Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
169 results about "Artificial fever" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
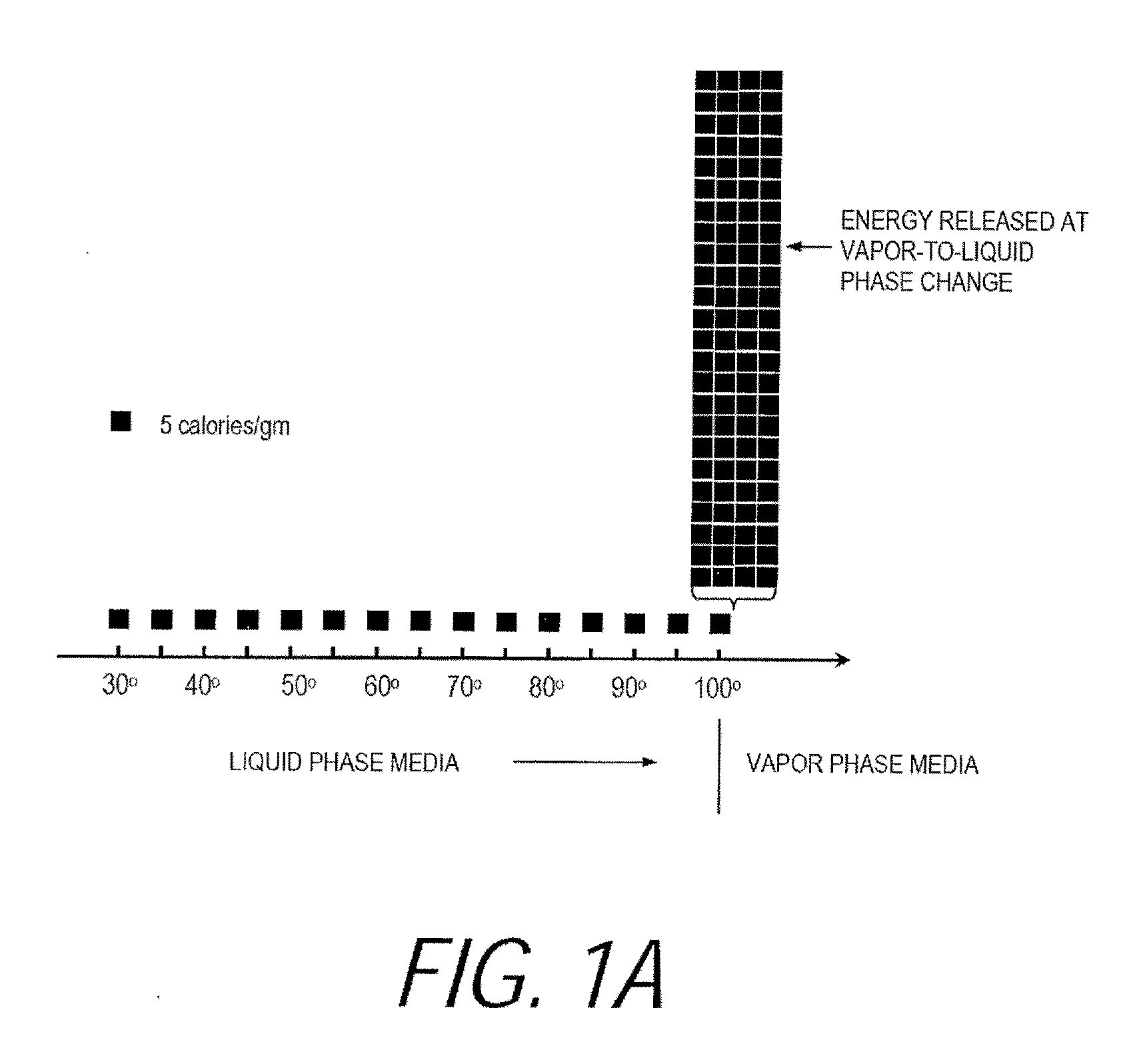
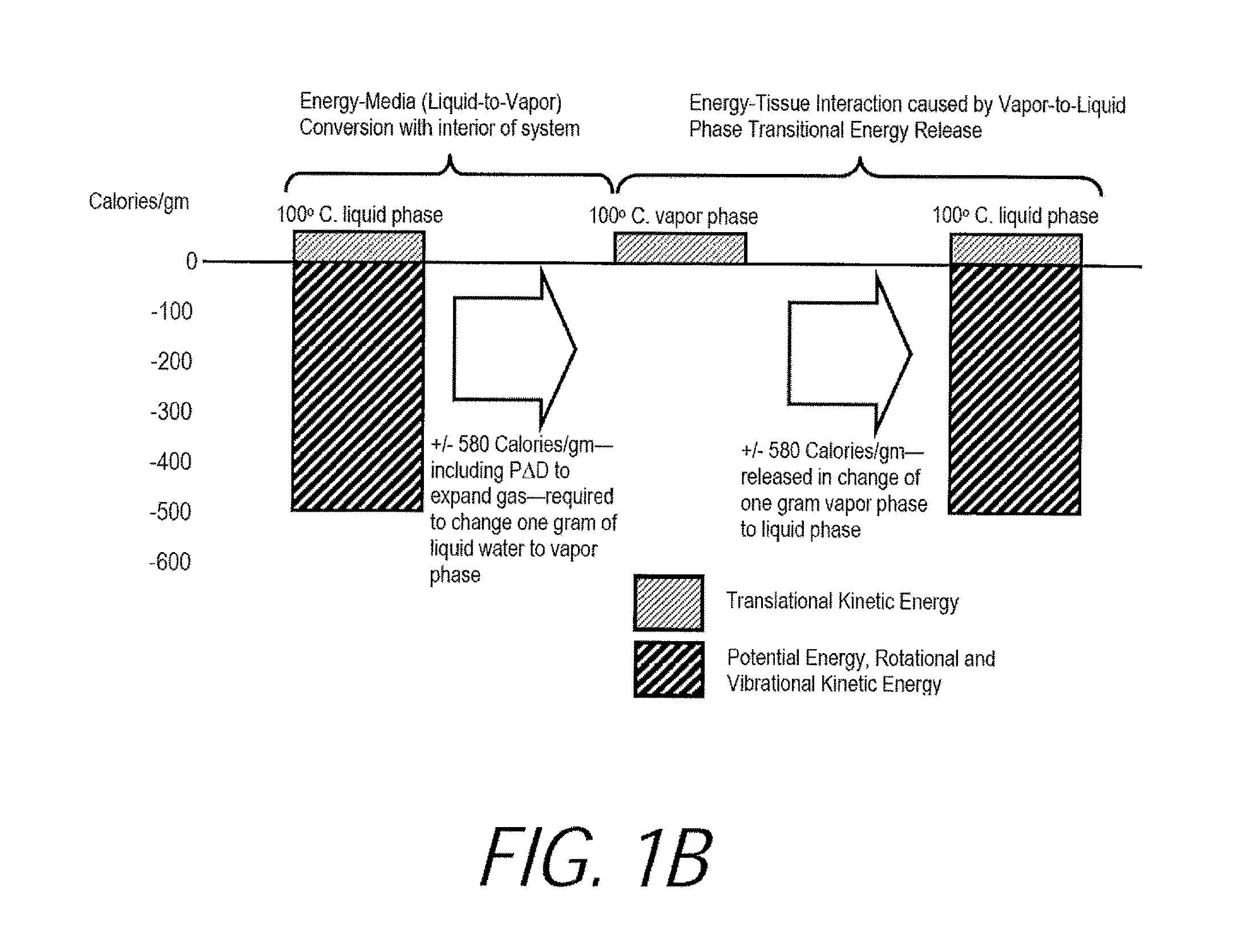
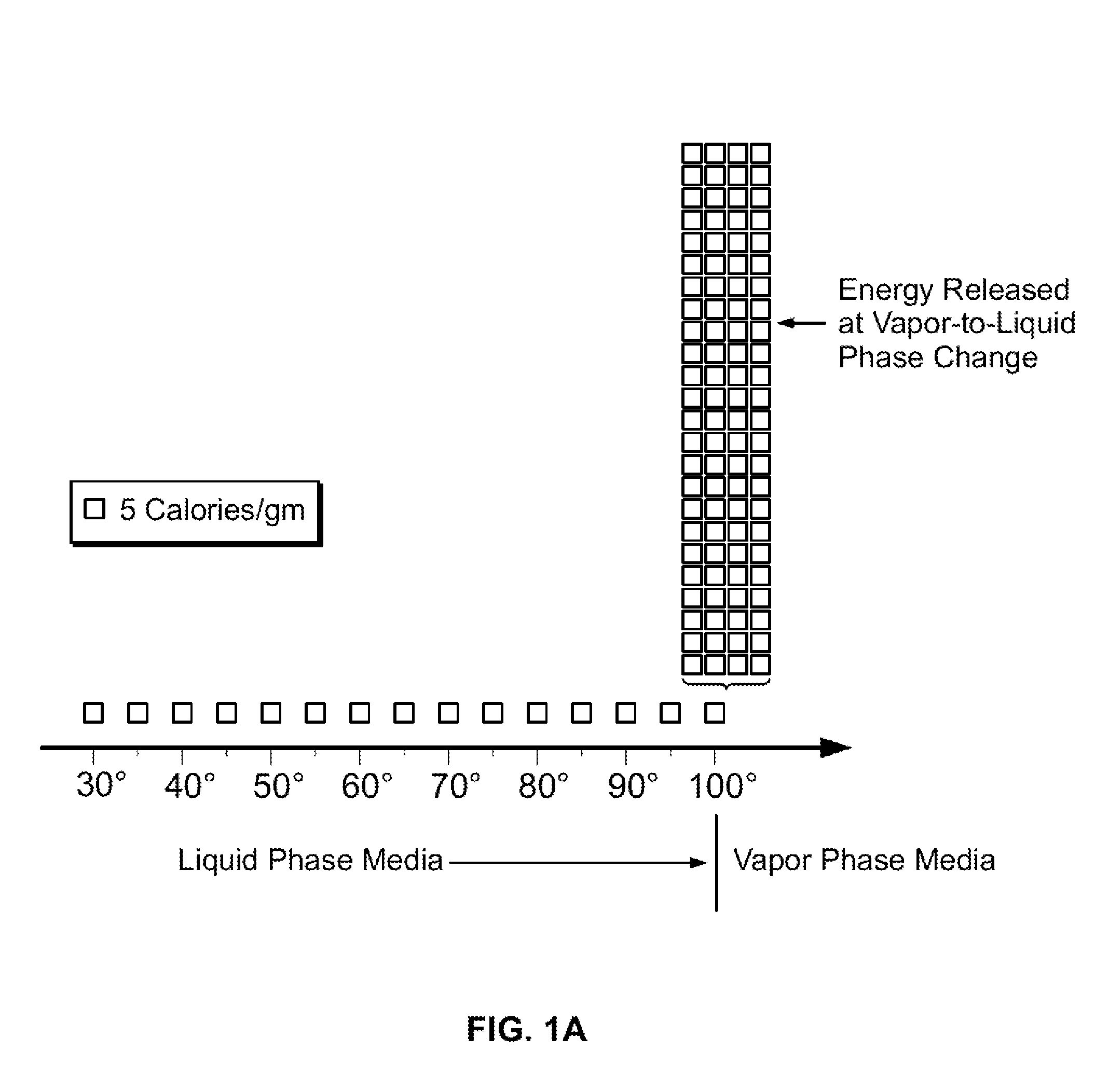
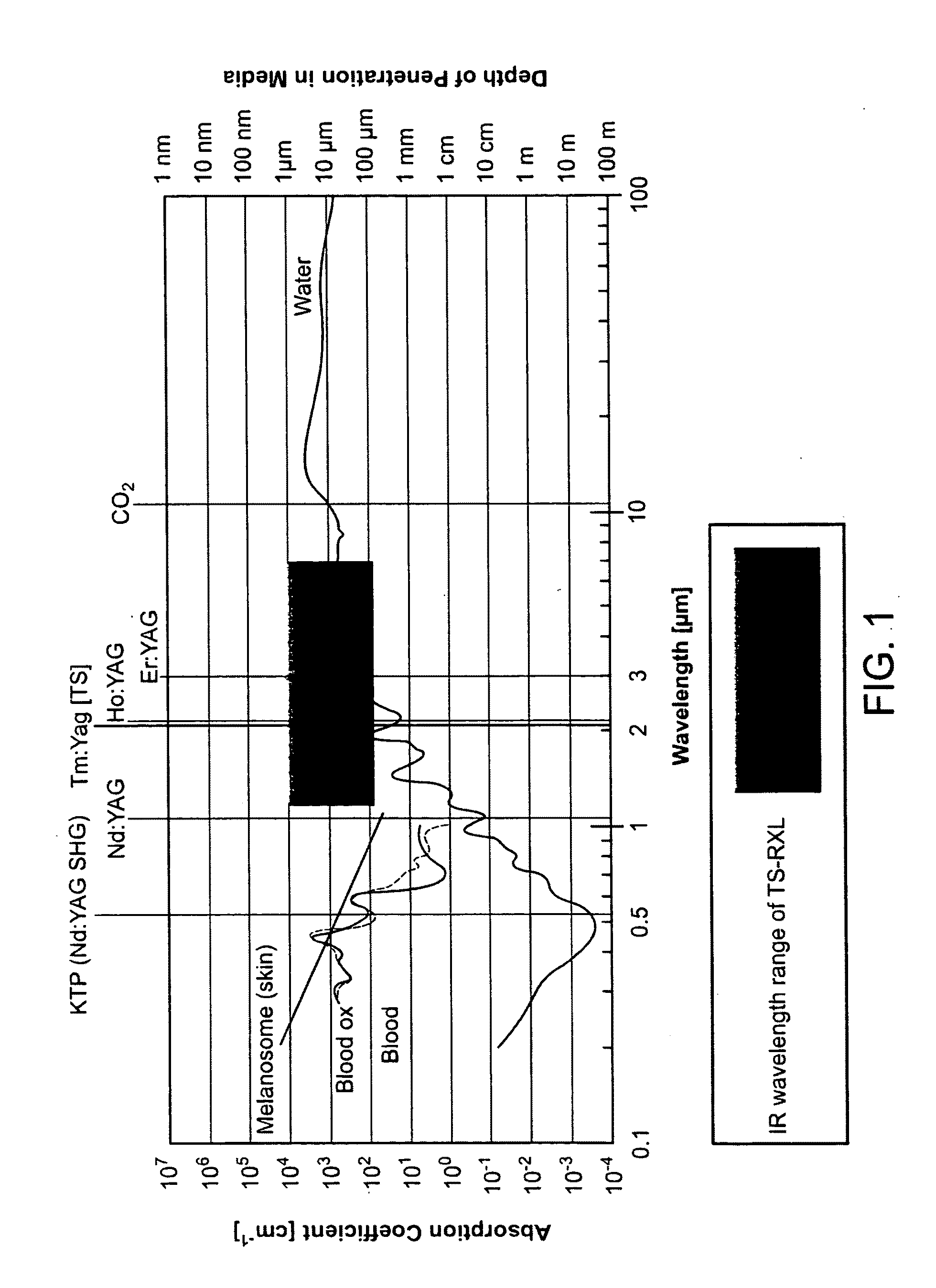
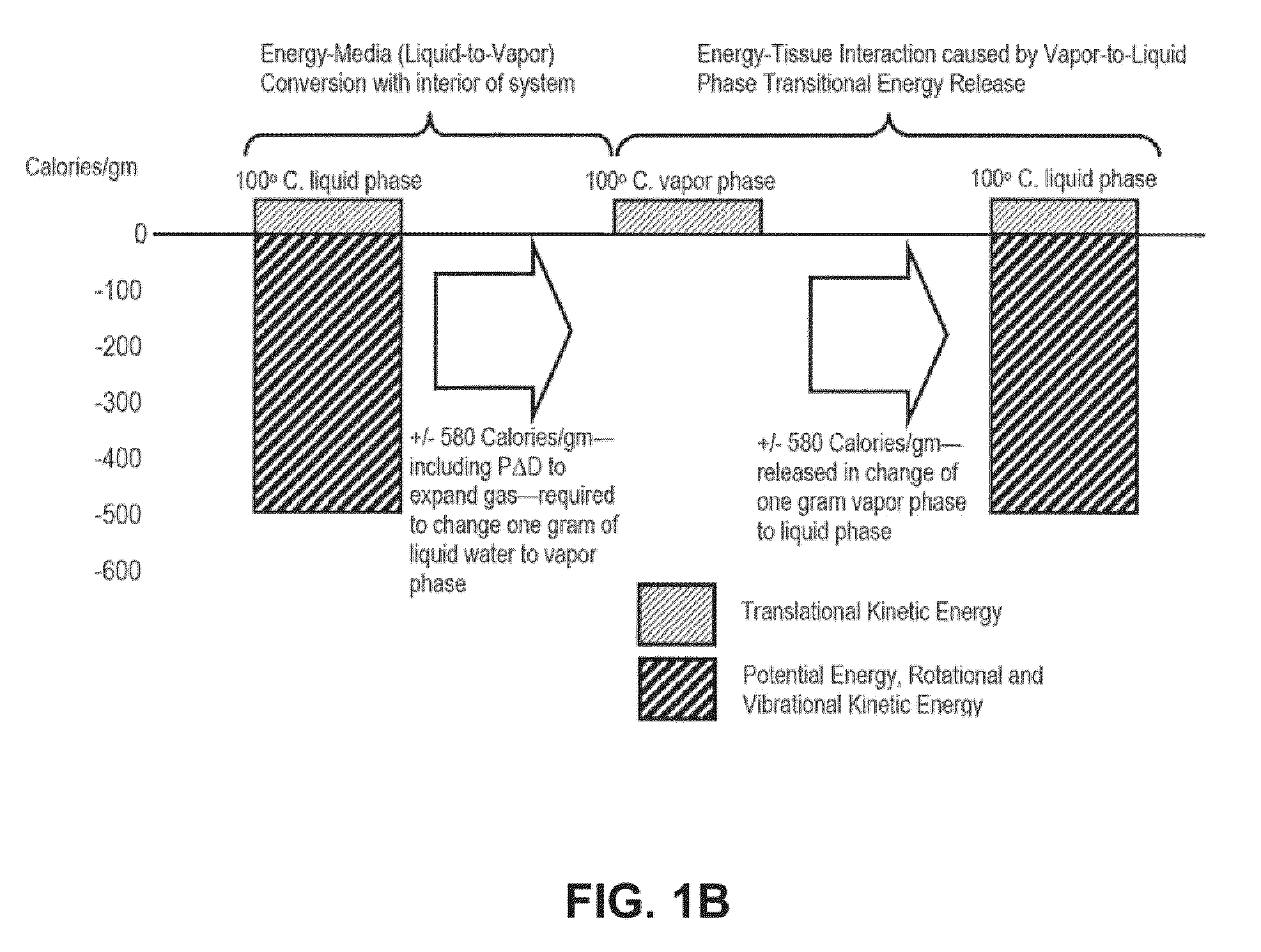
Pyrotherapy (artificial fever) is a method of treatment by raising the body temperature or sustaining an elevated body temperature (caused by a fever). In general, the body temperature was maintained at 41°C (105°F). Many diseases were treated by this method in the first half of the 20th century. In general, it was done by exposing the patient to hot baths, warm air, or (electric) blankets.
