Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
288 results about "Cellular dna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions for the development and function of living things. All known cellular life and some viruses contain DNA.
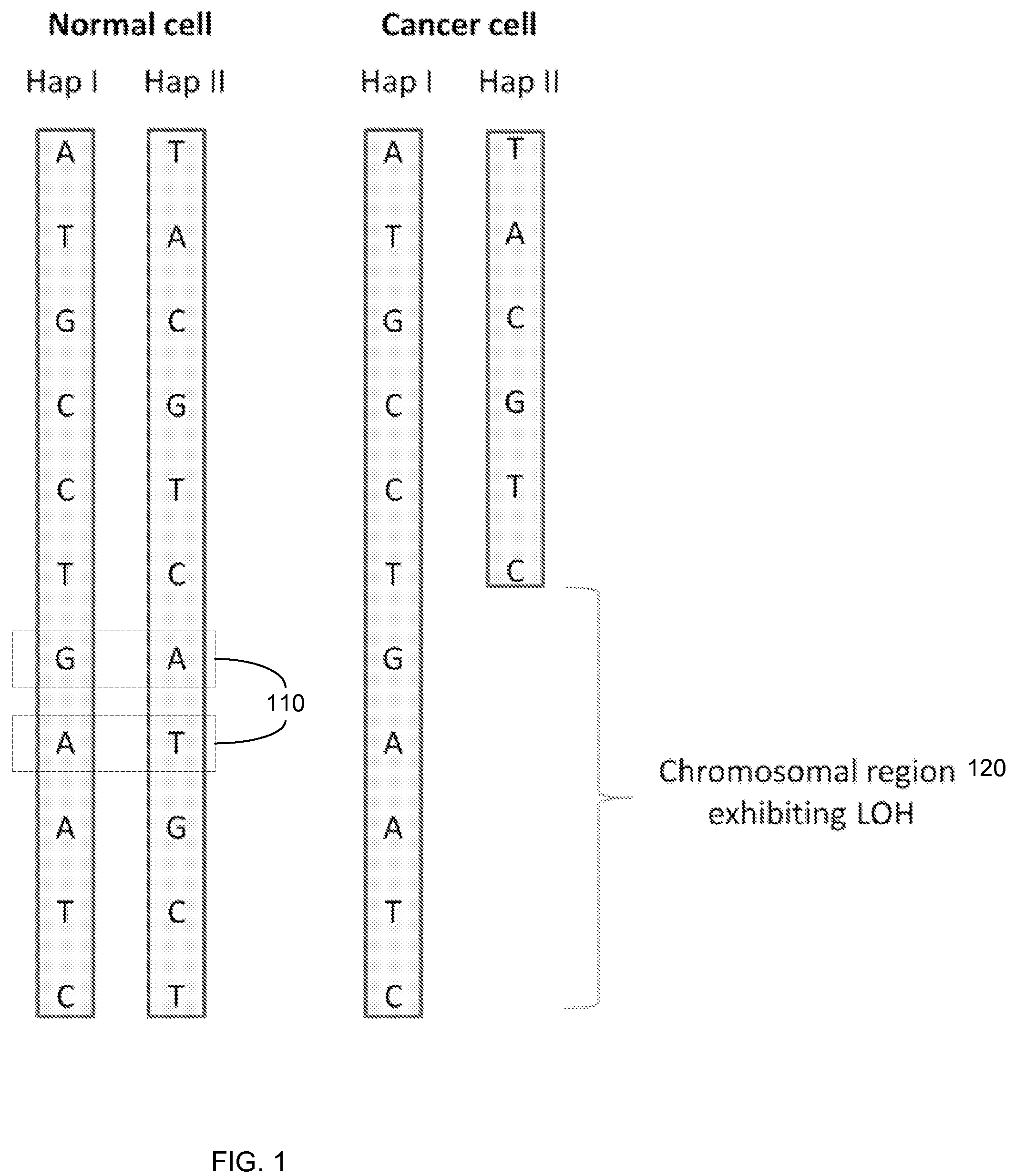
Detection of genetic abnormalities
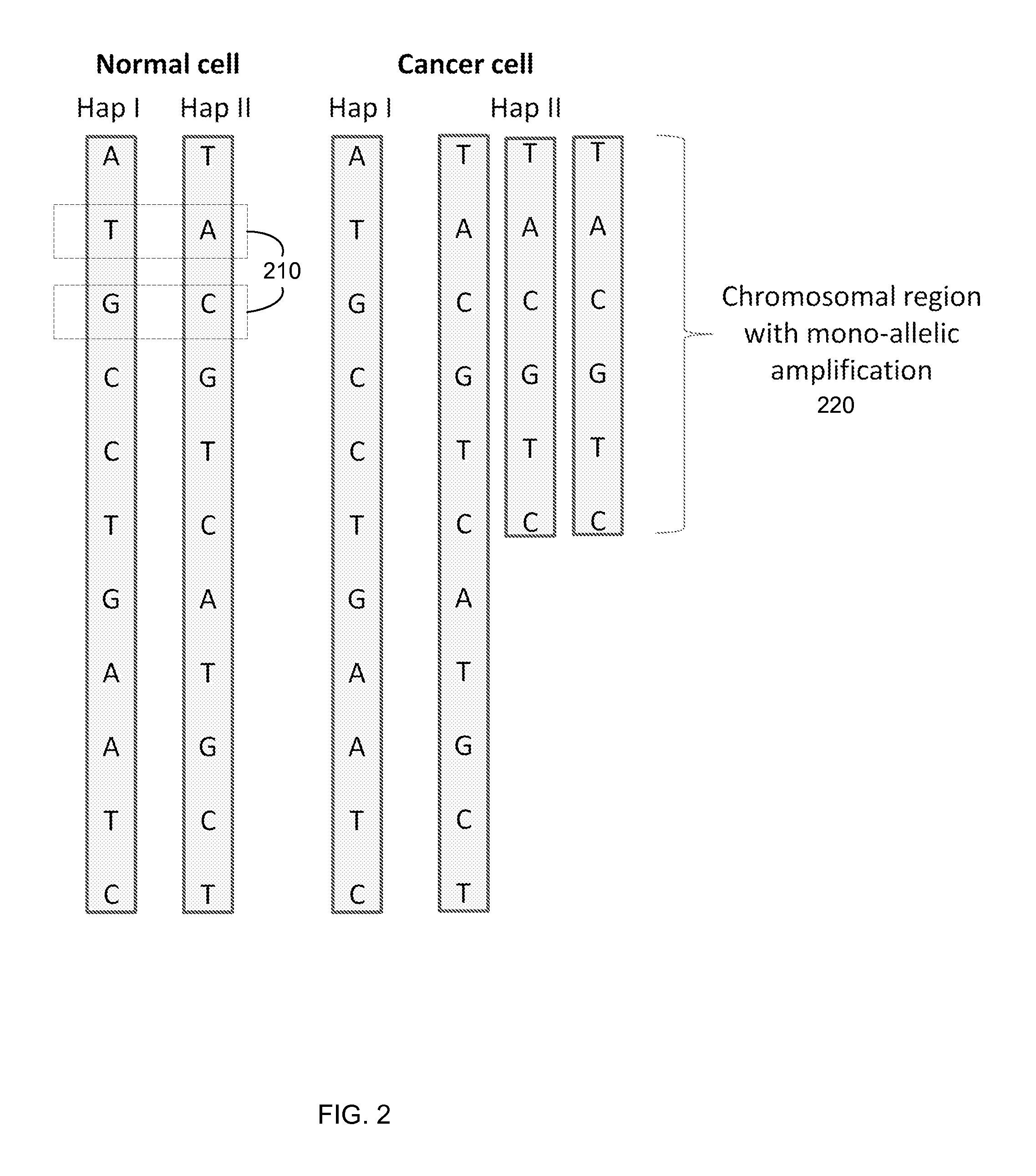
InactiveUS20120190020A1Quick sortingEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellNormal cell
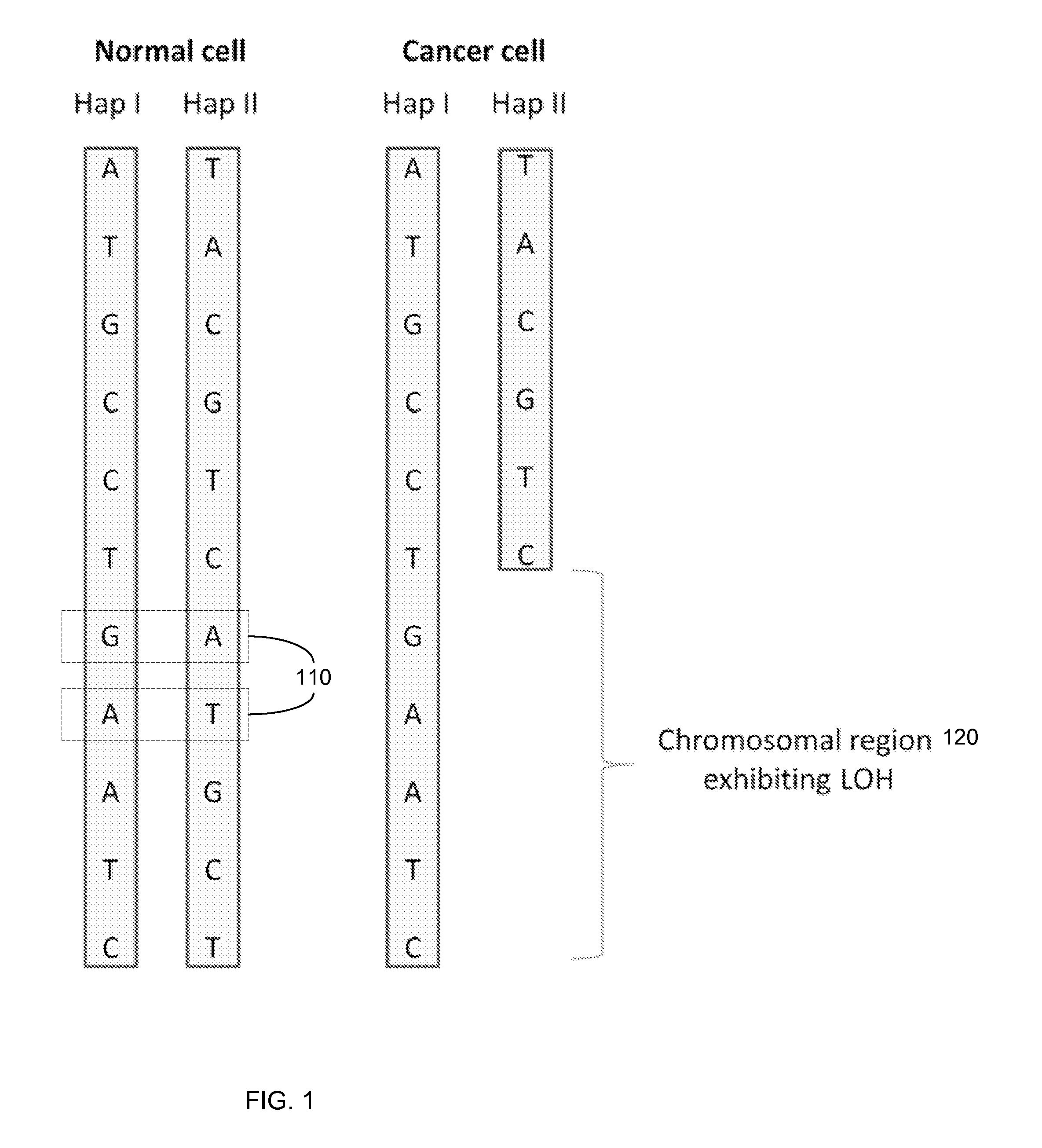
The present invention provides assay systems and related methods for determining genetic abnormalities in mixed samples comprising cell free DNA from both normal and putative genetically atypical cells. Exemplary mixed samples for analysis using the assay systems of the invention include samples comprising both maternal and fetal cell free DNA and samples that contain DNA from normal cells and circulating cancerous cells.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
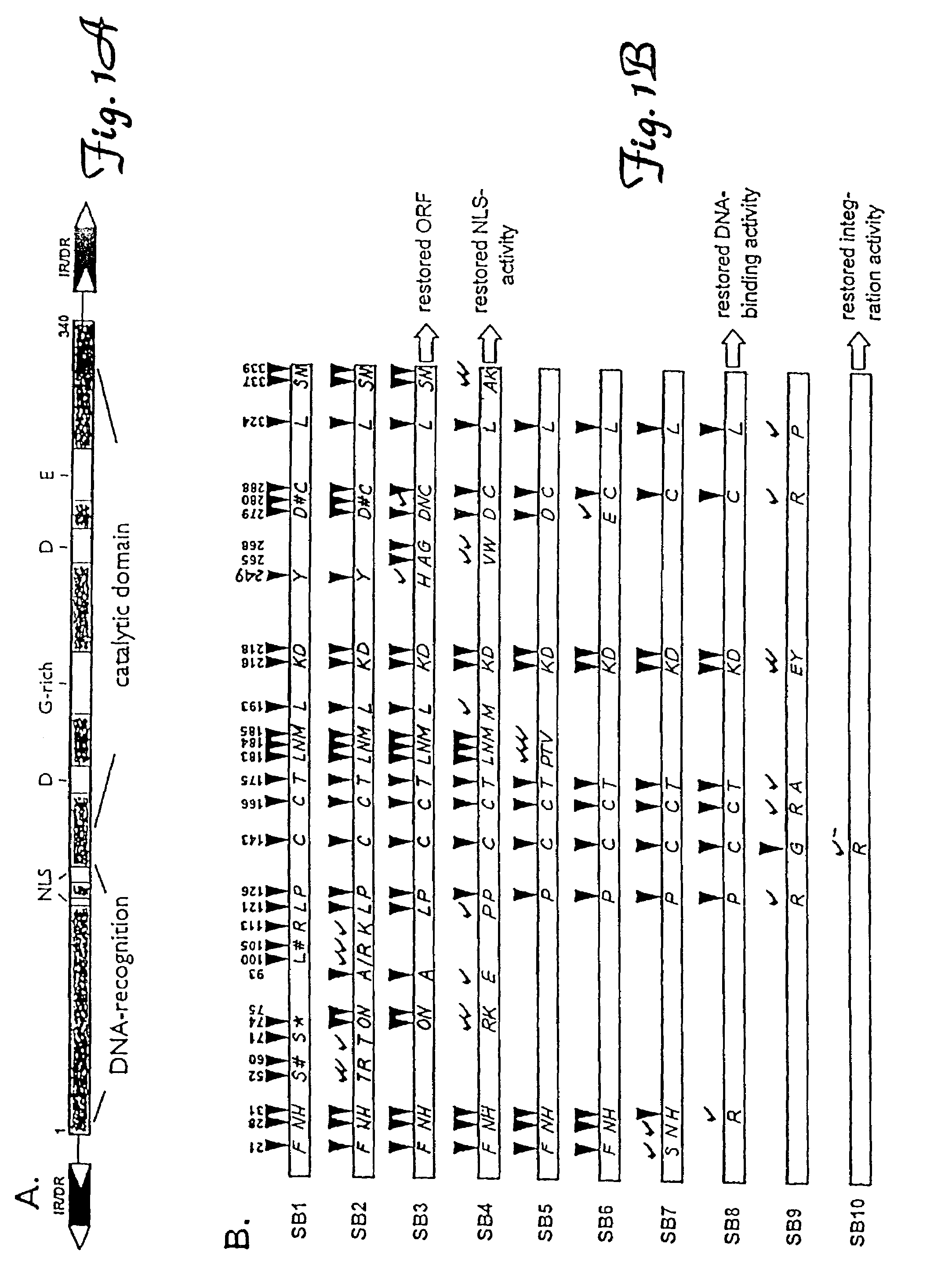
Nucleic acid transfer vector for the introduction of nucleic acid into the DNA of a cell
InactiveUS7148203B2Sugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsNucleic acid sequencingTransfer vector
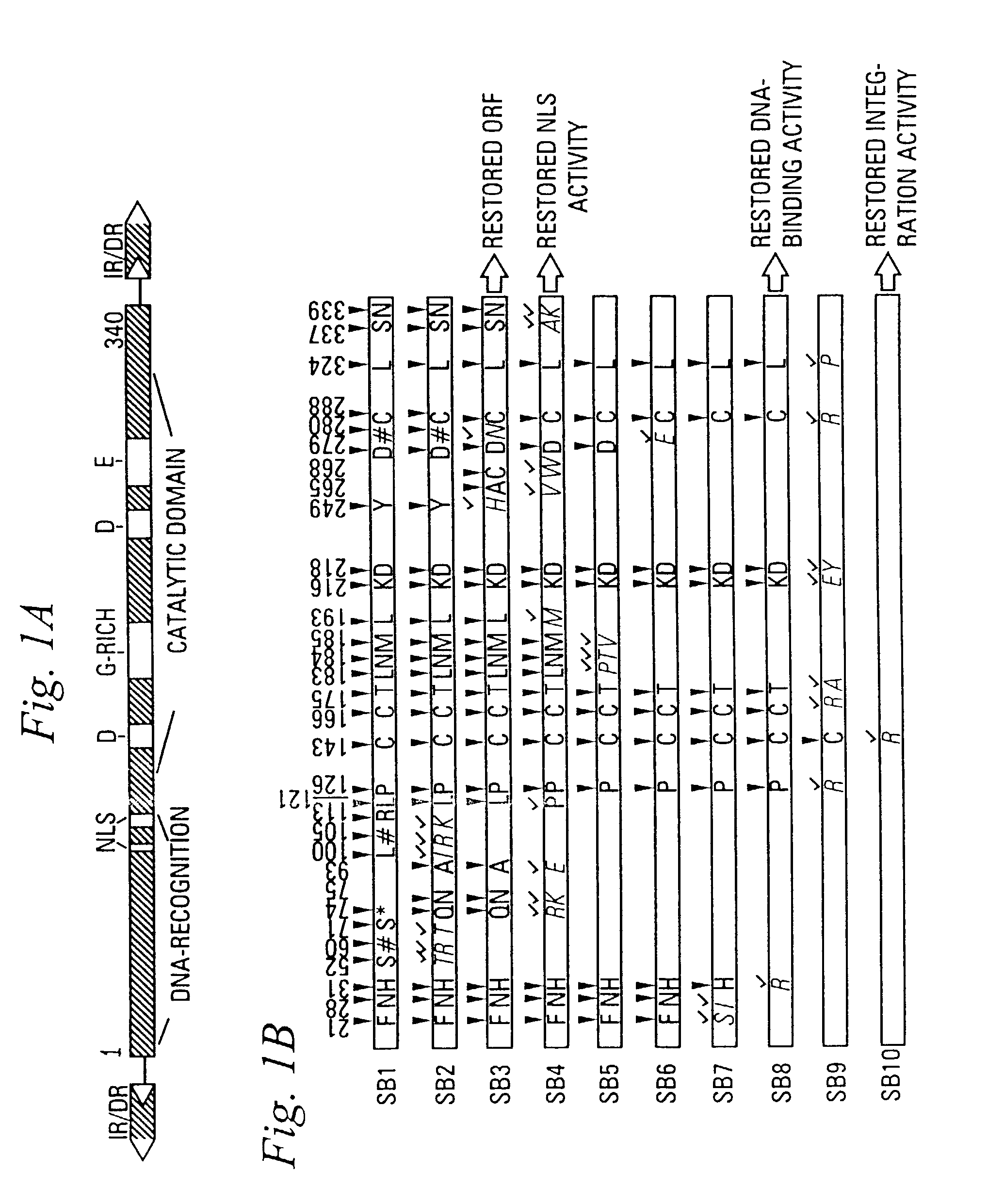
This invention relates to a system for introducing nucleic acid into the DNA of a cell. The system includes the use of a member of the SB family of transposases (SB) or nucleic acid encoding the transposase and a nucleic acid fragment that includes a nucleic acid sequence with flanking inverted repeats. The transposase recognizes at least a portion of an inverted repeats and incorporates the nucleic acid sequence into the DNA. Methods for use of this system are discussed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Detection of genetic abnormalities
InactiveUS20120190021A1Quick sortingEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellNormal cell
The present invention provides assay systems and related methods for determining genetic abnormalities in mixed samples comprising cell free DNA from both normal and putative genetically atypical cells. Exemplary mixed samples for analysis using the assay systems of the invention include samples comprising both maternal and fetal cell free DNA and samples that contain DNA from normal cells and circulating cancerous cells.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Nucleic acid transfer vector for the introduction of nucleic acid into the DNA of a cell
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Detection of genetic or molecular aberrations associated with cancer
ActiveUS20130040824A1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningAbnormal tissue growthAfter treatment
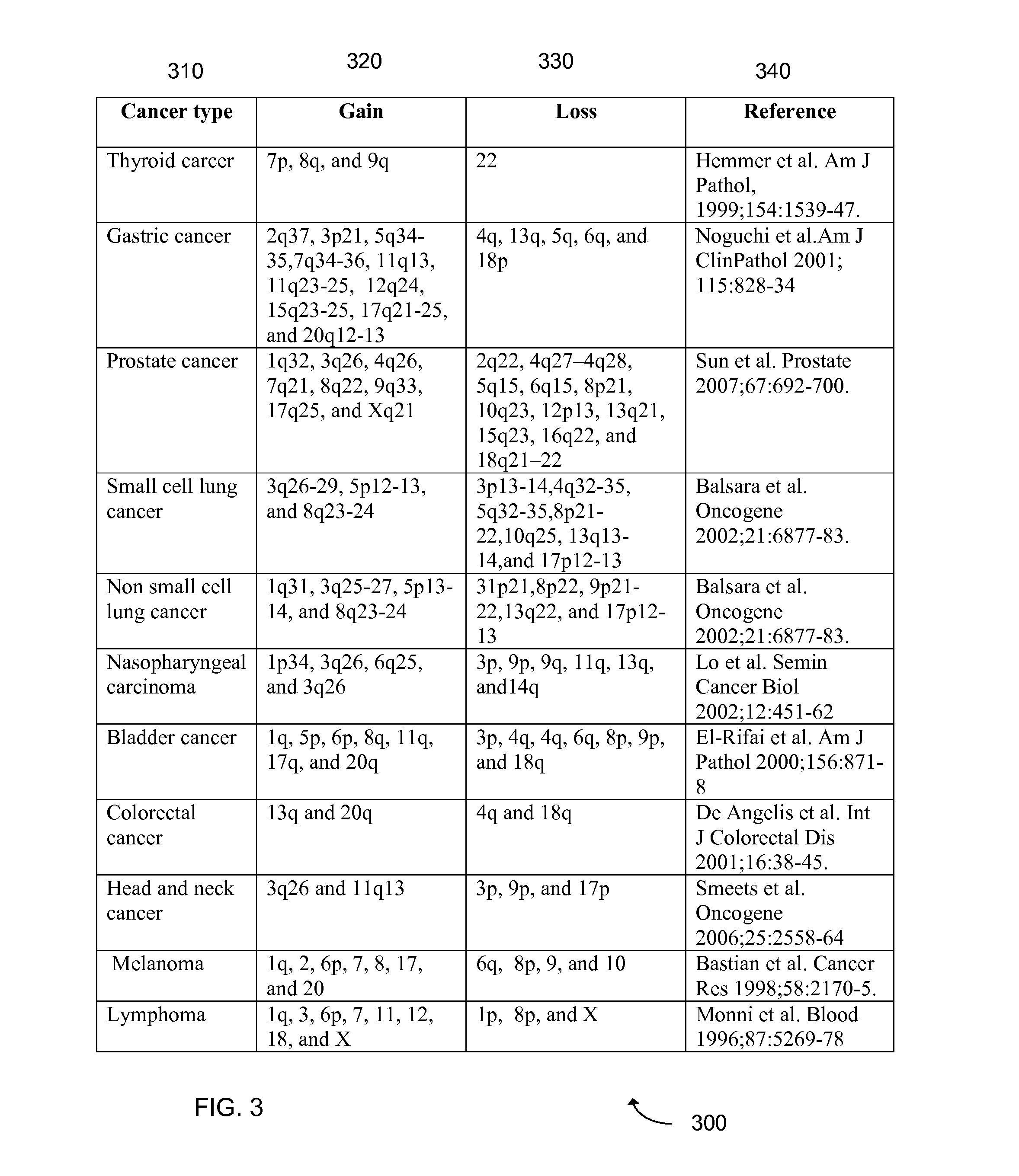
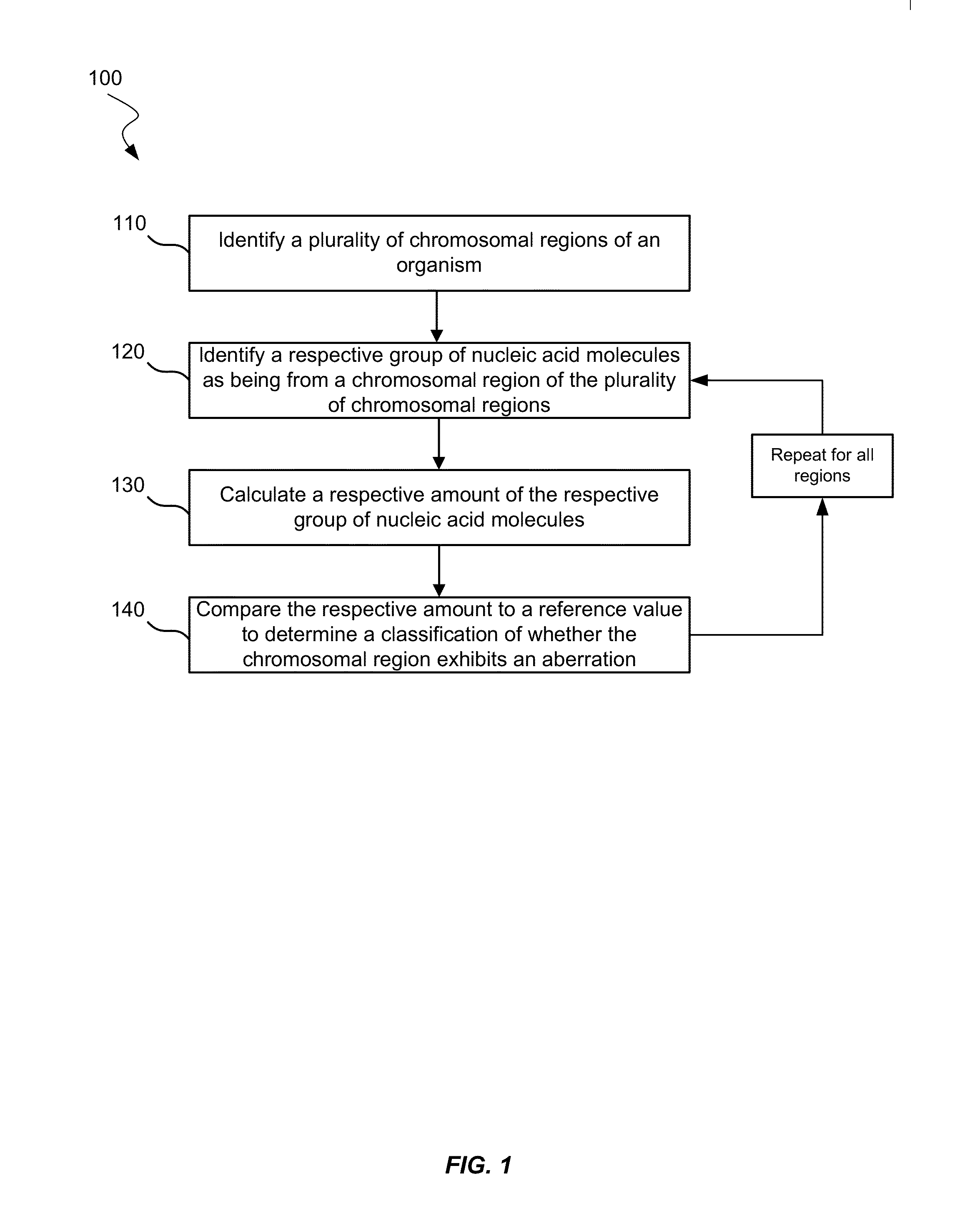
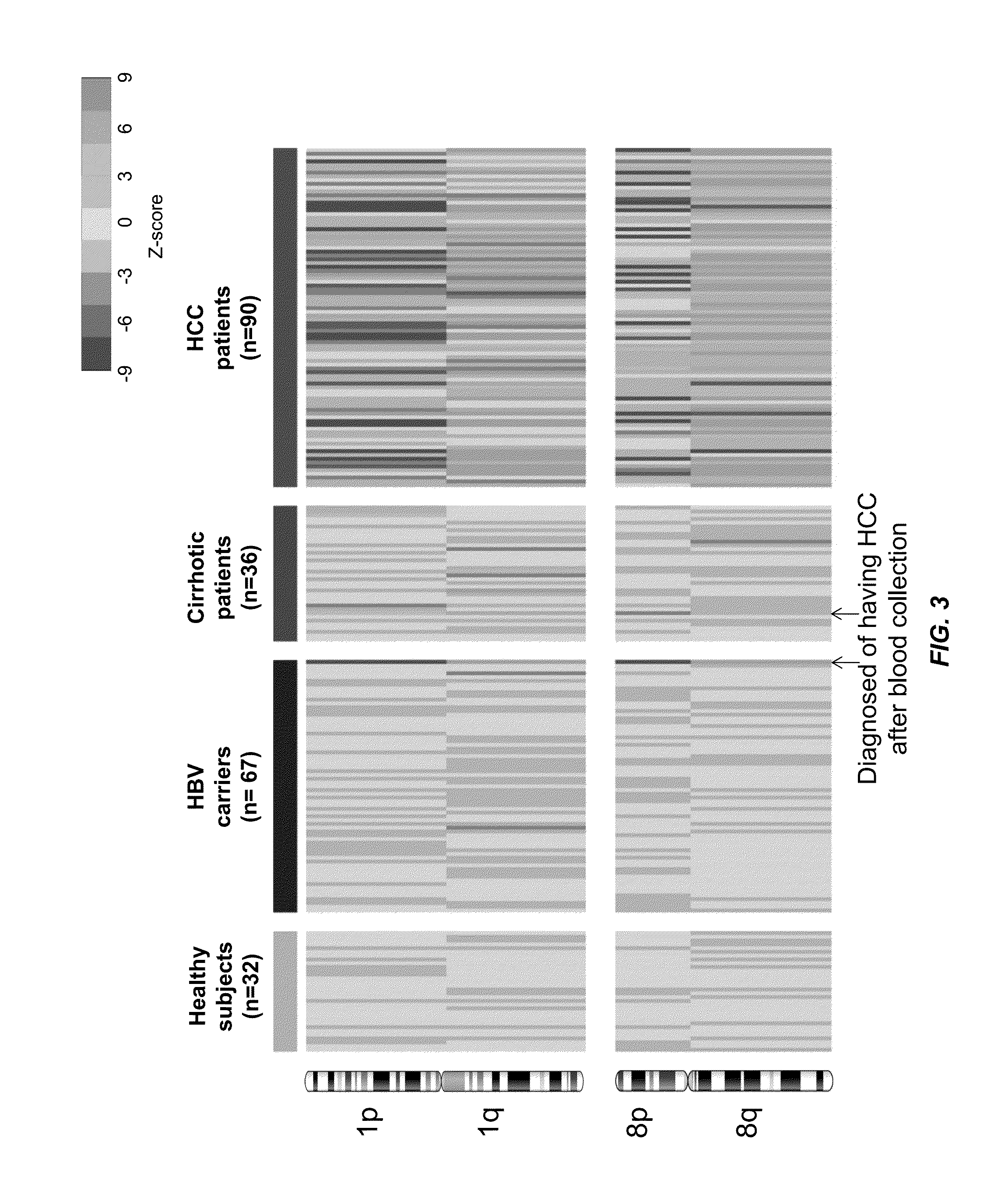
Biological samples including cell-free DNA fragments are analyzed to identify imbalances in chromosomal regions, e.g., due to deletions and / or amplifications in a tumor. Multiple loci are used for each chromosomal region. Such imbalances can then be used to diagnose (screen) a patient for cancer, as well as prognosticate a patient with cancer, or to detect the presence or to monitor the progress of a premalignant condition in a patient. The severity of an imbalance as well as the number of regions exhibiting an imbalance can be used. A systematic analysis of non-overlapping segments of a genome can provide a general screening tool for a sample. Additionally, a patient can be tested over time to track severity of each of one or more chromosomal regions and a number of chromosomal regions to enable screening and prognosticating, as well as monitoring of progress (e.g. after treatment).
