Microarray for detecting viable organisms
a microarray and organism technology, applied in biochemistry apparatus and processes, library screening, nucleotide libraries, etc., can solve the problems of laborious and time-consuming methods, rare use of process validation methods based on pcr, etc., and achieve selective detection and enumeration. , the effect of rapid detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Exclusion of Dead Cell DNA from Detection
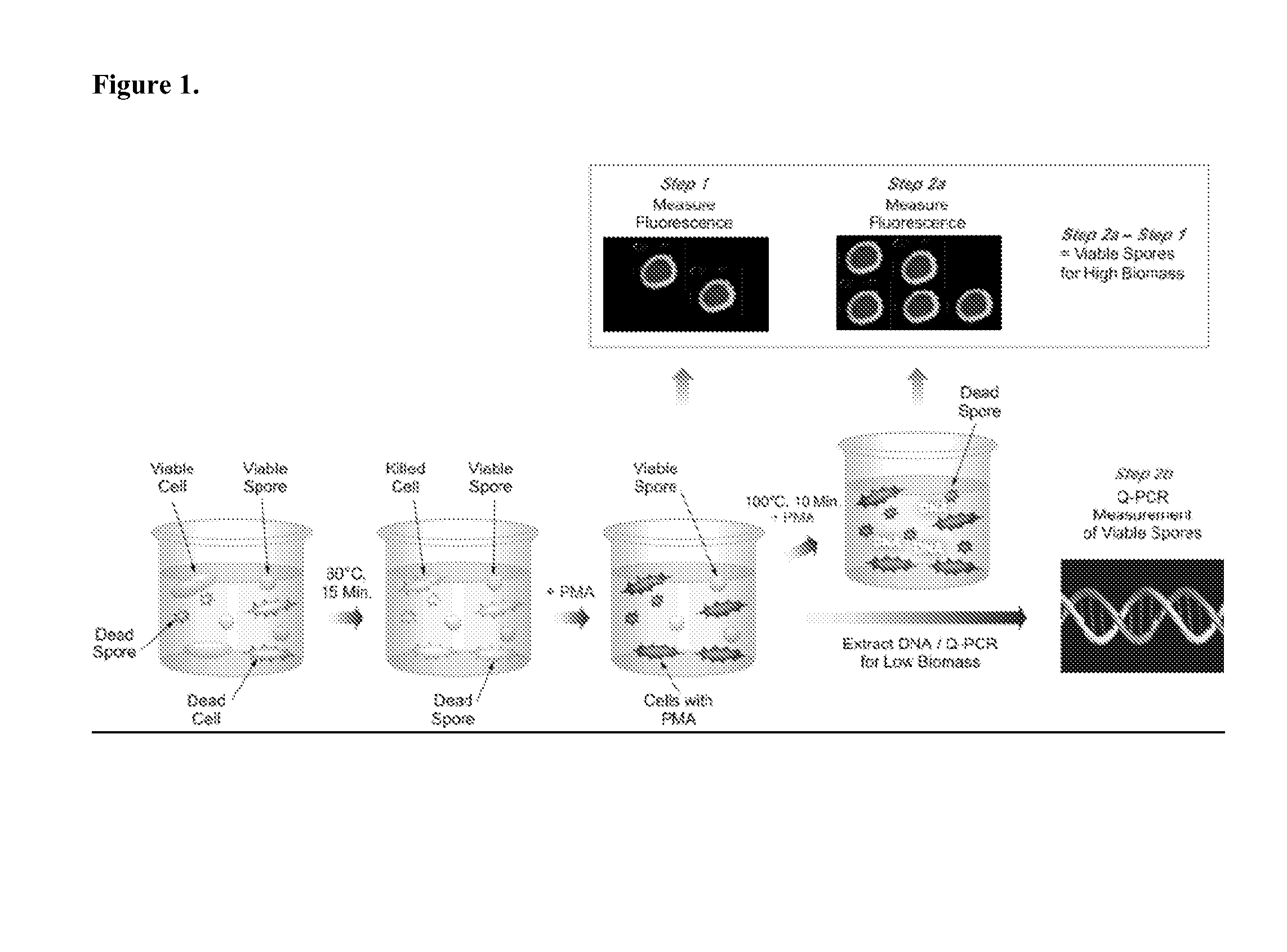
[0171]FIG. 1 illustrates one non-limiting embodiment of the present application. To briefly summarize, a test sample suspected of containing a mixture of vegetative cells, live, and dead bacterial endospores is first heat shocked at 80° C. for 15 minutes (Step 1). This step will eliminate any vegetative cells present in the sample, whereas spores will remain unaffected. The sample is then treated with PMA followed by incubation in the dark. Thereafter, the sample is exposed to visible light for 5 minutes, so that the DNA from dead cells only will be cross-linked. In general, excess PMA is removed from a sample after the treatment step and prior to or as part of subsequent nucleic acid extractions steps, such as by centrifugation and washing. Following the initial PMA treatment, the sample is concentrated by centrifugation and the fluorescence of the resulting reaction mixture, which contains dead cells and spores, is measured. The sample is t...
example 2
PMA Method
[0175]An objective was to evaluate a rapid and sensitive spore detection concept that will estimate viable microbial spores.
