Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
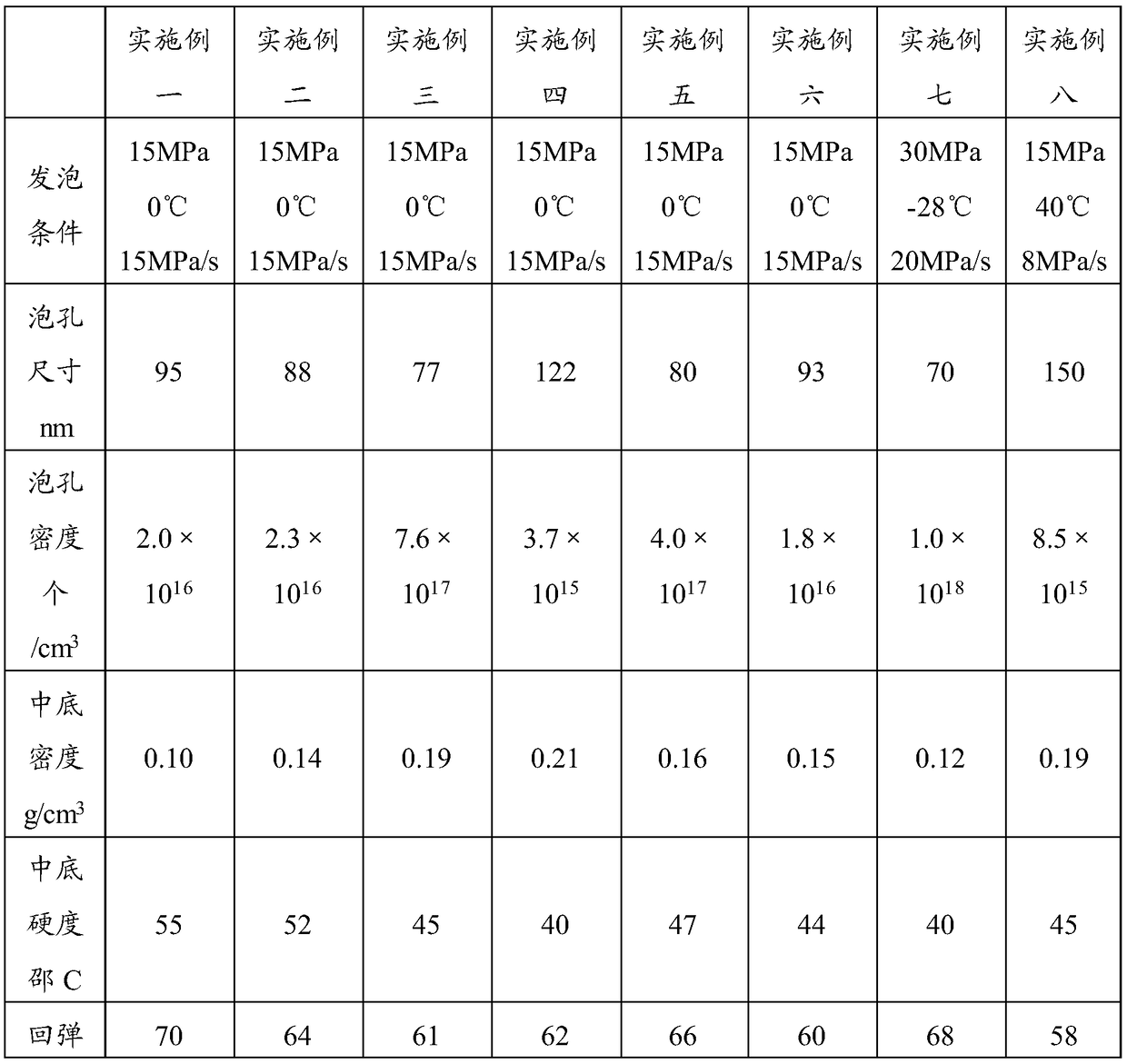
824 results about "Compressive deformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compressive stress results in deformation which shortens the object but also expands it outwards.
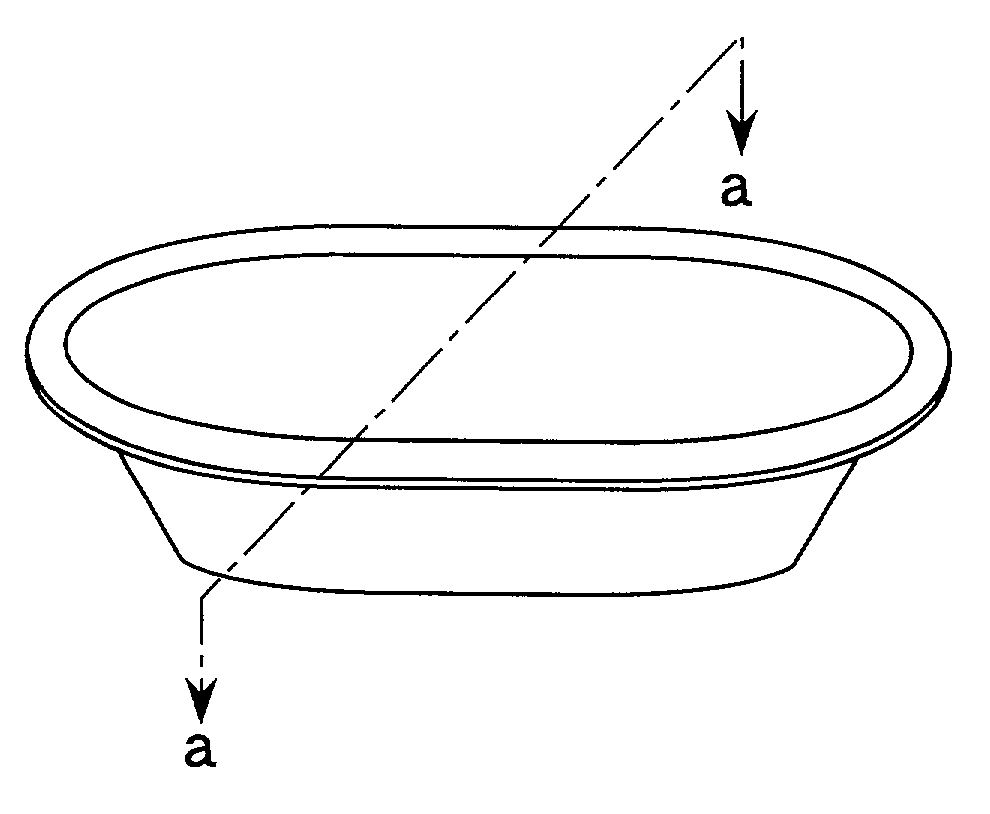
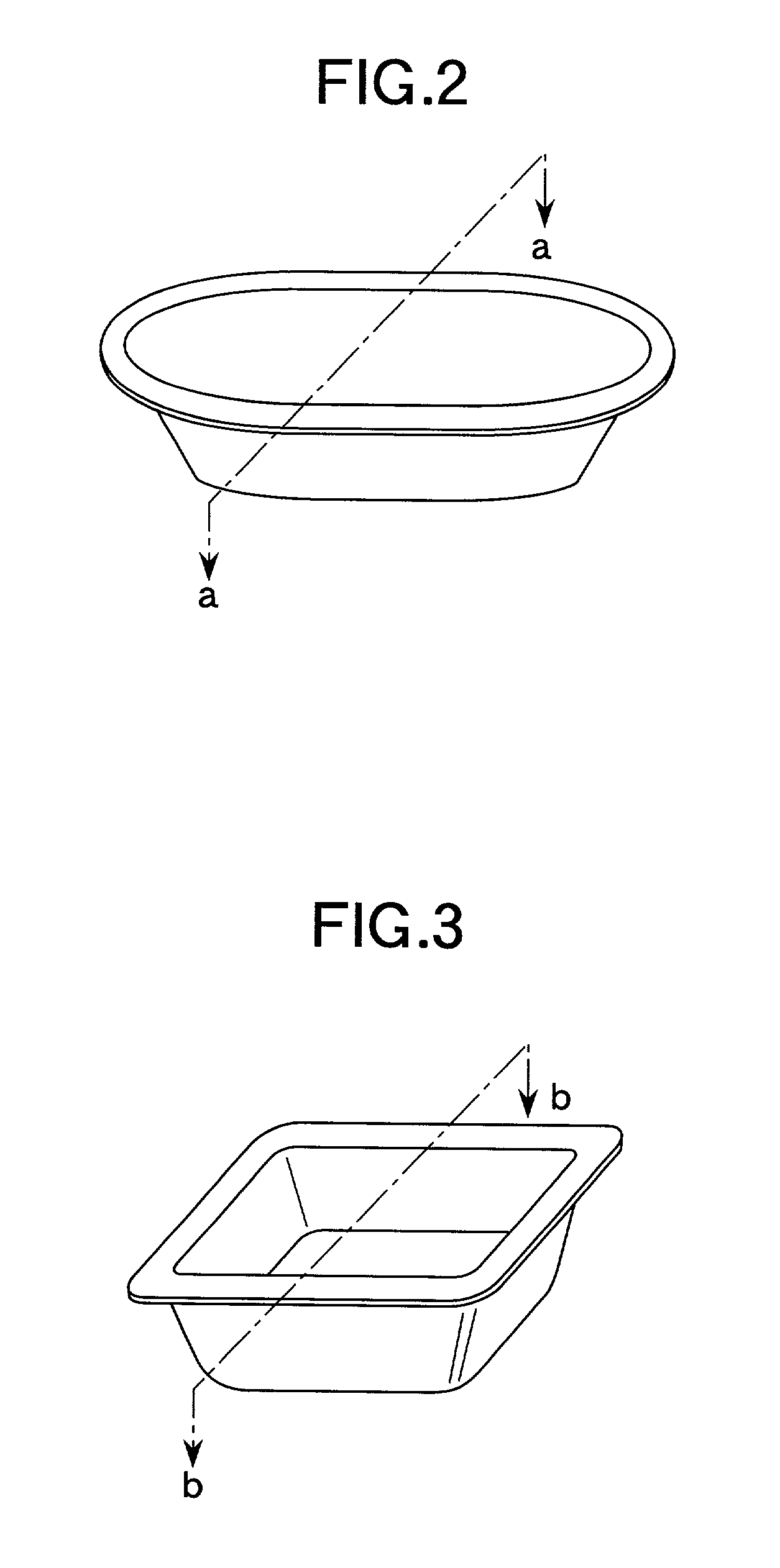
Molding base paper and molded paper vessel produced from it
InactiveUS20020012759A1Mechanical working/deformationSpecial paperCompressive strengthUltimate tensile strength
A molding base paper used for forming paper vessels such as a cup or tray for foods and various industrial products is disclosed which satisfies the following conditions (1) to (4): (1) a tensile strength (JIS-P 8113) of at least 2.0 kN / m, (2) an elongation at break (JIS-P 8113) of at least 1.5%, (3) a critical compression stress, defined by the following formula, in the range of 1 to 10 MPa: <paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>critical compression stress=A / B < / in-line-formula>wherein A represents the compression strength determined by JIS-P 8126, and B represents the area of loaded part of the test piece in the determination of the compression strength, and (4) an amount of the compression deformation, caused by applying compression stress of 20 kgf / cm2in thickness direction, of at least 10 %. The paper vessels are prepared by controlling the water content of the molding base paper at 10 to 20% and then drawing the molding base paper at 100 to 150° C.
Owner:OJI PAPER CO LTD
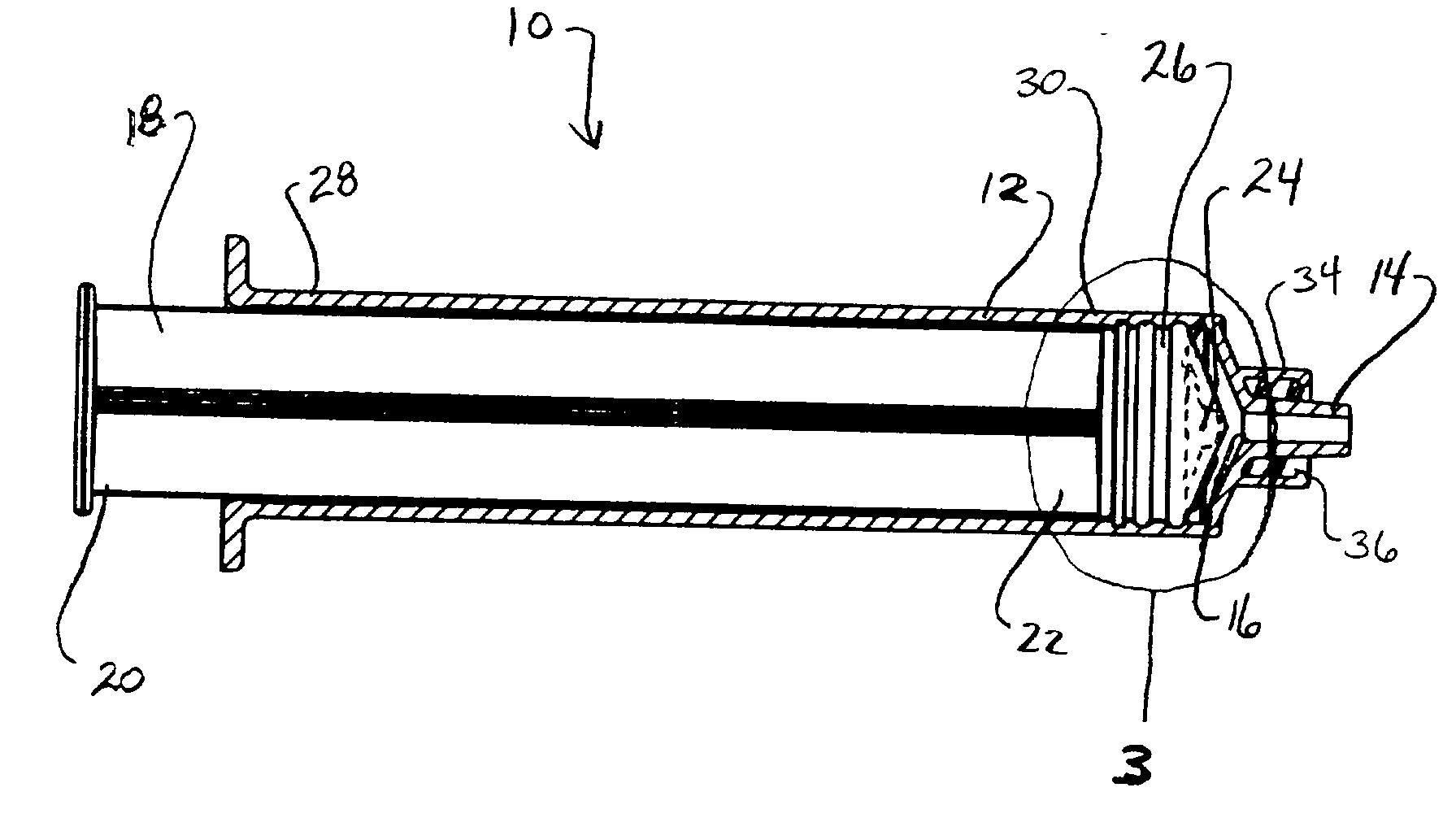
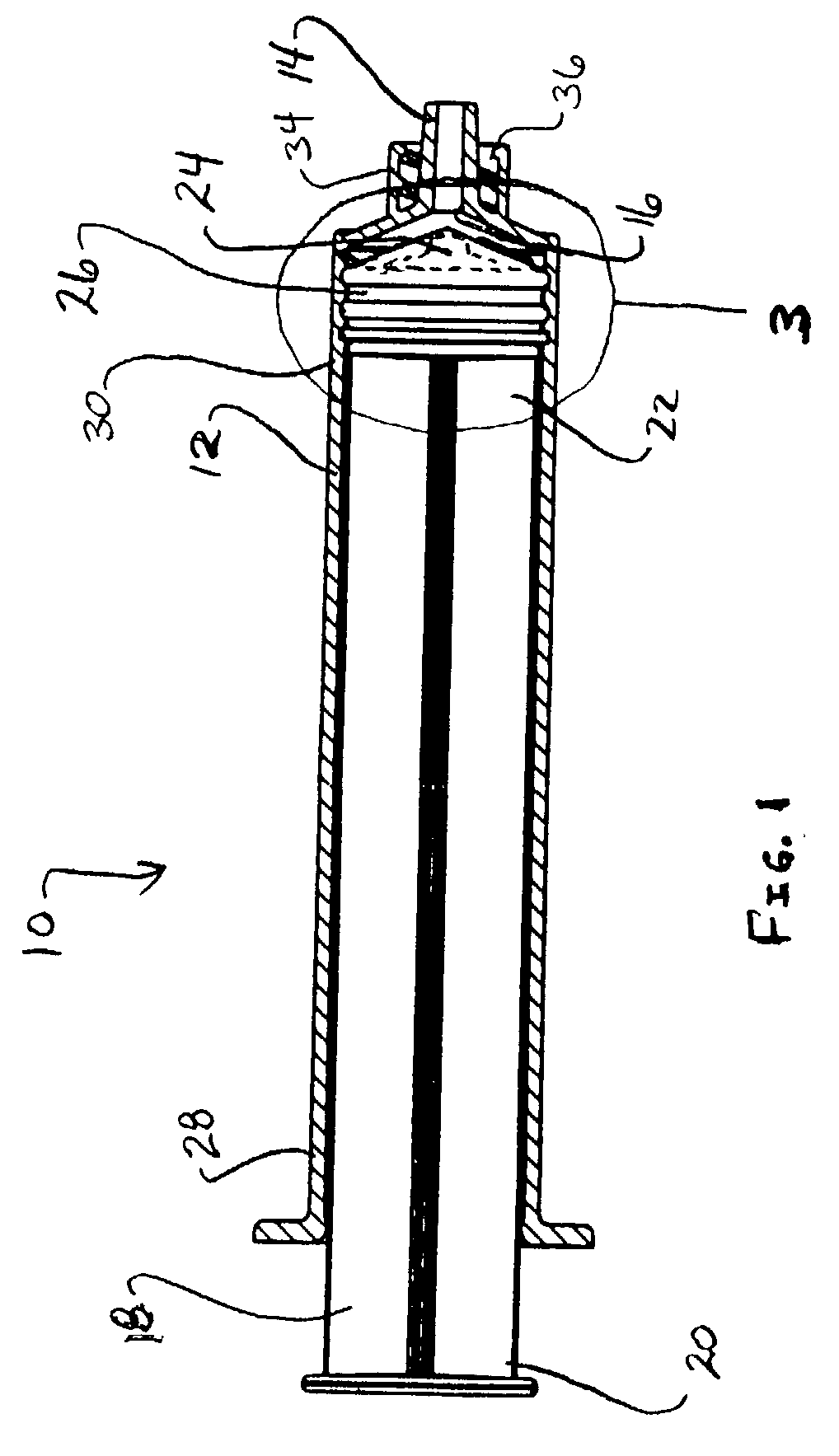
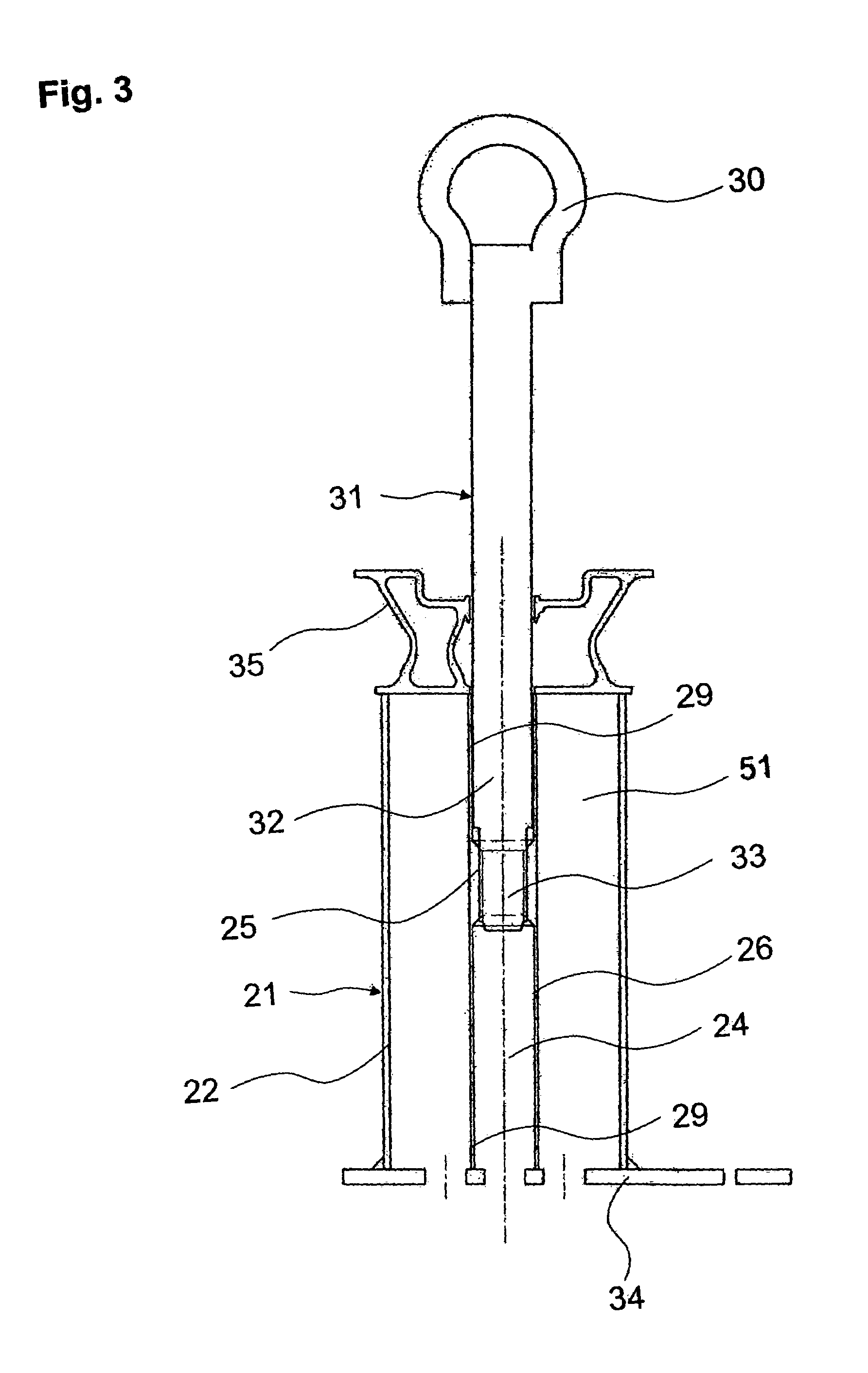
Anti-reflux syringe