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Methods for quantitative genetic analysis of cell free DNA
InactiveUS20160053301A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCell freeSpecific detection
The invention provides a method for genetic analysis in individuals that reveals both the genetic sequences and chromosomal copy number of targeted and specific genomic loci in a single assay. The present invention further provides methods for the sensitive and specific detection of target gene sequences and gene expression profiles.
Owner:RESOLUTION BIOSCI
Detecting mutations for cancer screening and fetal analysis
ActiveUS20170073774A1Accurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsCell freeEmbolization Therapy
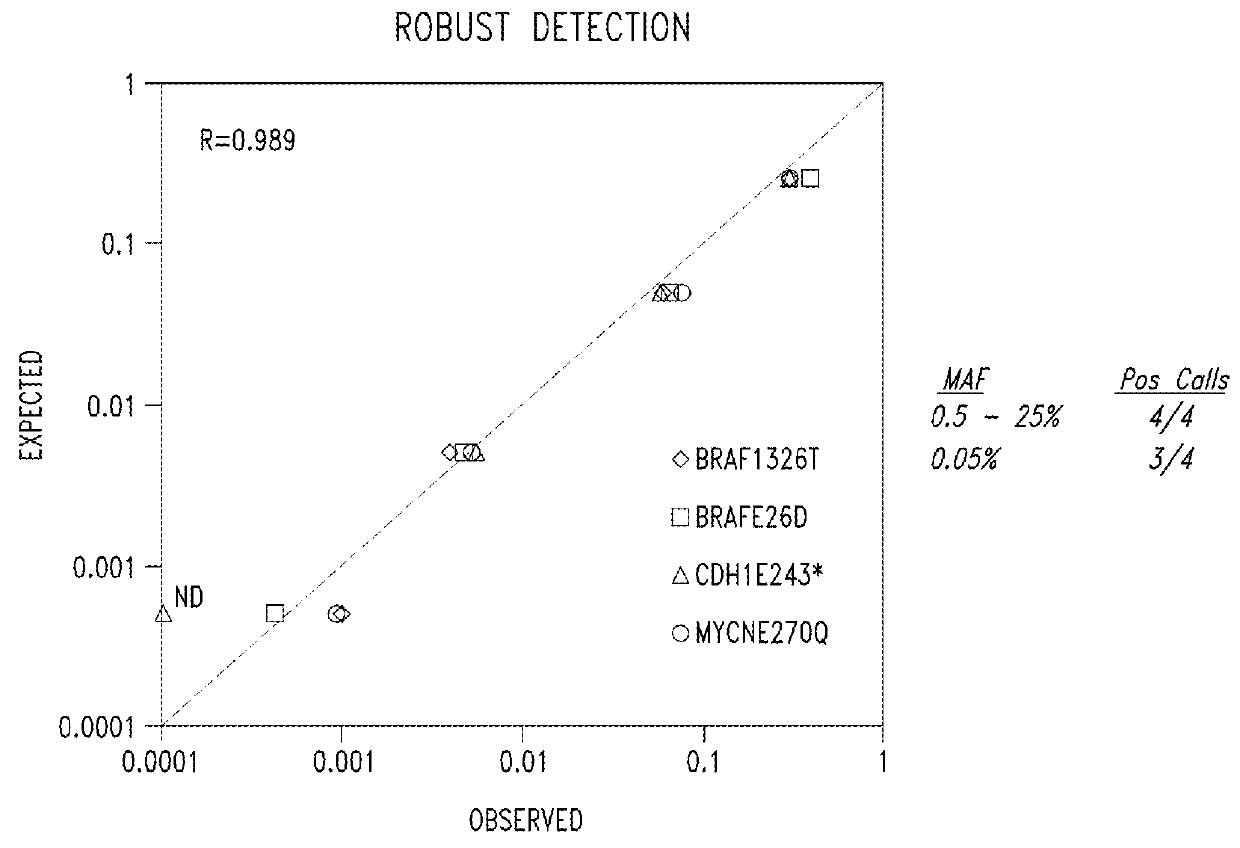
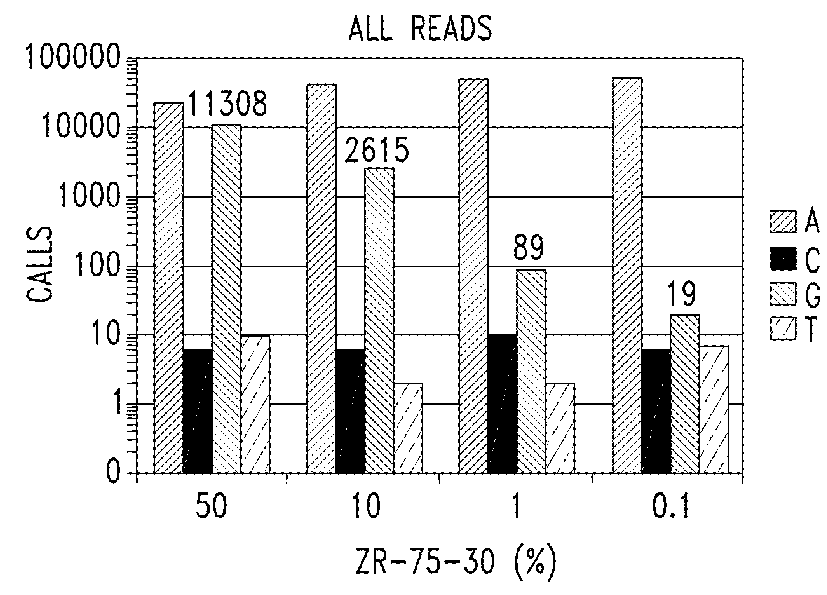
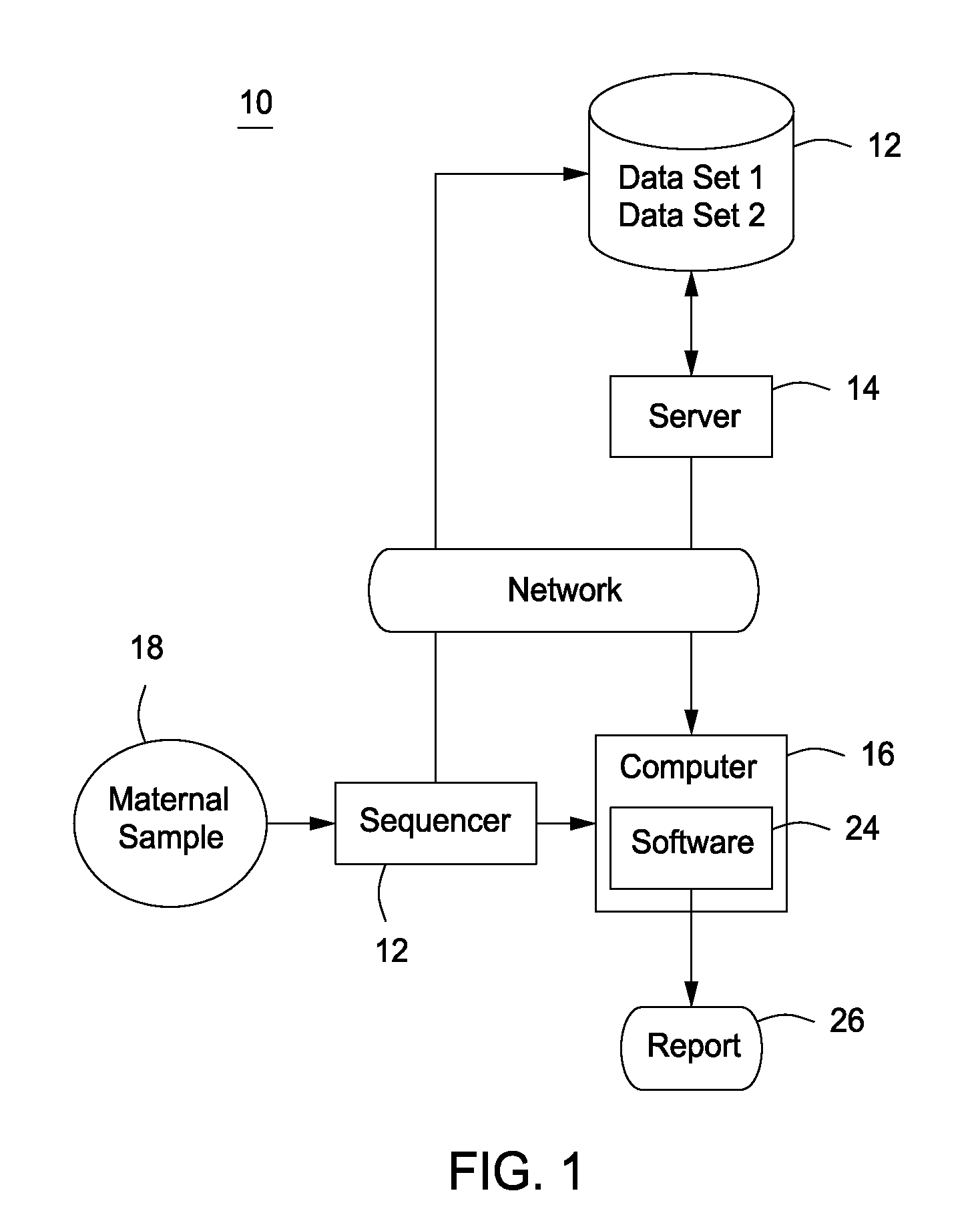
Embodiments are related to the accurate detection of somatic mutations in the plasma (or other samples containing cell-free DNA) of cancer patients and for subjects being screened for cancer. The detection of these molecular markers would be useful for the screening, detection, monitoring, management, and prognostication of cancer patients. For example, a mutational load can be determined from the identified somatic mutations, and the mutational load can be used to screen for any or various types of cancers, where no prior knowledge about a tumor or possible cancer of the subject may be required. Embodiments can be useful for guiding the use of therapies (e.g. targeted therapy, immunotherapy, genome editing, surgery, chemotherapy, embolization therapy, anti-angiogenesis therapy) for cancers. Embodiments are also directed to identifying de novo mutations in a fetus by analyzing a maternal sample having cell-free DNA from the fetus.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Non-disruptive gene targeting
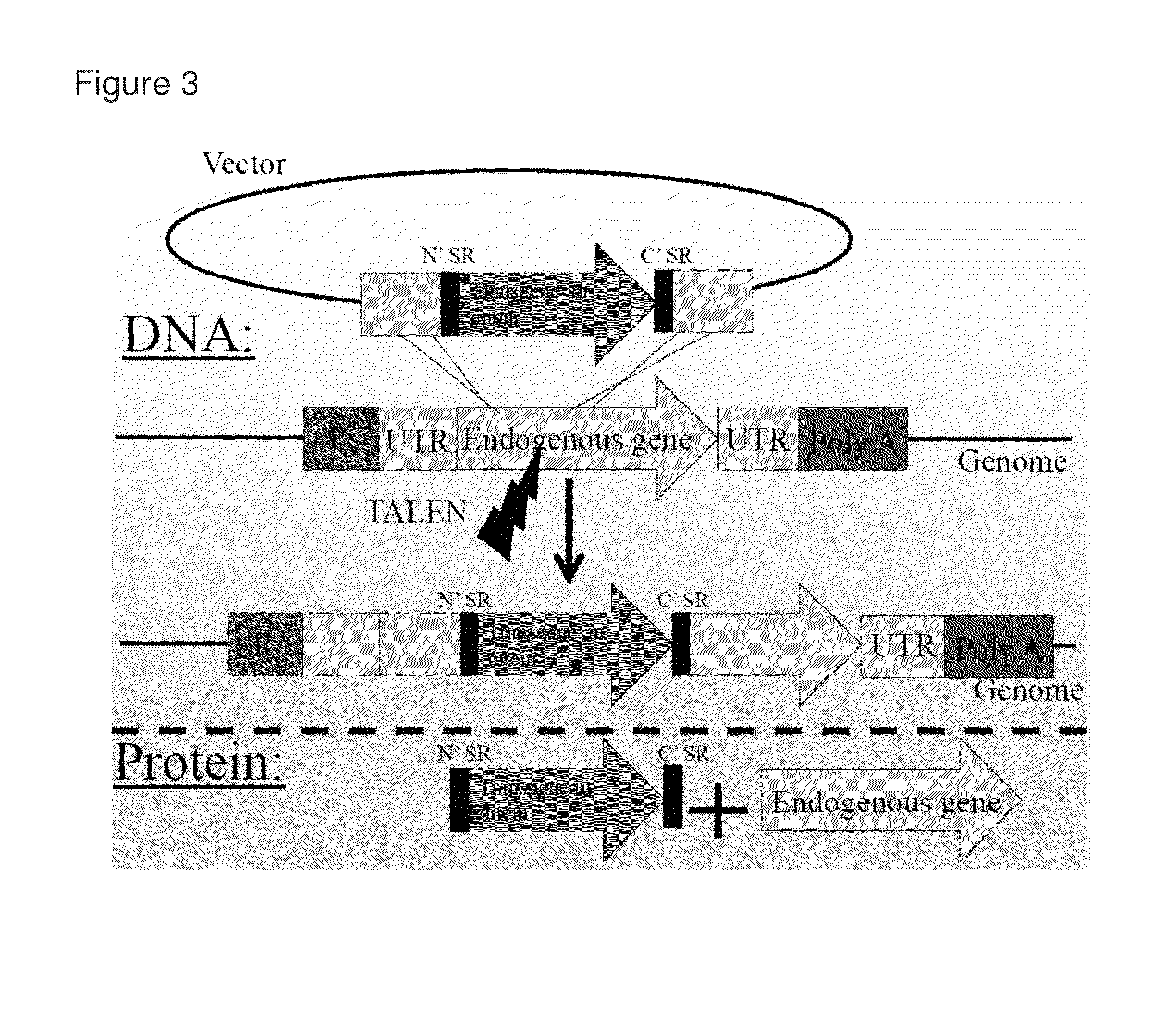
InactiveUS20130280222A1Easy to integrateBiocideFusion with DNA-binding domainDiseaseBiological studies
Compositions and methods are provided for integrating one or more genes of interest into cellular DNA without substantially disrupting the expression of the gene at the locus of integration, i.e., the target locus. These compositions and methods are useful in any in vitro or in vivo application in which it is desirable to express a gene of interest in the same spatially and temporally restricted pattern as that of a gene at a target locus while maintaining the expression of the gene at the target locus, for example, to treat disease, in the production of genetically modified organisms in agriculture, in the large scale production of proteins by cells for therapeutic, diagnostic, or research purposes, in the induction of iPS cells for therapeutic, diagnostic, or research purposes, in biological research, etc. Reagents, devices and kits thereof that find use in practicing the subject methods are also provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Cell free DNA diagnostic testing standards
Embodiments of the invention include methods and compositions for producing standards for noninvasive prenatal genetic diagnostics and for the detection and monitoring of cancer. The compositions can include a plurality of different nucleosomal DNA fragments derived from either primary cells or cell lines and can include one or more synthetic oligonucleotides. The amount of the different nucleosomal DNA fragments can be varied so as to simulate naturally occurring cell free DNA samples obtained from the blood of the pregnant woman or naturally occurring cell free DNA samples obtained from the blood of cancer patients.