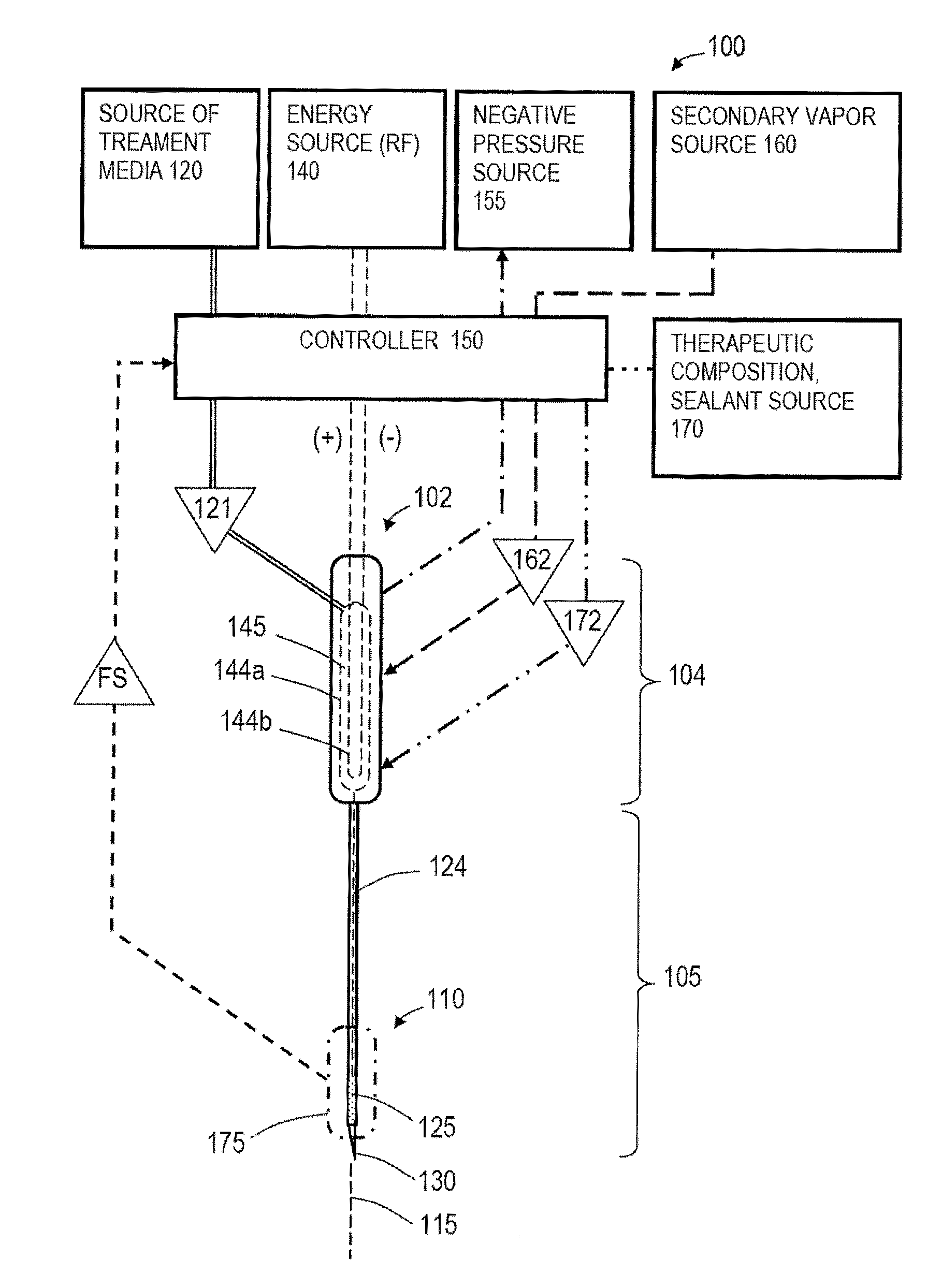
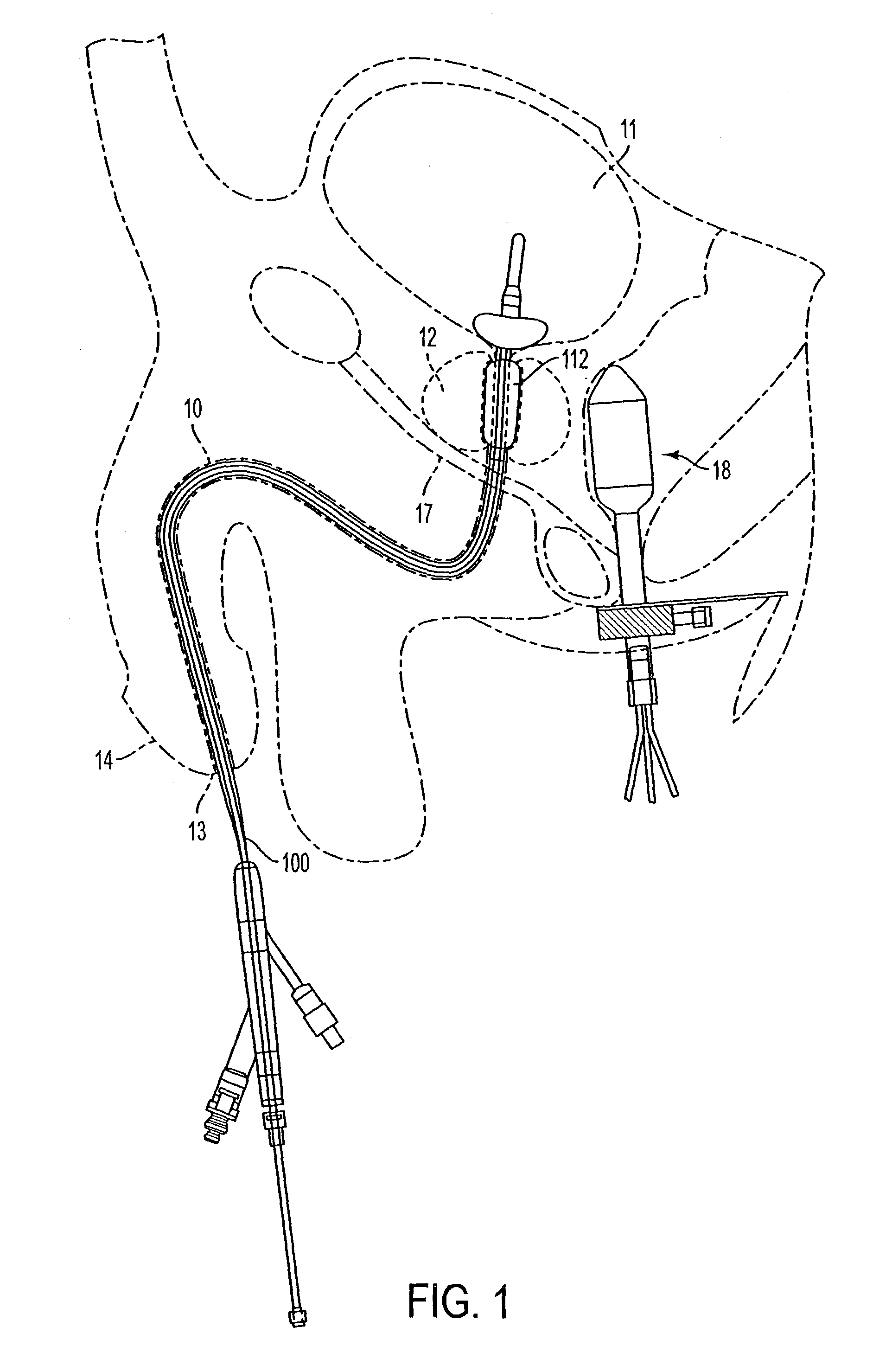
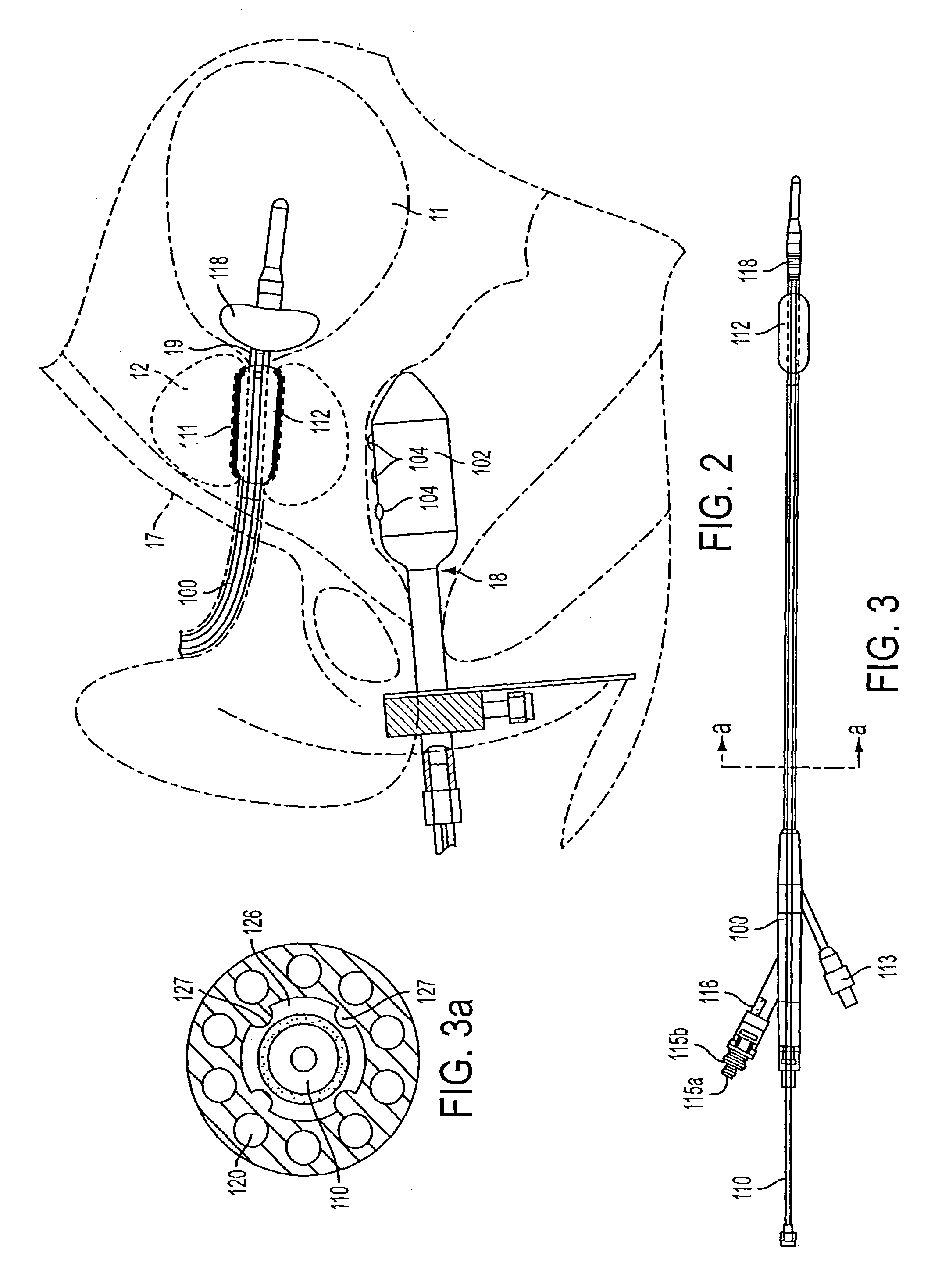
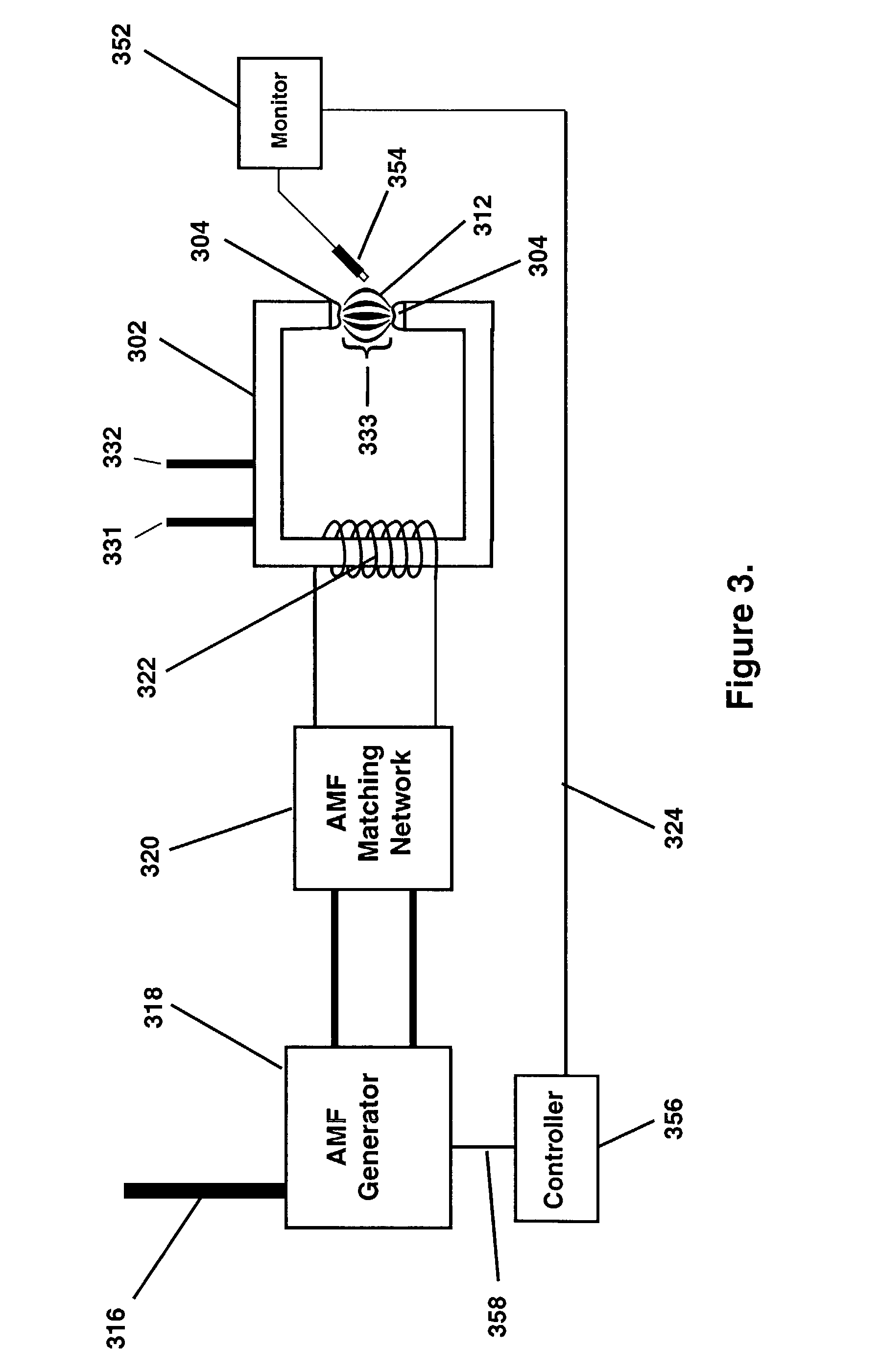
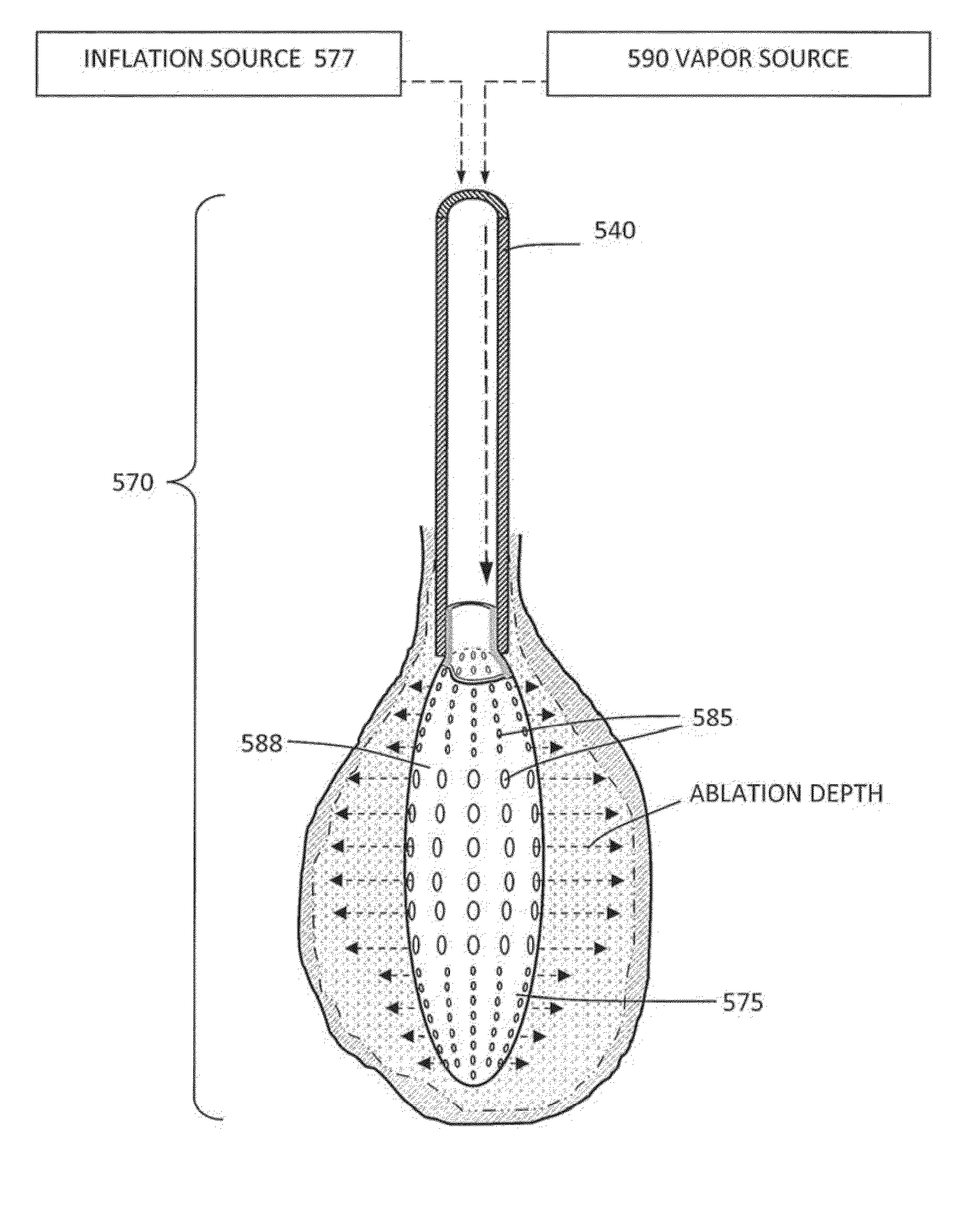
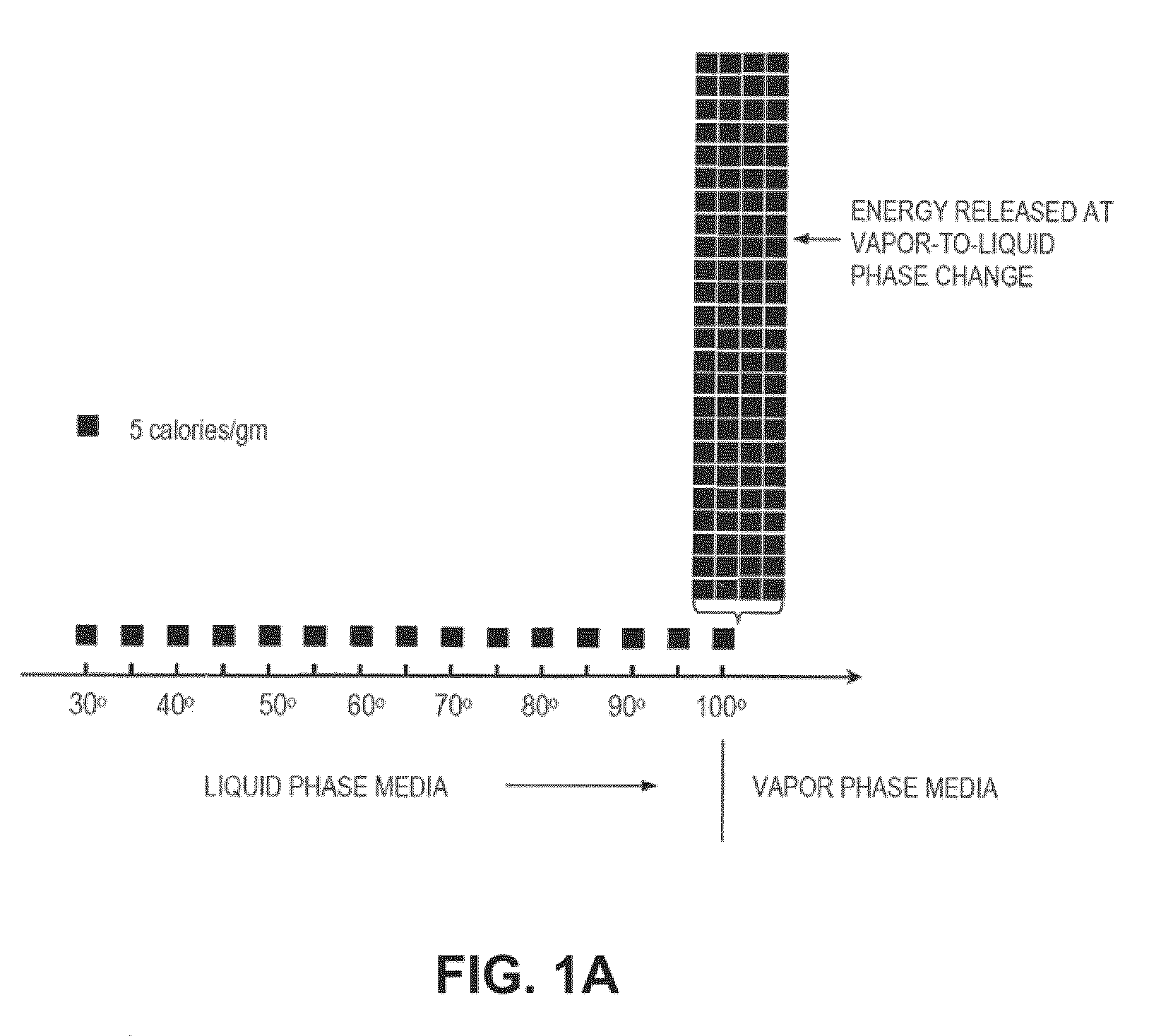
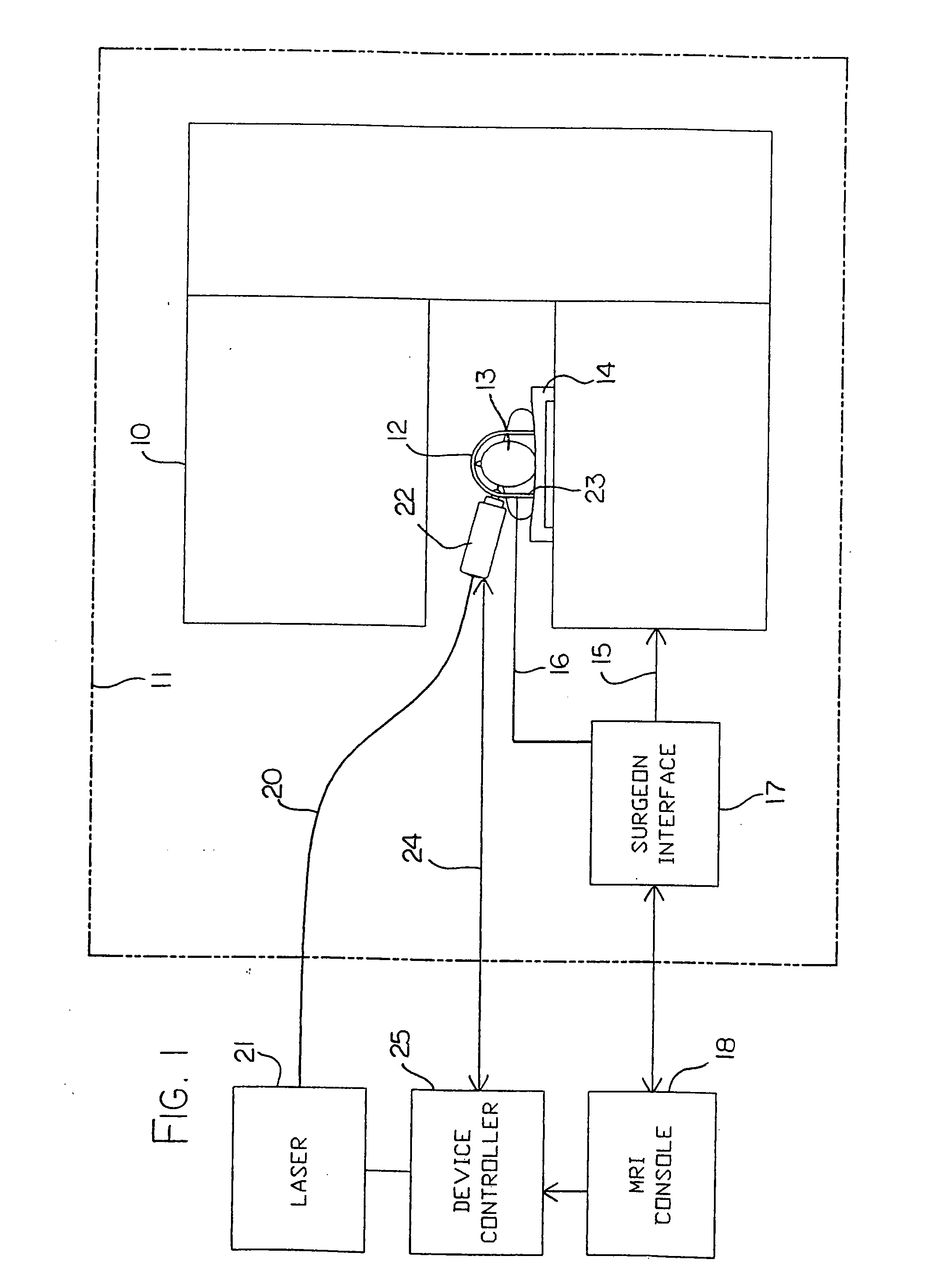
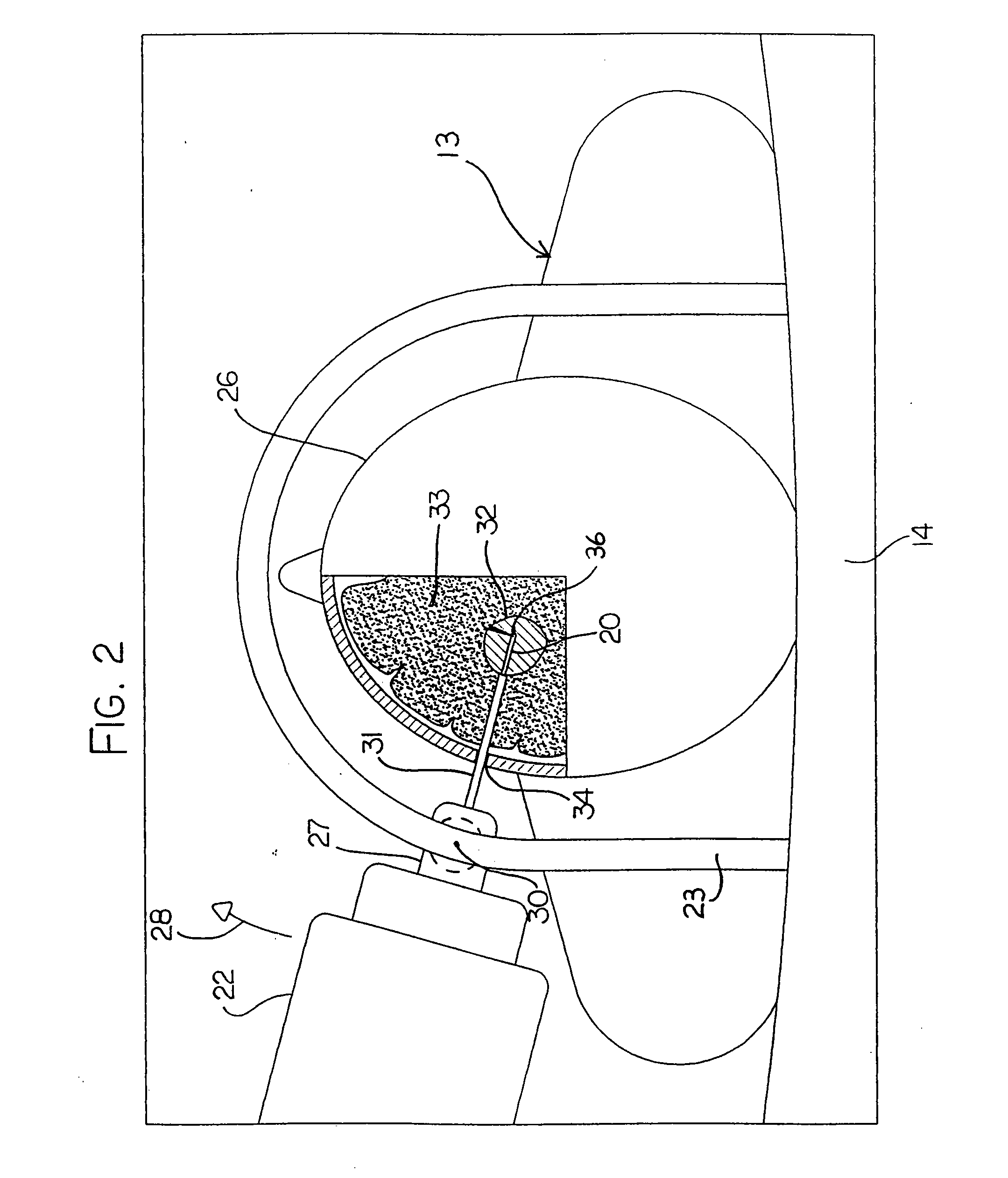
Medical system and method of use
InactiveUS20110077628A1Simple methodWithout the potential of carbonizing tissueSurgical instruments for heatingTherapeutic coolingThermal energyGas phase
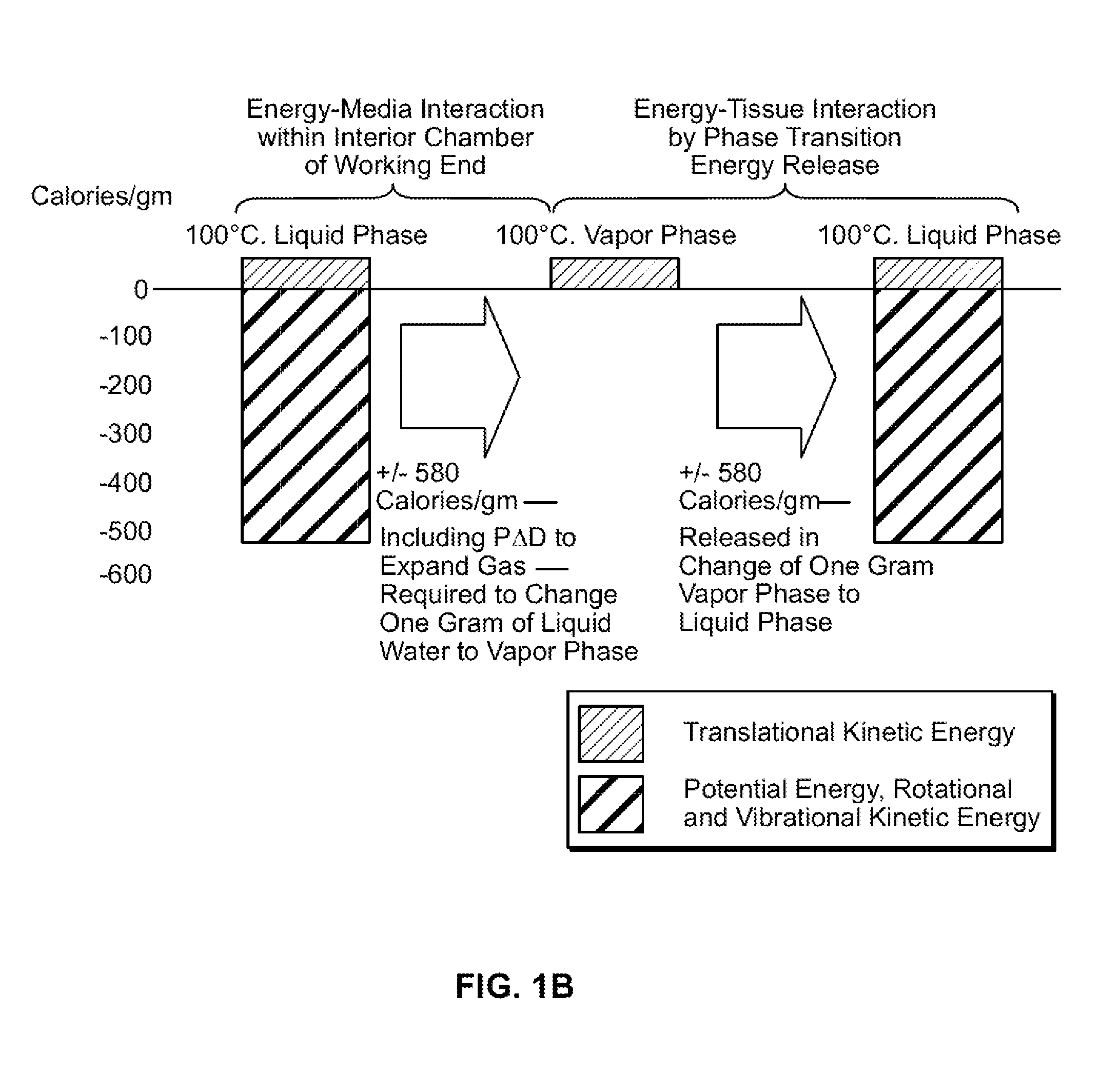
An instrument and method for tissue thermotherapy including an inductive heating means to generate a vapor phase media that is used for interstitial, intraluminal, intracavity or topical tissue treatment. In one method, the vapor phase media is propagated from a probe outlet to provide a controlled vapor-to-liquid phase change in an interface with tissue to thereby apply ablative thermal energy delivery.
