations as low as 0.02 milligrams / deciliter.
Owner:LEUVEN RES & DEV VZW
Polyolefin resin composition
The present invention provides a polyolefin-based resin composition, comprising (A) a polyolefin I produced from at least one monomer selected from the group consisting of α-olefins, cyclic olefins and styrenes; (B) a polyolefin II produced from said at least one monomer, which differs in composition or properties from said polyolefin I; and (C) a graft copolymer produced by bonding said polyolefins I and II to each other through a polyene, wherein (a) a ratio [(1 / R1) / (1 / R1)0] of a relaxation velocity (1 / R1) of a long-term relaxation component measured by a solid 1H-NMR method about the composition to a relaxation velocity (1 / R1)0 of a long-term relaxation component measured by a solid 1H-NMR method about a resin mixture of only the components (A) and (B) is 1.01 or higher; and (b) an intrinsic viscosity [η] of the composition is in the range of 0.1 to 10 deciliter / g as measured in decalin at 135° C. The resin composition is readily controlled in property-determining factors such as morphology and interfacial strength, and is capable of providing a composite material composed of polyolefin-based resins according to properties as required.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Polyester compositions, methods of manufacture, and uses thereof
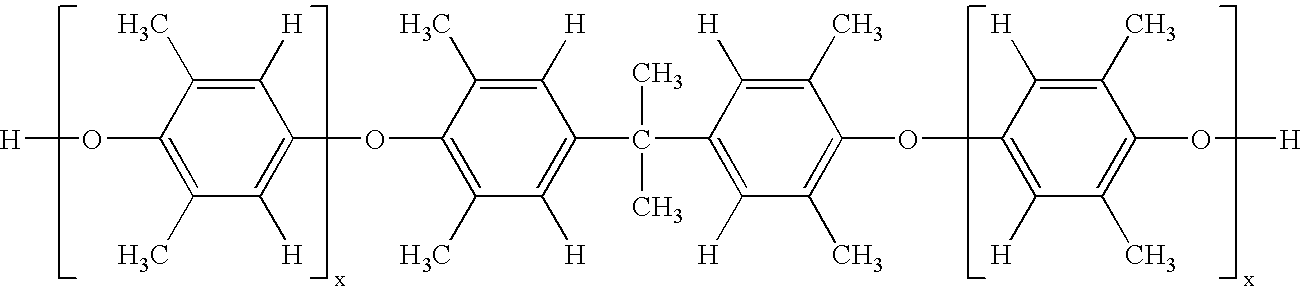
A composition is disclosed, comprising, based on the total weight of the composition, a combination of from 44 to 80 weight percent of a thermoplastic poly(butylene terephthalate); from 20 to 50 weight percent of a thermoplastic poly(ethylene terephthalate) having an intrinsic viscosity of 0.5 to 0.8 deciliters per gram, measured in a 60:40 by weight phenol / 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane mixture at 23° C. using a relative viscometer operating with a closed loop