A syringe is provided that includes a barrel including a nozzle having an interior opening. A plunger rod of the syringe has a first end and a second end. The second end includes an extension dimensioned to ensure that a member, disposed with the second end and enclosing the extension, abuts the interior opening. The barrel may include a distal wall that supports the nozzle and the plunger rod may include a correspondingly configured distal face. The extension may include a longitudinal length such that upon engagement of the member with the interior opening, the length of the extension prevents compressive deformation of the member between the distal wall and the distal face. The member can have a transverse wall and a cylindrical sidewall extending along the second end of the plunger rod. The transverse wall may have a substantially uniform thickness. The extension defines a distal portion which may be dimensioned for selective engagement of the member with the interior opening.
Owner:SHERWOOD SERVICES AG
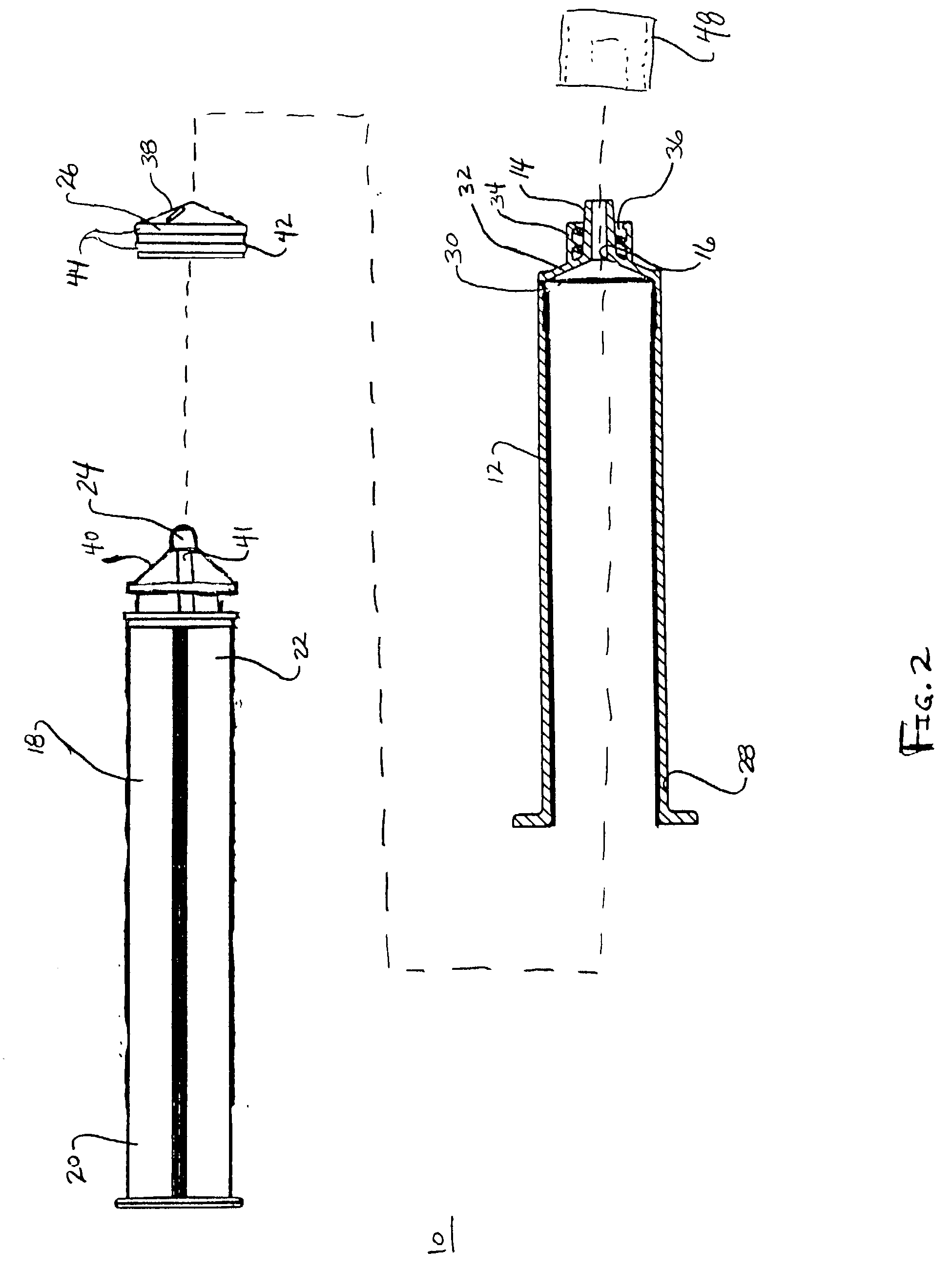
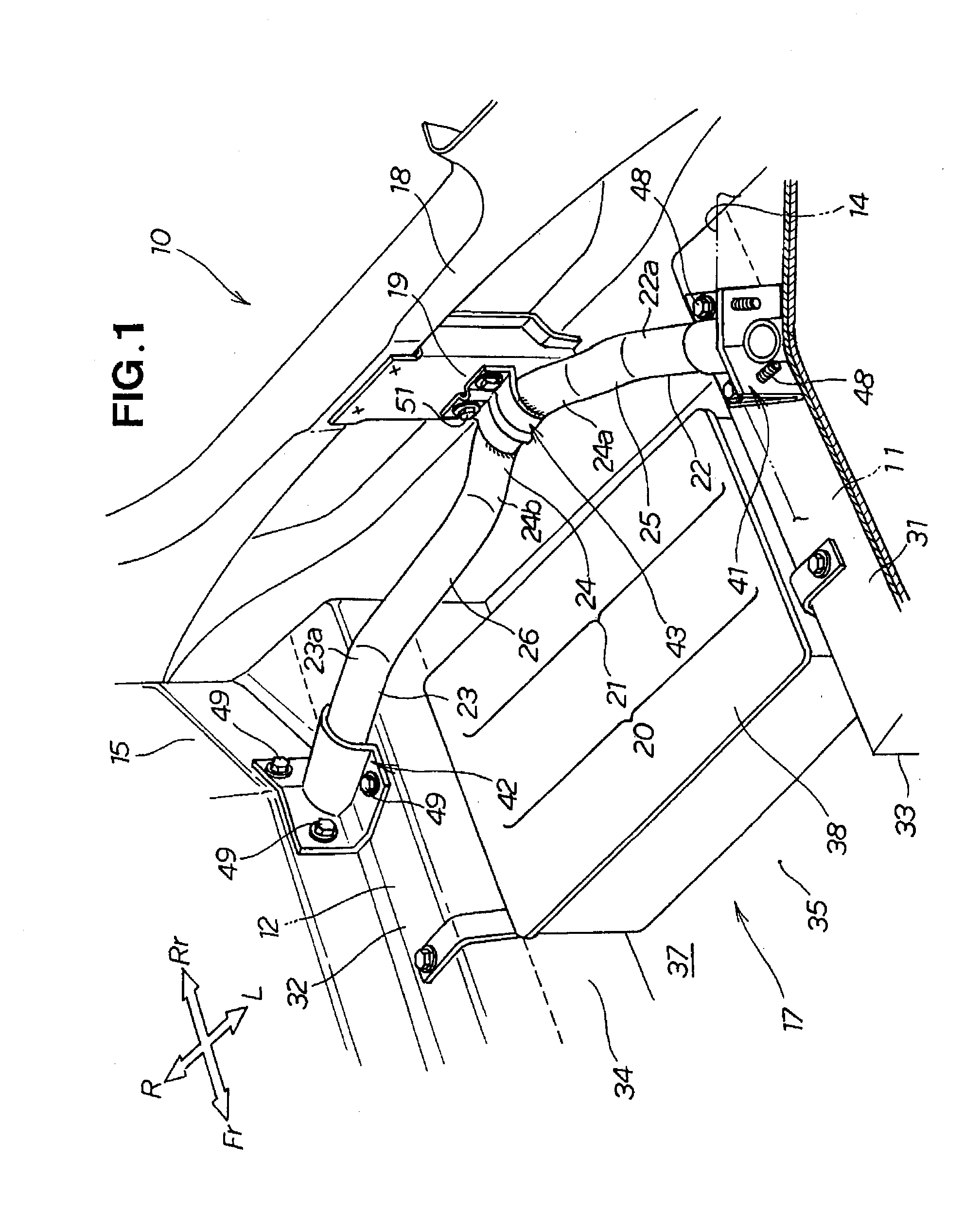
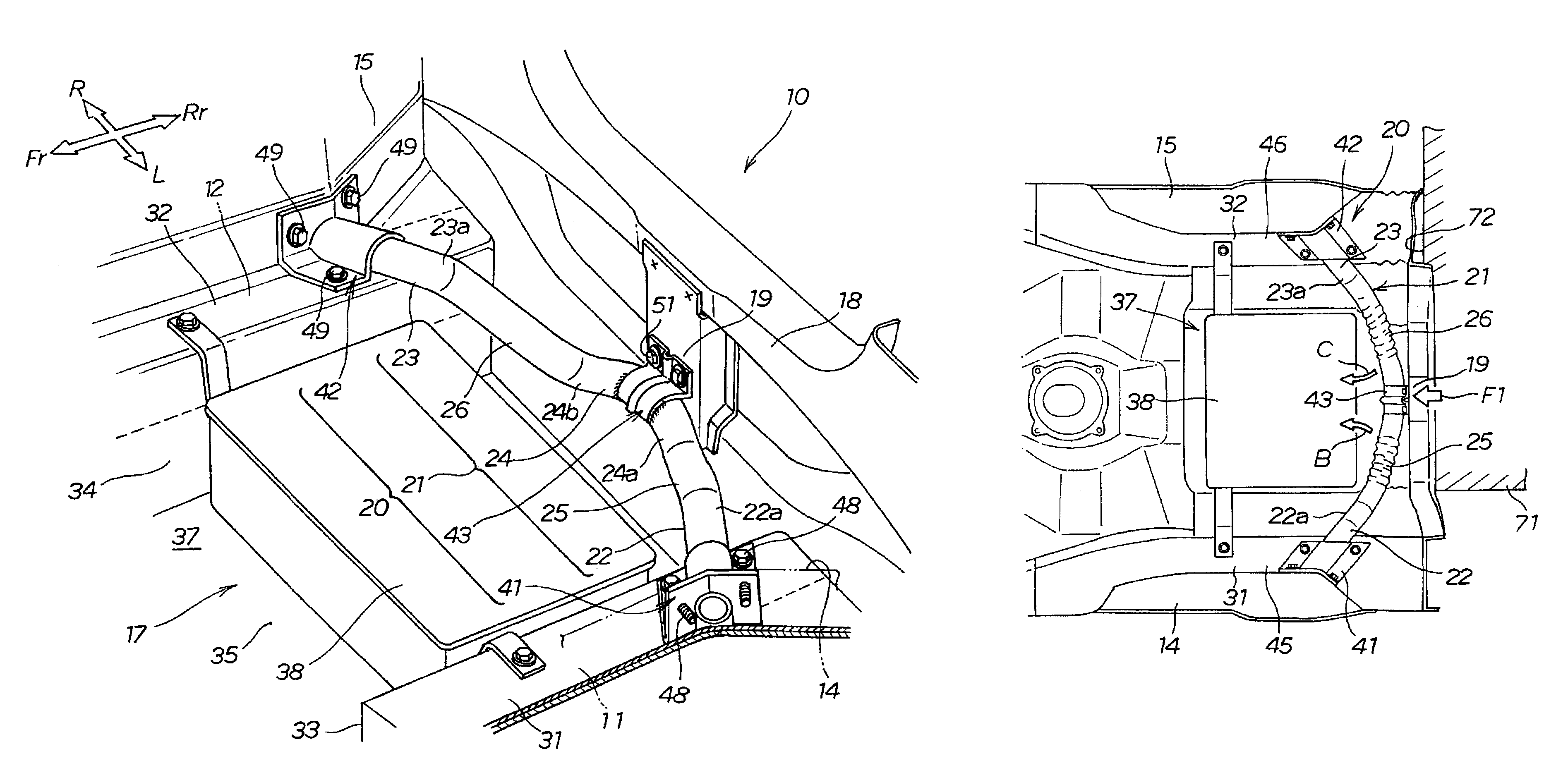
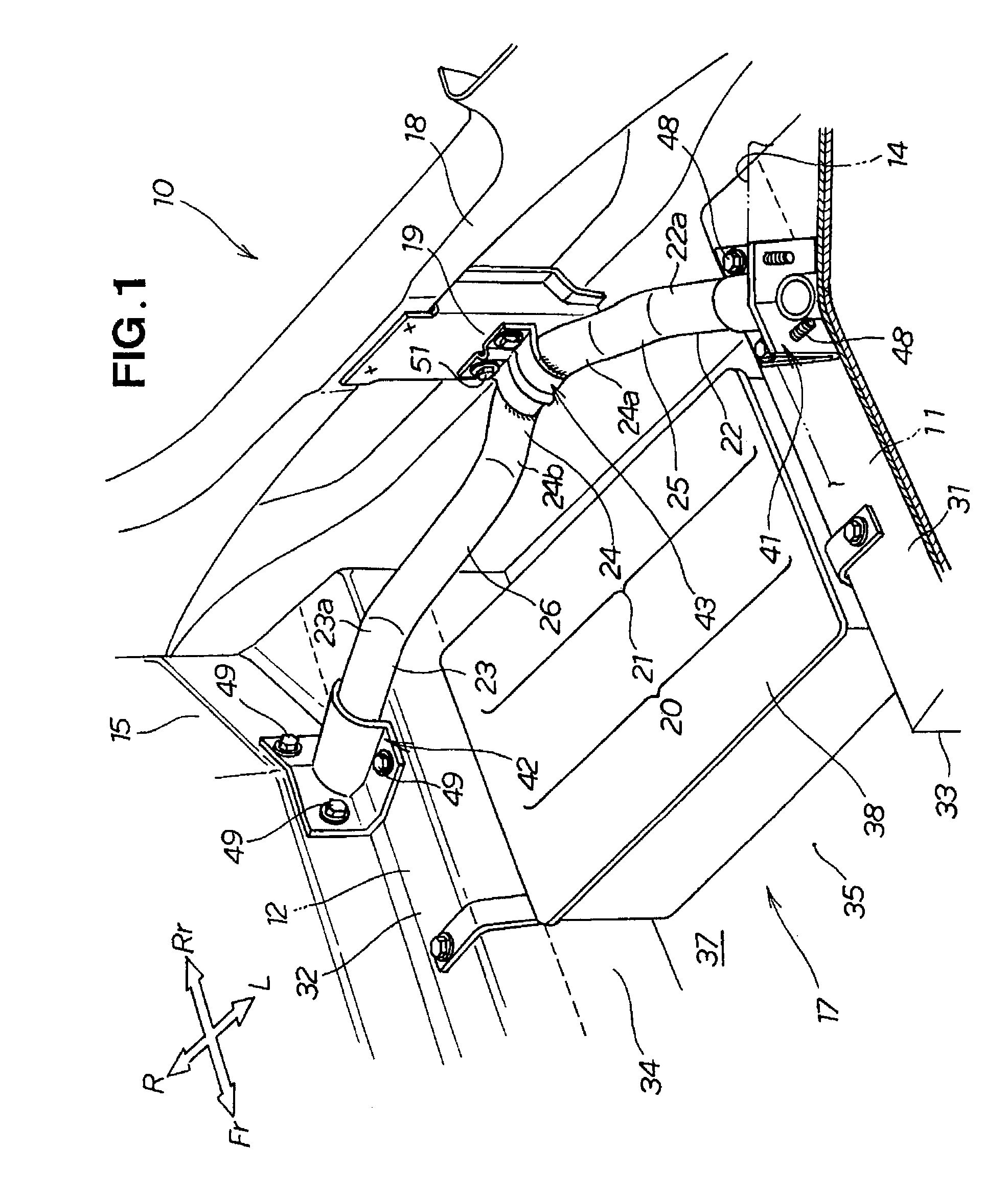
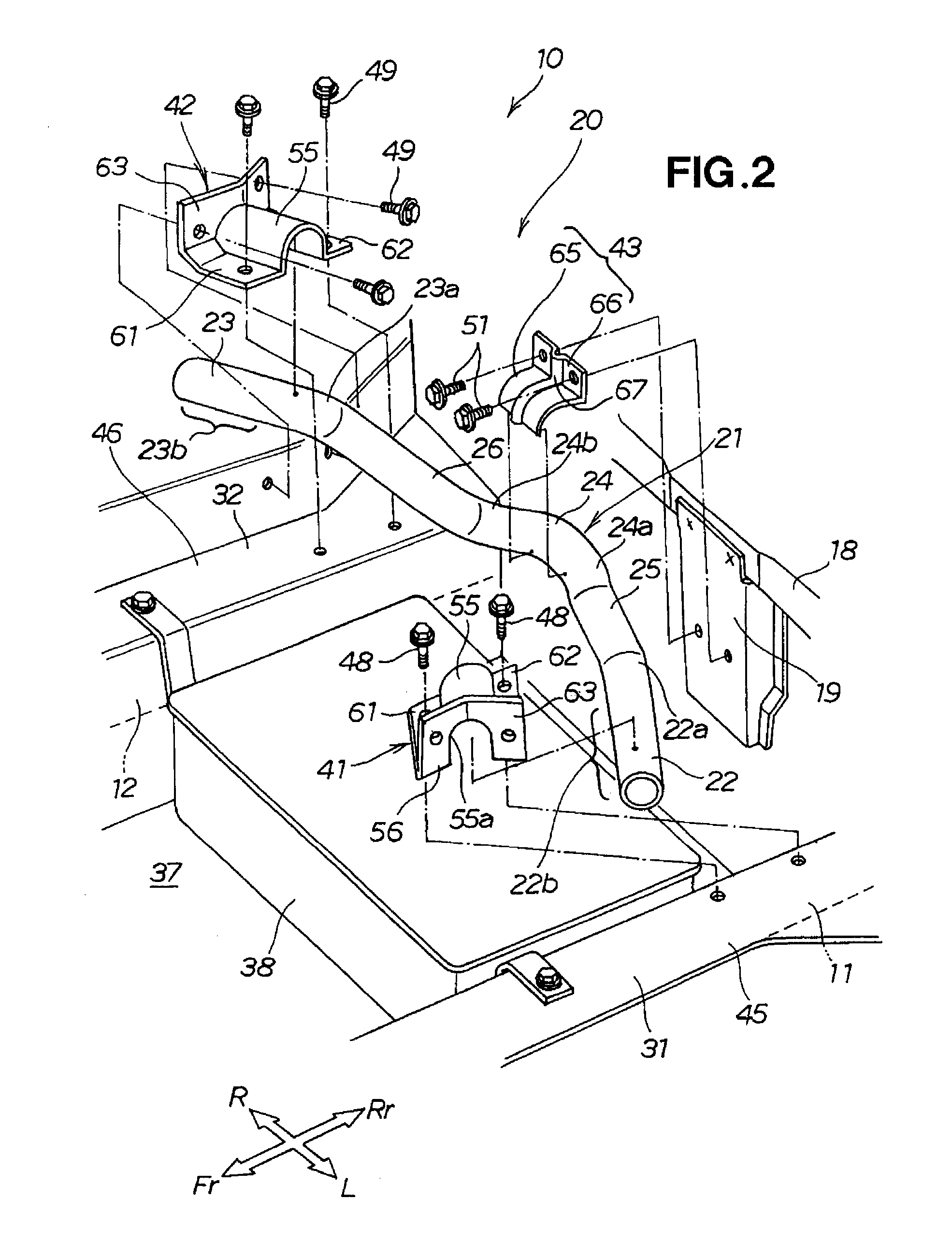
Rear frame structure for vehicle
InactiveUS20090026802A1Increasing vertical dimensionFully absorbedVehicle seatsUnderstructuresVehicle frameCompressive deformation
A rear frame structure for a vehicle is disclosed, wherein an impact load can be satisfactorily absorbed in the case of a collision with a rear surface of the vehicle. The rear frame structure includes a pipe-shaped impact-absorbing member located between left and right rear frames. The impact-absorbing member has a center pipe that has a V shape