Owner:NATERA
Method of using histone deacetylase inhibitors and monitoring biomarkers in combination therapy
ActiveUS20080153877A1Lower Level RequirementsInhibitory activityBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementPharmaceutical drugBiologic marker
Provided herein are methods for using at least one histone deacetylase inhibitor to decrease cellular DNA repair activity, methods for monitoring the decrease of cellular DNA repair activity using at least one biomarker, methods of treating cancer by using at least one histone deacetylase inhibitor to decrease cellular DNA repair activity in combination therapy, methods of combination therapy where at least one histone deacetylase inhibitor interferes with a DNA repairing mechanism involving RAD51, methods for predicting a induction time period between a first administration of at least one histone deacetylase inhibitor and a second administration of at least one other therapeutic treatment, and pharmaceutical compositions for combination therapy.
Owner:PHARMACYCLICS
Compounds and method for PDT of intimal hyperplasia and other diseases
A broad class of photosensitive compounds having enhanced in vivo target tissue selectivity and versatility in photodynamic therapy. Many furocoumarin compounds, such as psoralens, exhibit cytostatic activity when photoactivated but exhibit little in vivo specificity for selectively accumulating in any particular target tissue such as atheromatous plaques. Reactive Oxygen Producing Photosensitizers ("ROPPs") are photoactivatable compounds having an affinity for hyperproliferating cells (such as atheromatous plaque cells), which when photoactivated, produce cytotoxic reaction products. The photoactivity of a ROPP, such as a porphyrin, may be reduced by metalating the porphyrin while the selective affinity of the metalized ROPP for hyperproliferating tissue remains substantially unchanged. By linking a furocoumarin compound to a ROPP to form a F-ROPP, the cytostatic properties of the furocoumarin portion of the F-ROPP can be exploited while the selective affinity of the ROPP portion of the compound for hyperproliferating cells such as atheromatous plaque provides enhanced tissue selectivity without cytotoxicity. In vivo, certain F-ROPPs may be forced to selectively accumulate in a target tissue by illuminating only the target tissue with light having a wavelength operable for photoactivating the F portion of the F-ROPP thereby causing the F-ROPP to either form a monoadduct with or crosslink the cellular DNA in the target tissue. Light of a second wavelength can then be delivered to the target tissue to photoactivate the ROPP portion causing further interference with cellular activity.
Owner:ADGERO BIOPHARM
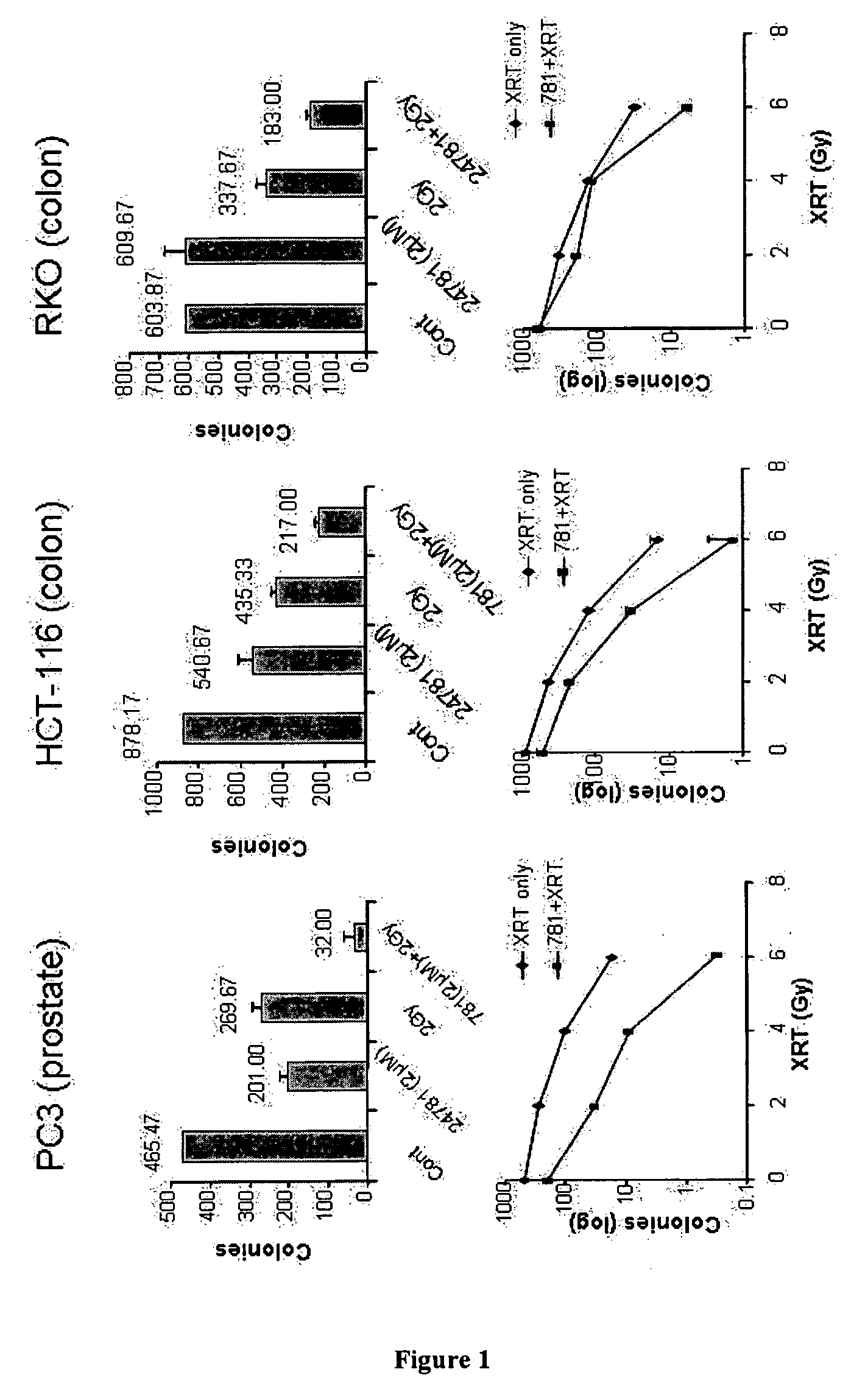
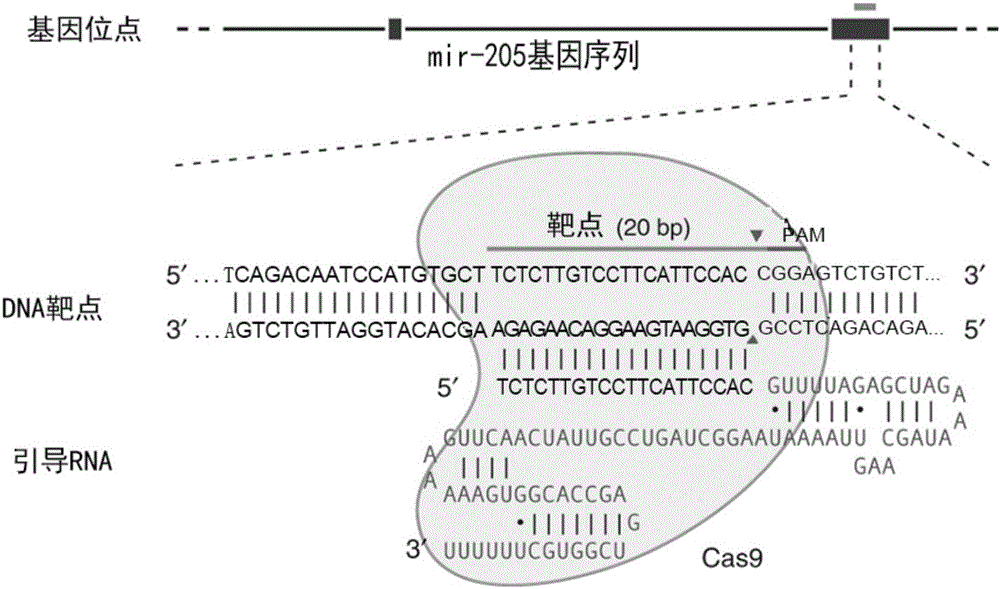
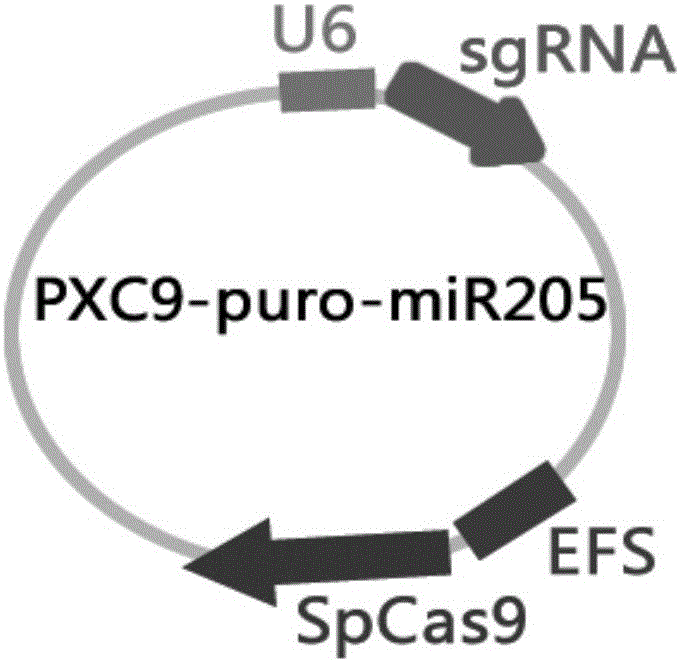
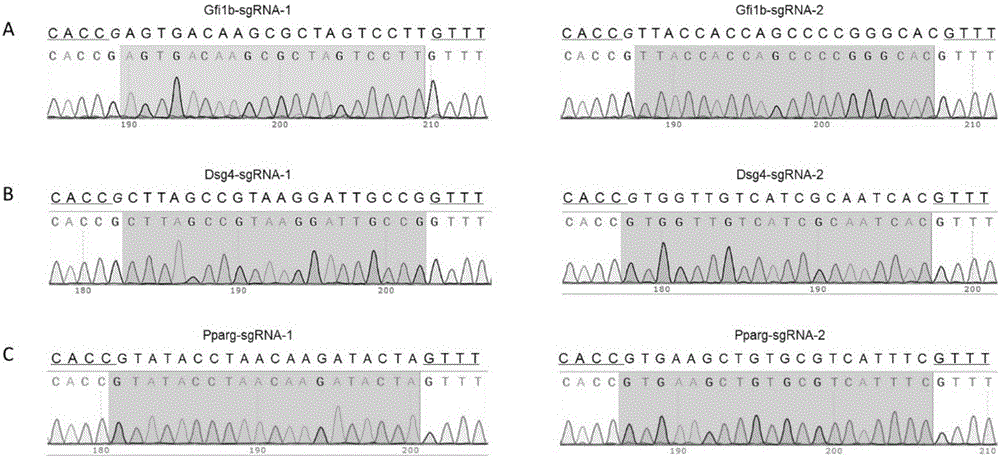
MiR-205 gene knockout kit based on CRISPR-Cas9 gene knockout technology
ActiveCN105112445AVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationEnzyme digestionFluorescence