system, which measures the solvent and sample viscosity simultaneously; from 5 to less than 20 weight percent of a talc filler having an average largest dimension of less than 0.9 micrometers, a median particle size of less than 0.9 micrometers, or both; and from 0.1 to 0.5 weight percent of a mold release agent. The compositions are useful in the manufacture of lighting articles, which can be directly metallized without the inclusion of a base coat.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
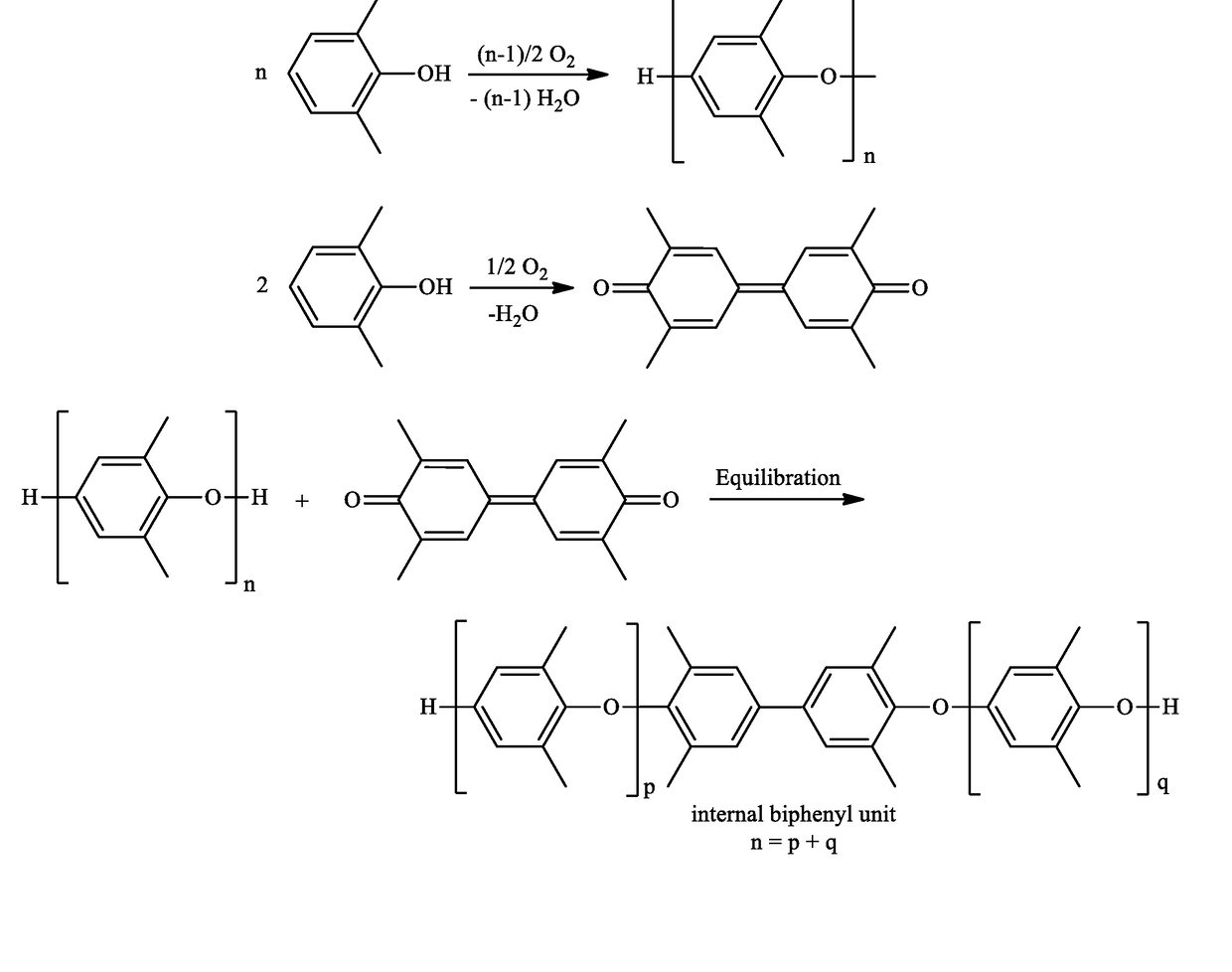
Method for poly(phenylene ether) manufacture and associated poly(phenylene ether)
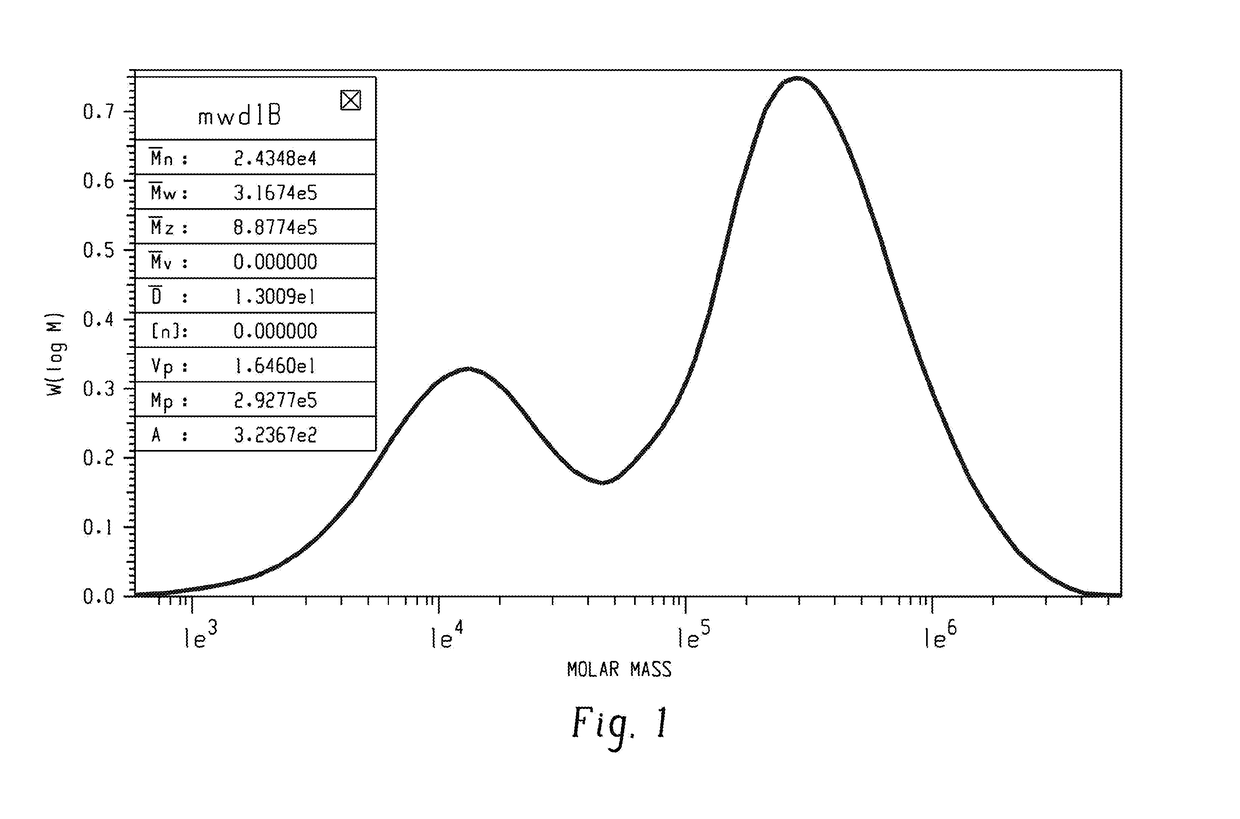
A method of making a poly(phenylene ether) comprises: in an exotherm period, continuous addition of oxygen and a monohydric phenol to a non-polar solvent and a polymerization catalyst comprising a metal salt, an amine, and a quaternary ammonium salt in a vessel, to form a polymerization mixture, wherein the oxygen and monohydric phenol are added in a mole ratio of 0.5:1 to 1.2:1; and cessation of the continuous addition of the monohydric phenol; and in a build period, continuation of oxygen addition until there is no further increase in viscosity of the polymerization mixture. A poly(phenylene ether) having an intrinsic viscosity of 0.5 to 2.0 deciliters per gram, measured in chloroform using an Ubbelohde capillary glass viscometer at 25° C., a polydispersity of 1 to 10, and a unimodal molecular weight distribution, is made by the method.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Syndiotactic polystyrene blends
InactiveUS20030216503A1Low intrinsic viscosityReduce the amount presentFilm/foil adhesivesSpecial tyresGramEther
A syndiotactic polystyrene blend comprises syndiotactic polystyrene and poly (arylene ether) wherein the poly(arylene ether) has an intrinsic viscosity less than about 0.25 grams / deciliter (g / dl) when measured in chloroform at 25° C.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Method of forming a crosslinked poly(arylene ether) film, and film formed thereby