in plan view, formed so as to protrude backward. The impact-absorbing member has left- and right-side pipes extending from the center pipe linearly upwardly to left and right end pipes. The impact load applied to the center pipe causes the left- and right-side pipes to undergo compressive deformation in their axial longitudinal directions as well as bending deformation towards the front of the vehicle body, whereby the impact load is absorbed.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
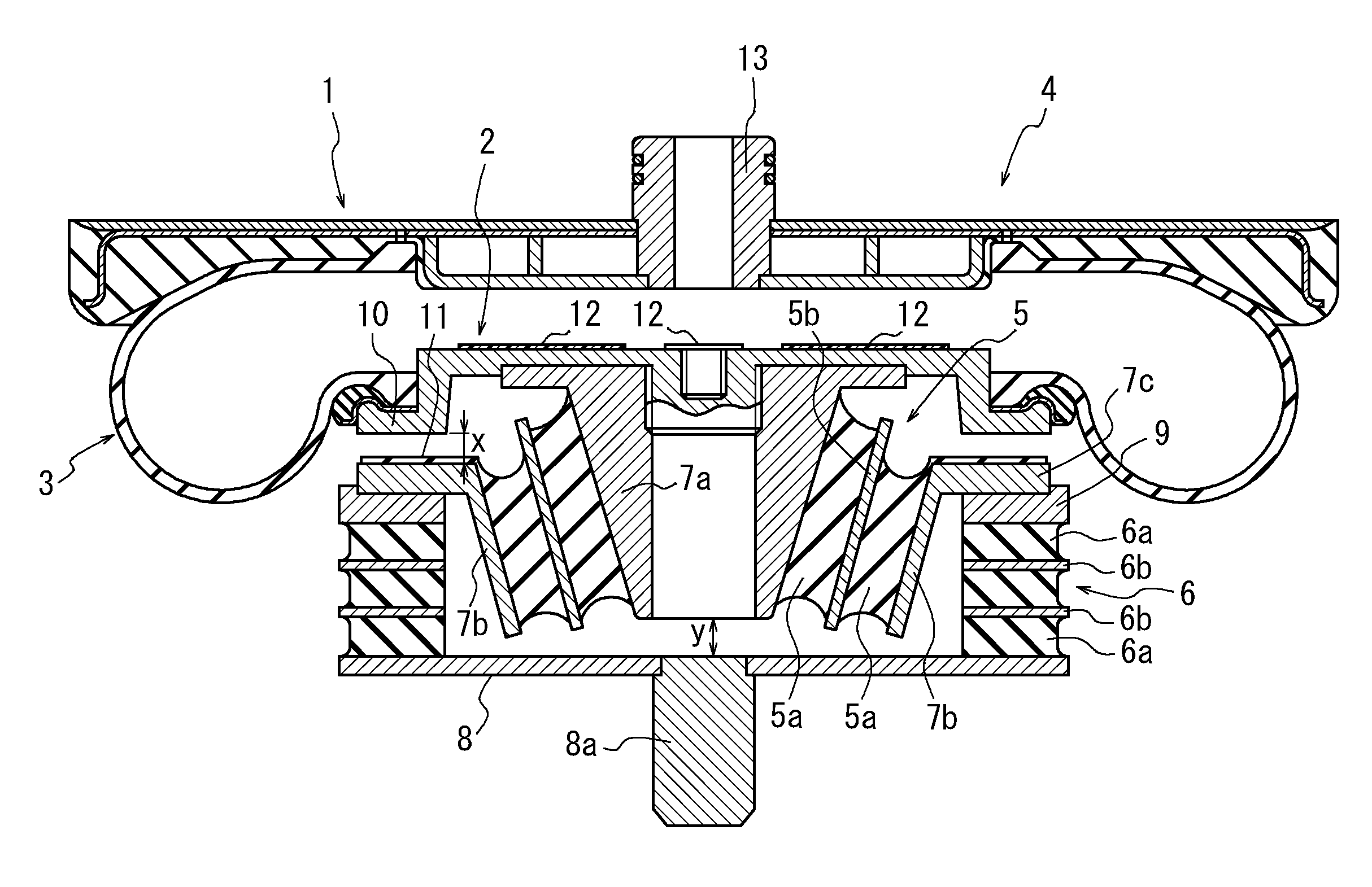
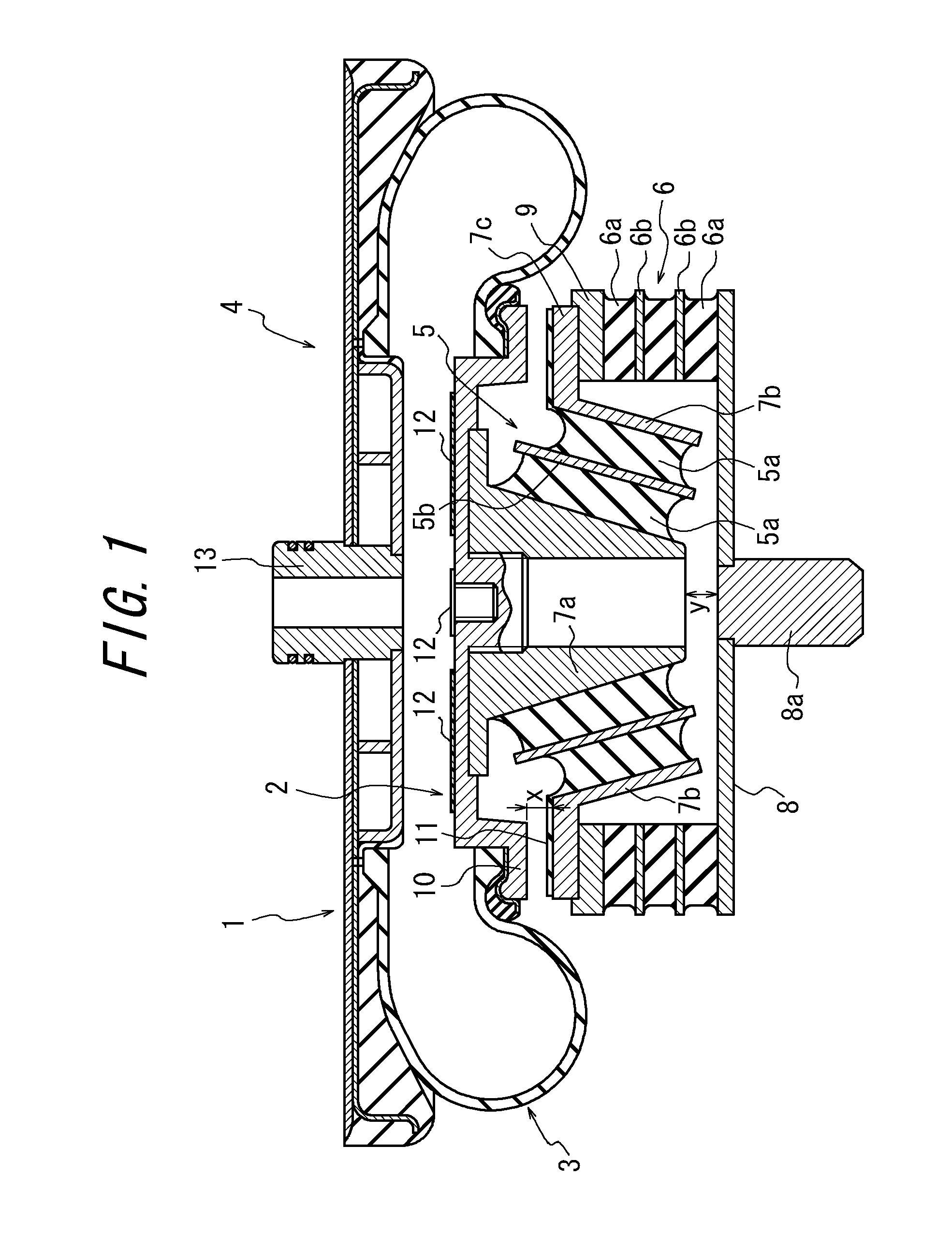
Air spring device
InactiveUS20110031662A1Stiff constantSimple structureNon-rotating vibration suppressionMultiple spring combinationsRubber materialAir spring
An air spring device includes an air spring (4) wherein gas is filled in an interior defined by an upper face plate (1), a lower face plate (2), as well as a cylindrical flexible diaphragm body (3) having opposite ends gas-tightly connected to the upper and lower face plates (1, 2), respectively. Between the lower face plate (2) and a lower supporting plate (8) spaced downward therefrom, a shear spring means (5) and a compression spring means (6) are series-connected, which are made mainly of rubber material. When a vertical load is applied to the air spring device, the shear spring means (5) and the compression spring means (6) are subjected mainly to shearing deformation and compressive deformation, respectively. The air spring device further includes an abutment member (10) allowing the compression spring means (6) to support the load in place of the shear spring means (5), after the deformation amount of the shear spring means (5) reaches a predetermined level.