The invention discloses a miR-205 gene knockout kit based on CRISPR-Cas9 gene knockout technology. According to the invention, an optimal CRISPR-Cas9 target sequence of a certain amount of miR-205 is obtained through target design software and an sgRNA single chain is synthesized in vitro; an insertion fragment is obtained through processing; then sgRNA is inoculated into a plasmid vector by using T4 ligase; and a miR-205 gene knockout cell strain is obtained through transfection of an LNCap cell strain, continuous drug screening and fluorescence detection. Heterogenous hybridization double strands are obtained by extracting DNAs of a cell, PCR amplification of miR-205, purification, denaturation of a PCR product and annealing; T7E1 enzyme digestion test is employed to determining shearing efficiency of a CRISPR-Cas9 system on miR-205; a verified optimized a miR-205 gene knockout CRISPR-Cas9 target sequence is obtained; and the kit is constructed on the basis of the target sequence and can be used for directional knockout of miR-205 genes. The kit has the characteristics of high gene knockout efficiency, fast speed, easiness and economic performance and has wide prospects in the aspects of construction of animal models and clinical research of medical science.
Owner:广州辉园苑医药科技有限公司
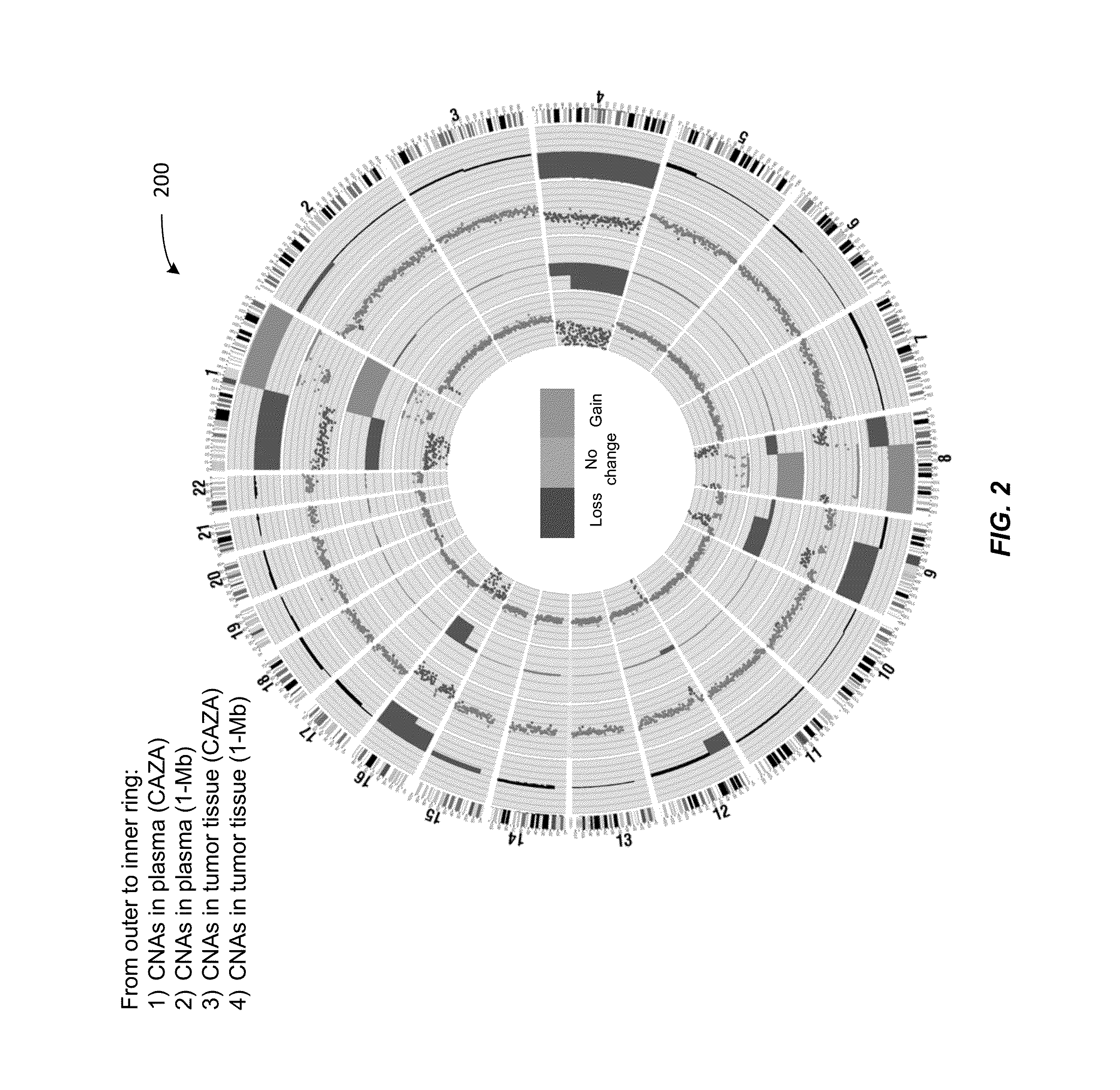
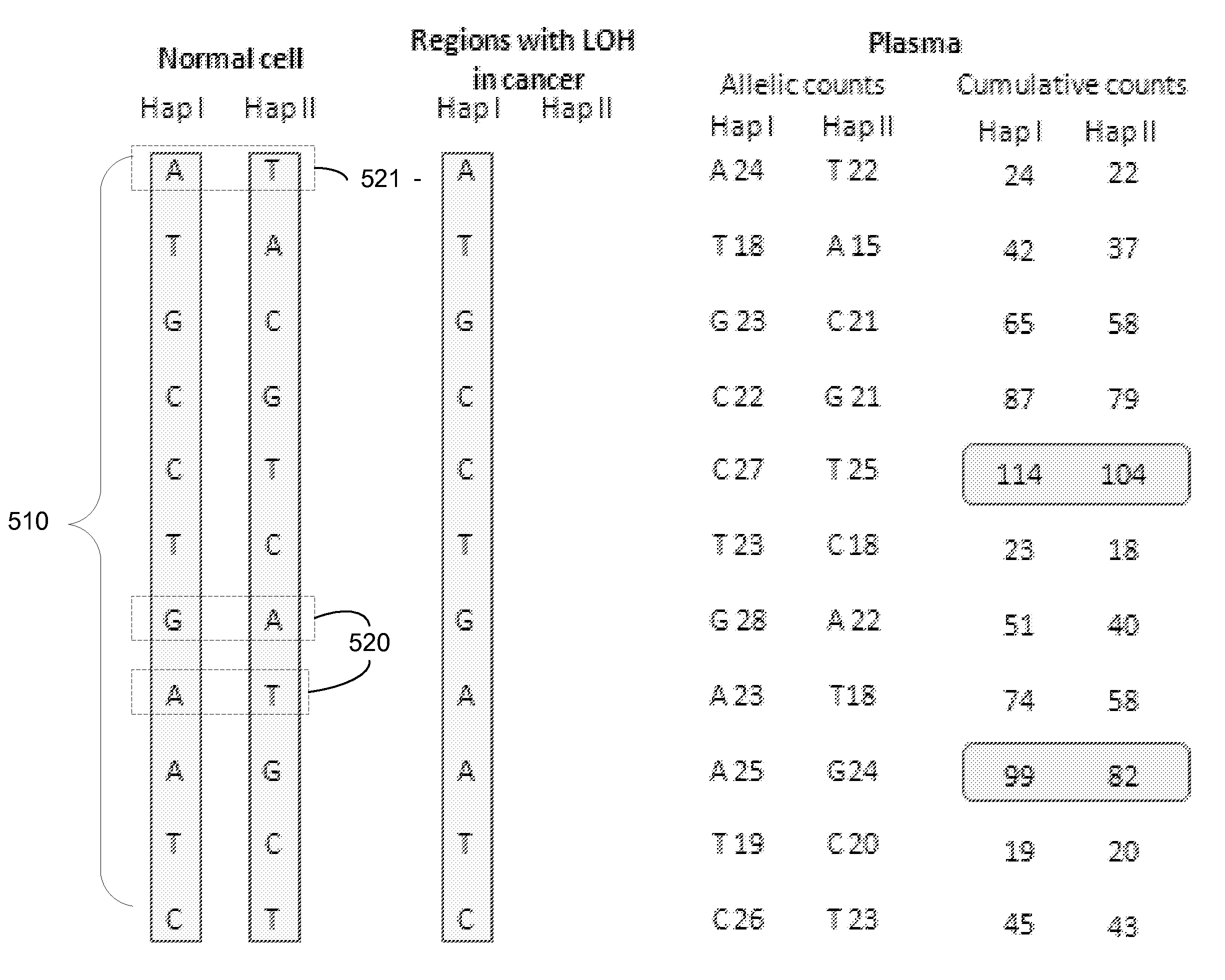
Using size and number aberrations in plasma DNA for detecting cancer
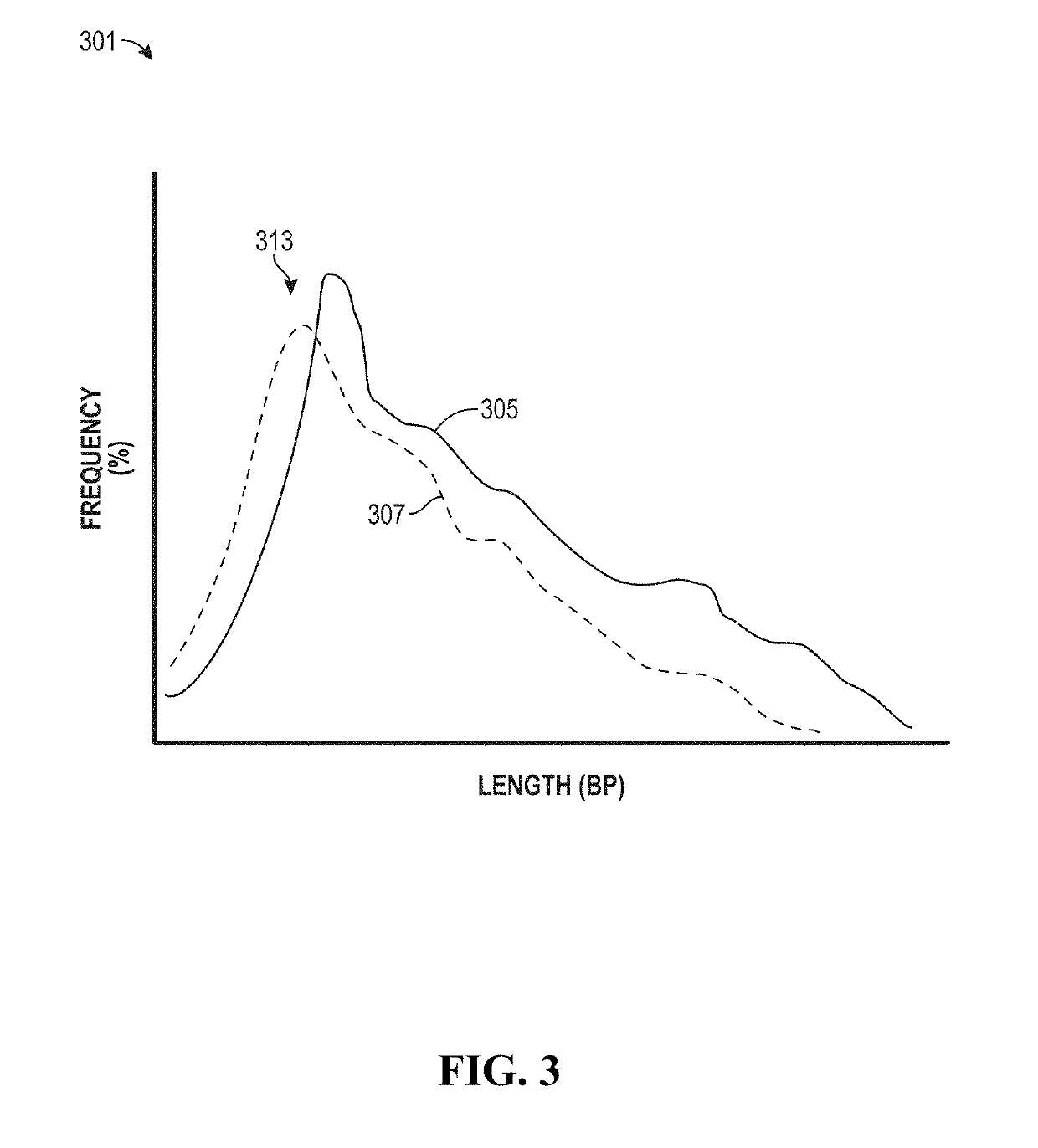
Analysis of tumor-derived circulating cell-free DNA opens up new possibilities for performing liquid biopsies for solid tumor assessment or cancer screening. However, many aspects of the biological characteristics of tumor-derived cell-free DNA remain unclear. Regarding the size profile of plasma DNA molecules, some studies reported increased integrity of tumor-derived plasma DNA while others reported shorter tumor-derived plasma DNA molecules. We performed an analysis of the size profiles of plasma DNA in patients with cancer using massively parallel sequencing at single base resolution and in a genomewide manner. Tumor-derived plasma DNA molecules were further identified using chromosome arm-level z-score analysis (CAZA). We showed that populations of aberrantly short and long DNA molecules co-existed in the plasma of patients with cancer. The short ones preferentially carried the tumor-associated copy number aberrations. These results show the ability to use plasma DNA as a molecular diagnostic tool.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
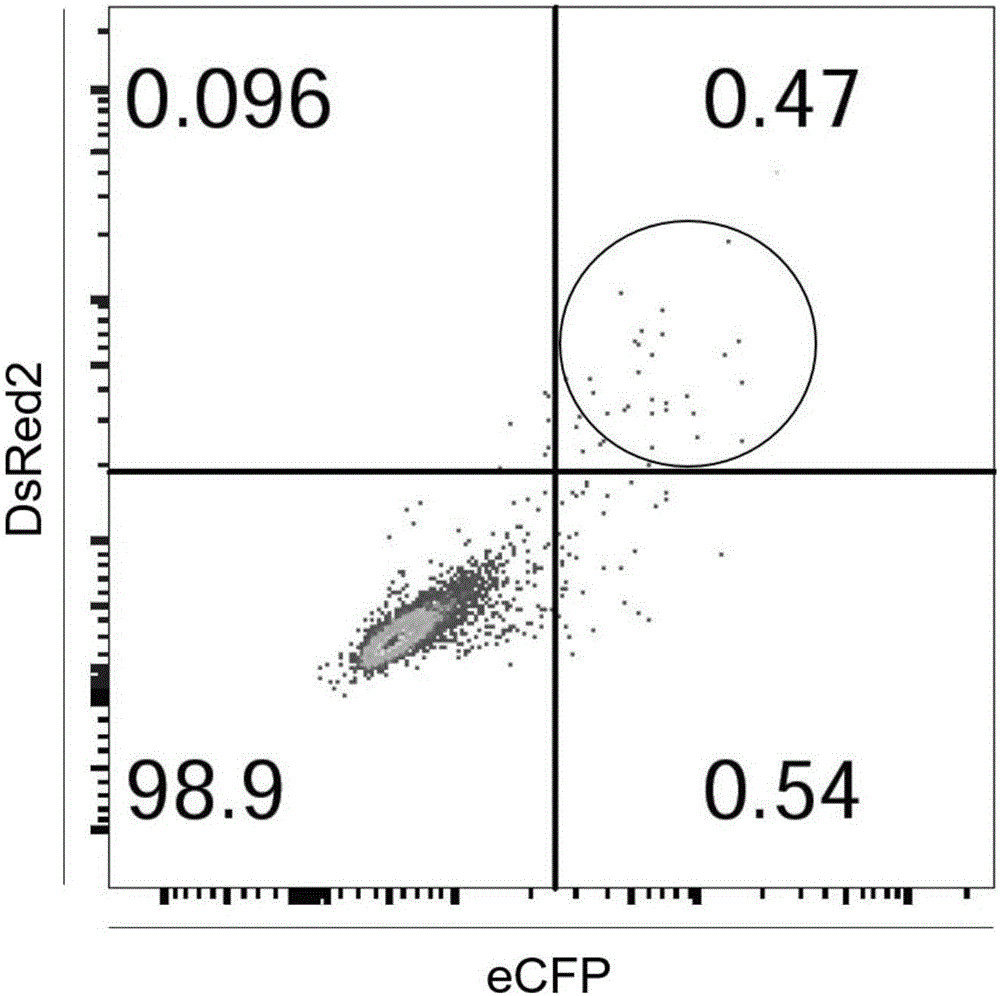
Cell line gene knock-out method for obtaining large fragment deletion through CRISPR/Cas9 system
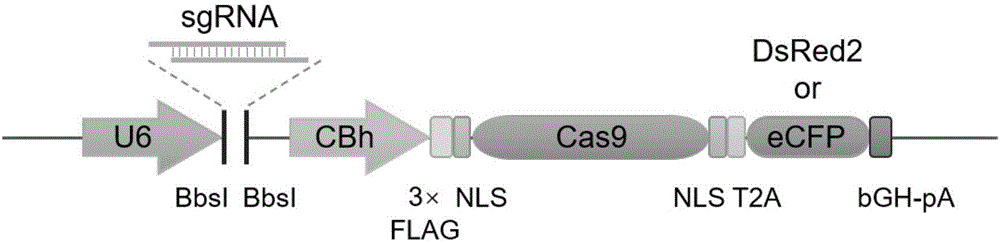
ActiveCN107435051AEasy accessImprove knockout productivityVectorsStable introduction of DNAFluorescenceLarge fragment
The invention relates to a cell line gene knock-out method for obtaining large fragment deletion through a CRISPR / Cas9 system, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and genetic modification. A pX458 vector is modified, so that the pX458 vector is provided with DsRed2 and ECFP (Enhanced Cyan Fluorescence Protein); then, a plurality of specific sgRNA sites are designed by aiming at a target gene and are connected into the modified vector; after the cell line transfection, cell groups are sorted by a flow cytometry; single cells subjected to genome editing can be very fast obtained; then, a single-cell DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequence is subjected to PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification; and single cells with large fragment deletion can be picked out from the single cells through gel electrophoresis. The CRISPR / Cas9 system, the flow cytometry single-cell sorting and fluorescent protein screening on the expression vector are combined, so that the positive monoclonal cells with the large fragment deletion can be obtained in a short time; and the work efficiency of the cell line gene knock-out is greatly improved.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