Owner:TSUNAMI MEDTECH
Apparatus for treatment of tissue adjacent a bodily conduit with a gene or drug-coated compression balloon
InactiveUS7837720B2Improve the heating effectEasy and less-expensive to manufactureStentsElectrotherapyGeneCatheter device
An apparatus for treatment of tissue within a body requiring thermotherapy includes a catheter to be inserted into a bodily conduit, an energy-emitting source disposed within the catheter, a compression balloon surrounding the energy-emitting source where the compression balloon has an inflated diameter that is greater than that of the bodily conduit in a relaxed state and an outside surface of the balloon is coated with one of gene modifiers and drug or medication, and means for activating the energy-emitting source to radiate energy to heat the drug-coated compression balloon and tissue to be treated whereby the heated drug-coated compression balloon effectively delivers the one of the gene modifiers and drug or medication to a target area of the diseased tissue. In addition, methods for using the above apparatus to treat diseased tissue are disclosed.
Owner:MEDIFOCUS
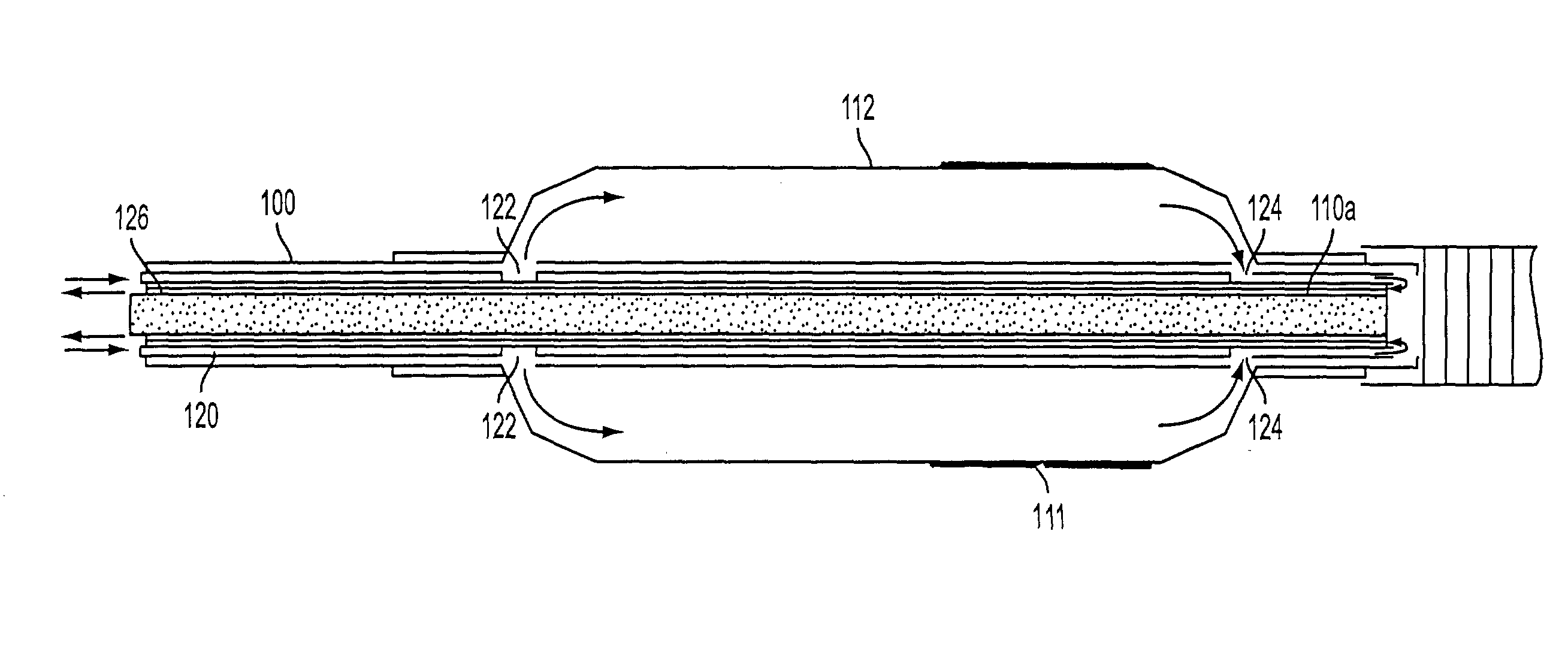
Thermotherapy device
InactiveUS7549987B2Prevent drynessControlled lateral marginsSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments using microwavesThermal energyNeurosurgery
This invention relates to the working end of a medical instrument that applies energy to tissue. In one embodiment, the instrument has a microfluidic tissue-engaging surface fabricated by soft lithography means together with optional superlattice cooling means that allows for very precise control of energy application, for example in neurosurgery applications. The tissue-engaging surface can eject a high-heat content vapor into the engaged tissue for treating tissue, while the superlattice cooling structure can prevent collateral thermal damage. Also, the superlattice cooling structure can be used to localize heat at a selected depth in tissue and prevent surface ablation. Also, the superlattice cooling structure can be used to prevent tissue sticking to a thermal energy delivery surface. In another embodiment, the tissue-engaging surface can be used in a jaw structure for sealing tissue together with hydrojet means for transecting the tissue.
Owner:TSUNAMI MEDTECH
Localized non-invasive biological modulation system
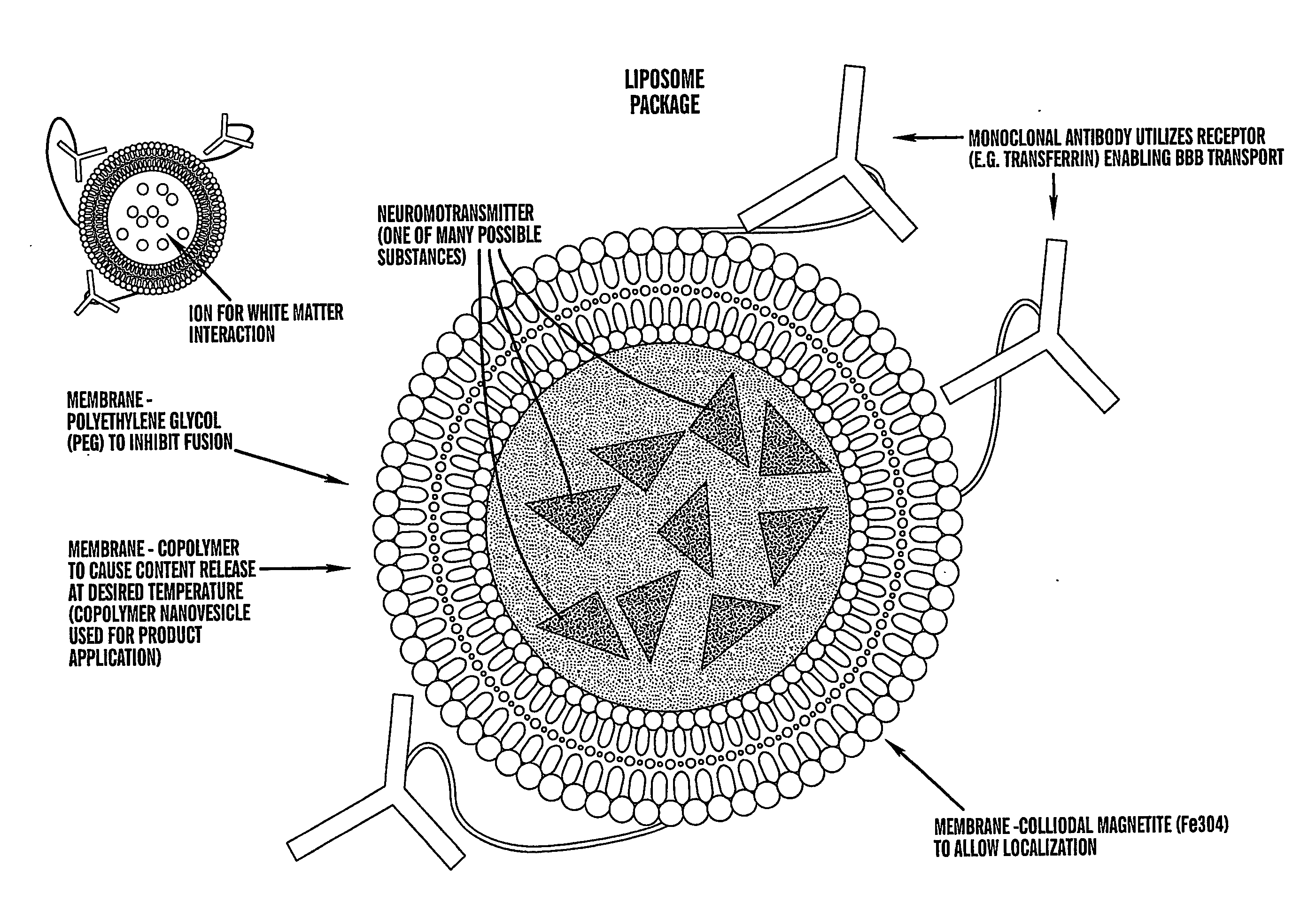
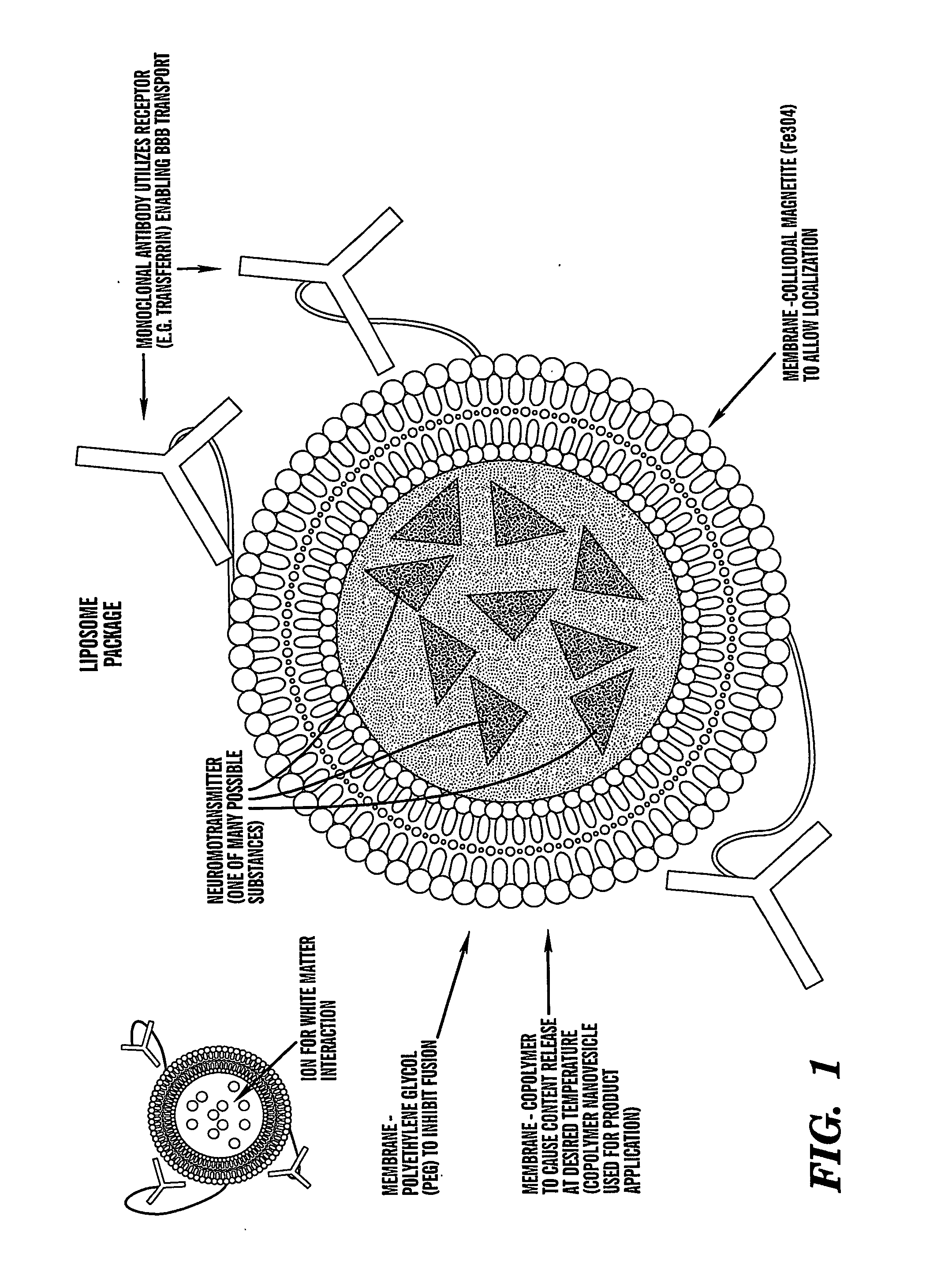
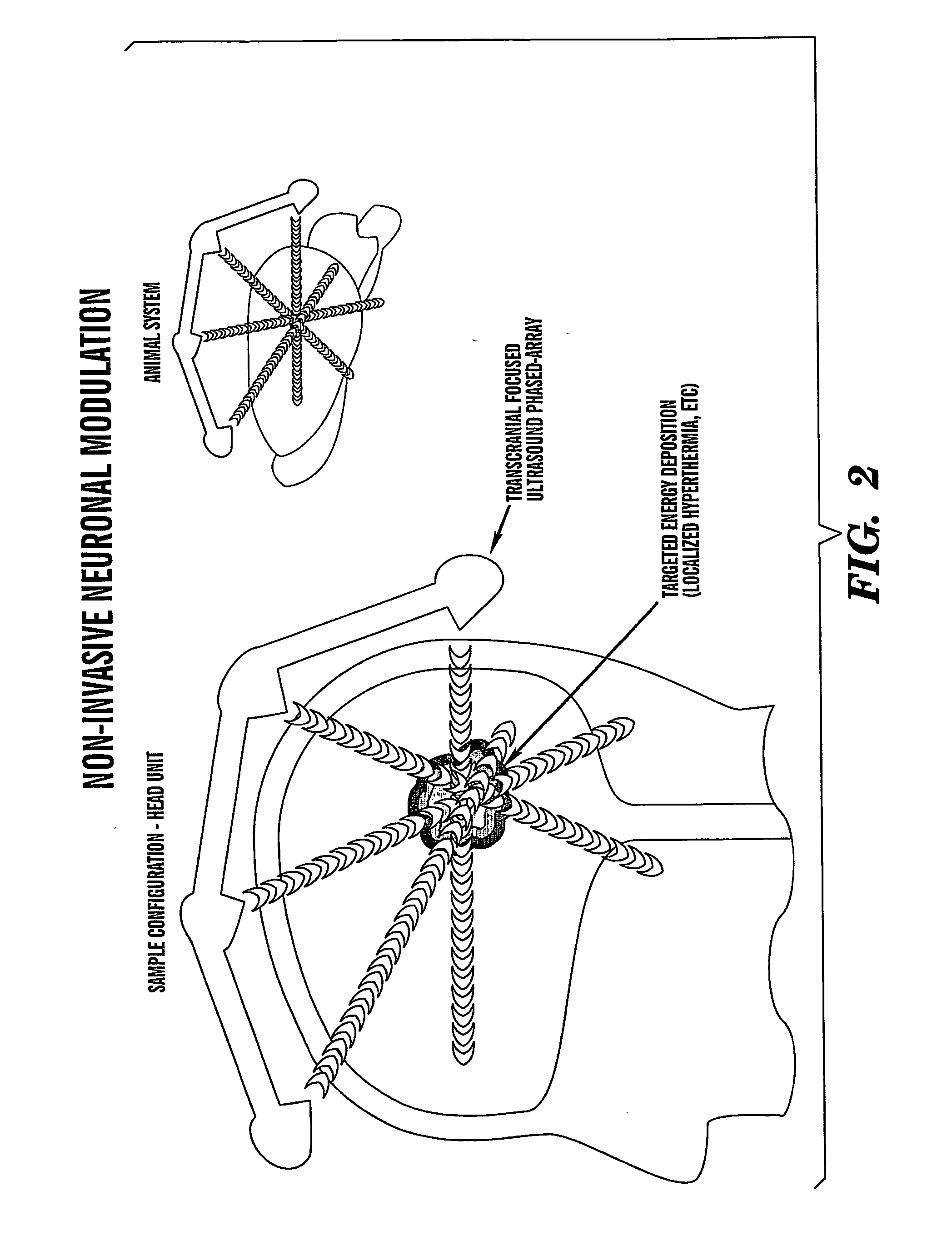
The present invention provides methods for non-invasive localized delivery of biologically active molecules, comprising packaging a molecule(s) of interest inside a thermosensitive particle, administering said particles to a subject, and inducing localized release of said molecules from said particles using a focused heat source. The thermosensitive particles may be thermosensitive polymer nanoparticles or thermosensitive liposomes. The particles may be delivered to a subject by any technique, including infusion. The molecules may be released from the particles using any method which induces localized hyperthermia, including focused ultrasound.
Owner:SAOIRSE CORP
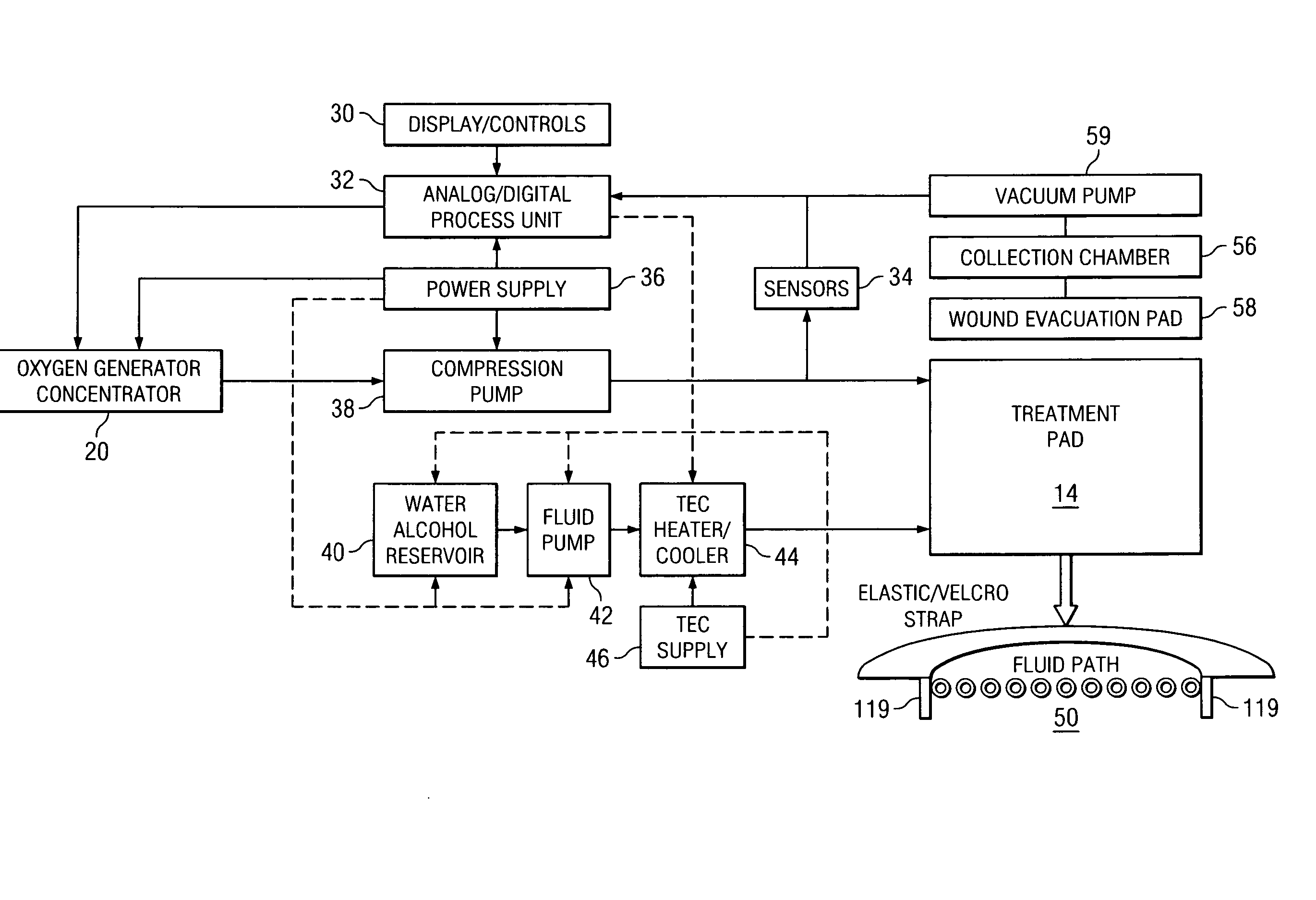
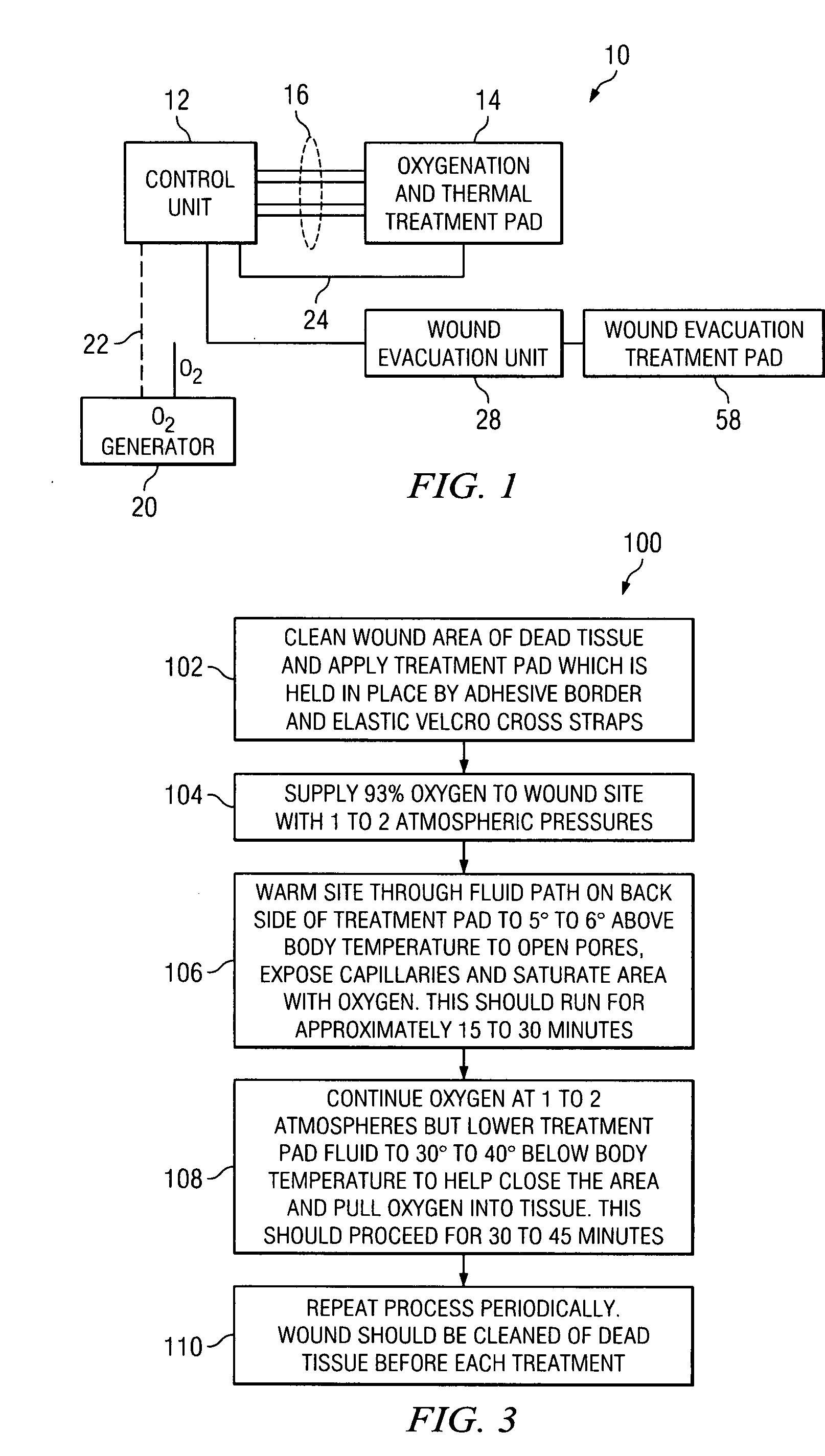
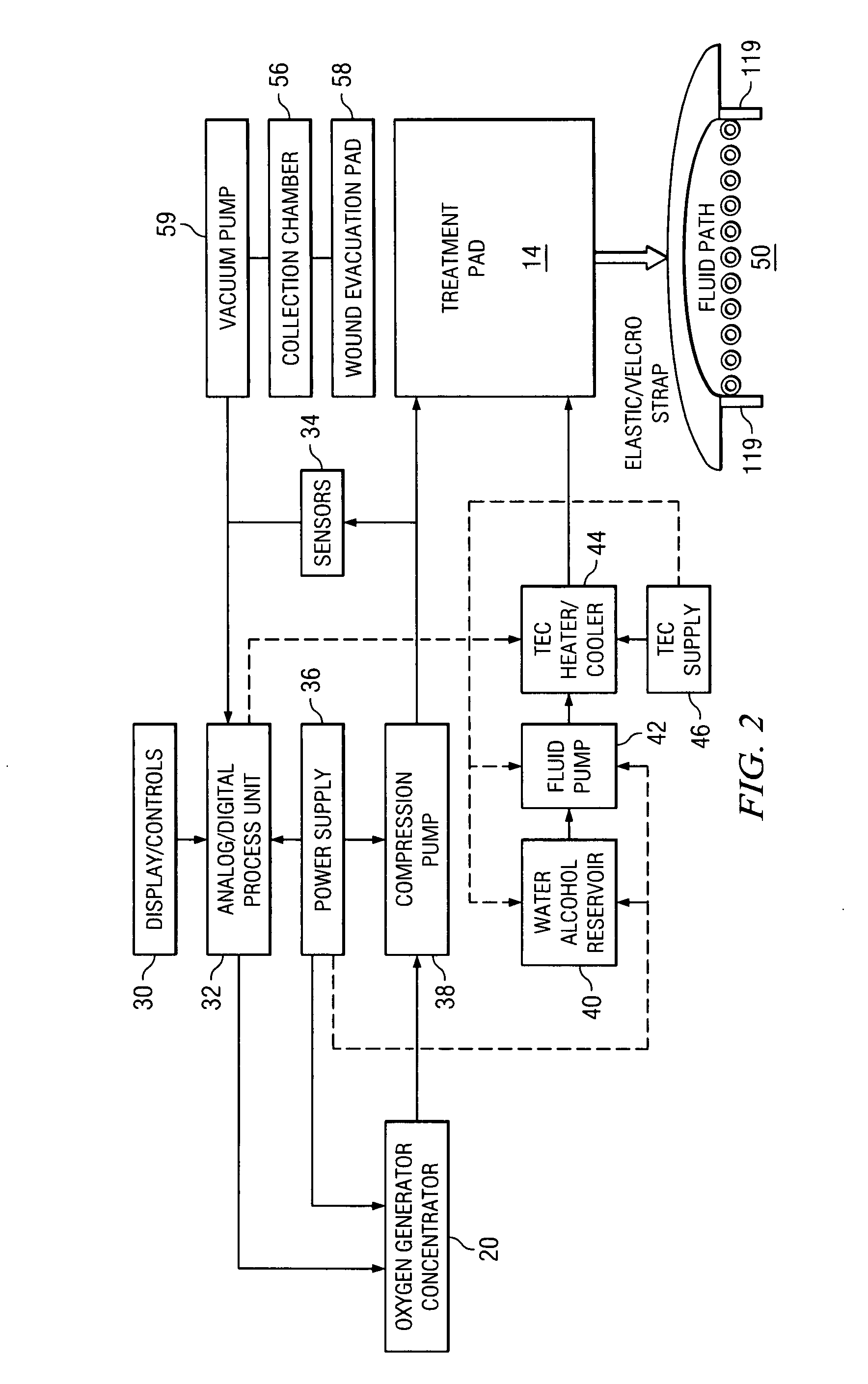
Method of and system for thermally augmented wound care oxygenation
ActiveUS20070282249A1Skin stimulationEasy to receiveMedical devicesMedical applicatorsWound careSubject matter
An oxygenation and temperature thermal therapy and oxygenation treatment pad with a plurality of air chambers is disclosed for treatment of skin wound tissues. The air chambers are filled and released by a valve assembly that may be separate from or integrated within the blanket. The thermal therapy and oxygenation treatment pad includes a fluid bladder for delivering hot and / or cold therapy to a patient in conjunction with oxygenation. The temperature therapy blanket may also include an air bladder for providing compression. Oxygenation is provided subsequent to initial heating in order to promote oxygen absorption by the wound tissues prior to the cooling thereof which facilitates pulling oxygen into the wound tissues. This Abstract is provided to comply with rules requiring an Abstract that allows a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain subject matter of the technical disclosure. This Abstract is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. 37 CFR 1.72(b).