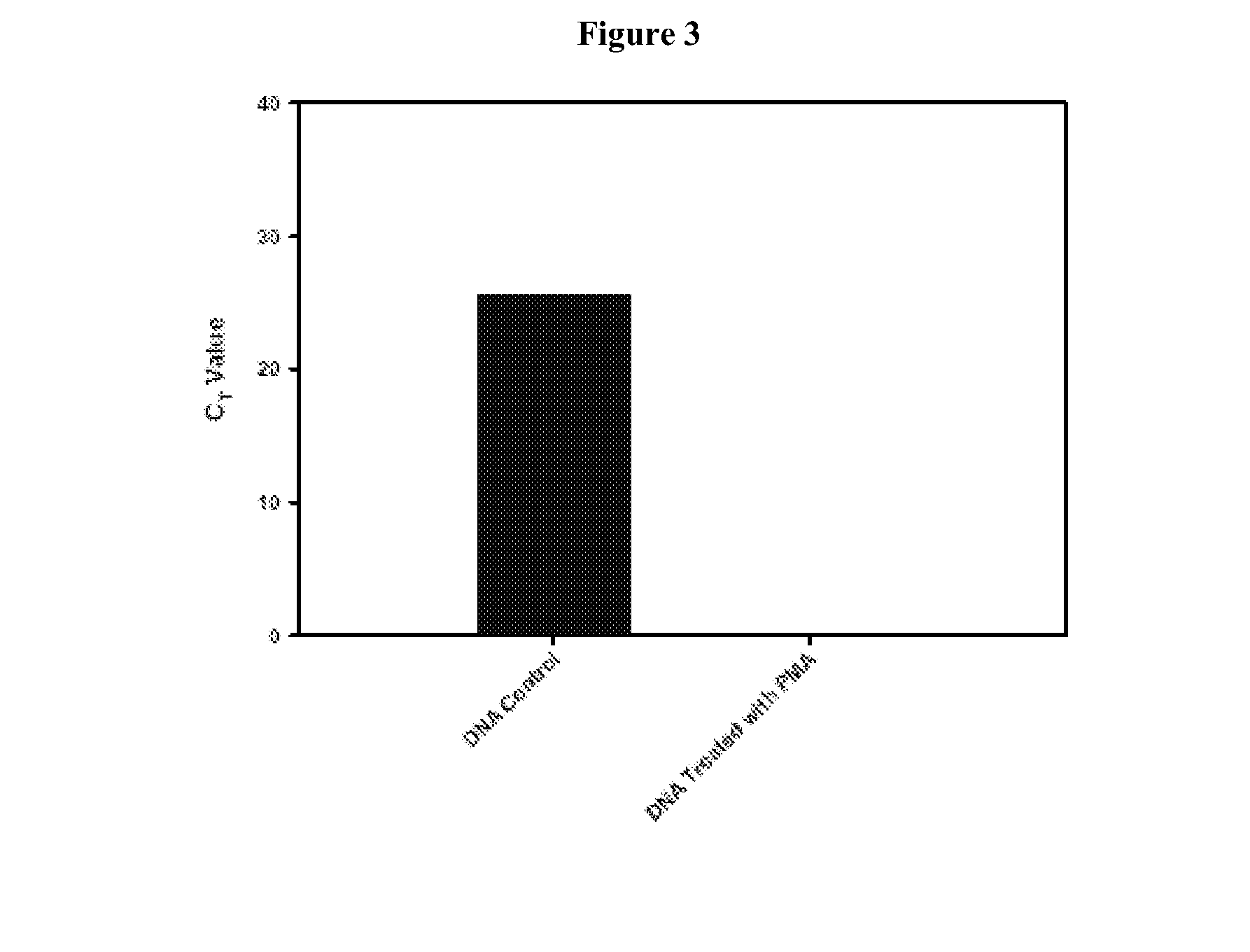
[0176]Real-time quantitative-PCR methods can be used to estimate microbial populations. This unique method is based on the use of a fluorescent DNA intercalating agent propidium monoazide (PMA), which can only penetrate the membranes of dead cells. The combination approach described in this example is referred to as the “PMA-method.” The present example describes the development of a reliable and efficient method for extracting DNA from spores. The spore structure is complex and made up of several layers that impart resistance to extreme environmental conditions. These several layers which include the cortex and coat structures together are probably responsible for difficulties in releasing DNA from spores. Using a urea-based extraction buffer, it was possible to degrade the outer spore coats. With the spore coats removed the spores were more suscepti...