Detection of genetic or molecular aberrations associated with cancer
ActiveUS8741811B2Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCell freeAfter treatment
Biological samples including cell-free DNA fragments are analyzed to identify imbalances in chromosomal regions, e.g., due to deletions and / or amplifications in a tumor. Multiple loci are used for each chromosomal region. Such imbalances can then be used to diagnose (screen) a patient for cancer, as well as prognosticate a patient with cancer, or to detect the presence or to monitor the progress of a premalignant condition in a patient. The severity of an imbalance as well as the number of regions exhibiting an imbalance can be used. A systematic analysis of non-overlapping segments of a genome can provide a general screening tool for a sample. Additionally, a patient can be tested over time to track severity of each of one or more chromosomal regions and a number of chromosomal regions to enable screening and prognosticating, as well as monitoring of progress (e.g. after treatment).
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Microarray for detecting viable organisms
InactiveUS20140155283A1Rapid and selective detection and enumerationLower levelNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismPropidium monoazide
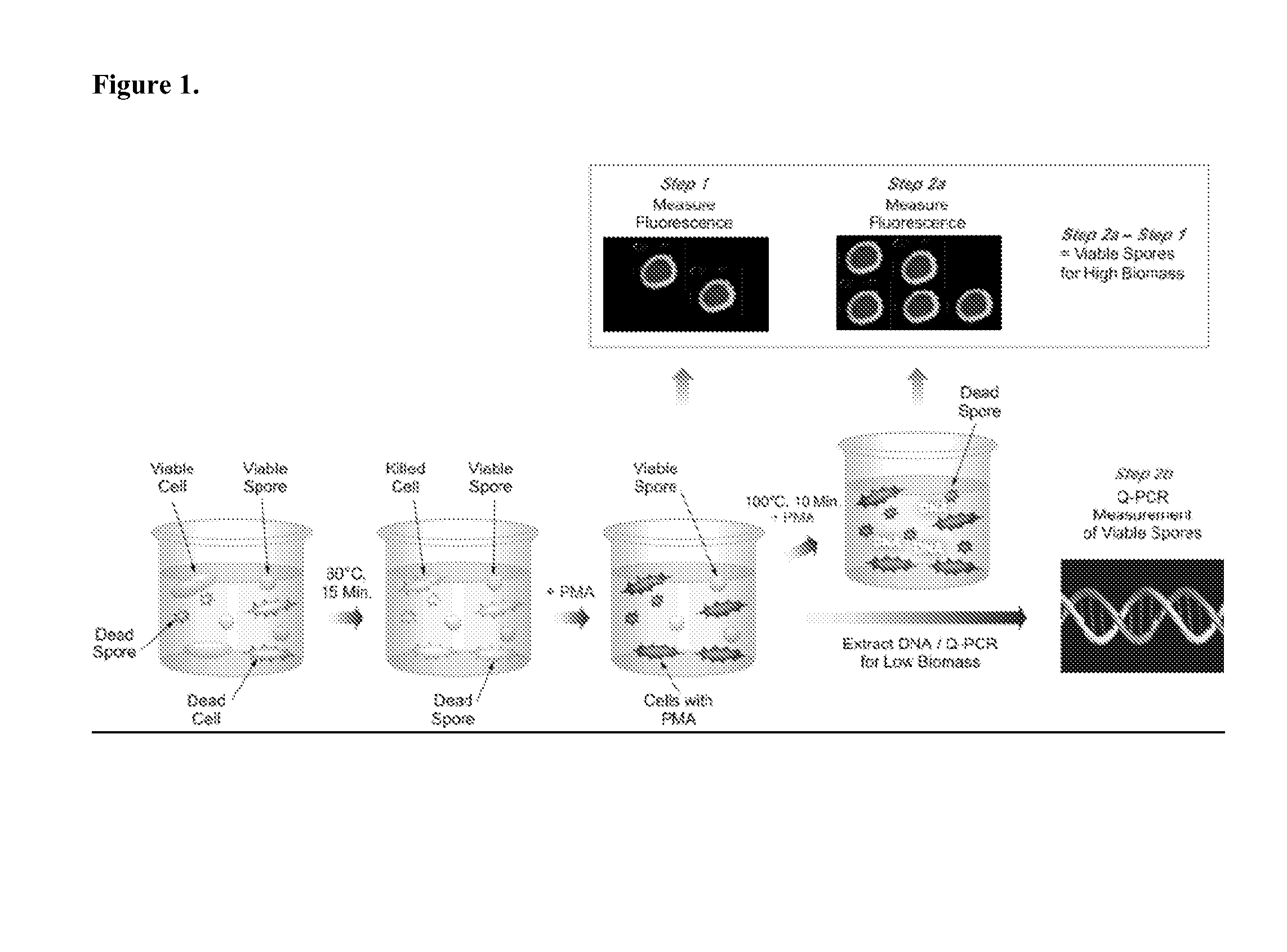
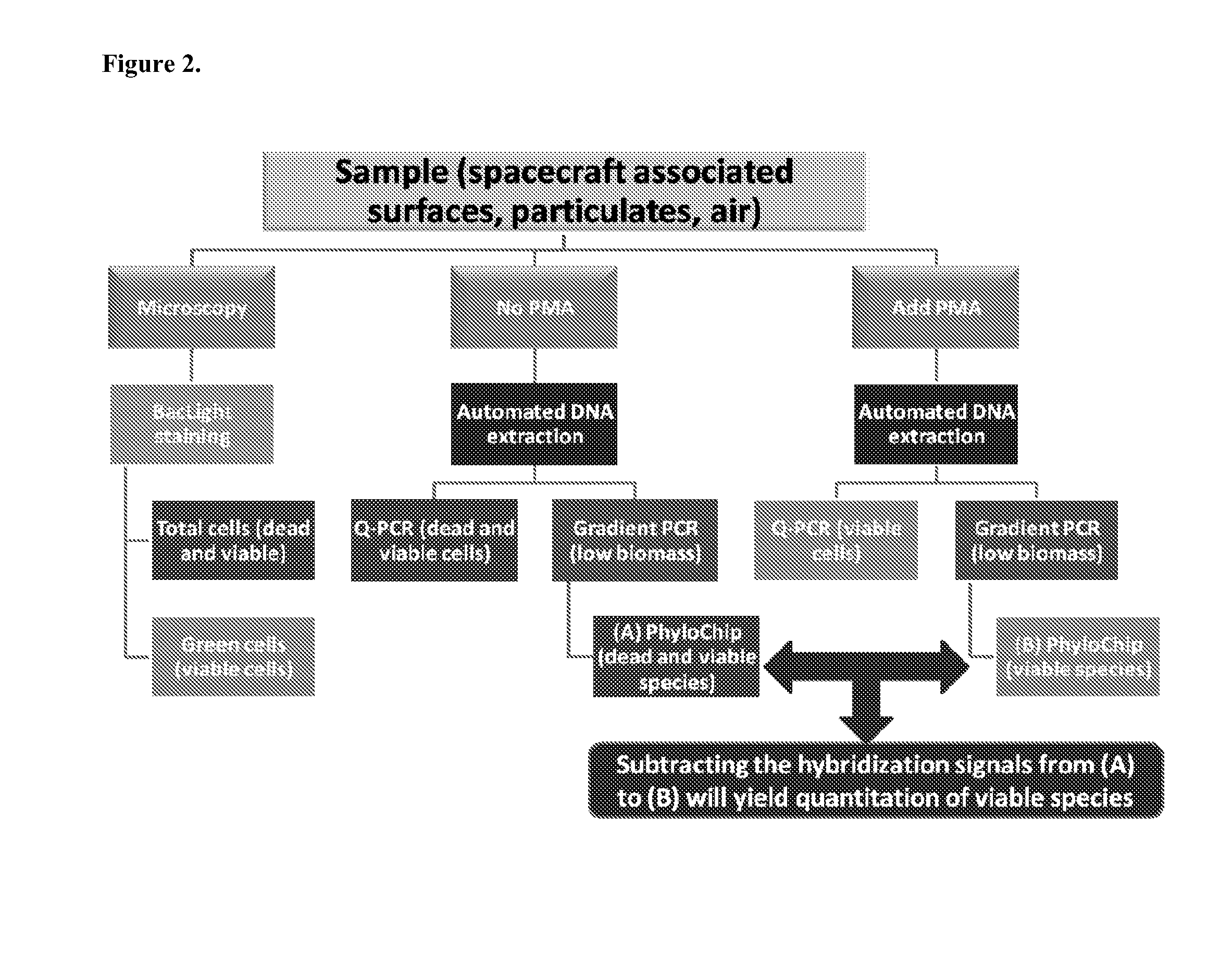
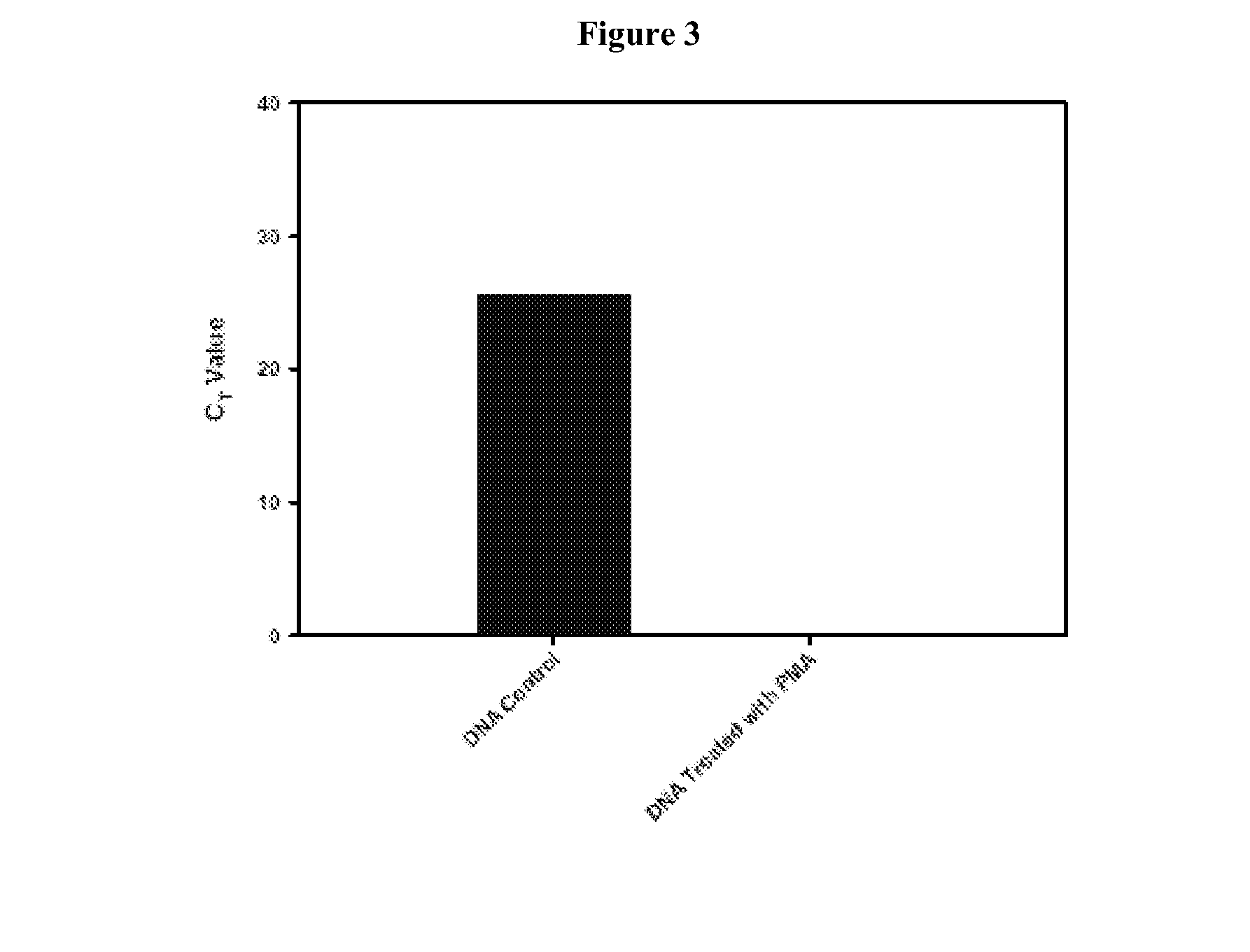
A methodology of microarray using the fluorescent DNA intercalating agent propidium monoazide (PMA) to selectively block DNA of dead cells from amplification and its application in detecting and enumerating viable microbes in complex microbial communities is described. A phylogenetic array is used in the preferred embodiment to enhance the sensitivity of the method. The PMA-Microarray assay is particularly applicable for monitoring samples from environments with extremely low microbial burden such as spacecraft surfaces.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
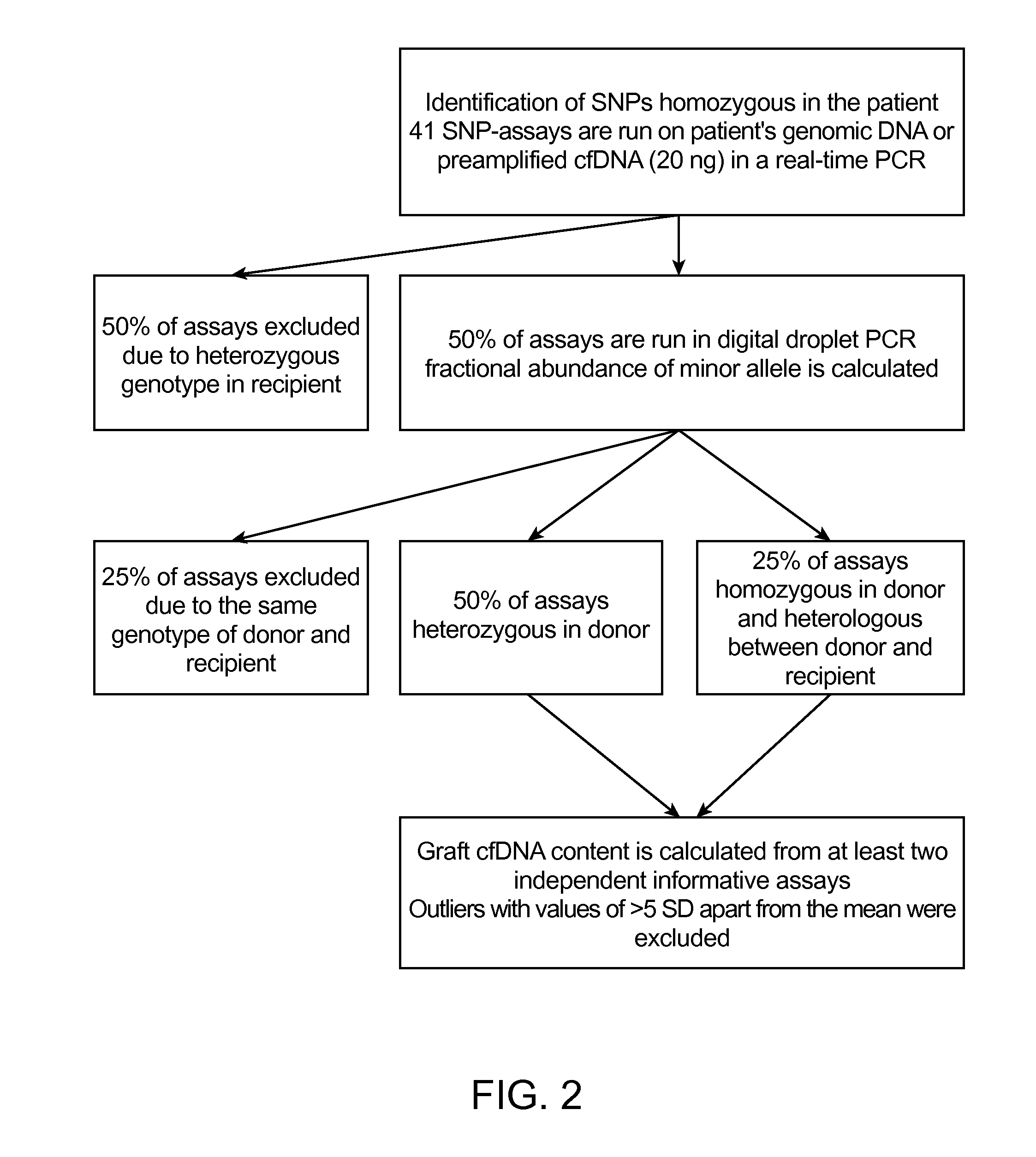
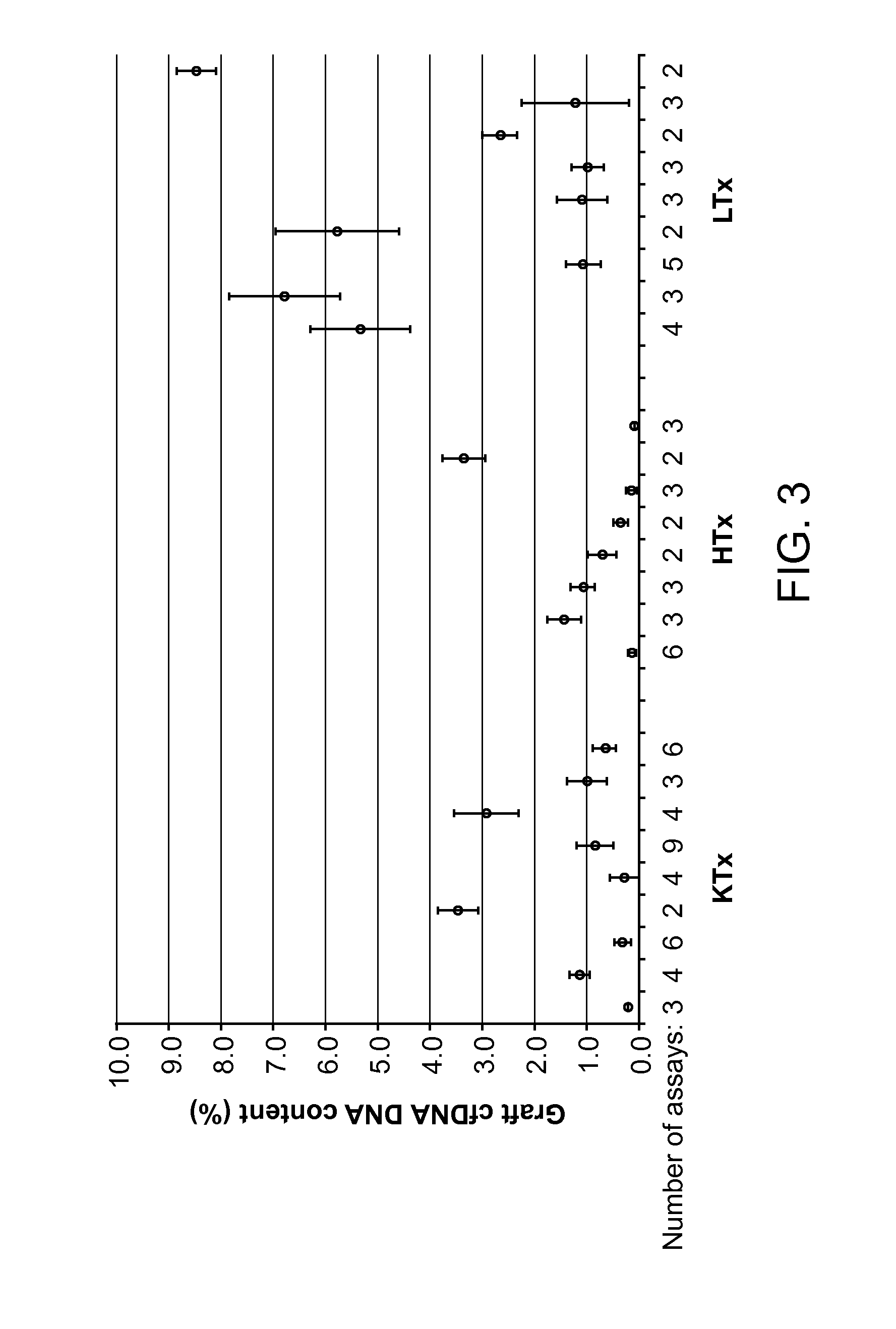
Detection and quantification of donor cell-free DNA in the circulation of organ transplant recipients
InactiveUS20160115541A1Detection of damageMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningBiologyCellular dna
This invention provides methods, compositions, and kits relating to detecting donor cell-free DNA in the circulation of an organ transplant recipient for the early identification of transplant rejection
Owner:CHRONIX BIOMEDICAL
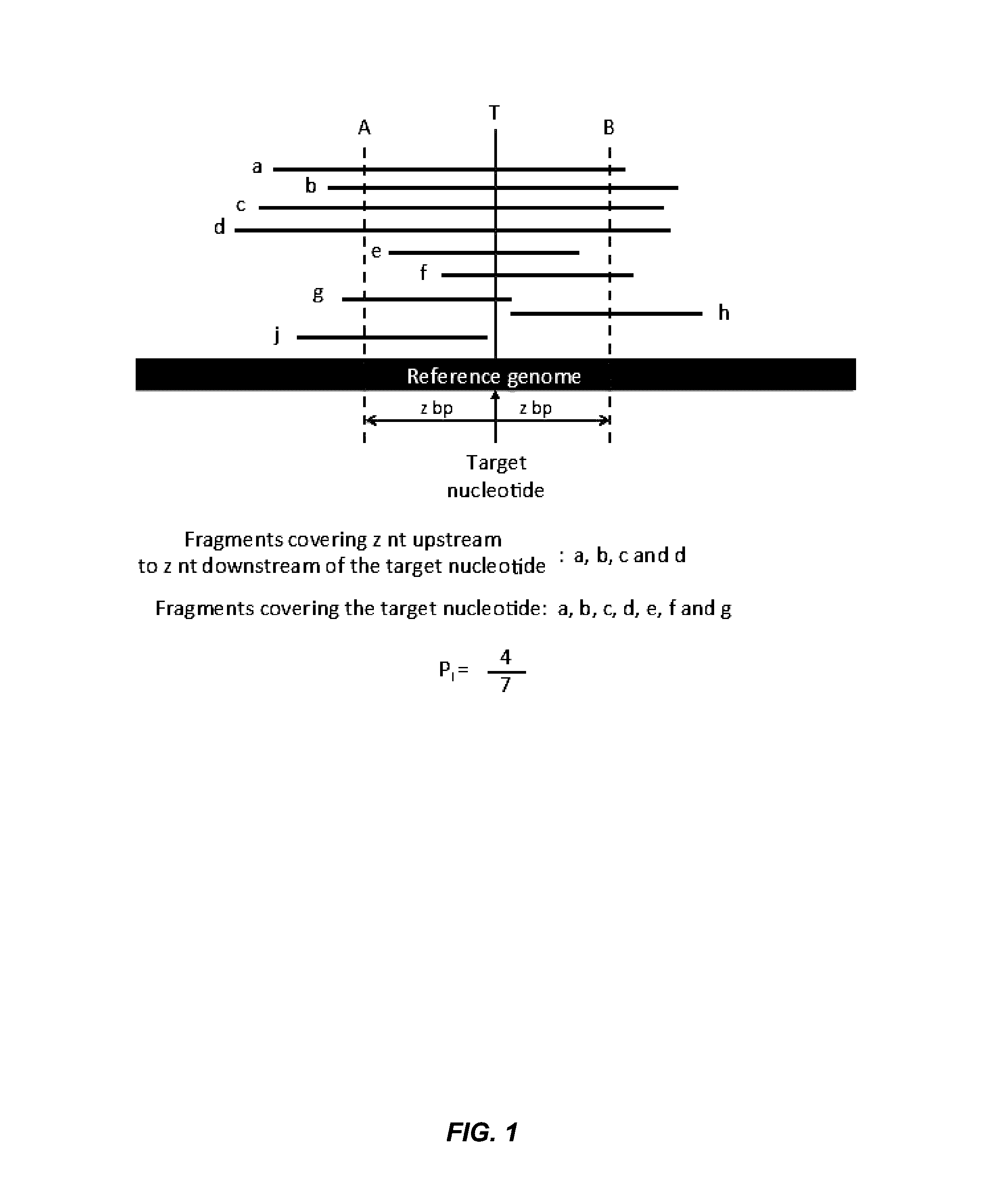
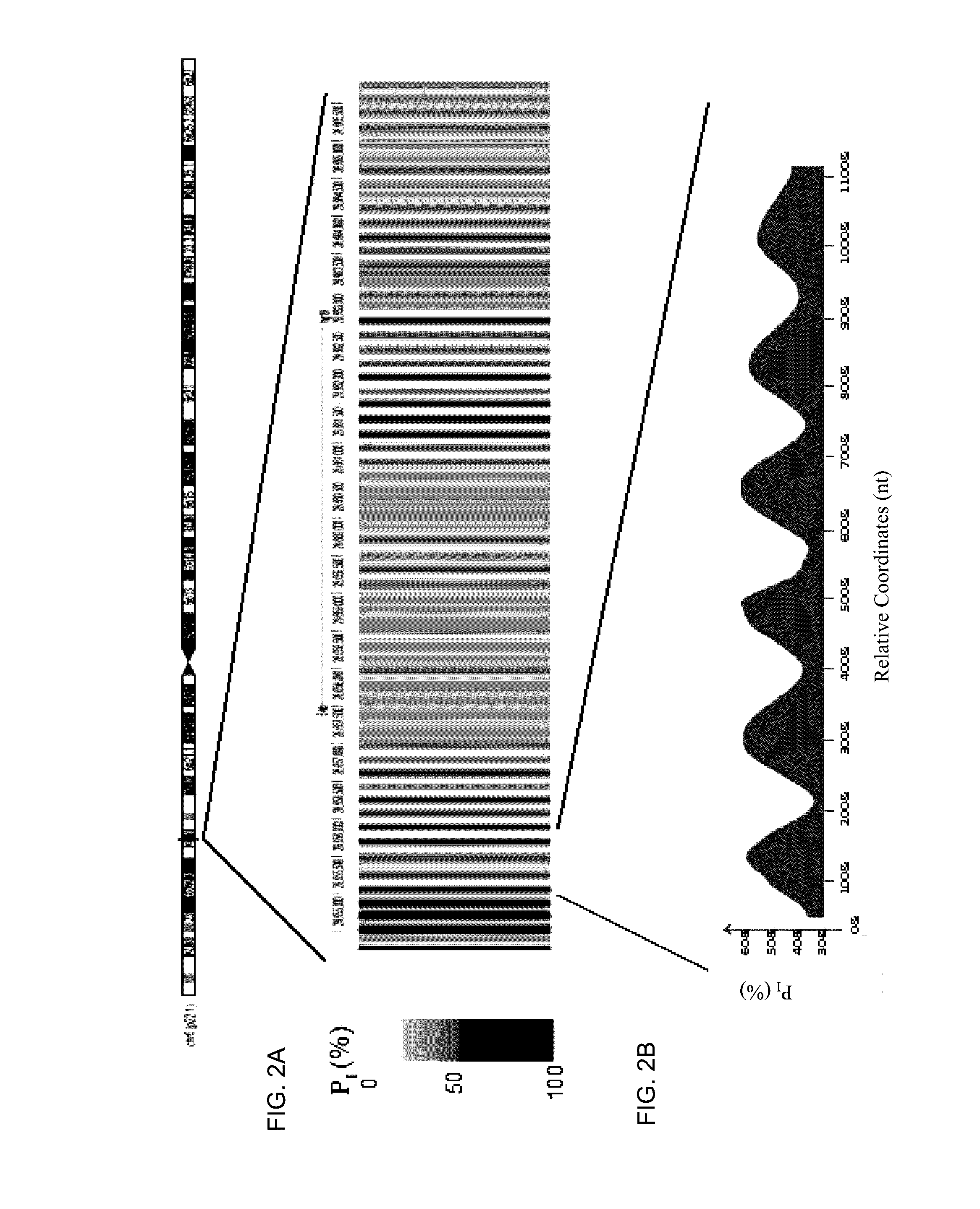
Analysis of fragmentation patterns of cell-free DNA
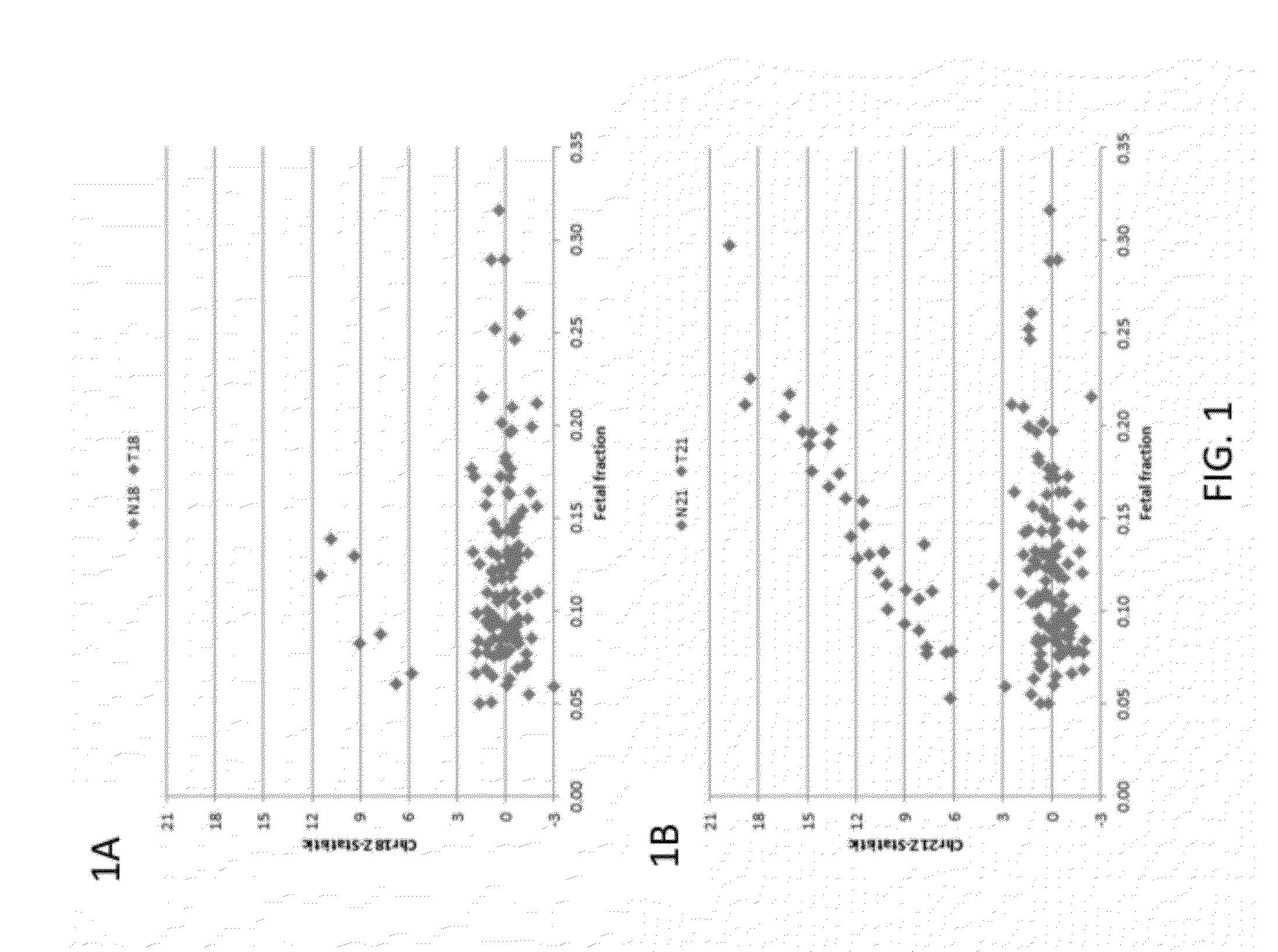
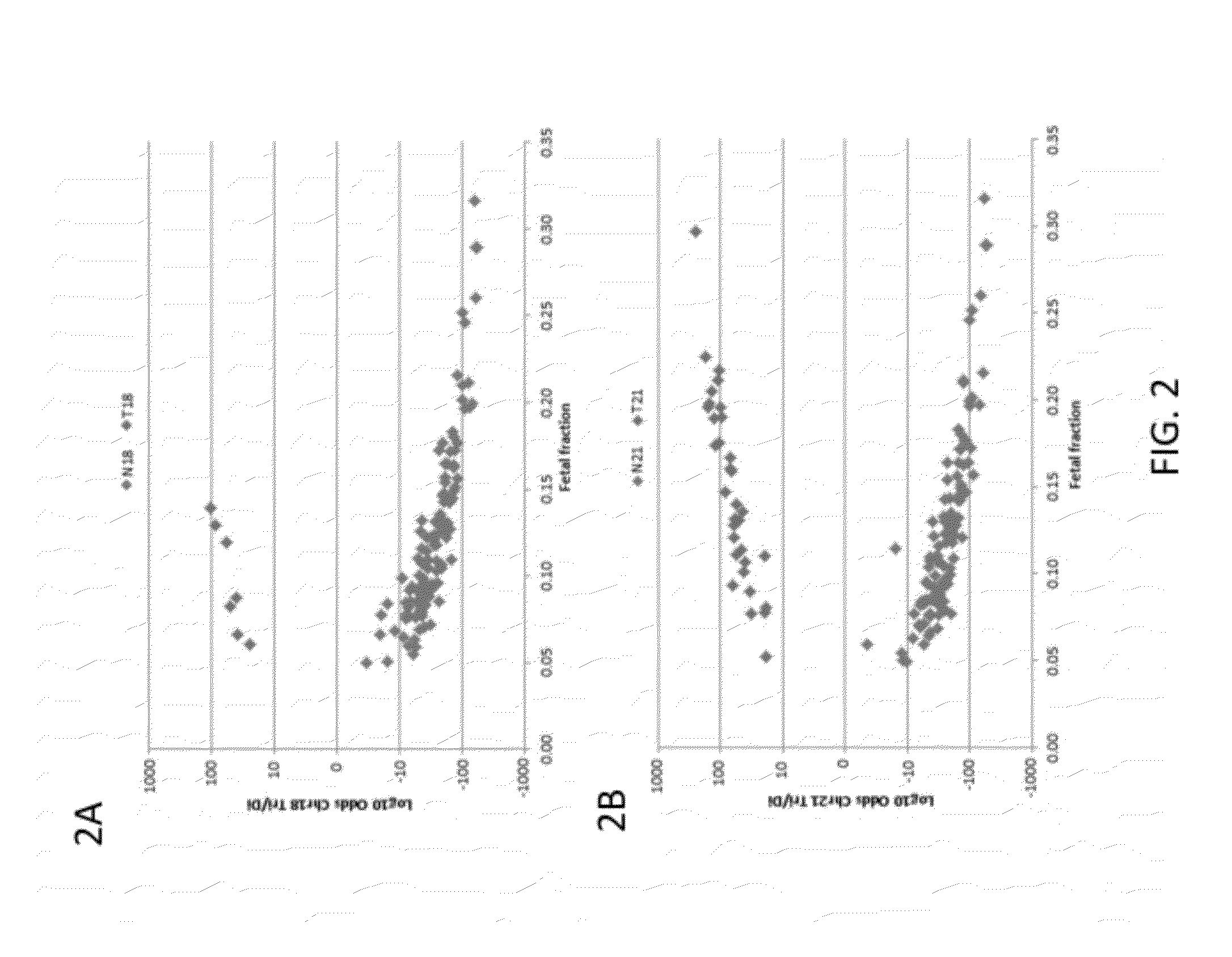
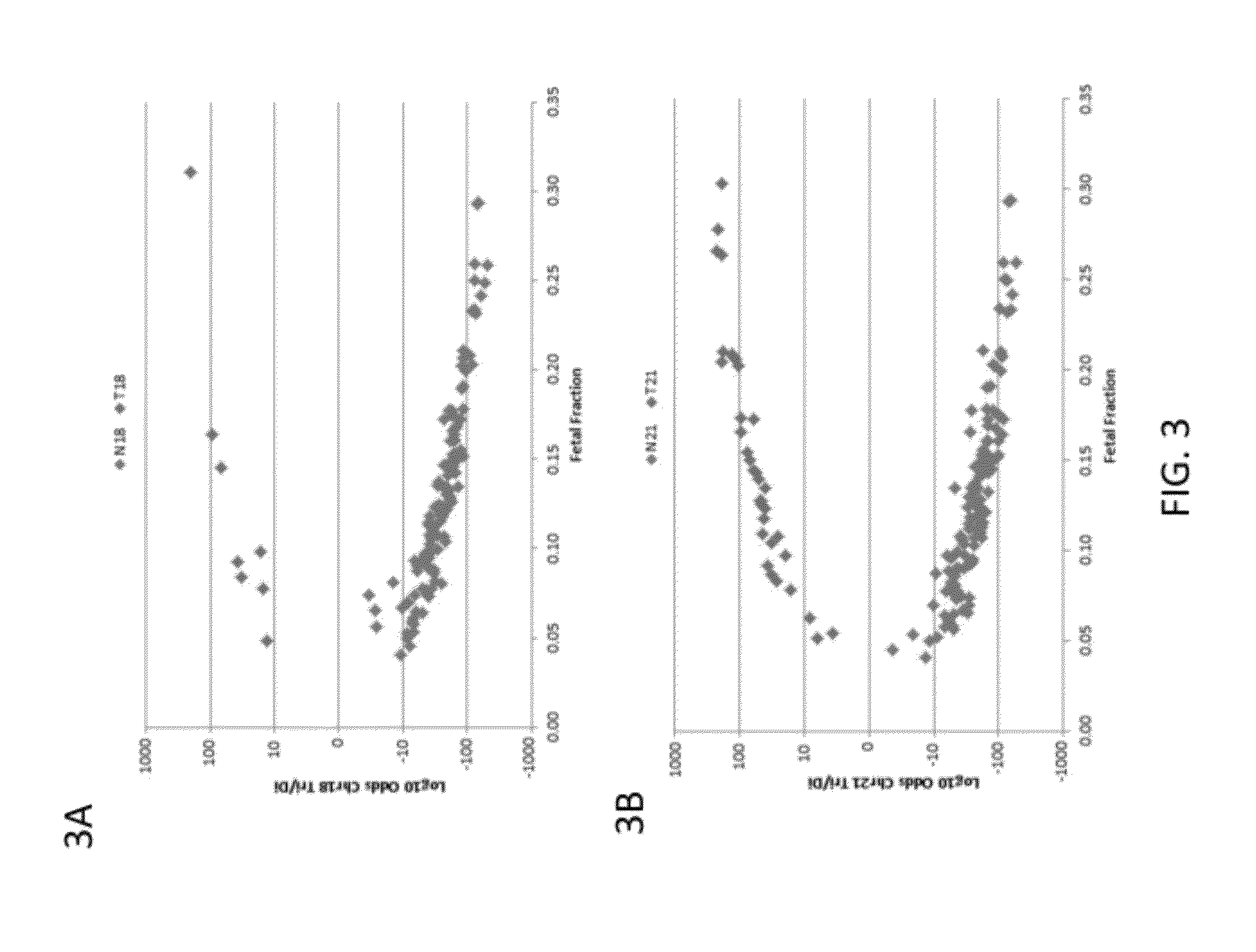