Owner:THERMOTEK
Microwave array applicator for hyperthermia
InactiveUS20100036369A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease surface areaMicrowave therapySurgical instruments for heatingEngineeringElectromagnetic field
Apparatus (10) for treating skin tissue with microwave radiation (e.g. having a frequency of 1 GHz to 300 GHz) is disclosed in which an array of radiating elements (18), e.g. patch antennas are arranged on a flexible treating surface (16) for locating over and conforming with a region of skin tissue (24) to be treated. The radiating elements (18) receive microwave energy from a feed structure and are configured to emit outwardly a electromagnetic field which permits the region of skin to a substantially uniform penetration depth. Each radiating element (18) may have an independently controllable power supply to permit relative adjustment of the field across the treatment surface. Each radiating element may have a monitoring unit to allow adjust based on detected reflected power. Each independently controllable power supply may include a dynamic impedance matching unit.
Owner:UNIV OF WALES BANGOR
Thermotherapy via targeted delivery of nanoscale magnetic particles
Disclosed are therapeutic methods for the treatment of disease material involving administration of a thermotherapeutic magnetic composition, which contains single-domain magnetic particles attached to a target-specific ligand, to a patient and application of an alternating magnetic field to inductively heat the thermotherapeutic magnetic composition. Also disclosed are methods of administering the thermotherapeutic magnetic material composition. The thermotherapeutic methods may be used where the predetermined target is associated with diseases, such as cancer, diseases of the immune system, and pathogen-borne diseases, and undesirable targets, such as toxins, reactions associated with organ transplants, hormone-related diseases, and non-cancerous diseased cells or tissue.
Owner:ASPEN MEDISYS +1
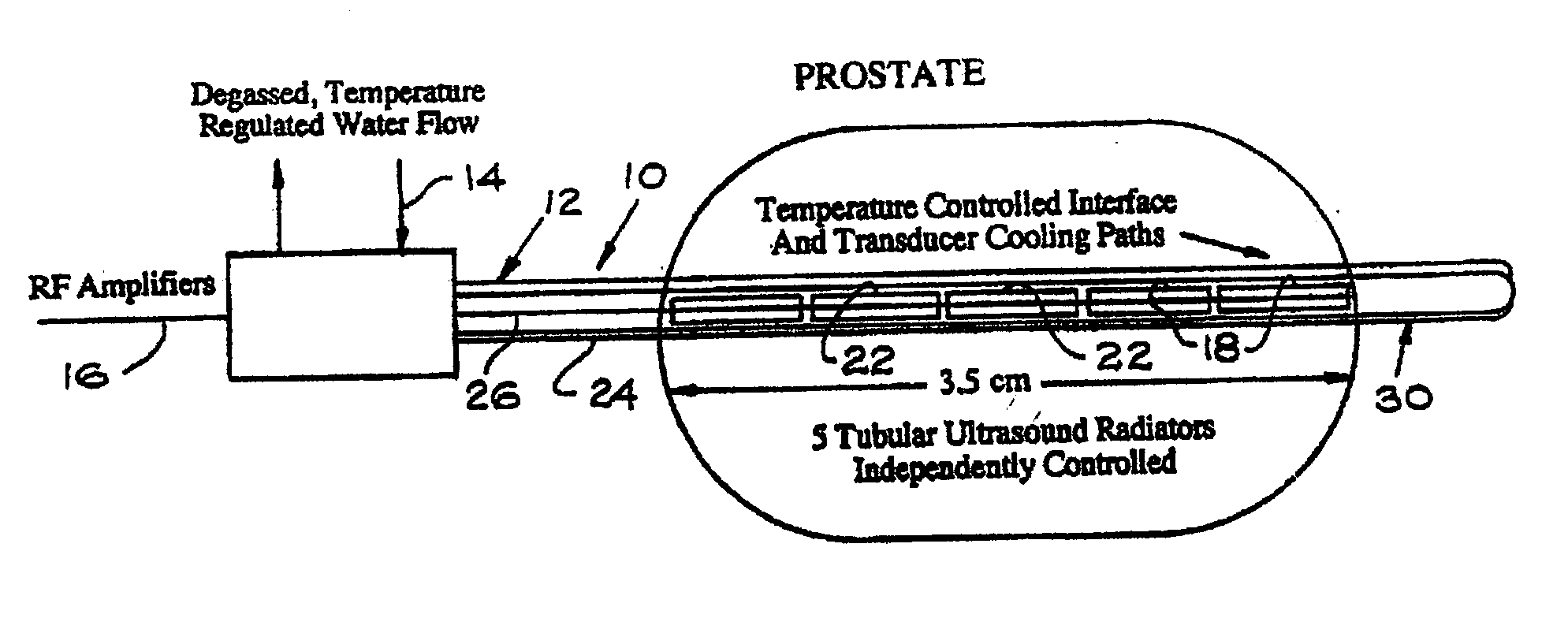
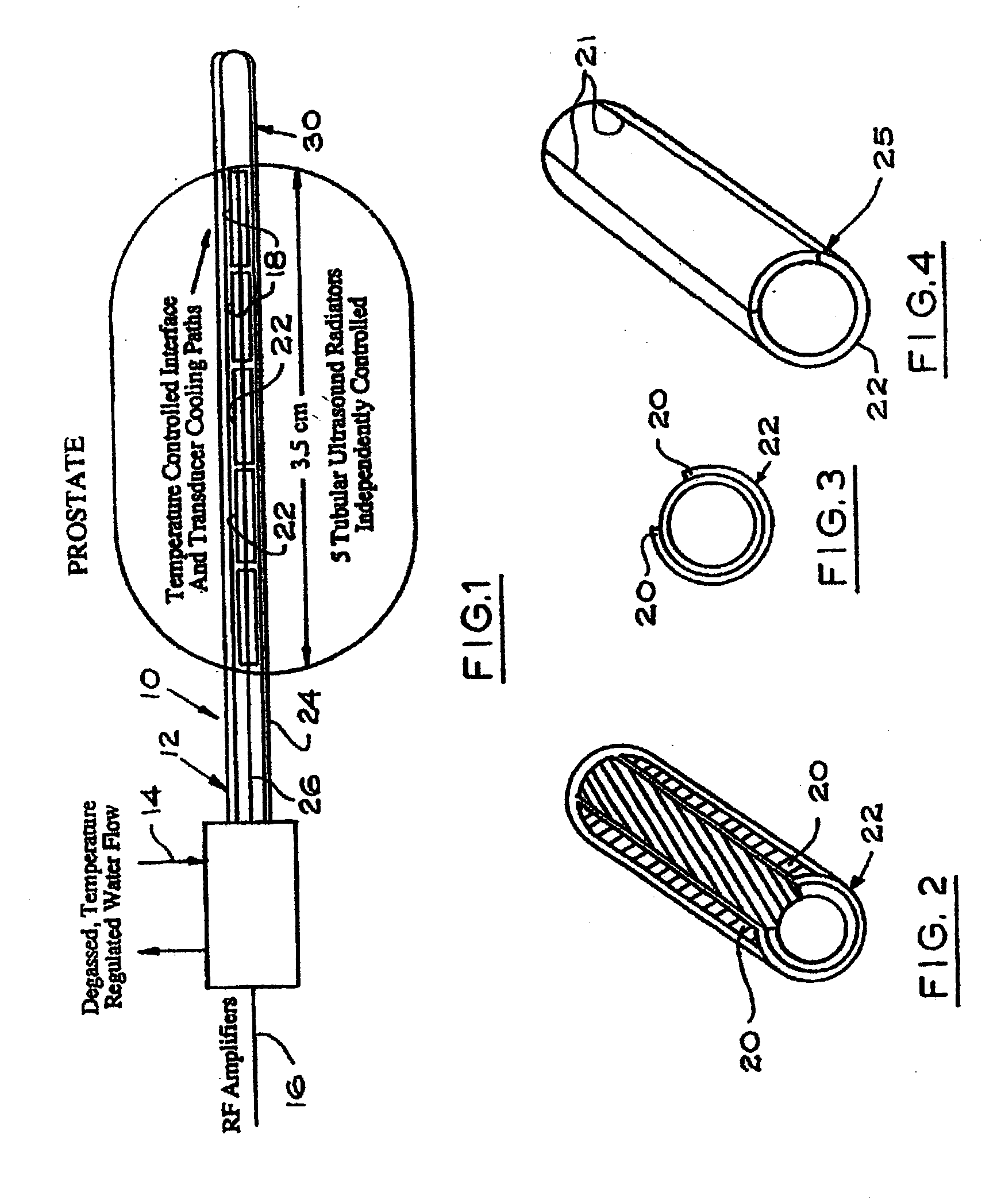
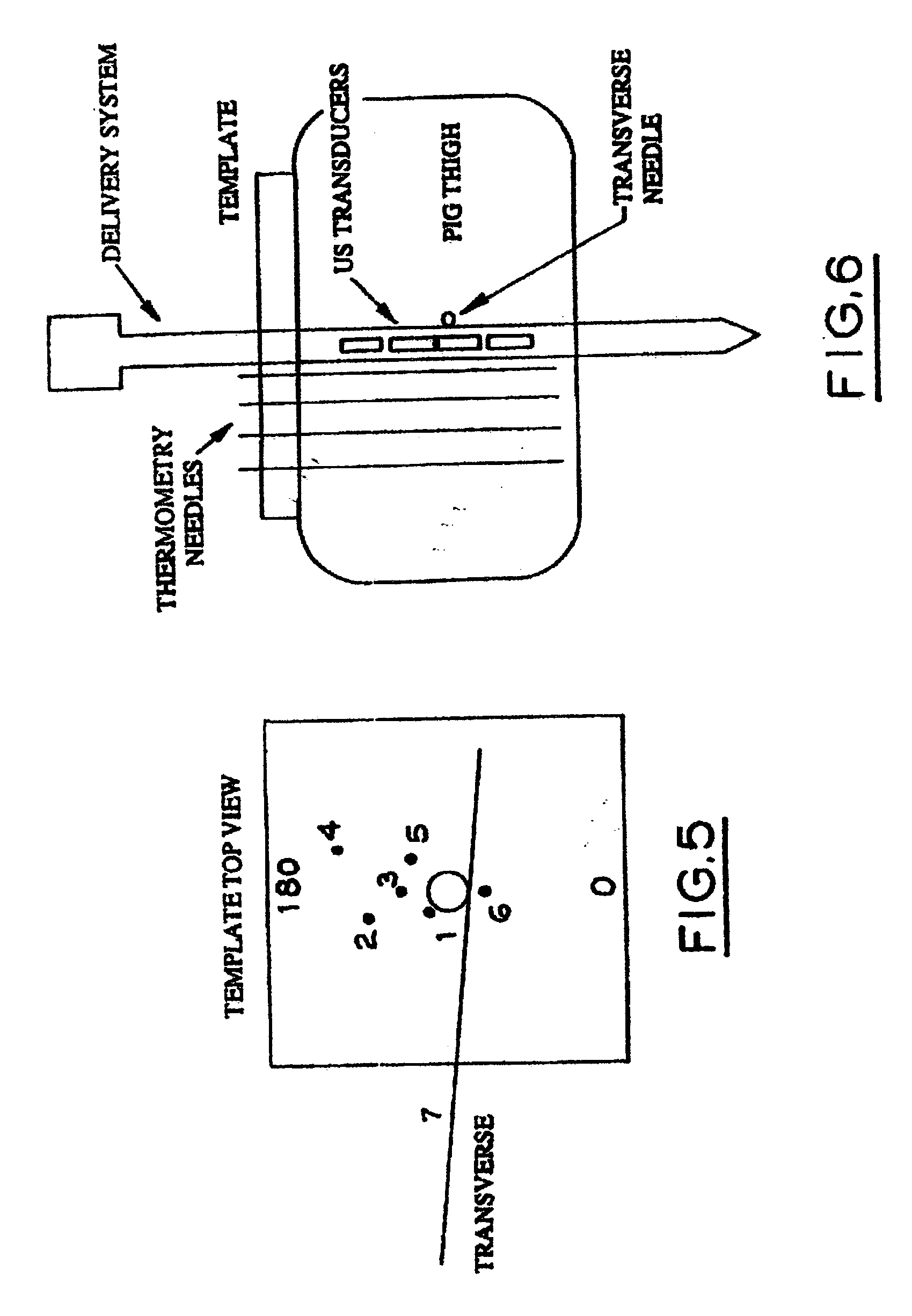
Method of manufacture of a transurethral ultrasound applicator for prostate gland thermal therapy
InactiveUS20040044375A1Increase energy outputEasy to controlUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUrethraSealant
An apparatus for applying thermal therapy to a prostate gland, comprising a support tube having a longitudinal central passageway, a power lead channeled through the longitudinal central passageway and an ultrasound crystal disposed around at least part of the support tube. The ultrasound crystal is coupled to the power lead which provides the power to energize the ultrasound crystal and generate ultrasound energy providing thermal therapy to the prostate gland. The ultrasound crystal further includes inactivated portions for reducing ultrasound energy directed to the rectal wall of the patient. A sealant is disposed in contact with the ultrasound crystal allowing vibration necessary for efficient ultrasound energy radiation for the thermal therapy to the prostate gland.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
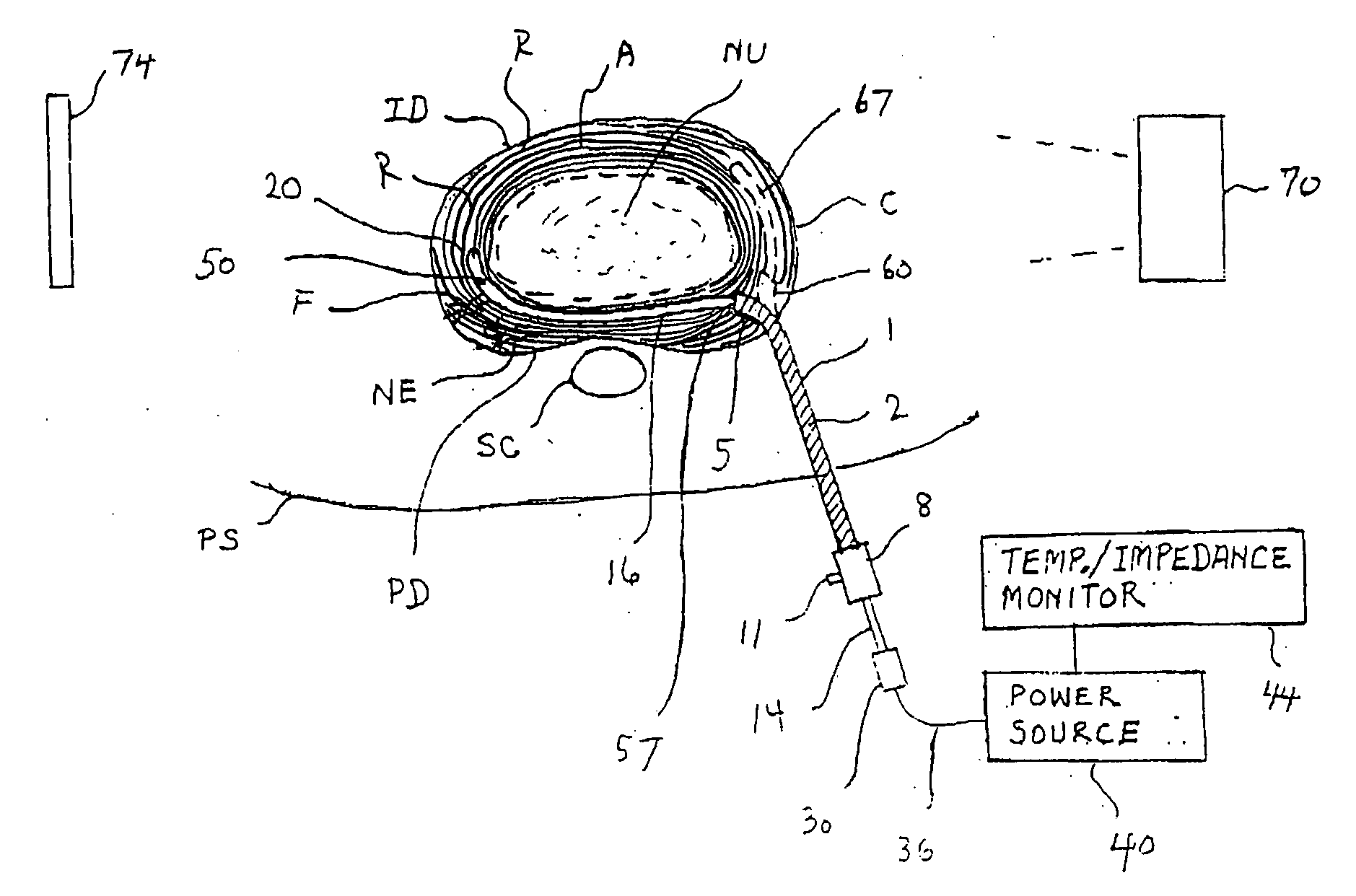
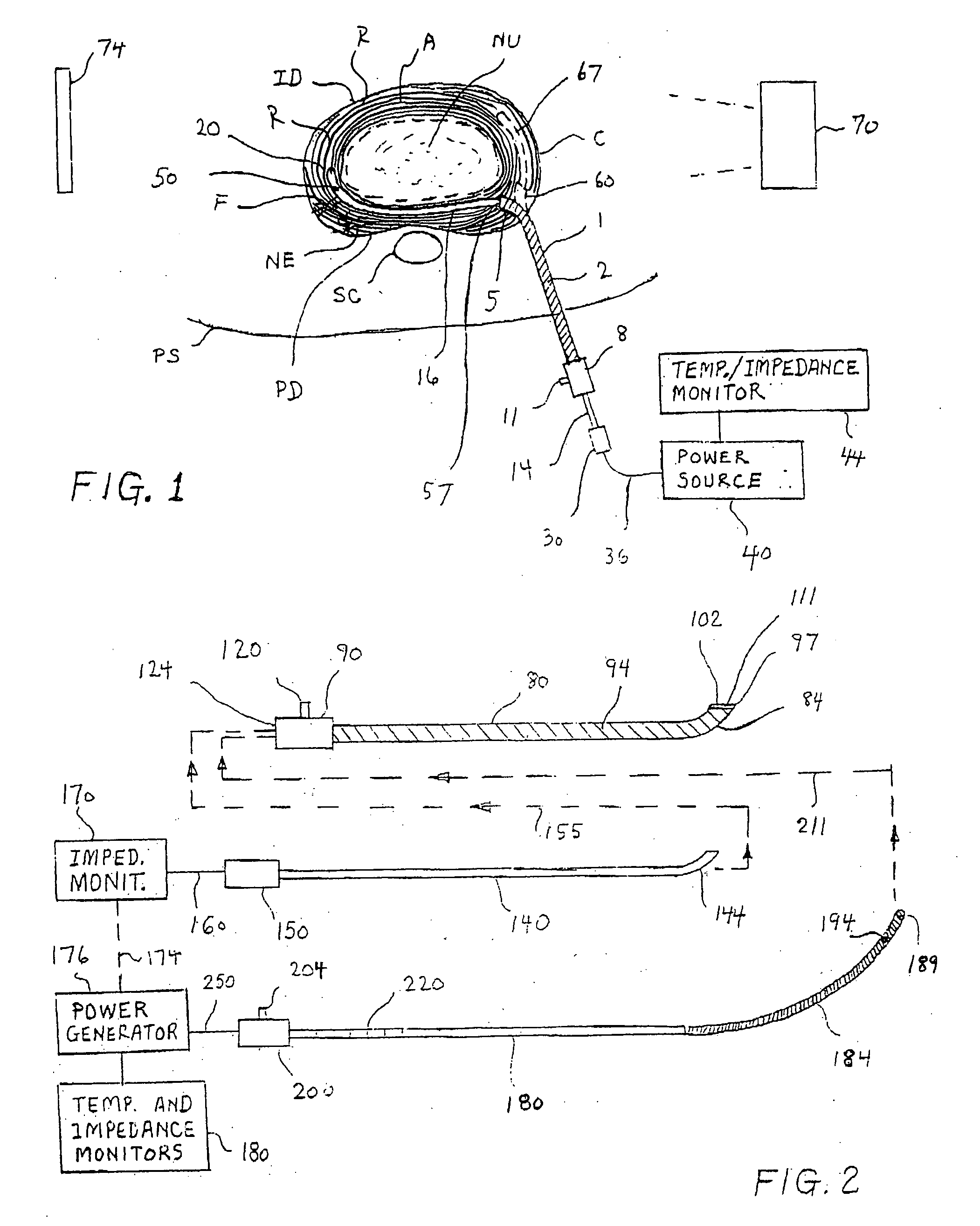
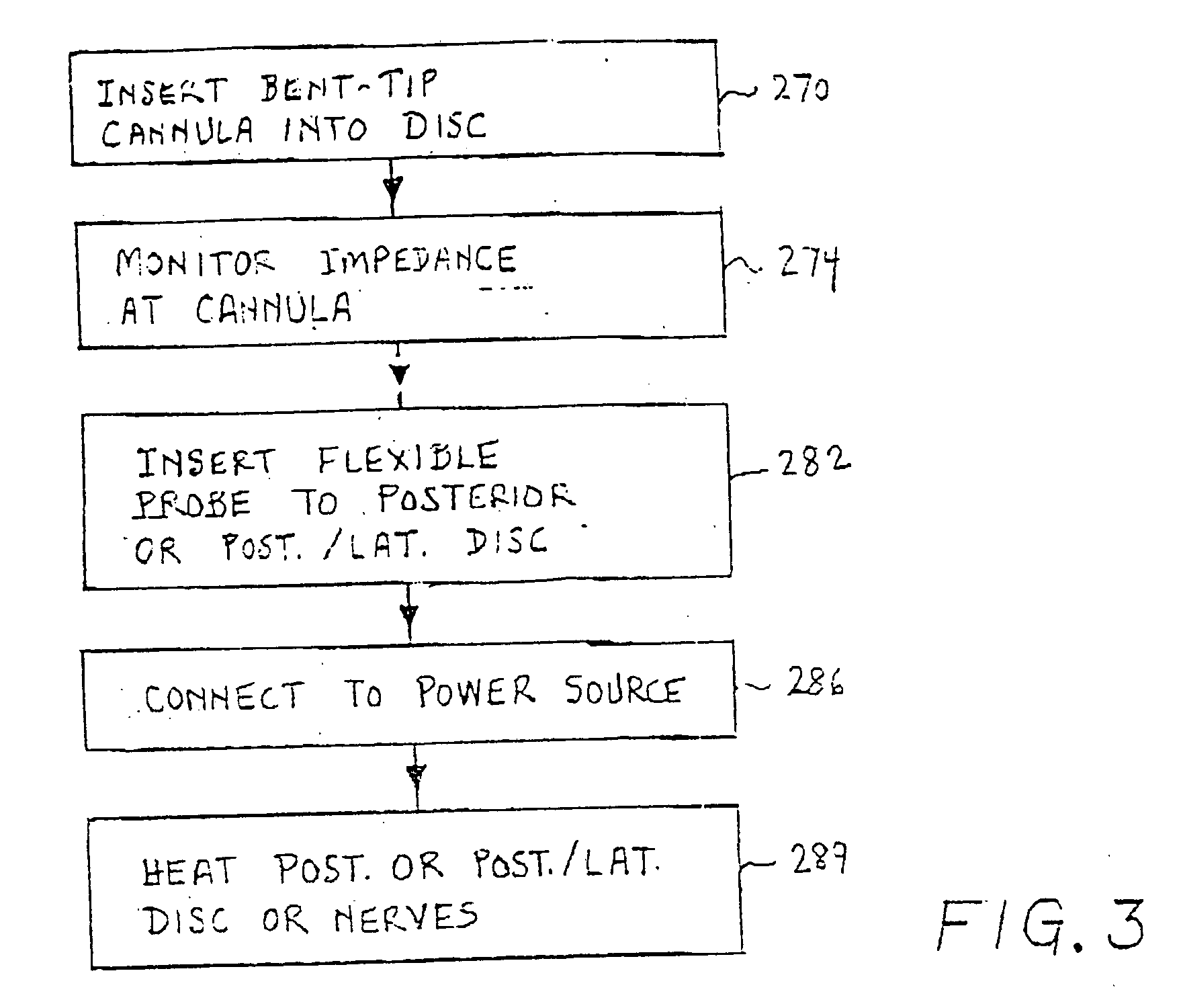
Apparatus for thermal treatment of an intervertebral disc
InactiveUS20040015218A1Surgical instruments for heatingTherapeutic coolingThermal energyThermal probe
An apparatus and method for treating an intervertebral disc having an inner nucleus pulpous and an outer annulus fibrous includes a thermal probe defining proximal and distal ends and having a guidable region adjacent the distal end thereof. The guidable region is characterized by having sufficient rigidity to advance within the annulus fibrous of the intervertebral disc in response to an axial force exerted on the proximal end of the thermal probe while having sufficient flexibility to substantially follow and conform to an azimuthal course defined by the natural striata of the annulus fibrous. The thermal probe is adapted for connection to a thermal energy source to provide thermal energy to the annulus fibrous to alleviate pain associated with the intervertebral disc.