A crosslinked poly(arylene ether) film is prepared by a method that includes forming a film from a composition that includes a poly(arylene ether) having an intrinsic viscosity of at least 0.25 deciliter per gram and a polydispersity index less than or equal to 10, and irradiating the poly(arylene ether) film with a dosage of about 50 to about 50,000 kiloGrays of accelerated electrons. The films exhibit good flexibility and solvent resistance. Films prepared by the method are described, as are articles that include such films.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Varnish compositions for electrical insulation and method of using the same
A varnish composition for producing an electrically insulative thermoset coating is disclosed. The varnish composition includes a functionalized poly(phenylene ether) having at least one aliphatic unsaturated group and exhibiting an intrinsic viscosity in the range of about 0.06 to about 0.25 deciliter per gram, measured in chloroform at 25° C. The varnish composition further includes an unsaturated polyester resin or vinyl ester resin, a reactive liquid monomer, and a compatibilizing agent. When cured, the polymers and reactive liquid monomer form an electrically insulative thermoset.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Poly(arylene ether) composition, method, and article
A curable composition includes an epoxy resin and a bifunctional poly(arylene ether) having an intrinsic viscosity of about 0.03 to about 0.2 deciliter per gram. After curing, the composition exhibits markedly improved impact strength relative to a corresponding composition prepared from mono functional poly (arylene ether). The composition is particularly useful for preparing electronic laminates, prepregs, and circuit boards.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