Factors affecting the fragmentation pattern of cell-free DNA (e.g., plasma DNA) and the applications, including those in molecular diagnostics, of the analysis of cell-free DNA fragmentation patterns are described. Various applications can use a property of a fragmentation pattern to determine a proportional contribution of a particular tissue type, to determine a genotype of a particular tissue type (e.g., fetal tissue in a maternal sample or tumor tissue in a sample from a cancer patient), and / or to identify preferred ending positions for a particular tissue type, which may then be used to determine a proportional contribution of a particular tissue type.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Non-invasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal genetic condition using cellular DNA and cell free DNA
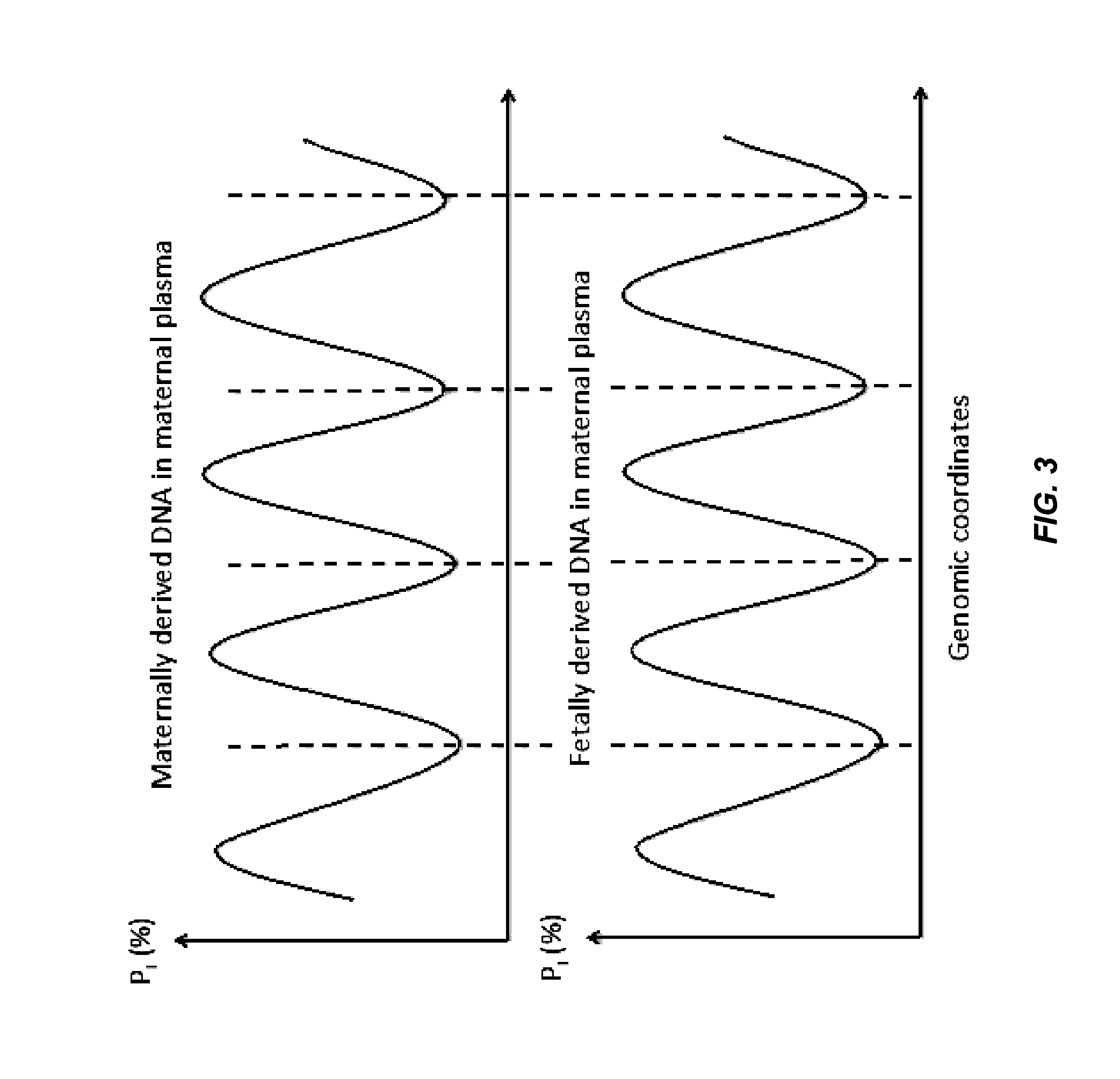
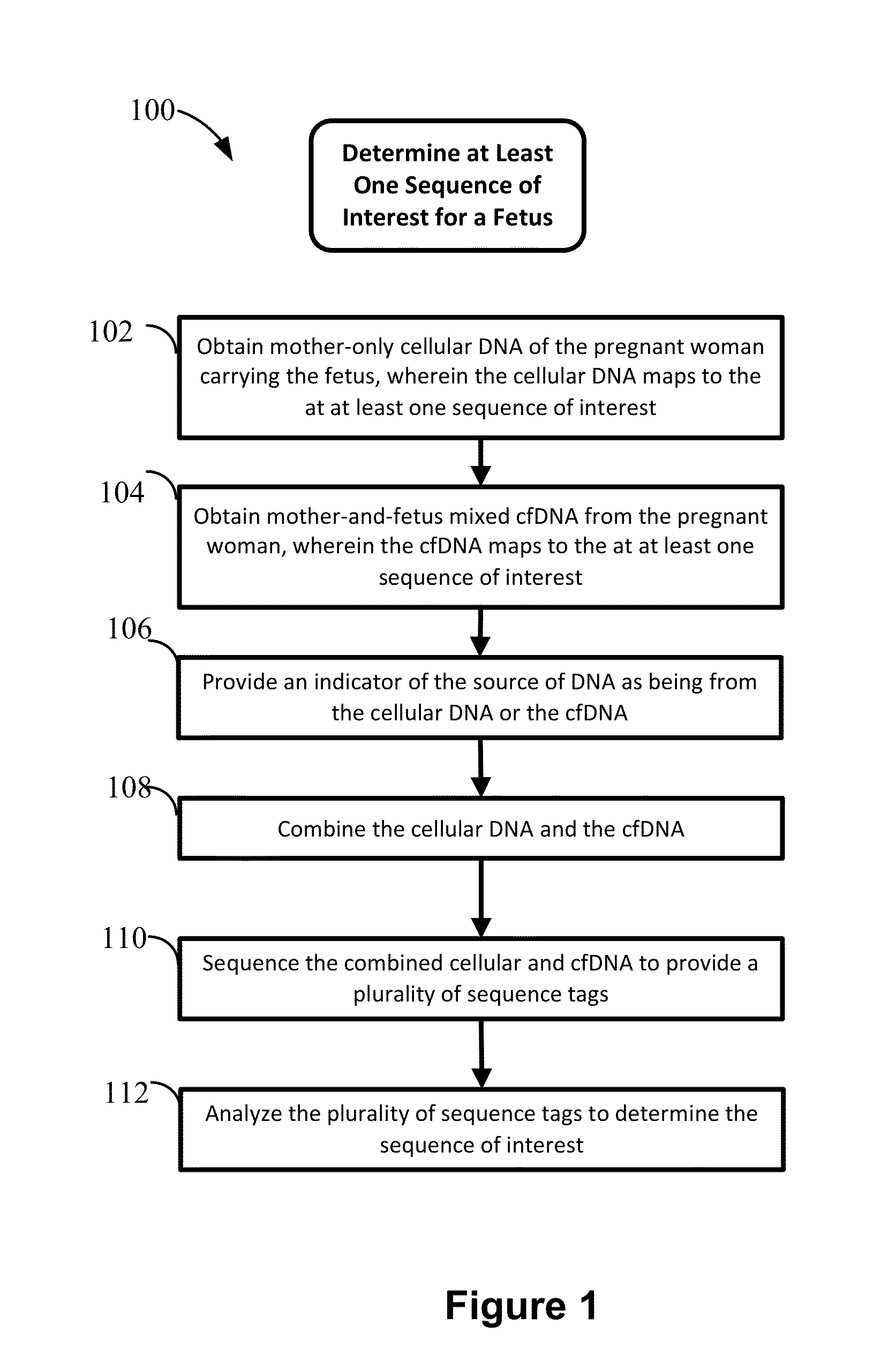
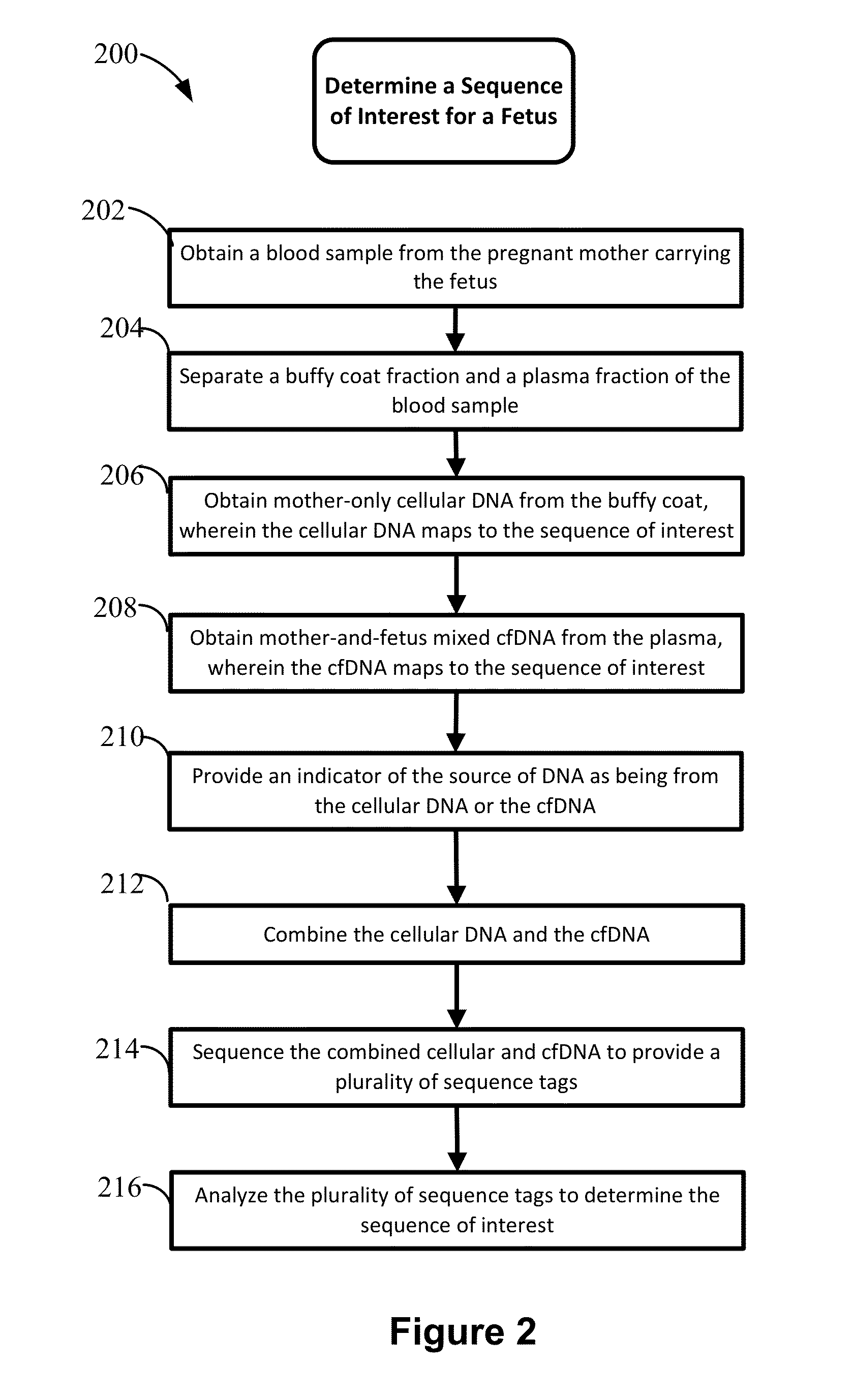
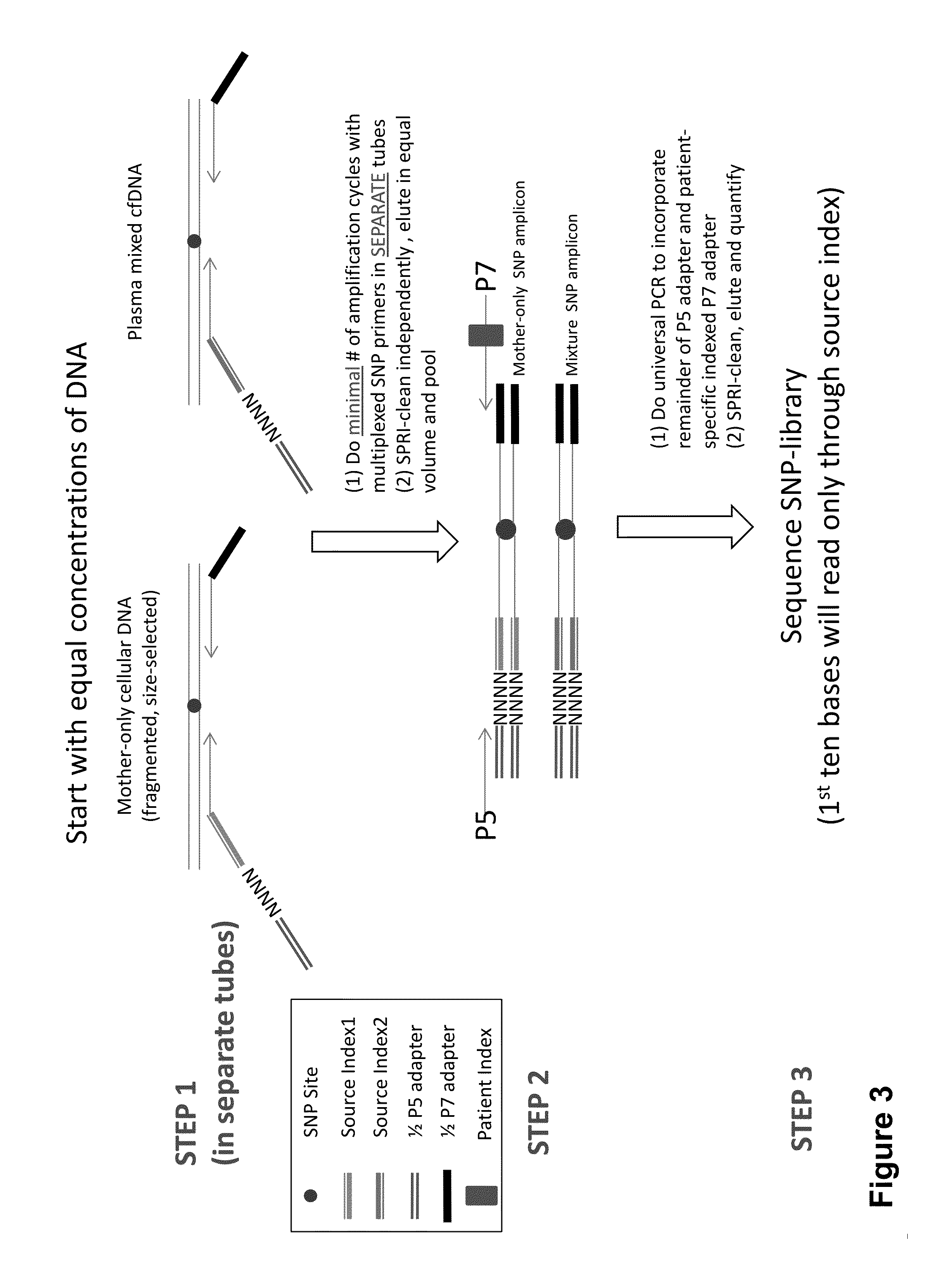
Disclosed are methods for determining at least one sequence of interest of a fetus of a pregnant mother. In various embodiments, the method can determine one or more sequences of interest in a test sample that comprises a mixture of maternal cellular DNA and mother-and-fetus cfDNA. In some embodiments, methods are provided for determining whether the fetus has a genetic disease. In some embodiments, methods are provided for determining whether the fetus is homozygous in a disease causing allele when the mother is heterozygous of the same allele. In some embodiments, methods are provided for determining whether the fetus has a copy number variation (CNV) or a non-CNV genetic sequence anomaly.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Methods and compositions for preparation of biological samples
InactiveUS20060240449A1Sufficient volumeIncrease usable surface areaMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid reductionLysisEnzyme
Methods and compositions for preparation of biological samples are disclosed. The methods include a prelysis step and a lysis step to make the cellular DNA available for further processing, amplification or analysis. The prelysis step includes the addition of a prelysis reagent to the cells. The prelysis reagent may include an enzyme to facilitate the disruption of the cells. The lysis step includes the addition of a lysis reagent to at least a portion of the prelysis reagent and cells.
Owner:ACCESS GENETICS
Method and pharmacological composition for the diagnosis and treatment of male
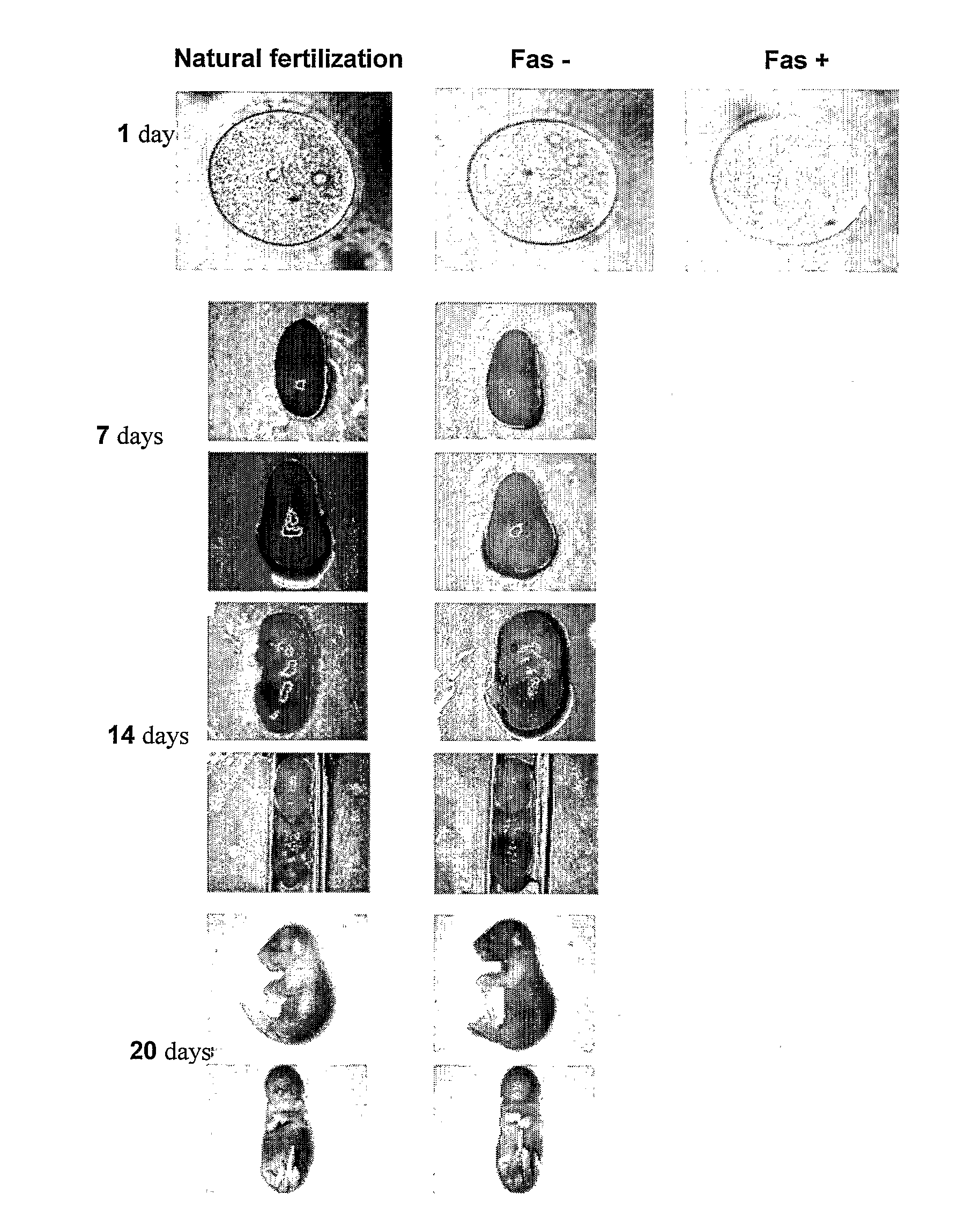
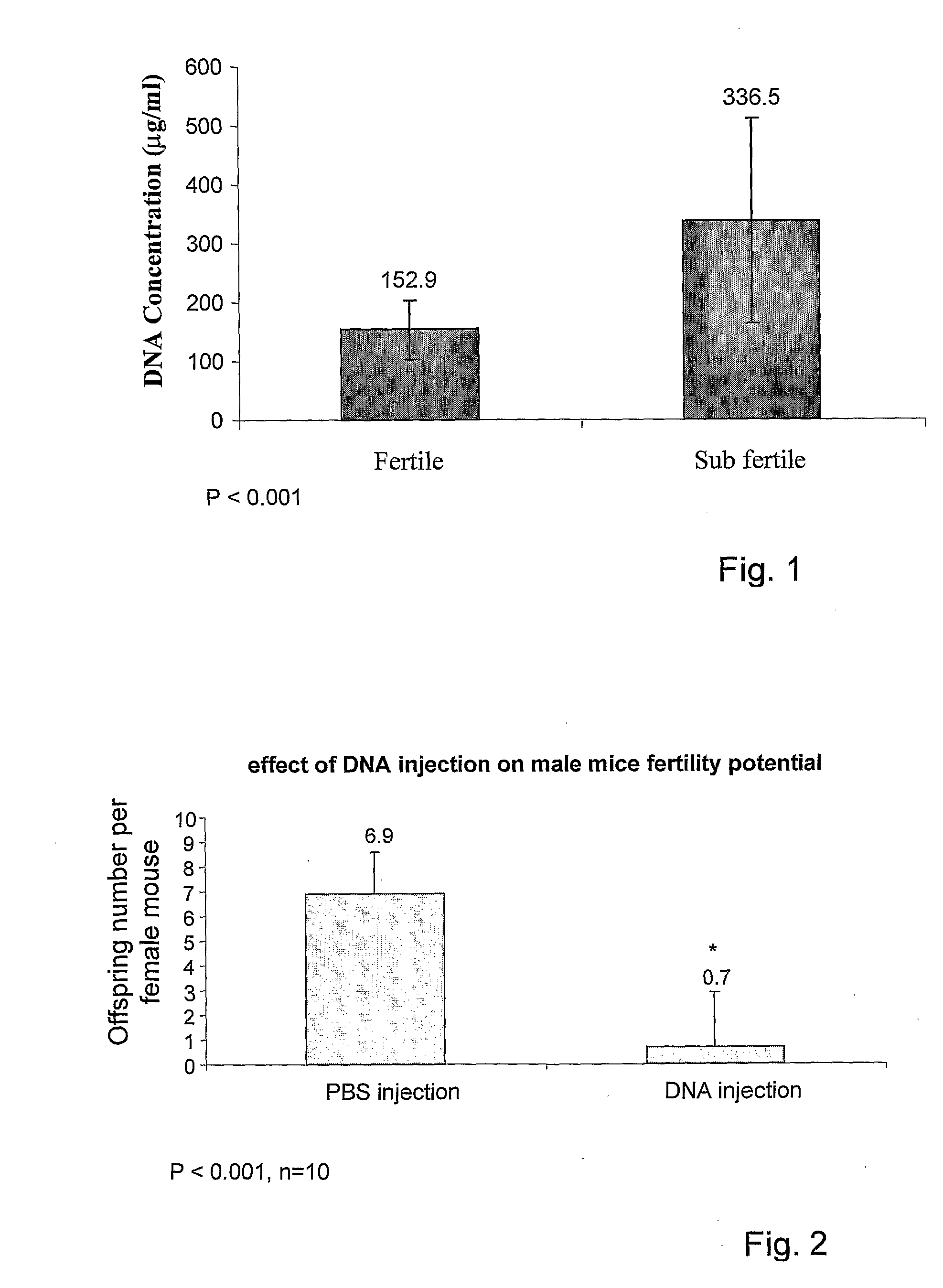
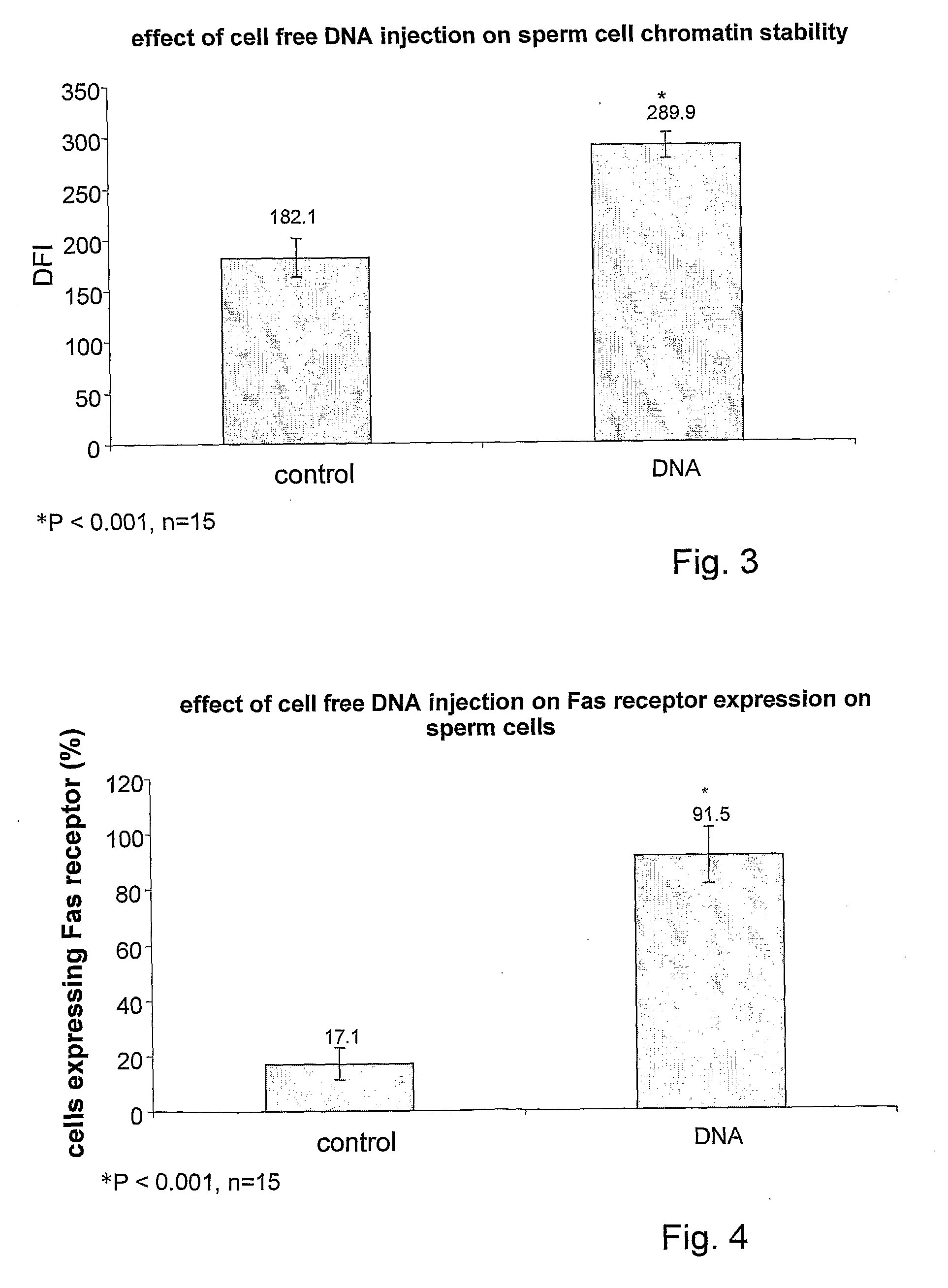
Pharmaceutical compositions for treating male sub-fertility that include an agent that causes a reduction in an effect of extracellular DNA on sperm cells, are provided. The agent may be, for example, an enzyme that degrades DNA such as DNase, a substance that blocks the interaction between cell free DNA and sperm cell surface receptors, a substance that binds to DNA, a substance that inhibits endogenous sperm cell DNase, a substance that inhibits a member of a signal transduction pathway mediated by DNA binding to sperm cell surface receptors, or an agent that stimulates production of an endogenous substance that causes a reduction in an antifertility effect of cell free DNA on sperm cells. Also provided are methods for treating male sub-fertility by administering the pharmaceutical composition to a subject in need thereof. Further provided are methods for determining a fertility status in a male subject, methods for assisted reproduction, methods for selecting an assisted reproduction technique (ART), and methods for selecting sperm cells in a sperm cell population for use in an assisted reproduction technique.