Owner:JTC TRUSTEES +1
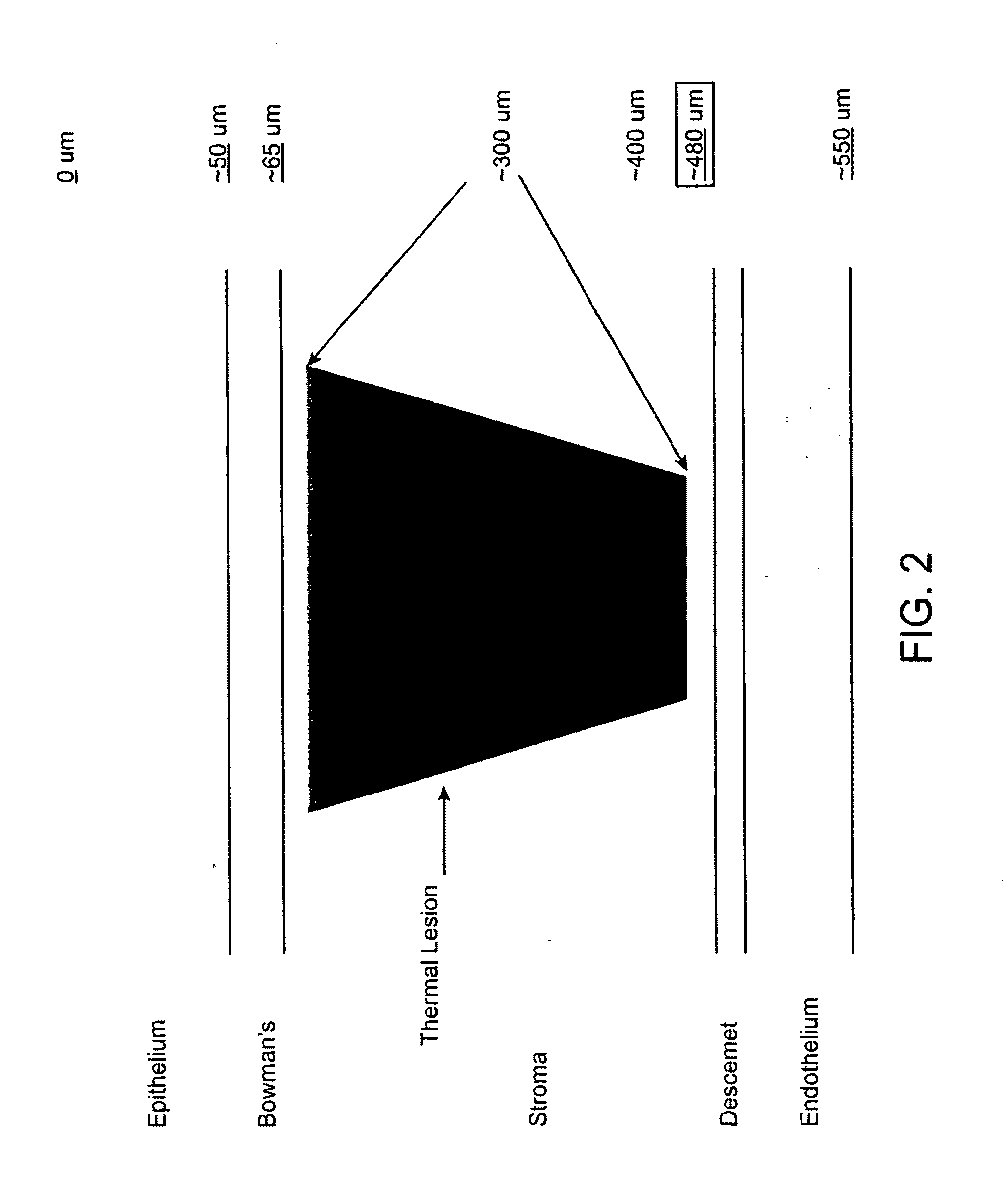
Method and apparatus for treatment of ocular tissue using combined modalities
ActiveUS20110282333A1Promote cornealFast cross-linkingLaser surgerySurgical instrument detailsHigh absorptionCollagen cross linking
An apparatus and a method are provided for treating a targeted area of ocular tissue in a tissue-sparing manner comprising use of two or more therapeutic modalities, including thermal radiation source (such as an CW infrared fiber laser), operative in a wavelength range that has a high absorption in water, and photochemical collagen cross-linking (CXL), together with one or more specific system improvements, such as peri-operative feedback measurements for tailoring of the therapeutic modalities, an ocular tissue surface thermal control / cooling mechanism and a source of deuterated water / riboflavin solution in a delivery system targeting ocular tissue in the presence of the ultraviolet radiation. Additional methods of rapid cross-linking (RXL), are provided that further enables cross-linking (CXL) therapy to be combined with thermal therapy.
Owner:ALEYEGN TECH LLC
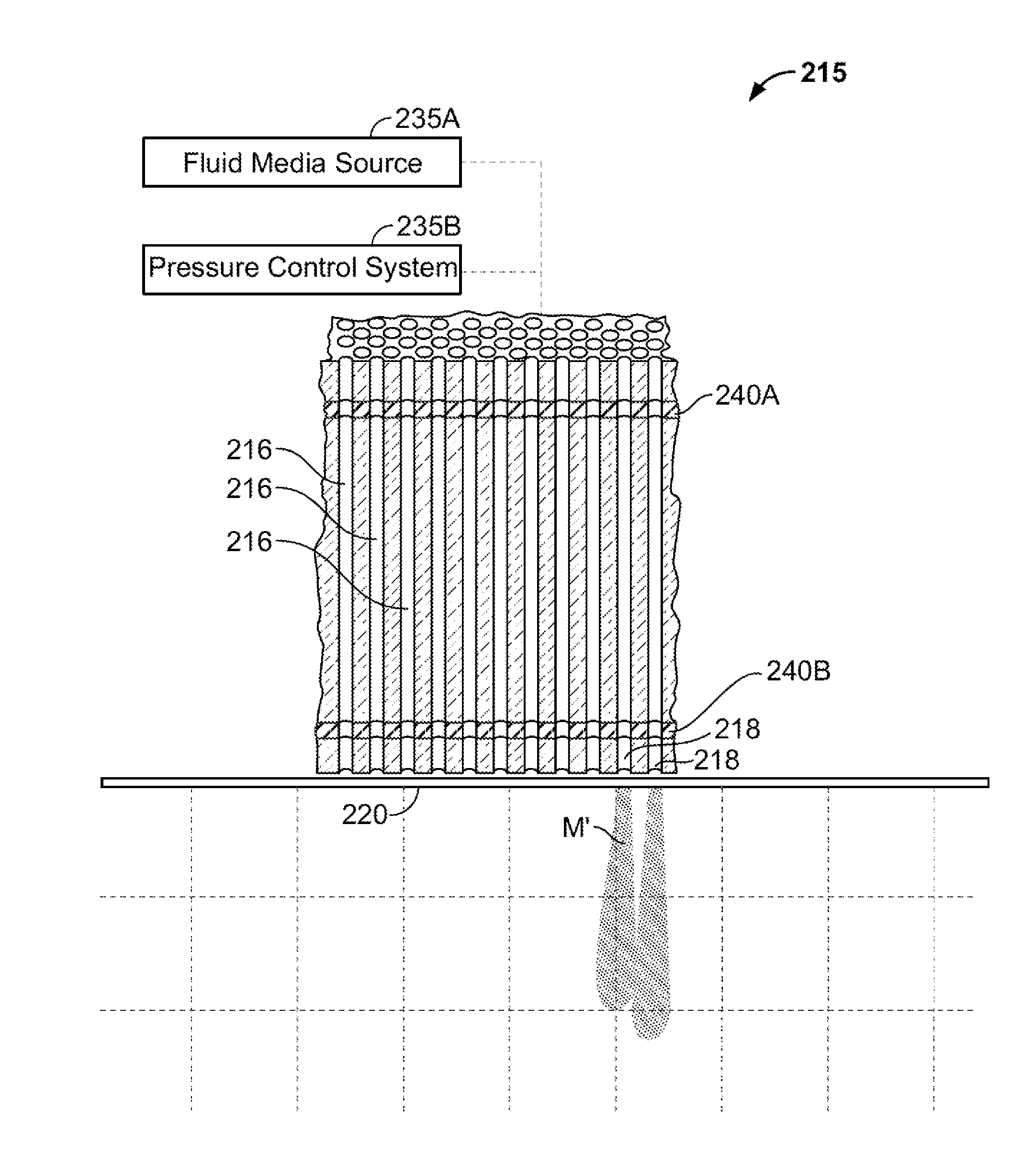
Methods for delivering energy into a target tissue of a body
InactiveUS8721632B2Without the potential of carbonizing tissueSimple methodSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingThermal energyGas phase
An instrument and method for tissue thermotherapy including an inductive heating means to generate a vapor phase media that is used for interstitial, intraluminal, intracavity or topical tissue treatment. In one method, the vapor phase media is propagated from a probe outlet to provide a controlled vapor-to-liquid phase change in an interface with tissue to thereby apply ablative thermal energy delivery.
Owner:TSUNAMI MEDTECH
Thermotherapy System Based on Redox Potential
InactiveUS20080255637A1Curb consumptionAvoid side effectsCavity massageBathing devicesTreatment effectMedicine
A method for treating a disease by returning the body to a natural condition. The method adjusts a parameter of a thermotherapy for treating or preventing the disease, disability, or condition of a patient and comprises (A) a step of measuring the redox potential (or pH value) of the patient and (B) a step of determining the parameter of thermotherapy suited to the patient according to the redox potential. Considering returning the biopotential to a range called homeostatic potential, a therapeutic potential of −75 mV to −90 mV (the potential in the cell is −75 mV) the absolute value of which is higher than that of the cell is given. It has been found that this therapy effects a cure.
Owner:CHICKEN CORP
Method for simultaneously carrying out magnetic induction heating, imaging and temperature detecting on tumor cells
InactiveCN101601607ADiagnostic recording/measuringSurgical instruments for heatingMicrosphereMagnetite Nanoparticles
A method for realizing simultaneous magnetic induction heating, imaging and intracellular temperature detecting on tumor cells by virtue of multi-functional nanospheres is provided aiming at the following problems: how magnetic nanoparticles in hyperthermia heat tumor cells as nano heaters after entering the cells and how the local temperature experienced by each cell is measured, so as to further promote the development of tumor magnetic induction hyperthermia technique. The method comprises the following steps: simultaneously combining the magnetic nanoparticles with the function of magnetic induction heating and fluorescent quantum dots with the functions of imaging and temperature detecting in polymeric or inorganic nanospheres, heating the cells by employing the nanospheres combined on the tumor cells under the alternating magnetic field and simultaneously carrying out imaging and temperature detecting on the cells by employing the fluorescent quantum dots under fluorescence microscopes.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
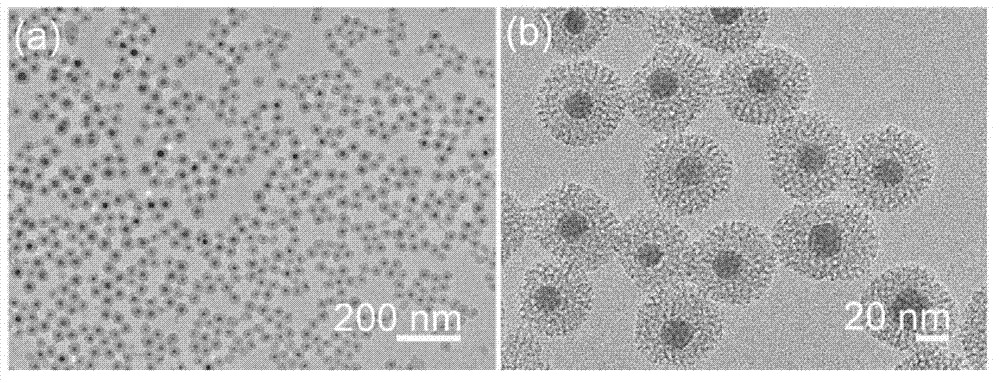
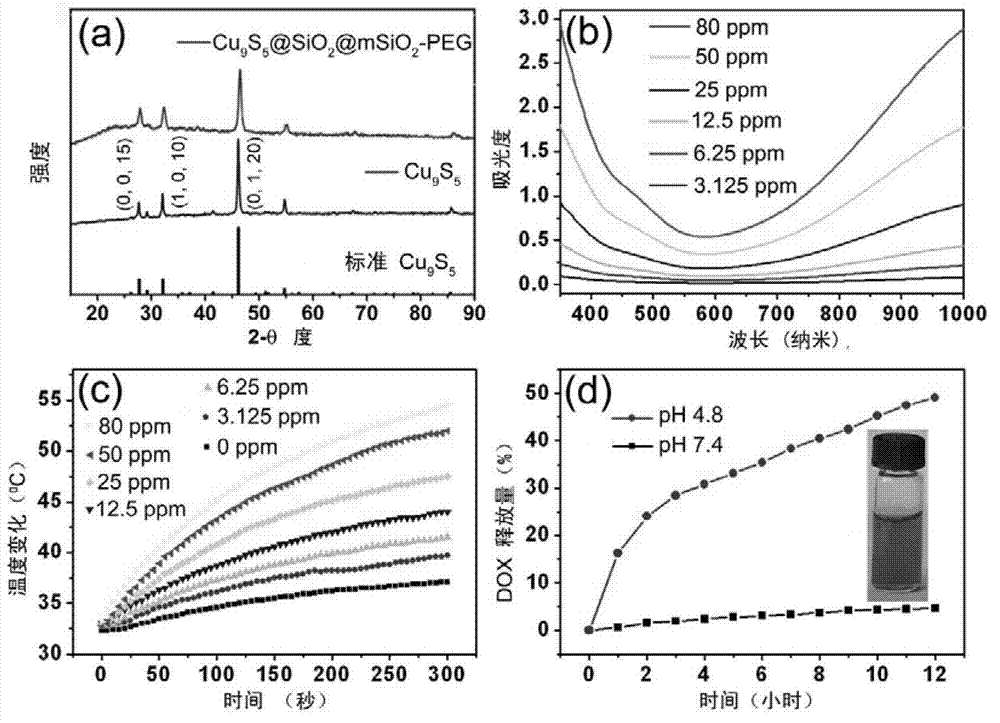
Copper sulfide/mesoporous silicon dioxide core-shell nano material as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102961753AEffective photothermal ablationGuaranteed normal transmissionEnergy modified materialsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMesoporous silicaNitrogen gas
The invention relates to a copper sulfide / mesoporous silicon dioxide core-shell nano material as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The chemical formula of the core-shell nano material is Cu9S5 / mSiO2-PEG. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) raising the temperature of oleylamine under the protection of nitrogen; adding a mixed solution of copper dibutyldithiocarbamate and the oleylamine and dispersing the mixed solution into chloroform to prepare a D solution; (2) dissolving a surfactant into water; raising the temperature and adding the D solution to prepare an E solution; and (3) taking the E solution and adding ethanol; raising the temperature and adding an NaOH solution; immediately adding TEOS (Tetraethylorthosilicate) and reacting; adding PEG-silane; continually reacting and carrying out hydrothermal reaction; and adding into a scrubbing solution to centrifuge and wash to obtain the product. The copper sulfide / mesoporous silicon dioxide core-shell nano material is applied to near-infrared photo-thermal treatment, anti-cancer drugs, chemotherapy of tumors and infrared heat imaging. The nano material disclosed by the invention has very low cell toxicity and very high blood compatibility; and the united effects of thermal therapy and the chemotherapy are good.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Core-excited nanoparticles and methods of their use in the diagnosis and treatment of disease
InactiveUS8197471B1Minimal side-effectsEffective and practicalPowder deliveryNanotechDiseaseCore shell nanoparticles
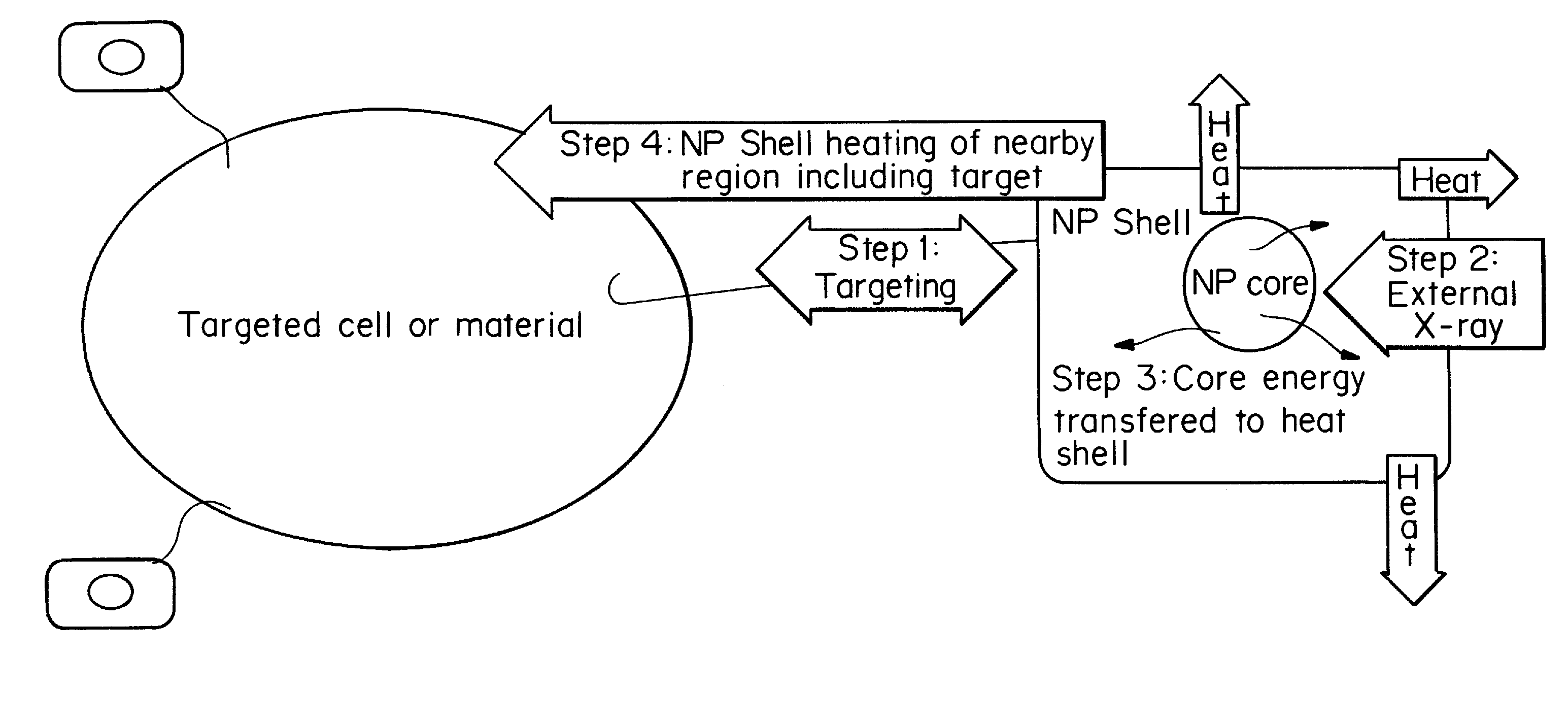
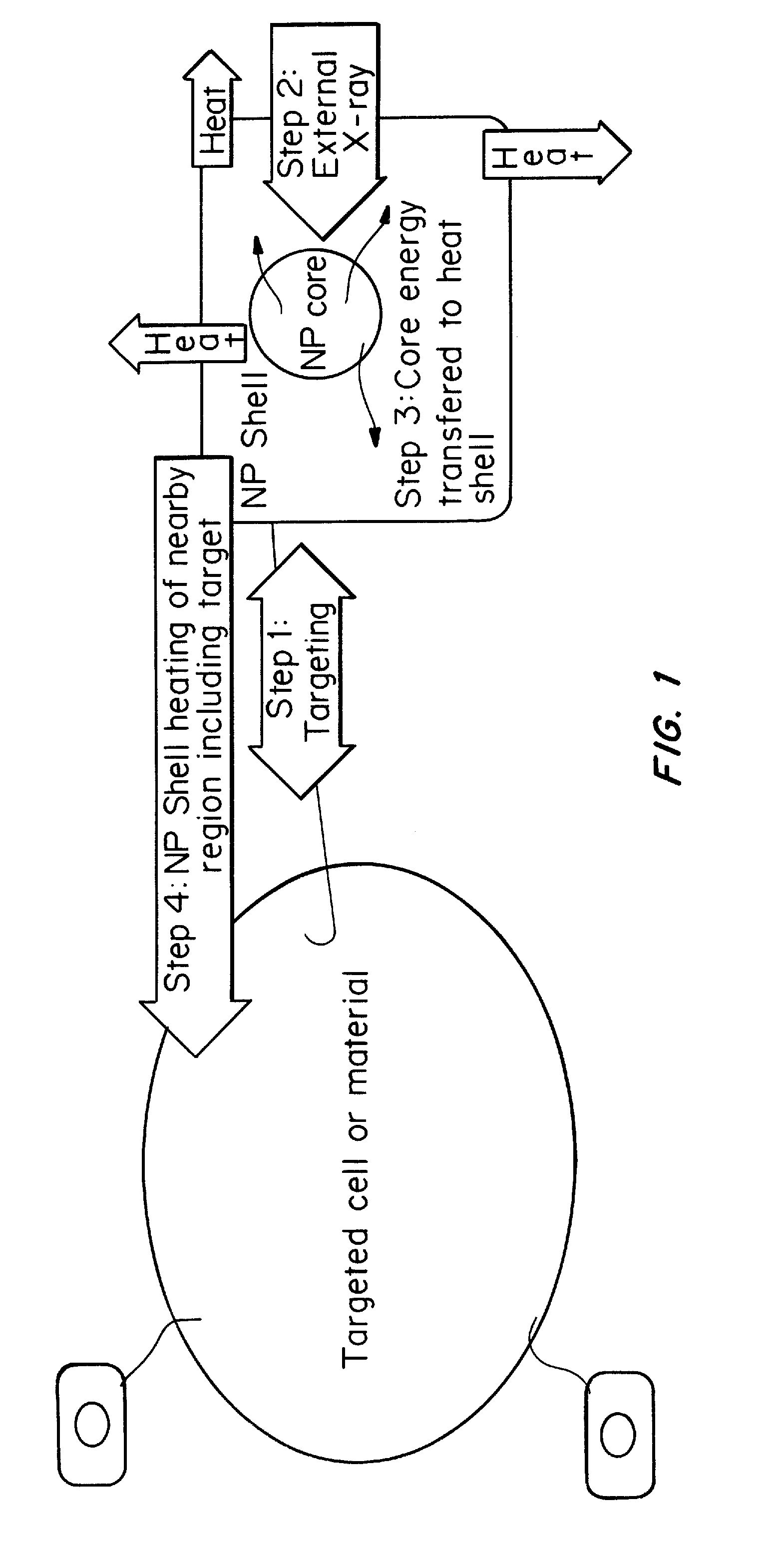
Core-excited nanoparticle thermotherapy (CENT), is an improved material for use in thermotherapy. The CENT method uses both core-exciting energy (including x-rays) and core-shell nanoparticles, specifically designed to absorb radiation in their core structure, then transfer energy from the core to the shell, to heat the outer shell of the nanoparticle. The heated nanoparticle then heats the surrounding region to a temperature sufficient to detect, affect, damage and / or destroy the targeted cell or material. CENT nanoparticles can be bound to targeting agents that deliver them to the region of the diseased cell.