Eigen antiflaming semi-aromatic copolymerization aromatic ether amide and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an eigen antiflaming semi-aromatic copolymerization aromatic ether amide and a preparation method thereof. Diphenol monomer containing phosphorus / silicon or difluoro-malonic acid diamide containing silicon or difluoro-malonic acid diamide monomer containing phosphorus is utilized, and solution polycondensation is carried out to prepare the antiflaming semi-aromatic copolymerization aromatic ether amide. Intrinsic viscosity number [eta] of the semi-aromatic copolymerization aromatic ether amide is 0.65-1.01 deciliters per gram, the vertical flaming class is V-2-V-0, thelimit oxygen index is 26.8-45.5%, and the tensile strength is 65-108 megapascals. The eigen antiflaming semi-aromatic copolymerization aromatic ether amide has the advantages of halogen-free flame retardant, non-molten drop performance, easy processing, high mechanical strength and the like, and the eigen antiflaming semi-aromatic copolymerization aromatic ether amide taken as engineering plasticsis wider in application.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Detection and determination of the stages of coronary artery disease
A method having clinically sufficient degree of diagnostic accuracy for detecting the presence of coronary artery disease in a human patient from the general population and for distinguishing between the stages of the disease in that patient is disclosed. The stages are, first, the non-acute stage, which is either asymptomatic coronary artery disease or stable angina, second, the acute stage known as unstable angina, and, third, the acute stage known as acute myocardial infarction. The diseased state (as opposed to the non-diseased state) is indicated by the clinically significant