Owner:PERINESS LTD
Enrichment of DNA comprising target sequence of interest
PendingUS20190360043A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementDownstream processingCell free
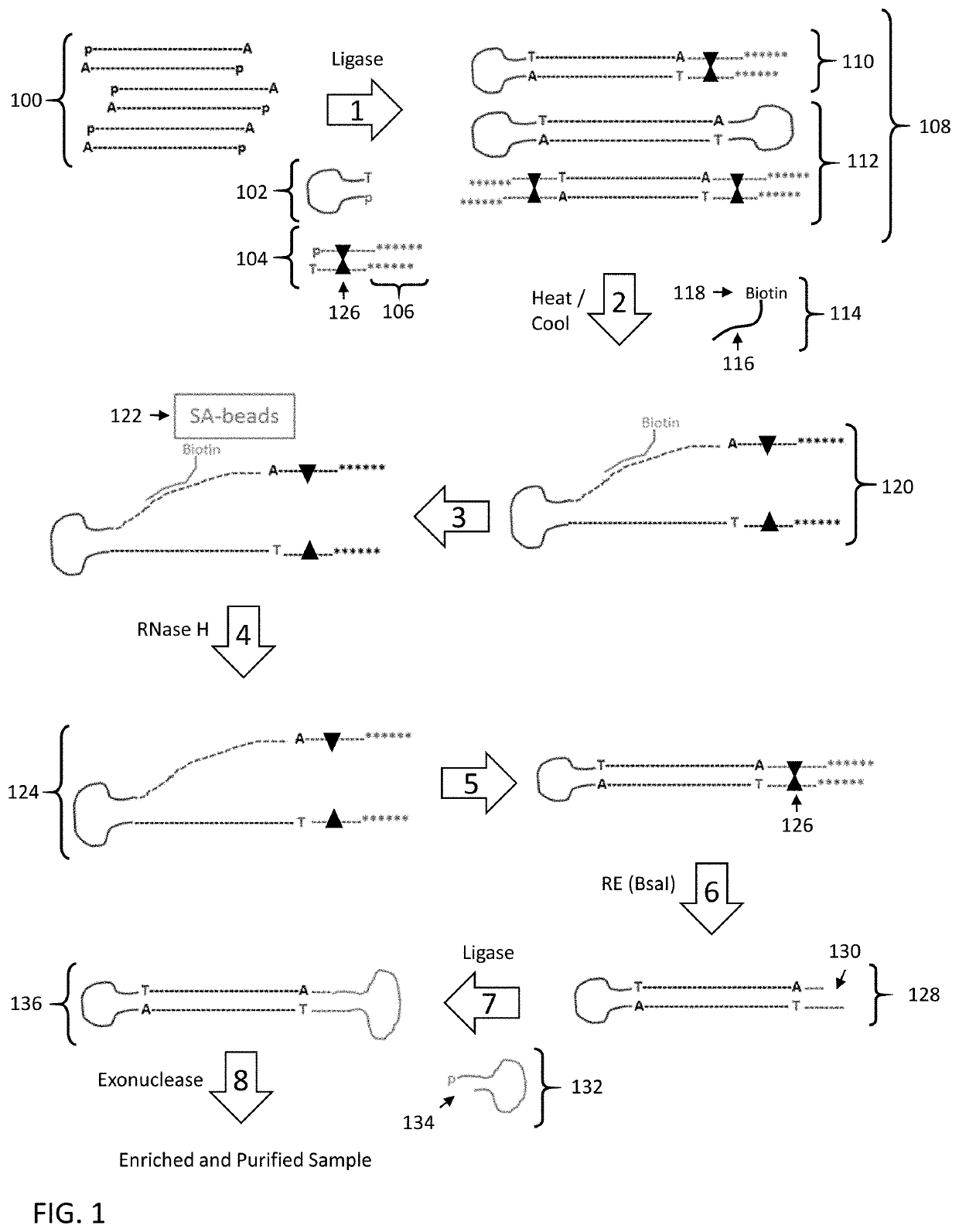
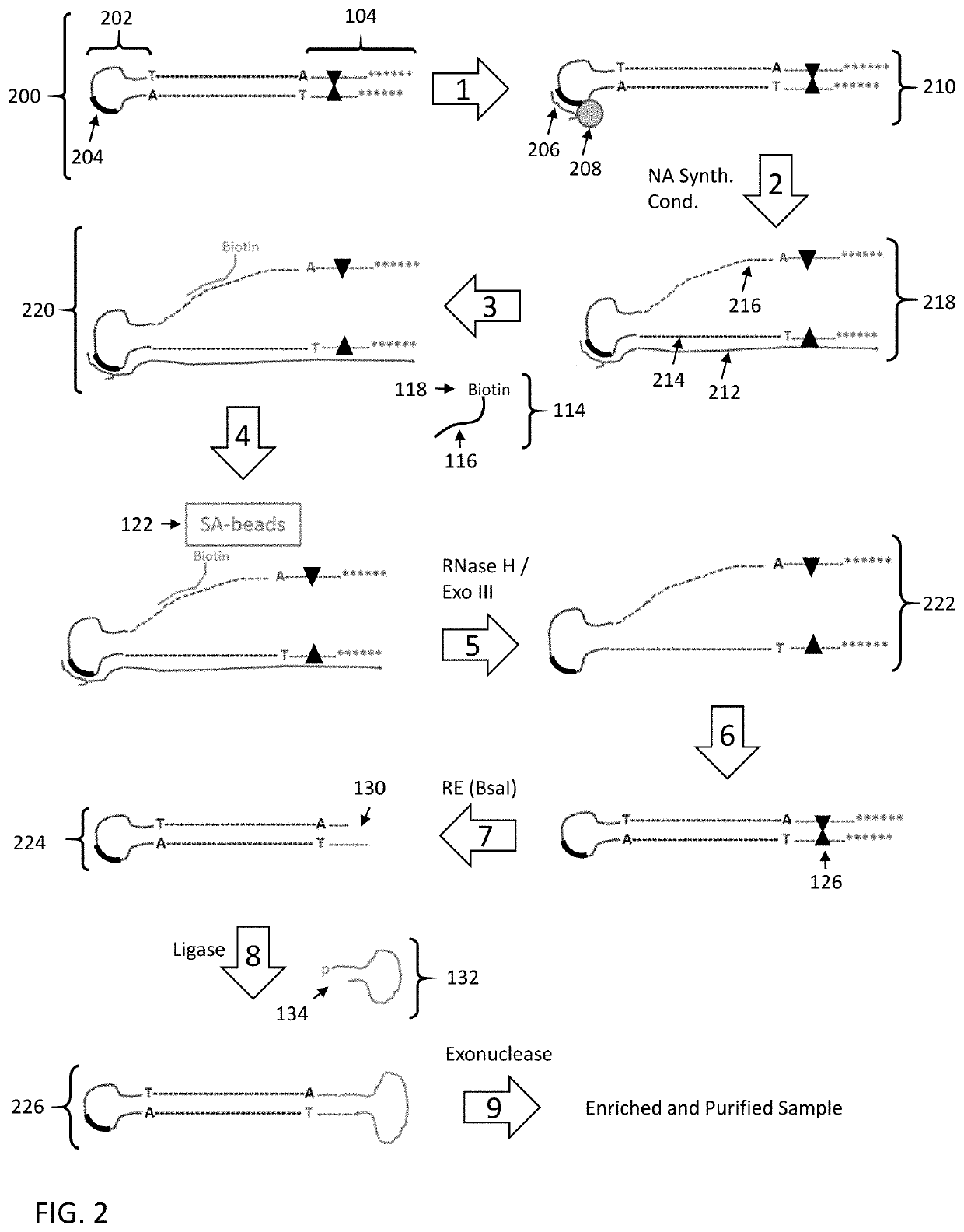
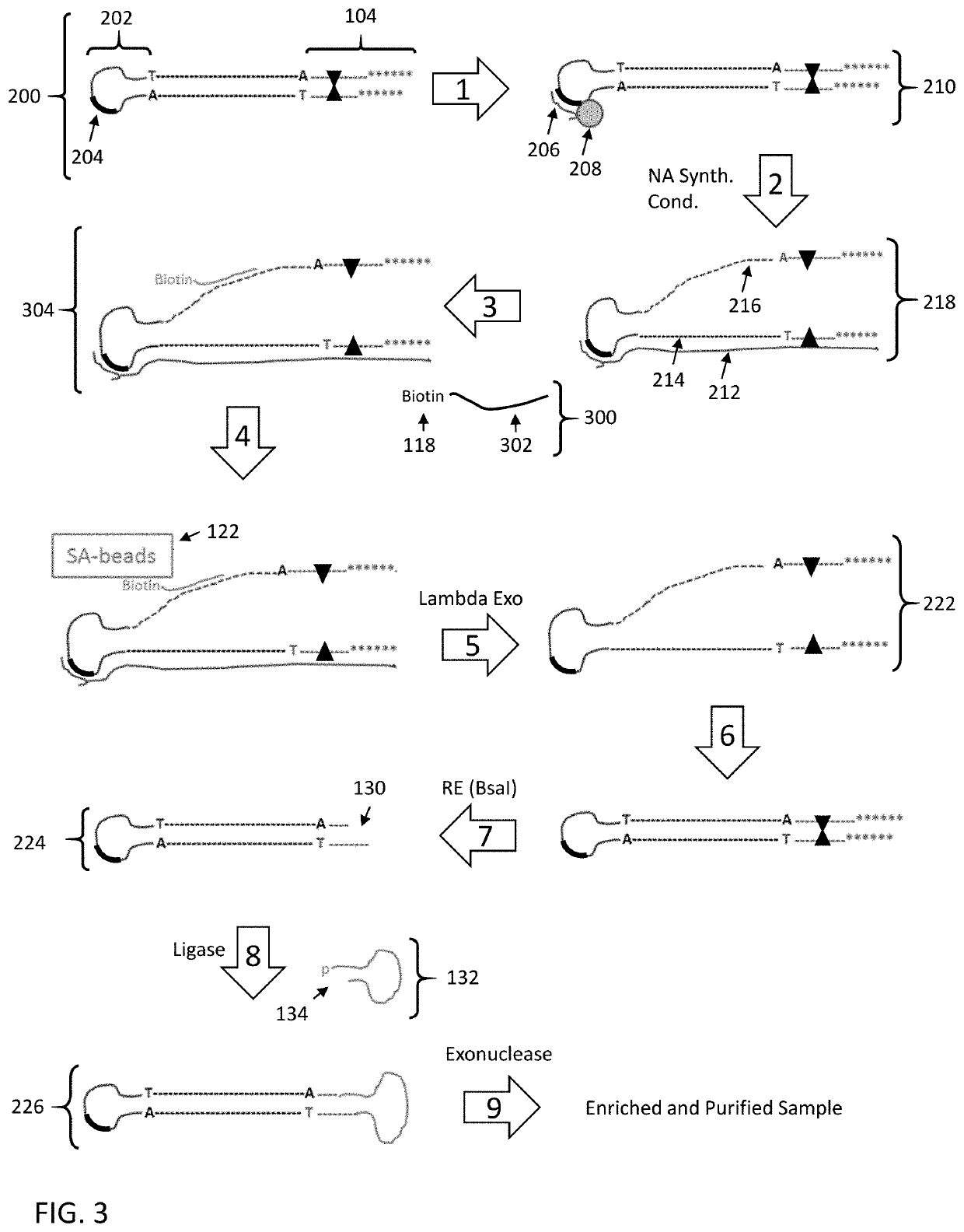
Disclosed are methods and compositions for enriching nucleic acid fragments from a sample that include one or more target region of interest. In certain aspects, a sample of double stranded nucleic acid fragments having a strand-linking adapter at one end and a non-strand-linking adapter at the other end are denatured and contacted with capture probes specific for a target sequence of interest. Capture probe-bound fragments are isolated from the sample, e.g., using a solid substrate specific for the binding moiety on the capture probes, and are renatured for downstream processing, thus maintaining the original double-stranded region. This enrichment process does not require amplification and as such maintains the nucleic acids in their native states. The disclosed enrichment process and compositions are suitable for analyzing nucleic acids that are fragmented and / or damaged, e.g., cell-free DNA such as circulating tumor DNA, as well as nucleic acids that are many kilobases in length.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Process for microsatellite instability detection
ActiveUS20190169685A1Useful in detectionIncrease the burdenTherapiesHealth-index calculationCell freeNucleotide
The invention provides methods for determining the MSI status of a patient by liquid biopsy with sample preparation using hybrid capture and non-unique barcodes. In certain aspects, the invention provides a method of detecting microsatellite instability (MSI). The method includes obtaining cell-free DNA (cfDNA) from a sample of blood or plasma from a patient and sequencing portions of the cfDNA to obtain sequences of a plurality of tracts of nucleotide repeats in the cfDNA. A report is provided describing an MSI status in the patient when a distribution of lengths of the plurality of tracts has peaks that deviate significantly from peaks in a reference distribution.
Owner:PERSONAL GENOME DIAGNOSTICS INC
Methods and applications of gene fusion detection in cell-free DNA analysis
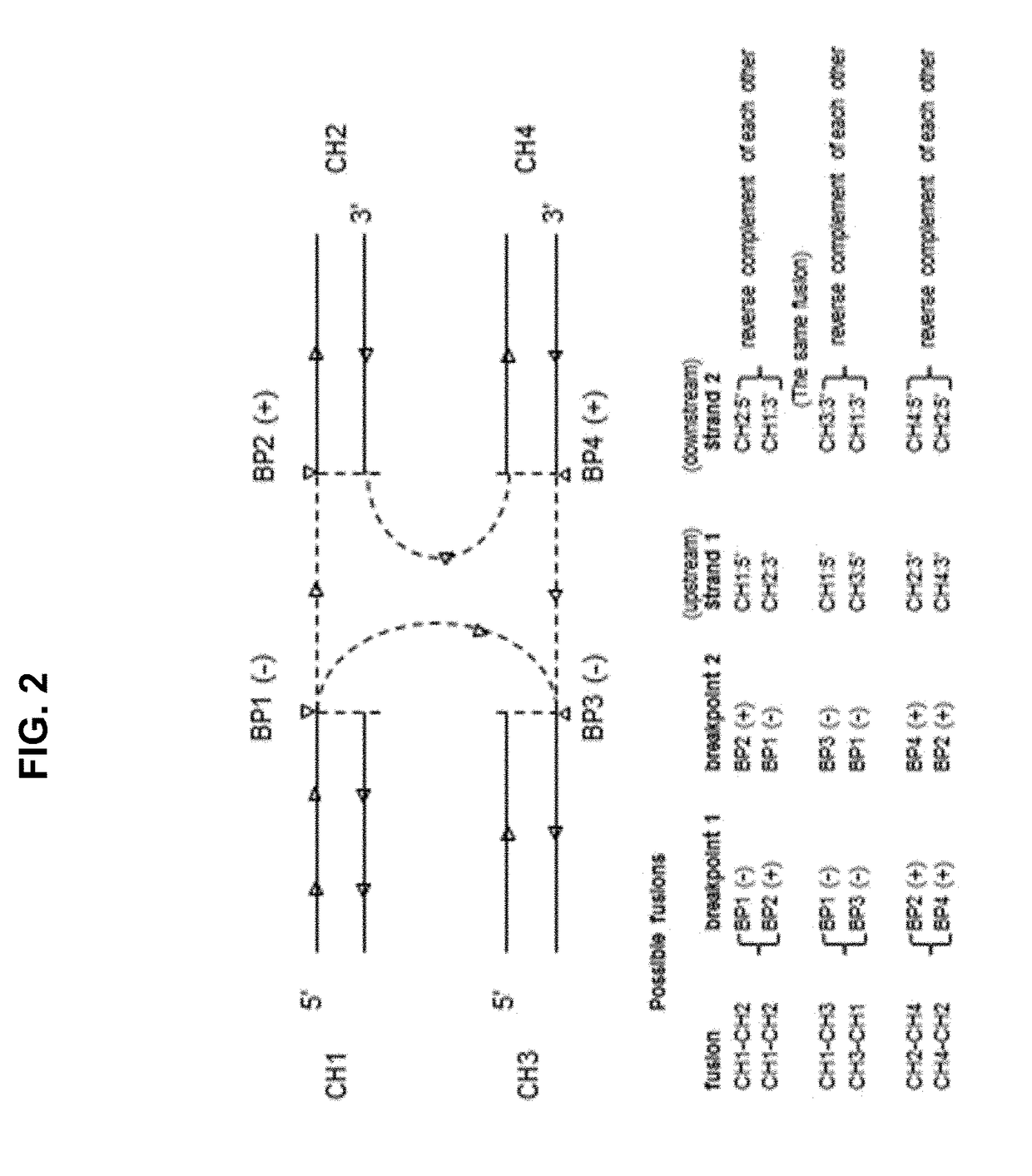
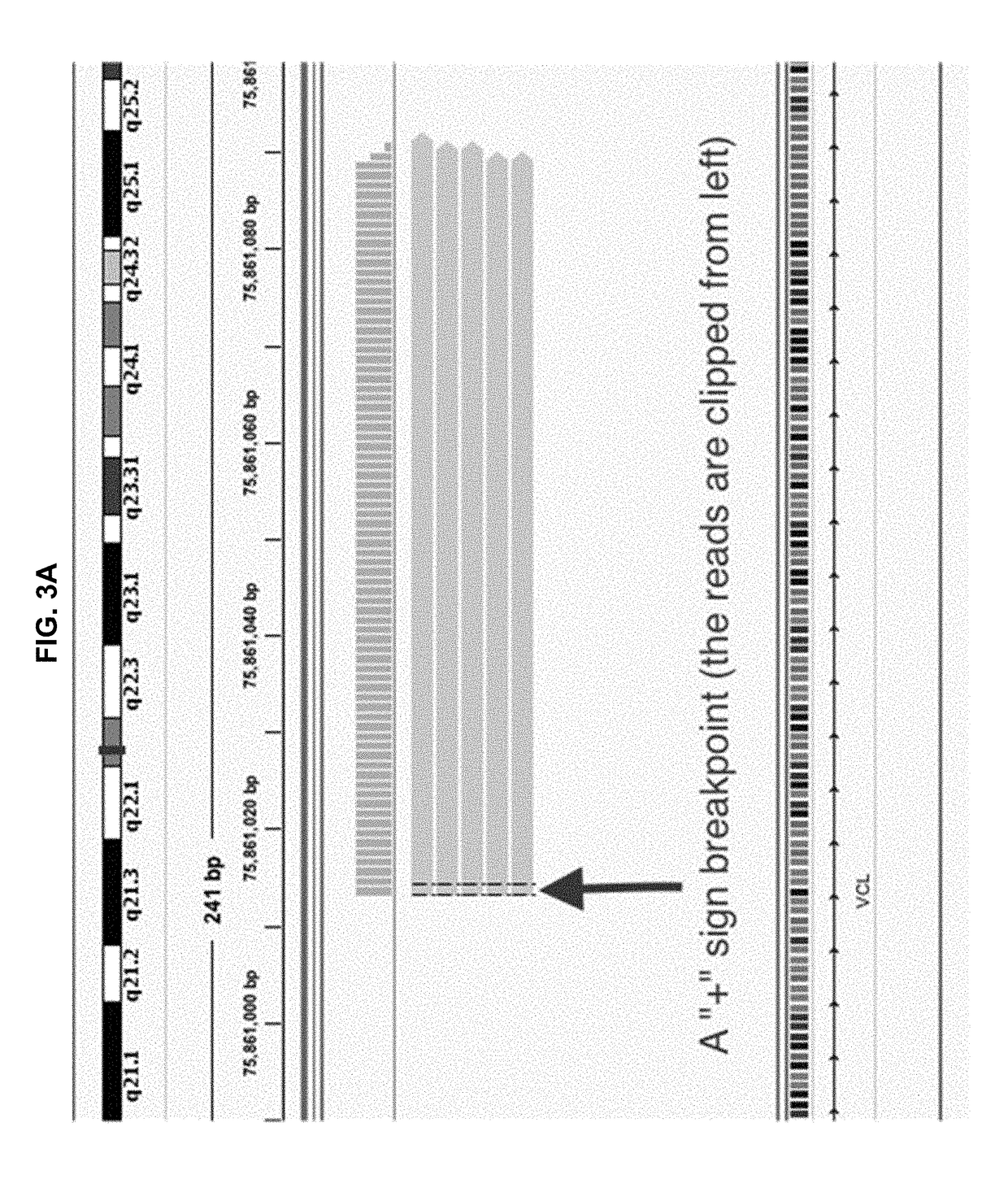
Systems and methods are disclosed for determining gene fusion by determining a fused read containing sequencing data of a portion of a fused chromosome DNA molecule; determining a predetermined point on the genome with least one mapped portion of the fused read clipped at the predetermined point (a breakpoint); identifying two mapped read portions from two breakpoints (breakpoint pair) as a potential fusion candidate; creating one or more fusion sets based on breakpoint pairs and clustering the fusion sets into one or more fusion clusters; and identifying each fusion cluster meeting a predetermined criterion as a gene fusion.