Owner:BRIDGESTONE CORP
Efficient distribution dryer
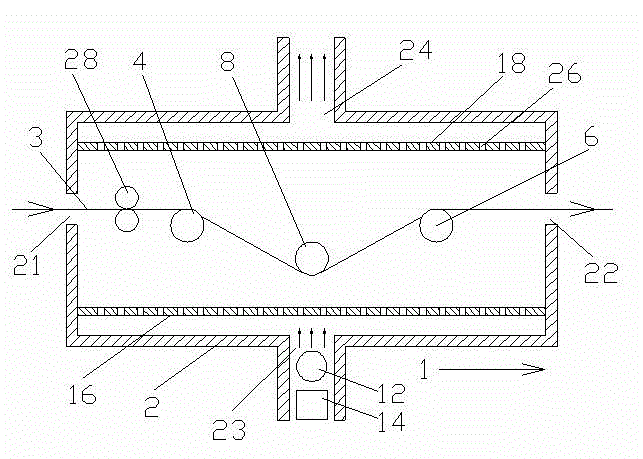
InactiveCN102914127AReduce the burden onPrevent local overheatingDrying chambers/containersDrying machines with progressive movementsSuperheatingCompressive deformation
The invention relates to an efficient distribution dryer which comprises a box housing. Two ends of the housing are provided with a cloth inlet and a cloth outlet. The housing is provided with an air inlet at the top and an air outlet at the bottom, or provided with an air inlet at the bottom and an air outlet at the top. A distribution conveying mechanism is disposed in an inner cavity of the housing. A heating pipe and a bower outside the heating pipe are disposed at the air inlet. The efficient distribution dryer is characterized in that transversely extending partitions are disposed in the inner cavity of the housing, and a plurality of intake through holes are arranged on the partitions in directions, along the distribution conveying direction and transversely perpendicular to the distribution conveying direction. The partitions with intake through holes are disposed in the efficient distribution dryer and disperse hot air from the single air inlet, so that local superheating and compressive deformation are prevented, drying quality is guaranteed and overall drying efficiency is also improved.
Owner:WUJIANG KESHIDA TEXTILE
Fiber reinforced rubber
The invention relates to a fiber reinforced rubber, for which the strength can be remarkably improved, the permanent compression set can be reduced and the anti-tear performance of rubber sheet can be enhanced. A method for preparing the fiber reinforced rubber comprises the following steps: a. mastication of rubber; b. reinforcing filler, fiber and accessory ingredient are added into the rubber for mixing; wherein, the fiber and the reinforcing filler is evenly mixed to prepare pre-dispersoid, and the pre-dispersoid is added into the rubber. As a preferred proposal, the method adopts styrene-butadiene rubber, nitrile rubber and neoprene which have the good properties of wearing resistance, pressure resistance, oil and water resistance and air tightness resistance as the rubber. The rubber sheet produced by the method can work under ultra-high temperature and pressure in various media for a long time with the maximum working temperature being 300 DEG C, and maintains good elasticity, less compressive deformation and excellent physical and mechanical properties which are reduced by not more than 20% compared with those at the normal temperature.
Owner:南京固柏橡塑制品有限公司
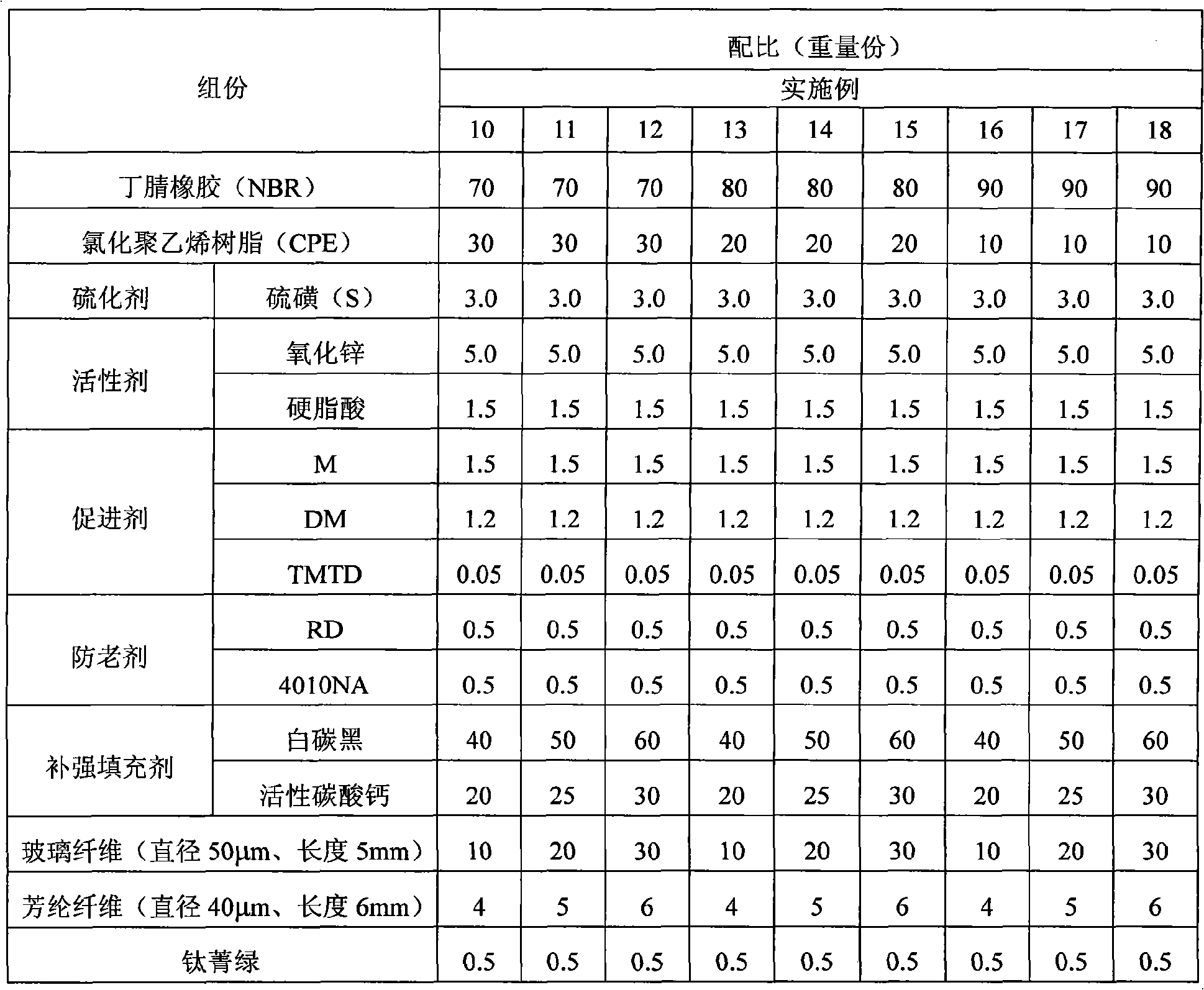
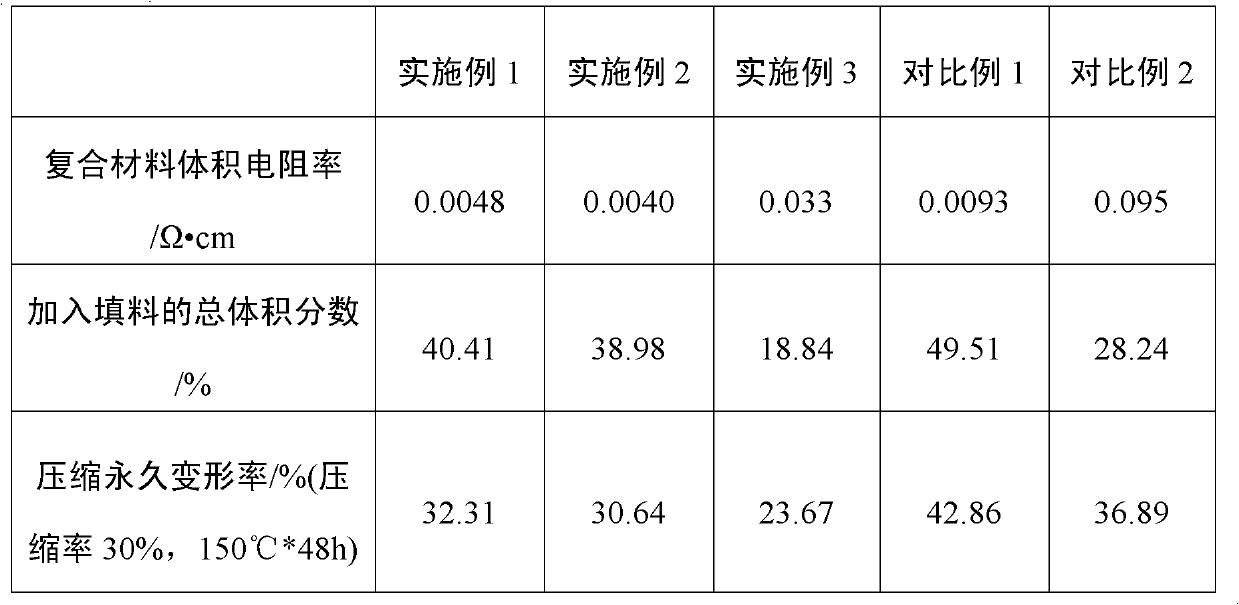
Low-compressive-deformation and high-conductivity rubber composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a low-compressive-deformation and high-conductivity rubber composite material and a preparation method thereof. The low-compressive-deformation and high-conductivity rubber composite material is prepared by the following steps of: taking silicon rubber as a base body and utilizing modified grain-shaped and fiber-shaped metal-plating conductive fillers containing a reactive double-bond silane coupling agent under a CO2 supercritical state to prepare low-compressive-deformation and high-conductivity rubber composite material. Under the condition of guaranteeing the high conductivity, the use amount of the conductive fillers is reduced and the composite material has low compressive deformation and high conductive property.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
Conductive particles and method of preparing the same
ActiveUS20080078977A1Improve suppression propertiesPromote recoveryConductive layers on insulating-supportsConductive materialParticle radiusCompressive deformation
Conductive particles each includes a polymer base particle and a conductive layer coating the polymer base particle. Let the compressive elastic deformation characteristic KX of one conductive particle when the displacement of particle diameter of the conductive particles is X % be defined by the following formula: KX=(3 / √2)·(SX−3 / 2)·(R−1 / 2)·FX. FX is the load (N) necessary for X % displacement of the conductive particles. SX is the compressive deformation amount (mm) upon X % displacement of the conductive particles. R is the particle radius (mm) of the conductive particles. The compressive elastic deformation characteristic K50 when the displacement of particle diameter of the conductive particles is 50% is 100 to 50000 N / mm2 at 20° C., and the recovery factor of particle diameter of the conductive particles when the displacement of particle diameter of the conductive particles is 50% is not less than 30% at 20° C.