presence of a first marker in a sample from the patient. The presence of one of the two acute stages, unstable angina or acute myocardial infarction, is indicated by the clinically significant presence of a second marker in a sample from the patient. The presence of the more severe acute stage known as acute myocardial infarction is indicated by the clinically significant presence of a third marker in a sample from the patient. Preferably the first marker comprises OxLDL, the second marker comprises MDA-modified LDL, and the third marker is a troponin. Preferably the OxLDL and MDA-modified LDL are detected using monoclonal antibodies that can detect the presence of those markers in undiluted human plasma at concentrations as low as 0.02 milligrams / deciliter.
Owner:LEUVEN RES & DEV VZW
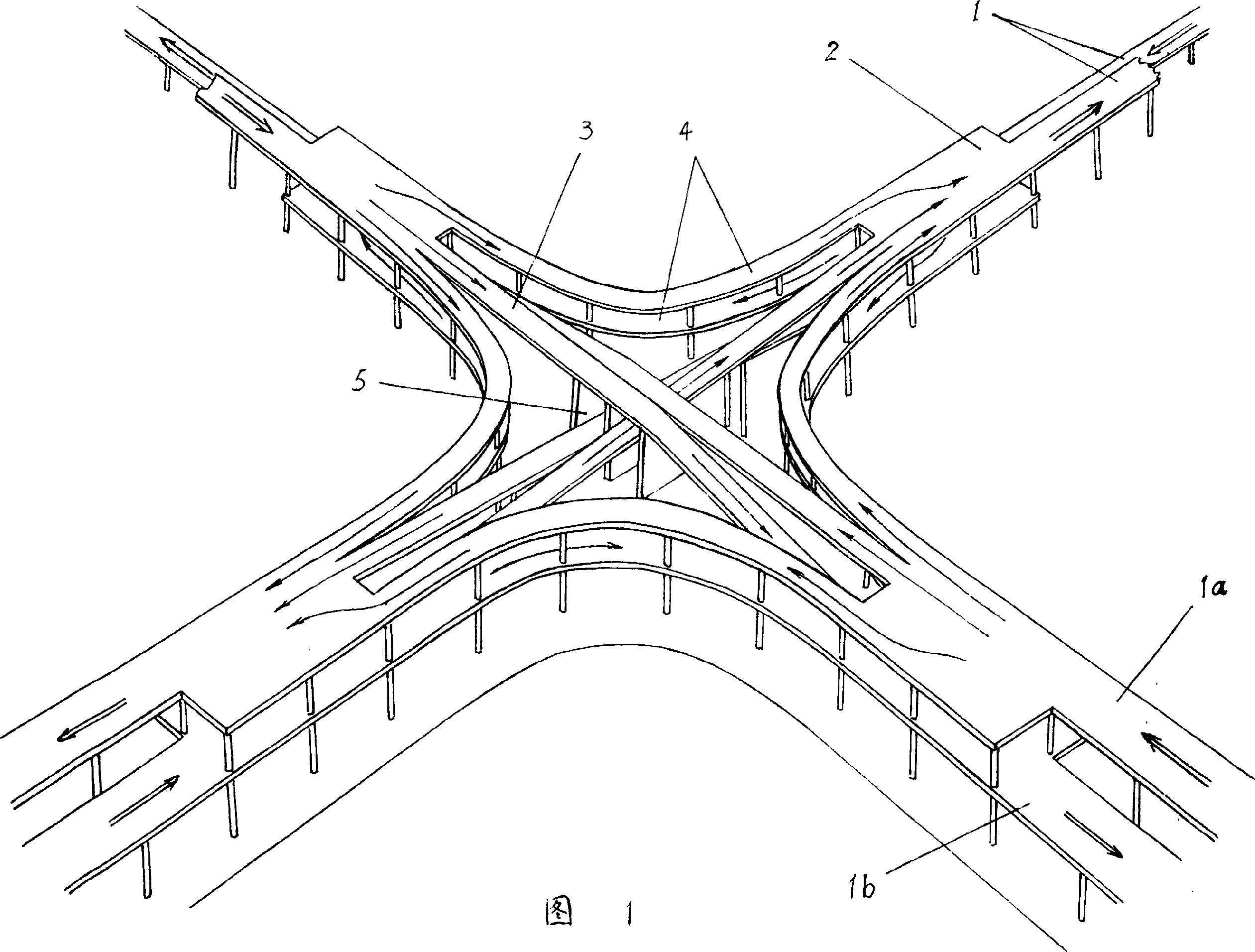
Two-deck full-directional direct-intercommunity overpass
InactiveCN1528982AConform to natural stateShort routeRoadwaysClimate change adaptationCross bridgeStructural engineering
The invention discloses double-layer full-orientation and direct-interconnection overpass, the overpass is made up of bridge approach, deciliter tilt hole, cross bridge and inner arc curved road, the deciliter tilt hole and curved road are double-layer structure with upper and subjacent layer, each bridge approach is a mutual double bridge which contain a long and a short bridge, which two are connected to the outer end of upper and subjacent layer of the hole, the two sides of each layer in deciliter tilt holes are connected through curved road bridge, the centre part of the each hole is connected to cross bridge, the cross bridge are straight bridges which are orthogonal, the cross bridge is bidirectional one-way bridge, the two ends of it are connected with the upper and subjacent layer of the hole. The overpass can realize full-orientation and direct-interconnection with small area and cost.