Owner:TERSIGNI SAMUEL HARRY
Prostate cancer ablation
Methods and systems for delivering electrical energy and controlled, mild hyperthermia to a prostate tissue of a patient for destruction of cancerous and / or hyperplastic tissue. A method includes positioning a plurality of electrodes in a target tissue region comprising the prostate tissue, and establishing an alternating electrical current flow through a volume of the prostate tissue to induce mild heating and destruction of cancerous cells in the volume.
Owner:LAZURE SCI
Method of hyperthemia treatment
Owner:FLORIDA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Interstitial microwave antenna with lateral effect for tissue hyperthermia in minimal invasive surgery
InactiveUS20060015161A1Reducing treatment invasivityElectrotherapyMicrowave therapyMinimal invasive surgeryElectrical conductor
Application device (1), for example, a metal needle or a plastic catheter that has in the end portion (2) of the free end a gradually increasing thickness to form substantially a chute guide (3) which ends at a side opening (4) made on the application device (1). This way, an interstitial antenna (10) is obtained formed by a co-axial tube having an external conductor (7), by a dielectric layer (9) and by a central conductor (8) embedded in the dielectric layer (9) that insulates it from the external conductor (7). The antenna (10) can be put in a target tissue, along an actuation direction forming an angle a with the introduction direction. This way, the antenna (10) achieves an actual surface isothermal, i.e. a mass of tissue actually coagulated within a curved surface (13), since the tip of the application device (1) is connected electrically with the external conductor (7) and increases its area of action.
Owner:LONGO IGNIO +1
Method and composition for hyperthermally treating cells in the eye with simultaneous imaging
InactiveUS20090240149A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyMedicinePhotoacoustic imaging in biomedicine
A method and composition for hyperthermally treating cells in the eye with simultaneous imaging. The heat (temperature) production inside the eye ( target) tissue is imaged. The desired temperature is achieved using a laser and photoacoustic imaging technique. Hyperthermia treatment of tissue in a target site applies a heat source to kill cells without protein denaturation. The method introduces an encapsulated dye that is released at a selected temperature in the target site to indicate that a threshold temperature has been reached to hyperthermally treat the tissue. In one embodiment, the composition releases the dye at a temperature of 42° C. to 50° C., and preferably about 45° C. to 49° C. The composition which can be a liposome composition encapsulating the dye can be introduced to the bloodstream of the patient to flow through the target site.
Owner:GHOLAM A PEYMAN
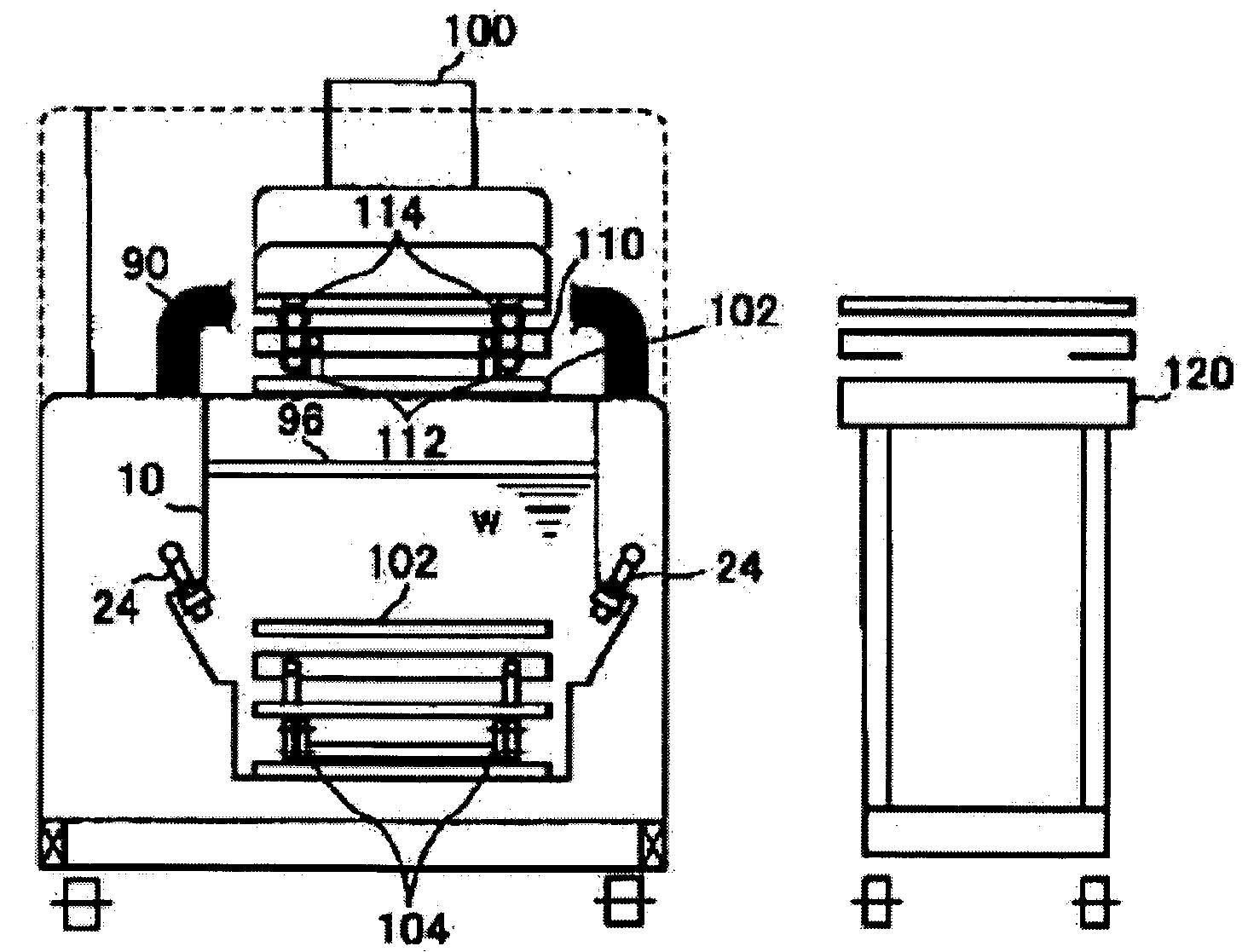
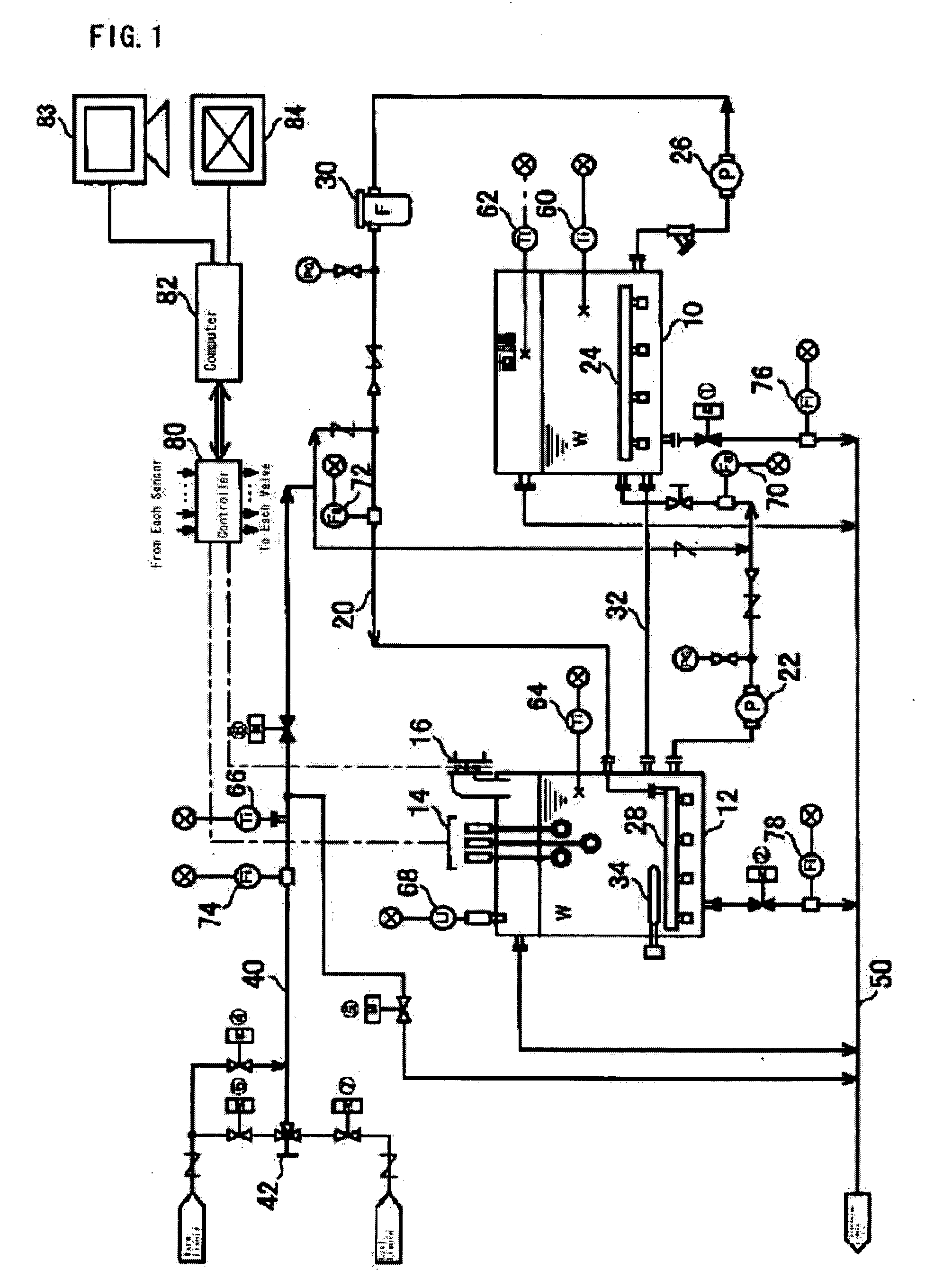
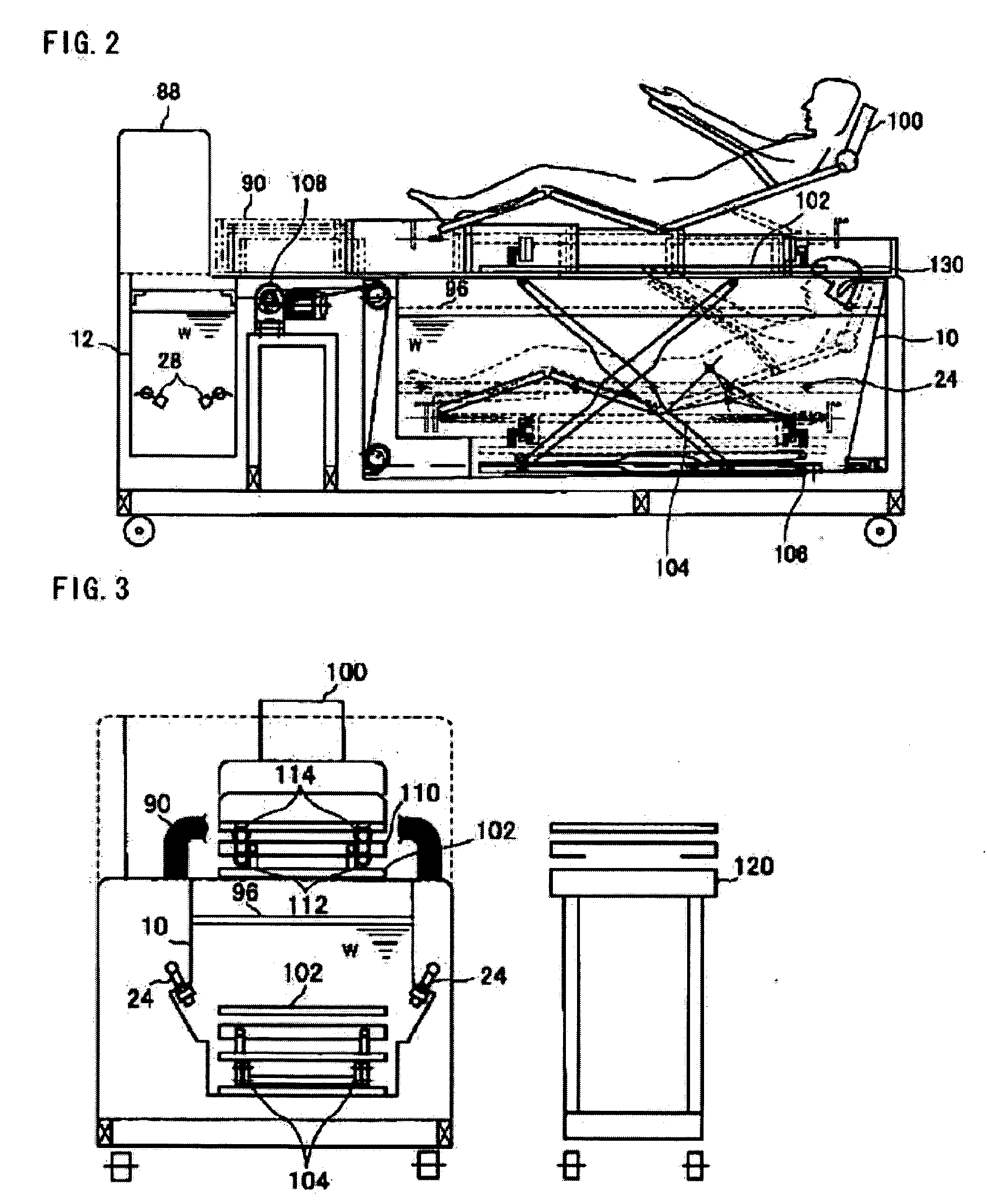
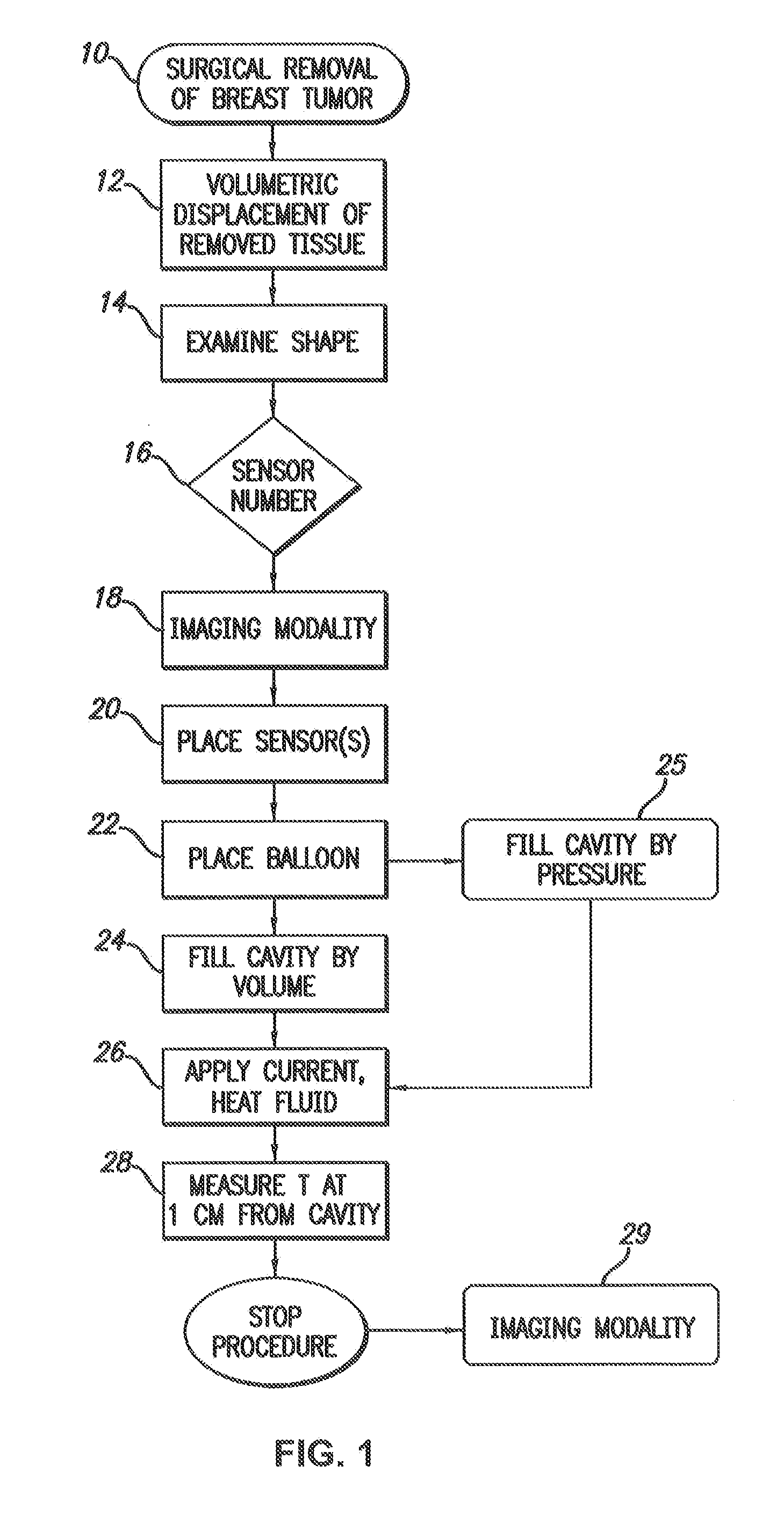
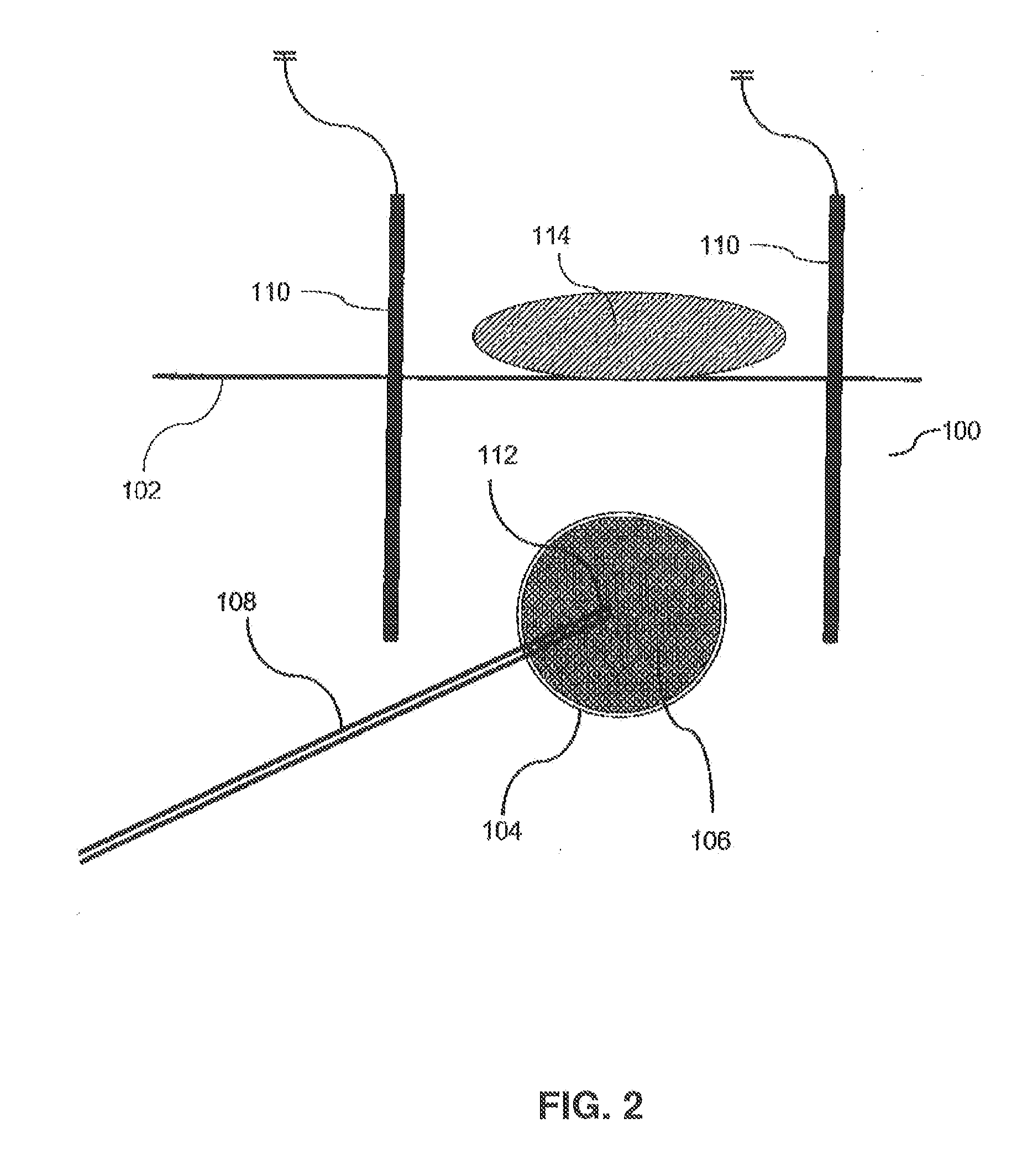
Image-guided removal and thermal therapy of breast cancer
InactiveUS20140025056A1Surgical navigation systemsSurgical instruments for heatingEarly breast cancerGeneral surgery
A method of removing undesirable cells and killing cells surrounding a cavity caused by the removal of the undesirable cells includes the step of inserting a probe through an incision made in the skin of a patient. The method further includes the steps of removing undesirable cells using the probe and using image-guided technology and inserting a balloon into the cavity formed by the removal of the undesirable cells. Still further, the method includes the steps of conforming the balloon to a shape of the cavity and providing sufficient fluid to fill the cavity based on the volume and reaching a temperature in the fluid to achieve a temperature in the tissue surrounding the cavity that kills cells surrounding the cavity.