Owner:NIPPON CHECMICAL IND CO LTD
Rear frame structure for vehicle
A rear frame structure for a vehicle is disclosed, wherein an impact load can be satisfactorily absorbed in the case of a collision with a rear surface of the vehicle. The rear frame structure includes a pipe-shaped impact-absorbing member located between left and right rear frames. The impact-absorbing member has a center pipe that has a V shape in plan view, formed so as to protrude backward. The impact-absorbing member has left- and right-side pipes extending from the center pipe linearly upwardly to left and right end pipes. The impact load applied to the center pipe causes the left- and right-side pipes to undergo compressive deformation in their axial longitudinal directions as well as bending deformation towards the front of the vehicle body, whereby the impact load is absorbed.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
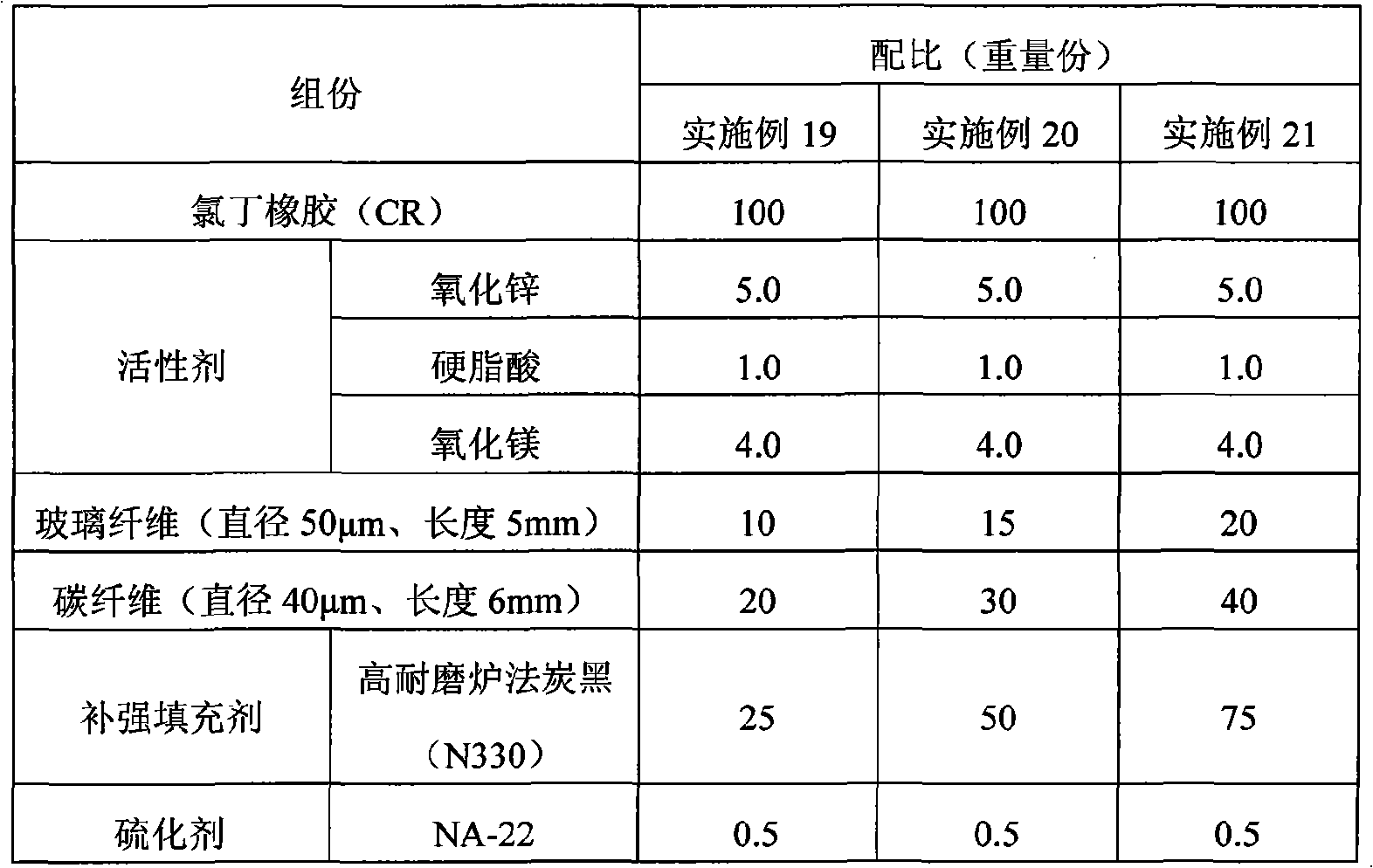
Conductive silicon rubber material with ultralow compressive deformation and low hardness and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103160128AReduce fillingIncrease elasticityNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialRubber materialCarbon nanotube
The invention relates to a conductive silicon rubber material with ultralow compressive deformation and low hardness and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of conductive silicon rubber materials. The rubber material is prepared by filling conductive fillers with different shape factors so as to ensure that a network passage is formed under the condition of low-usage conductive filler. The rubber material comprises the following ingredients in parts by mass: 100 parts of silicon rubber, 1-15 parts of vulcanizing agent, 0 or 1-8 parts of vulcanizing assistant, 5-15 parts of carbon black and 0.5-5 parts of carbon nanotubes. According to the material, the material is endowed with higher conductivity under the condition that lower compression permanent deformation and lower hardness are guaranteed; the preparation process is simple, and the cost is low; and through testing the electrical and mechanical properties of the material, the conductive silicon rubber material has the following properties: the Shore A hardness is not higher than 50, the 25% constant compression permanent deformation is not higher than 10% (100 DEG C * 24 h), the instantaneous resilience performance is not lower than 60%, and the volume resistivity is not higher than 50 omega.cm.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Inner sole structure for a sports shoe
InactiveUS20090241373A1Cushioning ability can be adjustedPrevents an excessive sinking of the upperSolesInsolesMechanical engineeringCompressive deformation
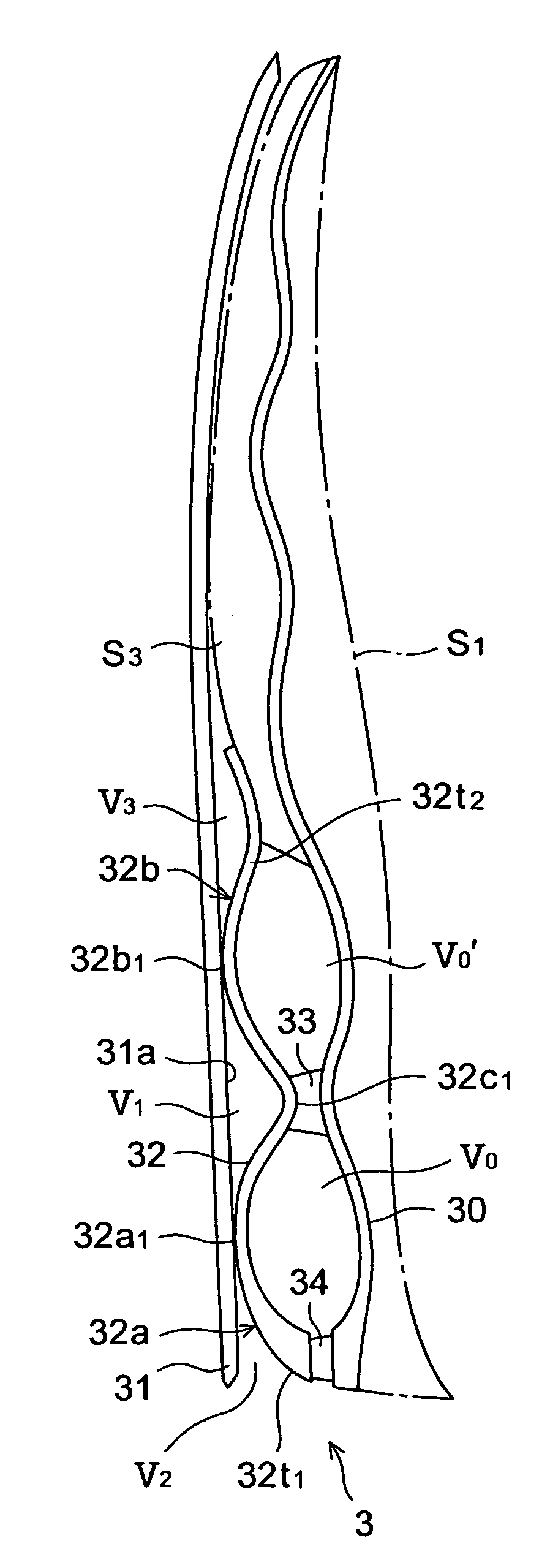
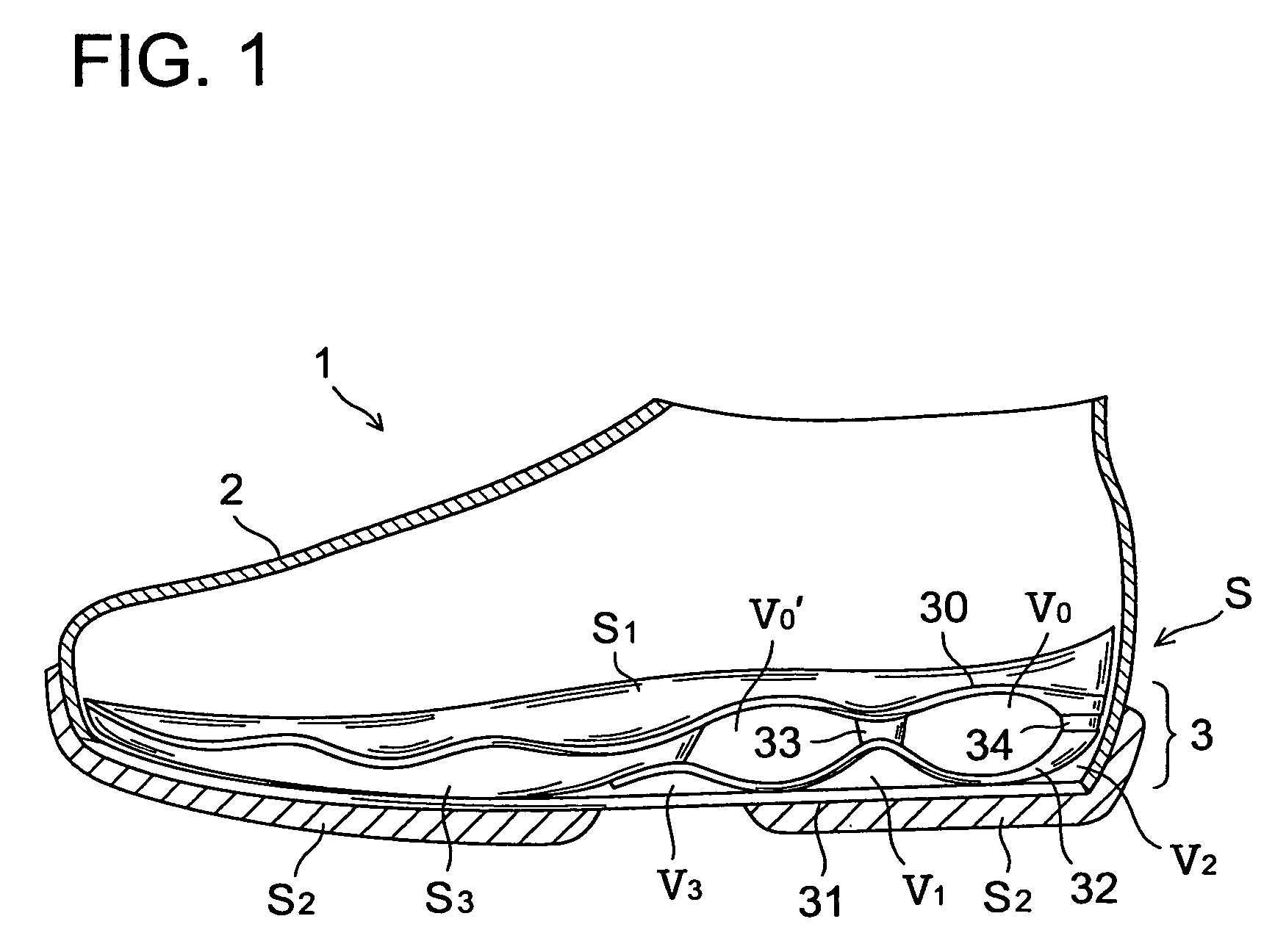
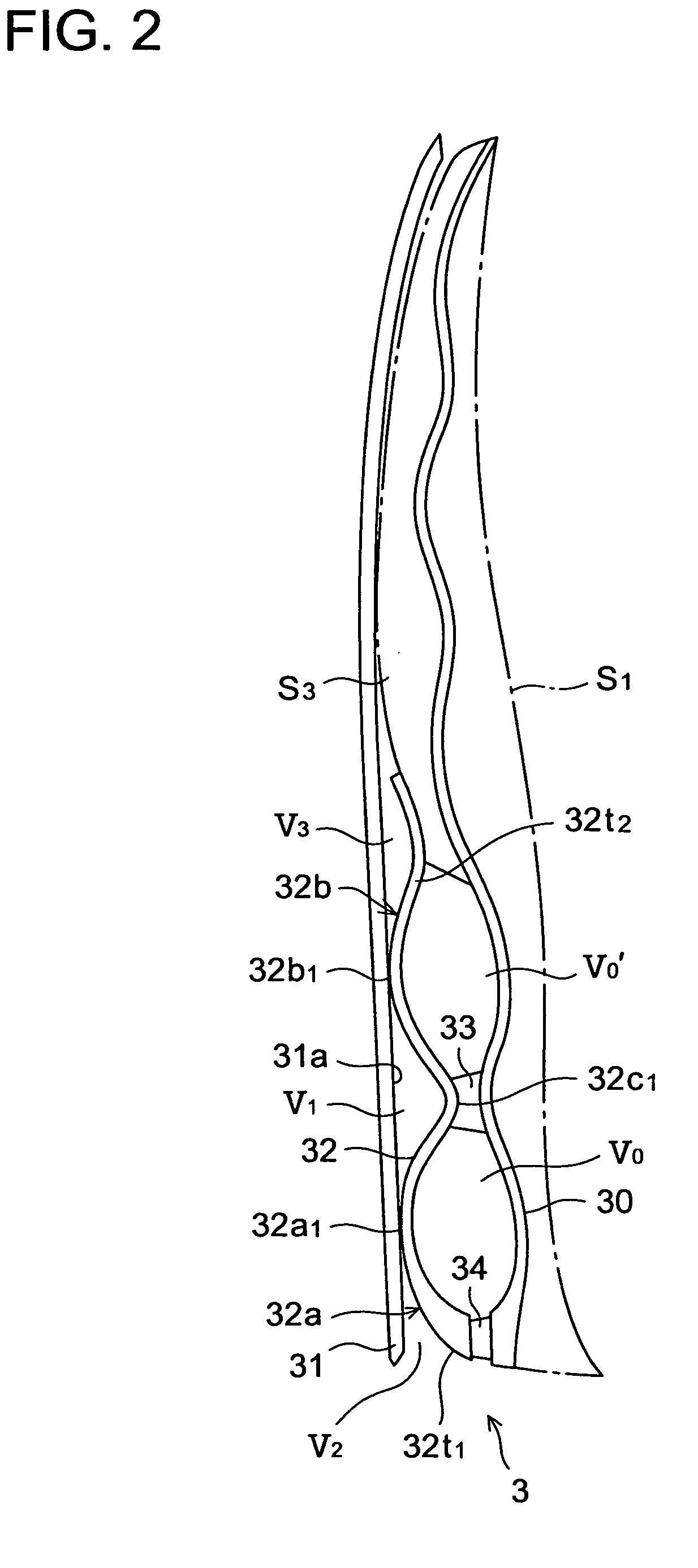
An inner sole structure 3 for a sports shoe 1 includes an upper sheet member 30 disposed on an upper side of a heel region of the shoe 1, a lower sheet member 31 disposed below the upper sheet member 30, and a wavy corrugated sheet member 32 that is interposed between the upper sheet member 30 and the lower sheet member 31, that has at least two downwardly protruding protrusions 32a, 32b adapted to form voids V0, V1′, V1 with the upper and lower sheet members 30, 31, and that is in contact with an upper surface 31a of the lower sheet member 31. Each of downwardly convex portions 32a1, 32b1 of the protrusions 32a, 32b of the wavy corrugated sheet member32 slides longitudinally on the lower sheet member 31 at the time of compressive deformation of the protrusions 32a, 32b.