Owner:吕乐民
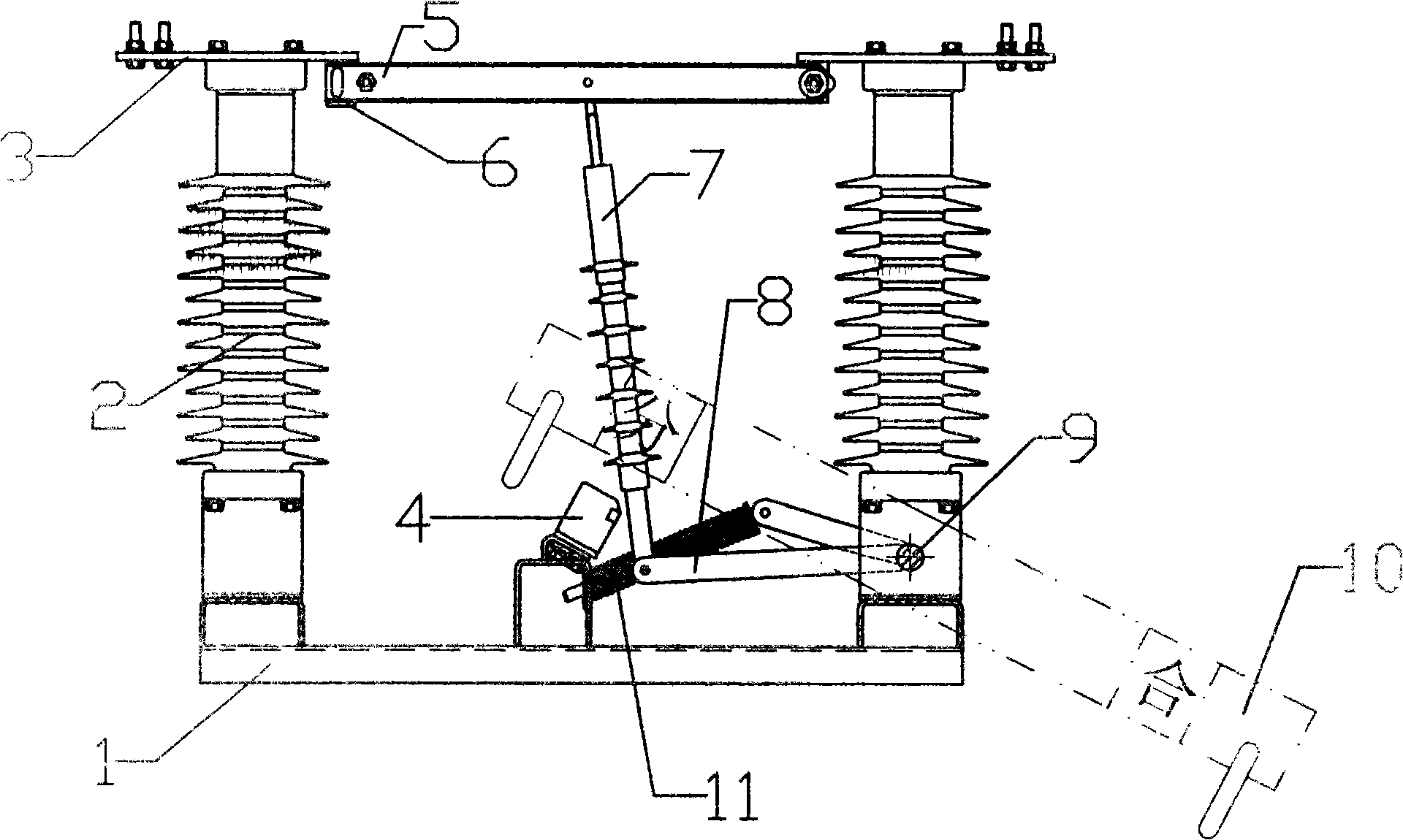
35kv outdoor ac isolation switch
ActiveCN101320649AReduce manufacturing costImprove safety and reliabilitySwitches with movable electrical contactsGround contactDrive shaft
A 35kV outdoors alternating current isolation switch is used for deciliter conversion of power circuit. The isolation switch comprises a under frame, an insulator, a connecting plate, a contact knife, an insulating tension pole, a crank and a rotating shaft; the under frame is provided with a ground contact; one end of the contact knife is hinged with the connecting plate; the other end is in contactable link with an income contact provided on the connecting plate, and is in contactable link with the ground contact on the under frame; middle of the contact knife is hinged with the upper end of the insulating tension pole; the lower end of the insulating tension pole is hinged with the crank; the crank is fixed with the rotating shaft provided on the under frame; the rotating shaft is a universal driving shaft permeating three phase; a spring is connected between the crank and the ground contact on the under frame. The invention not only realizes three phase breaking or closing brake by only once action, but also breaks off ground when closes brake, and realizes the three phase ground at breaking brake; and the isolation switch has the characters of low manufacturing cost, high safe reliability, good mechanical strength and long service life.