Owner:GUARDANT HEALTH
Modified triple-helix forming oligonucleotides for targeted mutagenesis
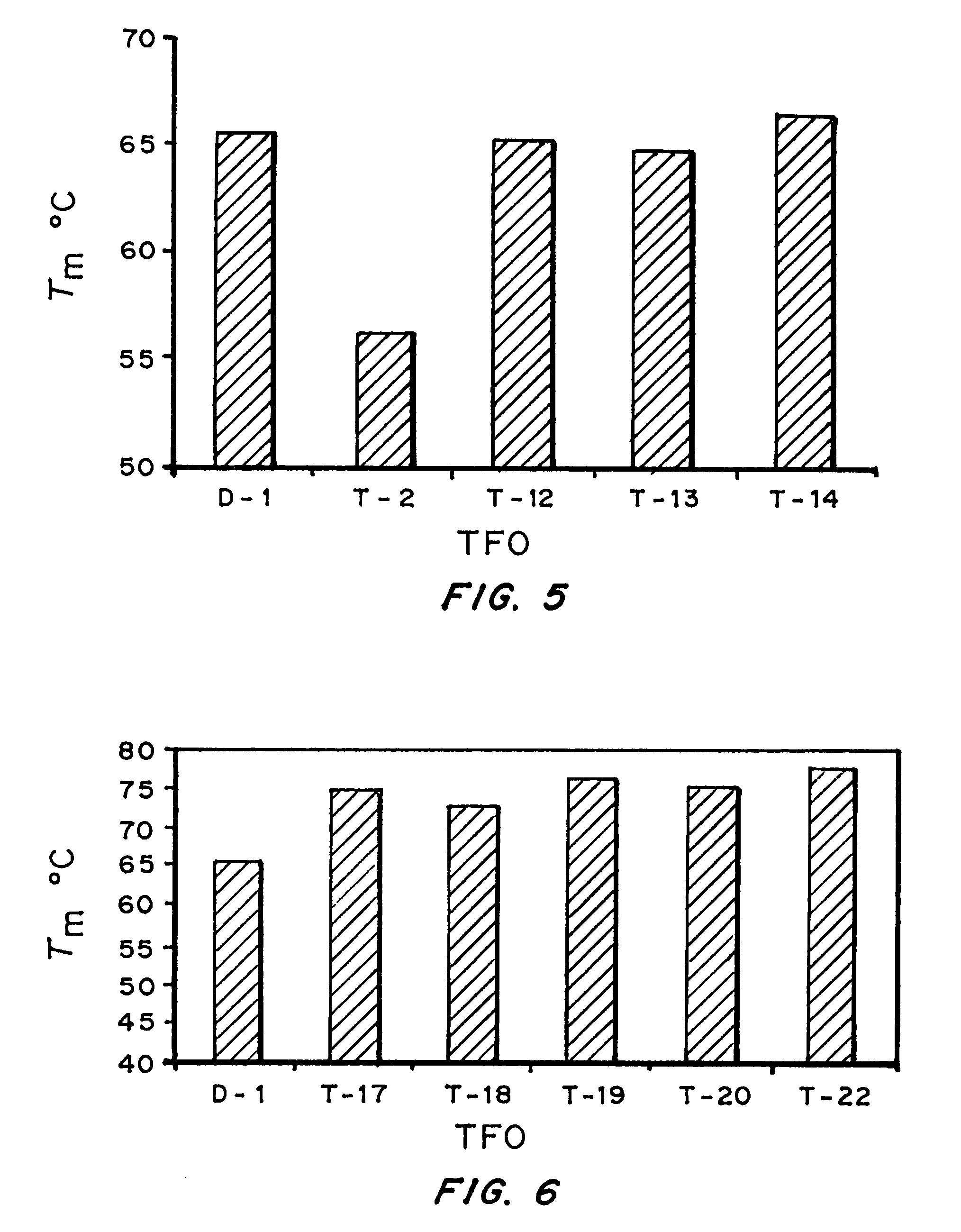
ActiveUS8658608B2Improve stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsBase JNucleotide
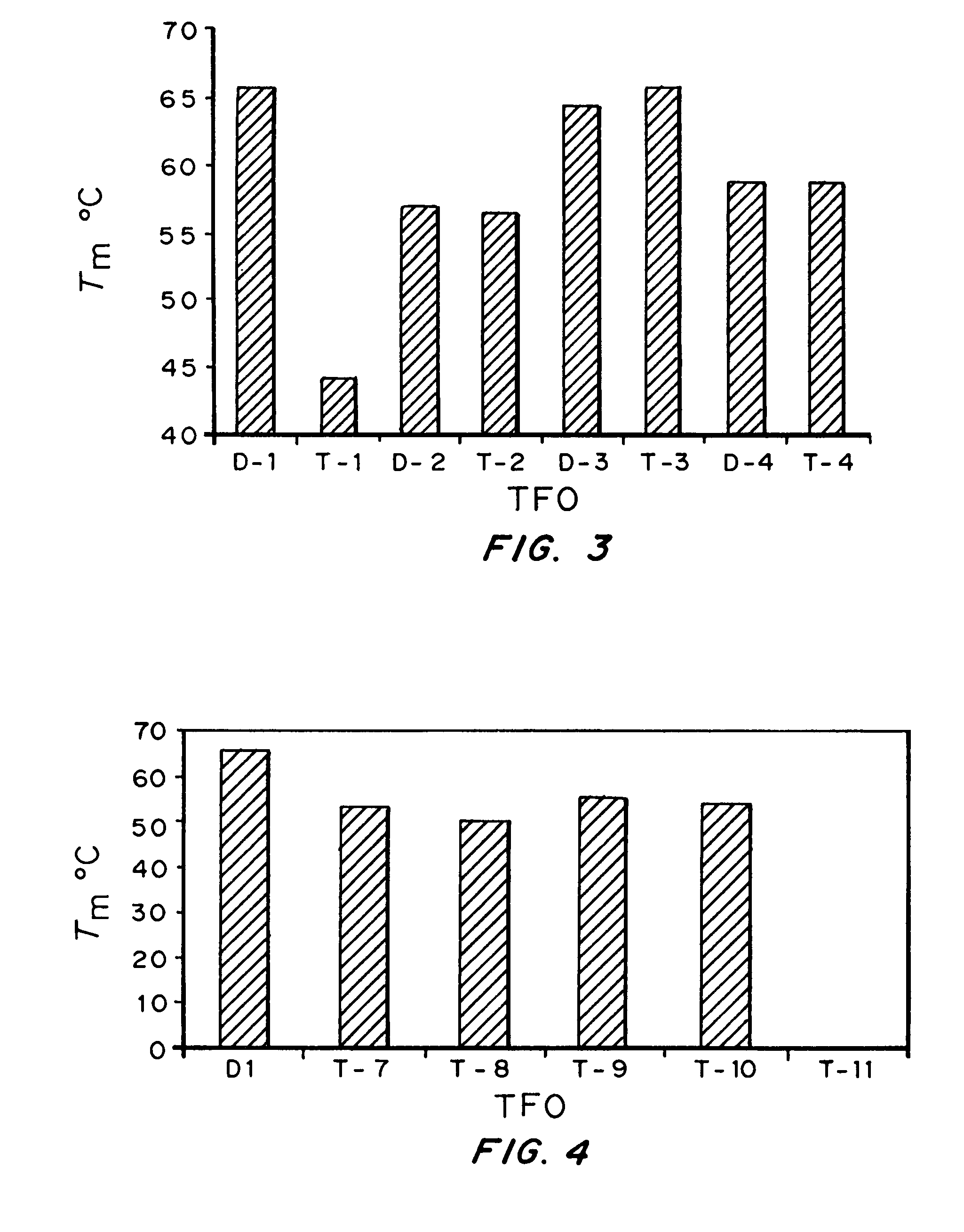
High affinity, chemically modified triplex-forming oligonucleotides (TFOs) and methods for use thereof are disclosed. TFOs are defined as triplex-forming oligonucleotides which bind as third strands to duplex DNA in a sequence specific manner. Triplex-forming oligonucleotides may be comprised of any possible combination of nucleotides and modified nucleotides. Modified nucleotides may contain chemical modifications of the heterocyclic base, sugar moiety or phosphate moiety. A high affinity oligonucleotide (Kd≦2×10−8) which forms a triple strand with a specific DNA segment of a target gene DNA is generated. It is preferable that the Kd for the high affinity oligonucleotide is below 2×10−10. The nucleotide binds or hybridizes to a target sequence within a target gene or target region of a chromosome, forming a triplex region. The binding of the oligonucleotide to the target region stimulates mutations within or adjacent to the target region using cellular DNA synthesis, recombination, and repair mechanisms. The mutation generated activates, inactivates, or alters the activity and function of the target gene.
Owner:CONCORD +2
Preparation of polyacrylic acid coated ferroferric oxide magnetic nano-particles and application thereof
InactiveCN101612541AReduce usageOvercoming Exposure to Toxic AgentsSugar derivativesOther chemical processesPurification methodsParticle-in-cell
The invention discloses preparation of polyacrylic acid (PAA) coated ferroferric oxide magnetic nano-particles and application thereof, and belongs to the technical fields of nano materials and bioengineering. The invention comprises a method for preparing the PAA ferroferric oxide magnetic nano-particles and application of the PAA ferroferric oxide magnetic nano-particles in cell DNA extraction and purification. The invention provides a method for preparing the PAA ferroferric oxide magnetic nano-particles by a high temperature decomposition method; and the prepared magnetic nano-particles are used for cell DNA high-efficiency extraction and purification, the extraction ratio is greatly improved, and the operation is more simple and convenient. The separation efficiency and the DNA yield of the DNA purification method based on the magnetic nano-particles are not lower than those of the conventional method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Full-automatic LCT (Liquid Cytologic Test) liquid-based thin-layer cell and cell DNA rapid slice production and dyeing integrated machine
InactiveCN101957279AQuality improvementEvenly distributedPreparing sample for investigationCancer preventionBiochemical engineering
The invention discloses a full-automatic LCT (Liquid Cytologic Test) liquid-based thin-layer cell and cell DNA rapid slice production and dyeing integrated machine. The slice production and dyeing integrated machine is placed in a box body, a centrifugal device and an annular rotating orbit share the same circle center and are arranged in the same horizontal position, and a sample bin liquid-adding cap and an annular orbit liquid-adding cap are respectively arranged above the centrifugal device and the annular rotating orbit; four mechanical arms and two suction nozzle bins are symmetrically arranged in a space between the centrifugal device and the annular rotating orbit. The invention can complete sample treatment, slice production and dyeing in one machine at one time. The prepared sample slice has stable quality, complete cell and uniform distribution. Moreover, the rapid slice production and dyeing of sample LCT liquid-based thin-layer cell and cell DNA can be realized simultaneously on the same machine. The machine has large-scale sample processing and high efficiency, and is especially applicable to large-scale cancer prevention census and the clinical diagnosis and screening of large special hospitals.
Owner:王珑
Detection of genetic abnormalities
ActiveUS20120164646A1Determine the prognosis of a diseaseMicrobiological testing/measurementCancer cellNormal cell
The present invention provides assay systems and related methods for determining genetic abnormalities in mixed samples comprising cell free DNA from both normal and putative genetically atypical cells. Exemplary mixed samples for analysis using the assay systems of the invention include samples comprising both maternal and fetal cell free DNA and samples that contain DNA from normal cells and circulating cancerous cells.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Compositions and methods for treatment of lysosomal storage disorders
InactiveUS20110293585A1Reduces and prevents break downBiocideSugar derivativesLipid formationLysosome
Compositions and methods for treating lysosomal storage diseases are disclosed. Lysosomal dysfunction is usually the result of deficiency of a single enzyme necessary for the metabolism of lipids, glycoproteins (sugar containing proteins) or mucopolysaccharides which are fated for breakdown or recycling. The compositions contain triplex-forming molecules which can be used to induce site-specific homologous recombination in mammalian cells when combined with donor DNA molecules, by stimulating cellular DNA synthesis, recombination, and repair mechanisms. The methods are particular useful for correcting point mutations in genes associated with lysosomal storage diseases such as Gaucher's disease, Fabry disease, and Hurler syndrome. Methods for determining the frequency of target gene repair and assessing the restoration of the enzymatic activity of corrected polypeptides are also disclosed. Ex vivo and in vivo methods of gene correction in patients are also provided.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Overall length cDNA sequence of micro-capsule algae toxins degrading enzyme MlrA, coded amino acid and application
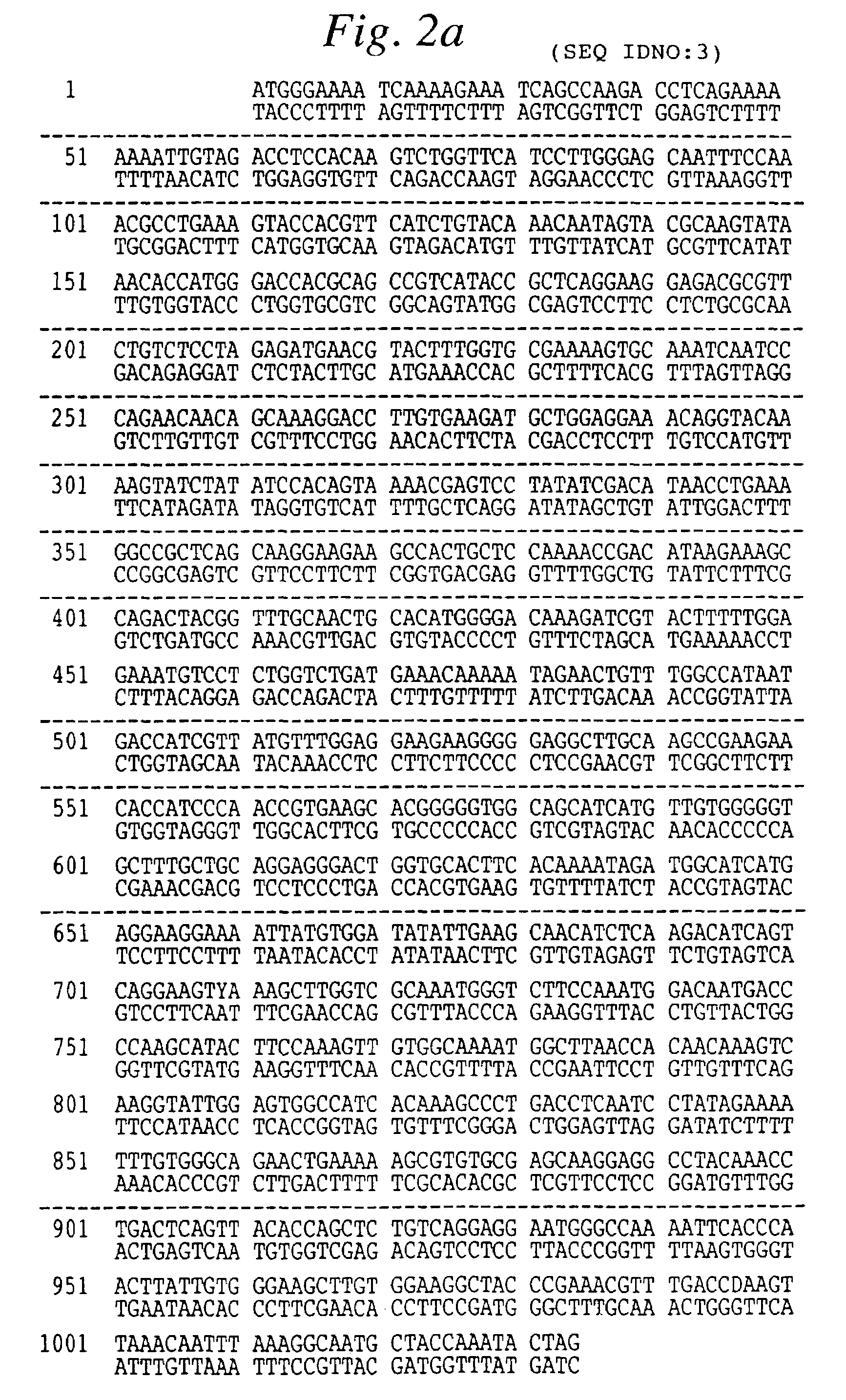
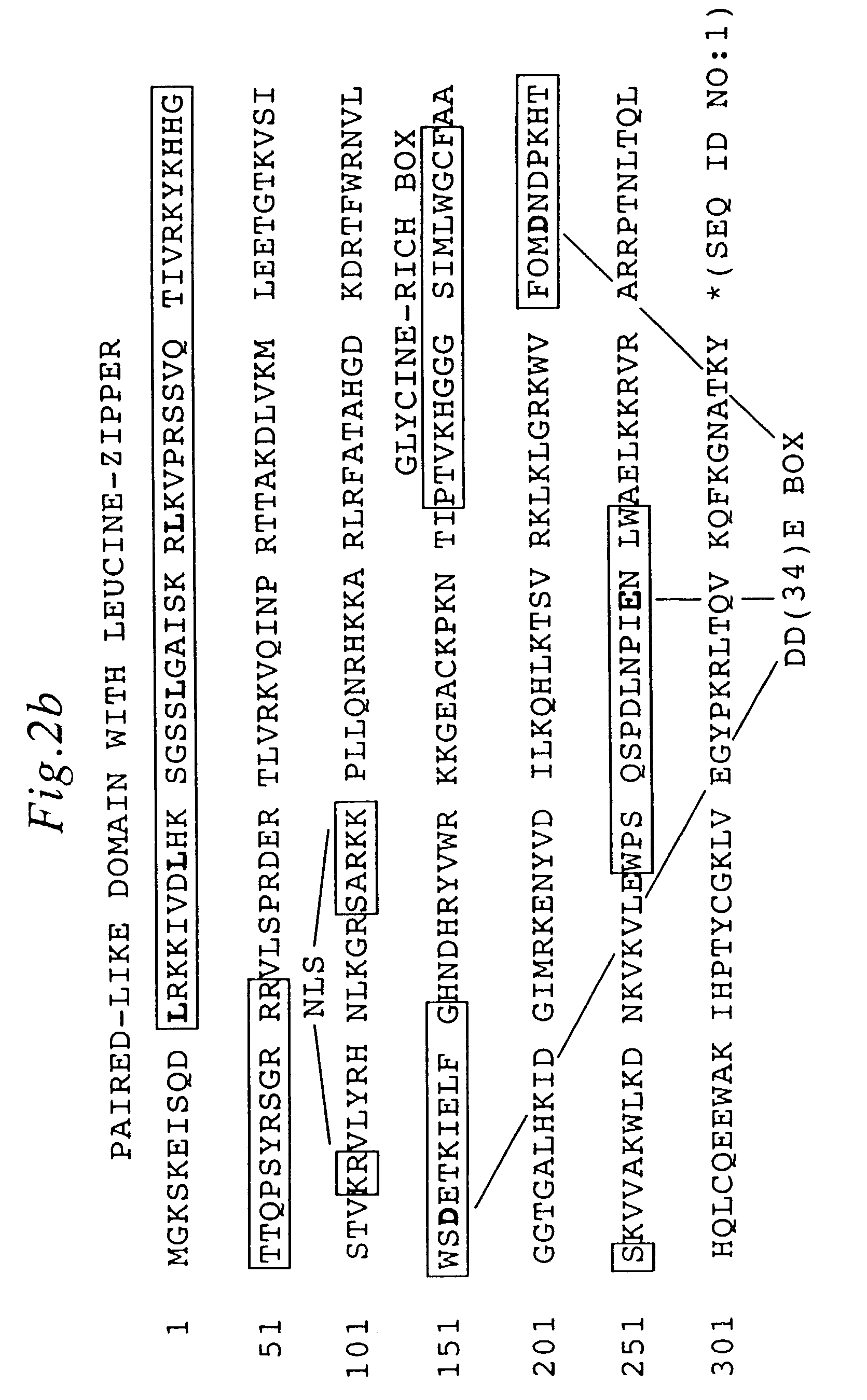
InactiveCN101775403AAvoid damageImprove food safetyBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffPhylum CyanobacteriaCyanophages
The invention provides an overall length cDNA sequence of micro-capsule algae toxins degrading enzyme MlrA, a coded protein and application. The nucleotide sequence of the overall length cDNA sequence of micro-capsule algae toxins degrading enzyme MlrA is shown as SEQ IDNO:1, and the coded amino acid sequence s shown as SEQ ID NO:3. The overall length cDNA sequence of micro-capsule algae toxins degrading enzyme MlrA in the invention has uniqueness and specifity for degradation of algae toxins, and can be used for detecting the situation of micro-capsule algae toxins in water body or fish products. The micro-capsule algae toxins degrading enzyme MlrA can be used as crude enzyme preparation in optimizing aquaculture water to effectively prevent and control damage of algae toxins on eating safety of bred aquatic products, and also can be used as fish bait additive to mitigate damage of micro-capsule algae toxins on fish hepatic cell DNA, maintain detoxication capacity of hepatic cells on algae toxins during blue-green algae bloom outbreak, and greatly improve eating safety of bred fish.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com