Owner:MIZUNO CORPORATION
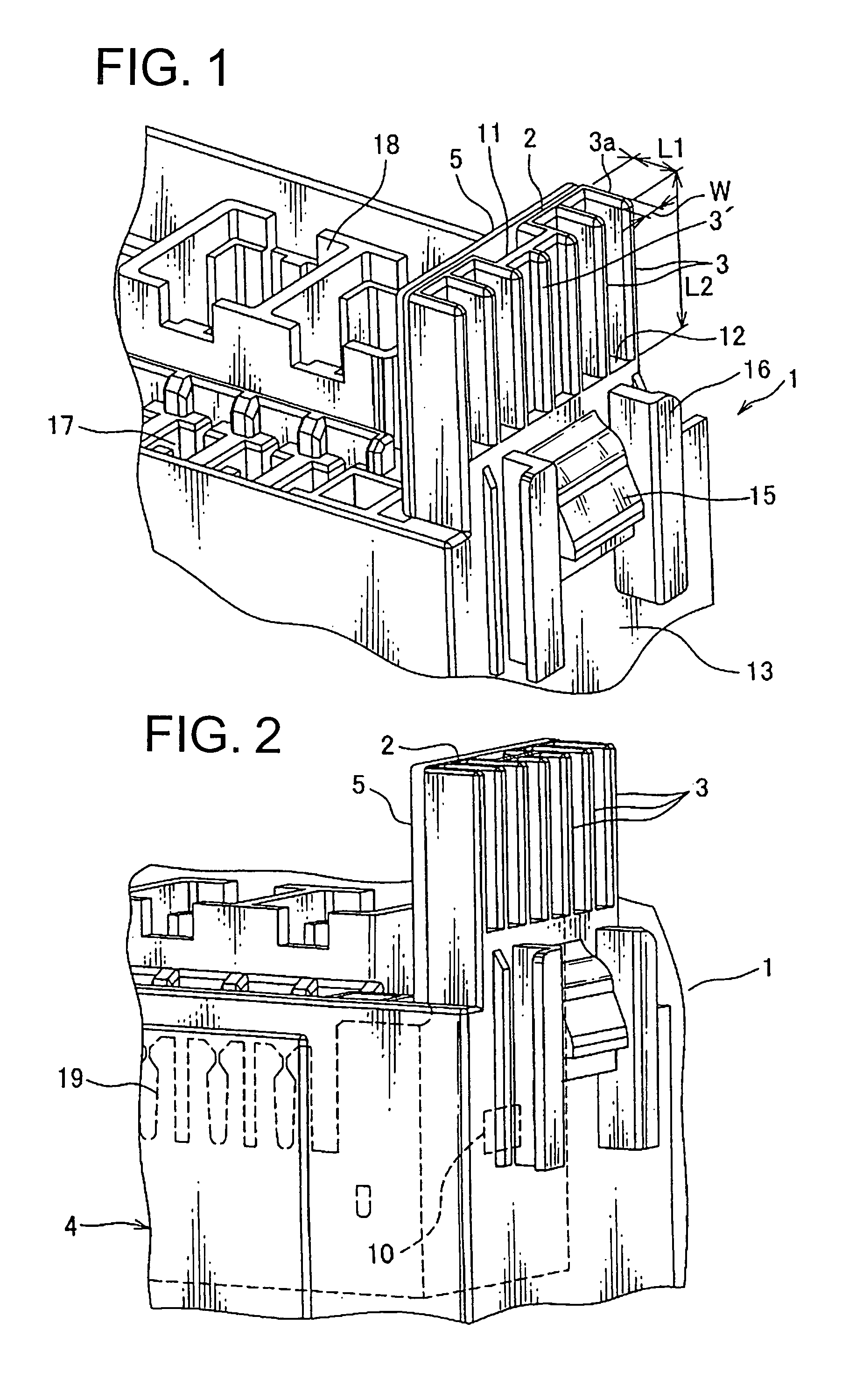
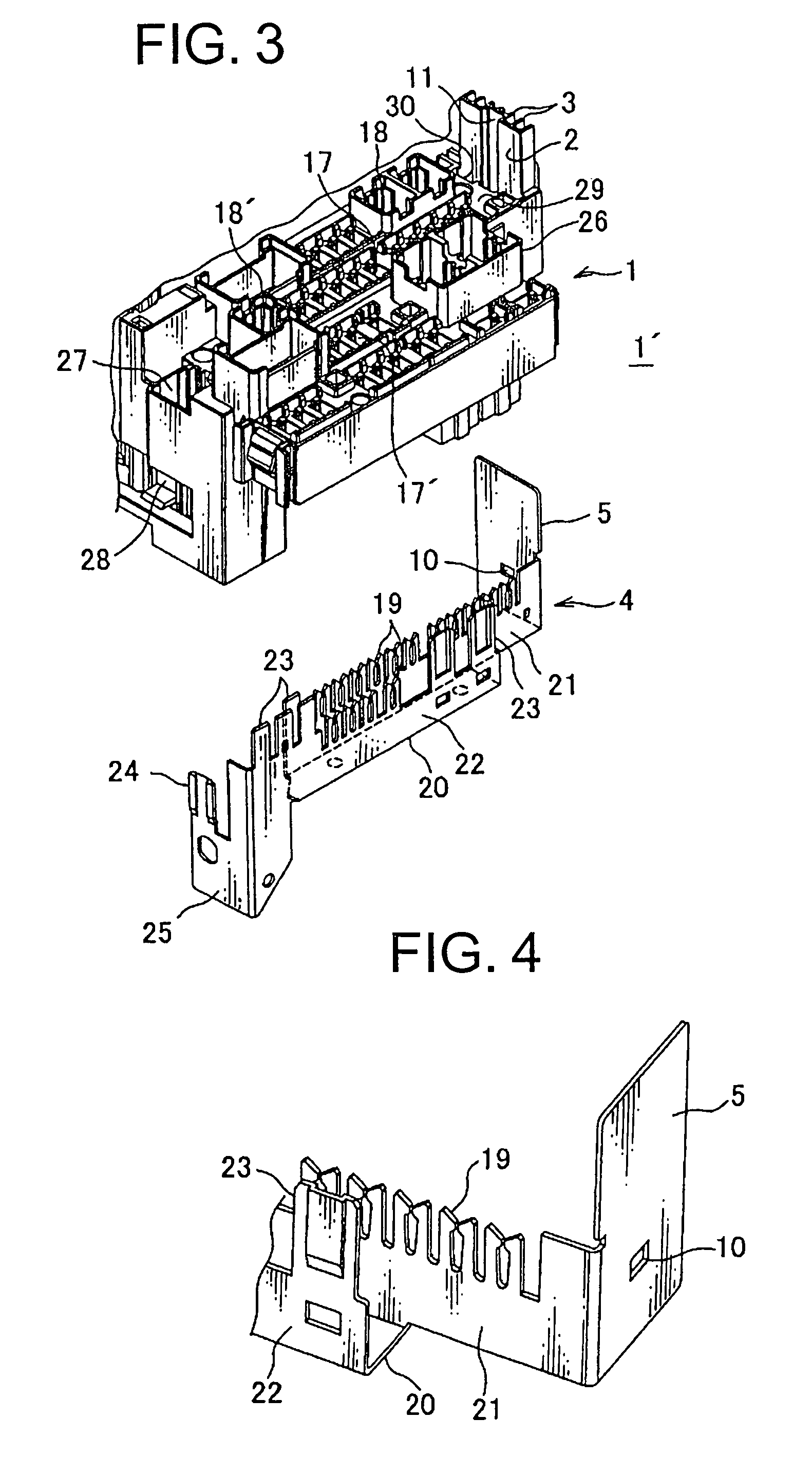
Rescue terminal structure
ActiveUS7785116B2Firmly connectedSafely and stably suppliedElectrically conductive connectionsPrinted circuitsEngineeringSynthetic resin
A block body made of insulating synthetic resin having a terminal supporting plate in one piece therewith. A plurality of elongated ribs project on one surface of the terminal supporting plate and a rescue terminal is arranged on the other surface of the terminal supporting plate. A bus bar is mounted in the block body. A clamping portion of a booster cable can grasp both the rescue terminal and the rib at one time. The plurality of ribs are parallel to each other. The dimension of the rib is defined such that the rib is placed under compressive deformation when the rib is clamped by the clamping portion. The block body has a hole through which the rescue terminal is passed such that the rescue terminal extends along and in contact with the other surface of the terminal supporting plate.
Owner:YAZAKI CORP
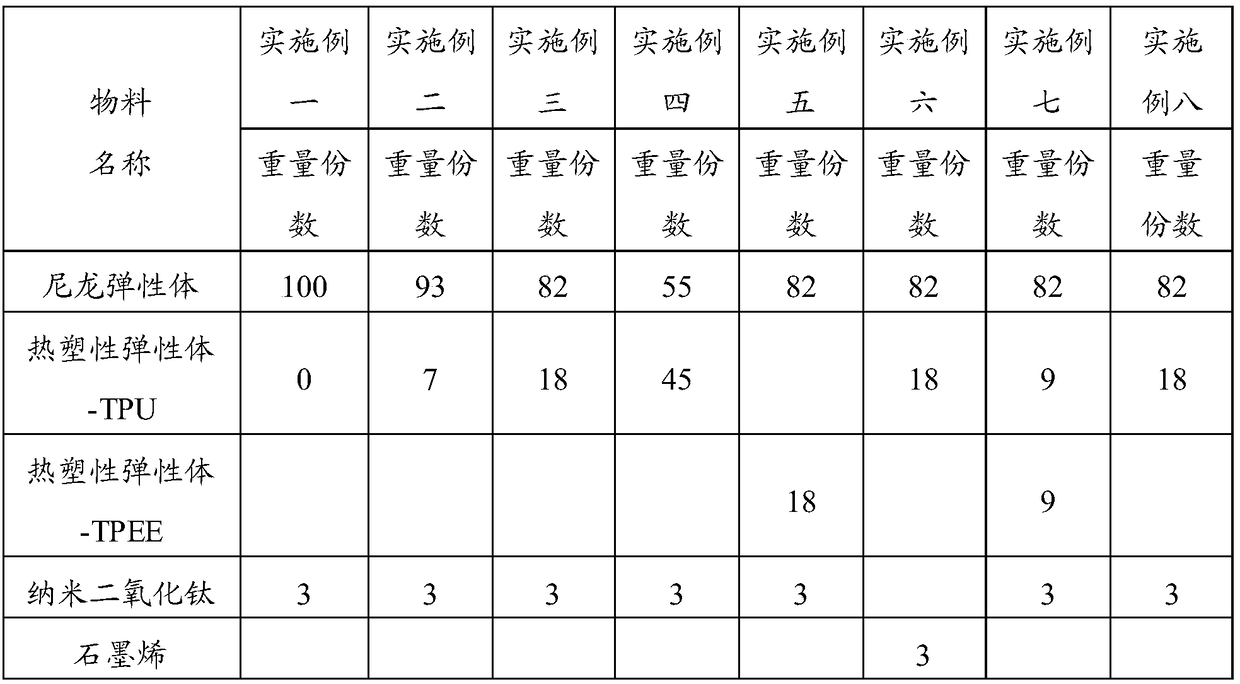
Foam material for shoe, preparation method and application of foam material
The invention provides a foam material for a shoe, a preparation method and application of the foam material. The foam material is prepared by sequentially performing the processes of injection molding and supercritical fluid foaming molding on a nylon elastomer composite material, and the nylon elastomer composite material comprises the following components in parts by mass: 50-100 parts of nylonelastomer resin, 0-50 parts of thermoplastic elastomer resin, 0.5-3 parts of a nanometer nucleating agent, 0-0.6 part of an antioxygen, 0-1.2 parts of stearic acid and 0-0.6 part of a foaming stabilizer. The foam material for the shoe has nanopores, is relatively light in weight, is endowed with relatively high hardness, further has the advantages of high resilience, low compressive deformation,relatively high tensile strength and the like, greatly reduces the weight of a sneaker and also is also relatively excellent in mechanical property and durability when used as an insole material of the shoe. In addition, the insole material of the shoe is prepared by rapidly releasing the pressure and foaming after dipping in supercritical fluid, the preparation flow is shorter, and the efficiencyis higher.
Owner:ANTA CHINA
Molded Foam Article, Foamed Sole, and Shoe
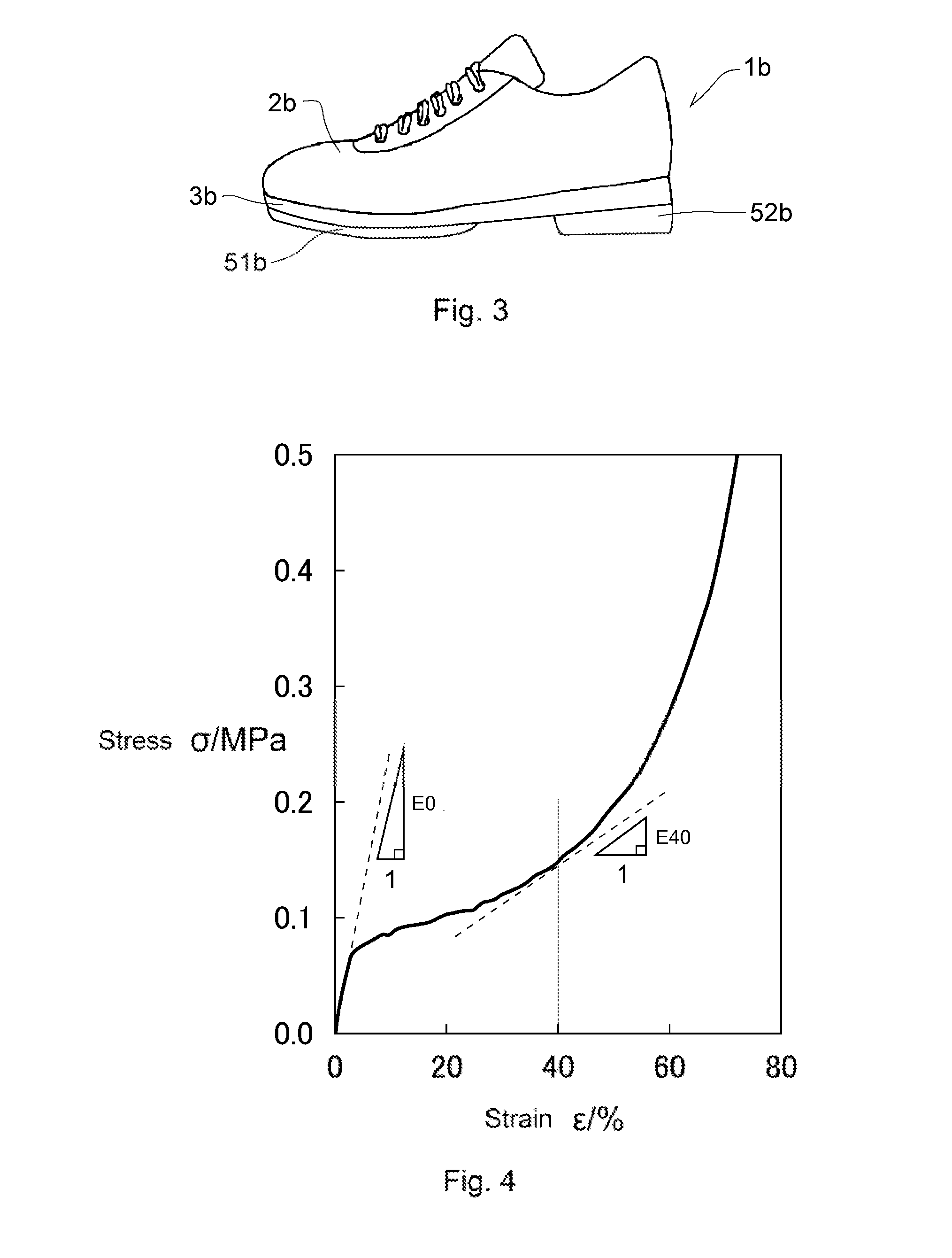
ActiveUS20150143723A1Little change in hardnessKeep elasticSolesAbsorbent padsCompressive deformationComposite material
There is provided a molded foam article including a foam obtained by foaming a formation material wherein the formation material contains a resin component, an Asker C hardness of the foam is 10 degrees or more, and a ratio E40 / E0 of the foam is 0.5 or more, the ratio E40 / E0 being a ratio of an elastic coefficient E40 at a strain of 40% in relation to an elastic coefficient E0 at a strain of 0% of the foam.The molded foam article has appropriate softness with a small change in hardness under compressive deformation.
Owner:ASICS CORP
Rubber compositions for oil seal of rubber framework and method for manufacturing same
Owner:青岛茂林橡胶制品有限公司
Method and device for ray bundle scanning for back scattering imaging
InactiveCN101644687AHandling using diaphragms/collimetersUsing wave/particle radiation meansEngineeringCompressive deformation
The invention discloses a method and a device for ray bundle scanning for back scattering imaging. The scanning device comprises a fixed shield plate and a rotary shield plate which are positioned atthe front of a ray source respectively, wherein the fixed shield plate is fixed relative to the ray source, and the rotary shield plate can be rotated relative to the fixed shield plate; the fixed shield plate and the rotary shield plate are provided with a ray passing region respectively; in the process of rotary scanning of the rotary shield plate, the ray passing region of the fixed shield plate and the ray passing region of the rotary shield plate are continuously crossed to form a scanning collimating hole; the scanning collimating hole is always kept in a preset shape relative to the raysource so that the section shape of the ray bundle passing through the scanning collimating hole is kept unchangeable. The scanning device can complete ideal ray bundle scanning, can implement the uniform scanning for target objects, and can conveniently realize the uniform sampling for the target objects, so longitudinal compressive deformation cannot be generated in obtained back scattering images.
Owner:NUCTECH CO LTD +1
Electrostatic image forming toner and resin for toner
An electrostatic image forming toner including: a colorant; a binder resin; and a releasing agent, wherein the binder resin contains at least two types of polyester resins A and B, wherein a difference of (T1 / 2−Tg) is 65° C. or more but less than 90° C., where T1 / 2 denotes a softening point of the electrostatic image forming toner and Tg denotes a glass transition temperature of the electrostatic image forming toner, and wherein the electrostatic image forming toner has a TMA compressive deformation rate (TMA %) at 50° C. which is 5% or less.
Owner:RICOH KK
Toner for forming electrostatic image, developer, process cartridge, and image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20140080046A1Low temperature fixing abilityLow anti-blocking property propertyDevelopersElectrographic process apparatusEngineeringPolyester resin
To provide a toner, which contains a colorant, a binder resin, and a releasing agent, wherein the toner satisfies the following (a) to (c); (a) the toner contains at least a polyester resin as the binder resin; (b) the toner has Tg1st of 25° C. to 50° C.; and (c) the toner has a TMA compressive deformation rate (TMA %) of 10% or lower at 50° C. under a condition having relative humidity of 70%, wherein the Tg1st is glass transition temperature of the toner for first heating, as the toner is measured by a DSC system (a differential scanning calorimeter).
Owner:RICOH KK
Toner, development agent, image forming apparatus, and image forming method
InactiveUS20140080050A1Toner accumulatingLow viscosityElectrographic process apparatusDevelopersPulse nuclear magnetic resonanceImage formation
Toner contains a binder resin, wherein the binder resin contains a block copolymer A containing a crystalline segment X and a non-crystalline segment Y, wherein the toner has a thermo-mechanical analysis (TMA) compressive deformation amount (TMA %) of 10% or less at 50° C. and a relative humidity of 90%, wherein the toner has a spin-spin relaxation time (t130) of 10 ms or greater at 130° C. as measured by pulse nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), wherein the toner has a spin-spin relaxation time (t′70) of 1 ms or less at 70° C. as measured by pulse NMR when descending from 130° C. to 70° C.