Owner:DOWLATSHAHI KAMBIZ
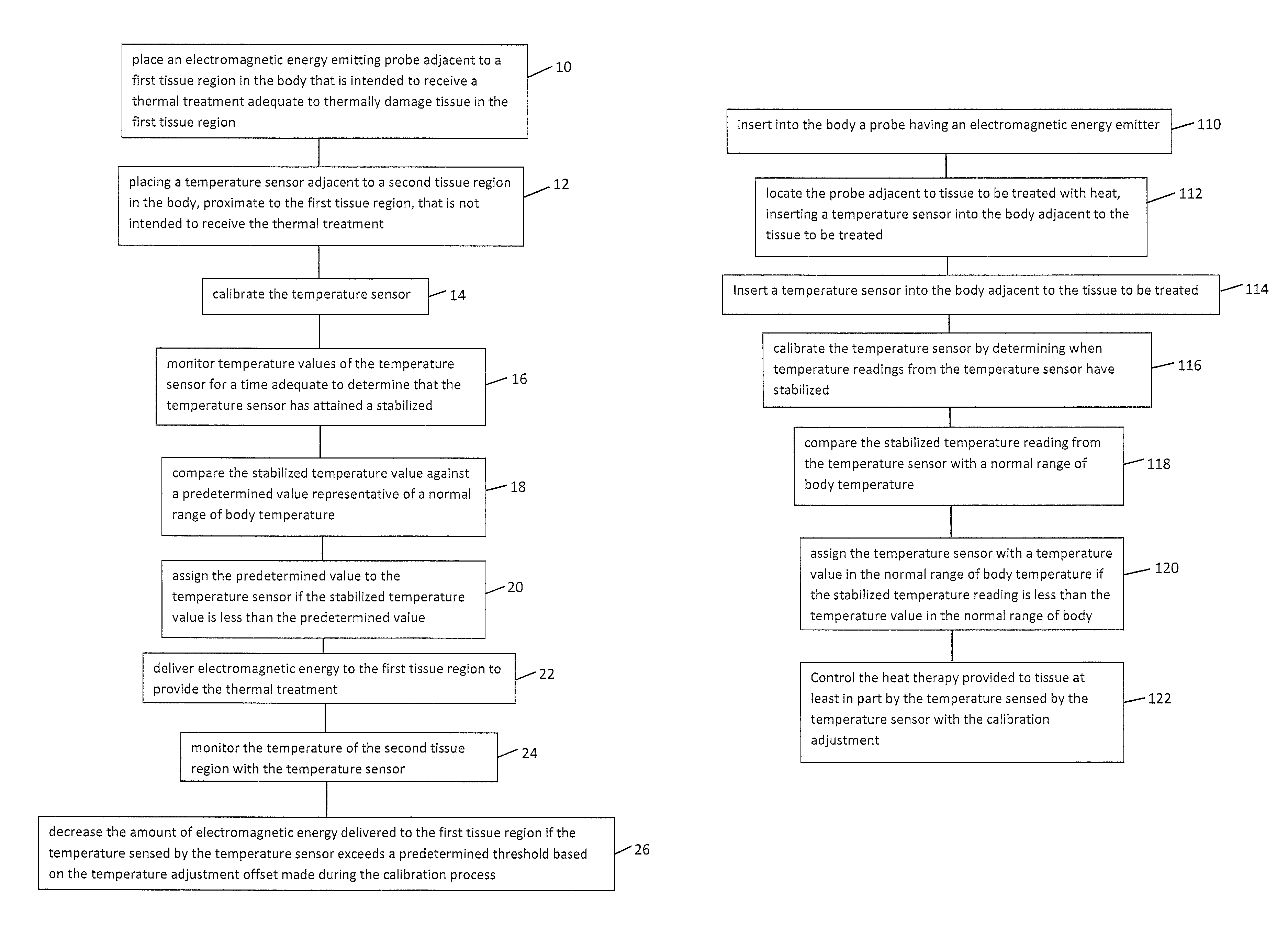
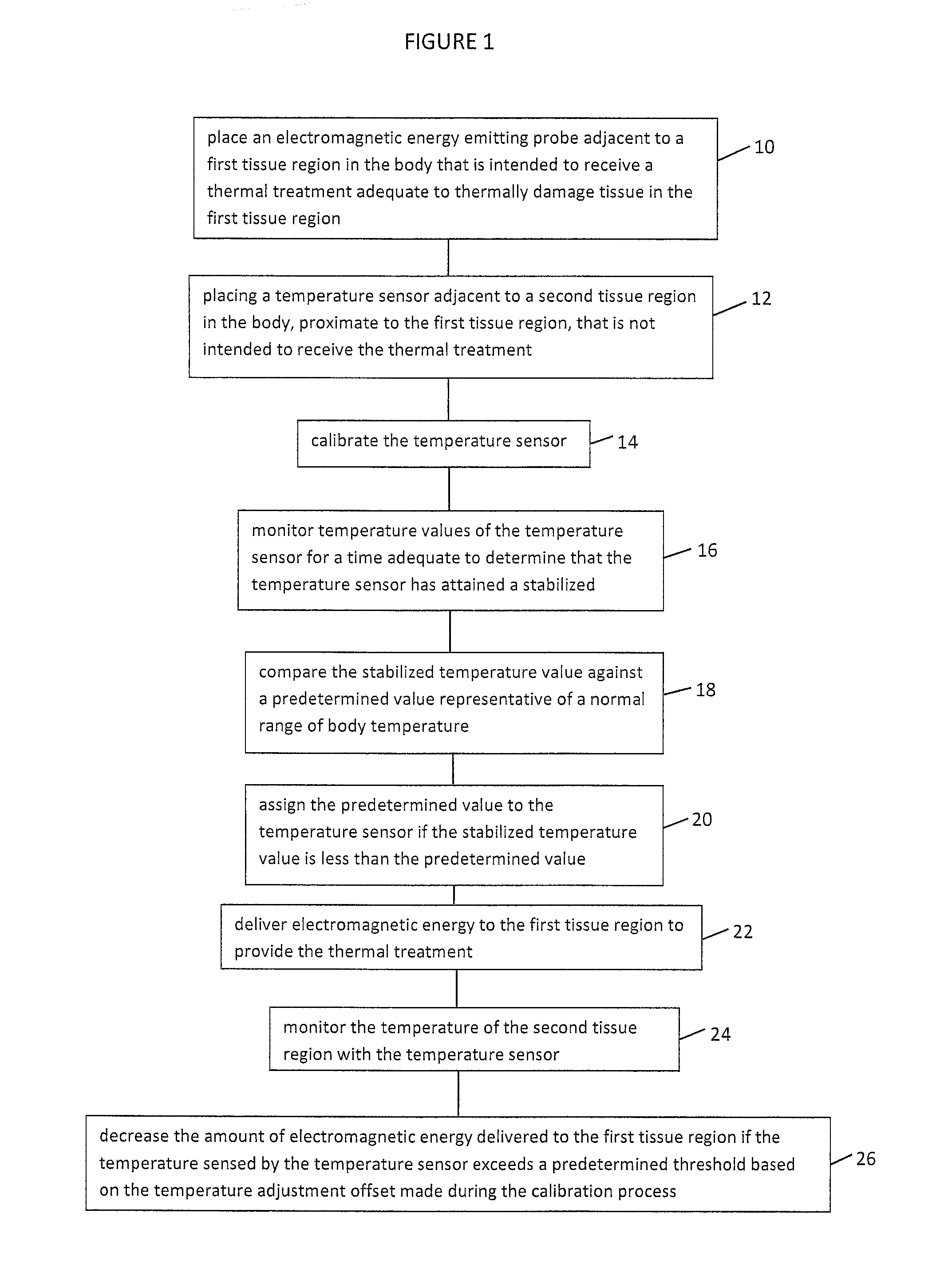
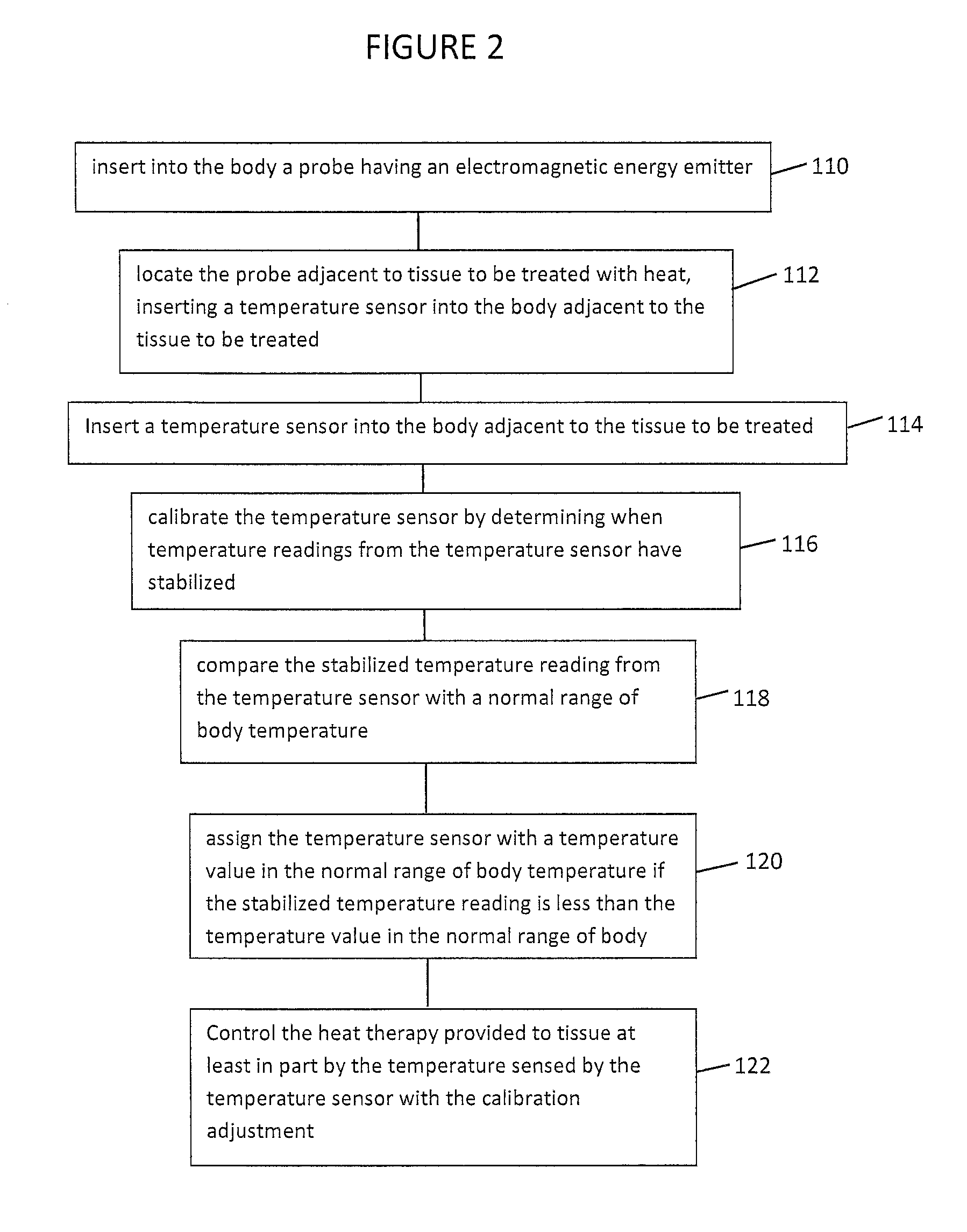
Thermal therapy temperature sensor calibration method
A thermal therapy of body tissue with electromagnetic energy is controlled by feedback from one or more temperature sensors placed in the vicinity of the tissue to be treated. The temperature sensors are calibrated by comparing stabilized temperature values of the one or more temperature sensors against a normal range of body temperature and adjusting sensed temperature to a value within a normal body temperature range if the actual temperature value of a stabilized temperature sensor is less than the normal body temperature range. The temperature adjustment to the temperature sensor is maintained throughout the thermal therapy which reduces the risk of thermal damage to healthy tissue located near the tissue to be treated.
Owner:UROLOGIX
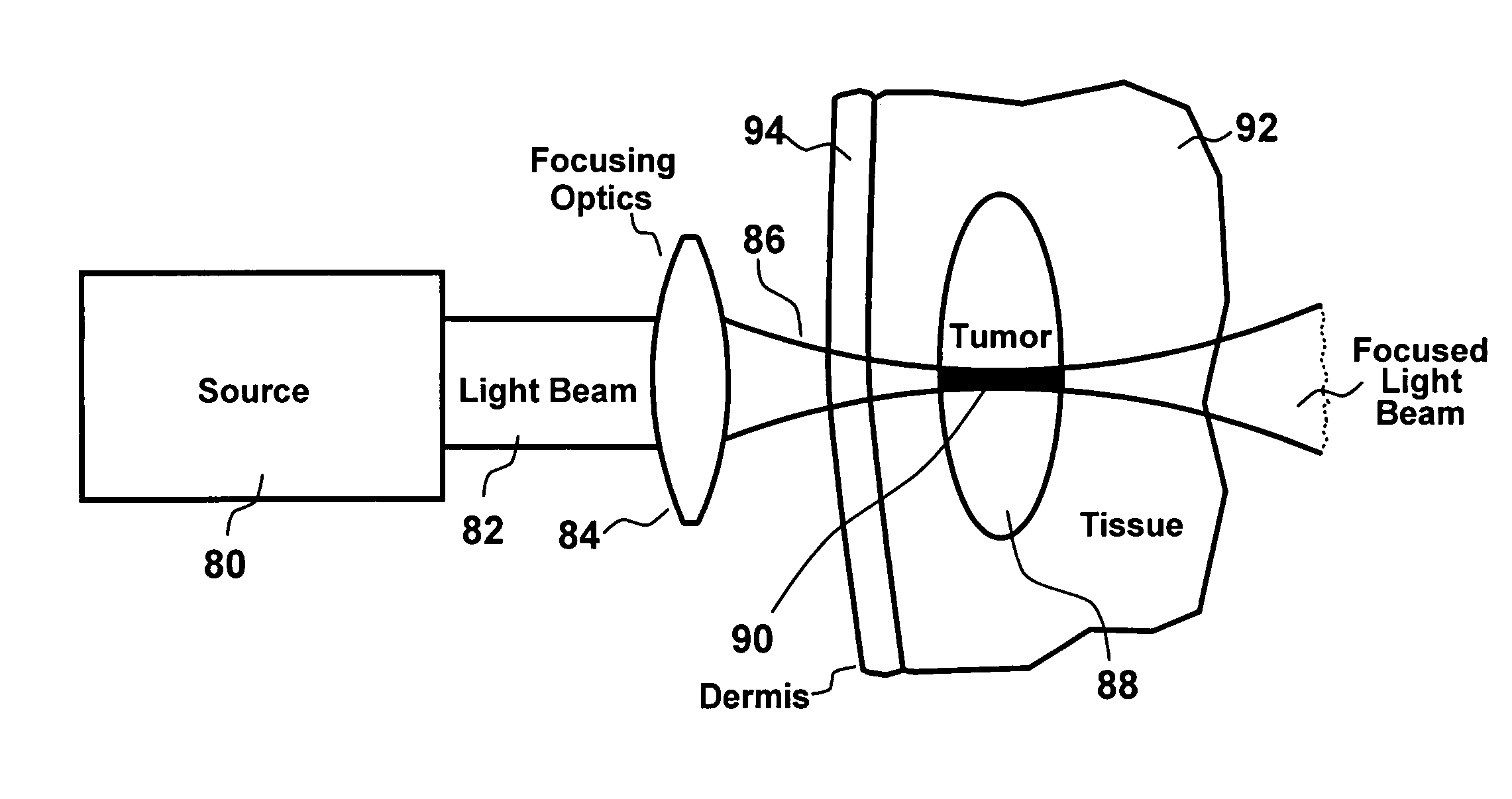
Treatment of pigmented tissues using optical energy
InactiveUS7036516B1Improve efficiencyElectrotherapyEnergy modified materialsThermal DestructionsOptical energy
A method and apparatus for selectively photobleaching or killing pigmented tissues by photochemically converting pigments in the tissues using light and specifically two-photon excitation. Phototoxic products thereby produced then kill pigmented cells. Hyperthermia or an exogenous agent can also be added to augment efficacy. The present invention is also directed to selective thermal destruction of pigmented tissues using related optical means.
Owner:PROVECTUS DEVICETECH
Thermal therapy sleeve
A flexible thermal therapy sleeve is disclosed. The sleeve includes a first layer including a first phase change material having a transition temperature of from about −10° C. to about 40° C., and a second layer including a second phase change material having a transition temperature of from about 35° C. to about 65° C. The first layer is joined to the second layer to form at least a partial enclosure having an opening through which a thermoactive material may be inserted and removed.
Owner:O&M HALYARD INC
Drug carrier, preparation method thereof, pharmaceutical composition made from drug carrier, and applications of drug carrier and pharmaceutical composition
InactiveCN103893764AAvoid reunionIncrease loadInorganic non-active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsDiseaseFluorescence
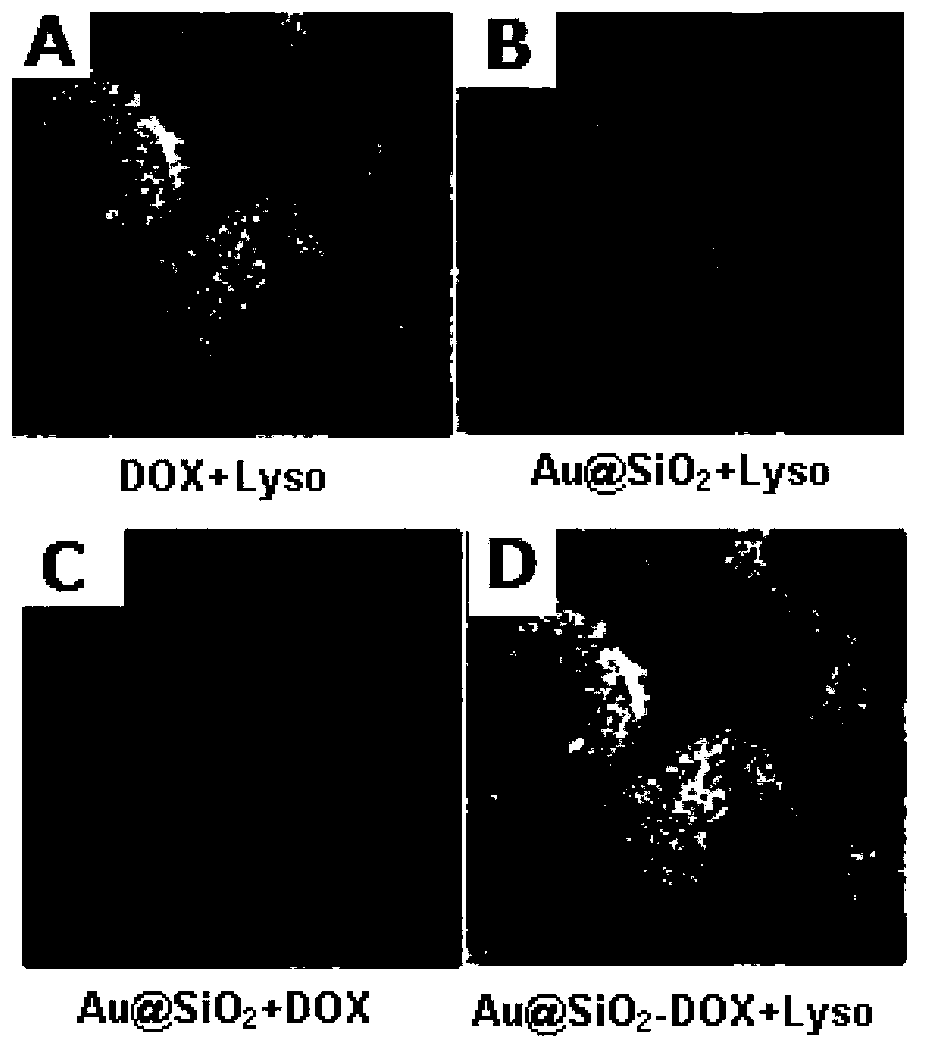
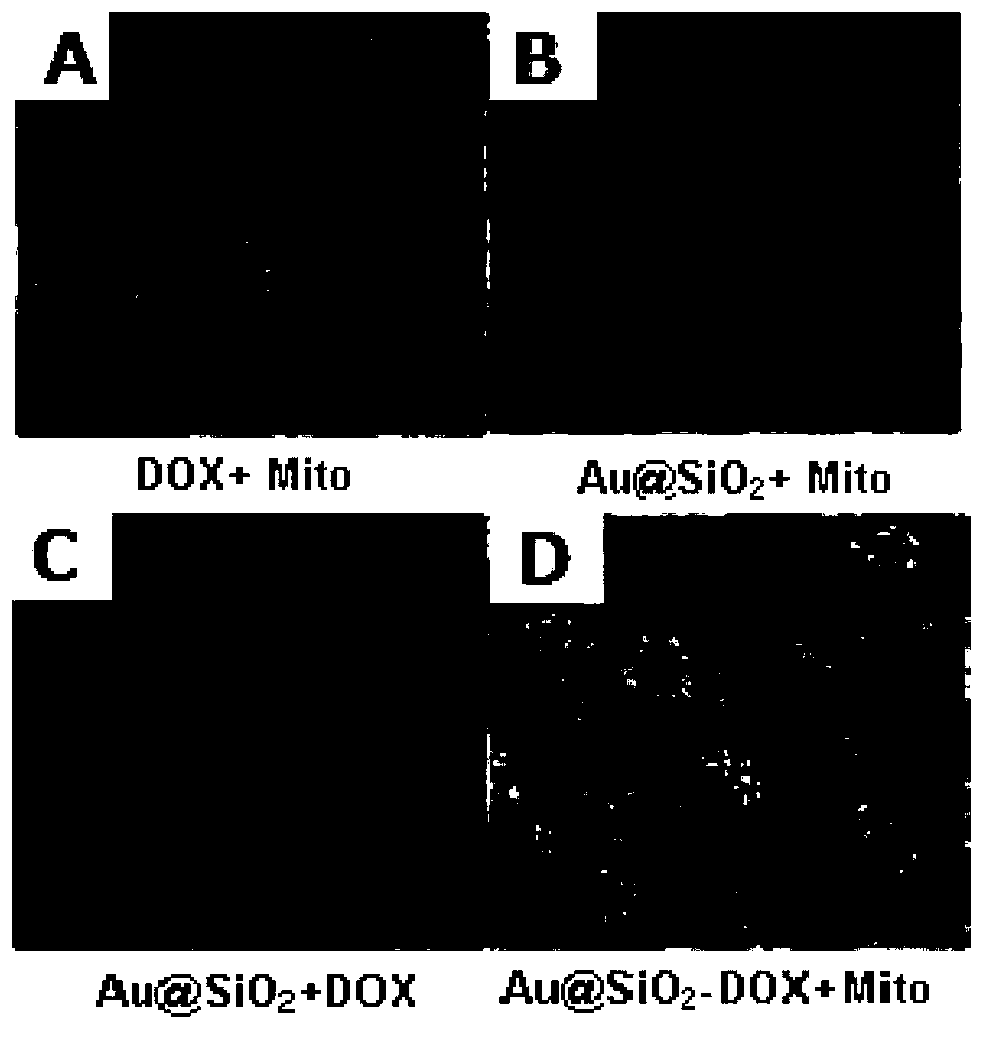
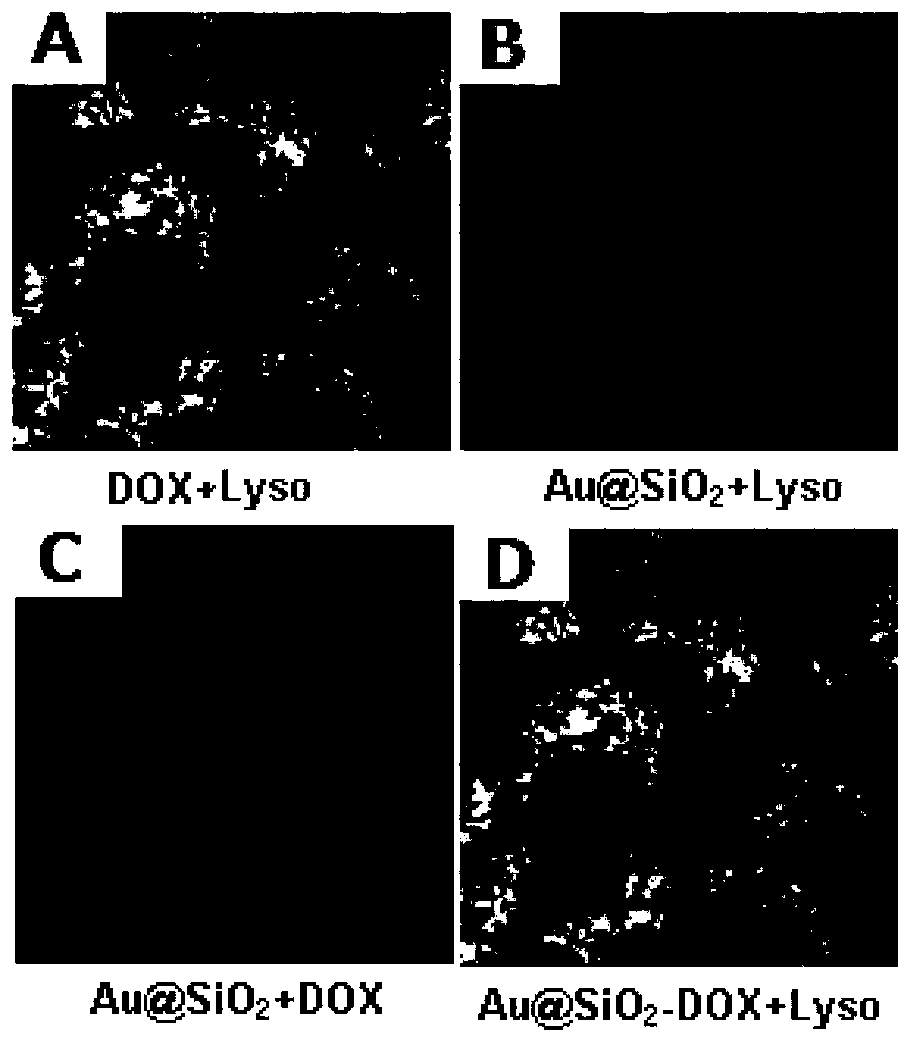
The invention discloses a drug carrier, a preparation method, a pharmaceutical composition made from the drug carrier, and applications of the drug carrier and the pharmaceutical composition. The mesoporous silica-coated gold nanorod (Au@SiO2) carrier is characterized in that: gold nanorods are coated with a layer of mesoporous silica. According to the preparation method, the Au@SiO2 carrier is prepared by taking hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide-coated gold nanorods as raw materials via hydrolytic polymerization with orthosilicate ester, can be used for coating a plurality of drugs and probe molecules, and delivering the drugs and the probe molecules to parts of diseases so as to realize targeting therapy. After absorption of near-infrared laser, the Au@SiO2 carrier, or drug-loaded Au@SiO2 nanoparticles are capable of emitting fluorescence and transforming a part of light energy into heat energy, so that the Au@SiO2 carrier and the drug-loaded Au@SiO2 nanoparticles can be used for bioimaging, light-dependent control drug release (chemotherapy), and thermotherapy. The preparation method of the Au@SiO2 carrier is simple; the Au@SiO2 carrier can be used for a plurality of diagnosis and treatment methods, and the plurality of diagnosis and treatment methods can be combined, so that it is beneficial for avoiding defects of a single diagnosis and treatment method, and the drug carrier and the pharmaceutical composition are especially suitable for tumor diagnosis and treatment with complex requirements.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Treatment of pigmented tissues using optical energy
InactiveUS20060095101A1Improve efficiencyEnergy modified materialsSurgical instrument detailsThermal DestructionsOptical energy
A method and apparatus for selectively photobleaching or killing pigmented tissues by photochemically converting pigments in the tissues using light and specifically two-photon excitation. Phototoxic products thereby produced then kill pigmented cells. Hyperthermia or an exogenous agent can also be added to augment efficacy. The present invention is also directed to selective thermal destruction of pigmented tissues using related optical means.