Owner:宁波鹿鼎电子科技有限公司
Varnish compositions for electrical insulation and method of using the same
A varnish composition for producing an electrically insulative thermoset coating is disclosed. The varnish composition includes a functionalized poly(phenylene ether) having at least one aliphatic unsaturated group and exhibiting an intrinsic viscosity in the range of about 0.06 to about 0.25 deciliter per gram, measured in chloroform at 25° C. The varnish composition further includes an unsaturated polyester resin or vinyl ester resin, a reactive liquid monomer, and a compatibilizing agent. When cured, the polymers and reactive liquid monomer form an electrically insulative thermoset.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Method for producing rayon by using PTT and PET
InactiveCN108315830AMaximum curl elasticityGood curl elasticityMelt spinning methodsConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsFiberGram
The invention discloses a method for producing rayon by using PTT and PET. Firstly, the rayon is prepared from ,by mass, 41-55 parts of PTT raw materials and 41-55 parts of PET raw materials, PET slices with low viscosity is selected as the PET raw materials, and the viscosity of the PET slices is not higher than 0.53 deciliter per gram; the PTT raw materials make the viscosity of PTT slices higher than 1.18 deciliters per gram through drum tackifier, so that the viscosity difference of the PTT raw materials and PET raw materials is increased as much as possible, and then the rayon is formed by melting, spinning and stretching. The method for producing the rayon by using the PTT and the PET makes fibers exert maximum elastic performance, and improves spinnability.
Owner:TONGKUN GRP
Varnish compositions for electrical insulation and method of using the same
A process for preparing a redistributed poly(phenylene ether), comprising reacting a poly(phenylene ether) in a reactive diluent monomer with a polyhydric phenol in the presence of a redistribution catalyst to form a composition comprising a redistributed poly(phenylene ether) in the reactive monomer diluent. The redistributed poly(phenylene ether) exhibits an intrinsic viscosity in the range of about 0.06 deciliters per gram to about 0.25 deciliters per gram, measured in chloroform at 25° C. The redistributed poly(phenylene ether) can be functionalized and admixed with unsaturated resin such as an unsaturated polyester resin or vinyl ester resin to obtain a varnish composition that, when cured, can form an electrically insulative thermoset.
Owner:SHPP GLOBAL TECH BV
Polyester compositions, methods of manufacture, and uses thereof
A composition is disclosed, comprising, based on the total weight of the composition, a combination of from 44 to 80 weight percent of a thermoplastic poly(butylene terephthalate); from 20 to 50 weight percent of a thermoplastic poly(ethylene terephthalate) having an intrinsic viscosity of 0.5 to 0.8 deciliters per gram, measured in a 60:40 by weight phenol / 1,1,2,2-tetrachloroethane mixture at 23° C. using a relative viscometer operating with a closed loop system, which measures the solvent and sample viscosity simultaneously; from 5 to less than 20 weight percent of a talc filler having an average largest dimension of less than 0.9 micrometers, a median particle size of less than 0.9 micrometers, or both; and from 0.1 to 0.5 weight percent of a mold release agent. The compositions are useful in the manufacture of lighting articles, which can be directly metallized without the inclusion of a base coat.
Owner:SABIC GLOBAL TECH BV
Polyethylene compositions, and articles made therefrom
The invention provides ethylene-based composition comprising a blend of an ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene having an intrinsic viscosity from 5 to 50 deciliters / gram; a thermoplastic polyolefin elastomer having a density of from 0.850 to 0.910 g / cc; and, optionally, a fluoropolymer.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Parenteral administration of pyrophosphate for prevention or treatment of phosphate or pyrophosphate depletion
A pharmaceutical composition for therapeutic administration of pyrophosphate for phosphate repletion may be in either liquid or solid form and may be usable as or usable for preparing a hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis solution containing a pyrophosphate compound present in an amount that provides a concentration in the dialysis solution equivalent to an inorganic phosphorus concentration of at least 0.5 mg per deciliter.
Owner:GUPTA AJAY
Polyethylene compositions and articles made therefrom
The present invention provides a composition suitable for use in plumbing applications, the composition comprising: an ultra-high molecular weight ethylene-based polymer having an inherent viscosity of 5 to 50 deciliters / gram; a polyethylene resin comprising a first molecular weight ethylene-based polymer a polymer component and a second molecular weight ethylene-based polymer component, wherein the polyethylene resin has a density of 0.930 to 0.960 g / cc; a thermoplastic polyolefin elastomer has a density of 0.850 to 0.910 g / cc; and optionally of fluoropolymers.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com