example 3
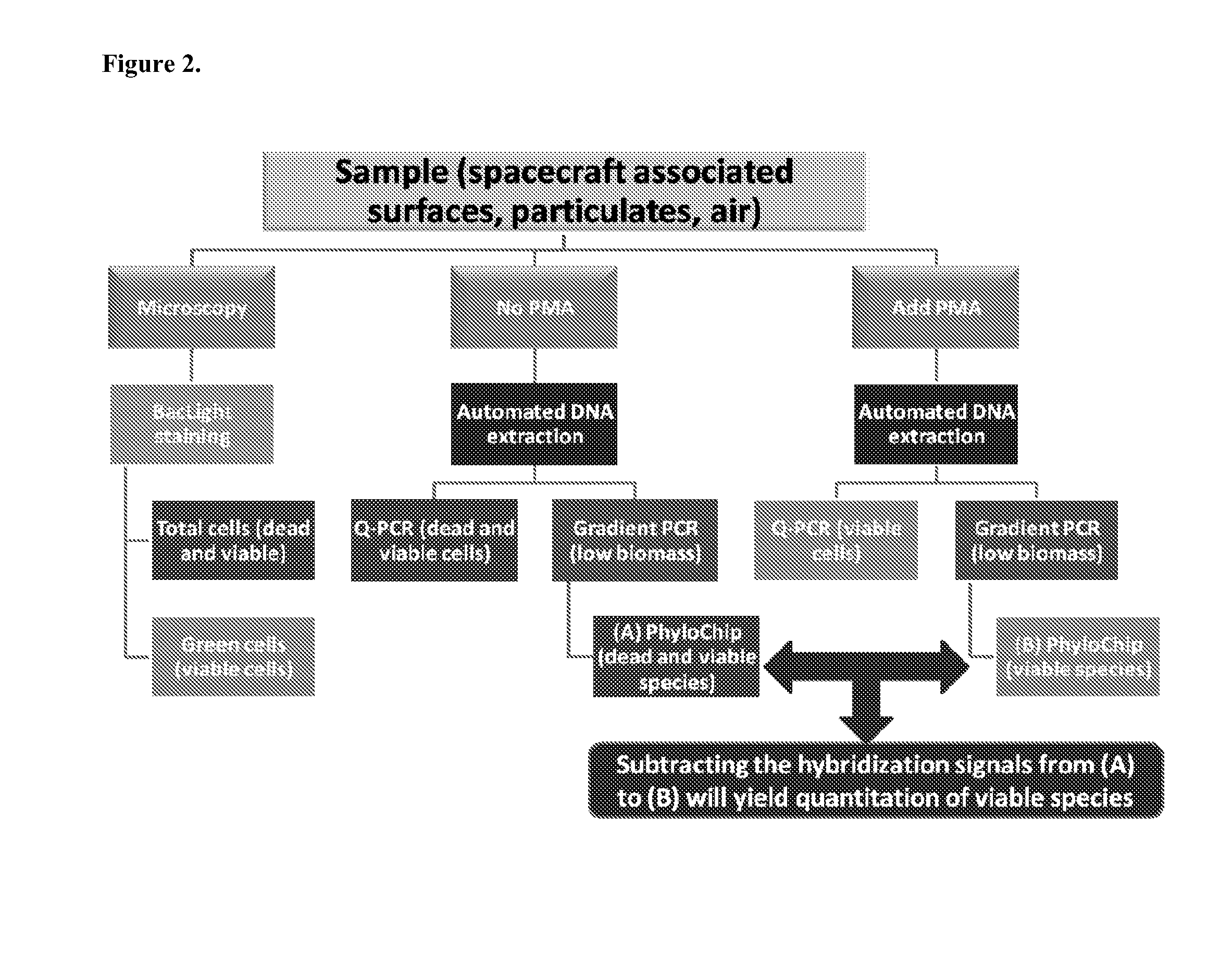
Evaluation of PMA-Treated Sample by Phylogenetic Array
[0182]A phylogenetic array is fabricated with some of the organism-specific and OTU-specific 16s rRNA probes selected by the methods described herein and in co-pending international application PCT / US2010 / 040106. The phylogenetic array in this example consists of 1,016,064 probe features, arranged as a grid of 1,008 rows and columns. Of these features, −90% are oligonucleotide perfect match (PM) or mis-match (MM) probes with exact or inexact complementarity, respectively, to 16s rRNA genes. In general, MM probes have one or more sequence differences with respect to PM probes, resulting in one or more mismatches with a target sequence. Each PM probe is paired with a mismatch control probe to distinguish target-specific hybridization from background and non-target cross-hybridization. The remaining probes are used for image orientation, normalization controls, or for pathogen-specific signature amplicon detection using additional t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| heat resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| threshold | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com