Owner:PROVECTUS DEVICETECH
Wearable multi-field radiation whole-body hyperthermia device
ActiveCN101856290AIncrease body temperatureIncreased heating radiation doseTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingMulti fieldWhole body
The invention relates to medical healthcare equipment, in particular to a wearable multi-field radiation whole-body hyperthermia device. Heat is introduced into a radiating target (i.e., a great vessel) by means of probe beams, and the energy of ultrasound, infrared, laser, microwave, radio frequency and electromagnetic probes at each frequency range is introduced into a vascular circulation system through the radiation probe network composed of probe beams distributed on an attachment in the form of optimum biological heat absorption, and then heat is transferred throughout the body through a hemoperfusion method, so that the vivo tissue is rapidly heated through conduction of biological heat in the tissue. The device has the characteristics of high thermal utilization ratio, high blood flow rate and high specific heat, and thermal convection is rapidly conducted between the radiant heat and the tissue to realize whole-body hyperthermia, therefore, the device not only can realize the purposes of uniformity of the machine body and rapid temperature rise, but also avoid the phenomenon of local overheating, simultaneously, has the accessibility of a wearable device and is a high-efficiency hyperthermia equipment without ache.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Heat therapy
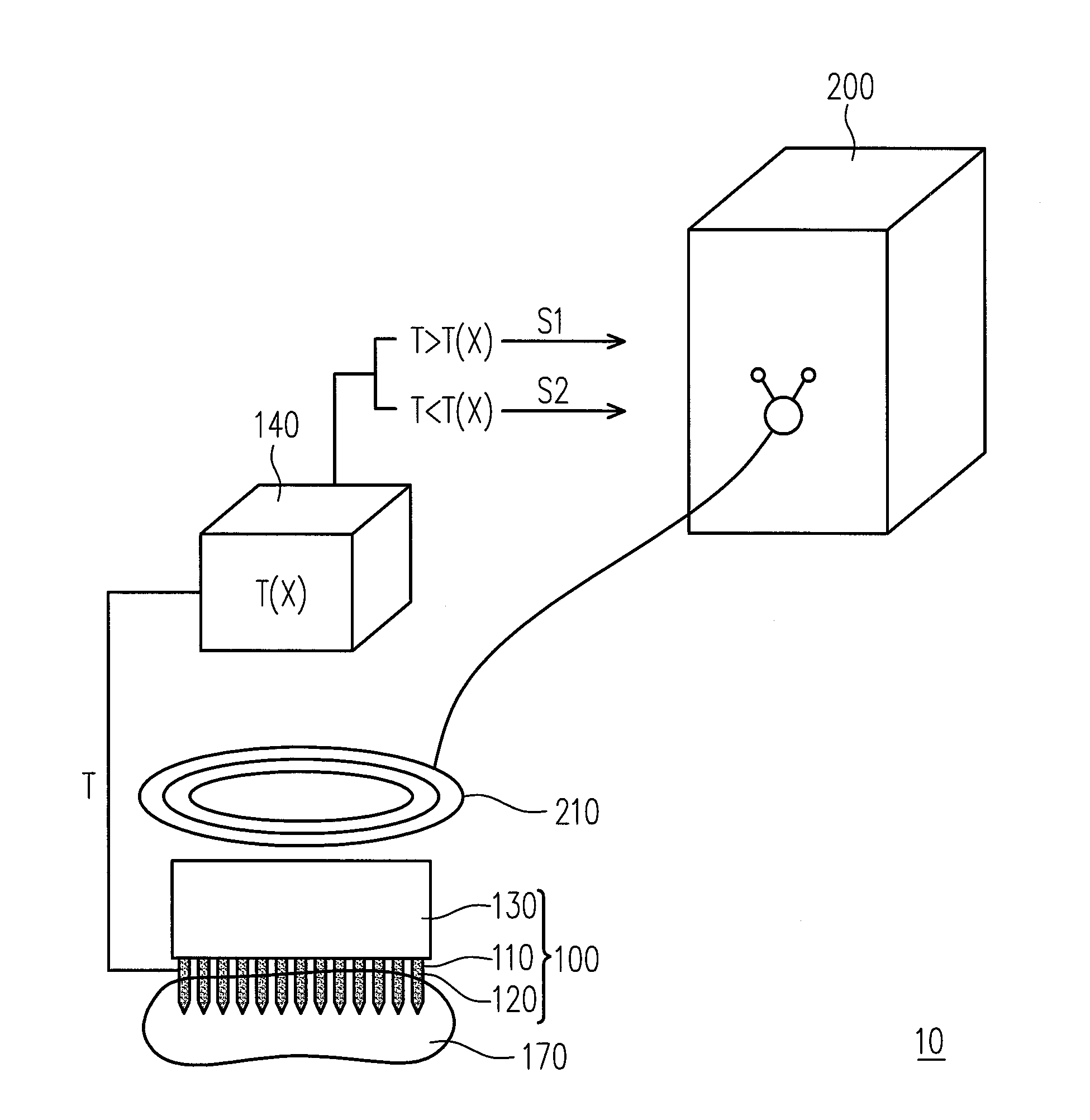
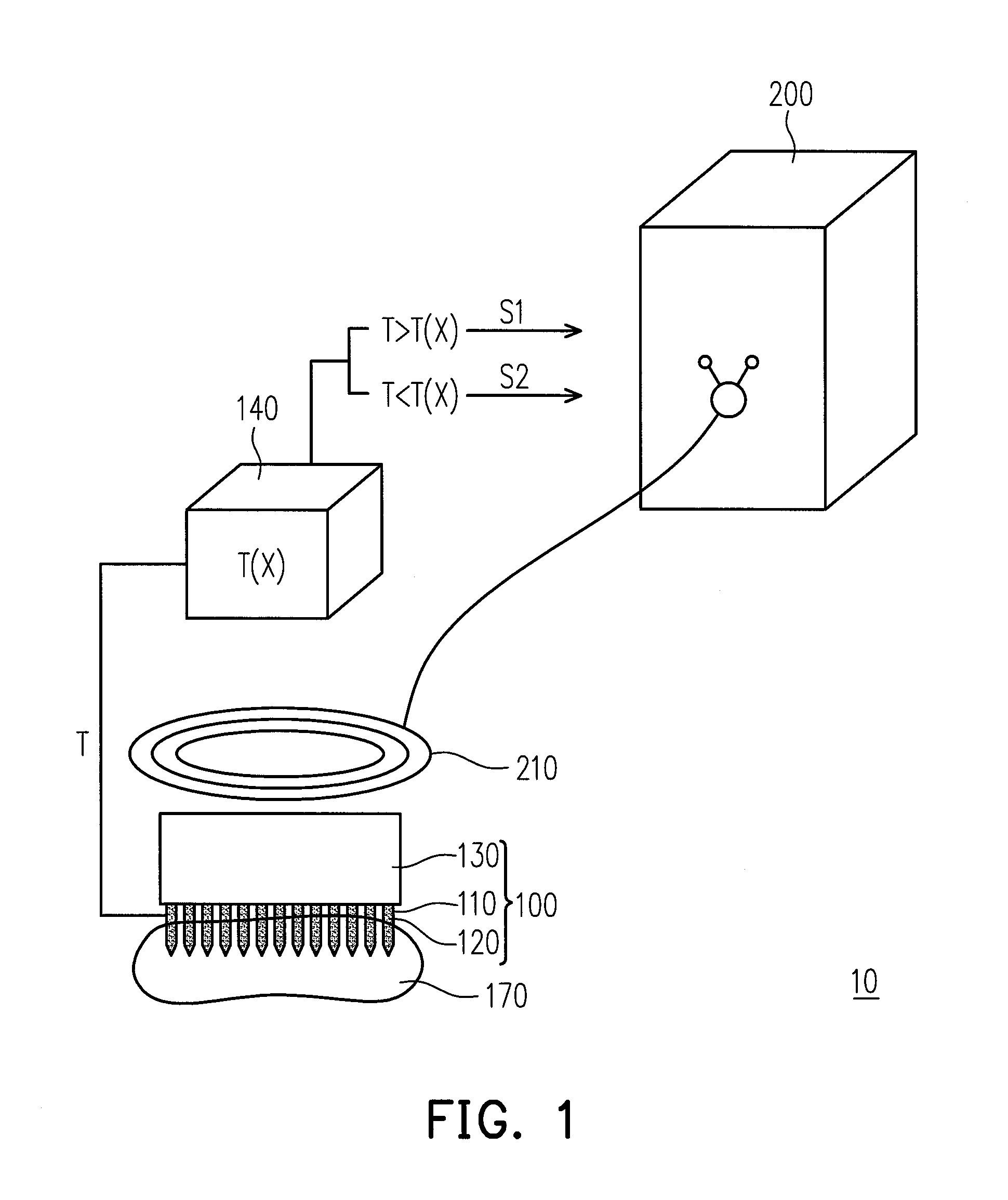
InactiveUS20120157749A1Avoid stickingStable temperatureElectrotherapyMagnetotherapyElectromagnetic fieldTarget tissue
A heat therapy for thermally treating a target tissue within a living body by using a treating apparatus including a treating device with a magnetic part is provided. The magnetic part is heated to a first temperature by a high frequency electromagnetic field with a heating rate ranging from 1 to 5° C. / sec, wherein the magnetic part is contacted the target tissue. Temperature controlling steps are performed to the magnetic part having the first temperature, and therefore the magnetic part has a final temperature higher than the first temperature, and a treatment is performed to the target tissue under the final temperature. Each of the temperature controlling steps is a heating step, a cooling step or a temperature conservation step, and the magnetic part is heated or cooled by the high frequency electromagnetic field with a heating rate or a cooling rate ranging from 1 to 5° C. / sec.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Alternating magnetic field thermotherapeutic system for tumor
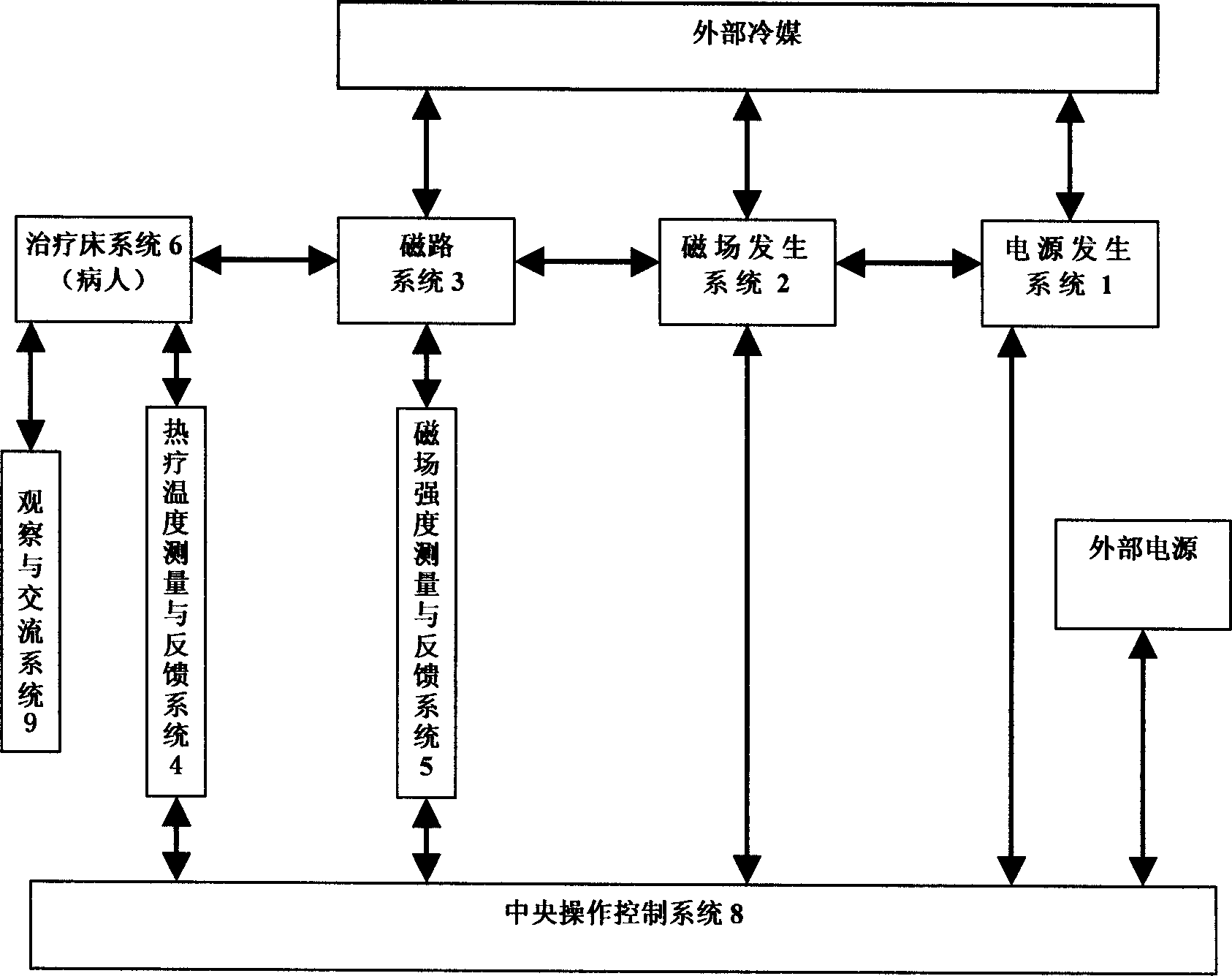
InactiveCN1748814AReduce areaUniform magnetic fieldElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingMedical equipmentEngineering
The tumor treating thermotherapeutic alternate magnetic field system in medical equipment field includes alternate power source system, magnetic field generating system, magnetic path system thermotherapeutic temperature measuring and feeding back system, alternate magnetic field strength measuring and feeding back system, treating bed system, shielding system and central operation and control system. The alternate magnetic field system has power source output frequency of 1-500 KHz, magnetic conductor made of soft magnetic material of high magnetic conductivity, cross section area of the magnetic conductor gap in 10-1000 sq cm, fixed or adjustable gap of 5-60 cm, and magnetic field strength inside the gap of 1-50 kA / m. Owing to magnetic path system comprising magnetic conductor and gap, the treating part of the alternate magnetic field system has homogeneous magnetic field distribution, high heating efficiency and reasonable heating mode.
Owner:SHANGHAI ALLRUN NANO SCI & TECH
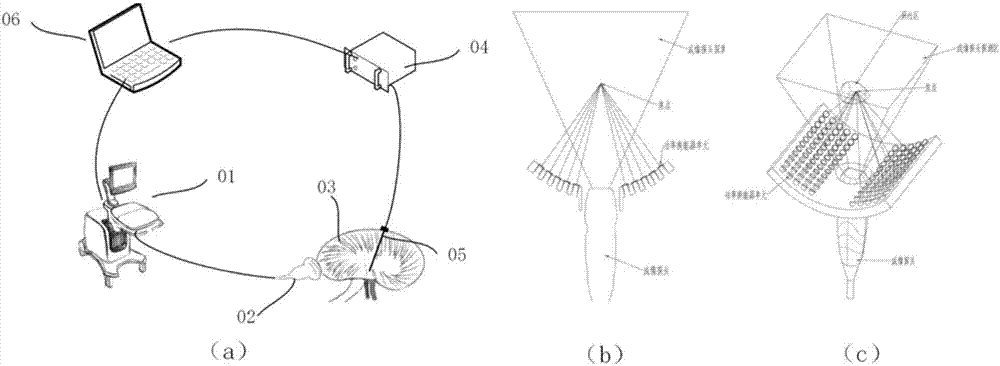
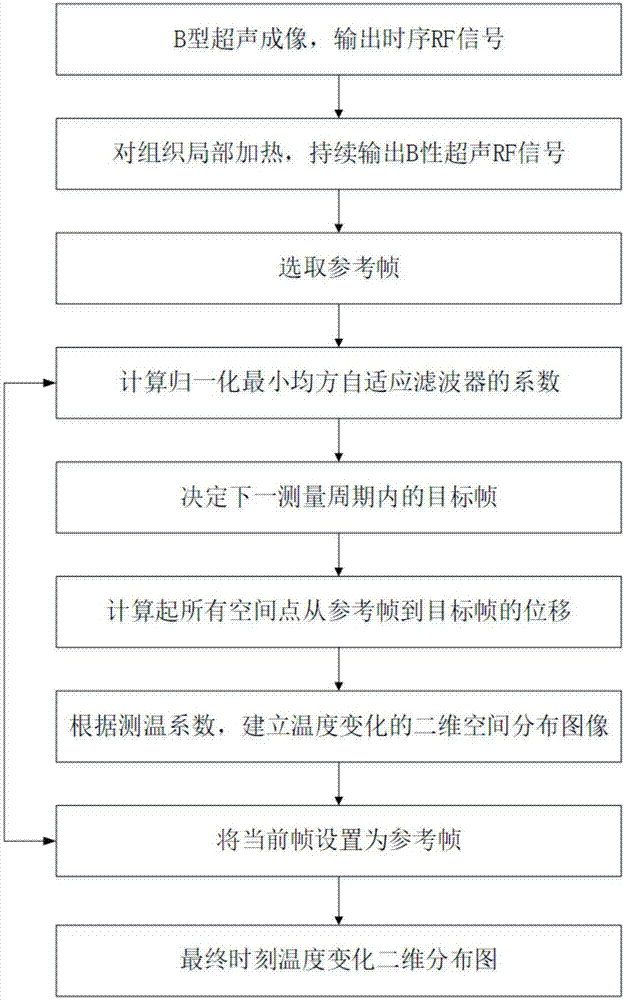
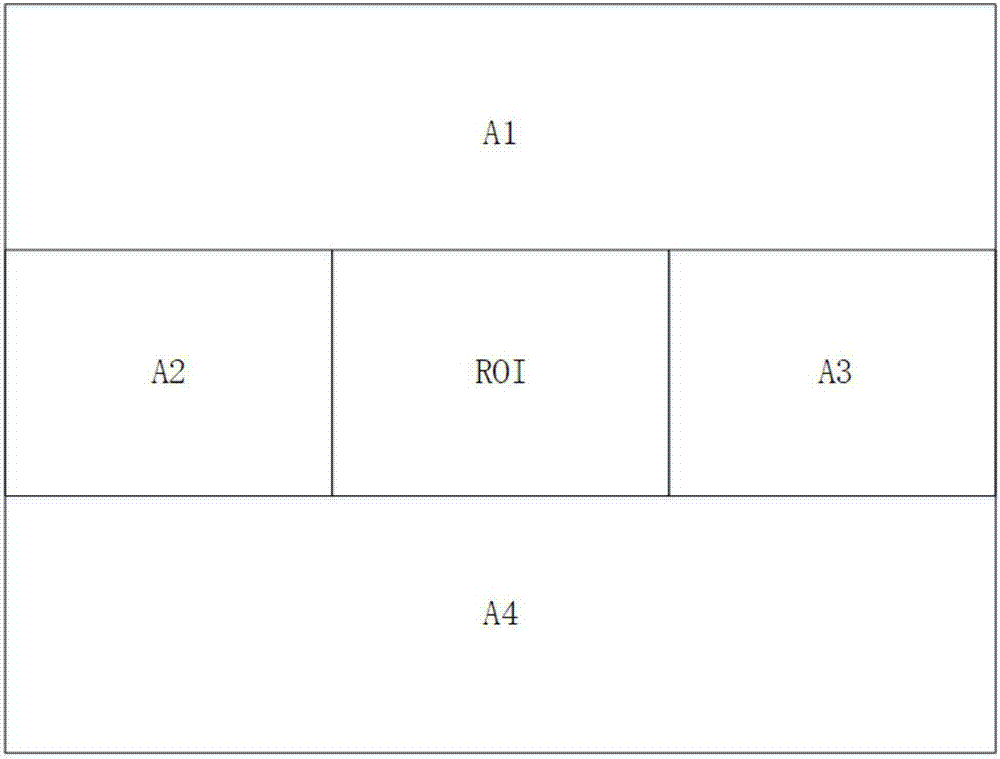
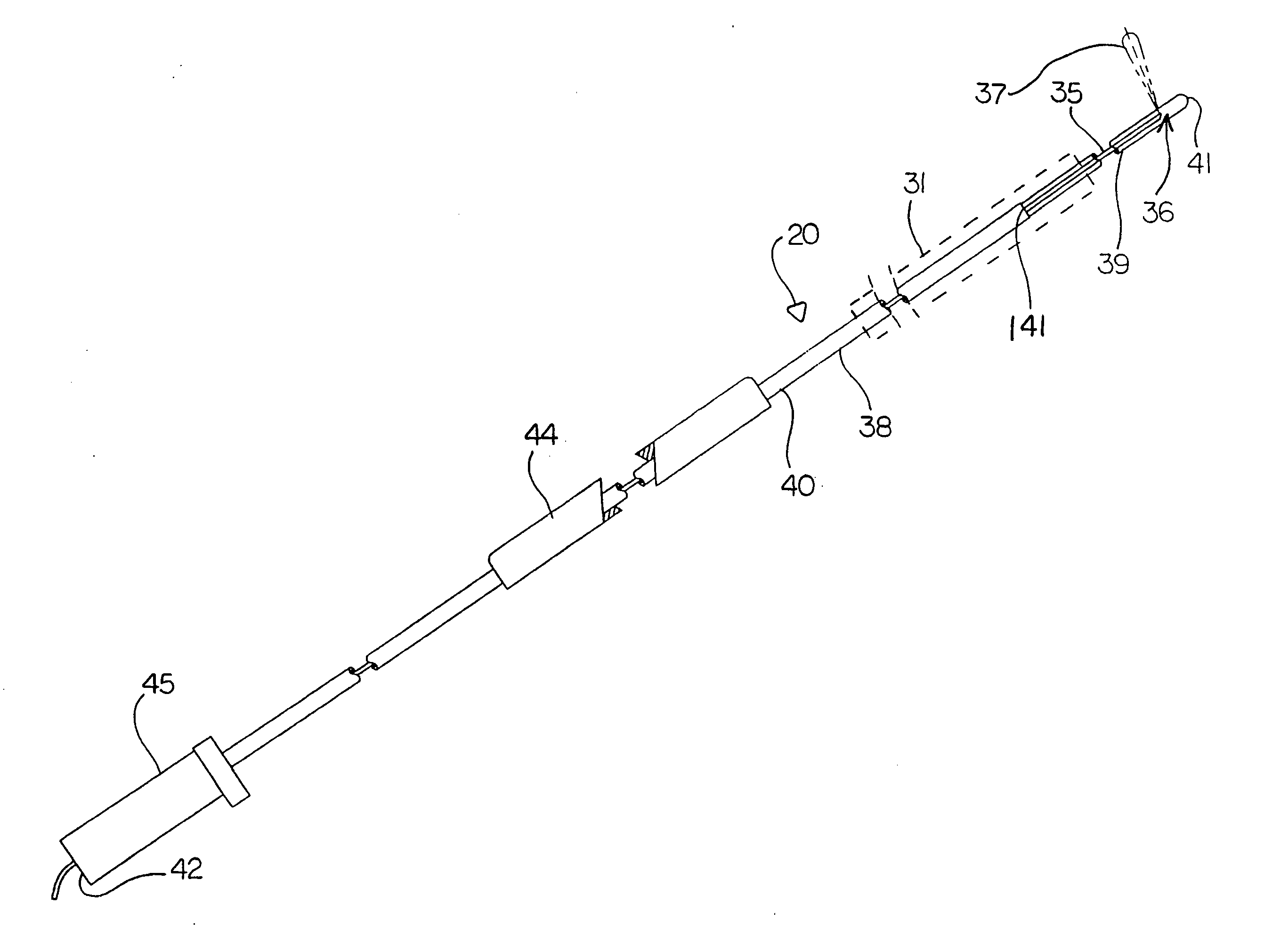
Ultrasonic method for measuring temperature change of biological tissue based on thermal expansion and gating algorithm
ActiveCN107569256ALow costEasy to deploy at scaleOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsDiseaseTissue heating
The invention discloses an ultrasonic method for measuring temperature change of biological tissue based on thermal expansion and gating algorithm. Aiming at the problem that temperature increment ofa target area cannot be effectively monitored in methods for treating diseases based on various current body tissue heating modes, a method for evaluating the temperature change of the biological tissue by using B-mode ultrasound RF signals is established. According to the method, methods such as focused ultrasound, radio frequency and microwave are used for locally heating the biological tissue,B-mode ultrasound is used for imaging the target area and collecting the RF signals of the target area, a target frame is selected based on B-mode ultrasound timing sequence images, time delay imagesthat ultrasound passes through the tissue are calculated, and accordingly temperature change images are obtained; according to images outside a heating area, the coefficient of a self-adaption filteris calculated, and the obtained temperature change images are subjected to noise suppression. According to the ultrasonic method, the error in the temperature increment range of 18 DEG C is smaller than or equal to 2 DEG C, the temperature increment monitoring technology of B-mode ultrasound is promoted to be applied to thermal therapy, and the safety and effectiveness of the thermal therapy can be remarkably improved.
Owner:NANJING GUANGCI MEDICAL TECH
Hyperthermia Treatment and Probe Therefor
ActiveUS20080154252A1Avoid overall overheatingPrevent overheating cellsSurgical instrument detailsDiagnostic recording/measuringPiezo electricTitanium
A method of using a probe that emits energy to coagulate lesions is disclosed. The probe is constructed and arranged to emit light from its distal end, either at an angle to its longitudinal axis, or along its longitudinal axis. Optionally, an end reflector may be used to direct the energy in a beam to one side of the fiber end. A reinforcing sleeve for the fiber is mounted to a shielded, Piezo-electric motor constructed and arranged to move the fiber both longitudinally and rotationally within an optional elongate cannula. An MRI system is arranged to generate a series of output signals indicative of temperature in the targeted area. The application of energy is stopped when the temperature at the boundary of the lesion reaches the required hyperthermic temperature. Cooling of the tip portion of the probe is effected by expansion of a supplied cooling fluid through a restrictive orifice into an expansion zone at the probe end. The fiber is encased in a stiff tubular titanium probe with a relatively small fluid supply duct inside the probe with the interior of the probe acting as a return duct for the expanded liquid. The temperature of the probe end is monitored by a sensor in the probe end and controlled by controlling the pressure in the supplied cooling fluid.
Owner:MONTERIS MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com