Owner:RICOH KK
Ring spun negative-Poisson's-ratio yarn and compound spinning device and method and application thereof
ActiveCN107400947ASolving Feed ProblemsFix stability issuesContinuous wound-up machinesYarnEngineeringCompressive deformation
The invention provides a ring spun negative-Poisson's-ratio yarn which includes relatively rigid and externally wrapped-wound endless tows and relatively flexible short fiber strands located in a yarn core. The negative-Poisson's-ratio compound structural yarn obtained through asymmetrical two-axis system compound spinning on a ring spinning frame. When the yarn is stressed and stretched, the stretch wound spirally and externally are straightened, the original straightened and thicker short fiber strands are thus spirally wound externally, so that a yarn body becomes thick to form negative-Poisson's-ratio deformation. The invention also provides a compound spinning device and method and application of the ring spun negative-Poisson's-ratio yarn. The short fiber strands are directly straightened through compound spinning on the ring spinning frame and are output at a central shaft position from a front roller jaw. The endless tows are output from the front roller jaw in a tension-free overfeeding mode and are externally wrapped, wound, compounded and twisted with the short fiber strands at a certain converging angle in an obvious-compressive deformation mode to form the yarn. The device is simple in structure and convenient to operate, and the obtained negative-Poisson's-ratio yarn can be used for negative-Poisson's-ratio fabrics and has a more obvious negative-Poisson's-ratio effect.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Toner, developer and image forming apparatus
ActiveUS20130337374A1Excellent low temperature fixabilityHigh temperature-resistant offset propertyElectrographic process apparatusDevelopersImaging equipmentThermomechanical analysis
To provide a toner including a binder resin and a colorant, wherein the toner has a glass transition temperature by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) of 20° C. or greater and less than 50° C., an endothermic peak temperature by DSC of 50° C. or greater and less than 80° C. and an amount of compressive deformation at 50° C. by a thermomechanical analysis of 5% or less.
Owner:RICOH KK
Friction factor measuring and calculating method during metal plastic forming
InactiveCN102944513AConvenient and accurate calculation methodAvoid inconvenienceUsing mechanical meansMaterial analysisMetallic materialsLubrication
The invention discloses a friction factor measuring and calculating method during metal plastic forming. Firstly, a standard metal material tensile test is performed to obtain mechanical characteristic parameters of a metal material to be measured, a cylindrical workpiece is subjected to upsetting and compressive deformation, geometric data of the workpiece before and after deformation are obtained by measuring, and the mechanical parameters and the upsetting geometric data are combined to figure out the friction factor between an upsetting forming mold and an upsetting forming workpiece. The measuring and calculating method is convenient and accurate, material characteristics are considered, and inconveniences and deviation caused by curve correlation method and the like are avoided. The method is mainly specific to evaluation of friction and lubrication conditions during metal forming and has an important application value in the metal forming machining technology.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
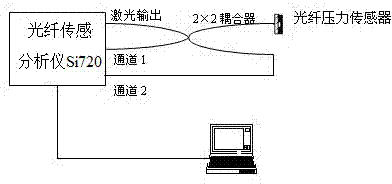
Miniature optical fiber Fabry-Perot pressure sensor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103528735AHigh measurement accuracyHigh precisionForce measurement by measuring optical property variationFluid pressure measurement by optical meansLight energyEngineering
The invention discloses a novel miniature optical fiber Fabry-Perot pressure sensor and a manufacturing method thereof. According to the sensor, the defects that large light energy loss is caused because a traditional optical fiber Fabry-Perot sensor generates non-planar movement when a pressure sensitive film is pressed can be effectively overcome, and higher measurement accuracy can be obtained. The provided miniature optical fiber Fabry-Perot pressure sensor comprises a monocrystalline silicon film and a borosilicate optical fiber which are connected through an anodic bonding process, wherein the monocrystalline silicon film comprises a boss; the borosilicate optical fiber comprises a concave cavity; one side of the monocrystalline silicon film with the boss and the concave cavity of the borosilicate optical fiber relatively form a Fabry-Perot cavity; a reflecting surface is formed on the top of the boss. The sensor has the advantages that two reflecting surfaces of the Fabry-Perot cavity are always kept to be parallel to each other in the compressive deformation of the sensitive film, and the measurement accuracy is greatly improved.
Owner:广州烽鼎医疗科技有限公司
Flexible conductive composite fabric, and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN106183316AGood flexibilityImprove electrical performanceFibre treatmentSynthetic resin layered productsComposite filmAdhesive
The invention relates to a flexible conductive composite fabric, and preparation and application thereof. The flexible conductive composite fabric comprises a conductive composite film (1), a base fabric (2) and an adhesive (3), wherein the base fabric (2) is adhered on the upper and lower surfaces of the conductive composite film through the adhesive (3); and two ends of the conductive composite film (1) are respectively adhered with an electrode. The flexible conductive composite fabric is prepared through the following steps: impregnating a carbon nanotube thin film in a graphene suspension, then taking the carbon nanotube thin film out of the graphene suspension, and carrying out drying in the air so as to obtain a carbon nanotube / graphene composite film; allowing a polyaniline nanowire array to grow in situ on the surface of the carbon nanotube / graphene composite film so as to obtain a carbon nanotube / graphene / polyaniline composite film; and respectively adhering an electrode at two ends of the composite film, coating the base fabric on the upper and lower surfaces of the composite film through the adhesive, and carrying out curing so as to obtain the flexible conductive composite fabric. The prepared conductive fabric provided by the invention has good conductivity, can reach 103 S / m to 105 S / m, can bear a certain degree of bending and compressive deformation, and is extensively applied in the fields of intelligent textile structures and intelligent materials.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
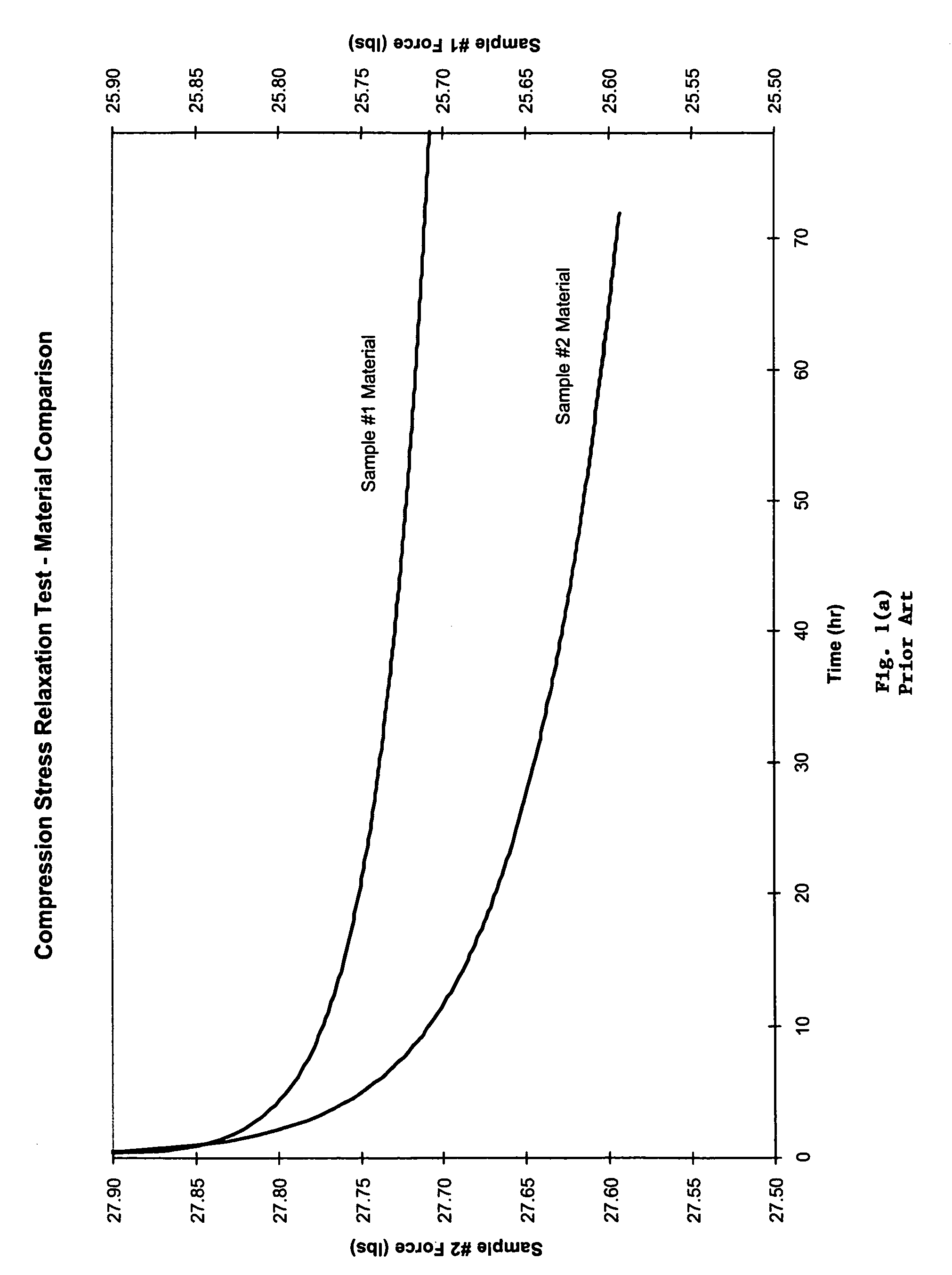
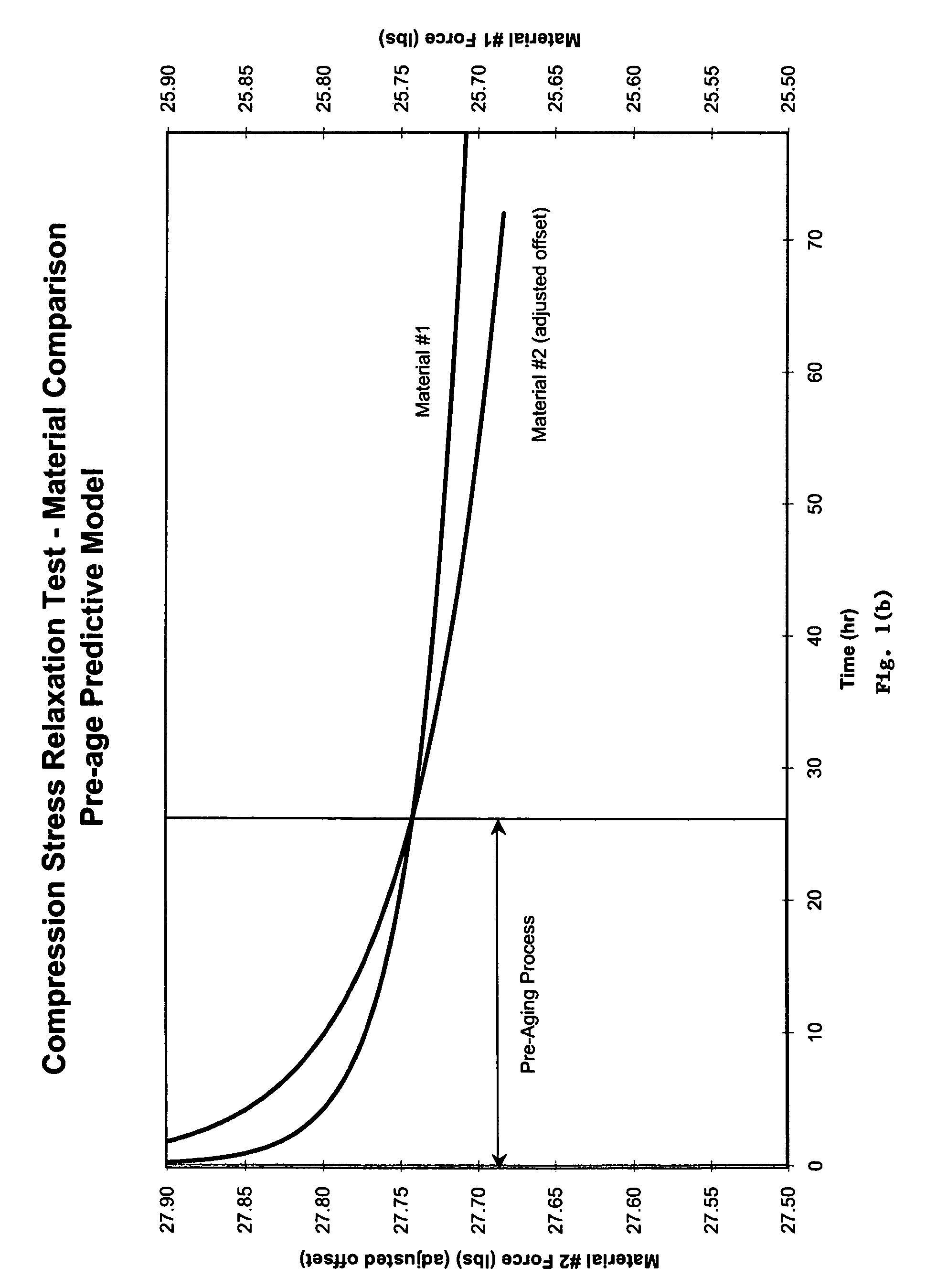
Pre-aging of rollers, gaskets, or o-rings to improve material response to compression set and compression stress relaxation
Provided is a method of stabilizing an elastomeric property of an elastomeric material. The method includes placing the elastomeric material in a pressurizing chamber and applying a suitable hydrostatic pressure to the elastomeric material within the pressurizing chamber to at least partially compress the elastomeric material. Application of the hydrostatic pressure is maintained for a period of time suitable to at least partially stabilize a restorative force exhibited by the elastomeric material in response to subsequent exposures of the elastomeric material to a compressive force.
Owner:CODONICS
Foaming section bar of multi-point positive feedback springback material with memorability and preparation method thereof
PendingCN107722602AWith positive multi-point feedback functionUnable to adjust melt viscosity in real timeSolesFoaming agentThermoplastic elastomer
The invention relates to a foaming section bar of multi-point positive feedback springback material with memorability and a preparation method thereof. The foaming section bar comprises a structural support which is composed of distributed enclosed air bags, and network pressure releasing structures which are distributed between enclosed air bags and comprise intercommunicated and open air passages that extend to the outside; the formula comprises the following components: 70-98 parts of degradable thermoplastic elastomers, 0.1-15 parts of a foaming agent, 0.05-0.5 parts of a nucleating agent,and 0-10 parts of a functional auxiliary agent. Compared with the prior art, compressive deformation and bounciness of countless enclosed air bags in the foaming section bar product are restrained and concentrated on relatively uniform surfaces by open air passages or capillaries, so that the product has positive multi-point feedback function.
Owner:上海德亿化工有限公司
Bumper system
ActiveUS7300080B2Easy to integrateFacilitate transmissionSuperstructure subunitsTowing devicesCompressive deformationImpact energy
A bumper system having a bumper running transverse to the longitudinal direction of a vehicle and at least one connecting element mounted thereon for the purpose of attaching the bumper to a vehicle, in particular to a longitudinal beam of a passenger car. The connecting element is a multi-chamber extruded section of metal with longitudinal axis running in the longitudinal direction of the vehicle. The connecting element is in the form of a safety element which, under impact, absorbs impact energy by compressive deformation. For the purpose of connecting a towing device, an attachment member is provided that is situated in one of the hollow chambers of the connecting element.
Owner:CONSTELLIUM SWITZERLAND
Severe plastic deformation method and severe plastic deformation device for pressing and rolling corner of non-equivalent passage
The invention discloses a severe plastic deformation method and a severe plastic deformation device for pressing and rolling the corner of a non-equal channel. According to the severe plastic deformation method and the severe plastic deformation device for pressing and rolling the corner of the non-equal channel, an equal-channel angular pressing (ECAP) technology and an ARB (Accumulative Roll Bonding) technology are integrated. The concrete process comprises the following steps that pressing force is applied after a test sample, a punching head and a mould are simultaneously preheated to pressing and rolling temperature, so that the test sample passes through the position of the channel corner of the device for pressing and rolling the corner of the non-equal channel completely; compressive deformation is generated when shear deformation is generated by the test sample so as to finish a first pass pressing and rolling process; the test sample is cut into L1 / L2 parts along a length direction, and the L1 / L2 parts are placed in an I channel; and the steps are repeated so as to finish multi-pass pressing and rolling deformation. The mould of the device is provided with the I channel and an II channel which are intersected and also have non-equal sections. The design is reasonable, the structure is simple, and the manufacturing cost is low. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the advantages of the ECAP technology and the ARB technology are integrated, and the mechanical property of a material is effectively enhanced. The process is short in procedure, high in efficiency and low in cost and is simple to operate. The severe plastic deformation method and the severe plastic deformation device for pressing and rolling the corner of the non-equal channel can be widely used for the field of processing metal materials, such as pure metal and alloy.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Bumper system
ActiveUS20060255603A1Facilitate transmissionReduce decreaseSuperstructure subunitsTowing devicesEngineeringCompressive deformation
A bumper system having a bumper running transverse to the longitudinal direction of a vehicle and at least one connecting element mounted thereon for the purpose of attaching the bumper to a vehicle, in particular to a longitudinal beam of a passenger car. The connecting element is a multi-chamber extruded section of metal with longitudinal axis running in the longitudinal direction of the vehicle. The connecting element is in the form of a safety element which, under impact, absorbs impact energy by compressive deformation. For the purpose of connecting a towing device, an attachment member is provided that is situated in one of the hollow chambers of the connecting element.
Owner:CONSTELLIUM SWITZERLAND
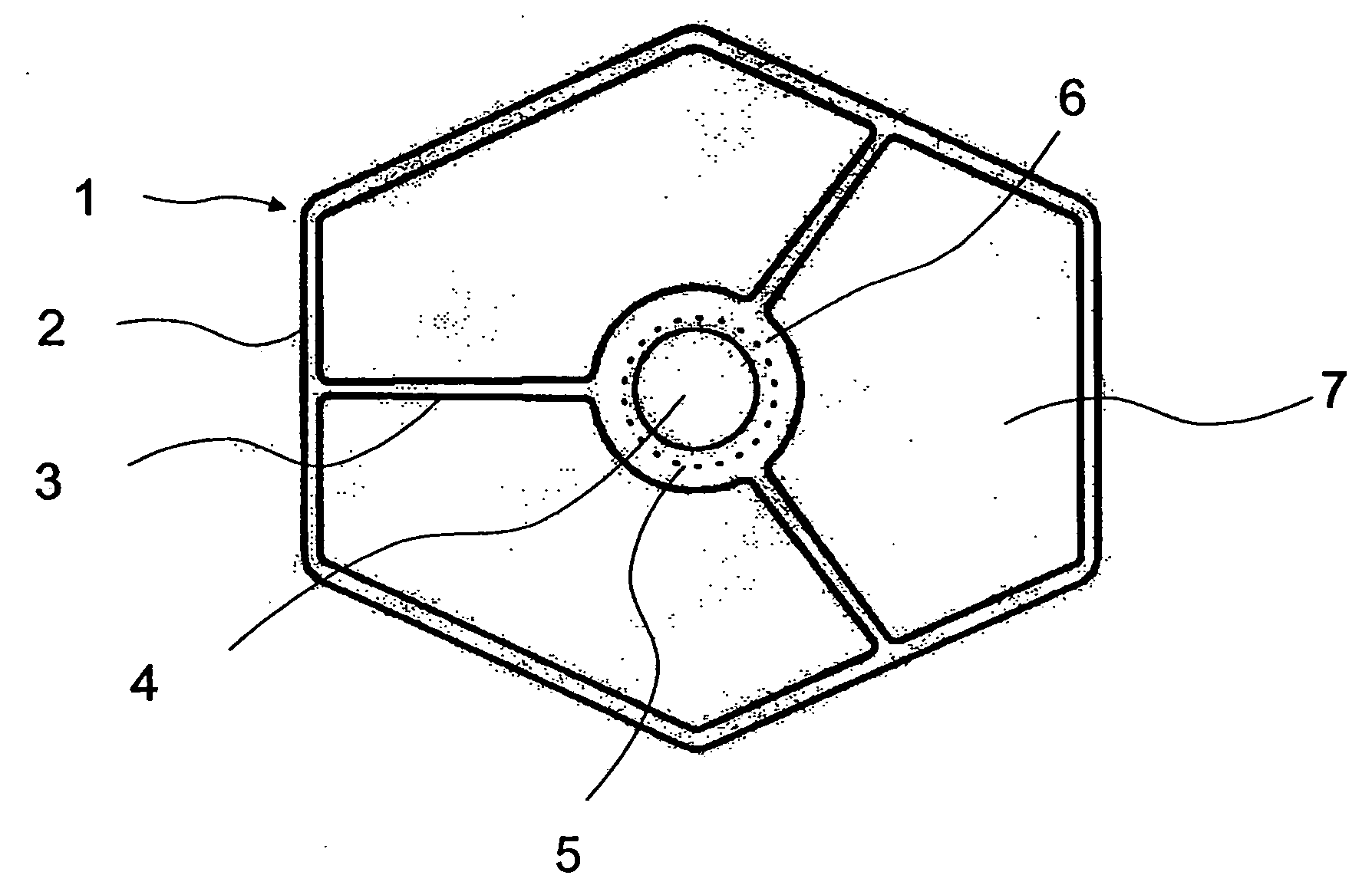
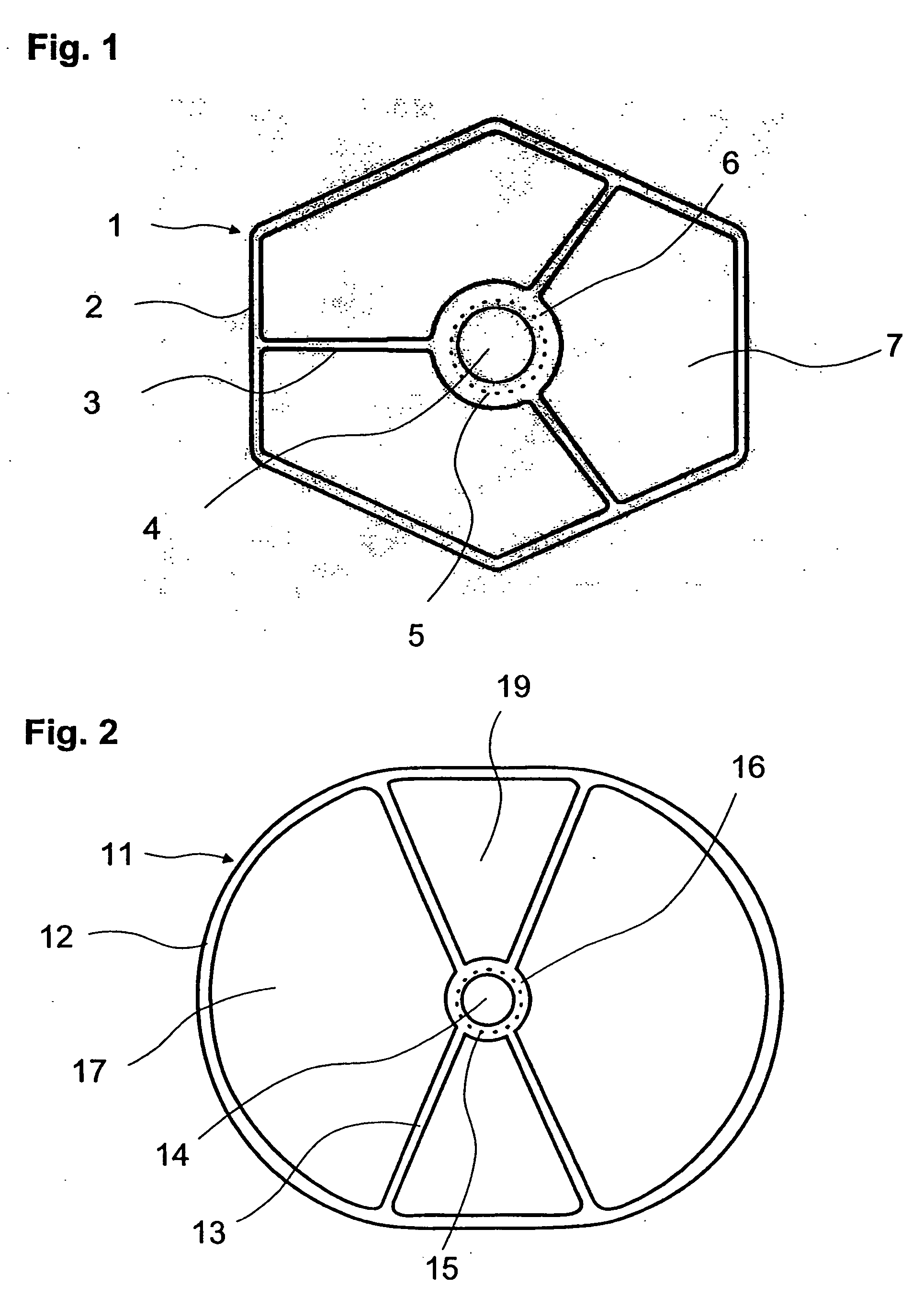
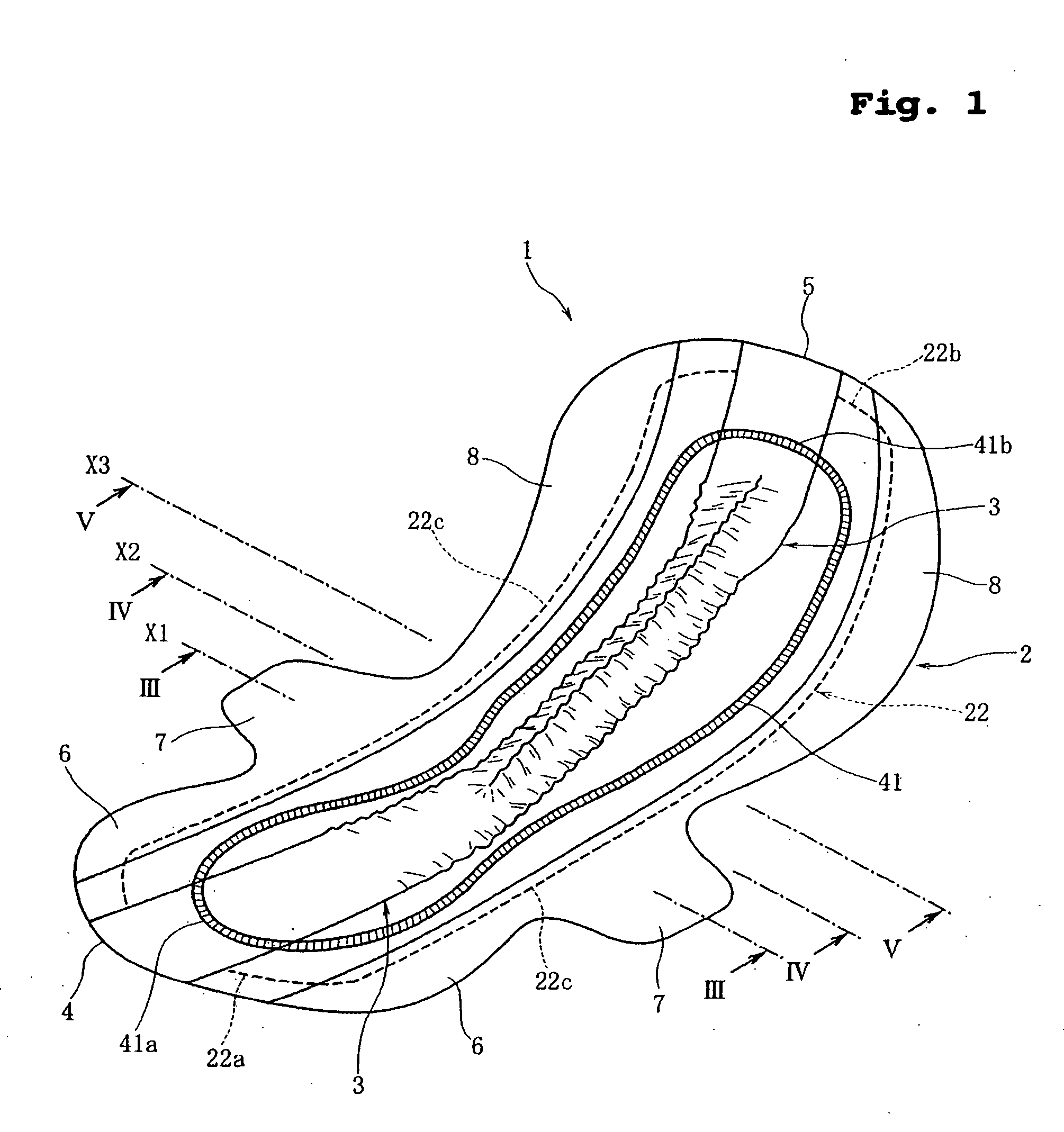
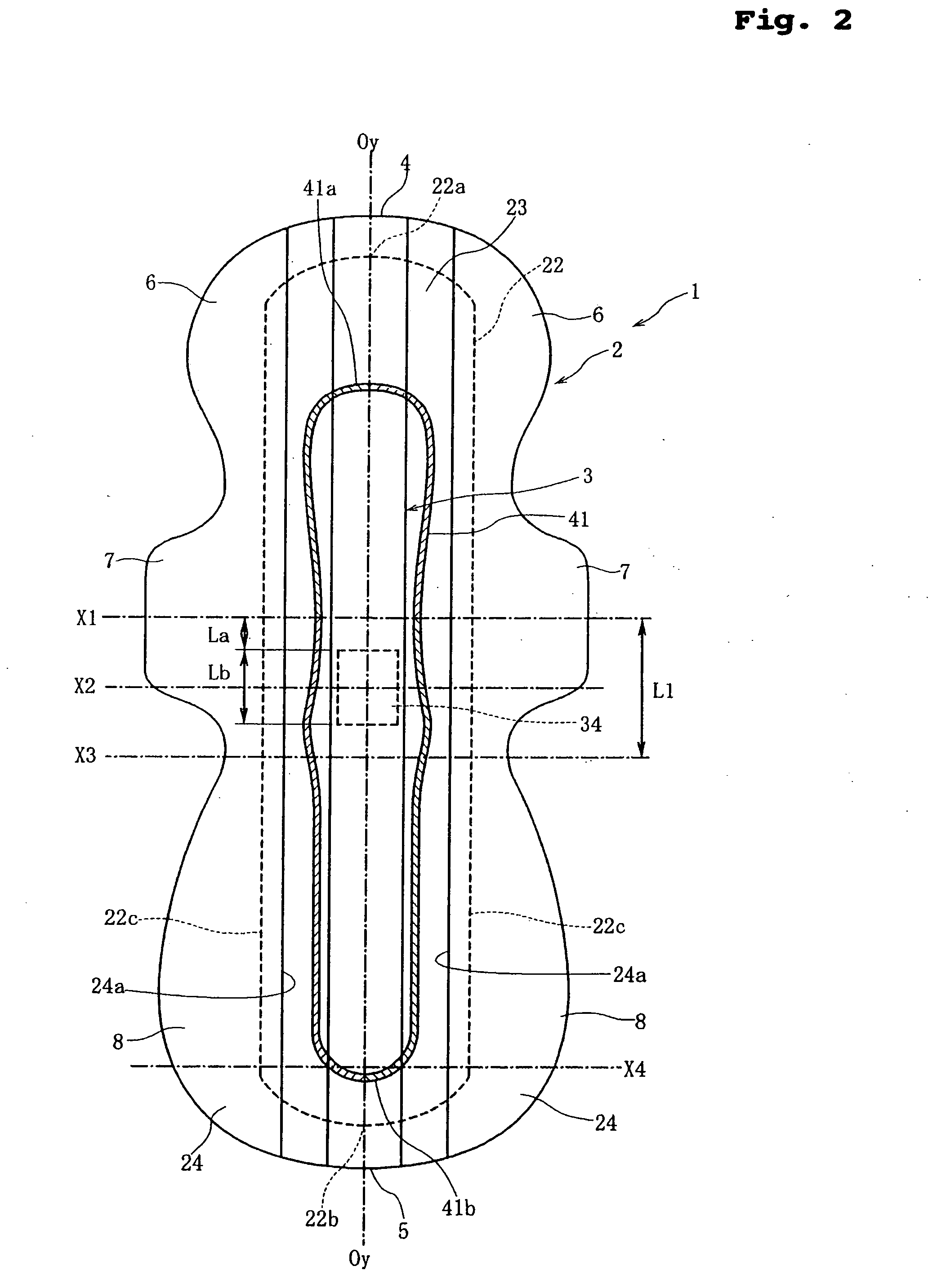
Sanitary napkin
InactiveUS20060271008A1Eliminate gapsPrevent backward leakageSanitary towelsBaby linensMechanical engineeringCompressive deformation
A sanitary napkin includes a main body having a liquid-absorbent layer for absorbing and retaining liquid and a projection disposed on a body surface of the main body. The projection has a resistive portion provided with a resistive member for resisting compressive deformation of the projection toward the main body and a flexible portion not provided with the resistive member. The flexible portion is longitudinally stretchable and subjected to a longitudinal elastic contractive force.
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com